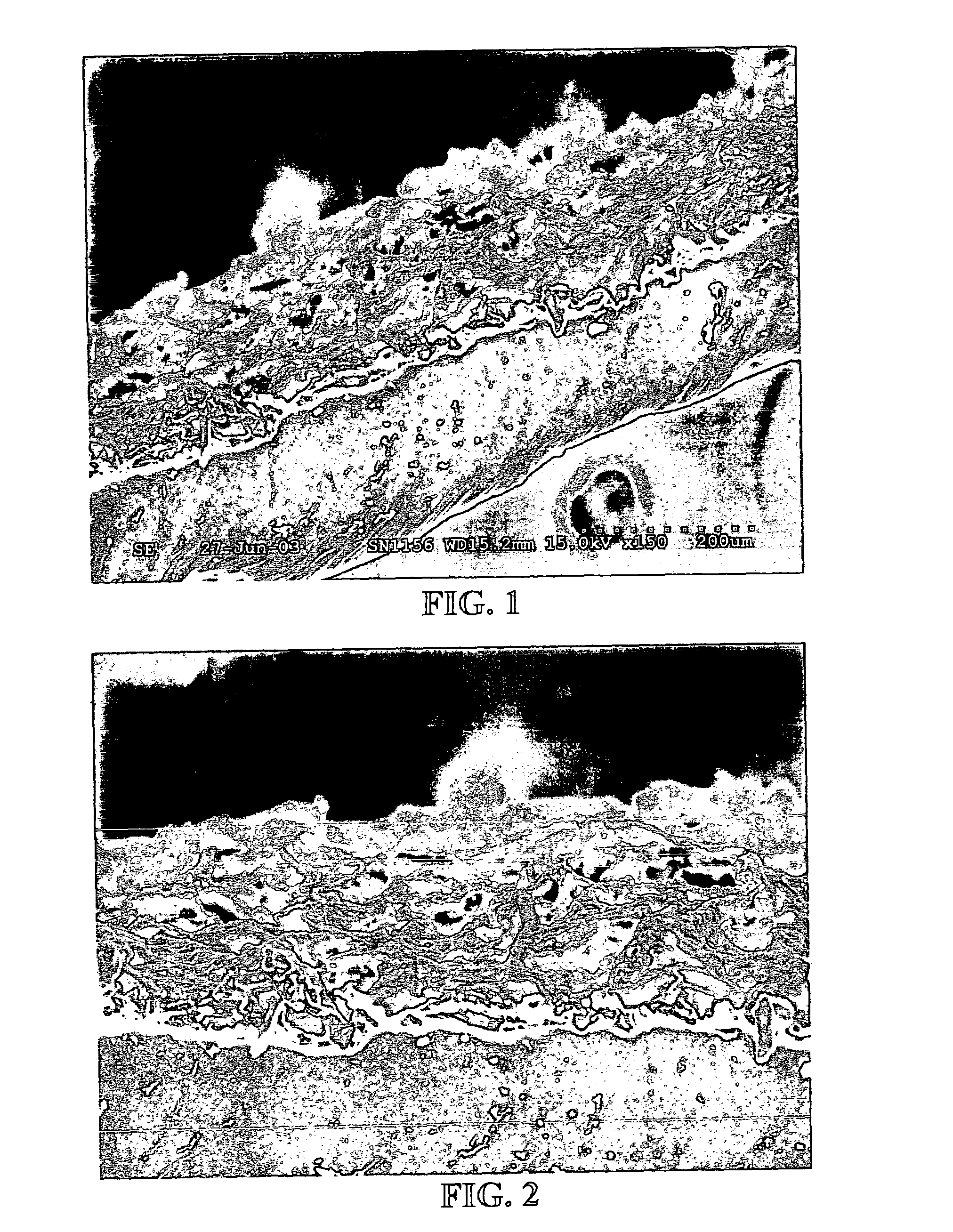
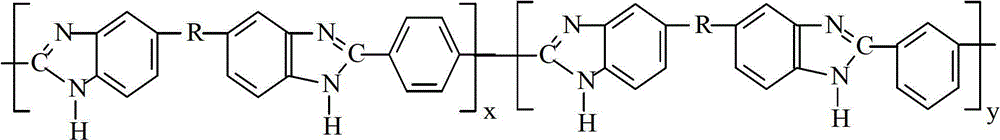
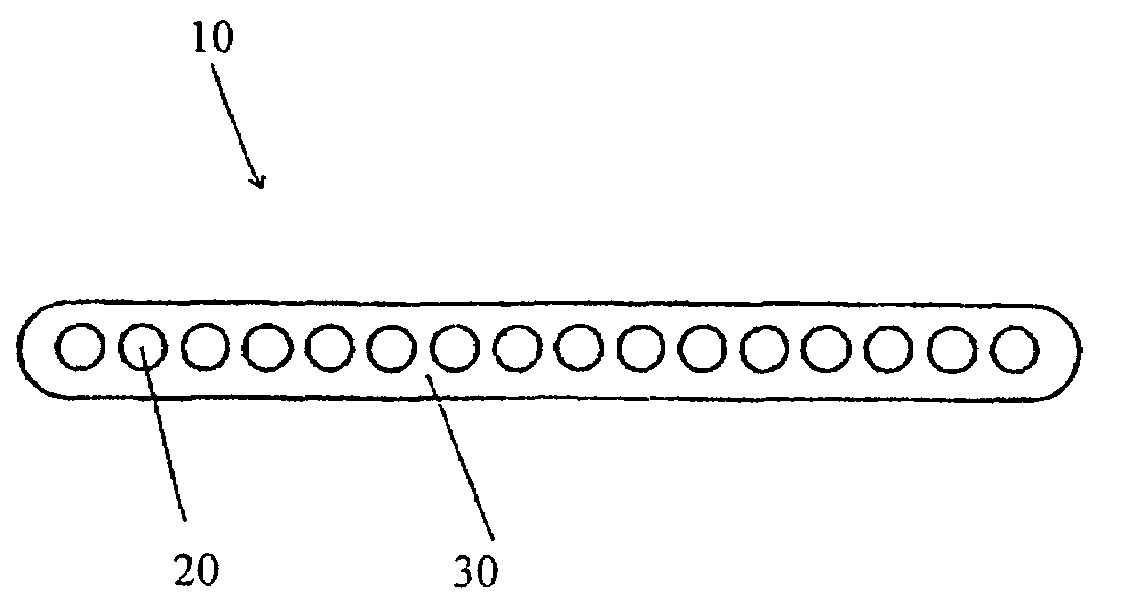
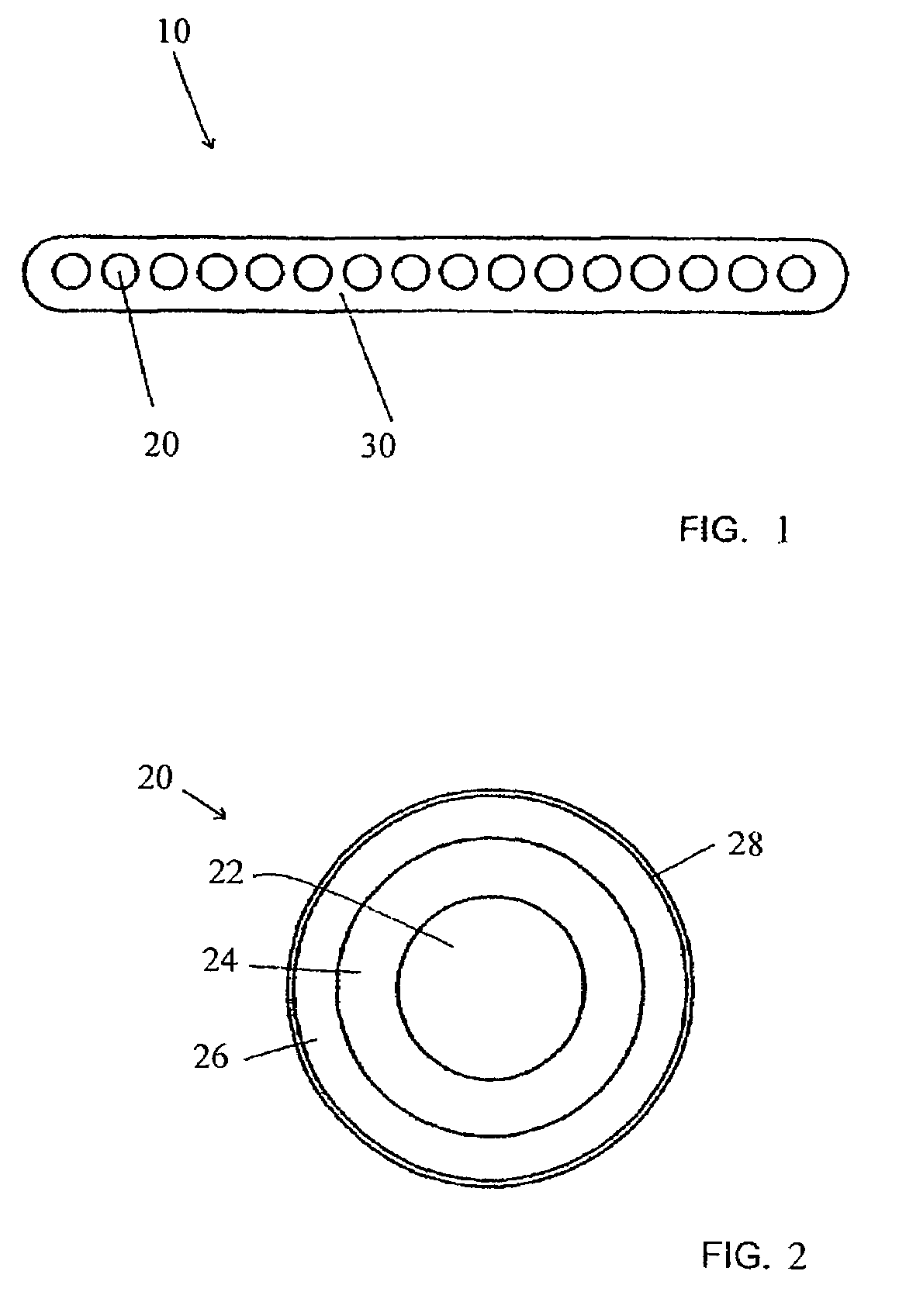
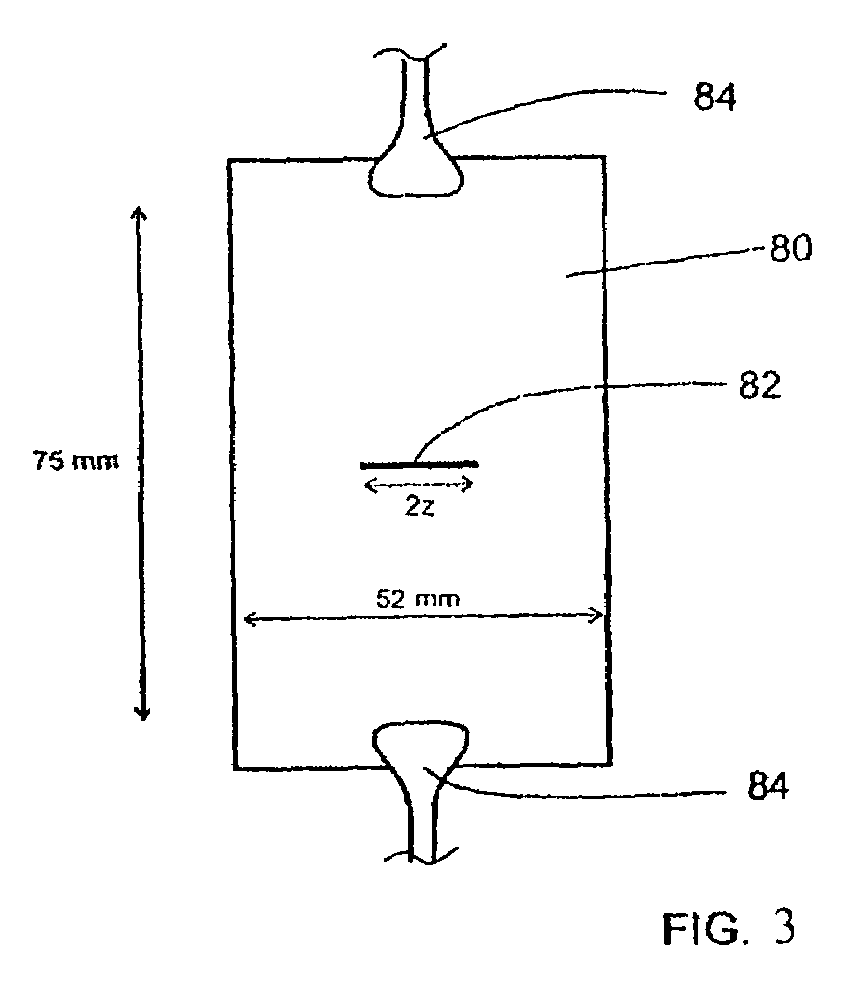
Patents
Literature
551 results about "Fiber coating" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
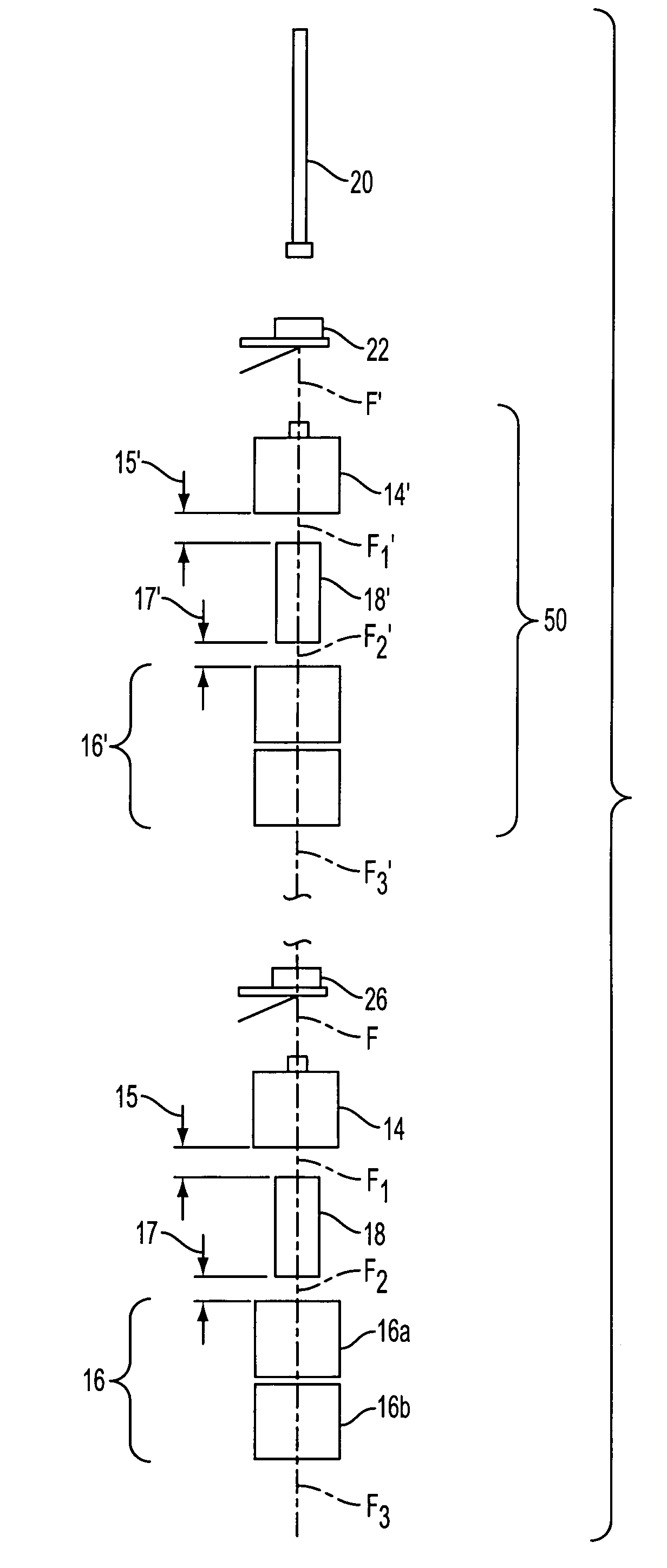
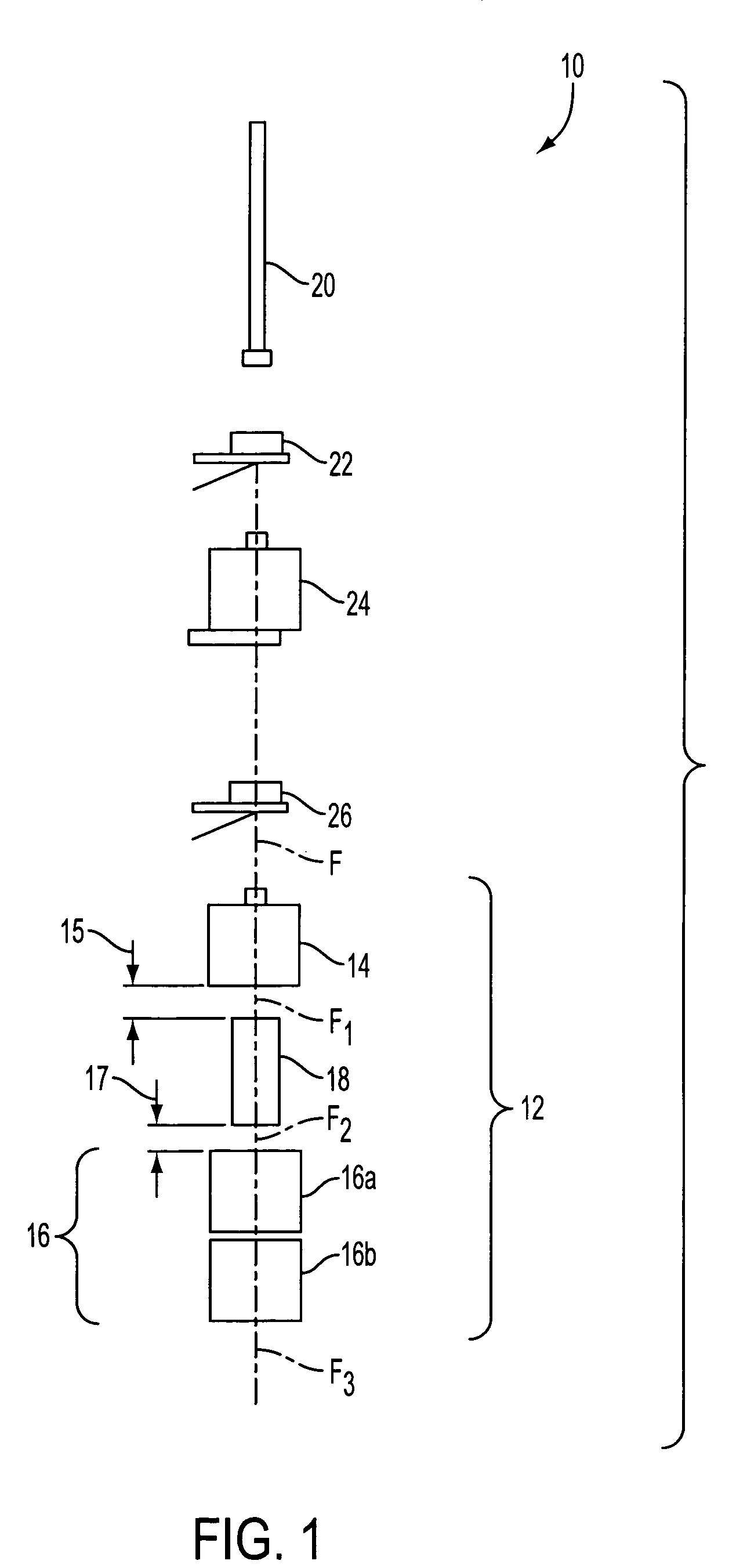
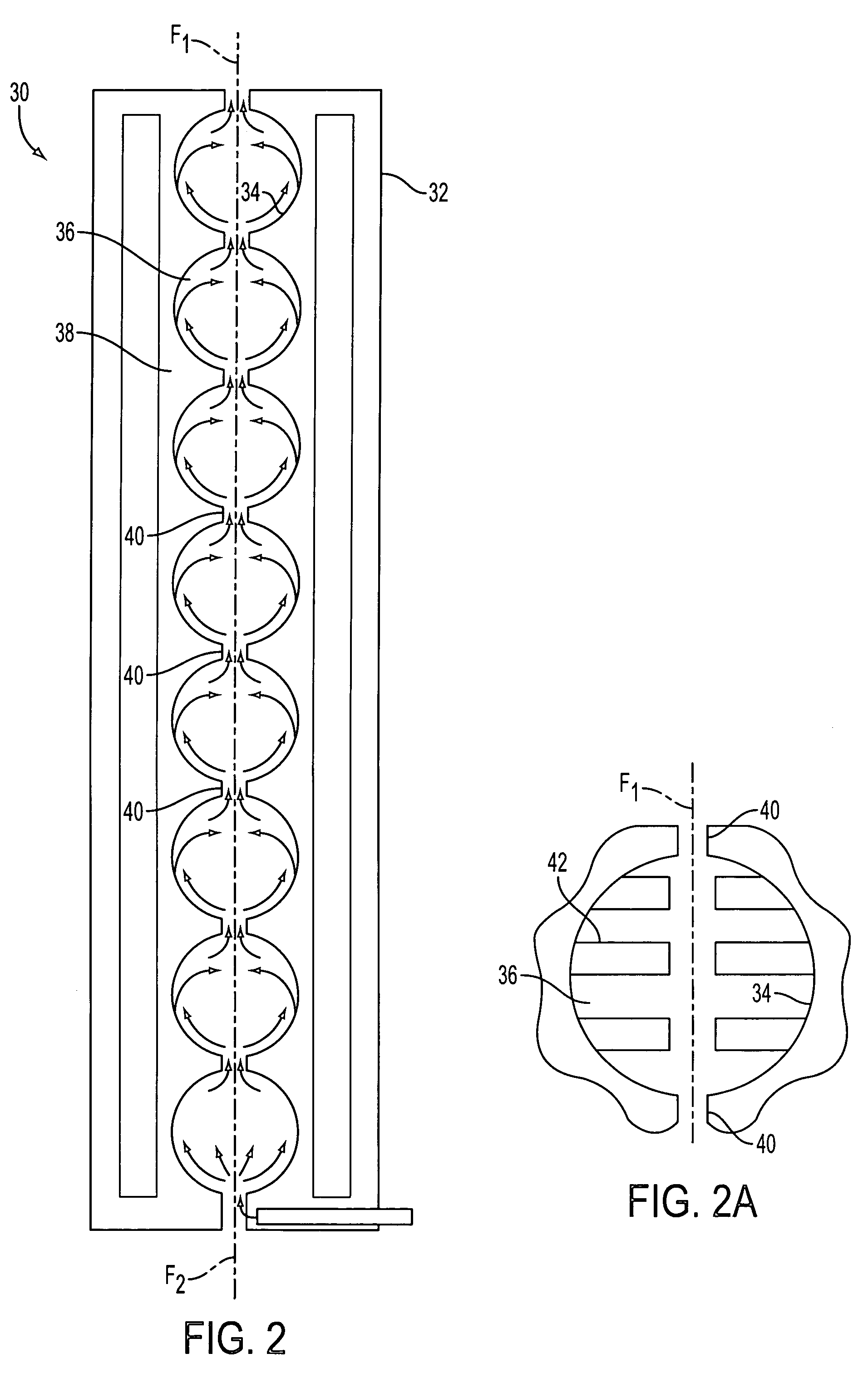
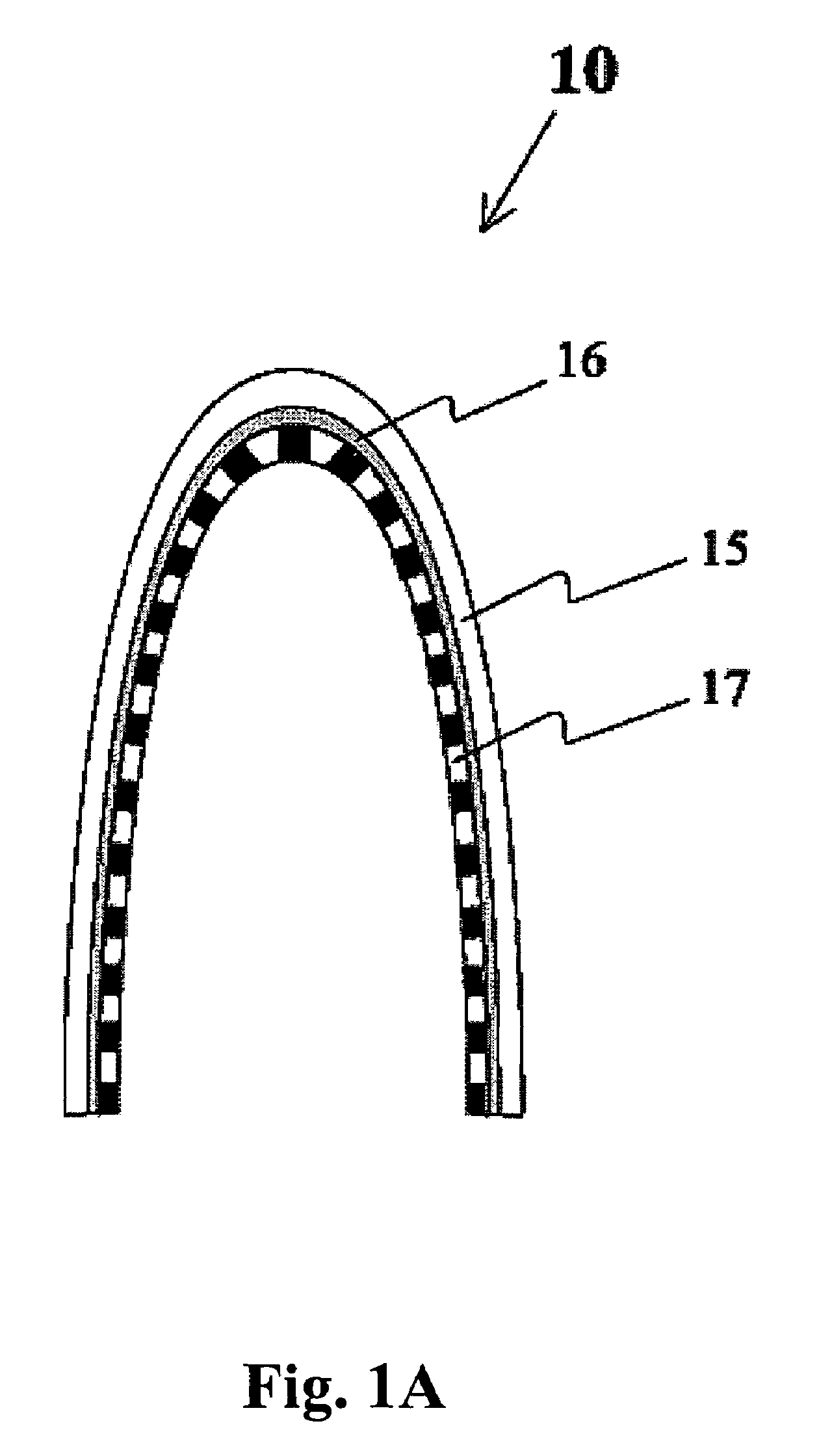
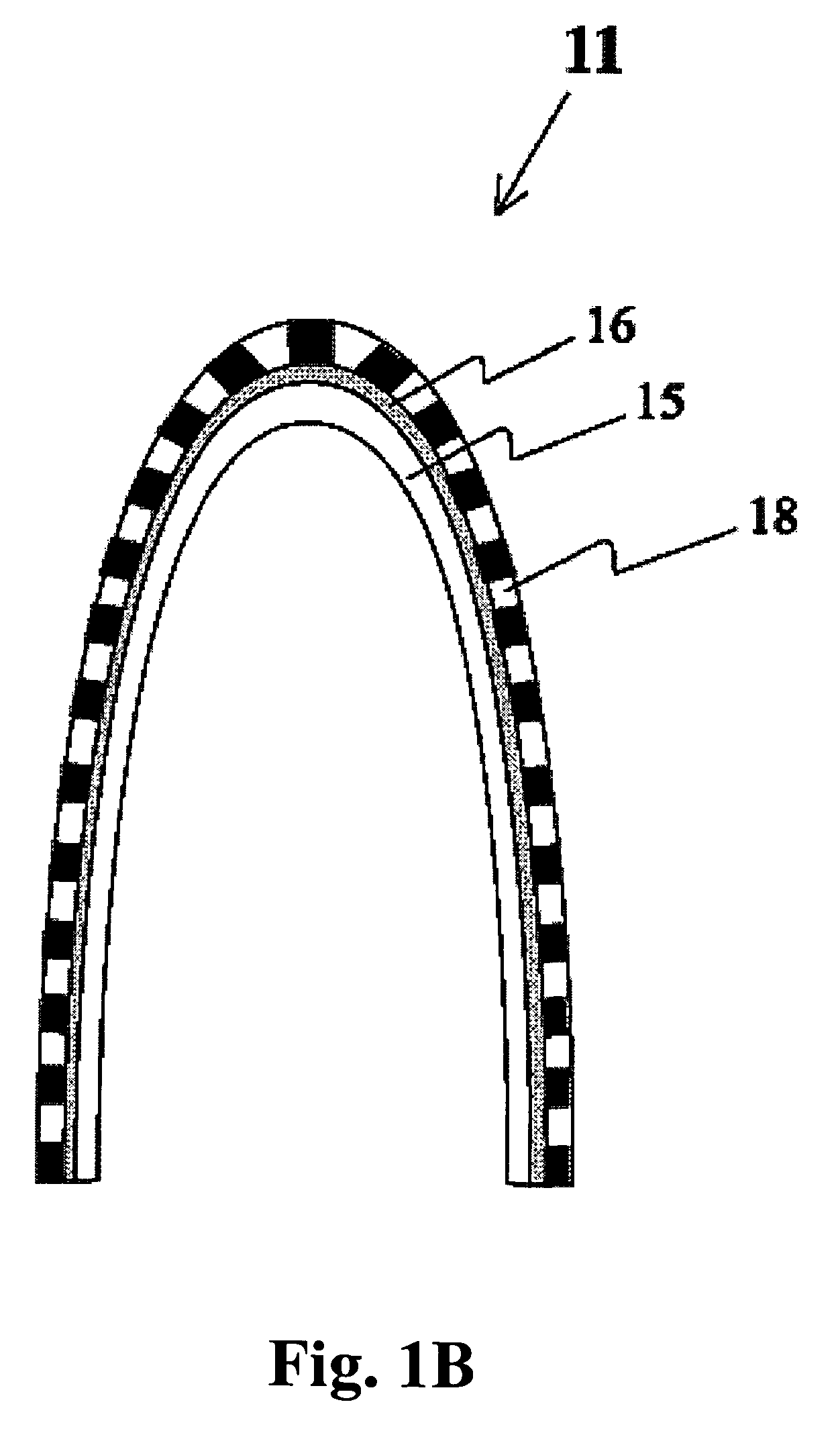
Method and apparatus for curing a fiber having at least two fiber coating curing stages
InactiveUS7322122B2Maintenance savingImprove drawing speedOptical articlesPretreated surfacesTime delaysIrradiation
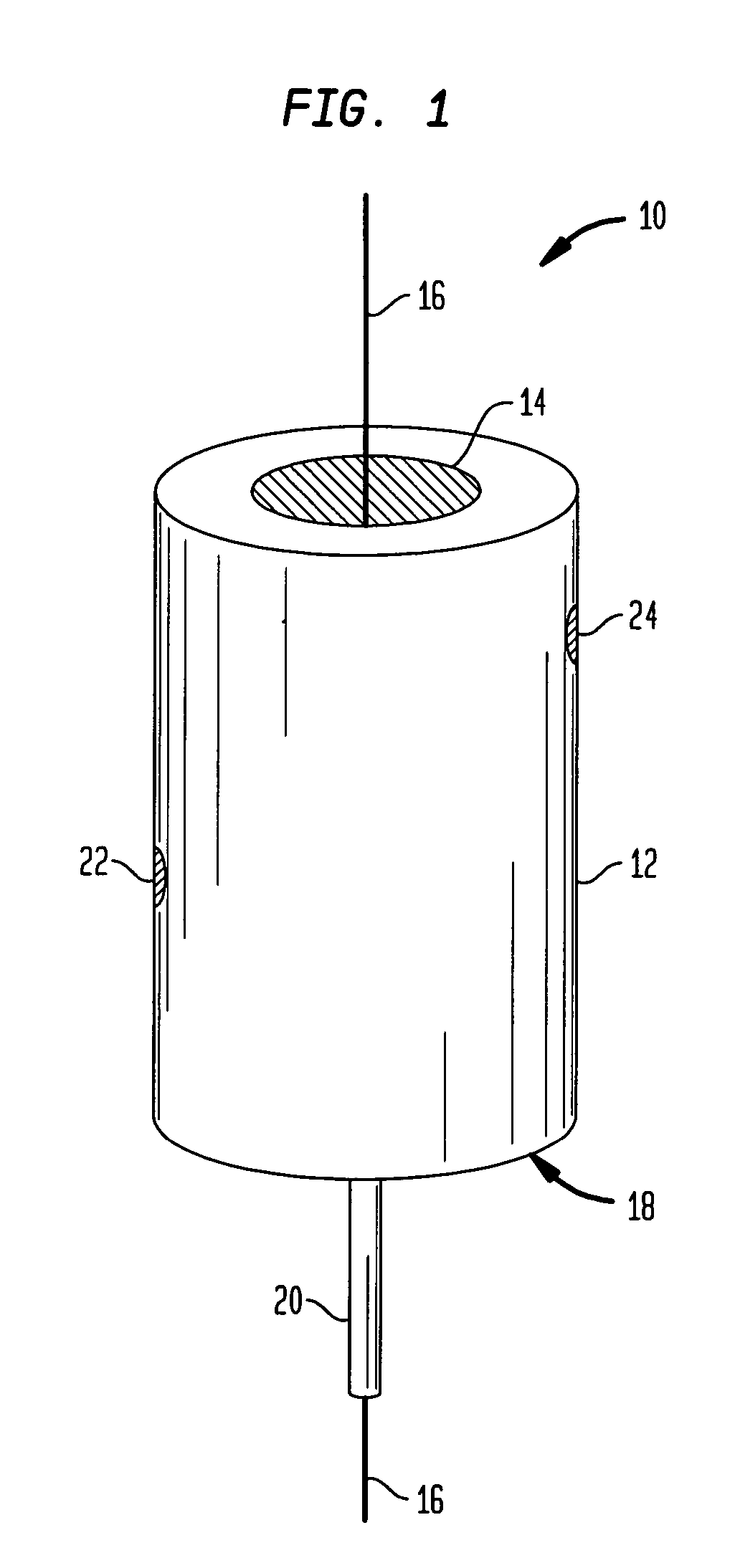
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for curing a coated fiber, comprising either two fiber coating curing stages separated by a cooling stage, or two fiber coating curing stages separated by a distinct time interval, or both. One of the two fiber coating curing stages responds to the coated fiber, and provides a partially cured fiber coating. The other of the two fiber coating curing stages responds to the partially cured coated fiber for further curing the coating of the fiber. In one embodiment of the invention, a cooling stage is placed between the two curing stages, while in the other the curing stages are placed a set distance apart such that polymerization of the coating initiated by the first curing stage has time to complete prior to the coating being irradiated by the second curing stage. The cooling stage is used to actively remove heat generated during the cure process from the fiber coating, while the time delay is used to allow complete polymerization to occur before subsequent irradiations. These embodiments of the present invention can be used separately or in combination to achieve optimal fiber coating cure.
Owner:DRAKA COMTEQ BV
Polymer composite fibrous coating on dipped rubber articles and method
The present invention provides a method of making an elastomeric article including preparing a non-woven fibrous polymer composition for dip-coating onto a layer of carboxylated acrylonitrile-butadiene elastomeric surface and in particular making industrial or household gloves. By dipping a former into a salt-based coagulant, followed by dipping into an elastomeric dispersion, and finally dipping into a polymer composite fibrous coating, a useful elastomeric article is prepared. The invention also provides an elastomeric article having a first layer, the first layer comprising a natural or synthetic polymer; and a second layer bonded to the first layer, the second layer comprising a polymer composite fibrous coating. The polymer composite fibrous coating includes at least one elastomer or elastomer blend, a fiber or fiber blend, a surfactant, and a micronised wax. The coating can be foamed, and provides improved sweat management and non-shredding properties to a user.
Owner:ANSELL HEALTHCARE PRODS
Heat reflective coated structural article
InactiveUS6872440B1Energy efficiencyLow costRecord information storageCeramic layered productsElastomerCeramic coating
The present invention relates to a heat reflective coated structural article comprising a heat reflective component and a coated structural article component which comprises a substrate having an ionic charge coated with a coating having essentially the same ionic charge. The coating of the coated structural article consists essentially of a filler material and a binder material wherein the binder material bonds the filler material together and to the substrate and wherein the coating does not bleed through the substrate. Nonlimiting examples of the heat reflective component include, elastomeric coatings, aluminum fiber coatings, acrylic and polyurethane coating systems, ceramic coatings insulating paints, metal pigment paints, metal pigment pastes and aluminum flakes. The heat reflective coated structural article of the present invention may be incorporated into commercial roofing products.
Owner:ELK PREMIUM BUILDING PROD
Non-reactive additives for fiber coatings
InactiveUS20070100039A1Easy to operateImprove performanceLayered productsPolyurea/polyurethane coatingsOligomerMonomer
The present invention relates to a curable composition having an oligomer, at least one monomer, and an amount of a substantially non-reactive oligomeric additive. The substantially non-reactive oligomeric additive is present in an amount effective to yield a cured product having a fracture toughness value that is higher than the fracture toughness value of a cured product of an otherwise identical composition lacking the non-reactive oligomeric additive. The present invention also relates to coated optical fibers, optical ribbons or bundles, and telecommunication systems having the curable composition.
Owner:CORNING INC
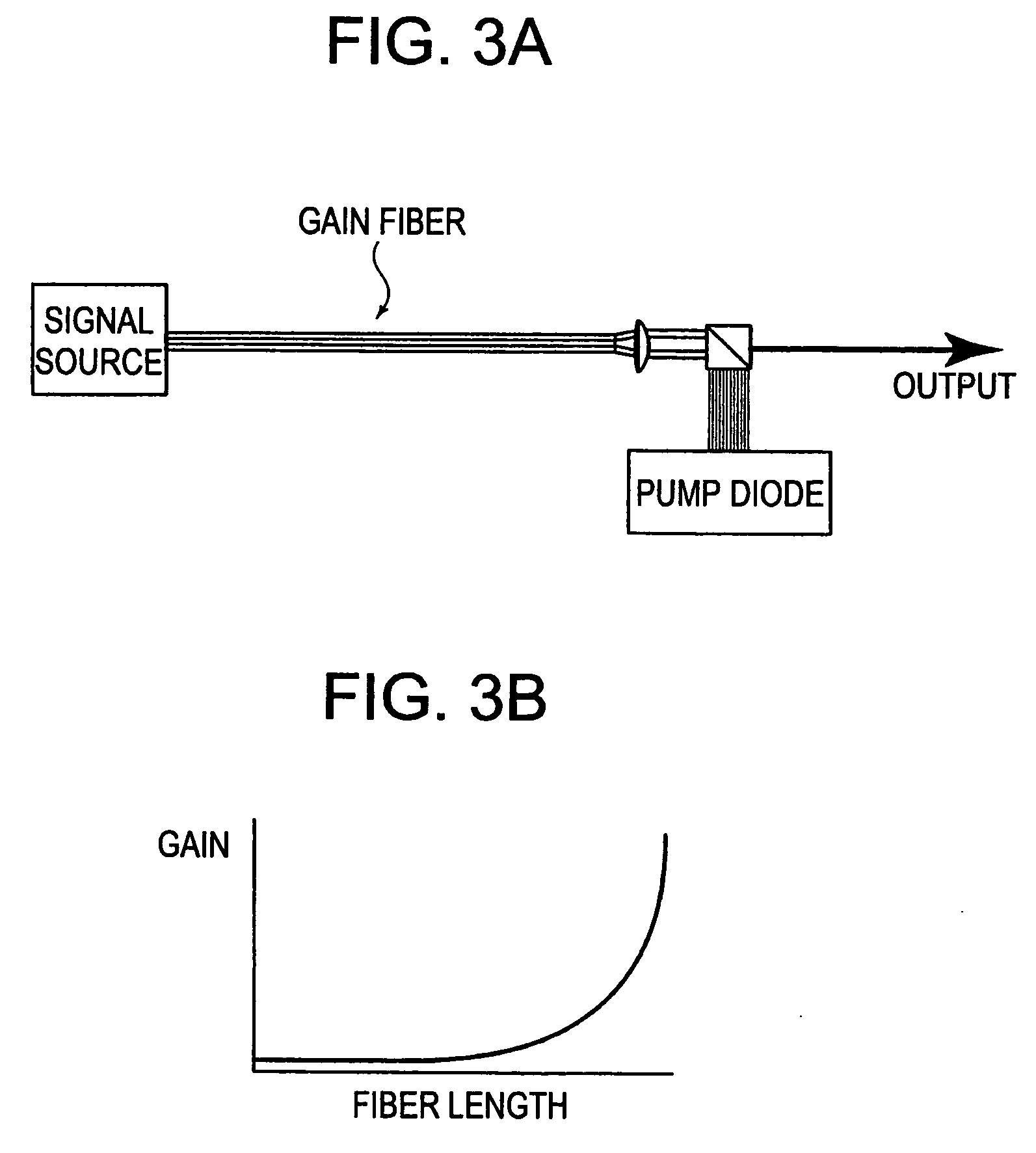
Single-polarization high power fiber lasers and amplifiers
InactiveUS20050232313A1Reduce absorptionMinimize nonlinearityLaser using scattering effectsOptical fibre with polarisationAudio power amplifierPolarization-maintaining optical fiber
A novel polarization maintaining optical fiber, which can be used as a high-power polarization maintaining fiber laser or amplifier, is described. Insensitivity of the polarization state to external fiber bending and temperature changes is accomplished by minimizing polarization mode-coupling via reducing stresses inside the fiber core via increasing the fiber diameter. Alternatively, polarization mode-coupling can be minimized by an optimization of the fiber coating to minimize stresses at the interface between the fiber and the coating. As a result insensitivity to polarization mode-coupling is obtained at greatly reduced values of birefringence compared to small-diameter fibers. The fiber is of significant use in any application where polarization stability is important, and will be useful in telecommunications applications in particular for reducing polarization mode dispersion. An implementation in a parabolic pulse-producing fiber laser is also described as one specific high power example.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
Triple-clad rare-earth doped optical fiber and applications
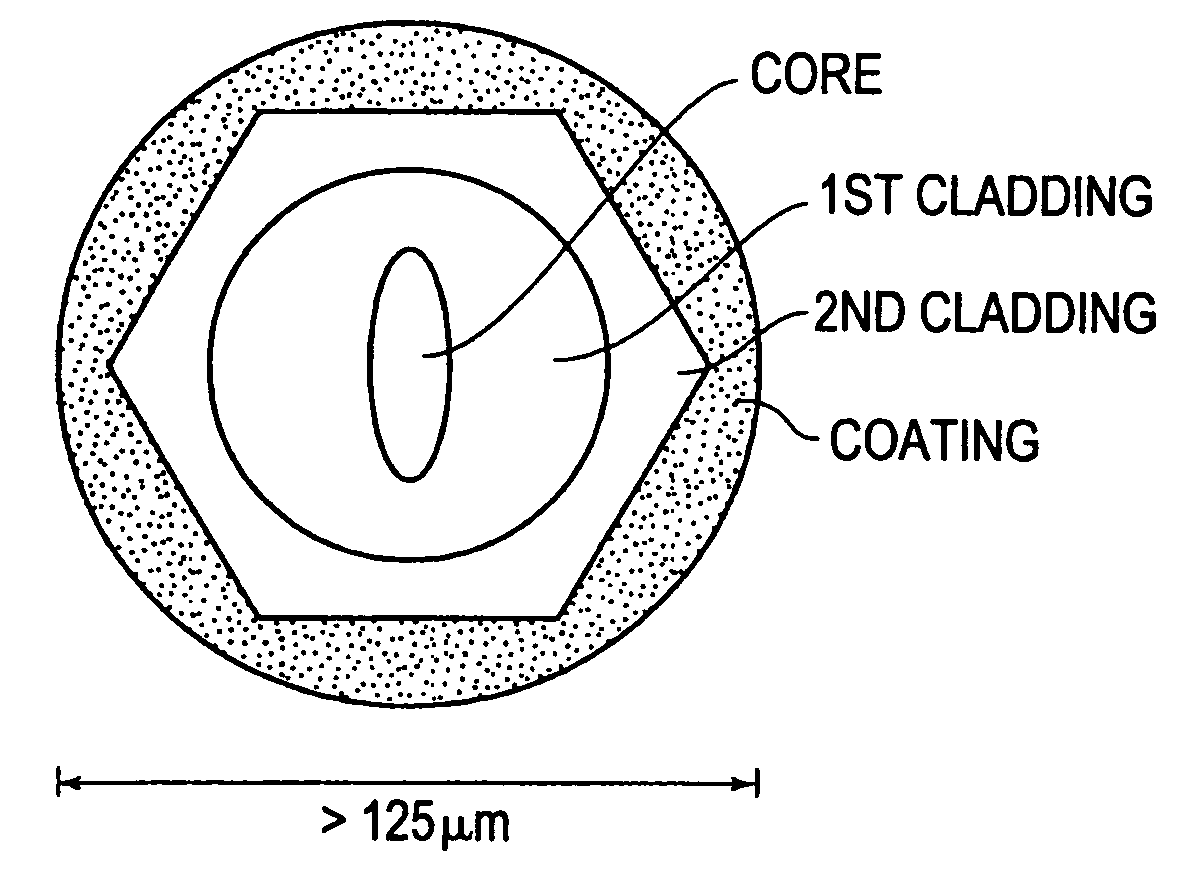
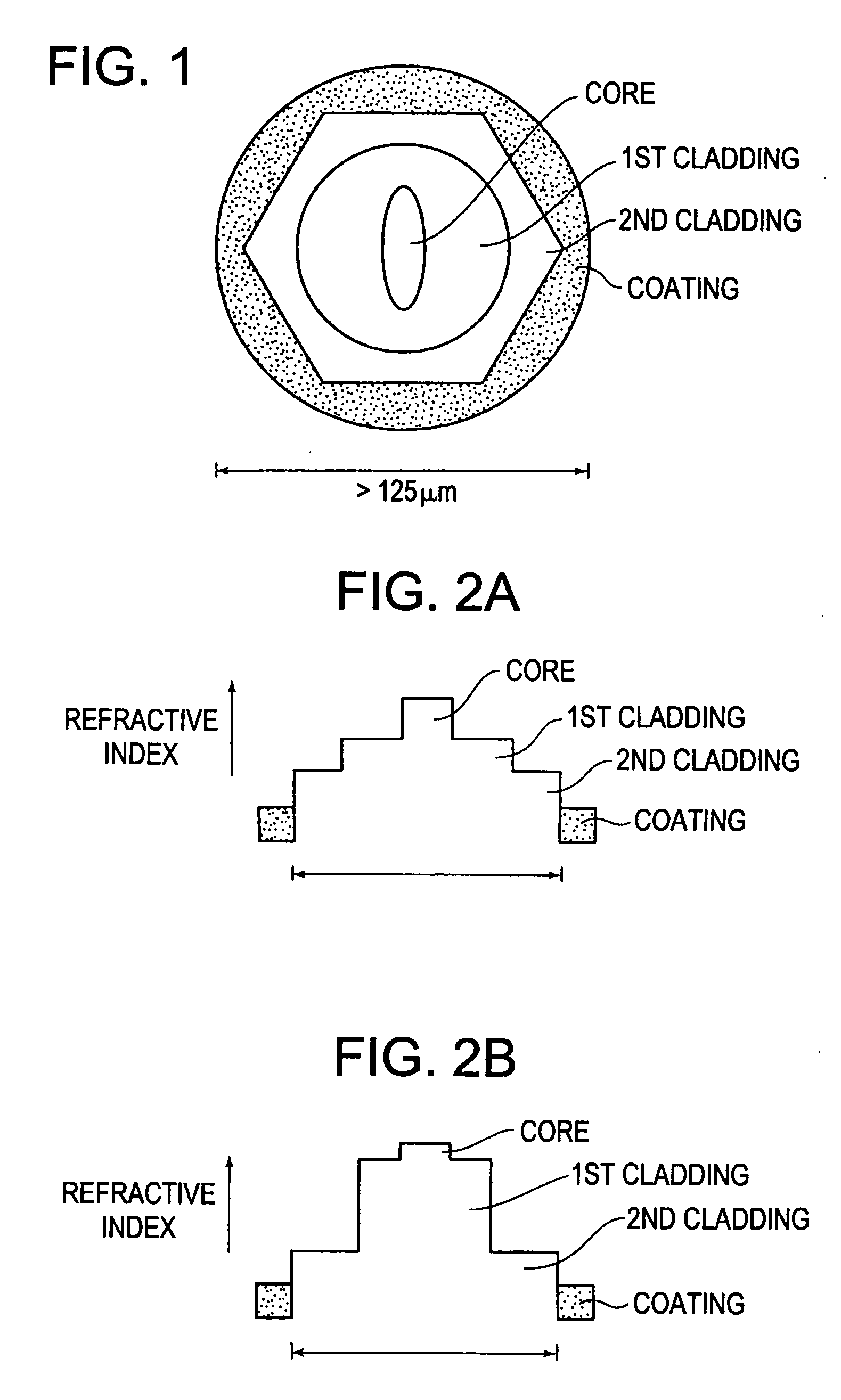
InactiveUS6941053B2Promote absorptionAccurate guideOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingActive medium shape and constructionRare-earth elementRefractive index
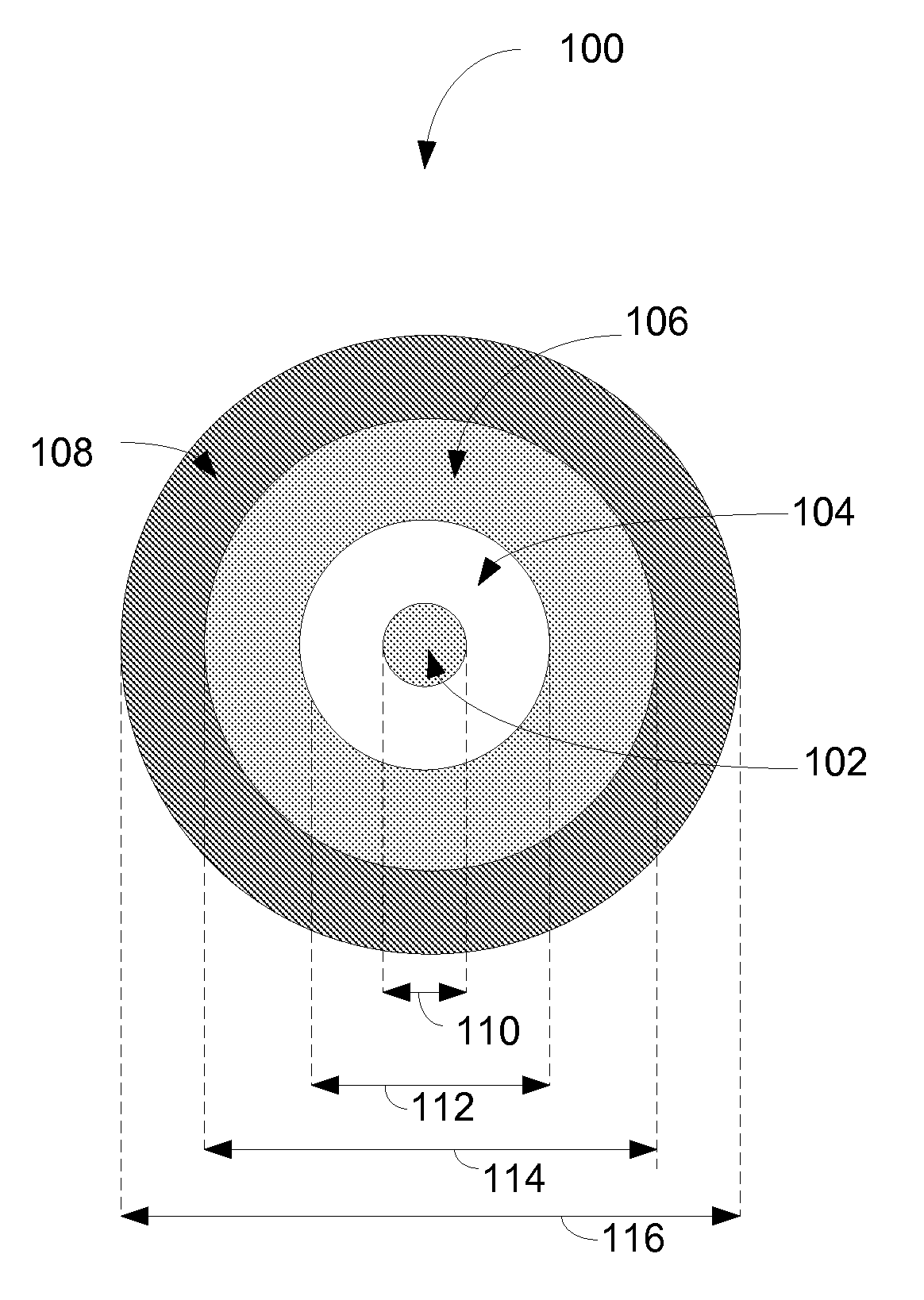
An optical fiber comprises a singlemode core, and an inner cladding disposed around said core, an intermediate cladding disposed around said inner cladding and an outer cladding disposed around said intermediate cladding thereby forming a triple-clad geometry. The core is doped with rare-earth elements and represents the waveguide section of higher refractive index through which the signal is transmitted and amplified. A fiber coating is provided around said outer cladding. The core has a higher refractive index than said inner cladding, said inner cladding having a higher refractive index than said intermediate cladding, and said intermediate cladding having a higher refractive index than said outer cladding. The inner cladding has a fairly high refractive index to limit the numerical aperture (NA) of said core. The inner cladding is within said intermediate, larger, cladding which is made of glass, that is used to guide multimode, high-power pump, said inner cladding acting as an intermediate level between said core and said multi-mode pump guiding intermediate cladding, with said outer cladding being present in said optical fiber for allowing said intermediate cladding to guide the pump power properly. The outer cladding is made of glass or of a low-index polymer material. The inner cladding is adapted to trap some of the pump signal into a smaller section in order to accelerate the absorption of the pump power.
Owner:INSTITUT NATIONAL D'OPTIQUE
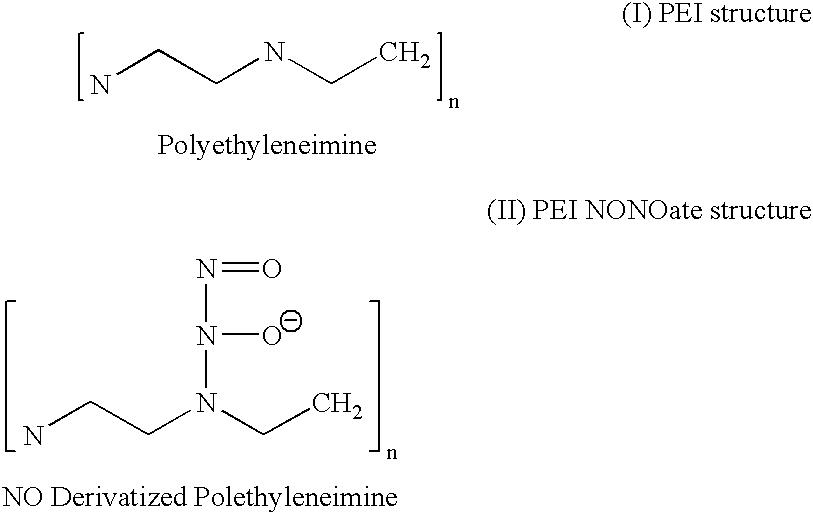
Polymer No Donor Predrug Nanofiber Coating for Medical Devices and Therapy
The present invention relates to nanofibers that produce therapeutic amounts of nitric oxide after a delay period, which allows time to install or implant the device into a patient. The nitric oxide release is thus localized to the area of the organism where NO dosing is indicated. The delay time is achieved by cospinning the NO-producing fiber with a fiber that tends to sequester the former's NO-producing functional groups. Fibers of the present invention may be incorporated into medical devices such as stents or other implantable medical devices to prevent the formation of adhesions or scarring in the area of the implant.
Owner:THE UNIVERSITY OF AKRON
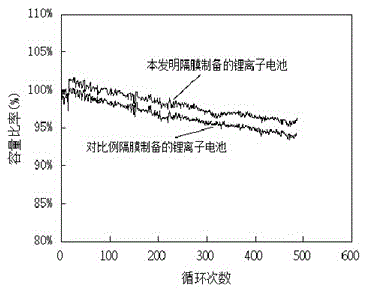
Composite coating lithium-ion battery separator and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105552284AImprove thermal performanceImprove mechanical propertiesCell component detailsWater basedPole piece
The invention relates to a composite coating lithium-ion battery separator. The composite coating lithium-ion battery separator is composed of a base film, an aramid fiber coating coated on one side of the base film and a PVDF coating coated on the other side of the base film; the aramid fiber coating is obtained by an aramid fiber sizing agent after coating, soaking and drying, and the thickness of the coating is 0.5-4 microns; the PVDF coating is obtained by a water-based PVDF sizing agent after coating and drying, and the thickness of the coating is 0.1-2 microns. The invention also provides a preparation method of the separator. According to the composite coating lithium-ion battery separator and the preparation method thereof, the separator has the characteristics that the aramid fiber coating is good in thermal performance and mechanical performance and the PVDF coating has good wettability and liquid retention property for electrolytes, can effectively adhere batteries and pole pieces and is little in environmental pollution, and is beneficial for preparing lithium-ion batteries with longer cycle life and higher safety. Tests indicate that the separator has good air permeability, liquid absorption rate, thermal contraction and tensile strength, so that the cycle life of the batteries can be obviously prolonged by using the lithium-ion batteries prepared by the separator.
Owner:CANGZHOU MINGZHU SEPARATOR TECH CO LTD
Apparatus for forming a microfiber coating
InactiveUS7105058B1Accelerates the removal of moistureReduce moistureLiquid surface applicatorsSpray nozzlesEngineeringAmbient air
An apparatus and method for forming a microfiber coating includes directing a liquid solution toward a deposition surface. The apparatus includes a tube defining a volume through which the liquid solution travels. An electric field is applied between the origin of the liquid solution and the surface. A gas is injected into the tube to create a vortex flow within the tube. This vortex flow protects the deposition surface from entrainment of ambient air from the surrounding atmosphere.
Owner:POLYREMEDY
Capacitive gas sensor and method of fabricating the same
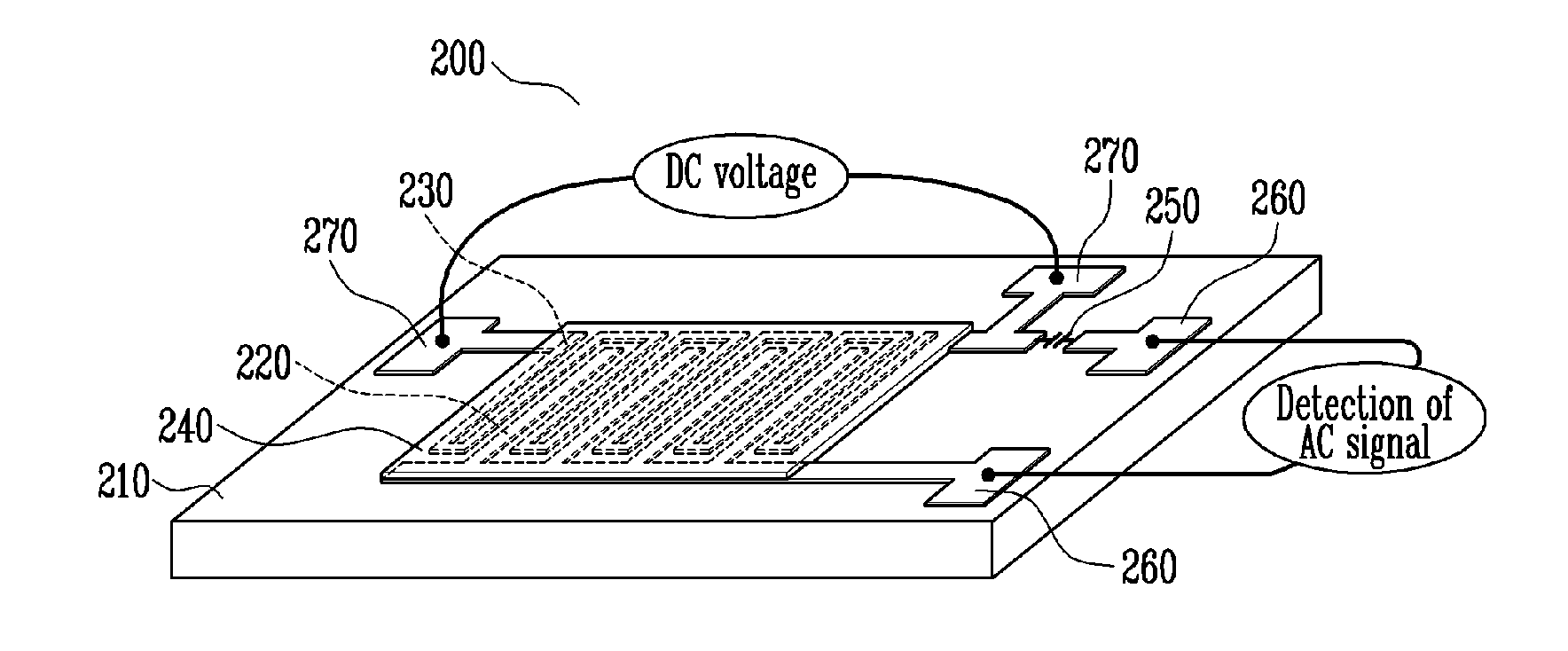
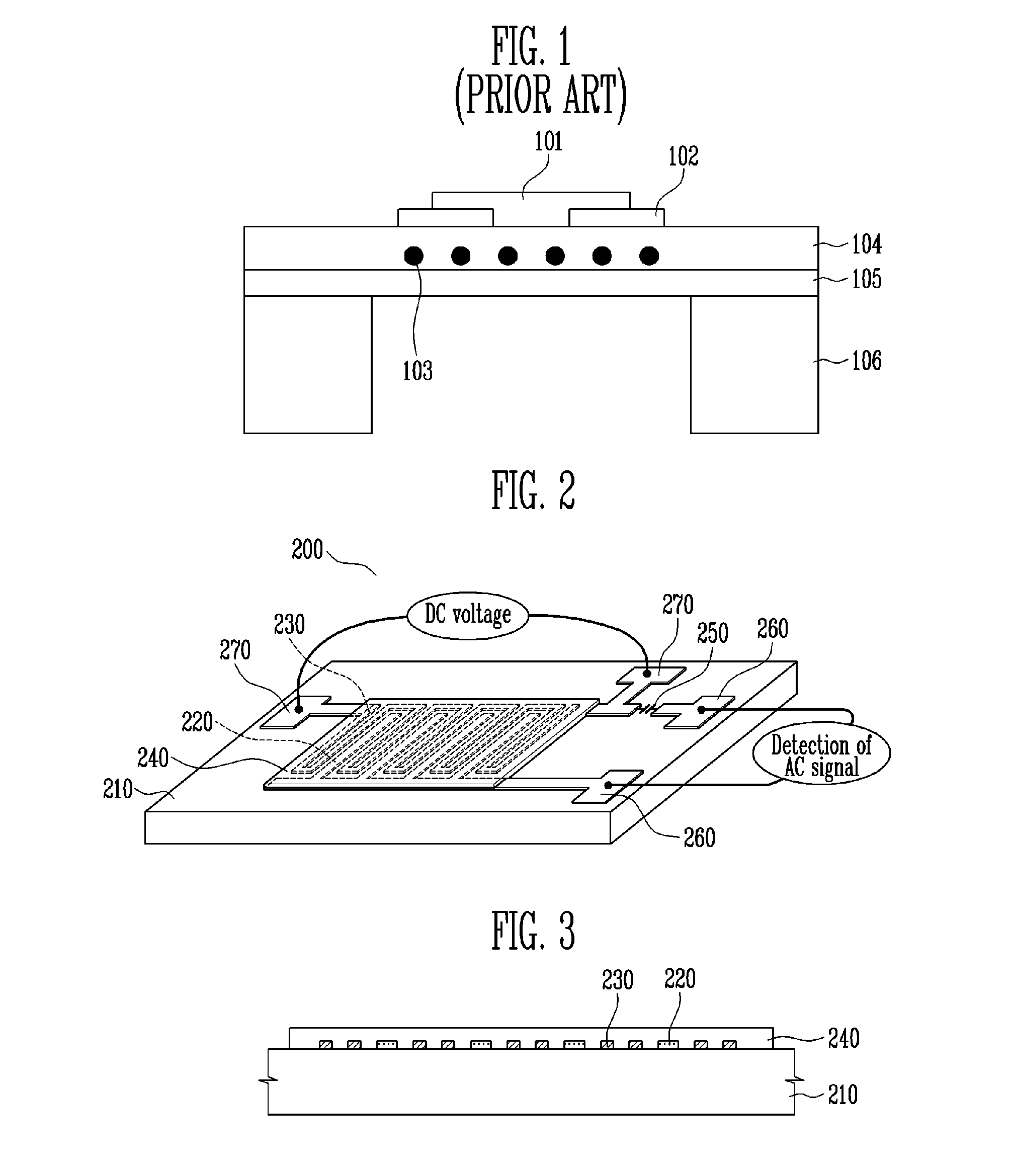
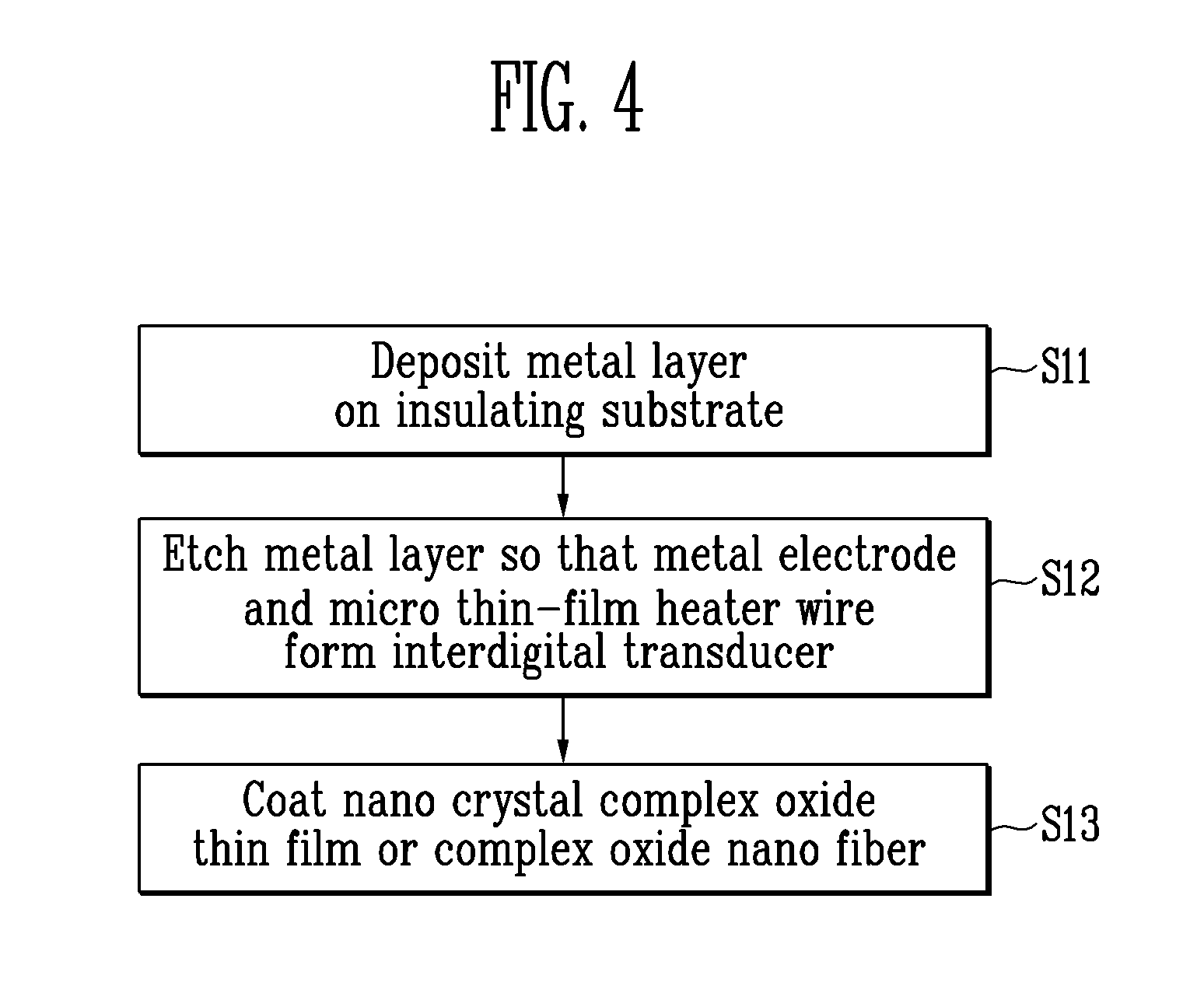
ActiveUS20100133528A1Excellent gas reaction characteristicSimple processNanotechSolid-state devicesNanofiberOptoelectronics
A capacitive gas sensor and a method of fabricating the same are provided. The capacitive gas sensor includes an insulating substrate, a metal electrode and a micro thin-film heater wire integrally formed on the same plane of the insulating substrate, and an oxide detection layer coated on the metal electrode and the micro thin-film heater wire. The fabrication method includes depositing a metal layer on an insulating substrate, etching the metal layer so that a metal electrode and a micro thin-film heater wire form an interdigital transducer on the same plane, and forming a nano crystal complex oxide thin film or a complex oxide nano fiber coating layer on the metal electrode and the micro thin-film heater wire as a detecting layer. The capacitive gas sensor can be easily fabricated and can have excellent characteristics such as high sensitivity, high selectivity, high stability, and low power consumption.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Polymeric shell adherently supported by a liner and a method of manufacture
ActiveUS7803438B2Preventing adhesive delaminationLimit stretch abilityDiagnosticsGlovesHot meltEngineering
An article comprising at least one cured, liquid-impervious polymeric shell substantially free from defects, at least one liner, and a non-tacky, thermoplastic adhesive layer between the shell and the liner, wherein the adhesive layer is melted and solidified to create a non-tacky bond between the shell and the liner, which can be moisture-absorbing or cut-resistant, whereby the liner supports and limits stretch ability of the shell, thereby preventing adhesive delamination between the adhesive layer and either of the shell and / or the liner; a method for the manufacture of an article comprising a supported, polymeric shell, such as a glove, a gauntlet, an apron, or a boot, comprising providing a cured, liquid-impervious, polymeric shell, providing a knitted / woven liner, incorporating a non-tacky, thermoplastic adhesive layer between the shell and the liner, such as by hot-melt spraying, dry-powder spraying or fiber-coating, creating intimate contact between the shell, the adhesive layer, and the liner, subjecting the shell, the adhesive layer, and the liner to infrared radiation to melt the adhesive layer and create a bond between the shell and the liner, and cooling the shell; as well as other methods.
Owner:ANSELL HEALTHCARE PRODS
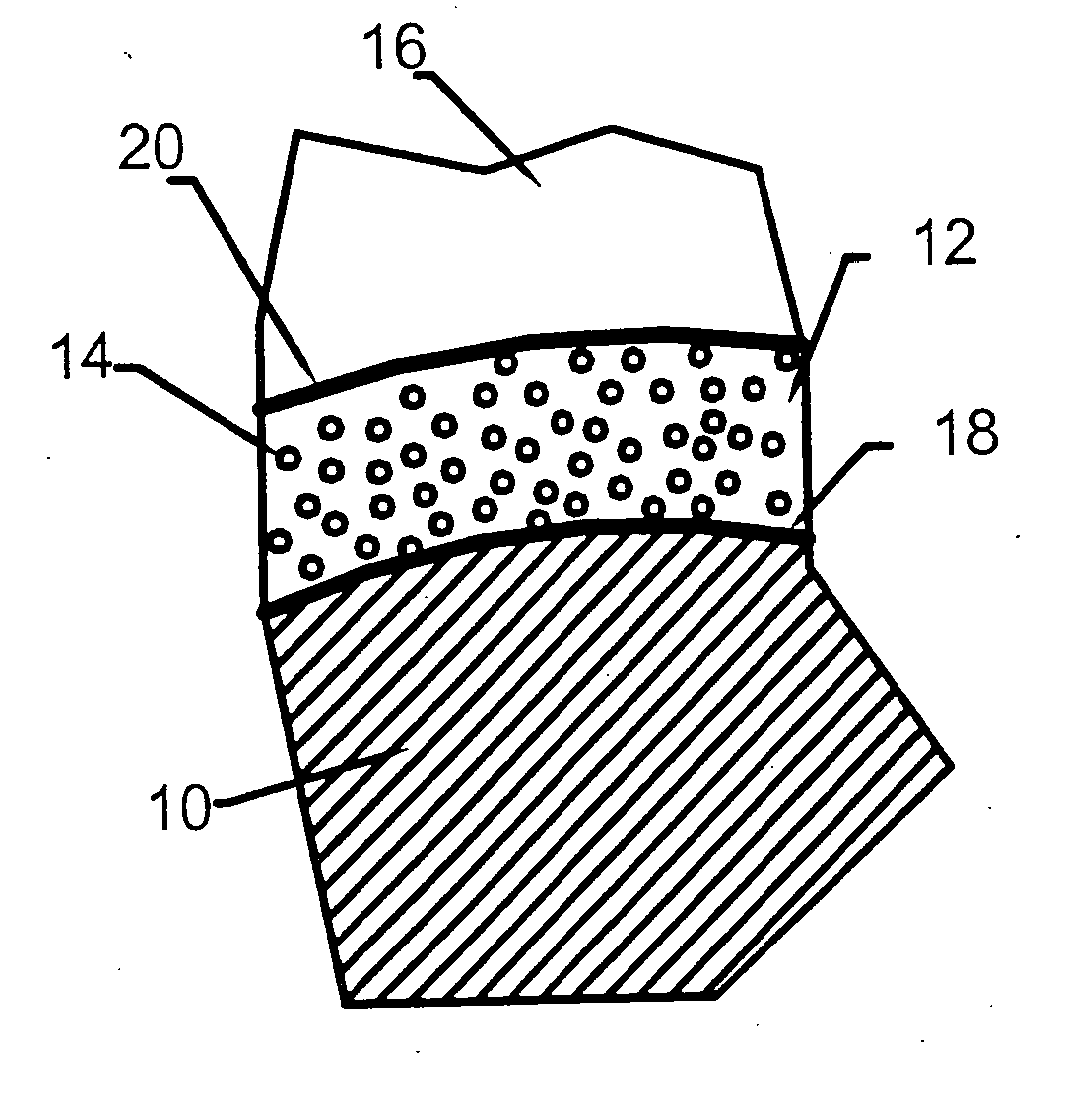
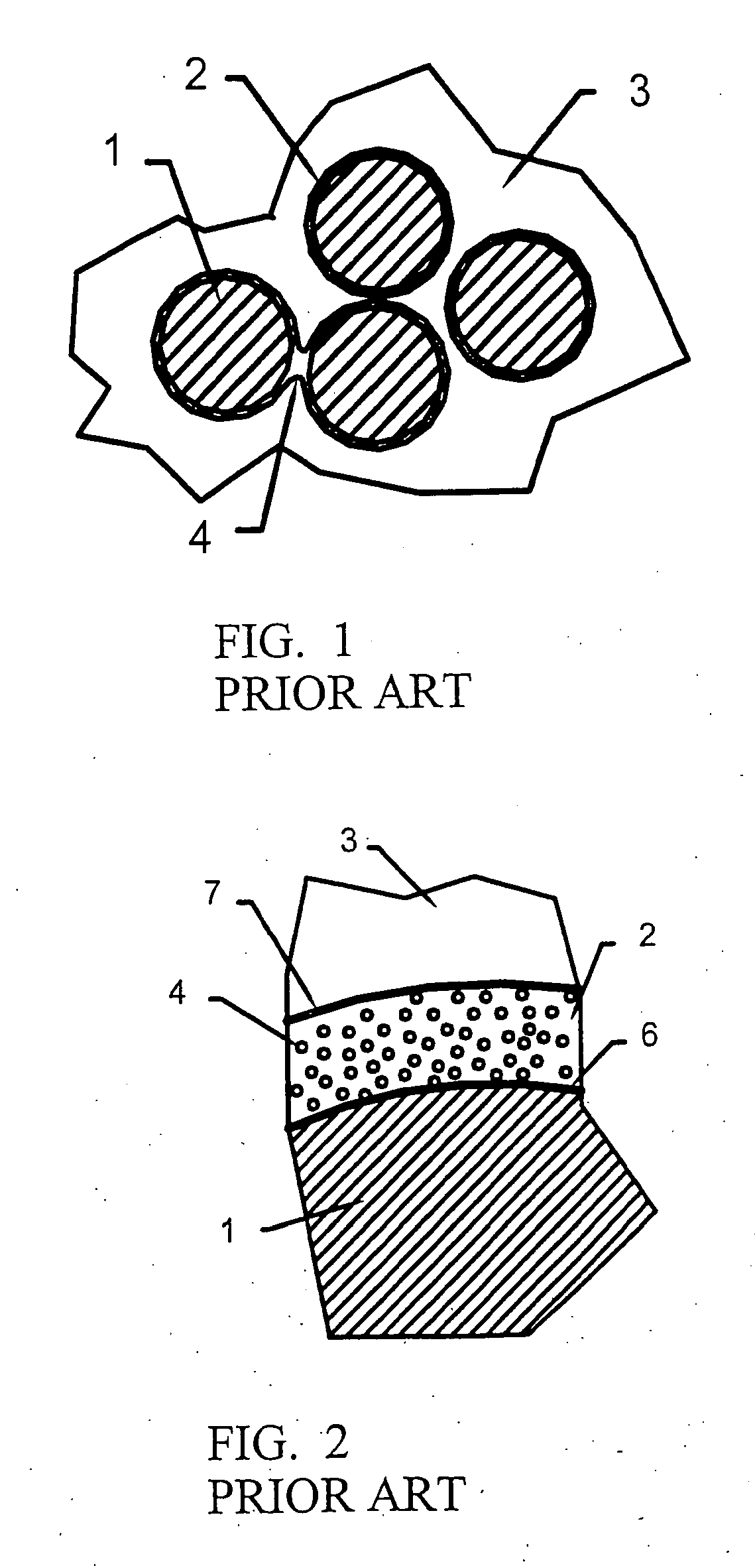
Ceramic-forming polymer material
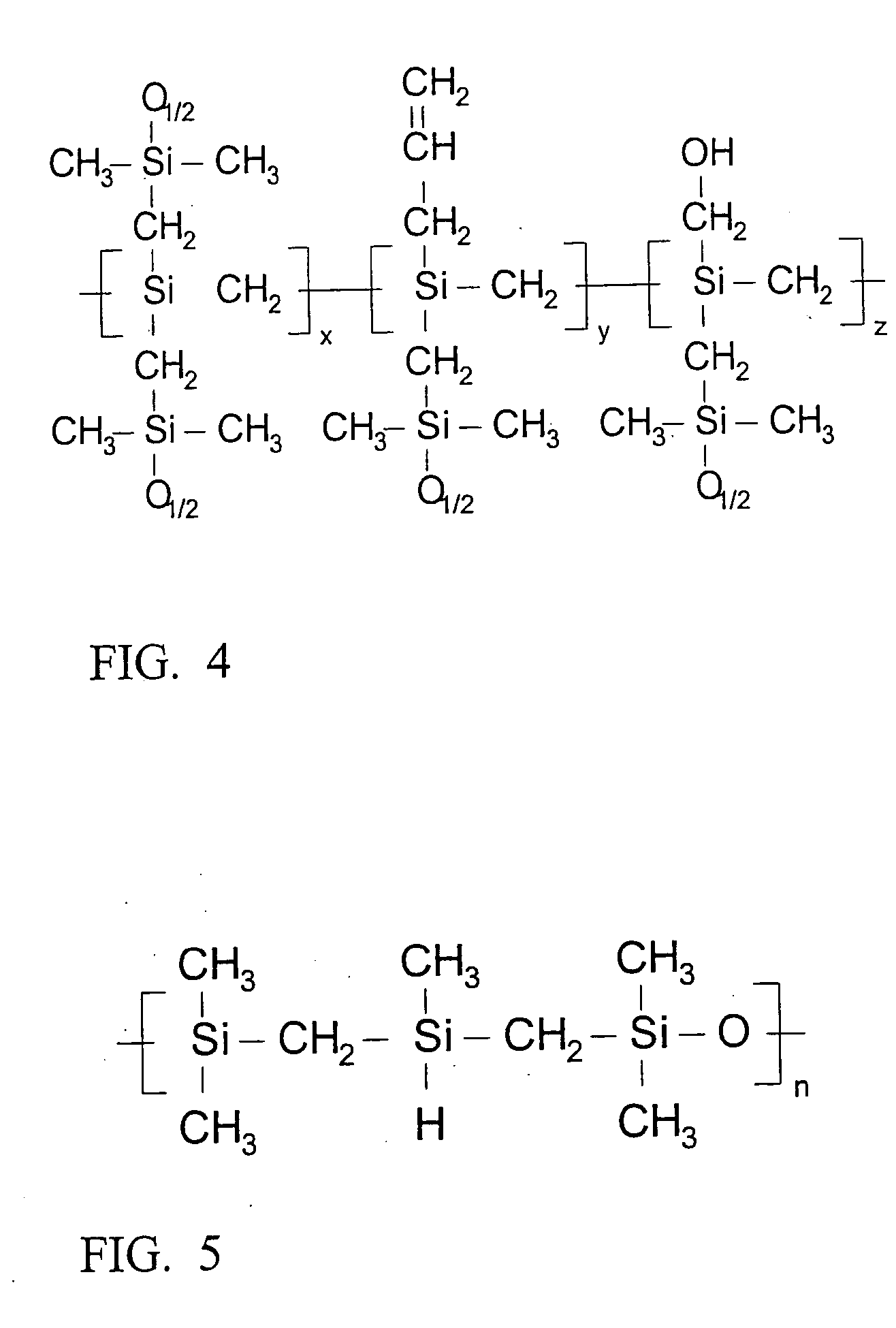
Disclosed is a polymer material comprised of at least one non-cyclic ceramic-forming polymer. The porosity and elemental composition of the resulting ceramic can be varied by inclusion of polymers with particular ratios of carbon, silicon, oxygen, and hydrogen and by manipulation of the conditions under which the polymer material is converted to a ceramic. The resulting ceramic may be useful in fiber-reinforced ceramic matrix composites (CMCs), semiconductor fabrication, fiber coatings, friction materials, and fire resistant coatings. A first aspect of the invention provides a compound of formula I wherein x is between about 0.75 and about 0.9, y is between about 0.05 and about 0.15, and z is between about 0.05 and about 0.20.
Owner:STARFIRE SYST
Solvent-free, radiation-curable, optical glass fiber coating composition and solvent-free method for making a solvent-free, radiation-curable, optical glass fiber coating composition
InactiveUS6107361AViscosity of mixtureViscosity of the mixture formed by this invention can be fine-tunedPhotomechanical apparatusCoatingsCarbamateSolvent free
The invention relates to a solvent-free radiation curable, optical glass fiber coating composition containing: a) a urethane oligomer having a functional group capable of polymerization in the presence of actinic radiation, with an average functionality of at least about 1.2, having a vinyl addition polymer as backbone. b) a urethane compound having a functional group capable of polymerization in the presence of actinic radiation, with an average functionality of at least about 1, containing an organic moiety having about 5 or more carbon atoms as backbone. c) a reactive diluent. Furthermore, the invention relates to a solvent-free method for producing a solvent-free, radiation curable urethane oligomer composition.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
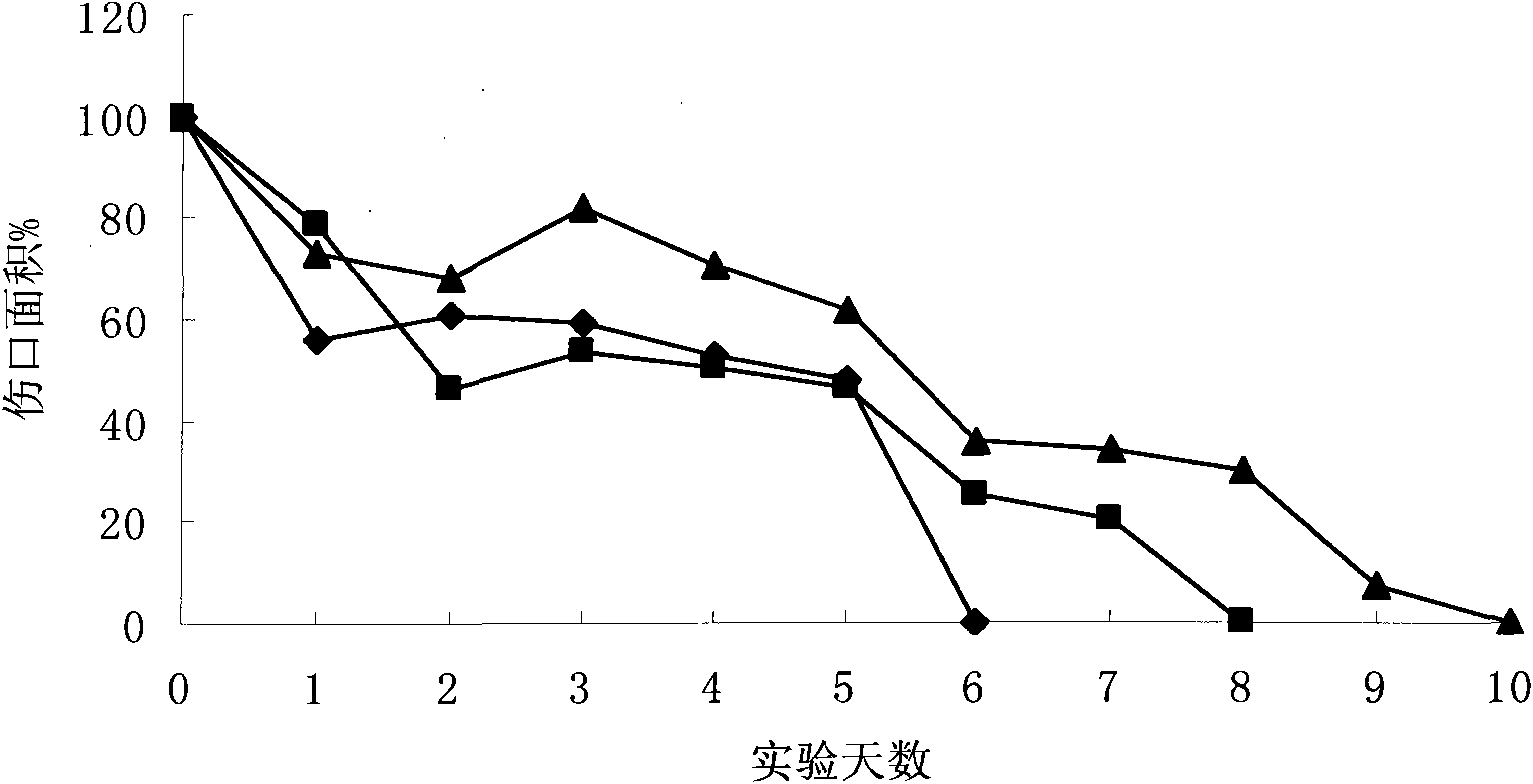
Dressing composition used for inhibiting scars and accelerating wound healing and application thereof
InactiveCN101897990APromote healingShorten healing timeAbsorbent padsBandagesCarboxymethyl-chitosanSodium hyaluronate
The invention discloses a dressing composition used for inhibiting scars and accelerating wound healing and application thereof. The dressing composition consists of chitosan, acidic polysaccharide and panax notoginseng saponins in a weight proportion of 100:10-50:10-100, wherein the chitosan is selected from chitosan, chitosan lactate, acetate and hydrochloride; the acidic polysaccharide is selected from sodium carboxymethyl chitosan, sodium hyaluronate, zinc hyaluronate, sodium alginate and sodium carboxymethyl cellulose; and the panax notoginseng saponins accounts for no less than 40.0 percent of the total weight of ginsenosides Rg1 and Rb1. The formulations of the dressing composition are xerogel powder, capsules, gel membranes, hydrogels and fiber coatings. The dressing composition is used for wounds, burns, scalds, crush injuries, skin ulcers, gastroenteric ulcers and no healing of the wounds, has the advantages of rapid hemostasis, exudate reduction, moisturizing, air permeability, bacteriostasis, inflammation diminishing, itch relieving, no adhesion, effective inhibition of scarring, remarkable reduction of wound healing time and no need of replacing dressings, so that thedressing composition basically meets requirements of perfect functional external dressings.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Preparation of solid-phase microextraction (SPME) fiber and extraction device assembled by same
InactiveCN102989432AOvercoming the problem of poor mechanical strengthUnique designComponent separationOther chemical processesSolid-phase microextractionMetal-organic framework
Disclosed is a preparation of an SPME fiber. A covalent bond method is adopted to prepare metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) as a coating for the extraction fiber. The fiber preparing method includes performing APTES amino-functionalization on a quartz fiber, namely, placing the fiber with amino on the surface into an MOF solution for reaction. An extraction device assembled by the prepared SPME coating comprises a device body, a microsyringe outer tube, a microsyringe needle, a push-pull rod and the extraction fiber with the coating, wherein the push-pull rod is arranged in the microsyringe outer tube and forms a sliding matching with the inner wall of the tube, the lower end of the push-pull rod is corroded by an aqua regia solution to obtain a corrosion end which is inserted into the extraction fiber with the coating, and a handle is arranged at the upper end of the push-pull rod. The preparation and the device have the advantages that an organic ligand of the extraction fiber coating and the MOFs is highly ordered and controllable, the extraction device has a novel structure, the coating fiber fixation is firm, and the stability and service life of the extraction fiber coating are improved.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
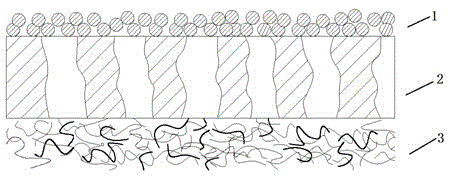
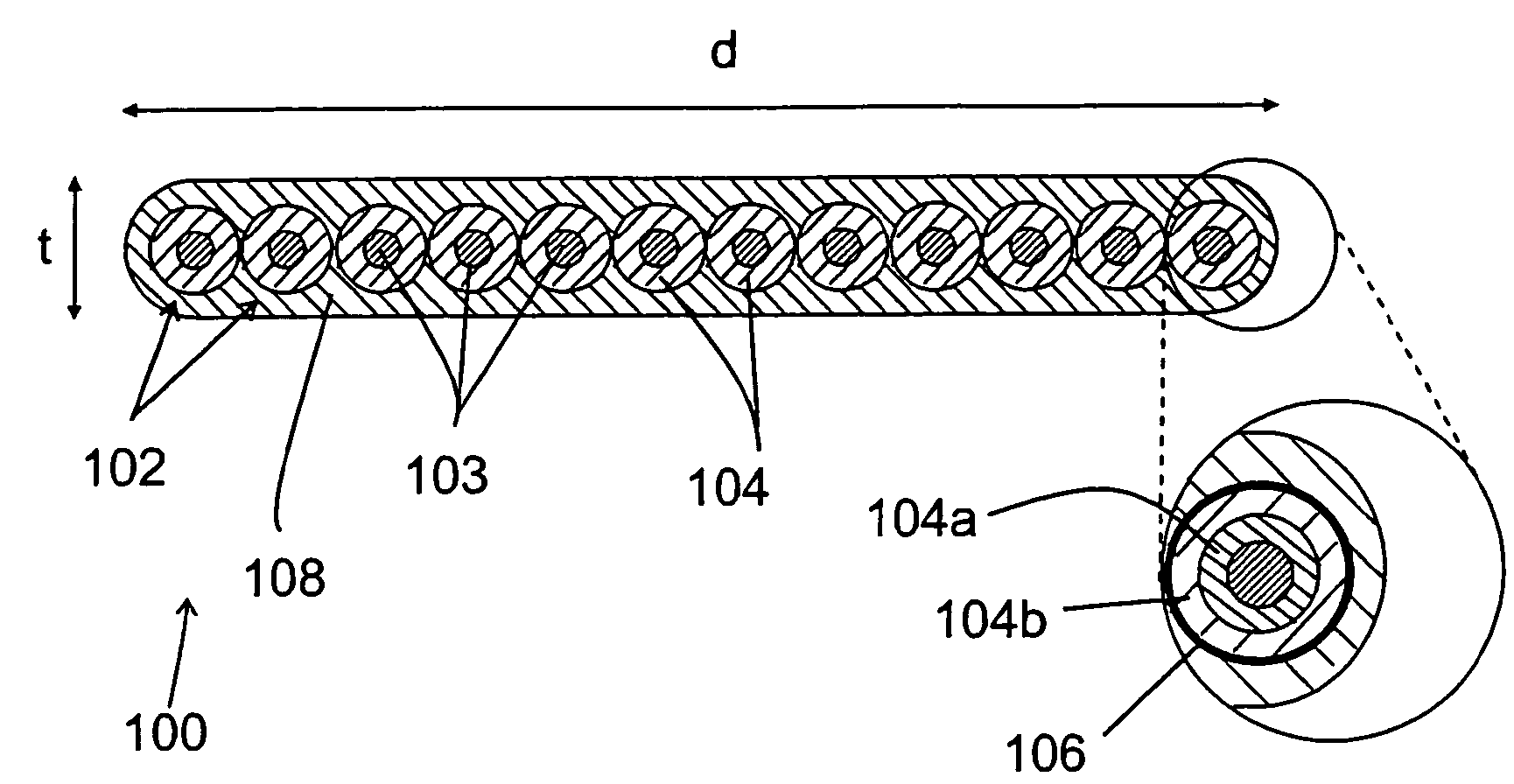
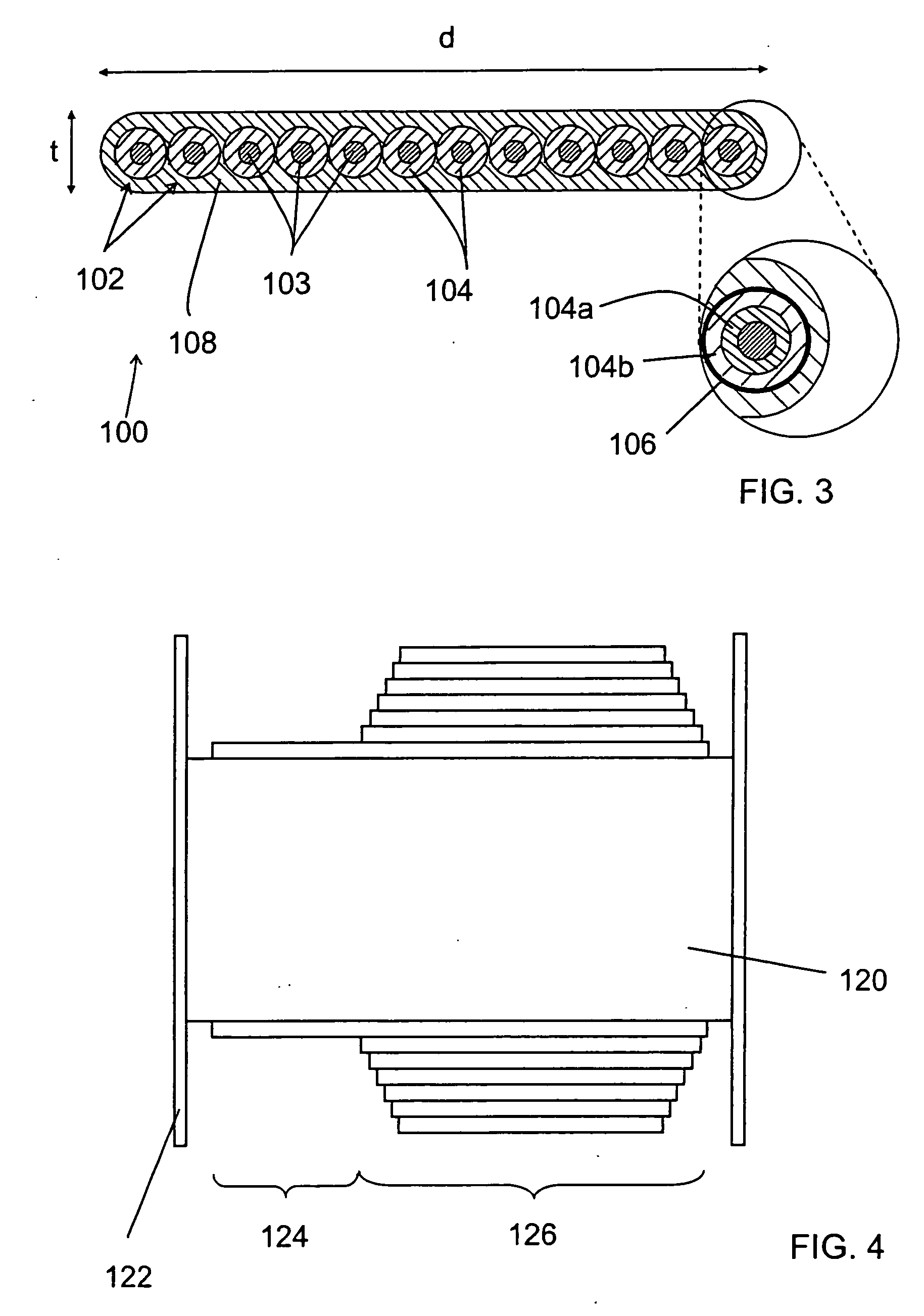
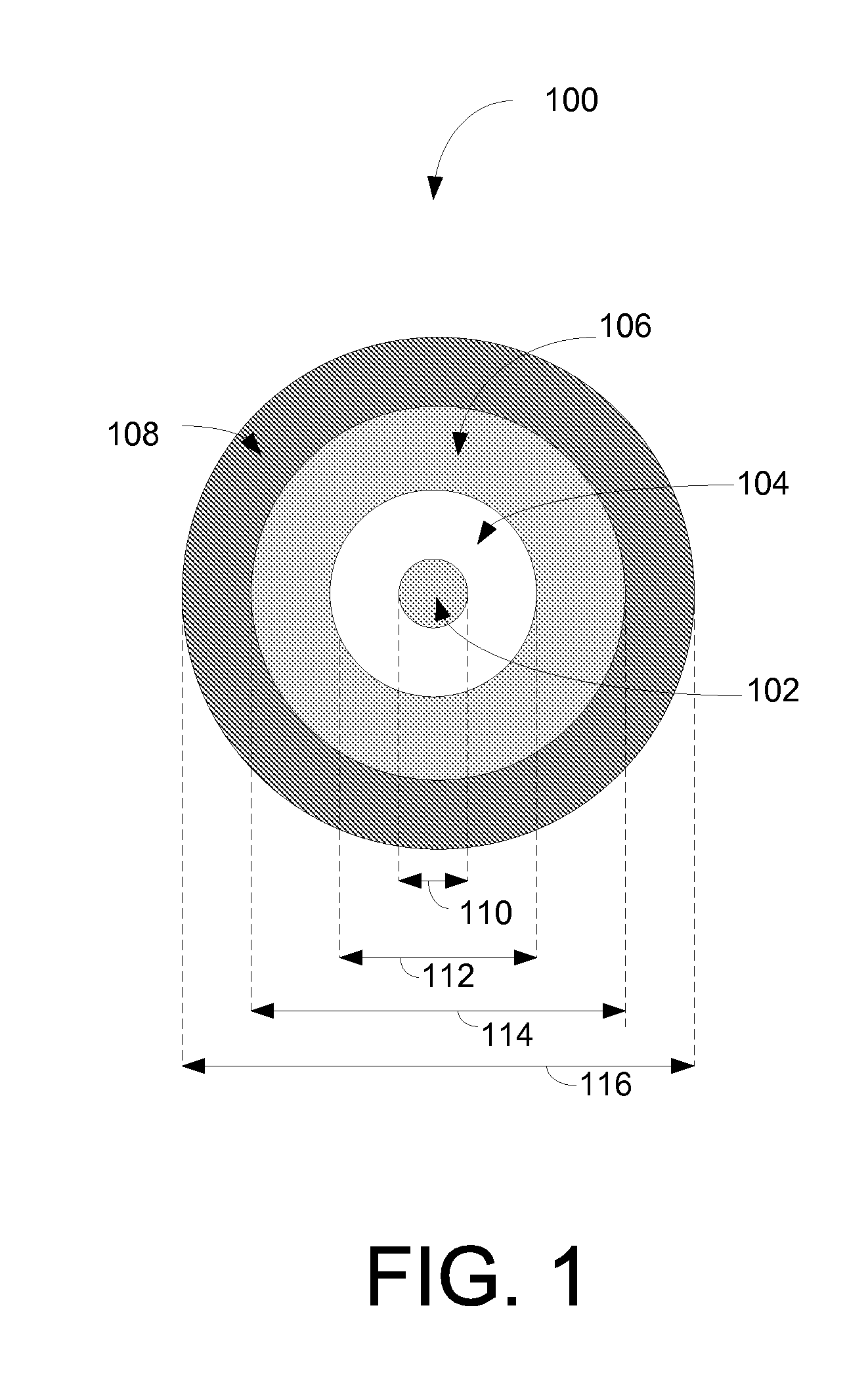
Optical fiber coating system and coated optical fiber
ActiveUS20050031283A1Low microbending lossEnvironmentalGlass optical fibreOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingUltrasound attenuationCoating system
The present invention relates to optical fiber coating systems capable of providing a high degree of microbend protection to an optical fiber, and an optical fiber coated therewith. According to one embodiment of the invention, an optical fiber coating system includes a primary coating and a secondary coating, wherein when a ribbon having twelve large effective area optical fibers coated with the coating system is subjected to the ribbon optical performance test at a wavelength of 1550 nm, the average change in attenuation is about 0.020 dB / km or less.
Owner:CORNING INC
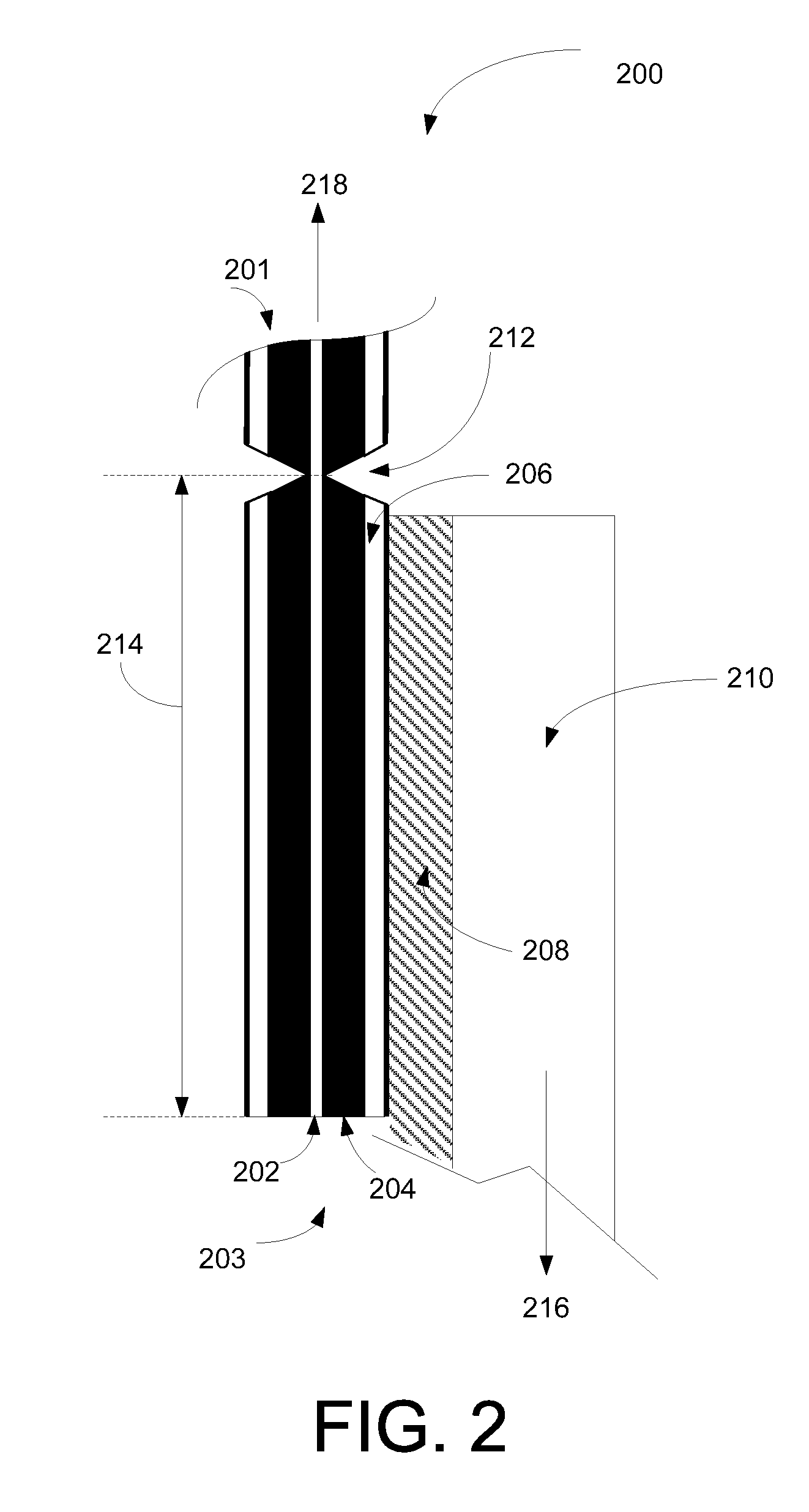
Systems and methods for coating optical fiber
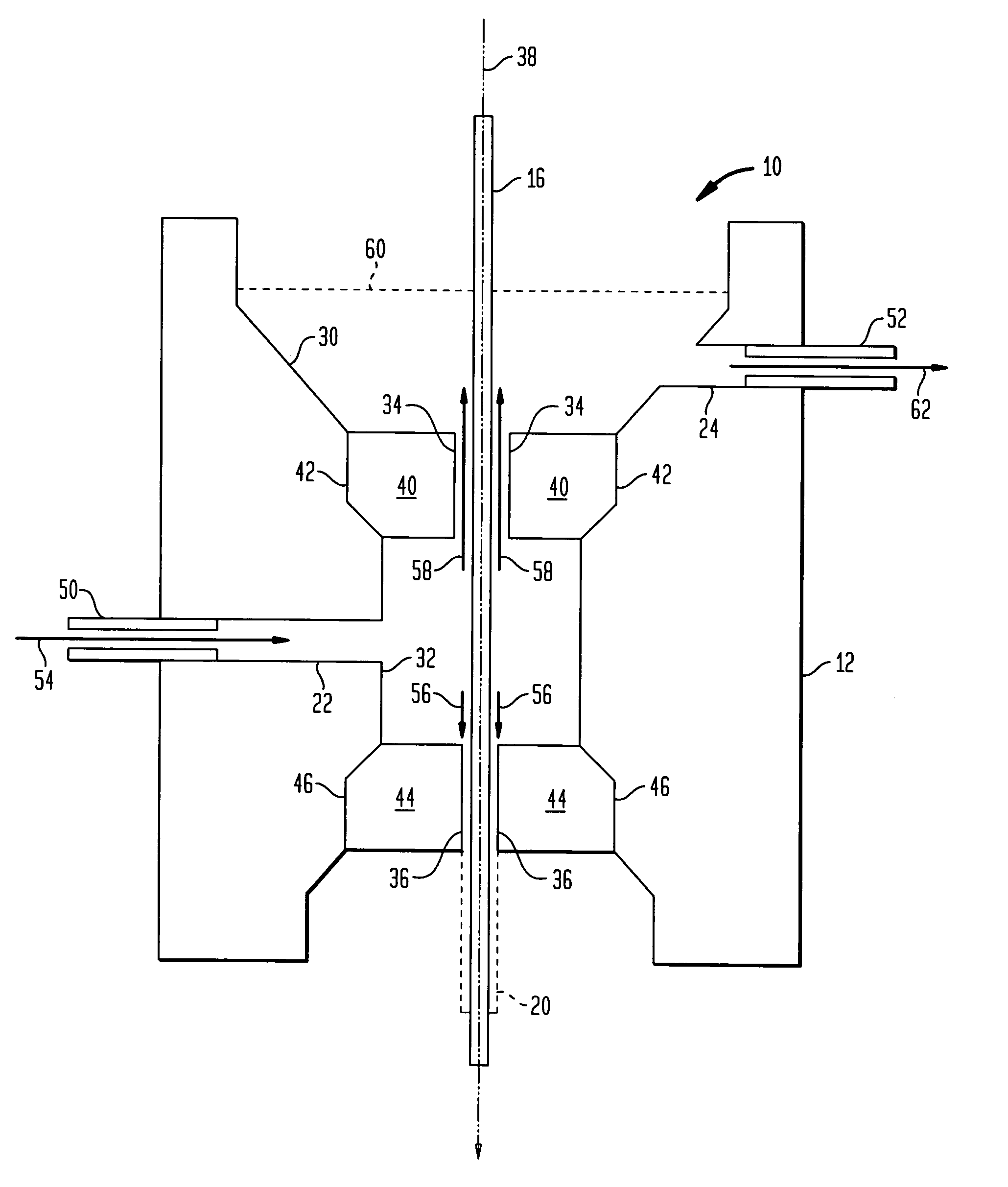
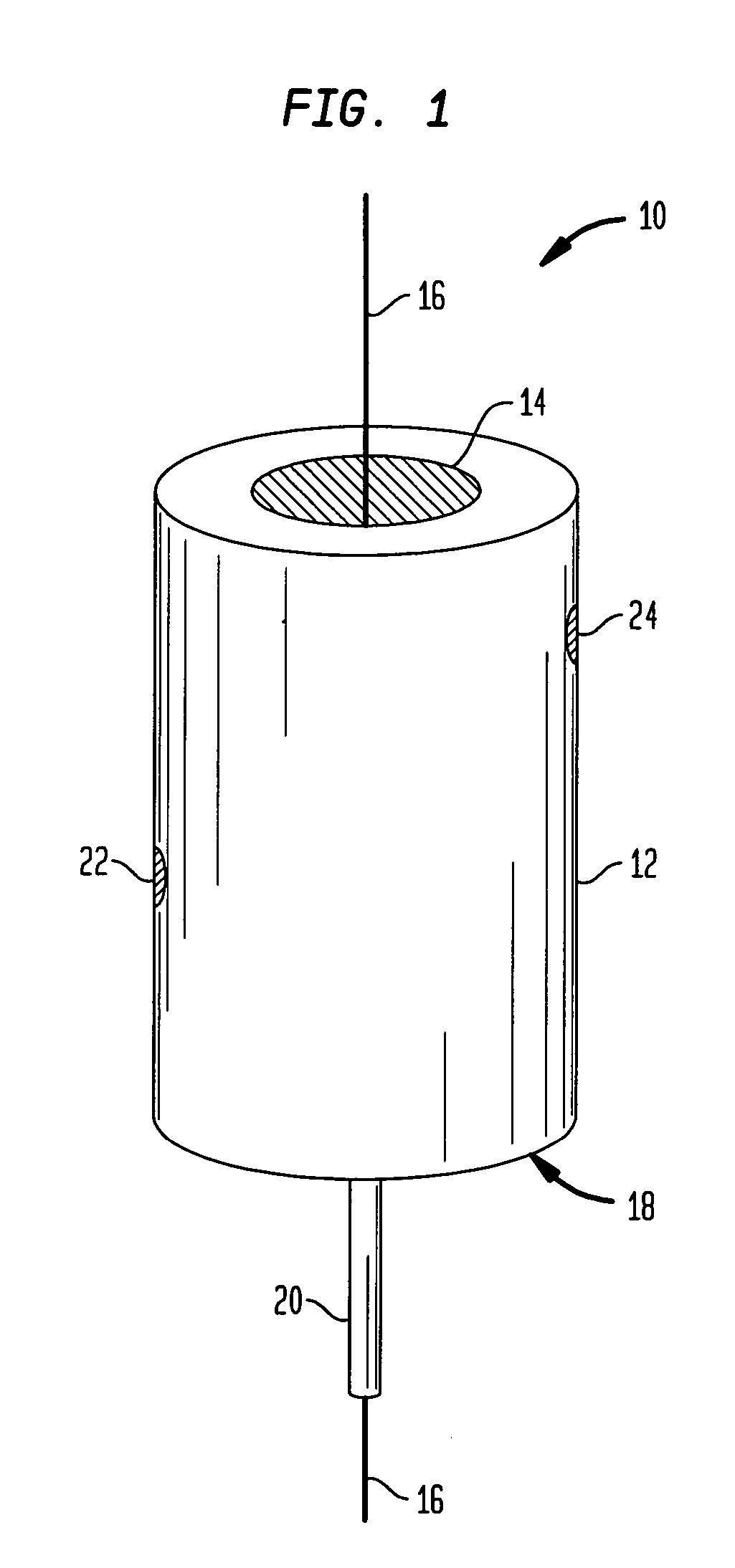
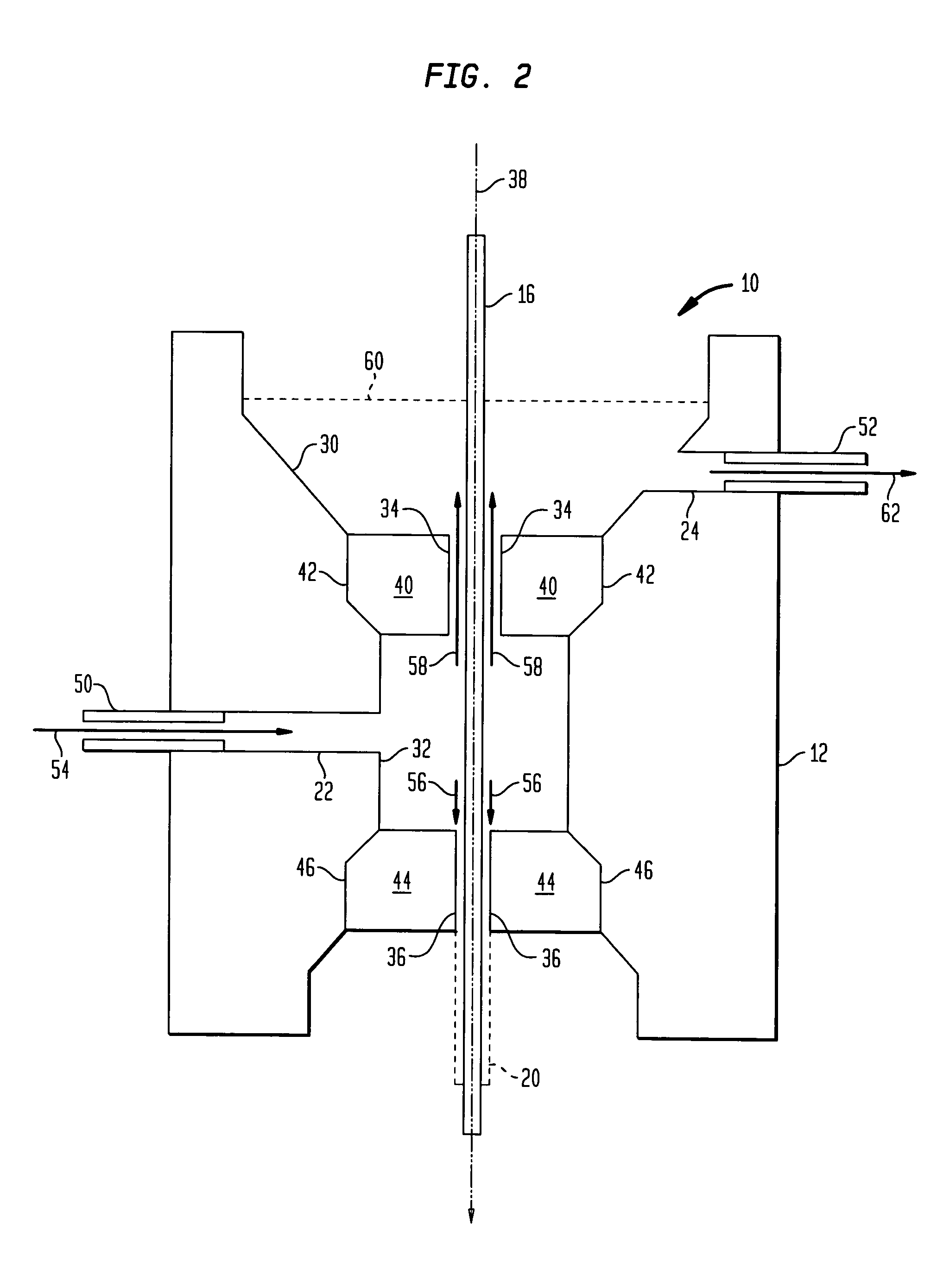
A fiber coating applicator includes a chamber and a cup positioned over the chamber. The cup is connected to the chamber by an entrance aperture. The chamber includes an exit aperture opposite the entrance aperture. The cup, entrance aperture, chamber, and exit aperture define a pathway for a fiber, such as an optical fiber, to be coated. The chamber further includes an input port for pumping a coating material into the chamber. The entrance aperture is dimensioned such that as a fiber travels along the pathway and coating material is pumped into the chamber, coating material travels upward through the entrance aperture around the fiber into the cup, the upward flow of coating material being restricted by the fiber and entrance aperture such that there is a hydrostatic pressure in the chamber. The exit aperture is dimensioned to shape coating material around a fiber traveling along the pathway.
Owner:FURAKAWA ELECTRIC NORTH AMERICA INC
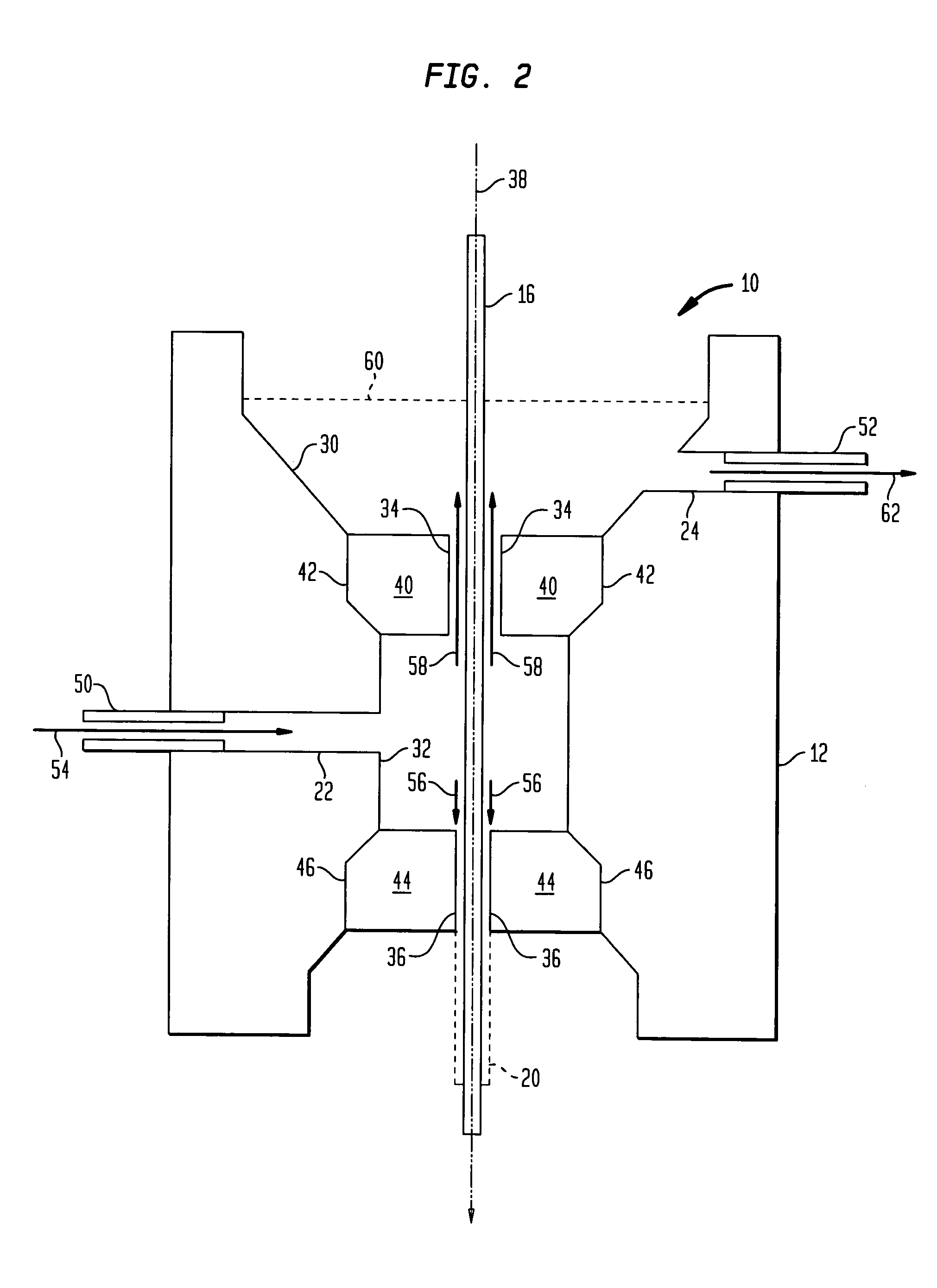
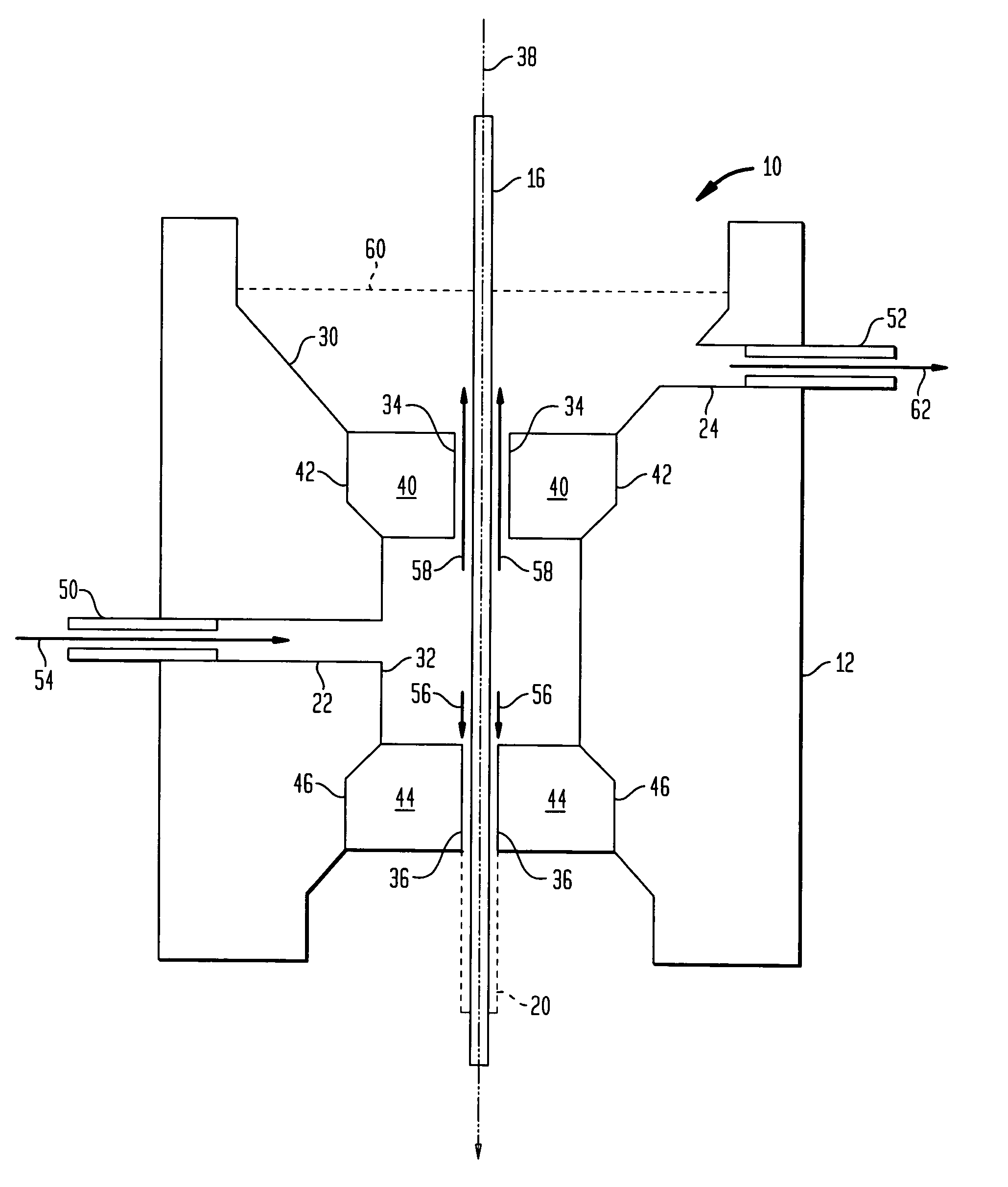
Systems and methods for coating optical fiber
A fiber coating applicator includes a chamber and a cup positioned over the chamber. The cup is connected to the chamber by an entrance aperture. The chamber includes an exit aperture opposite the entrance aperture. The cup, entrance aperture, chamber, and exit aperture define a pathway for a fiber, such as an optical fiber, to be coated. The chamber further includes an input port for pumping a coating material into the chamber. The entrance aperture is dimensioned such that as a fiber travels along the pathway and coating material is pumped into the chamber, coating material travels upward through the entrance aperture around the fiber into the cup, the upward flow of coating material being restricted by the fiber and entrance aperture such that there is a hydrostatic pressure in the chamber. The exit aperture is dimensioned to shape coating material around a fiber traveling along the pathway.
Owner:FURAKAWA ELECTRIC NORTH AMERICA INC
Water-tolerant decorative fiber coating
The invention discloses a water-tolerant decorative fiber coating which can be used as a special wall coating for interior and exterior walls. The water-tolerant decorative fiber coating comprises the following raw materials in parts by weight: 10-100 parts of fibers, 0.1-10 parts of a thickener, 5-150 parts of an emulsion, 0.1-10 parts of an auxiliary material, 10-1000 parts of a liquid and 0-20 parts of other components. The emulsion is one or more of a vinyl acetate-acrylic emulsion, a silicone acrylic emulsion, a styrene-acrylic emulsion and a pure acrylic emulsion. The auxiliary material is one or more of a foamer, a flame retardant, a mildew preventive, a preservative, a dispersant and essence. The liquid is water. The other components are one or more of glitter powder, metallic yarns, cannetille, pearl powder and noctilucent powder. The water-tolerant decorative fiber coating disclosed by the invention is good in decorative effect, can be used to draw and puzzle, fully improves the decorative grade, and has the advantages of weather fastness, scrubbing resistance, long service life, no crack, washability, seamlessness, no mildew, flame retardance and the like. Many defects of conventional fiber coatings such as fall of powdered gold, gold wires and fiber, water funk and short service life are remarkably improved, and many problems of seam, mildew, edge warping and the like of wallpaper are solved.
Owner:FUZHOU TONAK DECORATIVE MATERIAL
Water management properties of pem fuel cell bipolar plates using carbon nano tube coatings
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Ceramic forming polymer derived ceramic composite and methods
InactiveUS20040138046A1Resists oxidationLess-expensive to applyLiquid surface applicatorsCoatingsCeramic compositeHydrogen
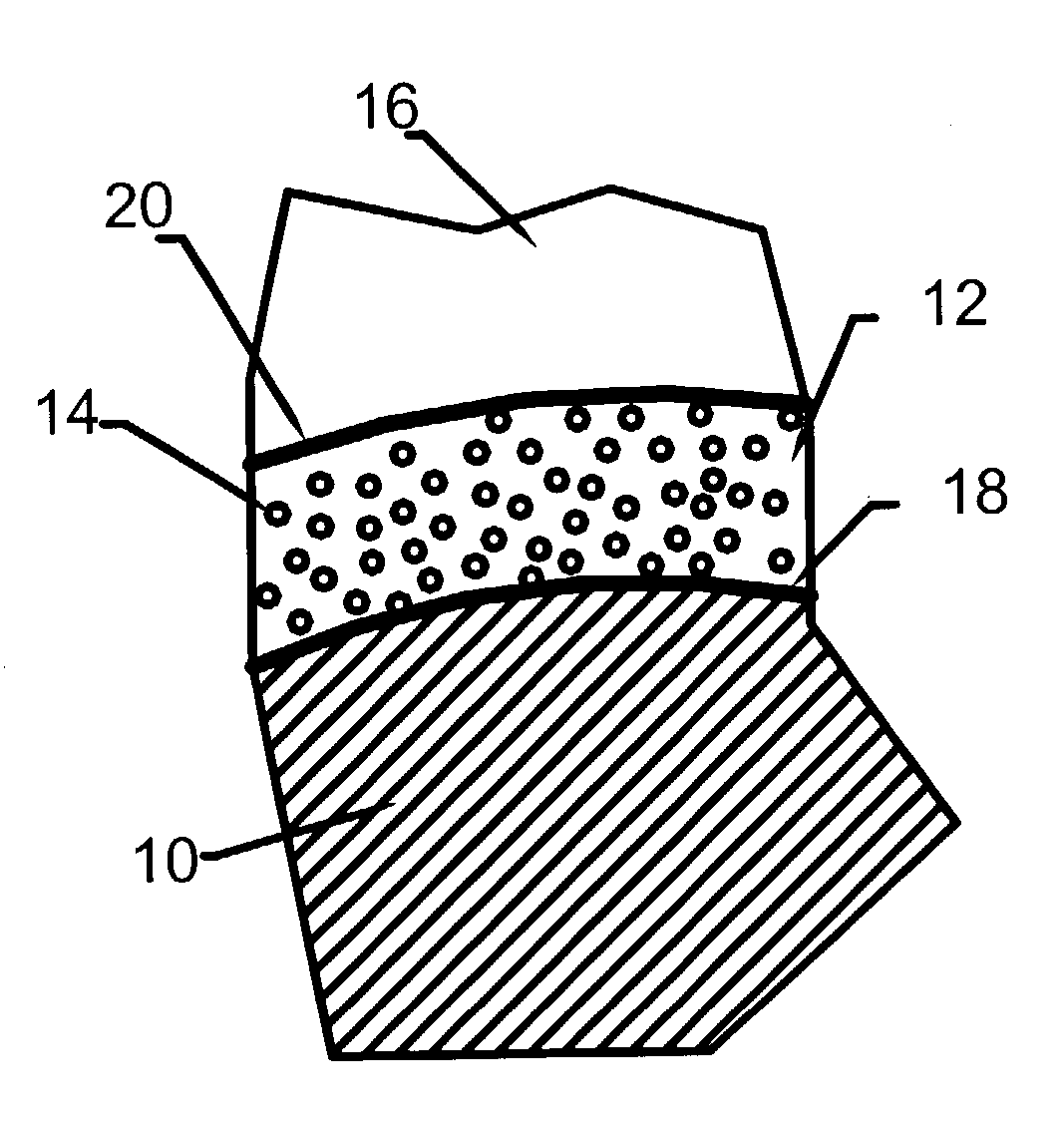
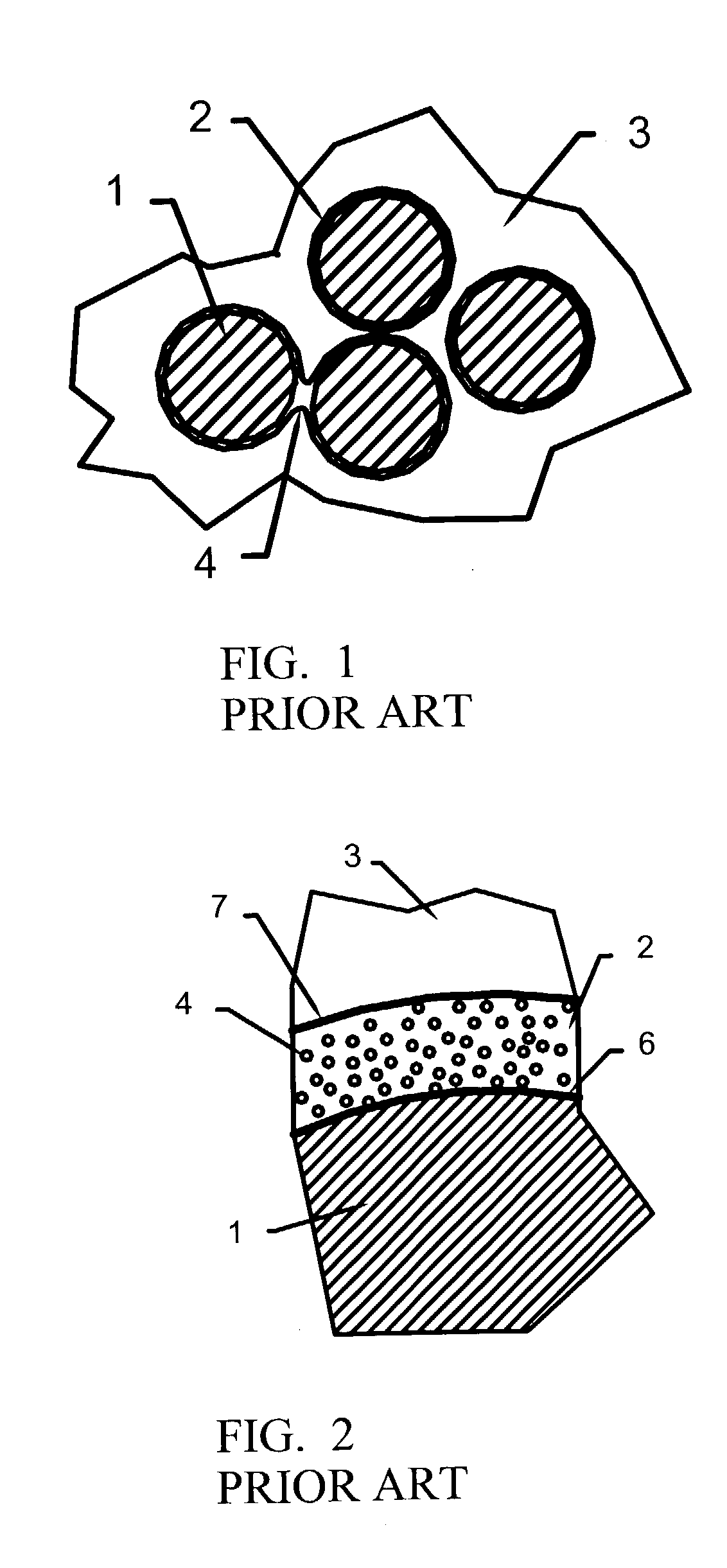
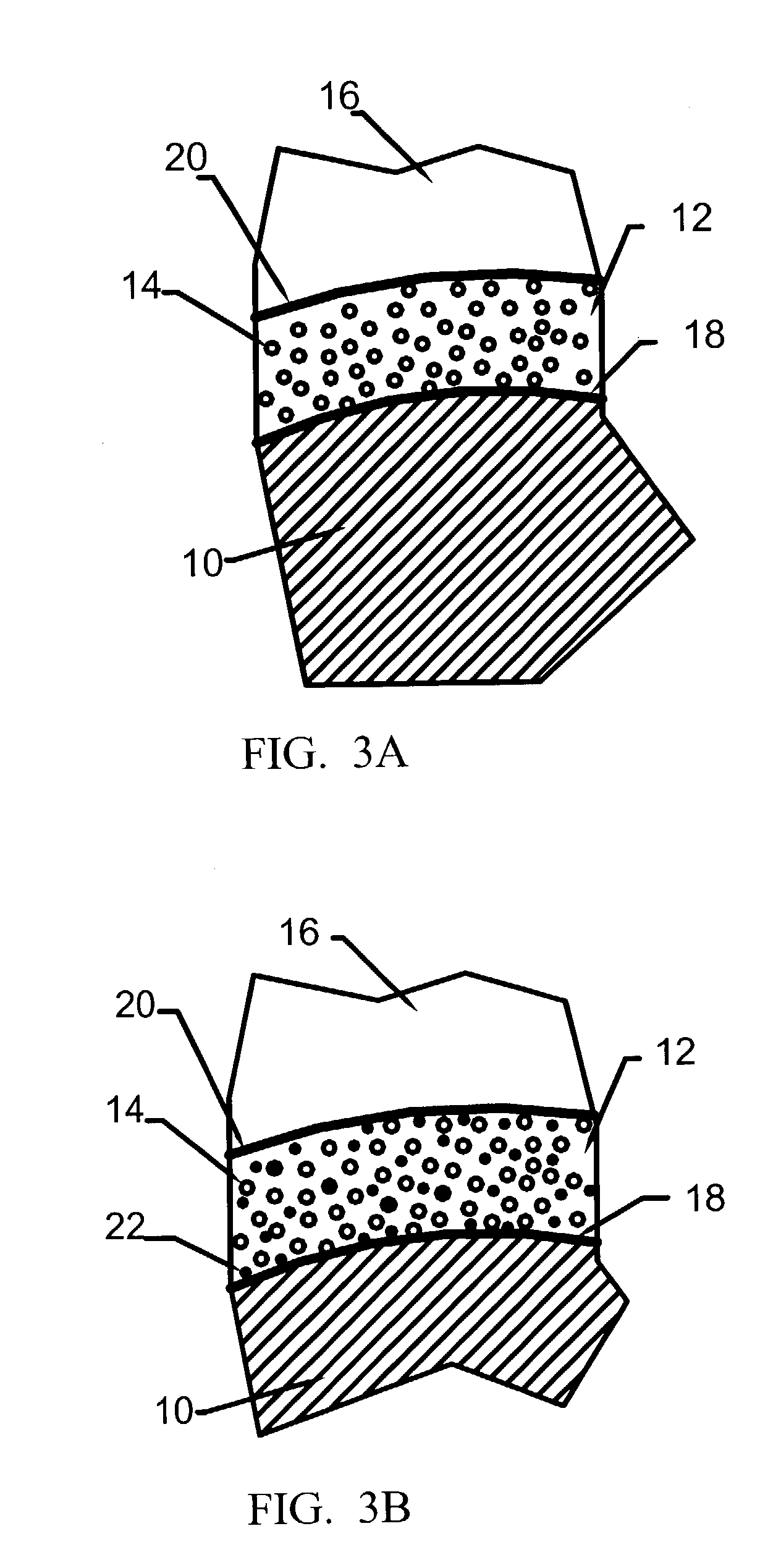
A ceramic composite having a ceramic coating formed from a ceramic forming polymer of adjustable composition. The ceramic forming polymer is capable of producing a weak interface-type fiber coating for the ceramic composite, resists oxidation and is less expensive to apply. The invention also includes methods of using a ceramic forming polymer to provide fiber coatings tailored to the type of matrix, fiber, or other reinforcement used. The material forms micro-porous and nano-porous coatings on the fibers. The porosity in the coatings provides a low strength interface between the fiber and matrix that imparts the toughness needed in the composite. The material can be provided with controlled ratios of carbon, silicon, oxygen and hyrdrogen to optimize bonding to the fibers, bonding of the matrix to the fiber coating, and environmental protection of the fibers.
Owner:STARFIRE SYST
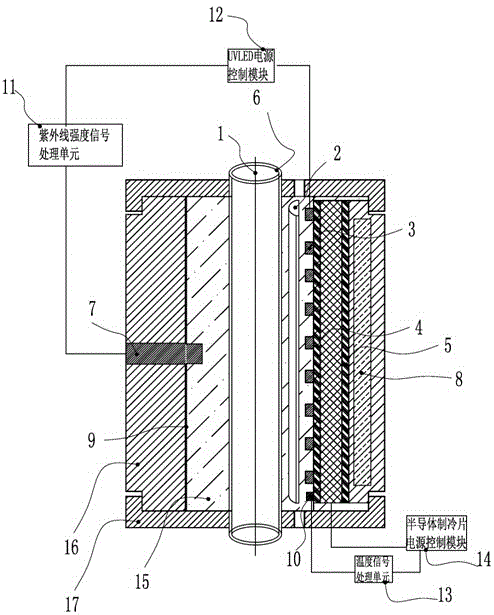
Light intensity-adjustable fiber coating layer ultraviolet curing apparatus
ActiveCN105060739AEfficient use ofSmall operating temperature fluctuationsElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesClosed loopUltraviolet lights
The invention relates to a light intensity-adjustable fiber coating layer ultraviolet curing apparatus. The apparatus comprises a cylindrical mounting base, UVLED light source modules are circumferentially and axially arranged in the inner cavity of the cylindrical mounting base, a cylindrical focusing lens is arranged in front of the luminescence surfaces of the UVLED light source modules to make ultraviolet lights emitted by the UVLED light source modules focused on a curing axis, an ultraviolet sensor is arranged in the inner cavity of the cylindrical mounting base, the ultraviolet sensor is connected with an UVLED power supply control module through an ultraviolet intensity signal processing module, and the UVLED power supply control module is connected with the UVLED light source modules to make the fiber drawing speed and the ultraviolet intensity form a control closed loop. The apparatus allows the output of UVLED light sources and the fiber drawing speed to be adjusted and matched in real time in order to guarantee and improve the fiber coating layer curing quality, efficiently utilize the UVLED light sources and save electric energy; and the apparatus has the advantages of reasonable and simple structure, high curing efficiency, less energy consumption, high automation degree, good coating layer quality and simple use.
Owner:YANGTZE OPTICAL FIBRE & CABLE CO LTD
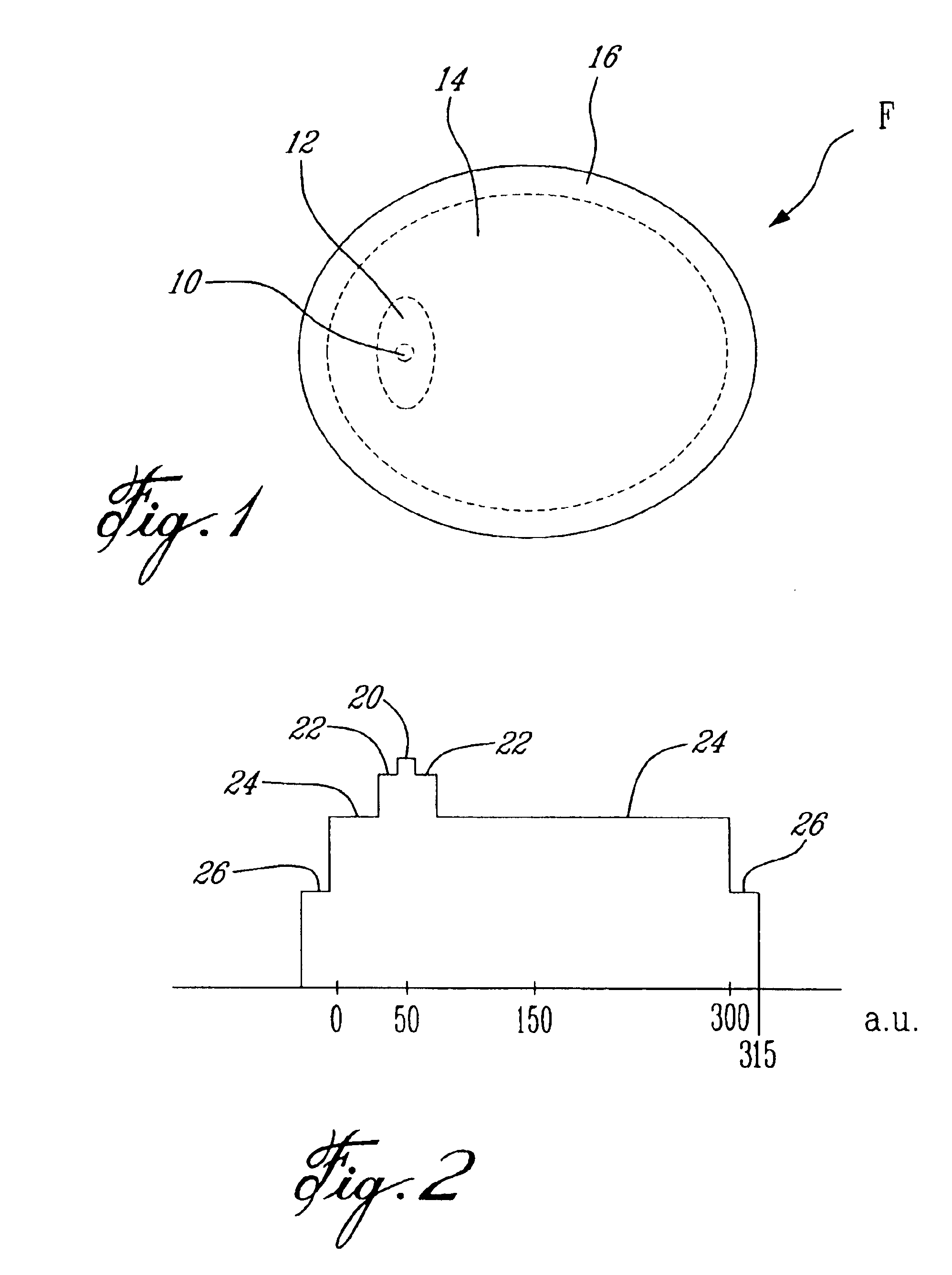
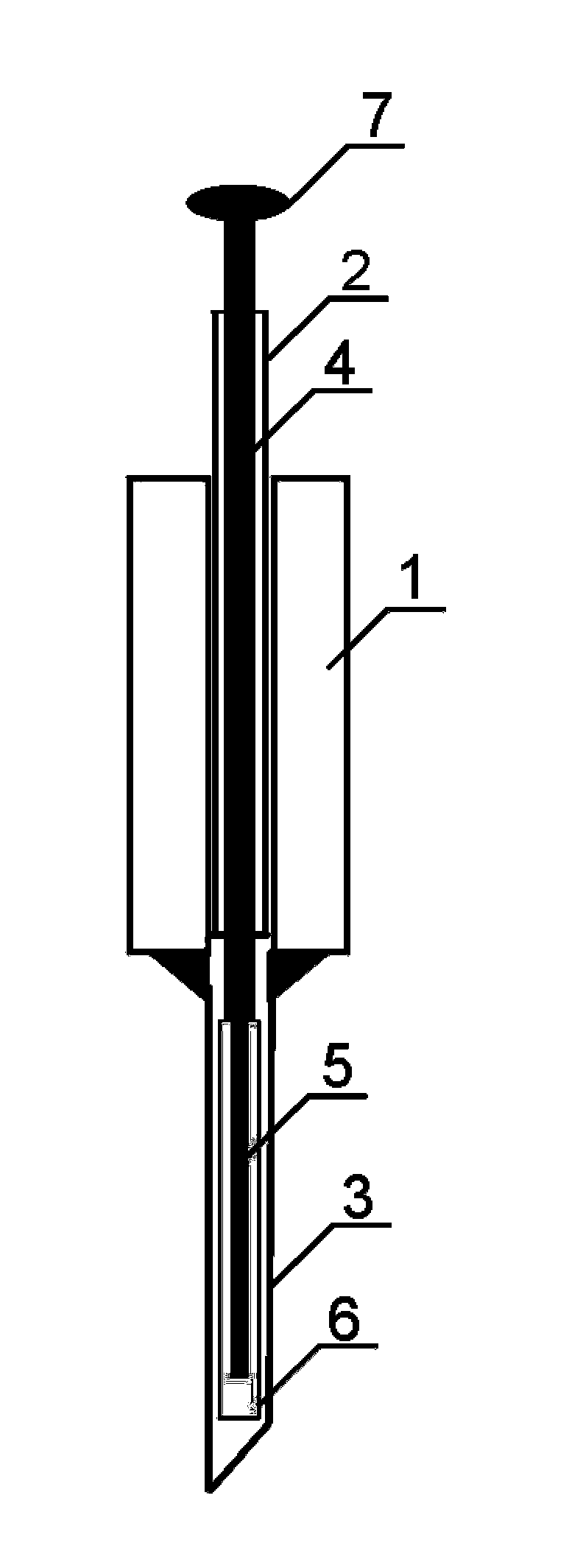
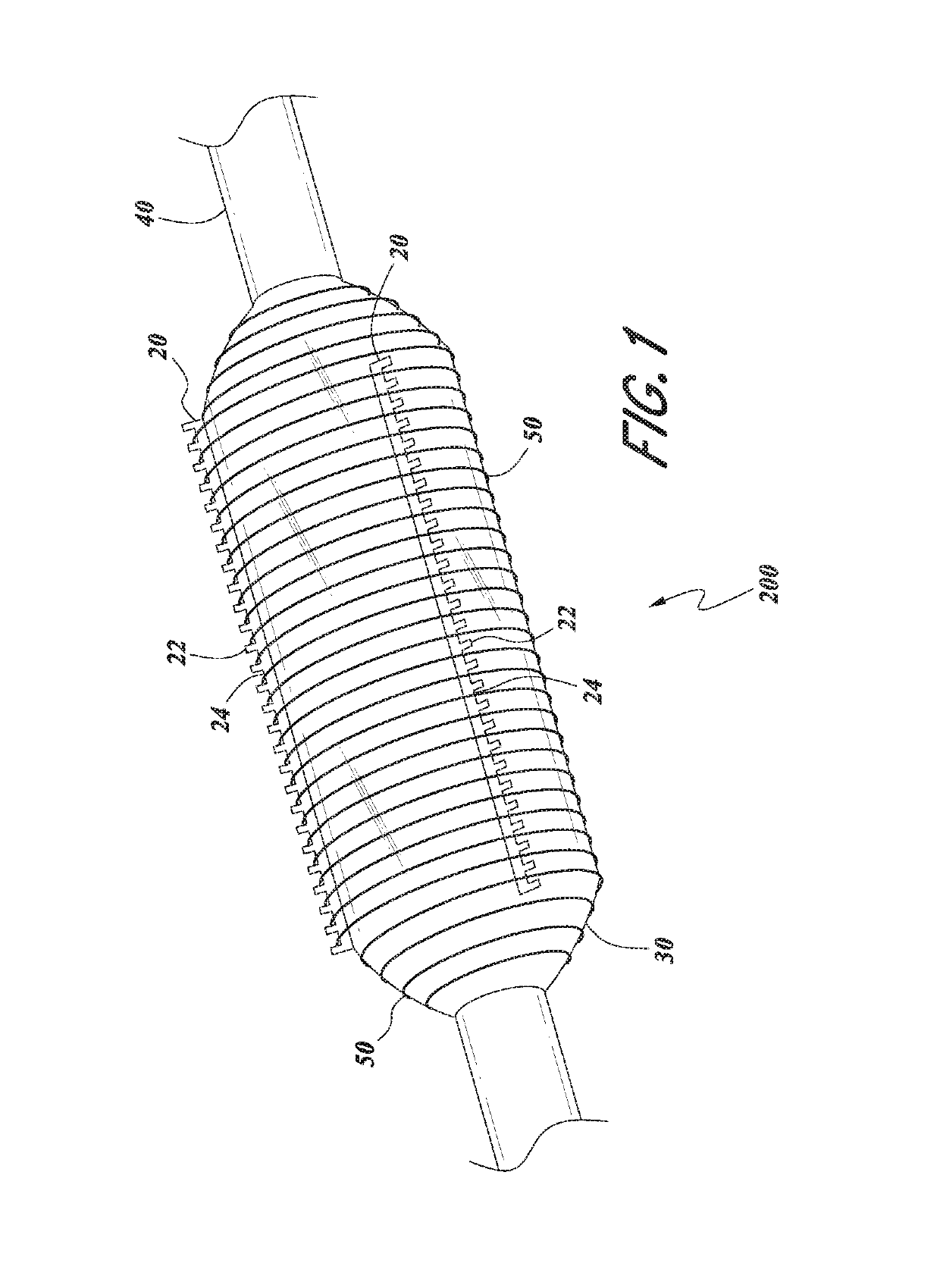
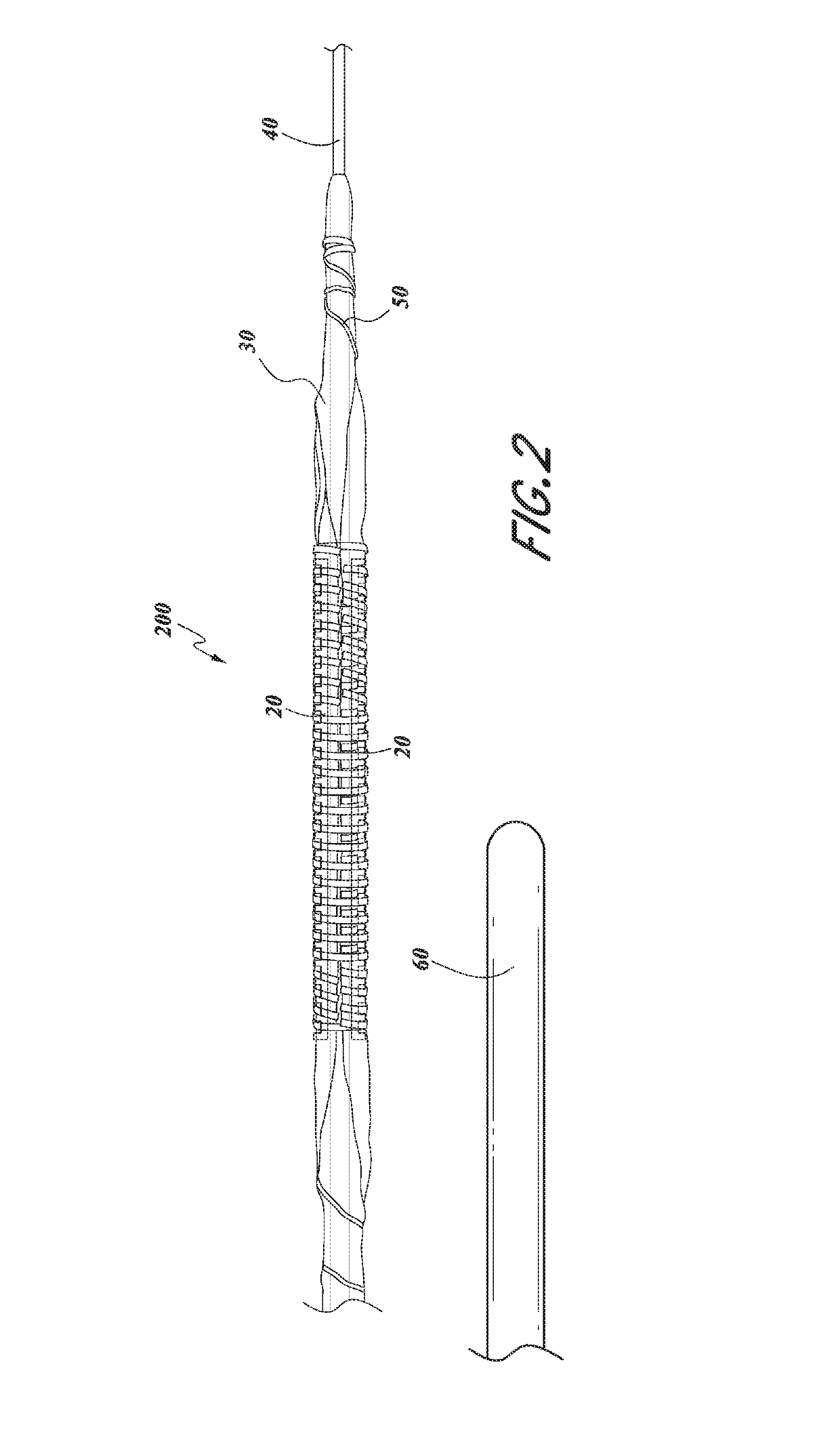
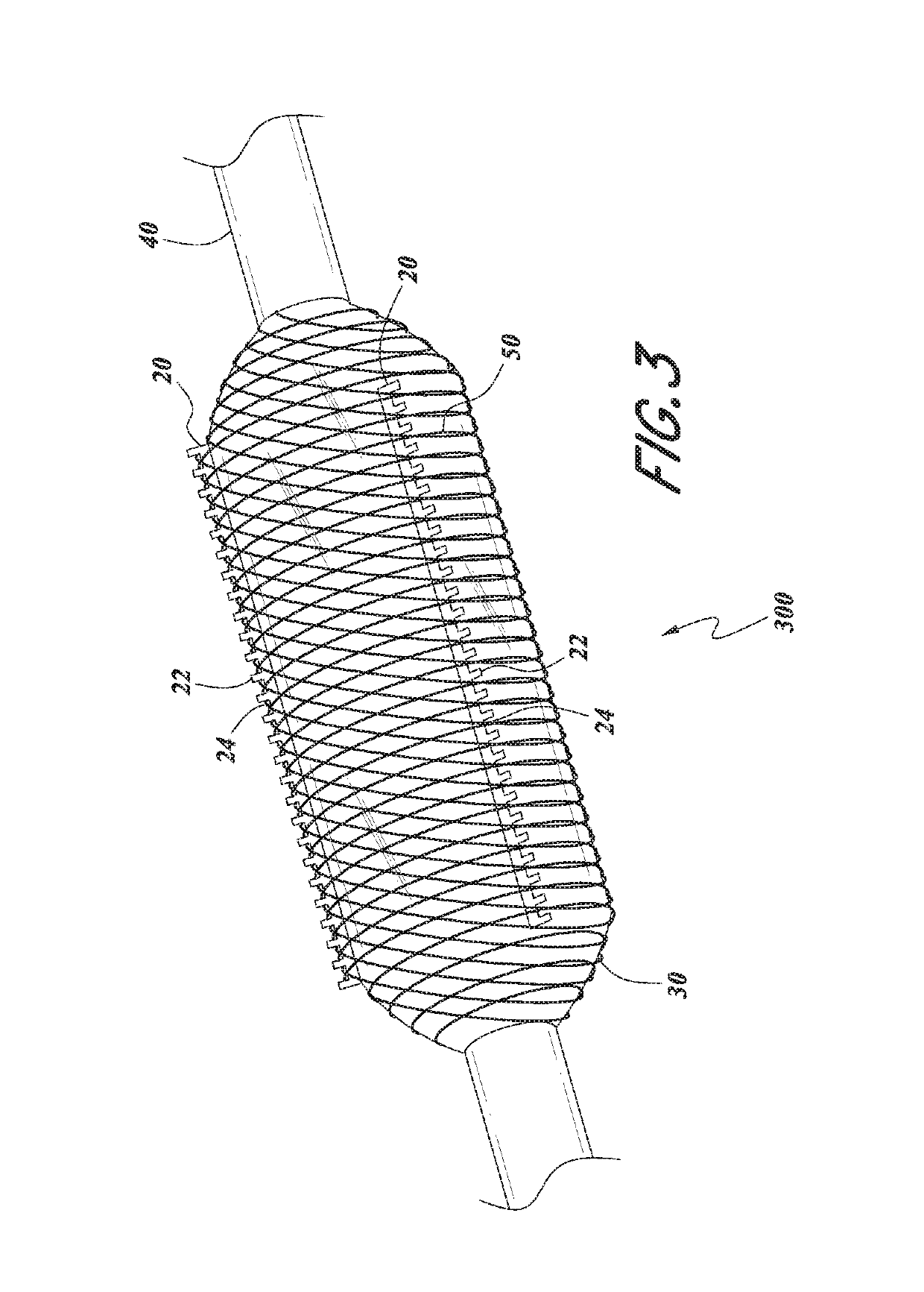
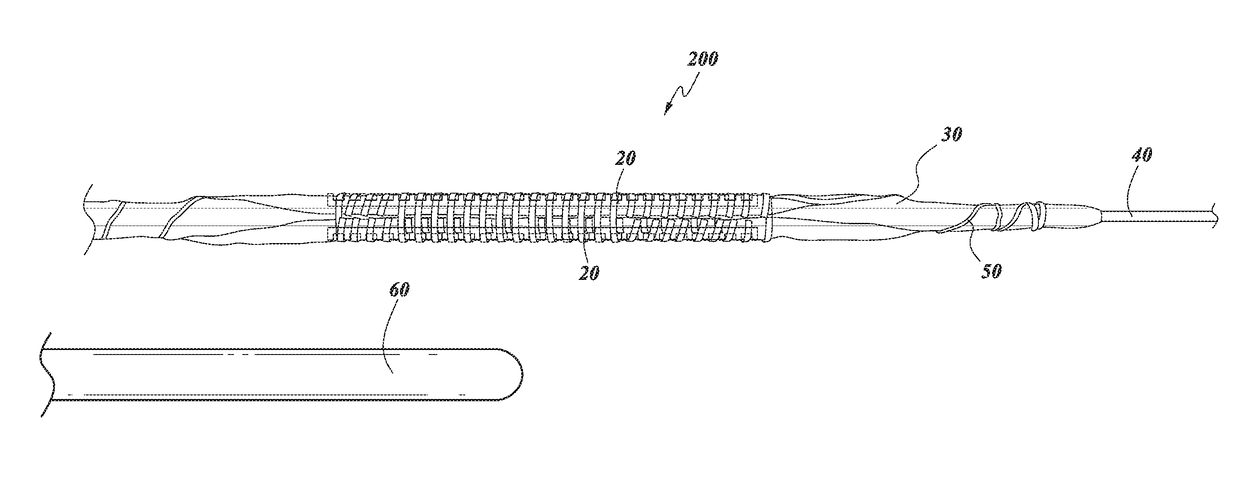
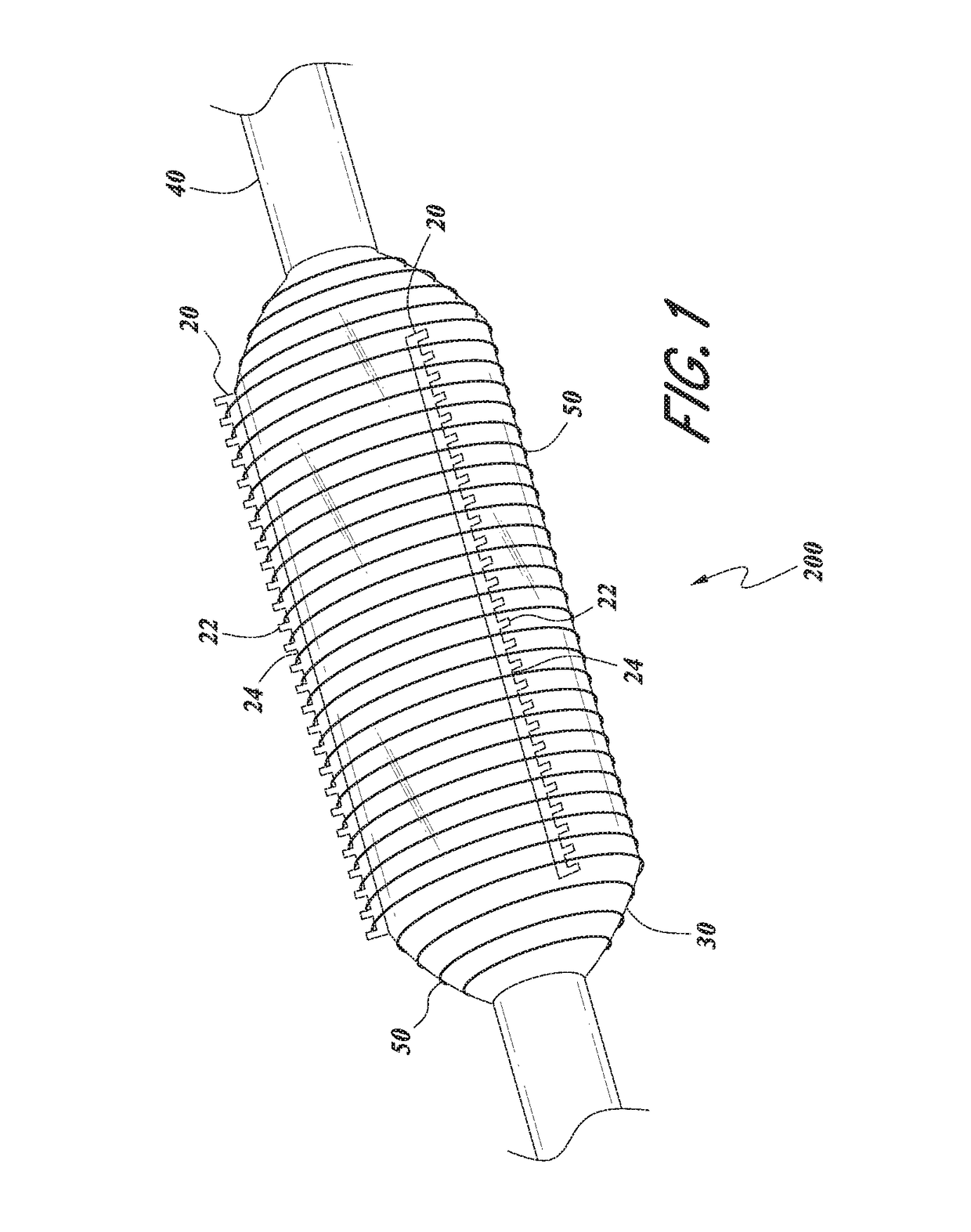
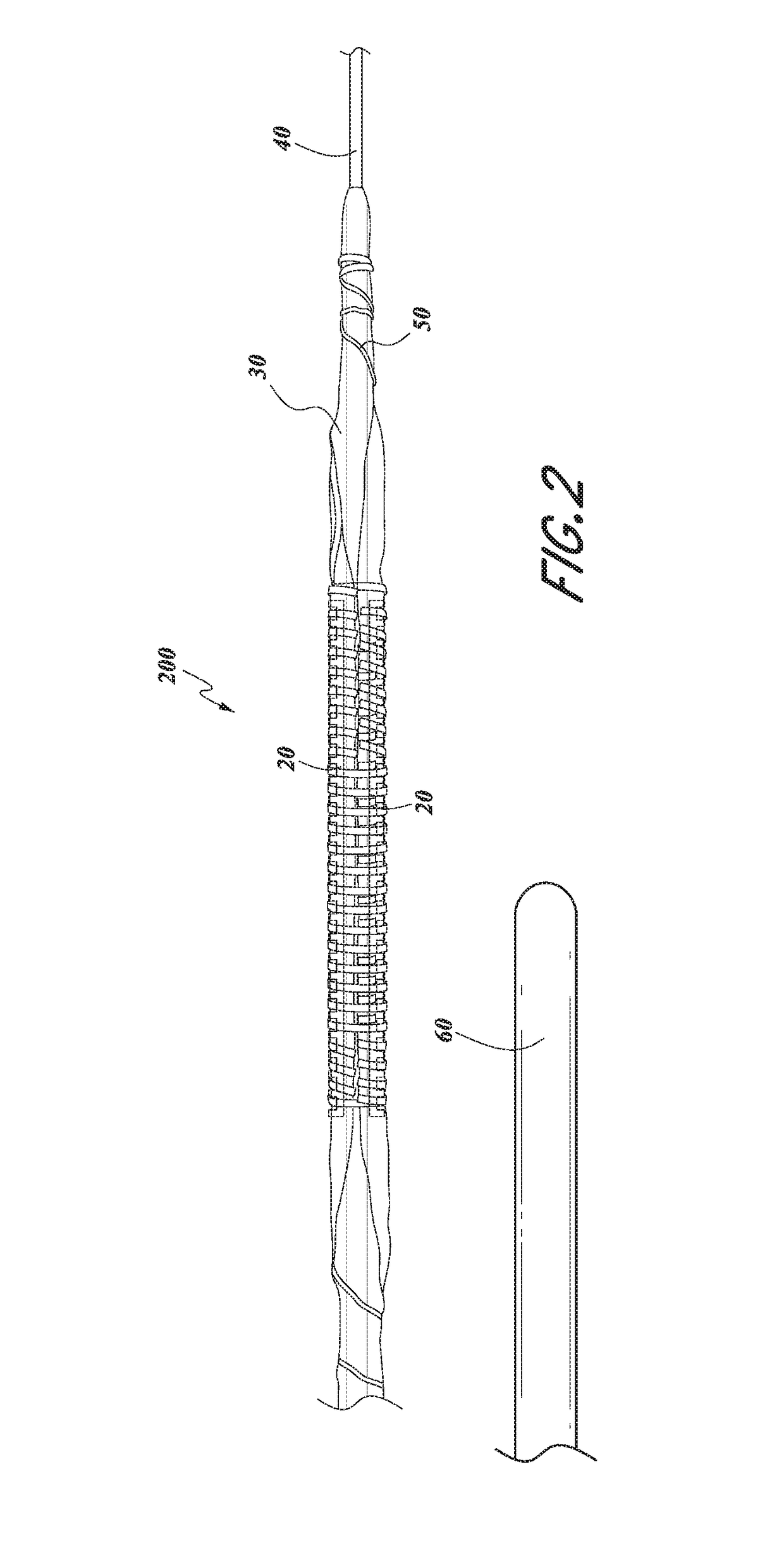
Serration balloon
A serration balloon can have a number of different components and can be made in a number of different manners. One or more longitudinally extending members with periodic raised wedges can be attached to a medical balloon. They can be attached with a fiber coating, a polymer coating, or other methods. A polymer matrix can be used to bond the longitudinally extending member to the surface of the balloon. The fiber coating can be, for example, a thread or mesh that secures the longitudinally extending member to the balloon. The medical balloon can be an angioplasty balloon, such as an off-the-shelf angioplasty balloon.
Owner:CAGENT VASCULAR INC
Optical fiber coatings for reducing microbend losses
InactiveUS20110188822A1Reducing microbend lossReducing microbend lossesGlass optical fibreElectrostatic spraying apparatusRoom temperaturePolarization mode dispersion
Certain embodiments of the invention may include systems and methods for providing optical fiber coatings to reduce microbend losses. According to an example embodiment of the invention, a method is provided for coating an optical fiber to reduce microbend losses and polarization mode dispersion (PMD). The method includes applying a primary layer to the optical fiber, wherein the optical fiber comprises a core region surrounded by a cladding region. The method includes applying a secondary layer to the primary layer, and curing the primary and secondary layers, wherein the cured primary layer adheres to the cladding region with a minimum pullout adhesion of 6 N / cm, and the cured secondary layer has an in situ modulus of about 700 MPa to about 1200 MPa at room temperature.
Owner:OFS FITEL LLC
Ceramic-forming polymer material
Disclosed is a polymer material comprised of at least one non-cyclic ceramic-forming polymer. The porosity and elemental composition of the resulting ceramic can be varied by inclusion of polymers with particular ratios of carbon, silicon, oxygen, and hydrogen and by manipulation of the conditions under which the polymer material is converted to a ceramic. The resulting ceramic may be useful in fiber-reinforced ceramic matrix composites (CMCs), semiconductor fabrication, fiber coatings, friction materials, and fire resistant coatings.
Owner:SHERWOOD WALTER J JR +1
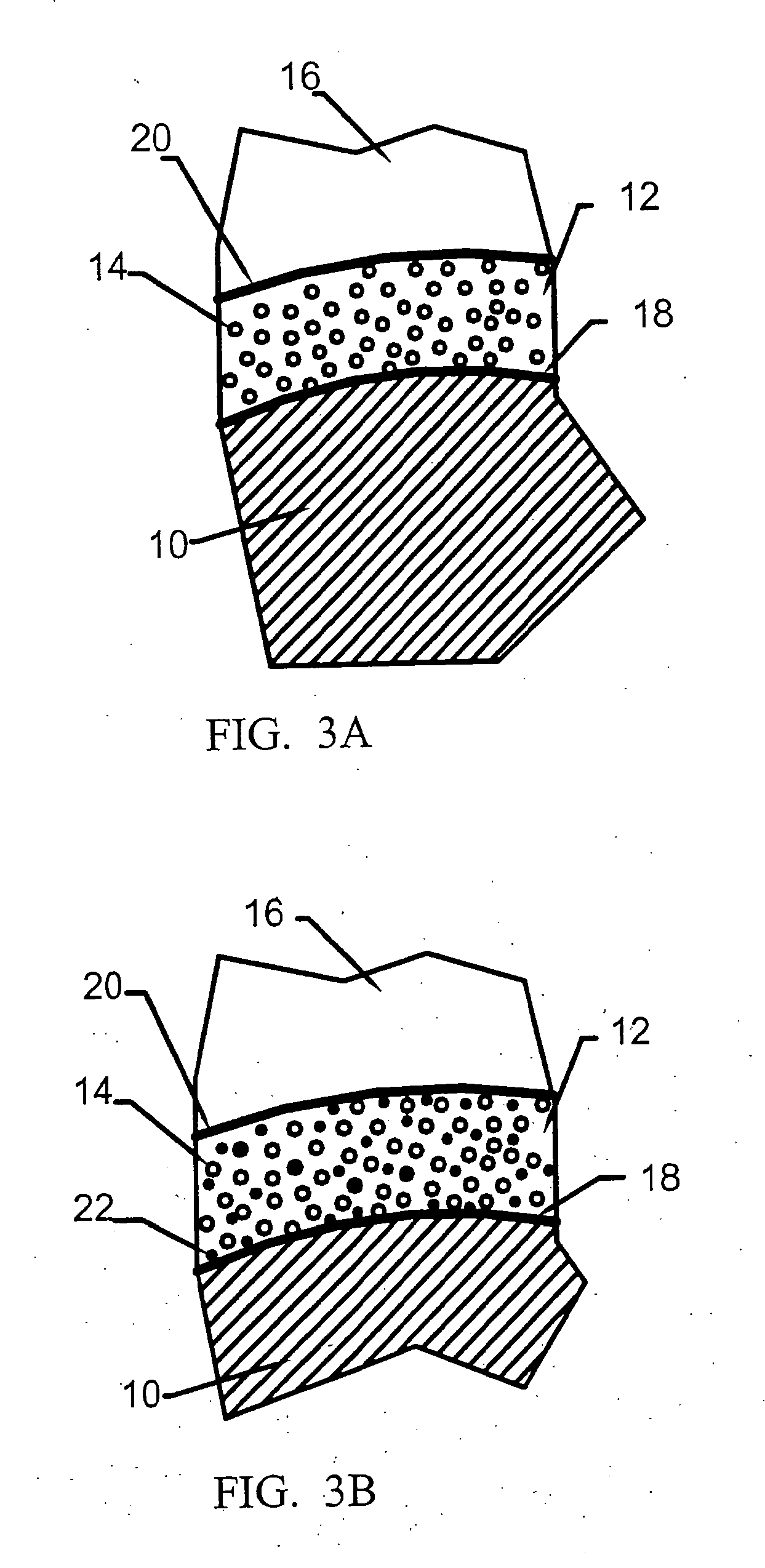
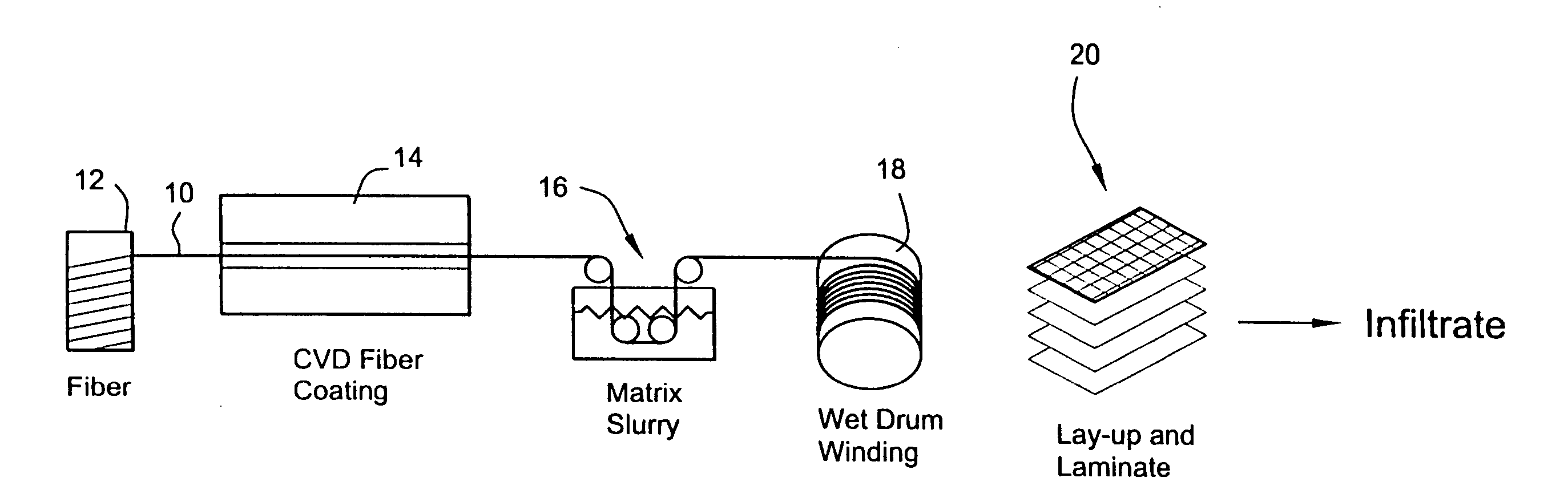
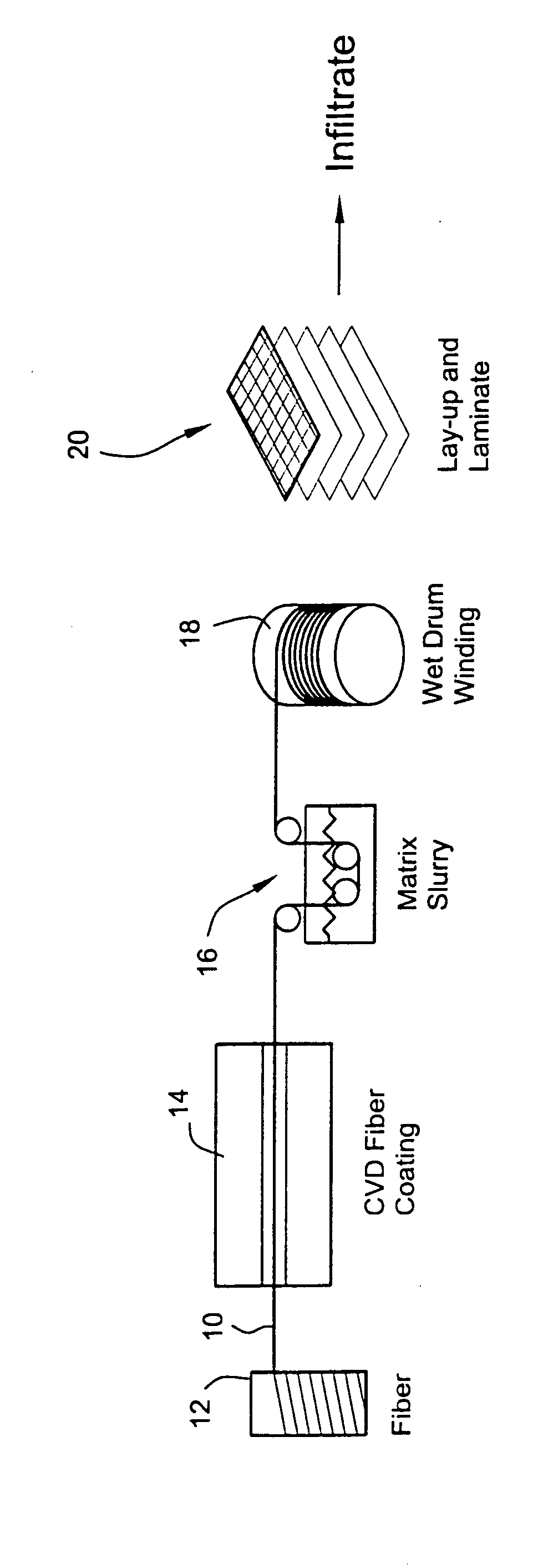
CMC process using a water-based prepreg slurry
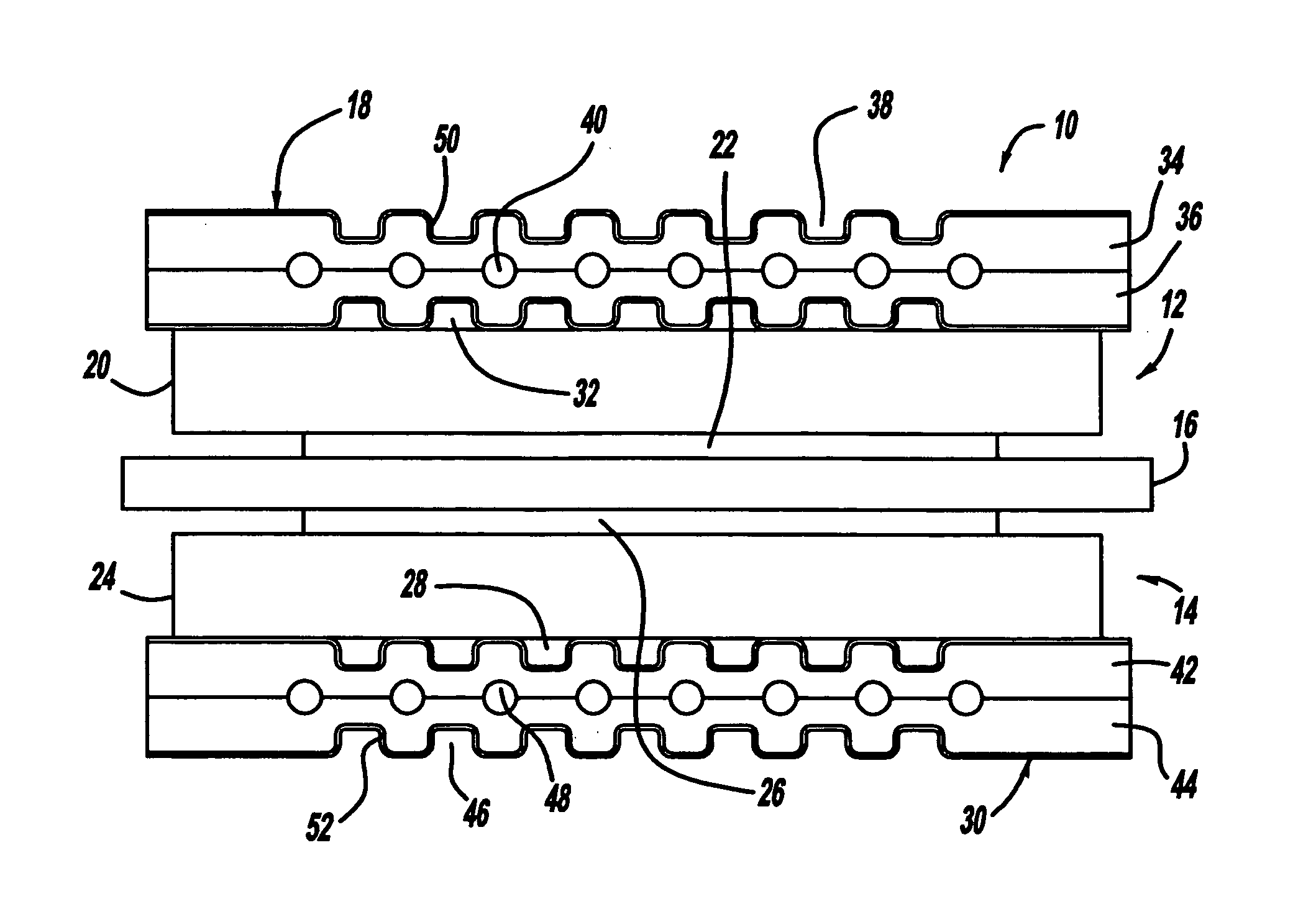
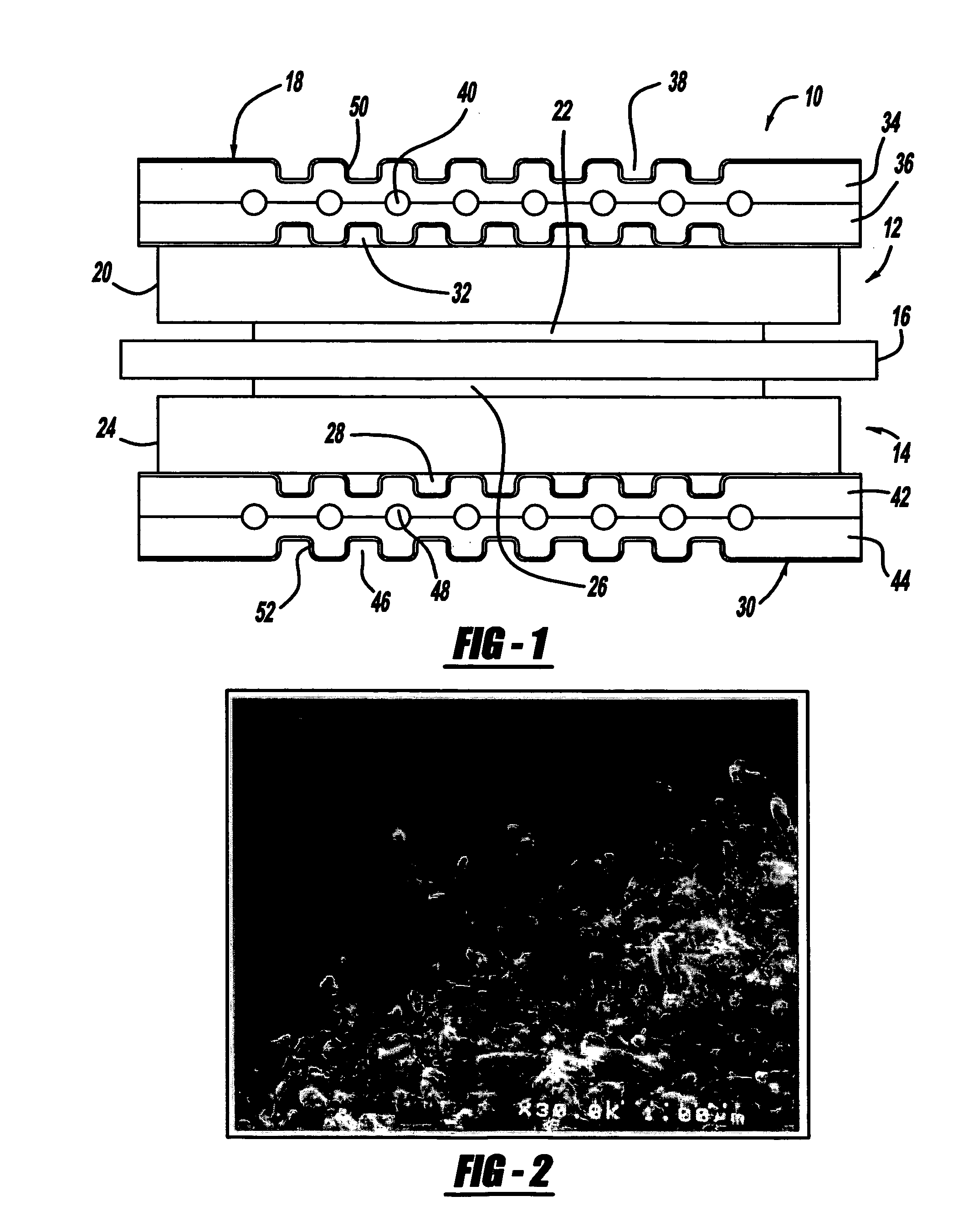
A process for forming a ceramic matrix composite component, for example, a turbine component, includes (a) applying a fiber coating to a fiber tow by chemical vapor deposition; (b) pulling the fiber tow through an aqueous slurry composed of high and low temperature binders, silicon carbide powder, carbon black and water to thereby form a prepreg tape; and (c) winding the prepreg tape on a drum.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method for preparing polyaniline composite nano silver conductive fibers
InactiveCN102444023AWith antistatic functionWith electromagnetic shielding functionFibre typesConductive coatingRoom temperature
The invention discloses a method for preparing polyaniline composite nano silver conductive fibers. The method comprises the following steps of: 1) preparation of a conductive coating solution, preparing polyaniline particles ground by a mortar and formic acid solutions of different mass fractions into the conductive coating solution, wherein the mass fractions of the formic acid solutions are 60 to 80 percent; 2) preparation of coated conductive fibers: coating the conductive coating solution on the surface of fibers by adopting a roller type fiber coating machine to prepare the coated conductive fibers, and washing and drying the coated conductive fibers to obtain conductive fibers; and 3) in-situ synthesis of a nano silver-polyaniline layer: soaking the conductive fibers A into 0.1 to 1.0mol / L aqueous solution of silver nitrate (AgNO3) for 0.5 to 2 hours, soaking the conductive fibers A into 0.2 to 2 mol / L aqueous solution of NaBH4, reacting for 6 to 10 hours at room temperature, washing by using ethanol and deionized water respectively, performing natural airing or drying, and thus obtaining the polyaniline / nano silver composite conductive fibers. The conductive fibers have high electric conductivity, the electric conductivity of the fibers can be regulated by controlling the process conditions, and different electric conductivity requirements are met.
Owner:翔瑞(泉州)纳米科技有限公司
Organosilicon polyimide benzimidazole photoconductive fiber coating layer and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to an organosilicon polyimide benzimidazole photoconductive fiber coating layer represented by the following molecular structural general formula and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: dissolving silane containing diamino in an organic mixed solution, adding aromatic dianhydride, stirring at room temperature to react for 1-2 h, then adding 2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-5-aminobenzimidazole monomer and aromatic diamine monomer, stirring to react for 4-5h to obtain an organosilicon polyimide benzimidazole resin solution, homogeneously coating the organosilicon polyimide benzimidazole resin solution on the surface of photoconductive fibers, and thermocuring to obtain the organosilicon polyimide benzimidazole photoconductive fiber coating layer. According to the invention, the coating layer disclosed herein had the advantages of simple curing process, excellent high temperature resistance, extremely excellent mechanical property and electrical property, etc.; the preparation method is simple, the comprehensive performance is excellent, and the coating layer and the preparation method have good market prospect.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV +1
Optical fiber ribbon with improved stripability
ActiveUS7289706B2Optical fibre with multilayer core/claddingCoupling light guidesMaterials scienceFiber coating
An optical fiber ribbon includes a plurality of optical fibers encapsulated within a matrix material, where the optical fiber coating(s) and the matrix material(s), and optionally any ink layers thereon, are characterized by compatible chemical and / or physical properties, whereby the fiber coating and matrix and any ink layers therebetween can be reliably stripped from the optical fibers to afford a suitable strip cleanliness. Novel ink formulations that can be used in the making of such fiber optic ribbons, methods of making such ribbons, and their use are also described.
Owner:CORNING INC
Serration balloon
A serration balloon can have a number of different components and can be made in a number of different manners. One or more longitudinally extending members with periodic raised wedges can be attached to a medical balloon. They can be attached with a fiber coating, a polymer coating, or other methods. A polymer matrix can be used to bond the longitudinally extending member to the surface of the balloon. The fiber coating can be, for example, a thread or mesh that secures the longitudinally extending member to the balloon. The medical balloon can be an angioplasty balloon, such as an off-the-shelf angioplasty balloon.
Owner:CAGENT VASCULAR INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com