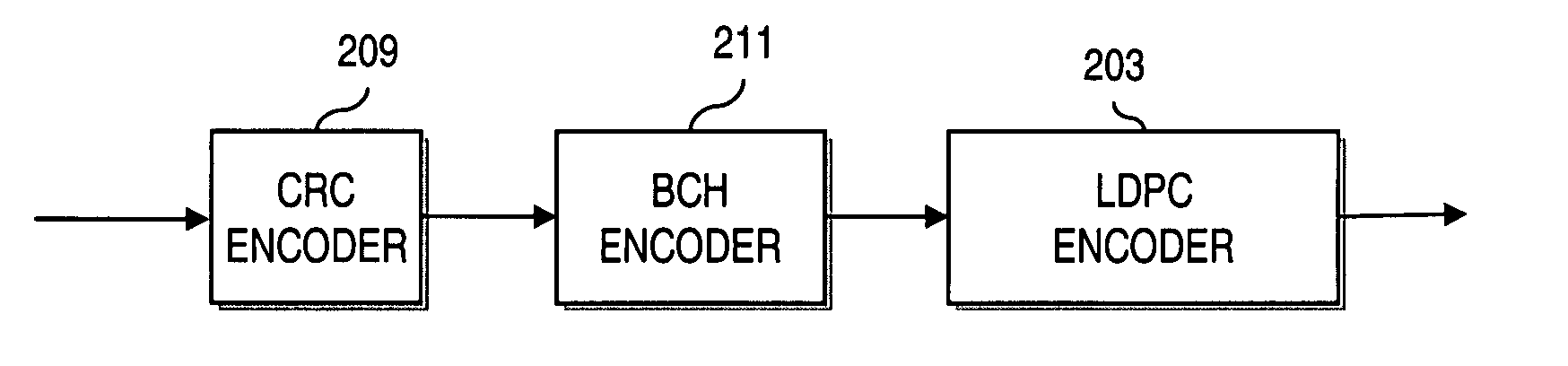
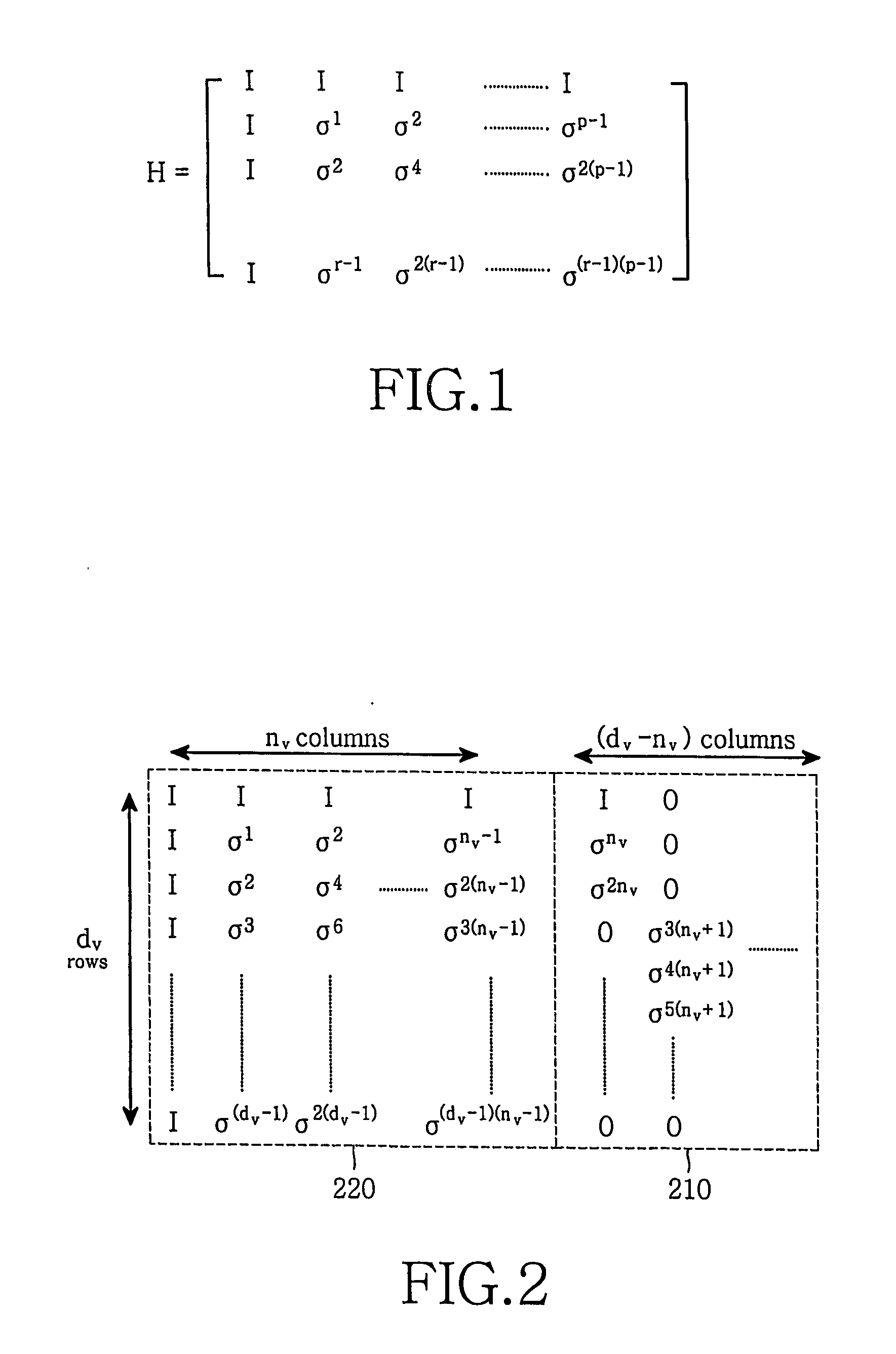
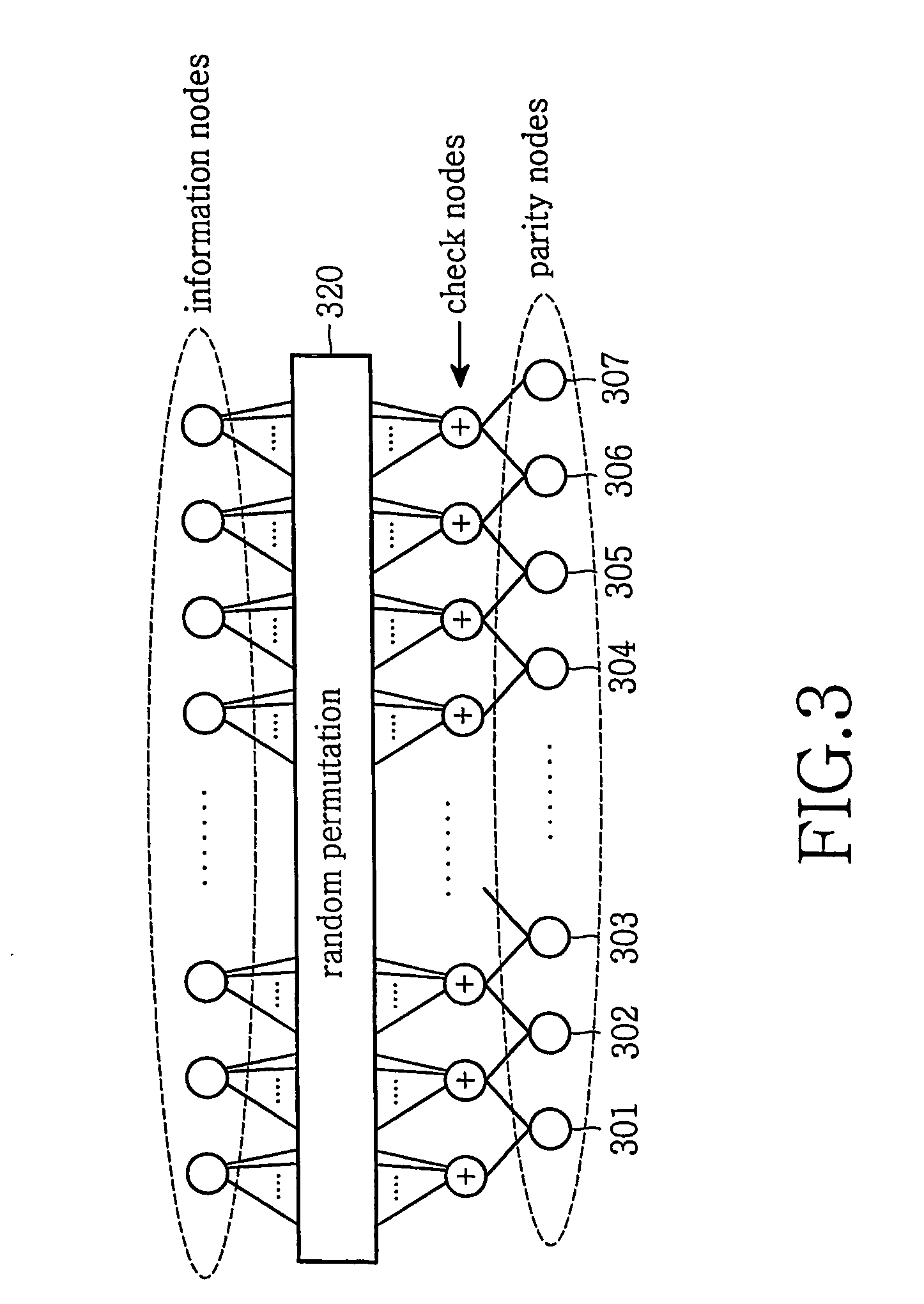
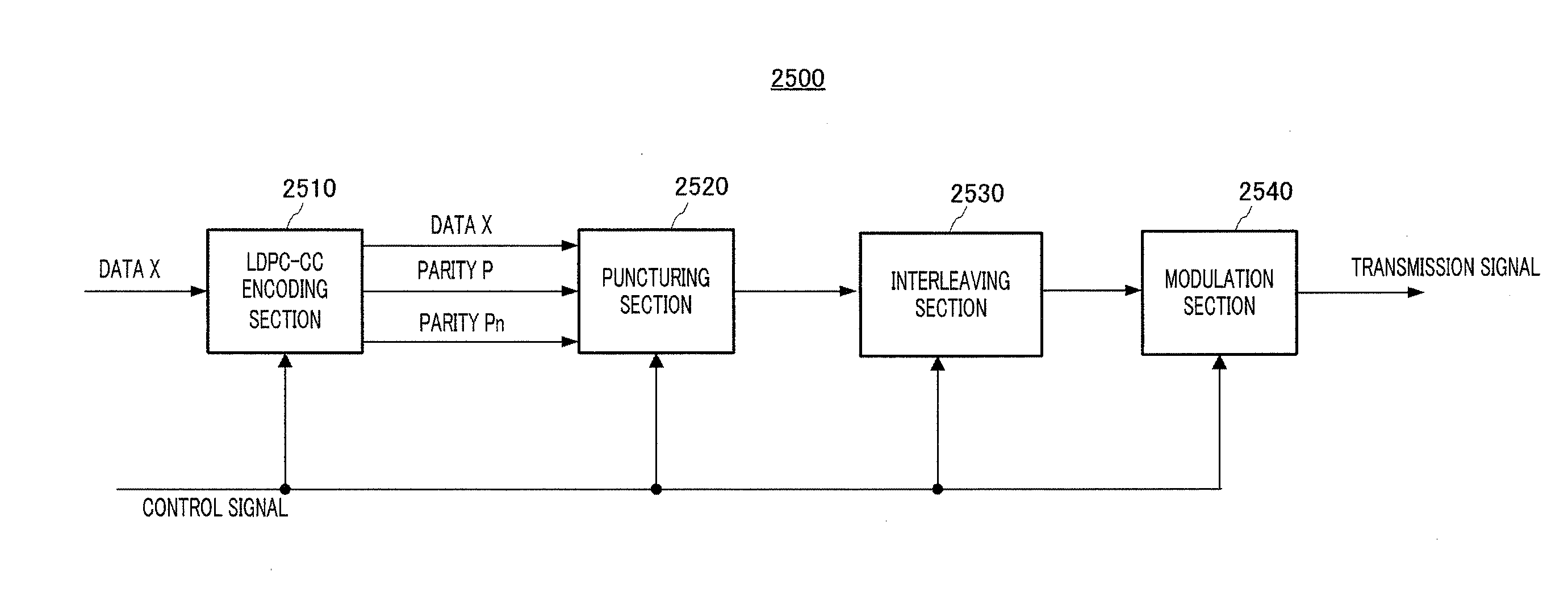
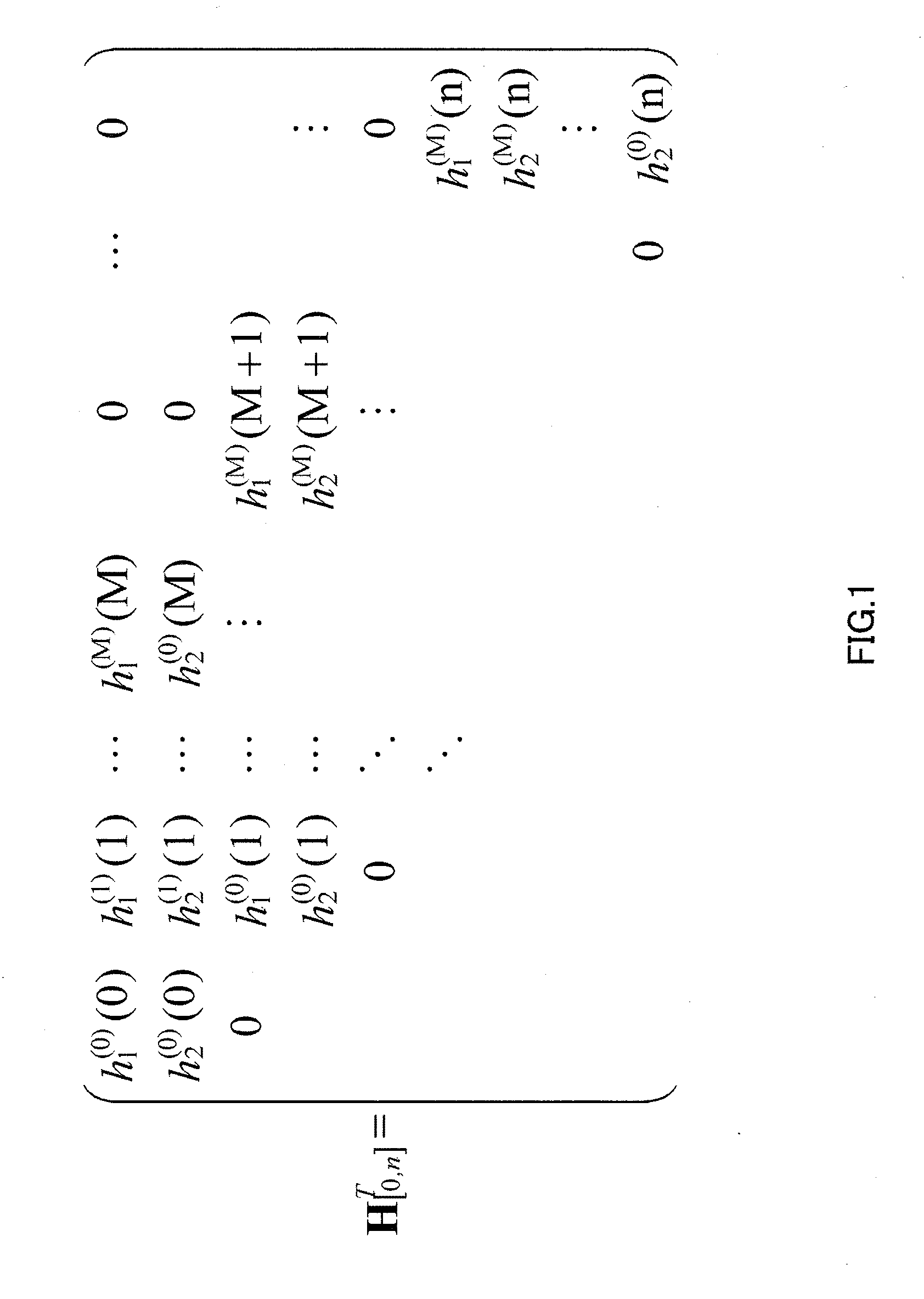
Patents
Literature
468 results about "Parity check code" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
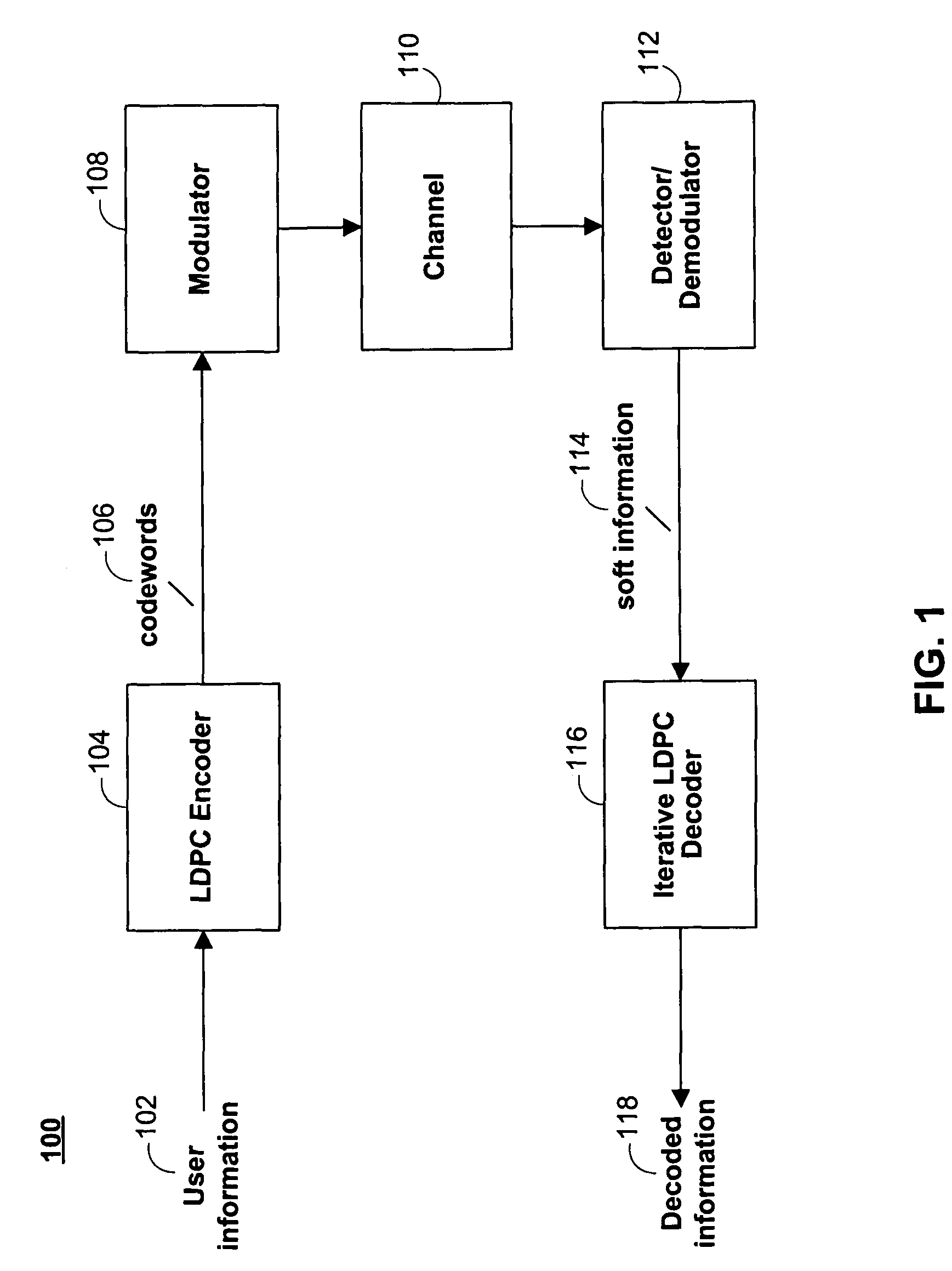
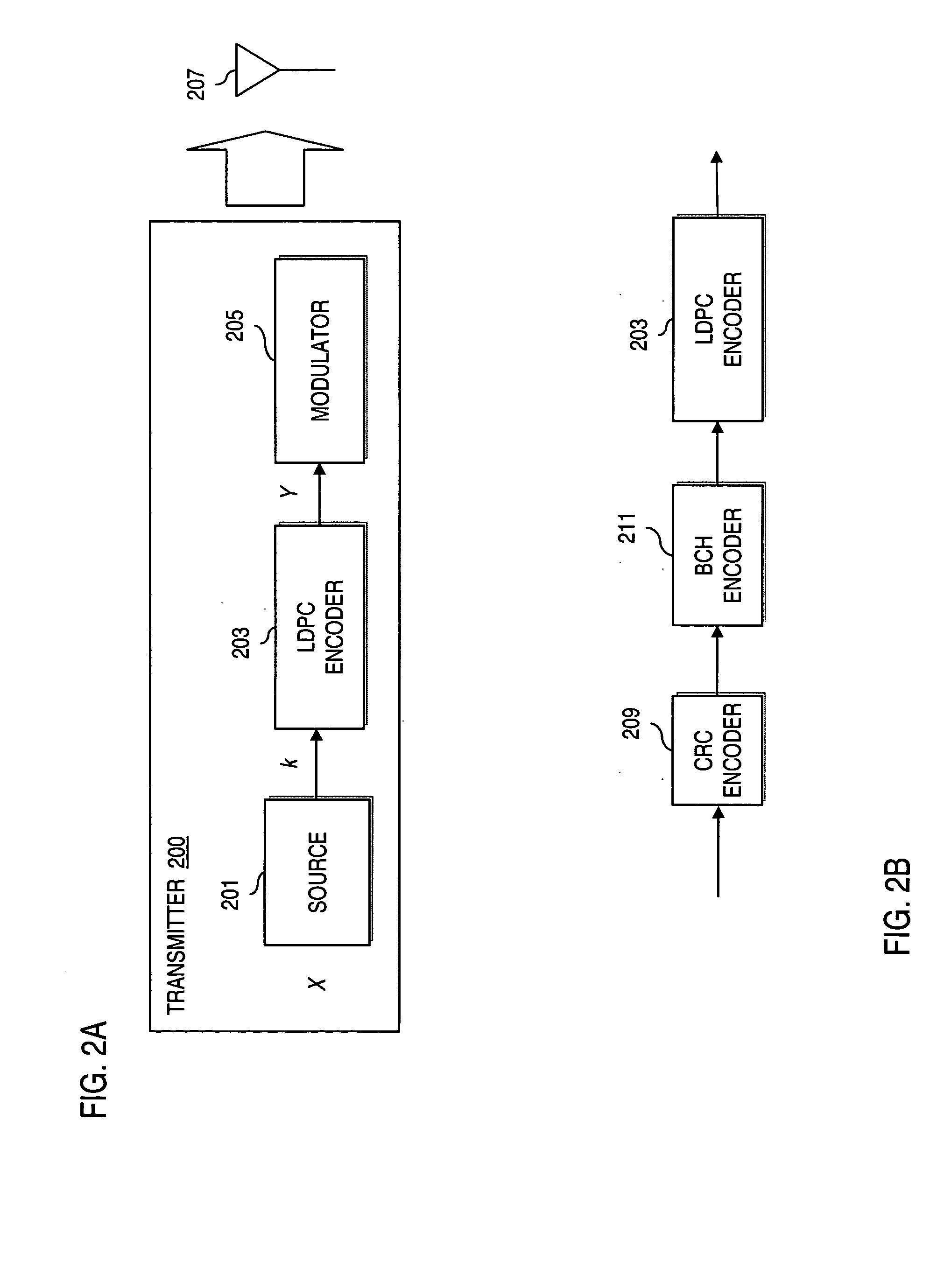
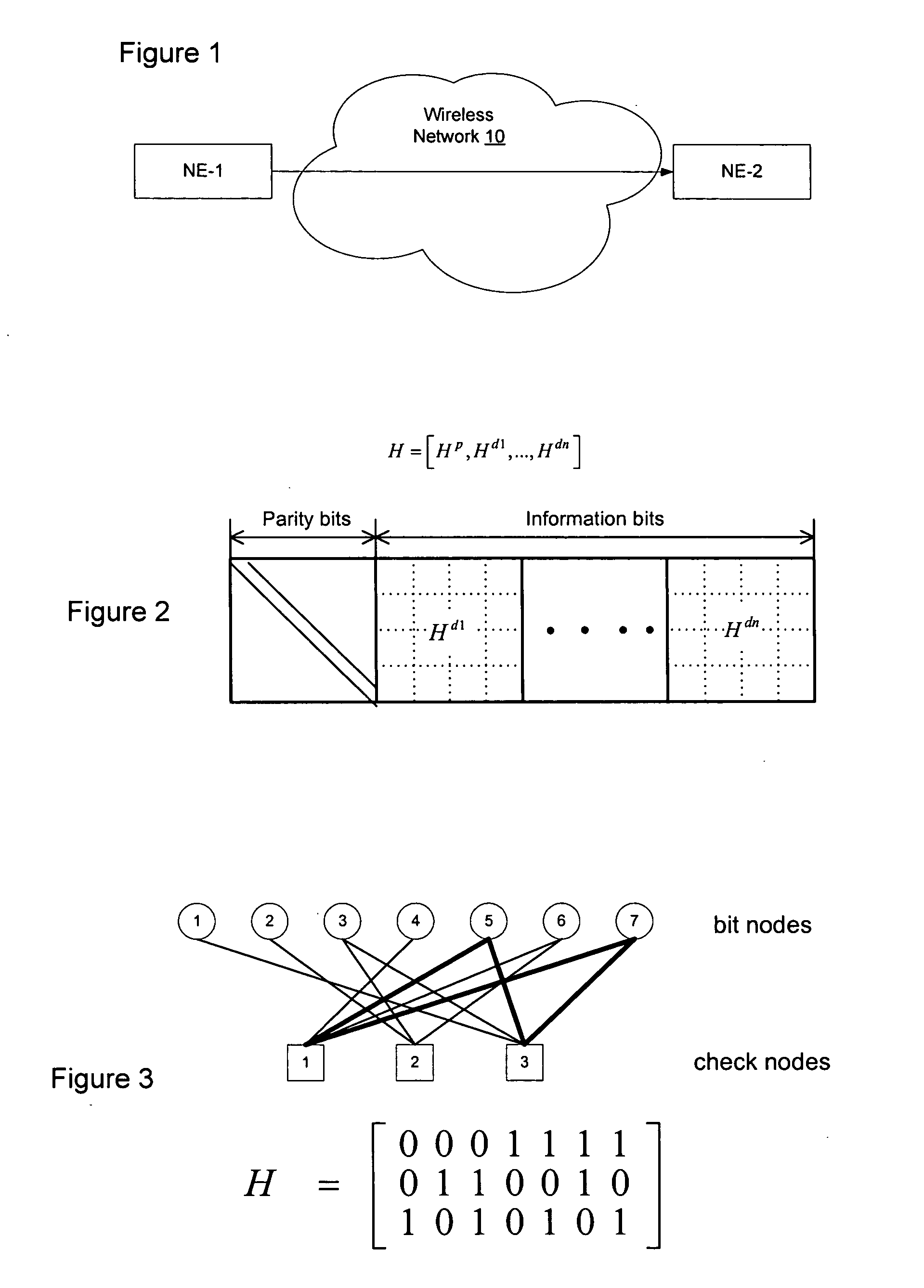
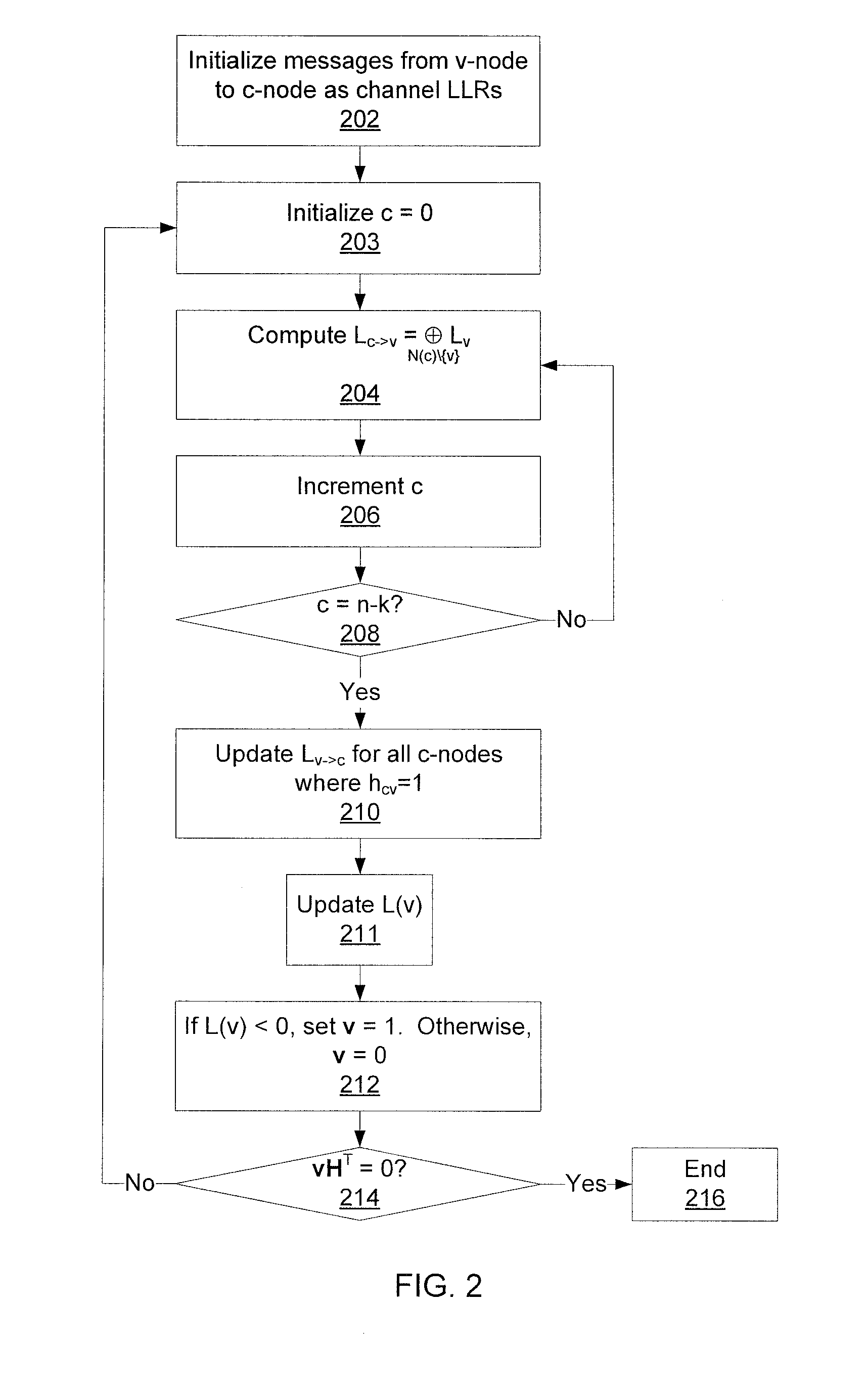
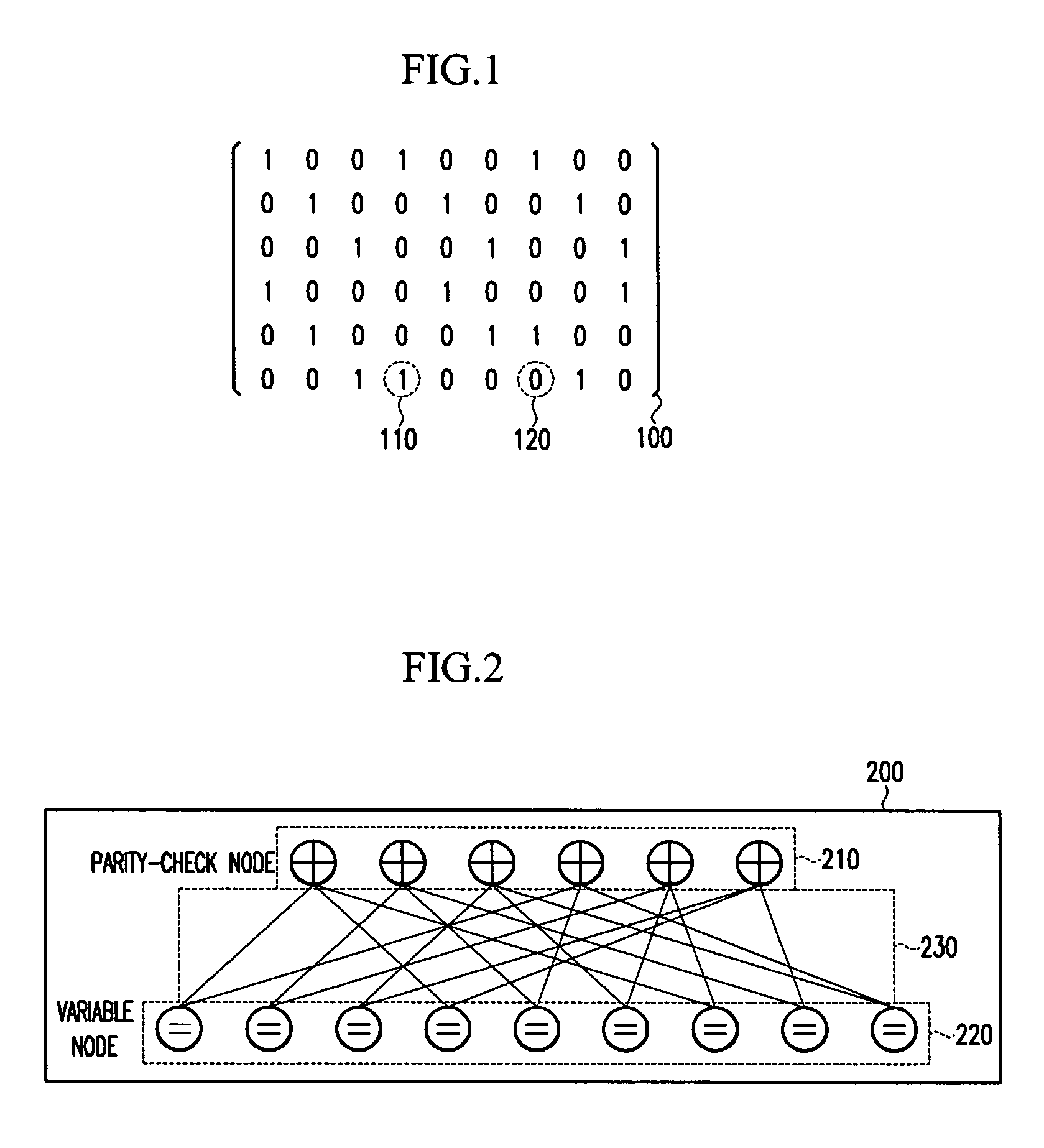
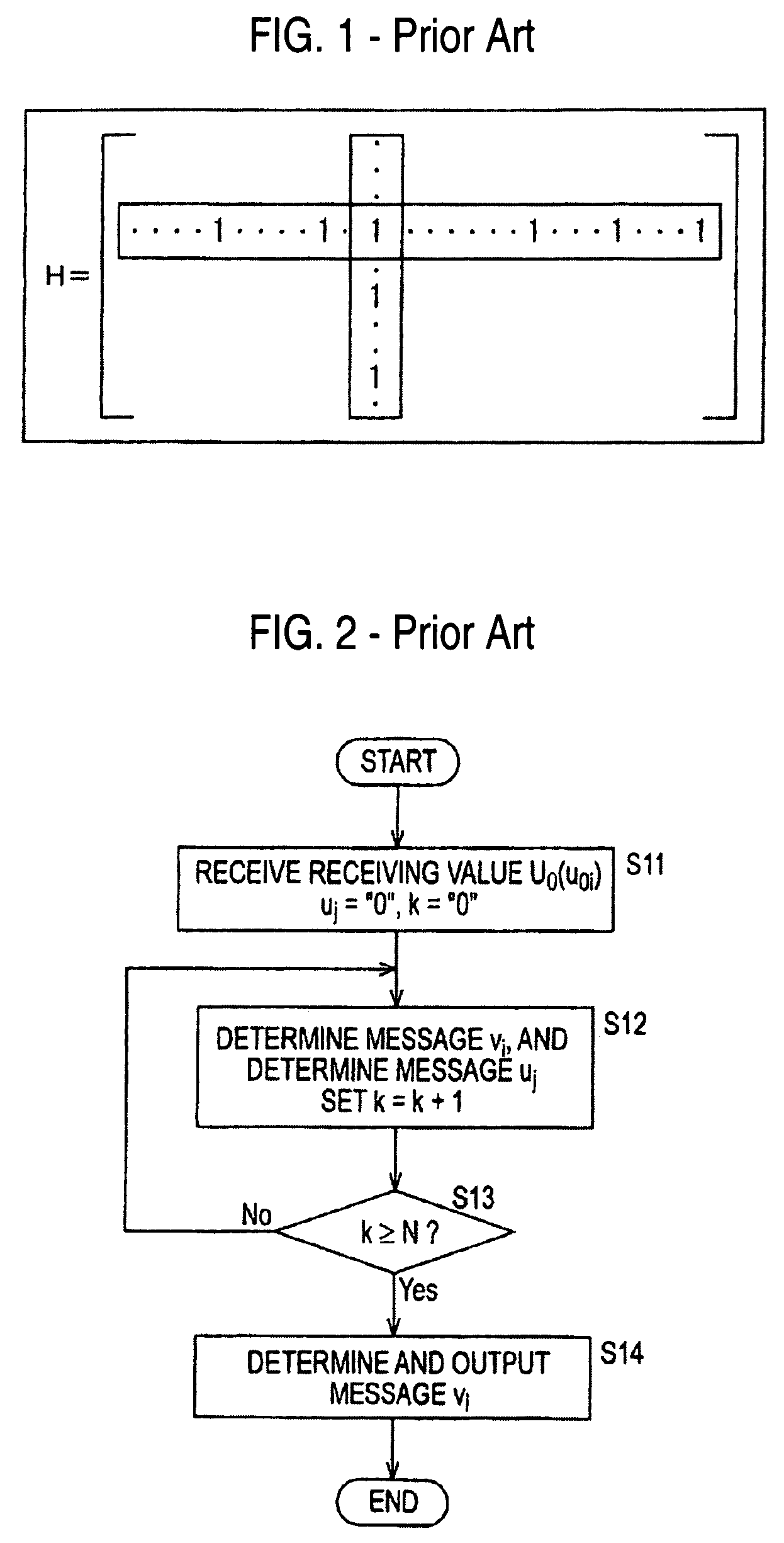
The simple parity-check code is the most familiar error-detecting code. In this code, a k-bit data word is changed to an n-bit code word where n = k + 1. The extra bit, called the parity bit, is selected to make the total number of 1s in the code word even. Although some implementations specify an odd number of 1s.
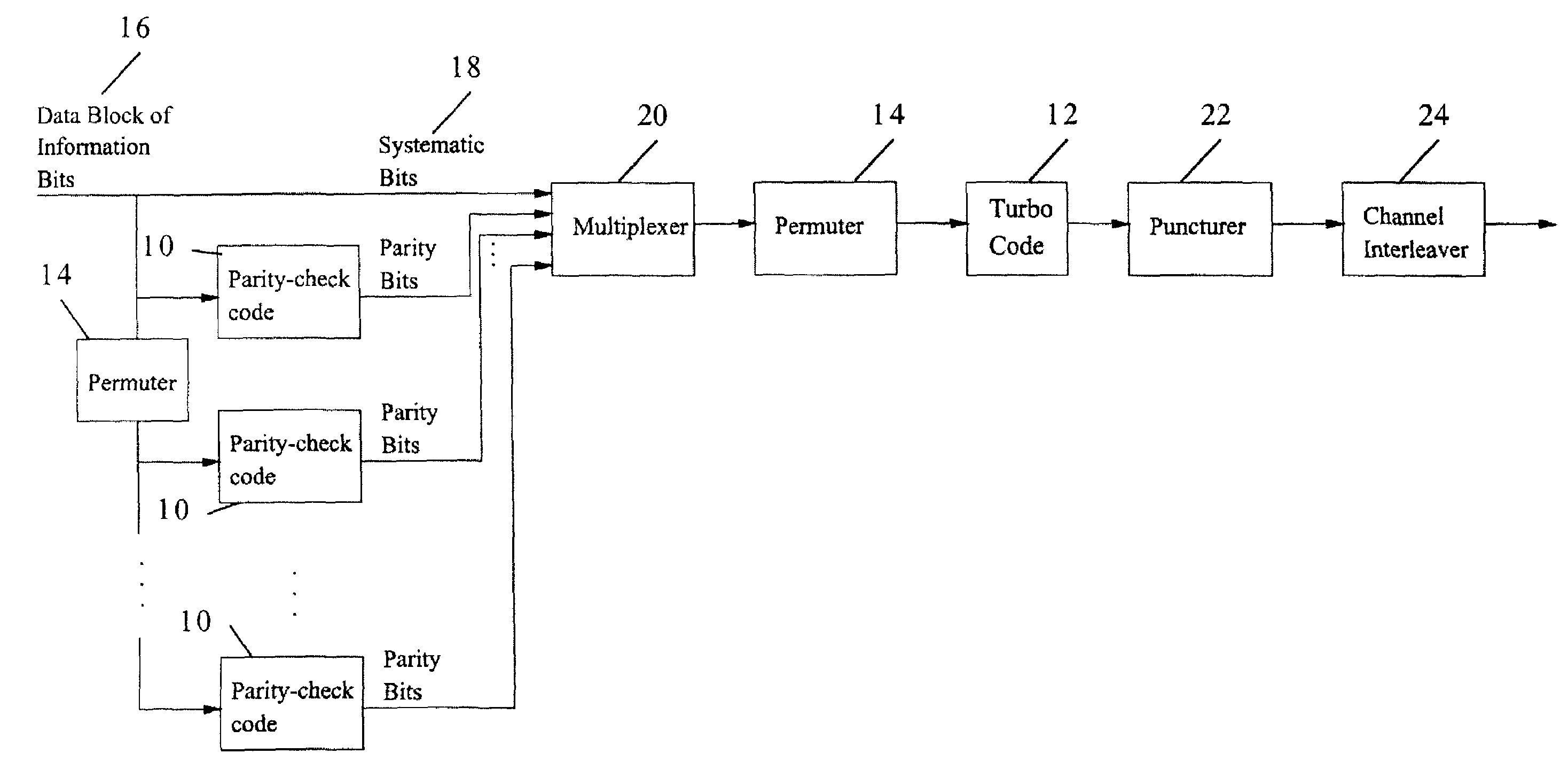
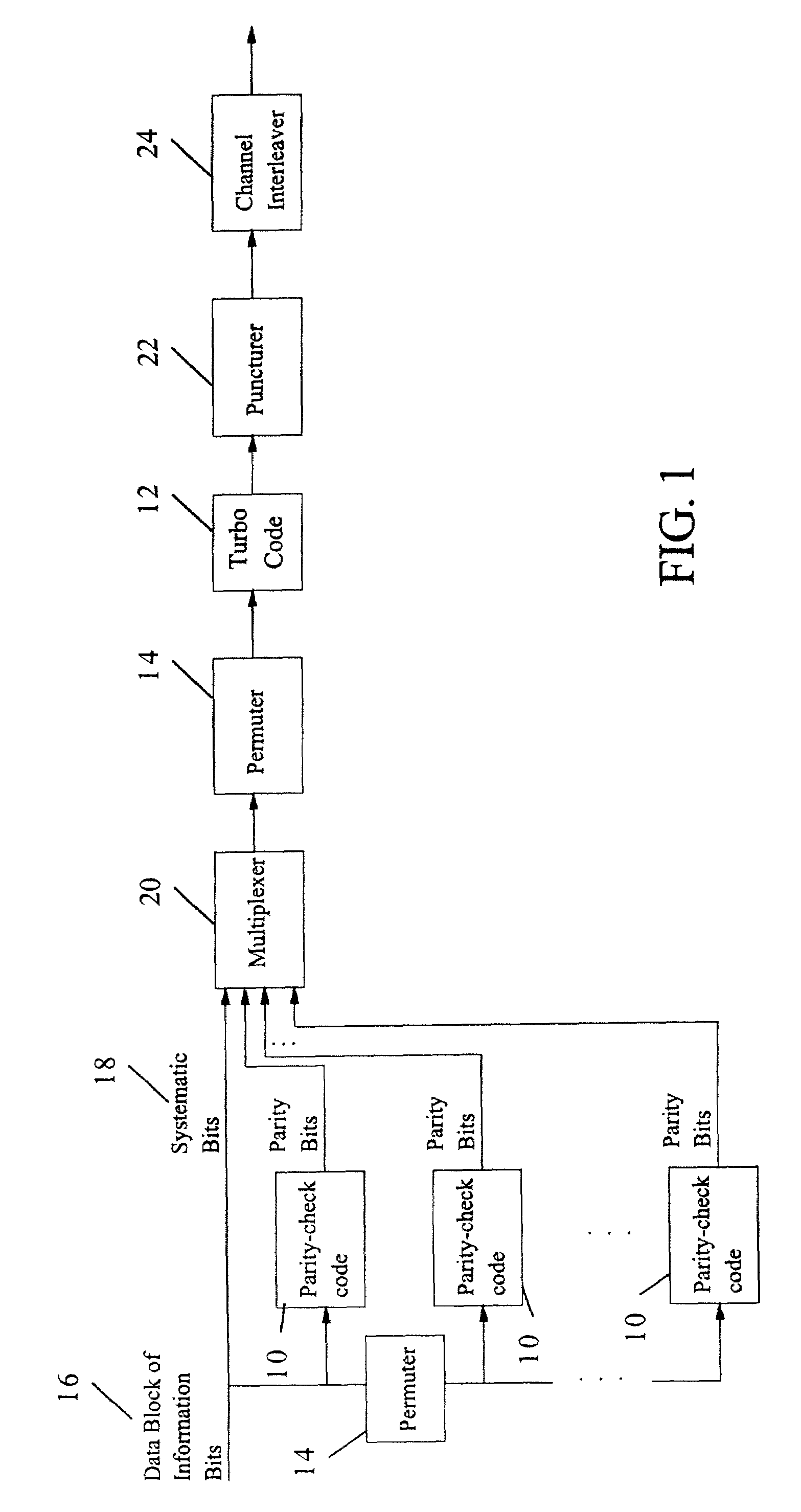
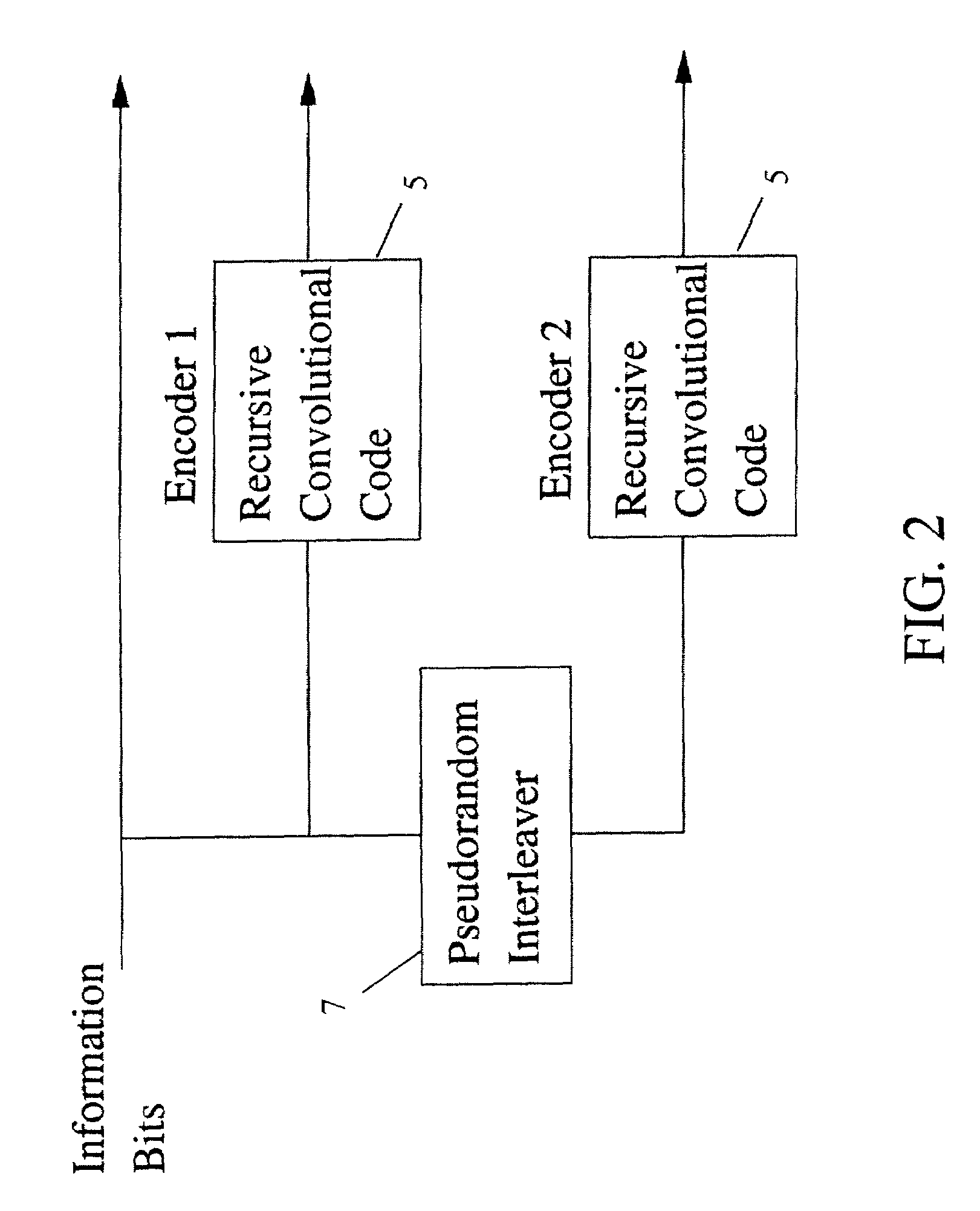
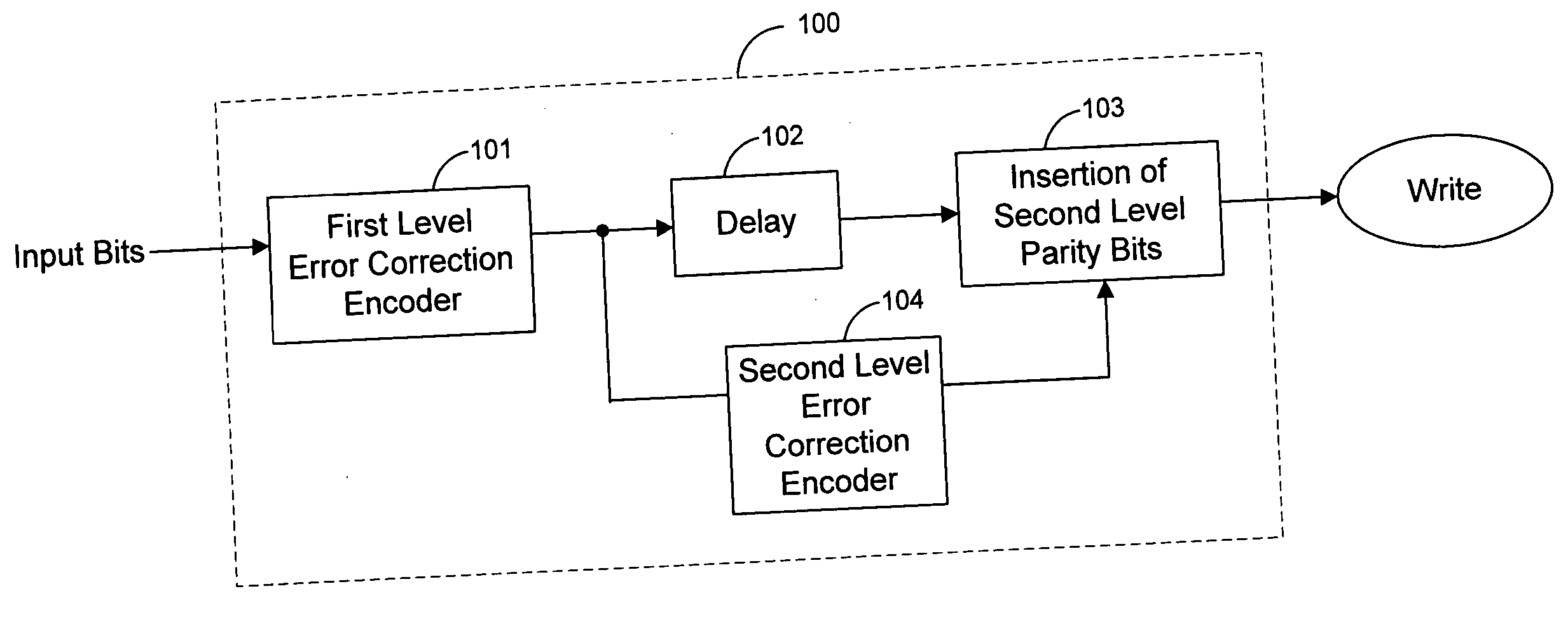
Method and coding means for error-correction utilizing concatenated parity and turbo codes
InactiveUS7093179B2Reduction in rateImprove overall utilizationError preventionError detection/correctionParallel computingTurbo coded
A method and apparatus for encoding and decoding data using an overall code comprising an outer parity-check and an inner parallel concatenated convolutional, or turbo code. The overall code provides error probabilities that are significantly lower than can be achieved by using turbo codes alone. The output of the inner code can be punctured to maintain the same turbo code rate as the turbo code encoding without the outer code. Multiple parity-check codes can be concatanated either serially or in parallel as outer codes. Decoding can be performed with iterative a posteriori probability (APP) decoders or with other decoders, depending on the requirements of the system. The parity-check code can be applied to a subset of the bits to achieve unequal error protection. Moreover, the techniques presented can be mapped to higher order modulation schemes to achieve improved power and bandwidth efficiency.
Owner:FLORIDA UNIV OF A FLORIDA +1
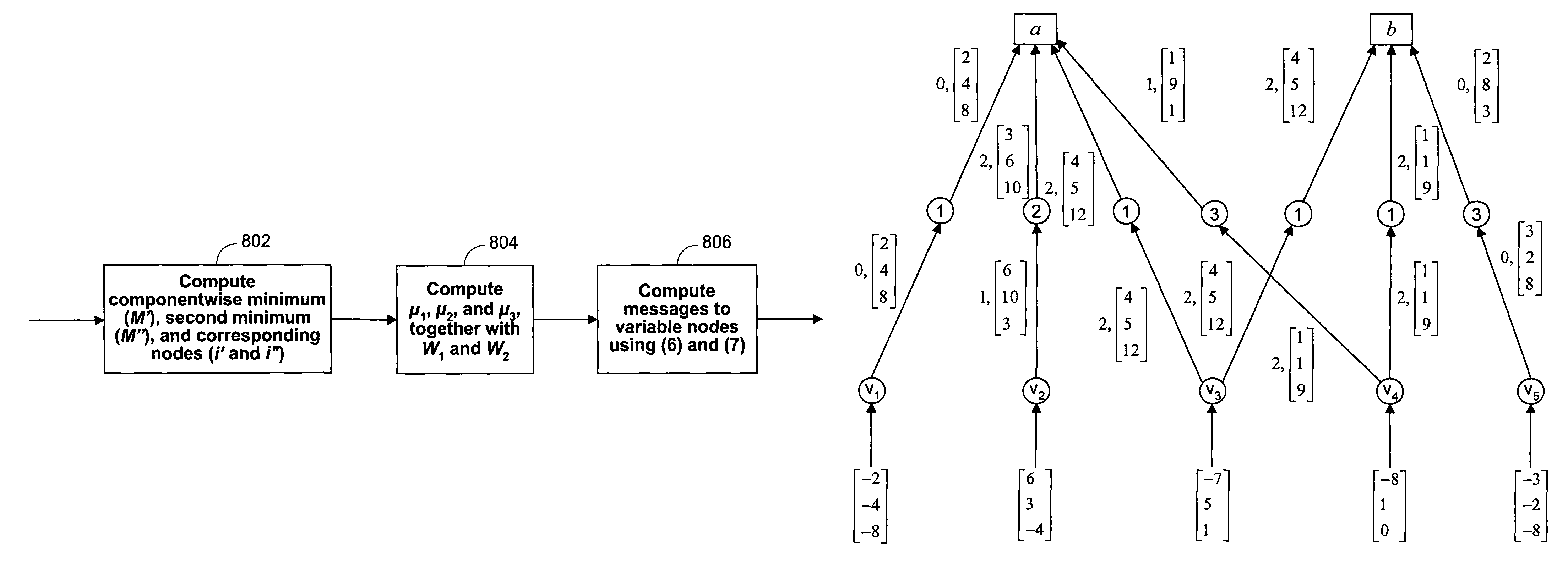
Reduced-complexity decoding of parity check codes
ActiveUS7752523B1Less resourcesData representation error detection/correctionCode conversionRound complexityTheoretical computer science
The disclosed technology provides a less resource intensive way to decode a parity check code using a modified min-sum algorithm. For a particular parity check constraint that includes n variable nodes, an LDPC decoder can compute soft information for one of the variable nodes based on combinations of soft information from other variable nodes, wherein each combination includes soft information from at most a number d of other variable nodes. In one embodiment, soft information from one of the other variable nodes is used in a combination only if it corresponds to a non-most-likely value for the other variable node.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
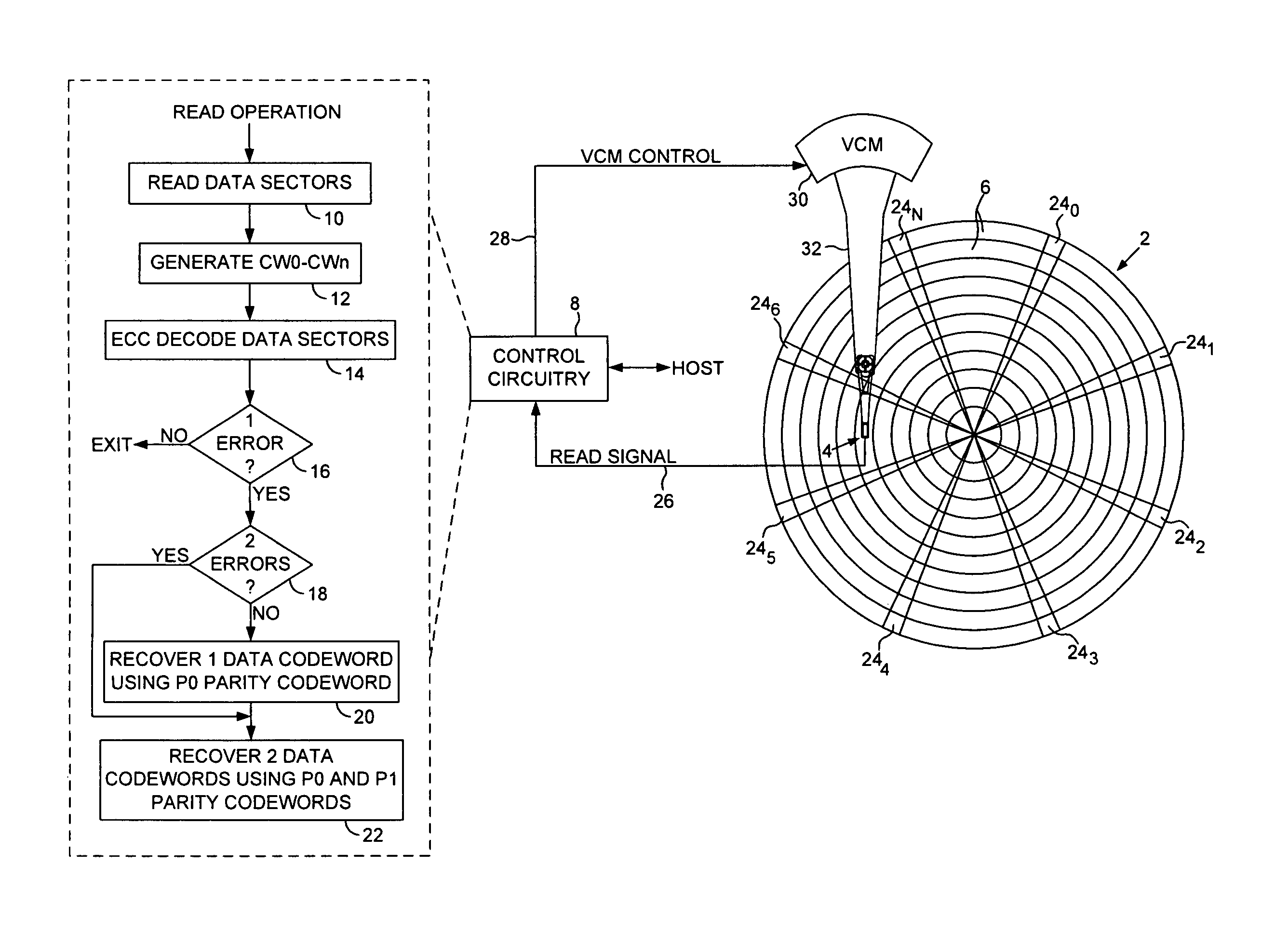
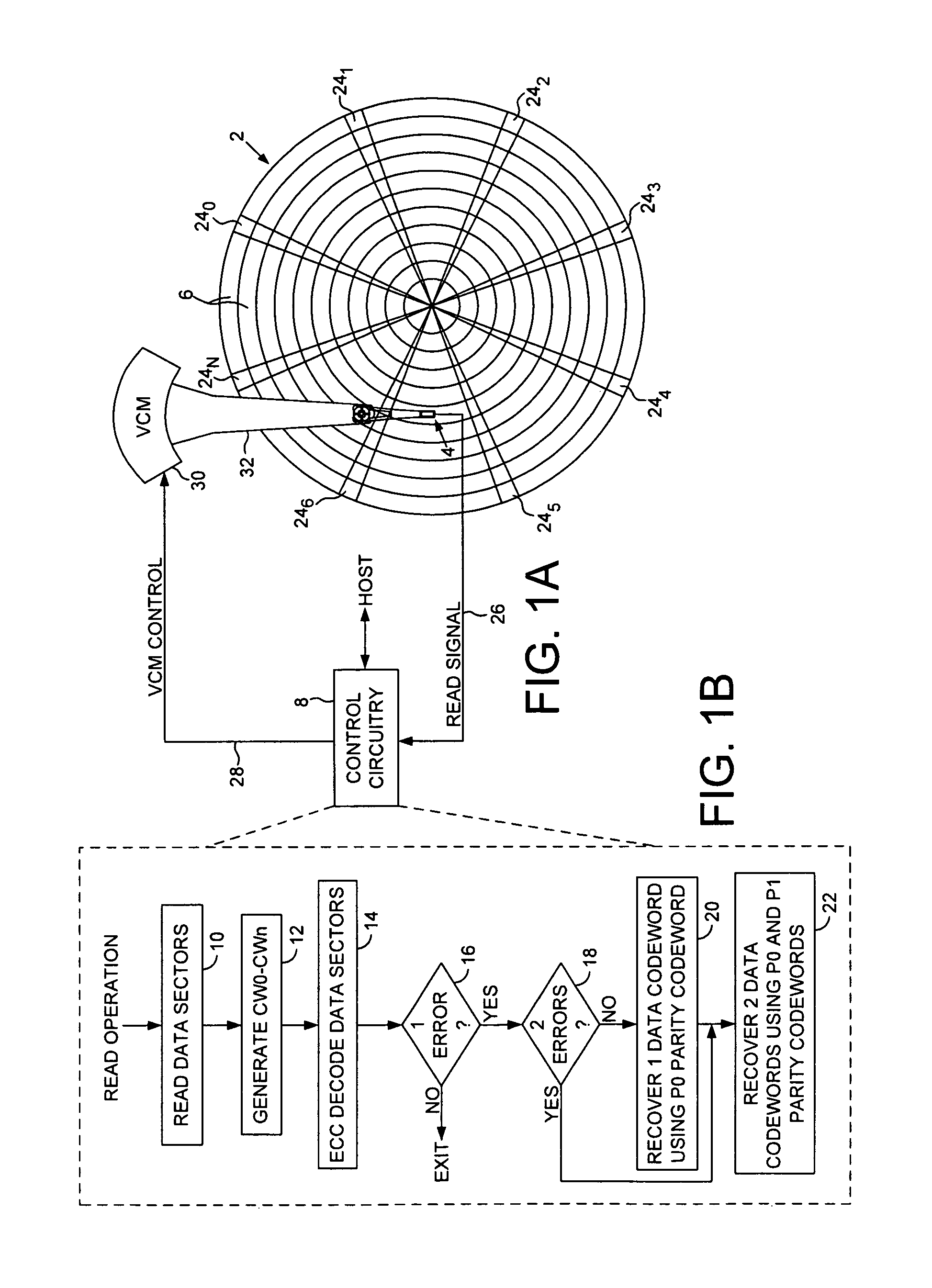
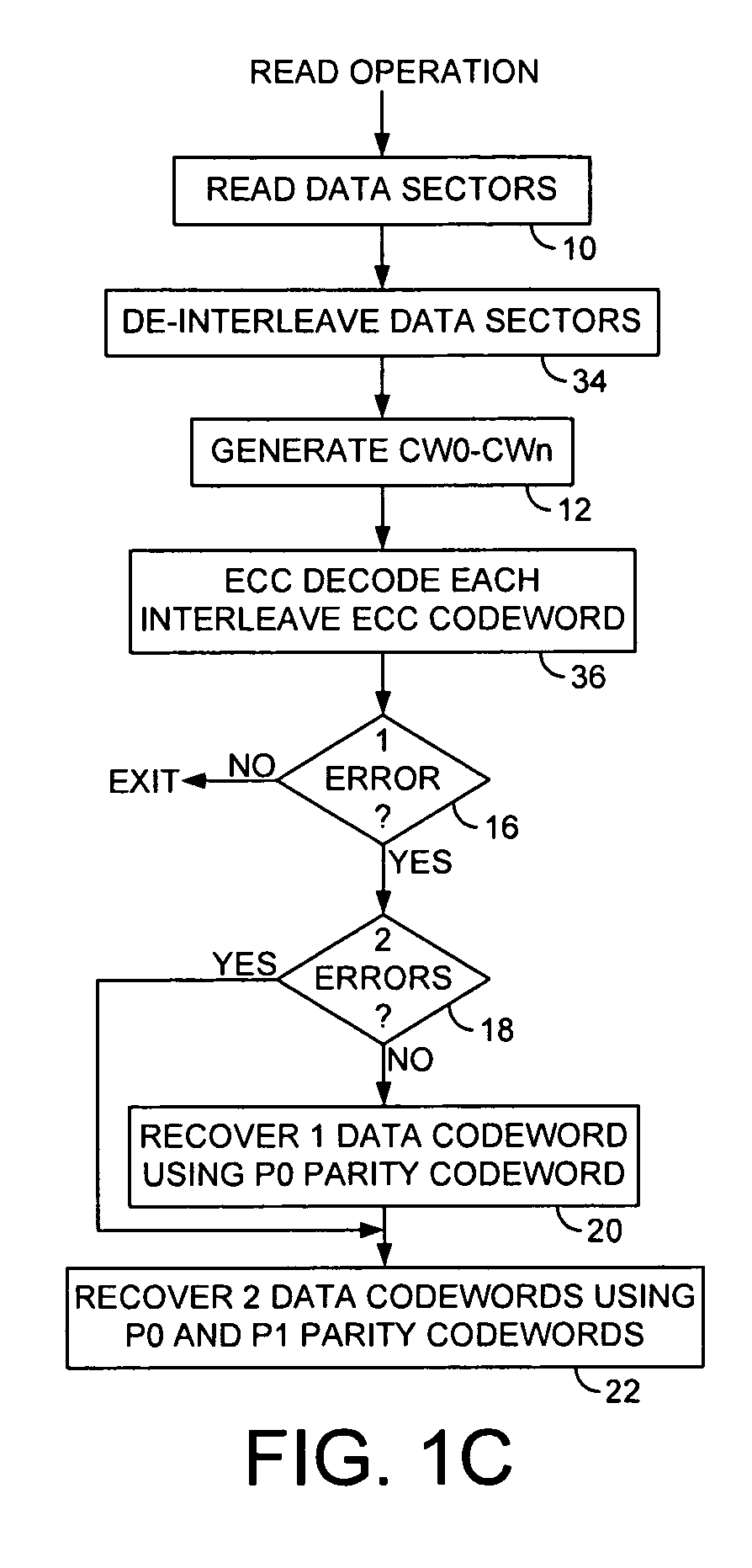
Disk drive recovering multiple codewords in data sectors using progressively higher order parity codewords
A disk drive is disclosed comprising a disk and a head actuated over the disk. The disk comprises a plurality of tracks, wherein each track comprises a plurality of data sectors including a parity sector, the parity sector comprising at least a P0 parity codeword and a P1 parity codeword. A plurality of data sectors are read from the disk (including the parity sector) to generate a plurality of data codewords CW0-CWn. The data sectors are decoded using an error correction code (ECC) decoder. When a single data codeword in CW0-CWn is unrecoverable using the ECC decoder, the single data codeword is recovered using the P0 parity codeword. When two data codewords in CW0-CWn are unrecoverable using the ECC decoder, the two data codewords are recovered using the P0 and P1 parity codewords.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
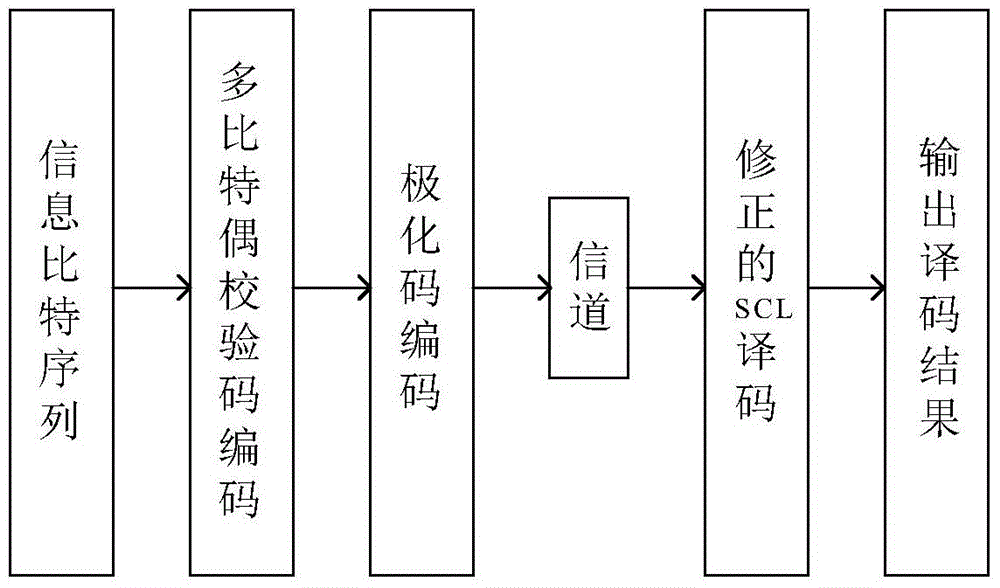
Polarization code and multi-bit even parity check code cascaded error correction coding method
ActiveCN105680883AImprove error correction performanceBreakthrough in error correction performanceCode conversionError correction/detection by combining multiple code structuresComputer hardwareError correction coding
The invention discloses a polarization code and multi-bit even parity check code cascaded error correction coding method. The method comprises the steps: a transmitting end encoder utilizes a multi-bit even parity check code as an outer code, and utilizes a polarization code as an inner code; a receiving end decoder decodes by utilizing a modified successive cancellation list (SCL) decoding algorithm. On the aspect of error correction performance, comparing with the prior art utilizing middle-short code length non-cascaded polarization codes of the SCL decoding algorithm, the polarization code and multi-bit even parity check code cascaded error correction coding method has the advantages that frame error rate performance of a system can be remarkably improved, and a maximum likelihood bound (ML Bound), which cannot be broken through by the SCL decoding algorithm, can be remarkably broken through. On the aspect of engineering realization, according to the polarization code and multi-bit even parity check code cascaded error correction coding method, the outer code utilizes the multi-bit even parity check code, which is simple to code; the modified SCL decoding algorithm is utilized to decode, bit decision and even parity check are combined to be carried out in a decoding process, and compared with the original SCL decoding algorithm, the method provided by the invention does not increase the decoding complexity, and facilitates the engineering realization.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
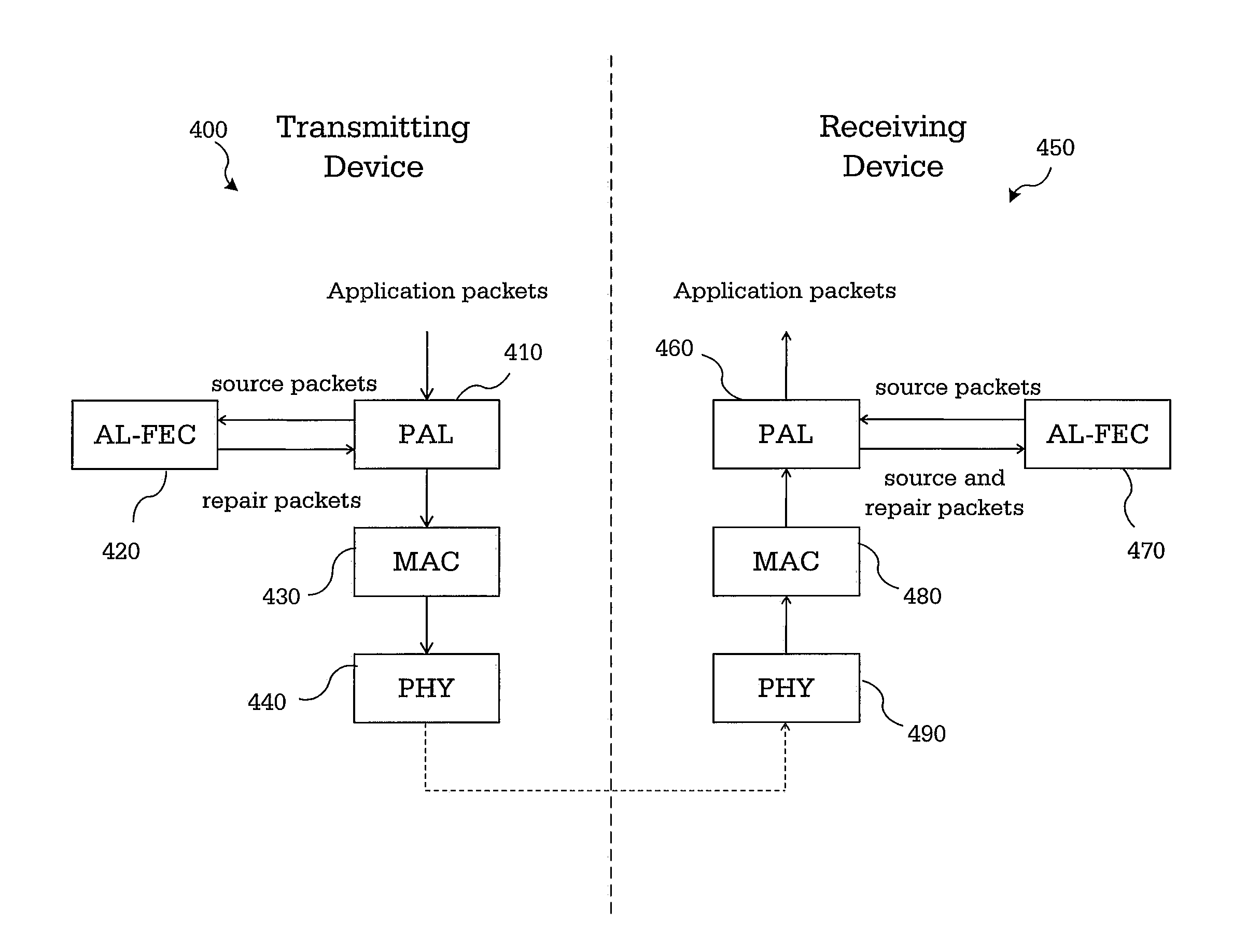
APPLICATION LAYER FEC FRAMEWORK FOR WiGig
InactiveUS20110219279A1Error correction/detection using convolutional codesError preventionComputer hardwareSingle parity check
A method and apparatus perform forward error correction in a wireless communication device in a wireless communication network. Application layer forward error correction (AL-FEC) capability information is transmitted during a capabilities exchange. A set of source packets are reshaped to k equal-sized source symbols. Systematic packets for the source symbols and at least one parity packet is encoded using a single parity check (SPC) AL-FEC code on the k source symbols. A header of each encoded packet includes a parity packet indicator. The encoded packets are processed in a media access control (MAC) layer and a physical (PHY) layer for transmission.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
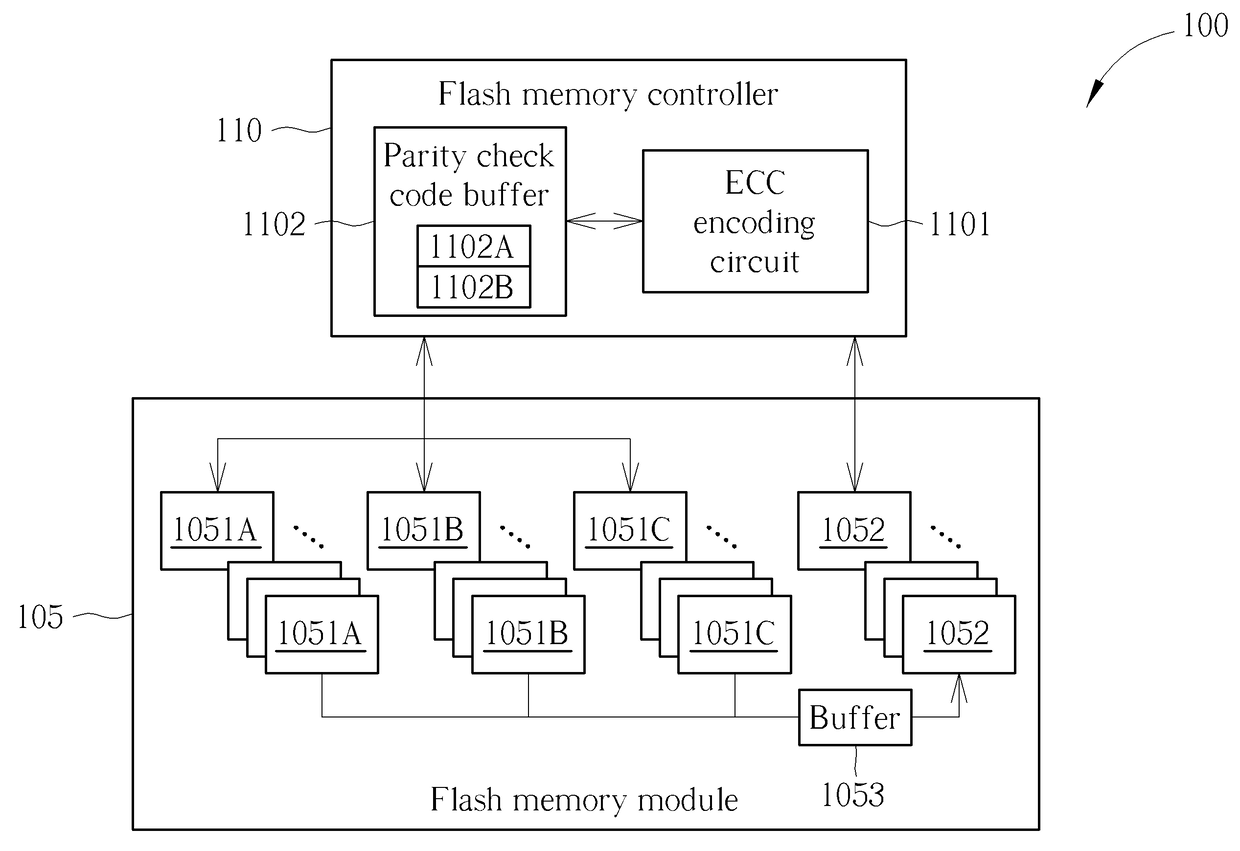
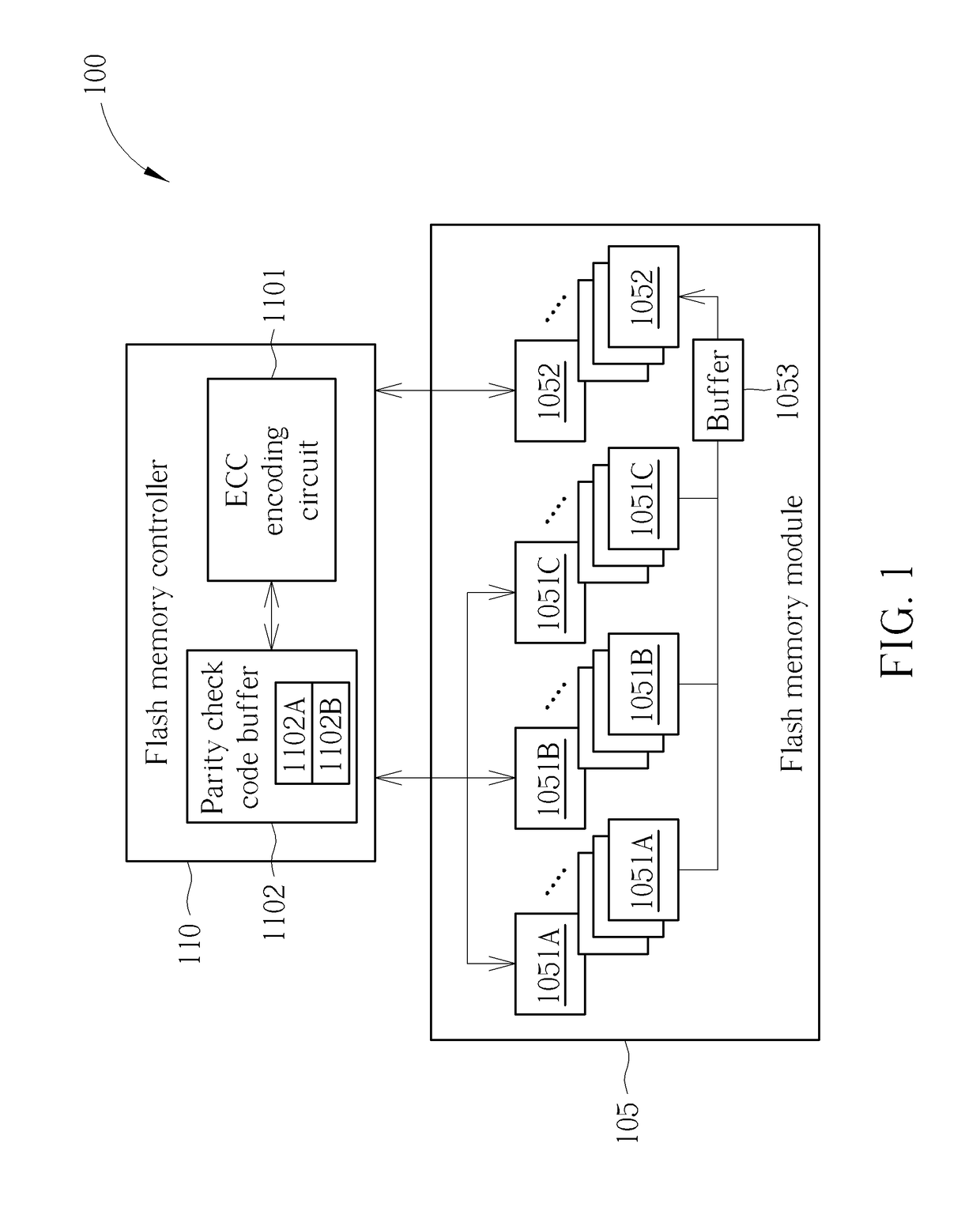
Flash memory apparatus and storage management method for flash memory
A method used for a flash memory module having a plurality of storage blocks each can be used as a first block or a second block includes: classifying data into a plurality of groups of data; respectively executing error code encoding to generate a first corresponding parity check code to store the groups of data and the first corresponding parity check code into the flash memory module as first blocks; reading out the groups of data from the first blocks; executing error correction and de-randomize operation upon read out data to generate de-randomized data; executing randomize operation upon the de-randomized data according to a set of seeds to generate randomized data; performing error code encoding upon the randomized data to generate a second corresponding parity check code; and storing the randomized data and the second corresponding parity check code into the flash memory module as the second block.
Owner:SILICON MOTION INC (TW)
Algebraic low-density parity check code design for variable block sizes and code rates
InactiveUS7260763B2Readily implemented in hardwareHigher code rate parityError detection/correctionError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsVariable-length codeSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
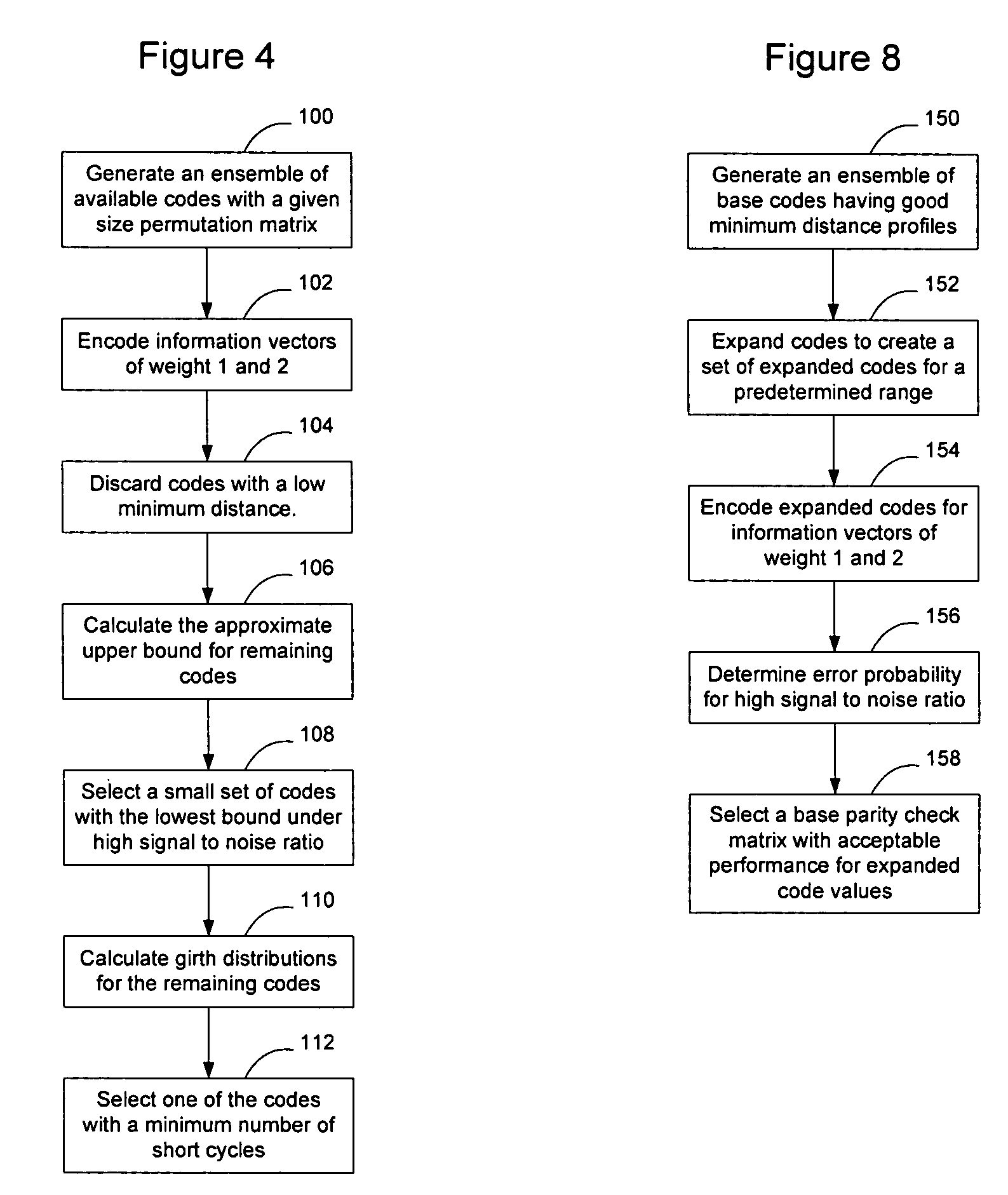
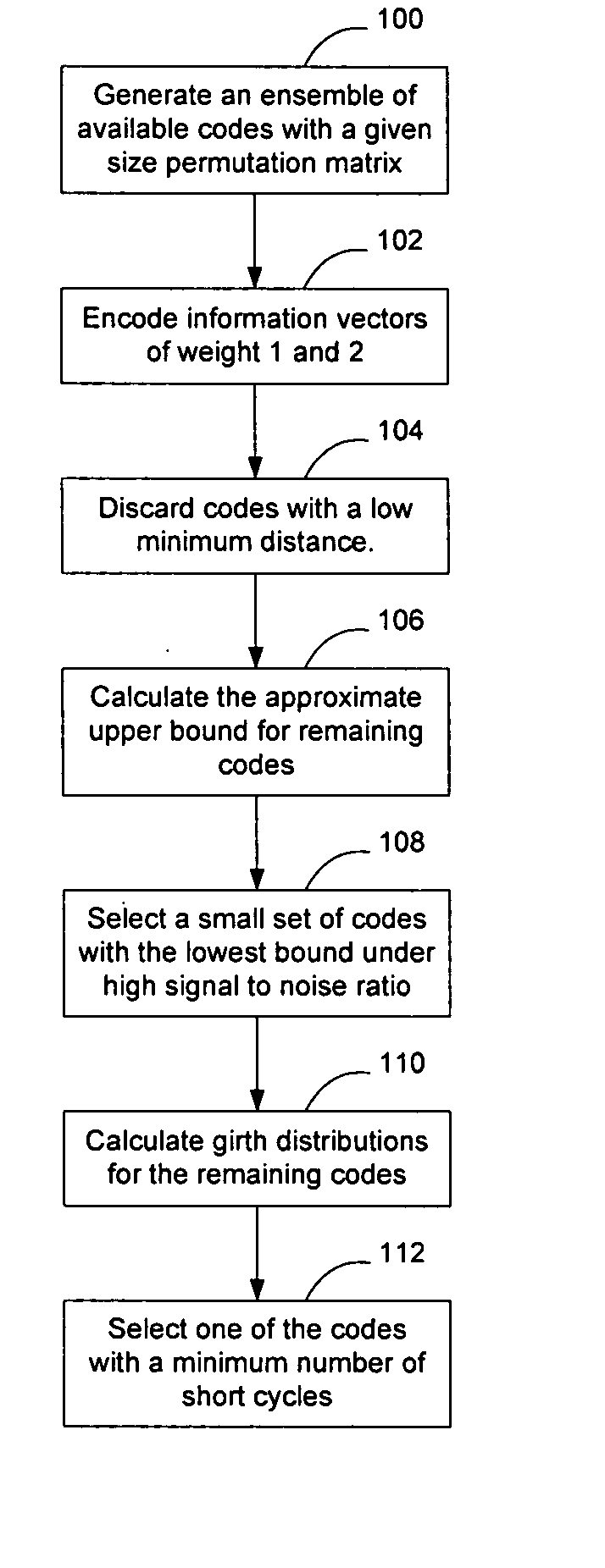
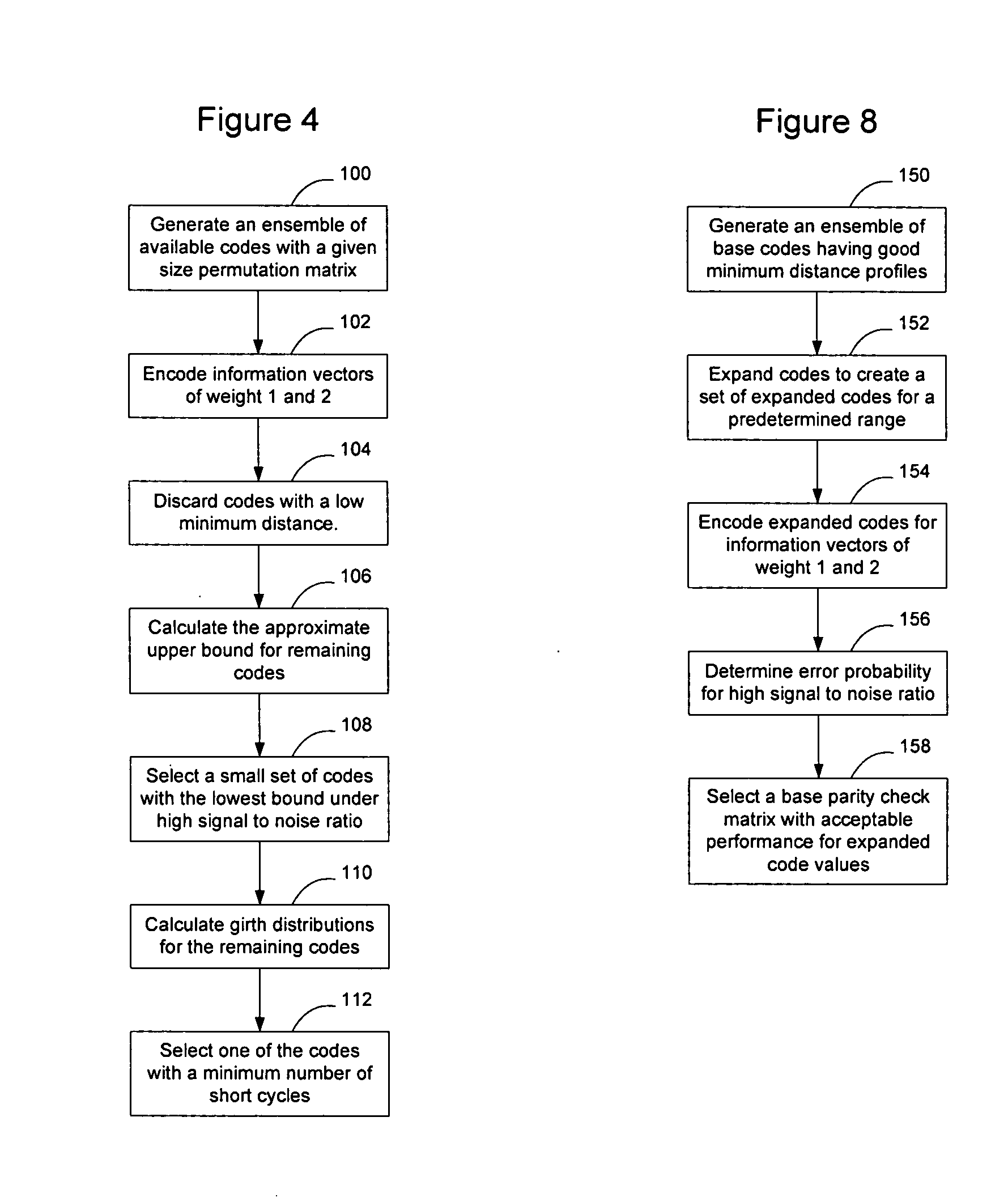
A higher code rate Low-Density Parity Check (LDPC) matrix may be designed by concatenating additional matrices to a π-rotation parity check matrix. The concatenated matrix may be selected such that the resultant LDPC matrix exhibits good expansion characteristics to enable the LDPC matrix to be used with variable block length codes. The codes may be designed by generating an ensemble of available codes, encoding them with information vectors of weight 1 and 2 and discarding codes with a low minimum distance. The approximate upper bounds for the remaining codes are then calculated and a small set of codes with the lowest bound under high signal to noise ratio is selected. The girth distributions for the remaining codes are then calculated and the code that has the minimum number of short cycles is selected. The selected code is concatenated to the original π-rotation parity check matrix.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Block Modulus Coding (BMC) Systems and Methods for Block Coding with Non-Binary Modulus
InactiveUS20090204877A1Reduce memory requirementsFacilitate interleavingData representation error detection/correctionOther error detection/correction/protectionCommunications systemBlock code
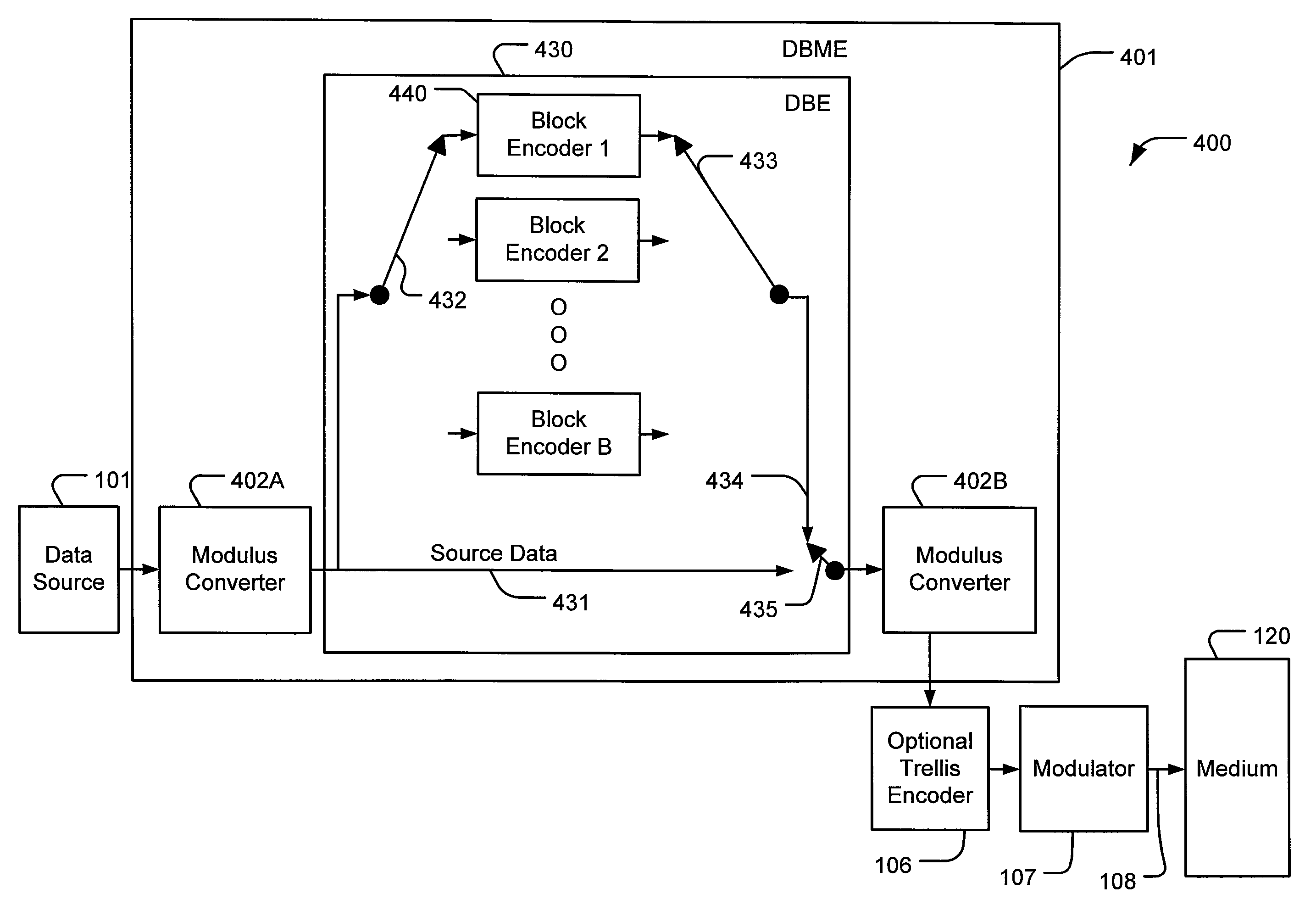
Block modulus coding (BMC) systems implement block coding on non-binary modulus m symbols, where m is greater than 2. BMC systems can be used for, among other things, forward error correction (FEC) of source data in communication systems or parity backup for error correction of source data in storage systems where the source data is represented by non-binary symbols that may be corrupted by burst errors. The block coding is preferably performed using a distributed arrangement of block encoders or decoders. A distributed block modulus encoder (DBME) encodes sequential source data symbols of modulus m with a plurality of sequential block encoders to produce interleaved parity codewords. The codewords utilize modulus m symbols where the medium can reliably resolve m symbol states. The interleaved parity codewords enable decoding of error-corrected source data symbols of modulus m with a distributed block modulus decoder (DBMD) that utilizes a plurality of sequential block decoders to produce the error-corrected source data symbols.
Owner:SUNRISE IP
Apparatus for encoding and decoding of low-density parity-check codes, and method thereof
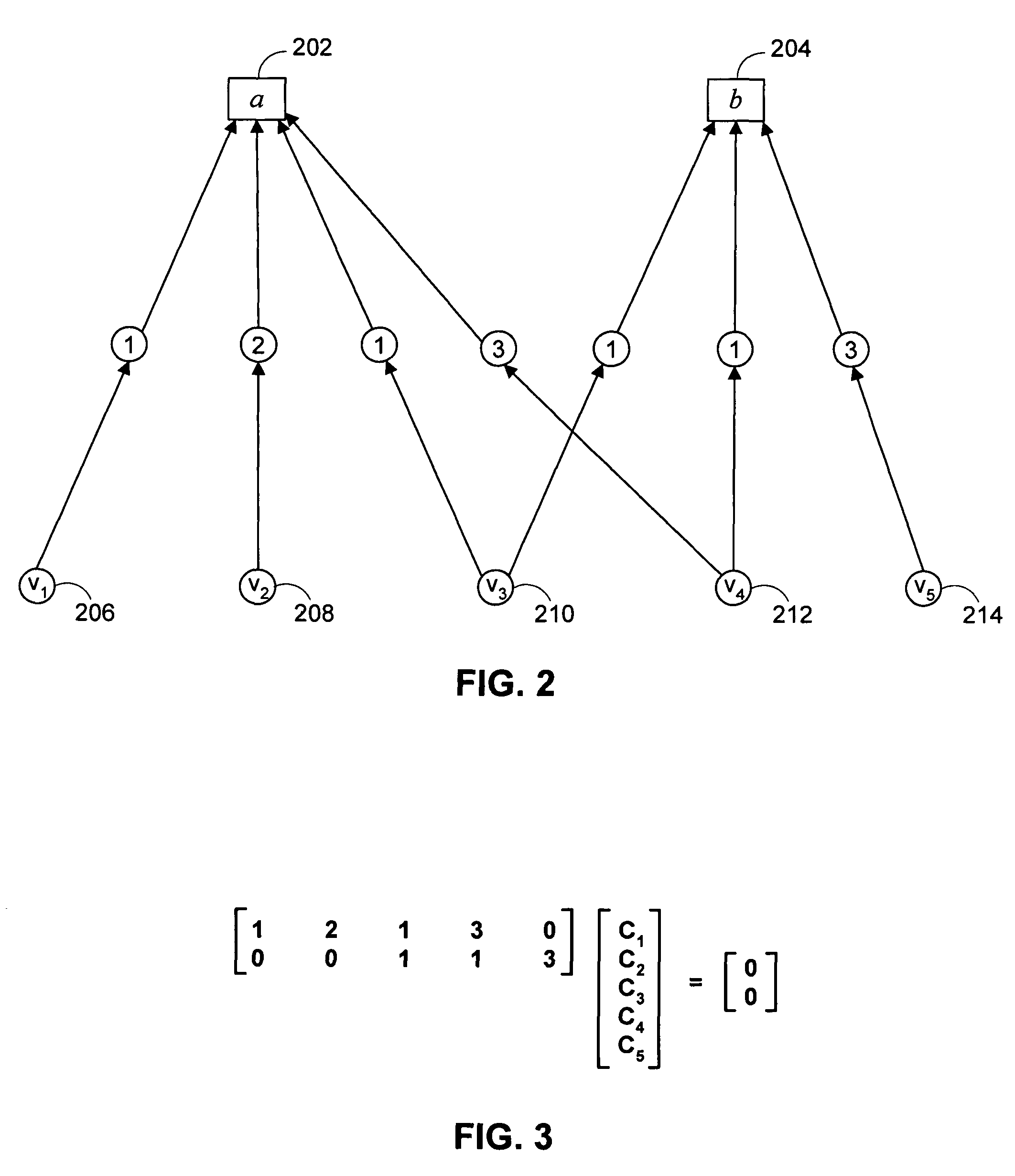
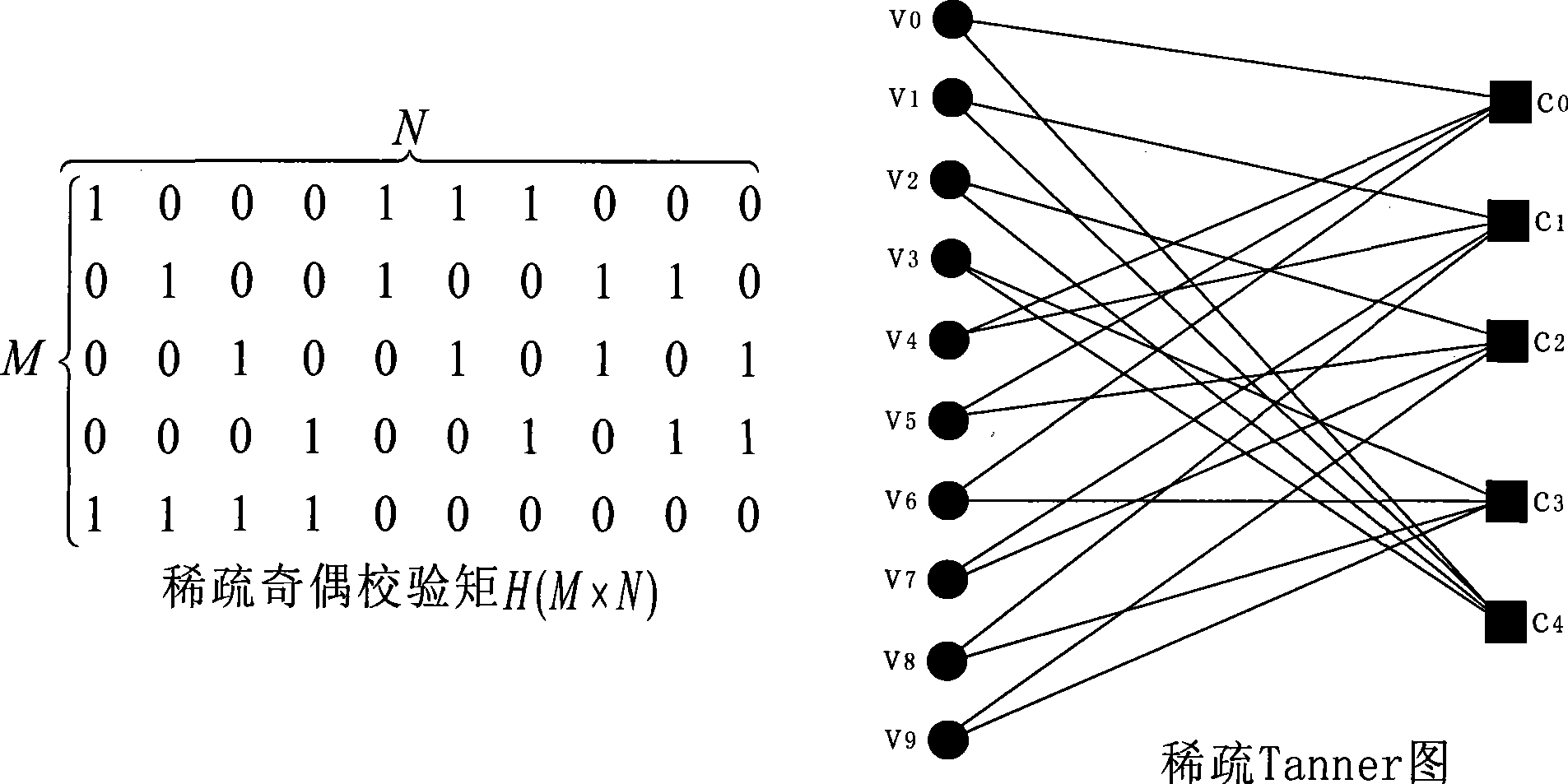
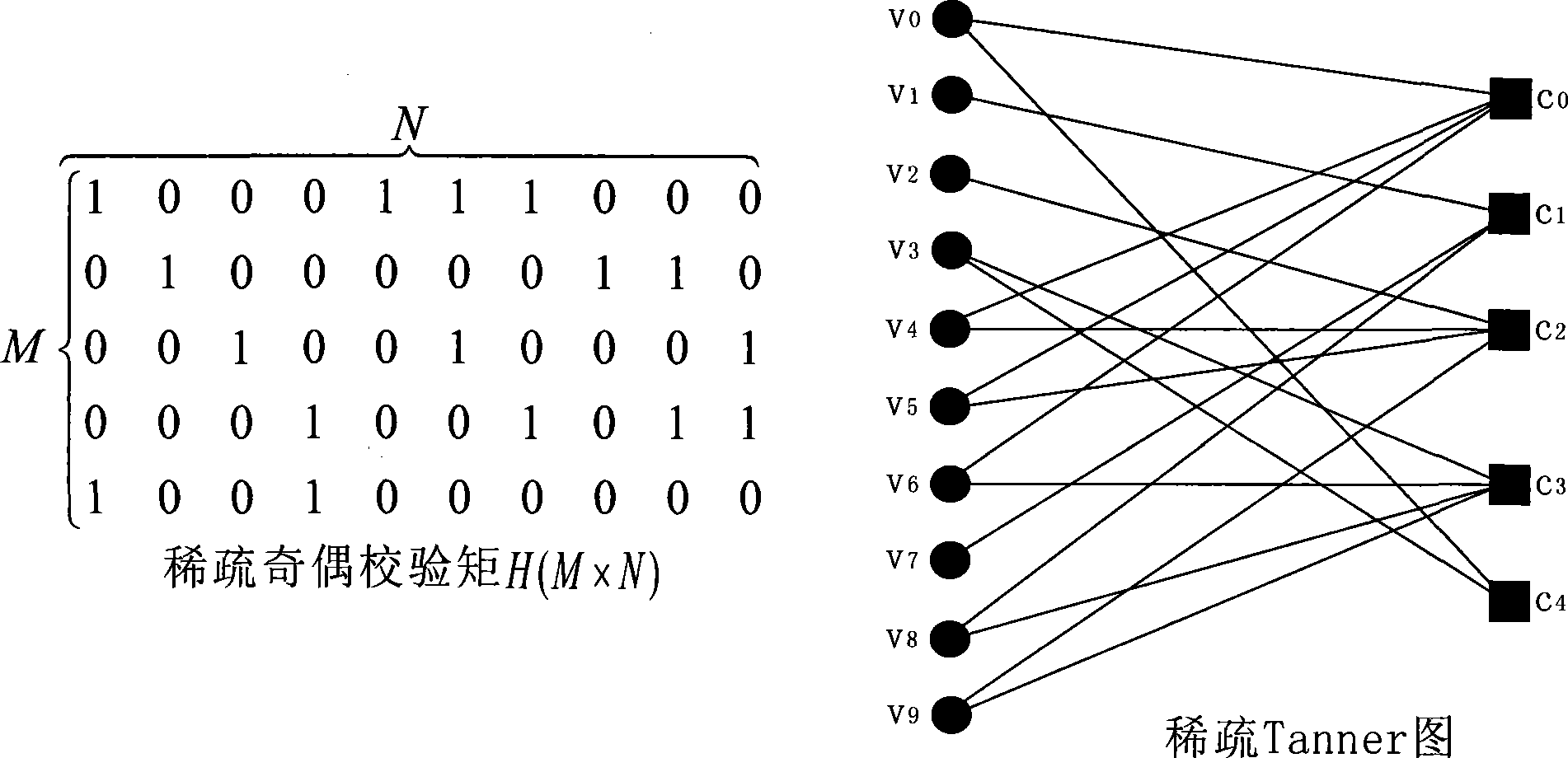
ActiveUS20050149840A1Reduce memory sizeHigh-speed and simple hardwareError detection/correctionError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsTanner graphAlgorithm
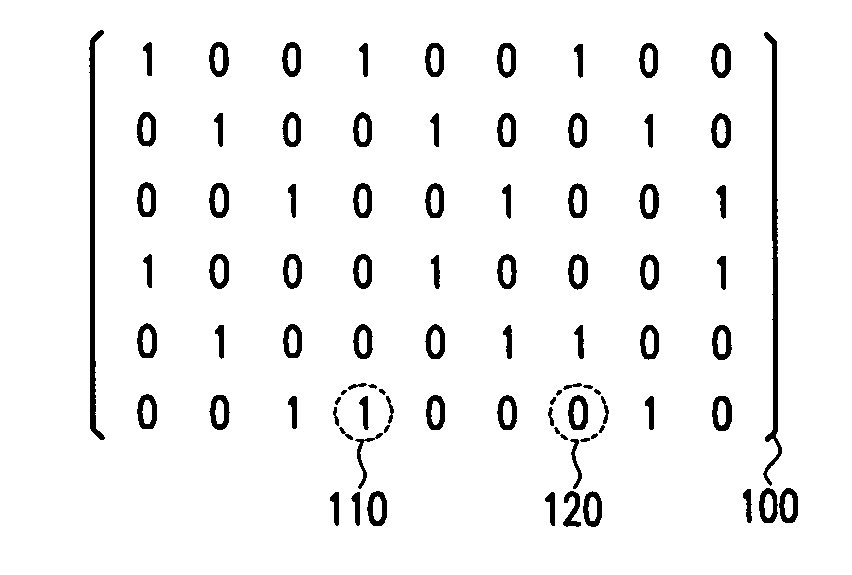
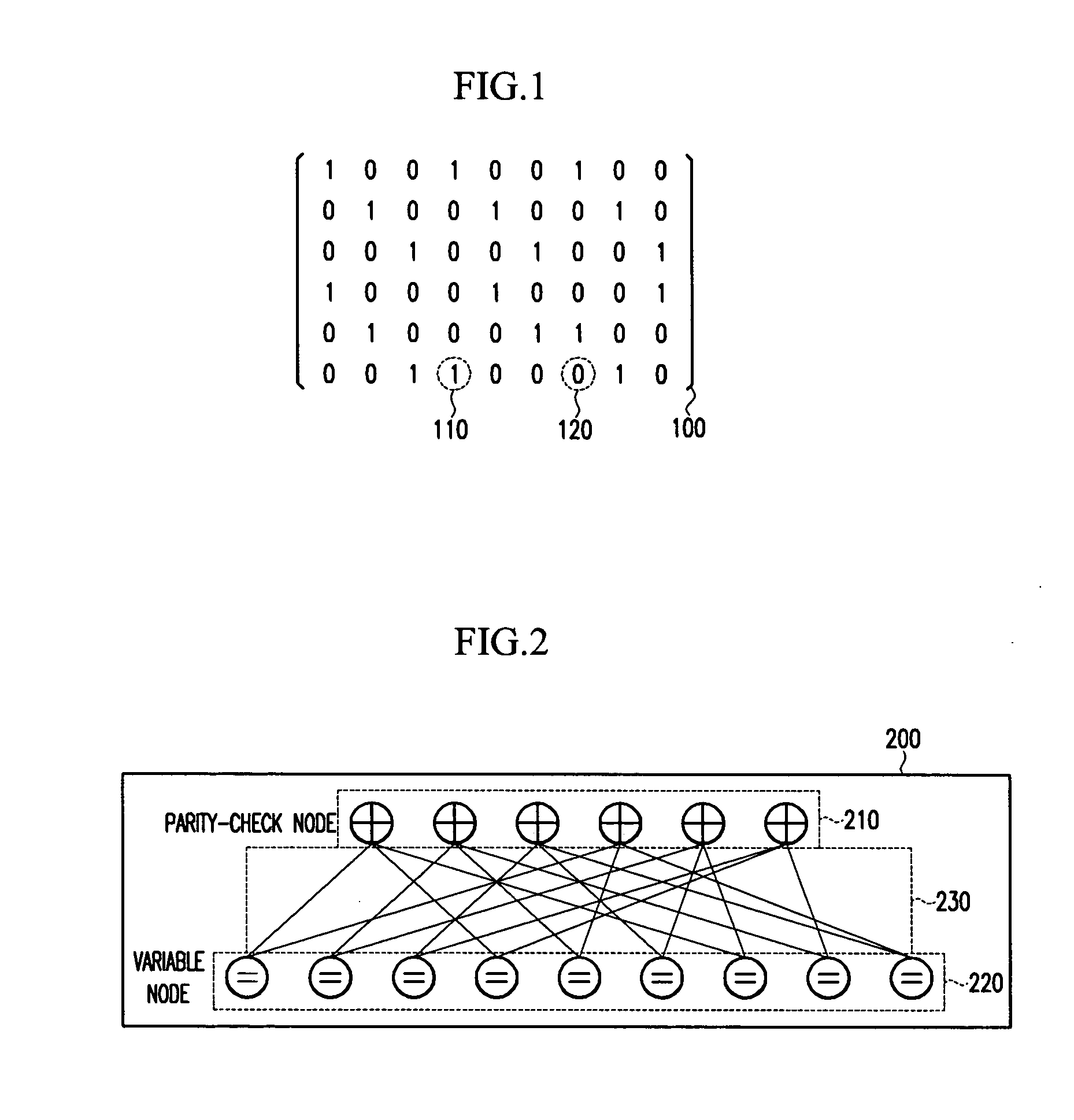
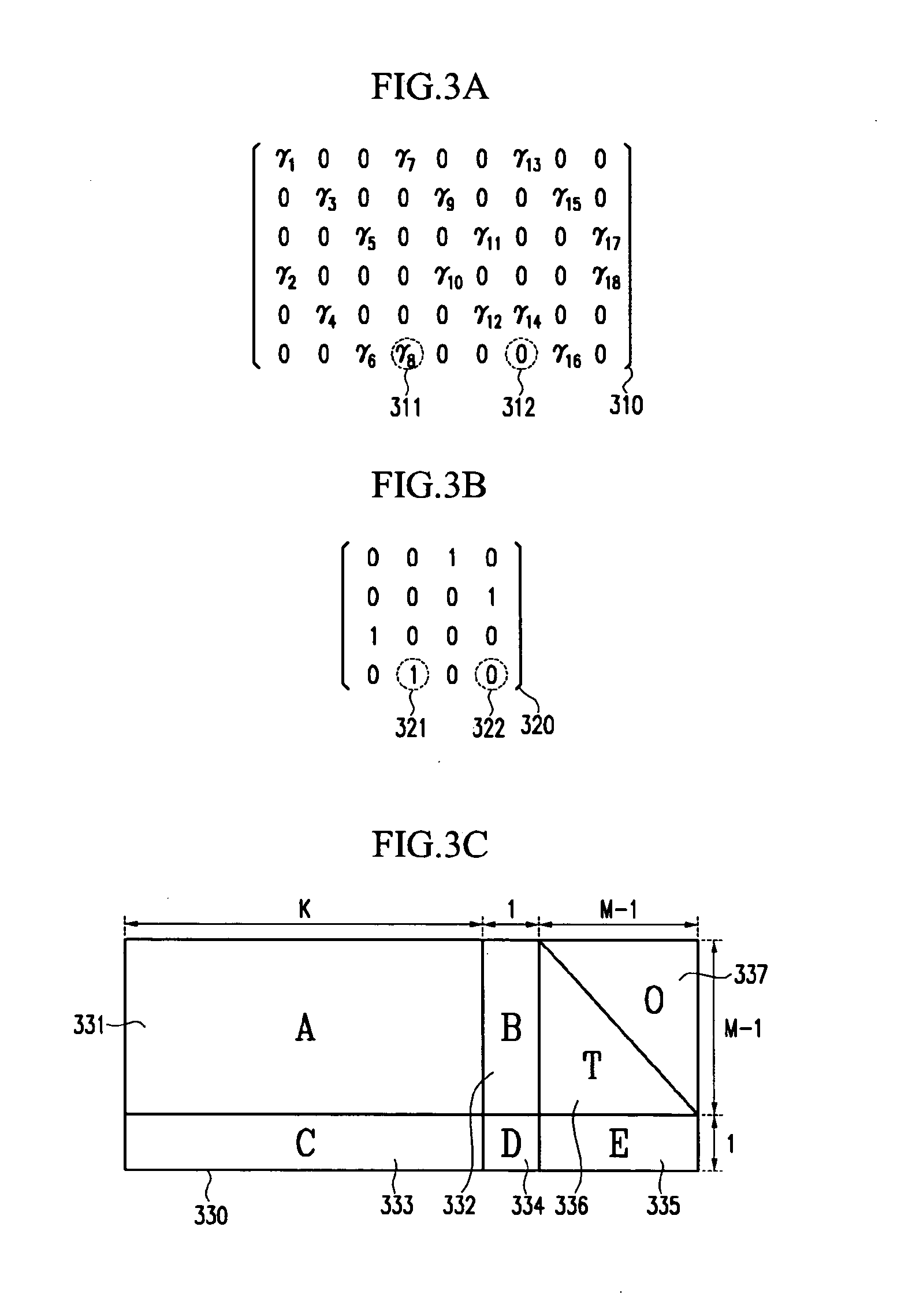
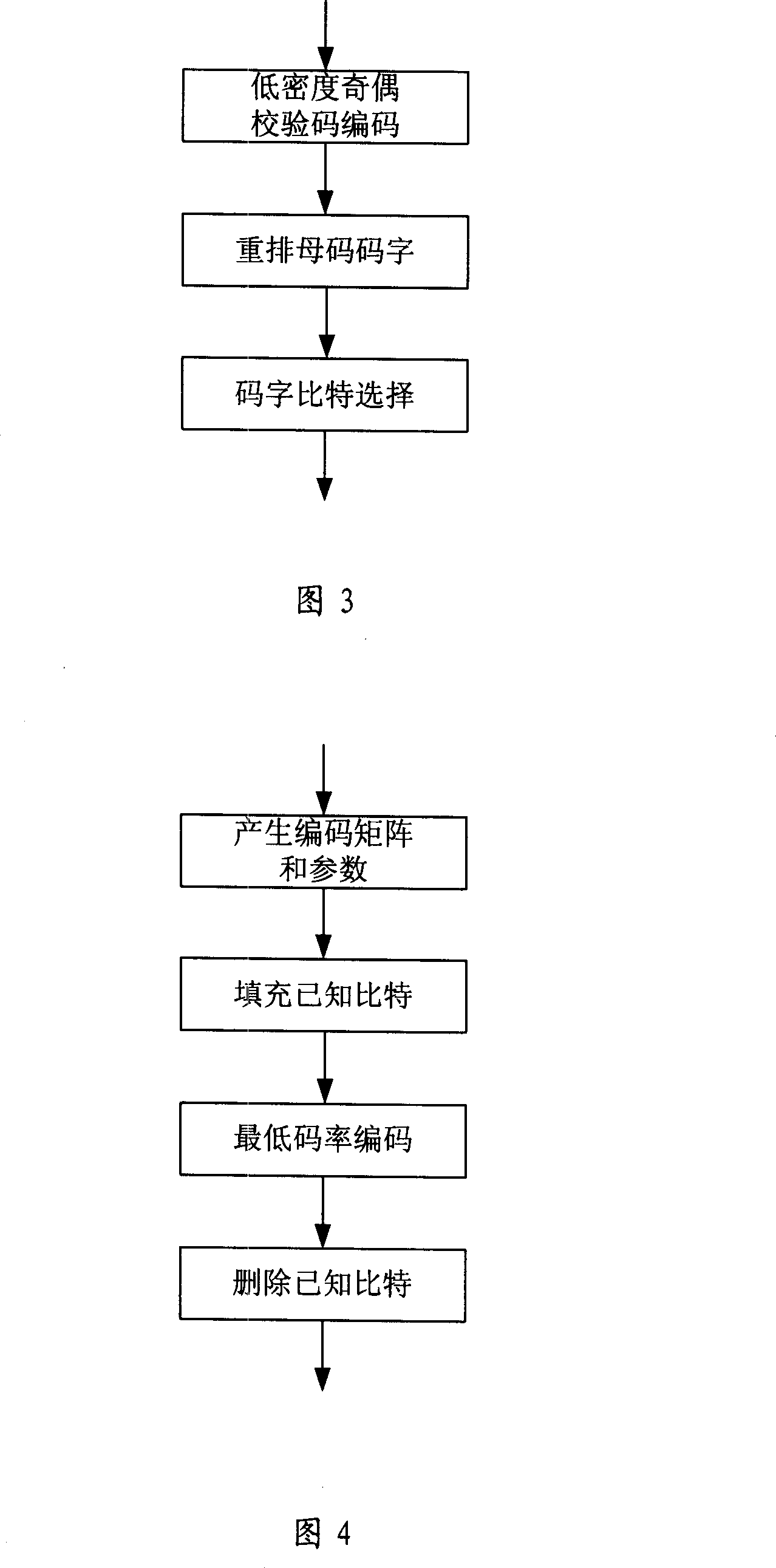
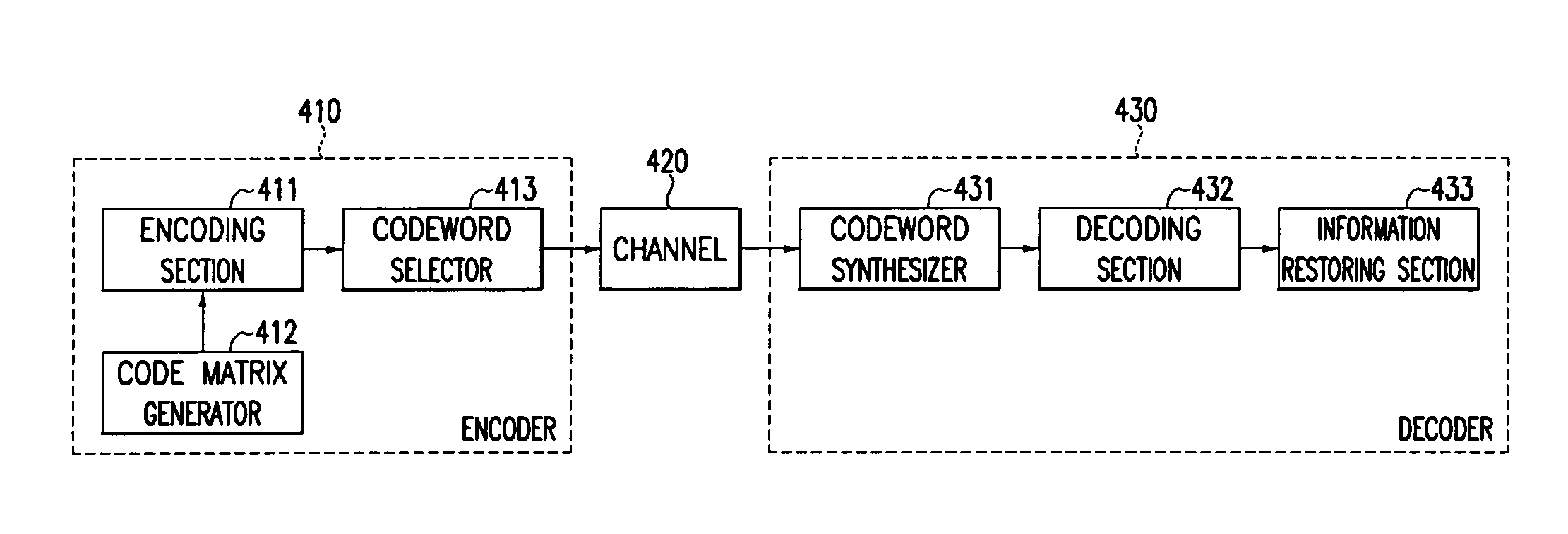
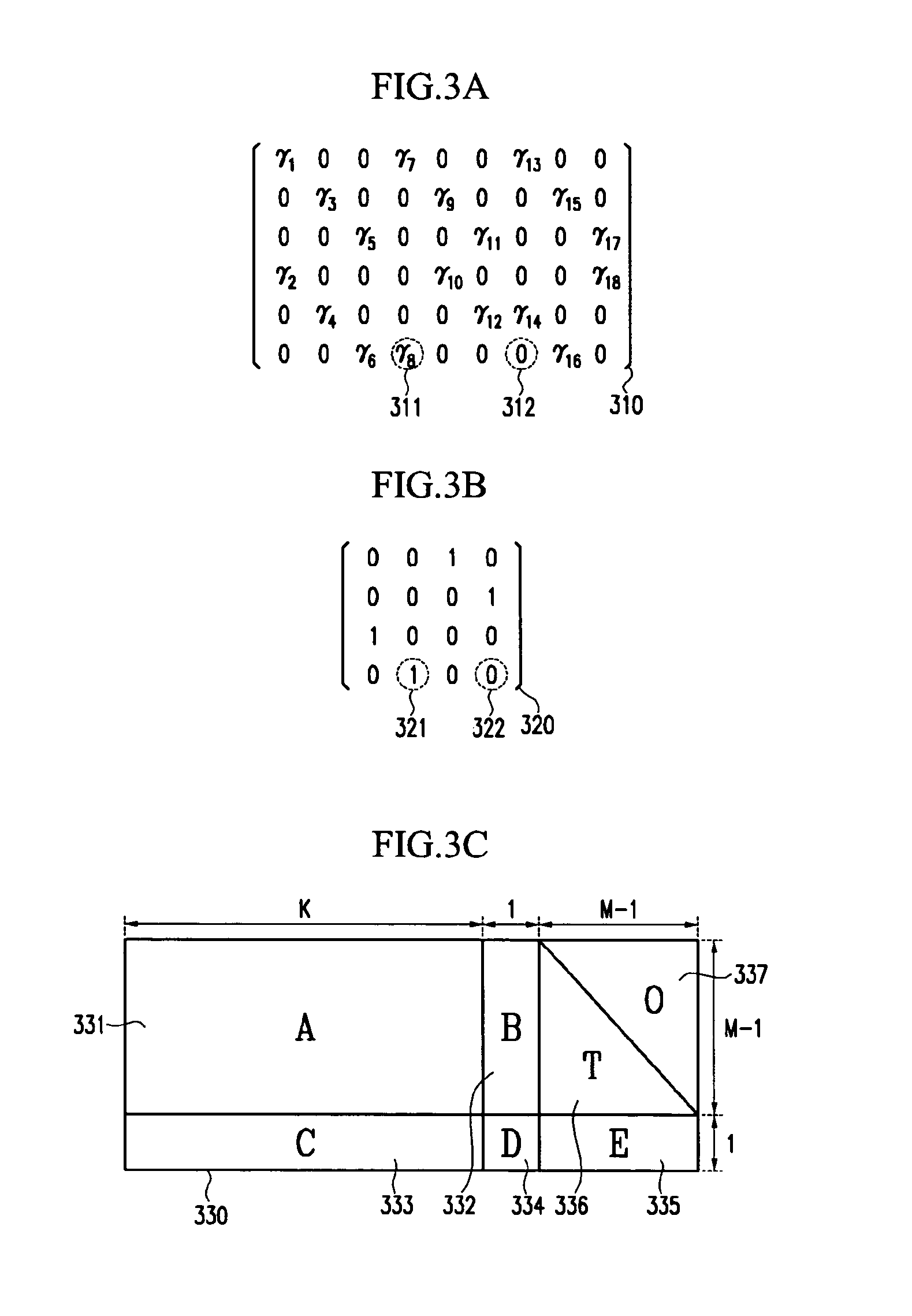
An LDPC code encoding apparatus includes: a code matrix generator for generating and transmitting a parity-check matrix comprising a combination of square matrices having a unique value on each row and column thereof; an encoding means encoding block LDPC codes according to the parity-check matrix received from the code matrix generator; and a codeword selector for puncturing the encoded result of the encoding means to generate an LDPC codeword. The code matrix generator divides an information word to be encoded into block matrices having a predetermined length to generate a vector information word. The encoding means encodes the block LDPC codes using the parity-check matrix divided into the block matrices and a Tanner graph divided into smaller graphs in correspondence to the parity-check matrix.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Method and apparatus for providing reduced memory low density parity check (LDPC) codes
ActiveUS20050091565A1Reduce memory requirementsAffect performanceError preventionError correction/detection using LDPC codesDigital videoTheoretical computer science
An approach is provided for generating Low Density Parity Check (LDPC) codes. An LDPC encoder generates a LDPC code with an outer Bose Chaudhuri Hocquenghem (BCH) code. For a rate 3 / 5 code, the approach provides a degree profile that yields reduced memory requirements for storage of the edge values without significantly affecting the performance with respect to an “unmodified” rate 3 / 5 code. The relevant parameters for the reduced memory LDPC codes are as follows: q=72, nldpc=64800, kldpc=nBCH=38880, kBCH=38688. The above approach has particular application in digital video broadcast services over satellite.
Owner:DTVG LICENSING INC
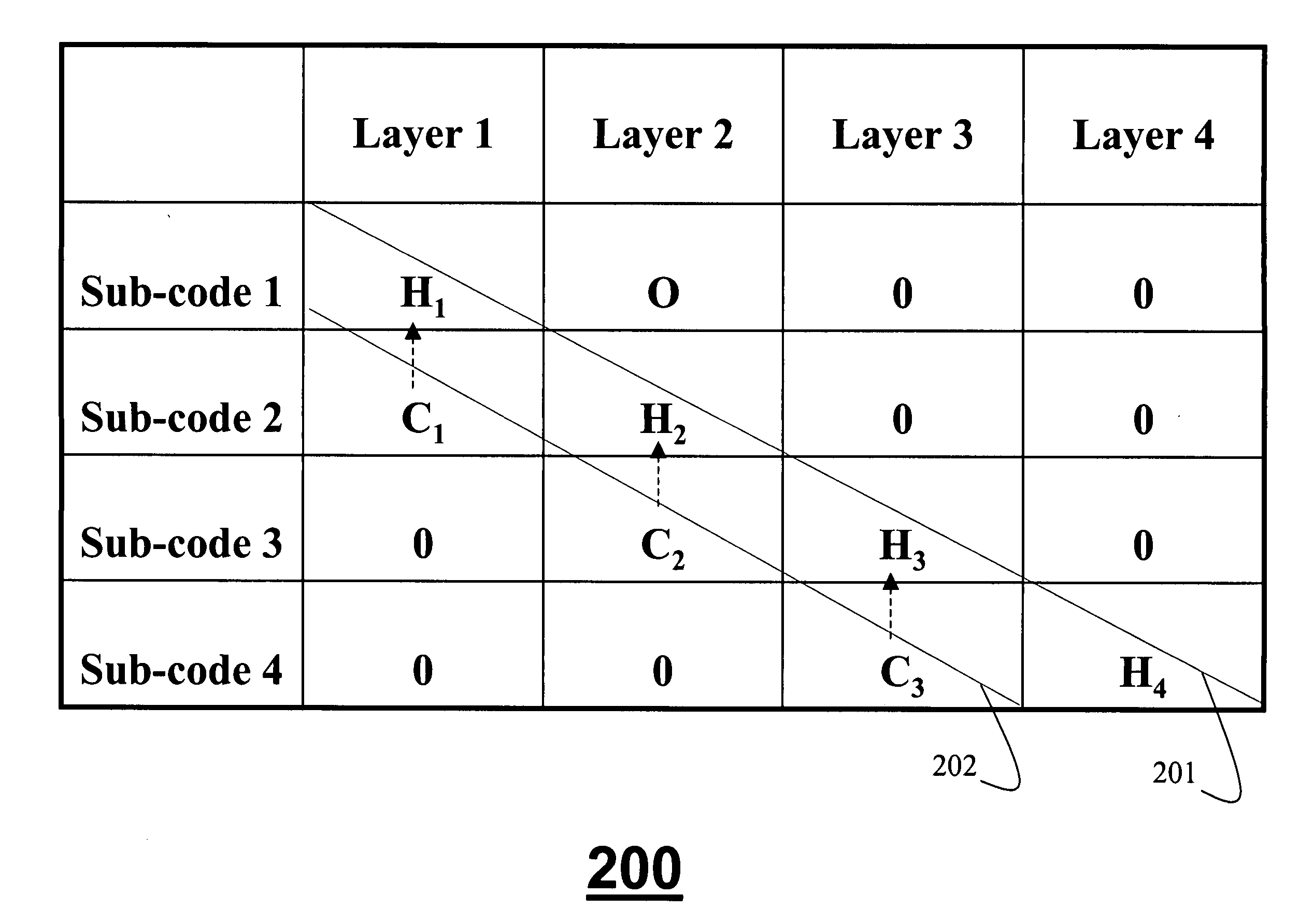
Quasi-block diagonal low-density parity-check code for MIMO systems
InactiveUS20050268202A1Easy to detectReduce error propagationMultiplex communicationCode conversionData streamCommunications system
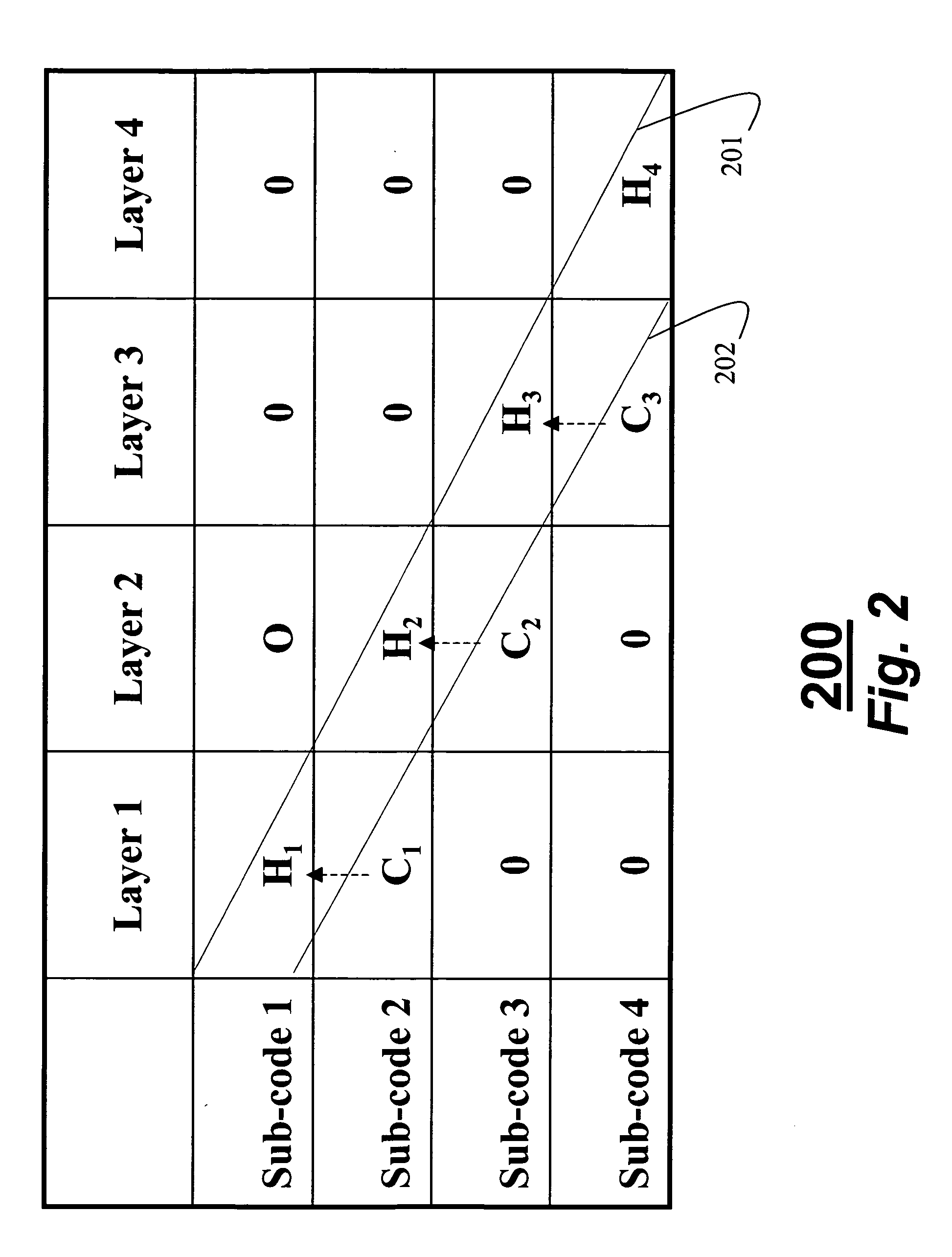
A method codes multiple data streams in multiple-input, multiple-output communications systems. In a transmitter, an input bitstream is encoded as codewords b in multiple layers. Each layer is modulated. A quasi-block diagonal, low-density parity-check code is applied to each layer, the quasi-block diagonal, parity-check code being a matrix H, the matrix H including one row of blocks for each subcode, and one row of blocks for each layer such that Hb=0 for any valid codeword. The layers are then forwarded to transmit antennas as a transmitted signal x.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Decoder and decoding method for low-density parity check codes constructed based on reed-solomon codes
ActiveUS20110126078A1Easy to useMitigate increase in implementation complexityCode conversionError correction/detection by combining multiple code structuresComputer architectureLow density
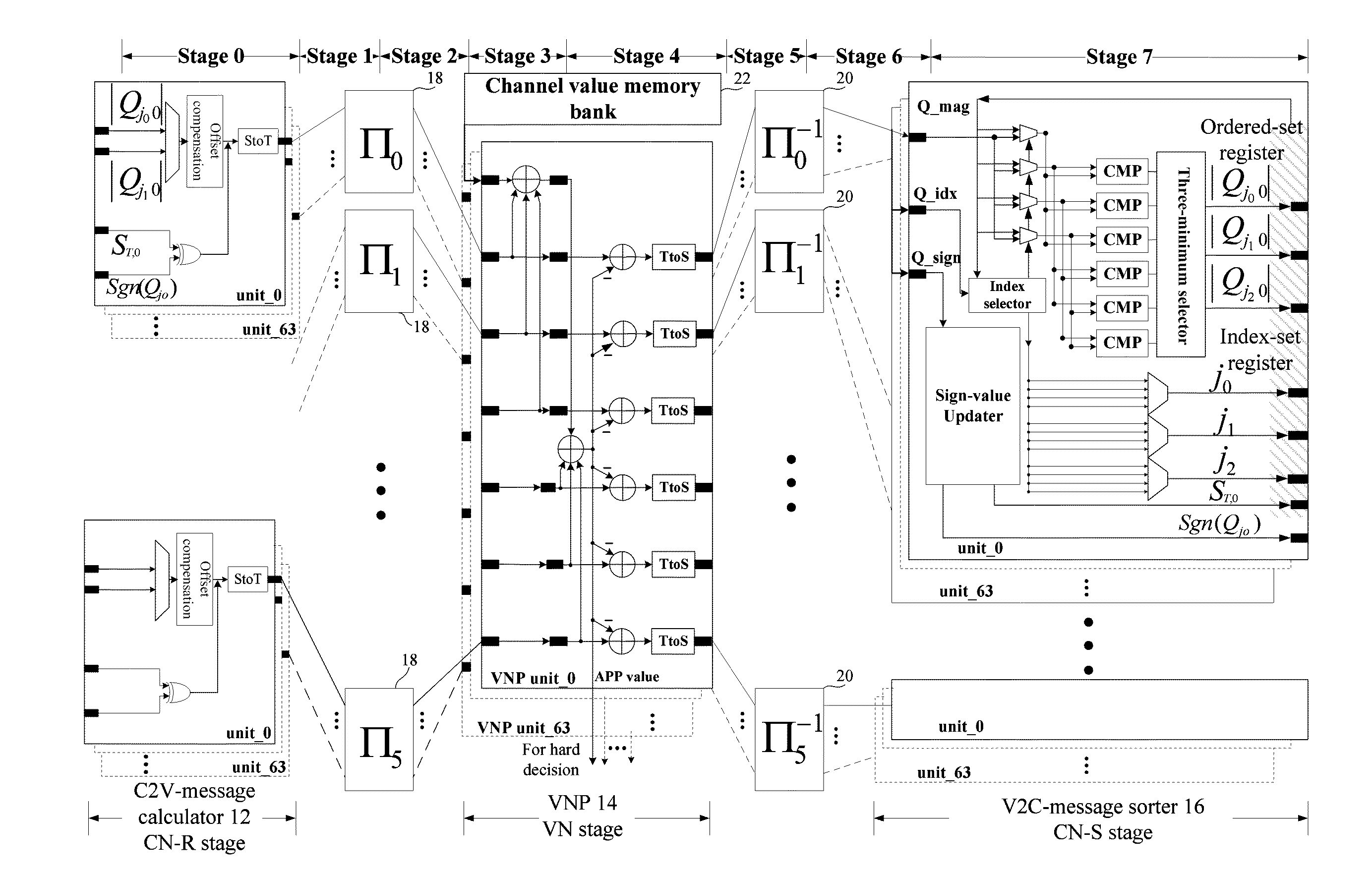
Configurable permutators in an LDPC decoder are provided. A partially-parallel architecture combined with the proposed permutators is used to mitigate the increase in implementation complexity for the multi-mode function. To overcome the difficulty in efficient implementation of a high-throughput decoder, the variable nodes are partitioned into several groups, and each group is processed sequentially in order to shorten the critical-path delay and, hence, increase the maximum operating frequency. In addition, shuffled message-passing decoding can be adopted in decoders according to the invention to increase the convergence speed, which reduces the number of iterations required to achieve a given bit-error-rate performance.
Owner:NATIONAL TSING HUA UNIVERSITY
Layered quasi-cyclic LDPC decoder with reduced-complexity circular shifter
ActiveUS8291283B1Improve computing efficiencyDecreased routing congestionError detection/correctionCode conversionRound complexityParallel computing
This disclosure relates generally to data decoding, and more particularly to iterative decoders for data encoded with a low-density parity check (LDPC) encoder. LDPC decoders are disclosed that use reduced-complexity circular shifters that may be used to decode predefined or designed QC-LDPC codes. In addition, methods to design codes which may have particular LDPC code performance capabilities and which may operate with such decoders using reduced-complexity circular shifters are provided. The generation of quasi-cyclic low density parity check codes and the use of circular shifters by LDPC decoders, may be done in such a way as to provide increased computational efficiency, decreased routing congestion, easier timing closure, and improved application performance.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
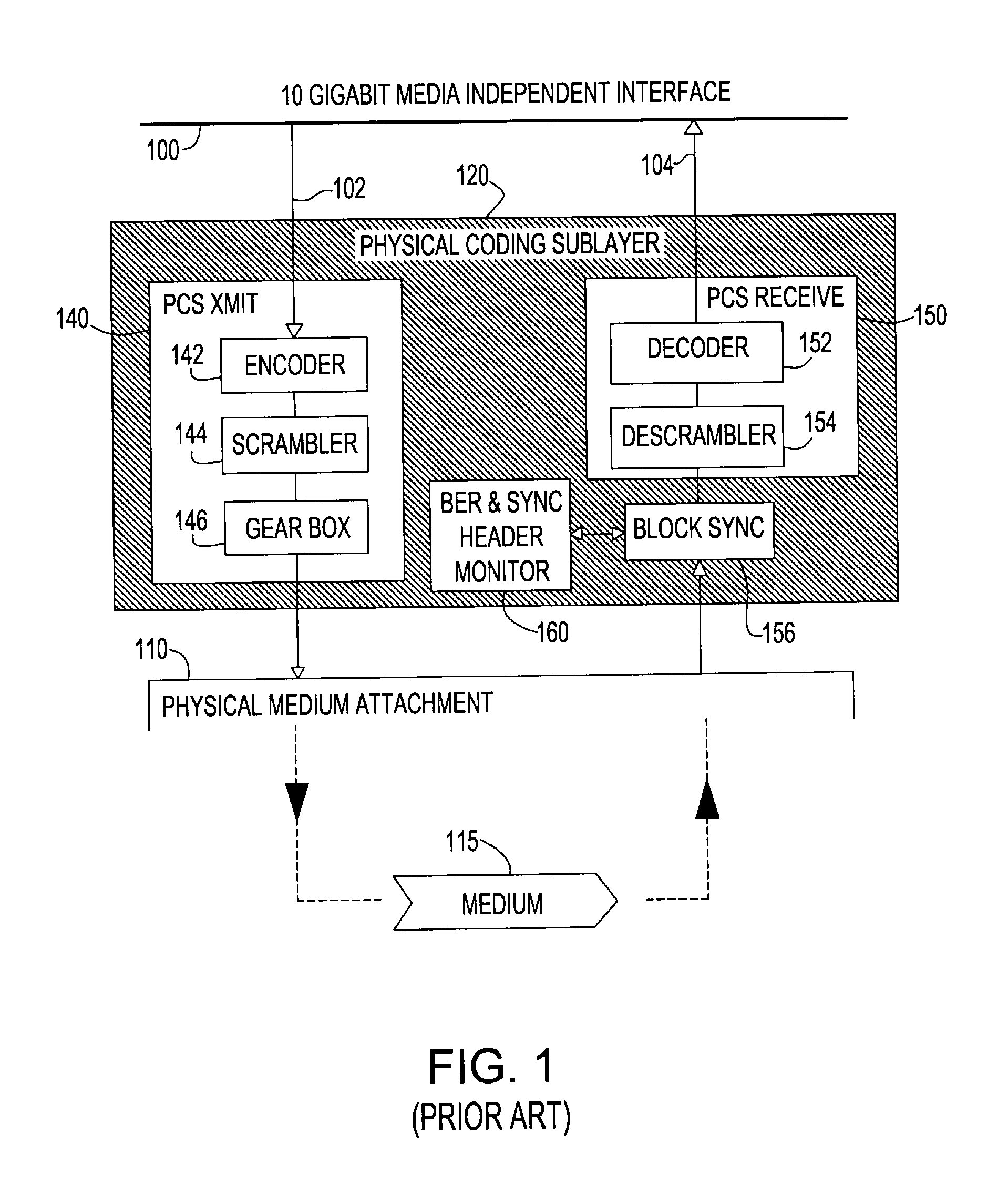
Forward error correction encoding for multiple link transmission capatible with 64b/66b scrambling
InactiveUS20080109707A1Reduce overheadCorrection errorError detection/correctionCode conversionHamming codeHigh bandwidth
Owner:IBM CORP
Method and system for providing long and short block length low density parity check (LDPC) codes
ActiveUS20050091570A1Minimizing storageMinimizing processing resourceError preventionCode conversionDigital videoLow density
An approach is provided for generating Low Density Parity Check (LDPC) codes. An LDPC encoder generates a LDPC code with an outer Bose Chaudhuri Hocquenghem (BCH) code. For ⅓ rate, the relevant parameters are as follows: q=120, nldpc=64,800, kldpc=nBCH=21600, kBCH=21408 (12 bit error correcting BCH). For ¼ rate, the LDPC code has the following relevant parameters: q=135, nldpc=64,800, kldpc=nBCH=16200, kBCH=16008 (12 bit error correcting BCH). For ⅖ rate, the following parameters exist: q=108, nldpc=64800, kldpc=nBCH=25920, kBCH=25728 (12 bit error correcting BCH). The above approach has particular application in digital video broadcast services over satellite.
Owner:DTVG LICENSING INC
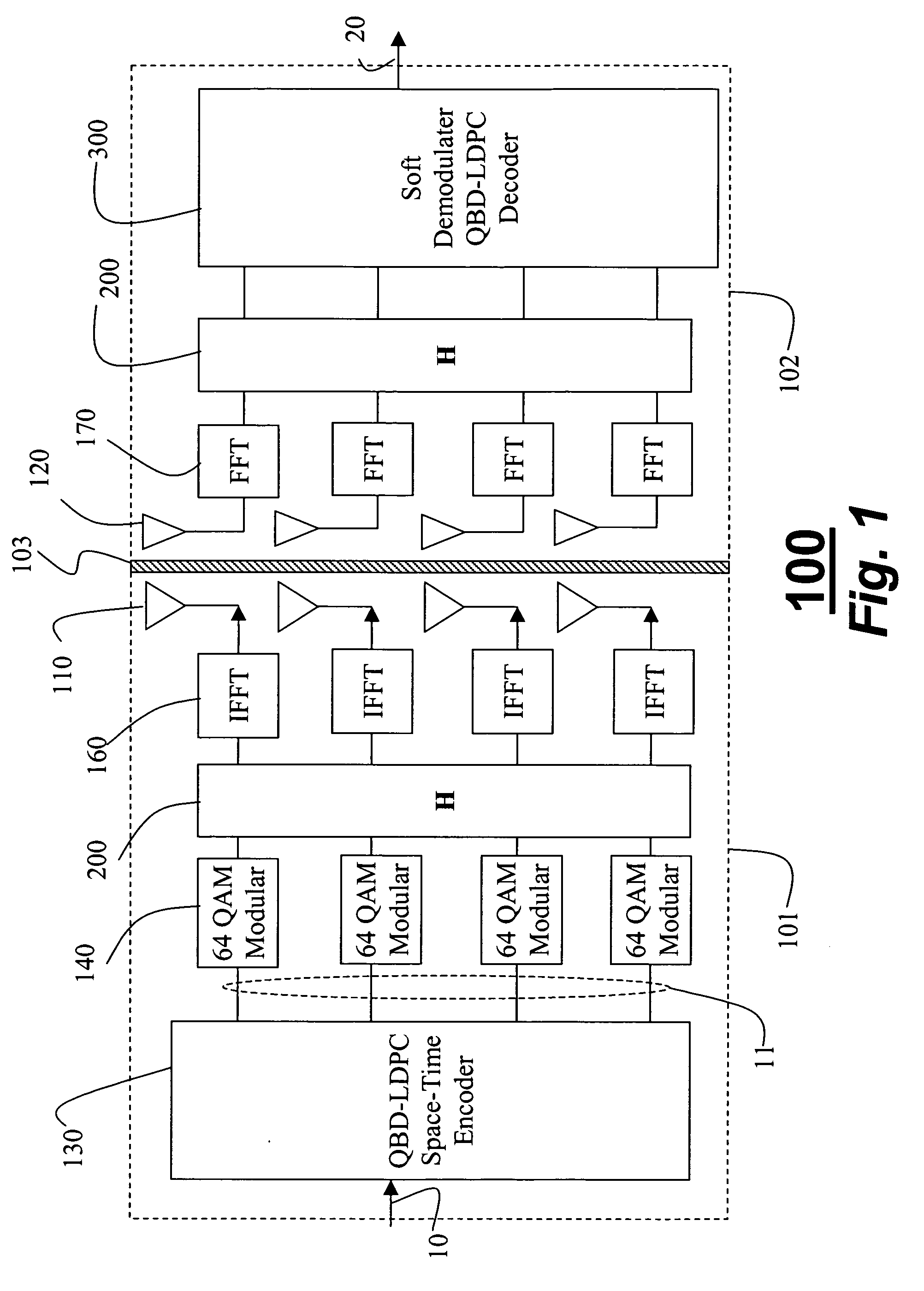
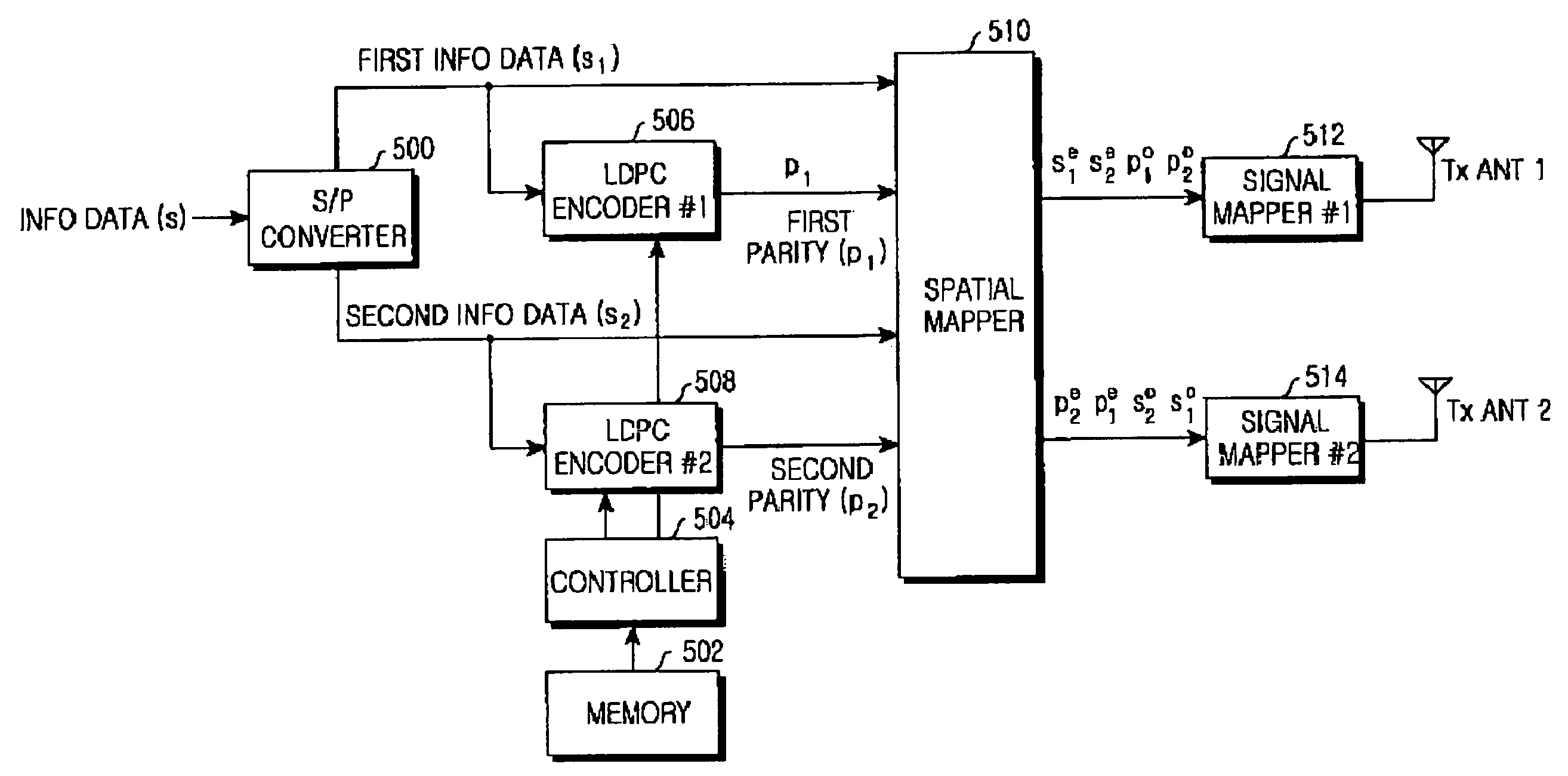
Apparatus and method for encoding and decoding a space-time low density parity check code with full diversity gain
ActiveUS20050204273A1Modulated-carrier systemsPolarisation/directional diversityAlgorithmParity-check matrix
In a mobile communication system including a transmitter and a receiver, an LDPC code is generated by encoding received information data such that a fifth partial matrix obtained by combining a second partial matrix having even-numbered columns of a first partial matrix corresponding to the information data with a fourth partial matrix having odd-numbered columns of a third partial matrix corresponding to a parity, and an eighth partial matrix obtained by combining a sixth partial matrix having odd-numbered columns of the first partial matrix with a seventh partial matrix having even-numbered columns of the third partial matrix correspond to a ninth partial matrix obtained by exclusive-ORing the first partial matrix and the third partial matrix and a parity check matrix having a predetermined rank in a binary field. A space-time LDPC code is generated by spatial-mapping the LDPC code according to a predetermined spatial mapping scheme.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and system for providing short block length low density parity check (LDPC) codes
ActiveUS20050060635A1Minimizing storageMinimizing processing resourceTransmission systemsError correction/detection using LDPC codesDigital videoTheoretical computer science
An approach is provided for generating Low Density Parity Check (LDPC) codes. An LDPC encoder generates a short LDPC code by shortening longer mother codes. The short LDPC code has an outer Bose Chaudhuri Hocquenghem (BCH) code. According to another aspect, for an LDPC code with code rate of 3 / 5 utilizing 8-PSK (Phase Shift Keying) modulation, an interleaver provides for interleaving bits of the output LDPC code by serially writing data associated with the LDPC code column-wise into a table and reading the data row-wise from right to left. The above approach has particular application in digital video broadcast services over satellite.
Owner:DTVG LICENSING INC
Algebraic low-density parity check code design for variable block sizes and code rates
InactiveUS20050204253A1Increase heightReadily implemented in hardwareError detection/correctionError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsVariable-length codeSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
A higher code rate Low-Density Parity Check (LDPC) matrix may be designed by concatenating additional matrices to a π-rotation parity check matrix. The concatenated matrix may be selected such that the resultant LDPC matrix exhibits good expansion characteristics to enable the LDPC matrix to be used with variable block length codes. The codes may be designed by generating an ensemble of available codes, encoding them with information vectors of weight 1 and 2 and discarding codes with a low minimum distance. The approximate upper bounds for the remaining codes are then calculated and a small set of codes with the lowest bound under high signal to noise ratio is selected. The girth distributions for the remaining codes are then calculated and the code that has the minimum number of short cycles is selected. The selected code is concatenated to the original v-rotation parity check matrix.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
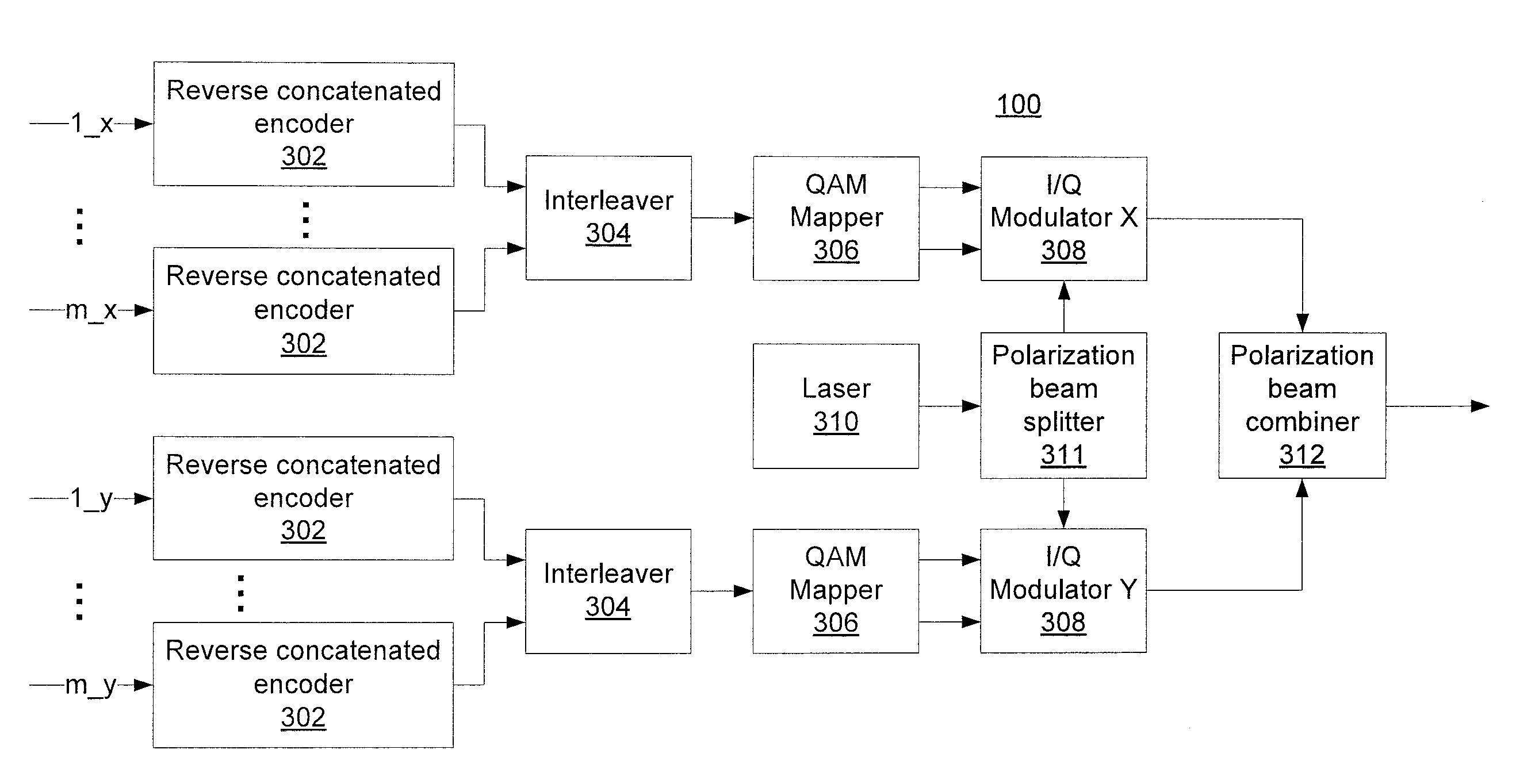
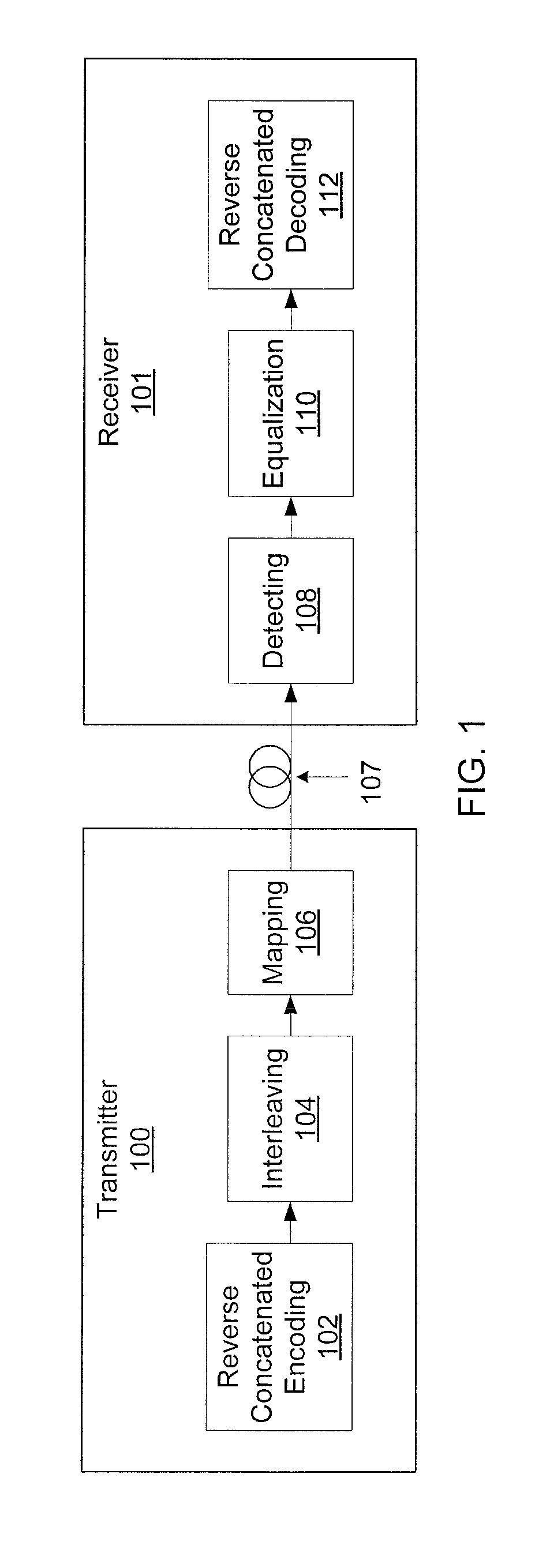
Reverse concatenated encoding and decoding
ActiveUS20120047415A1Improve decoding performanceReed-muller codesCode conversionComputer hardwareBlock code
Methods and systems for transmitting and receiving data include reverse concatenated encoding and decoding. Reverse concatenated decoding includes inner decoding the encoded stream with an inner decoder that uses a low-complexity linear-block code to produce an inner-decoder output stream, outer decoding the inner-decoder output stream with an outer decoder that uses a low-density parity-check code to produce an information stream, and iterating extrinsic bit reliabilities from the outer decoding for use in subsequent inner decoding to improve decoding performance.
Owner:NEC CORP
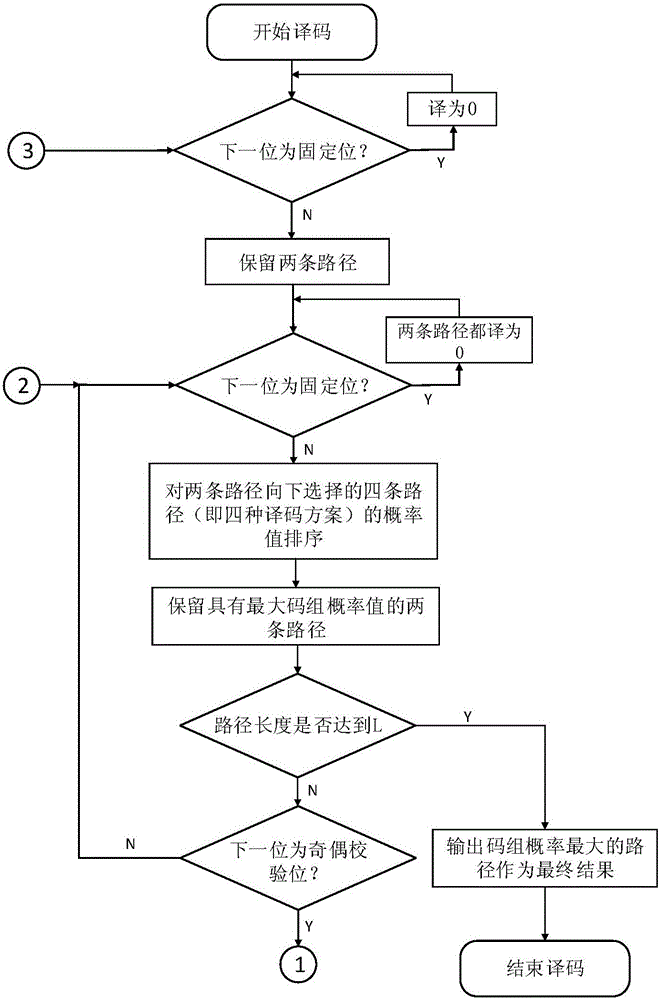
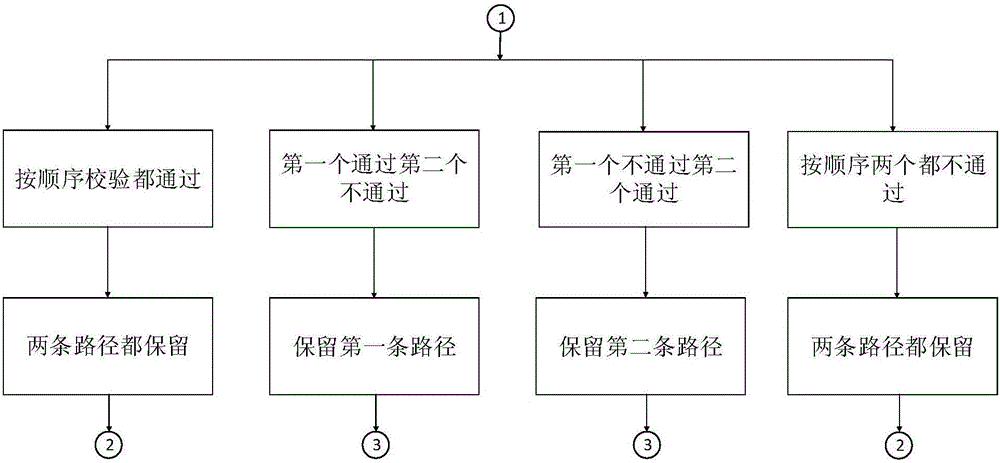
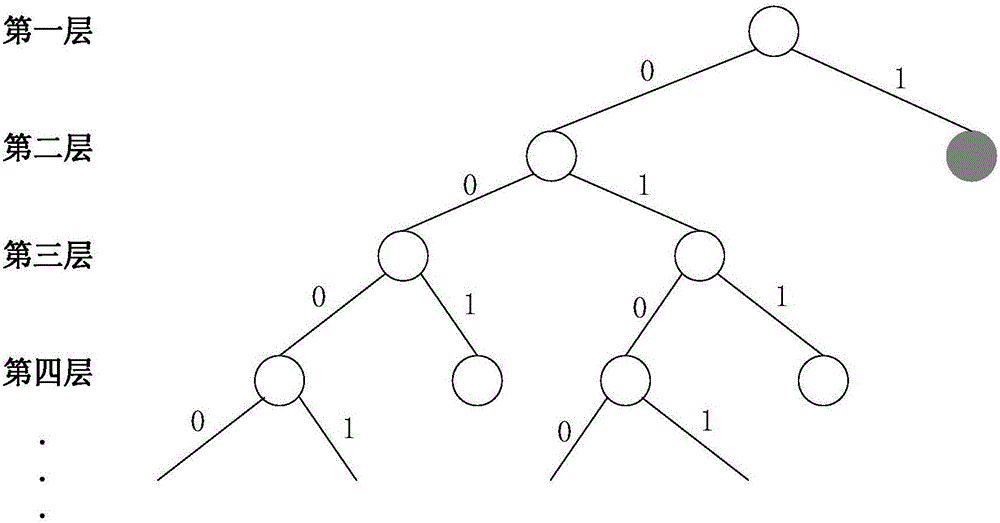
Low-complexity polarization code decryption SCL algorithm based on segmented verification assistance
InactiveCN105933010AReduce time complexityPrevent error propagationError correction/detection using linear codesError detection onlyRound complexitySignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
The invention discloses a low-complexity polarization code decryption SCL algorithm based on segmented verification assistance, and the algorithm selects a parity check code, repeatedly uses the parity check code in a decryption process, and achieves the performances of SCL-CRC24. Moreover, compared with a conventional scheme, the algorithm is better in low signal to noise ratio anti-noise performance and error rate. In addition, the spatial complexity of the algorithm is lower than that of the SCL-CRC24, the time complexity is greatly reduced, and the decoding speed is greatly improved. Compared with a CRC-24 verification algorithm sacrificing multiple information bits, the algorithm employs a parity check method, enables verification elements to be distributed in the information bits, is repeatedly used in the decoding process, and is lower in time complexity than the prior art.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
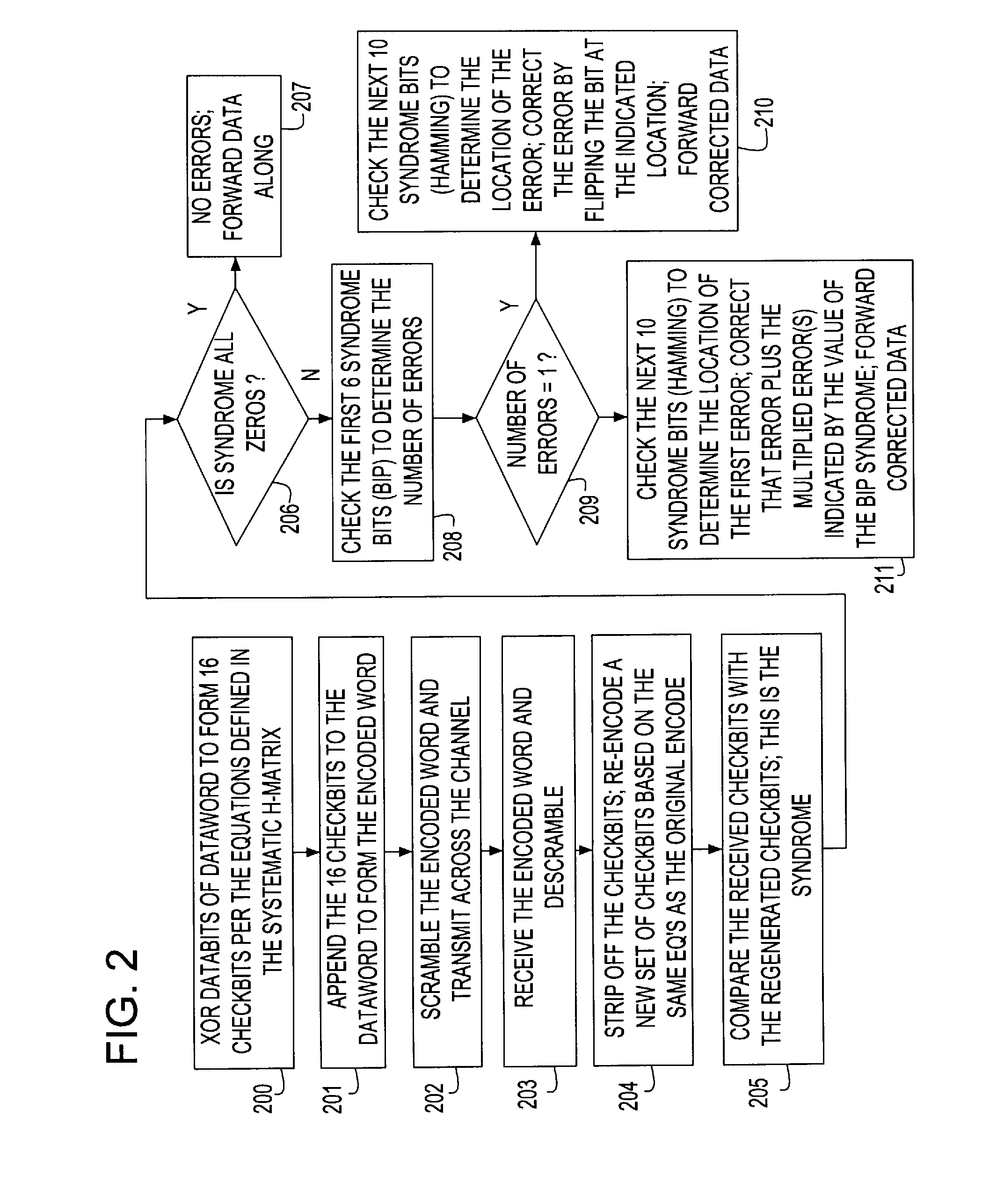
Generalized parity stripe data storage array
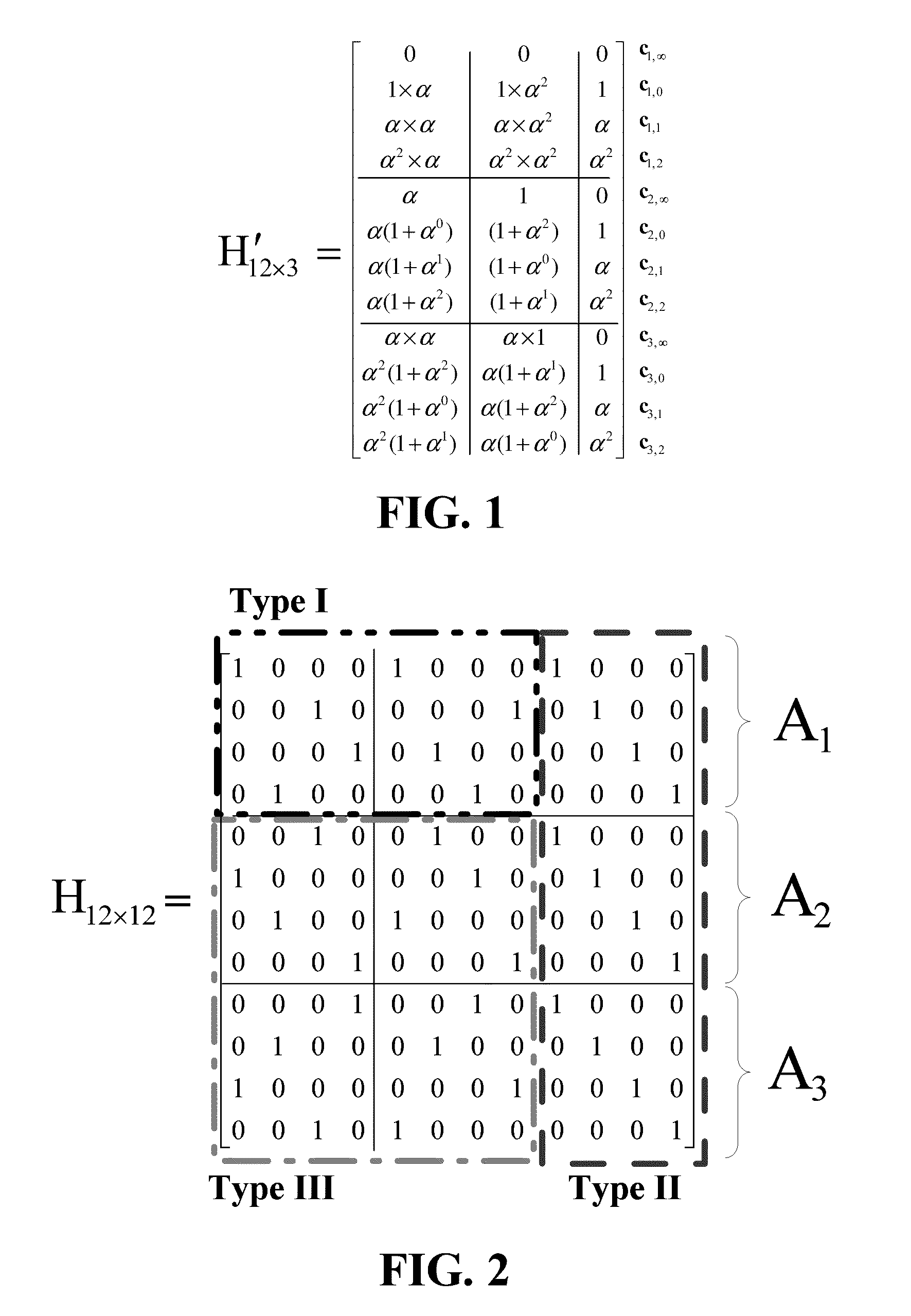
InactiveUS20050086575A1Increased Hamming distanceIncrease distanceNon-binary linear block codesError detection/correctionOn columnTheoretical computer science
The Hamming distance of an array of storage devices is increased by generating a parity check matrix based on column equations that are formed using an orthogonal parity code and includes a higher-order multiplier that changes each column. The higher order multiplier is selected to generate a finite basic field of a predetermined number of elements. The array has M rows and N columns, such that M is greater than or equal to three and N is greater than or equal to three. Row 1 through row M-2 of the array each have n-p data storage devices and p parity storage devices. Row M-1 of the array has n-(p+1) data storage devices and (p+1) parity storage devices. Lastly, row M of the array has N parity storage devices.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method for forming mixed automatic request re-sending packet of low density parity check code
ActiveCN101005334AAddresses flaws in Incremental Redundancy HARQ supportImprove performanceError prevention/detection by using return channelCode conversionComputer hardwareCrate
The method includes following steps: (1) based on inputted K bits information packet, encoder for low-density parity check code crates code word in NFIR bits LDPC HARQ parent code; the code word includes bit information packet, expanded check bit packet, and remaining check bit packet after deletion; the created code word is sent to HARQ buffer; (2) rearranging bits of code word of LDPC HARQ parent code in HARQ buffer, and keeping sequence of information bits and expanded check bits unchanged, and changing sequence of remaining check bits; (3) selecting bits code word in sequence from rearranged code word of HARQ parent code, i.e. first transmission starts up from first system bits, and then, start position of each transmission follows close to position of ending the previous transmission so as to generate binary sequence of HARQ packet.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Apparatus for encoding and decoding of low-density parity-check codes, and method thereof
ActiveUS7395494B2Reduce memory sizeHigh-speed and simple hardwareError detection/correctionError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsTanner graphParity-check matrix
An LDPC code encoding apparatus includes: a code matrix generator for generating and transmitting a parity-check matrix comprising a combination of square matrices having a unique value on each row and column thereof; an encoding means encoding block LDPC codes according to the parity-check matrix received from the code matrix generator; and a codeword selector for puncturing the encoded result of the encoding means to generate an LDPC codeword. The code matrix generator divides an information word to be encoded into block matrices having a predetermined length to generate a vector information word. The encoding means encodes the block LDPC codes using the parity-check matrix divided into the block matrices and a Tanner graph divided into smaller graphs in correspondence to the parity-check matrix.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Quasi-cyclic low-density parity-check code decoder and decoding method
ActiveCN101534166AFast convergenceSmall scaleError preventionError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsTheoretical computer scienceLow density
Owner:上海明波通信技术股份有限公司
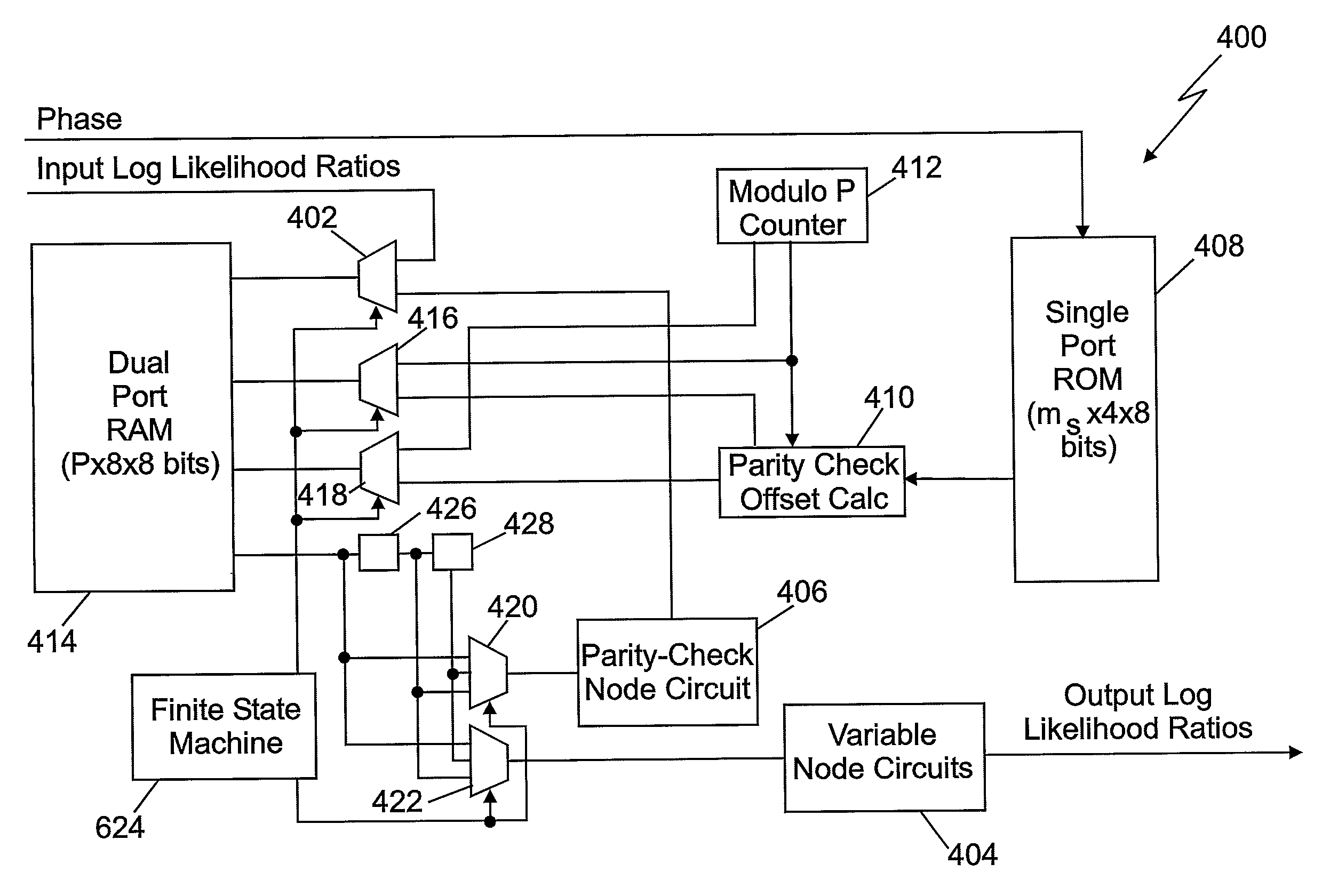
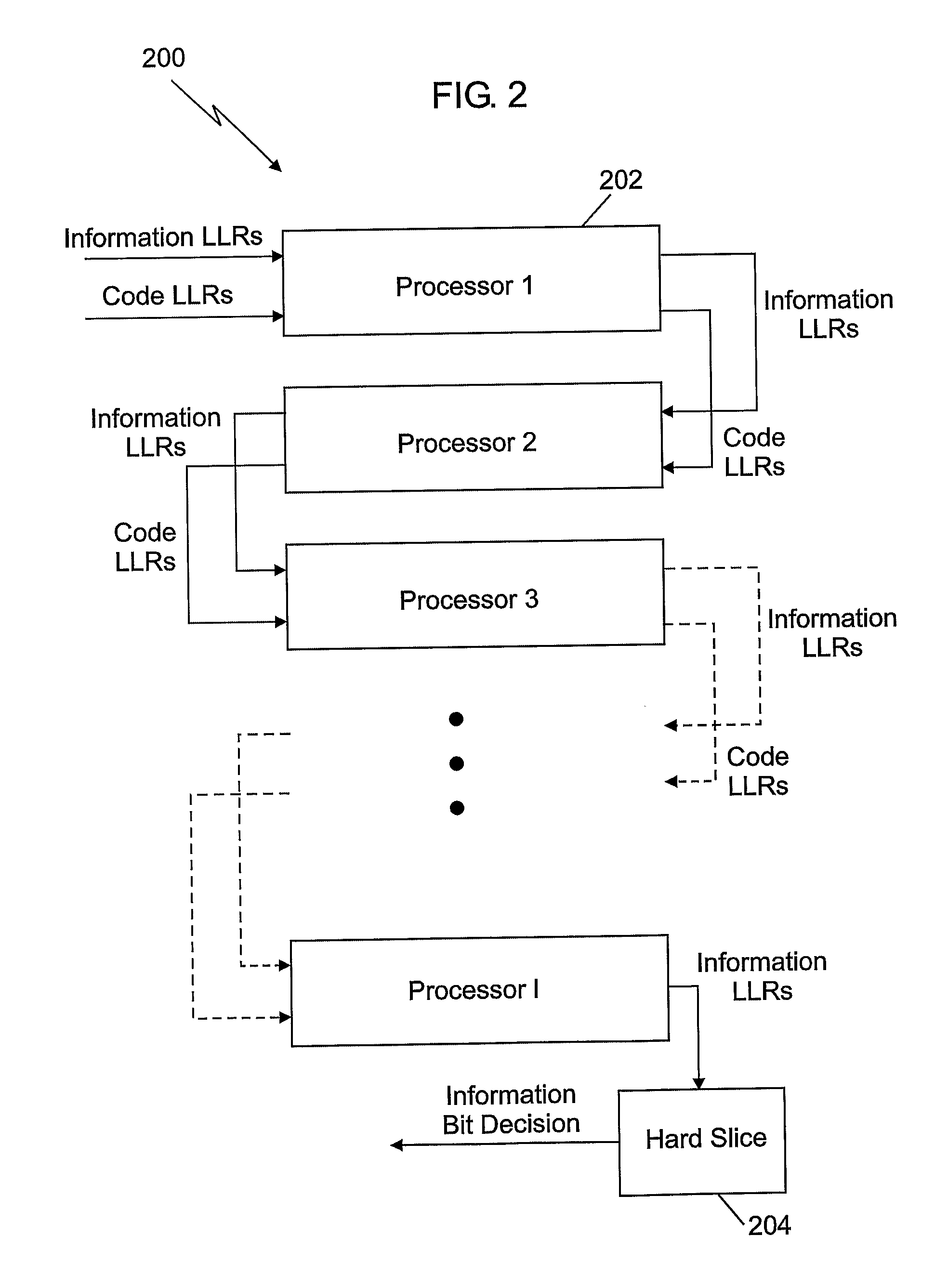
Decoder for Low-Density Parity-Check Convolutional Codes
InactiveUS20080195913A1Accurately decisionedImprove accuracyError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsCode conversionRandom access memoryParallel computing
Decoder for low-density parity check convolutional codes. In at least some embodiments, a decoder (200) for arbitrary length blocks of low-density, parity-check codes includes a plurality of interconnected processors (202), which further include a plurality of interconnected nodes. A memory can be interconnected with the nodes to store intermediate log likelihood ratio (LLR) values based on channel LLR values. Thus, LLR values having successively improved accuracy relative to the channel LLR values can be output from each processor, and eventually used to decision information bits. In some embodiments, the memory is a random access memory (RAM) device that is adapted to store the intermediate LLR values in a circular buffer. Additionally, a storage device such as a read-only memory (ROM) device can be used to generate a predetermined plurality of addresses for reading and writing LLR values.
Owner:THE GOVERNORS OF THE UNIV OF ALBERTA
Method for encoding low-density parity check code
ActiveUS20070022354A1Simplify the coding processImprove performanceError detection/correctionError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsTheoretical computer scienceDiagonal matrix
An apparatus and method for encoding low-density parity check (LDPC) codes. The method for generating a low-density parity check code formed of an information-part matrix and a parity-part matrix comprises the steps of converting the information-part matrix into an array code structure and assigning a degree sequence to each submatrix column; extending a dual-diagonal matrix corresponding to the parity-part matrix such that an offset value between diagonals has a random value; lifting the normalized dual-diagonal matrix; determining an offset value for cyclic column shift for each submatrix of the lifted normalized dual-diagonal matrix; and determining a parity symbol corresponding to a column of the parity-part matrix.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
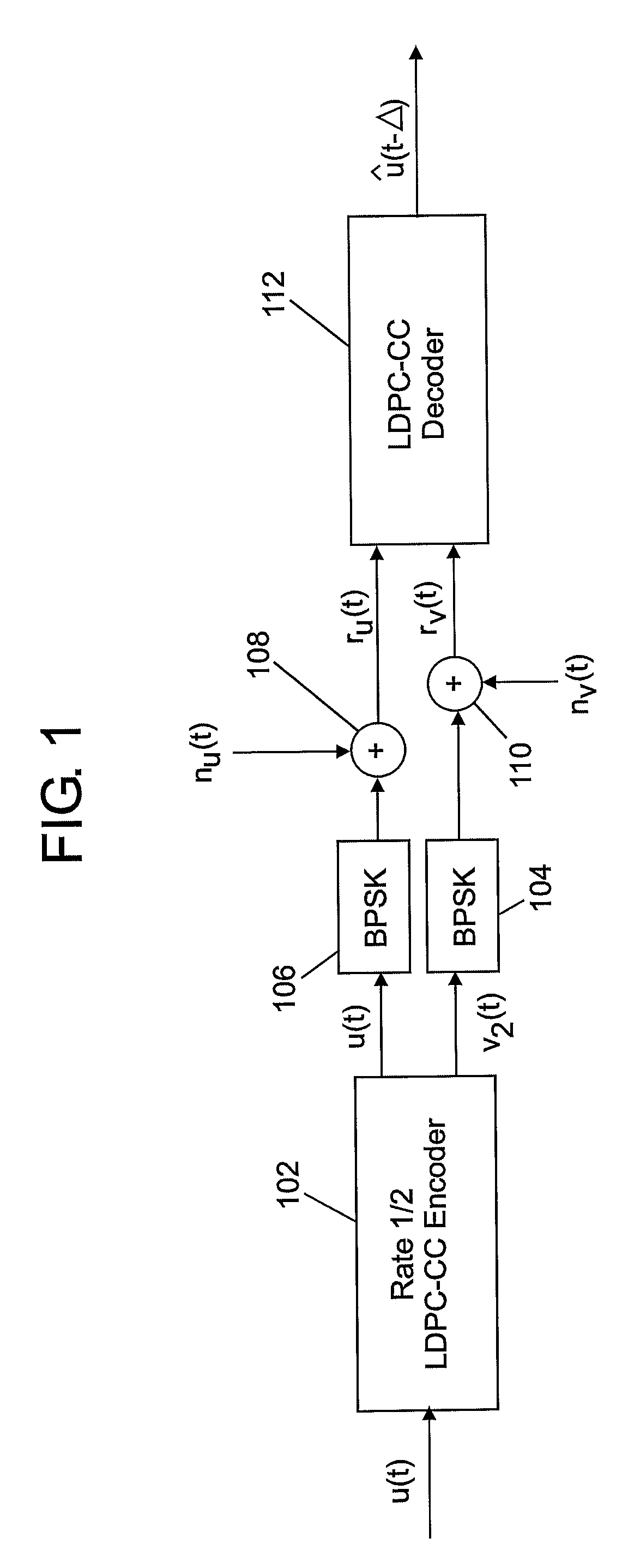
Encoding method, encoder, and decoder
ActiveUS20100205511A1Good reception qualityImprove reception qualityError correction/detection using convolutional codesError preventionLinear operationConvolution
A low-density parity check convolution code (LDPC-CC) is made, and a signal sequence is sent after subjected to an error-correcting encodement using the low-density parity check convolution code. In this case, a low-density parity check code of a time-variant period (3g) is created by linear operations of first to 3g-th (letter g designates a positive integer) parity check polynomials and input data.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
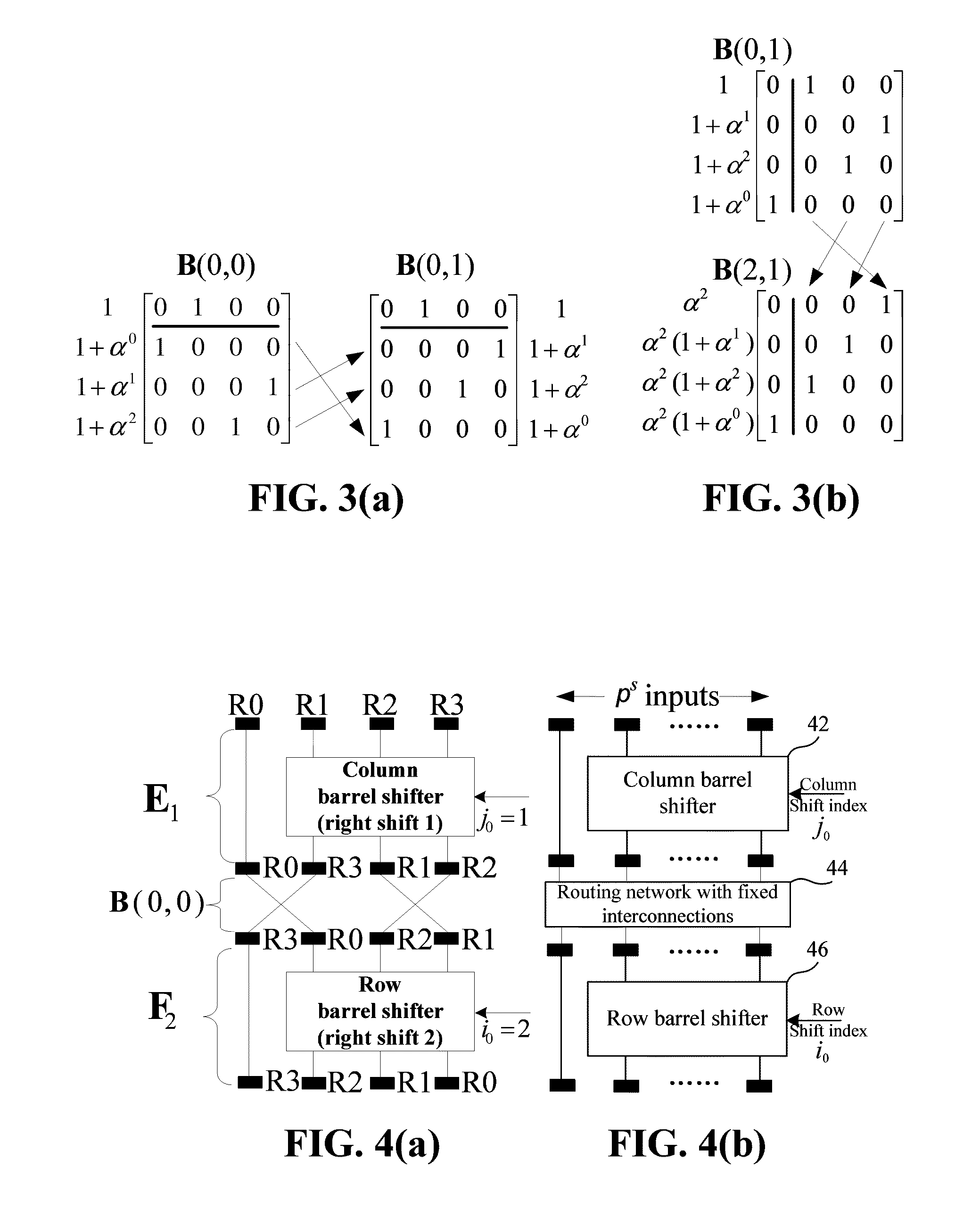
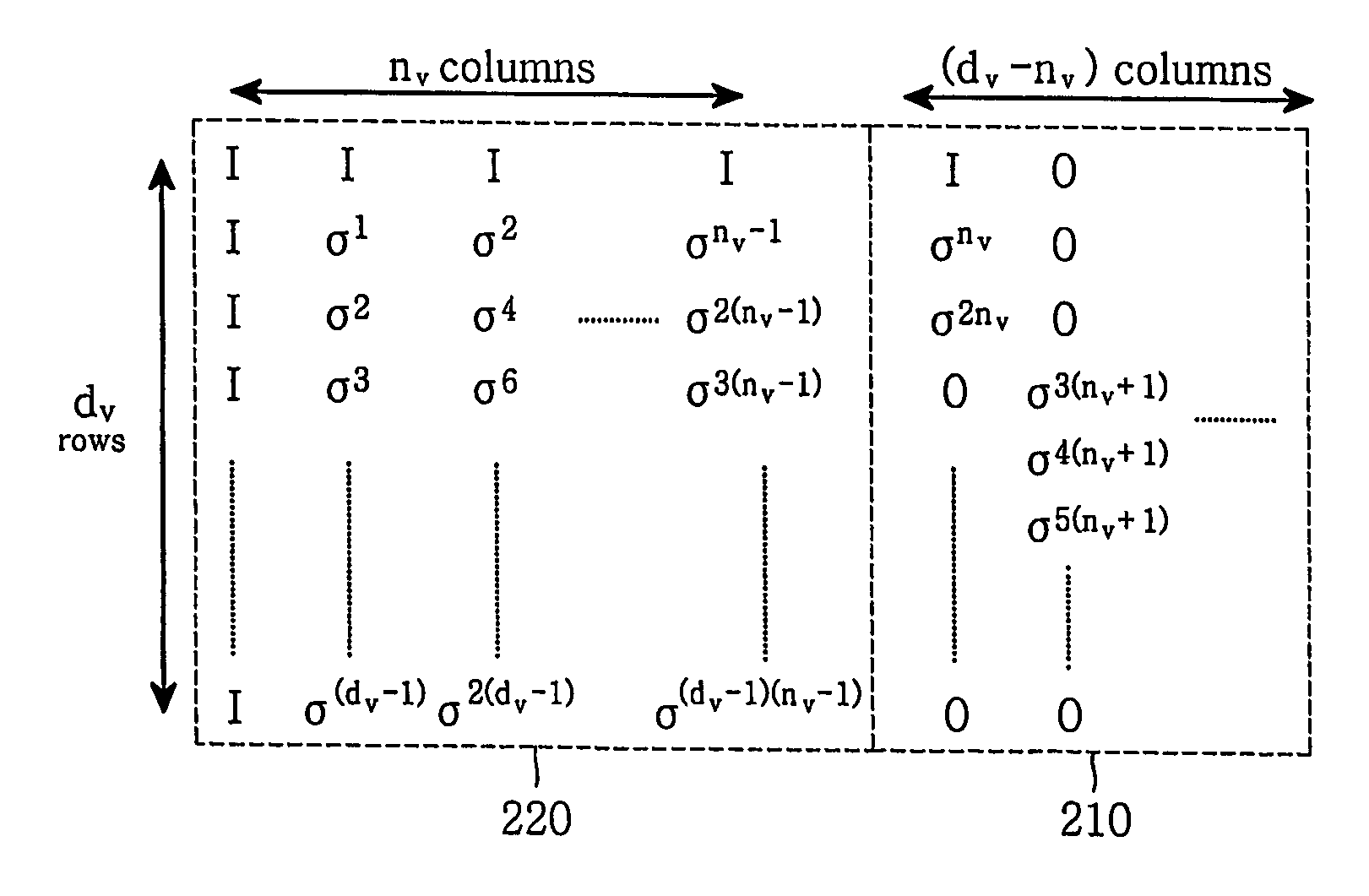
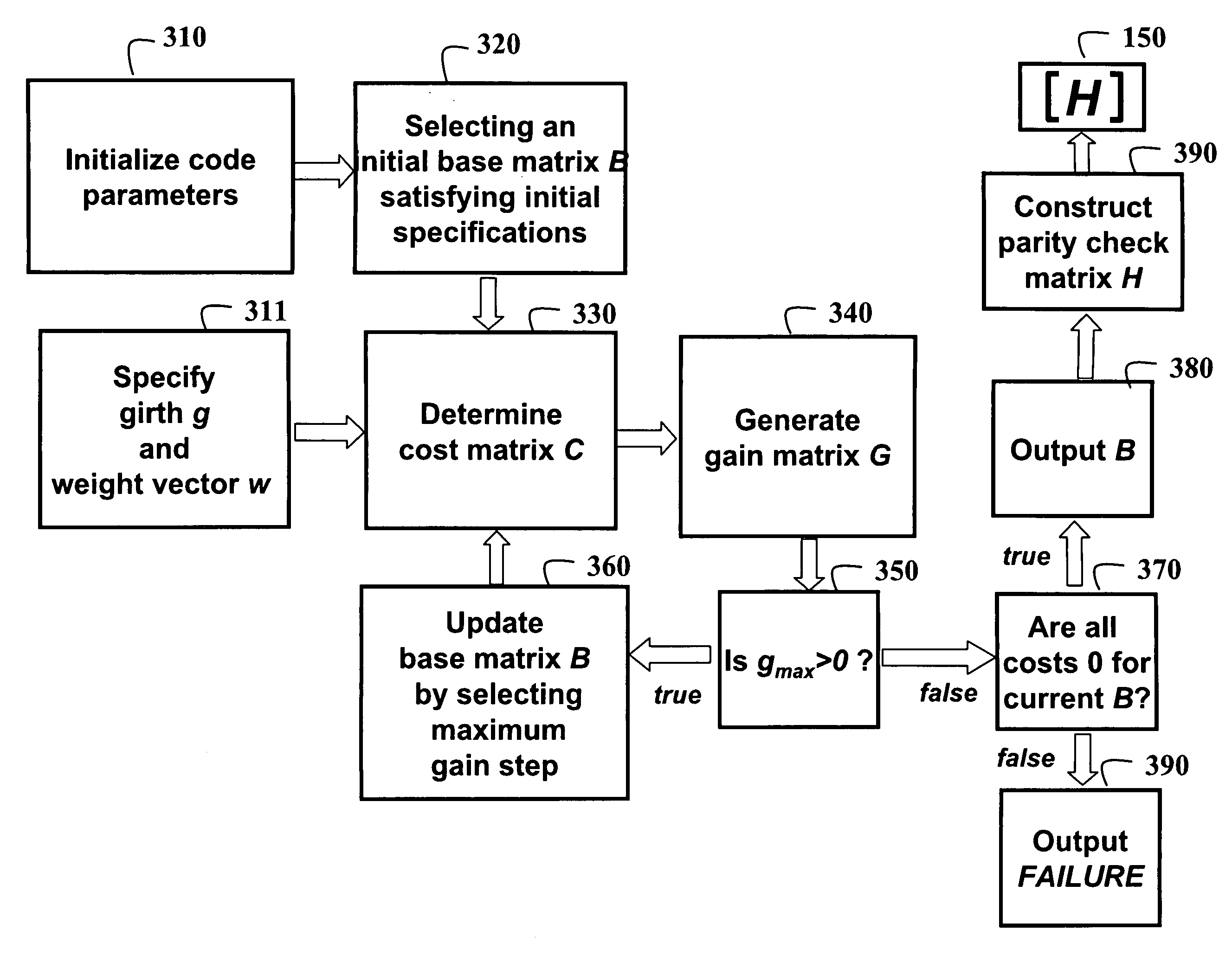
Method for constructing large-girth quasi-cyclic low-density parity-check codes
ActiveUS8103931B2Short block-lengthLess timeCode conversionChecking code calculationsSingle elementTheoretical computer science
A method constructs a code, wherein the code is a large-girth quasi-cyclic low-density parity-check code. A base matrix is selected for the code. A cost matrix corresponding to the base matrix is determined. A single element in the base is changed repeatedly maximize a reduction in cost. A parity check matrix is constructing for the code from the base matrix when the cost is zero, and an information block is encoded as a code word using the parity check matrix in an encoder.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Decoding apparatus, decoding method, and program to decode low density parity check codes
ActiveUS7299397B2Easy to controlSuppression frequencyError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsCode conversionComputer architectureLow density
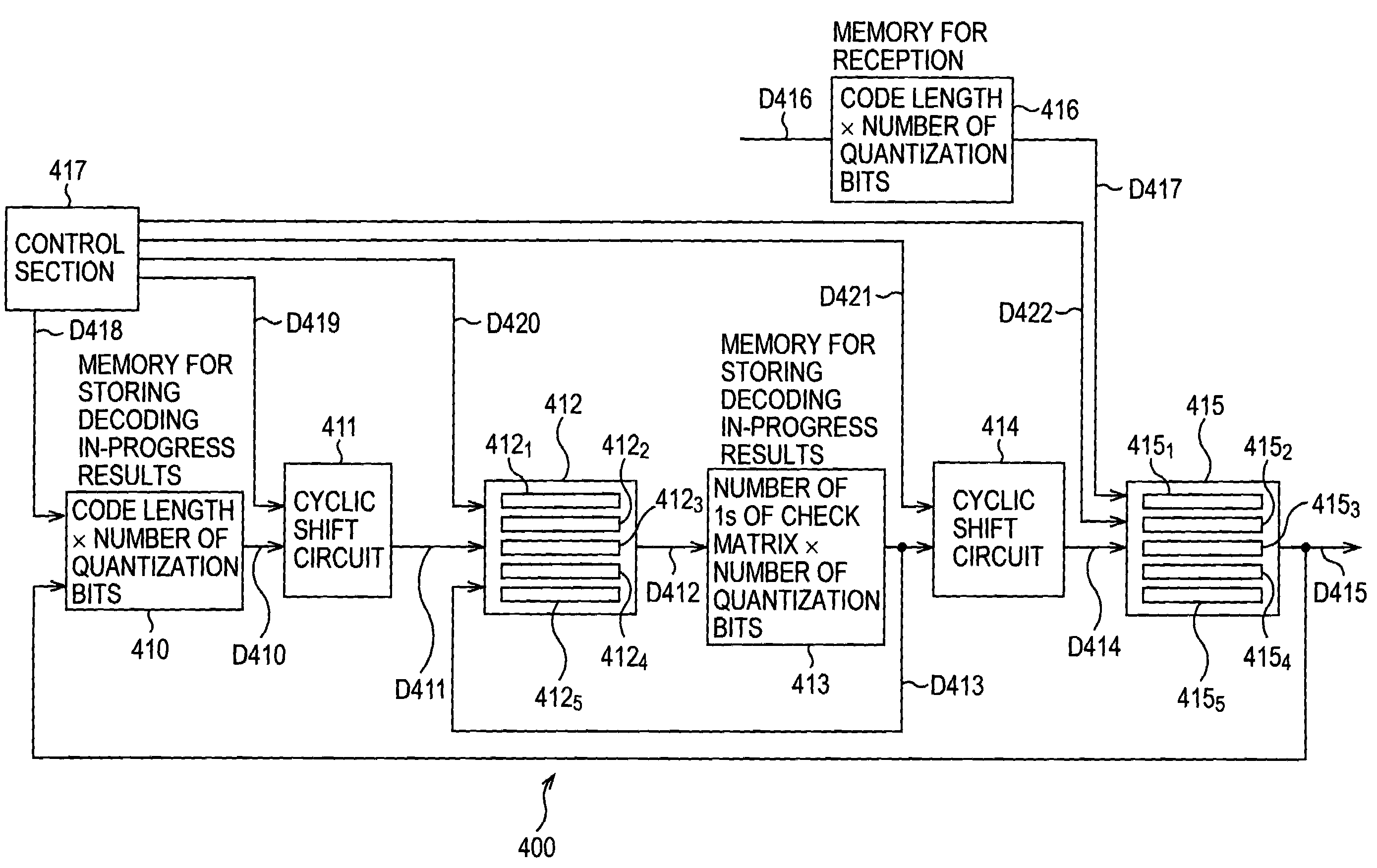
The present invention relates to a decoding apparatus and a decoding method for realizing the decoding of LDPC codes, in which, while the circuit scale is suppressed, the operating frequency can be suppressed within a sufficiently feasible range, and control of memory access can be performed easily, and to a program therefor. A check matrix of LDPC codes is formed by a combination of a (P×P) unit matrix, a matrix in which one to several 1s of the unit matrix are substituted with 0, a matrix in which they are cyclically shifted, a matrix, which is the sum of two or more of them, and a (P×P) 0-matrix. A check node calculator 313 simultaneously performs p check node calculations. A variable node calculator 319 simultaneously performs p variable node calculations.
Owner:SONY CORP
Reduced complexity error correction encoding techniques
InactiveUS20070043997A1Reduce complexityImprove system reliabilityCode conversionError correction/detection by combining multiple code structuresComputer hardwareData stream
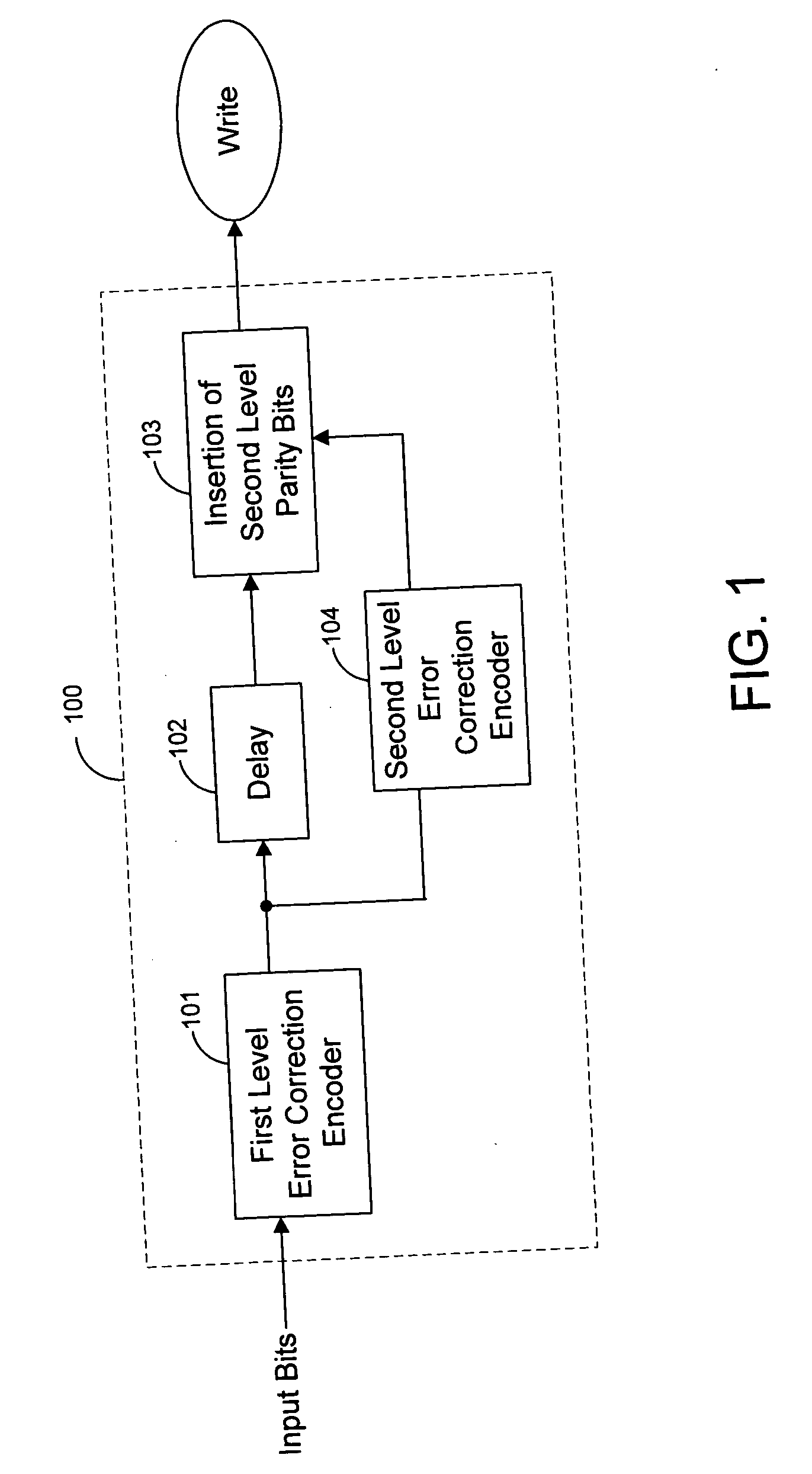
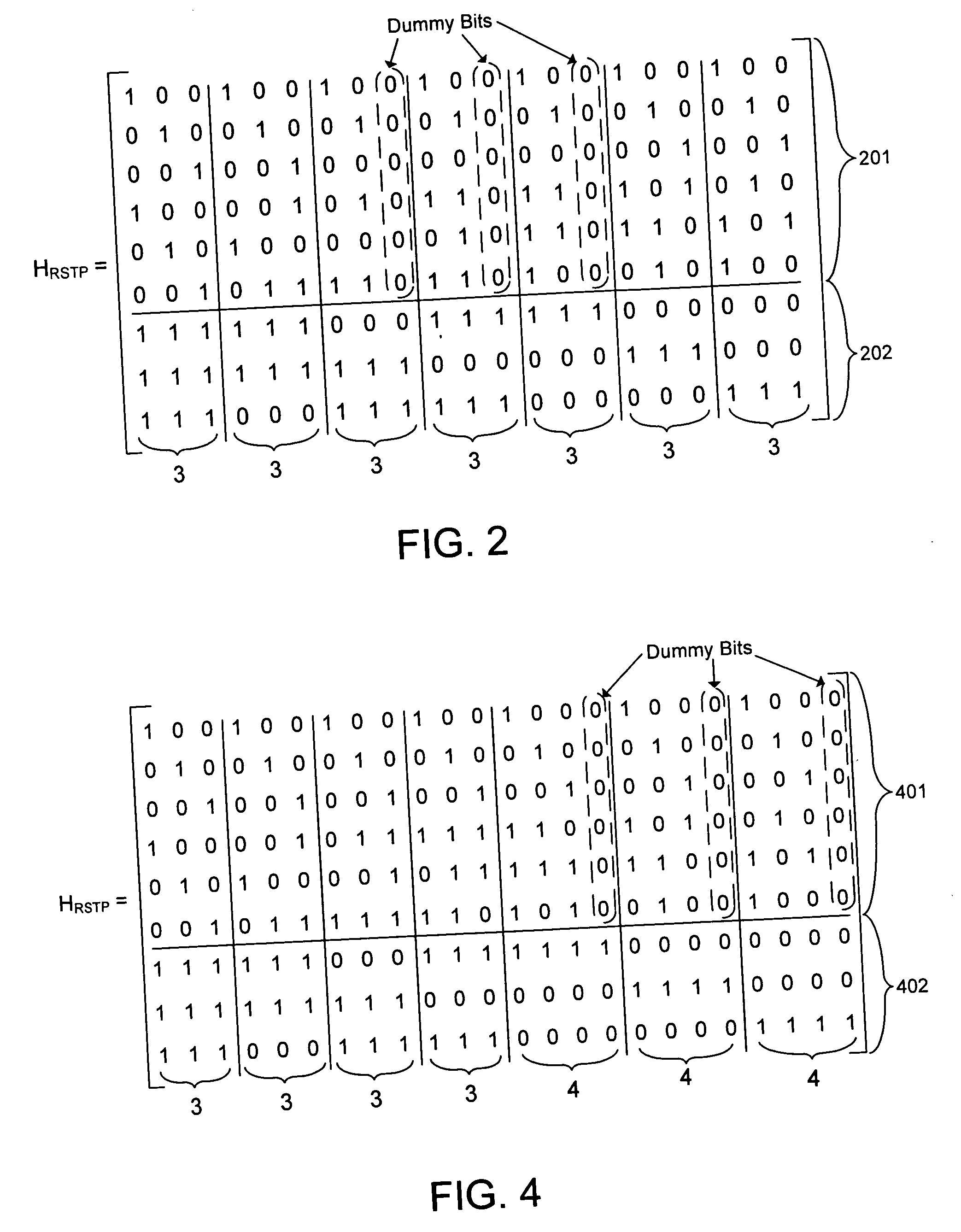
An error correction encoder inserts redundant parity information into a data stream to improve system reliability. The encoder can generate the redundant parity information using a composite code. Dummy bits are inserted into the data stream in locations reserved for parity information generated by subsequent encoding. The error correction code can have a uniform or a non-uniform span. The span corresponds to consecutive channel bits that are within a single block of a smaller parity code that is used to form a composite code. The span lengths can be variant across the whole codeword by inserting dummy bits in less than all of the spans.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com