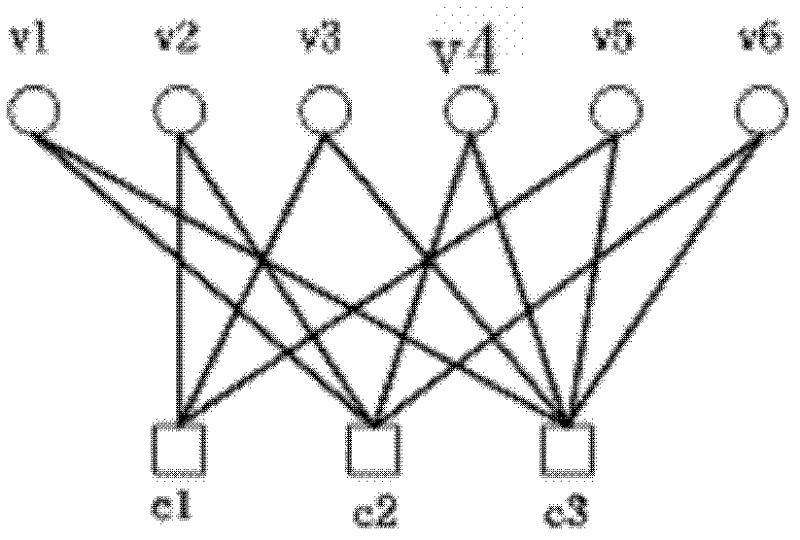
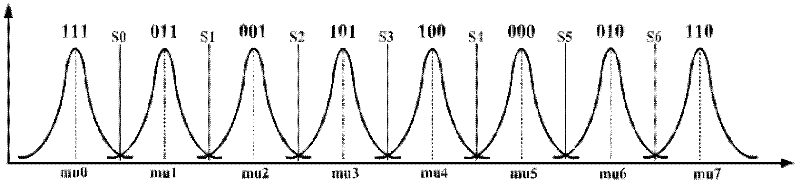
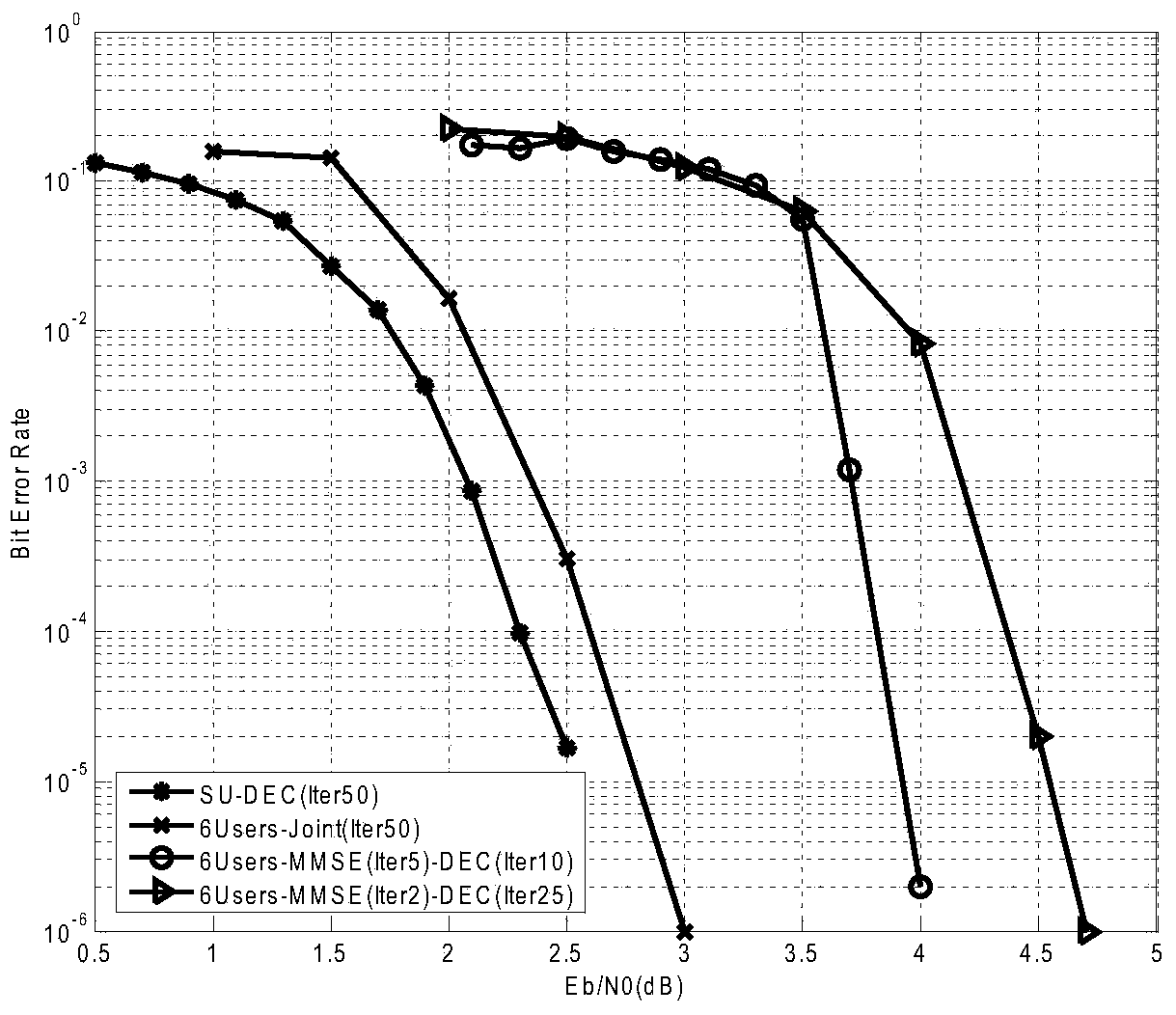
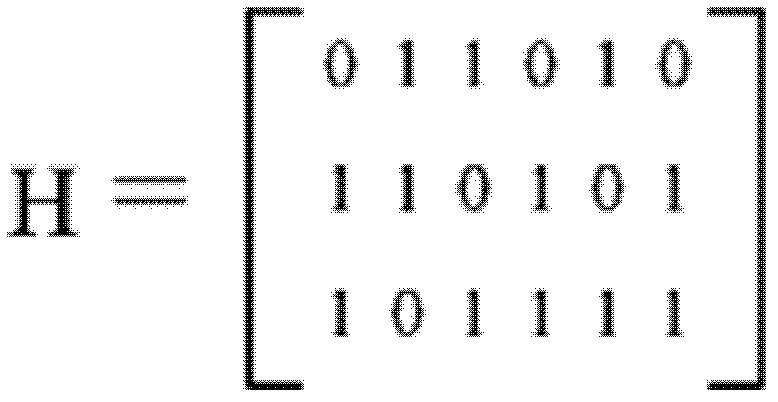Patents
Literature
675 results about "Soft information" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
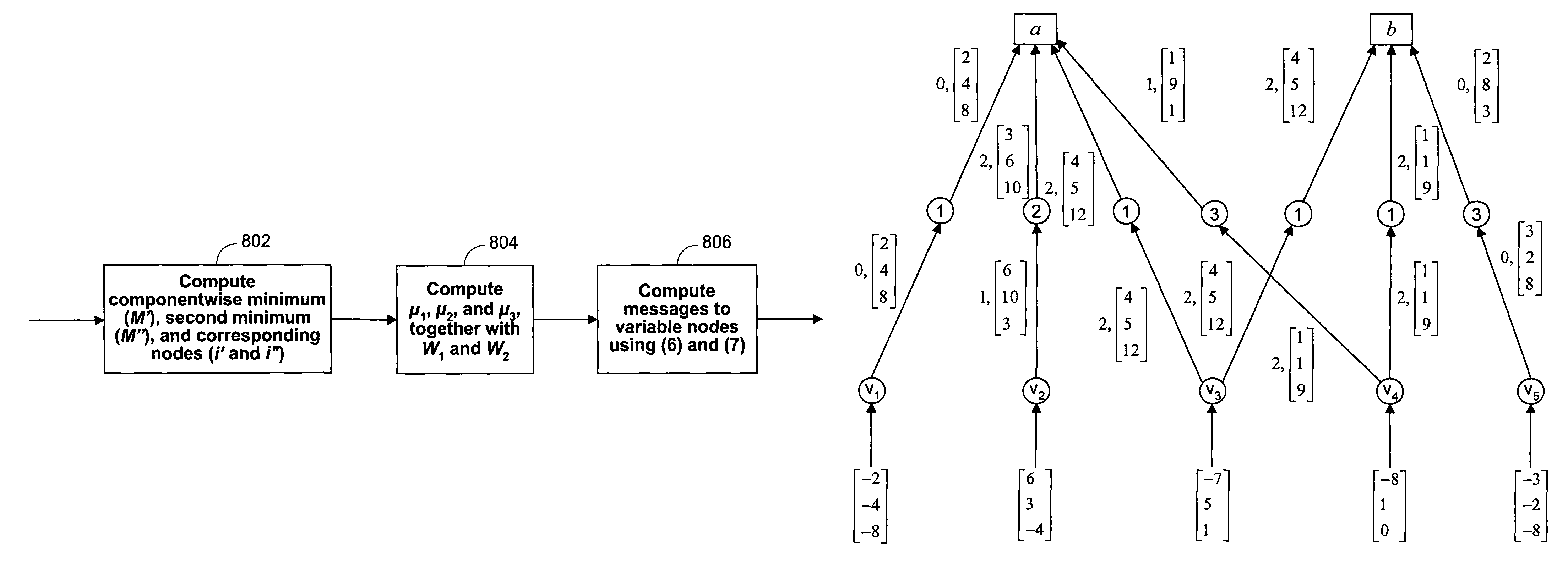
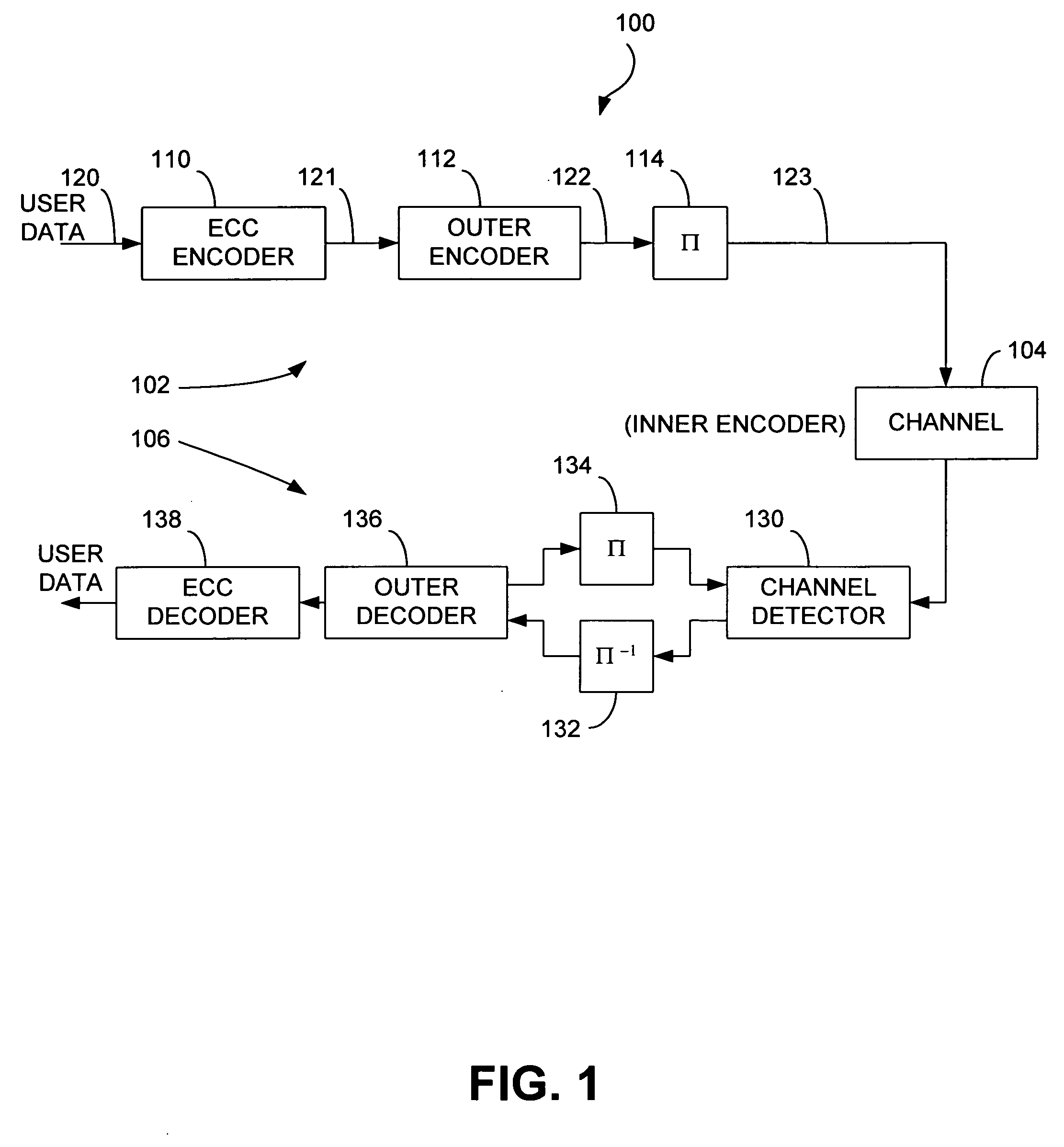
Reduced-complexity decoding of parity check codes
ActiveUS7752523B1Less resourcesData representation error detection/correctionCode conversionRound complexityTheoretical computer science
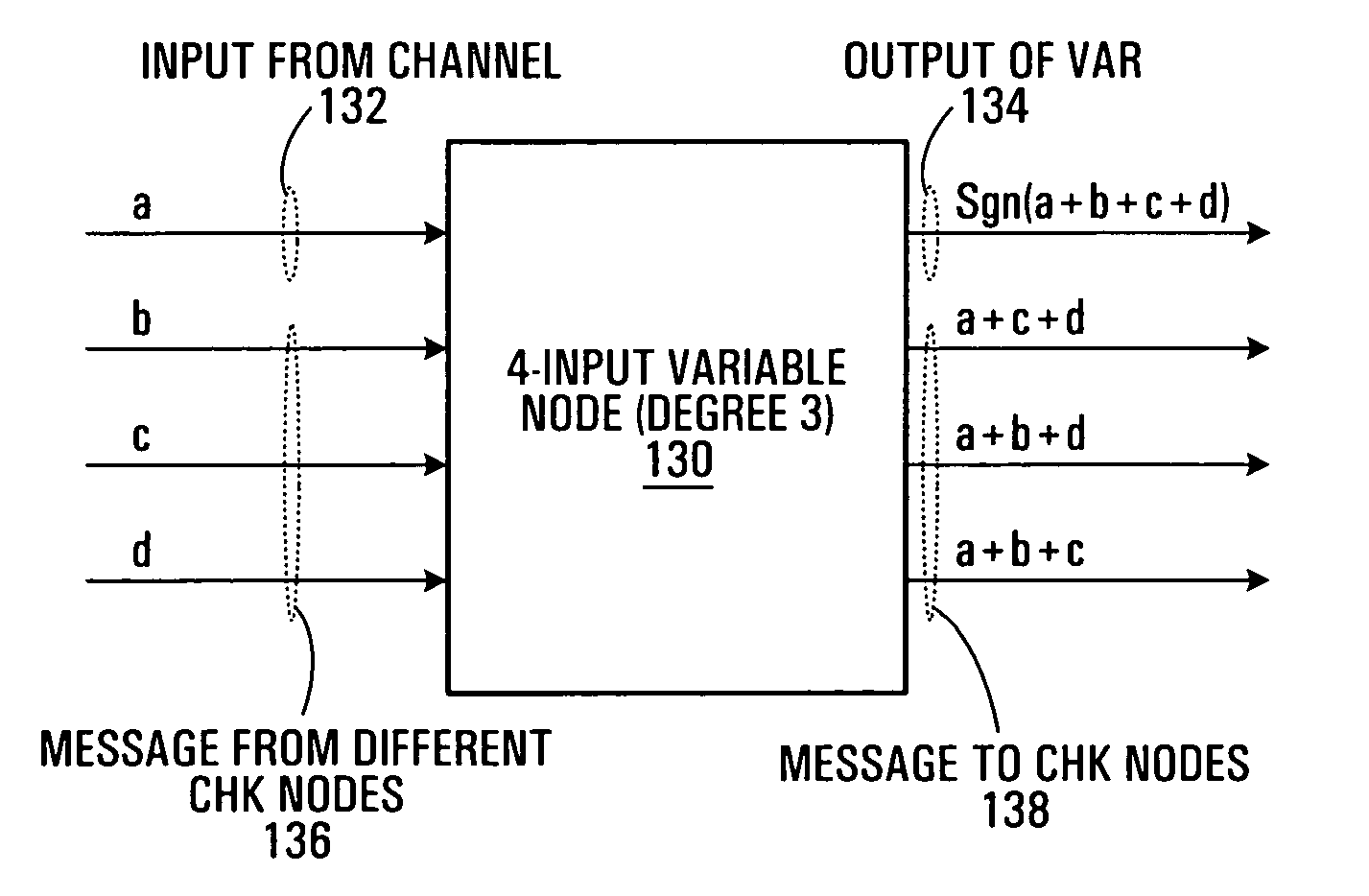
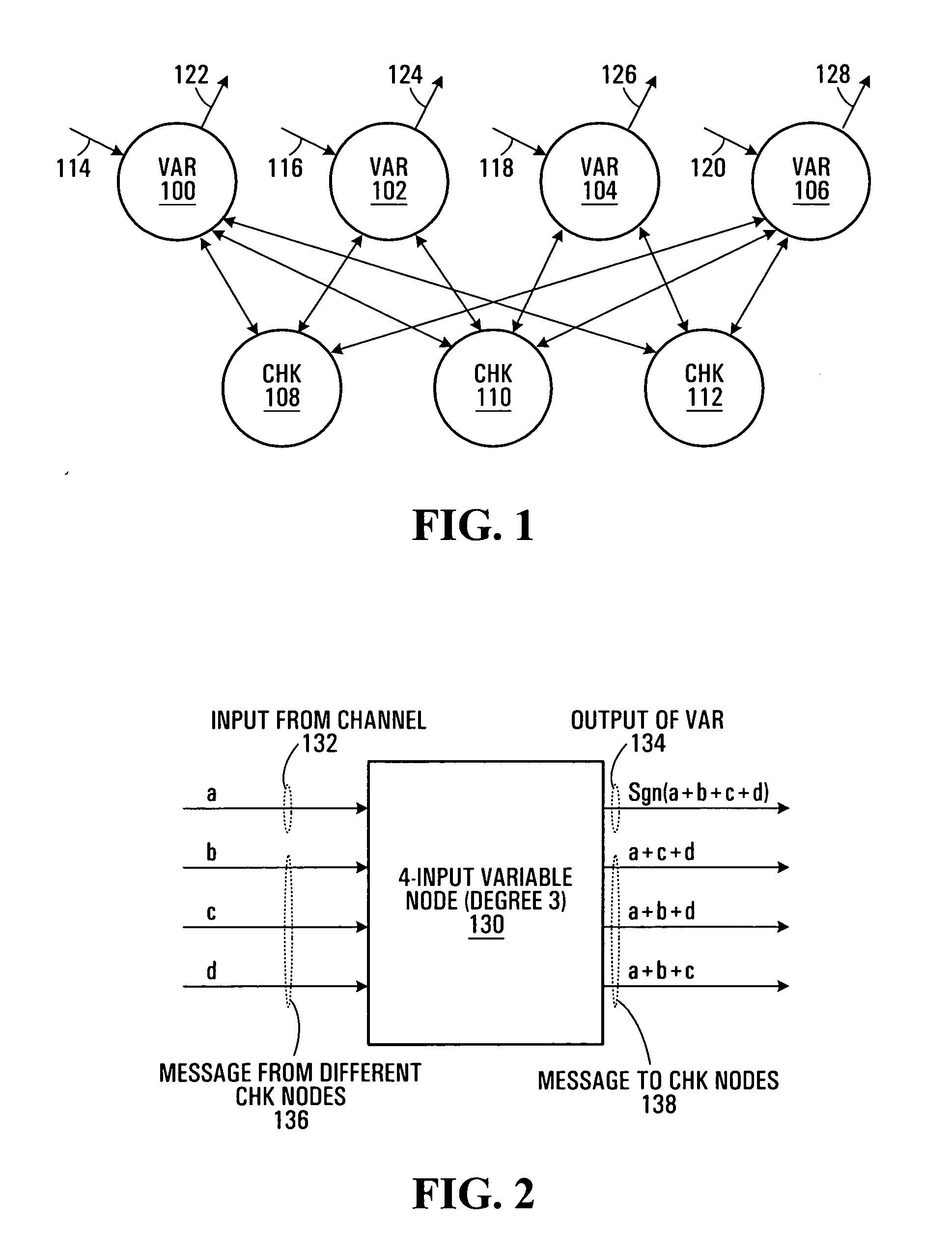
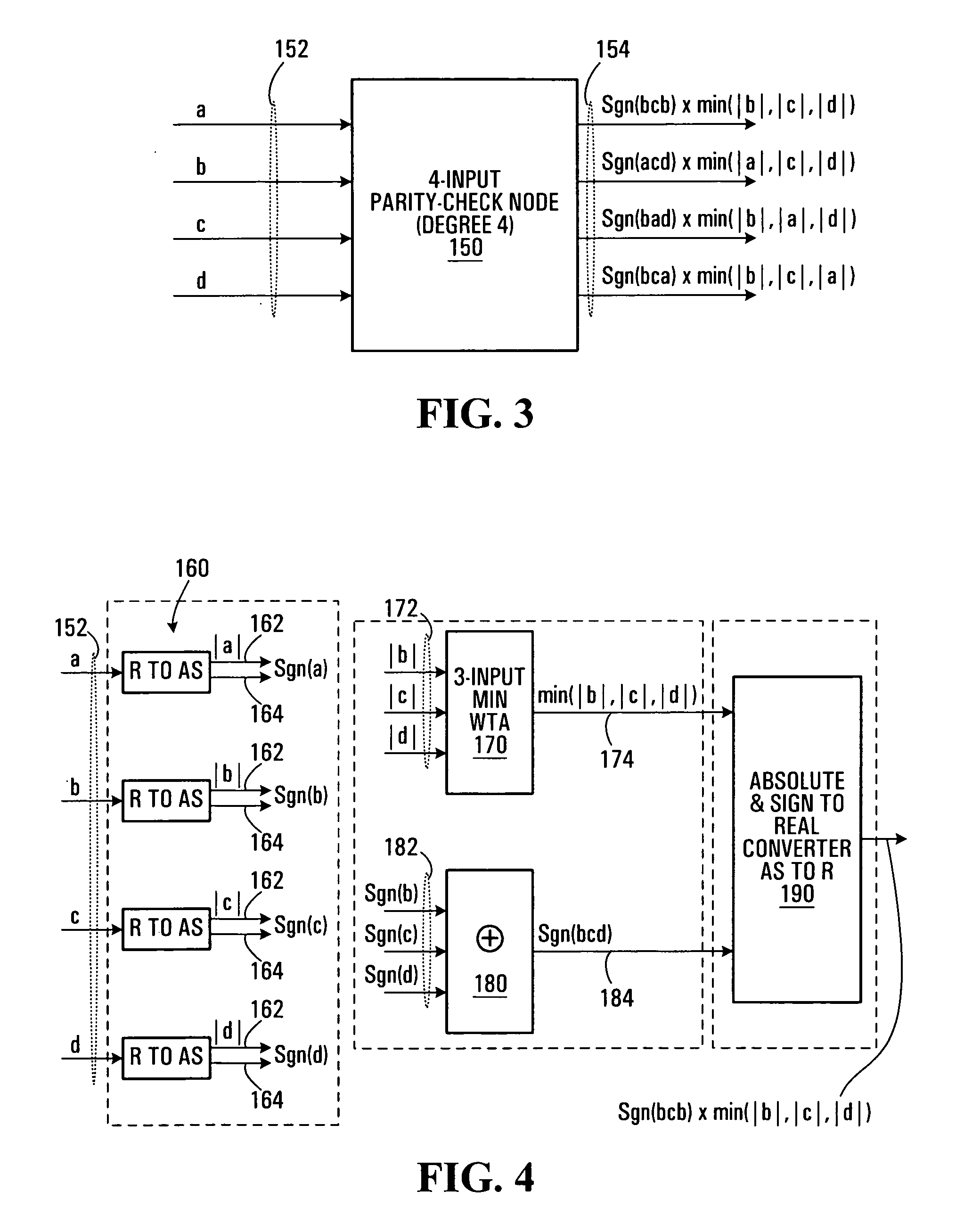
The disclosed technology provides a less resource intensive way to decode a parity check code using a modified min-sum algorithm. For a particular parity check constraint that includes n variable nodes, an LDPC decoder can compute soft information for one of the variable nodes based on combinations of soft information from other variable nodes, wherein each combination includes soft information from at most a number d of other variable nodes. In one embodiment, soft information from one of the other variable nodes is used in a combination only if it corresponds to a non-most-likely value for the other variable node.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
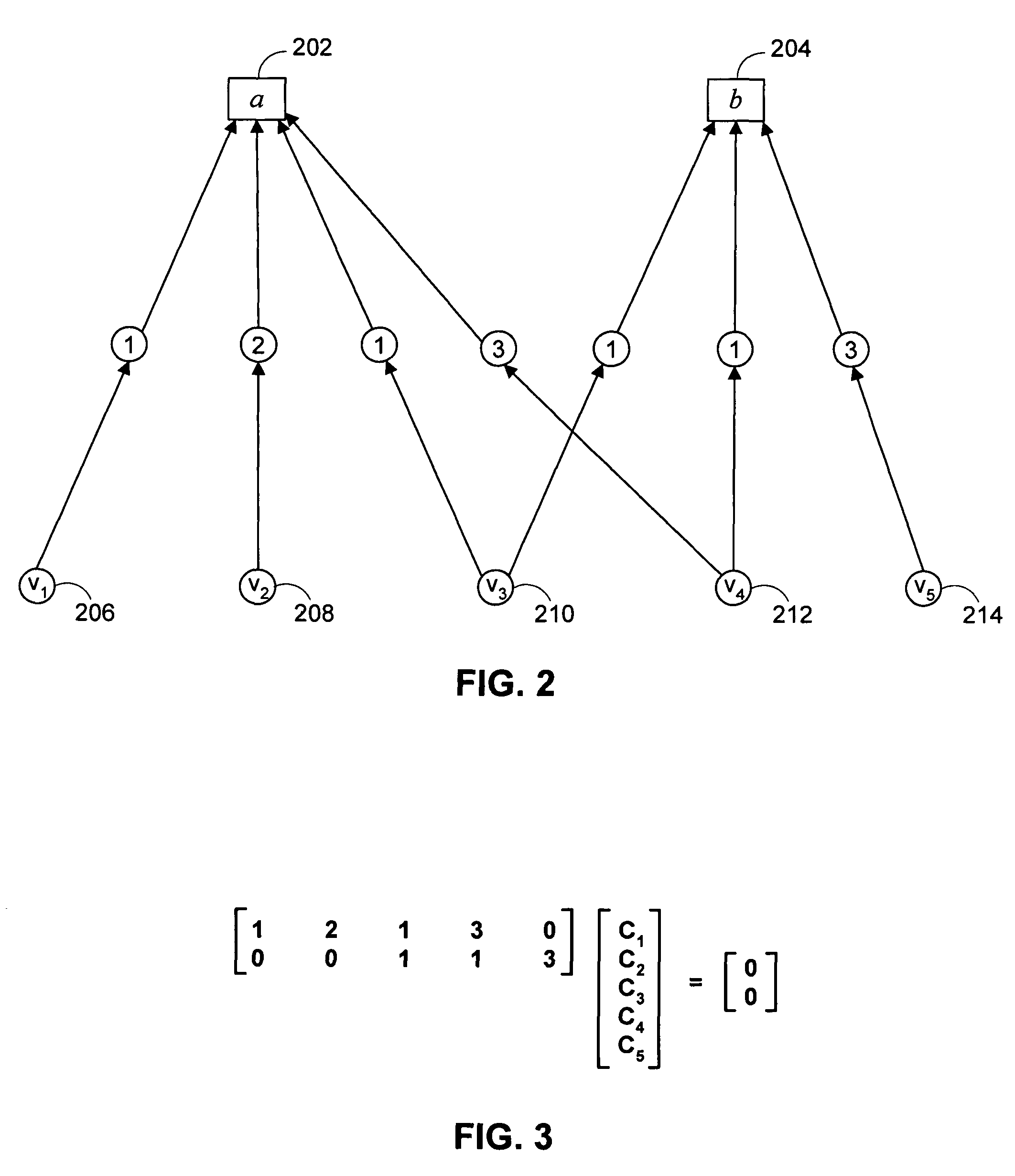
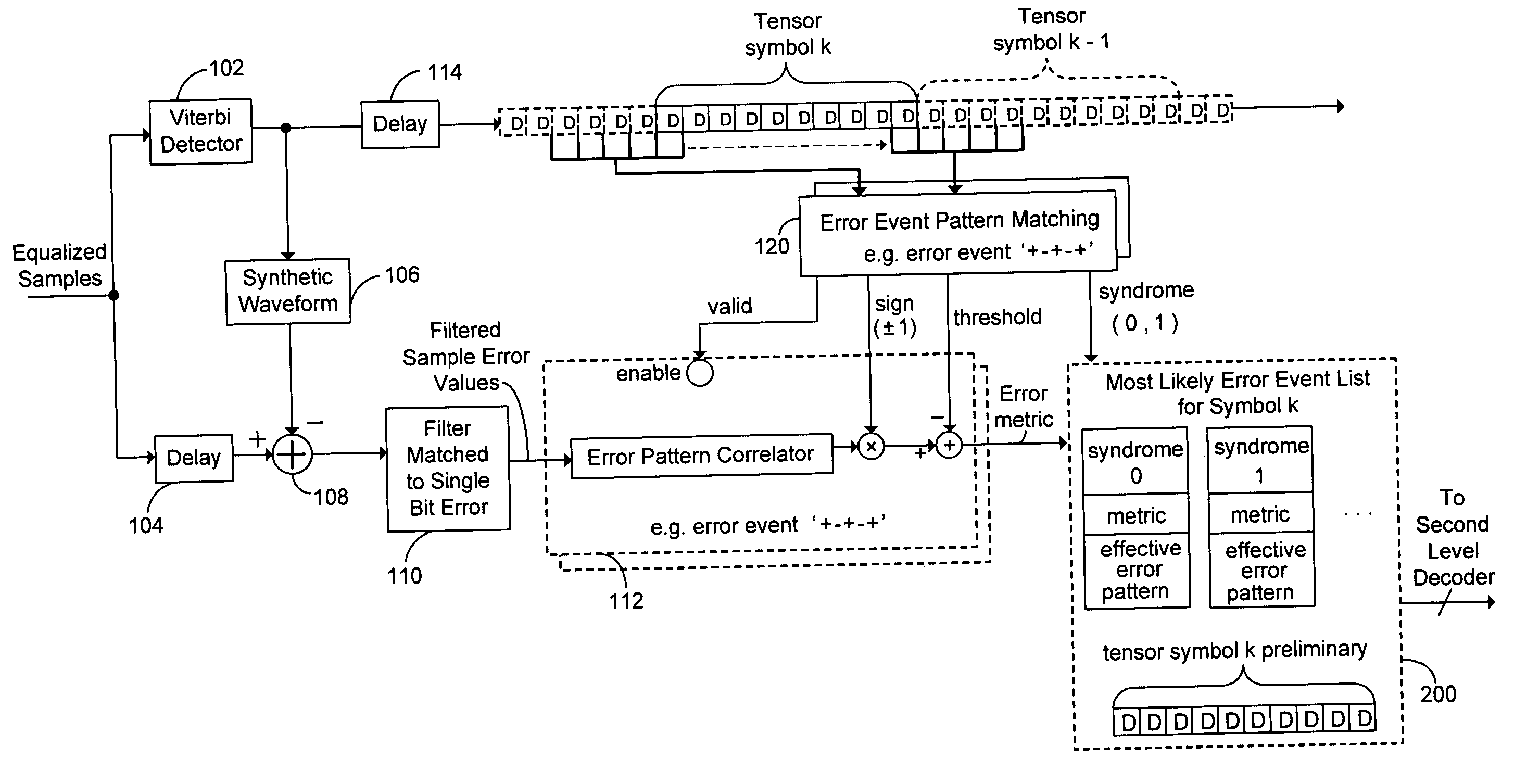
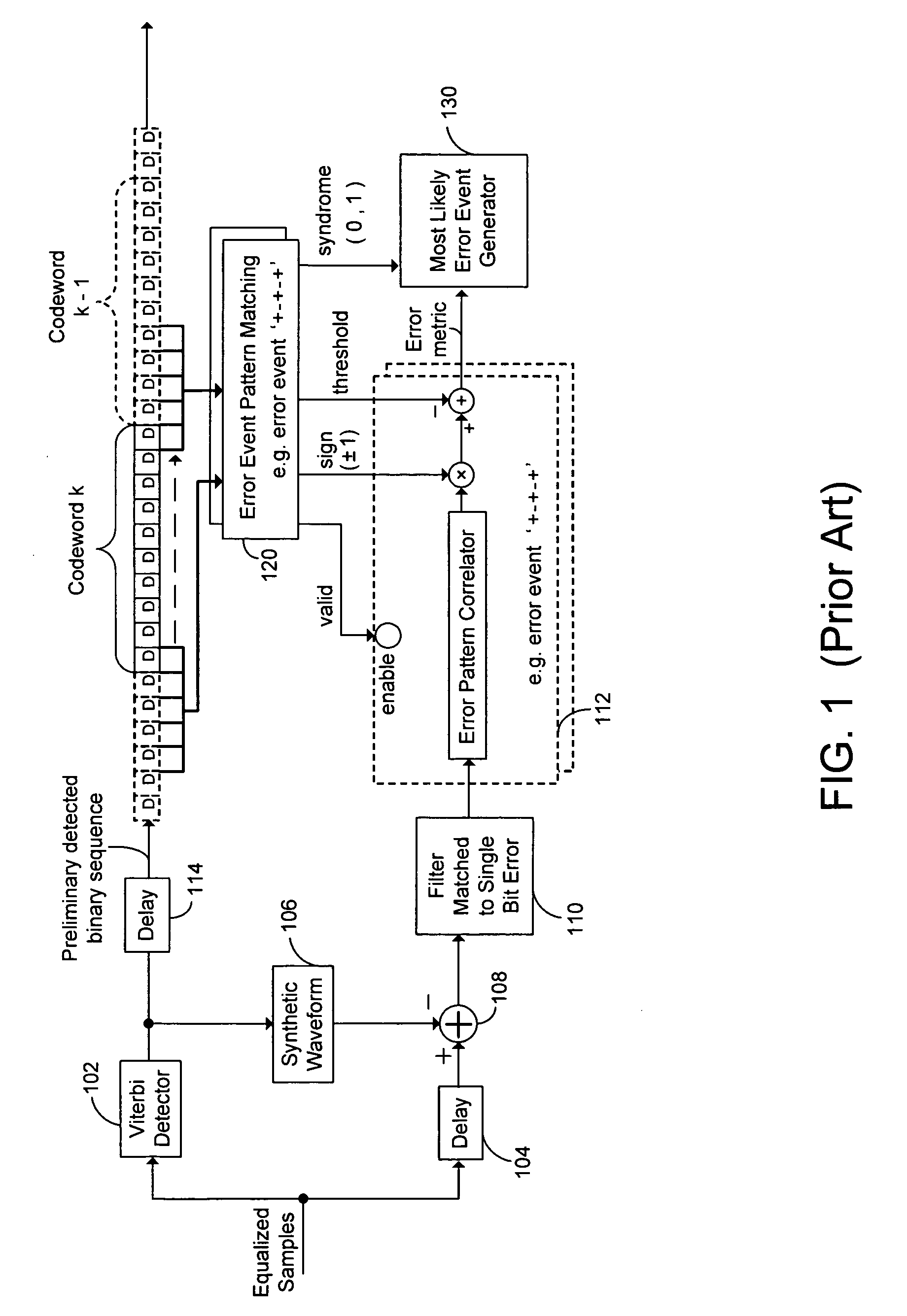
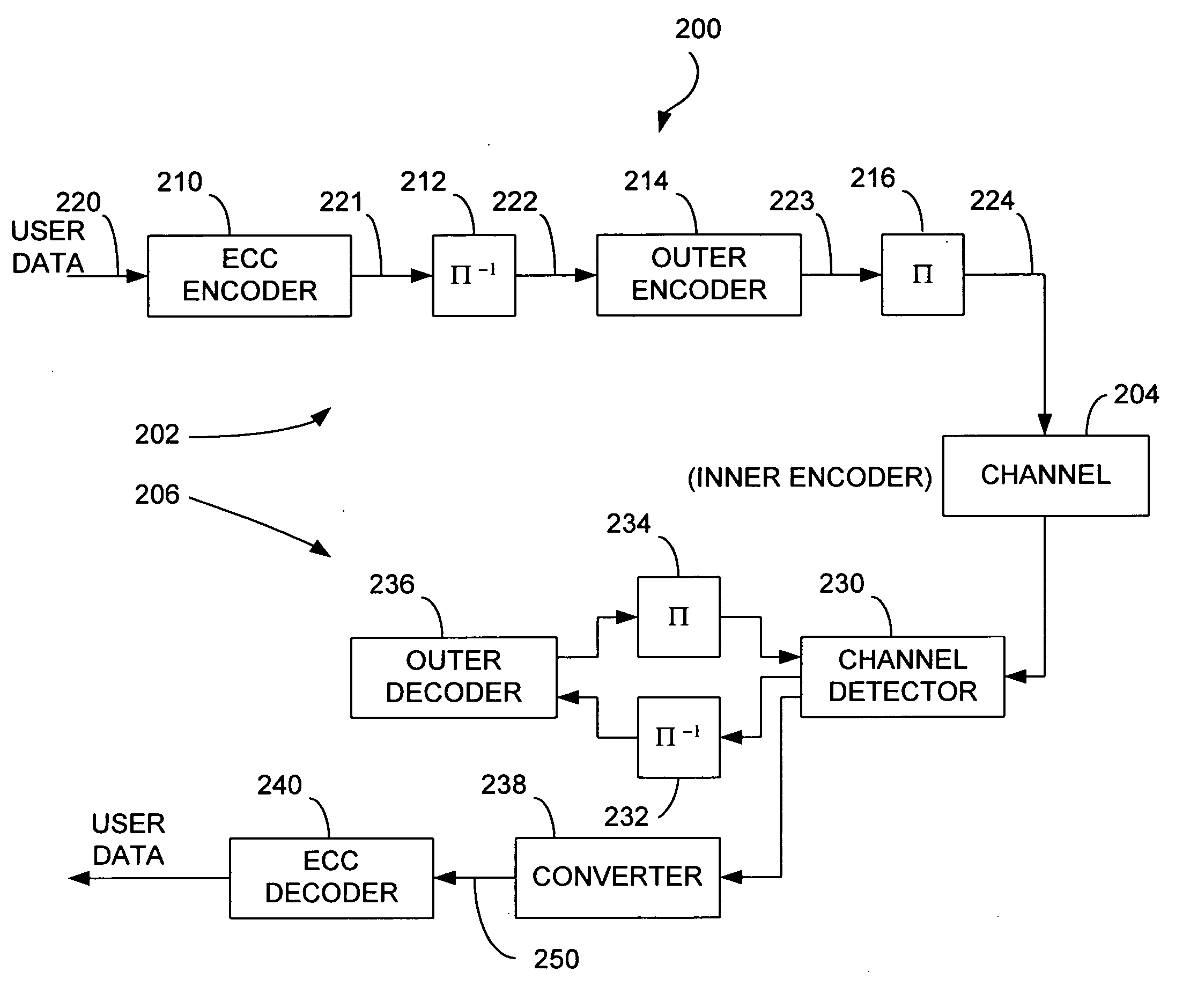
Decoding techniques for correcting errors using soft information
ActiveUS20070044006A1Increase ratingsData representation error detection/correctionOther decoding techniquesComputer hardwareSoft information
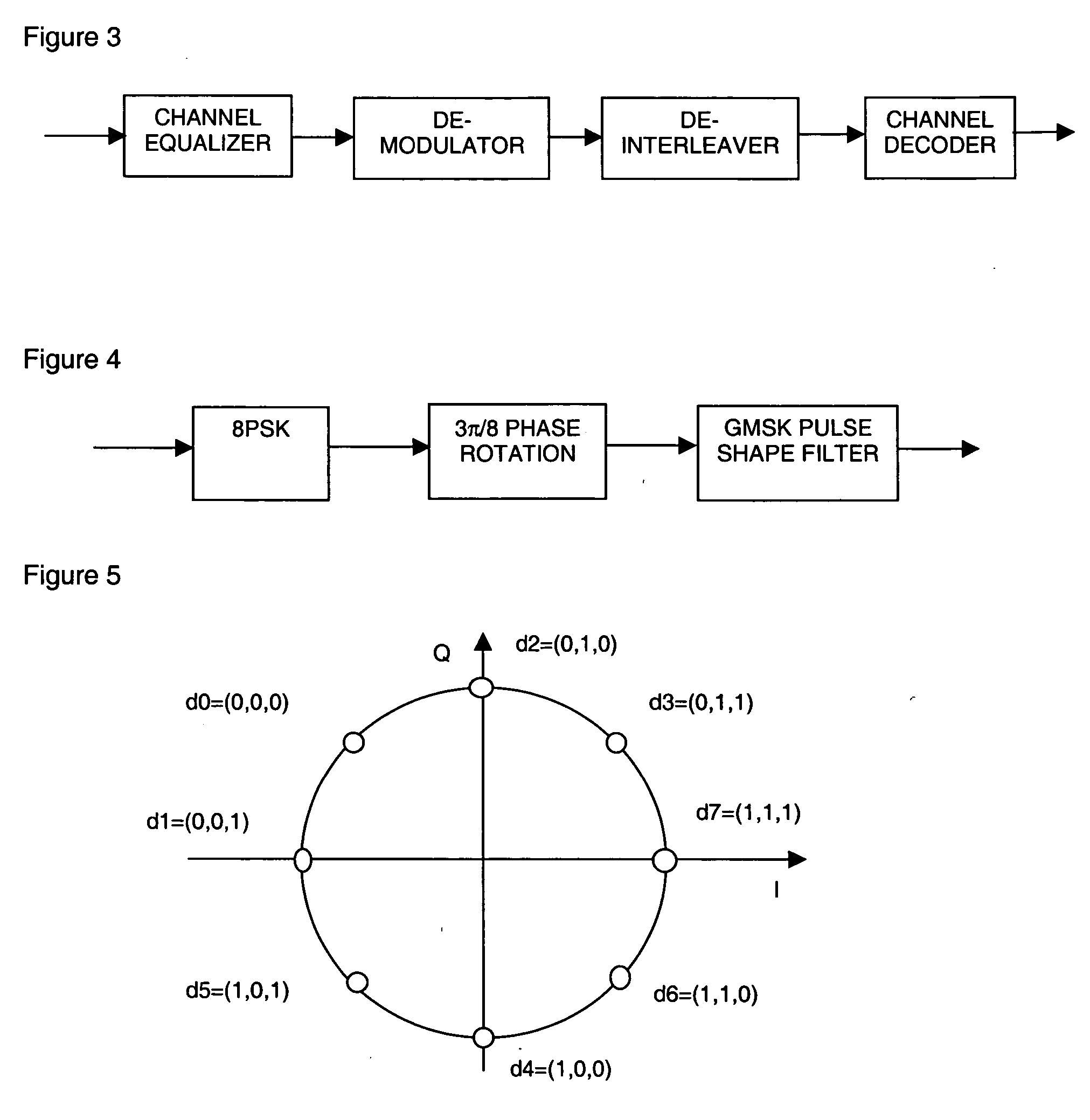
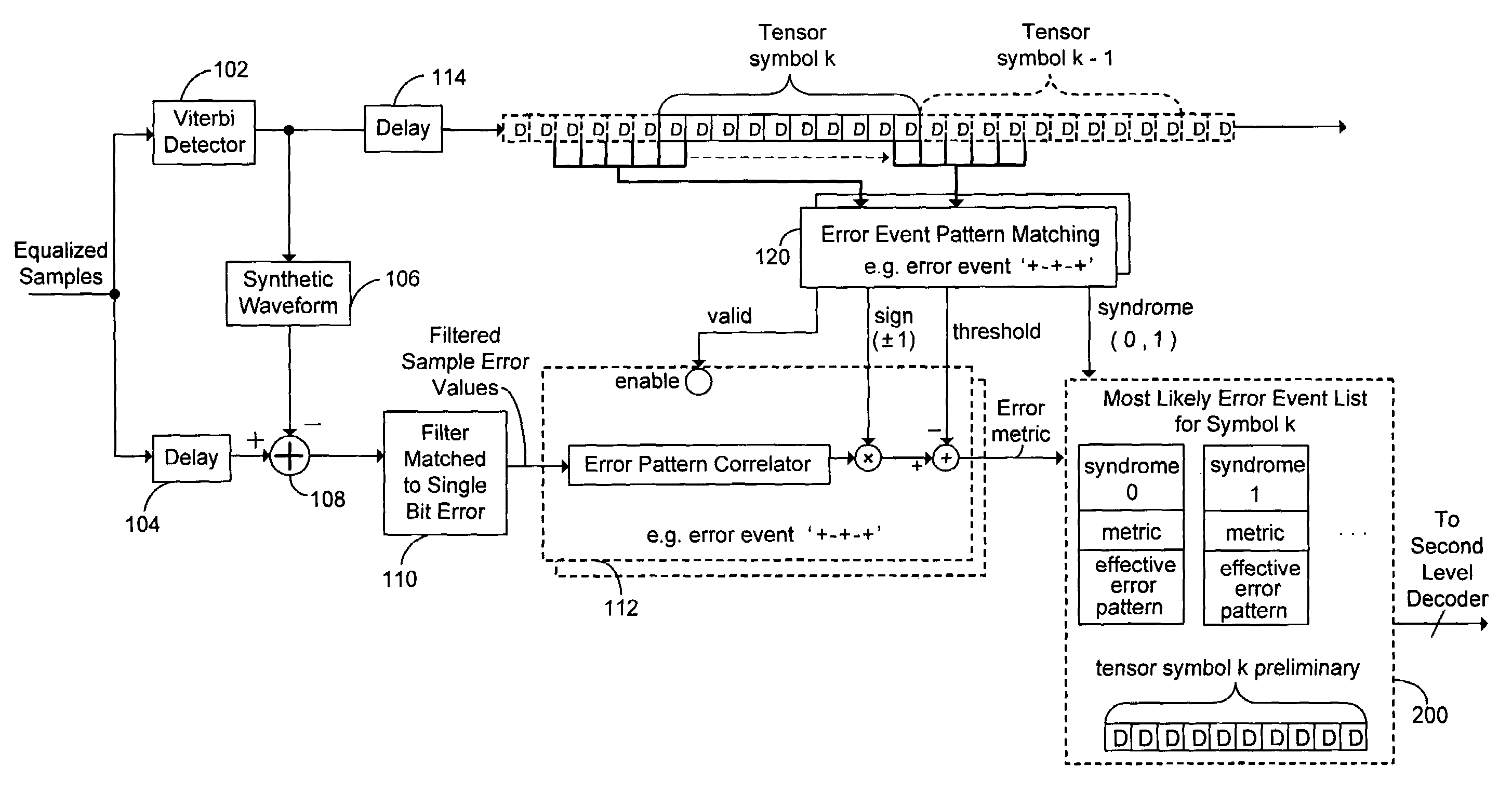
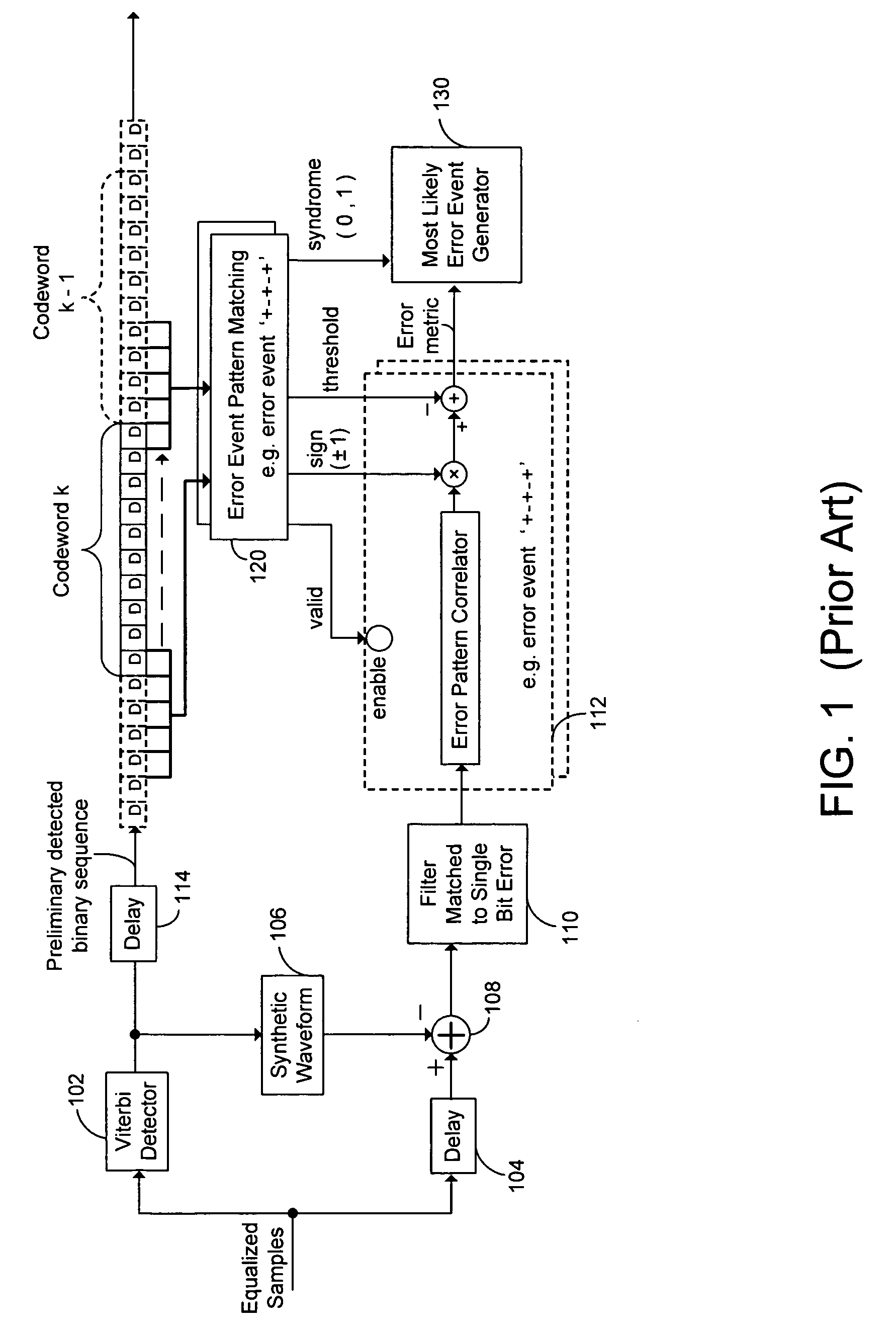
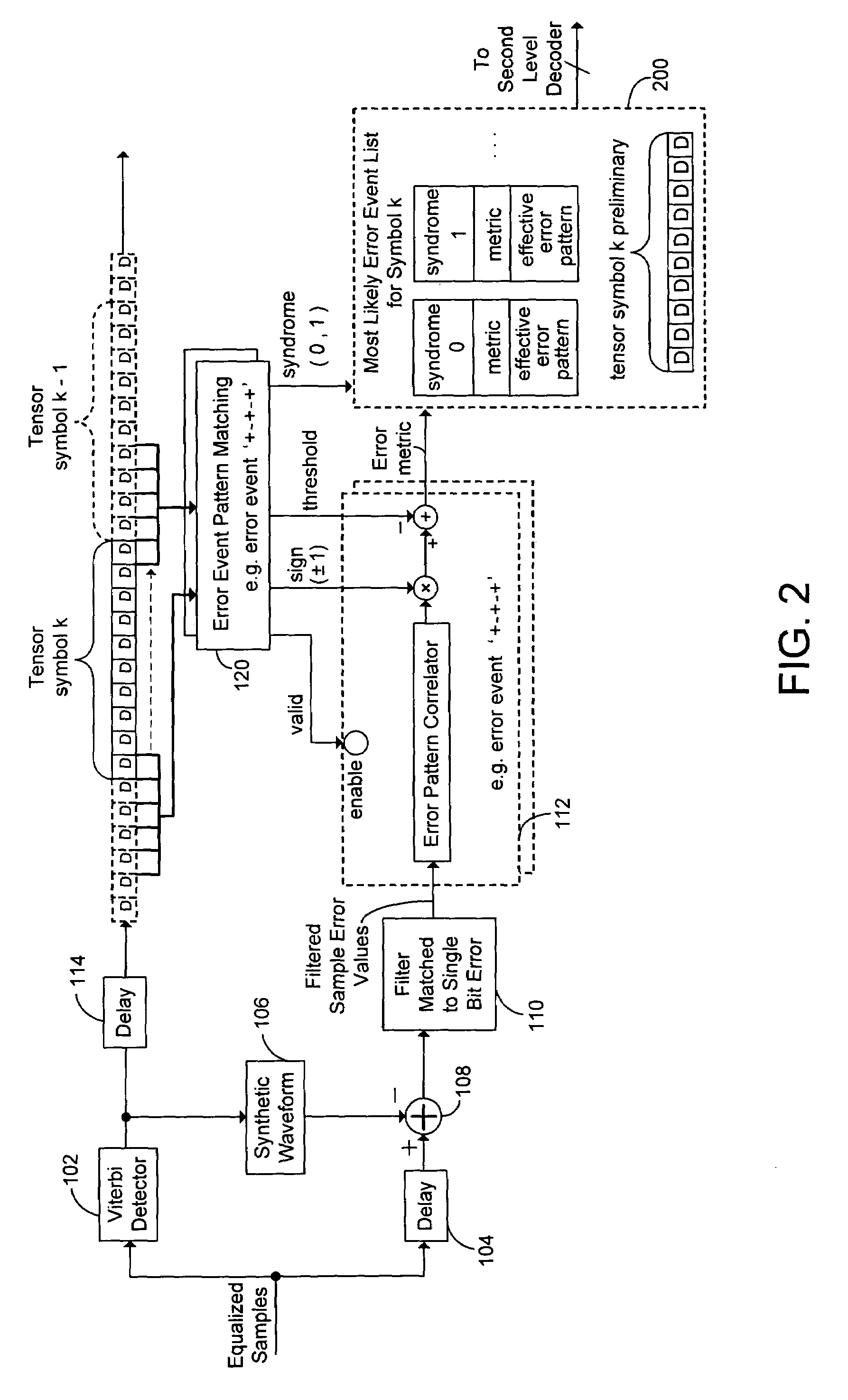
Two levels of error correction decoding are performed using first and second level decoders. A composite code formed by combining an inner component code and an outer component code can be used to decode the data and correct any errors. Performing two level decoding using a composite code allows the size of the inner parity block to be reduced to a single Reed-Solomon symbol while keeping a good code rate. The first level decoder generates soft information. The soft information can indicate a most likely error event for each possible syndrome value of the inner component code. The soft information can also include error metric values for each of the most likely error events. The second level decoder generates corrected syndrome values based on the soft information using the outer component code. The most likely trellis path that corresponds to the corrected syndrome values is then selected.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
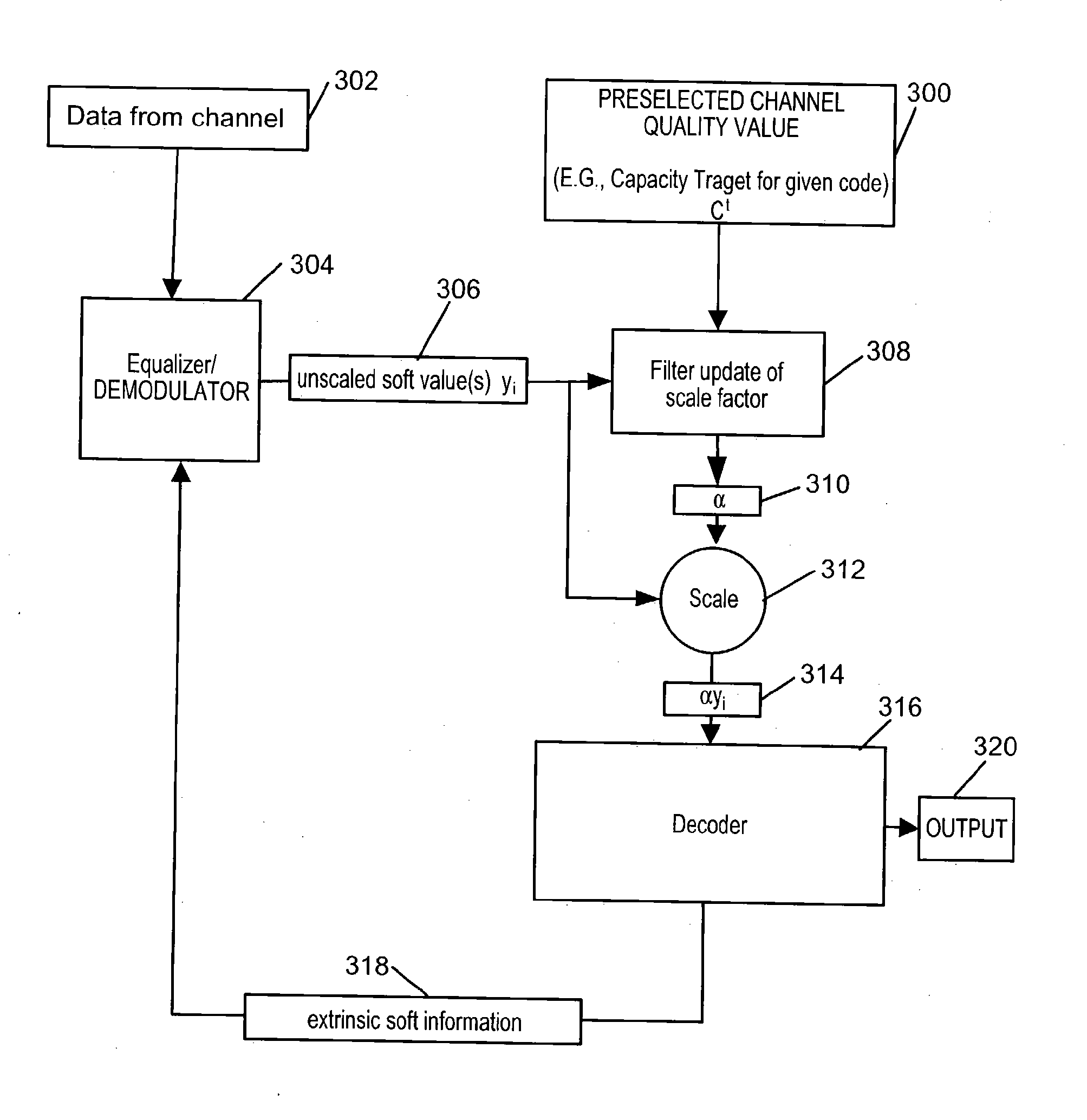
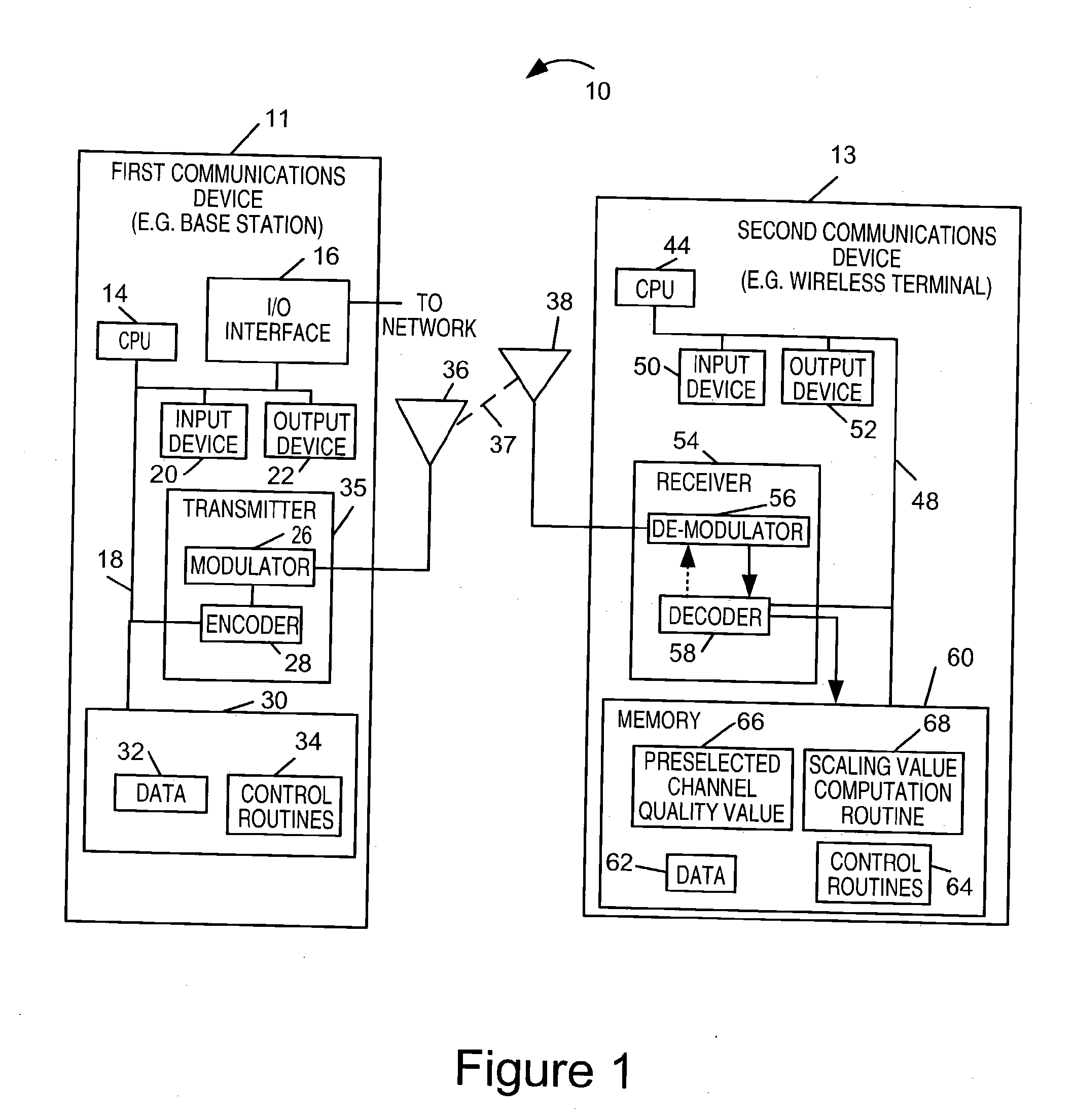
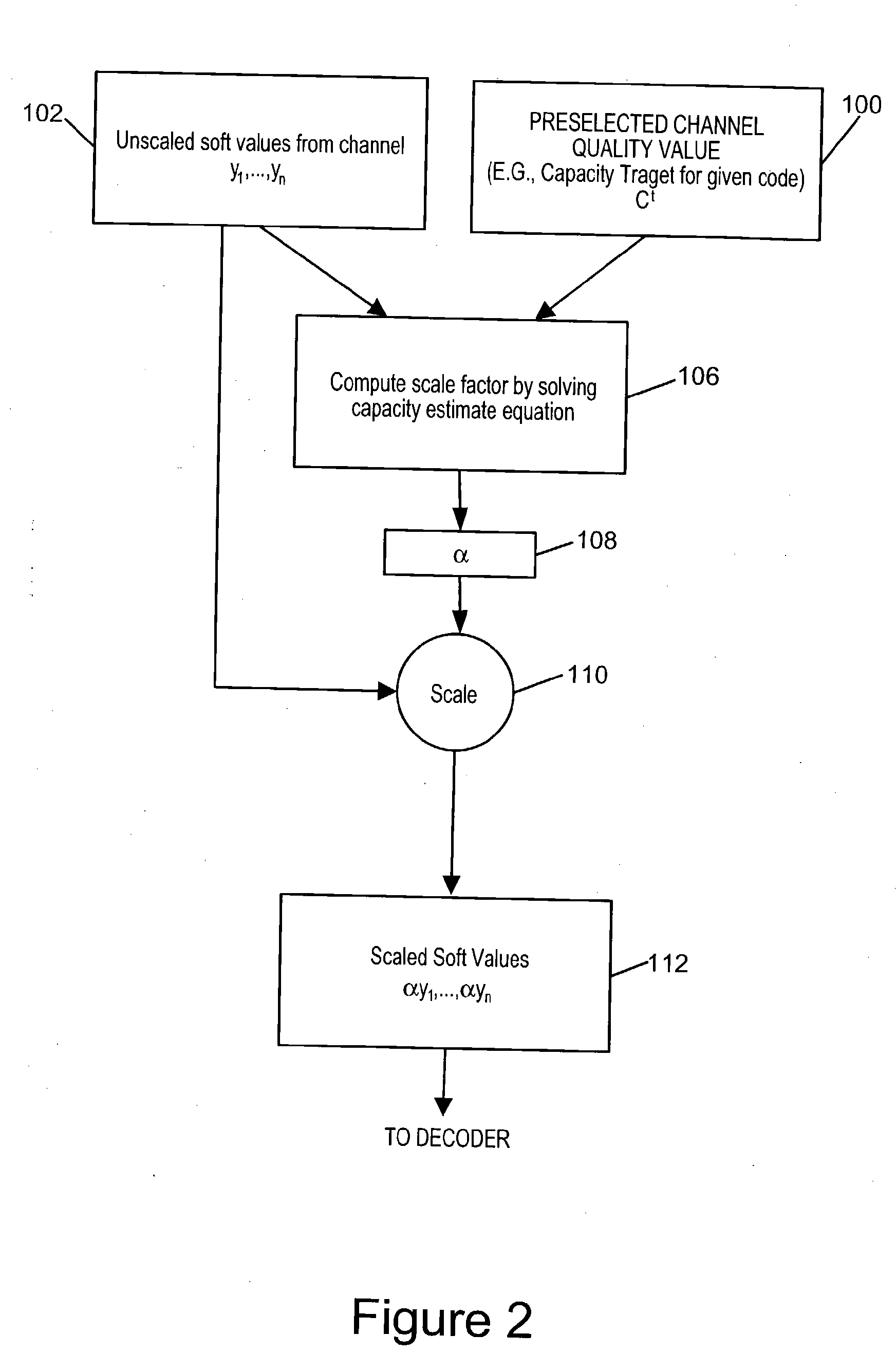
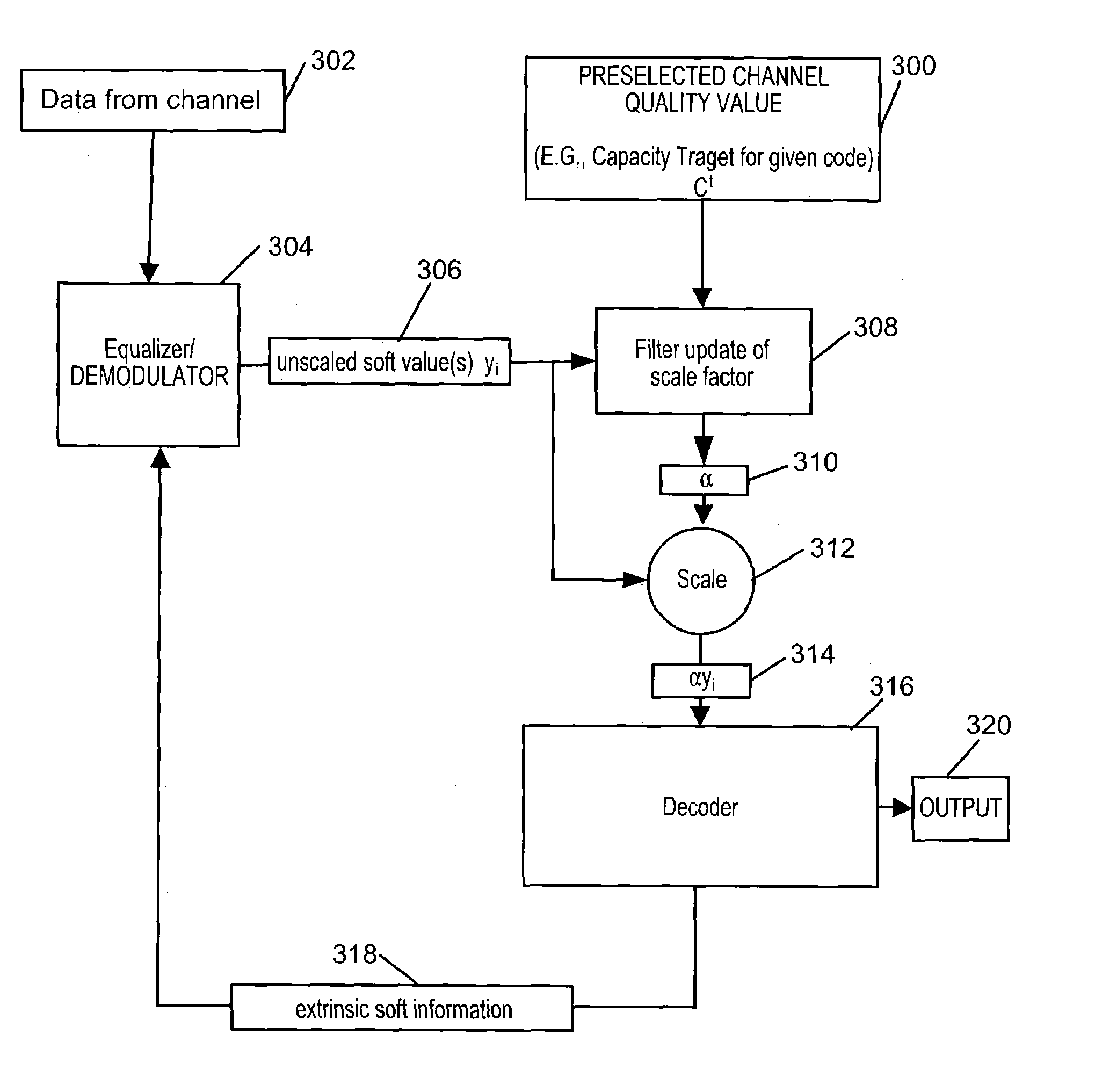
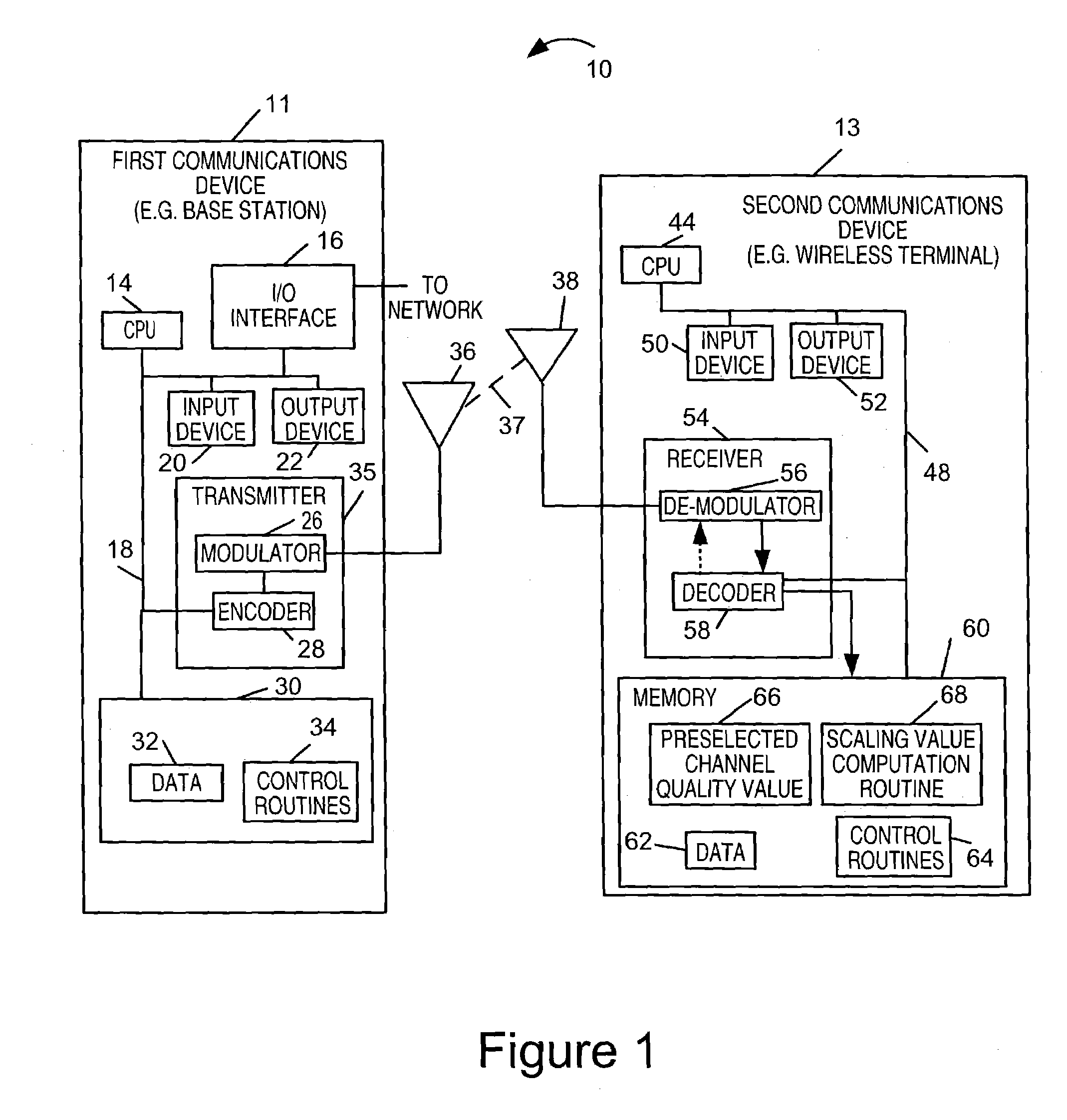
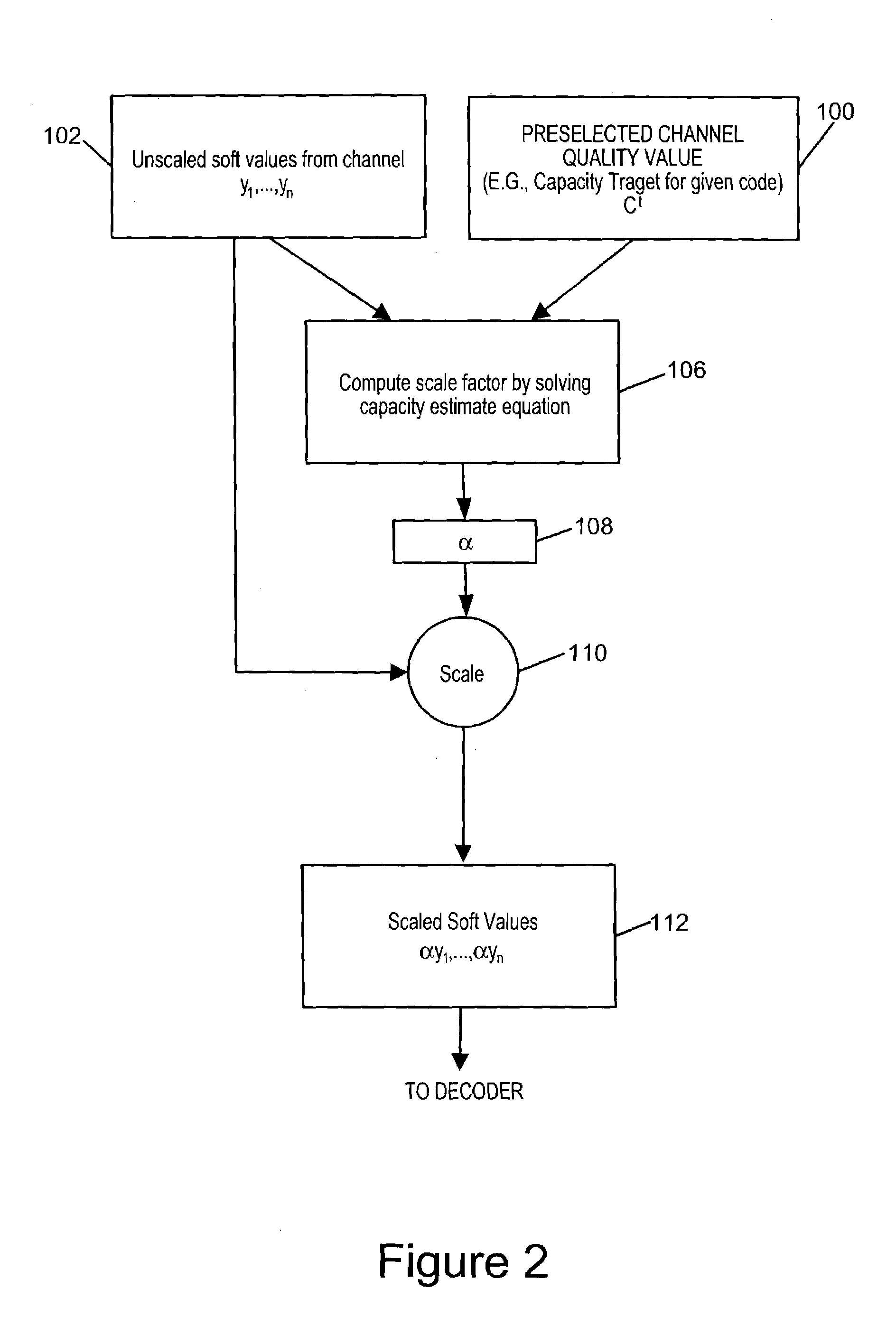
Soft information scaling for interactive decoding
InactiveUS20070234178A1Improve performancePerformance can be improved and optimizedOther decoding techniquesCode conversionComputer scienceSoft information
Methods and apparatus for scaling soft values as part of an error correction decoding process are described. Accurate decoding depends on use of the appropriate scale factor. Selection and use of the scale factor to scale soft values is designed to improve and / or optimize decoder performance without the need for prior knowledge of the correct scale factor or the actual channel conditions at the time the signal from which the soft values were obtained was transmitted through a communications channel. The techniques of the present invention assume that the soft values to be processed were transmitted through a communications channel having a quality that can be accurately described by a channel quality value. A scale factor is determined from the distribution of soft values to be scaled and an assumption that the channel through which they were transmitted was of the quality corresponding to a preselected channel quality value.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Symbol by symbol map detection for signals corrupted by colored and/or signal dependent noise
ActiveUS20070226599A1Data representation error detection/correctionModification of read/write signalsHard disc driveCommunications system
Symbol by symbol MAP detection for signals corrupted by colored and / or signal dependent noise. A novel means is presented for recursive calculation of forward metrics (α), backward metrics (β), and corresponding soft information (e.g., which can be provided as LLRs (log likelihood ratios)) within communication systems in which a trellis can be employed to perform demodulation of a received signal sequence. For signals that have been corrupted by colored and / or signal dependent noise, this means provides for the ability to perform novel soft information calculation for subsequent use in iterative decoding processing. Many types of communication channels can benefit from this novel means of detection including communication channels within hard disk drives (HDDs).
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
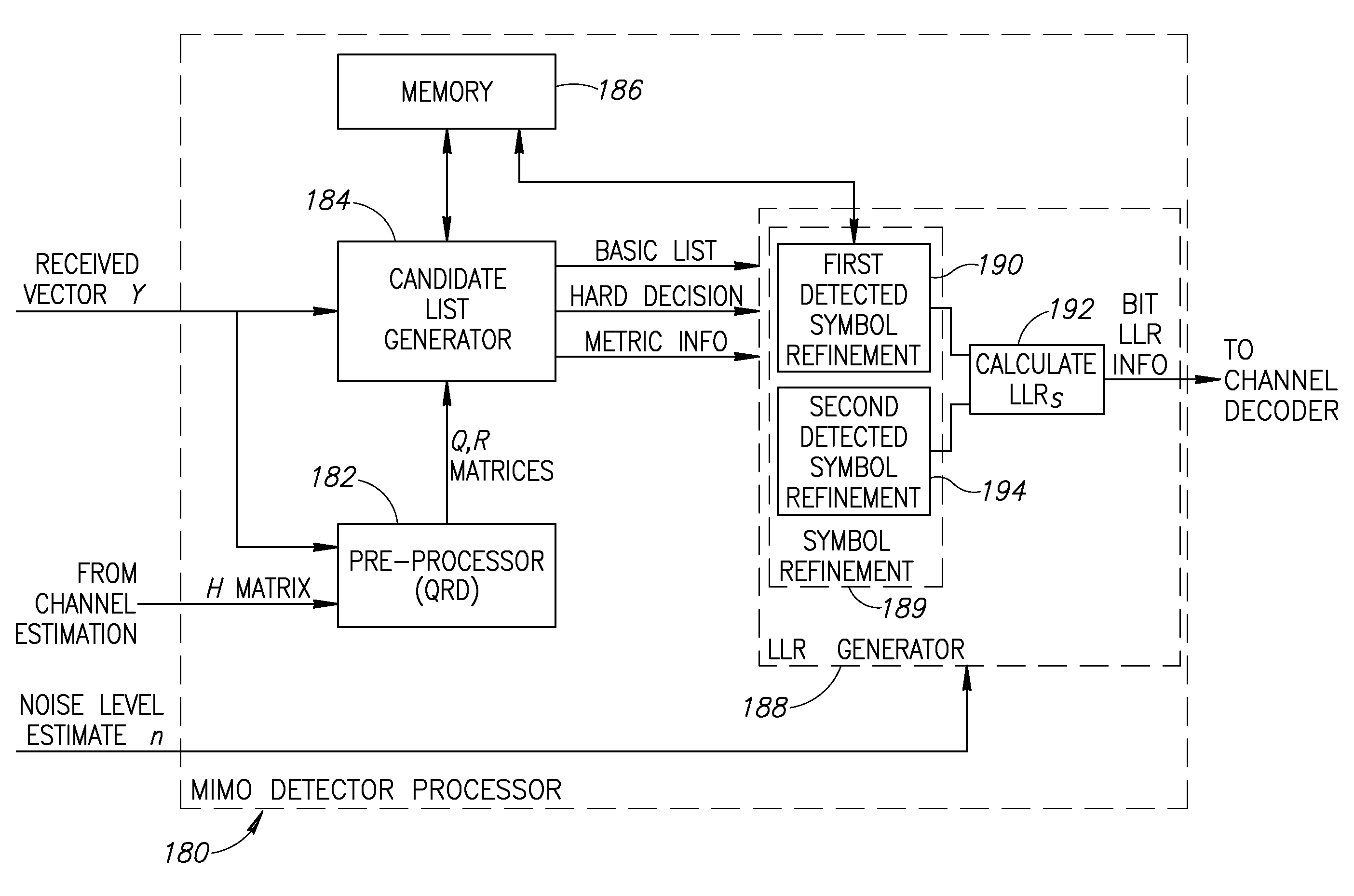
Multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) detector incorporating efficient signal point search and soft information refinement
InactiveUS20080279299A1Reduce computational complexityImproved receiver bit error rate (BER) performancePolarisation/directional diversityAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsCommunications systemSingle stage
A novel and useful apparatus for and method of multiple input multiple output (MIMO) detection for use in MIMO based communication systems. The mechanism of the invention performs a simplified tree search utilizing a single stage expansion of the most likely first symbol candidates, in the case of a 2×2 MIMO system. The invention also provides a refinement mechanism that is operative to significantly improve the soft information (i.e. log likelihood ratio) of the list of candidates. To improve the soft information, the mechanism applies one or more refinements rounds to generate additional candidates for both first and second detected symbols.
Owner:COMSYS COMM & SIGNAL PROC
Dynamic switching between MLSE and linear equalizer for single antenna interference cancellation in a GSM communication system
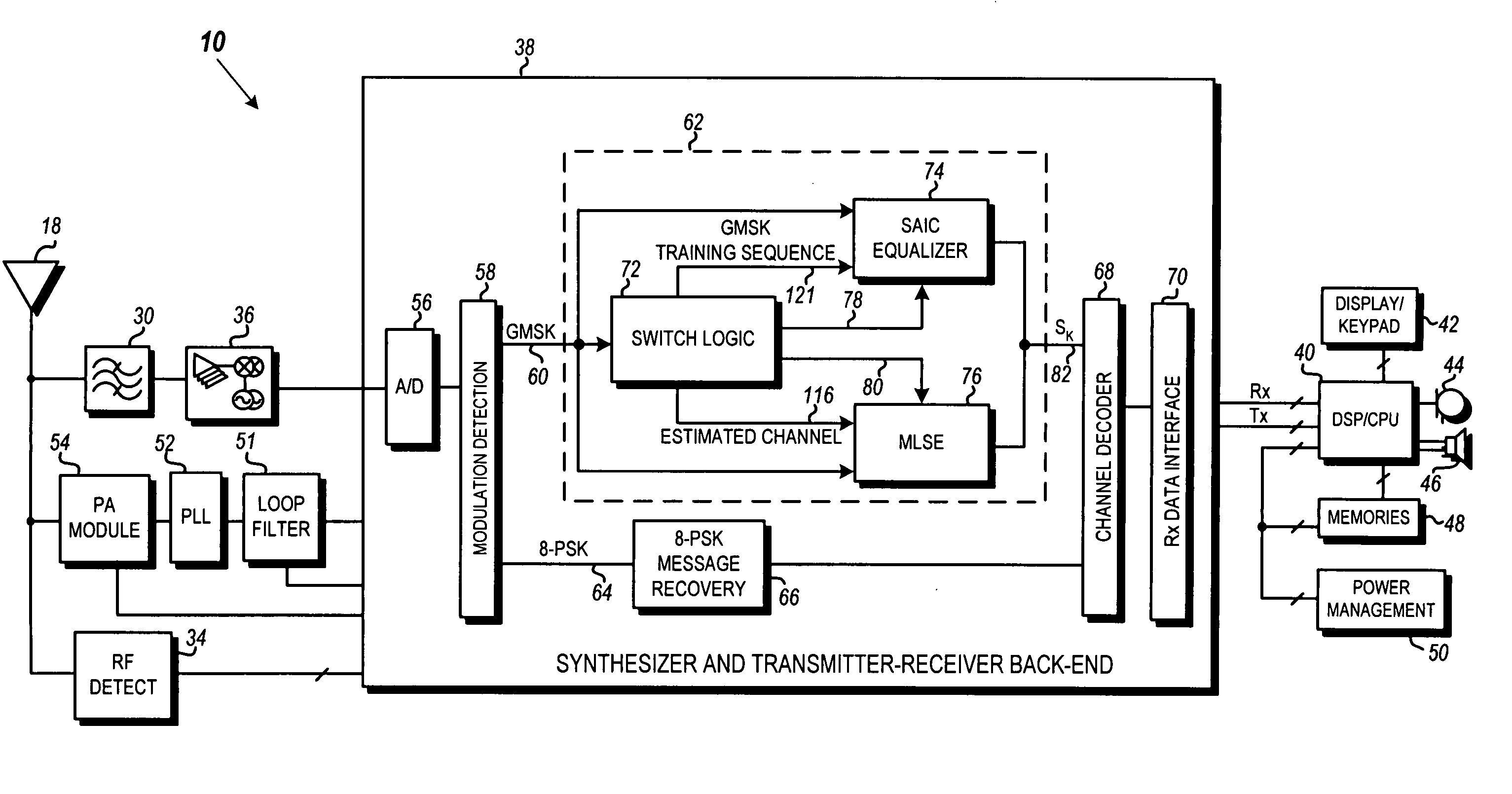
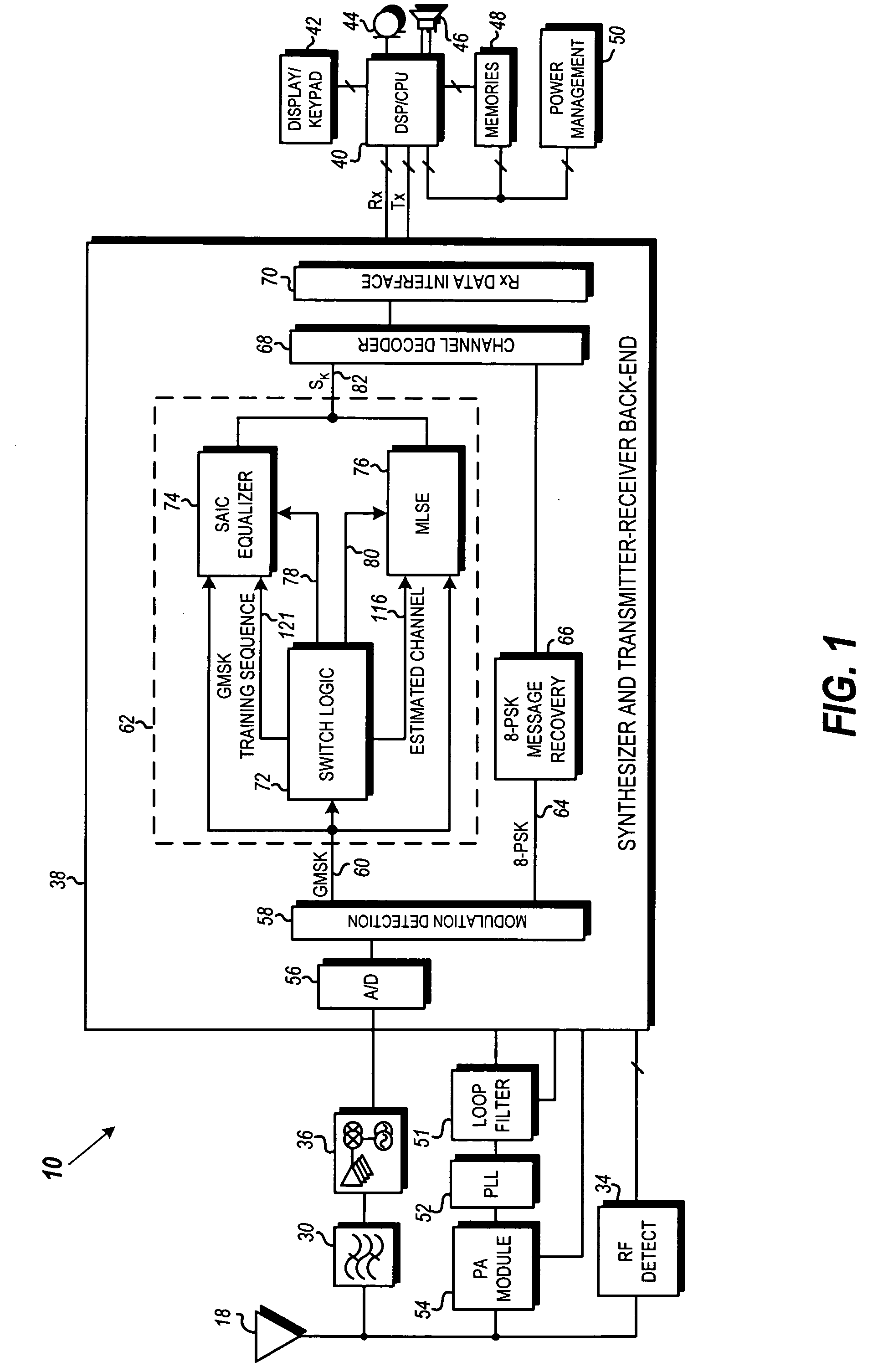
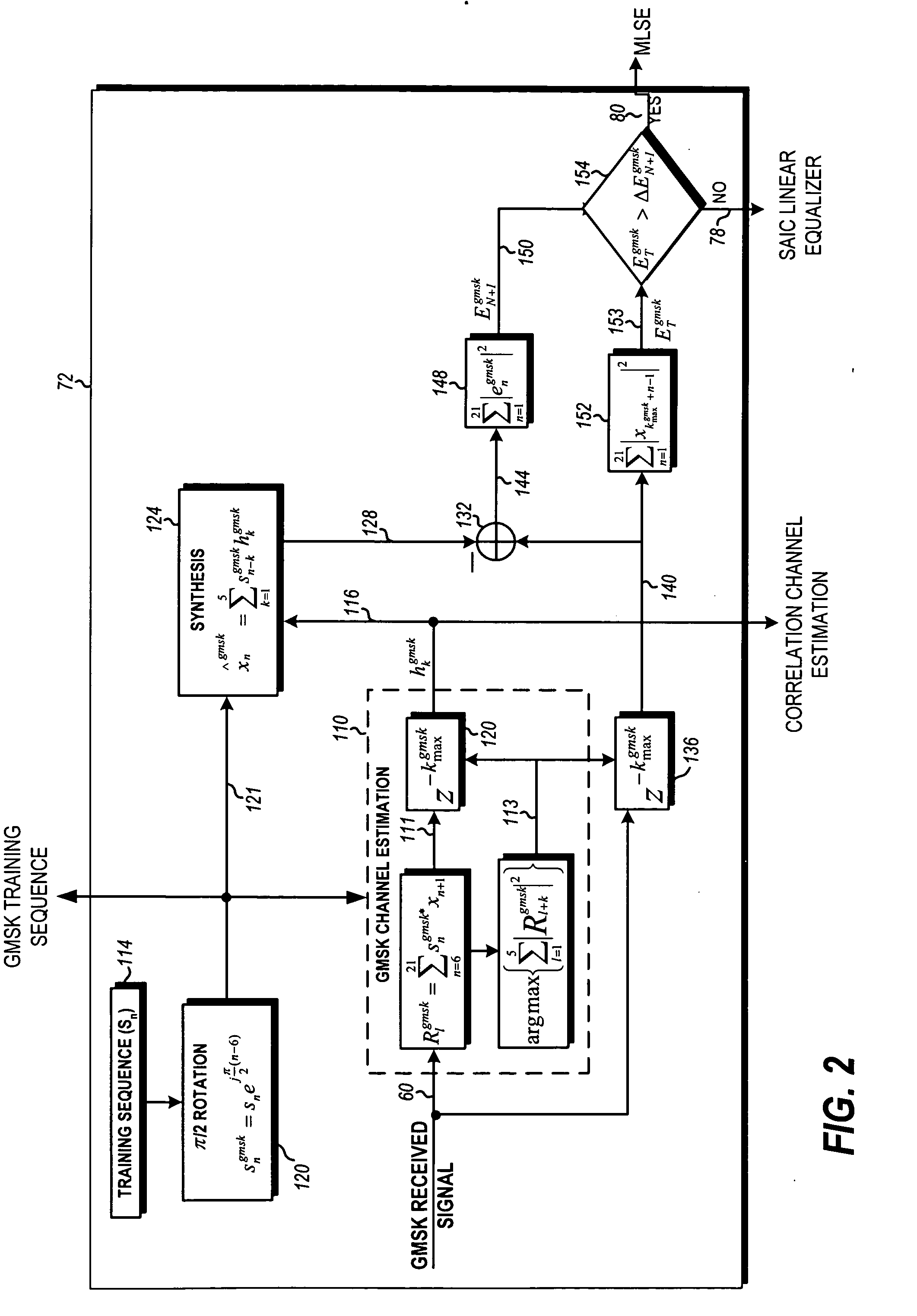
ActiveUS20070058709A1Multiple-port networksDelay line applicationsCommunications systemMobile station
In a GSM / EDGE Single Antenna Interference Cancellation (SAIC) operation environment, a mobile station is required to operate in a wide range of interference levels. An SAIC linear equalizer that takes advantage of the GMSK signal structure performs better than a conventional Maximum Likelihood Sequence Estimation (MLSE) equalizer in high interference levels, while it performs worse in low interference levels. A dynamic selection between the SAIC linear equalizer and the MLSE equalizer for each received burst is achieved to provide the optimal performance across the entire required operation environments. The dynamic selection is based on the estimated noise plus interference energy relative to the total received signal energy. The soft information calculated by the two categories of equalizers is properly scaled to generate soft information with balanced magnitude.
Owner:APPLE INC
High speed, low-cost process for the demodulation and detection in EDGE wireless cellular systems
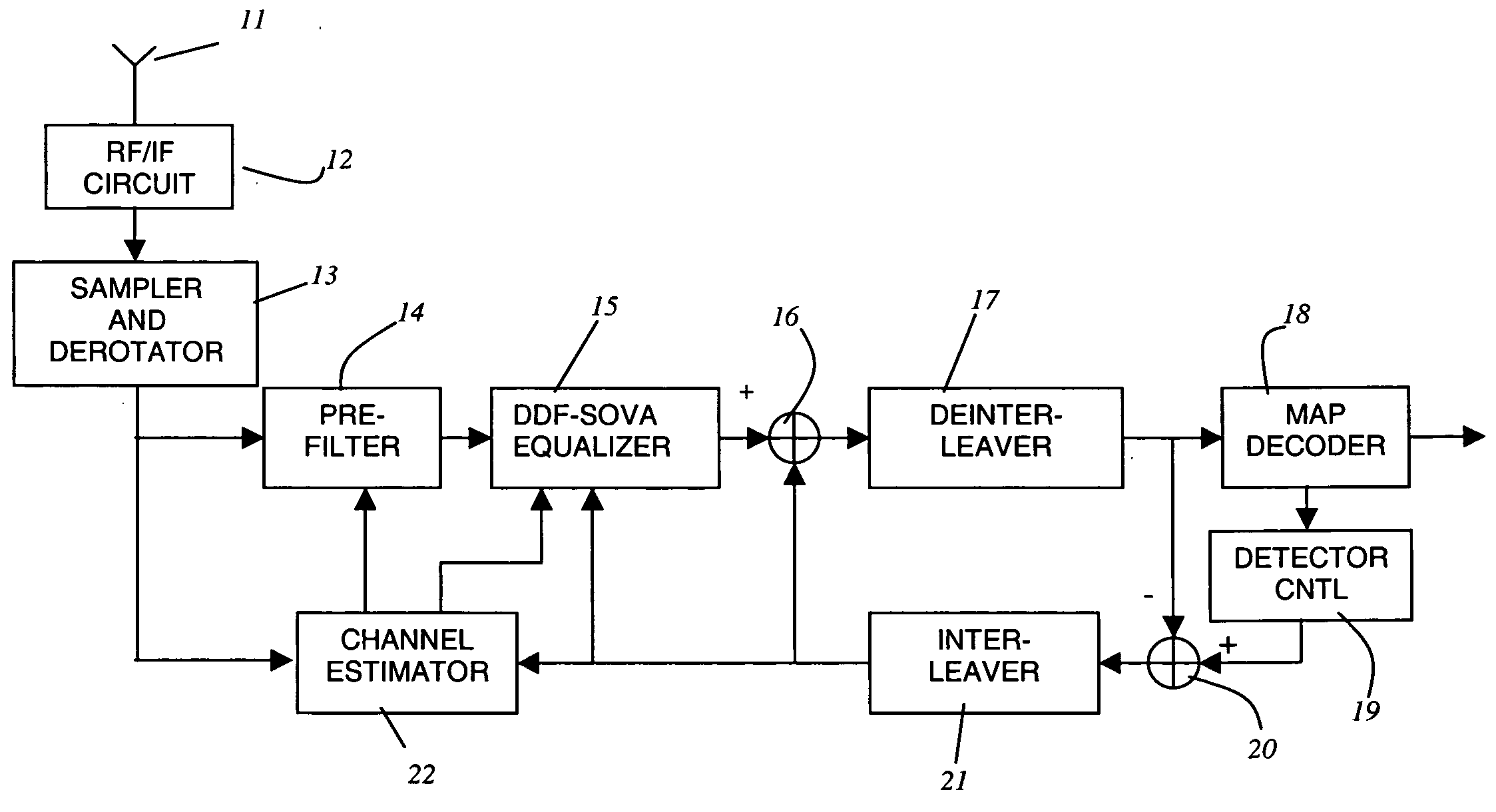
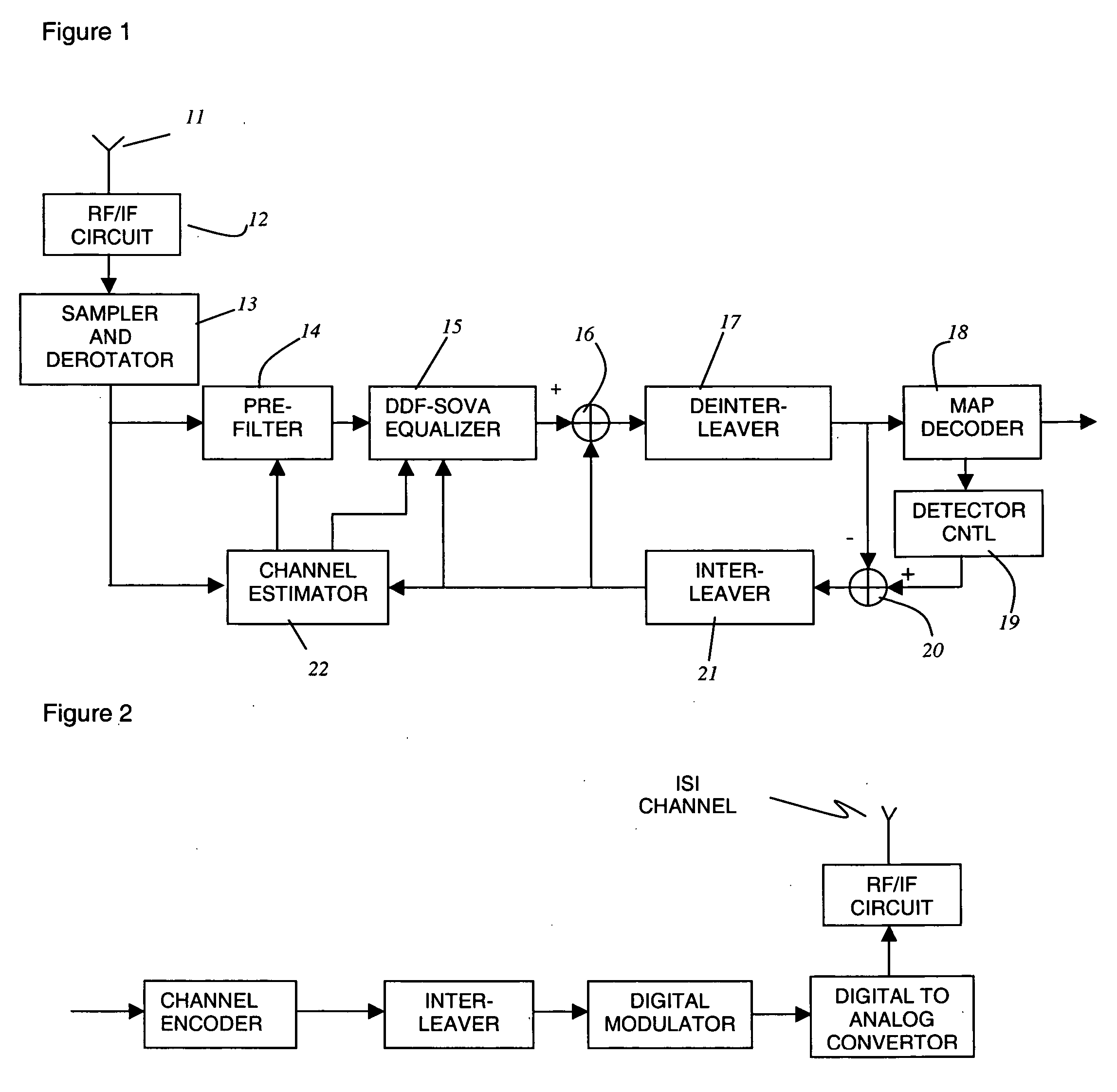
InactiveUS20050018794A1Low costEasy to detectAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsPhase-modulated carrier systemsReverse orderForward error correction
A process for signal detection in EDGE cellular systems is presented with the step of wireless channel estimation, a time-reversed signal processor, a soft-output Viterbi signal detector consisting of forward and reverse block processing, a MAP decoder that exchange soft information with the equalizer. Claim 1. A signal detection mechanism to demodulate received data frame that includes an accurate estimator to obtain channel responses, a forward filter and a FIR decision feedback filter to be used in soft-output equalizer, a time-reversal device storing received data in a time-reversed order for reverse block processing, an interference removal apparatus in both forward and reverse processing blocks, and a soft-input soft-output reduced state equalizer that utilizes the forward processing and reversed time processing blocks to generate iterative soft-output signals to the forward error correction decoder within the receiver system.
Owner:TANG XIANGGUO +2
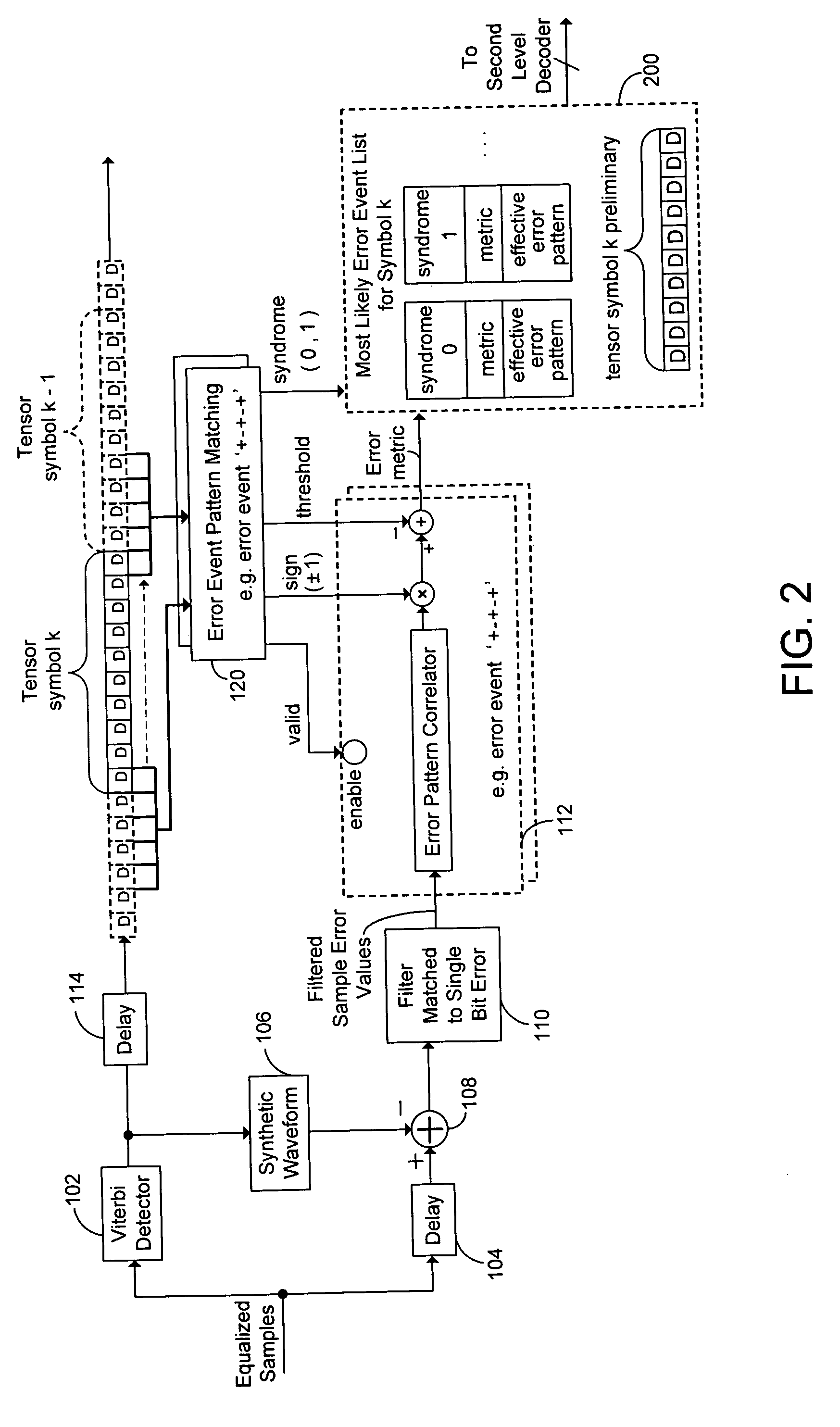
Decoding techniques for correcting errors using soft information
ActiveUS7725800B2Increase ratingsData representation error detection/correctionOther decoding techniquesComputer hardwareSoft information
Two levels of error correction decoding are performed using first and second level decoders. A composite code formed by combining an inner component code and an outer component code can be used to decode the data and correct any errors. Performing two level decoding using a composite code allows the size of the inner parity block to be reduced to a single Reed-Solomon symbol while keeping a good code rate. The first level decoder generates soft information. The soft information can indicate a most likely error event for each possible syndrome value of the inner component code. The soft information can also include error metric values for each of the most likely error events. The second level decoder generates corrected syndrome values based on the soft information using the outer component code. The most likely trellis path that corresponds to the corrected syndrome values is then selected.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
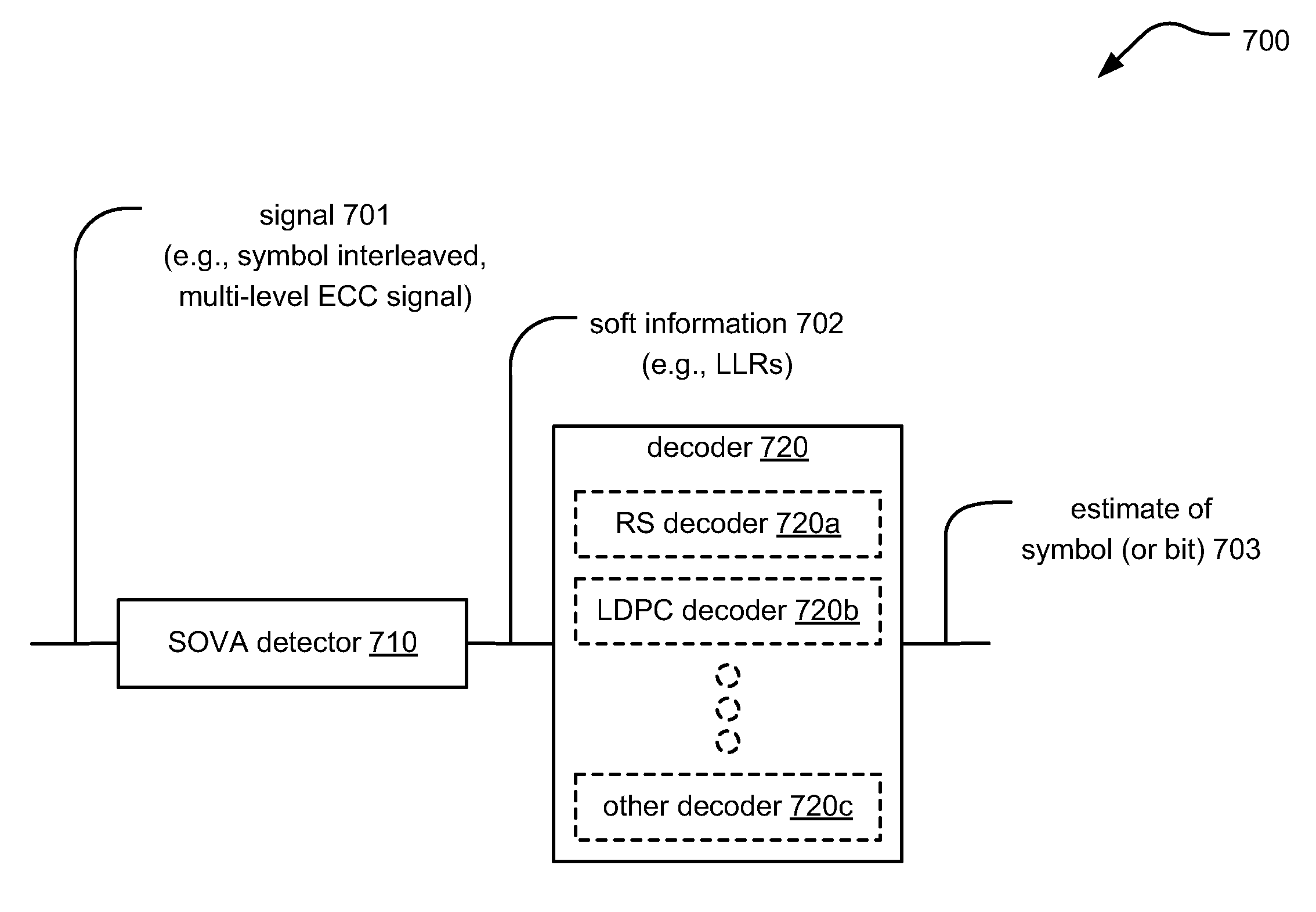
Error correction coding using soft information and interleaving
Error correction coding using soft information and interleaving. A symbol interleaved ECC signal (which can be a symbol interleaved multi-level ECC signal) initially undergoes detection (e.g., such as using SOVA detection) to generate soft information. A decoder uses the soft information to generate estimates of at least one symbol (or at least one bit) of the symbol interleaved multi-level ECC signal. Initially, each of the interleaves of the symbol interleaved multi-level ECC signal undergo decoding to determine whether or not any of the interleaves has correctable errors. If not, then a receiving device can request re-transmission of the symbol interleaved multi-level ECC signal from a transmitting device (or a re-read from media of a hard disk drive (HDD)). Interleaves having uncorrectable errors are associated with interleaves having correctable errors. Uncorrectable errors can be corrected via the use of erasure pointers or bit-flipping, among other means.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
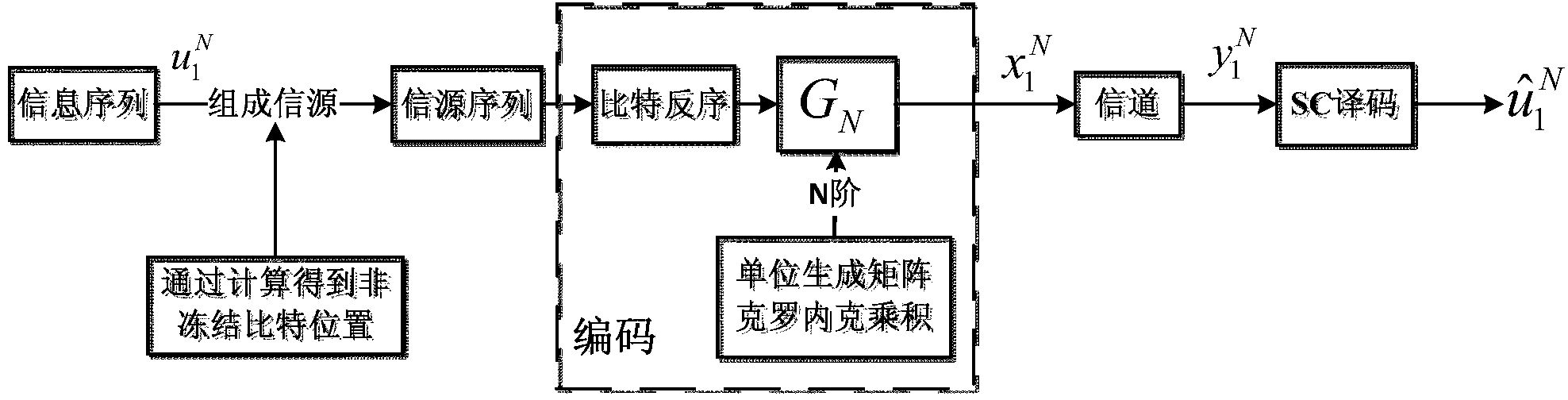
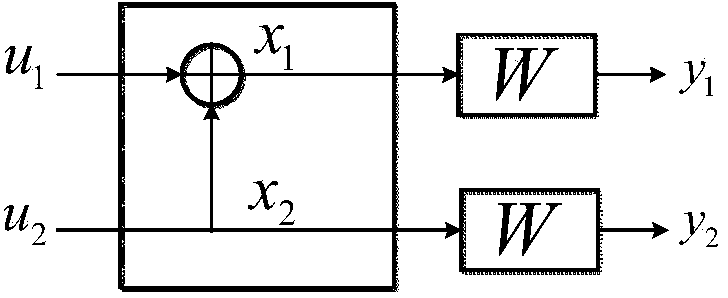
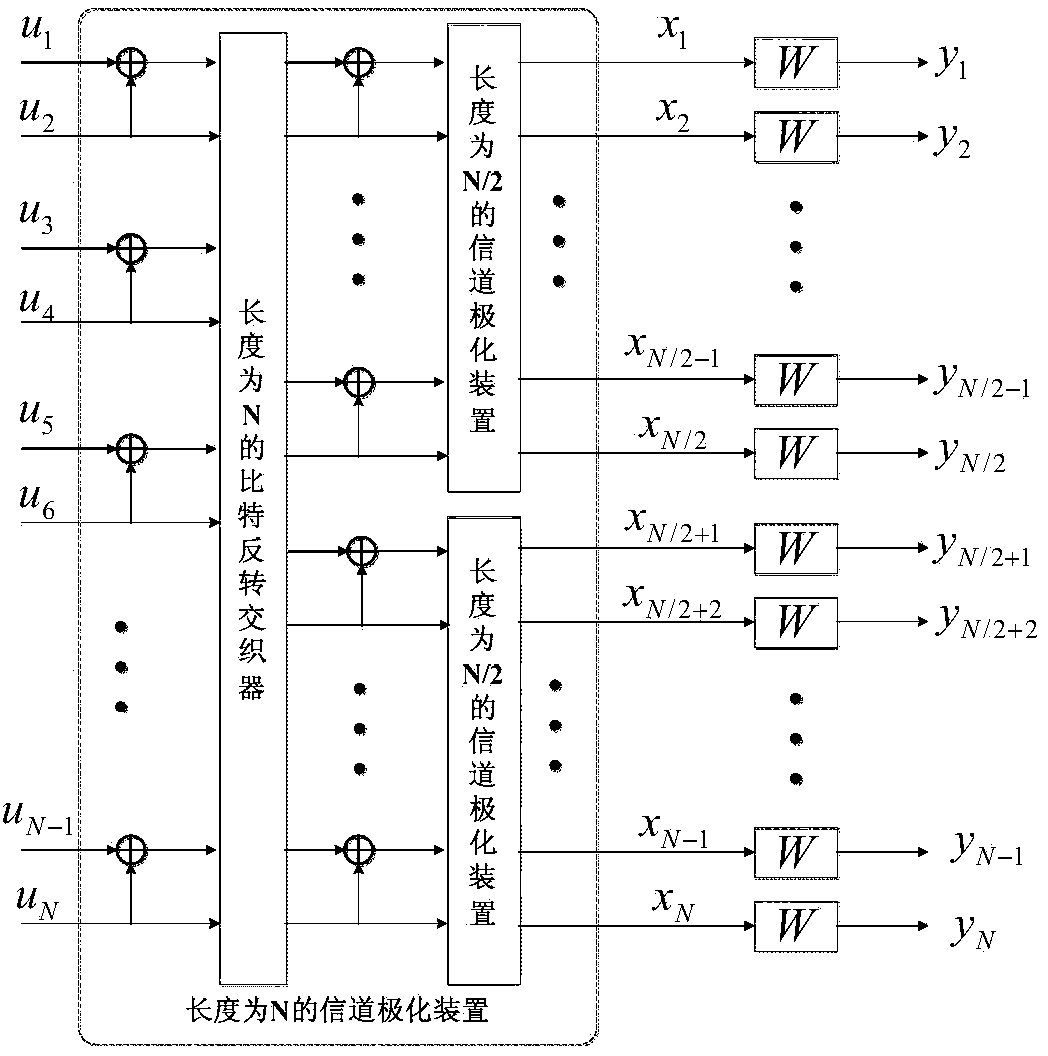
Polar code decoder and polar code decoding method based on probability calculation
ActiveCN104079382AImprove throughputDoes not affect the structureError preventionSequence transformationSoft information
The invention provides a polar code decoder and a polar code decoding method based on probability calculation. The polar code decoder comprises a probability sequence transformation module, a successive interference cancellation decoding module and a decision device, wherein the probability sequence transformation module is used for transforming received channel information into a first probability sequence; the successive interference cancellation decoding module is used for performing iteration processing on the first probability sequence based on a decision result of the decision device so as to obtain a second probability sequence and transforming the second probability sequence into a soft information value; and the decision device is used for performing hard decision on the soft information value and returning the decision result to the decoding module. According to the polar code decoder and the polar code decoding method based on probability calculation, the idea of the probability calculation is applied to the design of the polar code decoder, so that the processing delay of the polar code decoder can be reduced, and the total throughput of the polar code decoder can be increased greatly; and meanwhile, the polar code decoder and the polar code decoding method are simple in operation and good in universality and have better practical prospect.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) detector incorporating efficient signal point search and soft information refinement
InactiveUS7720169B2Increase probabilityEnhanced informationPolarisation/directional diversityAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsCommunications systemSingle stage
A novel and useful apparatus for and method of multiple input multiple output (MIMO) detection for use in MIMO based communication systems. The mechanism of the invention performs a simplified tree search utilizing a single stage expansion of the most likely first symbol candidates, in the case of a 2×2 MIMO system. The invention also provides a refinement mechanism operative to significantly improve the soft information (i.e. log likelihood ratio) of the list of candidates. To improve the soft information, the mechanism applies one or more refinement rounds to generate additional candidates for both first and second detected symbols.
Owner:COMSYS COMM & SIGNAL PROC
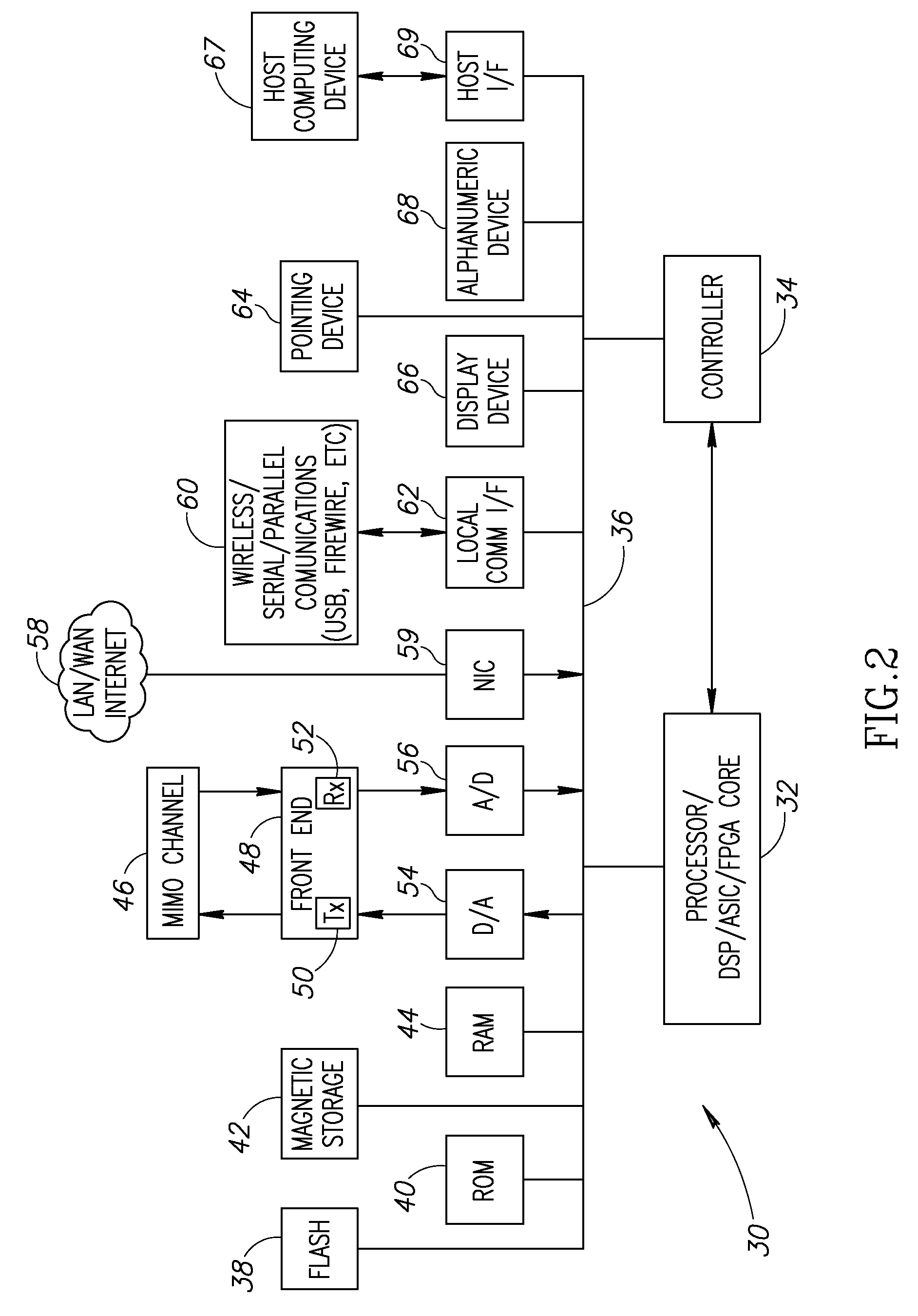
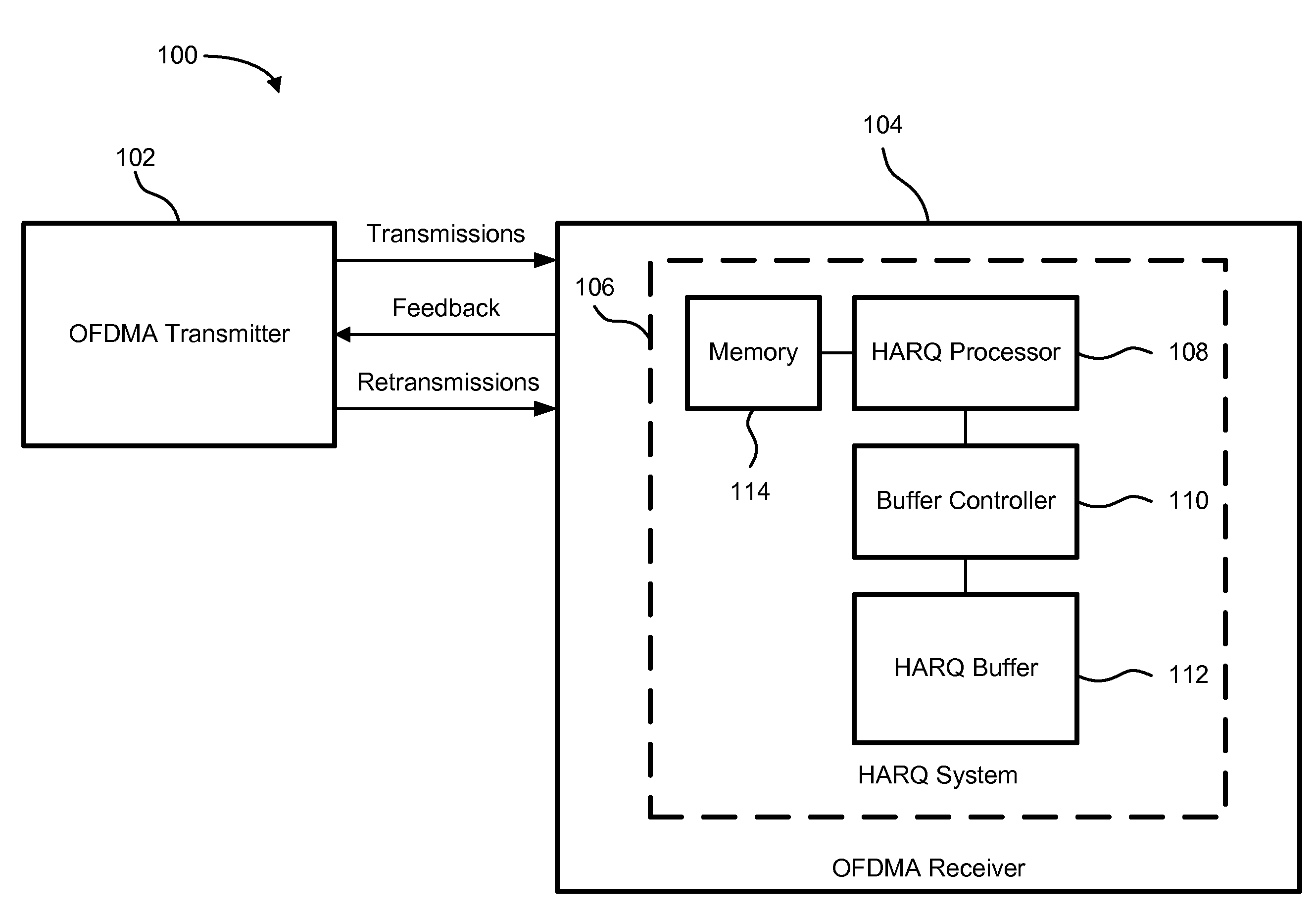
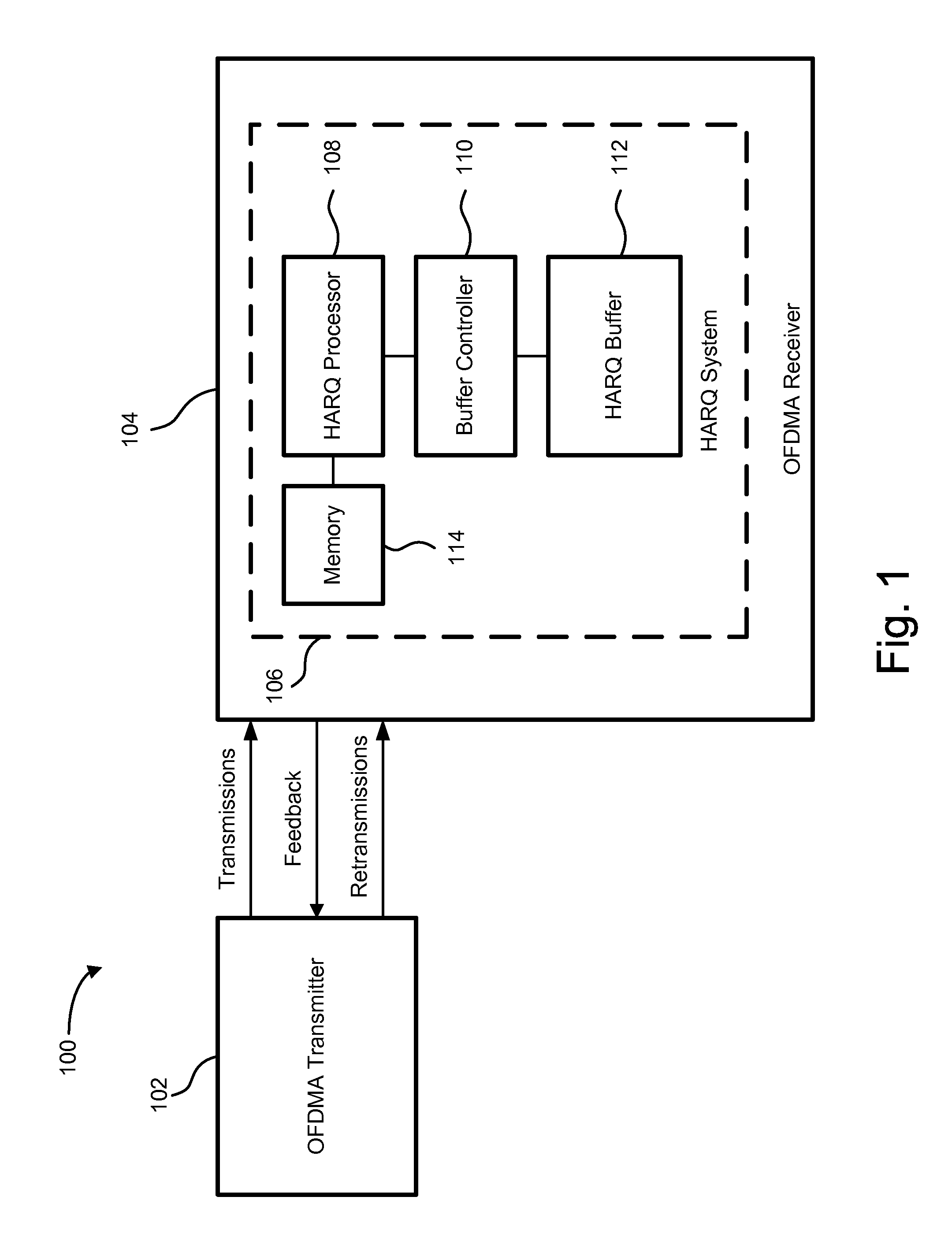
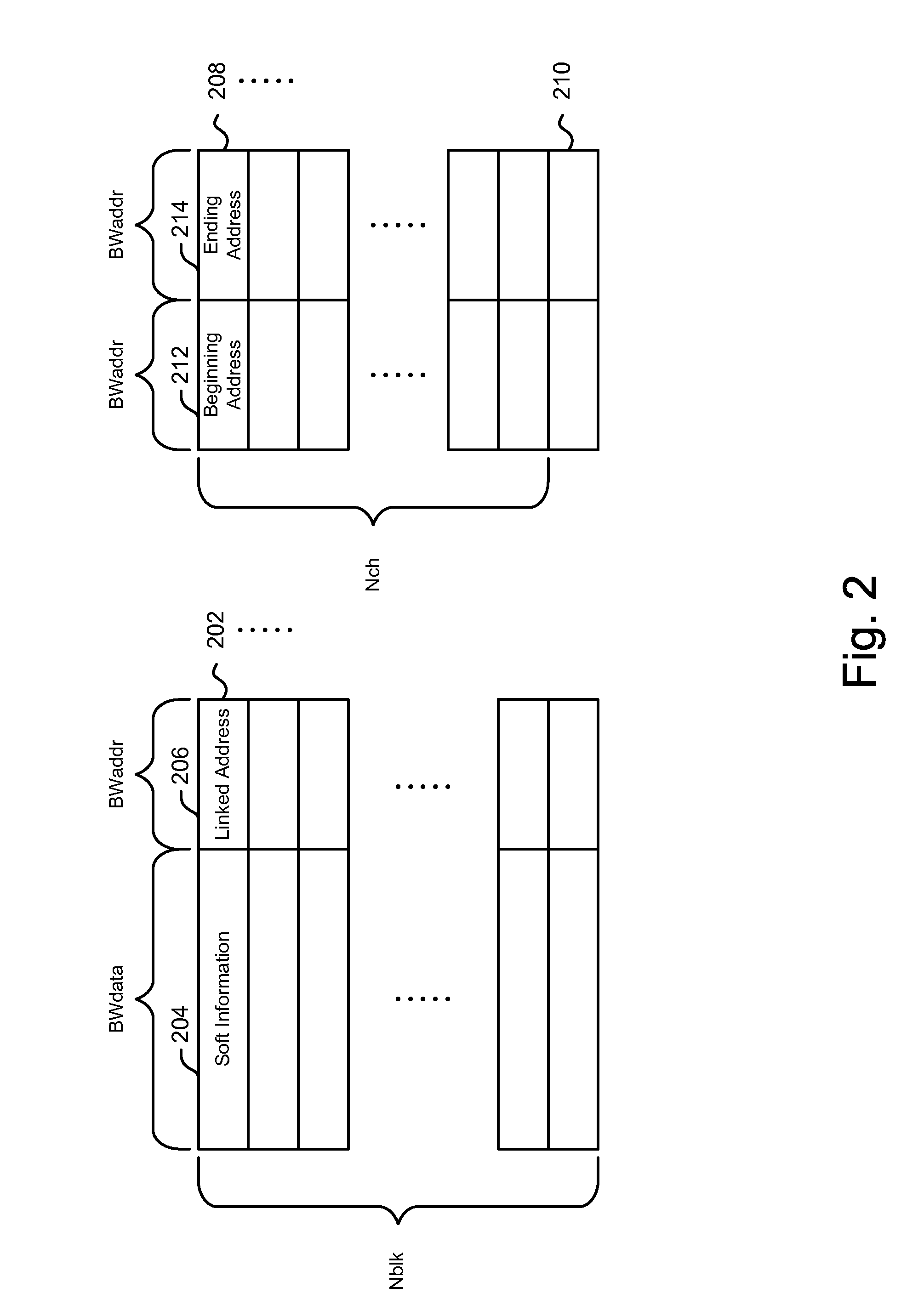
System and method for performing a HARQ operation in an ofdm-based receiver
InactiveUS20080276147A1Reduce complexityMeet cutting requirementsError prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission systemsData miningSoft information
A system and method for performing a HARQ operation in an OFDM-based receiver utilizes a linked list scheme for a HARQ buffer, which is used to store soft information for HARQ entities with decoding errors. The device and method also combine soft information of a particular HARQ entity with previous updated soft information of the particular HARQ entity using a combined scaling factor that depends on a current scaling factor and a previous combined scaling factor.
Owner:GHO GWANG HYUN +2
Dynamic LDPC error correction code method for flash memory
ActiveCN102394113AImprove read timeImprove reliabilityStatic storageDigital signal error detection/correctionAccess timeData error
The invention discloses a dynamic LDPC error correction code method for a flash memory, which belongs to the field of datum error correction of the non-volatile memory. According to the method, the quantification precision of soft information of LDPC codes is changed according to the page error rate of the NAND type flash memory. The method of the invention has the following beneficial effects: 1, in the initial usage phase of the NAND type flash memory, the program erasing frequency of each page in the flash memory is small, so the page error rate is small when, and the LDPC code soft information with the quantification precision of 1-bit is adopted to improve the read access time of the NAND type flash memory and reduce the power consumption of an LDPC decoder; and 2, when the flash memory is continuously used, the page error rate gradually rises, and the quantification precision of the LDPC codes is increased, so the error correction capability of the LDPC codes is improved, and the reliability of the NAND type flash memory can be improved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
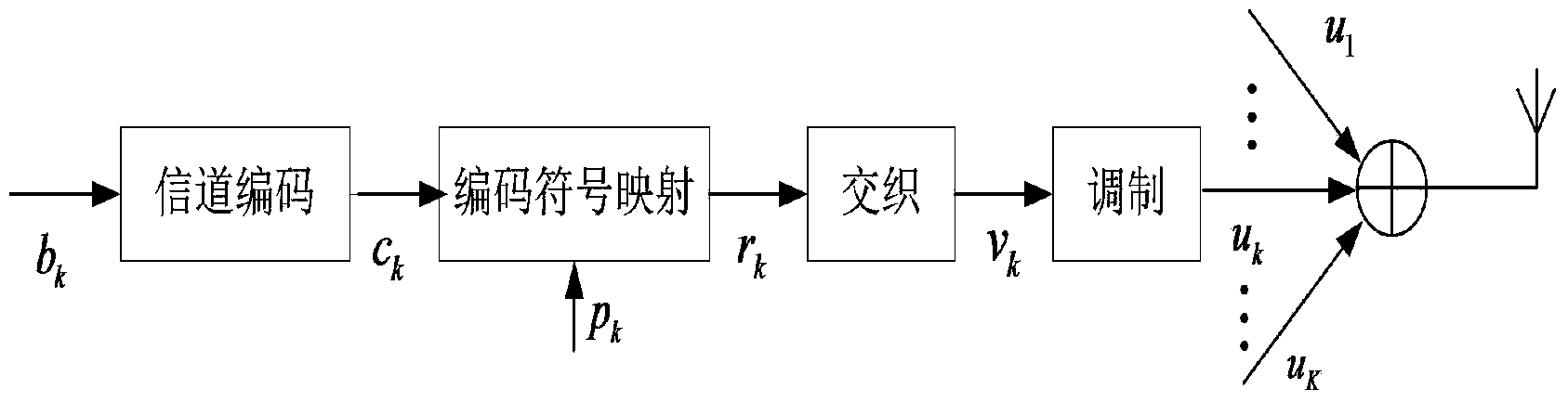
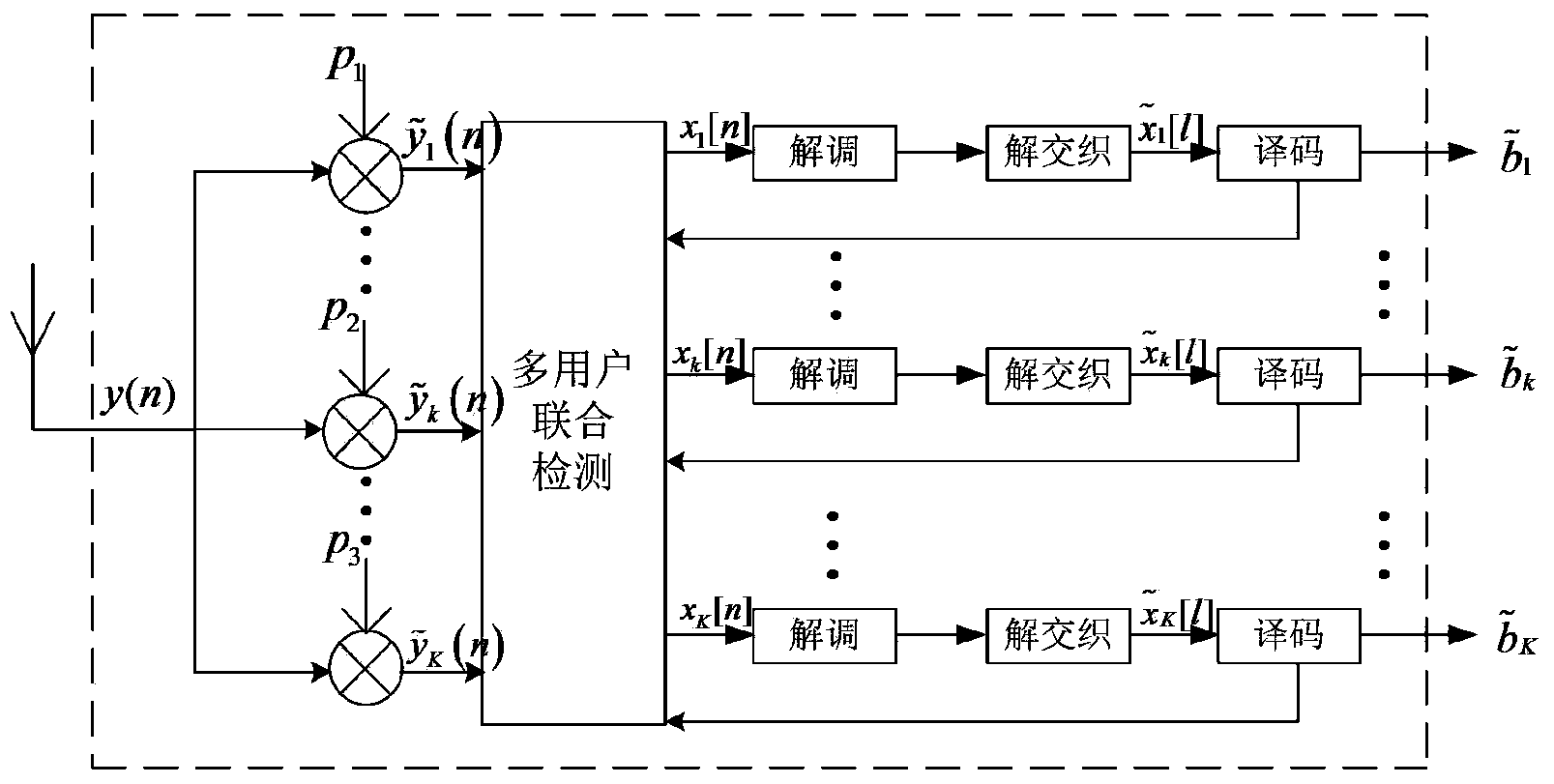
Non-orthogonal multi-user access and sending and combined receiving, demodulation and coding system and method
ActiveCN103841065AStrong interference abilityReduce operational complexityModulated-carrier systemsLine-faulsts/interference reductionReliable transmissionComputation complexity
The invention discloses a non-orthogonal multi-user access and sending and combined receiving, demodulation and coding system and method, and belongs to the technical field of communication. The method is characterized in that at a sending end, multiple users have access to the system in a non-orthogonal mode, and channel coding, coded symbol mapping, interleaving and modulation are carried out on a signal; at a receiving end, the received signal is multiplied by the feature sequence of each user, multi-user detection, demodulation, de-interleaving and decoding are sequentially carried out on the received signal, then multi-user detection is carried out on an output result again, and the iteration process is achieved. Based on the message passing conception, output soft information of a decoder is directly sent to undergo multi-user detection so as to achieve decoding and multi-user detection combined iteration processing. By means of the method, based on linear computation complexity, good interference elimination performance can be achieved, influence, caused by environmental noise and interference, on signal information is effectively reduced, and good BER performance and a more reliable transmission effect are achieved; meanwhile, multi-user interference elimination and decoding can be combined to be carried out, and therefore a parallel structure can be easily realized.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
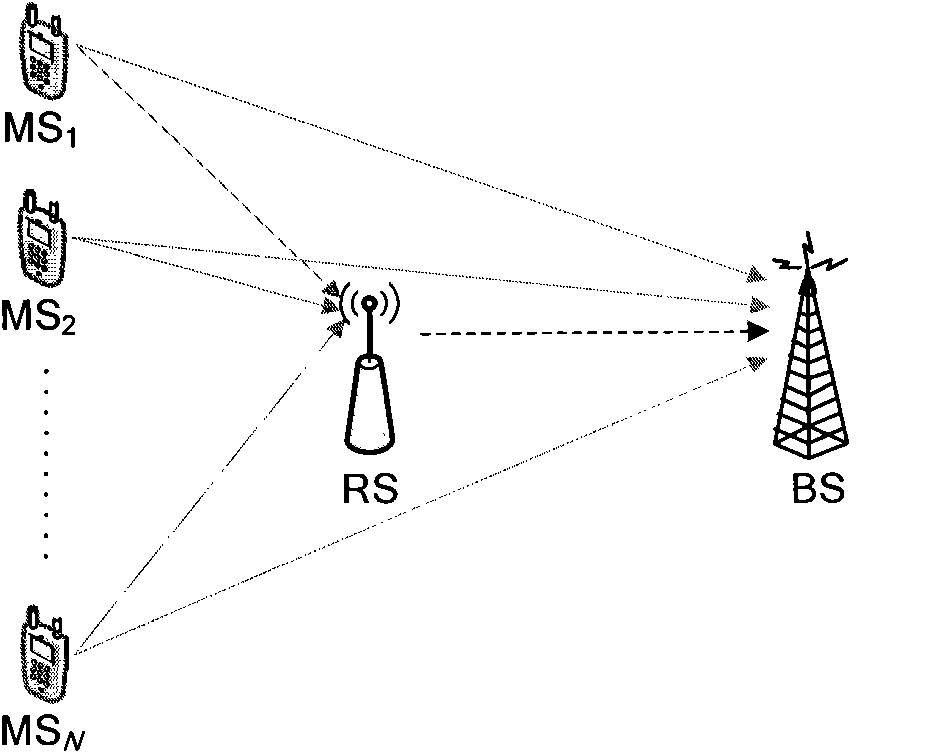
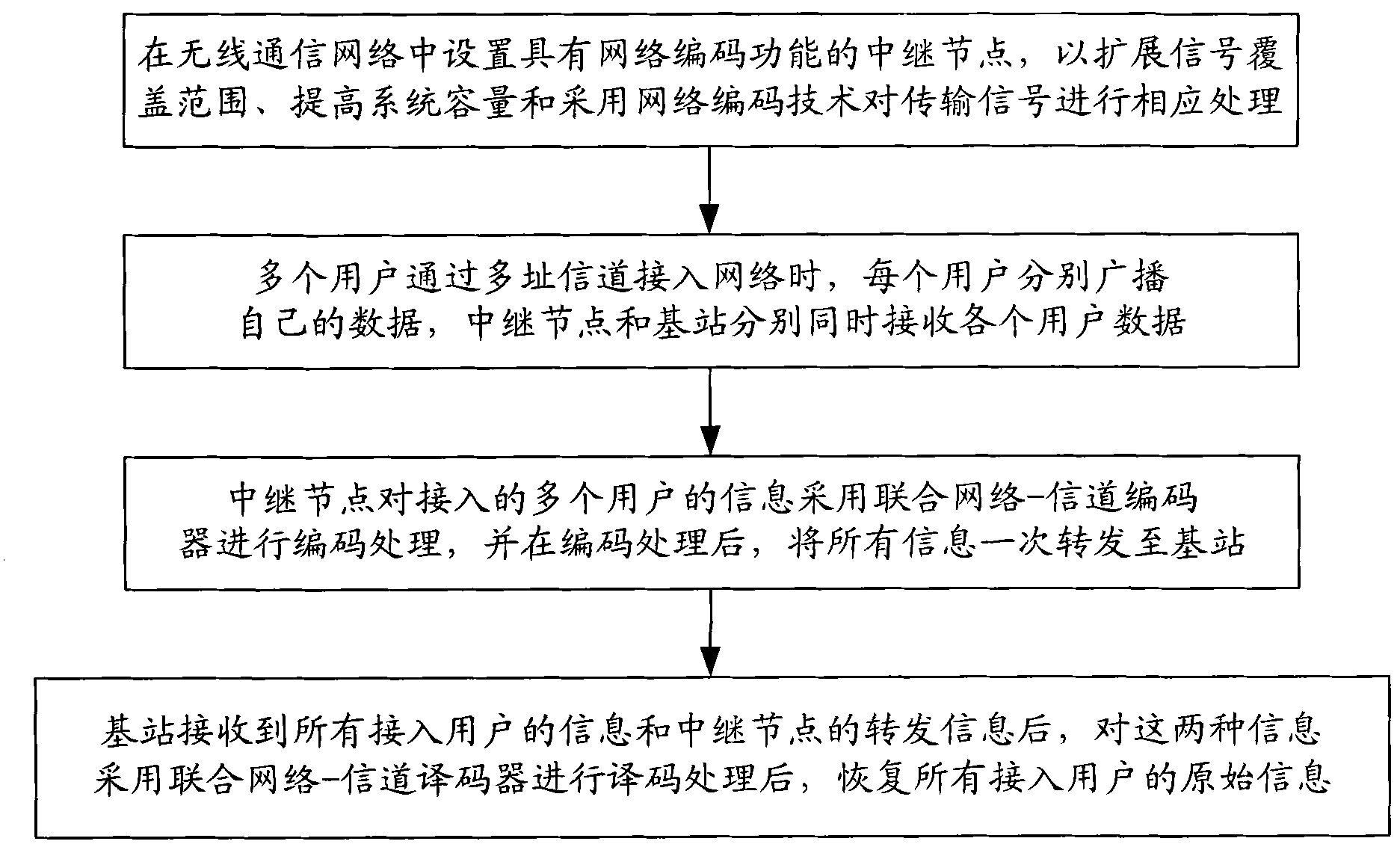
Multi-user network coding communication method with high-speed parallel encoding and decoding structure
InactiveCN101867451ASolve the problem of simultaneous network encodingGreat interleaving gainError preventionParallel encodingOriginal data
The invention discloses a multi-user network coding communication method with a high speed parallel encoding and decoding structure, which comprises the following steps: in a wireless relay network, multiple accessed user information is integrally interweaved by a relay node, serial / parallel conversion is carried out on the interweaved sequence, multiple groups of converted parallel data are input to a high speed parallel encoder to be encoded, and finally encoded data is broadcasted, thus realizing network encoding. A base station carries out teration decoding by means of a combined network-channel decoder according to original data broadcasted by users and data obtained by network encoding and channel encoding and forwarded by the relay node to obtain the original information of the users. The decoder of the base station comprises two parallel decoder groups, i.e. a user decoder group and a relay decoder group; iteration decoding is realized through transmitting soft information between two parallel decoder groups, thus not only recovering the original information of all accessed users but also improving decoding reliability and reducing decoding time delay. By adopting the method, the relay uplink transmission efficiency and the quality of transmission signal are improved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
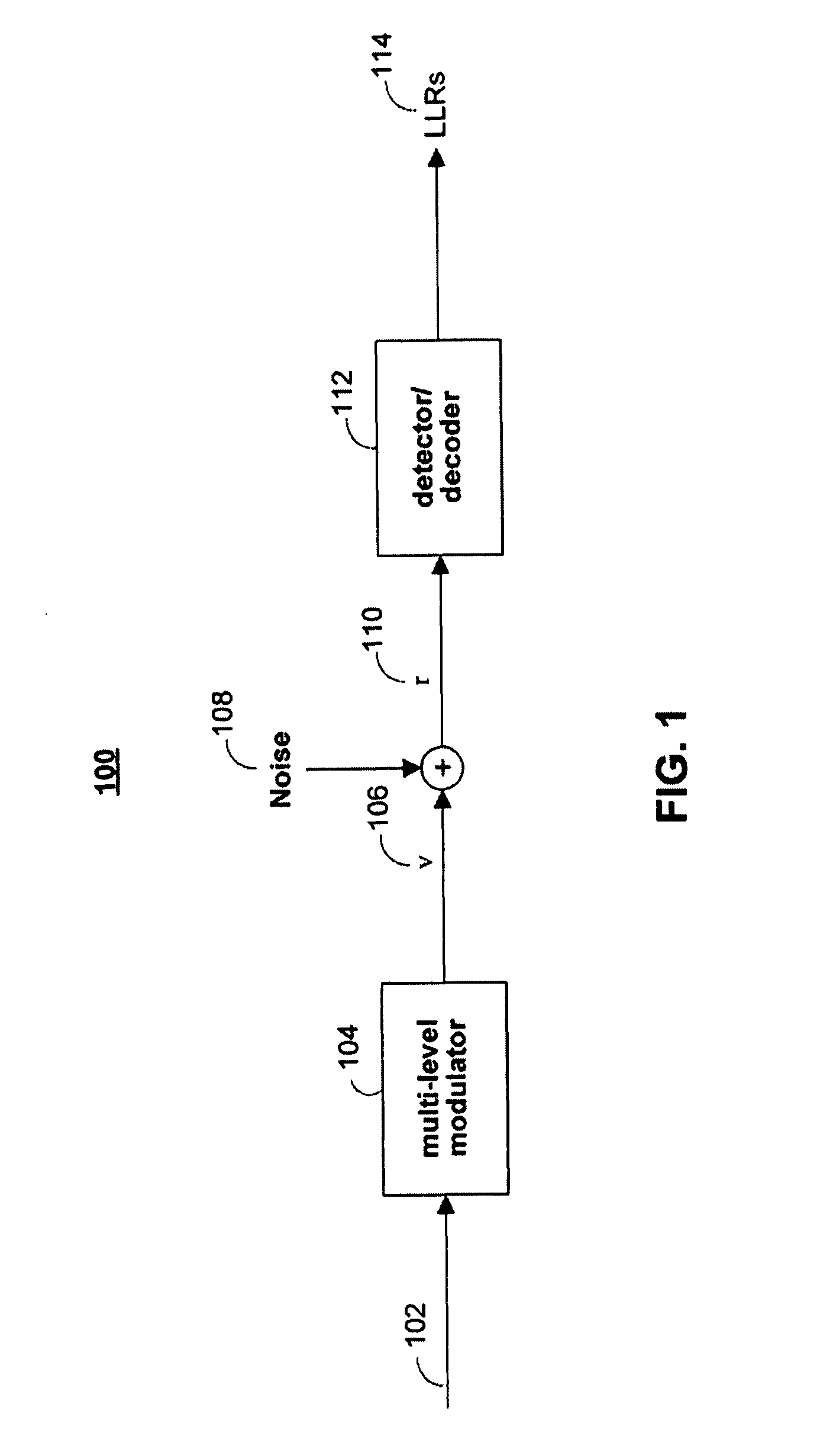
Method of hybrid soft/hard decision demodulation of signals with multilevel modulation
InactiveUS6977972B1Dc level restoring means or bias distort correctionAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsCommunications systemForward error correction
The performance of forward error correction decoders for digital communication systems can be improved if soft information relating the reliability of the value representing the demodulated signal is provided to the decoder with a value for the signal. On the other hand, soft information increases the quantity of information that must be processed, increasing the cost and complexity of the decoder.
Owner:SHARP LAB OF AMERICA INC
Variable rate soft information forwarding
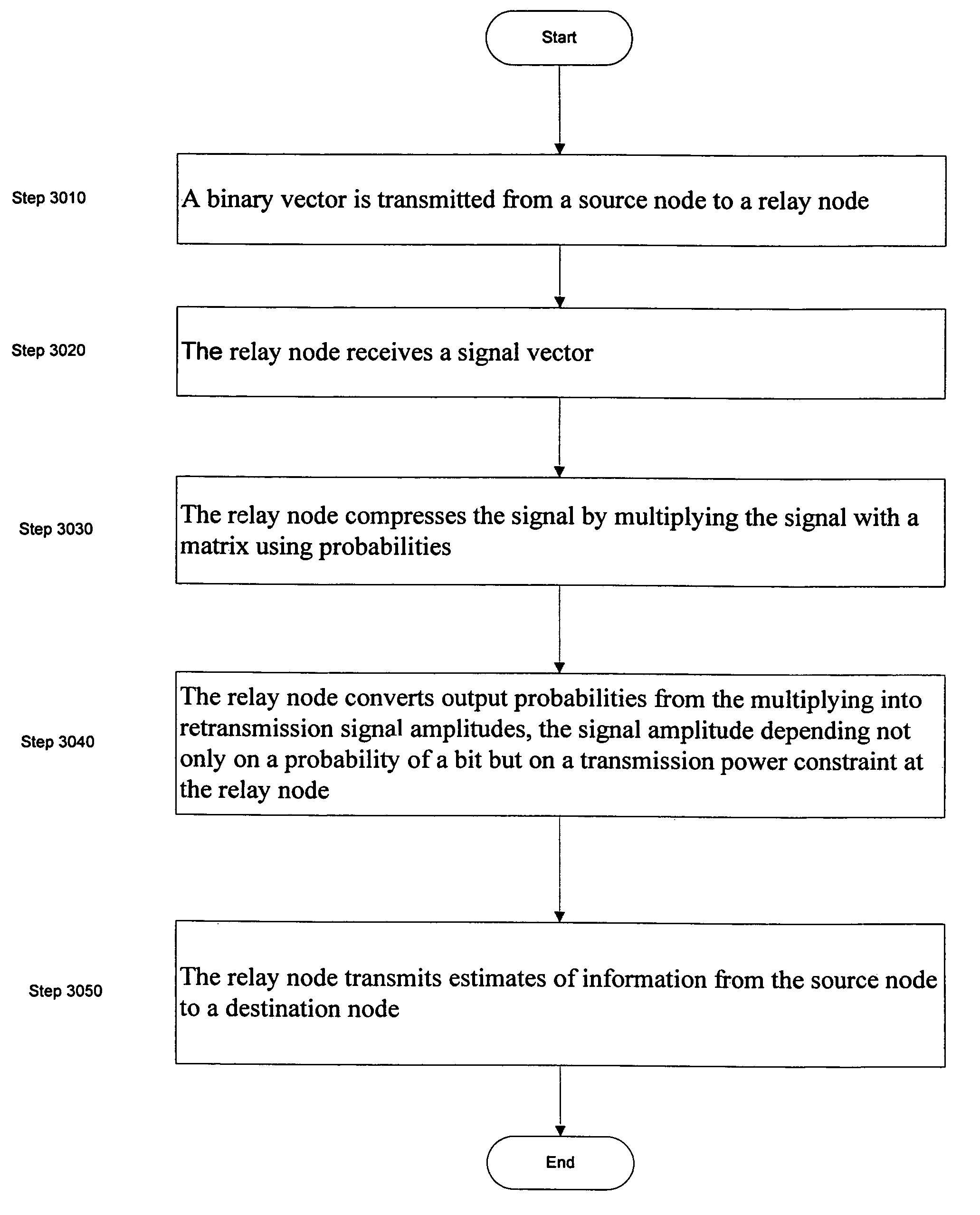
InactiveUS7821980B2Frequency-division multiplex detailsTransmission systemsComputer scienceSoft information
A method including transmitting a binary vector from a source node to a relay node and receiving a signal vector at the relay node. The method also includes compressing the signal at the relay node by multiplying the signal with a matrix using probabilities and converting output probabilities from the multiplying into retransmission signal amplitudes, the signal amplitude depending not only on a probability of a bit but on a transmission power constraint at the relay node. The method also includes transmitting, by the relay node, estimates of information from the source node to a destination node.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
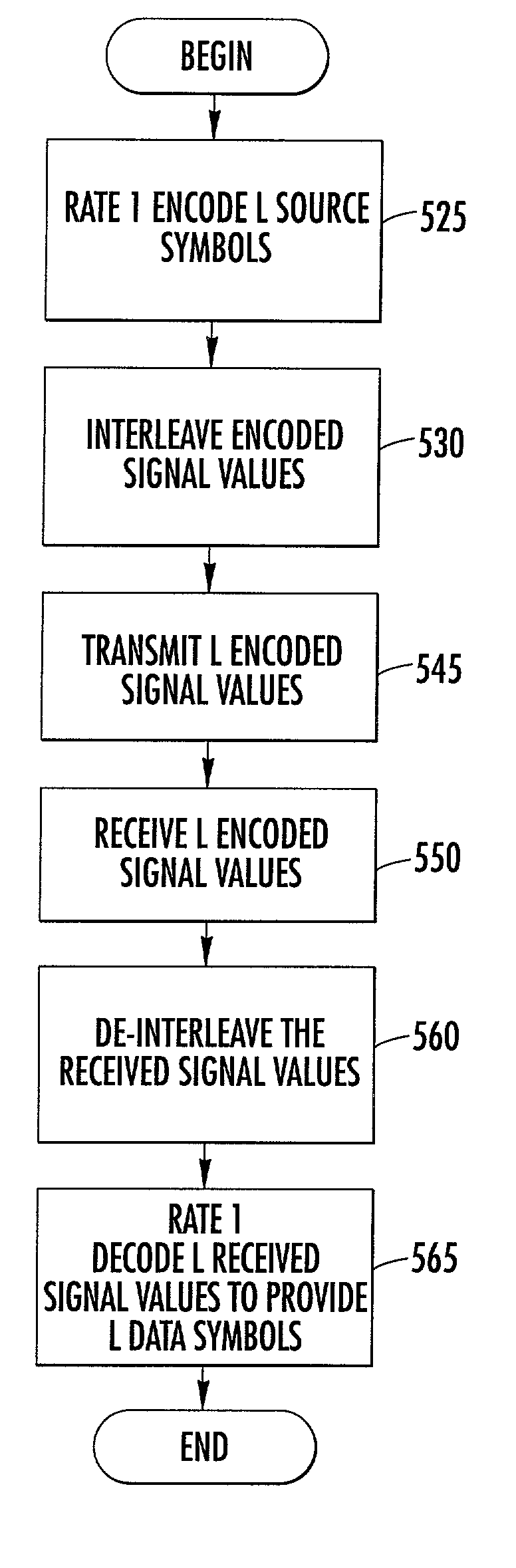
Rate one coding and decoding methods and systems
InactiveUS6944206B1Amplitude-modulated carrier systemsAmplitude demodulationFrequency spectrumSoft information
Methods and systems are provided for communicating encoded data. L received encoded signal values including soft information are received and transformed to L data symbols. In various embodiments, the L received encoded signal values are demodulated and the demodulated L received encoded signal values are convolutional decoded using a rate one convolutional decoder having only one output symbol per input symbol to provide the L data symbols, wherein the L received encoded signal values are convolutional encoded using a rate one convolutional encoder having only one output symbol per input symbol. In other embodiments of the present invention the L received encoded signal values are transformed using associated spectral energy at a plurality of frequency ranges within a bandwidth of a channel over which the L received encoded signal values are received for at least one of the L received encoded signal values.
Owner:UNWIRED PLANET
Symbol-level combining for MIMO systems with HARQ and/or repetition coding
ActiveUS20080025427A1Reduce decoding complexityWhitens noiseSpatial transmit diversityModulated-carrier systemsCritical path methodMimo systems
Systems and methods are provided for decoding signal vectors in multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) systems, where the receiver has received one or more signal vectors from the same transmitted vector. The symbols of the received signal vectors are combined, forming a combined received signal vector that may be treated as a single received signal vector. The combined signal vector is then decoded using a maximum-likelihood decoder. In some embodiments, the combined received signal vector may be processed prior to decoding. Systems and methods are also provided for computing soft information from a combined signal vector based on a decoding metric. Computationally intensive calculations can be extracted from the critical path and implemented in preprocessors and / or postprocessors.
Owner:NXP USA INC
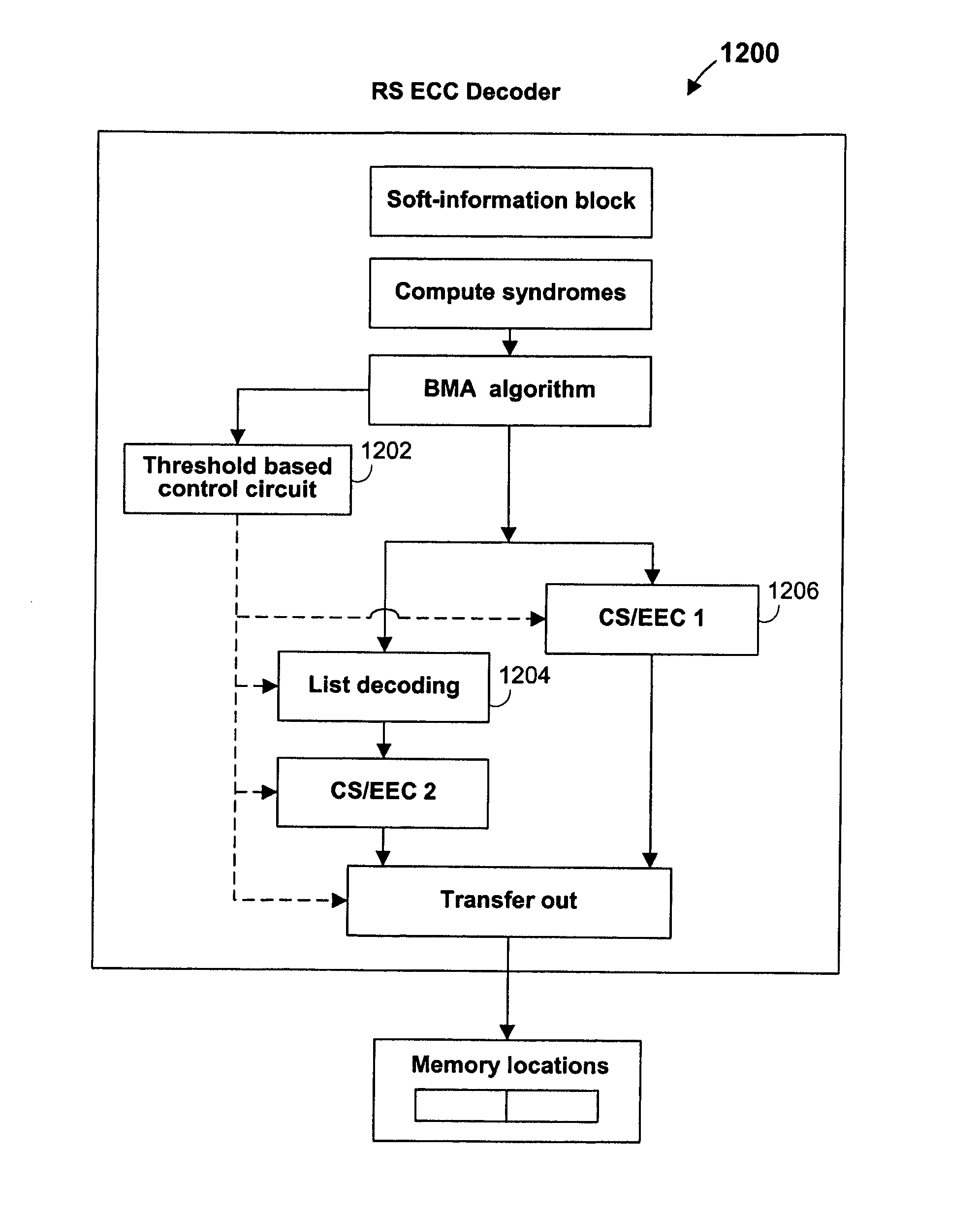
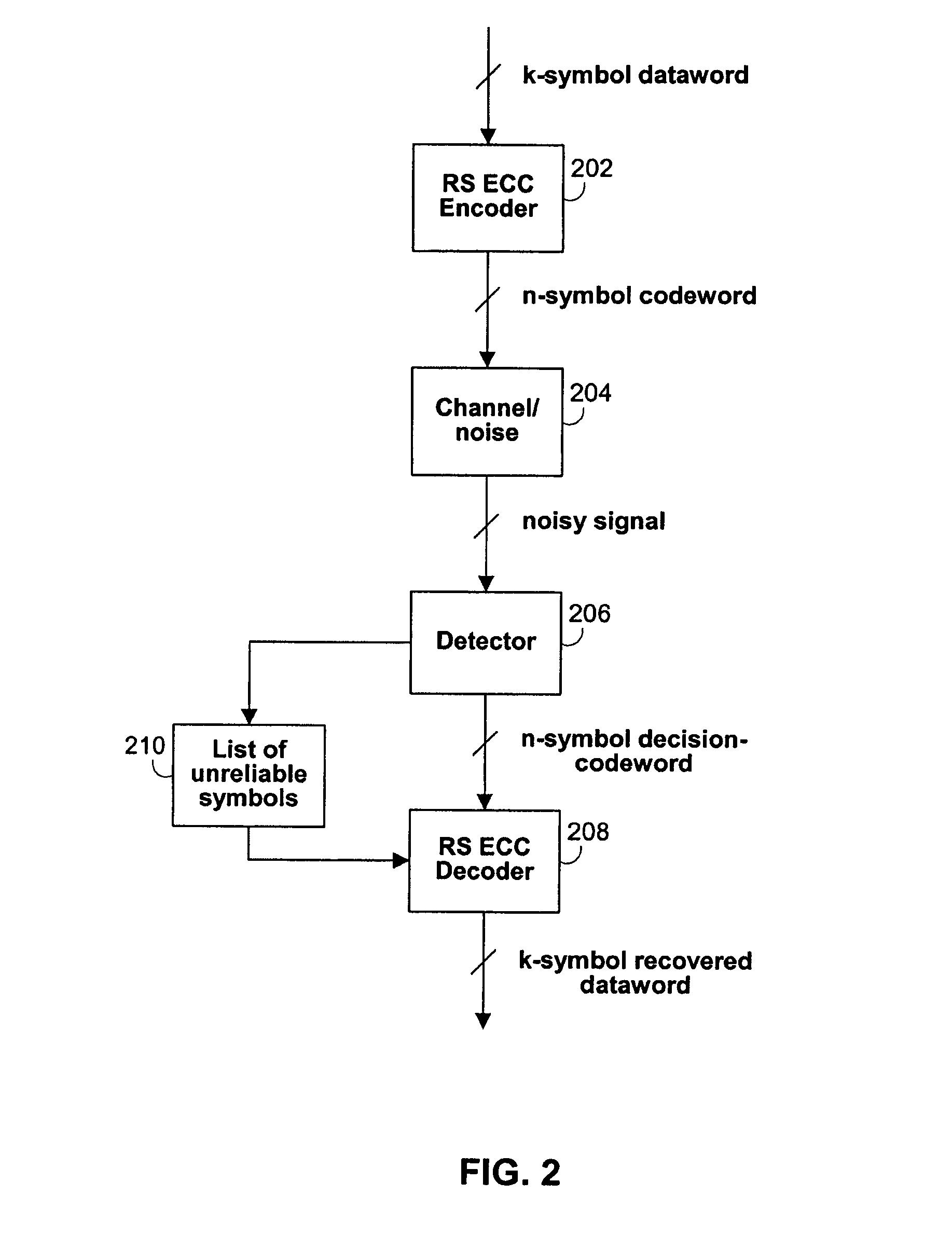
Architecture and control of reed-solomon error-correction decoding
ActiveUS7444582B1Joint error correctionOther decoding techniquesComputer architectureBerlekamp–Massey algorithm
Systems and methods are provided for implementing various aspects of a Reed-Solomon (RS) error-correction system. A detector can provide a decision-codeword from a channel and can also provide soft-information for the decision-codeword. If the decision-codeword corresponds to an inner code and an RS code is the outer code, a soft-information map can process the soft-information for the decision-codeword to produce soft-information for a RS decision-codeword. A RS decoder can employ the Berlekamp-Massey algorithm (BMA), list decoding, and a Chien search, and can include a pipelined architecture. A threshold-based control circuit can be used to predict whether list decoding will be needed and can suspend the list decoding operation if it predicts that list decoding is not needed.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
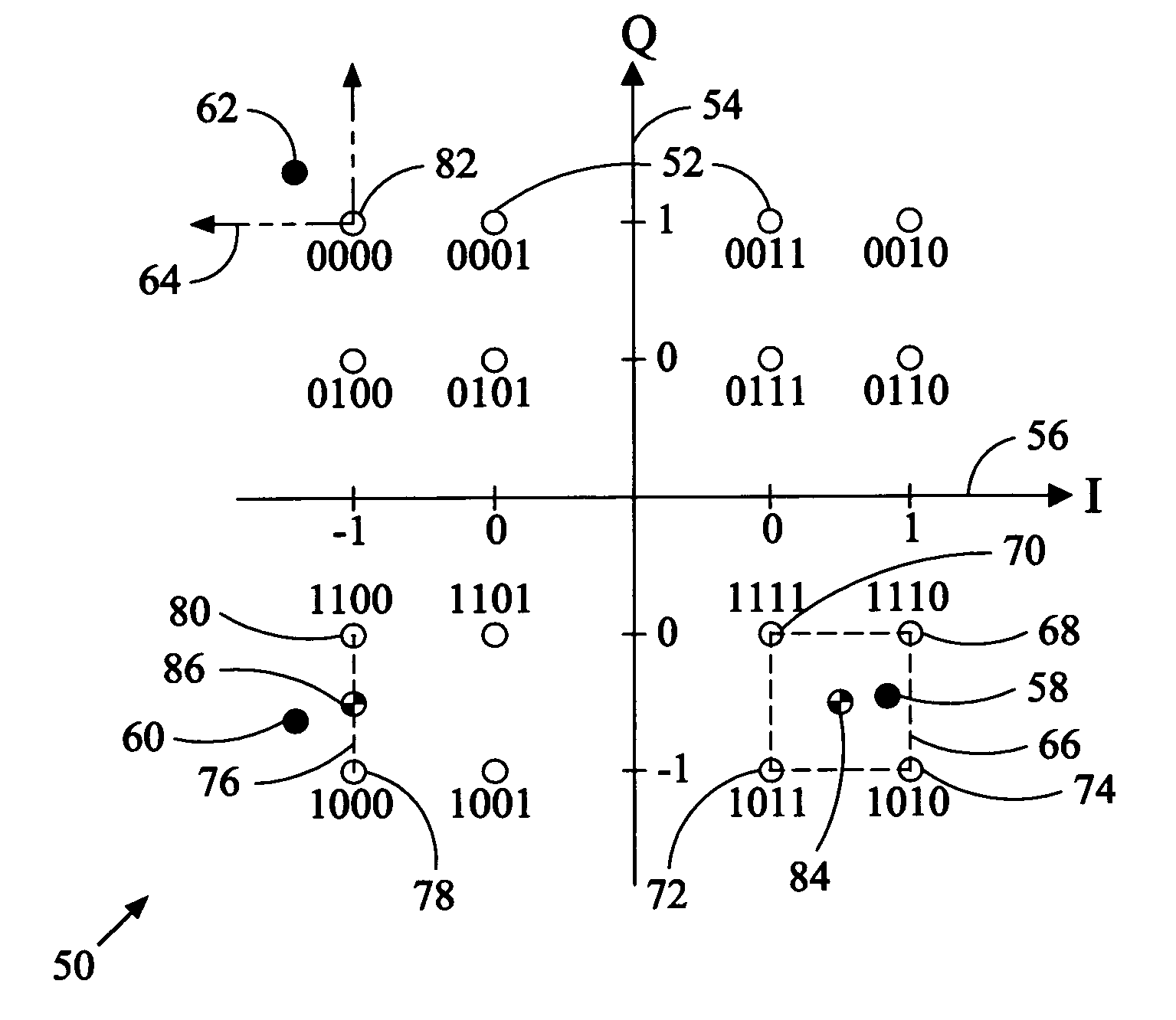
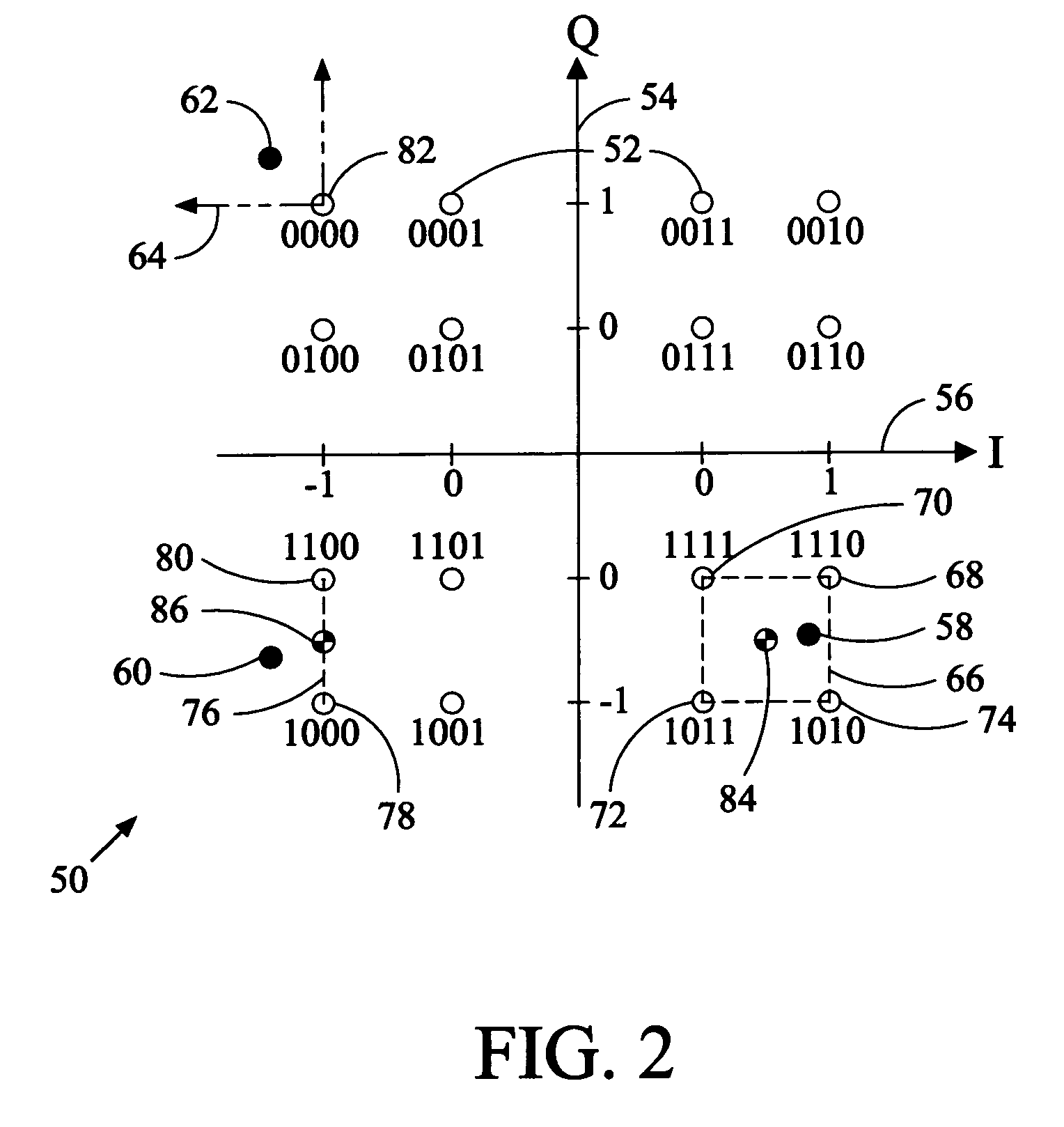
Calculating soft information from a multi-level modulation signal
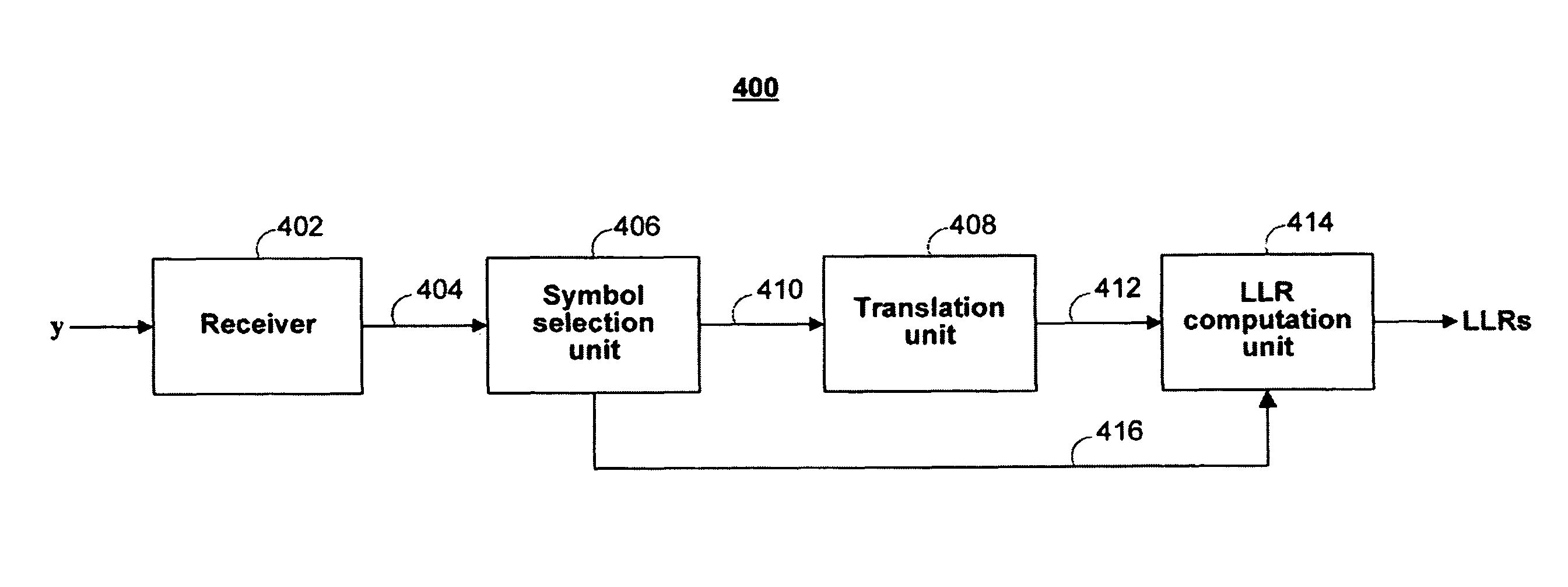
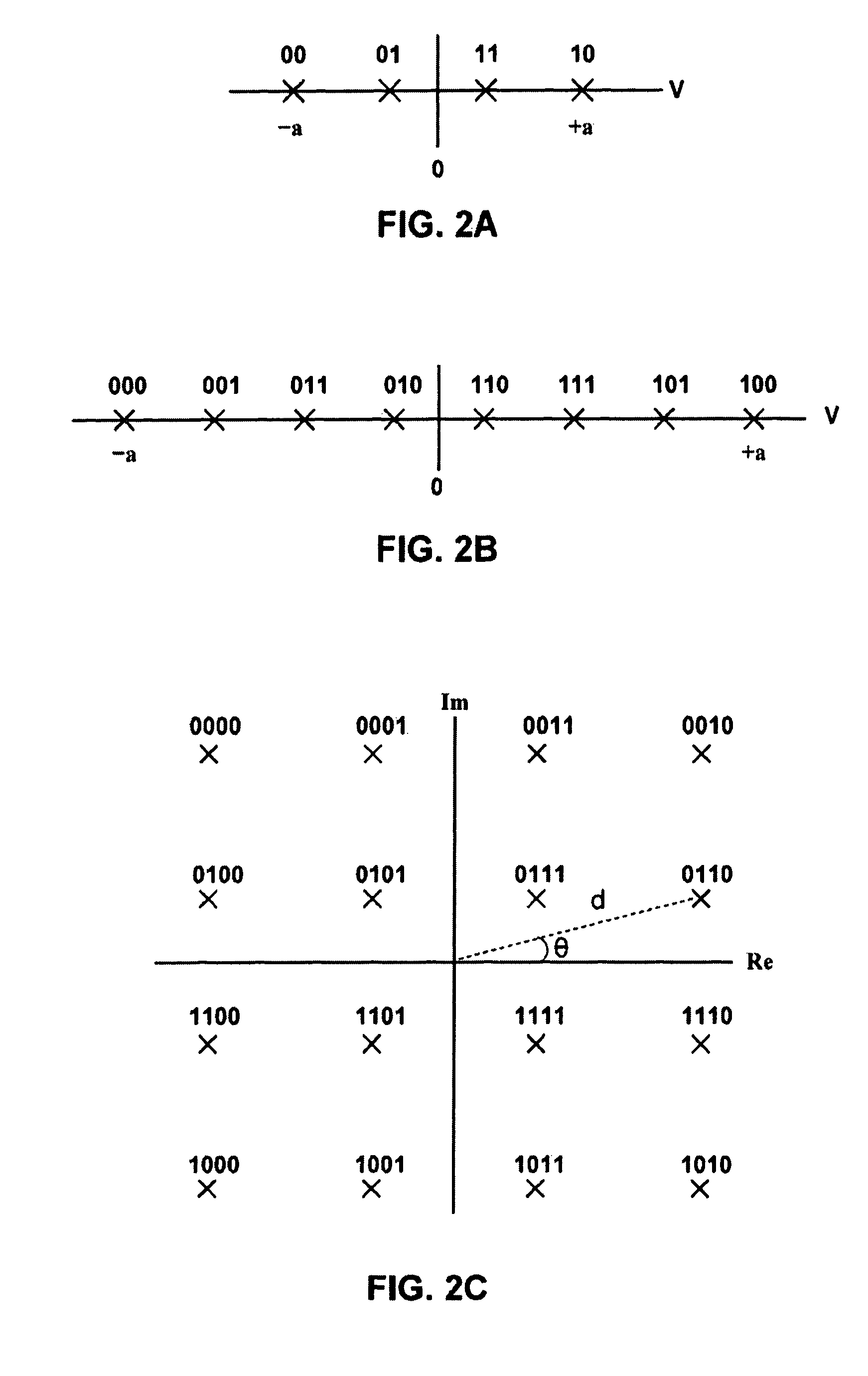
ActiveUS8166379B1Reduce complexityLess complexError correction/detection using convolutional codesError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsSymbol mappingNear neighbor
Apparatus and methods are provided for calculating soft information in a multi-level modulation scheme using one or more nearest neighbors. The nearest neighbors correspond to signal points in a signal constellation set nearest to the value of a received signal. The nearest neighbors of a received signal can be found by using a second symbol-to-signal point mapping for the signal constellation set that is different from the mapping actually used by the signal modulator. The second symbol mapping can be used to simplify the discover of nearest neighbors. Once the nearest neighbors are found in the second symbol mapping, the nearest symbols can be translated back into the actual symbol mapping using, for example, table lookup. The nearest neighbors in the actual symbol mapping can then be used to compute soft information in the form of, for example, log-likelihood ratios (LLRs).
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
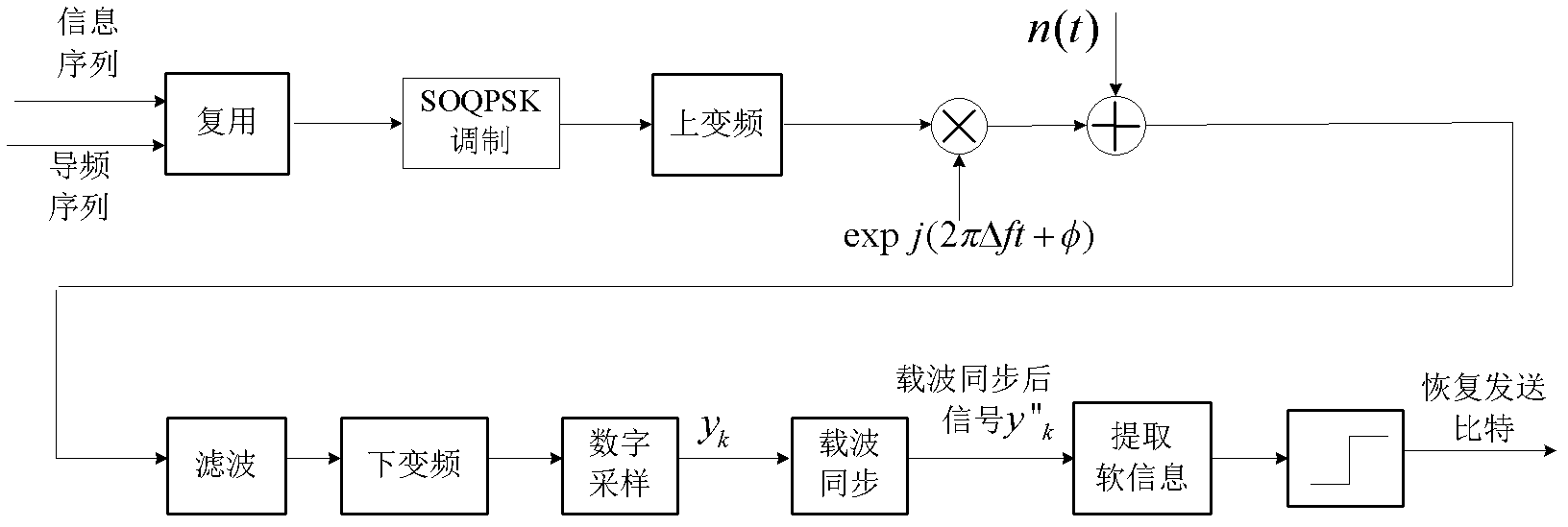
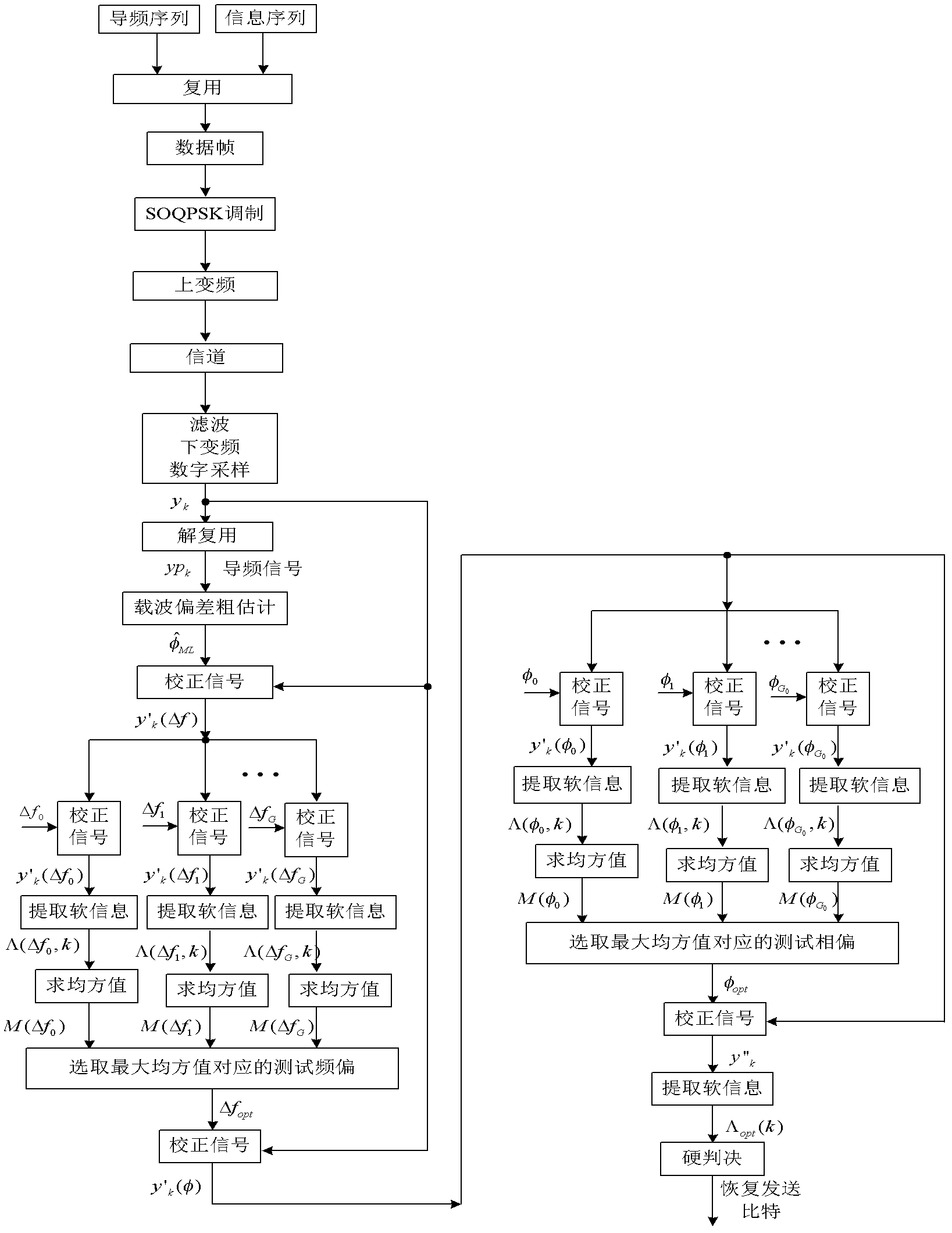
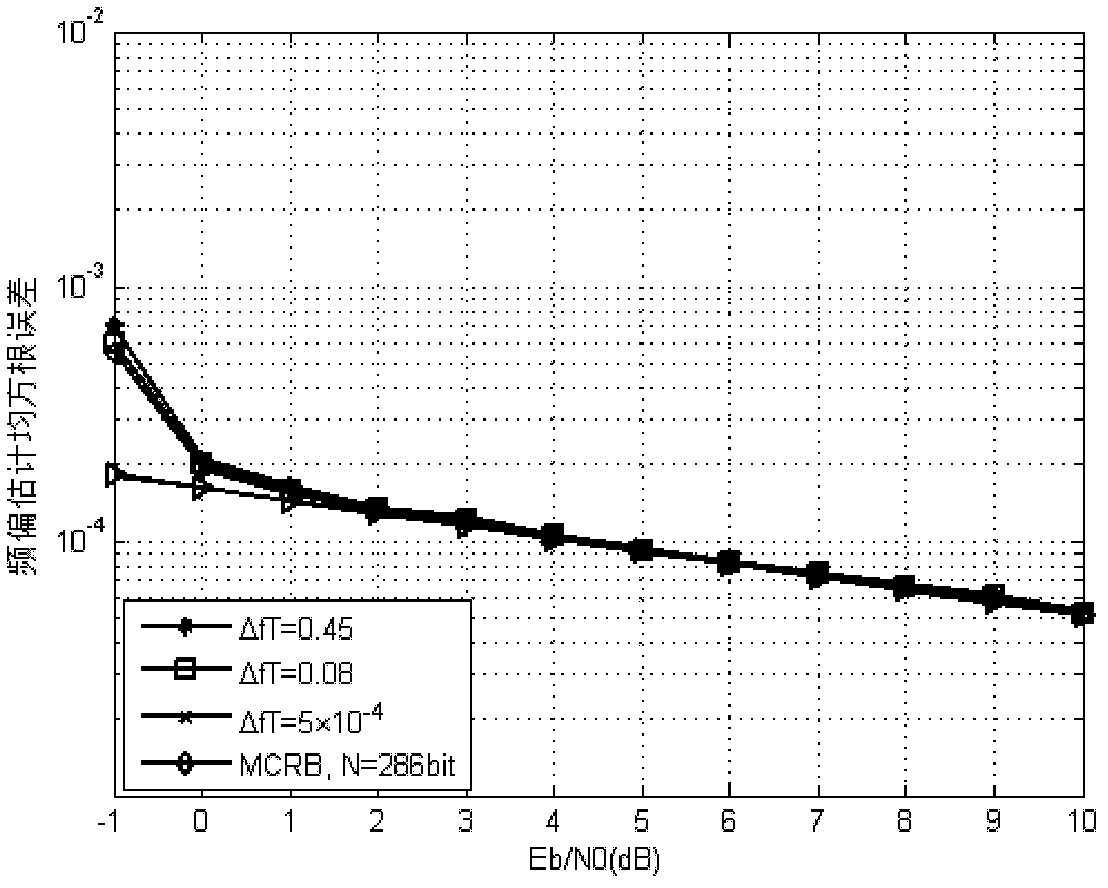
SOQPSK (shaping offset quadrature phase shift keying) carrier synchronization method based on pilot frequency and soft information combined assistance
InactiveCN102546500ASimplify operational complexityBaseband system detailsPhase-modulated carrier systemsCommunications systemMean square
The invention discloses an SOQPSK (shaping offset quadrature phase shift keying) carrier synchronization method based on pilot frequency and soft information combined assistance, mainly solves the problem in the existing short frame burst communication system carrier synchronization technique that the complexity is high and the carrier deviation estimation range is small. The implementation steps are as follows: firstly, according to pilot frequency assistant maximum likelihood carrier synchronization method, the rough estimation values of carrier frequency deviation and phase deviation are obtained, and the phase rough estimation value is used to revise the receiving signals; then, the frequency deviation one dimensional fine estimation interval, and phase deviation one dimensional fine estimation interval are respectively determined; and in the frequency deviation and phase deviation fine estimation intervals, according to the rule of maximizing the mean square value obtained during demodulation of soft information by SOQPSK, one dimensional search is performed to obtain the precise estimation value of carrier frequency deviation and phase deviation. A small amount of pilot frequency overhead is utilized, large carrier deviation with comparatively low operation complexity is revised, effective carrier synchronization is realized, nearly ideal bit-error performance of coherent demodulation is obtaind, and the method is suitable for the short frame burst communication system.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
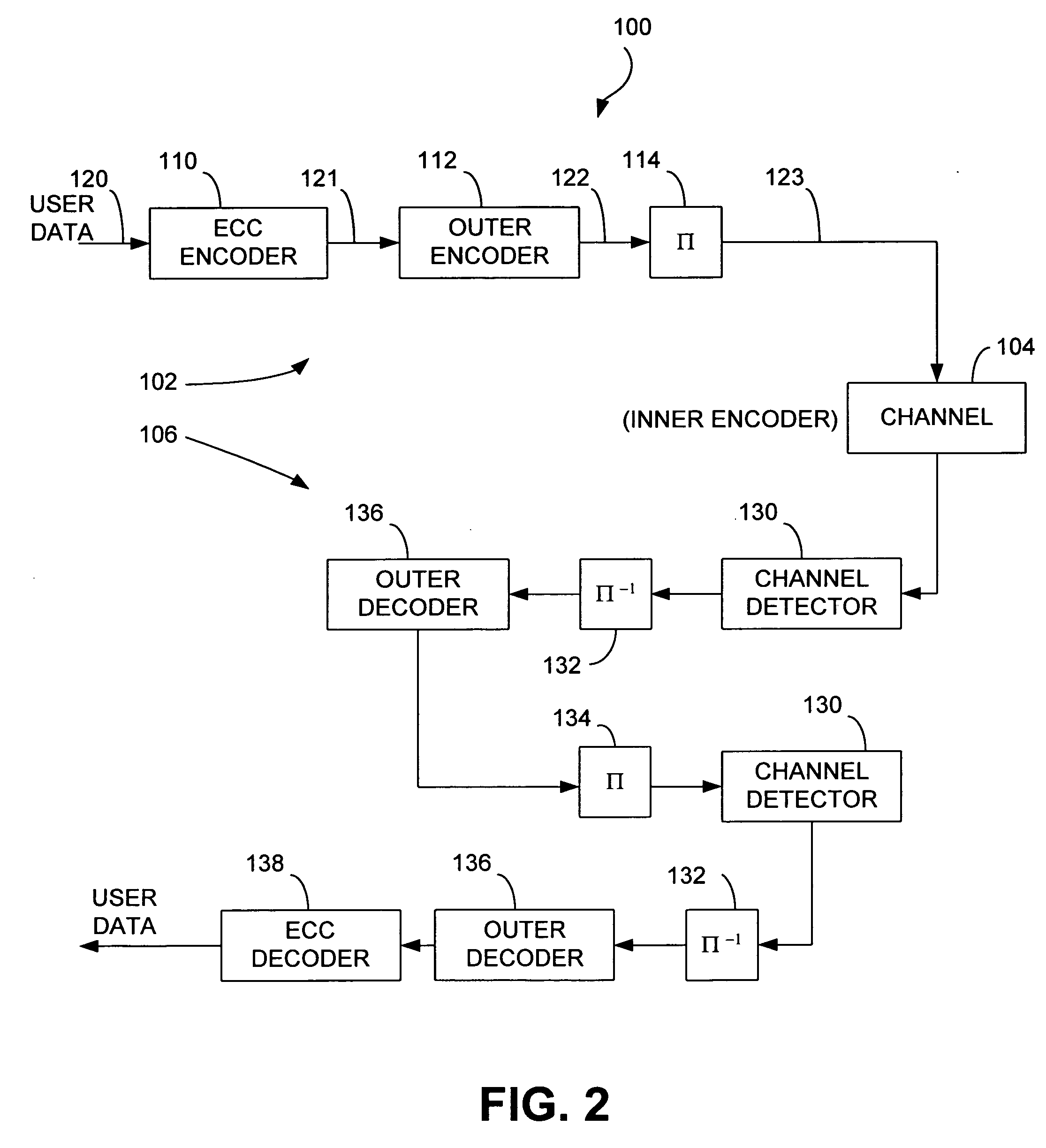
Iterative detector with ECC in channel domain
ActiveUS20060265634A1Data representation error detection/correctionCode conversionTelecommunicationsSoft information
A communications channel is provided, which includes a receive path having an iterative decoder and an ECC decoder. The iterative decoder has a soft channel detector with a soft output. The ECC decoder is coupled to decode bits produced from soft information received from the soft output and operates on the bits in a bit order that is the same as that on the soft output.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Obtaining soft information using a hard interface
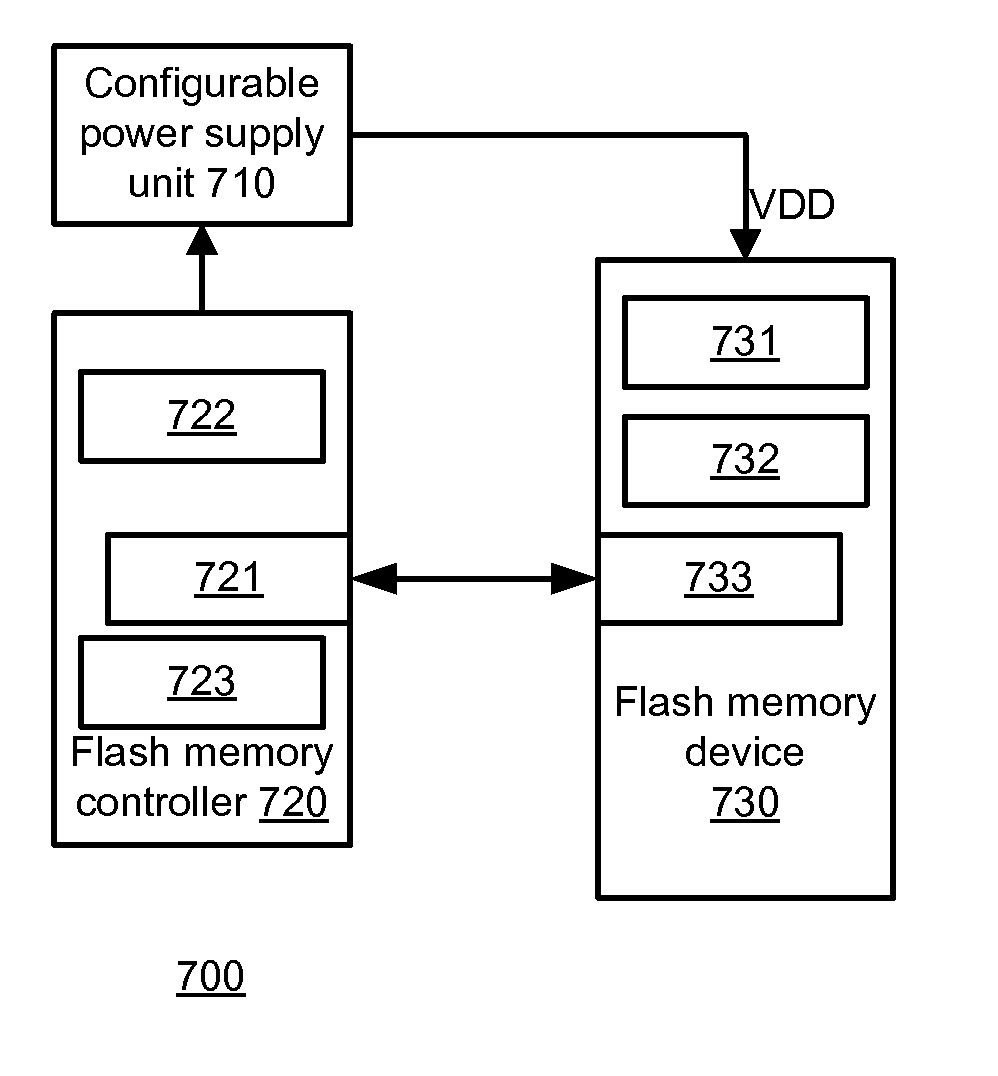
ActiveUS20120236638A1Prevent change of directionAvoid changeRead-only memoriesDigital storageVoltage referenceFlash memory controller
A flash memory controller, a computer readable medium and a method for generating reliability information using a hard information interface, the method may include performing multiple read attempts, while using the hard information interface, of a plurality of flash memory cells to provide multiple read results; wherein each flash memory cell is read by providing a reference voltage to the flash memory cell; wherein a same reference voltage is provided during the multiple read attempts; and generating, for each flash memory cell, reliability information based upon multiple read results of the flash memory cell.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Full CMOS min-sum analog iterative decoders
InactiveUS20050240647A1Reduce manufacturing costSimple designDigital data processing detailsError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsMOSFETCMOS
Analog iterative decoders are provided that are based on the so-called min-sum algorithm (also referred to as max-sum or max-product, Max-Log-MAP or BP-based decoding) and can be used to decode powerful coding schemes such as low-density parity-check (LDPC) codes and turbo codes. The circuits can be implemented by standard CMOS technology, which means lower fabrication cost and / or simpler design compared to previously reported analog iterative decoders that are based on BiCMOS or sub-threshold CMOS technology. Soft information is passed among variable nodes and parity-check nodes. A low-voltage high-swing Max WTA circuit is also provided. The circuit can be implemented by short channel MOSFET transistors and yet provide a reasonably high degree of accuracy. Applications include soft computing, and analog signal processing, in general. A Min WTA circuit can also be built based on this circuit by subtracting the input currents from a large reference current.
Owner:BANIHASHEMI AMIR +1
Self-adaptive mixture automatic request retransmission method
InactiveCN101183919AReduce the number of retransmissionsImprove performanceError prevention/detection by using return channelSpatial transmit diversityDiversity schemeData transmission
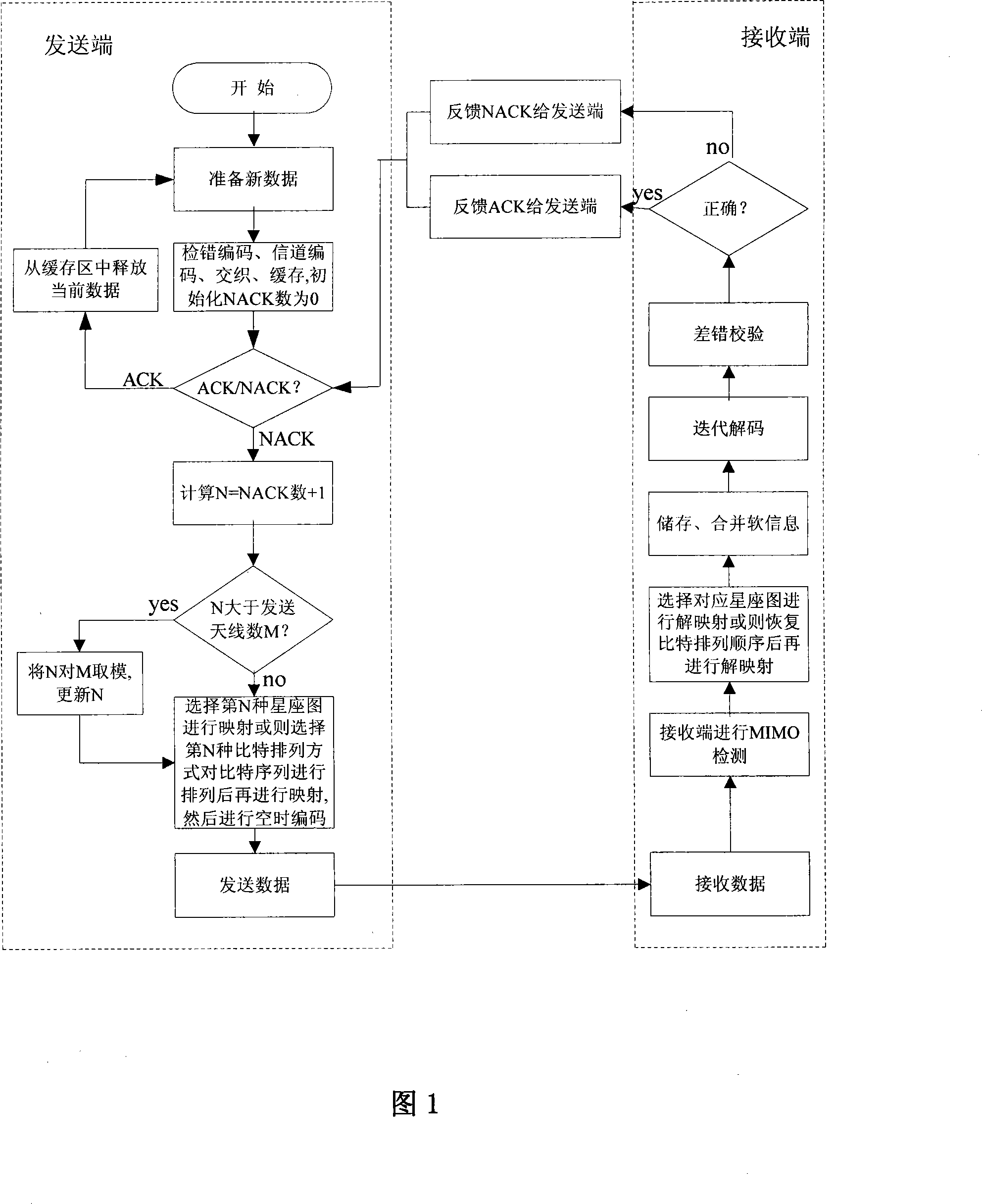
The invention discloses a combined hybrid automatic repeat request (HARQ) method, belonging to the field of wireless communication technology, aiming to effectively reduce the signal error rate, reduce retransmission number and increase throughout rate. The utility model is characterized that: a data transmission link is established between the sending end and the receiving end, the channel coding and the space-time coding structure are cascade connected; wherein, the number of the transmitting antenna at the sending end M is larger than one, M constellations or M kinds of bit sequence are stored at the sending end and the receiving end; one constellation is mapped or a bit sequence is rearranged and then mapped on a fixed constellation before each retransmission; then space-time coding is done according to a space-time coding structure; finally soft information combination and iterative decoding is done at the receiving end. The utility model has an advantage that the antenna diversity gain and the bit-symbol mapping diversity gain can effectively reduce the retransmission number and optimize system performance.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
System and method for realizing iterative timing synchronization of continuous phase modulation signal
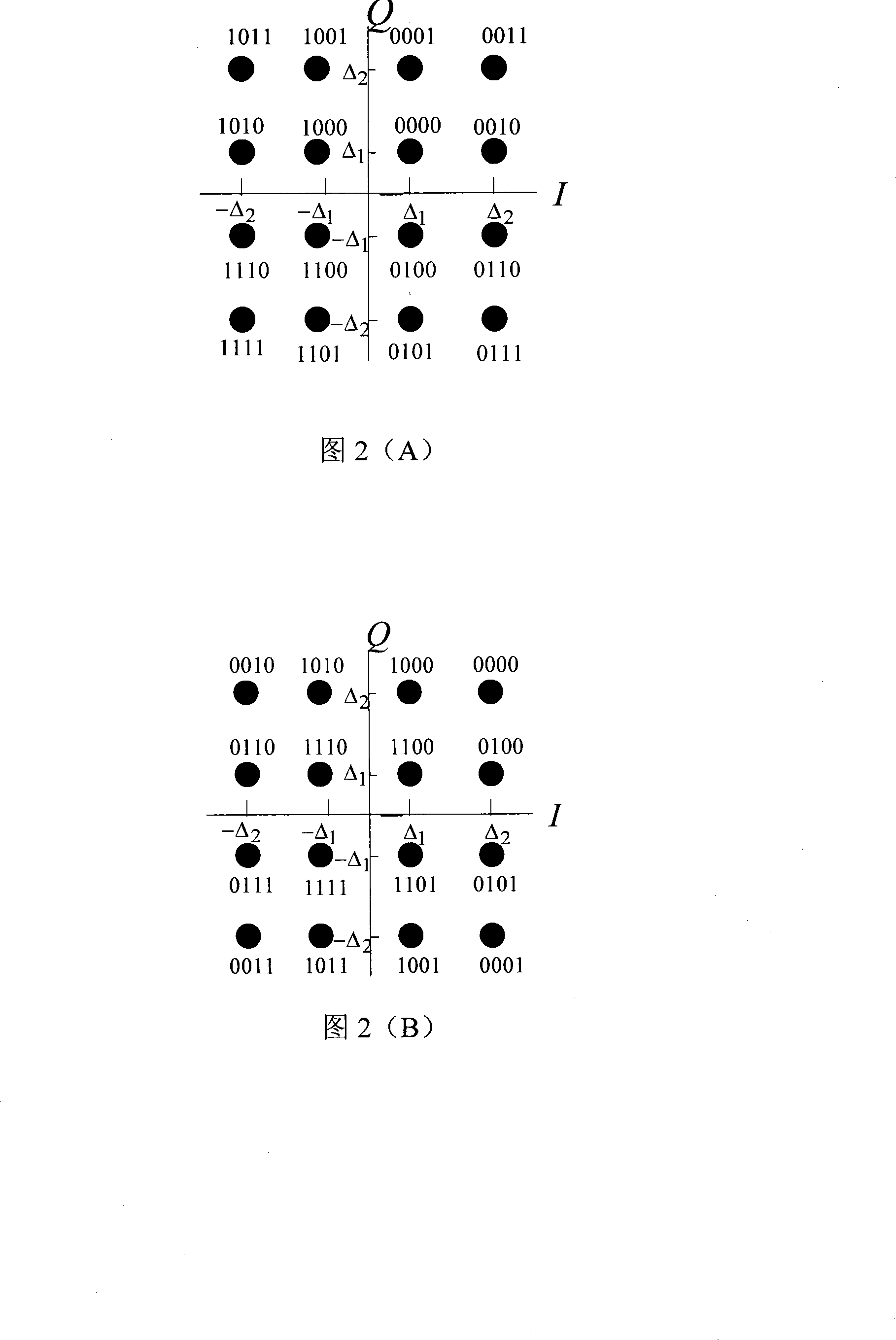
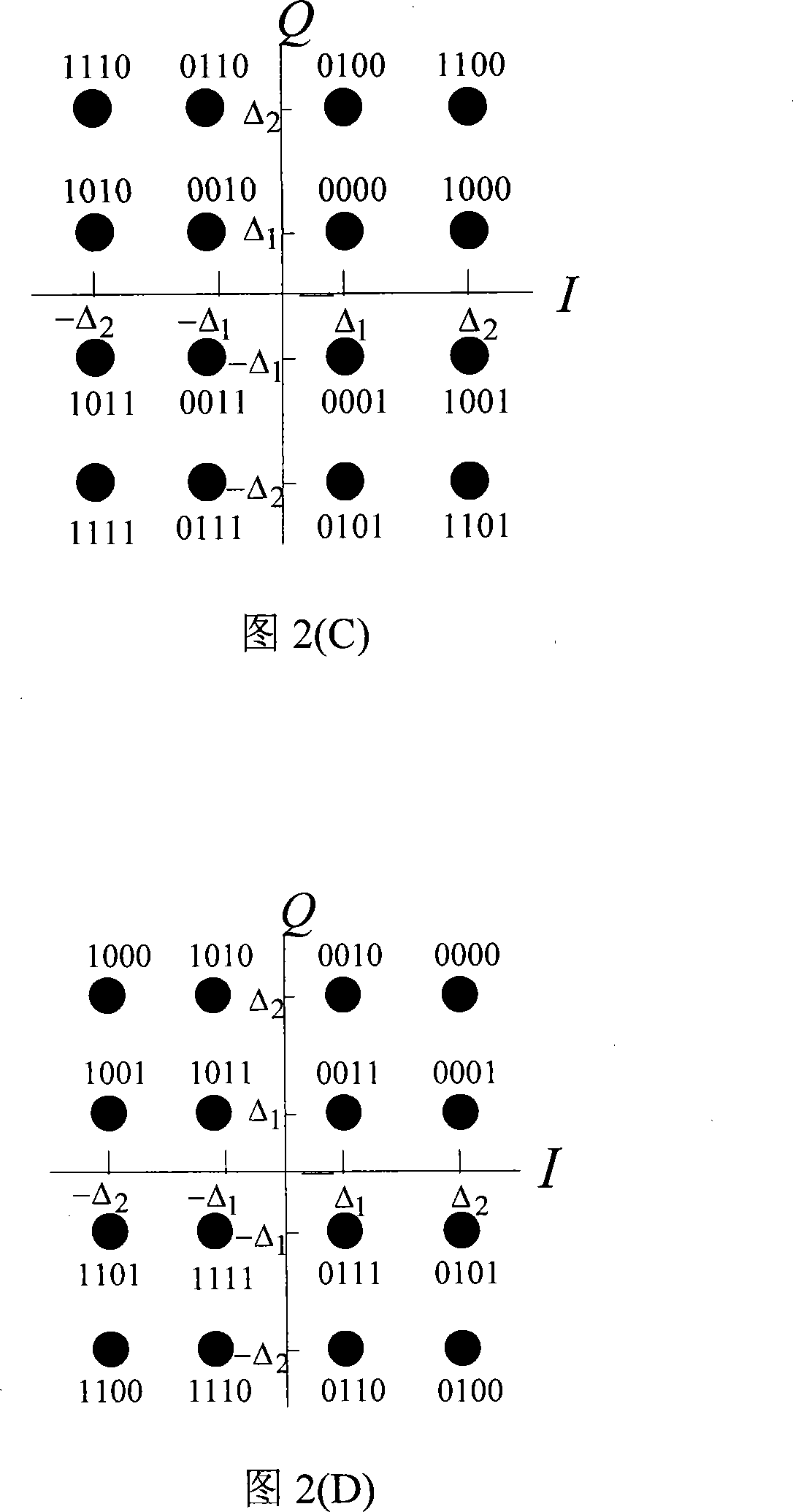
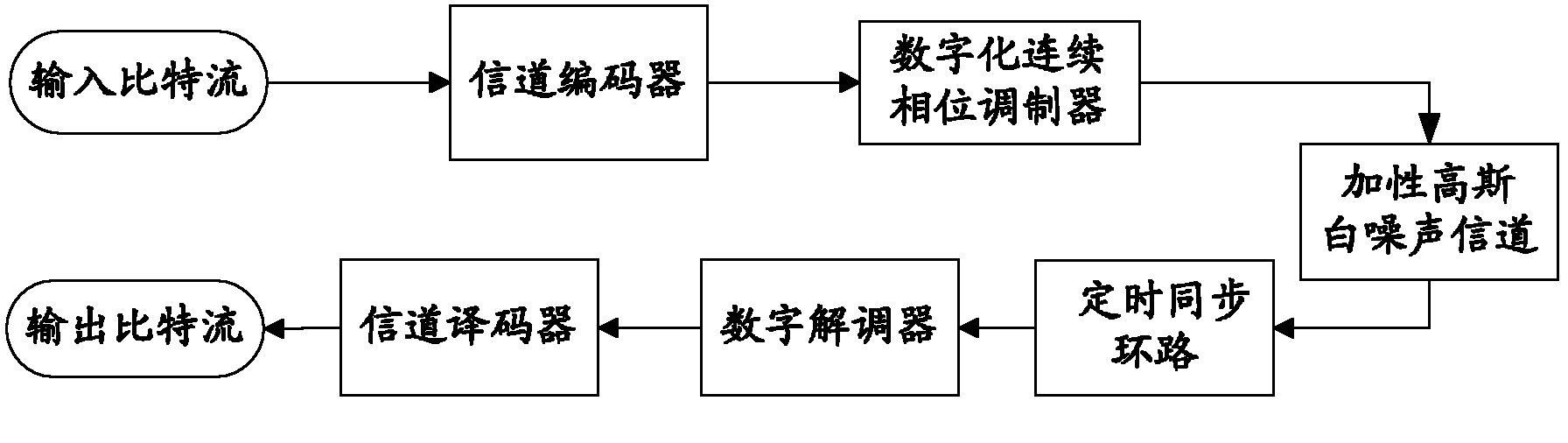
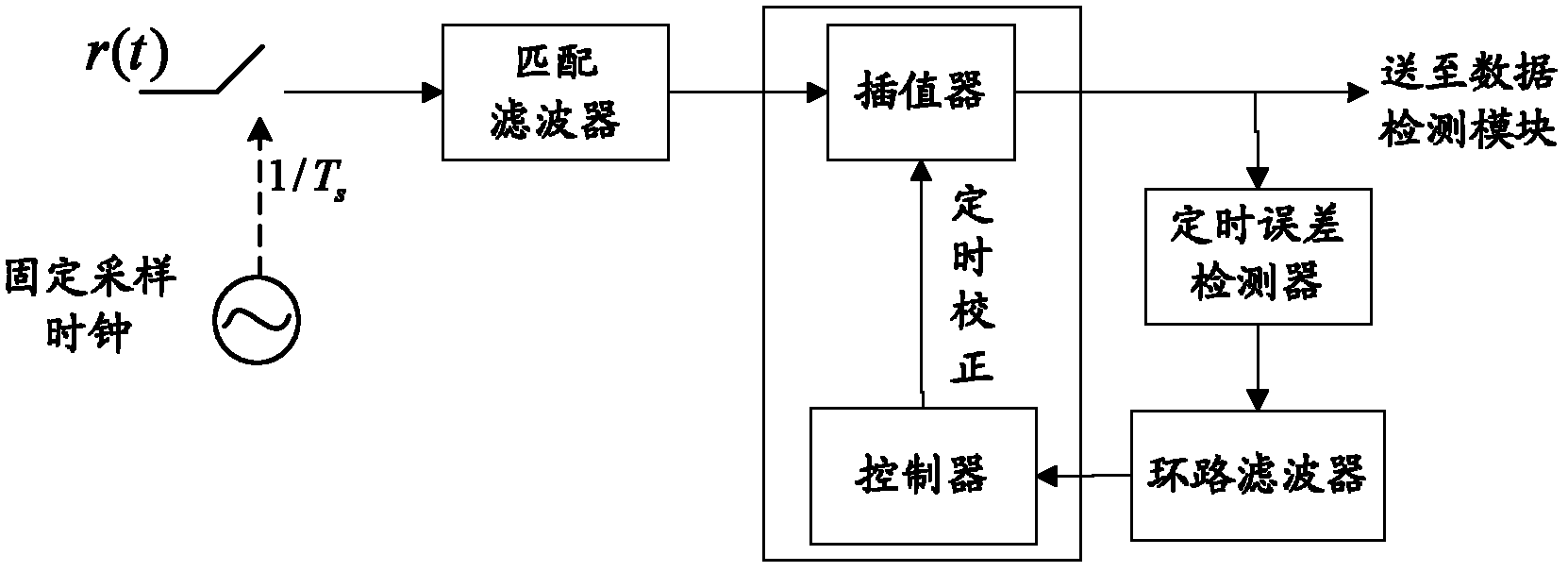
InactiveCN102148681AReduce complexityReliable Timing RecoveryError preventionTransmitter/receiver shaping networksTime delaysChannel decoder
The invention discloses a system and a method for realizing iterative timing synchronization of a continuous phase modulation (CMP) signal; the system is provided with a sender, and is composed of a maximum likelihood detector, a de-interleaver, a channel decoder and an information destination which are connected in order, and an interleaver which is used for interleaving an output signal of the channel decoder and feeding back the interleaved output signal to the maximum likelihood detector; a built-up circuit of the maximum likelihood detector comprises a match filter set, a demodulator, and a timing synchronization loop circuit arranged between the match filter set and the demodulator; a detecting method based on a maximum likelihood criterion is used for demodulating the received CPM signal, detecting and computing a timing error value and adjusting the time delay, and outputting a bit likelihood ratio of each symbol. Based on a timing error detecting method of the maximum likelihood criterion, a soft information assistance fed back by the channel decoder is used for realizing the timing synchronization to obtain an accurate timing deviation estimation; meanwhile, an iterativeprocess is used between the demodulation and the decoding to maximally improve an error bit ratio of the system; and the system and method for realizing iterative timing synchronization of the CMP signal can be applied in long-distance communication with the requirement of high performance.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Soft information scaling for iterative decoding
ActiveUS7231577B2Improve performancePerformance can be improved and optimizedError prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission systemsComputer scienceSoft information
Methods and apparatus for scaling soft values as part of an error correction decoding process are described. Accurate decoding depends on use of the appropriate scale factor. Selection and use of the scale factor to scale soft values is designed to improve and / or optimize decoder performance without the need for prior knowledge of the correct scale factor or the actual channel conditions at the time the signal from which the soft values were obtained was transmitted through a communications channel. The techniques of the present invention assume that the soft values to be processed were transmitted through a communications channel having a quality that can be accurately described by a channel quality value. A scale factor is determined from the distribution of soft values to be scaled and an assumption that the channel through which they were transmitted was of the quality corresponding to a preselected channel quality value.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
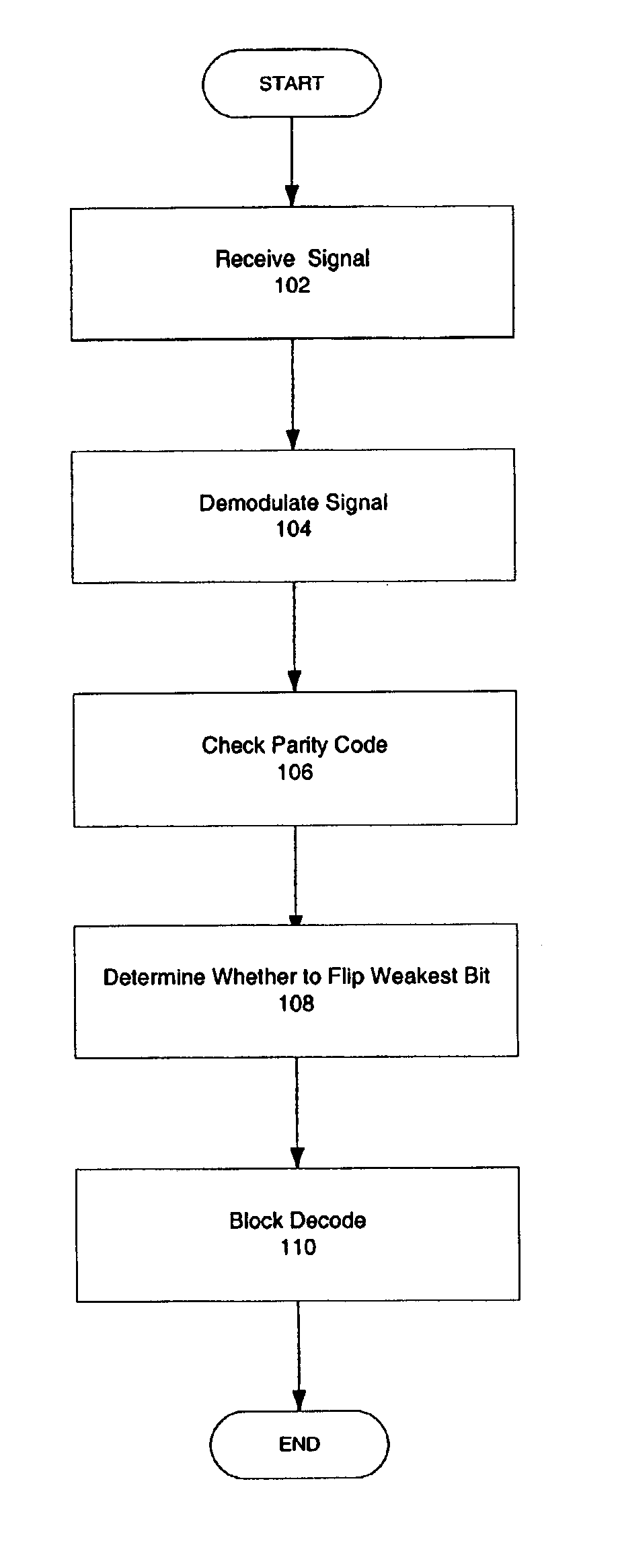
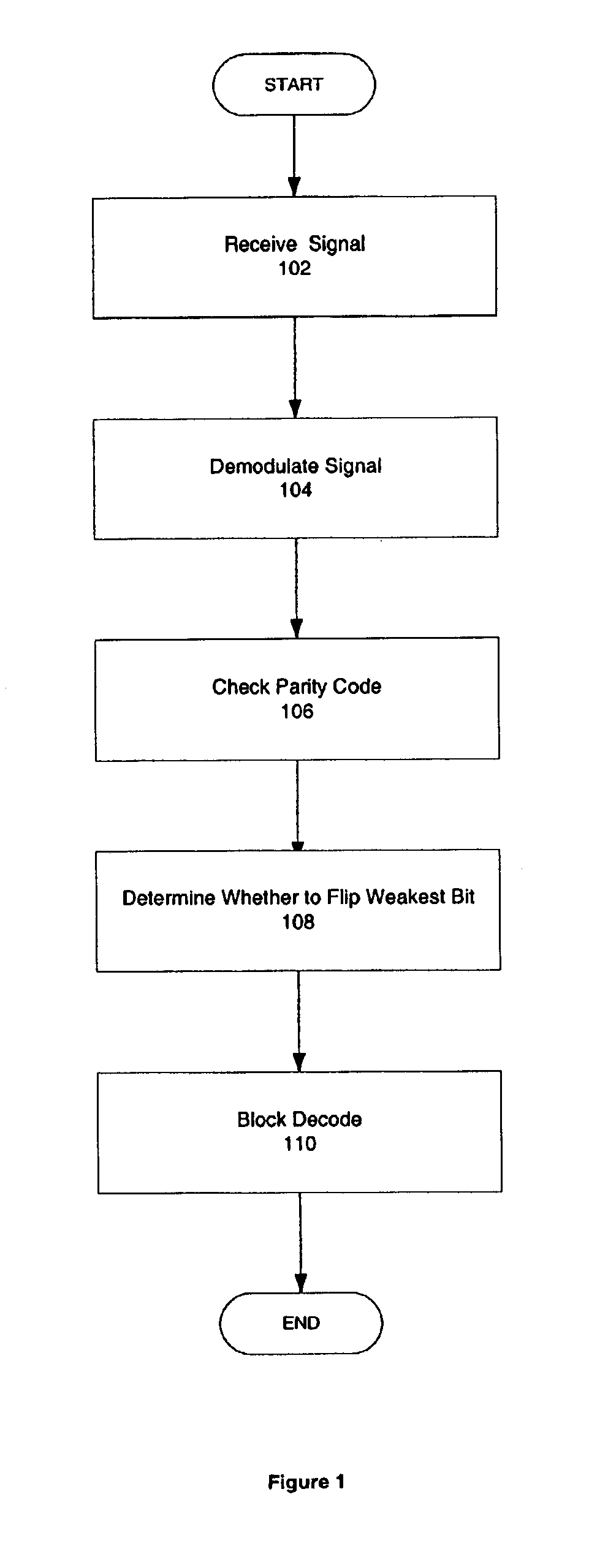
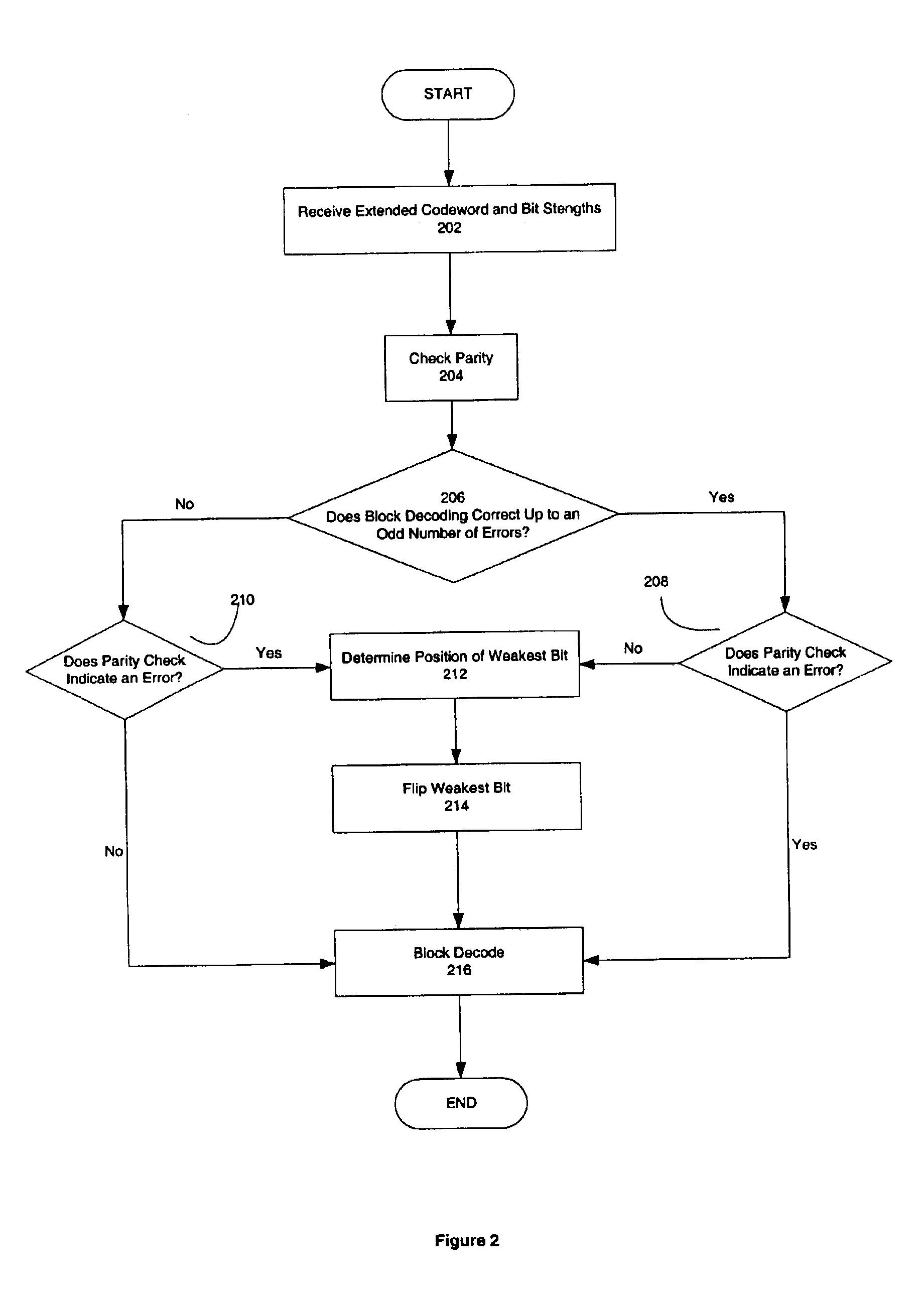
Decoding extended error correcting codes using soft information
InactiveUS6931583B2Correction errorOther decoding techniquesError detection/correctionSingle parity checkComputer hardware
In one embodiment, the present invention can be used to correct one more error in an extended codeword encoded with a block code and a single parity check code than the block code is able to correct. In one embodiment, a communications device includes a decoder that has a soft decoder to receive an extended codeword and a strength of each bit of the extended codeword, and to produce a codeword by soft decoding the extended codeword using the received strengths, and a block decoder coupled to the soft decoder to produce a corrected codeword by block decoding the codeword using an error correcting block code.
Owner:INTEL CORP
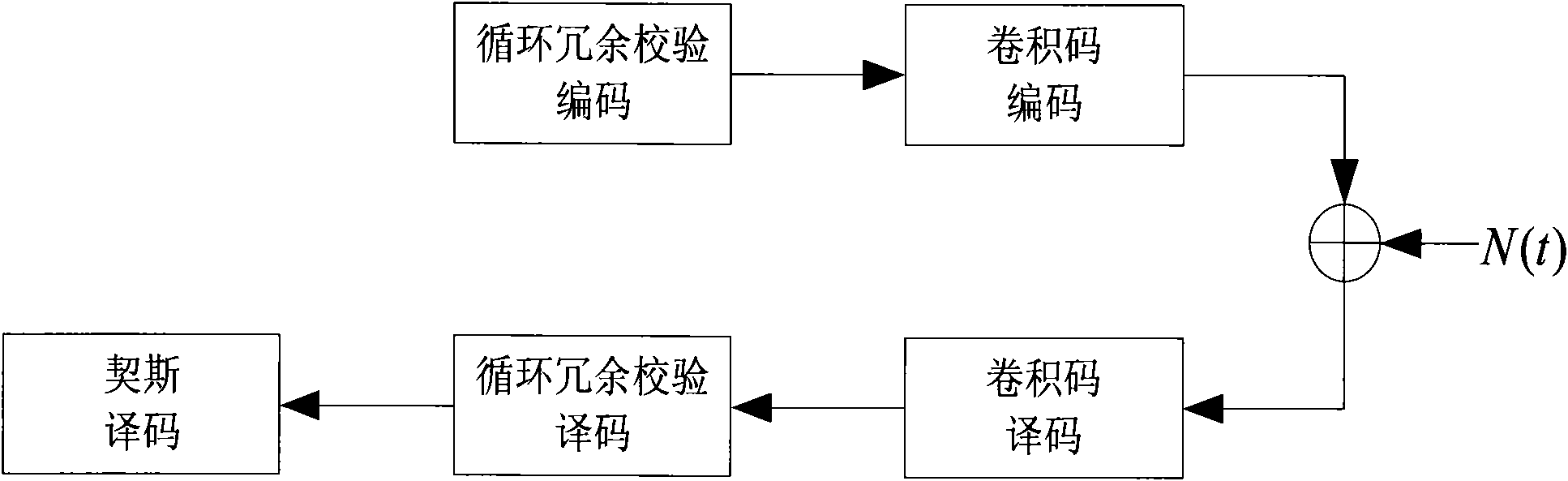
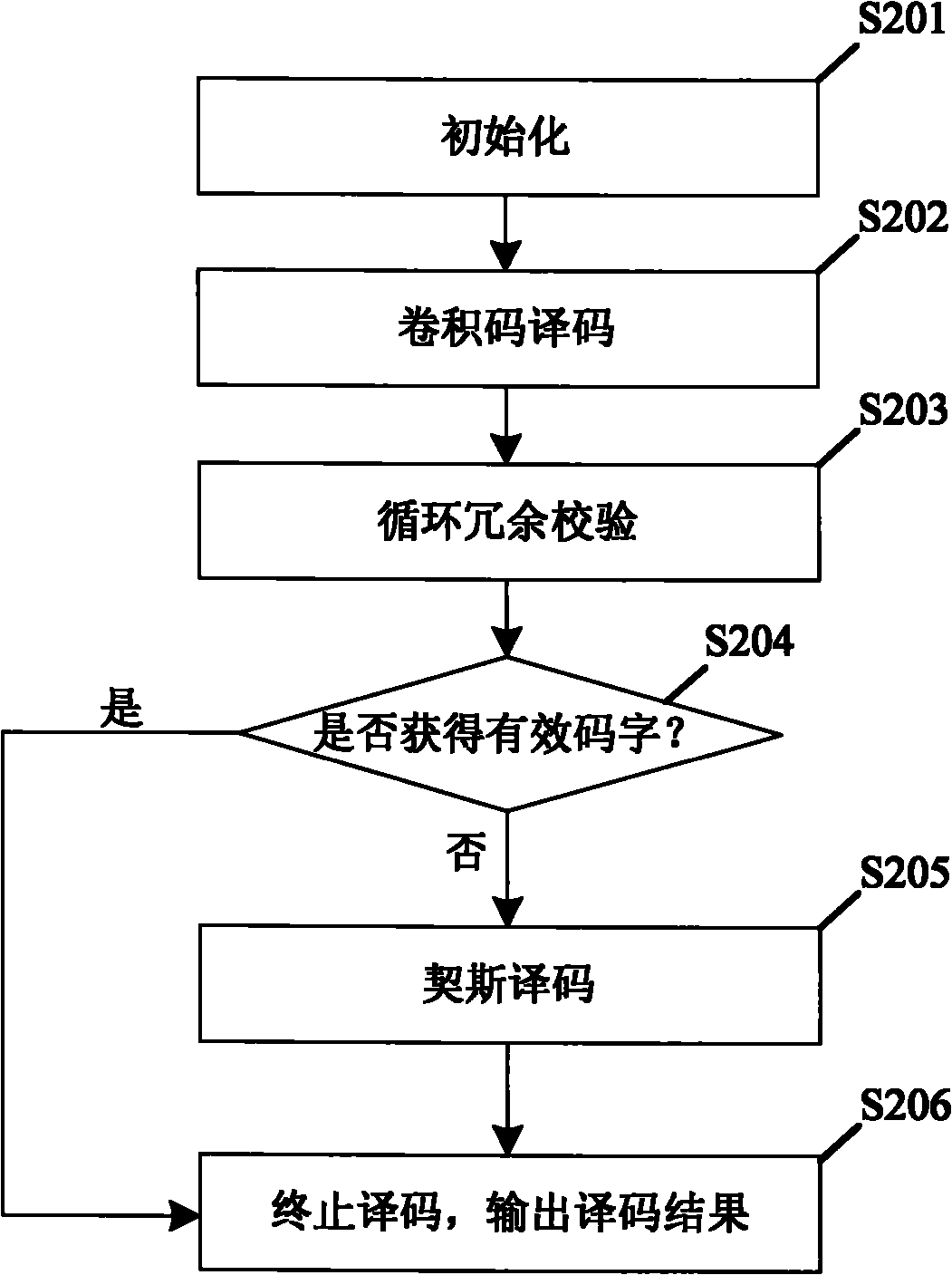
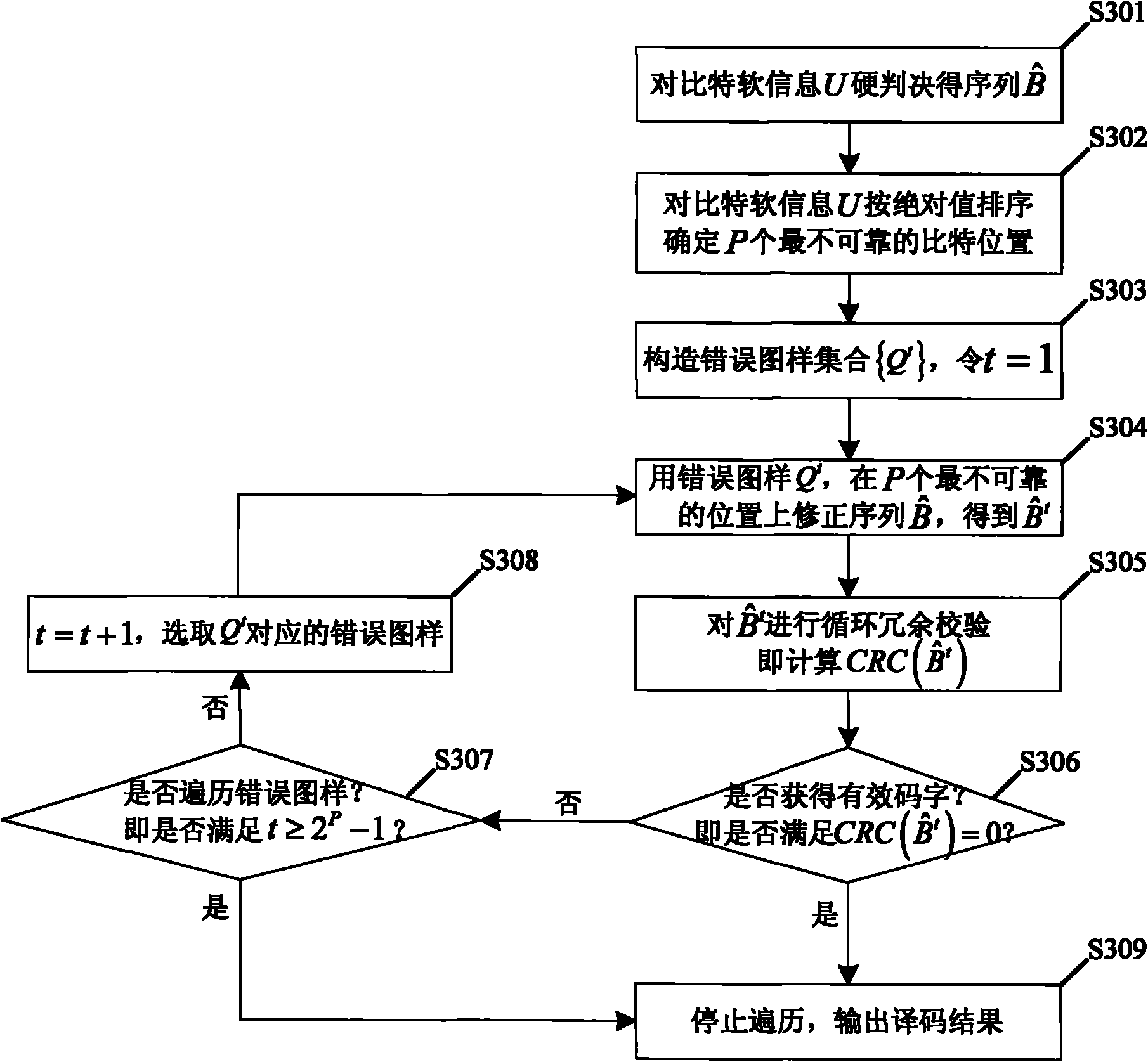
Cyclic redundancy check-assisted convolutional code decoding method
InactiveCN101867379ATake advantage ofImprove decoding performanceError correction/detection using convolutional codesError detection onlyConvolutional codeSoft information
The invention discloses a cyclic redundancy check-assisted convolutional code decoding method. Improved Chase decoding is applied to a cyclic redundancy check and convolutional code-cascaded coding / decoding scheme. The decoding method mainly comprises the following steps of: first performing corresponding convolutional code decoding on a received sequence according to an ending way of convolutional code coding, and performing primary cyclic redundancy check to judge whether a code word output by the convolutional code decoding is valid or not by utilizing cyclic redundancy check data in coding information bits; if the cyclic redundancy check determines the code word is valid, stopping the decoding and taking the code word as decoding output; if the cyclic redundancy check determines the code word is invalid, decoding bit soft information output by the convolutional code decoding by using the improved Chase decoding, and performing cyclic redundancy check on the code words output by the improved Chase decoding one by one; if the cyclic redundancy check determines a certain code word is valid, stopping the improved Chase decoding and taking the code word as the decoding output; and if the cyclic redundancy check determines no valid code word is obtained by the improved Chase decoding, stopping the decoding and determining the decoding is failed.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com