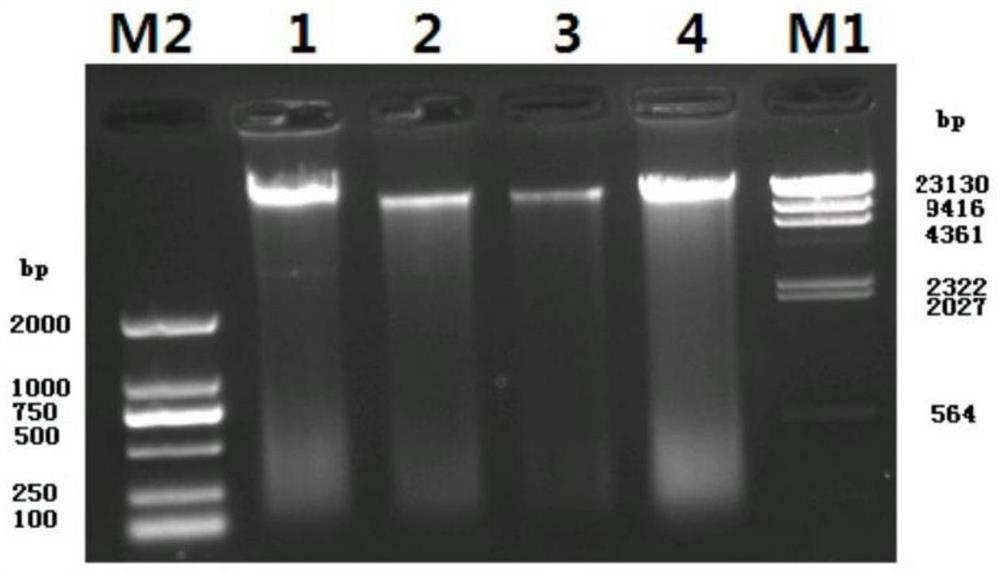
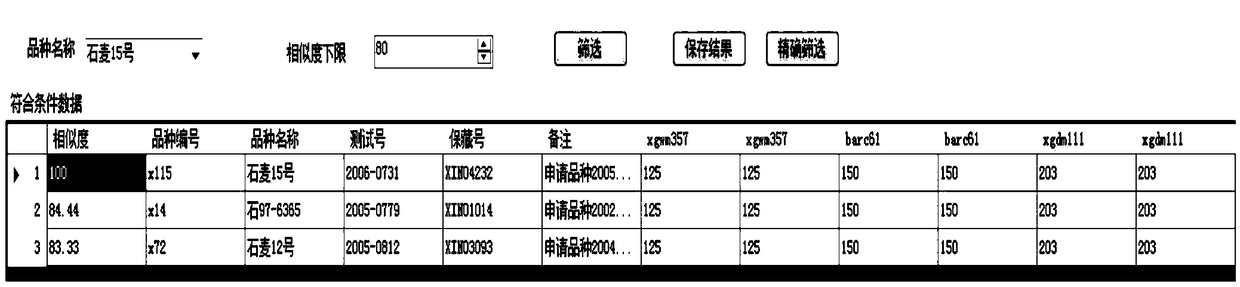
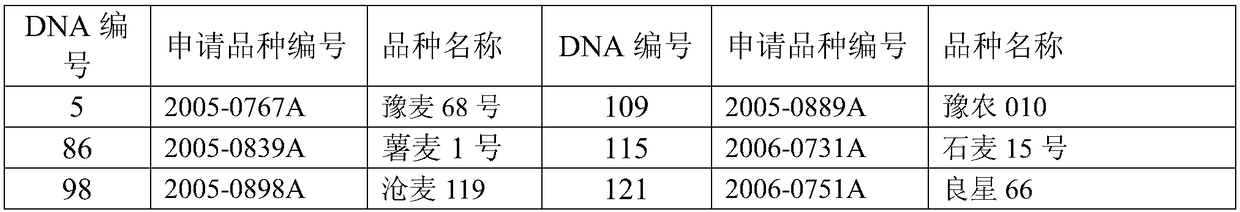
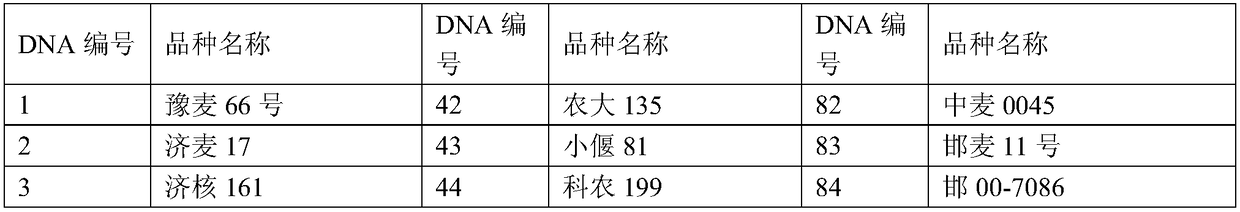
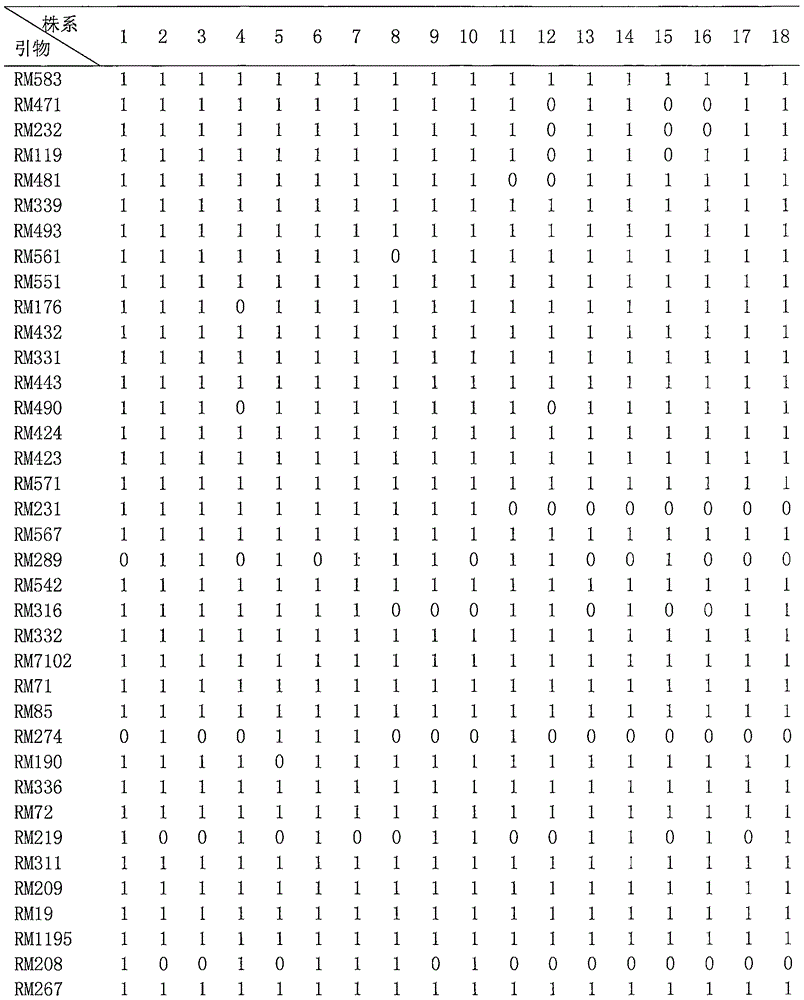
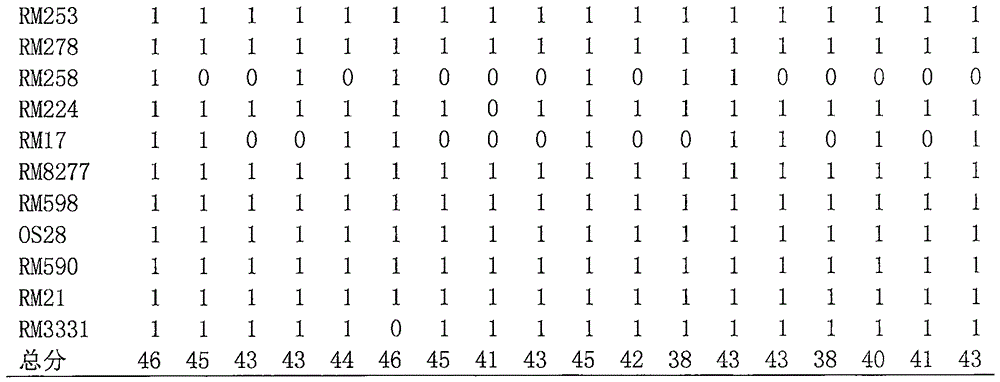
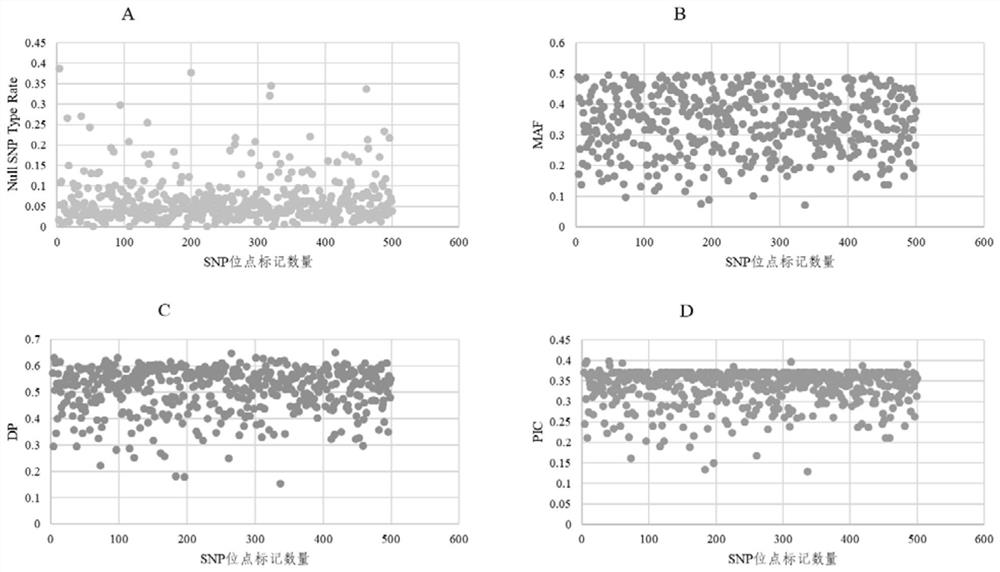
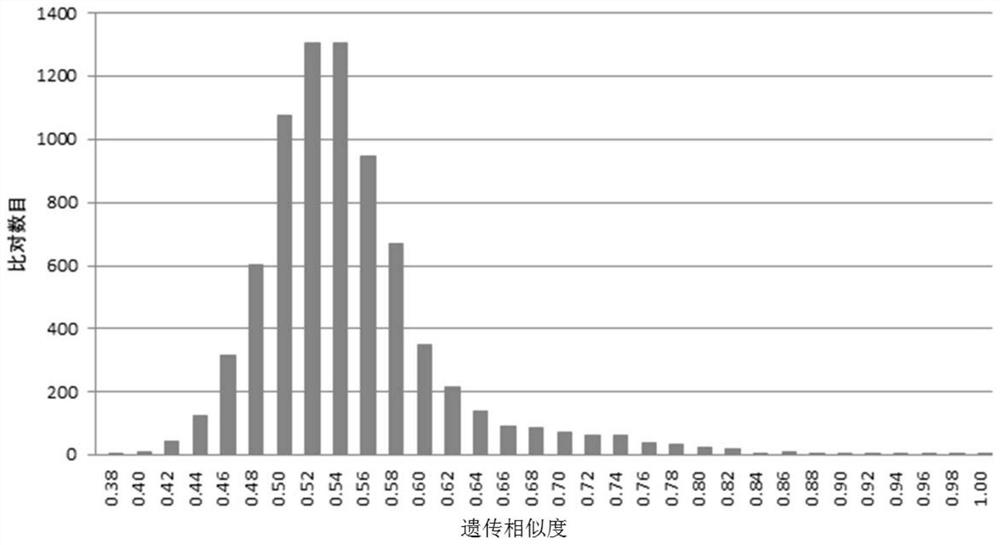
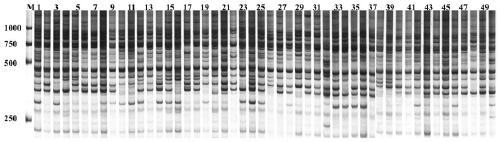
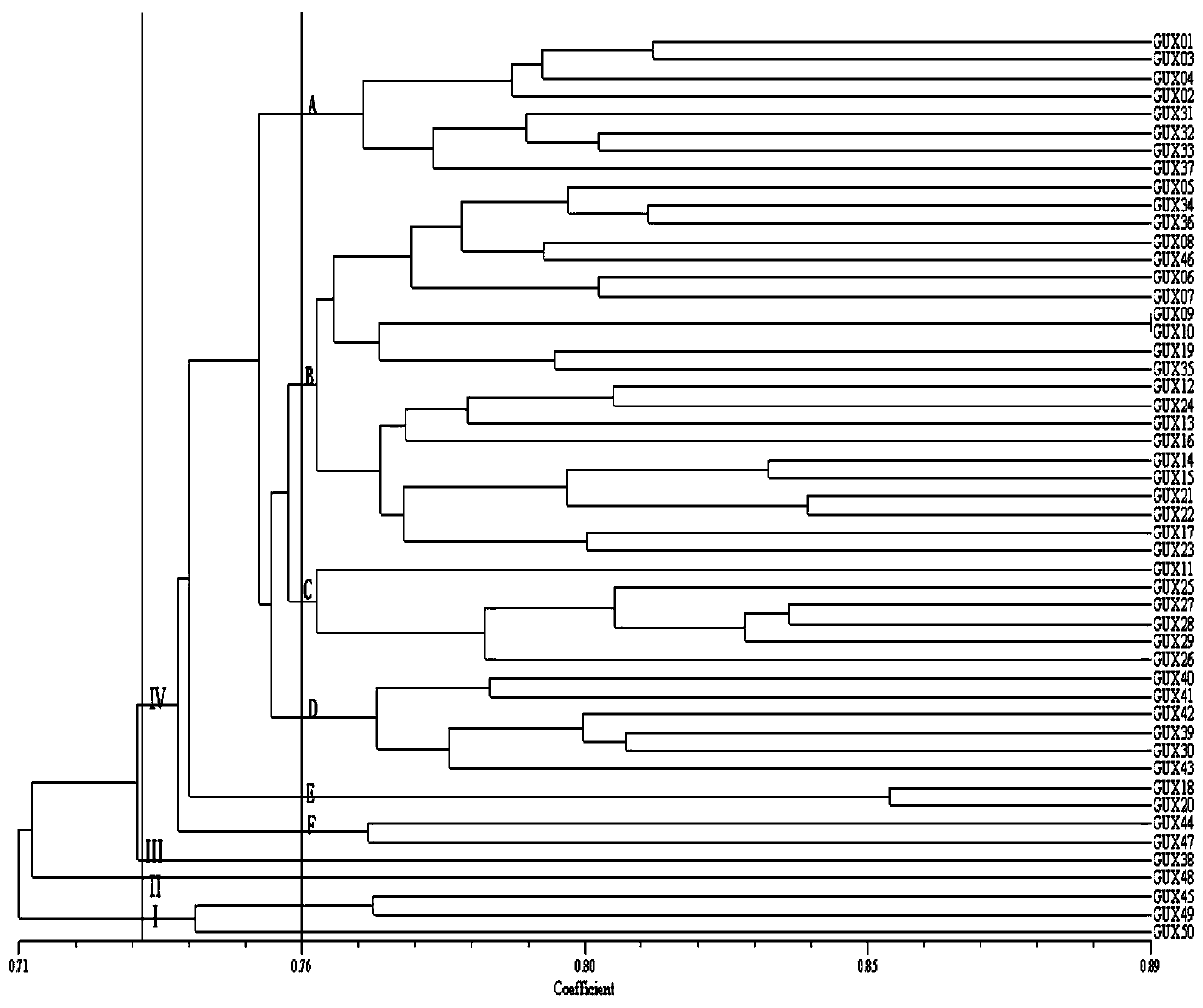
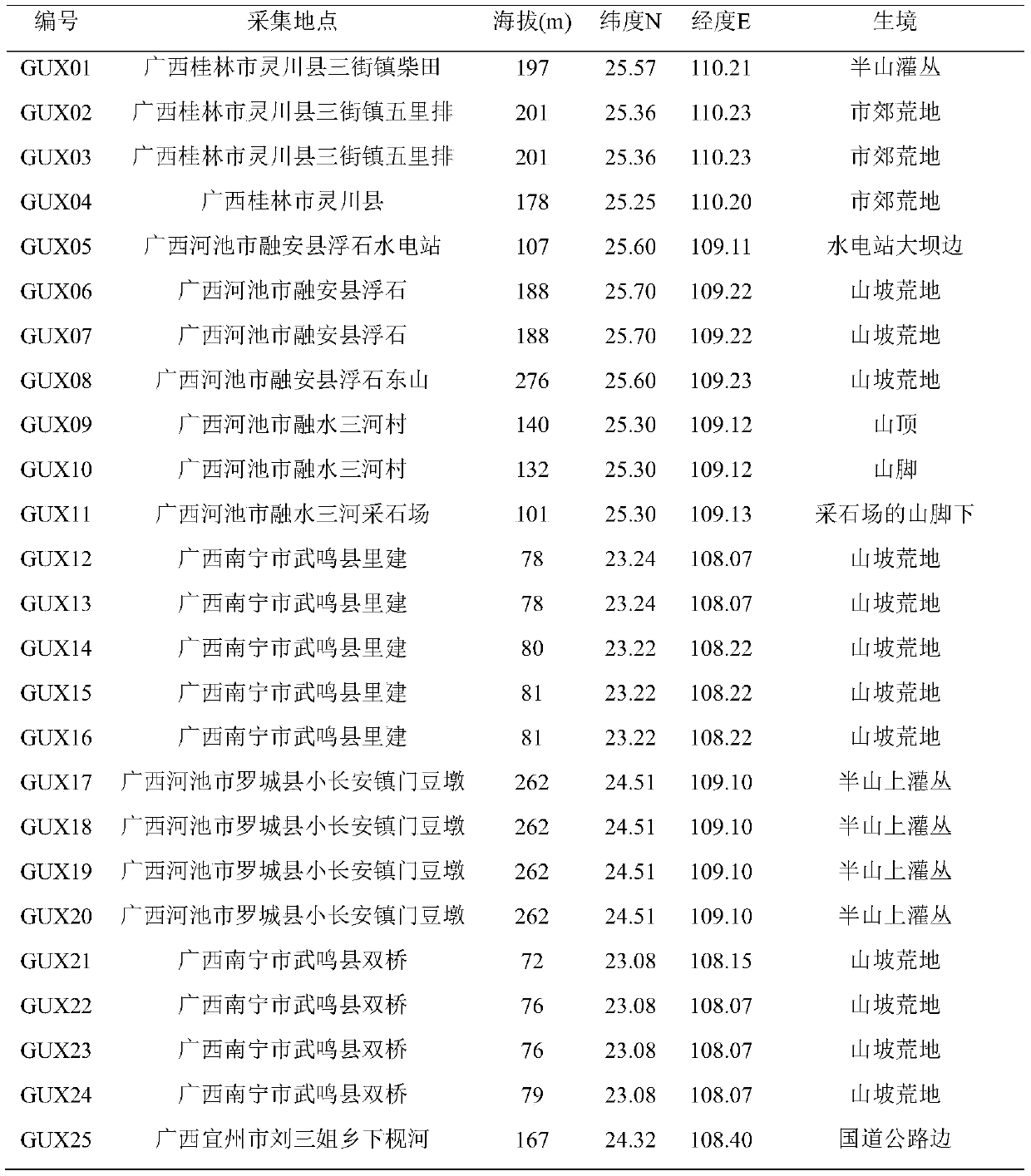
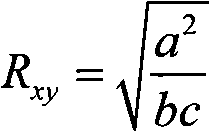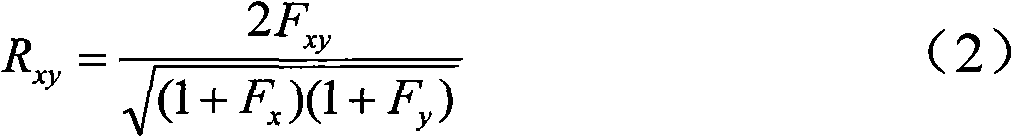Patents
Literature
36 results about "Genetic similarity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Genetic similarity theory, an extension of the kin-selection theory of altruism, postulates that people detect genetic similarity in oth ers ("nonkin" as well as "kin") in order to provide mutually sup portive environments, such as marriage, friendship, and social groups.
Method for identifying prunus persica plant species based on SSR molecular markers
InactiveCN105512513APromote healthy developmentMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsGenetic divergenceGenetic similarity
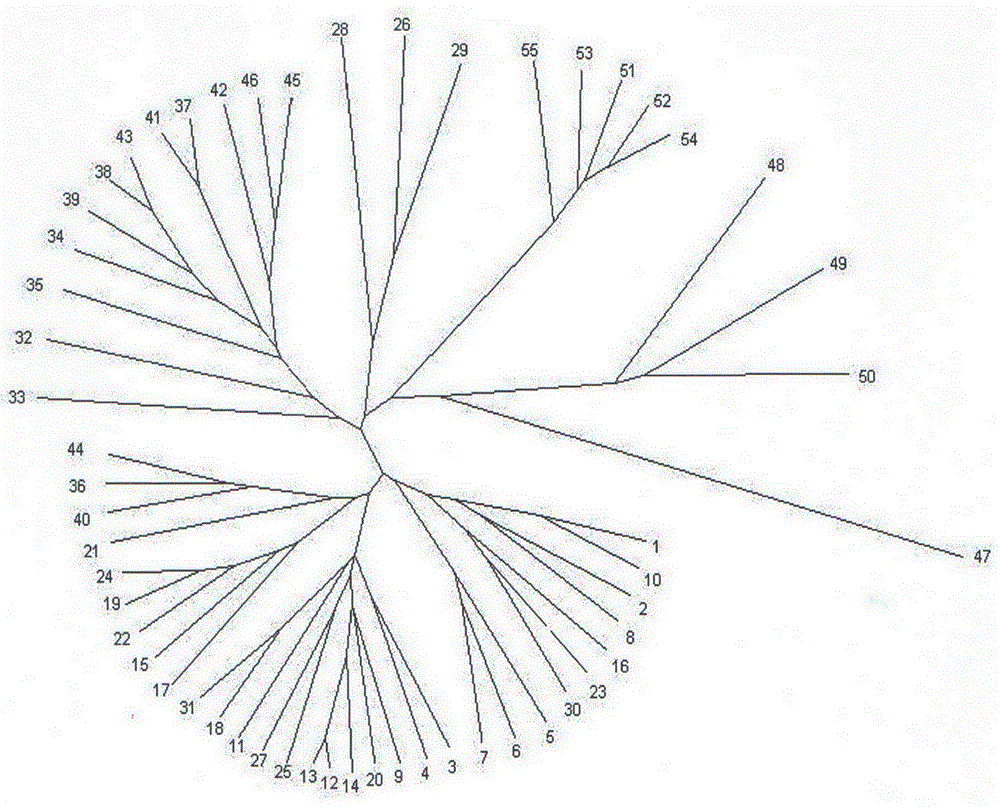
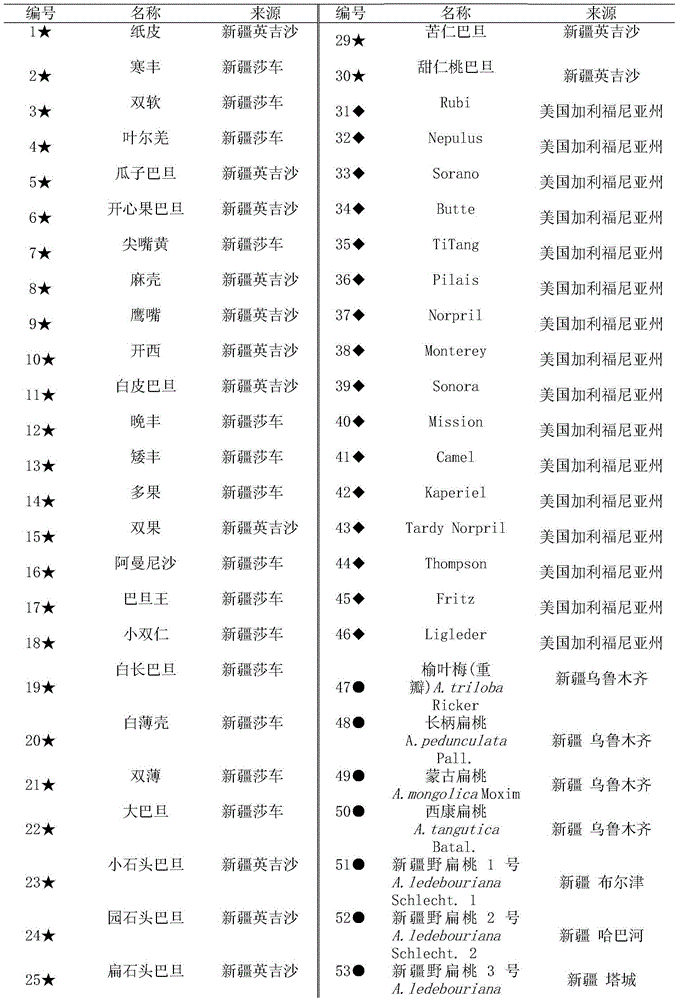
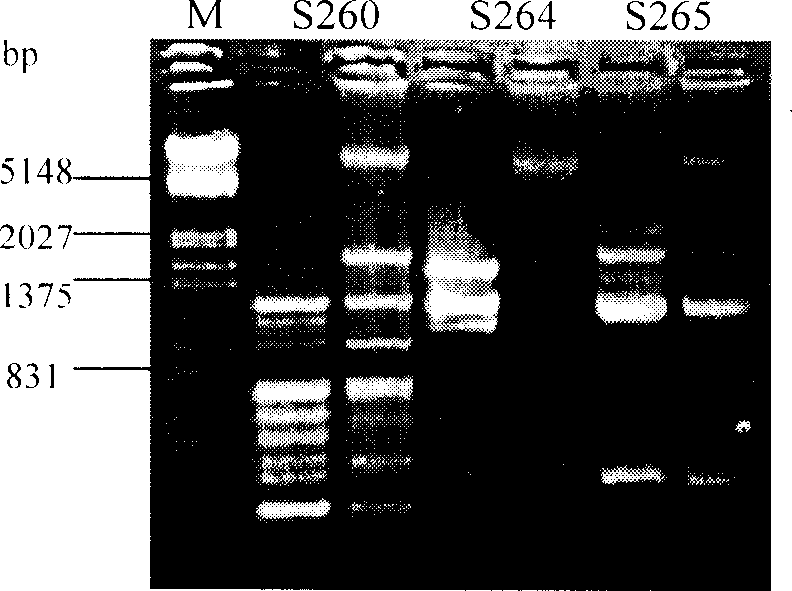
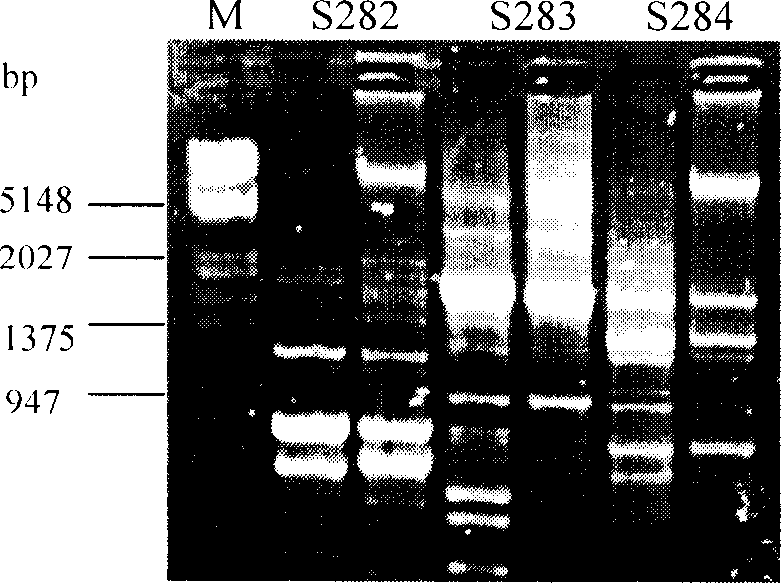
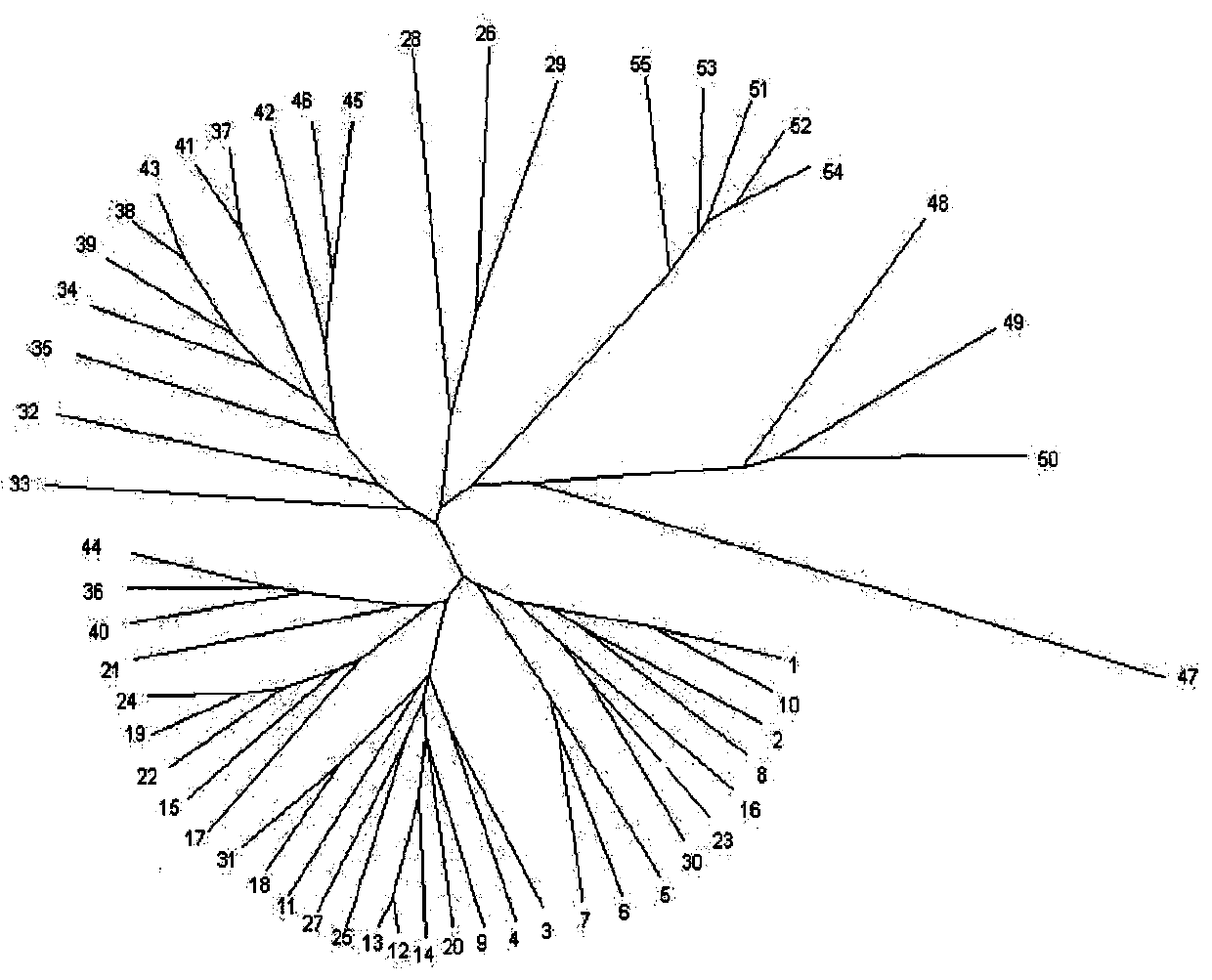
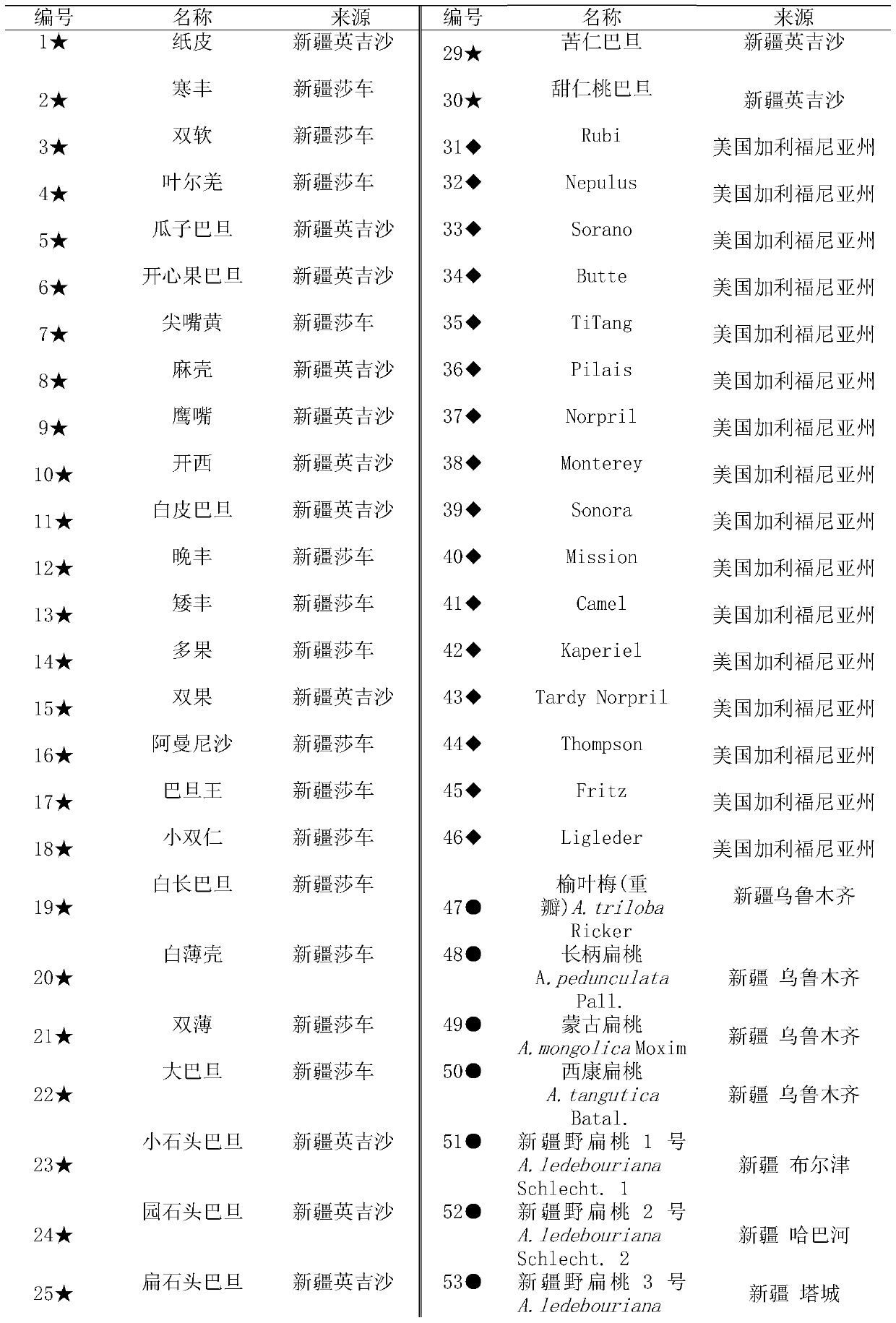
The invention relates to a method for identifying prunus persica plant species based on SSR molecular markers. According to the method, SSR primers with high polymorphism are selected for carrying out the SSR-PCR amplified reaction, electrophoresis detection and system analysis on 55 parts of prunus persica plant specie materials. The result shows that 10 pairs of primers, with high polymorphism, screened from 100 pairs of SSR primers are used for carrying out SSR-PCR amplification on genome DNA of the prunus persica plant specie materials, 63 amplified bands are amplified together, the number of polymorphic bands is 60, the polymorphic rate is 95.2%, and the better amplification result is obtained. Similarity coefficient and cluster analysis is carried out, the genetic similarity coefficient is 0.4133-0.9600, and the average similarity coefficient is 0.6867; the genetic difference among the 55 parts of prunus persica plant specie materials shows that the different species and the genetic distances among the different species are different, when the similarity coefficient is smaller than 0.68, most cultivated varieties are clustered into one cluster, and most cultivated varieties in the same provenance can be clustered together. An important way is provided for further distinguishing the genetic relationship among the prunus persica plant specie resources.
Owner:XINJIANG AGRI UNIV
Method for identifying varieties of lilium brownii by adopting SSR (simple sequence repeat) molecular marking technology
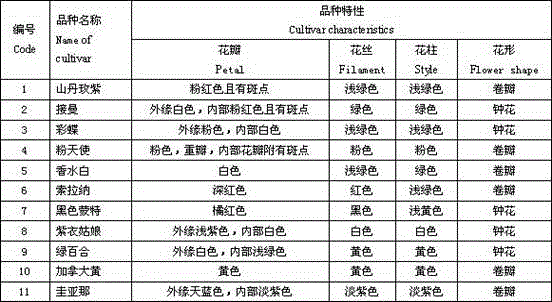
InactiveCN104263835AHigh polymorphismGood repeatabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementGermplasmPetal
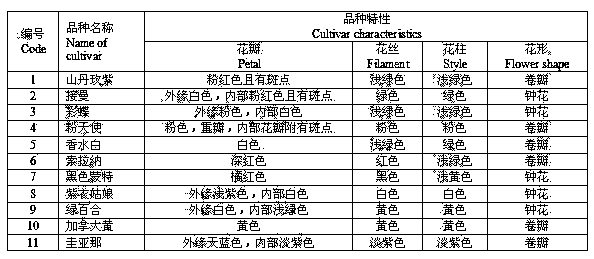
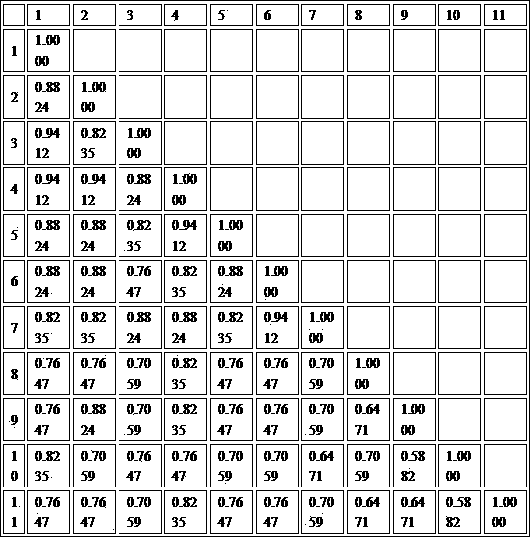
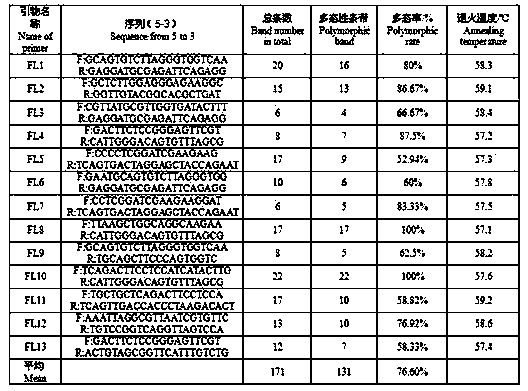
The invention relates to the method for identifying the varieties of lilium brownii by adopting an SSR (simple sequence repeat) molecular marking technology. A result shows that: two pairs of high-polymorphism and high-repeatability primers are screened from 13 pairs of primers for detecting 171 fragments comprising 131 polymorphic fragments, 4 to 22 fragments can be detected by each pair of primers with the sizes of 100 to 250bp, 1.69 bands are amplified by each pair of primers, and the polymorphism rate is 76.70 percent; NTSYS-pc2.11 is used for similarity coefficient and cluster analysis, the genetic similarity coefficient is 0.5882 to 09412, and the average similarity coefficient is 0.7647; materials are divided into six major classes by cluster analysis, the genetic differences between 11 lilium brownii germplasms are irrelevant to varietal characteristics, flower forms, the colors of filaments and styluses, but have certain correlation with the colors of petals, flower genes can better reflect genetic relationships between the lilium brownii germplasms, different varieties have different colors, and the primers can be designed by controlling related genes of flowers to provide an important means for further distinguishing the genetic relationships.
Owner:KAILI UNIV
Establishment method of porphyra haitanensis core germplasm bank
InactiveCN106222283AMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationSmall sampleGenetic similarity
The invention provides an establishment method of a porphyra haitanensis core germplasm bank and relates to porphyra haitanensis. The method includes the following steps that porphyra haitanensis germplasm is collected and purified; 2, strain genome DNA of all the germplasm of porphyra haitanensis is extracted; 3, porphyra haitanensis germplasm strain genetic diversity analysis based on an SSR molecular marker is carried out; 4, the genetic similarity coefficient between all germplasm strains is calculated; 5, gradual clustering sampling is carried out to establish the core germplasm bank. The obtained core germplasm bank can preserve the genetic diversity of original germplasma to the maximum degree with a smallest sample number, therefore, parent assembly links carried out during following porphyra haitanensis crossbreeding are simplified, and the breeding efficiency and the breeding effect are improved.
Owner:JIMEI UNIV
Ultraviolet mutagenic obtained low temperature salina and its identifying method
InactiveCN1944643AExtend the breeding timeLong breeding cycleUnicellular algaeMicrobiological testing/measurementUV-MutagenesisGenetic similarity
The present invention relates to saline algae, provides one kind of low temperature tolerant saline algae and its ultraviolet mutagenesis breeding process and identifying method. The low temperature tolerant saline algae features its light illuminating growth at 3-10deg.c to reach (1.05-8.11)x10<6> cell / ml in the cell density 2.1-21 times higher than the contrast; the genetic similarity coefficient to wild strain of 0.680-0.910; and increased or decreased protein zone(s) compared with wild strain.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
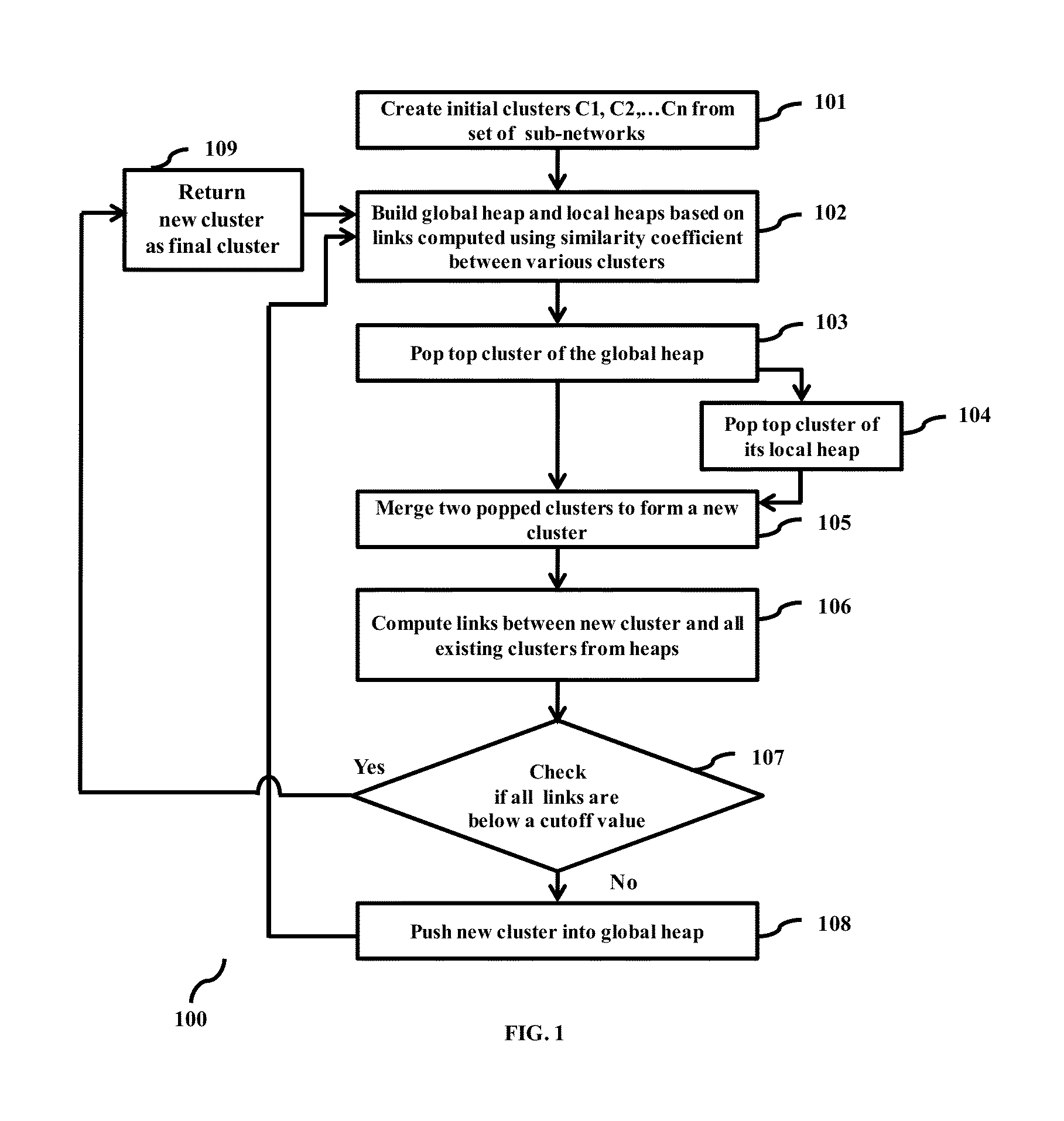
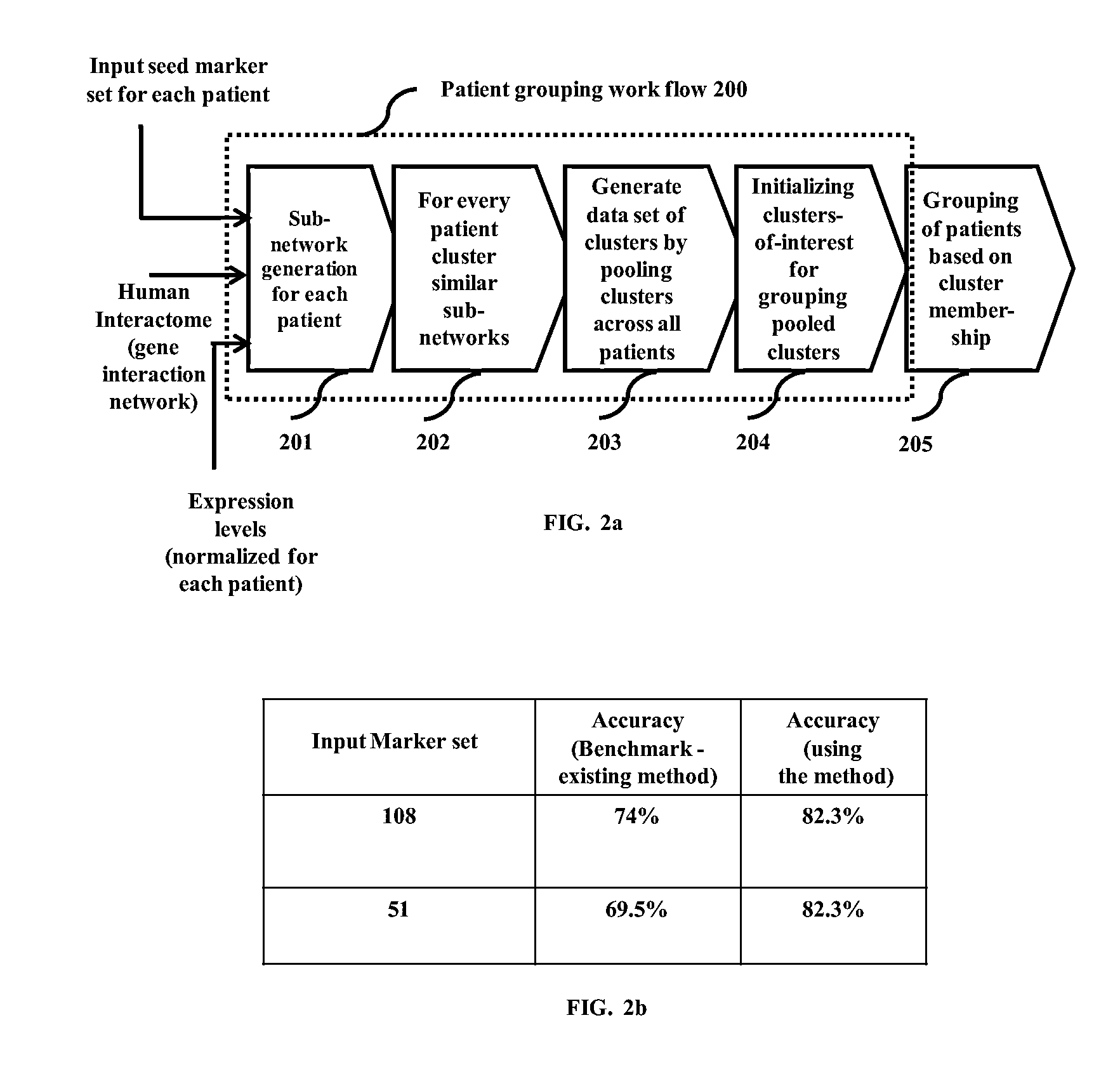
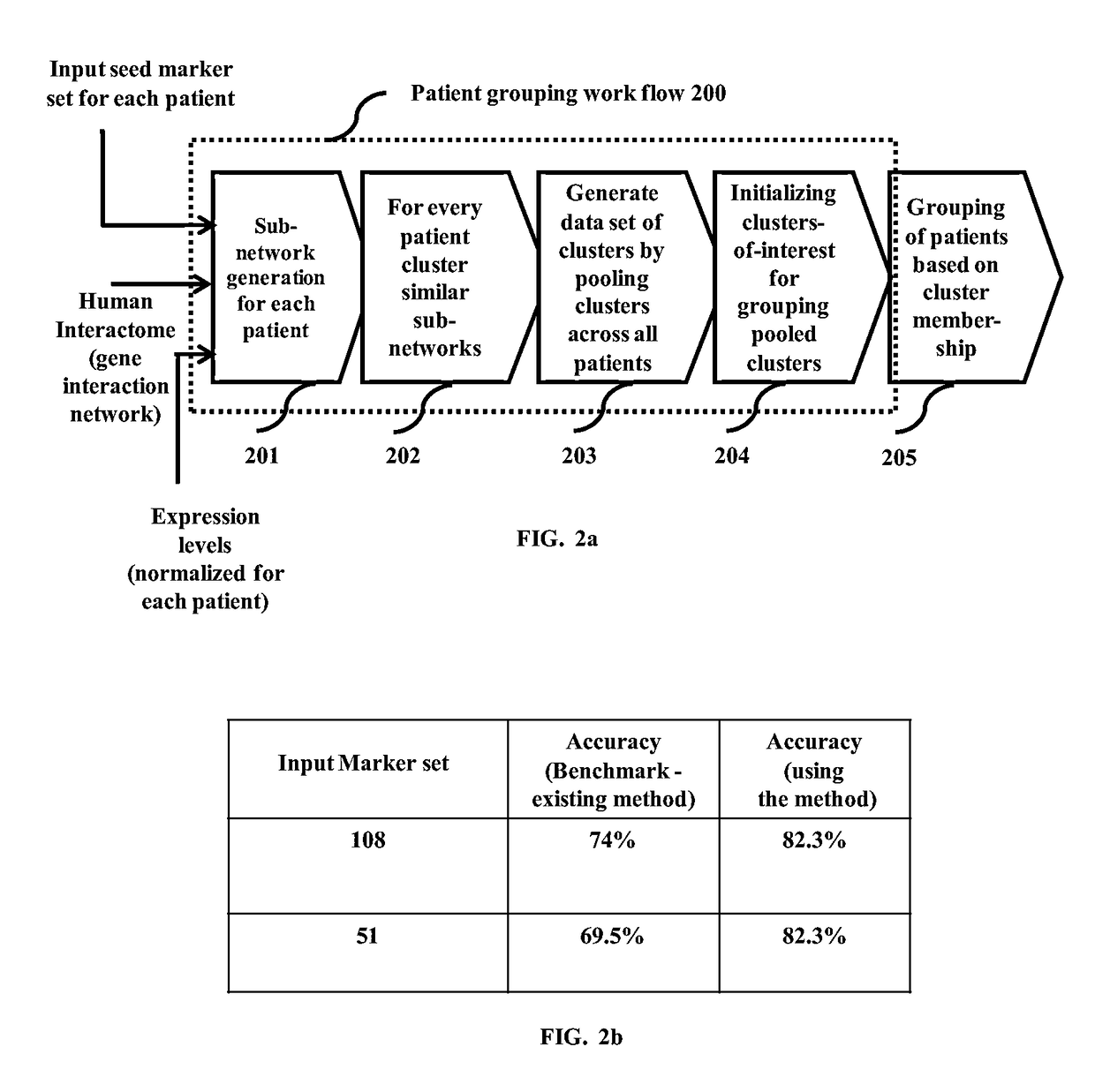
Methods and systems for customizable clustering of sub-networks for bioinformatics and health care applications
InactiveUS20150213115A1Digital data processing detailsRelational databasesInteraction netsPersonalization
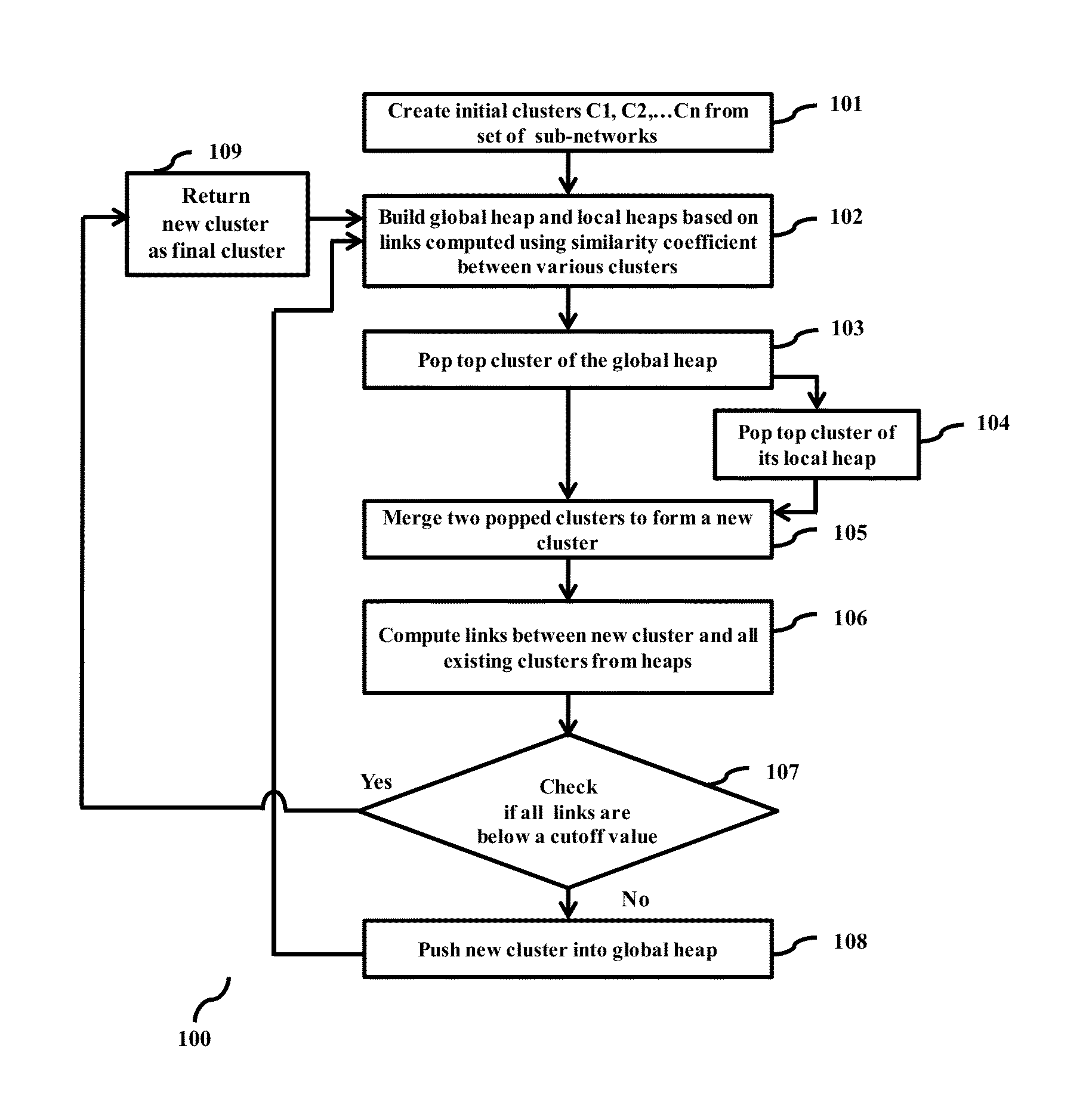
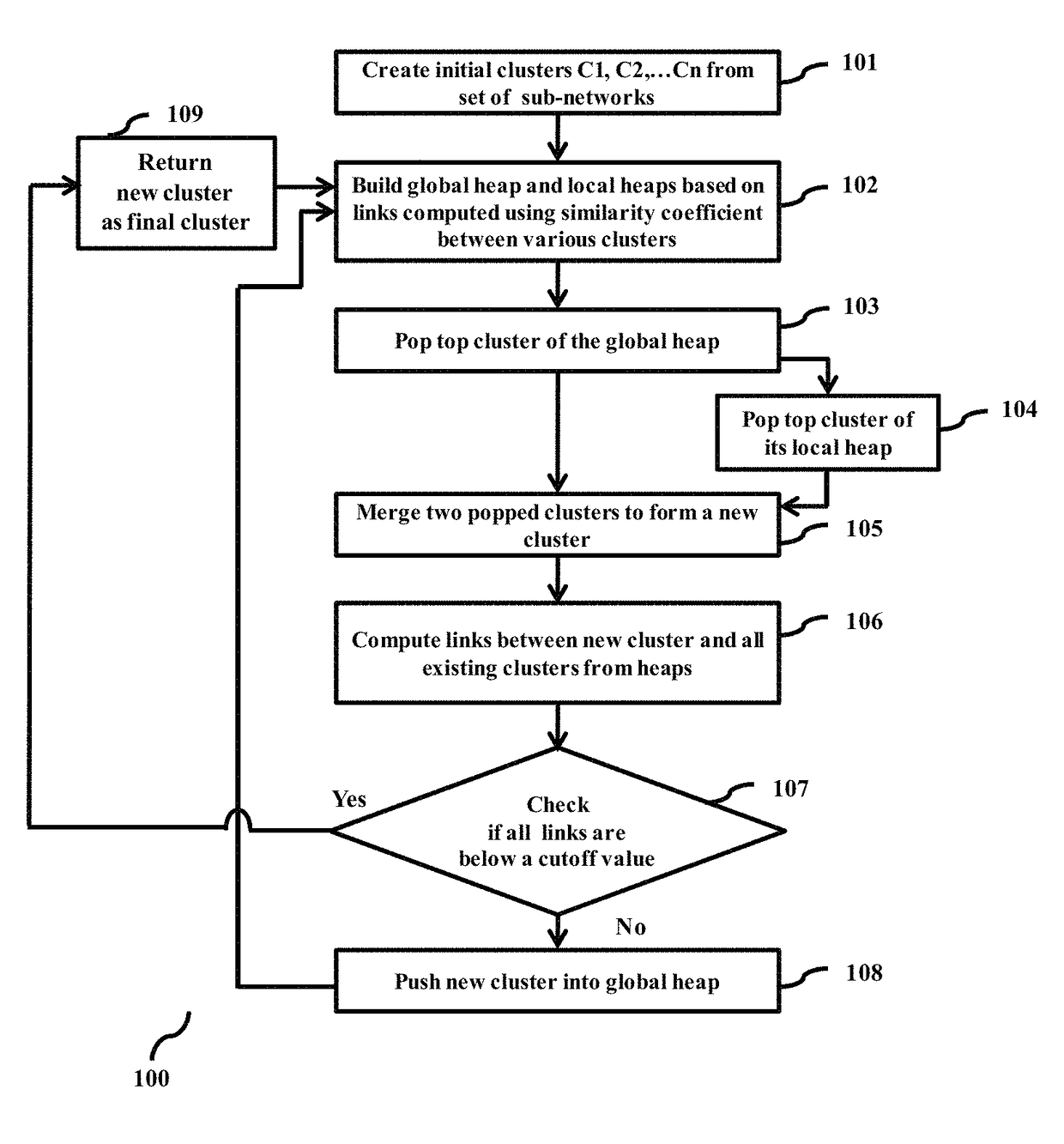
Methods and devices for clustering a plurality of sub-networks of a larger interaction network using an enhanced hierarchical clustering algorithm are disclosed. The methods provide expression based sub-network generation using differentially expressed markers. The enhanced hierarchical clustering algorithm clusters the generated sub-networks based on a user defined customizable similarity coefficient. The methods use non-Boolean links to cluster similar sub-networks. This provides consideration of indirect relationships among sub-networks. The customizable similarity coefficient enables the methods to be used for diverse applications such as biomarker detection, patient stratification, personalized therapy, drug efficacy prediction, genetic similarity analysis in genetic diseases. The methods enable patient grouping based on the enhanced hierarchical clustering algorithm.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Molecular markers and method for identifying Dimocarpus and related genera plants thereof
ActiveCN108913810AMake up for the lackAccurate and effective distinctionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationSpectral bandsGenomic DNA
The invention discloses molecular markers and a method for identifying Dimocarpus and related genera plants thereof, and belongs to the technical field of classification and identification of plant germplasm resources. According to the present invention, the genomic DNA of the Dimocarpus and the related genera plant are extracted by using the longan EST-SSR marker as the molecular marker, PCR amplification is performed with 9 pairs of universal EST-SSR primers, the amplified product is subjected to polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, the spectral bands are read, the 0 / 1 data matrix is established, the genetic similarity coefficient is calculated, and cluster analysis is performed. According to the present invention, the universal EST-SSR primers compensate for the lack of the universal SSRmarkers in the Sapindaceae, and provides the effective markers for the classification research on the plant in the Sapindaceae; and the provided EST-SSR markers can accurately and effectively distinguish the Dimocarpus and the four related genera plants thereof, and has advantages of high repeatability, neat banding pattern, simple operation and the like.
Owner:POMOLOGY RES INST FUJIAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Estimating method of genetic similarity index of codominance molecular marker based on relative correlation coefficient
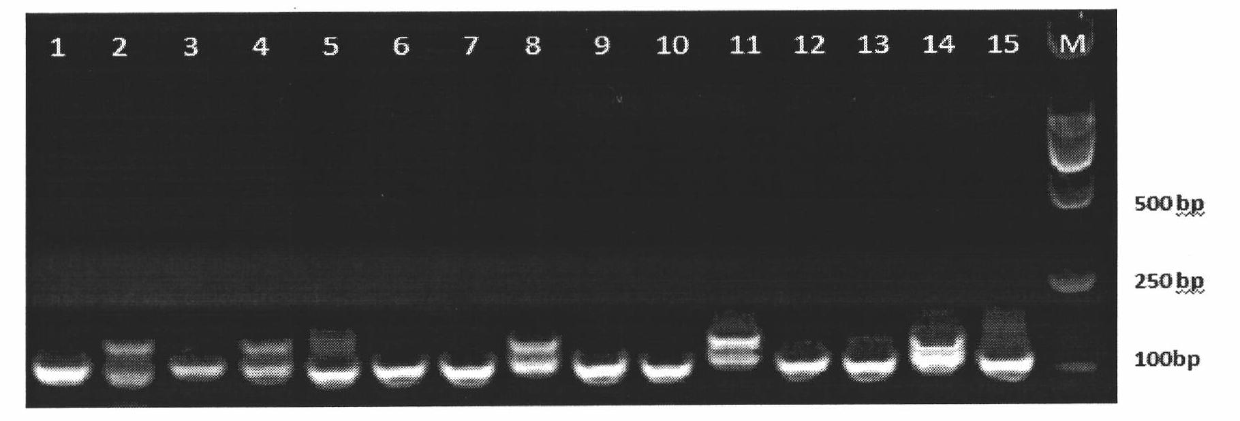
ActiveCN101984446AOvercome the defect that the degree of kinship is not necessarily relatedMicrobiological testing/measurementSpecial data processing applicationsCorrelation coefficientElectrophoresis
The invention discloses a calculation method of genetic similarity index of codominance molecular marker based on relative correlation coefficient. The technical scheme is as follows: obtaining an electrophoresis pattern of each variety or kind of plant by adopting the current codominance molecular marker method; comparing in pairs according to the amplification strip information of the variety or kind of the plant; respectively calculating a genetic similarity index between each two plant varieties and kinds according to a calculation formula of the genetic similarity index; and taking the genetic similarity index as the estimation of the corresponding relative extent of the individuals. The calculation method of genetic similarity index is applied to the codominance molecular marker. The calculation method of the obtained genetic similarity index can effectively respond the relative relationship extent among the colonies based on the relative correlation coefficient.
Owner:YUNNAN ACAD OF TOBACCO AGRI SCI +1
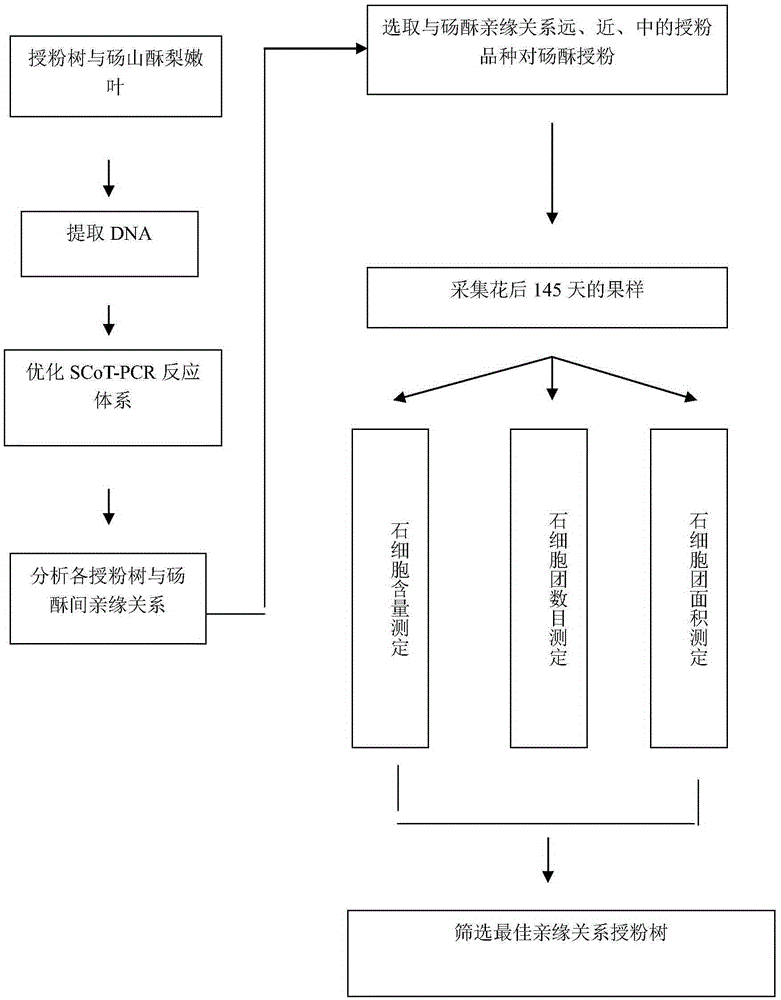
Method for screening pollination pear varieties suitable for Dangshan pears
InactiveCN105400887APromote amplificationClear bandMicrobiological testing/measurementPEARGenetic similarity
A method for screening pollination pear varieties suitable for Dangshan pears comprises the specific steps that 1, DNA of leaves of the pollination pear varieties is extracted; 2, a SCoT-PCR is carried out, a genetic similarity coefficient is calculated, and a genetic relationship dendrogram between the pollination pear varieties is constructed; 3, according to a clustering analysis result, the pollination pear varieties with the far, intermediate and near genetic relationships are selected to pollinate the Dangshan pears; 4, the number and area of sclereid groups of pulp tissue of mature fruits borne by each pollination pear variety are microscopically observed and calculated, and the content of sclereid is measured; 5, the pollination pear varieties with the optimal generic relationship are screened out through the analysis result of the step 4. According to the method, the genetic relationships between different pear variety resources can be revealed fast and accurately from the molecular level, the influence of the different genetic relation pollination pear varieties on the size and content of the sclereid of Dangshan pear fruits is analyzed, then the excellent pollination varieties with the proper genetic relationship are screened out, the sclereid content of the Dangshan pear fruits is improved, and the quality of the Dangshan pear fruits is improved.
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Mutagenesis, selective breeding and identification method of cold tolerant Danaliella
InactiveCN1888047AExtend the time of outdoor cultivationLong breeding cycleUnicellular algaeElectrical/wave energy microorganism treatmentUltravioletWild type
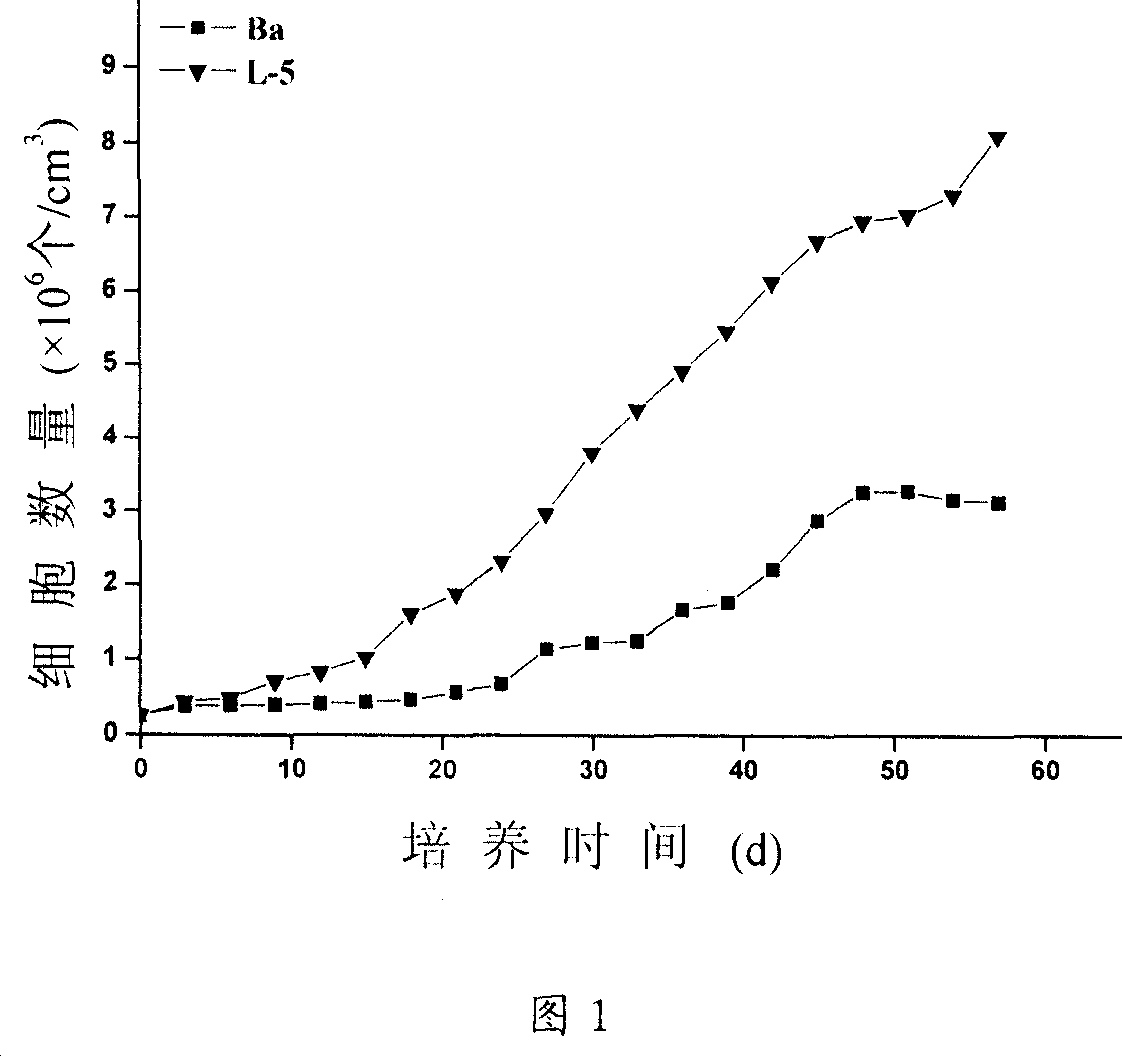
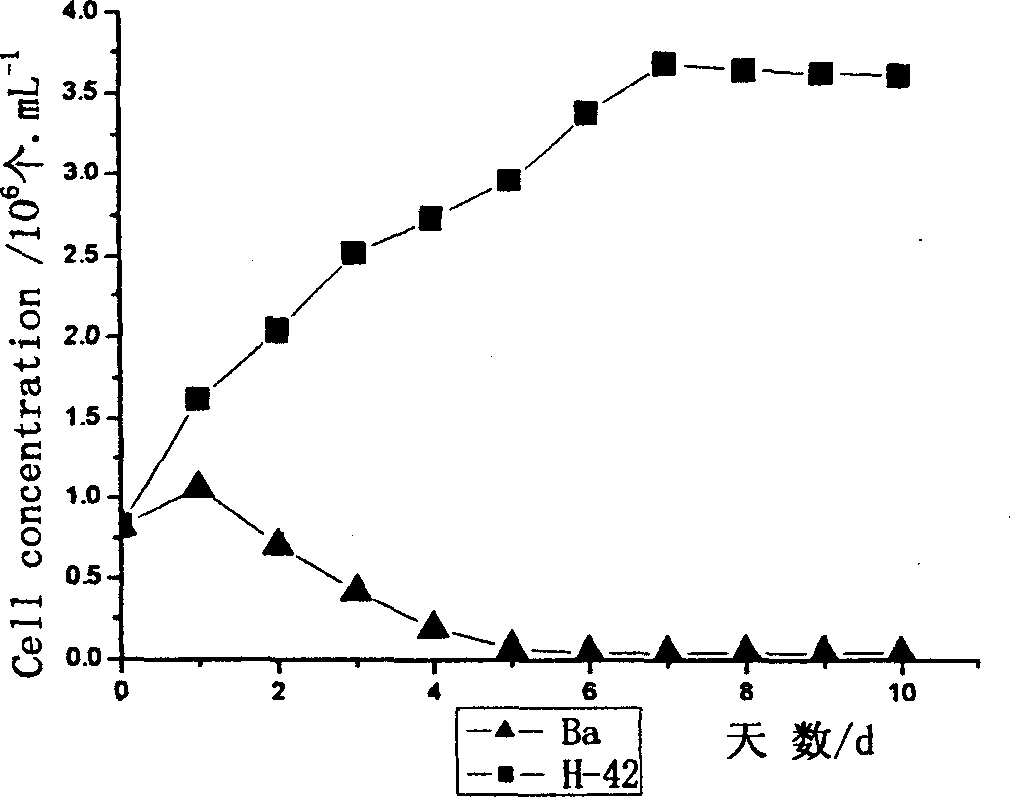
The ultraviolet ray mutagenesis, selective breeding and identification method of cold tolerant Dunaliella includes: inoculating Dunaliella to culture medium; lighting and dark inducing for synchronized growth; mixing Dunaliella liquid with iodine solution or bromophenol blue solution to deactivate Dunaliella, injecting Dunaliella liquid to culture dish, mutagenesis under ultraviolet lamp before dark culturing, mixing with fresh culture liquid and painting the mixture to Dunaliella culture medium for low temperature lighting culture; inoculating single Dunaliella colony to the culture liquid and low temperature lighting culturing; sampling detection to comparing the low temperature lighting growth curves of cold tolerant Dunaliella mutant and wild prototype strain; extracting total DNA for RAPD comparison; calculating genetic similarity coefficient; extracting total protein and post-electrophoresis staining while record results; comparing protein electropherogram; and confirming the obtained cold tolerant Dunaliella mutant.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Methods and systems for customizable clustering of sub-networks for bioinformatics and health care applications
InactiveUS9690844B2Relational databasesSpecial data processing applicationsPatient stratificationEfficacy
Methods and devices for clustering a plurality of sub-networks of a larger interaction network using an enhanced hierarchical clustering algorithm are disclosed. The methods provide expression based sub-network generation using differentially expressed markers. The enhanced hierarchical clustering algorithm clusters the generated sub-networks based on a user defined customizable similarity coefficient. The methods use non-Boolean links to cluster similar sub-networks. This provides consideration of indirect relationships among sub-networks. The customizable similarity coefficient enables the methods to be used for diverse applications such as biomarker detection, patient stratification, personalized therapy, drug efficacy prediction, genetic similarity analysis in genetic diseases. The methods enable patient grouping based on the enhanced hierarchical clustering algorithm.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Mutagenic breeding method of high temperature resistant pasteur Du algae
InactiveCN1757707AIncrease productivityExtend the time of outdoor cultivationMicrobiological testing/measurementUnicellular algaeUltravioletCulture mediums
A method for mutagenizing and selectively culturing a refractory single-cell green alga includes such steps as sterilizing and cooling culture medium, inoculating alga liquid, culturing, mixing with iodine solution or bromophenol blue, deactivating, calculating alga density in alga liquid, ultraviolet mutagenizing, dark culturing, mixing the cultured alga liquid with fresh culture medium, culturing, high-temp screening, amplifying culture of living alga cells, culturing under light radiation, inoculating yellow alga, culturing, testing its mutagenized effect, measuring the long and short diameters of cell, extracting DNA, random amplifying of polymorphic DNA, calculating genetic similarity coefficient, extracting H-42 and general protein, electrophoresis, dyeing with Coomassic brilliant blue, recording result and observing the electropherogram to obtain result.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
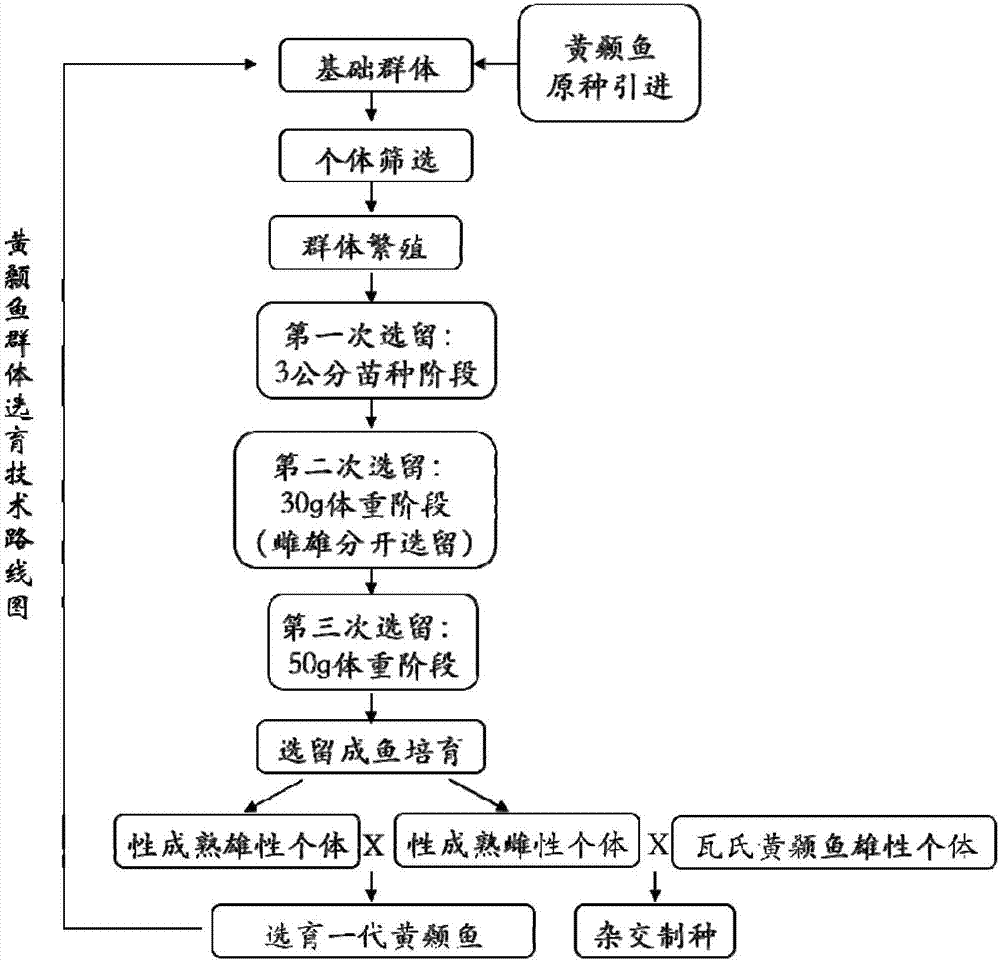
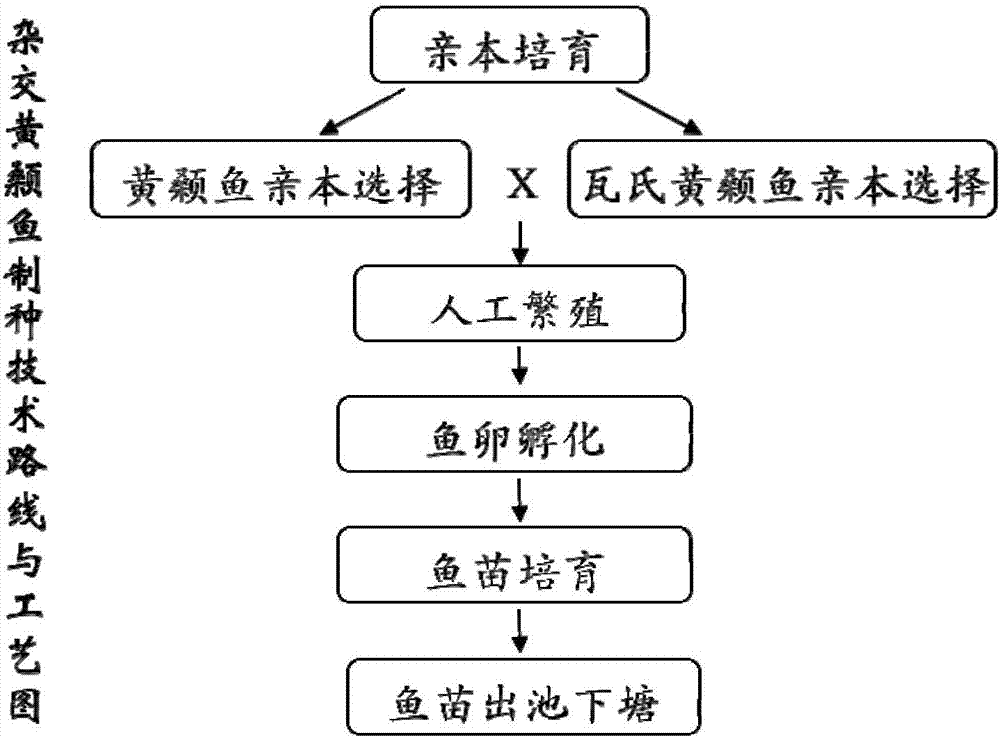
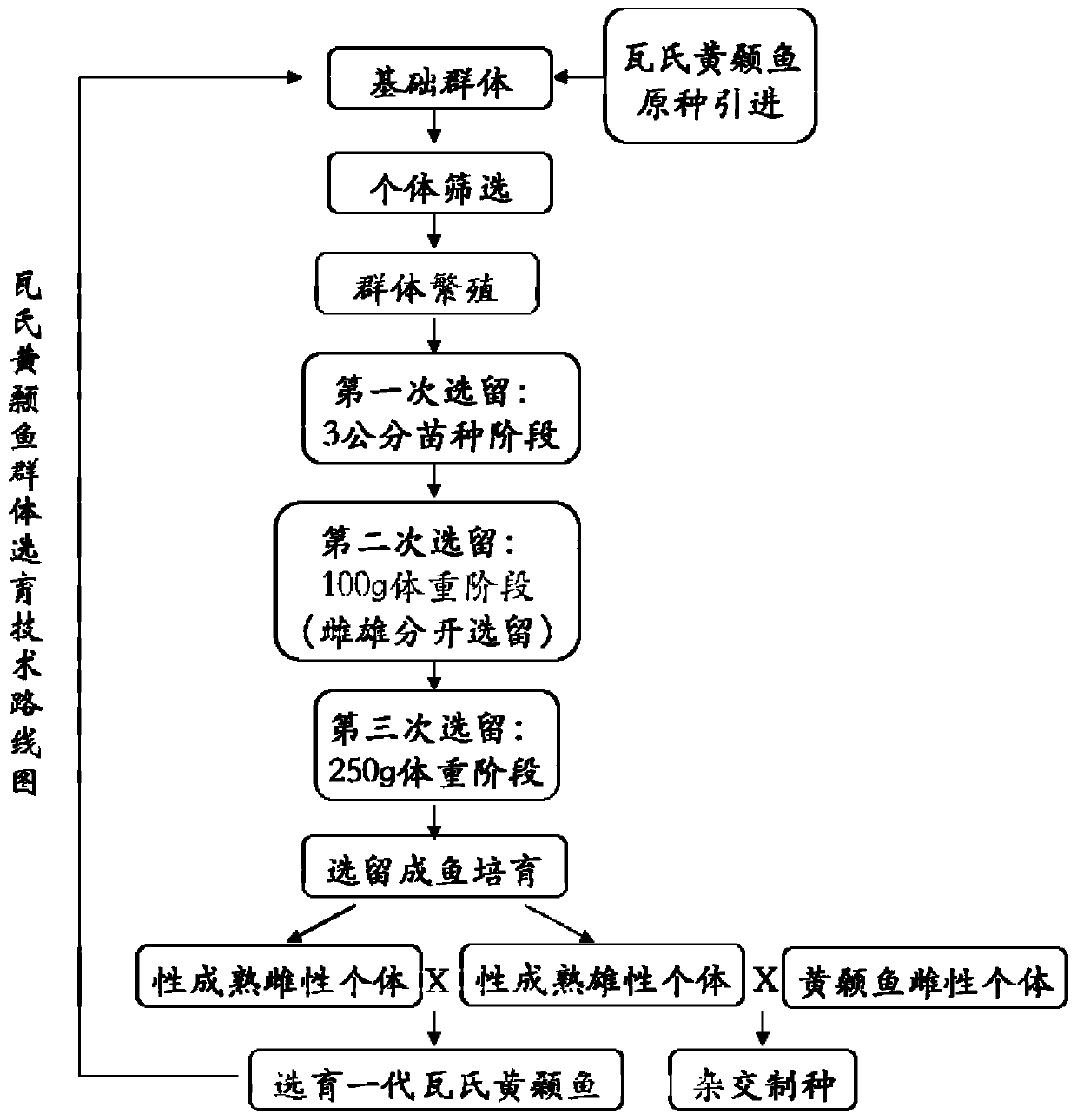
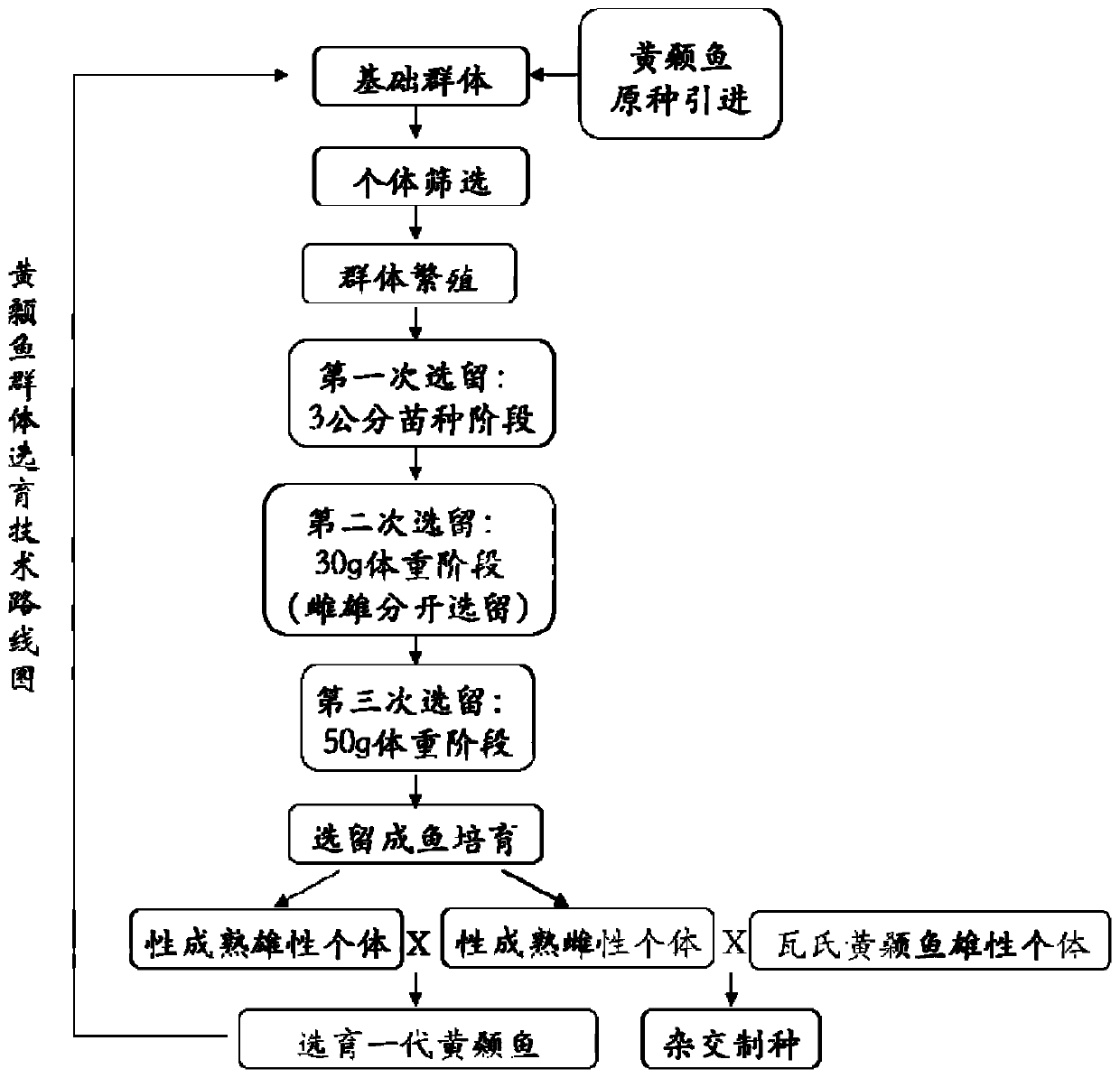
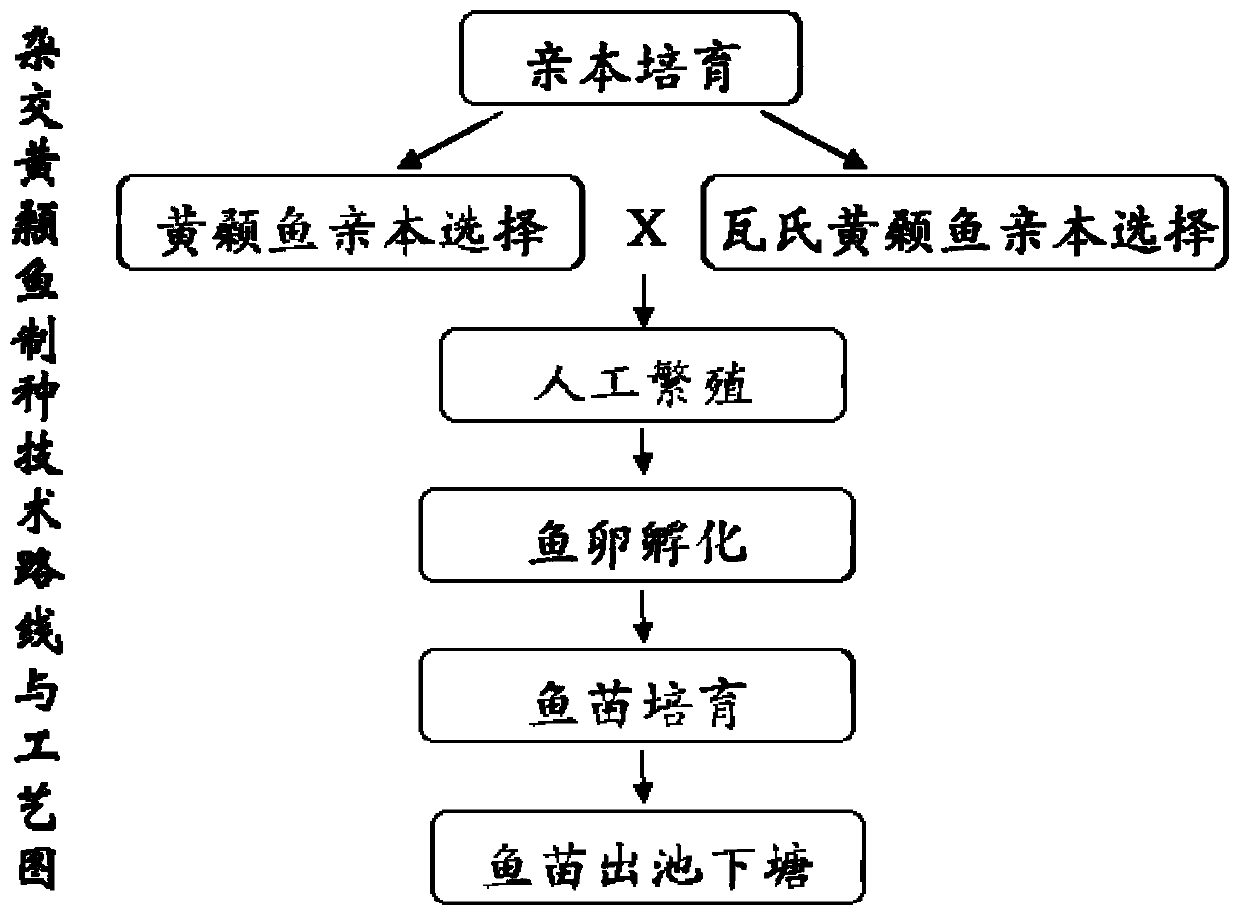
Complex breeding method for improving growth trait of Pelteobagrus fulvidraco
ActiveCN107155959AImprove efficiencyImprove survival rateMicrobiological testing/measurementClimate change adaptationGenetic similarityPelteobagrus
The invention relates to a complex breeding method for improving a growth trait of Pelteobagrus fulvidraco. The complex breeding method includes the following steps: acquiring high-quality Pelteobagrus fulvidraco and Pelteobagrus vachelli parent library through second generation group breeding; using microsatellite markers to detect Pelteobagrus fulvidraco and Pelteobagrus vachelli parents, selecting parent individuals having the genetic similarity of above 90% as a reproduction group; using female Pelteobagrus fulvidraco as female parents and male Pelteobagrus vachelli as male parents to perform hybrid breeding; and acquiring hybrid Pelteobagrus fulvidraco having the growth speed above 20% faster than common Pelteobagrus fulvidraco, wherein the hybrid Pelteobagrus fulvidraco has both excellent traits of dual parents, an attracting color ( female parents) and fast growth speed ( male parents). The complex breeding method can acquire improved hybrid Pelteobagrus fulvidraco, and has important significance for increasing the unit yield, the breeding benefits, and serving production practice.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
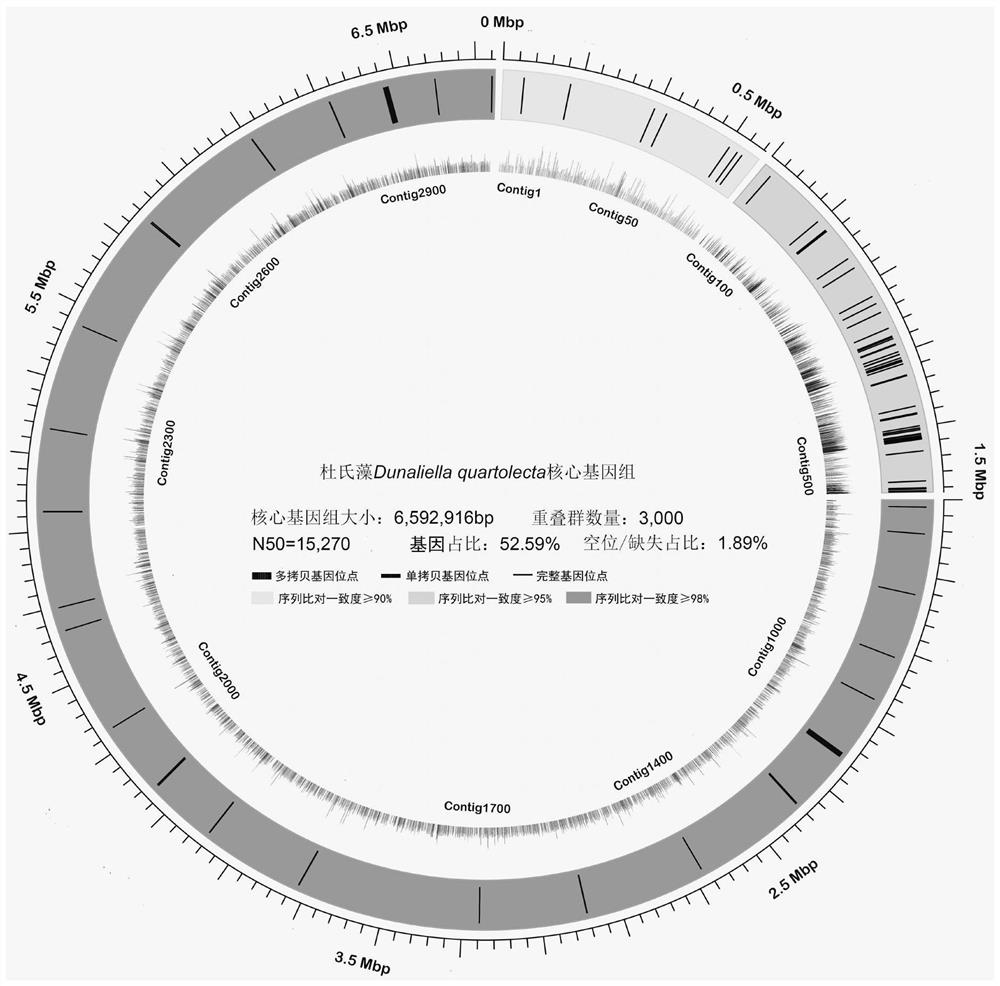
Strain identification method based on dunaliella core genome sequence
ActiveCN112349350AAvoid and overcome disadvantages such as high costRigorous program settingMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesGenomic sequencingMolecular identification
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant molecular identification, and particularly relates to a strain identification method based on a dunaliella core gene sequence. The method mainly comprises the following steps: collecting, purifying and culturing a sample; extracting the DNA of the whole genome; constructing a DNA sequencing library; obtaining whole genome sequencing data of thealgae strain to be detected and the Dunaliella Quartolecta; screening and de novo assembly of sequencing fragments of the D. Quartolecta core genome are carried out, and genome segmentation, proteinfunction annotation and genome contig colinearity analysis are carried out on the assembled core genome sequence; constructing a phylogenetic tree by utilizing single nucleotide polymorphism, and whenan algae strain to be detected and Dunaliella Quartolecta are gathered into a cluster, the data support rate of branches is 0.99-1.00, the genetic similarity percentage is greater than or equal to 99%, and the algae strain to be detected is D.quartolecta.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
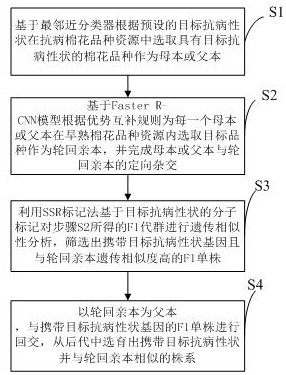
Specificity test approximate variety effective screening method based on genetic similarity
InactiveCN108796121AImprove work efficiencyOvercome the shortcomings of cumbersome selection operations, long time-consuming, and high error ratesMicrobiological testing/measurementCompletion timeScreening method
The invention discloses a specificity test approximate variety effective screening method based on genetic similarity. The method can be used for efficiently screening plant approximate varieties of wheat, corn, Chinese cabbages, soybeans and the like. The method is characterized in that firstly, for application varieties and known varieties, the DNA fingerprints of a group of SSR (simple sequencerepeat) markers or SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism) markers are collected; then, a DNA fingerprint database system of the known varieties is built; approximate variety screening database softwareis developed; the genetic similarity of the application varieties and the known varieties can be automatically calculated by the software; the approximate variety of each application variety can be selected according to any genetic similarity threshold value. A database technology is used for managing variety DNA fingerprint data; the genetic similarity is calculated; the approximate variety is selected; the work efficiency is greatly improved; the completion time of the approximate variety screening is shortened from several days to moment; the defects of approximate variety selection operation complexity, long consumed time and high error rate of the existing method are overcome.
Owner:CROP RES INST SHANDONG ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Cytoplasm type dividing method of millet breeding materials
InactiveCN102750458AImprove resultsImprove consistencyMicrobiological testing/measurementSpecial data processing applicationsHybrid seedGenetic similarity
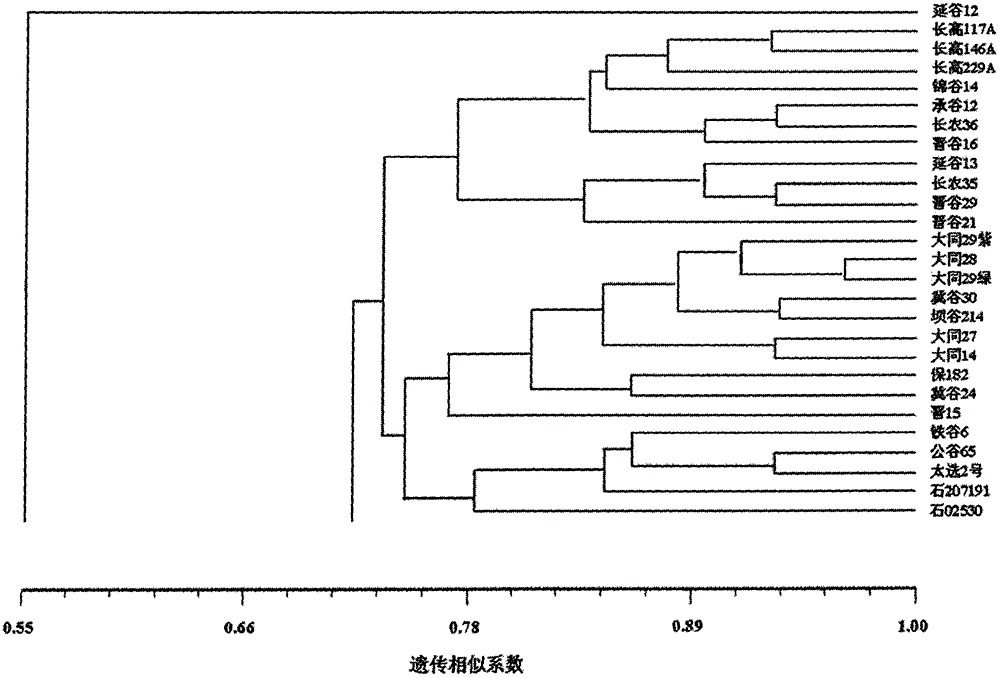
The invention discloses a cytoplasm type dividing method of millet breeding materials. The cytoplasm type dividing method is characterized by comprising the following steps of (1) cytoplasm source evolutionary tree building; (2) female parent derivation evolution chart building; (3) specific genetic similarity coefficient determination and cytoplasm source molecular clustering; and (4) cytoplasm type determination of the millet breeding materials. The method has the advantages that the foundation is laid for culturing the sterile system and the hybrid seed of different cytoplasm types, and the foundation is laid for creating the millet sterile system of different cytoplasm types and culturing the millet hybrid seed of different cytoplasm types.
Owner:GRAIN RES INST HEBEI ACAD OF AGRI & FORESTRY SCI
Breeding method for rapidly introducing rice target characters
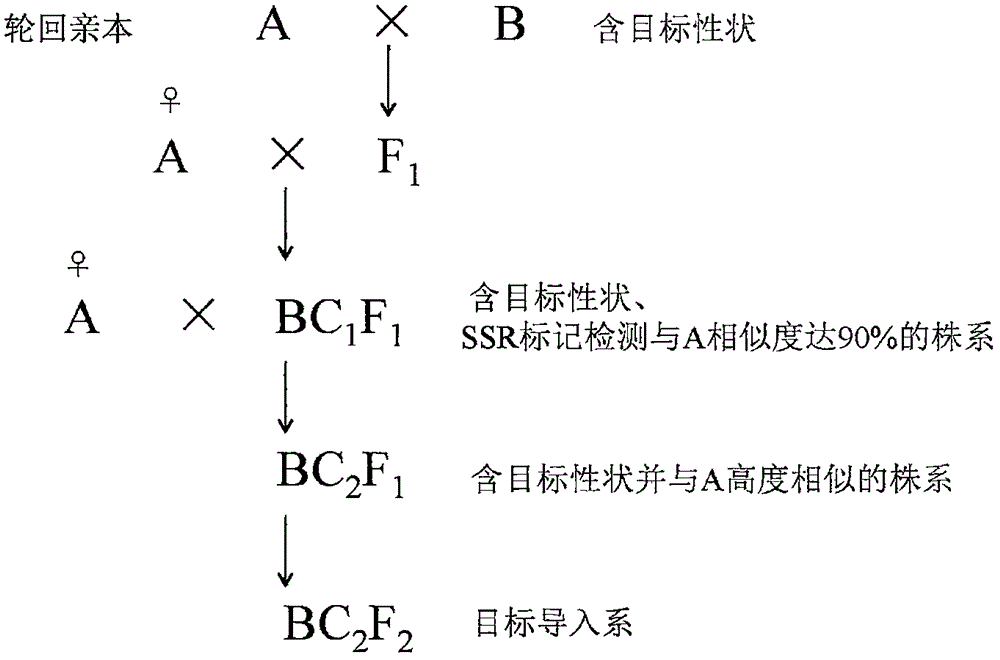
InactiveCN106577256AFast and efficient importSpeed up breedingMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant genotype modificationGenetic similarityGermplasm
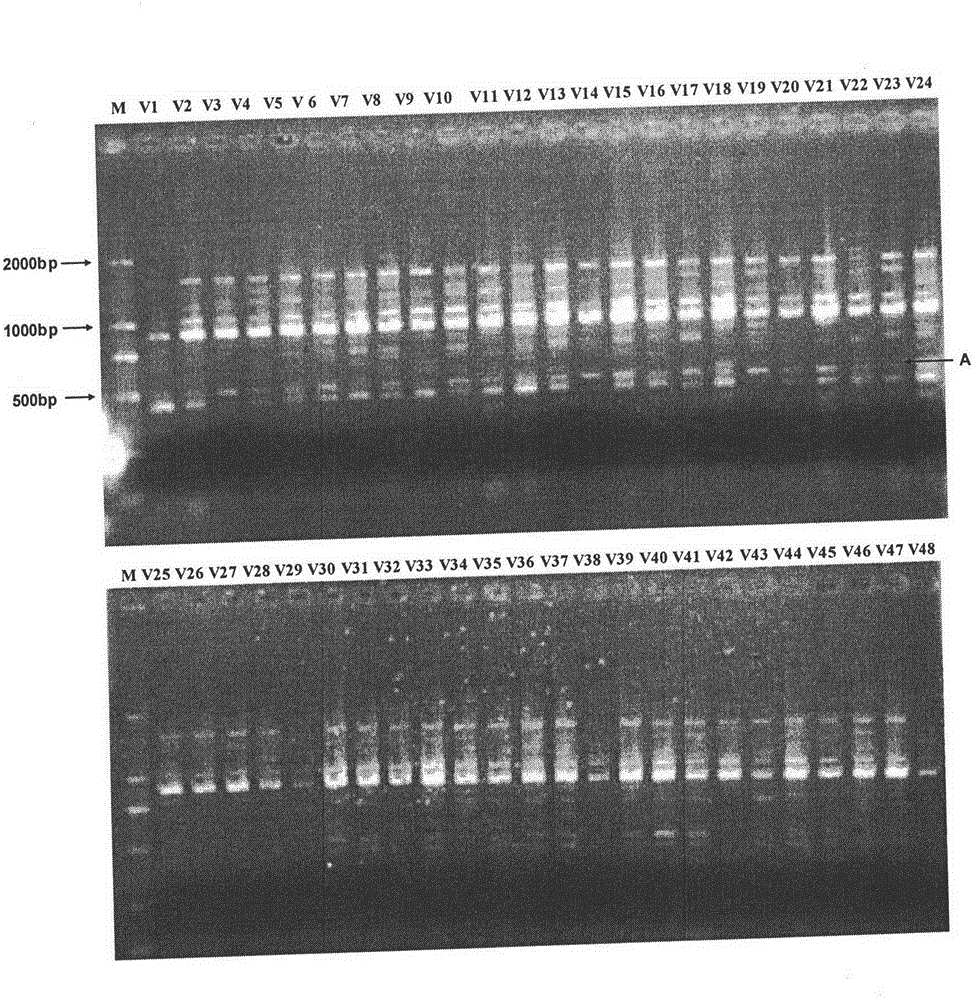
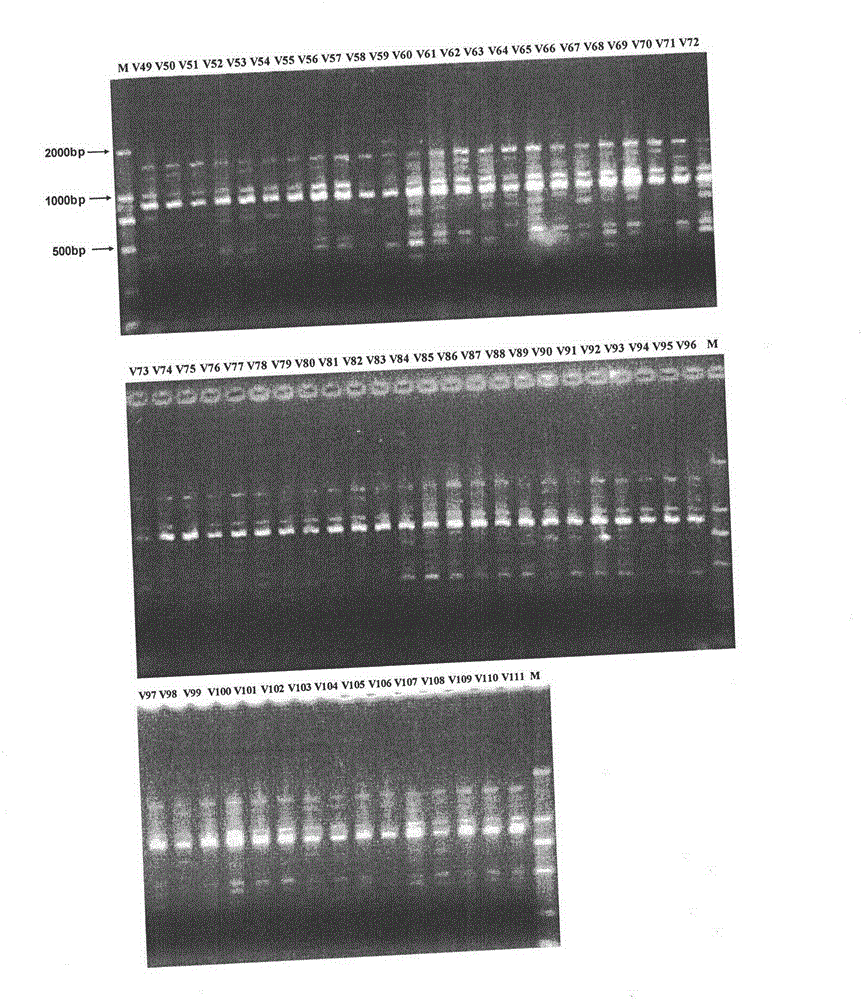
The invention discloses a breeding method for rapidly introducing rice target characters. The method includes the following steps that rice resources carrying target characters serve as a male parent or a female parent and are hybridized with a recurrent parent to obtain a hybrid F1; the recurrent parent serves as a female parent to be hybridized with the hybrid F1 to obtain a BC1F1 group; according to 48 molecular markers distributed evenly on 12 chromosomes of rice in the SSR labeling method of a rice variety identification technical regulation, genetic similarity analysis is conducted on a single plant of the BC1F1 group, and a BC1F1 single plant is screened, wherein the BC1F1 single plant carries the target characters and the genetic similarity is higher than 90% compared with the recurrent parent; the recurrent parent serves as a female parent to be hybridized with the BC1F1 single plant, and a plant carrying the target characters and similar to the recurrent parent is bred and selected from later generations. Through the comparison of SSR molecular markers with the recurrent parent, when the genetic similarity is high, the target characters are introduced rapidly and more-efficiently, and the genetic resource innovative breeding speed is greatly increased.
Owner:RICE RES ISTITUTE ANHUI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
SRAP molecular marking method for genetic diversity analysis of tetracera asiatica
PendingCN111471784AHigh polymorphismThe band is clearMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGeneticsGenetic similarity
The invention provides an SRAP molecular marking method for genetic diversity analysis of tetracera asiatica, and belongs to the technical field of molecular biology. According to the method, an SRAPmolecular marker primer system of tetracera asiatica is established, and the primer system comprises nine specific primer pairs; then the primer system is used for carrying out SRAP-PCR reaction amplification on a tetracera asiatica sample, genetic similarity and genetic distance are calculated according to a DNA random amplification result, clustering analysis is carried out, and a clustering graph is constructed. Amplified fragments obtained by using the screened primers are good in repeatability and clear in strip and exhibit high polymorphism; and meanwhile, the SRAP molecular marker primer system is used for carrying out clustering analysis on tetracera asiatica, a new method is established for variety identification and genetic diversity analysis of tetracera asiatica, and technicalguidance and theoretical support are provided for scientific research of resource identification, genetic diversity analysis and the like of tetracera asiatica.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV OF CHINESE MEDICINE
Screening method of saccharum arundinaceum breeding material
InactiveCN105838810AThe result is accurateSensitive resultMicrobiological testing/measurementScreening methodGermplasm
The invention provides a screening method of a saccharum arundinaceum breeding material. The method comprises the following steps: collecting saccharum arundinaceum resources, and performing variation analysis of phenotypic character and correlation analysis among characters on the resources; extracting the genome DNA of saccharum arundinaceum as a template, adopting SCoT labeled primers to perform amplification, detecting amplified products through polyacrylamide electrophoresis, and obtaining a DNA finger-print chromatogram; performing polymorphic analysis and J genetic similarity coefficient analysis on the saccharum arundinaceum resources, and constructing UPGMA phylogenetic trees; performing comprehensive analysis on different ecological positions, phenotypic variation characteristics and phylogenetic trees of different saccharum arundinaceum resources, so as to obtain the screened material. By adopting the technical scheme and in combination with the phenotypic character variation analysis and a molecular marker technology, screening results are more sensitive and accurate; the utilization potential of saccharum arundinaceum germplasm resources is comprehensively evaluated, the accharum arundinaceum breeding material is screened, and the method can serve cane breeding.
Owner:SUGARCANE RES INST GUANGXI ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Maize Molecular Breeding Core SNP Site Combination and Its Application
ActiveCN110129470BImprove breeding efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyGenetics
The invention discloses the core SNP site combination of corn molecular breeding and its application. The invention provides the application of 300 SNP sites in at least one of the following (1)-(4): (1) detecting the genetic similarity of corn inbred lines; (2) detecting the heterozygosity of corn hybrids; (3) ) Molecular marker-assisted background selection for maize backcross breeding; (4) maize molecular breeding; the present invention screens and determines a set of SNP site combinations suitable for maize molecular breeding from 740 pairs of SNP primers. Therefore, based on the high-throughput KASP detection platform of samples, the present invention screens the combination of core SNP sites suitable for molecular breeding of maize, which can significantly improve the breeding efficiency.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
A kind of screening method of spotgrass breeding material
InactiveCN105838810BThe result is accurateSensitive resultMicrobiological testing/measurementScreening methodGermplasm
The invention provides a screening method of a saccharum arundinaceum breeding material. The method comprises the following steps: collecting saccharum arundinaceum resources, and performing variation analysis of phenotypic character and correlation analysis among characters on the resources; extracting the genome DNA of saccharum arundinaceum as a template, adopting SCoT labeled primers to perform amplification, detecting amplified products through polyacrylamide electrophoresis, and obtaining a DNA finger-print chromatogram; performing polymorphic analysis and J genetic similarity coefficient analysis on the saccharum arundinaceum resources, and constructing UPGMA phylogenetic trees; performing comprehensive analysis on different ecological positions, phenotypic variation characteristics and phylogenetic trees of different saccharum arundinaceum resources, so as to obtain the screened material. By adopting the technical scheme and in combination with the phenotypic character variation analysis and a molecular marker technology, screening results are more sensitive and accurate; the utilization potential of saccharum arundinaceum germplasm resources is comprehensively evaluated, the accharum arundinaceum breeding material is screened, and the method can serve cane breeding.
Owner:SUGARCANE RES INST GUANGXI ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Molecular marker SSR primer for identifying genetic relationship and variety of rehmannia glutinosa variety, kit and application
PendingCN114703314ATaking into account stabilityConvenienceMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyGenetic similarity
The invention relates to the technical field of molecular biology and genetic breeding, in particular to a molecular marker SSR primer for genetic relationship and variety identification of rehmannia glutinosa varieties, a kit and application. The 50 pairs of SSR primers provided by the invention are used for respectively amplifying DNA of 17 planting resources in the Huanghuai region, and the derivative relationship, genetic difference, evolution relationship and the like among different varieties are determined through clustering analysis and genetic similarity analysis, so that a scientific basis can be provided for breeding and breeding. Meanwhile, by adopting the 15 pairs of SSR primers provided by the invention, different rehmannia varieties can be accurately distinguished through difference combination of amplification products among different primer pairs, so that the rehmannia varieties in 17 Huanghuai production areas can be distinguished and identified on the DNA level, and the SSR fingerprint spectrum of the rehmannia varieties is formed.
Owner:HENAN ACAD OF SCI INST OF BIOLOGY LIABILITY +1
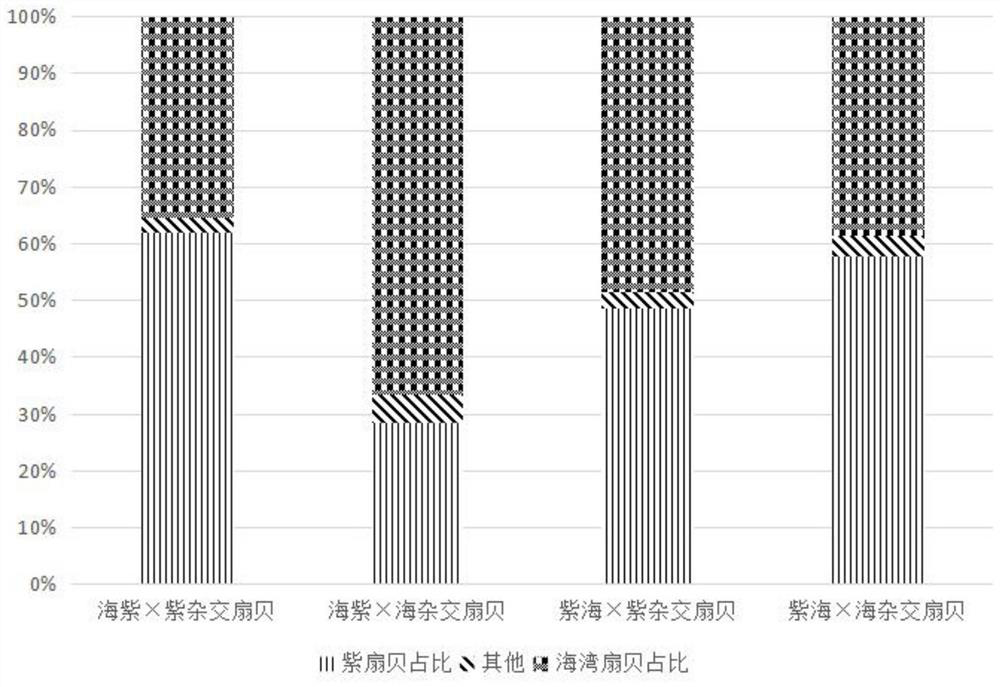
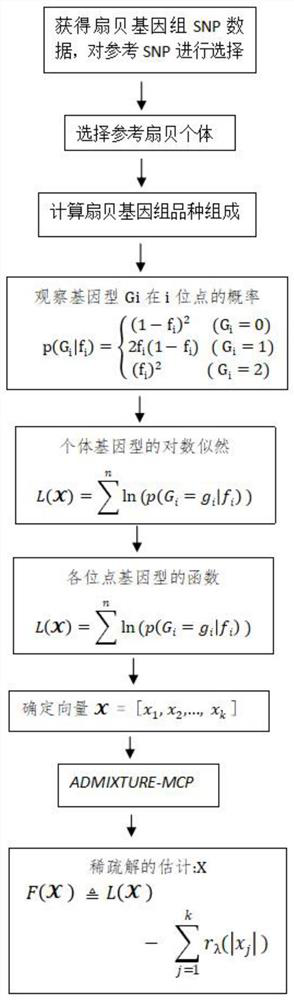
A new method for estimating the species composition of aquatic animal genomes based on the admixture-mcp model
ActiveCN111354417BReduce small portion problemsReduce noiseProteomicsGenomicsAlgorithmAquatic animal
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Estimating method of genetic similarity index of codominance molecular marker based on relative correlation coefficient
ActiveCN101984446BOvercome the defect that the degree of kinship is not necessarily relatedMicrobiological testing/measurementSpecial data processing applicationsCorrelation coefficientElectrophoresis
The invention discloses a calculation method of genetic similarity index of codominance molecular marker based on relative correlation coefficient. The technical scheme is as follows: obtaining an electrophoresis pattern of each variety or kind of plant by adopting the current codominance molecular marker method; comparing in pairs according to the amplification strip information of the variety or kind of the plant; respectively calculating a genetic similarity index between each two plant varieties and kinds according to a calculation formula of the genetic similarity index; and taking the genetic similarity index as the estimation of the corresponding relative extent of the individuals. The calculation method of genetic similarity index is applied to the codominance molecular marker. The calculation method of the obtained genetic similarity index can effectively respond the relative relationship extent among the colonies based on the relative correlation coefficient.
Owner:YUNNAN ACAD OF TOBACCO AGRI SCI +1
PCR primers, methods and kits for analyzing grass genetic diversity
ActiveCN106434971BRich genetic variationImprove detection efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiological interactionGermplasm
Owner:TROPICAL CORP STRAIN RESOURCE INST CHINESE ACAD OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
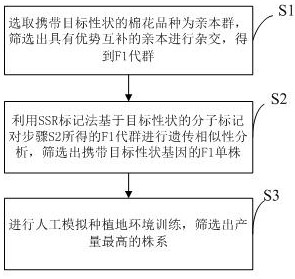
Breeding method of high-yield high-quality multi-resistance cotton
InactiveCN111887150ASpeed up breedingShorten the timeMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant genotype modificationBiotechnologyGermplasm
The invention discloses a breeding method of high-yield high-quality multi-resistance cotton. The breeding method comprises the following steps: S1, selecting a cotton variety carrying target traits as a parent group, screening out parents being in complementary in advantages, and performing hybridizing to obtain an F1 generation group; S2, performing genetic similarity analysis on the F1 generation group obtained in the step S2 by utilizing an SSR marking method based on a molecular marker of a target character, and screening out F1 single plants carrying target character genes; and S3, performing artificial simulation planting land environment training, and screening out a strain with the highest yield. Through combination of SSR molecular marking and artificial simulation planting landenvironment training, the breeding speed for germplasm resource innovation is greatly increased, and besides, varieties suitable for different planting environments can be screened out at the same time.
Owner:INST OF CEREAL & OIL CROPS HEBEI ACAD OF AGRI & FORESTRY SCI
A method for identifying germplasm of almonds based on ssr molecular markers
InactiveCN105512513BPromote healthy developmentMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsBiotechnologyGermplasm
The invention relates to a method for identifying prunus persica plant species based on SSR molecular markers. According to the method, SSR primers with high polymorphism are selected for carrying out the SSR-PCR amplified reaction, electrophoresis detection and system analysis on 55 parts of prunus persica plant specie materials. The result shows that 10 pairs of primers, with high polymorphism, screened from 100 pairs of SSR primers are used for carrying out SSR-PCR amplification on genome DNA of the prunus persica plant specie materials, 63 amplified bands are amplified together, the number of polymorphic bands is 60, the polymorphic rate is 95.2%, and the better amplification result is obtained. Similarity coefficient and cluster analysis is carried out, the genetic similarity coefficient is 0.4133-0.9600, and the average similarity coefficient is 0.6867; the genetic difference among the 55 parts of prunus persica plant specie materials shows that the different species and the genetic distances among the different species are different, when the similarity coefficient is smaller than 0.68, most cultivated varieties are clustered into one cluster, and most cultivated varieties in the same provenance can be clustered together. An important way is provided for further distinguishing the genetic relationship among the prunus persica plant specie resources.
Owner:XINJIANG AGRI UNIV
A method for identifying lily varieties using ssr molecular marker technology
InactiveCN104263835BHigh polymorphismGood repeatabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementGeneticsGenetic similarity
Owner:KAILI UNIV
System and method for forming online social network using genome information
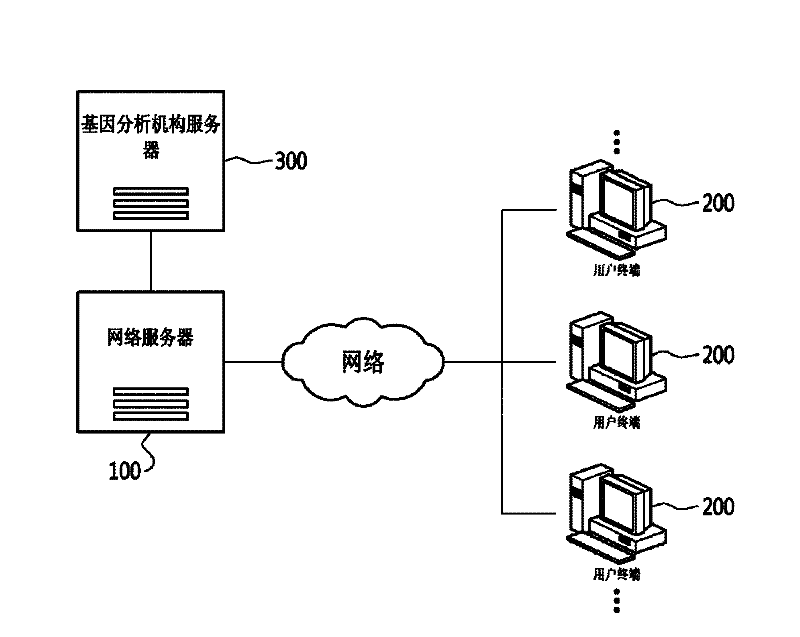
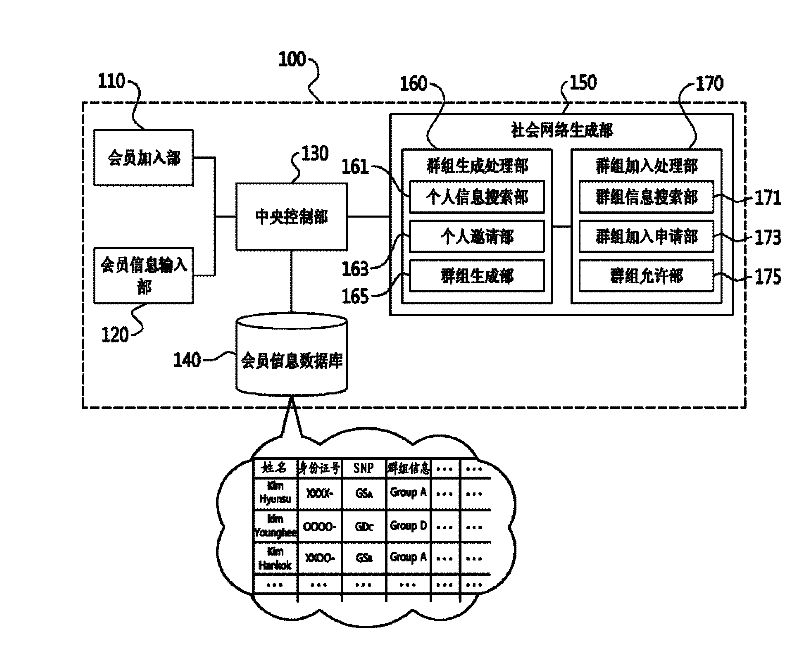
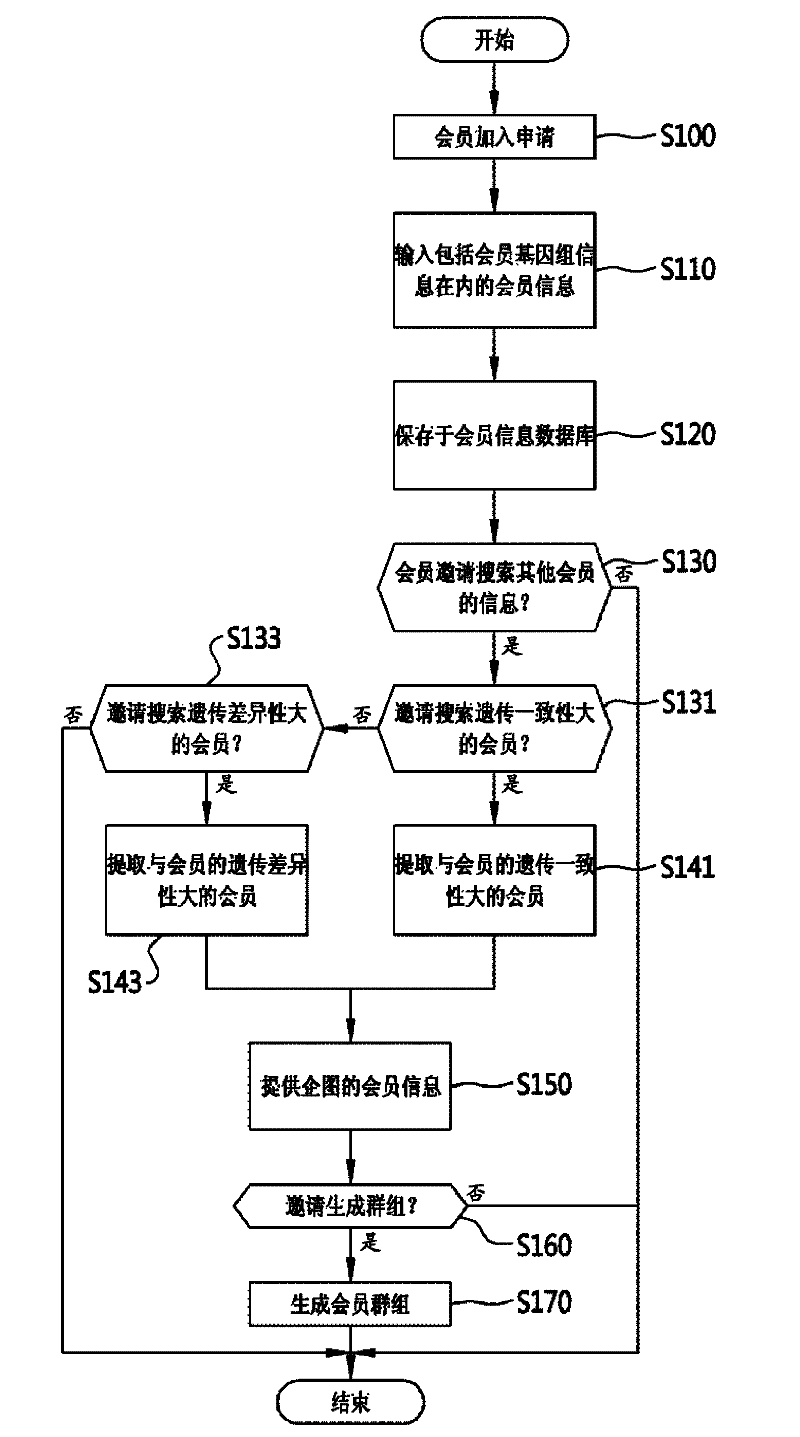
InactiveCN102289722AMeet various requirementsData processing applicationsMedical equipmentGenetic similaritySocial network
The present invention relates to a system and method for forming an online social network using genome information. To be more specific, an embodiment of the invention may include a web server that creates a database of detailed information of members, including genome information of the member, as inputted from member terminals, and which generates a social network on the world wide web based on the genome information of the members. An embodiment of the invention can be utilized to satisfy the various personal demands of members by analyzing the gene information of members to form a database of the members' genome information and forming a social network online according to the degree of genetic similarity or distance of the genome information.
Owner:GENOME RES FOUND
A compound breeding method for improving the growth traits of yellow catfish
ActiveCN107155959BImprove efficiencyImprove survival rateMicrobiological testing/measurementClimate change adaptationBiotechnologyMicrosatellite
The invention relates to a complex breeding method for improving a growth trait of Pelteobagrus fulvidraco. The complex breeding method includes the following steps: acquiring high-quality Pelteobagrus fulvidraco and Pelteobagrus vachelli parent library through second generation group breeding; using microsatellite markers to detect Pelteobagrus fulvidraco and Pelteobagrus vachelli parents, selecting parent individuals having the genetic similarity of above 90% as a reproduction group; using female Pelteobagrus fulvidraco as female parents and male Pelteobagrus vachelli as male parents to perform hybrid breeding; and acquiring hybrid Pelteobagrus fulvidraco having the growth speed above 20% faster than common Pelteobagrus fulvidraco, wherein the hybrid Pelteobagrus fulvidraco has both excellent traits of dual parents, an attracting color ( female parents) and fast growth speed ( male parents). The complex breeding method can acquire improved hybrid Pelteobagrus fulvidraco, and has important significance for increasing the unit yield, the breeding benefits, and serving production practice.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Efficient breeding method for early-maturing disease-resistant cotton
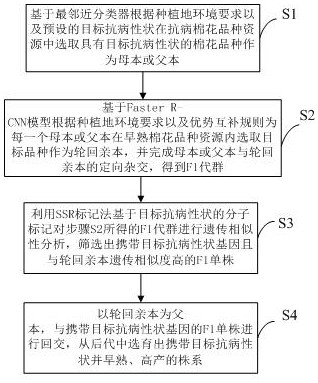
InactiveCN111887151AShorten the timeIncrease success rateMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant genotype modificationBiotechnologyGermplasm
The invention discloses an efficient breeding method for early-maturing disease-resistant cotton. The method comprises the following steps: screening a target cotton variety as a female parent or a male parent based on a preset target disease-resistant character; selecting a target early-maturing cotton variety as a recurrent parent based on a preset advantage complementation rule, and finishing directional hybridization of the female parent or the male parent and the recurrent parent to obtain an F1 generation group; performing genetic similarity analysis on the F1 generation group obtained in the step S2 based on a molecular marker of a target disease resistance character by utilizing an SSR marking method; and carrying out backcross on the recurrent parent serving as a father parent andthe F1 single plant carrying a target disease-resistant character gene, and breeding an early-maturing and high-yield strain carrying the target disease-resistant character from offspring. Through combination of SSR molecular markers and deep learning, the breeding speed of germplasm resource innovation is greatly increased, and meanwhile, varieties integrating multiple excellent traits can be screened out.
Owner:INST OF CEREAL & OIL CROPS HEBEI ACAD OF AGRI & FORESTRY SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com