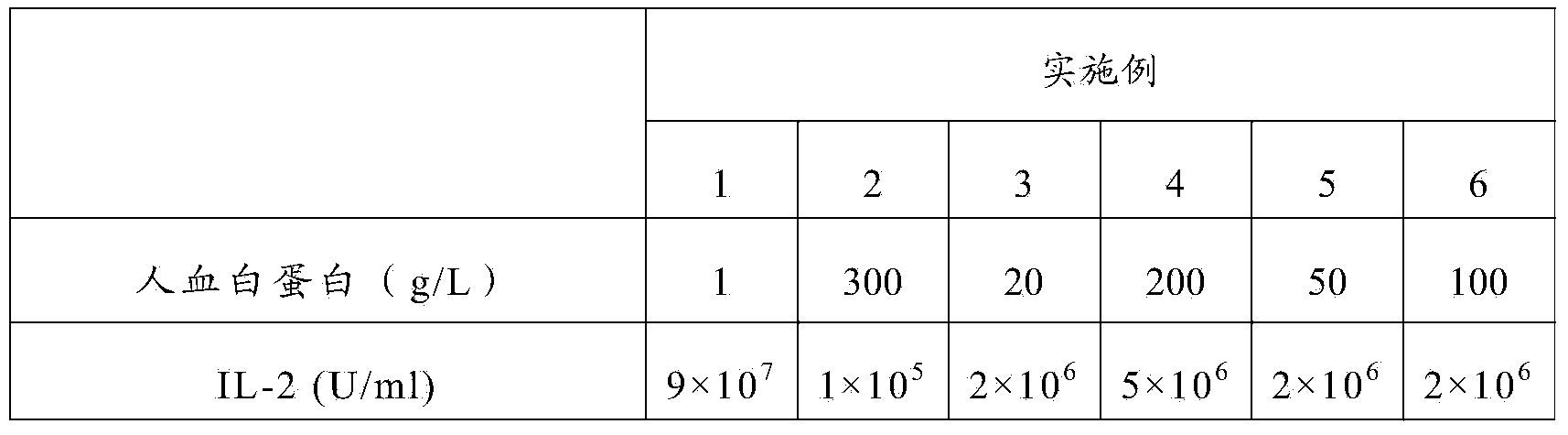Patents
Literature
86 results about "Cellular density" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
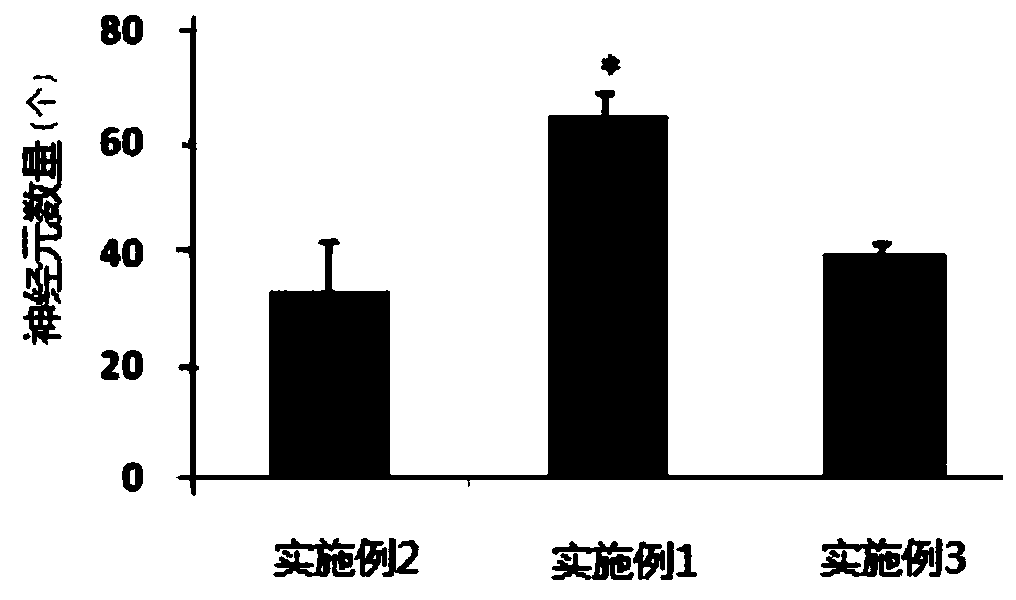
This suggests that cell density is not merely a function of cellular environment or the concentration of certain cellular components, and that cell density (and the distribution of densities in a population of cells) may be an independent and useful diagnostic.
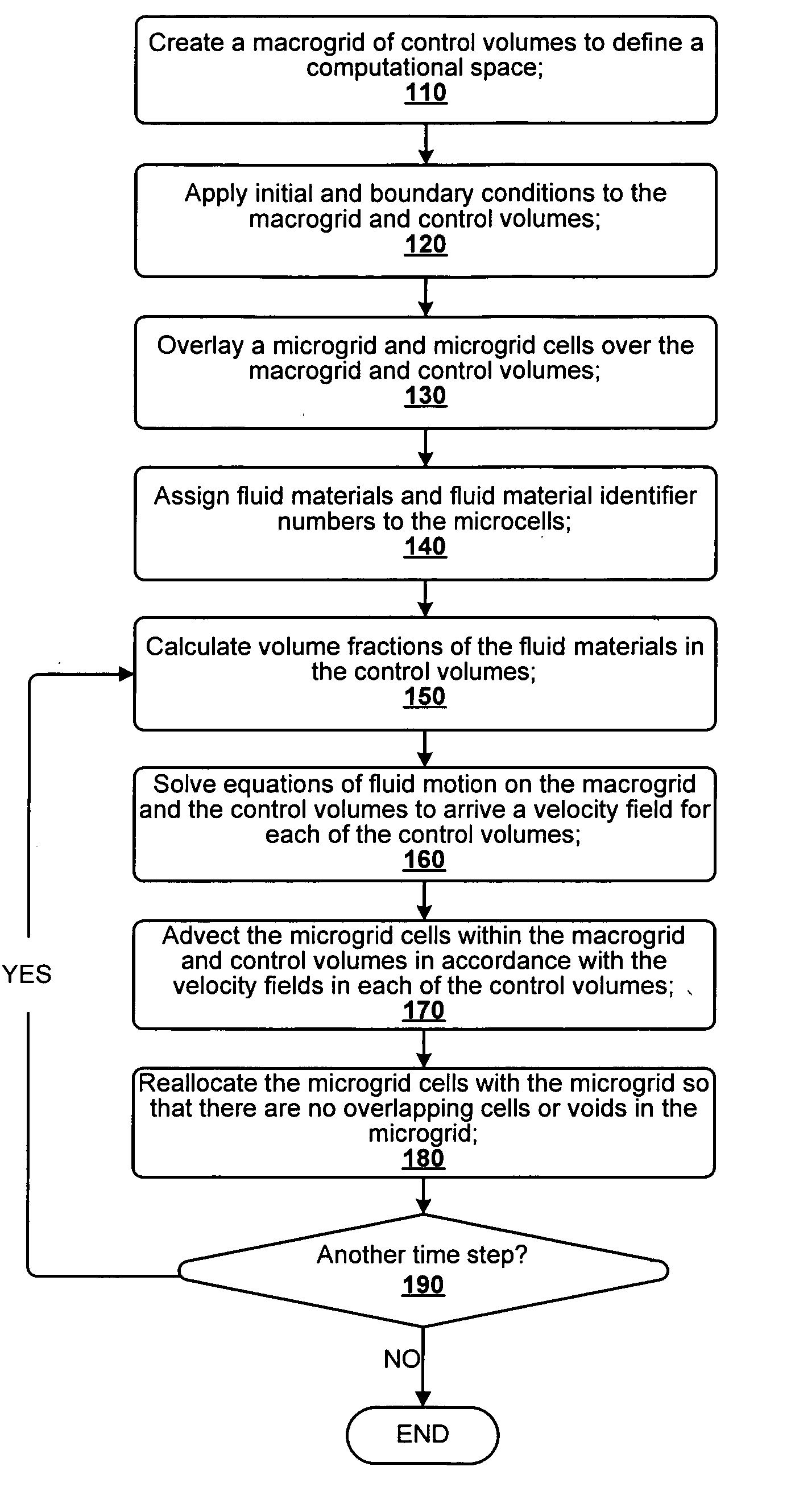
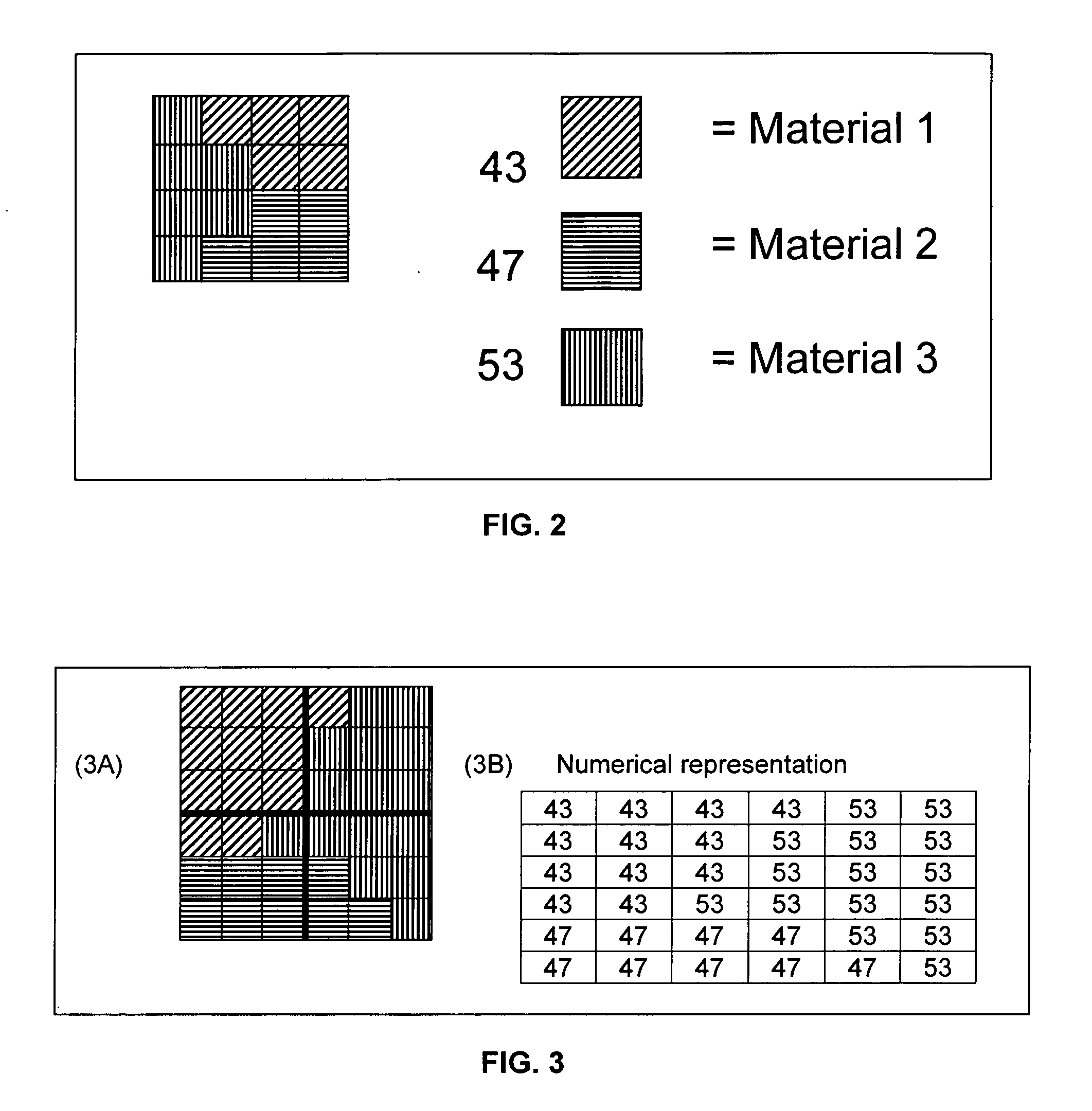
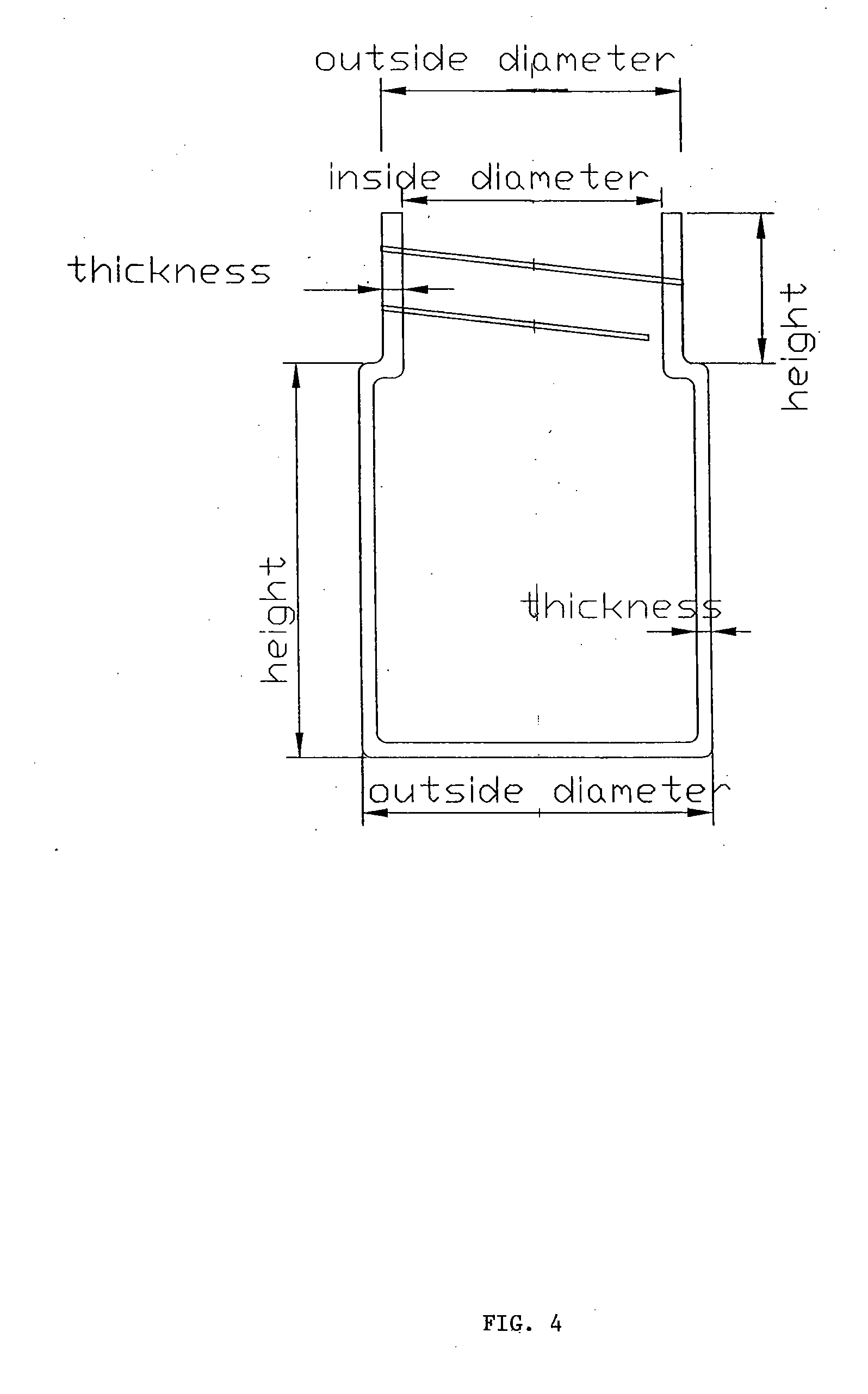
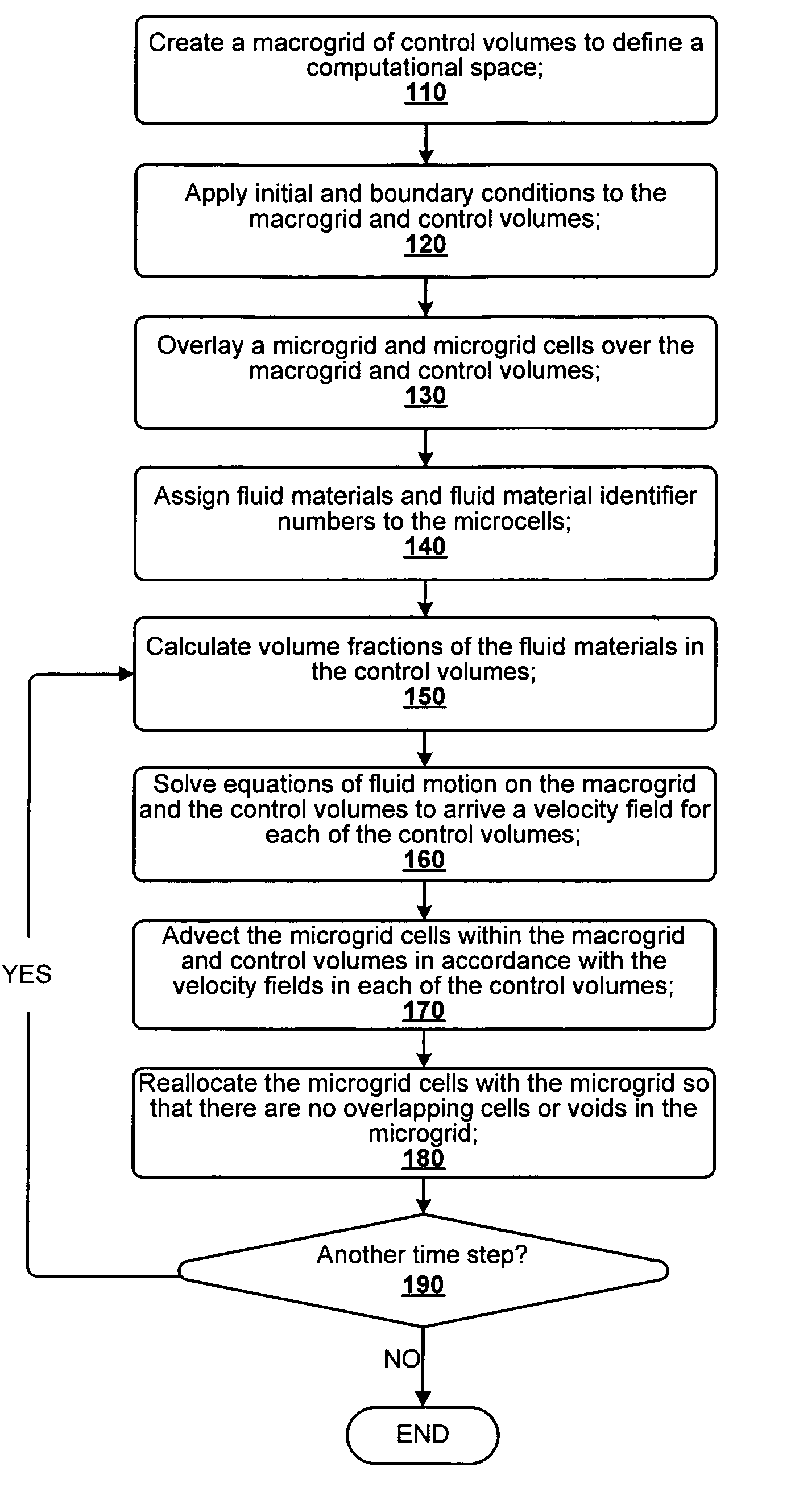
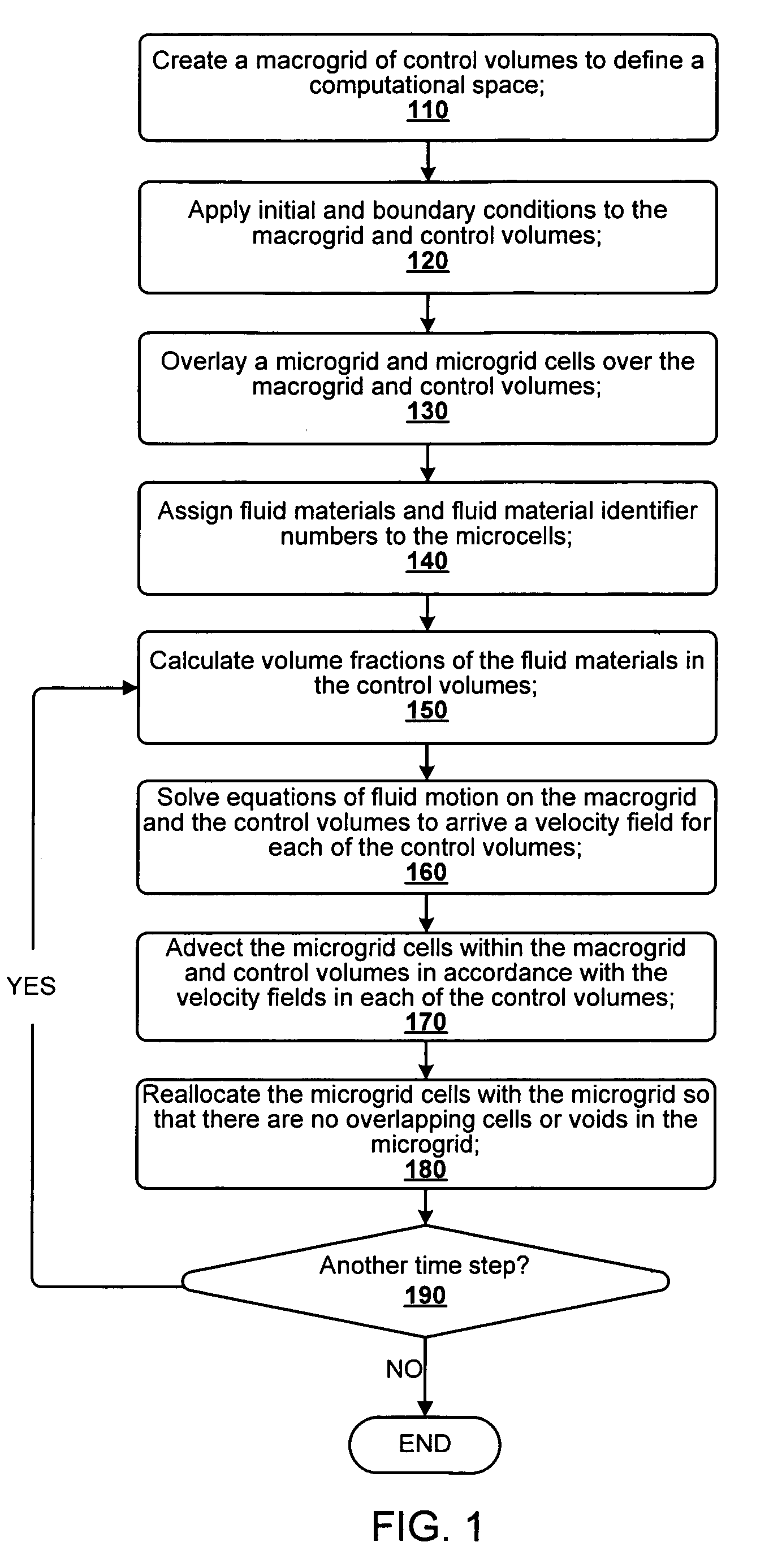
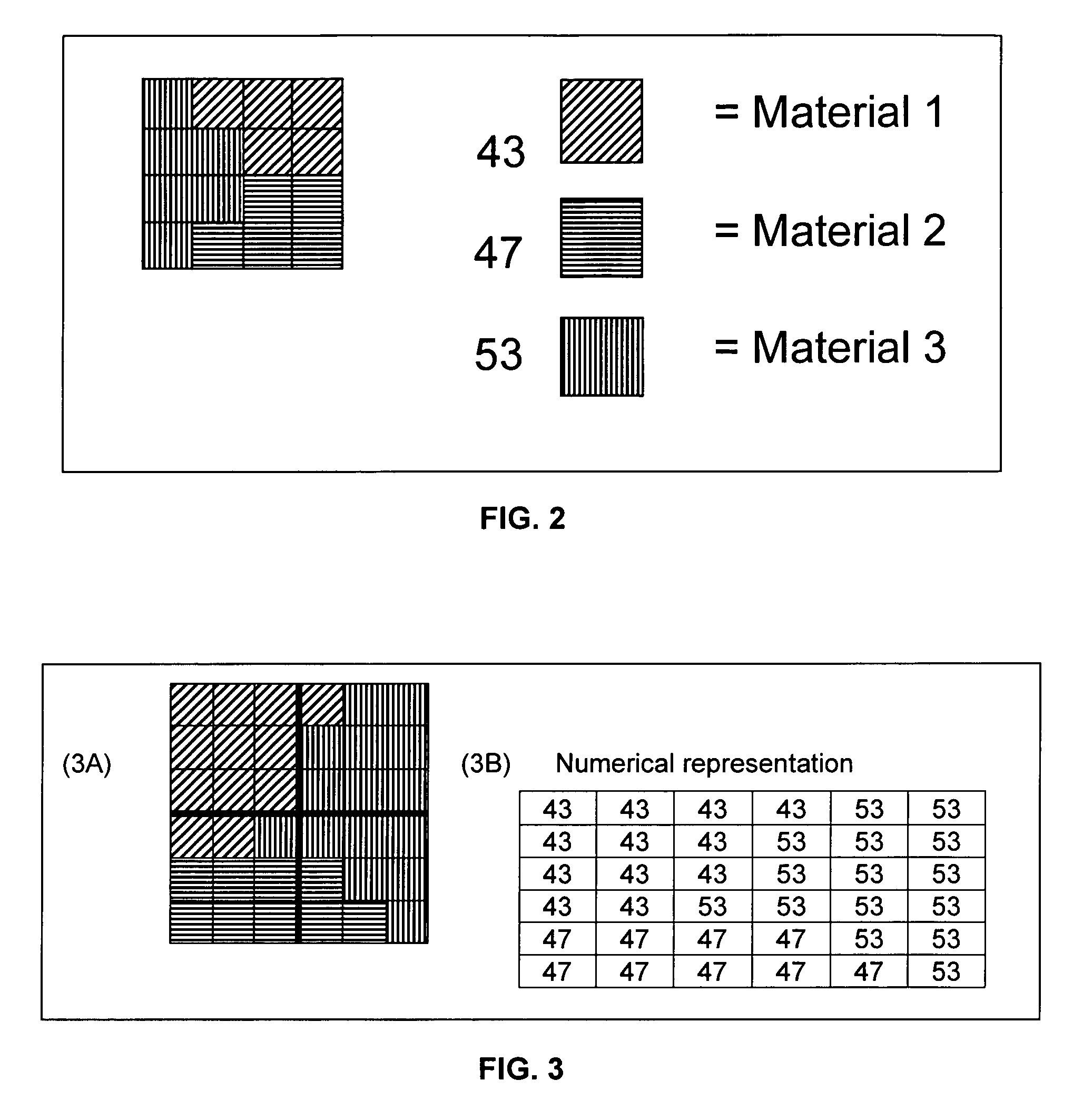
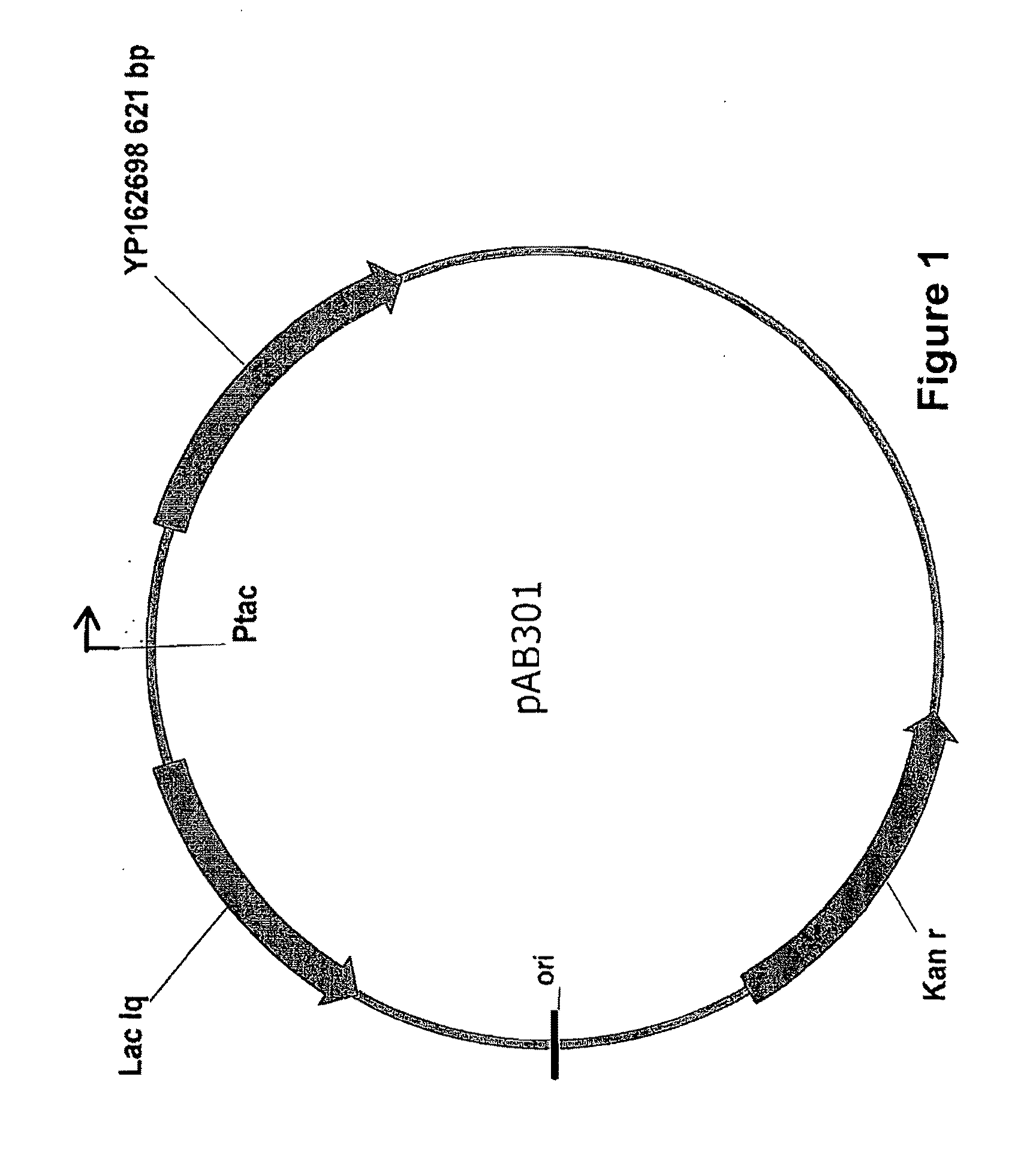
N-phase interface tracking method utilizing unique enumeration of microgrid cells
InactiveUS20050182603A1Easy to handleFluid to flowComputation using non-denominational number representationDesign optimisation/simulationMicrogridEngineering
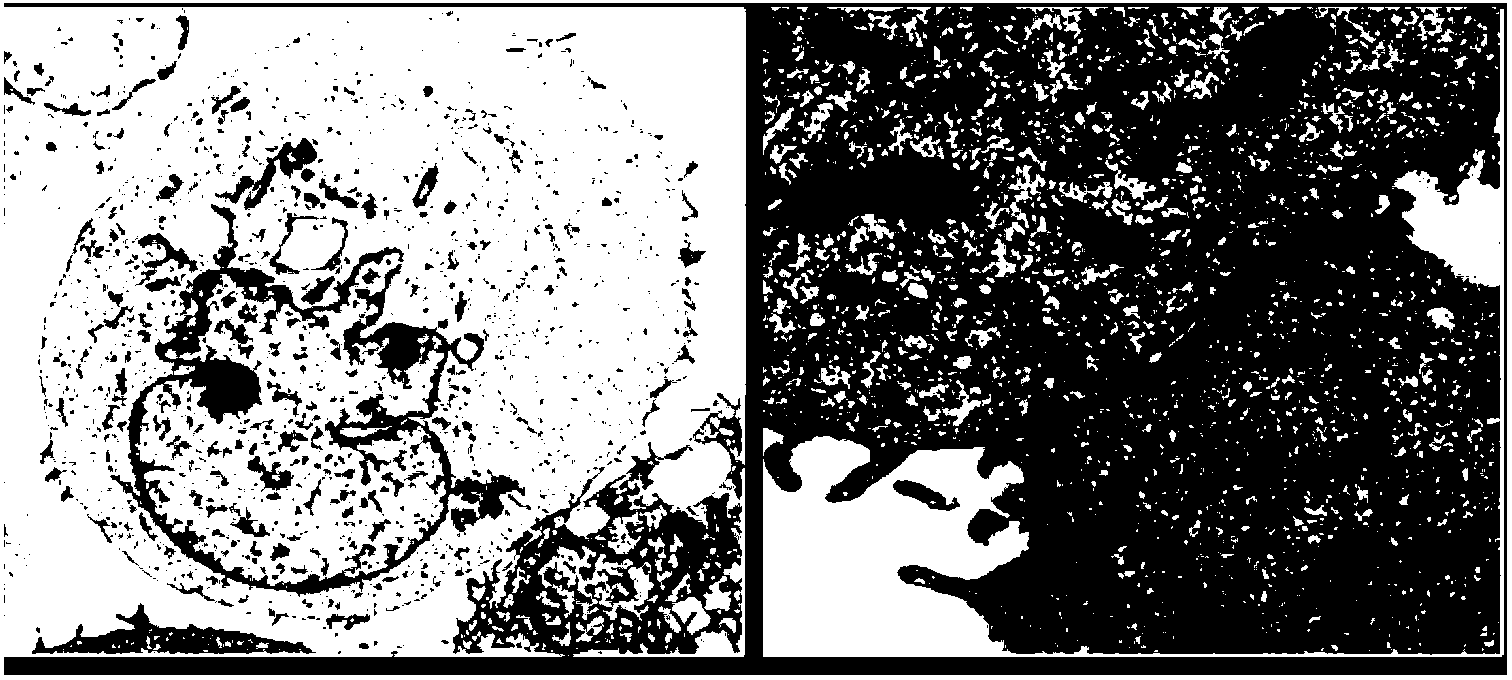
A method for tracking N fluid materials and their associated interfaces during simulated fluid flow is disclosed. A microgrid cell methodology is embedded on a regular macrogrid to subdivide and then tag fluid materials in a computational system preferably using a prime numbering algorithm. The motion of microgrid cells is tracked based on local velocity conditions, rectifying small anomalies by a coupled evaluation of local volume fraction fields and global mass conservation. Volume fractions can be calculated at any time step via an evaluation of the prime locations so that average cellular density and viscosity values can be regularly updated.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
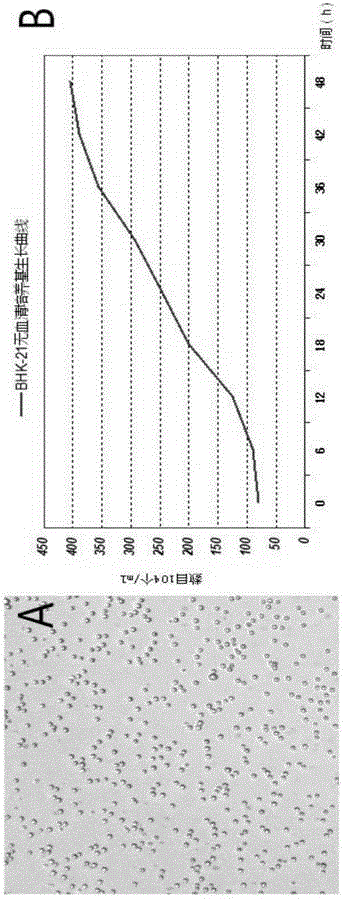
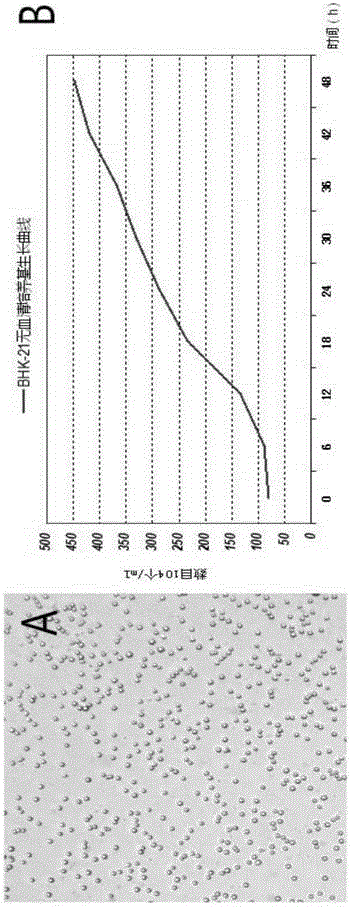
Serum-free animal origin-free culture medium for suspension culture of BHK-21 cells and preparation method of serum-free animal origin-free culture medium
ActiveCN105018416AProliferate fastIncrease vitalityArtificial cell constructsVertebrate cellsAntigenDouble-time
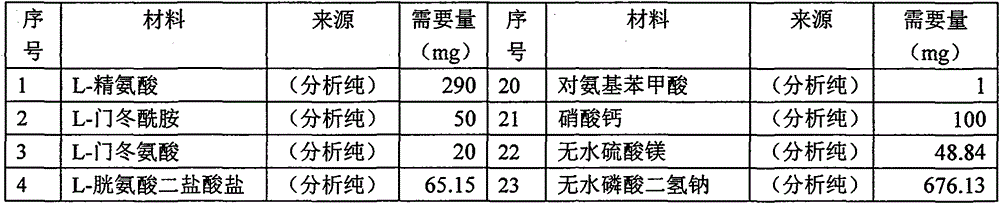
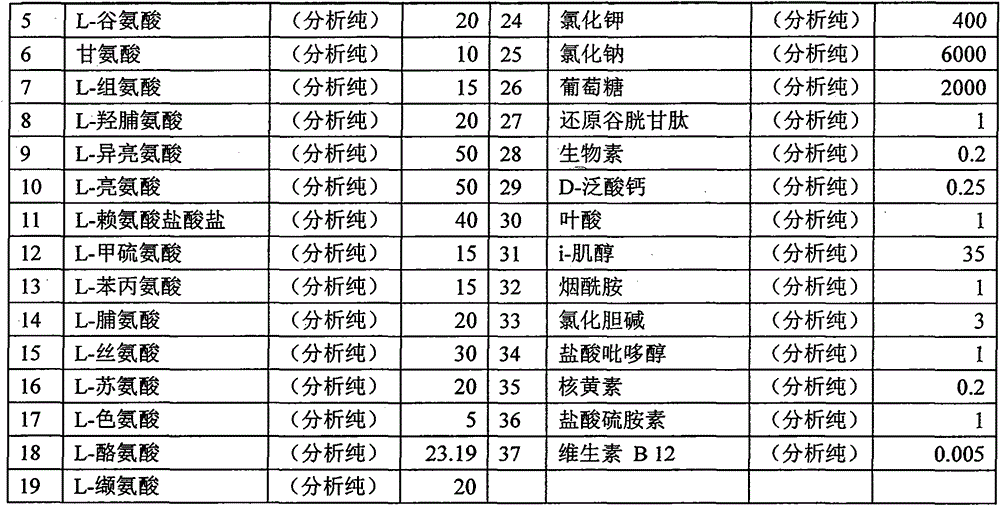
The invention discloses a serum-free animal origin-free culture medium for suspension culture of BHK-21 cells and a preparation method of the serum-free animal origin-free culture medium. According to the serum-free animal origin-free culture medium for suspension culture of the BHK-21 cells and the preparation method of the serum-free animal origin-free culture medium, through the addition and component optimization of amino acids, inorganic salt, vitamins, lipids, hydrolysates and the rest of additives in the culture medium, the multiplication speed of the BHK-21 cells is remarkably improved, the doubling time is shortened, and the high activity is maintained while the cells reach higher growth density. The culture medium is suitable for high-density suspension culture of the BHK-21 cells, low in cost, free of serum, free of animal origins and low in protein, the biological function of the serum is completely replaced through the addition of the ingredients including the lipids, the vitamins, the microelements, recombinant protein and the hydrolysates,, and some negative effects caused by the serum to later purification and separation of an antigen are avoided. Through optimization on the components of the culture medium, the multiplication speed of the BHK-21 cells in suspension culture is higher, the cell density is higher, the cell activity is higher, and the BHK-21 cells are more suitable for large-scale industrial production.
Owner:内蒙古金源康生物工程股份有限公司
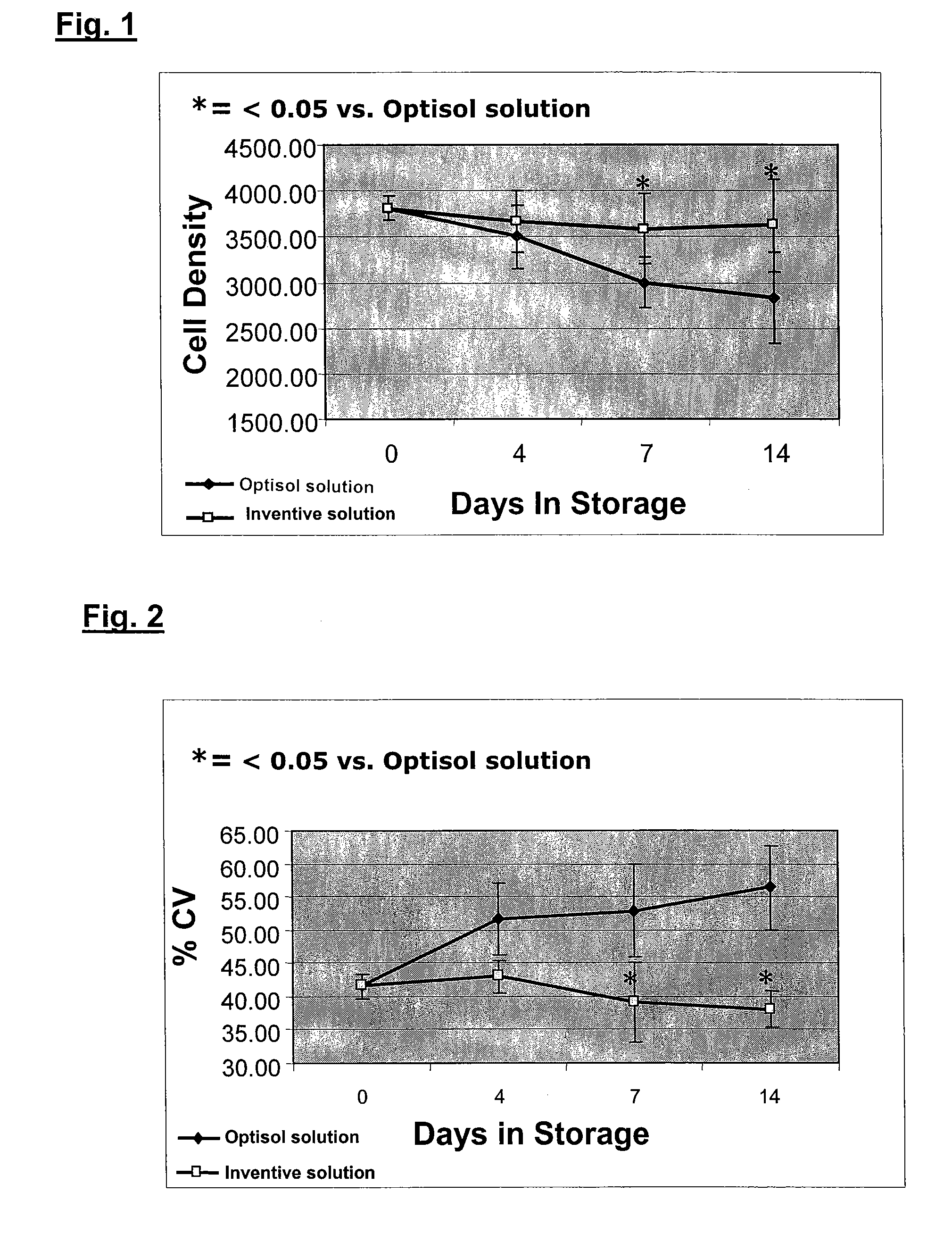
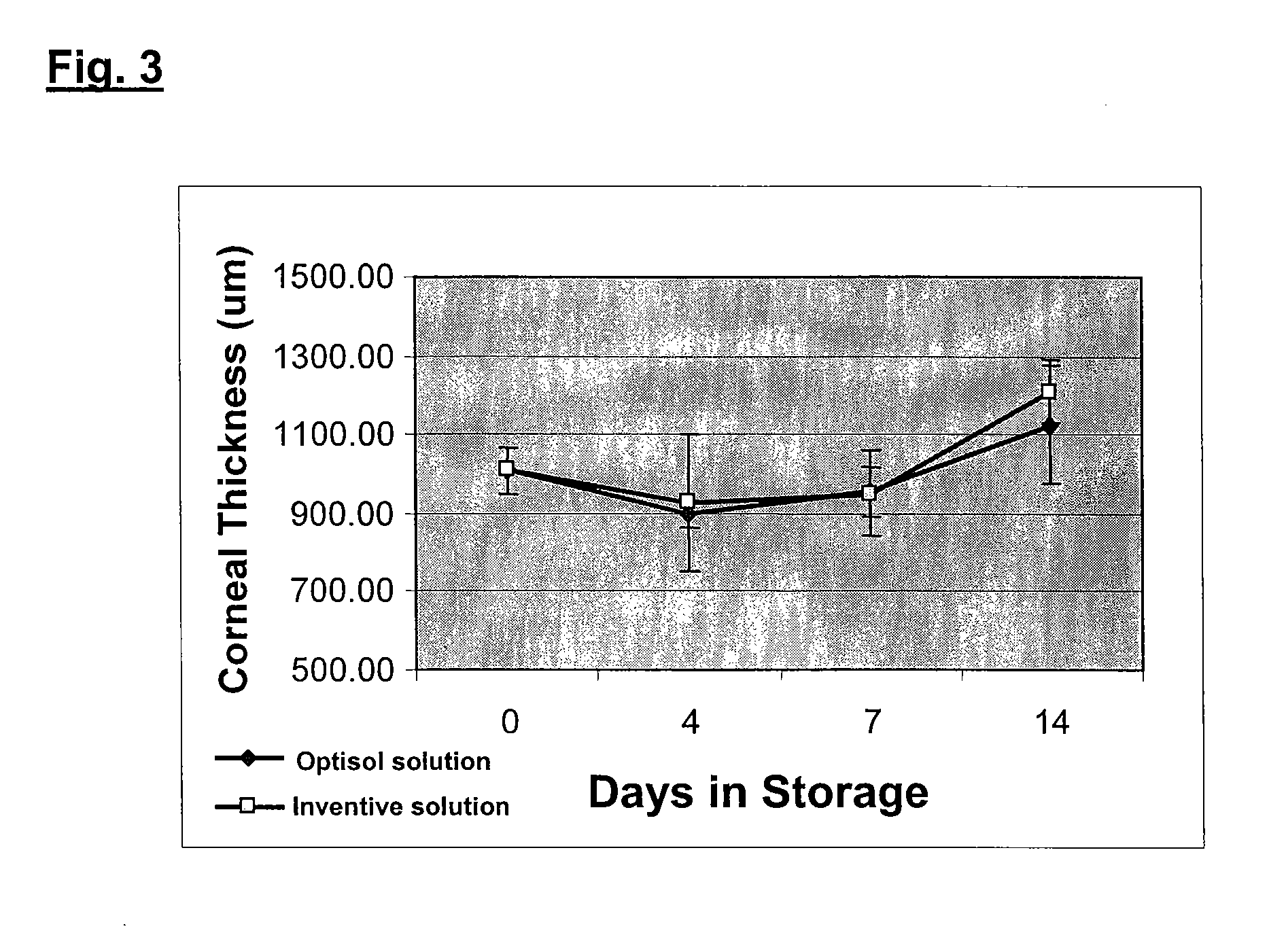
Composition and method for in vitro preservation of corneal tissues
A corneal storage solution which maintains cell density and cell viability of corneas stored in vitro for a period of greater than four days up to about two weeks is provided. The solution contains a buffered, balanced, nutrient and electrolyte aqueous solution, at least one colloidal osmotic agent, a phenolic antioxidant compound, a non-lactate-generating substrate, a thiol-containing compound, insulin, and at least one antibiotic. A method for in vitro storage and preservation of the viability of human corneal endothelial cells for subsequent use includes the steps of removing a cornea from an eye globe and placing the cornea in the above corneal storage solution.
Owner:SOLL DAVID B M D +1
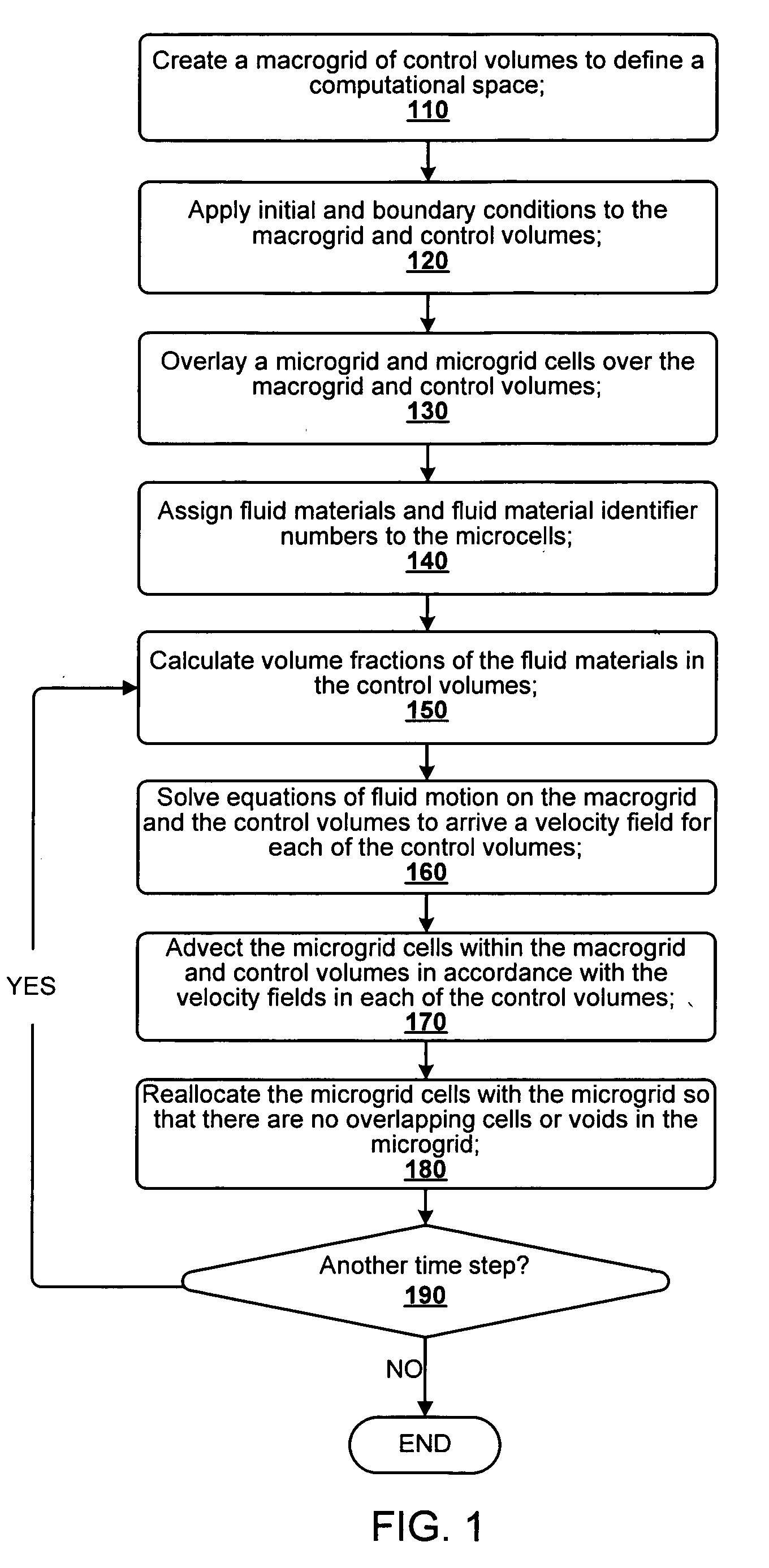
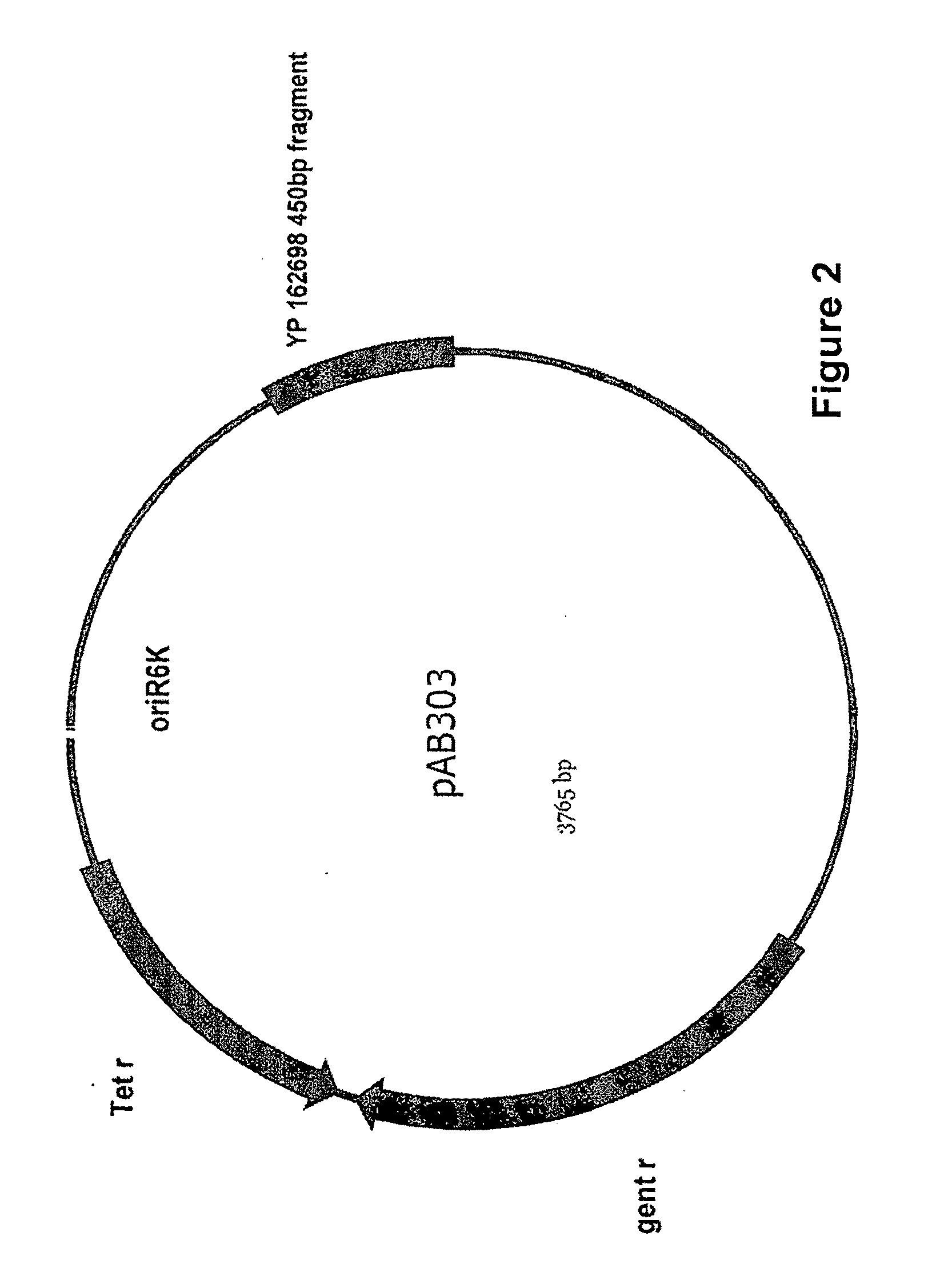
N-phase interface tracking method utilizing unique enumeration of microgrid cells
InactiveUS7379852B2Easy to handleComputation using non-denominational number representationDesign optimisation/simulationMicrogridPower grid
A method for tracking N fluid materials and their associated interfaces during simulated fluid flow is disclosed. A microgrid cell methodology is embedded on a regular macrogrid to subdivide and then tag fluid materials in a computational system preferably using a prime numbering algorithm. The motion of microgrid cells is tracked based on local velocity conditions, rectifying small anomalies by a coupled evaluation of local volume fraction fields and global mass conservation. Volume fractions can be calculated at any time step via an evaluation of the prime locations so that average cellular density and viscosity values can be regularly updated.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
Supercritical CO2 micro-foaming polylactic acid/wood-flour composite material and preparation method thereof
The invention provides a supercritical CO2 micro-foaming polylactic acid / wood-flour composite material and a preparation method of the supercritical CO2 micro-foaming polylactic acid / wood-flour composite material, and relates to a micro-foaming composite material and a preparation method of the micro-foaming composite material, solving the problems of common wood-plastic composite material that the density is high, the impact strength is low, and the resulting waste is easy to pollute the environment. The preparation method comprises the following steps: getting raw materials such as polylactic acid, wood flour, a coupling agent, a toughening agent and a lubricant; mixing the raw materials in a high-speed mixer based on a certain ratio; melting and blending by a two-roll mill; preparing a sample by compression molding; then swelling the sample by adopting the supercritical carbon dioxide as the foaming agent; and finally quickly releasing the pressure, thus obtaining the micro-foaming polylactic acid / wood-flour composite material. The supercritical CO2 micro-foaming polylactic acid / wood-flour composite material has the advantages that the temperature for foaming is low, the pressure is held within a short time, a cellular structure is easy to control, and the prepared micropore composite material is small in aperture and high in cellular density; and the supercritical CO2 micro-foaming polylactic acid / wood-flour composite material is a green and environment-friendly foaming material with good performance.
Owner:SOUTHWEAT UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Extracellular matrix gel model used for researching development and differentiation of embryonic stem cells
The invention relates to an extracellular matrix gel model used for researching development and differentiation of embryonic stem cells, belonging to the research field of tissue engineering and regenerative medicine, and mainly solving the problem that no ideal model exists for the research of differentiation and development of embryonic stem cells in vitro. We the extracellular matrix gel adopt as the in vitro three dimensional model of the differentiation and development of embryonic stem cells, inoculate the embryonic stem cells to the three dimensional model in different cell densities, and observe the phenomena of the forming of embryoid body by self-differentiation of the embryonic stem cells and the law of the embryoid body being differentiated into cells of different ancestries; and the microenvironment in which the embryonic stem cells grow is regulated, the extracellular matrix gel is taken as the main body to carry out the directional differentiation and development research of the embryonic stem cells, thus disclosing the inherent law and mechanism of the in vitro differentiation and development of the embryonic stem cells, and searching for new methods for directional differentiation of embryonic stem cells to the functional cells of important vital organs at the terminal differentiation period; and the invention will provide a new technical method for exploring the development mechanism of the embryonic stem cells.
Owner:INST OF BASIC MEDICAL SCI ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF PLA
Method for extracting myelomonocyte and differentiating to osteoclast
InactiveCN104651302AStable traitsLower requirementSkeletal/connective tissue cellsOsteocyteCellular density
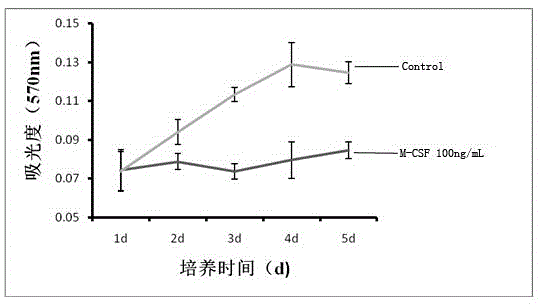
The invention belongs to the field of cell extraction and differentiation authentication, and discloses a method for extracting myelomonocyte and differentiating to osteoclast. The method comprises the following steps: (A) performing sterile myelomonocyte separation, culturing in a complete medium of 20-100ng / mLM-CSF, replacing the complete medium every other day, and observing the morphological characteristics of monocyte; (B) when the density of monocyte is 80-90%, taking out a part of the cells for surface antigen authentication; (C) drawing a growth curve of other cells and performing differentiation induction for osteoclast on other cells. The method for extracting myelomonocyte and differentiating to osteoclast is simple, convenient and reliable, low in requested condition requirements, low in cost and short in time, the extracted monocyte is stable in property, and C57BL / 6 mice myelomonocyte which is reliable and stable in resource can be provided for medical basis, clinical research, tissue engineering study, and the like.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF SOOCHOW UNIV
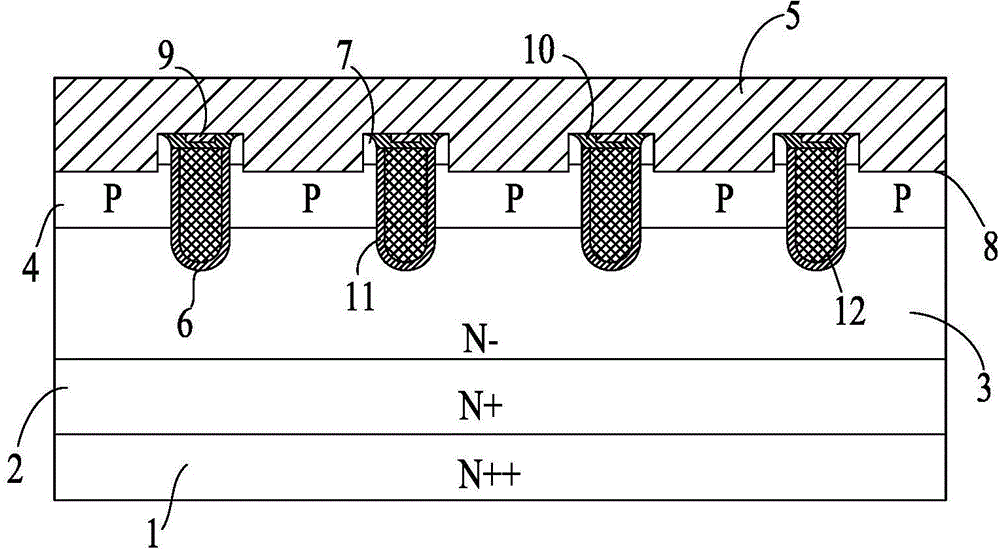
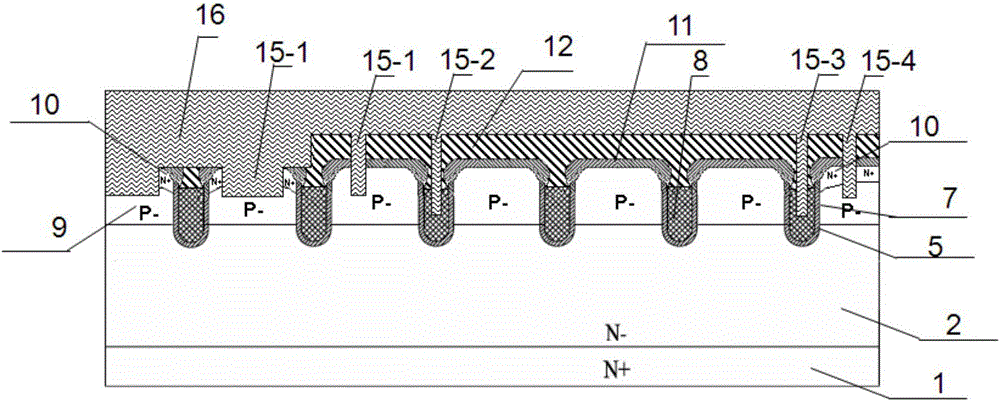
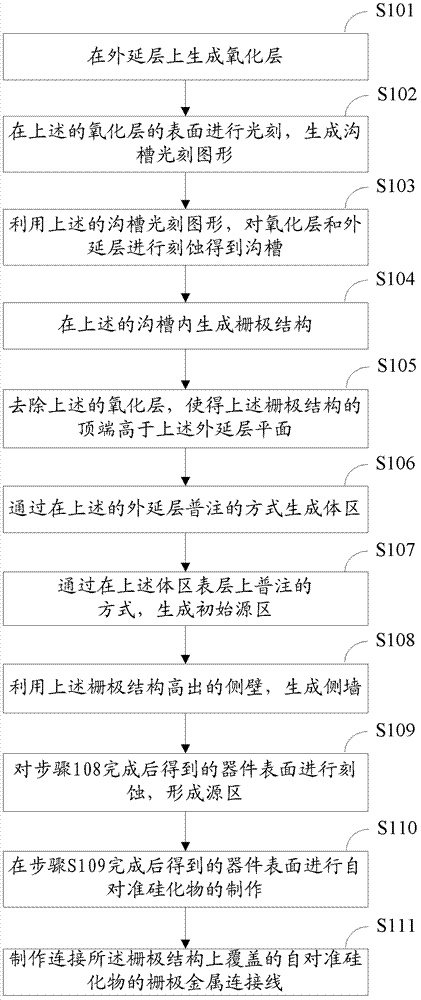
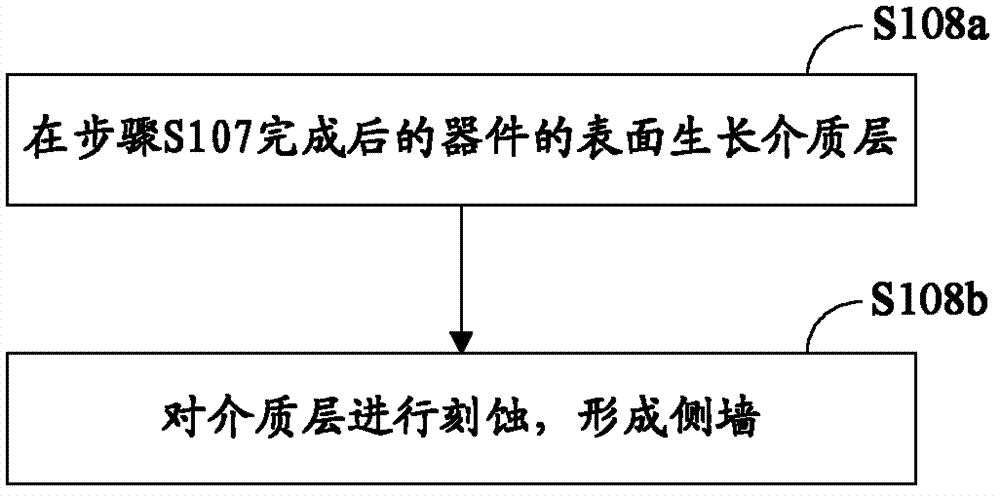
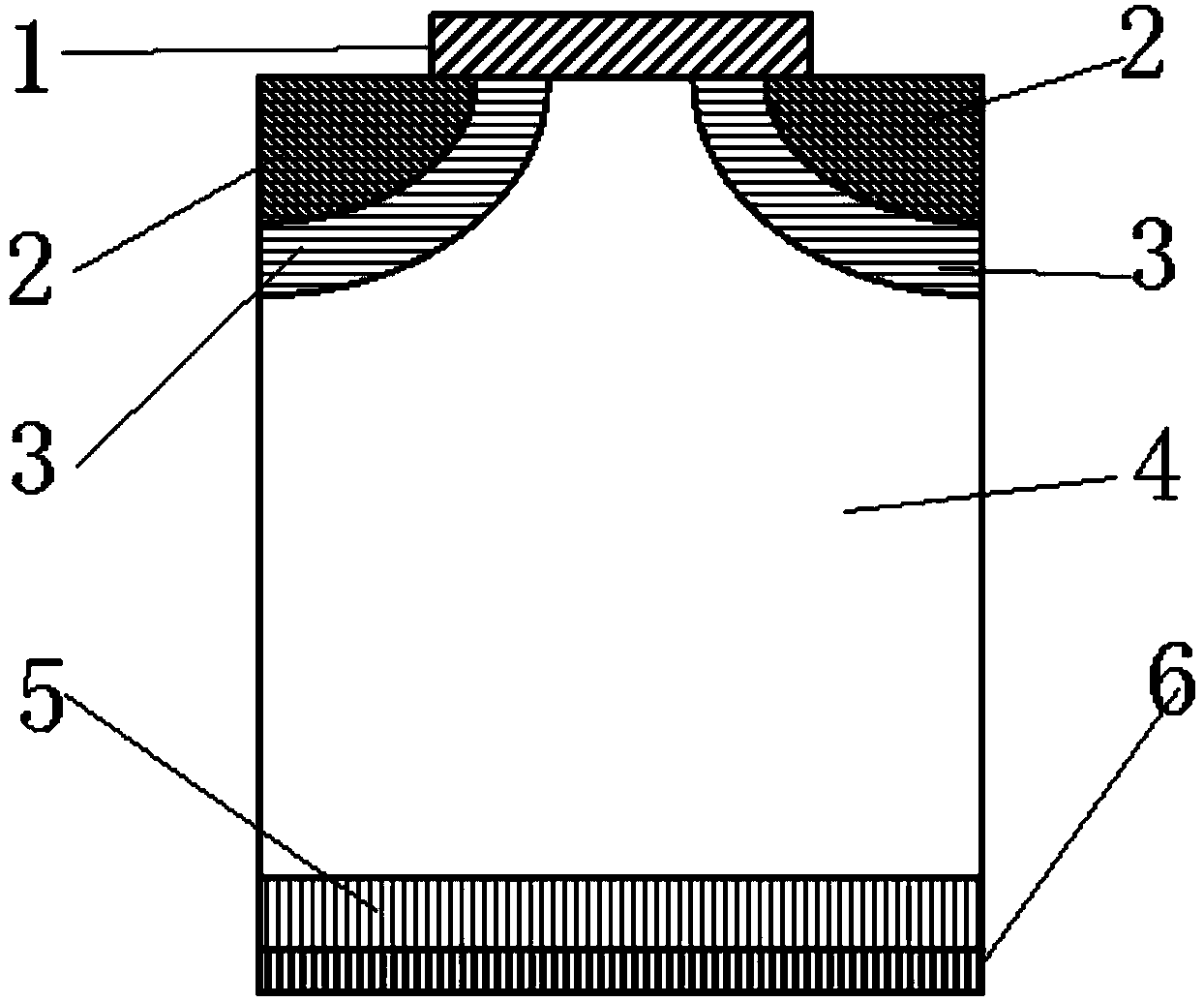
Deep-groove power MOS (metal oxide semiconductor) device with ultrahigh cellular density and manufacturing method of deep-groove power MOS device
ActiveCN104576743ASelf-Aligned EtchingLower channel resistanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesElectrical resistance and conductanceOhmic contact
The invention relates to a deep-groove power MOS (metal oxide semiconductor) device with ultrahigh cellular density and a manufacturing method of the deep-groove power MOS device. Cells in a cellular area adopt groove structures, gate oxidation layers are grown on the section of the power MOS device and the inner wall and the bottom of cellular grooves, and conductive polycrystalline silicon is deposited in the cellular grooves. Thermal oxidation layers are arranged in notches of the cellular grooves, insulation medium layers are deposited on the thermal oxidation layers, and the insulation medium layers and the thermal oxidation layer are distributed in the notches of the cellular grooves only. On the section of the power MOS device, source contact holes extend into a second conductive type trap layer downwards from a first conductive type source electrode and are filled with source metal, and the source metal contacts with the first conductive type source area and the second conductive type trap layer. The deep-groove power MOS device is compact in structure, groove resistance of the MOS device can be greatly reduced, and characteristic conduction resistance of the integral device is reduced.
Owner:WUXI NCE POWER
Compound for promoting the growth of neural cells
ActiveUS7585892B2Small molecular sizeImprove survival rateBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsNeural cellNeuron
Disclosed is a compound capable of promoting the growth and development of neurons, the proliferation of neural stem cells and inducing the neural stem cells to differentiate into neurons, which is represented by a general formula as (I).The compound of the present invention can increase the survival rate of neural cells even at a low cellular density in a culture medium. The compound of the present invention can also promote the growth of neurons, which is revealed by the increase in the thickness, length and number of branches in the neurites (neural fibers). In addition, the compound of the present invention can be used to promote the development of neural stem cells and induce them to differentiate into neurons.
Owner:NATURE WISE BIOTECH & MEDICALS CORP
Ultraviolet mutagenic obtained low temperature salina and its identifying method
InactiveCN1944643AExtend the breeding timeLong breeding cycleUnicellular algaeMicrobiological testing/measurementUV-MutagenesisGenetic similarity
The present invention relates to saline algae, provides one kind of low temperature tolerant saline algae and its ultraviolet mutagenesis breeding process and identifying method. The low temperature tolerant saline algae features its light illuminating growth at 3-10deg.c to reach (1.05-8.11)x10<6> cell / ml in the cell density 2.1-21 times higher than the contrast; the genetic similarity coefficient to wild strain of 0.680-0.910; and increased or decreased protein zone(s) compared with wild strain.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Method for determining baculovirus titer
InactiveCN103364560AGood repeatabilityThe test result is accurateMaterial analysisCytopathic effectFluorescence microscope
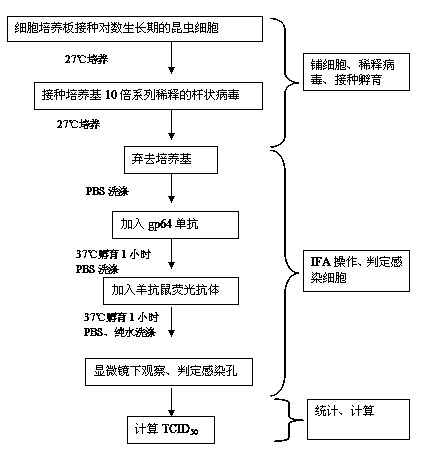
The invention discloses a method for determining baculovirus titer. The method comprises the following steps: paving a cell culture plate with insect cells in the logarithmic phase at the cell density of 2*104-4*104 / 0.1mL / hole, placing the cell culture plate into an incubator for culture and sticking the insect cells to hole bottom; inoculating baculovirus to be detected into the insect cell plate and culturing in the incubator; removing a medium in the cell plate, fixing, washing the cell plate, adding gp64 McAb for incubation, washing the cell plate, adding goat-anti-mouse fluorescent antibody for incubation, washing the cell plate, and observing under a fluorescence microscope; and calculating TCID50 of the virus. The method for determining baculovirus titer is combined with indirect immunofluorescence, is a TCID50 determination method for directly judging whether each hole cell is infected and has good repeatability. Obtained detection results are more accurate. It is not necessary to combine cytopathic effect for determination, and there is no influence from aspects of subjective and experience factors.
Owner:WUHAN CHOPPER BIOLOGY
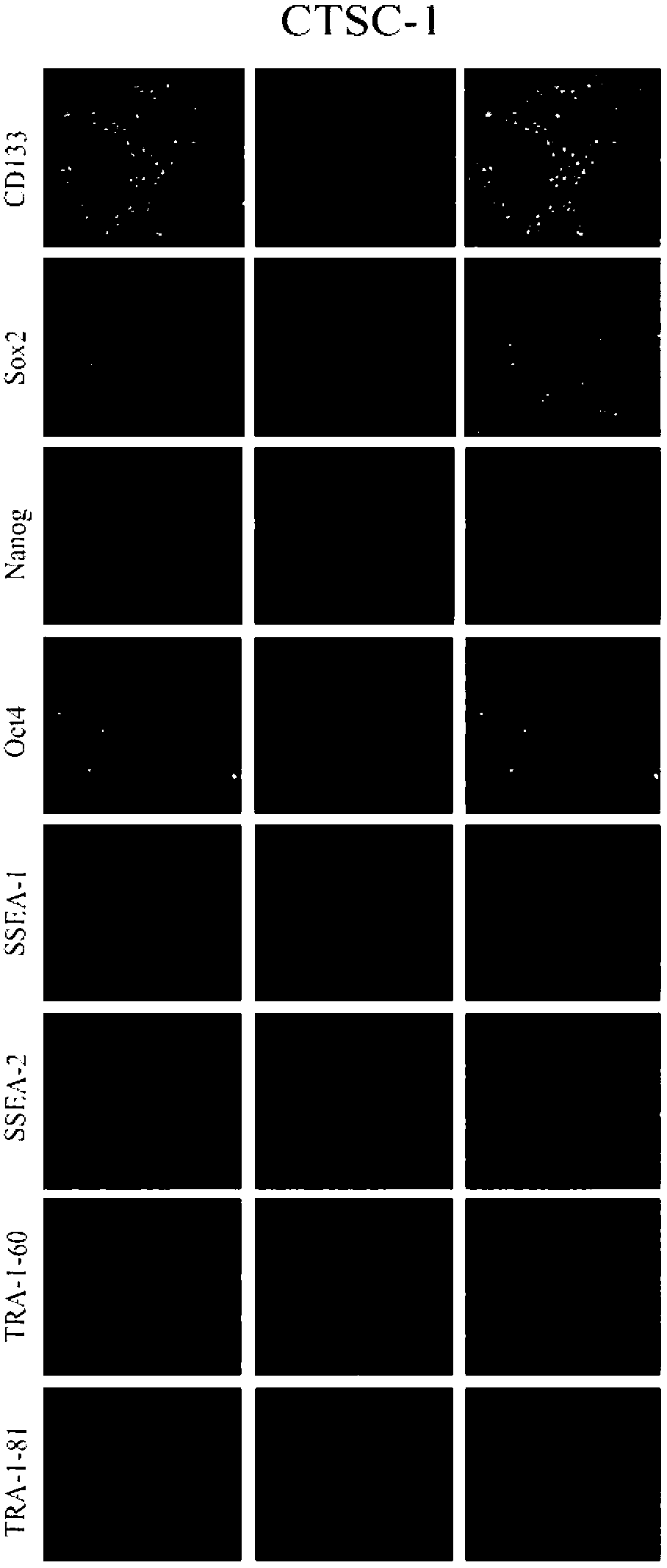
Chinese tongue squamous cancer cell line (CTSC-1) and establishing method thereof
InactiveCN102911915AAchieve enrichmentMicrobiological testing/measurementTumor/cancer cellsSquamous cancerMolecular level
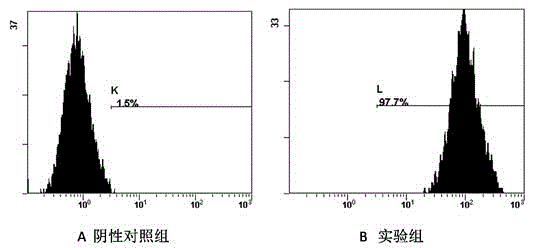
The invention provides an establishing method of a Chinese tongue squamous cancer cell line (CTSC-1), and provides a material base for researching the characteristics of tongue squamous cancer and therapeutics thereof. The establishing method comprises the steps of: carrying out primary culture on the tongue squamous cancer cells by adopting a tissue explants adherent method; subculturing when the cell density reaches about 80 percent; carrying out RT-PCR (Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction) detection on stably subcultured cells to indicate that the cells express tongue squamous cancer cell symbolic molecules CK 8, 18 and 19; and detecting adherent cells through a western blot test to express proteins of the tongue squamous cancer cell symbolic molecules CK 8 and 18, therefore, proving on a molecular level the successful establishment of the CTSC-1.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
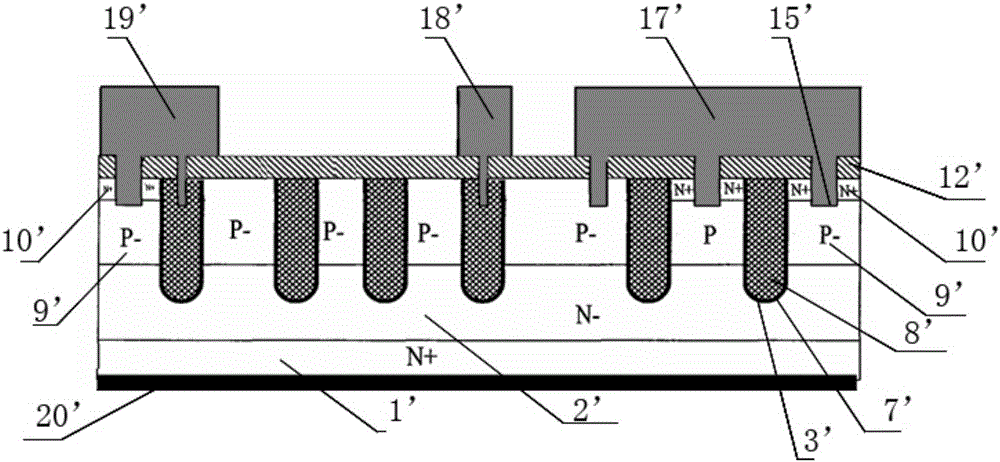
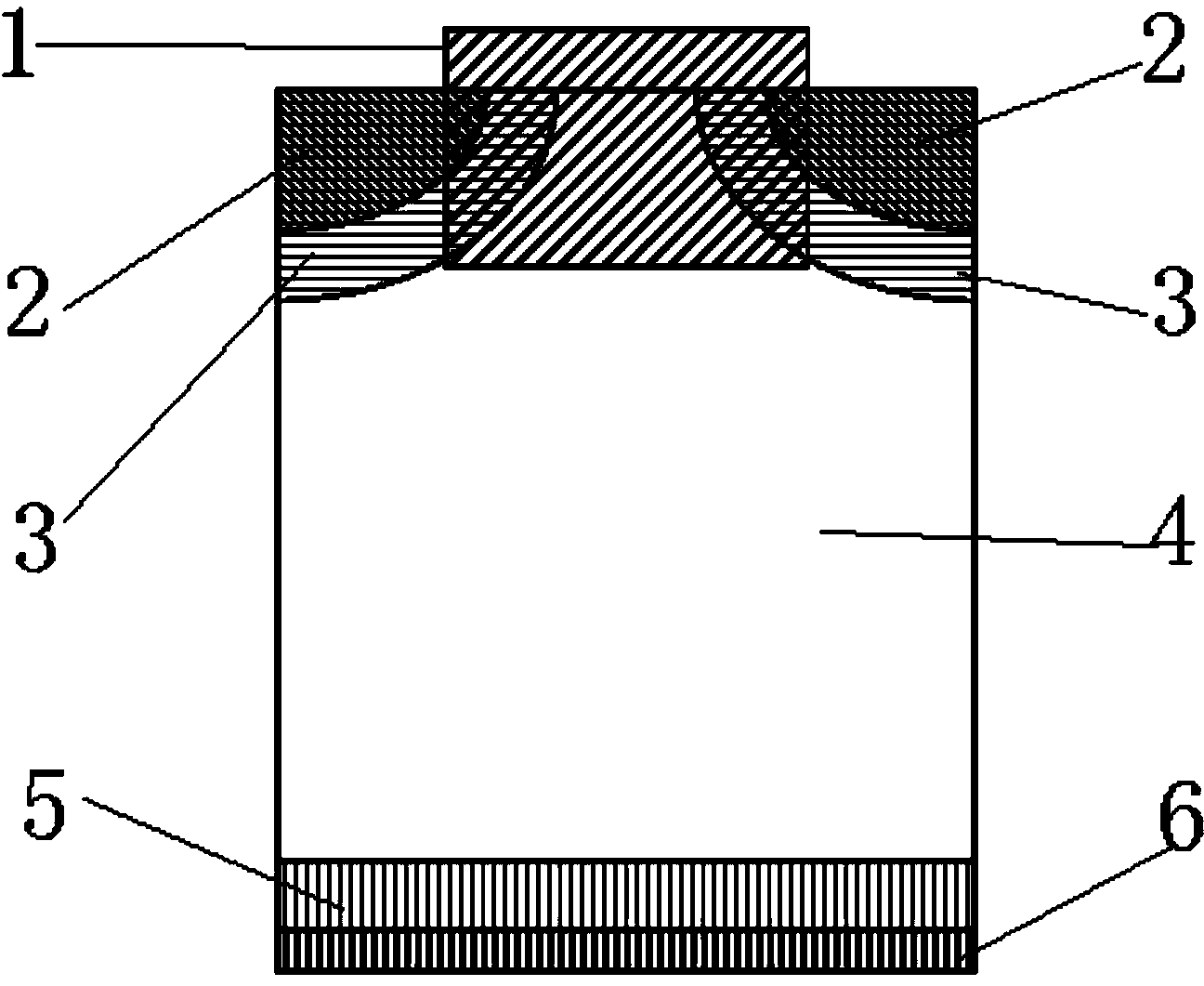
High density low voltage trench power MOS device and method of manufacturing same
PendingCN106653831AIncreased density (integratedObvious process stepsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesElectrical resistance and conductanceEtching
The invention relates to a high density low voltage trench power MOS device and a method of manufacturing the same. A bowl structure of a trench is formed by performing thermal oxidation (a thickness of 500A-5000A) to the upper part of the trench, and a dry general etching method of a high selection ratio (silicon dioxide: silicon) is also selected for etching only silicon under the premise of not etching silicon dioxide, so that the etching of a contact hole in a cellular region of a trench power MOS device is realized, also known as self-aligned etching of the contact hole. Meanwhile, the invention also achieves the etching of a lead-out hole in a terminal protection region of the device, without increasing apparent process steps. As is well known in the industry, for self-aligned etching, the registration deviation of lithography can be considered to be zero. In this way, in the current 8-inch fab lithography machine operation, the invention can greatly reduce the cellular width of a minimum cell of the cellular region from 0.9 <mu>m to 0.5 <mu>m, thus greatly improving the cellular density (an integration degree) and reducing the overall specific on-resistance.
Owner:YANGZHOU YANGJIE ELECTRONIC TECH CO LTD
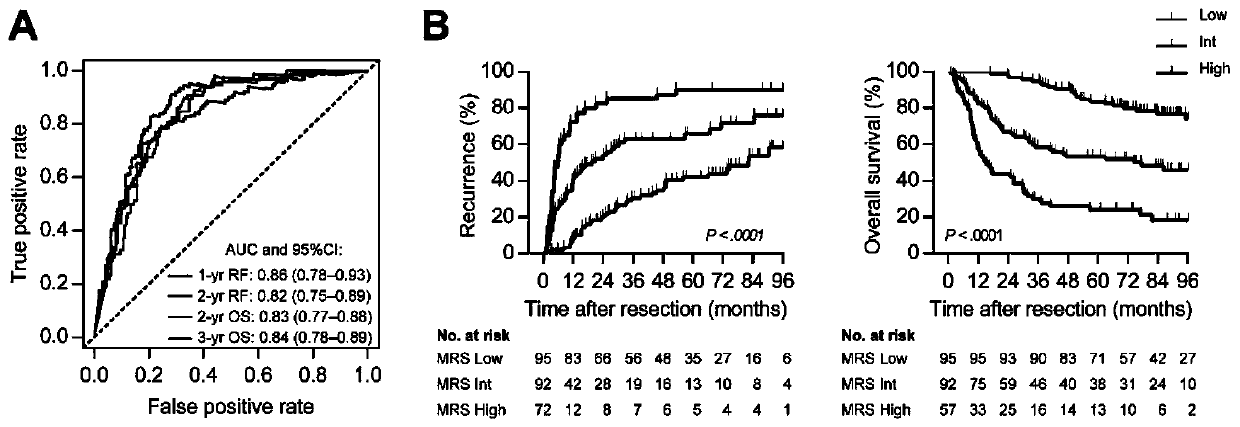
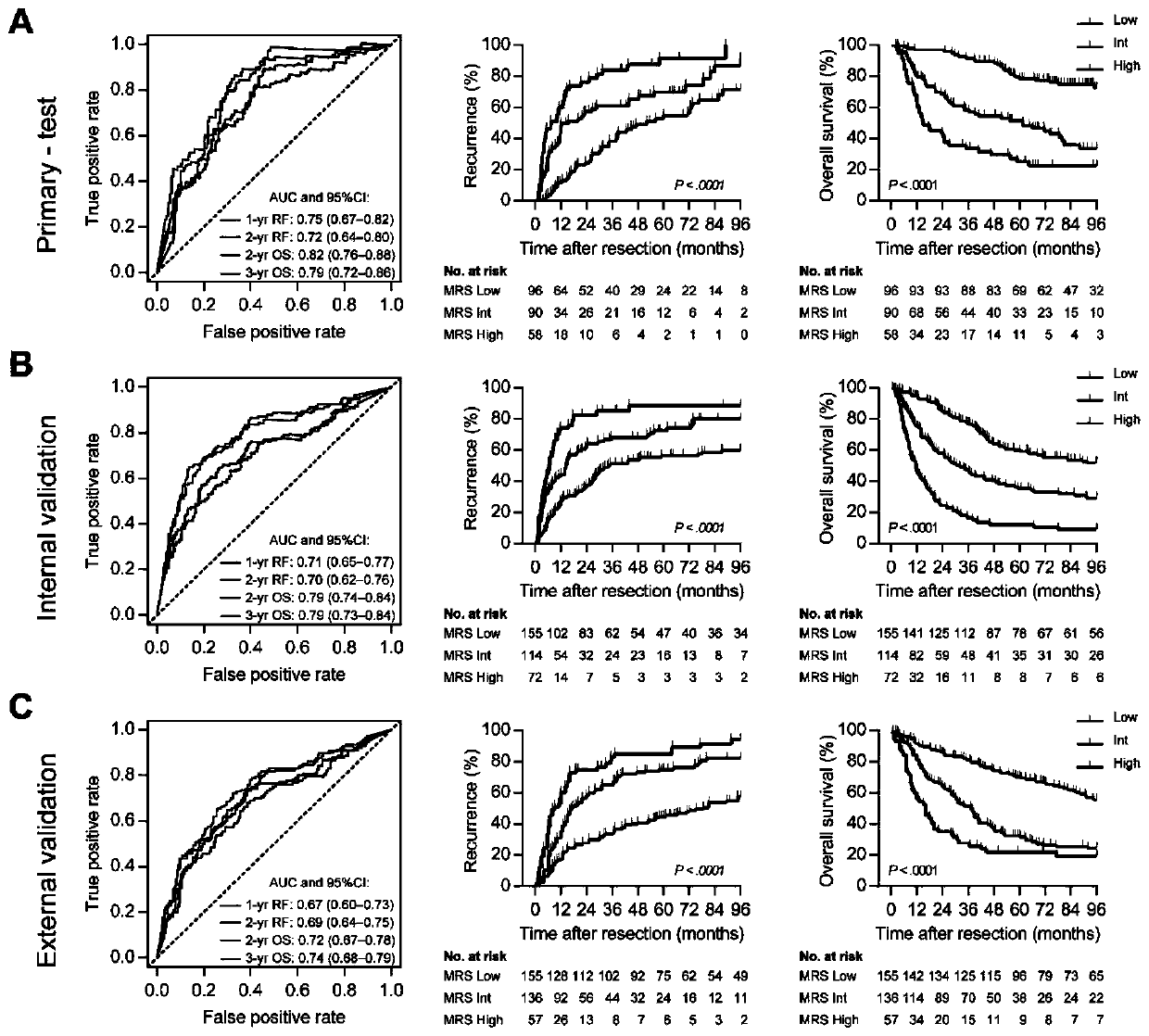
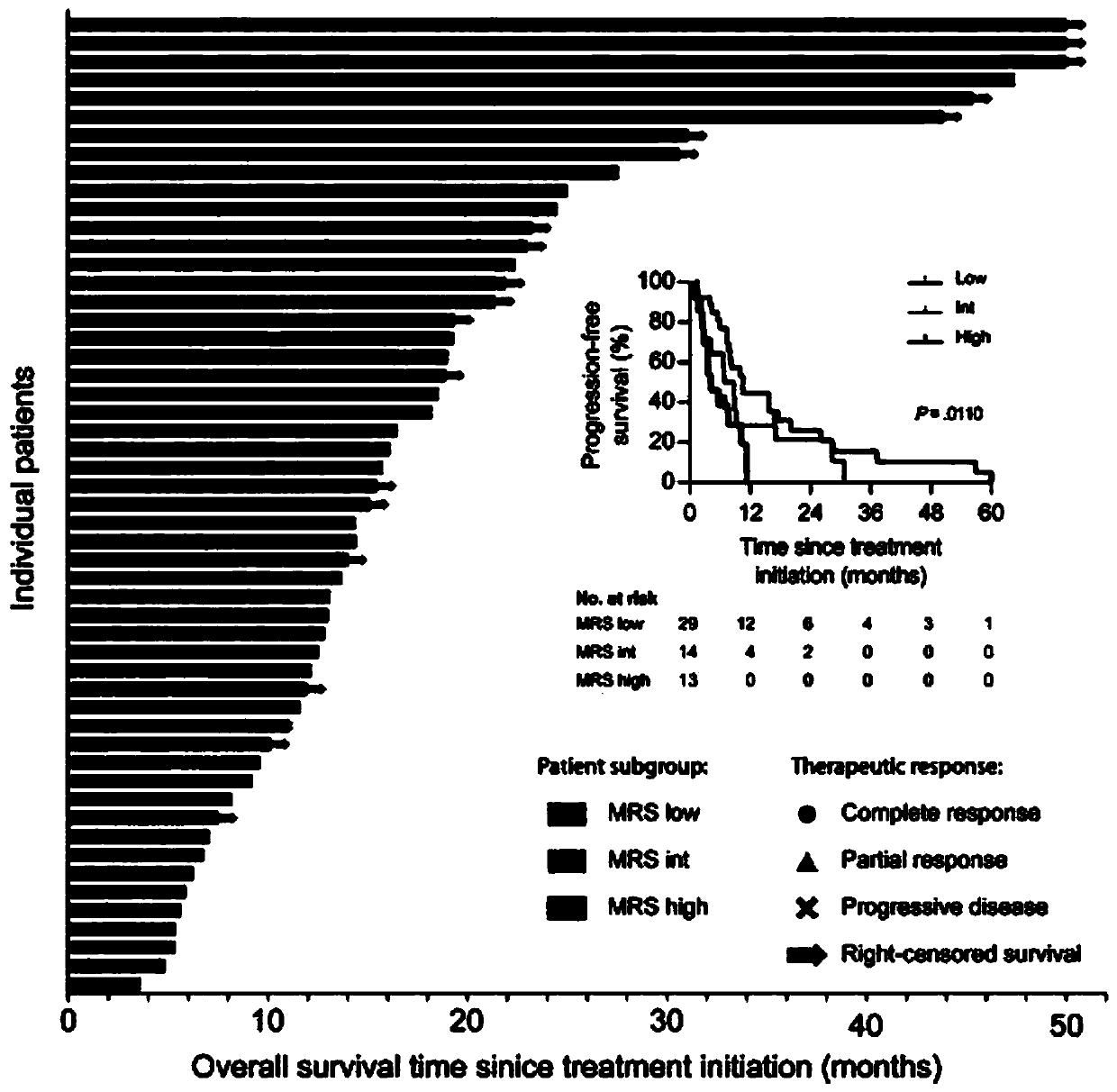
Marker for prognosis prediction of liver cancer based on CD11b and CD169 protein molecules
InactiveCN111122865AImprove reliabilityStrong specificityDisease diagnosisProtein moleculesLymphocyte
The invention discloses a marker for prognosis prediction of liver cancer based on CD11b and CD169 protein molecules. The marker is MRS, and the MRS=0.161*CD11bT-0. 106*CD169T+35. According to the MRSprovided by the invention, a marker of myeloid cells instead of a marker of lymphocytes is utilized; the prediction ability of postoperative recurrence and survival of a patient undergoes multi-center and large-sample verification, and the reliability is higher; the marker can further be used for predicting the curative effect of subsequent sorafenib or TACE treatment on postoperative recurrent patients; prognostic indexes with high prognosis specificity, high sensitivity and high clinical application value can be obtained only by detecting the CD11b+cell density and the CD169+cell density inthe liver cancer tissue, and the detection method is simple and convenient.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
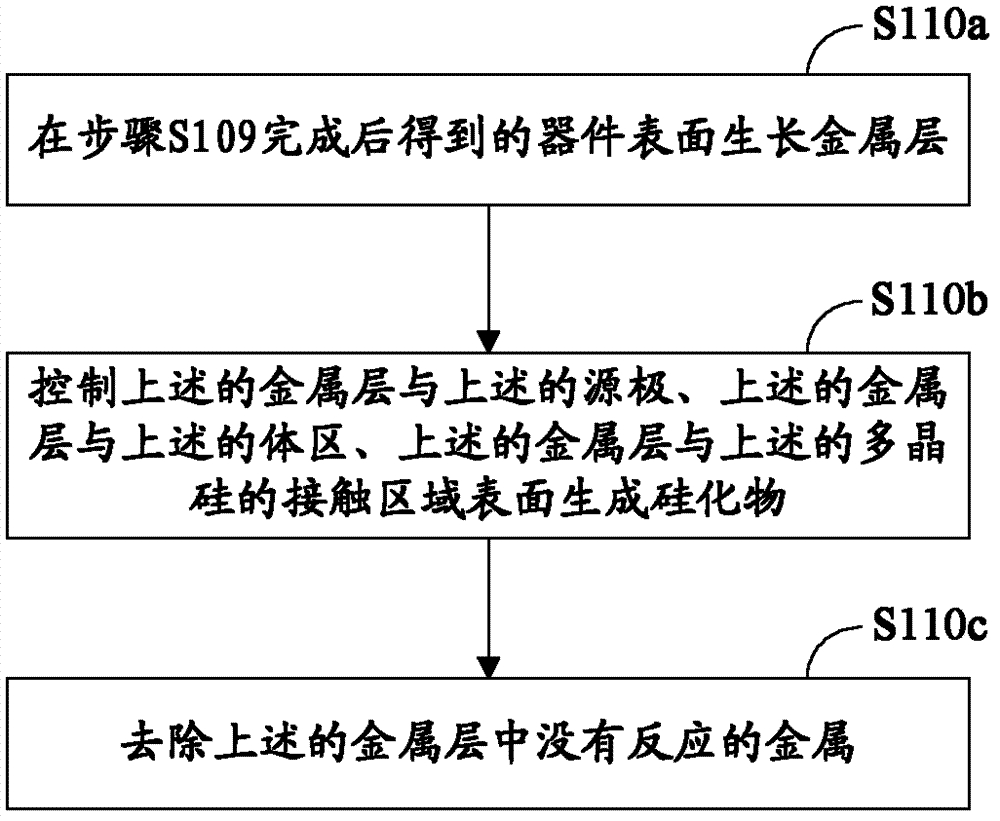
Trench VDMOS device and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN103367145AHigh densityReduce the number of photolithography layersSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesEngineeringBody region
The invention discloses a manufacturing method of a trench VDMOS device. The method comprises the steps of manufacturing a gate structure of which the top end is higher than the plane of an epitaxial layer; generating a body region and an initial source region through injection on the epitaxial layer; generating a flank by using a raised side wall of a polycrystalline silicon; etching the surface of a device to generate a source region, wherein the height of the side wall makes a part, covered by the flank, of the initial source region not etched in the etching process of the acquired source region; growing a metal layer on the surface of the device; controlling contact surfaces between the metal layer and a source electrode, between the metal layer and the body region and between the metal layer and the polycrystalline silicon to generate a silicide; and removing metal failing to react in the metal layer. The invention further provides a trench VDMOS device. As photo-etching is not required when the source region is manufactured and no contact hole needs to be manufactured, the number of photolithographic layers is reduced. Influence and restriction of factors such as photolithographic resolution and registration accuracy to the technological processes are reduced, the cellular density can be increased, and the manufacturing cost is lowered.
Owner:PEKING UNIV FOUNDER GRP CO LTD +1
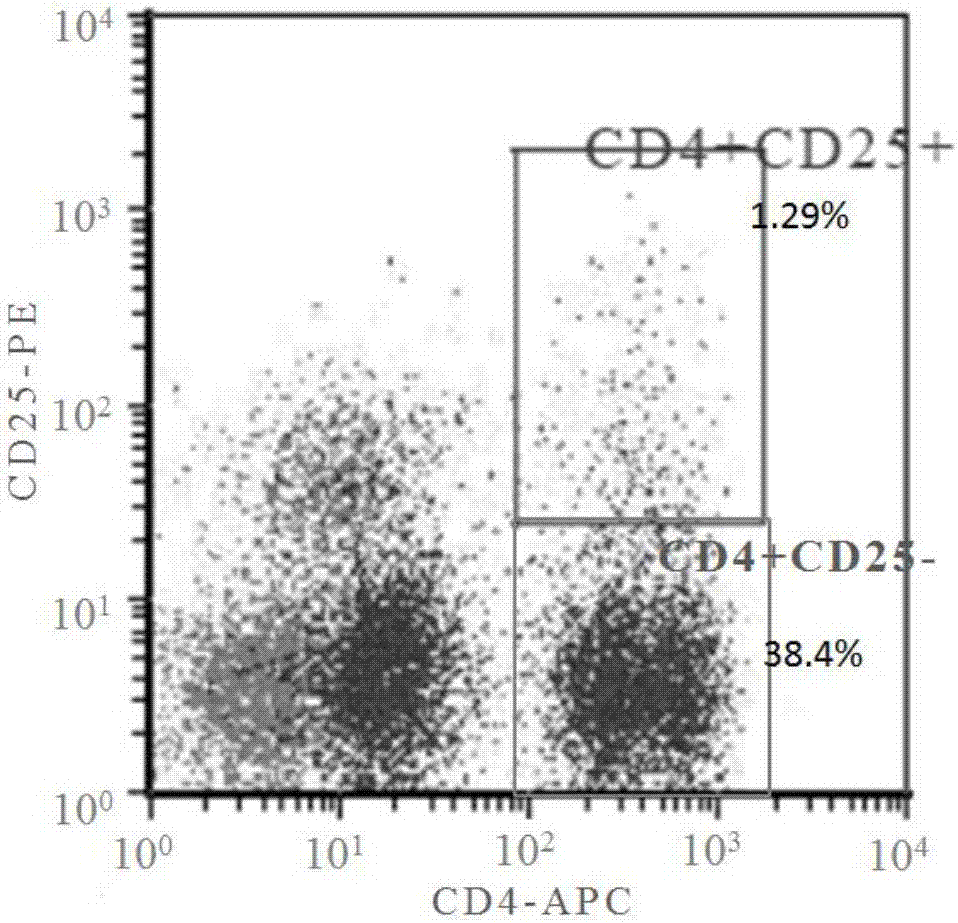
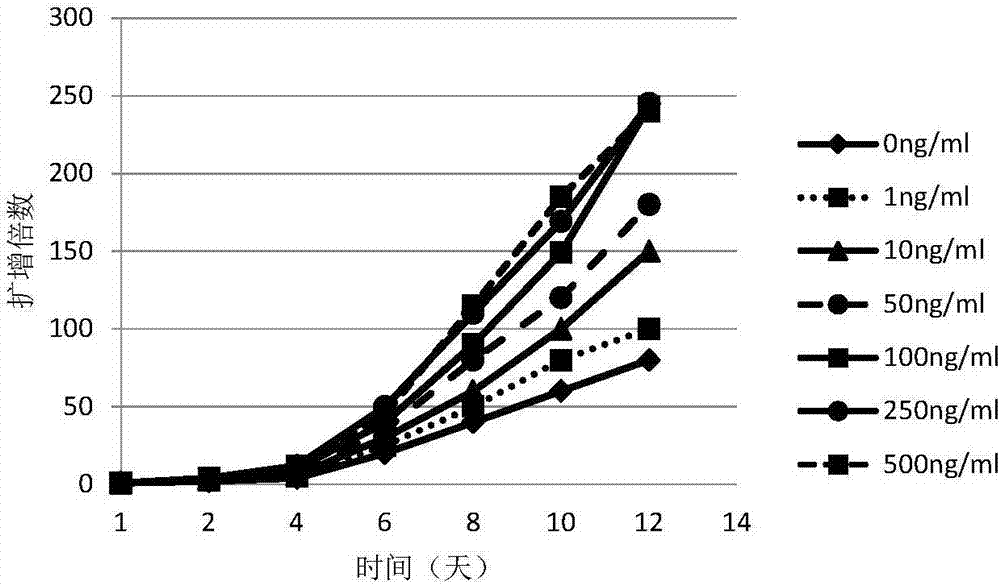
In-vitro amplification method of cord blood Treg cells
ActiveCN107164324AHigh purityIncrease multipleBlood/immune system cellsCell culture active agentsCord blood stem cellT reg cells
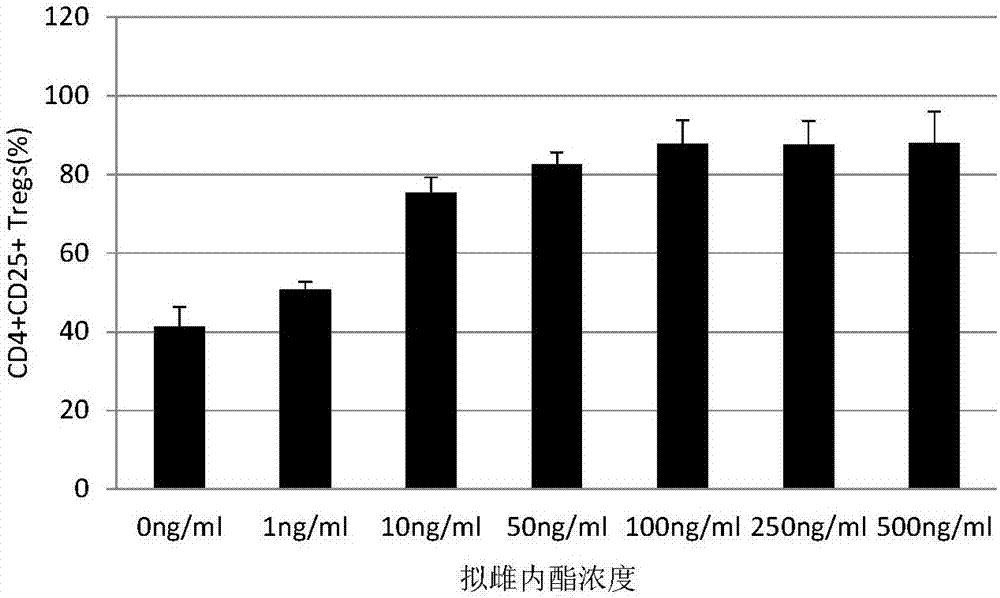
The invention relates to an in-vitro amplification method of cord blood Treg cells, comprising the steps of S1, isolating mononuclear cells; S2, adjusting cellular density, inoculating to a culture flask, and adding inactivated plasma; on the first day, adding coumestrol, TGF-beta, CD3 / CD28 monoclonal antibody and IL-2; S3, on the fourth day, supplementing a culture medium, adding inactivated plasma, coumestrol and TGF-beta, and keeping the final concentration constant; S4, on the sixth day, supplementing the culture medium, and keeping the final concentrations of other components unchanged; S5, on the ninth day, supplementing the culture medium, and keeping the final concentrations of other components unchanged; S6, on the twelfth day, collecting cells. The amplification of CD4, CD25 and Tregs is induced under the coaction of coumestrol and TGF-beta, the amplifying efficiency is high, and high-purity Treg cells can be acquired without pre-purification.
Owner:深圳市沃英达生命科学有限公司
Micro-heterotypic cell-loaded alginic acid gel, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN111195371AGuaranteed independencePromote rapid formationProsthesisBiologic scaffoldTissue repair
The invention discloses a micro-heterotypic cell-loaded alginic acid gel, and a preparation method and an application thereof. The micro-heterotypic cell-loaded alginic acid gel is of a four-layer structure and sequentially comprises cells and a nutrient solution, inner-layer heterotypic gel, a drug solution and outer-layer gel from inside to outside. The inner-layer heterotypic gel of the microheterotypic cell-loaded alginic acid gel provides a biological scaffold for directional propagation of cells; the drug solution enables the cells to generate functional differentiation to form a cell population of specific tissues / organs; and the outer-layer gel ensures the relative independence of internal substances. According to the preparation method , the micro-special-shaped carrier cell gel with good uniformity can be rapidly formed in a large flux, the cell-loaded gel with different functions can be prepared by changing cell types, cell density and medicines contained in a water phase, the cell-loaded gel can be widely applied to transplantation of various engineering organs and repair of damaged organs and tissues, and different functional requirements of the engineering organs aremet.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Formula of density gradient solution used for tissue and cell purification
InactiveCN105886454AGood separation resultEasy to separateCell dissociation methodsPancreatic cellsSodium DiatrizoateAdditive ingredient
The invention provides a formula of a density gradient solution used for tissue and cell purification. According to the formula, the density gradient solution contains density gradient ingredients, such as iohexol, sodium diatrizoate and iodixanol, wherein the substances capable of improving the osmotic pressure and preventing tissue and cell edema, such as raffinose and mycose are added, then magnevist solution is also added, and culture solutions such as DMEM culture solution and buffer solutions such as HBSS buffer solution are adopted as the solvents. With the adoption of the formula, the problems that at present, the density gradient separation for tissues and cells of large animals and human beings is difficult, and the separated tissues and cells are low in activity are solved, and the cells and tissues with different densities after dissociation or mechanical dispersion can be separated by the density gradient solution under the centrifugal condition. Due to the design of the density gradient solution, a certain application value is achieved for promoting the domestic and overseas study on the separation of tissues and cells. The principle is simple, the preparation is easy, the use is convenient, and the large-scale preparation can be realized; due to the declaration of the patent, a foundation is laid for the development and application of the density gradient separating solution.
Owner:WENZHOU YIKANG CELL TRANSPLANTATION CO LTD
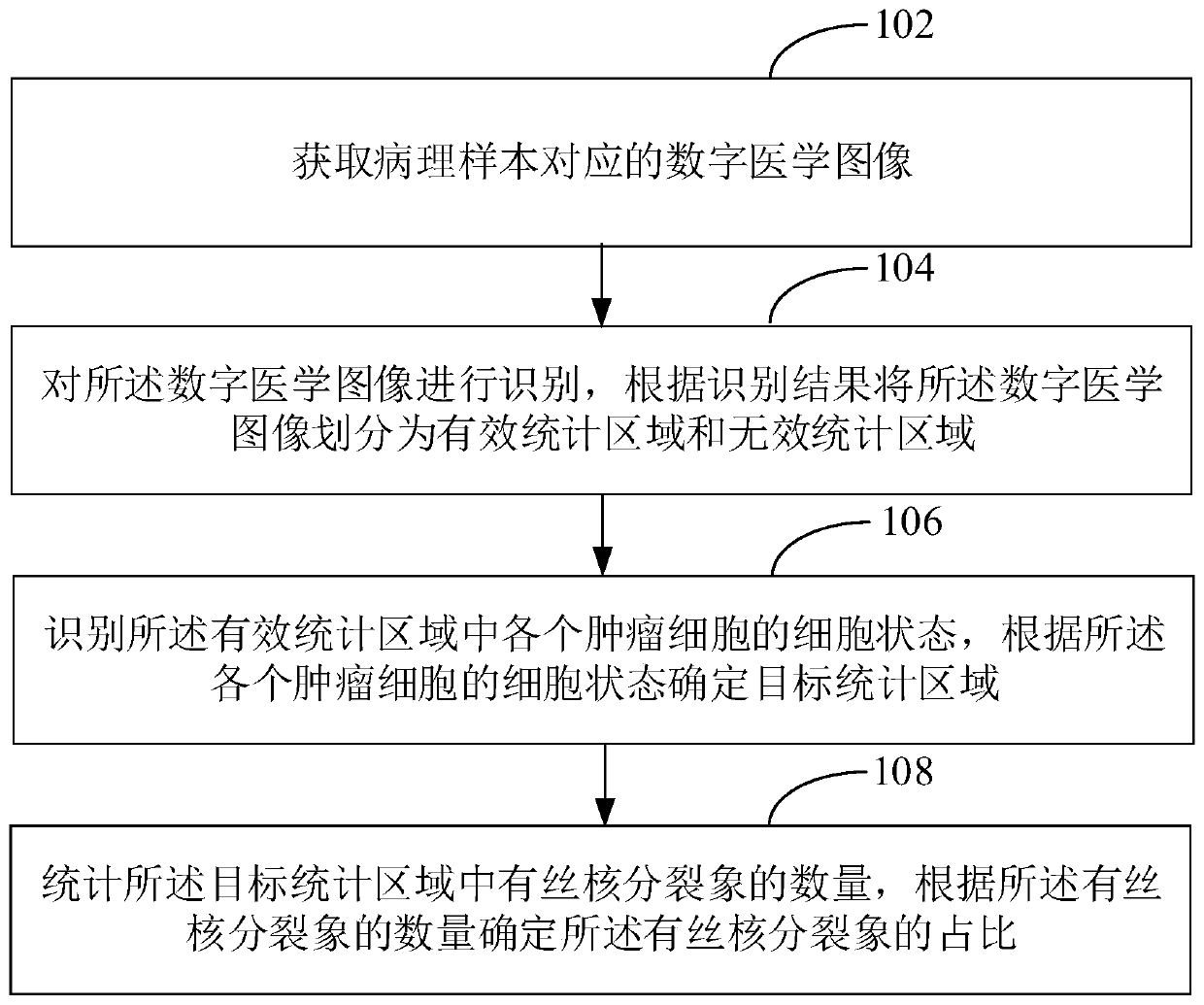
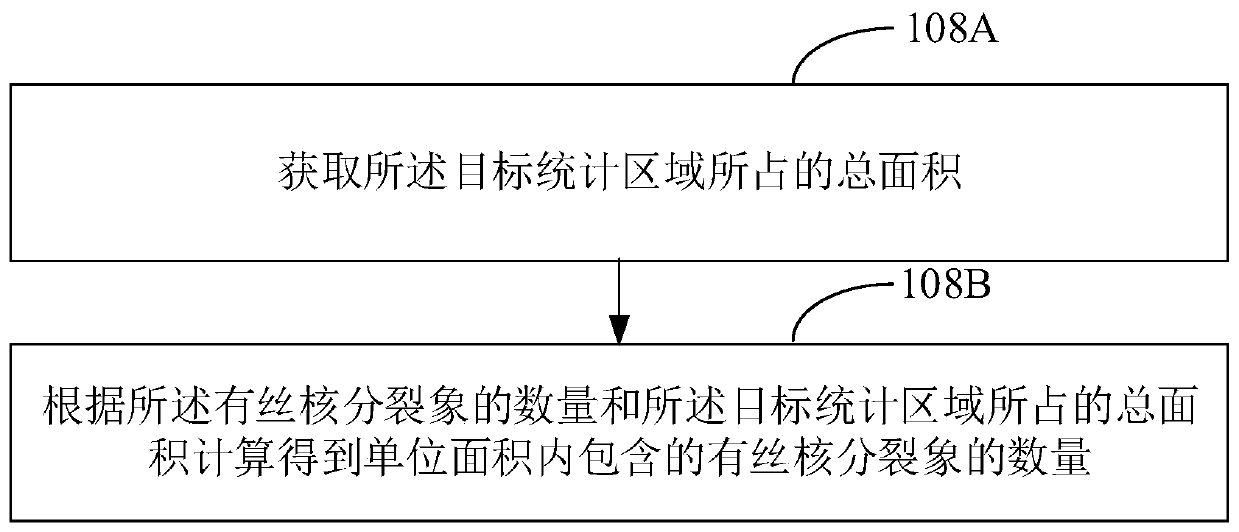
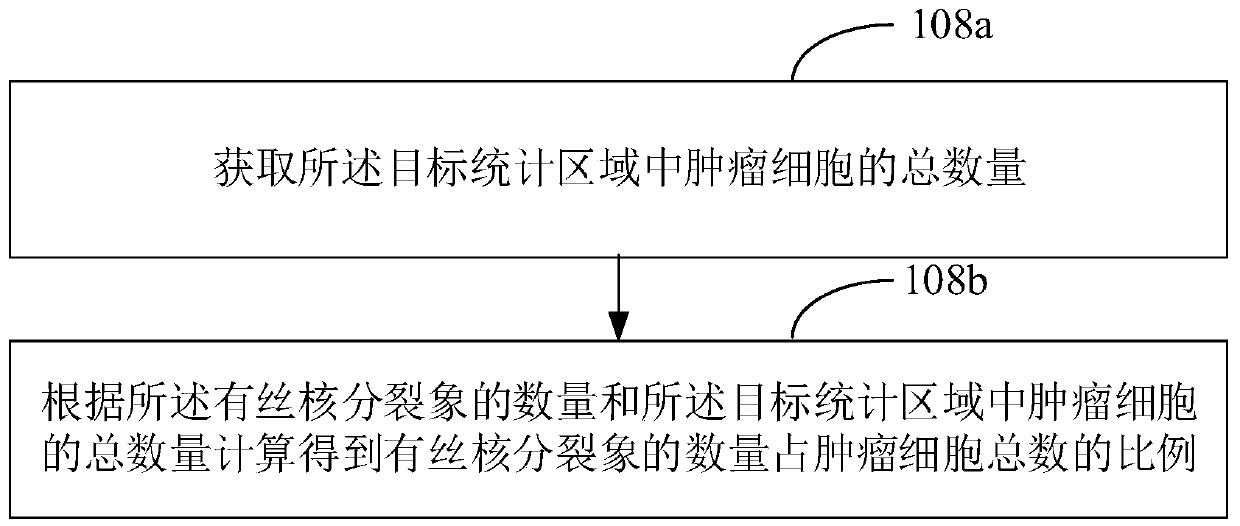
Digital pathological section mitotic image statistical method, device, equipment and medium
The embodiment of the invention discloses a digital pathological section mitotic image statistical method. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring a digital medical image corresponding toa pathological sample; identifying the digital medical image, and dividing the digital medical image into an effective statistical area and an invalid statistical area according to an identification result; identifying the cell state of each tumor cell in the effective statistical area, and determining a target statistical area according to the cell state of each tumor cell; and counting the number of the filament nuclear split images in the target statistical area, and determining the proportion of the filament nuclear split images according to the number of the filament nuclear split images.According to the digital pathological section mitotic image statistical method, the number of mitotic images in the statistical target statistical area is determined; therefore, diagnostic junction deviation caused by factors such as microscope specification, tumor stromal ratio and cell density is eliminated, and meanwhile, due to the combination of computer recognition and machine vision, rapidand accurate quantitative detection and analysis can be realized.
Owner:GUANGZHOU KINGMED DIAGNOSTICS CENT
Enhanced DCIK (dendritic cell activated cytokine-induced killer) cell preparation method and cell preparation
ActiveCN103966163AIncrease the value-added multiplePromote conversionMammal material medical ingredientsBlood/immune system cellsPeripheral blood mononuclear cellDendritic cell
The invention discloses an enhanced DCIK (dendritic cell activated cytokine-induced killer) cellpreparation method and cell preparation. The method comprises the steps as follows: a PBMC (peripheral blood mononuclear cell) is separated from collectedperipheral blood of a patient; the PBMC is placed in a blood-free medium for culture to obtain nuclear cells with the concentration of 1-3*10<6> / ml, IFN-gamma (interferon-gamma), phytohemagglutinin and PGE2 (prostaglandin E2) are added, and the mixture is transferred into a culture flask or a culture bag to be cultured for 24 h; then a CD3 monoclonal antibody, IL-2 (interleukin-2), IL-1alpha, IL-4 and a GM-CSF (granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor) are added, the mixture is cultured for 3-5 days, the cell density is controlled in a range of 1-6*10<6> / ml, the mixture is cultured for 14-21 days continuously, and an enhanced CIK cell is obtained through centrifugal collection. The enhanced DCIK cell preparation comprises the enhanced DCIK cell, human blood albumin, the IL-2, amino acid, vitamins and inorganic salt. The preservation time of the DCIK cell preparation is substantially longer than those of preparations in previous patents and is prolonged to 36 hours from 6 hours under the room temperature condition. The preparation is higher in reliability in clinical applications, and the safety is effectively guaranteed.
Owner:武汉光谷高新科技发展有限公司
Serum-free suspension domestication method of Vero cells
InactiveCN110904025ALarge number of proliferation and expansionThe cultivation process is easy to scale upCulture processArtificial cell constructsBiotechnologyPancreatinum
The invention relates to the field of biology. A serum-free suspension domestication method of Vero cells comprises the steps of step I, performing adherent culture on the Vero cells until the convergence rate reaches 80%, discarding supernatant, adding D-PBS free from calcium and magnesium ions, and performing washing; step II, discarding the D-PBS, adding pancreas enzymes, discarding trypsinization liquid, remaining a few pancreas enzymes which are enough to cover cells, performing incubation until the cells become round or performing incubation for definite time, and patting the bottom of aflask to dissociate cells; step III, performing re-suspension with a Vero-S suspension serum-free culture medium; step VI, discarding the supernatant, and performing re-suspension with Vero-S suspension serum-free culture medium; step V, diluting the density of the cells, performing inoculation to a disposable shake flask, and performing culture; step VI, when the density of the cells reaches 3*10<6> cells / ml, performing cell passage; and step VII, once the density of the cells can reach 3*10<6> cells / ml or above in 48h for continuous 10 generations or above and the motility rate of the cellsis not less than 95%, thinking that the cells are adapted to suspension culture.
Owner:上海源培生物科技股份有限公司
Hyperuricemia cell model, building method thereof and application of model to uric acid reduction efficacy evaluation
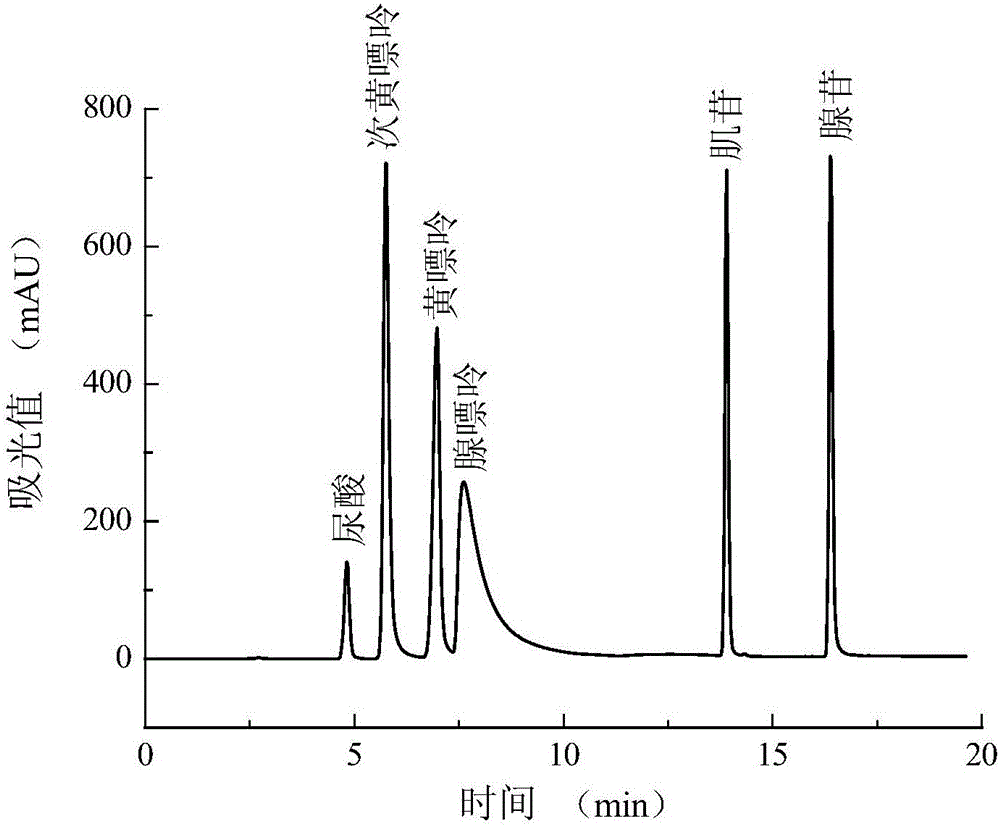
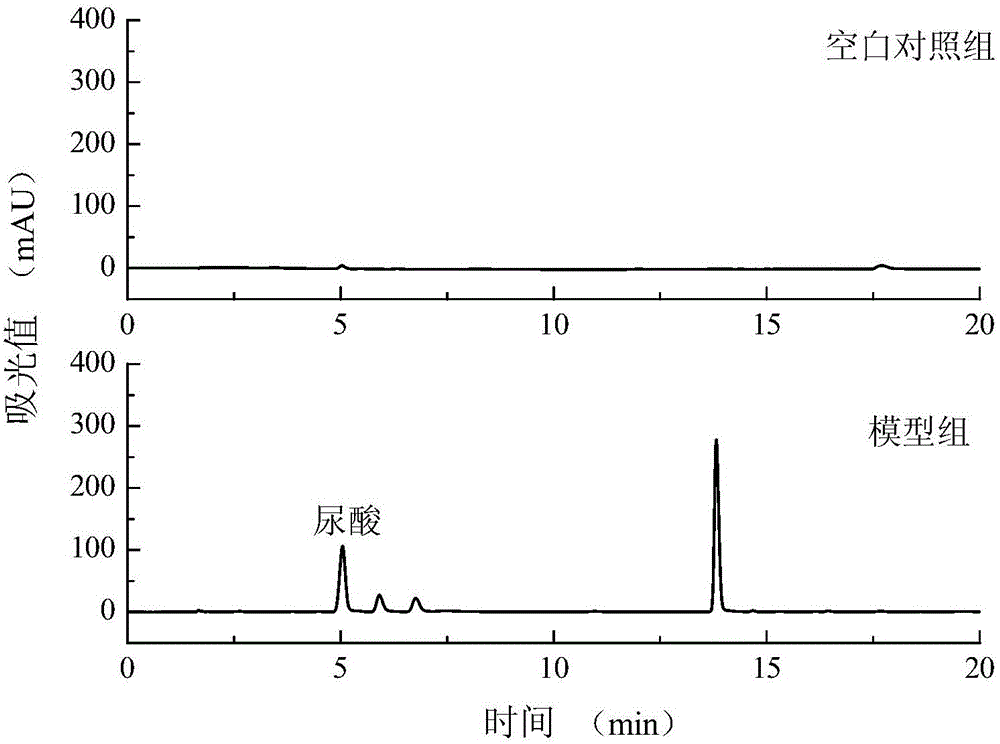
ActiveCN106190953AShort cycleEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementCulture processAdenosinePhosphate
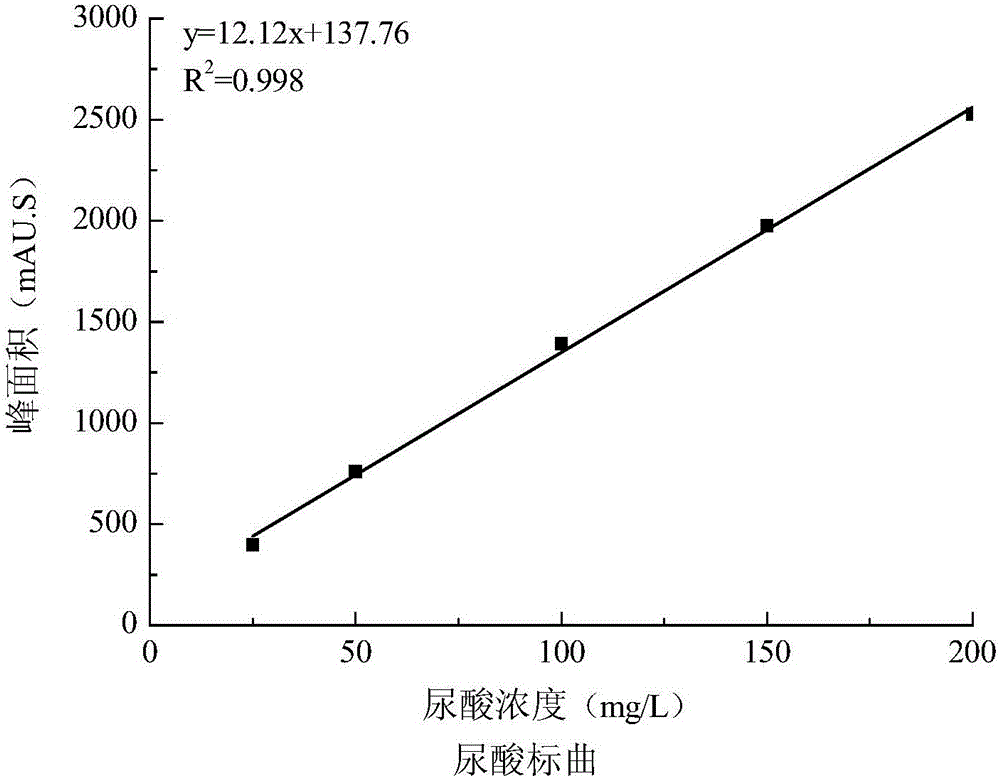
The invention relates to a hyperuricemia cell model, a building method thereof and an application of the model to uric acid reduction efficacy evaluation. The building method includes the steps: (1) taking human proximal tubular epithelial cells (HK-2 cells) as model making cells, dissociating the HK-2 cells in a logarithmic phase to prepare cell suspension, adjusting cell density and culturing the cells in a cell culture box for 12-36 hours after planking; (2) removing cell supernatant, cleaning the cells with PBS (phosphate buffer solution) for 2-3 times, adding adenosine and continuing incubation for 12-36 hours; (3) adding xanthine oxidase into the cell supernatant, continuing culture for 12-36 hours, taking out the cell supernatant, and performing efficient liquid detection of uric acid content. Experimental results indicate that the hyperuricemia cell model can be obtained by the aid of the inductor adenosine and the xanthine oxidase. The hyperuricemia cell model is built for the first time, uric acid reduction efficacy of a medicine can be simply and rapidly analyzed, and the model is of great significance for gout medicine research.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Microcellular foam film-coated packaging paper material and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to film-coated packaging paper and a preparation method thereof, in particular to a microcellular foam film-coated packaging paper material and a preparation method thereof. Thematerial is prepared from, by weight, 70-90 parts of polyvinyl alcohol, 1-10 parts of a melt reinforcing agent, 1-10 parts of a flow modifier, 1-10 parts of a foaming agent, 0.5-3 parts of an anti-adhesion agent, 1-5 parts of a foaming auxiliary agent and 0.5-2 parts of other auxiliary agents. The material is excellent in melt forming and stretching performance, small in foam hole diameter and high in cellular density, the foam film thickness can reach 20micron or below, and a product is light in weight, high in tensile strength and tear resistance and excellent in heat resistance and can be applied to the field of packaging with the requirement of high temperature of 80 DEG C or above; in addition, the product is environmentally friendly and biologically degradable; the product is excellent in oil substance barrier property; furthermore, due to high paper adhesiveness, a film surface aftertreatment process is avoided, and high productivity is realized.
Owner:NANJING JULONG SCI&TECH CO LTD
Method for inducing neural stem cells in vitro to directionally differentiate into neurons
ActiveCN110699321APromotes purity differentiationSimple methodNervous system cellsCell culture supports/coatingSingle cell suspensionNeurosphere
The invention relates to a method for inducing neural stem cells in vitro to directionally differentiate into neurons. The method includes: using fetal rat brain tissue of an ICR (institute of cancerresearch) pregnant rat as a raw material to carry out primary culture on neural stem cells so as to obtain neurospheres, centrifuging to remove supernate, washing precipitate with PBS (phosphate buffered solution), allowing digestion to occur, adding a culture solution to terminate the digestion, centrifuging to remove supernate, adding a growth culture solution into the precipitate, carrying outsecondary culture on the neural stem cells, digesting the fourth-generation or fifth-generation neurospheres to prepare a single-cell suspension, spreading the single-cell suspension to a 12-orifice cell culture plate coated with poly-l-ornithine and laminin under the cell density of 5*104 to 5*106 cells per mL, culturing overnight, adding a differentiation culture solution on the second day, andcarrying out differentiation culture to obtain mature neurons. The method is simple and well repeatable, allows the differentiation ratio of neural stem cells to neurons to be evidently increased, canpromote purity differentiation of neurons and helps attain the neurons with good growth state and high purity.
Owner:XINYANG NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Loquat fruit quality evaluation and prediction method for guiding loquat sales strategy
The invention relates to a loquat fruit quality evaluation and prediction method for guiding a loquat sales strategy, and solves the problem that a current loquat fruit evaluation method can only reflect the current quality state of fruits and cannot predict and judge the future change trend of the quality of the fruits in advance. According to the method, the equatorial plane of the loquat fruit is subjected to slice dyeing, the lignified cell density P of the equatorial plane of the loquat fruit is counted to guide the current value of the loquat fruit in the batch, the lower the P value is, the higher the current selling price is, the development stage of each lignified cell is counted to predict the quality change trend T of the loquat fruit in the batch, the warehousing strategy is guided according to the T value, the loquat fruits are suitable for storage and transportation if the T value is high, and the loquat fruits should be sold as soon as possible if the T value is low. According to the invention, the current quality of the loquat fruits is evaluated according to the density of the lignified cells, and the quality change trend of the batch of loquat fruits is predicted according to the development stage of each lignified cell, so that the sales strategy of the loquat fruits is guided.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for preclinical testing of immunomodulatory drugs
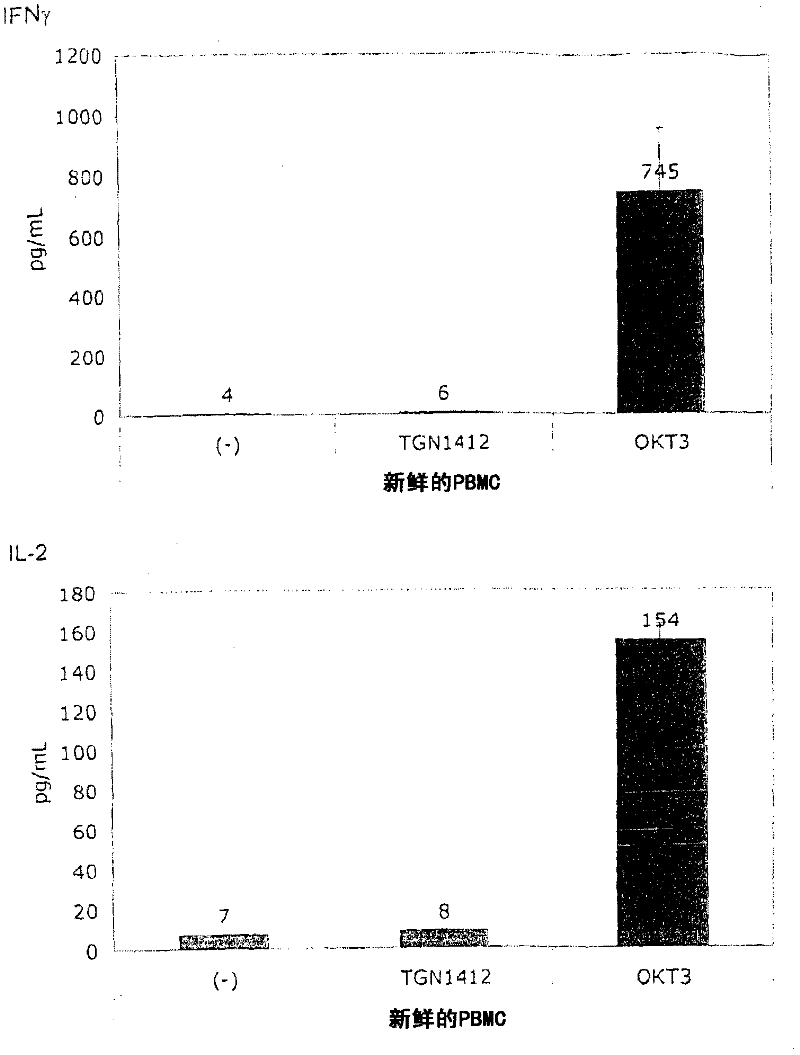
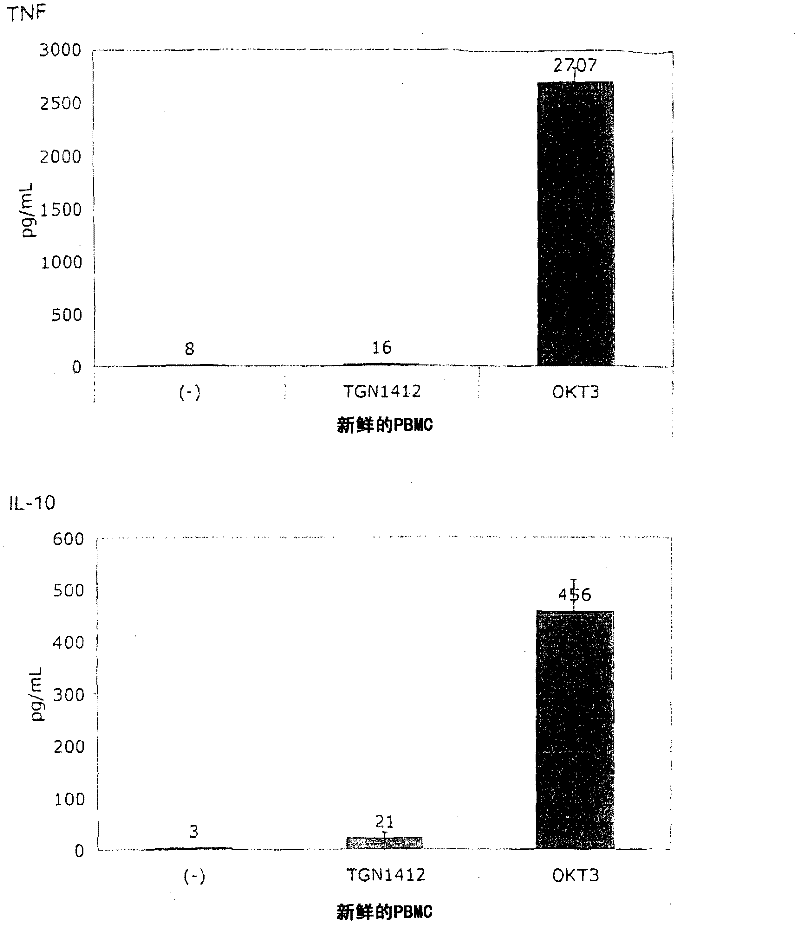
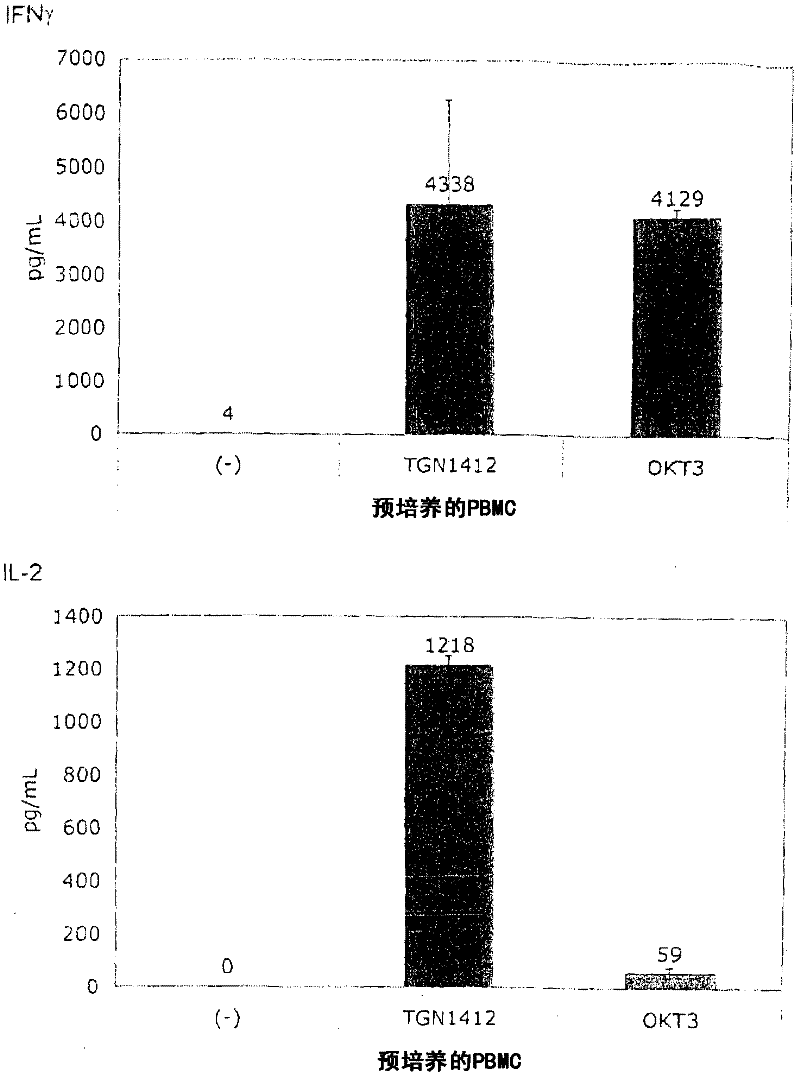
The invention teaches a method for testing a prospective or known immunomodulatory drug for T-ceil activation, comprising the steps of contacting in-vitro a peripheral blood mononuclear cell (PBMC) culture with a predetermined amount of the prospective or known immunomodulatory drug and observing the PBMC culture for T-ceil activation using a readout system, upon contact with the prospective or known immunomodulatory drug, wherein the ceil density of a PBMC preculture is adjusted such that cell-cell contact of the PBMC is enabled and wherein the PBMC preculture is cultured for at least 12h.
Owner:THERAMAB
Methods of Disrupting Quorum Sensing to Affect Microbial Population Cell Density
InactiveUS20110124522A1High volumetric productivityReduce deliveryBacteriaLibrary screeningMicroorganismMicrobiology
The present invention relates to the modulation of quorum sensing mechanisms in a microorganism for the purpose of exploiting the fermentation capabilities of the microorganism.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER USA
Grid-controlled vertical double-diffusion metal-oxide semiconductor field effect transistor
ActiveCN104009088APrevent punch-throughEasy to shareSemiconductor devicesDouble diffusionEngineering
The invention discloses a grid-controlled vertical double-diffusion metal-oxide semiconductor field effect transistor. A channel region and a JFET region of the transistor are wrapped in gate electrodes from the upper surface, the front side face and the rear side face, so that when the transistor is powered on in the forward direction, majority carrier accumulation layers are formed on the channel region of a device and the JFET region of the device respectively through the expanded grid electrodes, the on resistance can be decreased remarkably, and the output current can be increased. Moreover, due to the capability of folding grids for controlling electric charges of the JFET region, the punch through problem caused by the shrinkage of the size of the JFET region can be avoided, so that the charge sharing effect of cellular cells is promoted, vertical electric field distribution is optimized, and the puncture voltage of the device is increased. Besides, cellular miniaturization is facilitated due to the shrinkage of the size of the JFET region, cellular density is increased, and thus the larger current can be obtained.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
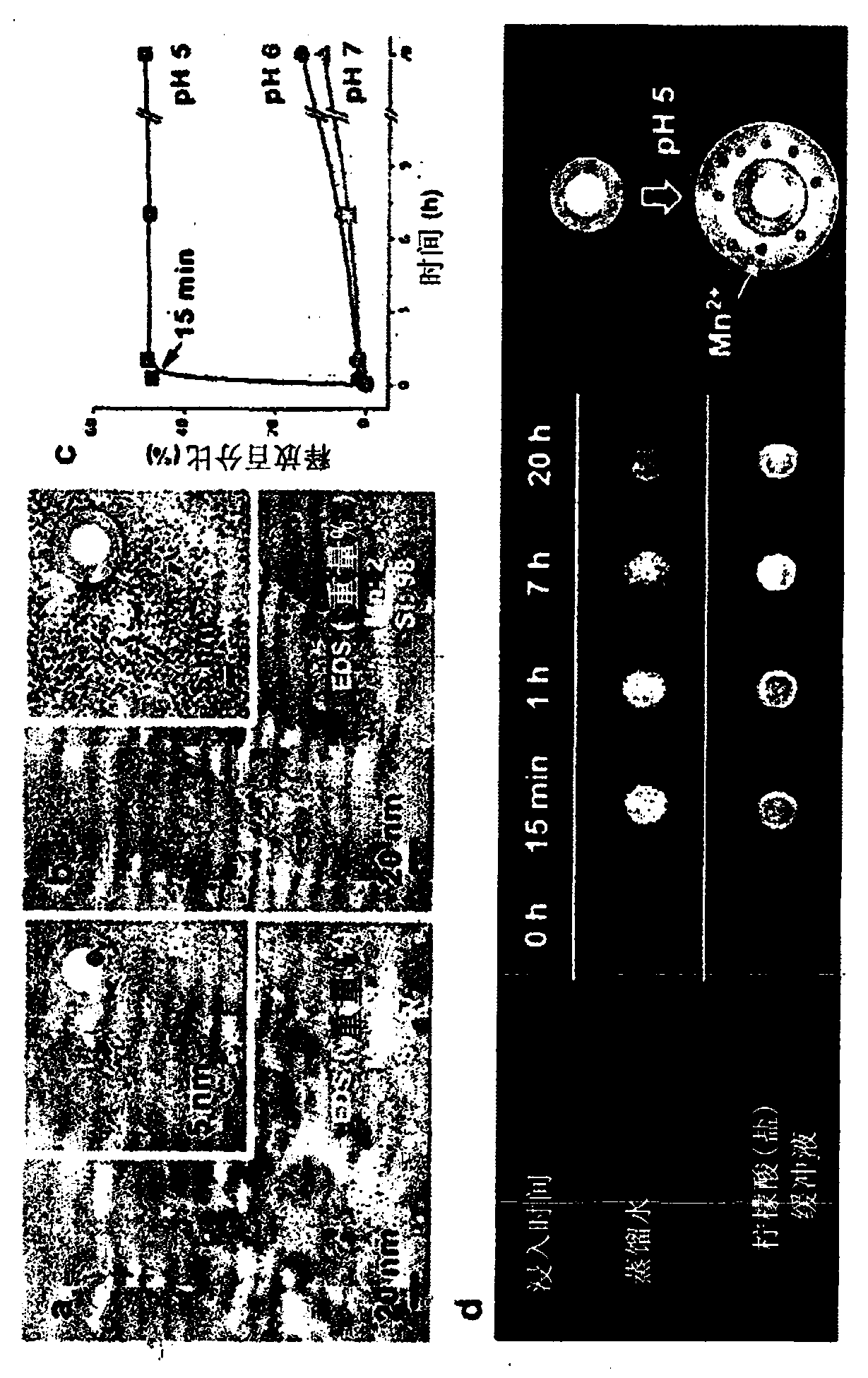
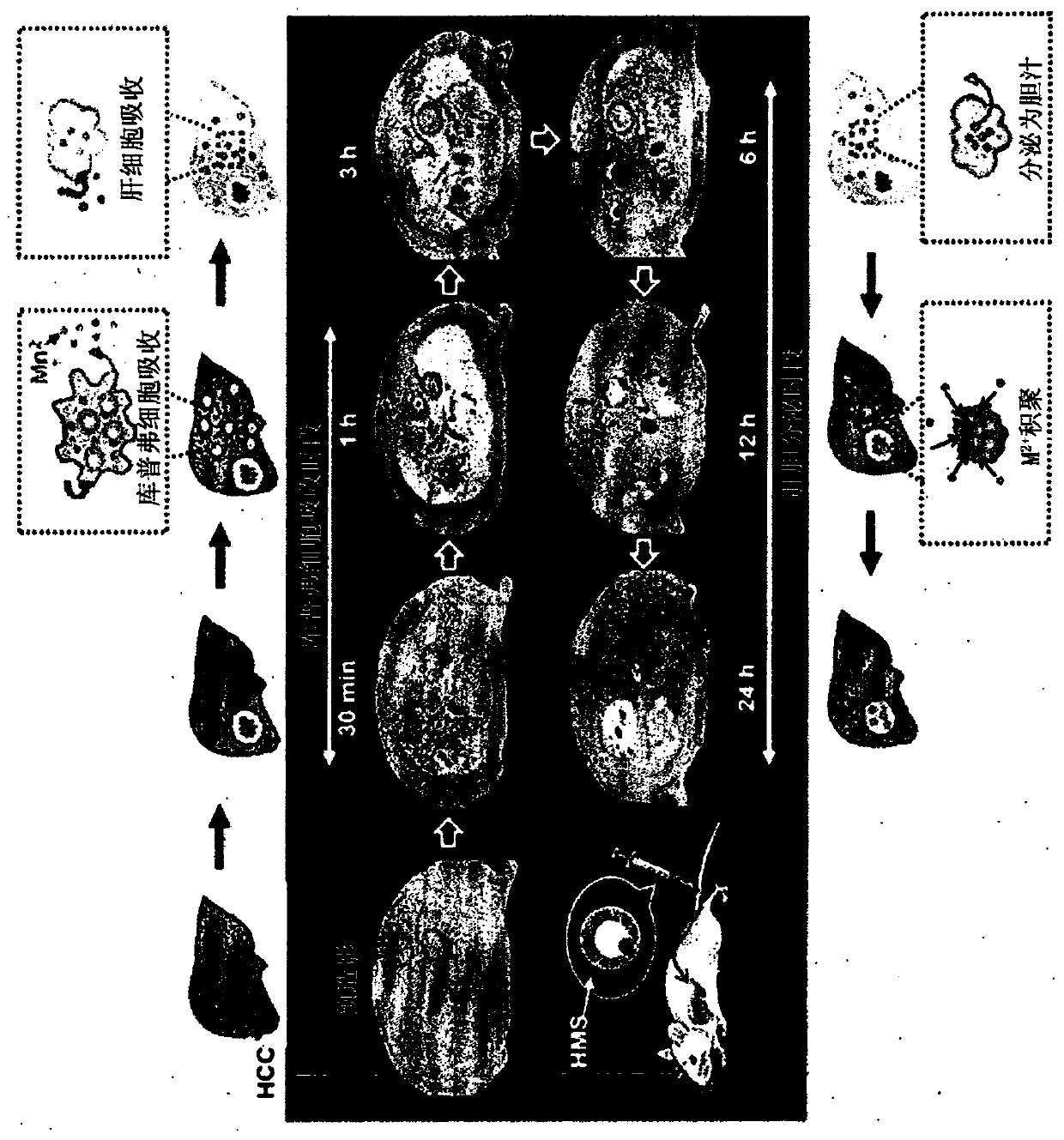
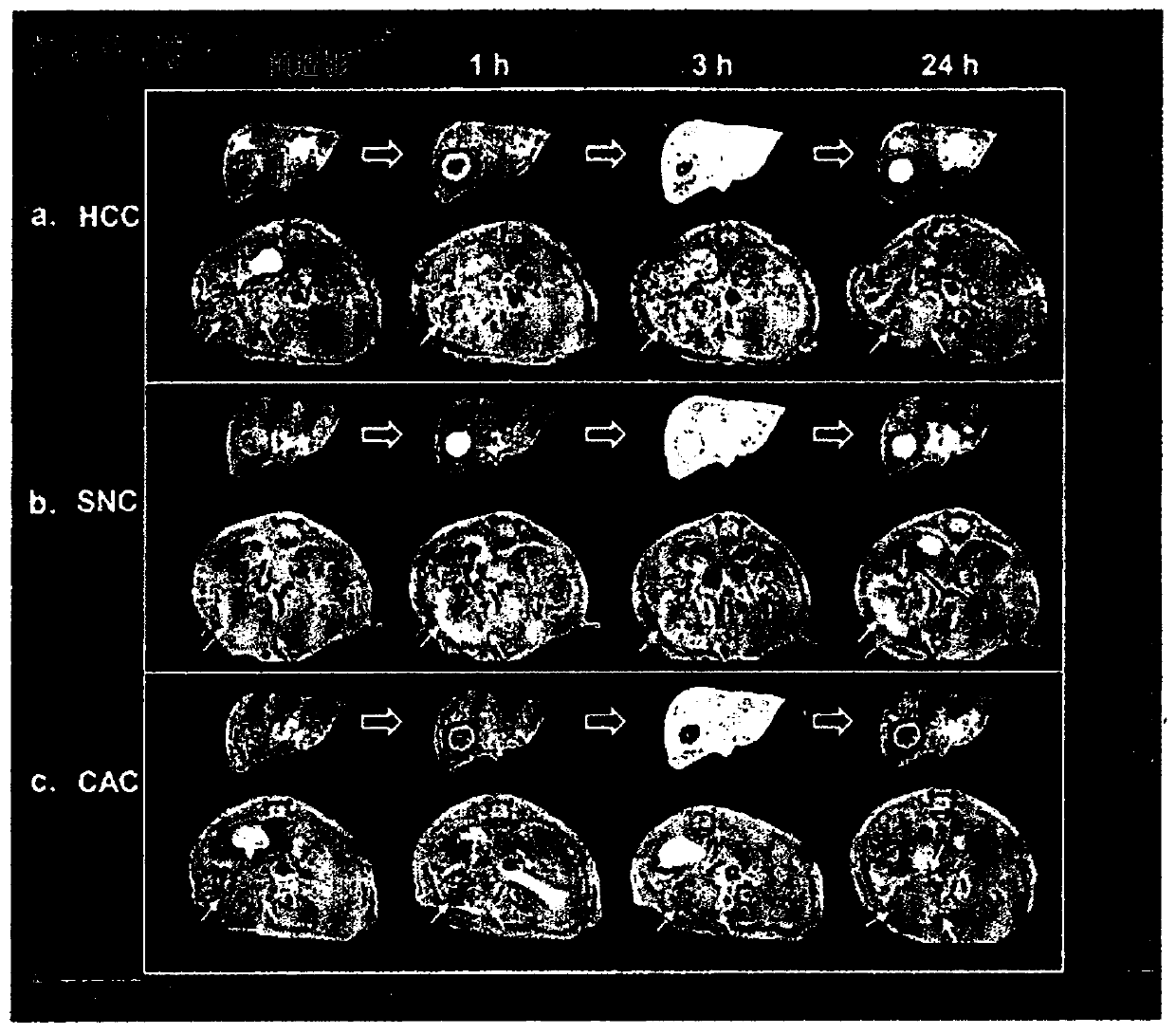
Diagnostic imaging hepatic tissue-specific contrast medium comprising manganese silicate nanoparticle
ActiveCN110505889AInhibition distributionNanomedicineNMR/MRI constrast preparationsDiseaseTherapeutic effect
The present invention relates to a diagnostic imaging manganese silicate hepatic tumor-specific MRI contrast medium which releases manganese ions (Mn2+) in an acidic condition and a method for characterizing a hepatic tissue, using the same. Exhibiting different patterns of T1-weighted imaging including vascularity, cell density, mitochondrial activity, hepatocellular affinity, etc., according totissue specificity of normal hepatic tissues and diseased liver tissues (particularly hepatic tumor), within relatively short period of time, the present invention allows disease-specific characteristics of hepatic tumor to be detected at an appropriate time through the analysis of such T1-weighted imaging. Particularly, the present invention is expected to be very effectively used in discerning and diagnosing kinds of hepatic tumor or in determining therapeutic effects and further to be helpful in diagnosing diseases generated in organs other than the liver according to tissue specificity.
Owner:POSTECH ACAD IND FOUND +1
Determining method of content of antigen virus of inactivated vaccine of recombinant bird flu cellgen
ActiveCN102703602AReduce mistakesOperational benchmarks are reliableMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesCanine kidneyWater baths
The invention provides a novel determining method of the content of antigen virus of an inactivated vaccine of a recombinant bird flu H5N1 cellgen. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) preparation of MDCK (madin darby canine kidney), wherein 1.5ml of MDCK frozen cell with density of 2.0*10<6> is extracted and put in a water bath at a temperature of 37 DEG C, 10 to 15ml of cell culturefluid is added to culture for 72 hours, the cell is digested with 0.25 percent EDTA (ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid)-pancreatin, the cell nutrient fluid is diluted into MDCK cell suspension of 4.0*10<5>, the MDCK cell suspension is spread to a 96-mesh cell plate in a cell density of 40,000 per pore (0.1ml per pore), the cell plate is put in a CO2 culture case at a temperature of 37 DEG C and humidity of 5 percent to culture for 24 hours to form a compact monolayer for later use; and (2) inoculation of a recombinant bird flu H5N1 antigen, wherein recombinant bird flu H5N1 cellgen antigens in different batches are extracted and respectively added into the compact monolayer with 100mu l in each pore, and 100mu l of cell maintenance fluid is added to culture for four days, and a TCID50 (50% tissue culture infection dose) value is calculated by the number of cytopathic pores in a Reed-Muench method. The method is applicable to a cellgen vaccine for detecting the virus content by an erythrocyte agglutination test, which means that different viruses use corresponding sensitive cells.
Owner:吉林冠界生物技术有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com