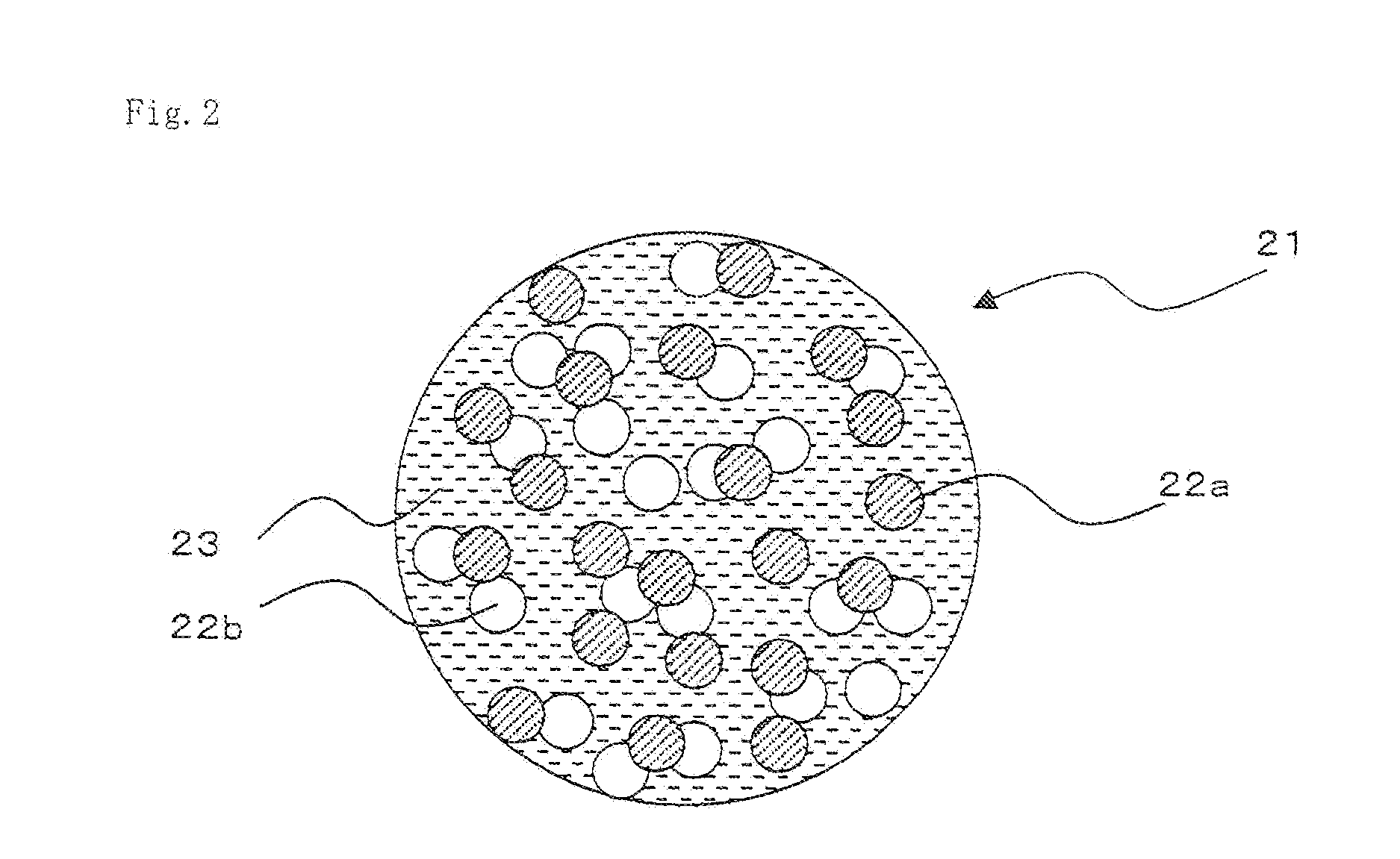
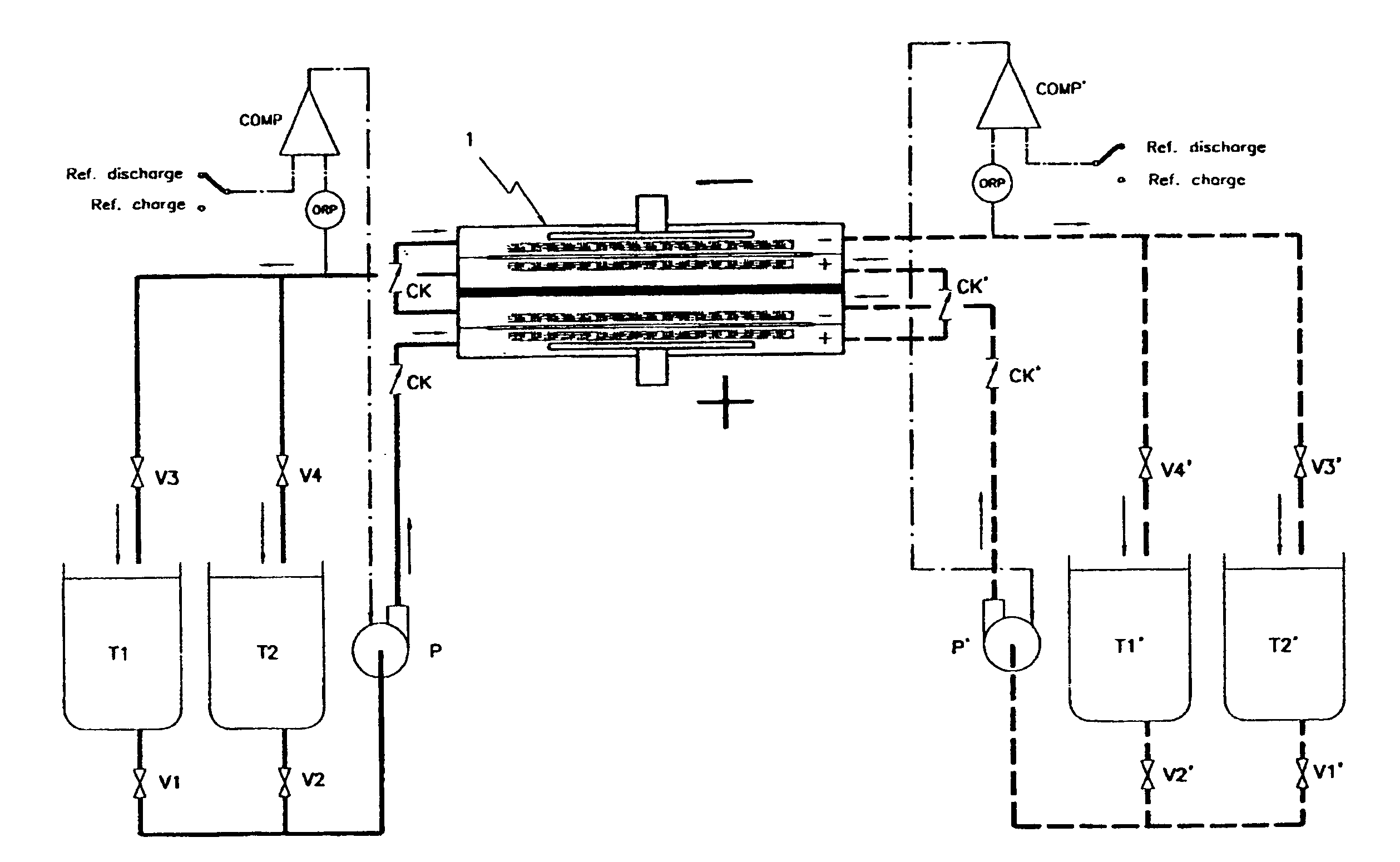
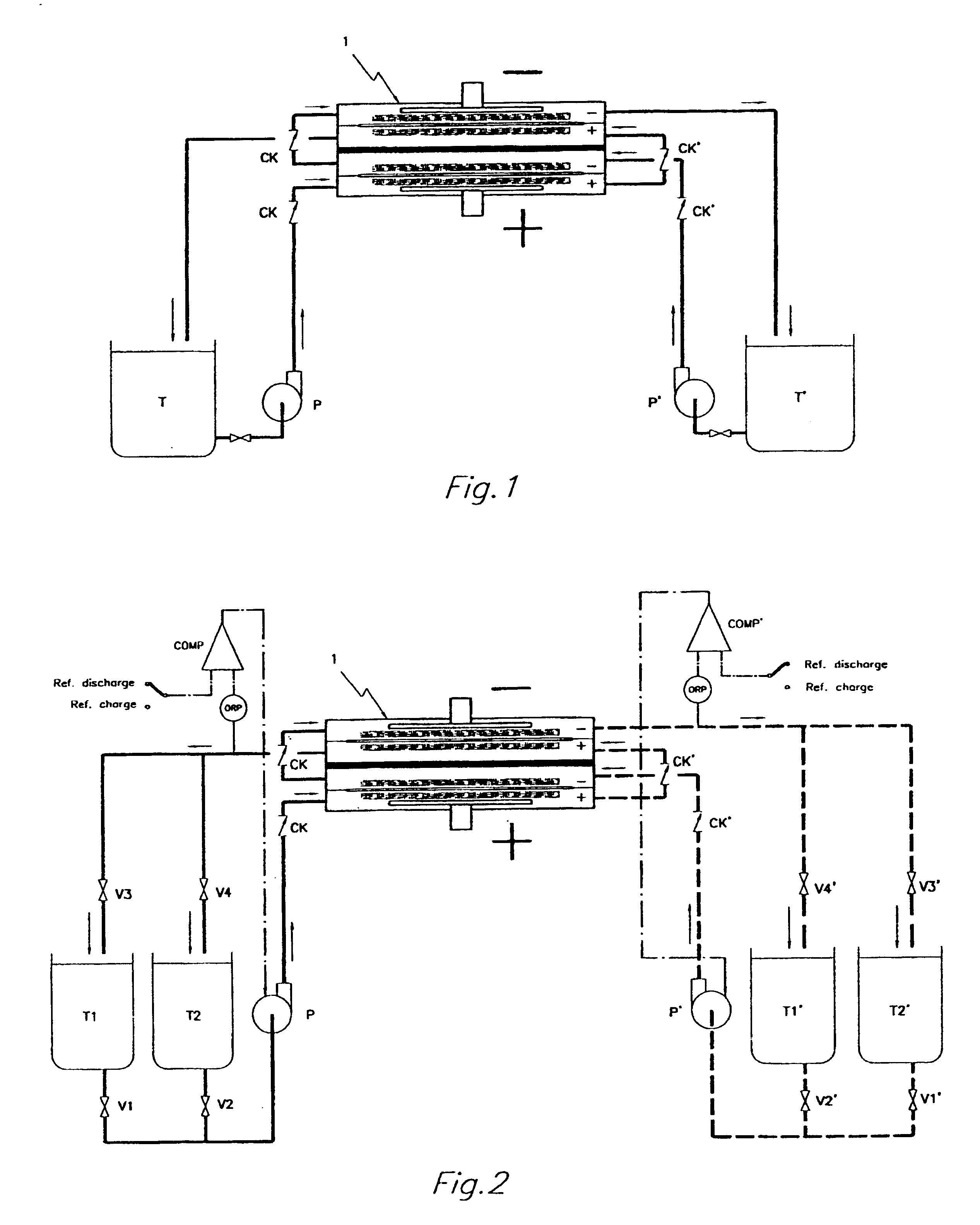
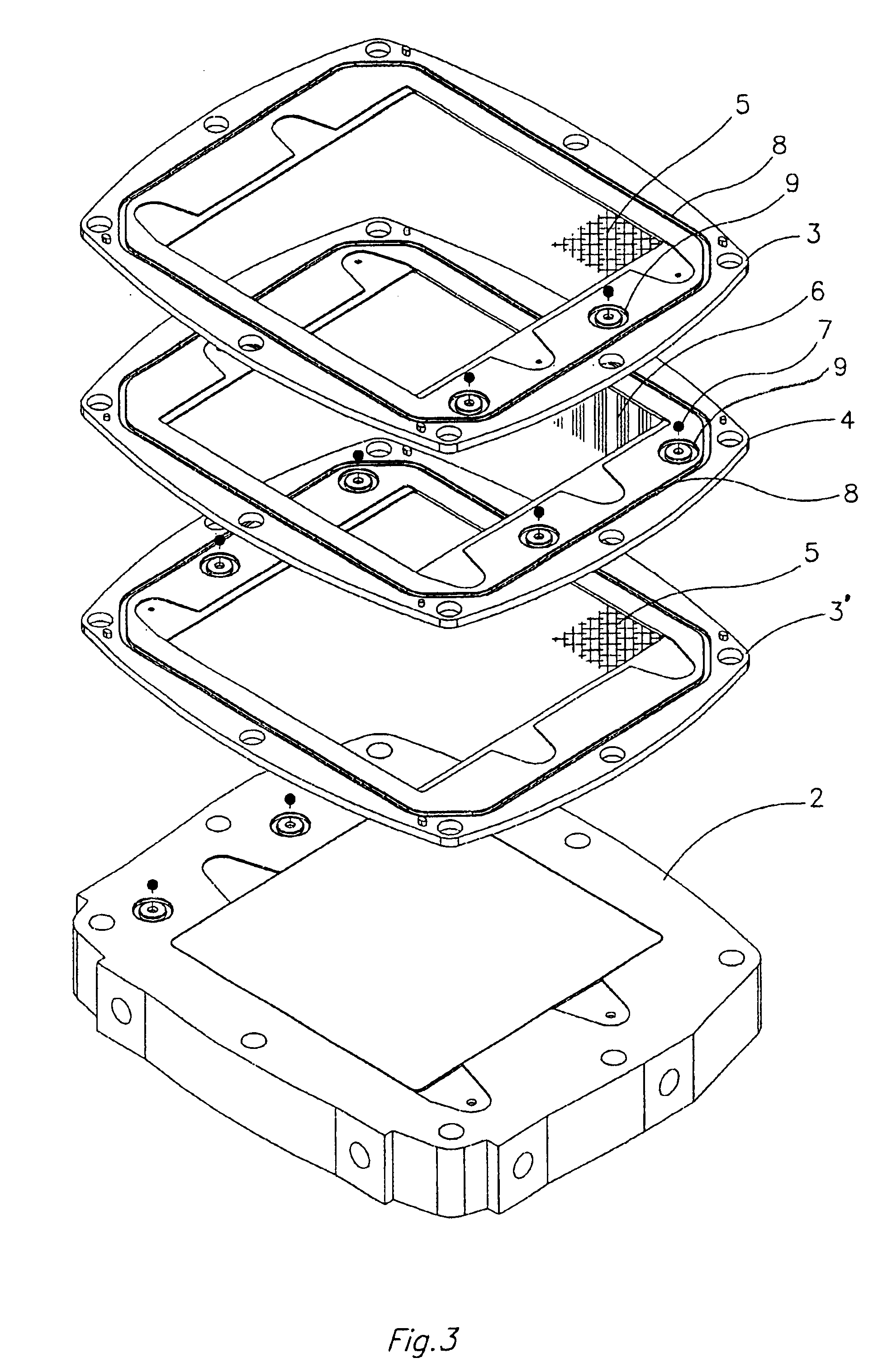
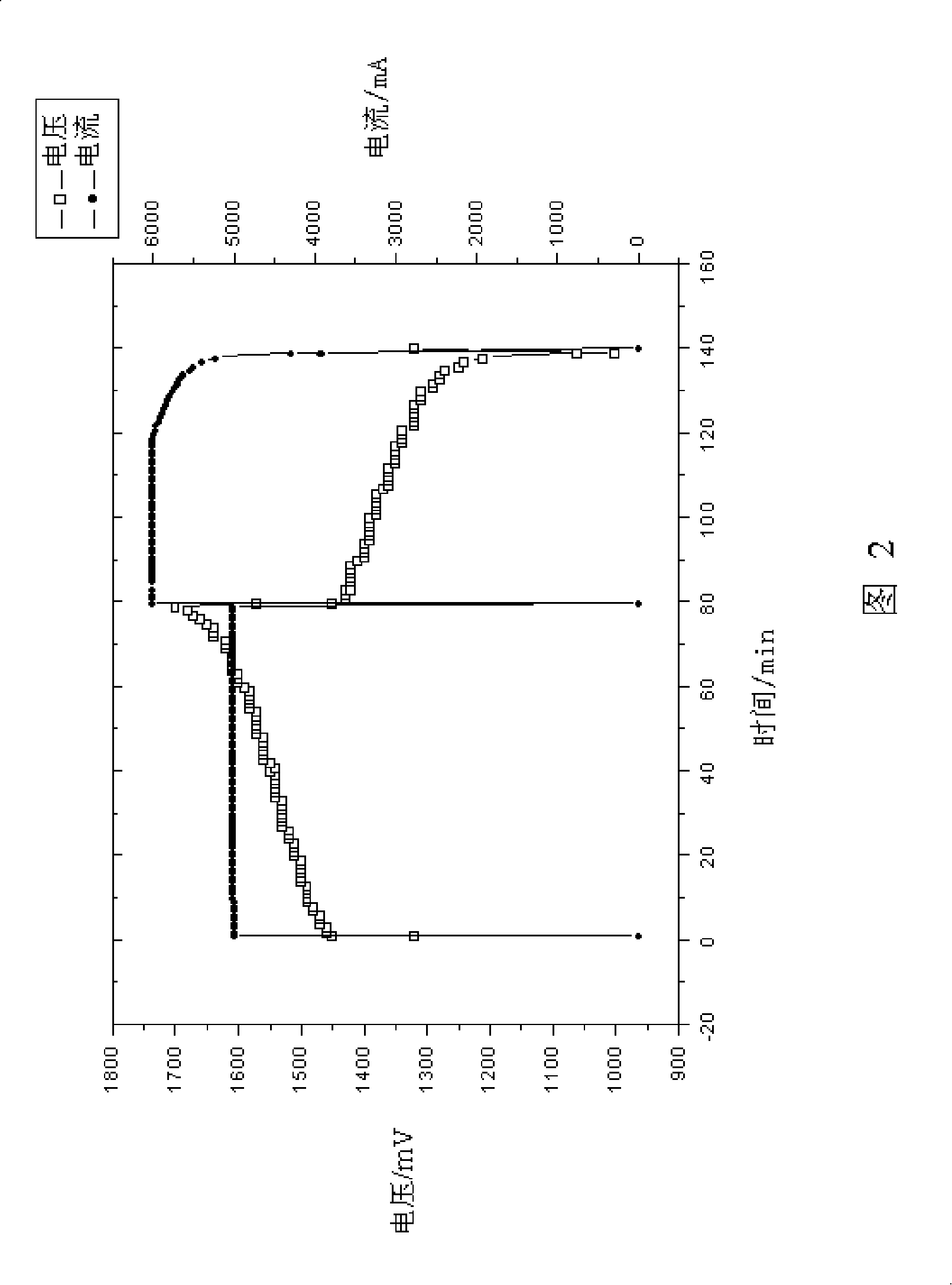
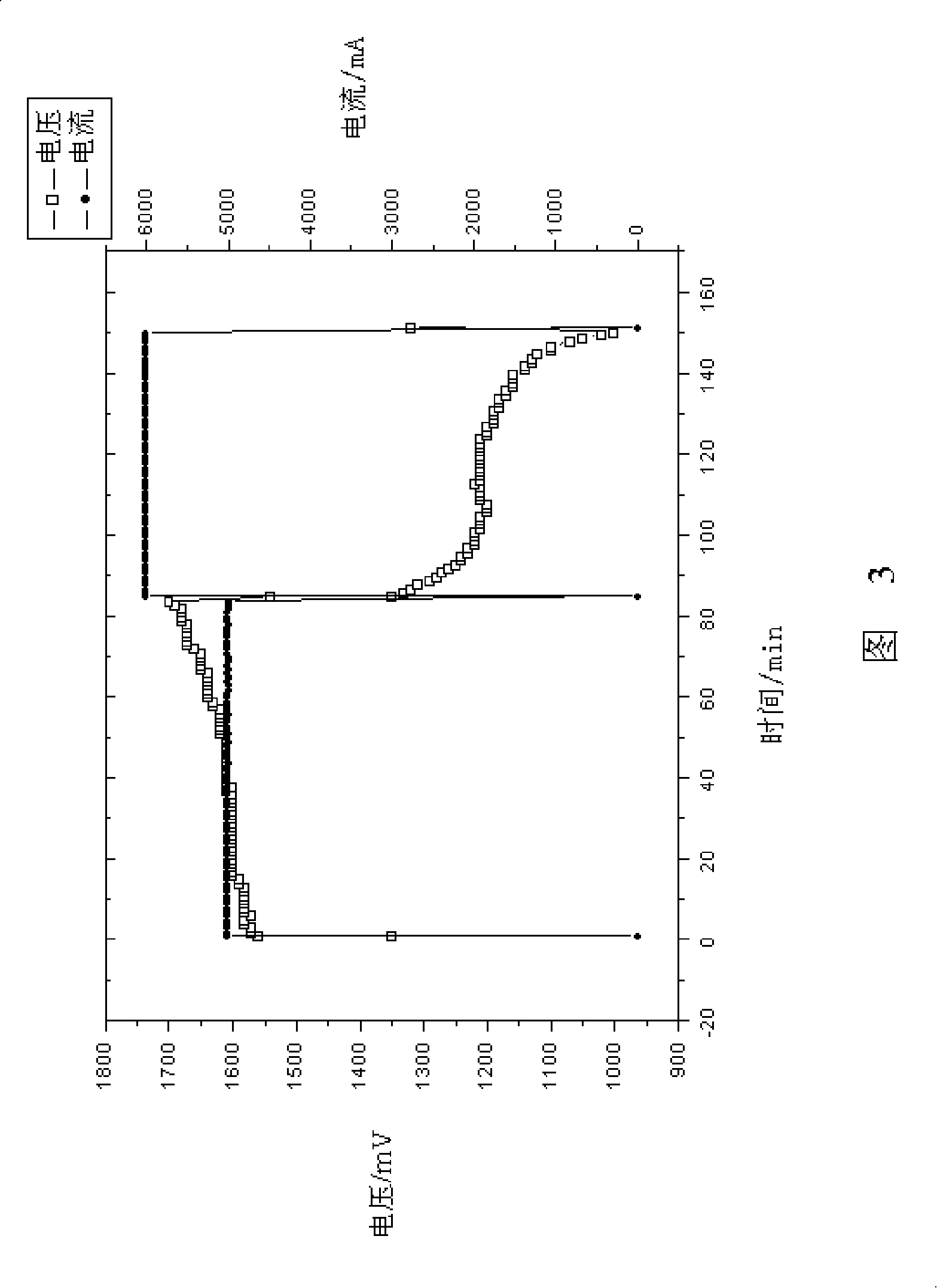
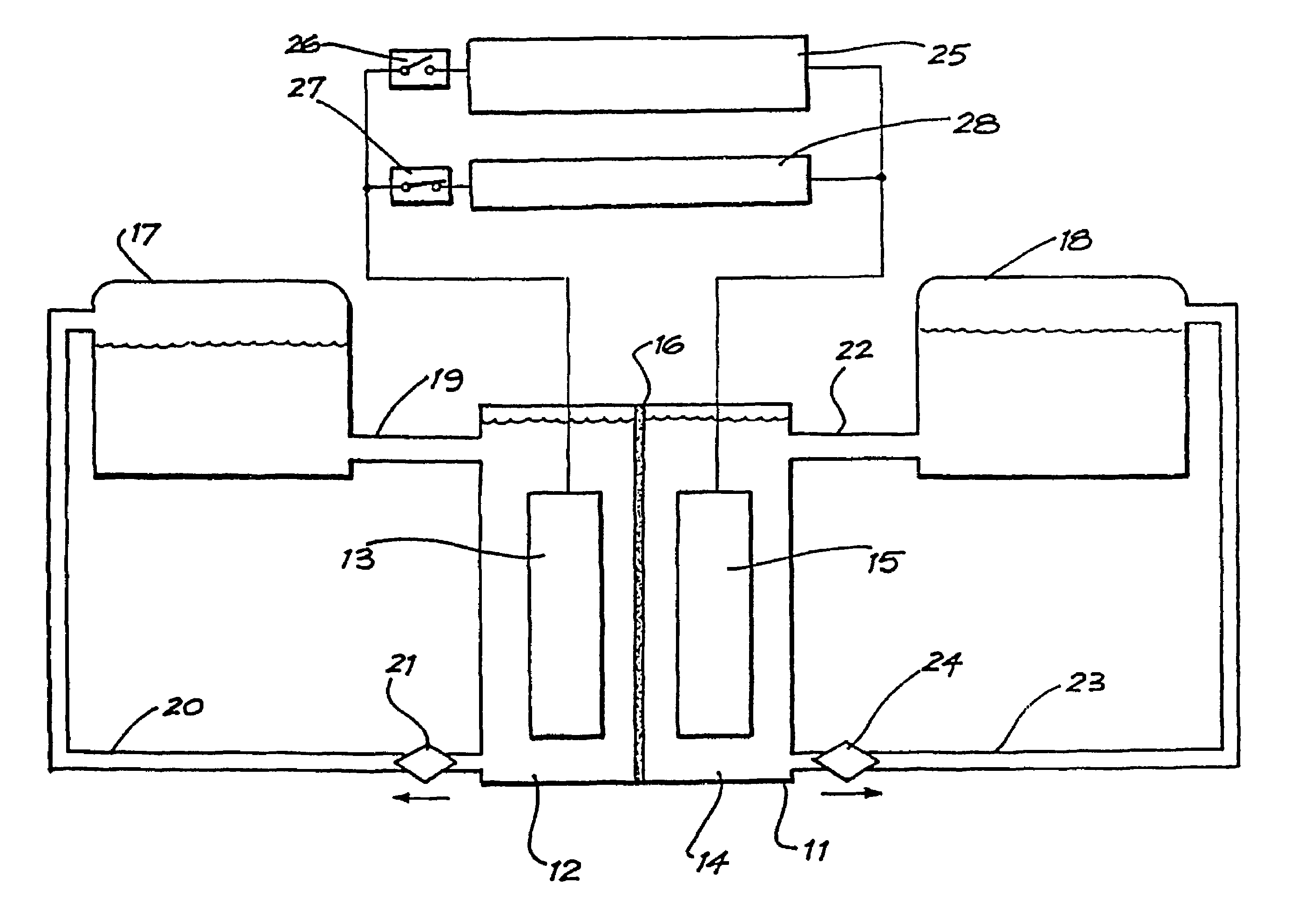
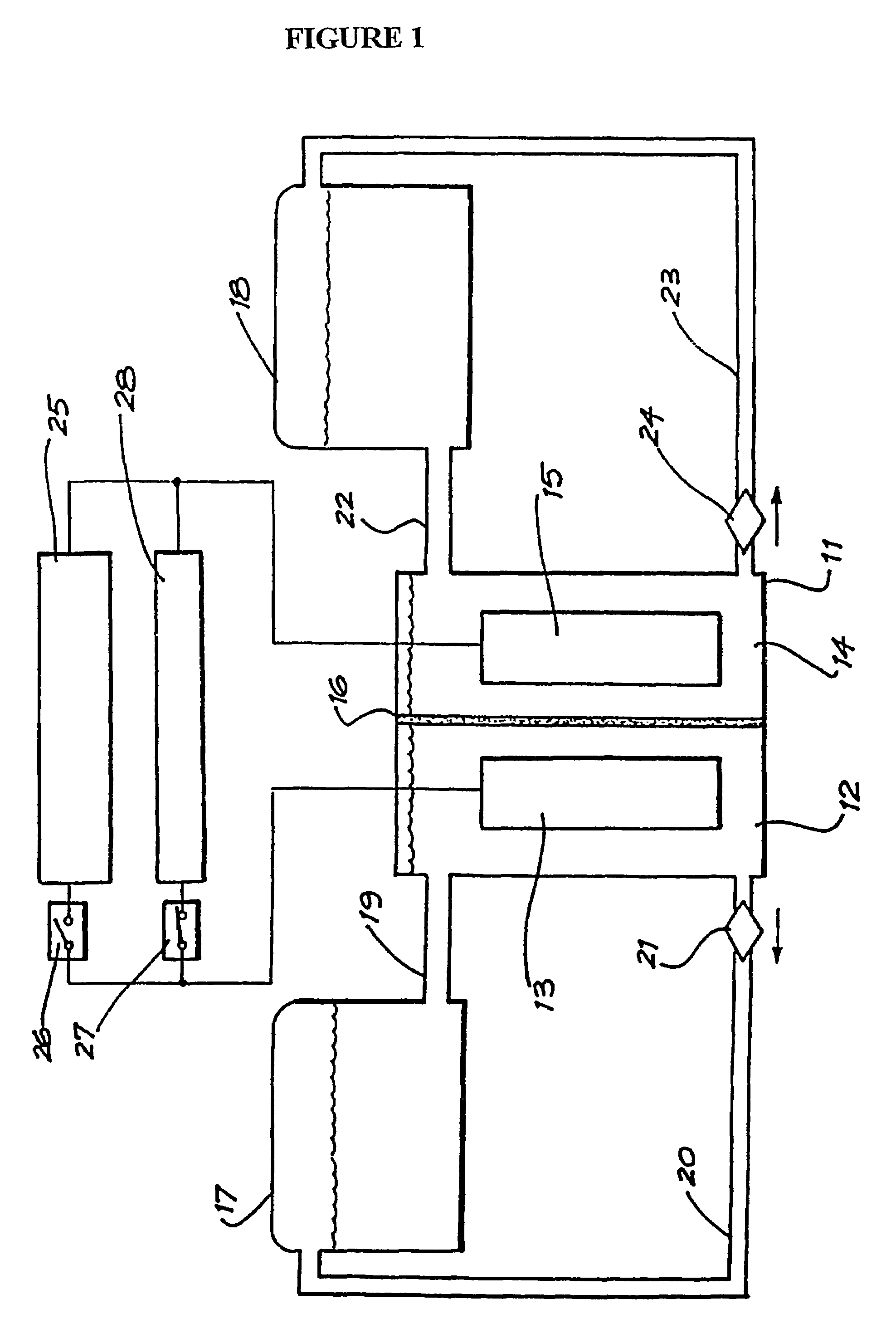
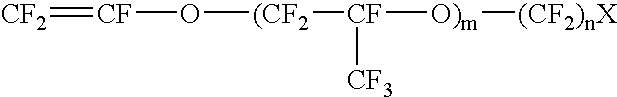Patents
Literature
2935 results about "Flow battery" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
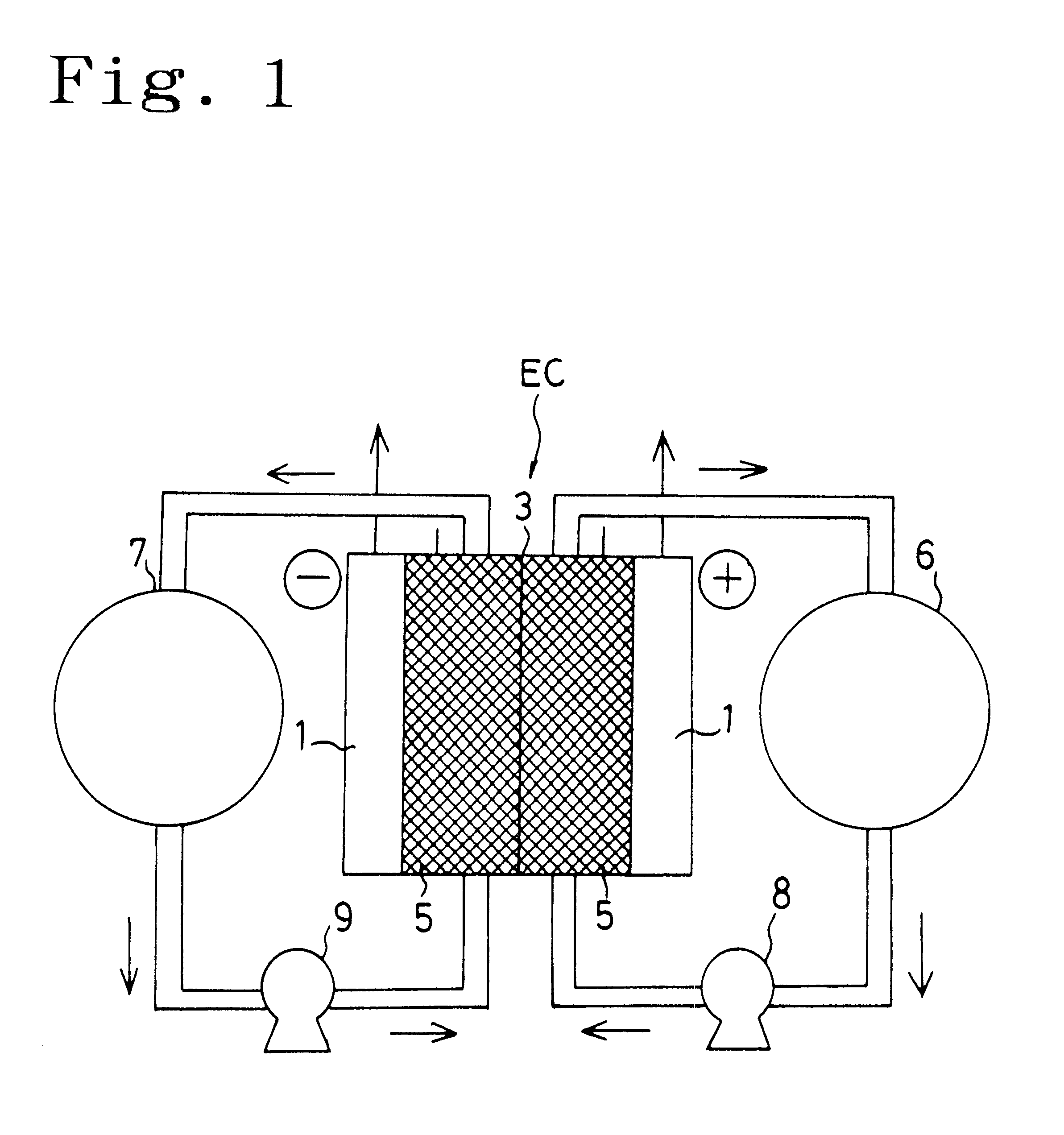
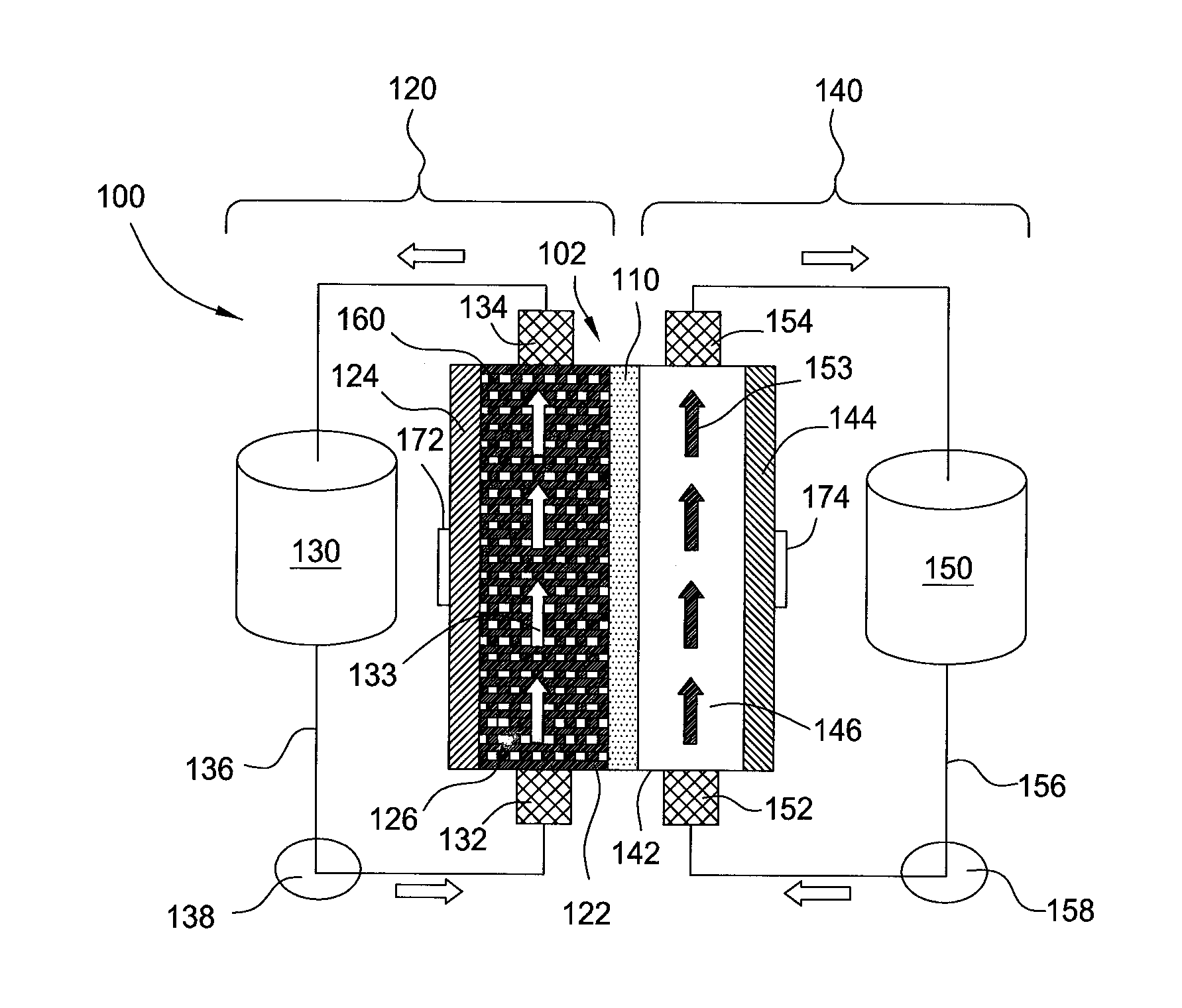
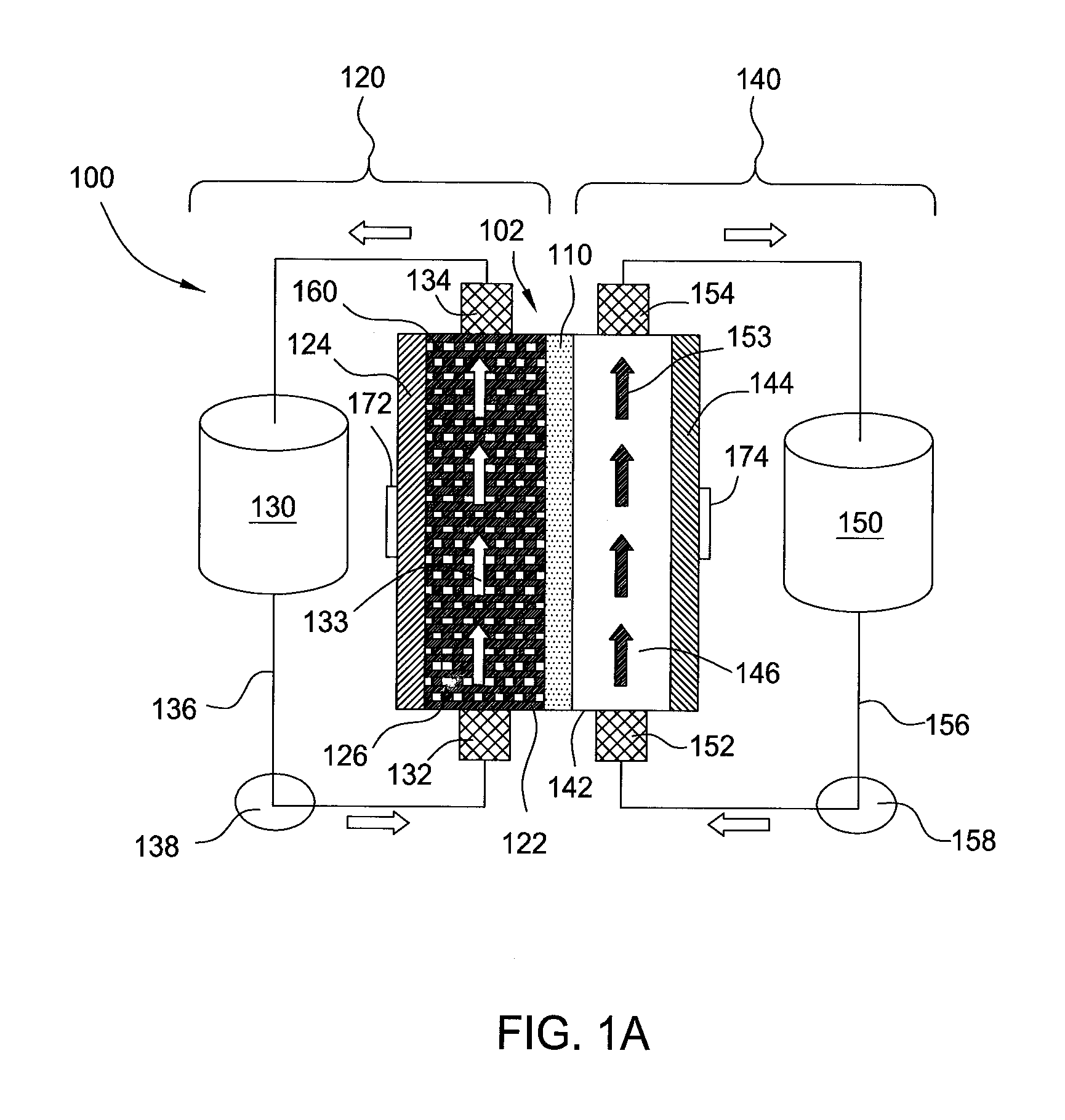
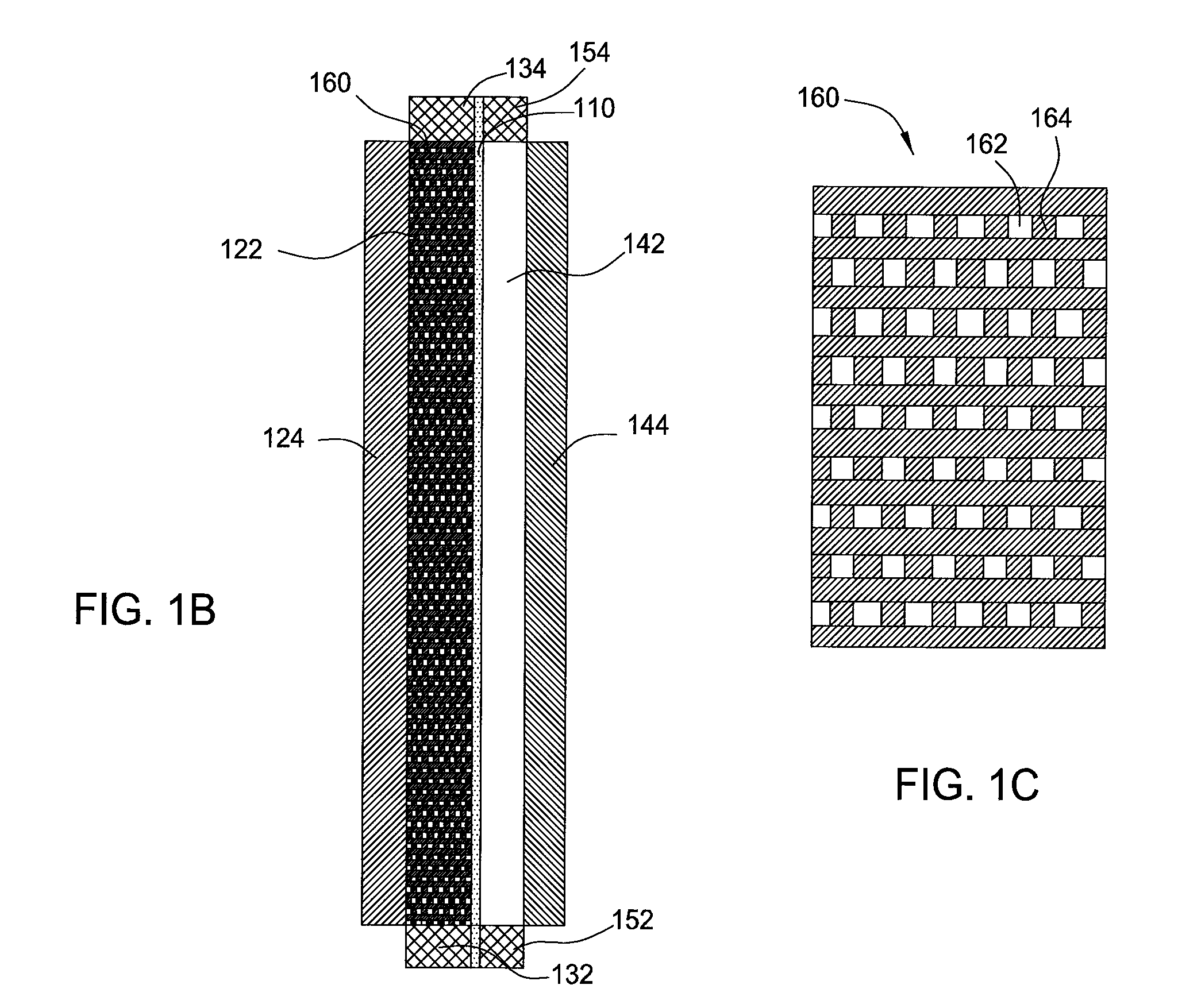
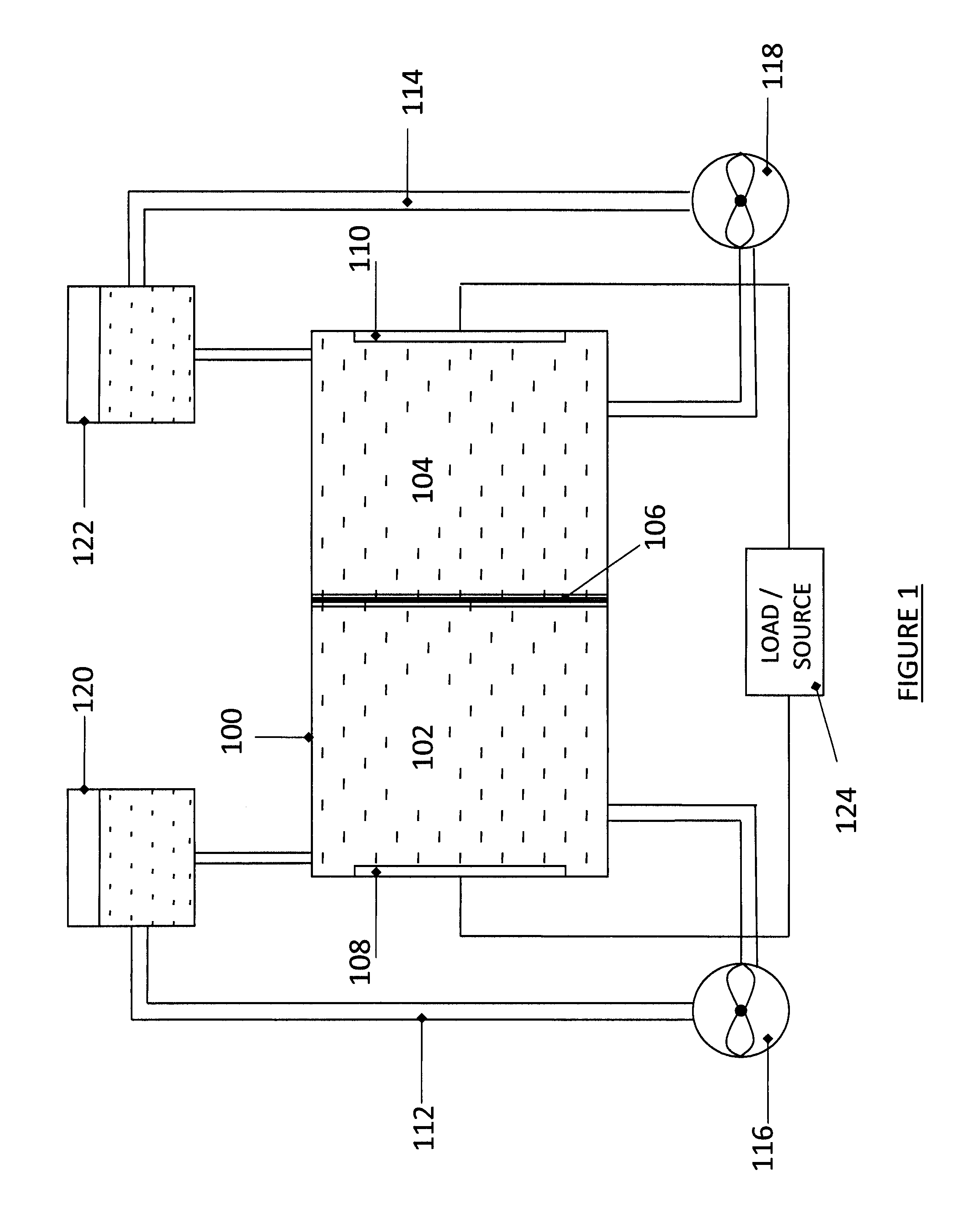
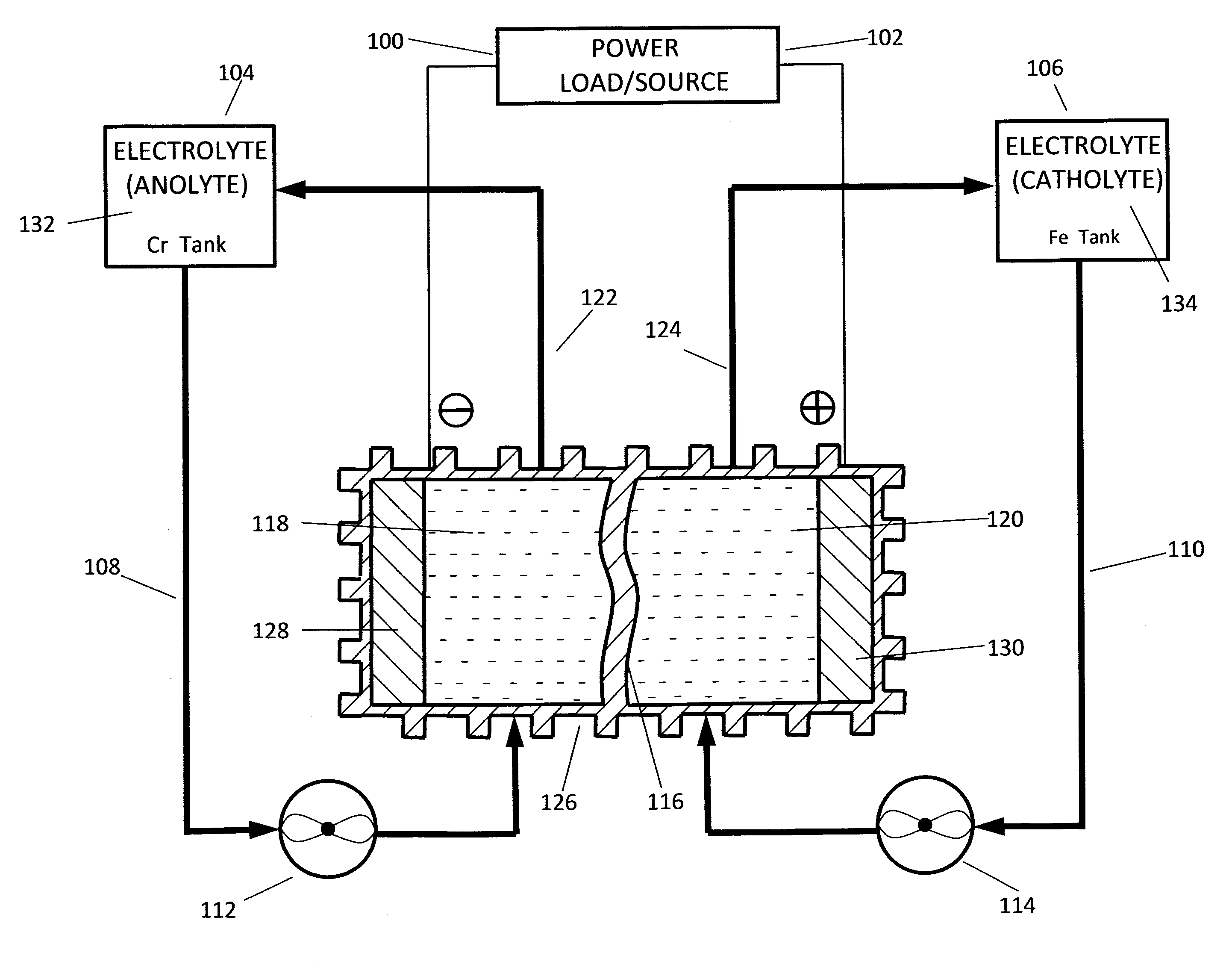
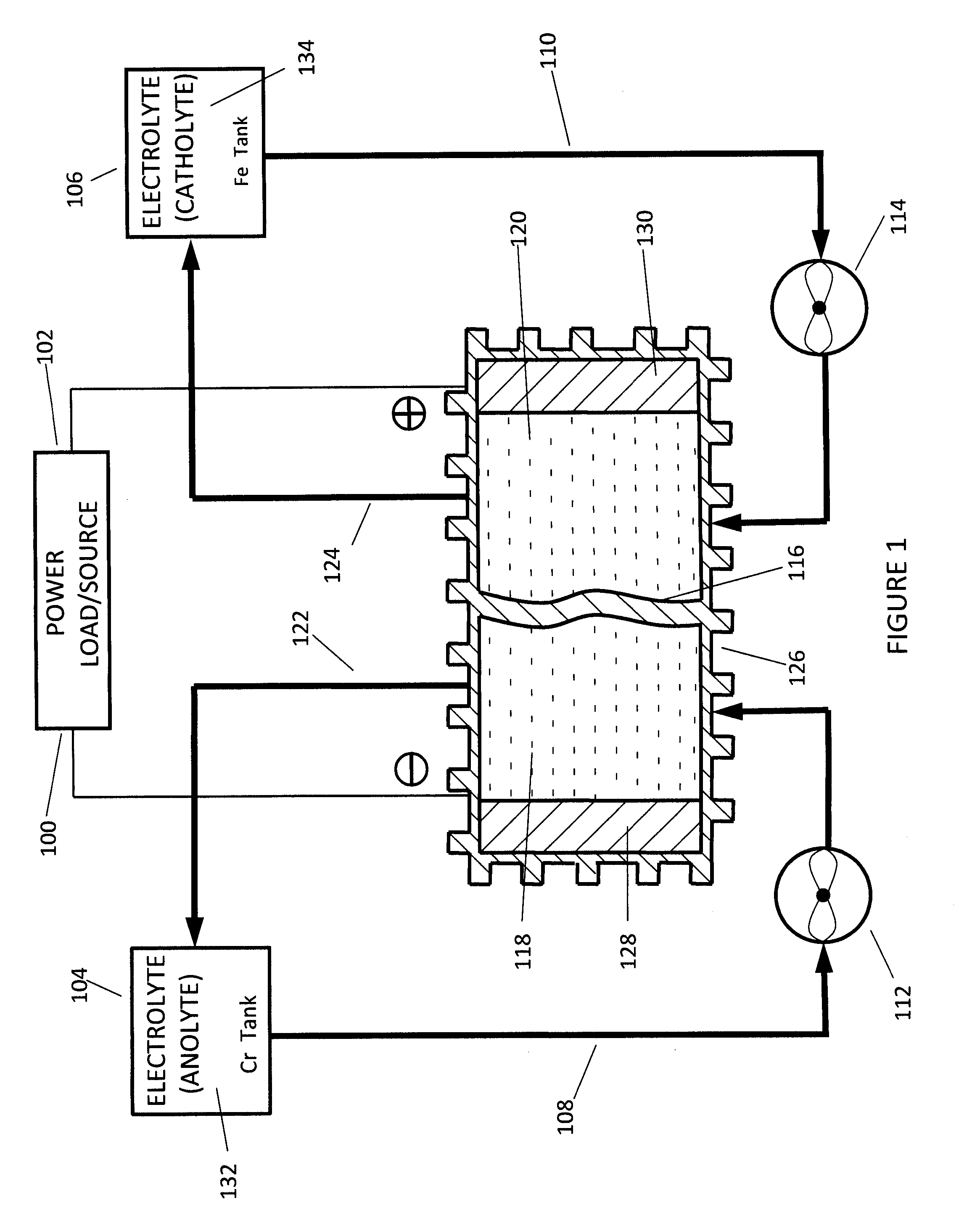
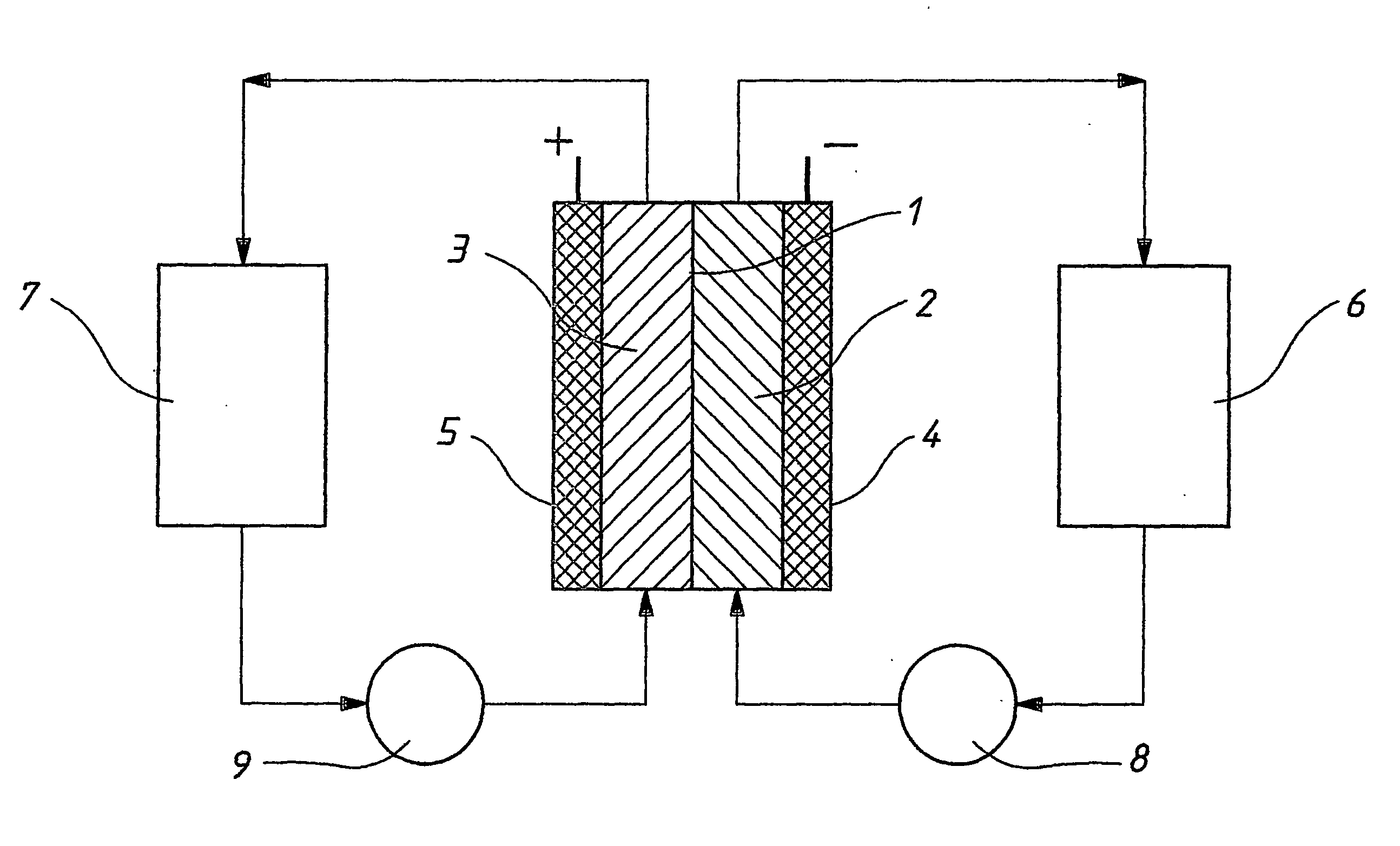
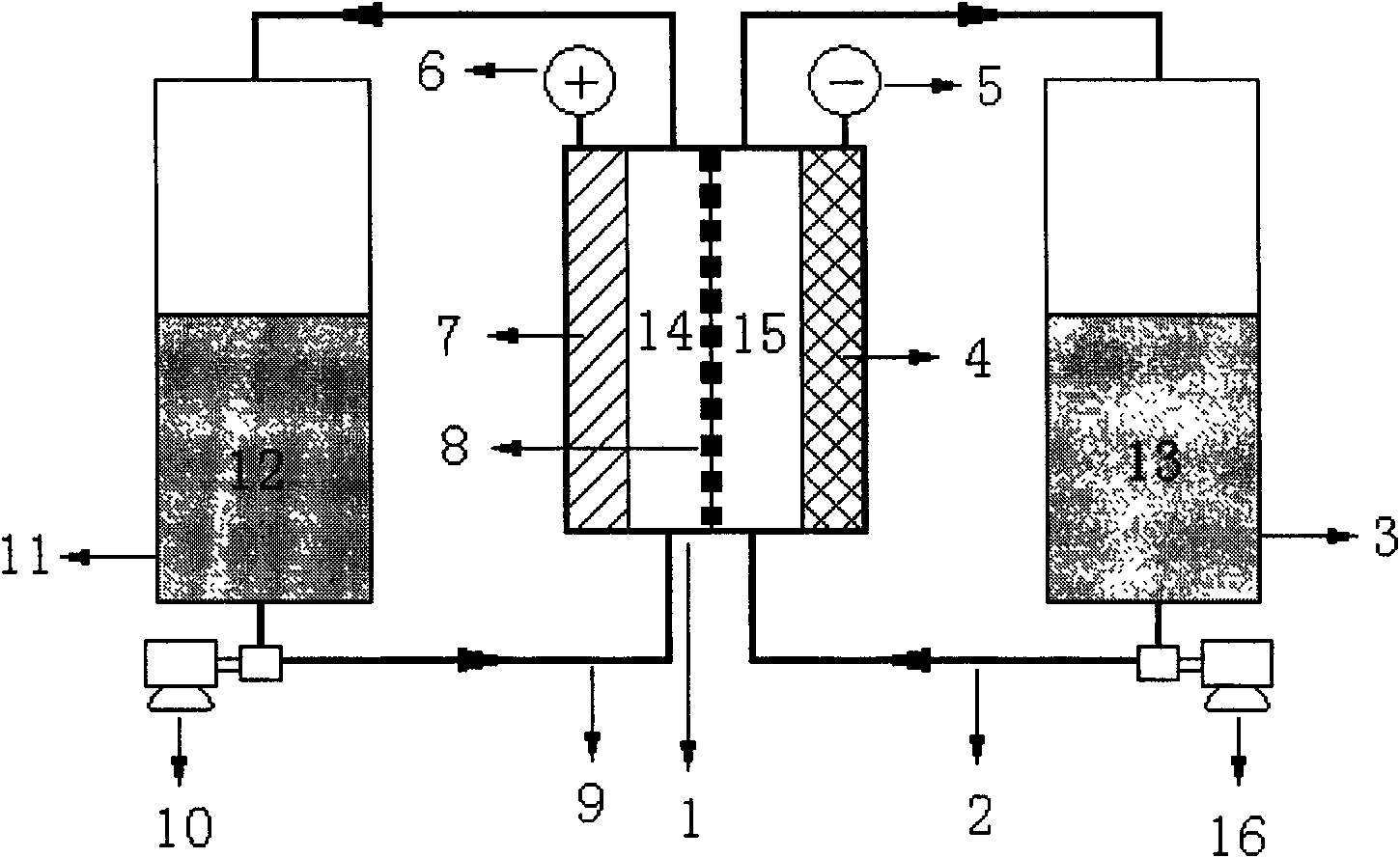
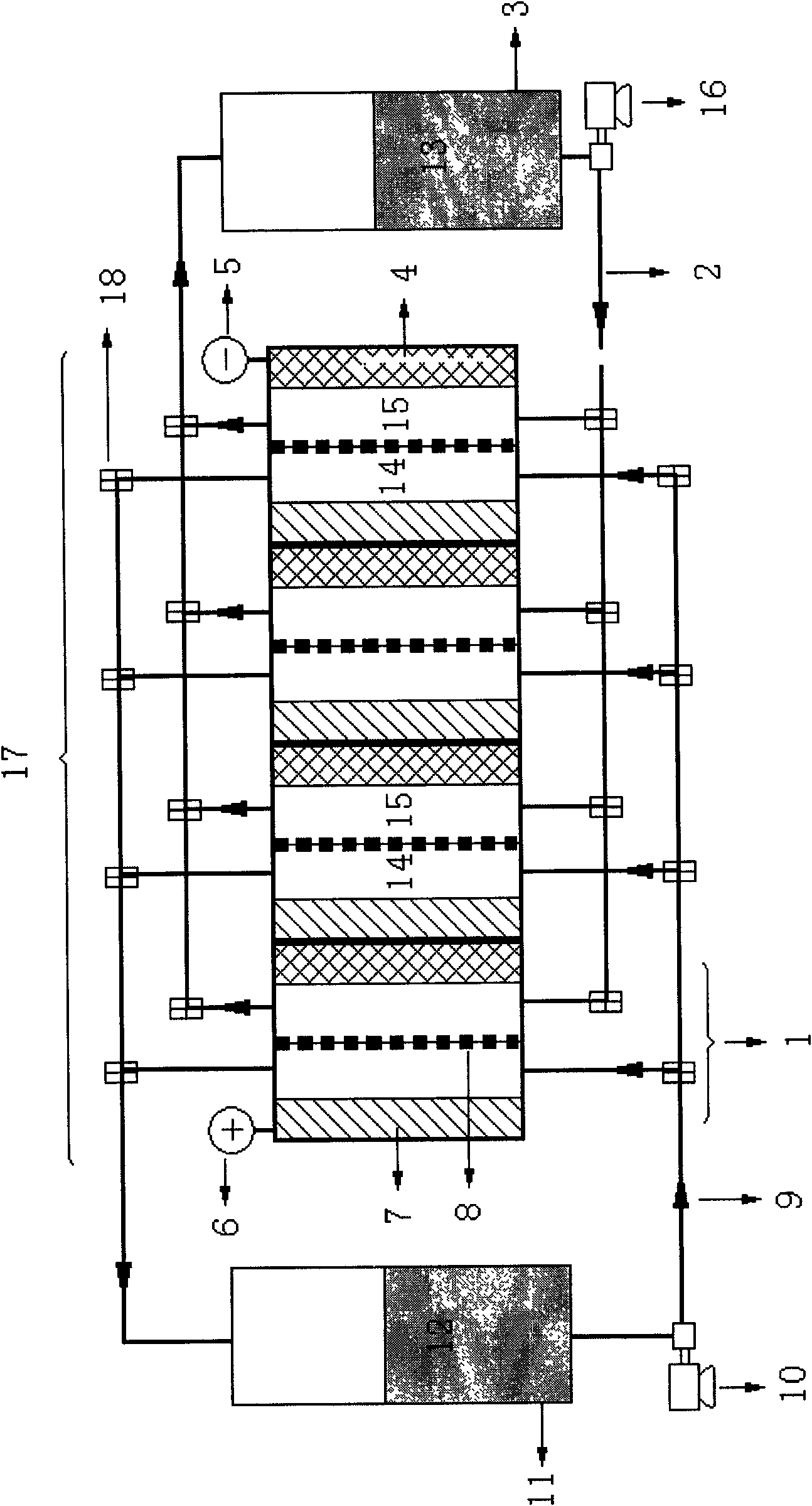
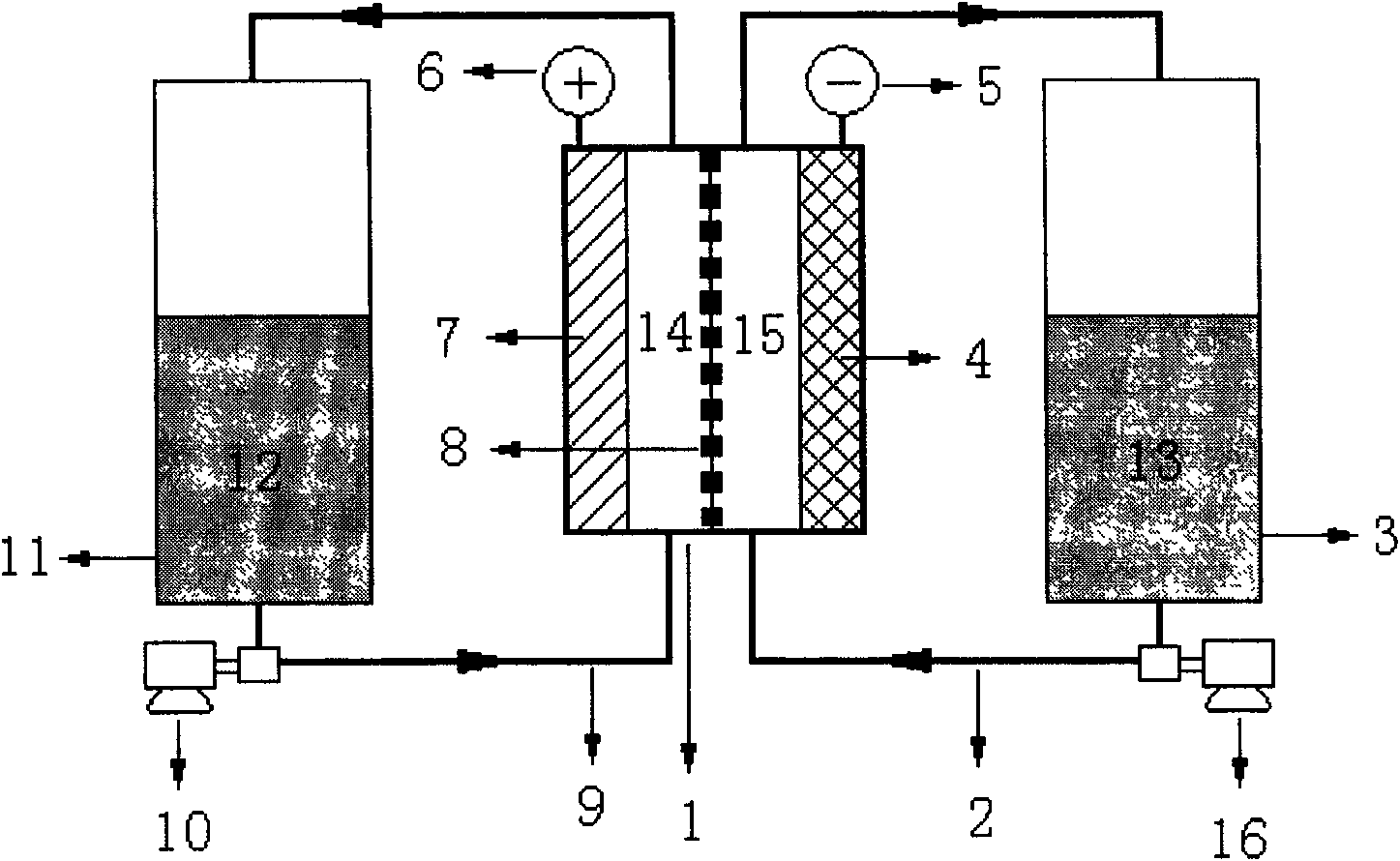
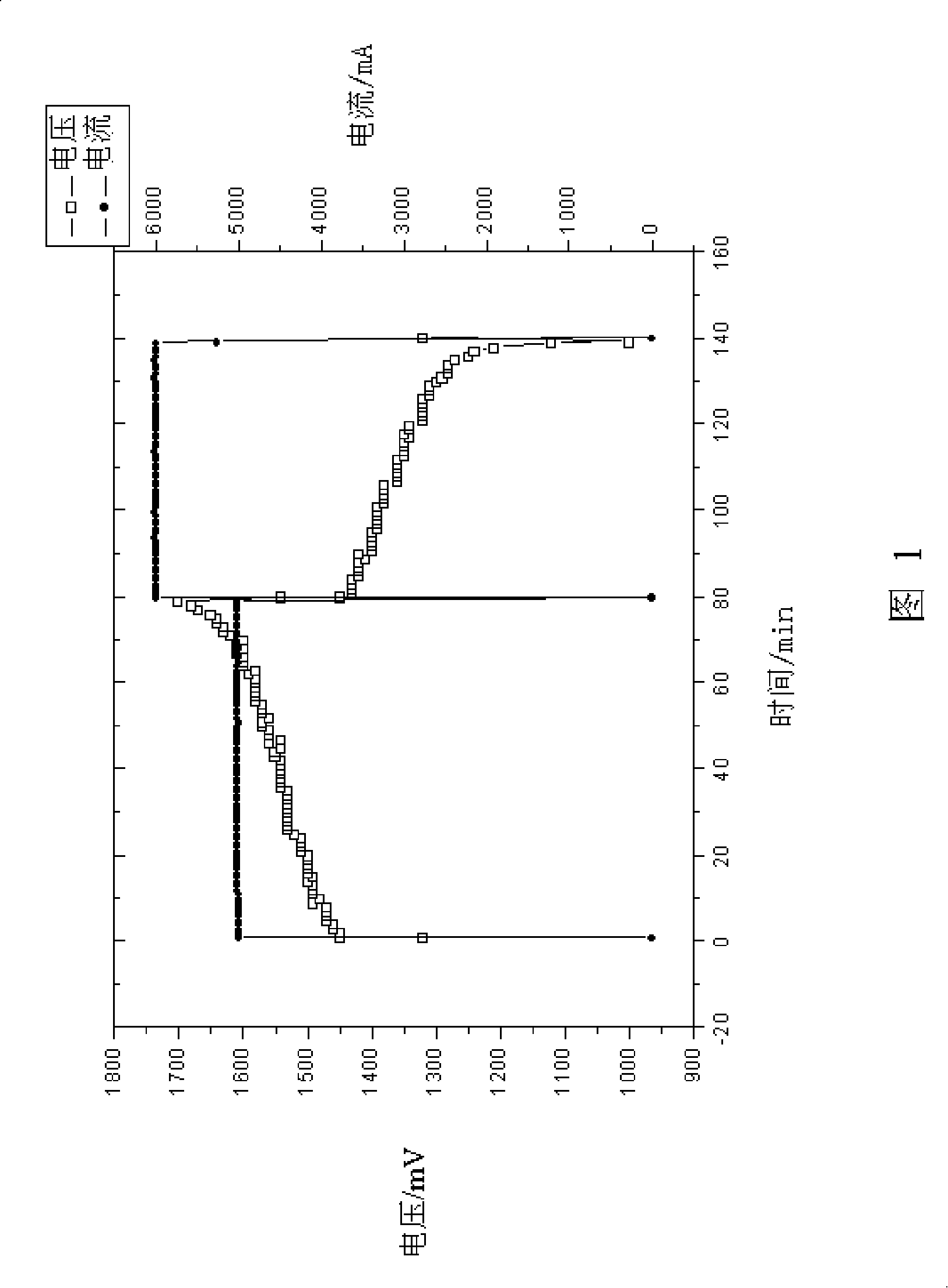
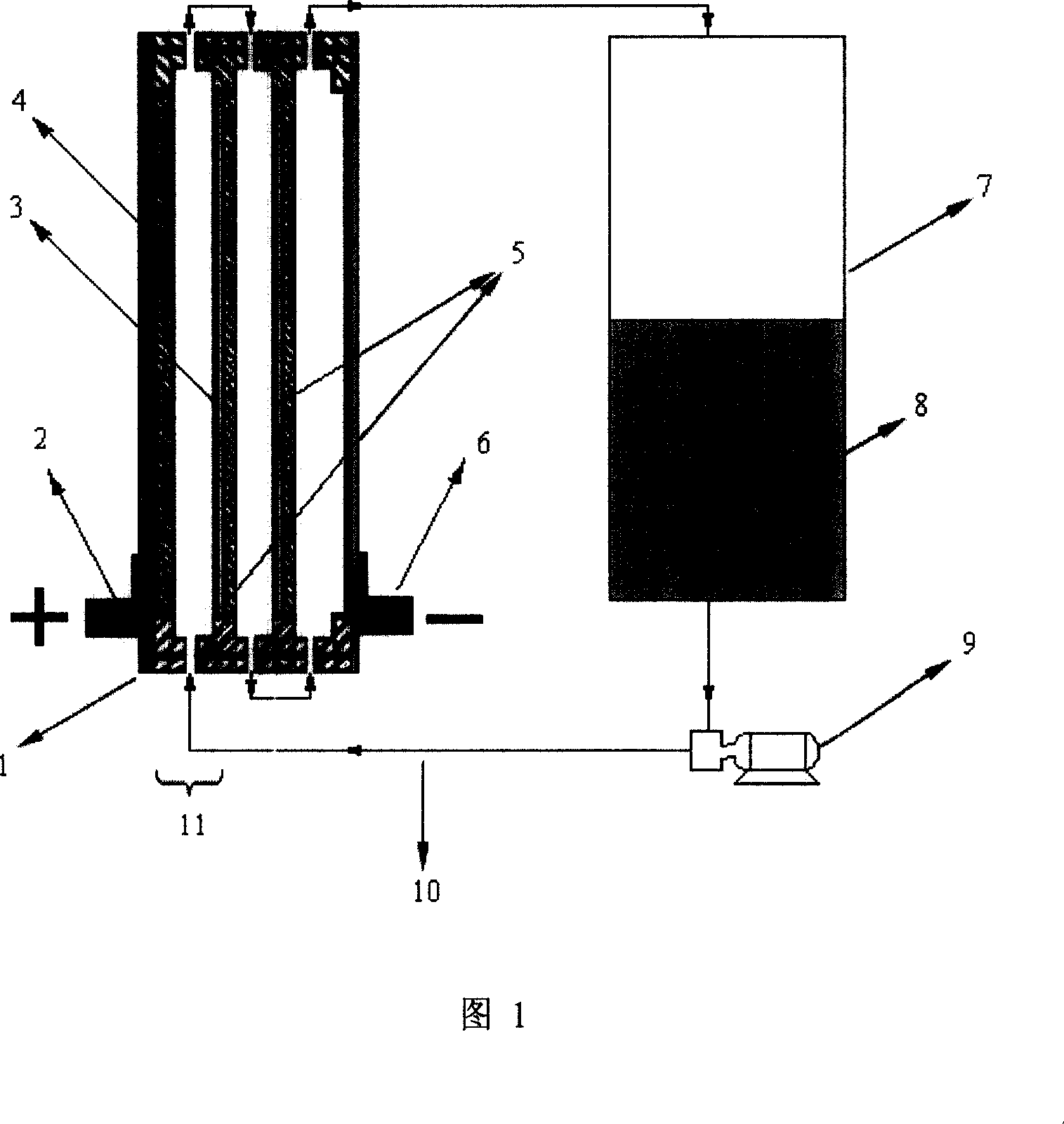
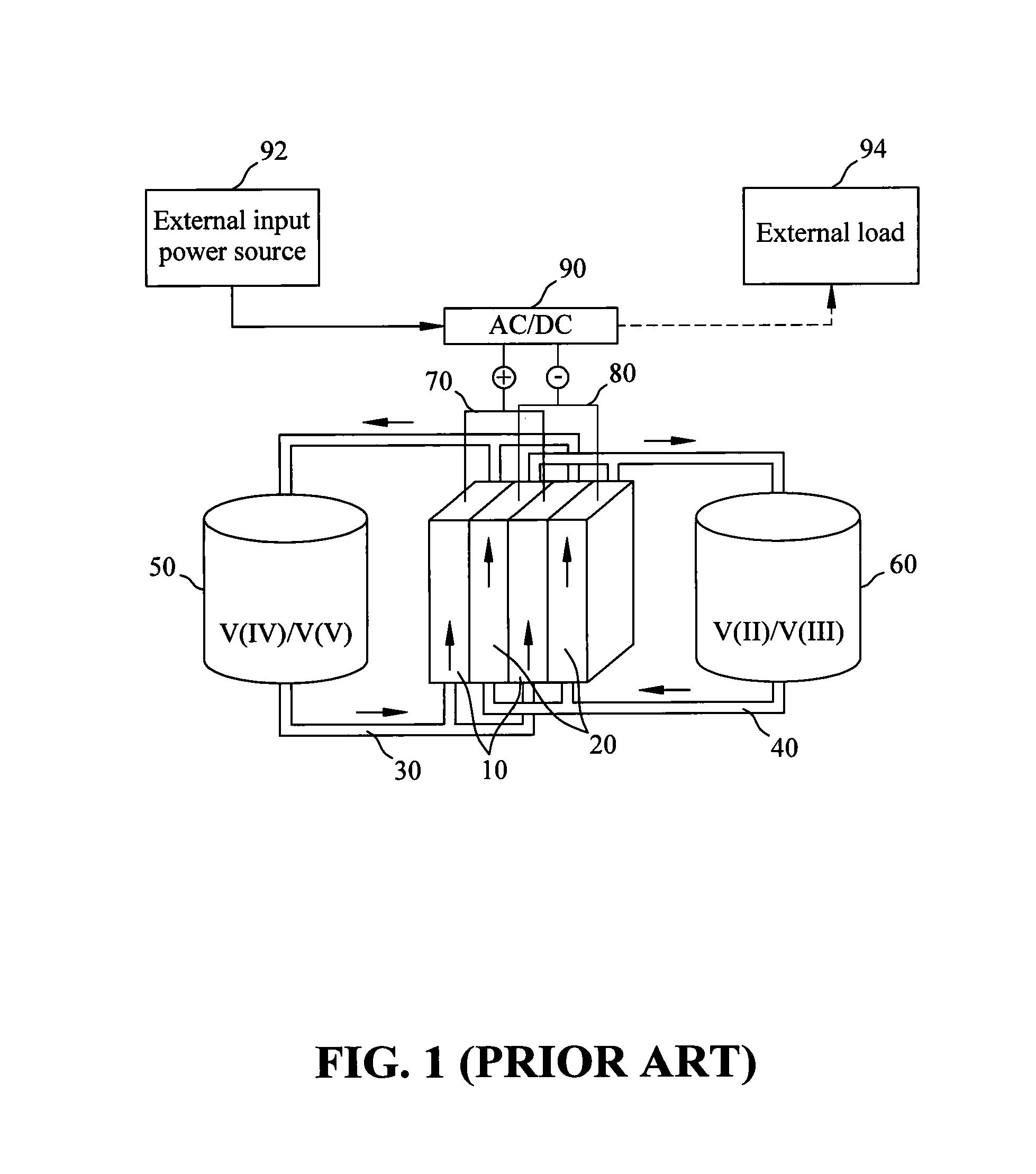
A flow battery, or redox flow battery (after reduction–oxidation), is a type of electrochemical cell where chemical energy is provided by two chemical components dissolved in liquids contained within the system and separated by a membrane. Ion exchange (accompanied by flow of electric current) occurs through the membrane while both liquids circulate in their own respective space. Cell voltage is chemically determined by the Nernst equation and ranges, in practical applications, from 1.0 to 2.2 volts.
Carbon electrode material for a vanadium-based redox-flow battery
The carbon electrode material of the present invention is used for a vanadium redox-flow cell. The carbon electrode material has quasi-graphite crystal structure in which <002> spacing obtained by X-ray wide angle analysis is 3.43 to 3.60 Å, size of a crystallite in c axial direction is 15 to 33 Å and size of crystallite in a axial direction is 30 to 70 Å. In addition, an amount of surface acidic functional groups obtained by XPS surface analysis is 0.1 to 1.2% and total number of surface bound-nitrogen atoms is 5% or smaller relative to total number of surface carbon atoms. The carbon electrode materials formed of a non-woven fabric of a carbonaceouss fiber is preferable.
Owner:TOYO TOYOBO CO LTD
Redox flow battery
InactiveUS6764789B1Reduce capacityReduce frequencyElectrolyte holding meansCell electrodesRedoxAqueous solution
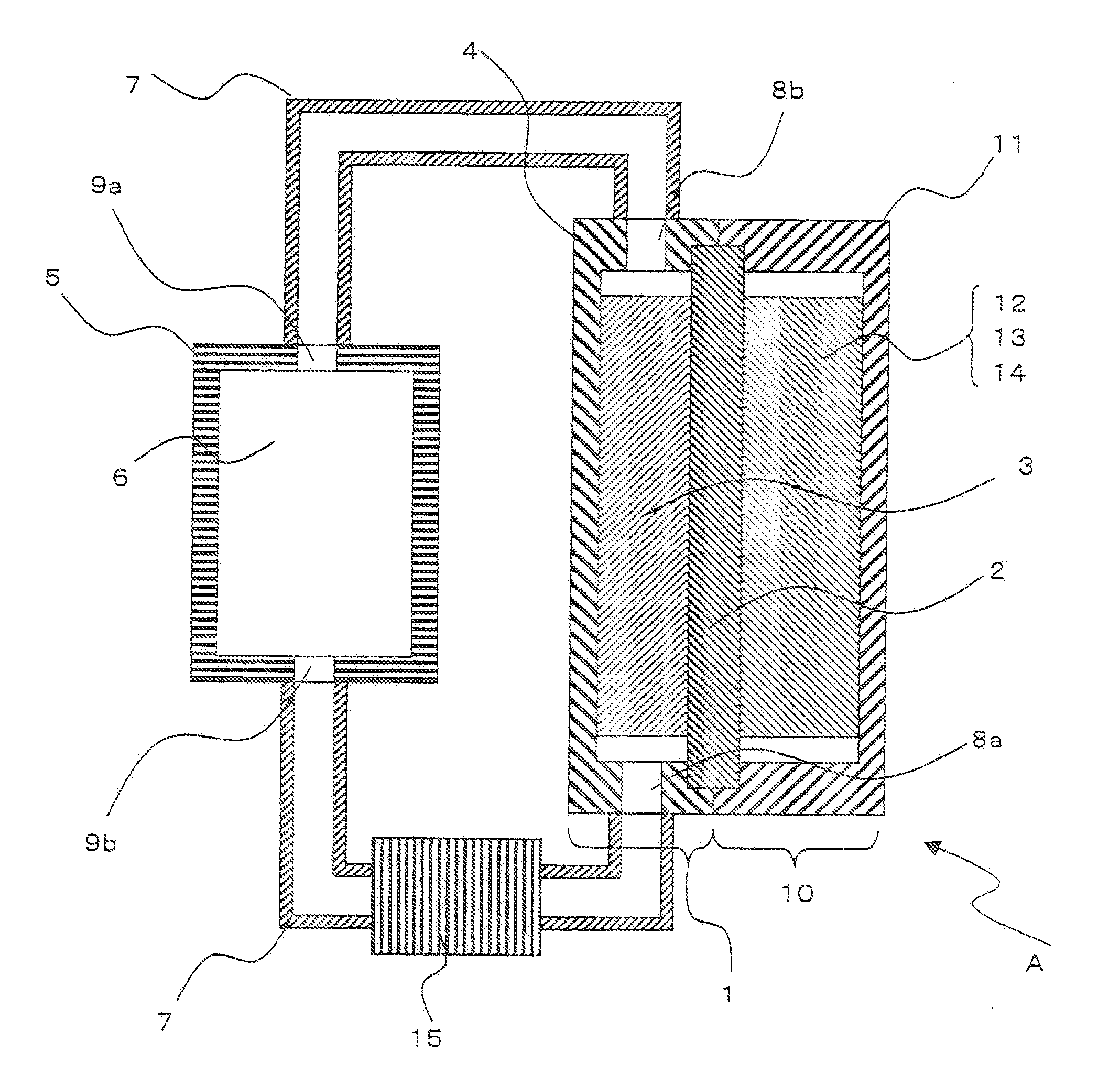
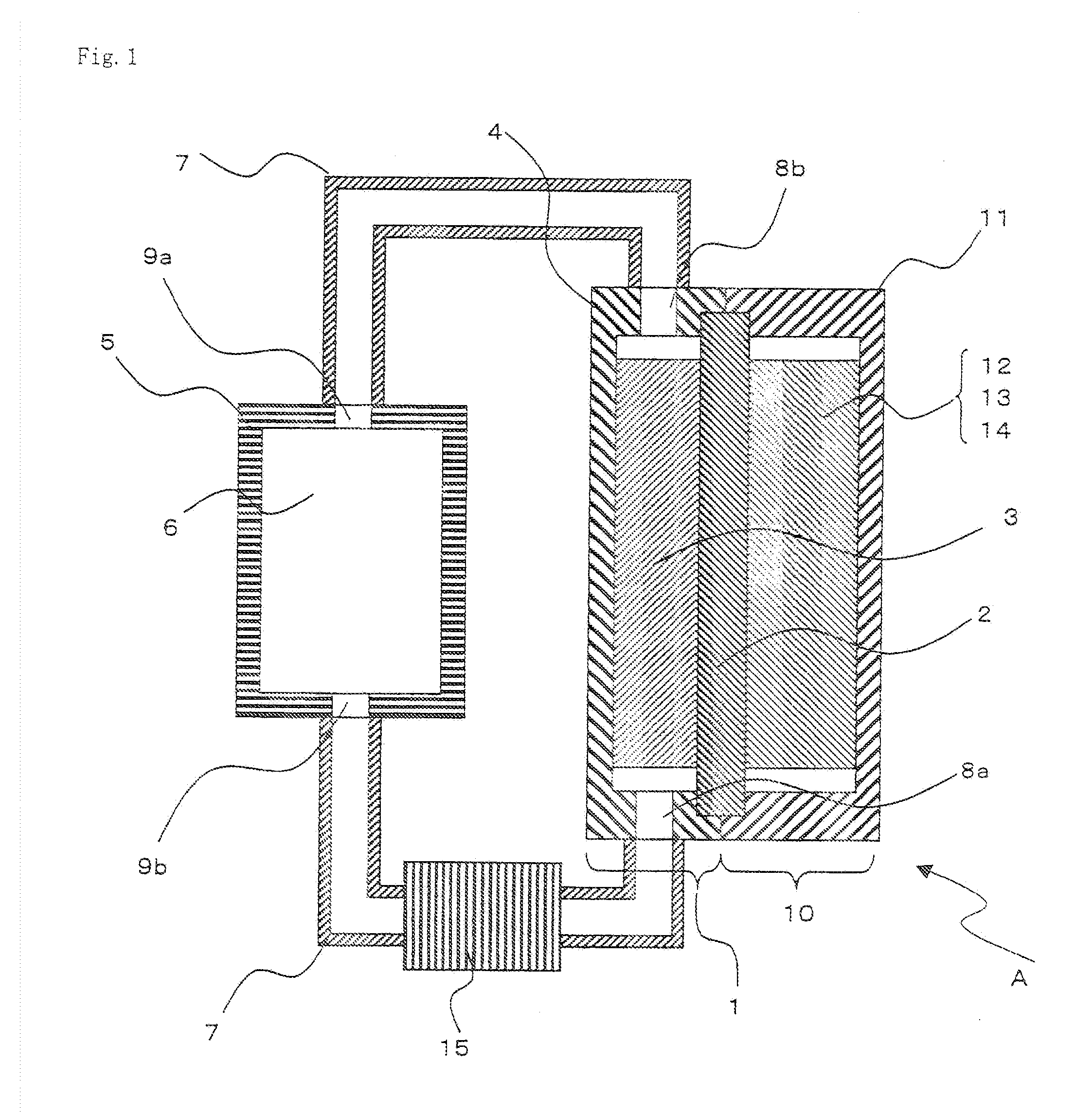
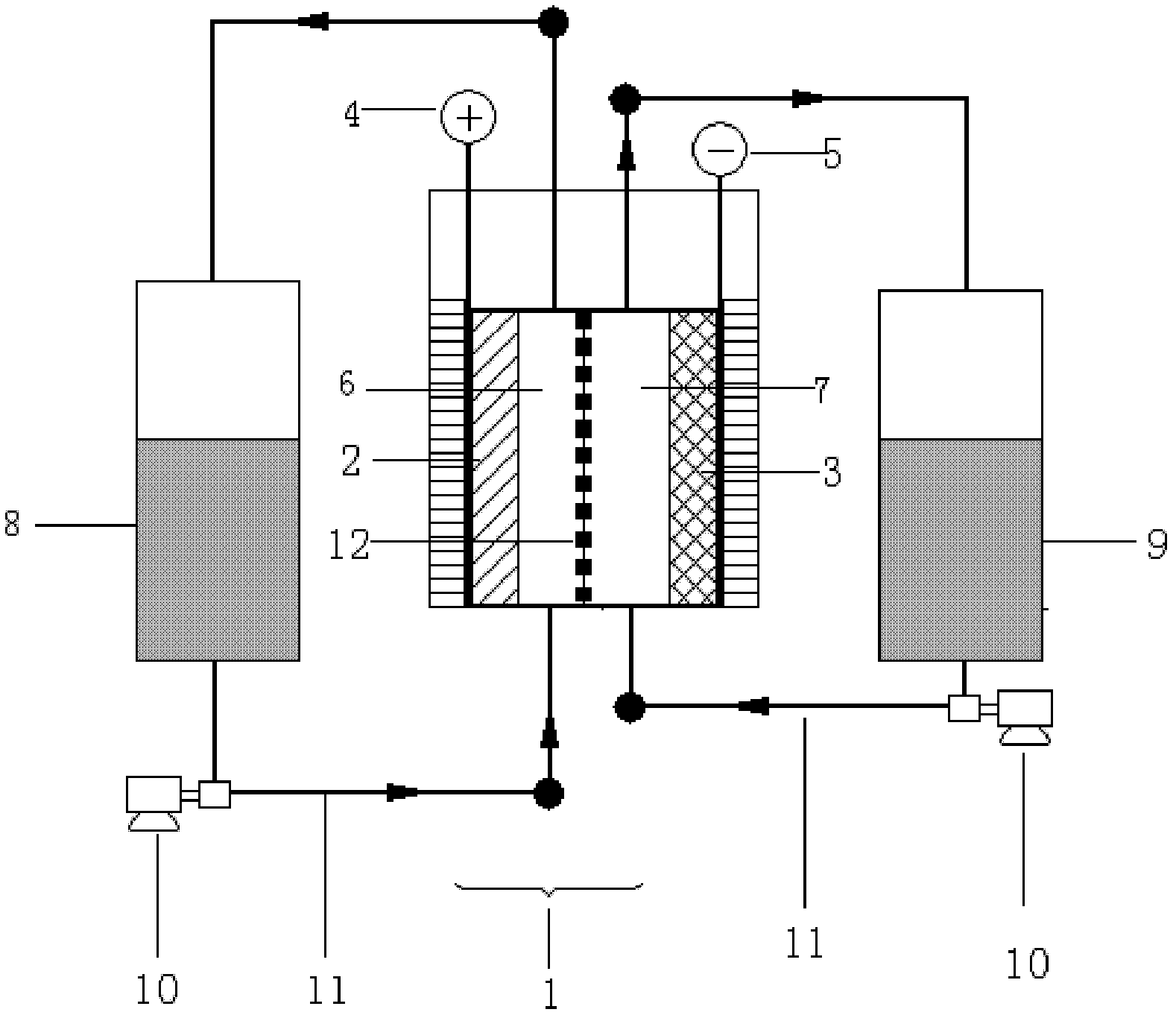
The present invention provides a redox flow type battery which a liquid-circulating battery comprising a battery cell and storage tanks for positive and negative electrolytes, wherein the battery cell is separated by a membrane to provide a positive cell and a negative cell, each cell having a liquid-permeable porous electrode disposed therein, wherein the positive and negative electrolytes are sulfuric acid aqueous solutions with vanadium ion concentrations of 0.5 mol / l to 8 mol / l and the electrolyte which migrates through the membrane over cycles of charge and discharge is returned from the storage tank where the liquid increases to the storage tank where the liquid decreases in order to keep the change in the amounts of the positive and negative electrolytes in a certain range while charge and discharge are carried out.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Redox flow battery
InactiveUS20120135278A1High charge-discharge efficiencyIncrease energy densityCell electrodesFinal product manufactureRedoxSlurry
A redox flow battery comprising an electrode cell including a negative electrode cell, a positive electrode cell and a separator for separating them, in which at least one of the negative electrode cell and the positive electrode cell includes a slurry type electrode solution, a porous current collector and a casing; a tank for storing the slurry type electrode solution; and a pipe for circulating the slurry type electrode solution between the tank and the electrode cell.
Owner:SHARP KK
Redox flow battery and method of operating it
InactiveUS6692862B1Easy dischargeImprove efficiencyElectrolyte moving arrangementsFuel cells groupingWork cycleRedox
By realizing or installing check valve liquid vein interrupters in each compartment of the battery the phenomenon of slow discharge of the retained volumes of electrolytes during long periods of inactivity of a redox flow battery, with the electrolyte pumps stopped altogether, can be practically eliminated with the effect that the battery is perfectly ready to deliver electric power immediately upon request even after prolonged periods of inactivity. Moreover, the presence of liquid vein interrupters on each compartment in either an outlet or an inlet port substantially preventing by-pass current during a not pumping phase, permits to increase the by pumping the electrolytes through the compartments of a battery stack intermittently, in other words in a pulsed manner, with a certain duty-cycle. Relatively brief pumping phases at relatively high flow rate alternated to phases of not pumping provide for a volumetrically adequate refreshing of the electrolytes present in the battery compartments and contrast the formation of gradients in the bodies of electrolyte.
Owner:SQUIRREL HLDG
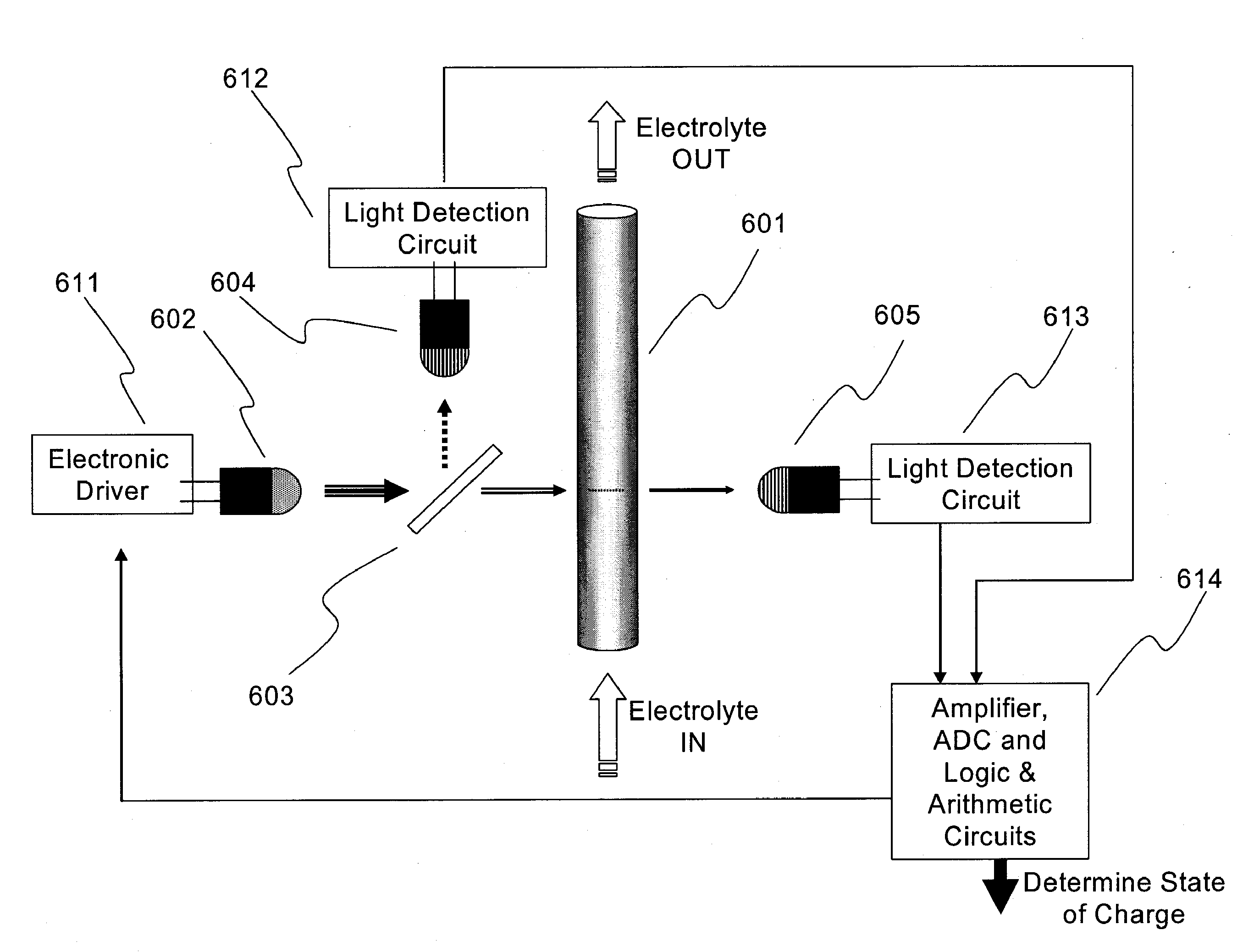
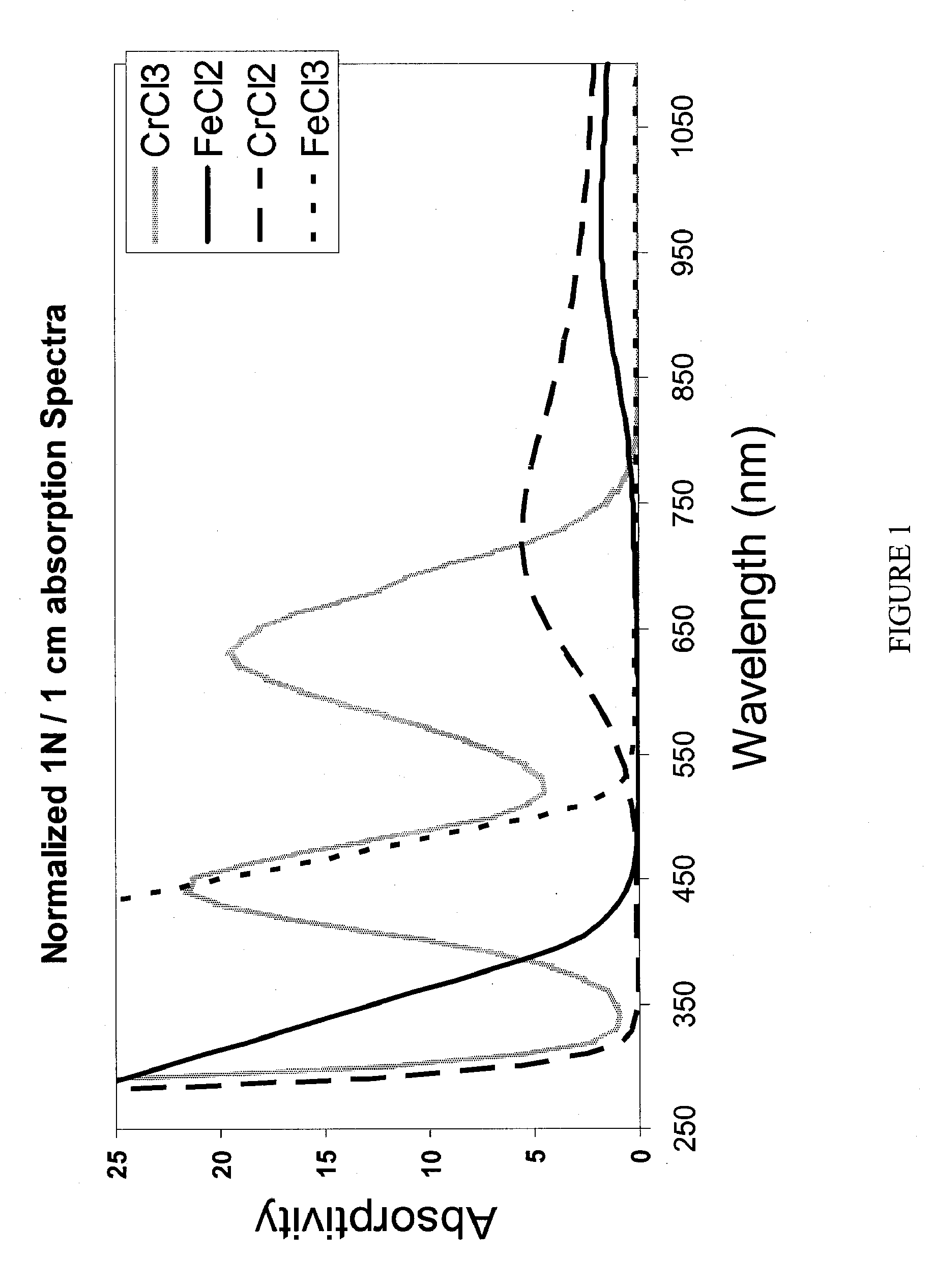
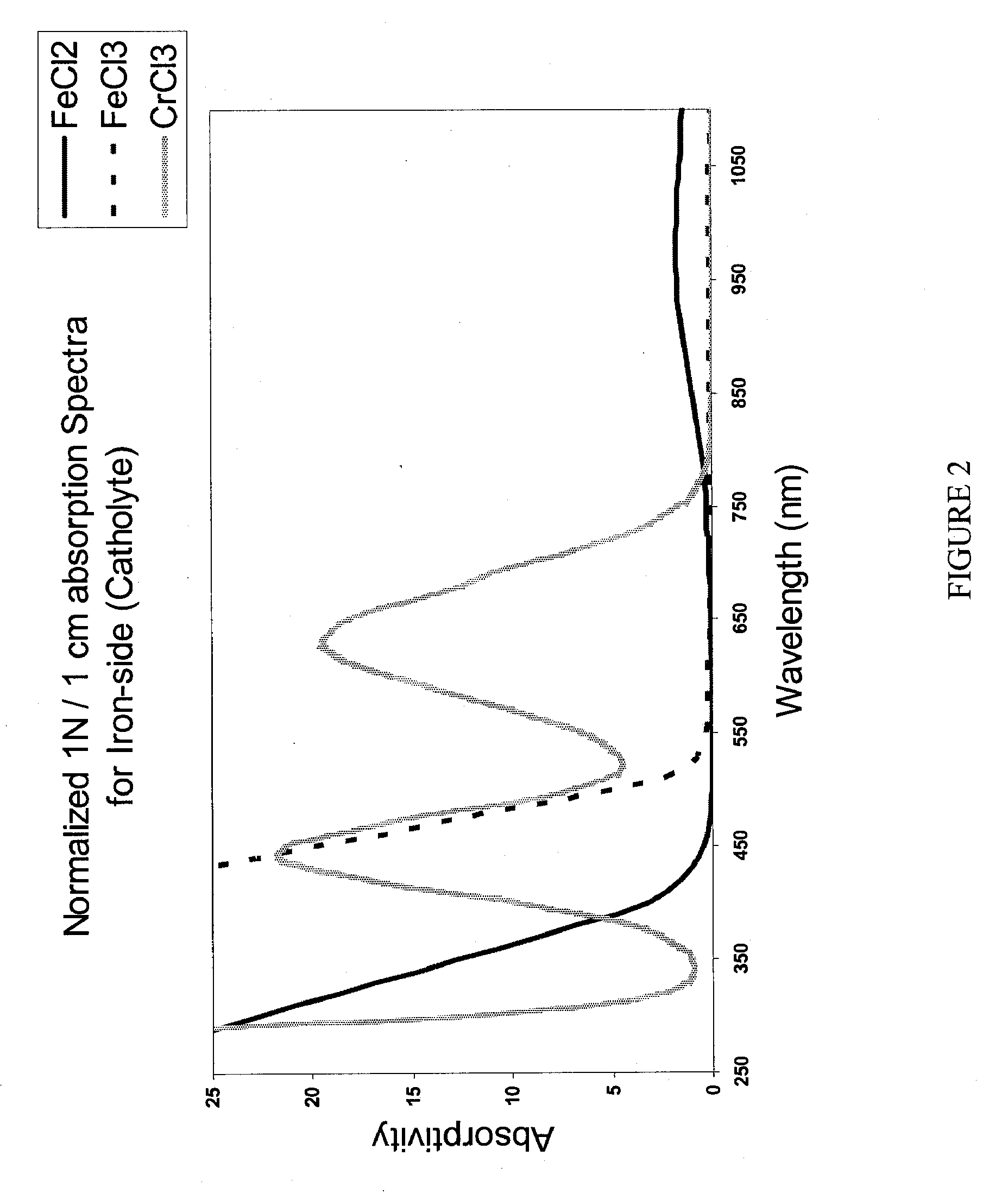
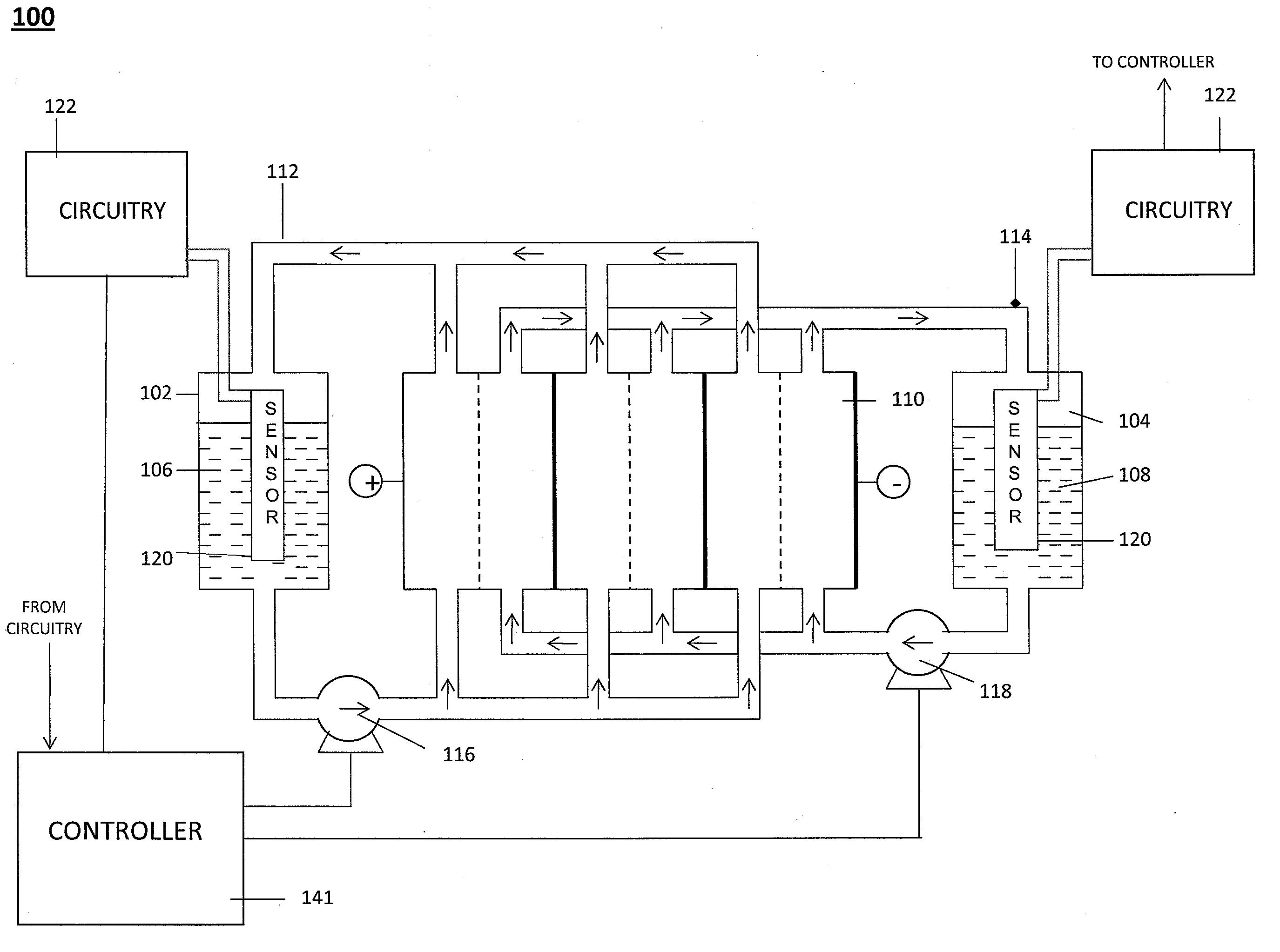
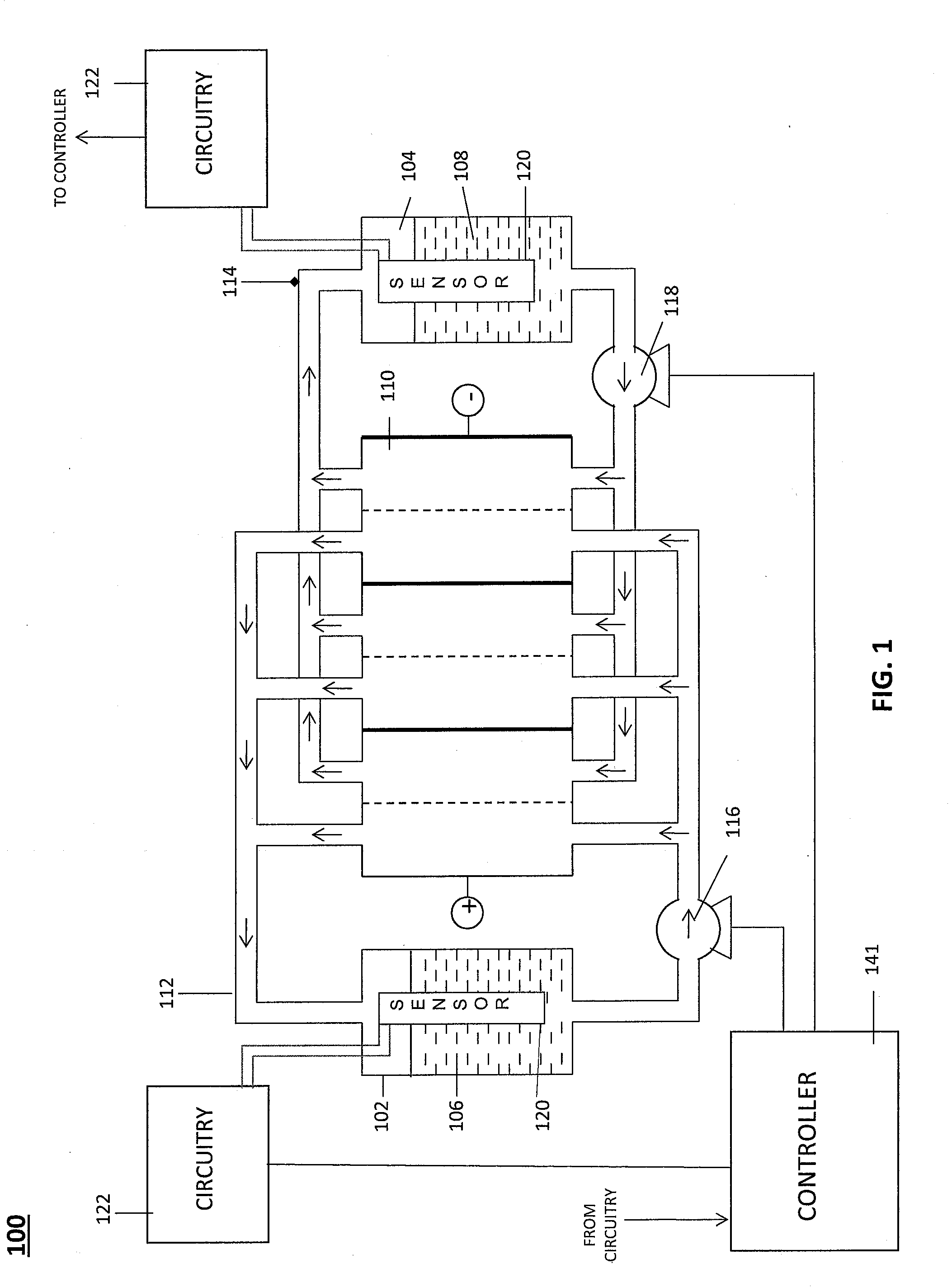
Apparatus and Methods of Determination of State of Charge in a Redox Flow Battery
InactiveUS20080193828A1Batteries circuit arrangementsMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorRedoxState of charge
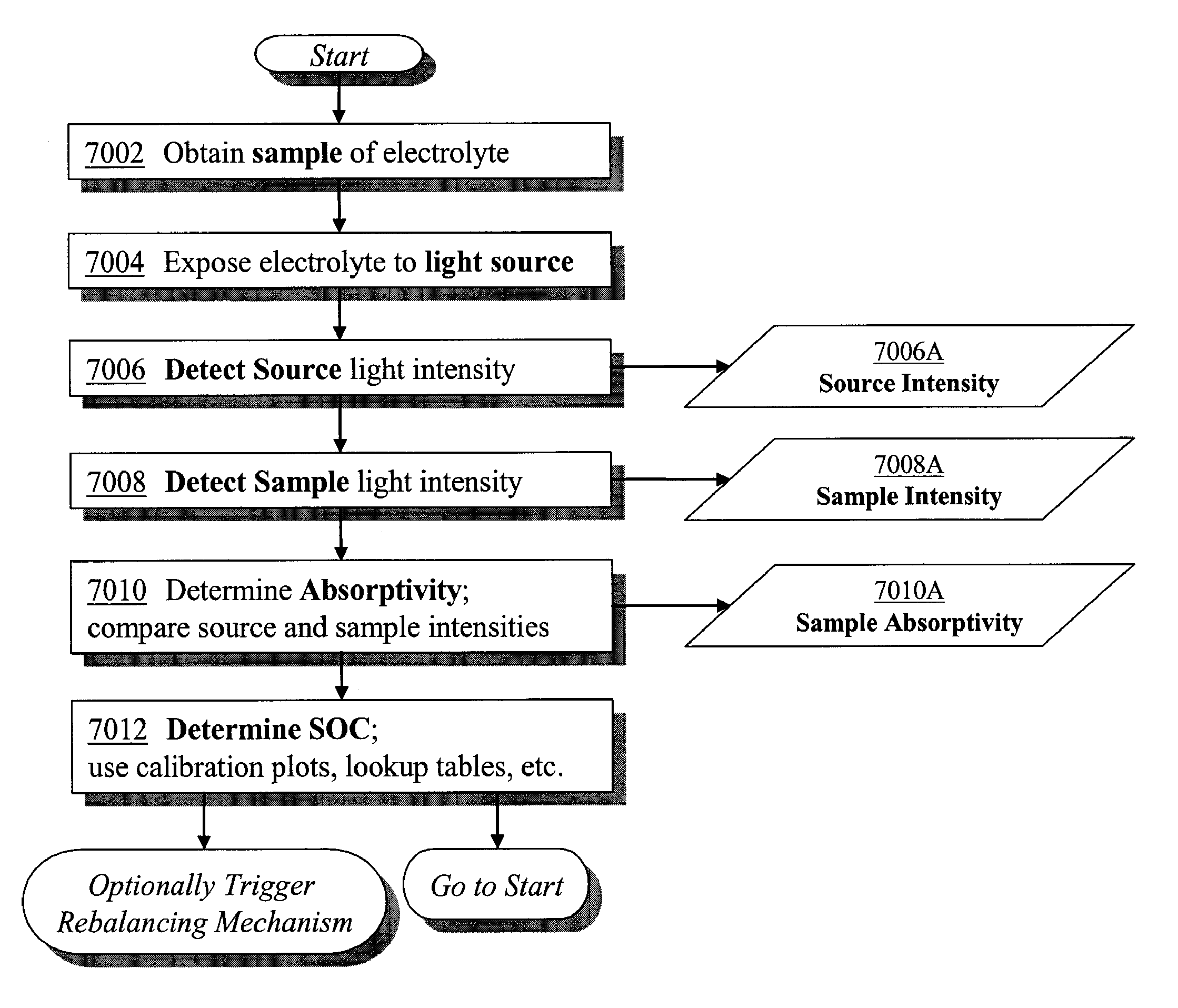
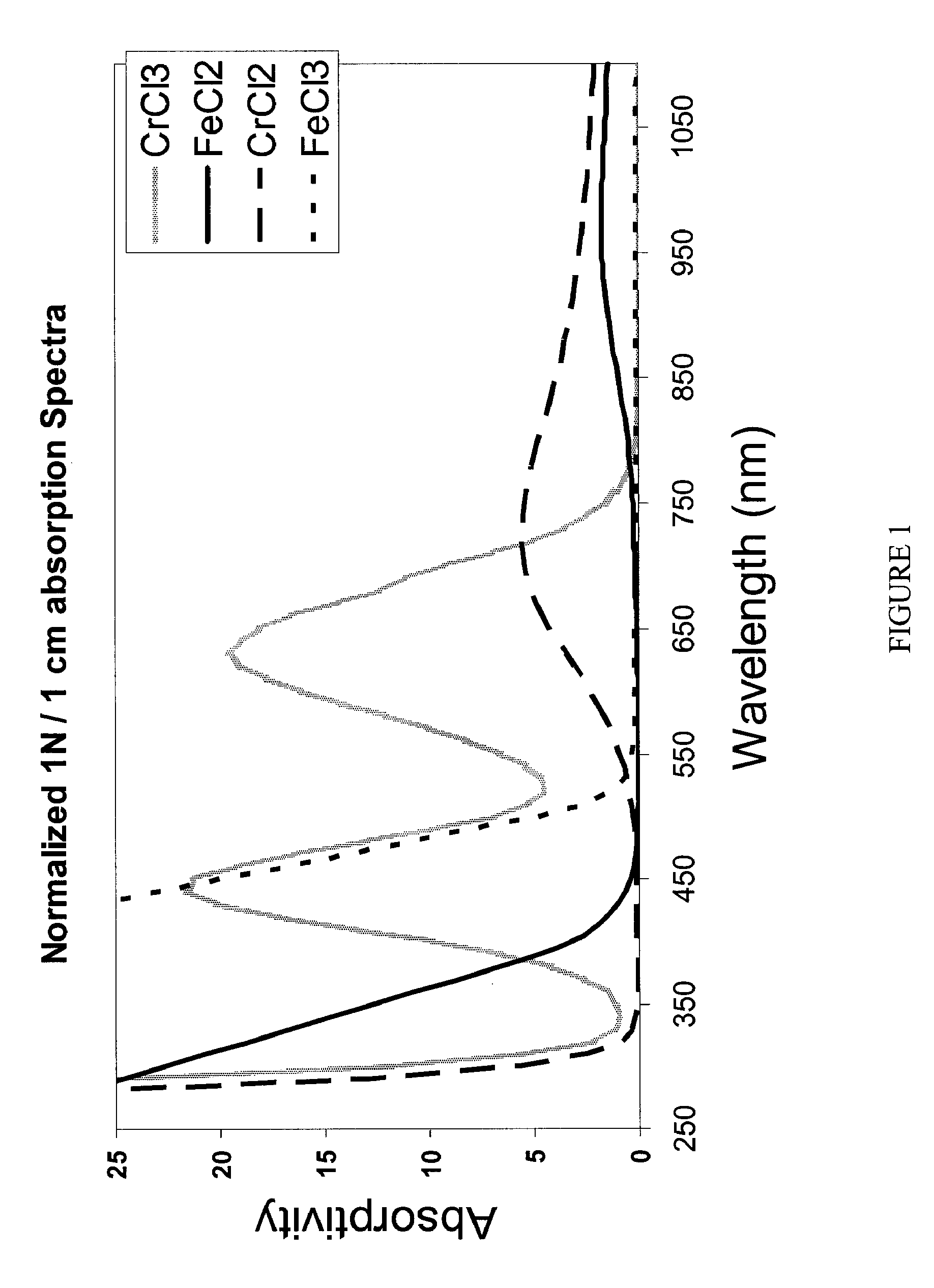
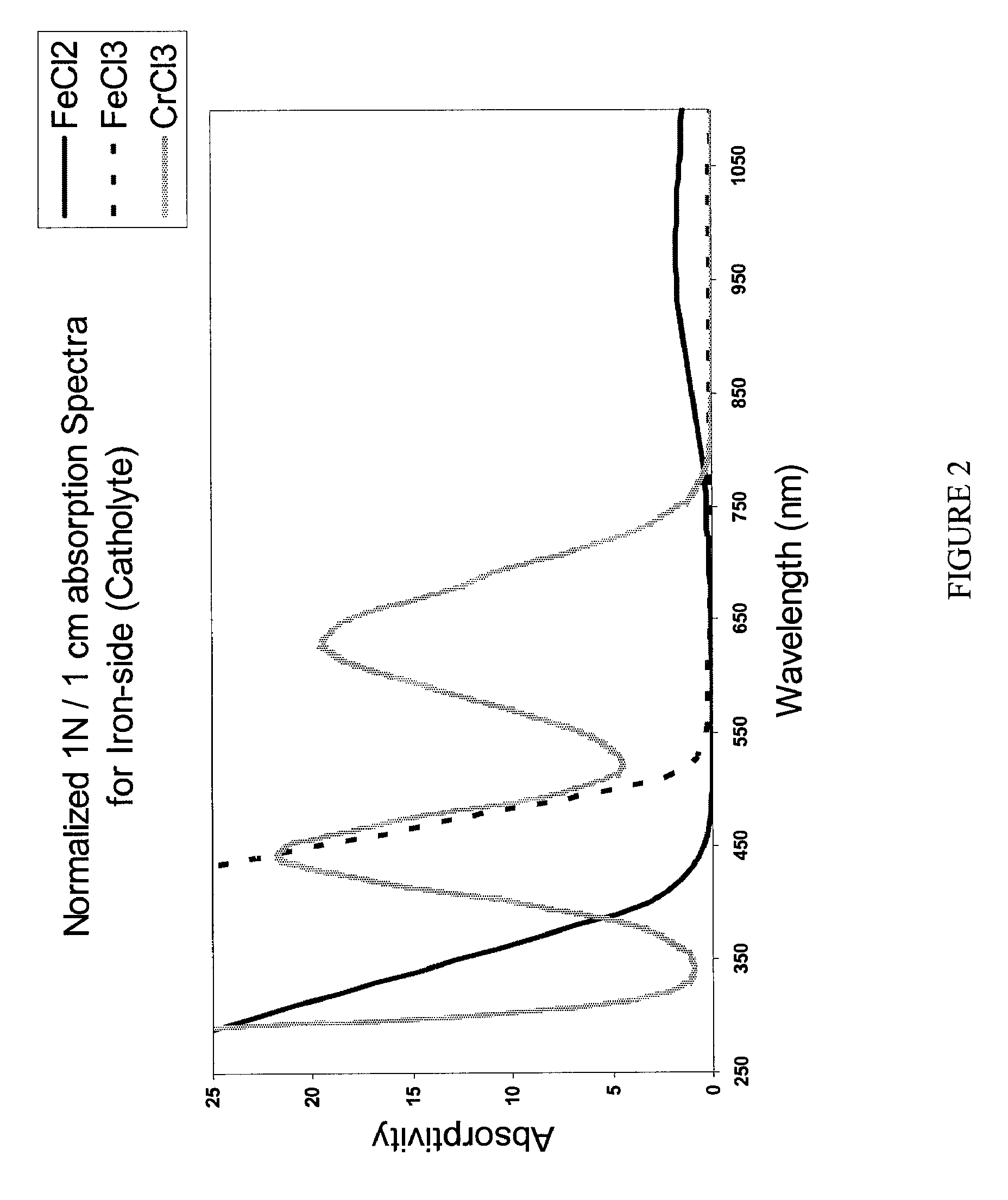
Apparatus and methods for determining the individual states of charge of electrolytes in a redox battery with mixed or unmixed reactants by optical absorption spectrophotometry are disclosed. The state of charge thus obtained may serve as a gauge for the amount of electro-chemical energy left in the system. Further, the information on anolyte and catholyte charge states may be used for any rebalancing mechanism if the states are different.
Owner:IMERGY POWER SYST
Flow battery systems
ActiveUS20120052347A1Uniform metal platingHigh cell current densityFuel and secondary cellsCell electrodesEngineeringMetal
Embodiments of the invention generally provide for flow battery cells and systems containing a plurality of flow battery cells, and methods for improving metal plating within the flow battery cell, such as by flowing and exposing the catholyte to various types of cathodes. In one embodiment, a flow battery cell is provided which includes a cathodic half cell and an anodic half cell separated by an electrolyte membrane, wherein the cathodic half cell contains a plurality of cathodic wires extending perpendicular or substantially perpendicular to and within the catholyte pathway and in contact with the catholyte, and each of the cathodic wires extends parallel or substantially parallel to each other. In some examples, the plurality of cathodic wires may have at least two arrays of cathodic wires, each array contains at least one row of cathodic wires, and each row extends along the catholyte pathway.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
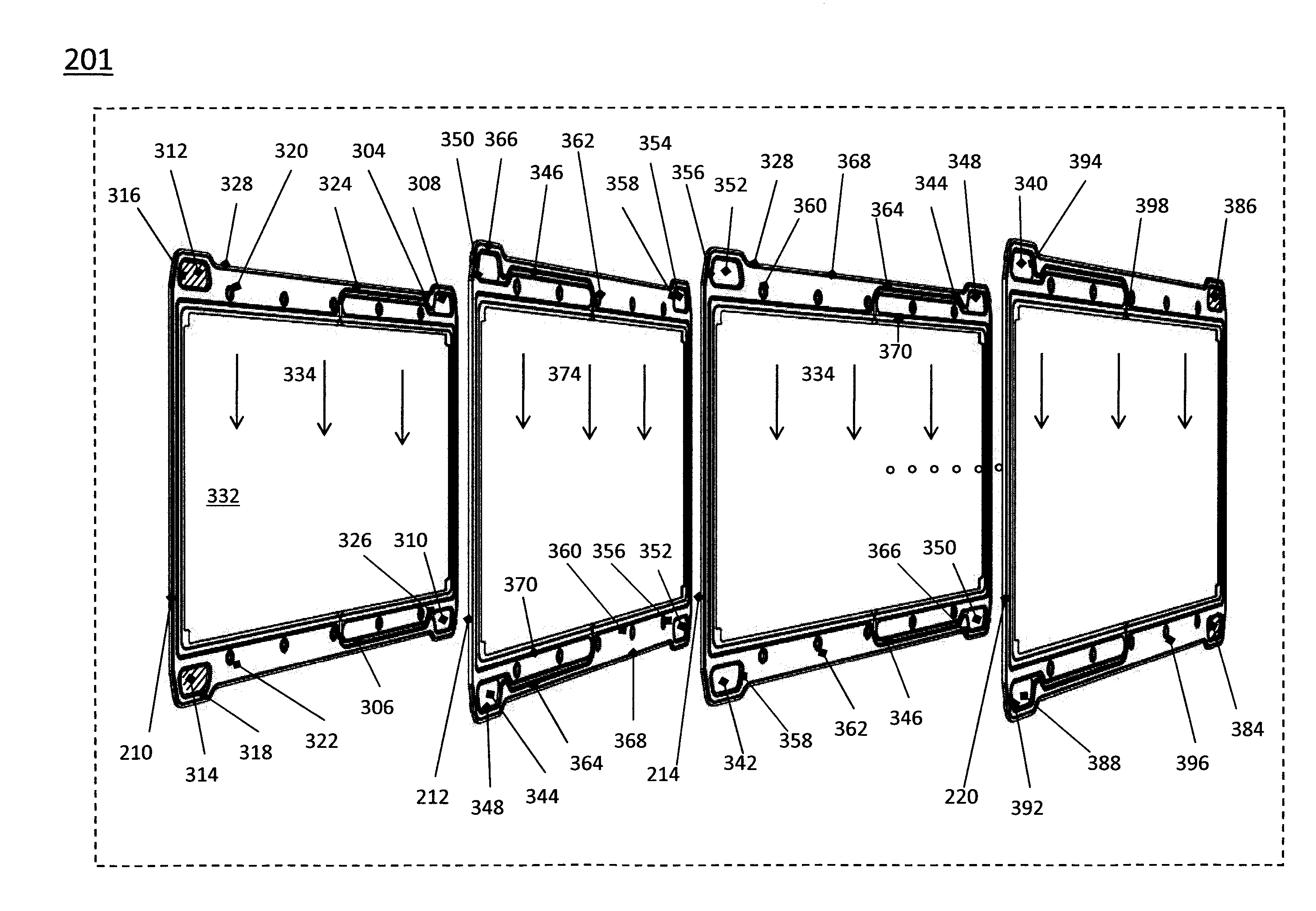
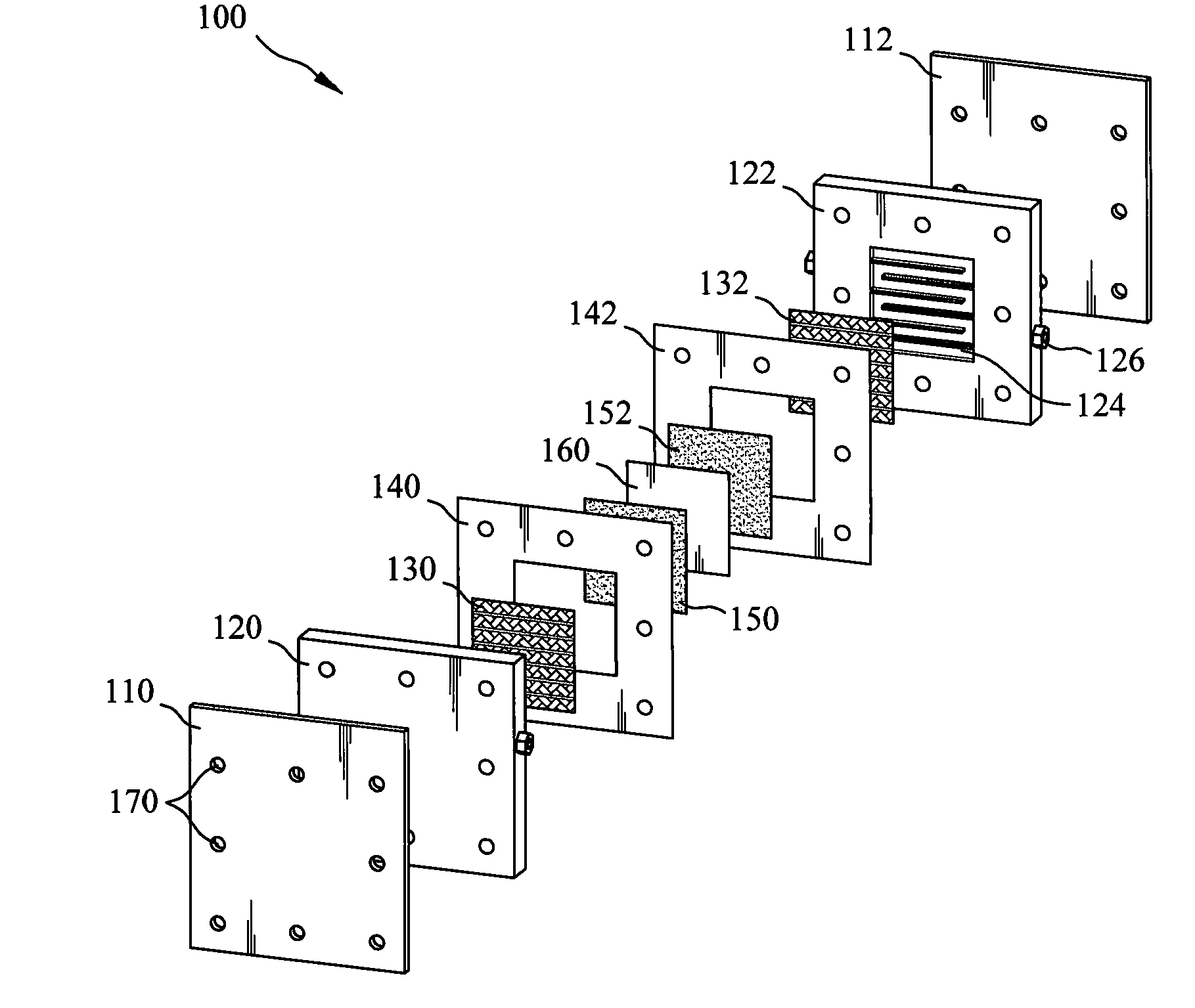
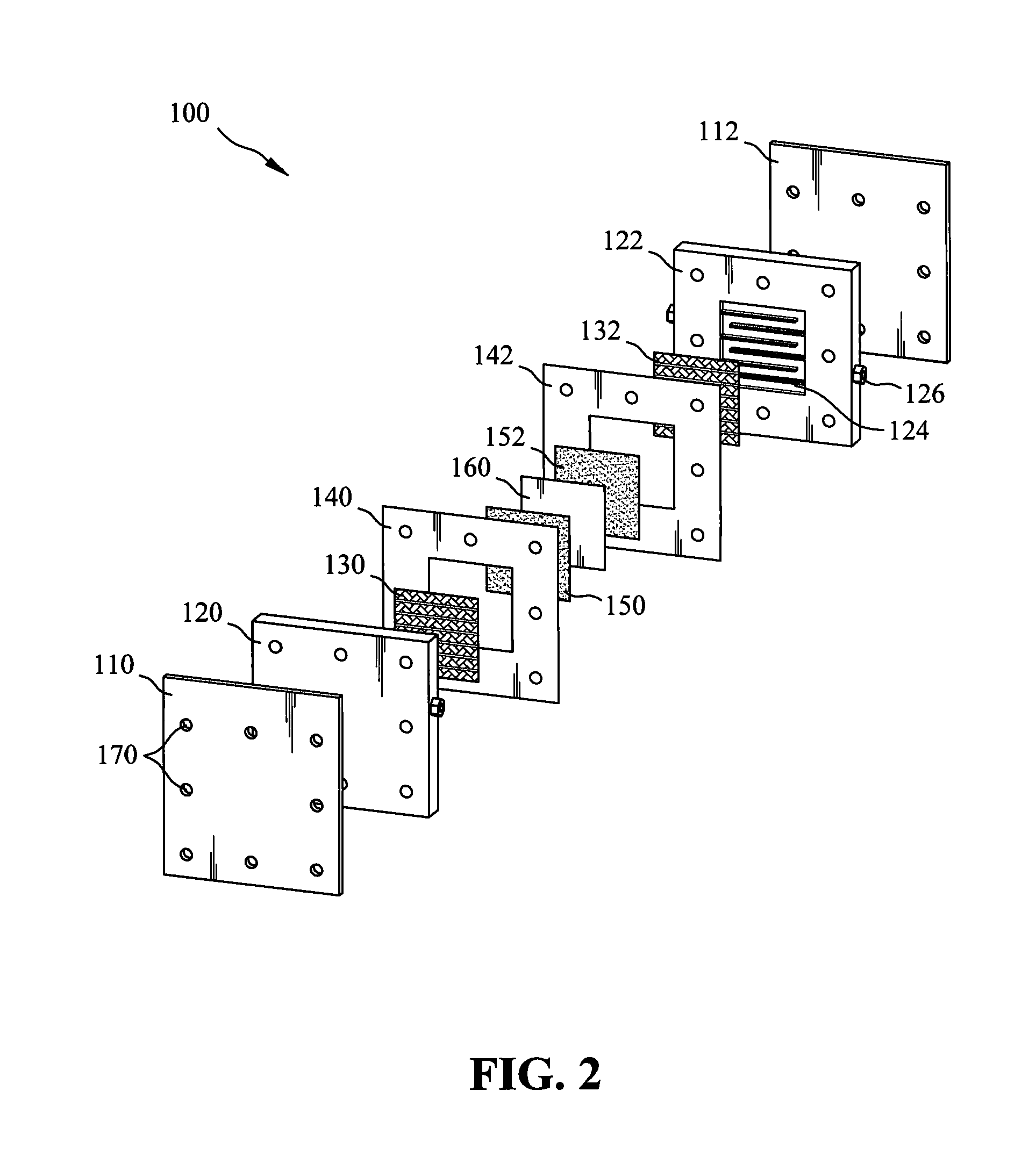
Common Module Stack Component Design
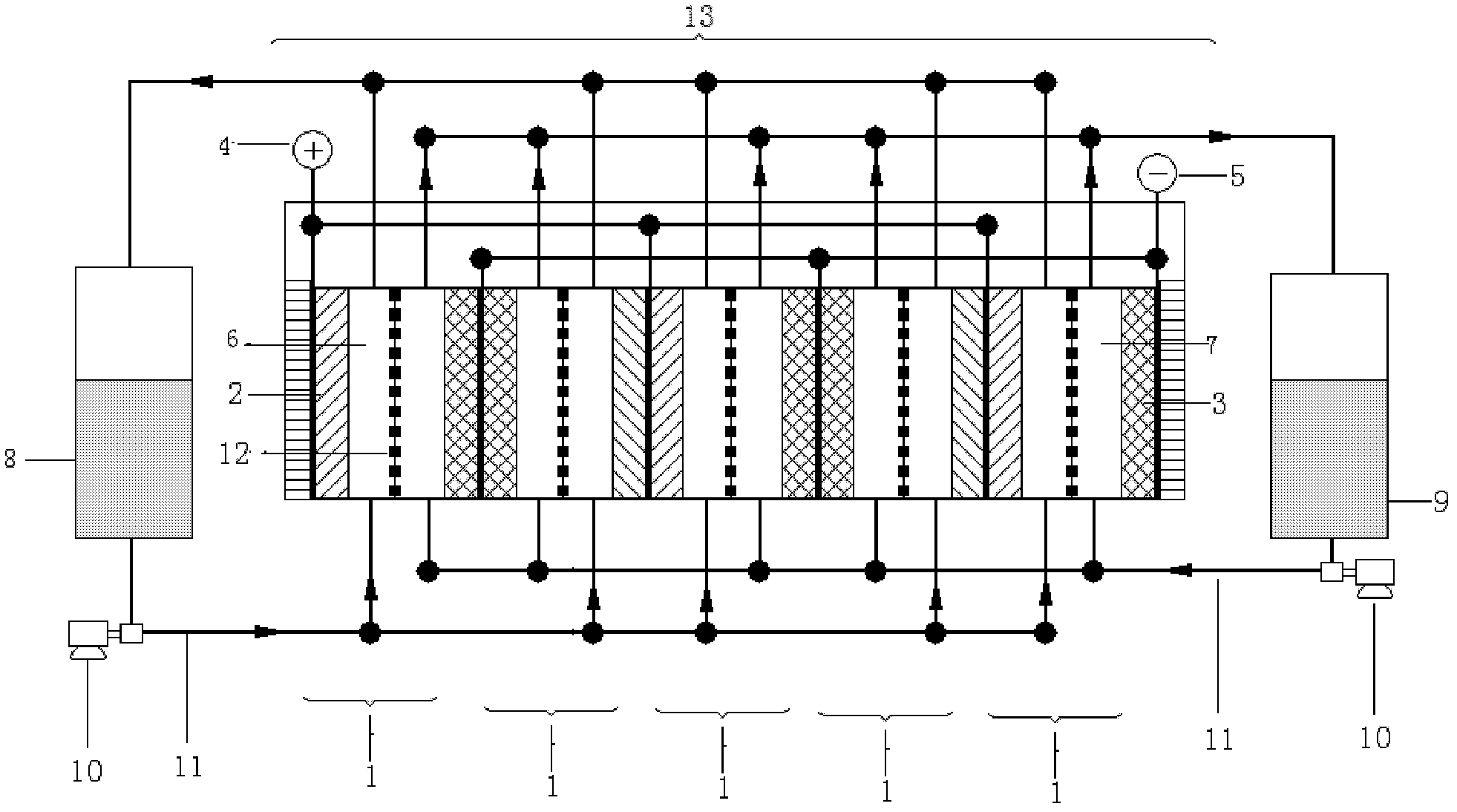
A stack for use in a flow battery, the stack comprising an odd number of interior elements positioned between two end elements, the two end elements each including an electrode, and the odd number of interior elements including membrane elements alternating with electrode elements, wherein the membrane elements include an interior frame and a membrane, the electrode elements include the interior frame and an electrode, wherein the interior frame is rotated by 180° from the frame of the membrane elements.
Owner:IMERGY POWER SYST
Functionalized Carbon Electrode, Related Material, Process for Production, and Use Thereof
InactiveUS20140113200A1Low costSimple processElectrolytic capacitorsHybrid capacitor electrodesFuel cellsPorous carbon
The present invention relates to a material for use as an electrode for electrochemical energy storage devices such as electrochemical capacitors (ECs) and secondary batteries, primary batteries, metal / air batteries, fuel cells, flow batteries and a method for producing the same. More specifically, this invention relates to an electrode material consisting of a functionalized porous carbon, a method for producing the same, and an energy storage device using said electrode materials.
Owner:SEYMOUR FRASER
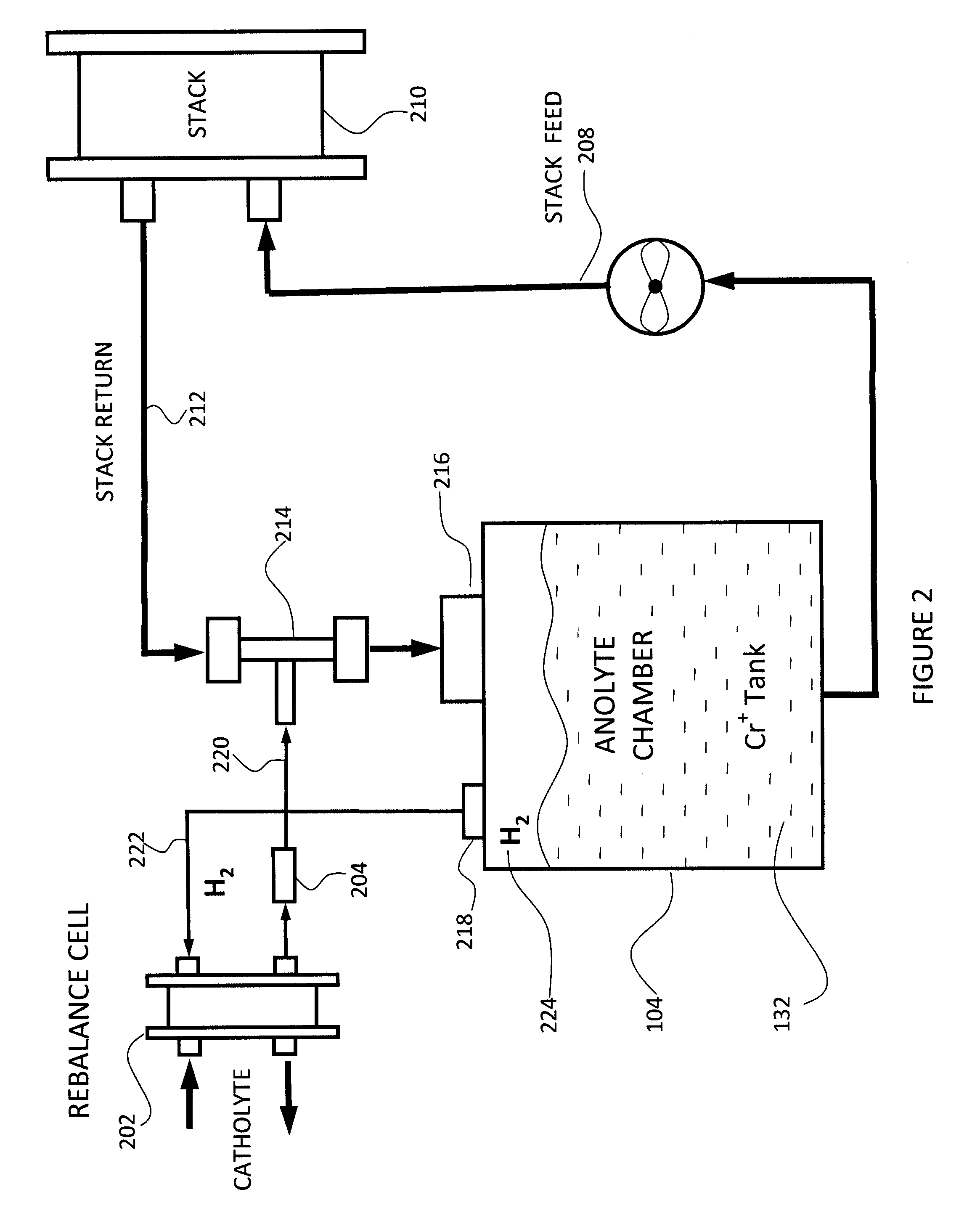
Venturi pumping system in a hydrogen gas circulation of a flow battery
InactiveUS20100092843A1Increase capacity and performanceElectrolyte stream managementIndirect fuel cellsHydrogenRedox
A redox flow battery system is presented that utilizes a rebalancing cell. A pump based on the Venturi principle is coupled to the rebalancing cell in order to actively circulate hydrogen gas through the rebalancing cell. The venturi pump requires no moving parts which eliminates problems of reliability and cost. Utilizing the venturi pump to actively circulate gas can significantly enhanced the function of the rebalance cell thereby providing enhanced capacity and performance of the flow battery system.
Owner:DEEYA ENERGY TECH INC
Level Sensor for Conductive Liquids
A sensor for measuring a level of a conductive liquid, is provided. The sensor includes at least two electrodes that can be positioned in a holding tank so as to be partially submerged in the conductive liquid, sensor leads coupled to the at least two electrodes, and circuitry and a controller for determining the properties of the electrolyte, the circuitry being coupled to the at least two electrodes via the sensor leads, and the controller being coupled to the circuitry. The sensor may be used as an electrolyte level sensor in a flow battery system.
Owner:IMERGY POWER SYST
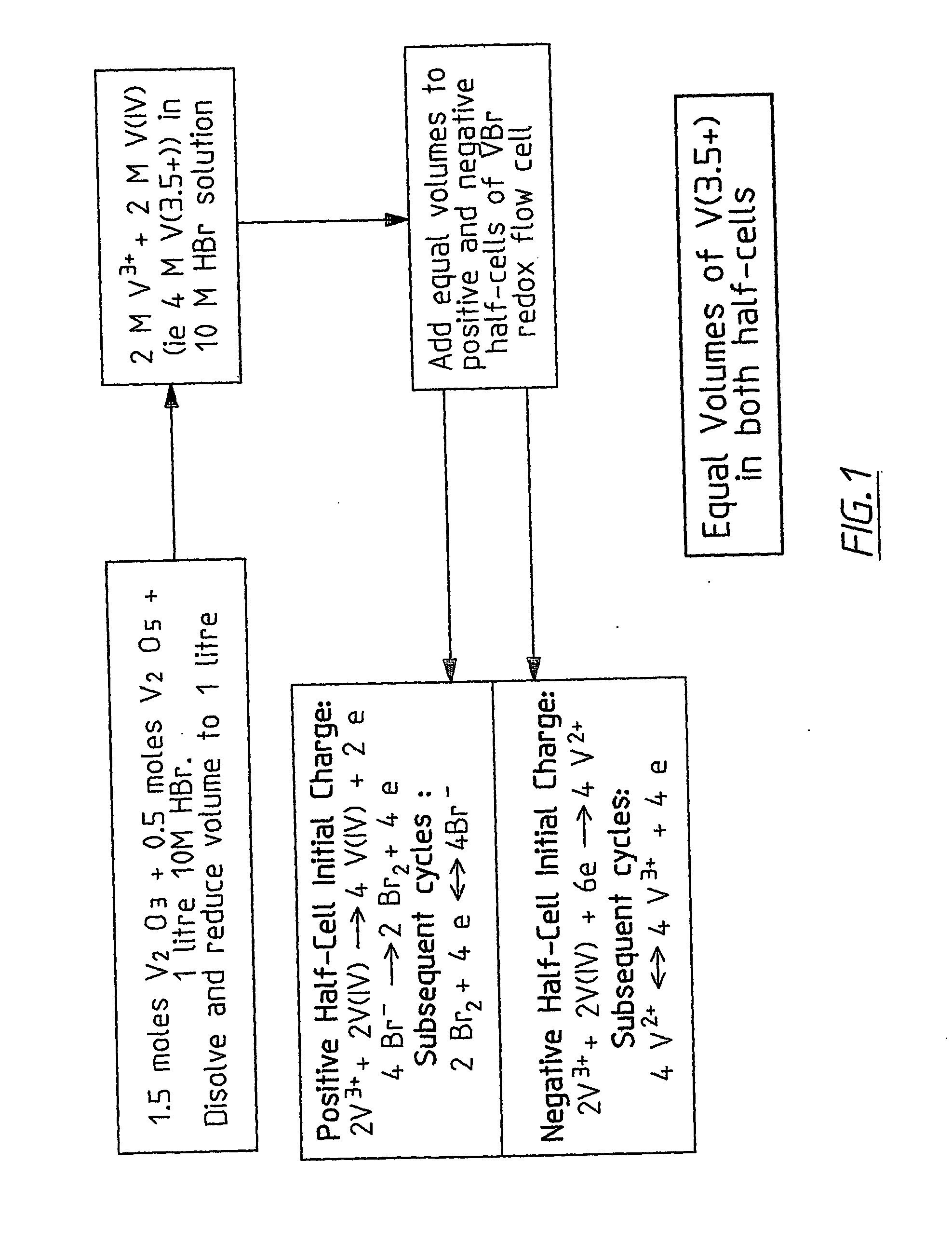
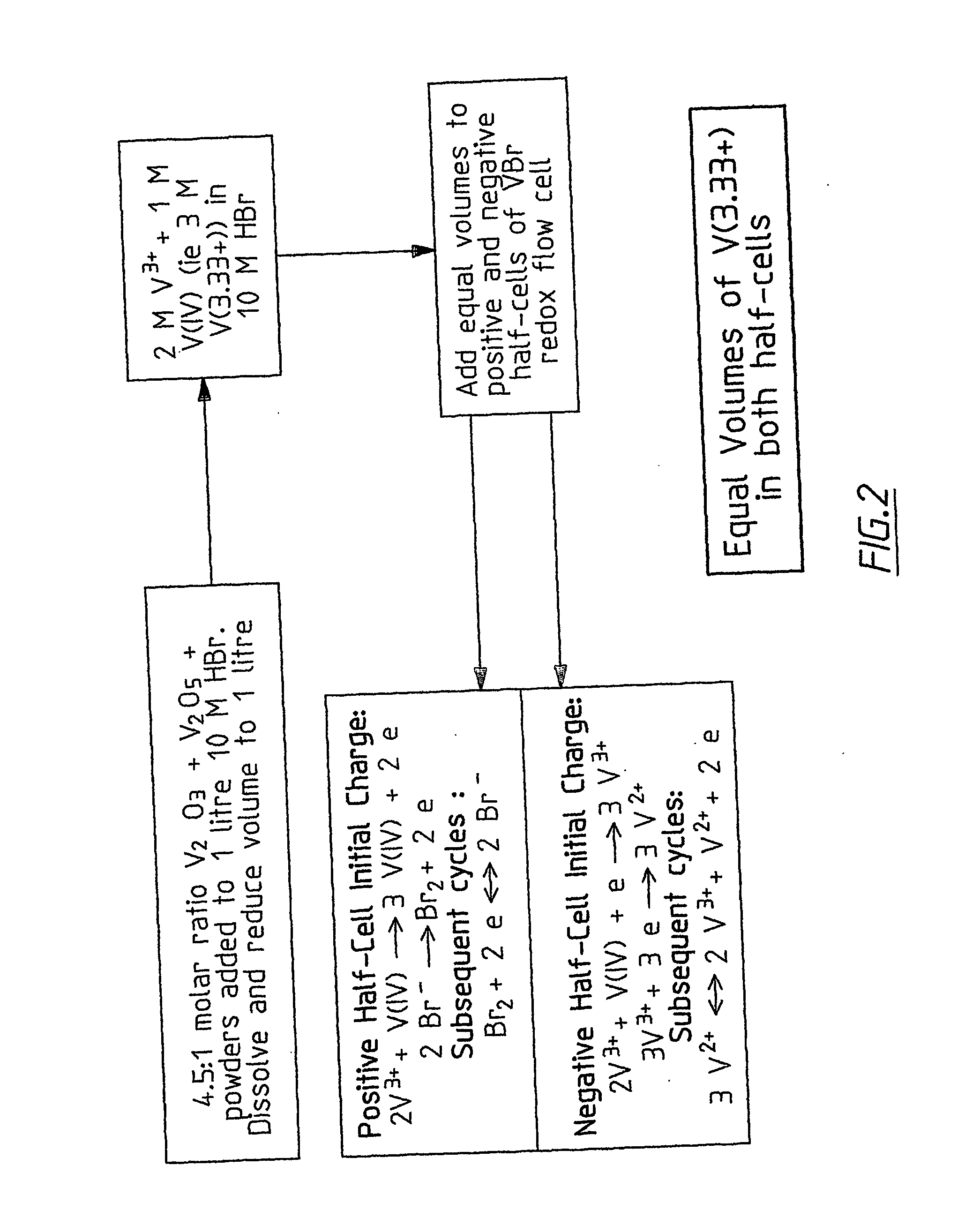
Novel vanadium halide redox flow battery
InactiveUS20060183016A1Avoid excessive bromine generationStabilise the bromine producedCharging stationsCell electrodesRedoxPhysical chemistry
A prior to charge vanadium halide redox cell, a vanadium halide redox cell which is at a state of charge selected from the group consisting of a zero state of charge and a near zero state of charge and vanadium halide redox cell which are fully charged and partially charged are described. The prior to charge vanadium halide redox cell comprises a positive half cell containing a positive half cell solution comprising a halide electrolyte, vanadium (III) halide and vanadium (IV) halide, a negative half cell containing a negative half cell solution comprising a halide electrolyte, vanadium (III) halide and vanadium (N) halide wherein the amounts of vanadium (III) halide, vanadium (IV) halide and halide ions in the positive and negative half cell solutions are such that in a first charging step comprising charging the prior to charge vanadium halide redox cell, a vanadium halide redox cell having a state of charge selected from the group consisting of a zero state of charge and a near zero state of charge comprising predominantly vanadium (N) halide in the positive half cell solution and predominantly V(III) halide in the negative half cell solution can be prepared. The vanadium halide redox cell which is at a state of charge selected from the group consisting of a zero state of charge and a near zero state of charge comprises a positive half cell containing a positive half cell solution comprising a halide electrolyte and a vanadium halide which is predominantly vanadium (N) halide, a negative half cell containing a negative half cell solution comprising a halide electrolyte and a vanadium halide which is predominantly vanadium (III) halide wherein the amount of vanadium (N) halide in the positive half cell solution and the amount of vanadium (III) halide in the negative half cell solution are such that the vanadium halide redox cell is at a state of charge selected from the group consisting of a zero state of charge and a near zero state of charge. The vanadium halide redox cell which is fully charged comprises a positive half cell containing a positive half cell solution comprising a halide electrolyte, a polyhalide complex, vanadium (IV) halide and vanadium (V) halide, a negative half cell containing a negative half cell solution comprising a halide electrolyte and vanadium (II) halide wherein the molar concentration of vanadium (V) and polyhalide complex:molar concentration of vanadium (II) halide is about stoichiometrically balanced. The vanadium halide redox cell which is partially charged comprises a positive half cell containing a positive half cell solution comprising a halide electrolyte, a polyhalide complex, vanadium (IV) halide and vanadium (V) halide, a negative half cell containing a negative half cell solution comprising a halide electrolyte, vanadium (II) halide and vanadium (III) halide wherein the number of moles of moles of polyhalide complex and vanadium (V): number of moles of vanadium (II) halide is about stoichiometrically balanced.
Owner:NEWSOUTH INNOVATIONS PTY LTD
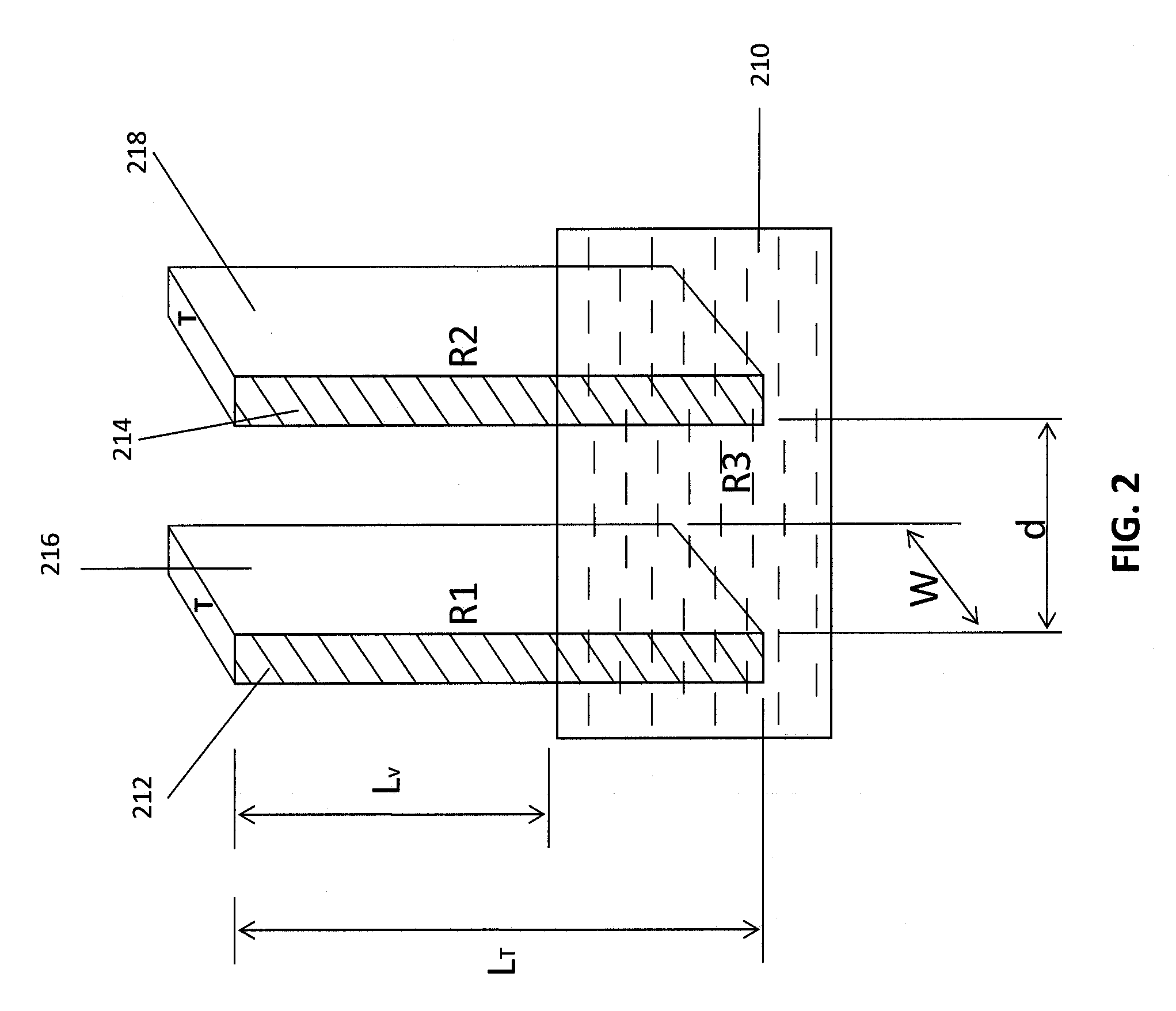
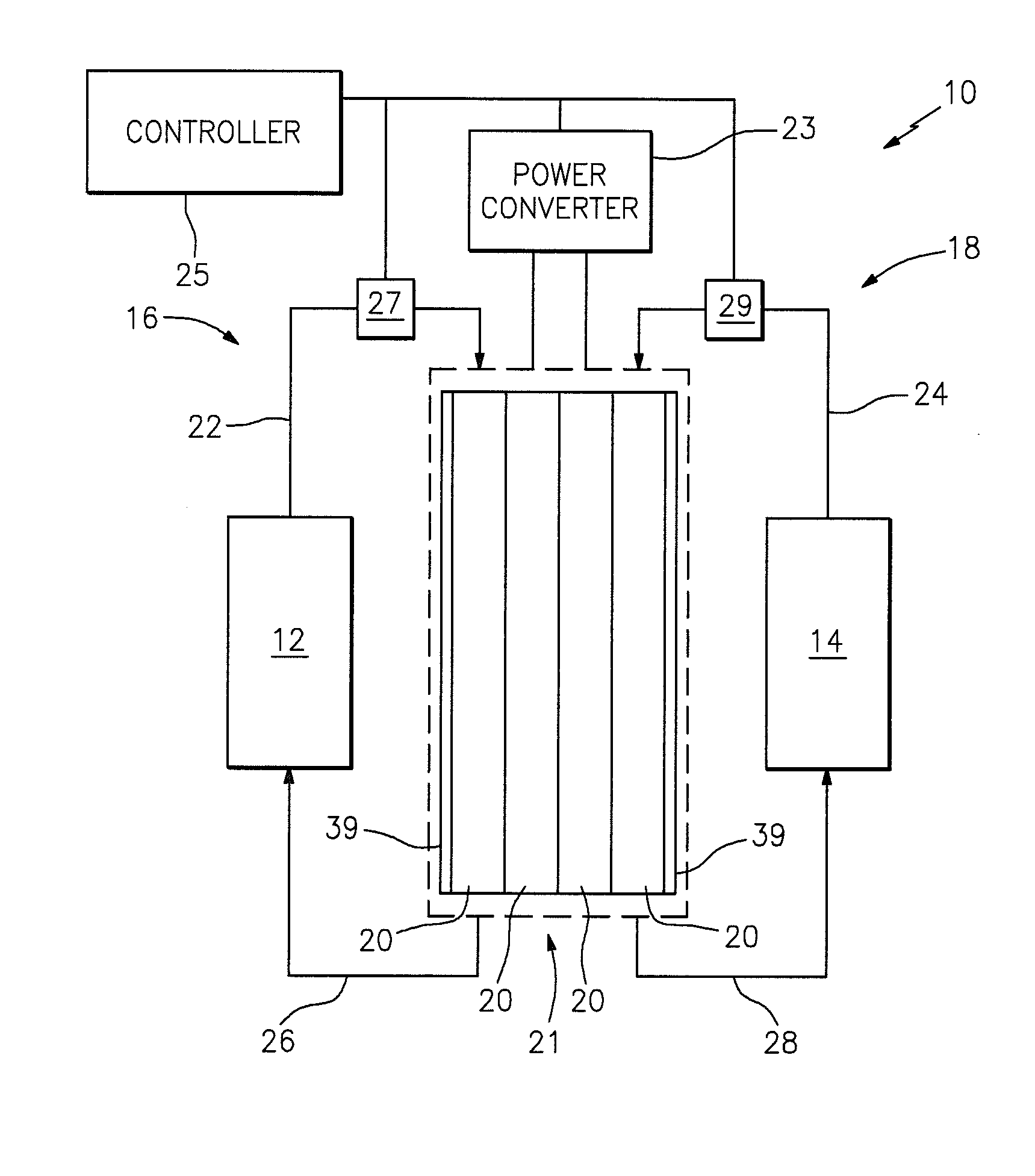
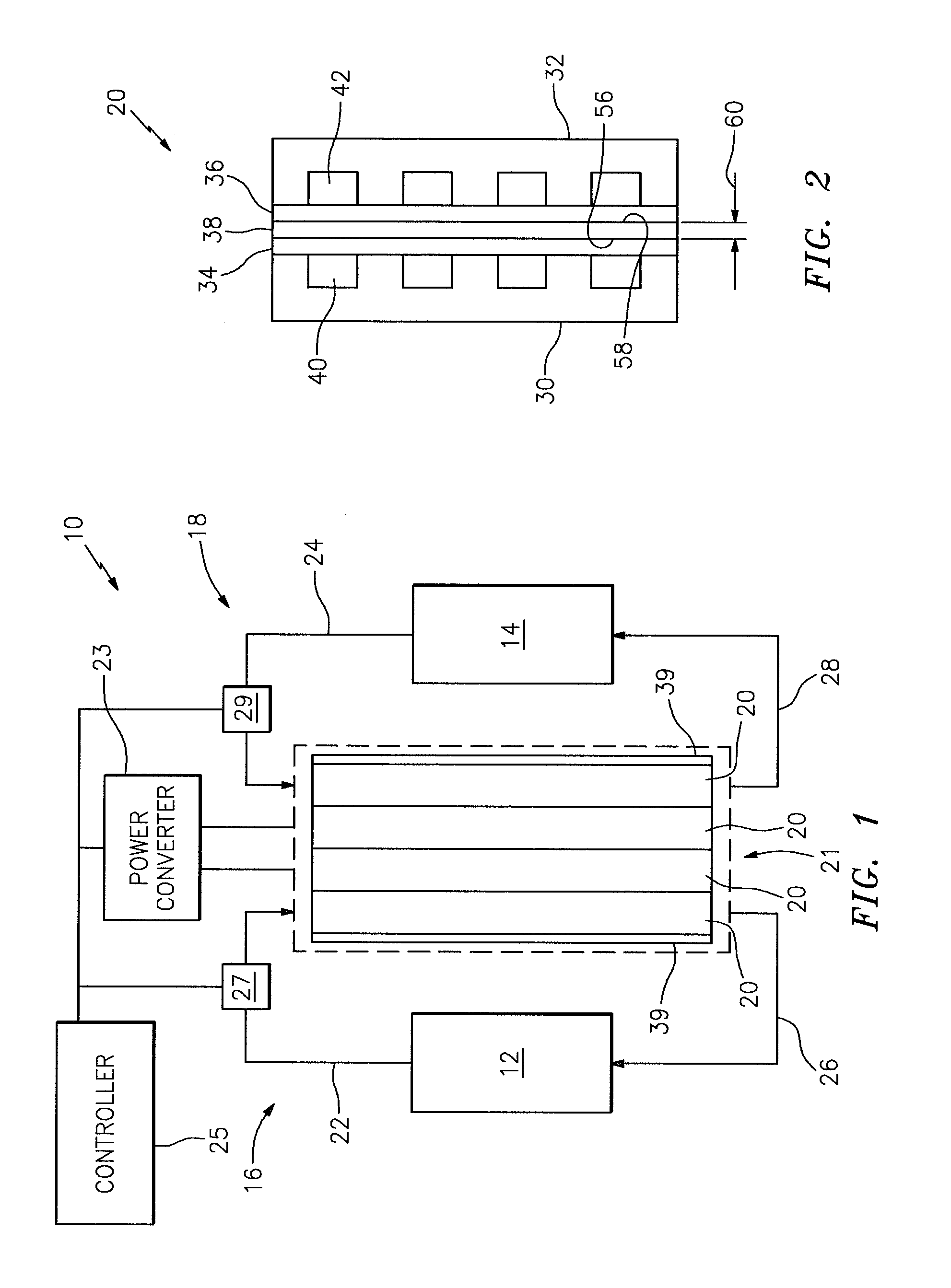
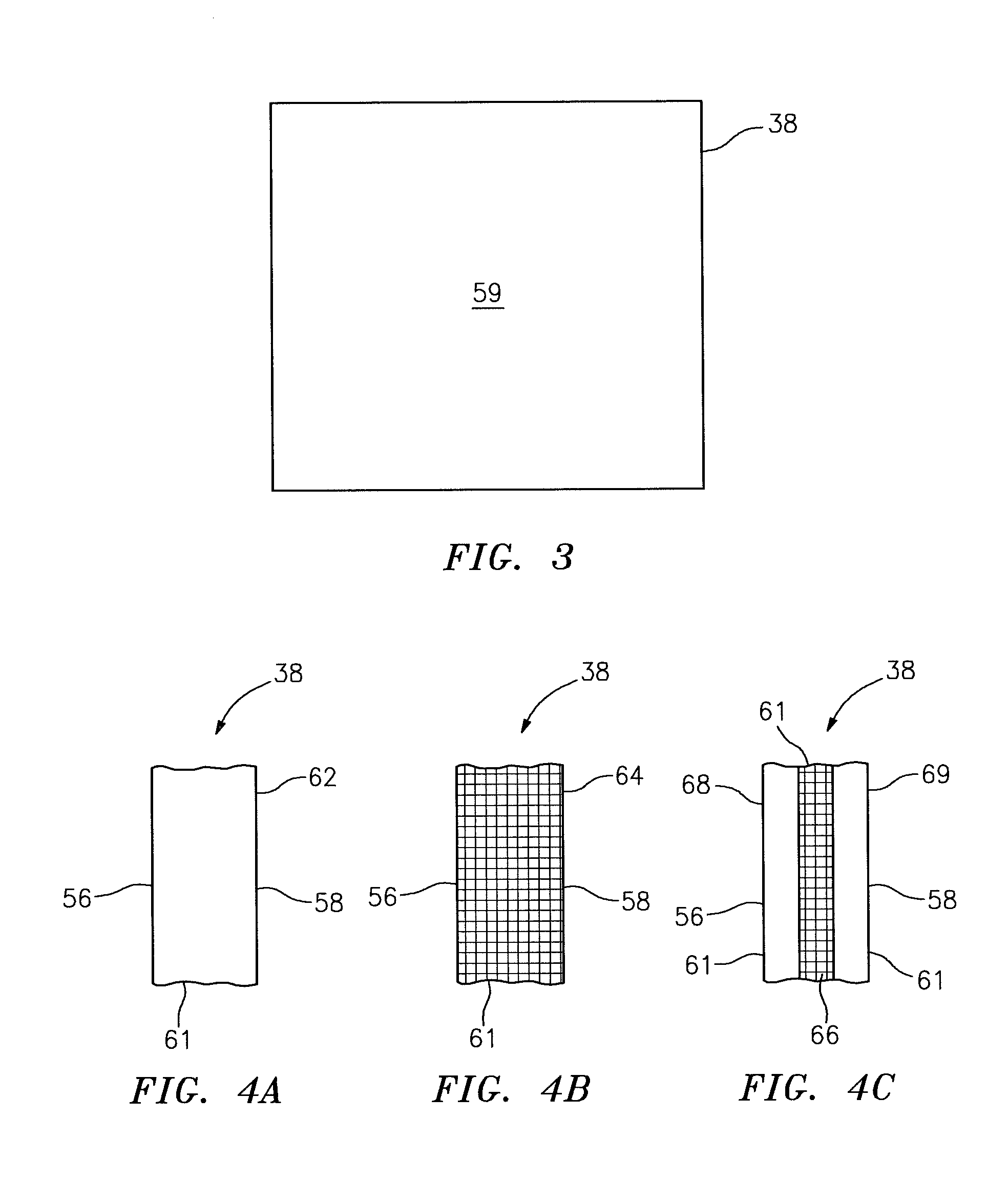
Flow battery having a low resistance membrane
A flow battery includes a membrane having a thickness of less than approximately one hundred twenty five micrometers; and a solution having a reversible redox couple reactant, wherein the solution wets the membrane.
Owner:UNITED TECH CORP
Redox flow battery
ActiveUS20120045680A1Suppress generationHigh electromotive forceElectrolyte moving arrangementsCell electrodesManganesePhysical chemistry
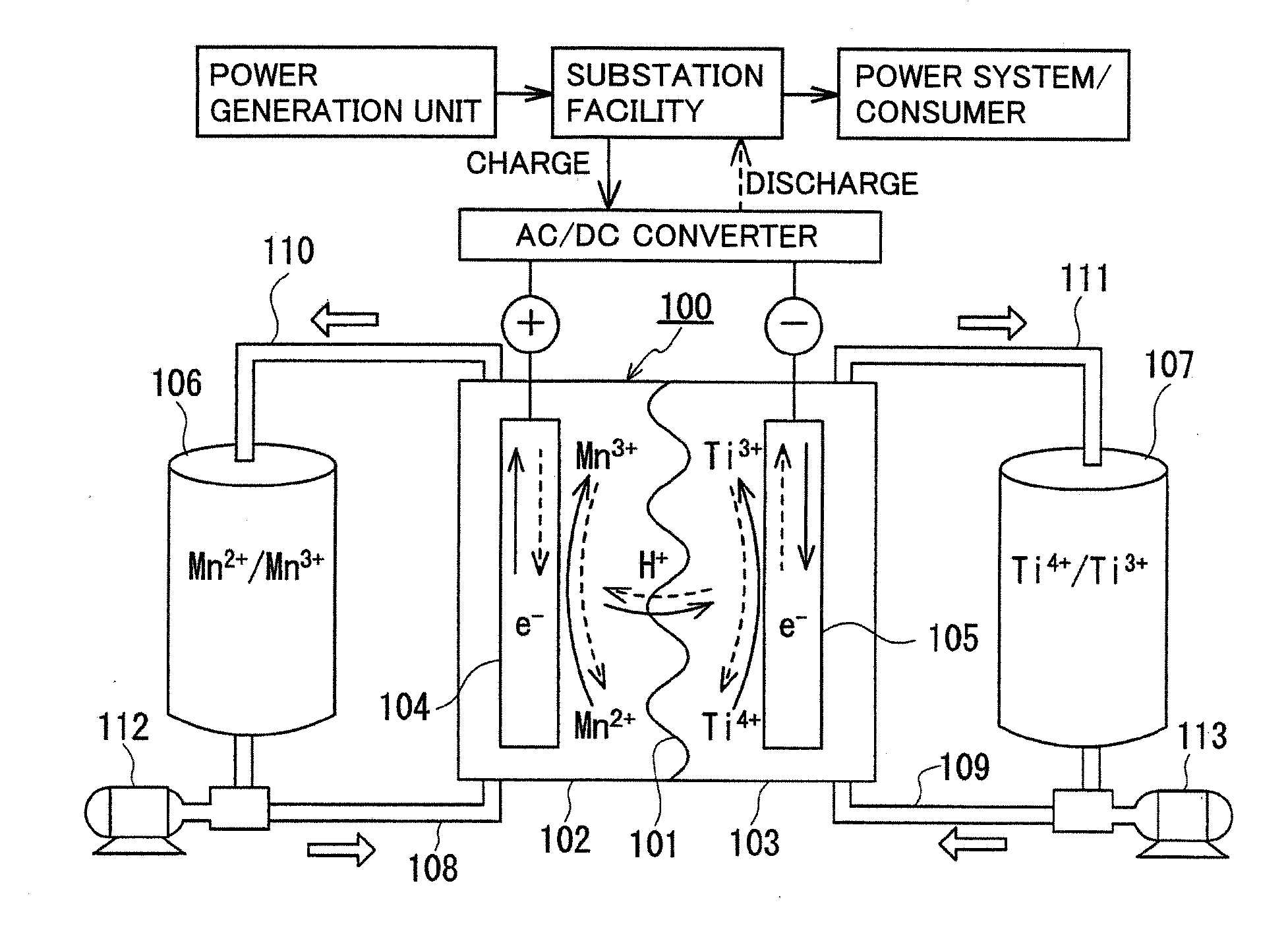
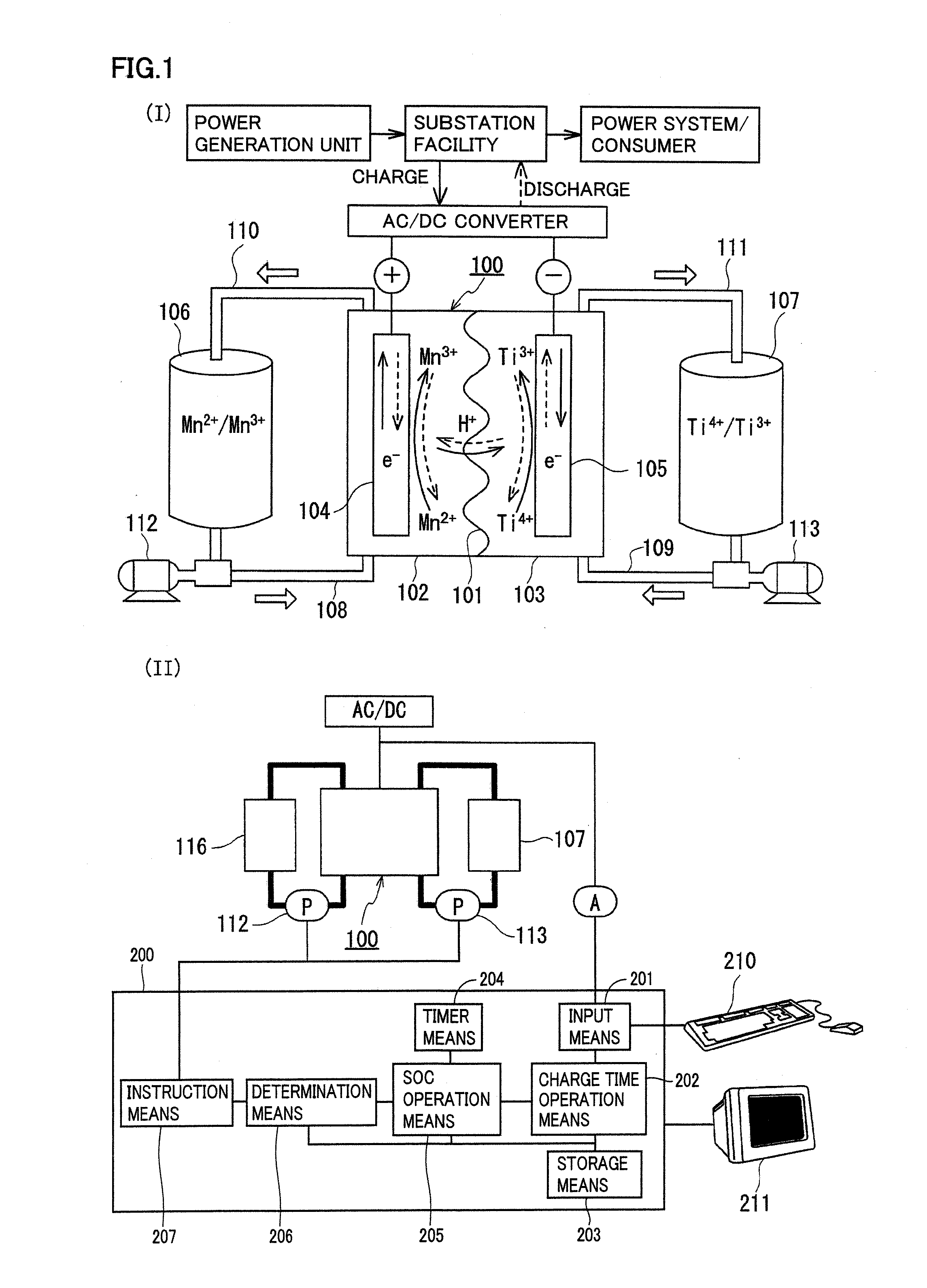
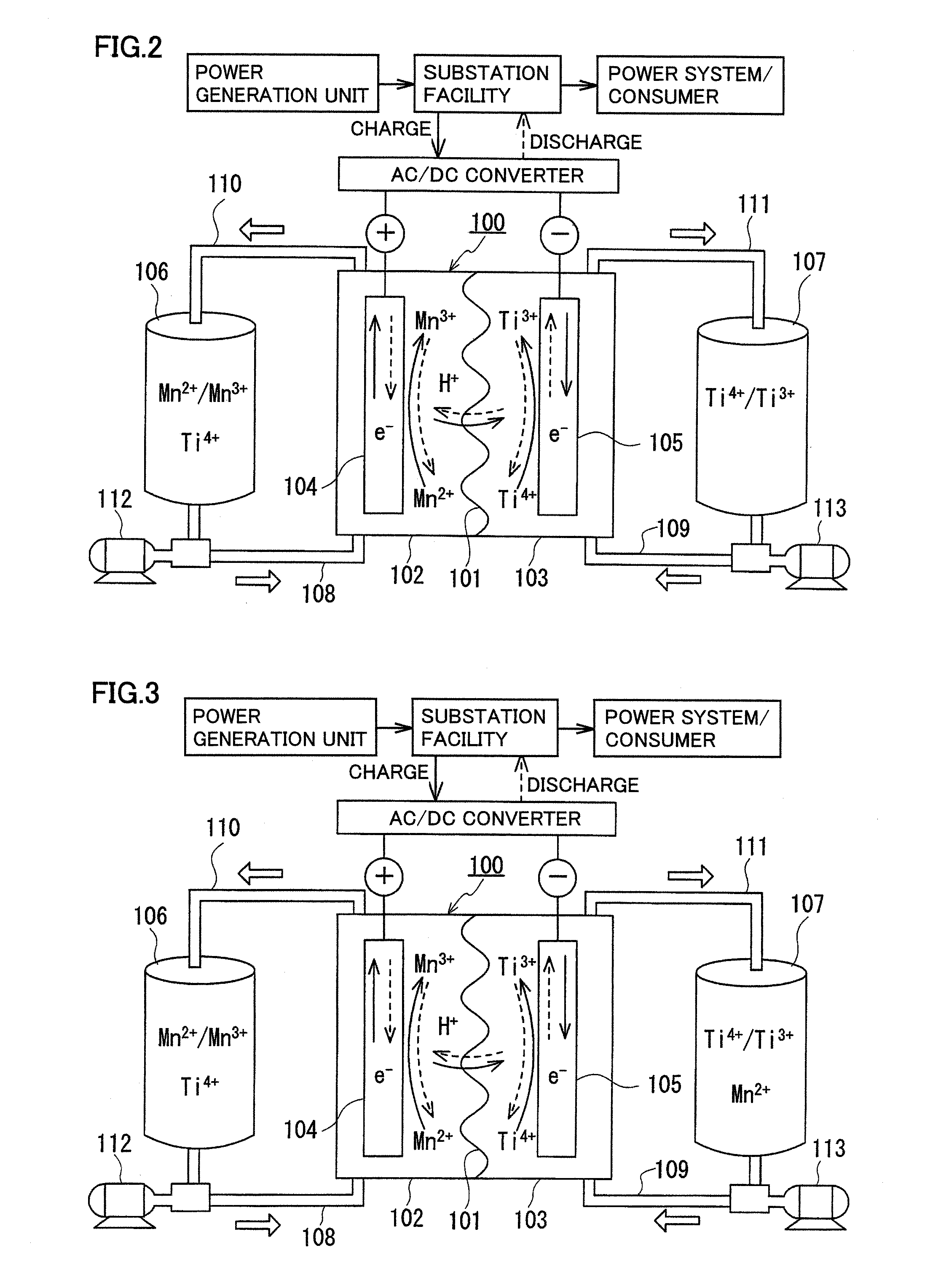
A redox flow battery having a high electromotive force and capable of suppressing generation of a precipitation is provided. In a redox flow battery 100, a positive electrode electrolyte and a negative electrode electrolyte are supplied to a battery cell including a positive electrode 104, a negative electrode 105, and a membrane 101 interposed between the electrodes 104 and 105, to charge and discharge the battery. The positive electrode electrolyte contains a manganese ion, or both of a manganese ion and a titanium ion. The negative electrode electrolyte contains at least one type of metal ion selected from a titanium ion, a vanadium ion, a chromium ion, a zinc ion, and a tin ion. The redox flow battery 100 can suppress generation of a precipitation of MnO2, and can be charged and discharged well by containing a titanium ion in the positive electrode electrolyte, or by being operated such that the positive electrode electrolyte has an SOC of not more than 90%. In addition, the redox flow battery 100 can have a high electromotive force equal to or higher than that of a conventional vanadium-based redox flow battery.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Thermal Control of a Flow Cell Battery
A flow battery with thermal management is presented. The flow battery is housed in an enclosure where fluid is uniformly circulated about holding tanks of electrolyte to control the temperature inside the enclosure.
Owner:IMERGY POWER SYST
Method for designing redox flow battery system
InactiveUS20050181273A1Improve system efficiencySure easyCell electrodesFuel cell auxillariesOxidation-Reduction AgentRedox
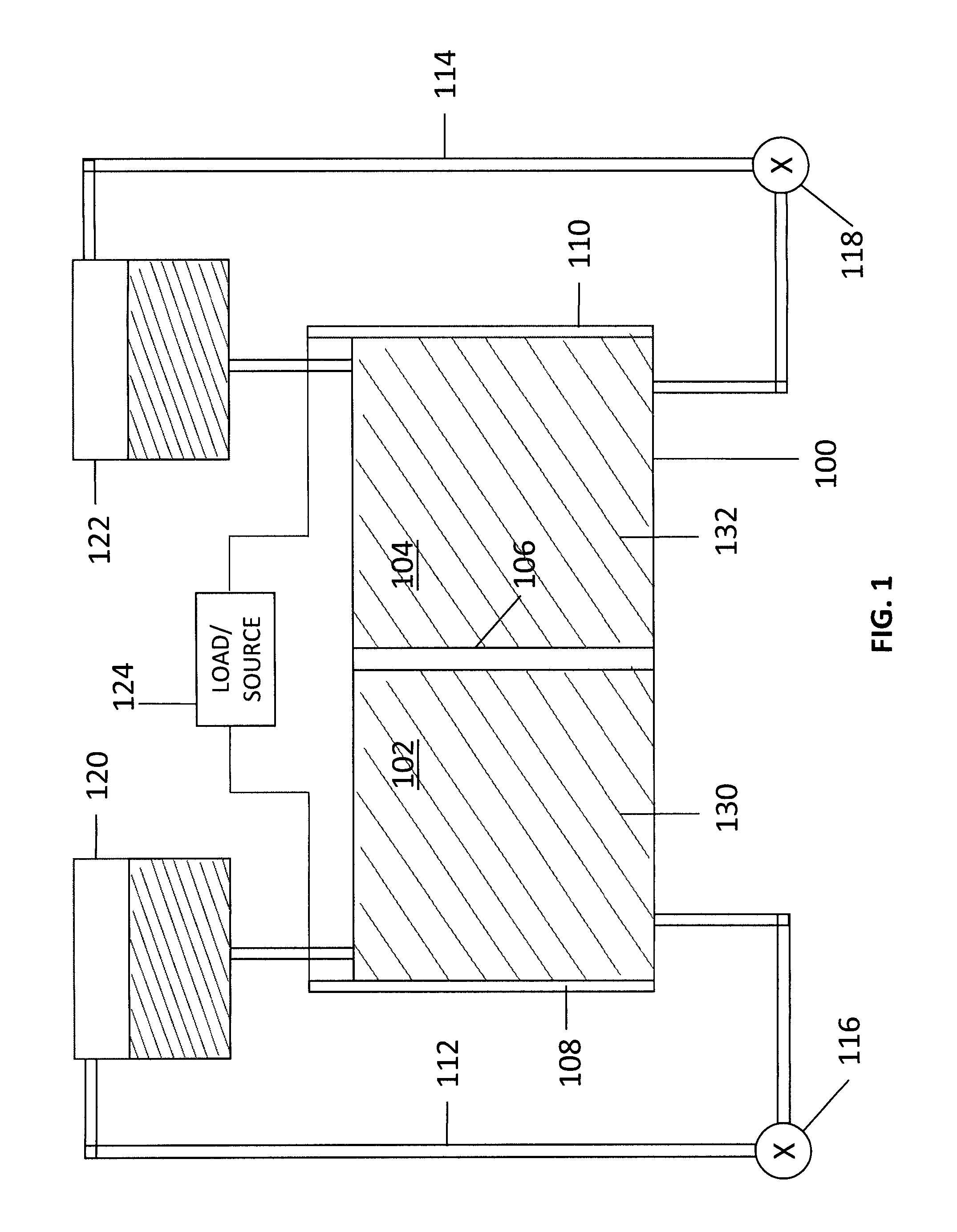
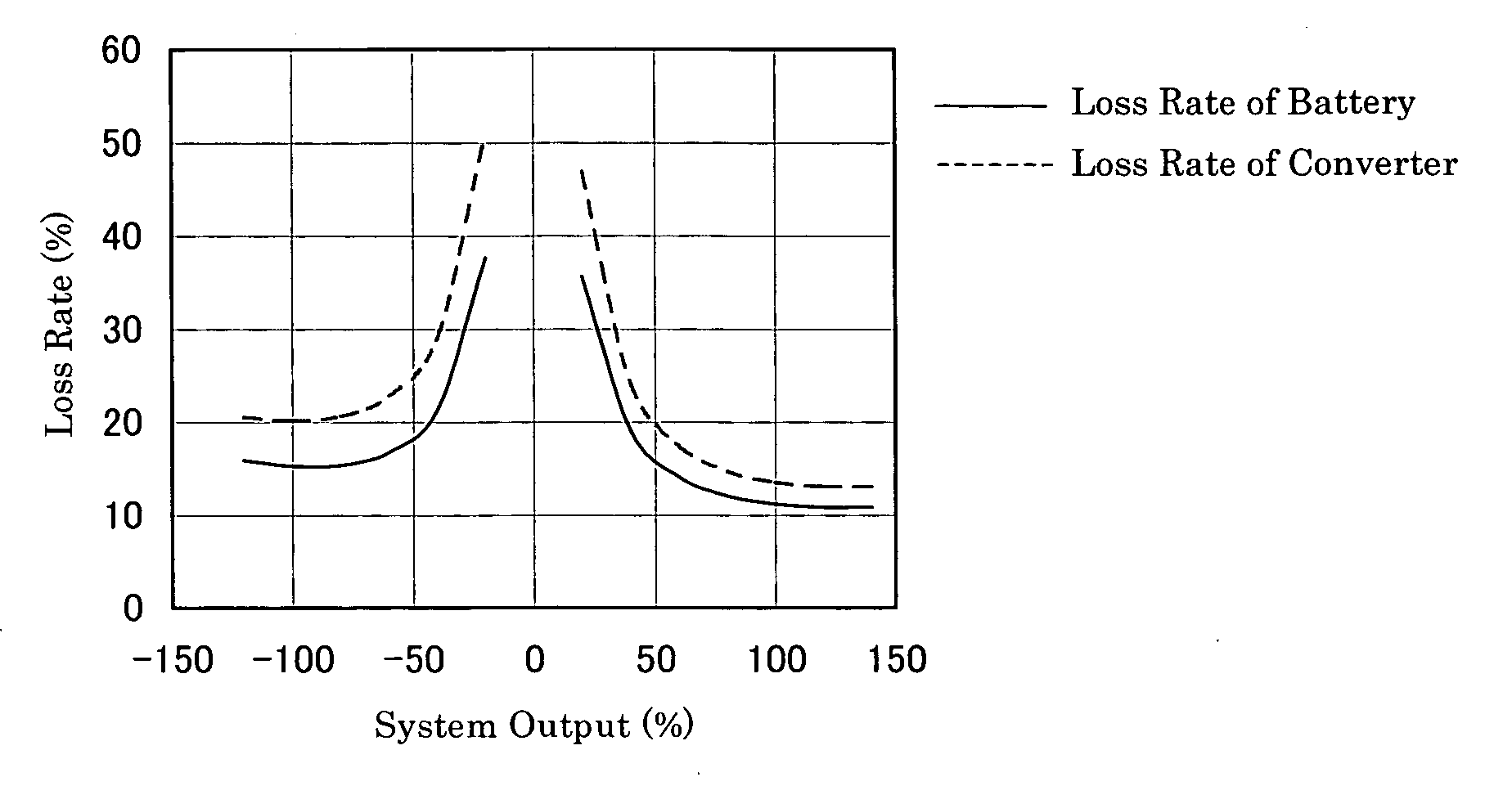
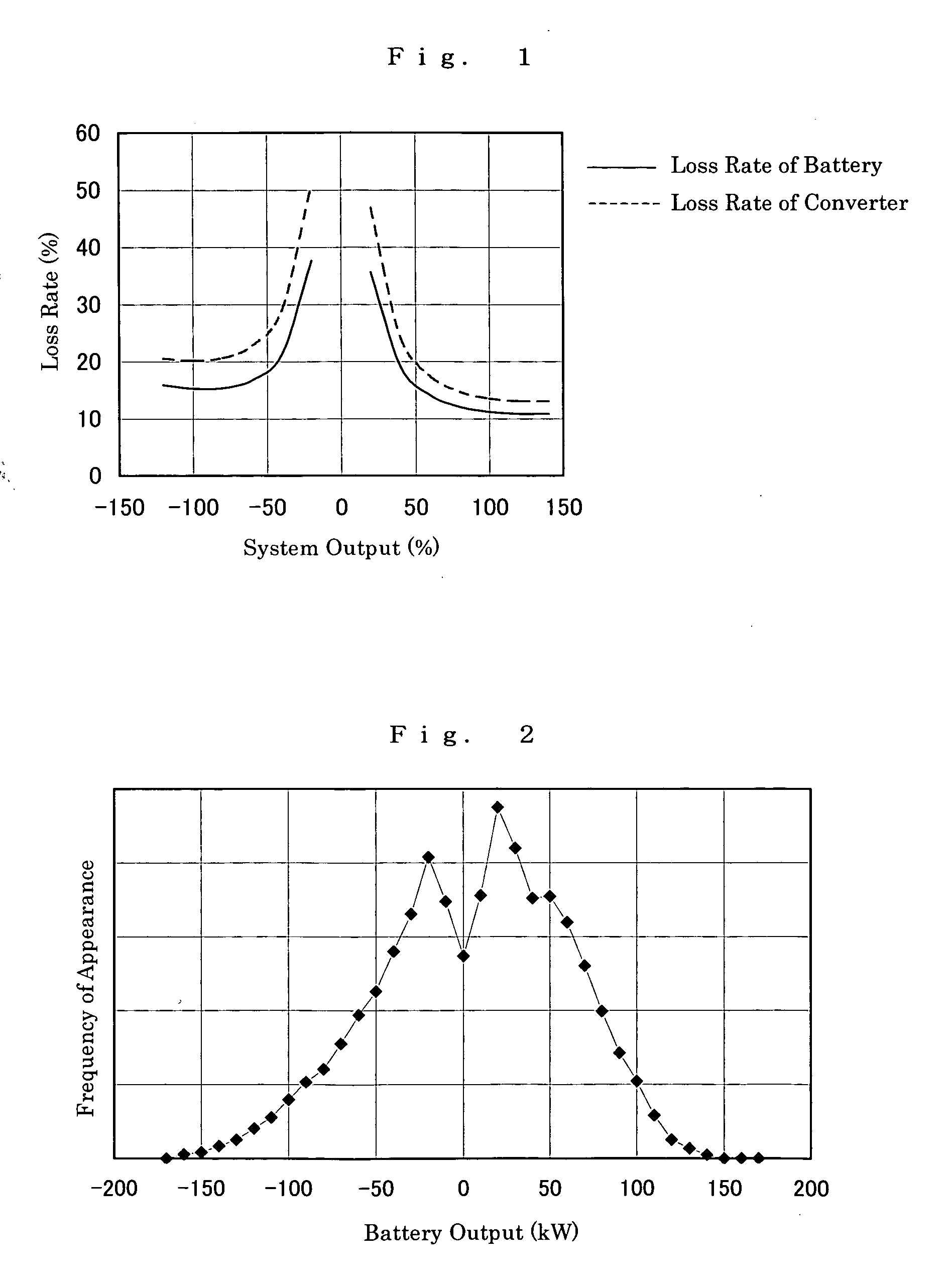
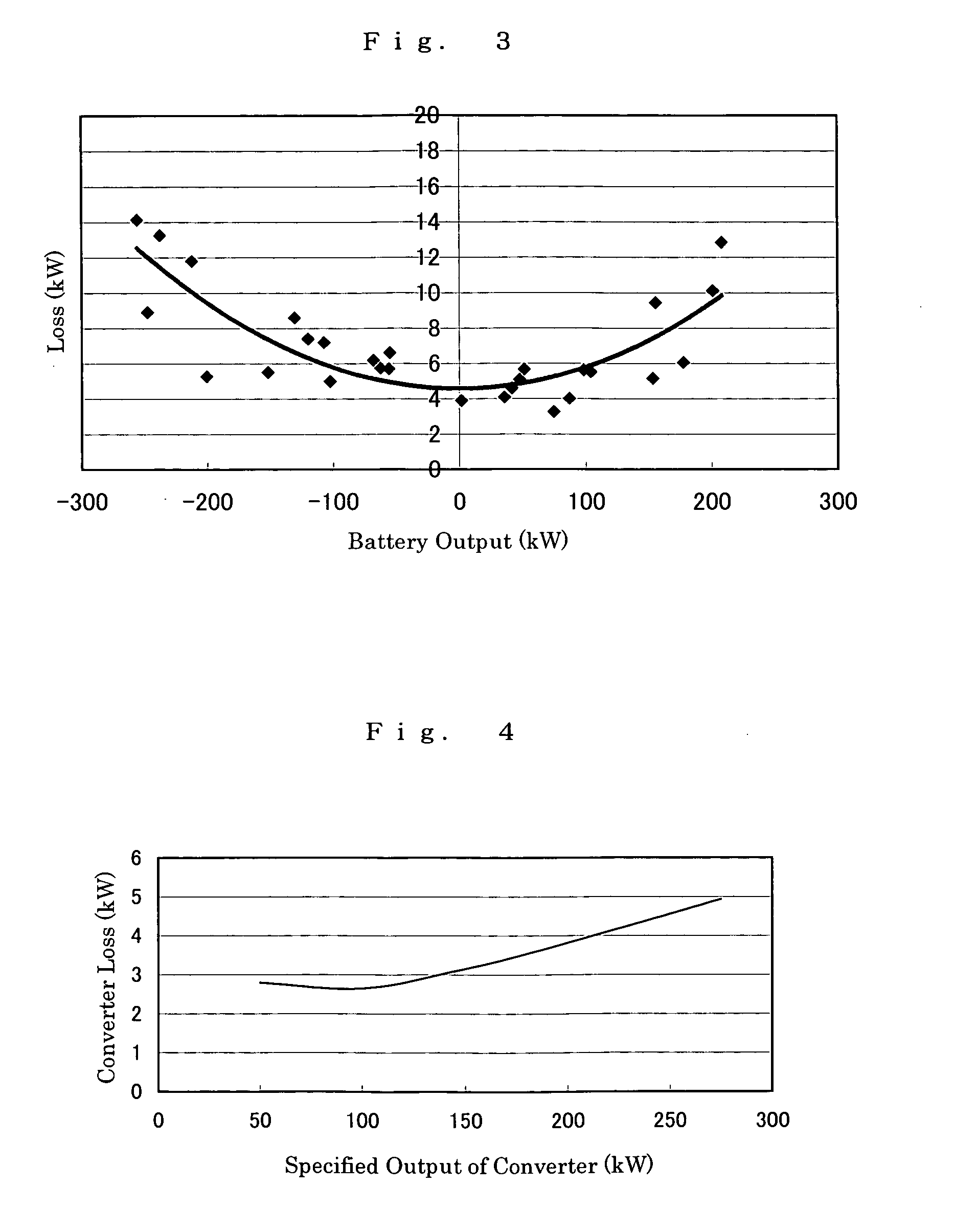
The present invention provides a method of designing a redox flow battery system that can prevent system efficiency loss caused by weak generation power or load power at the time of electric charge or discharge, without using any lead storage battery, and can also provide further improved system efficiency. In the present invention, generating equipment that varies irregularly in output of power generation is provided with the redox flow battery to smooth the output of power generation. An average value of output distribution of the battery with respect to the smoothed output of power generation and standard deviation are determined. Then, at least either of a specified output of the battery and a specified output of the converter for converting the battery output is determined based on the standard deviation.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD +1
Cell frame for redox flow battery, and redox flow battery
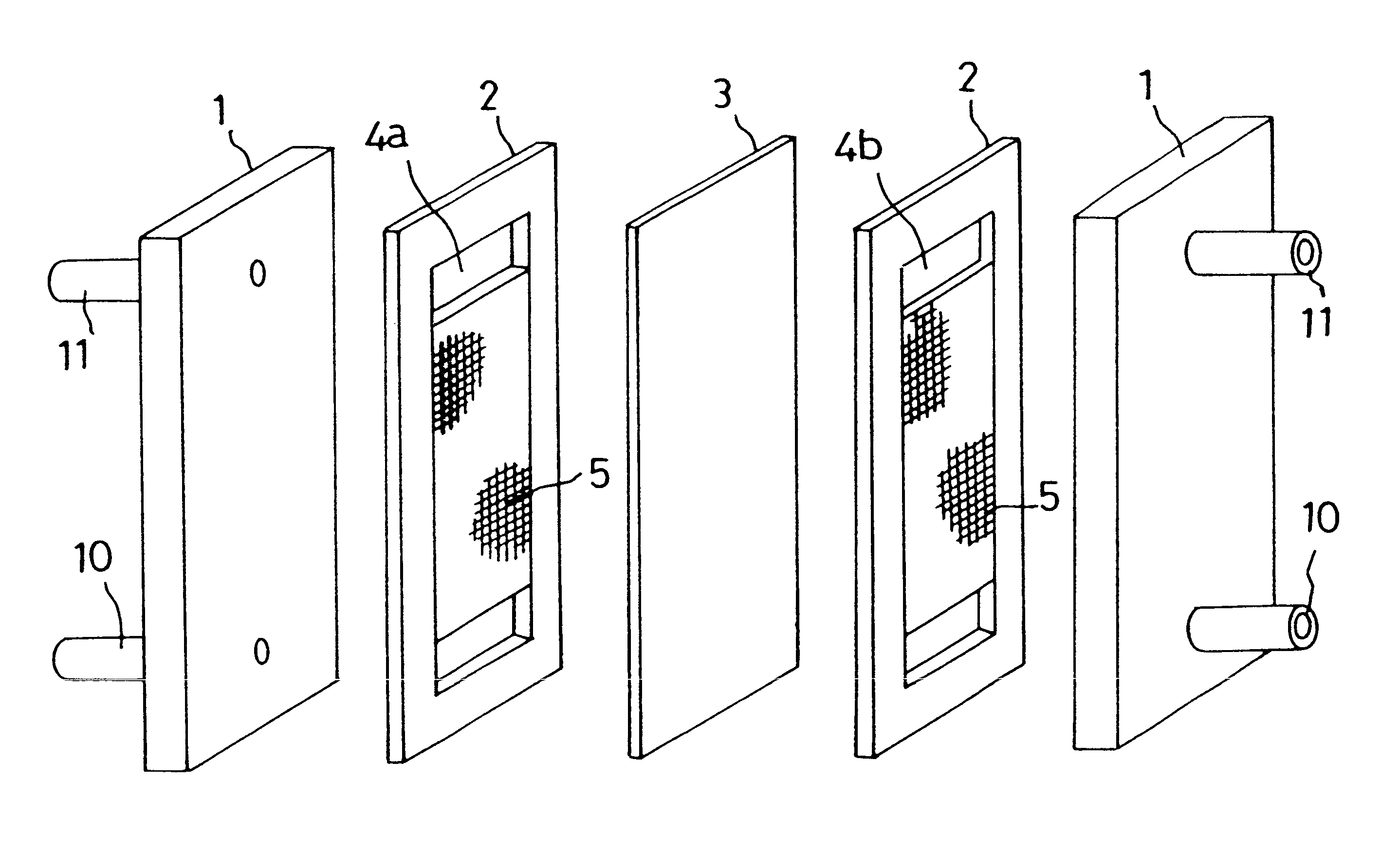
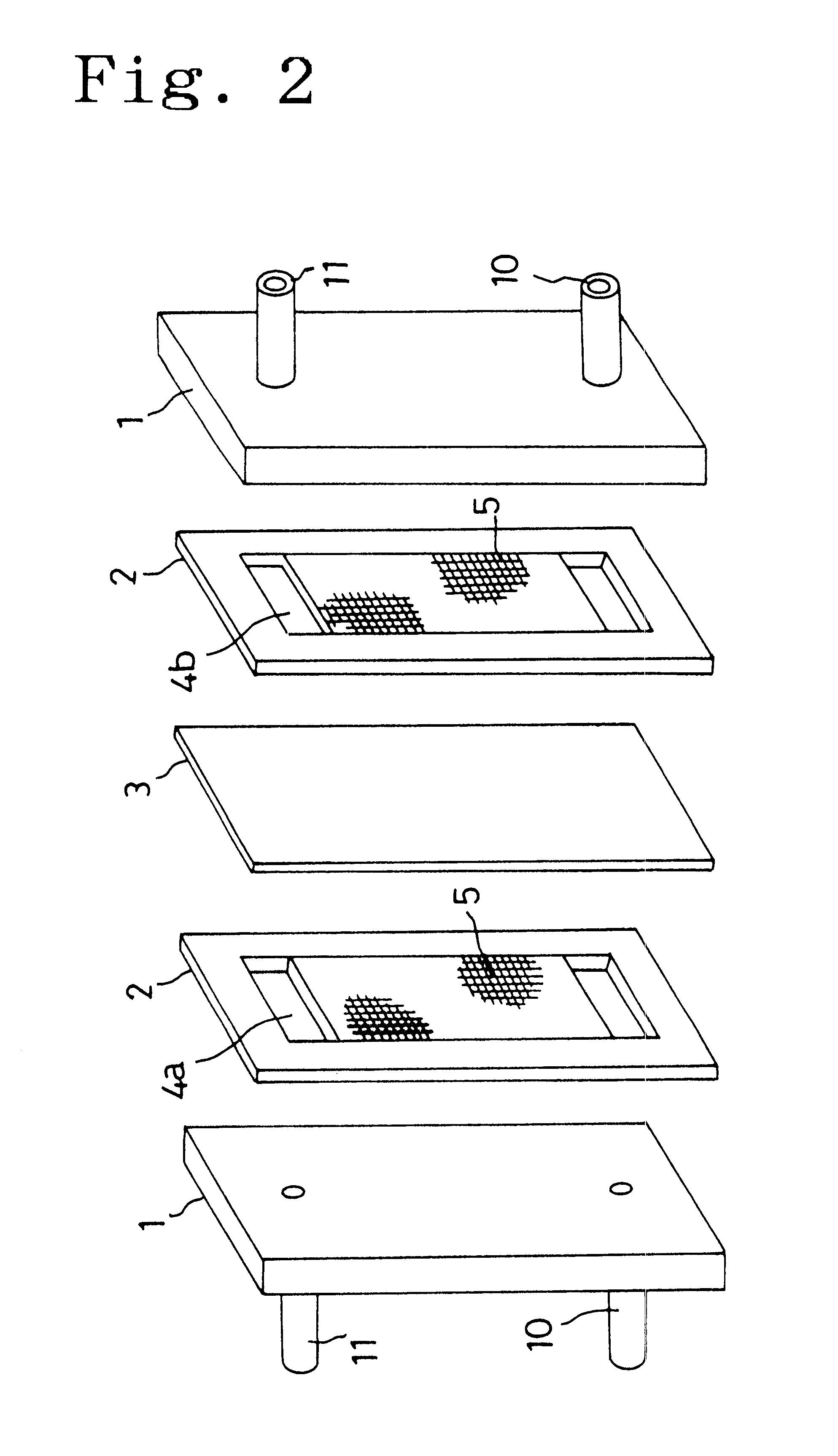
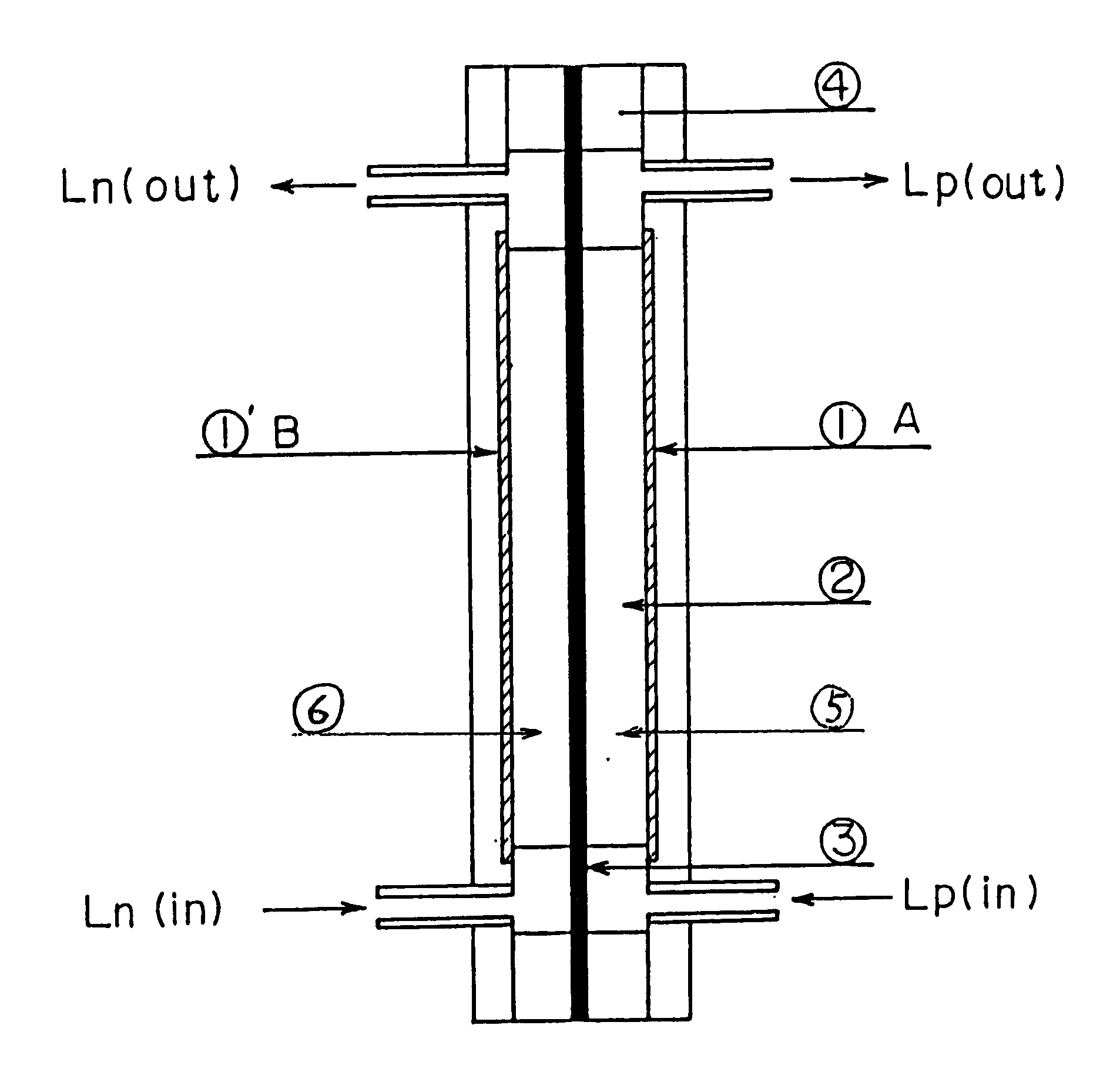
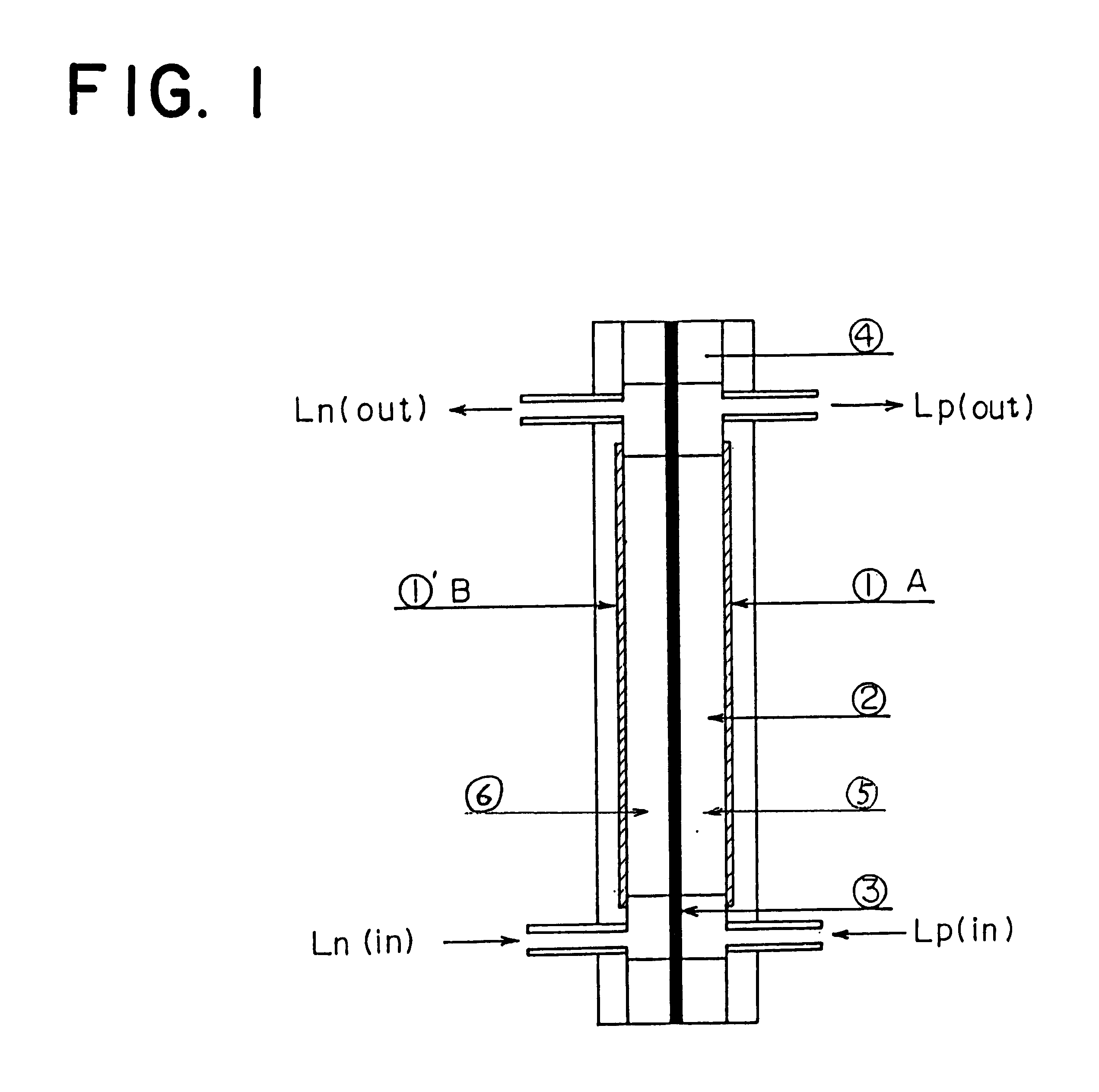
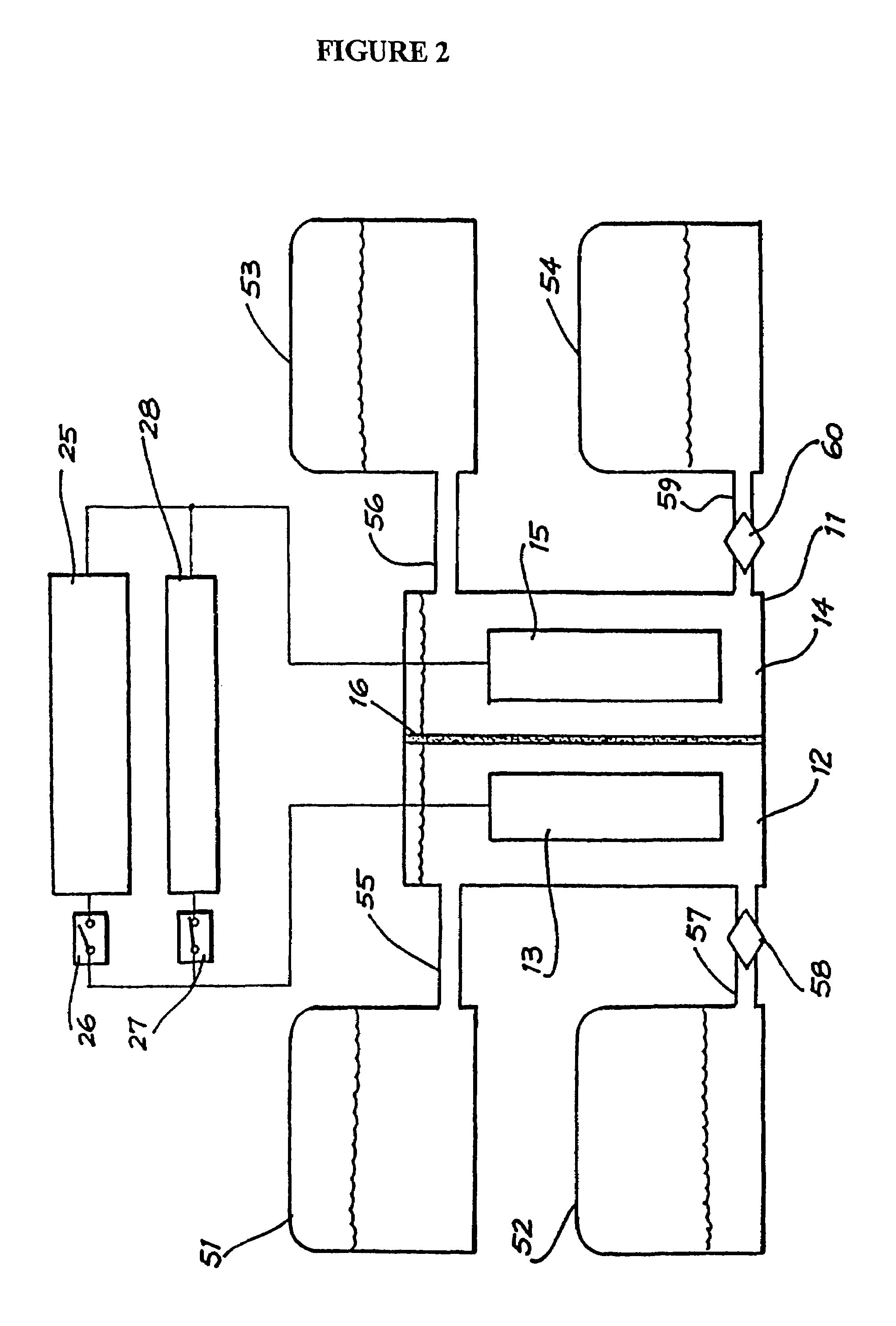
InactiveUS20080081247A1Avoid breakingPrevent a break in the membraneElectrolyte holding meansEngine sealsElectrolyte leakageOxidation-Reduction Agent
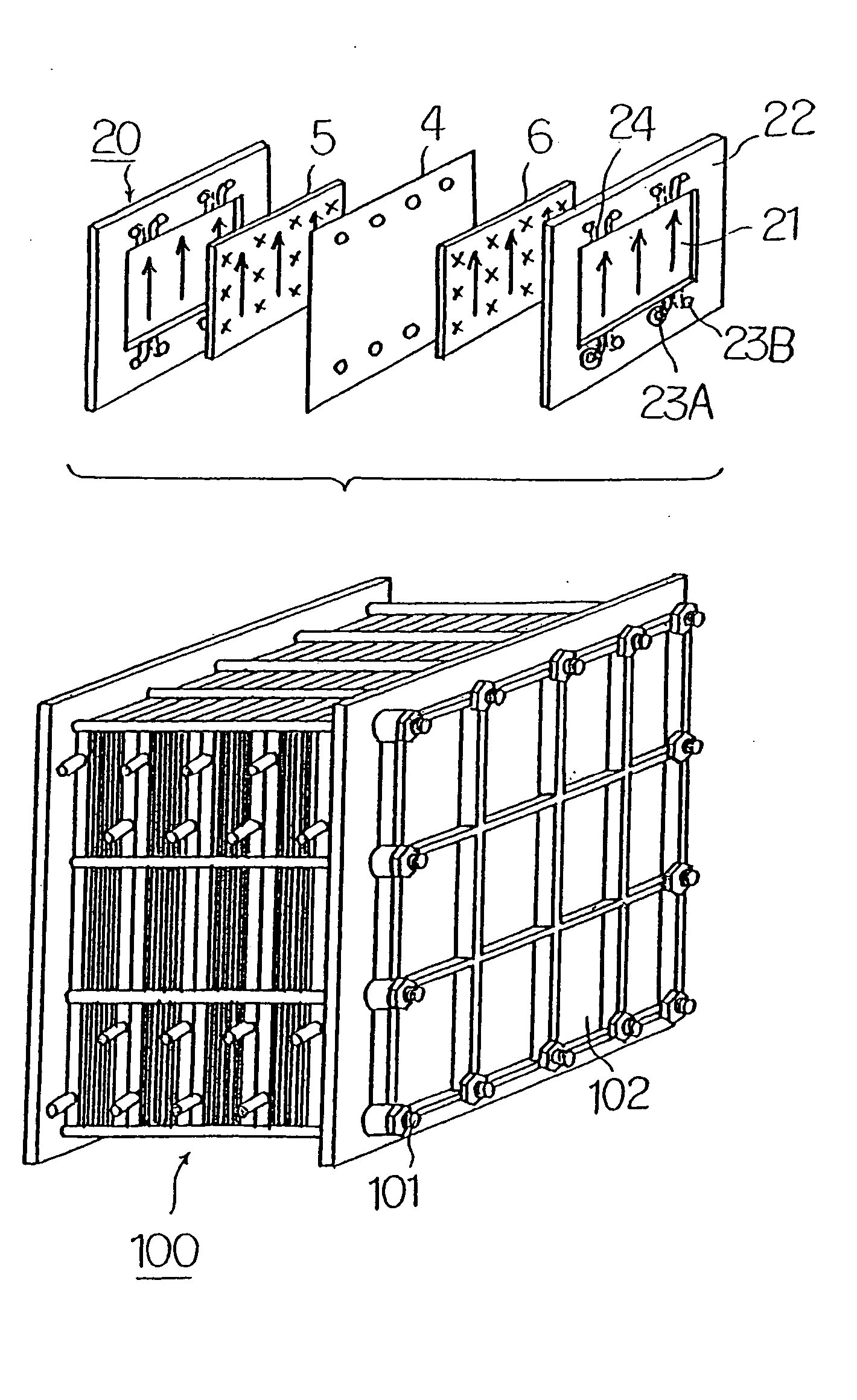
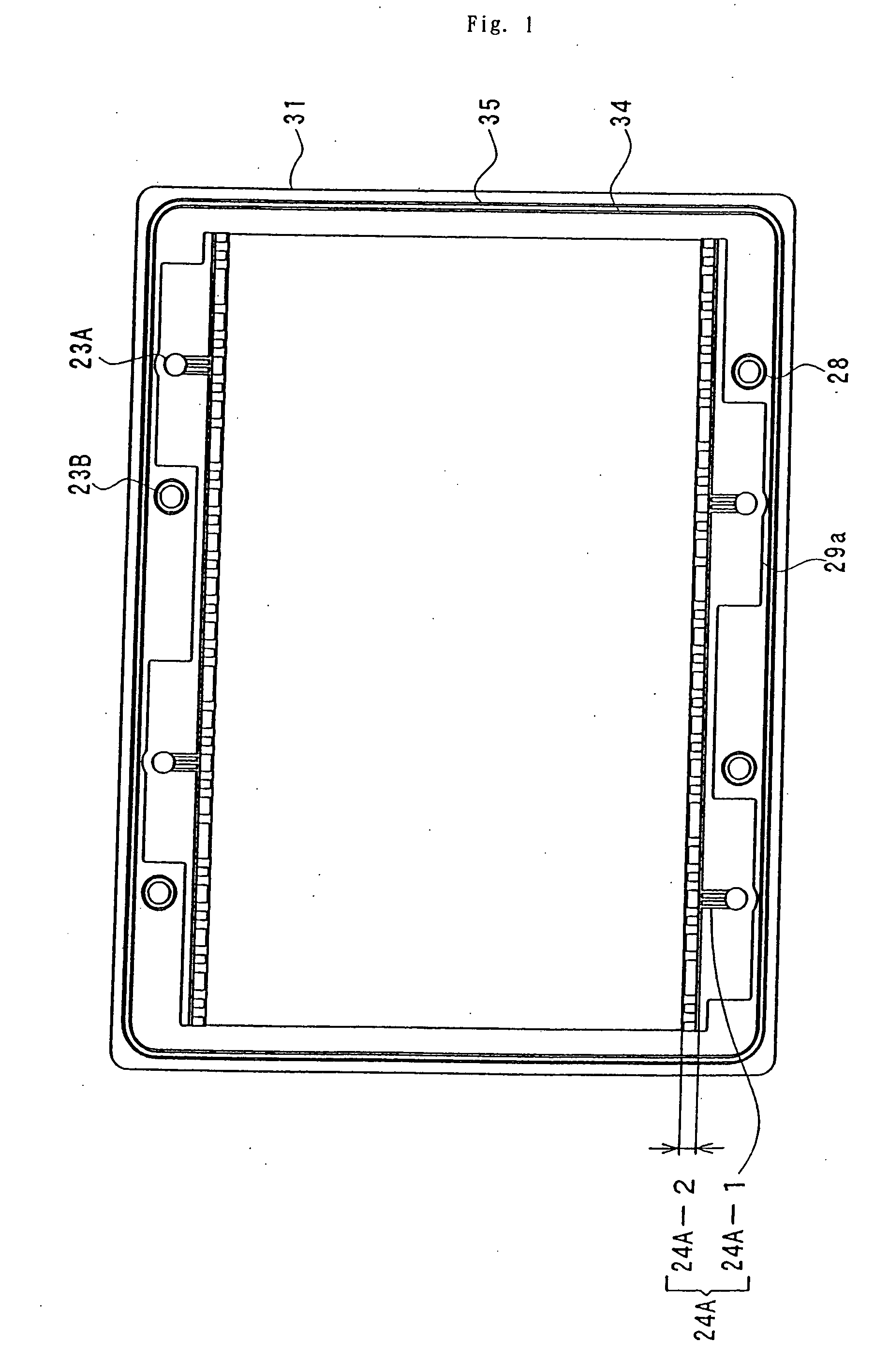
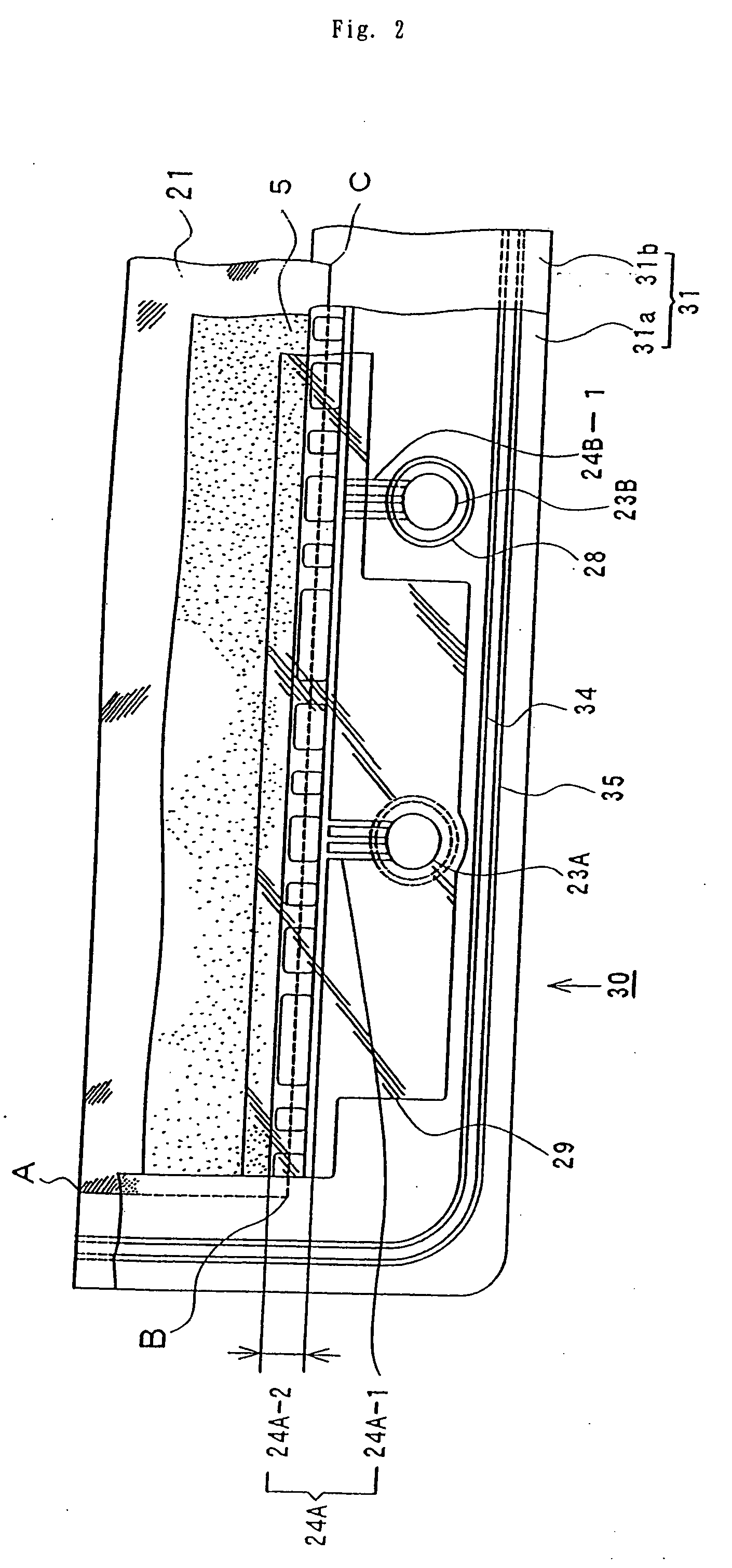
This invention provides a cell frame for a redox flow battery that prevents leakage of electrolyte out of the cell frame and also provides a good workability in assembling the redox flow battery. Also, this invention provides a redox flow battery using the cell frame. In the cell frame 30 for the redox flow battery 30 comprising a bipolar plate 21 and a frame 31 fitted around a periphery of the bipolar plate 21, the frame 31 has, on each side thereof, an inner seal and an outer seal to press-contact with a membrane and also seal electrolyte. The frame 31 has, on each side thereof, an inner seal groove 34 and an outer seal groove 35 for placing therein the inner seal and the outer seal, respectively, to prevent the electrolyte from leaking out, and O-rings are placed in the respective seal grooves.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD +1
Water-soluble organic couple redox flow battery
InactiveCN102035007AReduce polarizationImprove energy efficiencyFuel cells groupingRegenerative fuel cellsElectrode potentialElectrical battery
The invention relates to a water-soluble organic couple redox flow battery which comprises an anode, electrolyte thereof, a diaphragm thereof, a cathode and electrolyte thereof, wherein one of two active substances of the anode / cathode is a water-soluble organic couple, and the other one is an inorganic couple or organic couple; and the electrolyte of the anode / cathode is stored in an external storage tank, flows through the battery in a circulating way through a pump and undergoes oxidation / reduction reaction on the anode / cathode divided by the diaphragm to carry out the charging / discharging process. Organic couple materials are not limited by mining deposits, the charge capacity depends on the volume of the storage tank, the size of the battery can be singly designed according to the power requirement, and electrode potential and a reaction electron amount can be designed and controlled by organic molecules. Therefore, the redox flow battery has the advantages of rich raw materials, convenient preparation, high power conversion efficiency, environmental protection, safe use and the like and is suitable for scale electricity storage.
Owner:NO 63971 TROOPS PLA
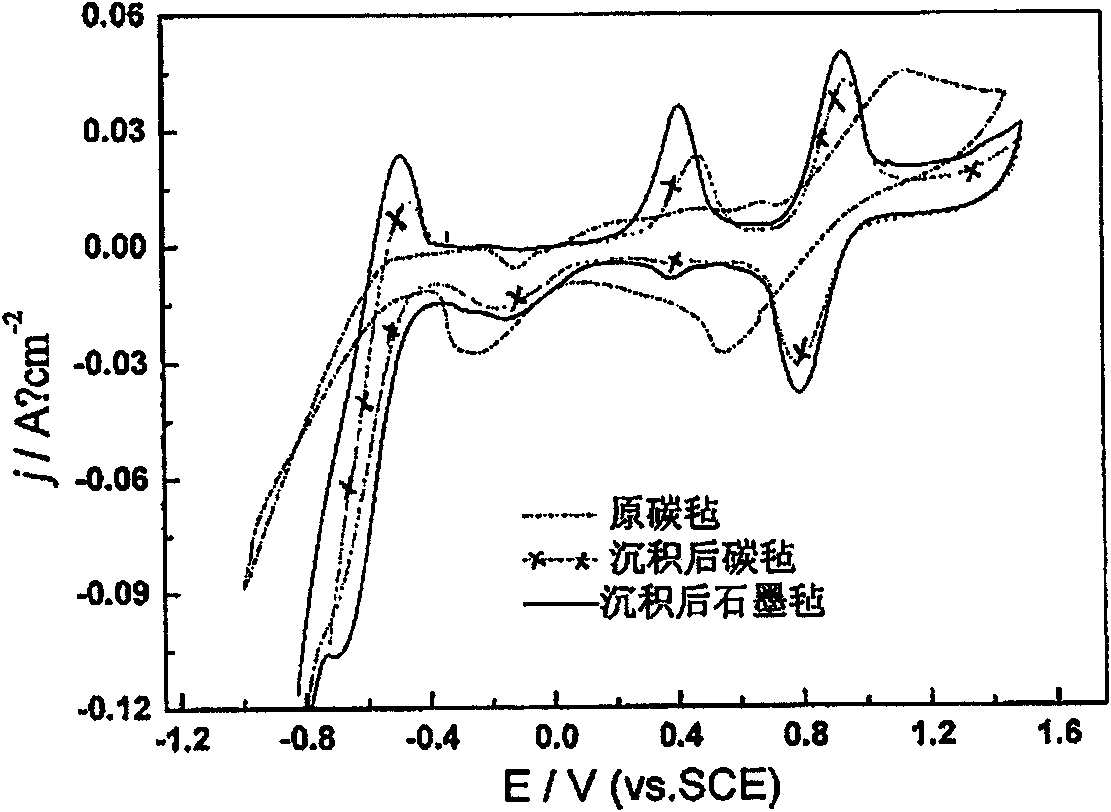
Graphite felt watch surface modified method and modified mineral carbon felt
InactiveCN101182678AImprove wettabilityImprove charge and discharge performanceElectrode manufacturing processesPhysical treatmentFiberVanadium redox battery
The invention relates to a graphite fiber felt surface modification method and a modified graphite fiber felt, and belongs to the all vanadium redox flow battery electrode manufacture technical field. The method step is that the electrochemical cathode modification treatment is conducted before the anode oxidation treatment. When used as an electrode, a modified graphite fiber felt greatly improves the electrochemical activity in the preparation of an all vanadium redox flow battery, promotes the voltage efficiency and the battery energy efficiency during the battery discharging, and increases the stable discharging time, so the recharging and discharging performance of the all vanadium redox flow battery is greatly improved. Moreover, the method is easy for implantation and low in the cost. No particular devices are required. The invention provides a good-performance electrode material for the battery manufacture field.
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON & STEEL RES INST OF PANGANG GROUP +1
Vanadium/polyhalide redox flow battery
InactiveUS7320844B2Minimise potential cross-contaminationCell electrodesRegenerative fuel cellsElectricityRedox
The invention relates to a redox flow cell containing a polyhalide / halide redox couple in the positive half-cell electrolyte and a V(III) / V(II) redox couple in the negative half-cell electrolyte. The invention also relates to a method of producing electricity by discharging the fully charged or partially charged redox flow cell, and a method of charging the discharged or partially discharged redox flow cell.
Owner:WATTJOULE
A Zn-Ni liquid battery
ActiveCN101127393AIncrease transfer speedDetoxificationElectrolyte moving arrangementsAlkaline accumulatorsEngineeringNickel electrode
The utility model relates to a zinc-nickel sap fluid cell, which comprises a galvanic pile which is a multi-section series connection of cell monomers, electrolyte, a storage tank, a liquid pump and a plurality of pipelines; wherein, the cell monomer comprises a nickel electrode anode, a cathode current collector of deposit zinc, and electrolyte; wherein, the electrolyte is a zincous alkaline solution, and two cell monomers are connected in series via a bipolar plate. In the process of charge and discharge, the electrolyte continuously flows between the storage tank and the galvanic pile via the pipelines driven by the liquid pump. Zinc settles onto the cathode current collector and becomes a cathode active substance from the electrolyte at the time of charging, while zinc dissolves into the electrolyte from the cathode current collector at the time of discharging. The utility model has the advantages of simple fabrication technology, low cost, high cycle life and other advantages.
Owner:NO 63971 TROOPS PLA +1
Electrode materials and all-vanadium redox flow battery containing electrode materials
InactiveCN101651201AReduce dosageLow costElectrode manufacturing processesRegenerative fuel cellsCarbon nanotubeRedox
The invention provides an electrode for a vanadium battery, comprising a carbon basal body and a carbon nano-tube layer formed on the surface of the basal body, wherein the carbon basal body is selected from a graphite felt, a carbon felt, a carbon paper and carbon cloth. The invention also provides an all-vanadium redox flow battery containing the electrode. The electrode has improved electrochemical activity and reliable mechanical strength.
Owner:BIG PAWER ELECTRICAL TECH XIANGYANG +1
Organic phase dual flow battery
InactiveCN103000924AIncrease energy densitySimple preparation processRegenerative fuel cellsLiquid storage tankFerrocene
The present invention discloses an organic phase dual flow battery, which comprises at least a battery monomer, wherein the battery monomer comprises a positive electrode and a negative electrode, the positive electrode and the negative electrode are respectively connected with a positive electrode terminal and a negative electrode terminal, a separation membrane is arranged between the positive electrode and the negative electrode, a positive electrode flow channel is arranged between the separation membrane and the positive electrode, a negative electrode flow channel is arranged between the separation membrane and the negative electrode, the positive electrode flow channel is filled with a positive electrode electrolyte liquid, the negative electrode flow channel is filled with a negative electrode electrolyte liquid, both ends of the positive electrode flow channel are respectively communicated with a positive electrode electrolyte liquid storage tank, both ends of the negative electrode flow channel are respectively communicated with a negative electrode electrolyte liquid storage tank, an active substance of the positive electrode electrolyte liquid is ferrocene or a derivative thereof, and an active substance of the negative electrode electrolyte liquid is anthraquinone or a derivative thereof. The organic phase dual flow battery of the anthraquinone or the derivative thereof / the ferrocene or the derivative thereof has advantages of simple manufacturing process, low cost, high cycle life and the like, has characteristics of high energy density, high power density and high energy utilization efficiency, and can be widely used in electric power, transportation, electronics and other industries.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
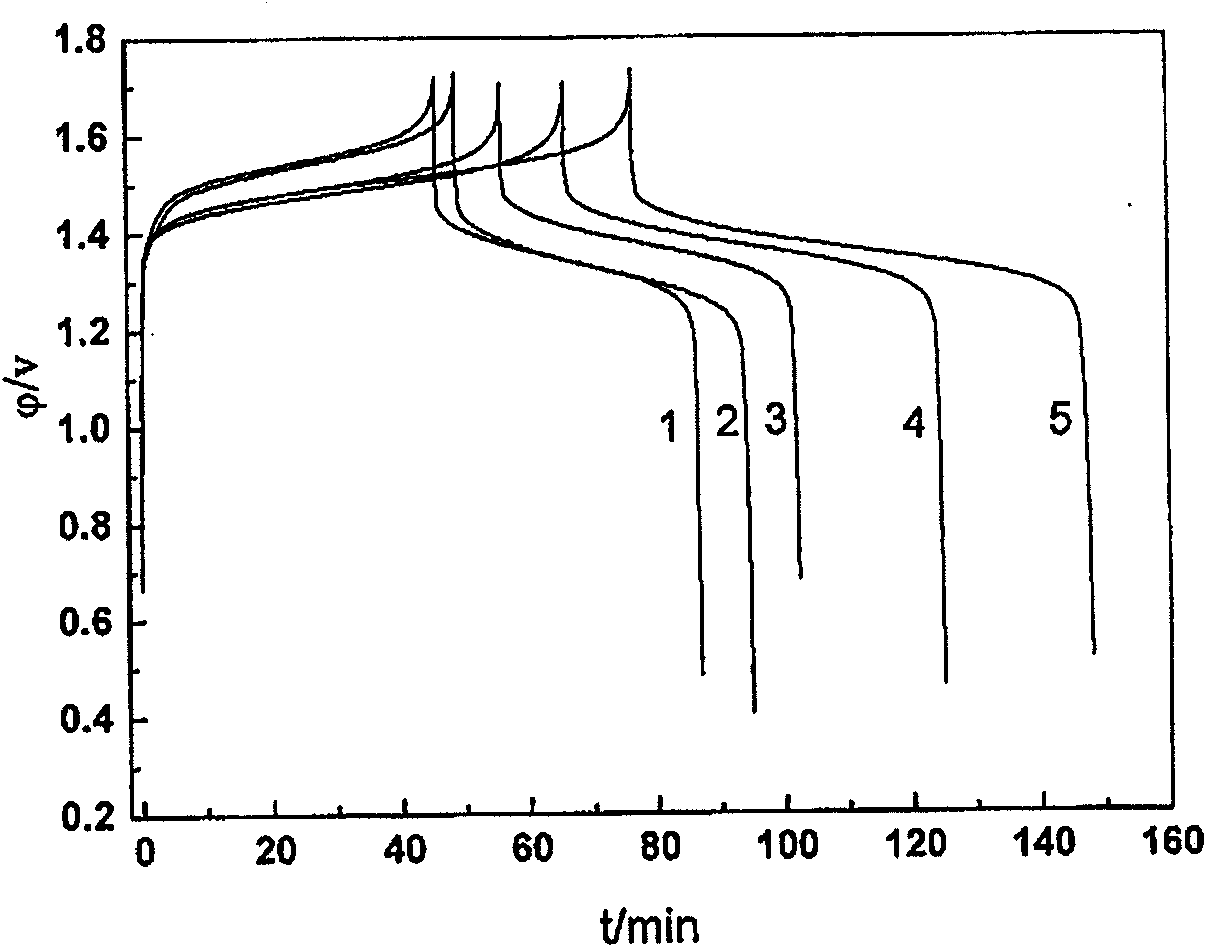
Method for preparing all vanadium ion redox flow battery electrolyte
ActiveCN101110481AIncrease concentrationIncrease discharge voltageRegenerative fuel cellsSecondary cellsHigh concentrationElectrochemistry
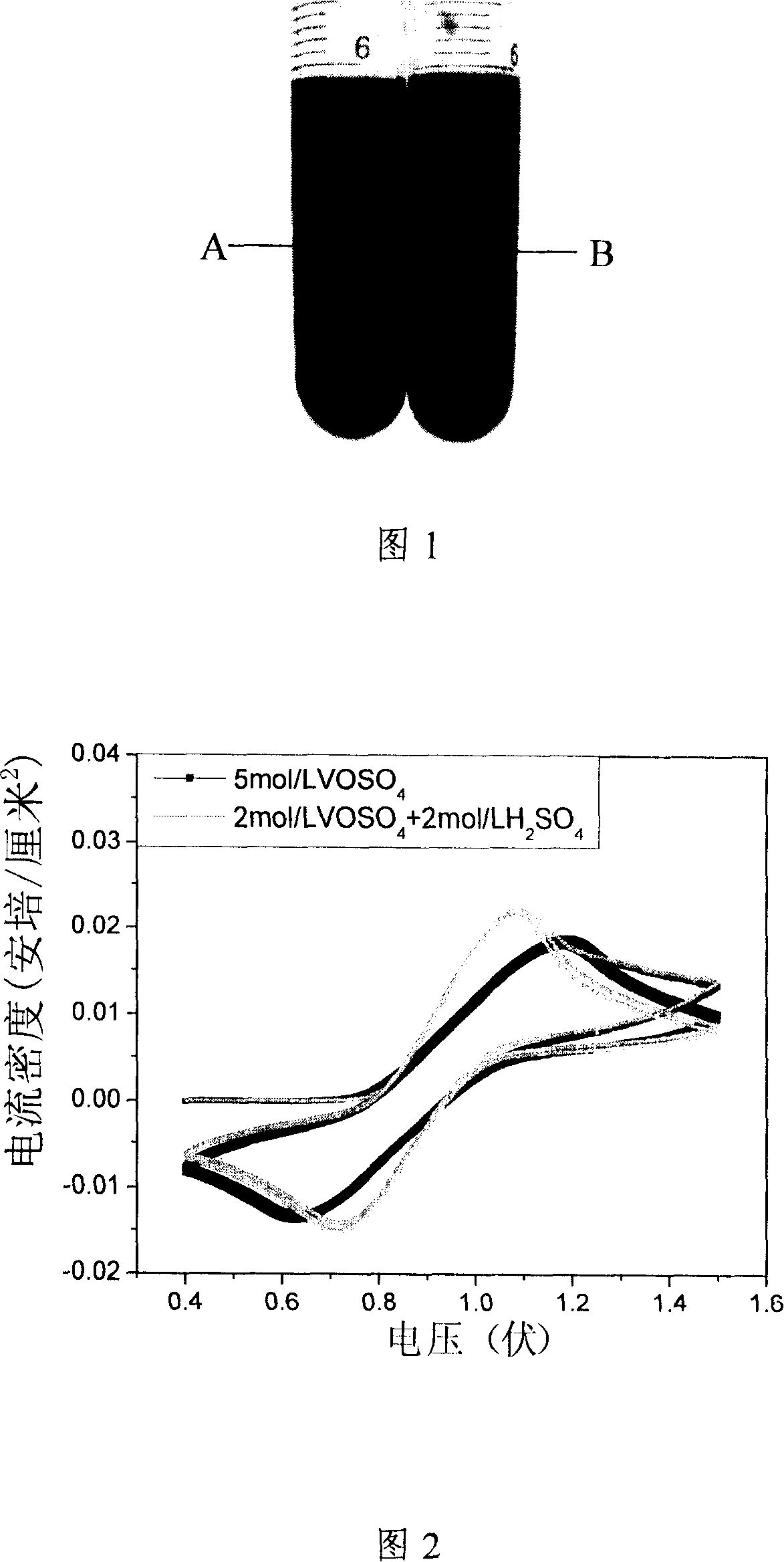
The present invention relates to a method to produce high concentration full vanadium ion oxidation and reduction liquid flow battery (vanadium battery) electrolyte, which produces 5-6mol / L vanadium battery electrolyte by proportionally adding organic-inorganic compound stabilizing agents. The present invention has the advantages of simple technical method, convenient operation and easy raw material acquisition, produces stable high-concentration vanadium battery electrolyte with excellent electrochemical reversibility and electrical conductivity approximate to conventional 2mol / L electrolyte and realizes battery charge and discharge.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Vanadium ion redox flow battery electrolyte, preparation method thereof and battery thereof
ActiveCN101635363ASimple production processReduce lossesRegenerative fuel cellsFuel cell detailsManufacturing technologyVanadyl sulfate
The invention provides vanadium ion redox flow battery electrolyte, comprising vandic salt, sulphuric acid, additive, deionized water and metal salt can be dissolved in a sulphuric acid system. The electrolyte can greatly improve the cathode system evolution overpotential of the vanadium battery and anode system evolution overpotential, greatly reduce the ratio of gas evolution in the electrolyte caused by various polarizations in the process of operating the vanadium battery, and improve the stability of the electrolyte in the process of charge and discharge. The invention further provides a preparation method of the vanadium ion redox flow battery electrolyte, which eliminates a step of electrolyzing the obtained vanadyl sulfate solution to obtain 50% of trivalent vanadium and 50% of tetravalent vanadium, greatly simplifies the manufacture technology of the vanadium electrolyte which can be directly used for charging and discharging, reduces the lose of the vanadium in the process of preparation, and reduces the preparation cost of the electrolyte.
Owner:BYD CO LTD
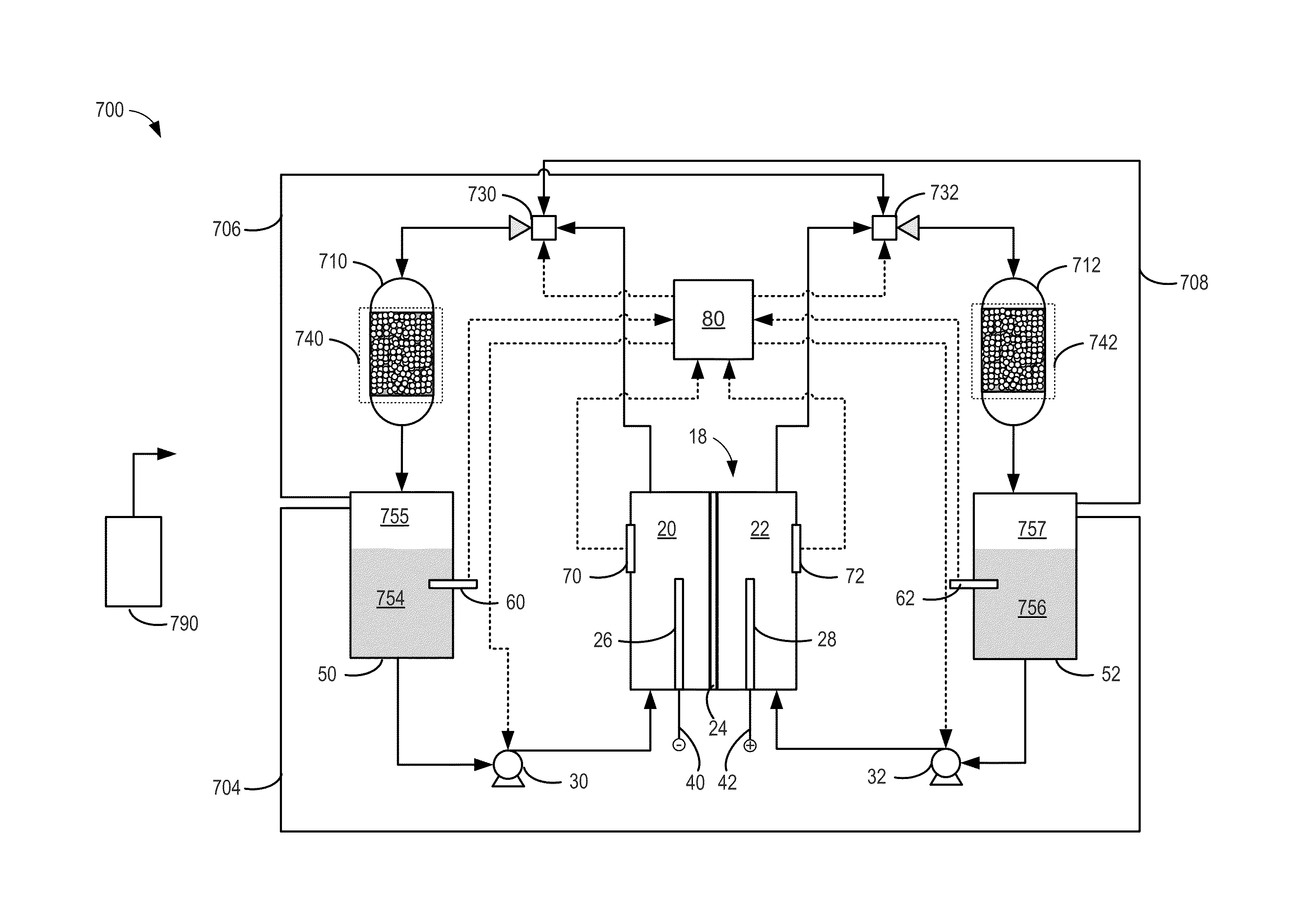
Method and system for rebalancing electrolytes in a redox flow battery system
A method of rebalancing electrolytes in a redox flow battery system comprises directing hydrogen gas generated on the negative side of the redox flow battery system to a catalyst surface, and fluidly contacting the hydrogen gas with an electrolyte comprising a metal ion at the catalyst surface, wherein the metal ion is chemically reduced by the hydrogen gas at the catalyst surface, and a state of charge of the electrolyte and pH of the electrolyte remain substantially balanced.
Owner:ESS TECHNOLOGY
Method for preparing electrode material for all-vanadium flow battery
InactiveCN102522568AImprove energy storage efficiencyHigh specific surface areaCell electrodesCarbon fibersTraditional Use
The invention relates to the field of cell manufacturing and energy storage, and concretely relates to a method for preparing an electrode material for an all-vanadium flow battery. The method comprises the following steps: preparing a composite spinning liquid needed by experiments, uniformly mixing carbon nanotubes with the electrode catalysis, graphite oxide, a transition metal oxide or a transition metal nitrate or halide, and the like with the composite spinning liquid, preparing a raw electrode material through a static spinning process, preoxidizing an electrode material precursor (the raw electrode material) through utilizing a vacuum / atmosphere furnace (at 200-500DEG C), and carbonizing in an inert atmosphere (at 800-1500DEG C) to obtain the needed electrode material. The obtained electrode material can be subjected to charge and discharge tests of the cell after cleaning and drying. According to the vanadium cell electrode material prepared through adopting the method of the invention, the carbon fiber diameter is in the nanometer level, the specific surface area is substantially higher than specific surface areas of traditional used electrode materials, and the oxygen content of the fiber surface is greatly improved because of the late preoxidation processing.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for operating redox flow battery system
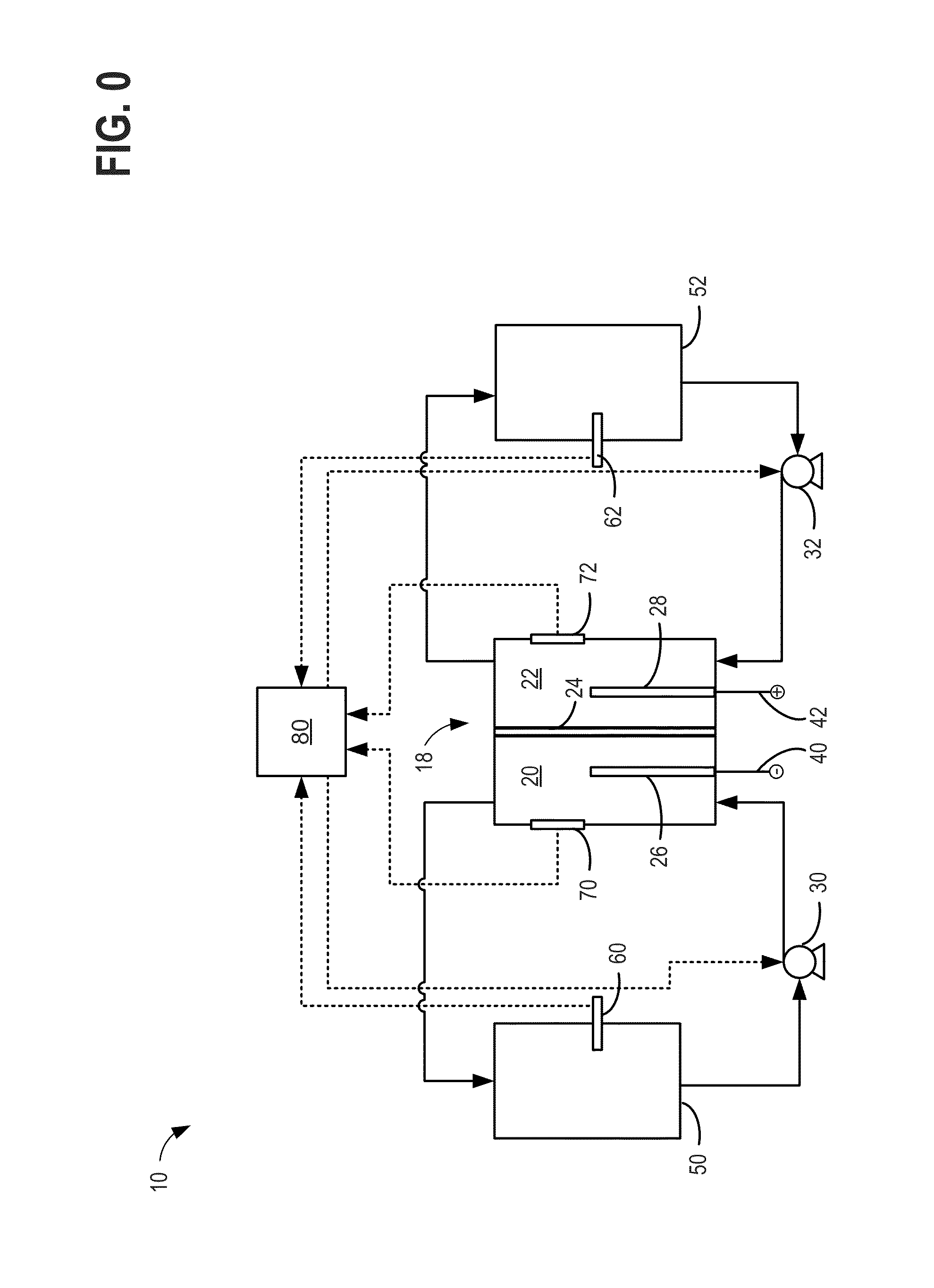
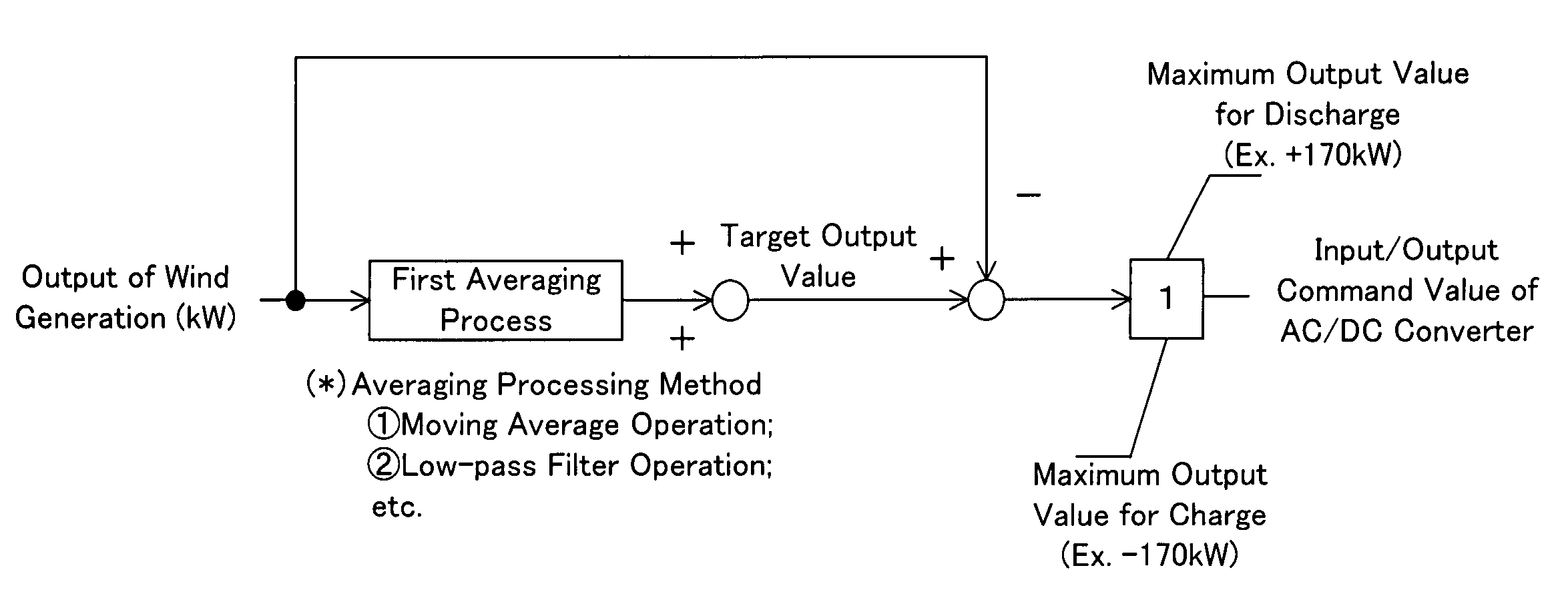
InactiveUS7061205B2Improve energy efficiencyBatteries circuit arrangementsWind motor controlElectrical batteryTime segment
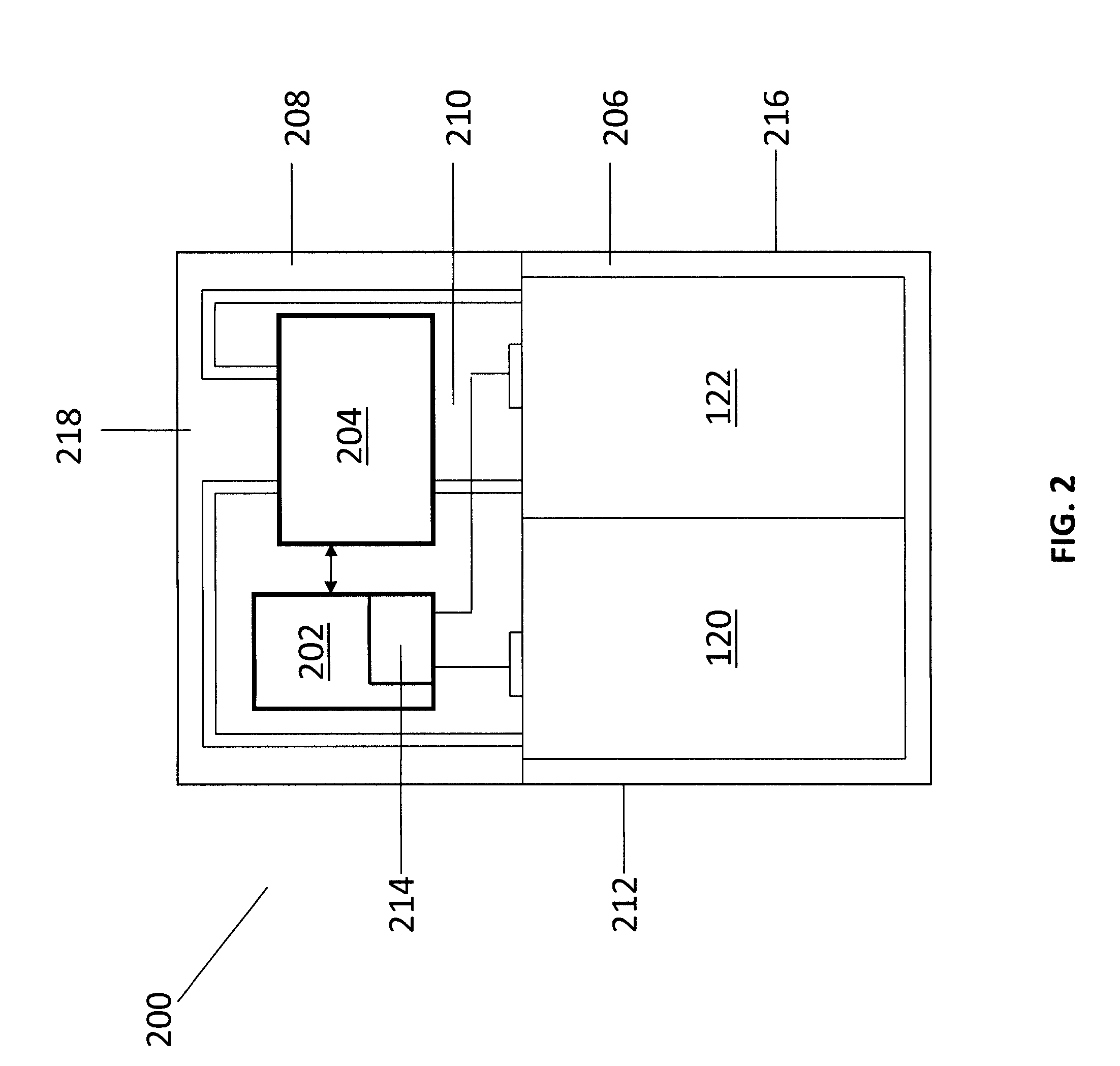
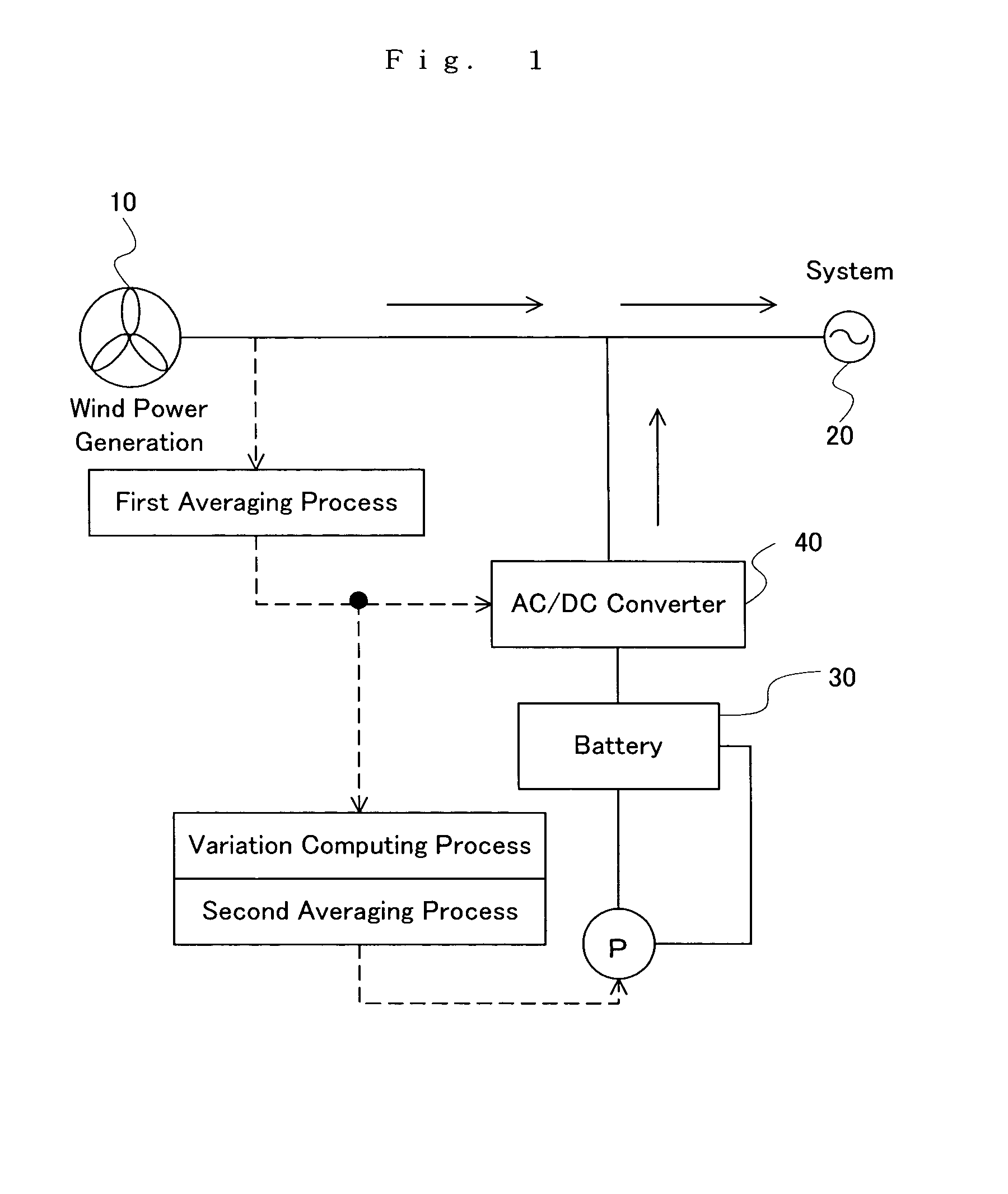
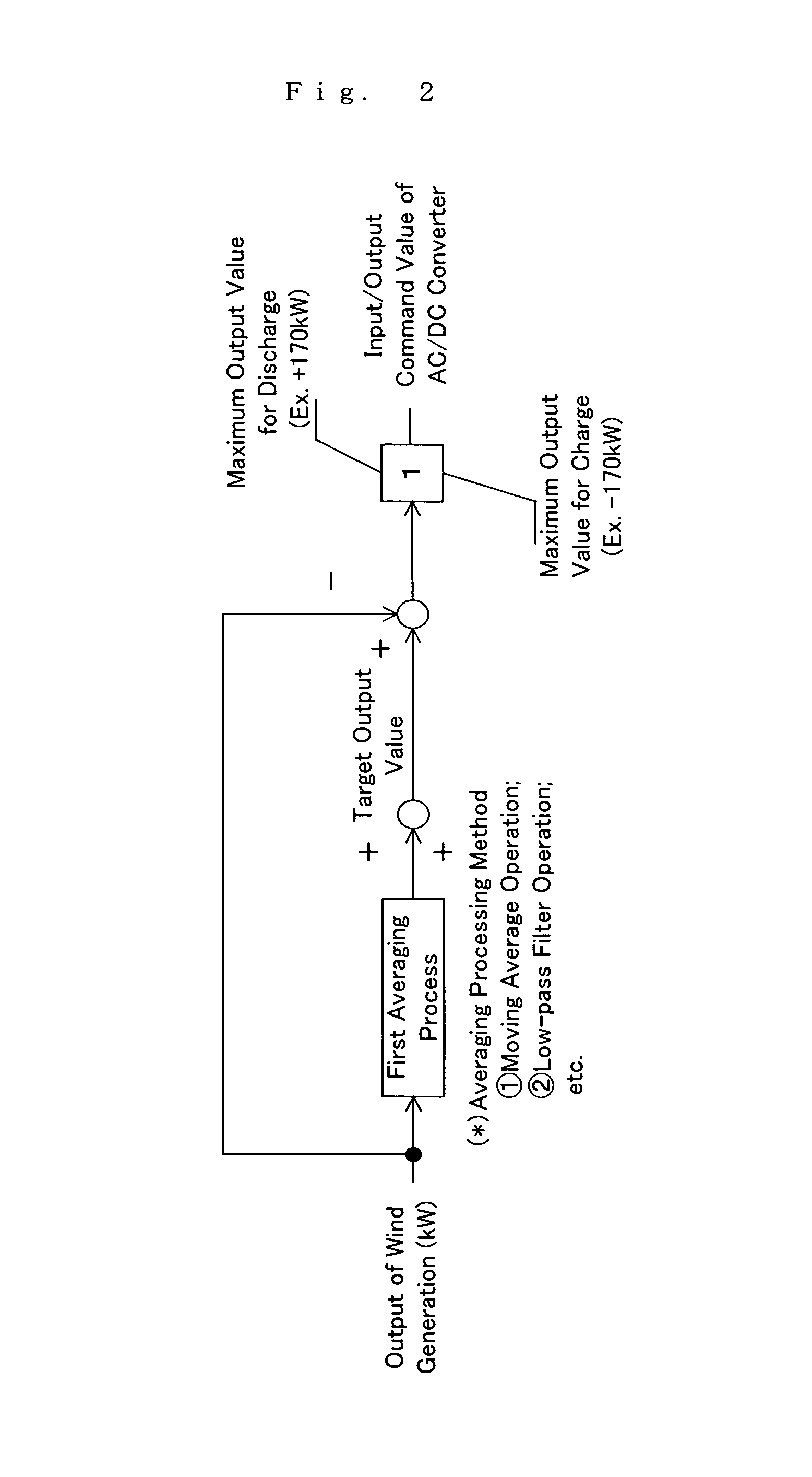
An operating method of a redox flow battery system that can provide a stabilized output to a system from a redox flow battery system annexed to a wind power generator, to produce an improved battery efficiency. The redox flow battery system comprises the wind power generator 10, a redox flow battery 30 annexed to the wind power generator, and an AC / DC converter 40 connected to the redox flow battery. In the operating method, an output of the wind power generator within a certain period of time in the past is subjected to a first averaging process; a present output value of the wind power generator is subtracted from the resulting value of the first averaging process, from which an input / output command value to the AC / DC converter 40 is determined; the input / output command value is subjected to a variation computing process to find variation without any consideration of a sign of the input / output command value; the resulting value obtained by the variation computing process is further subjected to a second averaging process, and an output command value for a pump P to circulate electrolytic solution of the redox flow battery is determined based on the result of the second averaging process.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD +1
Apparatus and methods of determination of state of charge in a redox flow battery
InactiveUS7855005B2Batteries circuit arrangementsMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorState of chargeRedox
Methods for determining the state of charge of an electrolyte solution in a redox battery by optical absorption spectrophotometry are disclosed. The state of charge thus obtained may serve as a gauge for the amount of electro-chemical energy left in the system.
Owner:IMERGY POWER SYST
Electrode structure of vanadium redox flow battery
ActiveUS20130022846A1Improve concentrationImprove electrochemical efficiencyCell electrodesCell component detailsProtonRedox
An electrode structure of a vanadium redox flow battery is disclosed, which includes a proton-exchange membrane, two graphite papers, two graphite felt units, two pads, two graphite polar plates, two metal plates and a lock-fixing device which are symmetrically stacked in sequence from center to outside. wherein each graphite polar plate has the flow channels with a grooved structure, and each graphite felt unit is embedded in the flow channels of one of the graphite polar plates, and then the graphite felt units are covered by the graphite papers such that the different electrolytes flow in their corresponding flow channels. The storage tanks of vanadium electrolyte are connected through the connection pipelines, and the redox reaction is performed through the flows of the vanadium electrolyte. The electrode structure of the vanadium redox flow battery can be stacked for forming a large-scale electrode structure to increase the electrical power.
Owner:JEN CATHOLIC UNIV
Preparation method of metal-organic framework material/polymer composite proton exchange membrane
ActiveCN105789668AStrong penetrating powerImprove performanceRegenerative fuel cellsVanadium redox batteryMetal-organic framework
The invention relates to a preparation method of a metal-organic framework material / polymer composite proton exchange membrane. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: dissolving a polymer matrix and a certain amount of metal-organic framework material with an organic solvent and carrying out ultrasonic dispersion to form a uniform membrane liquid; coating the flat and smooth surface of a glass plate with the obtained membrane liquid, and then removing the organic solvent to obtain a composite membrane; and carrying out vacuum drying on the composite membrane for 24 hours to prepare the composite proton exchange membrane for an all-vanadium redox flow battery. The composite proton exchange membrane is smooth in surface; the internal structure of the membrane is regular; the membrane is uniform in thickness and free of a defect; and the thickness is 10-300 microns. The composite proton exchange membrane provided by the invention has excellent vanadium ion permeation blocking ability, keeps excellent proton transfer performance, overcomes the defect of relatively high vanadium ion permeability of an existing all-vanadium redox flow battery membrane, and has the advantages of being simple in preparation process, high in proton transmittance, excellent in vanadium blocking property, excellent in oxidative resistance, easy to industrially amplify and the like.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com