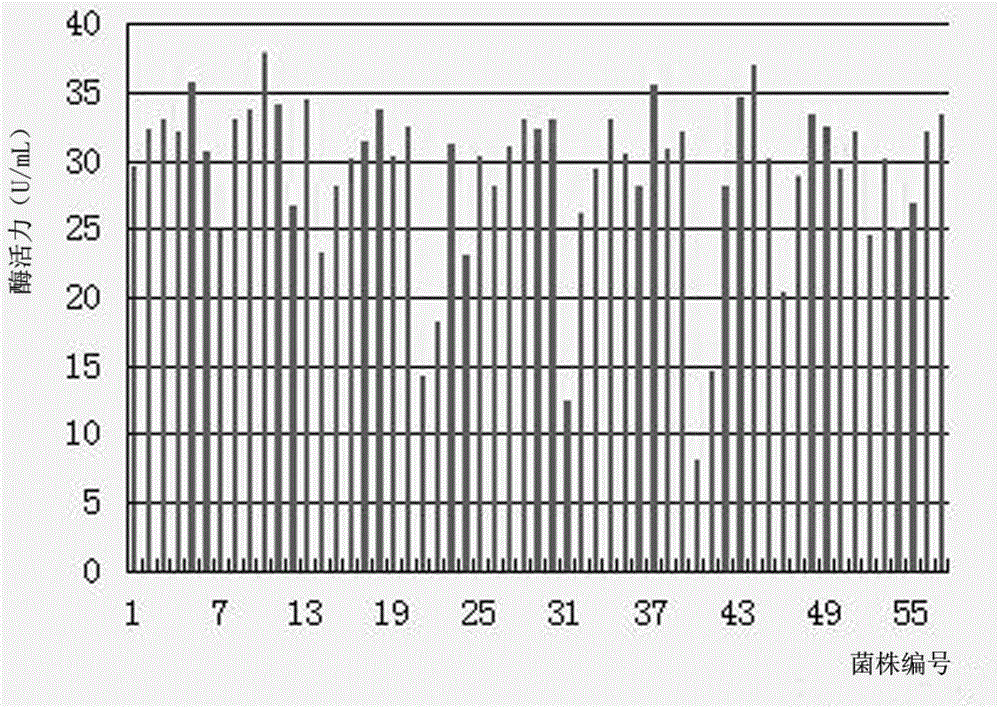
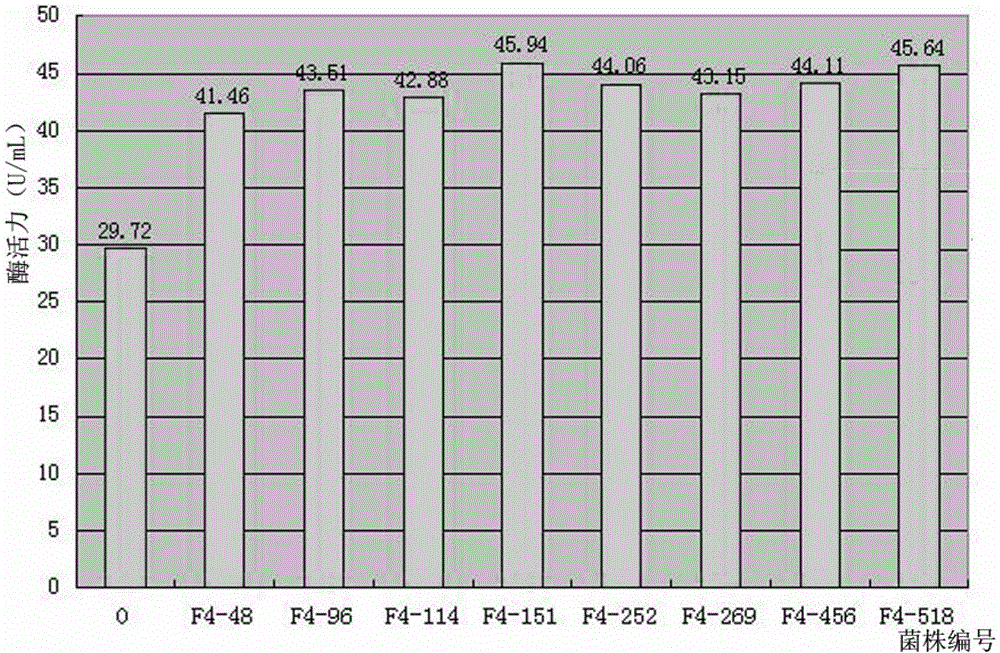
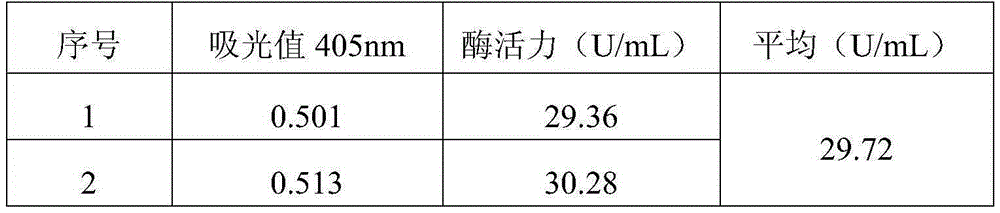
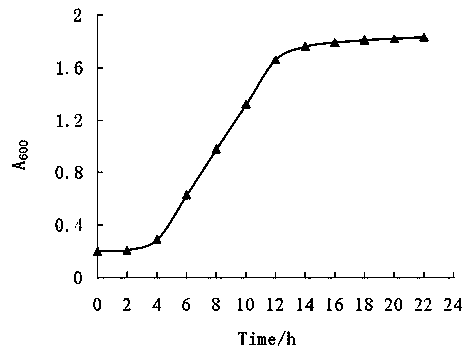
Patents
Literature
87 results about "UV-Mutagenesis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Abamectin producing bacterium and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102154168AImprove Abamectin B ComponentLess componentsBacteriaMutant preparationLithium chlorideHydroxylamine
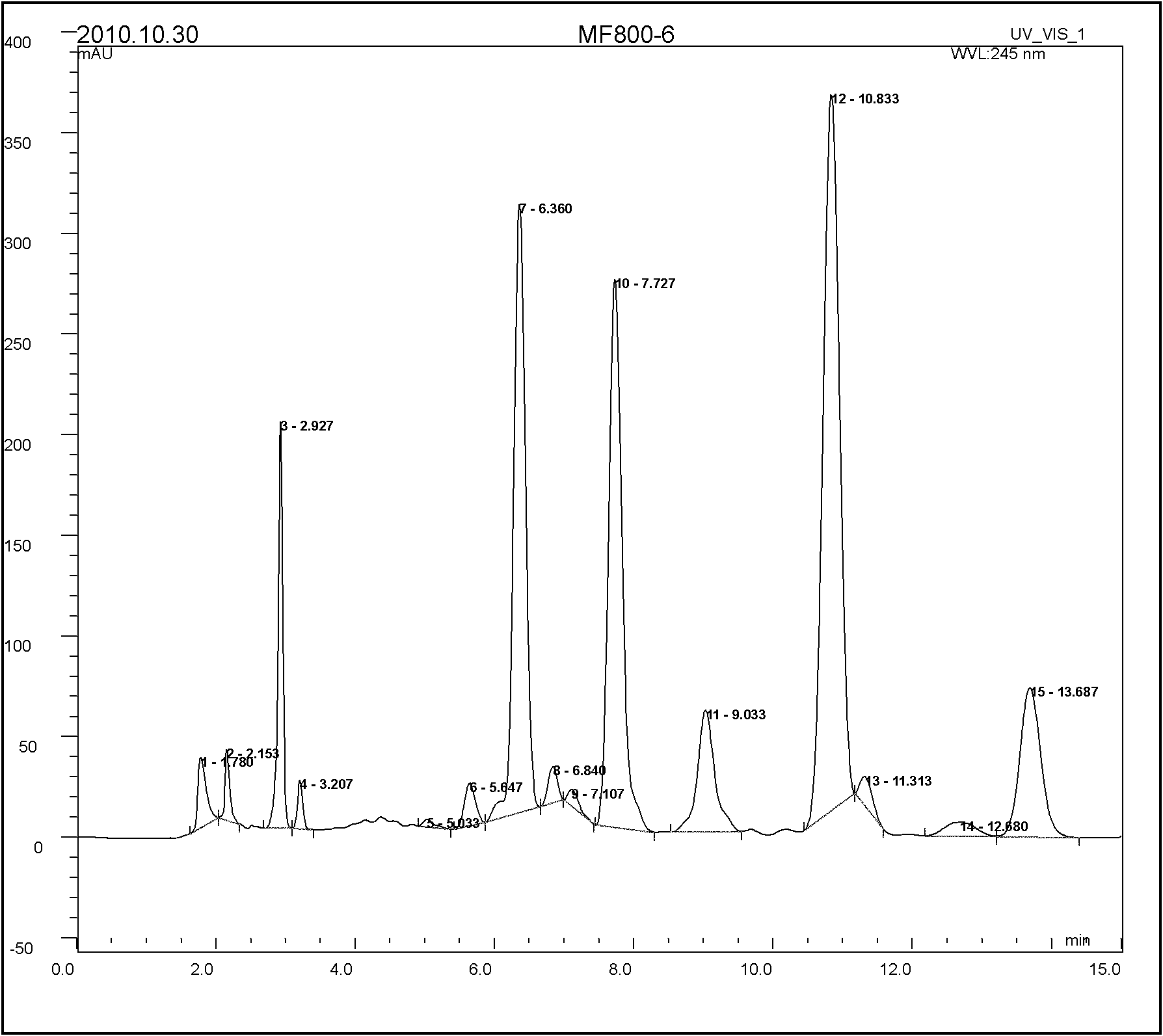
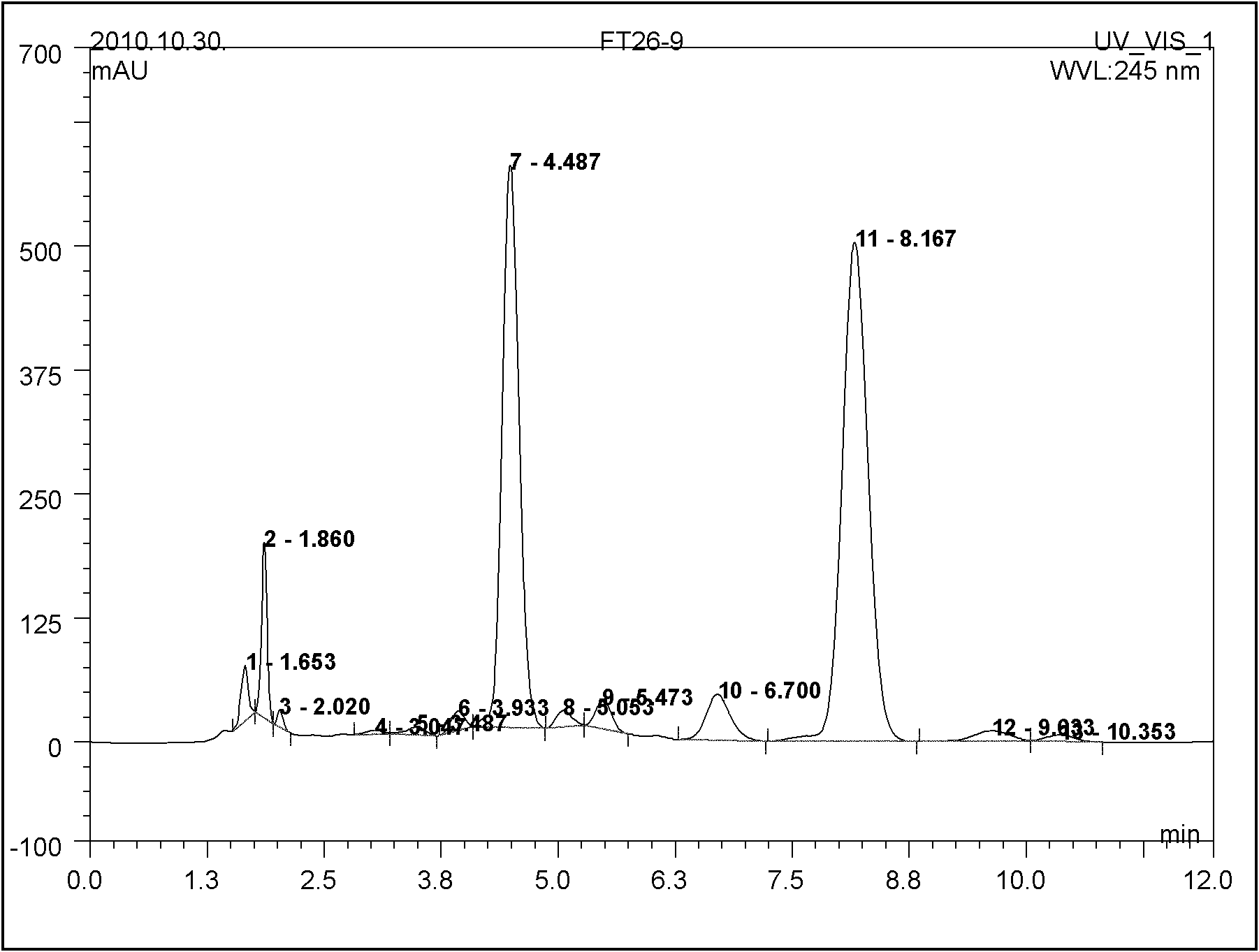
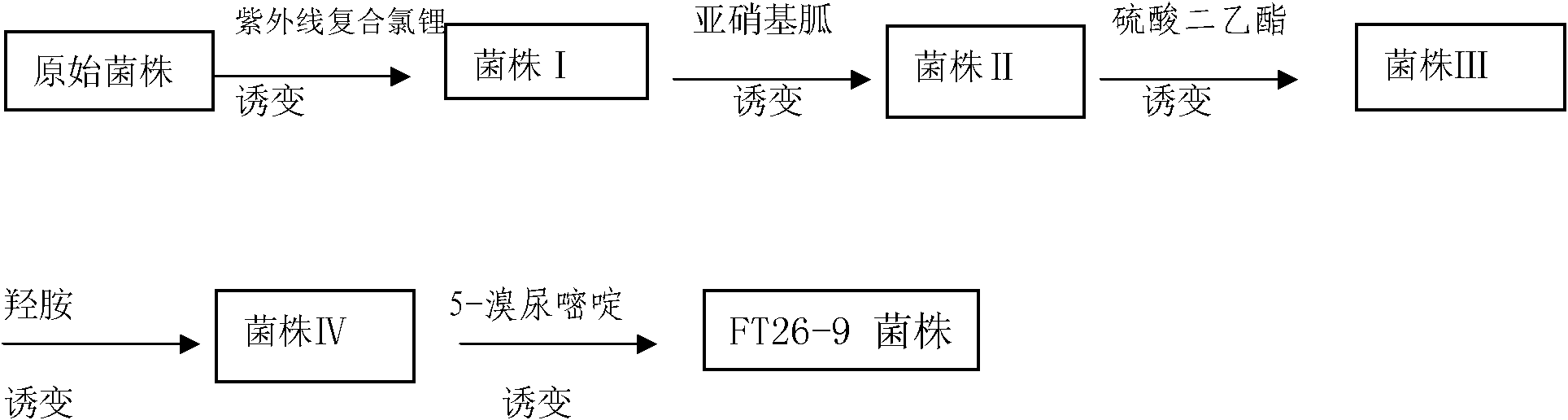
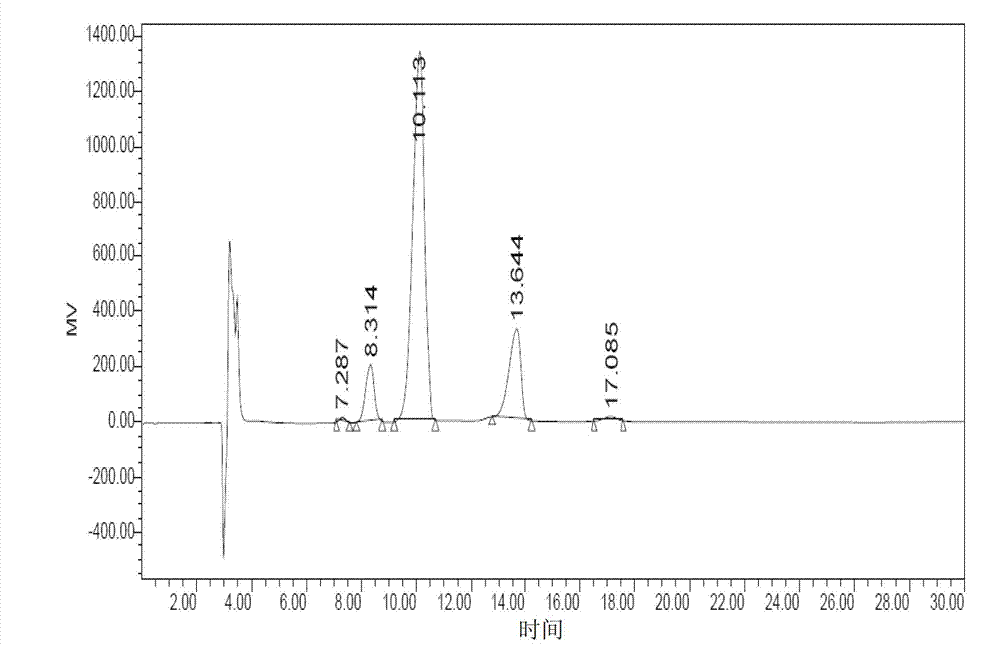
The invention discloses abamectin producing bacterium and a preparation method thereof. The collection name of the bacterium is FT26-9 and the collection number of the bacterium is CGMCC No.4341. The bacterium was collected on November 12th, 2010. The preparation method comprises: performing ultraviolet and lithium chloride combined mutation induction treatment of a starting strain; screening an induced-mutation strain; performing mutation induction by nitrosoguanidine and screening; performing mutation induction by diethyl sulfate and screening; performing mutation induction by hydroxylamine and screening; performing mutation induction by 5-bromouracil and ultraviolet and screening; and finally obtaining the FT26-9 strain which can greatly improve the abamectin B component content in a fermentation product and reduce the abamectin A component content in the fermentation product. When the bacterium is used in industrial production of abamectin, the fermentation unit is improved by about 40 percent, and the product cost is reduced by about 35 percent.
Owner:HEBEI XINGBAI AGRI SCI & TECH CO LTD
Fermentable silk spore yeast strains and application for preparing microbial oil thereof
InactiveCN101967452AEfficient accumulationReduce yieldFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The invention discloses fermentable silk spore yeast strain and a method for preparing microbial oil with lignocellulose hydrolyzate. The method for preparing the yeast strain comprises the following steps of: taking the fermentable silk spore yeast CICC 1368 as the original strains, performing the ultraviolet ray mutagenesis and the composite mutagenesis of the ultraviolet ray and the LiCl, obtaining the high-yield strains by means of fermenting and screening, and naturalizing the obtained strains in the lignocellulose hydrolyzate to finally obtain the oil yeast strain CCTCC M209060 which can effectively accumulate the oil in the lignocellulose hydrolyzate. The strains has high oil yield compared with the original strains, can effectively accumulate the oil in the lignocellulose hydrolyzate which contains the inhibitor with higher concentration, and offers the probability for preparing the microbial oil with low cost, high efficiency and large scale.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Bacterial strain for producing fructosyl transferase and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a bacterial strain for producing fructosyl transferase and a preparation method thereof. The bacterial strain disclosed herein is prepared by the following steps: firstly screening a bacterial strain by lithium chloride and UV mutagenesis, and then changing the property of fructosyl transferase in the bacterial strain by genome shuffling. The bacterial strain is named Aspergillus oryzae scut209, preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC) in Wuhan, China, on April 10, 2012 with CCTCC Designation CCTCC No:M 2012106. The bacterial strain has high capability of producing fructosyl transferase and has high industrial application value, wherein the capability of producing fructosyl transferase reaches 34987U / g cell.
Owner:QUANTUM HI TECH (CHINA) BIO CO LTD +1
Method of producing neutral beta-konjak mannase preparation
The invention discloses a preparing method of bacillus subtilis TQS6 CCTCC M207001 of highly effective expression neutral beta-mannase through adopting UV (ultraviolet mutagenesis ) and NTG (nitrosoguanidine mutagenesis) compositing mutagenesis, which comprises the following steps: bevel-culturing bacterial strain; proceeding ferment culture after one grade and two grade culture; choosing culture medium; adding into not exclusively degraded liquid from centrifuging sugar liquid; venting into oxygen-enriched air during the course of yeast; increasing dissolved oxygen; getting high active neutral beta-konjak mannase. The product possesses high enzyme production, high enzyme activator, short period of production and low cost, which can invert low mannan effectively.
Owner:WUHAN TAIYUAN INVESTMENT GUARANTEE
Mutagenized strain Bacillus licheniformis TKPG091 for generating great amount of gamma-poly glutamic acid
InactiveCN101838619AIncrease production capacityHigh yieldBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyBacillus licheniformis
Owner:天津北洋百川生物技术有限公司
Method for restructuring/breeding Actinobacillus succinogenes strain, and method for producing succinic acid by fermenting Actinobacillus succinogenes strain
InactiveCN101531972AImproved sodium toleranceImprove fermentation characteristicsBacteriaMutant preparationGenome shufflingX-ray
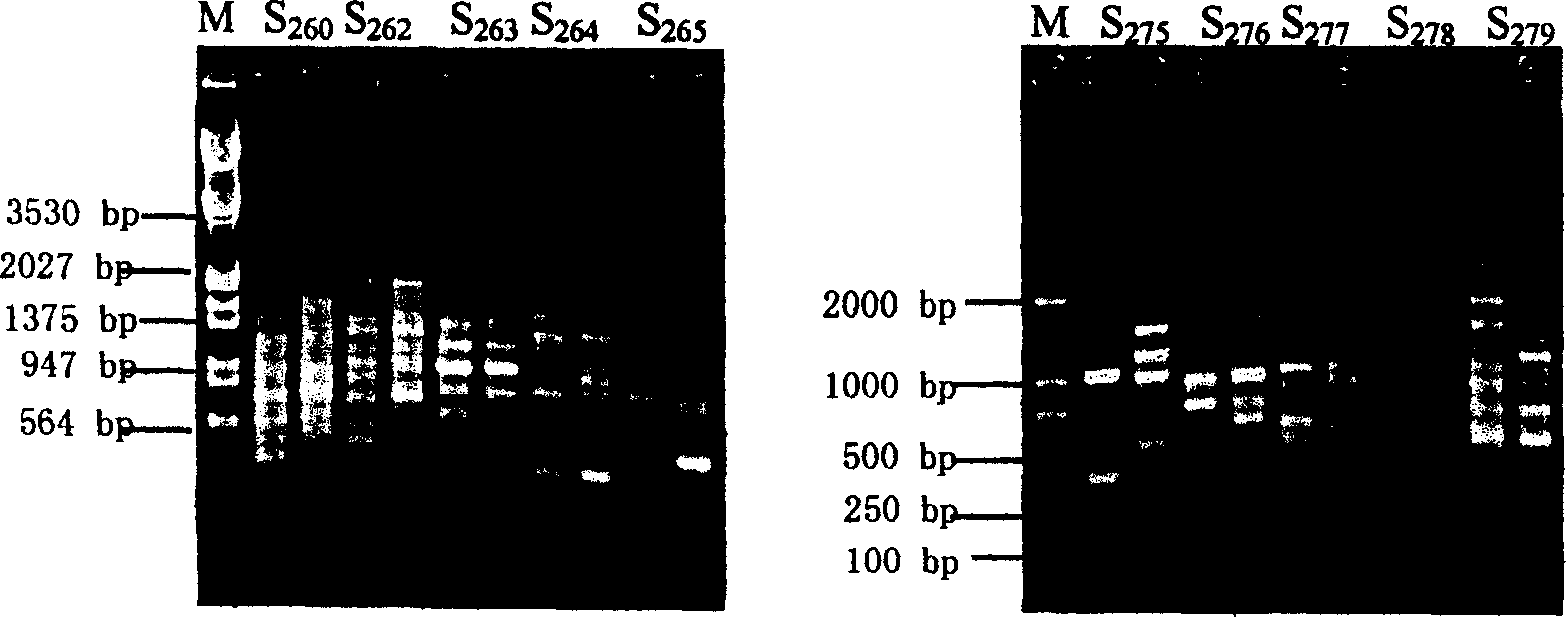
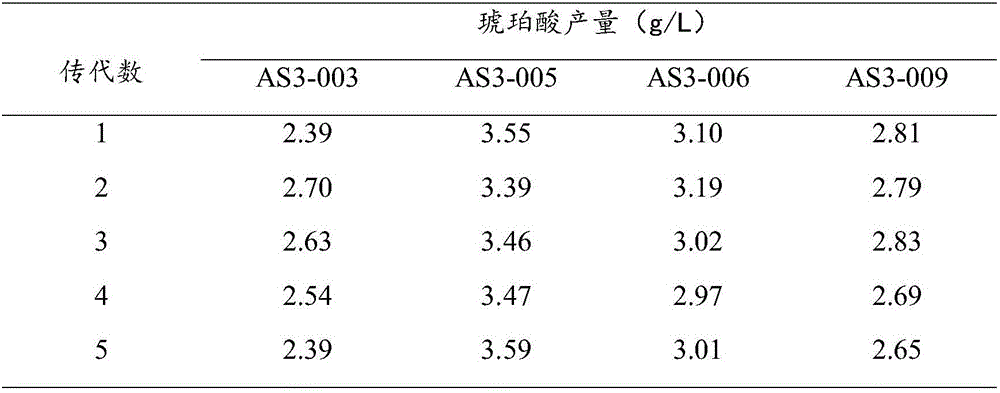
The invention relates to an Actinobacillus succinogenes strain CGMCC 2653 (namely F3-10) with better sodium-ion tolerance and acid-producing performance, a method for breeding the strain and a method for producing succinic acid by fermenting the strain. Actinobacillus succinogenes CGMCC 1593 is taken as an original strain and then subjected to X-ray mutation, ultraviolet mutation, diethyl sulfate (EMS) chemical mutation and nitrosoguanidine (NTG) chemical mutation respectively; three strains X-8, UV-17 and SE-6 with improved fermentative acid-producing performance and particularly improved sodium-ion tolerance, as well as a high-yield strain SF-9 with fluoroacetate resistance, are obtained by screening the obtained product; and a genome restructuring method is used for breeding the strains so as to obtain the strain F3-10 with high yield, sodium tolerance and fluoroacetate resistance. The strain F3-10 takes sugarcane molasses as raw material, adopts Na2CO3 to control fermentation pH, and performs fed-batch fermentation in a 5L fermenter, and produces 53.96 grams of succinic acid per liter in 48 hours; the yield of consumed sugar is 89.2 percent; the utilization rate of sugar is 94.0 percent; and the ratio of succinic acid to heteroacid is 6.58:1. Therefore, the strain F3-10 is remarkably improved as compared with the original strain CGMCC 1593.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
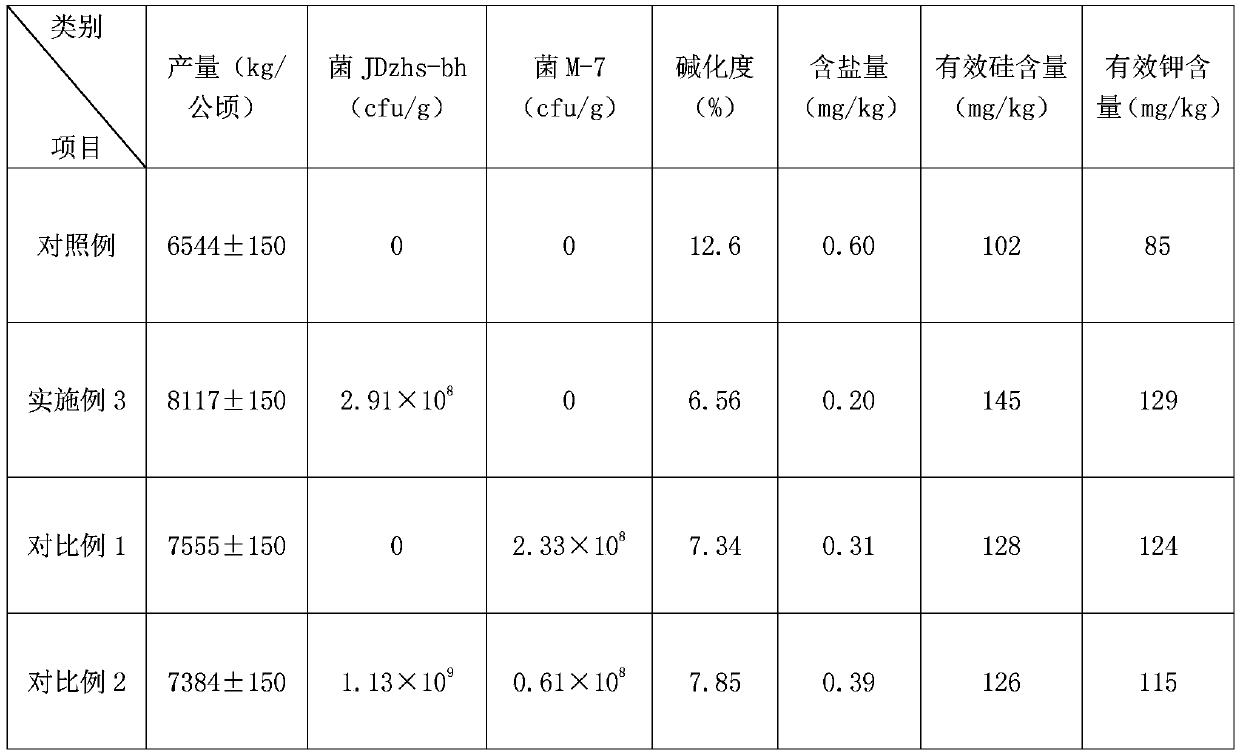
Bacillus mucilaginosus and application thereof for preparing saline alkali soil improvement agent
ActiveCN110106126AResilienceFacilitated releaseAgriculture tools and machinesBacteriaAlkali soilMutation screening
The invention relates to bacillus mucilaginosus and application thereof for preparing a saline alkali soil improvement agent. The bacillus mucilaginosus JDzhs-bh is preserved at the China Center for Type Culture Collection on March 20th, 2019, the address is No.3, courtyard 1, the western Beichen road, Chaoyang district of Beijing, and the strain preservation number is CGMCC No.17376. The invention discloses bacillus mucilaginosus capable of resisting high temperature and saline alkali and being cultivated through ultraviolet mutation screening for the first time. The bacillus mucilaginosus has the stress resistance for high temperature and saline alkali, and can effectively adapt to saline alkali hardening soil. Meanwhile, the effect of degrading silicon and phosphorus is achieved, release of elements such as soluble silicon and phosphorus in soil is promoted, crop stress resistance is enhanced, the utilization rate of the soil repairing agent is achieved, saline alkali soil is repaired and improved, and salinization is lowered.
Owner:INST OF AGRI RESOURCES & ENVIRONMENT SHANDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Method for producing high-activity chitosanase preparation
InactiveCN101148646AHigh activityHigh efficiency of enzymatic hydrolysis processBacteriaHydrolasesUV-MutagenesisChitin formation
The present invention is production process of UV and NTG mutagenizing Bacillus subtilis TQS6 to culture high efficiency expressing chitosanase strain TQK and fermentation producing high activity chitosanase. The chitosanase strain is first slant cultured and then fermentation cultured while introducing oxygen-rich air to increase dissolved oxygen to 30-80 %; and after culturing for 18-24 hr, average enzyme activity may reach 718 mu / ml. High activity chitosanase may be obtained through fermentation in optimized enzyme producing condition. The process of the present invention can obtain chitosanase with high yield, high stability and high activity, and the produced chitosanase is applied in converting chitosan into chitin oligose effectively and economically.
Owner:WUHAN EAST ANGEL BIOENG
Bacillus subtilis and its application
ActiveCN1609189ALower burn valueHas industrial application valueBacteriaHydrocarbon oils refiningMicroorganismUV-Mutagenesis
The present invention relates to Bacillus subtilis Fds-1 with the preservation number of CGMCC No. 0644. The strain of the present invention is obtained through separation from the soil near high sulfur oil well, ultraviolet mutagensis and screening. The growing cell and the rest cell of the strain can make the C-S bond oxidized to break and thus eliminate organic sulfur from organic compound, so that the strain is especially suitable for eliminate organic sulfur from petroleum fractions in high desulfurizing rate.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Endogenous bacillus subtilis positive mutant strain, preparation method thereof, prepared biocontrol agent and application of biocontrol agent in preventing and controlling pomegranate dry rot
InactiveCN104017749AHigh activityThe cultivation method is simpleBiocideBacteriaDiseaseUV-Mutagenesis
The invention relates to an endogenous bacillus subtilis positive mutant strain, a preparation method thereof, a prepared biocontrol agent and an application of the biocontrol agent in preventing and controlling pomegranate dry rot, including (1) screening of a Bacillus subtilis wild-type strain NS04 and ultraviolet mutation and breeding of a positive mutant biocontrol strain NS04307; (2) antibacterial stability of the positive mutant strain NS04307; (3) a preparation method of the positive mutant strain NS04307 biocontrol agent; and (4) application of the positive mutant strain NS04307 in preventing and controlling plant diseases. The biocontrol agent disclosed by the invention has the characteristics of wide bactericidal spectrum, good effect, difficulty in disease drug resistance generation, safety on human, livestock and crops, environmental friendliness and the like and has a better effect on the field control of the pomegranate dry rot especially. In addition, the biocontrol agent disclosed by the invention achieves outstanding inhibition activity on the growth of 15 different pathogenic bacteria, such as Sclerotiumrolfsii, Trichotheciumroseum, Exserohilumrostratum, Fusariumoxysporum, Alternariaalternate and the like.
Owner:ZAOZHUANG UNIV
Glucomannan enzyme preparation method
InactiveCN101182500AEfficient degradationIncrease enzyme activityFungiHydrolasesCell wallOligosaccharide
The invention relates to a preparation method of glucomannanase, which is characterized in that Trichoderma viride (Trichoderma viride) CGMCC3.2942 selected and bred by ultraviolet mutagenesis is used as an enzyme-producing strain, and the koji is cultivated in a solid koji culture medium. The solid koji medium is composed of solid medium and nutrient saline with a mass ratio of 1:2.2-2.3, wherein the solid medium is composed of bagasse 65%-73%, bran 15%-20%, yeast cell wall 10%-15% %, 2.0% to 4.0% of konjac powder, and then through the steps of enzyme liquid extraction, enzyme sludge precipitation, purification, etc., to obtain glucomannanase. The invention has the advantages of simple process, low equipment investment, low cost, no pollution, easy product extraction and purification, and the obtained glucomannanase can efficiently degrade plant-like glucomannan to obtain glucomannan oligosaccharides, and can more effectively degrade Yeast-like cell walls obtain yeast glucomannan-oligosaccharides.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF MICROORGANISM +1
High-throughput screening method for bacillus circulans
InactiveCN105274086AIncrease screening volumeSpeed up the breeding processMutant preparationMicroorganism based processesLithium chlorideHigh-Throughput Screening Methods
The invention belongs to the technical field of fermentation engineering and microbial breeding, and discloses a high-throughput screening method for bacillus circulans for generating beta-galactosidase. The high-throughput screening method includes main steps of activating initial strains; carrying out ultraviolet mutation and lithium chloride mutation; carrying out high-throughput screening by the aid of 96 pore plates to obtain bacillus circulans mutant strains with improved enzyme capacity. The high-throughput screening method has the advantages that the mutation probability of the strains can be improved by the aid of the traditional physical and chemical combined mutation modes, the screening workload can be reduced by the aid of high-throughput screening tools, the screening efficiency can be improved, strain breeding procedures can be accelerated, and the optimal strains can be screened.
Owner:QUANTUM HI TECH (CHINA) BIO CO LTD
Bacillus circulans and application for same in preparation for ferulic acid decarboxylase
InactiveCN103451133AHigh deacidase activitySimple production processBacteriaMicroorganism based processesYeastUV-Mutagenesis
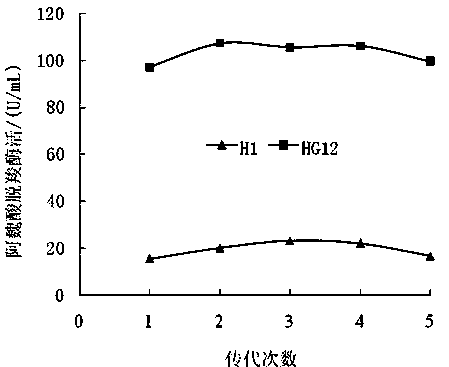
The invention belongs to the technical field of bioengineering, and particularly discloses bacillus circulans and an application of the same in preparation for ferulic acid decarboxylase. The bacillus circulans is characterized in that a bacillus circulans HG12 strain is obtained by separating from a high-temperature yeast for brewing Maotai-flavour liquor in the white wine plants of China, and screening by virtue of ultraviolet mutation, as well as has the characteristics of being fast in growth and propagation speeds, capable of producing the ferulic acid decarboxylase under the induction of ferulic acid, stable in performance of producing the ferulic acid decarboxylase, and high in enzymatic activity. According to the bacillus circulans and the application disclosed by the invention, continuous and large-scale production for the ferulic acid decarboxylase can be realized, and industrialized production for the ferulic acid decarboxylase is facilitated; moreover, the enzyme is simple and convenient in production process, short in production cycle, and low in cost.
Owner:QILU UNIV OF TECH
Liquid state fermentation lower citrinin and high color value monascus red pigment preparing method and product
ActiveCN104893983AGood biological propertiesLarge amount of inoculationFungiMutant preparationMicroorganismMonascus anka
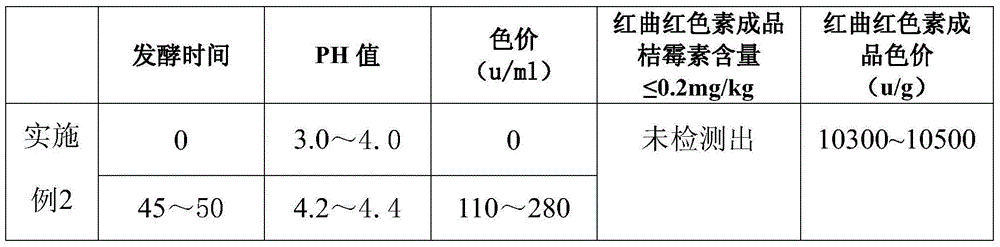
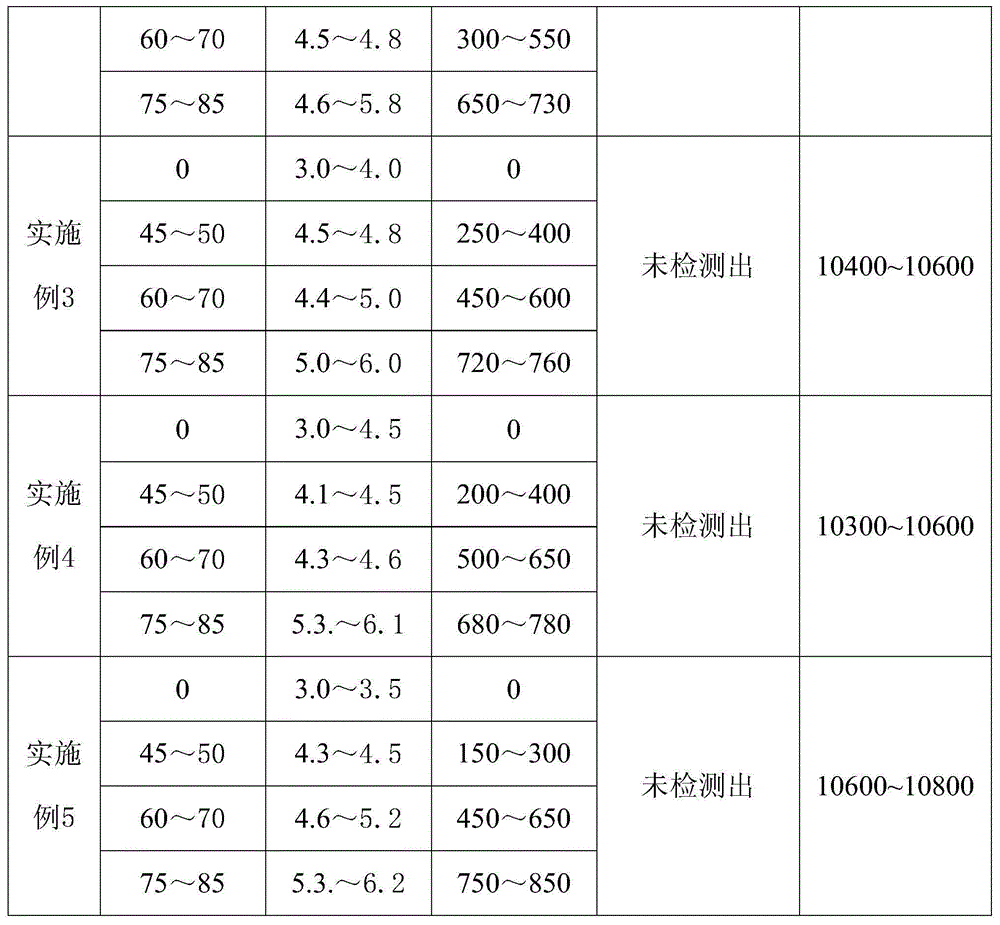
The invention discloses Monascus anka Yang YZ 301 and a cultivation method thereof, wherein the microbial preservation number of the Monascus anka Yang YZ 301 is CGMCC9707. The invention further discloses a method for preparing lower citrinin and high color value monascus red pigment through liquid state fermentation of the Monascus anka Yang YZ 301. The method includes the first step of strain breeding, the second step of seed cultivation and enlarged cultivation, and the third step of liquid state fermentation, extraction and purification, spray drying and the like. The strains are the Monascus anka Yang YZ 301 obtained by cultivation, repeated UV mutagenesis and repeated isolation and screening of Monascus anka Nakazawa et Sato YZ201 developed by the Tianyi Biological Fermentation Technology Co., Ltd in Dongguan. The invention further discloses a lower citrinin and high color value monascus red pigment product obtained through the preparing method. The provided strains are excellent, and the technology is reasonable and stable. The obtained product is high in yield and stable in quality. The content of citrinin in the product is not more than 0.2 mg / kg (calculated by unit color value of 500 mu / g), and the color value of monascus red pigment ranges from 10,300 mu / g to 10,800 mu / g.
Owner:佛山市真红生物技术有限公司
Astaxanthin high-production mutant strain of haematococcus pluvialis
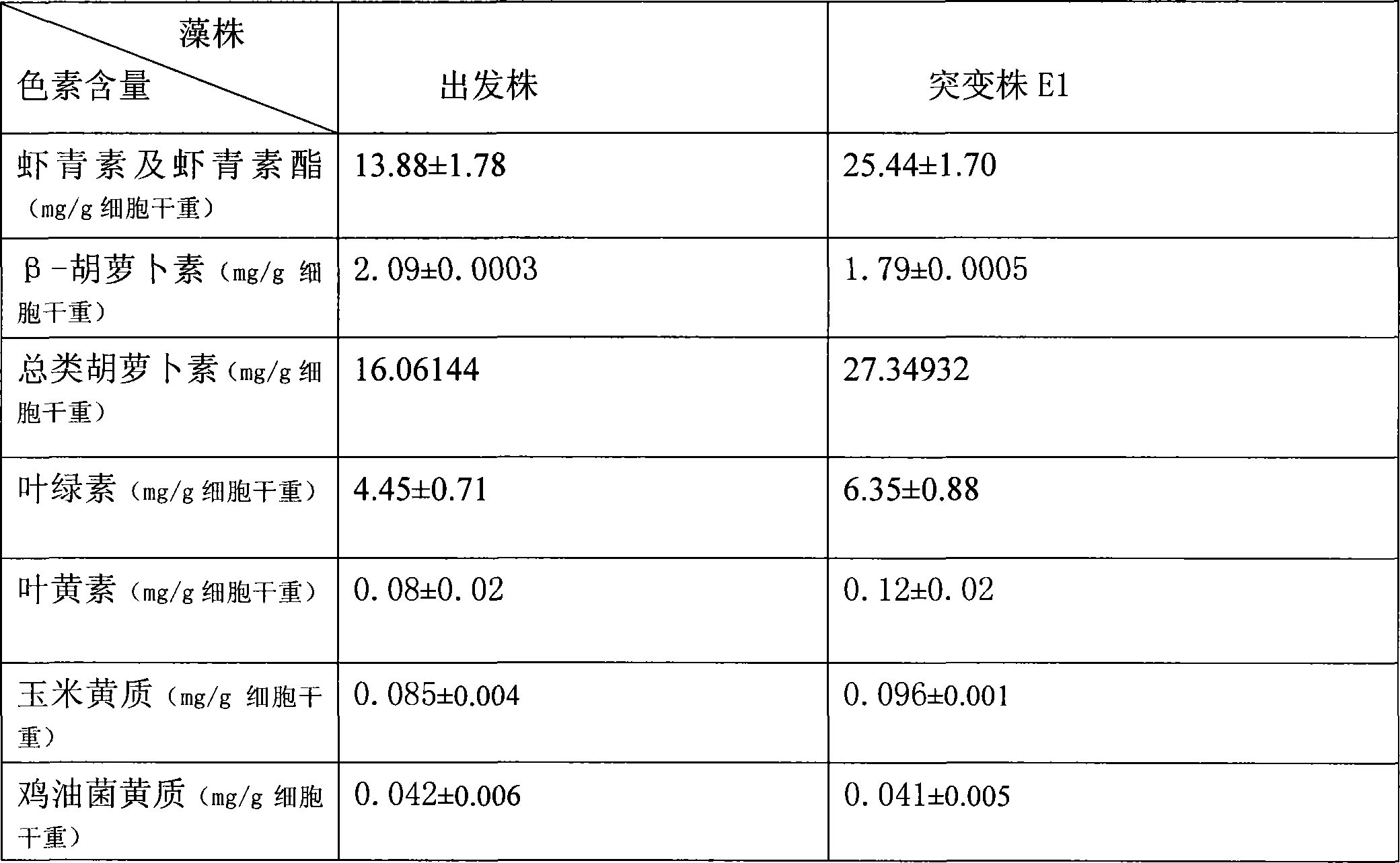
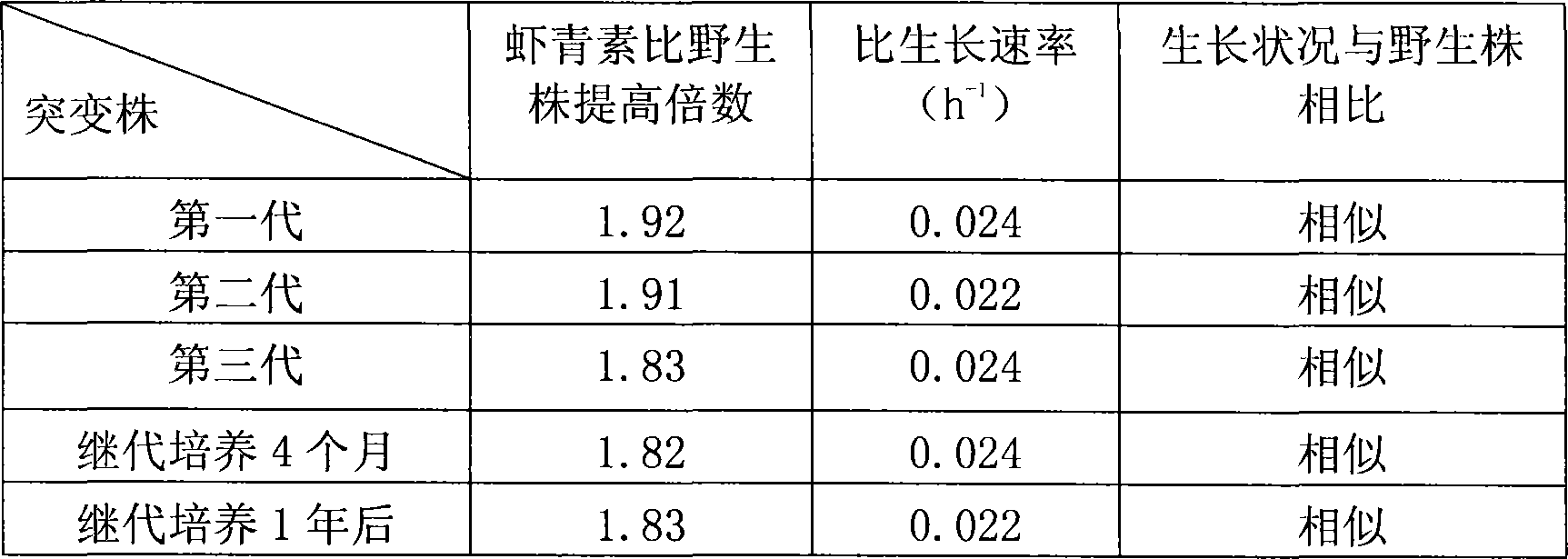
The present invention provides a high-yielding astaxanthin mutant strain of Haematococcus pluvialis (Haematococcus pluvialis) E1 CCTCC M 207164, which uses the wild strain of Haematococcus pluvialis as material , using ultraviolet chemical compound mutagenesis, mutagenesis selection of carotenoid biosynthesis inhibitor screening. The astaxanthin content of the algal strain is 1.83 times higher than that of the original strain, the growth rate is 14% higher than that of the original strain, the physiological and biochemical characteristics are stable, and it has stable genetic properties. It is an excellent algal strain for producing natural astaxanthin and can be used as a source of industrial production. Industrial production of natural astaxanthin.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Ultraviolet mutation breeding and acclimatization method of salt-resisting domestic fungus
InactiveCN102487821AOpen up a new way of mutation breedingEasy to operateHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureDry weightUltraviolet
The invention discloses an ultraviolet mutation breeding and acclimatization method of a salt-resisting domestic fungus. According to the invention, initial domestic fungus strains are activated and are subject to mycelium ultraviolet mutation; salt-resisting stains are subject to primary screening, acclimatization and secondary screening by using salt-containing selective culture media, such that the salt-resisting stain is obtained. The method is suitable to be used in salt-resisting stain breeding and acclimatization of domestic fungus varieties such as cap fungus, shiitake fungus and Jew's ear. The method is advantaged in that: the high-salt-resisting mutation strain is obtained with the mycelium ultraviolet mutation and acclimatization method, such that a novel approach of salt-resisting cap fungus breeding is developed. The operation processes are simple, a small amount of equipment is required, the cost is low, such that the domestic fungus breeding method is easy to popularize. A mutation period is short, a forward mutation rate is improved, and an effect is substantial. The obtained strain has a salt-resisting capacity of 2%, stable hereditary characters, and excellent agronomic characters. When the method is used in the productions in saline alkali lands, the quality of cap fungus fruiting bodies is improved; and a fresh-to-dry weight ratio and a storing tolerance are improved by more than 50%. Therefore, the quality of cap fungus is effectively improved, the production cost is reduced, and the economic benefits are substantially improved.
Owner:天津市林业果树研究所
Ultraviolet mutagenic obtained low temperature salina and its identifying method
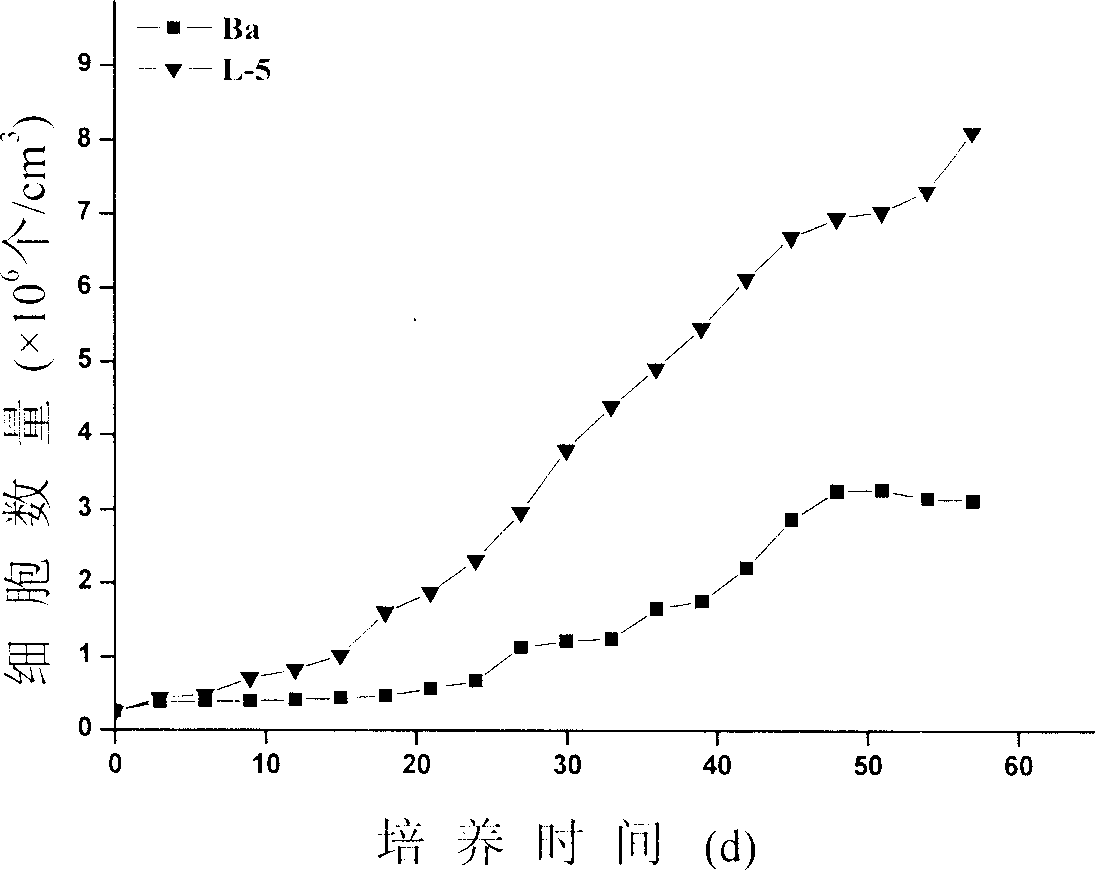
InactiveCN1944643AExtend the breeding timeLong breeding cycleUnicellular algaeMicrobiological testing/measurementUV-MutagenesisGenetic similarity
The present invention relates to saline algae, provides one kind of low temperature tolerant saline algae and its ultraviolet mutagenesis breeding process and identifying method. The low temperature tolerant saline algae features its light illuminating growth at 3-10deg.c to reach (1.05-8.11)x10<6> cell / ml in the cell density 2.1-21 times higher than the contrast; the genetic similarity coefficient to wild strain of 0.680-0.910; and increased or decreased protein zone(s) compared with wild strain.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Torulaspora delbrueckii and application thereof
The invention discloses torulaspora delbrueckii and an application thereof. A preservation number of torulaspora delbrueckii is CGMCC No.8740 and CGMCC No.8742. An ultraviolet mutation method is adopted to mutate torulaspora delbrueckii; then mutated strains having high active phytase under an acid condition are screened out, so that mutated phytase produced by the mutated strains can hydrolyze phytic acid under pH conditions of a stomach environment relatively well. The mutated strain can be used for producing feed or food phytase or producing microbial phosphate fertilizer or bioorganic fertilizer. Besides, the mutated phytase gene sequence can be cloned to prokaryotic or eukaryotic gene expression vectors to construct gene engineering strains or transgenic plants by gene engineering technology, so as to efficiently express the mutated phytase genes, thereby producing the mutated phytase.
Owner:ANHUI SCI & TECH UNIV
Inhibitor-resistant saccharomyces cerevisiae and selective culture method and application thereof
ActiveCN110358690AIncrease profitShort fermentation timeFungiMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The invention relates to an inhibitor-resistant saccharomyces cerevisiae and a selective culture method and application thereof. The inhibitor-resistant saccharomyces cerevisiae is named as ZR / SC-UV-2, classified and named as saccharomyces cerevisiae, and deposited in the China general microbiological culture collection center, the preservation number is CGMCCNo.17924, and the preservation addressis No.3, yard 1, Beichen west road, Chaoyang district in Beijing. The selective culture method includes the following steps that the saccharomyces cerevisiae of xylose can be used as a starting strain, and the inhibitor-resistant saccharomyces cerevisiae is obtained after UV-induced screening. The UV mutagenesis condition includes the following steps that under a light-shading condition, a UV lamp of 15-20 W is used for irradiating for 30-600 seconds at a distance of 15-20 cm for UV mutagenesis. Compared with the prior art, the saccharomyces cerevisiae has strong resistance to an inhibitor incellulose hydrolysate, the degradation rate of the xylose is high, the fermentation time is short, and the system is suitable for the industrialized production of ethanol prepared from agricultural straw.
Owner:ZHONGRONG TECH CORP LTD
Method for screening methionine resistant deinsectization streptomyces avermitilis strain
ActiveCN101948826AImprove efficiencySimple and fast operationMutant preparationElectrical/wave energy microorganism treatmentSporeMicroorganism
The invention discloses a method for screening a methionine resistant deinsectization streptomyces avermitilis strain, which belongs to the field of the screening of microbial strains. The method comprises the following steps of: performing ultraviolet mutagenesis on deinsectization streptomyces avermitilis spore suspension; performing enrichment on tolerant strains by using a methionine-containing liquid culture medium; screening methionine solid-plate tolerant strains; and screening strains of which the shake flask capacity is improved compared with that of parent strains through preliminary screening, secondary screening and genetic stability research so as to provide a feasible method for screening the deinsectization streptomyces avermitilis strain. The shake flask production capacity of the deinsectization streptomyces avermitilis strain screened by the method is greatly improved, and the genetic stability is high.
Owner:XINYU PHARM CO LTD
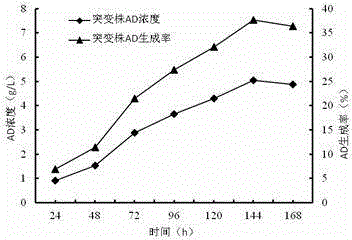
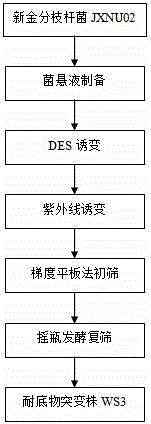
Androstenedione substrate-tolerant mutant strain and mutation breeding method thereof
InactiveCN104531548AImprove the ability to degrade phytosterolsStrong conversion potentialBacteriaMutant preparationMycobacterium neoaurumPhytosterol
The invention discloses an androstenedione substrate-tolerant mutant strain and a mutation breeding method thereof. A mutant strain of mycobacterium neoaurum WS3 is preserved in China center for type culture collection with an accession number of CCTCC NO: M 2014322, and the preservation date is July 4, 2014. According to the invention, mycobacterium neoaurumJXNU02 is used as a starting strain; compound mutation is carried out by diethyl sulfate and an ultraviolet mutation method; primary screening is performed by a gradient plate method; secondary screening and verification are carried out by a shake flask fermentation method; and thus the mutant strain of mycobacterium neoaurum WS3 with high substrate tolerance and genetic stability is bred. The method of the invention effectively improves the capability of mycobacteria for degrading phytosterol to generate androstenedione, provides an excellent strain for producing androstenedione by a microbiological method, and has important significance on the pharmaceutical industry of our country.
Owner:JIANGXI NORMAL UNIV
Method for increasing antibiotic yield by virtue of mutagenesis of erythromycin producing strain
InactiveCN103667248AImprove toleranceImprove production capacityMutant preparationElectrical/wave energy microorganism treatmentUV-MutagenesisTiter
Owner:SHANDONG FANGMING PHARMACEUTICAL CO LTD
Mutagenesis, selective breeding and identification method of cold tolerant Danaliella
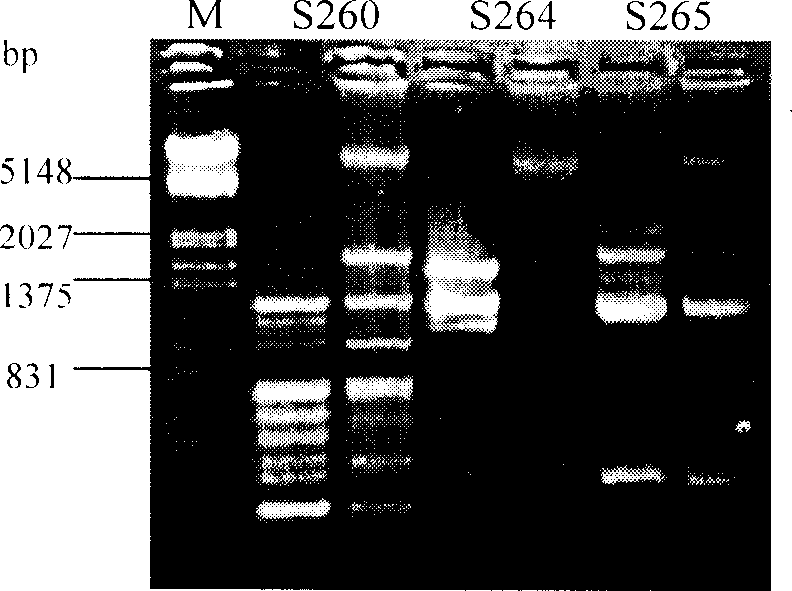
InactiveCN1888047AExtend the time of outdoor cultivationLong breeding cycleUnicellular algaeElectrical/wave energy microorganism treatmentUltravioletWild type
The ultraviolet ray mutagenesis, selective breeding and identification method of cold tolerant Dunaliella includes: inoculating Dunaliella to culture medium; lighting and dark inducing for synchronized growth; mixing Dunaliella liquid with iodine solution or bromophenol blue solution to deactivate Dunaliella, injecting Dunaliella liquid to culture dish, mutagenesis under ultraviolet lamp before dark culturing, mixing with fresh culture liquid and painting the mixture to Dunaliella culture medium for low temperature lighting culture; inoculating single Dunaliella colony to the culture liquid and low temperature lighting culturing; sampling detection to comparing the low temperature lighting growth curves of cold tolerant Dunaliella mutant and wild prototype strain; extracting total DNA for RAPD comparison; calculating genetic similarity coefficient; extracting total protein and post-electrophoresis staining while record results; comparing protein electropherogram; and confirming the obtained cold tolerant Dunaliella mutant.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Method for inducing wild cabbage type cole in vitro microspores and screening mutant
InactiveCN101250516AStrong mutagenic effectEfficient use ofMutant preparationElectrical/wave energy microorganism treatmentSaccharumPlant cell
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant cell engineering and in particular relates to a method for screening brassica napus in vitro microspores ultraviolet mutation and mutants, which is characterized in that the method comprises: using aqueous sucrose solution to separate brassica napus microspores, suspending the microspores on NLN culture medium which is modified through adding colchicine to be irradiated with ultraviolet and to be doubled with chromosome, transferring doubled microspores on the NLN culture medium which is modified to induce embryoid, then, transferring the embryoid on B5 culture medium to be induced into double haploid plants, transplanting the plants into filed to indentify, and screening out the mutants. The morphological character mutant rate is 10.53-21.57%, and the variant rates of sulfuric glucoside, the oil content and the erucic acid content are respectively 25.53-78.7%, 22.22-59.09% and 38.89-46.97%. The method of the invention has the advantages that the operation procedure is convenient, the time is saved, the cost is low, and the like. The method is suitable for screening the microspores ultraviolet mutation and mutants of cruciferae crops.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Mutagenesis breeding method for high-fat dunaliella salina
The invention relates to a mutation breeding method for high lipid dunaliella, in particular to a mutation breeding method to obtain high lipid content dunaliella through ultraviolet mutation and extraction and screening by ether and other reagent, which belongs to dunaliella field; wherein, the obtained high lipid dunaliella is Danaliella bardawil var. HL. The invention is characterized in that: sterilized culture medium is cooled to inoculate dunaliella, and a dunaliella solution is obtained; the dunaliella solution is light-cultured, and the OD630 value is measured; parent strain is coated on the culture medium, and is cultured after ultraviolet radiation mutation; single colonies after mutation treatment is selected and cultured; the culture medium is subject to centrifugal elutriation, and a fresh dunaliella is obtained; the fresh dunaliella is collected and extracted, and the extract is dried and weighted; a mutational strain is selected, and is inoculated with the parent strain for culture; dunaliella cell is collected through centrifugation, and is dried into dunaliella powder; the total lipid content of the dunaliella powder is measured, and is determined higher than that of the mutational strain of the parent strain; lipid in the dunaliella powder of the high lipid mutational strain is subject to secondary screening, and the mutational train is verified to be a high lipid dunaliella mutational train.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Mutagenic breeding method of high temperature resistant pasteur Du algae
InactiveCN1757707AIncrease productivityExtend the time of outdoor cultivationMicrobiological testing/measurementUnicellular algaeUltravioletCulture mediums
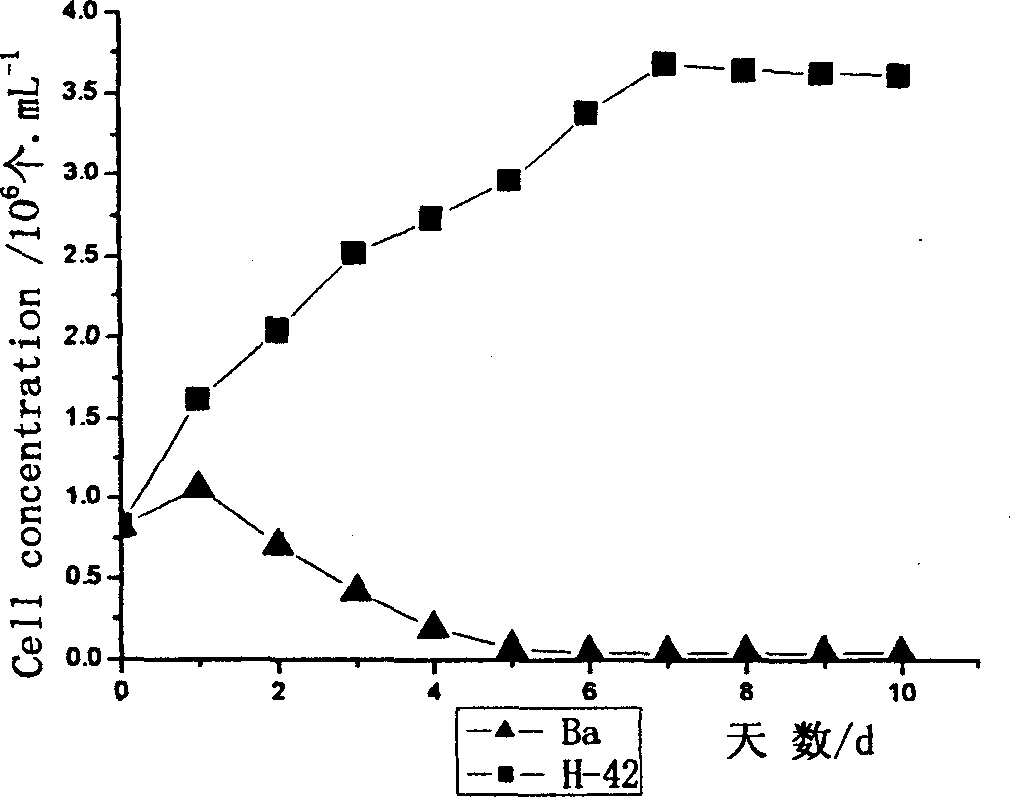
A method for mutagenizing and selectively culturing a refractory single-cell green alga includes such steps as sterilizing and cooling culture medium, inoculating alga liquid, culturing, mixing with iodine solution or bromophenol blue, deactivating, calculating alga density in alga liquid, ultraviolet mutagenizing, dark culturing, mixing the cultured alga liquid with fresh culture medium, culturing, high-temp screening, amplifying culture of living alga cells, culturing under light radiation, inoculating yellow alga, culturing, testing its mutagenized effect, measuring the long and short diameters of cell, extracting DNA, random amplifying of polymorphic DNA, calculating genetic similarity coefficient, extracting H-42 and general protein, electrophoresis, dyeing with Coomassic brilliant blue, recording result and observing the electropherogram to obtain result.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Fusion method for breeding high-efficiency cadmium-resistant microbial protoplast multi-parent strains
InactiveCN101955926AMicrobiological testing/measurementMutant preparationMicroorganismUV-Mutagenesis
The invention discloses a method for improving cadmium tolerance of bacillus through mutation, which comprises the following steps of: (1) taking bacillus subtilis as a starting bacterium, and pre-culturing the bacillus on a beef extract peptone culture medium for 10 hours; and (2) performing ultraviolet mutation on pre-cultured active colony: irradiating by using 15W ultraviolet lamp under the condition of a fixed distance of 30cm for 5 minutes, performing mutation, screening by fermenting on a concentration gradient culture medium plate and in a shake flask, wherein the obtained active colony is the mutated bacillus with high tolerance to cadmium. Through the method, the mutated bacillus B38 fully tolerating high concentrate cadmium is obtained, and the cadmium tolerant concentration is 3mmol / L.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Method for breeding high-producing strains through acid protease by means of ultraviolet mutation
InactiveCN105779431AWeaken hydrogen bonds between double bondsImprove fermentation effectMicroorganism separationElectrical/wave energy microorganism treatmentUltravioletVariant strain
The invention discloses a method for breeding high-producing strains through acid protease by means of ultraviolet mutation.The method comprises the following steps of a, preparation of spore suspension liquid, wherein tablet spores cultured in a constant temperature incubator are taken, shaken and then diluted with sterile distilled water, and the spore suspension liquid is obtained for use; b, ultraviolet mutation, wherein the spore suspension liquid is taken and put under an ultraviolet lamp for irradiation, culture is carried out under a dark condition, and finally the fatality rate is calculated; c, strain screening, wherein c1, based on strains with the fatality rate between 70% and 80% in the step b, variant strains with the HC value higher than the mean value are picked out as preliminarily screened strains for secondary screening; c2, a conical flask containing a potato culture medium is inoculated with the strains obtained in the step c1, and after culture in a shaker, the enzymatic activity of acid protease is measured through a foline-phenol method; the mutated variant strains with the enzymatic activity higher than the mean value are selected for six times of continuous passage, and the high-producing strains are obtained.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Succinic acid-rich strain for brewing soy sauce as well as mutation breeding method and application of succinic acid-rich strain
InactiveCN106222094AIncrease concentrationGenetically stableFungiMutant preparationSuccinic acidFood flavor
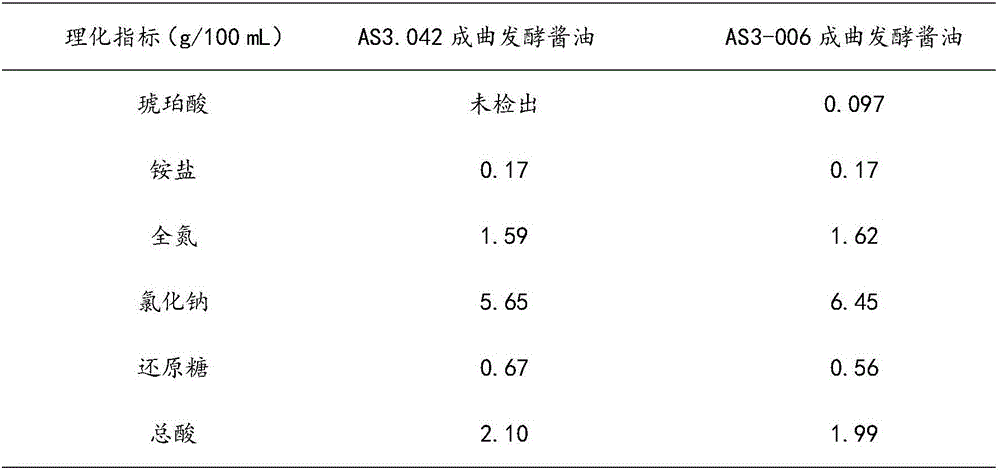
The invention relates to a succinic acid-rich strain for brewing soy sauce as well as a mutation breeding method and application of the succinic acid-rich strain. The strain is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on June, 2016, with a preservation number of CGMCC No.12629. The mutation breeding method comprise the steps of firstly preparing Aspergillus oryzae Huniang 3.042 spore suspension, preparing a spore protoplast, carrying out ultraviolet mutation, coating culturing, preliminary screening, secondary screening and genetic stability research, and applying the obtained product to the preparation of soy sauce finished koji in a soy sauce brewing process. Compared with the prior art, the strain for brewing the soy sauce has the advantages that the genetic property is stable, and a large number of succinic acid can be produced during the fermentation of the soy sauce, so that the concentration of succinic acid in the finished soy sauce is substantially increased, the delicate flavor of the finished soy sauce is obviously improved, and the quality of the finished soy sauce is improved; the mutation breeding method is simple, the operation is simple, the input cost is low, the soy sauce finished koji prepared from the strain has high succinic acid content and good enzymatic activity, and the sense and the quality of the finished soy sauce prepared from the strain can be obviously improved.
Owner:YANTAI UNIV
Method for improving tolerance of erythromycin-producing strain against n-propanol through mutagenesis
InactiveCN103160446AImprove toleranceIncrease concentrationBacteriaMutant preparationHigh concentrationUV-Mutagenesis
The invention discloses a method for improving the tolerance of erythromycin-producing strain against n-propanol through mutagenesis. The method comprises the steps that: (1) an erythromycin-producing strain is adopted as an initial strain, and is pre-cultured for 7 days on a slant culture medium; (2) the pre-cultured erythromycin-producing strain is subjected to ultraviolet mutagenesis, wherein the strain is irradiated for 3min under conditions of an ultraviolet lamp with a power of 15W and a fixed distance of 20cm; and the obtained product is instantly smeared on a culture medium plate; (3) live colonies after mutagenesis are subjected to ion beam irradiation mutagenesis, wherein a mutagenesis temperature is 25 DEG C and mutagenesis dose is 55Gy; after mutagenesis, culture medium plate pre-screening and shaking flask fermentation secondary-screening are carried out, and the obtained live colonies are the mutant erythromycin-producing strain with tolerance to n-propanol. With the method, the mutant erythromycin-producing strain with tolerance to high-concentration n-propanol is obtained. The n-propanol tolerance concentration is higher than 2%. Therefore, erythromycin-producing strain tolerance against n-propanol is improved, such that n-propanol concentration in a culture medium can be increased. Under a condition that producing strain conversion rate is unchanged, with the increasing of n-propanol concentration, erythromycin yield is increased. A draw-off titer of a 100L fermentation tank can be higher than 13000u / ml.
Owner:SHANDONG FANGMING PHARMACEUTICAL CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com