Patents
Literature
93 results about "Routing congestion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
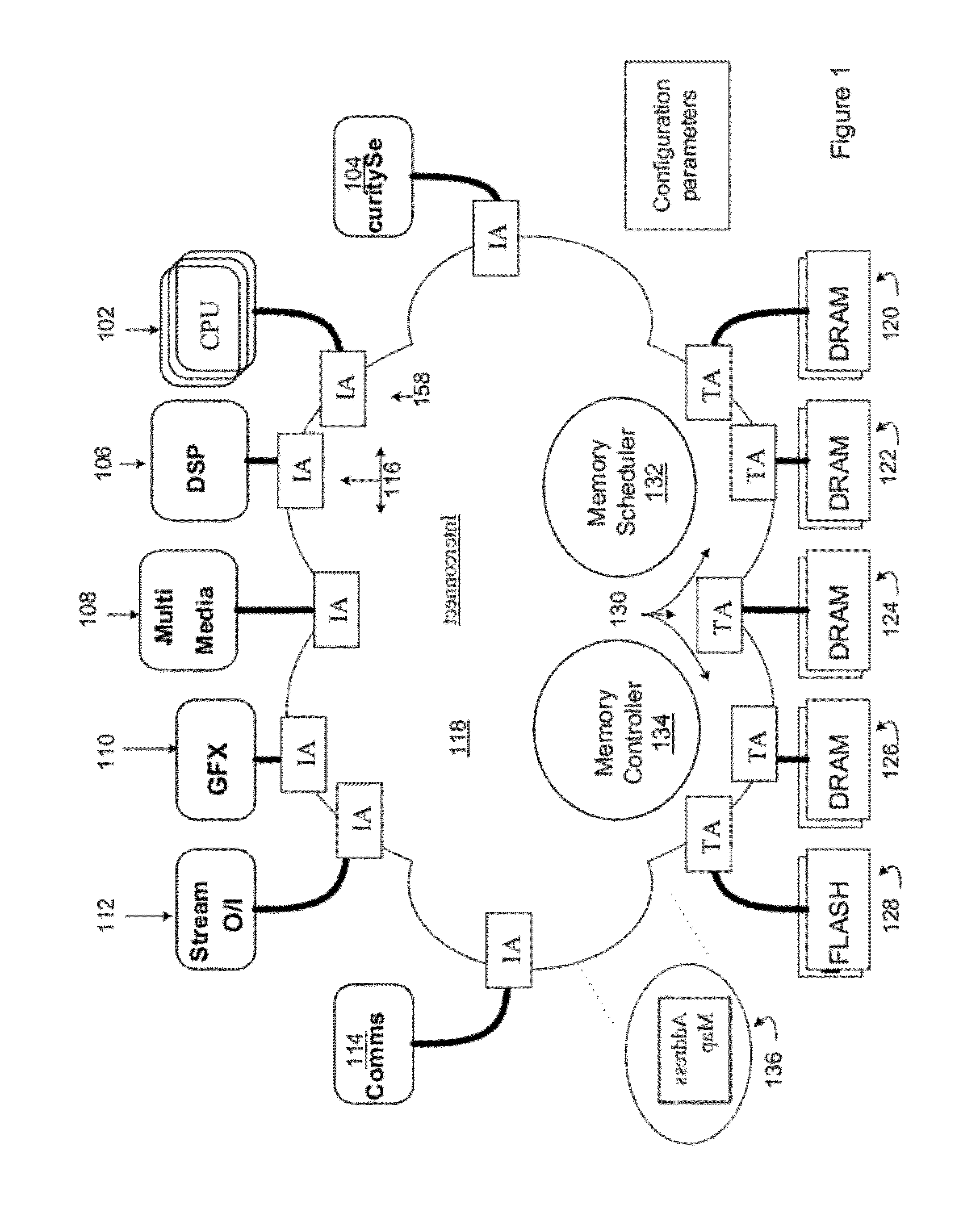
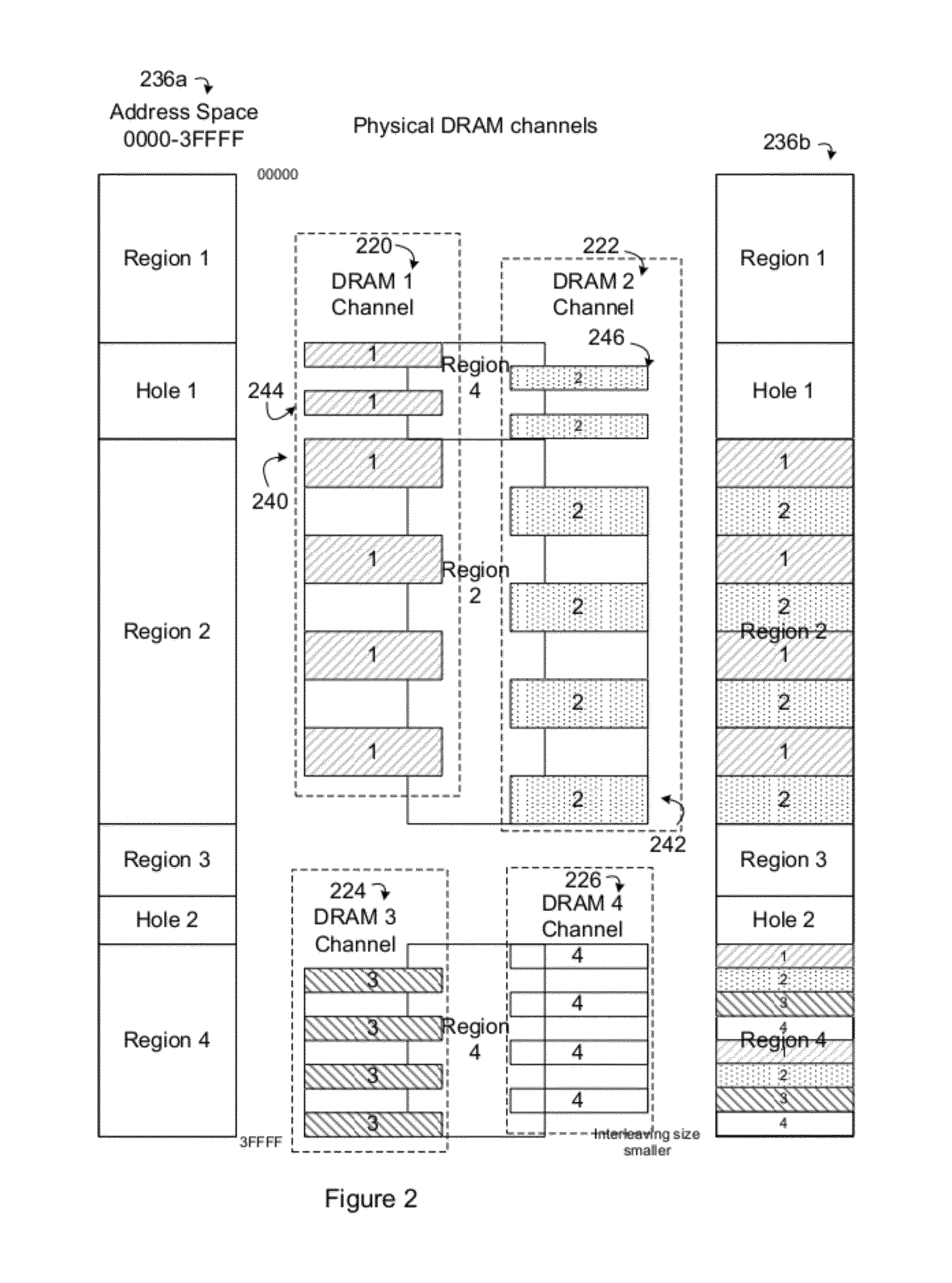
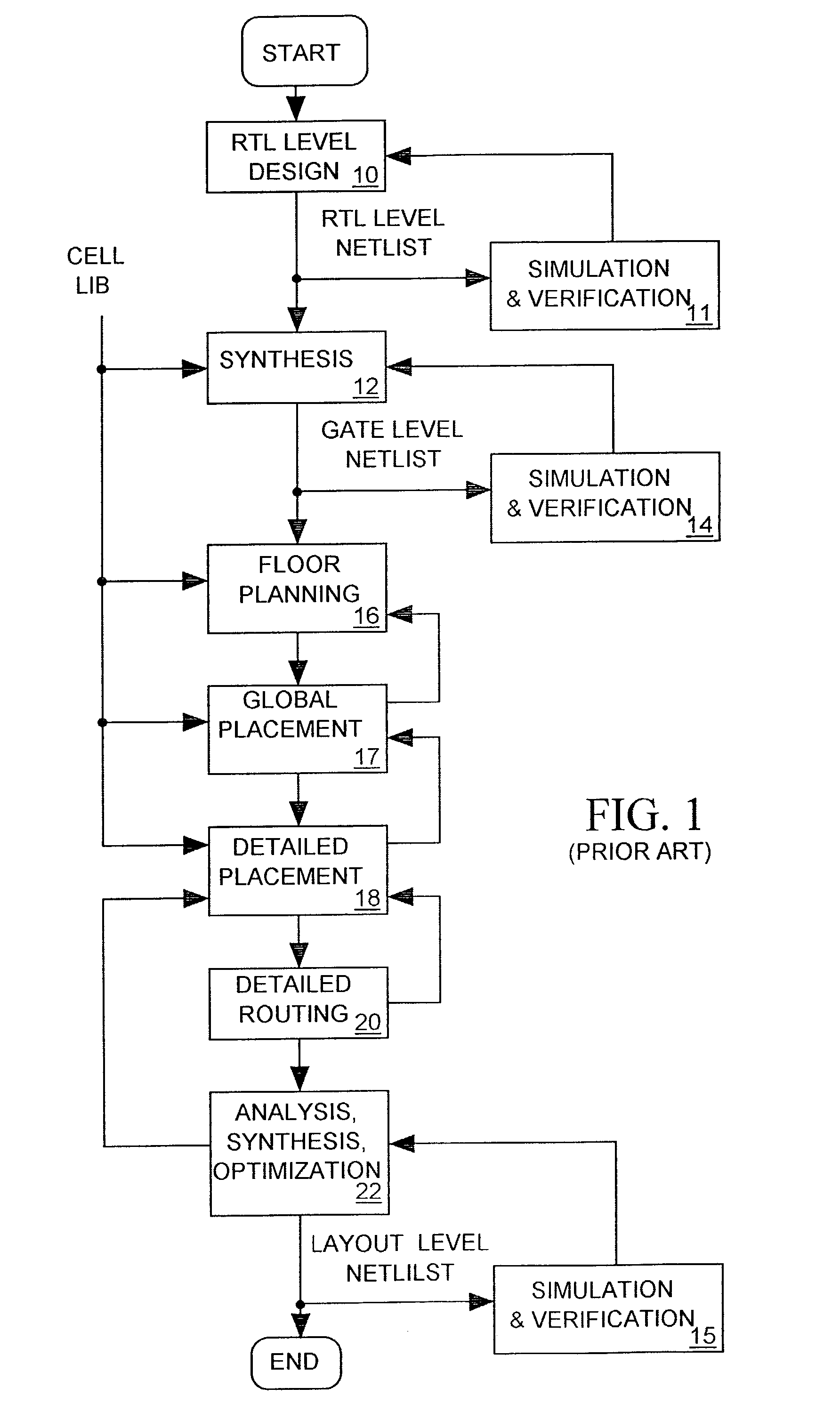
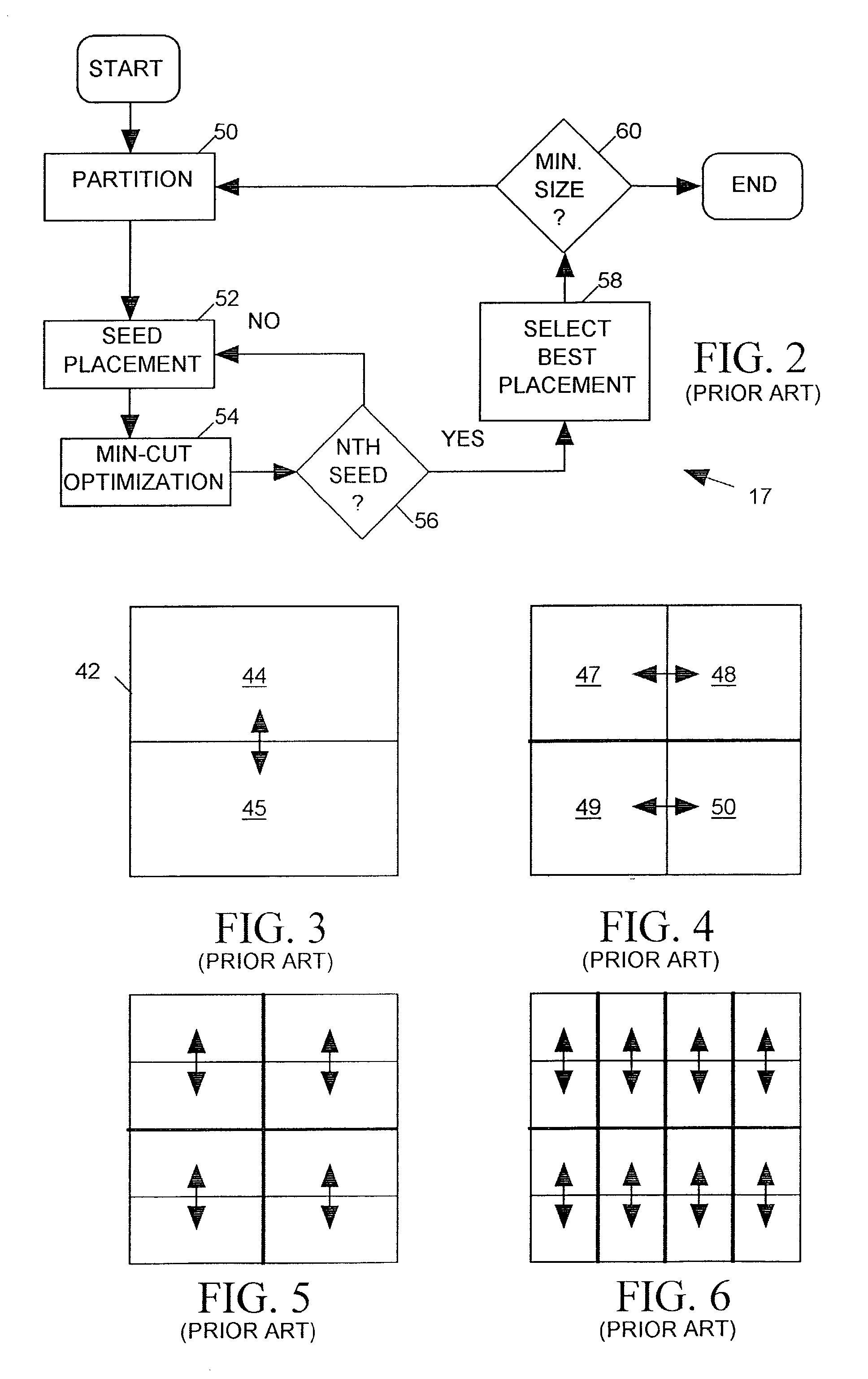
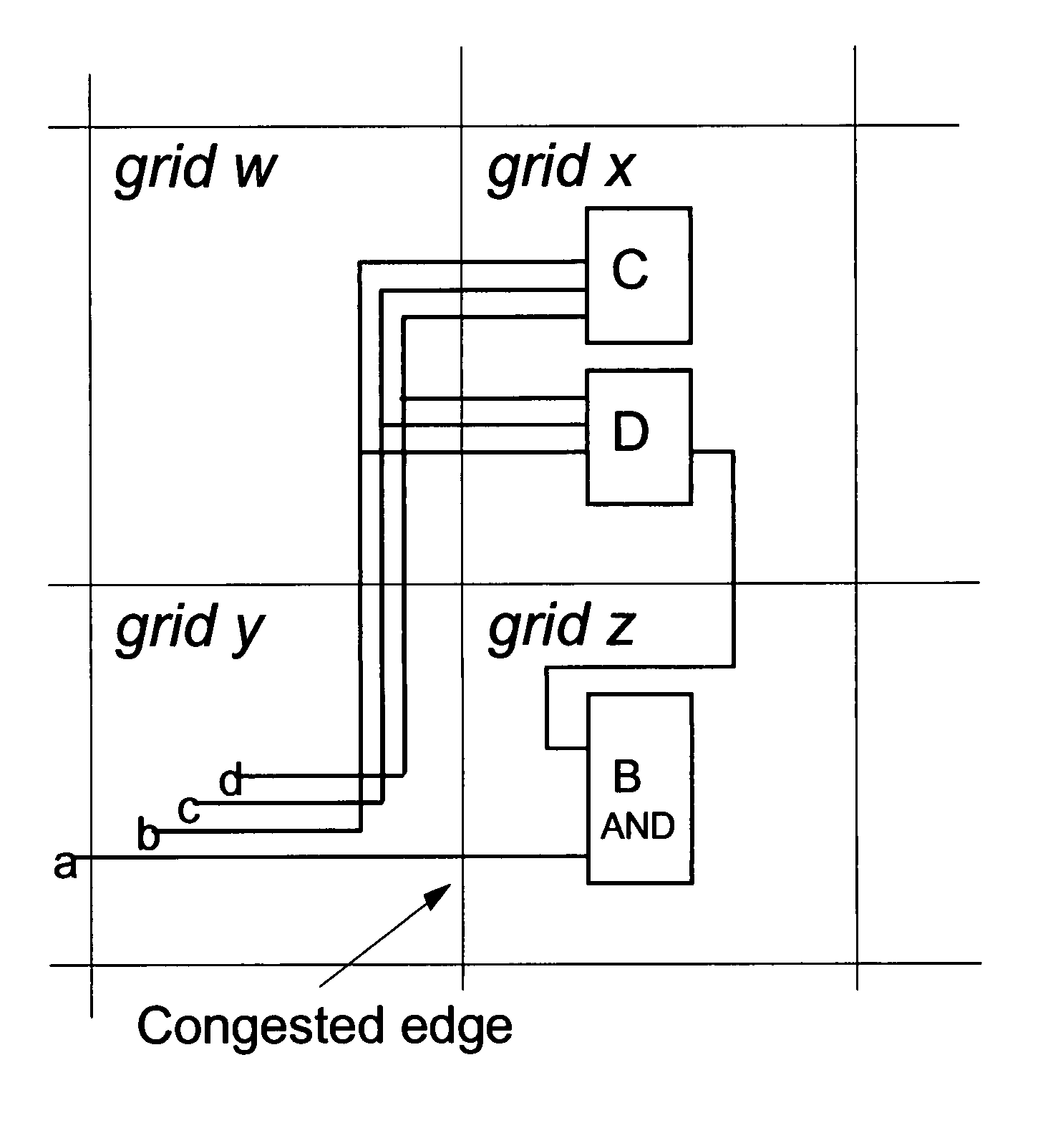
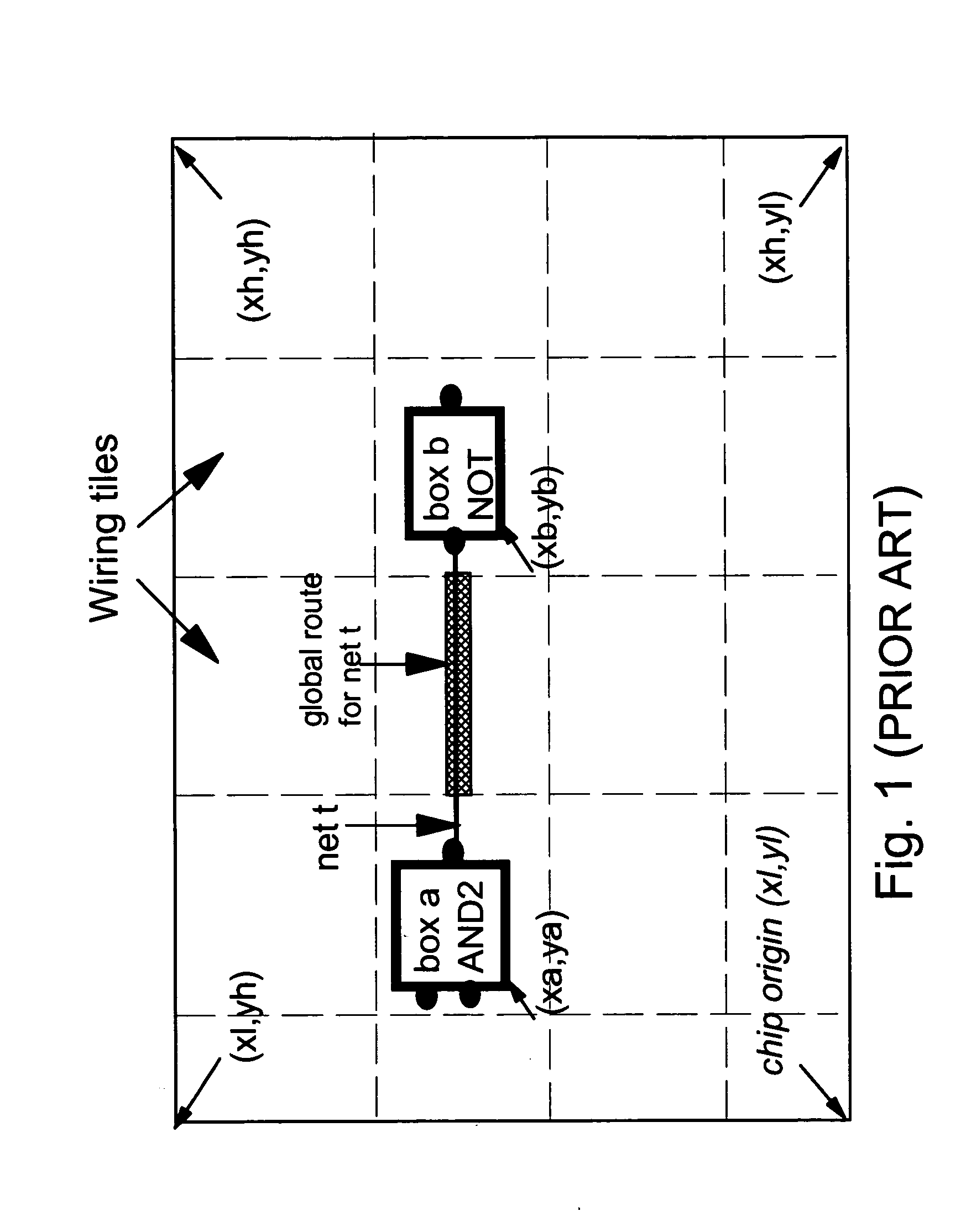
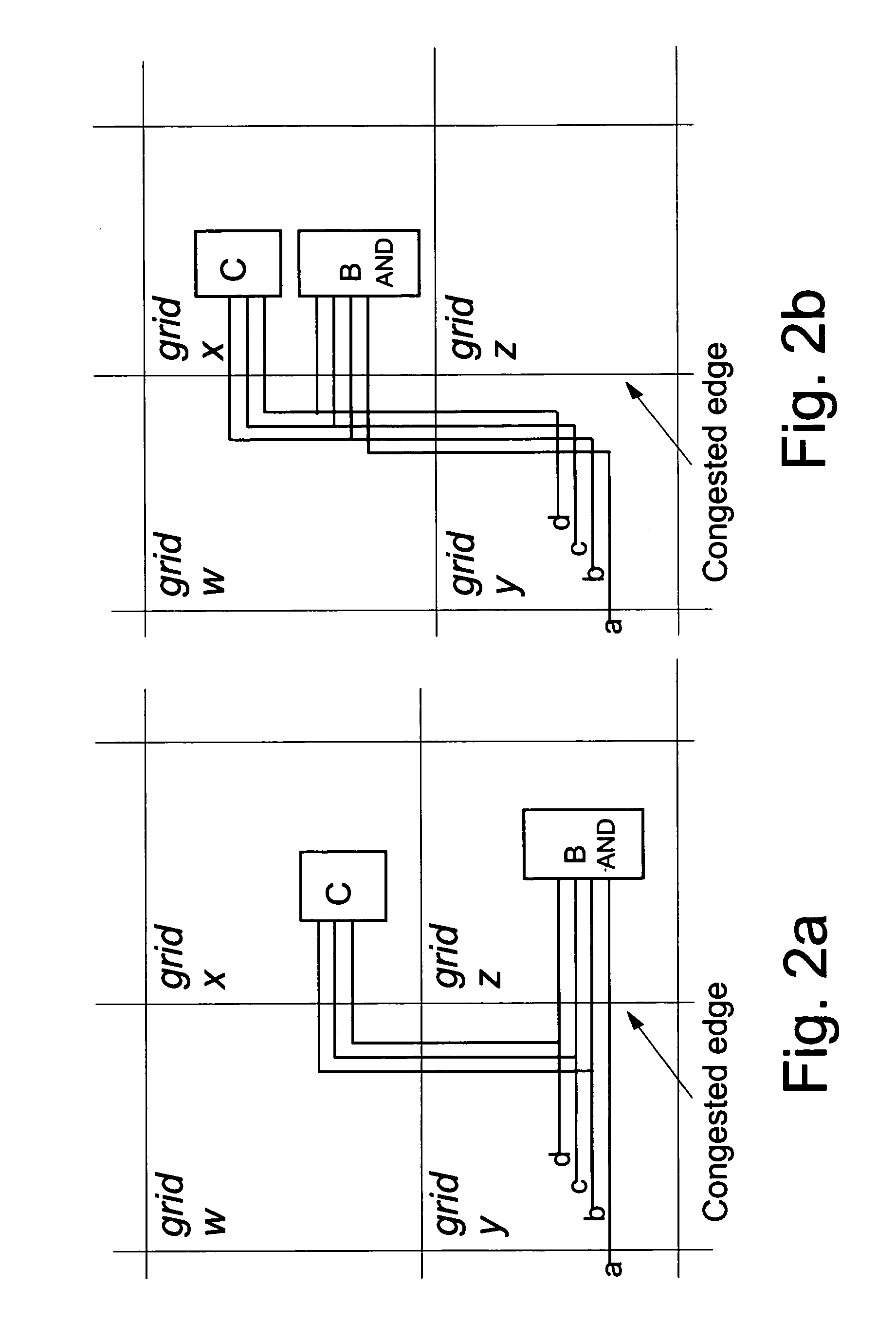
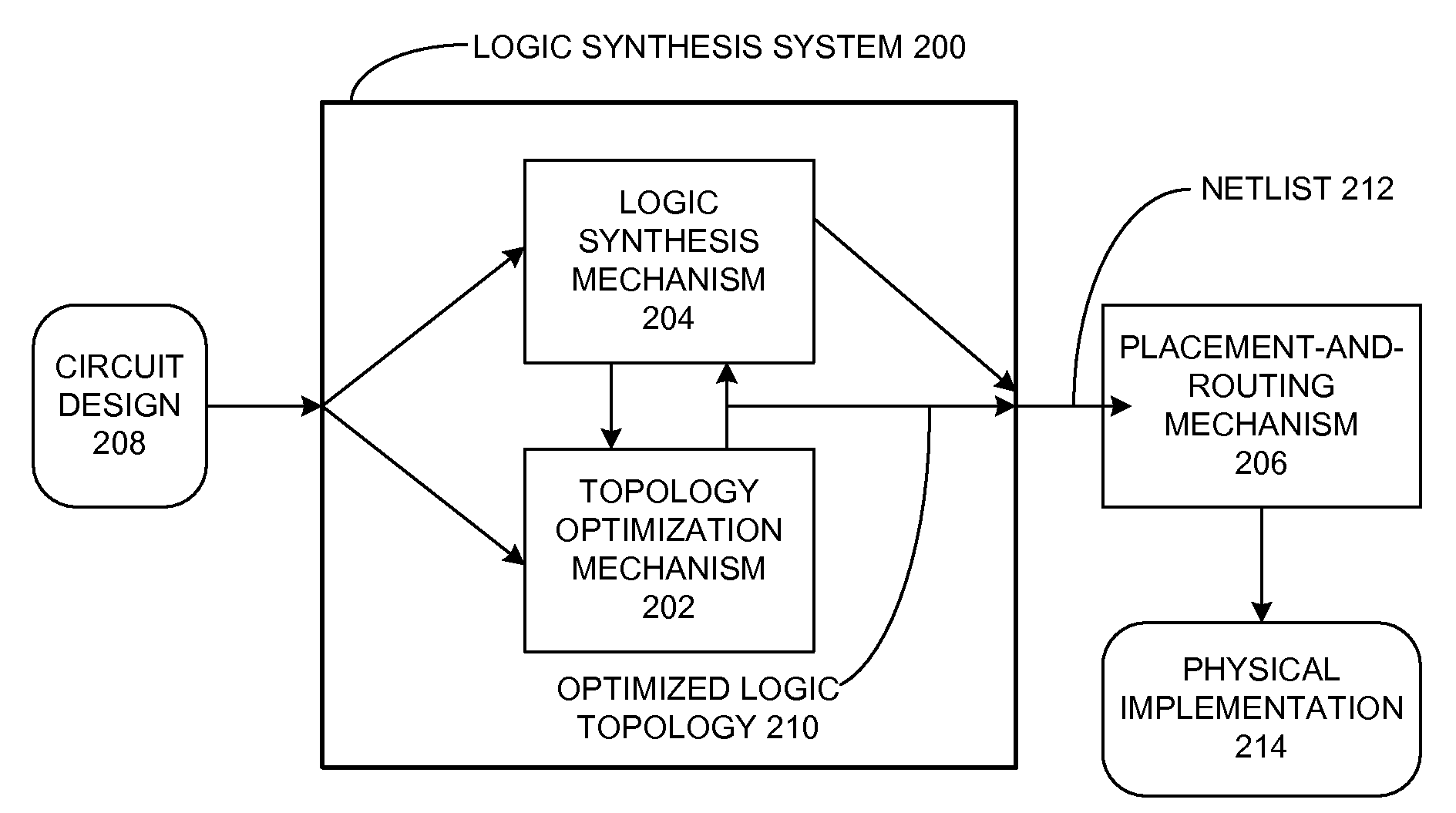
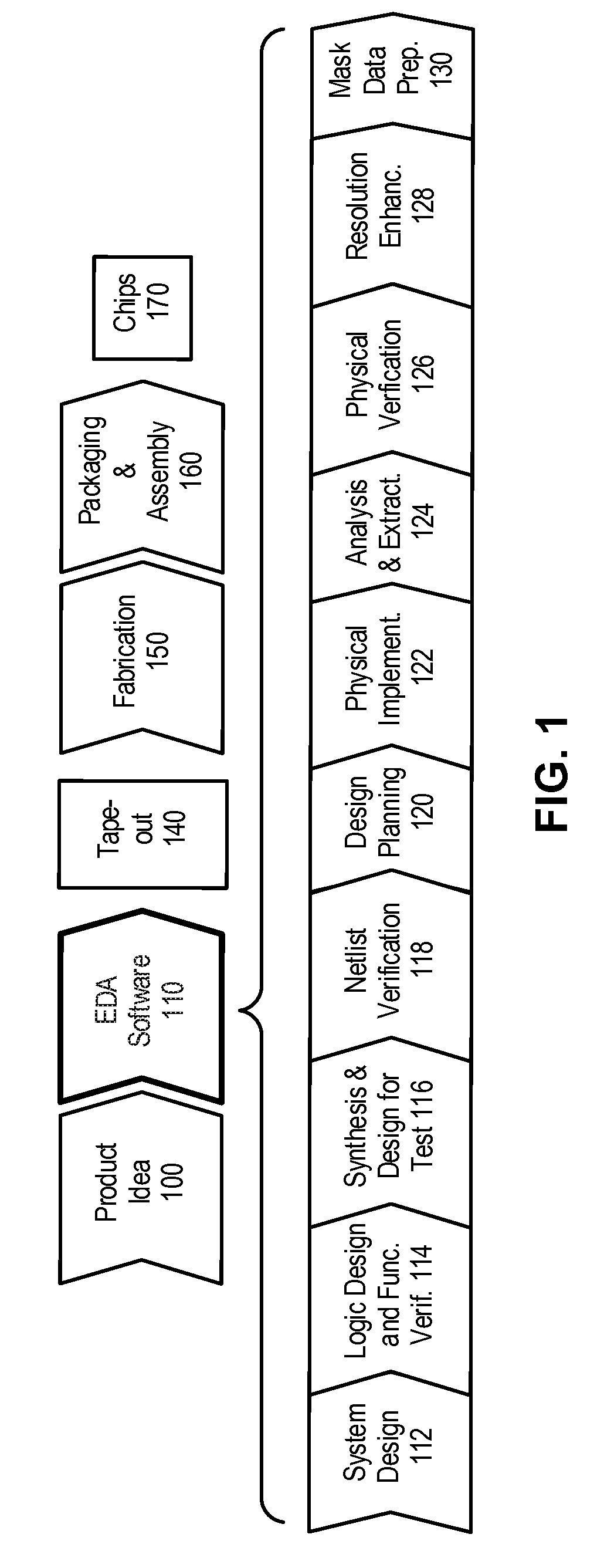
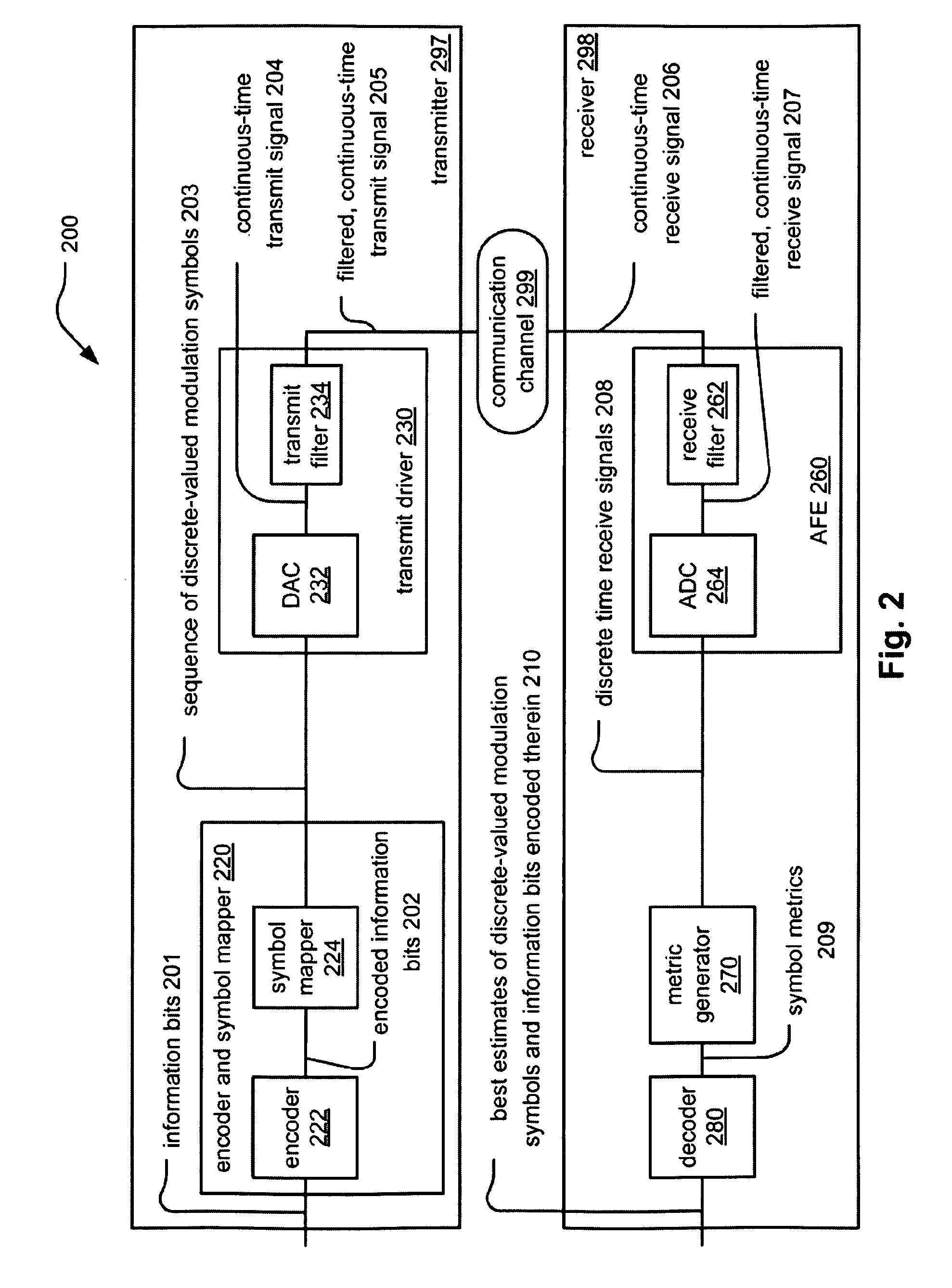
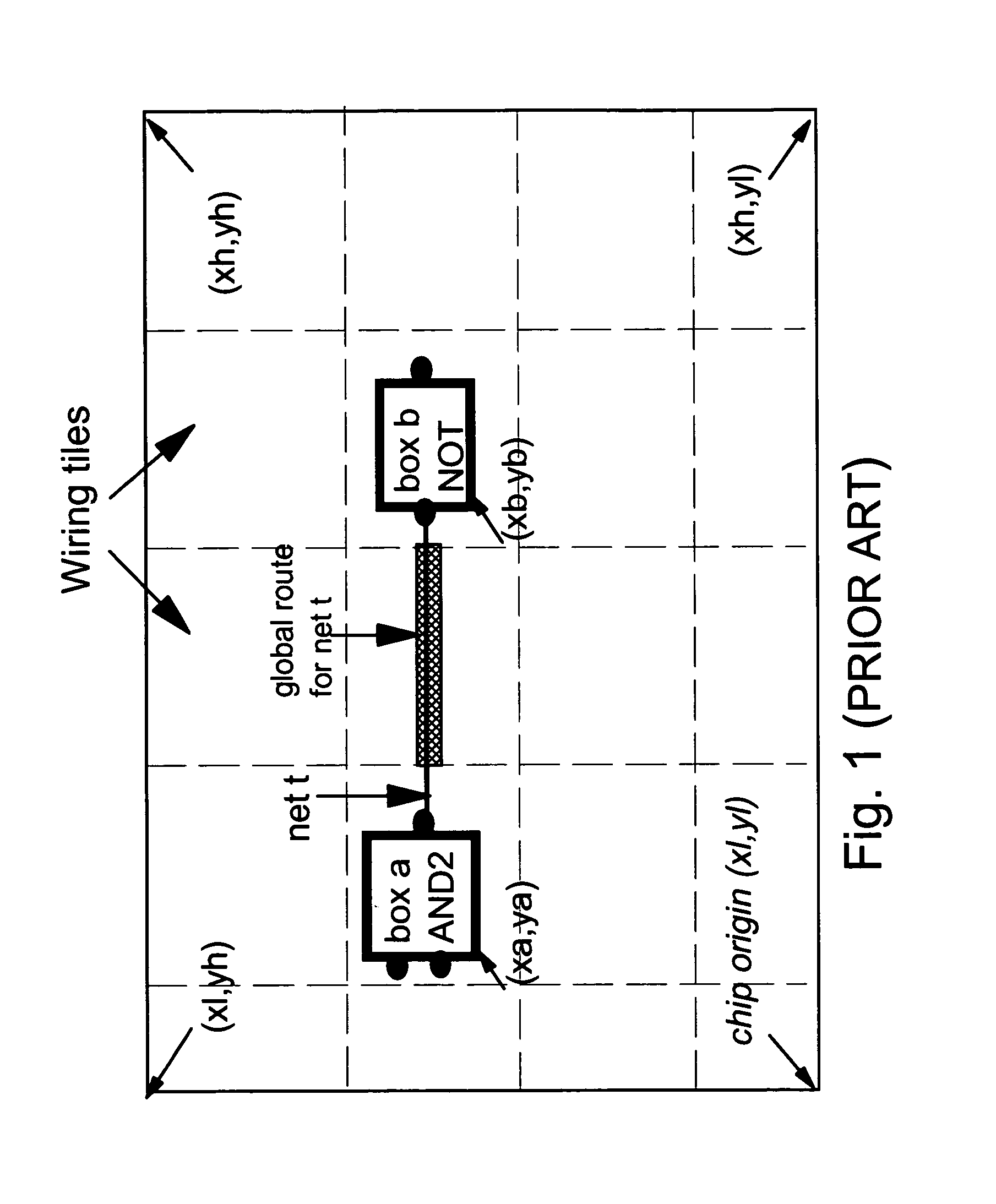
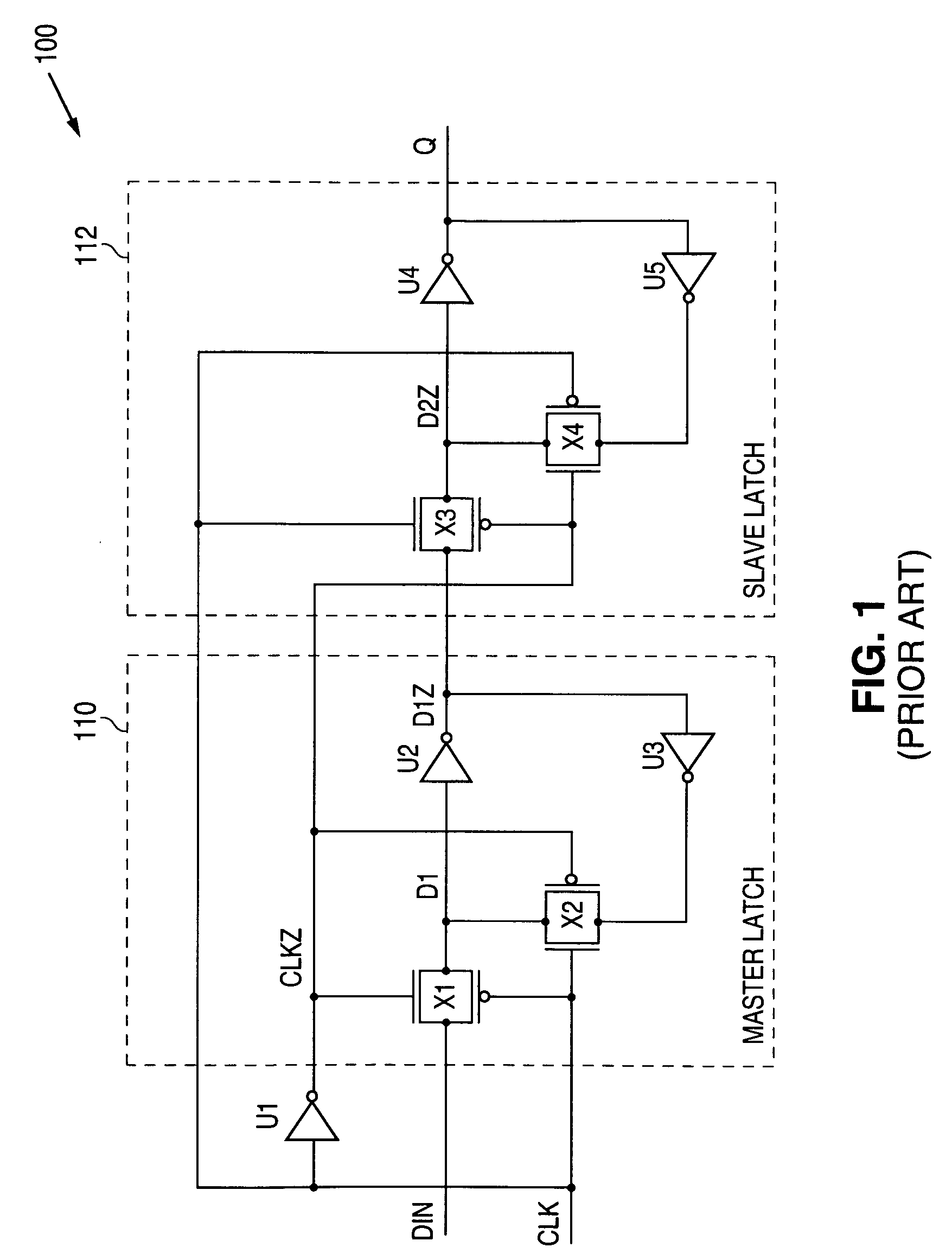
Wire routing congestion occurs on a system-on-chip when a lot of wires (or metal lines) are routed in a narrow space. It becomes prevalent in the on-chip interconnect fabric because it must be routed in the floorplan "white space" between IP block restrictions.
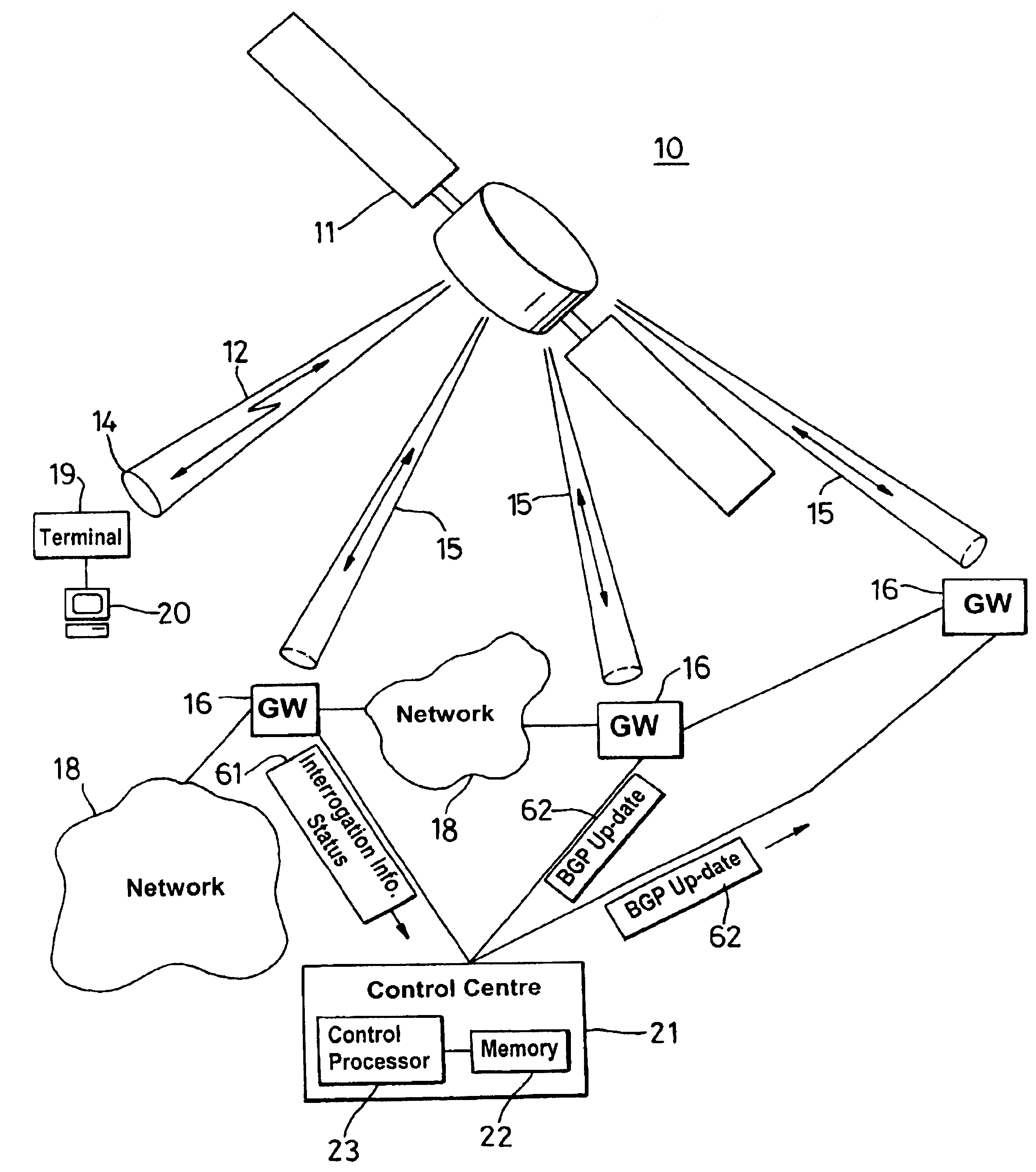
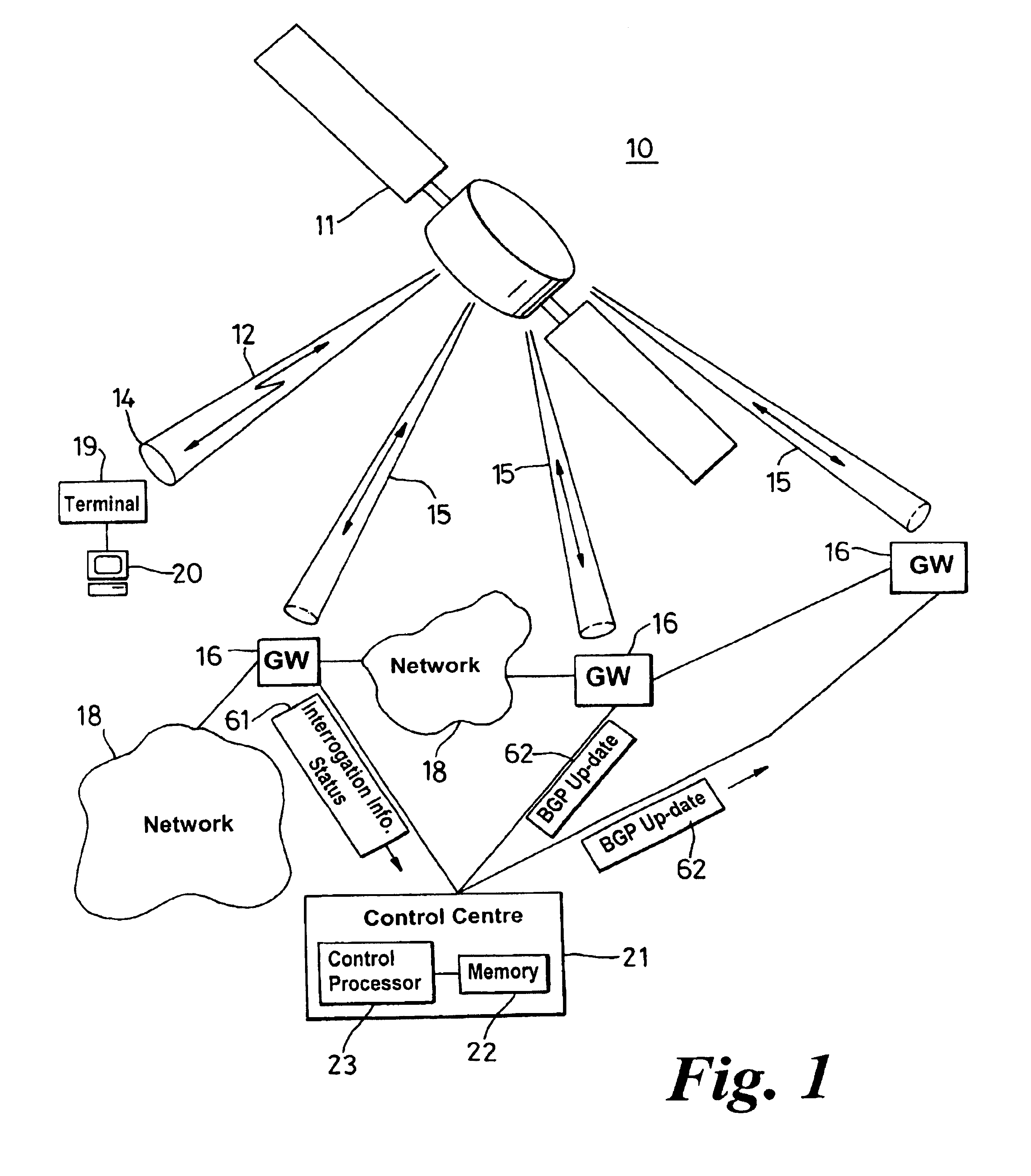
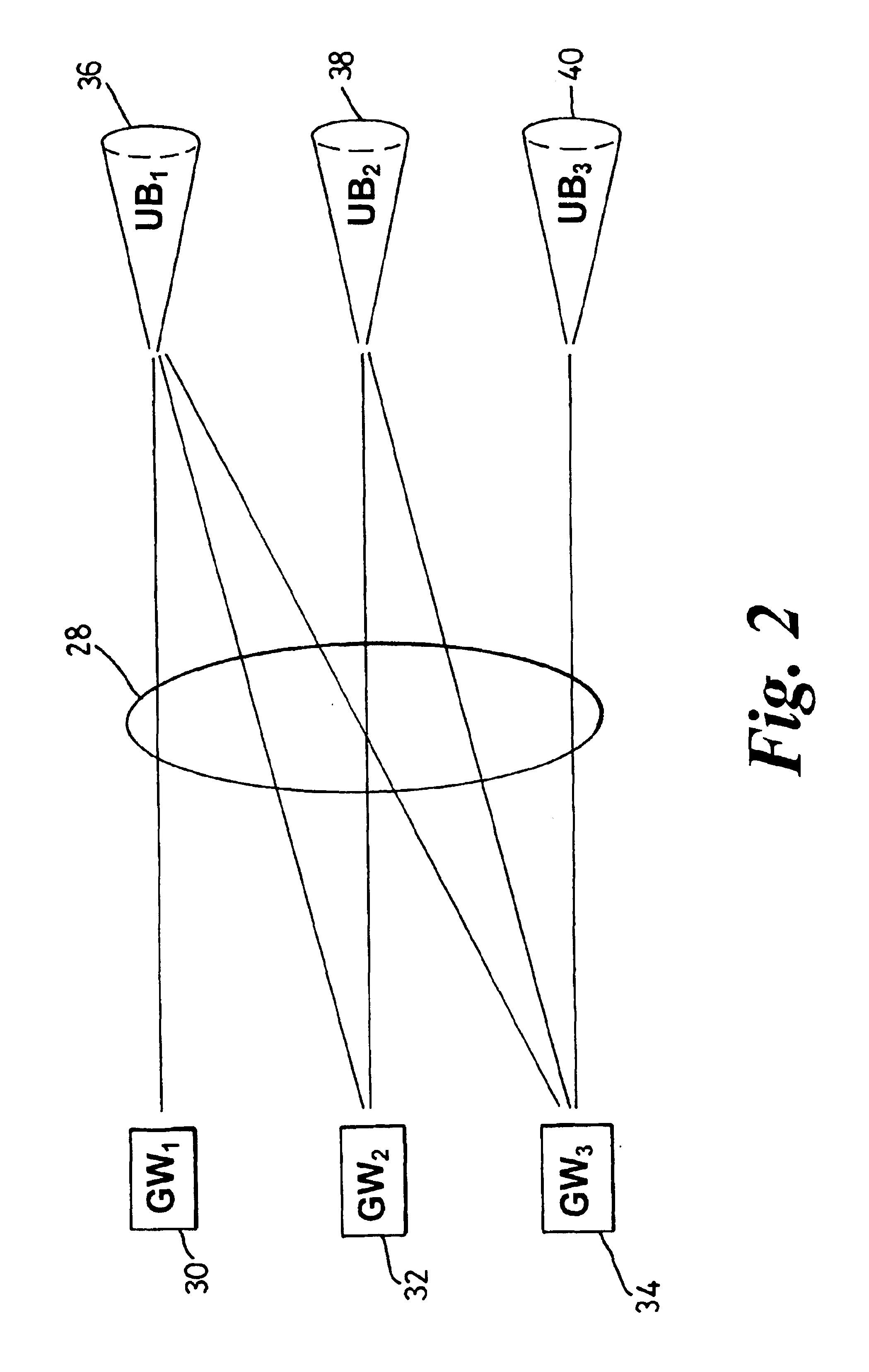
Border gateway protocol manager and method of managing the selection of communication links
InactiveUS6829221B1Avoid congestionLeast costError preventionTransmission systemsBorder Gateway ProtocolCommunication link
A border gateway protocol (BGP) management system (10) dynamically determines an optimum or preferred data route (12) from wireline networks (18) into a satellite communication system (11). Multiple gateways (16, 30-34) provide access points to the wireline networks. The management system includes a connectivity matrix which processes (74) information, such as bandwidth availability and route congestion, and then generate a BGP update that is communicated (80) into at least one of the gateways. The BGP update promotes preferred gateways and so identifies a preferred access path to the satellite system. Specifically, the BGP update instruction contains a metric altering a weighting of an identified route data route, which metric effects path selection at a gateway receiving IP datagrams. The metric is derived from information pertaining to a connectivity matrix associated with the satellite system.
Owner:NORTEL NETWORKS LTD
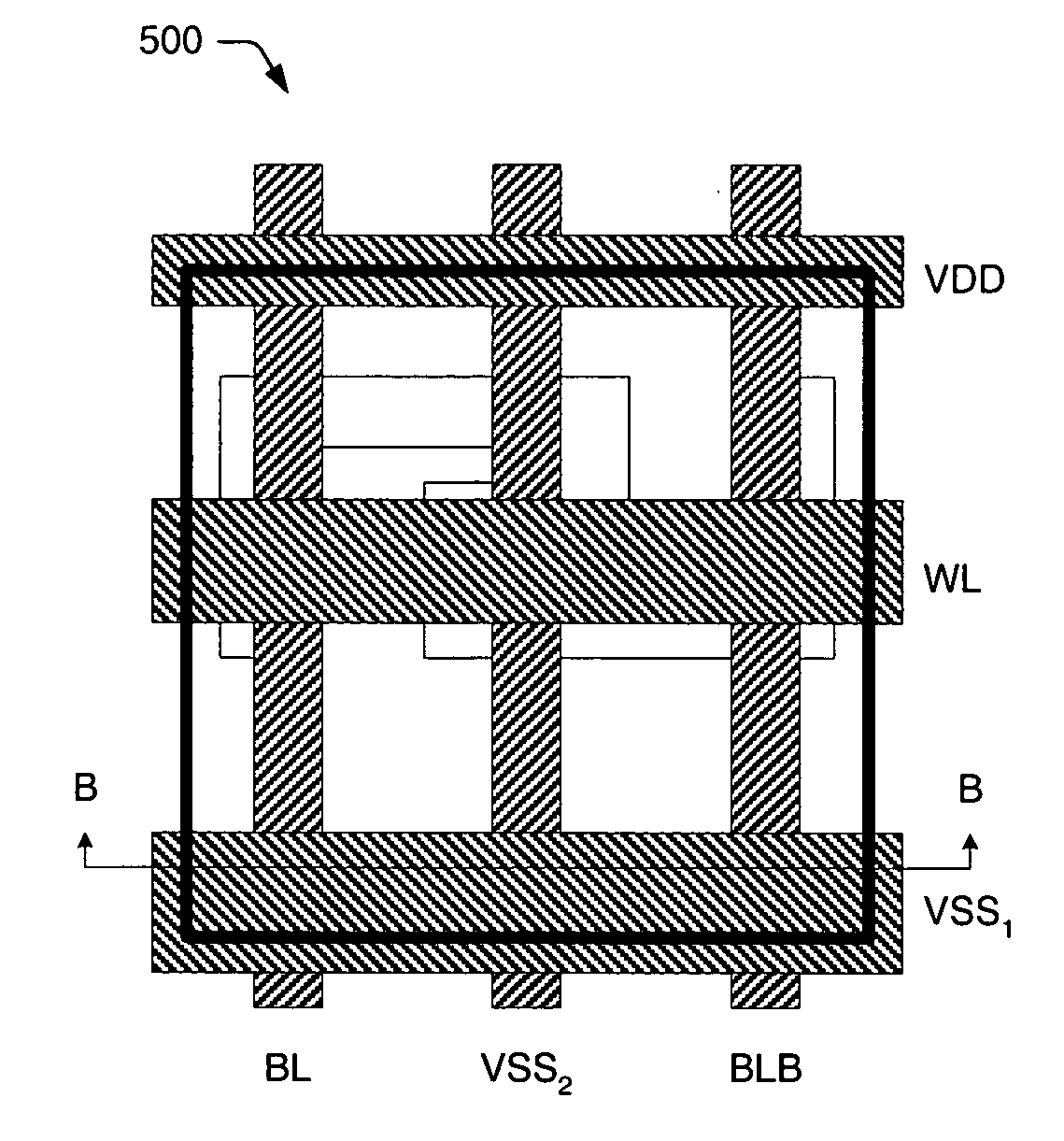
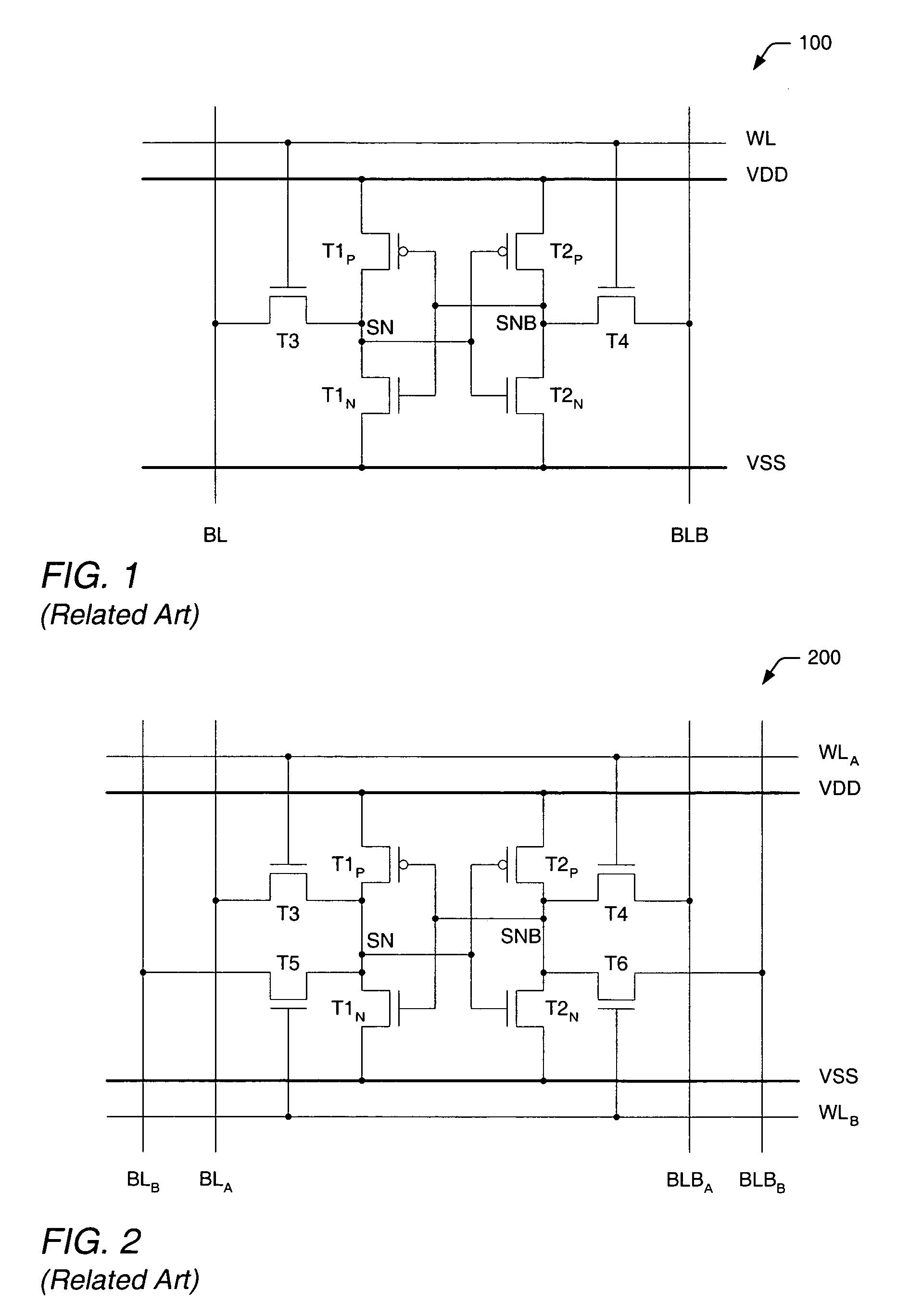
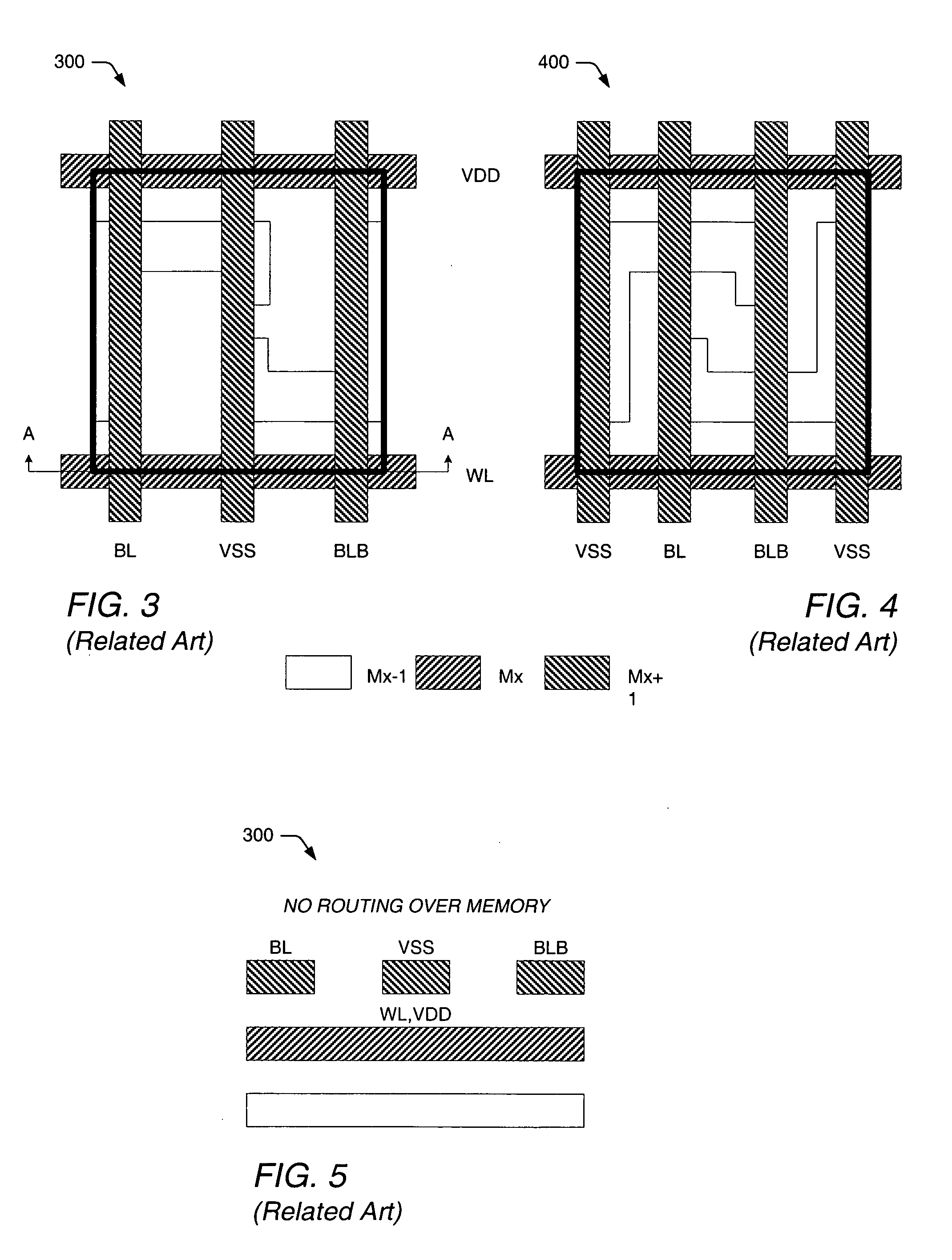
Memory cell architecture for reduced routing congestion
ActiveUS6980462B1Effective shieldingReduce the environmentSolid-state devicesDigital storageComputer architectureRouting congestion
An improved memory cell architecture is provided herein for reducing, or altogether eliminating, chip-level routing congestion in System-on-Chip environments. Though only a few embodiments are provided herein, features common to the described embodiments include: the formation of bitlines in a lower-level metallization layer of the memory array, and the use of word lines and ground supply lines, both formed in inter-level metallization layer(s) of the memory array, for effective shielding of the bitlines against routing signals in the chip-level routing layer.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
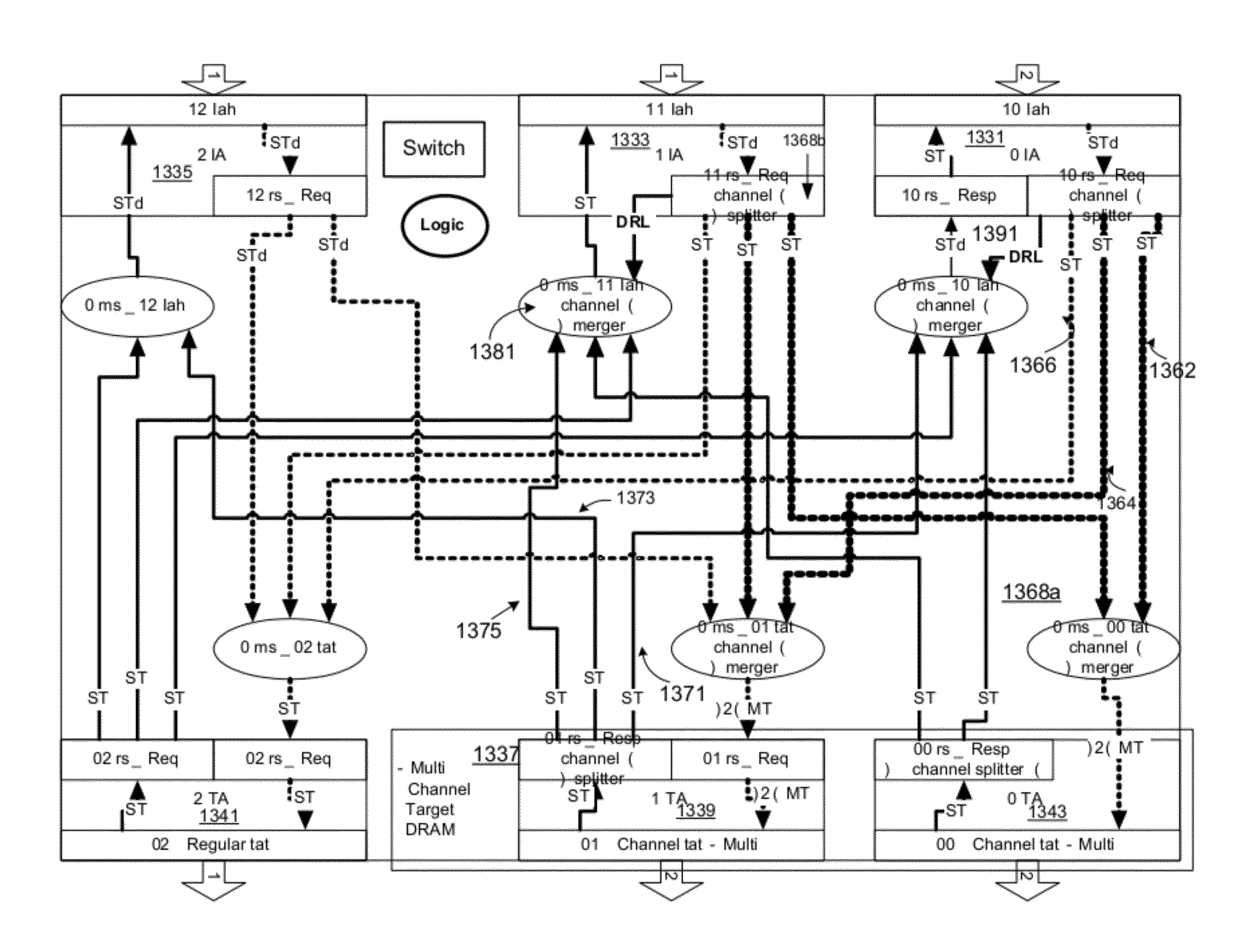
Interconnect that eliminates routing congestion and manages simultaneous transactions
InactiveUS20120036296A1Digital computer detailsDigital storageProtocol for Carrying Authentication for Network AccessRouting congestion
A method, apparatus, and system are described, which generally relate to an integrated circuit having an interconnect. The flow control logic for the interconnect applies a flow control splitting protocol to permit transactions from each initiator thread and / or each initiator tag stream to be outstanding to multiple channels in a single aggregate target at once, and therefore to multiple individual targets within an aggregate target at once. The combined flow control logic and flow control protocol allows the interconnect to manage simultaneous requests to multiple channels in an aggregate target from the same thread or tag at the same time.
Owner:META PLATFORMS TECH LLC
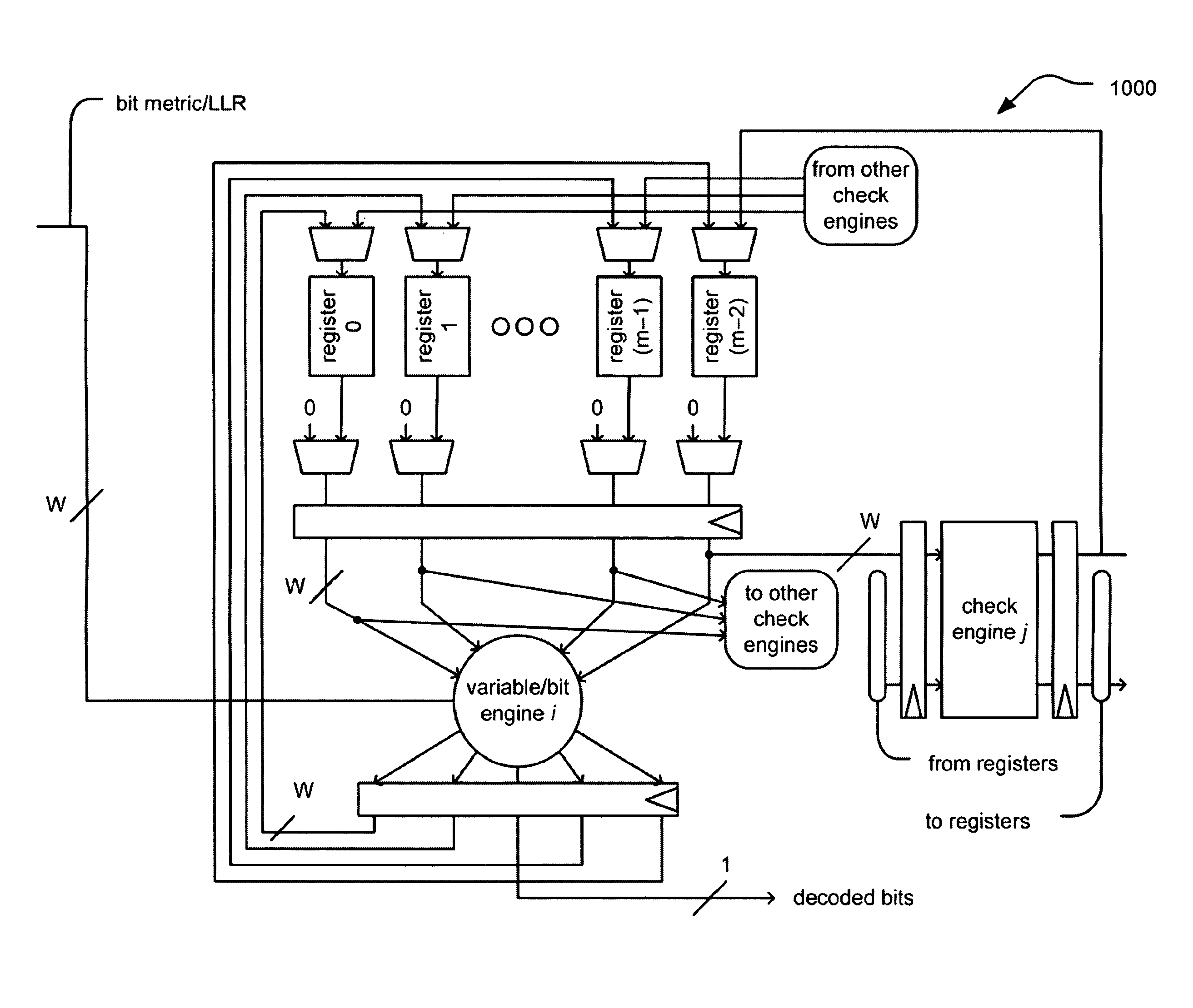
Distributed processing LDPC (low density parity check) decoder
ActiveUS20090013237A1Error correction/detection using multiple parity bitsCode conversionCommunication deviceThroughput
Distributed processing LDPC (Low Density Parity Check) decoder. A means is presented herein that includes an LDPC decoding architecture leveraging a distributed processing technique (e.g., daisy chain) to increase data throughput and reduce memory storage requirements. Routing congestion and critical path latency are also improved thereby. Each daisy chain includes a number of registers, and a number of localized MUXs (e.g., MUXs having merely 2 inputs each). The means presented herein also does not contain any barrel shifters, high fan-in multiplexers, or interconnection networks; therefore, the critical path is relatively short and it can also be pipelined to further increase data throughput. If desired, a communication device can include multiple configurations of such daisy chains to accommodate the decoding of various LDPC coded signals (e.g., such as for an application and / or communication device that must decoded LDPC codes using different low density parity check matrices).
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
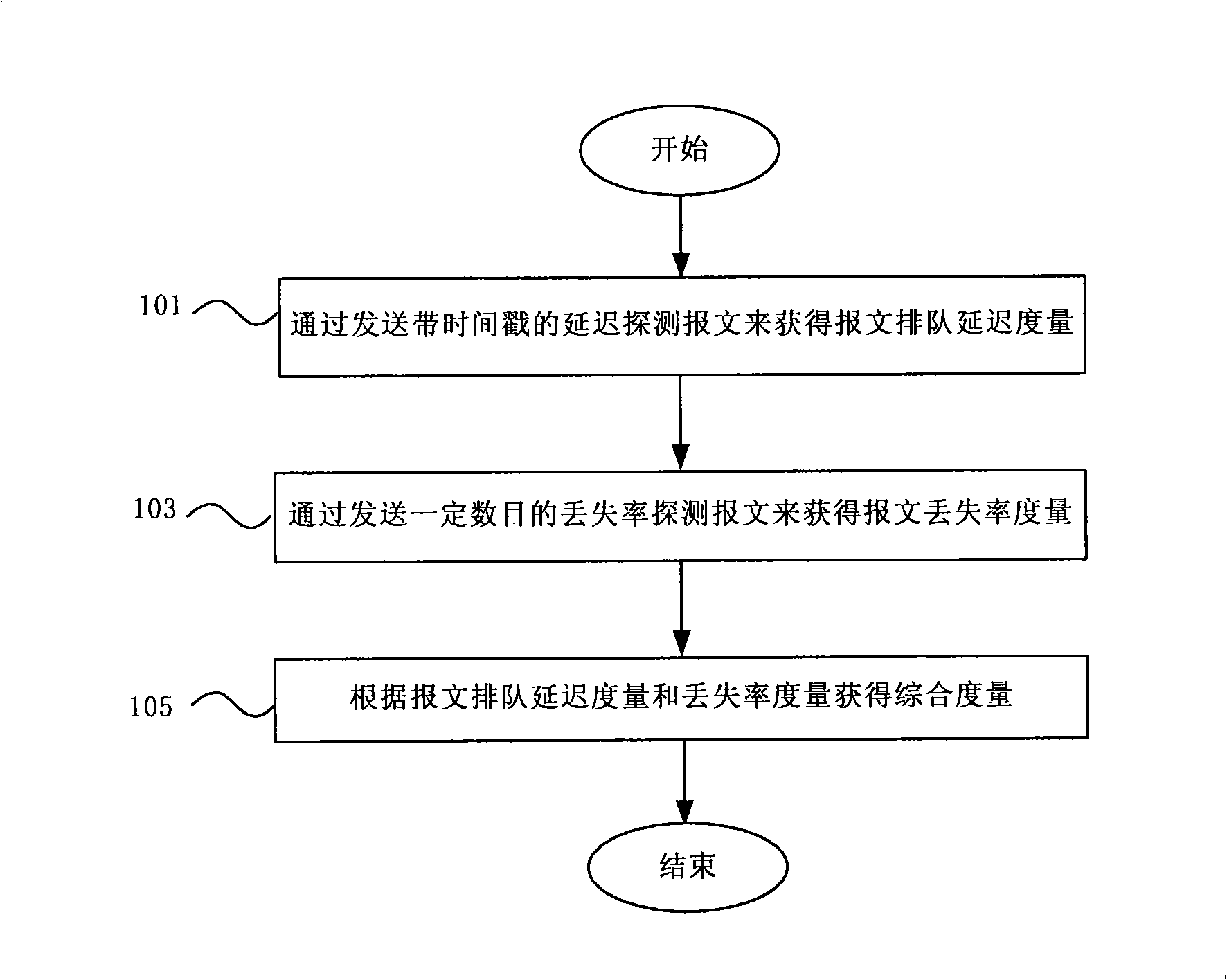
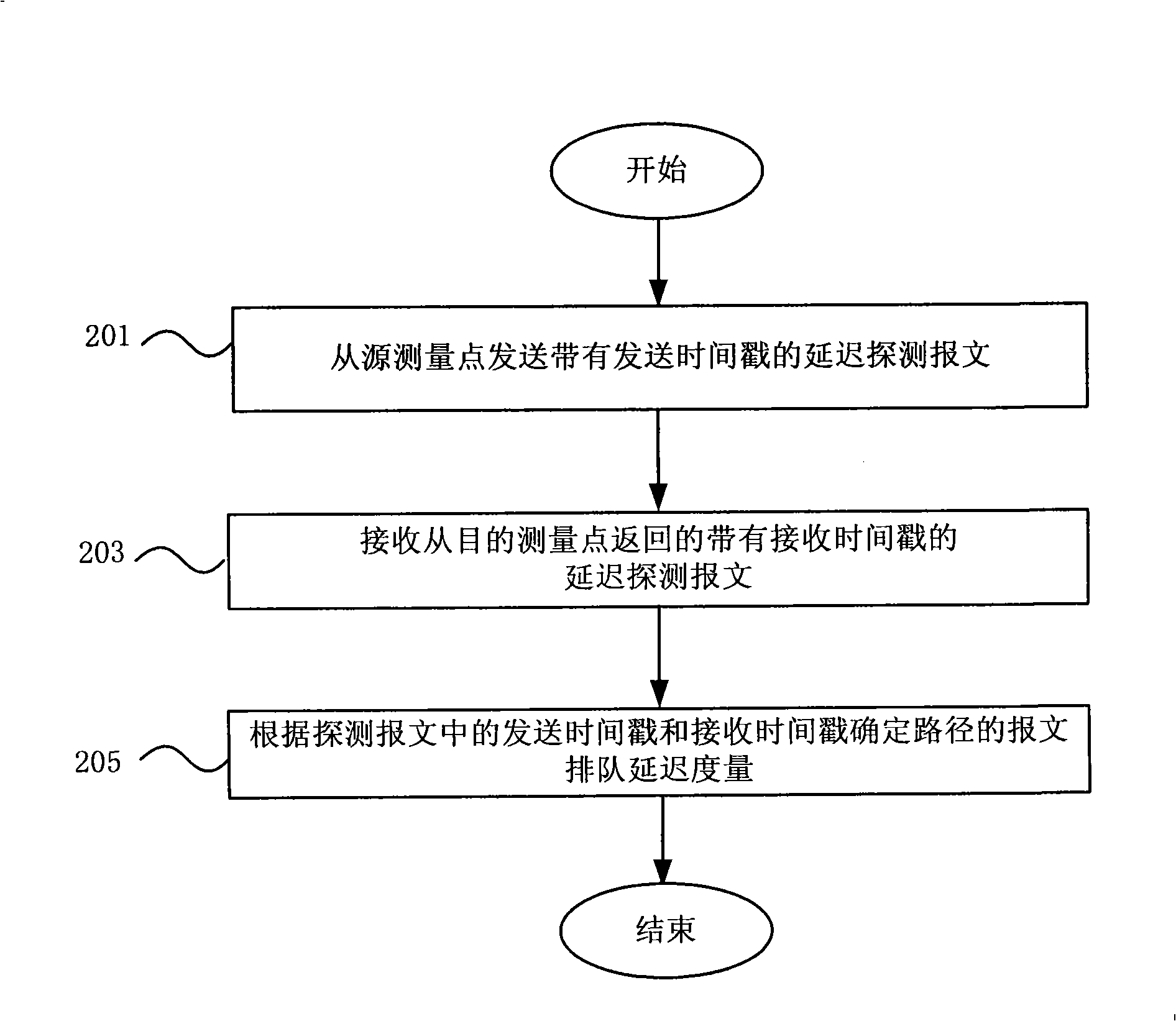
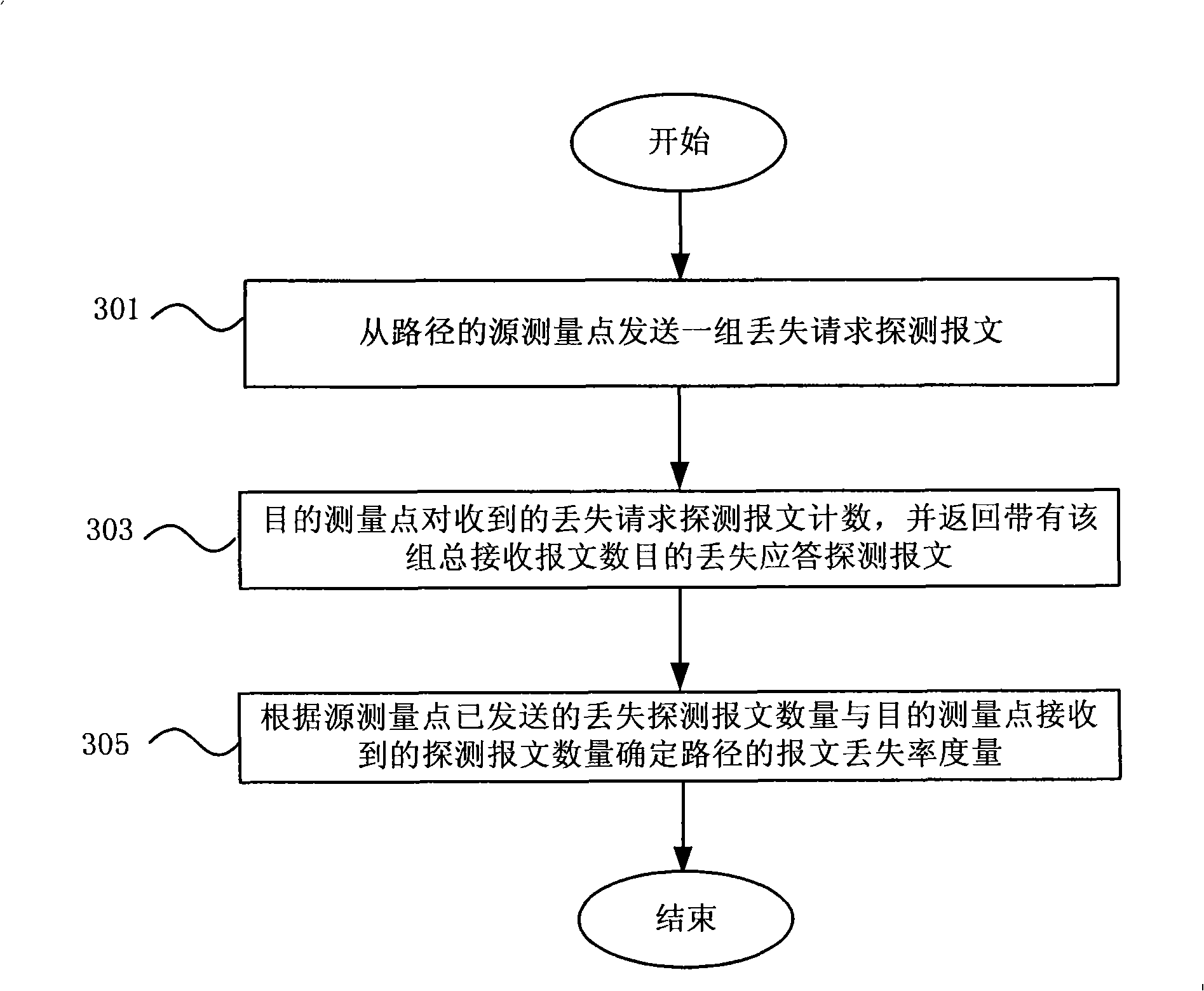
Measuring method, measuring apparatus and forwarding device for route congestion state in IP network
ActiveCN101272290AReflect the load levelAccurately reflect load levelsData switching networksLoss rateRouting congestion
The invention discloses a measurement method for path congestion status in an IP network, a measuring device and a data retransmitting device thereof. The measurement method comprises the steps: measuring the measurement of message queuing delay of the path in the network; measuring the measurement of message loss rate of the path in the network; acquiring a comprehensive measurement of the congestion status of the path according to the measurement of message queuing delay and the measurement of message loss rate. The measurement method of the invention acquires the comprehensive measurement through measuring the measurement of message queuing delay and the measurement of message loss rate, thus can reflect path load level in real network more exactly.
Owner:CHINA TELECOM CORP LTD
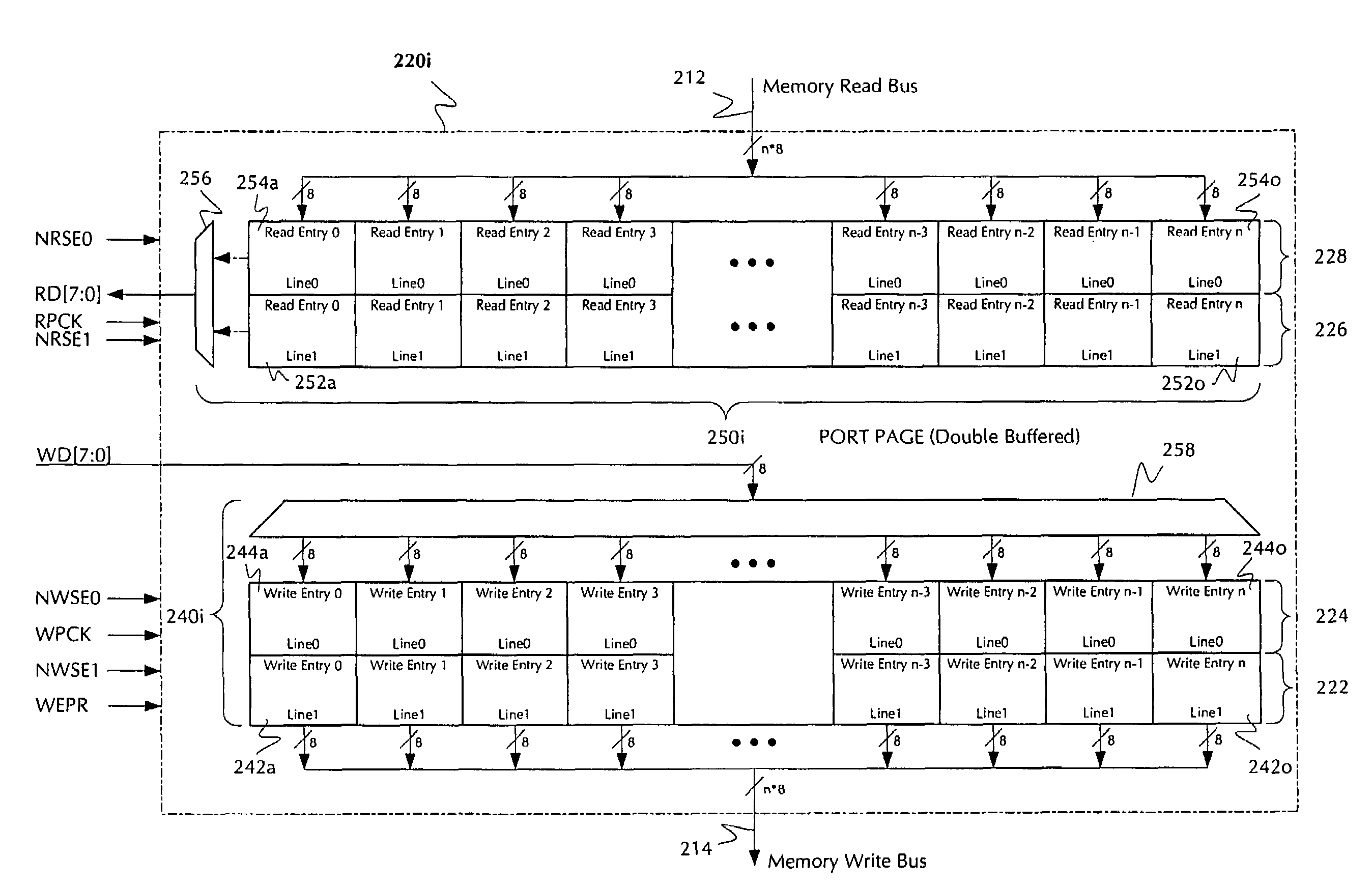
Multiport memory architecture, devices and systems including the same, and methods of using the same
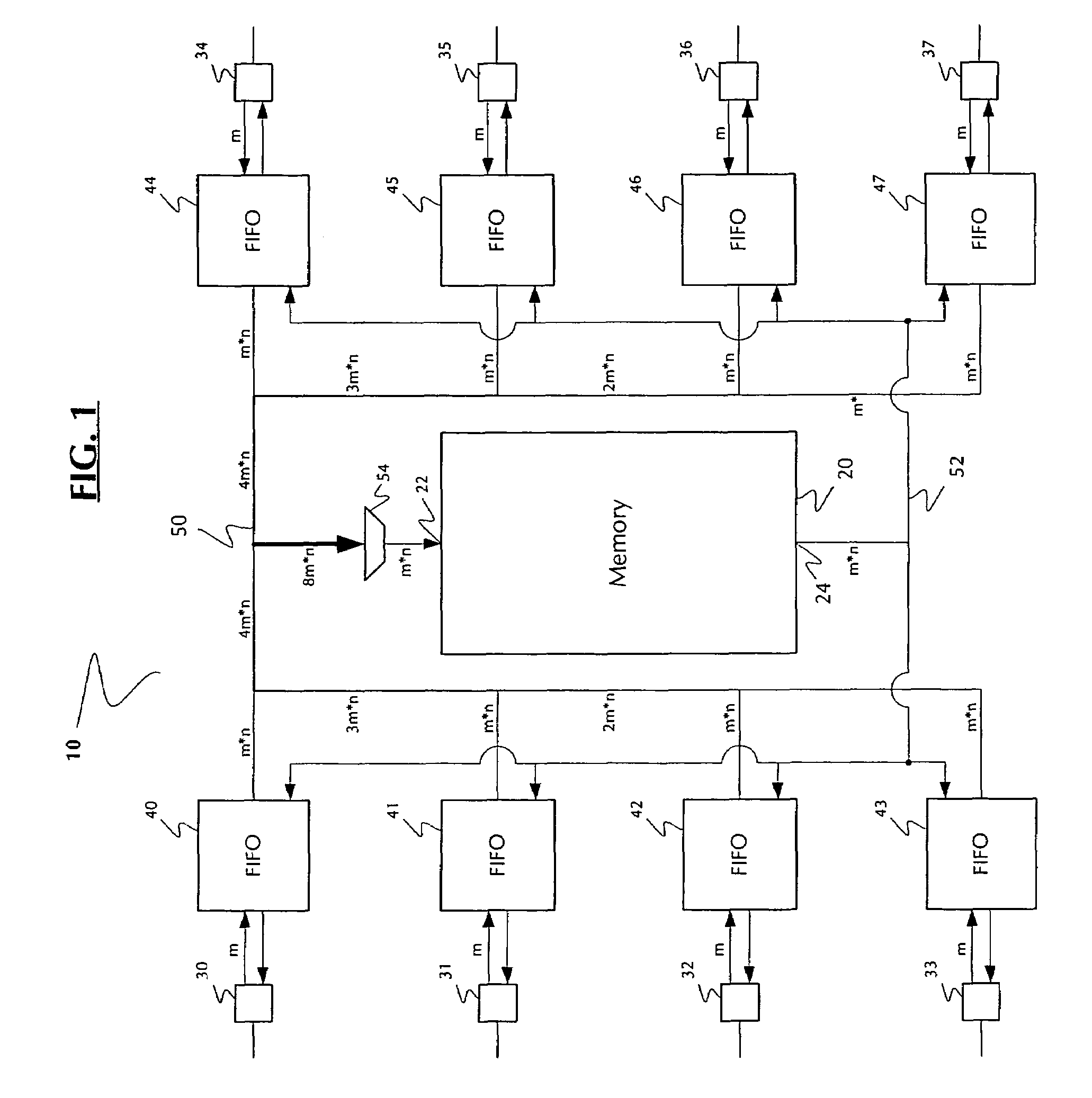
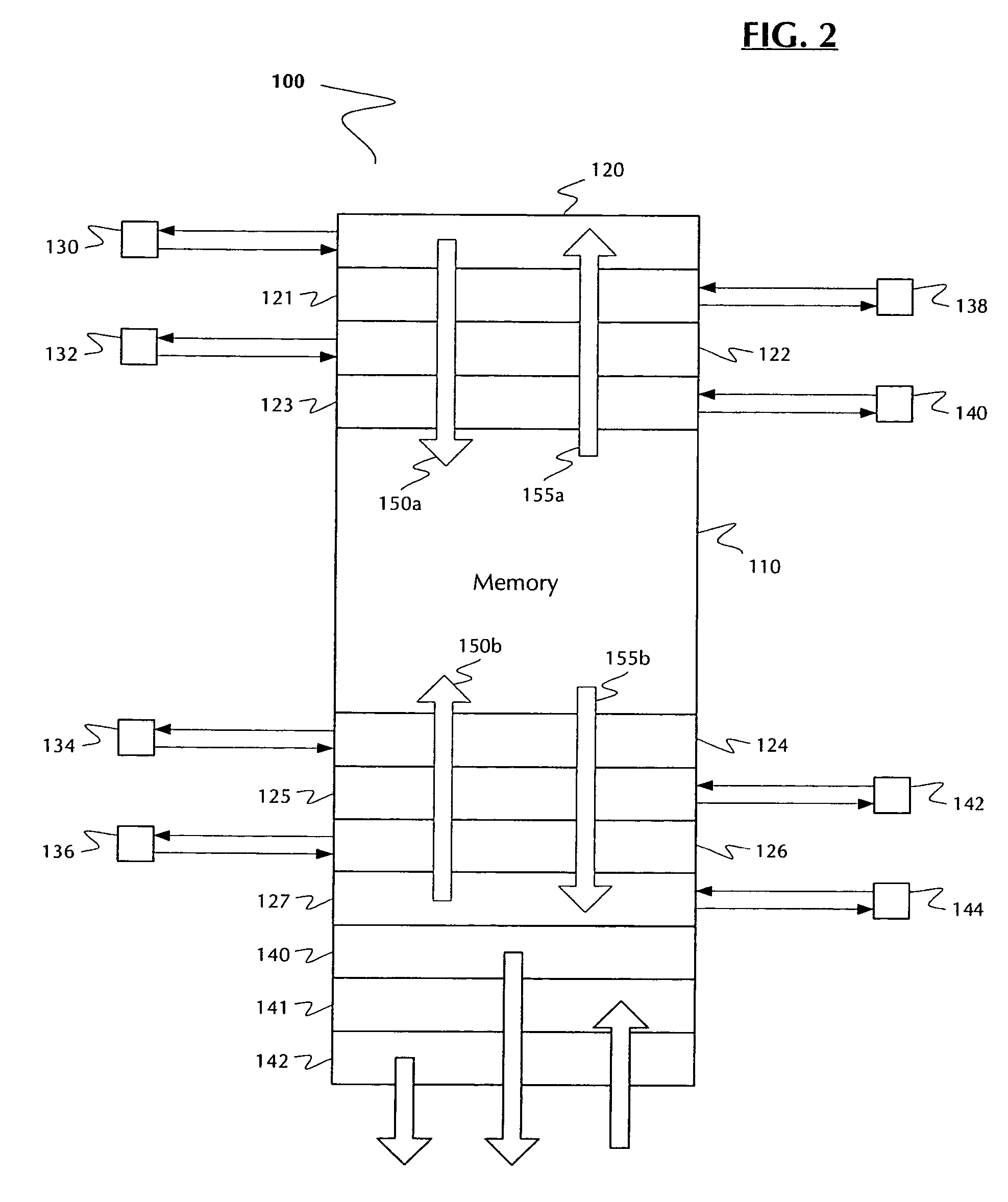
A multiport memory architecture, systems including the same and methods for using the same. The architecture generally includes (a) a memory array; (b) a plurality of ports configured to receive and / or transmit data; and (c) a plurality of port buffers, each of which is configured to transmit the data to and / or receive the data from one or more of the ports, and all of which are configured to (i) transmit the data to the memory array on a first common bus and (ii) receive the data from the memory array on a second common bus. The systems generally include those that embody one or more of the inventive concepts disclosed herein. The methods generally relate to writing blocks of data to, reading blocks of data from, and / or transferring blocks of data across a memory. The present invention advantageously reduces latency in data communications, particularly in network switches, by tightly coupling port buffers to the main memory and advantageously using point-to-point communications over long segments of the memory read and write paths, thereby reducing routing congestion and enabling the elimination of a FIFO. The invention advantageously shrinks chip size and provides increased data transmission rates and throughput, and in preferred embodiments, reduced resistance and / or capacitance in the memory read and write busses.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Node Spreading via Artificial Density Enhancement to Reduce Routing Congestion
ActiveUS20080216039A1Influence optimizeImprove performanceCAD circuit designSpecial data processing applicationsInterconnectionRouting congestion
Simultaneous Dynamical Integration modeling techniques are applied to global placement of elements of integrated circuits as described by netlists specifying interconnection of morphable-devices. Solutions to a system of coupled ordinary differential equations in accordance with Newtonian mechanics are approximated by numerical integration. A resultant time-evolving system of nodes moves through a continuous location space in continuous time, and is used to derive placements of the morphable-devices having one-to-one correspondences with the nodes. Nodes under the influence of net attractive forces, computed based on the interconnections between the morphable devices, tend to coalesce into well-organized topologies. Nodes are also affected by spreading forces determined by density fields that are developed based on local spatial node populations.
Owner:CALLAHAN CELLULAR L L C
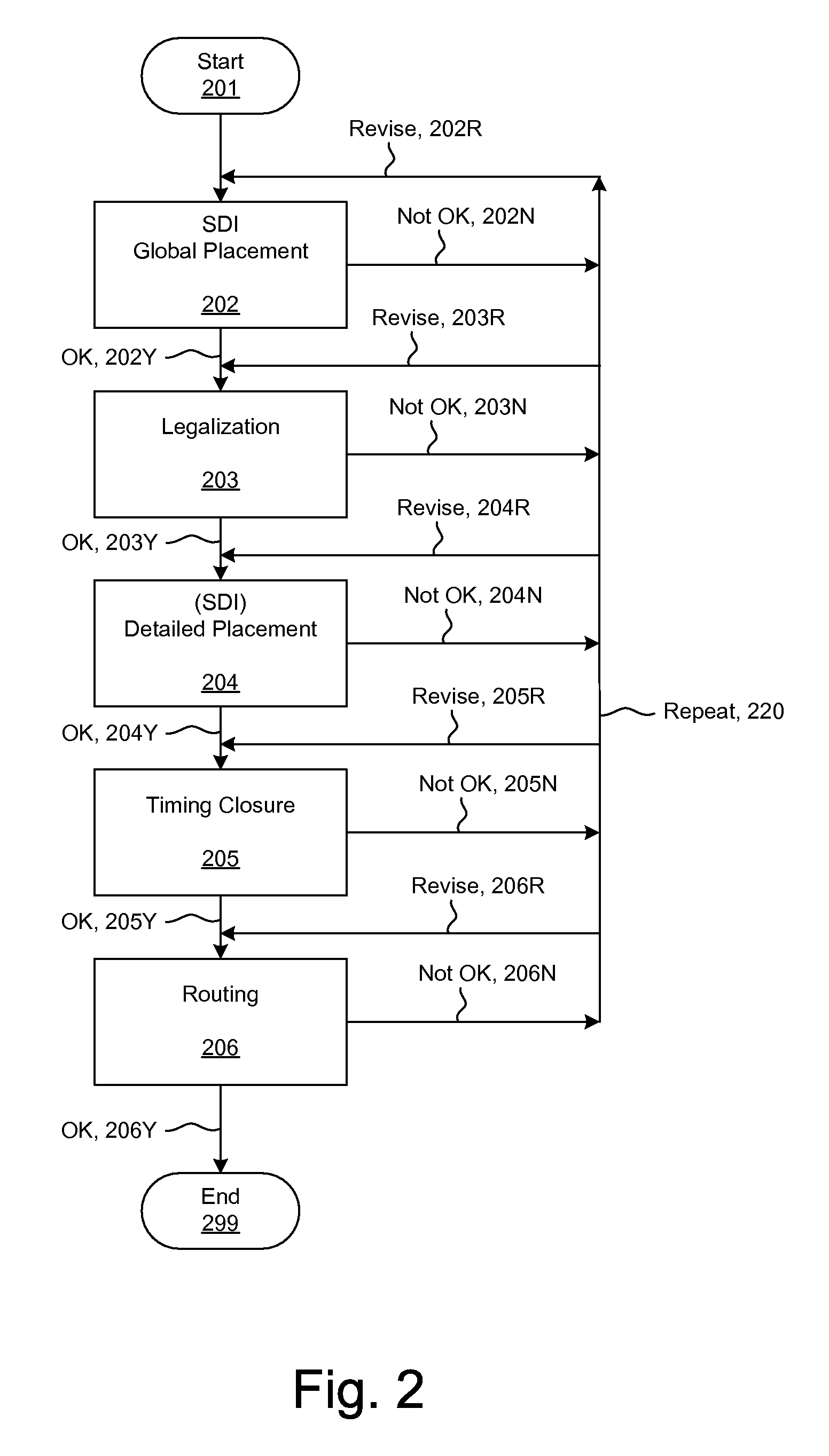
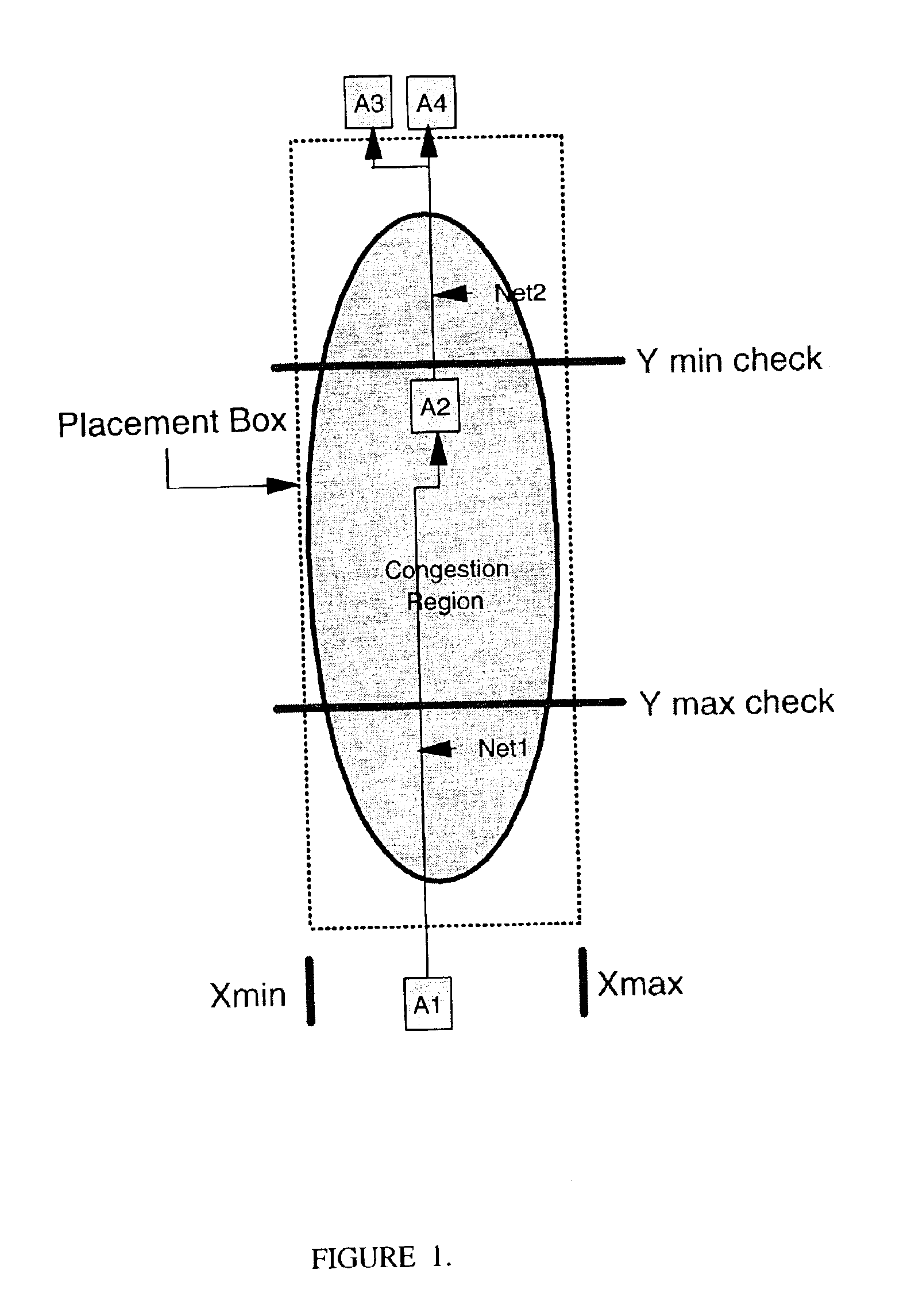
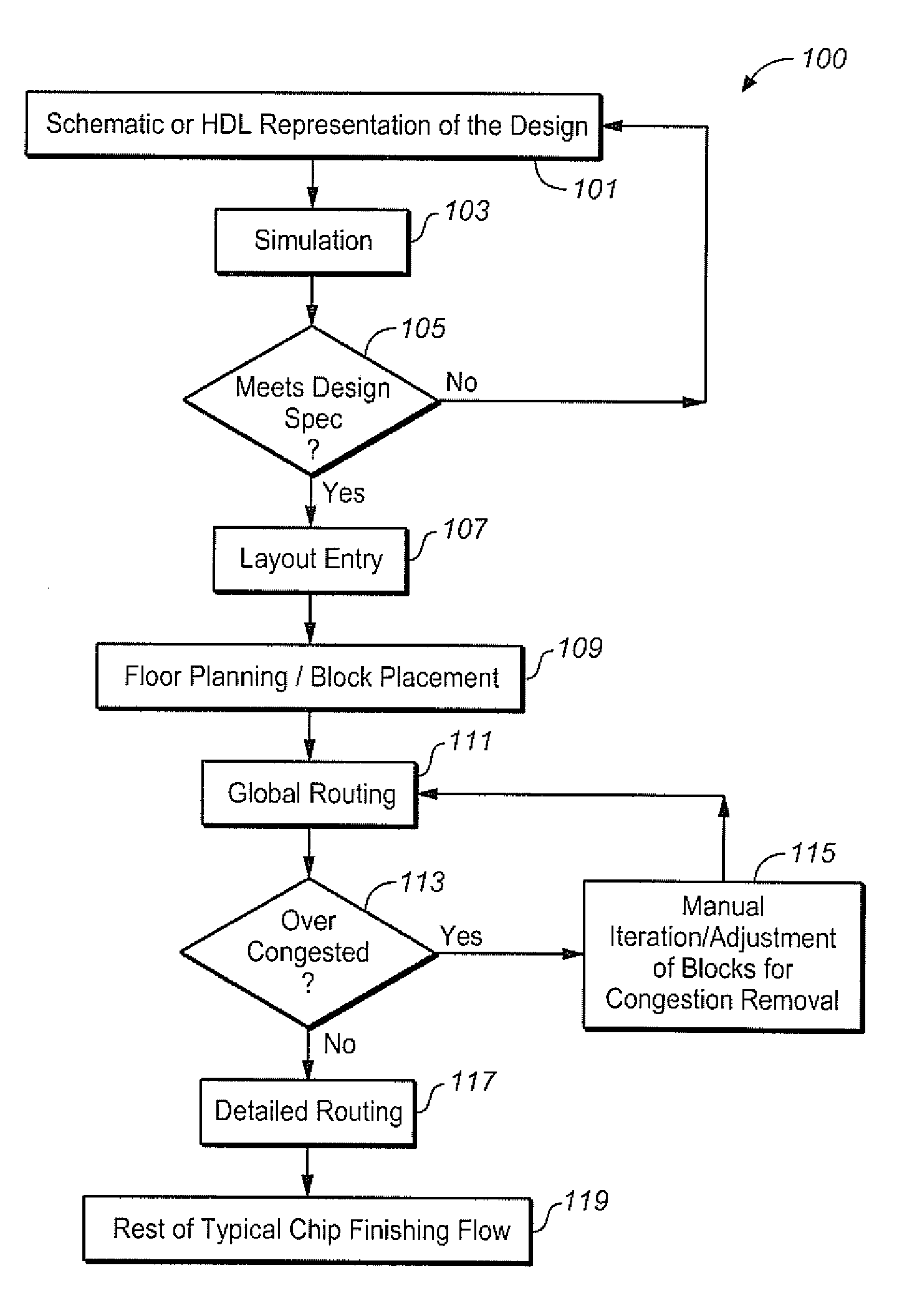
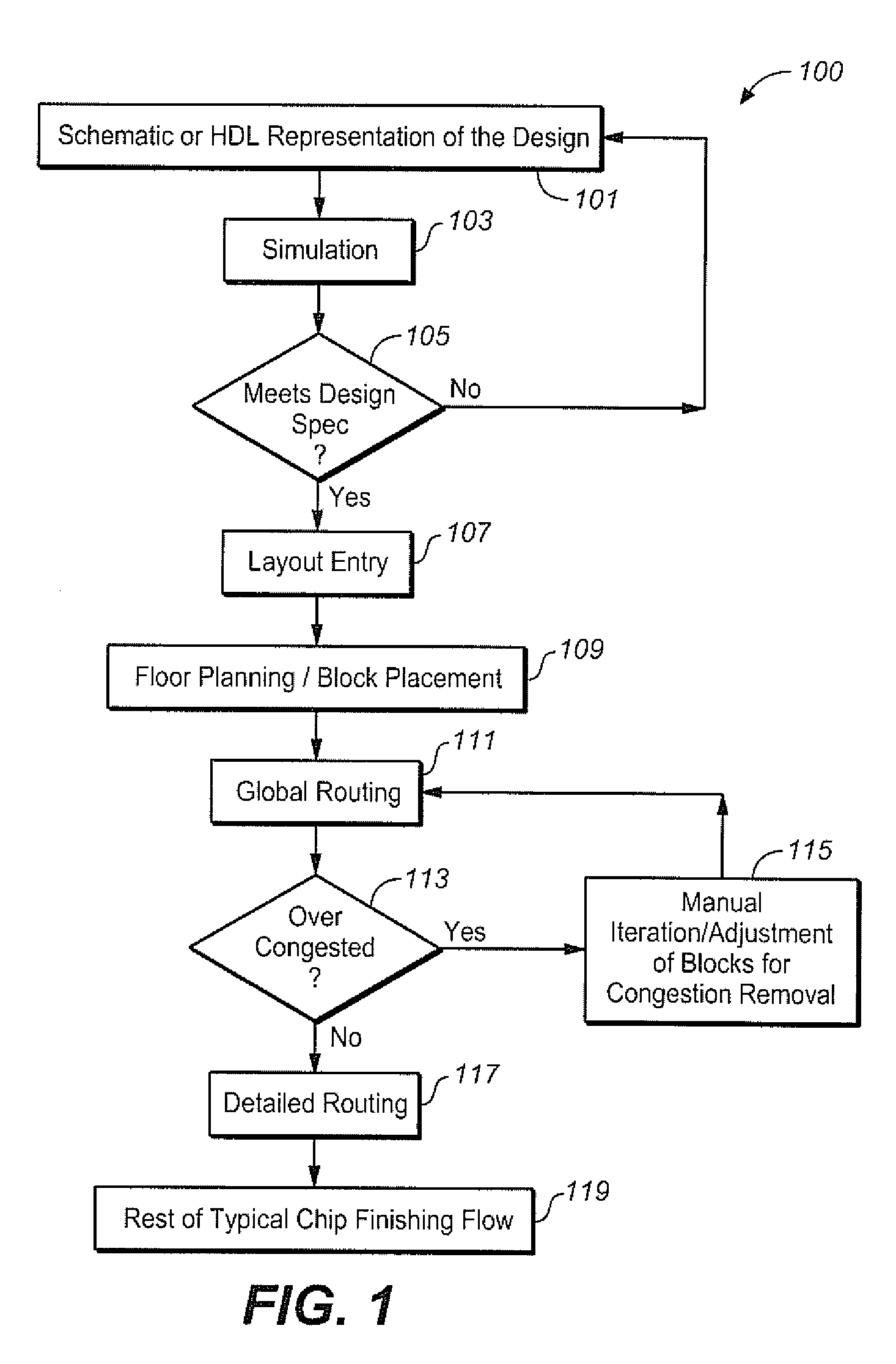
Congestion aware pin optimizer
InactiveUS7971174B1Computer aided designSpecial data processing applicationsComputer scienceRouting congestion
A circuit design process for the reduction of routing congestion is described. This process includes a block placement operation, an initial pin optimization for the block placement, and global routing based upon the initial pin optimization. Congestion data is generated from the global routing and, in an automated process, the pins are re-optimized, based upon the congestion data. This process can be used as part of a custom layout design process, for example.
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
Probabilistic congestion prediction with partial blockages
InactiveUS7299442B2Easy to predictFast and Accurate EstimationComputer aided designSpecial data processing applicationsTheoretical computer scienceRouting congestion
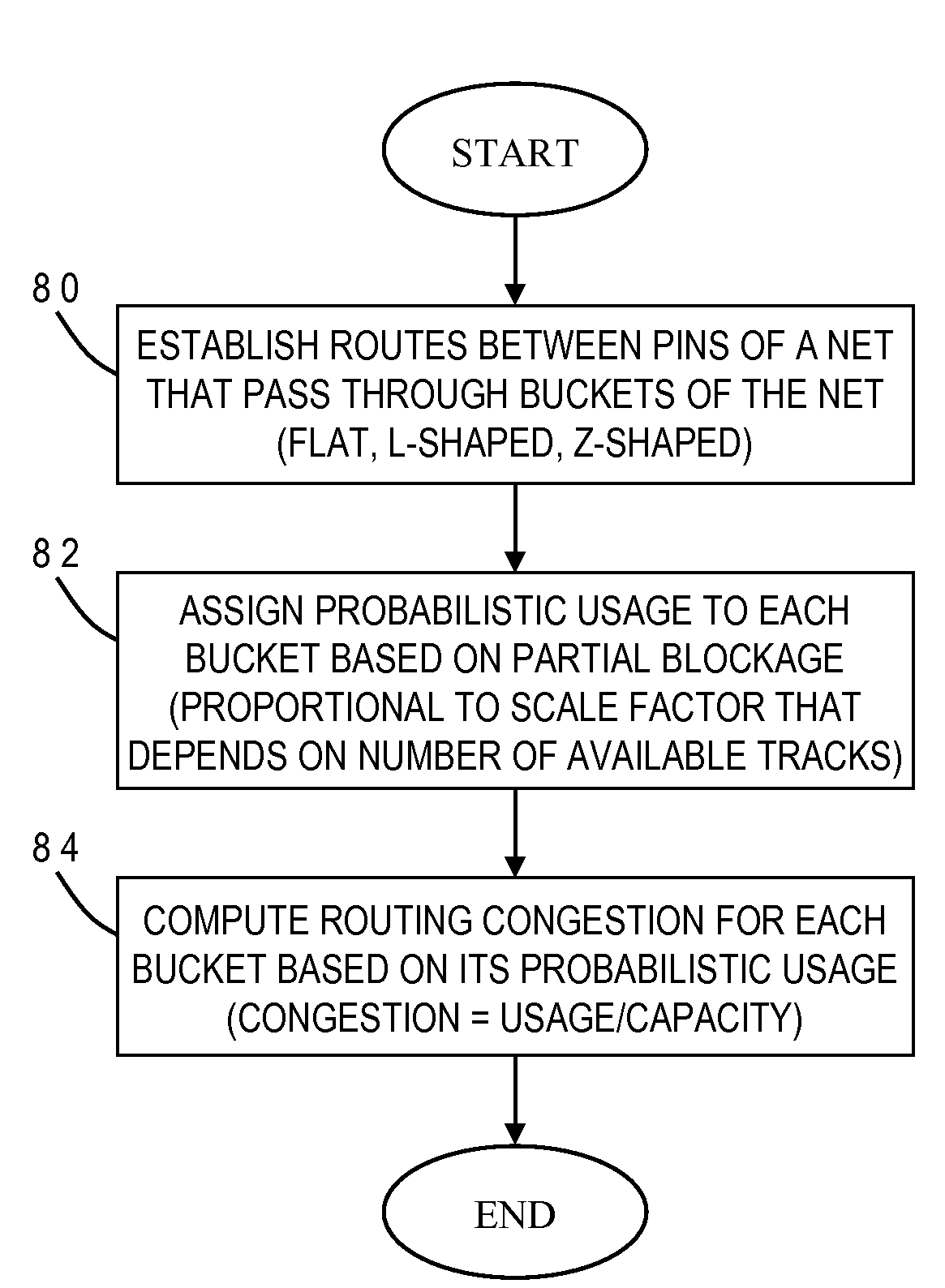
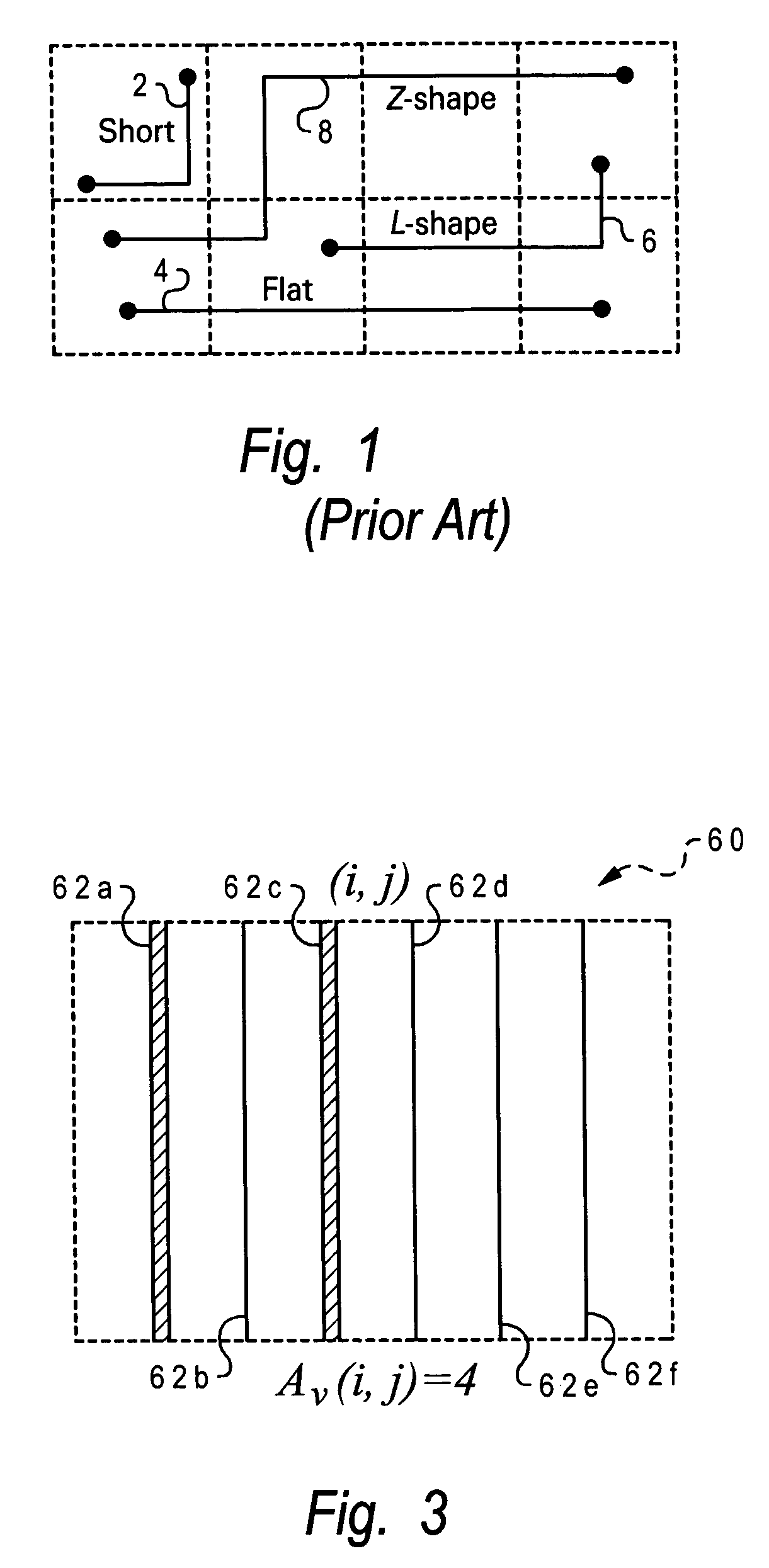
A method of estimating routing congestion between pins in a net of an integrated circuit design, by establishing one or more potential routes between the pins which pass through buckets in the net, assigning a probabilistic usage to each bucket based on any partial blockage of the wiring tracks in each bucket, and computing routing congestion for each bucket using its probabilistic usage. When the net is a two-pin net that is a part of a larger multi-pin net, and a tree is constructed to bridge the two-pin net to another pin of the multi-pin net. The routing congestion for each bucket is computed as a ratio of the bucket usage to bucket capacity. For L-shaped routes (having at least one bend in a bucket), the probabilistic usage is proportional to a scale factor a which is a ratio of a minimum number of available wiring tracks for a given route to a sum of minimum numbers of available wiring tracks for all possible routes. For Z-shaped routes (having at least two bends in two respective buckets), the probabilistic usage is equal to a ratio of a minimum capacity of a given route to a sum of minimum capacities of all routes having an associated orientation with the given route. Assignment of the usage values may entail the creation of a temporary usage map of the net buckets with an initial value of zero usage in every temporary usage map bucket, thereafter storing usage values in corresponding buckets of the temporary usage map, and deriving a final usage map from the temporary usage map.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Method for eliminating routing congestion in an IC layout
InactiveUS7225116B2Reduce congestionReduce the amount requiredComputer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationEngineeringRouting congestion
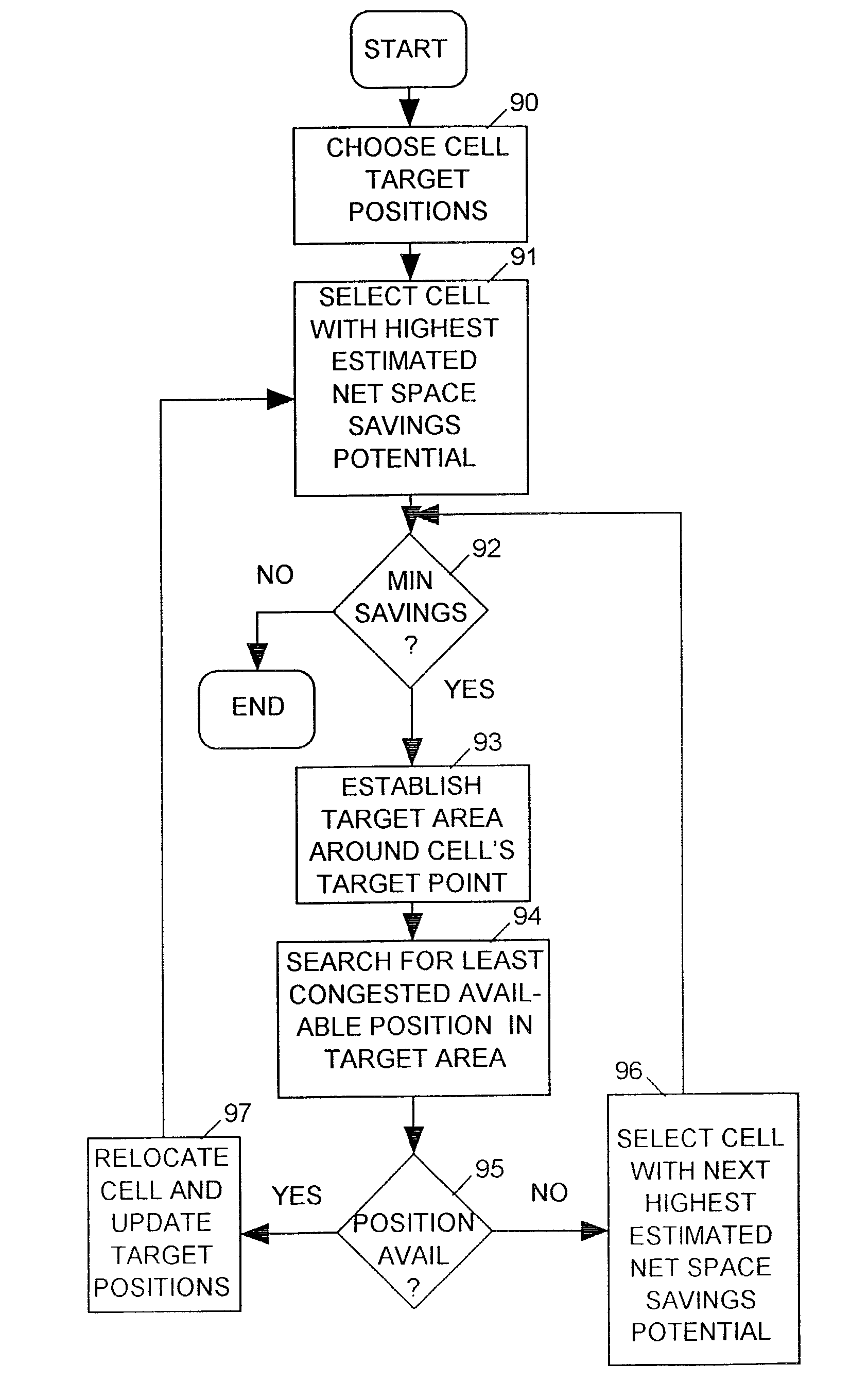
The invention relates to a method for eliminating routing congestion in an integrated circuit (IC) layout defined by a placement plan indicating a position within the layout of each cell forming the IC and routing plan describing routes followed by nets interconnecting the cells. Routing congestion is eliminated by estimating routing congestion in various areas of the layout and relocating each cell to least routing congested areas of the layout for which cell relocation results in a reduction in the total lengths of the nets connected to the cell that exceeds a predetermined minimum reduction.
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
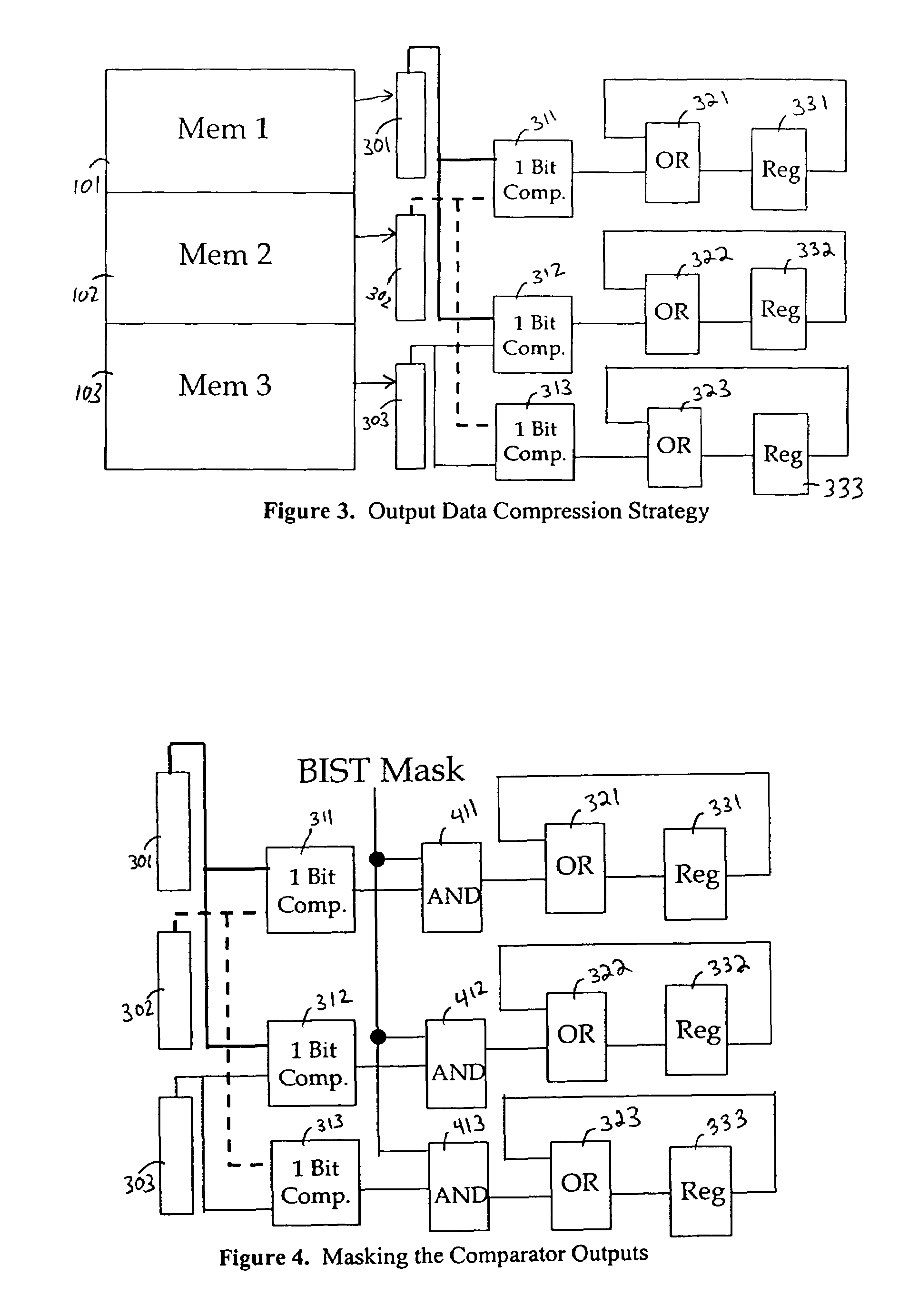
Method and apparatus for routing efficient built-in self test for on-chip circuit blocks
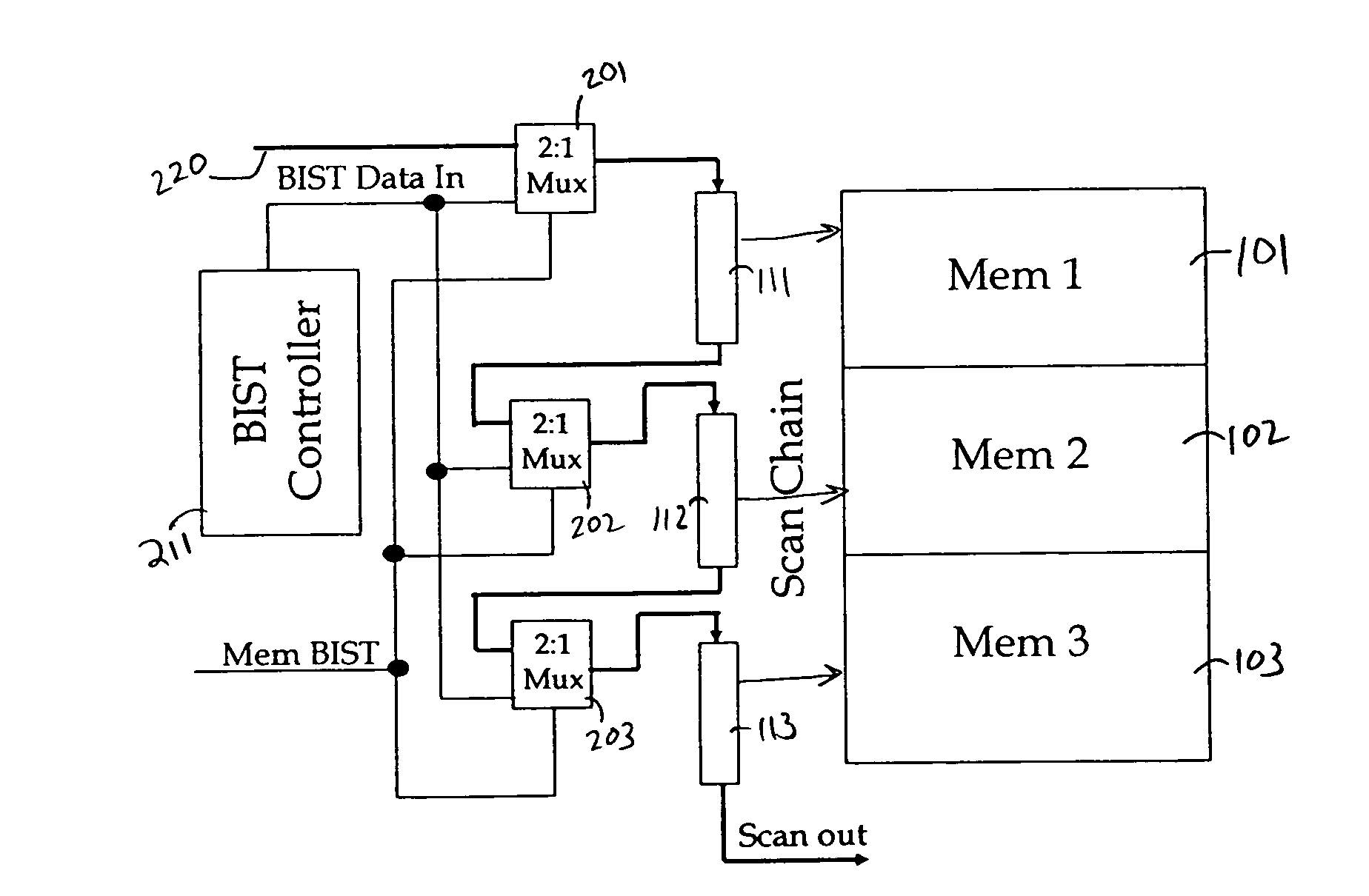
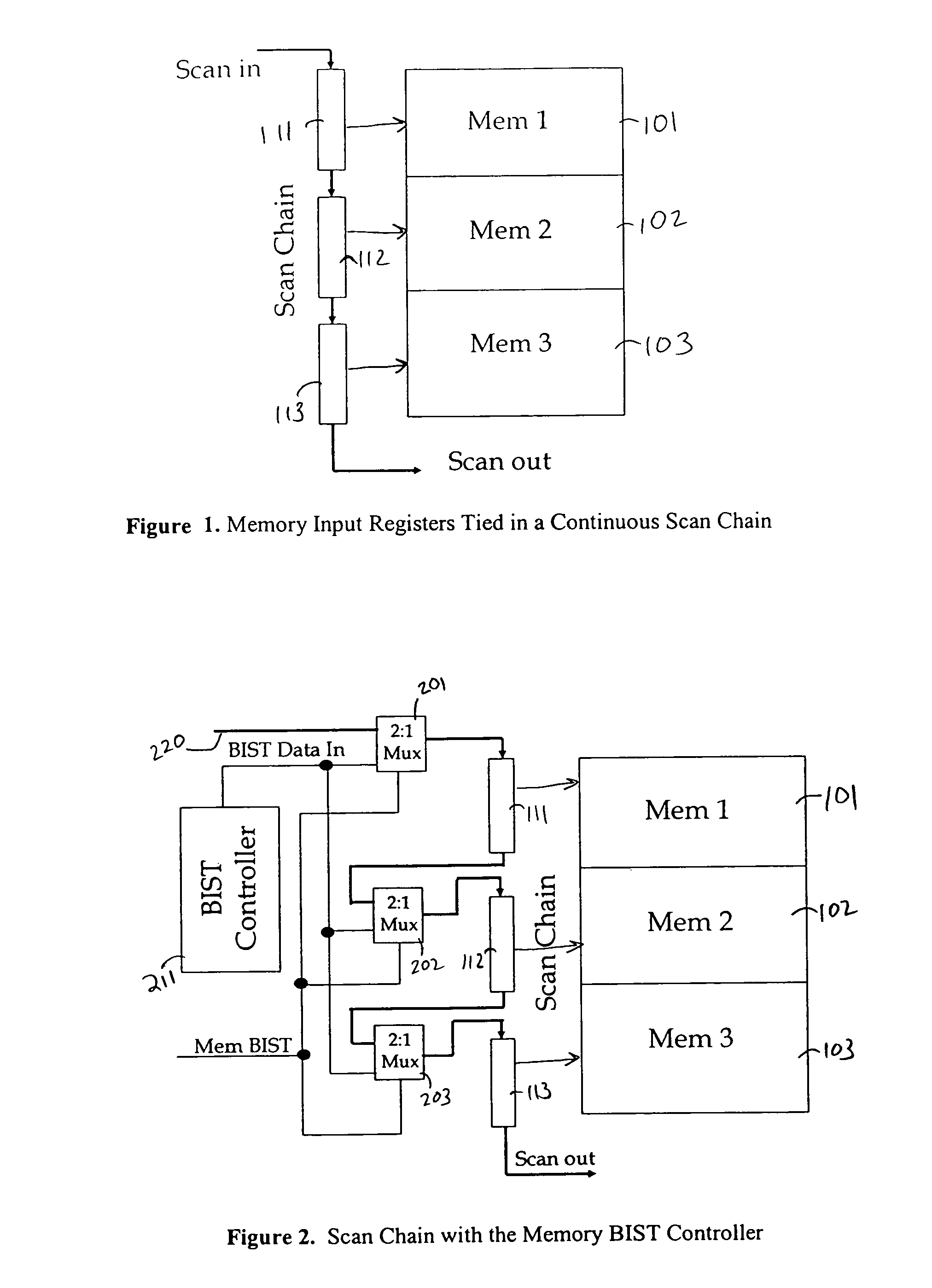
InactiveUS7707472B1Avoids high routing congestionReduce in quantityElectronic circuit testingStatic storageElectricityRouting congestion
Built-in self test techniques for testing circuit blocks on integrated circuits are provided. A BIST controller is provided on-chip to test two or more circuit blocks. High routing congestion is avoided by loading test data into the circuit blocks through scan chain segments that run continuously along the inputs and outputs of the circuit blocks. The BIST controller takes control of the scan chain segments during test and has the ability to partition the scan chains at specified intervals.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
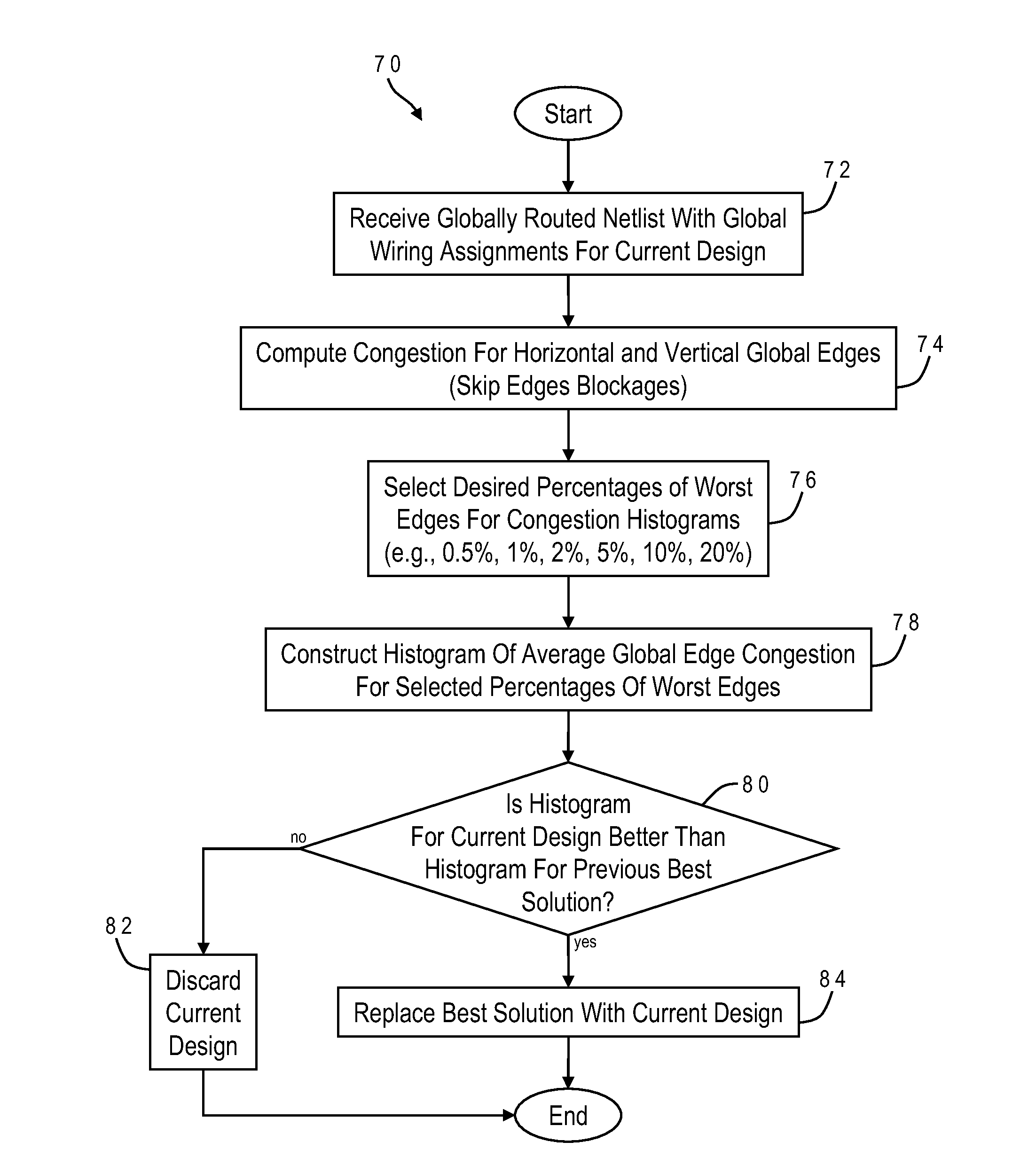
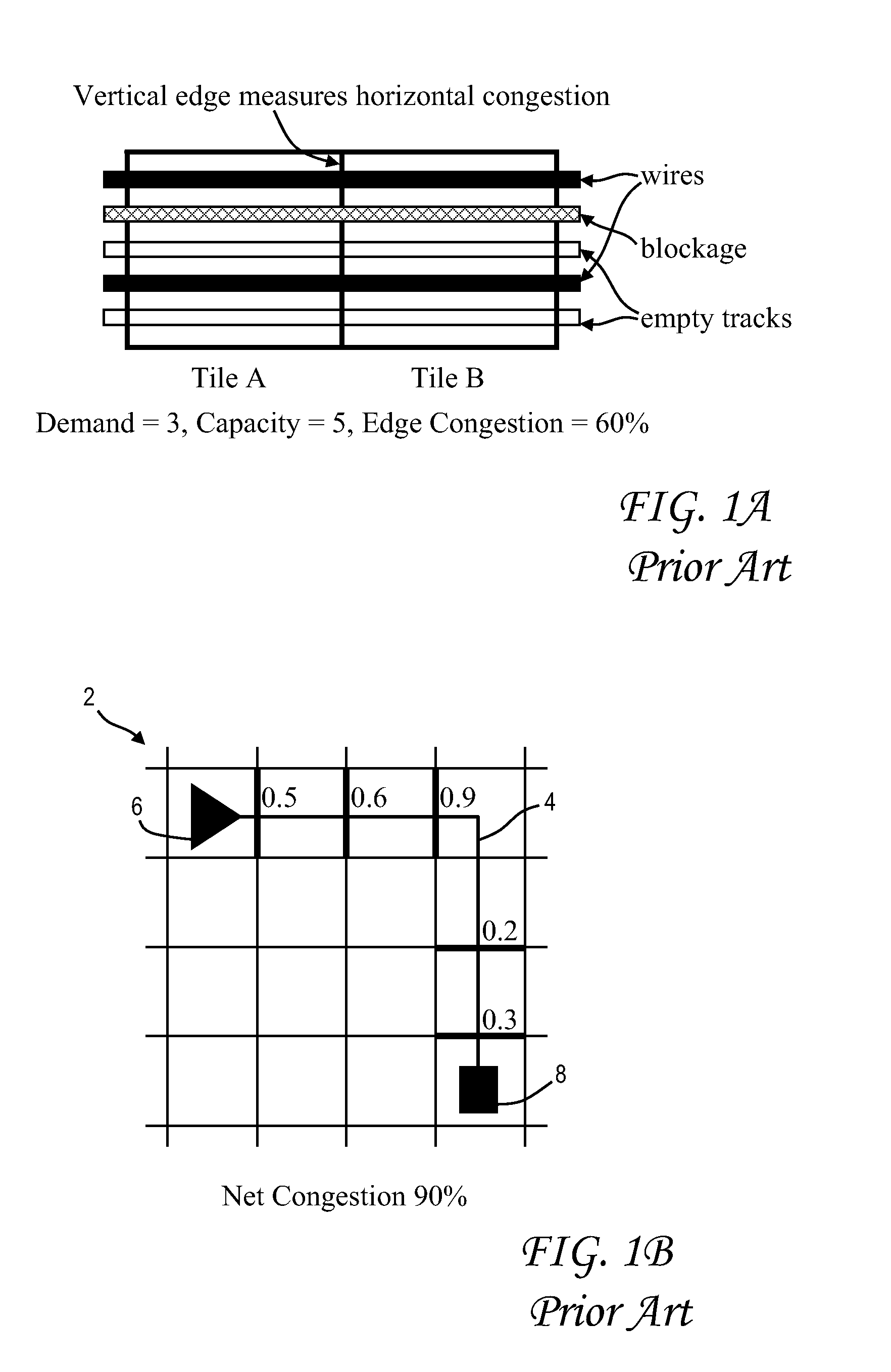
Evaluating routing congestion based on average global edge congestion histograms
InactiveUS20130086545A1Computer aided designSpecial data processing applicationsHorizontal and verticalRouting congestion
Global routing congestion in an integrated circuit design is characterized by computing global edge congestions and constructing a histogram of averages of the global edge congestions for varying percentages of worst edge congestion, e.g., 0.5%, 1%, 2%, 5%, 10% and 20%. Horizontal and vertical global edges are handled separately. Global edges near blockages can be skipped to avoid false congestion hotspots. The histogram of the current global routing can be compared to a histogram for a previous global routing to select a best routing solution. The histograms can also be used in conjunction with congestion-driven physical synthesis tools.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Method for reducing wiring congestion in a VLSI chip design
InactiveUS20050151258A1Reduced wiring areaReduce congestionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesLogic cellAnd logic unit
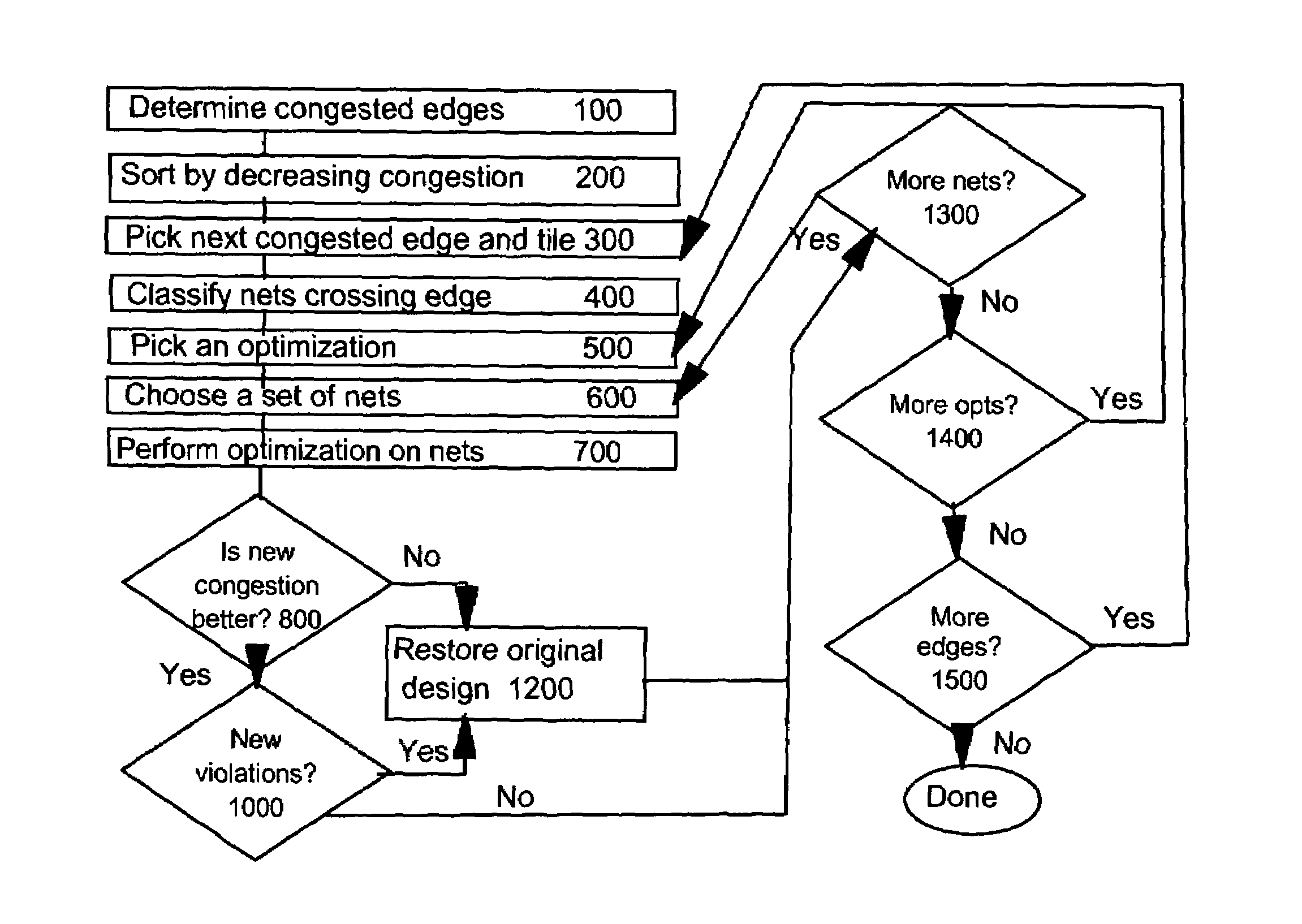
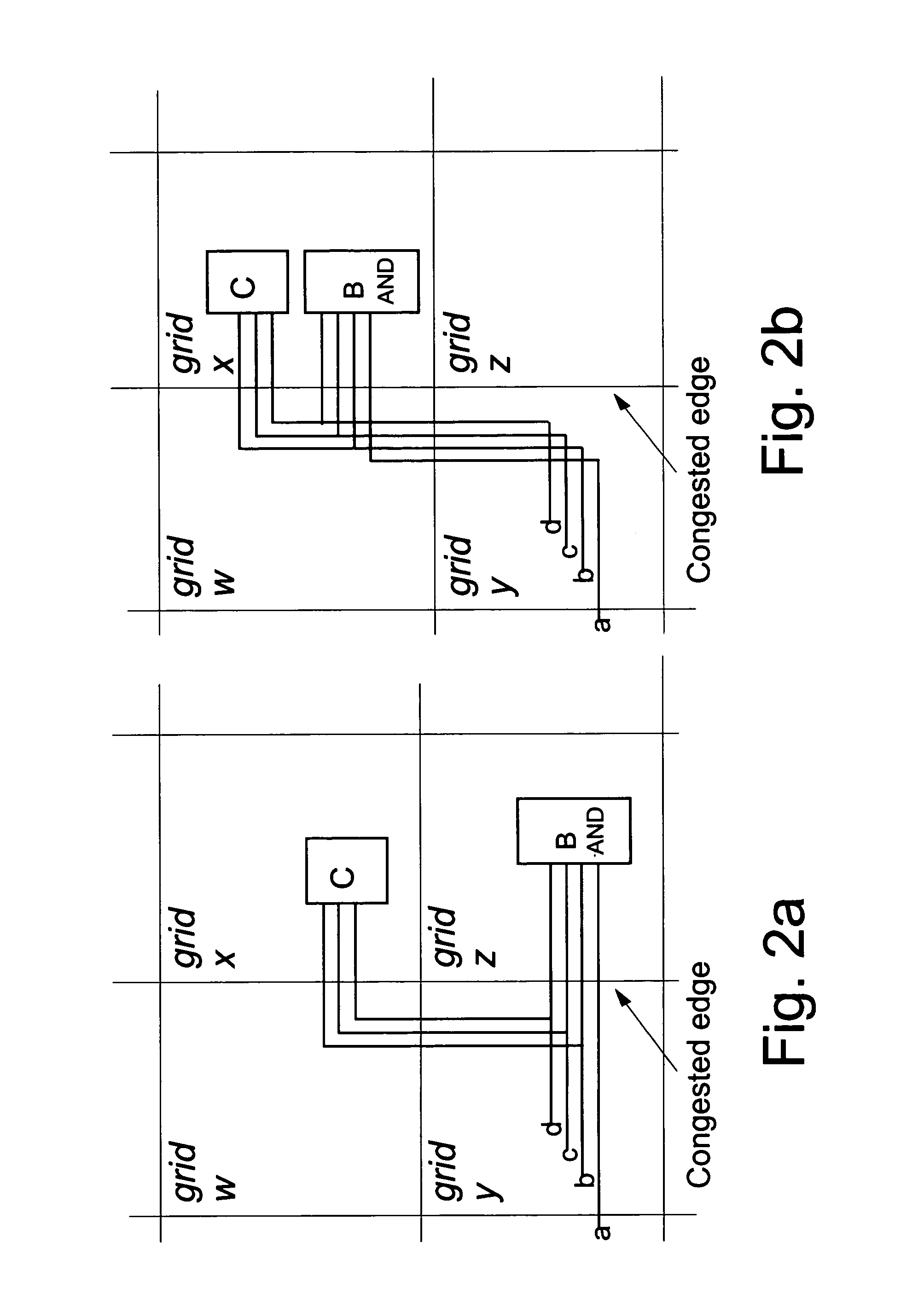
A system and method for correcting wiring congestion in a placed and partially or fully globally-routed VLSI chip design while avoiding adding new timing or electrical violations or other design constraints. Globally-congested areas are identified along with determining terminated and non-terminated wires in the congested areas. The process includes optimizing the identified congestion areas, incrementally rerouting affected nets, testing the resultant design legality and congestion metrics, and committing or reversing the optimizations and reroutings. The optimizations further includes the movement of logic cells and decomposition, recomposition or any other modification of logic cell structures (possibly combined with cell movement) to move terminated wires to less congested grid edges, rearrangement of commutative connections within or between cells, or addition of buffers to cause reroutes of feedthrough wires.
Owner:IBM CORP
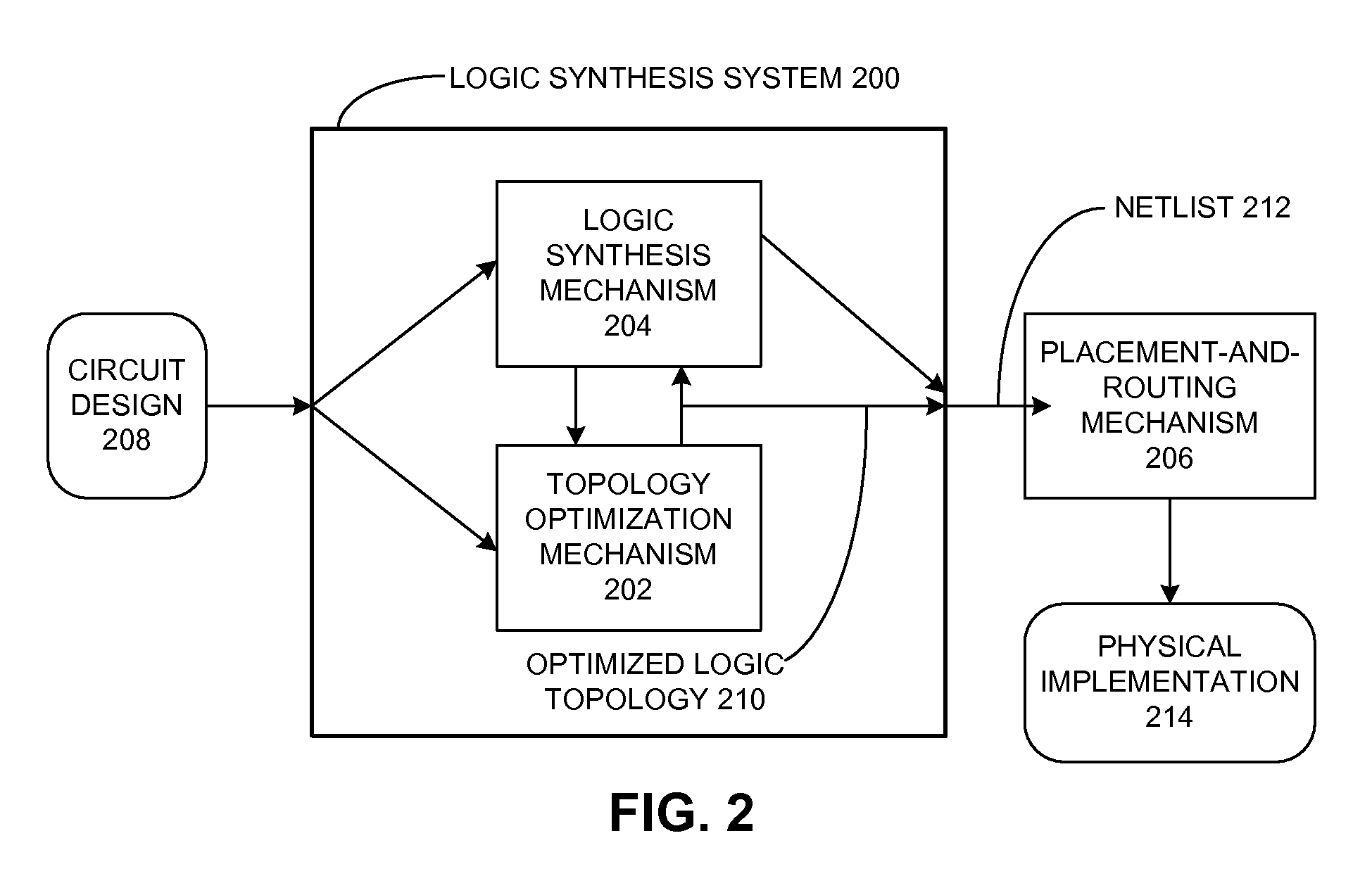
Congestion optimization during synthesis
ActiveUS20100115476A1Reduces routing congestionReduce crossoverComputer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationDesign stageSystem identification
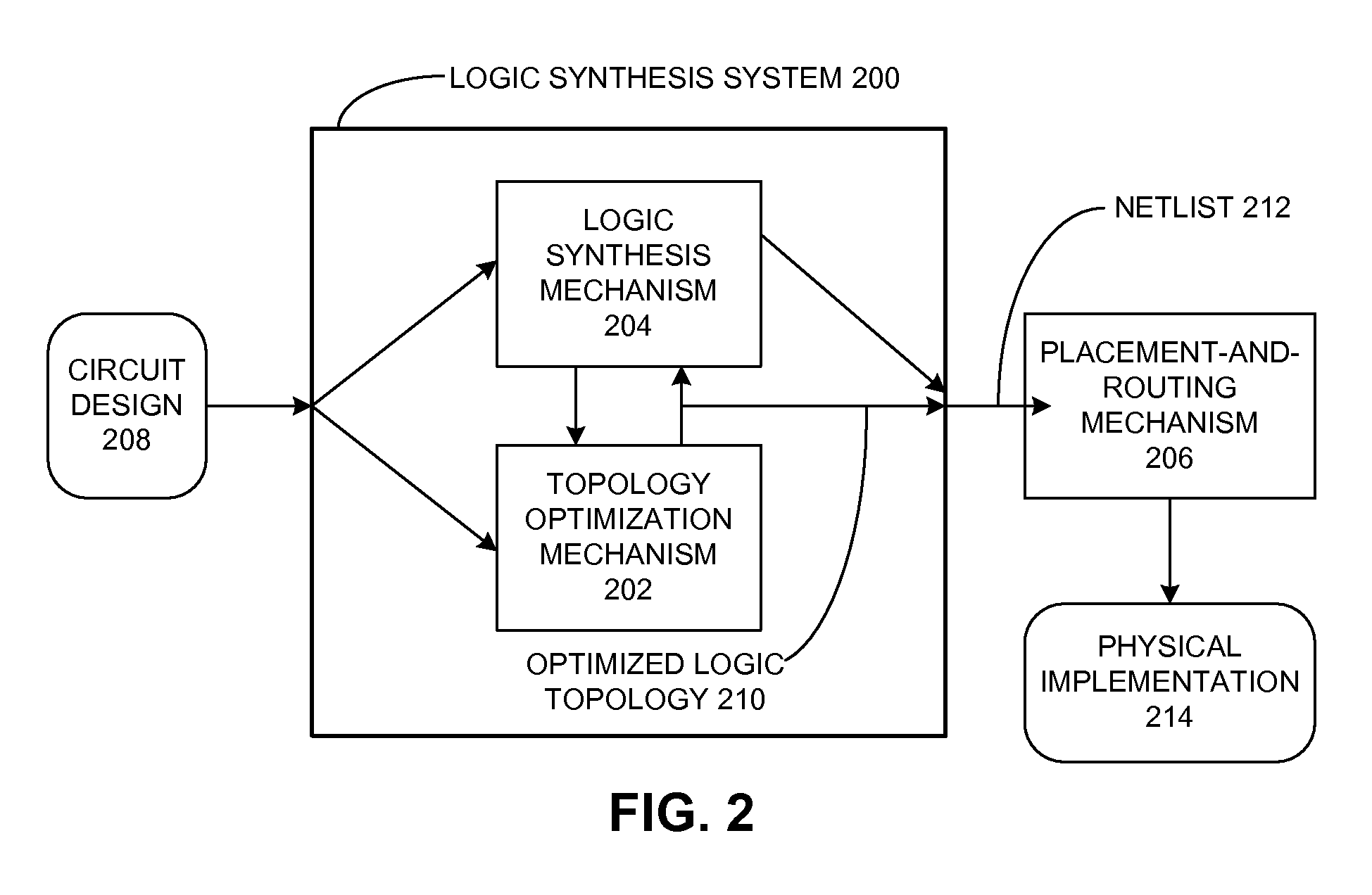
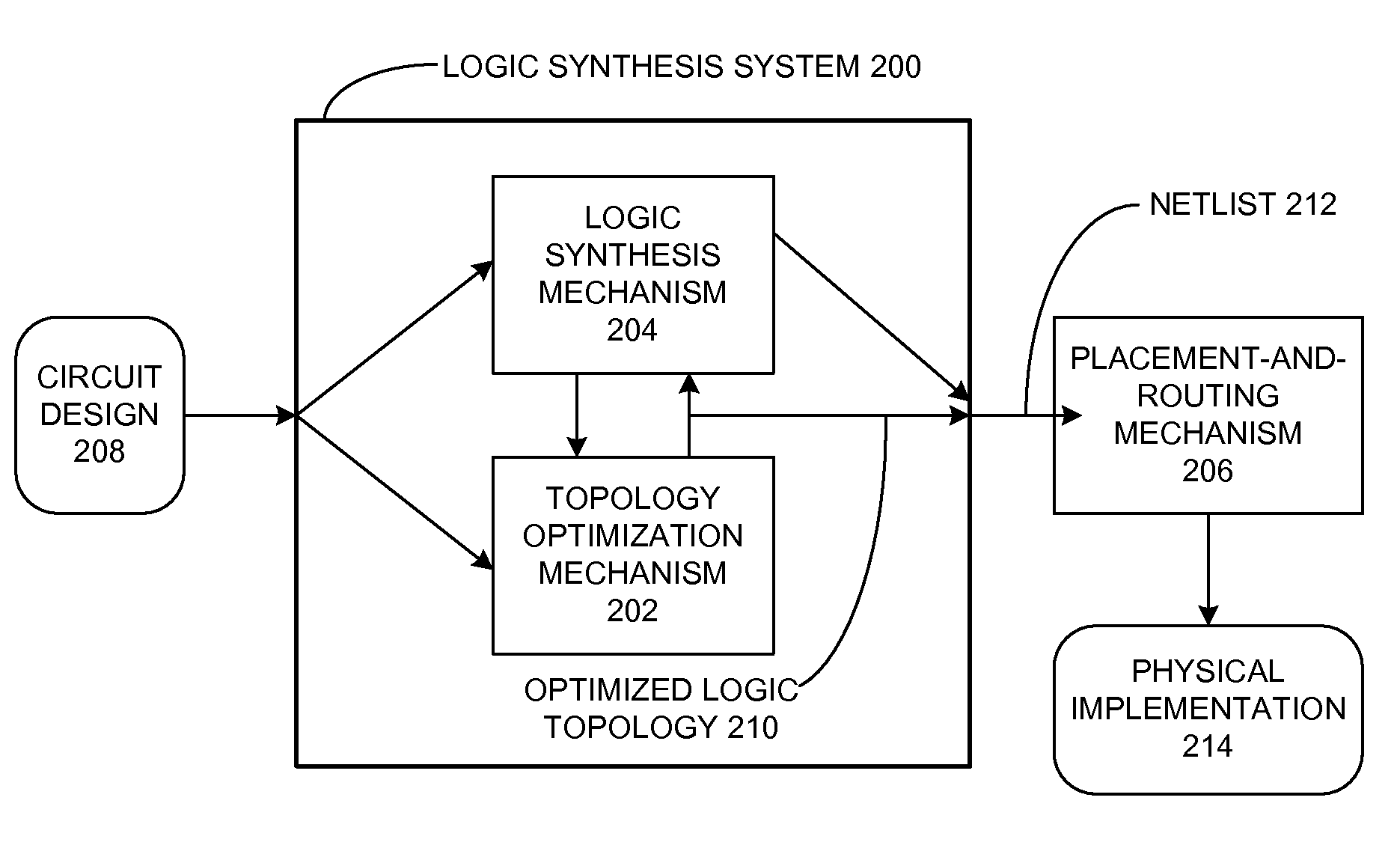
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system that optimizes a circuit design during a logic design stage to reduce routing congestion during a placement and routing stage. During operation, this system identifies a first circuit structure in the circuit design which is expected to cause routing congestion during the placement and routing stage. Next, the system generates a second circuit structure which is functionally equivalent to the first circuit structure, and is not expected to cause routing congestion during the placement and routing stage. The system then replaces the first circuit structure in the circuit design with the second circuit structure, thereby mitigating routing congestion during the placement and routing stage.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Congestion optimization during synthesis
ActiveUS8024693B2Reduce crossoverReduce congestionComputer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationDesign stageSystem identification
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
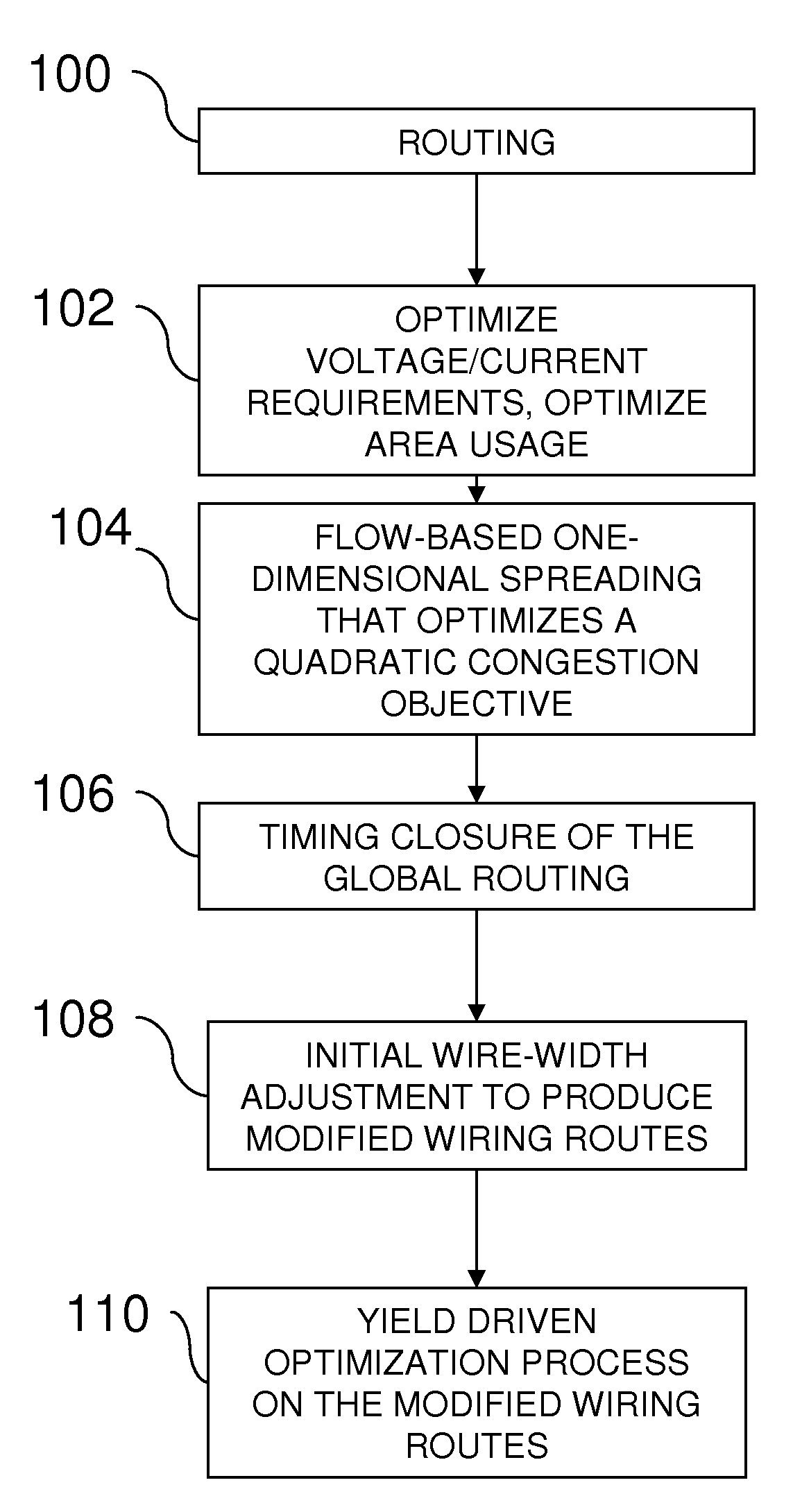
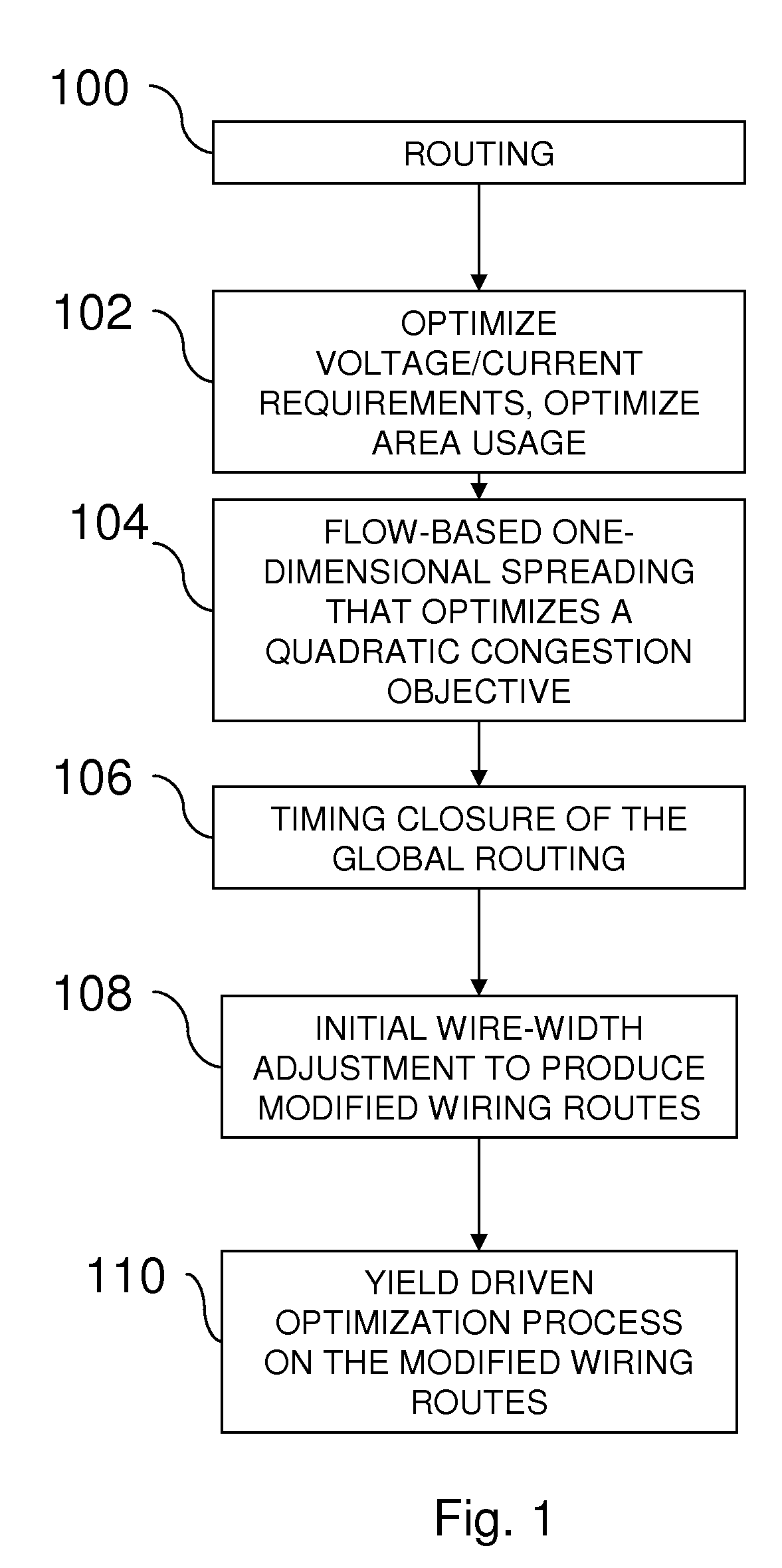
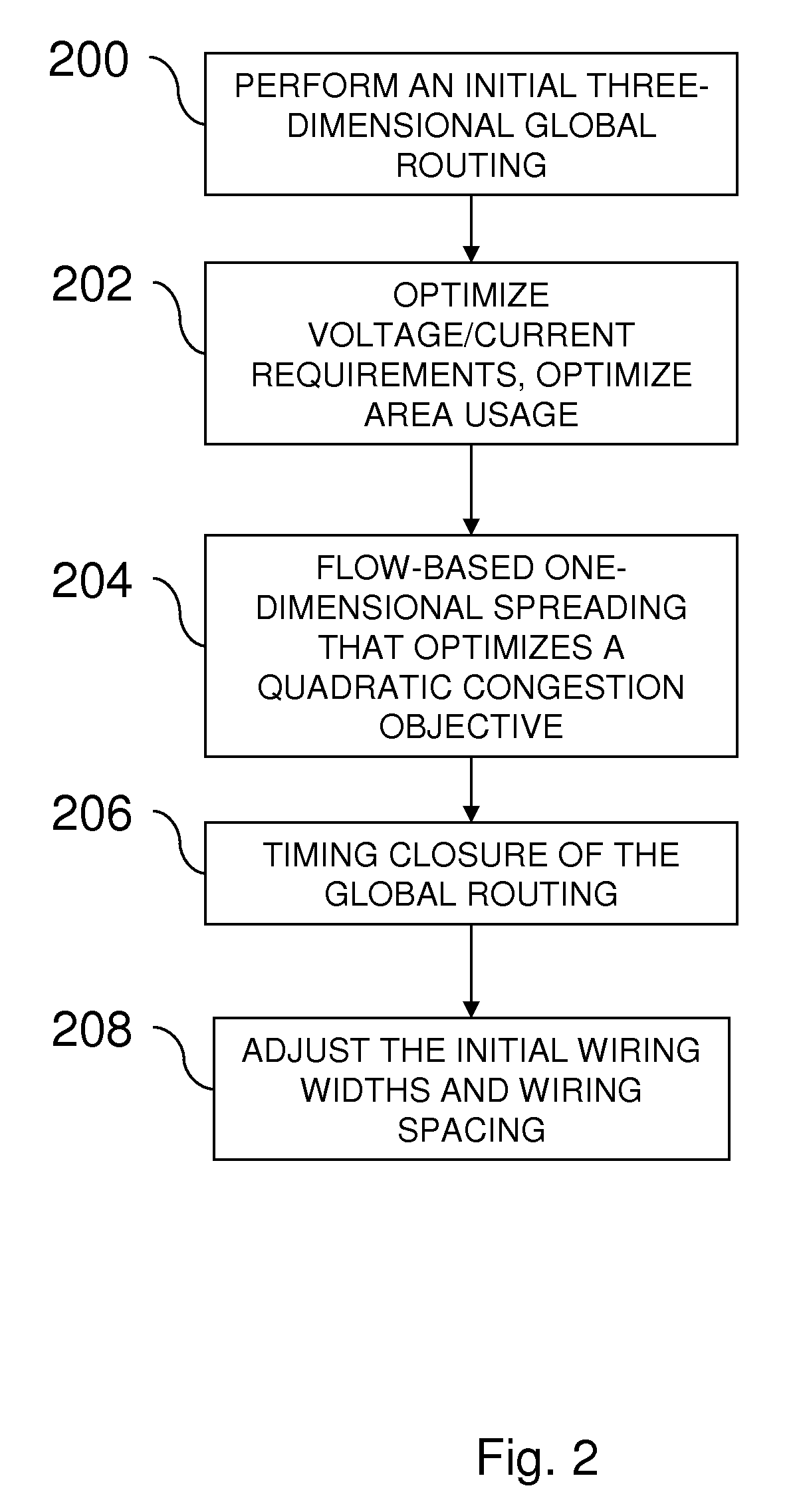
Method for IC wiring yield optimization, including wire widening during and after routing
InactiveUS20100023913A1Good yieldReduce areaComputer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationTiming closureIc routing
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Method and system for placing logic nodes based on an estimated wiring congestion
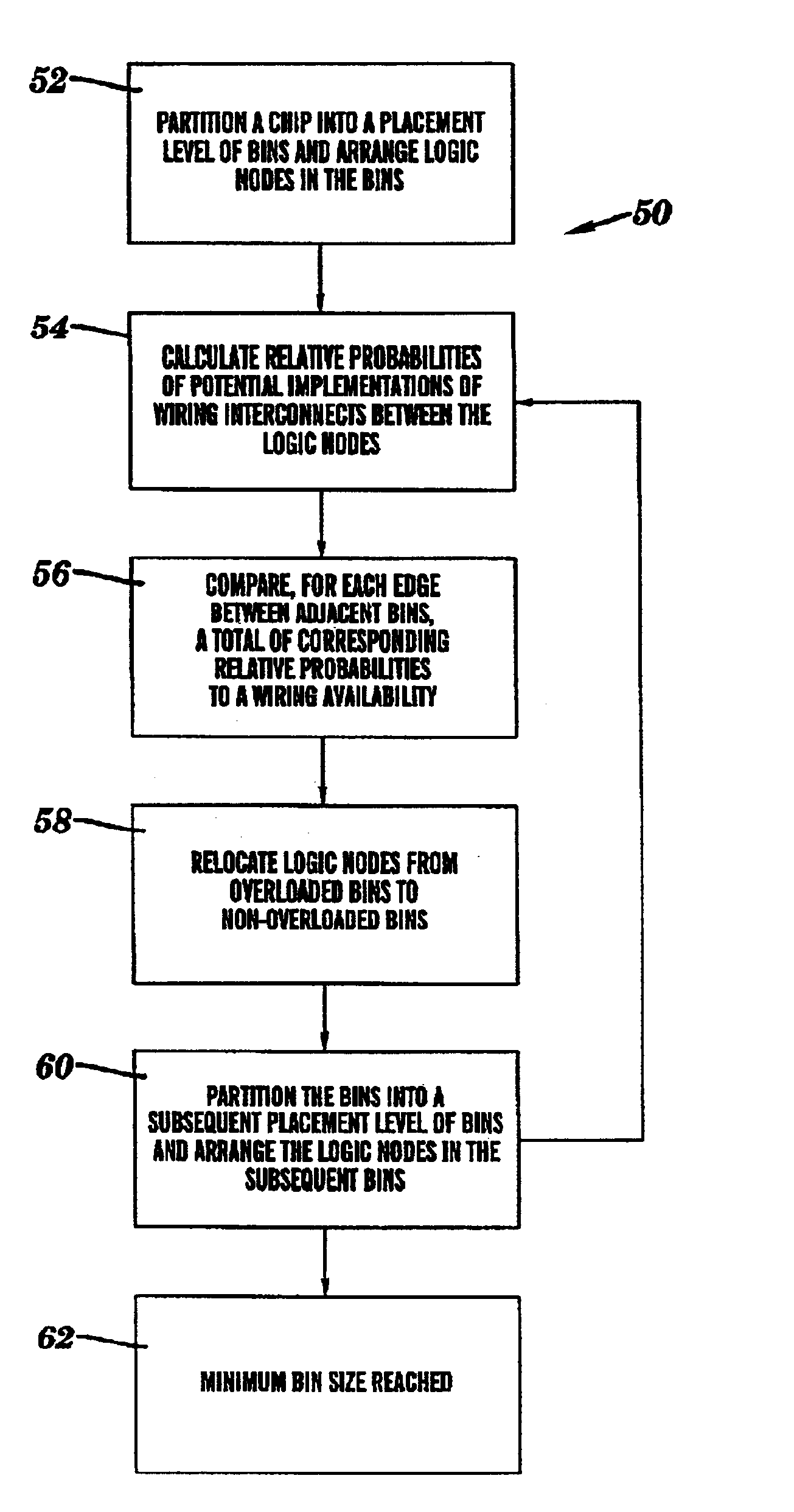
InactiveUS6904584B2Computer aided designSpecial data processing applicationsRelative probabilityRouting congestion
A method and system for placing logic nodes based on an estimated wiring congestion are provided. Specifically, under the present invention, relative probabilities for potential implementations of wiring interconnects between logic nodes are determined. Then, for each edge between adjacent bins, a total of corresponding relative probabilities is compared to a wiring availability. Based on the comparison, the logic nodes can be placed within wiring constraints.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
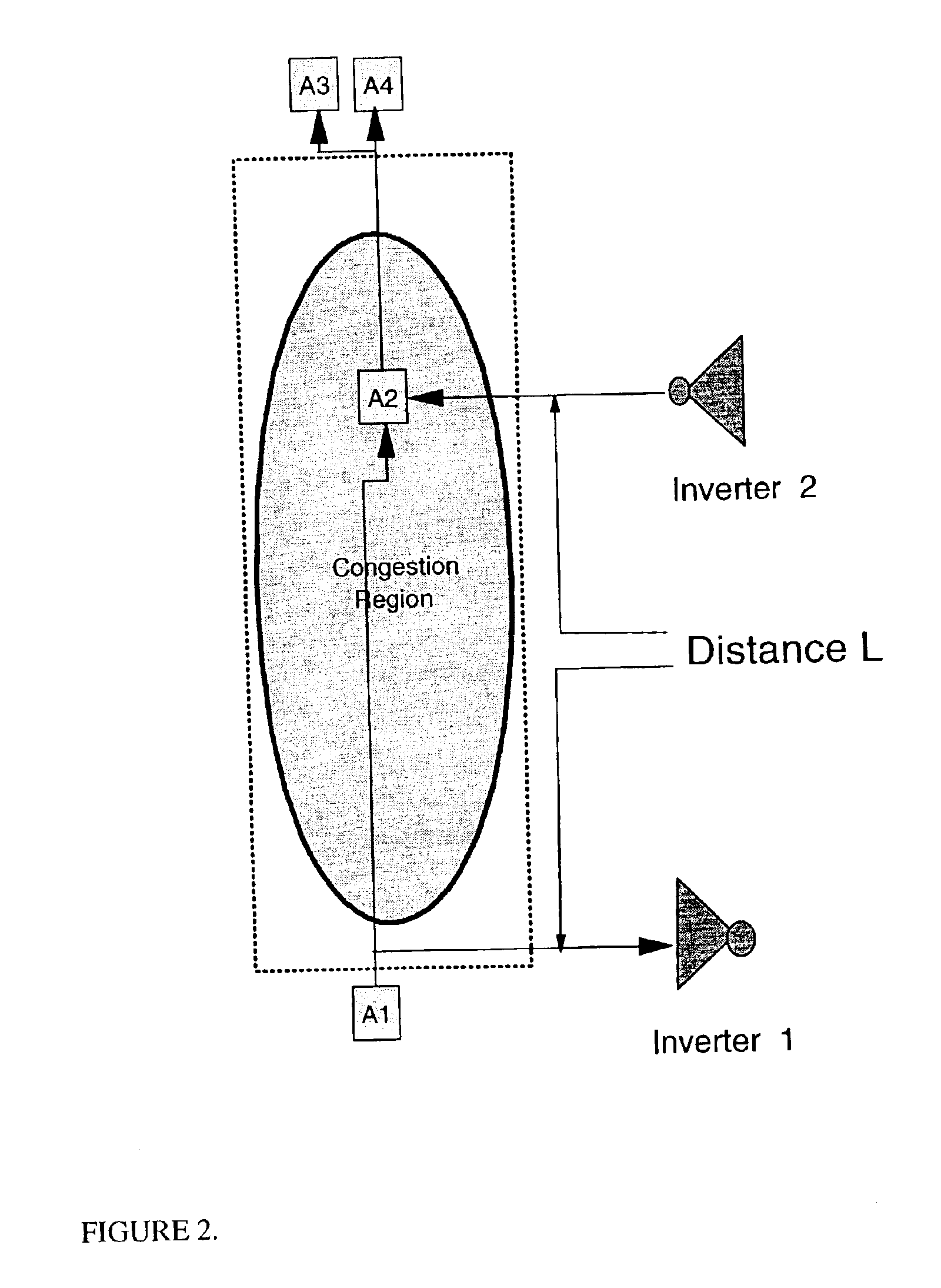
Method for identification and removal of non-timing critical wire routes from congestion region
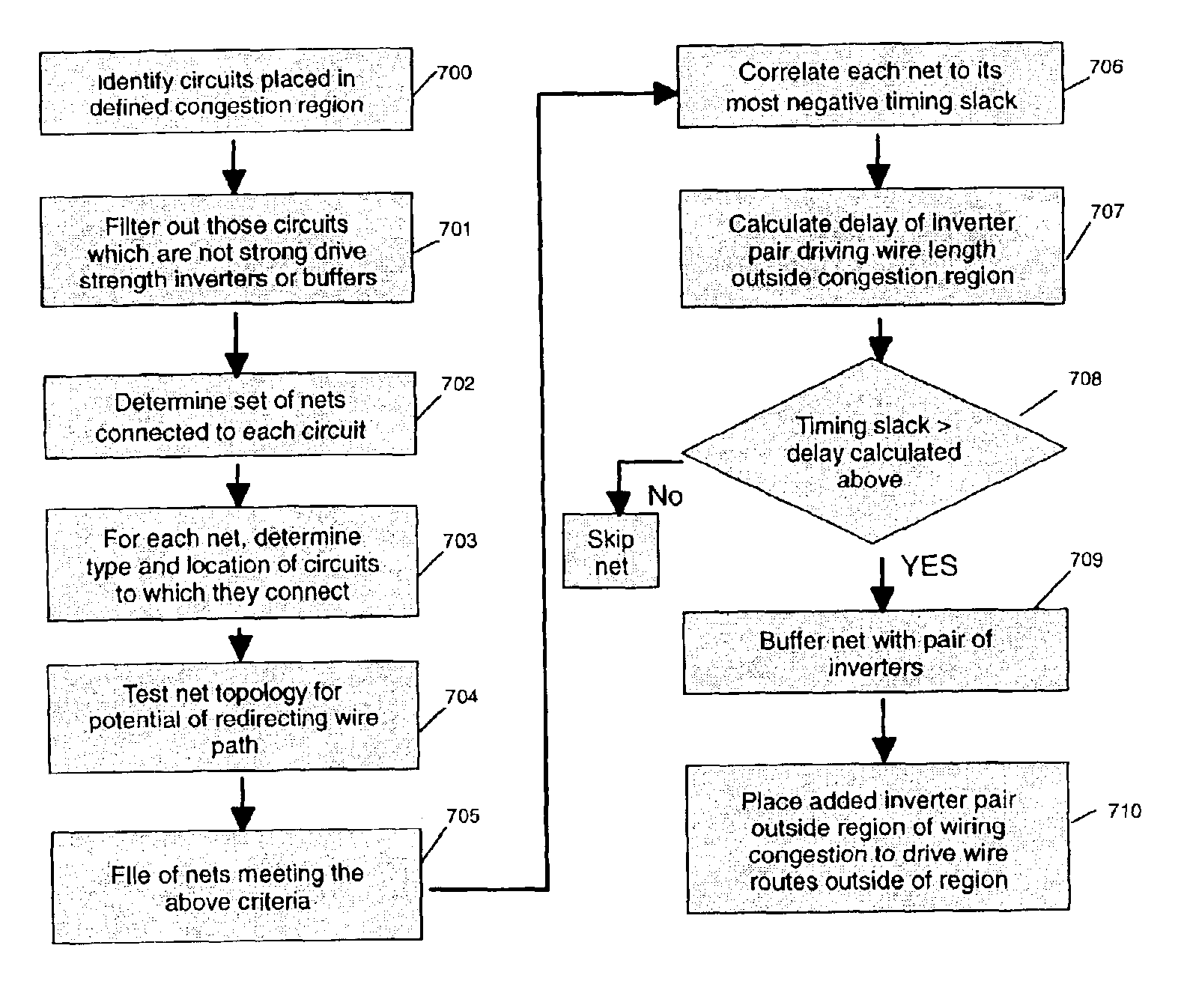
InactiveUS6904585B2Congestion increaseSlow changeProgram controlComputer aided designVlsi chip designCongestion detection
A method for identifying and modifying, in a VLSI chip design, wire routes within a region of wiring congestion that can be routed around that region without inducing timing violations by the insertion and proper placement of inverters. Circuits and nets are examined in the vicinity of the wiring congestion to determine those nets with high potential to drive a route outside the region. Circuit locations are analyzed to determine if the net connecting them creates a path through the region of wiring congestion. Timing slacks are derived from the timing reports for such nets and compared against a timing value representing the additional delay of using an inverter pair to drive the wire route outside the region of wiring congestion. If a net has sufficient timing slack, it is buffered with an inverter pair which is then placed in a manner as to force the wire routes for the modified path around the region of wiring congestion, thereby reducing the wire utilization within the region.
Owner:IBM CORP
3D integrated circuit
ActiveUS20160211241A1Improve system performanceReduce power consumptionSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device details3d integrated circuitElectric distribution network
A three-dimensional integrated circuit (3D-IC) architecture incorporates multiple layers, each layer including at least one die and at least one switch to connect the dies on the different layers. In some aspects, a power distribution network (PDN) is routed from a first layer through the switches to supply power to at least one other layer, thereby reducing routing congestion on the layers. The switches can be placed around the periphery of an IC package to improve heat dissipation (e.g., by improving heat transfer from the center to the edge of the IC package). The switches can be used for routing test signals and / or other signals between layers, thereby improving test functionality and / or fault recovery.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
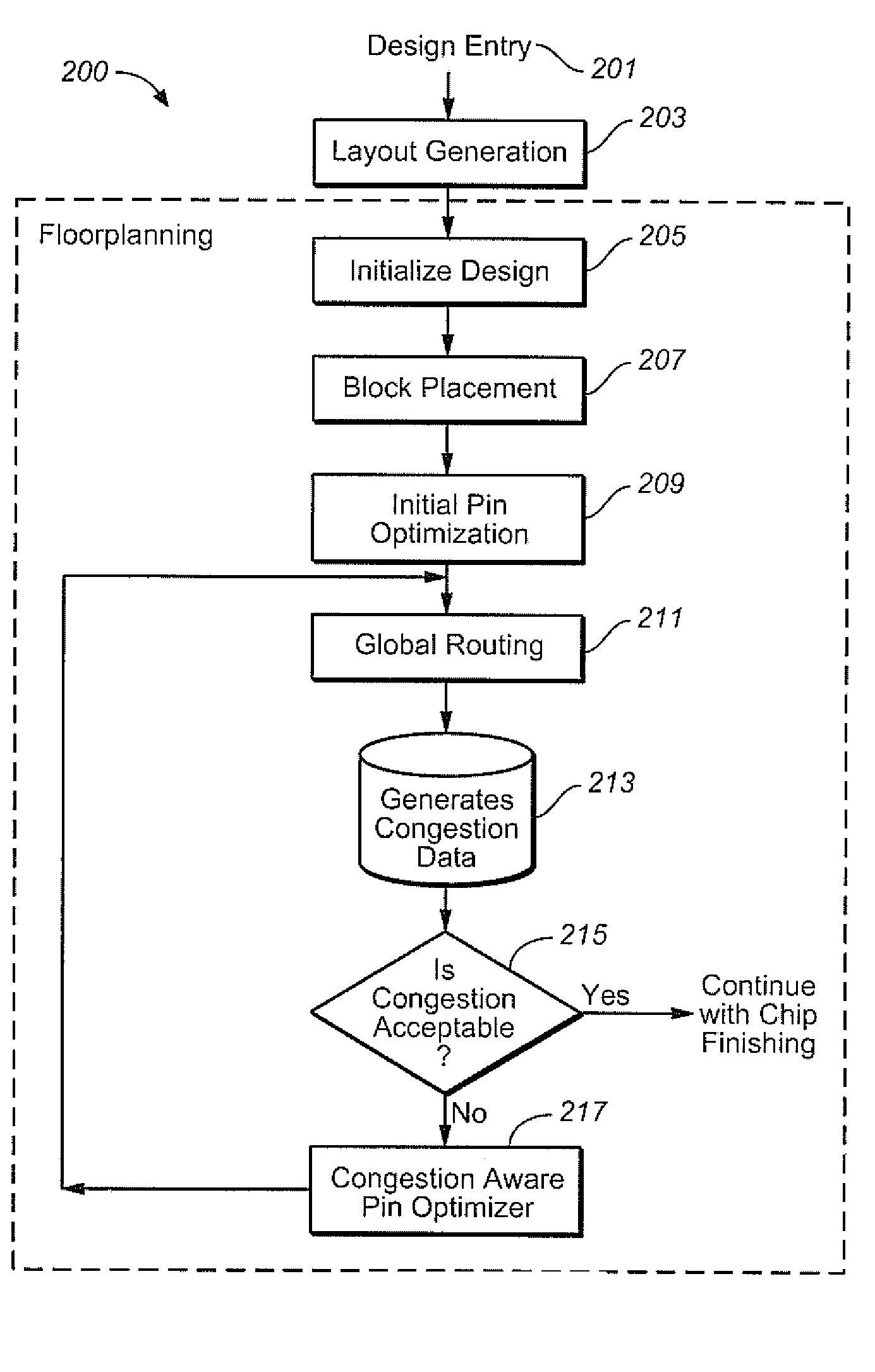
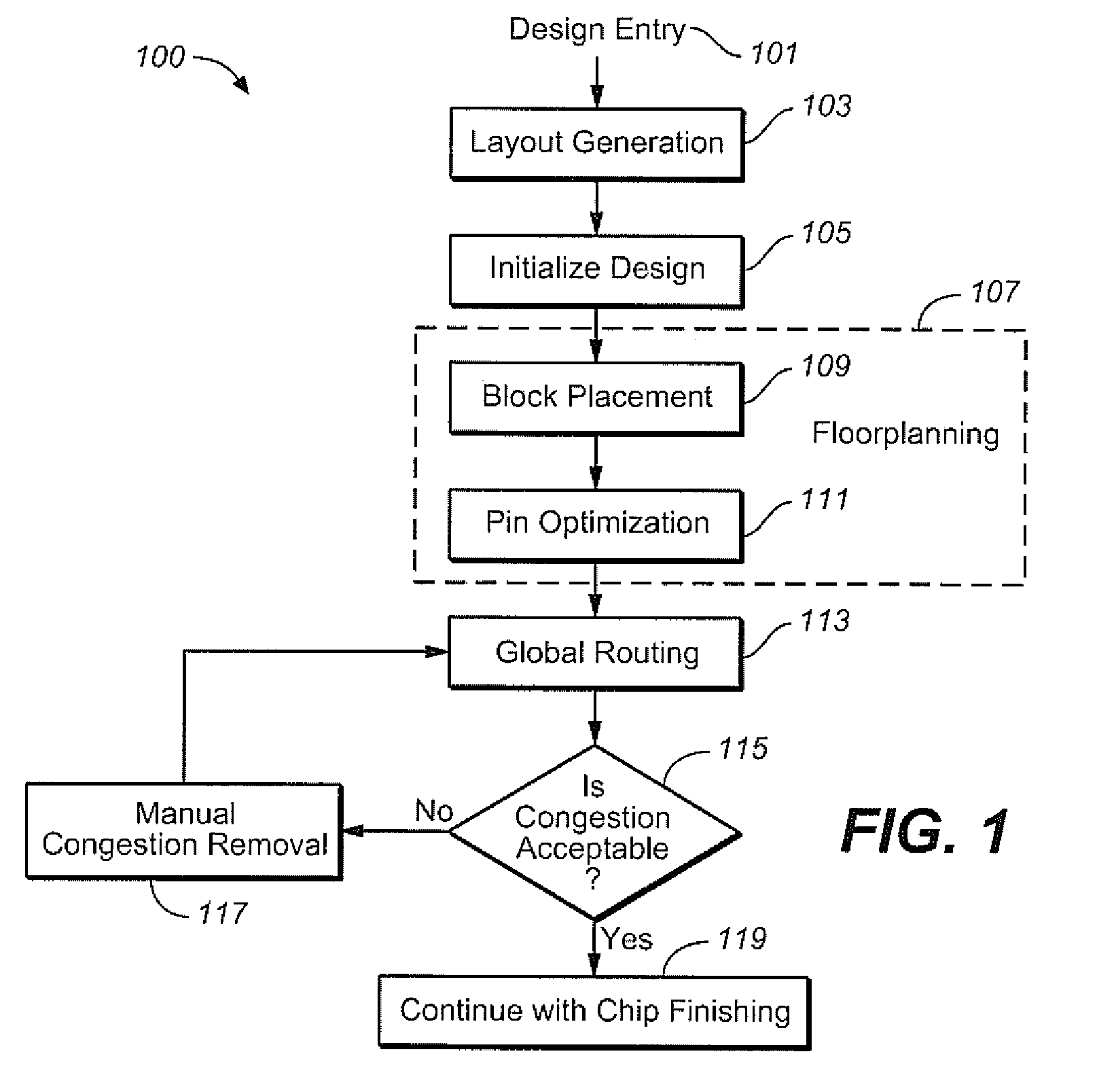
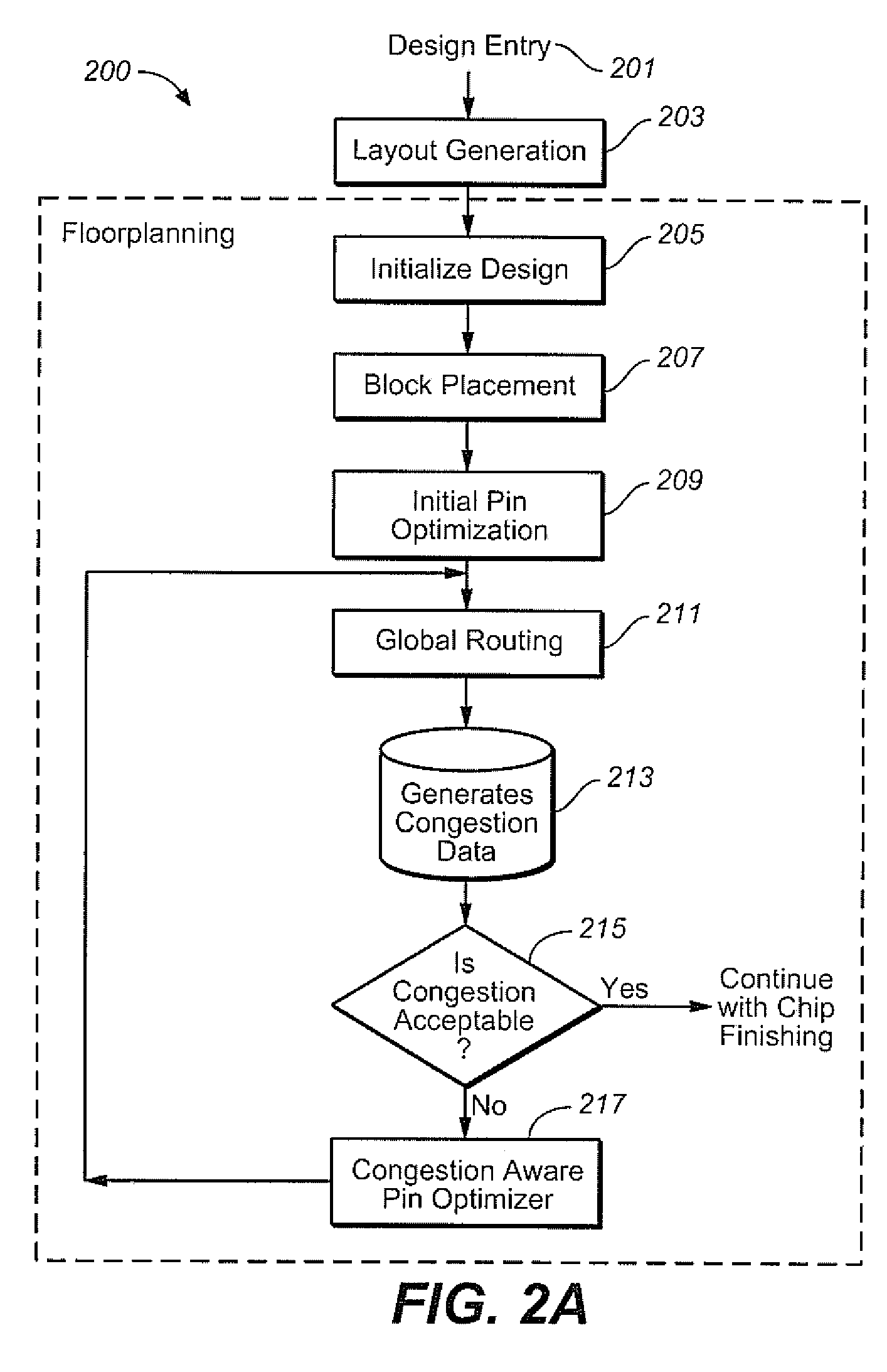
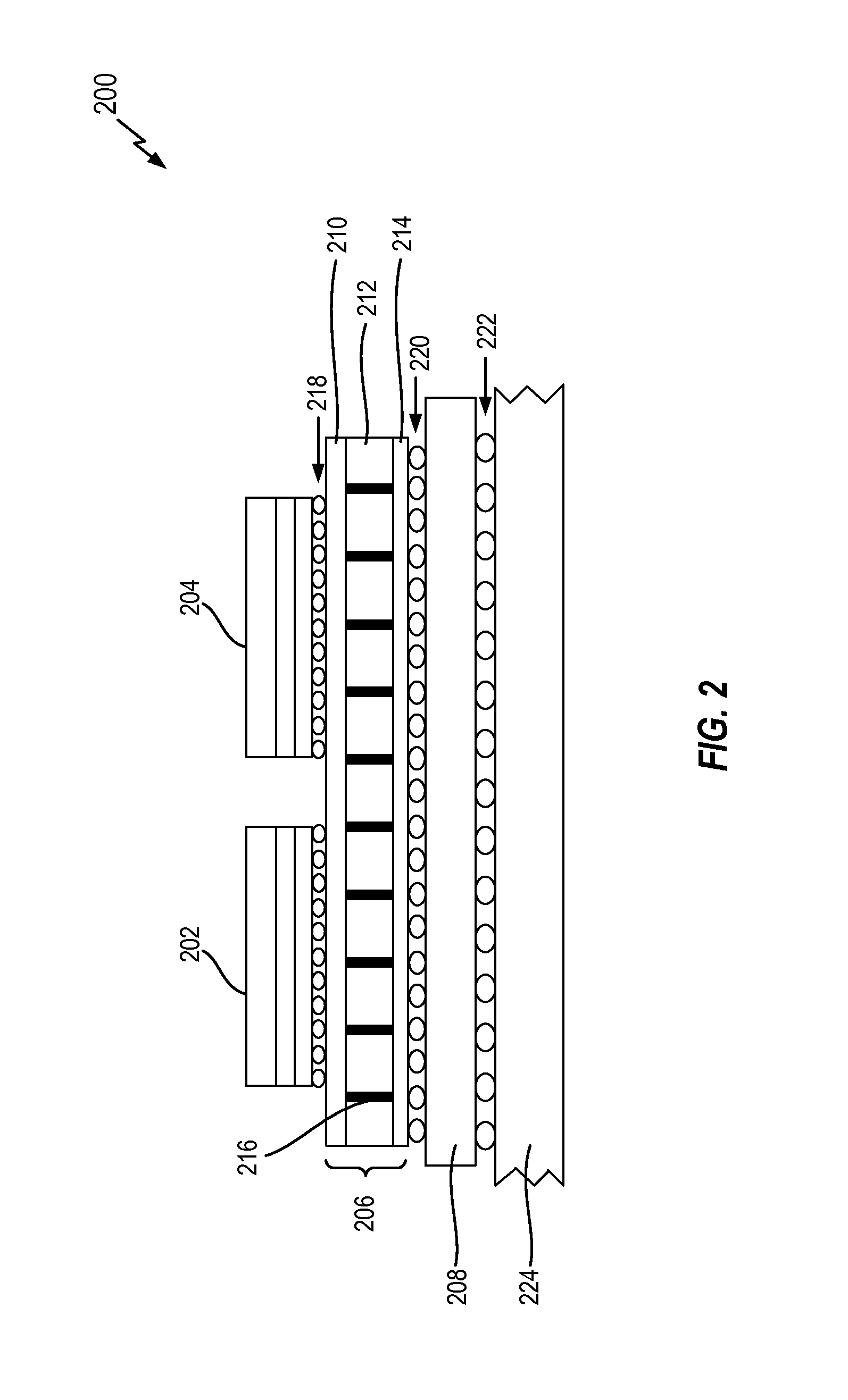
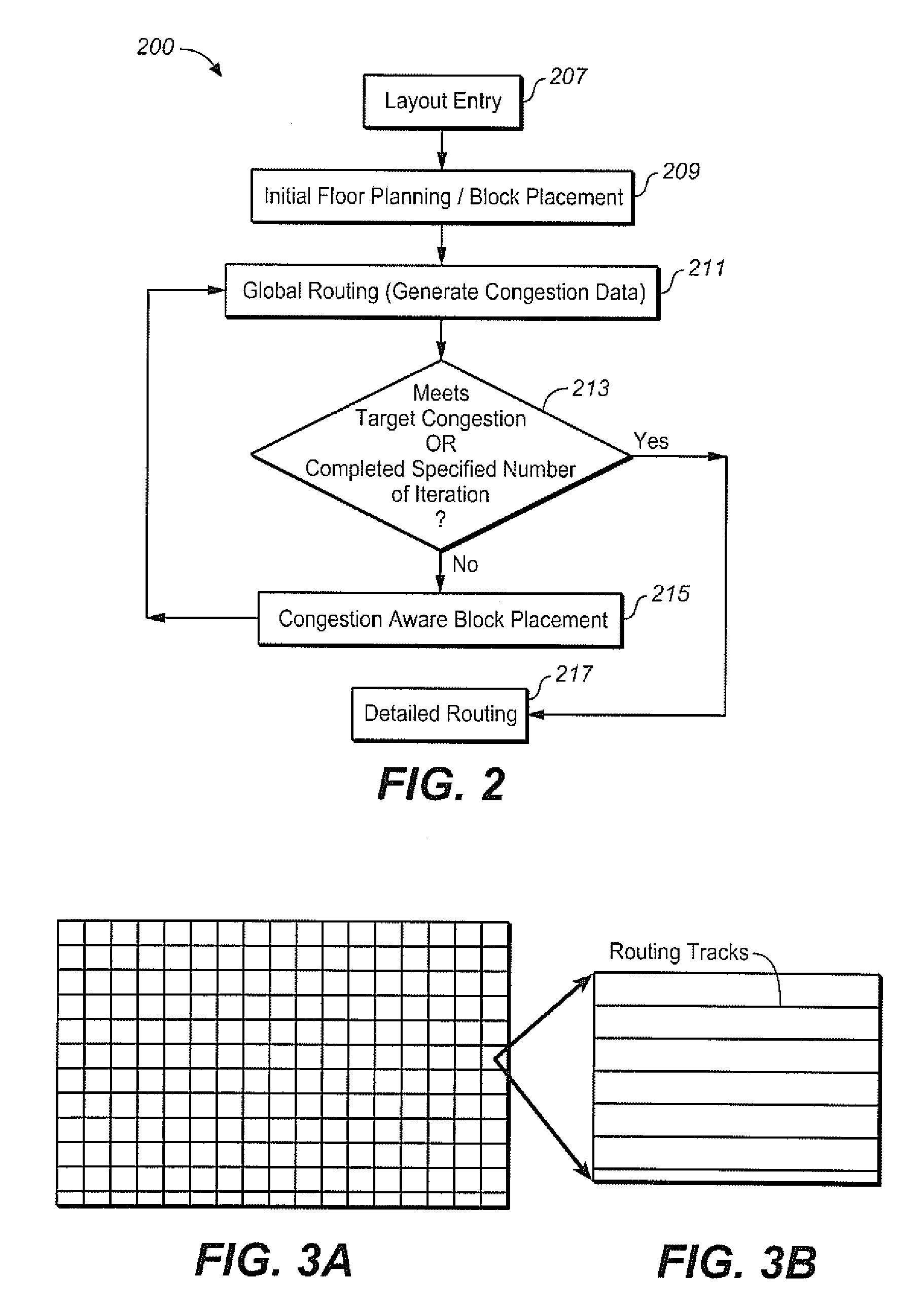
Congestion aware block placement
ActiveUS8239797B1Reduce routing congestionComputer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationComputer architectureRouting congestion
A circuit design process is presented that includes a block placement operation, followed by global routing based upon the initial placement of the blocks. Congestion data is generated from the global routing and, in an automated process, the blocks are placed again based upon the congestion data to reduce the routing congestion of the design. This can be used as part of a custom layout design process, for example.
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
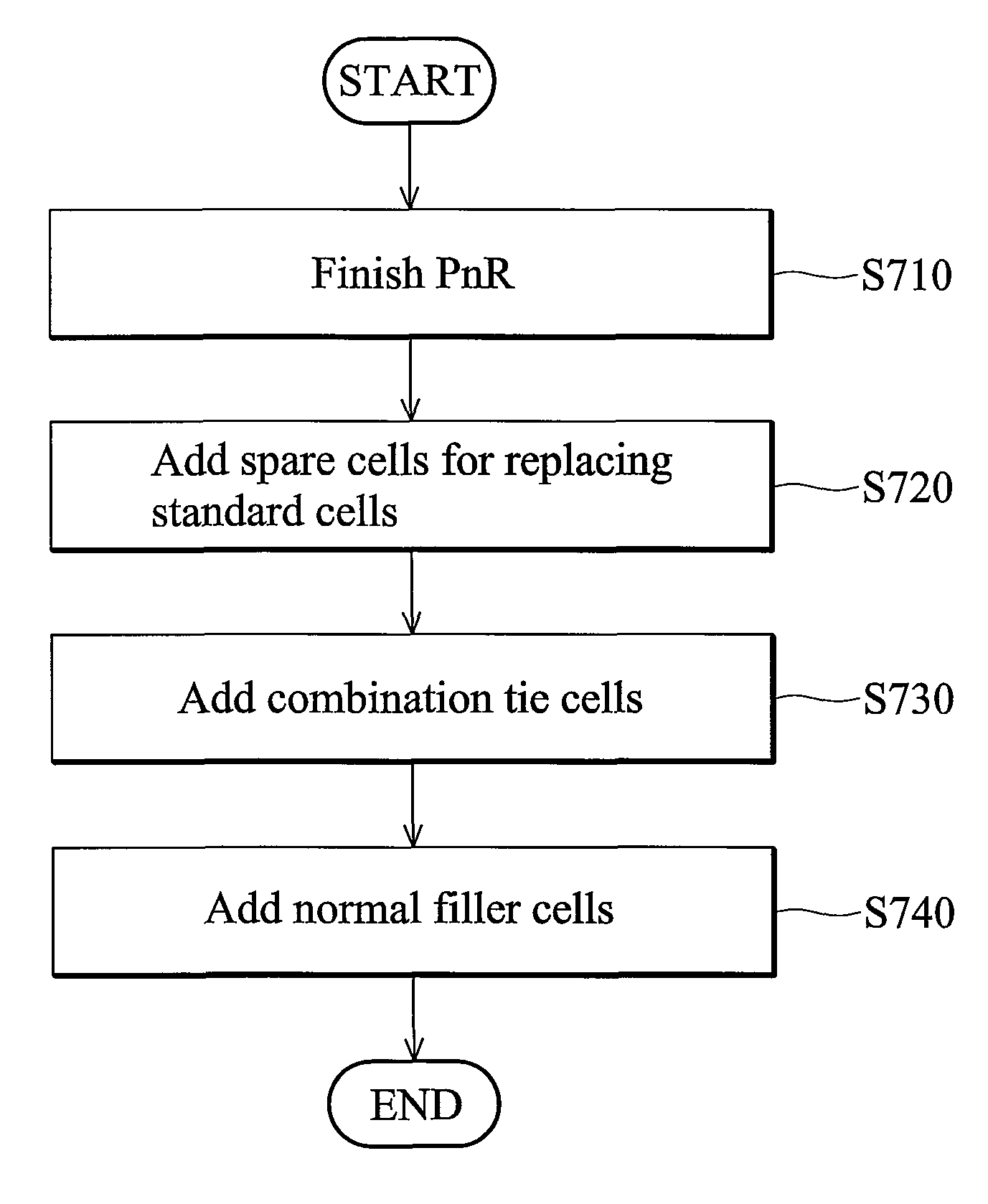
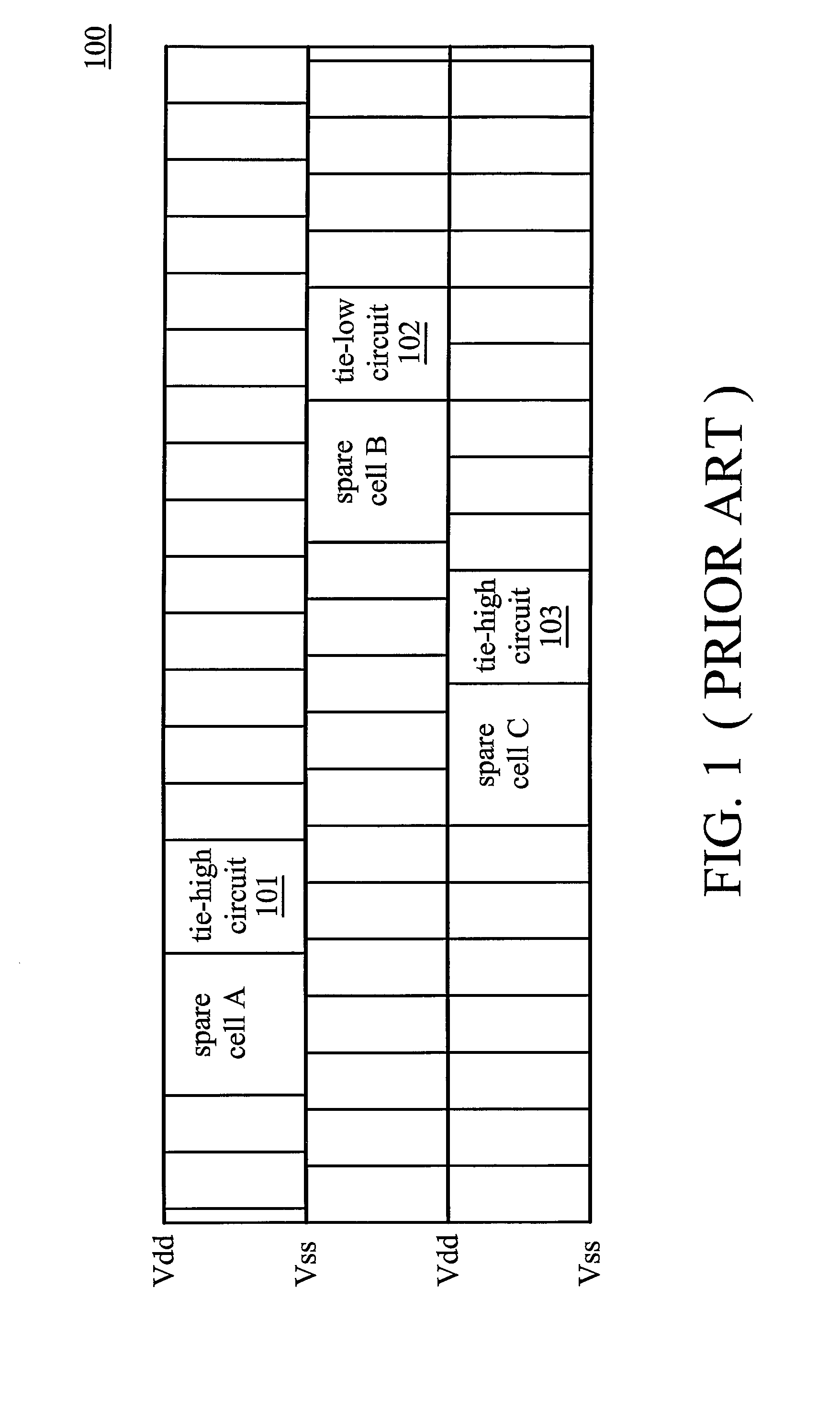
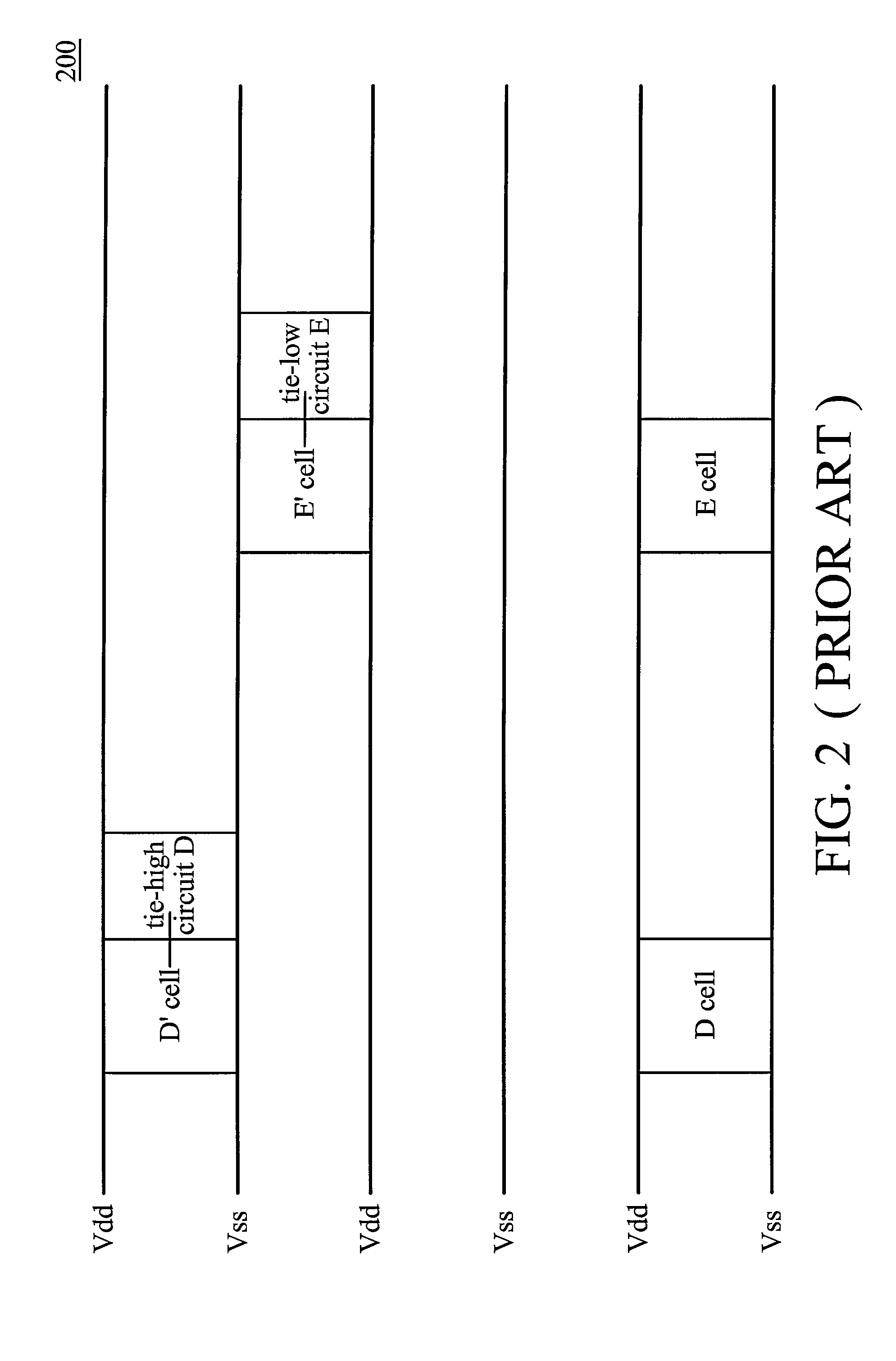
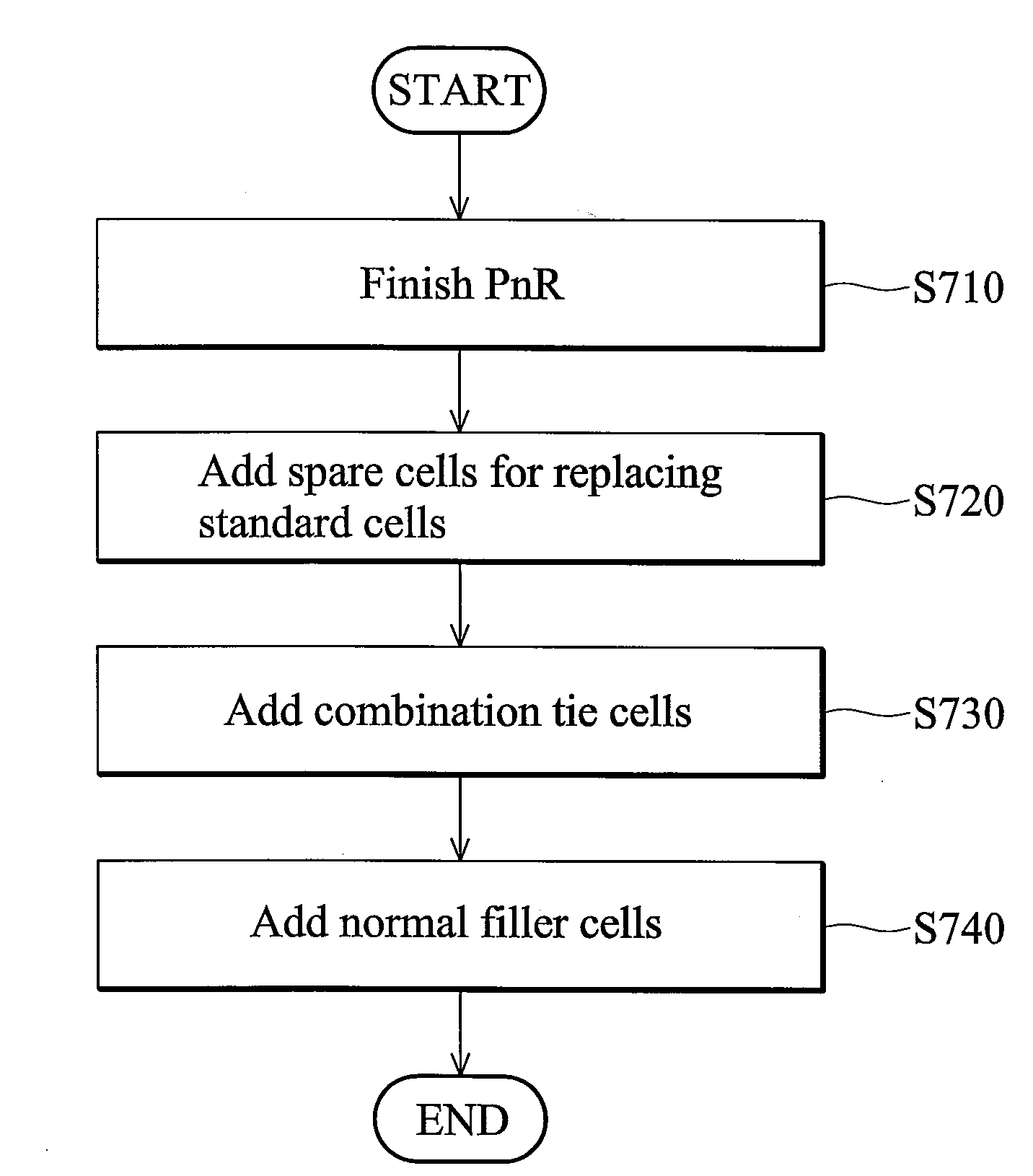
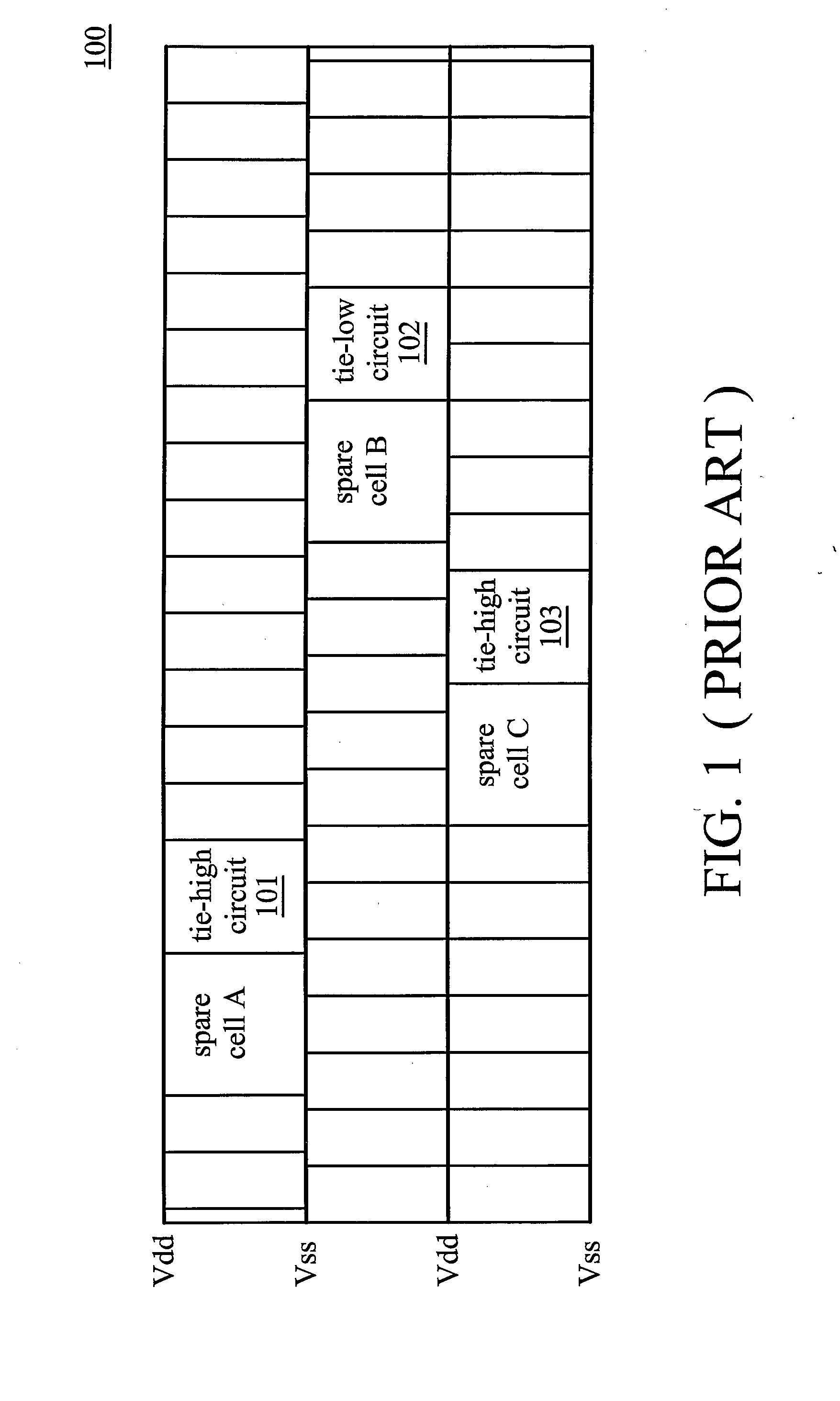
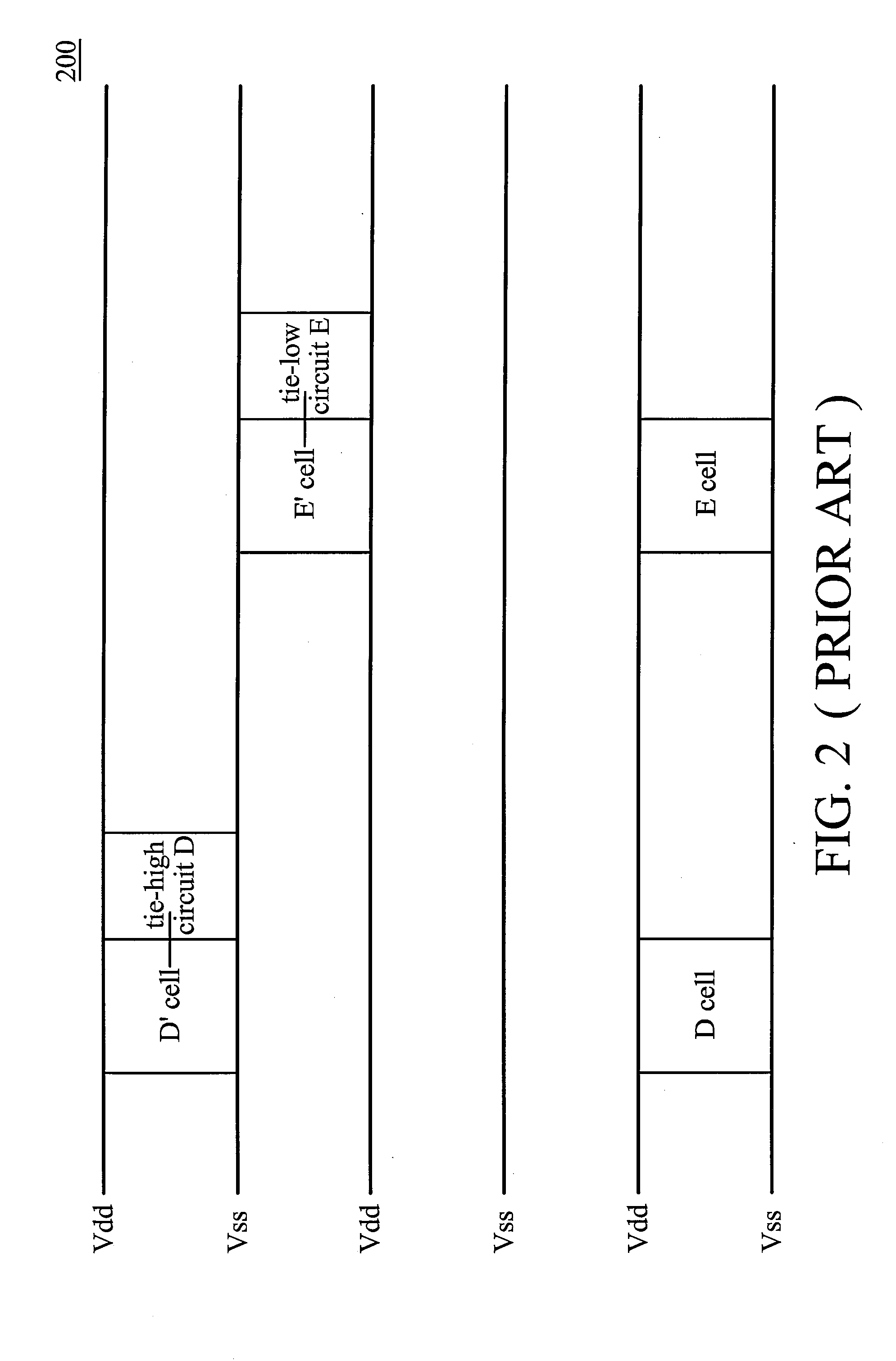
Layout circuit having a combined tie cell
ActiveUS7949988B2Switching accelaration modificationsReliability increasing modificationsCapacitanceEngineering
A layout circuit is provided, comprising standard cells, a spare cell, combined tie cells and normal filler cells. The standard cells are disposed and routed on a layout area. The spare cell is added on the layout area and provided for replacing one of the standard cells while adding or changing functions later. The combined tie cells are added on the layout area. The normal filler cells are added on the rest of the layout area. The combined tie cell comprises a tie-high circuit, a tie-low circuit and a capacitance circuit. Some standard cells are disposed near at least one combined tie cell for avoiding routing congestion between the combined tie cells and the replaced standard cell. A circuit layout method is also provided.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
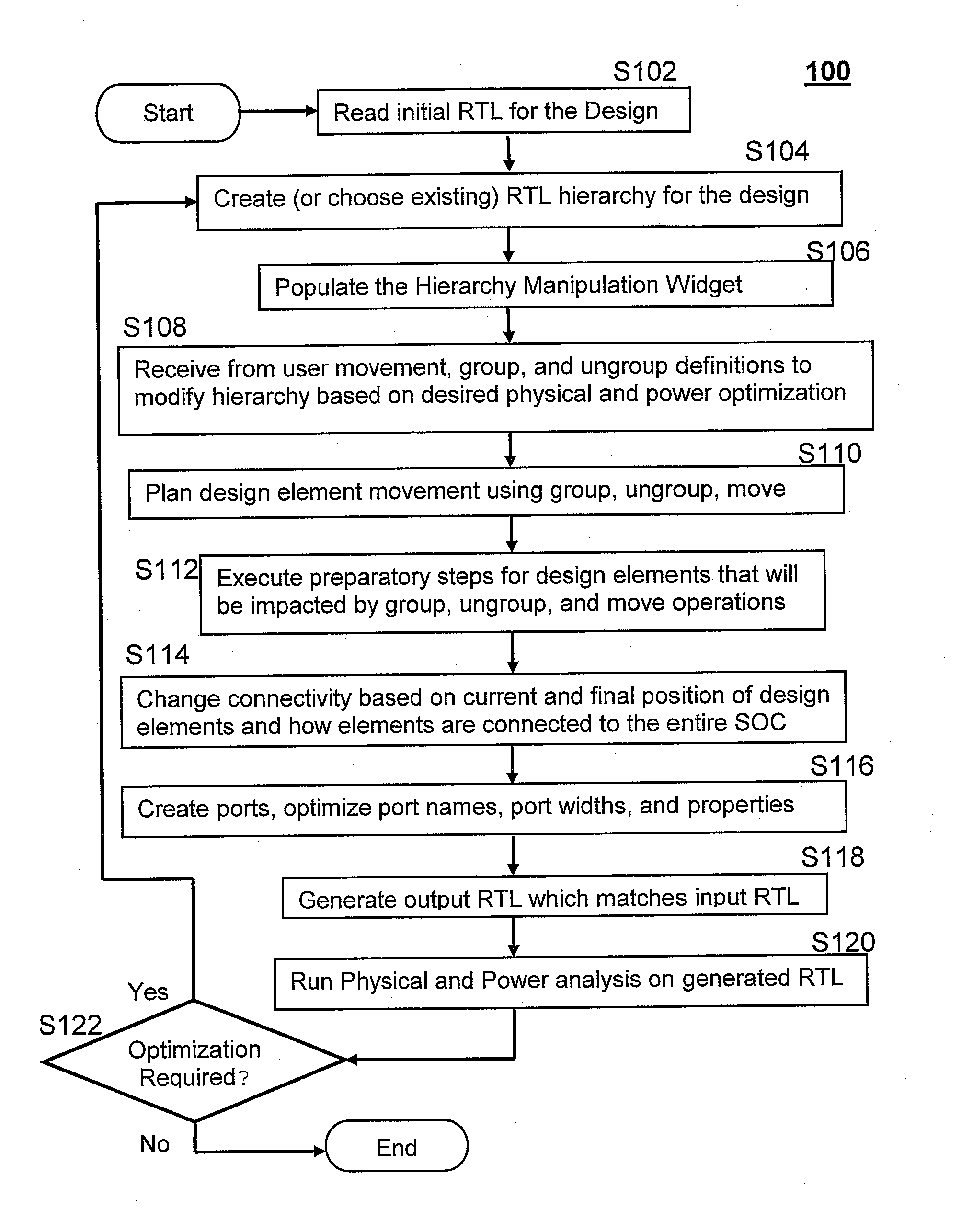
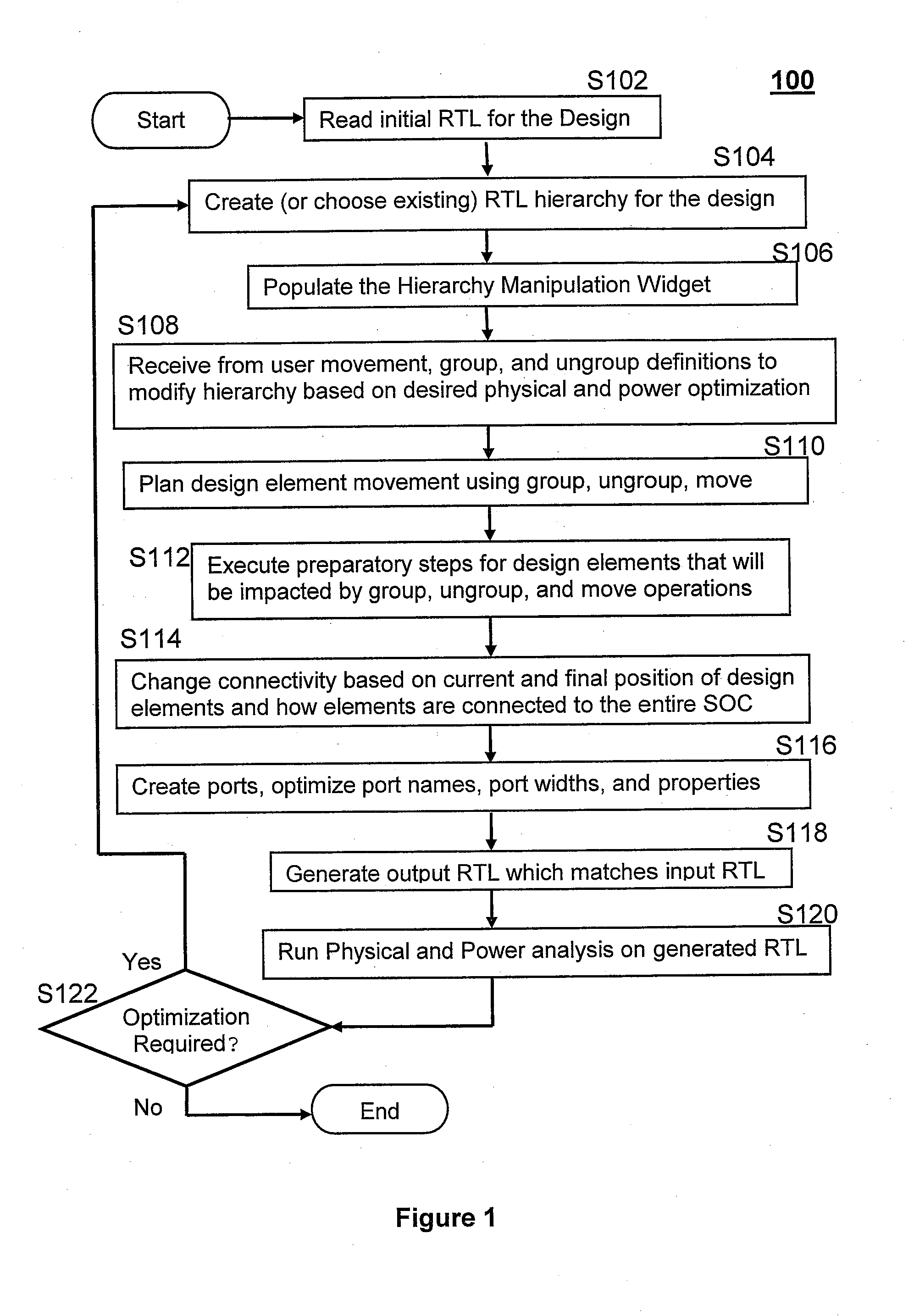
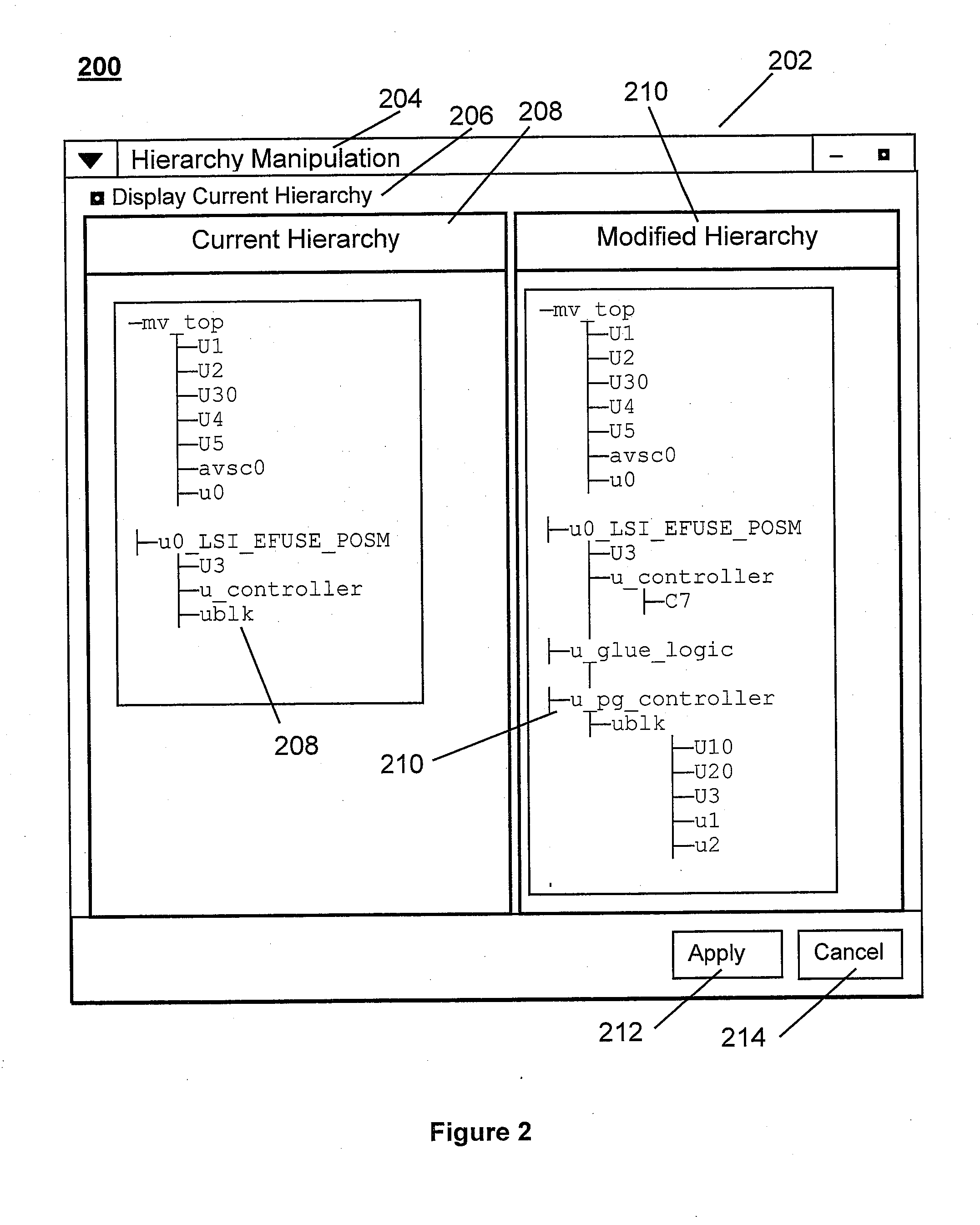
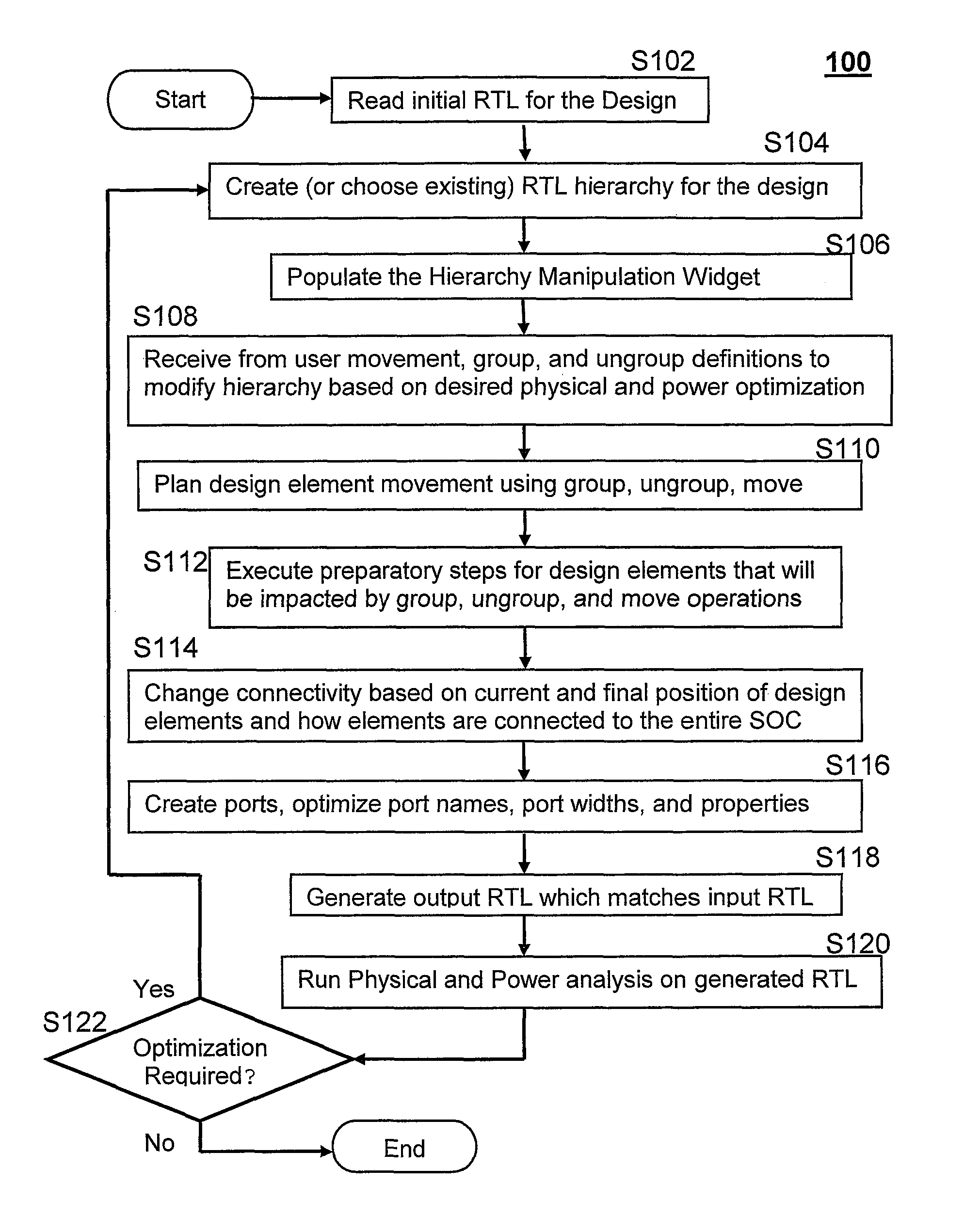
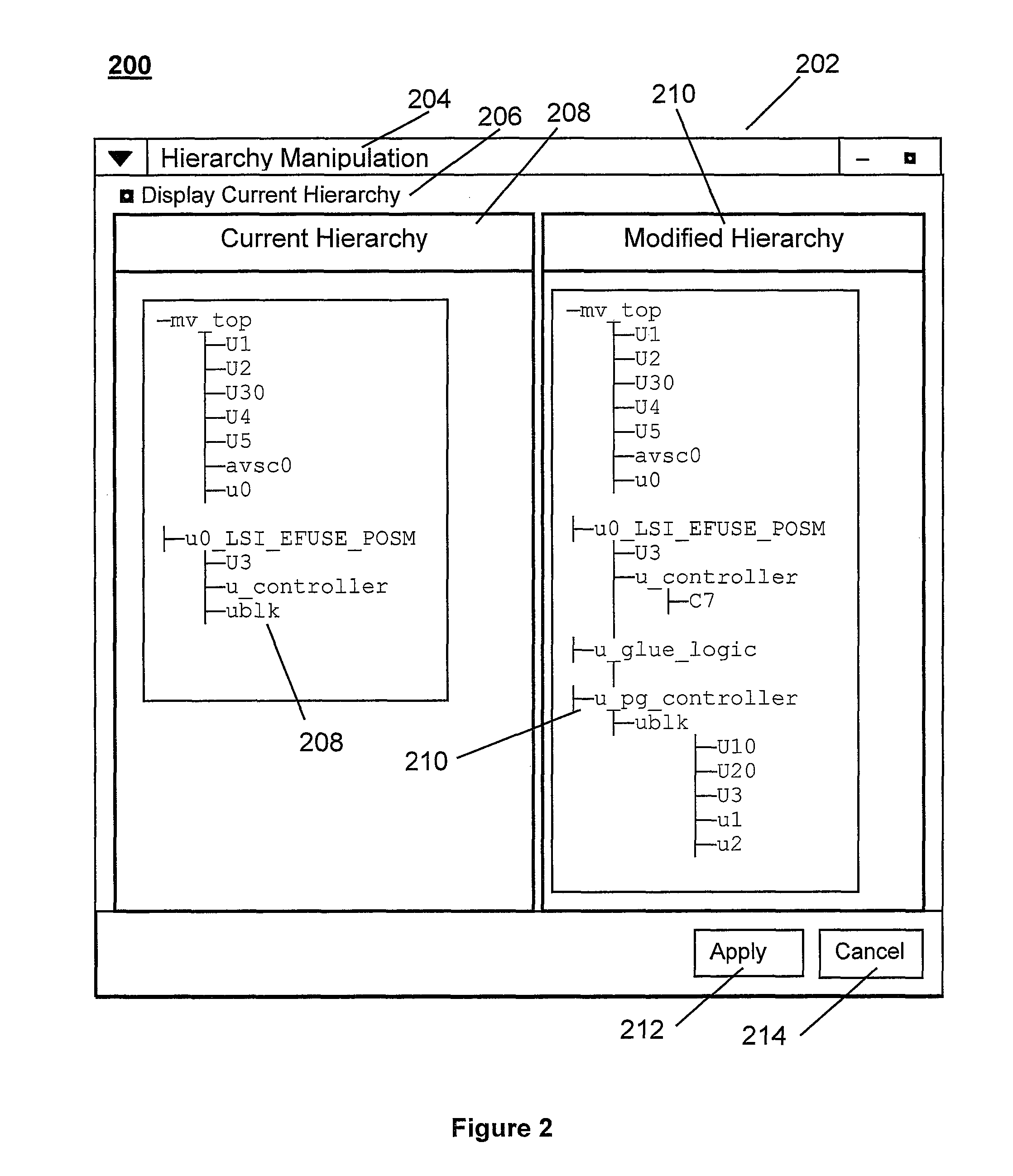
System and method for altering circuit design hierarchy to optimize routing and power distribution
ActiveUS20140282338A1Raise the level of performanceAvoid distributingSystems intergating technologiesComputer aided designEffective powerDistribution system
Systems and methods are disclosed for modifying the hierarchy of a System-on-Chip and other circuit designs to provide better routing and performance as well as more effective power distribution. A user specifies desired modifications to the design hierarchy and then the system automatically alters the hierarchy by performing group, ungroup, and move operations to efficiently and optimally implement the desired hierarchy modifications. Any modifications to port and signal names are automatically resolved by the system and the resultant RTL matches the function of the input RTL. The user then evaluates the revised hierarchy with regard to power distribution and routing congestion, and further hierarchy modifications are performed if necessary. A widget user interface facility is included to allow user-guided direction of hierarchy modifications in an iterative fashion.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
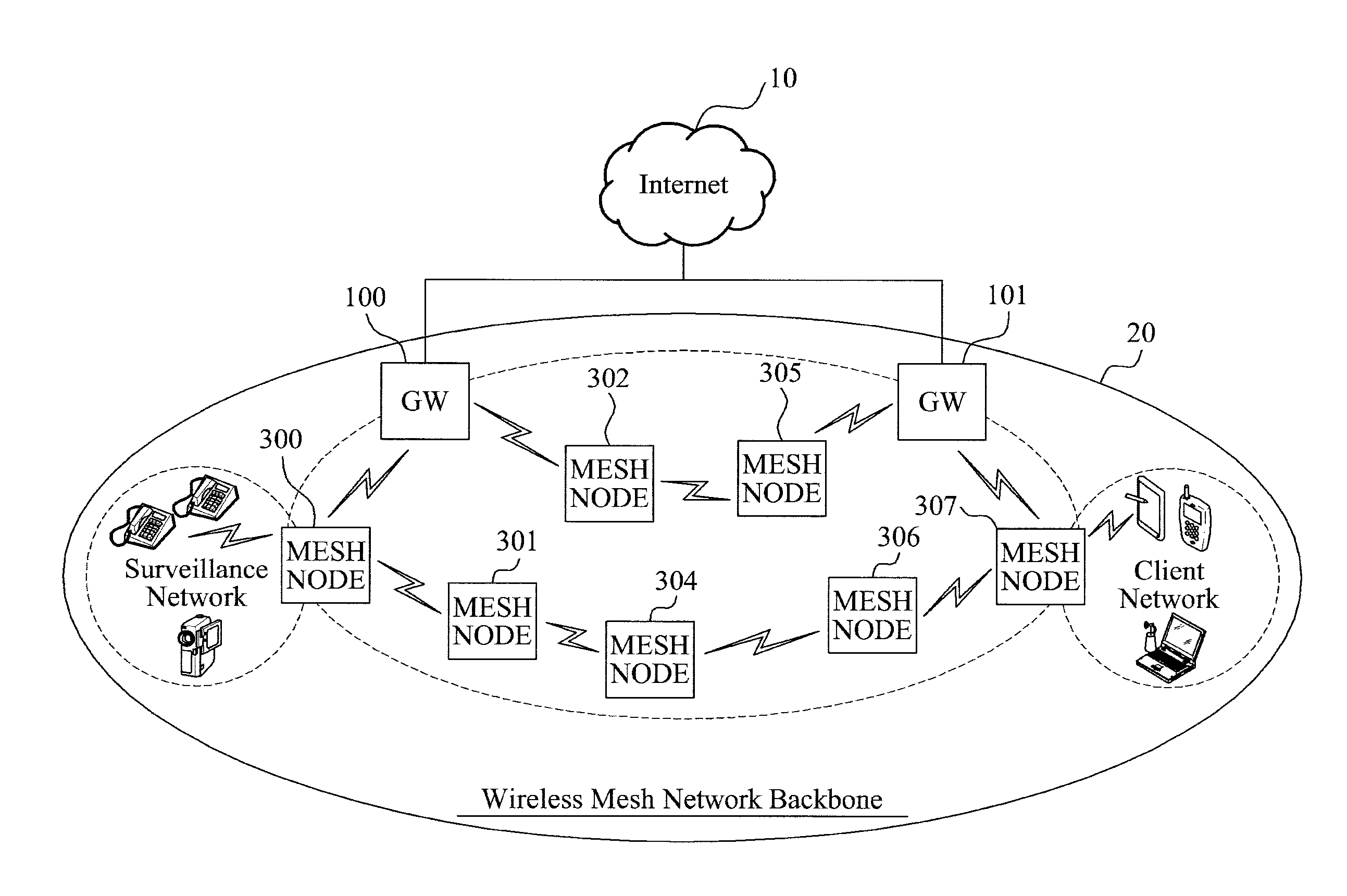
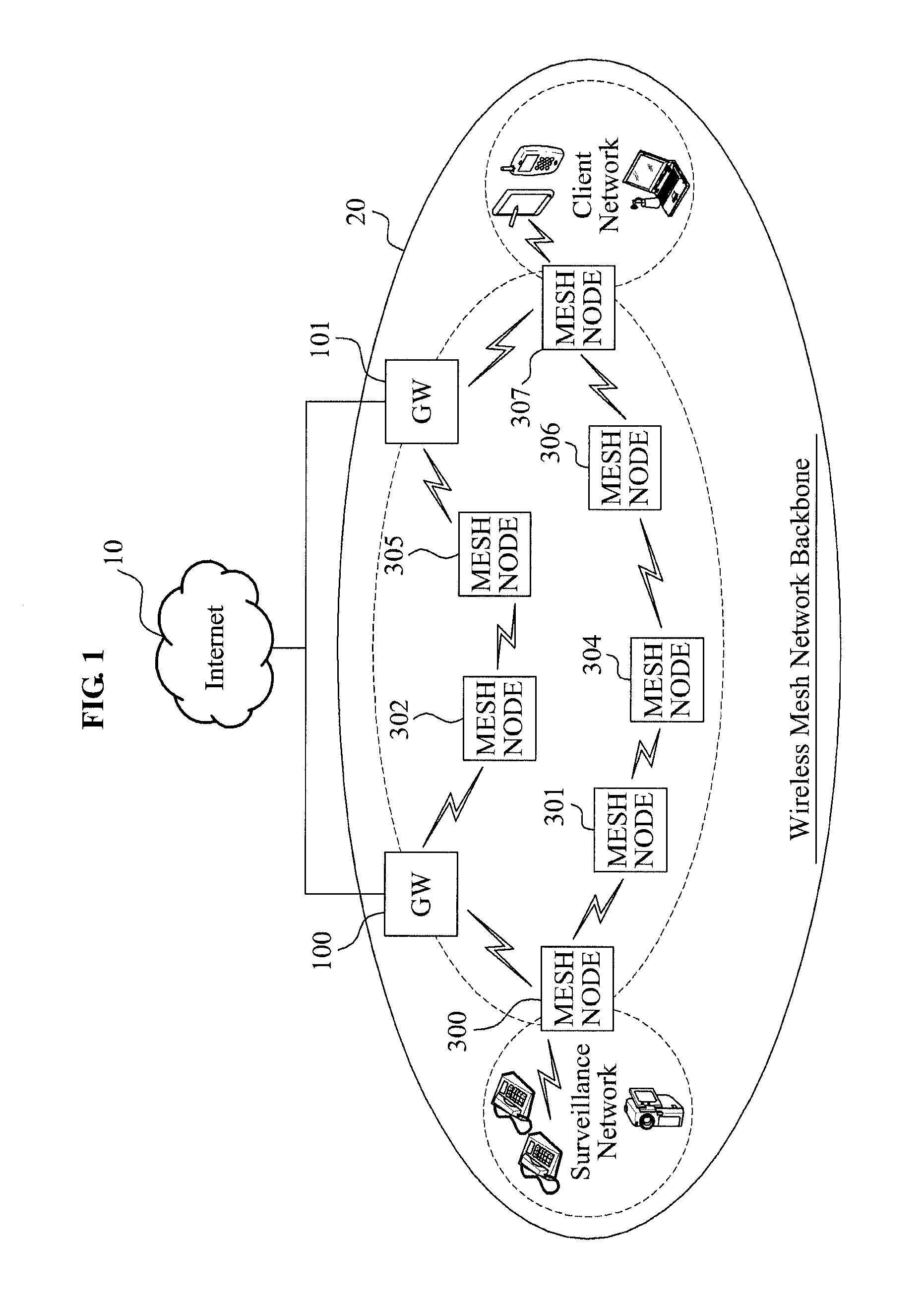
Method for notifying about/avoiding congestion situation of data transmission in wireless mesh network, and mesh node for the same
InactiveUS20120044806A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsReal time servicesData transmission
Provided is a multi-route routing scheme that supports Quality of Service (QoS) in the wireless mesh network. A method of notifying about and avoiding congestion situation in data transmission in a wireless mesh network and a mesh node may also be provided. Data may be differentially transmitted to multiple routes by obtaining a route congestion level existing in a current multi-hop route and thus, data providing a real-time service, such as a video streaming service, may avoid congested routes and may be promptly transmitted. Multiple queues in a mesh node may be divided into divided queues based on a congestion situation of a transmission route in a network and the divided queues may be transmitted through multiple routes and thus, an efficiency of the overall network may increase.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST +1
Method and apparatus for controlling congestion during integrated circuit design resynthesis
InactiveUS20070094631A1CAD circuit designSpecial data processing applicationsInterconnectionRouting congestion
The present disclosure is directed to a method and apparatus for dividing an integrated circuit design field into a plurality of congestion rectangles having user-selectable sizes. A routing congestion value is estimated for each congestion rectangle prior to routing interconnections within the design field. The congestion values are stored in machine-readable memory and are updated in response to wire changes within the design field.
Owner:BELL SEMICON LLC
System and method for altering circuit design hierarchy to optimize routing and power distribution using initial RTL-level circuit description netlist
ActiveUS8930863B2Raise the level of performanceAvoid distributingSystems intergating technologiesComputer aided designEffective powerComputer architecture
Systems and methods are disclosed for modifying the hierarchy of a System-on-Chip and other circuit designs to provide better routing and performance as well as more effective power distribution. A user specifies desired modifications to the design hierarchy and then the system automatically alters the hierarchy by performing group, ungroup, and move operations to efficiently and optimally implement the desired hierarchy modifications. Any modifications to port and signal names are automatically resolved by the system and the resultant RTL matches the function of the input RTL. The user then evaluates the revised hierarchy with regard to power distribution and routing congestion, and further hierarchy modifications are performed if necessary. A widget user interface facility is included to allow user-guided direction of hierarchy modifications in an iterative fashion.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Layout circuit having a combined tie cell
ActiveUS20090249273A1Reliability increasing modificationsLogic circuits characterised by logic functionCapacitanceRouting congestion
A layout circuit is provided, comprising standard cells, a spare cell, combined tie cells and normal filler cells. The standard cells are disposed and routed on a layout area. The spare cell is added on the layout area and provided for replacing one of the standard cells while adding or changing functions later. The combined tie cells are added on the layout area. The normal filler cells are added on the rest of the layout area. The combined tie cell comprises a tie-high circuit, a tie-low circuit and a capacitance circuit. Some standard cells are disposed near at least one combined tie cell for avoiding routing congestion between the combined tie cells and the replaced standard cell. A circuit layout method is also provided.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
Distributed processing LDPC (low density parity check) decoder
ActiveUS7958429B2Error correction/detection using multiple parity bitsCode conversionMultiplexerParity-check matrix
Distributed processing LDPC (Low Density Parity Check) decoder. A means is presented herein that includes an LDPC decoding architecture leveraging a distributed processing technique (e.g., daisy chain) to increase data throughput and reduce memory storage requirements. Routing congestion and critical path latency are also improved thereby. Each daisy chain includes a number of registers, and a number of localized MUXs (e.g., MUXs having merely 2 inputs each). The means presented herein also does not contain any barrel shifters, high fan-in multiplexers, or interconnection networks; therefore, the critical path is relatively short and it can also be pipelined to further increase data throughput. If desired, a communication device can include multiple configurations of such daisy chains to accommodate the decoding of various LDPC coded signals (e.g., such as for an application and / or communication device that must decoded LDPC codes using different low density parity check matrices).
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Method for reducing wiring congestion in a VLSI chip design
InactiveUS6958545B2Reduced wiring areaReduce congestionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesAnd logic unitLogic cell
A system and method for correcting wiring congestion in a placed and partially or fully globally-routed VLSI chip design while avoiding adding new timing or electrical violations or other design constraints. Globally-congested areas are identified along with determining terminated and non-terminated wires in the congested areas. The process includes optimizing the identified congestion areas, incrementally rerouting affected nets, testing the resultant design legality and congestion metrics, and committing or reversing the optimizations and reroutings. The optimizations further includes the movement of logic cells and decomposition, recomposition or any other modification of logic cell structures (possibly combined with cell movement) to move terminated wires to less congested grid edges, rearrangement of commutative connections within or between cells, or addition of buffers to cause reroutes of feedthrough wires.
Owner:IBM CORP
Routing path determination method and device, control equipment and storage medium
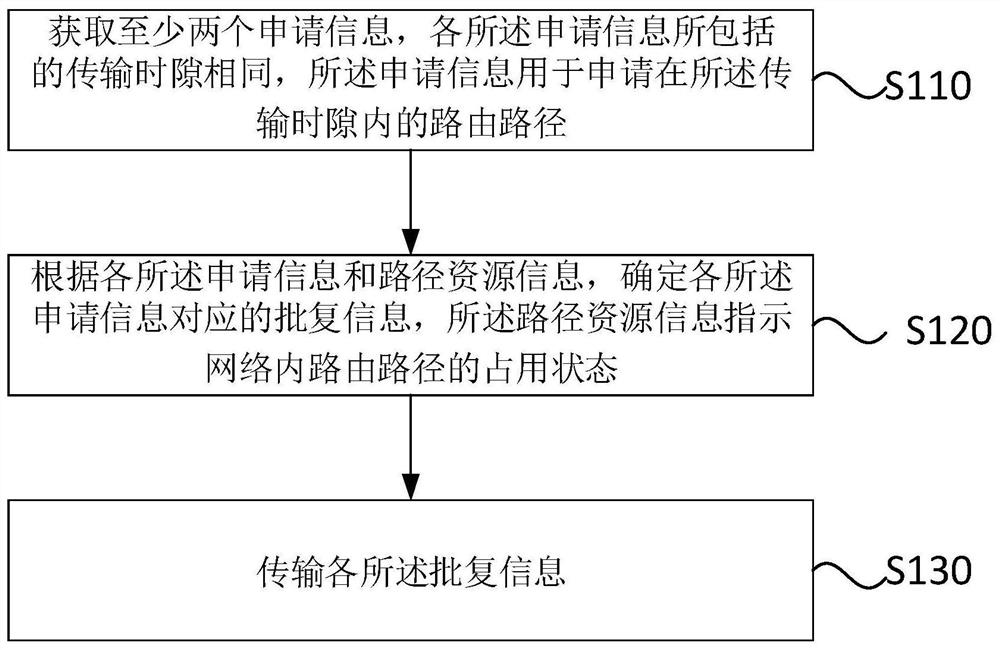
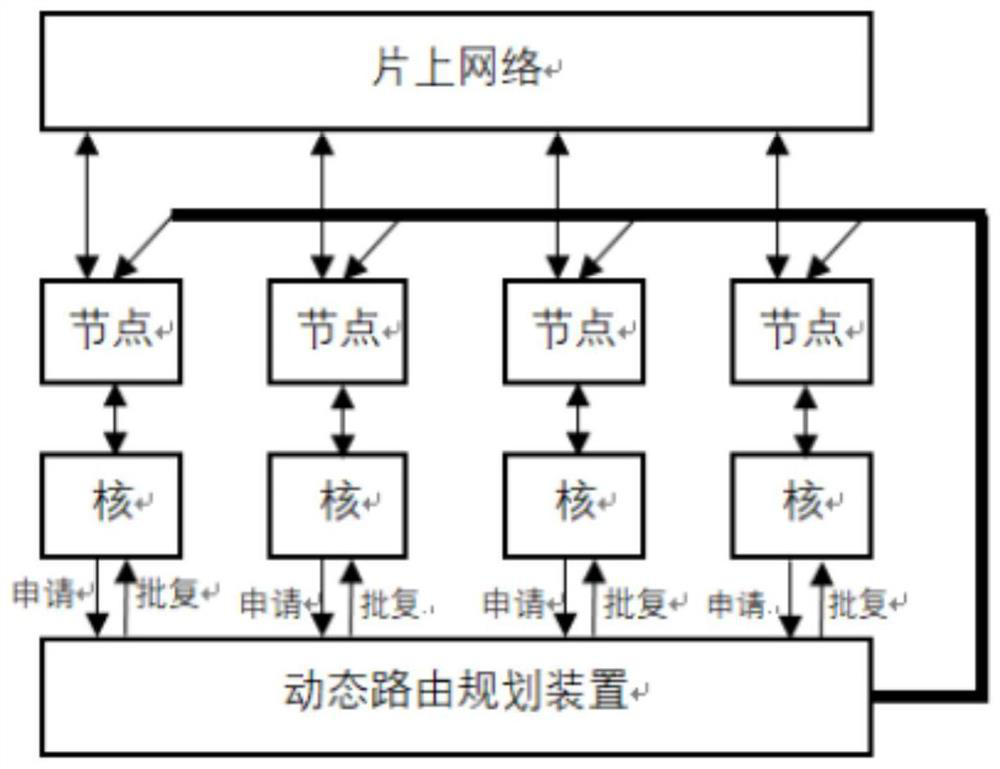
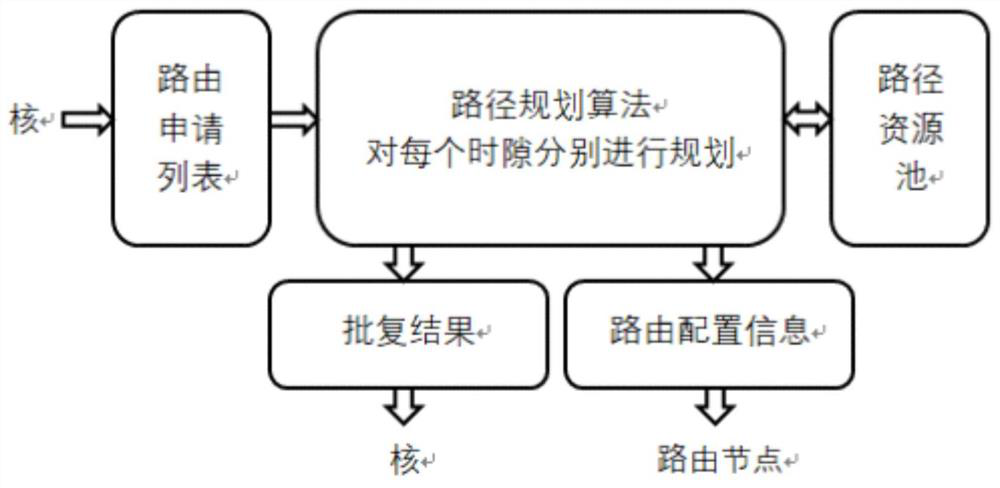
ActiveCN112003787AReduce lagData switching networksHigh level techniquesPathPingResource information
The invention discloses a routing path determination method and device, control equipment and a storage medium. The routing path determination method comprises the steps of: acquiring at least two pieces of application information, wherein transmission time slots included in the application information are the same, and the application information is used for applying for a routing path in the transmission time slot; determining reply information corresponding to each piece of application information according to each piece of application information and path resource information, wherein thepath resource information indicates an occupation state of a routing path in a network; and transmitting each piece of reply information. By means of the routing path determination method, the reply information can be determined before route congestion, and the hysteresis quality of route optimization is effectively reduced.
Owner:LYNXI TECH CO LTD
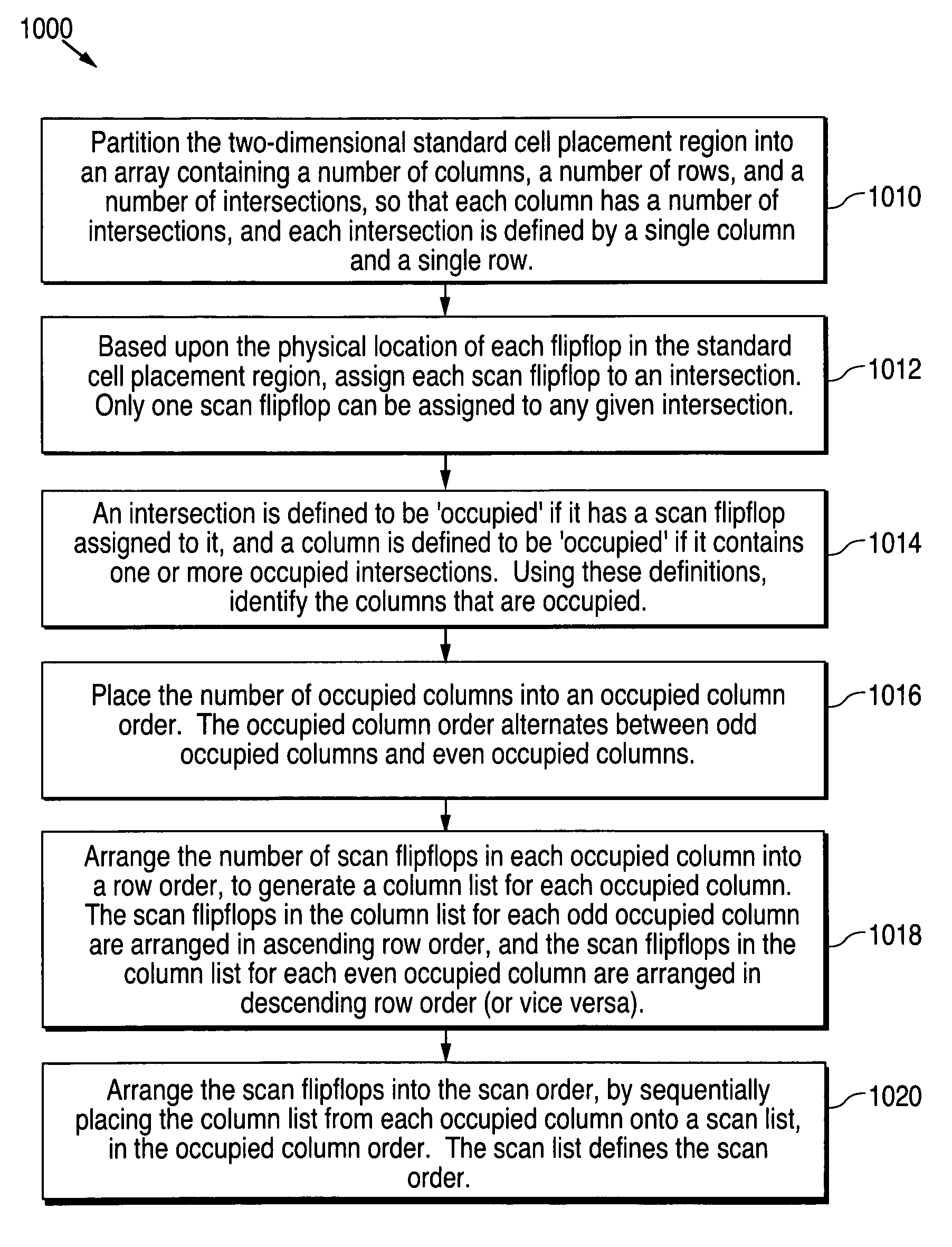
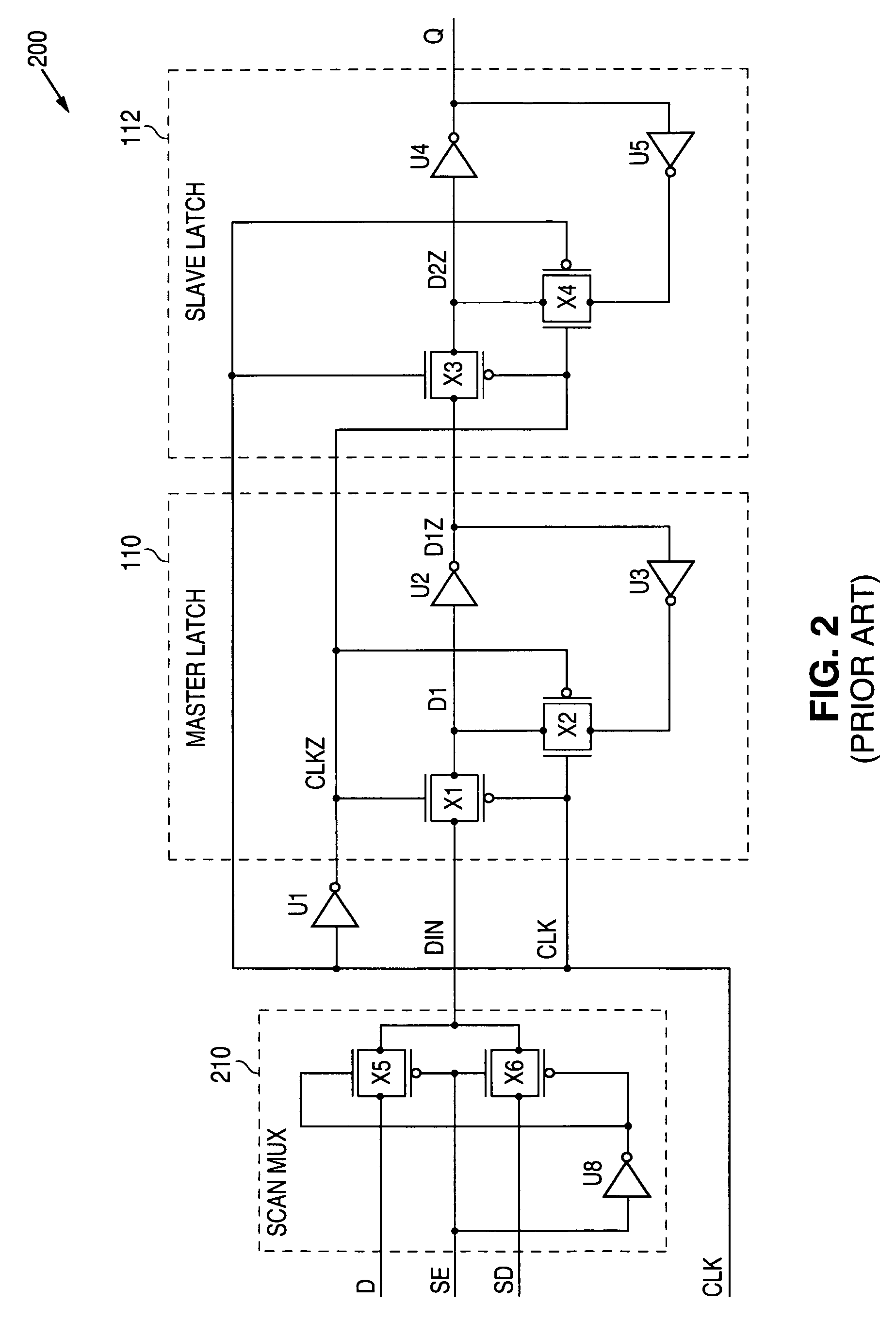
Method of stitching scan flipflops together to form a scan chain with a reduced wire length
The scan flipflops on a semiconductor chip are stitched together to form one or more scan chains, located in one or more standard cell placement regions, after the optimal physical location of each scan flip-flop has been determined. As a result, the total length of the scan chain wires is substantially reduced, thereby reducing on-chip wiring congestion, flip-flop load capacitance, and flipflop power dissipation.
Owner:NAT SEMICON CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com