Patents
Literature
347 results about "Common battery" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
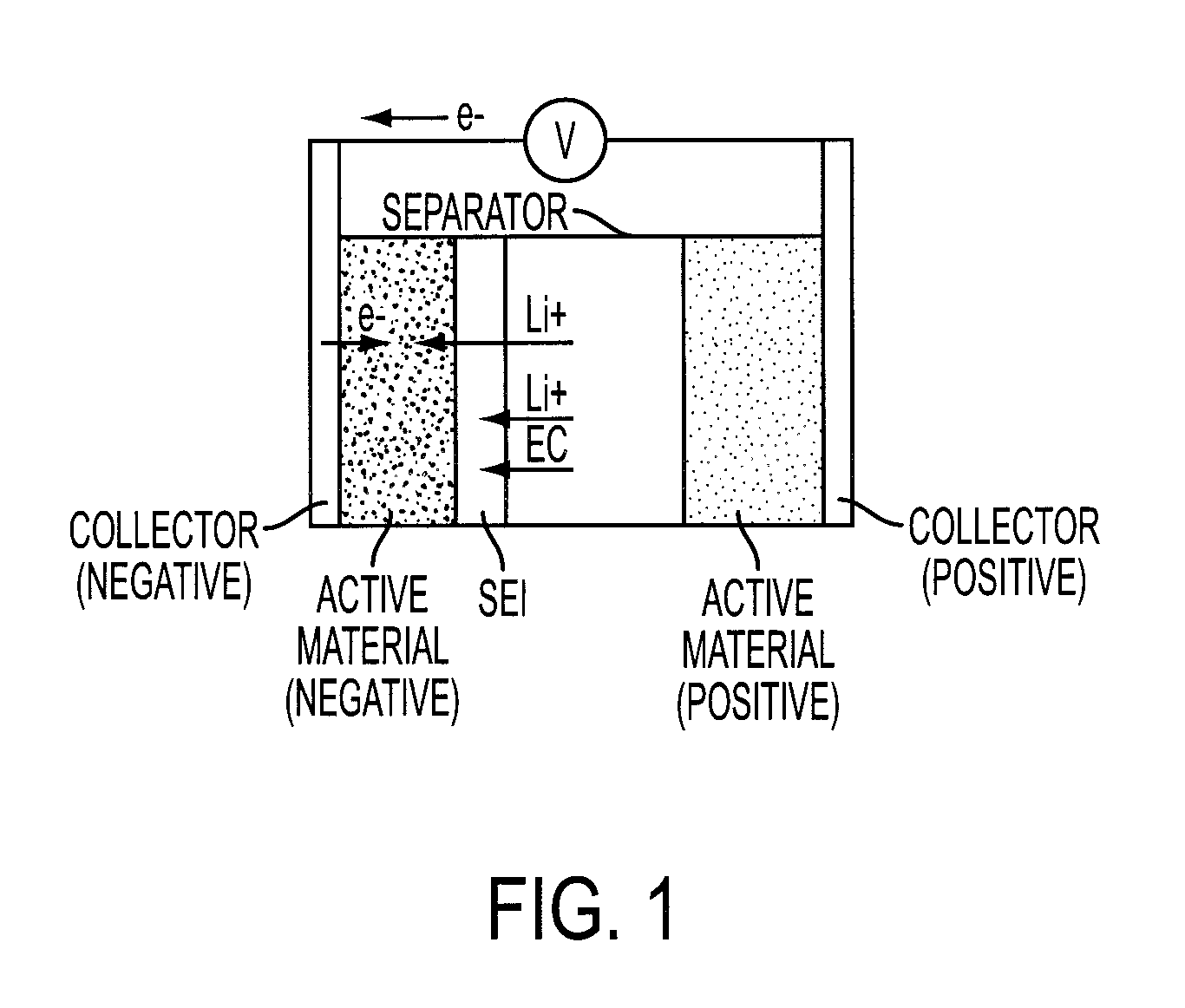
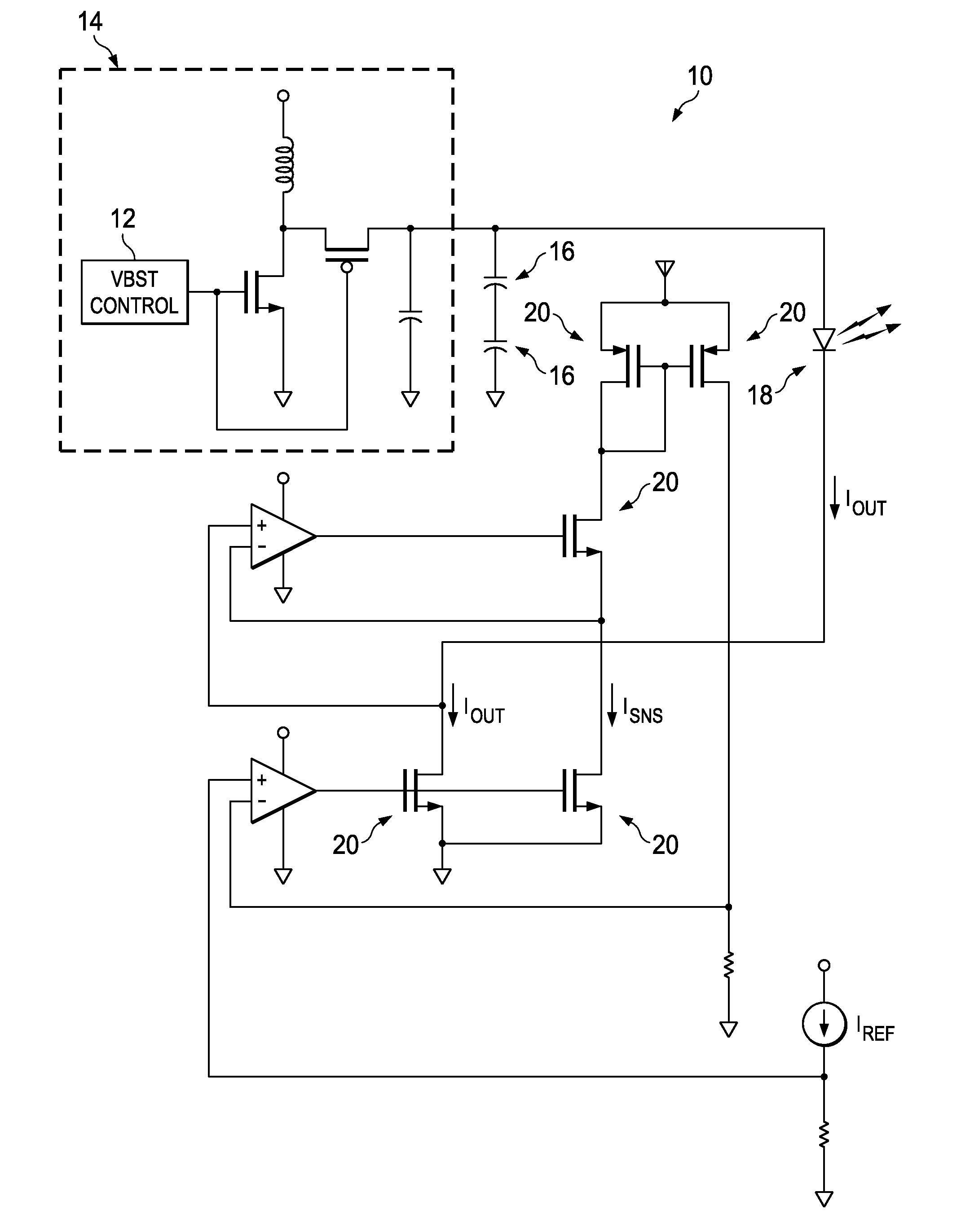
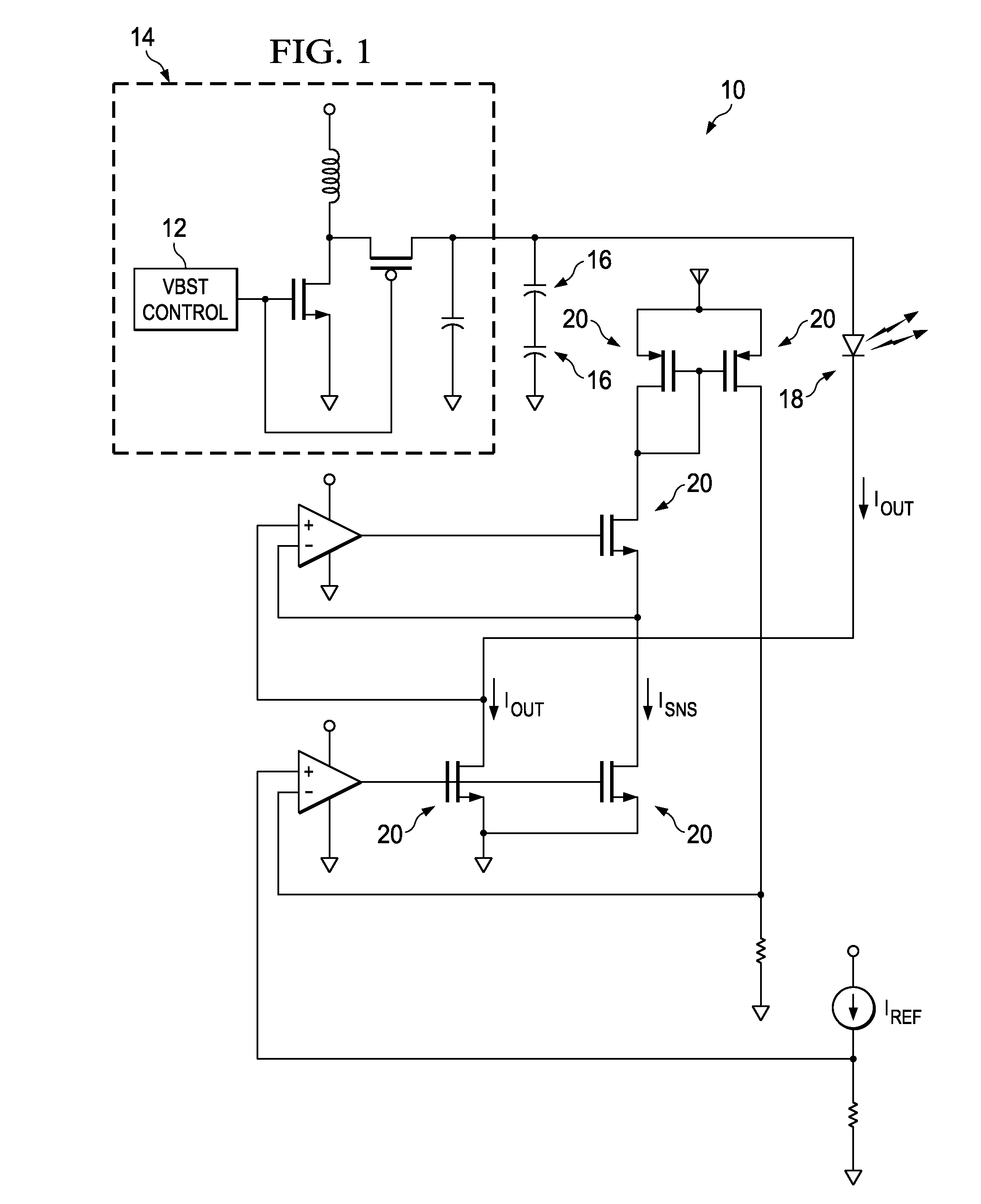
In telecommunication, a common battery is a single electrical power source used to energize more than one circuit, electronic component, equipment, or system. A common battery is usually a string of electrolytic cells and is usually centrally located to the equipment that it serves. In many telecommunications applications, the common battery is at a nominal −48 VDC. A central office common battery in the battery room supplies power to operate all directly connected instruments. Common battery may include one or more power conversion devices to transform commercial power to direct current, with a rechargeable battery floating across the output. Common battery operation largely replaced local batteries in each telephone in the early 20th century. It consists of two ends that emit opposing positive and negative charges
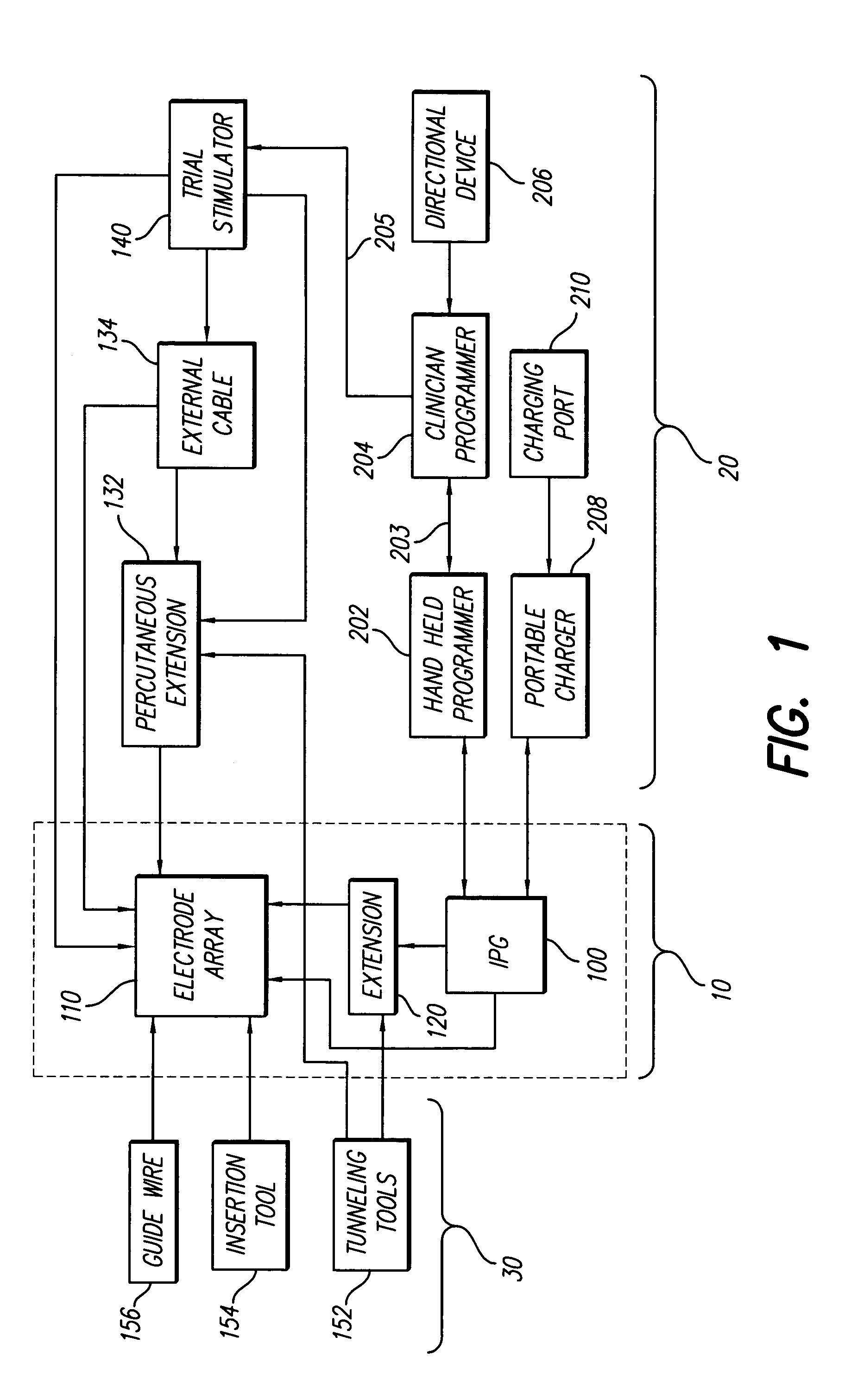
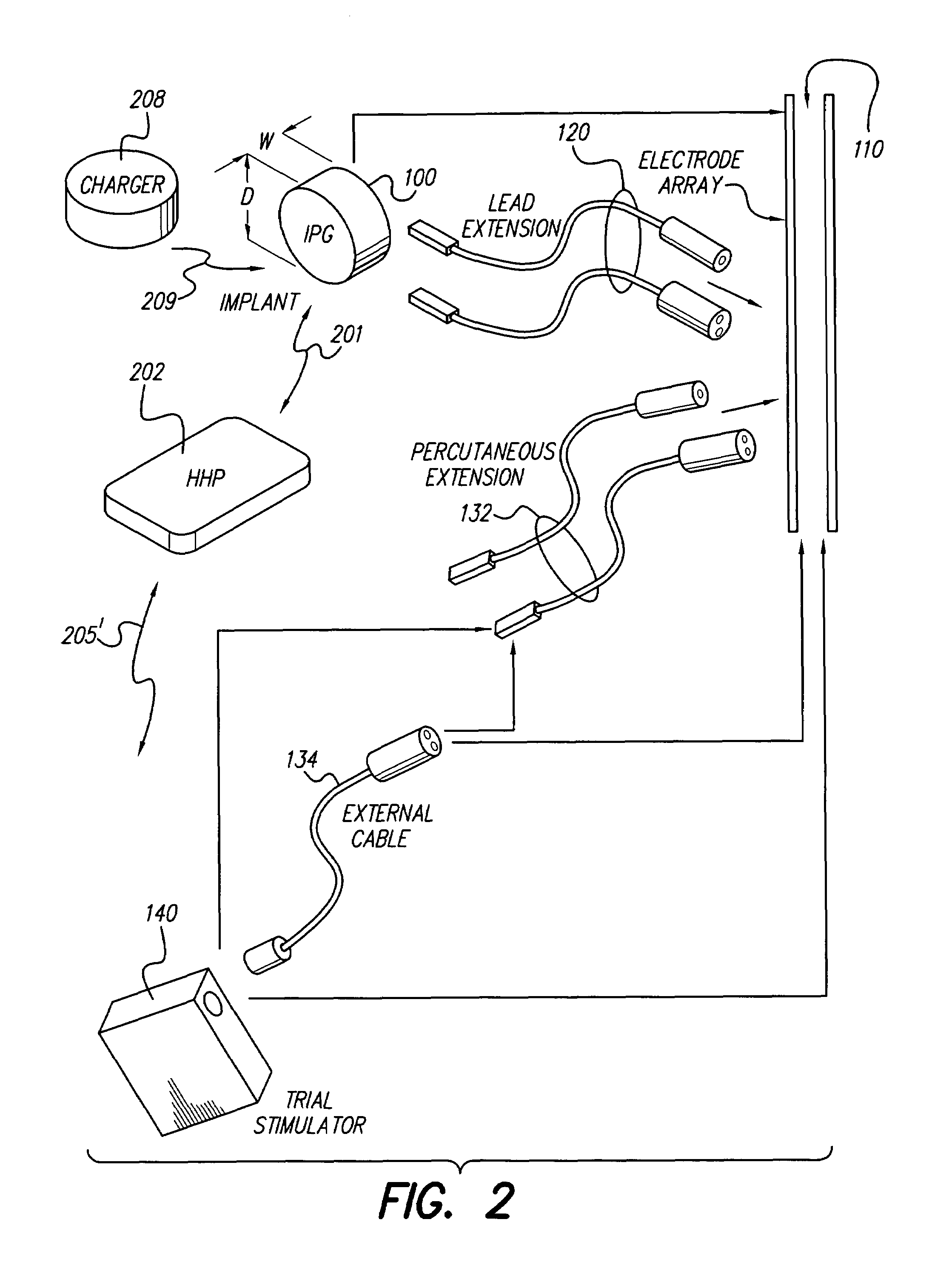
Implantable devices using rechargeable zero-volt technology lithium-ion batteries
InactiveUS7184836B1Assures safe and reliable operation of systemFirmly connectedElectrotherapyLoad circuitLow voltage
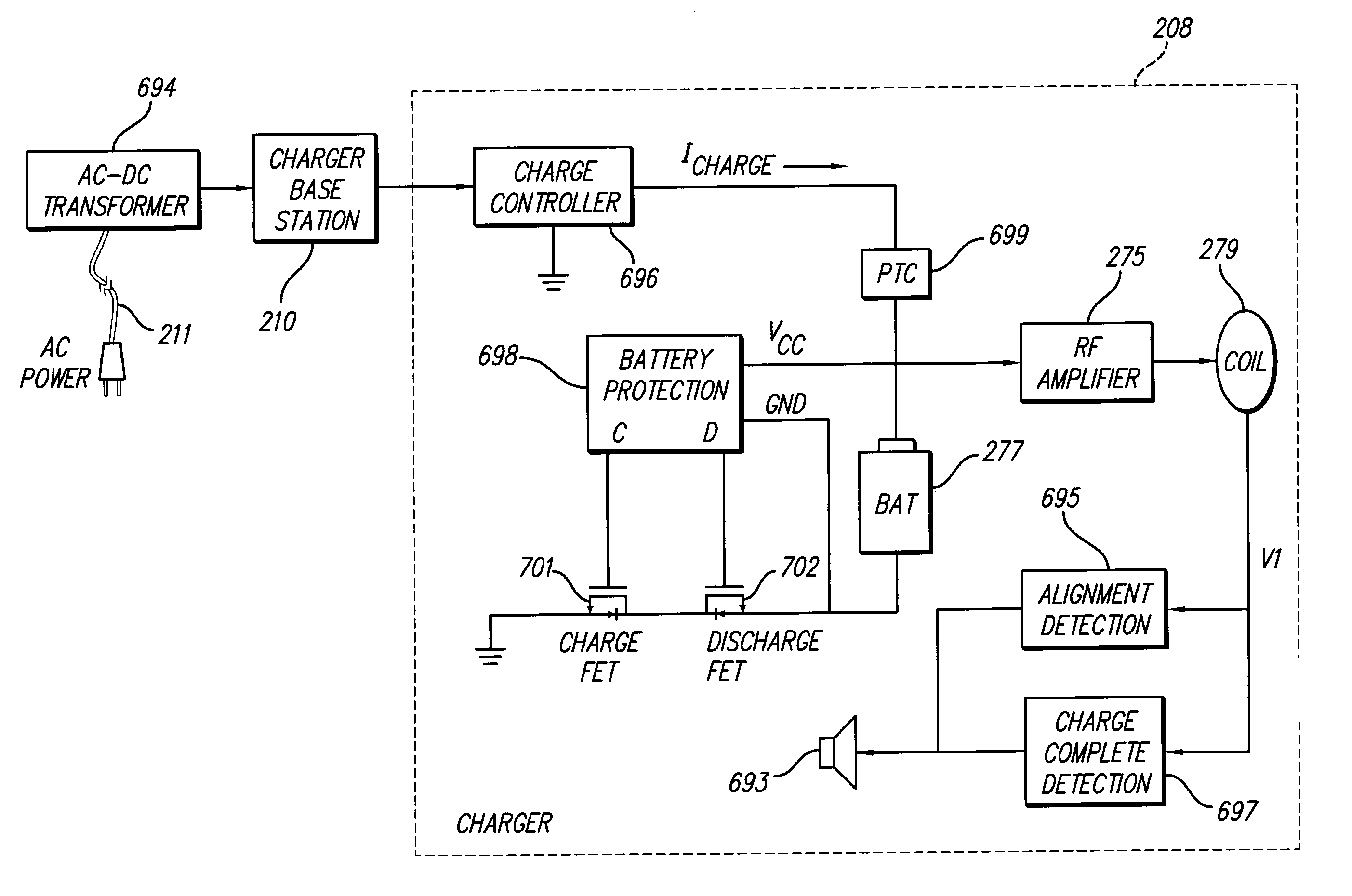
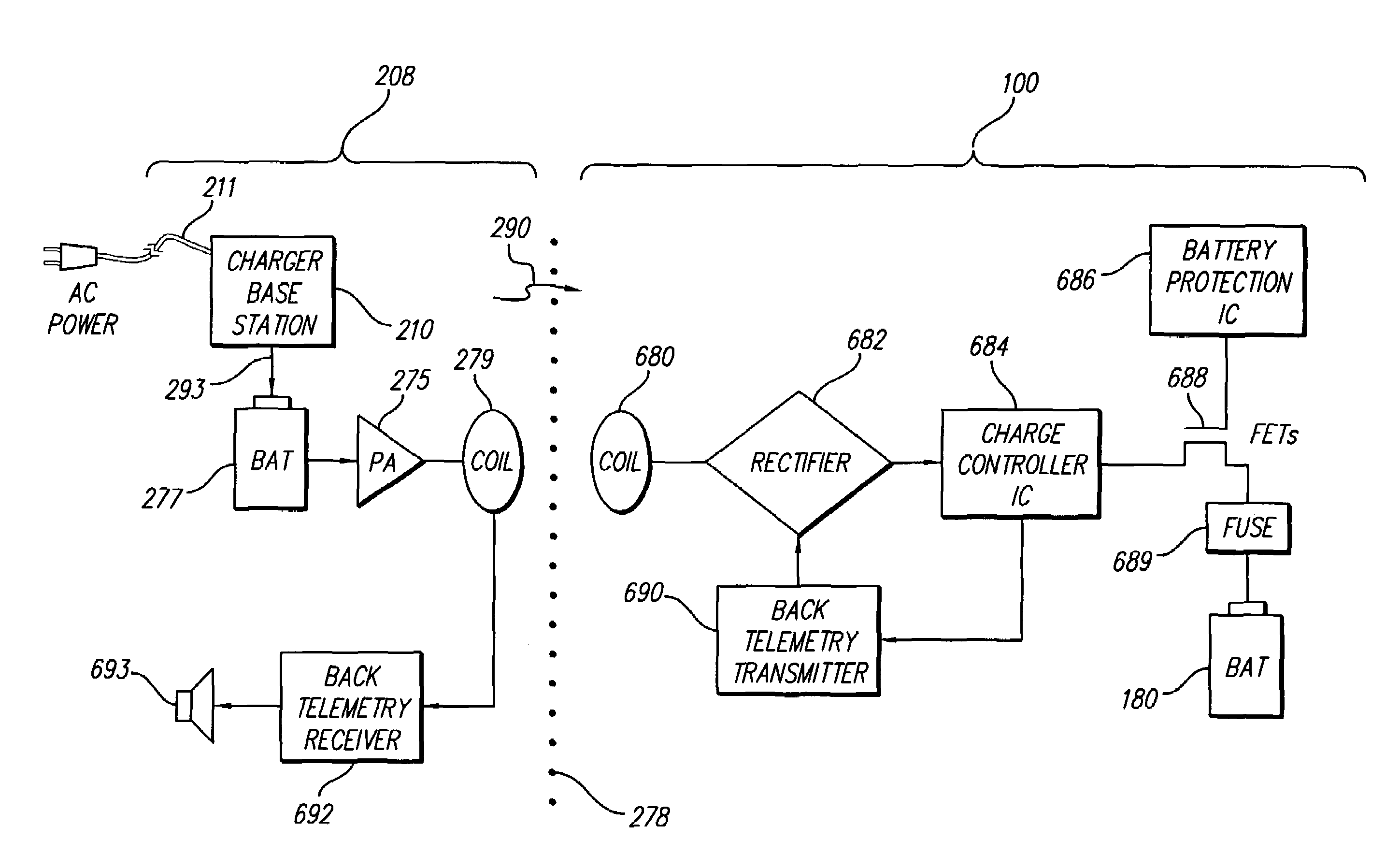
An implantable medical device, such as an implantable pulse generator (IPG) used with a spinal cord stimulation (SCS) system, includes a rechargeable lithium-ion battery having an anode electrode with a substrate made substantially from titanium. Such battery construction allows the rechargeable battery to be discharged down to zero volts without damage to the battery. The implantable medical device includes battery charging and protection circuitry that controls the charging of the battery so as to assure its reliable and safe operation. A multi-rate charge algorithm is employed that minimizes charging time while ensuring the battery cell is safely charged. Fast charging occurs at safer lower battery voltages (e.g., battery voltage above about 2.5 V), and slower charging occurs when the battery nears full charge higher battery voltages (e.g., above about 4.0 V). When potentially less-than-safe very low voltages are encountered (e.g., less than 2.5 V), then very slow (trickle) charging occurs to bring the battery voltage back up to the safer voltage levels where more rapid charging can safely occur. The battery charging and protection circuitry also continuously monitors the battery voltage and current. If the battery operates outside of a predetermined range of voltage or current, the battery protection circuitry disconnects the battery from the particular fault, i.e. charging circuitry or load circuits.
Owner:QUALLION +1
Implantable devices using rechargeable zero-volt technology lithium-ion batteries
InactiveUS7295878B1Assures safe and reliable operation of systemFirmly connectedImplantable neurostimulatorsLoad circuitLow voltage
An implantable medical device, such as an implantable pulse generator (IPG) used with a spinal cord stimulation (SCS) system, includes a rechargeable lithium-ion battery having an anode electrode with a substrate made substantially from titanium. Such battery construction allows the rechargeable battery to be discharged down to zero volts without damage to the battery. The implantable medical device includes battery charging and protection circuitry that controls the charging of the battery so as to assure its reliable and safe operation. A multi-rate charge algorithm is employed that minimizes charging time while ensuring the battery cell is safely charged. Slow charging occurs at lower battery voltages (e.g., battery voltage below about 2.5 V), and fast charging occurs when the battery voltage has reached a safe level (e.g., above about 2.5 V). When potentially less-than-safe very low voltages are encountered (e.g., less than 2.5 V), then very slow (trickle) charging occurs to bring the battery voltage back up to the safer voltage levels where more rapid charging can safely occur. The battery charging and protection circuitry also continuously monitors the battery voltage and current. If the battery operates outside of a predetermined range of voltage or current, the battery protection circuitry disconnects the battery from the particular fault, i.e. charging circuitry or load circuits.
Owner:QUALLION +1
Battery determination system for battery-powered devices
ActiveUS20050099156A1Boards/switchyards circuit arrangementsMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansCommon batteryEngineering
This system provides a method for determining whether ordinary battery cells, a battery pack, and / or a charger unit are attached to a portable electronic device. The system provides a center contact in a battery shaft that contacts a battery pack or a point on an individual battery and allows the device regulation unit to measure the voltage at that point. If the voltage is below a particular threshold, then the system determines that a battery pack may be inserted in the battery shaft and the portable electronic unit enters a battery pack mode. If the voltage is above the threshold voltage, then the portable electronic device enters the battery operation mode. If a voltage transition is sensed on the DEVICE START line, the portable electronic device determines that the charger is installed and the portable electronic device enters the appropriate mode.
Owner:AKG ACOUSTICS
Universal serial bus powered battery charger
InactiveUS20020130638A1Batteries circuit arrangementsVolume/mass flow measurementElectrical batteryHand held
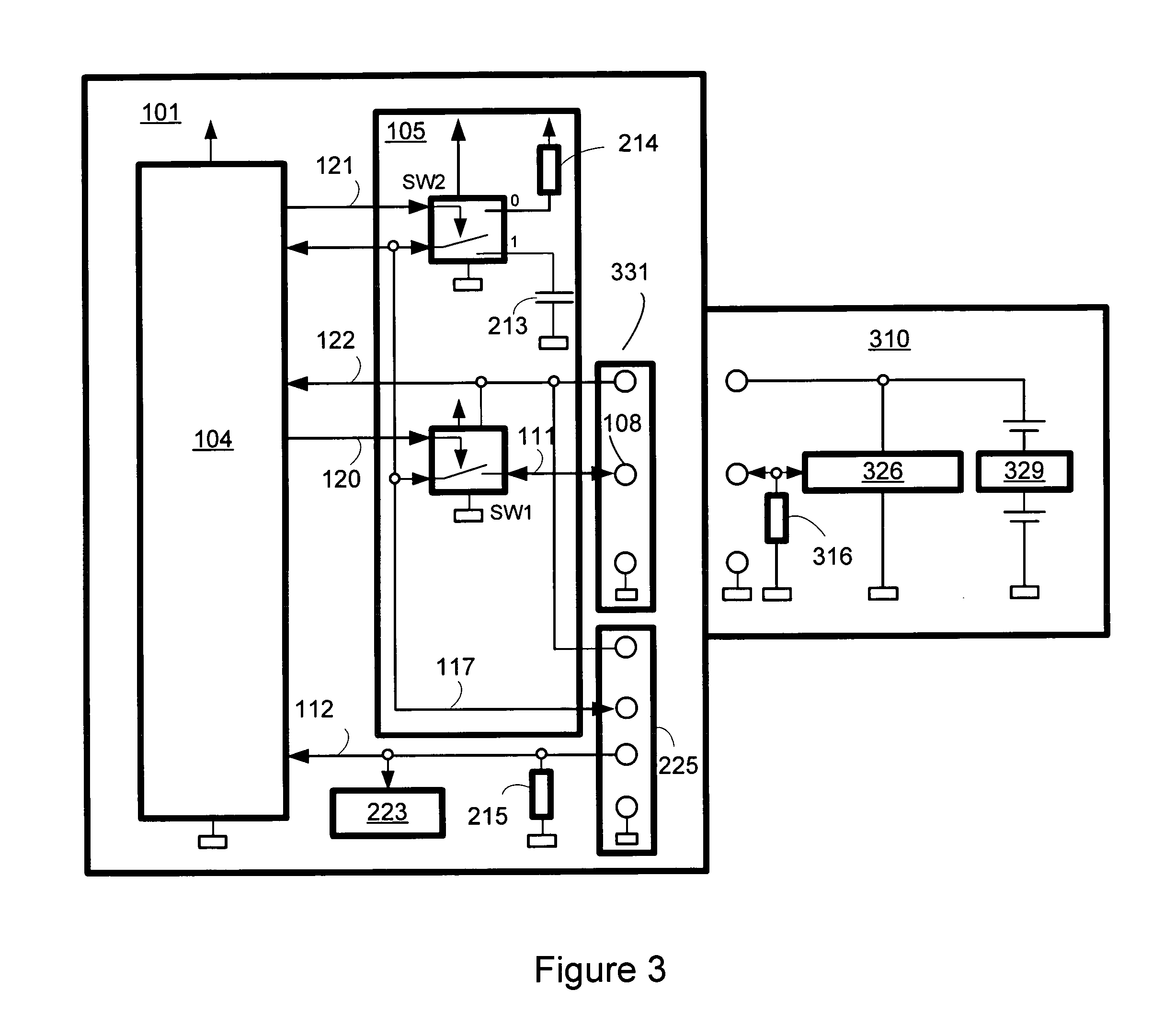
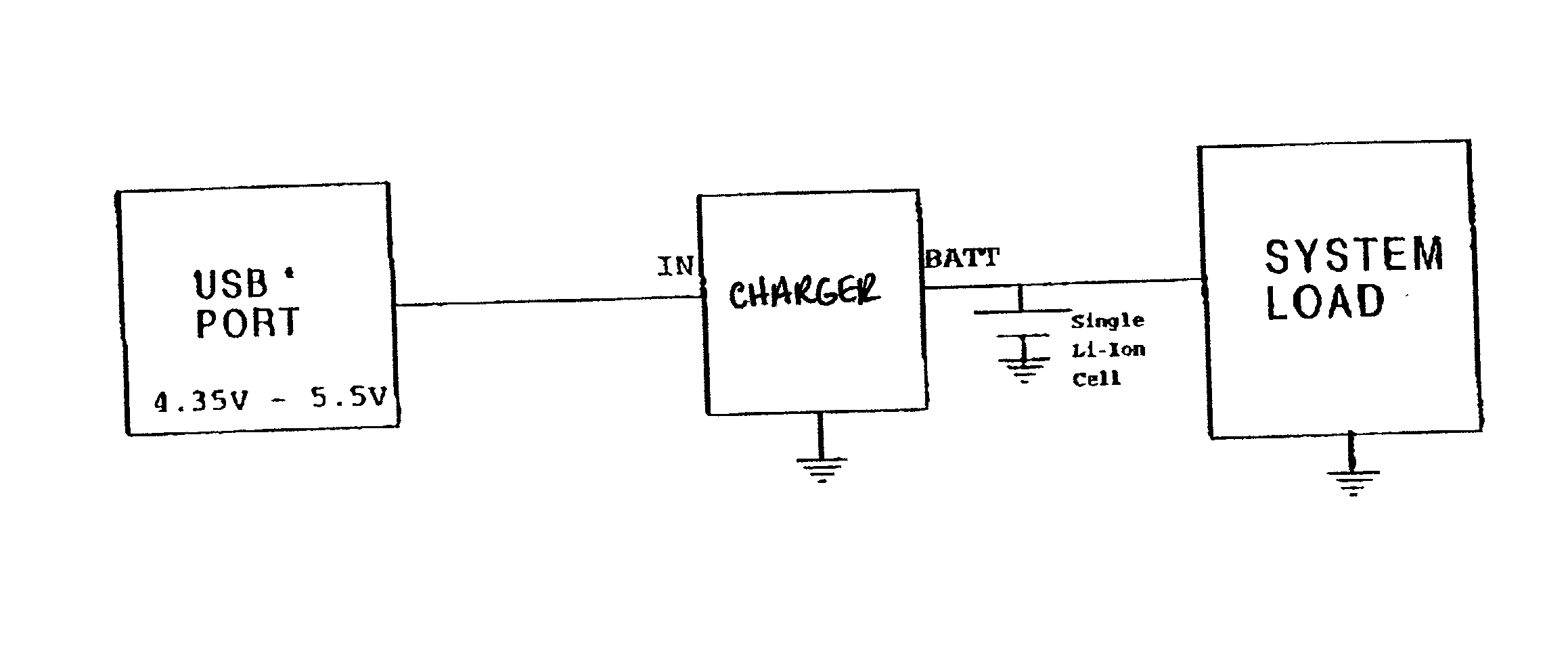
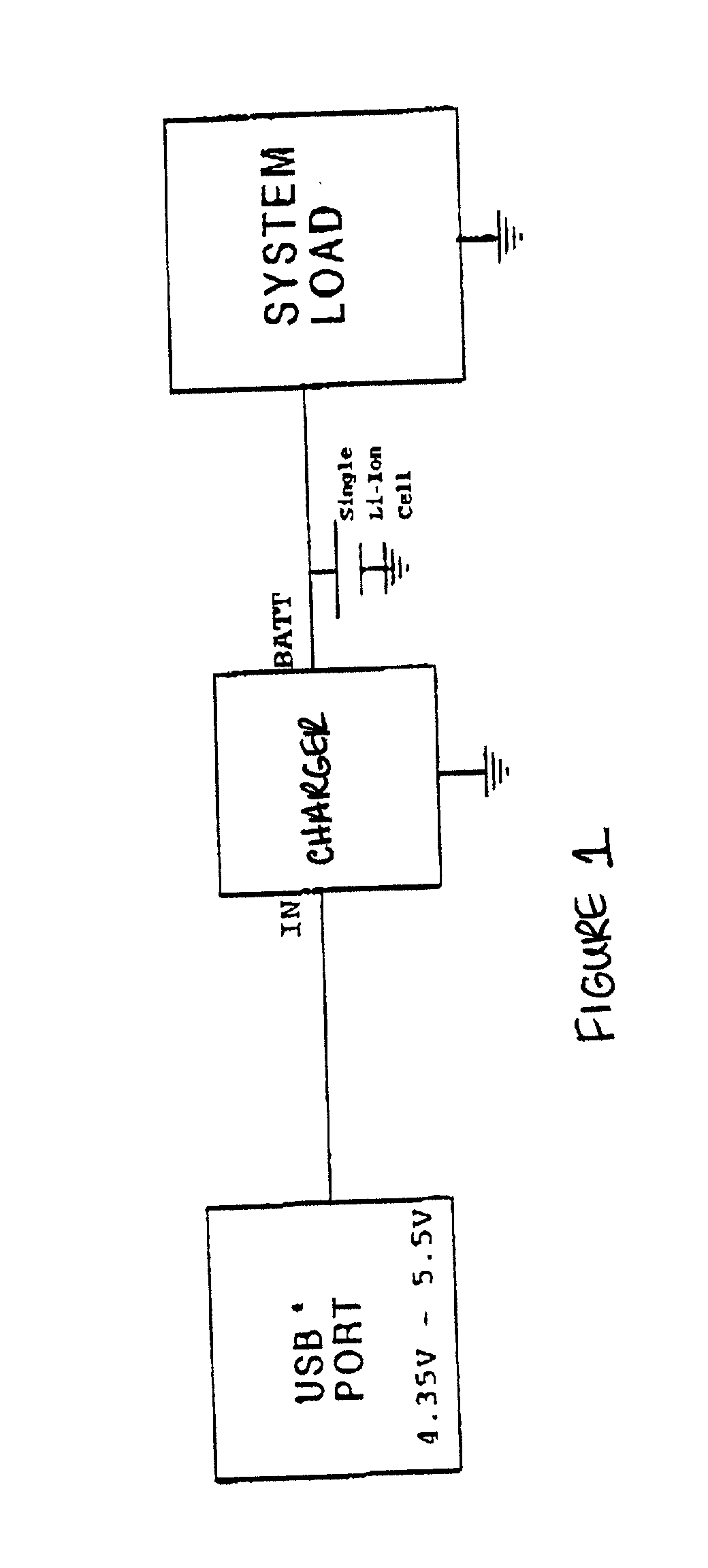
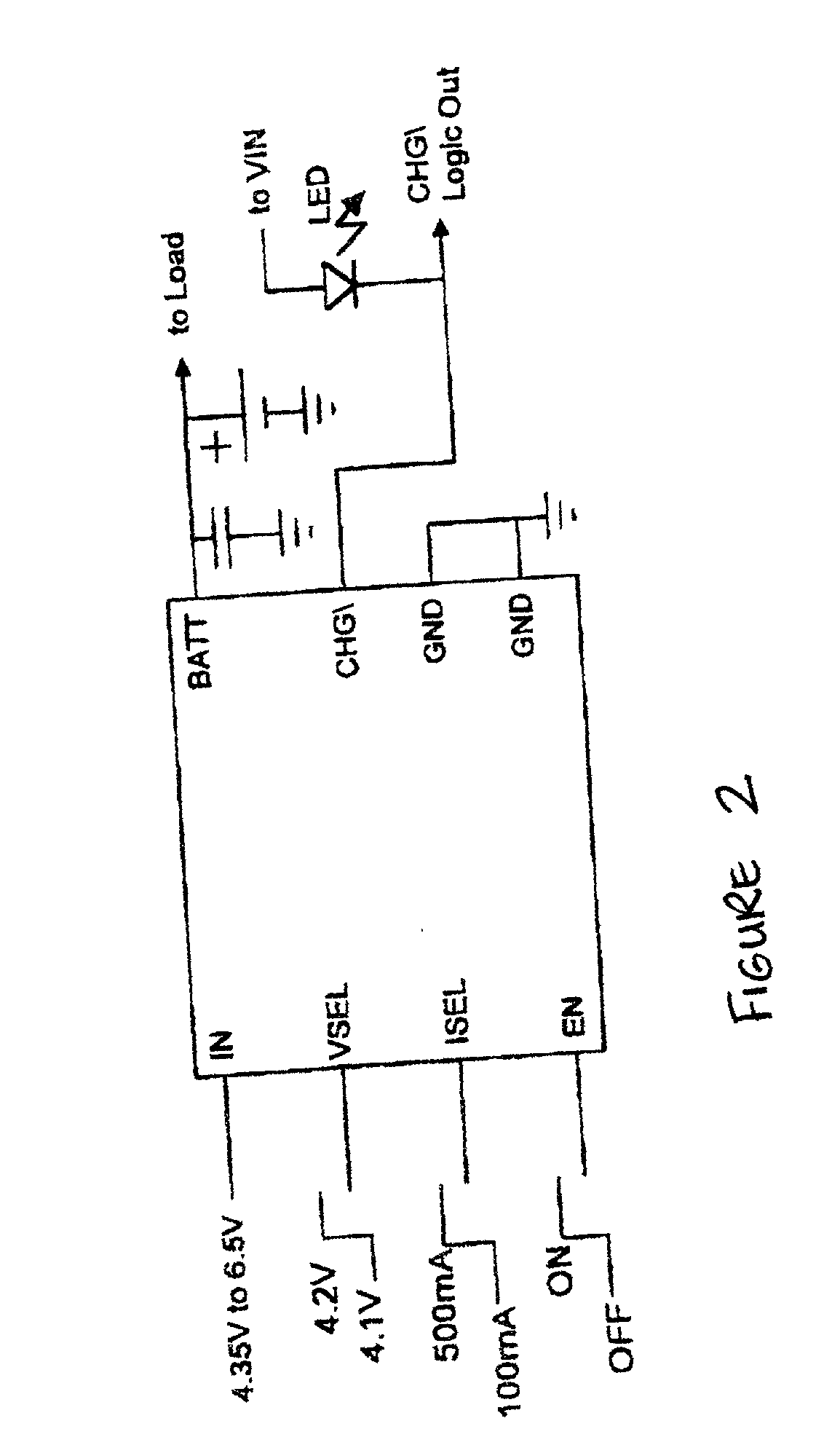
Universal serial bus powered battery charger primarily intended for use in battery powered hand-held and other portable devices to charge the battery or batteries within the battery powered device when the same is connected to a host device, powered hub or a bus powered hub through a universal serial bus (USB) port. The battery charger includes one or more current limits to conform to the universal serial bus current supply limit set in the USB specification. Any of the universal serial bus voltage and current limits may be used to charge batteries in the battery powered device, such as single cell lithium-ion batteries. Various features are disclosed.
Owner:MAXIM INTEGRATED PROD INC
Batteries for optimizing output and charge balance with adjustable, exportable and addressable characteristics
ActiveUS8901888B1Eliminate overshootingEasy loadingBatteries circuit arrangementsCylindrical casing cells/batteryThermodynamicsElectrical battery
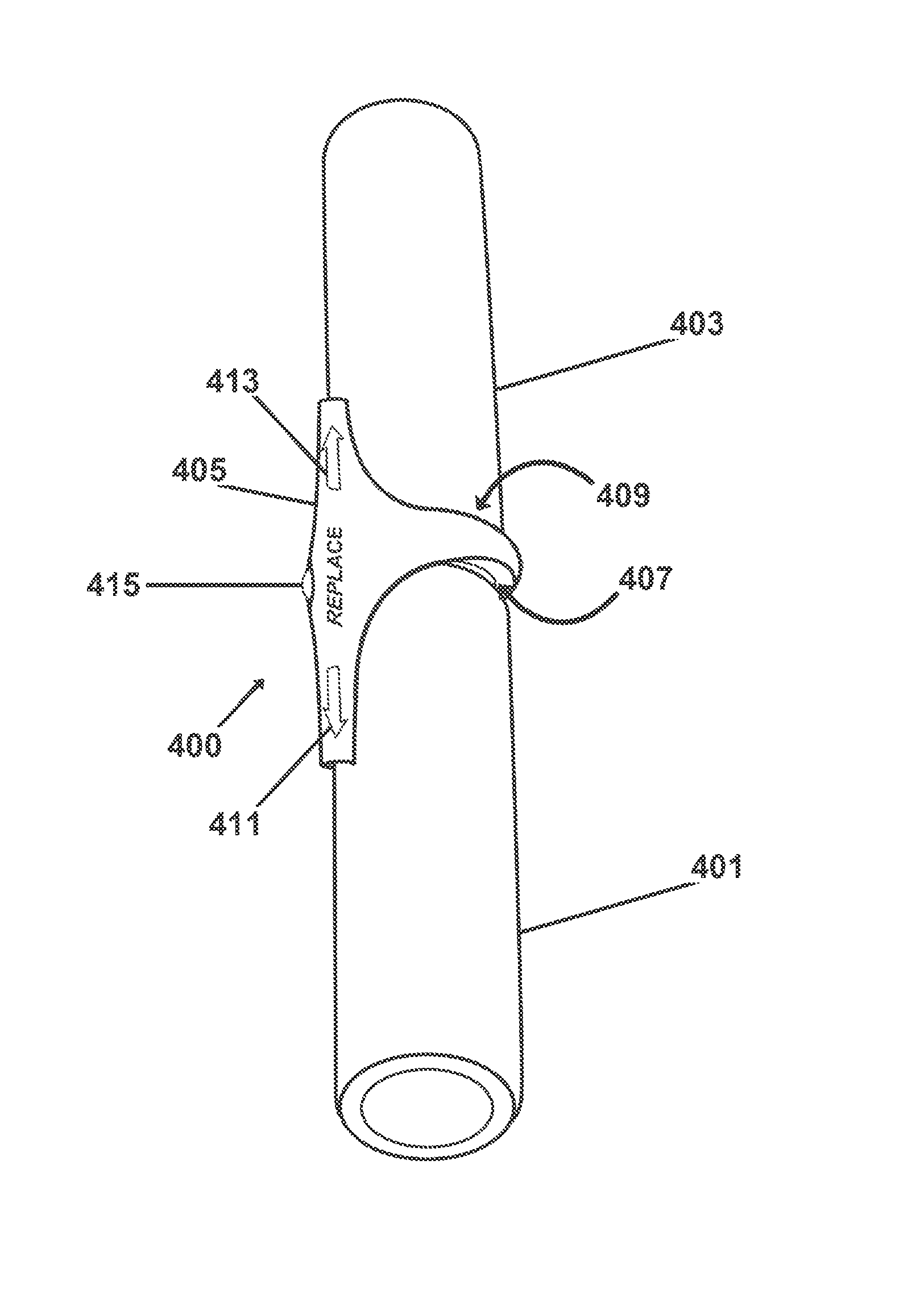
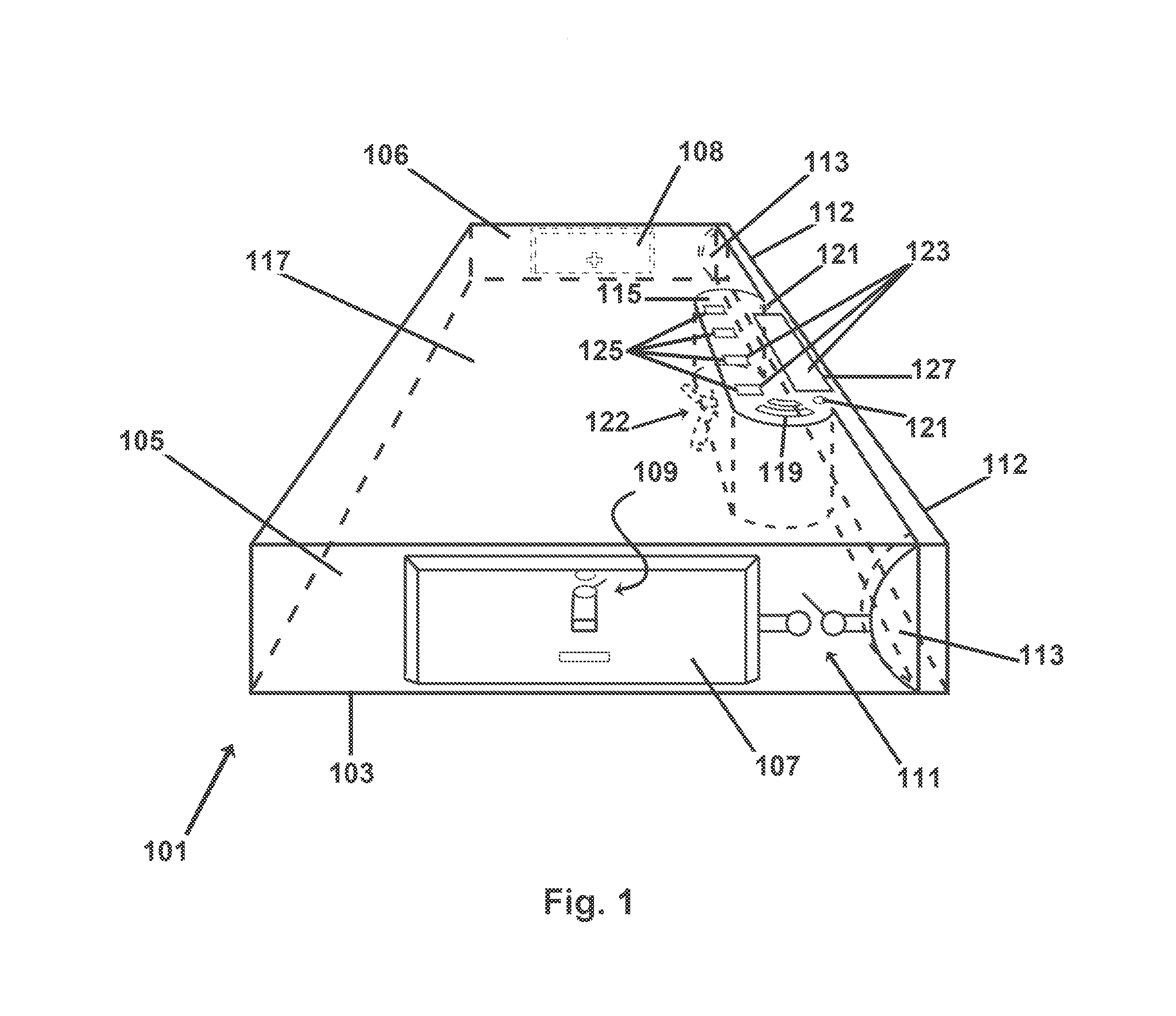
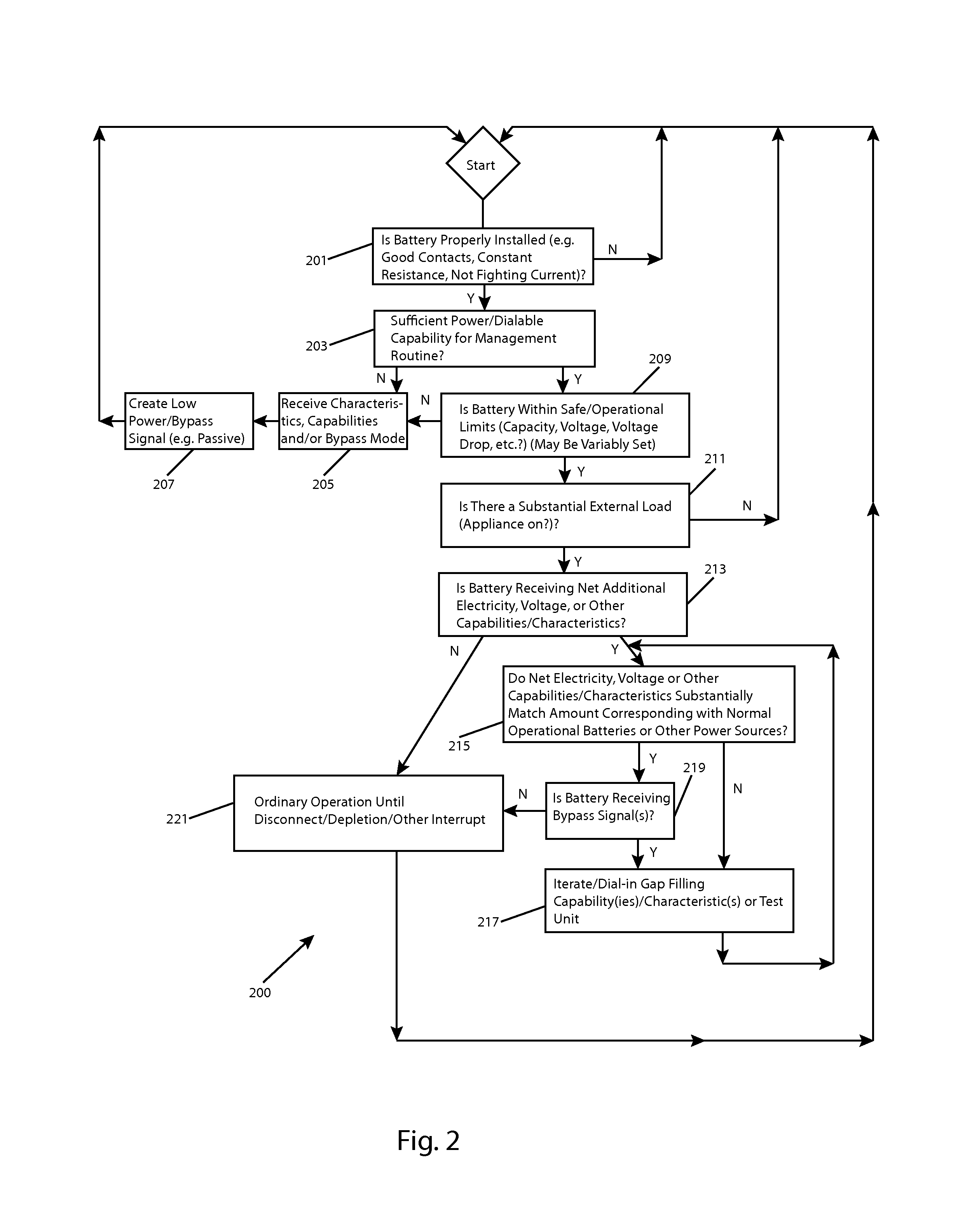
New battery management systems are provided that maintain voltage, current, cell balance and other electrical characteristics, without wasteful cell-to-cell recharging or resistive bleeding. In some aspects of the invention, a lagging or deteriorated battery may be at least partially bypassed, and the output of another, stronger battery is altered and addressed to supply the resulting power, voltage or other “gap.” In other aspects, the invention is implemented in an insert with battery mimicking and replacement hardware, and with a form factor for installation in a wide variety of possible battery compartments along with ordinary batteries.
Owner:BECKMAN CHRISTOPHER V
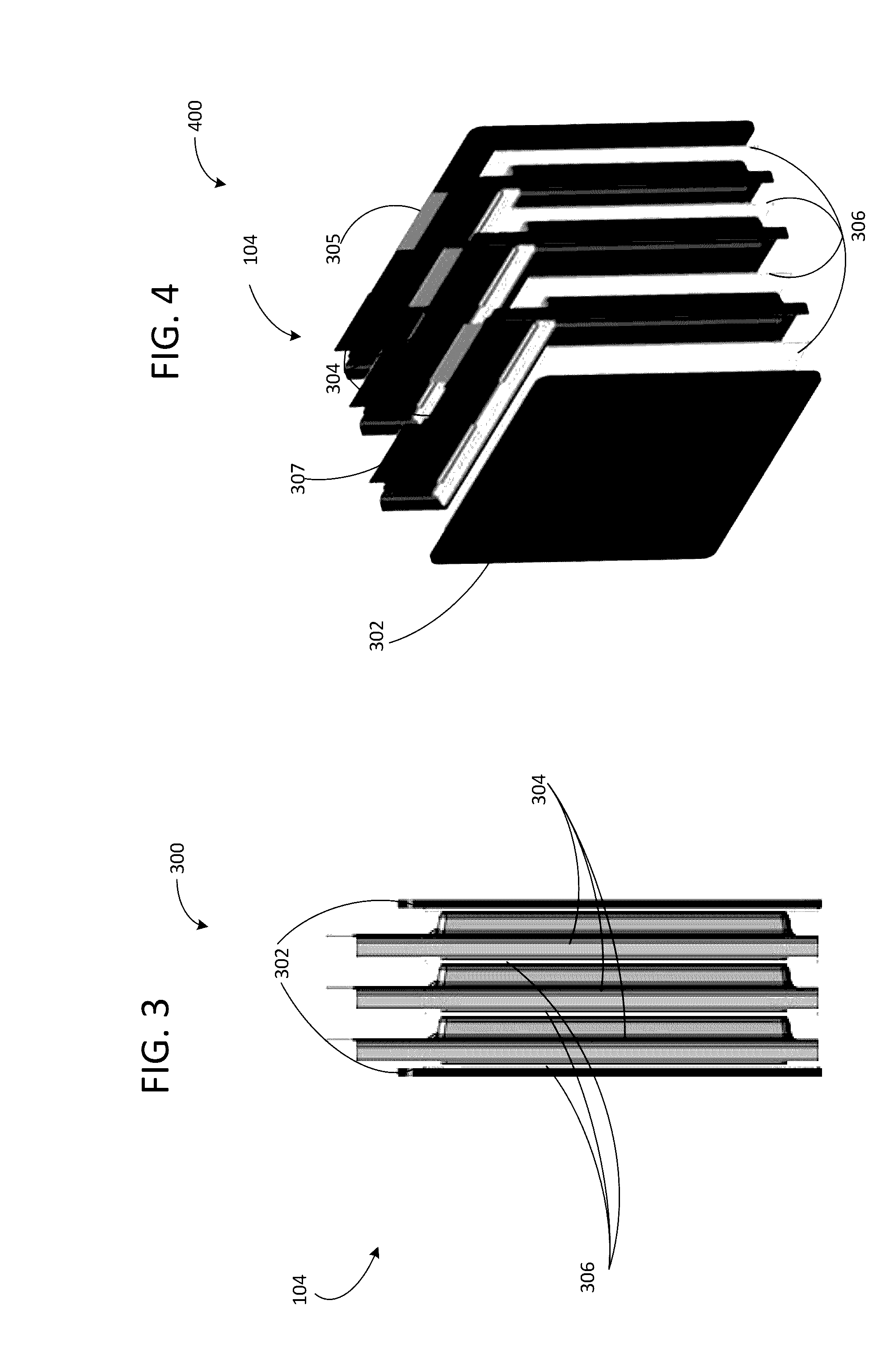
Super battery plate
ActiveCN101556997AIncrease specific energyHigh specific powerElectrolytic capacitorsHybrid capacitor electrodesFiberCarbon fibers
The invention discloses a super battery plate which comprises a positive plate and a negative plate; the raw materials of the positive plate consist of lead powder, carbon fibers, carbon materials, short fibers and sulfuric acid solution; the raw materials of the negative plate consist of lead powder, PTFE, barium sulphate, humic acid, lignin sodium sulplate, carbon fibers, carbon materials, short fibers and dilute sulfuric acid; the super battery prepared by the super battery plate has the advantages of high specific power and specific energy as well as long charge and discharge service life of a large pulse current. Moreover, the discharge of a low-temperature large current is batter than that of a common battery.
Owner:CHISEN POWER JIANGSU CO LTD
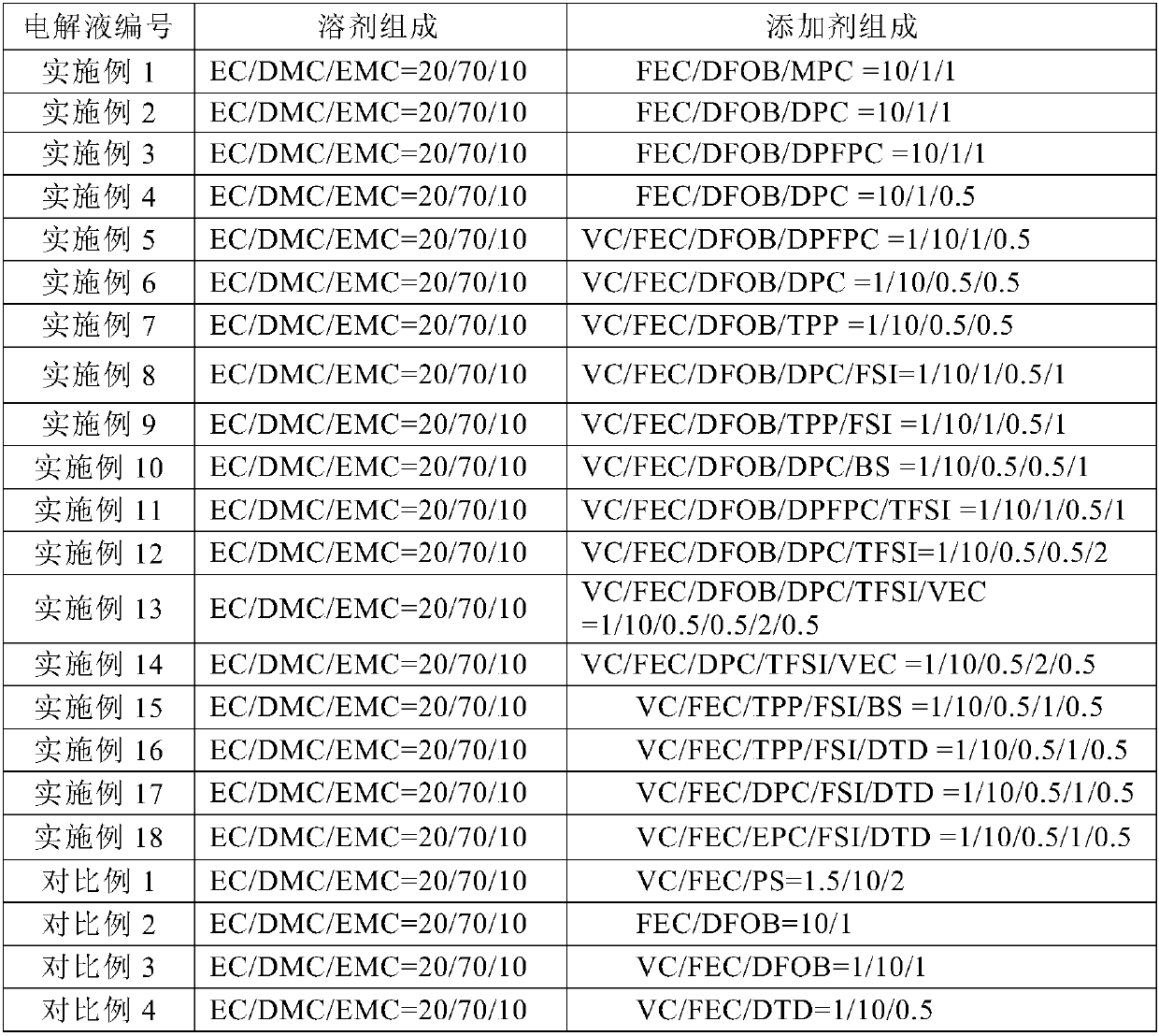
Lithium-ion battery electrolyte and lithium-ion battery
InactiveCN107834110AImprove cycle performanceImprove charge and discharge efficiencySecondary cells servicing/maintenanceHigh temperature storageCyclic process
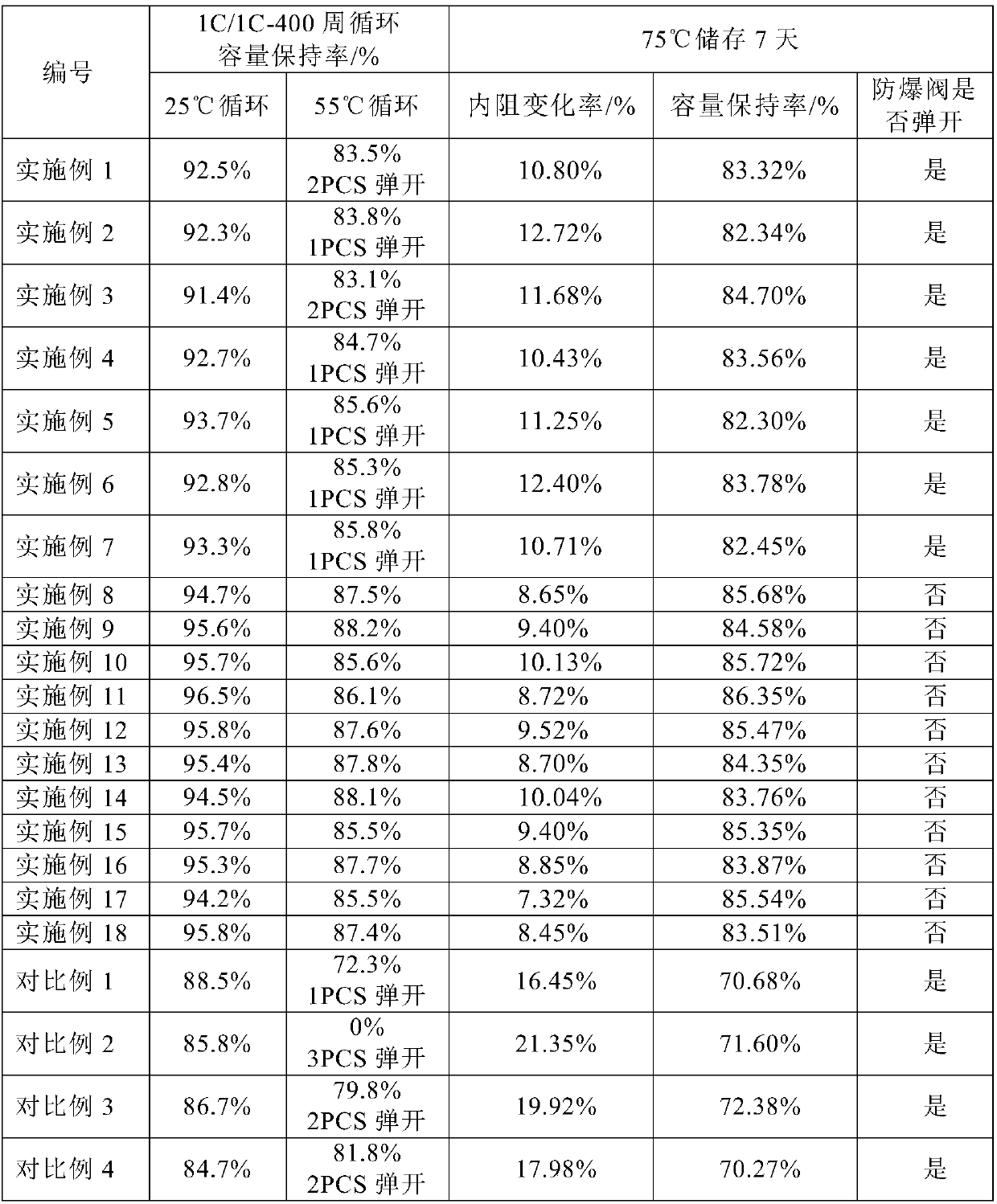
The invention belongs to the technical field of lithium-ion batteries, in particular to a lithium-ion battery electrolyte and a lithium-ion battery. Three additives, namely an additive A, an additiveB and an additive C, are added in the in the electrolyte, wherein the additive A can improve the cycle performance of a high-nickel material battery and inhibit the battery from increasing internal resistance in high-temperature storage and cyclic processes, the charging and discharging efficiency of the battery in charging and discharging processes can be improved, and self-discharging is reduced; the additive B can form a thin and compact SEI membrane on a negative electrode interface, so that a high-nickel material has relatively low interface impedance when matching with a high-volume high-compaction negative electrode material, and lithium-ions are favorably diffused; the additive C can inhibit a high-nickel battery from producing too much gas so that a battery explosion-proof valveis sprung in the long-term storage process at high temperature, and meanwhile has positive influence on the cycle life of the battery; therefore, the electrolyte guarantees that the battery has a relatively good cyclic life, the internal resistance of the battery in the use process is reduced, and when the battery is used at high temperature, potential safety hazards, which appear as the explosion-proof valve is sprung, are avoided.
Owner:DONGGUAN SHANSHAN BATTERY MATERIALS
Method of controlling battery charging
InactiveUS8040106B2Lighter and more inexpensive energy storage devicesHybrid vehiclesBatteries circuit arrangementsBattery chargePresent method
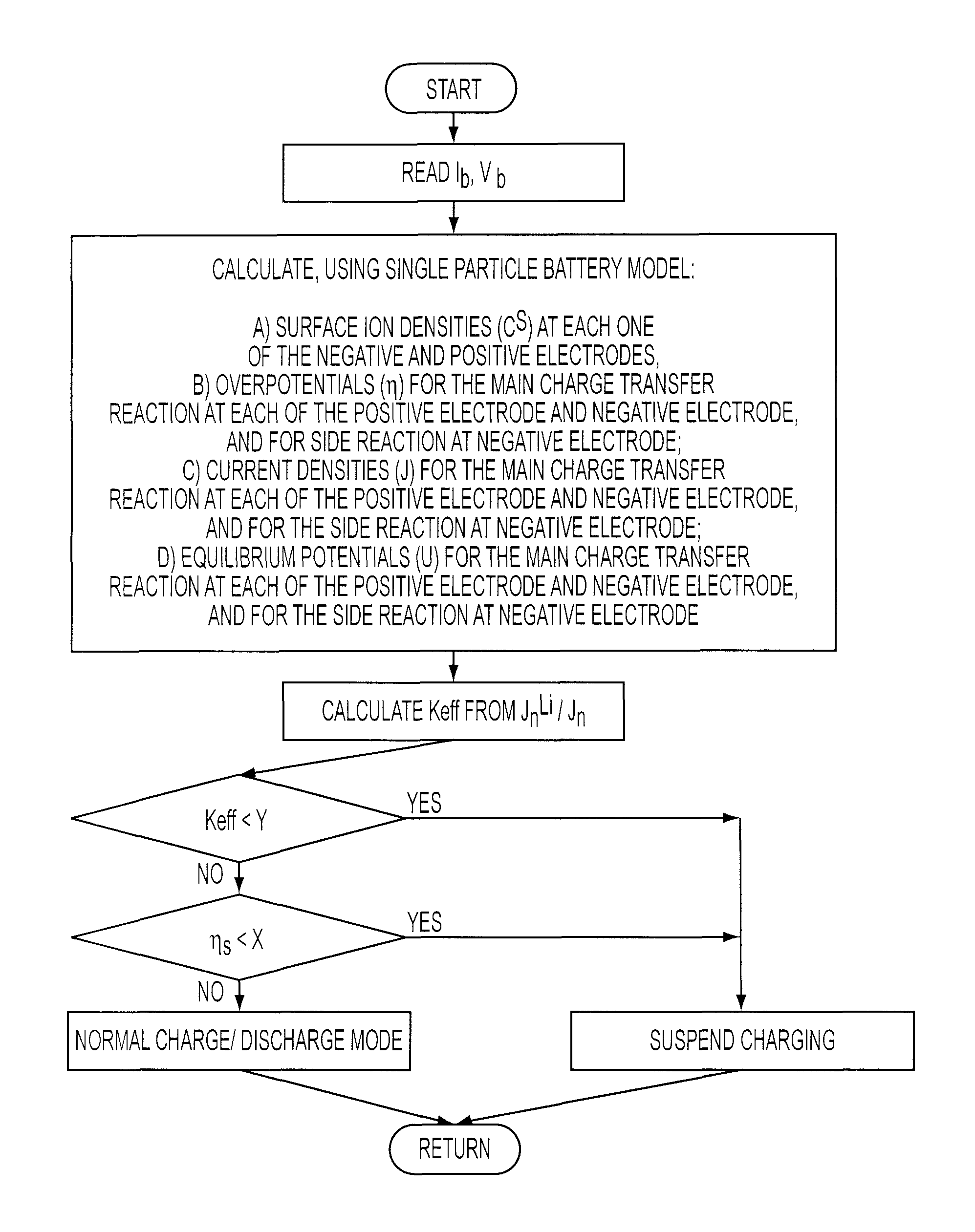
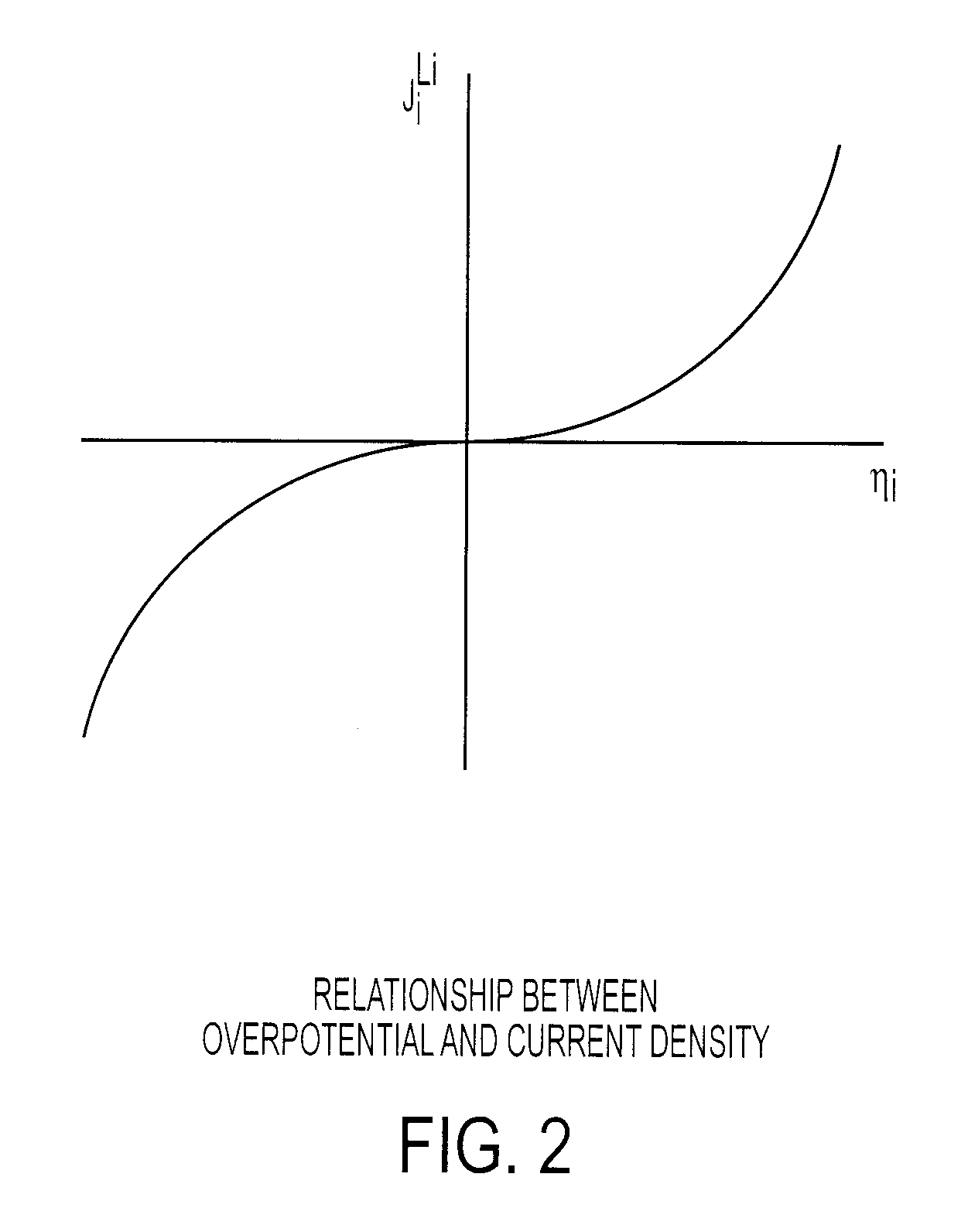
The present teachings are directed toward methods of controlling the charging of a battery. The method includes the steps of receiving current and voltage output information for the battery during a charging / discharging cycle at a certain time interval, and using a model to determine both charging efficiency of the battery and the overpotential for a side reaction. These values for the charging efficiency and the overpotential of the side reaction are then compared to respective first and second given values. If either the charging efficiency or the overpotential is less than their respective given values, then the charging of the battery is suspended. The present method is particularly applicable to Li-ion batteries.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
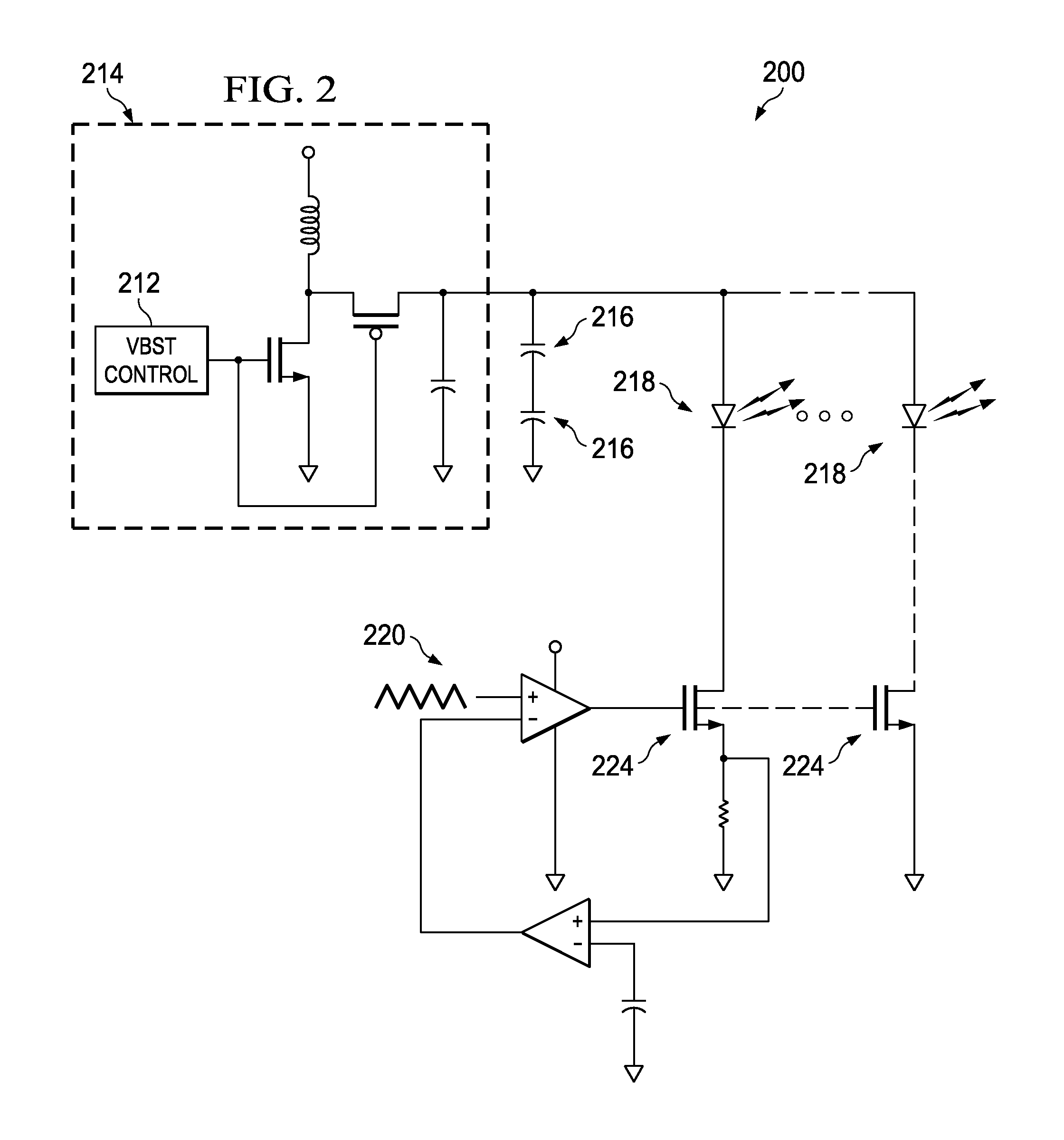
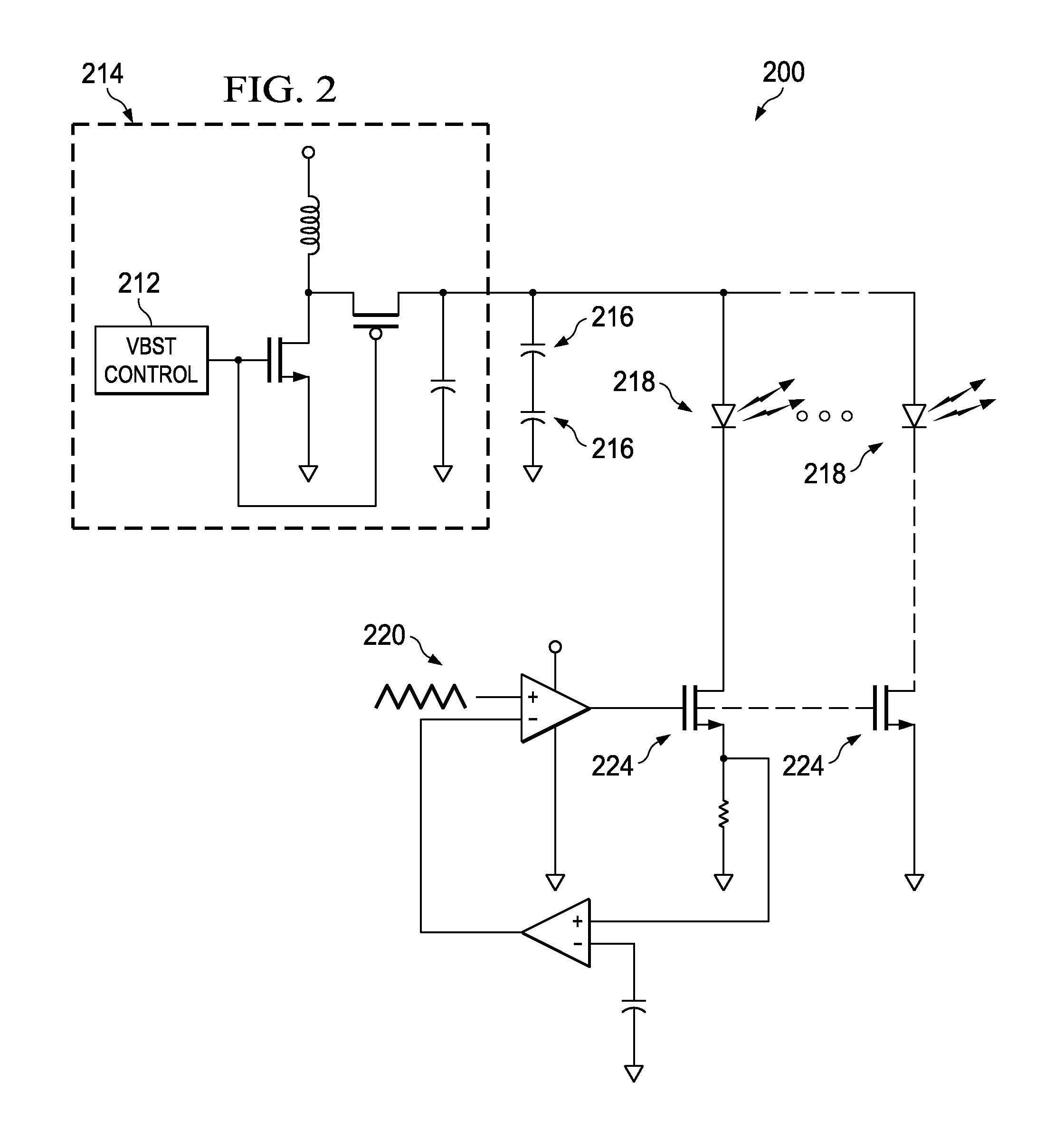
Flash LED Controller
InactiveUS20120104962A1Increase drive currentElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesElectricityElectrical resistance and conductance
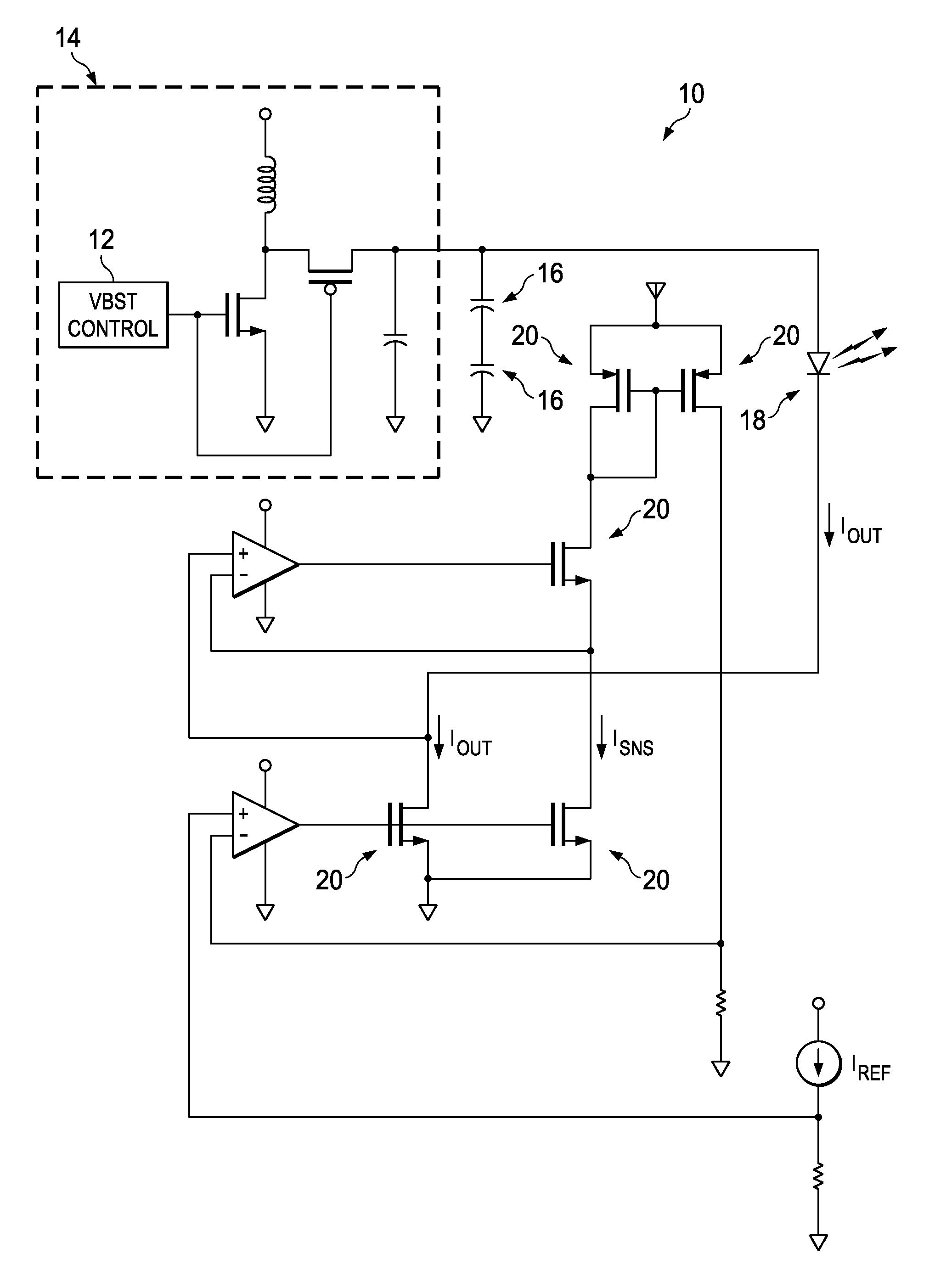
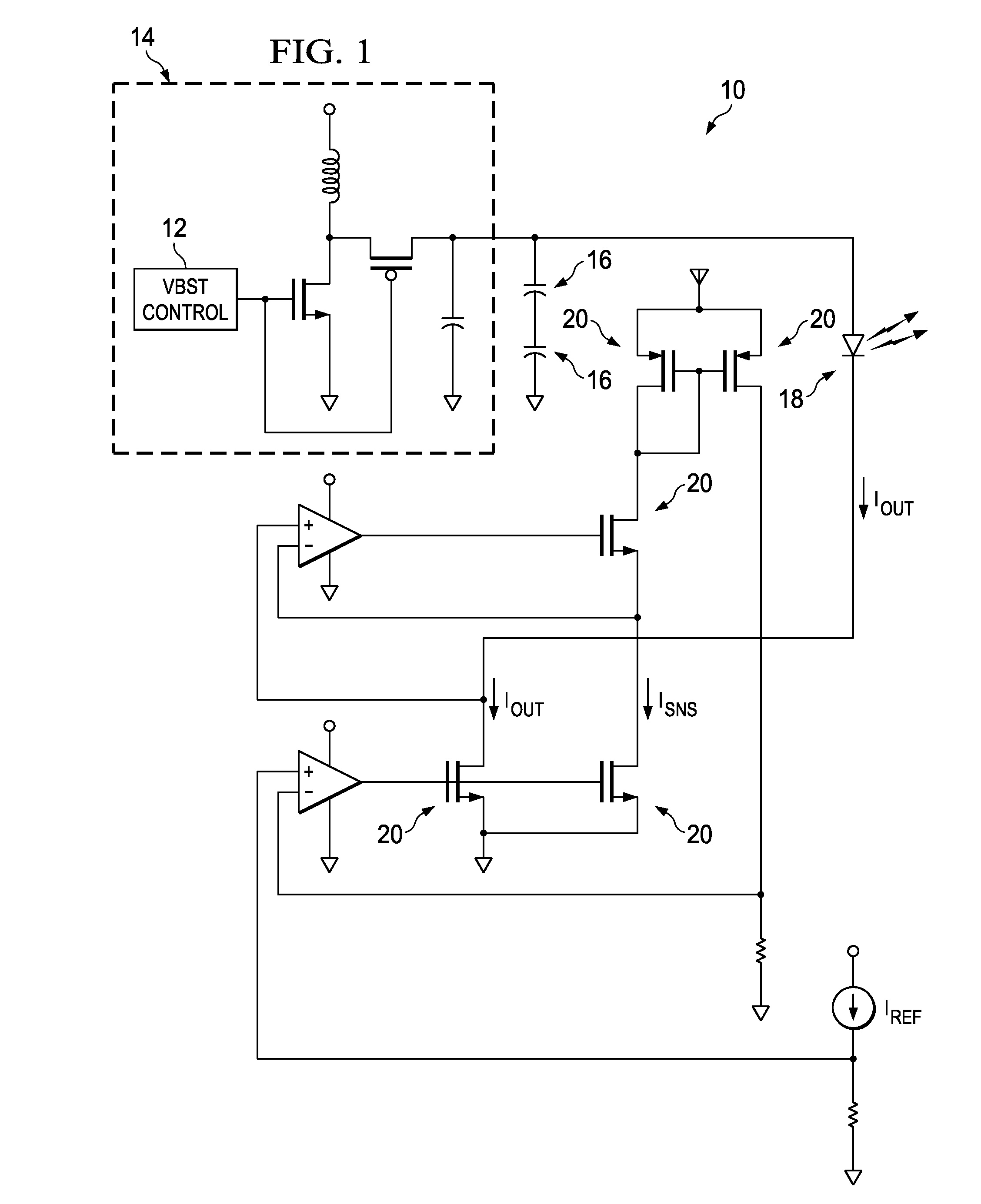
The invention provides integrated power supplies, circuit drivers, and control methods for relatively high-current drivers, usable with common battery power sources. Preferred embodiments include one or more high series resistance super-capacitors electrically connected with a power. A low resistance driver circuit regulates power supplied from the super-capacitors to the load.
Owner:TRIUNE IP
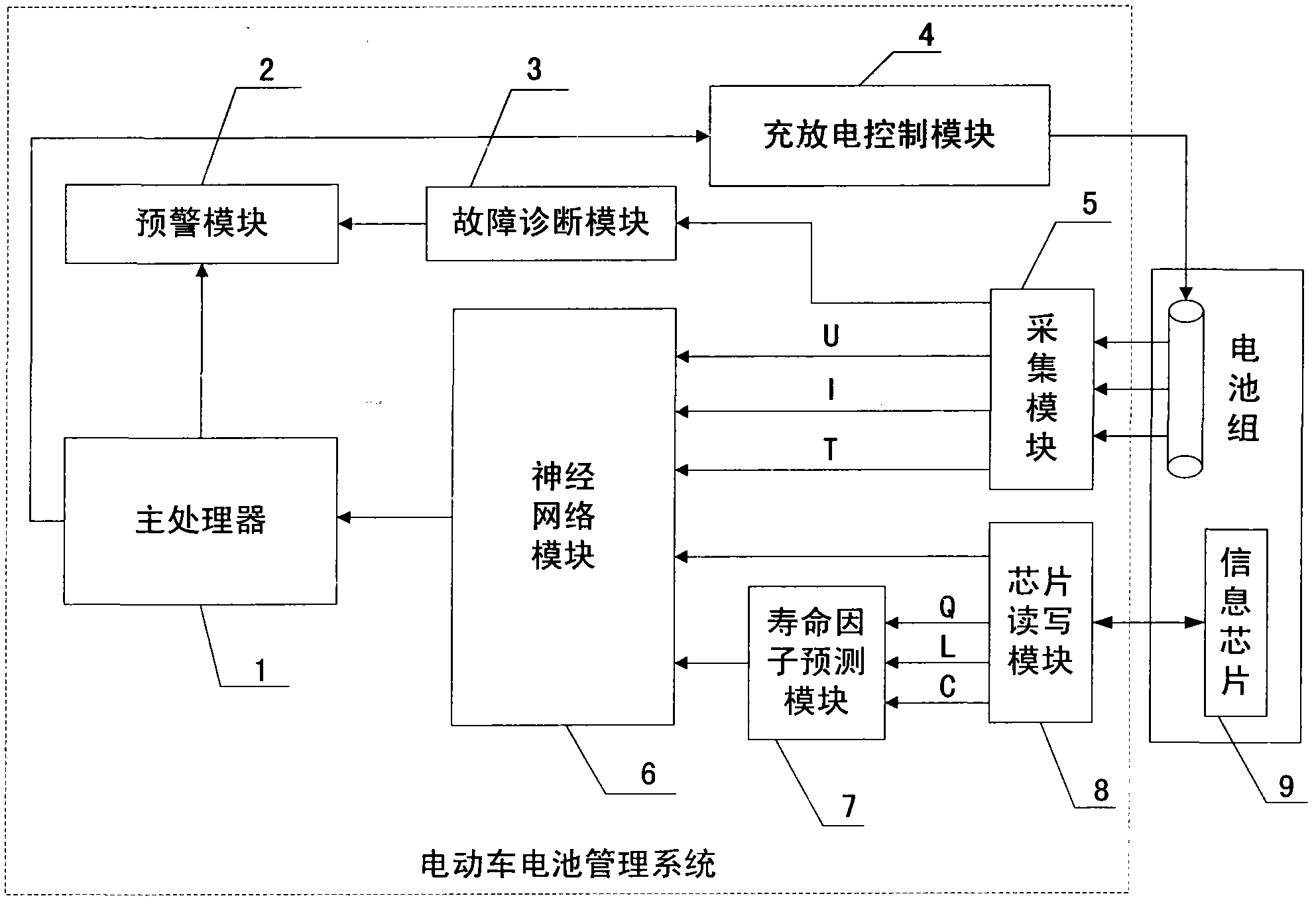
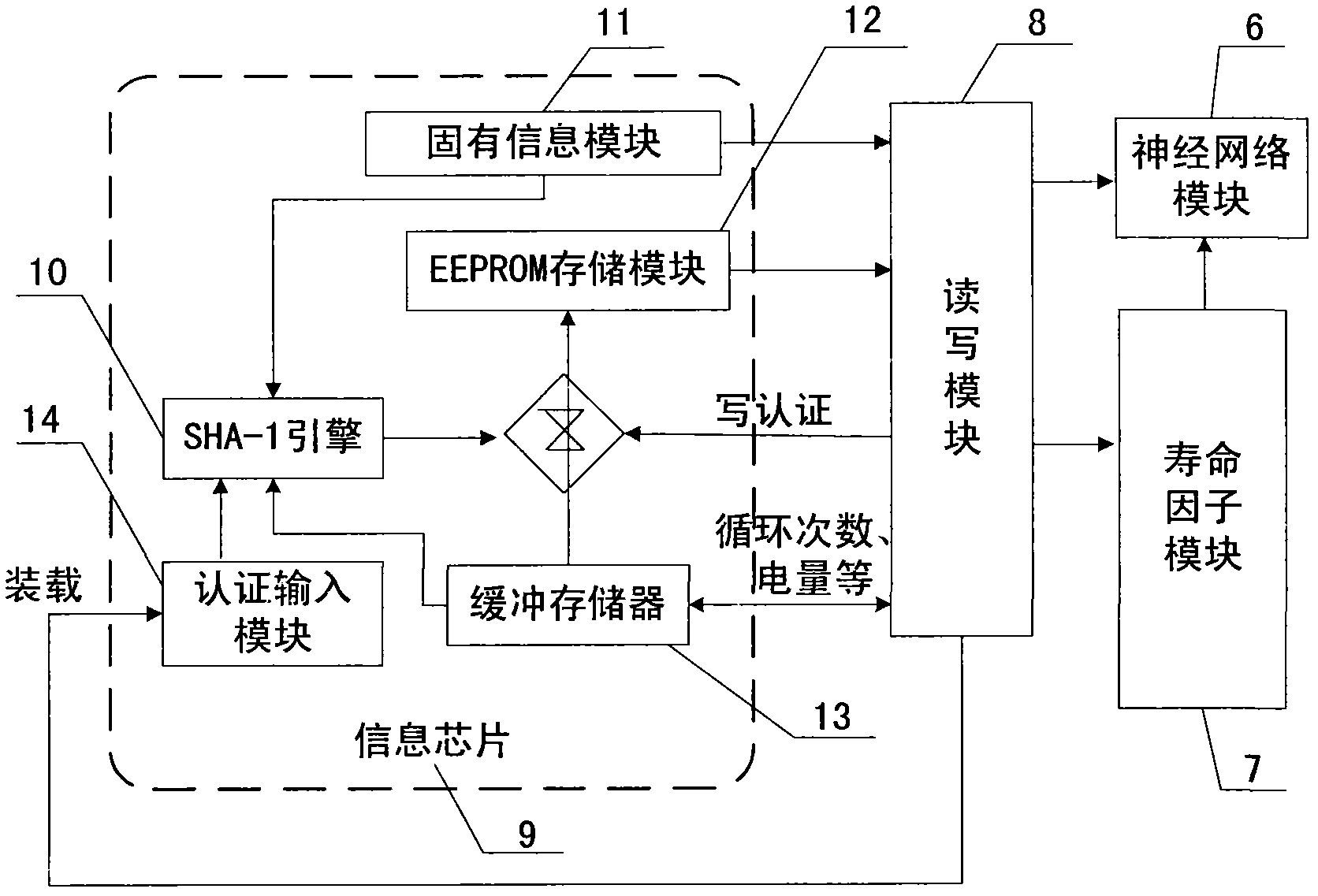
SOC estimation method of battery of electric vehicle
InactiveCN101964018AResolve identity issuesTrack usage in real timeSpecial data processing applicationsPower batteryElectrical battery
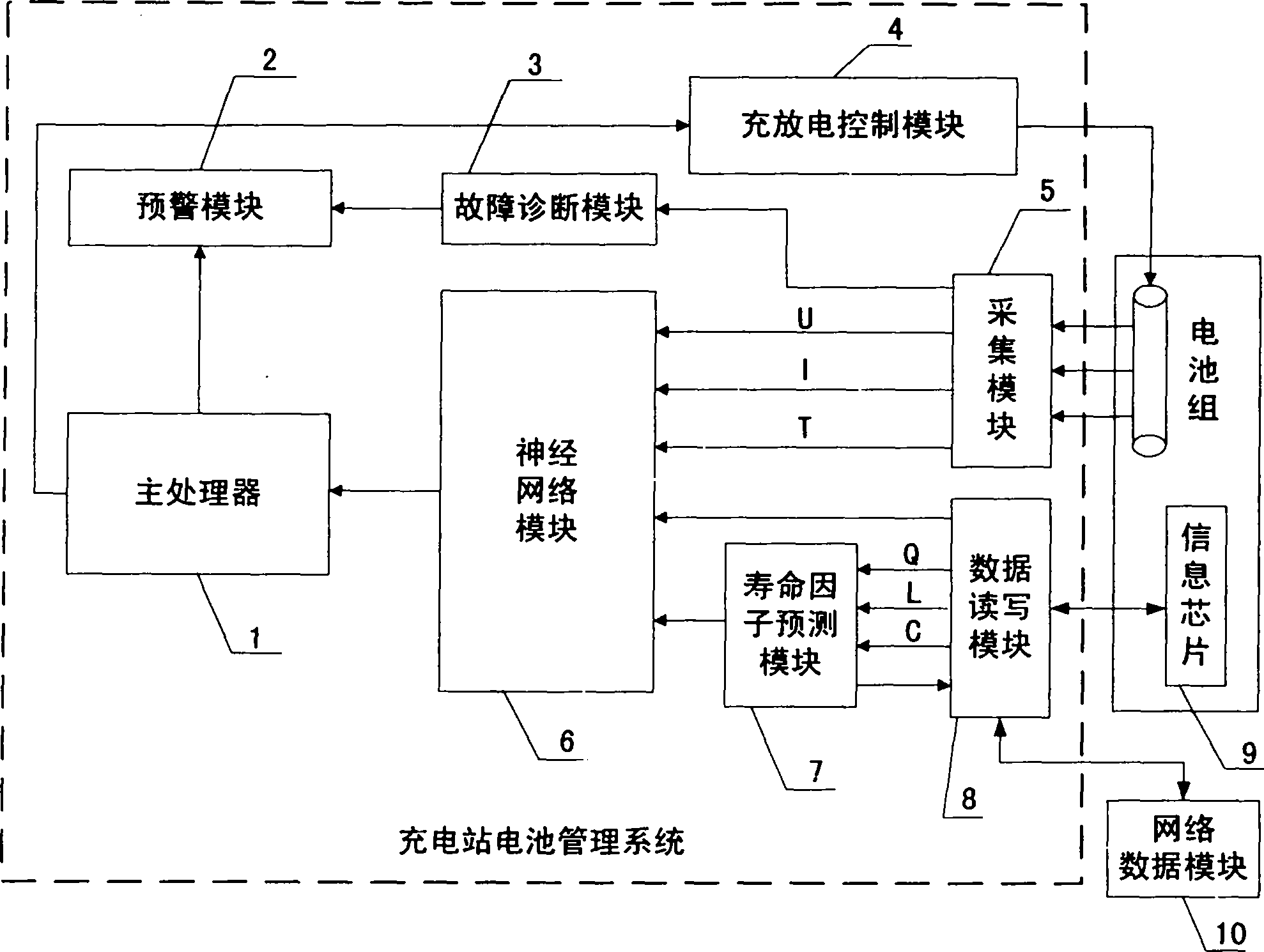
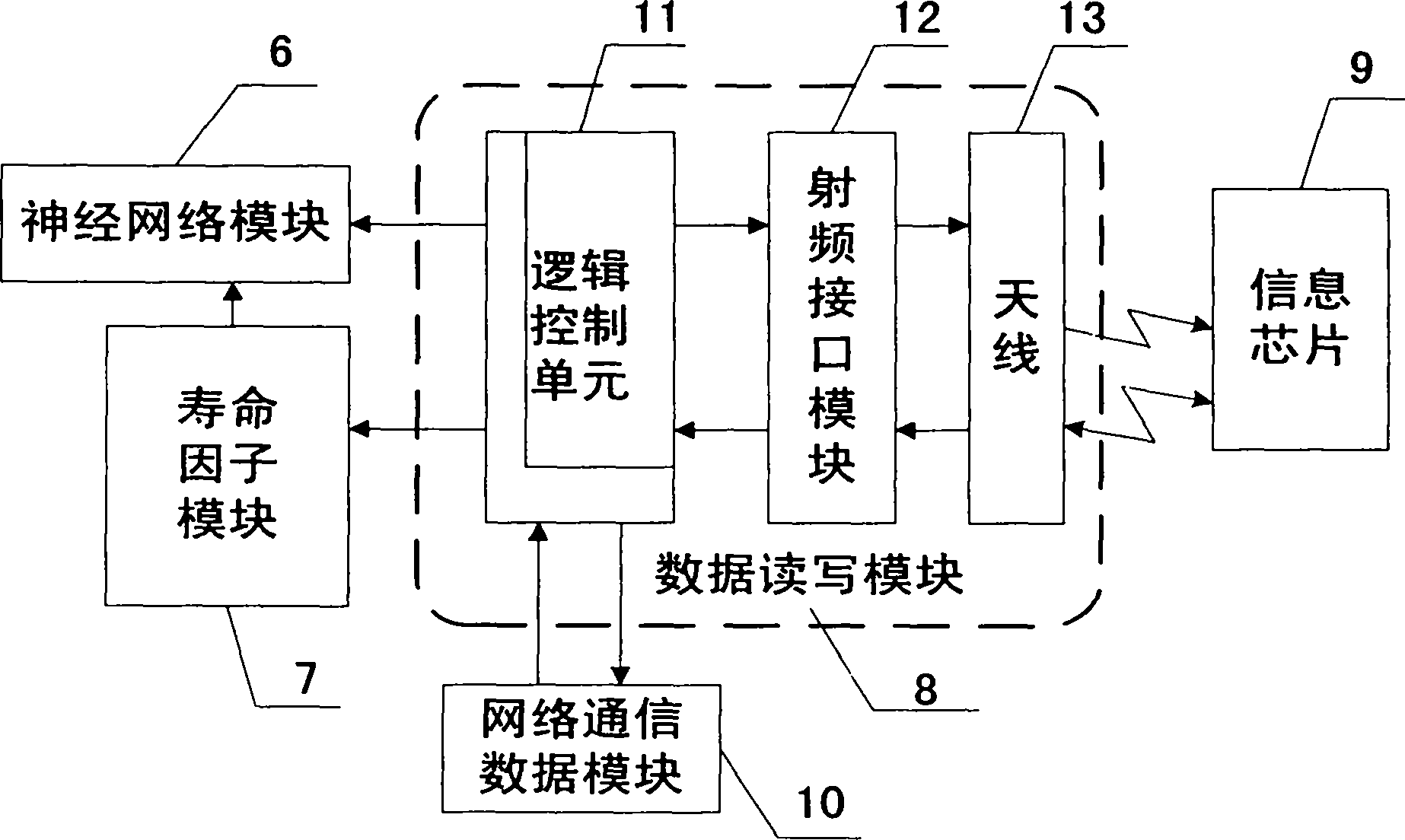
The invention relates to an SOC estimation method of a battery of an electric vehicle, which is mainly used for solving the technical problems of safety circulation of the battery, the SOC estimation algorithm of the power battery and the like. The technical scheme provides a chip for implanting information in an ordinary battery pack and a SOC neutral network estimation method based on the type of the battery and a life factor of the battery of the electric vehicle on the basis of certification requirement during the circulation of the battery and analysis of a standard module of a neutral network SOC estimation method. The information chip can ensure the compatibility of a manufacturer, a charging station and the electric vehicle with the battery pack and high safety, avoid leading counterfeit batteries to enter into the circulation field, be easy to construct a unified battery network management information platform and form a stable battery using management market scheme; and the type of the battery, the recorded charge and discharge data in recent plural times and the number of cycles, which are obtained from the information chip in the battery, as well as rated capacity recorded in the chip are inputted into a life factor analysis module, then the life state of the battery is judged, and the type of the battery and the life factor are increased as the input on the basis of taking voltage, current and temperature as the input in a neutral network standard module, thereby realizing the precise estimation of the state of charge of the battery of the electric vehicle.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
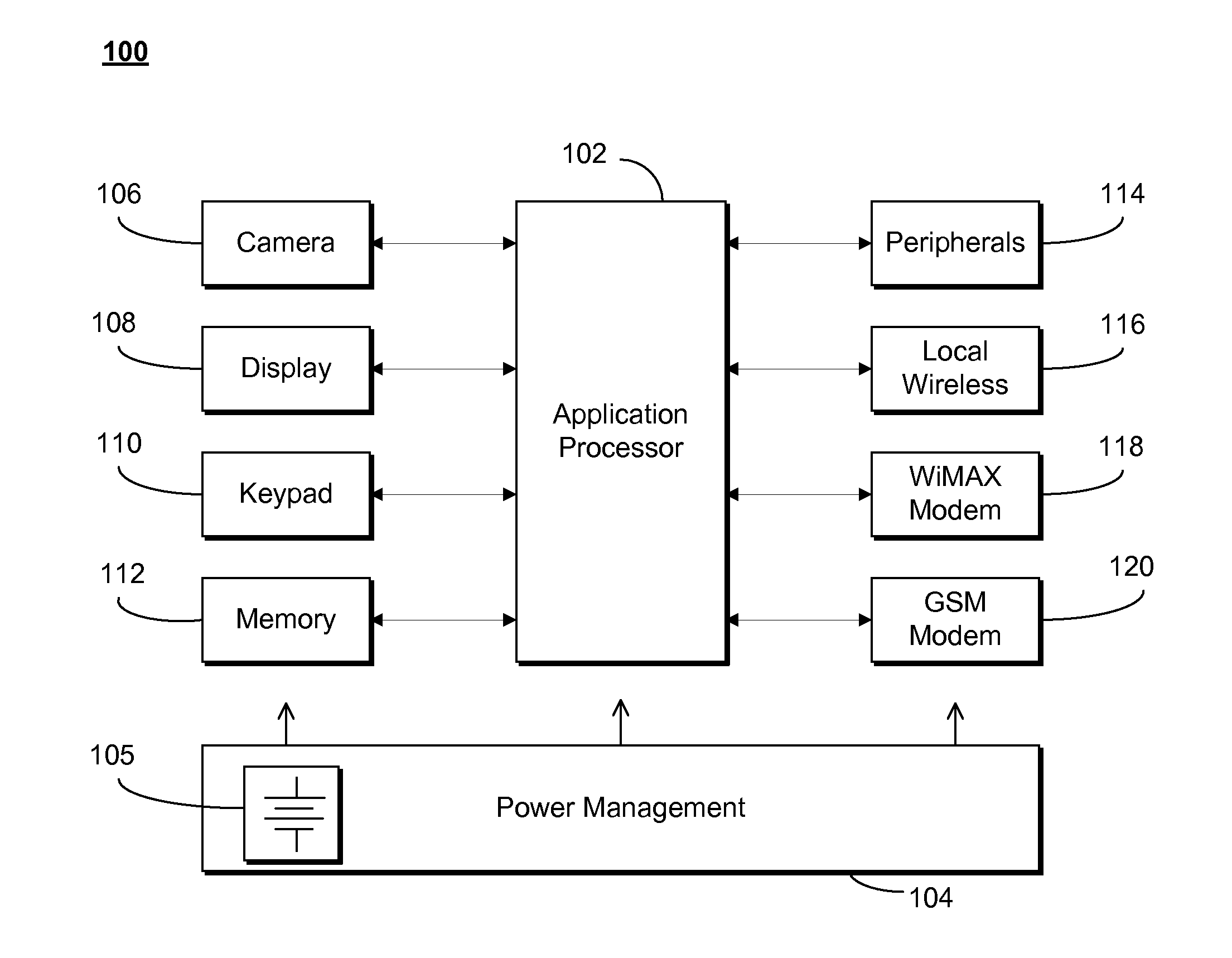
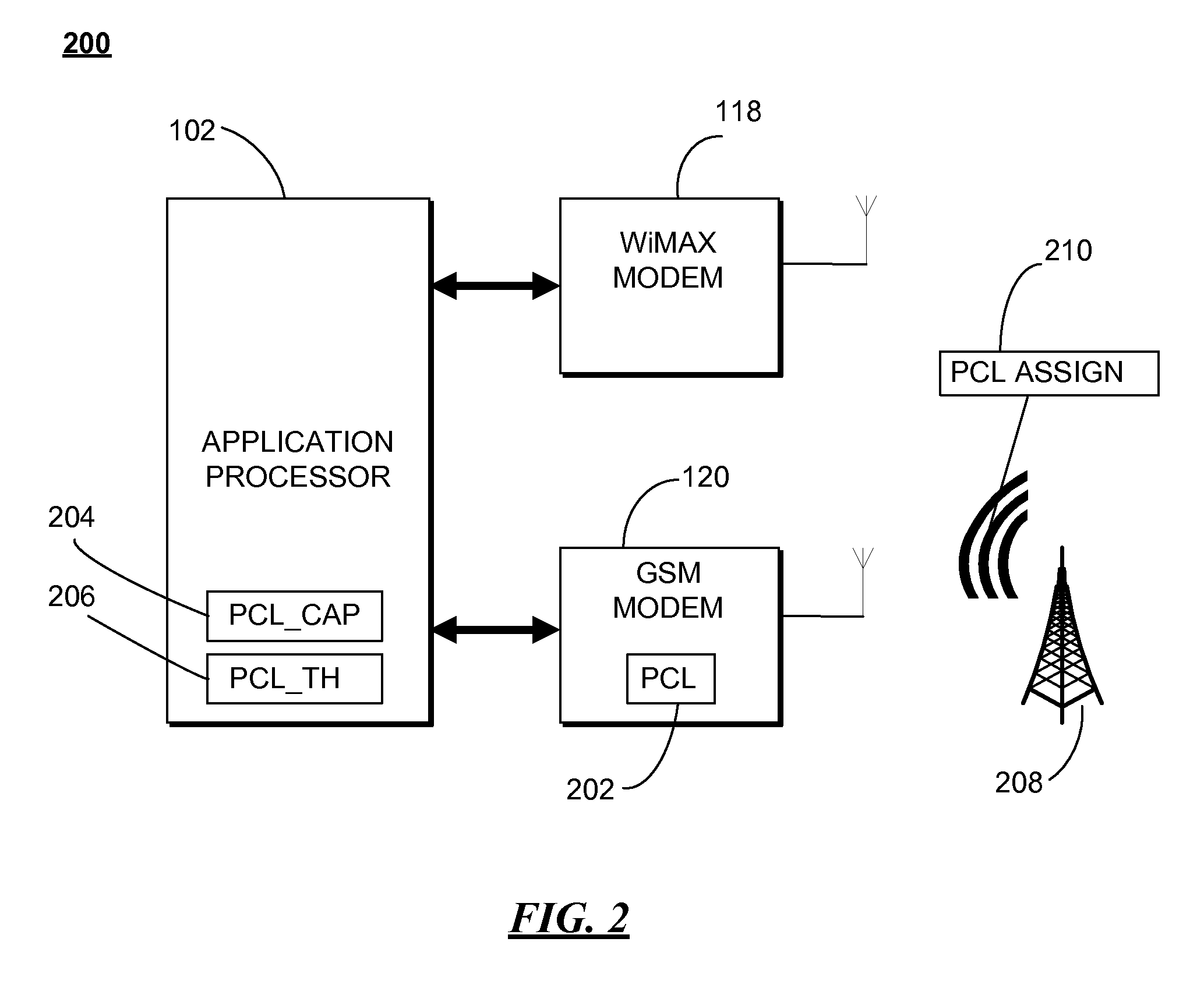
Method and apparatus for controlling power among modems in a multi-mode mobile communication device
ActiveUS20090275355A1Lower Level RequirementsEnergy efficient ICTPower managementControl powerModem device
A multi-mode communication device (100) uses a first wireless modem (118) and a second wireless modem (120) which operates independently to facilitate communication over different air interfaces. Both modems are powered by a common battery (105). When the first wireless modem engages in a communication activity, the second wireless modem's maximum operating power level is reduced. When the first wireless modem ceases communication activity, the second wireless modems full operating power range is restored.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
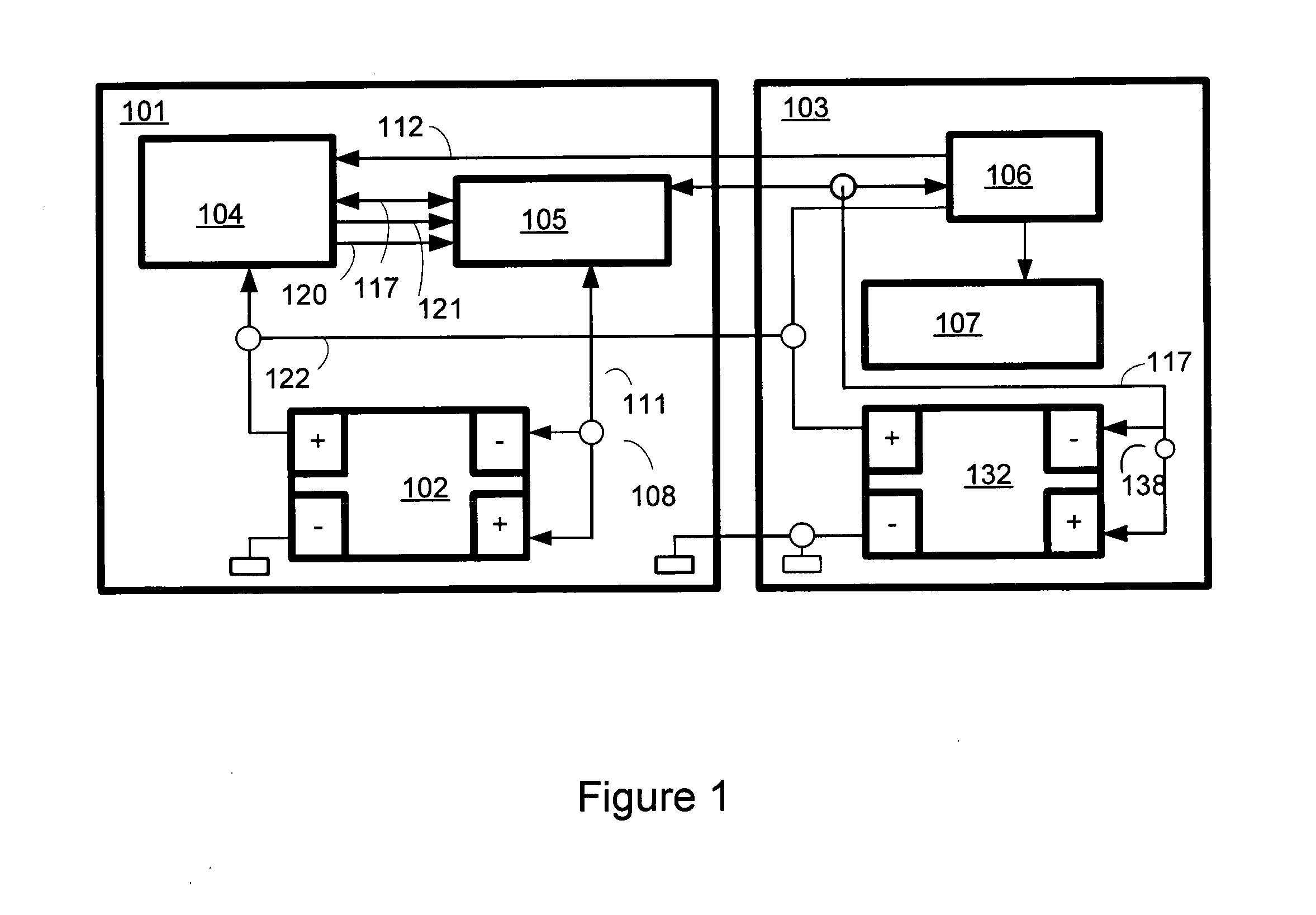
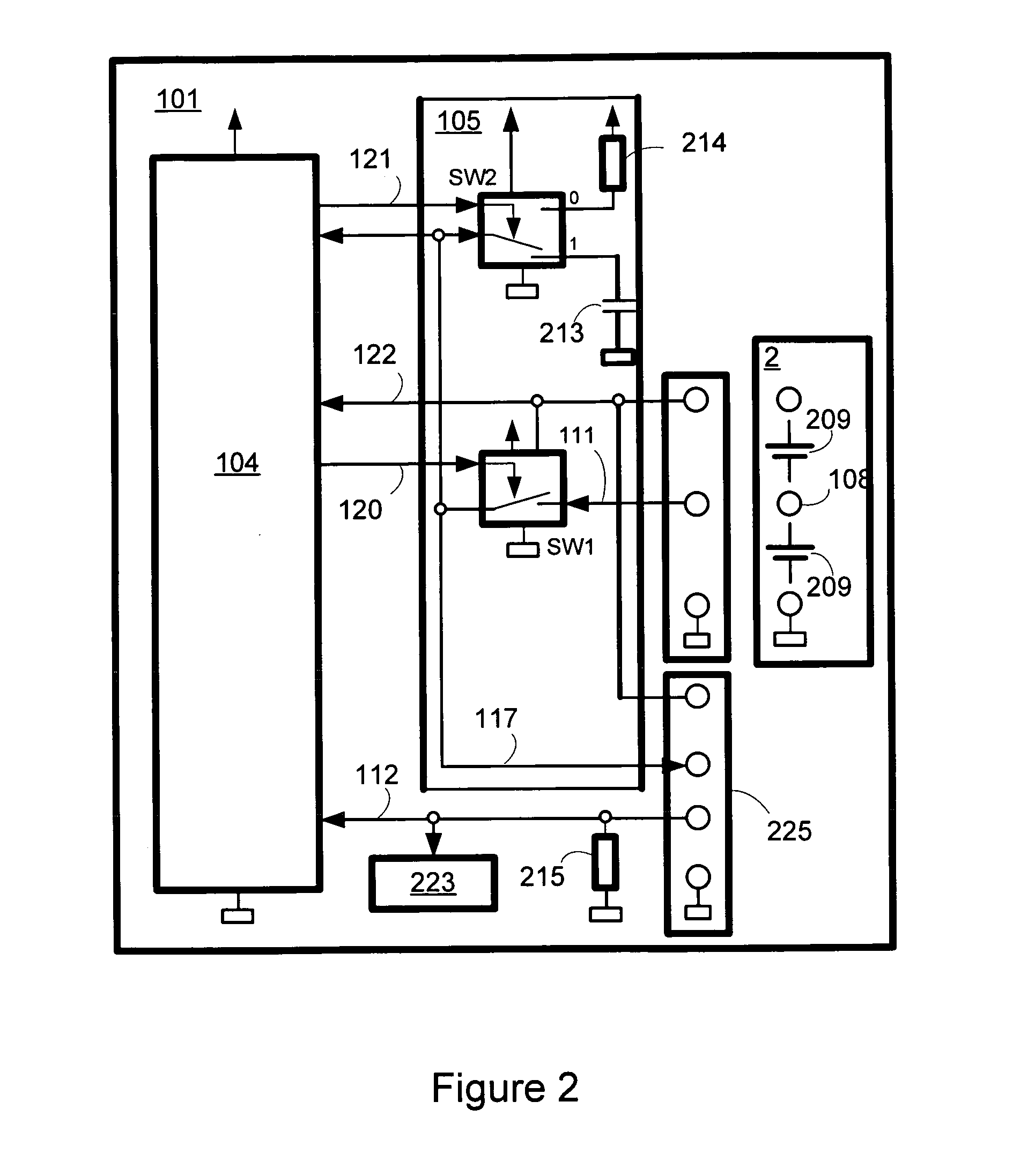
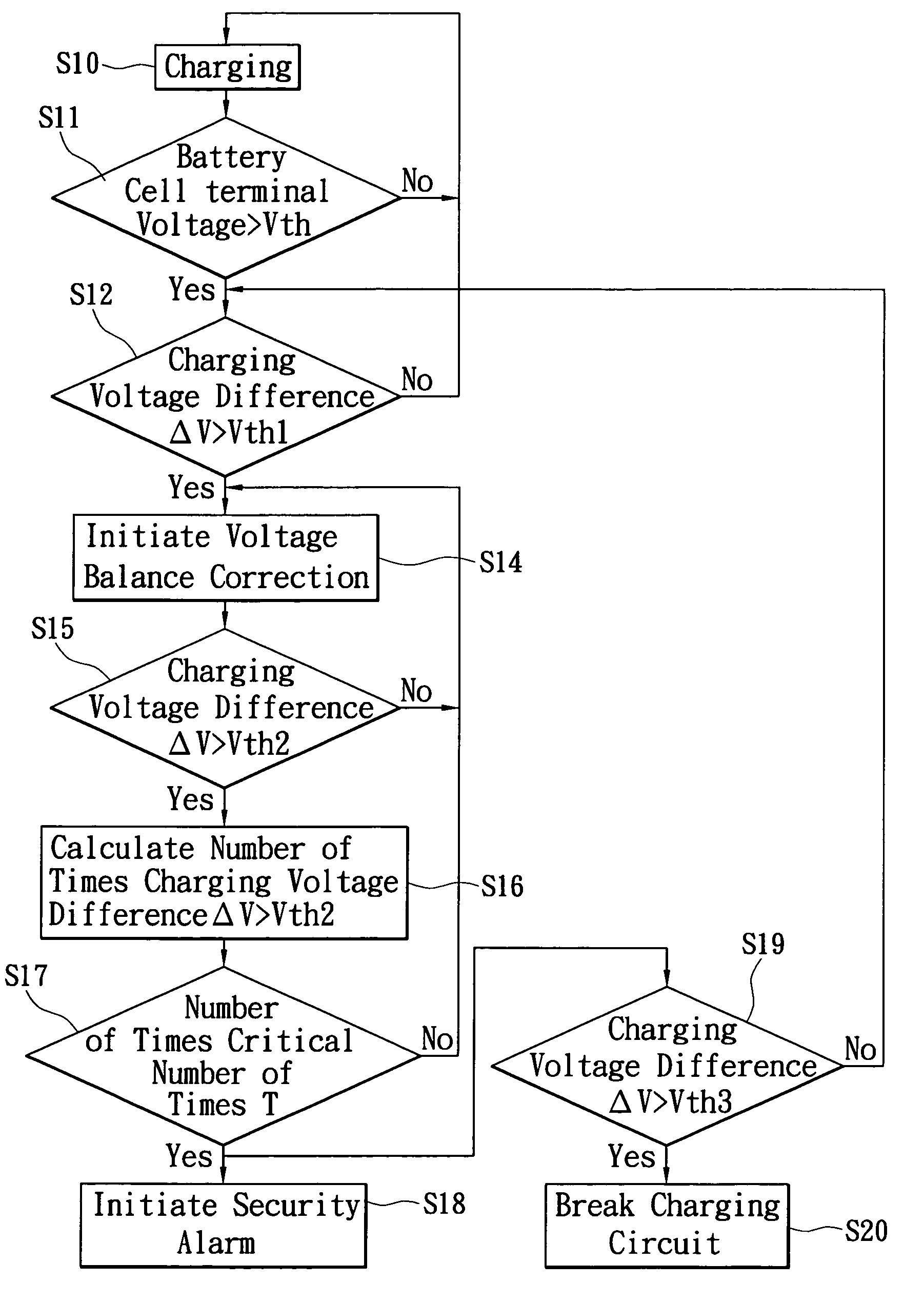
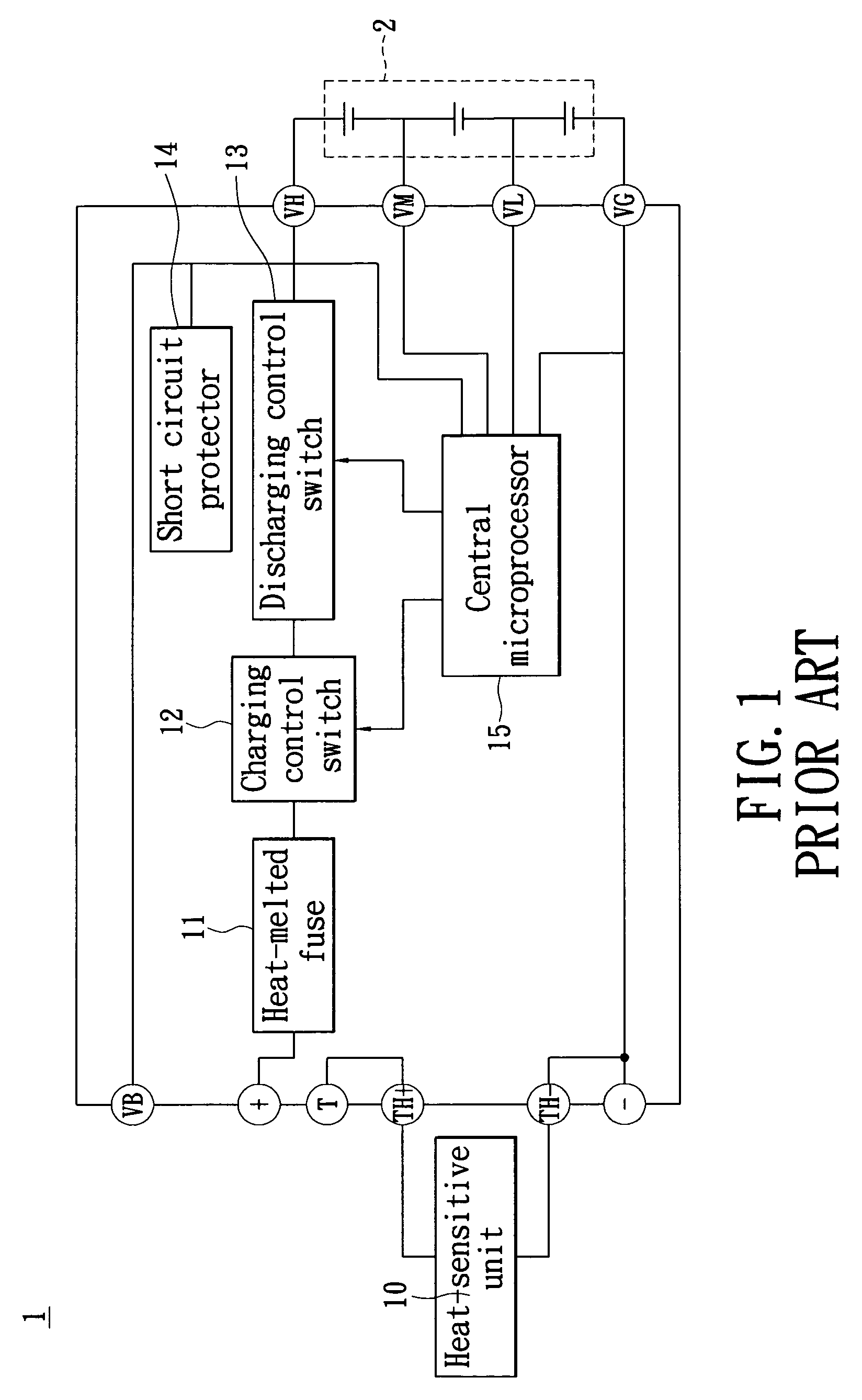
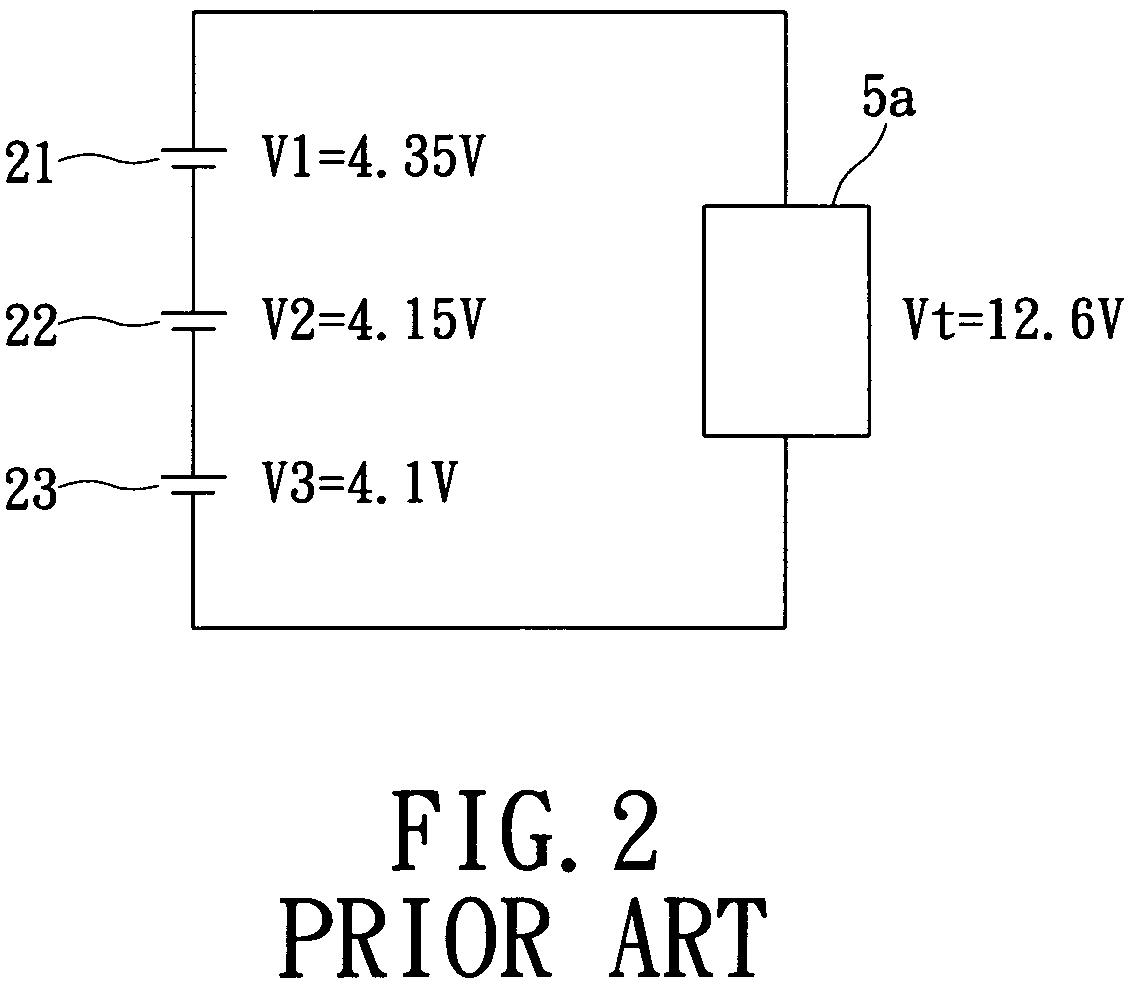
Alarm-including protection apparatus for lithium-ion battery and method thereof
InactiveUS8030898B2Avoid damageAvoid it happening againCharge equalisation circuitCurrent/voltage measurementElectrical batteryTerminal voltage
An alarm-including protection apparatus and method thereof are used to protect a lithium-ion battery with a plurality of series cells. The protection apparatus includes a voltage balance controller for detecting the terminal voltage of each cell and correcting the terminal voltage of each cell. A protection unit and the lithium-ion battery are connected in series. A microprocessor connects to the voltage balance controller and the protection unit for receiving the terminal voltage of each cell and figuring out a voltage difference between the maximum terminal voltage and the minimum terminal voltage of the series cells. According to the comparison result of the voltage difference and a plurality of critical voltage differences, the microprocessor is used to correct the terminal voltage of each cell, generate an alarm signal or stop charging to the lithium-ion battery.
Owner:CELXPERT ENERGY CORP +1
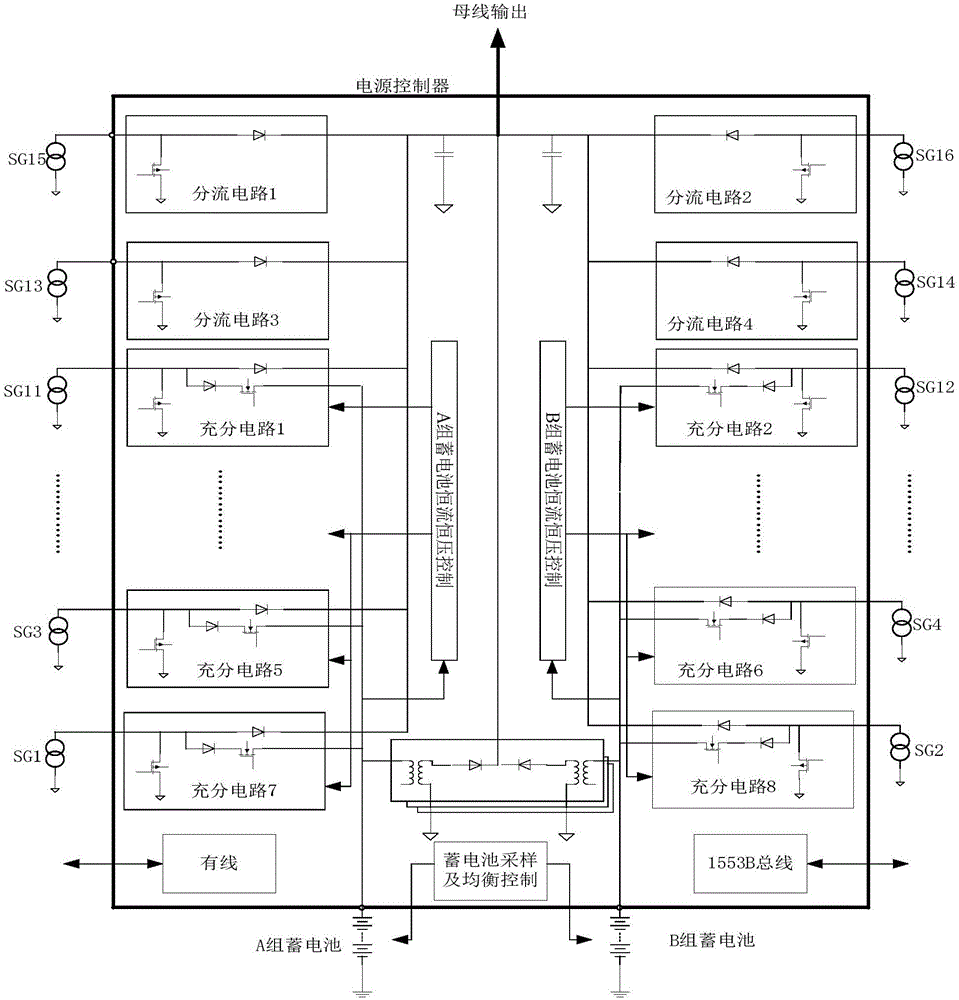
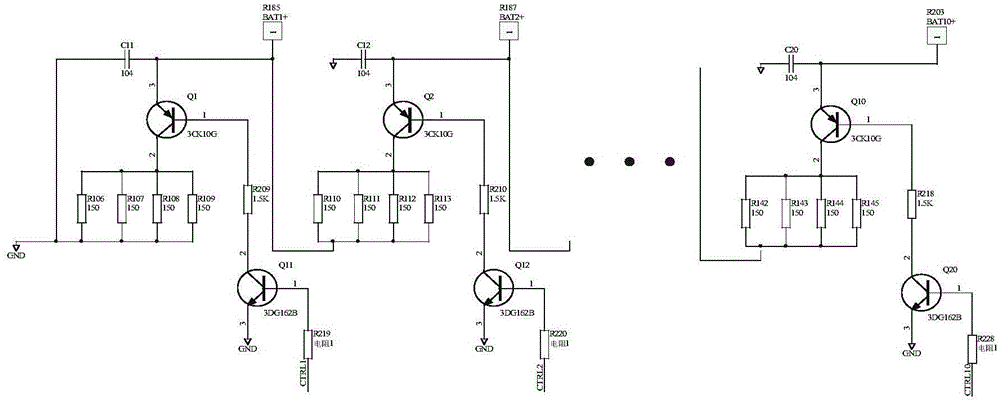
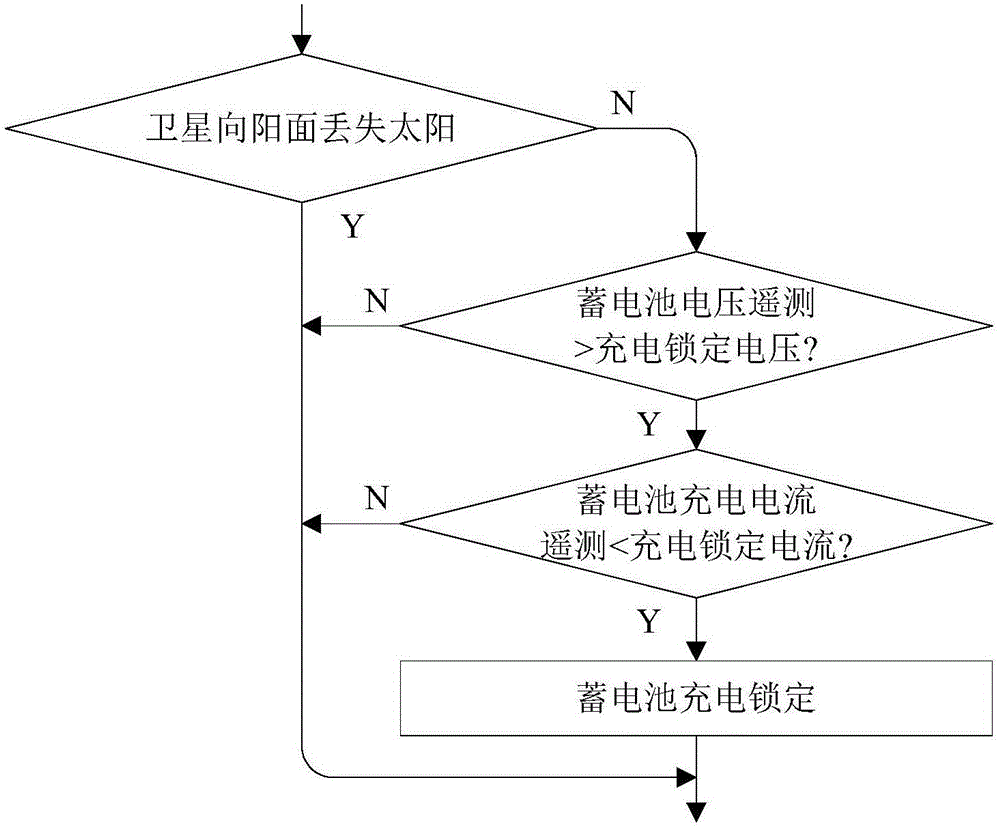
Autonomous management system of satellite lithium-ion battery pack power supply subsystem
InactiveCN105140984AStable power supplyMeet power supply and distribution requirementsEmergency protective circuit arrangementsSecondary cellsElectrical batterySolar cell
The invention discloses an autonomous management system of a satellite lithium-ion battery pack power supply subsystem. The autonomous management system comprises an in-orbit management module, an emergency protection module, a balance control module and a lower computer module, wherein the in-orbit management module is used for preventing a lithium-ion battery pack from being excessively charged; the emergency protection module is used for preventing the lithium-ion battery pack from being excessively discharged; the balance control module is used for balancing the voltage among various single lithium-ion batteries in the lithium-ion battery pack; and the lower computer module is used for sampling and comparing the voltage of various single lithium-ion batteries in the lithium-ion battery pack. Through charging and discharging adjustment control on the battery pack and shunt adjustment of excessive power output by a solar cell array, transform control on the power supply subsystem is finished; the power supply stability of a busbar and various subsystems is kept; and the power supply and distribution requirements of load on the satellite are met. According to the autonomous management system, in-orbit full-autonomous control on the satellite lithium-ion battery pack power supply subsystem is achieved; and the reliability of the system is also greatly improved fundamentally.
Owner:SHANGHAI SATELLITE ENG INST
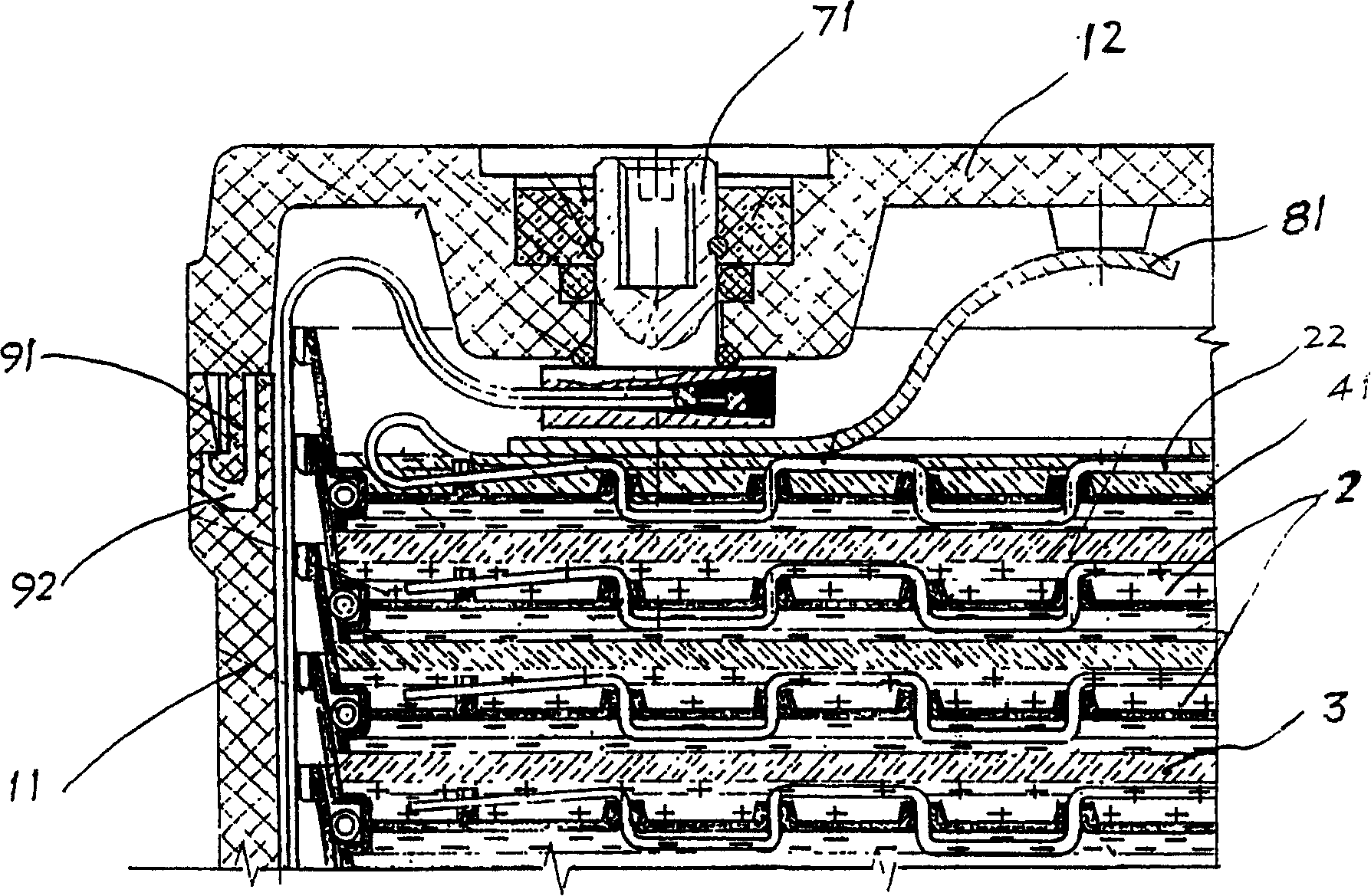
Long life high capacity bipolar-type pole plate lead acid battery for electric automobile
InactiveCN101202355AImprove corrosion resistanceReduce the likelihood of feverFinal product manufactureSmall-sized cells cases/jacketsElectrical batteryEngineering
The invention provides a dual-pole polar plate lead-acid accumulator with long service life and high capacity used for an electric vehicle. A polar plate group consists of a dual-pole polar plate, an upper end polar plate, a lower end polar plate and a clapboard; the polar plate group is arranged in a battery frame which presses the polar plate group and gives a suitable pressure to active matter. The invention is technically characterized in that one surface of an anode of a baseplate of the dual-pole polar plate is provided with a conductive needle and one surface of a cathode is provided with a conductive column; furthermore, electrode modification is carried out for the baseplate and the conductive needle. After the modification, the specific capacity of the battery is 45-50Wh / kg, which is improved by 20%-30% compared with the existing normal battery. The design service life is 3-8 years, which is improved 2-3 times compared with the normal battery. The battery is mainly used for electric vehicles, electric bicycles, etc., as power supplies, and can be also used for all sites where the existing normal lead-acid batteries are applied.
Owner:夏振明
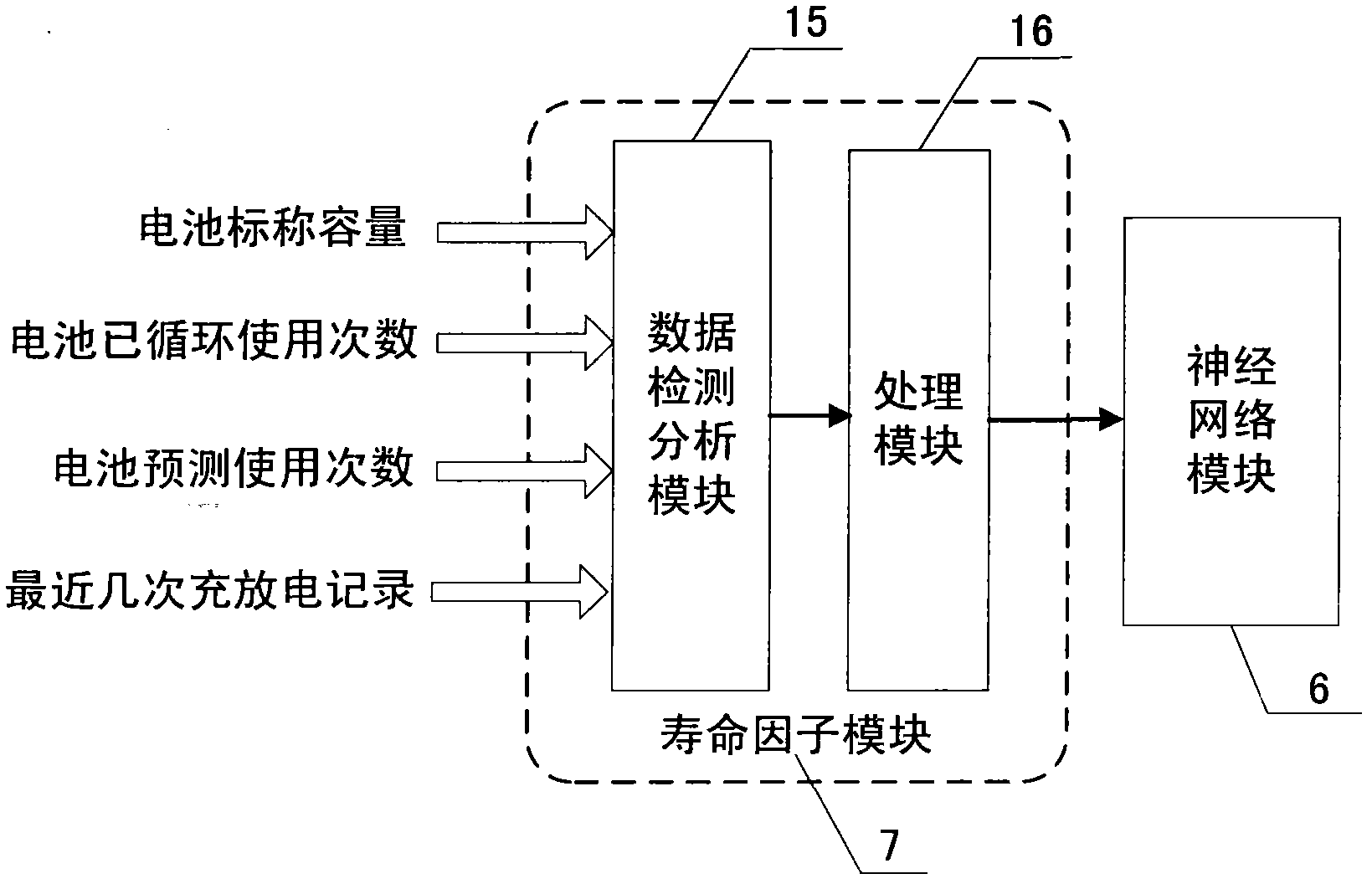
Evaluation method for system on chip (SOC) of charging station battery
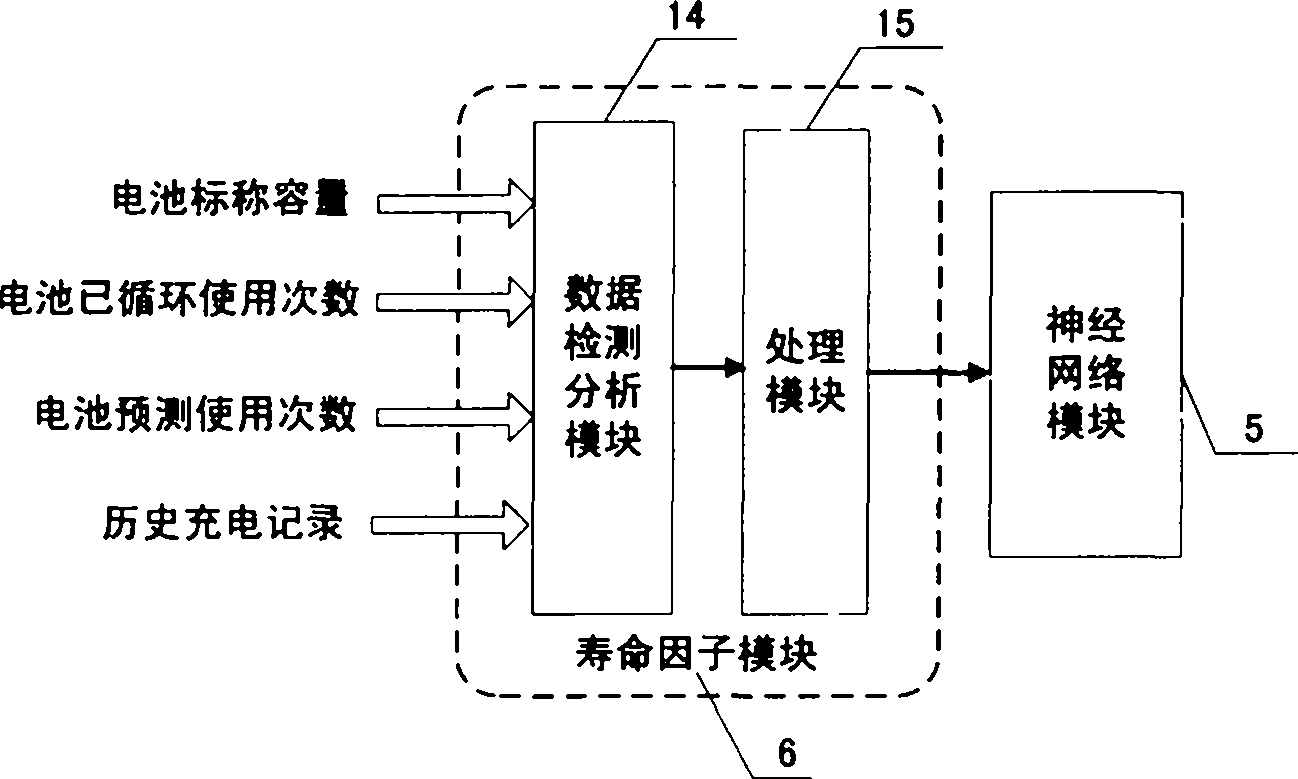
InactiveCN102385660AResolve identity issuesImprove real-time performanceBiological neural network modelsSpecial data processing applicationsNerve networkElectrical battery
An evaluation method for a system on a chip (SOC) of a charging station battery mainly solves the technical problem of charging station battery identity authentication and management and SOC evaluation algorithm of a charging station battery. The technical scheme is that: providing a charging station battery SOC nerve network evaluation method on the basis of standard model analysis of a charging station battery management scheme and a SOC evaluation method of a nerve network under the environment of an intelligent power grid based on type and life factor. A reading-writing module in a management system is used for reading inherent output information including a sole battery information identify (ID) number, a battery type, rated capacity and the like stored in an information chip of an ordinary battery, and rapid battery authentication under an united authentication system can be achieved. The charging station battery management system can use historic charging data of a battery from a network server through communication of a process layer network and a between station network of the charging battery so as to fit a curve of circulation time and electricity amount value, work out the life factor and judge the life state of the battery. On the basis that voltage, current and temperature serve as an input in the standard model of the nerve network, the battery type and life factor are added as input so as to achieve accurate evaluation of the charge state of the charging station battery.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
Lithium-ion battery and electric vehicle utilizing the same
InactiveUS20170214018A1Avoid fireAvoid explosionSmall-sized cells cases/jacketsLarge-sized cells cases/jacketsElectrical batteryEngineering
The present invention relates to a lithium-ion battery and an electric vehicle utilizing the lithium-ion battery. The lithium-ion battery comprises a housing, and battery cell group disposed in the housing, wherein, a fire-extinguishing material layer is provided between the battery cell group and the housing, and the housing is provided with drain hole. The technical scheme of the present invention can effectively prevent fire and explosion of lithium-ion battery, and can significantly improve the safety of lithium-ion battery in use.
Owner:ZHEJIANG CHAOWEI CHUANGYUAN INDUSTRAIAL
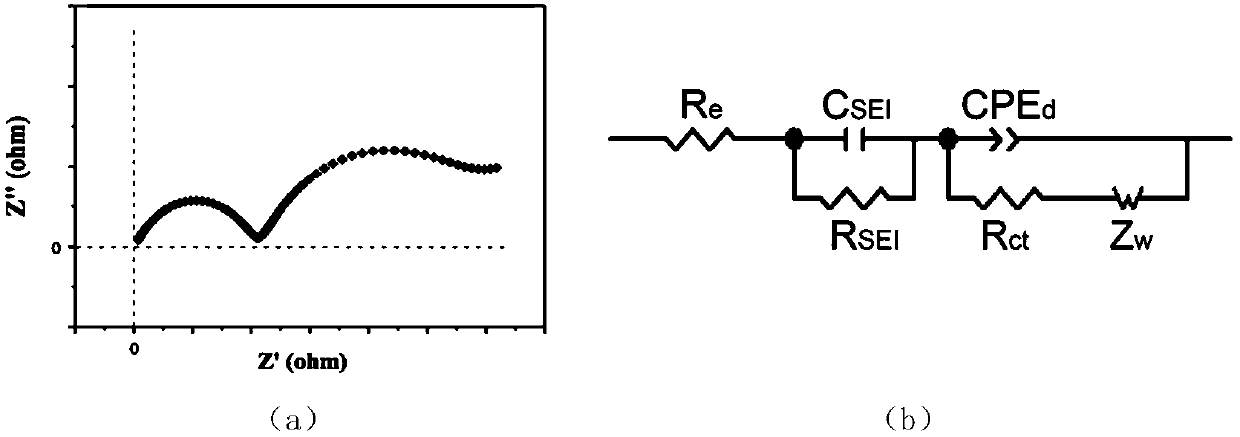
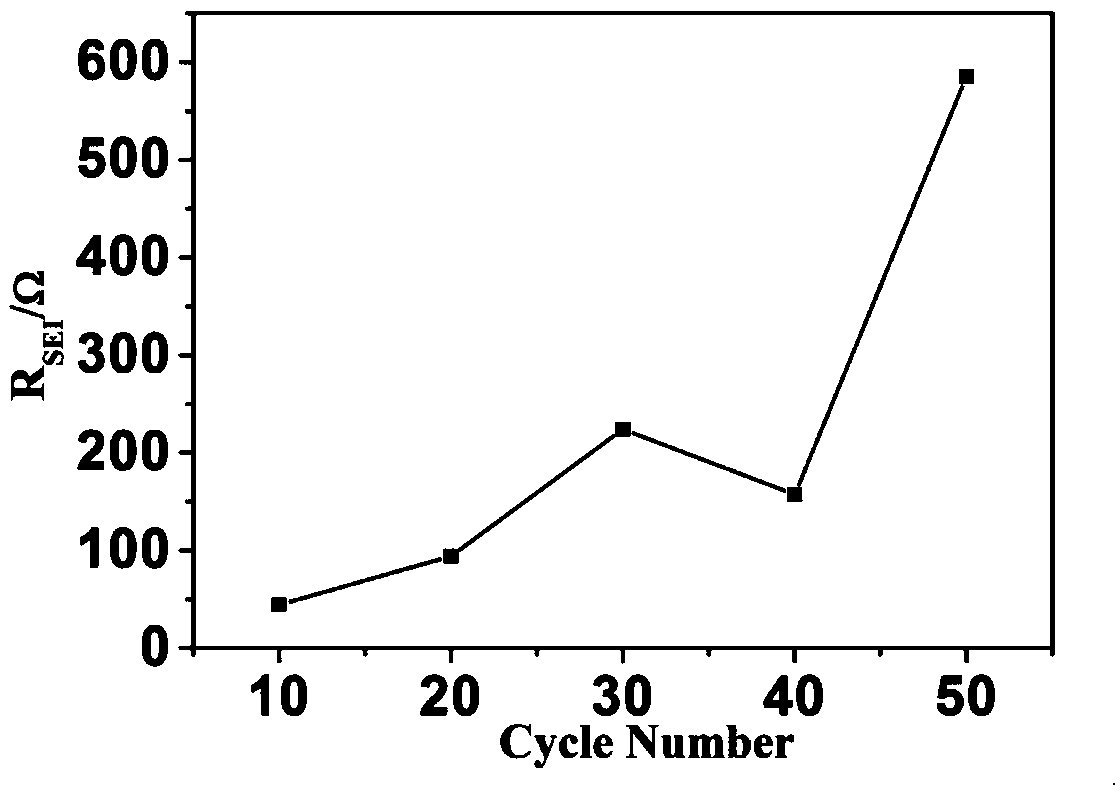
Lithium ion battery failure analysis method based on alternating current impedance method
ActiveCN109581240AAssess lifeAssess securityElectrical testingSecondary cells charging/dischargingFilm resistanceElectrical battery
The invention provides a lithium ion battery failure analysis method based on an alternating current impedance method. The safety performance of a lithium-ion battery has attracted much attention, anda negative electrode of the lithium ion battery is easily subjected to lithium evolution under the abuse condition, so that a lithium dendritic crystal is formed, and thermal runaway or even explosion of the battery is caused. According to the lithium ion battery failure analysis method based on the alternating current impedance method provided by the invention, an electrochemical alternating current impedance testing method is adopted, a relationship between an alternating current impedance spectrum signal and the internal environment of the battery is analyzed, the SEI film resistance change can be analyzed from an alternating current impedance spectrum, and therefore the state of short circuit in the dendritic crystal of the battery can be quickly and accurately predicted without damaging the battery, thereby evaluating the service life and the safety of the battery.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Battery crush protection system
ActiveUS20160329538A1Reduce functionIncrease the amount of compressionFinal product manufactureBattery isolationElectrical batteryEngineering
The following description relates to systems and methods for a vehicle battery. The vehicle battery may be a Lithium-ion battery, and may comprise a plurality of prismatic shaped battery cells, arranged and stacked to form a series of battery cell groups, and where protective casings or partitioned chambers of a protective casing enclose each battery cell group. The protective casings, or component segments of a protective casing, may be coupled to one another by a series of ridges and mating grooves. A protective casing may alternatively comprise of a monolithic extrusion comprising a plurality of partitioned chambers. The protective casing may be configured to absorb a threshold compressive force without resulting in deformation of the battery cell groups.
Owner:A123 SYSTEMS LLC
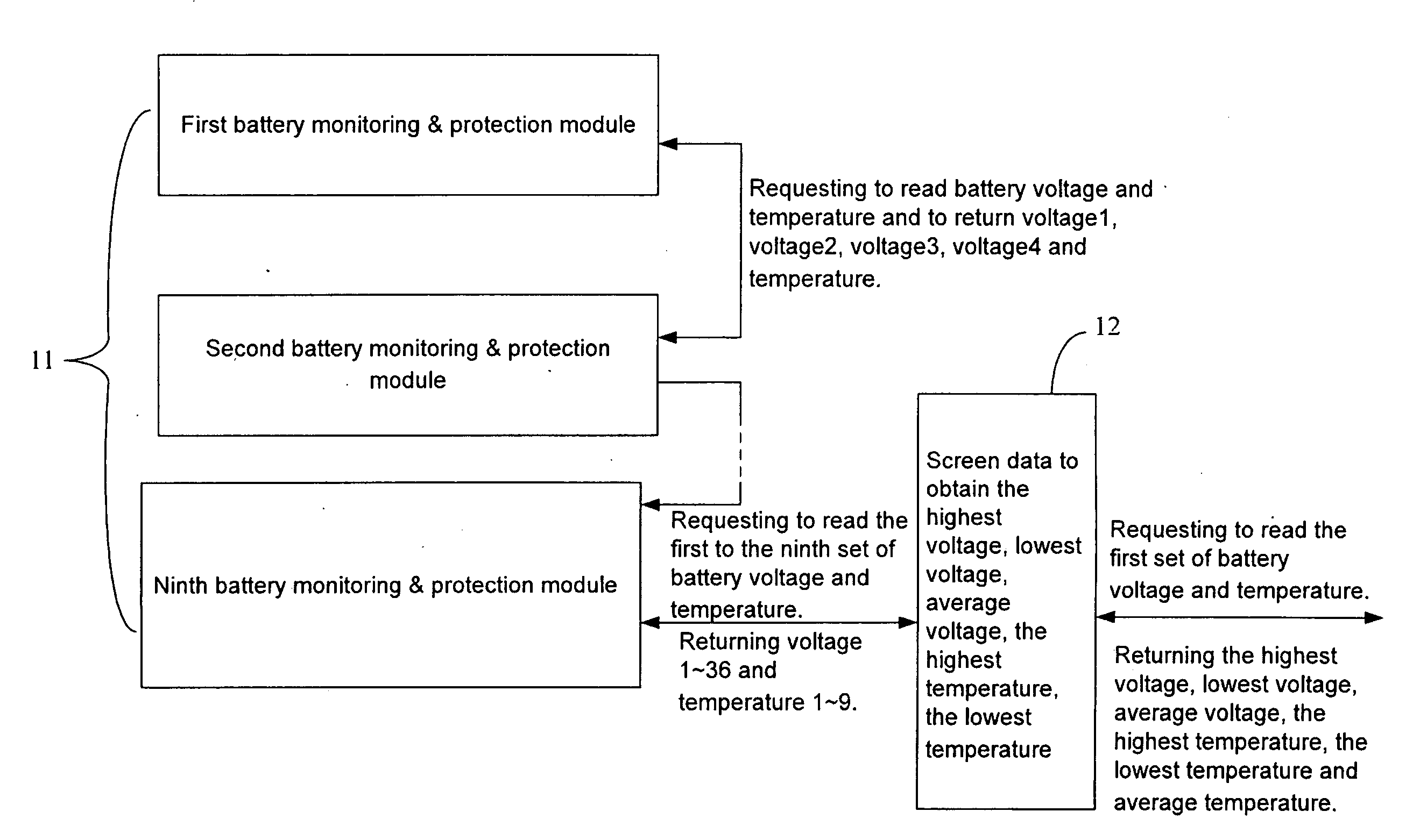
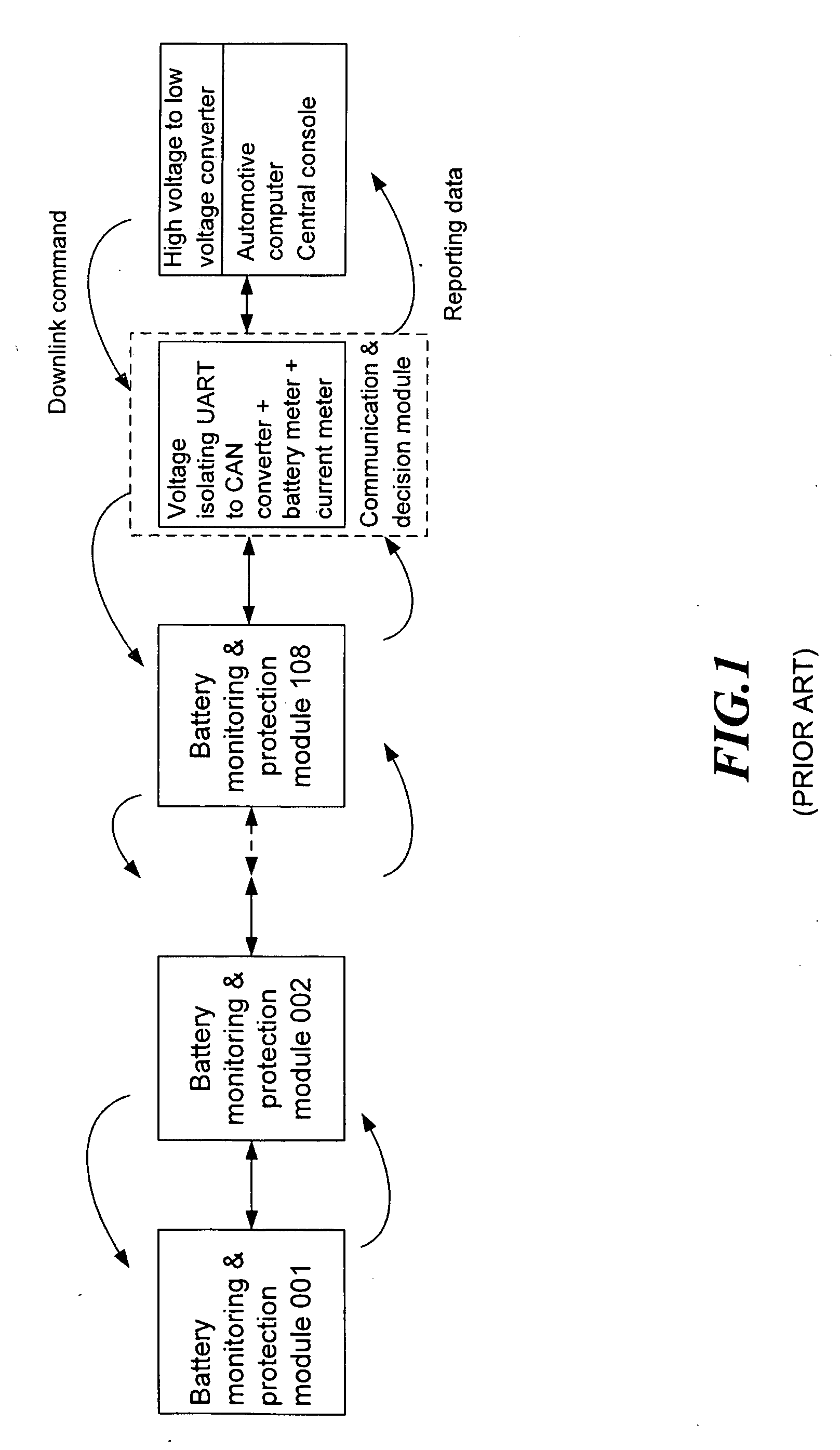
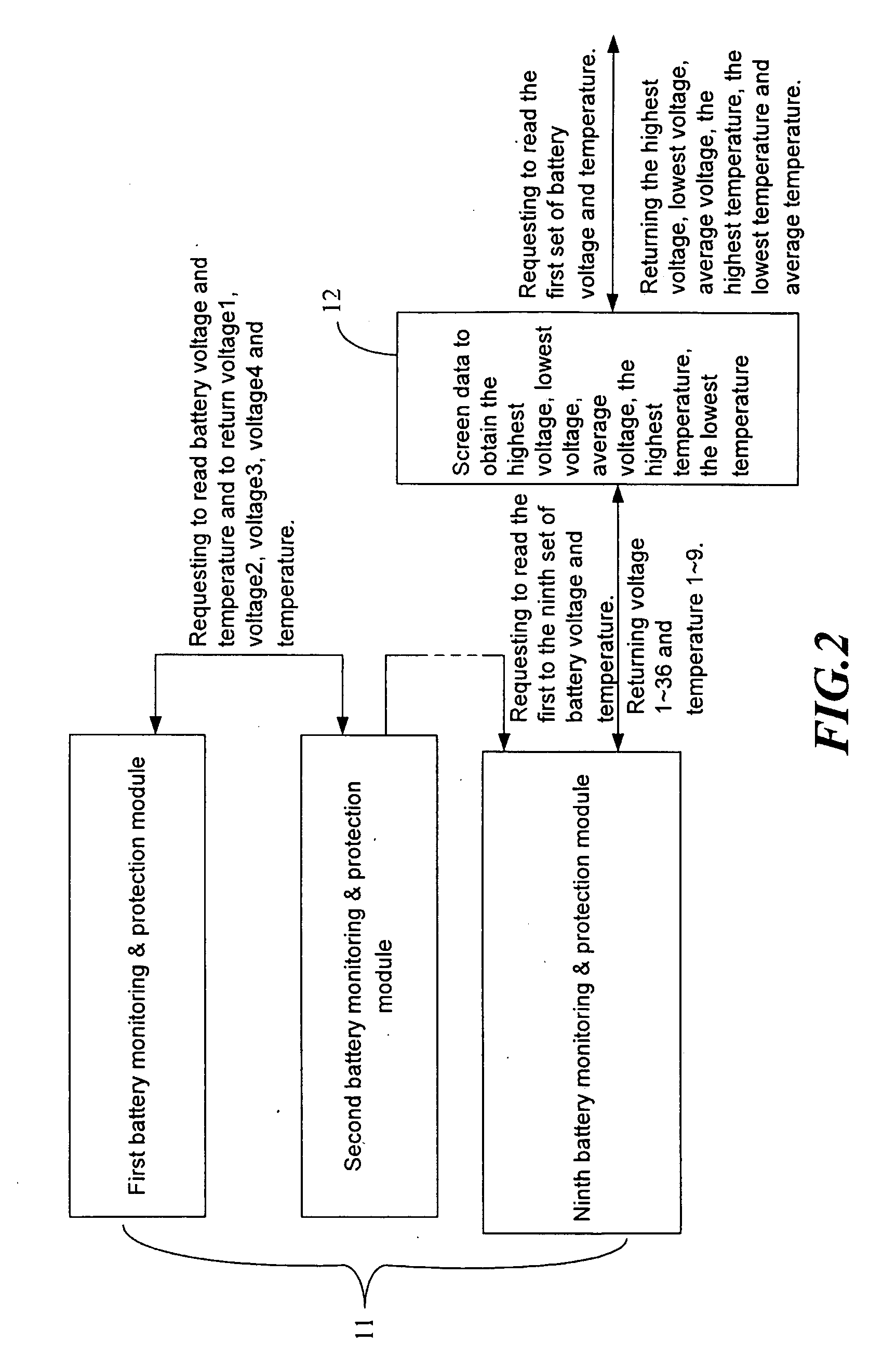
Hierarchical battery management system
InactiveUS20100097034A1Reduce the amount requiredSpeed up decision processCharge equalisation circuitCircuit monitoring/indicationElectricityElectric power system
A hierarchical battery-management system mainly comprises a monitoring and equalizing module, an intermediary module and a communication and decision module. The monitoring and equalizing module electrically couples with the battery. The intermediary module electrically couples with the monitoring and equalizing module and the communication and decision module; besides, the communication and decision module electrically couples with a power system or an electronic / electrical apparatus. The present invention uses a digital transmission interface constructed from an uplink / downlink circuit with a DC isolation component for common battery management, and a hierarchical management structure constructed by the intermediary module to screen data and to transmit meaningful cell data to meet real time managing requirements of the large battery set.
Owner:ALL NEW ENERGY TECH CORP
Composite solid electrolyte material, preparation method thereof, and all-solid-state lithium ion secondary battery containing electrolyte material
InactiveCN106887638AOvercoming Assembly Operations ProblemsImprove stabilitySolid electrolytesSecondary cellsAll solid stateSulfur
The invention discloses a composite solid electrolyte material, a preparation method thereof, and an all-solid-state lithium ion secondary battery containing the electrolyte material. The composite solid electrolyte material comprises a core and a surface coating which covers the surface of the core, the core is inorganic chalcogenide glass ceramic state electrolyte, and the surface coating is a lithium compound which does not react with air and moisture in air. The preparation method of the composite solid electrolyte material is as follows: firstly the inorganic chalcogenide glass ceramic state electrolyte core is prepared, and then a radio frequency sputtering method or pulse laser deposition is used for coating the lithium compound which does not react with air and moisture in air on the surface of the inorganic chalcogenide glass ceramic state electrolyte. The composite solid electrolyte material has high stability in air, and can be assembled into all-solid-state batteries in the environment of common battery plant, in order to overcome the problem that prior chalcogenide electrolyte must be assembled and operated in an anhydrous condition.
Owner:CHINA AUTOMOTIVE BATTERY RES INST CO LTD +1
Technique for making polar plate of dried-charge tube-type dynamic lead acid battery
InactiveCN101355152AHigh content of lead dioxideHigh lead contentLead-acid accumulator electrodesSecondary stageEngineering
The invention provides a formation process for a polar plate of a dry-charged tube type power lead-acid battery, comprising the preparation of the polar plate, solidification and drying, formation, washing, the soakage of a negative plate, and drying and manufacturing of the polar plate. The formation process is characterized in that the solidification and drying process of the polar plate comprises the following stages: the first stage is the solidification stage which is performed at a temperature of between 35 and 45 DEG C, and the humidity above 95 percent for 24 hours; the second stage is the drying stage which comprises two stages, wherein the first drying stage is performed at a temperature of between 40 and 50 DEG C, and the humidity between 60 and 70 percent for 24 hours; and the second drying stage is performed at a temperature of between 65 and 75 DEG C, and the humidity between 40 and 50 percent for 24 hours. With the invention, Pb02 of a positive plate is more than or equal to 85 percent, Pb of the negative plate is more than or equal to 85 percent, and the water content in the polar plate is below 0.5 percent. Under the conditions of the same volume and the same weight, the capacity and the service life of the polar plate exceed the common battery by 10 to 15 percent; and the dry-charged performance of the polar plate is as follows: initial charge is not needed after liquid is added, and the polar plate can be used after standing for 4 hours.
Owner:江苏快乐电气股份有限公司
Safe battery solvents
ActiveUS7285362B2Reduced effectivenessEasily polarizableOrganic electrolyte cellsElectrolyte accumulators manufactureBackbone chainSolvent
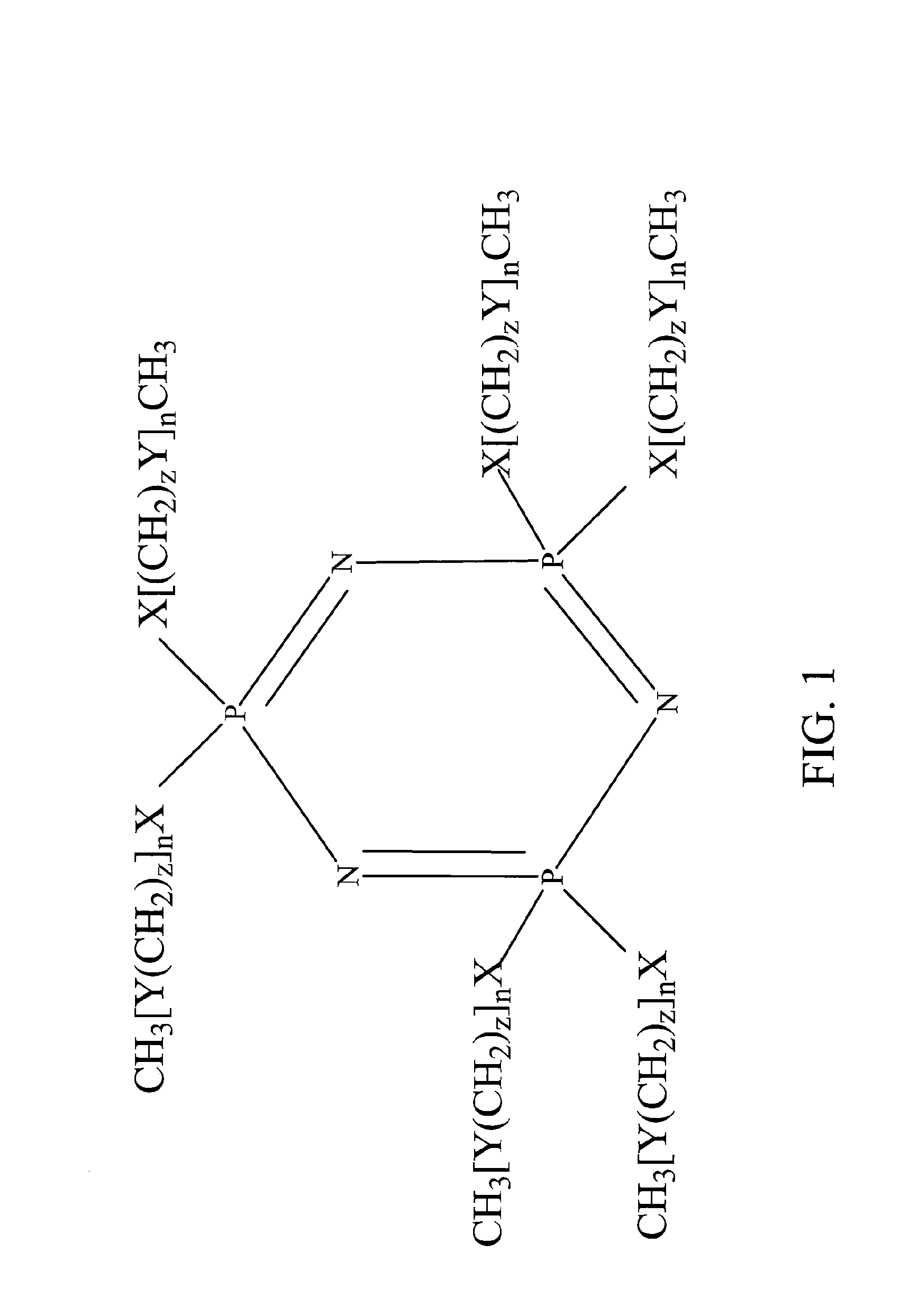
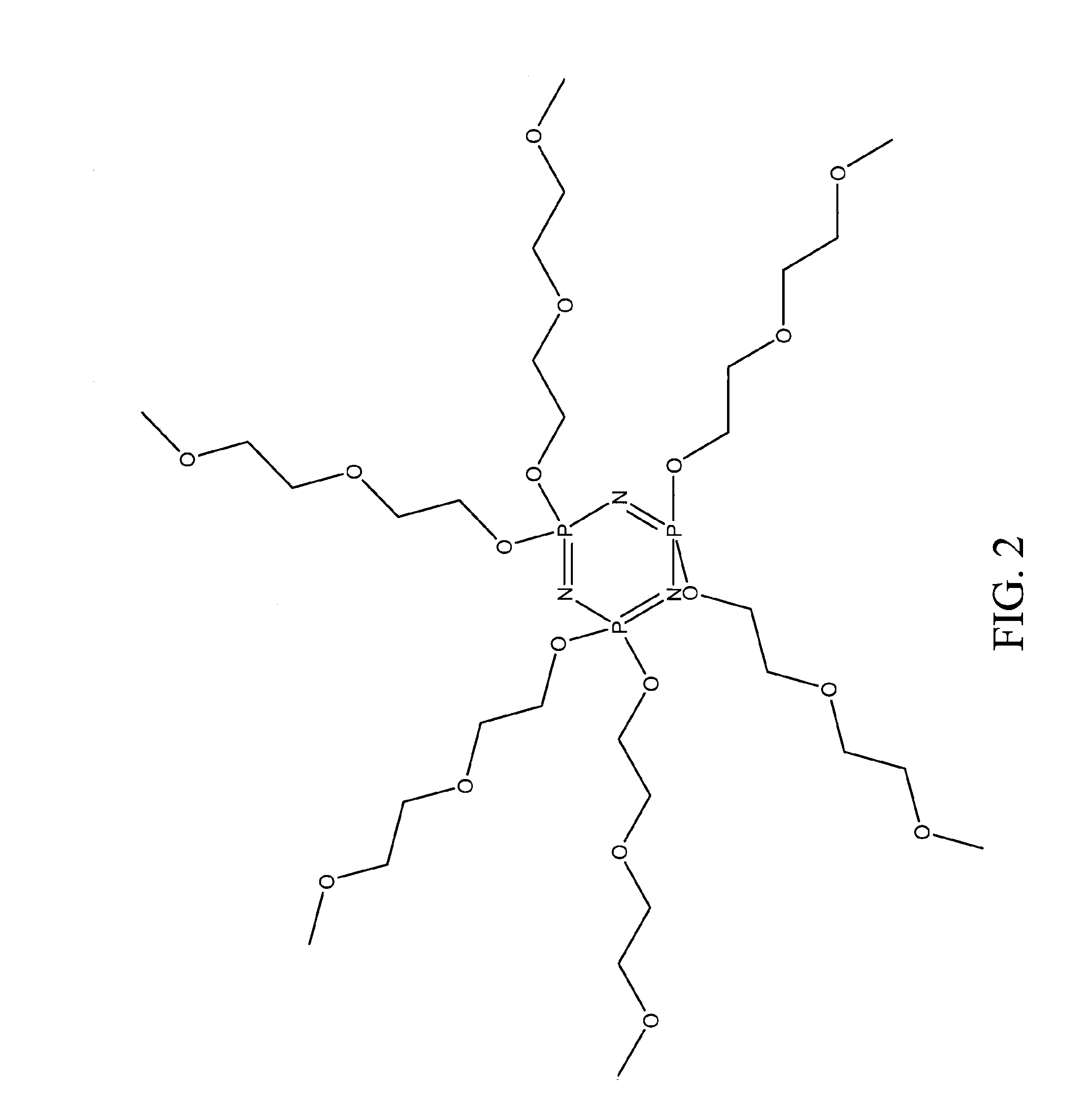
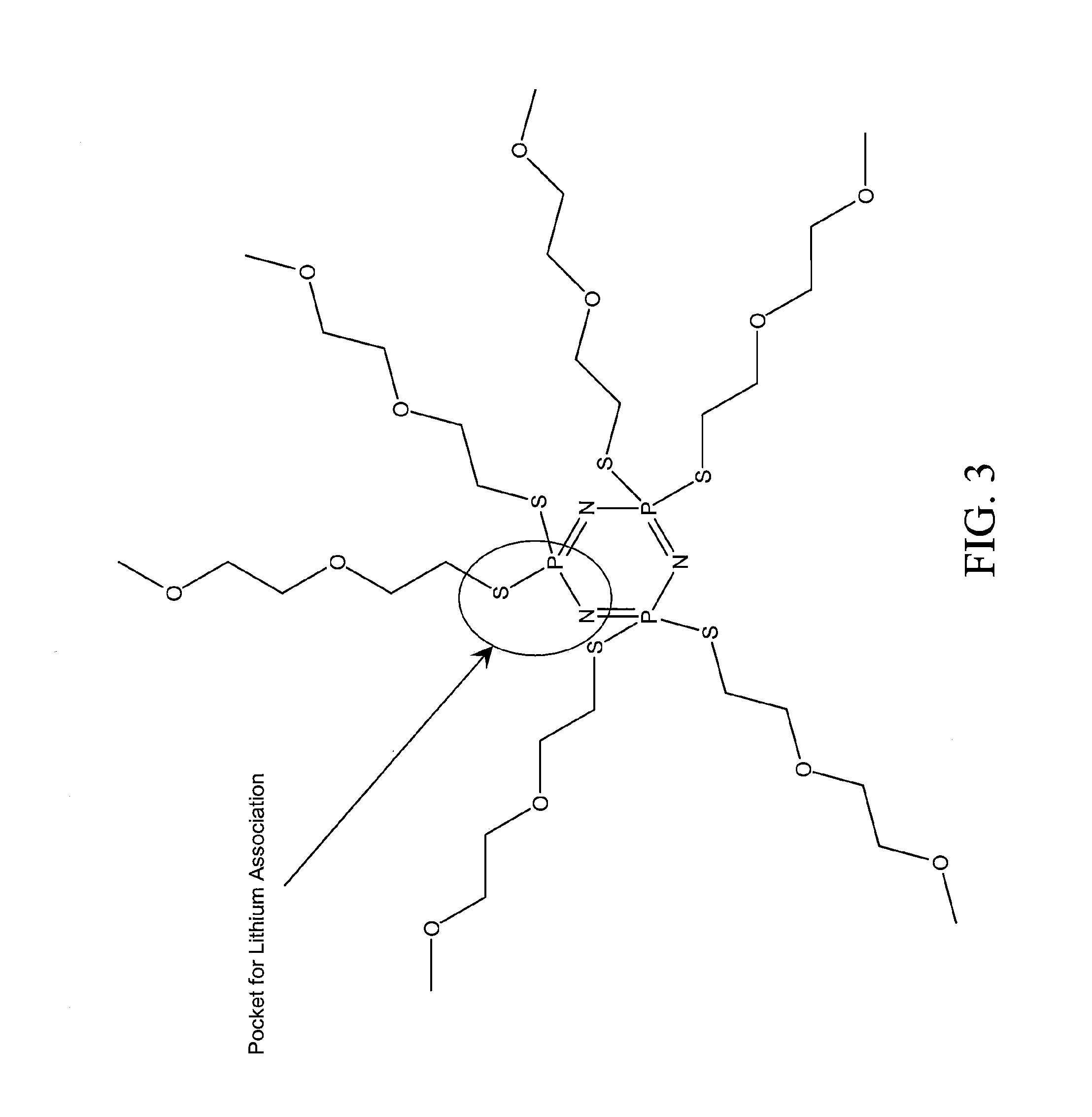
An ion transporting solvent maintains very low vapor pressure, contains flame retarding elements, and is nontoxic. The solvent in combination with common battery electrolyte salts can be used to replace the current carbonate electrolyte solution, creating a safer battery. It can also be used in combination with polymer gels or solid polymer electrolytes to produce polymer batteries with enhanced conductivity characteristics. The solvents may comprise a class of cyclic and acyclic low molecular weight phosphazenes compounds, comprising repeating phosphorus and nitrogen units forming a core backbone and ion-carrying pendent groups bound to the phosphorus. In preferred embodiments, the cyclic phosphazene comprises at least 3 phosphorus and nitrogen units, and the pendent groups are polyethers, polythioethers, polyether / polythioethers or any combination thereof, and / or other groups preferably comprising other atoms from Group 6B of the periodic table of elements.
Owner:BATTELLE ENERGY ALLIANCE LLC
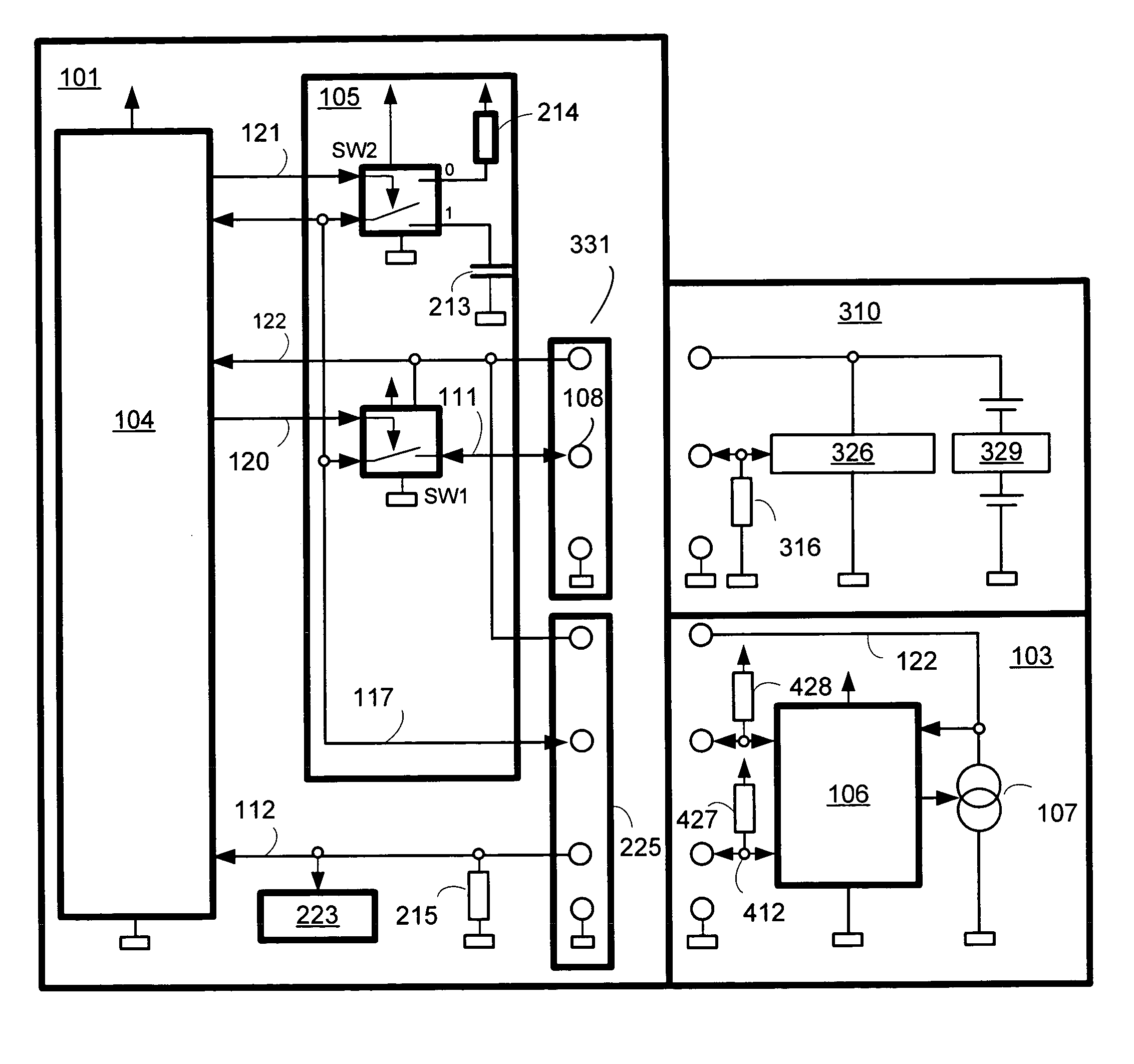
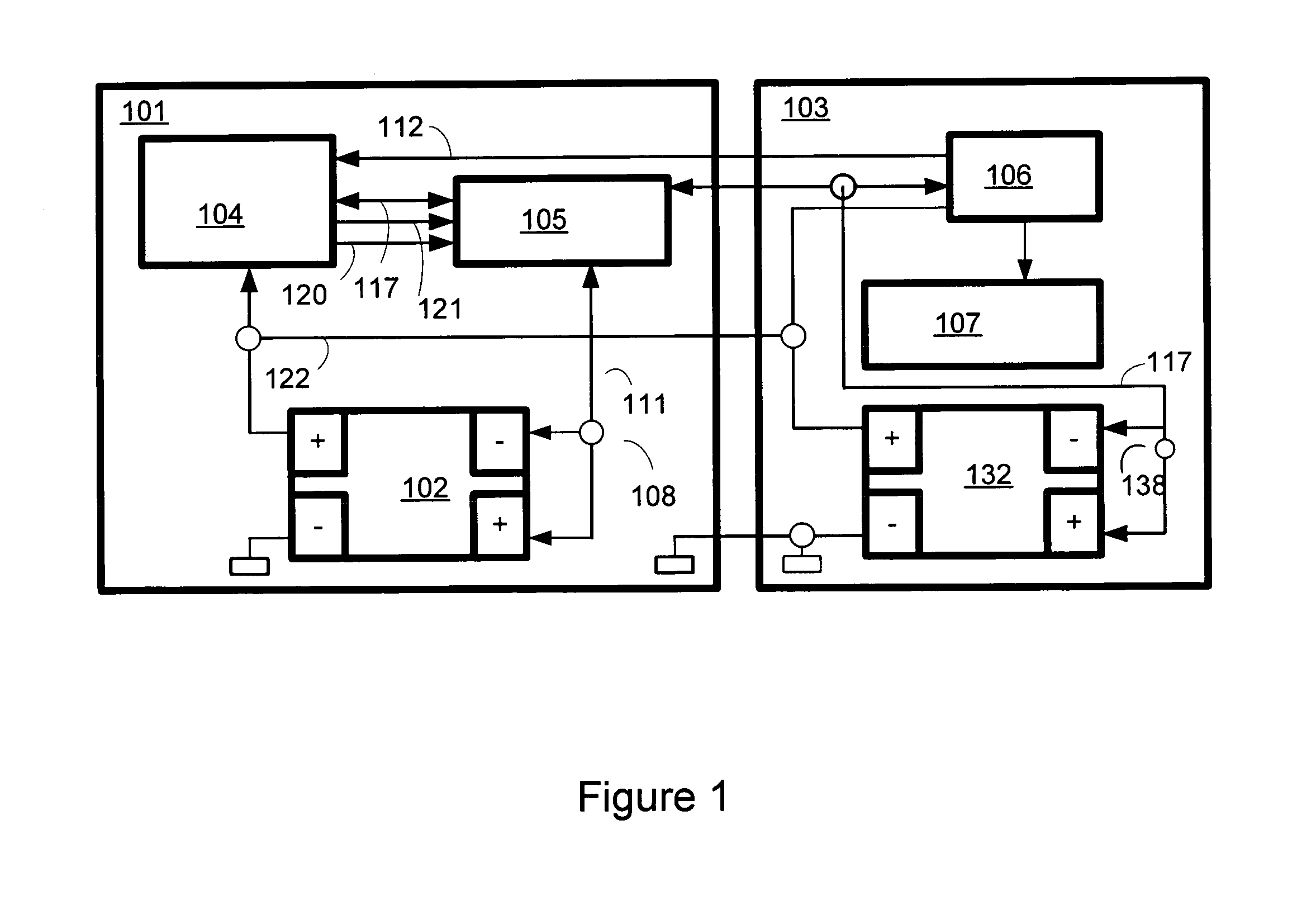
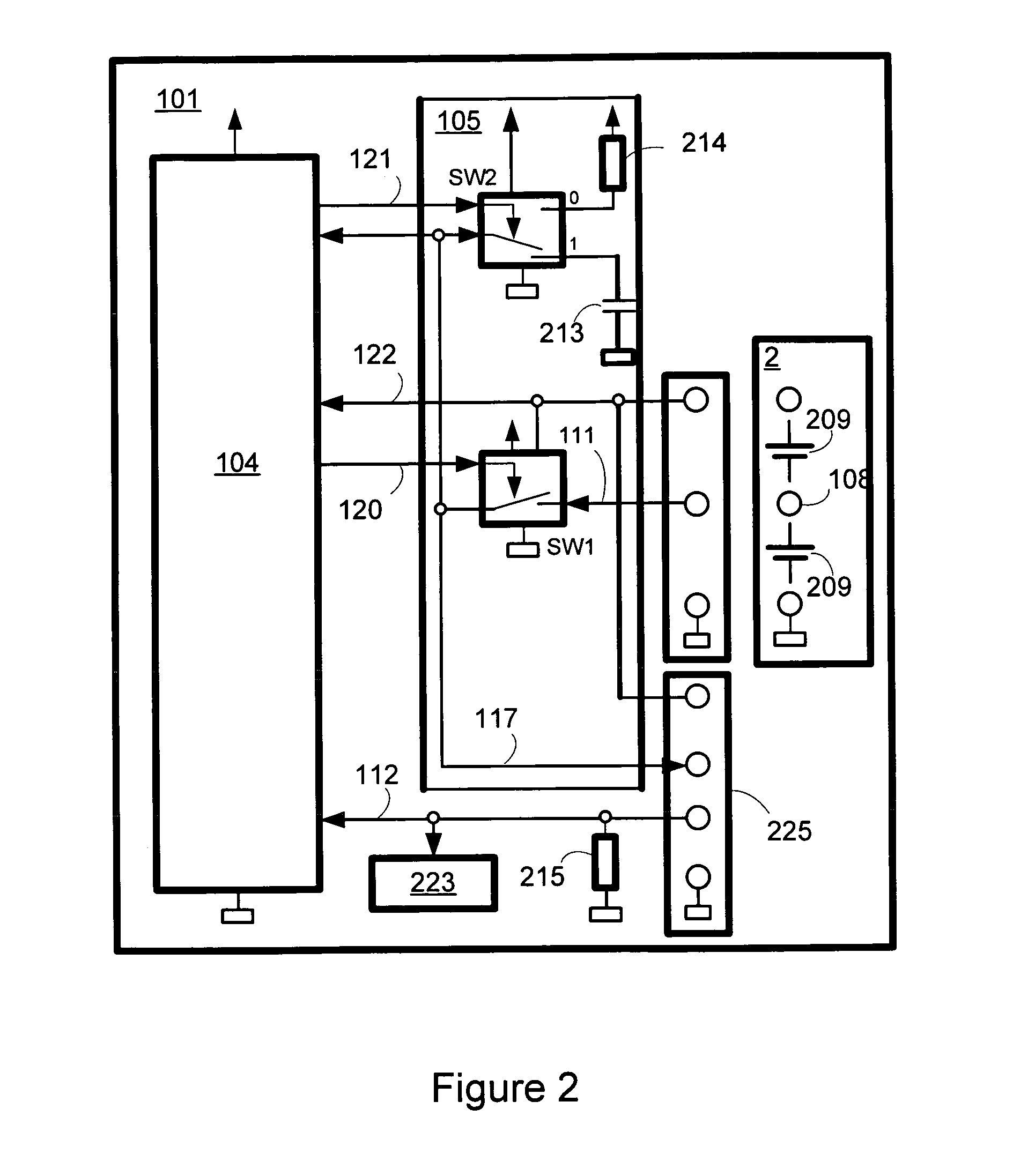
Battery arrangement
InactiveUS20100059299A1Small installation space requirementEliminate effectiveCell temperature controlGas pressure propulsion mountingEngineeringBattery cell
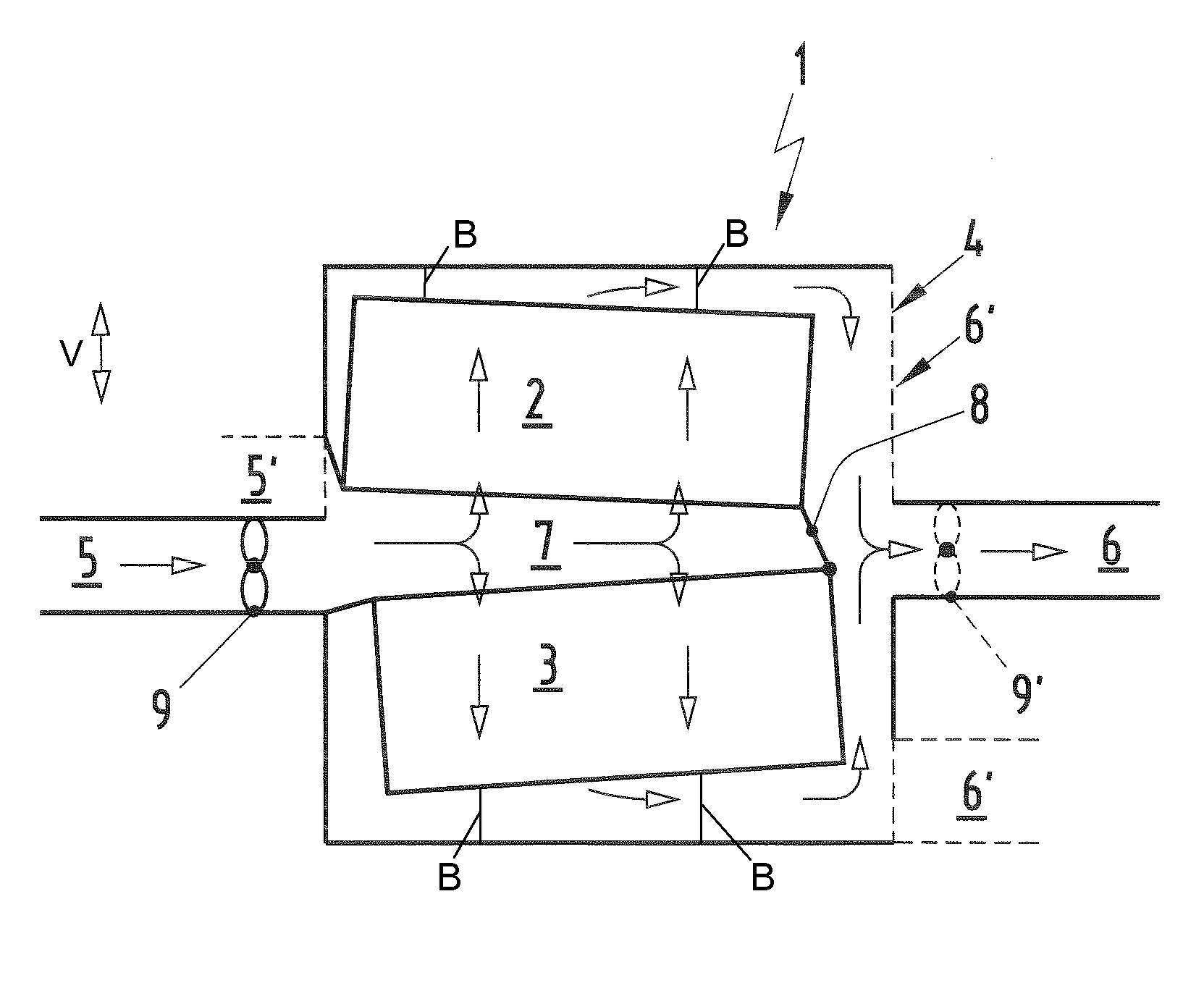
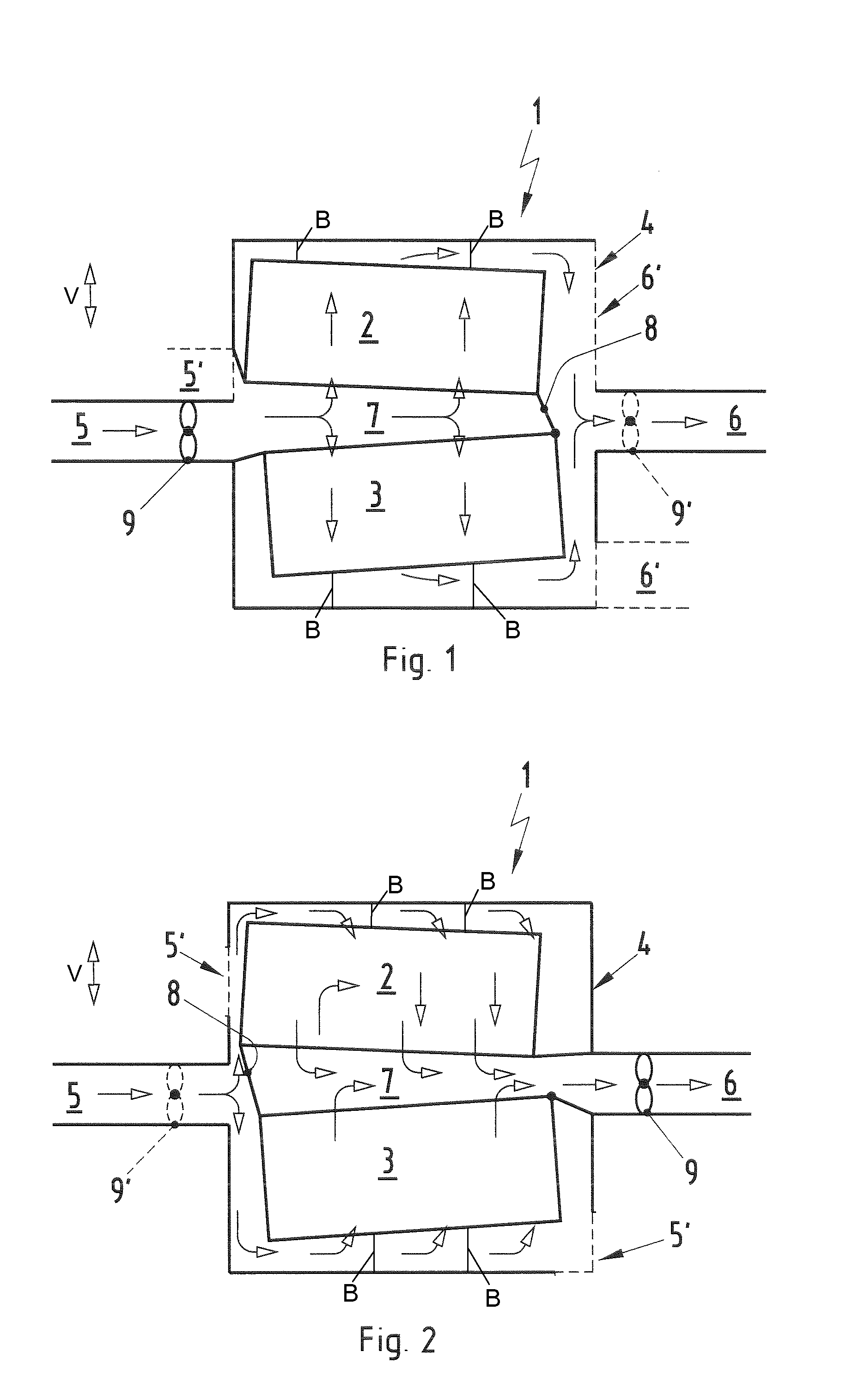
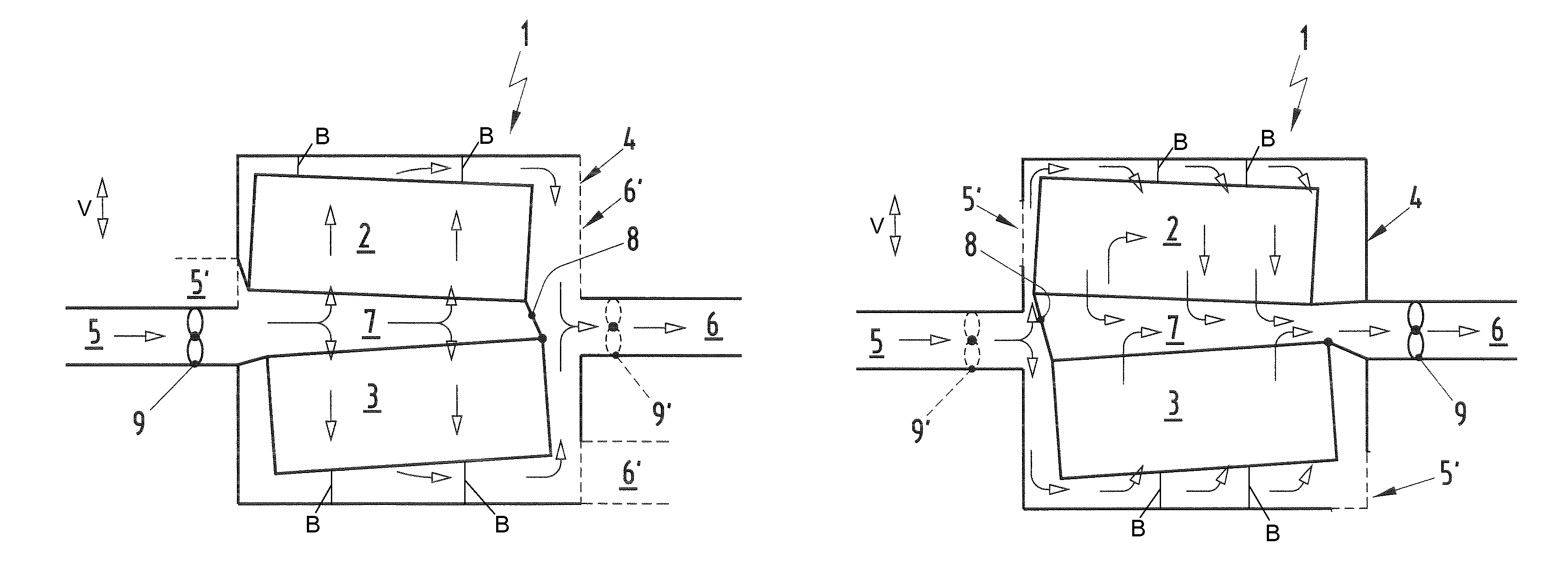
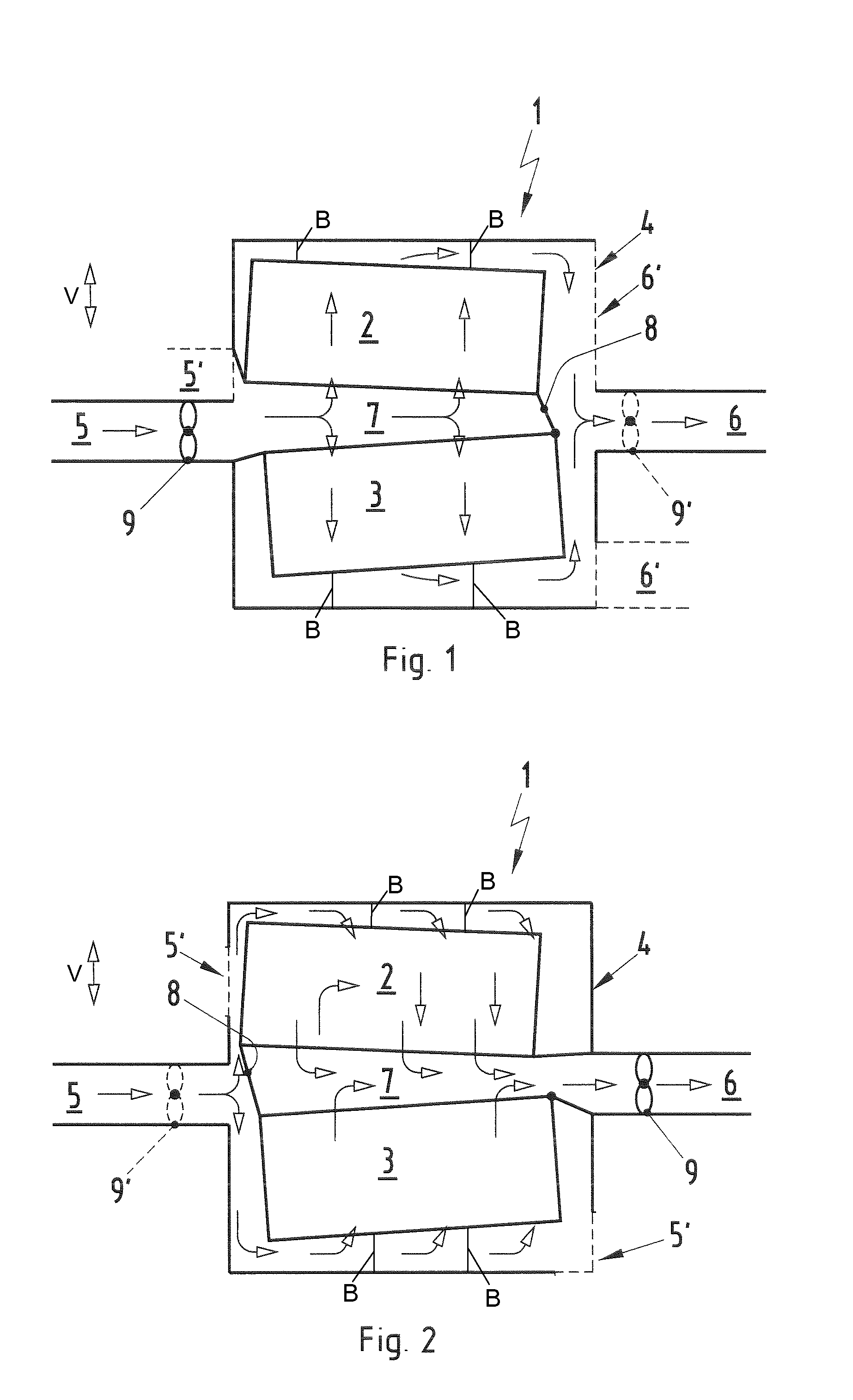
A battery arrangement (1) has at least two battery cell packs (2, 3) arranged in a common battery housing (4). The battery housing (4) has at least one first opening (5) for supplying cooling air and at least one second opening (6) for discharging heated air. The battery cell packs (2, 3) are arranged one above the other and delimit a tunnel (7) therebetween in a height direction. At least one of the first and second openings (5, 6) is arranged substantially at the same level as the tunnel (7). The tunnel (7) is closed at a side facing one of the first and second openings (5, 6) so that air flowing between the first and second openings (5, 6) is channeled through or around the battery cell packs (2, 3).
Owner:DR ING H C F PORSCHE AG
Universal rechargeable battery formed by adopting lithium-ion battery and control method thereof
ActiveCN103490099AImplement charging modeRealize the charging rateFinal product manufactureElectrical testingElectrical batteryCharge control
The invention provides a universal rechargeable battery formed by adopting a lithium-ion battery and a control method thereof. The universal rechargeable battery formed by adopting the lithium-ion battery comprises an external packing casing as well as a charging / discharging controller, a positive electrode crimping sheet, a lithium-ion battery and a negative electrode end cover, which are sequentially assembled in the external packing casing in a press fit manner; the charging / discharging controller comprises a charging / discharging controller casing as well as a charging / discharging control circuit welding body, an insulating spacer, a charging / discharging controller support which are arranged in the charging / discharging controller casing; a lithium-ion battery charging / discharging control circuit is welded on the charging / discharging control circuit welding body; the lithium-ion battery charging / discharging control circuit comprises a lithium-ion battery charging control circuit welded on a circuit board, electrically connected with the lithium-ion battery and the positive electrode end cover respectively, and further electrically connected with the negative electrode end cover via the charging / discharging controller casing and the external packing casing, a lithium-ion battery detection and control circuit and a DC-DC buck voltage stabilizing discharging circuit.
Owner:麦格松(湖北)电源系统有限责任公司
Battery arrangement
InactiveUS8205702B2Small space requirementEliminate effectiveCell temperature controlPlural diverse prime-mover propulsion mountingEngineeringBattery cell
Owner:DR ING H C F PORSCHE AG
Flash LED controller
InactiveUS8704450B2Electrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesElectrical resistance and conductanceElectricity
The invention provides integrated power supplies, circuit drivers, and control methods for relatively high-current drivers, usable with common battery power sources. Preferred embodiments include one or more high series resistance super-capacitors electrically connected with a power. A low resistance driver circuit regulates power supplied from the super-capacitors to the load.
Owner:TRIUNE IP
Battery determination system for battery-powered devices
ActiveUS7439706B2Boards/switchyards circuit arrangementsMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansElectrical batteryOperation mode
This system provides a method for determining whether ordinary battery cells, a battery pack, and / or a charger unit are attached to a portable electronic device. The system provides a center contact in a battery shaft that contacts a battery pack or a point on an individual battery and allows the device regulation unit to measure the voltage at that point. If the voltage is below a particular threshold, then the system determines that a battery pack may be inserted in the battery shaft and the portable electronic unit enters a battery pack mode. If the voltage is above the threshold voltage, then the portable electronic device enters the battery operation mode. If a voltage transition is sensed on the DEVICE START line, the portable electronic device determines that the charger is installed and the portable electronic device enters the appropriate mode.
Owner:AKG ACOUSTICS
Common-battery deposition producing method for Mg La Pr Ce intermediate alloy
The present invention belongs to a coelectrodeposition prepartion method of magnesium-lanthanum, praseodymium and cerium intermediate alloy. In the electrolytic furnace said invention uses potassium chloride, magnesium chloride and lanthanum-praseodymium-cerium chloride as electrolyte, its cathodic current density is 10-30 A / sq.cm, and its temperature is 700-900 deg.C, so that said invention can utilize the coelectrodeposition process to prepare the invented magnesium-lanthanum-praseodymium-cerium intermediate alloy.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF APPLIED CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for monitoring potentials of anode and cathode of lithium-ion battery
ActiveCN102593539AThere is no potential drift problemAccurate monitoringSecondary cells servicing/maintenancePotential changeElectrical battery
The invention belongs to the technical field of lithium-ion batteries, and in particular relates to a method for monitoring potentials of an anode and a cathode of a lithium-ion battery. The method includes packing a working cell and a reference cell in the same packaging bag, immitting electrolyte to obtain a four-electrode lithium-ion battery after formation, aging and capacity sorting, wherein an electronic insulating film is arranged between the working cell and the reference cell, a positive lug and a negative lug are arranged at the front end of the working cell, and a first lug and a second lug are arranged at the front end of the reference cell; connecting the positive lug and the negative lug with either the first lug or the second lug respectively, and monitoring the potential of the anode and the cathode of the lithium-ion battery. Compared with the prior art, the method for monitoring the potential of the anode and the cathode of the lithium-ion battery has the advantages that both anode and cathode of the reference cell have stable potentials with small drifting and little variation over time in a half-charged state; and potential change of the anode and the cathode of the battery in a test and in work can be effectively monitored.
Owner:DONGGUAN AMPEREX TECH
Low-temperature heating device for lithium-ion battery and electric car
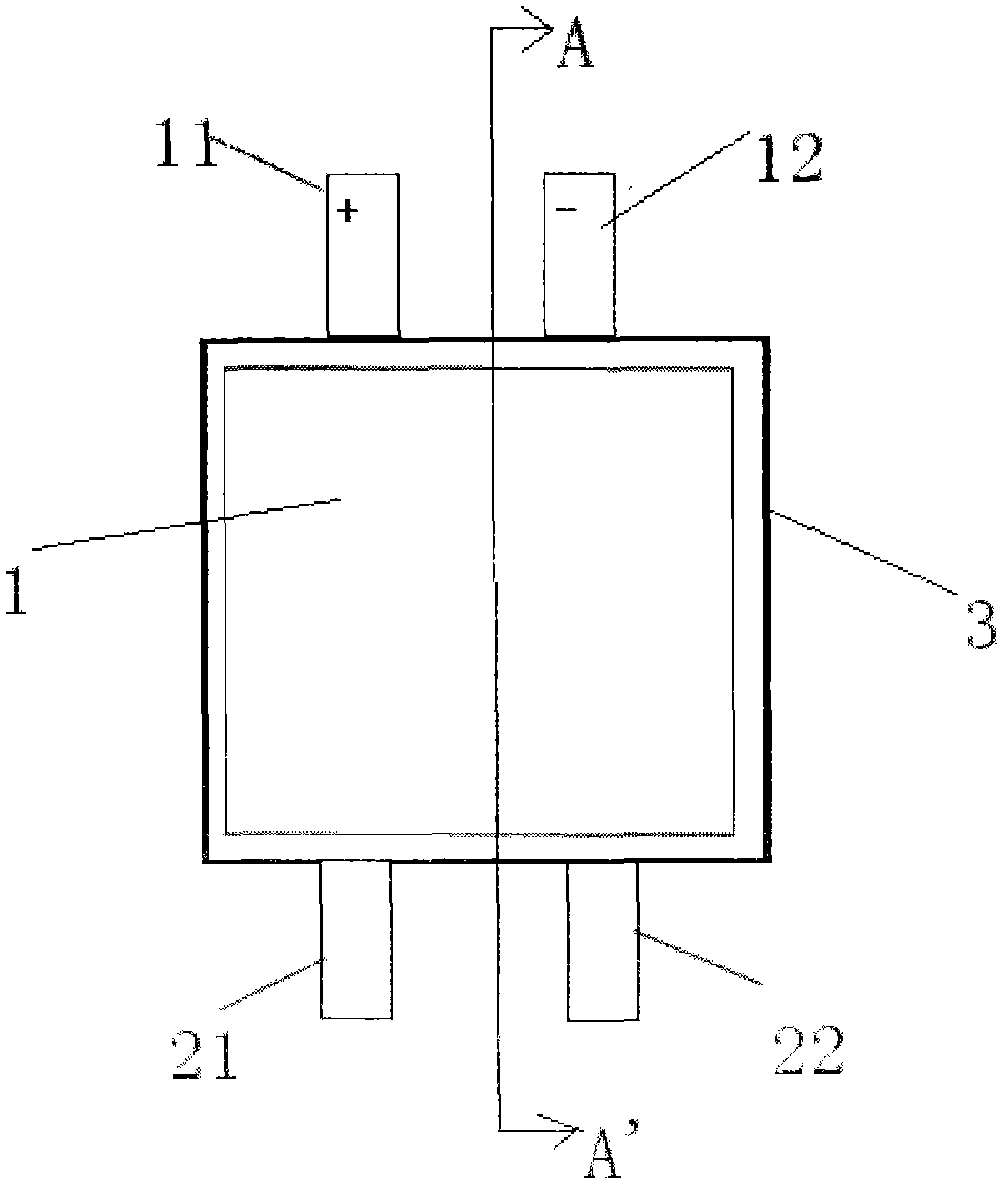
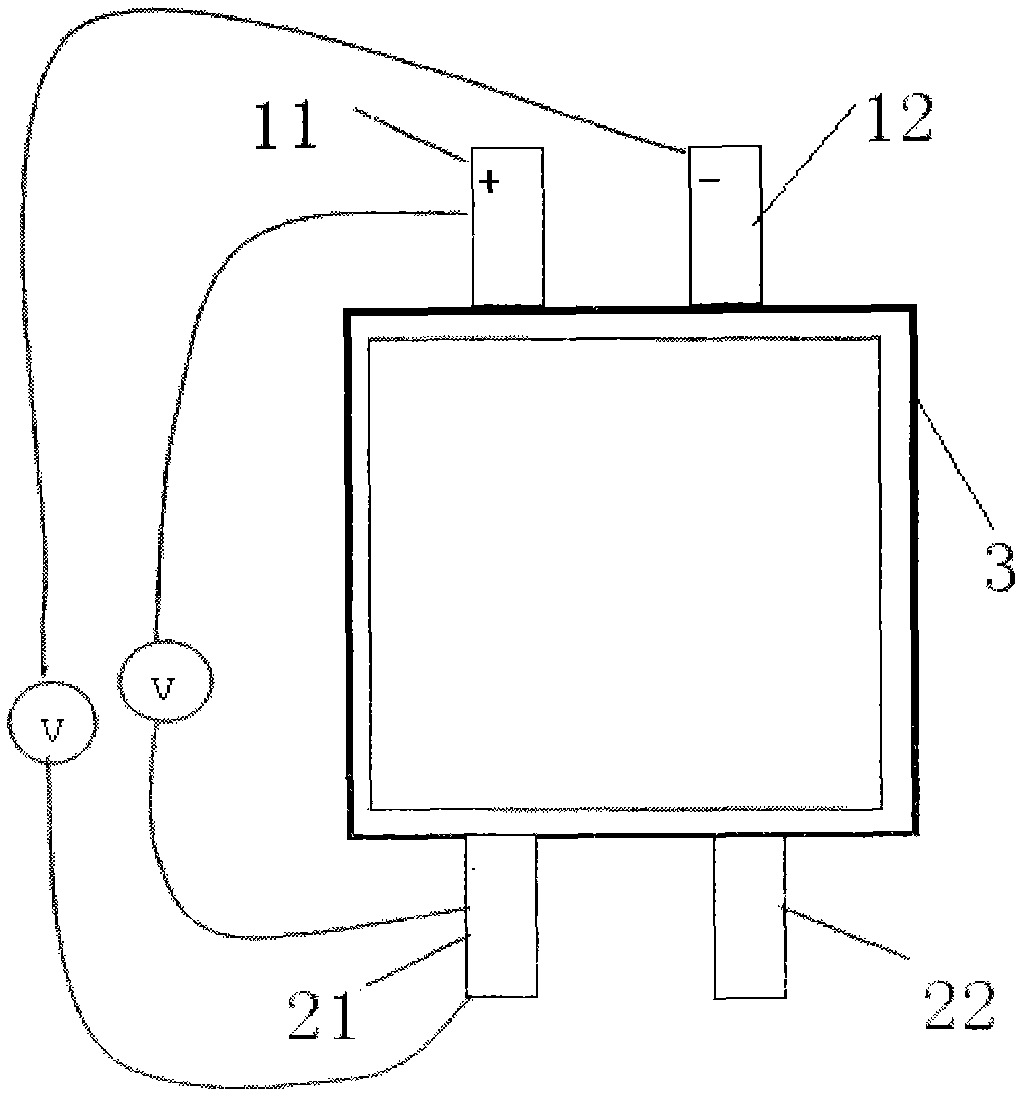
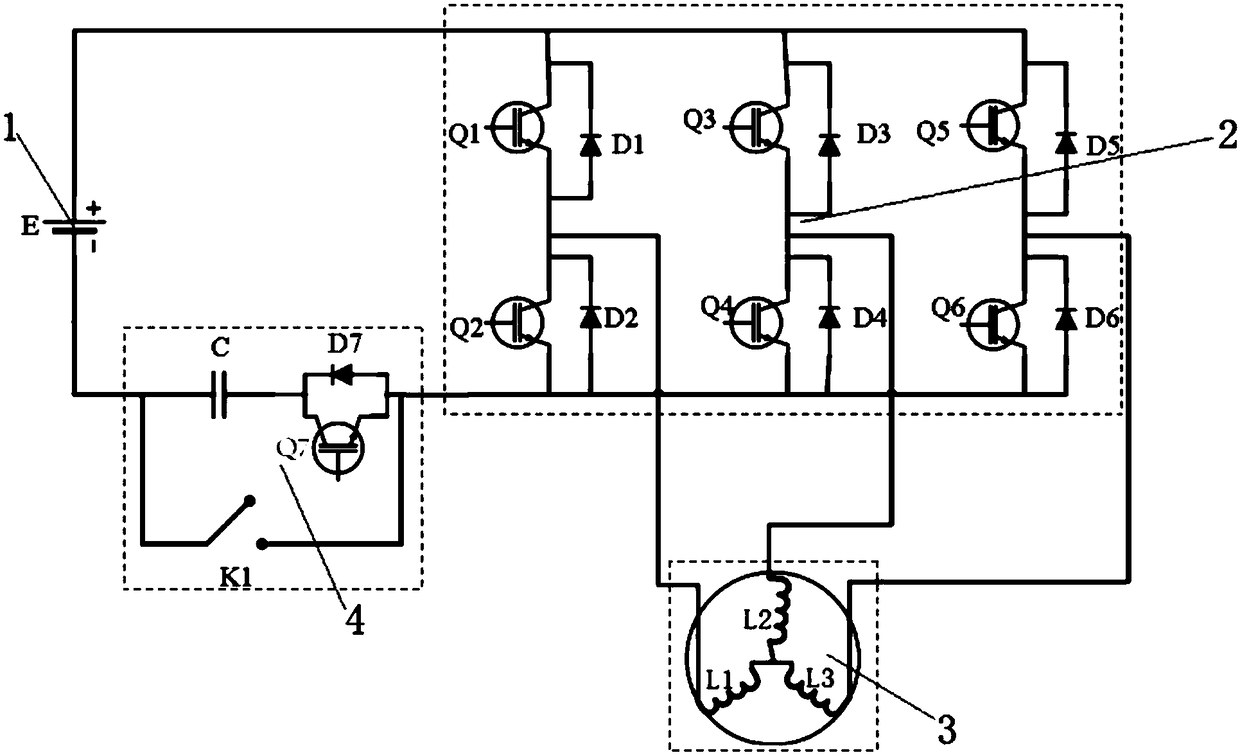
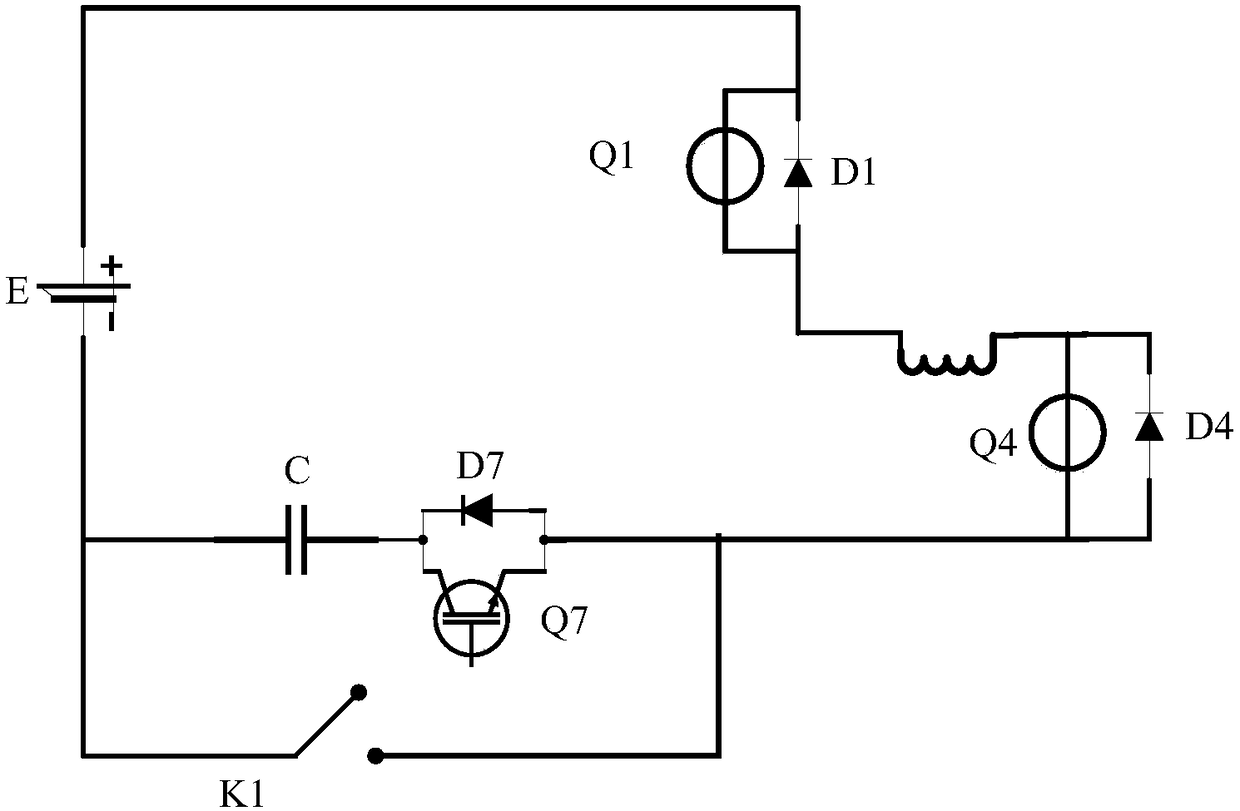
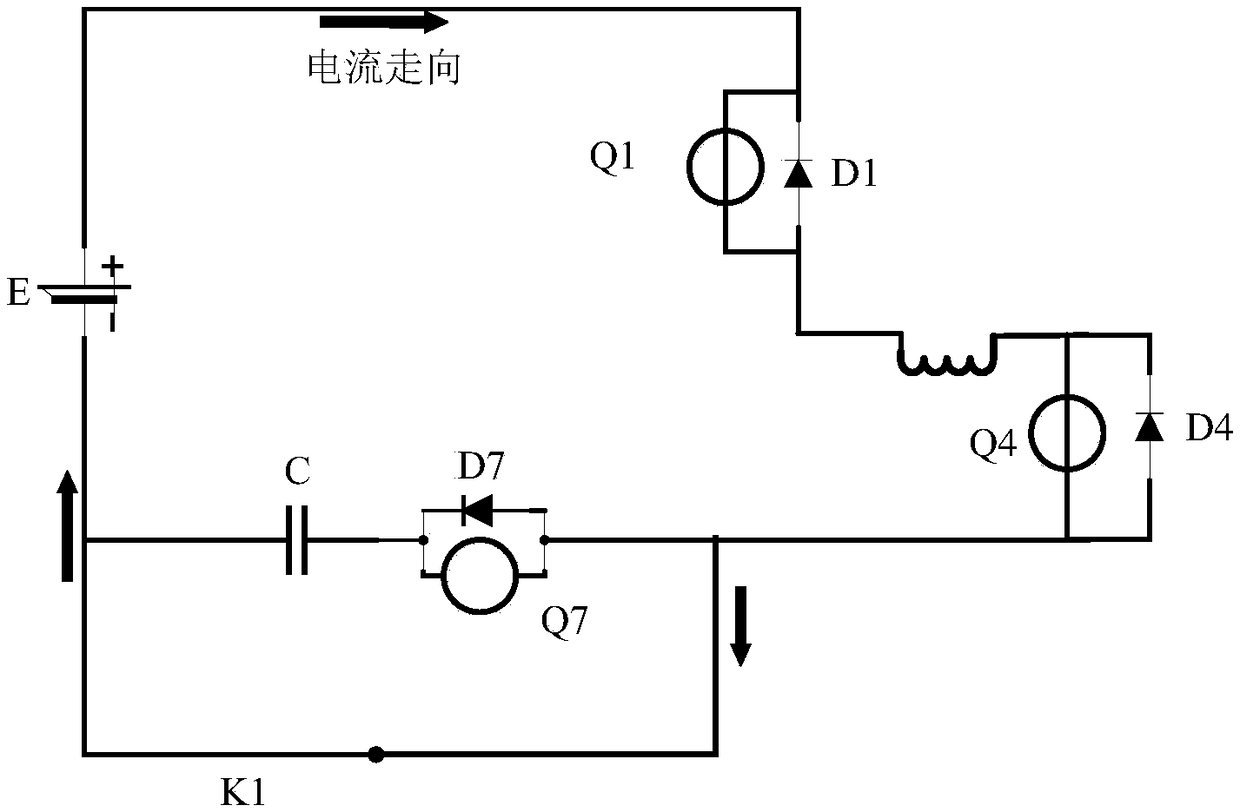
ActiveCN108511822ALow costSimple structureSecondary cells servicing/maintenanceElectrical batteryElectric cars
The invention relates to a low-temperature heating device for a lithium-ion battery; the low-temperature heating device comprises the lithium-ion battery, two power devices of a motor controller and two winding inductors of a motor; the low-temperature heating device also comprises a heating control circuit arranged between the power devices of the motor controller and a negative electrode of thelithium-ion battery. The lithium-ion battery, the two power devices of the motor controller, the two winding inductors of the motor and the heating control circuit are successively connected to form acircuit. The heating control circuit comprises a capacitive element, an additional power device and a switching device. The capacitive element and the additional power device are connected in seriesand then connected in parallel with the switching device. An LC oscillating circuit is formed by the capacitive element and the winding inductors through opening and closing of the switching device and the additional power device respectively, and the high-frequency alternating current is generated. According to Joule's law, the heat is generated in the battery, and then the interior of the battery is heated. The device can be used for quickly and efficiently heating, and has uniform speed and good effect.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com