Patents
Literature
119 results about "Spare cell" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
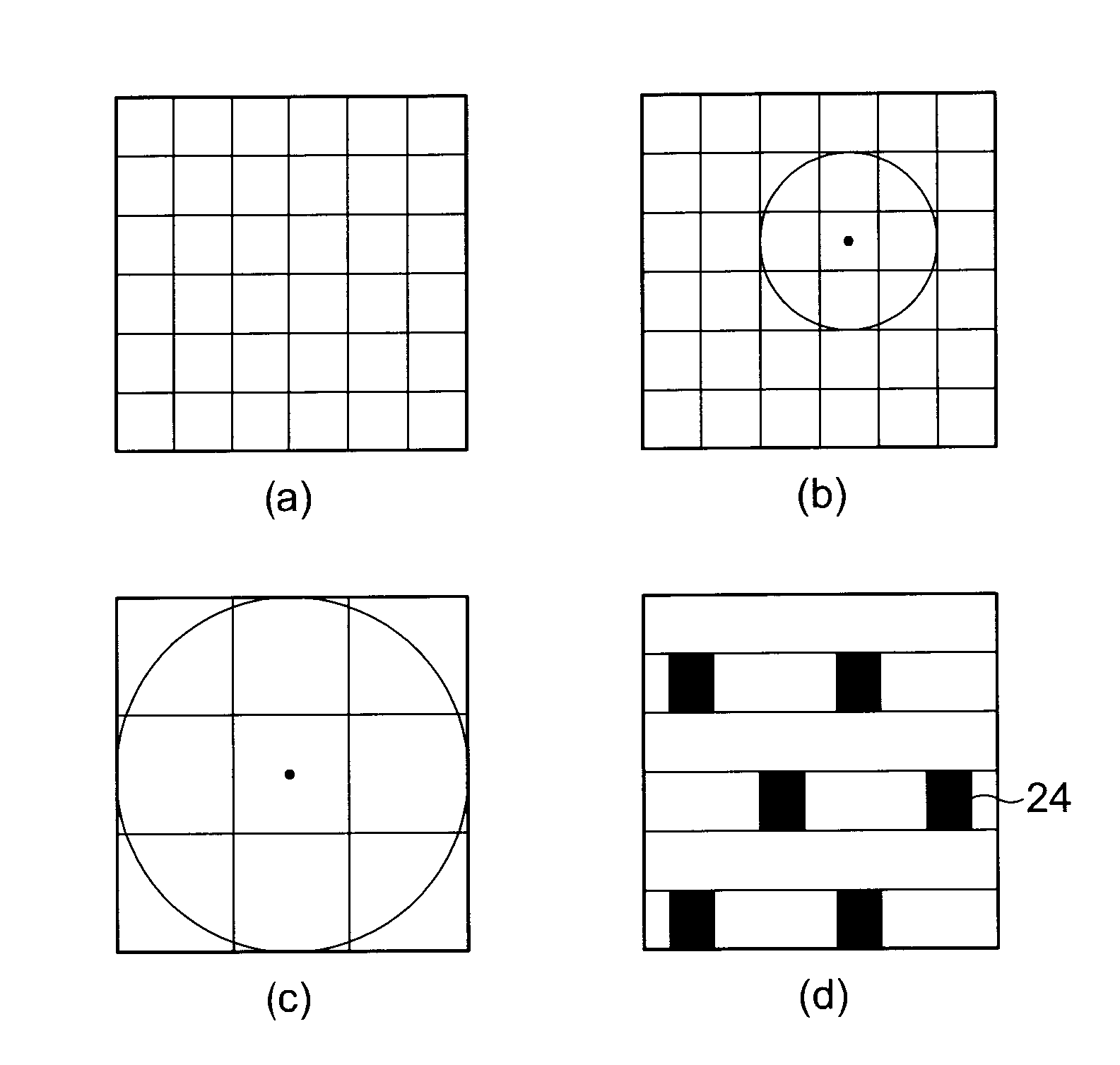
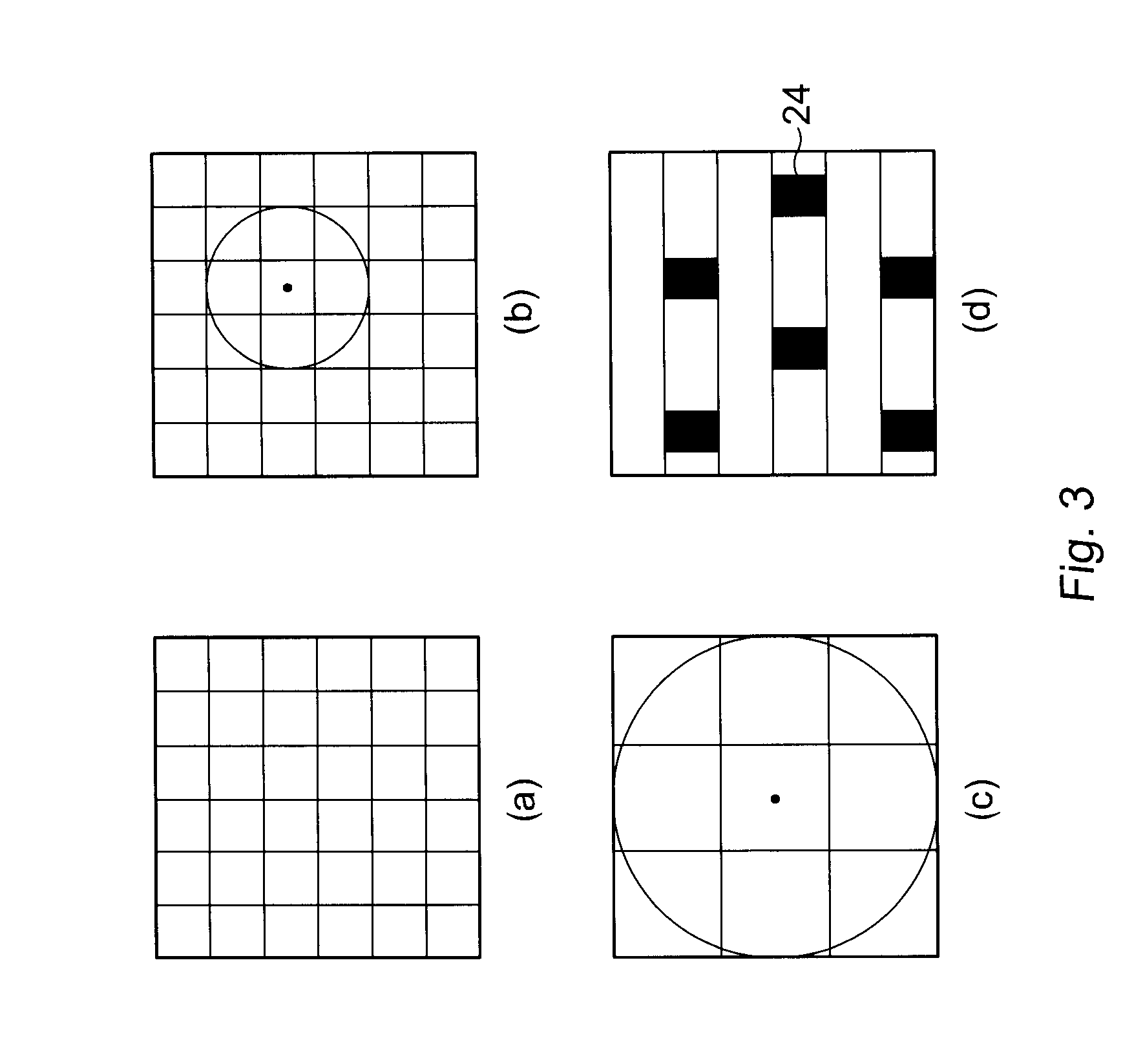
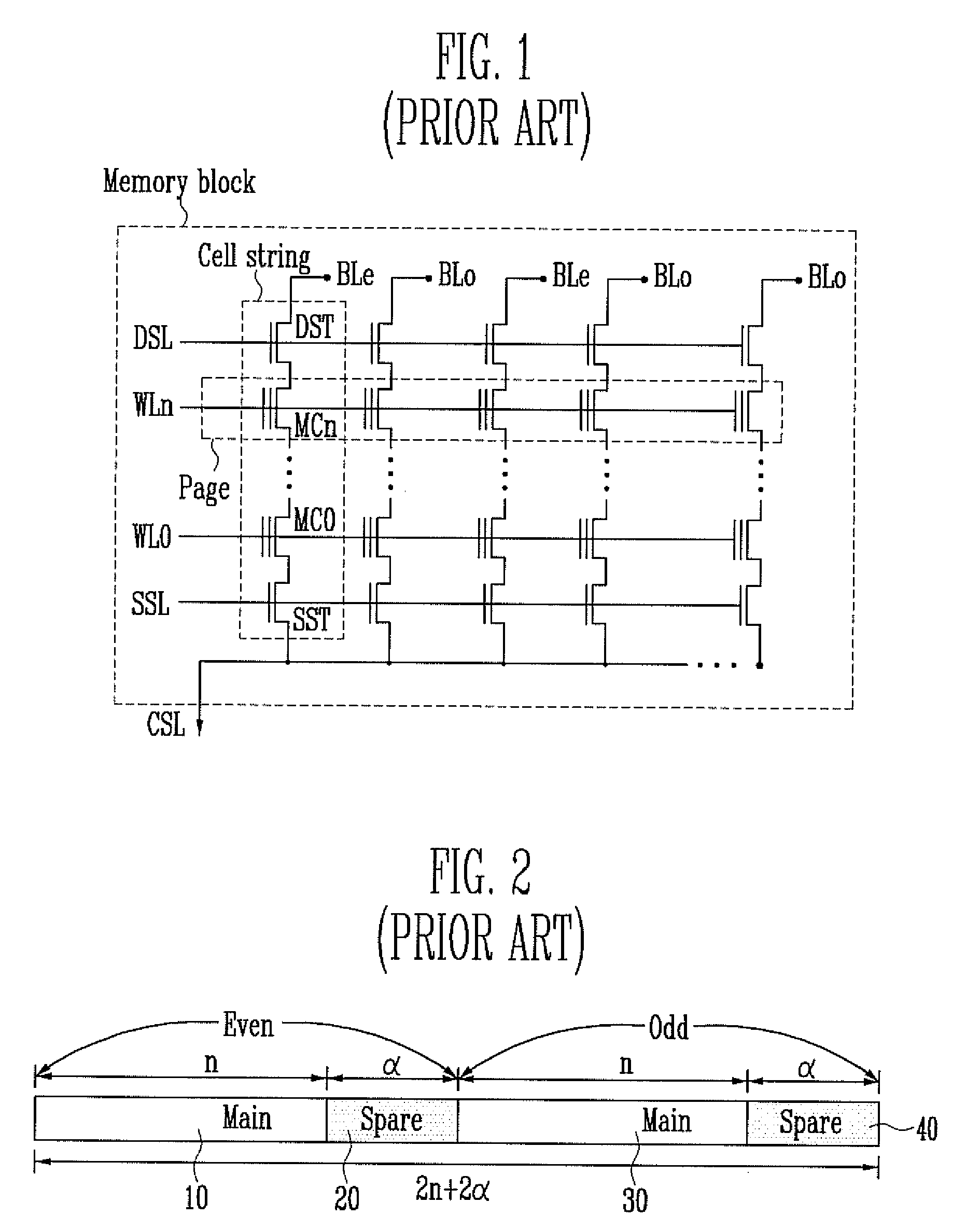
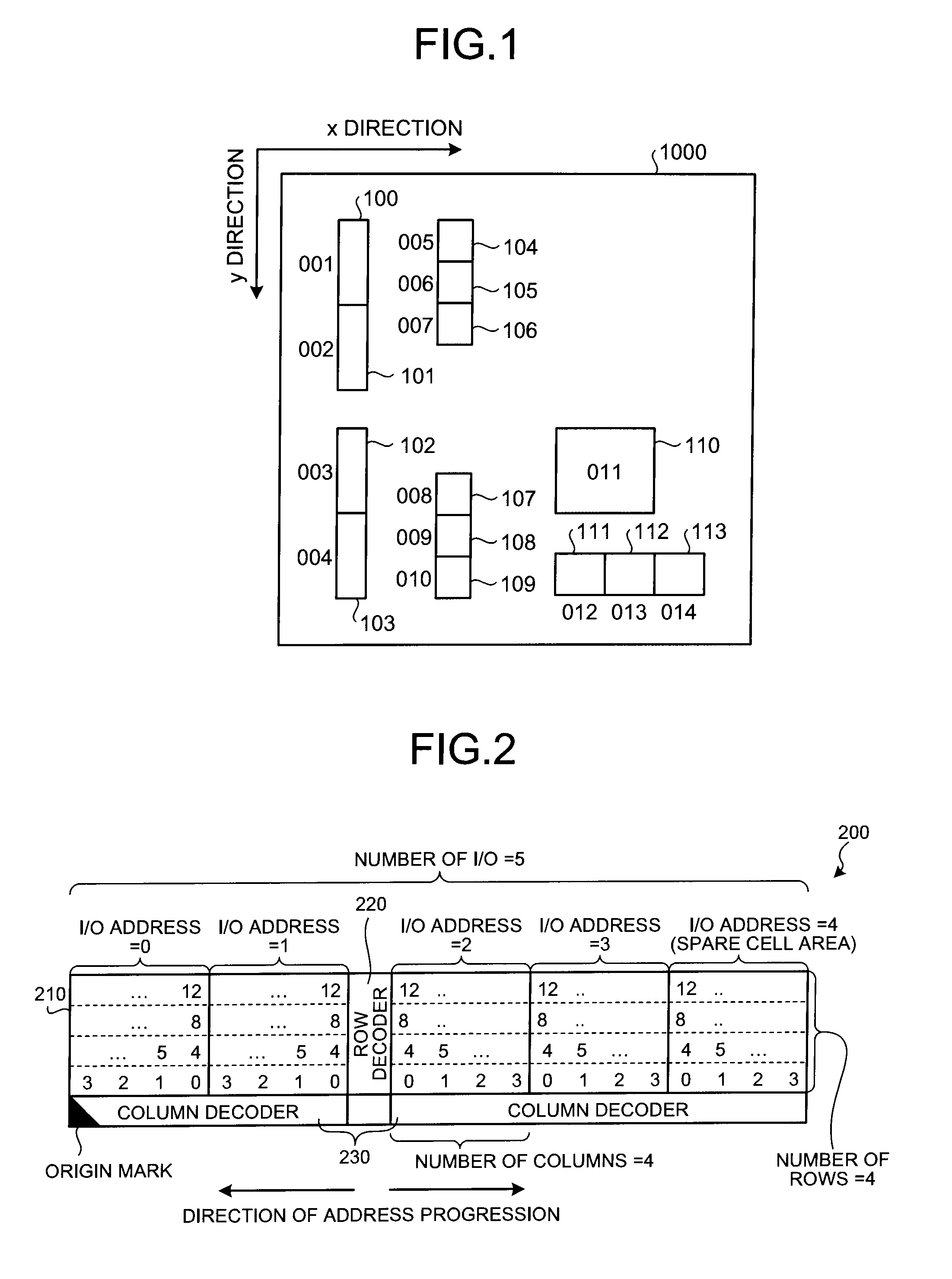
Spare cells are most useful when they are physically near the location of the logic that needs to be changed. Therefore, spare cells need to be dispersed across the chip rather than gathered in one or several tight locations. To add and place spare cells in a design, do one of the following steps:
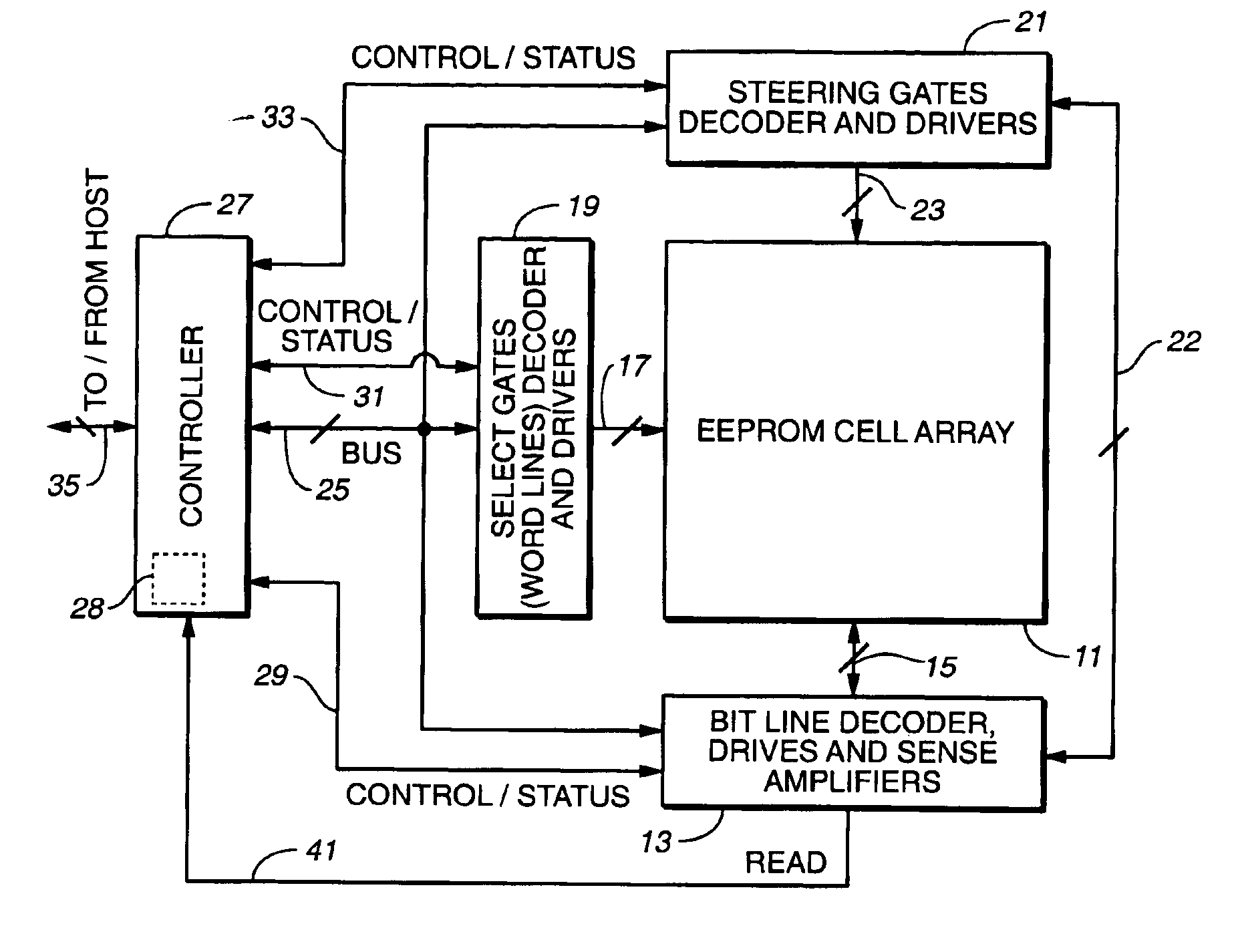
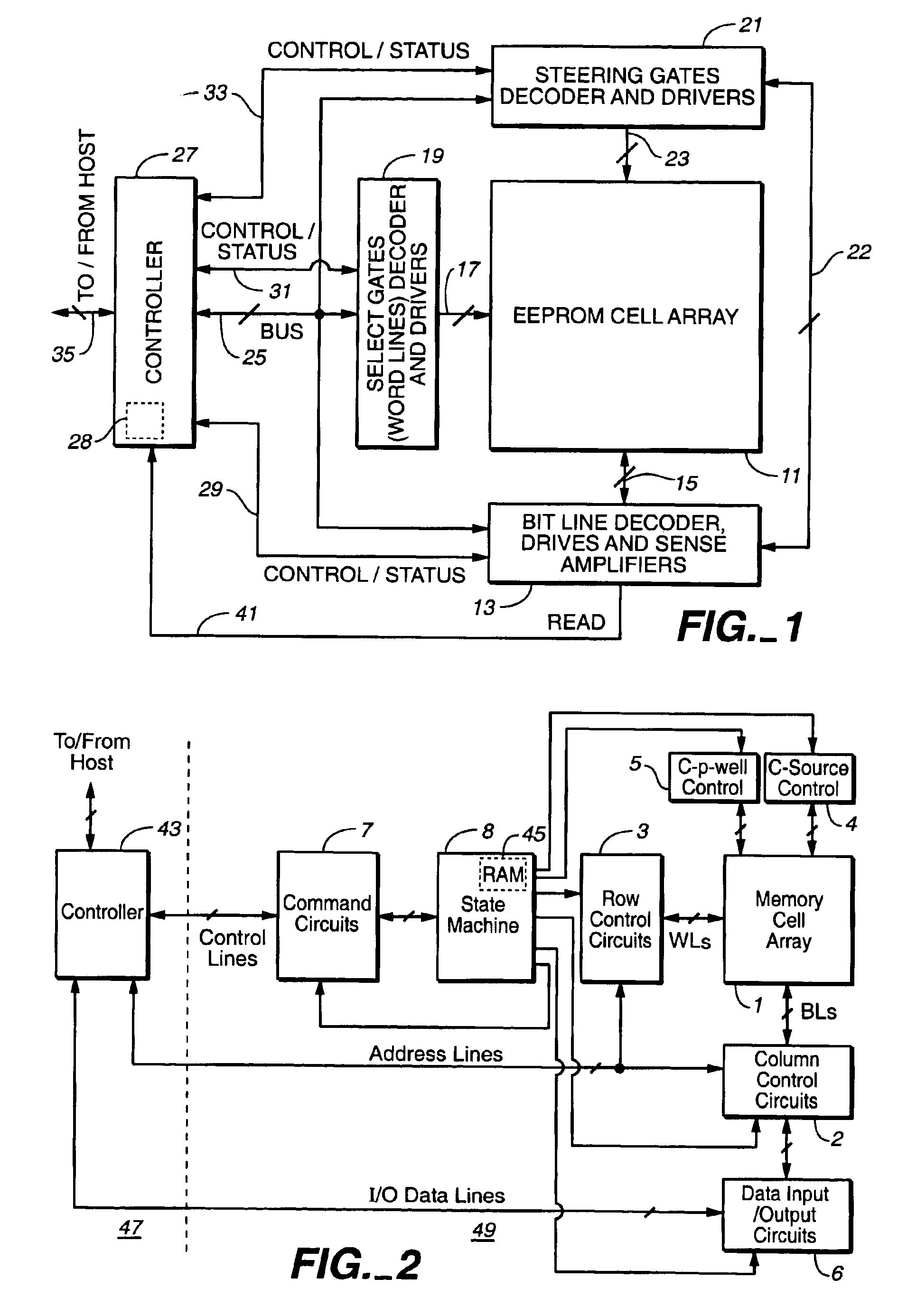
Non-volatile semiconductor memory with large erase blocks storing cycle counts
InactiveUS6944063B2Increase volumeReduce the amount of noiseError detection/correctionSolid-state devicesComputer scienceCorrection code
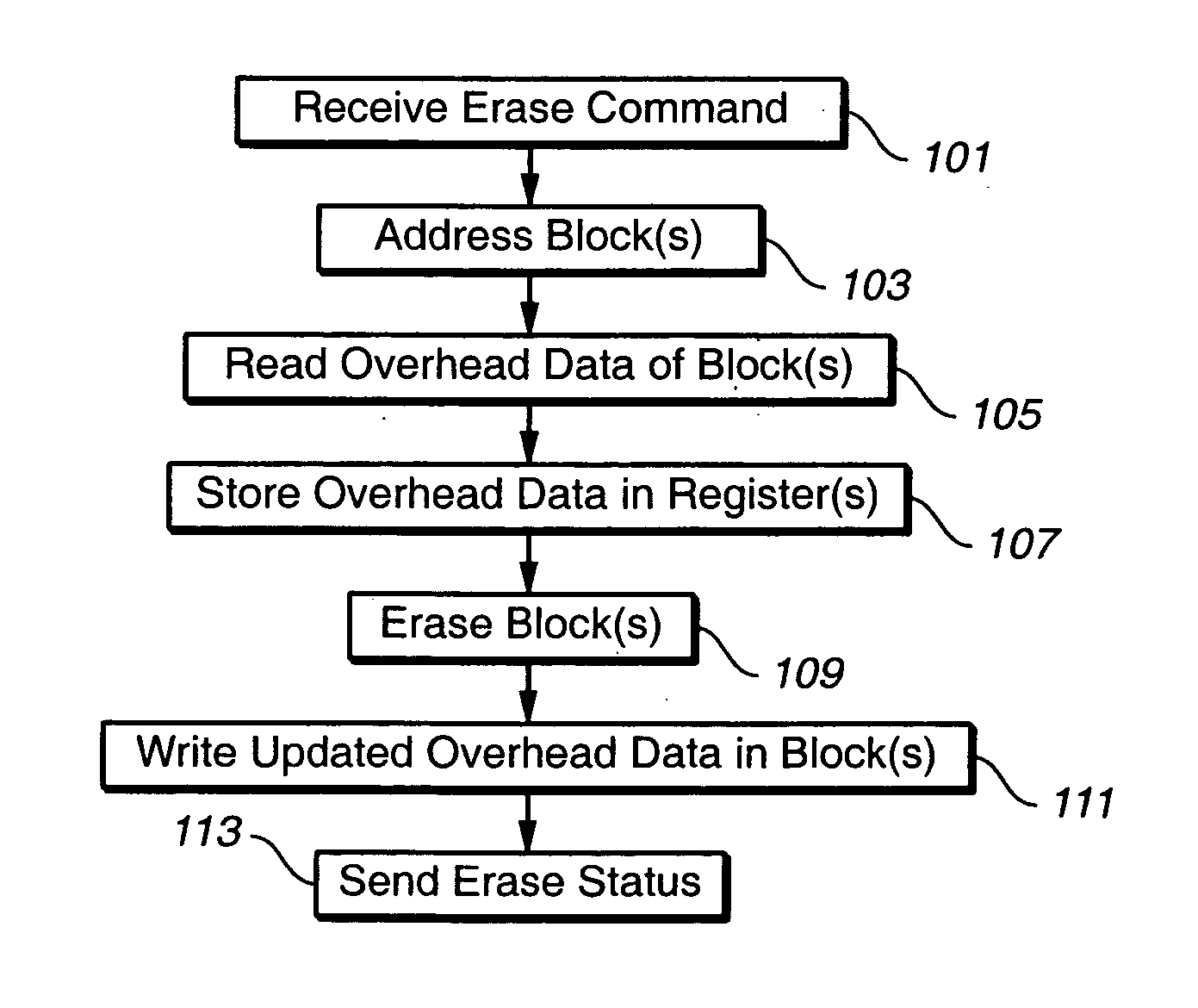
In a flash EEPROM system that is divided into separately erasable blocks of memory cells with multiple pages of user data being stored in each block, a count of the number of erase cycles that each block has endured is stored in one location within the block, such as in spare cells of only one page or distributed among header regions of multiple pages. The page or pages containing the block cycle count are initially read from each block that is being erased, the cycle count temporarily stored, the block erased and an updated cycle count is then written back into the block location. User data is then programmed into individual pages of the block as necessary. The user data is preferably stored in more than two states per memory cell storage element, in which case the cycle count can be stored in binary in a manner to speed up the erase process and reduce disturbing effects on the erased state that writing the updated cycle count can cause. An error correction code calculated from the cycle count may be stored with it, thereby allowing validation of the stored cycle count.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP +1
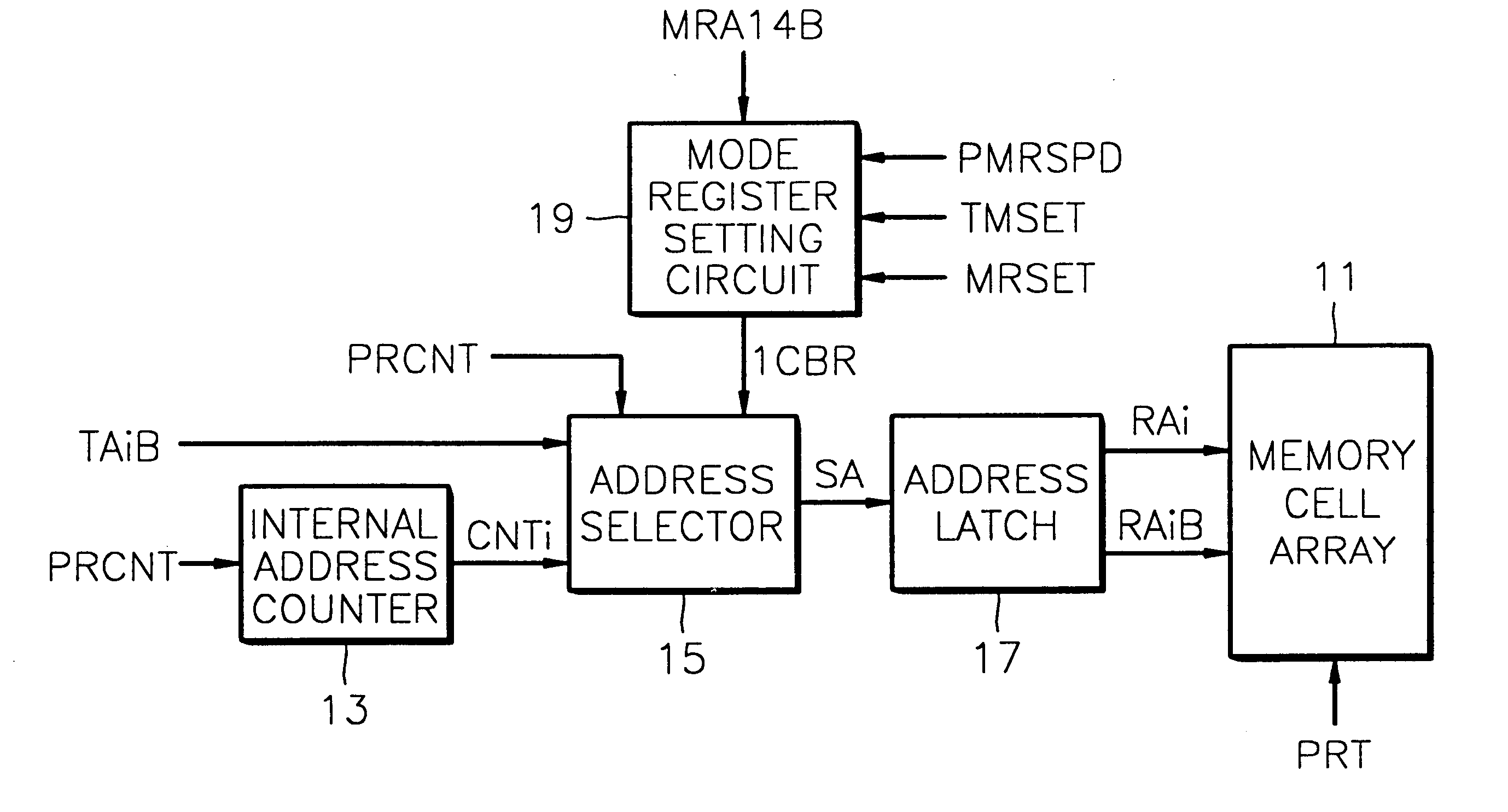
Synchronous DRAM having test mode in which automatic refresh is performed according to external address and automatic refresh method
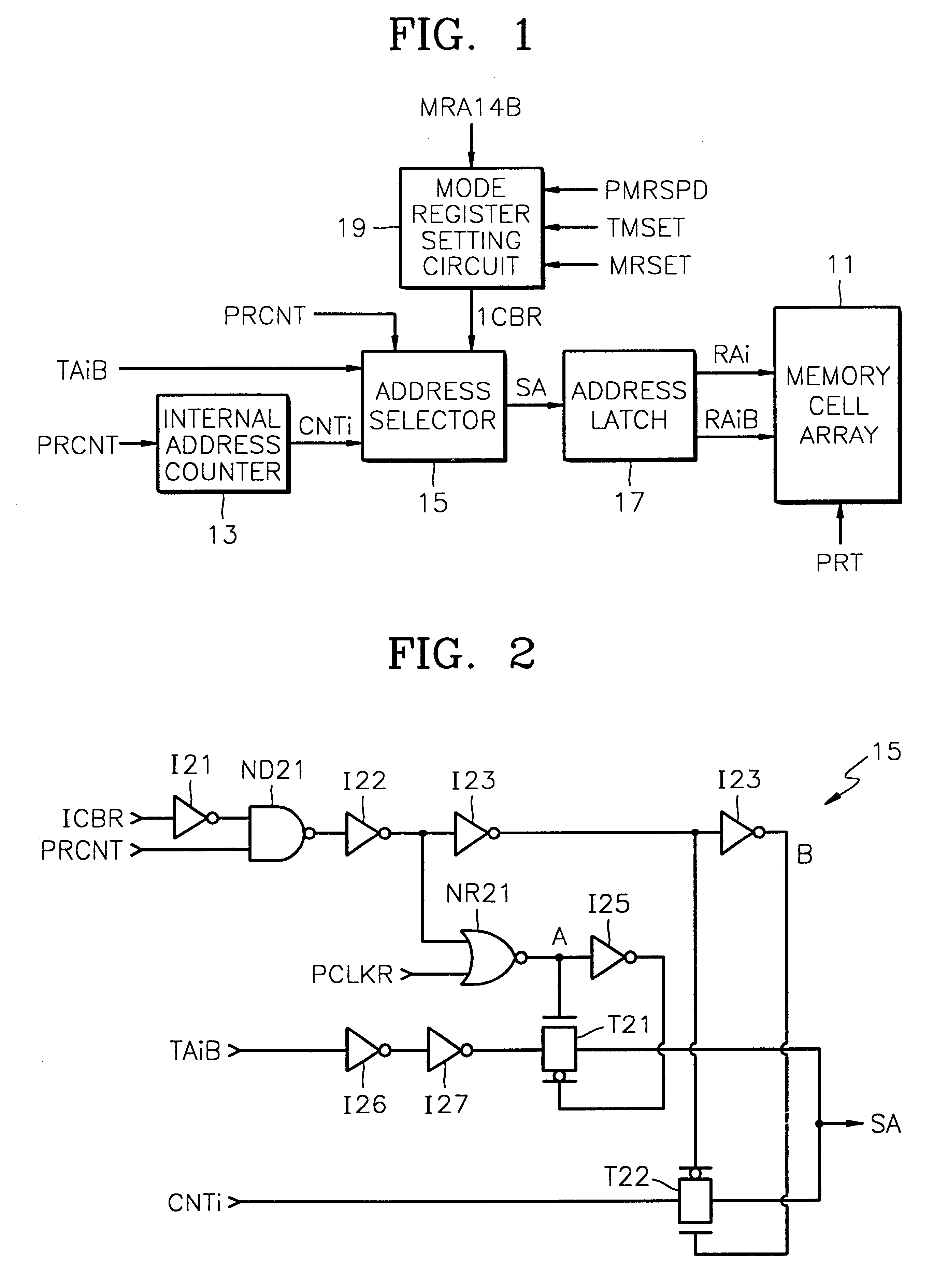
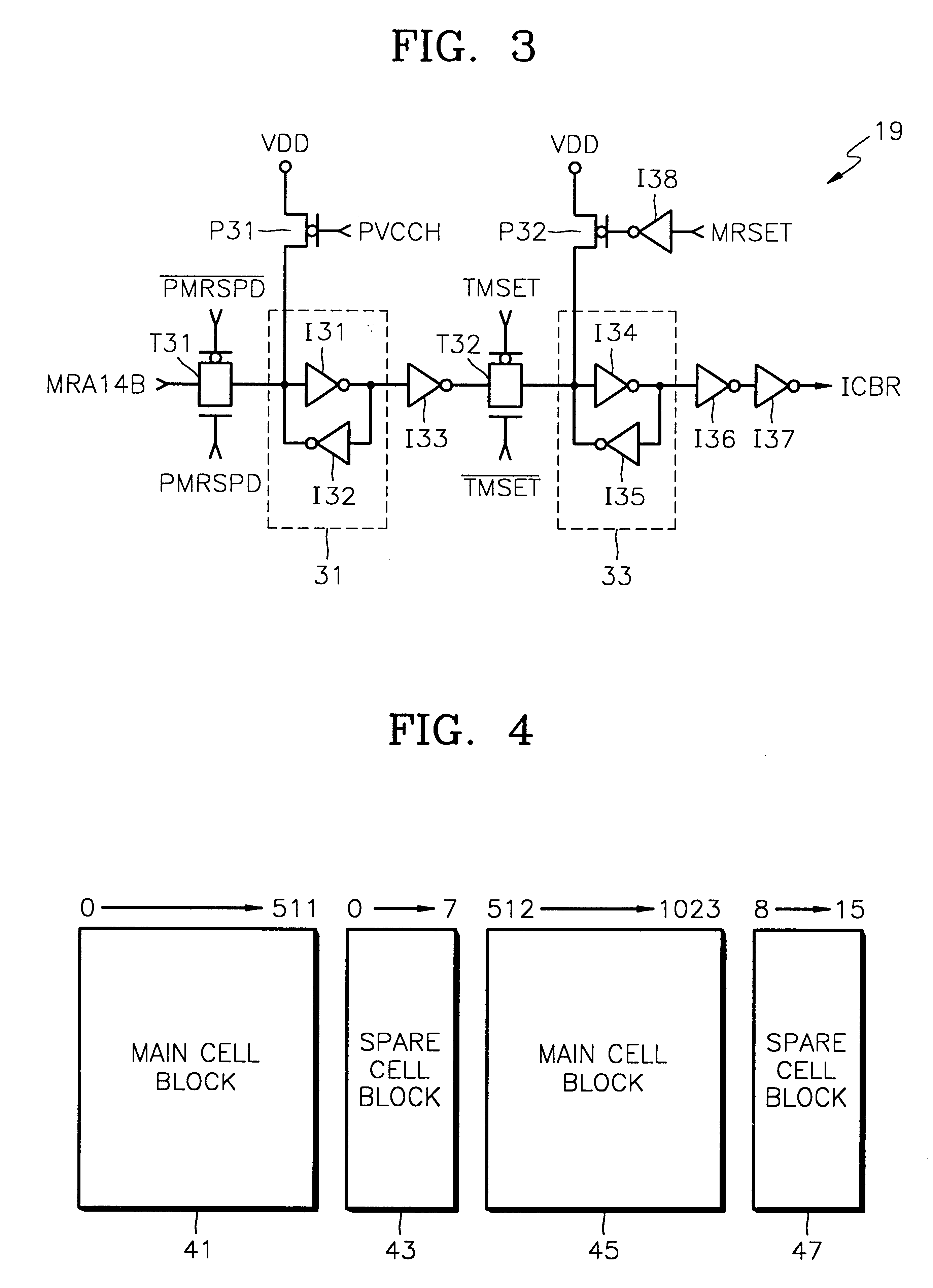
A synchronous DRAM and method are provided in which main cells and spare cells are accessed by an external address during automatic refresh of a test mode. In the synchronous DRAM, a mode register setting circuit receives an external signal in response to a plurality of control signals to generate a mode register setting signal, during an automatic refresh operation in a test mode. An address selector selects and outputs an external address to the memory cell array, in response to the activation of the mode register set signal, during the automatic refresh operation in the test mode. The address selector selects and outputs an internal address to the memory cell array, in response to the deactivation of the mode register set signal, during an automatic refresh operation in a normal mode. Therefore, the main cells and the spare cells in the memory cell array are sequentially accessed and refreshed by the external address during the automatic refresh operation in the test mode.< / PTEXT>
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
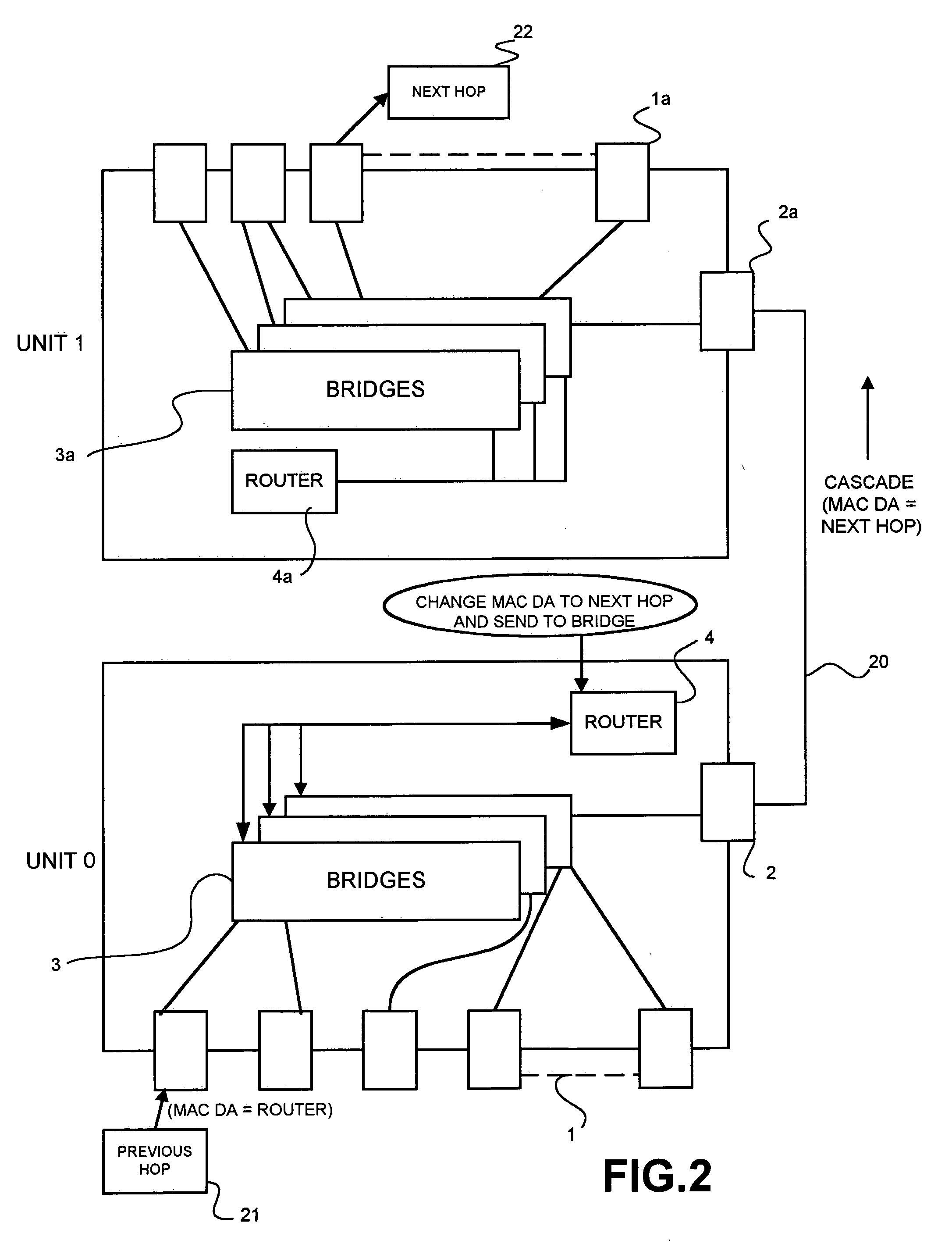
Stackable routers employing a routing protocol
ActiveUS20050135357A1Reduce bandwidth requirementsMaintain relationshipData switching by path configurationPrimary stationNetwork router
A stack of network routers is composed of at least one (elected) master unit and one or more slave units each capable of running a routing protocol. Only the master unit runs the entire routing protocol at a given time. It forwards direct update messages via a transmission control protocol to each of the slave units. These direct update messages may include specific packet formats for the protocol state machinery where such machinery is required by the routing protocol, e.g. the interface state machine and the neighbor state machine for the OSPF protocol, and for the net databases, e.g. the link state databases for the OSPF protocol, in each of the slave units. Each slave unit may run its protocol state machinery (where provided) based purely on the direct update messages received from the master. The synchronisation of the net databases may be based on snooping net update packets and a comparison of the information received thereby with verification data messages sent from the master unit. The synchronization allows the running of the routing protocol on multiple physical routers in a stack without requiring the overhead of a back-up unit that would not perform routing unless a master router unit became unavailable.
Owner:VALTRUS INNOVATIONS LTD
Fault tolerant cell array architecture
InactiveUS7299377B2Single instruction multiple data multiprocessorsStatic indicating devicesData processing systemComputer architecture
A data processing system containing a monolithic network of cells with sufficient redundancy provided through direct logical replacement of defective cells by spare cells to allow a large monolithic array of cells without uncorrectable defects to be organized, where the cells have a variety of useful properties. The data processing system according to the present invention overcomes the chip-size limit and off-chip connection bottlenecks of chip-based architectures, the von Neumann bottleneck of uniprocessor architectures, the memory and I / O bottlenecks of parallel processing architectures, and the input bandwidth bottleneck of high-resolution displays, and supports integration of up to an entire massively parallel data processing system into a single monolithic entity.
Owner:NORMAN RICHARD S
Memory system and method of operating the same
InactiveUS20120173920A1Read-only memoriesRedundant hardware error correctionComputer scienceTotal error
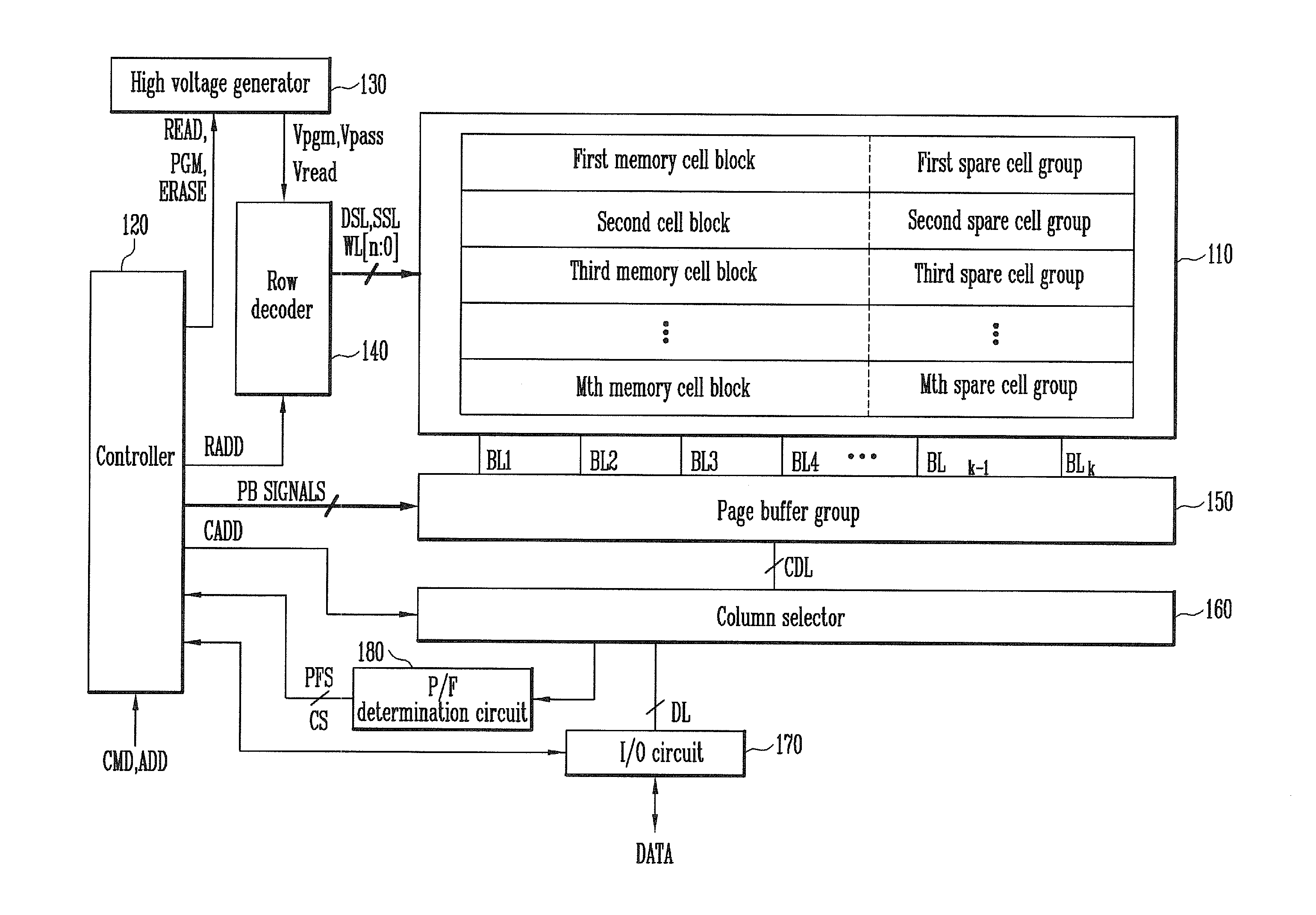
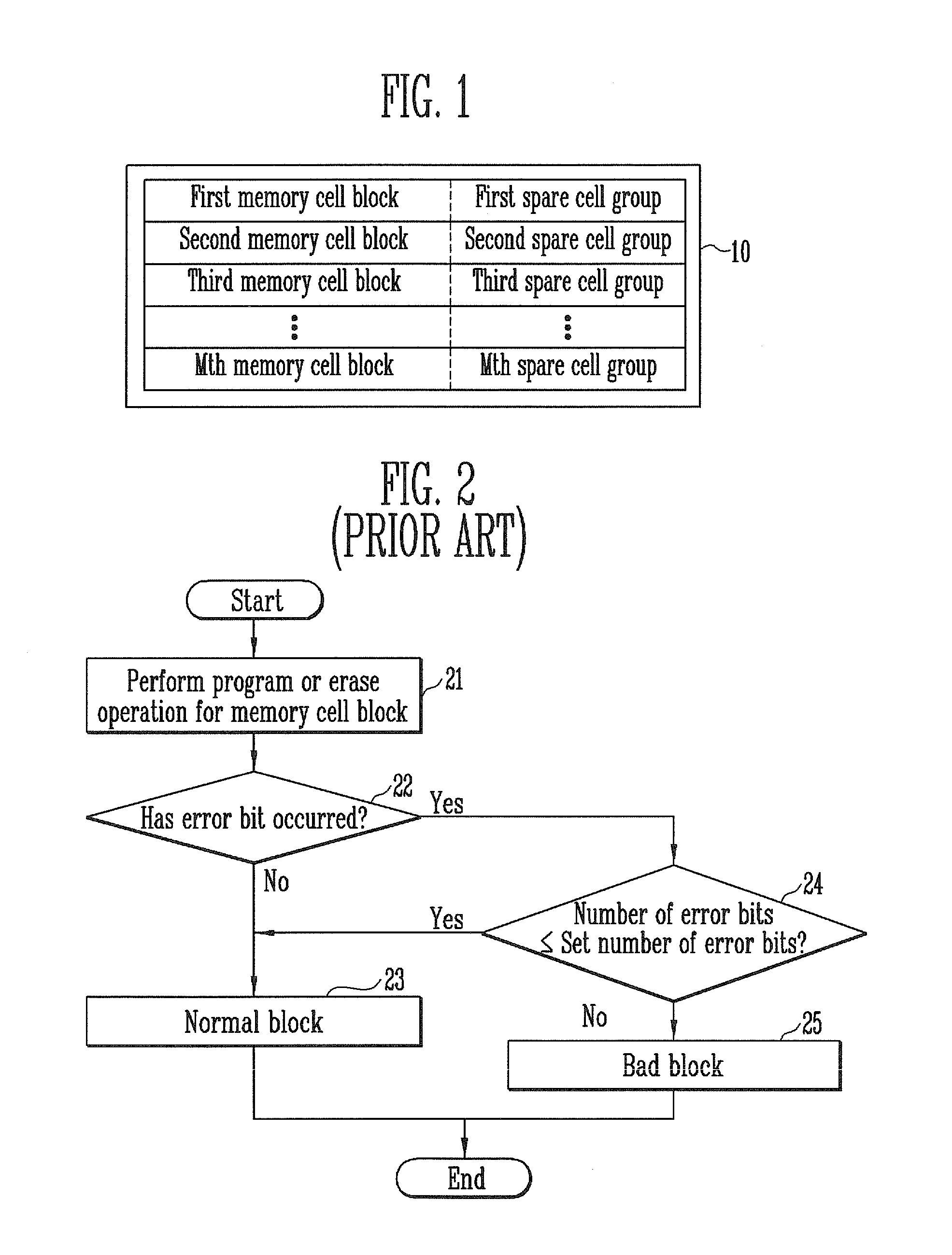
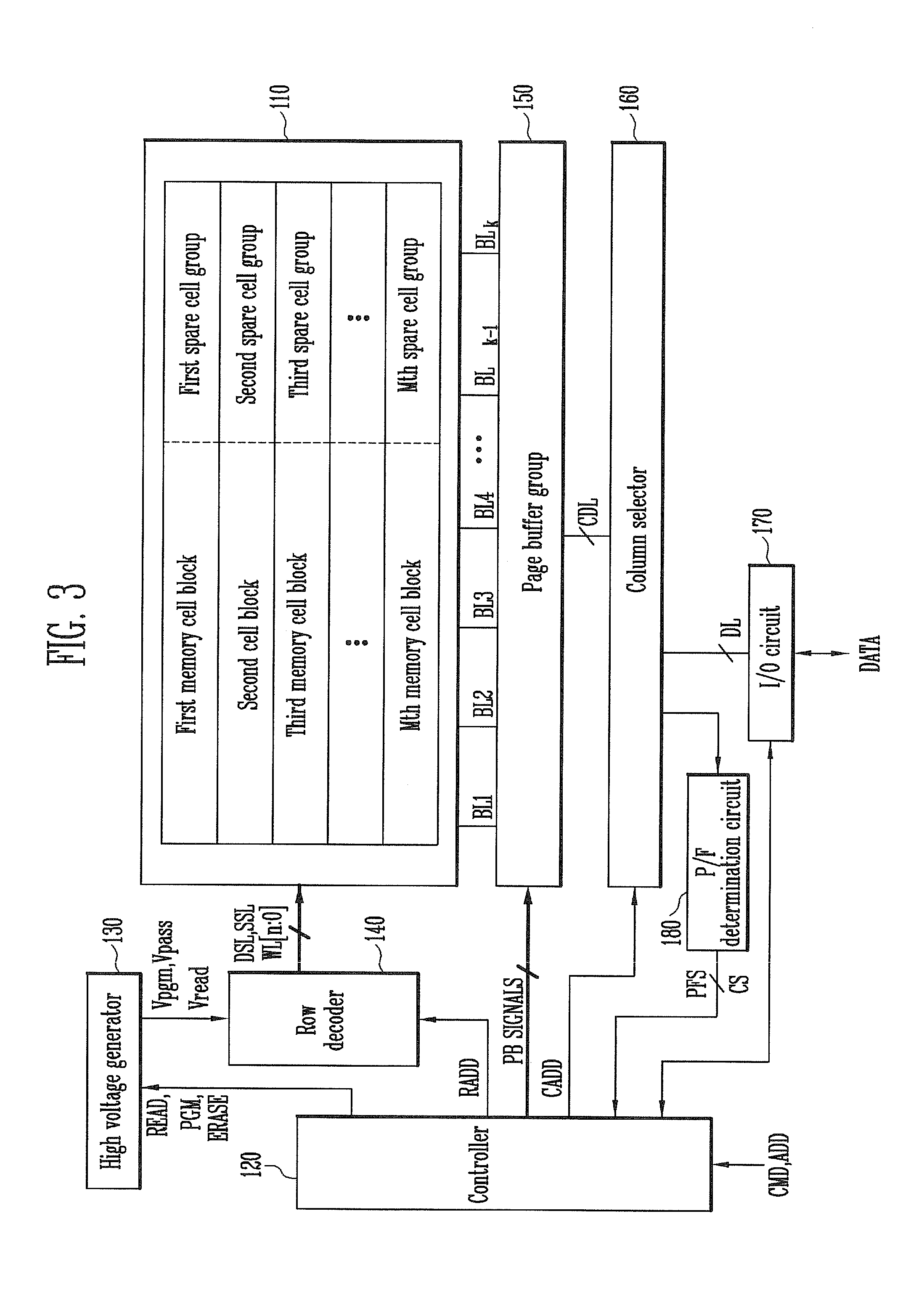
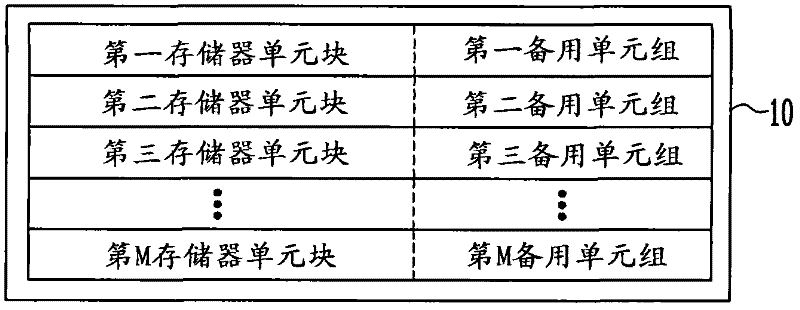
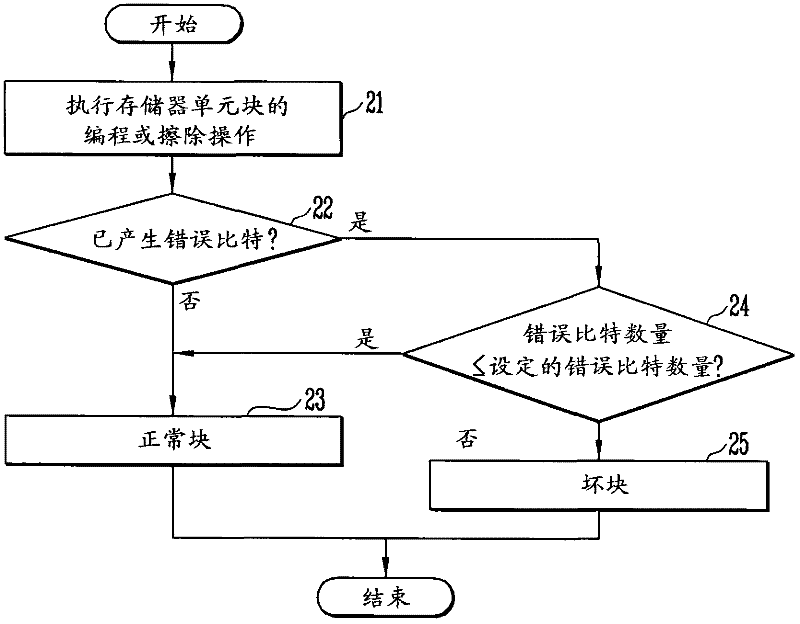
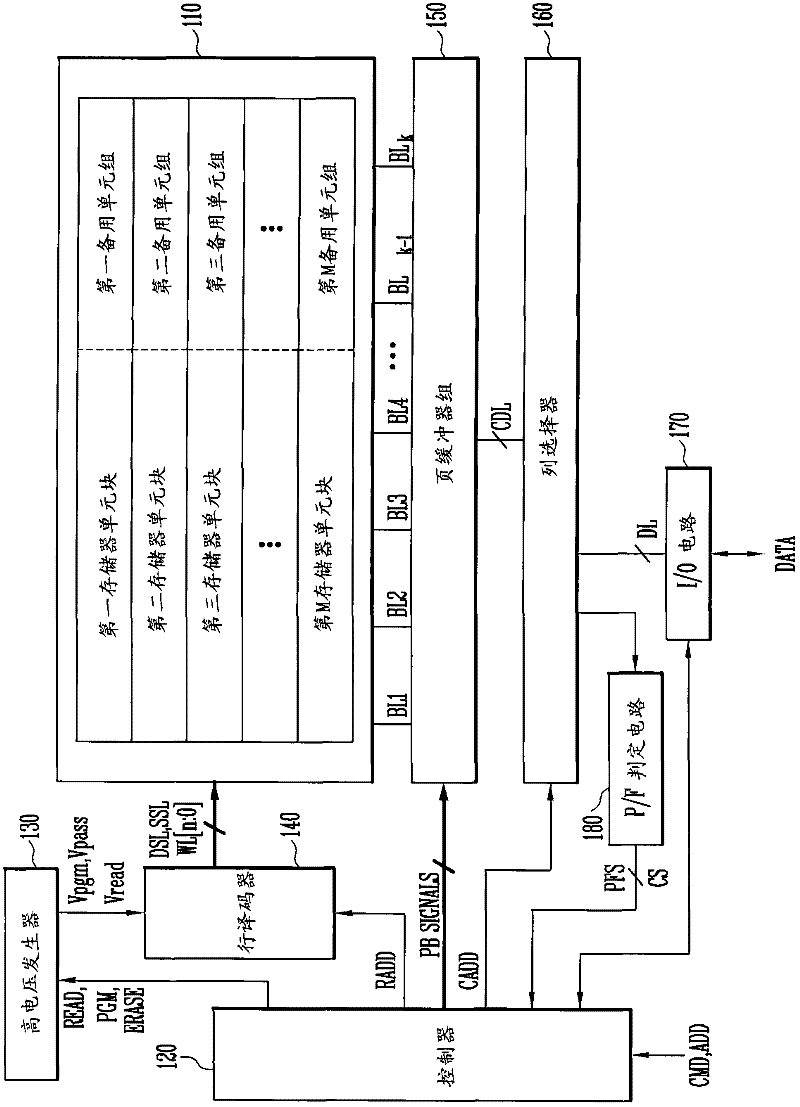
A method of operating a memory system includes classifying numbers of total error bits into a plurality of ranges, assigning a plurality of data to the plurality of ranges, respectively, counting a number of detected error bits for a memory cell block, and storing a selected one of the plurality of data in at least one spare cell when the number of the detected error bits is within one of the ranges that corresponds to the selected data.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
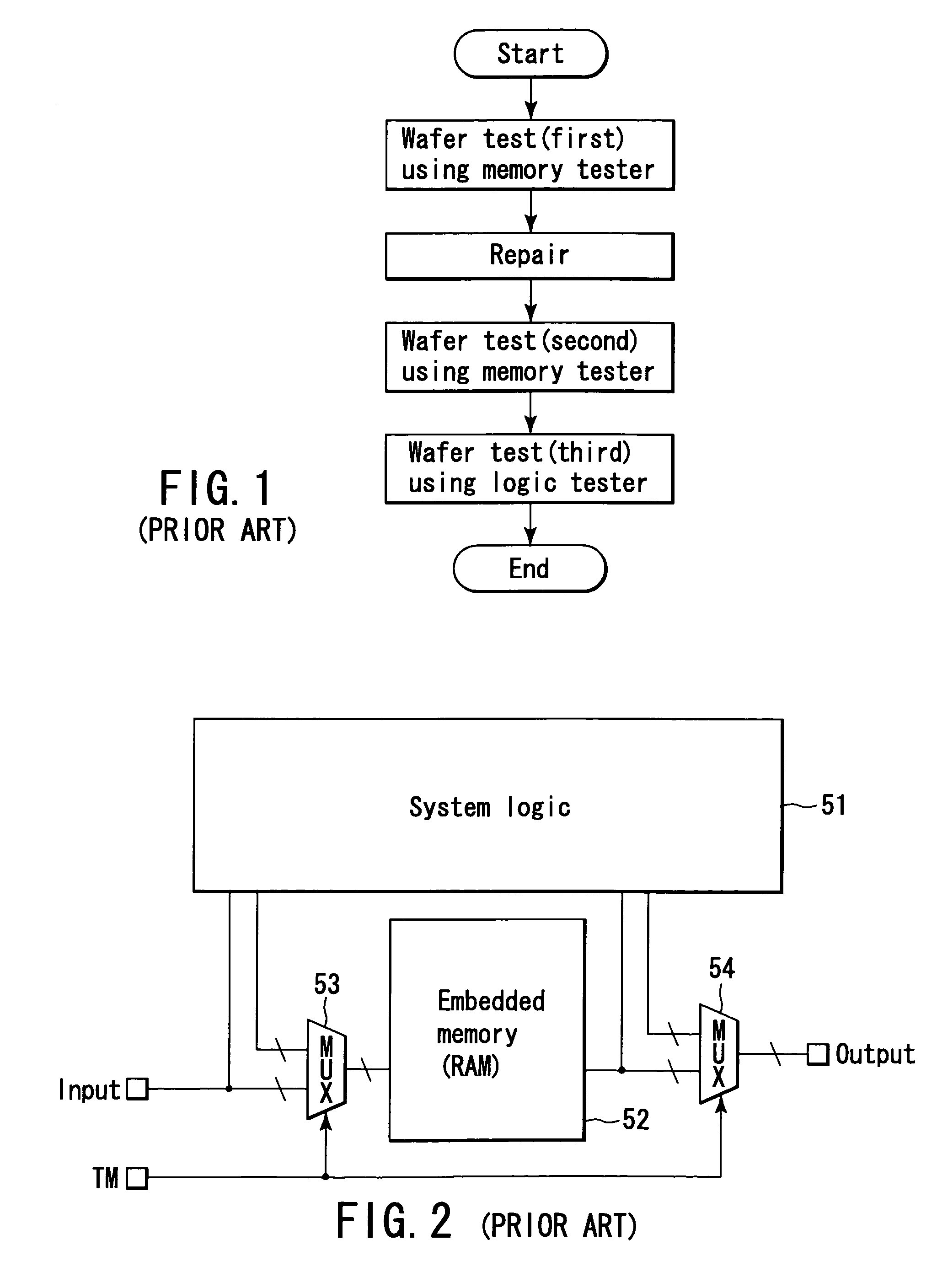
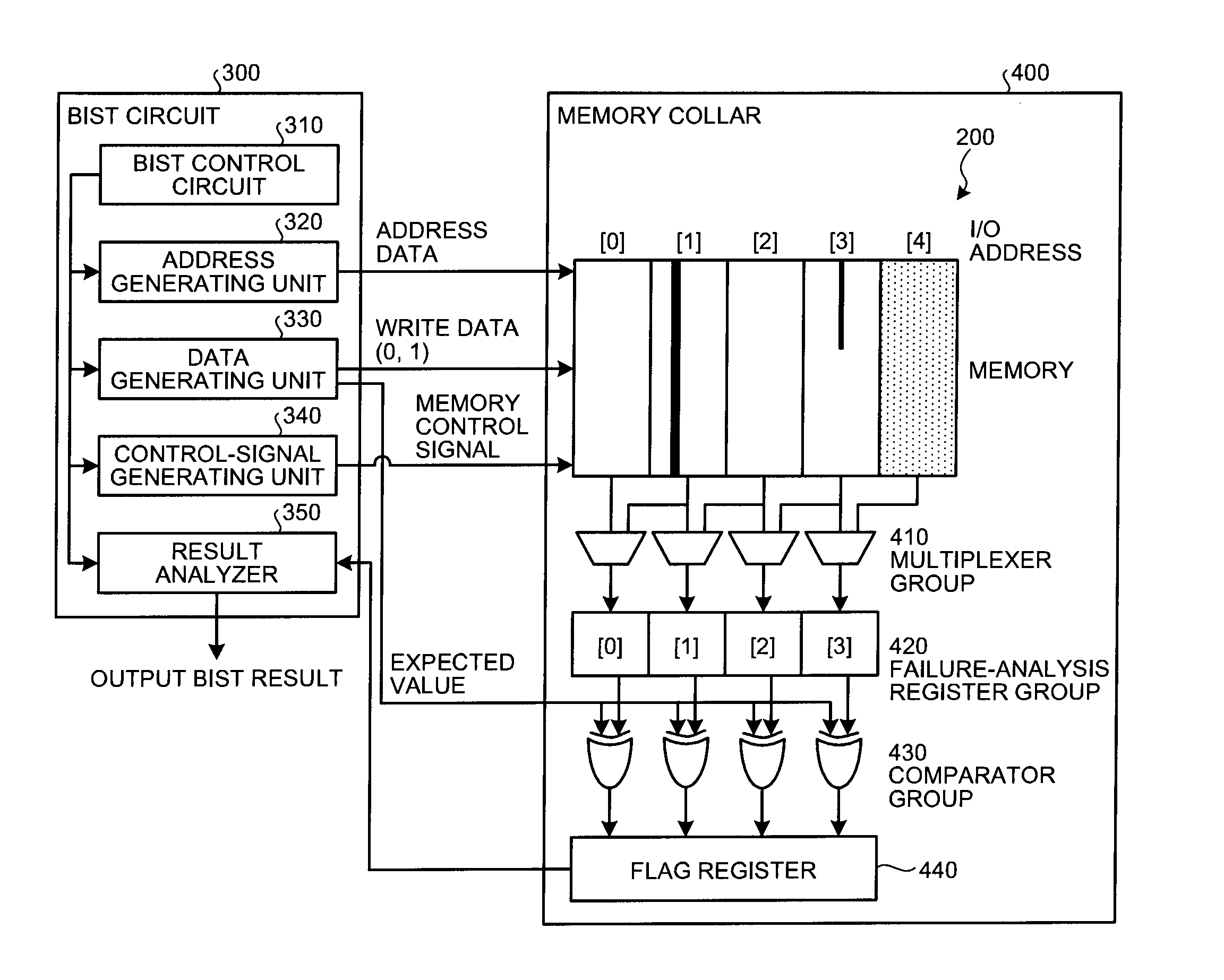
Semiconductor integrated circuit device having a test function
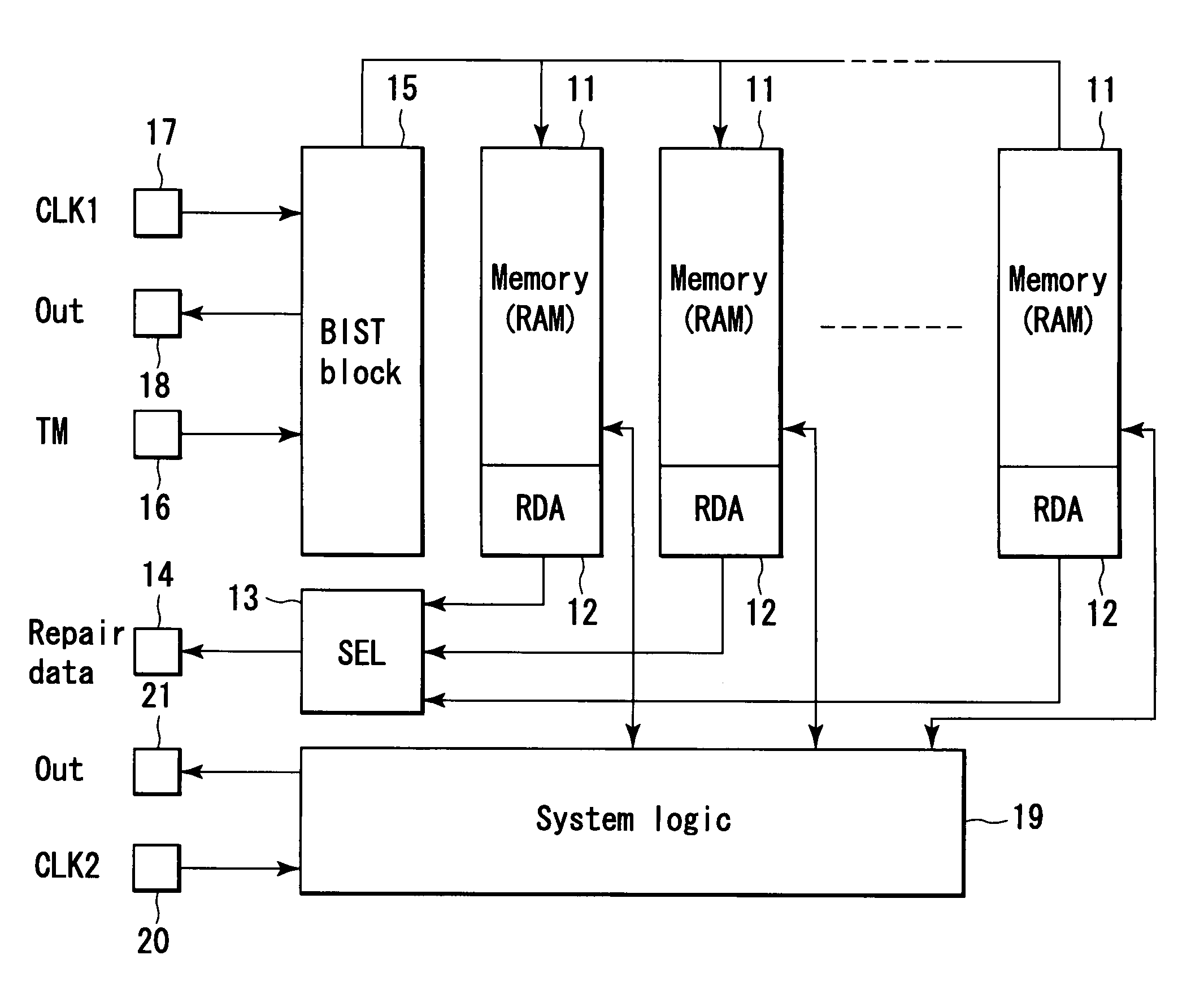
A semiconductor memory device includes a memory collar, a repair data analyzer, a BIST block, and a system logic. The memory collar includes a memory cell and a spare cell and have a redundancy function of replacing fail memory cell with the spare cell if fail memory cell exists. The repair data analyzer determines whether or not memory cell included in the memory collar is defective, and generates fail address corresponding to the memory cell determined as being defective. The BIST block operates in synchrony with a first clock signal inputted to a first clock signal terminal in a test operation mode, and controls the operation of the memory collar. The system logic operates in synchrony with a second clock signal inputted to a second clock signal terminal in the test operation mode.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
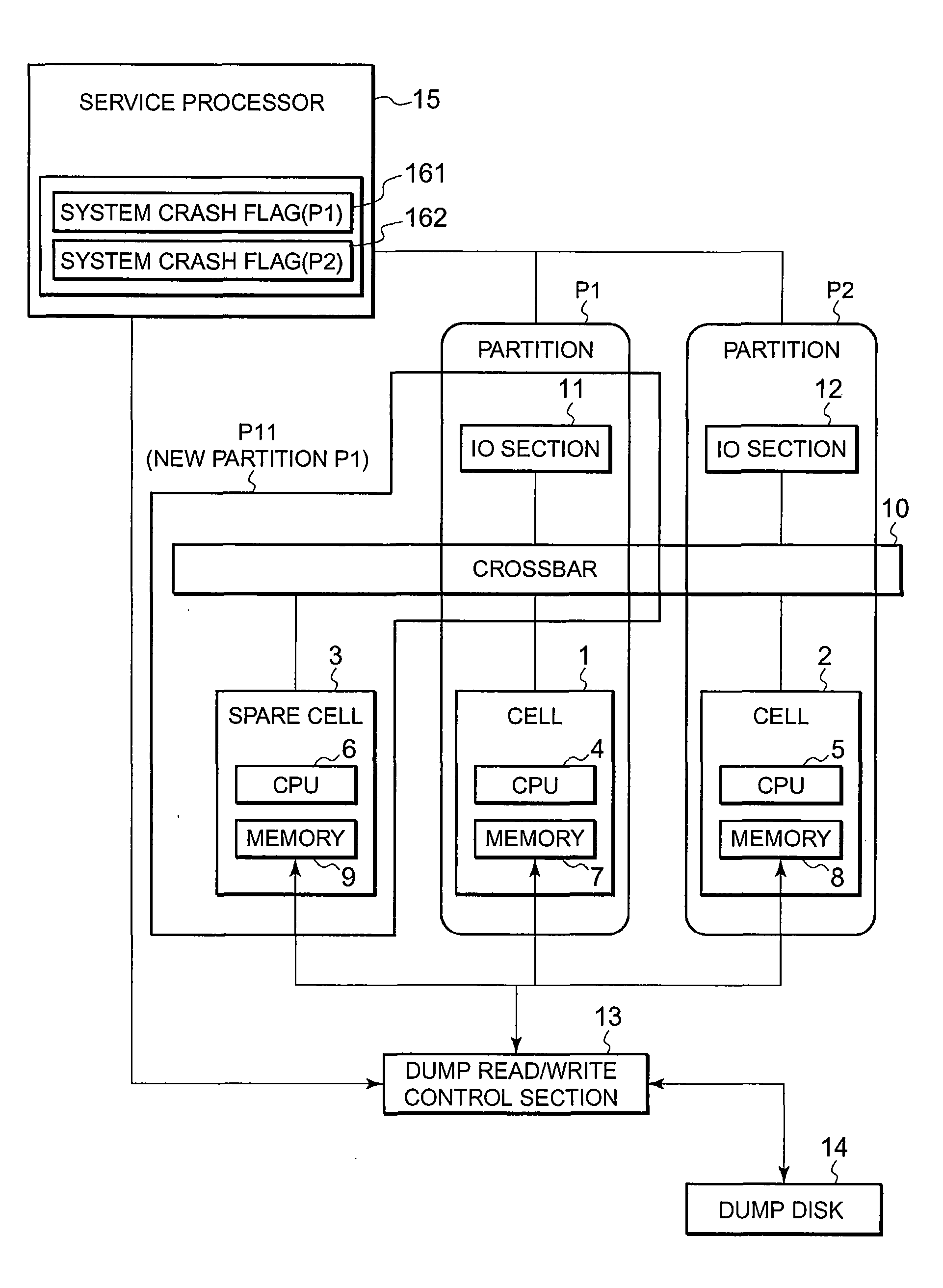
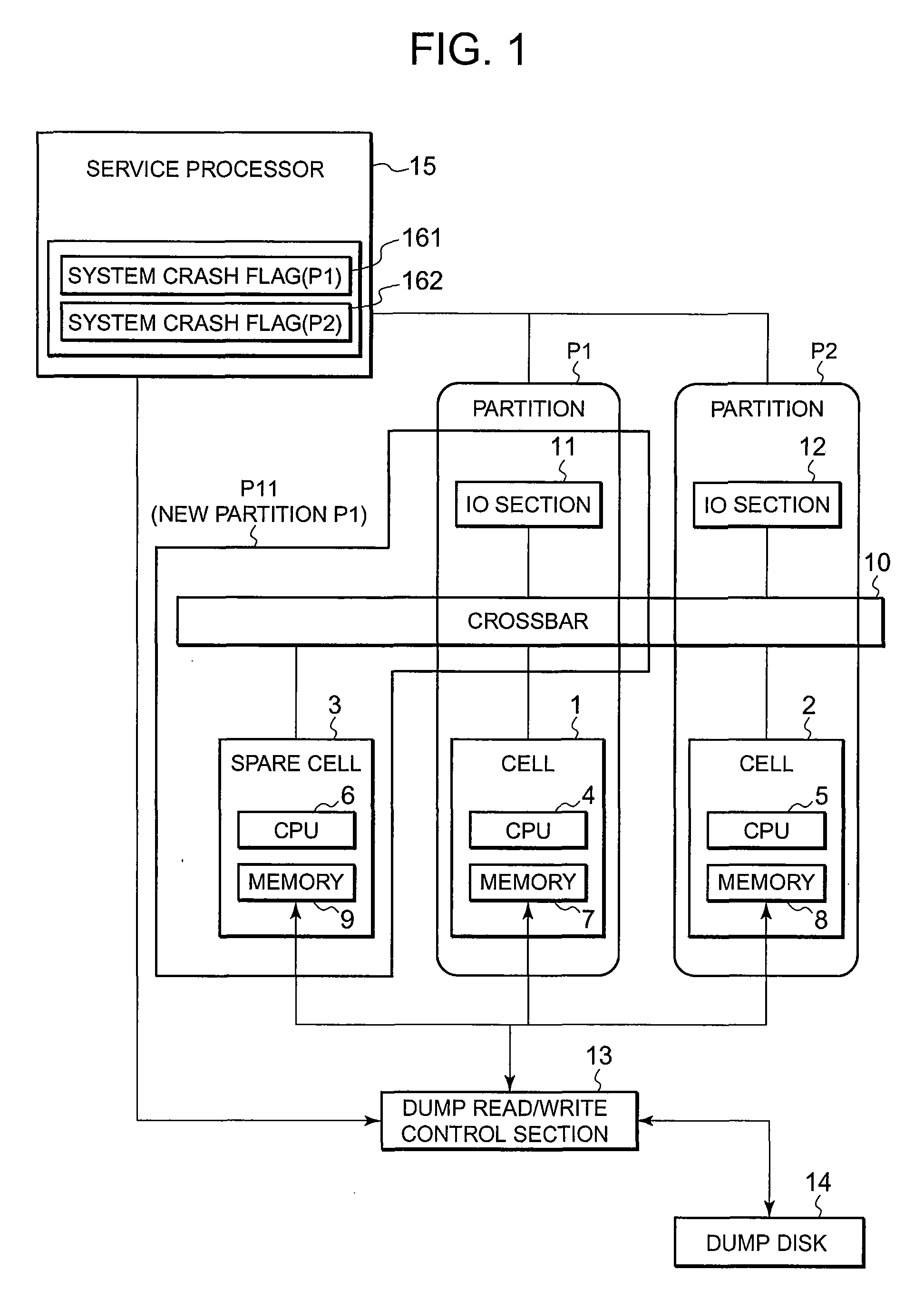
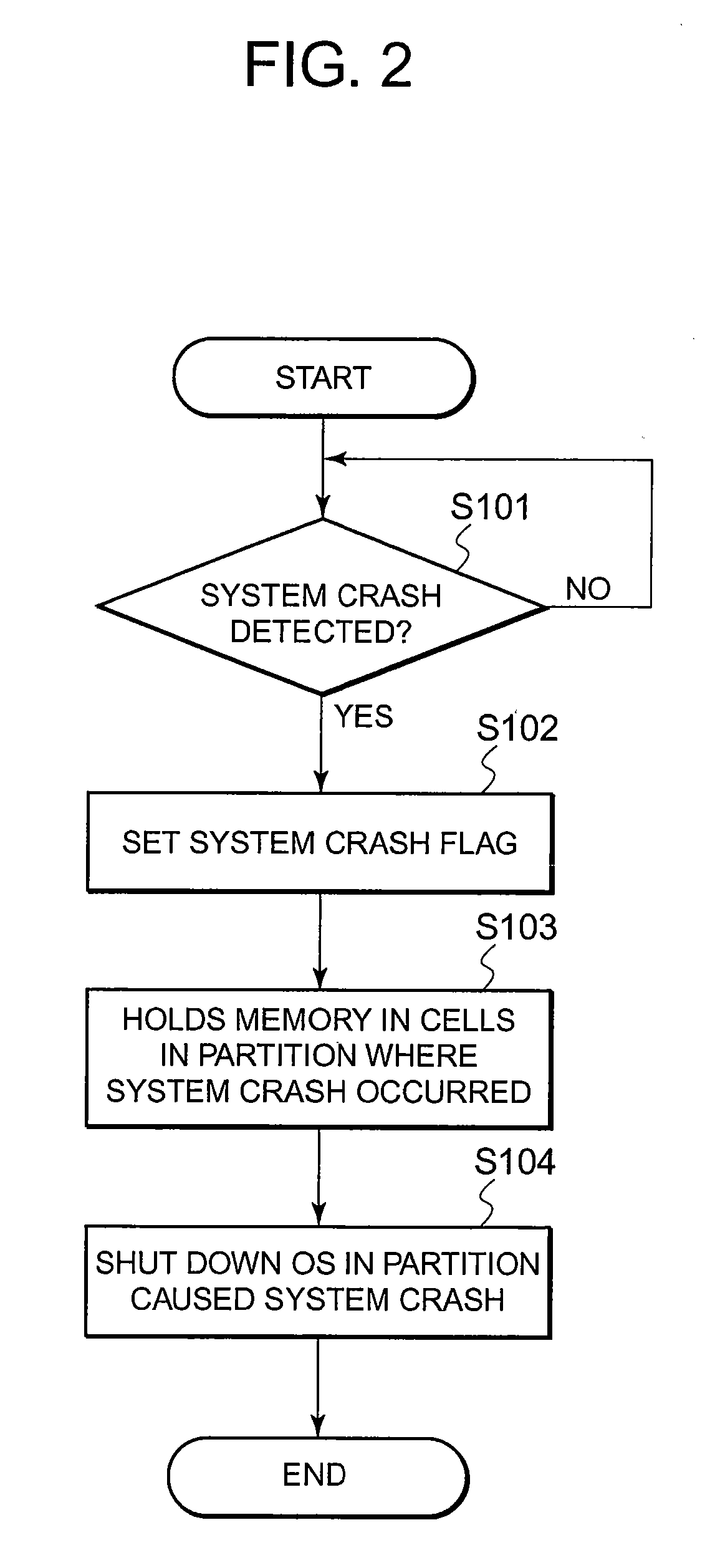
Memory dump method, computer system, and memory dump program
InactiveUS20070101191A1Down time of systemNon-redundant fault processingComputer architectureTerm memory
A computer system of the present invention includes cells each of which includes a CPU and a memory, and partitions each of which is configured by combining any number of the cells. A service processor and a control element which controls reading and writing data for memory dumping are provided with the computer system. The cells includes a spare cell which does not belong to any of the partitions. If any of the partitions shuts down because of a system crash, the service processor disconnects the cell in the partition in which the system crash has occurred from the partition with memory information contained in the memory in the cell being held, and sets the spare cell into the partition. After the partition is booted, the control element writes the memory information contained in the memory in the disconnected cell onto the recording medium.
Owner:NEC CORP
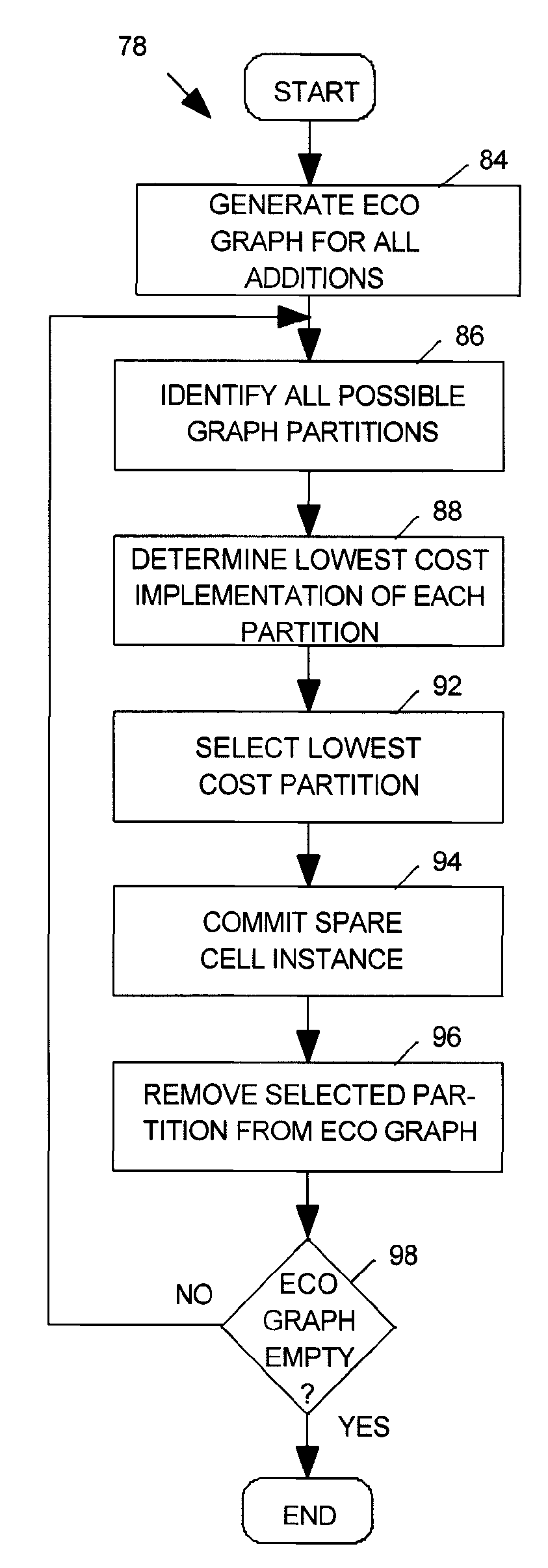
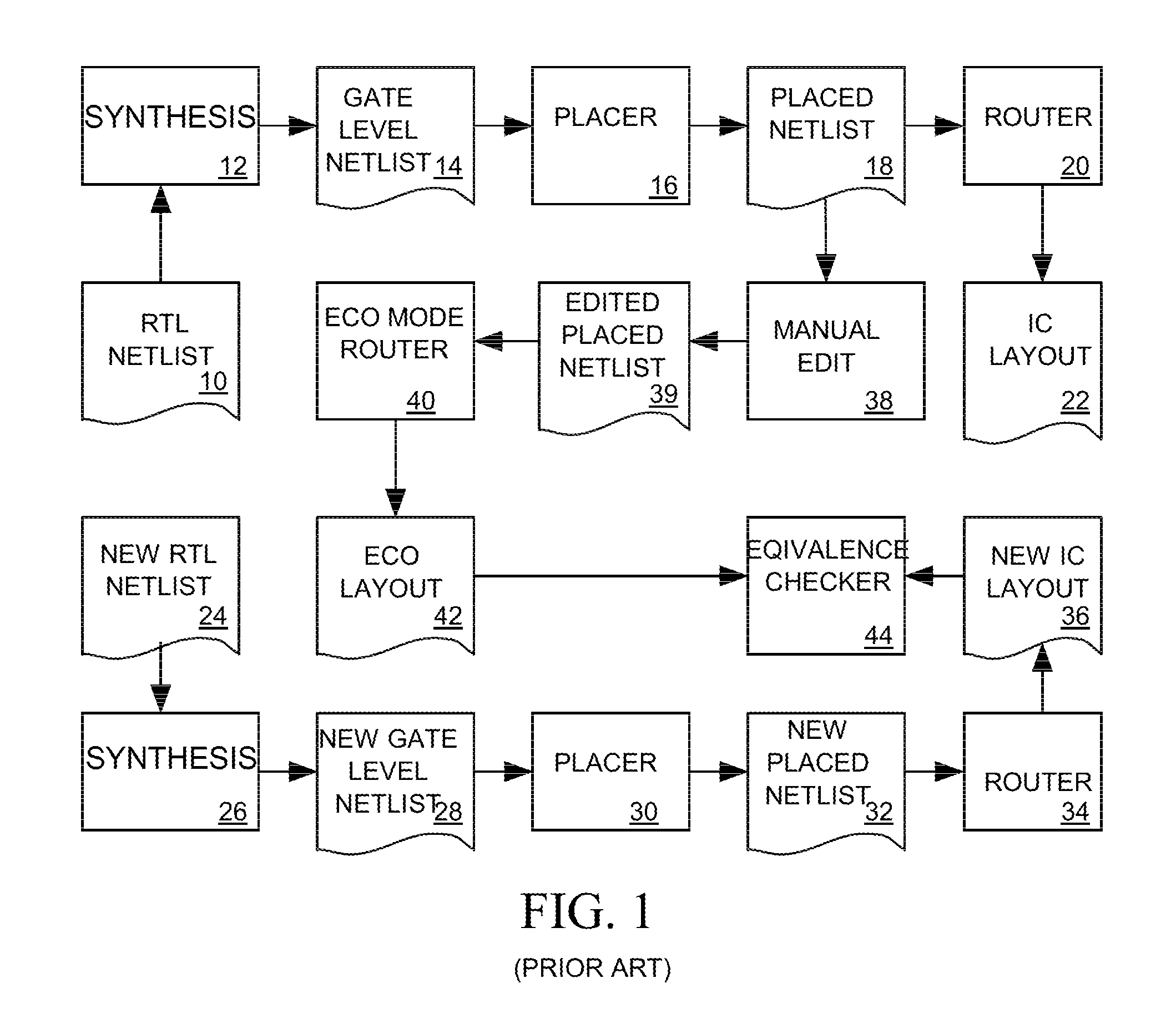
System for implementing post-silicon IC design changes
ActiveUS20090178013A1Improve routeablityCAD circuit designMulti-objective optimisationEngineeringActive cell
An engineering change order (ECO) modifying an IC having spare cell instances is implemented by converting active cell instances implementing portions of the IC to be deleted into additional spare cell instances, by creating a technology independent behavioral model of portions of the IC to be added, by selecting spare cell instances to implement the behavior model, and by routing nets to the selected spare cell instances in a way that minimizes a number of metal layers of the IC that are modified.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
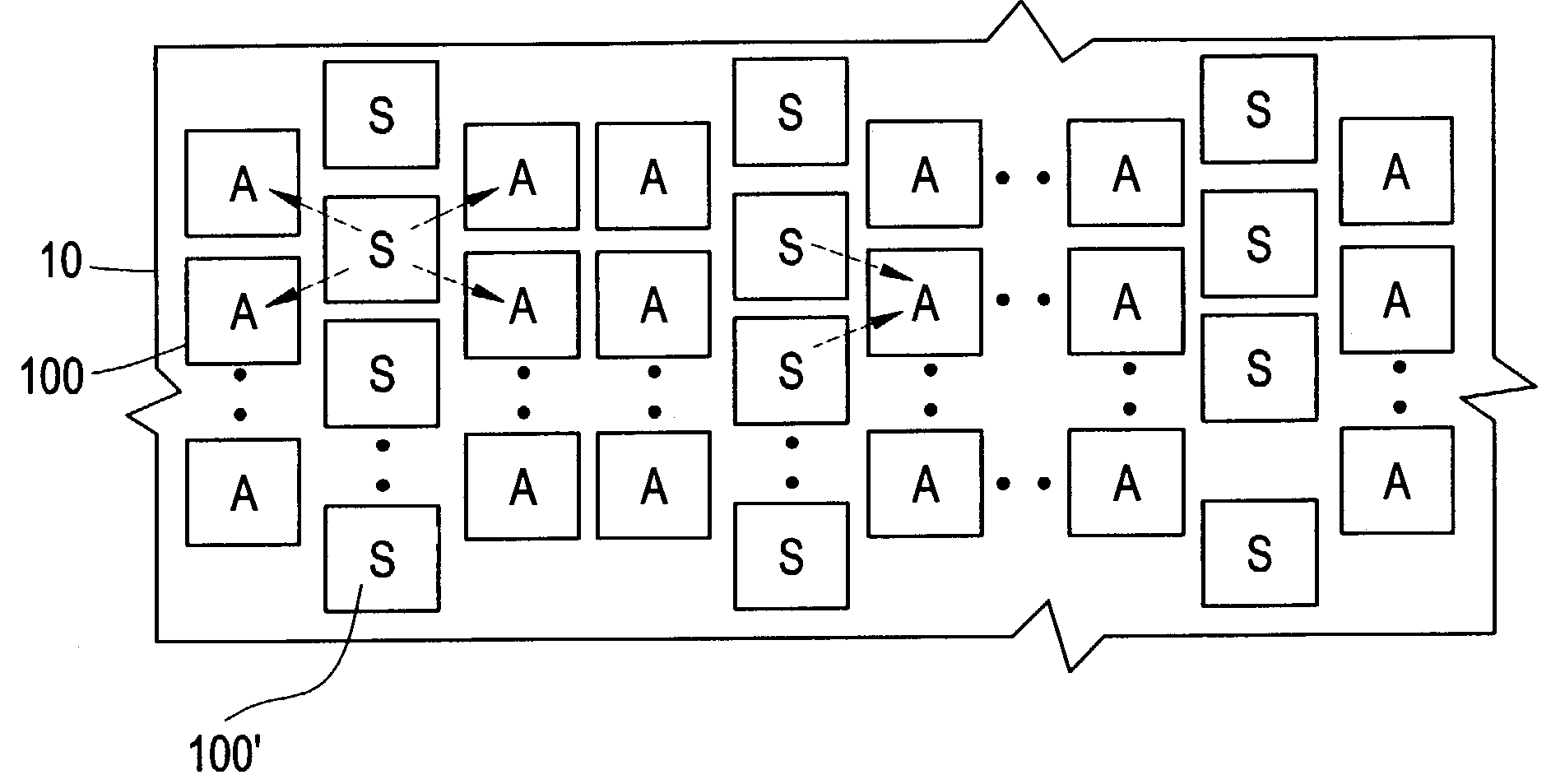
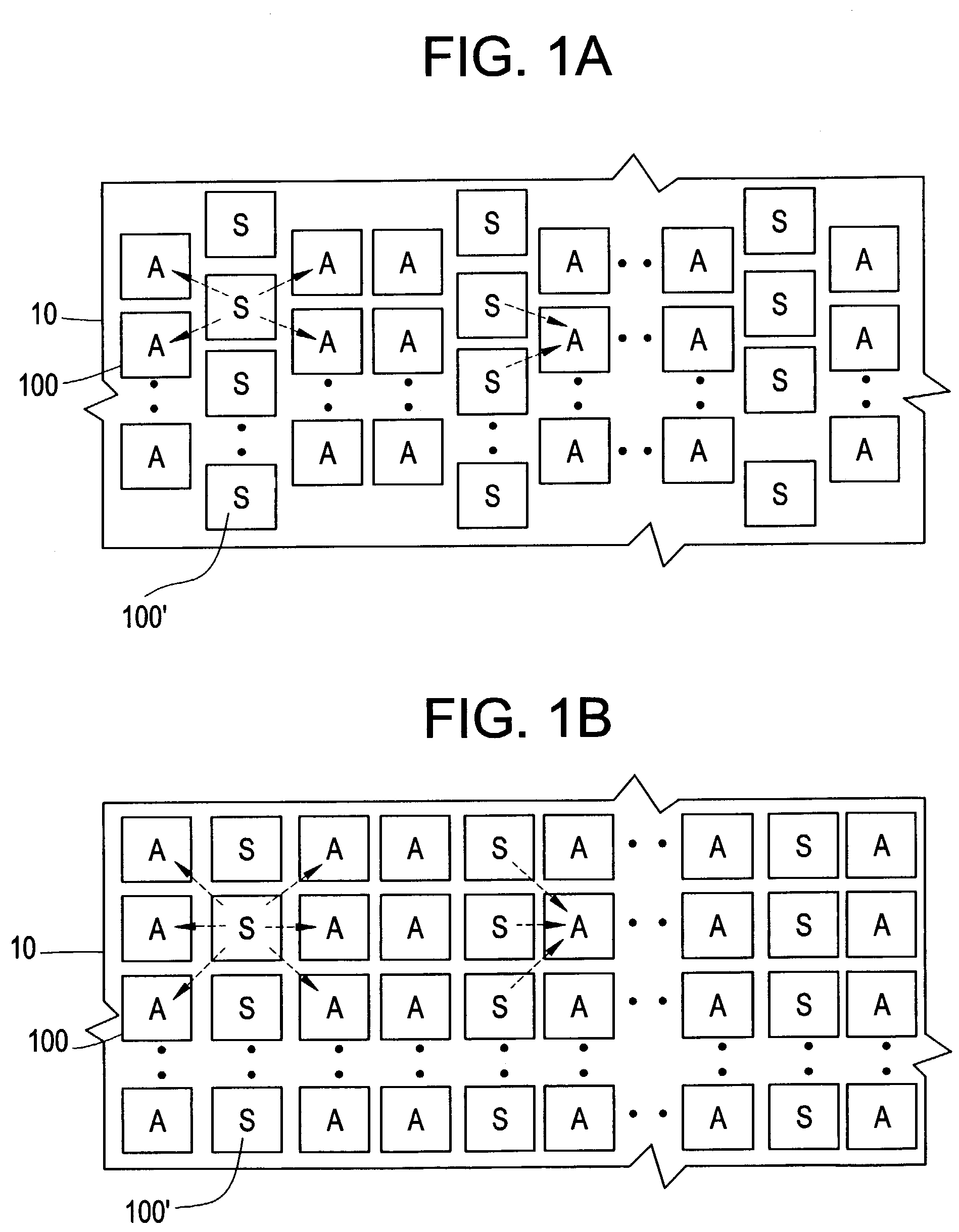
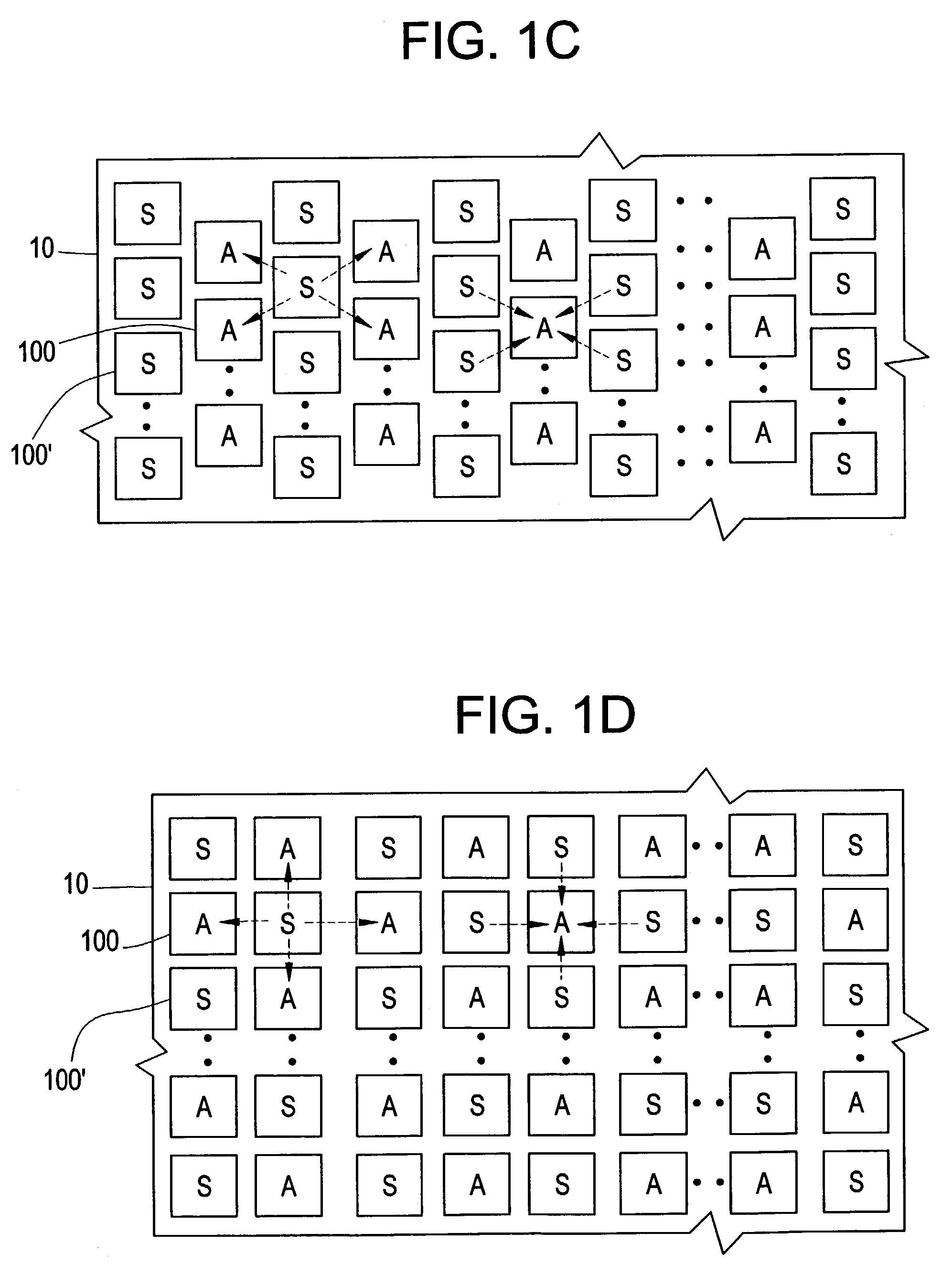
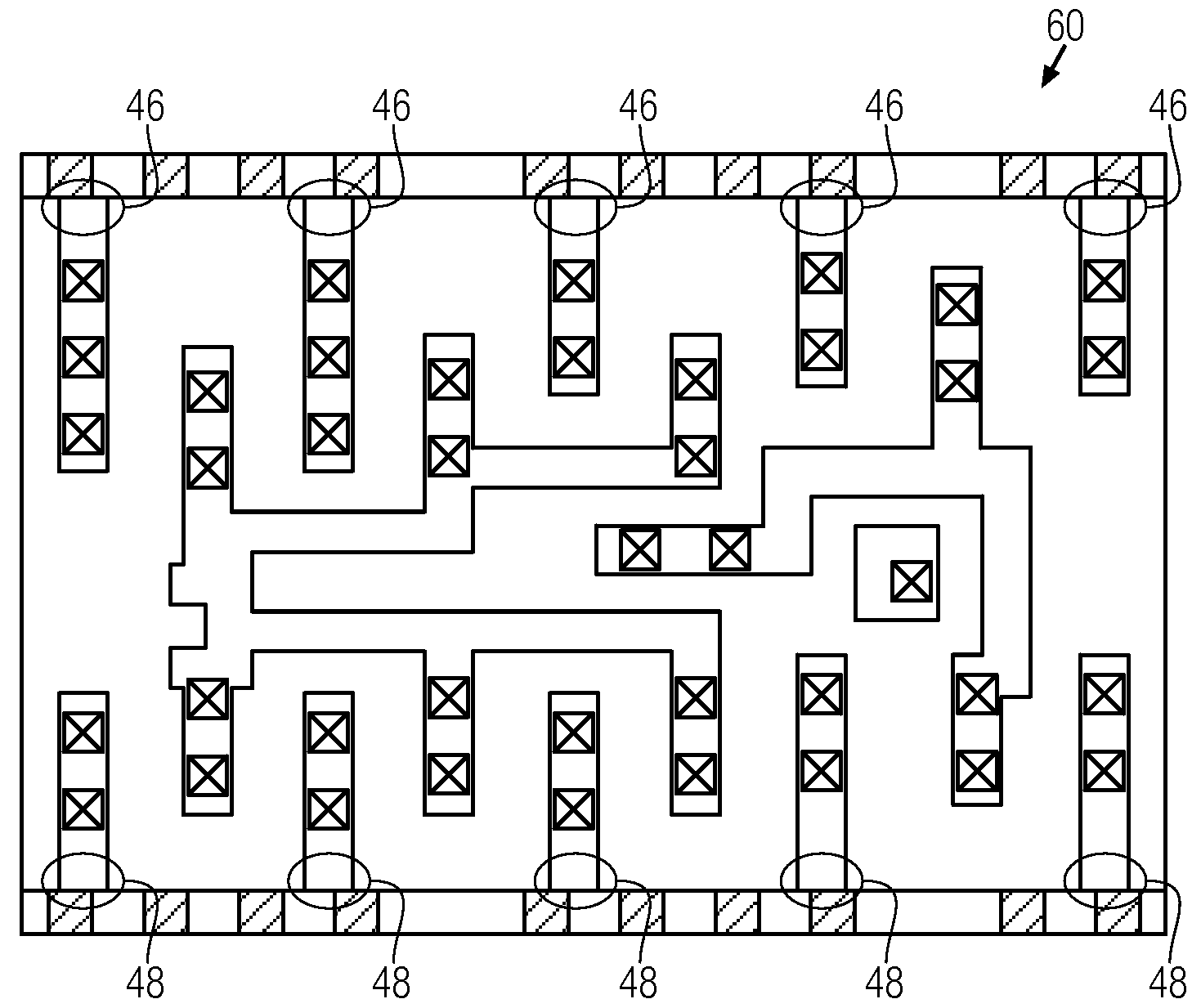
Spatially aware drive strength dependent die size independent combinatorial spare cell insertion manner and related system and method
InactiveUS20080237644A1Raise countIncrease design areaSolid-state devicesComputer aided designReserve CellChip size
A design method for an integrated circuit adds spare cells in a System-on-Chip to allow for Engineering Change Orders (ECOs) to be performed at a later stage in the design. This method can be used to provide a second version of the chip having minimal alterations performed in a short cycle time. The spare cells can be divided into combinational and sequential cells. There is an optimum spread of combinational cells in the design for post placement repairs of the chip with just metal layer changes. The method takes into account the drive strength of the spare cells as the main factor in their placement on the chip.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
Ad hoc flash memory reference cells
In a nonvolatile memory, that includes cells organized in a plurality of bit lines and a plurality of word lines, user data are stored in respective portions of each of two of the word lines. Control information is stored in a cell that is common to one of the bit lines and one of the two word lines. A cell that is common to the bit line and the other word line is used as a reference cell. A flash memory, that includes a plurality of primary cells and a plurality of spare cells, is interrogated to determine which spare cells have been used to replace respective primary cells. At least some of the other spare cells are used as reference cells.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
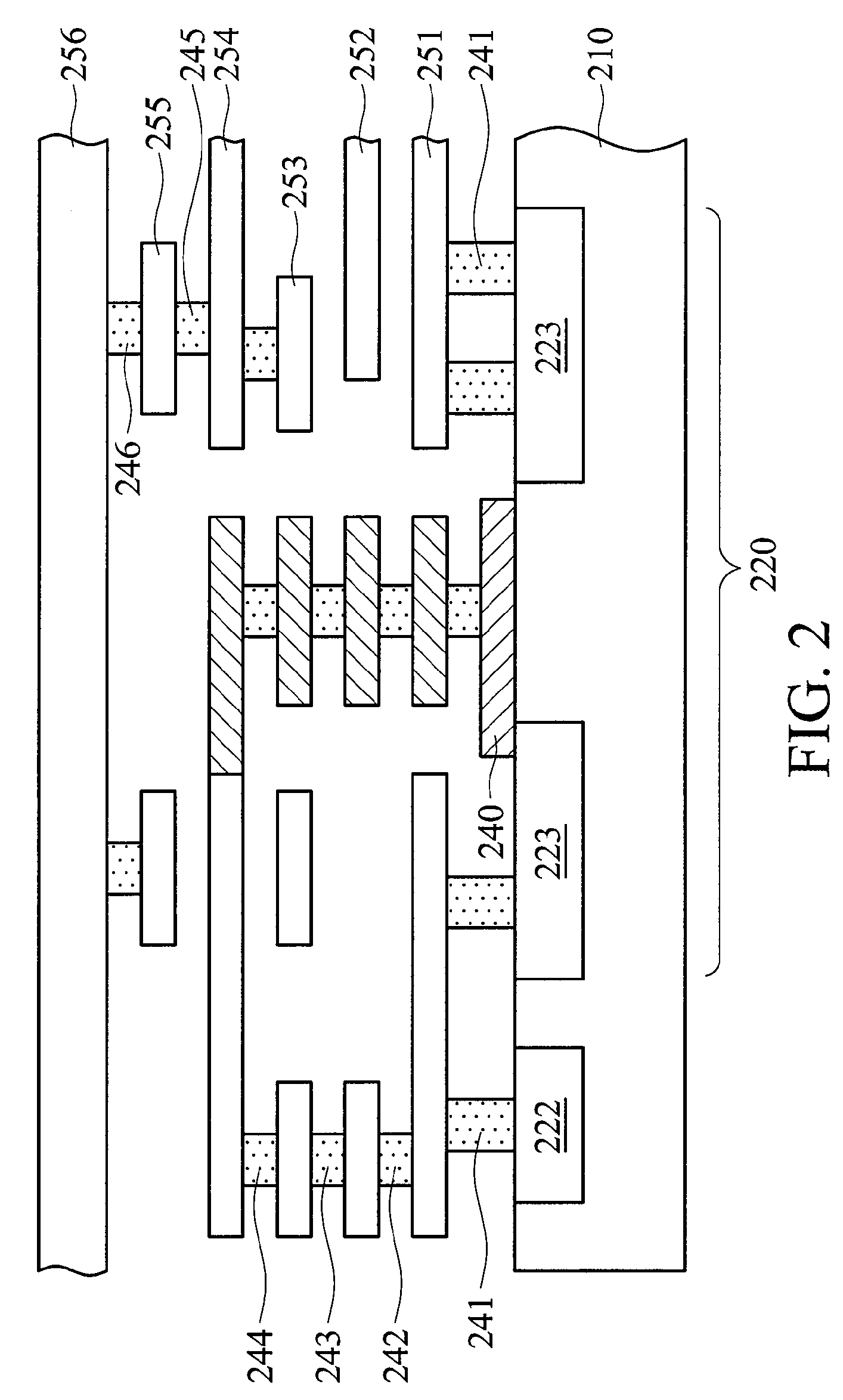
Integrated circuit with spare cells
An integrated circuit with spare cells. The integrated circuit comprises a substrate, spare cells formed on the substrate, and a plurality of metal layers and metal vias stacked over an input or output. A metal layer outermost from the substrate, among the plurality of metal layers, electrically connects to a power or ground voltage.
Owner:VIA TECH INC
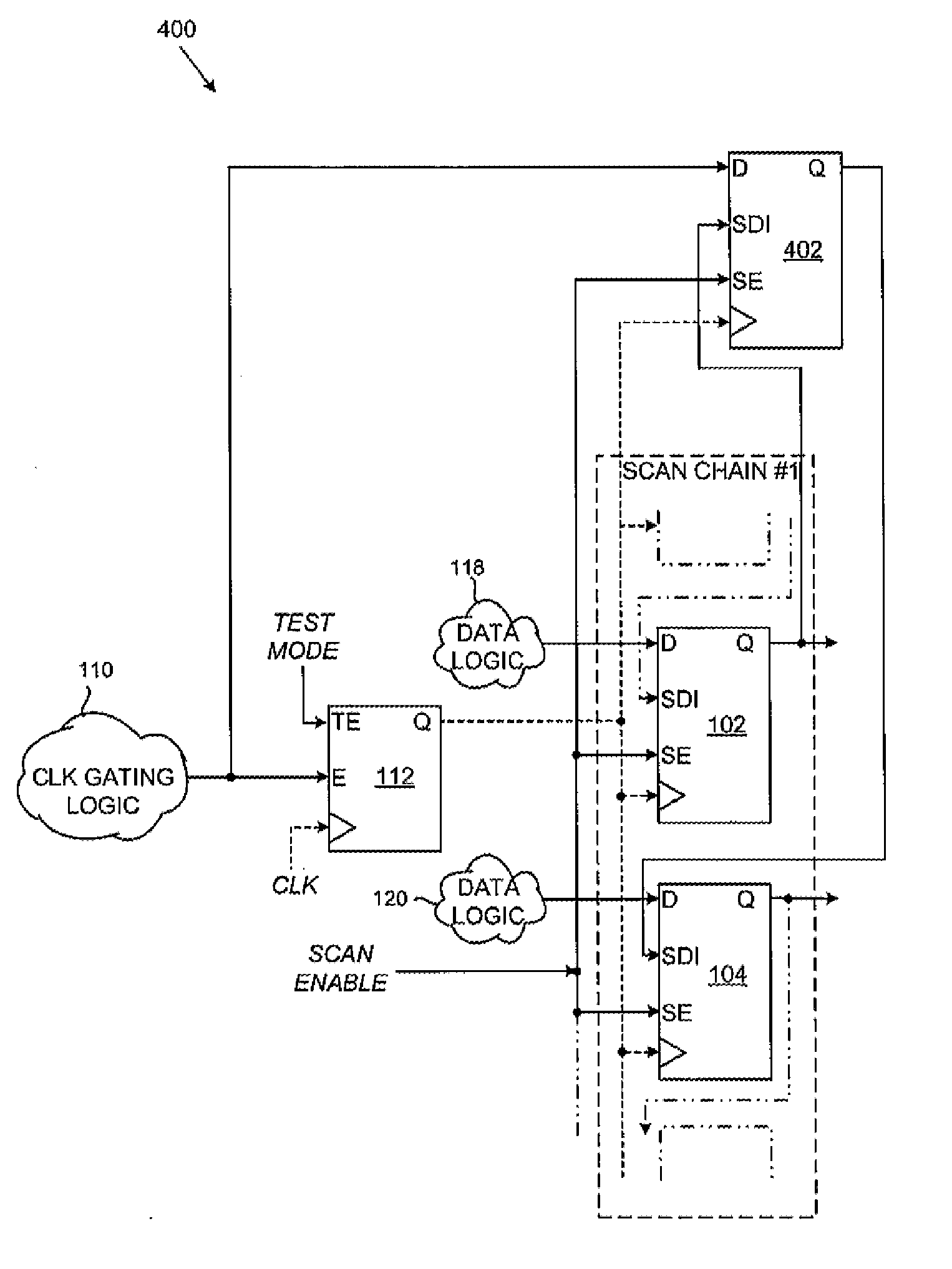
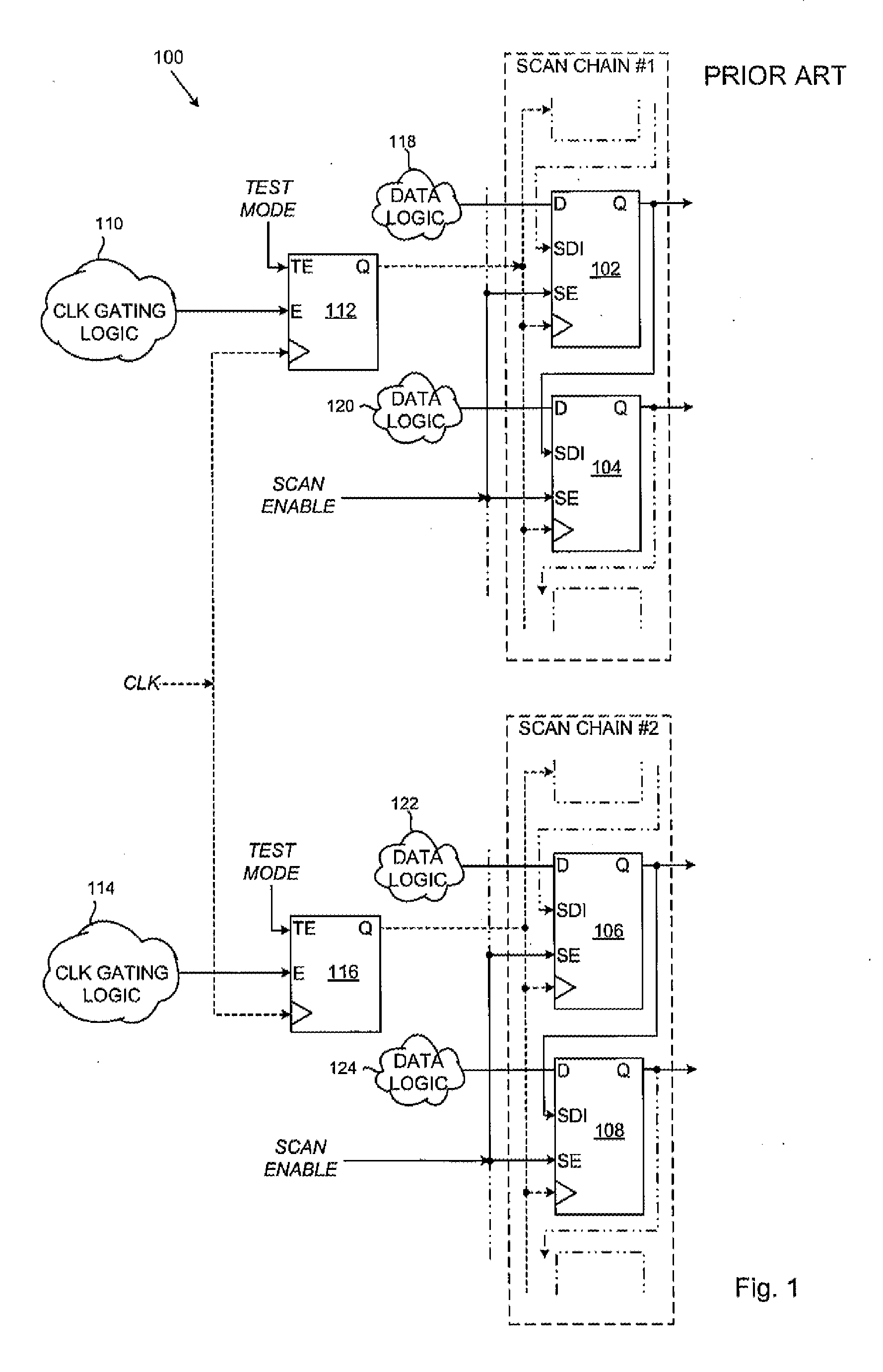
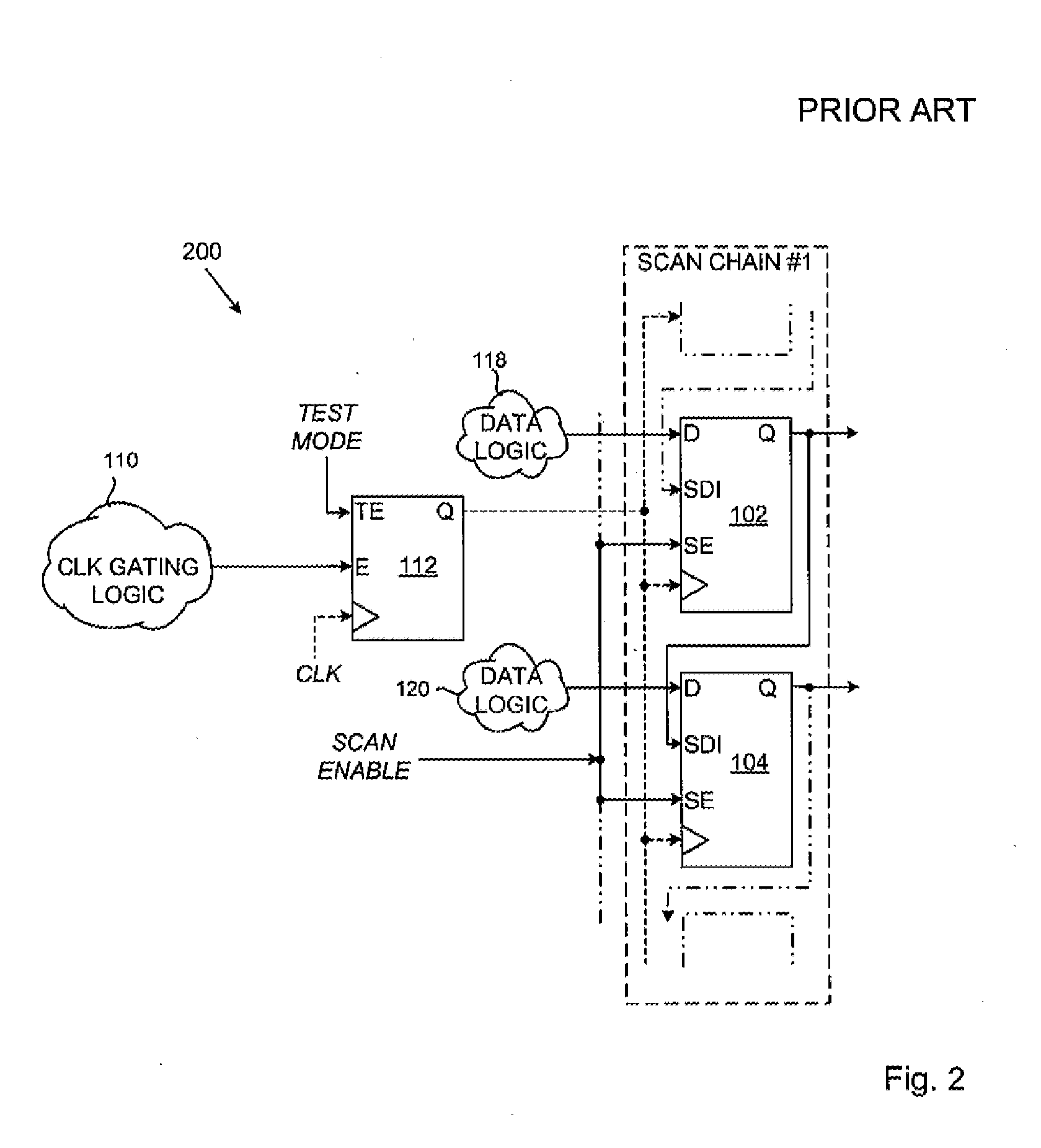
Scan testing of integrated circuit with clock gating cells
InactiveUS20130117618A1Electronic circuit testingDetecting faulty computer hardwareEngineeringClock gating
An integrated circuit includes a set of cells for operation in a functional mode and in a scan testing mode, and a spare cell. The cells are connected in a scan chain with scan data inputs connected to the outputs of preceding cells in the scan chain and respond to assertion of a scan enable signal. A clock gating element applies a functional clock signal to clock inputs of the cells in response to a gating enable signal in functional mode and a test clock signal in response to a test mode signal in scan testing mode. A functional data input of the spare cell latches the gating enable signal during the scan testing mode in response to de-assertion of the scan enable signal. The output of the spare cell is connected to the scan data input of one of the cells in response to the scan enable signal.
Owner:FREESCALE SEMICON INC
Cone-aware spare cell placement using hypergraph connectivity analysis
ActiveUS20120054707A1Simple methodAccurate placementConfiguration CADCAD circuit designNODALHypergraph
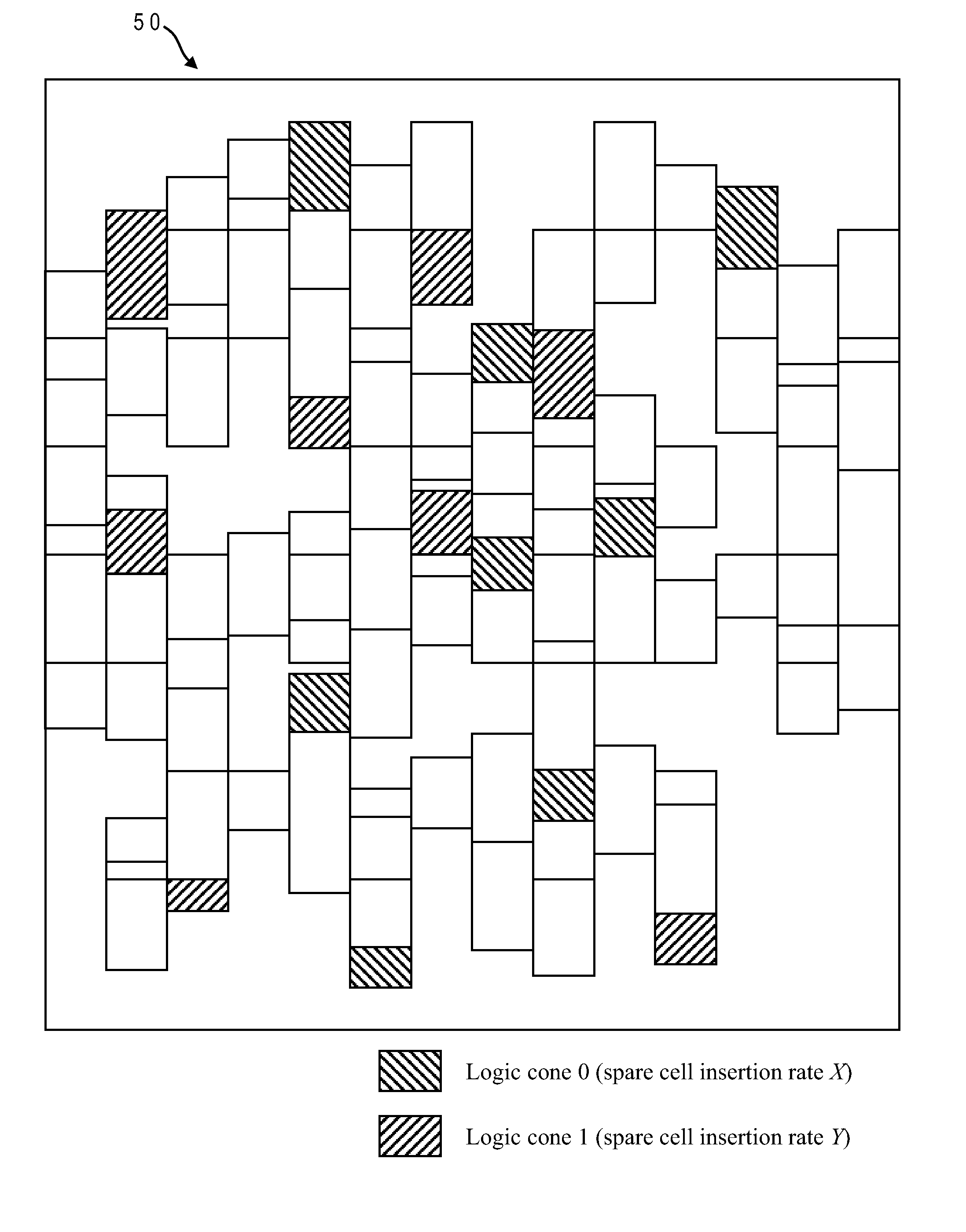
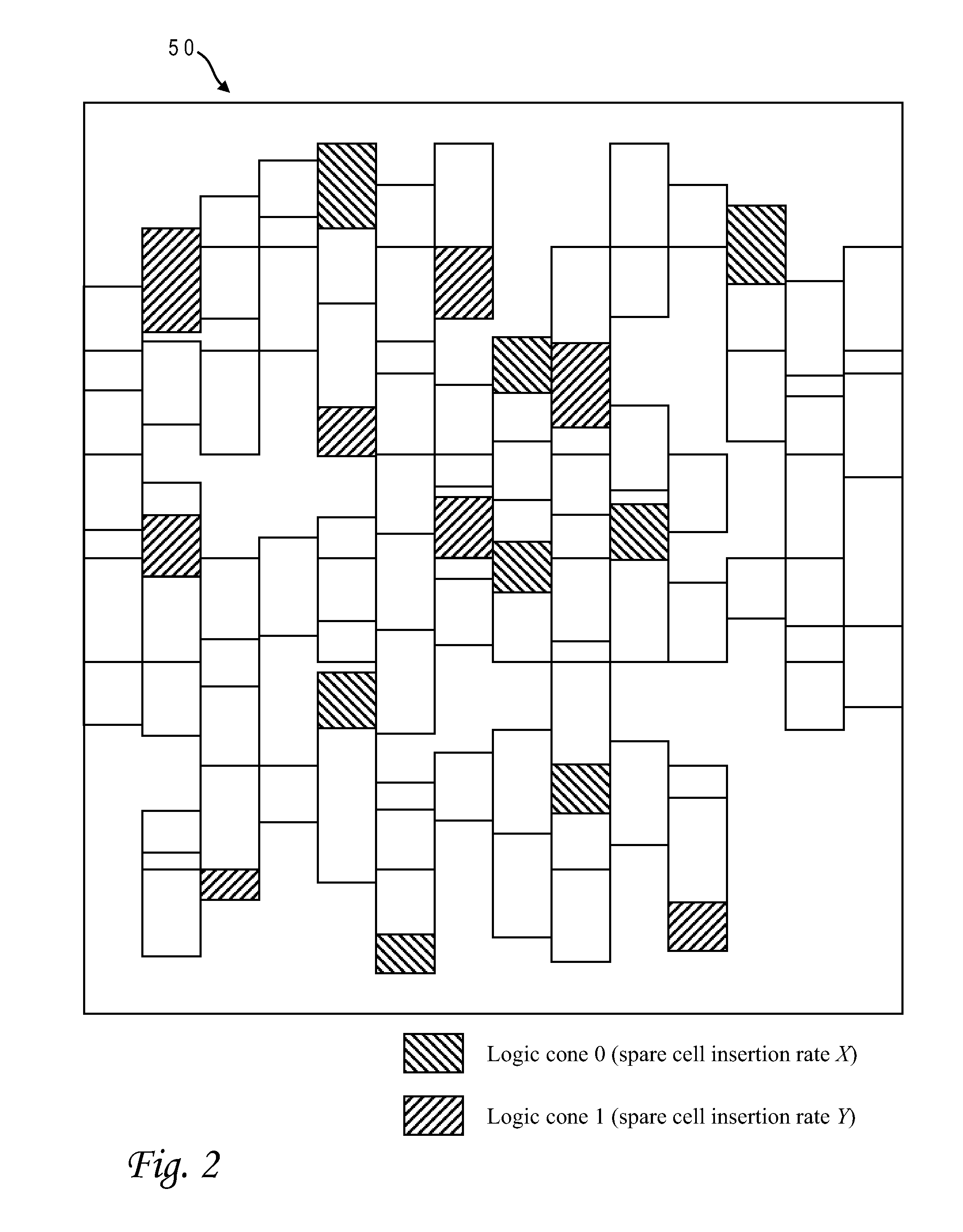
Spare cells are placed in an IC design by assigning different spare utilization rates to logic cones, applying the rates to corresponding spare cell regions surrounding cells in the cones, identifying any overlap of regions from different logic cones, and inserting a spare cell at the overlapping region having the highest spare utilization rate. The best location for the spare cell is computed using a hypergraph wherein the cells are edges and the regions are nodes. Any node that is dominated by another node is removed and its edge is extended to the dominating node. The spare cell is inserted in the region having the most edges (the edges can be weighted). The process is repeated iteratively, updating the hypergraph by removing nodes connected to spare cell location, and inserting the next spare cell at a region corresponding to the node which then has the greatest number of connected edges.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
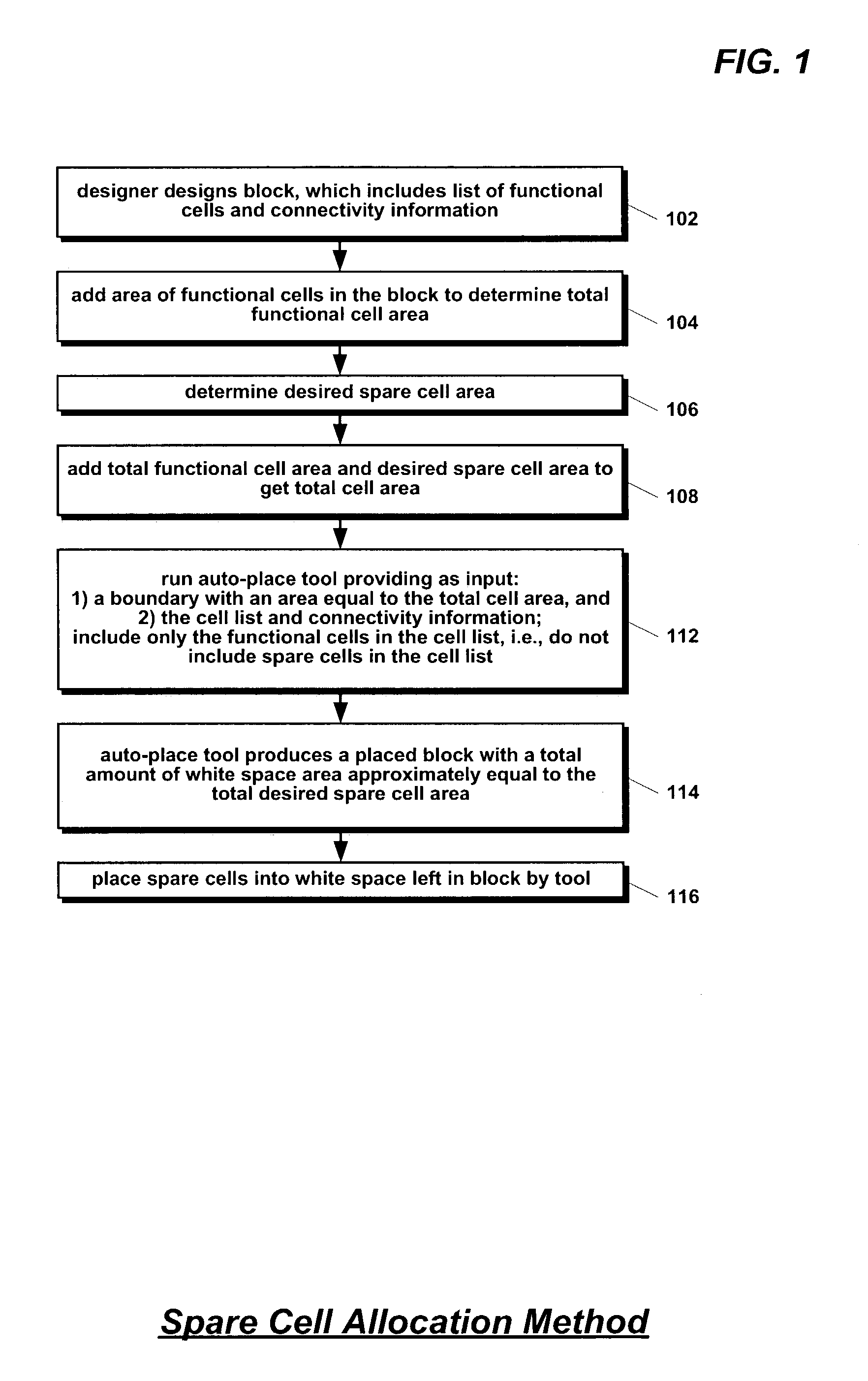
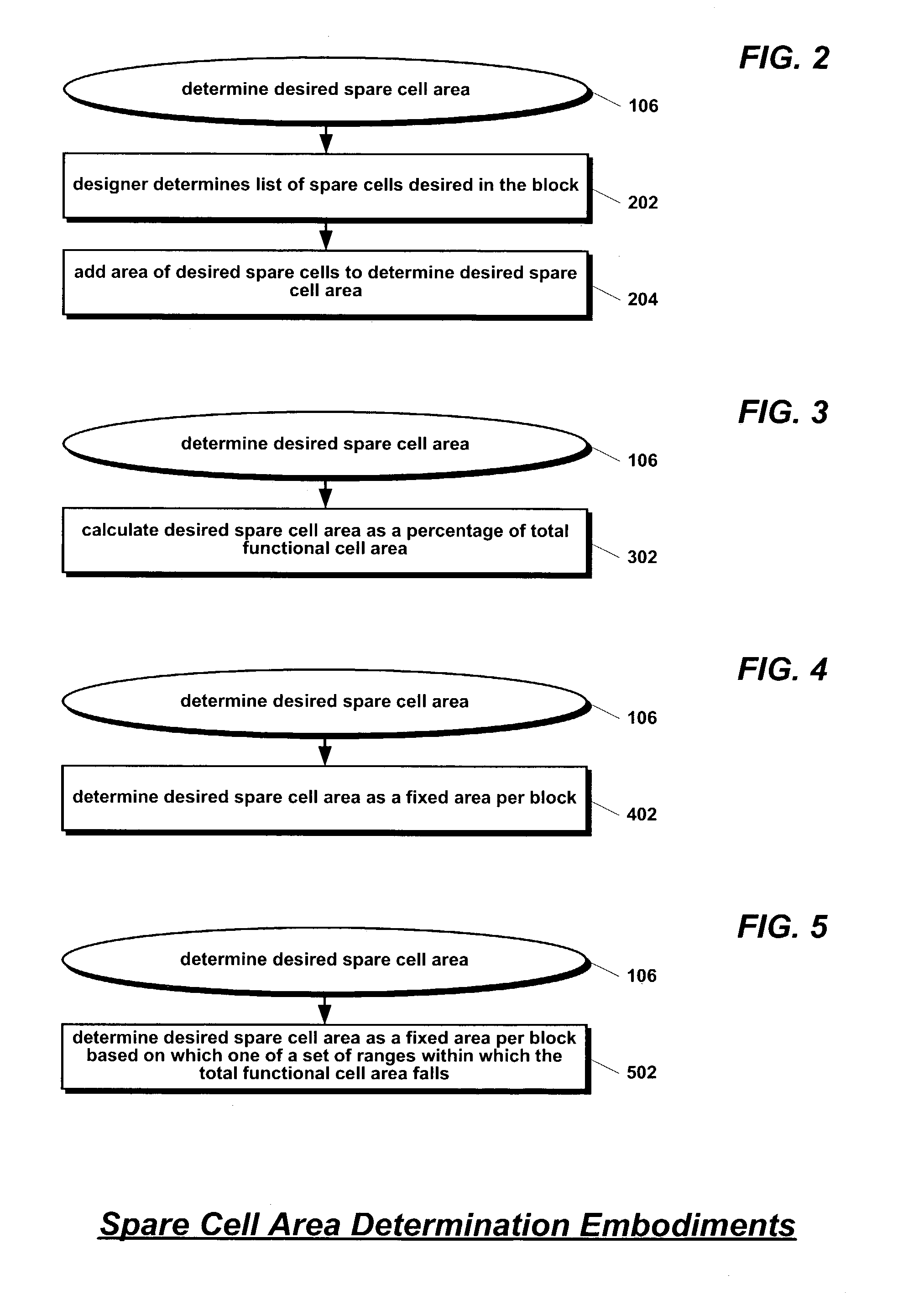
Method for allocating spare cells in auto-place-route blocks
ActiveUS6993738B2High yieldLow costSolid-state devicesCAD circuit designReserve CellTheoretical computer science
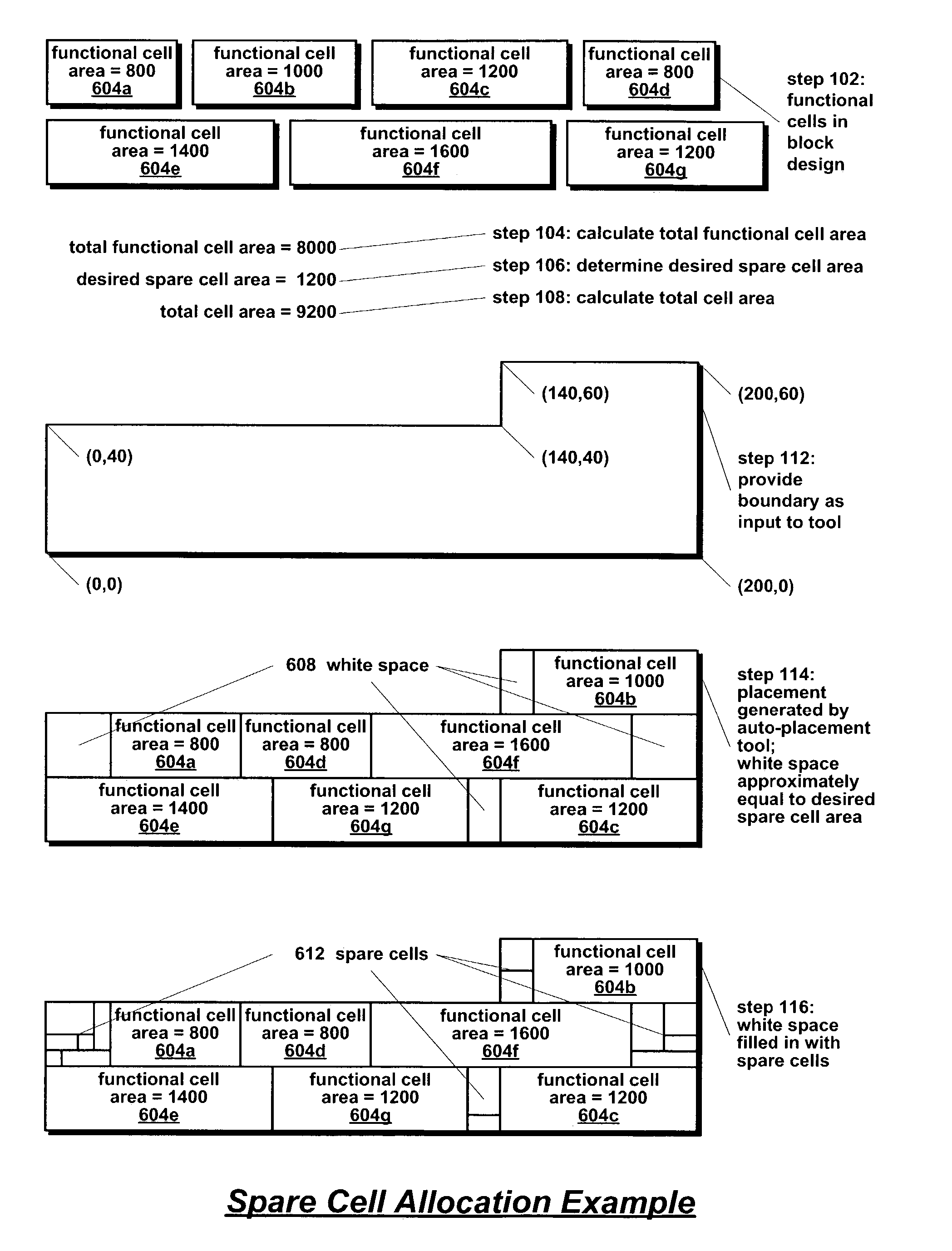
A method for placing spare cells into an auto-place-route (APR) block of an integrated circuit is disclosed. The list of functional cells to be included in the block is determined along with the netlist. The sum of the areas of the functional cells and the desired spare cell area is used as the area of the block boundary. The boundary is provided as input to an auto-placement tool along with the netlist and the list of functional cells. The list of functional cells specifically does not include the spare cells so that the tool does not place spare cells in the boundary. Consequently, the spare cell area may be utilized as wiggle-room by the tool to efficiently place the functional cells. The tool produces a placement of the functional cells that includes white space in the boundary. Spare cells are then placed into the white space.
Owner:IP FIRST
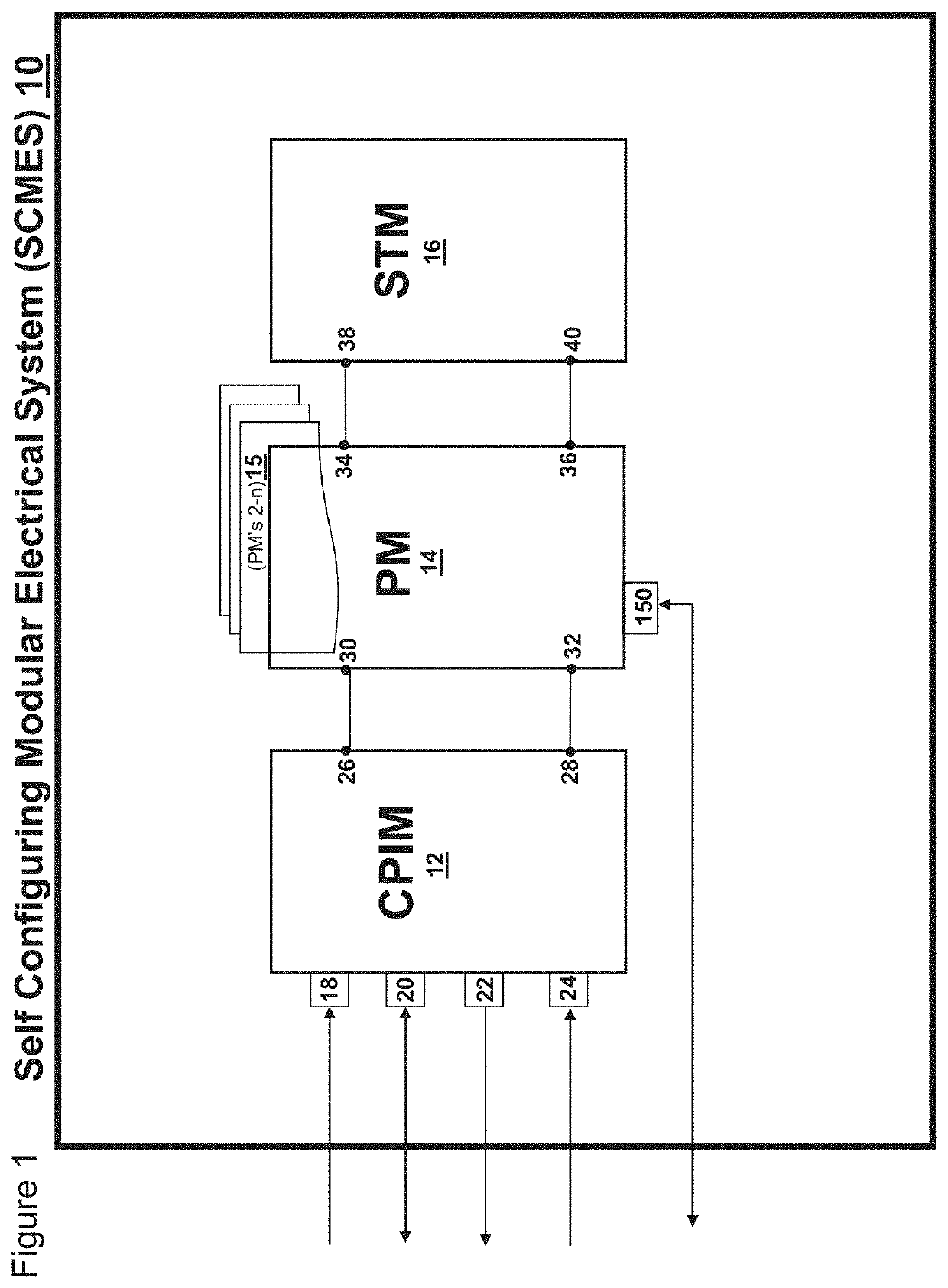
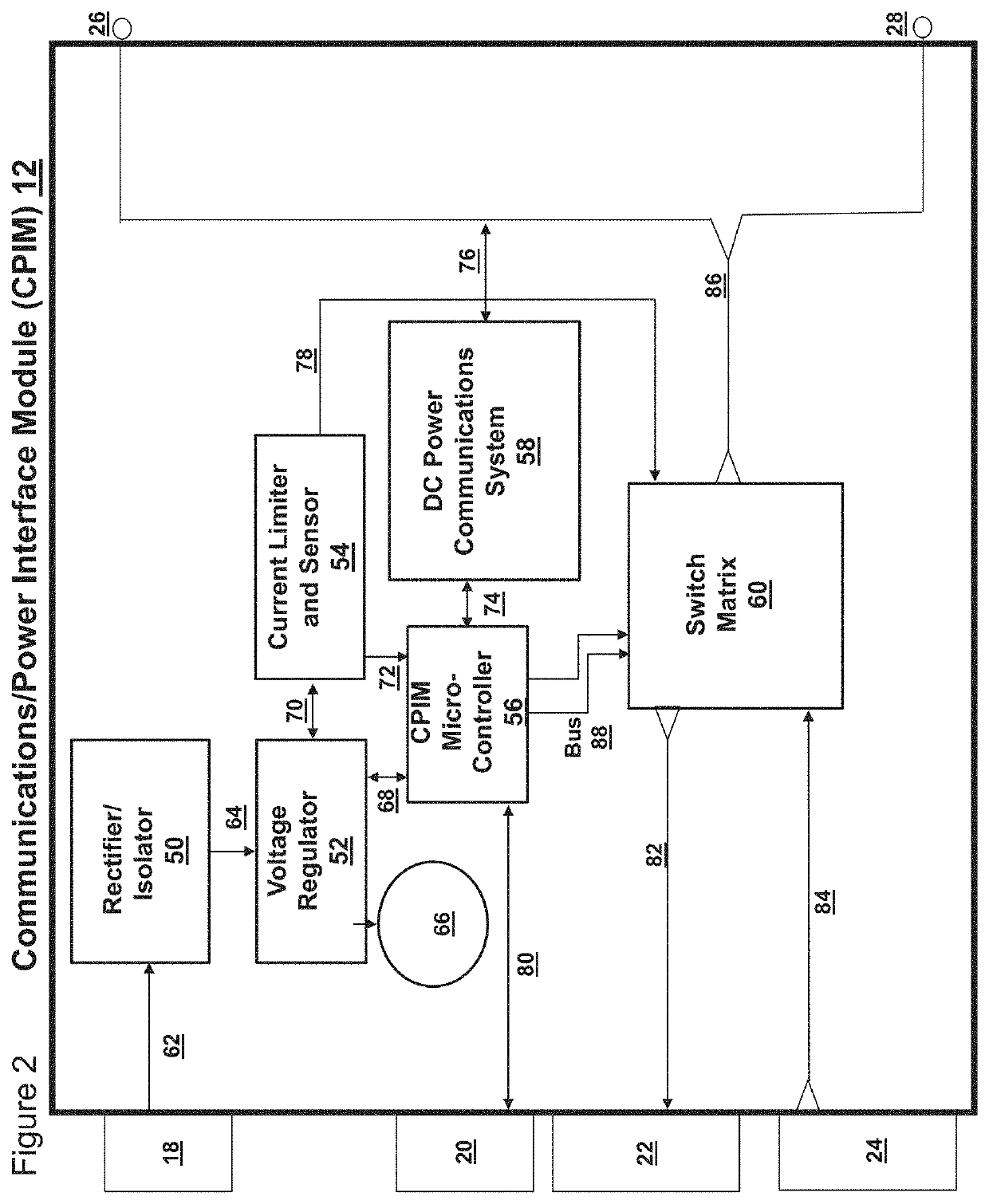
Self configuring modular electrical system
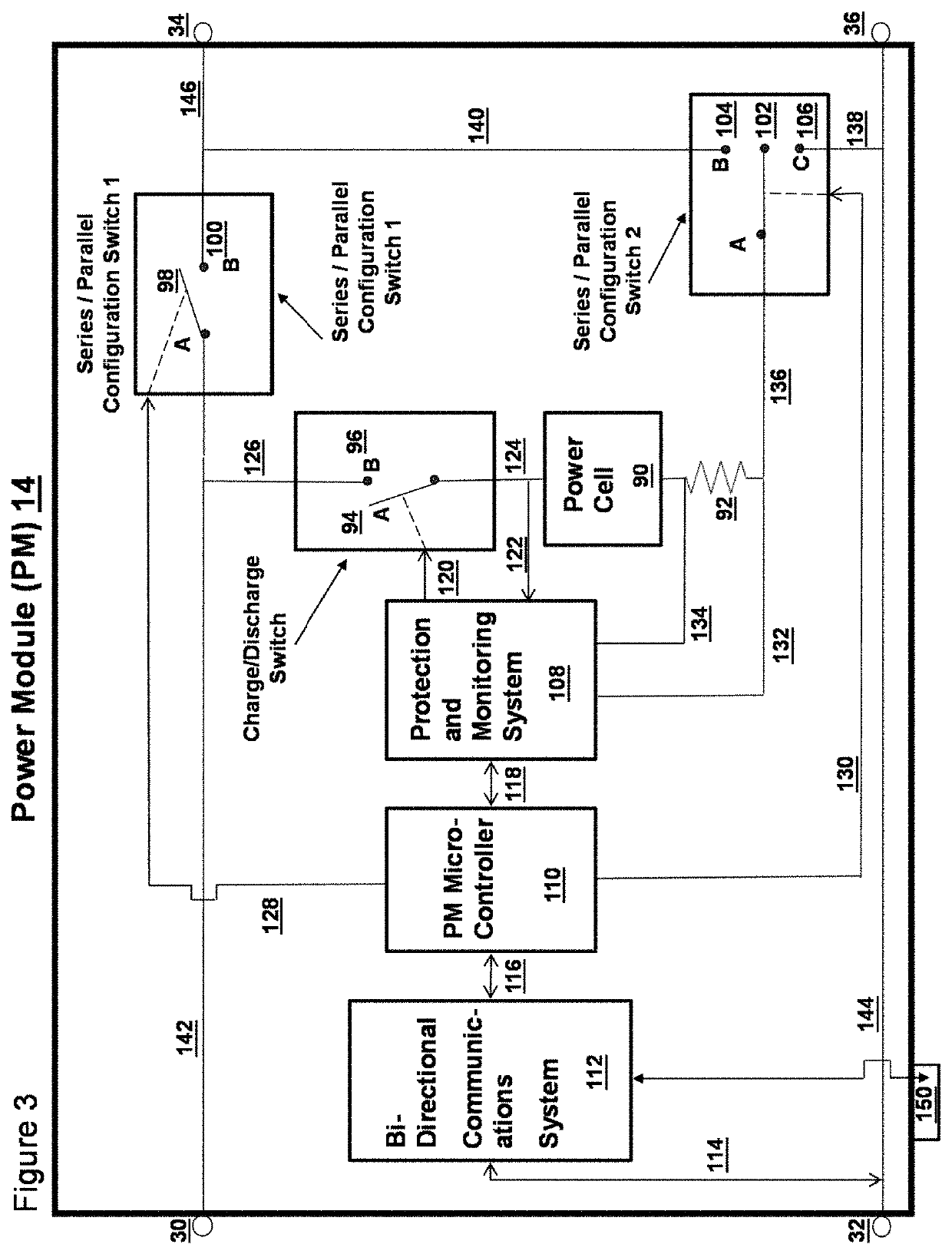
ActiveUS20210313830A1Dc network circuit arrangementsCharge equalisation circuitElectrical batteryEngineering
As an improvement to existing matrix-like power / communications systems, a decentralized array of power and communications components defining a self-configuring modular electrical system which is comprised of components that are completely scalable, easily replaceable, intelligent and combinable in a series, parallel, bypassed state or even capable of elegantly switching in a spare cell(s) to replace a dead cell while interfacing with common battery power chemistry, an external power supply input, a standardized bi-directional data communication input and is combinable and arrangeable into practically any mechanical footprint whereby energy density and communications capability is maximized along with simplicity in accordance with weight and balance considerations and integrated as an autonomous system at the lowest possible cost while being survivable in the harshest of environments including physical shock, vibration, vacuum, radiation, thermal, and electromagnetic interference and providing a communications interface for external control or monitoring via human or other control system input while simultaneously being capable of fully and simply reconfiguring itself if an internal battery cell failure occurs within the system, allowing for instant stabilization to maintain the required uninterrupted power output while providing uninterrupted communications through the system during the upset event while being instantly reconfigurable from series to parallel or vice versa ordering, and being capable of reconfiguring itself autonomously into an arrangement of series / parallel states within its architecture for charge / discharge while enabling cell balancing and continual monitoring all individual cell health status parameters, and only using two wires for all component interconnection.
Owner:SPACE INFORMATION LABS
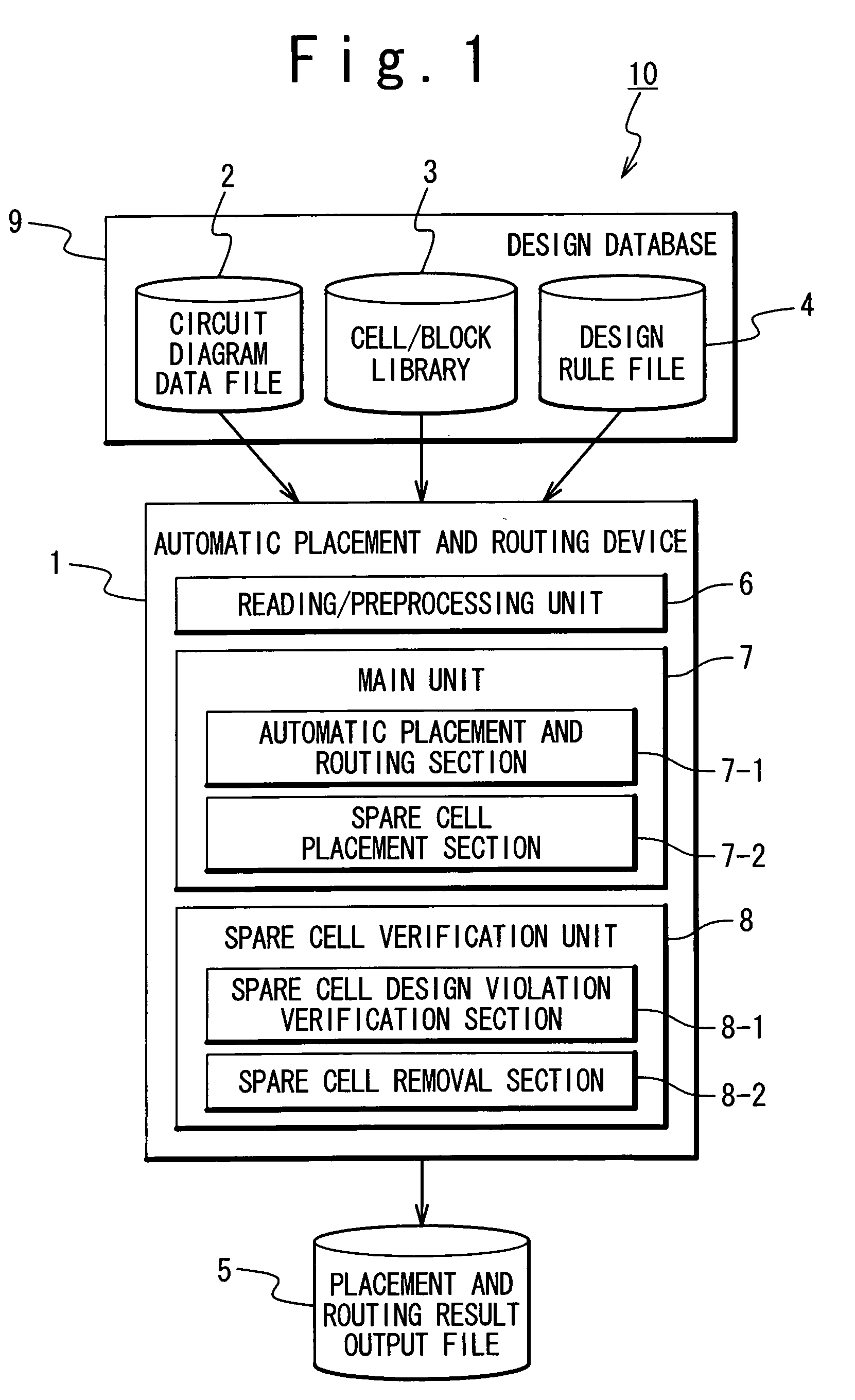
Automatic placement and routing device, method for placement and routing of semiconductor device, semiconductor device and manufacturing method of the same
InactiveUS20050172253A1Reduce loadReduce memory capacitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingComputer architectureDevice material
A method of placement and routing of a semiconductor device, includes steps (a) to (c). The step (a) is a procedure of executing placement of functional blocks and executing routing of interconnections in a placement and routing area of a semiconductor device based on circuit diagram data, functional block data and design rule data. The step (b) is a procedure of executing placement of spare cells in first areas of the placement and routing area, disregarding the routing result, wherein the functional blocks are not placed in the first areas, the spare cells are spare functional blocks. The step (c) is a procedure of removing first spare cells of the spare cells from the first areas, wherein the first spare cells are in violation of a design rule with regard to a relation to the interconnections, the design rule is described in the design rule data.
Owner:NEC ELECTRONICS CORP
Spare cell library design for integrated circuit
InactiveUS20100231256A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringIntegrated design
A cell based design layout of an application specific integrated circuit (ASIC) having a function has reduceddecreased power leakage because functionally unconnected additional cells or spare cells of the integrated design layout are unconnected to the power supplies Vdd and Vss.
Owner:FREESCALE SEMICON INC
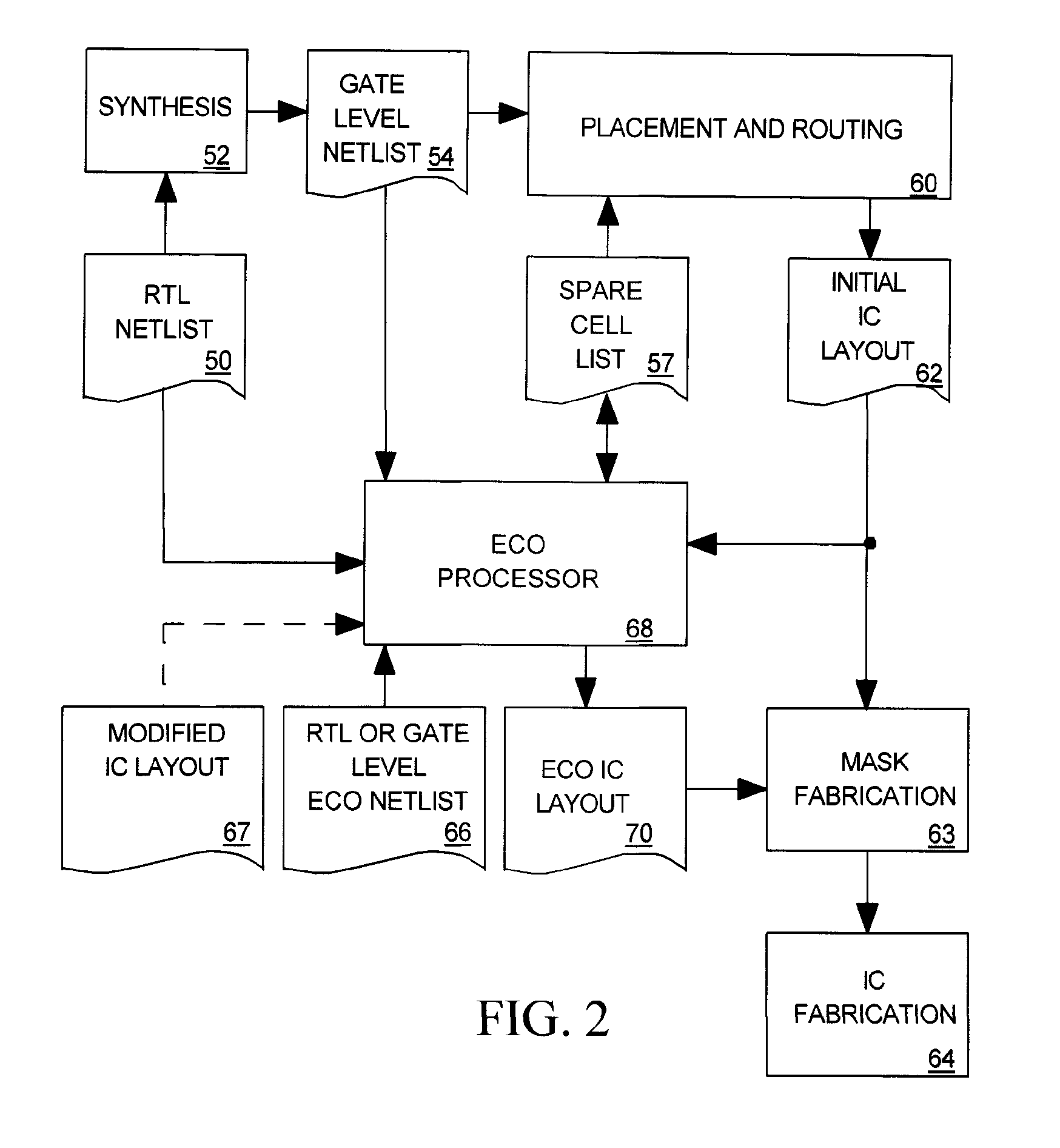
System for implementing post-silicon IC design changes
ActiveUS8015522B2Computer programmed simultaneously with data introductionCAD circuit designActive cellEngineering
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Redox flow battery system and method of controlling it
ActiveUS20150325874A1Improve reliabilityEasily monitorable by external instrumentsFuel cells groupingCell electrodesVanadium redox batteryElectronic controller
A novel multi cell stack architecture has specific features allowing deployment of simple electrical instrumentation of data collection / monitoring of crucial hydraulic, electrical and electrochemical quantities, on the basis of which the operator or electronic controller is able to gather / process critical information of such a depth and enhanced reliability, for immediately identifying any cell in “state of sufferance” and eventually to exclude it from the system and possibly substitute it with a spare cell. A method of monitoring / controlling the operation of an all-vanadium redox flow battery system is also disclosed.
Owner:HYDRAREDOX TECH HLDG
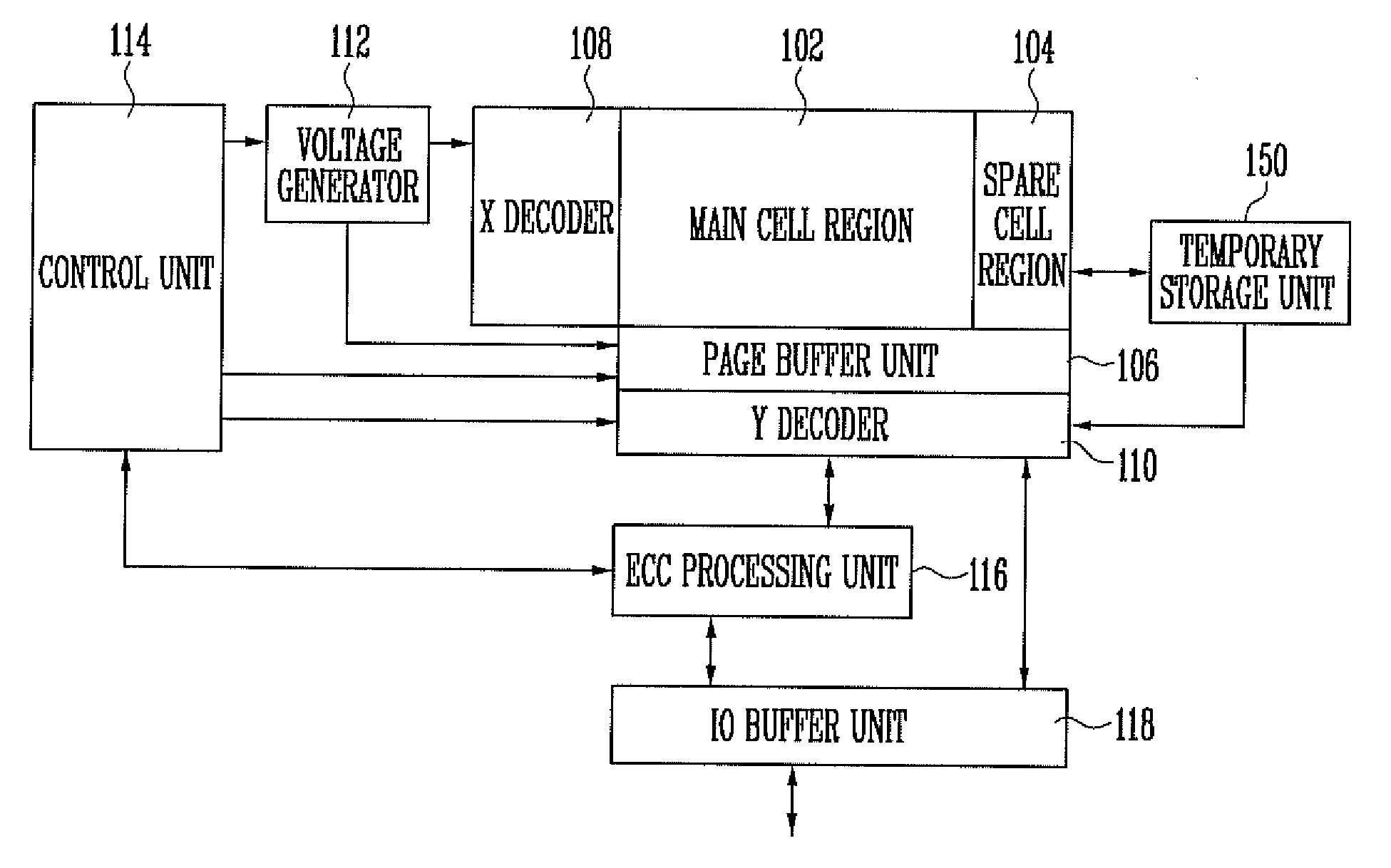
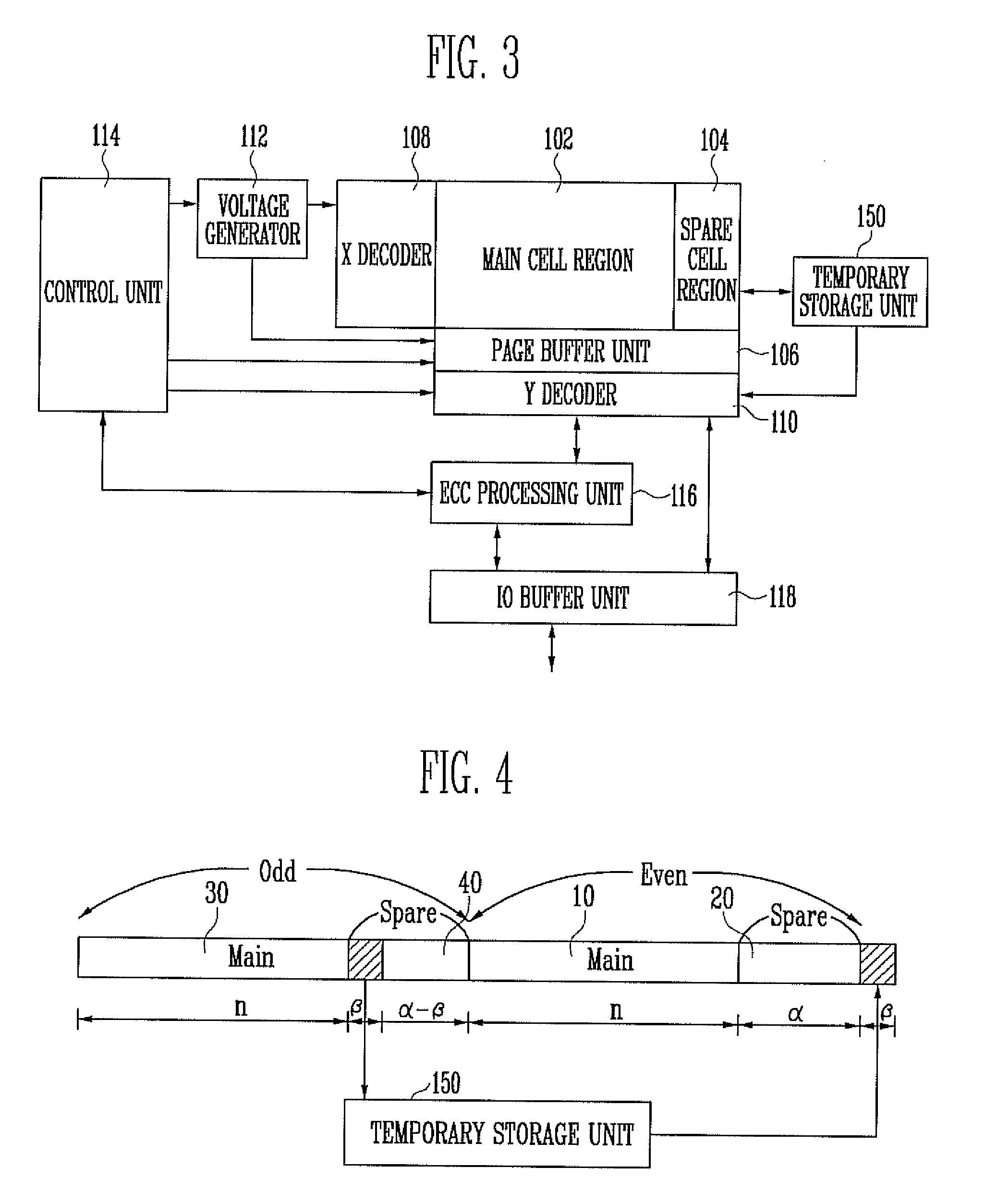
Method of operating nonvolatile memory device and nonvolatile memory device for implementing the same
InactiveUS20100332946A1Improve performanceRead-only memoriesError correction/detection using interleaving techniquesParallel computingData storing
A method of operating a nonvolatile memory device including a memory cell array having first and second main cells for storing external input data, first spare cells for storing data for error correction code (ECC) processing on the data stored in the first and second main cells and second spare cells for storing data for ECC processing on the data stored in the first and second main cells which involves reading the data stored in the first spare cells, reading the data stored in the second main cells and the data stored in the second spare cells, and performing the ECC processing on the data read from the second main cells using the data read from the first spare cells and the data read from the second spare cells.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
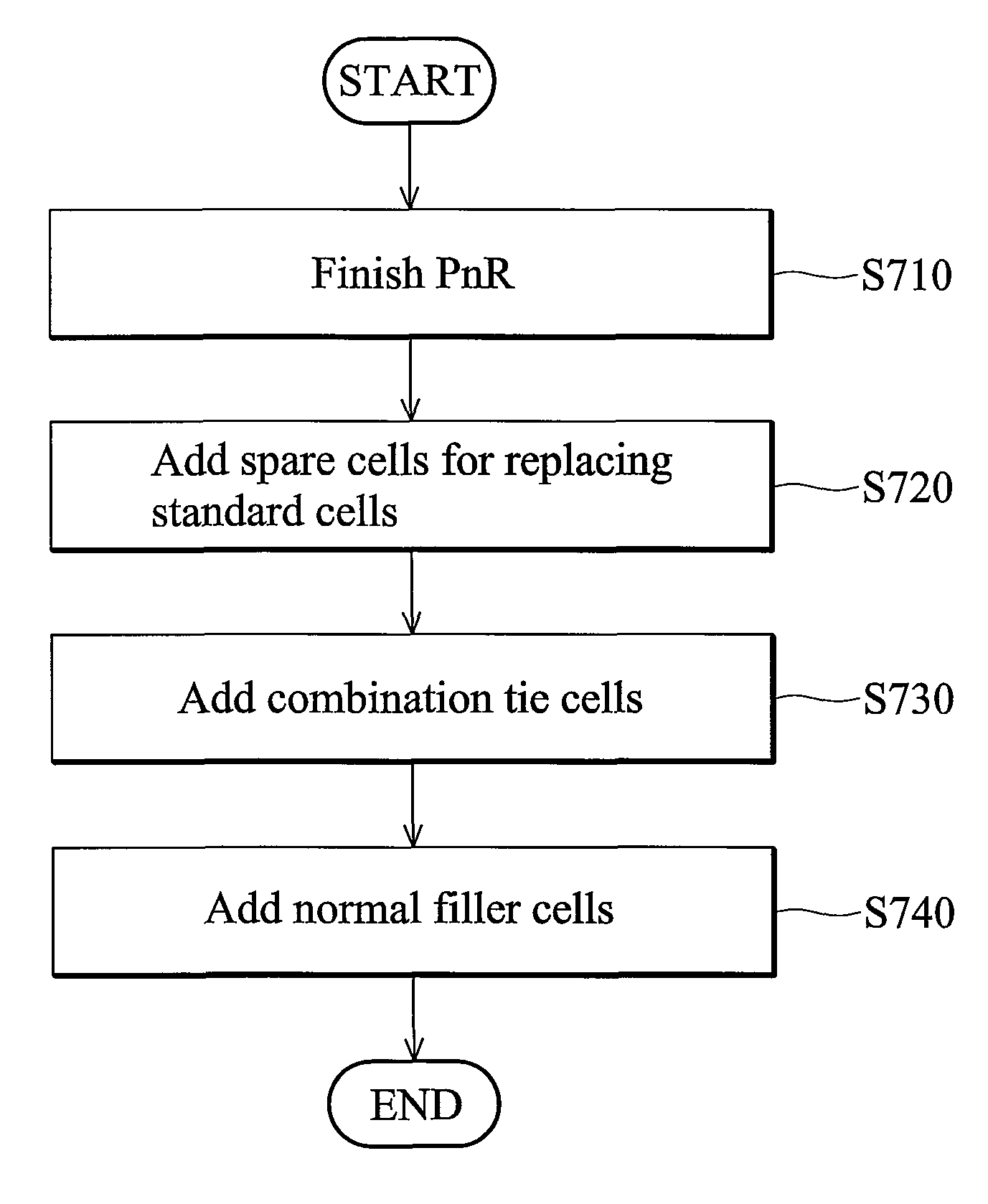
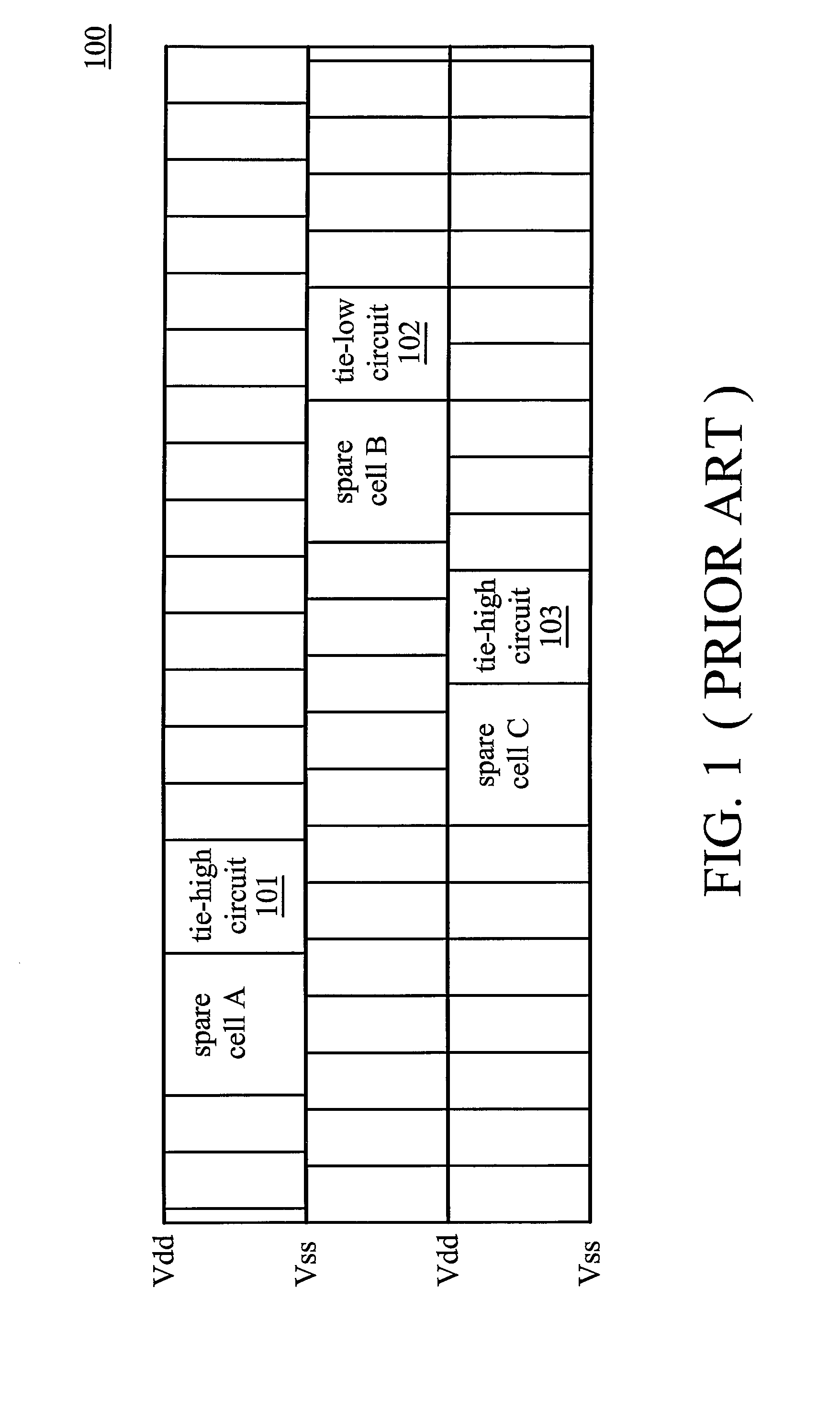
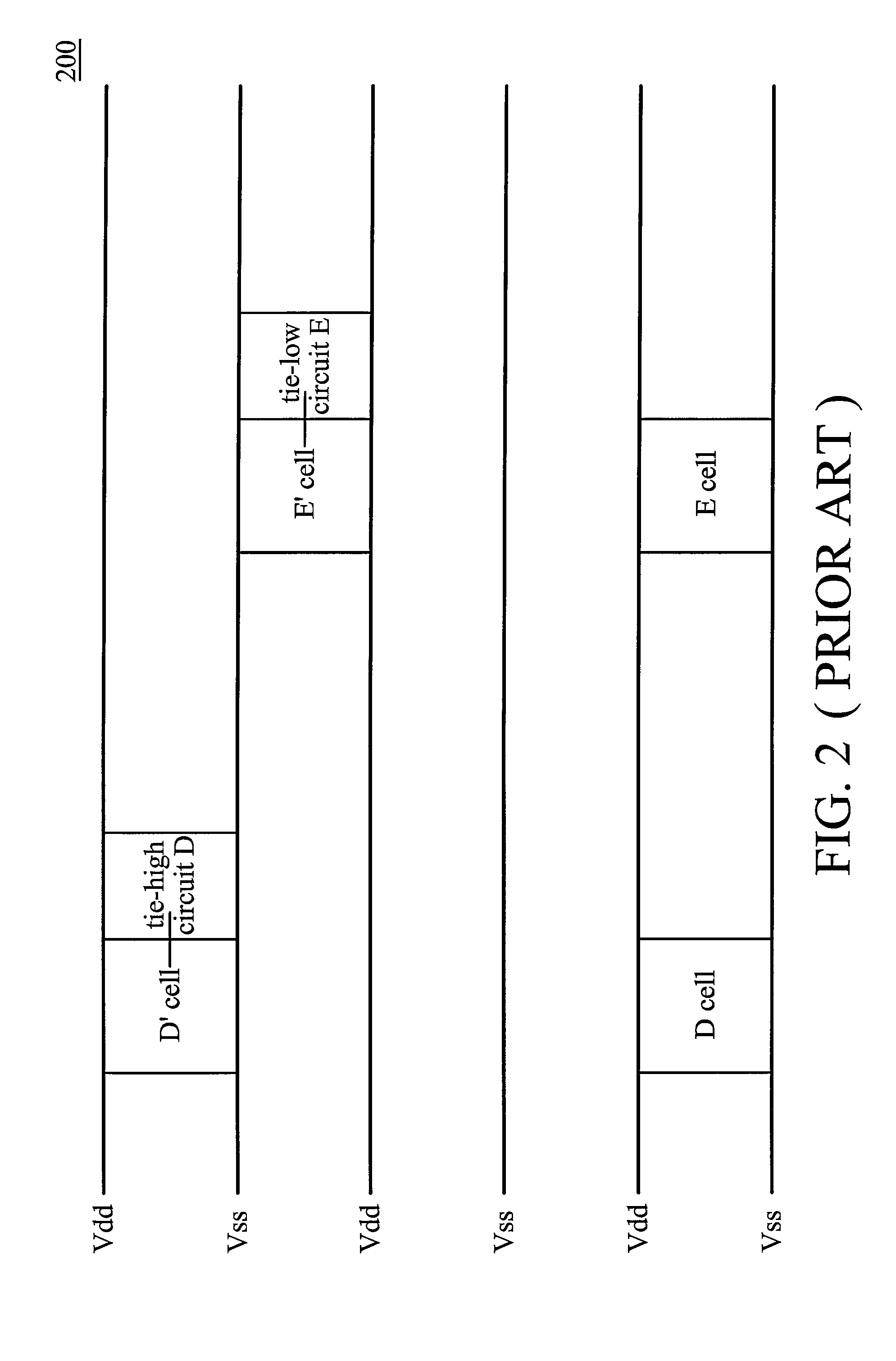
Layout circuit having a combined tie cell
ActiveUS7949988B2Switching accelaration modificationsReliability increasing modificationsCapacitanceEngineering
A layout circuit is provided, comprising standard cells, a spare cell, combined tie cells and normal filler cells. The standard cells are disposed and routed on a layout area. The spare cell is added on the layout area and provided for replacing one of the standard cells while adding or changing functions later. The combined tie cells are added on the layout area. The normal filler cells are added on the rest of the layout area. The combined tie cell comprises a tie-high circuit, a tie-low circuit and a capacitance circuit. Some standard cells are disposed near at least one combined tie cell for avoiding routing congestion between the combined tie cells and the replaced standard cell. A circuit layout method is also provided.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
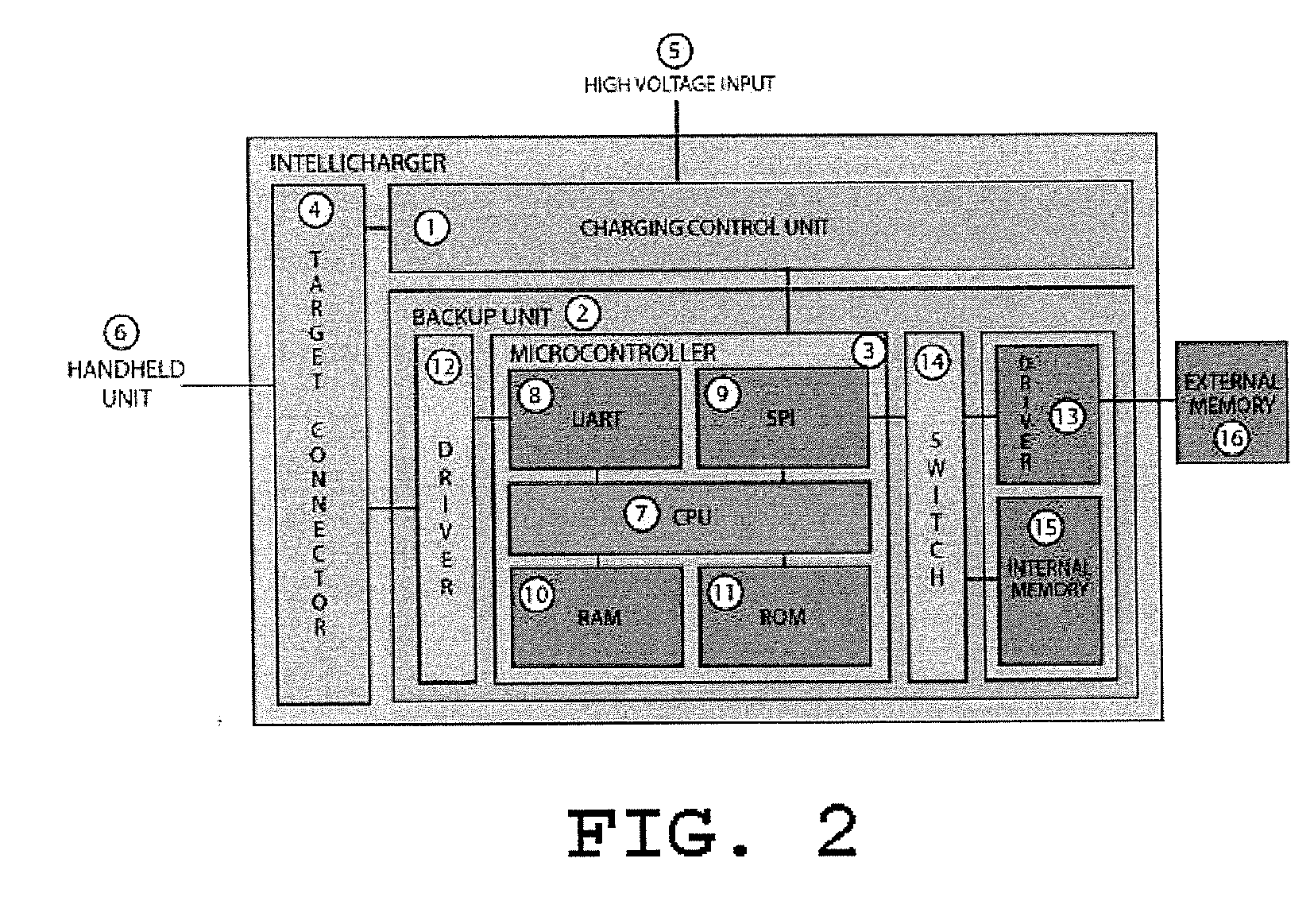
Apparatus for charging handheld units
InactiveUS20070096685A1Increase storage spaceStorage moreSubstation equipmentElectric powerTransmission protocolEngineering
A charger for handheld units is also an automatic backup unit for data stored in the handheld unit. The communication with the handheld unit is performed through a predefined object transfer protocol. By using an object transfer protocol, it is up to the handheld unit how to interact with the charger / backup unit when the communication has been initiated. Previous versions of the data may be stored and retrieved. It is possible to access the stored data and control the settings of the charger / backup unit from a handheld or a computer.
Owner:Q - DOG
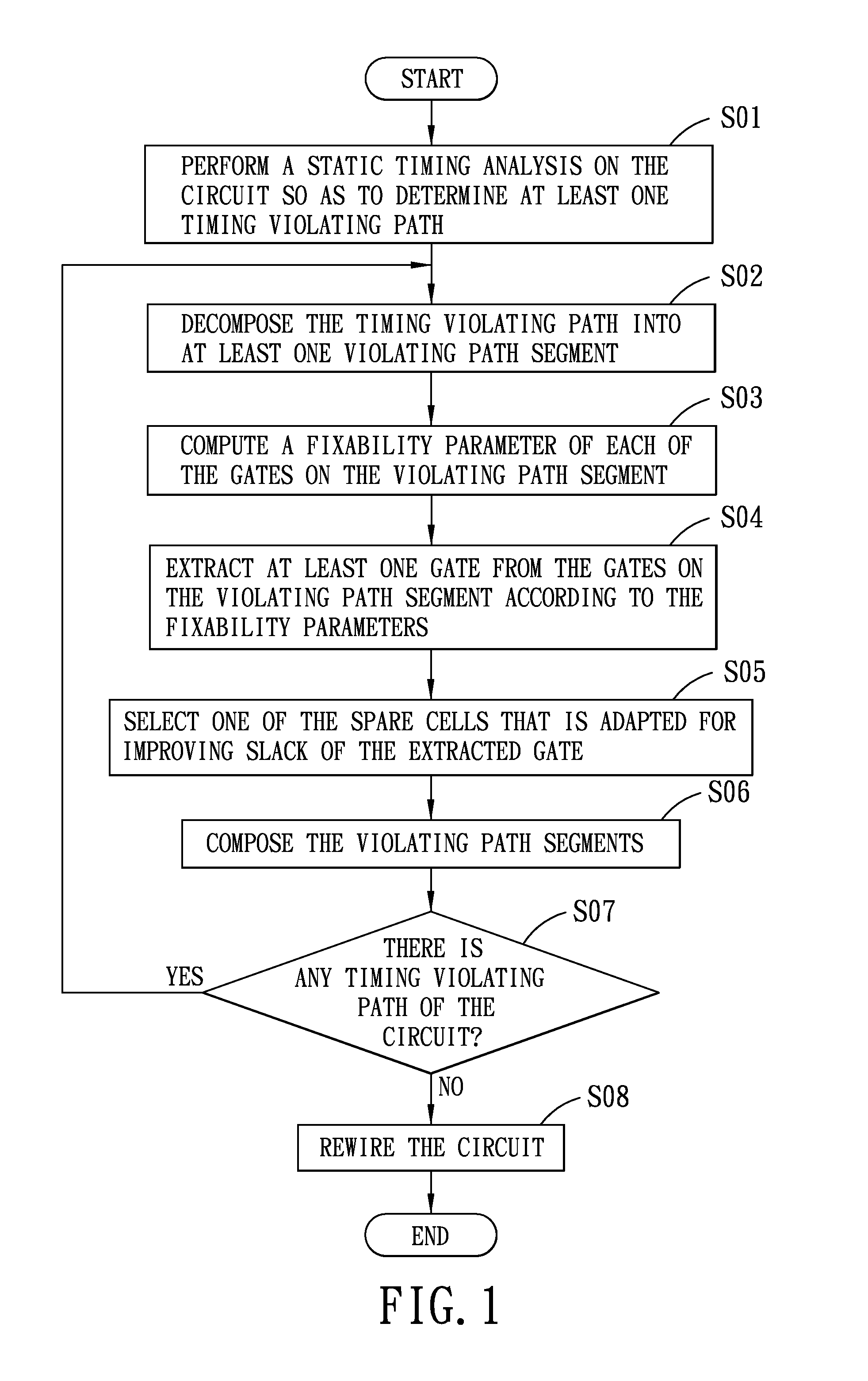
Method of implementing timing engineering change order
InactiveUS20130298097A1Efficient implementationCAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationStatic timing analysisAlgorithm
A method of implementing timing ECO in a circuit includes the steps of performing a static timing analysis on the circuit so as to determine at least one timing violating path of the circuit, decomposing the timing violating path into at least one violating path segment, determining a smooth curve from each timing violating path and determining a plurality of reference points along the smooth curve, computing a fixability parameter of each gate on the violating path segment, extracting at least one gate according to the fixability parameters, and selecting one spare cell and disposing the selected spare cell on the violating path segment.
Owner:NAT CHIAO TUNG UNIV +1
Non-volatile semiconductor memory with large erase blocks storing cycle counts
ActiveUS20050102466A1Increase volumeReduce the amount of noiseError detection/correctionSolid-state devicesComputer scienceStorage cell
In a flash EEPROM system that is divided into separately erasable blocks of memory cells with multiple pages of user data being stored in each block, a count of the number of erase cycles that each block has endured is stored in one location within the block, such as in spare cells of only one page or distributed among header regions of multiple pages. The page or pages containing the block cycle count are initially read from each block that is being erased, the cycle count temporarily stored, the block erased and an updated cycle count is then written back into the block location. User data is then programmed into individual pages of the block as necessary. The user data is preferably stored in more than two states per memory cell storage element, in which case the cycle count can be stored in binary in a manner to speed up the erase process and reduce disturbing effects on the erased state that writing the updated cycle count can cause. An error correction code calculated from the cycle count may be stored with it, thereby allowing validation of the stored cycle count.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA +1
Failure analysis method, failure analysis system, and memory macro system
Configuration information including number of normal cell areas and number of spare cell areas arranged in a memory macro and a size of each cell area is extracted from circuit design information, and electrical test results of the normal cell areas and the spare cell areas arranged in the memory macro are collected. Arrangement information corresponding to a collection order of the electrical test results is converted to a two-dimensional coordinate value for two-dimensionally displaying the arrangement information corresponding to a collection order of the electrical test results in a unit of cell area in association with a physical layout of a memory cell in the memory macro based on the configuration information. The collected electrical test results are displayed based on the two-dimensional coordinate value so that the normal cell areas and the spare cell areas can be distinguished.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
Spare cell insertion based on reachable state analysis
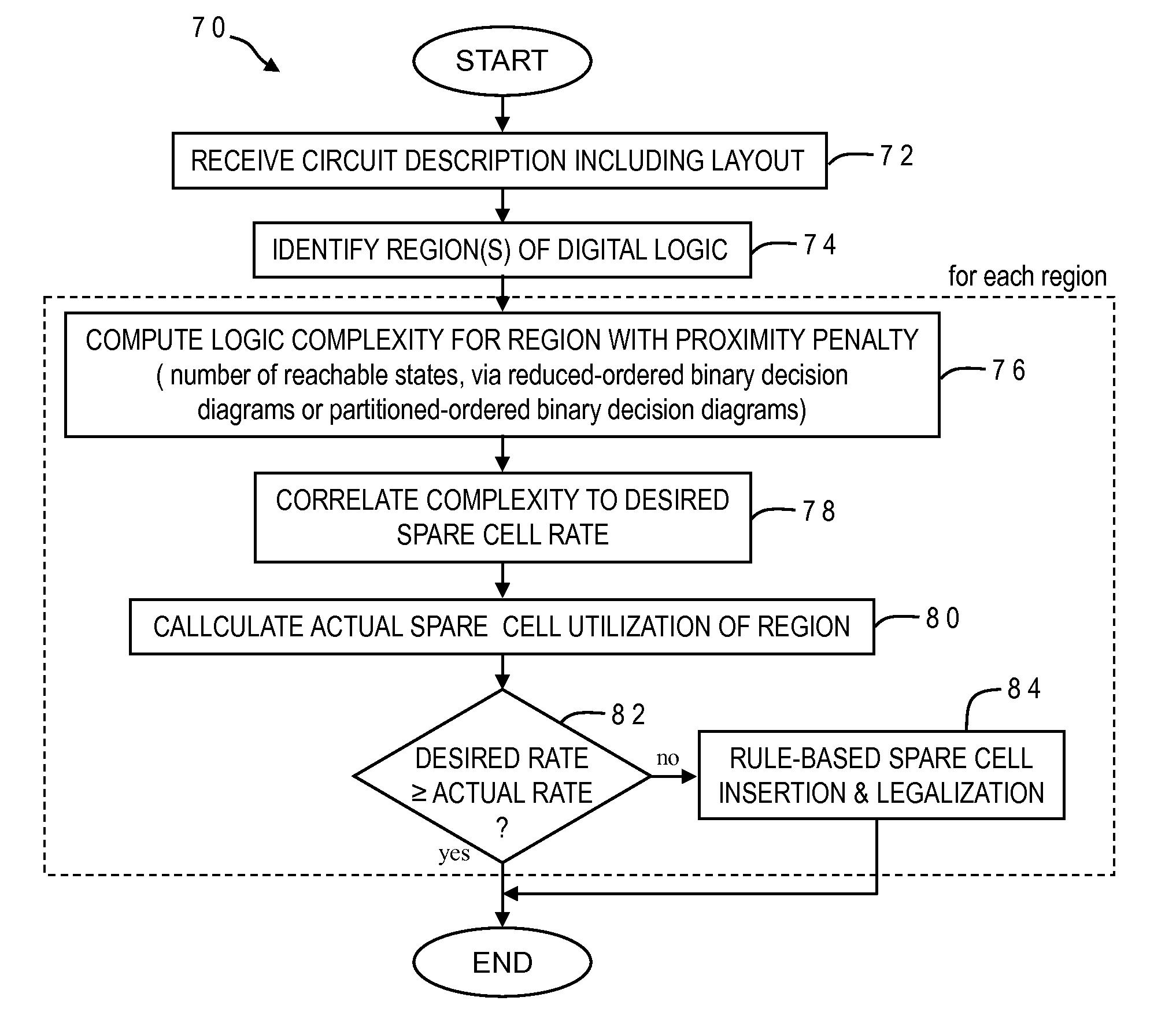
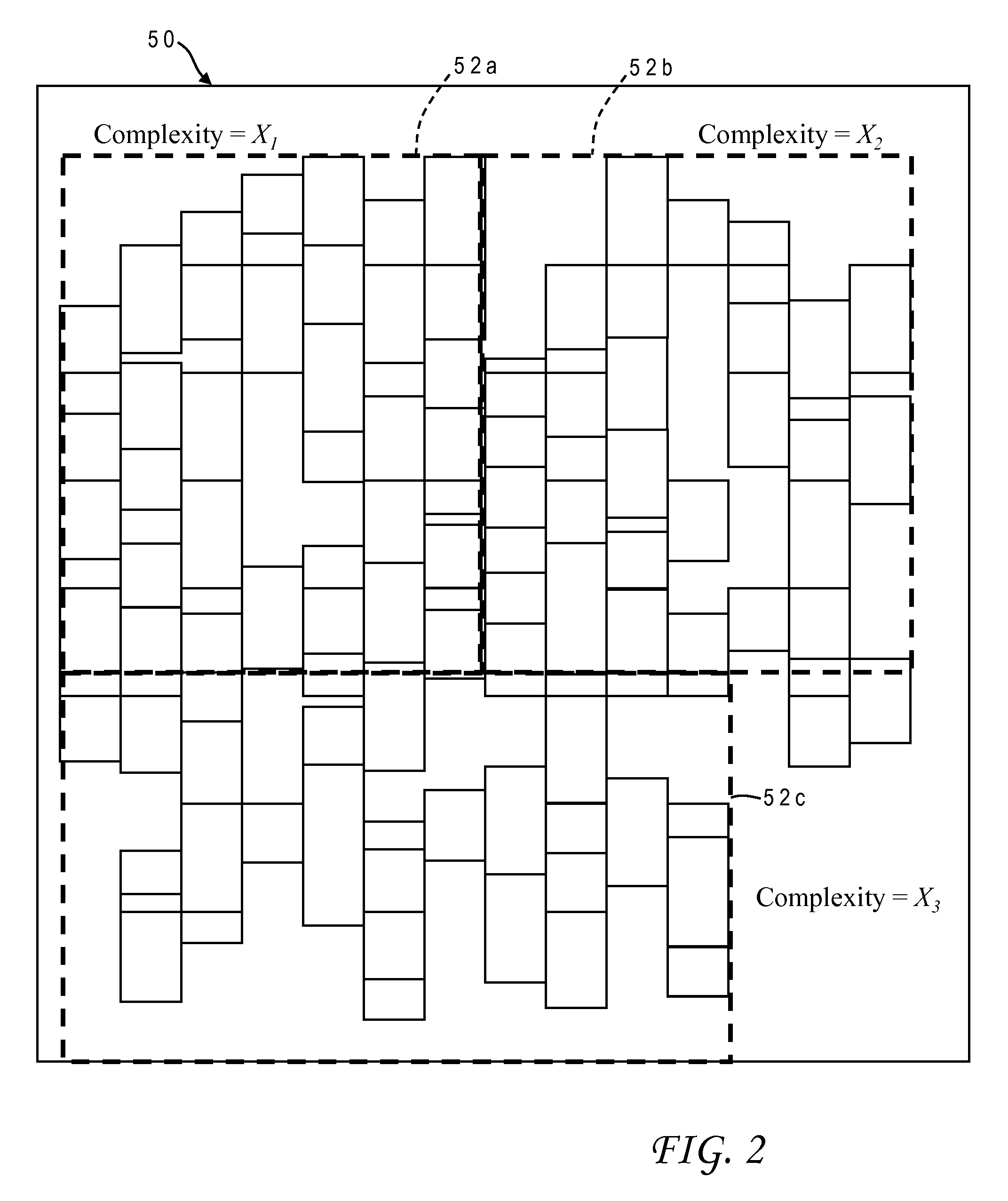
InactiveUS8661391B1CAD circuit designSpecial data processing applicationsLogic complexityEngineering
Spare cells are inserted in a region of an integrated circuit design based on a logic complexity of the region. The logic complexity can be computed based on the number of reachable states of digital logic in the region, and can be correlated to a desired spare cell insertion rate which is then compared to the actual spare cell utilization in the region. The target spare cell rate can further based on logic complexity values for neighboring regions with a proximity penalty.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Memory system and method of operating the same
A method of operating a memory system includes classifying numbers of total error bits into a plurality of ranges, assigning a plurality of data to the plurality of ranges, respectively, counting a number of detected error bits for a memory cell block, and storing a selected one of the plurality of data in at least one spare cell when the number of the detected error bits is within one of the ranges that corresponds to the selected data.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Replacement of a faulty memory cell with a spare cell for a memory circuit
ActiveUS20130176768A1Improve performanceImproved lifetimeDigital storageComputer architectureMemory cell
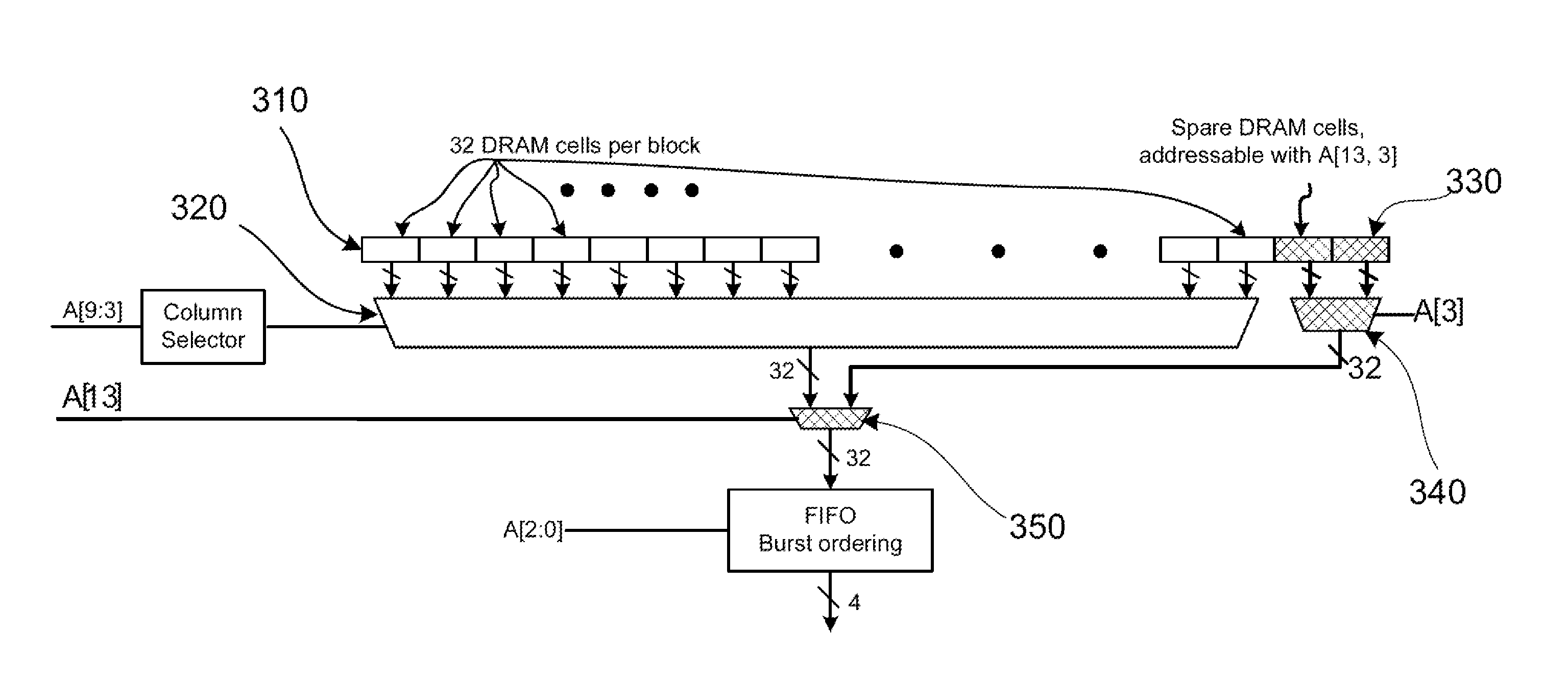
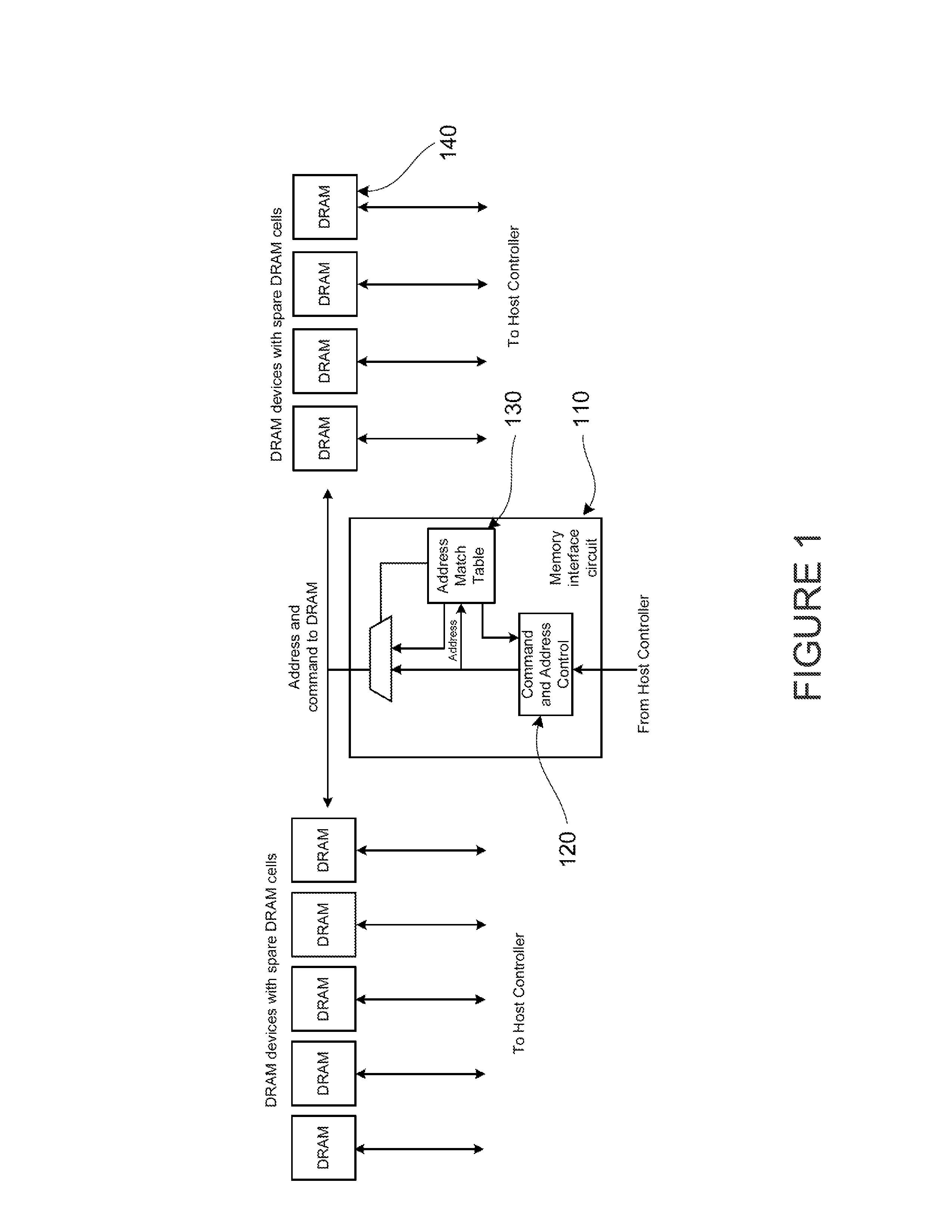
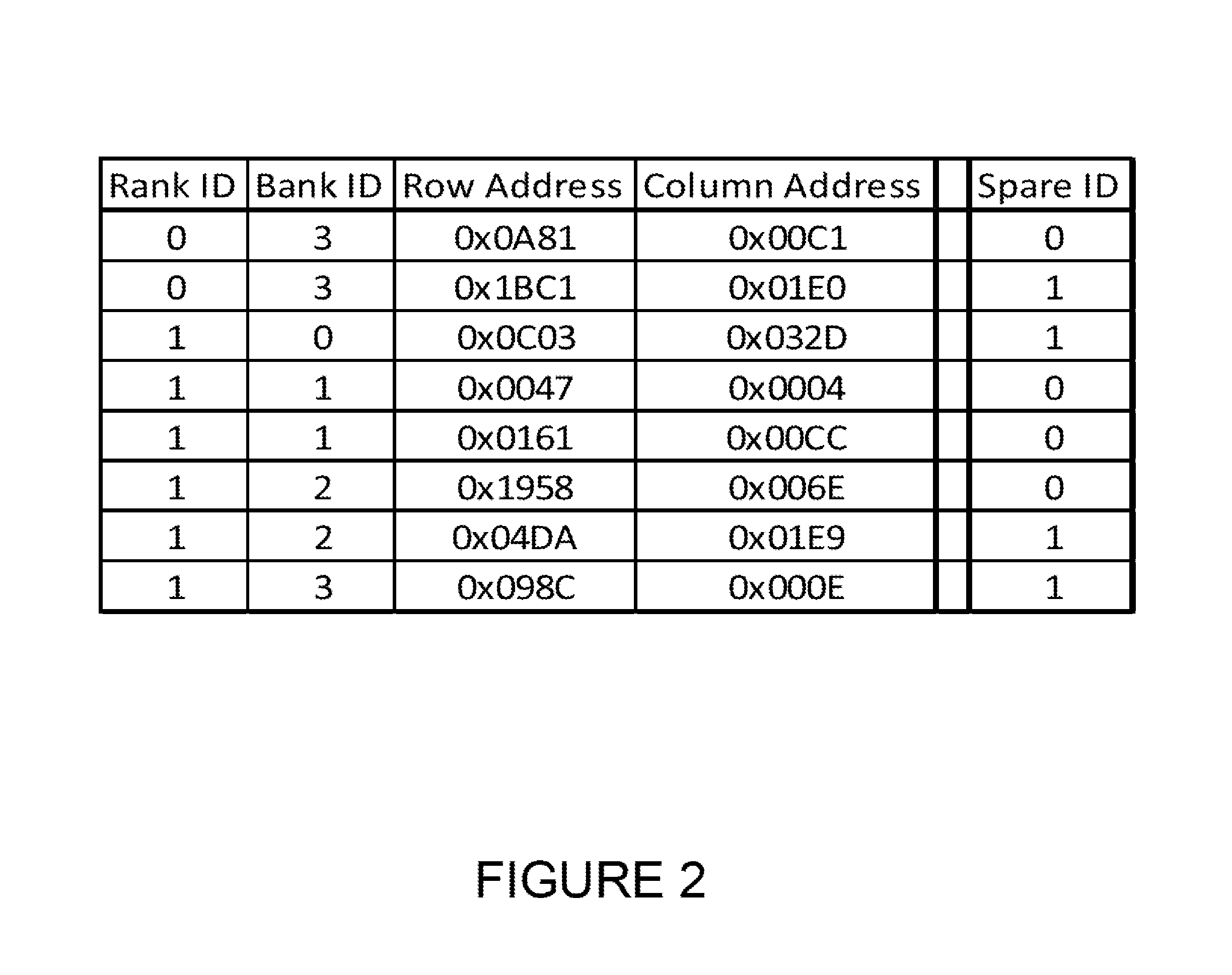
A memory integrated circuit device is provided. The device includes a plurality of regular address inputs and at least one spare address input configured for a selected mode or an unselected mode. The device includes a plurality of control inputs, a plurality of data inputs, and a plurality of data outputs. The device has a plurality of memory arrays. Each of the memory arrays comprises a plurality of memory cells. Each of the plurality of memory cells is coupled to a data input / output. The device has a spare group of memory cells comprising a plurality of spare memory cells. Each of the plurality of spare memory cells is externally (or internally) addressable using the address match table and configured with the spare address input; whereupon the spare address input is coupled to the address match table to access the spare memory cells.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
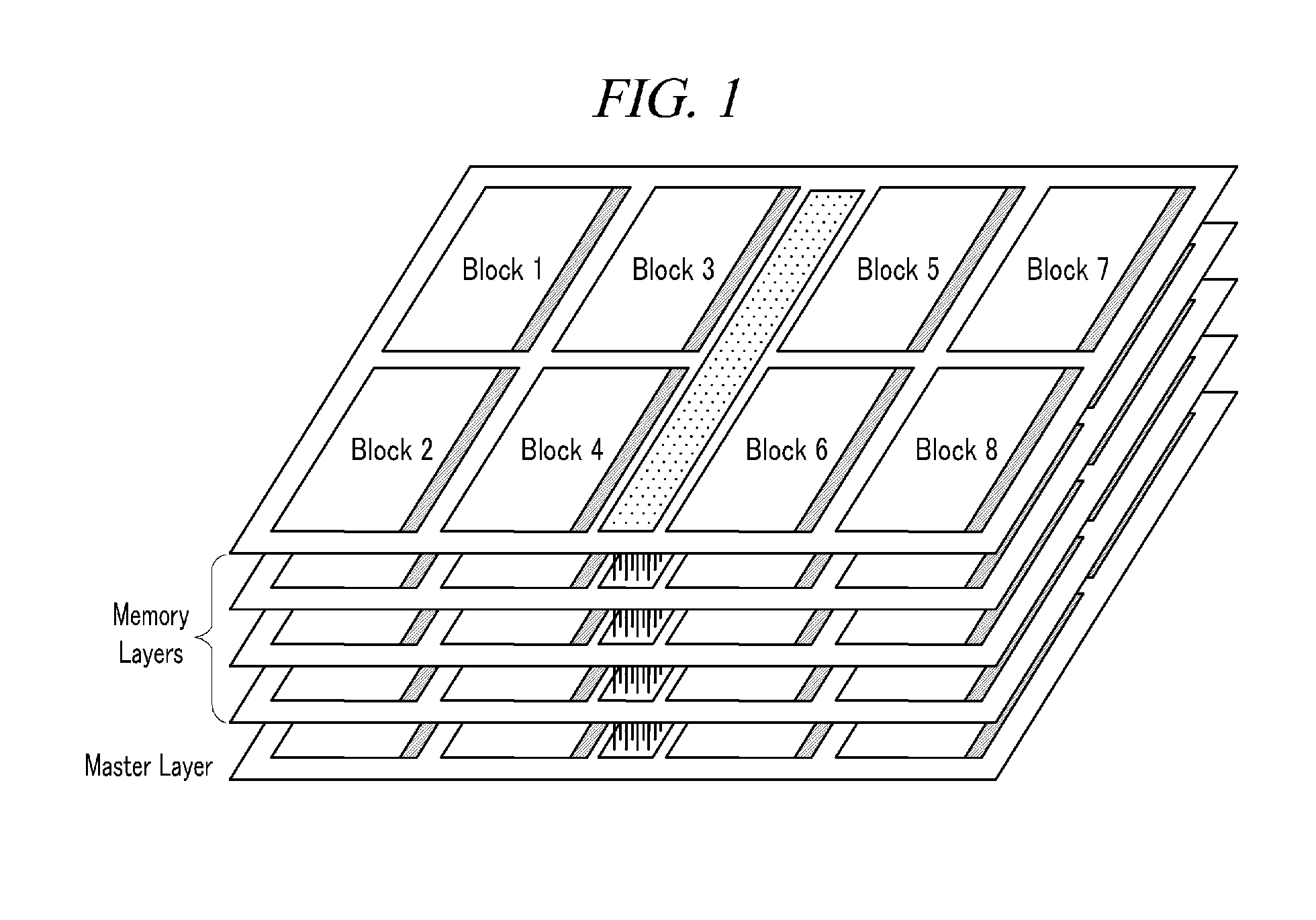
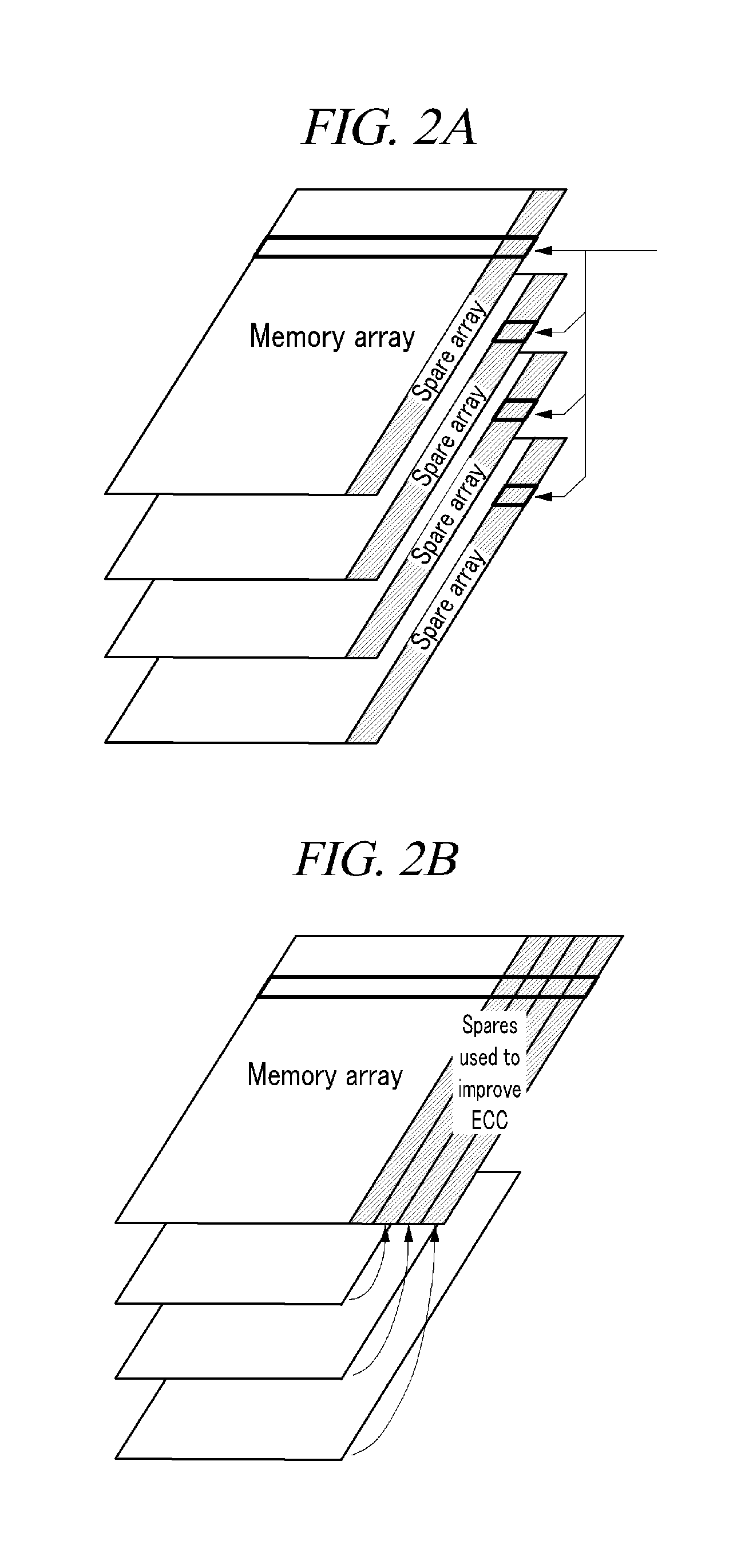
3D memory with error checking and correction function
ActiveUS20160124810A1Improving error checkImprove correction performanceStatic storageRedundant data error correctionError checkingParallel computing
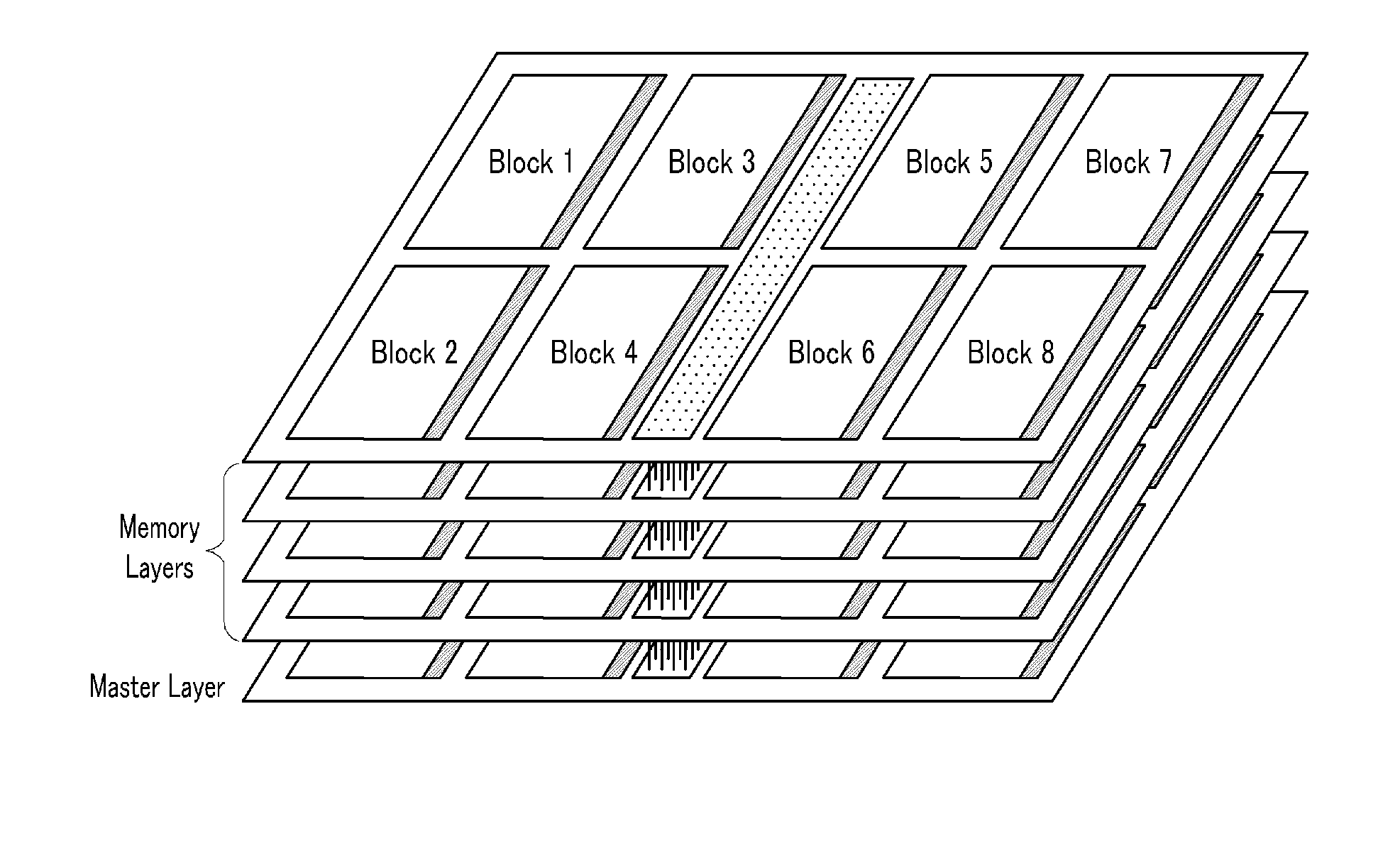
An error check and correction method of a 3D memory include a) storing check bits, which is used for error check and correction of an upper memory among the plurality of the memory layers, in one or more of spare cell arrays of a lower memory layer stacked below the upper memory layer and the upper memory layer; and b) performing error check and correction of the upper memory layer by using the stored check bits, wherein in the 3D memory, there are stacked a plurality of memory layers comprising a memory cell array with a matrix structure consisting of memory cells and a spare cell array with a matrix structure consisting of spare memory cells for replacing a fault memory cell, in which a fault occurs, and the 3D memory comprises a master layer for controlling the plurality of the memory layers.
Owner:RES & BUSINESS FOUND SUNGKYUNKWAN UNIV
Method and device for establishing active/standby intermediate frequency cell protection
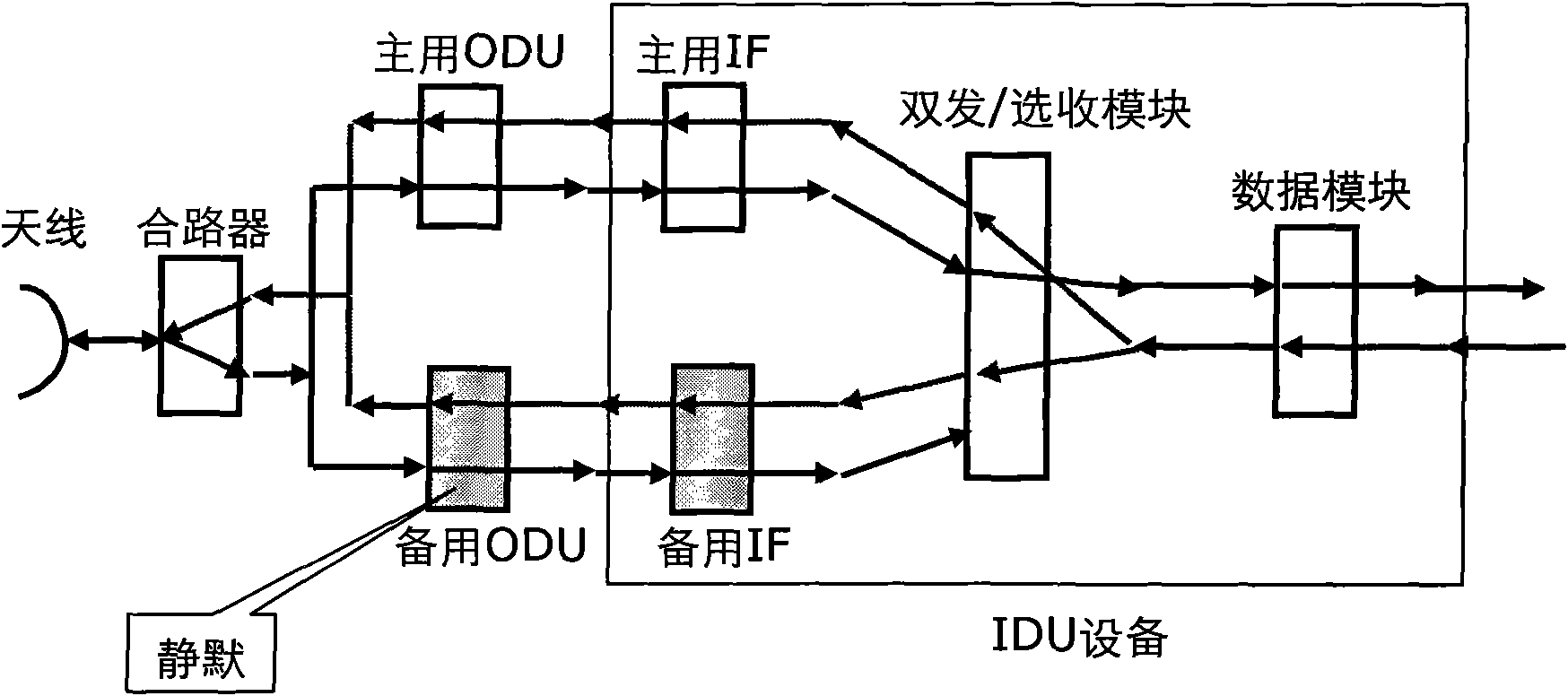
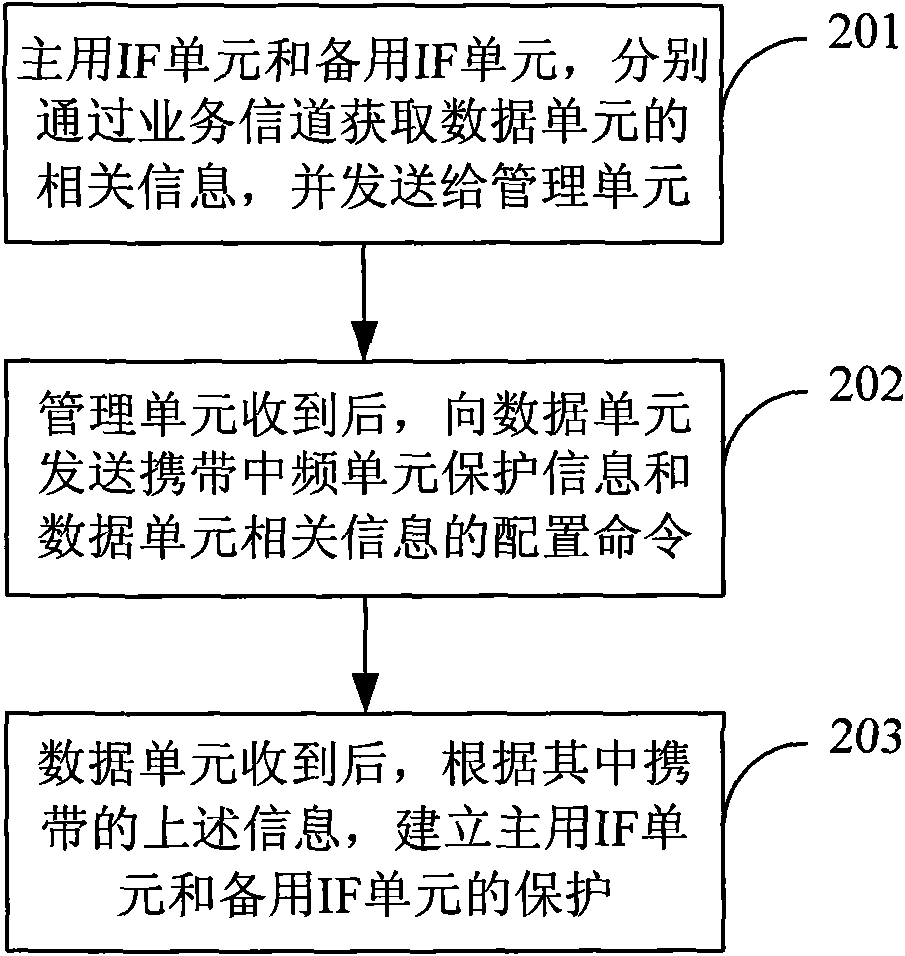
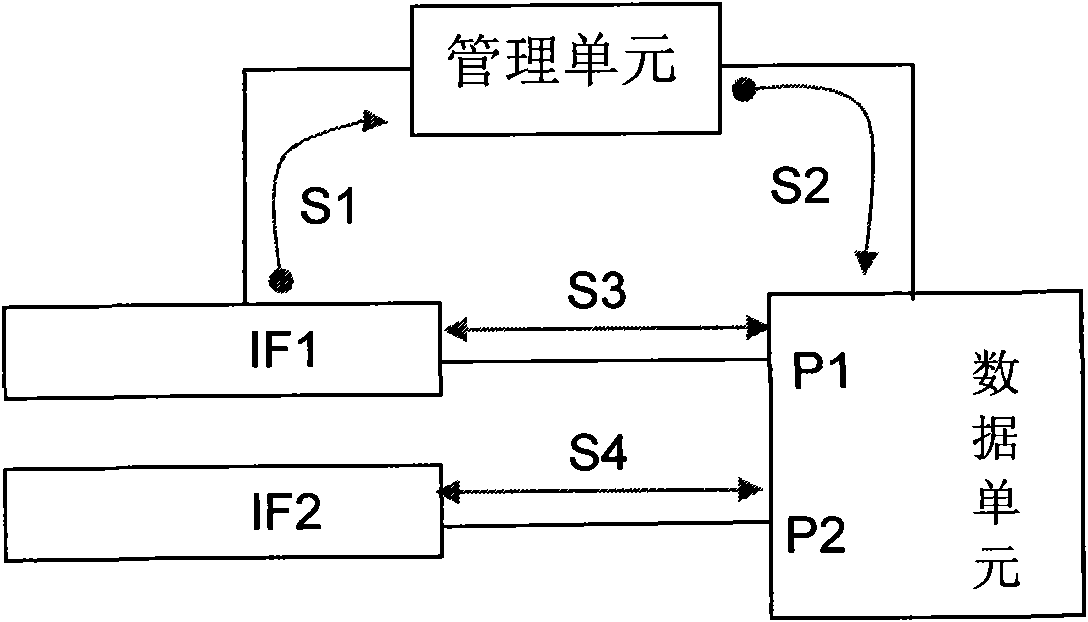
InactiveCN101848102AIncrease flexibilityEasy to manageError prevention/detection by using return channelData switching networksRelevant informationIntermediate frequency
The invention discloses a method and device for establishing active / standby intermediate frequency (IF) cell protection, belonging to the microwave technical field. The method comprises the following steps: an active IF cell and a standby IF cell obtain the relevant information of a data cell through the traffic channels thereof with the data cell and send the obtained relevant information to a management cell through the traffic channels respectively; after receiving the relevant information sent by the active IF cell and the standby IF cell, the management cell sends a configuration order containing the IF cell protection information and the relevant information of the data cell to the data cell; and after receiving the configuration order, the data cell establishes protection for the active IF cell and the standby IF cell according to the content of the order. The device of the invention comprises the active IF cell, the standby IF cell, the data cell and the management cell. By using the device, the flexibility of active / standby IF cell protection can be increased; and the device is convenient to manage and maintain.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com