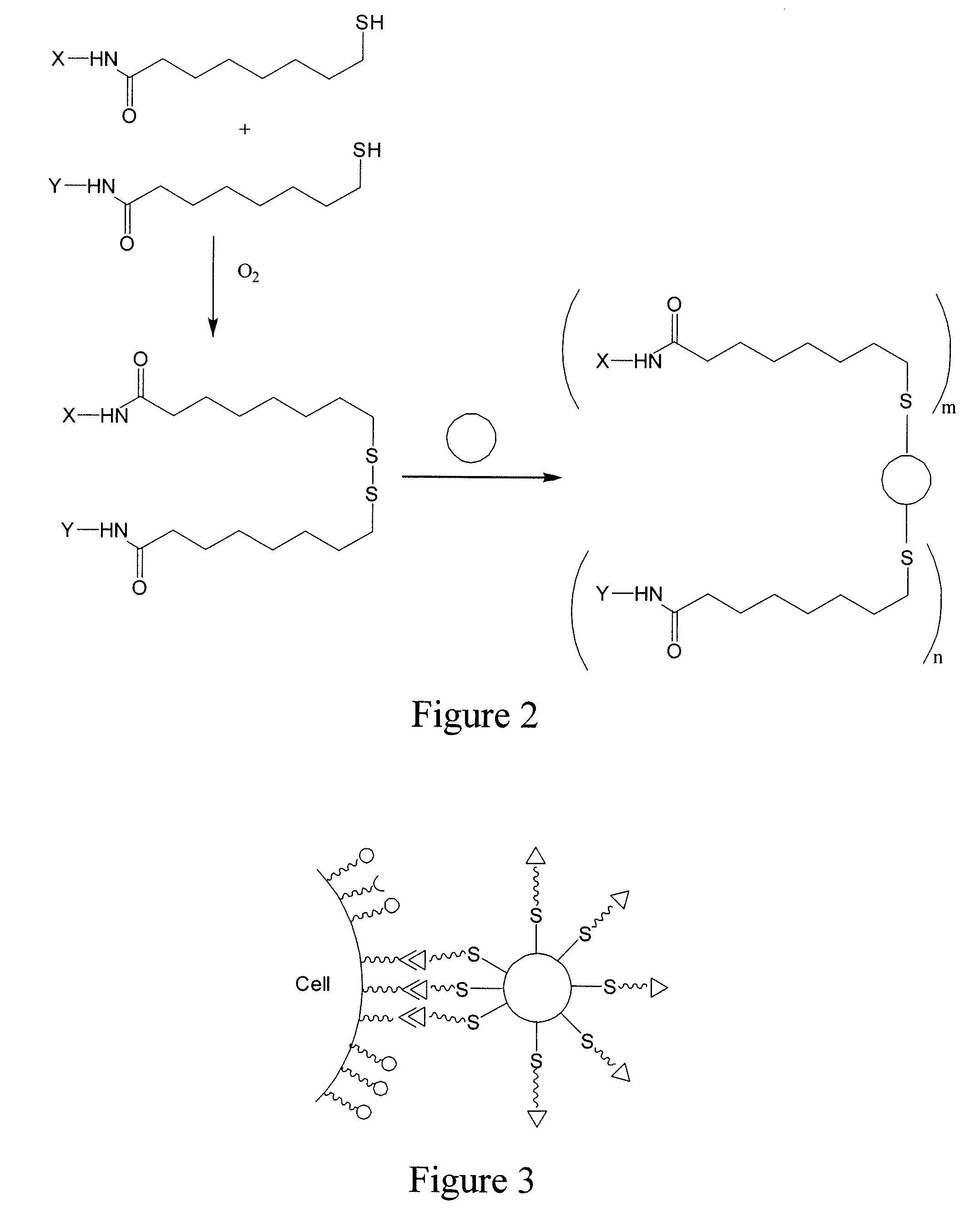
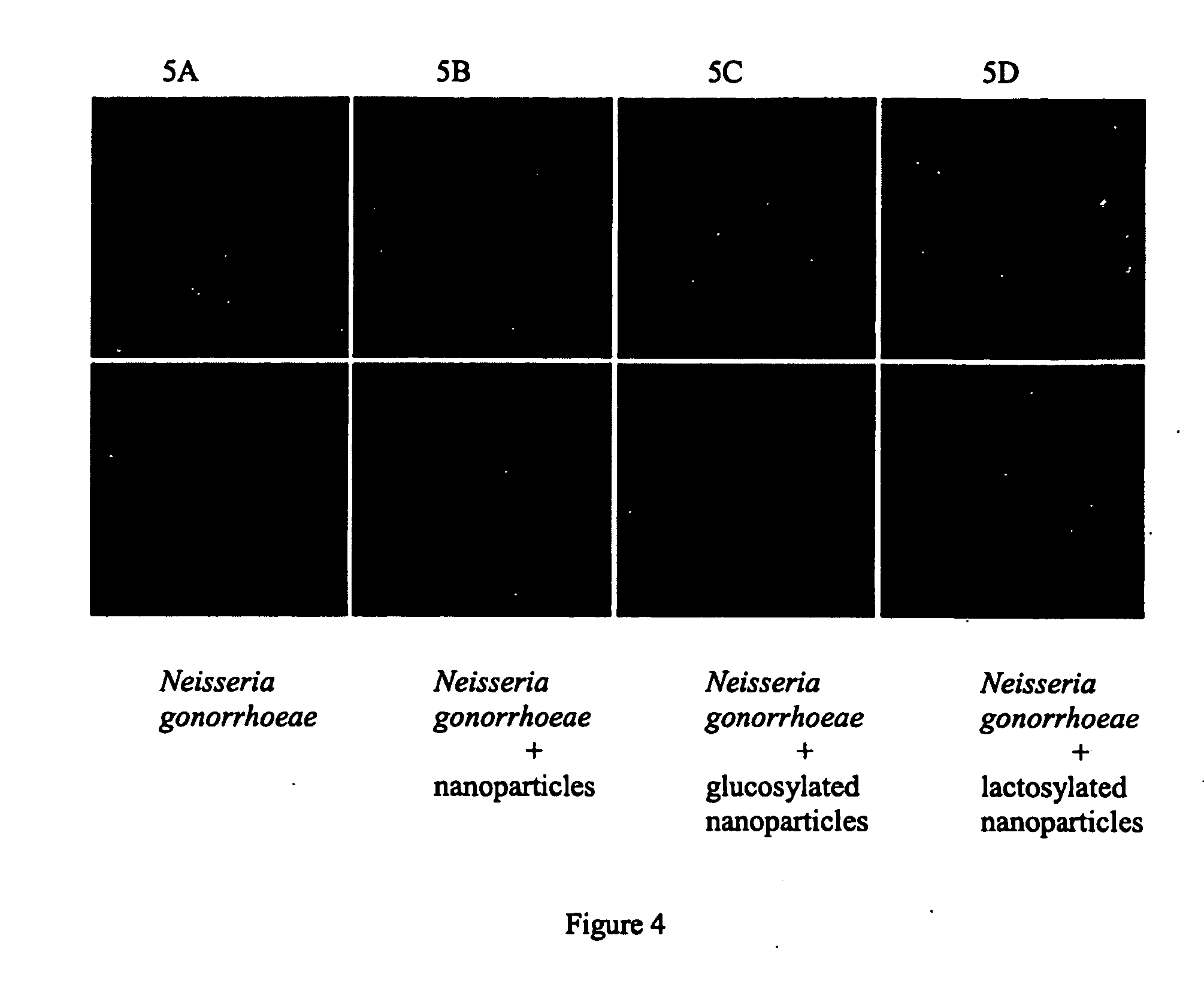
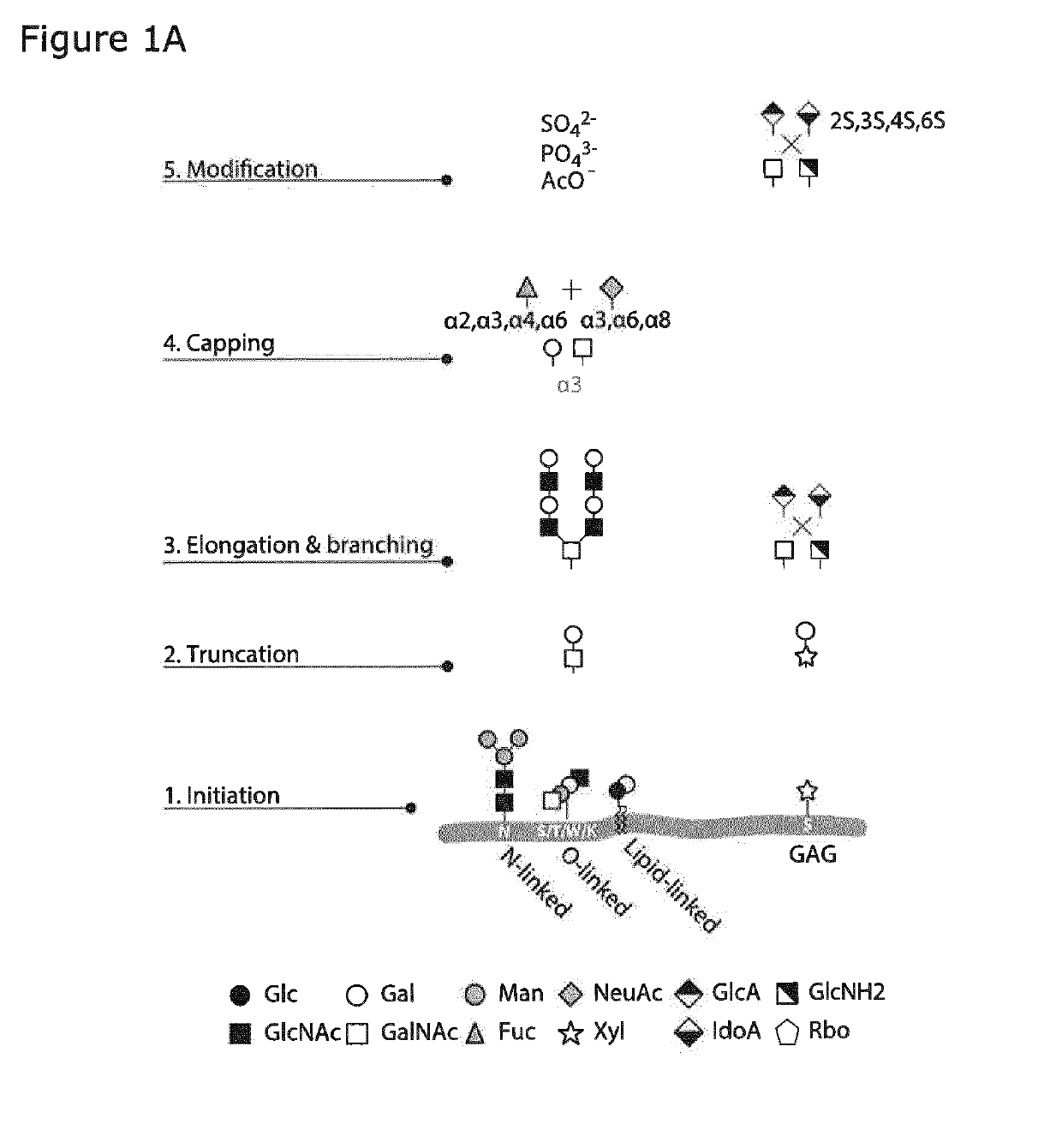
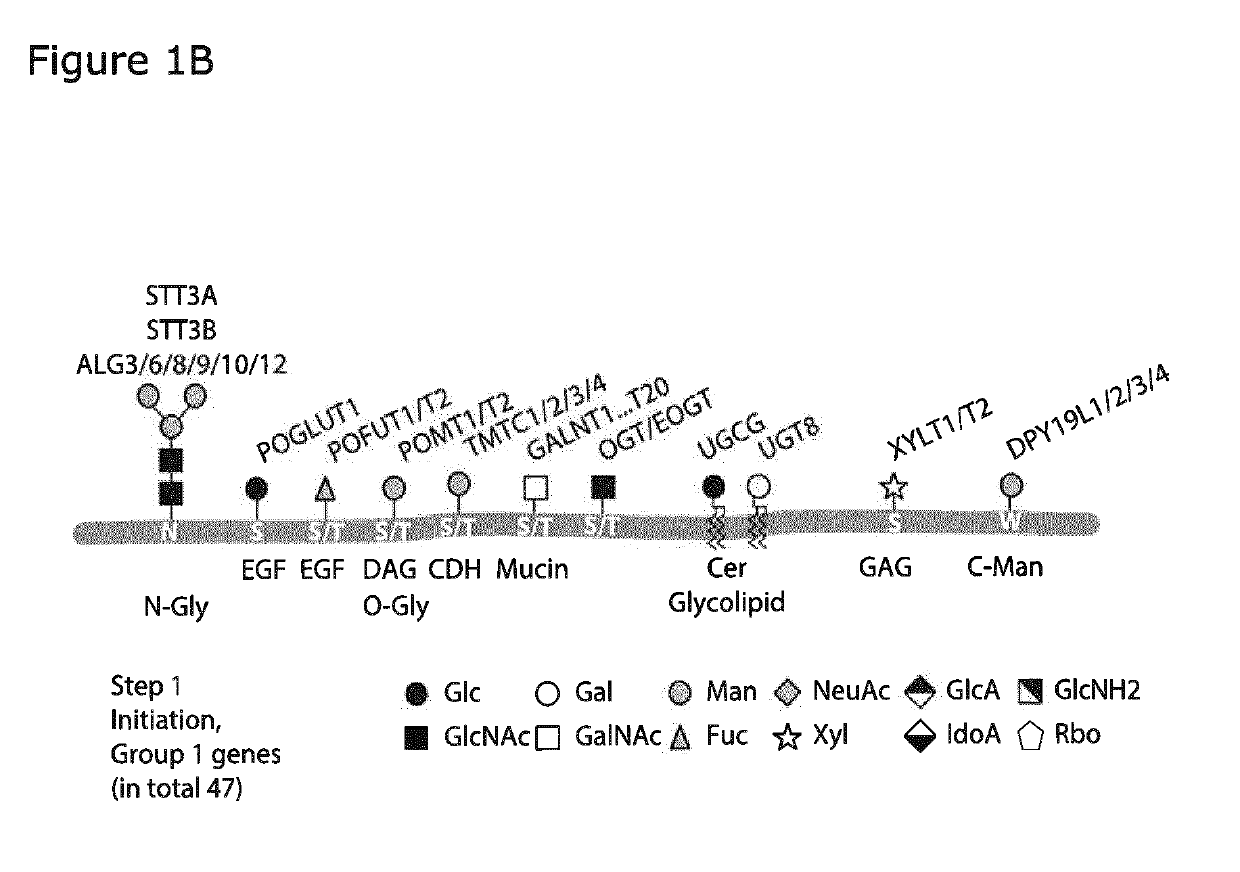
Patents
Literature
43 results about "Biological interaction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In ecology, a biological interaction is the effect that a pair of organisms living together in a community have on each other. They can be either of the same species (intraspecific interactions), or of different species (interspecific interactions). These effects may be short-term, like pollination and predation, or long-term; both often strongly influence the evolution of the species involved. A long-term interaction is called a symbiosis. Symbioses range from mutualism, beneficial to both partners, to competition, harmful to both partners. Interactions can be indirect, through intermediaries such as shared resources or common enemies. This type of relationship can be shown by net effect based on individual effects on both organisms arising out of relationship.
Biocompatible materials
InactiveUS20050053642A1Reduce in quantityTime-stabilising natural conformationMaterial nanotechnologyPharmaceutical containersBiological interactionChemisorption
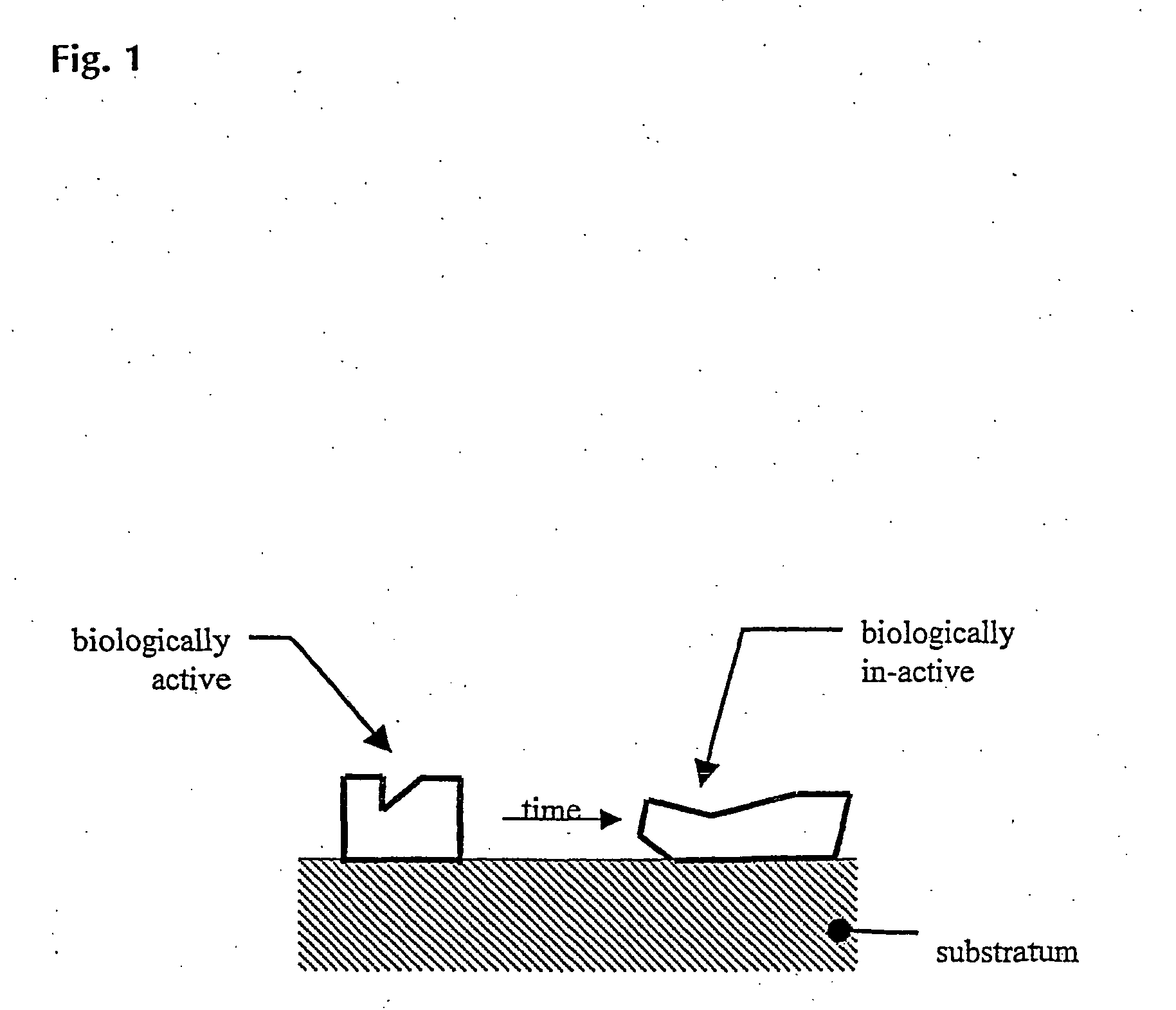
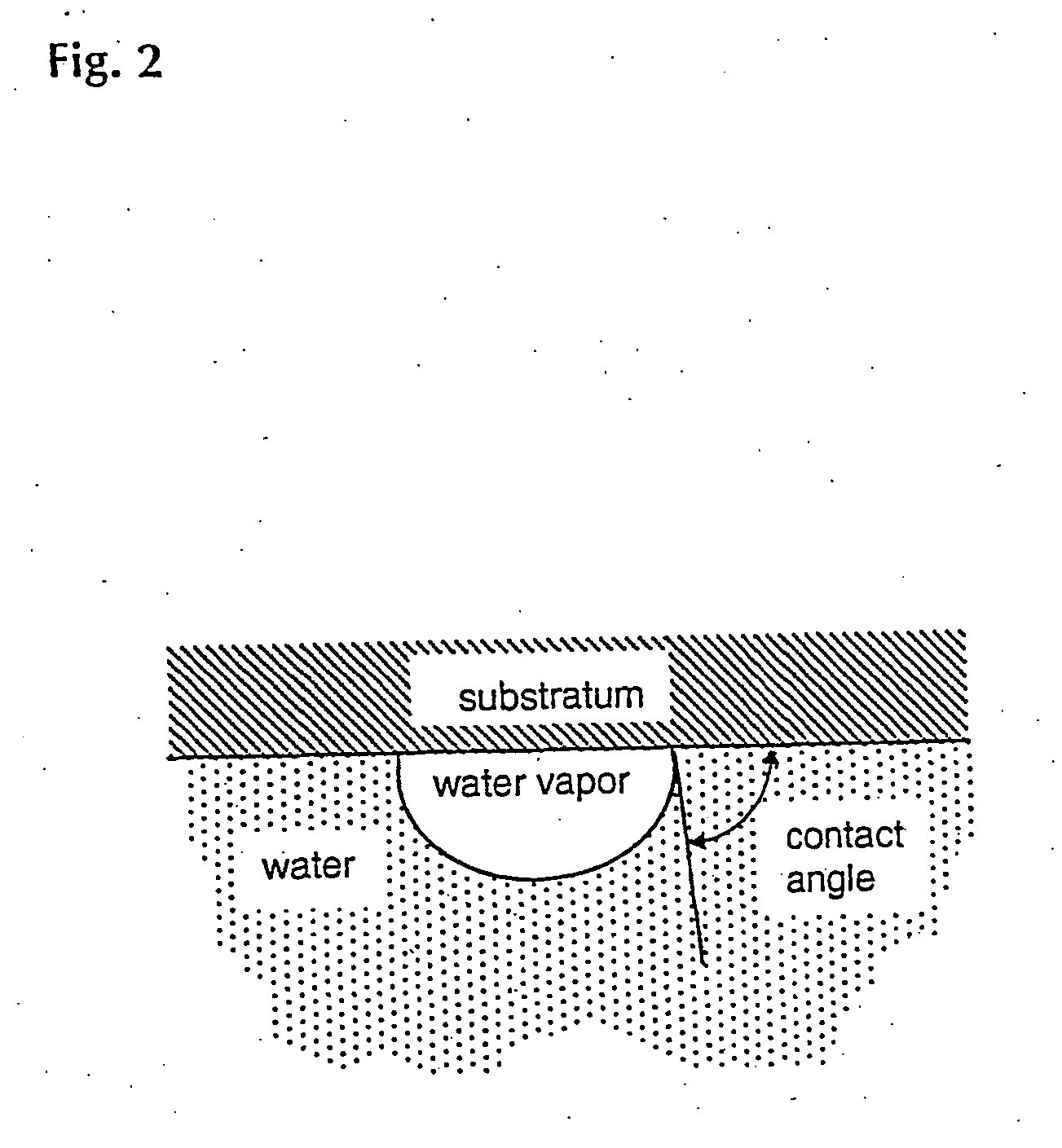
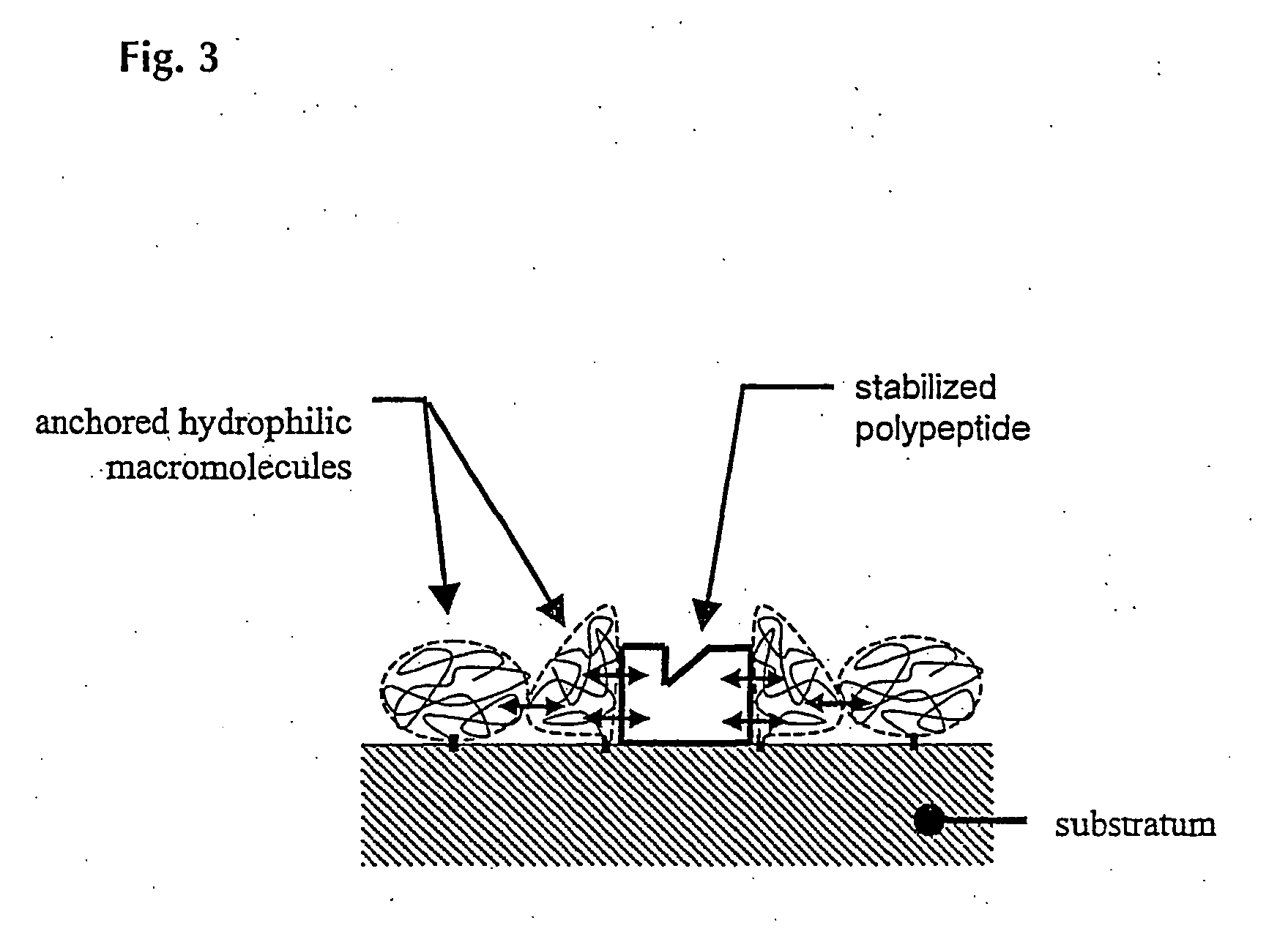
The present invention teaches a novel approach of creating biocmpatible surfaces, said surfaces being capable of functionally interact with biological material. SAid biocompatible surfaces comrise at least two comonents, such as a hydrophobic substratum and a macromolecule of hydrophilic nature, which, in a cooperativity, form together the novel biocoompatible surfaces. The novel approach is ased on contacting said hydrophobic substratum with a laterally patterned monomolecular layer of said hydrophilic and flexible macromolecules, exhibiting a pronounced excluded volume. The htus formed two component surface is, in respect to polarity and morphology, a molecularly heterogeneous surface. Structural features of said macromolecular monolayer (as e.g. the layer thickness or its lateral density) are determined by: i) the structural features of the layer forming macromolecules (as e.g. their MW or their molecular architecture) and ii) the method of creating said monomolecular layer (as e.g. by physi- or chemisorbing, or by chemically binding said macromolecules). The structural features of the layer forming macromolecules(s) is in turn determined by synthesis. AMount and conformation and thus also biological activity of biological material (as e.g. polypeptides) which contact the novel biocompatible surface, is determined and maintained by the cooperative action of the underlying hydrophobic substratum and the macromolecular layer. In this way it becomes possible to maintain and control biological interactions between said contacted polypeptides and other biological compounds as e.g. cells, antibodies and the like. Consequently, the present invention aims to reduce and / or eliminate the deactivation and / or denaturation associated with the contacting of polypeptides and / or other biological material to a hydrophobic substratum surface.
Owner:BIOSURF APS
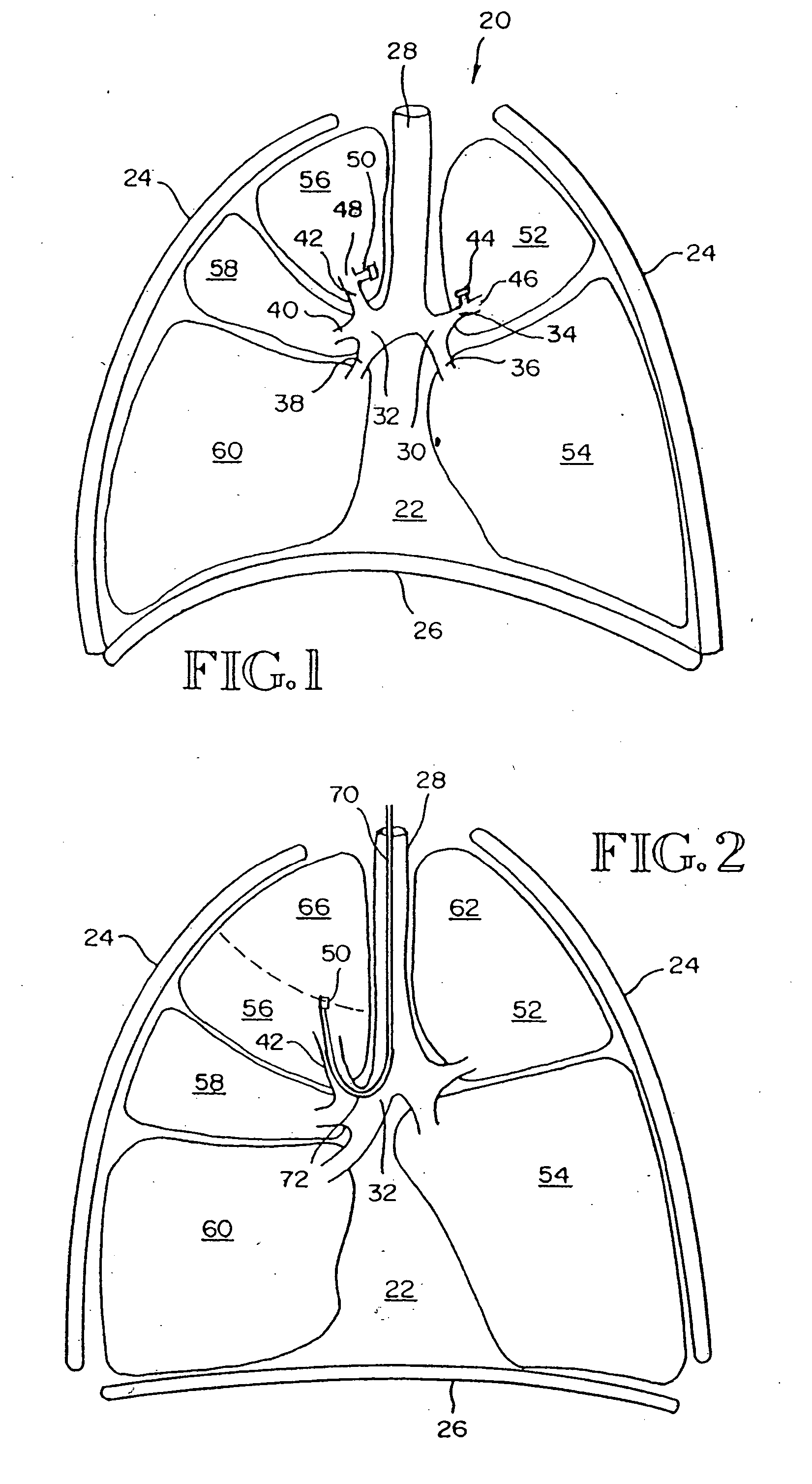
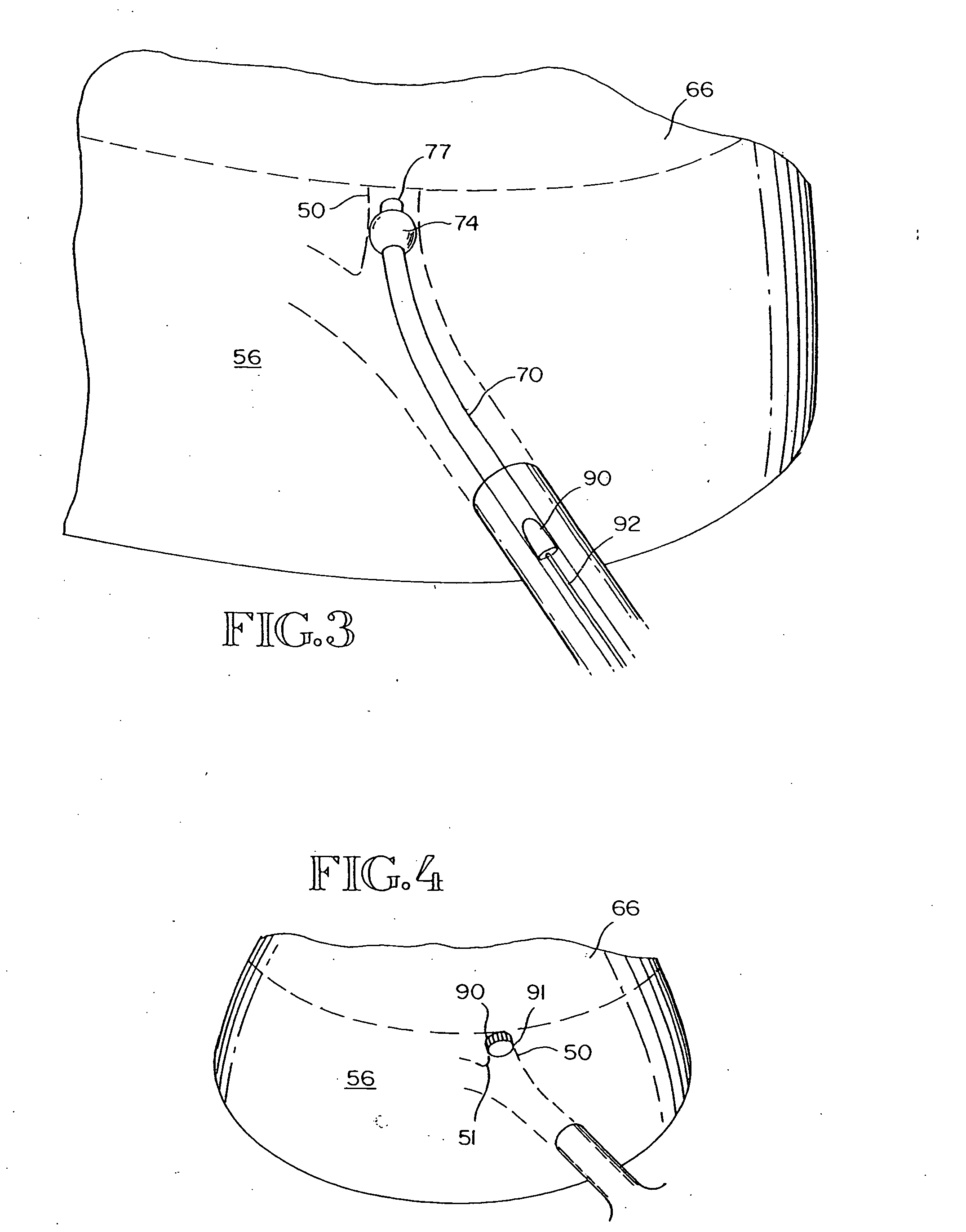
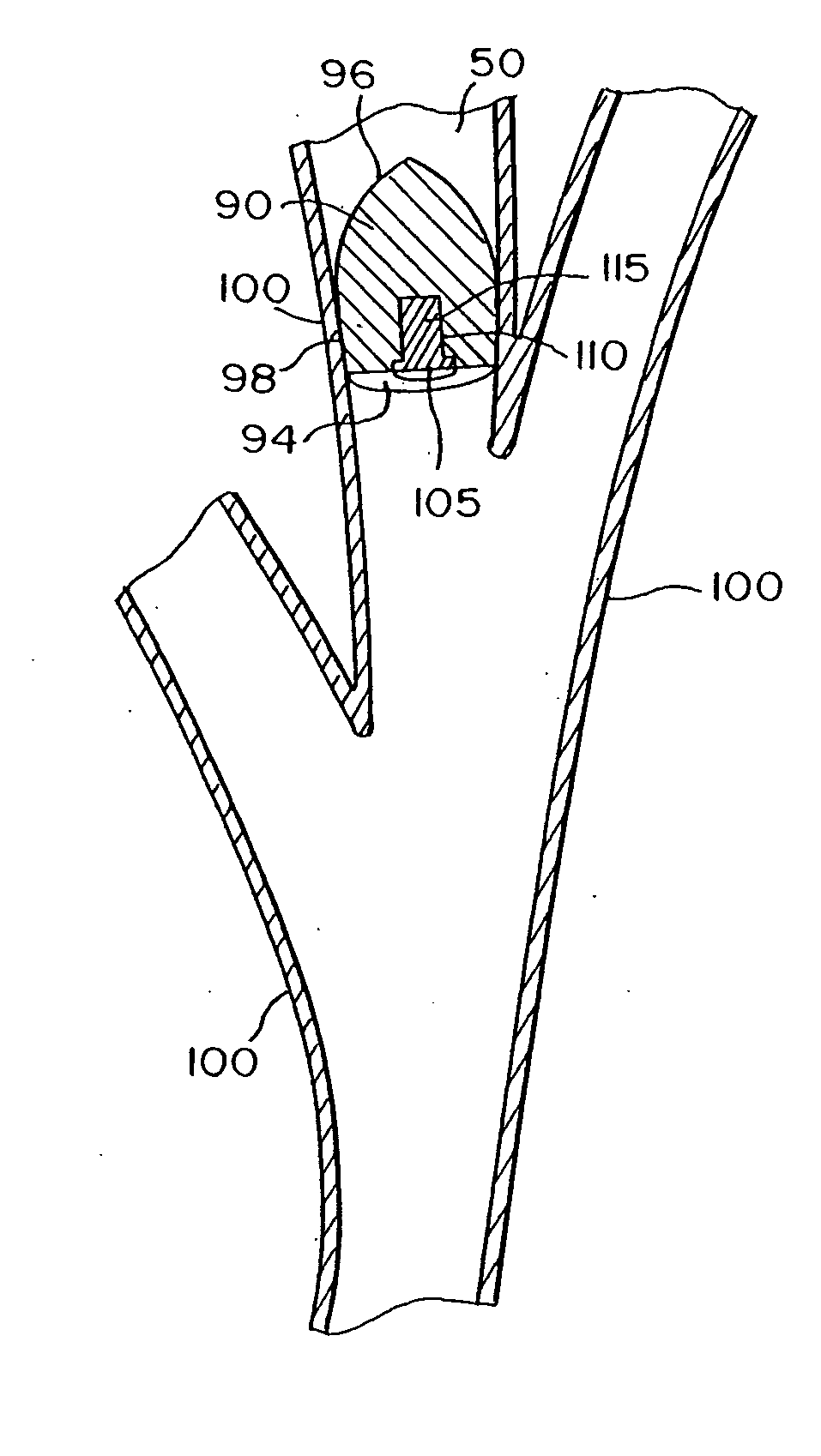
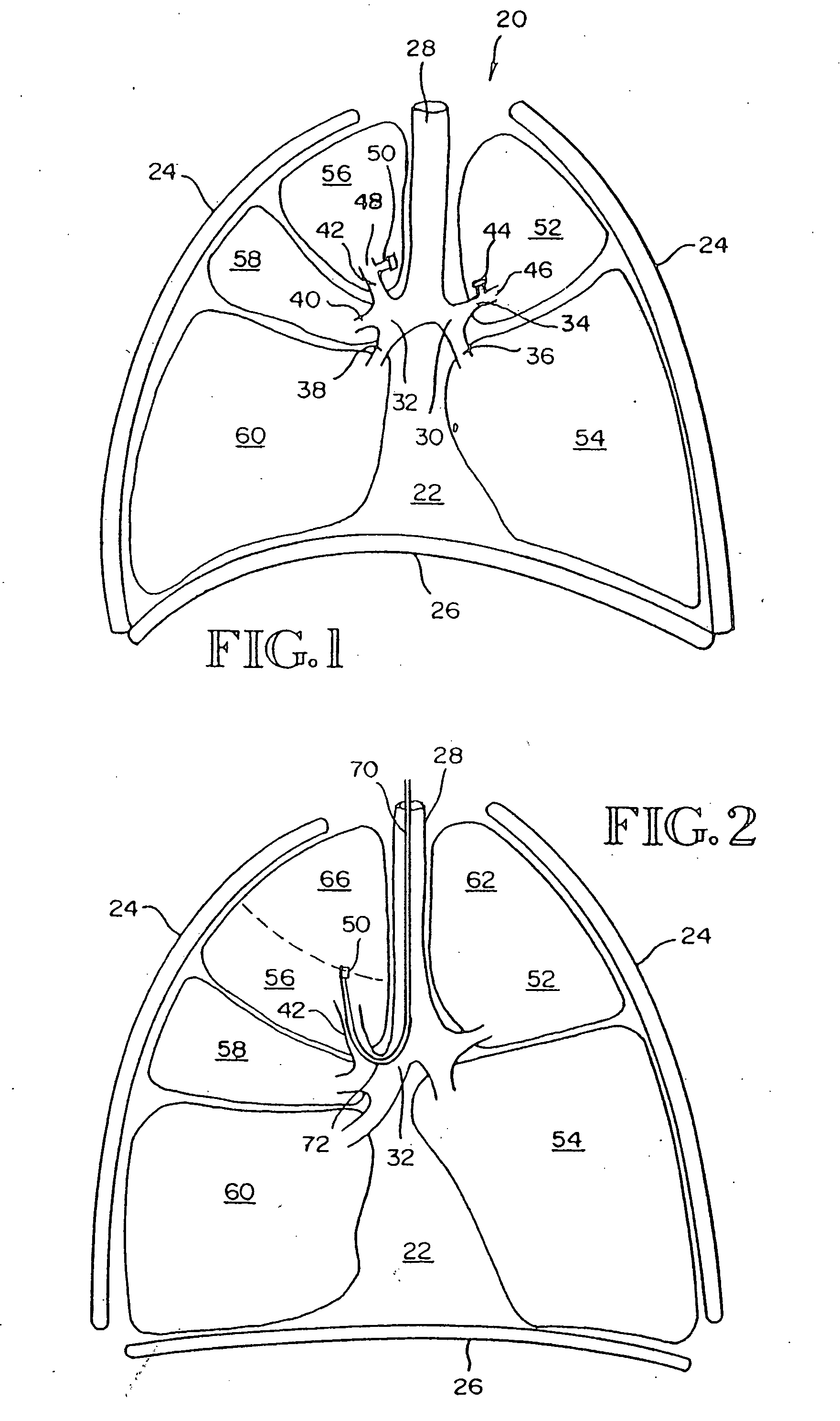
Intra-bronchial obstruction device that provides a medicant intra-bronchially to the patient
An intra-bronchial device provides a medicant intra-bronchially. The medicant may be used for controlling biological interaction of an intra-bronchial obstruction device with the patient, to treat a disease or condition of the lungs such as pneumonia or lung cancer, or to treat a systemic disease or condition. The medicant is provided by associating a medicant with the intra-bronchial device, either before, at the time of placement, or after placement. The medicant may overlie at least a portion of the intra-bronchial device, be absorbed into at least a portion of the intra-bronchial device, or be carried in a chamber. The intra-bronchial device may further include an absorptive member, and the medicant is absorbed by the absorptive member.
Owner:GYRUS ACMI INC (D B A OLYMPUS SURGICAL TECH AMERICA)
Intra-bronchial obstructing device that controls biological interaction with the patient
The present invention provides an intra-bronchial device and method that controls biological interaction of the device with the patient. The intra-bronchial device is adapted to be placed in an air passageway of a patient to collapse a lung portion associated with the air passageway. The device includes an obstructing member that prevents air from being inhaled into the lung portion to collapse the lung portion, and a medicant carried by the obstructing member. The medicant may overlie at least a portion of the obstructing member, or the medicant may be absorbed in at least a portion of the obstructing member. The obstructing member may further include an absorptive member, and the medicant is absorbed by the absorptive member.
Owner:GYRUS ACMI INC (D B A OLYMPUS SURGICAL TECH AMERICA)
Biological assays using gradients formed in microfluidic systems
InactiveUS7374906B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsMaterial nanotechnologyAssayBiological interaction
The present invention discloses a device for monitoring chemotaxis or chemoinvasion. The present invention further provides a flexible assay system and numerous assays that can be used to test biological interactions and systems. Laminar flow gradients are employed that mimic gradient situations present in vivo.
Owner:SURFACE LOGIX INC
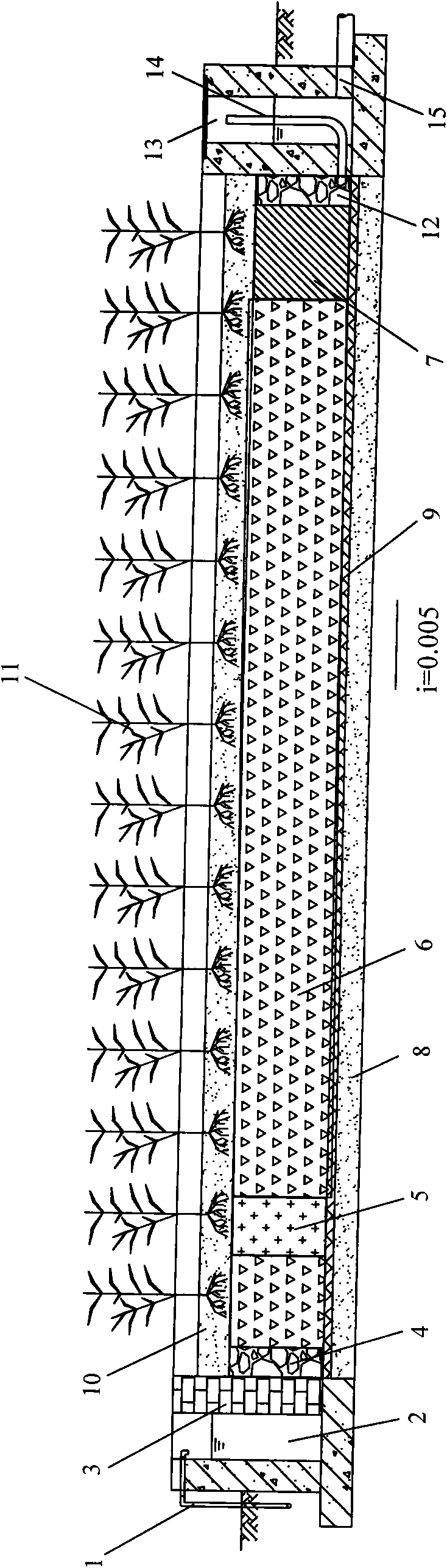
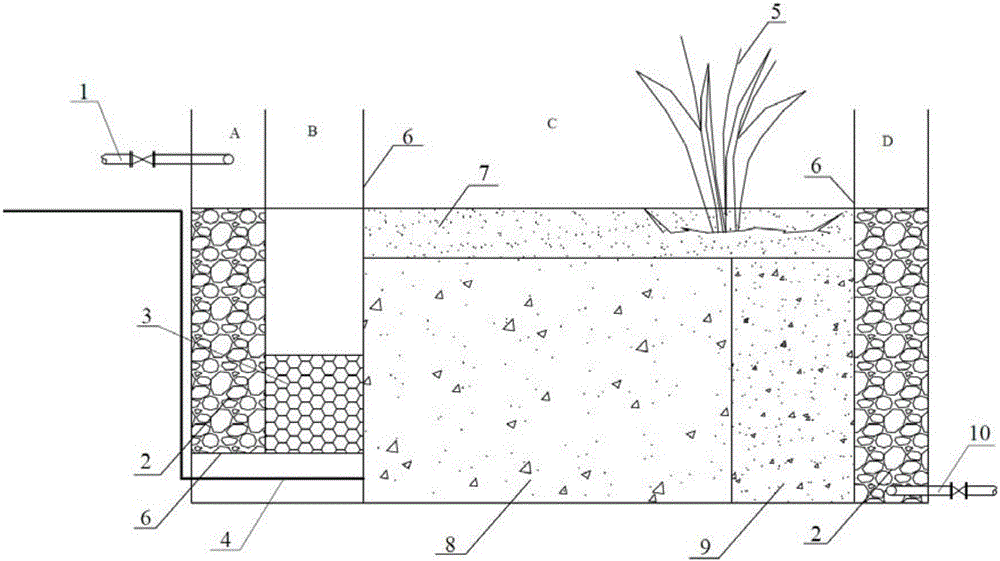
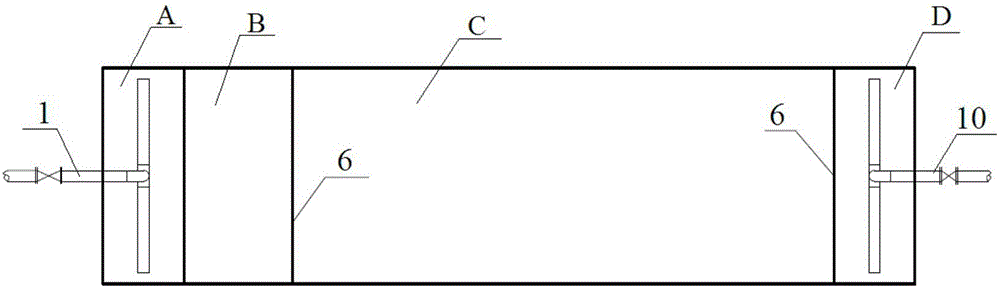
Artificial wetland with combined fillers and treating process thereof
ActiveCN102079579AGood at removingGood removal effectWater contaminantsWaste water treatment from metallurgical processConstructed wetlandTreatment effect
The invention provides an artificial wetland with combined fillers for the advanced treatment of the effluent coking wastewater of iron and steel enterprises, which sequentially comprises a water inlet area, a wetland processing unit area and a water outlet area, wherein the wetland processing unit area sequentially comprises a gravel filler section, an iron carbon filler section and a manganese sand filler section; and a soil covering layer and wetland plants are arranged on the surface of the wetland. By using iron carbon, manganese sand and gravels as combined fillers and using emerging plants (such as cattail, Scirpus tabernaemontani, Thalia dealbata, reed and the like) having large biomass, salinization resistance and high metal and organic substance adsorptive power as a composite plant bed, the invention forms a horizontal subsurface flow artificial wetland. Thus, when industrial waste water moves into the artificial wetland, pollutants can be removed on the basis of a series of physical, chemical and biological interaction among the fillers, plants and microorganisms. The process provided by the invention has high pollutant shock load resistance and good treatment effect. Besides, the outlet water is stable, and main indexes of the outlet water can meet the Reuse of Urban Recycling Water-Water Quality Standard for Industrial Uses (GB / T 19923-2005). Thus, the outlet water can be recycled as circulating cooling water for steel enterprises.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD +1
Biosensors
InactiveUS20070249063A1Microbiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisCrystallographyBiological interaction
Methods for detecting a biological interaction comprising administering a substrate comprising a ligand attached to the substrate wherein the ligand binds to a receptor and wherein a signal is produced. Also disclosed is a biosensor comprising a substrate and a ligand wherein the ligand is attached to the surface of the substrate and wherein the ligand preferentially binds to a receptor.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
Method for detecting proteinaceous inhibitors of protein-protein or DNA-protein interactions
The present invention relates generally to a method of identifying modulators of biological interactions and agents useful for same. More particularly, the present invention contemplates a method of detecting inhibitors of biological interactions involving proteinaceous and / or nucleic acid molecules and more particularly a method of identifying peptide inhibitors of biological interactions having adverse effects on living cells, tissue or organisms. The present invention provides the means by which a wide range of peptide-based therapeutic, prophylactic and diagnostic reagents may be developed.
Owner:PHYLOGICA
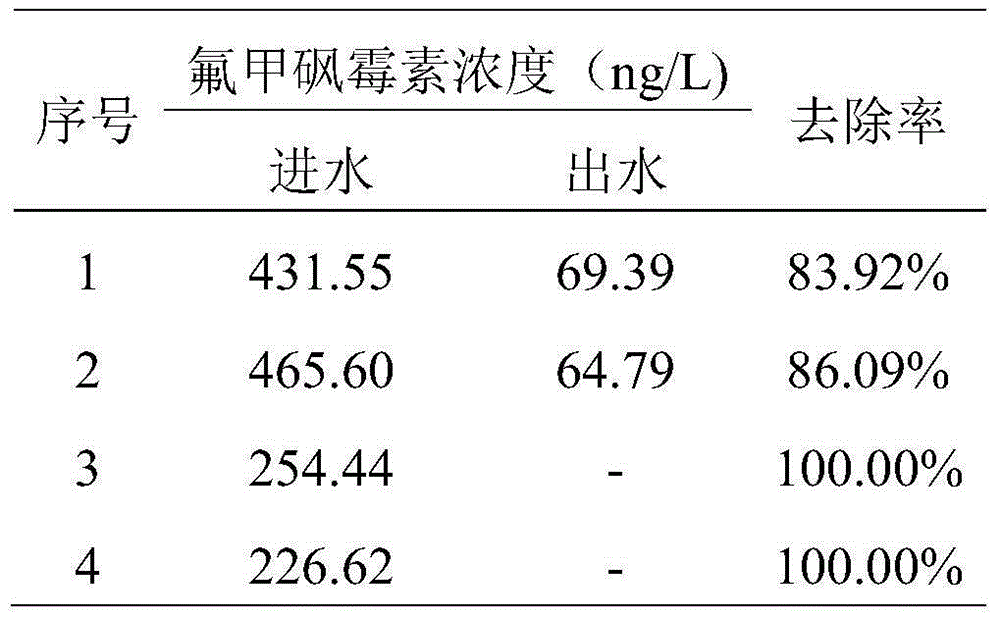
Iron-carbon-base artificial wetland purification system for removing florfenicol in aquaculture
InactiveCN105084655AReduce construction costsLow costWater contaminantsMultistage water/sewage treatmentConstructed wetlandBiological interaction
The invention belongs to the technical field of water treatment, and relates to an iron-carbon-base artificial wetland purification system for removing florfenicol in aquaculture. The system comprises a water inflow area, an iron-carbon microelectrolysis area, a wetland purification area and a water outflow area in sequence. The iron-carbon microelectrolysis area is filled with iron-carbon filler, and an aeration device is arranged below the iron-carbon filler. The wetland purification area comprises a lower filler layer and an upper soil covering layer, the filler layer comprises a gravel filler segment close to the iron-carbon microelectrolysis area and a zeolite filler segment close to the water outflow area, and wetland plants are planted on the soil covering layer. Compared with the prior art, the iron-carbon microelectrolysis area is additionally arranged, antibiotics in aquatic water are removed under the physical, chemical and biological interaction, and meanwhile other types of pollutants are removed as well; the system has the advantages of being low in construction cost, good in purification effect, capable of bringing good ecological benefits, easy and convenient to operate, stable in water outflow and the like, can be applied to purification and cyclic utilization of aquatic water and has great economical and environmental benefits.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Method for performing fed-batch operations in small volume reactors
InactiveUS20070178023A1Chemical/physical/physico-chemical microreactorsBiochemistry apparatusBiological interactionBatch operation
Methods for forming chemical and / or biological products in reactors, and / or analyzing chemical and / or biological interactions in reactors are provided. The methods relate, more specifically, to forming such products and / or carrying out such analyses in small volume reactors with control over overall fluid volume in the reactors. The methods can be used to mimic processes in large scale reactors and / or to obtain reaction or interaction information relevant to large scale reactors (e.g., to adjust / optimize large-scale reactor processes). Advantageously, the methods can allow parameters of small scale reactors to be correlated with those of large scale reactors, where desired.
Owner:BIOPROCESSORS CORP
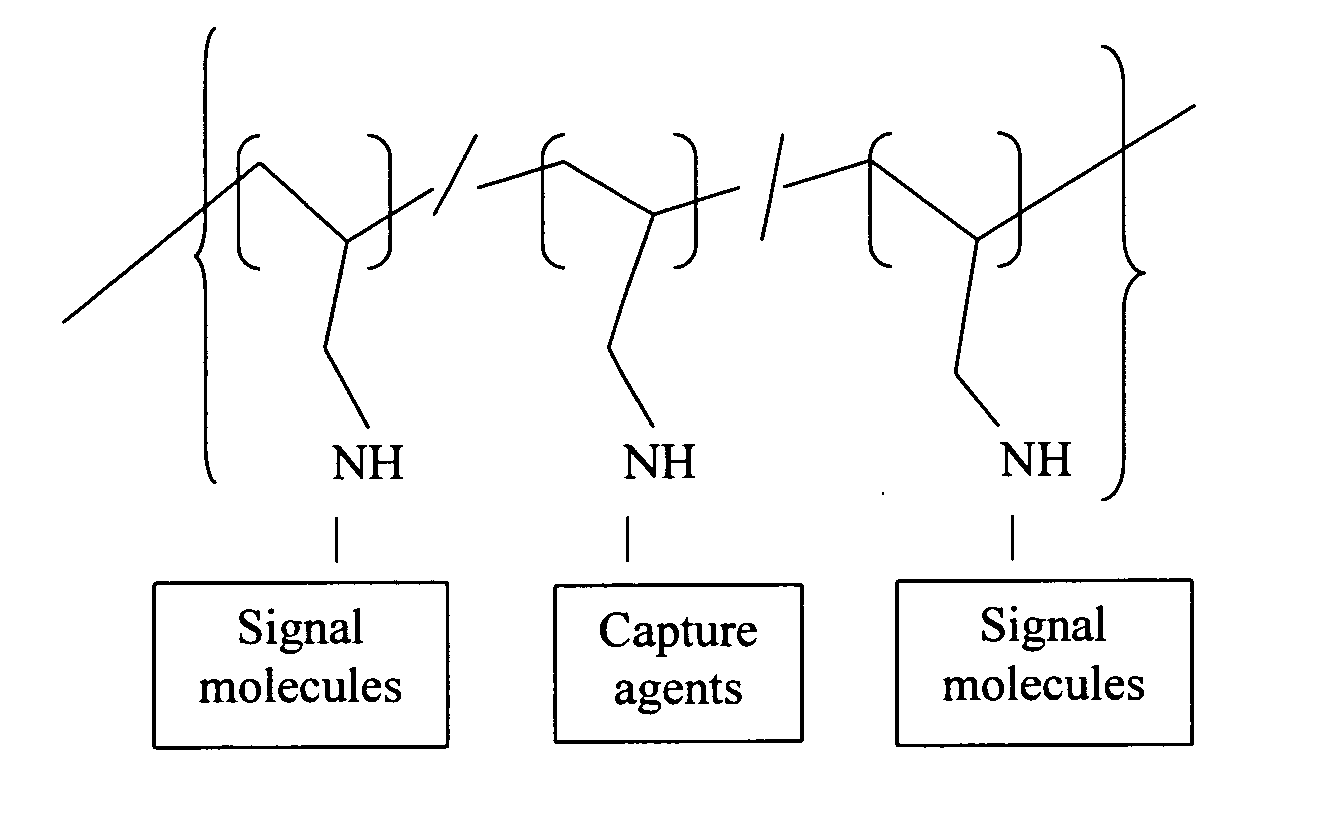
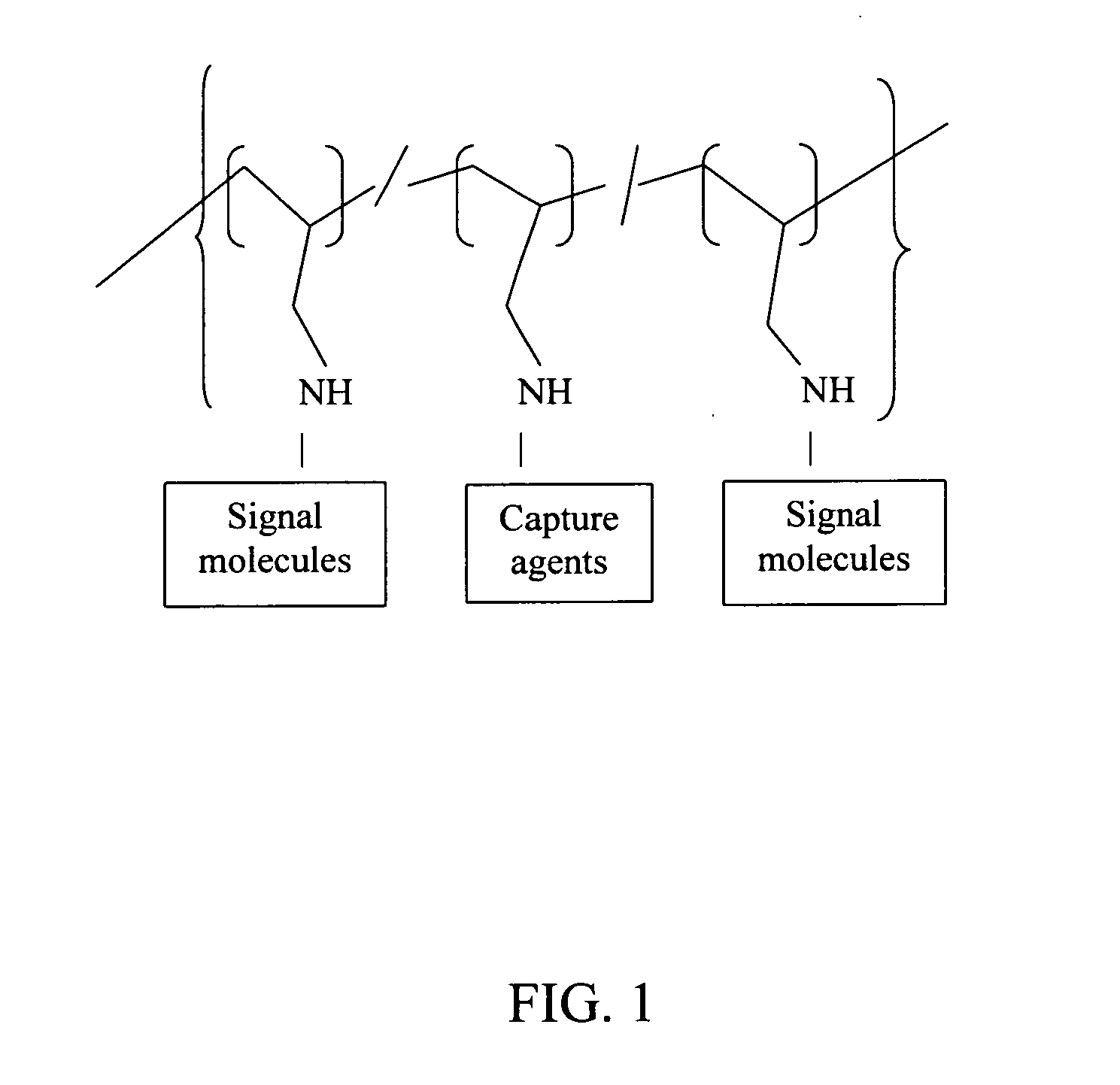
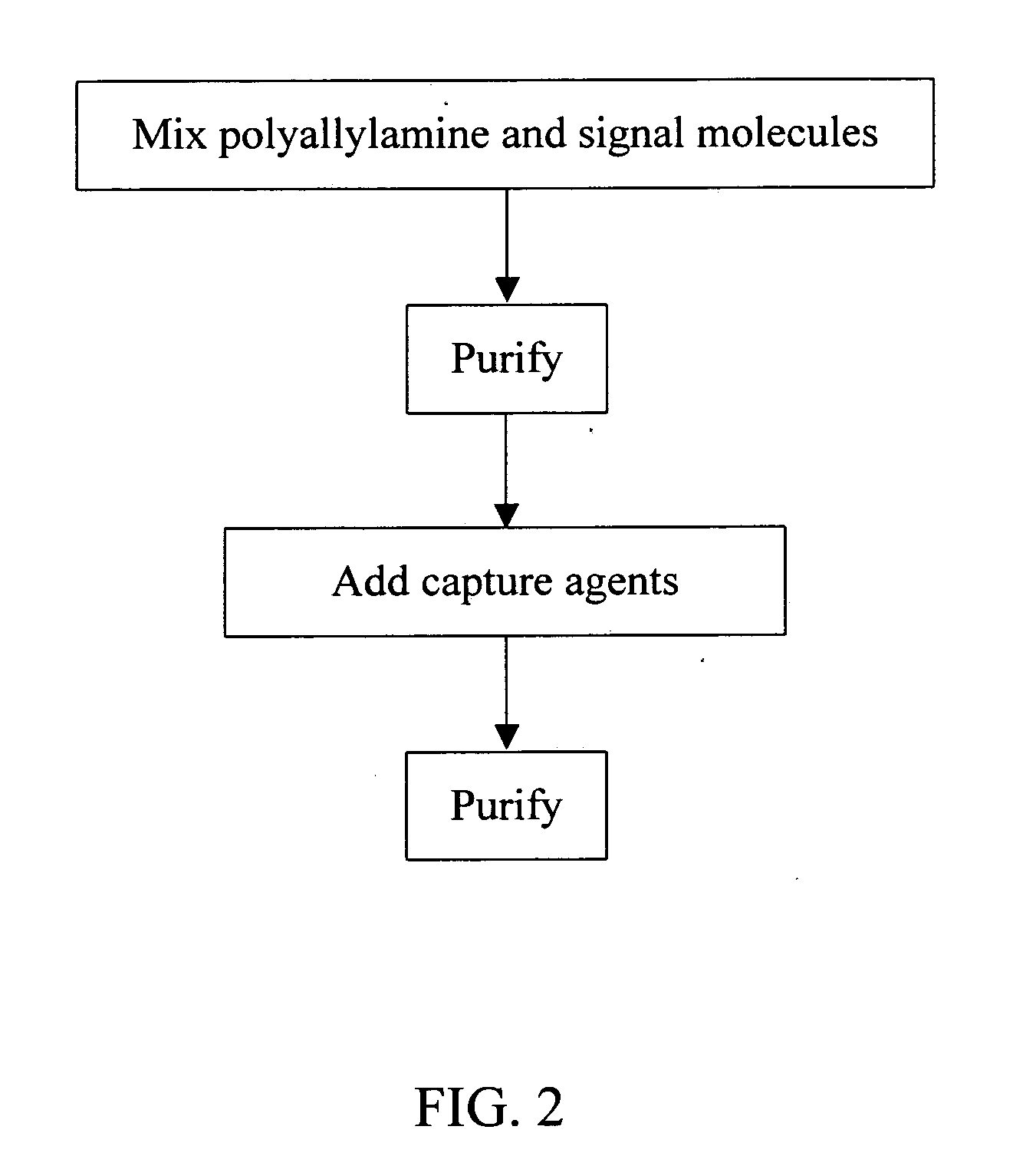
Polyallylamine conjugates and applications thereof for biological signal amplification
InactiveUS20050106649A1Reduce preparation timeMicrobiological testing/measurementPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsSignalling moleculesBiological interaction
Polyallylamine conjugates and applications thereof for biological signal amplification are provided by utilizing the essential amino group of polyallylamine to covalently bind with capture agents and signal molecules having the functional groups selected from a group consisting of —NHS, —CO, —S═O2 and —C═O—C═O. The resulting conjugates having more than one signaling entities can be further implemented for biological expression with enhancing effect on biological signal intensity, such that the sensitivity of detection for the variation between biological interactions is largely increased.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
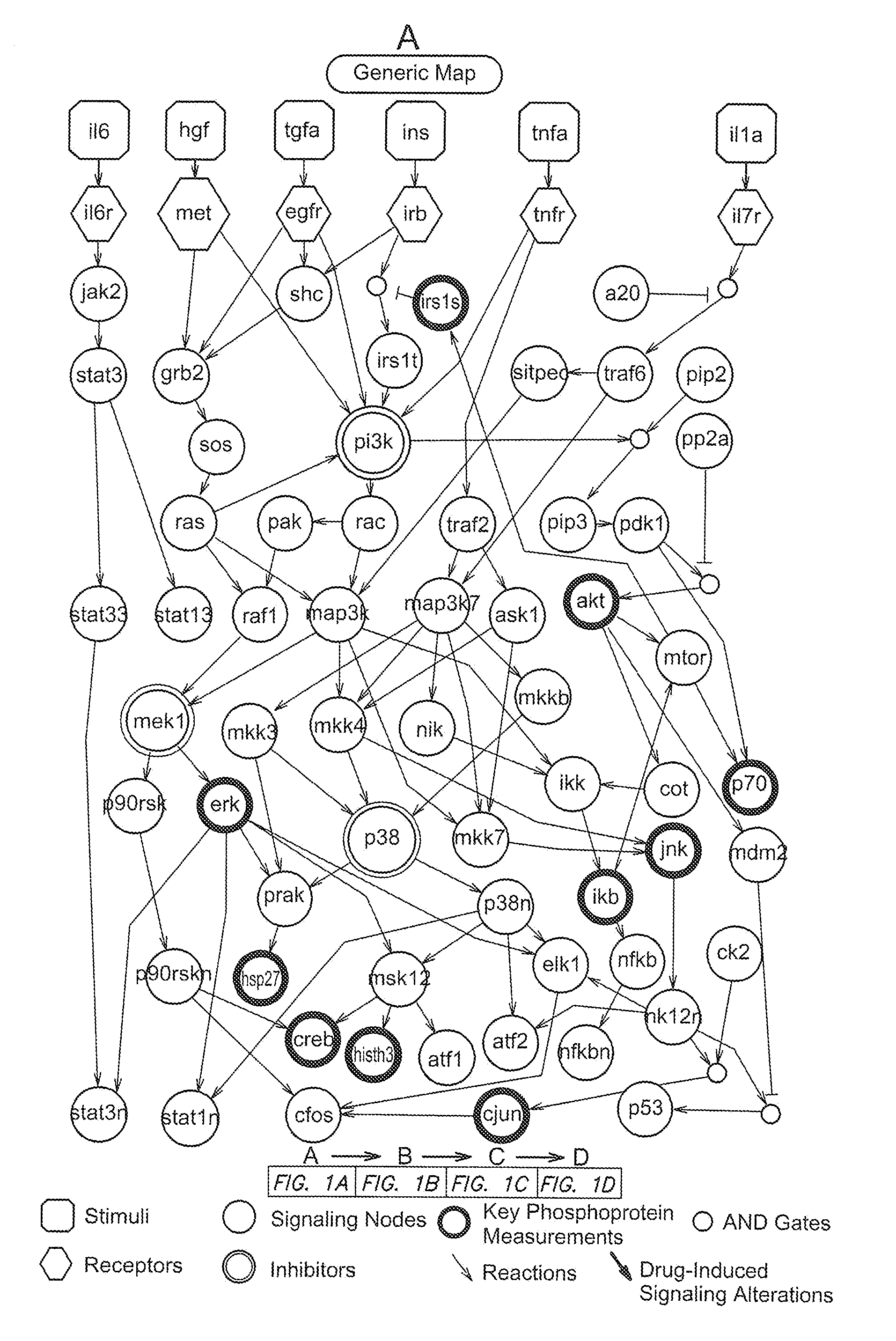
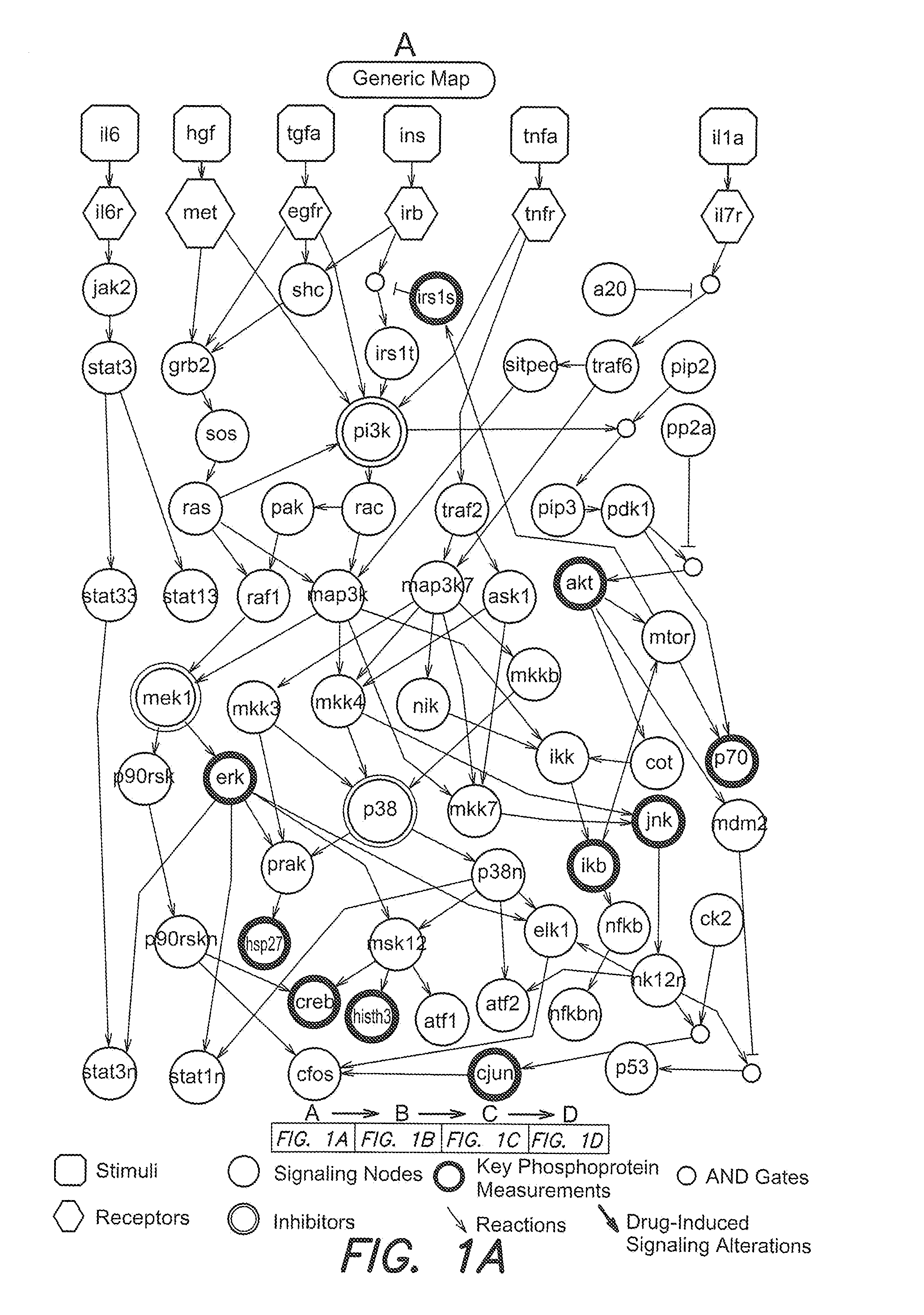
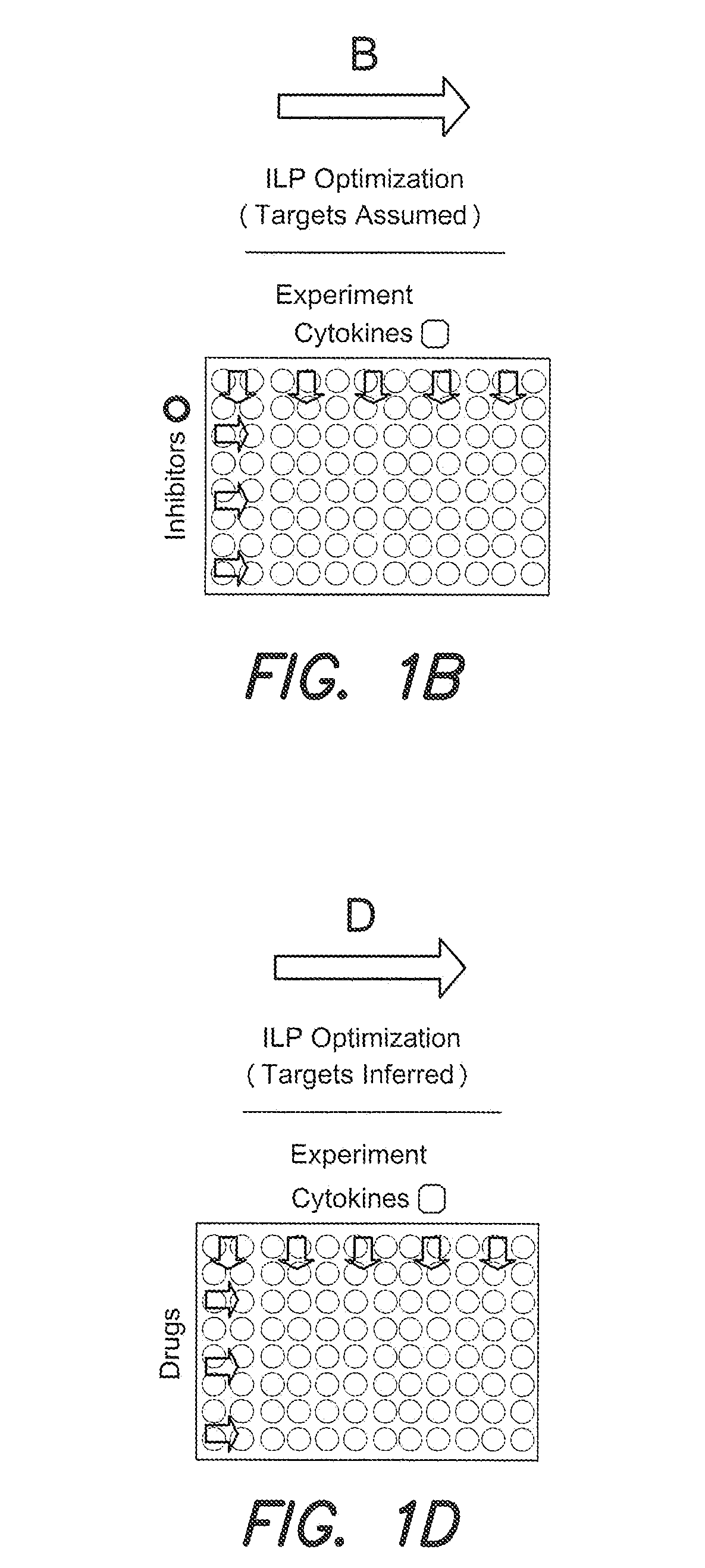
Identification of drug effects on signaling pathways using integer linear programming
InactiveUS20110153302A1Good effectImprove drug efficacyBiocideOrganic active ingredientsPersonalizationBiological interaction
Methods and algorithms for modeling biological interaction networks using integer linear programming (ILP) are provided. Methods to identify the effect of a drug on such interaction networks are also provided. Methods to use ILP-base modeling of biological interaction networks and drug effects to personalize clinical interventions are also provided.
Owner:NAT TECHN UNIV OF ATHENS RES COMMITTEE +1
Environmental factor-biological interaction simulation device for terrestrial ecological system
InactiveCN104535752ANo need to consider external interferenceMaterials are readily availableMaterial analysisBiological interactionAlloy
The invention discloses an environmental factor-biological interaction simulation device for a terrestrial ecological system. The simulation device comprises a computer and at least one ecological box, wherein the computer and each ecological box are connected by virtue of a circuit or a wireless transmission device; the computer used for controlling or detecting the conditions in the ecological boxes is arranged outside the ecological box or arranged in a master control box; each ecological box comprises an observation unit and a field simulation unit; the observation unit is arranged on the field simulation unit; a temperature and humidity sensor, illumination equipment and a camera shooting device are arranged on the upper part in the observation unit; and an alloy plate with pores is arranged on the middle lower part or the bottom in the field simulation unit. A group or multiple groups of terrestrial ecological system(s) can be continuously, dynamically and stably controlled to a certain degree in a temperature difference range under all-weather conditions throughout the year, and a reliable solution is provided for an experiment of simulating the action of the environmental factors on the organisms.
Owner:NANJING INST OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI MINIST OF ECOLOGY & ENVIRONMENT OF THE PEOPLES REPUBLIC OF CHINA
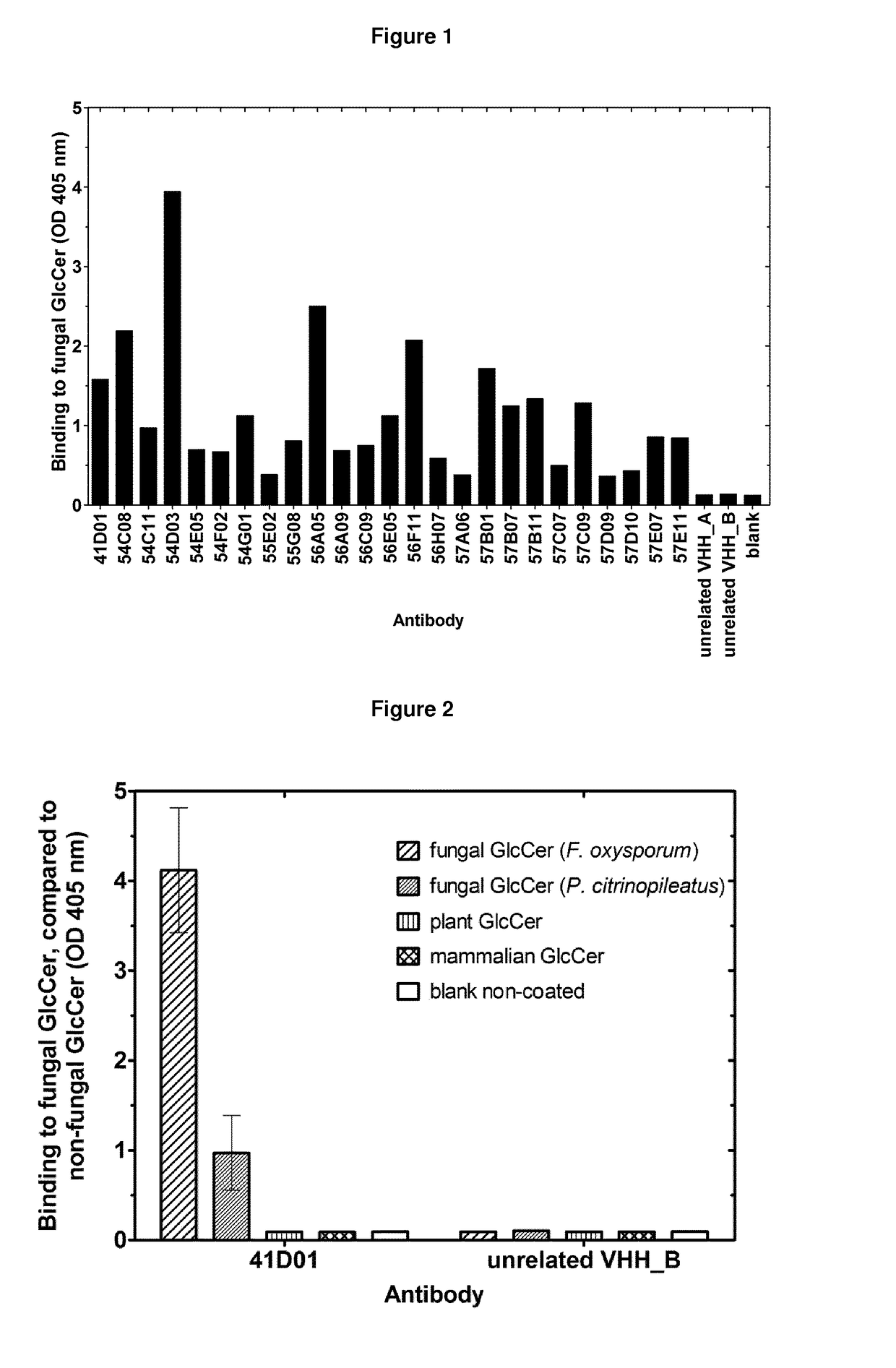
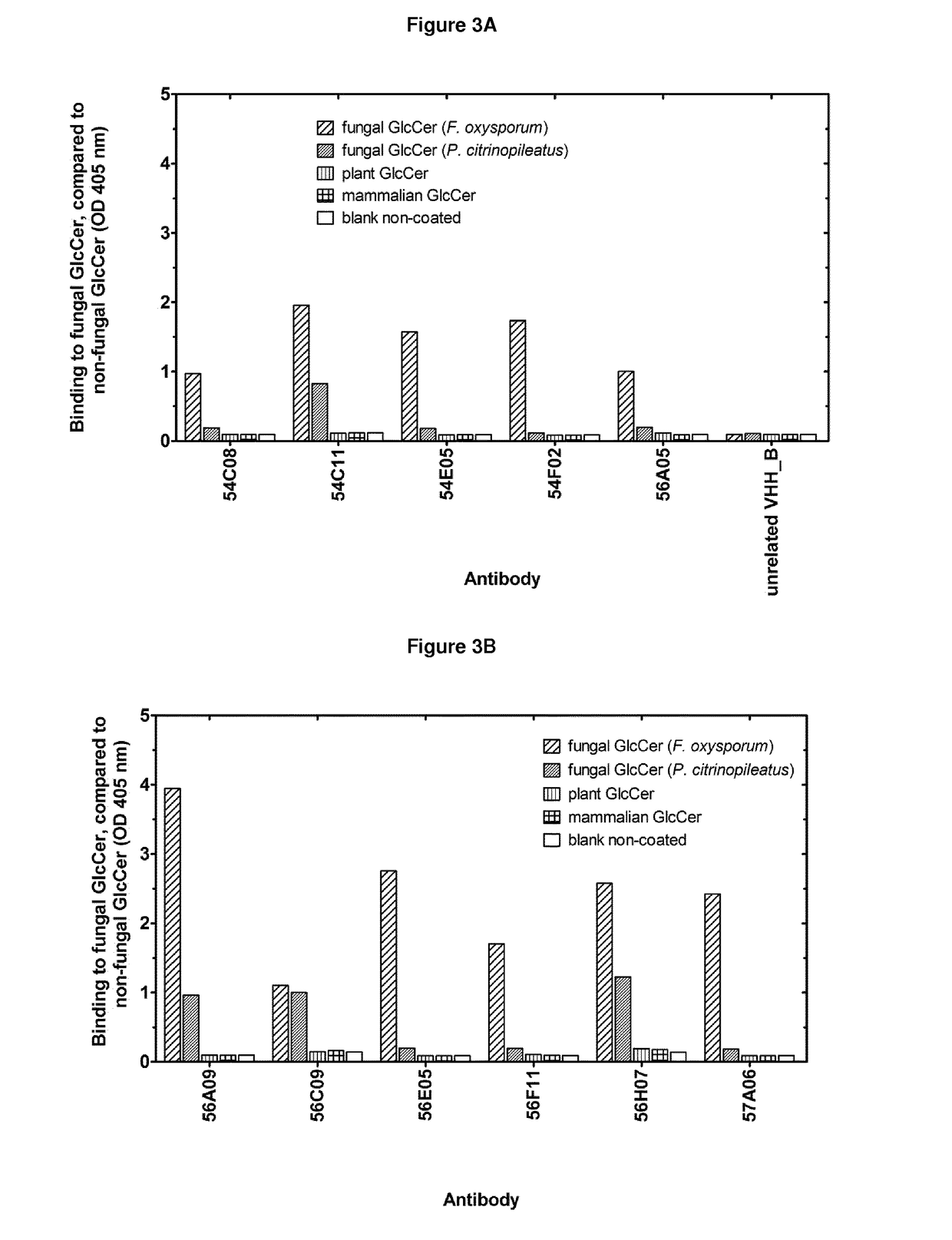
Agrochemical compositions comprising antibodies binding to sphingolipids
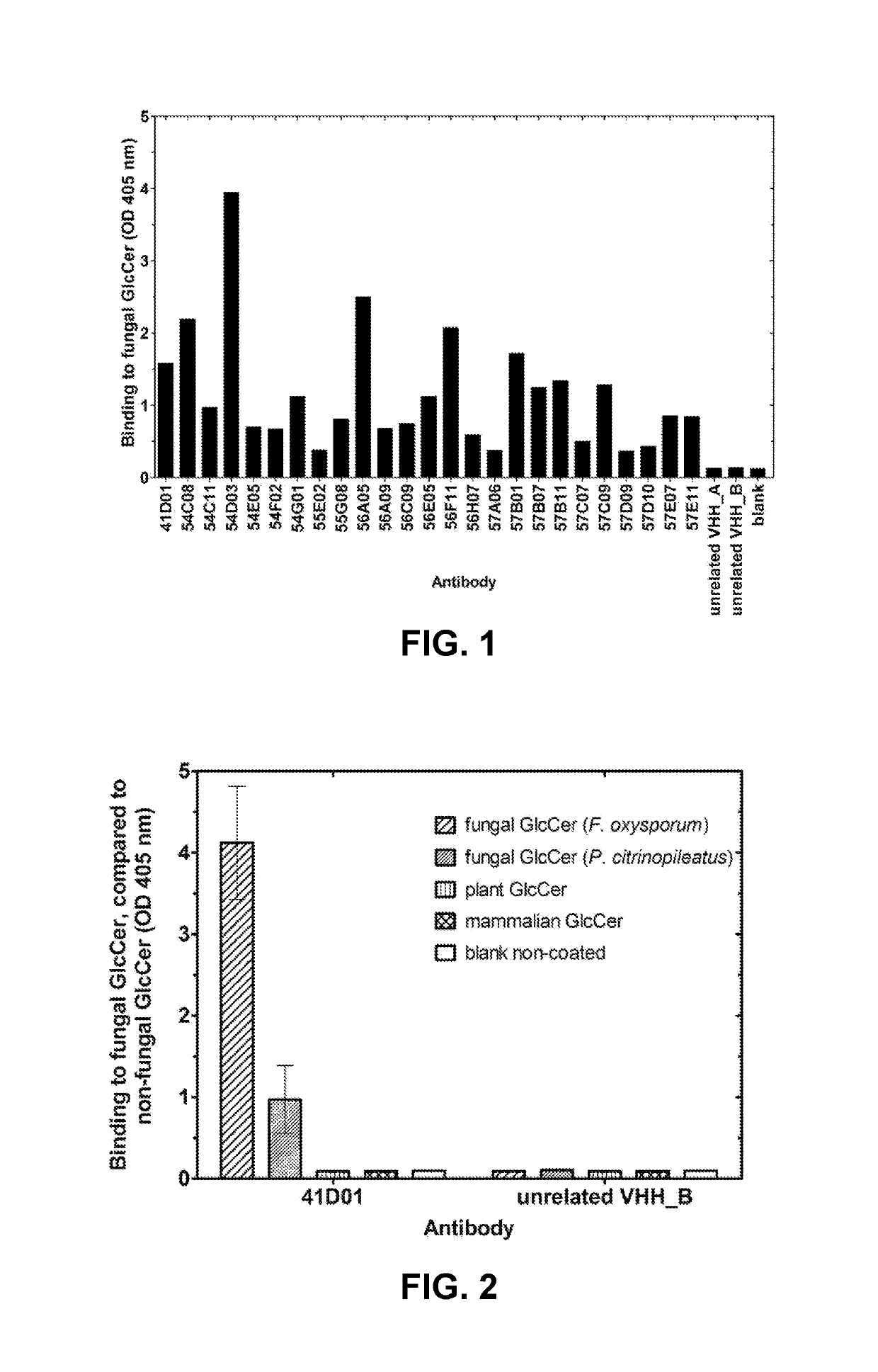
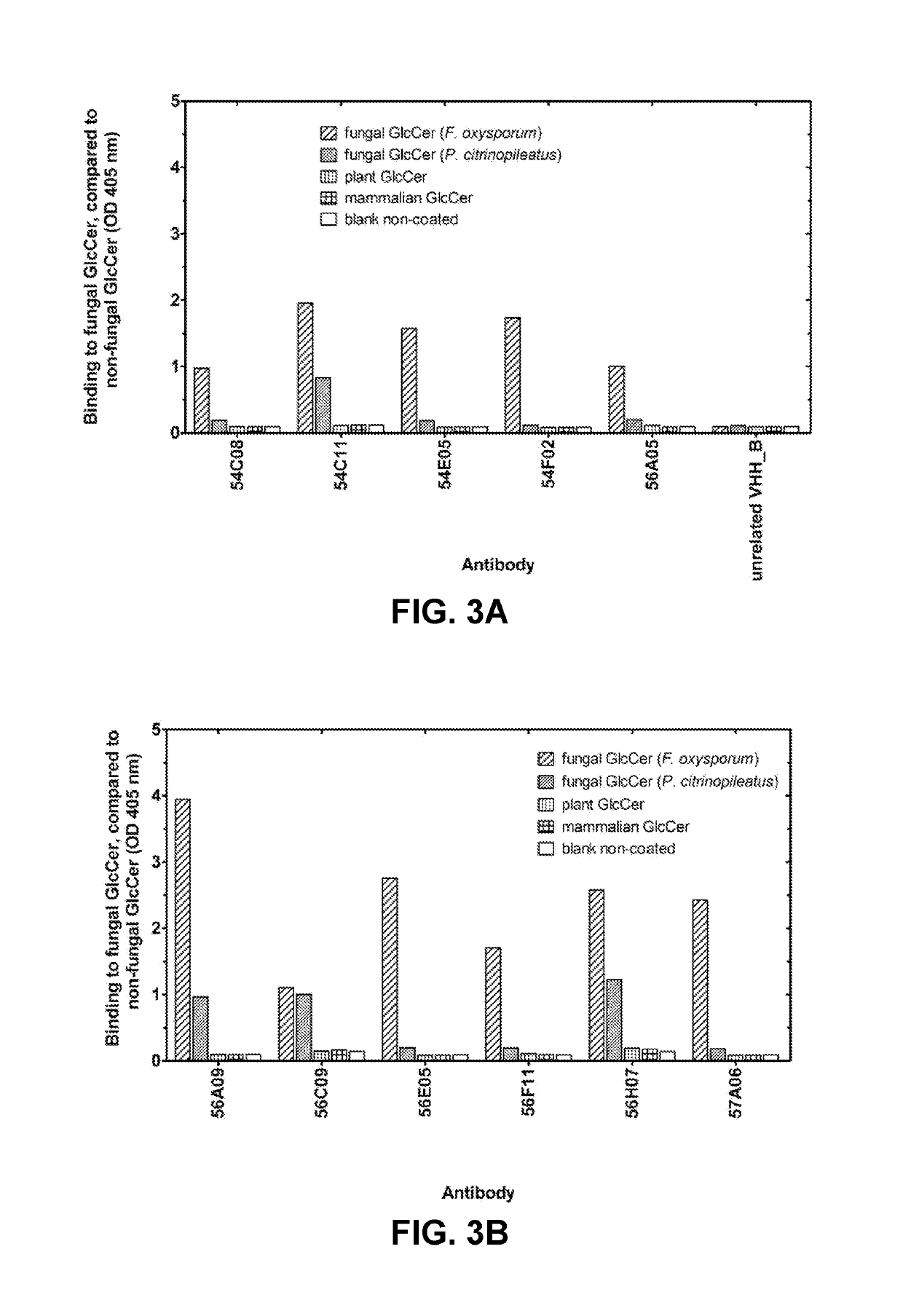
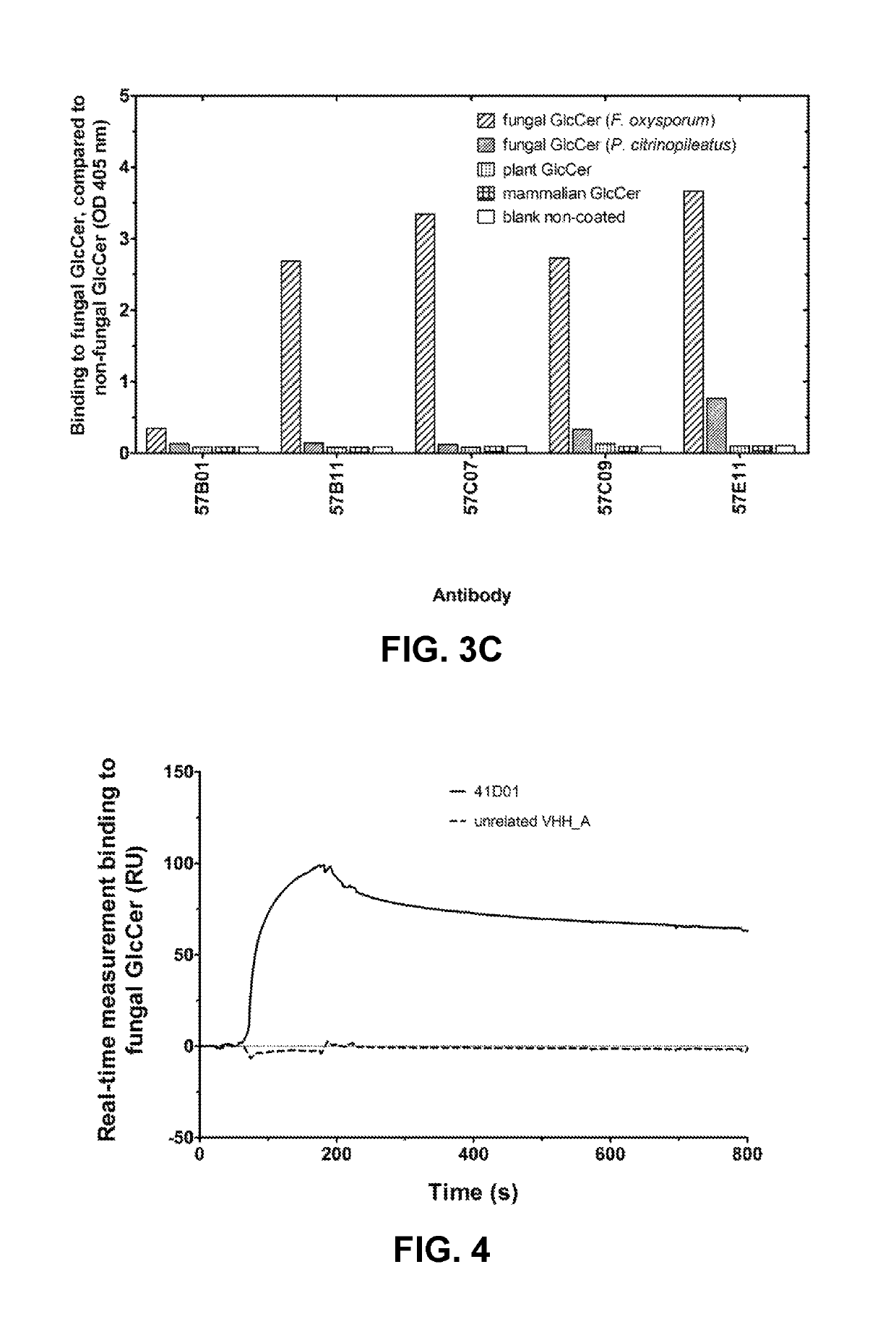
The present invention relates to agrochemical and biological control compositions for combating pests, more specifically plant pests, comprising at least one polypeptide, which specifically binds to a pest. The invention further provides methods for protecting or treating a plant or a part of a plant from an infection or other biological interaction with a plant pathogen, at least comprising the step of applying directly or indirectly to a plant or to a part of a plant, an agrochemical composition, under conditions effective to protect or treat a plant or a part of a plant against a infection or biological interaction with a plant pathogen. Further provided are methods for producing such agrochemical compositions and formulations, to polypeptides with a specific pesticidal activity comprised within an agrochemical formulation, to nucleic acids encoding such polypeptide and to plants comprising chimeric genes comprising such nucleic acids.
Owner:KATHOLIEKE UNIV LEUVEN +1
Controlled magnetohydrodynamic fluidic networks and stirrers
ActiveUS7371051B2Pump componentsTransportation and packagingBiological interactionMagneto hydrodynamic
The present invention relates to controlled, magnetohydrodynamically-driven, fluidic networks containing a plurality of individually controlled branches. The branches consist of conduits equipped with pairs of electrodes that are controlled by electrode controllers. In operation, the network is placed within a magnetic field and potentials or currents are applied across electrode pairs within the various branches of the network in specifically determined magnitudes and polarities for specifically determined time intervals in accordance with an activation sequence that may be determined by an algorithm. Placed within a temperature gradient, at least a part of the network can act as a thermal cycler for use in biological interactions that employ temperature variations. The invention also relates to magnetohydrodynamic stirrers comprising a conduit or cavity having at least two electrodes disposed in such an orientation that, upon the application of a potential or current across the electrode pair within a magnetic field, secondary flows such as chaotic advection is generated.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Electrochemical Patterning on Multi-Channel Microelectrode Array for Biosensing Applications
InactiveUS20080113352A1High selectivityConvenient investigationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsSequential/parallel process reactionsDesorptionBiological interaction
Described is a method for electrochemically patterning a microelectrode array (MEA) with at least two different kinds of macromolecules. Said method comprising the steps of: providing a platform with a surface that comprises individually addressable conductive microelectrode surfaces; covering said platform surface with an adlayer of resistant polymer; desorbing said adlayer from a first kind of conductive microelectrodes intended for the selective adsorption of a first kind of macromolecules, in particular proteins, by applying a potential; subjecting the desorbed surfaces to the first macromolecule under conditions such that said first macromolecule adsorbs to said desorbed surfaces, and repeating the desorption / adsorption steps with a second or further kind of macromolecules until all kinds of desired macromolecules are adsorbed. A microchip array produced by the inventive method is also described. Such chip arrays can be used to study a large diversity of biological interactions, e.g. protein-protein interactions, protein-cell interactions, protein-nucleic acid interactions, etc.
Owner:ETH TRANSFER +1
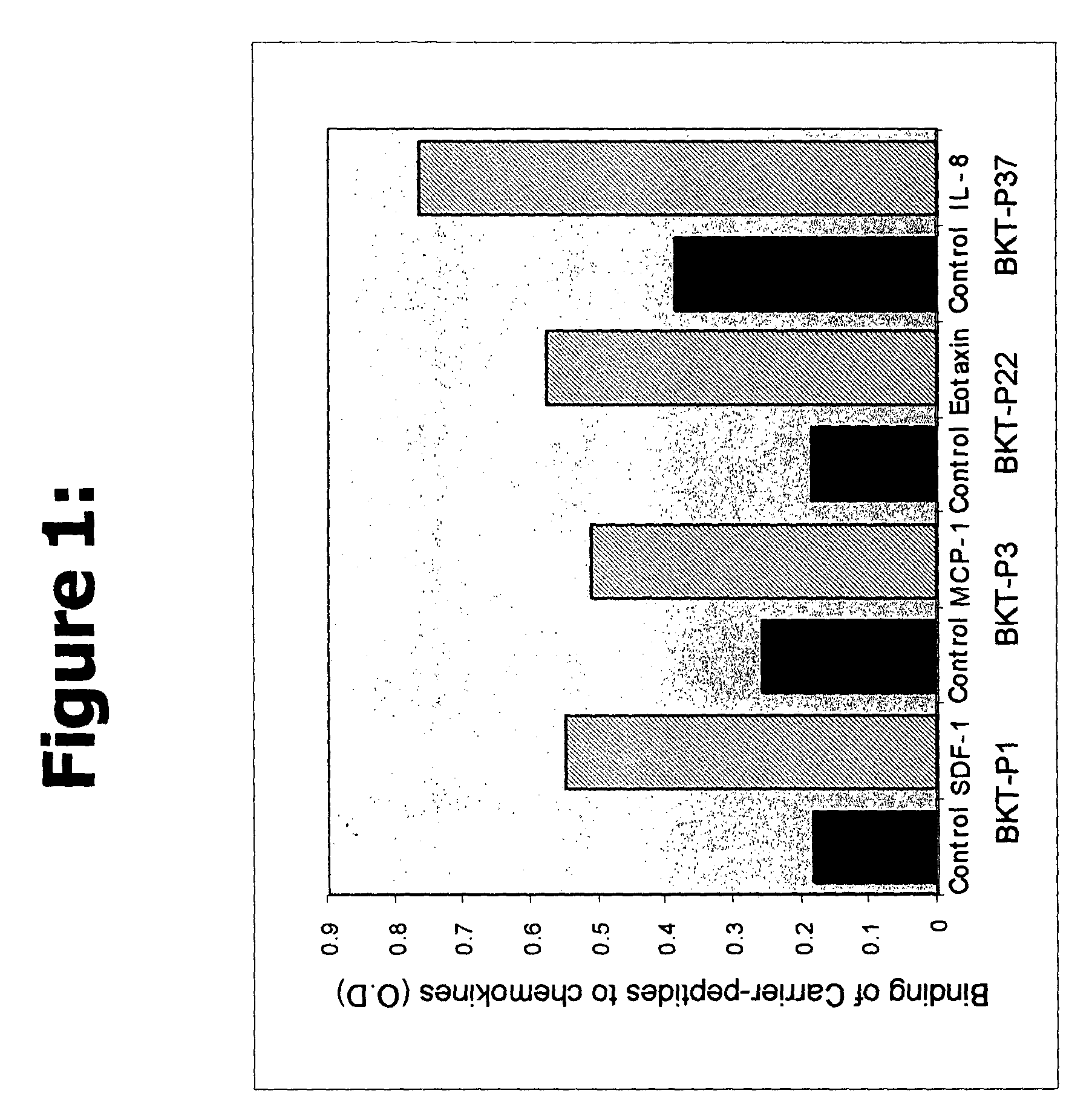
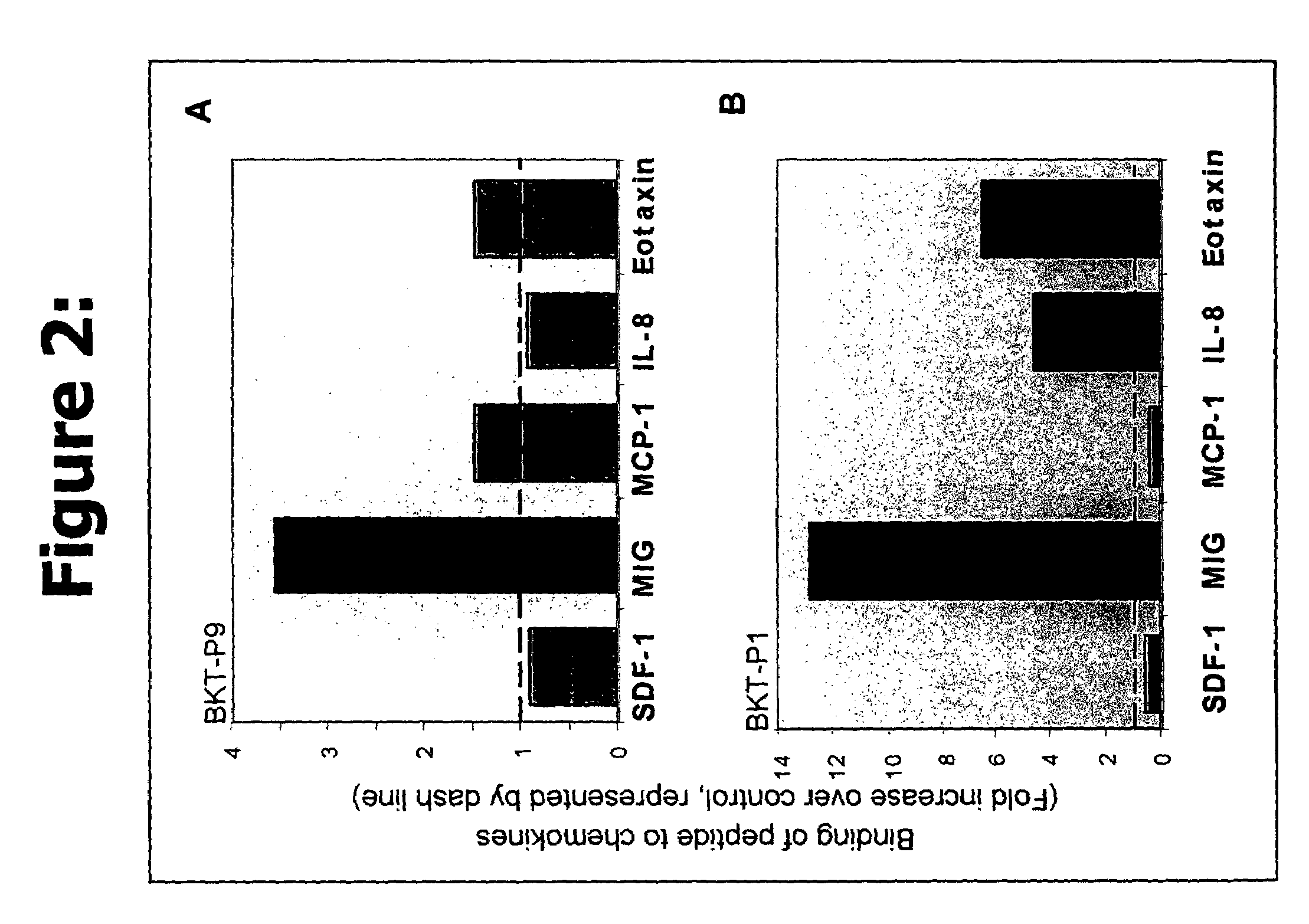
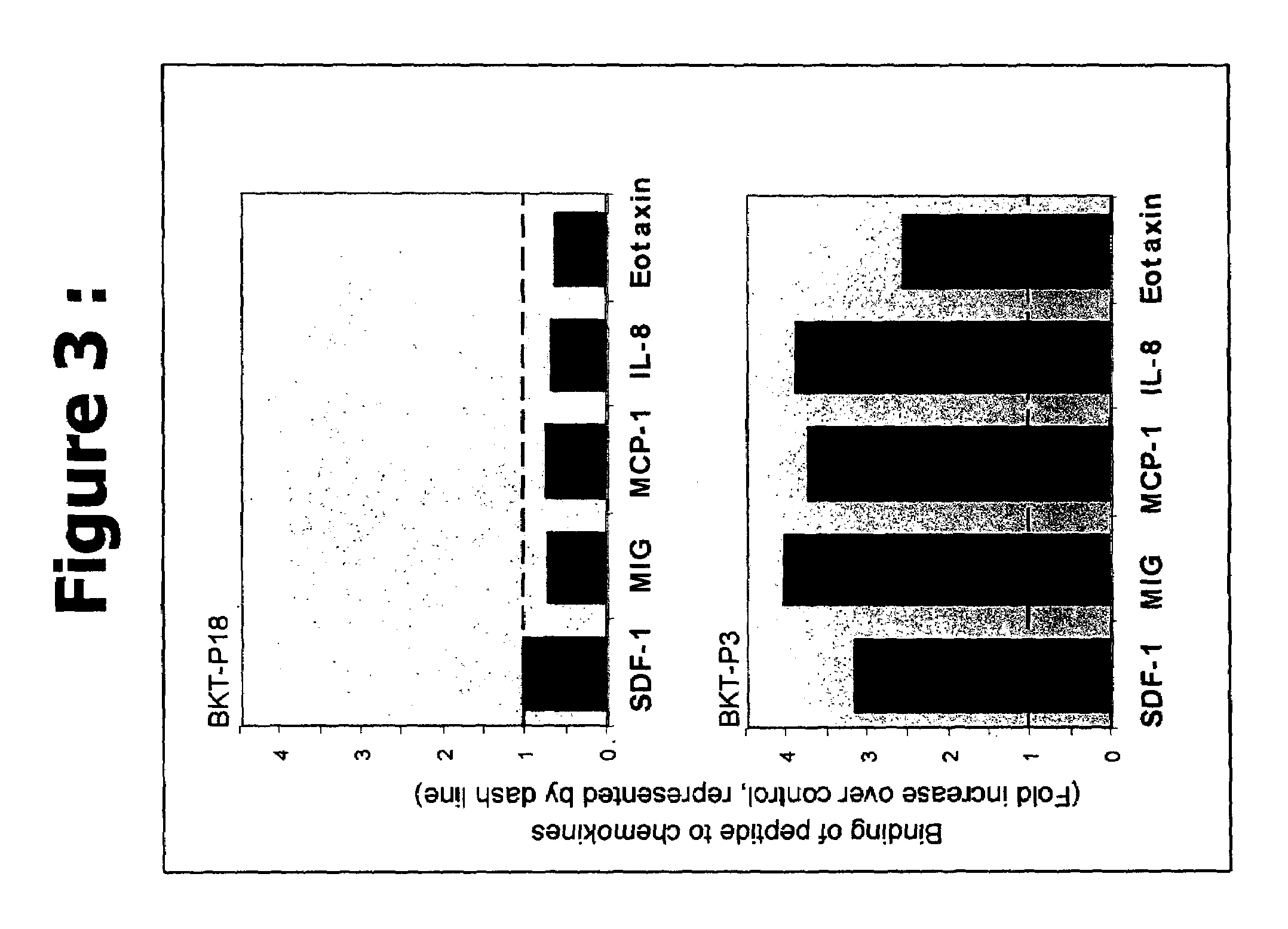
Methods of inhibiting chemokine binding to chemokine receptors
InactiveUS7488717B2Modulate effectImprove bindingBiocideAntipyreticBiological interactionChemokine receptor binding
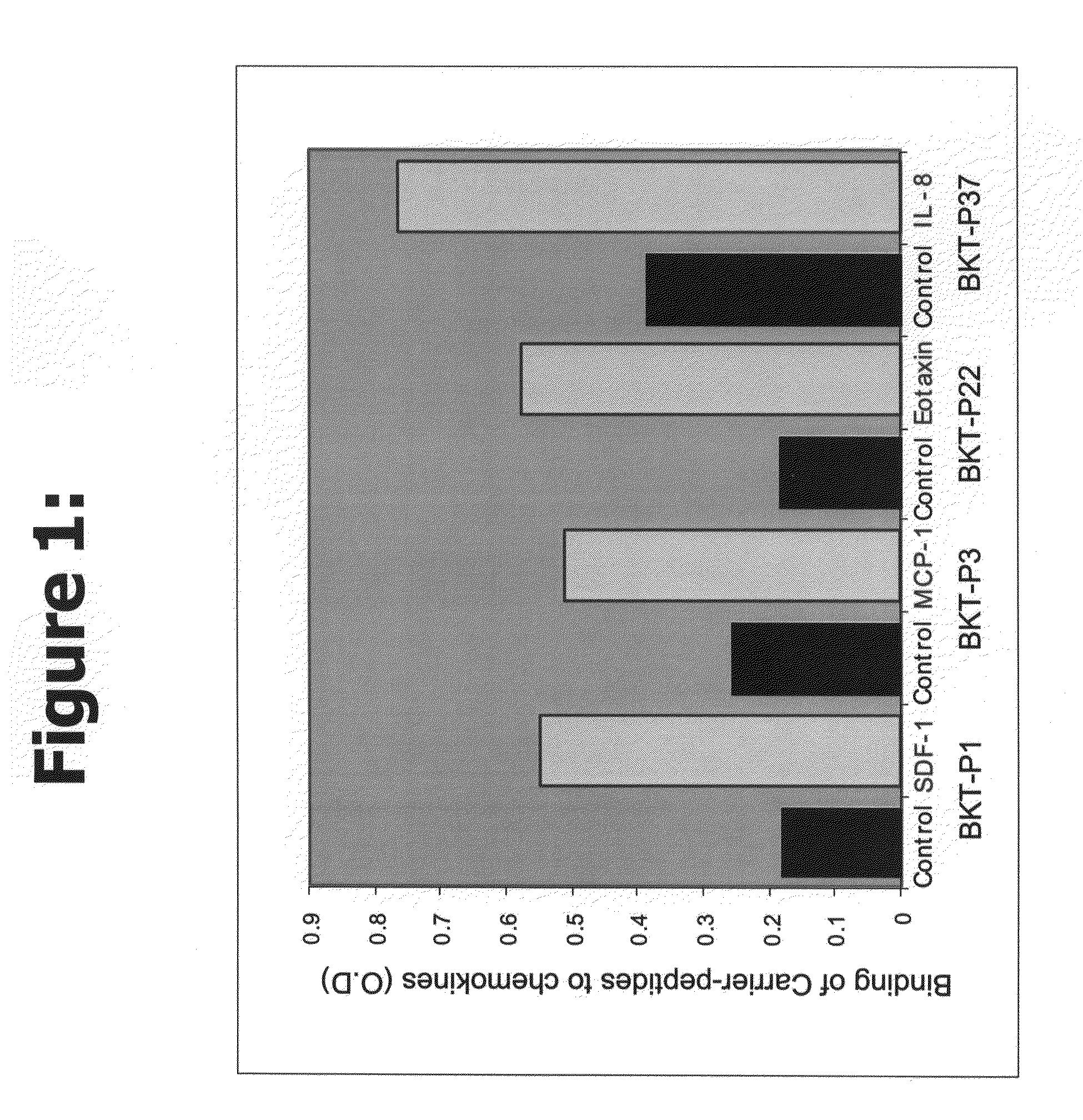
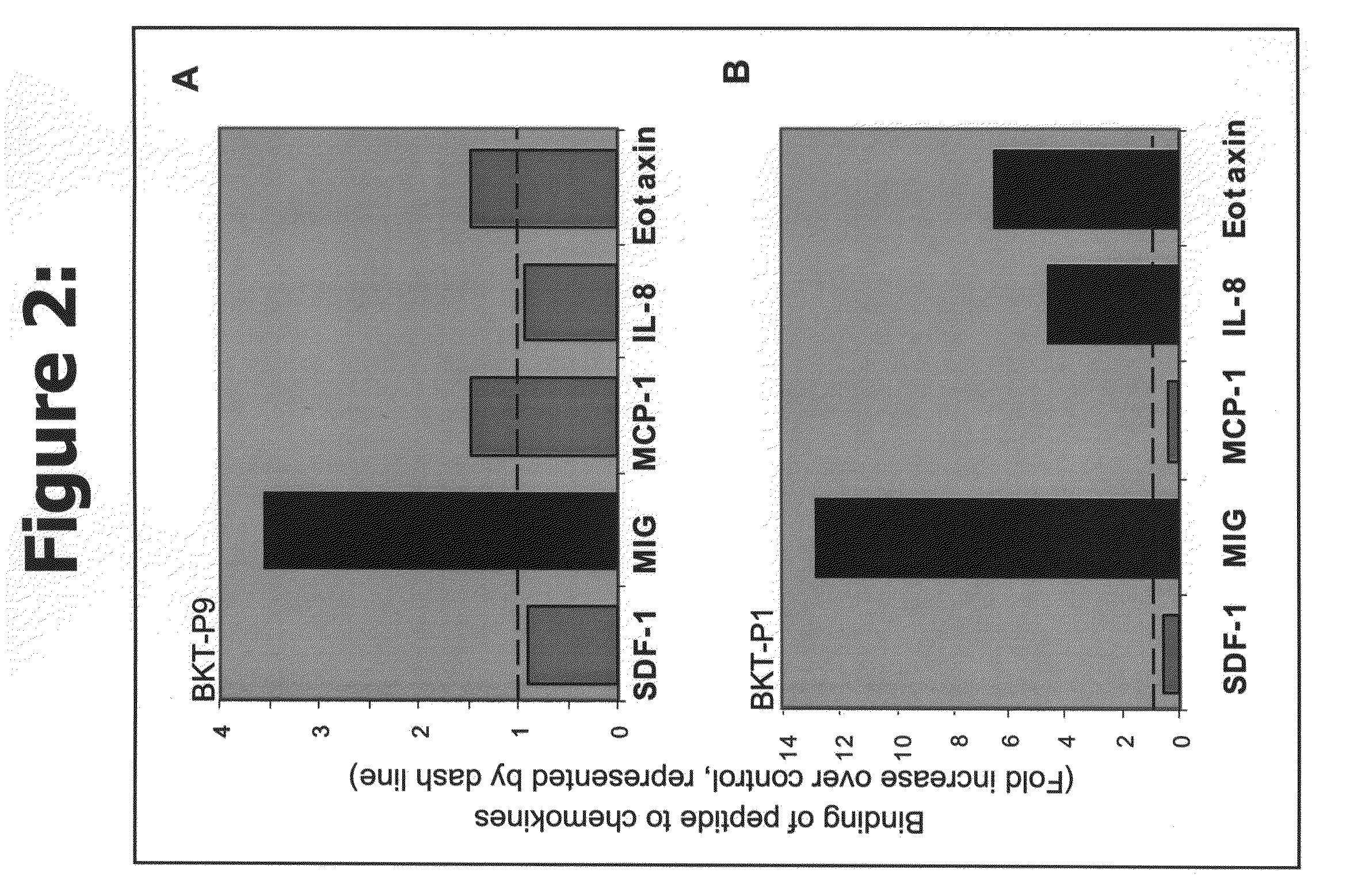
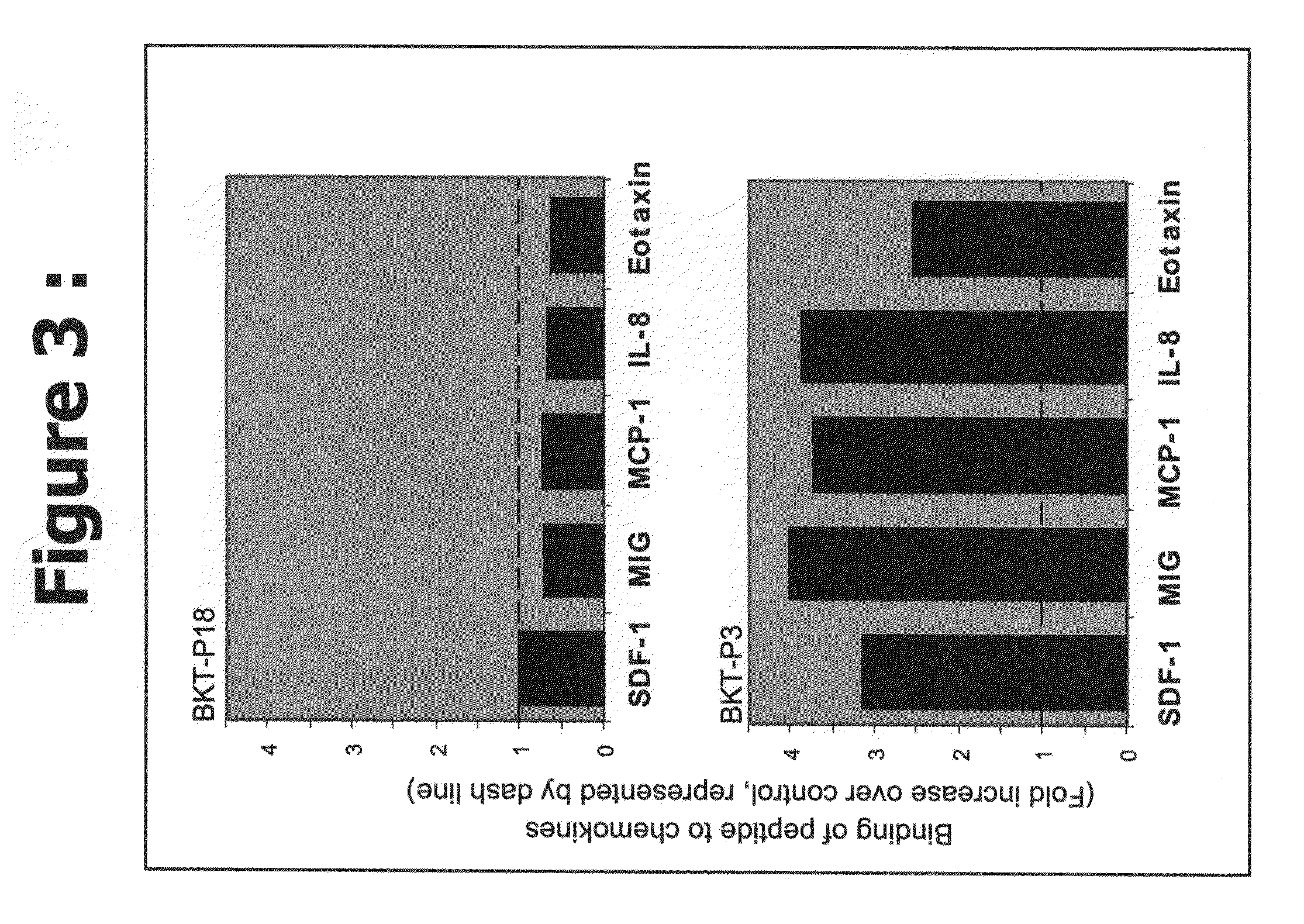
Novel peptides or peptidomimetic agents or small molecules for modulating the biological effect of a chemokine. According to the present invention, the therapeutic agents preferably are endowed with the capacity to bind to certain chemokines in order to modulate the biological interaction between the target ligand, chemokine, and the respective target receptor, chemokine receptor. These peptides may be described as agonist ligands or antagonists. Next, preferably certain peptides share consensus sequences are described which characterize the families or categories of these modulator peptides.
Owner:BIOKINE THERAPEUTICS LTD
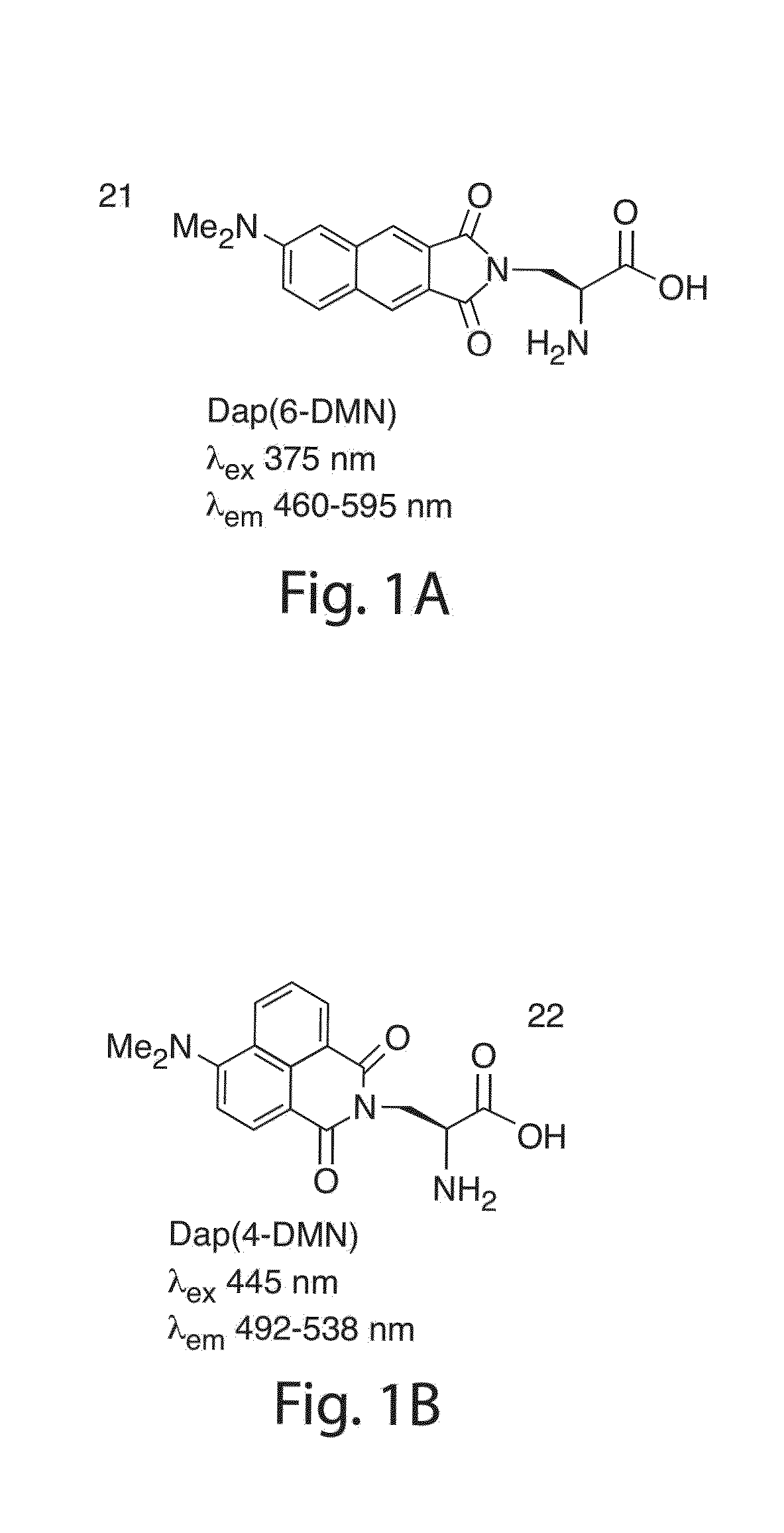
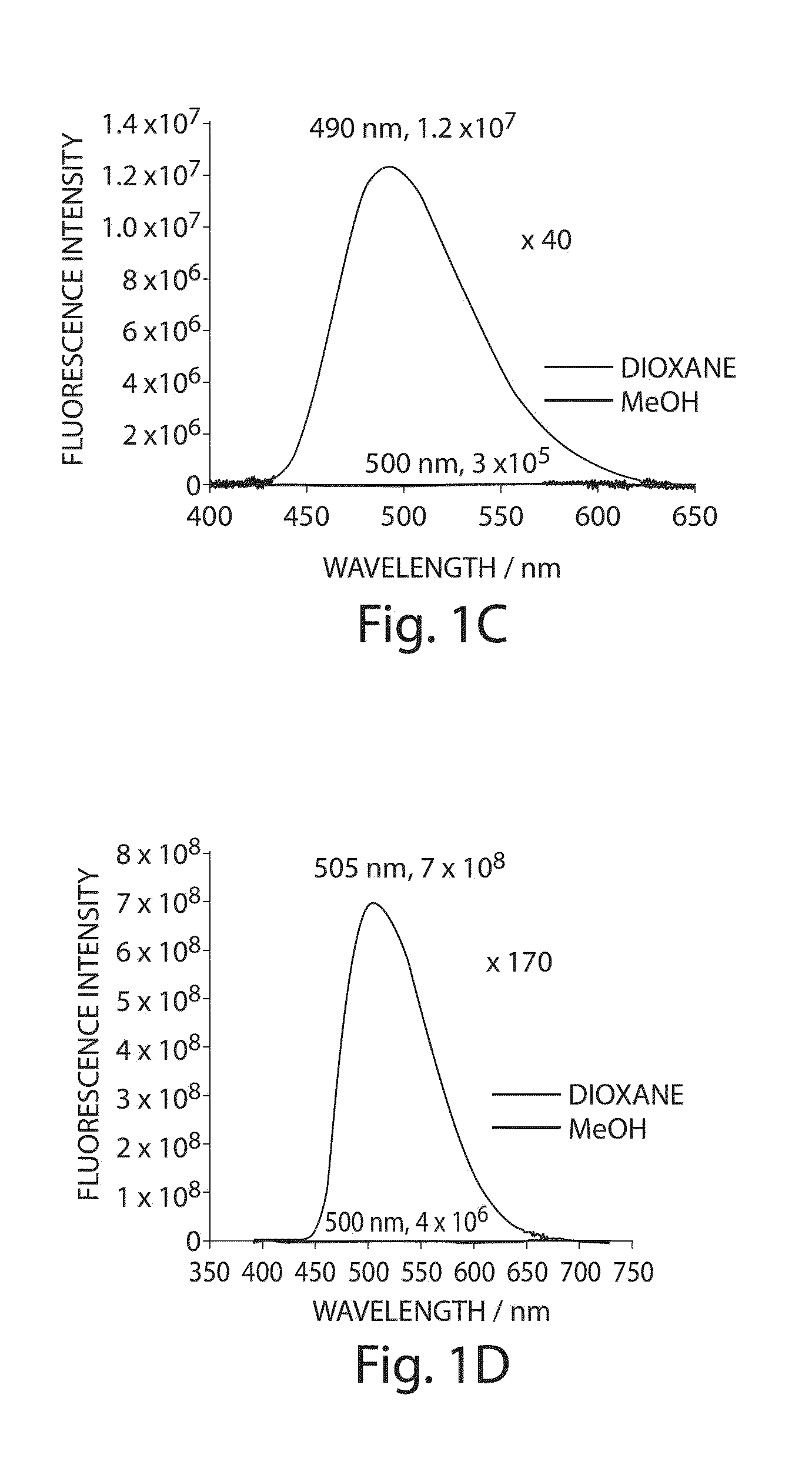
Environmentally sensitive fluorophores
ActiveUS8440835B2Improve propertiesGood chemical stabilityGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsPeptide preparation methodsPhosphorylationBiological interaction
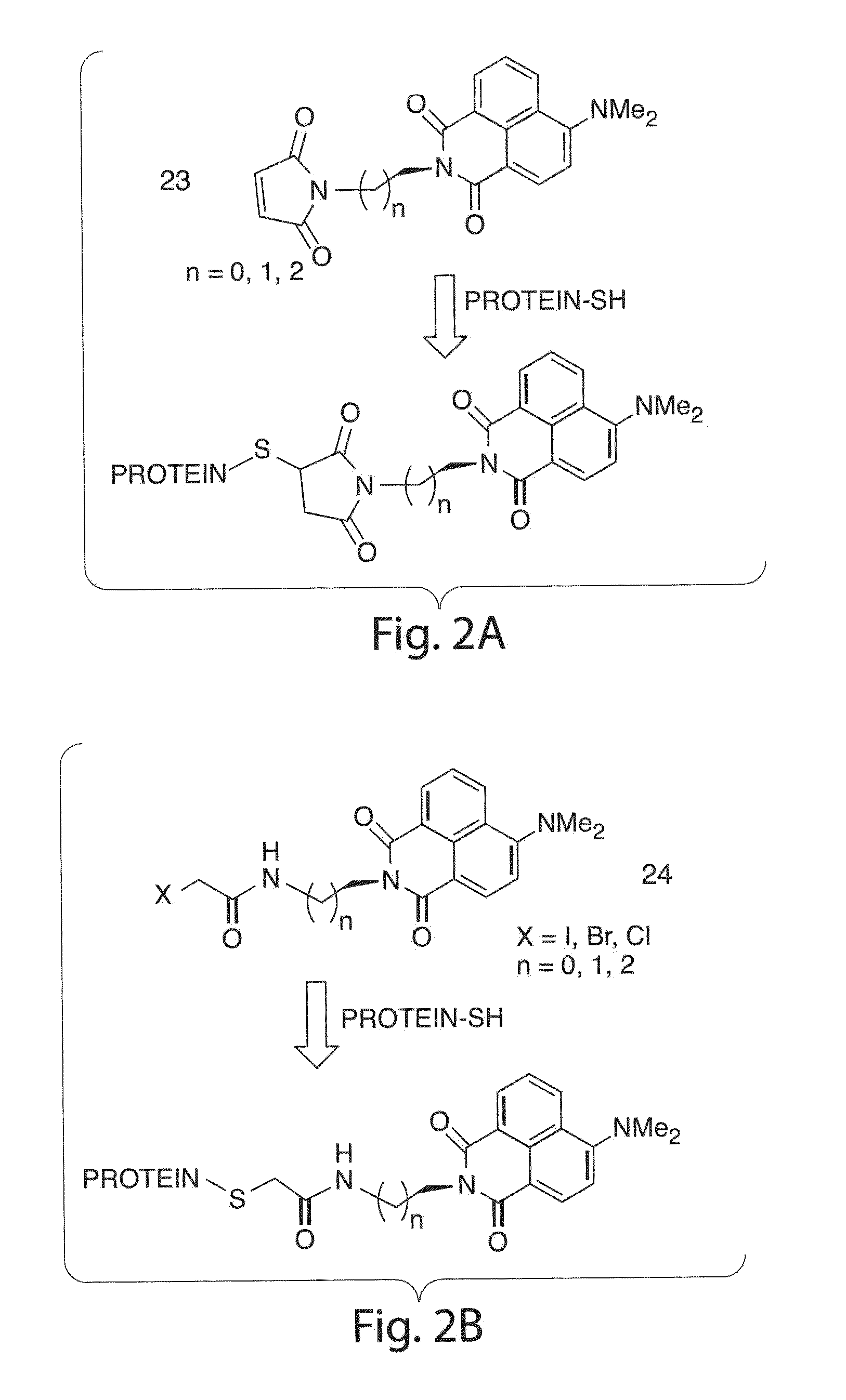
The present invention generally relates to environment-sensitive fluorophores, including environment-sensitive fluorophores for reporting protein / protein and peptide / protein interactions. In one aspect, the present invention is directed to compounds and salts thereof, compositions and methods useful in determining biological interactions. In some cases, the compounds of the present invention are environment-sensitive fluorophores that have spectroscopic behavior that may depend on factors such as the physicochemical properties of the surrounding environment. The compounds of the present invention can be used, in certain embodiments, to monitor ions, small molecules, and biological processes such as protein folding, protein-protein interactions and phosphorylation events.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Solid-phase array-based biocatalytic transformations
ActiveUS7202030B2Easy to operateMacromolecular librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseEnzymatic synthesis
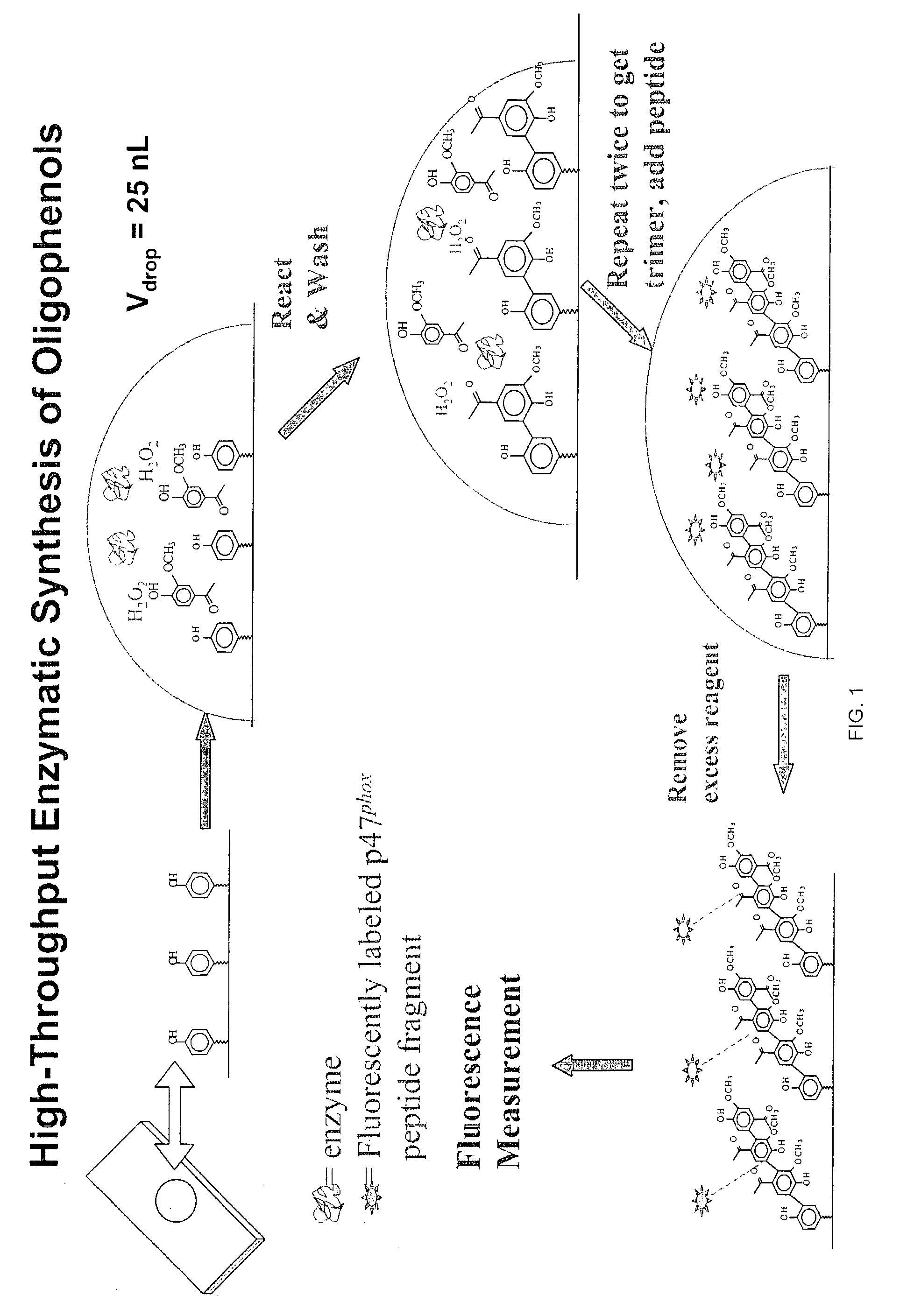
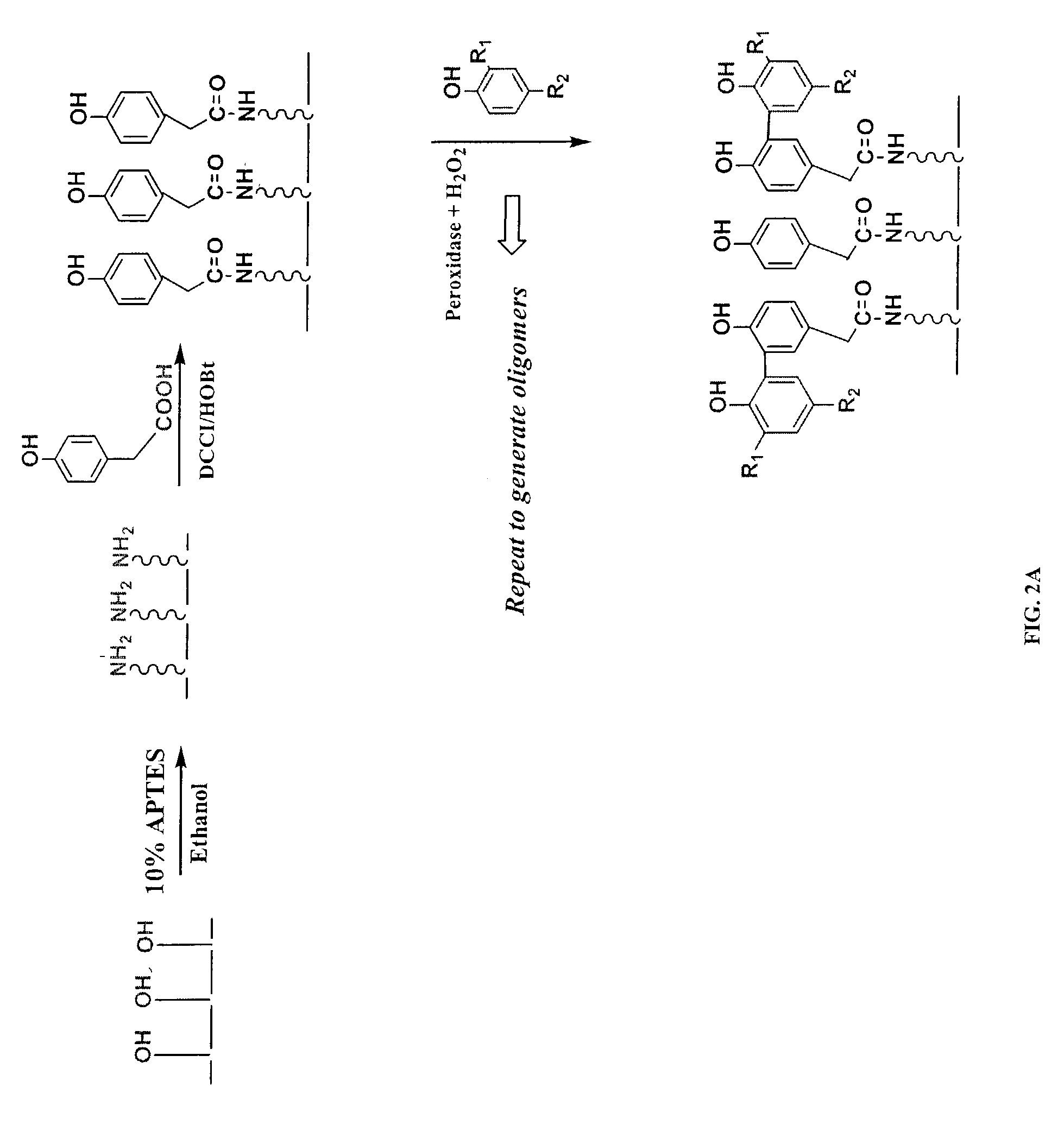
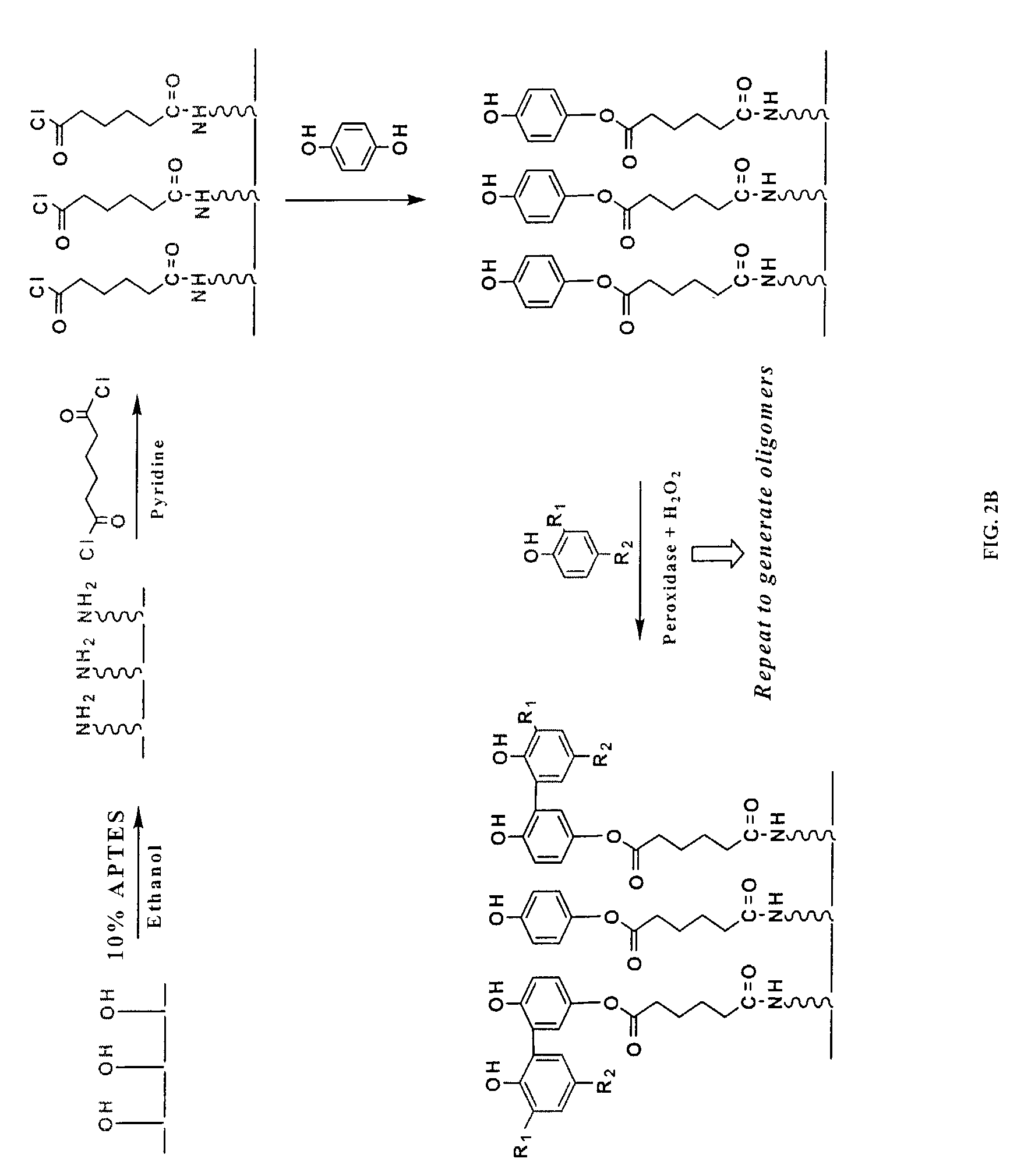
This invention relates to the enzymatic synthesis of oligophenols on solid support by sequential enzymatic addition of reaction solutions containing phenols. The oligomers are then selectively built up on the solid surface. When used in a specific format, the oligomers can be generated in a spatially addressable array, which can then be screened for some type of biological interaction. The synthetic compounds of the present invention are synthesized in a combinatorial manner on solid support using peroxidase or other related enzymatic catalysis, and the products are generated in spatially addressable microarrays. Oligophenols of the present invention have shown significance as potential inhibitors of NADPH oxidase assembly, an enzyme that has been implicated in a wide range of diseases stemming from vascular hyperpermeability.
Owner:RENESSELAER POLYTECHNIC INST +1
Drug interaction assay chip
InactiveUS20030059846A1Sequential/parallel process reactionsOrganic chemistry methodsDrug interactionFluorescence
A tool (a method, and a microarray apparatus) to enable evaluation of drug-drug interactions, by providing large numbers of pharmaceutical compounds on solid substrates in numerous replicate sets suitable for long-term storage. Ordinarily, the various compounds are present in extremely high densities. The libraries of pharmaceutical compounds, when used as a bioreaction assay chip, can be combined with a detection system that includes cells, cellular fractions, enzymes, organic molecules, and fluorescence or chromogenic reporter molecules along with a test drug agent. This method allows the detection of biochemical or biological interaction of the test drug agent with known pharmaceutical compounds in a defined biochemical or biological context of the assay.
Owner:MOREWOOD MOLECULAR +1
Methods of inhibiting chemokine binding to chemokines receptors
InactiveUS20100173848A1Improve bindingAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsBiological interactionChemokine Receptor Gene
Novel peptidic or peptidomimetic agents or small molecules for modulating the biological effect of a chemokine. According to the present invention, the therapeutic agents preferably are endowed with the capacity to bind to certain chemokines in order to modulate the biological interaction between the target ligand, chemokine, and the respective target receptor, chemokine receptor. These peptides may be described as agonist ligands or antagonists. Next, preferably certain peptides share consensus sequences are described which characterize the families or categories of these modulator peptides.
Owner:BIOKINE THERAPEUTICS LTD
Biosensors
Methods for detecting a biological interaction comprising administering a substrate comprising a ligand attached to the substrate wherein the ligand binds to a receptor and wherein a signal is produced. Also disclosed is a biosensor comprising a substrate and a ligand wherein the ligand is attached to the surface of the substrate and wherein the ligand preferentially binds to a receptor.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND OFFICE OF TECH COMMLIZATION
A cell-based array platform
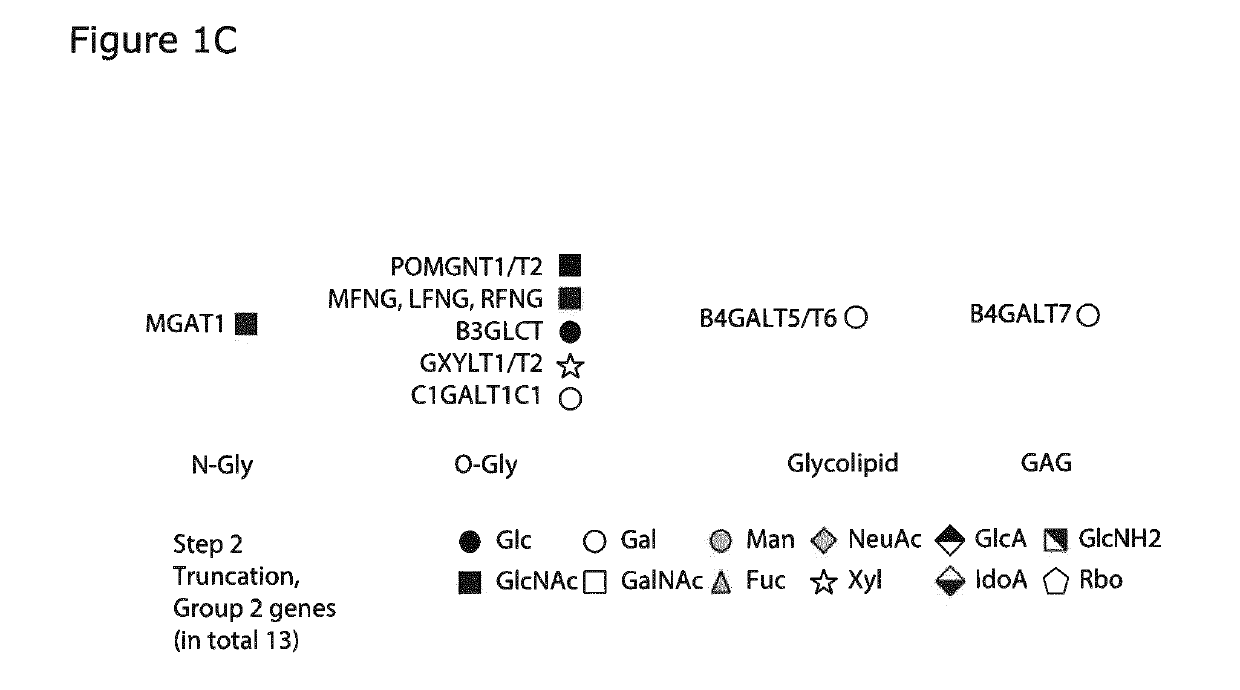
PendingUS20190330601A1Expansion of in complexityComplexity volumeBiological material analysisTransferasesMammalian GlycanBiological interaction
The present invention relates to a method for display of a plurality of mammalian glycans on cells or proteins for probing biological interactions and identifying glycan structures involved. A plurality of mammalian cells is genetically engineered in a combinatorial approach to differentially express the human glycome. Genetic engineering of the cell produces a plurality isogenic cells with different repertoires of glycosyltransferases and display of glycans that is used to interpret biological interactions. The plurality of engineered cells display glycans with and without the context of specific proteins exogeneously expressed, and is useful for detection and optimization of biological interactions for example binding of lectins, antibodies, viruses and bacteria and glycoproteins.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF COPENHAGEN
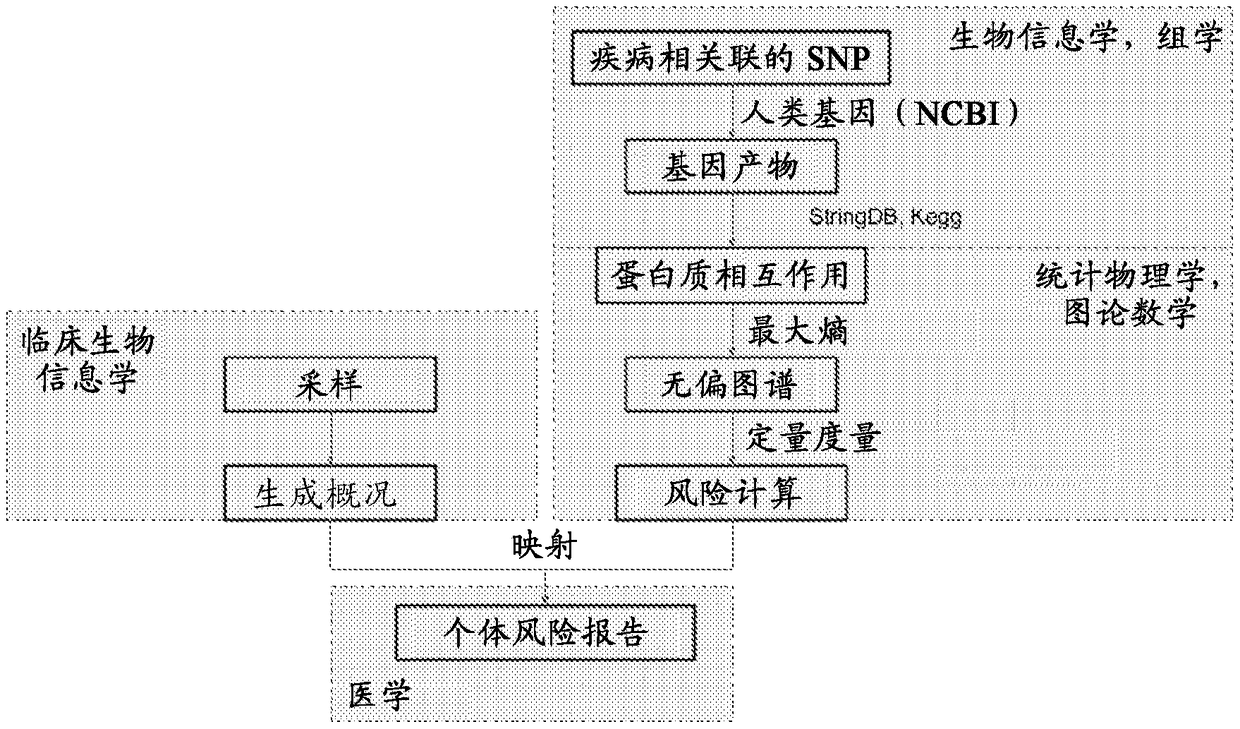
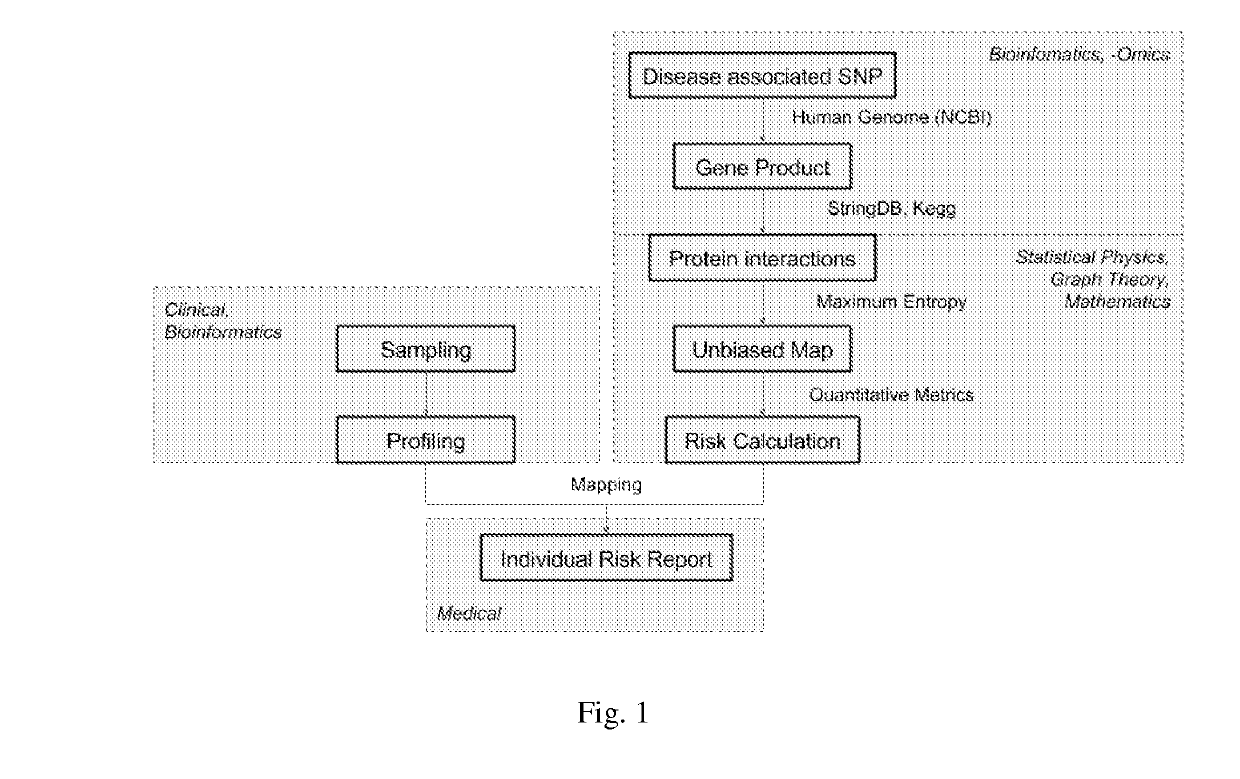
Methods for analysis of digital data
Methods for producing an enriched reference data map useful for identifying critical factors for the development of a condition of interest are disclosed. The reference data map may be used to assessthe risk or likelihood of a condition of interest being realized. In the context of medicine or genetics, the methods of the invention may be used to produce a risk assessment roadmap useful for identifying elements (biomolecular constructs, biological interactions, and biological pathways) that are critical to the development of a particular disease or syndrome. The roadmap may be consulted to design treatment methods having the greatest likelihood of successfully treating or preventing the development of a disease or syndrome. Also disclosed are methods for using such a risk assessment roadmap to evaluate a specific configuration of elements for determining the changes in the configuration of elements that will result in the achievement or the avoidance of a defined condition of interest. In the context of medicine or genetics, the invention provides methods for determining the susceptibility of an individual or group of individuals to develop a particular disease or syndrome utilizing biological data of the individual or group and assessing the level of risk by referencing a risk assessment roadmap prepared according to the invention herein. Uncertainty in diagnosis is minimizedor eliminated by these methods, and the targets, interactions, and pathways most likely to be critical for disease development, and so representing the best intervention points for treatment or prevention of the disease or syndrome, are identified.
Owner:WHITE ANVIL INNOVATIONS LLC
Method for detecting fragrance of silkworm chrysalis by headspace solid-phase microextraction and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry
InactiveCN106353413AFacilitates secondary metabolic processesSimple and fast operationComponent separationBiological interactionSolid-phase microextraction
The invention discloses a method for detecting fragrance of silkworm chrysalis by headspace solid-phase microextraction and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. The method utilizes the fact that headspace solid-phase microextraction technology integrates sampling, extraction and enrichment, and has the advantages that extraction speed is high, operating cost is low, and there is no need for solvent extraction and infusion and other operations; automated analysis is implemented by the use with gas chromatography-mass spectrometry technology, the types and contents of characteristic flavor substances in the insect food material silkworm chrysalis, the effect of different nymphosis temperatures upon the types and formation of characteristic flavor matters in black and yellow fresh silkworm chrysalises are studied, and the influences of boiling, deep frying and lyophilization upon the flavor substances are compared in order to push the deep-processed silkworm chrysalises to the production and development of characteristic flavor seasonings; the method of the invention has a certain assistance in further researches on secondary metabolic process of insects, biological interaction of insects and animal and plant ecological mutual influence.
Owner:辽宁中北方正检测服务有限公司
Methods for Analysis of Digital Data
Methods for producing an enriched reference data map useful for identifying critical factors for the development of a condition of interest are disclosed. The reference data map may be used to assess the risk or likelihood of a condition of interest being realized. In the context of medicine or genetics, the methods of the invention may be used to produce a risk assessment roadmap useful for identifying elements (biomolecular constructs, biological interactions, and biological pathways) that are critical to the development of a particular disease or syndrome. The roadmap may be consulted to design treatment methods having the greatest likelihood of successfully treating or preventing the development of a disease or syndrome. Also disclosed are methods for using such a risk assessment roadmap to evaluate a specific configuration of elements for determining the changes in the configuration of elements that will result in the achievement or the avoidance of a defined condition of interest. In the context of medicine or genetics, the invention provides methods for determining the susceptibility of an individual or group of individuals to develop a particular disease or syndrome utilizing biological data of the individual or group and assessing the level of risk by referencing a risk assessment roadmap prepared according to the disclosure herein. Uncertainty in diagnosis is minimized or eliminated by these methods, and the targets, interactions, and pathways most likely to be critical for disease development, and so representing the best intervention points for treatment or prevention of the disease or syndrome, are identified.
Owner:WHITE ANVIL INNOVATIONS LLC
Computer-Implemented Method For Simulating, In A Three-Dimensional Scene, The Evolution Of Biological Data
InactiveUS20140156247A1Easy to browseReduce usageMedical simulationData visualisationBiological interactionComputer science
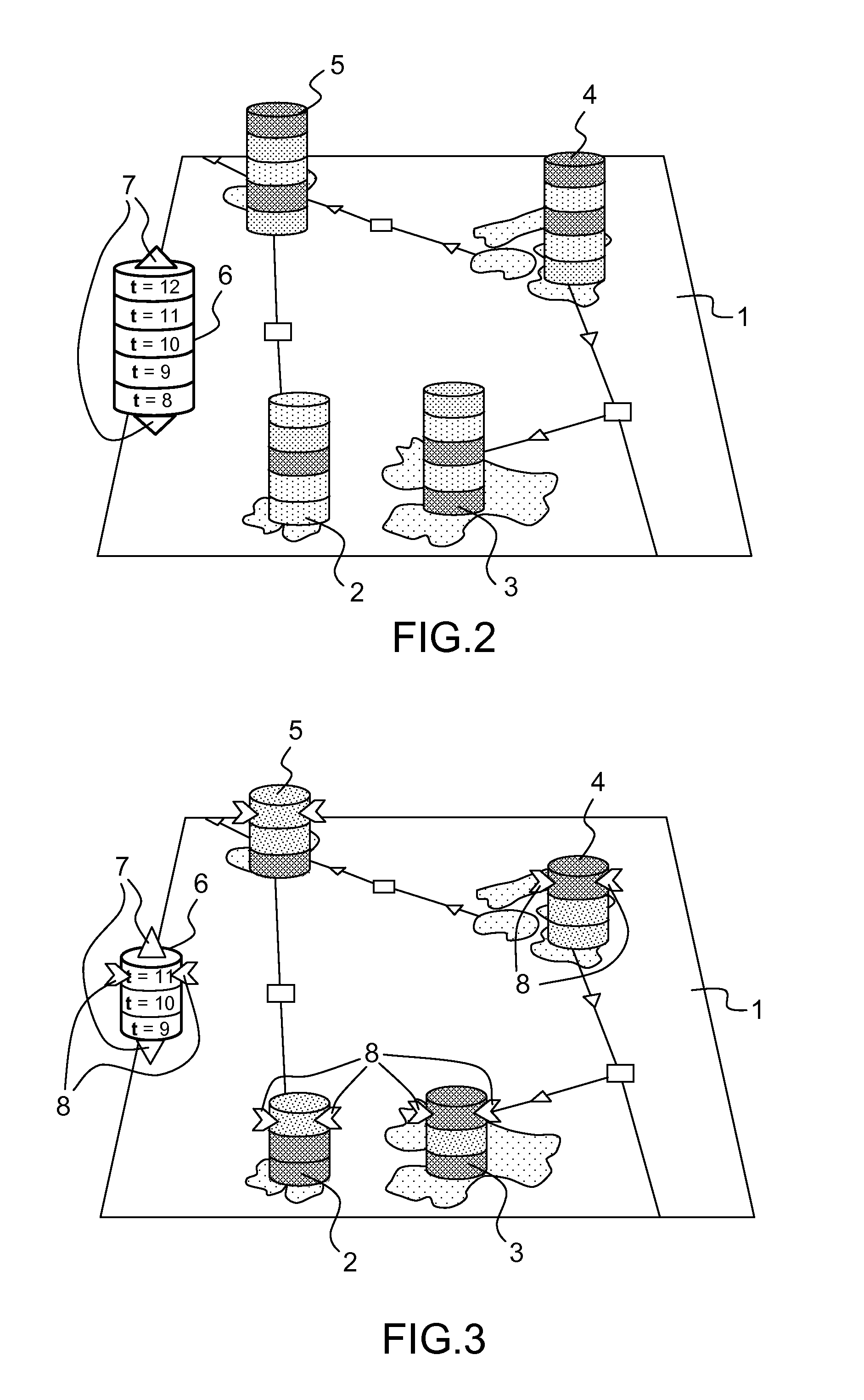
A computer-implemented method for simulating, in a three-dimensional scene, the evolution of biological data comprising the steps of:displaying an initial biological interaction network (BIN) of biological entities; anddetermining biological data for said interaction network (BIN);characterized in that the method further comprises the step of:displaying, in a three-dimensional scene, a biological data of each entity in a first layout (2, 3, 4, 5), a first layout comprising several levels, a level corresponding to the value of the biological data at a time instant (t).
Owner:DASSAULT SYSTEMES
Agrochemical compositions comprising antibodies binding to sphingolipids
This disclosure relates to agrochemical and biological control compositions for combating pests, more specifically plant pests, comprising at least one polypeptide, which specifically binds to a pest. The disclosure further provides methods for protecting or treating a plant or a part of a plant from an infection or other biological interaction with a plant pathogen, at least comprising the step of applying directly or indirectly to a plant or to a part of a plant, an agrochemical composition, under conditions effective to protect or treat a plant or a part of a plant against a infection or biological interaction with a plant pathogen. Further provided are methods for producing such agrochemical compositions and formulations, to polypeptides with a specific pesticidal activity comprised within an agrochemical formulation, to nucleic acids encoding such polypeptide and to plants comprising chimeric genes comprising such nucleic acids.
Owner:AGROSAVFE +1
Bioelectric signal operating system and method thereof
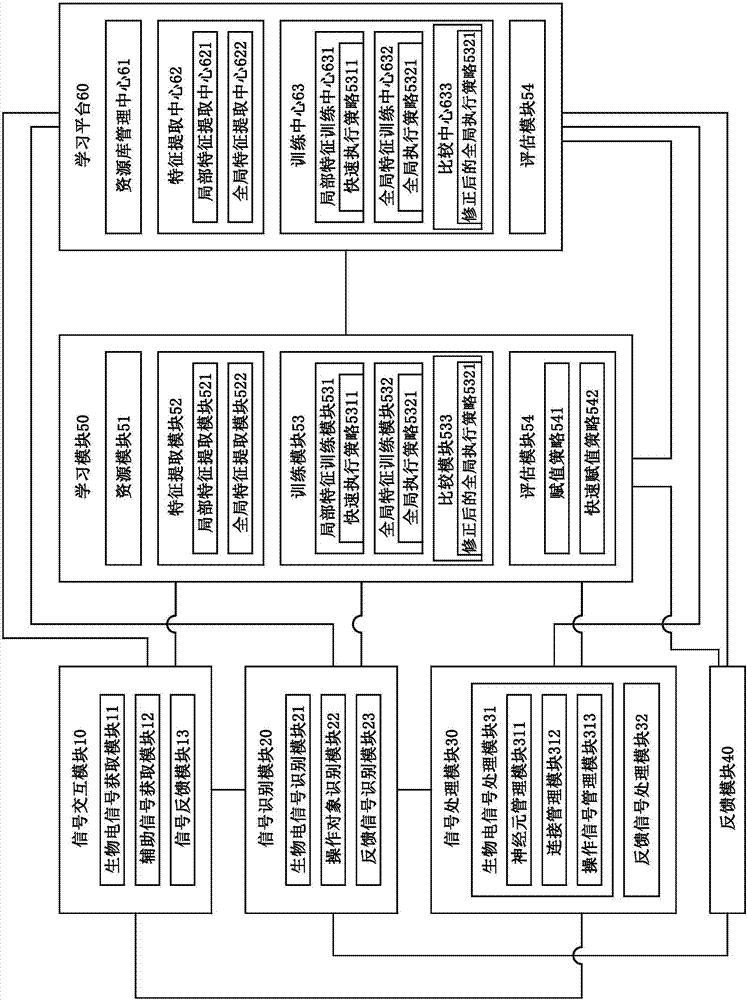
InactiveCN107305428AInput/output for user-computer interactionGraph readingElectricityBiological interaction
A bioelectric signal operating system includes: at least one signal interaction module, the signal interaction module is used to acquire the bioelectric signal; at least one signal identification module, the signal identification module is communicatively connected to the signal interaction module, wherein the A signal identification module identifies an operation intention according to the bioelectric signal; at least one signal processing module, the signal processing module is communicatively connected to the signal identification module; and a feedback module, the feedback module is respectively communicatively connected to the signal identification module module, and the feedback module is arranged on the operation object to provide a feedback signal of the operation object.
Owner:宁波原子智能技术有限公司
Photoelectrochemical biosensor and detection method thereof for BLM (bleomycin)
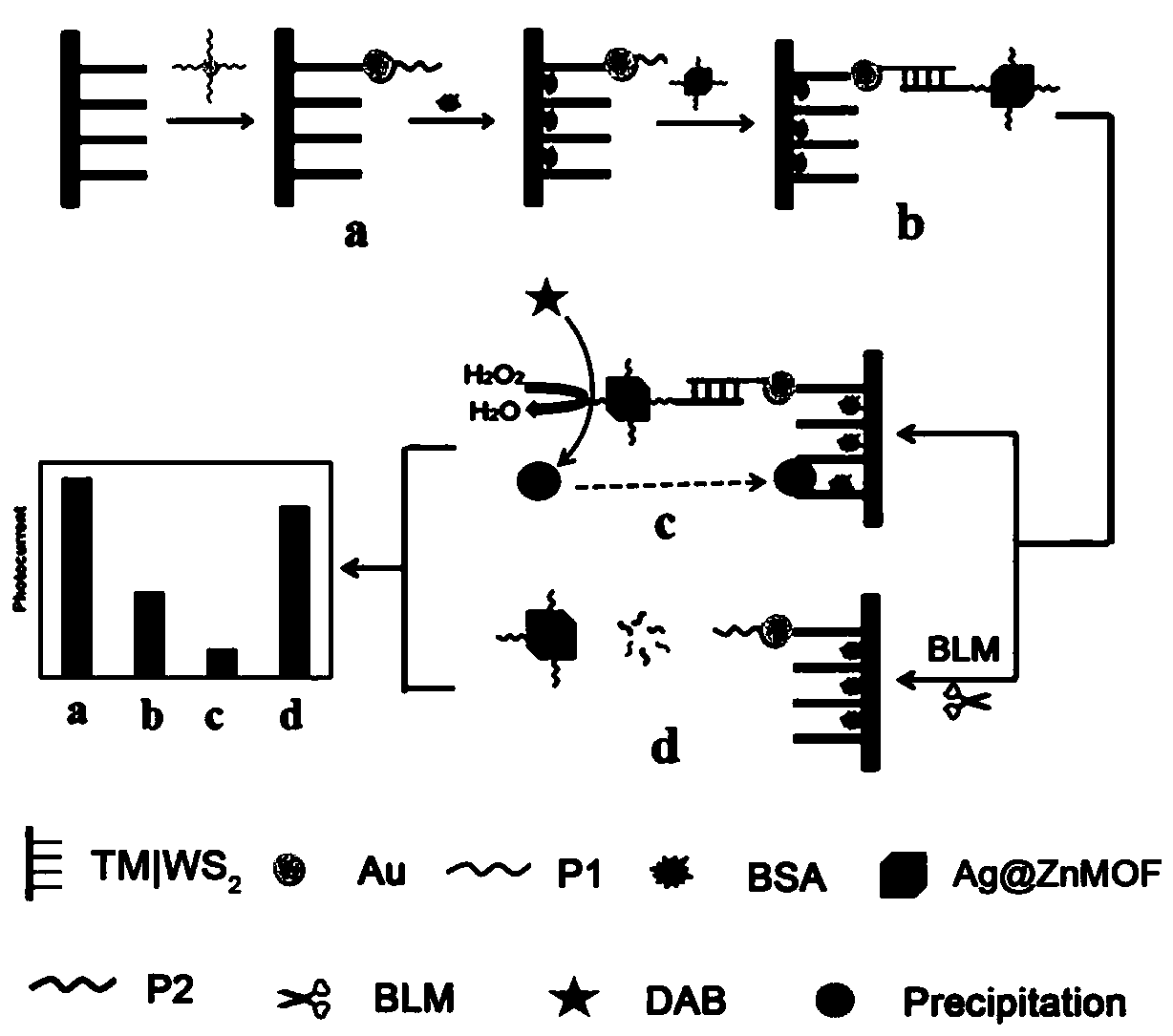
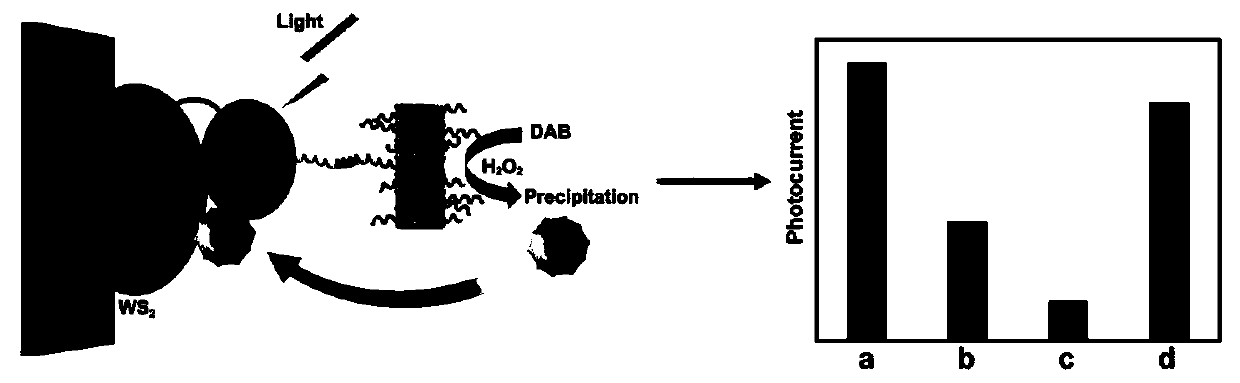
ActiveCN110426440AIncrease surface areaHigh densityMaterial nanotechnologyChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceBiological interactionWorkstation
The invention belongs to the technical field of nanometer new materials, and particularly relates to an application and preparation that a WS<2> nanorod array and a gold nanoparticle (WS<2>-Au) are taken as photoelectrochemical matrixes and an (Ag) / ZnMOF analog peroxide nanocomposite is taken as a signal amplifier. A photoelectrochemical biosensor comprises a working electrode, a reference electrode and a counter electrode, wherein the working electrode, the reference electrode and the counter electrode are connected with a photoelectrochemical workstation. The photoelectrochemical biosensor is characterized in that the working electrode is modified with the WS<2>-Au, and in addition, (Ag) / ZnMOF is connected to the surface of an electrode through hybridization chain reaction. On the basisof the utilization of the WS<2>-Au and the (Ag) / ZnMOF analog peroxide nanocomposite, a simple PEC (photoelectrochemical) bioanalysis platform used for monitoring BLM activity is designed. An experiment proves that the constructed photoelectrochemical biosensor platform is simple and economic, and exhibits high sensitivity, selectivity and reliability for BLM detection. The work is a basis of a newuniversal PEC immunoassay format, and can be expanded to be used for detecting other interested biological interactions.
Owner:QUFU NORMAL UNIV
DNA barcoding sequence and method for identifying Lycium barbarum species by using same
PendingCN111733273AIncrease the number ofValid identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyDNA barcoding
The invention discloses a DNA barcoding sequence and a method for identifying Lycium barbarum species by using the same, and belongs to the technical field of identification of Lycium barbarum species. According to the method, DNA barcoding of psbH-petB of Lycium barbarum is used to identify Lycium barbarum species and determine the interspecific relationship of Lycium barbarum, meanwhile, a psbH-petB barcoding database is obtained on the basis of the method, through comparison of a psbH-petB sequence of a sample to be identified with a sequence in the psbH-petB barcoding database, the Lyciumbarbarum species can be identified effectively, the interspecific relationship of the Lycium barbarum can be determined, and an effective basis is provided for the Lycium barbarum varieties.
Owner:WOLFBERRY ENG RES INST NINGXIA ACADEMY OF AGRI & FORESTRY SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com