Patents
Literature
562 results about "Polarization mode dispersion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Polarization mode dispersion (PMD) is a form of modal dispersion where two different polarizations of light in a waveguide, which normally travel at the same speed, travel at different speeds due to random imperfections and asymmetries, causing random spreading of optical pulses. Unless it is compensated, which is difficult, this ultimately limits the rate at which data can be transmitted over a fiber.
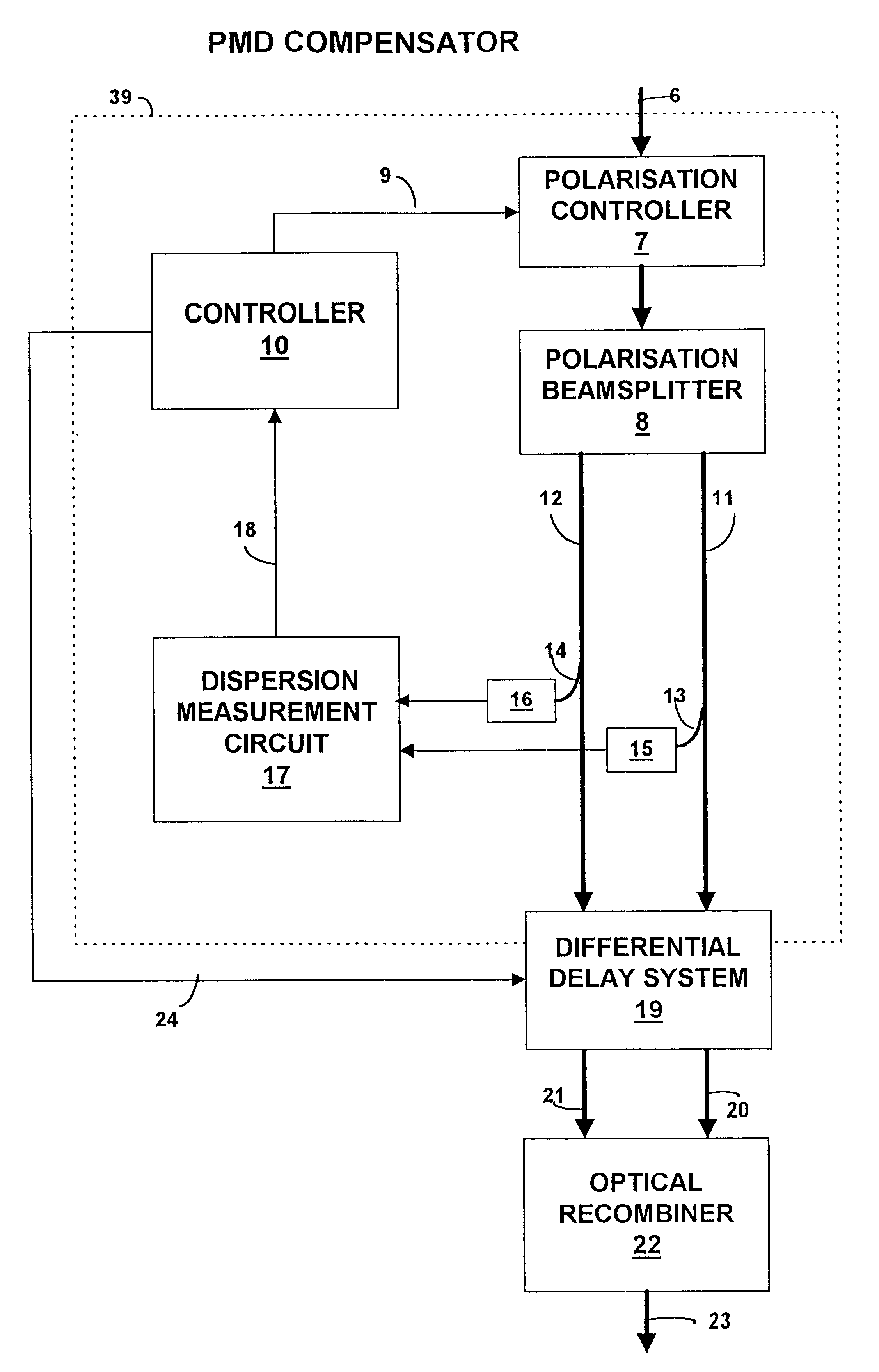
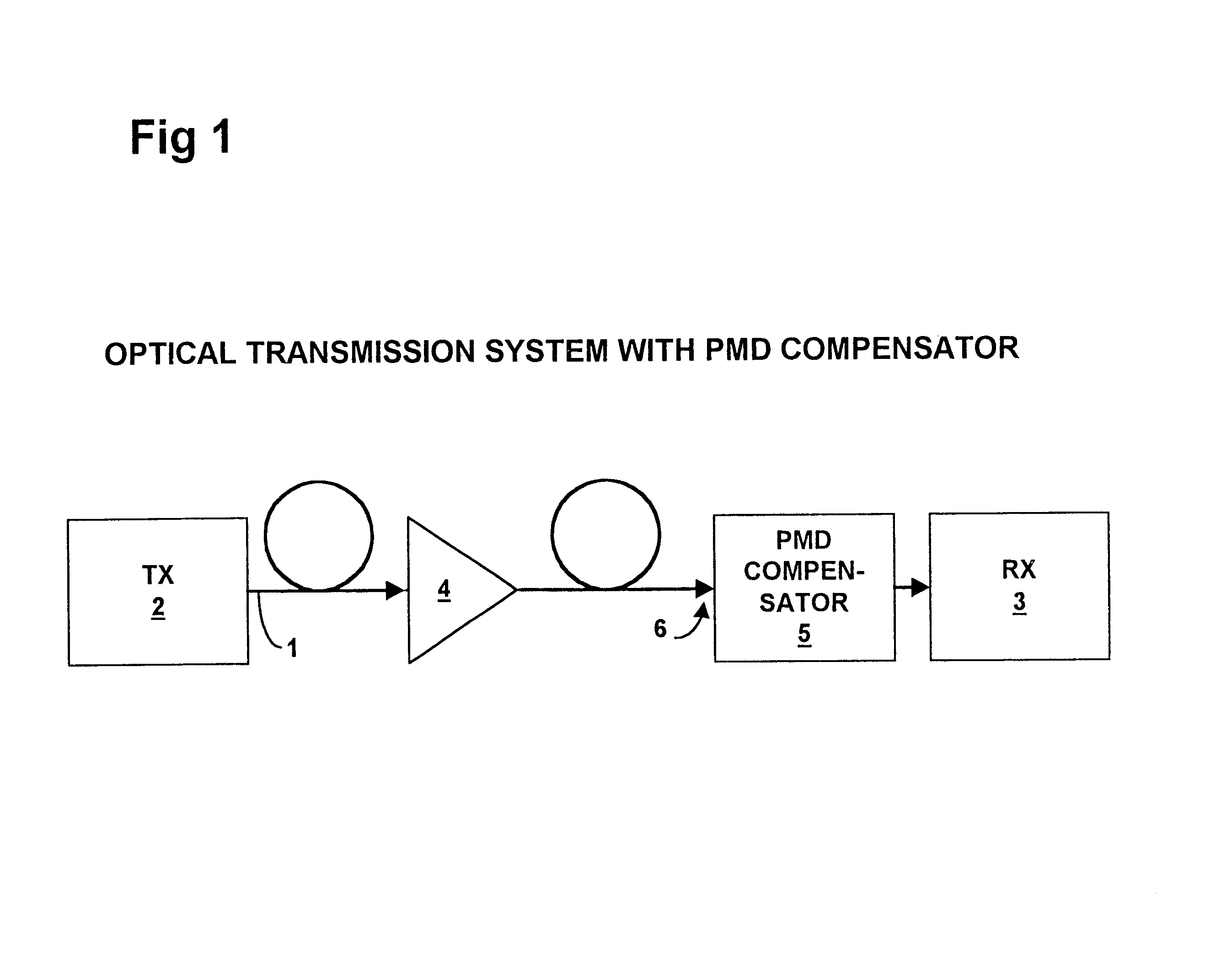
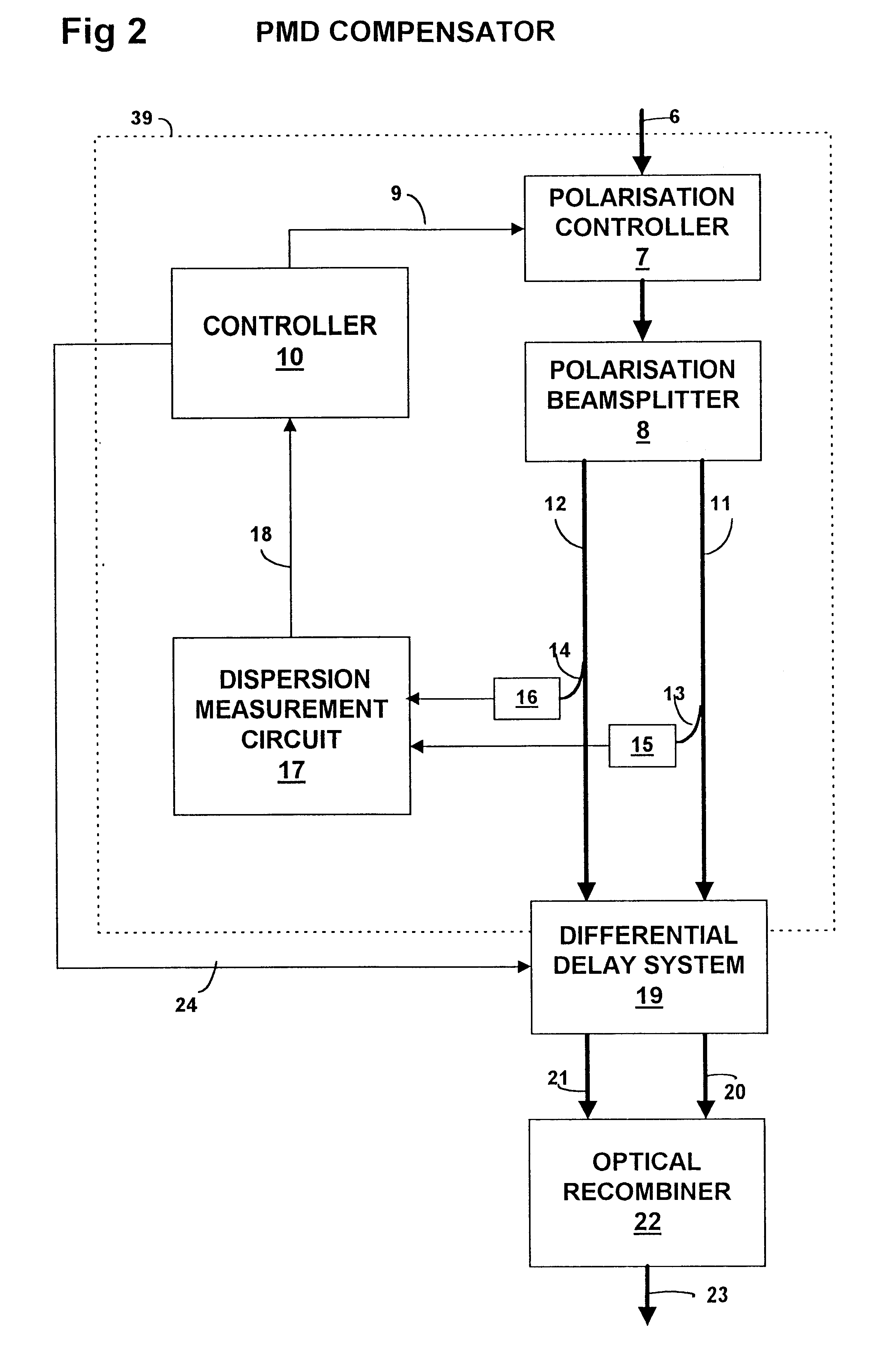
Polarization mode dispersion compensation
InactiveUS6271952B1Producing strainTransmission monitoringTransmission monitoring/testing/fault-measurement systemsGratingCommunications system
Polarization mode dispersion in an optical signal transmitted through a waveguide of a communications system is compensated by separating the dispersed signal into components corresponding to principal polarization states. The components are delayed by respective delays differing by a delay increment which is controlled to correspond to the dispersion delay and the delayed components are recombined to provide a dispersion compensated optical output signal. Each of the delays is provided by an chirped Bragg reflector forming part of a delay line, the Bragg reflectors comprising optical fibres with chirped intracore index gratings. Transducers or temperature controllers acting on one of the fibres allows dimensional control of the grating periodicity such that the position of Bragg reflection is variable. Wavelength division multiplexed optical signals are compensated using sampled gratings which allow a common Bragg reflection position for each wavelength.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
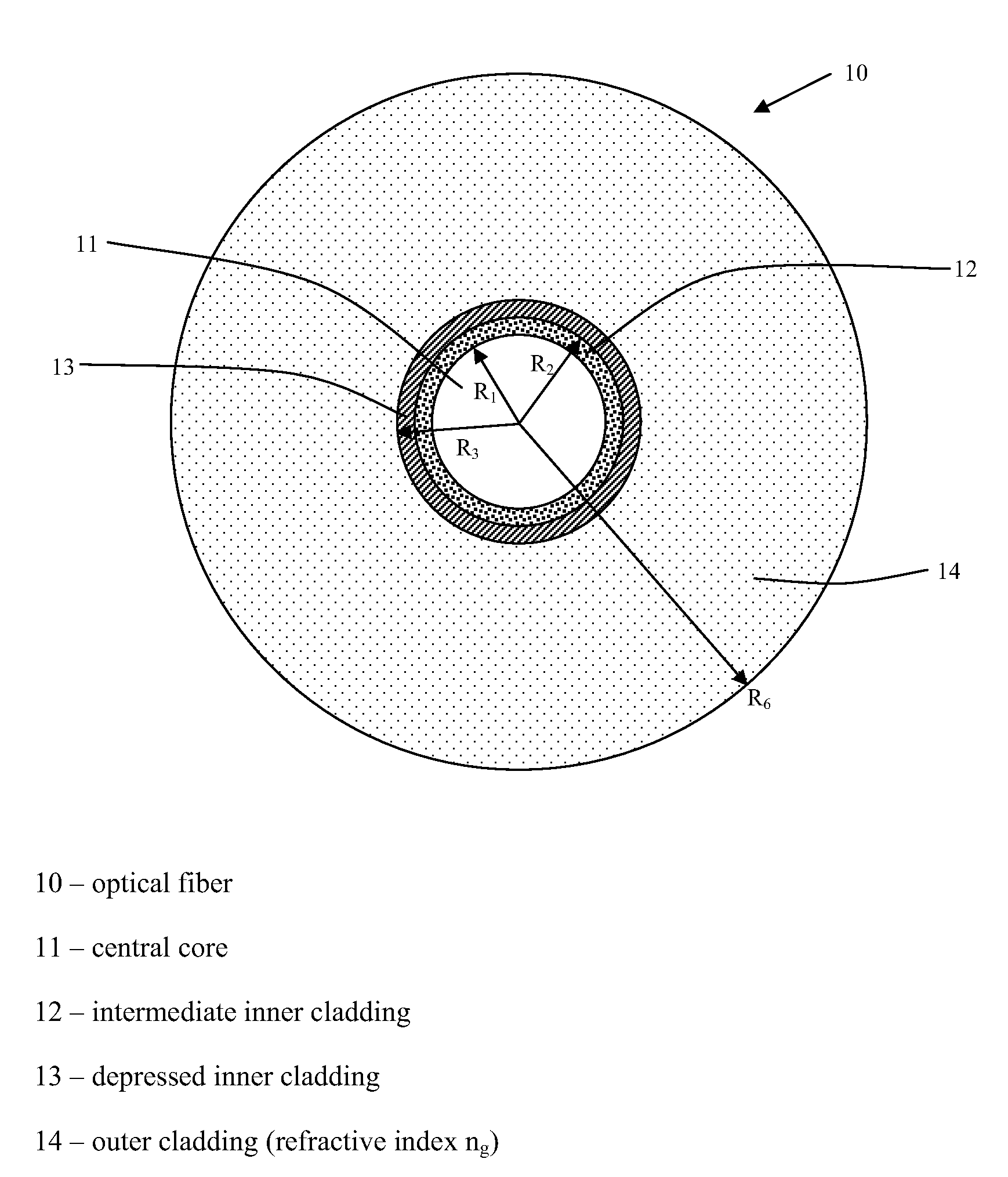
Chromatic dispersion compensating fiber
ActiveUS7356234B2Improved FOM valueLimited bending and micro-bending lossesOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingOptical waveguide light guideOptical ModuleRefractive index
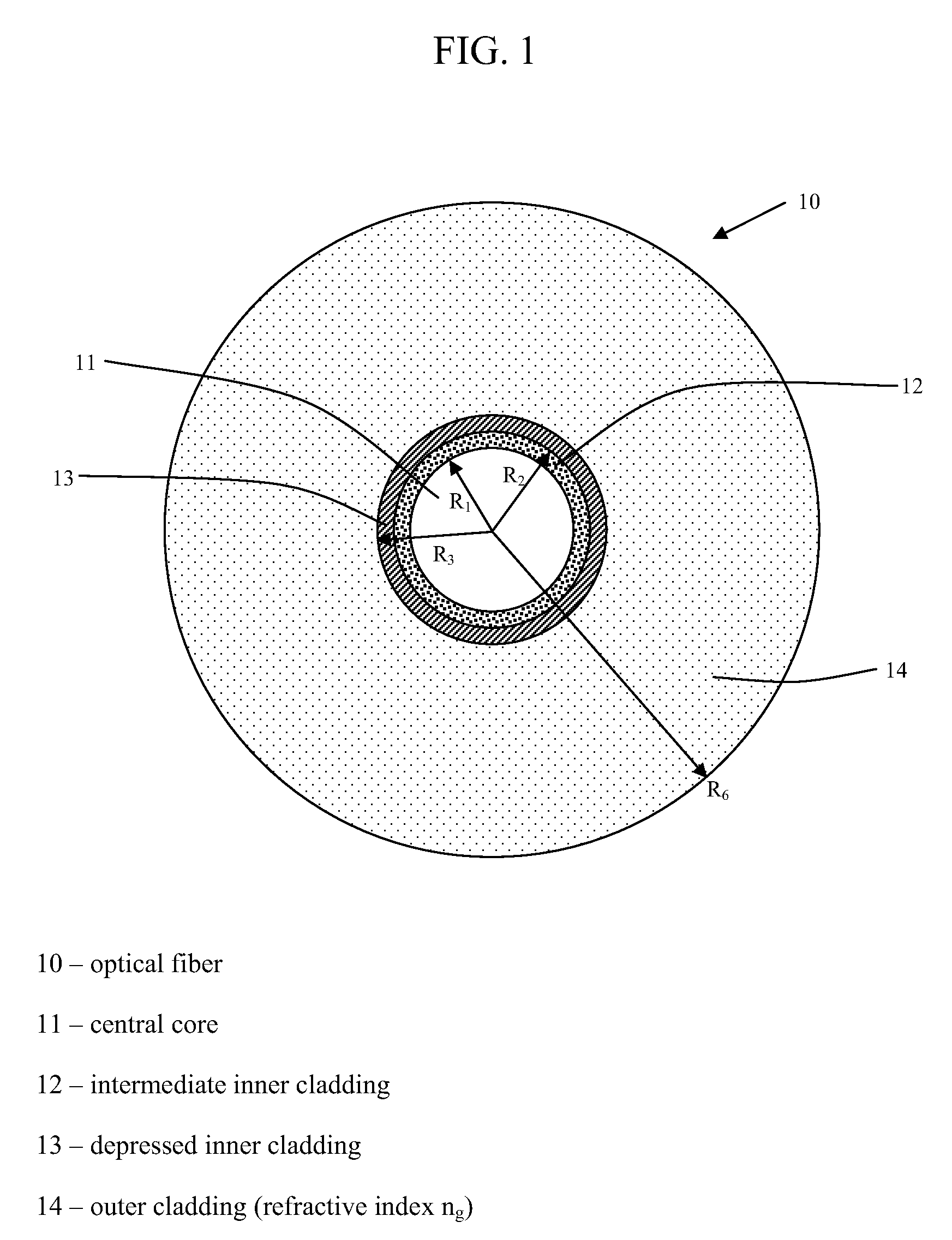
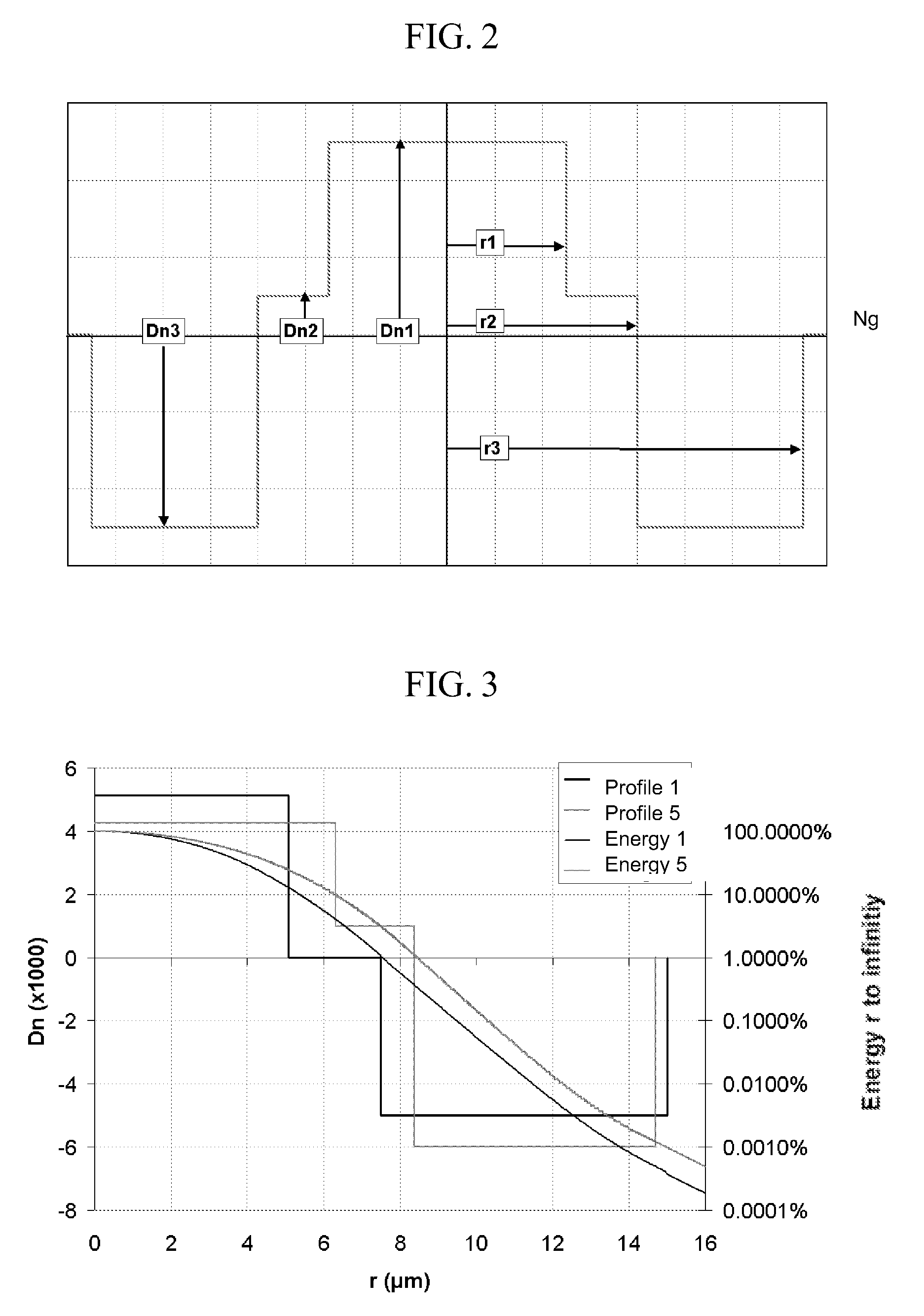
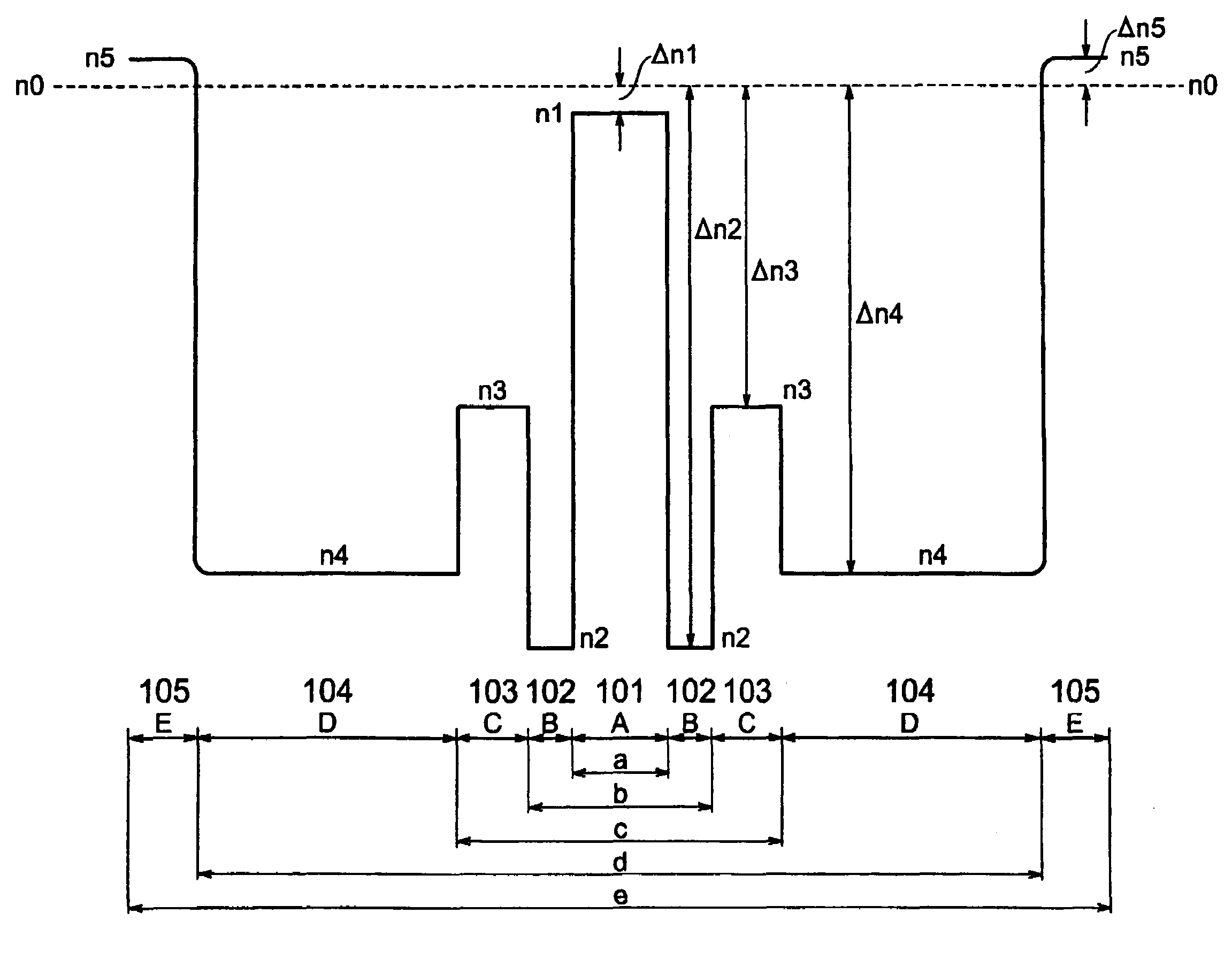
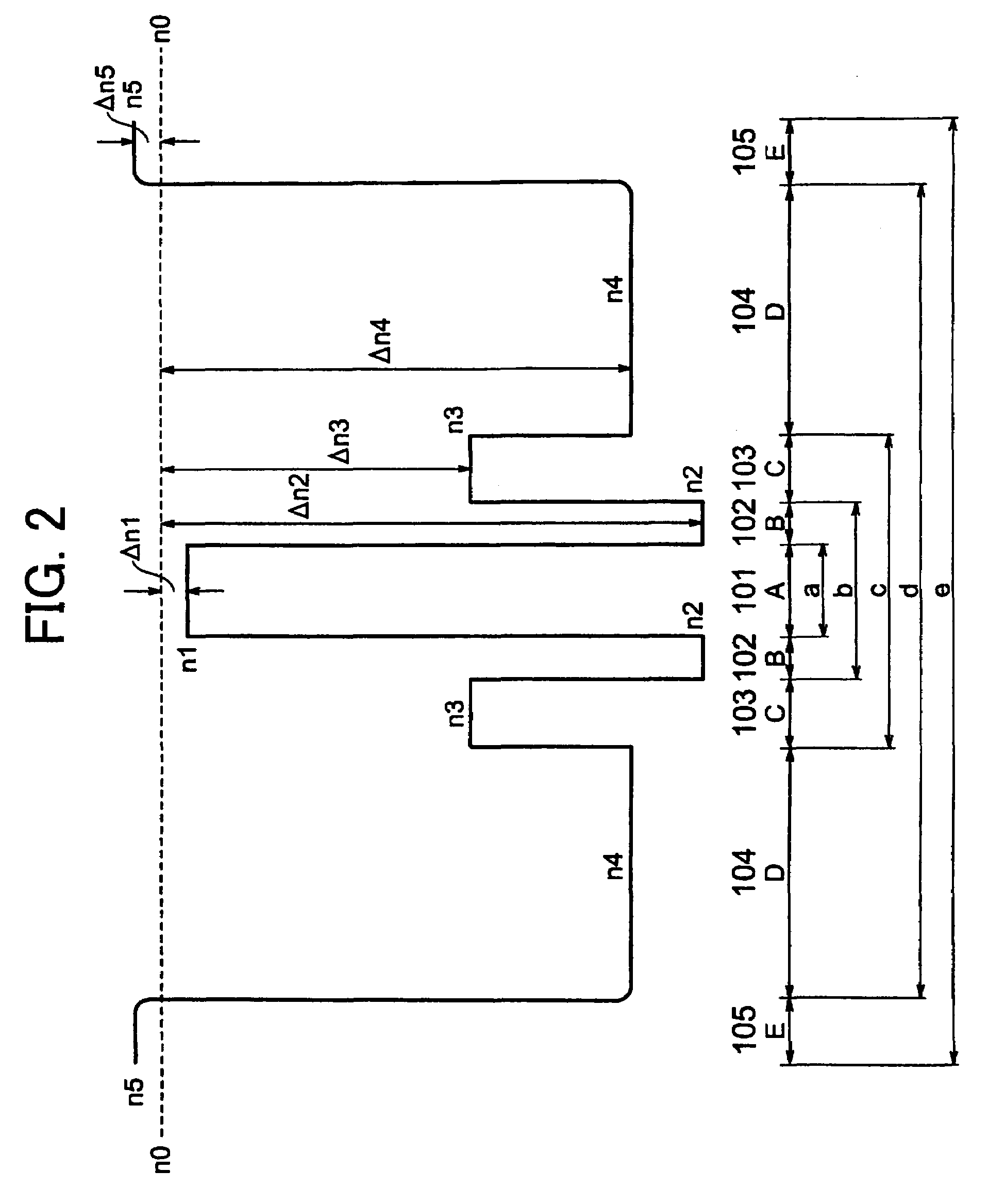
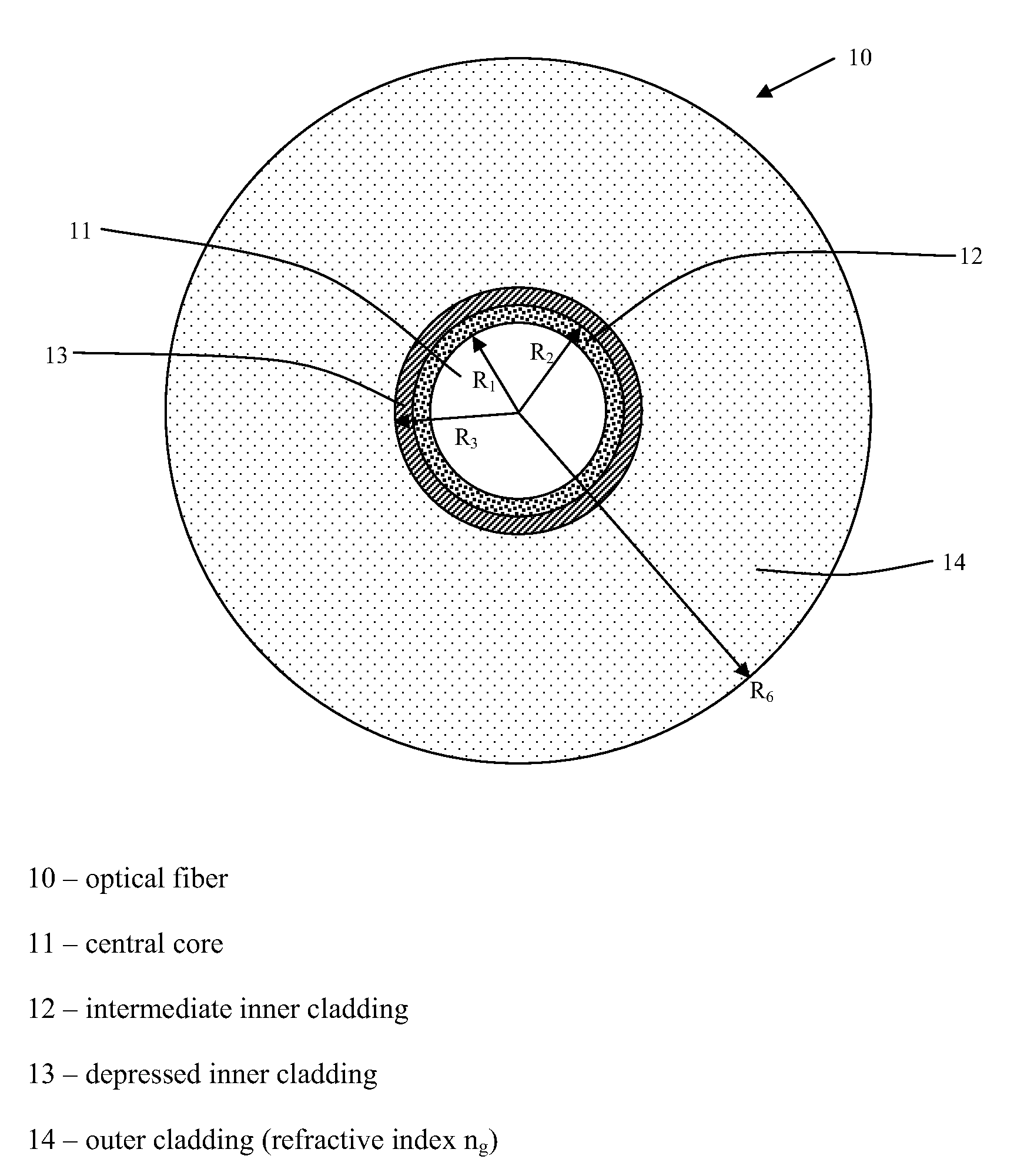
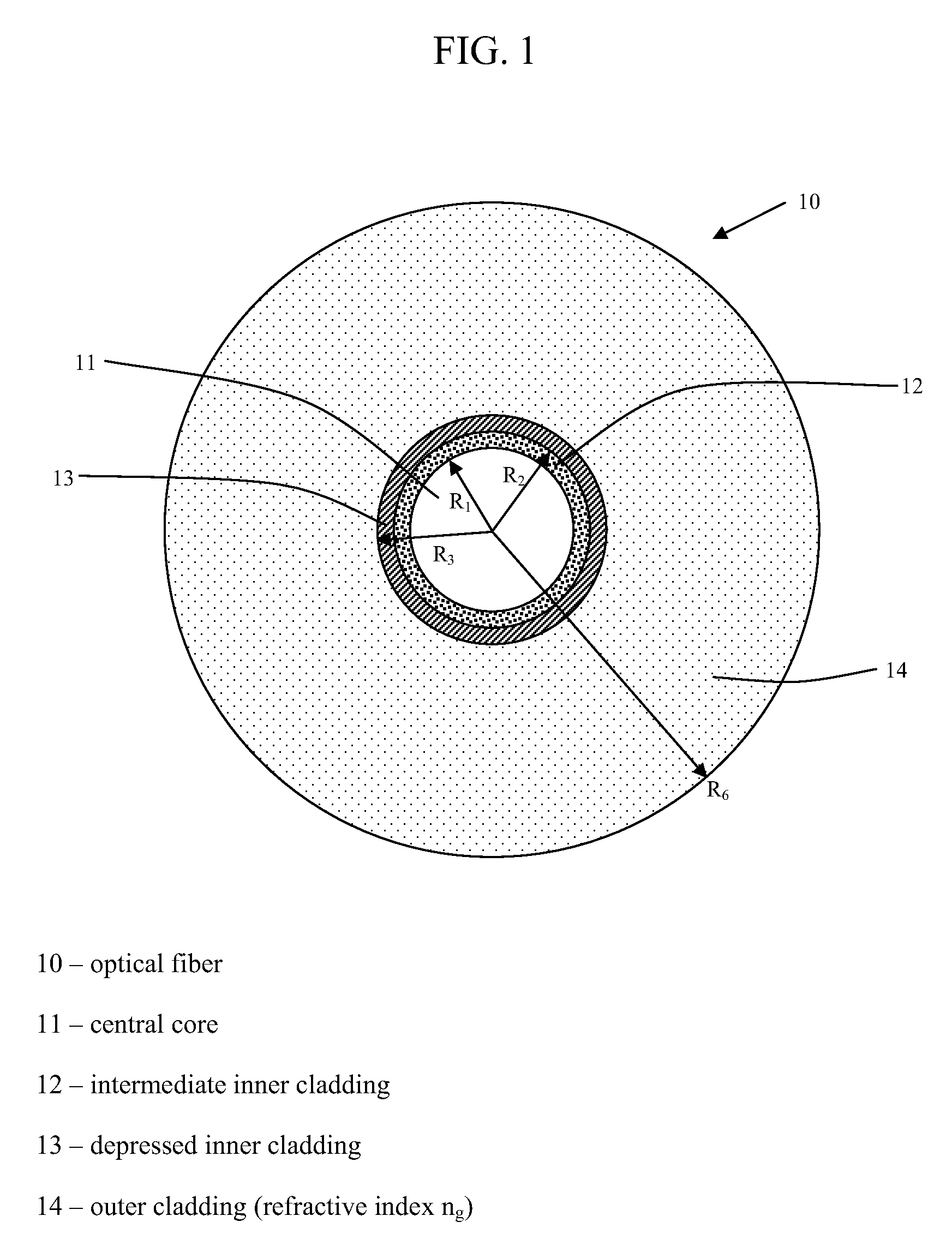
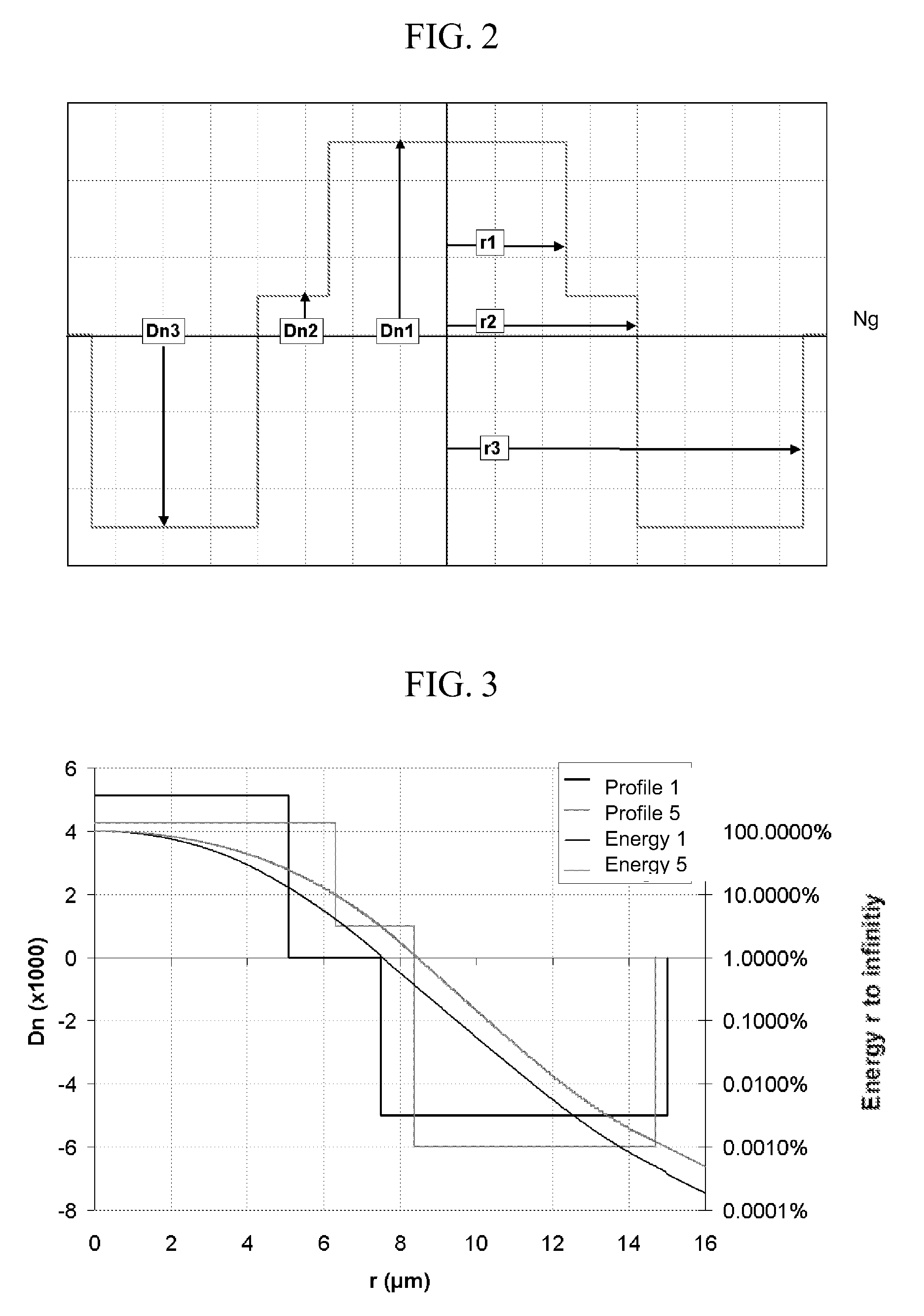
Disclosed is a chromatic dispersion compensating optical fiber comprising a central core, an intermediate cladding having a width (r2−r1) of 2.0 microns or greater, and a depressed inner cladding having a refractive index difference Dn3 with the external optical cladding of −3.0×10−3 or lower. At a wavelength of 1550 nm, the optical fiber exhibits a positive chromatic dispersion of 21 ps / (nm·km) or higher and a ratio of mode radius to intermediate cladding radius of (W02 / r2) of 0.7 or less. The present optical fiber has a good figure of merit value and limited bending and microbending losses. The optical fiber can be rolled up in a housing of reduced size in a chromatic dispersion compensating optical module having limited insertion losses and reduced polarization mode dispersion.
Owner:DRAKA COMTEQ BV
All-fiber chirped pulse amplification systems
InactiveUS20050105865A1Improve overall utilizationImprove performanceFibre transmissionCoupling light guidesLow noiseGrating
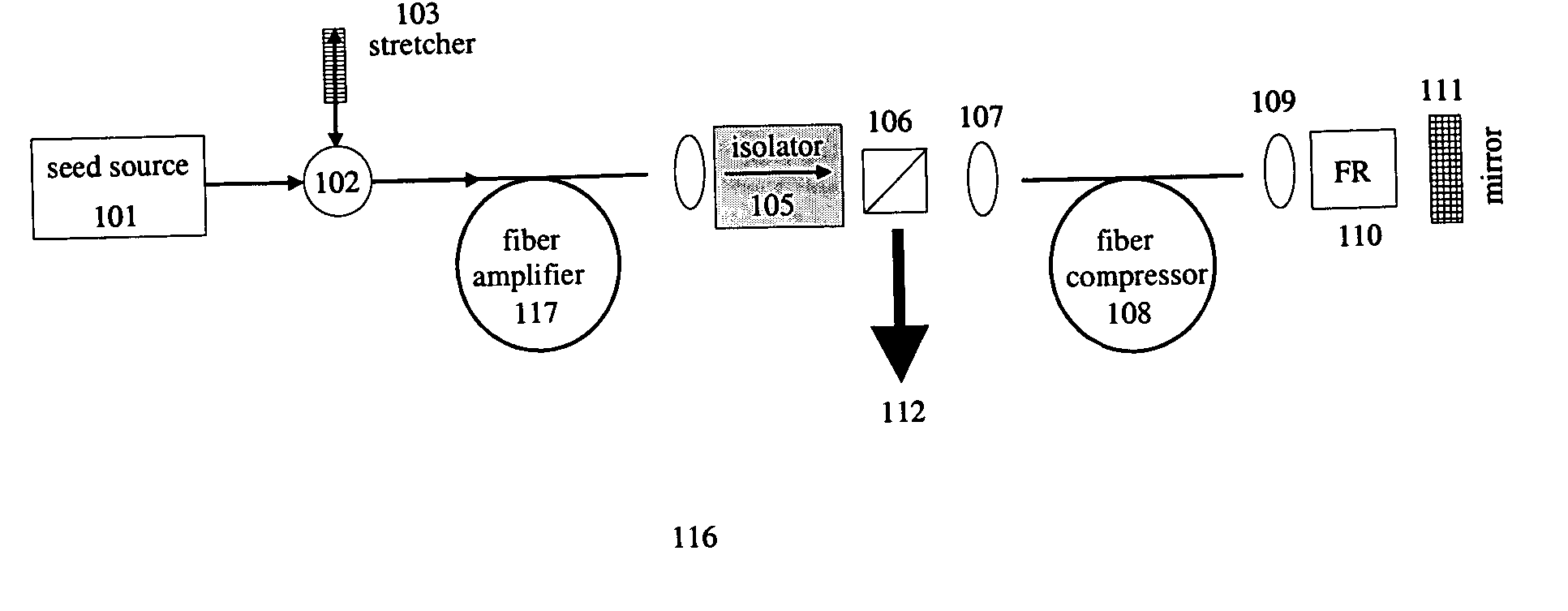
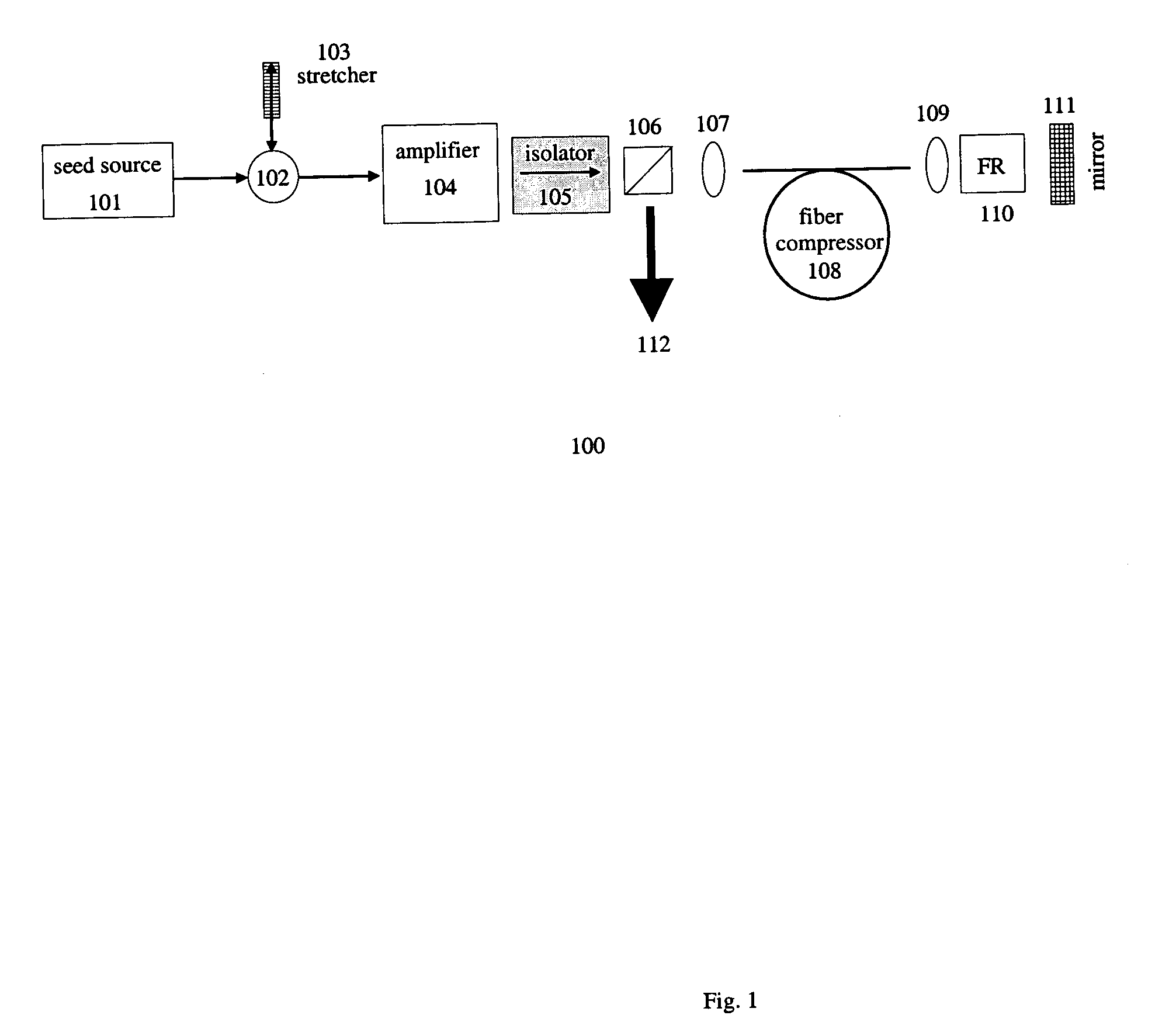
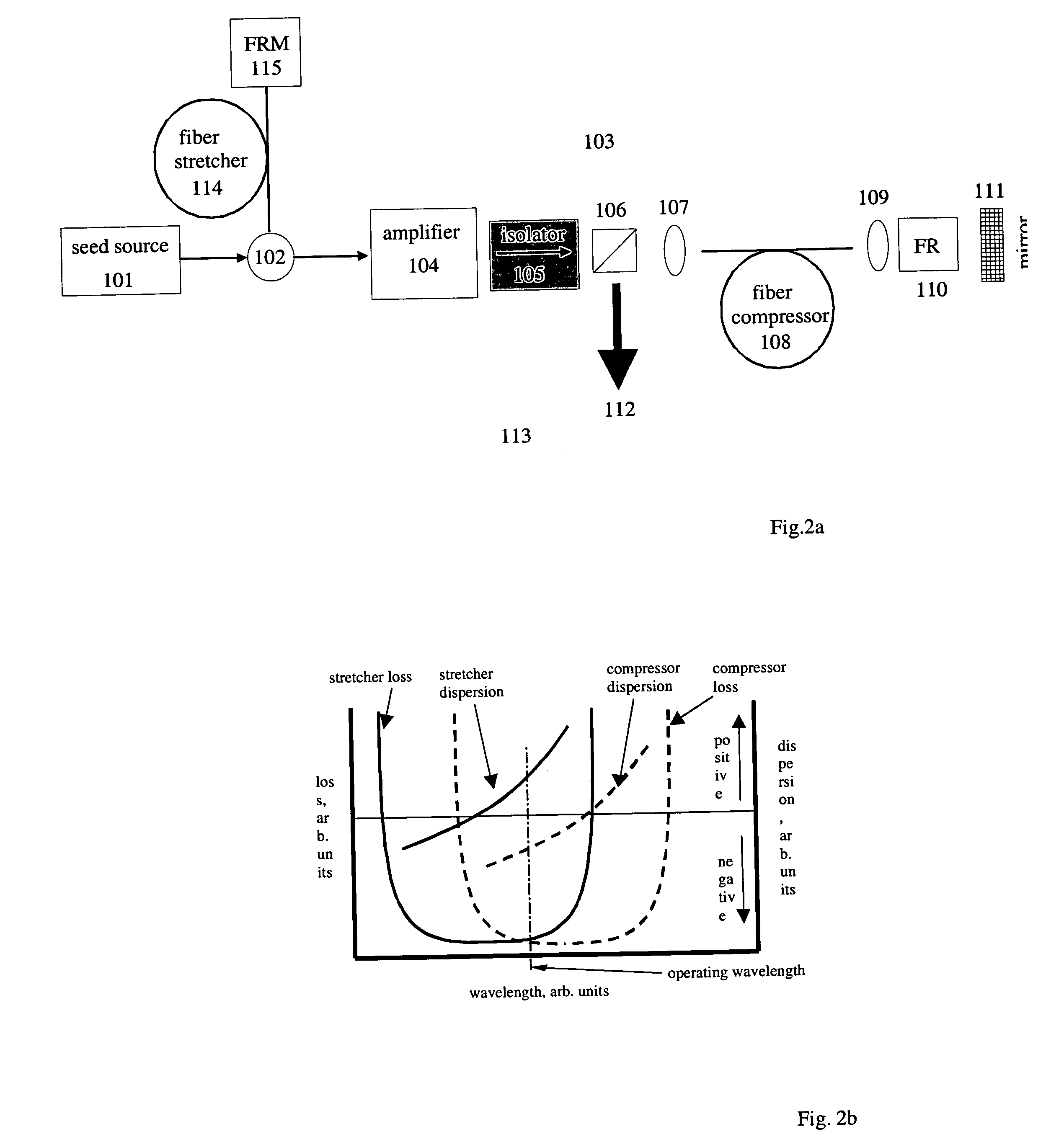
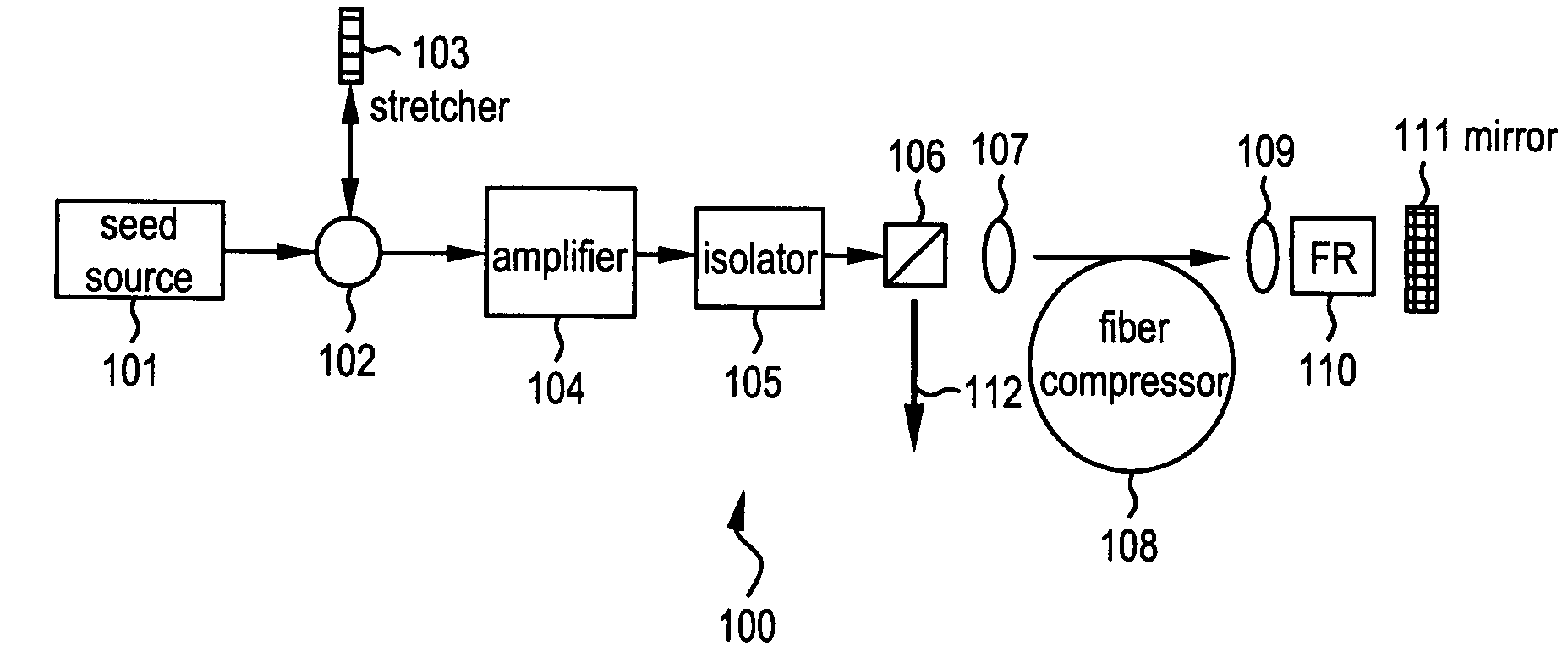
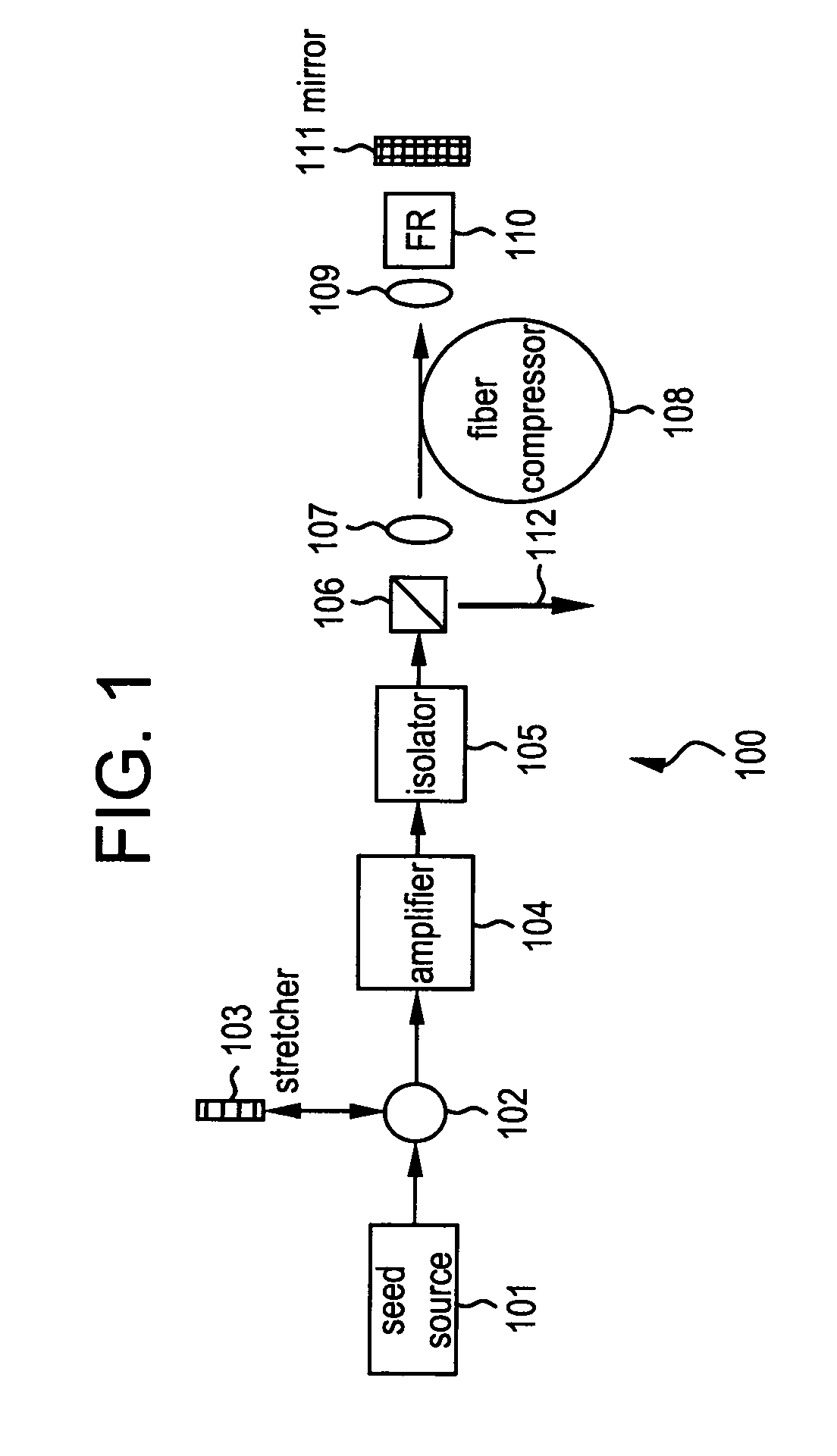
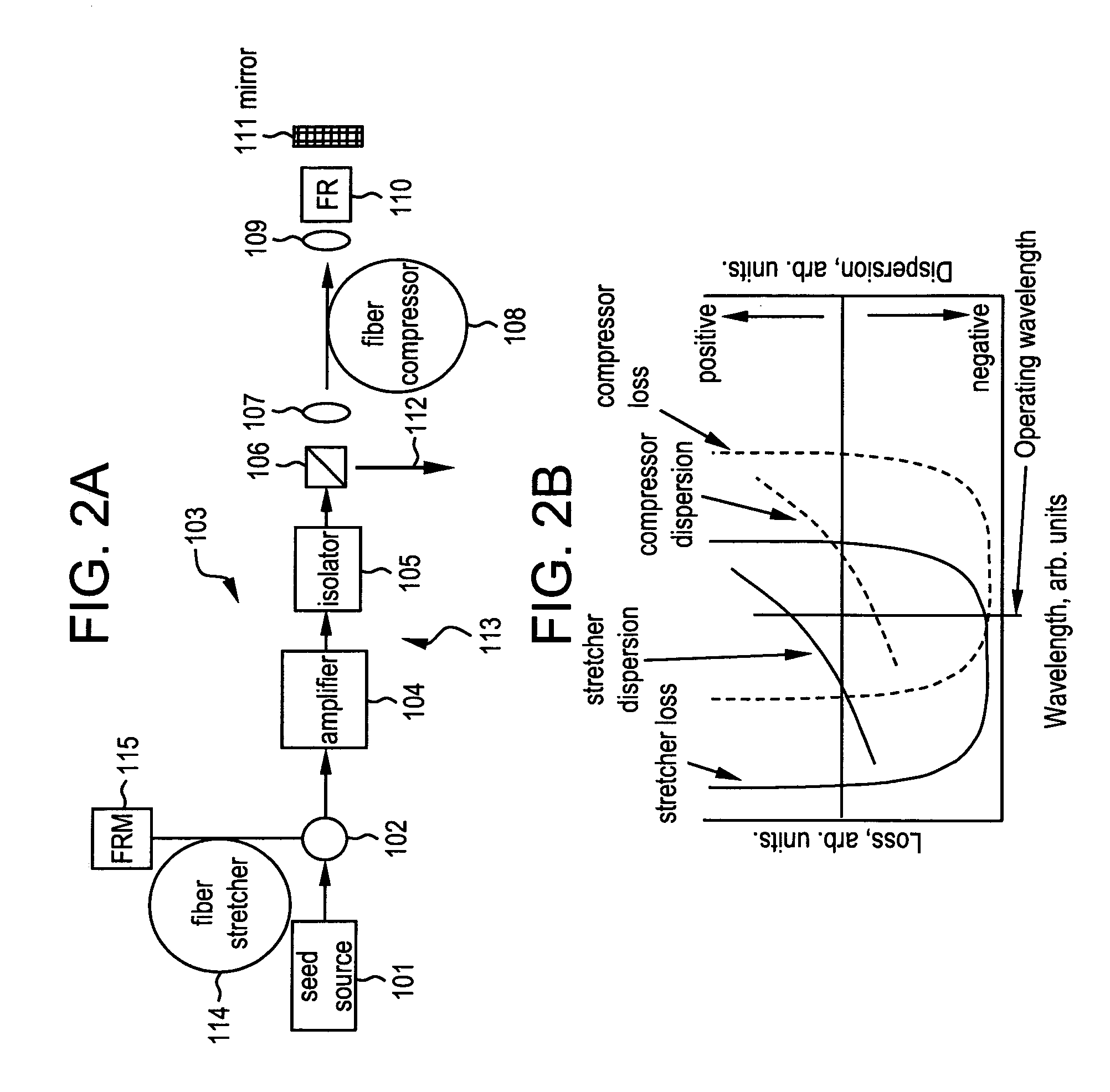
By compensating polarization mode-dispersion as well chromatic dispersion in photonic crystal fiber pulse compressors, high pulse energies can be obtained from all-fiber chirped pulse amplification systems. By inducing third-order dispersion in fiber amplifiers via self-phase modulation, the third-order chromatic dispersion from bulk grating pulse compressors can be compensated and the pulse quality of hybrid fiber / bulk chirped pulse amplification systems can be improved. Finally, by amplifying positively chirped pulses in negative dispersion fiber amplifiers, low noise wavelength tunable seed source via anti-Stokes frequency shifting can be obtained.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
All-fiber chirped pulse amplification systems
InactiveUS7414780B2Improve overall utilizationImprove performanceCoupling light guidesFibre transmissionLow noiseGrating
By compensating polarization mode-dispersion as well chromatic dispersion in photonic crystal fiber pulse compressors, high pulse energies can be obtained from all-fiber chirped pulse amplification systems. By inducing third-order dispersion in fiber amplifiers via self-phase modulation, the third-order chromatic dispersion from bulk grating pulse compressors can be compensated and the pulse quality of hybrid fiber / bulk chirped pulse amplification systems can be improved. Finally, by amplifying positively chirped pulses in negative dispersion fiber amplifiers, low noise wavelength tunable seed source via anti-Stokes frequency shifting can be obtained.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
Fault Localization and Fiber Security in Optical Transponders
ActiveUS20120224846A1Accurate locationTransmission monitoringElectromagnetic transmission optical aspectsDigital signal processingFiber
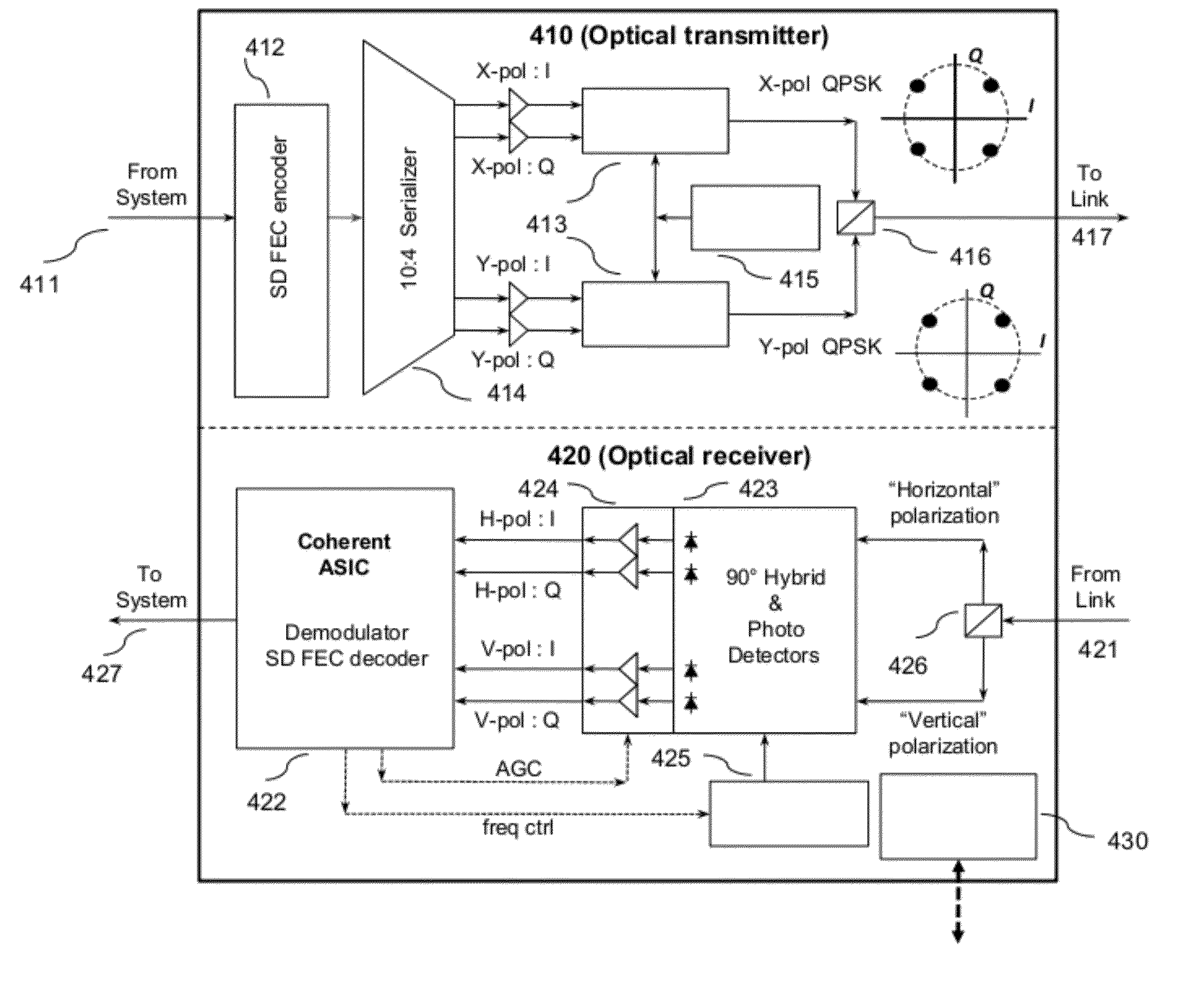
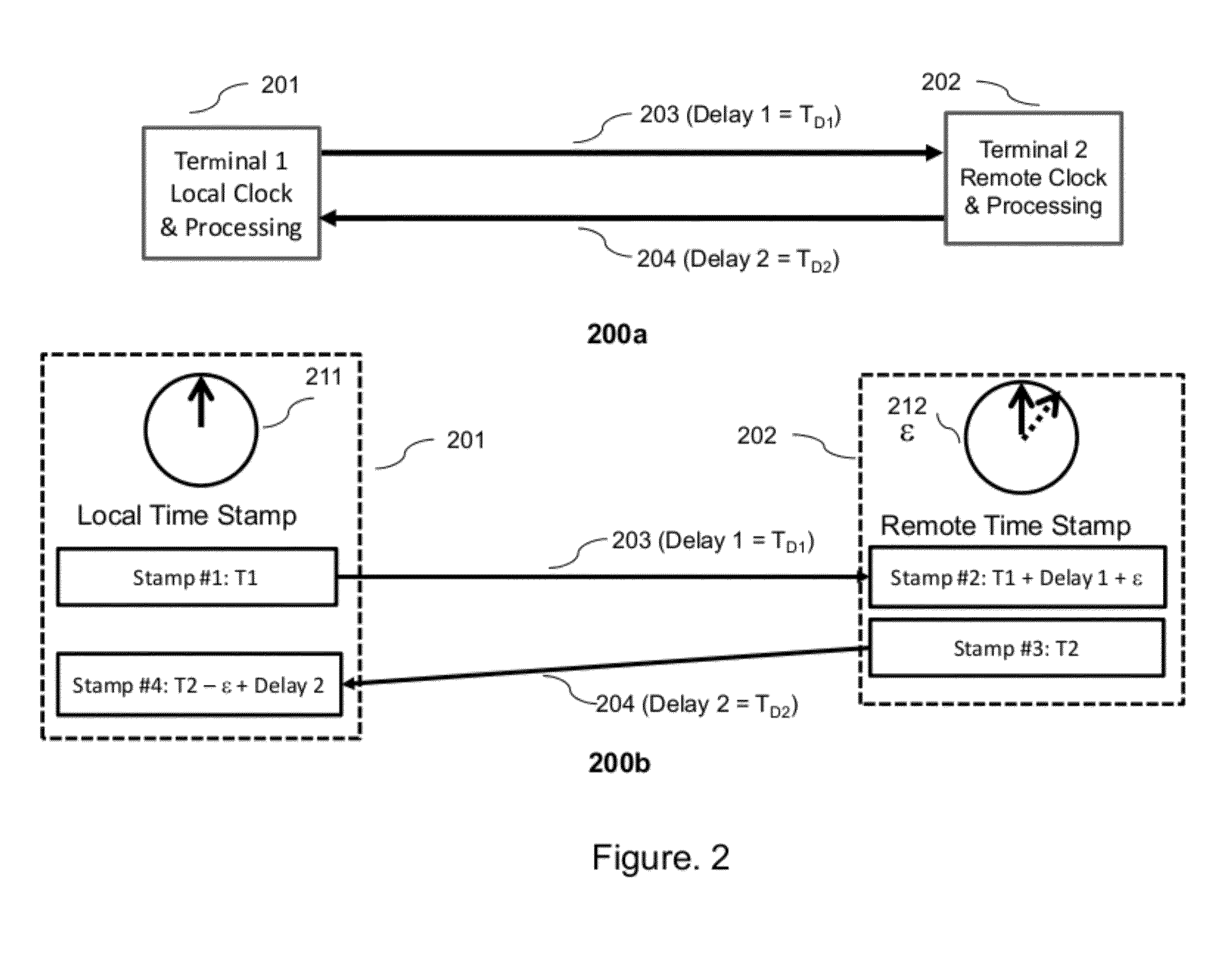
Designs, methods, and applications for fault localization and fiber security in optical transponders is described. In one embodiment a two-way time transfer protocol or other suitable method for synchronizing clocks between distant transponders is used. The clock synchronized transponders have digital signal processing to continually detect high precision time-histories of physical layer attributes in the transmission between the two transponders. Physical layer attributes can include: state-of-polarization changes, changes in polarization-mode-dispersion, change in propagation delay, changes or loss-of-light, changes in OSNR, changes in BER between the two nodes. By recording these physical layer changes and time-stamping them information on the magnitude and estimated location of the changes can be inferred by from the time records. In one aspect the method may be used in a distributed optical sensor for monitoring trespassing events that are a risk to fiber security of an optical transmission link.
Owner:ACACIA CHEM
Plasmon-photon coupled optical devices
InactiveUS20050275934A1Avoid spreadingImprove transmittanceBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsMaterial analysis by optical meansAngle of incidenceRefractive index
The present invention is directed to optical devices. More specifically, the disclosed devices include a film defining a periodic array of surface elements so as to give rise to surface plasmon polaritons. The film also includes at least a single aperture having a diameter less than the wavelength of light. In one embodiment, the surface elements can be an array of anisotropic apertures and the films can act as a polarizer. The disclosed devices can also include a material having a variable refractive index substantially adjacent to the metal film. For example, the refractive index of the adjacent material can vary according to some characteristic of the light incident to the device, for instance, the intensity or the angle of incidence of the light. In this embodiment, resonant coupling of incident light with the SPP, and hence transmittivity of the device, can depend upon the nature of incident light. The disclosed devices can be useful in, for example, remote polarizers, polarization mode dispersion, isolators, multi-color displays, switches, such as can be controlled according to incident sunlight, or optical filters, such as for eye protection devices, filtering out possibly harmful light.
Owner:CLEMSON UNIV RES FOUND
Single-polarization high power fiber lasers and amplifiers
InactiveUS20050232313A1Reduce absorptionMinimize nonlinearityLaser using scattering effectsOptical fibre with polarisationAudio power amplifierPolarization-maintaining optical fiber
A novel polarization maintaining optical fiber, which can be used as a high-power polarization maintaining fiber laser or amplifier, is described. Insensitivity of the polarization state to external fiber bending and temperature changes is accomplished by minimizing polarization mode-coupling via reducing stresses inside the fiber core via increasing the fiber diameter. Alternatively, polarization mode-coupling can be minimized by an optimization of the fiber coating to minimize stresses at the interface between the fiber and the coating. As a result insensitivity to polarization mode-coupling is obtained at greatly reduced values of birefringence compared to small-diameter fibers. The fiber is of significant use in any application where polarization stability is important, and will be useful in telecommunications applications in particular for reducing polarization mode dispersion. An implementation in a parabolic pulse-producing fiber laser is also described as one specific high power example.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
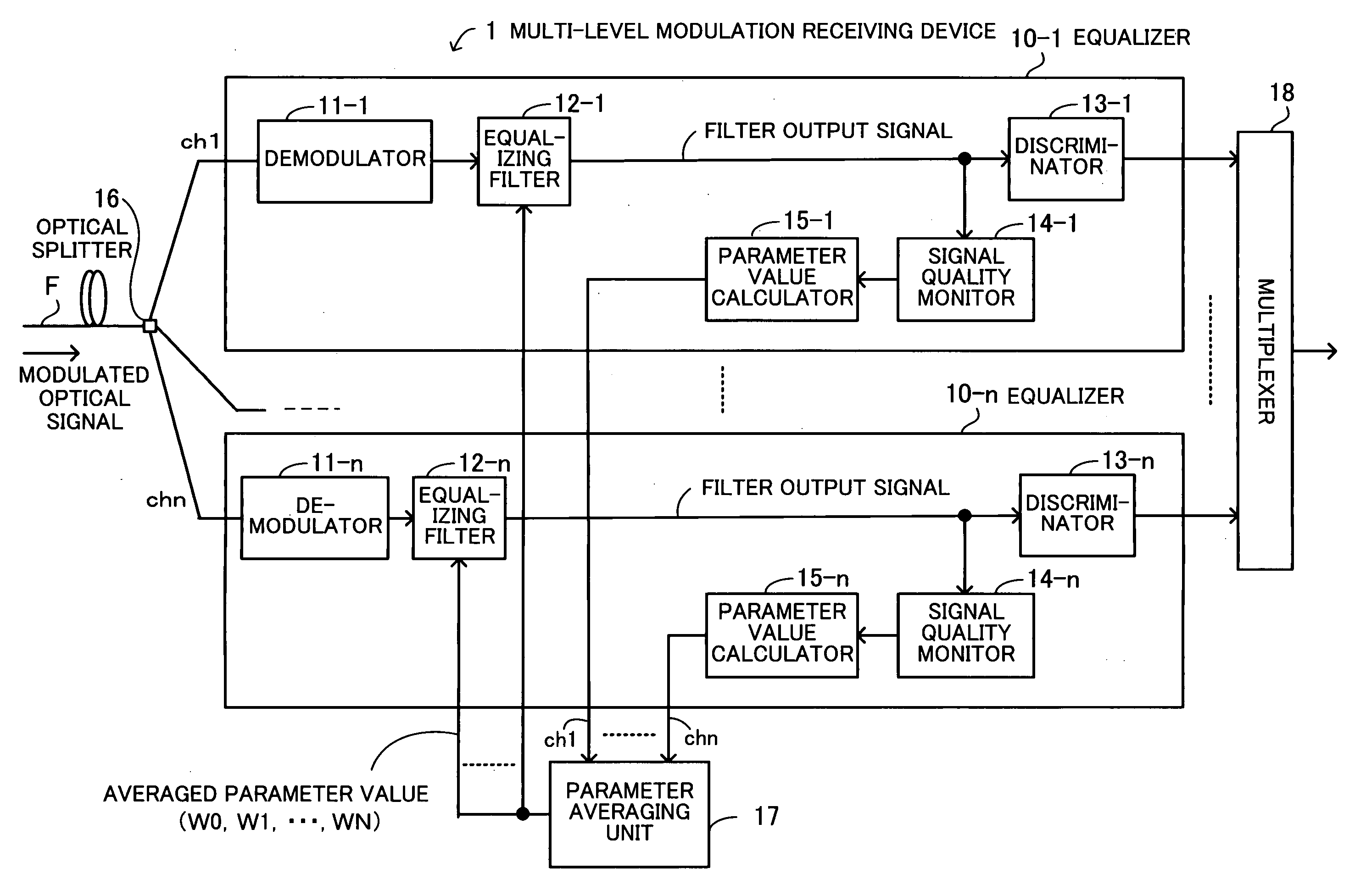
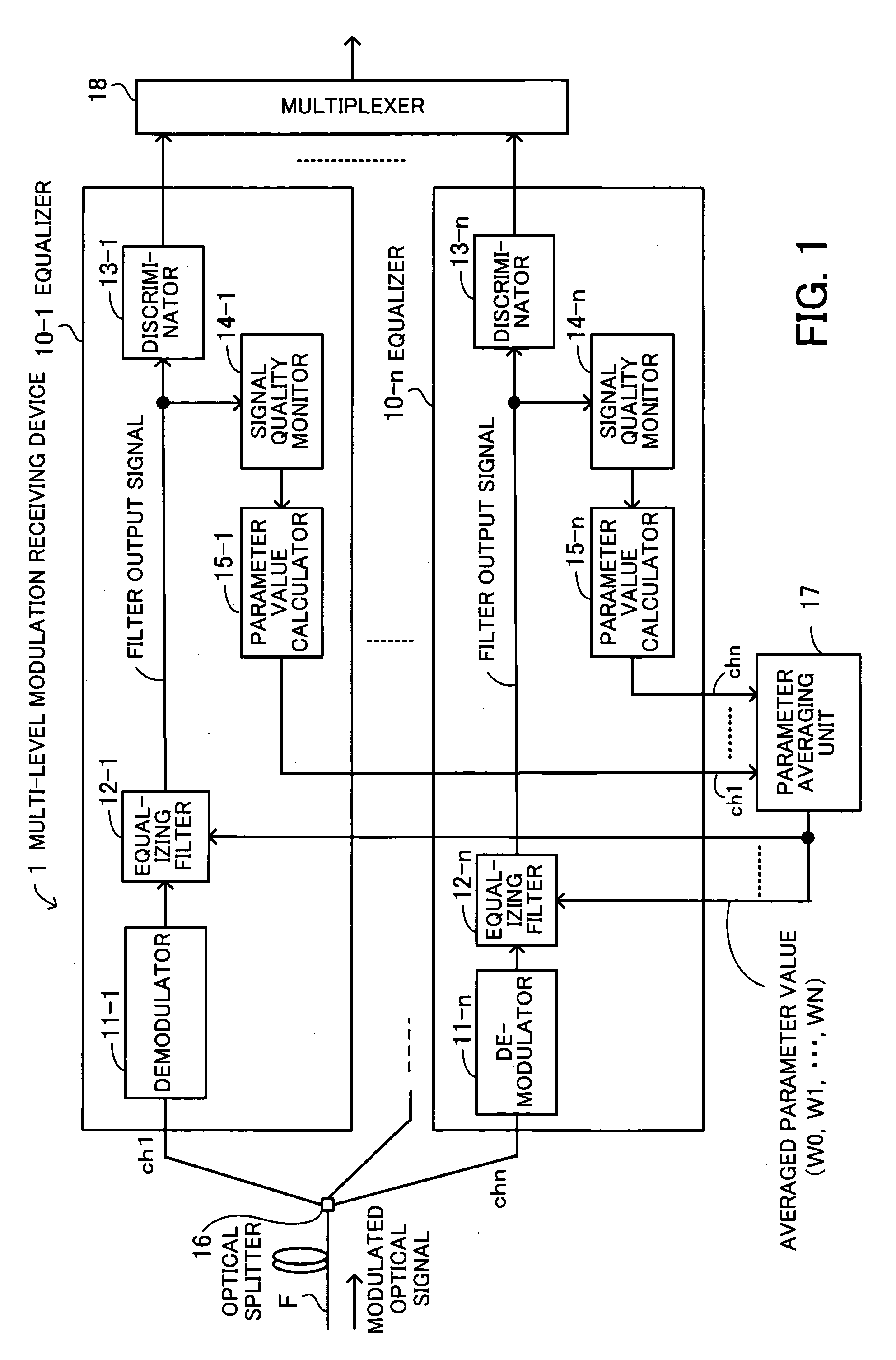
Multi-level modulation receiving device
ActiveUS20080031633A1Improve accuracyShort timeDistortion/dispersion eliminationElectromagnetic transmittersSignal qualityEngineering
A multi-level modulation receiving device for adaptively compensating for chromatic dispersion and polarization mode dispersion with high precision. Each equalizing filter has at least one variable parameter as a weight therefor and equalizes the waveform of a corresponding channel signal in accordance with an averaged variable parameter value. A signal quality monitor monitors the signal quality of the filter output signal, and a variable parameter value calculator calculates a variable parameter value to be set as the variable parameter, in accordance with the signal quality. A variable parameter averaging unit averages the variable parameter values calculated for respective channels, to generate an averaged variable parameter value, and sends the averaged variable parameter value to the equalizing filters such that the same weight is set in the equalizing filters associated with the n channels.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
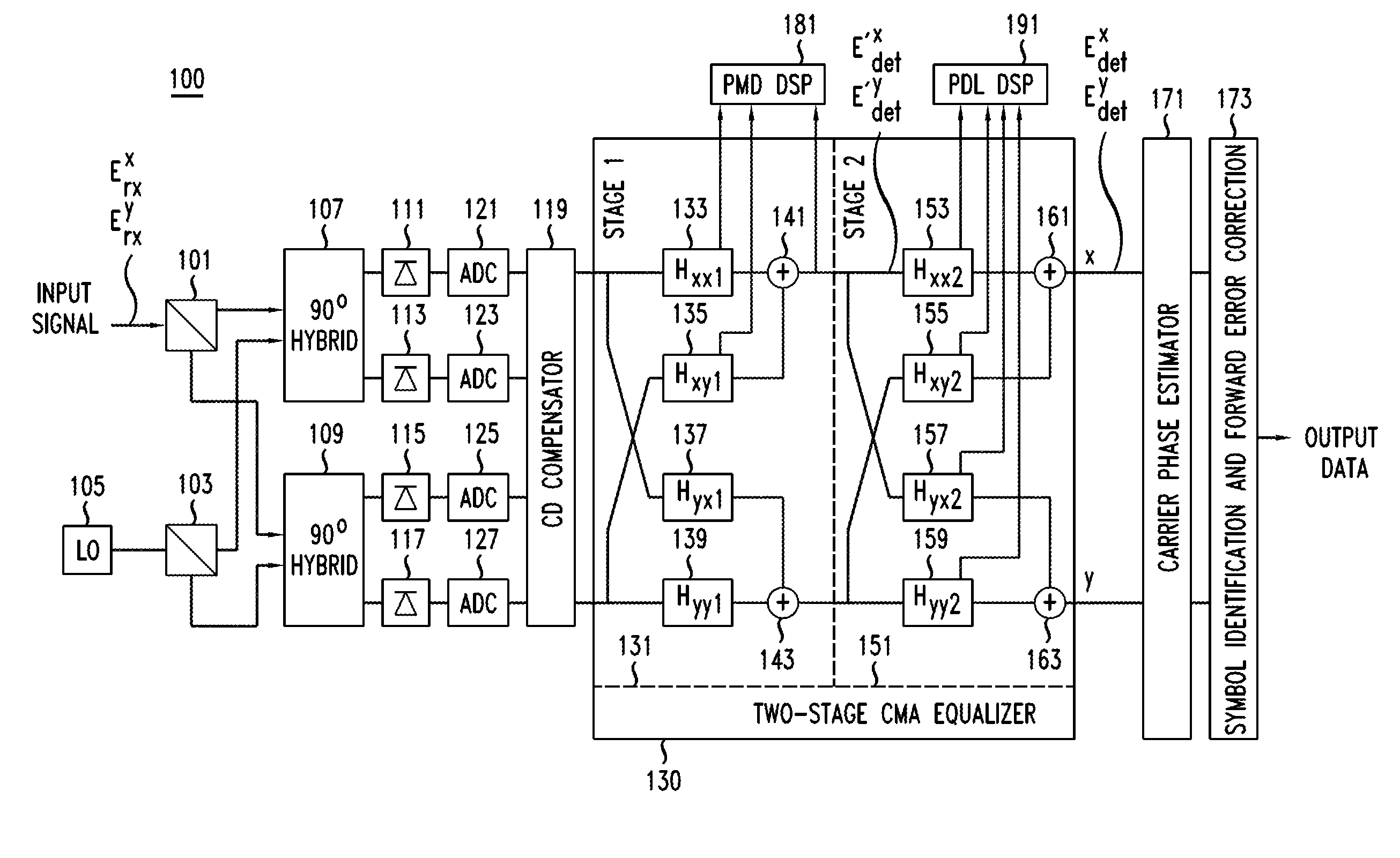
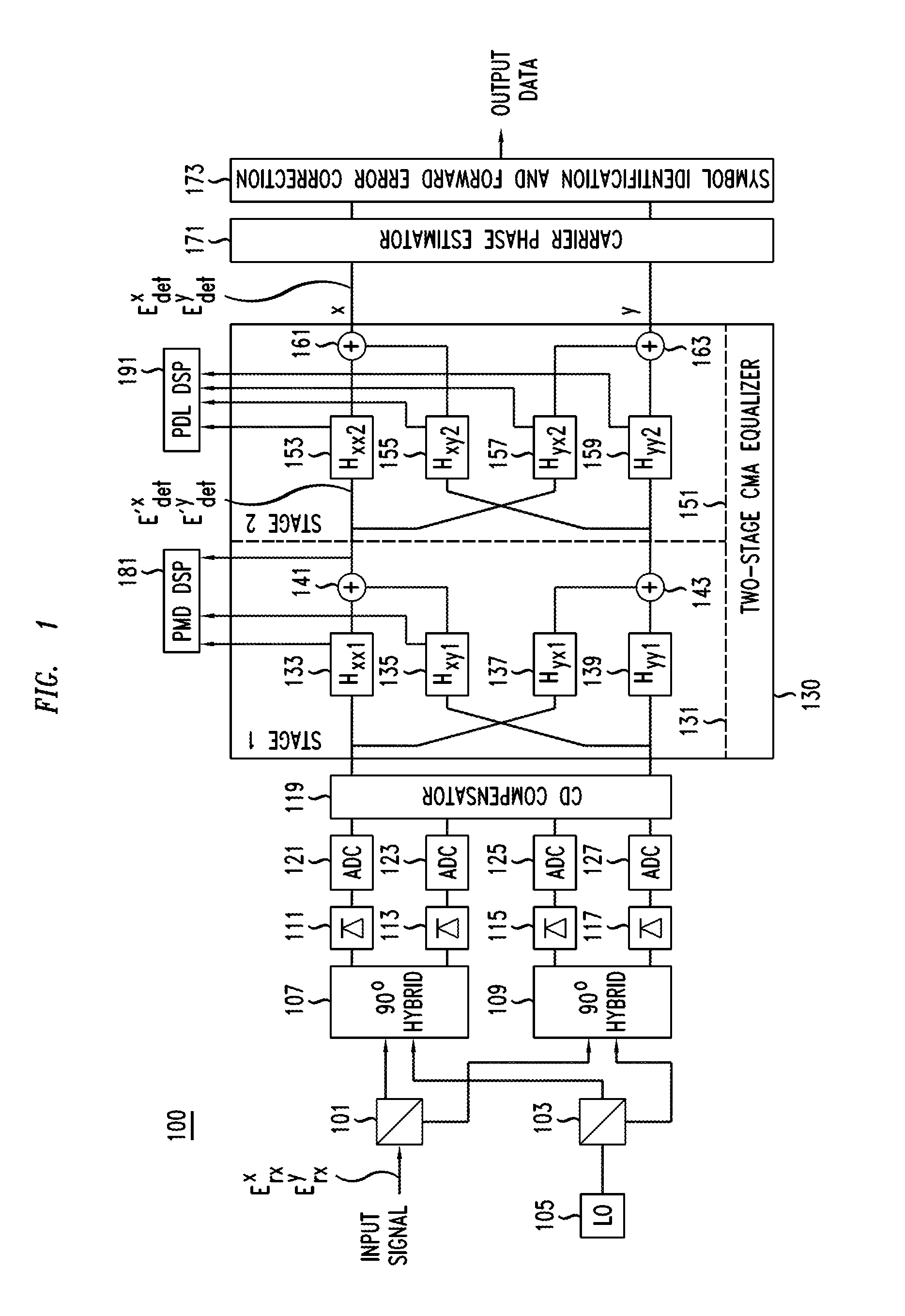
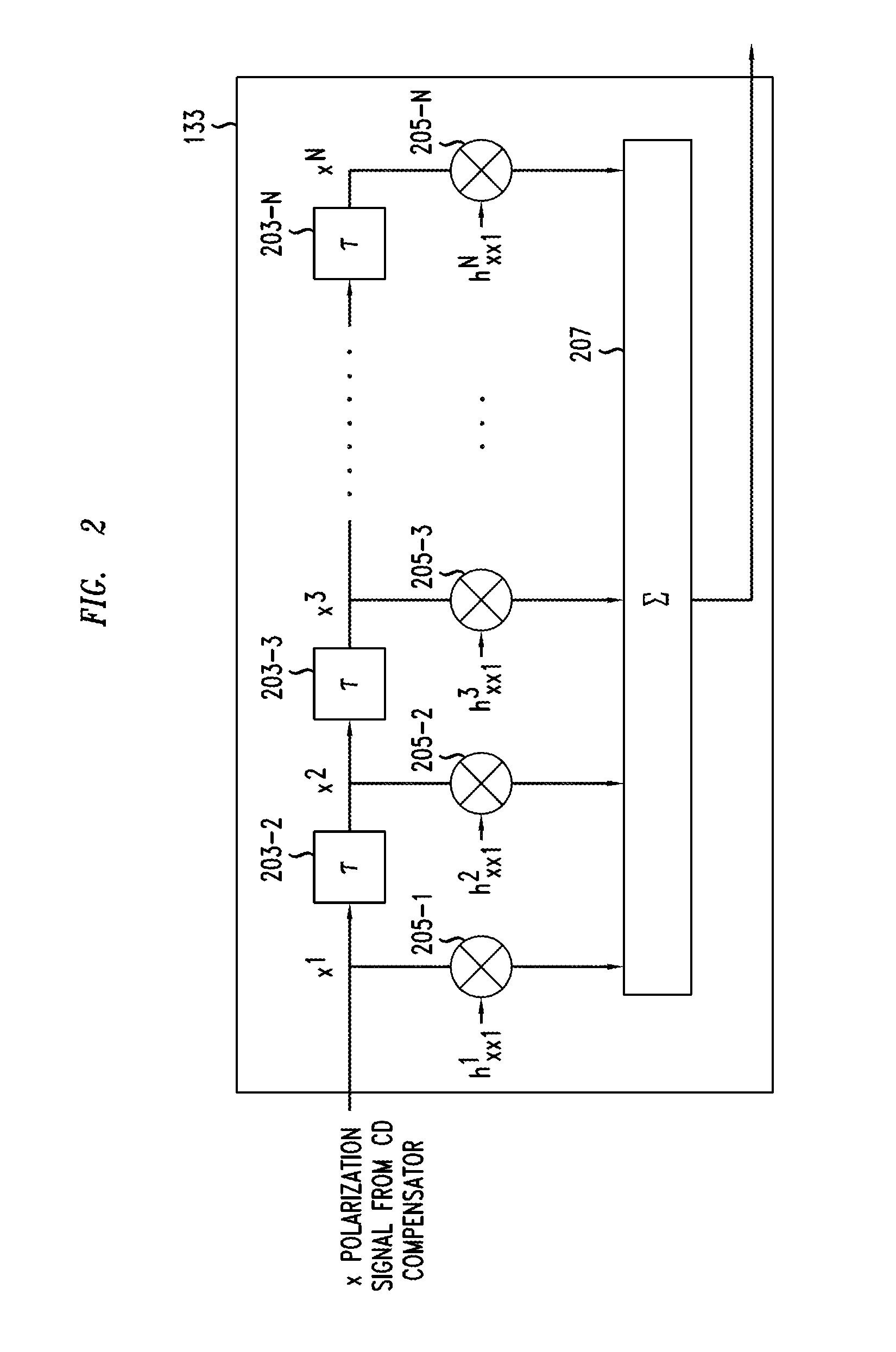
Method And Apparatus For Polarization-Division-Multiplexed Optical Receivers
ActiveUS20120002979A1Effective wayEliminate the problemElectromagnetic receiversEqualizationPolarization mode dispersion
An optical receiver includes a two-stage constant modulus algorithm (CMA) equalizer. The first stage is a modified version of a CMA equalizer and the second stage is a conventional CMA equalizer. The first stage may be made up of four sub-equalizers, of which only two of the sub-equalizers are independent, i.e., uncorrelated to each other. This first stage equalizer compensates for polarization-mode dispersion (PMD). The second stage equalizer is a conventional CMA equalizer made up of four sub-equalizers that are adjusted independently. This second stage equalizer may compensate for polarization-dependent loss (PDL). The receiver includes a first processor that determines PMD information based on a plurality of transfer function parameters of the modified CMA equalization of the first stage equalizer and the modified-equalized output and a second processor that determines PDL based on a plurality of transfer function parameters of the CMA equalization of the second stage equalizer.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
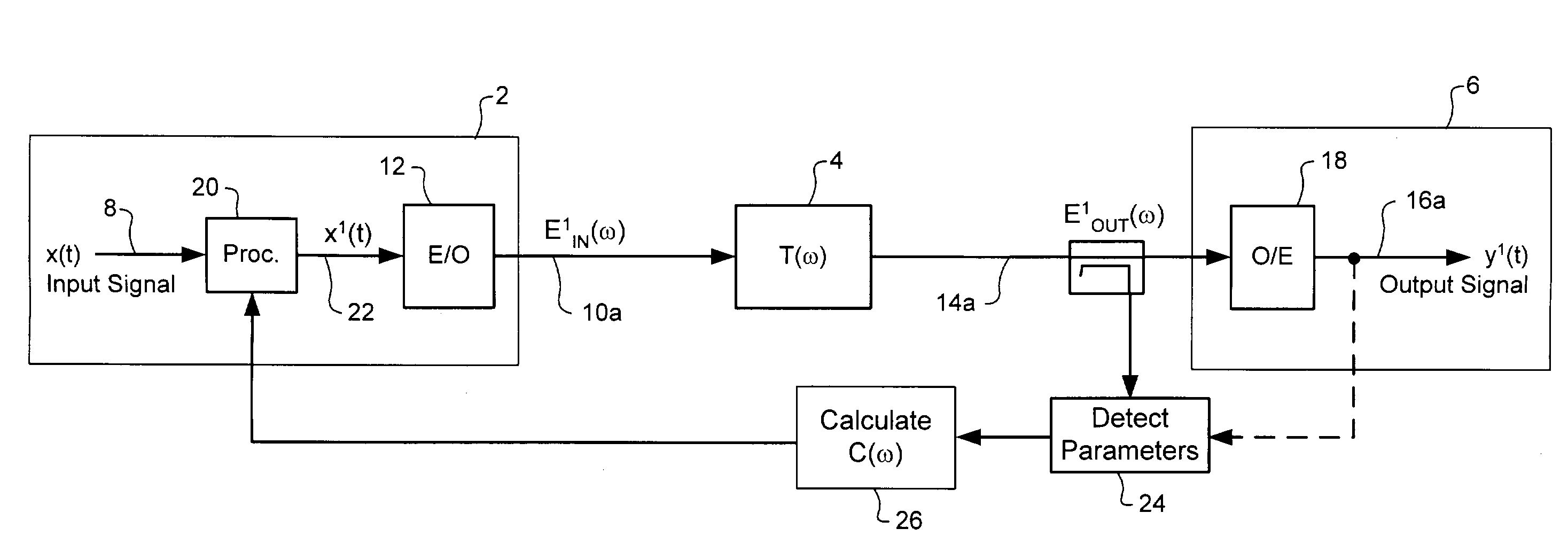
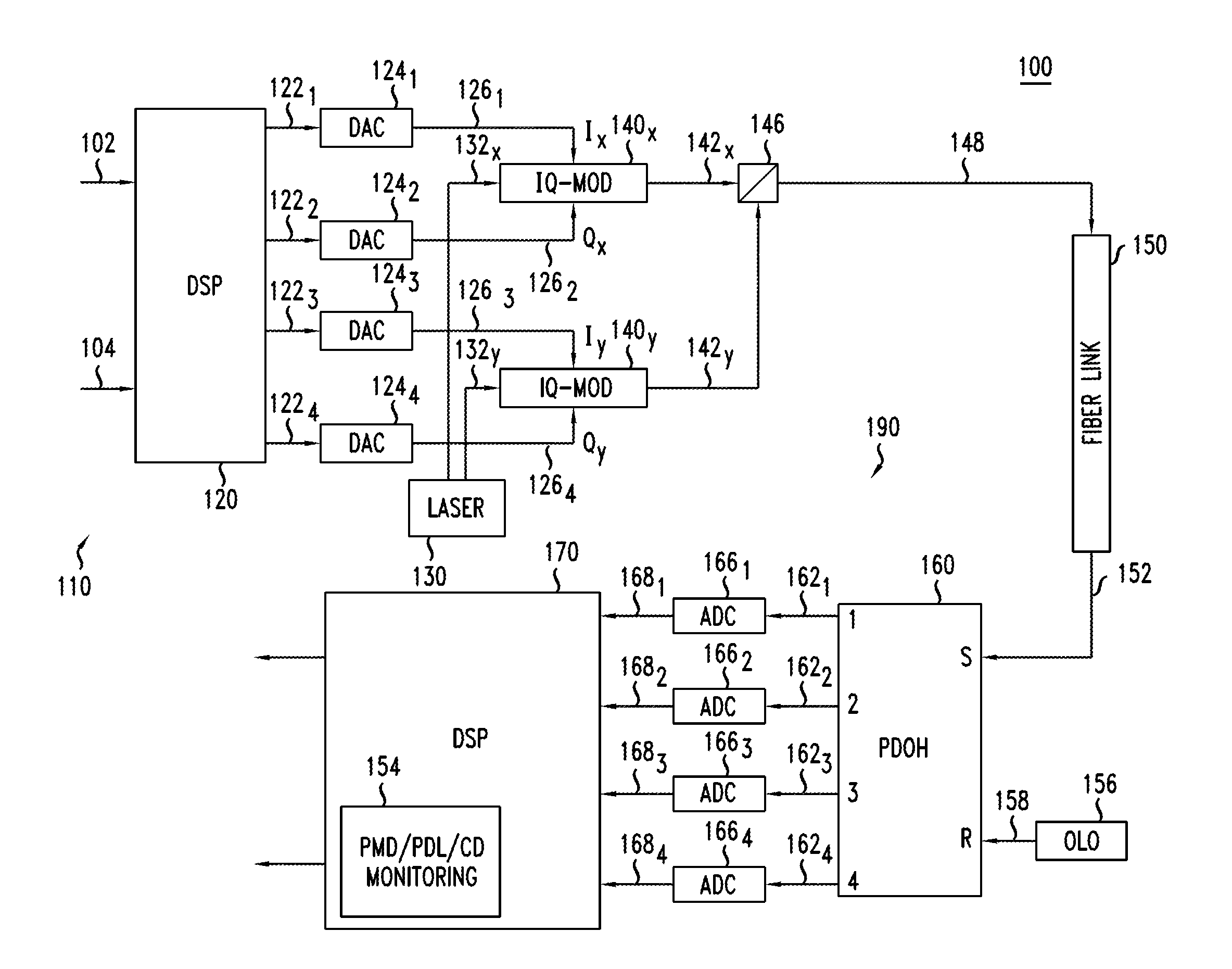
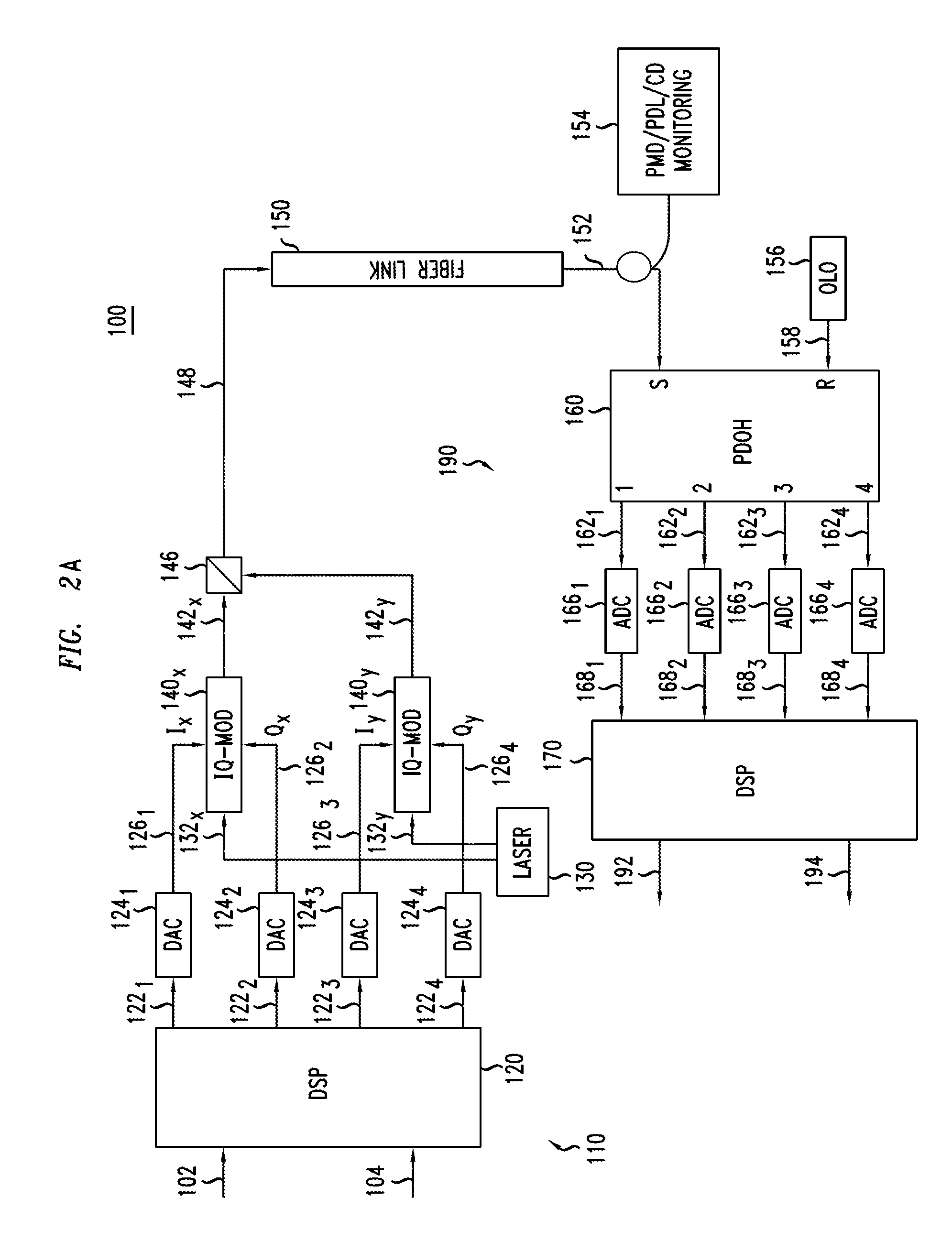
Electrical domain mitigation of polarization dependent effects in an optical communications system
ActiveUS7382985B2Reduce impactCost-effectiveDistortion/dispersion eliminationElectromagnetic transmittersCommunications systemPolarization mode dispersion
Polarization Dependent Effects (PDEs), including Polarization Mode Dispersion (PMD) and Polarization Dependent Loss (PDL) imposed on optical signals conveyed through an optical link are compensated by processing an input signal in the electrical domain prior to transmission. A compensation function is derived that at least partially compensates the PDEs. The communications signal is then processed in the electrical domain using the compensation function to generate an electrical predistorted signal. The electrical predistorted signal is then used to modulate an optical source to generate a corresponding predistorted optical signal for transmission through the optical link. The PDEs of the optical link operate of the predistorted optical signal such at that substantially undistorted optical signal is received at a receiving end of the link.
Owner:CIENA
Optical fiber, method for manufacturing same and optical transmission channel
ActiveUS20050089289A1Glass making apparatusOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingZero-dispersion wavelengthTransmission channel
The present invention provides an optical fiber of which a zero dispersion wavelength falls within a range of between 1,250 nm and 1,350 nm inclusive, transmission loss at 1,550 nm is equal to or less than 0.185 dB / km, chromatic dispersion at 1,550 nm is within the range of 19±1 ps / nm·km, a dispersion slope at 1,550 nm is equal to or less than 0.06 ps / nm2·km, an effective area Aeff is equal to or more than 105 μm2, a cable cutoff wavelength λcc is equal to or less than 1,530 nm, polarization mode dispersion is equal to or less than 0.1 ps / km1 / 2, and a loss when the optical fiber is wound on a mandrel having an outer diameter of 20 mm is equal to or less than 10 dB / m.
Owner:FURUKAWA ELECTRIC CO LTD
Plasmon-photon coupled optical devices
InactiveUS7110154B2Improve transmittanceTransmittivity of high intensity light is limitedBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsMaterial analysis by optical meansAngle of incidenceRefractive index
The present invention is directed to optical devices. More specifically, the disclosed devices include a film defining a periodic array of surface elements so as to give rise to surface plasmon polaritons. The film also includes at least a single aperture having a diameter less than the wavelength of light. In one embodiment, the surface elements can be an array of anisotropic apertures and the films can act as a polarizer. The disclosed devices can also include a material having a variable refractive index substantially adjacent to the metal film. For example, the refractive index of the adjacent material can vary according to some characteristic of the light incident to the device, for instance, the intensity or the angle of incidence of the light. In this embodiment, resonant coupling of incident light with the SPP, and hence transmittivity of the device, can depend upon the nature of incident light. The disclosed devices can be useful in, for example, remote polarizers, polarization mode dispersion, isolators, multi-color displays, switches, such as can be controlled according to incident sunlight, or optical filters, such as for eye protection devices, filtering out possibly harmful light.
Owner:CLEMSON UNIV RES FOUND
Electronically tunable optical filtering modules
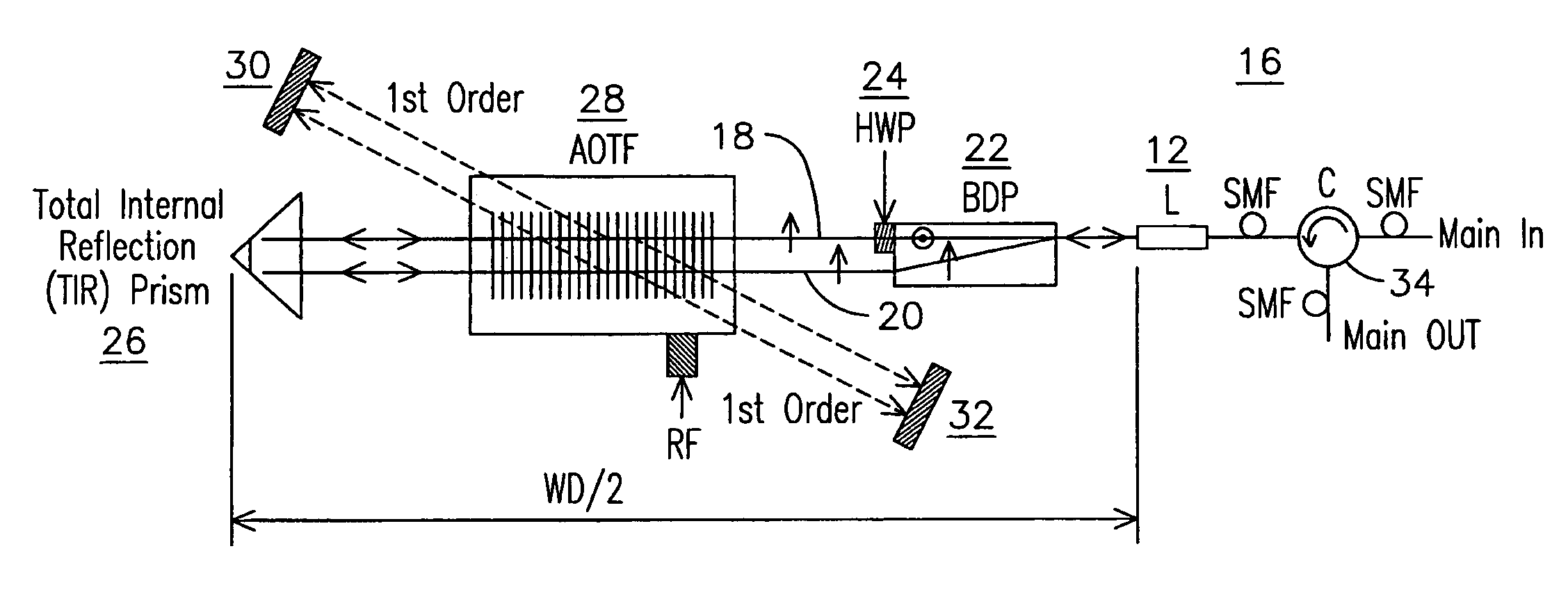
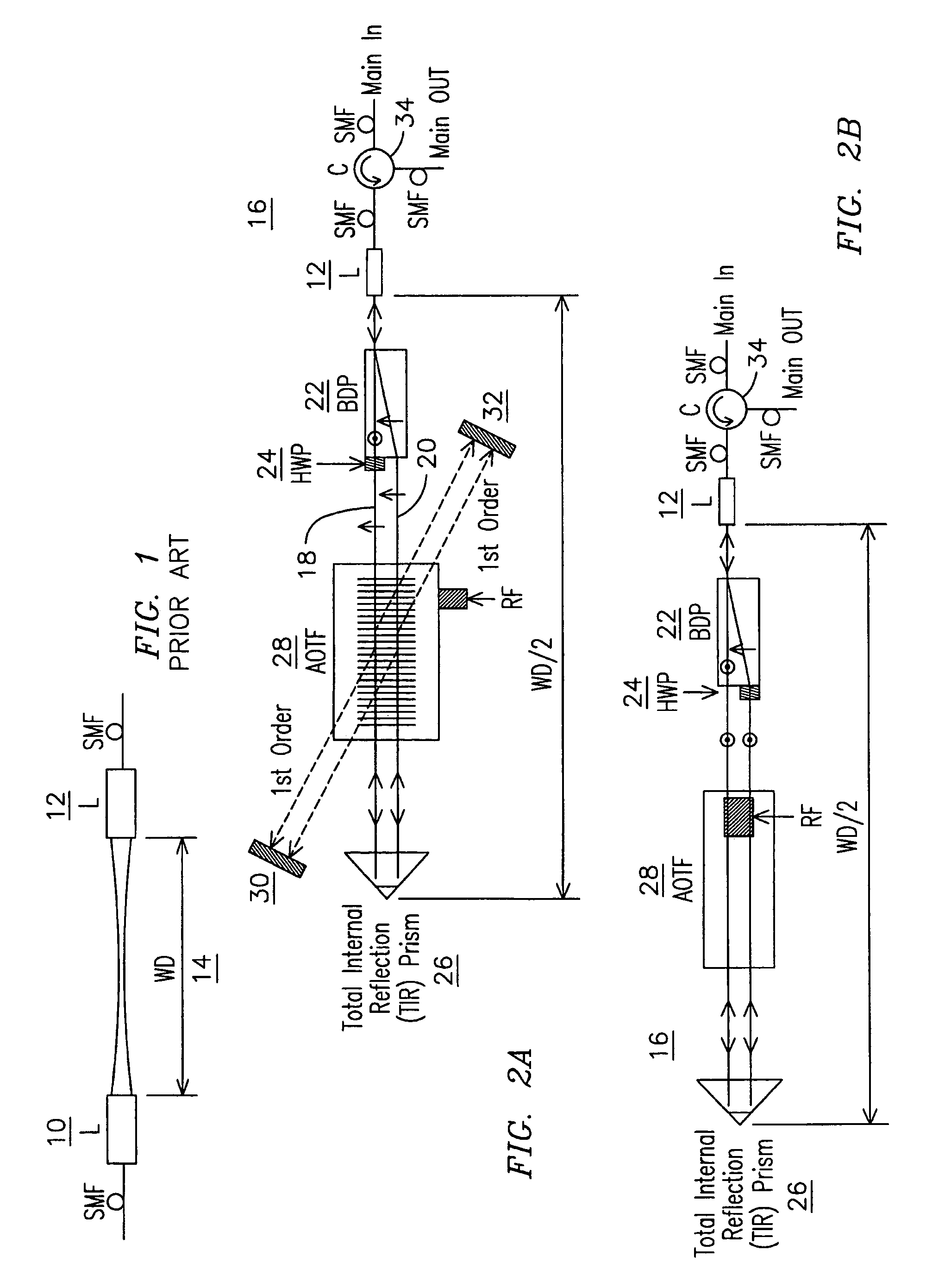
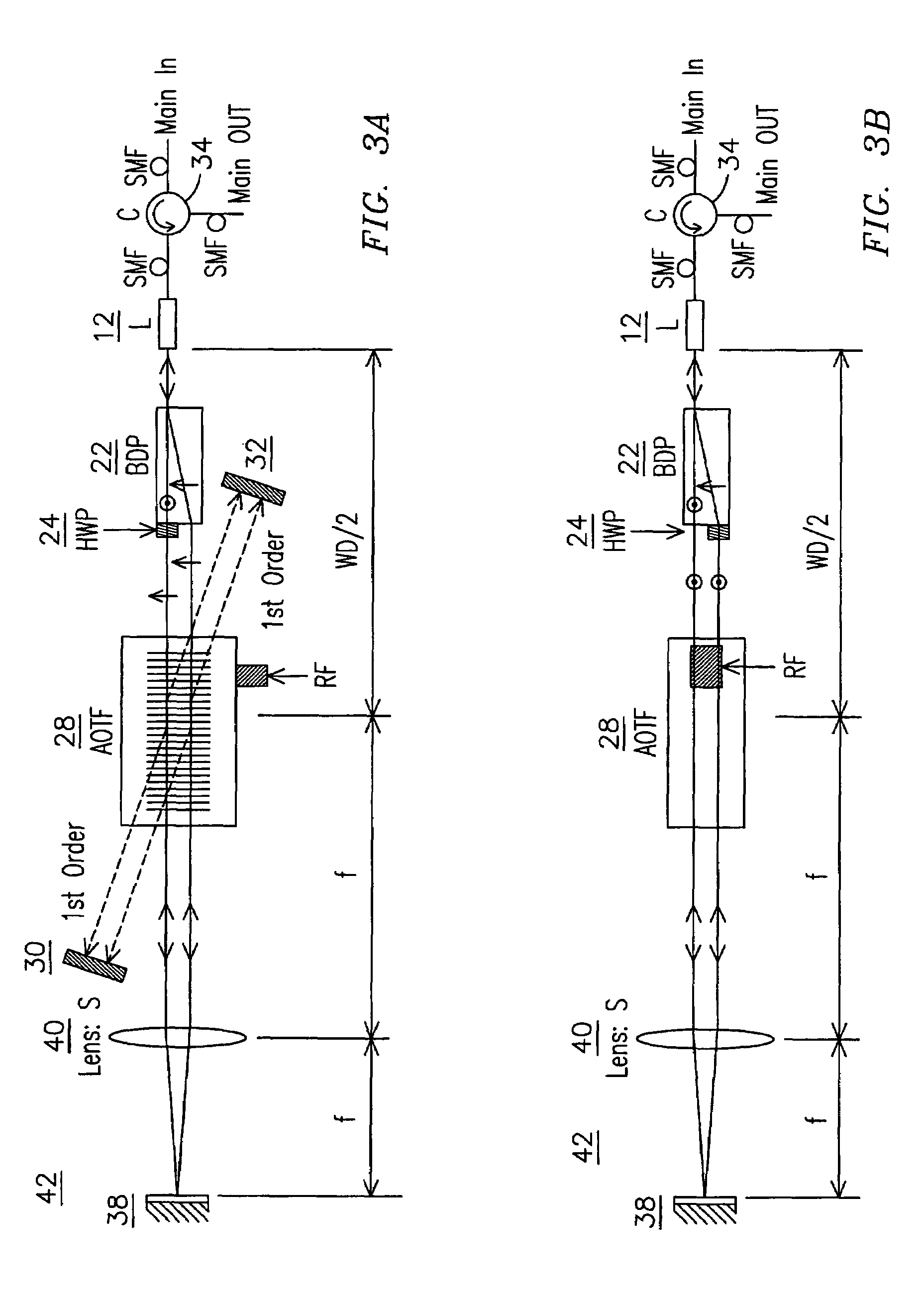
Electronically agile optical filtering modules for equalizing light propagation differences in at least two spaced optical beam pathways in the modules. The modules use optical polarization rotation devices that may include acousto-optic tunable filter (AOTF) devices, liquid crystal devices, and magneto-optic devices. Such devices may be subject to polarization dispersion losses (PDL) and polarization mode dispersion (PMD) that may be different for when light travel along different light paths through the device. By redirecting light beams back along a different bi-directional path through the devices which may exhibit non-uniform performance across orthogonal polarizations, PDL and PMD may be reduced.
Owner:NUONICS
Methods and apparatus for electromagnetic signal polarimetry sensing
ActiveUS20130332115A1Amplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDigital computer detailsPolarimetryRadio frequency signal
A system and method of identifying changes utilizing radio frequency polarization includes receiving a reflected and / or transmitted polarized radio frequency signal at a receiver, filtering, amplifying and conditioning the received signal, converting the received signal from an analog format to a digital format, processing the digital signal to elicit a polarization mode dispersion feature of the received signal, and comparing the polarization mode dispersion features to a known calibration to detect a change in a characteristic of the target object.
Owner:UNIV OF NOTRE DAME DU LAC
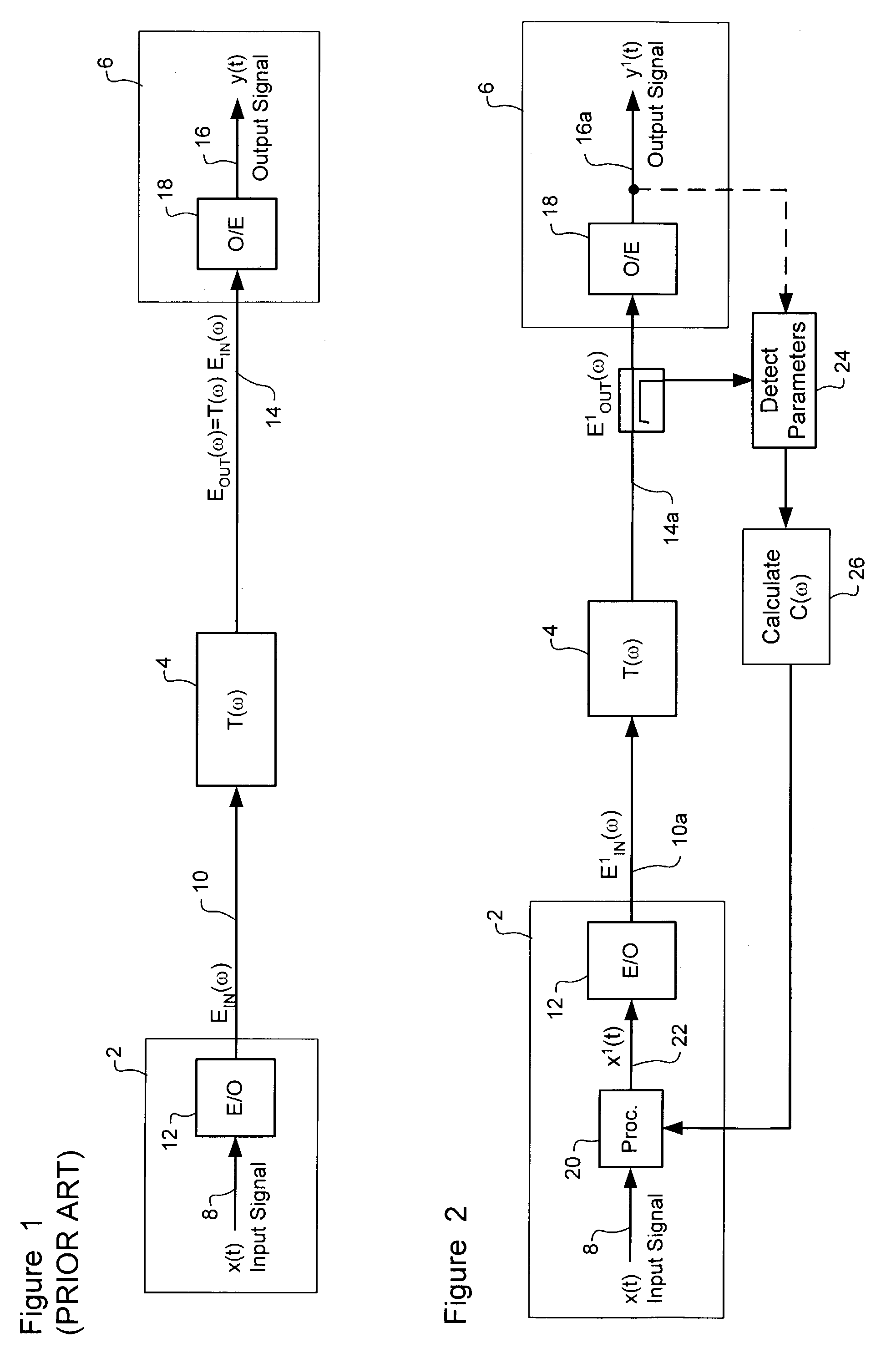
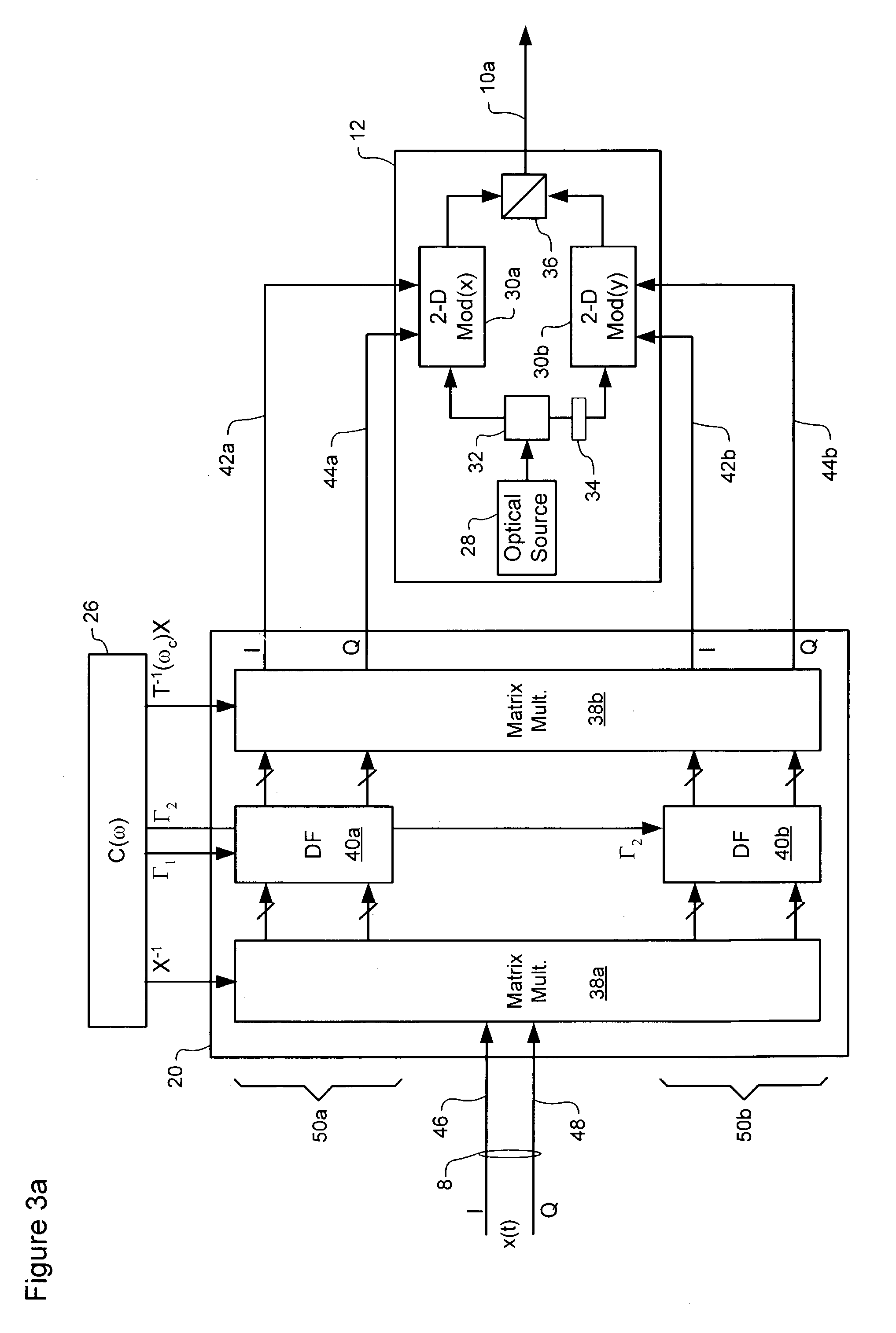
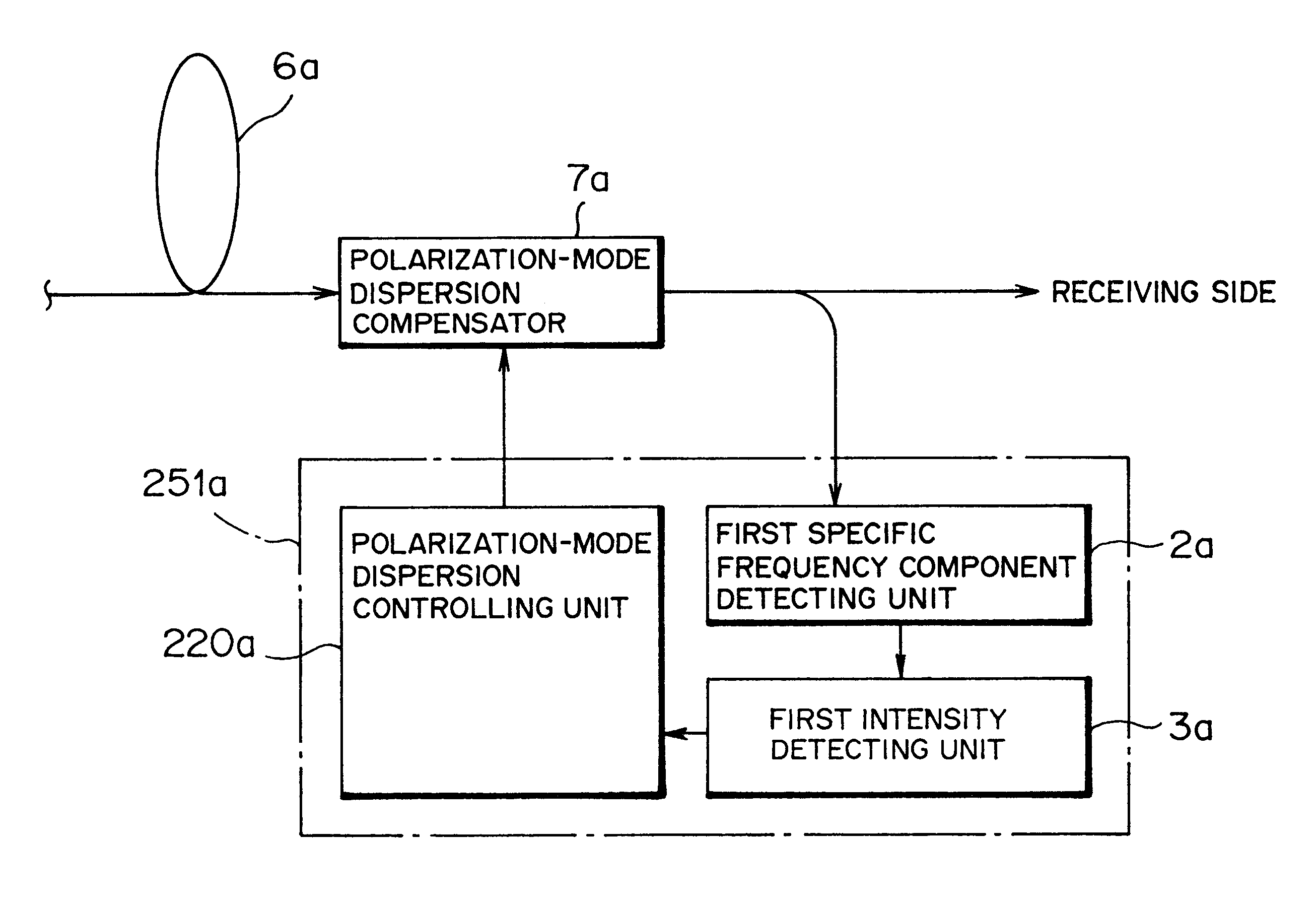
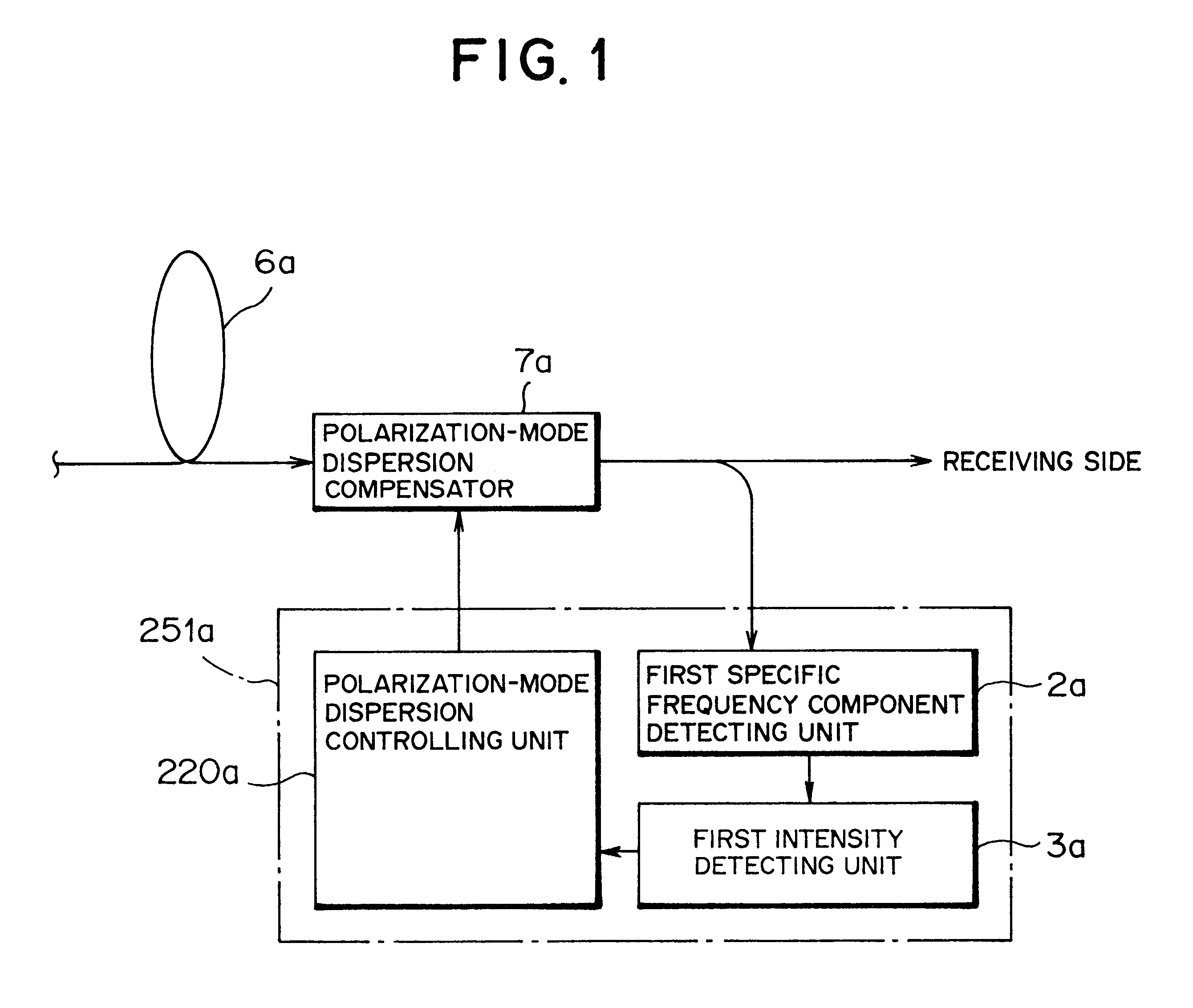
Polarization-mode dispersion detecting method, and a dispersion compensation controlling apparatus and a dispersion compensation controlling method
InactiveUS6728491B1Inhibit deteriorationGreat contributionDistortion/dispersion eliminationElectromagnetic transmittersUltra high speedFrequency spectrum
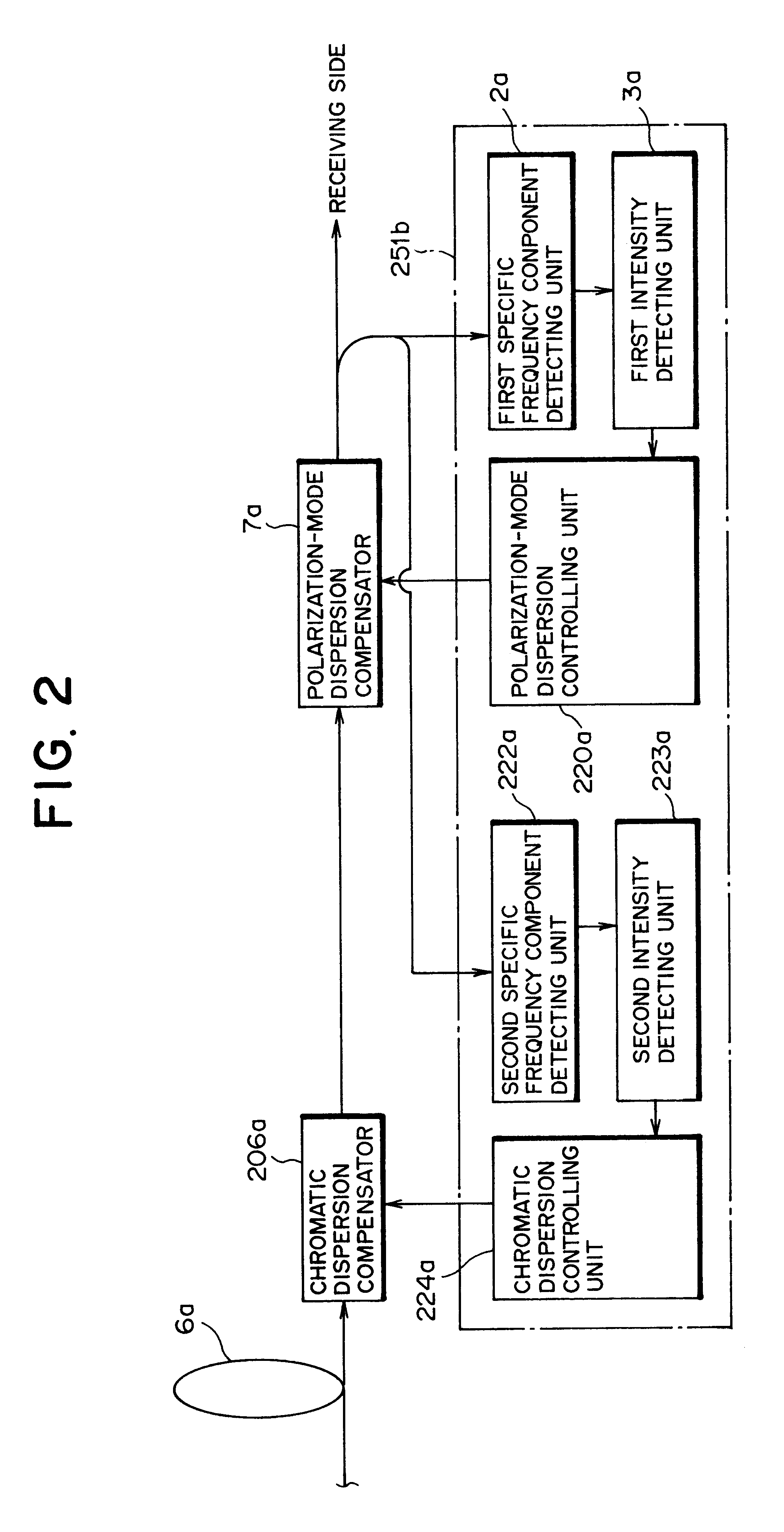
A dispersion compensation controlling apparatus used in a very high-speed optical communication system adopting optical time division multiplexing system comprises a first specific frequency component detecting unit (2a) detecting a first specific frequency component in a baseband spectrum in a transmission optical signal inputted to a receiving side over a transmission fiber as a transmission line (6a), a first intensity detecting unit (3a) detecting information on an intensity of the first specific frequency component detected by the first specific frequency component detecting unit (2a), and a polarization-mode dispersion controlling unit (220a) controlling a polarization-mode dispersion quantity of the transmission line (6a) such that the intensity of the first specific frequency component detected by the first intensity detecting unit (3a) becomes the maximum, thereby easily detecting and compensating polarization-mode dispersion generated in a high-speed optical signal.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Timing recovery in presence of optical impairments and optimization of equalization based on timing recovery moment strengths
ActiveUS20110268459A1Minimizing hardwarePolarisation multiplex systemsSynchronisation error detectionTransceiverEngineering
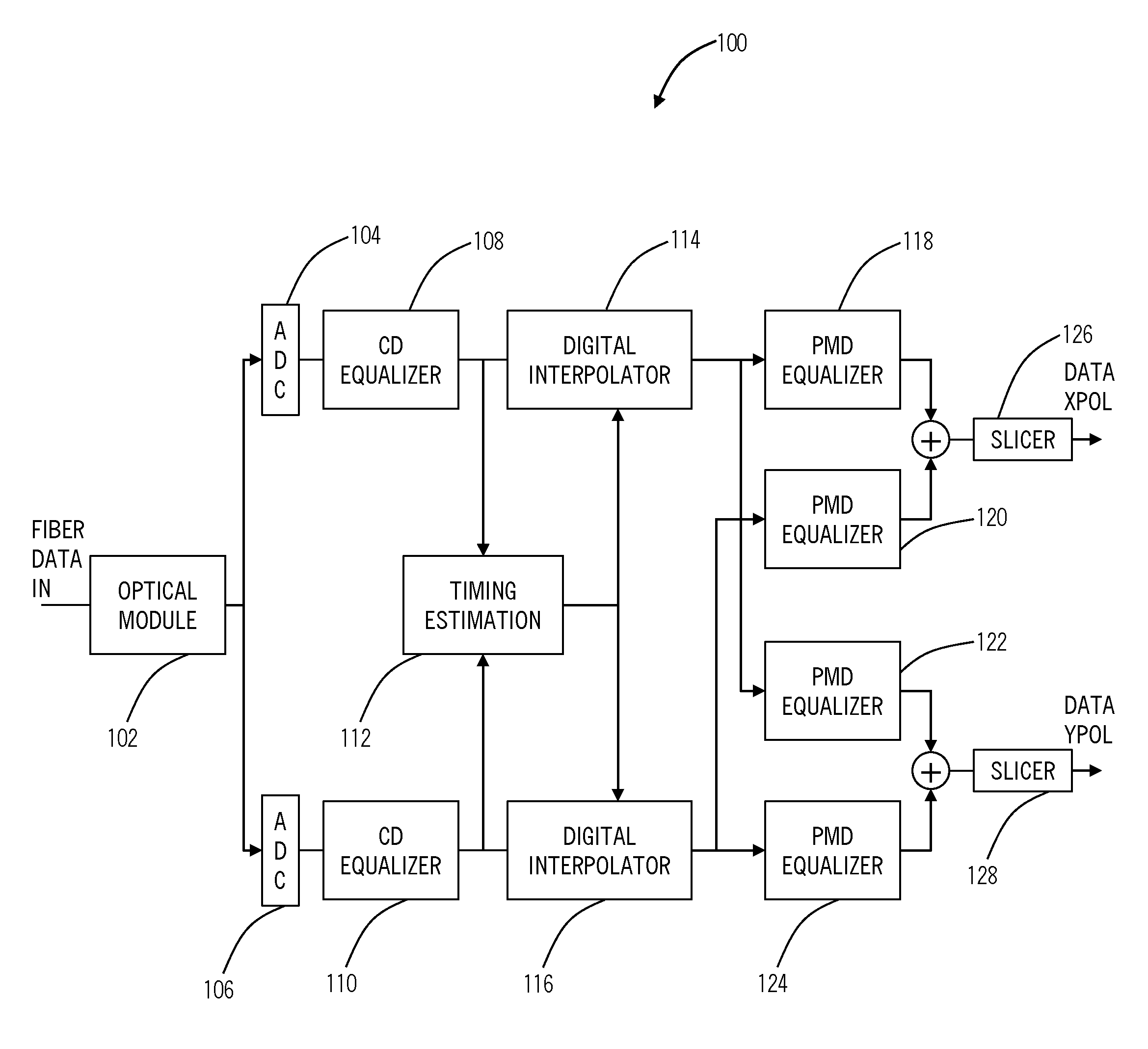
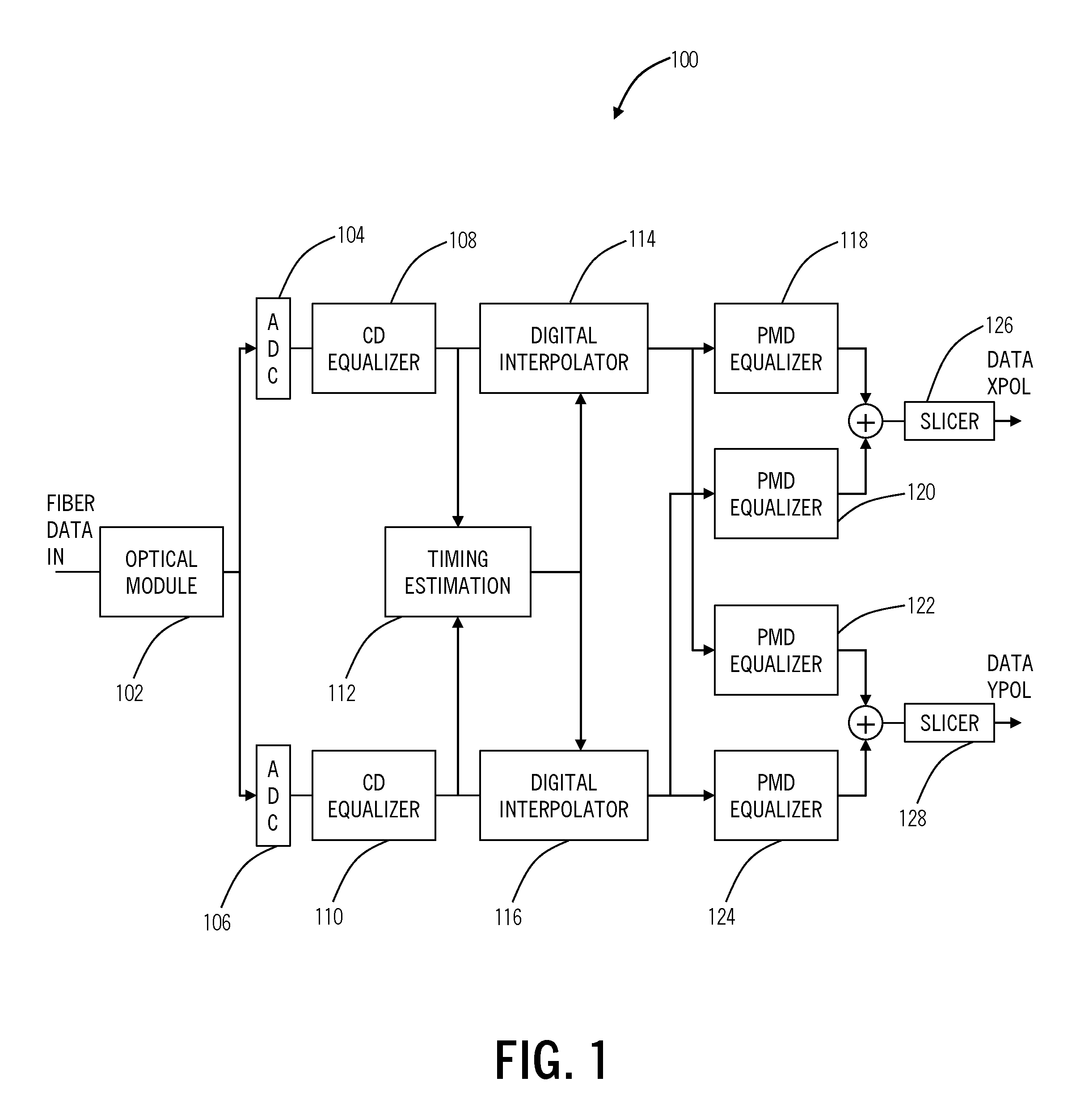
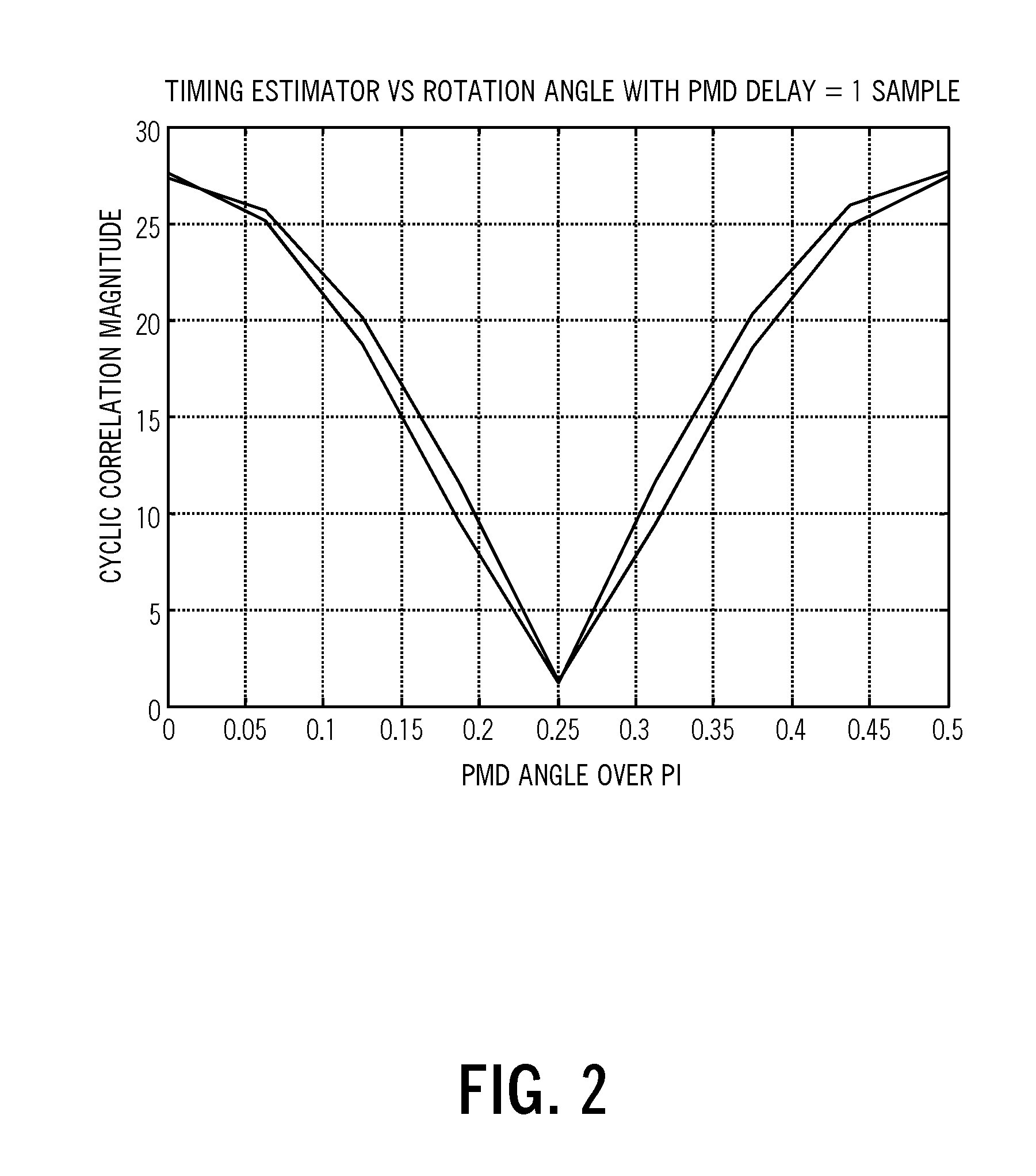
The present disclosure provides timing recovery in optical systems in the presence of chromatic dispersion (CD), polarization mode dispersion (PMD), and polarization dependent loss (PDL) and to optimization of equalization settings based upon timing recovery moment strengths. A stable timing point may be determined in the presence of PMD and PDL impairments, even when the direct estimate of timing becomes unreliable. This determination may be performed entirely in the digital domain providing precise, predictable performance. Also, the present invention utilizes a monotonic relationship between the timing metric and CD setting error to provide directed search in setting the CD equalizer thereby reducing significantly the overall search effort in optimizing CD equalizer settings. This utilizes computations already performed by the transceiver for timing recovery function yielding a computational advantage over competing methods.
Owner:CIENA
Optical fiber, method for manufacturing same and optical transmission channel
ActiveUS7095940B2Glass making apparatusOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingZero-dispersion wavelengthTransmission channel
The present invention provides an optical fiber of which a zero dispersion wavelength falls within a range of between 1,250 nm and 1,350 nm inclusive, transmission loss at 1,550 nm is equal to or less than 0.185 dB / km, chromatic dispersion at 1,550 nm is within the range of 19±1 ps / nm·km, a dispersion slope at 1,550 nm is equal to or less than 0.06 ps / nm2·km, an effective area Aeff is equal to or more than 105 μm2, a cable cutoff wavelength λcc is equal to or less than 1,530 nm, polarization mode dispersion is equal to or less than 0.1 ps / km1 / 2, and a loss when the optical fiber is wound on a mandrel having an outer diameter of 20 mm is equal to or less than 10 dB / m.
Owner:FURUKAWA ELECTRIC CO LTD
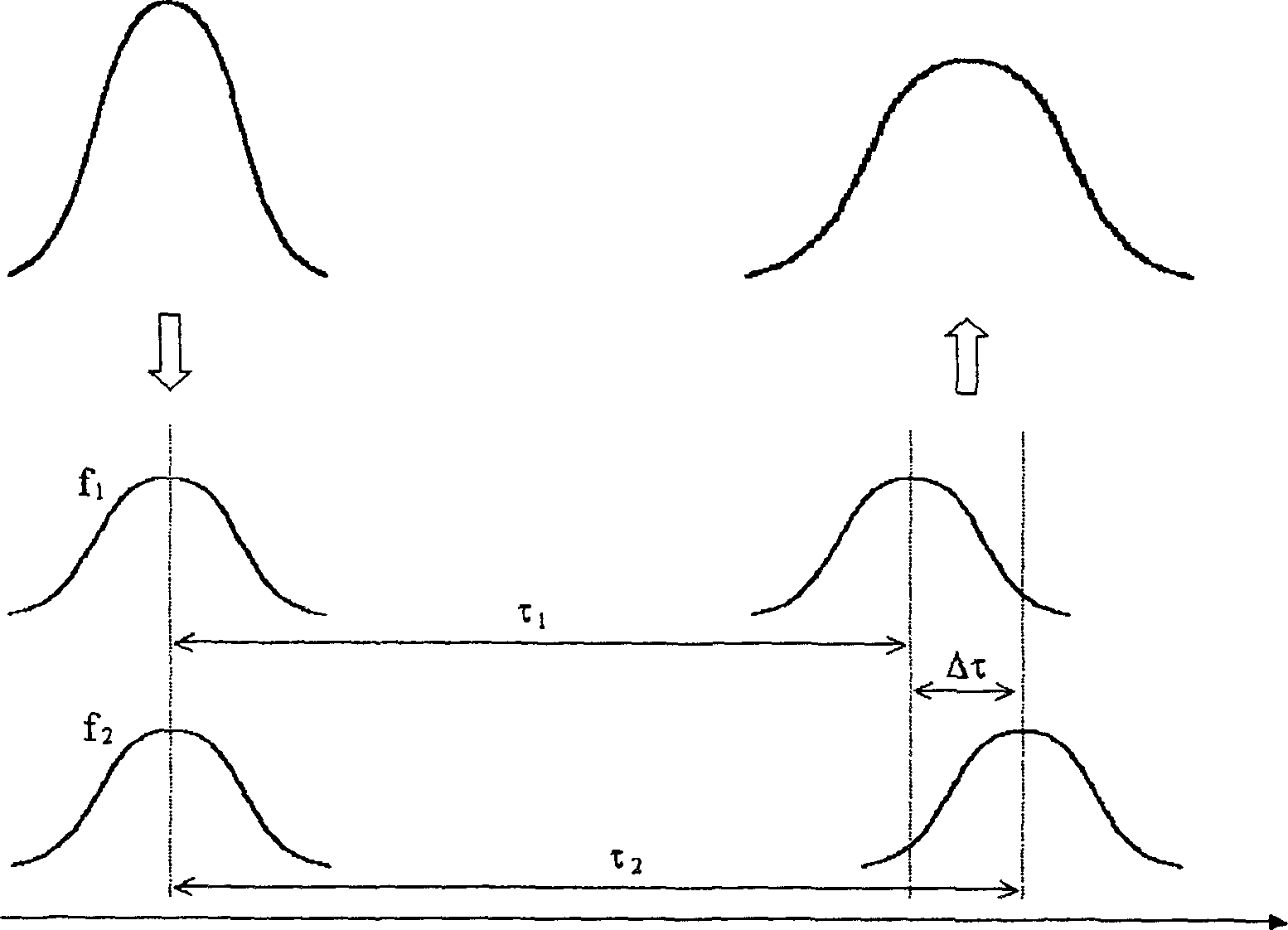
Method for increasing accuracy of measurement of mean polarization mode dispersion
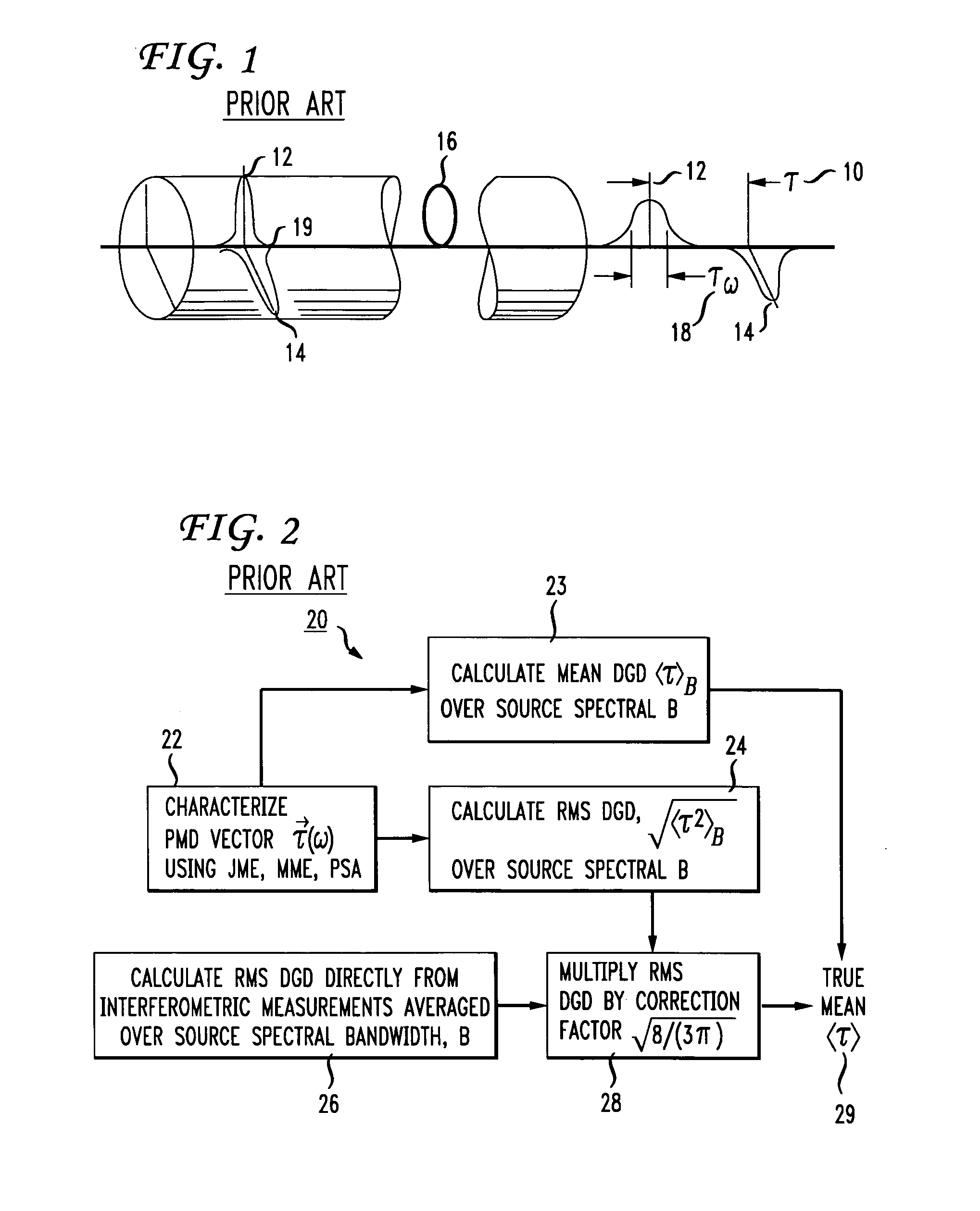
InactiveUS7292322B2High measurement accuracyError minimizationMaterial analysis by optical meansElectromagnetic transmissionMean squarePolarization mode dispersion
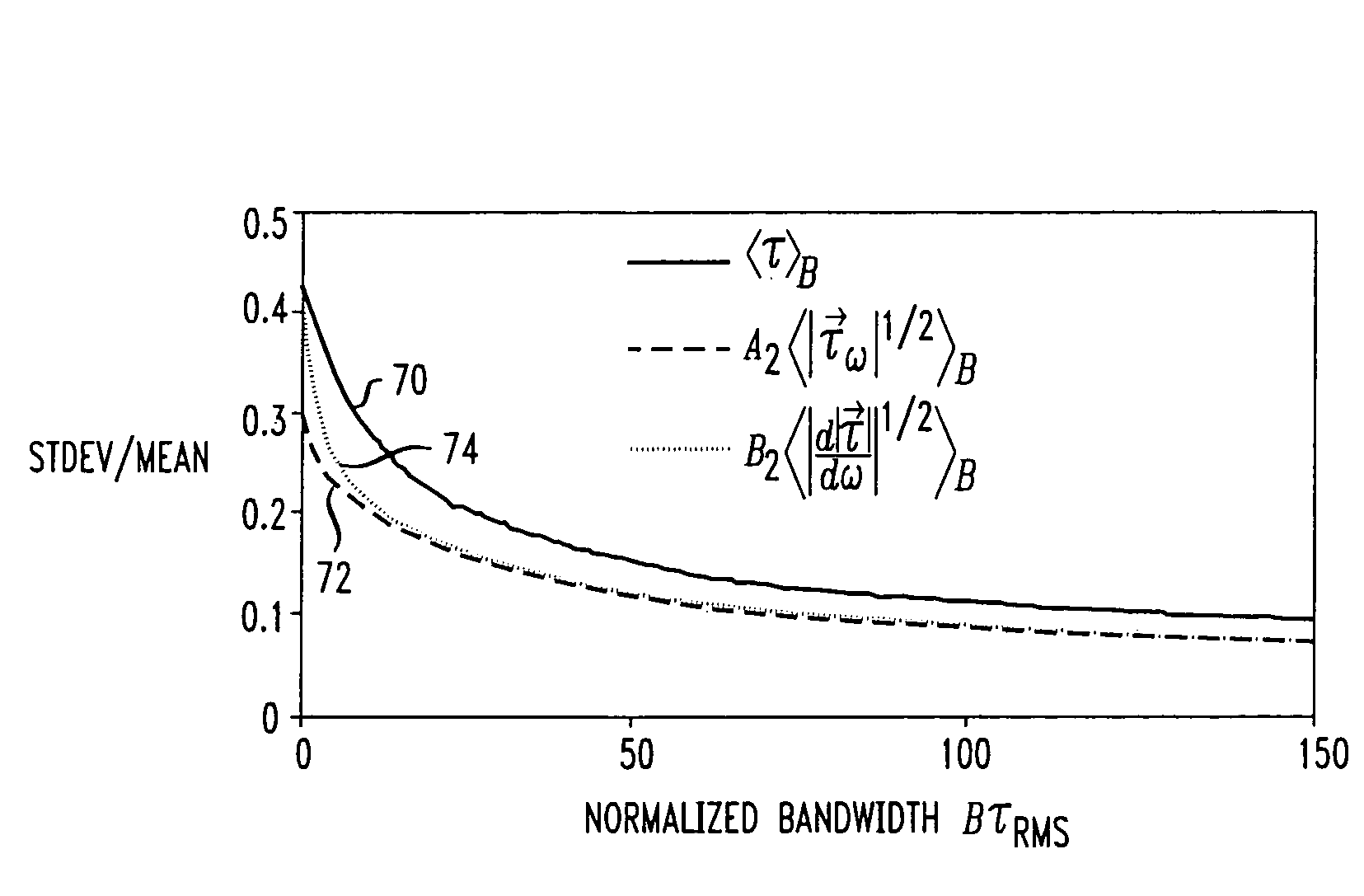
The present invention provides a method for increasing the accuracy of measurement of mean differential group delay (DGD) from the polarization mode dispersion (PMD) in optical fiber. The method includes a systematic correction to mean-square DGD measured with any conventional mean to minimize systematic error caused by finite source bandwidth. The method further includes a systematic correction to the measurement of mean DGD and mean square DGD from statistics of the second-order PMD (SOPMD) obtained with frequency domain PMD-measuring apparatus. The probability density function (PDF) of either the vector or scalar SOPMD is applied, depending on which quantity is measured. The systematic correction is made to minimize the systematic error in estimating mean DGD, caused by finite source bandwidth, to achieve a two-fold reduction of the measurement variance equivalent to doubling the source bandwidth.
Owner:FICO MIRRORS SA +1
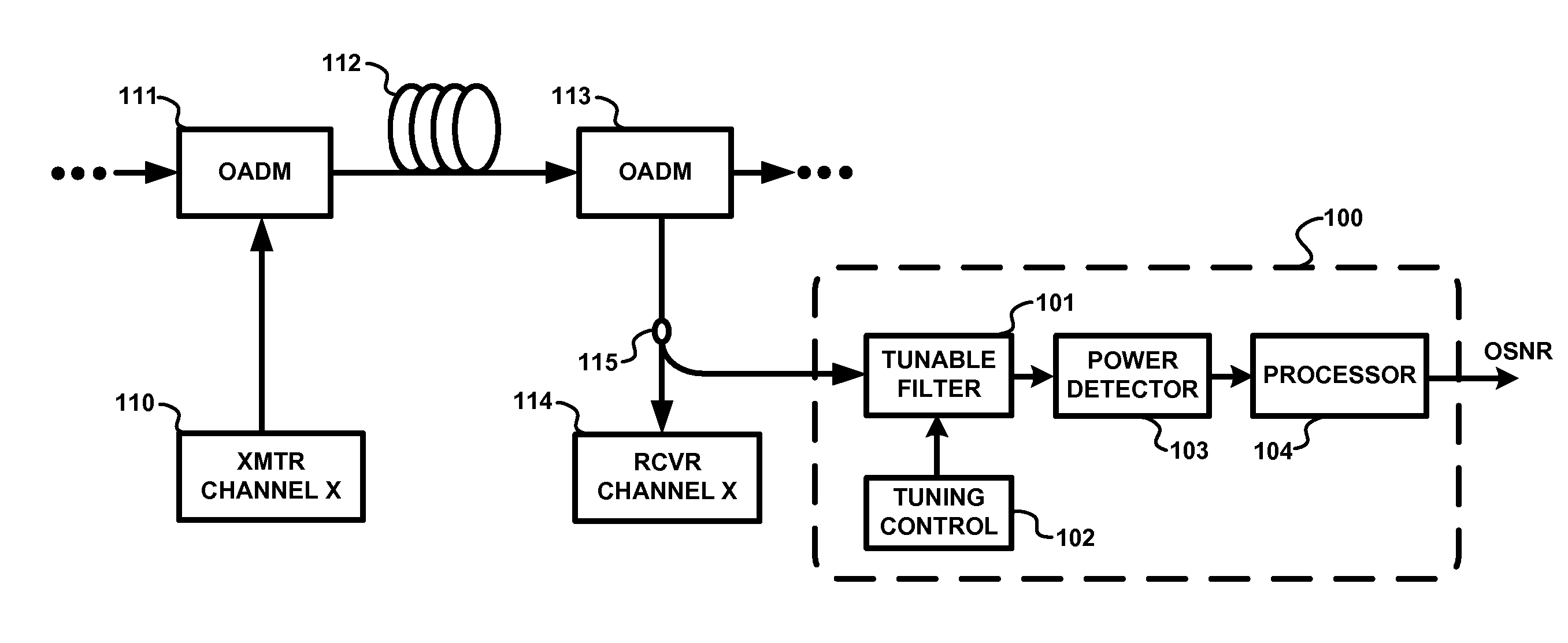
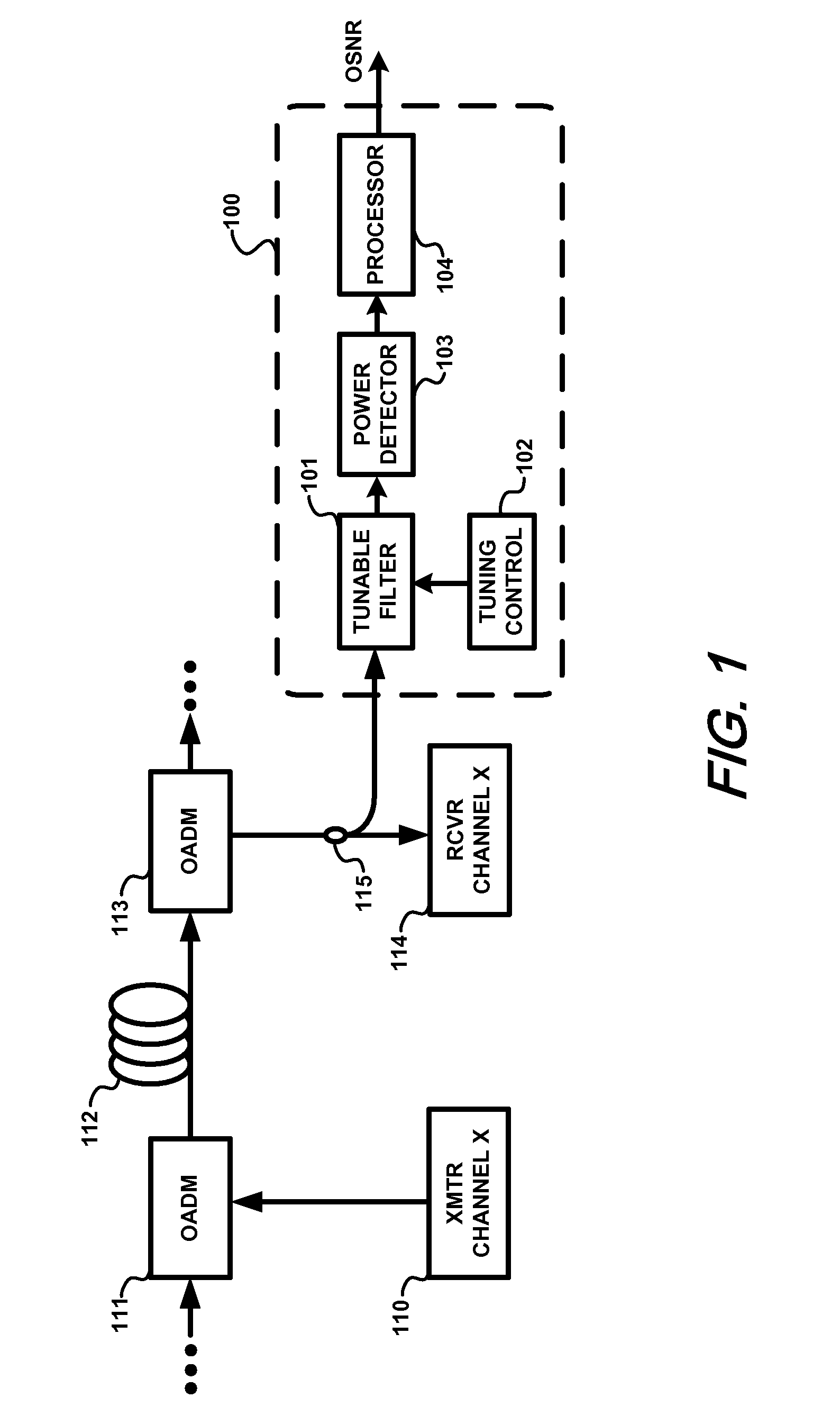
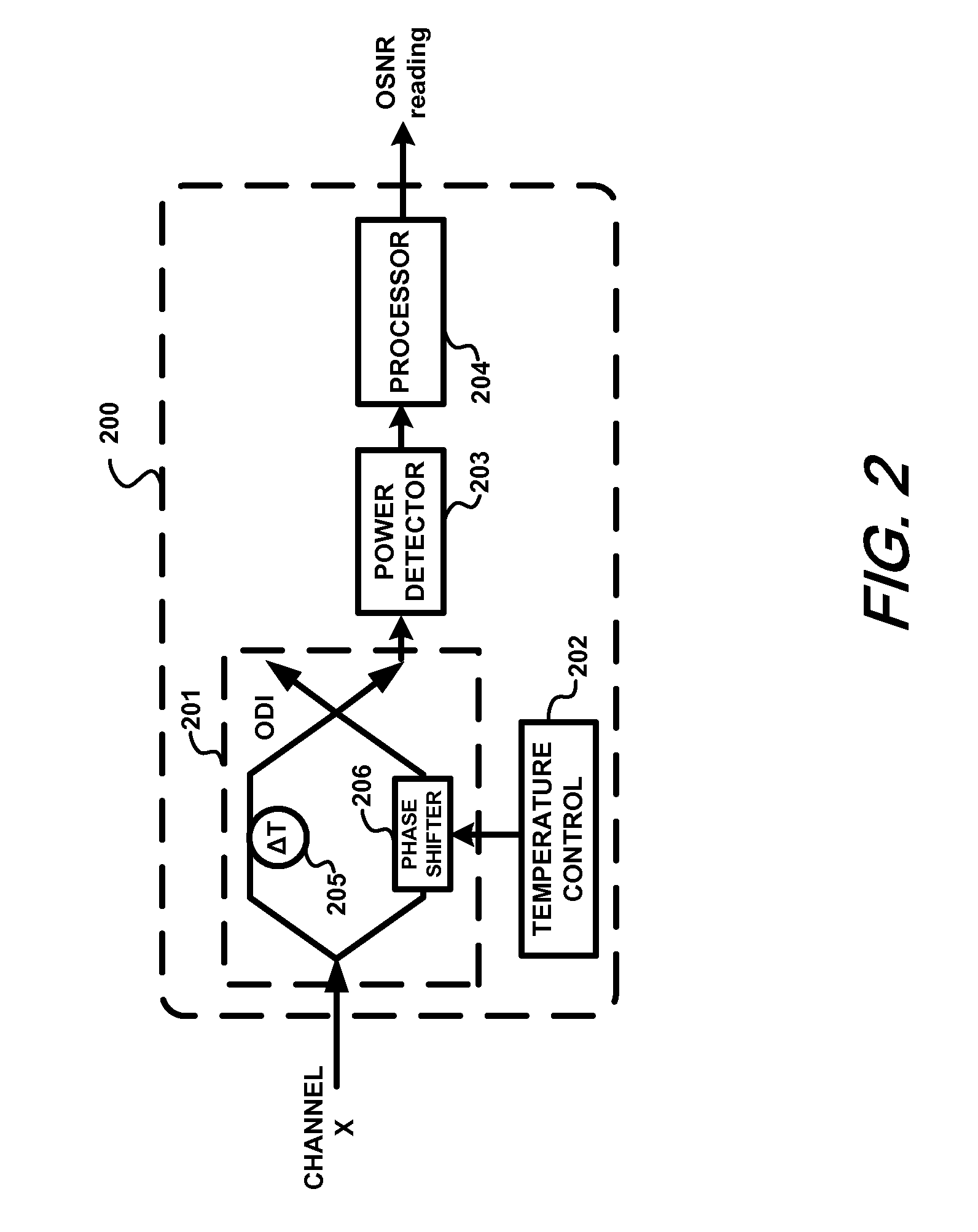
Method and apparatus for monitoring optical signal-to-noise ratio
ActiveUS20070297043A1Not affectLaser detailsFibre transmissionEngineeringPolarization mode dispersion
Optical signal-to-noise ratio (OSNR) monitoring methods and apparatus are described. A tunable optical filter filters an optical channel containing an optical signal and noise. The total signal and noise power at the output of the filter is measured as the transmittance passband of the filter is varied and the maximum and minimum powers are determined. The ratio between the maximum and minimum powers is then used to determine the OSNR of the optical channel, which, for example, can be a wavelength channel in a wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) system. The ratio of the maximum signal power to the minimum signal power and the ratio of the maximum noise power to the minimum noise power are pre-determined based on the signal modulation format type and filter passband characteristics. Because the OSNR monitoring method and apparatus rely on information obtained after spectrally filtering the signal and noise, their operation is independent of any transmission effect that does not affect the optical power spectra of the signal and the noise or affects them in a known manner. For example, effects such as chromatic dispersion (CD), polarization-mode dispersion (PMD), and changes in the signal degree of polarization (DOP) and noise DOP will not affect the OSNR reading thus obtained.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC +1
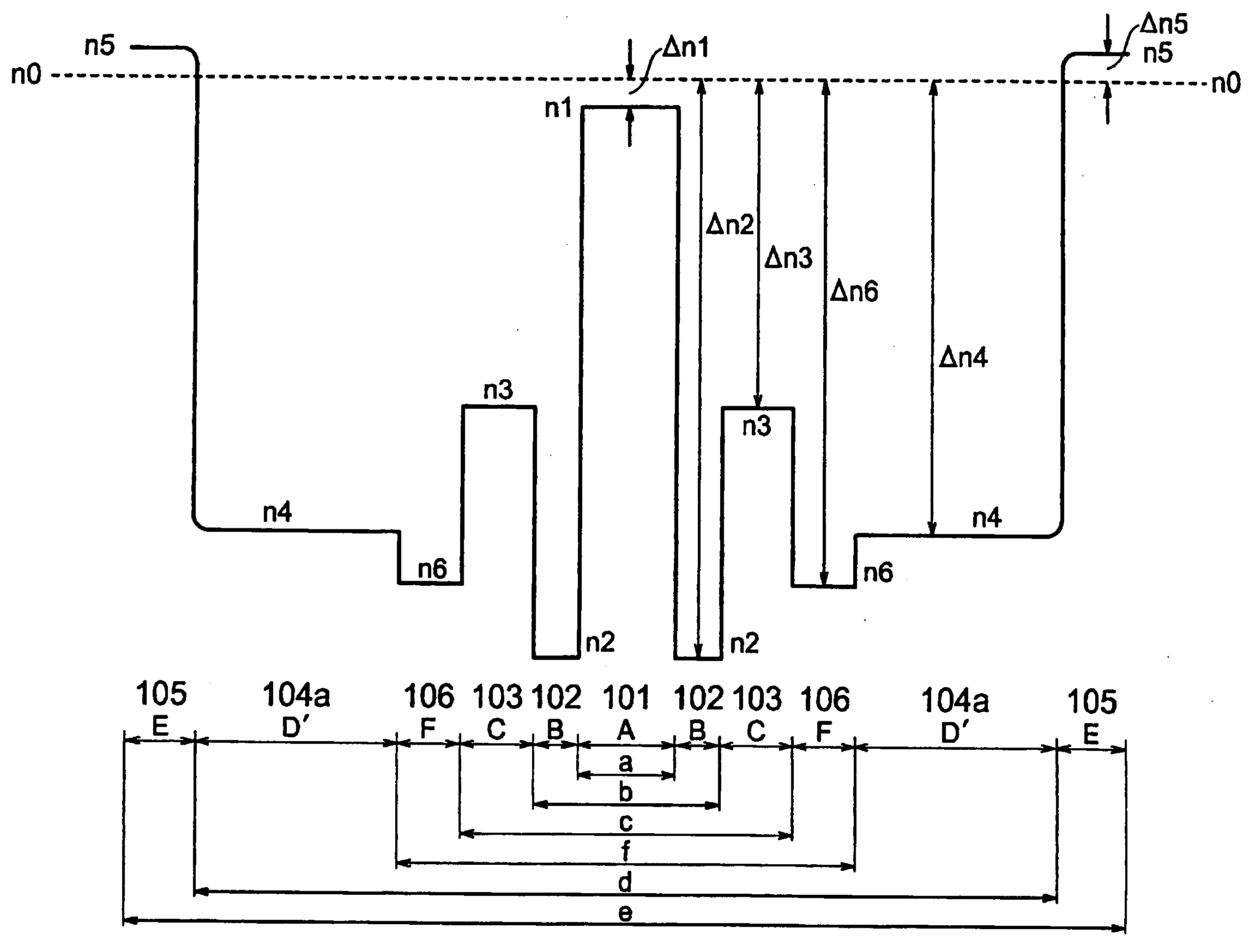
Method for fabricating a low polarization mode dispersion optical fiber
The method of fabricating an optical waveguide fiber from a preform having a centerline aperture which includes reducing the pressure in the centerline aperture, then increasing the pressure in the centerline aperture to a pressure in order to improve uniformity, circularity, and / or symmetry around the centerline aperture region.
Owner:CORNING INC
Chromatic Dispersion Compensating Fiber
ActiveUS20070258686A1Improved FOM valueLimited bending and micro-bending lossesOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingOptical waveguide light guideOptical ModuleRefractive index
Disclosed is a chromatic dispersion compensating optical fiber comprising a central core, an intermediate cladding having a width (r2−r1) of 2.0 microns or greater, and a depressed inner cladding having a refractive index difference Dn3 with the external optical cladding of −3.0×10−3 or lower. At a wavelength of 1550 nm, the optical fiber exhibits a positive chromatic dispersion of 21 ps / nm·km or higher and a ratio of mode radius to intermediate cladding radius of (W02 / r2) of 0.7 or less. The present optical fiber has a good figure of merit value and limited bending and microbending losses. The optical fiber can be rolled up in a housing of reduced size in a chromatic dispersion compensating optical module having limited insertion losses and reduced polarization mode dispersion
Owner:DRAKA COMTEQ BV
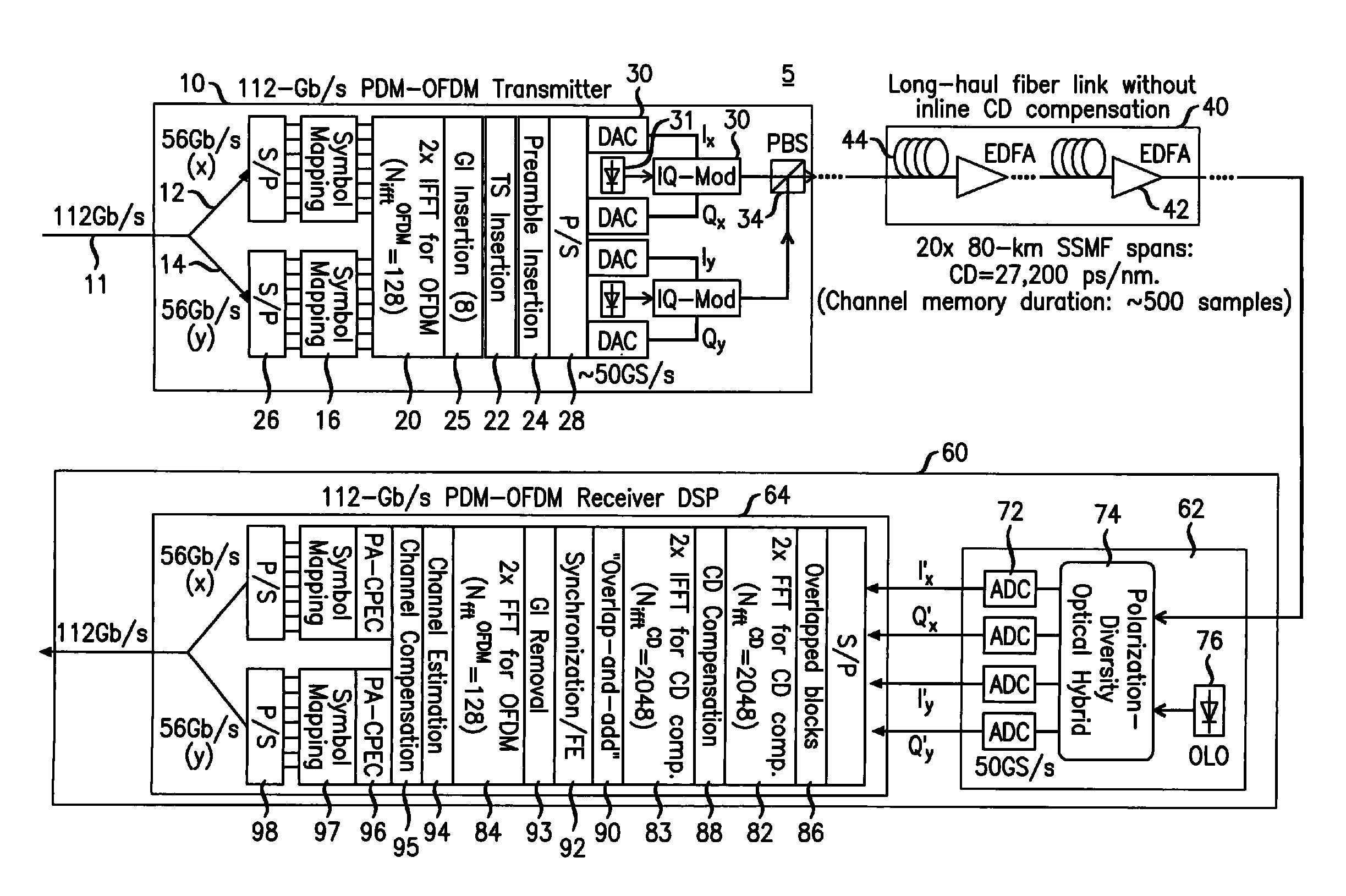
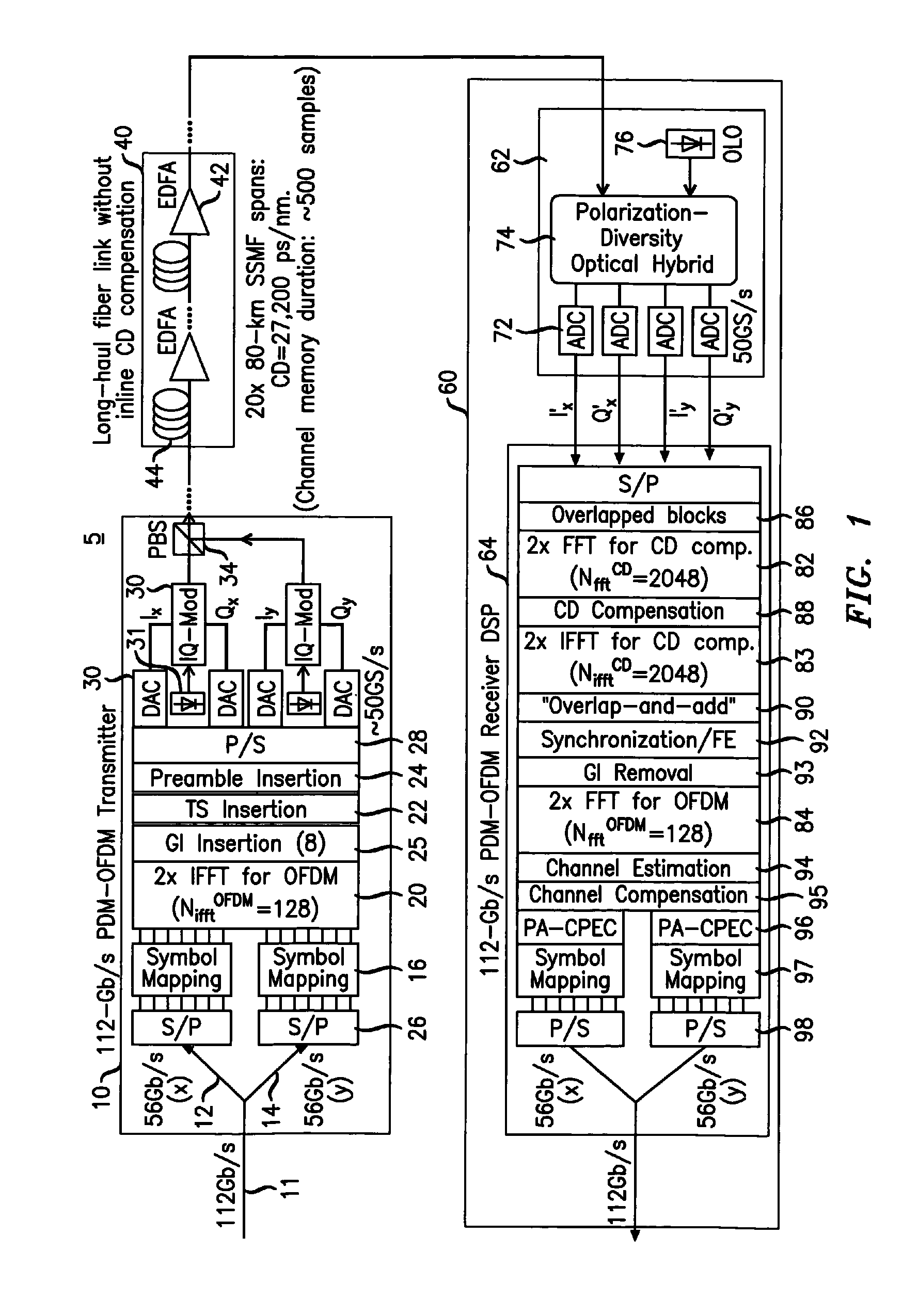
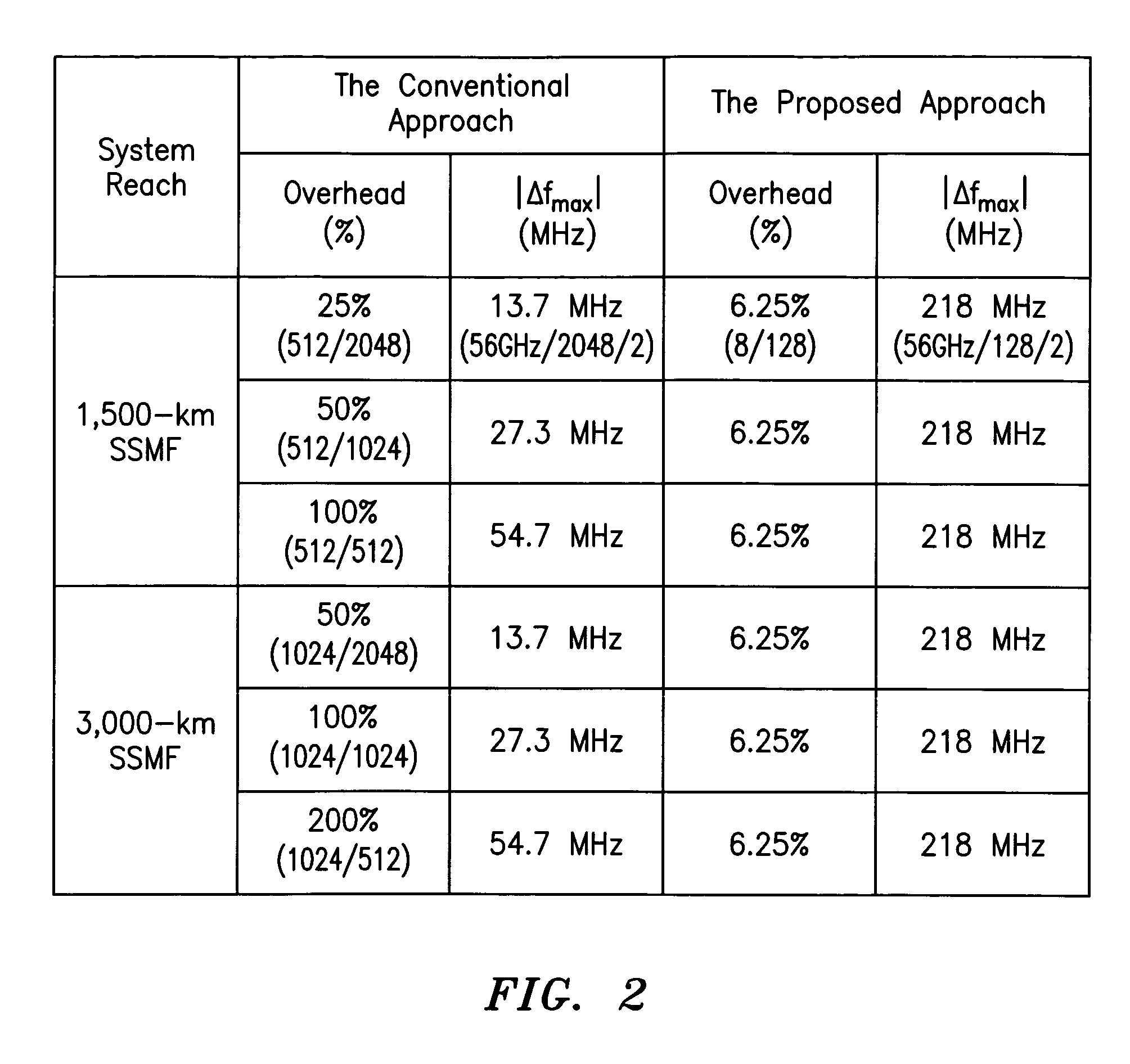
System, method and apparatus for coherent optical OFDM
ActiveUS8218979B2Facilitate frequency estimationEase the frequency stabilization taskModulated-carrier systemsWavelength-division multiplex systemsEngineeringPolarization mode dispersion
Digital compensation of chromatic dispersion (CD) effect experienced by optical orthogonal frequency-division multiplexed (OFDM) signal in fiber transmission is provided in the frequency domain using a Fast Fourier Transform / Inverse Fast Fourier Transform (FFT / IFFT) pair with equal length of digital samples prior to OFDM receiver signal processing, wherein the equal length is larger than the length of a FFT used for OFDM subcarrier demultiplexing of the received signal. The OFDM signal processing is independent of fiber CD, so small guard-interval (GI) can still be used to achieve high spectral efficiency even under the experience of large CD. The GI need only to be large enough to accommodate other effects such as polarization-mode dispersion. The length of an IFFT used for OFDM subcarrier multiplexing, as well as the FFT for OFDM demultiplexing can be sufficiently small so subcarrier spacing is sufficiently large to tolerate typical frequency offsets between the transmitter laser and the optical local oscillator.
Owner:RPX CORP
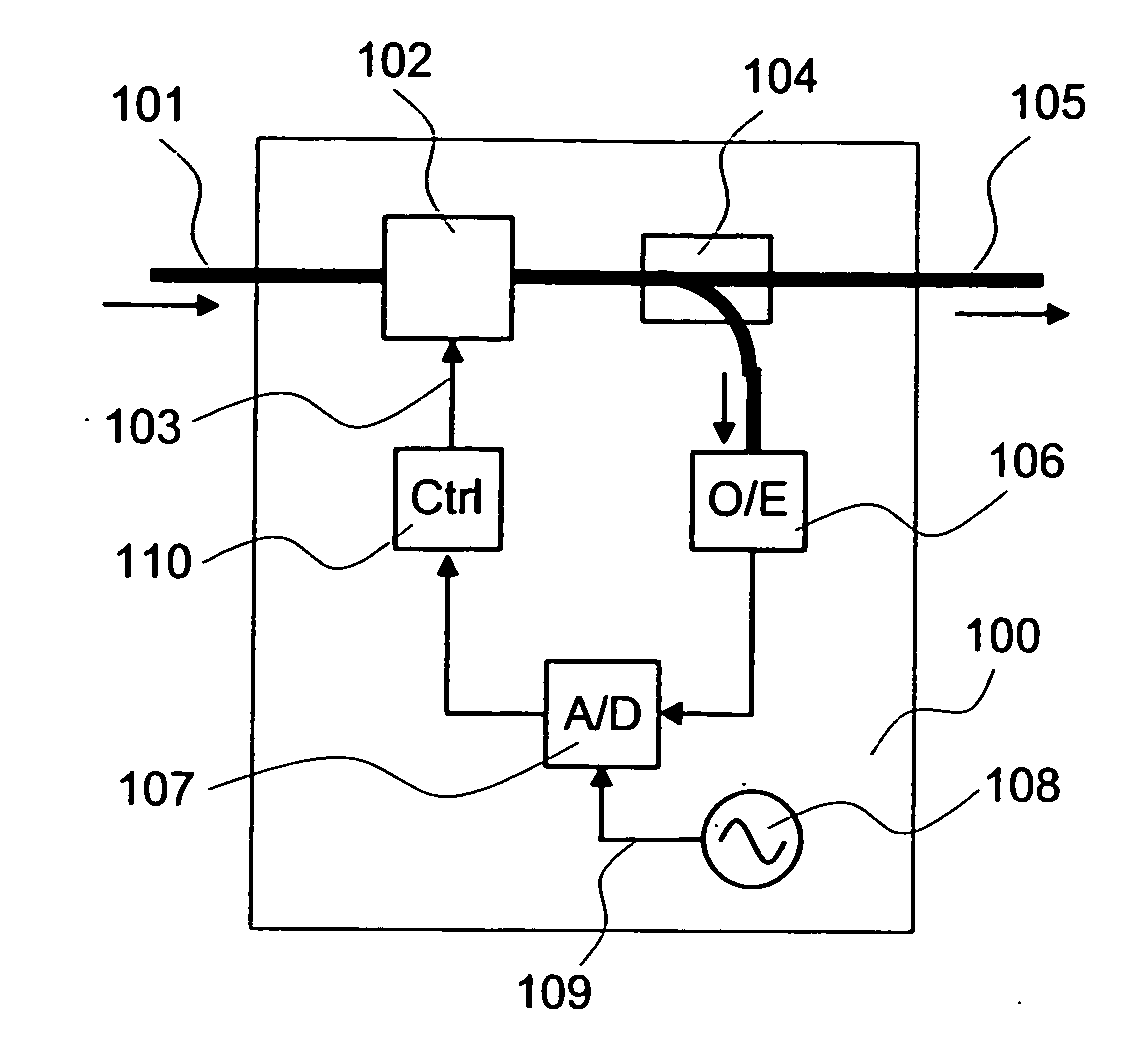
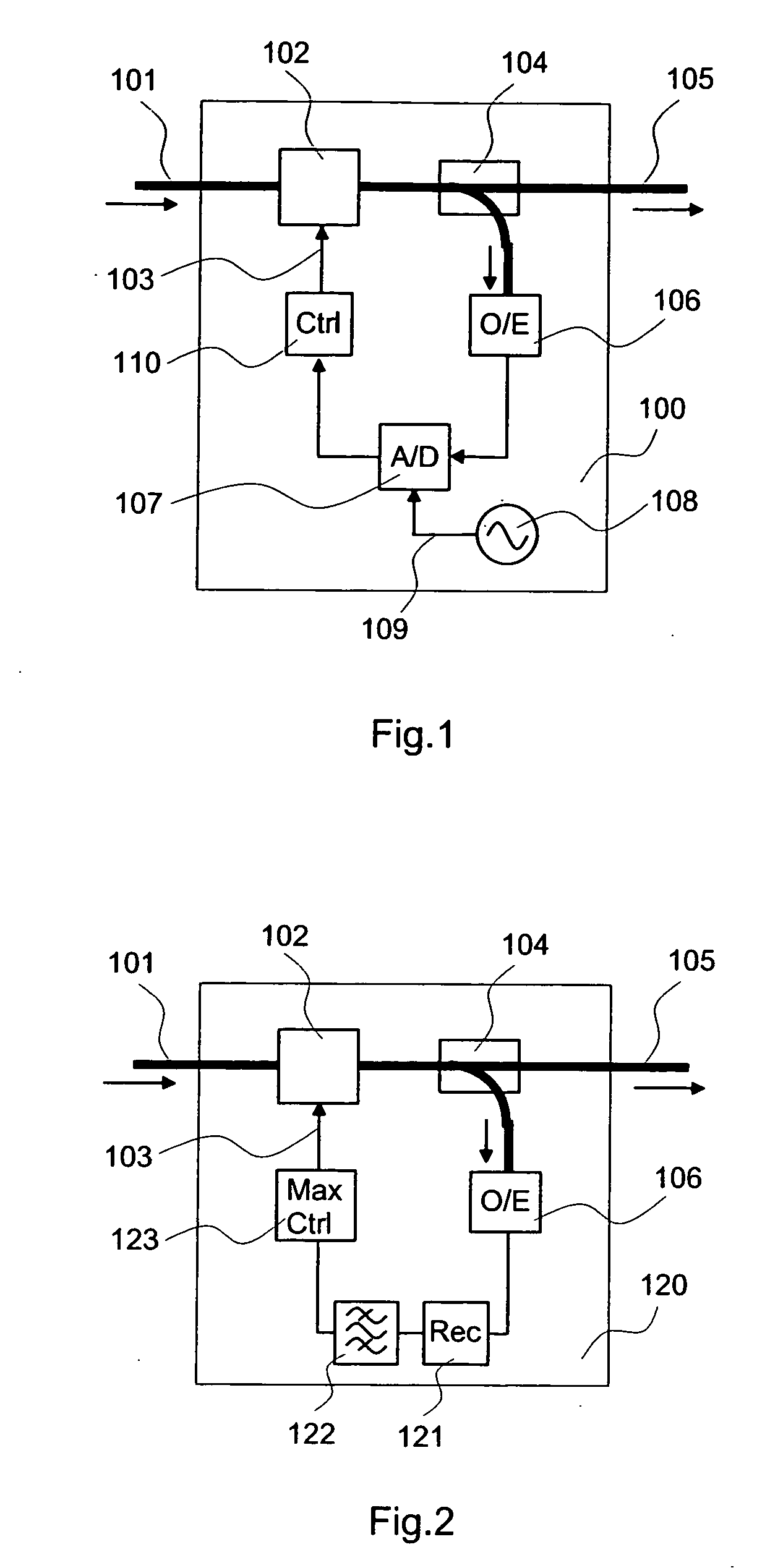
Signal waveform deterioration compensator
InactiveUS20070065162A1Minimizes waveform deteriorationSignal waveform to deteriorateWavelength-division multiplex systemsDistortion/dispersion eliminationFiberAmplitude histogram
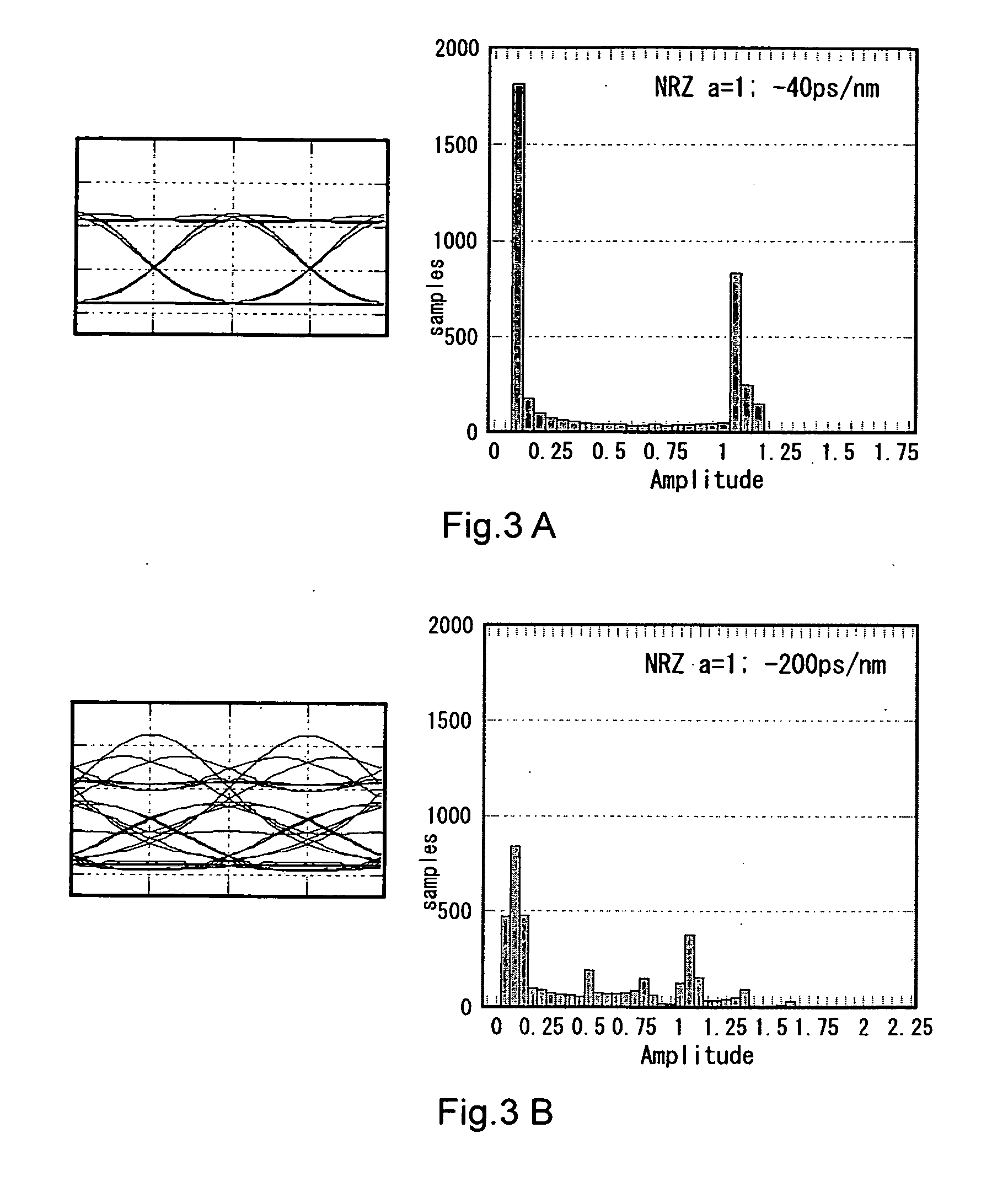
The waveform deterioration detection range is broadened and multi bit rates can be handled. A chromatic dispersion compensator (or polarization mode dispersion compensator) (102) receives a waveform-deteriorated NRZ optical signal entered through an input fiber (101) and compensates it. On the other hand, an optical detector (106) receives part of output light and a sampling circuit (A / D converter) (107) performs asynchronous sampling of received waveform intensity. A control circuit (110) calculates the nth even moment (n is 4 or more) from an obtained waveform amplitude histogram and performs control to minimize its value.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
PMD-insensitive method of chromatic dispersion estimation for a coherent receiver
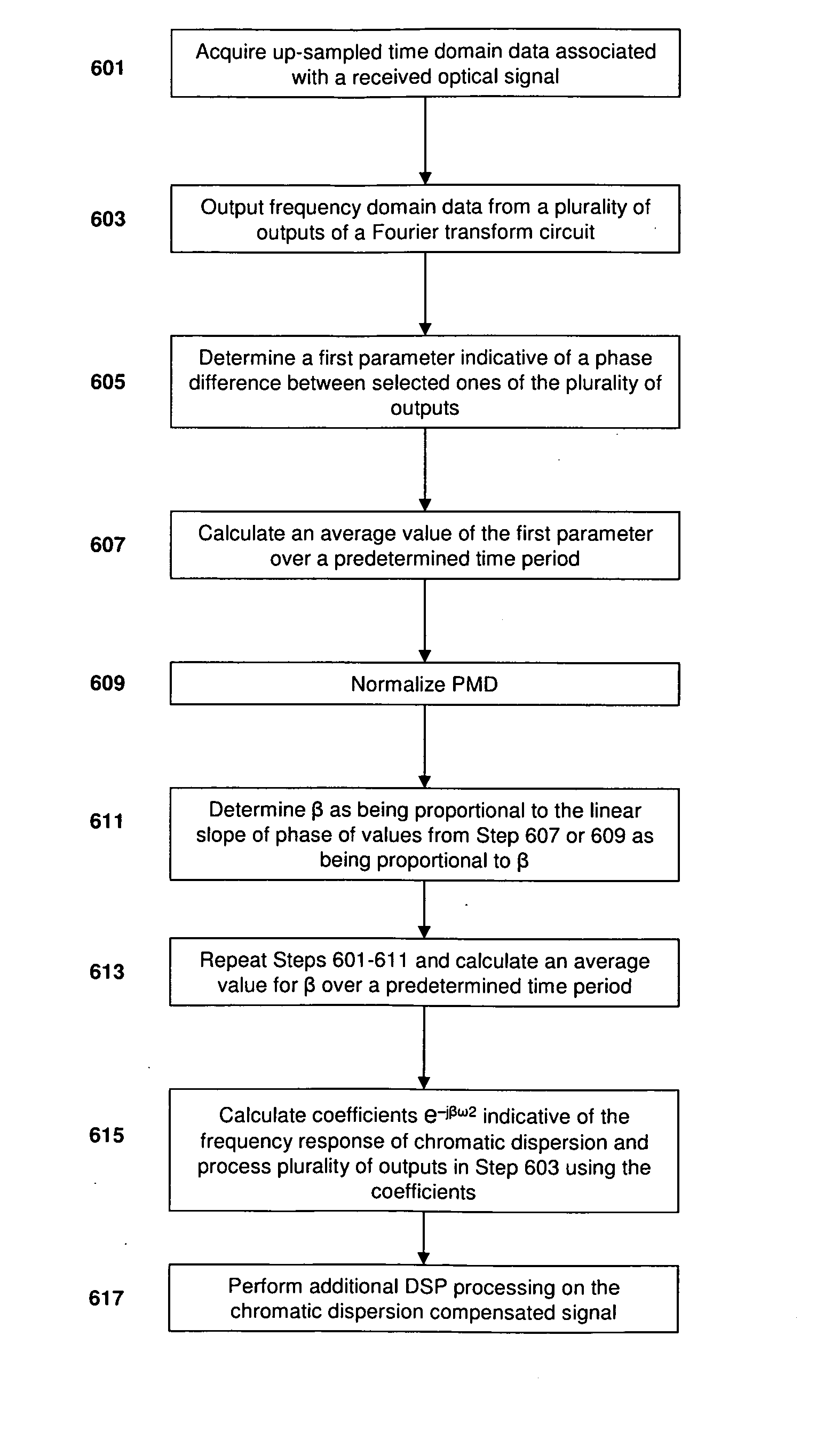
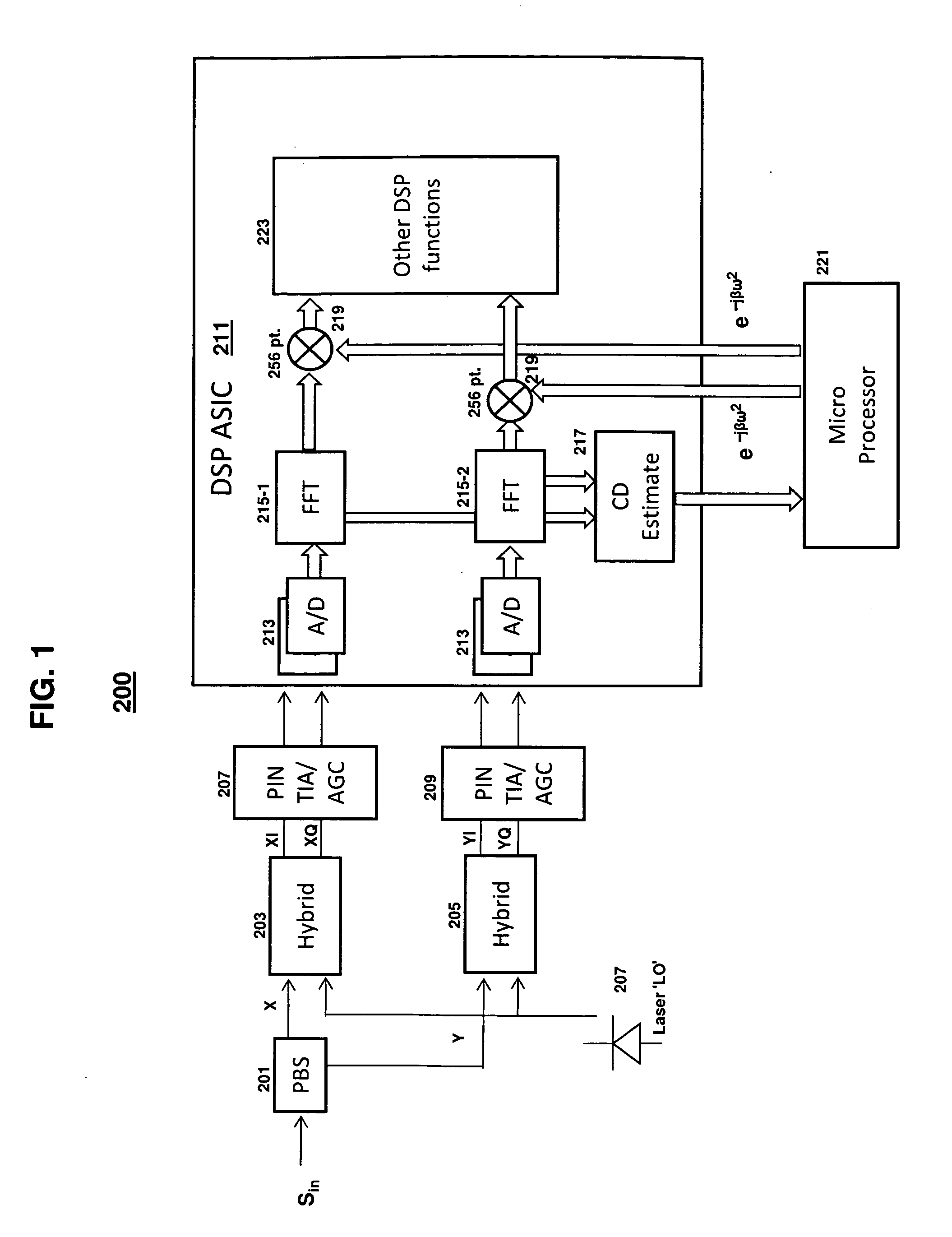
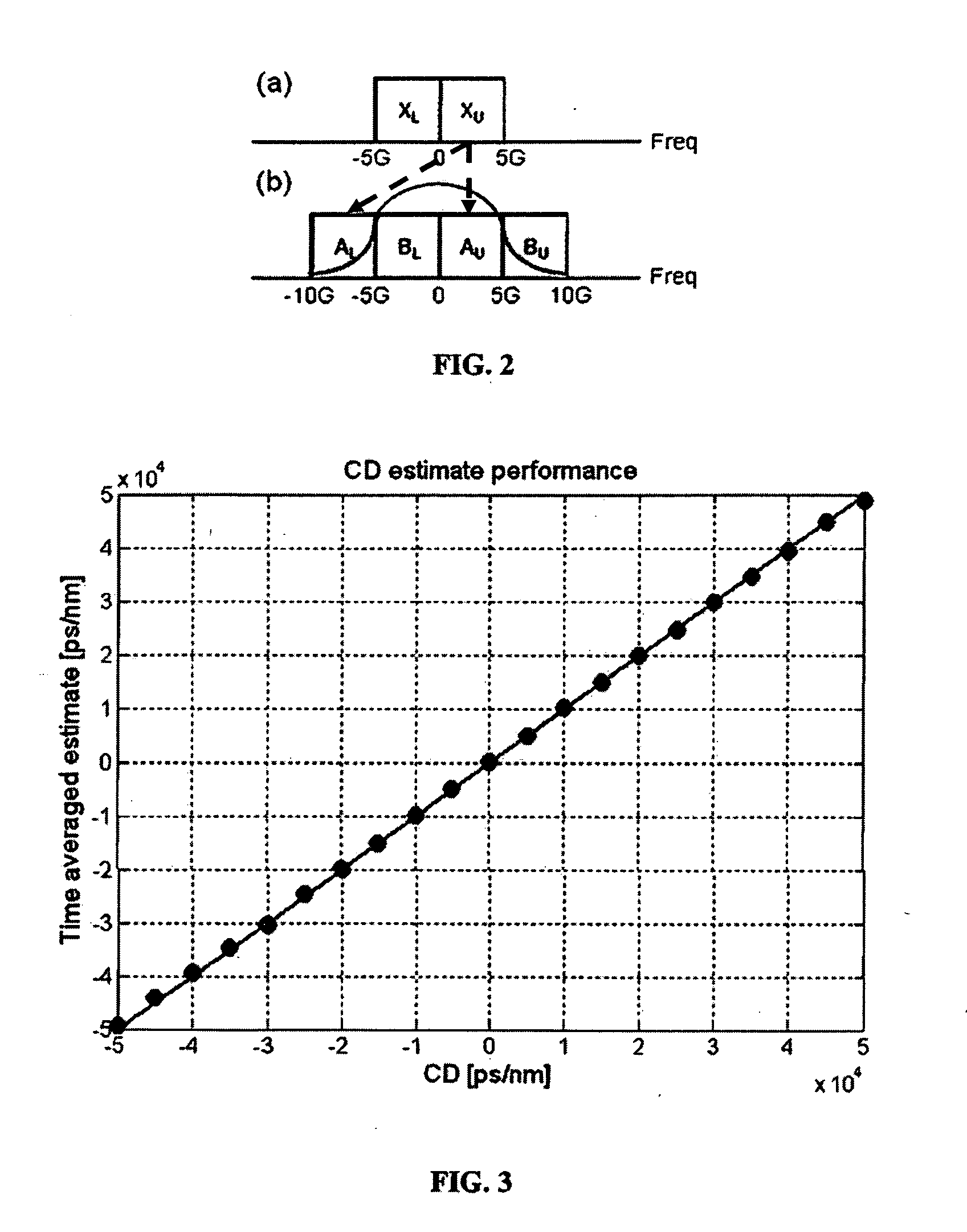
Consistent with the present disclosure, a method and system for estimating chromatic dispersion of an optical signal in a coherent receiver is provided that is insensitive to polarization mode dispersion (PMD) and other polarization effects in the optical communication system. The effects of chromatic dispersion in the optical system are estimated by first calculating a phase shift between a pair of related frequency domain data outputs of a Fourier transform circuit. The calculated phase shift includes a linear phase component that is proportional to the chromatic dispersion, a DC constant phase component, and a data spectrum component. The calculated phase shift is then averaged over a number of clock cycles to remove the data spectrum components. The time averaged result is used to normalize any effects of PMD from the received signal. A slope of the linear phase component as a function of frequency is then calculated and used to estimate the value for chromatic dispersion. The chromatic dispersion estimate is then used to determine a number of coefficients of an inverse frequency response of the chromatic dispersion in the system, and is used to compensate for the chromatic dispersion.
Owner:INFINERA CORP
Apparatus And Method For Monitoring An Optical Coherent Network
InactiveUS20120170929A1Transmission monitoringTransmission monitoring/testing/fault-measurement systemsPolarization mode dispersionComputer science
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
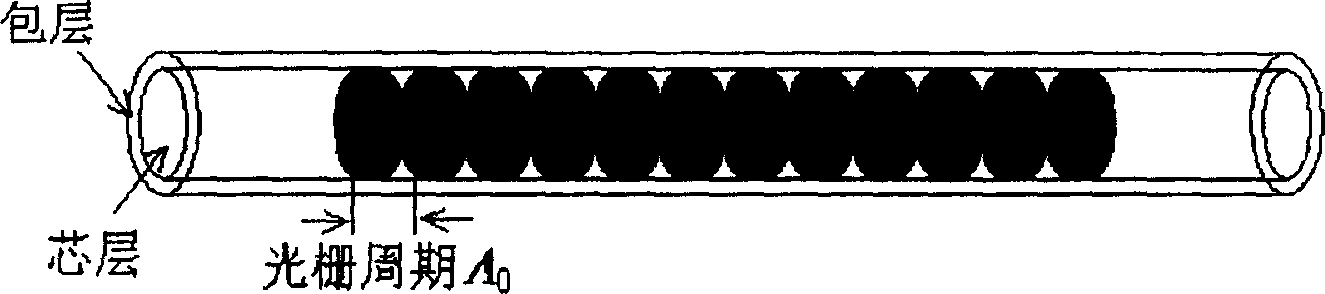
Bragg grating with new sampling structure for compensating dispersion and polarization mode dispersion
InactiveCN1434583AEasy to controlAvoid reducing manufacturing costsDistortion/dispersion eliminationNon-linear opticsGratingFiber Bragg grating
This invention provides a reflective Bragg grating used in dispersion compensatino in optical fiber communication which has effective refractive index perturbation expressed indiagram (1) in which z is a coordinate along the grating direction, A is period of grating beginning, delta ndc is a mean value in a grating period of effective refractive index perturbation, delta nac is the amplitude of that fast variable component is an added phase item, in which F(z) is a new sample structure with non-linear type II chirp display in diagram(2), therefore, this invented grating can provide various group time delay respoonse spectrums to compensate the dispersion in a certain reflecting band independent of chirp (type I) caused by the variation along z by delta ndc or diameter, and F(z) sample period is far more larger than the grating period.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
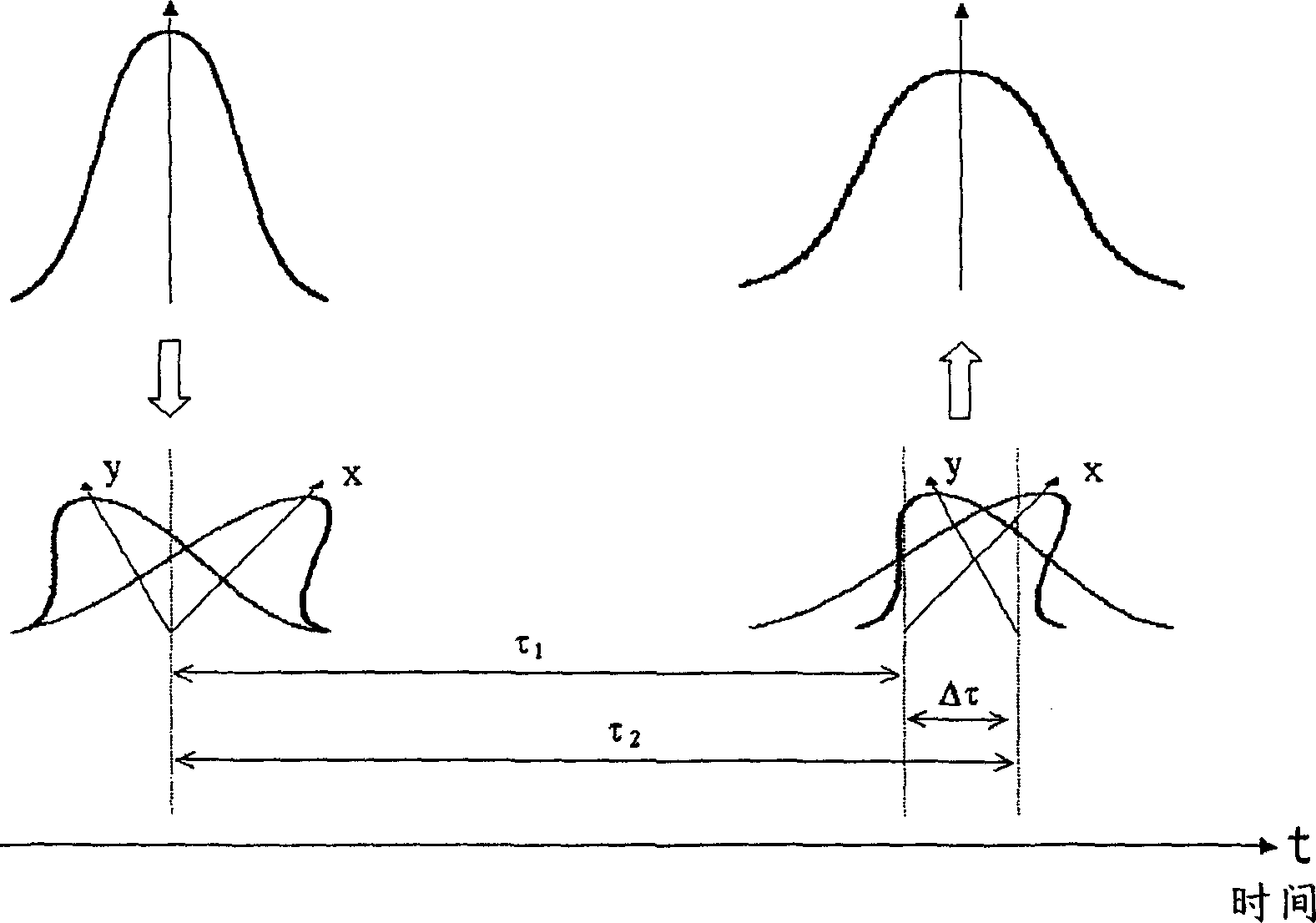
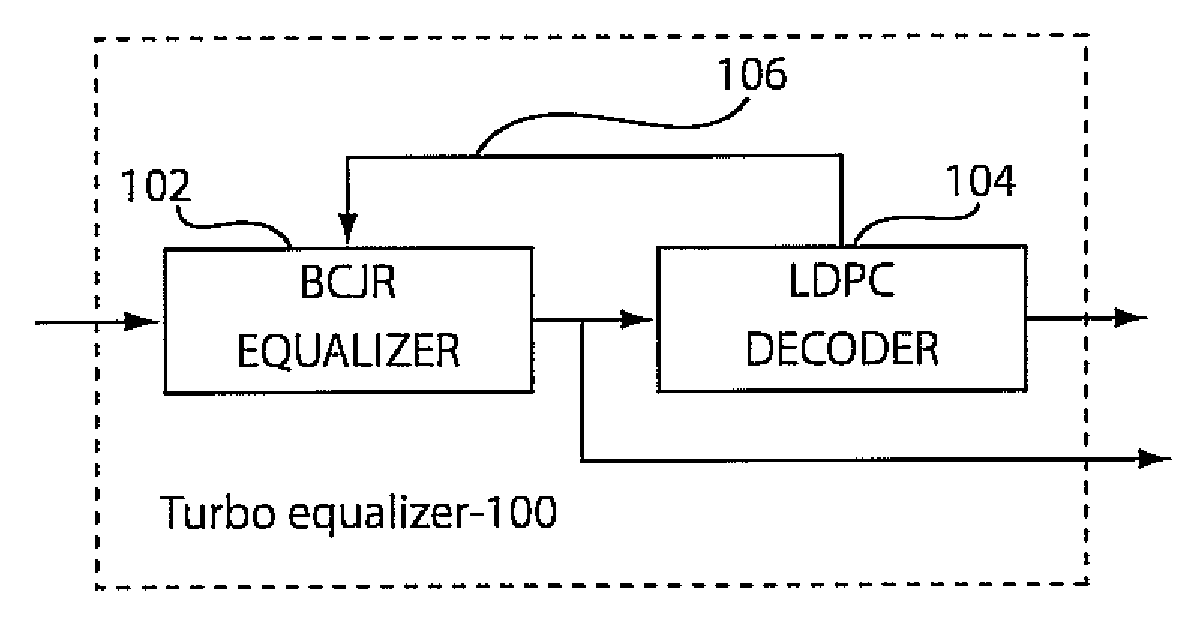
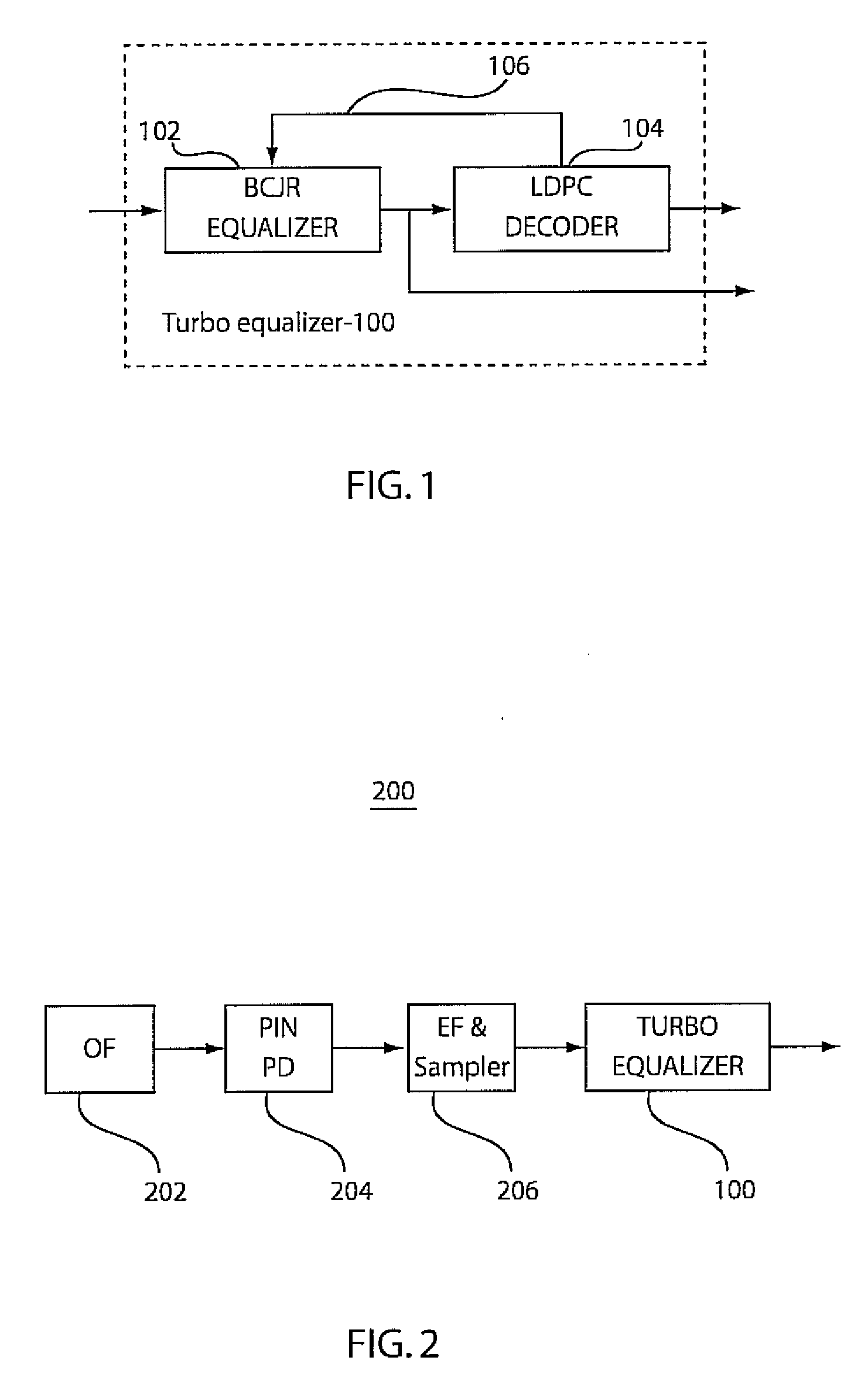
Polarization mode dispersion compensation using bcjr equalizer and iterative LDPC decoding
InactiveUS20090177945A1Error prevention/detection by using return channelCode conversionLow densityPolarization mode dispersion
A turbo equalizer includes a Bahl-Cocke-Jelinek-Raviv (BCJR) equalizer configured to receive a transmitted signal and partially cancel inter-symbol interference (ISI) due to polarization-mode dispersion (PMD). A low-density parity check (LDPC) decoder is coupled to the BCJR equalizer to receive channel bit reliabilities therefrom. The LDPC decoder iteratively provides extrinsic soft information feedback to the BCJR equalizer to compensate for PMD.
Owner:NEC CORP
Method of evaluating fiber PMD using polarization optical time domain reflectometry
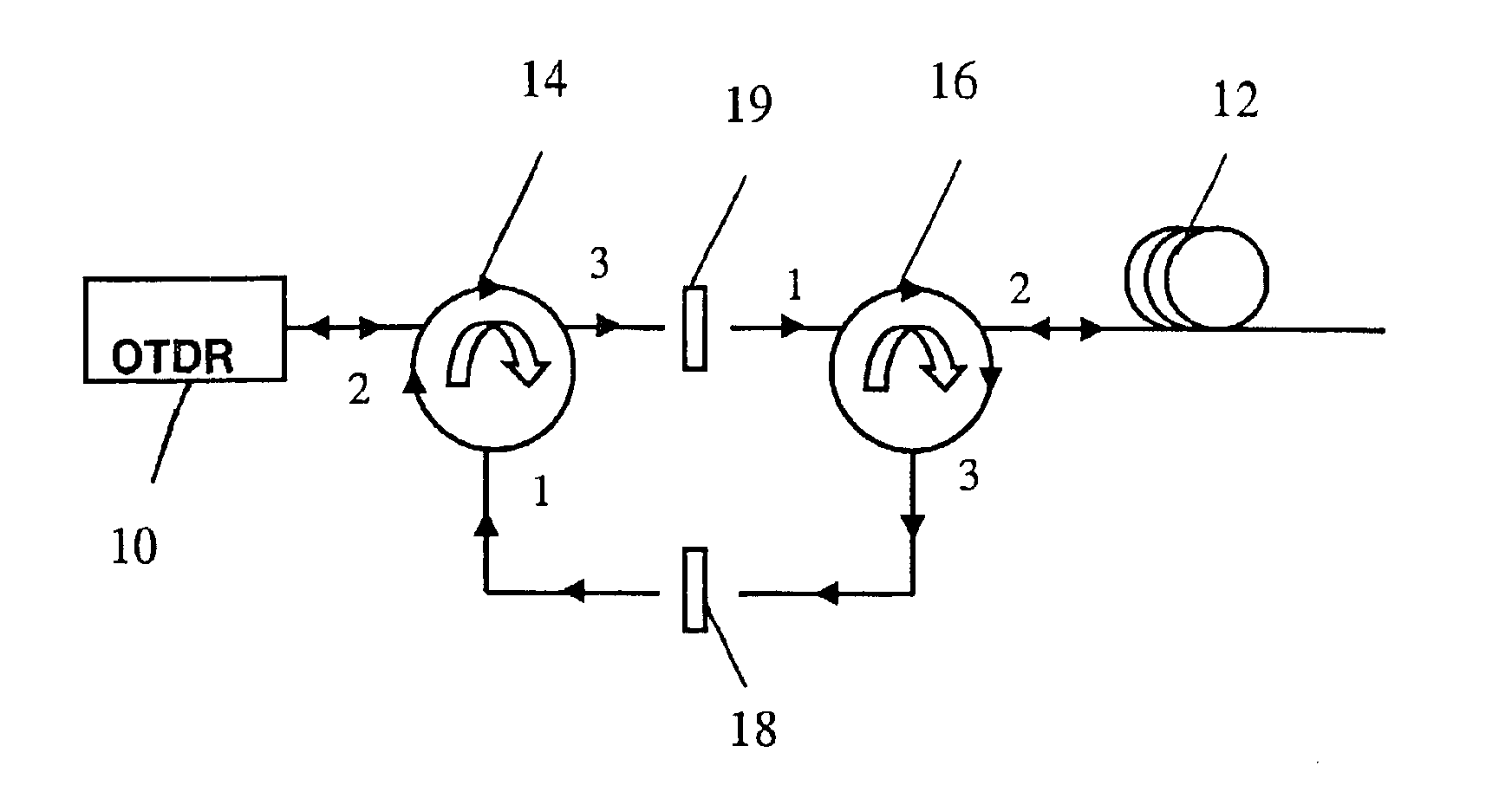
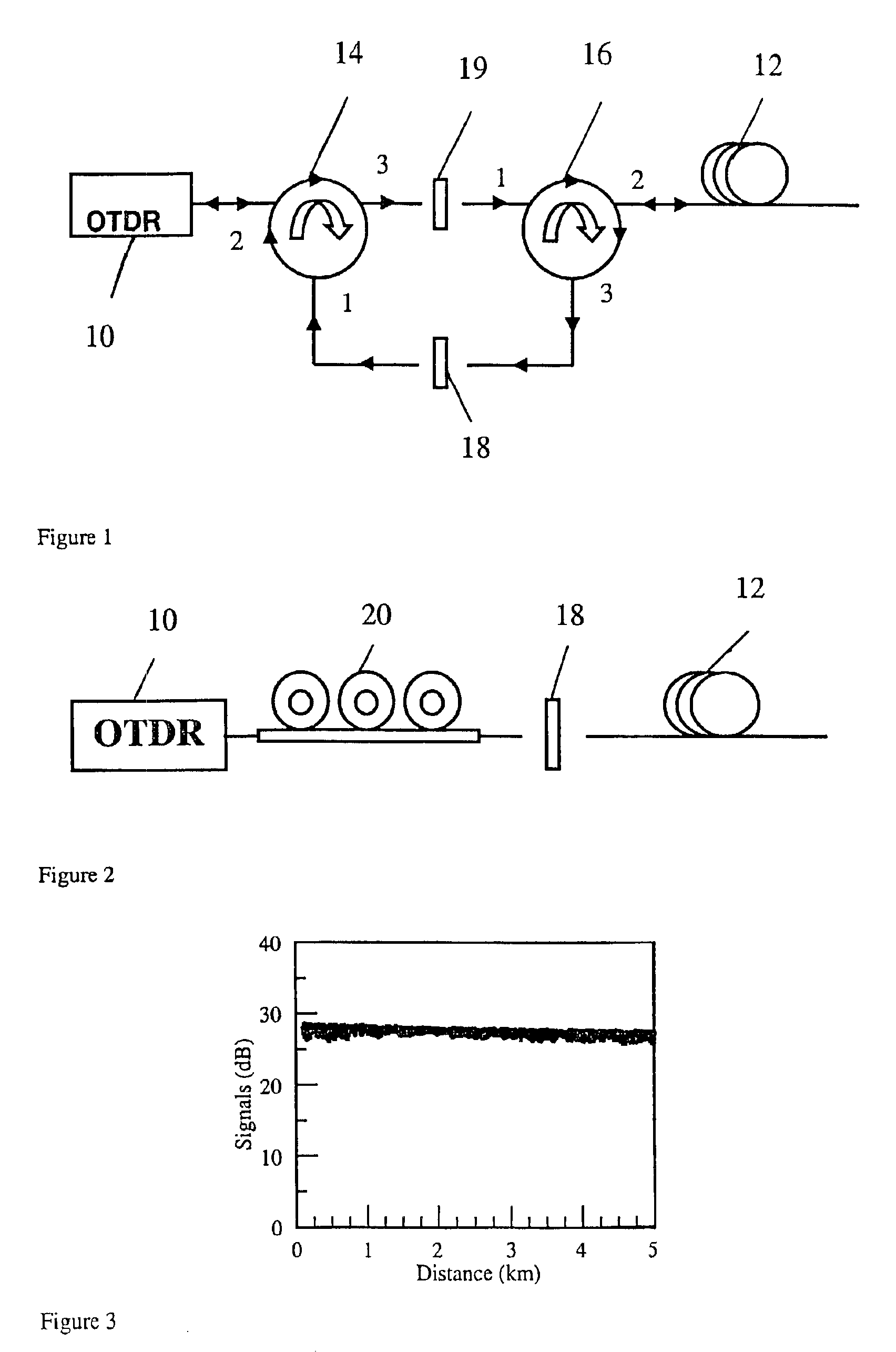
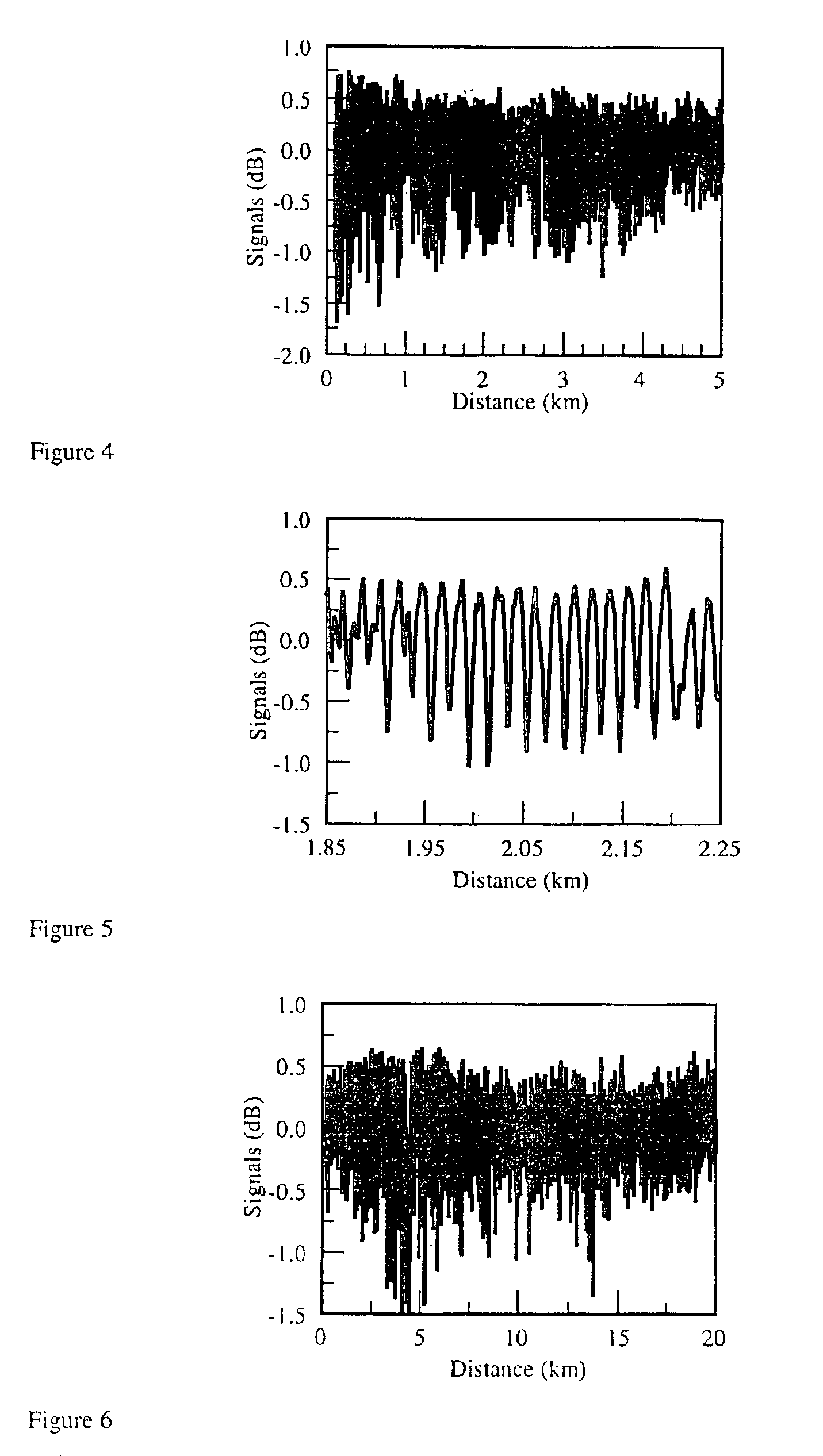
InactiveUS6946646B2Easy to identifyReflectometers dealing with polarizationRadiation pyrometryTime domainFiber
A method for screening fiber polarization mode dispersion using a polarization optical time domain reflectometer. A pulse radiation is emitted into the fiber under test, and the backscattered radiation is measured by the POTDR and used to obtain a POTDR trace. The POTDR trace is then analyzed to compare the variation of signals along the length of the fiber, the variation in signals relating to the level of PMD along the length of the fiber. Because high levels of PMD correspond to localized levels of low variability, by setting the variability of signal threshold sufficiently low, fibers having unacceptably high localized PMD can be identified and removed.
Owner:CORNING INC
Optical receiver having a signal-equalization capability
ActiveUS20140086594A1Large dispersion-compensation capacitySmall dispersion-compensation capacityElectromagnetic receiversMultiplexingEngineering
In one embodiment, an optical receiver has a bulk dispersion compensator and a butterfly equalizer serially connected to one another to perform dispersion-compensation processing and electronic polarization de-multiplexing. The bulk dispersion compensator has a relatively large dispersion-compensation capacity, but is relatively slow and operates in a quasi-static configuration. The butterfly equalizer has a relatively small dispersion-compensation capacity, but can be dynamically reconfigured on a relatively fast time scale to track the changing conditions in the optical-transport link. The optical receiver has a feedback path that enables the configuration of the bulk dispersion compensator to be changed based on the configuration of the butterfly equalizer in a manner that advantageously enables the receiver to tolerate larger amounts of chromatic dispersion and / or polarization-mode dispersion than without the use of the feedback path.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Multi-core optical fiber
InactiveCN103399374AUniform stress distributionIncrease sink ring widthOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingOptical waveguide light guideData centerLength wave
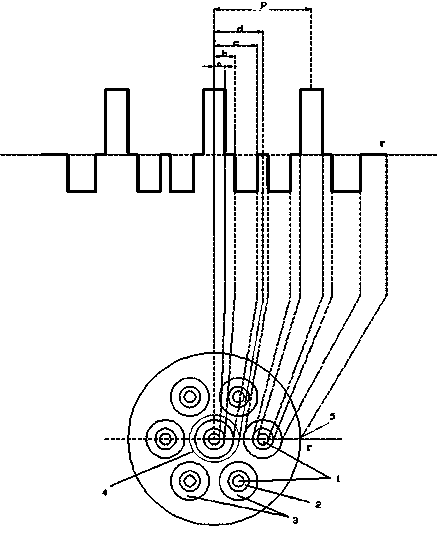
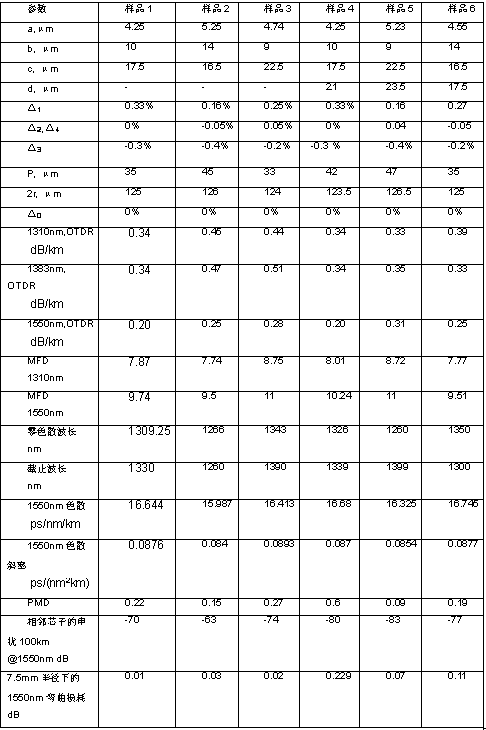
The invention relates to a multi-core optical fiber for communication. The multi-core optical fiber comprises 7 fiber core regions and a main wrapping layer, and is characterized in that the 7 fiber core regions consists of a center fiber core region and 6 outer fiber core regions which are uniformly distributed at the periphery of the center fiber core region; the core wrapping layer structures of the fiber core regions are the same; a fiber core distance between any two adjacent fiber core regions is the same; each fiber core region comprises a fiber core and an inner wrapping layer and a sunken wrapping layer which wrap a core layer; the residual part is the main outer wrapping layer. The fiber core regions of the multi-core optical fiber are reasonably arranged, so that the multi-core optical fiber is compact in structure and is particularly suitable for a dense wiring or long-distance optical fiber communication environment such as a data center; furthermore, the multi-core optical fiber is high in bending resistance and has extremely small influence on crosstalk between any two cores; under a bending condition, the crosstalk performance can completely meet an error rate requirement of high-speed transmission, and high practicability is achieved; the cutoff wavelength, the chromatic dispersion, the mode field, the PMD (polarization mode dispersion) and the like of the optical fiber can be compatible with those of an optical fiber G.652, thus meeting a requirement on multi-core optical fiber communication.
Owner:YANGTZE OPTICAL FIBRE & CABLE CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com