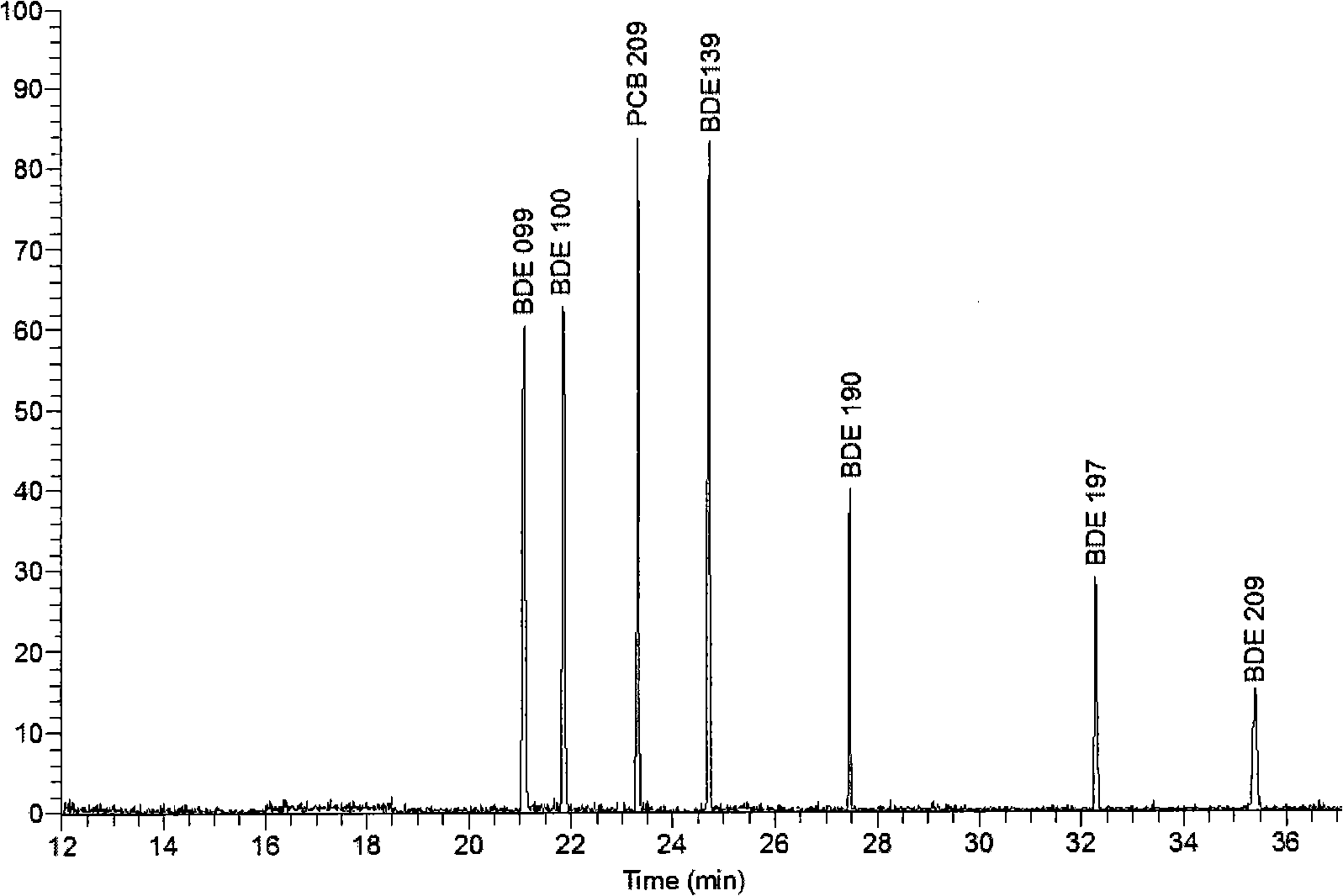
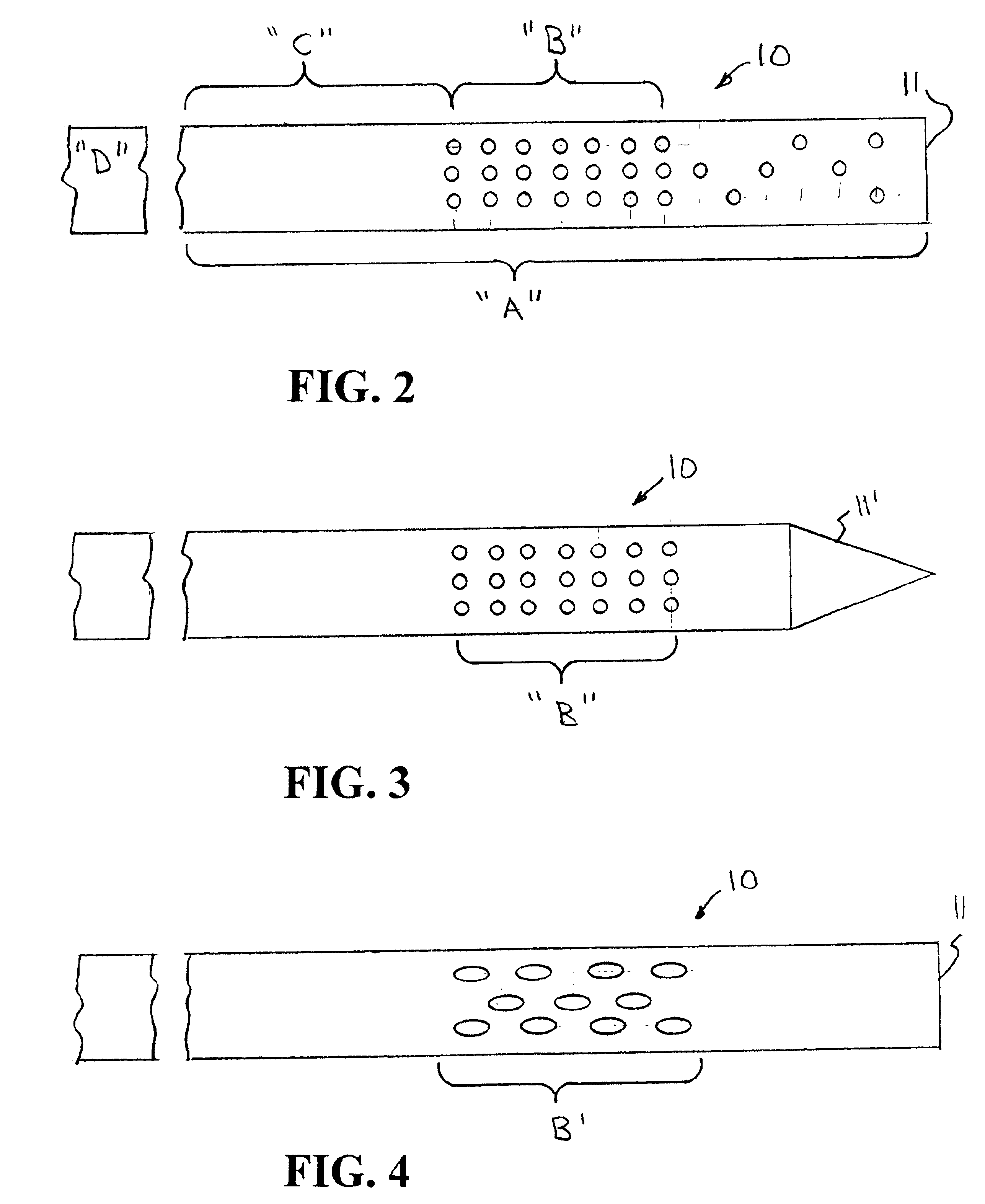
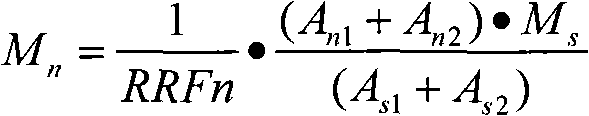Patents
Literature
718 results about "Solid-phase microextraction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
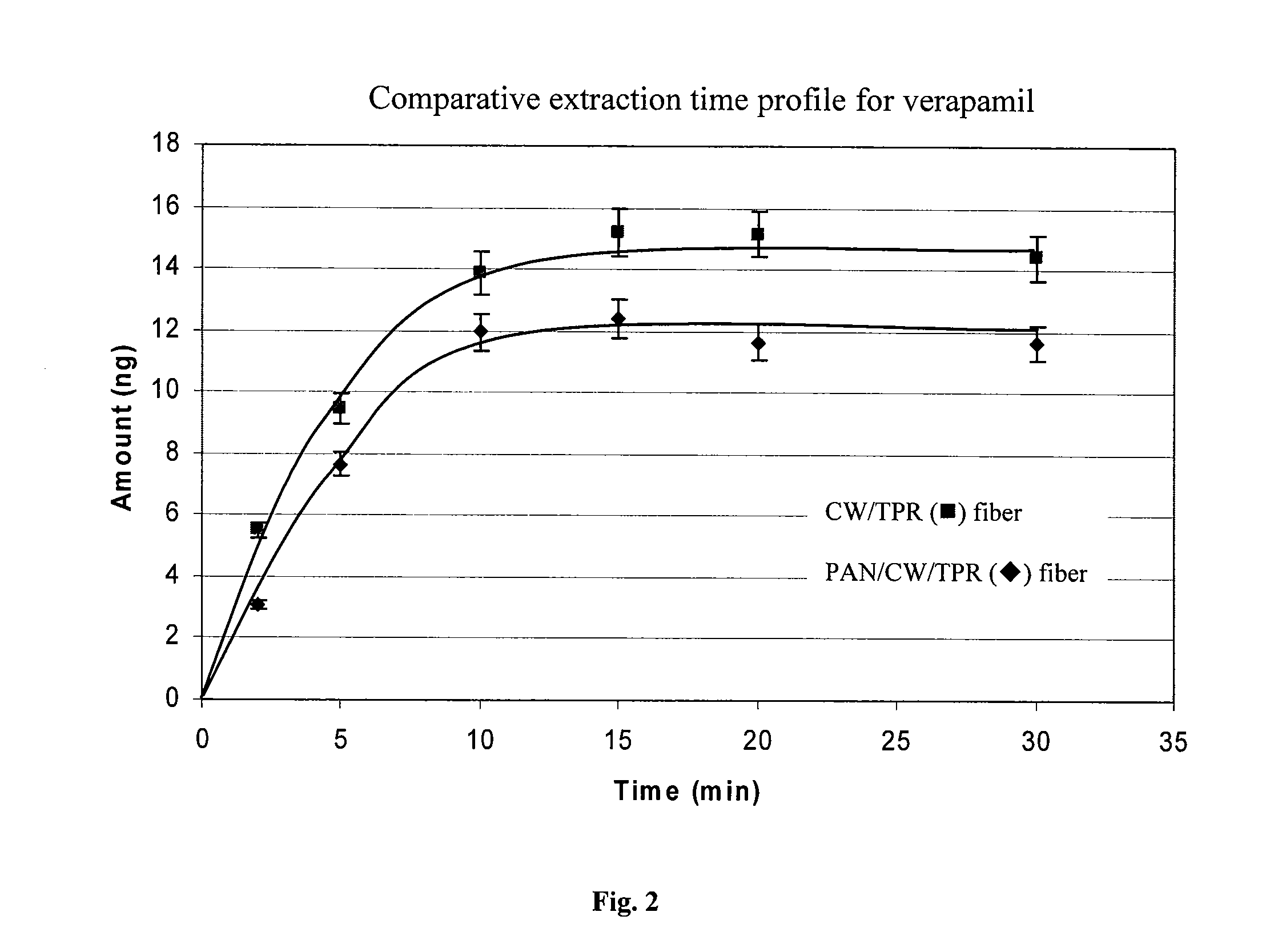
Solid-phase microextraction, or SPME, is a solid phase extraction sampling technique that involves the use of a fiber coated with an extracting phase, that can be a liquid (polymer) or a solid (sorbent), which extracts different kinds of analytes (including both volatile and non-volatile) from different kinds of media, that can be in liquid or gas phase. The quantity of analyte extracted by the fibre is proportional to its concentration in the sample as long as equilibrium is reached or, in case of short time pre-equilibrium, with help of convection or agitation.
Technique for detecting microorganisms
A technique for detecting the presence of microorganisms in a simple, rapid, and efficient manner is provided. More specifically, the technique involves identifying one or more volatile compounds associated with a particular microorganism of interest. The volatile compounds may be identified, for instance, using solid phase microextraction in conjunction with gas chromatography / mass spectroscopy (“GC / MS”) analysis methods. Once identified, an indicator may then be selected that is configured to undergo a detectable color change in the presence of the identified volatile compound(s). If desired, the indicator may be provided on a substrate to form an indicator strip for use in a wide variety of applications. In this manner, the presence of the microorganism may be rapidly detected by simply observing a color change of the indicator strip.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
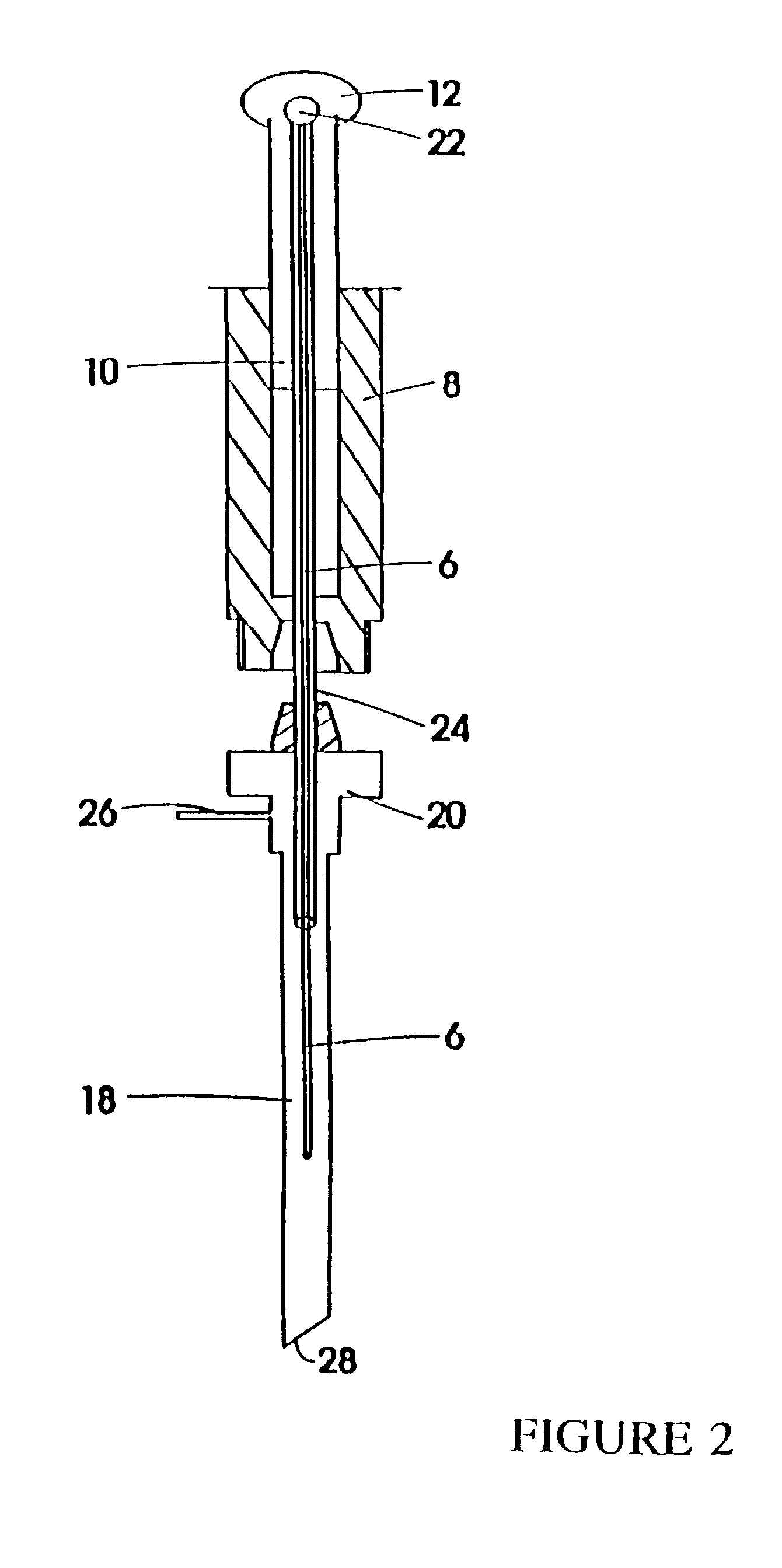
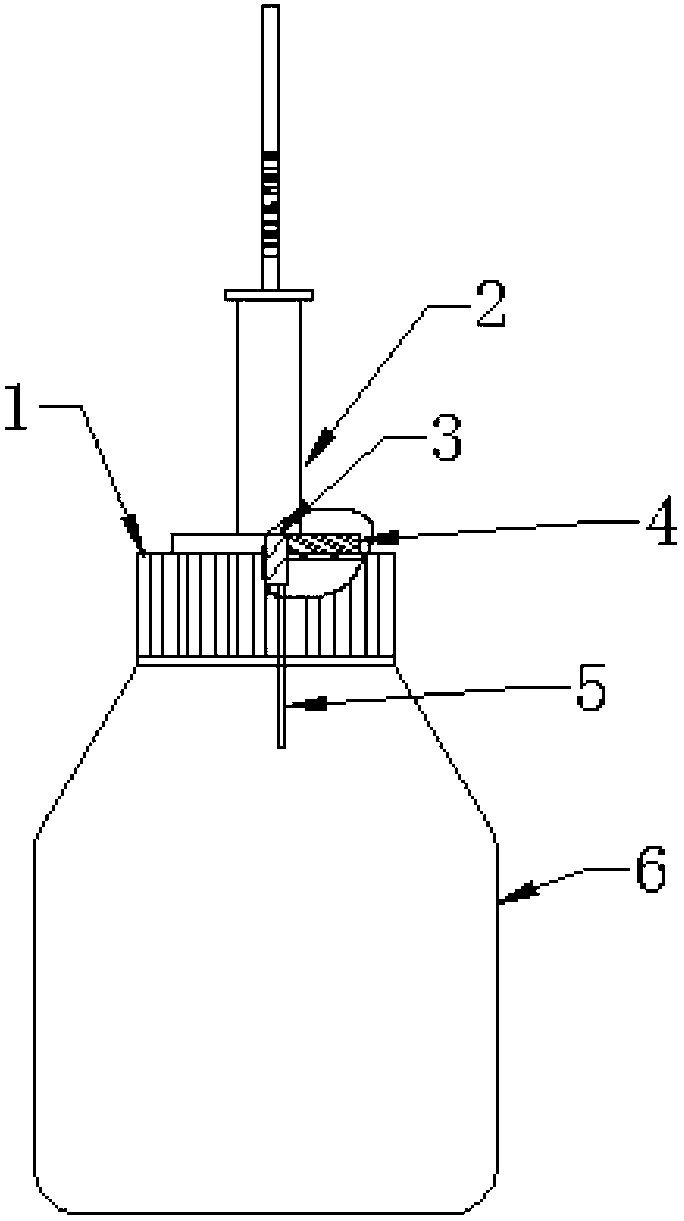
Method for Solid-Phase-Micro Extraction and Apparatus Therefor
InactiveUS20080064115A1Increase flow rateShorten the timeComponent separationMicrobiological testing/measurementAnalyteSolid phase extraction
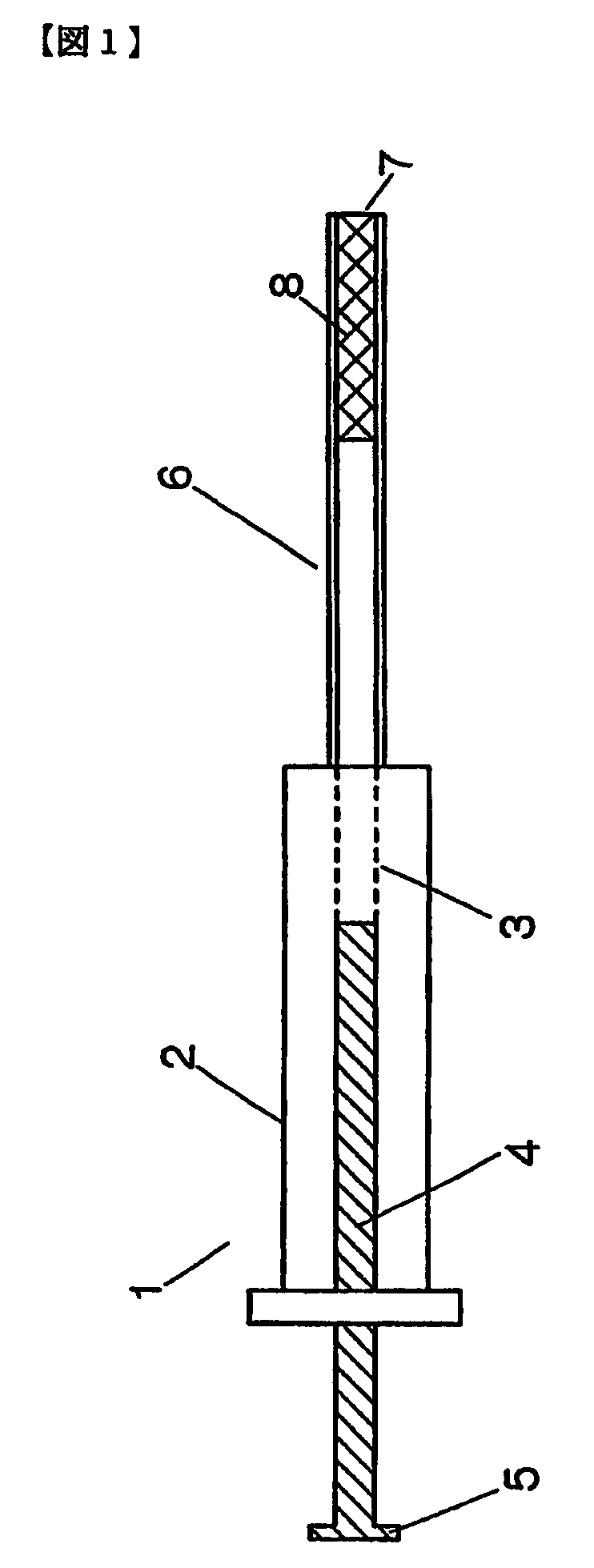
The present invention is directed to a system for pre-treatment of a sample to be introduced in a chromatograph, and a method for performing solid-phase extraction of a component present in a sample. The system uses a syringe having a needle being provided with a porous body having a monolithic structure along at least an appropriate length of the needle and across an overall diameter of the needle. The method includes the steps of inserting the needle into the sample, passing the sample through the needle to retain an analyte within the porous body, and desorbtion of the retained analyte from the porous body.
Owner:GL SCI
Device for solid phase microextraction and desorption
InactiveUS6042787AMaterial nanotechnologyAnalysis using chemical indicatorsAnalyteSolid-phase microextraction
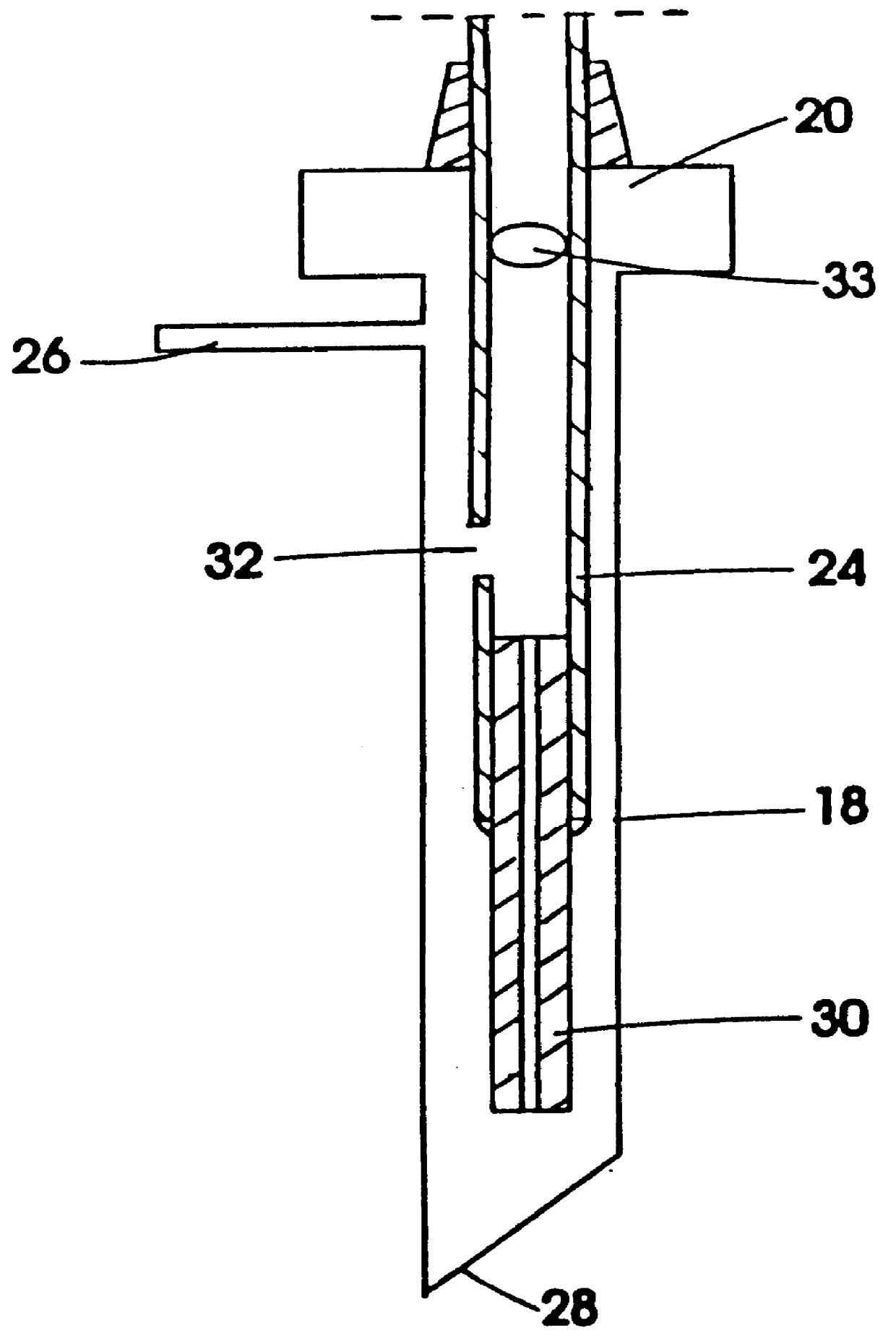
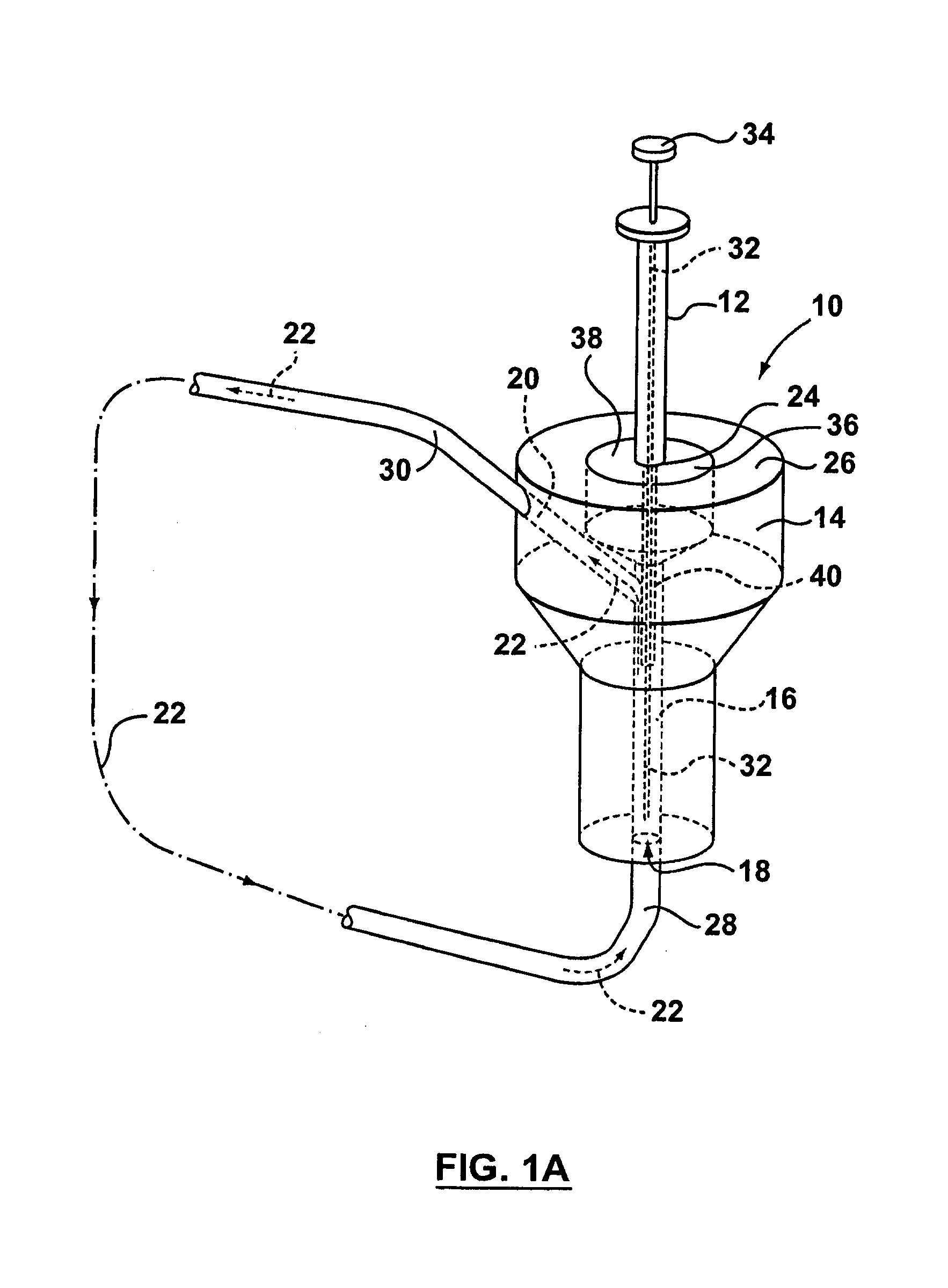
A device for carrying out solid phase microextraction is a tubular member having one closed end and one open end with an extracting surface within said tubular member. The extracting surface can be an extracting phase coating extending over a zone within the tubular member. The tubular member has a heater that can be used for either or both drawing fluid carrier into the tubular member or assisting in desorbing analytes into an injector of an analysis instrument. The tubular member can also be mounted in a housing with an airtight cavity and a plunger. A method of operation of the device is also provided. Previously, samples were analyzed using liquid-liquid extraction or using cartridges. Both of these methods are relatively expensive and time consuming. Both of these methods also require the use of solvents which can be difficult and expensive to dispose of.
Owner:PAWLISZYN JANUSZ B
Method and device to extract components contained in a fluid
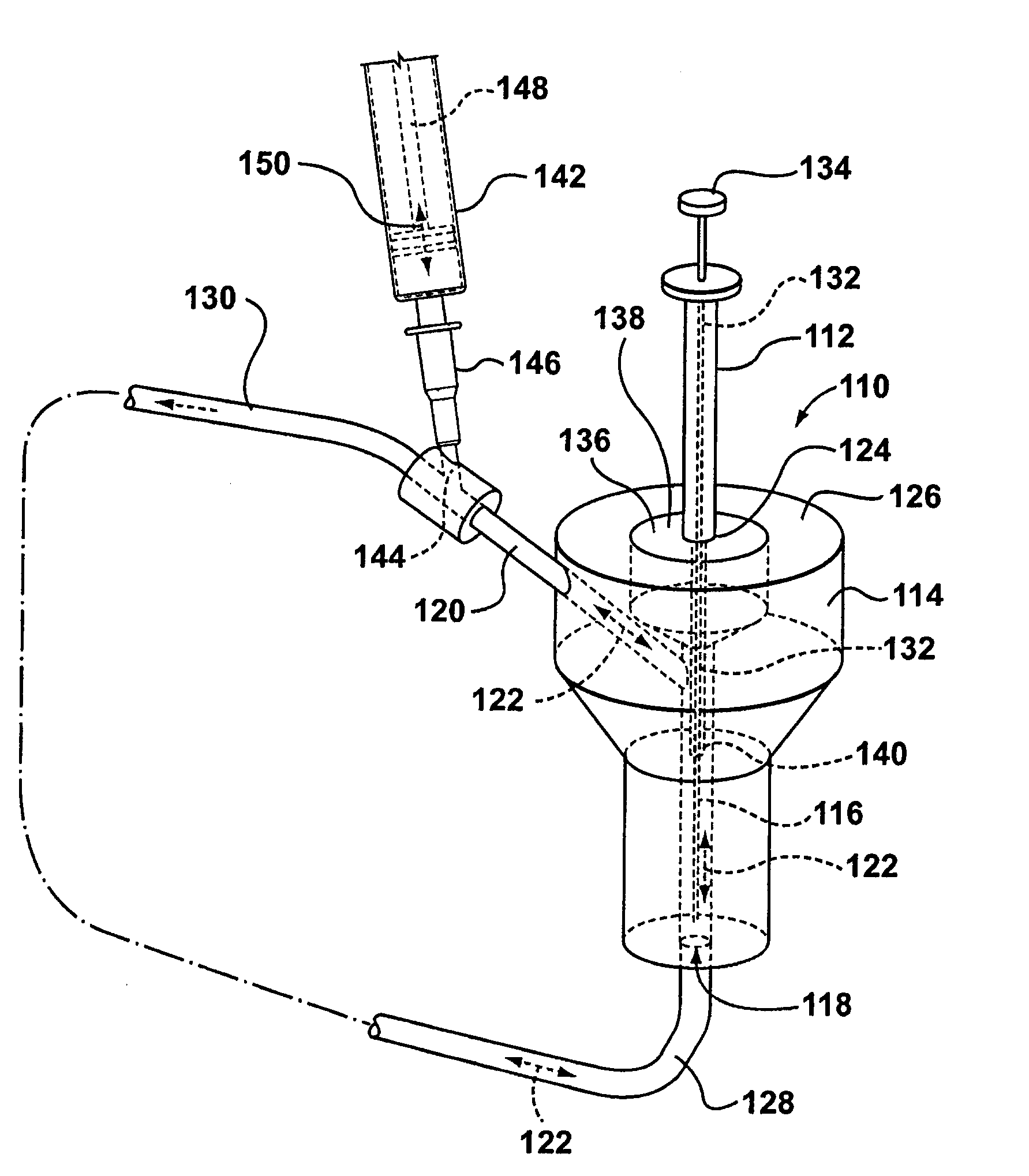
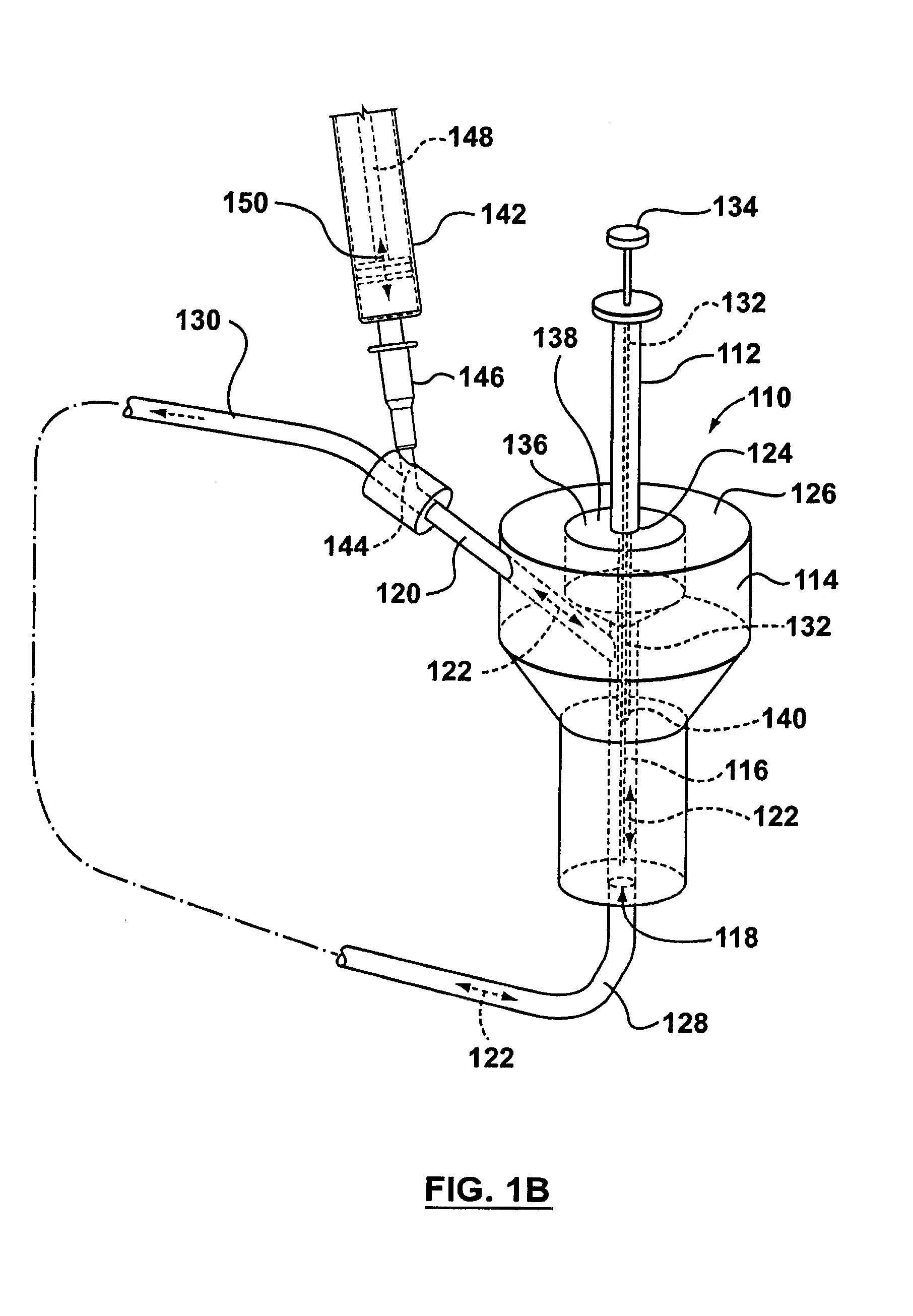
ActiveUS20100011888A1Simple interfaceWithdrawing sample devicesPreparing sample for investigationAnalyteSolid-phase microextraction
Applicants' teachings relate to a method and device to extract components contained in a fluid. More particularly, the applicants' teachings are directed towards a method and sampling device for quick extraction of targeted components from their in vivo surroundings. In accordance with various embodiments of applicants' teachings a sampling device and method to extract components, such as, for example, analytes, from a fluid is provided. The device is interfaced with a fluid source, such as, for example, but not limited to, a circulatory system of an animal, to enable extraction of target molecules with minimal loss of fluid (e.g., blood) to the source. The device facilitates an interface between the circulatory system of an animal and a suitable sampling probe such as, for example, a solid phase microextraction (SPME) probe. The targeted compounds are desorbed in small volumes of solvents that can be analyzed with highly specific instruments. In particular, in various embodiments of applicant's teachings a device to extract components contained in a fluid is provided. The device comprises a housing defining a cavity, with the housing having at least one opening to allow fluid flow into and out of the cavity. The device also comprises a probe insertable into the cavity of the housing. Moreover, the device comprises a channel, with the channel adapted to connect the cavity to a fluid pump, so that when the probe is inserted into the cavity the fluid pump causes fluid to flow into and out of the cavity through the at least one opening and contact the probe in the cavity.
Owner:NOAB BIODISCOVERIES +1
Metal-organic framework polymer for solid-phase microextraction
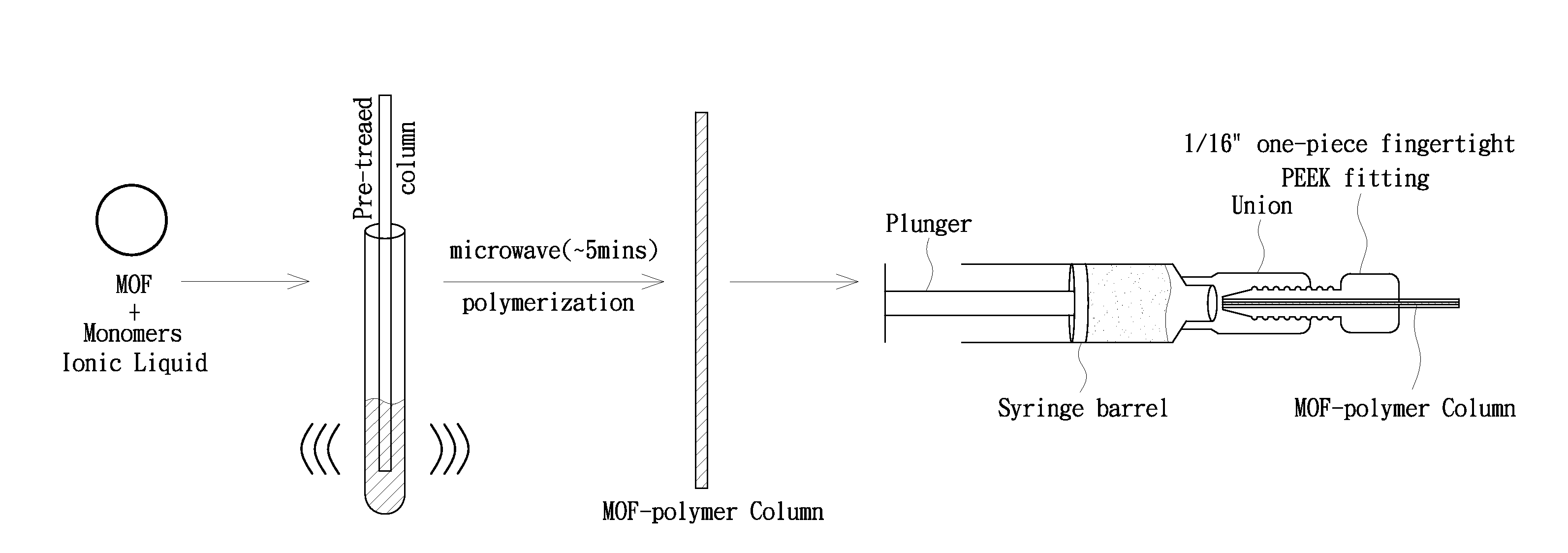
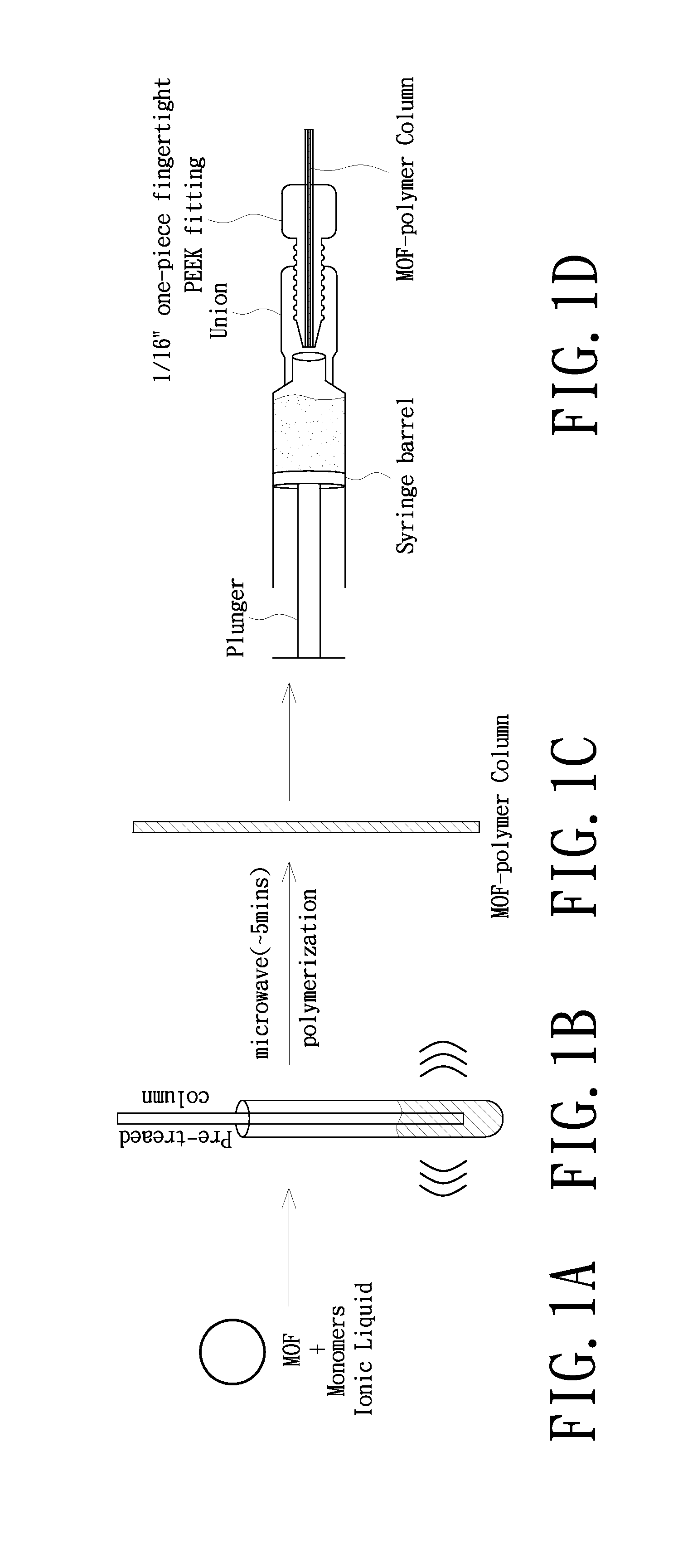
A metal-organic framework (MOF) polymer for solid-phase microextraction (SPME) includes an MOF including metal ions building units coordinating polytopic organic linkers; and a polymer coordinatively bonding to the MOF, wherein the polymer is composed of one or more vinyl monomers and a cross-linker those are polymerized in the presence of a radical initiator. A method for preparing a stationary phase for SPME is also provided.
Owner:CHUNG YUAN CHRISTIAN UNIVERSITY
Device and method for combined use of molecular imprinting solid phase microextraction and hollow fiber liquid phase microextraction, and application thereof
InactiveCN101637668AHigh enrichment factorAnalysis fitIon-exchange process apparatusIon-exchanger regenerationHollow fibre membraneFiber
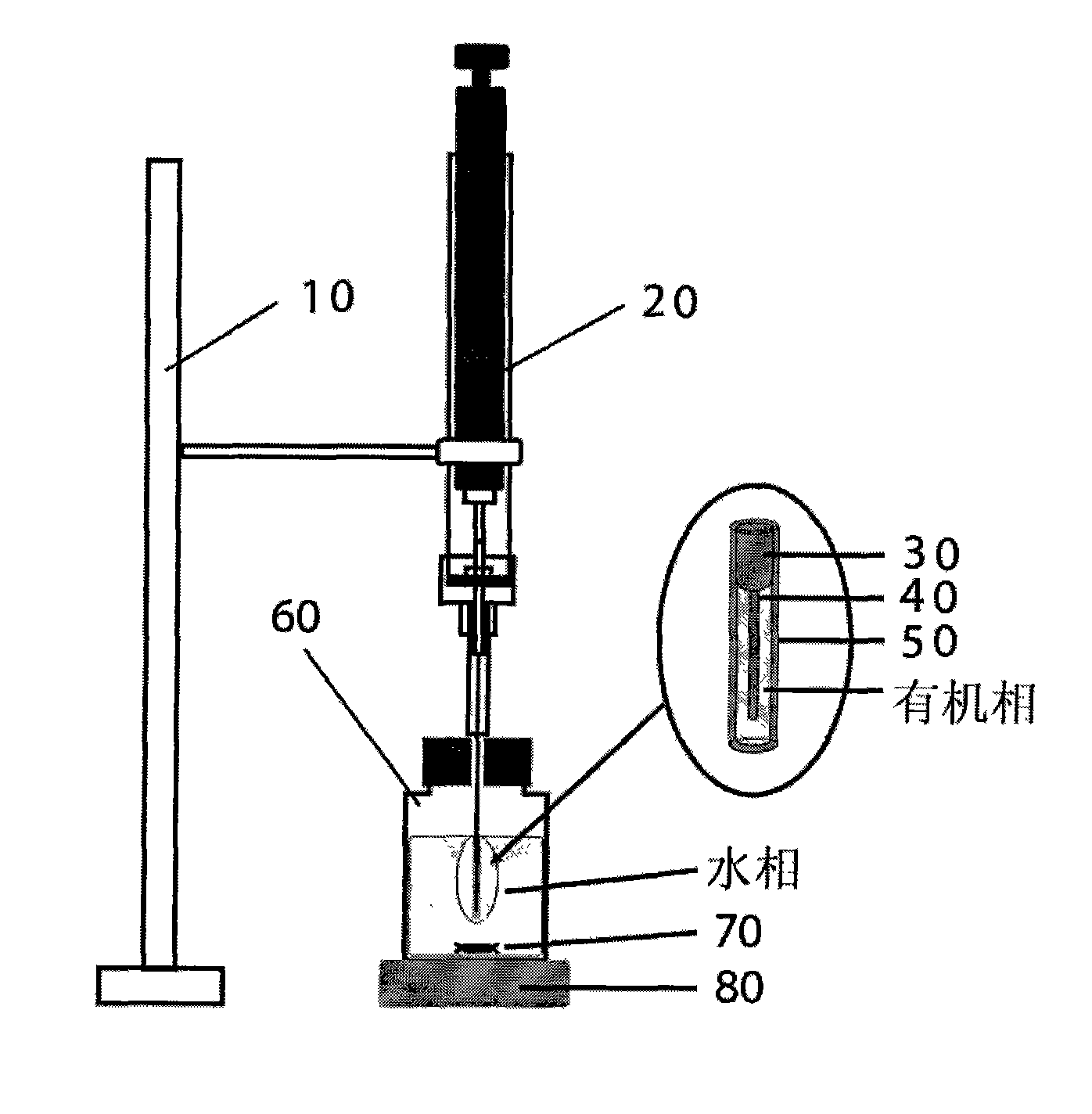
The invention discloses a device and a method for the combined use of molecular imprinting solid phase microextraction and hollow fiber liquid phase microextraction, and the application thereof. The device consists of a solid phase microextraction device, a molecular imprinting solid phase microextraction probe, a hollow fiber membrane, an extraction bottle and a stirrer. The molecular imprintingsolid phase microextraction probe is inserted in to a hollow fiber membrane cavity containing organic solvent, fixed and then directly positioned into a sample solution to be measured for purpose of liquid-solid phase synchronous microextraction. During the microextraction, analytes permeate the hollow fiber membrane, are then enriched in the organic solvent and then undergo secondary extraction and enrichment under the action of the molecular imprinting solid phase microextraction probe. The device is simple, operates conveniently, facilitates the combined use with an analyzer, is suitable for the separation and enrichment of organics with trace amounts in complex water phase samples obtained from the fields such as environment, food, medicine, biology and the like.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
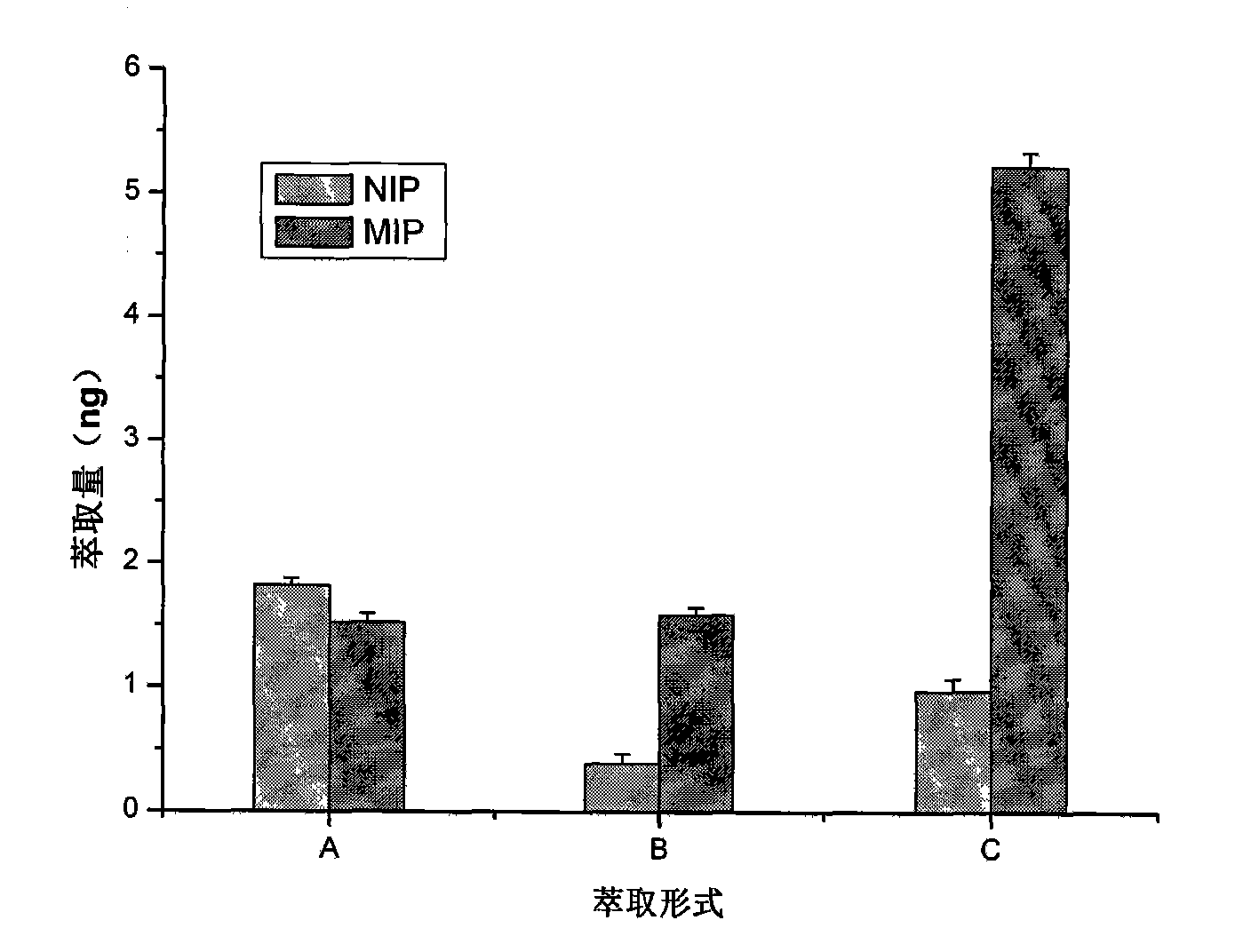
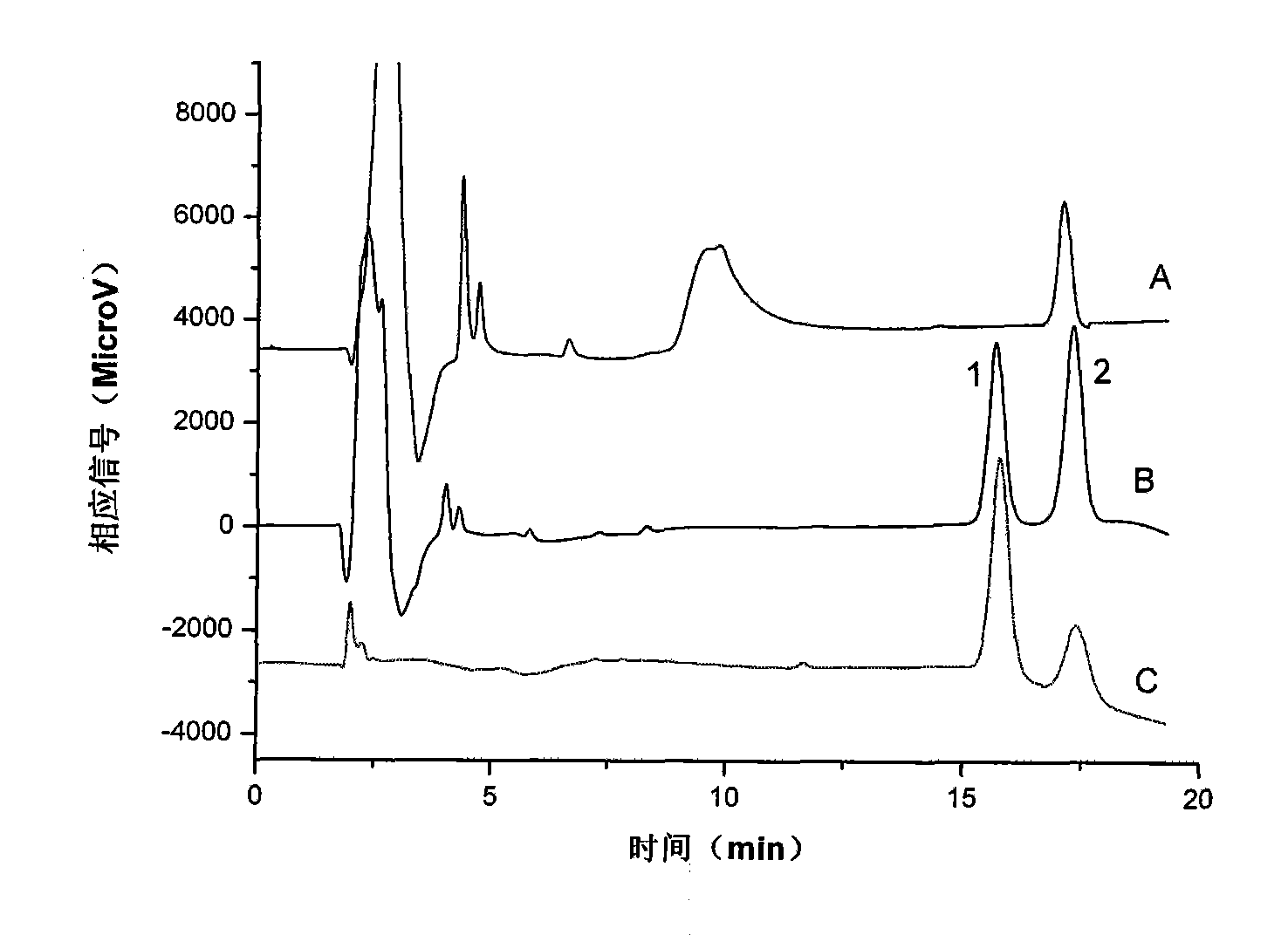
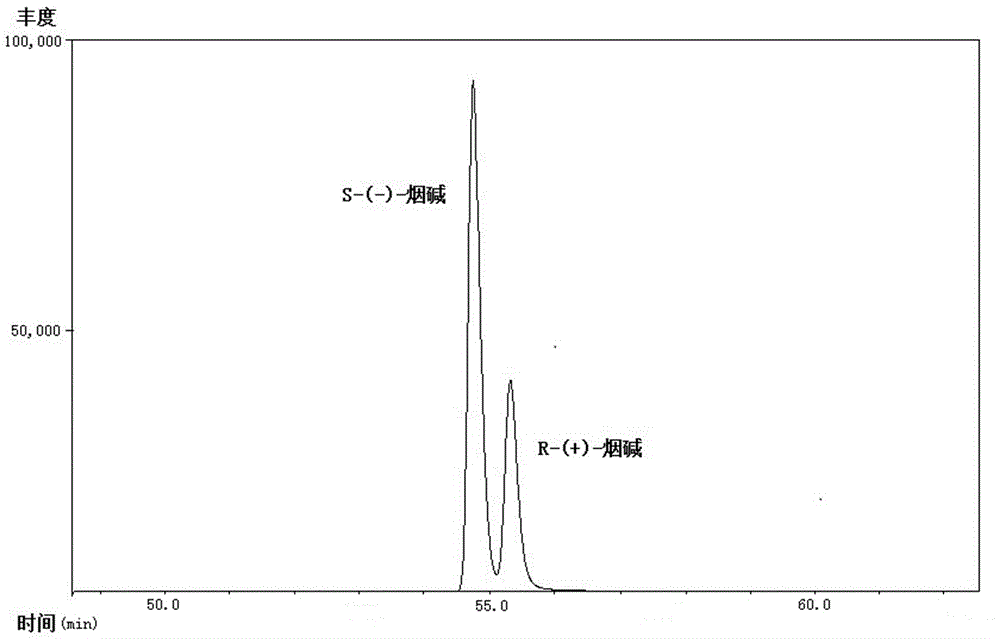
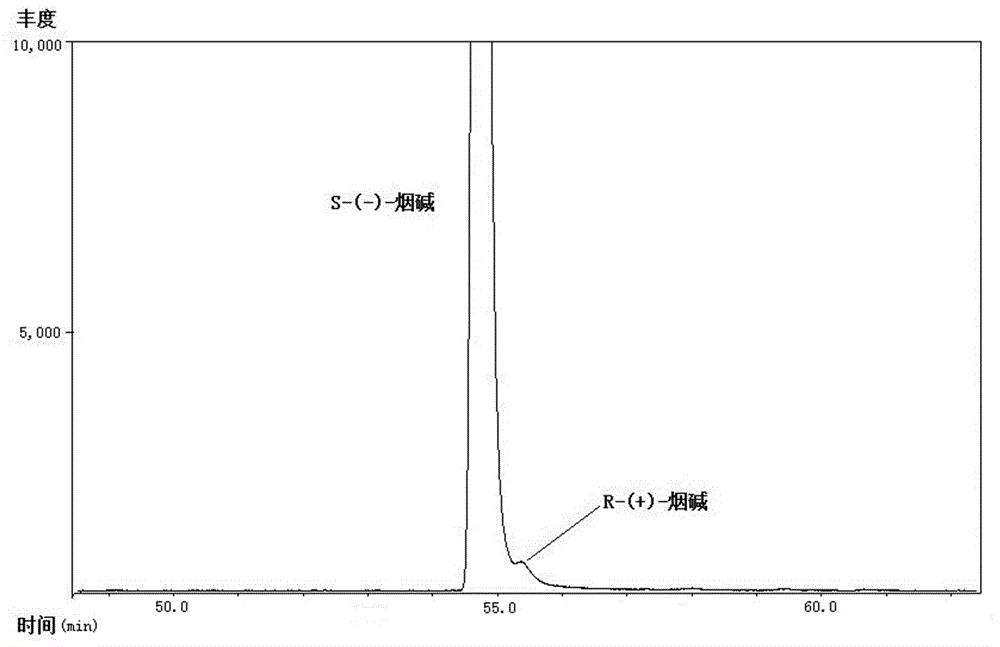
Chiral analysis method for nicotine in cigarette cut tobacco
InactiveCN106324130AGood effectThe pre-processing process is simpleComponent separationSolid-phase microextractionGas phase
The invention discloses a chiral analysis method for nicotine in cigarette cut tobacco. The chiral analysis method for nicotine in cigarette cut tobacco is characterized by including the steps that cut tobacco samples are dried, smashed and screened, extracting liquid is added, the mixture is extracted and filtered, then common cut-tobacco-sample extracting liquid is directly analyzed through a multidimensional gas phase chromatography and mass spectrometry detector, cut-tobacco-sample extracting liquid with the excessively-low nicotine content is subjected to automatic solid phase microextraction to be subjected to multidimensional gas-phase-chromatography tandem-mass-spectrum analysis, and the proportion of S-(-)-nicotine and R-(+)-nicotine in the cigarette cut tobacco is quantitatively detected with the peak area normalization method. The detection method is simple, fast and convenient in sample treatment, low in method detection limit, high in sensitivity and good in accuracy degree, and analysis of cigarette cut tobacco samples can be met.
Owner:CHINA NAT TOBACCO QUALITY SUPERVISION & TEST CENT
Respiration detecting method and its device for diagnosing early lung cancer
InactiveCN1647756AWide detection rangeHigh detection sensitivityRespiratory organ evaluationNerve networkSolid-phase microextraction
The present invention discloses a kind of respiration detecting method and apparatus for diagnosing lung cancer in early stage. The method includes solid phase micro extraction to pre-enrich the exhaled gas of the patient, inserting the solid phase micro extraction with adsorbed organic gas component into hot gas desorbing unit to desorb, separating the desorbed organic gas component with vapor capillary chromatographic column, adsorbing the organic gas component with the organic gas sensing film in the detecting head of one pair of HF delay line ASW sensors to detect the organic gas content, and performing image processing and nerve network mode distinction on 11 kinds of detected lung cancer labeling organic components to diagnose lung cancer patient. The technology of the present invention may be also used for detecting volatile organic matters in other various fields.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Continuous gas in-tube solid phase microextraction device combined with gas chromatography for use
InactiveCN102636595AAchieve complete extractionIncreased extraction surface areaComponent separationGas solid chromatographyPretreatment method
The invention discloses a continuous gas in-tube solid phase microextraction device combined with gas chromatography (GC) for use. The continuous gas in-tube solid phase microextraction device comprises a continuous gas in-tube solid phase microextraction device and a sampling device, wherein the continuous gas in-tube solid phase microextraction device is composed of an in-tube solid phase microextraction needle, a semiconductor condenser, a microheater and an inert gas connecting pipe, and the sampling device is composed of the in-tube solid phase microextraction needle, and a stop valve, a carrier gas flow controller and a gas source which are connected in sequence through a connector connected with a port of an extraction needle on one end of the in-tube solid phase microextraction needle and are used with the gas chromatography. According to the invention, the extraction needle performs thermal desorption at a GC sample inlet without changing the GC sample inlet and thus the continuous gas in-tube solid phase microextraction device is applied to the GC with any brand. The invention has the advantages of simple operating method, high extraction rate, accurate quantification, hydrophilic environment, convenient automatic operation and the like and also provides a sample pretreatment method integrated with extraction, separation and concentration. The continuous gas in-tube solid phase microextraction device can greatly promote the combination use of the SPME (solid phase microextraction) technology and the GC / MS (mass spectra) technology and applications of micro constituents in complex samples in aspects of on-site analysis, on-line analysis and in-situ analysis.
Owner:YANBIAN UNIV
Method for rapidly detecting polybrominated diphenyl ether residue in sample
InactiveCN101526508AFast extractionHigh detection limitOrganic chemistryComponent separationWater bathsFiber
The invention discloses a method for rapidly detecting polybrominated diphenyl ether residue in a sample, particularly in textiles. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: (1) the sample is crushed, dipped in base solution and ultrasonically extracted in water bath, and solid phase microextraction is employed to concentrate a target compound; and (2) polybrominated diphenyl ether is qualitatively and quantitatively determined by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry after thermal desorption. The method helps effectively solve the problem of matrix effect that fabric fibers have no solvent extraction, obtains a satisfactory result for the analysis of a selected target compound, has the advantages of low organic solvent consumption, rapid extraction speed, less interference from impurities, high sample recovery rate and the like, and can be applicable to rapidly detecting polybrominated diphenyl ether flame retardant residue in textiles.
Owner:陈军 +3
Preparation of solid-phase microextraction (SPME) fiber and extraction device assembled by same
InactiveCN102989432AOvercoming the problem of poor mechanical strengthUnique designComponent separationOther chemical processesSolid-phase microextractionMetal-organic framework
Disclosed is a preparation of an SPME fiber. A covalent bond method is adopted to prepare metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) as a coating for the extraction fiber. The fiber preparing method includes performing APTES amino-functionalization on a quartz fiber, namely, placing the fiber with amino on the surface into an MOF solution for reaction. An extraction device assembled by the prepared SPME coating comprises a device body, a microsyringe outer tube, a microsyringe needle, a push-pull rod and the extraction fiber with the coating, wherein the push-pull rod is arranged in the microsyringe outer tube and forms a sliding matching with the inner wall of the tube, the lower end of the push-pull rod is corroded by an aqua regia solution to obtain a corrosion end which is inserted into the extraction fiber with the coating, and a handle is arranged at the upper end of the push-pull rod. The preparation and the device have the advantages that an organic ligand of the extraction fiber coating and the MOFs is highly ordered and controllable, the extraction device has a novel structure, the coating fiber fixation is firm, and the stability and service life of the extraction fiber coating are improved.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
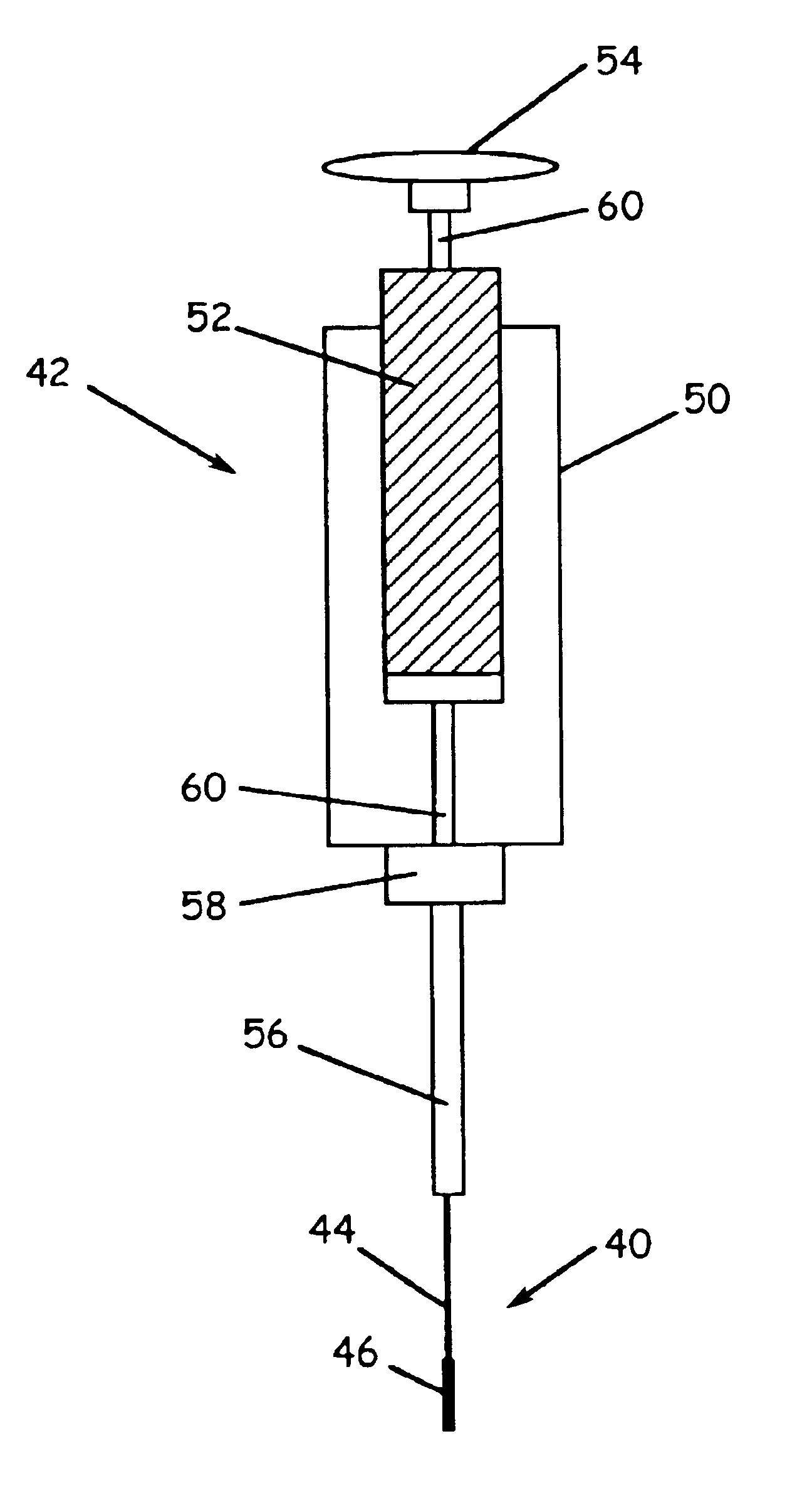
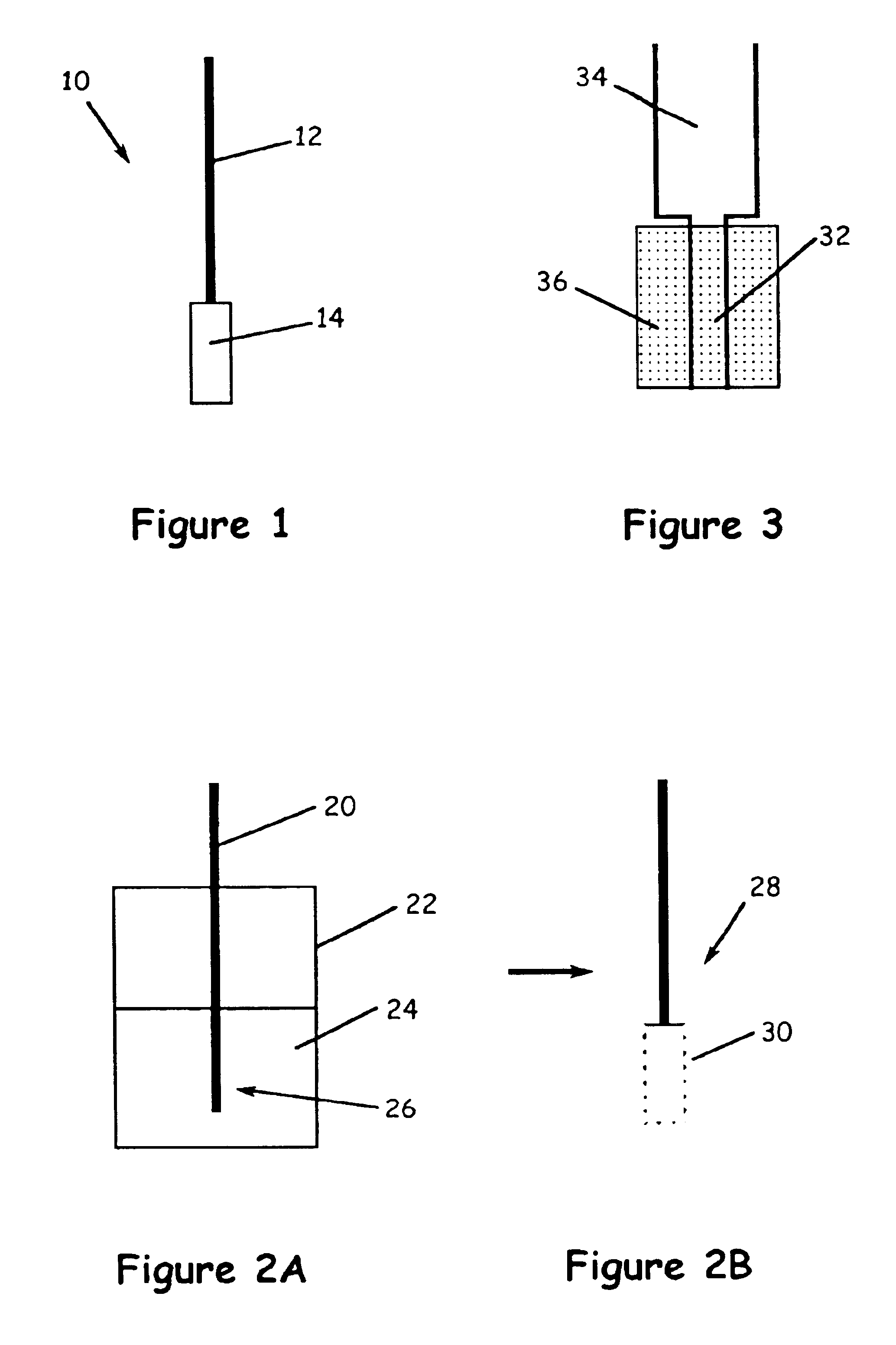
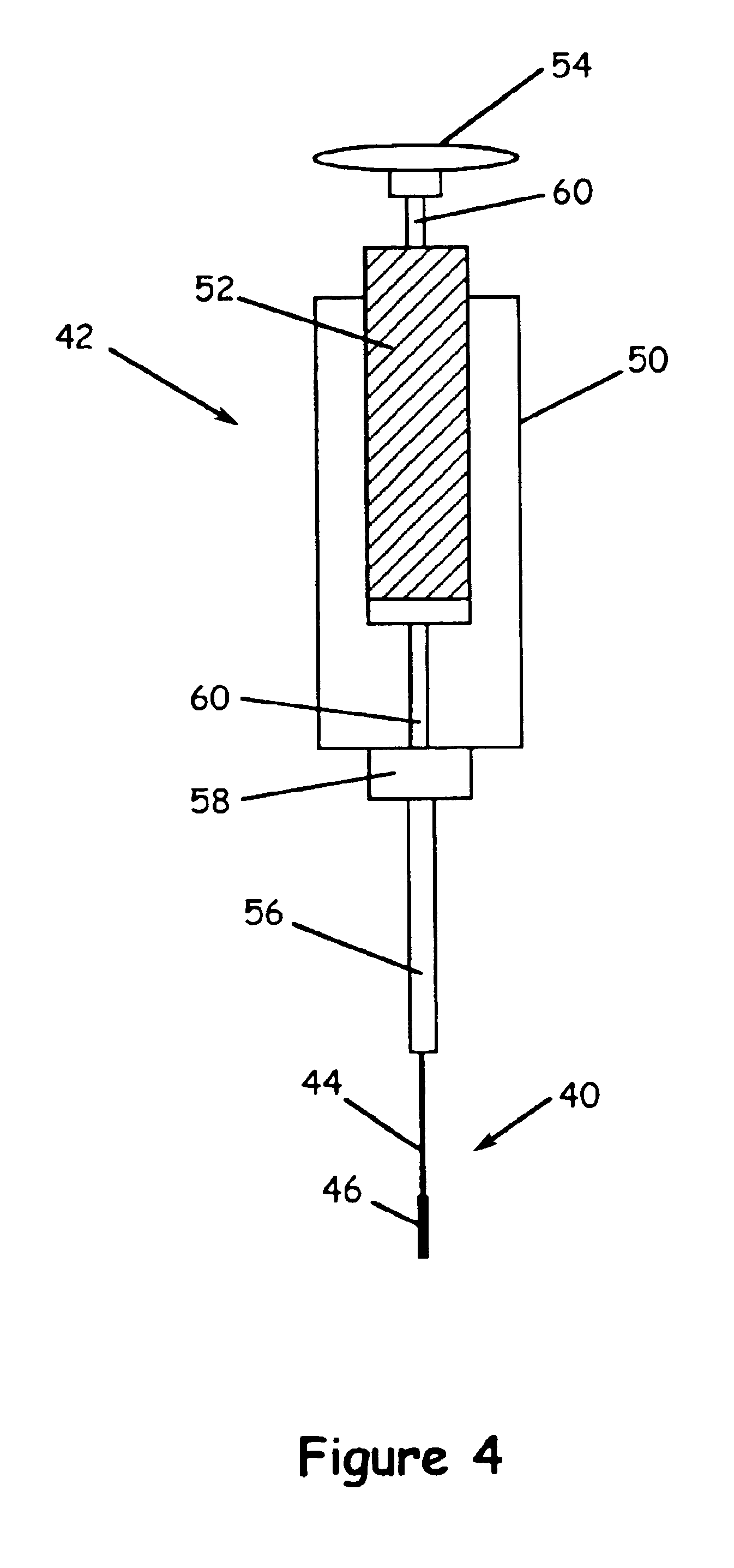
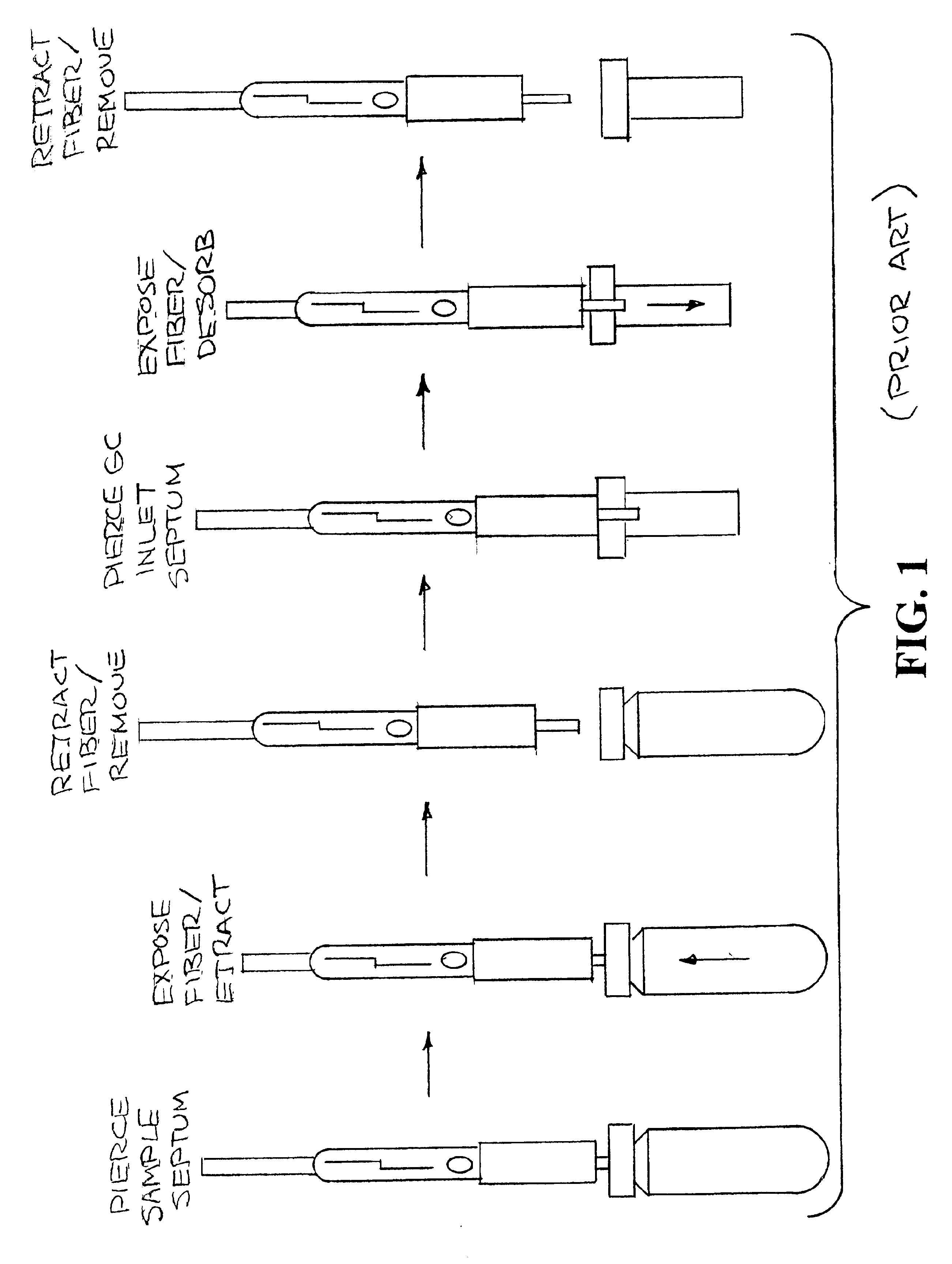
Method and device for solid phase microextraction and desorption
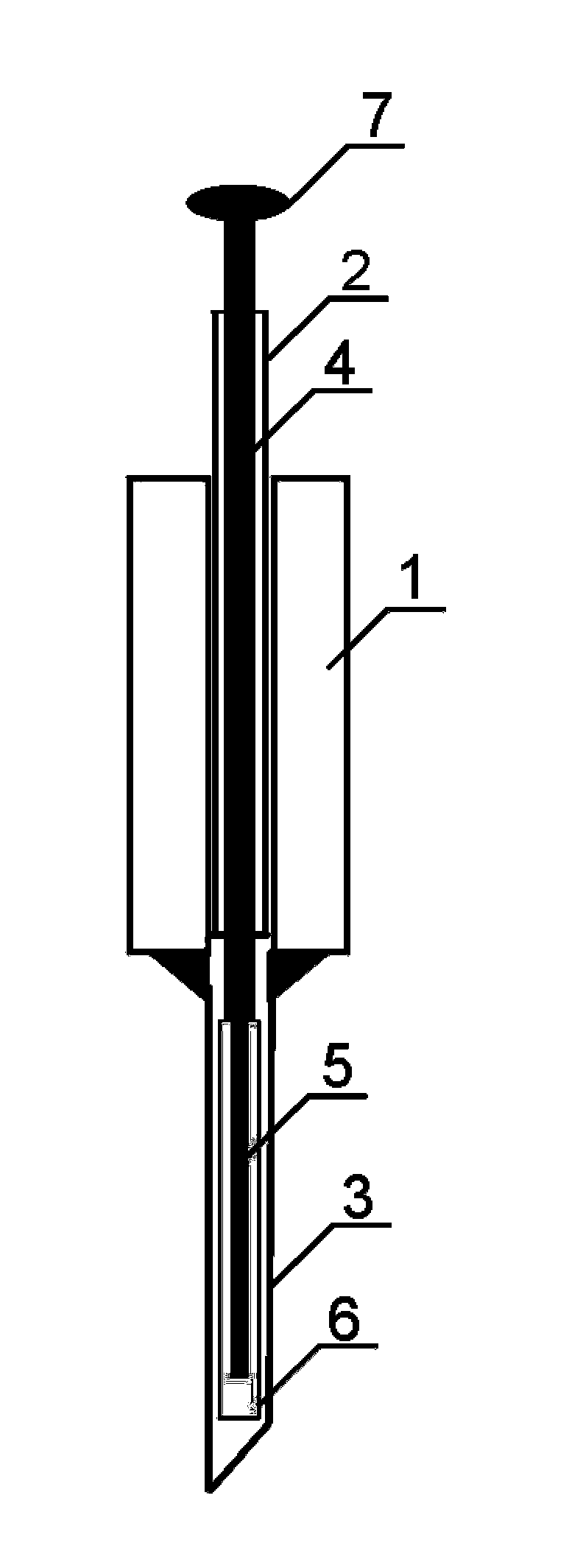
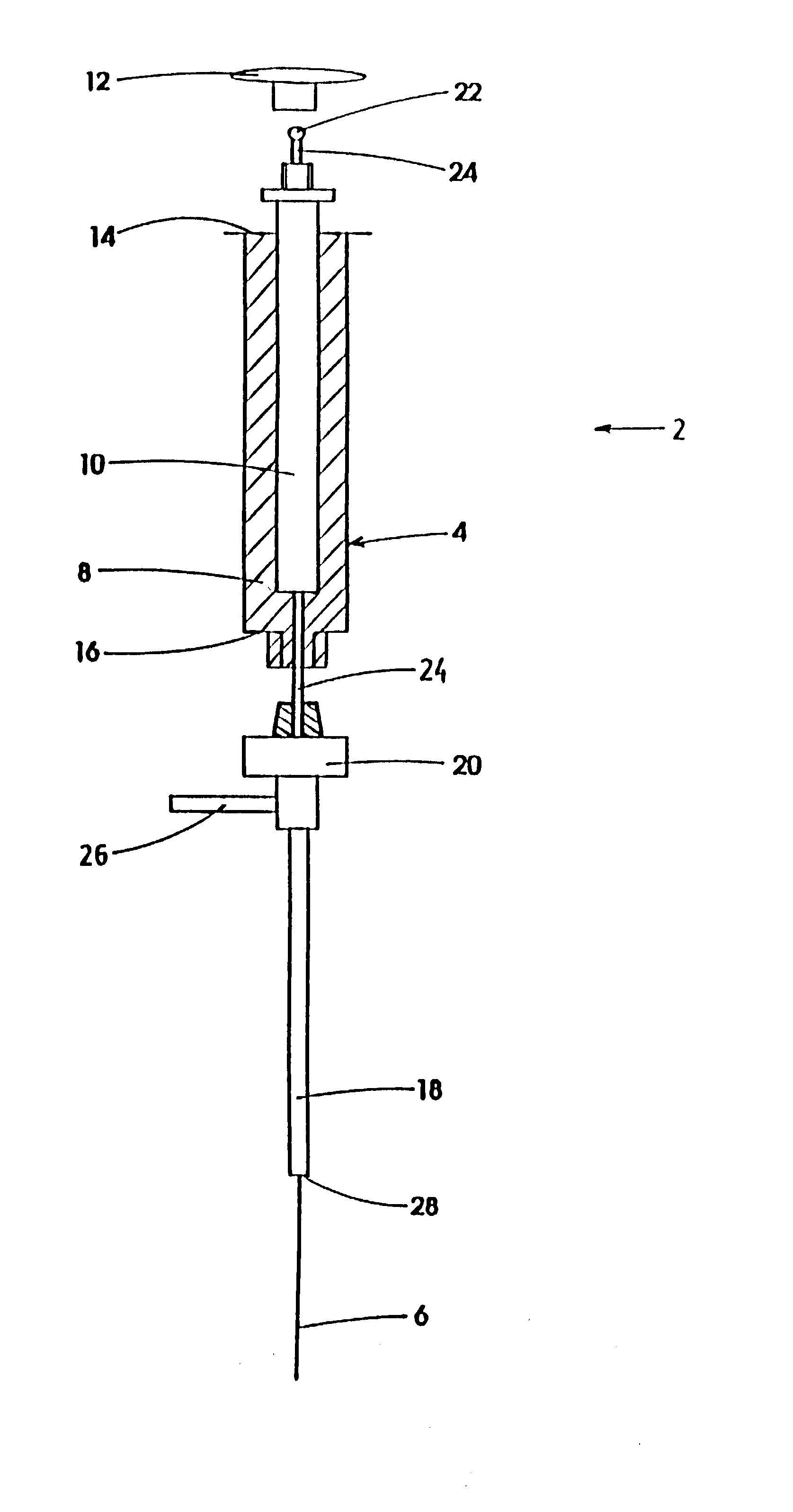
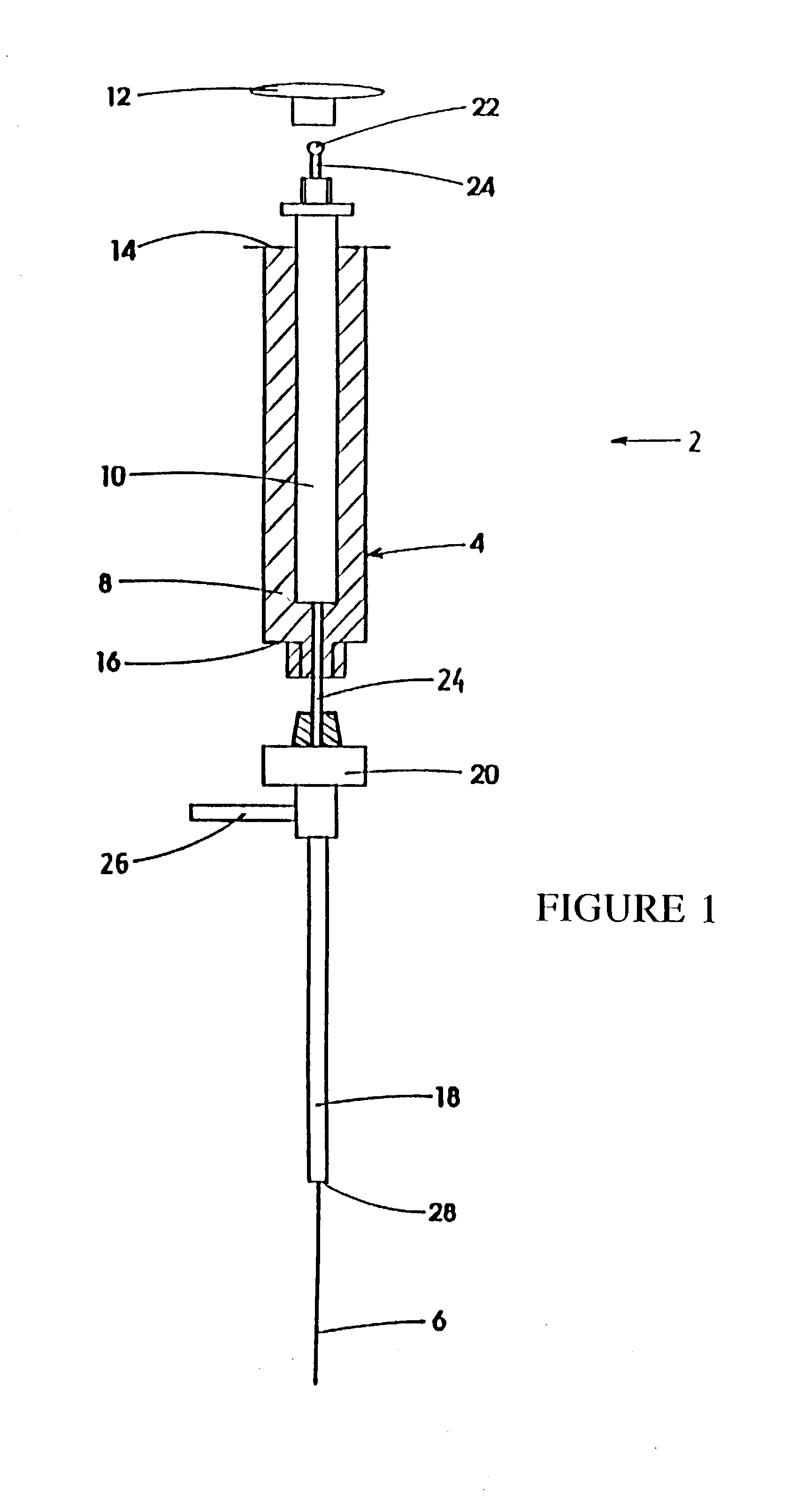
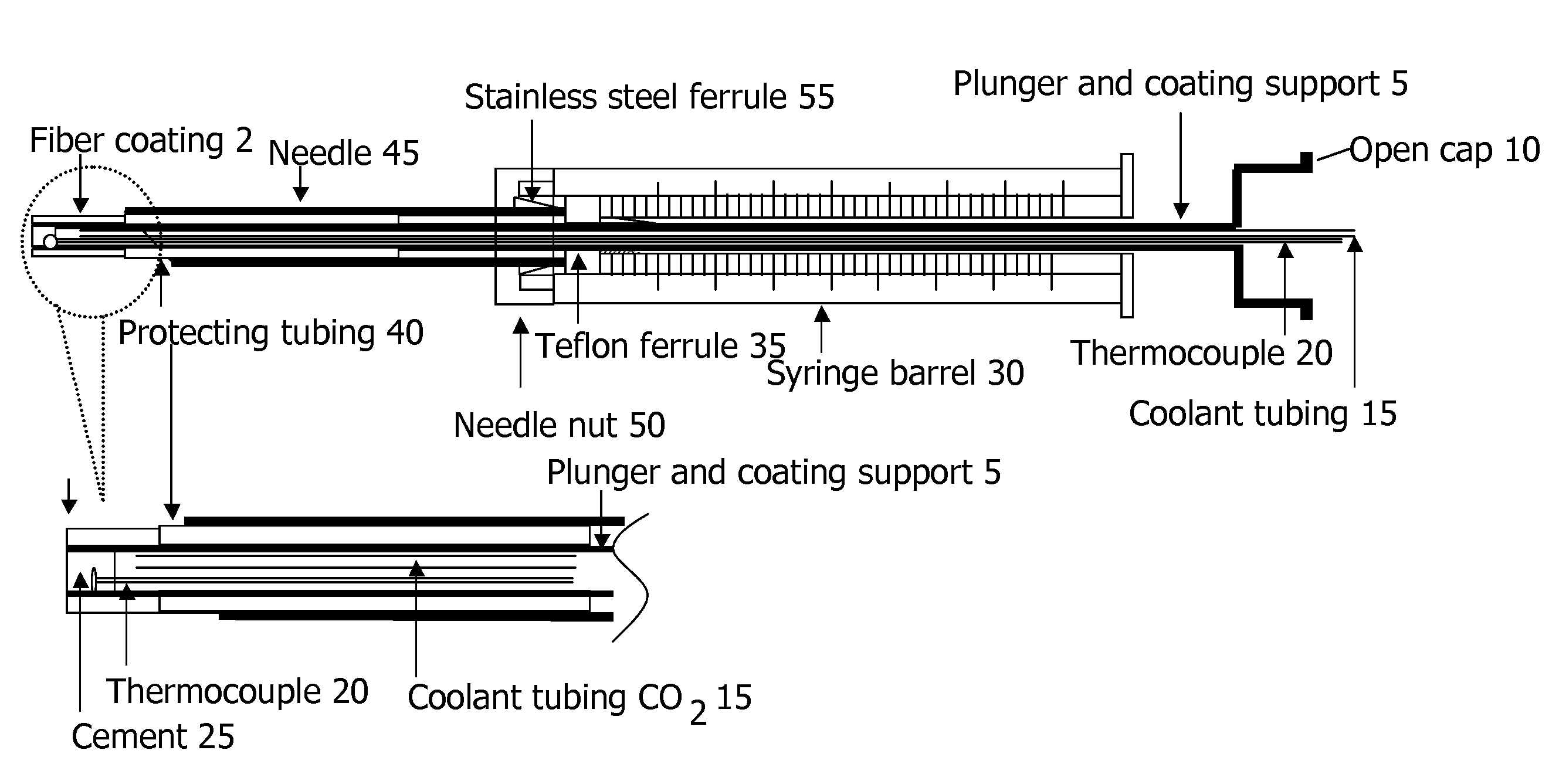
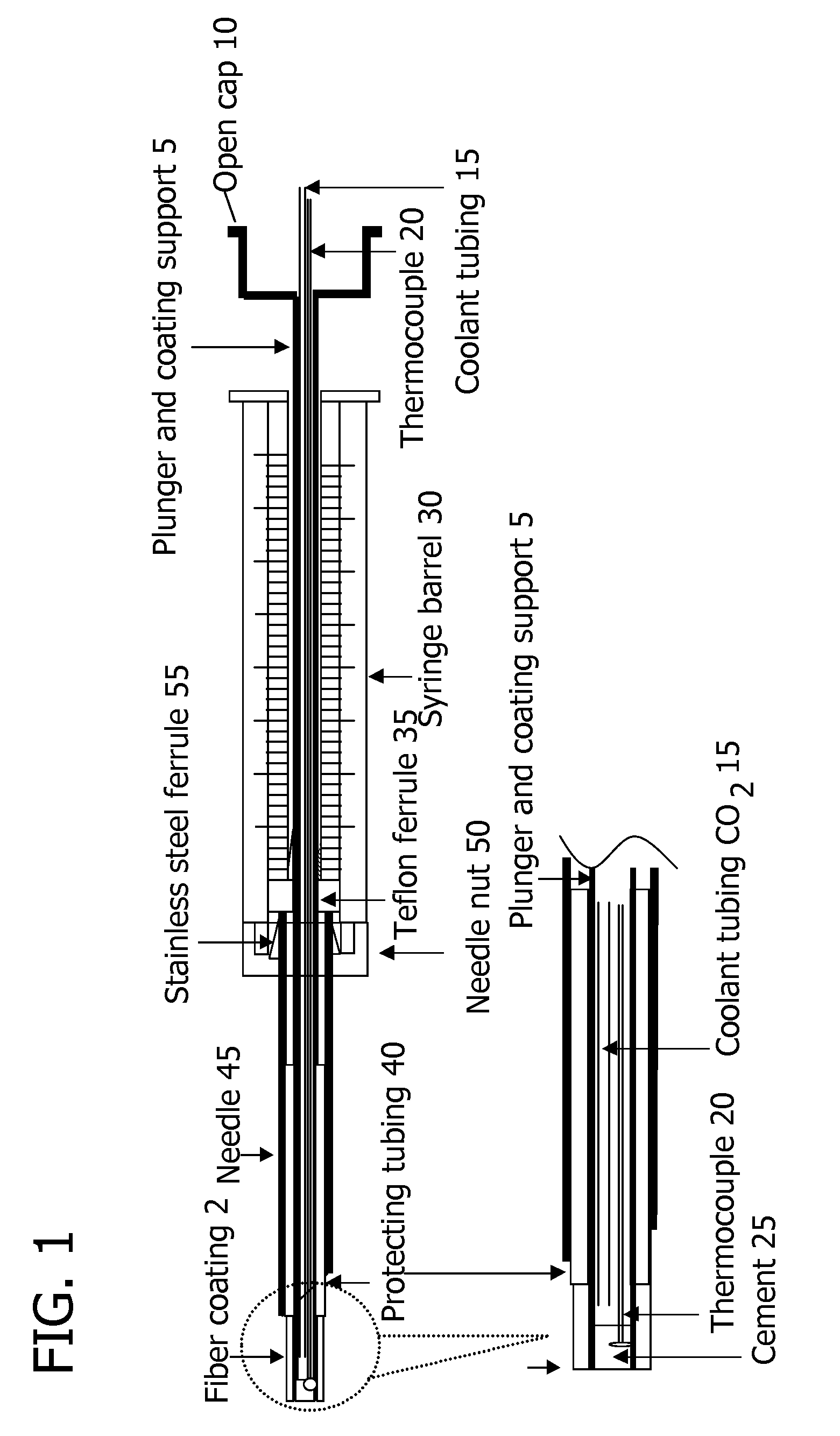
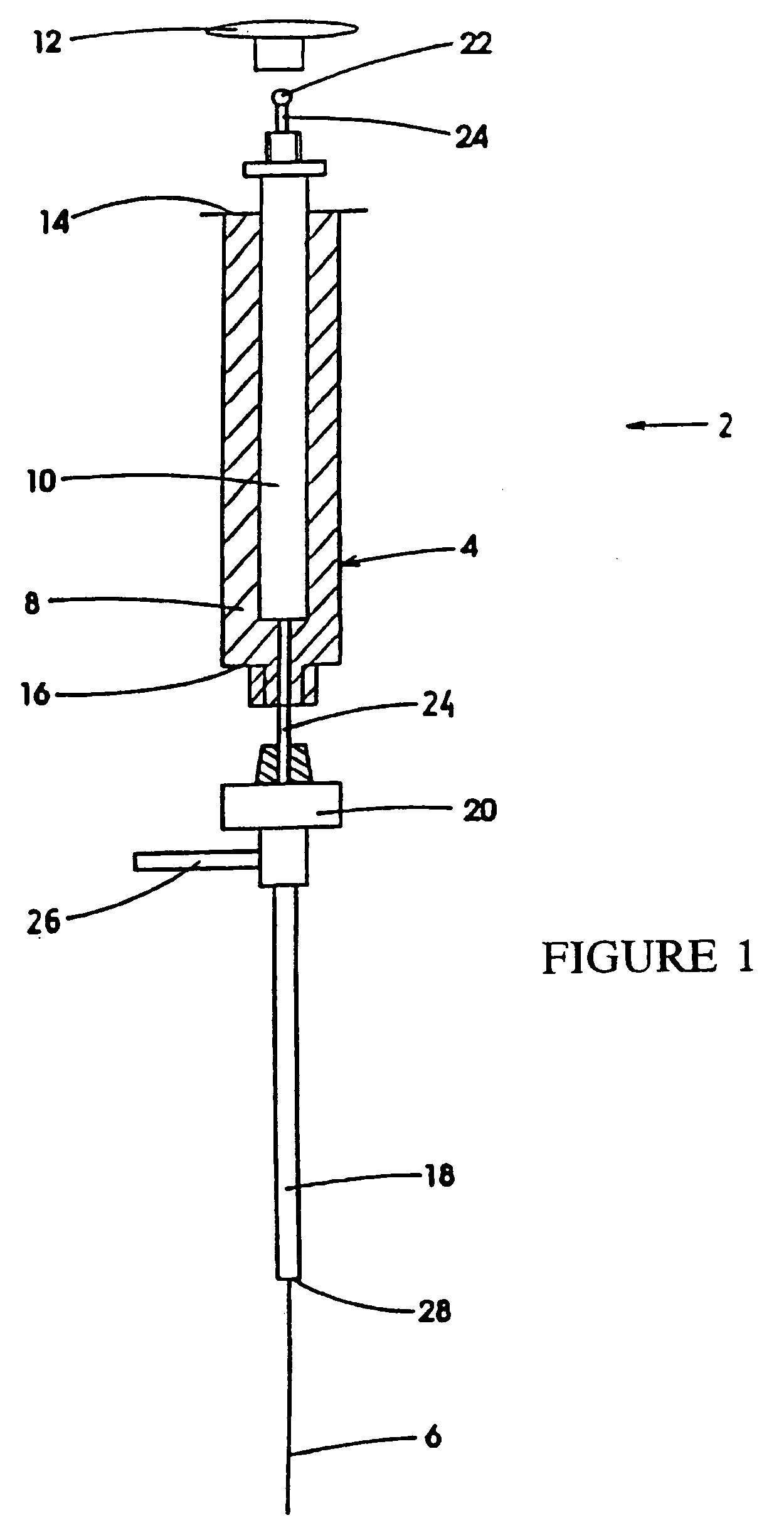
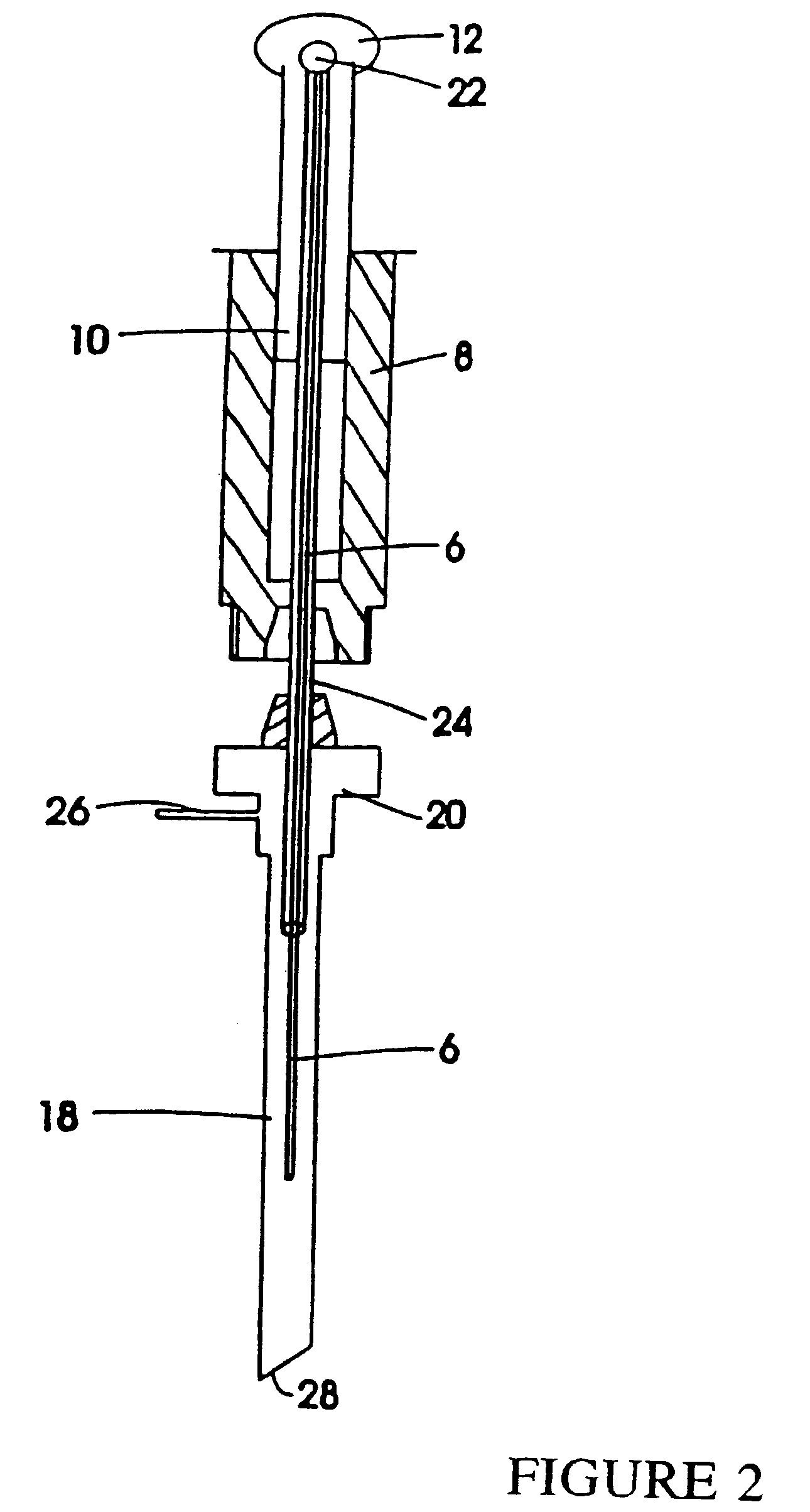
A device for carrying out solid phase microextraction is a fiber contained in a syringe. The fiber can be solid or hollow. The syringe has a barrel and a plunger slidable within the barrel, the plunger having a handle extending from one end of the barrel. A hollow needle extends from an end of the barrel opposite to the plunger. The fiber is contained in the needle. When the plunger is depressed, the fiber extends beyond a free end of the needle and when the plunger is in a withdrawn position, the fiber is located within the needle. The syringe protects the fiber from damage. When it is desired to analyze a sample in a bottle having a septum, the needle is inserted through the septum and the plunger is depressed so that the fiber will extend into the sample. After one or two minutes, the plunger is moved to the withdrawn position so that the fiber will return to the needle and the syringe is withdrawn from the sample bottle. The syringe is then inserted through a septum in a gas injection port of a gas chromatograph. The plunger is again depressed so that the fiber will extend into the gas chromatograph and an analysis of the components on the fiber is carried out. Then, the plunger is moved to the withdrawn and the syringe is withdrawn from the injection port. Previously, samples were analyzed using liquid-liquid extraction or using cartridges. Both of these methods are relatively expensive and time consuming. Both of these methods also require the use of solvents which can be difficult and expensive to dispose of.
Owner:PAWLISZYN JANUSZ B
Solid phase microextraction device using aerogel
InactiveUS6905031B1Quick and easy to manufactureEasily toleratedComponent separationSolid sorbent liquid separationSolid-phase microextractionKovar
A sample collection substrate of aerogel and / or xerogel materials bound to a support structure is used as a solid phase microextraction (SPME) device. The xerogels and aerogels may be organic or inorganic and doped with metals or other compounds to target specific chemical analytes. The support structure is typically formed of a glass fiber or a metal wire (stainless steel or kovar). The devices are made by applying gel solution to the support structures and drying the solution to form aerogel or xerogel. Aerogel particles may be attached to the wet layer before drying to increase sample collection surface area. These devices are robust, stable in fields of high radiation, and highly effective at collecting gas and liquid samples while maintaining superior mechanical and thermal stability during routine use. Aerogel SPME devices are advantageous for use in GC / MS analyses due to their lack of interfering background and tolerance of GC thermal cycling.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
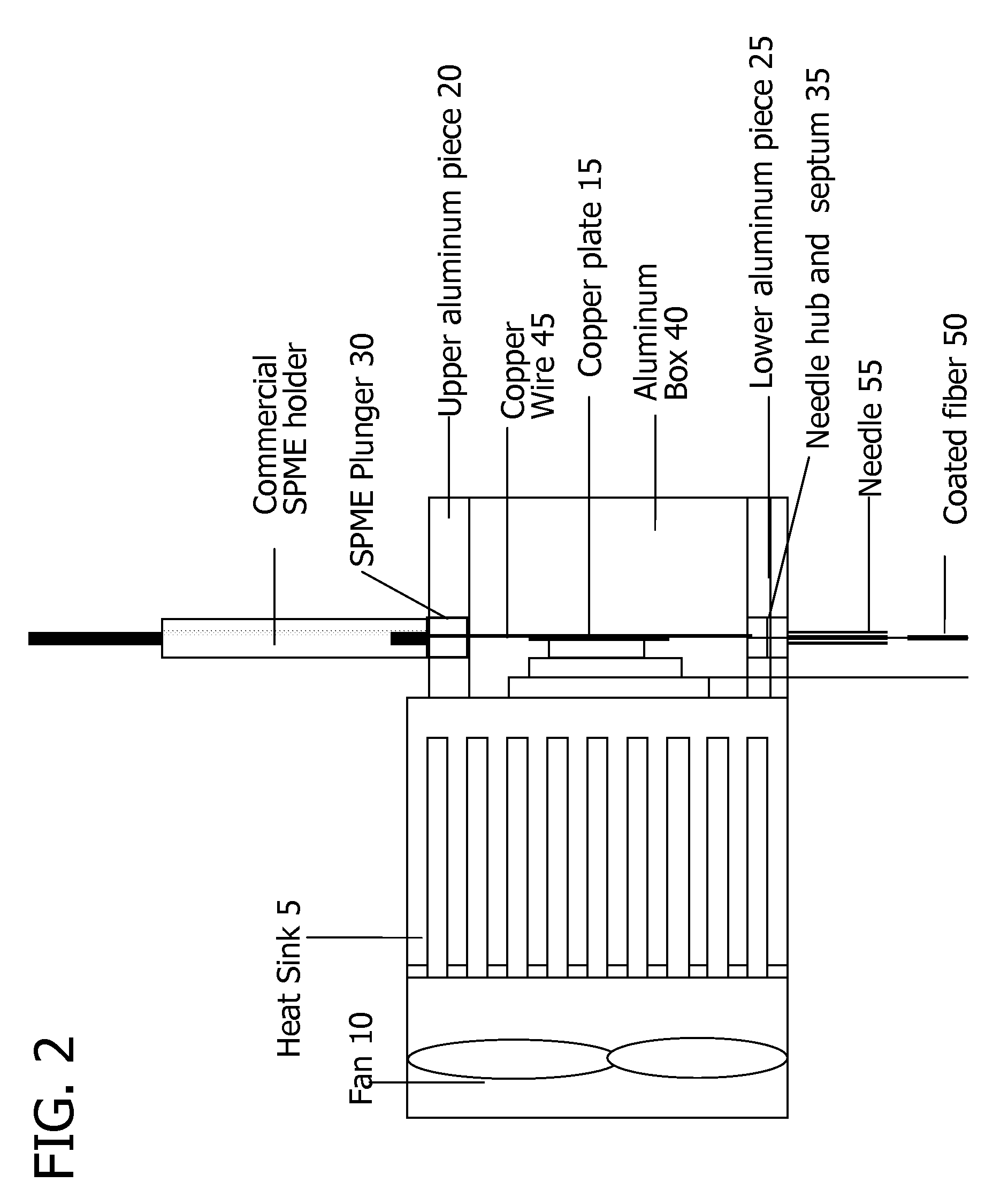
Internally cooled coated fiber device
An internally cooled solid phase microextraction device that provides for quantitative sampling of volatile and semi-volatile organic compounds in complex samples. The device temperature is controlled the device design enables repeated use without failure. The device is miniaturized allowing it to be used with autosamplers known in the art.
Owner:PAWLISZYN JANUSZ
Capillary solid phase microextraction device and extracting method
InactiveCN1500540ALarger than surfaceExtraction enrichment factor increasedSolid solvent extractionFour-way valveGas liquid chromatographic
The solid phase capillary miniature extractor includes mainly one four-way valve and one six-way valve connected via gas path; one capillary extracting column made of elastic hollow quartz capillary, stainless steel capillary or stainless steel capillary with inside quartz lining, connected to the six-way valve and with cross-linking coated fixing phase in the inside wall; one heater outside the extracting column for heating; one miniature three-way pipe connected to the extracting column, the six-way valve and conveying gas path for the desorption sample; and one conveying pipe inserted into the gas chromatographic sample injector. The liquid sample pushed by the auxiliary carrier gas enters first to the extracting column via the four-way valve and the six-way valve; the four-way valve is then turned and the extracting column is heated; and the six-way valve is finally turned for the desorbed component to enter the gas chromatographic sample injector.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Porous protective solid phase micro-extractor sheath
InactiveUS6871556B2Analysis using chemical indicatorsComponent separationBare fiberSolid-phase microextraction
A porous protective sheath for active extraction media used in solid phase microextraction (SPME). The sheath permits exposure of the media to the environment without the necessity of extending a fragile coated fiber from a protective tube or needle. Subsequently, the sheath can pierce and seal with GC-MS septums, allowing direct injection of samples into inlet ports of analytical equipment. Use of the porous protective sheath, within which the active extraction media is contained, mitigates the problems of: 1) fiber breakage while the fiber is extended during sampling, 2) active media coating loss caused by physical contact of the bare fiber with the sampling environment; and 3) coating slough-off during fiber extension and retraction operations caused by rubbing action between the fiber and protective needle or tube.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
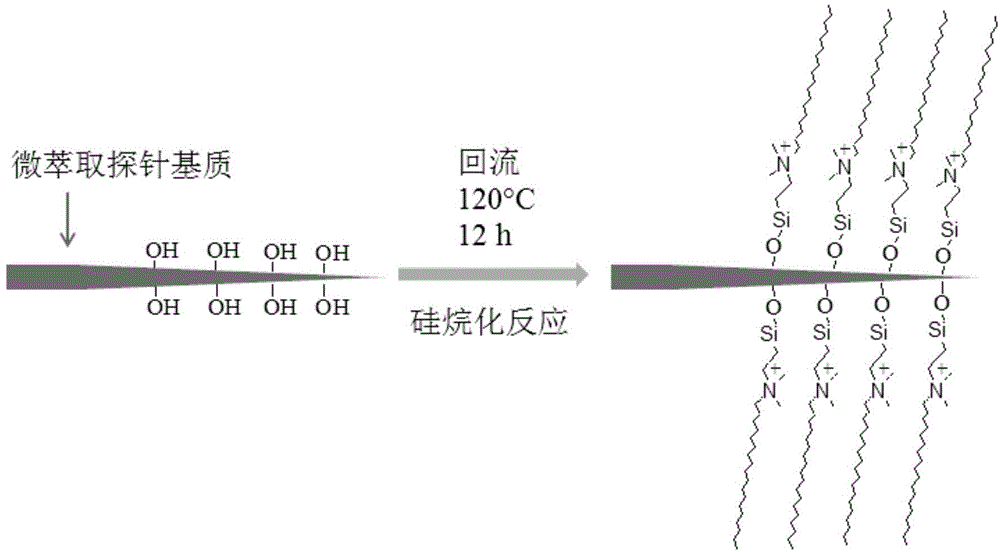
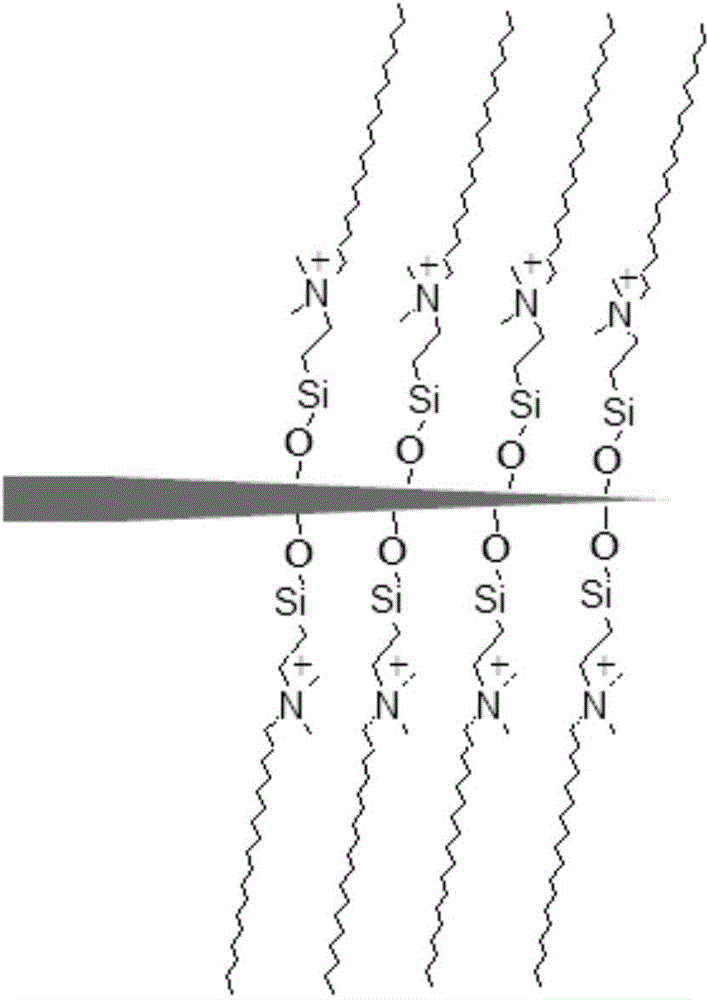
Microextraction probe electrospray ion source and manufacturing method and application of microextraction probe electrospray ion source
InactiveCN104134606AGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansSolid-phase microextractionMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
The invention belongs to the field of chemistry, and relates to a microextraction probe electrospray ion source and a manufacturing method and application of the microextraction probe electrospray ion source, in particular to a probe capable of being directly used for complex-matrix solid-phase microextraction and direct-electrospray mass spectrometry analysis and a manufacturing method and application of the probe. The probe is characterized in that a silanization reaction is carried out on adsorption materials containing silylation and pointed-shaped wood fiber matrixes with the surface rich in hydroxyl, and the microextraction probe is obtained. By means of the probe, high enrichment coefficients of trace target compounds in multiple kinds of complex matrixes can be directly extracted, the probe after extraction can carry out direct electrospray to ionize the target compounds in the normal-pressure open environment and carry out mass spectrometry analysis; the microextraction electrospray probe achieves solid-phase microextraction and ambient mass spectrometry combination analysis, can be used as the novel electrospray ion source and has the high sensitivity and the ideal reproducibility.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV +1
Analytical method for determining aromatic constituents in tea
InactiveCN103076411AReliable identificationEfficient retrieval matching analysisComponent separationKovats retention indexSolid-phase microextraction
The invention provides an analytical method for determining aromatic constituents in tea. The method adopts HS-SPME (headspace-solid phase microextraction), combines GC-MS (gas chromatography-mass spectrometer) with the Kovats retention index (KI), employs a 50 / 30mu m DVB / CAR / PDMS type SPME head, optimizes HS-SPME parameters, establishes an AMDIS (automated mass spectral deconvolution and identification system) combined with the KI, and establishes a tea aroma atlas database for analysis. Compared with the conventional tea aroma analysis, the provided analytical method is better in accuracy, efficiency, flexibility and comprehensiveness, and can be effectively applied to qualitative and quantitative analysis for identification of the aromatic constituents in the tea.
Owner:TEA RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method and device for solid phase microextraction and desorption
InactiveUS20050011831A1Component separationMaterial analysis by optical meansSolid-phase microextractionDesorption
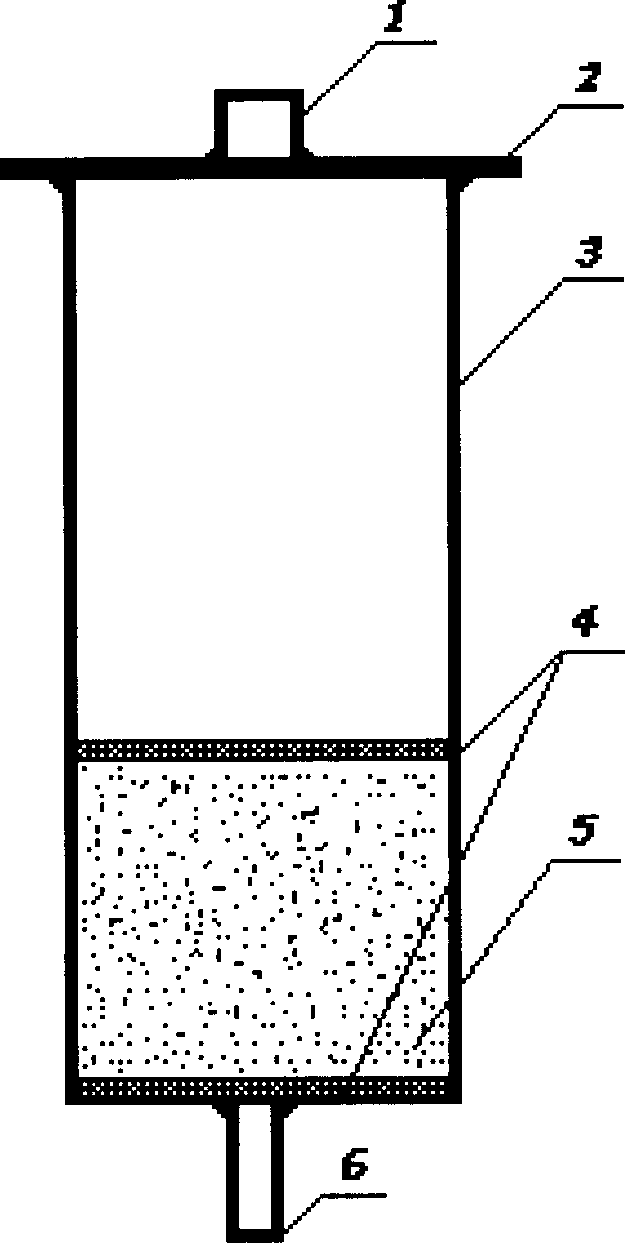
A device for carrying out solid phase microextraction on-site is a tubular member having one closed end and one open end with an extracting surface within said tubular member. The extracting surface can be an extracting phase coating extending over a zone within the tubular member. The tubular member is mounted in a housing with an airtight cavity. A method of operation of the device is also provided. The solid phase microextraction device facilitates the ultimate goal of chemist to perform analysis on-site at place where a sample is located rather than moving the sample to laboratory, as it is a common practice in many cases at present. This approach eliminates errors and reduces the time associated with sample transport and storage and, therefore, it results in more accurate, precise and faster analytical data.
Owner:PAWLISZYN JANUSZ B
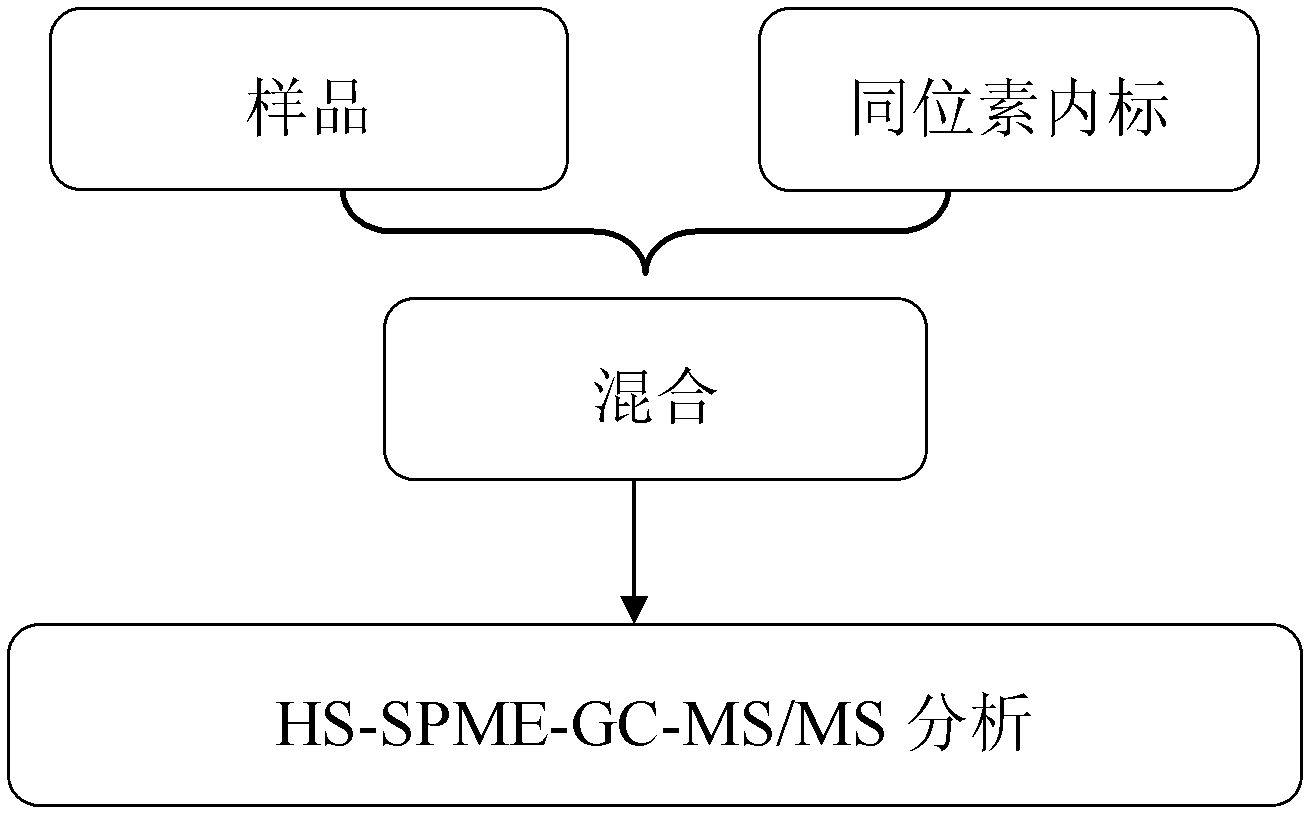
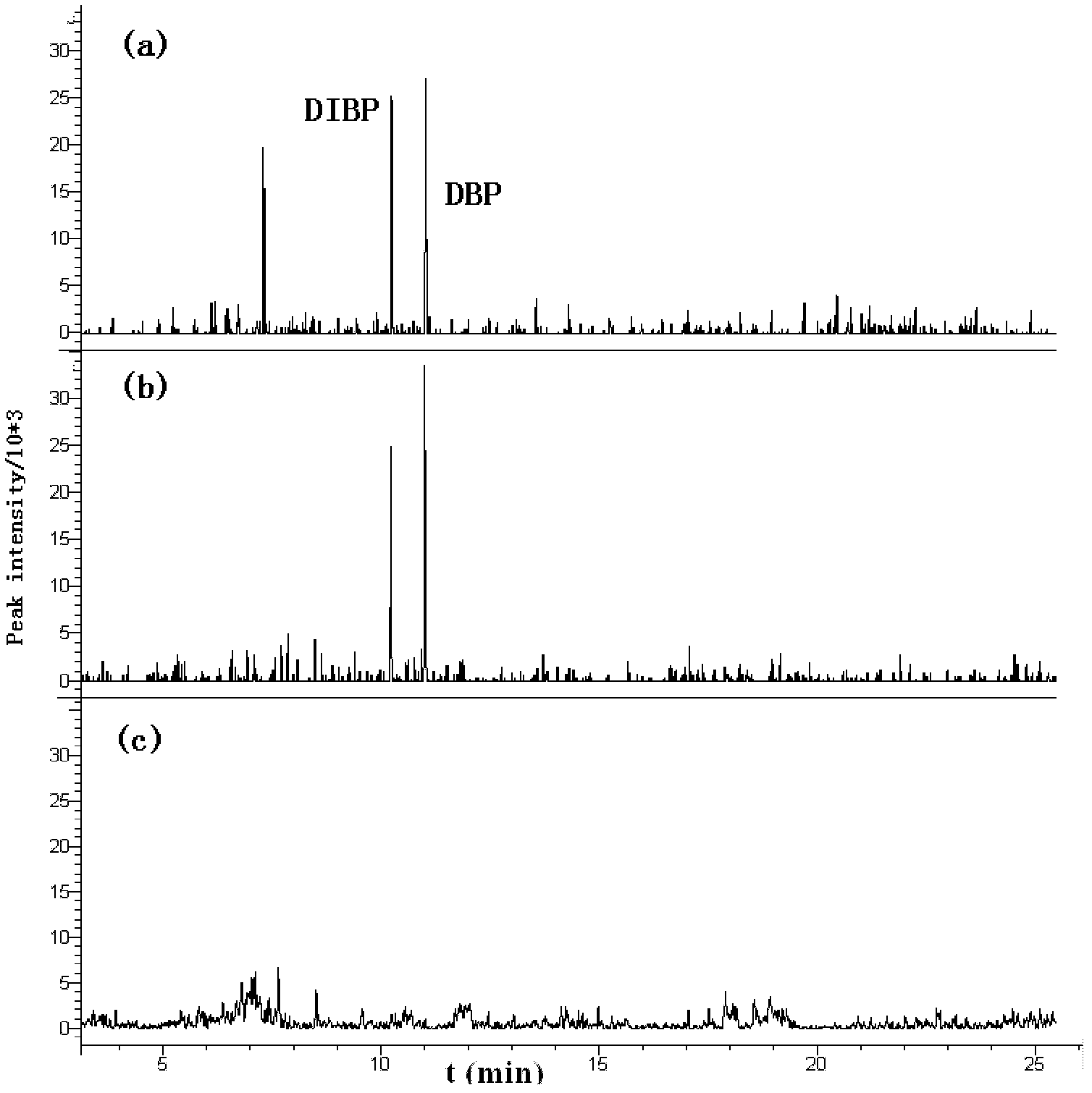
Method for detecting plasticizer content in solid sample by headspace solid phase microextraction gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry
InactiveCN102520091AImprove accuracyImprove efficiencyComponent separationSensitive analysisGas phase
The invention relates to a method for detecting the plasticizer content in a solid sample by headspace solid phase microextraction gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry, and the method combines an isotope internal standard and the headspace solid phase microextraction gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (HS-SPME-GC-MS / MS) analysis for qualitative or quantitative analysis of a dimethyl phthalate plasticizer in a sample. The method mainly comprises the following steps of: a) mixing the solid sample with the isotope internal standard, and conducting extraction with headspace solid phase microextraction equipment; b) carrying out sample analysis; C) performing GC-MS / MS analysis; and d) implementing result treatment and quantitative analysis. The method of the invention is a fast, efficient, sensitive analysis method.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF ORGANIC CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method and device for solid phase microextraction and desorption
A device for carrying out solid phase microextraction is a fiber contained in a syringe. When it is desired to analyze a sample in a bottle having a septum, the needle is inserted through the septum and the plunger is depressed so that the fiber will extend into the sample. After one or two minutes, the plunger is moved to the withdrawn position so that the fiber will return to the needle and the syringe is withdrawn from the sample bottle. The syringe is then inserted through a septum in a gas injection port of a gas chromatograph. The plunger is again depressed so that the fiber will extend into the gas chromatograph and an analysis of the components on the fiber is carried out. Then, the plunger is moved to the withdrawn position and the syringe is withdrawn from the injection port.
Owner:PAWLISZYN JANUSZ B
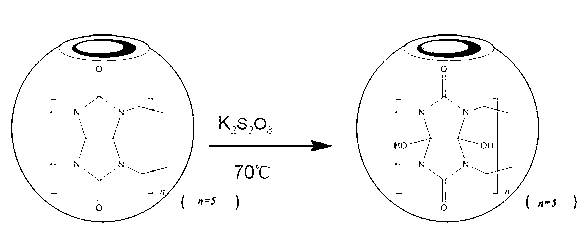
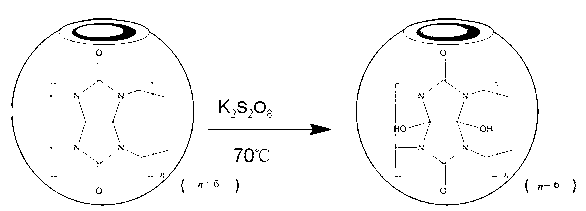
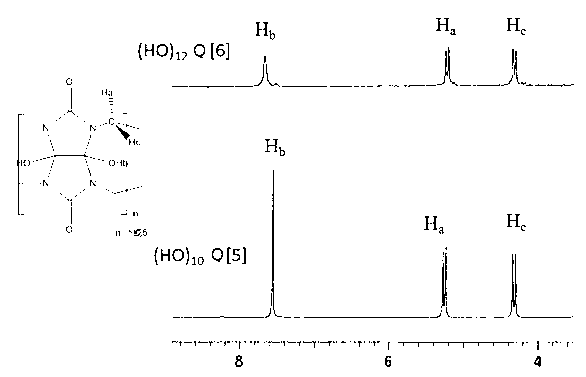
Solid phase microextraction coating of hydroxyl cucurbituril as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN103157453AIncrease surface areaHigh selectivityIon-exchange process apparatusComponent separationPotassium persulfateChemical reaction
The invention discloses a solid phase microextraction coating of a hydroxyl cucurbituril as well as a preparation method and an application thereof, relates to an analyzing sample pre-treatment technology, and belongs to the technical field of analytical chemistry. The solid phase microextraction coating is characterized in that a common pentabasic cucurbituril or six-membered cucurbituril is subjected to potassium peroxodisulfate oxidation and cation exchange resin separation and purification so as to obtain the hydroxyl cucurbituril through, the hydroxyl cucurbituril is bonded on a sol-gel mesh through a chemical reaction so as to obtain the solid phase microextraction coating, the coating is utilized to prepare a solid phase microextraction fibre which is combined with a gas chromatography, the environmental water sample containing polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon is analysed, and the coating is utilized to prepare a solid phase microextraction stirring rod which is combined with a high performance liquid chromatography so as to analyze non-steroid antiinflammatory drugs. The solid phase microextraction coating provided by the invention has the advantages that the superficial area of the coating is large, and the extraction capacity is large; and the solid phase microextraction coating is a novel solid phase microextraction coating, is used for analyzing, high in selectivity, low in detection limitation, wide in linearity range, and good in selectivity.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV
Packing material for solid phase extraction and solid phase exraction method
InactiveUS20020004561A1Easy to separateAmount of absorption decreaseCation exchanger materialsOther chemical processesHydrophilic monomerSolid-phase microextraction
An object of the present invention is to provide a packing material for solid phase extraction, ensuring excellent recovery of not only a hydrophobic substance but also an ionic substance by having hydrophobicity and an ion exchange group at the same time, and a solid phase extraction method, a packing apparatus, and a method for treating a sample, using the packing apparatus. A packing material for solid phase extraction of the present invention is a particle obtained by copolymerizing a hydrophobic monomer (A) and a hydrophilic monomer (B) and introducing thereinto an ion exchange group, in which the ion exchange group is introduced without impairing the hydrophobic site. The present invention also provides a solid phase extraction method, a packing apparatus for solid phase extraction and a method for treating a sample, using the packing material.
Owner:SHOWA DENKO KK
Biocompatible solid-phase microextraction coatings and methods for their preparation
InactiveUS20090026122A1Reduce adsorptionSamplingParticle separator tubesSolid-phase microextractionBiocompatible coating
A biocompatible coating for solid phase microextraction (SPME) of a small molecule from a biological matrix. The coating comprises SPME particles and a biocompatible polymer. The biocompatible polymer (e.g. polyacrylonitrile) reduces adsorption of proteins or macromolecules onto the SPME particles and allows the SPME particles to extract the small molecule from the matrix. A process for coating a flexible fiber with a biocompatible coating. The process comprises: coating the fiber with a suspension of SPME particles, the SPME particles being suspended in a solution of a biocompatible polymer and a solvent, the biocompatible polymer can comprise polyacrylonitrile (PAN); drying the coated fiber to remove the solvent; and curing the dried coated fiber at an elevated temperature.
Owner:PAWLISZYN JANUSZ B
Process for determining hydrocarbon composition of vacuum gas oil by combination of solid phase extraction and mass spectrum
ActiveCN1690704AEfficient separationEffective dosageComponent separationStationary phaseSolid-phase microextraction
A composition measurement method for hydrocarbon of vacuum gas oil by solid phase extraction combination mass spectrum comprises that separate the oil to three parts of saturated hydrocarbon, arene and gum by solid phase extraction, analyze their corresponding content by weighing or gas chromatography; detect makeup of saturated hydrocarbon and arene by mass spectrum; use normalization method to compute hydrocarbon composition of vacuum gas oil according to corresponding content of saturated hydrocarbon and arene; stationary phase of aforementioned solid phase extraction is silicon dioxide with specific surface is 450~750m2g, pore volume is 0.35~0.55ml / g, and pore with aperture 290~350nm takes up 50~70% of total pore volume. The method need less oil sample, and is quick and accurate.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Method for producing solid-phase microextraction capillaries
InactiveCN101073714AHigh selectivityEasy extractionIon-exchange process apparatusSolvent extractionGlycidyl methacrylateSolid-phase microextraction
The invention is concerned with the prepare method of capillary for solid phase microextraction. The methacrylic acid glycidyl is function monomer, the ethyleneglycol dimethacrylate is vulcanizing agent, toluene and dodecyl are mixed pore-causing agent, and 2,2'-azobisisobutyronitrile is initiator. Mix and mill the stuff and pour into quartz capillary disposed with ethylene, close and heat to polymerization. After the reaction, use solvent to clean capillary and remove the rudimental monomer, vulcanizing agent and pore-causing agent to get whole capillary with the polymer of methacrylic acid glycidyl and ethyleneglycol dimethacrylate. Use vitriol to clear the whole capillary to get hydroxylation, or clear the capillary with diethylamine and close to heat at 65 to 75 degree to get the capillary with the polymer of methacrylic acid glycidyl and ethyleneglycol dimethacrylate derived from diethylamine. The method is easy and low cost and the extraction agency stuff is fit to set up a credible and high sensitive analysis method.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Solid phase micro-extraction device and method for preparing fibre extraction head thereof
InactiveCN101496958AIngenious ideaUnique designIon-exchange process apparatusIon-exchanger regenerationMetal fiberSolid-phase microextraction
The invention relates to a solid phase micro-extraction device and a method for preparing a fiber extraction head thereof. The solid phase micro-extraction device comprises a micro sample injector, the inside of a sample injector push rod is provided with a stainless steel capillary pipe, and the lower end of the sample injector push rod is inserted with the fiber extraction head. The preparation method for the fiber extraction head comprises: corroding one end of a metal fiber into aqua regia, while corroding the other end in HF; dissolving metal salt and organic ligand in a solvent in a hot water reaction kettle to obtain a reaction mixed liquor; and immerging the one end of the metal fiber corroded by the HF after pretreatment into the reaction mixed liquor, and controlling the temperature to between 50 and 220 DEG C and the time to between 6 and 90 hours to prepare the solid phase micro-extraction head of which the surface is grown with metal organic porous skeleton materials in situ. The solid phase micro-extraction device has the advantages of difficult damage of extracted fibers, high temperature resistance, low cost, good extraction performance, capability of replacing the extraction head, and large adsorption capacity. The method can grow porous skeleton materials with different structures on the extraction head aiming at different compounds so as to design high-selectivity enrichment to a target object, and has wide application prospect in the aspect of analytical chemistry.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Method for simultaneously detecting six types of 24 antibiotics in water by solid phase extraction-liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry
InactiveCN107543877AShort timeHigh precisionComponent separationSolid-phase microextractionAntibiotic Y
The invention discloses a method for simultaneously detecting six types of 24 antibiotics in water by solid phase extraction-liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. The method comprises (1) carrying out water sample pretreatment through adding an internal standard substance indicating a recovery rate before solid phase extraction, (2) enriching and purifying a target antibiotic with a solid phase extraction small column and (3) detecting contents of six types of 24 antibiotics in water through a liquid chromatography-tandom mass spectrometer. The method can simultaneously detect residues of six types of 24 antibiotics in water, has low time consumption in detection and has the advantages of high precision, high sensitivity, high stability, high selectivity and low detection limit.In the water sample pretreatment, an organic reagent use amount is small, environmental friendliness is realized, operation is simple, an enrichment factor is high and reproducibility is good. The method utilizes the internal standard substance indicating a recovery rate before solid phase extraction, well shows the loss of the target substances in the pretreatment and produces a real and reliablefinal result.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACADEMY OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCES
Method and device for solid phase microextraction and desorption
InactiveUS7674631B2Component separationWithdrawing sample devicesDesorptionSolid-phase microextraction
A device for carrying out solid phase microextraction on-site is a tubular member having one closed end and one open end with an extracting surface within said tubular member. The extracting surface can be an extracting phase coating extending over a zone within the tubular member. The tubular member is mounted in a housing with an airtight cavity. A method of operation of the device is also provided. The solid phase microextraction device facilitates the ultimate goal of chemist to perform analysis on-site at place where a sample is located rather than moving the sample to laboratory, as it is a common practice in many cases at present. This approach eliminates errors and reduces the time associated with sample transport and storage and, therefore, it results in more accurate, precise and faster analytical data.
Owner:PAWLISZYN JANUSZ B
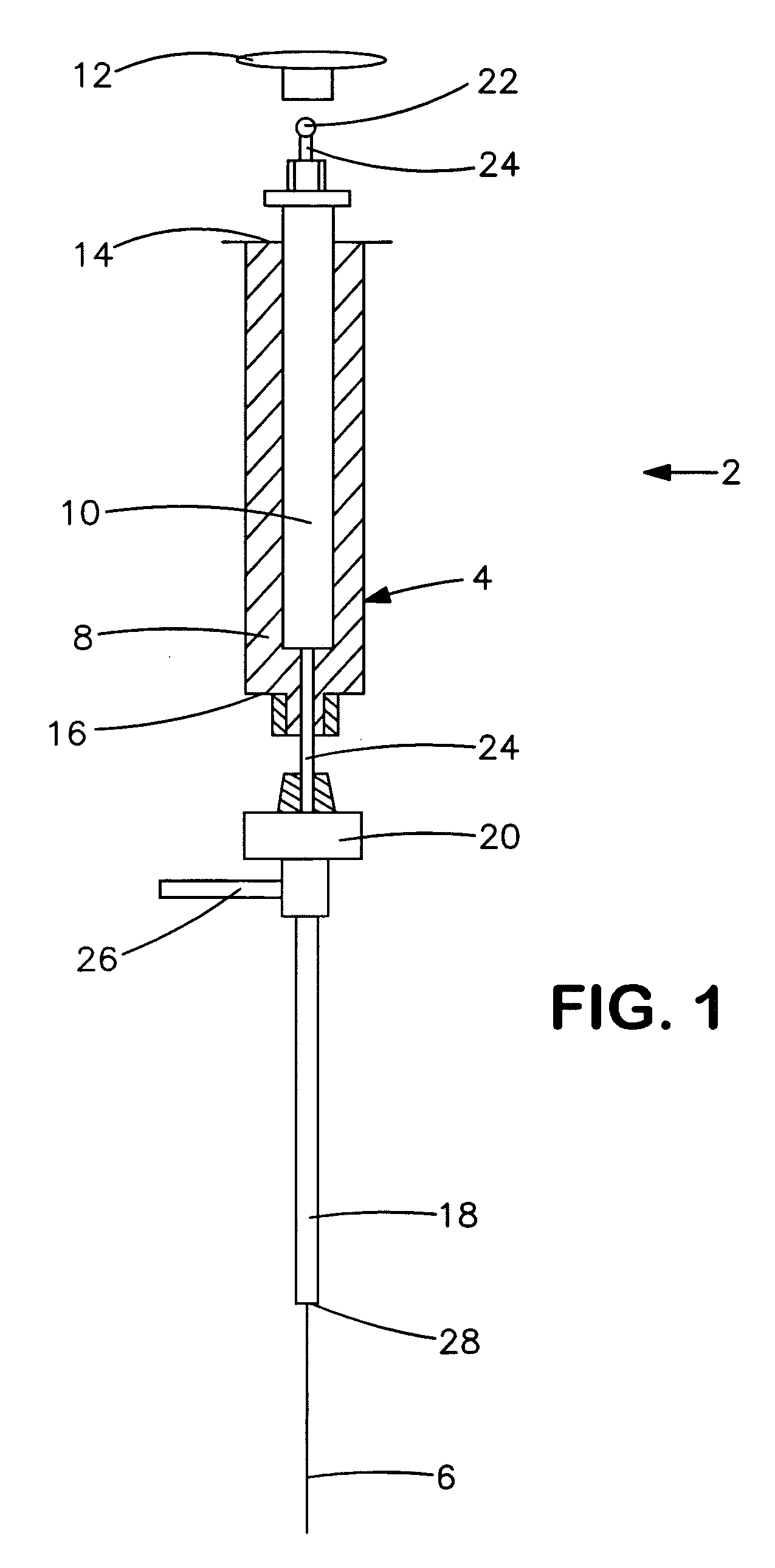
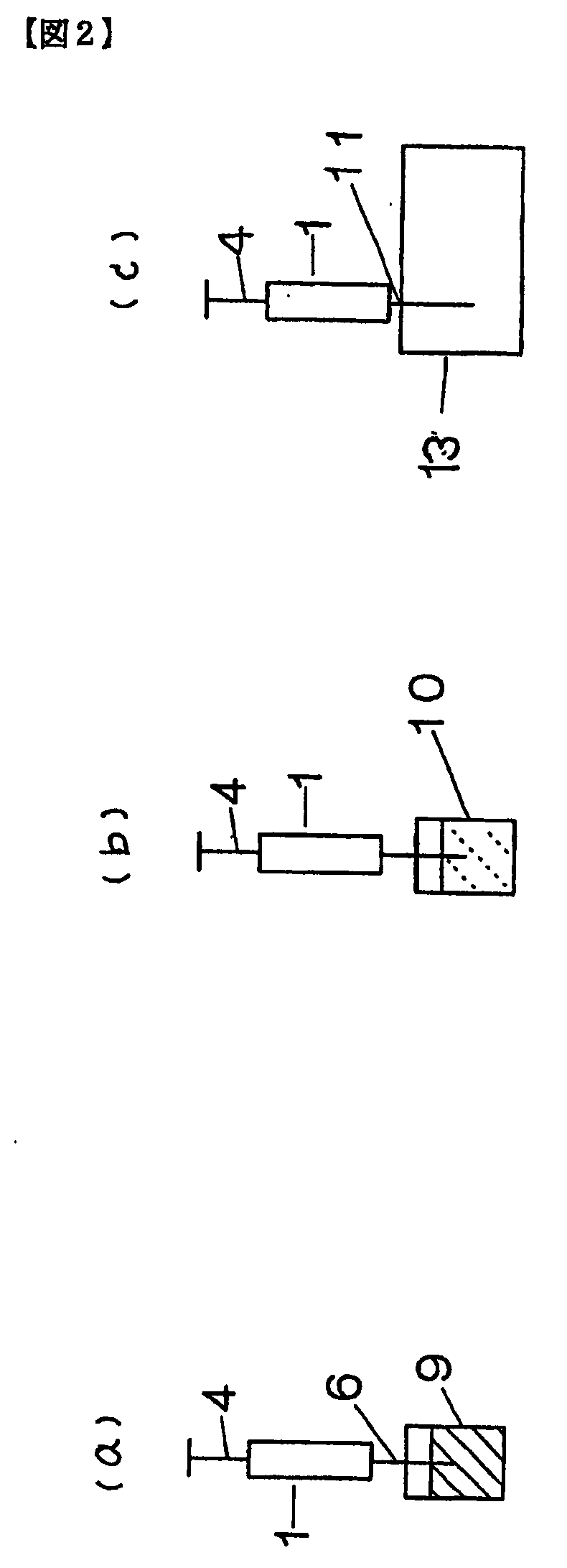
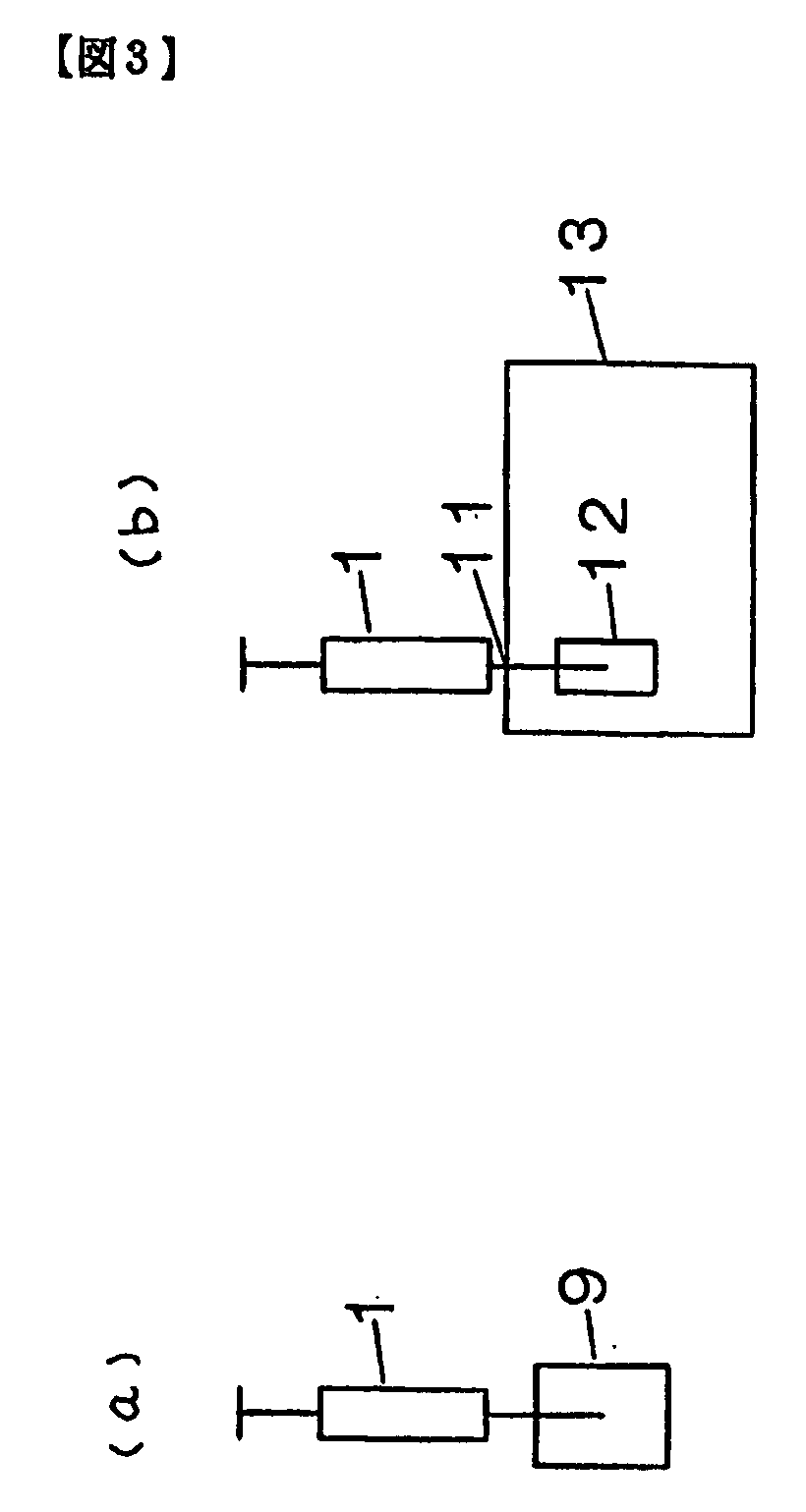
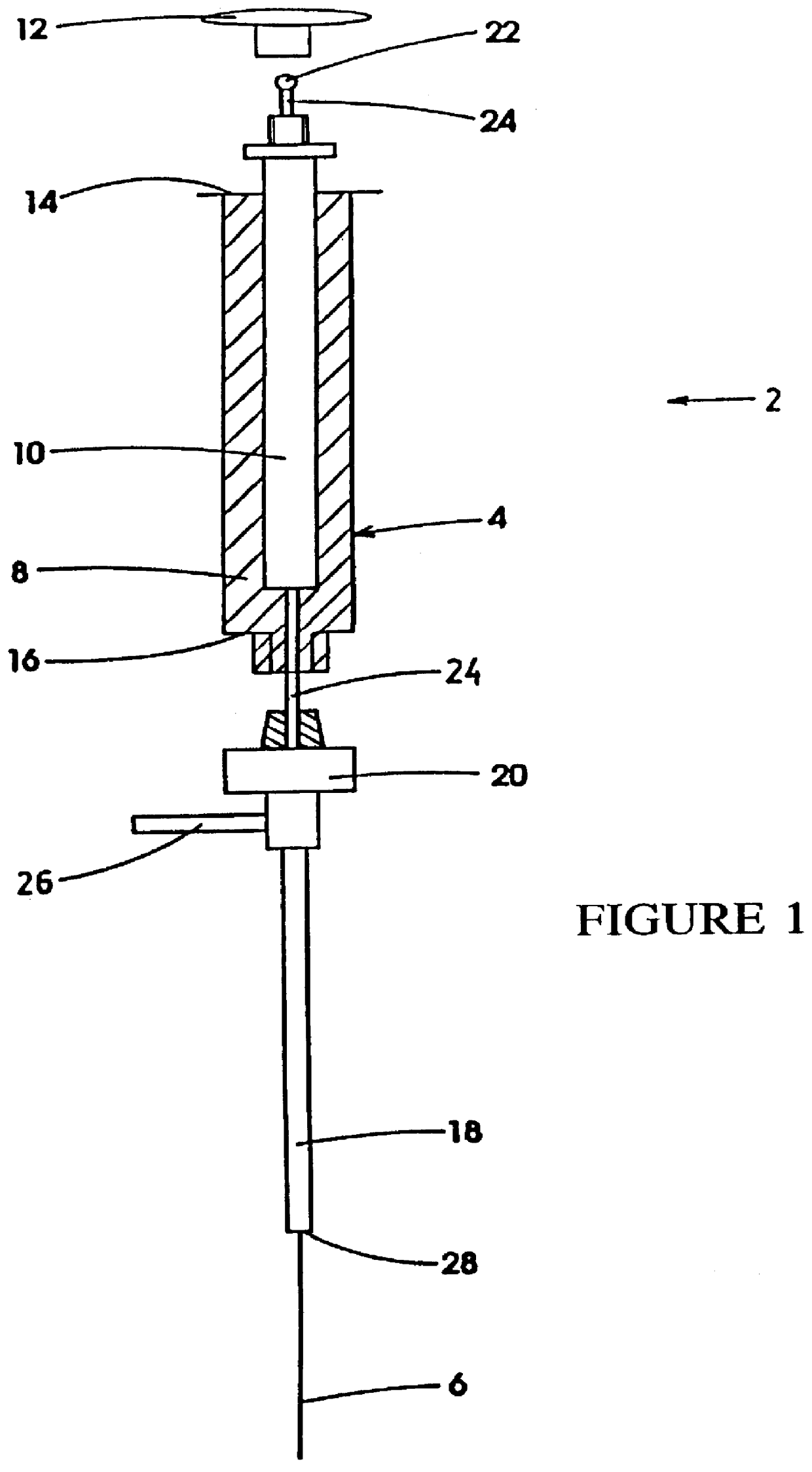
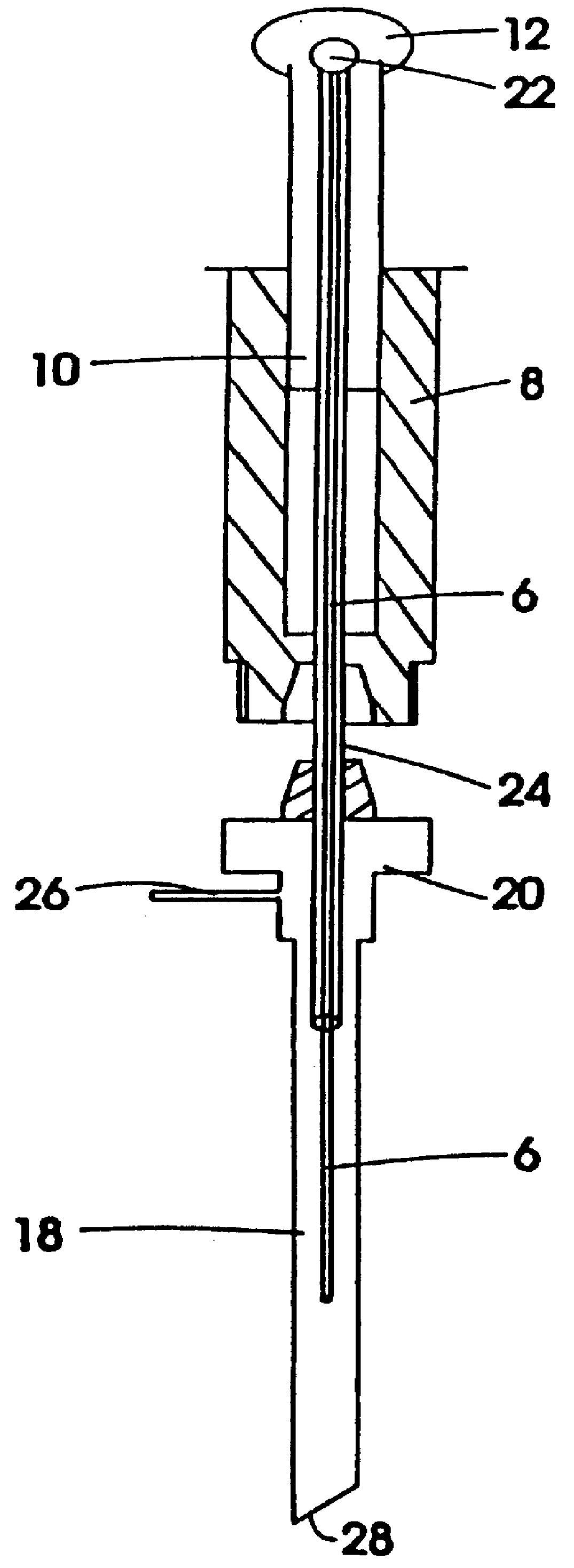
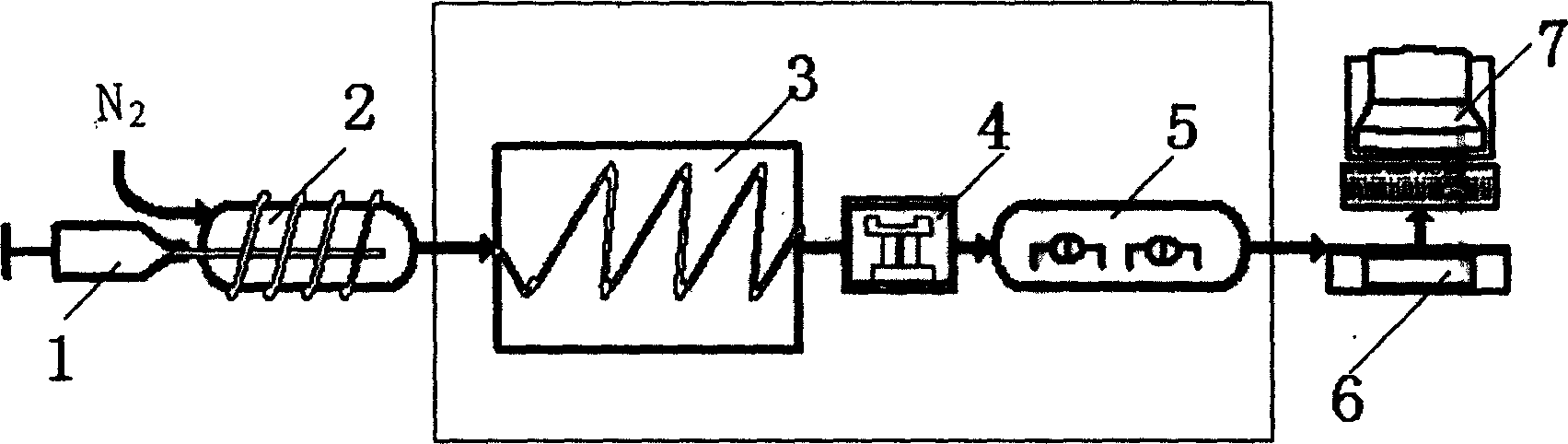
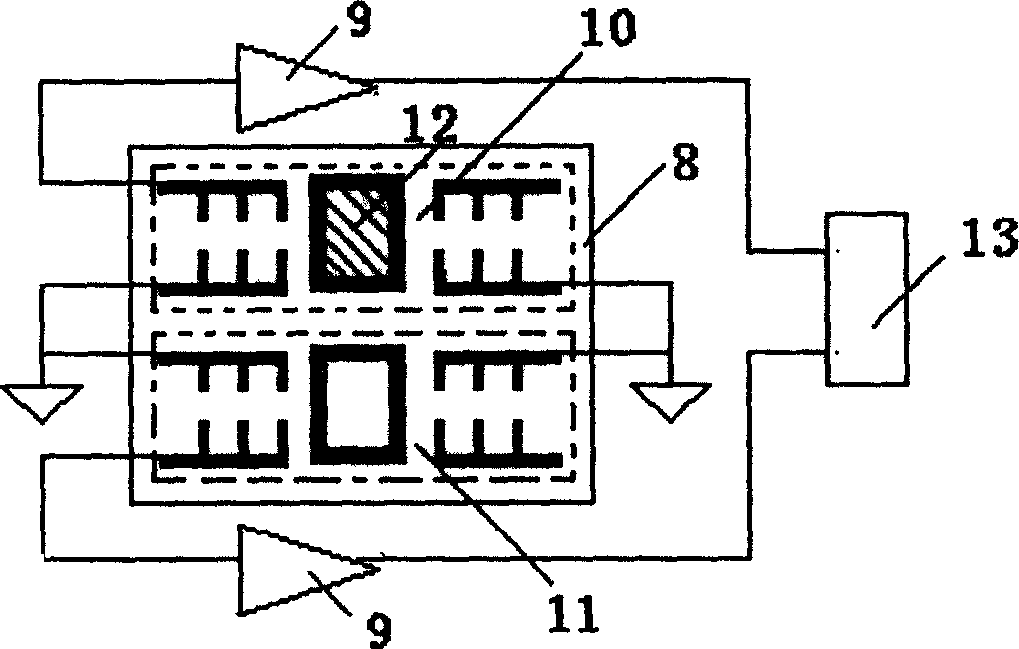
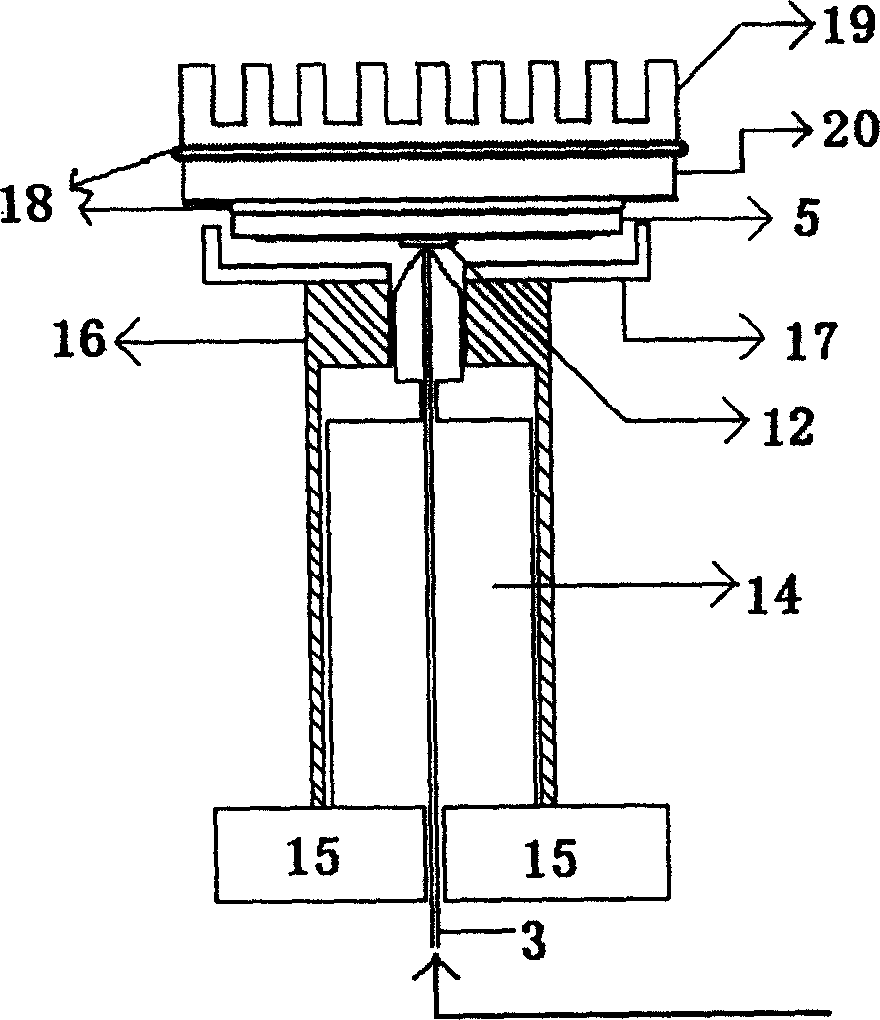
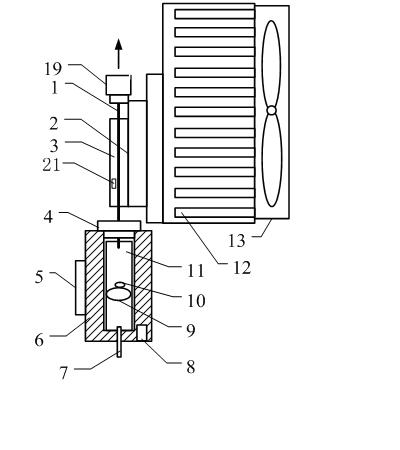
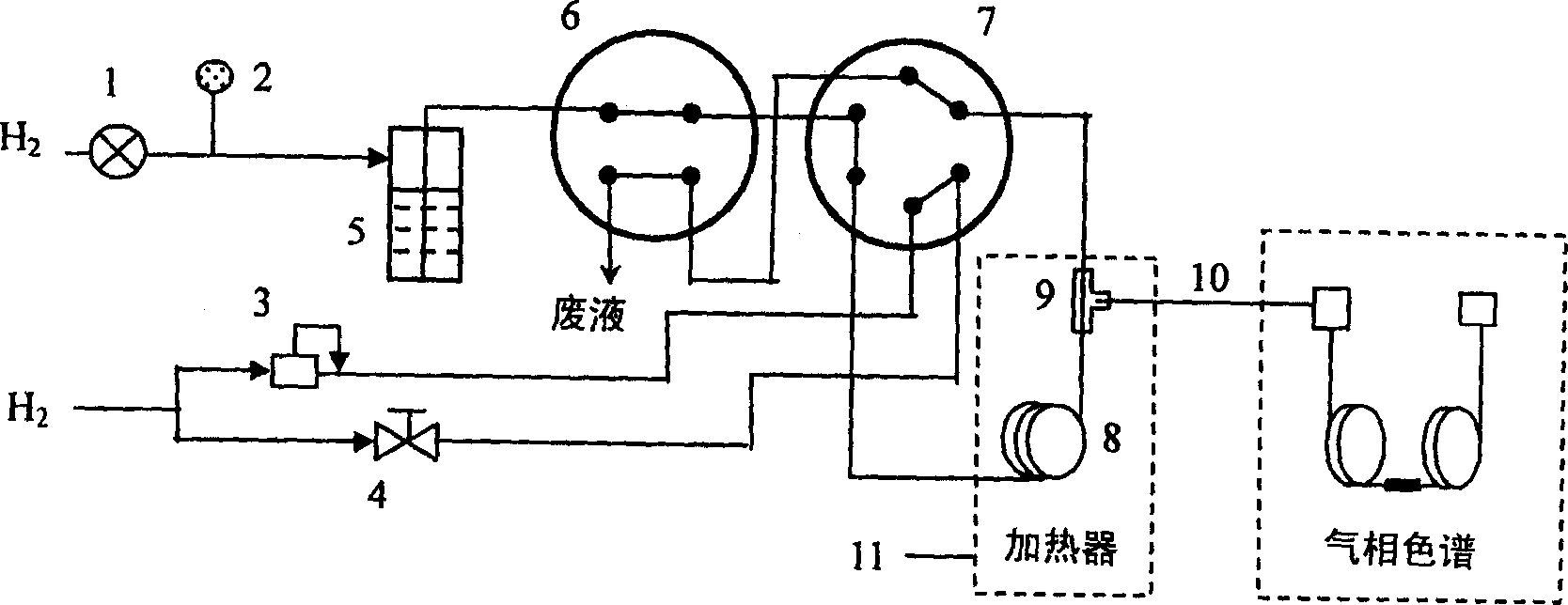
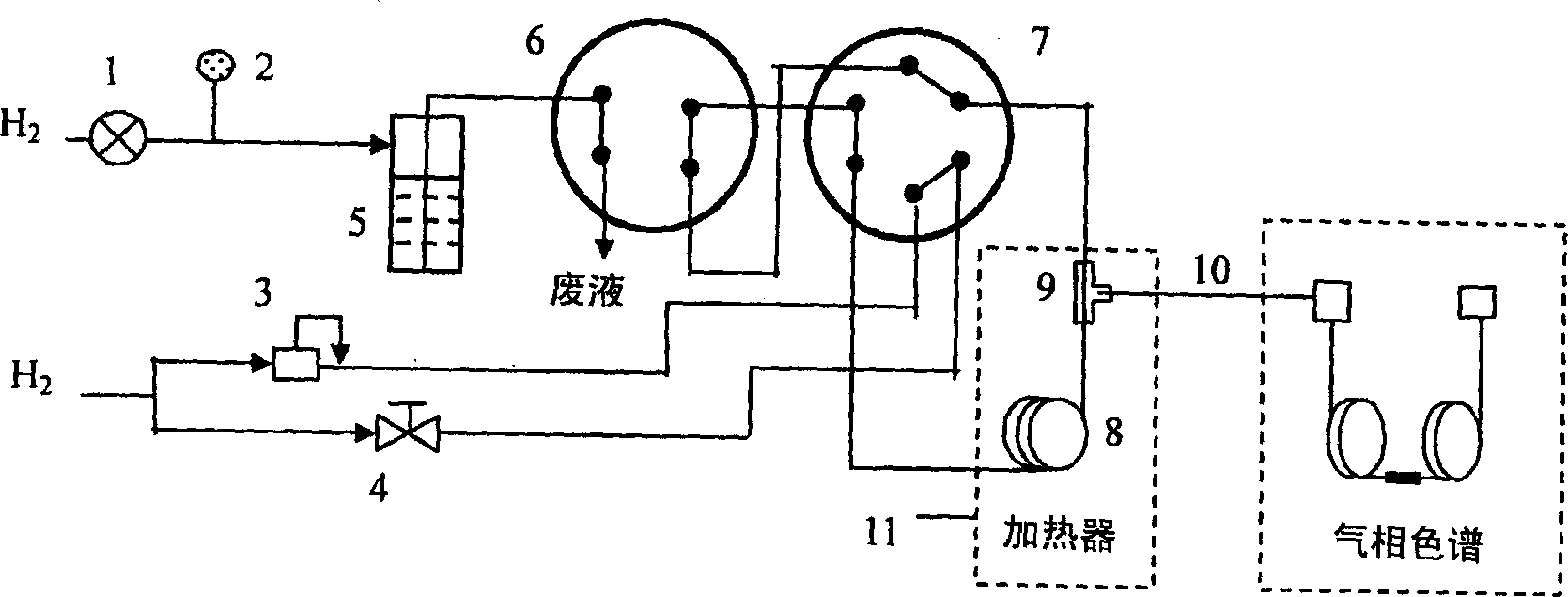
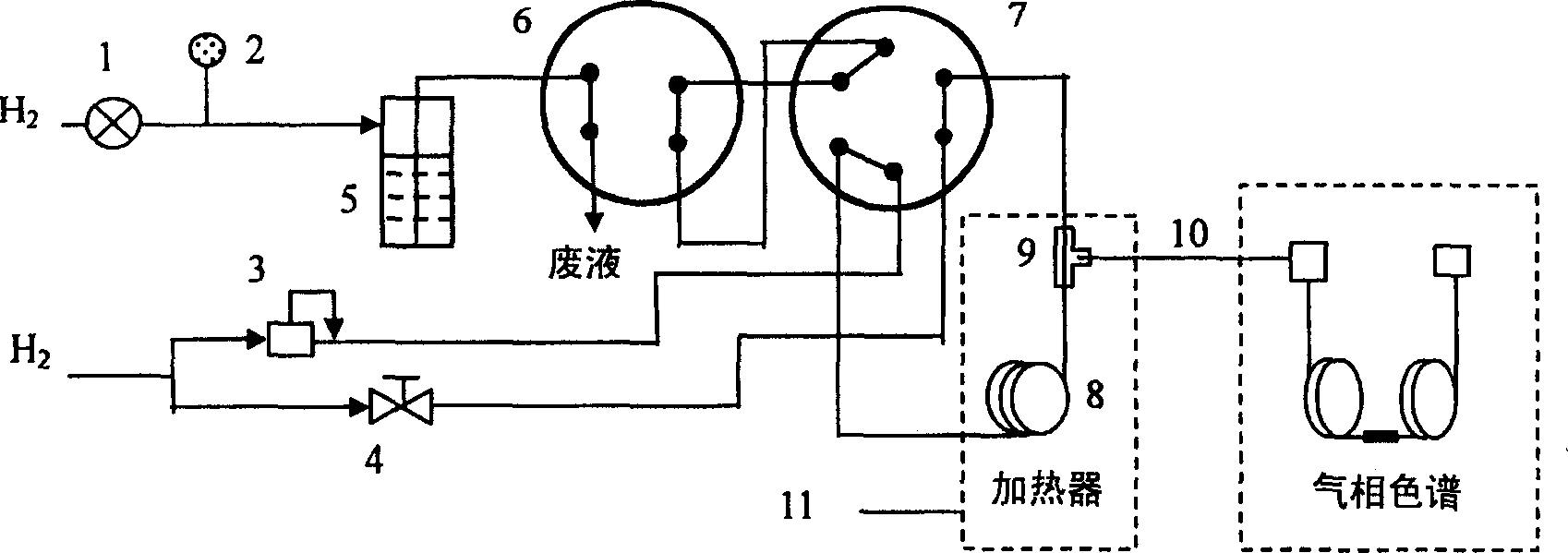
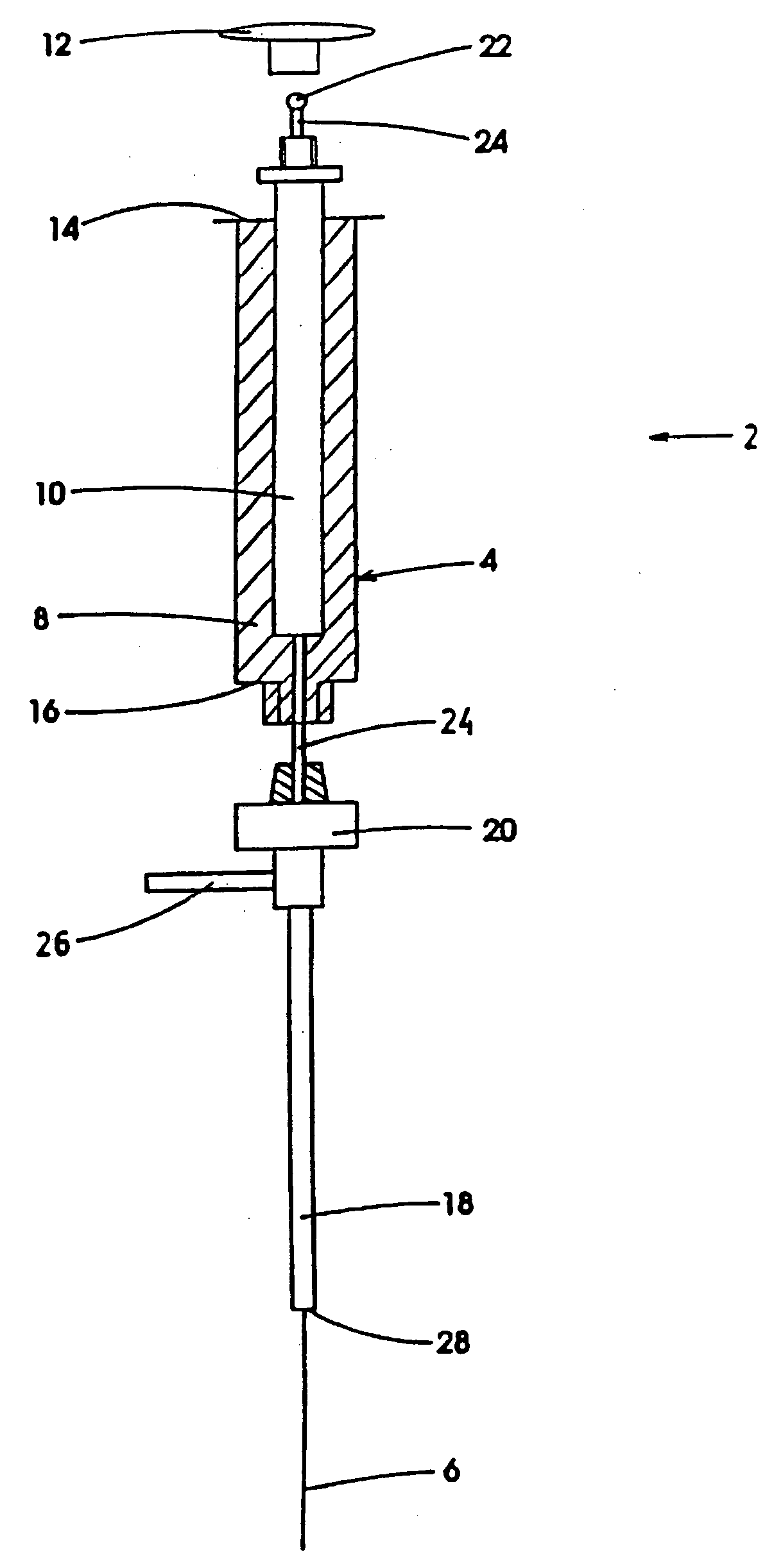
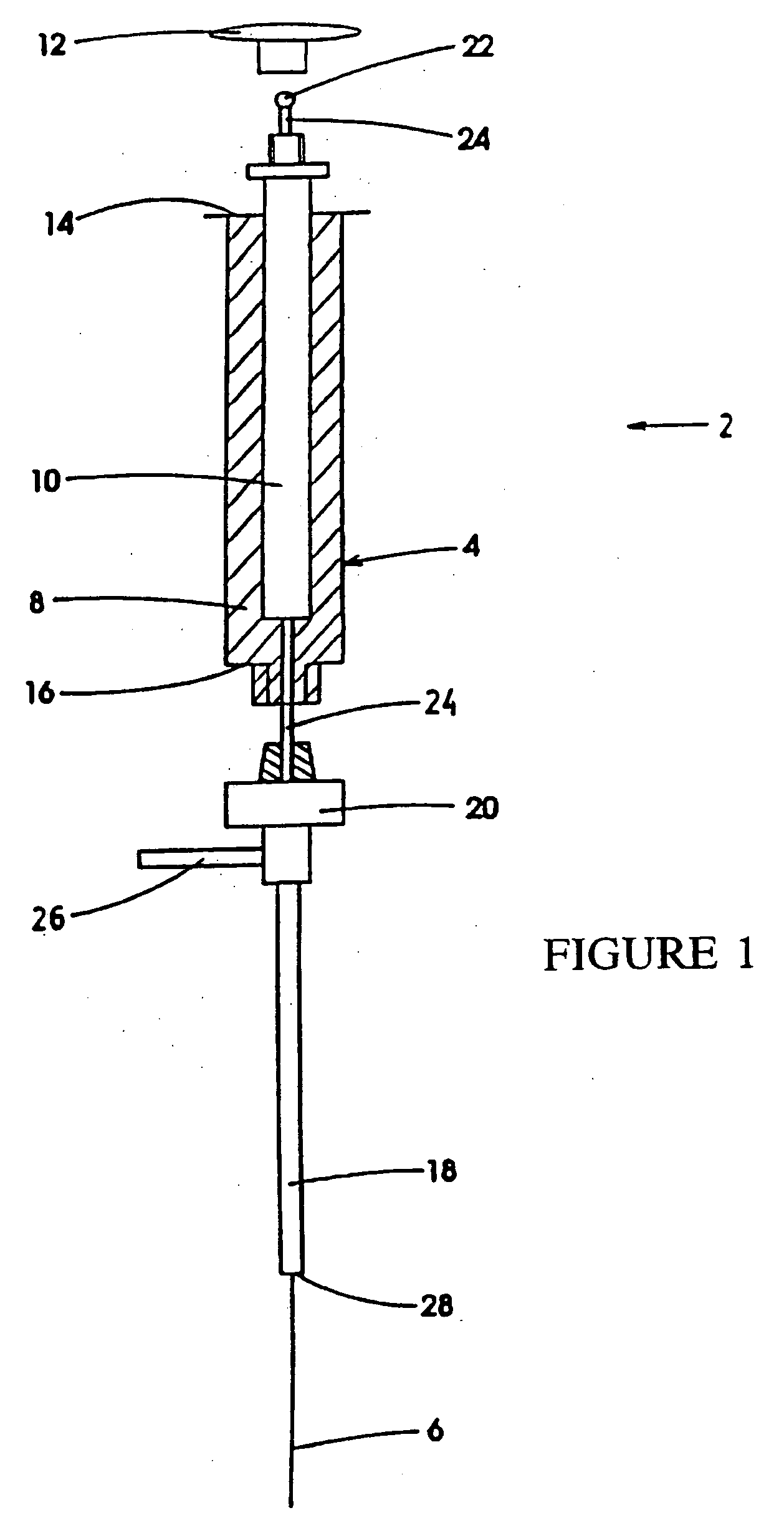
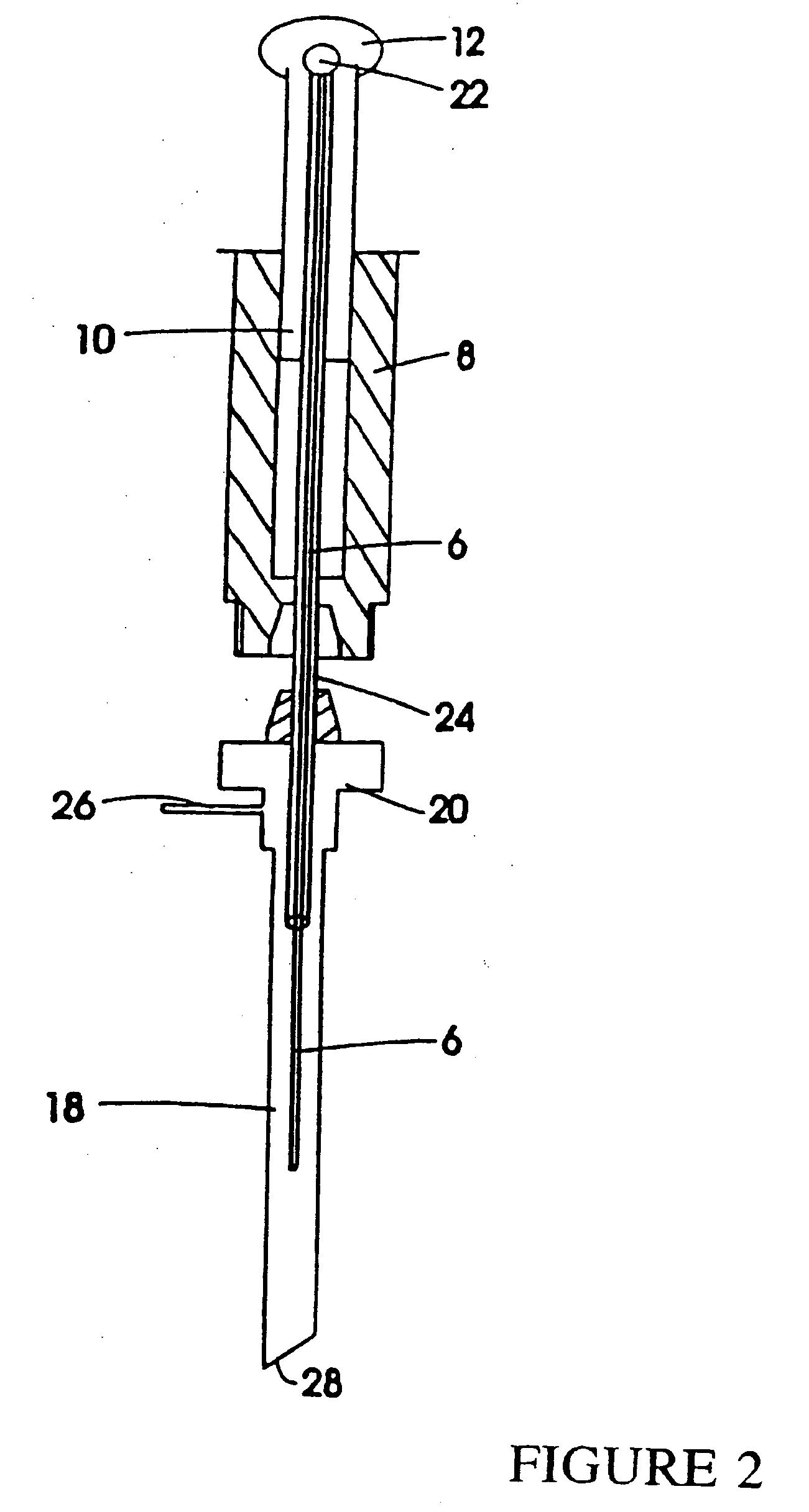
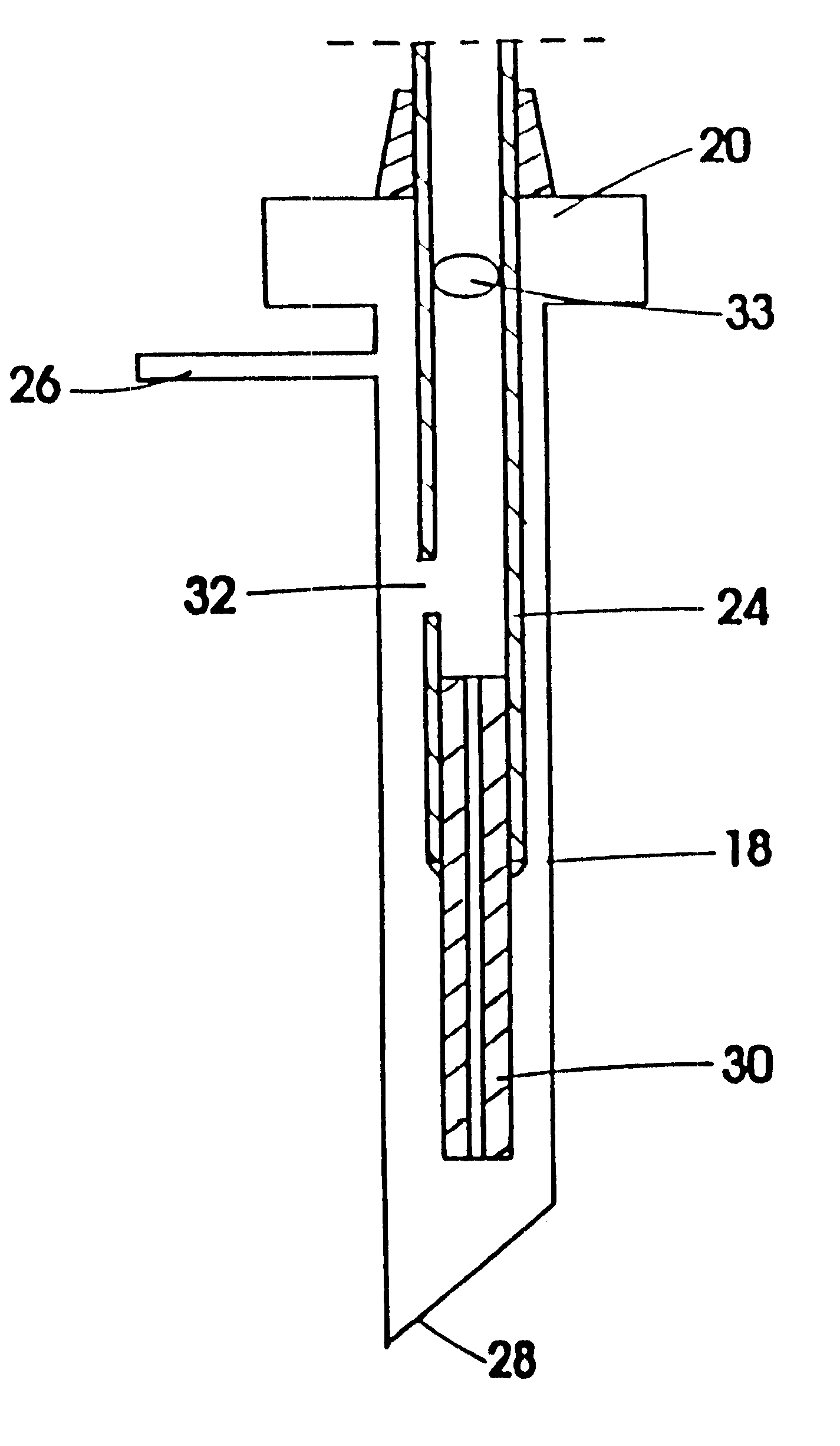
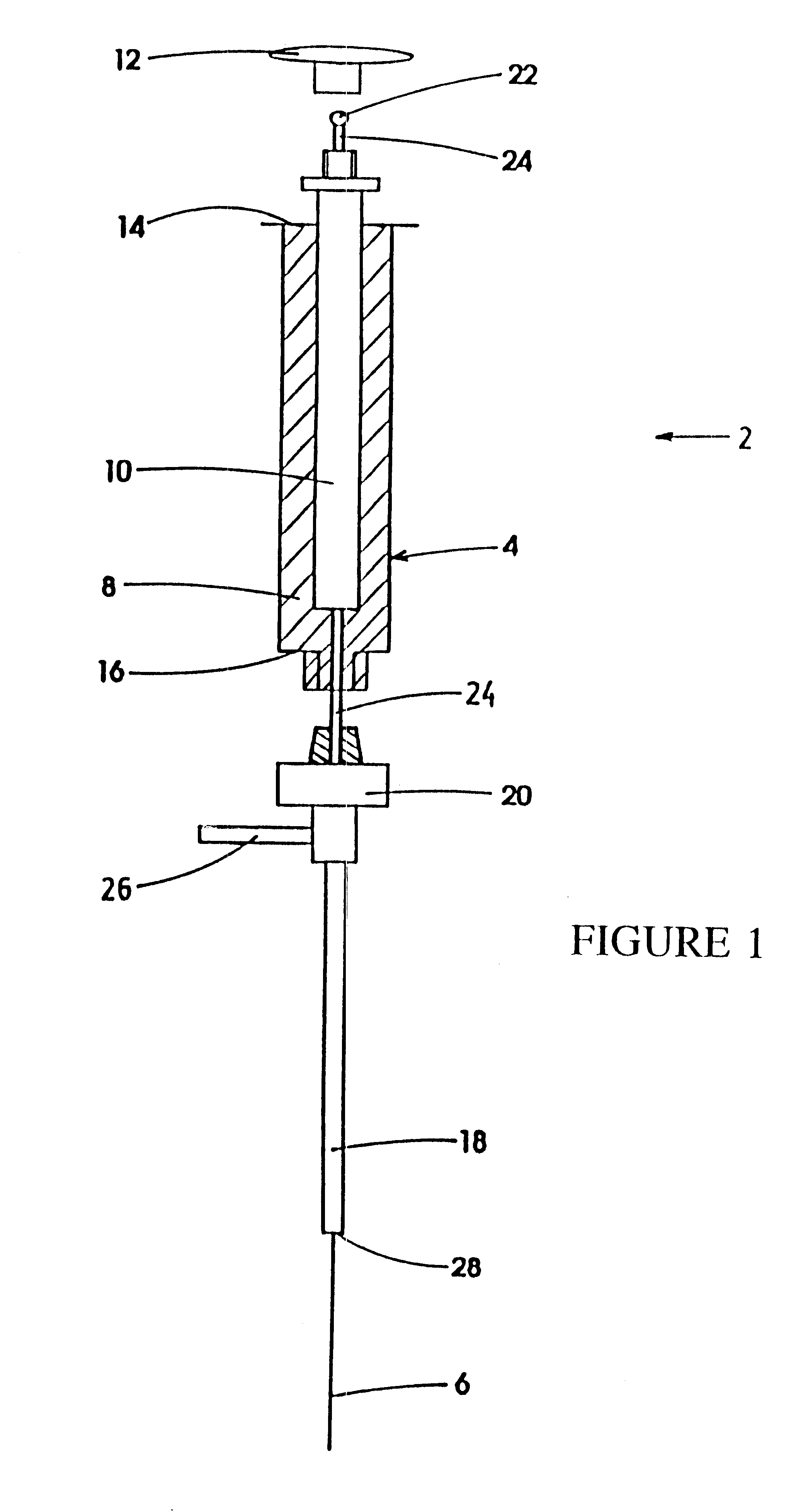
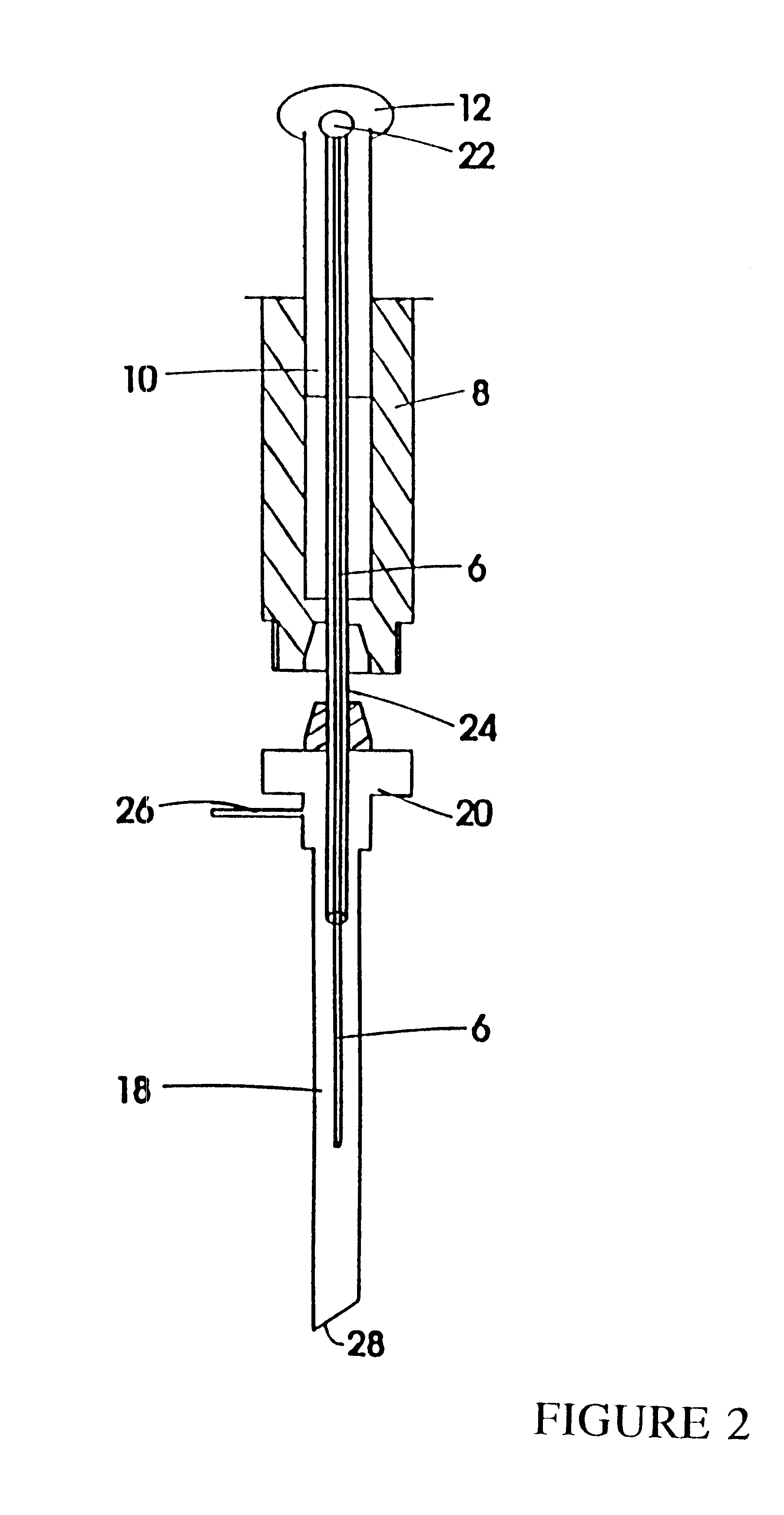
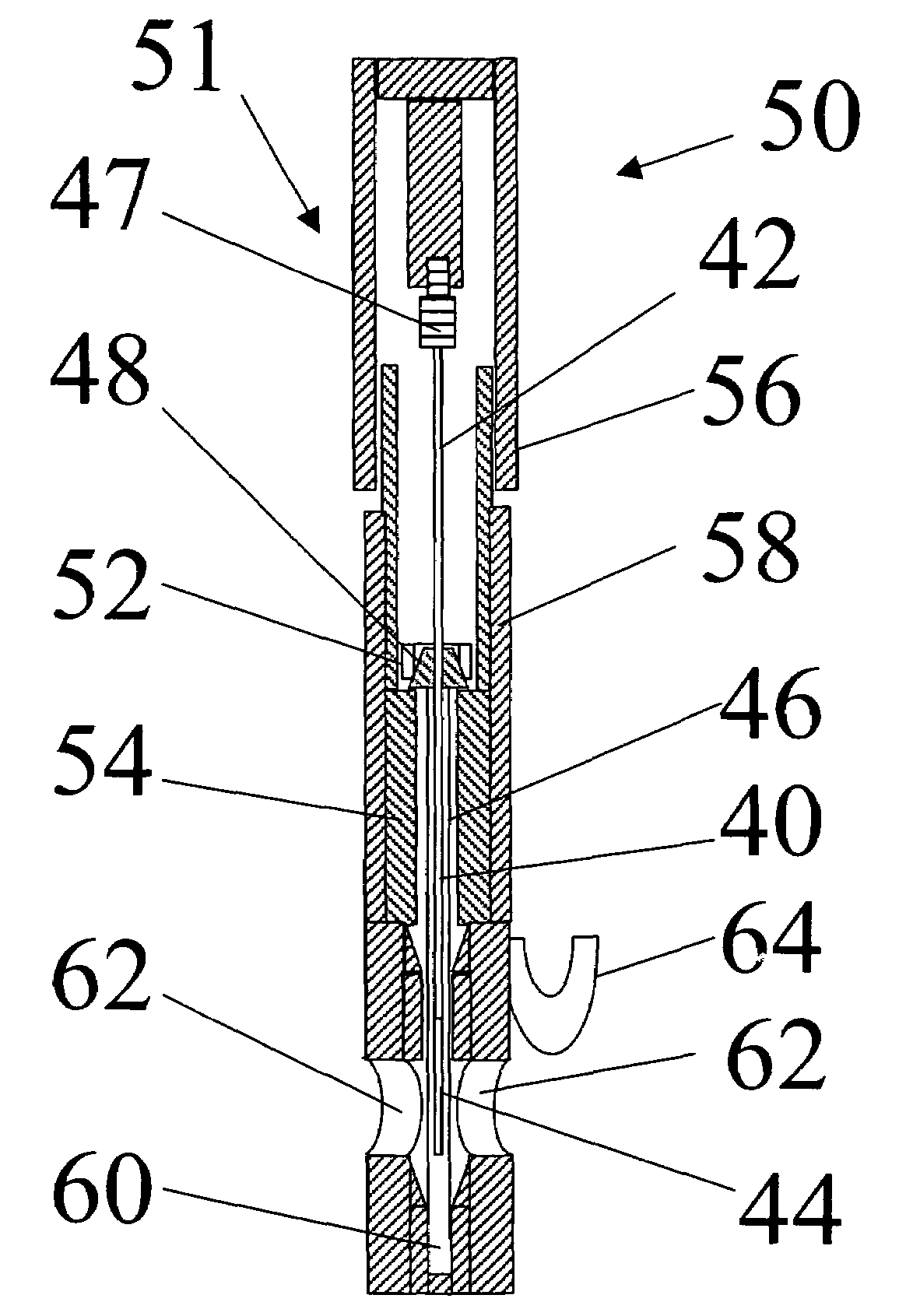
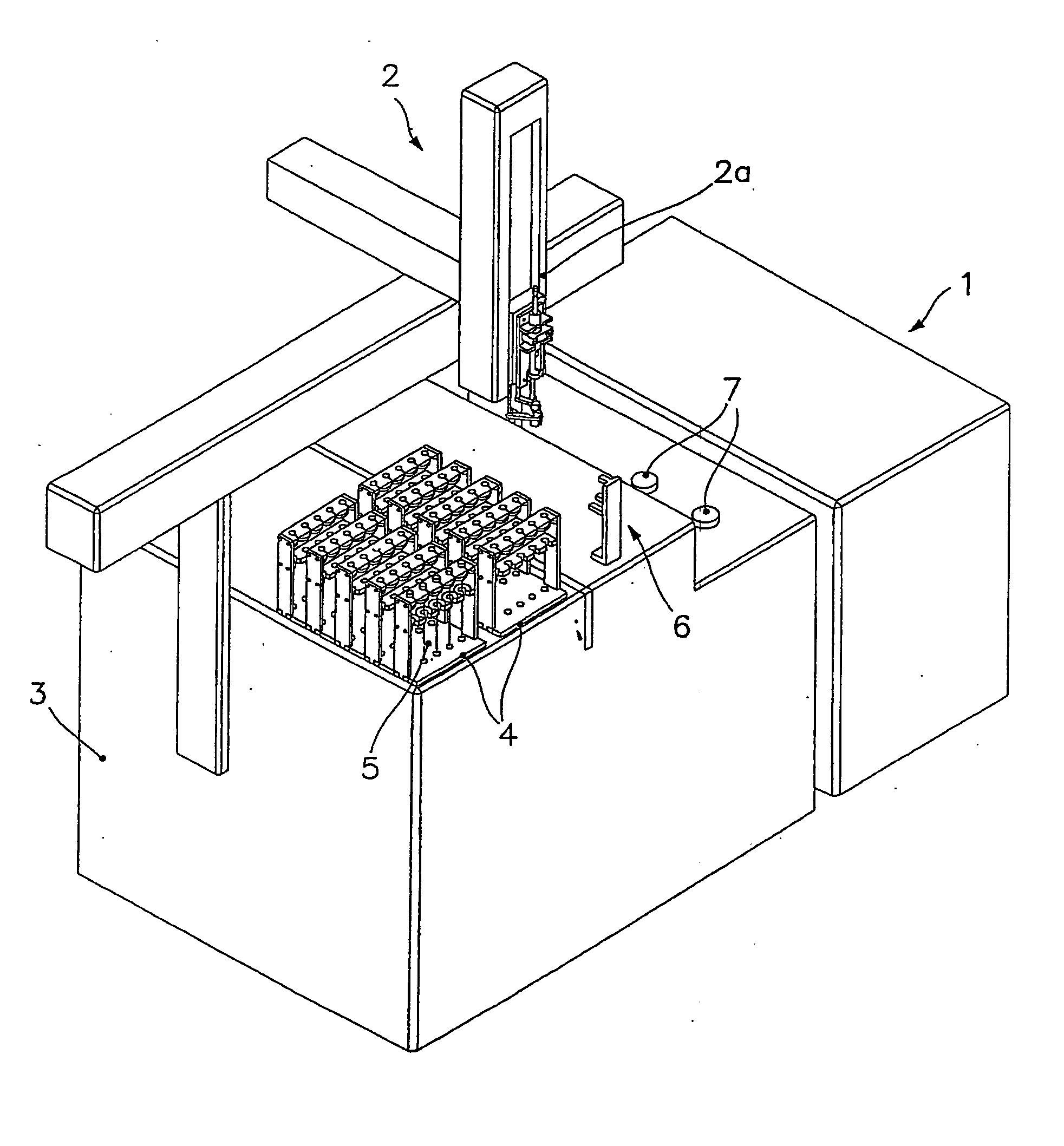
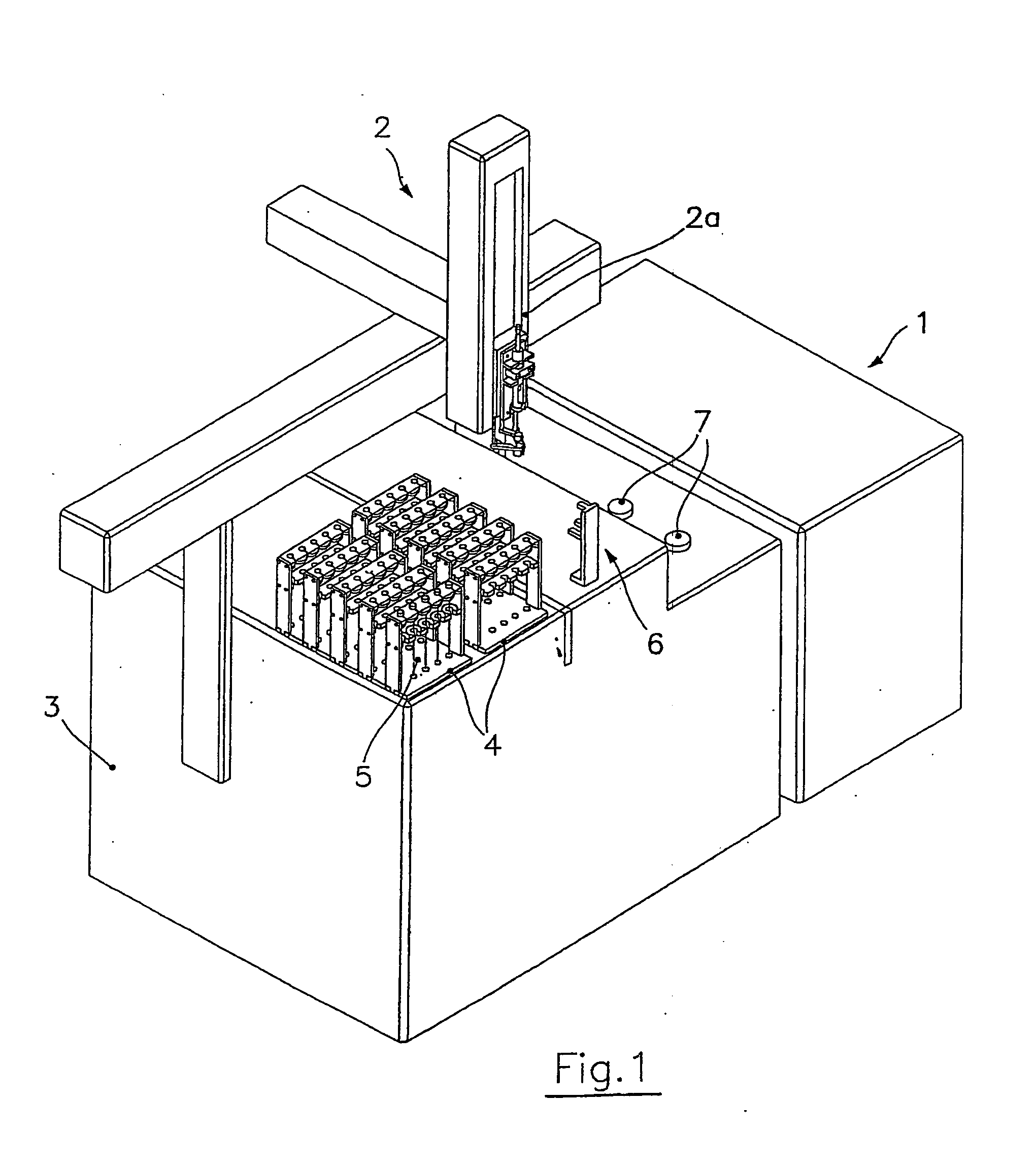
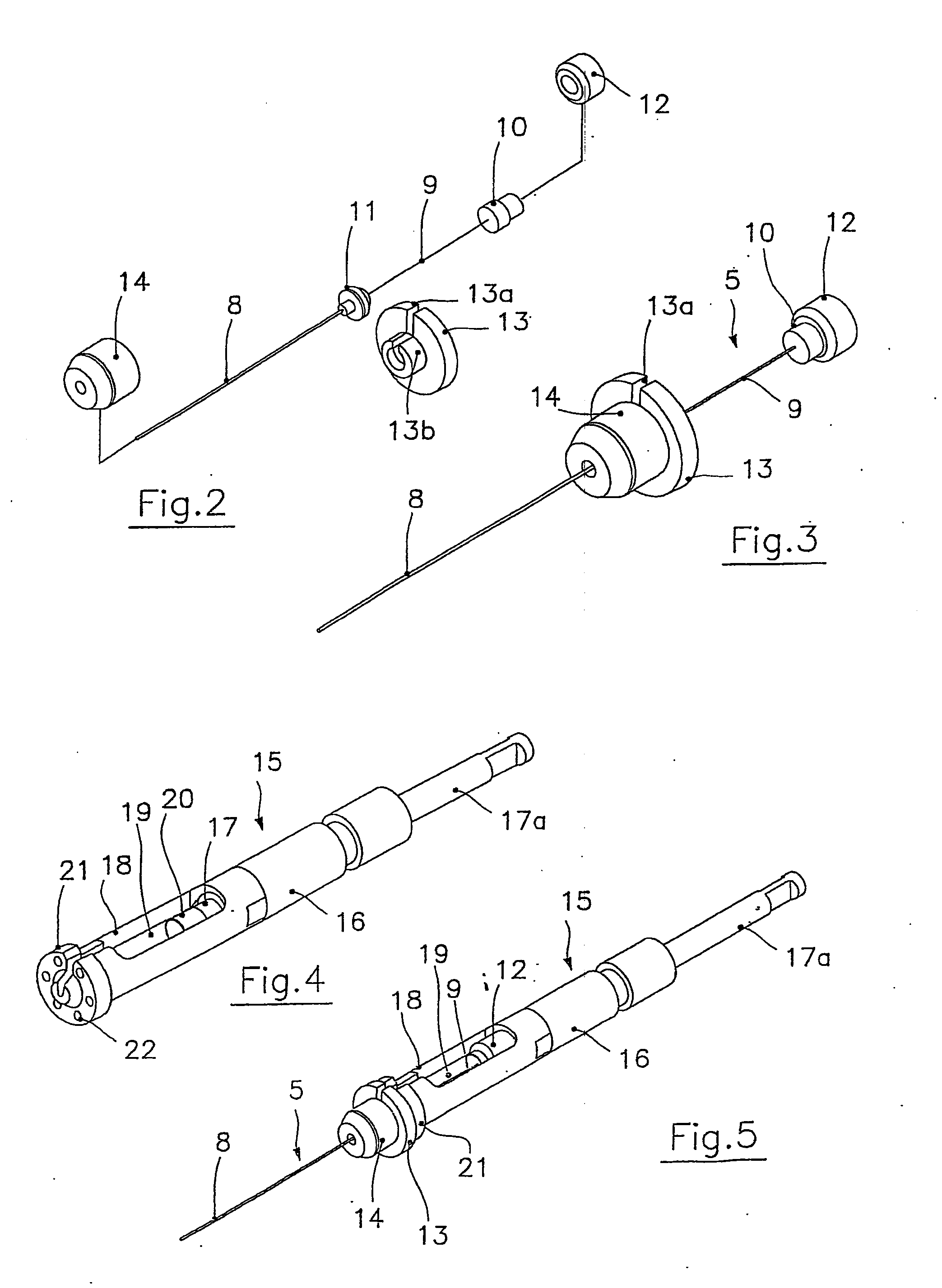
Automatic solid Phase Microextraction (Spme) Sampling Apparatus
An automatic solid-phase microextraction (SPME) sampling apparatus having a mobile sampler arm with a holder for a probe carrying a fiber 9 and an intermediate bracket for transferring the probe between a probe storage tray and the gas chromatograph injector. In the various probe handling stages, the probes are collected by a magnetic member attached to the end of the plunger in the holder, at the free end of the holder's body and at the lower end of the block for guiding the probe needle. The magnetic member interacts with a ferromagnetic connector attached to one end of the fiber and with a ferromagnetic flange attached to the end of the needle containing the fiber in order to place the probe on the transfer bracket or remove it therefrom. The apparatus can perform analyses on fibers that have already been exposed, extract analytes from samples, and subsequently transfer them for desorption in the gas chromatograph in a fully automatic way.
Owner:DEGLI ESPOSTI FILIPPO +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com