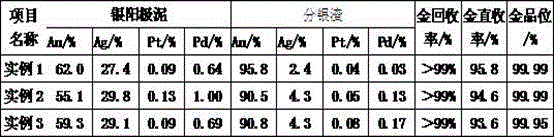
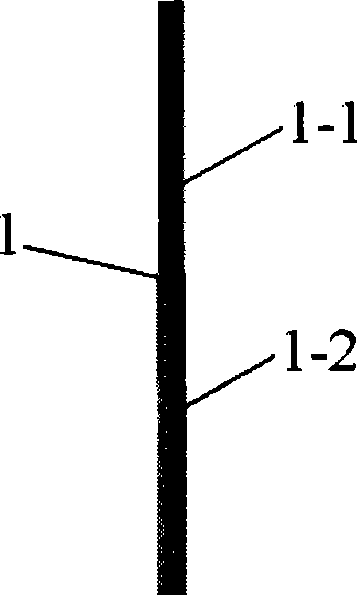
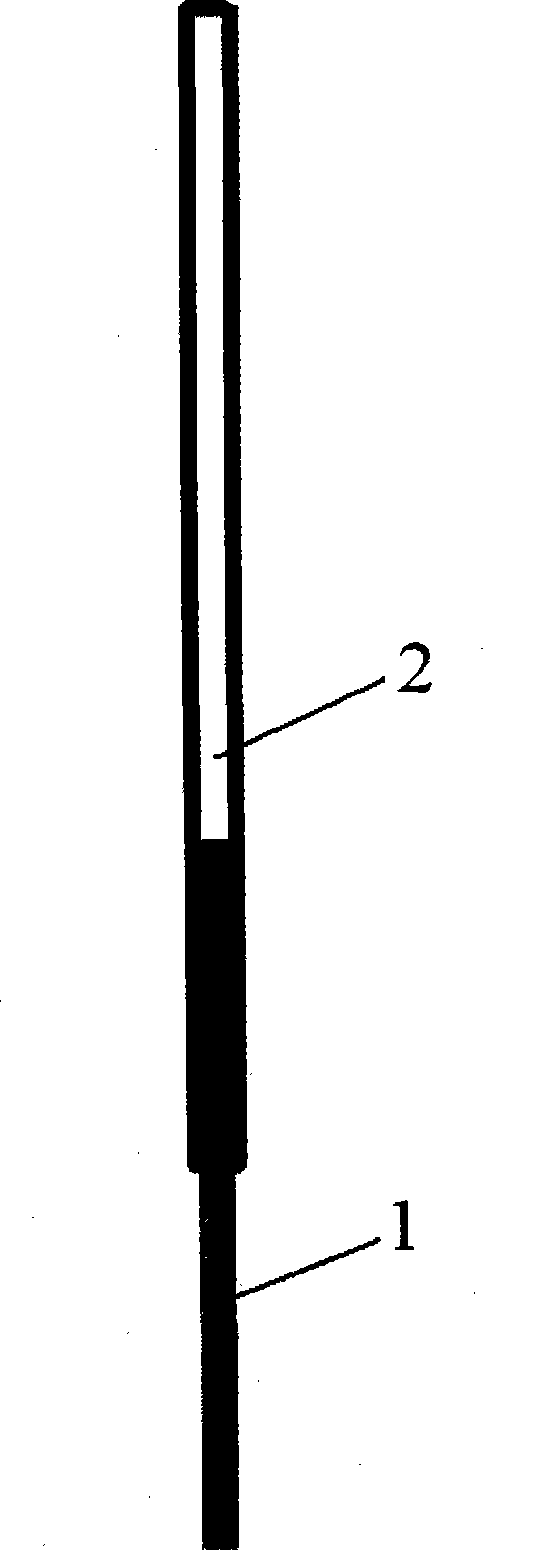
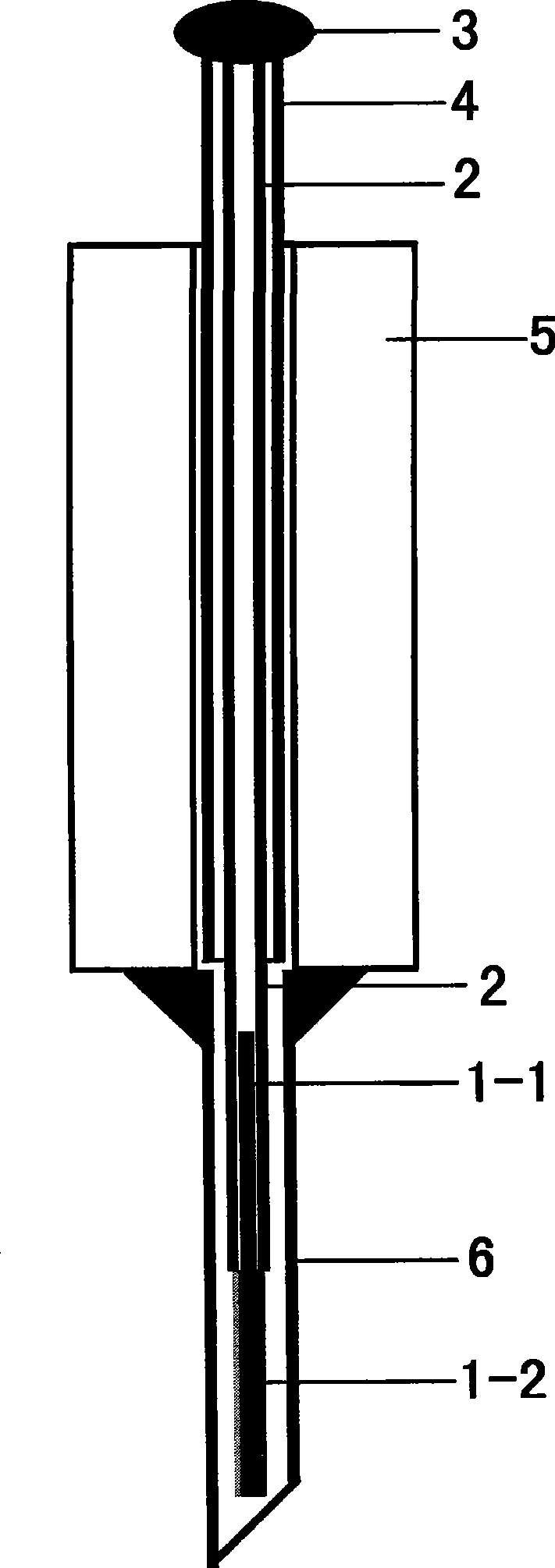
Patents
Literature
596 results about "Aqua regia" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Aqua regia (/ˈreɪɡiə, ˈriːdʒiə/; from Latin, lit. "regal water" or "king's water") is a mixture of nitric acid and hydrochloric acid, optimally in a molar ratio of 1:3. Aqua regia is a yellow-orange (sometimes red) fuming liquid, so named by alchemists because it can dissolve the noble metals gold and platinum, though not all metals.
Reclamation of a Titanosilicate, and Reconstitution of an Active Oxidation Catalyst
InactiveUS20080064591A1Acceptable product selectivityAcceptable selectivityMolecular sieve catalystsOther chemical processesCatalytic metalTitanium
A method of reclaiming a titanosilicate from a deactivated or spent oxidation catalyst containing a titanosilicate having deposited thereon one or more catalytic metals, such as gold, and optionally, one or more promoter metals, the method involving treating the deactivated catalyst with an oxidant; contacting the oxidant-treated catalyst with acid, preferably aqua regia; washing the titanosilicate to remove residual acid; and optionally drying and / or calcining. A method of reconstituting an active oxidation catalyst from a spent or deactivated oxidation catalyst, the method involving reclaiming the titanosilicate as noted above, and then depositing one or more catalytic metals and, optionally, one or more promoter metals onto the reclaimed titanosilicate.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Regenerating method and process for recycling rare precious metals from electronic wastes
ActiveCN103397186AAdvanced technologyLow costProcess efficiency improvementMagnetic separationTelevision setHigh voltage
The invention discloses a regenerating method and process for recycling rare precious metals from electronic and electric wastes, and particularly discloses a process for recycling non-ferrous and rare precious metals such as copper, tin, gold, silver, platinum, palladium, rhodium and the like from electronic wastes. The regenerating method comprises the following steps of: smashing circuit boards and elements dismounted from waste electronic and electric appliances such as waste computers, waste mobile phones, waste televisions and the like to 40-200 meshes; dissolving a binder by using an organic solvent; then, separating metals and nonmetals by using a high voltage electrostatic method; next, leaching the precious metals by using sulfuric acid and aqua regia; extracting silver, gold, platinum, palladium and rhodium step by step by using a liquid membrane; and finally, carrying out purification treatment to obtain nonferrous metals such as copper and tin and the rare precious metals such as gold, silver, platinum, palladium, rhodium and the like, so that the waste secondary resource is regenerated and recycled. The regenerating method has the advantages of simplicity and convenience in process, high comprehensive metal recycle ratio, few three wastes, easiness for treatment and low cost, is a favorable technical approach for efficient utilization of mineral resources of cities, and not only has an environment-friendly benefit, but also has favorable economic and social benefits.
Owner:HUNAN TONGLI ELECTRONICS WASTE RECOVERING DISSEMBLING & UTILIZATION
Method for recovering valuable metals from waste printed circuit board
ActiveCN101787547ASolve pollutionReduce energy consumptionPhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementElectrolysisFiltration
The invention discloses a method for recovering valuable metals from a waste printed circuit board. The method comprises the following steps: sorting and crushing the printed circuit board, evenly mixing powder containing multiple metal parts with a fluxing agent, and smelting at low temperature for 1-3.5h; adding hot water into smelting products for leaching; evaporating and concentrating filtrate after filtration, and then returning evaporation mother liquor to the water leaching process step; using solution after leaching for swirl electrodeposition of metal silver, and adding 5-25% of HNO3 into filter residue for leaching; filtering the solution after electrodeposition, and adding 1-5 times of the weight of aqua regia into the filter residue for leaching; using the solution after leaching by the aqua regia for the swirl electrodeposition of gold, adding saturated NH4Cl into the solution after the electrodeposition for reaction, then filtering, using ammonium chloroplatinate for refining the filter residue, obtaining sponge platinum, adding methanoic acid into the solution after precipitation, and carrying out reaction for obtaining crude palladium powder. The method can extract copper, nickel, silver, gold, platinum, palladium and other main products and other by-products, realize the maximization of reutilization of value metal resources in the waste printed circuit board and solve the environmental pollution problem; and the adoption of the swirl electrolysis technology can realize low energy consumption, low reagent consumption, short process flow and simple operation.
Owner:HUNAN JIANG YE MECHANICAL & ELECTRICAL TECH CO LTD
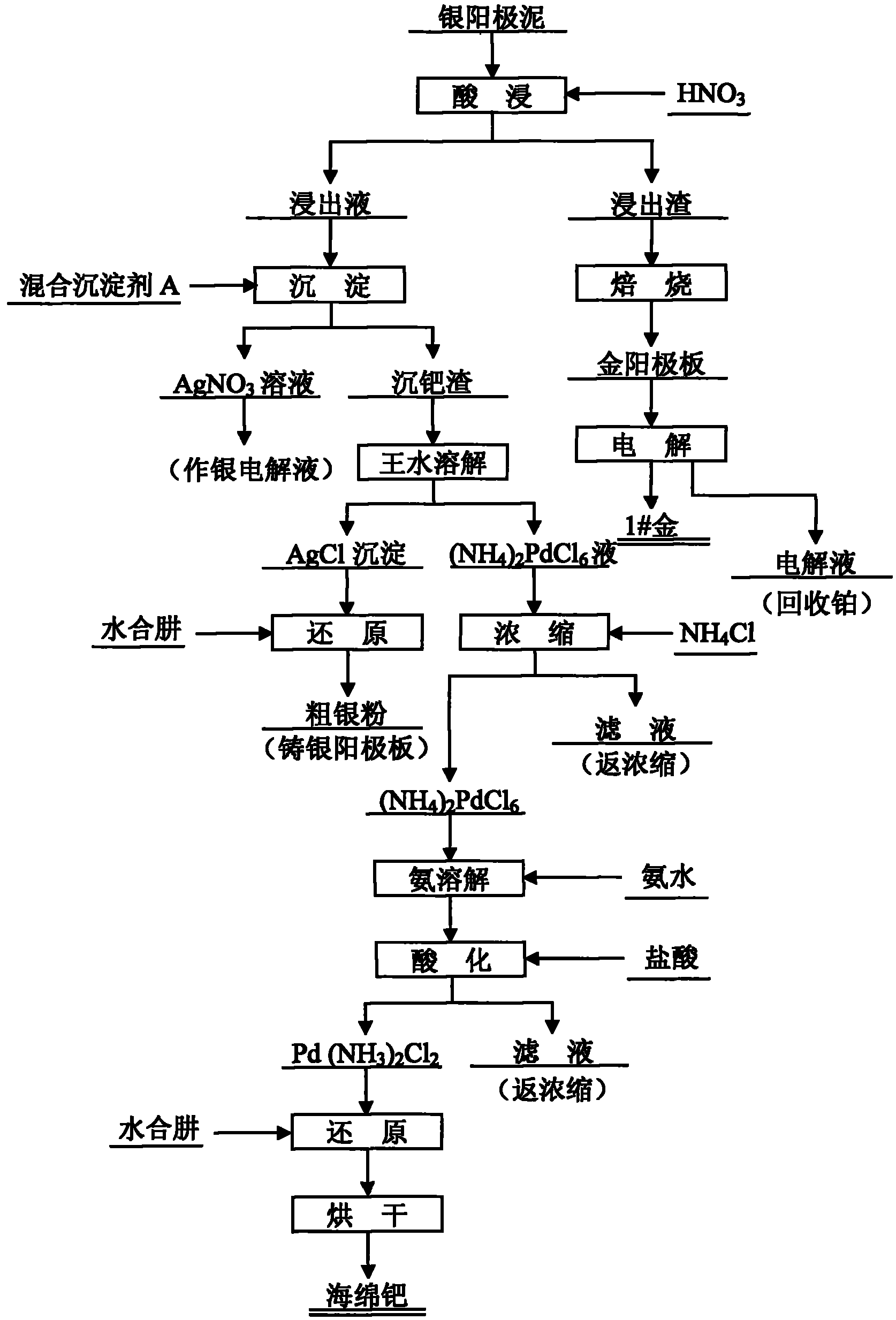
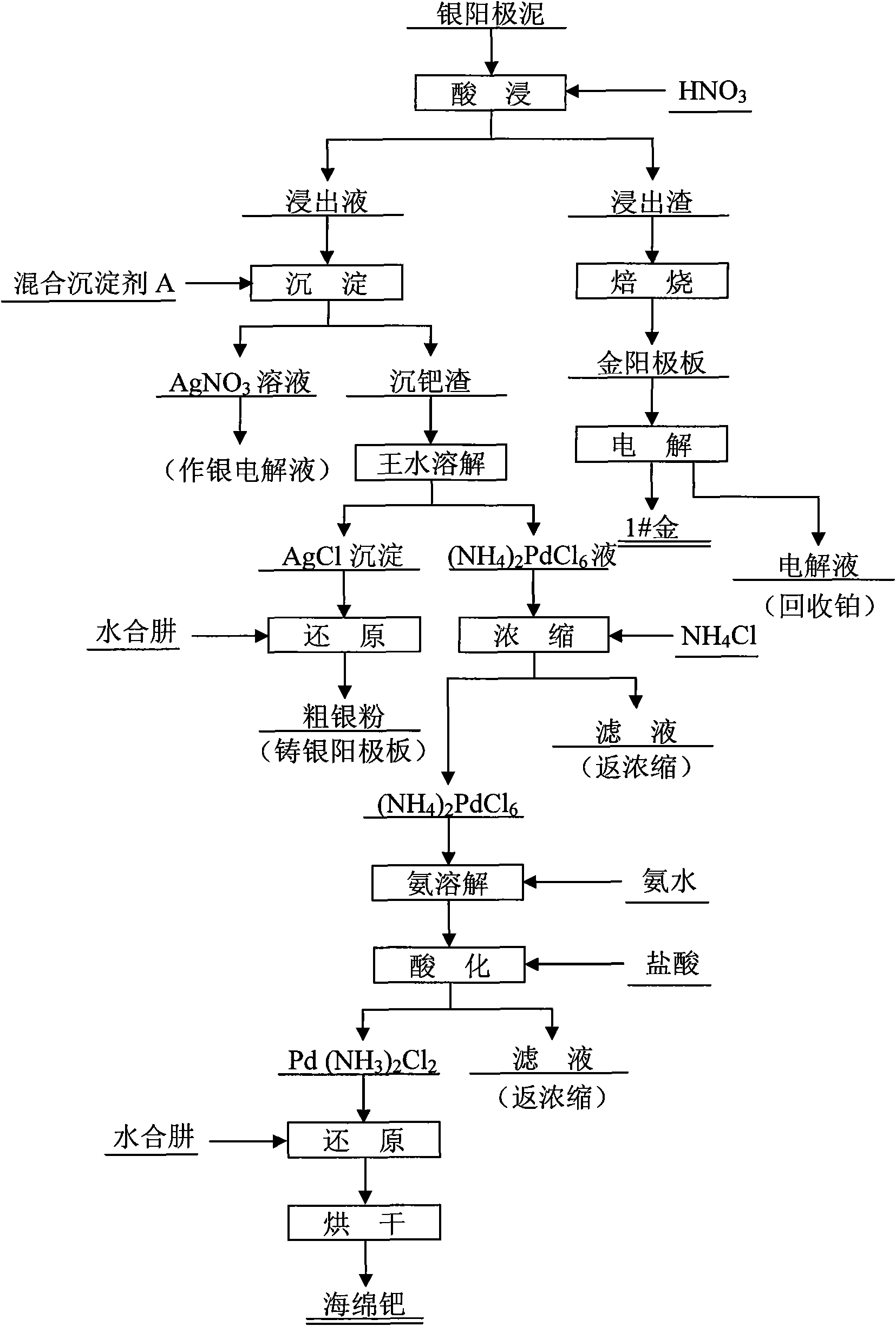
Silver anode mud treatment process
InactiveCN102041393AReduce lossLow costPhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementElectrolysisDissolution
The invention relates to a silver anode mud treatment process. The process is characterized by leaching silver anode mud with nitric acid, wherein silver, palladium and base metals enter into solution while gold and platinum remain in residue; after roasting the leaching residue and removing impurities, using a cast gold anode plate to electrolyze the leaching residue to obtain gold No. 1 and using electrolyte for recycling platinum; regulating the pH value of leachate and adding mixed precipitator A solution to selectively precipitate palladium to obtain palladium precipitate residues; solution after palladium precipitation mainly being AgNO3 solution and returning the AgNO3 solution to undergo silver electrolysis; dissolving the palladium precipitate residues with aqua regia and filtering the dissolved solution to obtain the filter residue which is mainly AgCl, reducing the filter residue with hydrazine hydrate to obtain crude silver powder and returning the crude silver powder to a cast silver anode plate; and concentrating and carrying out ammonium on the solution after dissolution to obtain (NH4)2PdCl6 precipitate, dissolving the (NH4)2PdCl6 precipitate with ammonia and acidizing the (NH4)2PdCl6 precipitate with hydrochloric acid to obtain Pd(NH3)2Cl2 precipitate, then reducing the Pd(NH3)2Cl2 precipitate with hydrazine hydrate and then drying the reduction product to obtain spongy palladium, wherein the produced filtrate is returned to the concentration process. The invention has the advantages of less precious metal loss, low cost, strong practicability, high comprehensive recoverability and obvious economic benefit.
Owner:CHENZHOU CITY JINGUI SILVER IND CO LTD
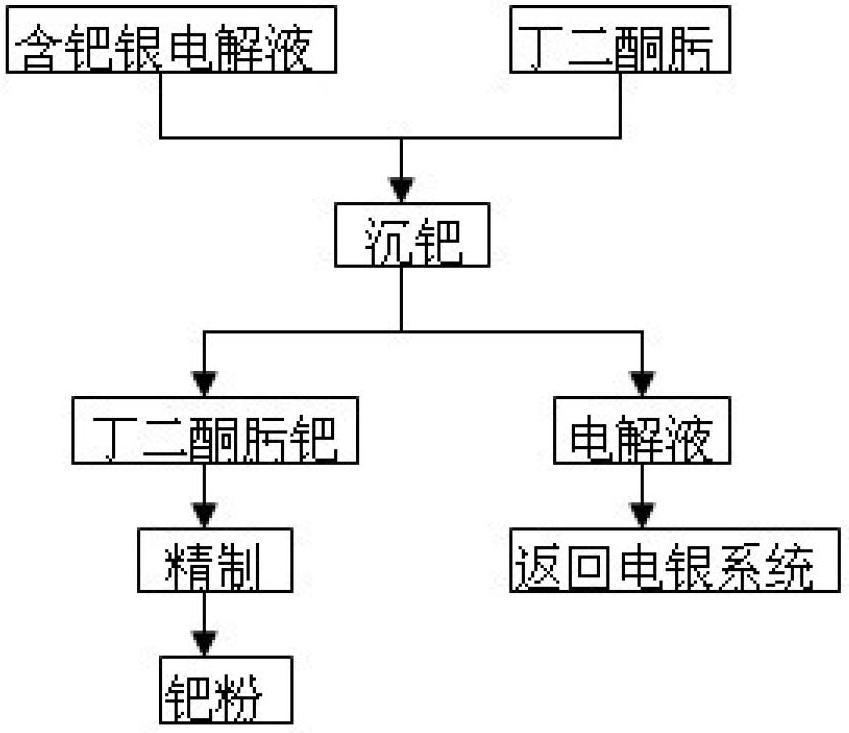
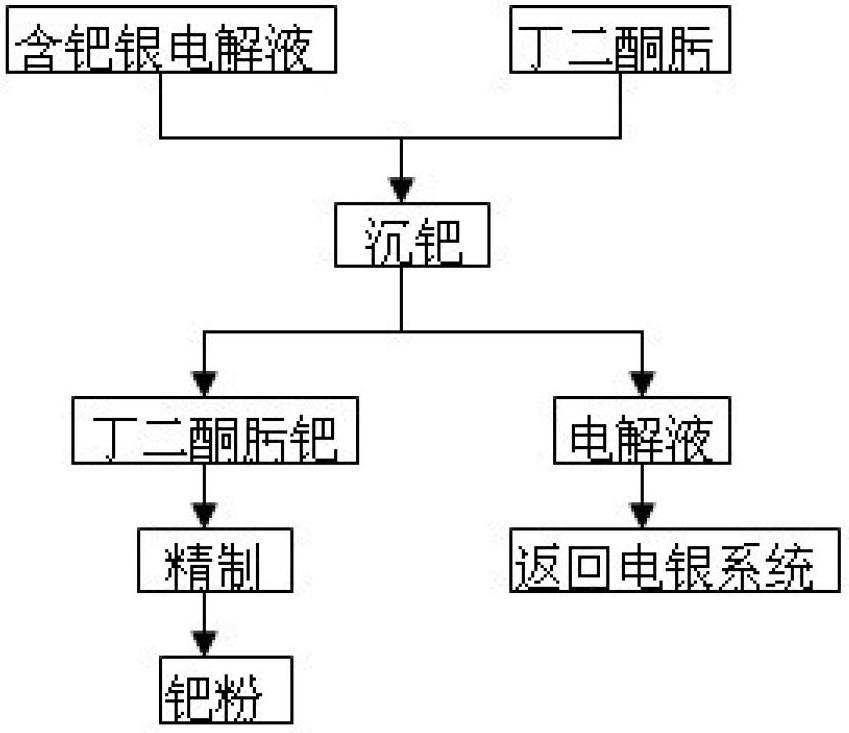
Method for recycling palladium from silver electrolyte by using dimethylglyoxime
InactiveCN102676837ANo heating requiredSimplify operating proceduresProcess efficiency improvementElectrolyteEthanol
The invention discloses a method for recycling palladium from a silver electrolyte by using dimethylglyoxime. The method comprises the following steps: adding dimethylglyoxime into a palladium-containing electrolyte for precipitating palladium; performing solid-liquid separation, returning filtrate as an electrolyte, and eluting filter residue with nitric acid acidification water to obtain a dimethylglyoxime palladium crude product; dissolving the dimethylglyoxime palladium crude product with aqua regia, and then precipitating palladium with ammonium chloride; eluting an obtained ammonium chloropalladate precipitate with an ammonium chloride solution until filtrate is colorless; and adding water, heating, and dissolving; filtering, and cooling filtrate; adding ammonia water, complexing and dissolving; cooling, filtering, and eluting the filter residue with ammonia water; adding hydrochloric acid for acidifying filtrate; filtering to obtain a diammonium dichloropalladite precipitate; and reducing the precipitate by hydrazine hydrate to obtain palladium sponge with the grade of 99.99%. Heating and pH regulation are not required, and only quantitative precipitation of palladium is required; the selectivity is good; and the precipitated dimethylglyoxime palladium can achieve a very high purity after simple eluting, so that the palladium purifying process is greatly shortened and the palladium recycling rate is improved; the using amount of dimethylglyoxime is low; and except a small amount of ethanol, other ions are not brought, so that the reuse of the electrolyte is not affected.
Owner:SIHUI CITY HONGMING PRECIOUS METALS
Copper alloy, copper alloy plate, and process for producing the same
This invention provides a copper alloy having excellent stress relaxation resistance, comprising Ni: 0.1 to 3.0% (% by mass; the same shall apply hereinafter), Sn: 0.01 to 3.0%, and P: 0.01 to 0.3% with the balance consisting of copper and unavoidable impurities, characterized in that the content of Ni in an extraction residue after extraction separation on a filter having an opening size of 0.1 [mu]m by an extraction residue method is not more than 40% in terms of the proportion to the content of Ni in the copper alloy. In the extraction residue method, 10 g of the copper alloy is immersed in 300 ml of a methanol solution having an ammonium acetate concentration of 10% by mass. This copper alloy is used as an anode. On the other hand, platinum is used as a cathode. Galvanostatic electrolysis is carried out at a current density of 10 mA / cm<2>. A solution containing this copper alloy dissolved therein is subjected to suction filtration by a polycarbonate membrane filter having an opening size of 0.1 [mu]m, and the insolubles as the residue are separated and extracted on the filter. The content of Ni in the extraction residue is determined by dissolving the insolubles as the residue on the filter in a solution composed of a mixture of aqua regia and water at a ratio of 1 : 1, and then analyzing the solution by ICP emission spectrometry.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
Method for reducing surface light reflectivity of silicon chip
InactiveCN102157608AReduce light reflectivityDoes not affect the preparation processFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesHydrofluoric acidSilicon chip
The invention discloses a method for reducing the surface light reflectivity of a silicon chip, and the method comprises the following steps: step 1): immerging the silicon chip into mixed solution of hydrofluoric acid and salts containing Ag ions, Cu ions, Ni ions or Mg ions for etching; and step 2): placing the silicon chip after etching into nitric acid or aqua regia for ultrasonic cleaning so as to remove a metal covering object on the surface. The method is simple in process, low in cost, convenient to operate and extensive in application conditions, the complex process is not required, the average light reflectivity of the silicon chip can be reduced to below 5% through only one step, and the method is suitable for large-scale industrial production.
Owner:INST OF PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for forming self-aligned metal silicide contacts
InactiveUS20070254479A1Minimizes deleterious formation of residual materialReduce riskSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEtchingPlatinum silicide
The present invention relates to a method for forming self-aligned metal silicide contacts over at least two silicon-containing semiconductor regions that are spaced apart from each other by an exposed dielectric region. Preferably, each of the self-aligned metal silicide contacts so formed comprises at least nickel silicide and platinum silicide with a substantially smooth surface, and the exposed dielectric region is essentially free of metal and metal silicide. More preferably, the method comprises the steps of nickel or nickel alloy deposition, low-temperature annealing, nickel etching, high-temperature annealing, and aqua regia etching.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Preparation of solid-phase microextraction (SPME) fiber and extraction device assembled by same
InactiveCN102989432AOvercoming the problem of poor mechanical strengthUnique designComponent separationOther chemical processesSolid-phase microextractionMetal-organic framework
Disclosed is a preparation of an SPME fiber. A covalent bond method is adopted to prepare metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) as a coating for the extraction fiber. The fiber preparing method includes performing APTES amino-functionalization on a quartz fiber, namely, placing the fiber with amino on the surface into an MOF solution for reaction. An extraction device assembled by the prepared SPME coating comprises a device body, a microsyringe outer tube, a microsyringe needle, a push-pull rod and the extraction fiber with the coating, wherein the push-pull rod is arranged in the microsyringe outer tube and forms a sliding matching with the inner wall of the tube, the lower end of the push-pull rod is corroded by an aqua regia solution to obtain a corrosion end which is inserted into the extraction fiber with the coating, and a handle is arranged at the upper end of the push-pull rod. The preparation and the device have the advantages that an organic ligand of the extraction fiber coating and the MOFs is highly ordered and controllable, the extraction device has a novel structure, the coating fiber fixation is firm, and the stability and service life of the extraction fiber coating are improved.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Silicon waste-slice surface metal removal and noblemetal silver-platinum-gold recovery method
InactiveCN1851016AEfficient removalEasy to recycleProcess efficiency improvementCleaning using liquidsRecovery methodMetal impurities
The invention discloses the method of wiping off the exterior metal of the silicon abandoned piece and reclaiming the noble metal platinum. The semiconductor parts of an apparatus and the semiconductor integrate circuit abandoned silicon piece are dipped in the hydrochloric acid or the dilute vitriol to wipe off the metal alive than the hydrogen, the nitric acid is used to melt the cooper or the silver on the silicon piece, the combination of thick hydrochloric acid and the thick nitric acid is used to melt the gold and the platinum on the surface of the silicon piece, then the combination of the hydrofluoric acid and the nitric acid is used to melt the metal silicon material on the surface of the silicon piece, the material silicon piece is gained with the cleaning, the drying or the setting off. The metal alive than the hydrogen is added in the said silver nitrate solution to gain the silver by the permutation, the aqua regia containing the gold and the platinum is heated or is added the alkali to get rid of the excessive hydrochloric acid and the nitric acid, the copper is added in the residual solution to gain the gold or the platinum by the permutation. The invention can wipe off the metal impurity and the metal silicon material on the surface of the abandoned silicon piece effectively, the disposed silicon piece can be used for the material of the sun energy silicon single crystal, the solar cell silicon piece can be gained by the more process, the noble metal is reclaimed, so it is useful for circle utilize of the resource.
Owner:浙江东源电子有限公司
Method for recycling platinum and rhodium from binary aqua regia insoluble slag
InactiveCN101476044AEmission reductionImprove protectionProcess efficiency improvementIsolation effectRecovery method
The invention relates to a precious-metal recovery method, specifically relates to a method of recovering platinum / rhodium from insoluble residue of dualistic royal water for solving problems of the existing platinum / rhodium recovering method that the process flow is lengthy and complicated, operational process is dangerous, the isolation effect is bad, and the like. The method comprises steps of preprocessing the insoluble residue of royal water by using barium superoxide, oxidizing the platinum and rhodium thereof, dissolving the oxidized platinum and rhodium in hydrochloric acid; using ammonium chloride to deposit platinum after being converted to a sodium type, adding hydrazine hydrate for recovering the spongy platinum, complexing by adding sodium nitrite into the filter liquor after platinum deposition, depositing rhodium by using ammonium chloride, adding hydrochloric acid for dissolving and sodium type conversion, eliminating base metal in the liquid by using ion exchange resin, finally using hydrazine hydrate and hydrogen gas flame for recovering rhodium powder. The method is a precious-metal-resource secondary recovery utilization and purification method, and has advantages of simple technique, short purification period, convenient operations, high coefficient of recovery, little discharging of waste gas and waste matter, and environment protection, and the like.
Owner:CNOOC TAIYUAN PRECIOUS METALS
Process for producing a free-standing iii-n layer, and free-standing iii-n substrate
InactiveUS20070141814A1Polycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingVapor phaseAqua regia
A process for producing a free-standing III-N layer, where III denotes at least one element from group III of the periodic system, selected from Al, Ga and In, comprises depositing on a Li(Al,Ga)Ox substrate, where x is in a range between 1 and 3 inclusive, at least one first III-N layer by means of molecular beam epitaxy. A thick second III-N layer is deposited on the first III-N layer by means of a hydride vapor phase epitaxy. During cooling of the structure produced in this way, the Li(Al,Ga)Ox substrate completely or largely flakes off the III-N layers, or residues can be removed if necessary, by using etching liquid, such as aqua regia. A free-standing III-N substrate being substantially free of uncontrolled impurities and having advantageous properties is provided.
Owner:FREIBERGER COMPOUND MATERIALS
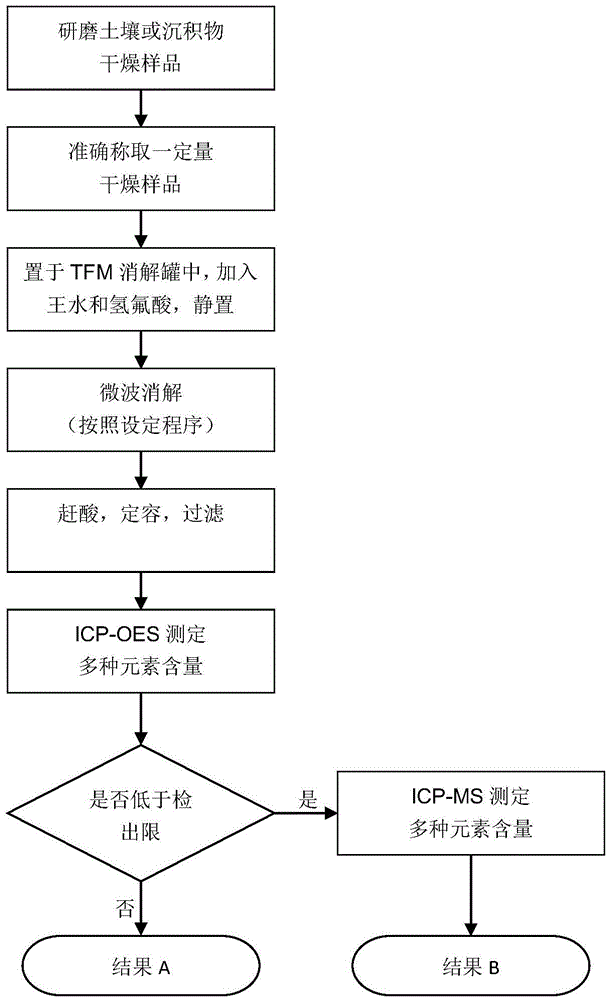
Method for simultaneously determining contents of various elements in soil or deposits
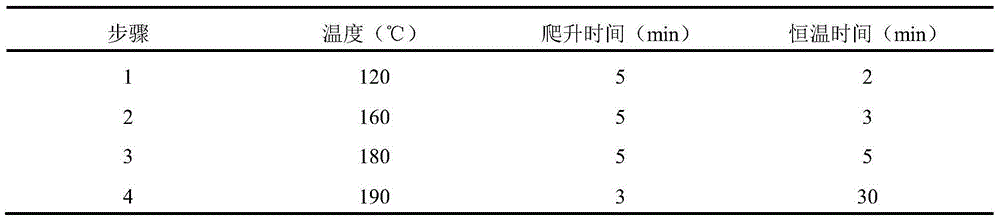
InactiveCN105606590AShorten digestion timeReduced measurement timePreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansManganeseDigestion
The invention relates to detection technology for element contents, and provides a method for simultaneously determining contents of arsenic, cadmium, lead, vanadium, zinc, manganese and phosphor in soil or deposits. The method mainly comprises the following steps: (1) 0.1g of a grinded drying soil sample is accurately weighed and placed in a TFM microwave digestion pot, a certain proportion of aqua regia and hydrofluoric acid are added, and a solution is allowed to stand; (2) an appropriate microwave digestion program is set, and microwave digestion is carried out for the solution in the step (1); (3) after the microwave digestion program ends, an acid-driving device is used for heating and evaporating the digestion solution in the step (2) to a dry state, and total transfer, volumetric flask preparation, and filtering are carried out; (4) ICP-OES is used for determining contents of arsenic, cadmium, lead, vanadium, zinc, manganese and phosphor in the clear liquor in the step (3); (5) ICP-MS is used for determining contents of elements in the clear liquor in the step (3) which do not reach detection limits in the step (4) once more. The method has the advantages of simple steps, simplified operation, saved soil samples, reduced personal error, minimized environment interference, and improved working environments.
Owner:RES CENT FOR ECO ENVIRONMENTAL SCI THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method and device for preparing high-purity ruthenium
InactiveCN101797649ASolve the sintered very hardSolve the problem of high chlorine and oxygen contentVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingHydrofluoric acidHydrogen
The invention relates to a method and a device for preparing high-purity ruthenium. The method comprises the following steps that: hydrogen dioxide is added into ruthenium hydrochloride solution to be undertaken one section of oxidation distillation reaction, then oxidant is added into the liquid to be undertaken a second section of adequate oxidation distillation reaction, then the oxidation distillation is repeatedly performed to extract the ruthenium, ruthenium tetroxide gas which is discharged from the second section of oxidation reaction is adequately collected, the ruthenium tetroxide gas is transformed to ruthenium hydrochloride absorption liquid, ammonium chloride is added into the ruthenium hydrochloride absorption liquid to be crystallized and precipitated, and the prepared ammonium chloride ruthenium precipitant is calcined and reduced to sponge ruthenium under the atmosphere of hydrogen; and the prepared sponge ruthenium is dried under the atmosphere of the hydrogen after being boiled and washed by mixed acid of aqua regia and hydrofluoric acid to obtain the high-purity ruthenium.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY
Method for preparing high pure gold and enriching silver, platinum and palladium from silver anode mud
ActiveCN106119554AHigh removal rateHigh gold contentProcess efficiency improvementSlagMaterials science
The invention discloses a method for preparing high pure gold and enriching silver, platinum and palladium from silver anode mud. The process of separating silver with nitric acid, recycling silver, platinum and palladium with silver-enriched liquid, decomposing silver separating slag with aqua regia and preparing high pure gold with a one-time unsaturation reduction method is adopted and comprises the steps: leaching the silver anode mud with nitric acid to obtain separated silver, adding sodium chloride into the silver separating liquid to deposit the silver to obtain silver chloride sediment and silver depositing liquid, adding iron powder into the silver chloride sediment for replacement, returning the crude silver back to a Kaldo furnace for melting, and adding sodium hydrogen sulfite into the silver depositing liquid to reduce, deposit and recycle platinum and palladium; performing gold separating on the silver separating slag with aqua regia to obtain gold separating liquid and gold separating slag, performing the iron powder replacement step on the gold separating slag, adding the sodium hydrogen sulfite into the gold separating liquid to perform unsaturation reduction to obtain gold powder and gold depositing liquid, washing, drying and ingotting the gold powder to obtain a product gold ingot, and adding the sodium hydrogen sulfite into the gold depositing liquid to reduce and recycle the platinum and palladium for the second time to obtain the crude gold powder, and returning back to the previous steps. The method solves the problems of long leaching flow, high agent cost, complex operation, more devices and low recycle rate of the silver anode mud.
Owner:ZIJIN MINING GROUP
Solid phase micro-extraction device and method for preparing fibre extraction head thereof
InactiveCN101496958AIngenious ideaUnique designIon-exchange process apparatusIon-exchanger regenerationMetal fiberSolid-phase microextraction
The invention relates to a solid phase micro-extraction device and a method for preparing a fiber extraction head thereof. The solid phase micro-extraction device comprises a micro sample injector, the inside of a sample injector push rod is provided with a stainless steel capillary pipe, and the lower end of the sample injector push rod is inserted with the fiber extraction head. The preparation method for the fiber extraction head comprises: corroding one end of a metal fiber into aqua regia, while corroding the other end in HF; dissolving metal salt and organic ligand in a solvent in a hot water reaction kettle to obtain a reaction mixed liquor; and immerging the one end of the metal fiber corroded by the HF after pretreatment into the reaction mixed liquor, and controlling the temperature to between 50 and 220 DEG C and the time to between 6 and 90 hours to prepare the solid phase micro-extraction head of which the surface is grown with metal organic porous skeleton materials in situ. The solid phase micro-extraction device has the advantages of difficult damage of extracted fibers, high temperature resistance, low cost, good extraction performance, capability of replacing the extraction head, and large adsorption capacity. The method can grow porous skeleton materials with different structures on the extraction head aiming at different compounds so as to design high-selectivity enrichment to a target object, and has wide application prospect in the aspect of analytical chemistry.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
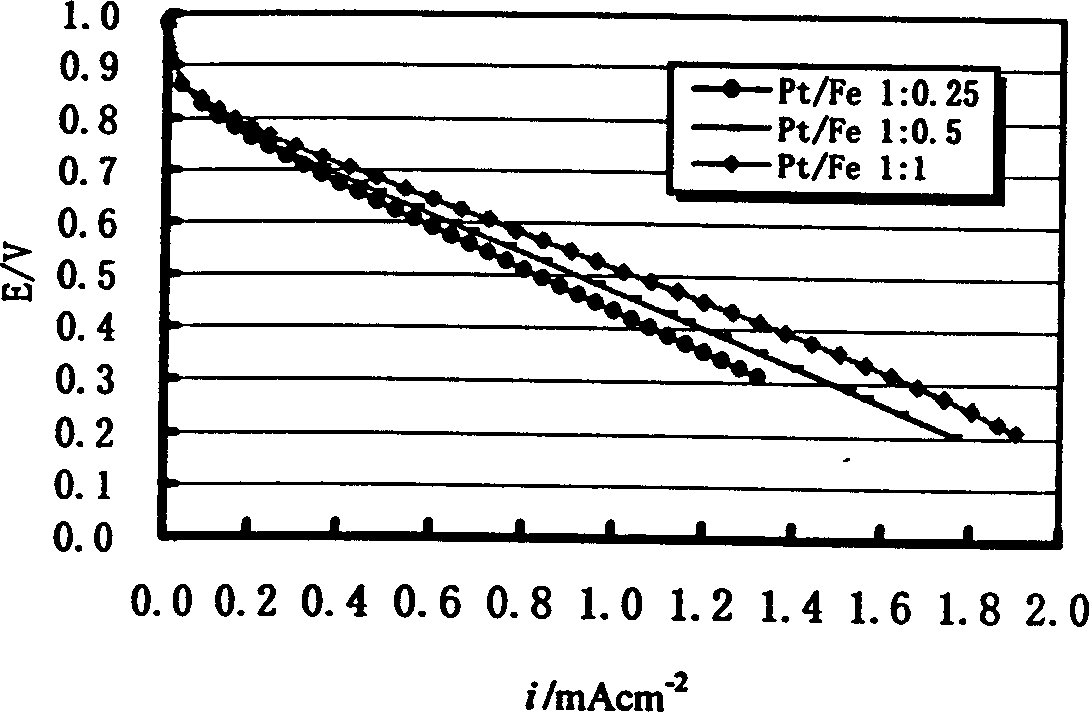
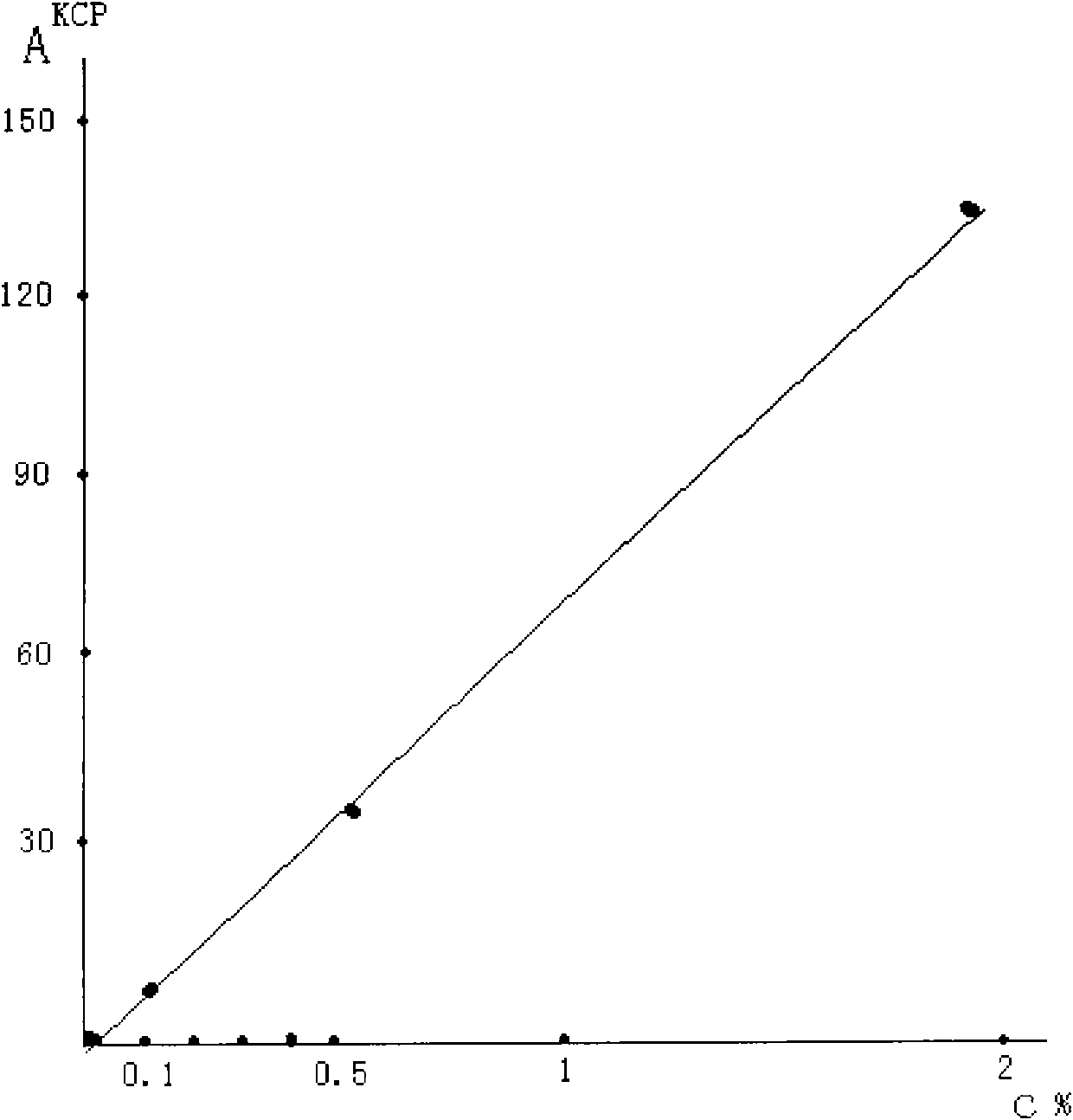
Carbon-bearing platinum-iron alloy electrocatalyst for PEM electrolyte fuel cell and its preparing method
This invention provides a carbon carrying PtFe alloy electric catalyst and its preparation method used in PEM electrolyte fuel cell electrode with Pt solution dissolved with aqua regia as the precursor and Fe as doped element to be uniformly deposited on the carbon powder carrier in liquid phase, then to carry out gas / solid reduction reaction in high temperature reduction farness with hydrogen asthe reducing agent to make Pt and Fe form carbon carrying PtFe electric catalyst uniformly distributed on the carbon carrier in the size small than 5nm.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
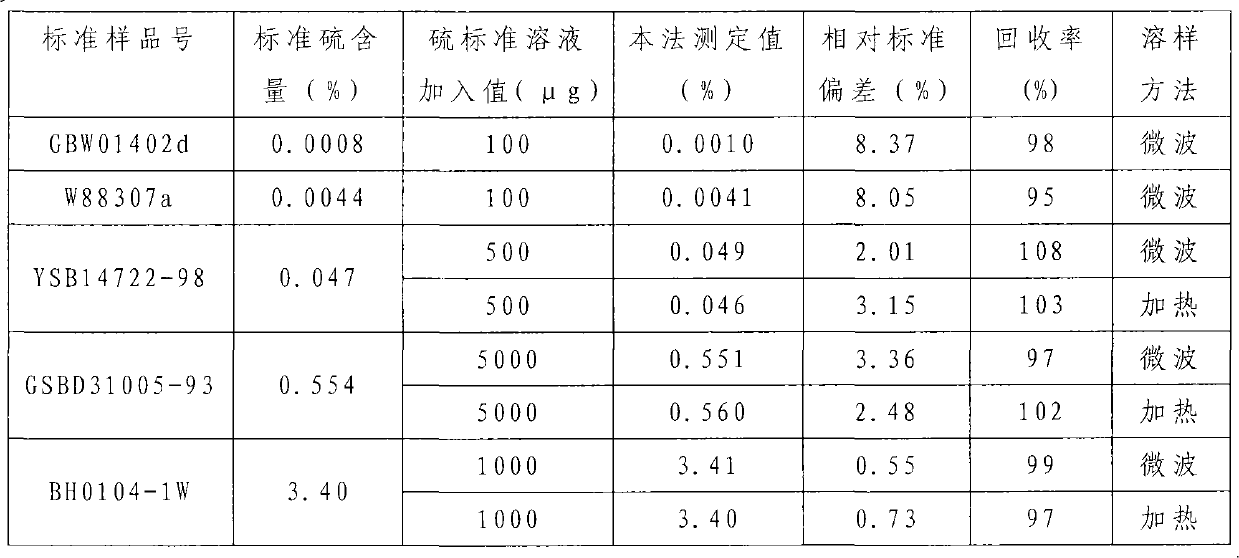
Method for measuring sulfur content in iron ore
InactiveCN101793830AReduce matrix effectImprove accuracyAnalysis by thermal excitationIronstoneMicrowave
The invention discloses a method for measuring sulfur content in iron ore. The method comprises the following steps: dissolving a sample in aqua regia by heating or using microwave to obtain the solution to be measured; measuring the spectral intensity of three or more types of ferrum-based solution of which the known sulfur content ranges comprise the sulfur content of the sample by using ICP-OES; establishing a calibration curve; measuring the spectral intensity of the solution to be measured; and performing regression calculation according to the calibration curve to obtain the sulfur content in the solution to be measured. Because the ICP-OES has the characteristics of wide linear detection range, high sensitivity, and accuracy, by using the method, the sulfur content over 0.0005 percent in the iron ore can be measured. Simultaneously, when the calibration curve is established, a matrix effect of an iron matrix can be eliminated by performing matrix matching, so that the measurement result is more accurate and reliable. In addition, in the method, the sample is dissolved by heating or using microwave, so that the method is more scientific and accurate. Moreover, the method can be realized only by simply dissolving the sample, measuring, establishing the calibration curve, and performing the regression calculation by using a computer, so the method has very high practicability.
Owner:WUHAN IRON & STEEL (GROUP) CORP
Platinum refining technology
A platinum refining technology comprises the steps of platinum family metal contained concentrate (slag, secondary resources and the like) chlorination dissolving, dissolved solution acidity adjustment, organic reducing agent ammonium oxalate precipitation, and precious metal filtering separation. The technology has the characteristics of wide material adaptability and simple operation, allows ammonium chloroplatinate of a platinum family metal contained material containing ammonium chloroplatinate to be efficiently and rapidly dissolved and precipitated, and allows the dissolving efficiency, the precipitation rate and the refining recovery efficiency to reach 95-99%, 99% and 90-95% respectively in the whole refining process; and compared with a traditional ammonium chloride repeated-precipitation method, the technology effectively solves a problem that nitrogen oxide cannot be discharged in a standard reaching mode, and eliminates the problems of large labor intensity of a aqua regia dissolved solution nitrate removing process and low production efficiency. The reducing agent ammonium oxalate is an organic reagent, and reacts to generate a pollution-free gas which can be directly discharged in the reaction process, so a solution system is not changed, thereby no influences on subsequent platinum precipitation by ammonium chloride are caused, and the yield and the quality of platinum family metal products are substantially improved.
Owner:JINCHUAN GROUP LIMITED
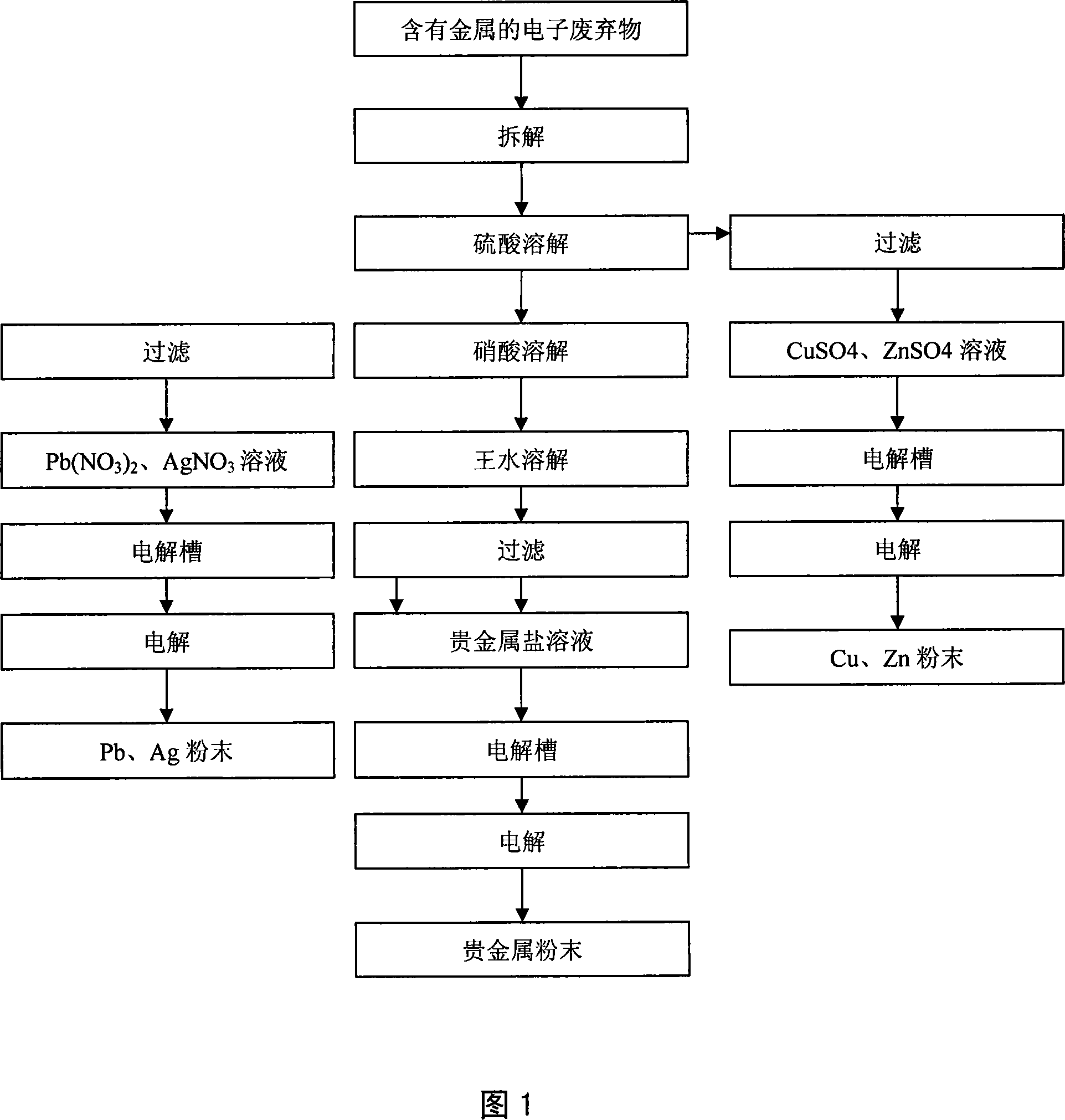
Method for reclaiming metals by classified electrolysis of electron wastes
InactiveCN101230470AHigh recovery rateLess investmentPhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementElectrolysisDecomposition
The invention relates to a method of recovering metal from electronic waste through a stepped electrolyzation and belongs to the field of electronic waste recovery processing technology. Firstly, a sulphuric acid solution, a nitric acid solution and an aqua regia solution are adopted to dissolve the metallic elements in the electronic waste step by step; secondly, a sulfate solution, a nitrate solution and a precious metal saline solution are obtained after the solutions are filtered; and thirdly, the electromotive force of the electrodes is regulated according to the decomposition voltages of the metallic ions, for different metallic ions have different decomposition voltages. Single metallic substances of Cu, Zn, Pb and Ag, the Au precious metal alloy and the Pt precious metal alloy are extracted through a stepped (from low to high) electrolyzation. The current density is 200 to 1000 A / m<2>, the electrolytic temperature is 20 to 60 DEG C, carbon or Pt is adopted as the anode material, and stainless steel, carbon or Pt is adopted as the cathode material. The invention has the advantages that the investment is small, the technique is simple, the process flow is short, the pollution is light, the metal recovery rate is high and the recovery cost is low. The invention is fit for industrialisation series manufacturing.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Copper alloy, copper alloy plate, and process for producing the same
InactiveUS20090116996A1High stress relaxation resistanceImprove bending performanceElectrolysisFiltration
A copper alloy with an excellent stress relaxation resistance including Ni: 0.1 through 3.0 mass %, Sn: 0.01 through 3.0 mass %, P: 0.01 through 0.3 mass % and remainder copper and inevitable impurities, and the Ni content in extracted residues separated and left on a filter having filter mesh size of 0.1 μm by using an extracted residues method accounting for 40 mass % or less of the Ni content in the copper alloy, wherein the extracted residues method requires that 10 g of the copper alloy is immersed in 300 ml of a methanol solution which contains 10 mass % of ammonium acetate, and using the copper alloy as the anode and platinum as the cathode, constant-current electrolysis is performed at the current density of 10 mA / cm2, and the solution in which the copper alloy is thus dissolved is subjected to suction filtration using a membrane filter of polycarbonate whose filter mesh size is 0.1 μm, thereby separating and extracting undissolved residues on said filter, and the Ni content in the extracted residues is identified through analysis by ICP after dissolving said undissolved residues separated and left on said filter into a solution prepared by mixing aqua regia and water at the ratio of 1:1.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
Method for preparing raw material for vapor-method aluminum nitride crystal growth
InactiveCN103643295AFulfil requirementsPolycrystalline material growthFrom condensed vaporsGas phaseSingle crystal
The invention discloses a method for preparing a raw material for vapor-method aluminum nitride crystal growth. The method comprises the specific steps of soaking a tungsten crucible and a crucible cover which are required to be used in aqua regia for 30-120 minutes, taking out the tungsten crucible and the crucible cover, cleanly flushing, and drying for later use; adding aluminum nitride powder into the tungsten crucible, and carrying out multi-layer compacting treatment; covering the tungsten crucible with the crucible cover, putting in a tungsten-mesh heating furnace, vacuumizing until the pressure is 1*10<-3>Pa, inflating with high-purity nitrogen gas until the pressure is 30kPa, heating to the temperature of 300 DEG C, keeping the temperature constant for 1 hour, heating to the temperature of 800 DEG C, and keeping the temperature constant for 1 hour; inflating the tungsten-mesh heating furnace with high-purity nitrogen gas until the pressure is 50kPa, heating to the temperature of 1800 DEG C, keeping the temperature constant for 5 hours, heating to the temperature of 2,050 DEG C, and keeping the temperature constant for 8 hours; cooling to room temperature, thereby obtaining an aluminum nitride sinter cake which serves as the raw material for vapor-method aluminum nitride crystal growth. According to the method, a compact sintered body is prepared from the aluminum nitride powder, so as to control vapor-phase reaction, thus the requirements of RVT (Physical Vapor Transport)-method aluminum nitride crystal material growth for raw materials are met.
Owner:BEIJING HUAJINCHUANGWEI ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Preparation method of low-mercury compound catalyst for producing vinyl chloride
ActiveCN102500421AExtended service lifeGood dispersionPreparation by halogen halide additionOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsEvaporationChloride
The invention discloses a preparation method of a low-mercury compound catalyst for producing vinyl chloride, which relates to the catalyst which contains metallic mercury and nickel, and comprises the steps that: firstly a coaly carbon carrier is soaked in aqua regia, and simultaneously flows back in the aqueous solution of triethylamine, is stirred and pre-treated; then surfactant hexadecyltrimethylammonium chloride and additive nickel chloride are added by the mass ratio that hexadecyltrimethylammonium chloride: HgCl2 is 2.85 to 7.65: 4 to 6.5 and NiCl2: HgC12 is 4:4 to 6.5, and impregnated in a vacuum rotary evaporation way, wherein the prepared HgCl2 accounts for 4 percent to 6.5 percent of the total mass of the catalyst and NiCl2 accounts for 4 percent of the total mass of the catalyst, the hexadecyltrimethylammonium chlorid accounts for 2.85 percent to 7.65 percent of the total mass of the catalyst, and the balance is the low-mercury compound catalyst of C, so that the activity, stability and selectivity of the low-mercury compound catalyst are also significantly improved while the mercury content is reduced.
Owner:内蒙古海驰高科新材有限公司
Method for determining precious metal in platinum-palladium ores
InactiveCN103940805AObserve spectral lines in real timeReal-time observation of measurement resultsPreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by thermal excitationWater bathsOptical Emission Spectrometer
The invention discloses a method for determining precious metal in platinum-group metal ores. The method comprises the following steps: (1) obtaining a nickel-sulfonium button from a nickel-sulfonium fire assay enriching sample; (2) grinding the nickel-sulfonium button with a grinder; (3) adding the ground nickel-sulfonium button in a hydrochloric acid solution and heating for dissolving to remove base metal and sulfonium from the nickel-sulfonium button; (4) adding a reductant and a coprecipitator to the solution obtained from the step (3) to recover a small quantity of precious metal lost in the solution; (5) performing suction filtration at negative pressure to obtain a precious metal precipitate; (6) dissolving the precipitate in the step (5) together with a filtering membrane with aqua regia in a water bath and diluting with pure water to a fixed volume; (7) drawing calibration curves of platinum, palladium, gold, rhodium, ruthenium and iridium by an ICP-OES (Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectrometer) and determining the intensity of spectral lines of platinum, palladium, gold, rhodium, ruthenium and iridium in the sample solution; (8) automatically calculating the content of to-be-detected elements by a computer according to the calibration curves and a sample information table. The method has good stability and high result accuracy degree. According to the method, six precious metal elements can be determined simultaneously just by one-time sample weighing and pretreatment, the working efficiency is increased greatly and the detection cost is lowered.
Owner:WANBAO MINING
Method for preparing nitrogen-containing carbon nano tube
InactiveCN104016328AHigh yieldSuitable for large-scale industrial productionCarbon nanotubesNanotechnologyMass ratioCarbon nanotube
The invention relates to a nitrogen-containing carbon nano tube and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method specifically comprises the following preparation steps: by taking Zn<2+> and Fe<2+> as co-metallic ions in a solvothermal system, complexing the metal ions and imidazole organic ligands, and synthesizing imidazole polymer nanospheres; mixing the spheres with dicyandiamide of different amounts (a mass ratio of the dicyandiamide to the imidazole polymer nanospheres is adjustable in a range from 2.5 to 20) or carbonizing pure imidazole polymer nanospheres at the temperature of 700-900 DEG C in N2 atmosphere for 3-4 hours, and obtaining a solid material; removing metals Zn and Fe by using aqua regia and nitric acid, and further obtaining the nitrogen-doped multi-walled carbon nano tube of which the tube diameter is adjustable in a range from 30 to 800nm and the nitrogen doping amount is adjustable in a range from 4 to 12 percent. The method is simple in process, low in equipment requirement, low in energy consumption and simple and easily controlled in reaction process; the tube diameter of the carbon nano tube is adjustable; and the nitrogen is uniformly distributed in the carbon tube and is high in content.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A kind of preparation method of high-purity platinum
The invention relates to a method for preparing high-purity platinum. The steps are as follows: (1) dissolving 100 grams of metallic platinum in aqua regia, and reacting with ammonium chloride to form ammonium chloroplatinate precipitation, and then draining to obtain platinum chloride (2) ion-exchange purification of ammonium chloroplatinate, (3) preparation of high-purity platinum, the ammonium chloroplatinate obtained in step (2) is packed into a quartz boat, put into a muffle furnace and calcined to obtain high-purity platinum pure platinum. In the present invention, metallic platinum and aqua regia are dissolved to generate ammonium chloroplatinate, and then the ammonium chloroplatinate is removed by ion exchange resin to generate chloroplatinic acid, and ammonium chloride is added to generate ammonium chloroplatinate, which is obtained by burning after drying. High purity platinum.
Owner:TIANJIN CHEM REAGENT RES INST
Deeply hydrodearomatized catalyst and preparation method
ActiveCN101745383AHigh Hydrodearomatization ActivityMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsRefining by aromatic hydrocarbon hydrogenationPtru catalystBase oil
The invention relates to a type of deeply hydrodearomatized catalyst and a preparation method. Slurry containing 1 percent to 5 percent by weight of aluminium ion, 40 percent to 60 percent by weight of silicon dioxide and 5 percent to 15 percent by weight of ammonium ion is prepared; the slurry is dried under the temperature of 100 DEG C to 200 DEG C; the produced powder is mixed with pseudo-boehmite with the total pore volume of 0.4ml / g to 0.45ml / g and the surface area of 200m2 / g to 240m2 / g, and the produced mixture is shaped, dried under the temperature of 100 DEG C to 150 DEG C and baked under the temperature of 450 DEG C to 530 DEG C, so that carrier is obtained; the aqua regia of Pt and Pd, the volume of which is equal to the water absorption capacity of the carrier, is added into the carrier, and the carrier is dried under the temperature of 80 DEG C to 120 DEG C and baked under the temperature of 450 DEG C to 480 DEG C, so that the catalyst is obtained; Pt accounts for 0.1 percent to 0.5 percent of the weight of the catalyst, and Pd accounts for 0.3 percent to 0.8 percent of the weight of the catalyst; and the catalyst can meet the requirement of the deep hydrodearomatization of naphthenic base oil with the viscosity from 8mm2 / s to 700mm2 / s under the temperature of 40 DEG C and from 2mm2 / s to 30mm2 / s under the temperature of 100 DEG C.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD +1
Method for measuring impurity in high pure gold by plasma atomic emission spectrometer
ActiveCN101349646AAccurate measurementEliminate distractionsPreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by electrical excitationAnalytical controlImpurity
The invention relates to a method for using a plasma atomic emission spectrometer to measure impurities in high-purity gold, which comprises the following steps: weighing one unit of sample in a bunsen beaker, adding aqua regia to dissolve, replenishing hydrochloric acid deionized water to do constant volume to a scale after dissolving, respectively getting sample solution in more than two colorimetric tubes, solution in each tube is 15ml, adding gold standard solution which is mixed by elements according to a multiple relation in turn, doing constant volume by deionized water, starting the plasma atomic emission spectrometer, starting a circulating water pump, opening analytic control software, entering a 'standard addition method' control procedure, choosing a spectral line for measuring in a spectral line base, setting the concentration value of curved lines, scanning a whole band, sucking sample solution in each colorimetric tube in an instrument in turn according to the sequence that the concentration is from low to high, clicking a feeler switch to get an initial curve point of the point after sucking in each time, assuring curved lines, and leading the linear coefficient to be more than 0.99, outputting the concentration value result of each determined element, and calculating the result of the percentage content of each determined element according to the calculating formula.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF NONFERROUS METALS & RARE EARTH
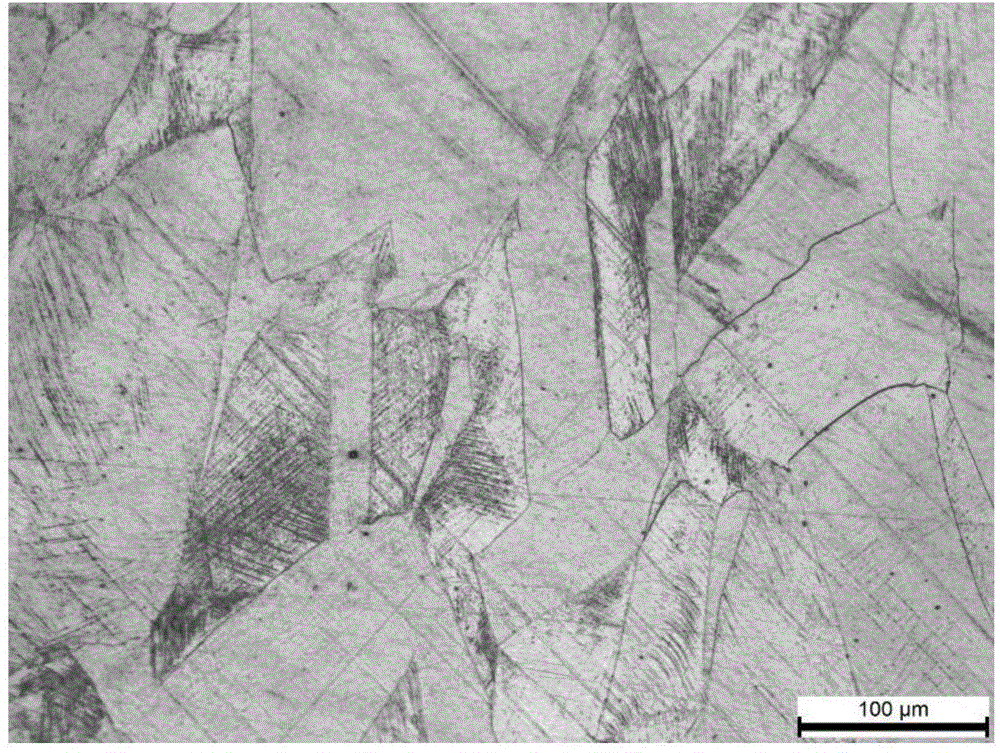
Austenite stainless steel erosion agent and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN105671553AClear and complete display of grain boundariesClear and complete display of precipitated phase morphologyPreparing sample for investigationAlloySolvent
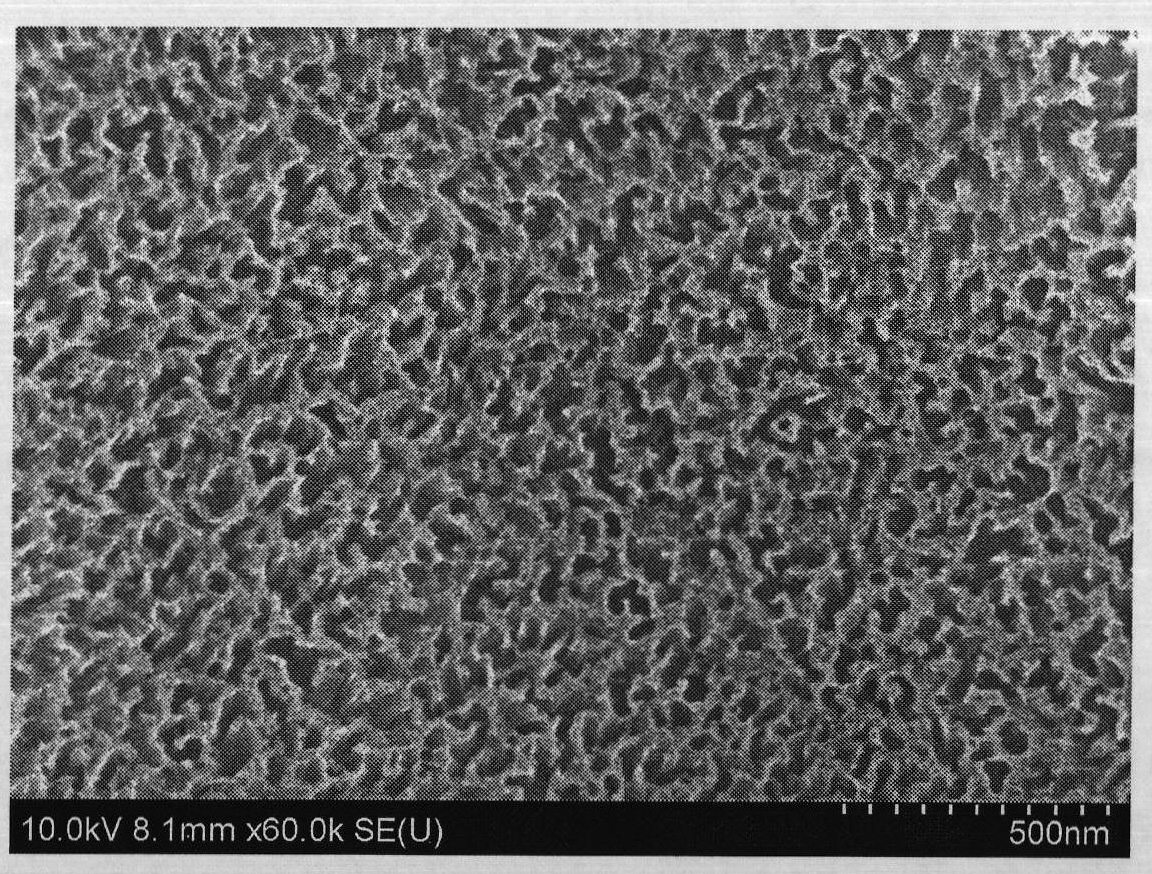
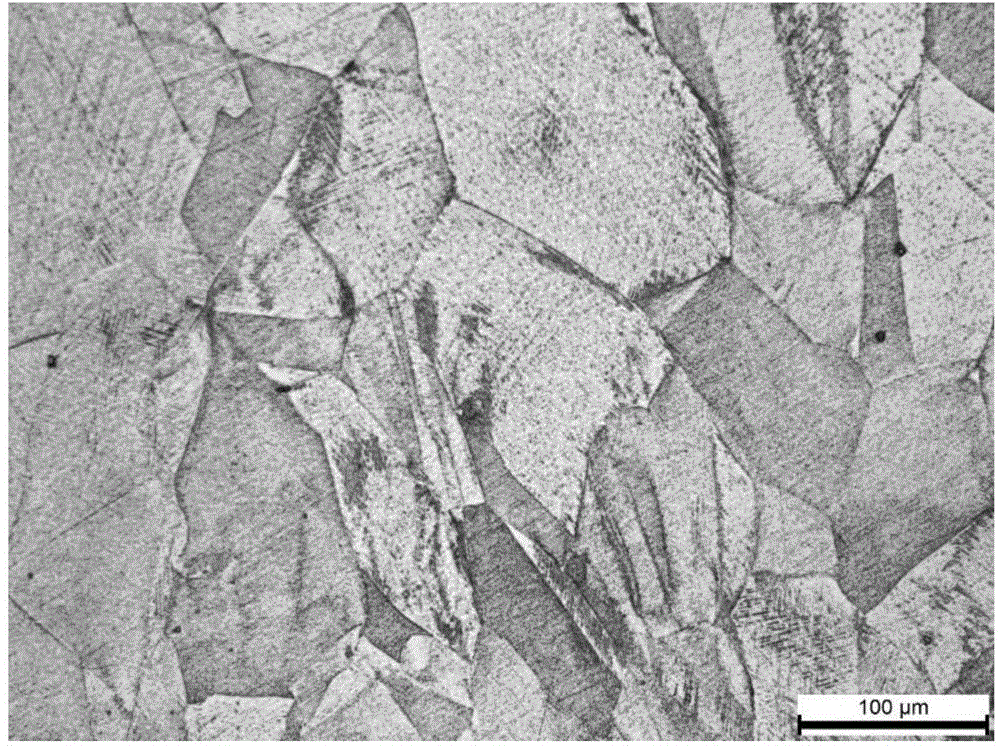
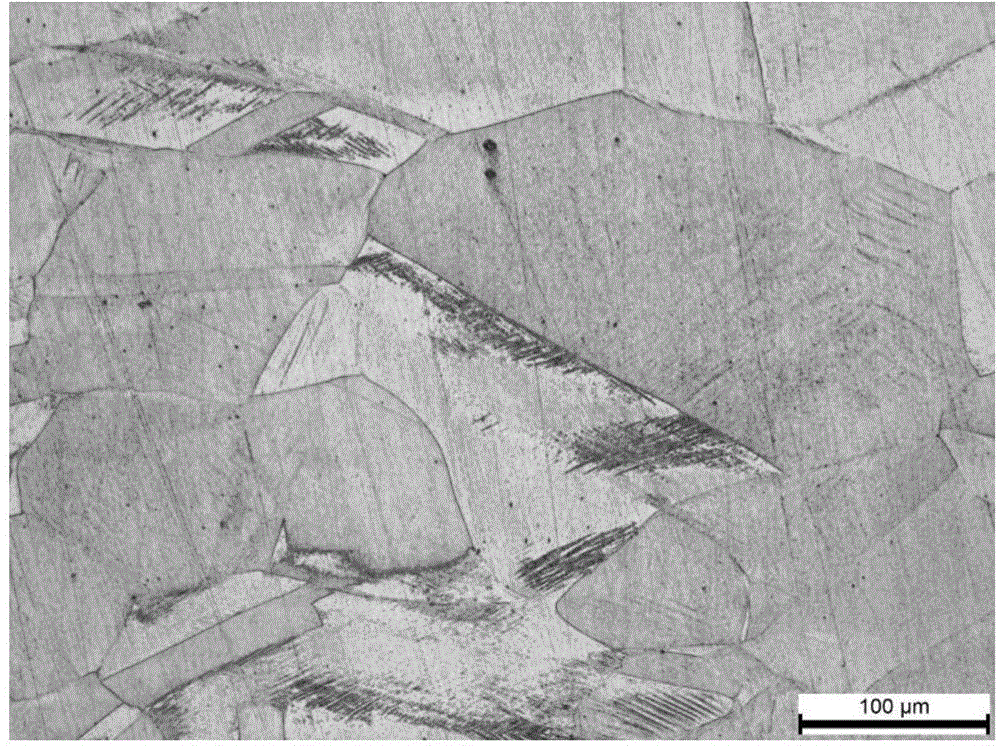
The invention provides an austenite stainless steel erosion agent and a preparation method and application thereof. Ethyl alcohol serves as a solvent of the erosion agent. The solvent comprises, by per liter, 60-120 ml / L of concentrated nitric acid, 150-300 ml / L of concentrated hydrochloric acid and 100-200 g / L of ferric chloride. According to the austenite stainless steel erosion agent provided by the invention, the erosion agent is a novel erosion agent obtained through repeated exploration in the experimental process, the adverse effects of the high volatility and corrosivity of aqua regia on a human body are avoided, the situation that dotted spots are produced due to uneven corrosion through a hydrochloric acid FeCl3 water solution and the other erosion agents, and the erosion process is easy to control; in addition, a polishing effect is achieved to a certain extent, tiny scratches on the surface of an austenite alloy sample can be removed, and austenite grain boundaries and the precipitated phase morphology can be clearly and completely shown; moreover, compared with other common erosion agents, the austenite stainless steel erosion agent is stable in component, capable of being stored for a long time under an airtight condition and high in using convenience.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com