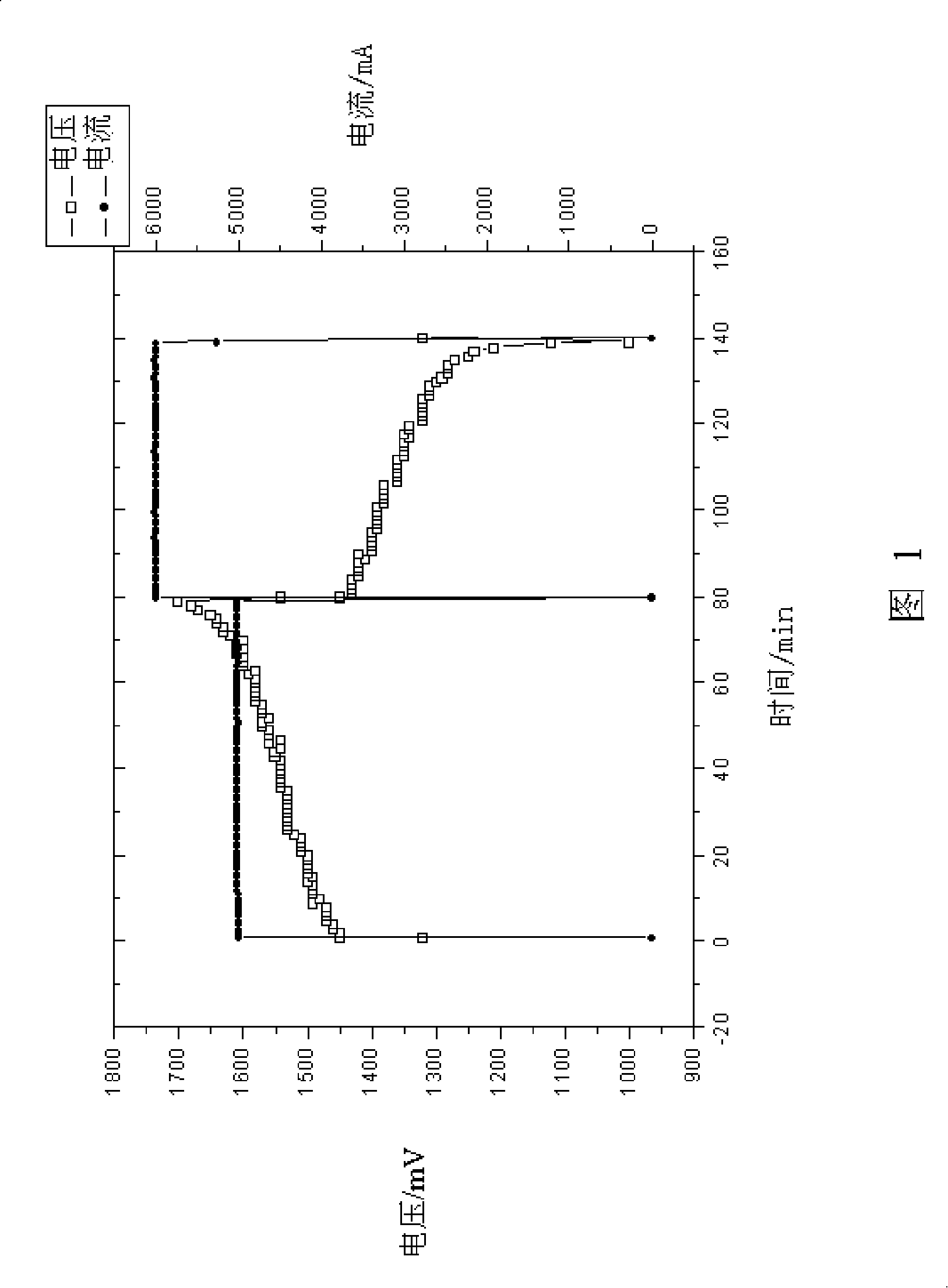
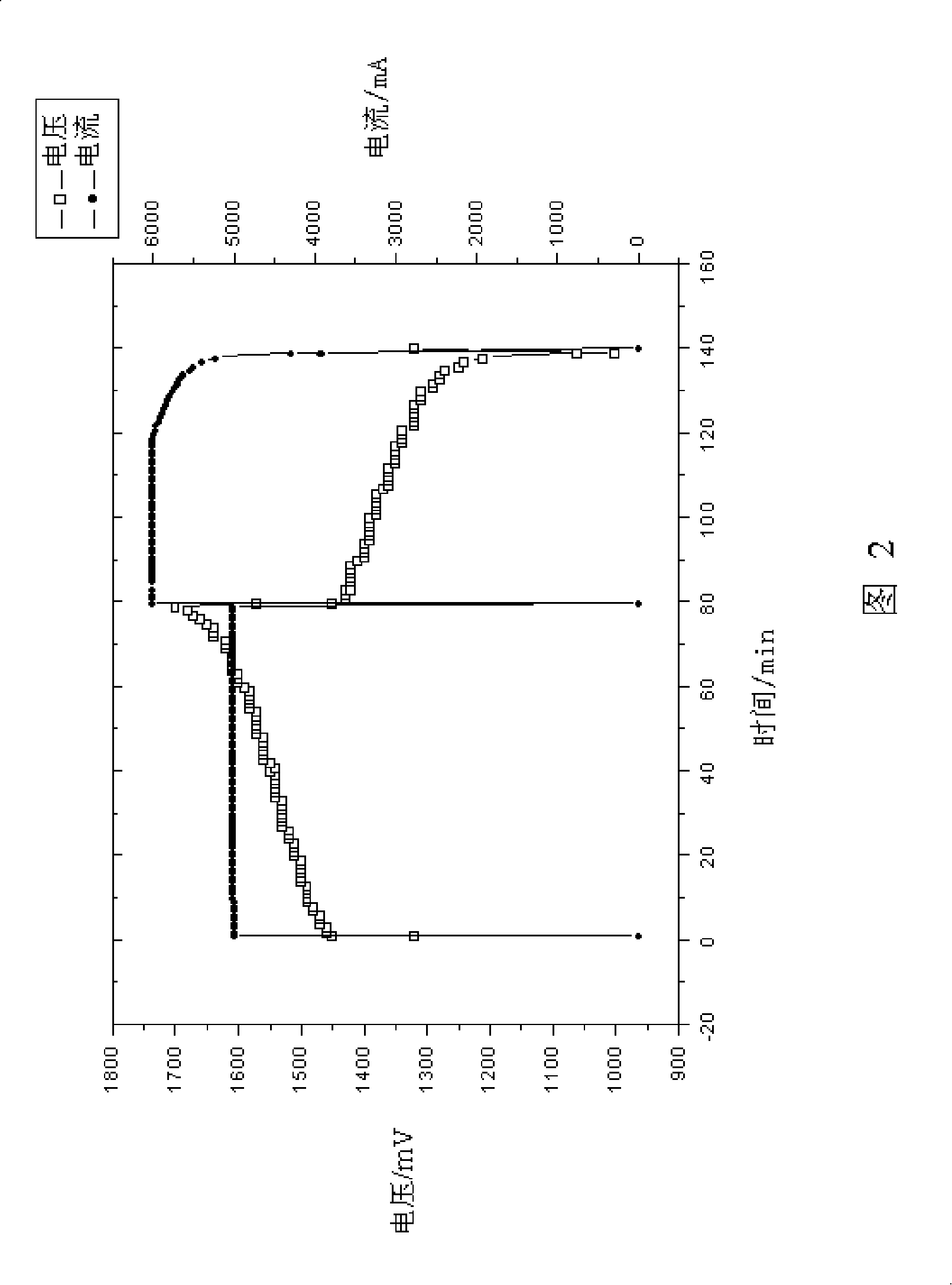
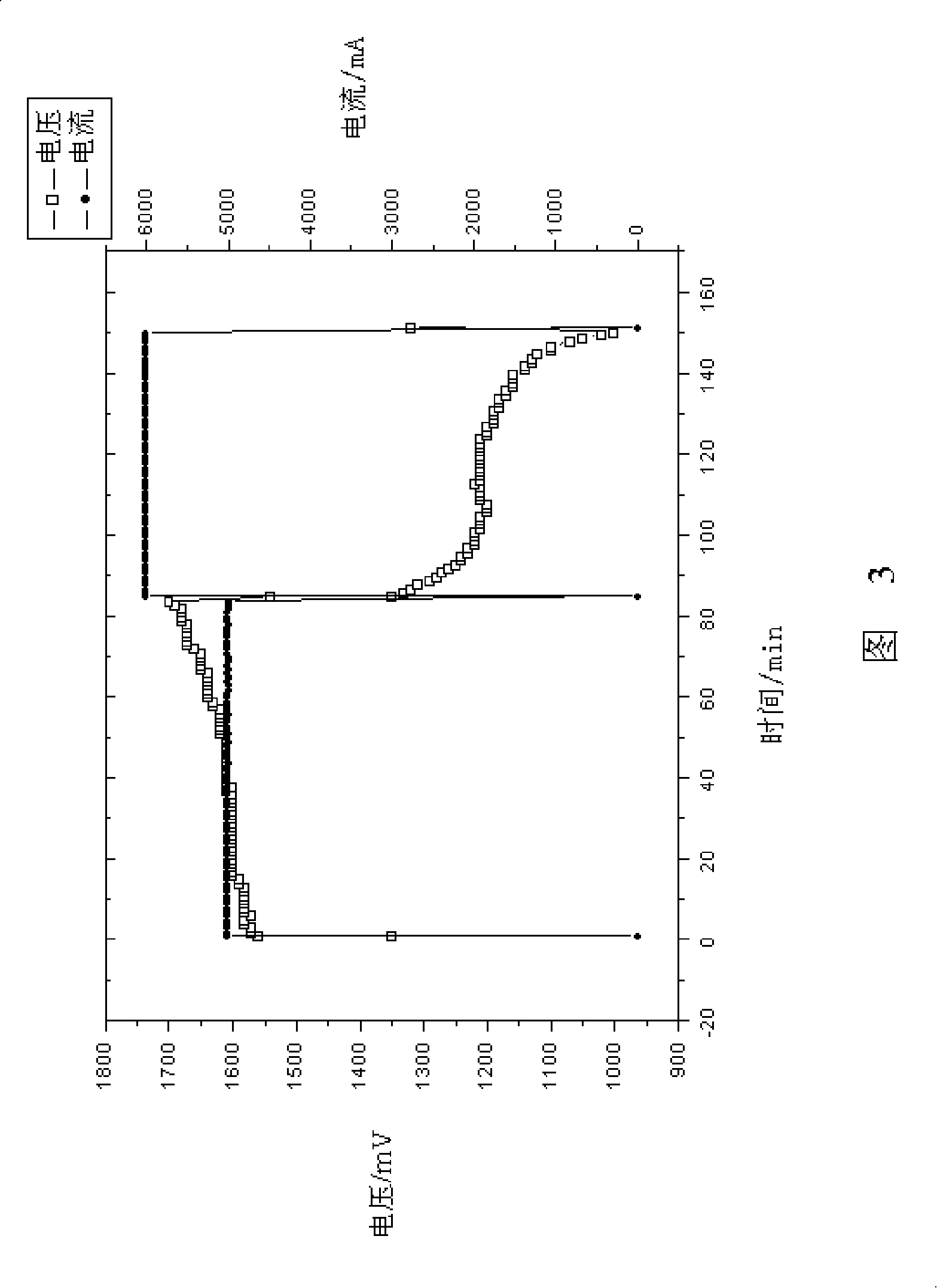
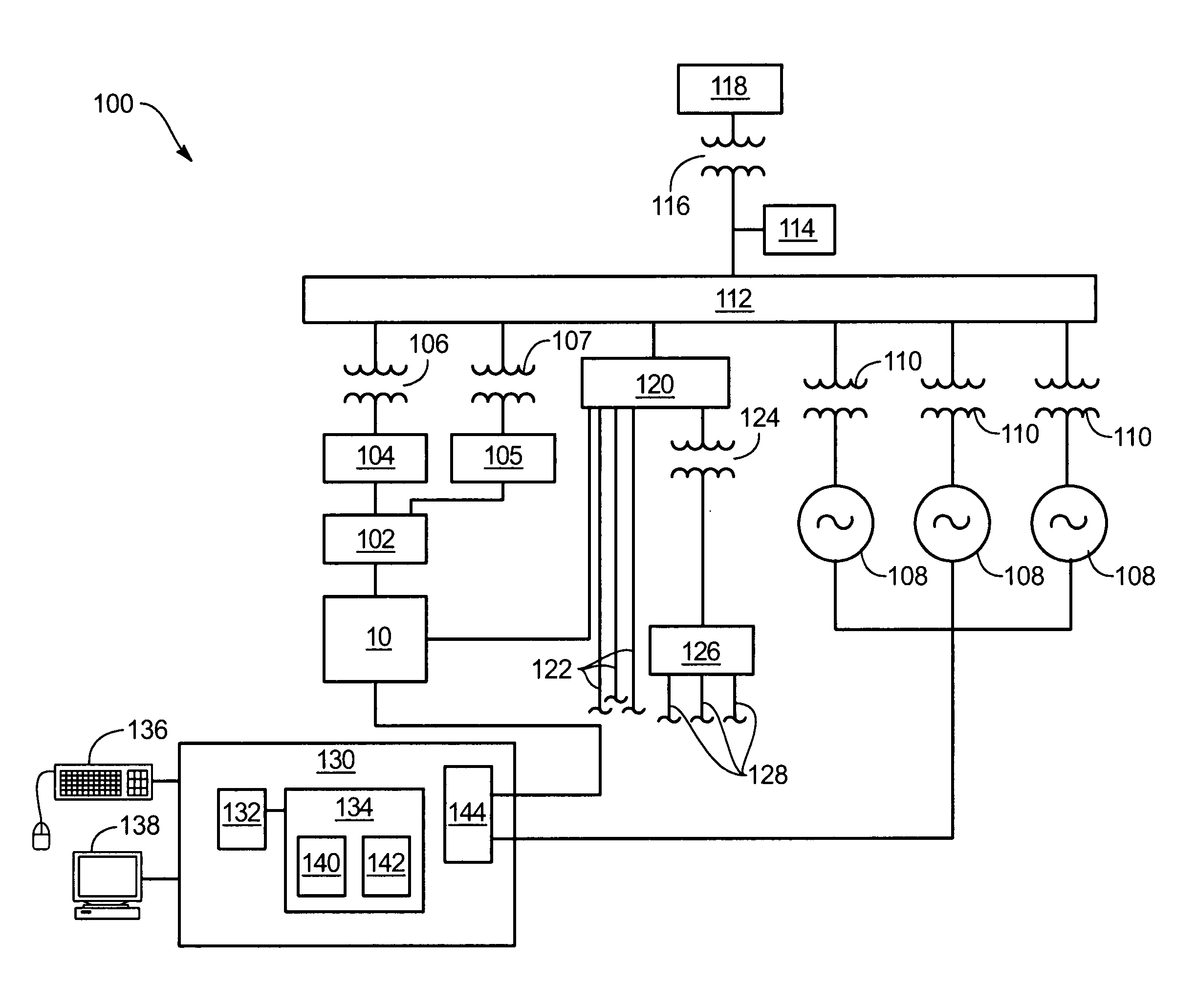
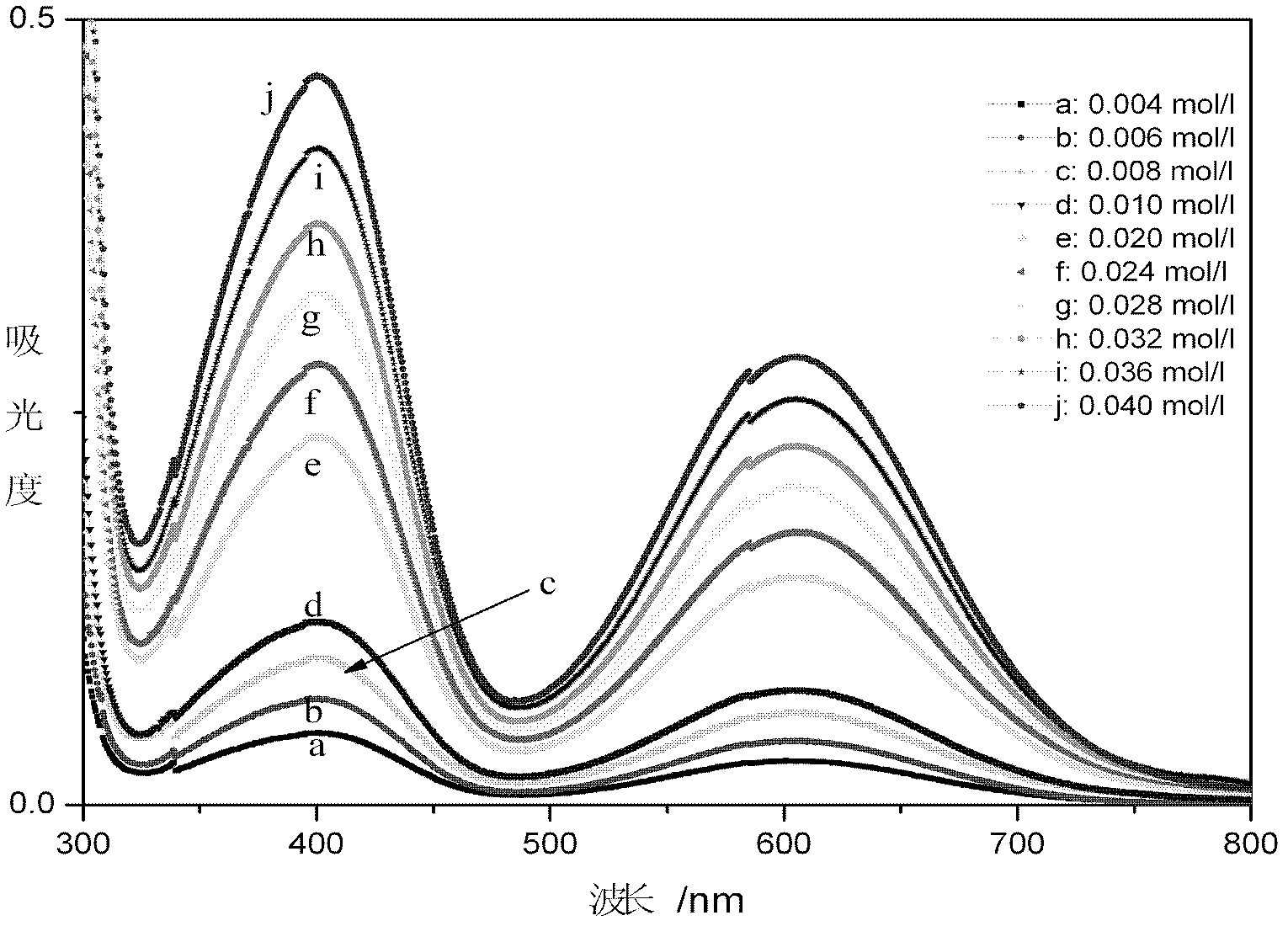
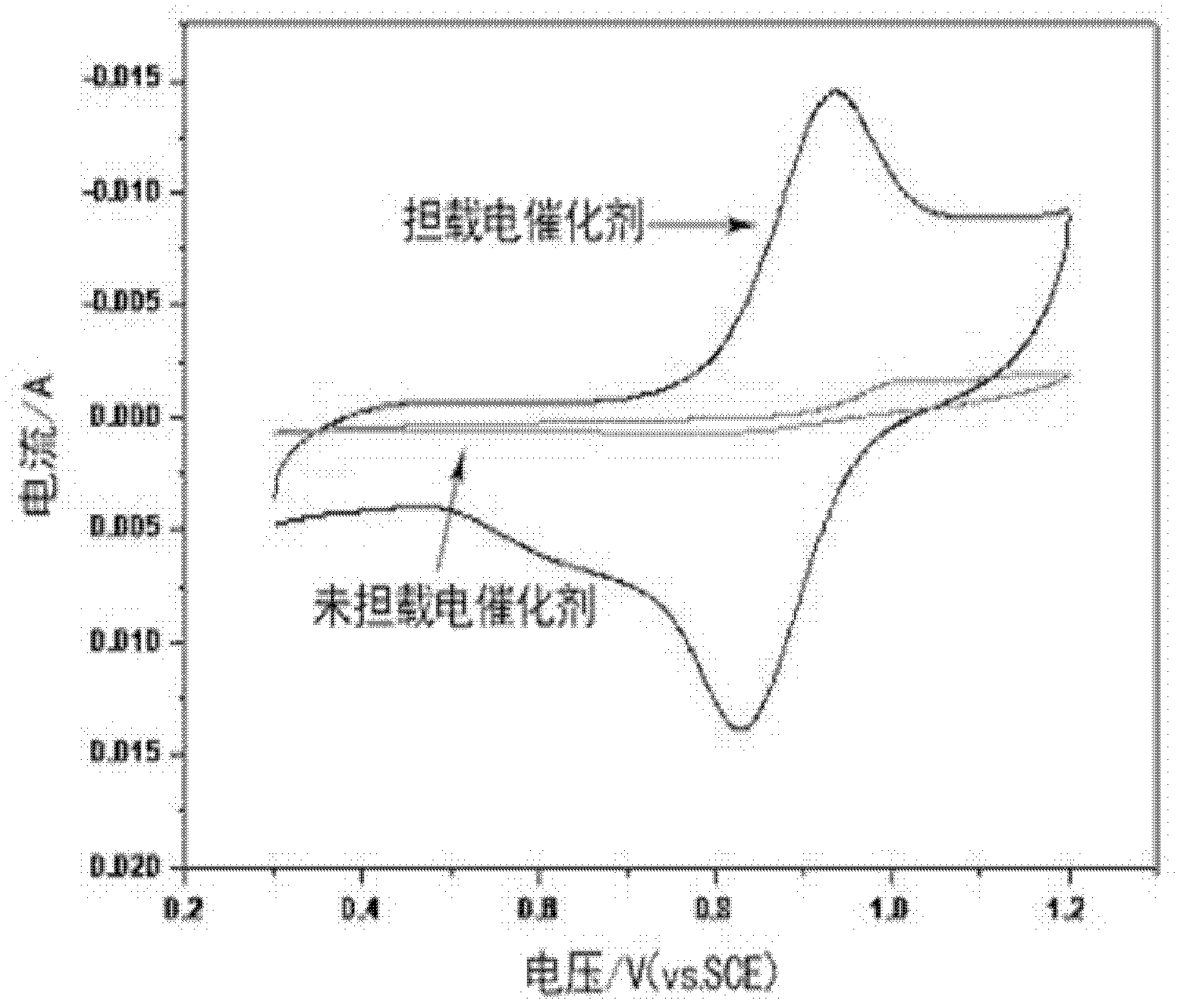
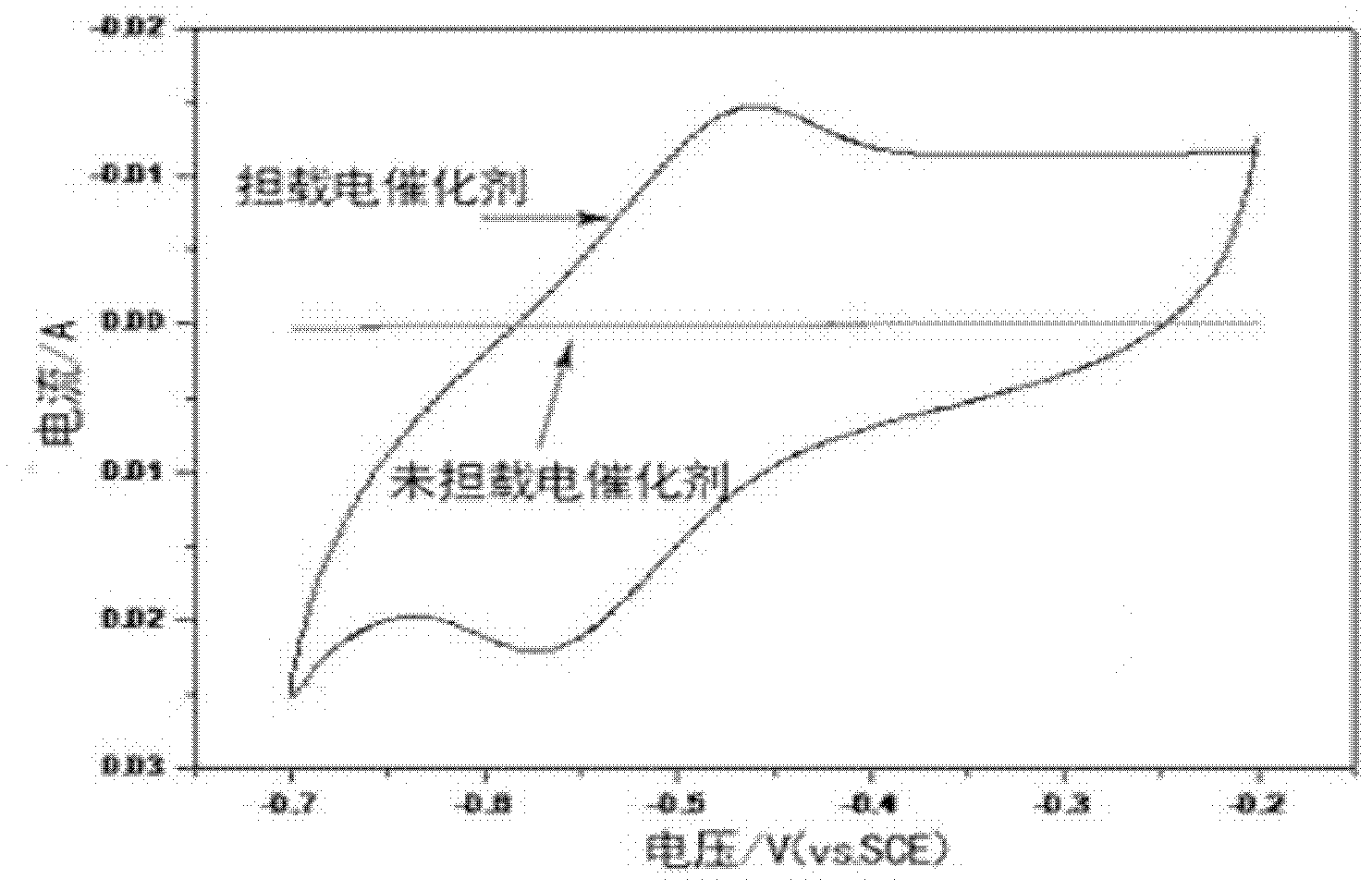
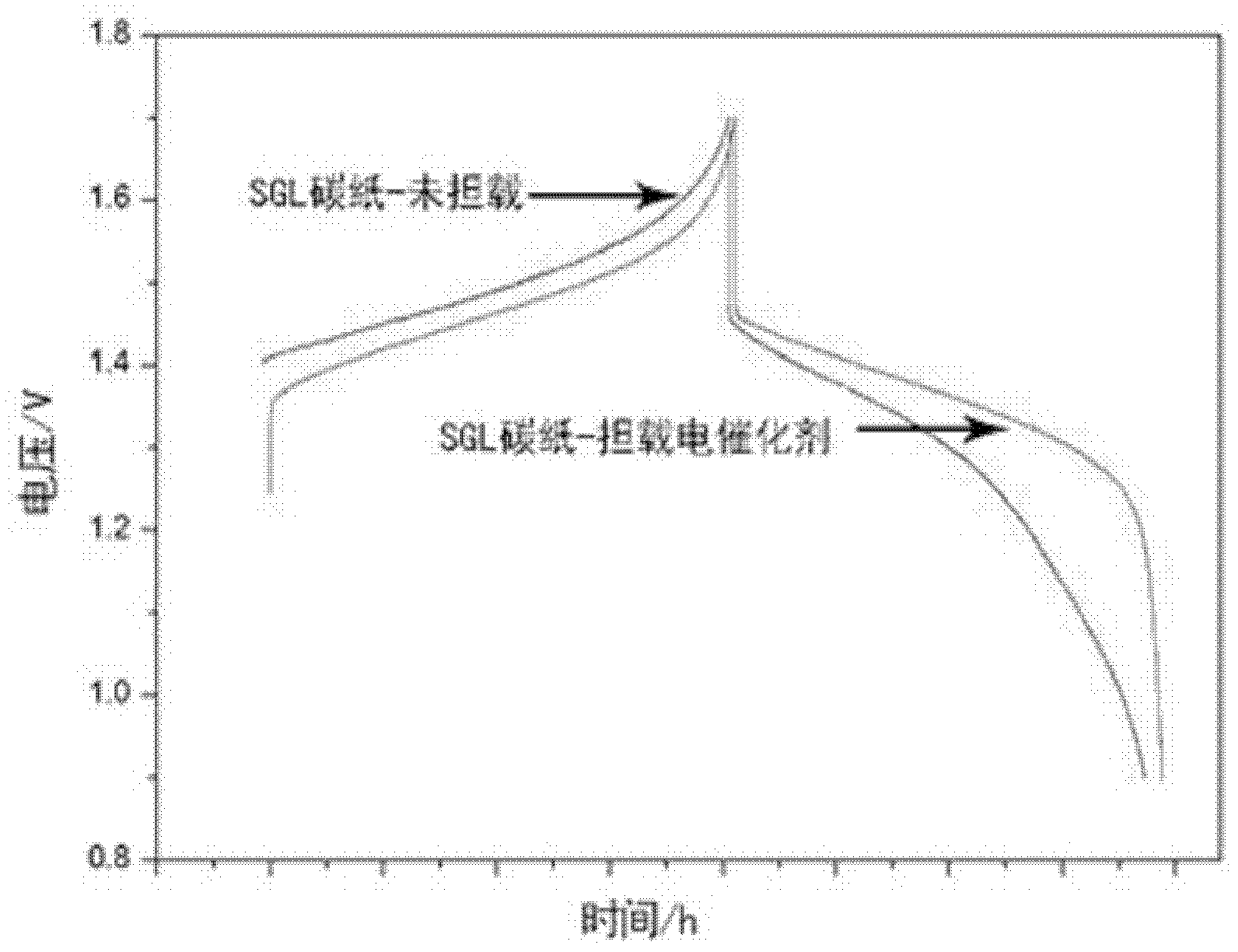
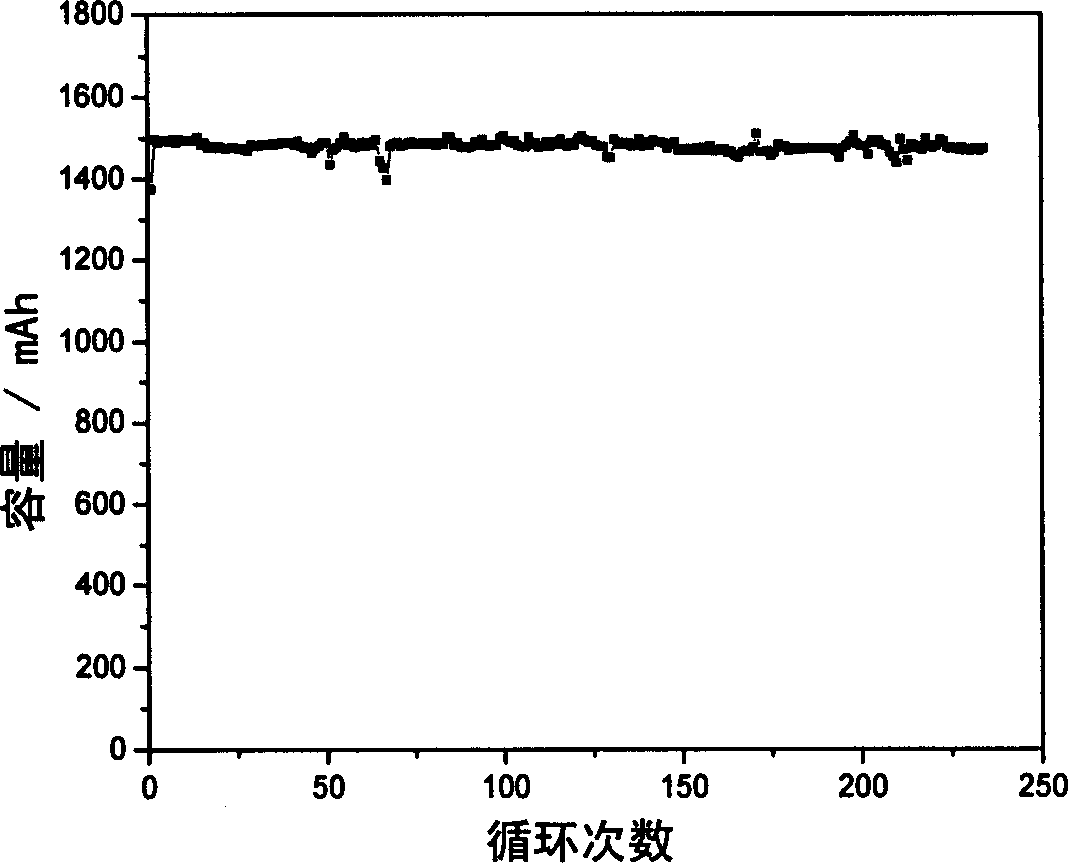
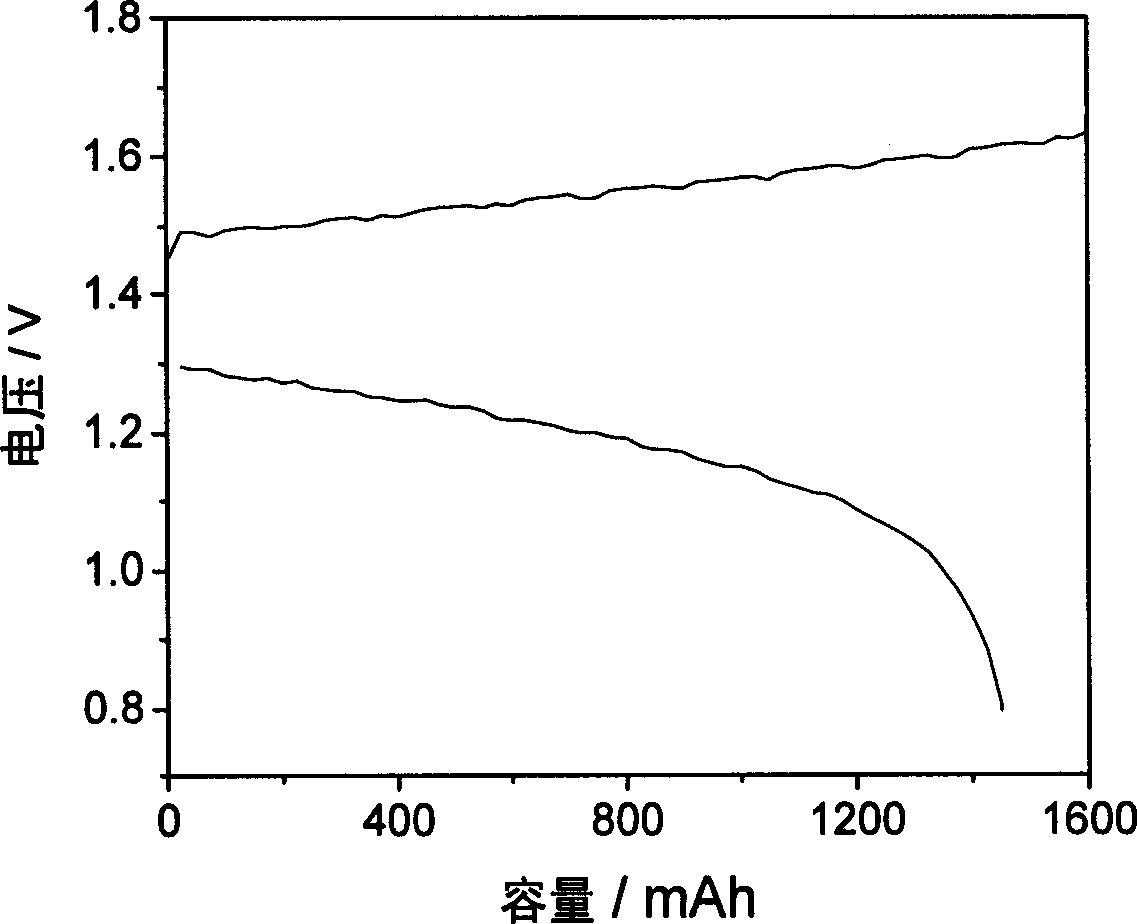
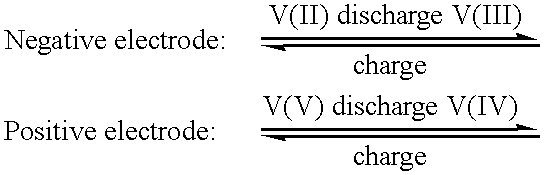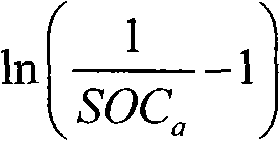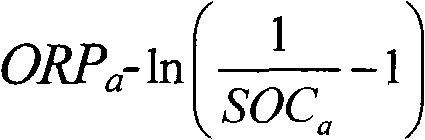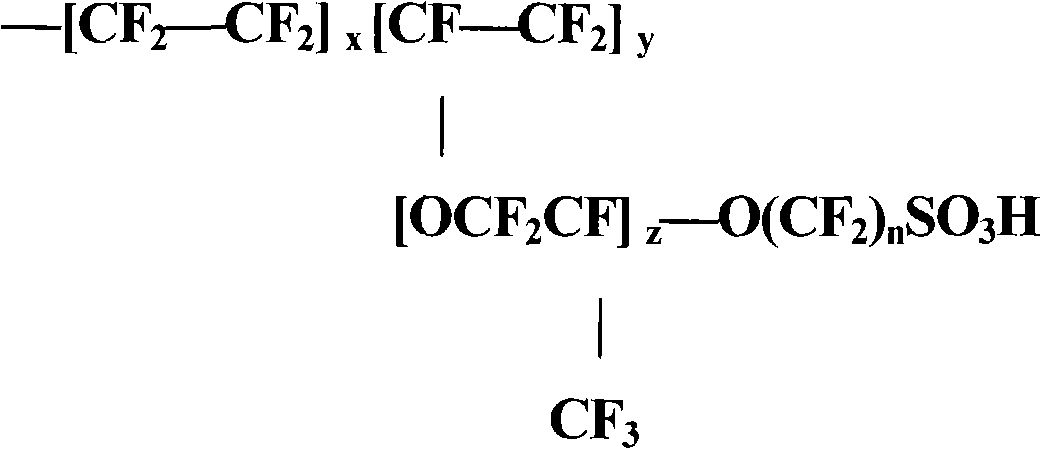Patents
Literature
215 results about "Vanadium redox battery" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The vanadium redox battery (VRB), also known as the vanadium flow battery (VFB) or vanadium redox flow battery (VRFB), is a type of rechargeable flow battery that employs vanadium ions in different oxidation states to store chemical potential energy. The vanadium redox battery exploits the ability of vanadium to exist in solution in four different oxidation states, and uses this property to make a battery that has just one electroactive element instead of two. For several reasons, including their relative bulkiness, most vanadium batteries are currently used for grid energy storage, i.e., attached to power plants or electrical grids.
High energy density vanadium electrolyte solutions, methods of preparation thereof and all-vanadium redox cells and batteries containing high energy vanadium electrolyte solutions
InactiveUS20010028977A1Effective amountEasy to modifyCharging stationsCell electrodesElectricityVanadium redox battery
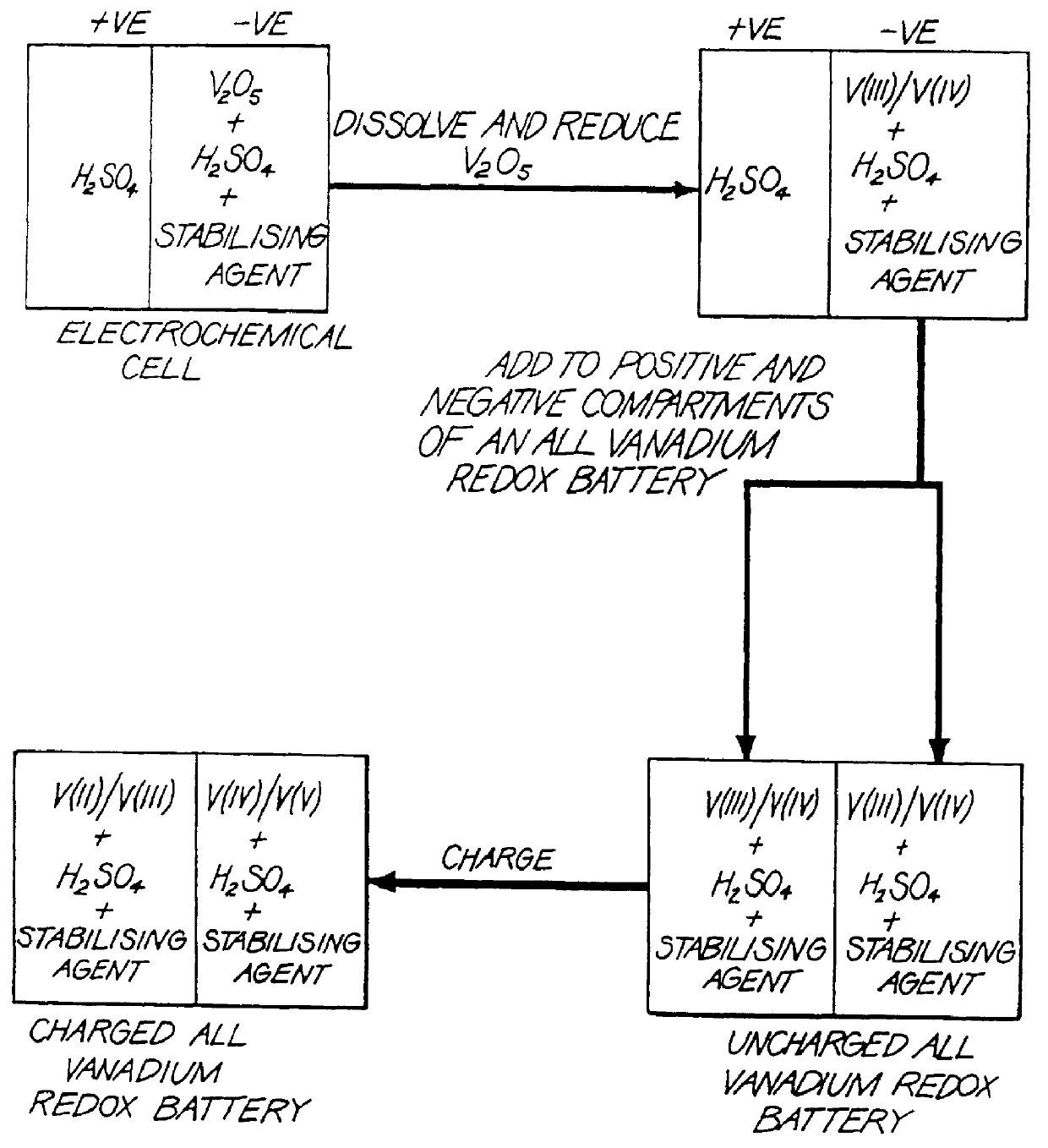
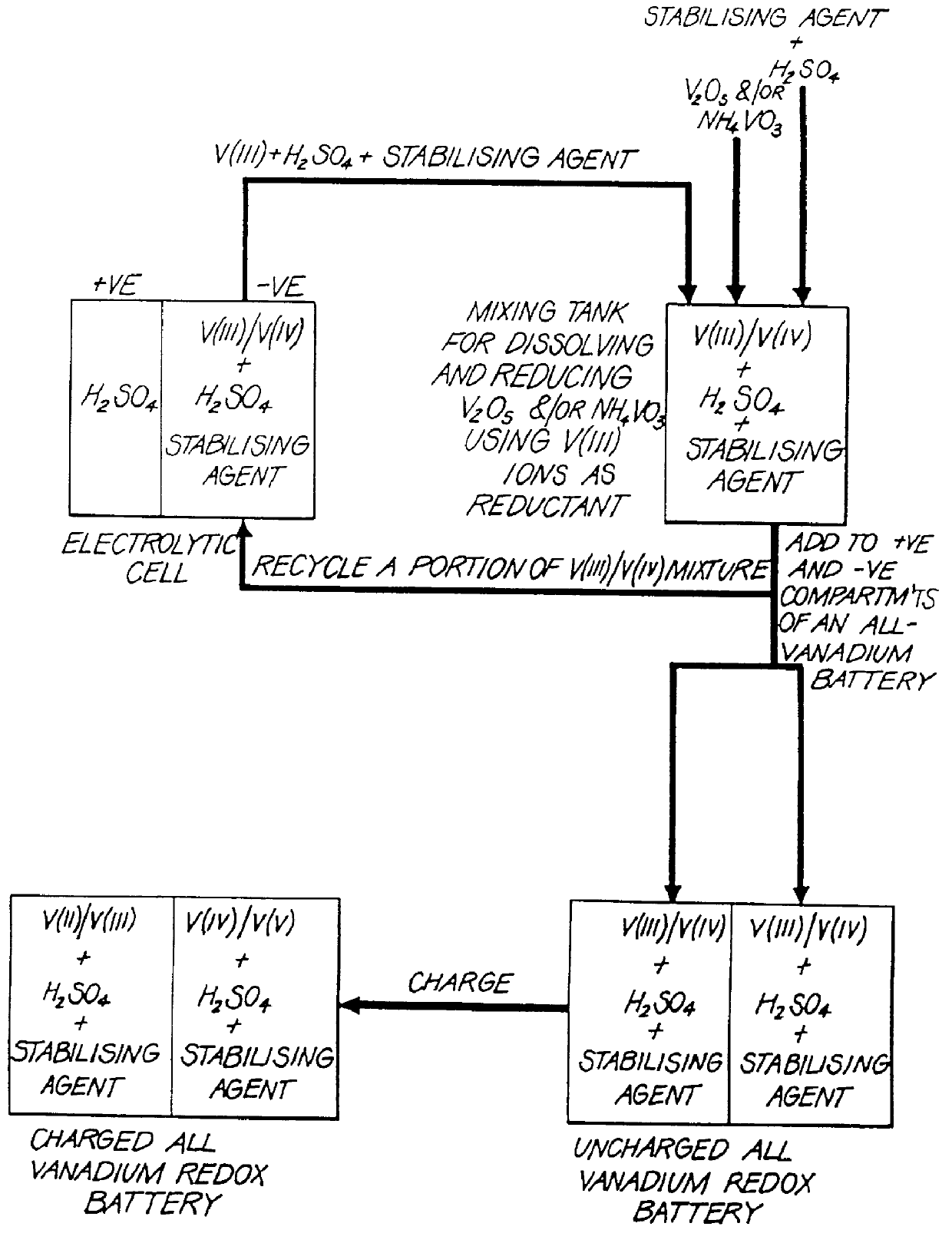
Disclosed is a method for preparing a high energy density (HED) electrolyte solution for use in an all-vanadium redox cells, a high energy density electrolyte solution, in particular an all-vanadium high energy density electrolyte solution, a redox cell, in particular an all-vanadium redox cell, comprising the high energy density electrolyte solution, a redox battery, in particular an all-vanadium redox battery, comprising the HED electrolyte solution, a process for recharging a discharged or partially discharged redox battery, in particular an all-vanadium redox battery, comprising the HED electrolyte solution, a process for the production of electricity from a charged redox battery, and in particular a charged all-vanadium redox battery, comprising the HED electrolyte, a redox battery / fuel cell and a process for the production of electricity from a redox battery / fuel cell. A method for stabilising an electrolyte solution for use in a redox cell, in particular for stabilising an electrolyte solution for use in an all-vanadium redox cell, a stabilised electrolyte solution, in particular an all-vanadium stabilised electrolyte solution, a redox cell, in particular an all-vanadium redox cell, comprising the stabilised electrolyte solution, a redox battery, in particular an all-vanadium redox battery comprising the stabilised electrolyte solution, a process for recharging a discharged or partially discharged redox battery, in particular an all-vanadium redox battery, comprising the stabilised electrolyte solution, and a process for the production of electricity from a charged redox battery, and in particular a charged all-vanadium redox battery, comprising the stabilised electrolyte solution are disclosed. Also disclosed are a redox battery / fuel cell and a process for the production of electricity from a redox battery / fuel cell.
Owner:JD HLDG INC
Stabilized electrolyte solutions, methods of preparation thereof and redox cells and batteries containing stabilized electrolyte solutions
InactiveUS6143443AReduce precipitationEffective amountLead-acid accumulatorsFinal product manufactureVanadium redox batteryFuel cells
Owner:VRB ENERGY INC
High energy density vanadium electrolyte solutions, methods of preparation thereof and all-vanadium redox cells and batteries containing high energy vanadium electrolyte solutions
InactiveUS6468688B2Effective amountEasy to modifyCharging stationsCell electrodesElectricityVanadium redox battery
Disclosed is a method for preparing a high energy density (HED) electrolyte solution for use in an all-vanadium redox cells, a high energy density electrolyte solution, in particular an all-vanadium high energy density electrolyte solution, a redox cell, in particular an all-vanadium redox cell, comprising the high energy density electrolyte solution, a redox battery, in particular an all-vanadium redox battery, comprising the HED electrolyte solution, a process for recharging a discharged or partially discharged redox battery, in particular an all-vanadium redox battery, comprising the HED electrolyte solution, a process for the production of electricity from a charged redox battery, and in particular a charged all-vanadium redox battery, comprising the HED electrolyte, a redox battery / fuel cell and a process for the production of electricity from a redox battery / fuel cell. A method for stabilising an electrolyte solution for use in a redox cell, in particular for stabilising an electrolyte solution for use in an all-vanadium redox cell, a stabilised electrolyte solution, in particular an all-vanadium stabilised electrolyte solution, a redox cell, in particular an all-vanadium redox cell, comprising the stabilised electrolyte solution, a redox battery, in particular an all-vanadium redox battery comprising the stabilised electrolyte solution, a process for recharging a discharged or partially discharged redox battery, in particular an all-vanadium redox battery, comprising the stabilised electrolyte solution, and a process for the production of electricity from a charged redox battery, and in particular a charged all-vanadium redox battery, comprising the stabilised electrolyte solution are disclosed. Also disclosed are a redox battery / fuel cell and a process for the production of electricity from a redox battery / fuel cell.
Owner:JD HLDG INC
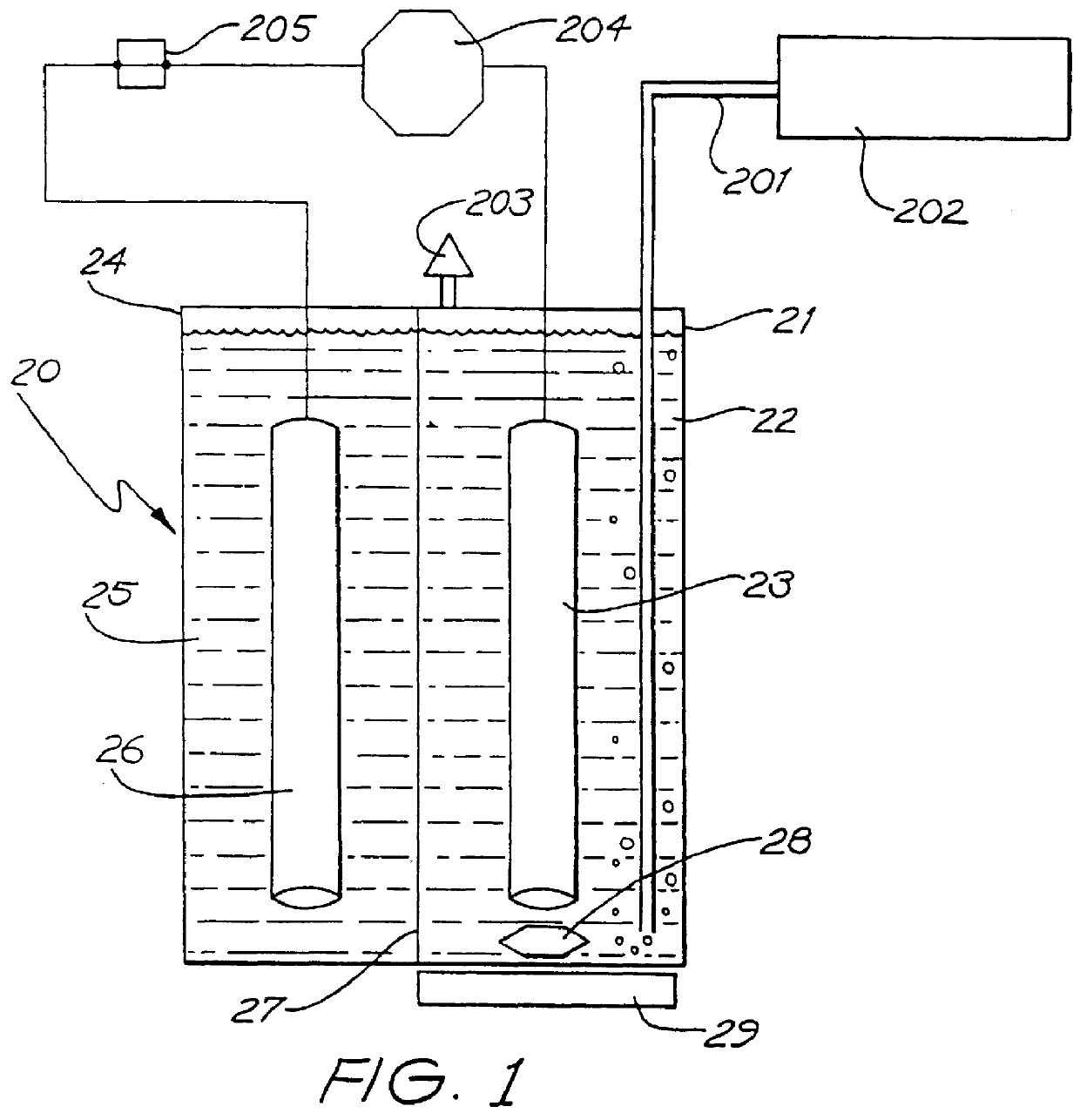
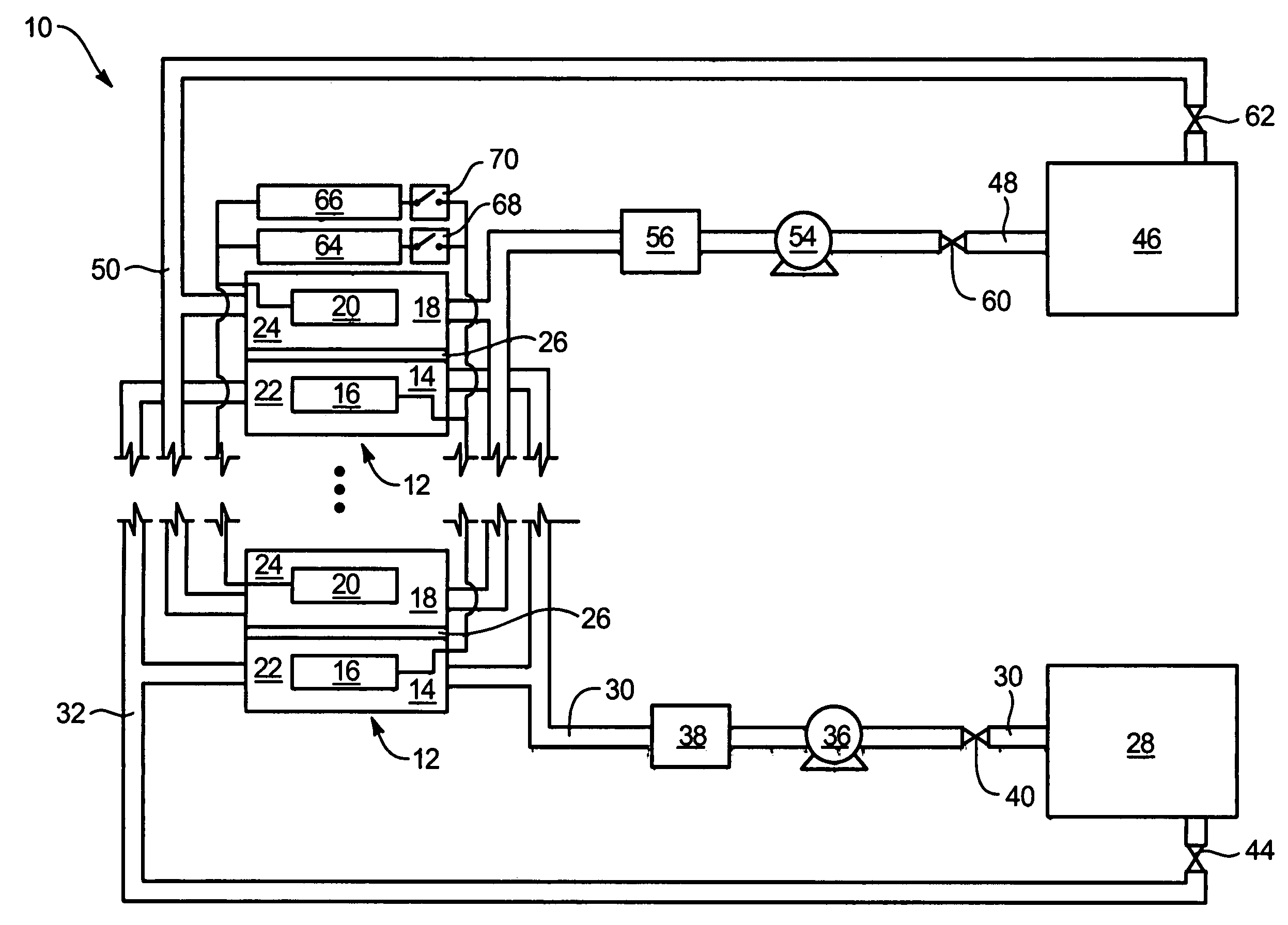
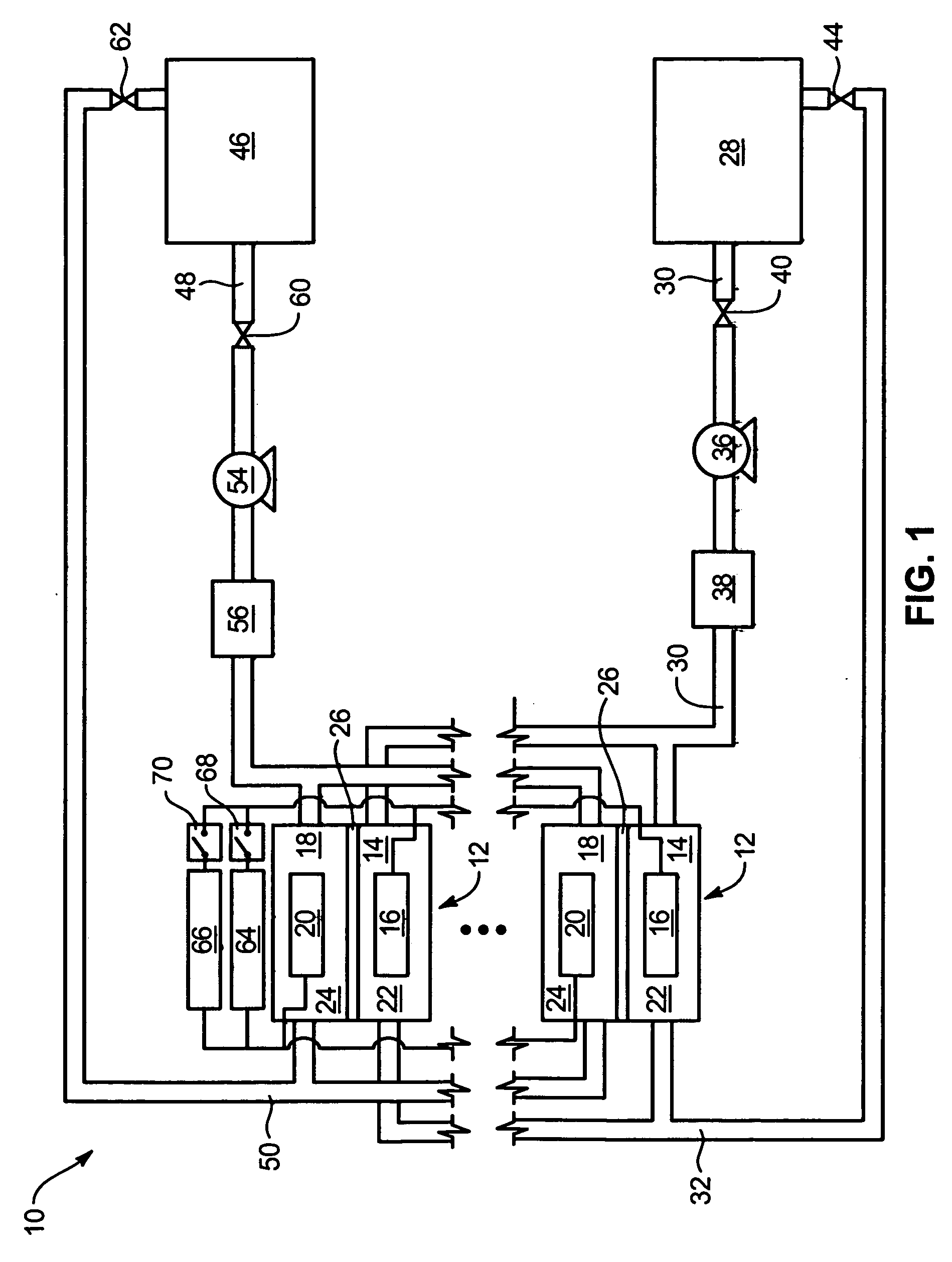
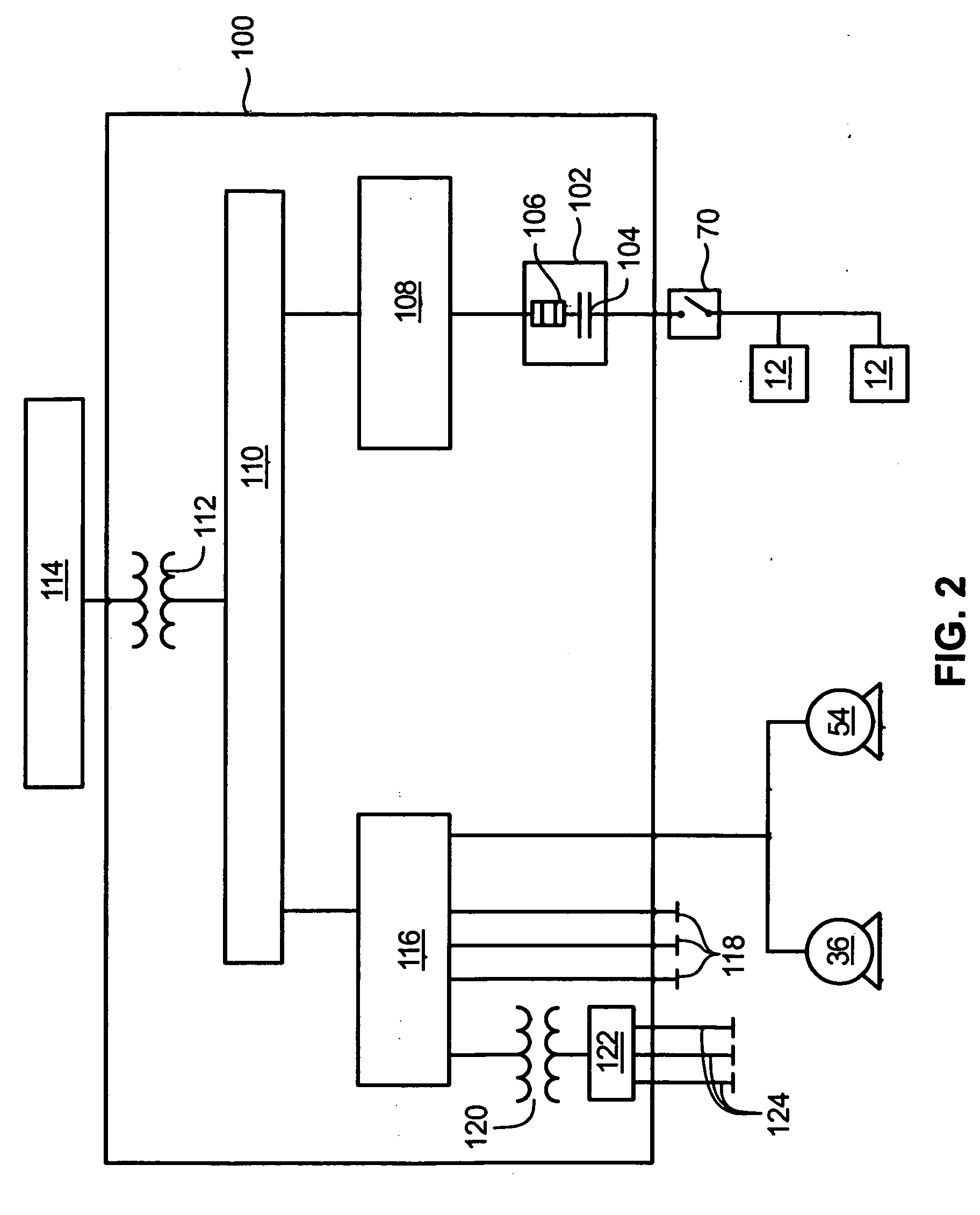
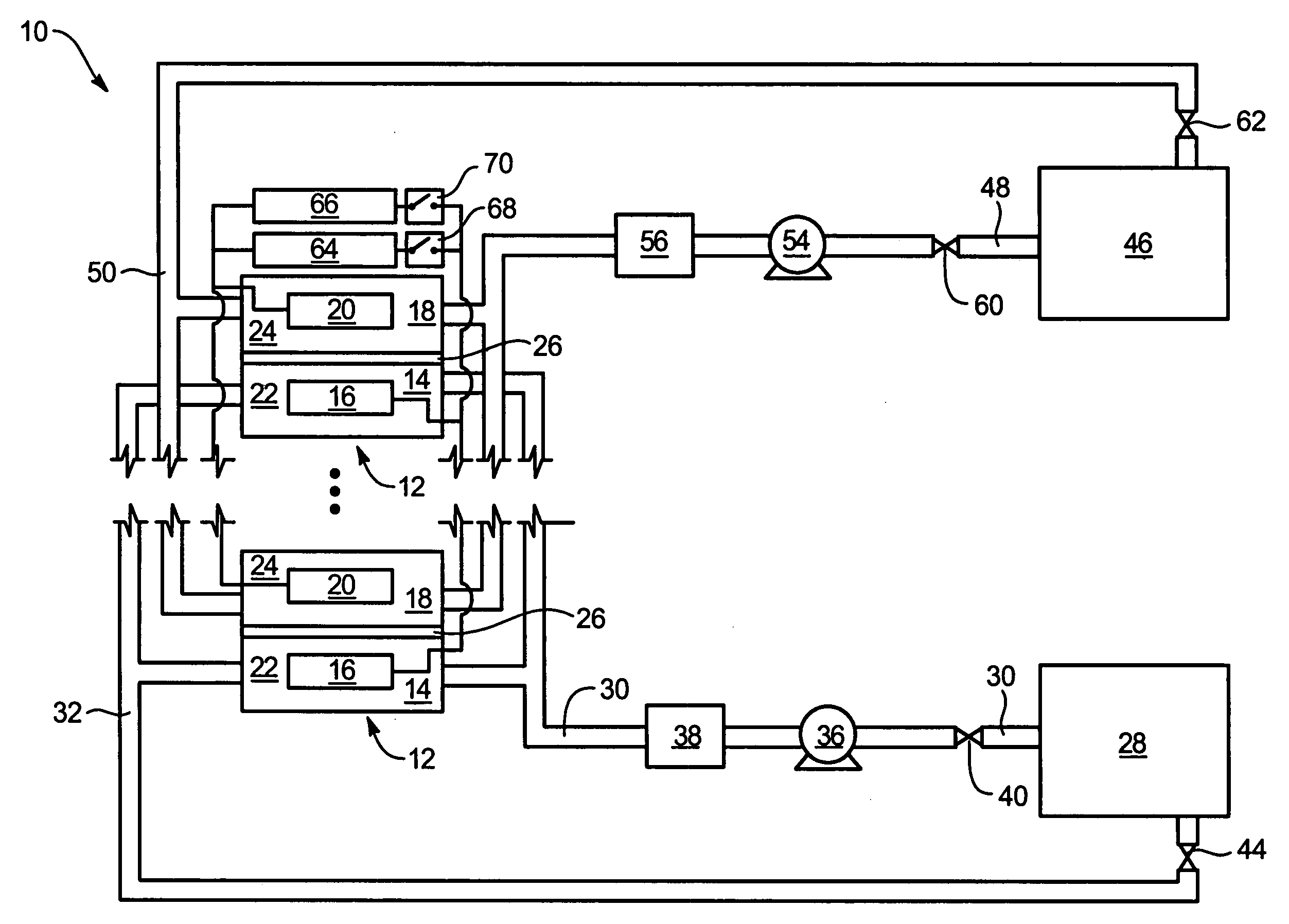
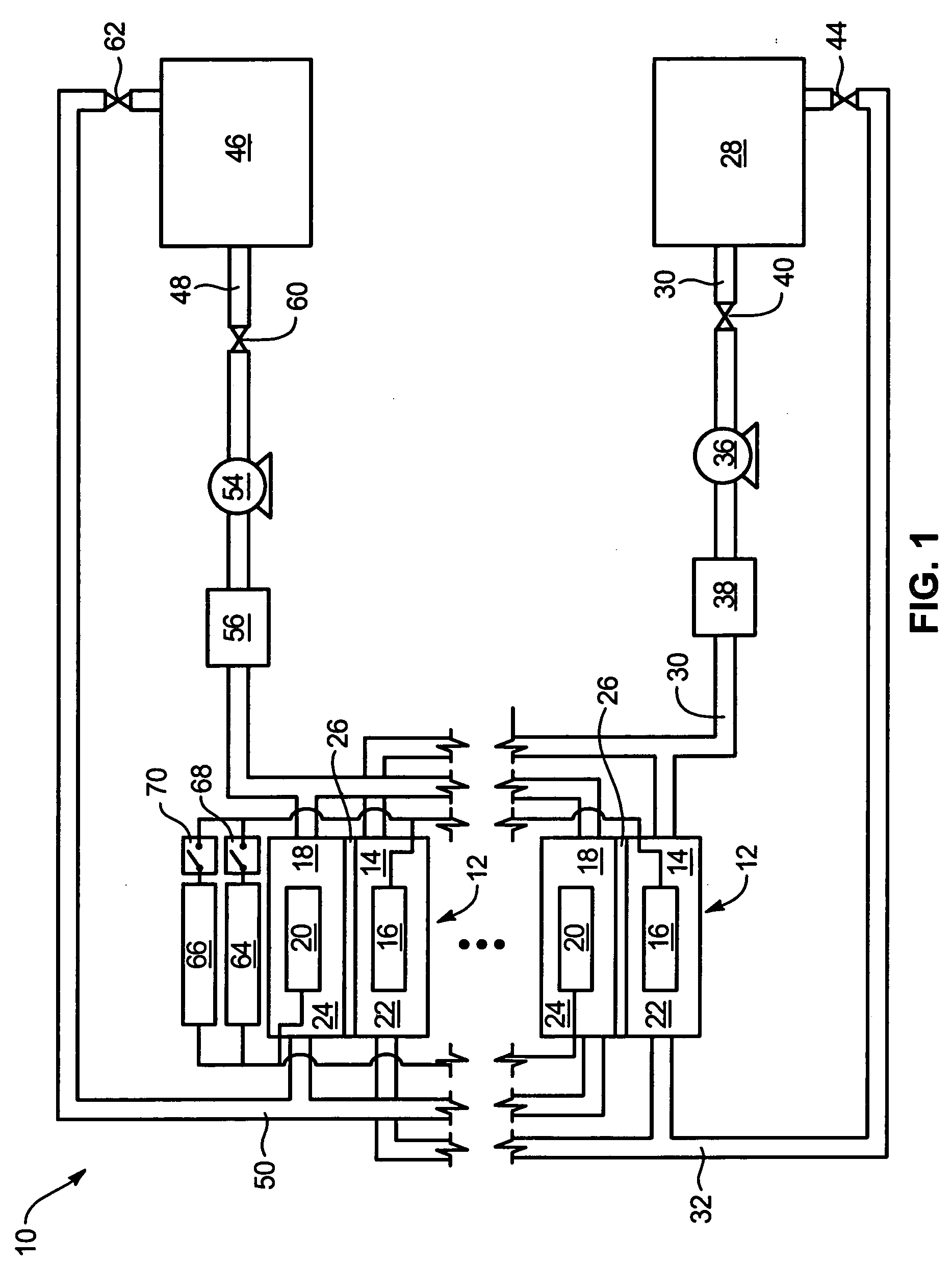
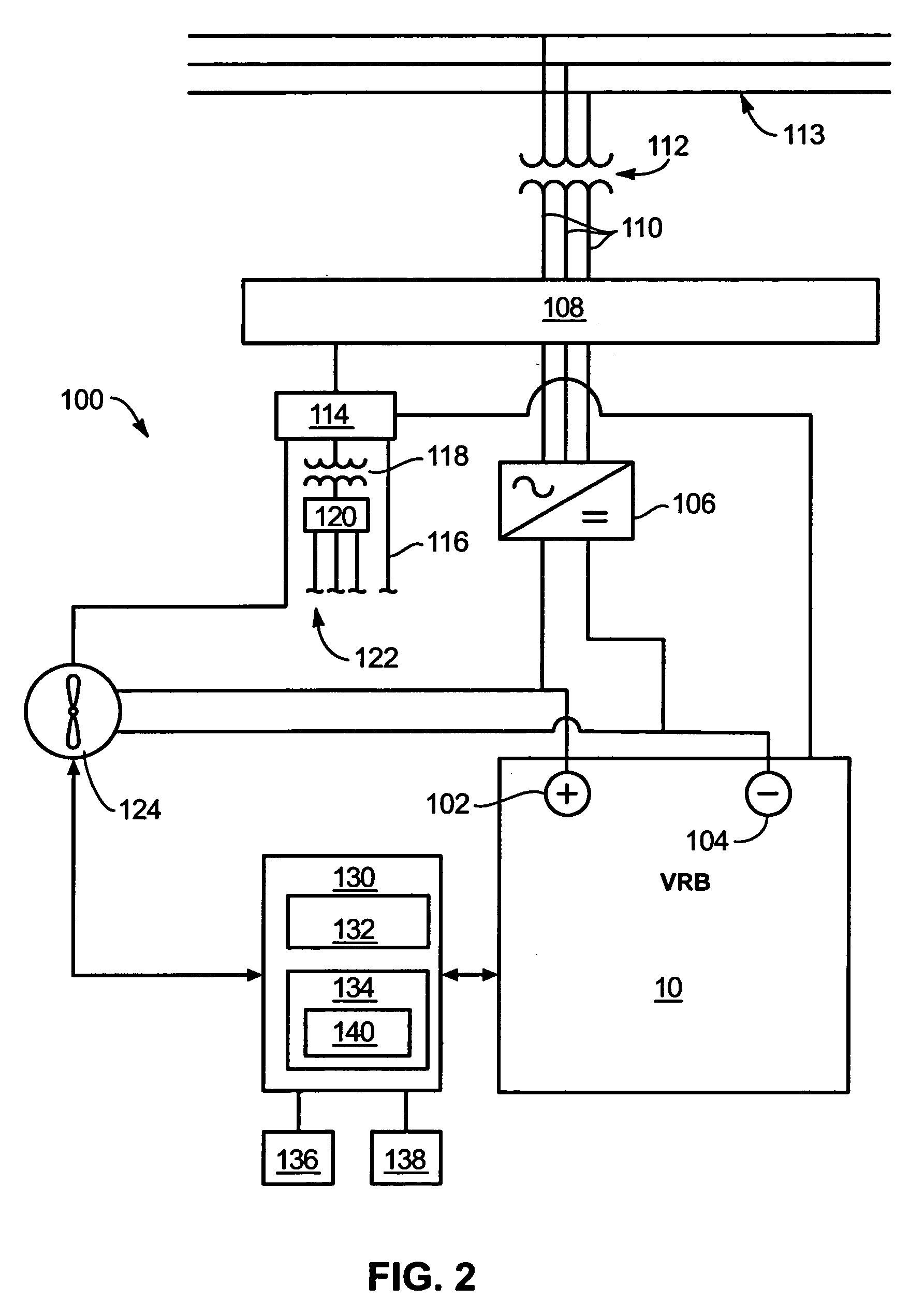
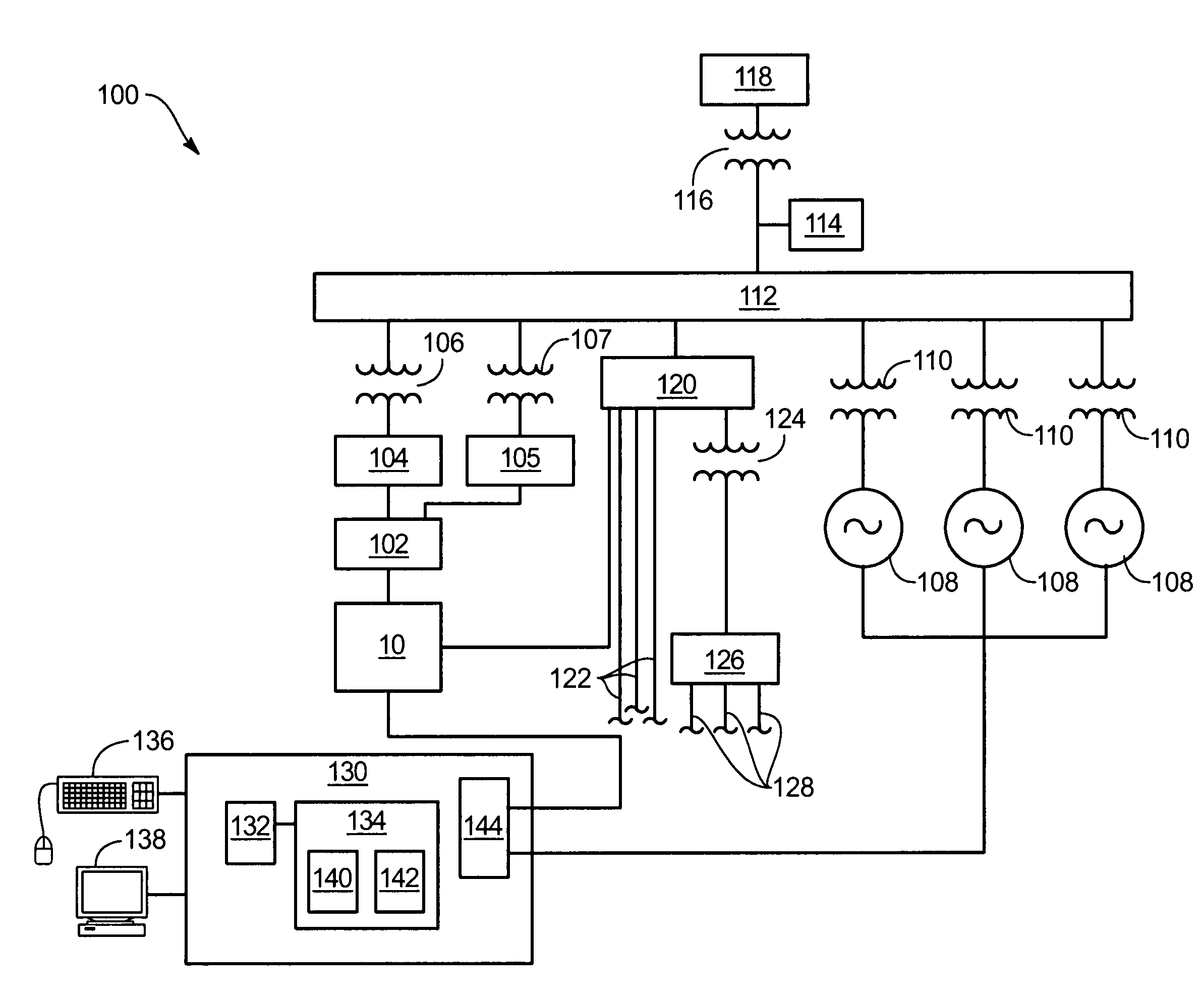
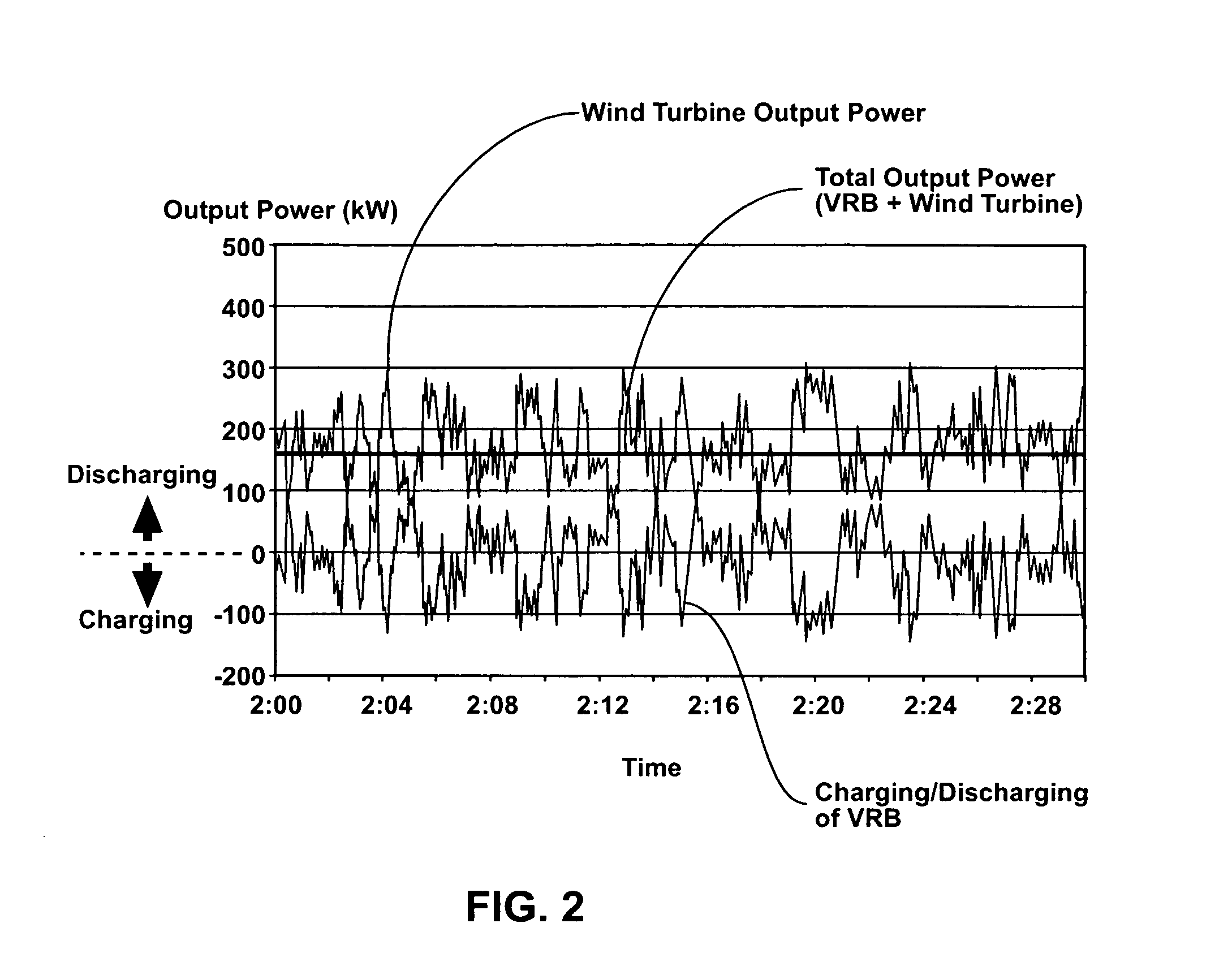
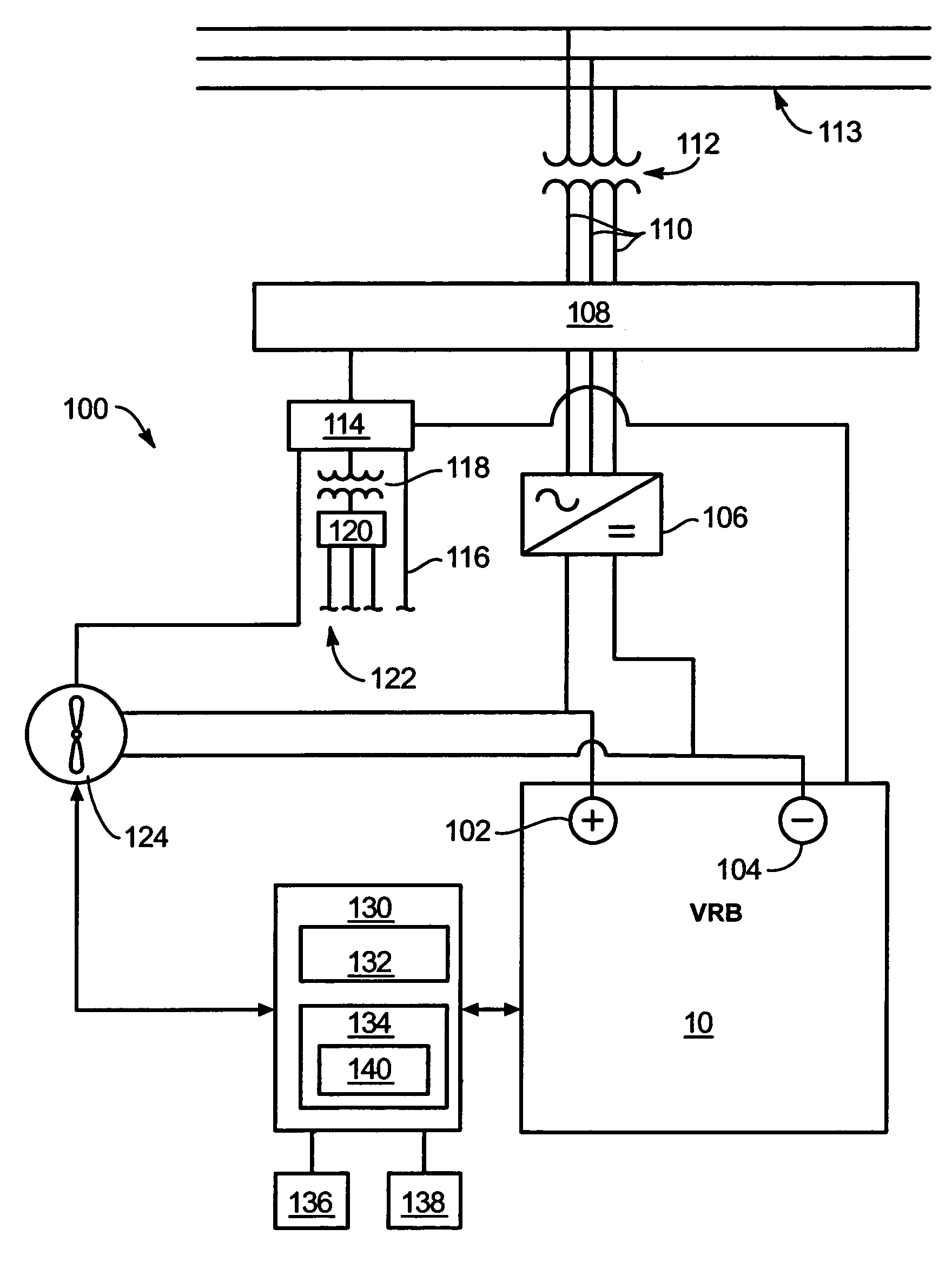
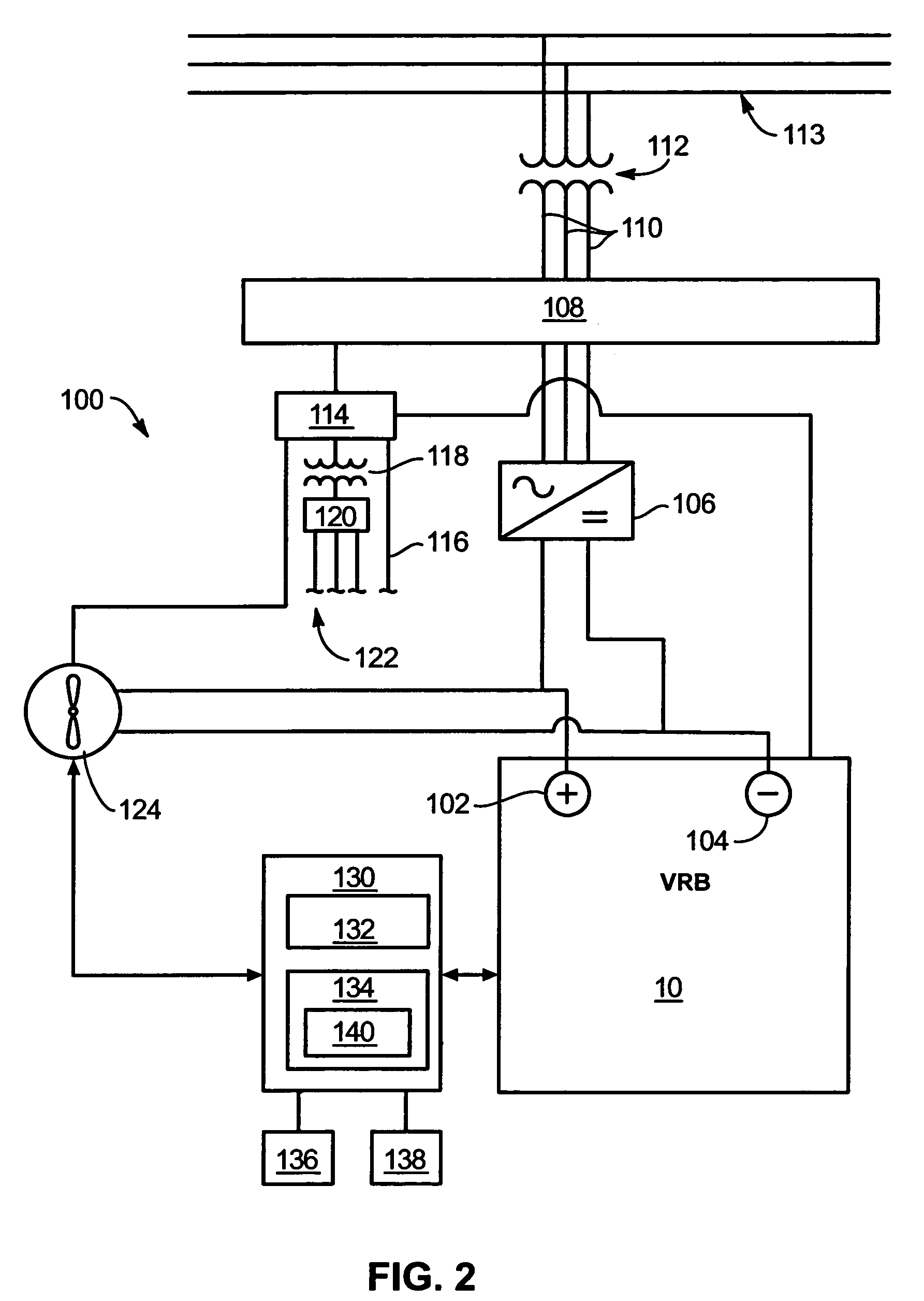
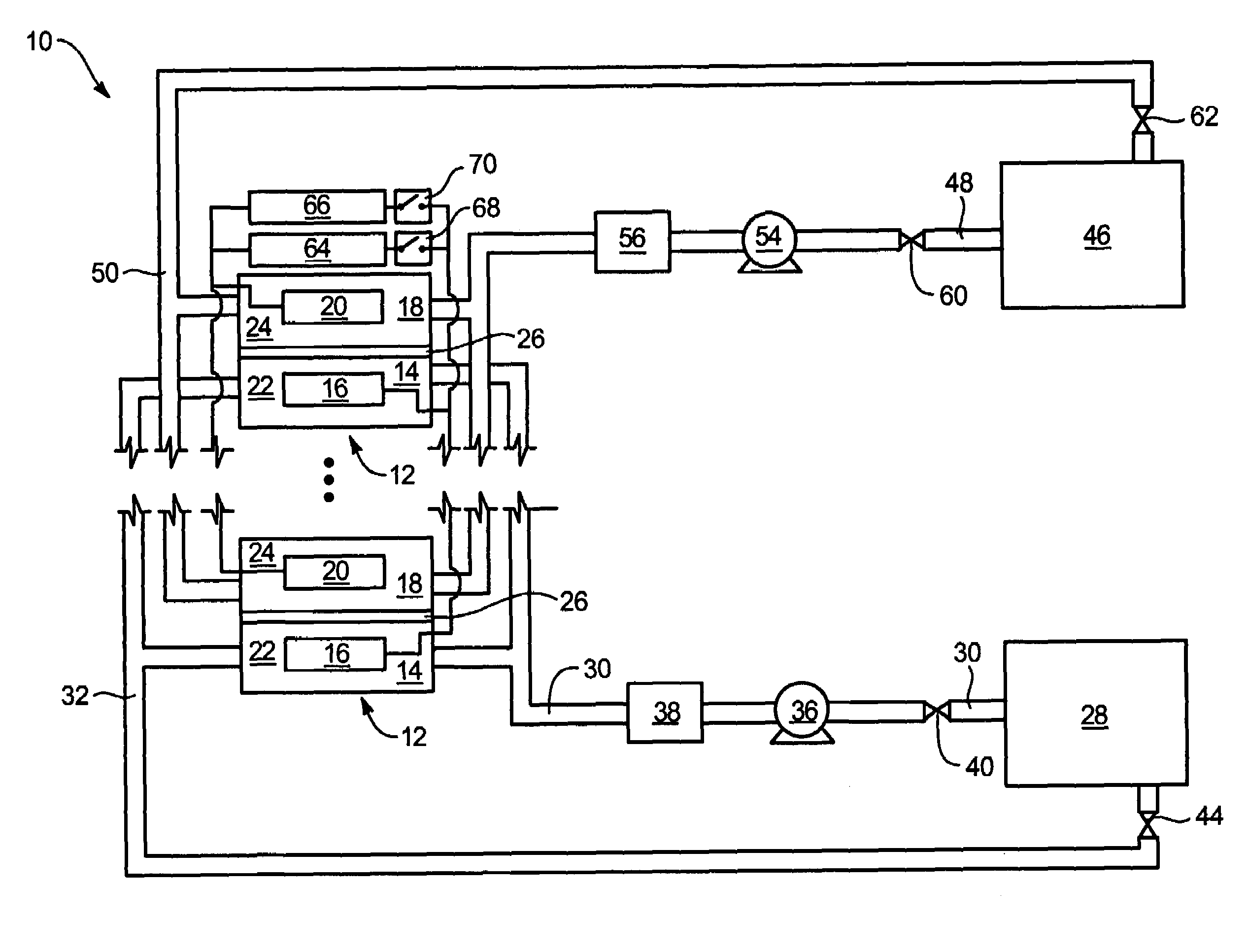
System and method for optimizing efficiency and power output from a vanadium redox battery energy storage system
An energy storage system includes a vanadium redox battery that interfaces with a control system to optimize performance and efficiency. The control system calculates optimal pump speeds, electrolyte temperature ranges, and charge and discharge rates. The control system instructs the vanadium redox battery to operate in accordance with the prescribed parameters. The control system further calculates optimal temperature ranges and charge and discharge rates for the vanadium redox battery.
Owner:VRB ENERGY INC
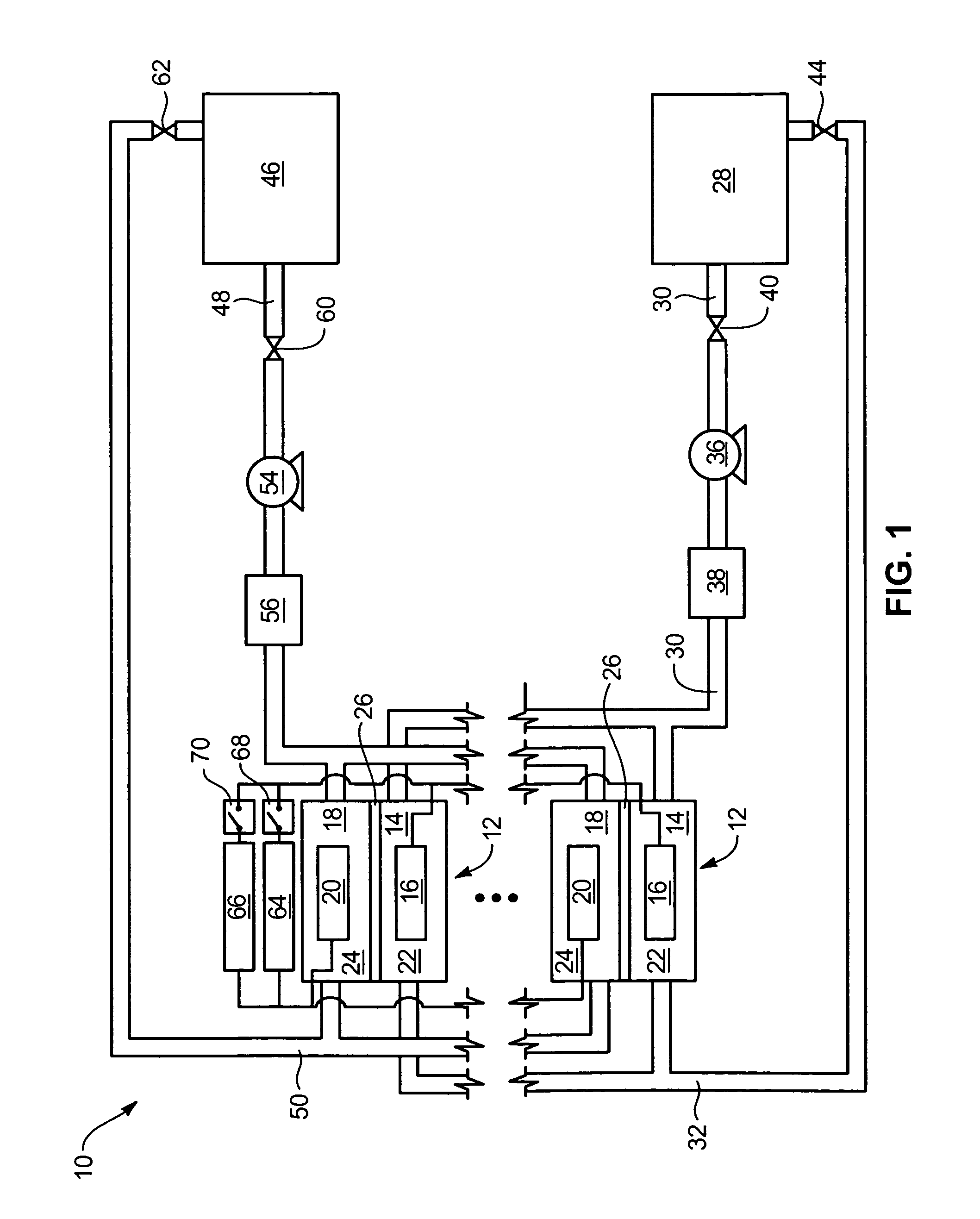
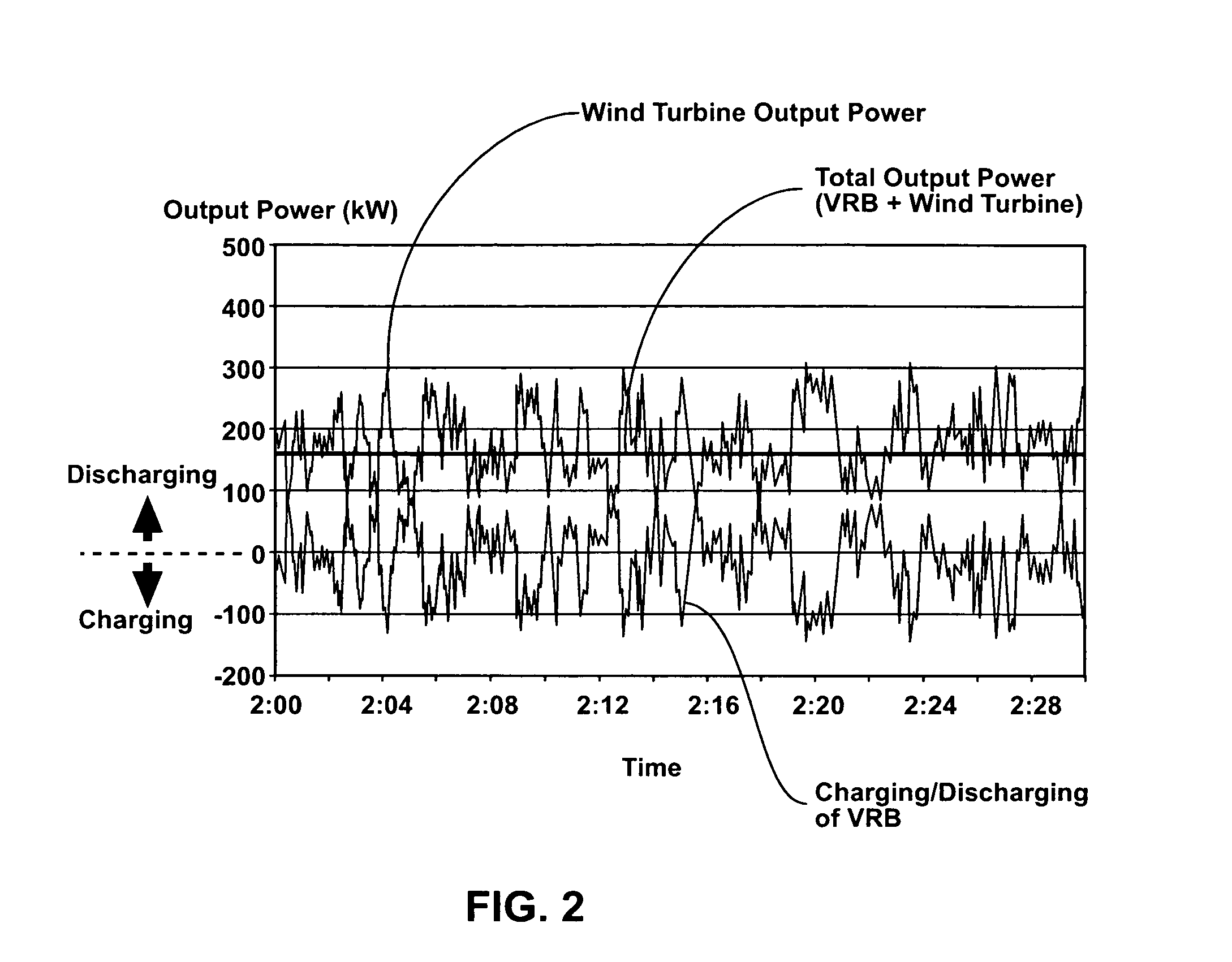
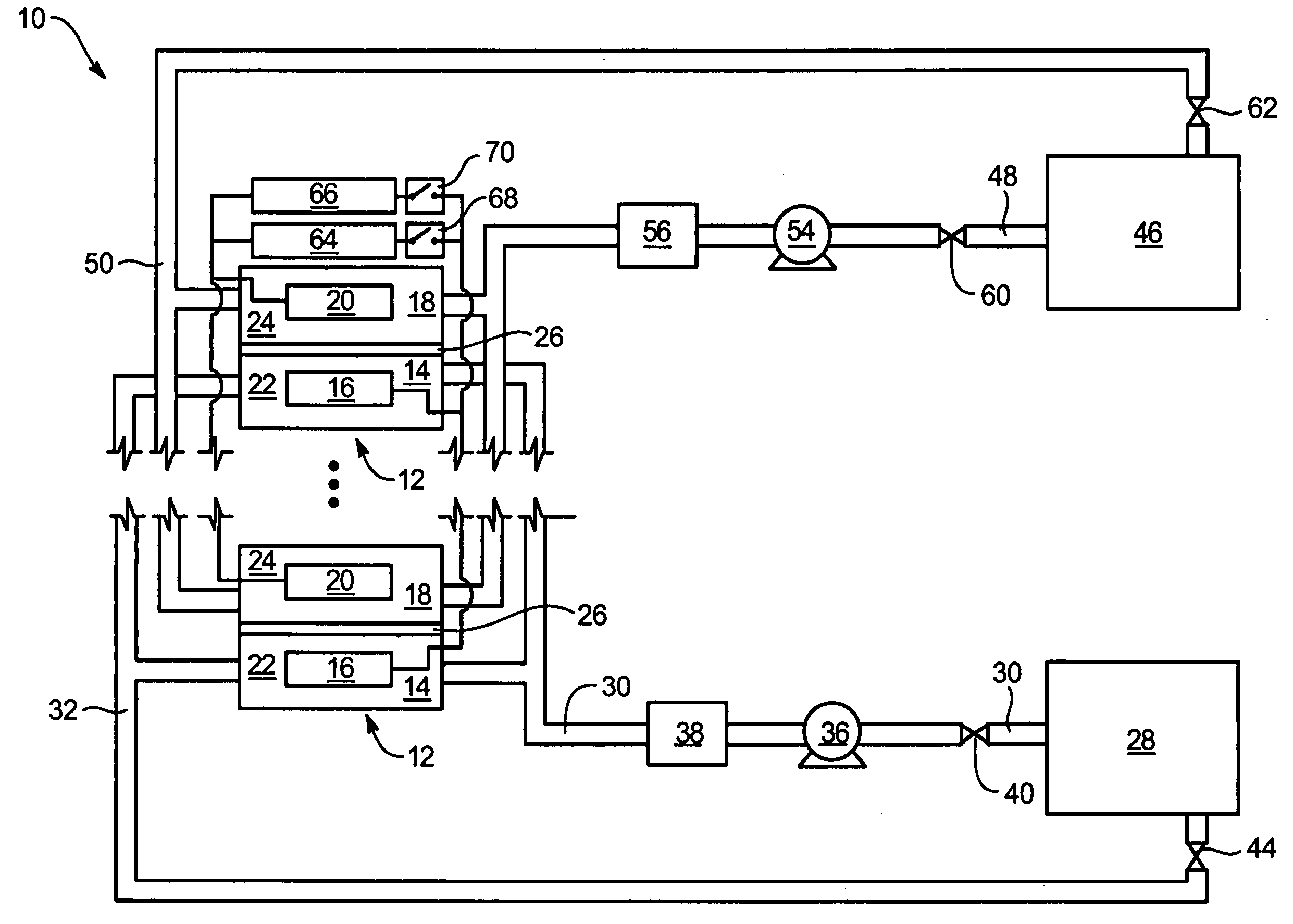
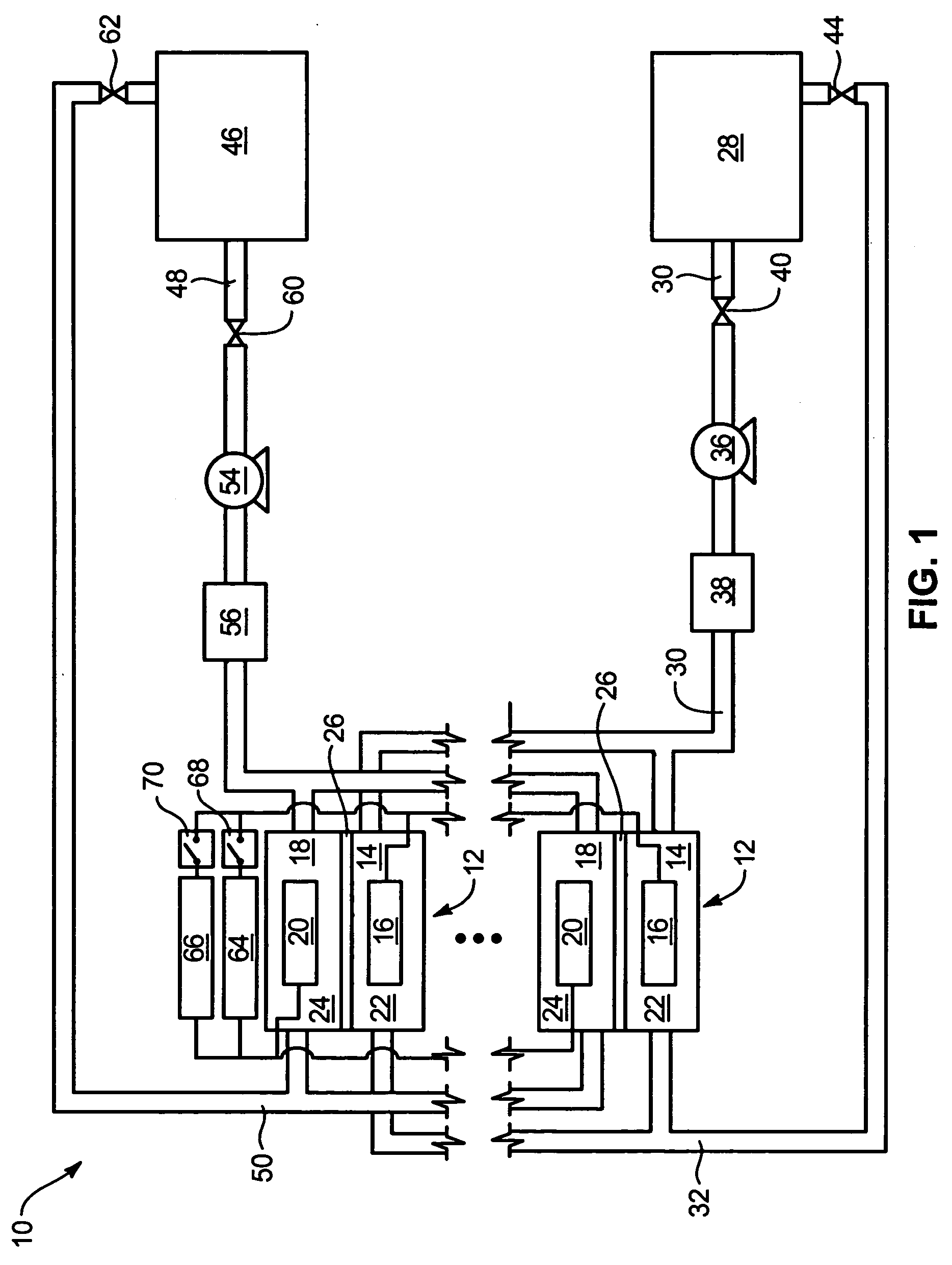
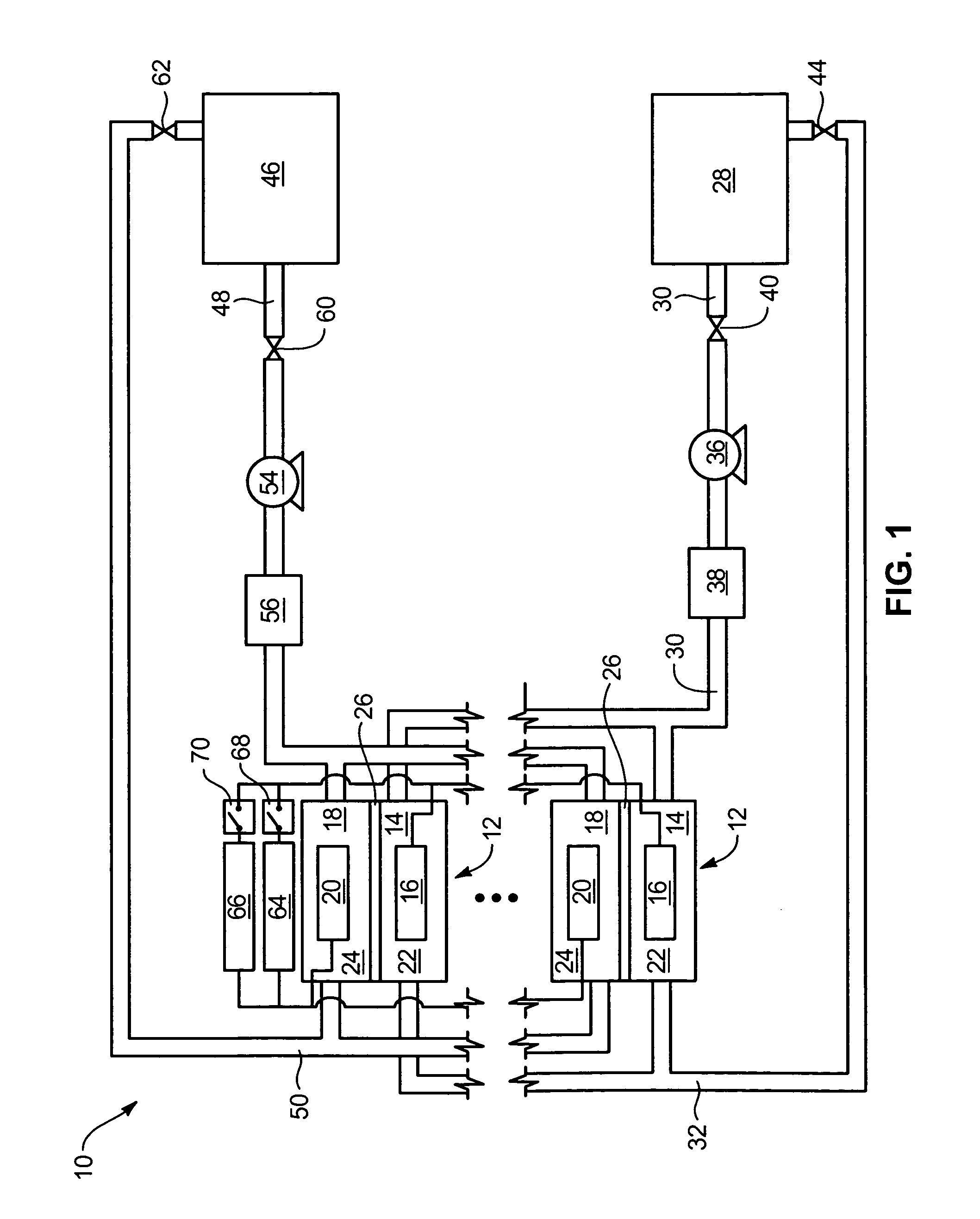
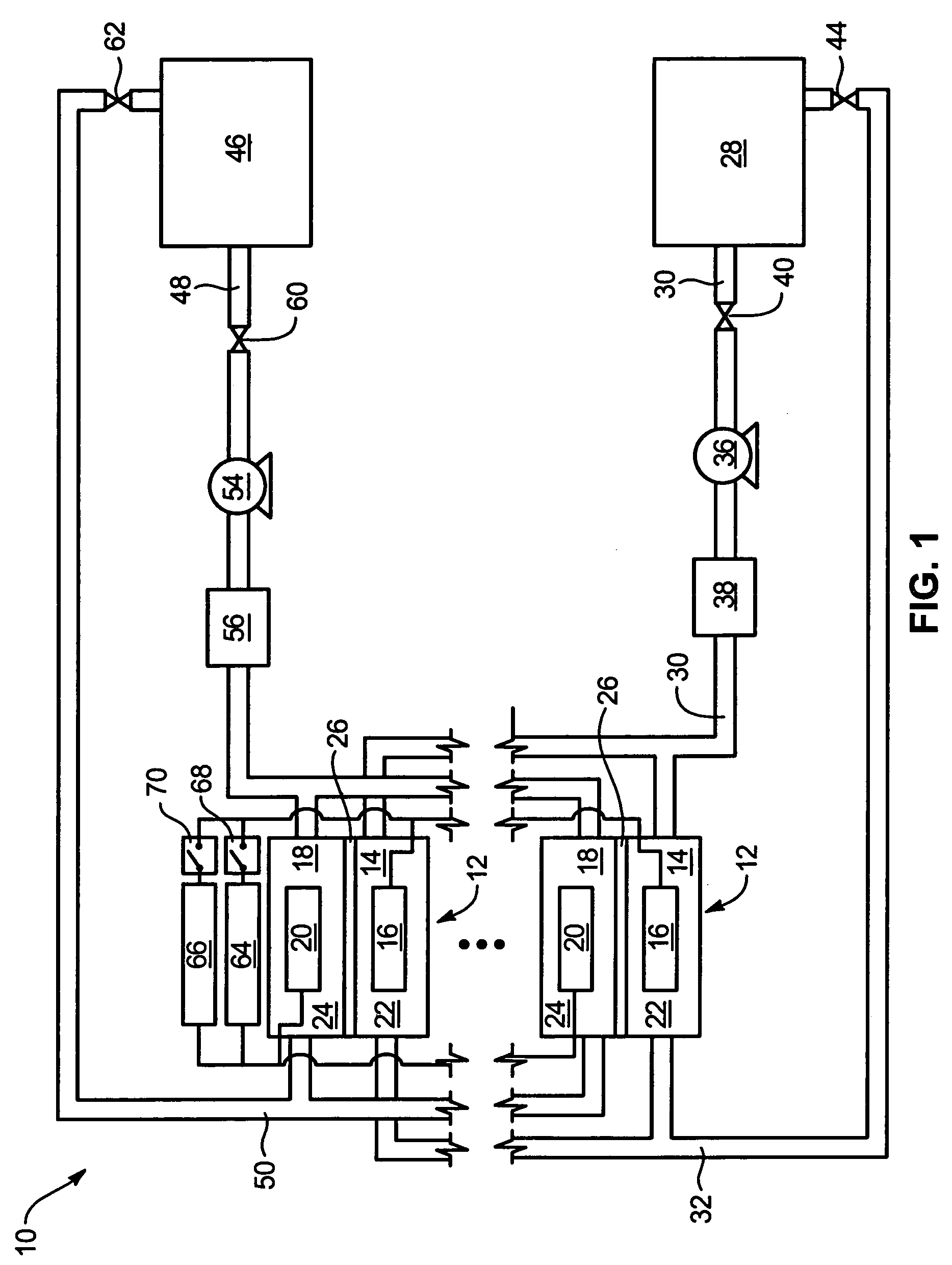
Power generation system incorporating a vanadium redox battery and a direct current wind turbine generator
ActiveUS20050156432A1Batteries circuit arrangementsWind energy with electric storageVanadium redox batteryControl system
A power generation system includes a wind turbine generator and a vanadium redox battery to compensate for fluctuations in wind power. The wind turbine generator provides DC power that may be used to charge the vanadium redox battery. Generated DC power may also be used for power distribution and, if required, supplemented by DC power from the vanadium redox battery. The power generation system interfaces with a control system to optimize performance and efficiency.
Owner:VRB ENERGY INC
Method for retrofitting wind turbine farms
ActiveUS7227275B2Wind energy with electric storageEnergy storageVanadium redox batteryControl system
A power generation system with a predetermined rating limit includes one or more wind turbine generators and a vanadium redox battery. The vanadium redox battery absorbs excess energy to ensure that the rating limit is not exceeded, provide system stability, and improve power generation availability. The power generation system may further include a control system to manage the vanadium redox battery's absorption and power generation to control system stability and system frequency.
Owner:VRB ENERGY INC
Vanadium redox battery energy storage and power generation system incorporating and optimizing diesel engine generators
ActiveUS20050156431A1Batteries circuit arrangementsLevel controlVanadium redox batteryElectrical battery
A power generation system includes a vanadium redox battery that interfaces with a control system to optimize performance and efficiency. The power generation system may include one or more wind turbine generators and one or more diesel fuel generators. The control system manages the vanadium redox battery's absorption and power generation to control system stability and system frequency. The control system further manages the operation of the wind turbine generators and diesel fuel generators to control system stability and voltage.
Owner:VRB ENERGY INC
Methods and apparatus for coupling an energy storage system to a variable energy supply system
ActiveUS20070080666A1Batteries circuit arrangementsSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsVanadium redox batteryElectricity
A method for coupling an energy storage system to a variable energy supply system includes providing an energy storage system including at least one Vanadium redox battery and at least one battery charge controller. The method also includes electrically coupling the at least one battery charge controller to the variable energy supply system such that the at least one battery is configured to supply a substantially consistent energy output during fluctuating energy loads of the energy supply system.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
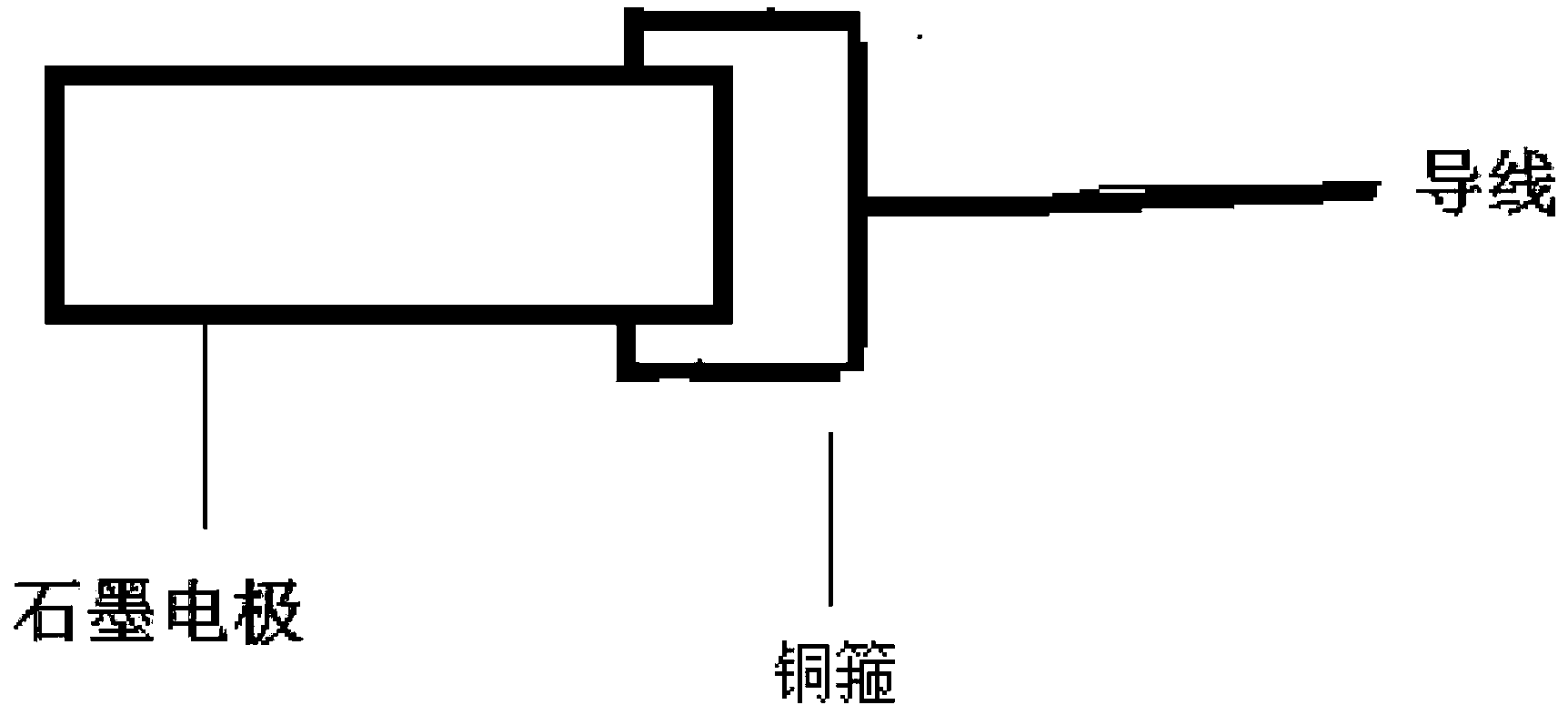
Graphite felt watch surface modified method and modified mineral carbon felt
InactiveCN101182678AImprove wettabilityImprove charge and discharge performanceElectrode manufacturing processesPhysical treatmentFiberVanadium redox battery
The invention relates to a graphite fiber felt surface modification method and a modified graphite fiber felt, and belongs to the all vanadium redox flow battery electrode manufacture technical field. The method step is that the electrochemical cathode modification treatment is conducted before the anode oxidation treatment. When used as an electrode, a modified graphite fiber felt greatly improves the electrochemical activity in the preparation of an all vanadium redox flow battery, promotes the voltage efficiency and the battery energy efficiency during the battery discharging, and increases the stable discharging time, so the recharging and discharging performance of the all vanadium redox flow battery is greatly improved. Moreover, the method is easy for implantation and low in the cost. No particular devices are required. The invention provides a good-performance electrode material for the battery manufacture field.
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON & STEEL RES INST OF PANGANG GROUP +1
Method for retrofitting wind turbine farms
ActiveUS20060171086A1Wind energy with electric storageEnergy storageVanadium redox batteryControl system
A power generation system with a predetermined rating limit includes one or more wind turbine generators and a vanadium redox battery. The vanadium redox battery absorbs excess energy to ensure that the rating limit is not exceeded, provide system stability, and improve power generation availability. The power generation system may further include a control system to manage the vanadium redox battery's absorption and power generation to control system stability and system frequency.
Owner:VRB ENERGY INC
Power generation system incorporating a vanadium redox battery and a direct current wind turbine generator
A power generation system includes a wind turbine generator and a vanadium redox battery to compensate for fluctuations in wind power. The wind turbine generator provides DC power that may be used to charge the vanadium redox battery. Generated DC power may also be used for power distribution and, if required, supplemented by DC power from the vanadium redox battery. The power generation system interfaces with a control system to optimize performance and efficiency.
Owner:VRB ENERGY INC
Preparation method of metal-organic framework material/polymer composite proton exchange membrane
ActiveCN105789668AStrong penetrating powerImprove performanceRegenerative fuel cellsVanadium redox batteryMetal-organic framework
The invention relates to a preparation method of a metal-organic framework material / polymer composite proton exchange membrane. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: dissolving a polymer matrix and a certain amount of metal-organic framework material with an organic solvent and carrying out ultrasonic dispersion to form a uniform membrane liquid; coating the flat and smooth surface of a glass plate with the obtained membrane liquid, and then removing the organic solvent to obtain a composite membrane; and carrying out vacuum drying on the composite membrane for 24 hours to prepare the composite proton exchange membrane for an all-vanadium redox flow battery. The composite proton exchange membrane is smooth in surface; the internal structure of the membrane is regular; the membrane is uniform in thickness and free of a defect; and the thickness is 10-300 microns. The composite proton exchange membrane provided by the invention has excellent vanadium ion permeation blocking ability, keeps excellent proton transfer performance, overcomes the defect of relatively high vanadium ion permeability of an existing all-vanadium redox flow battery membrane, and has the advantages of being simple in preparation process, high in proton transmittance, excellent in vanadium blocking property, excellent in oxidative resistance, easy to industrially amplify and the like.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Vanadium redox battery electrolyte
InactiveUS20040241552A1Loss in Coulombic efficiencyEvolution of hydrogen is thereby avoidedTantalum compoundsRegenerative fuel cellsVanadium redox batterySlurry
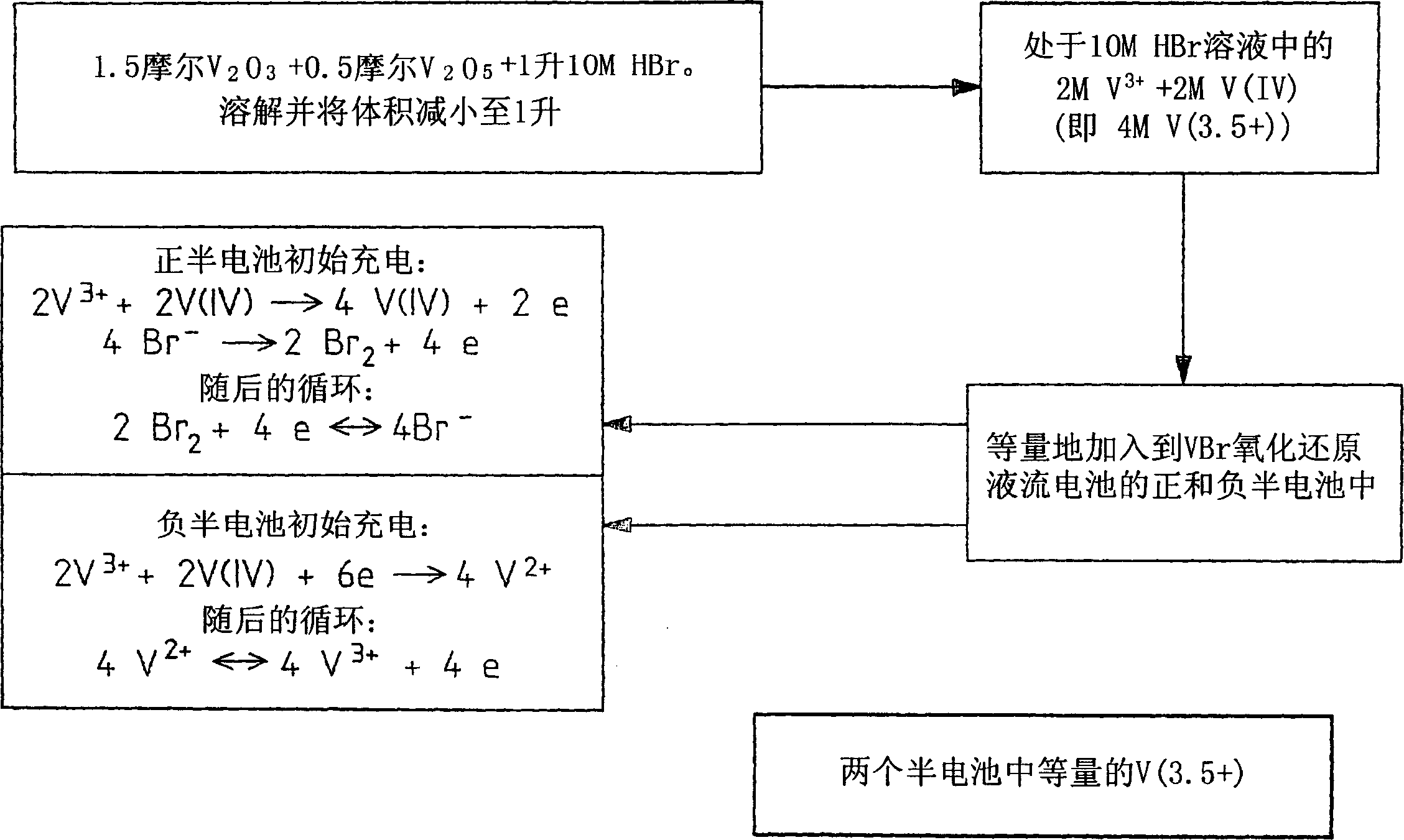
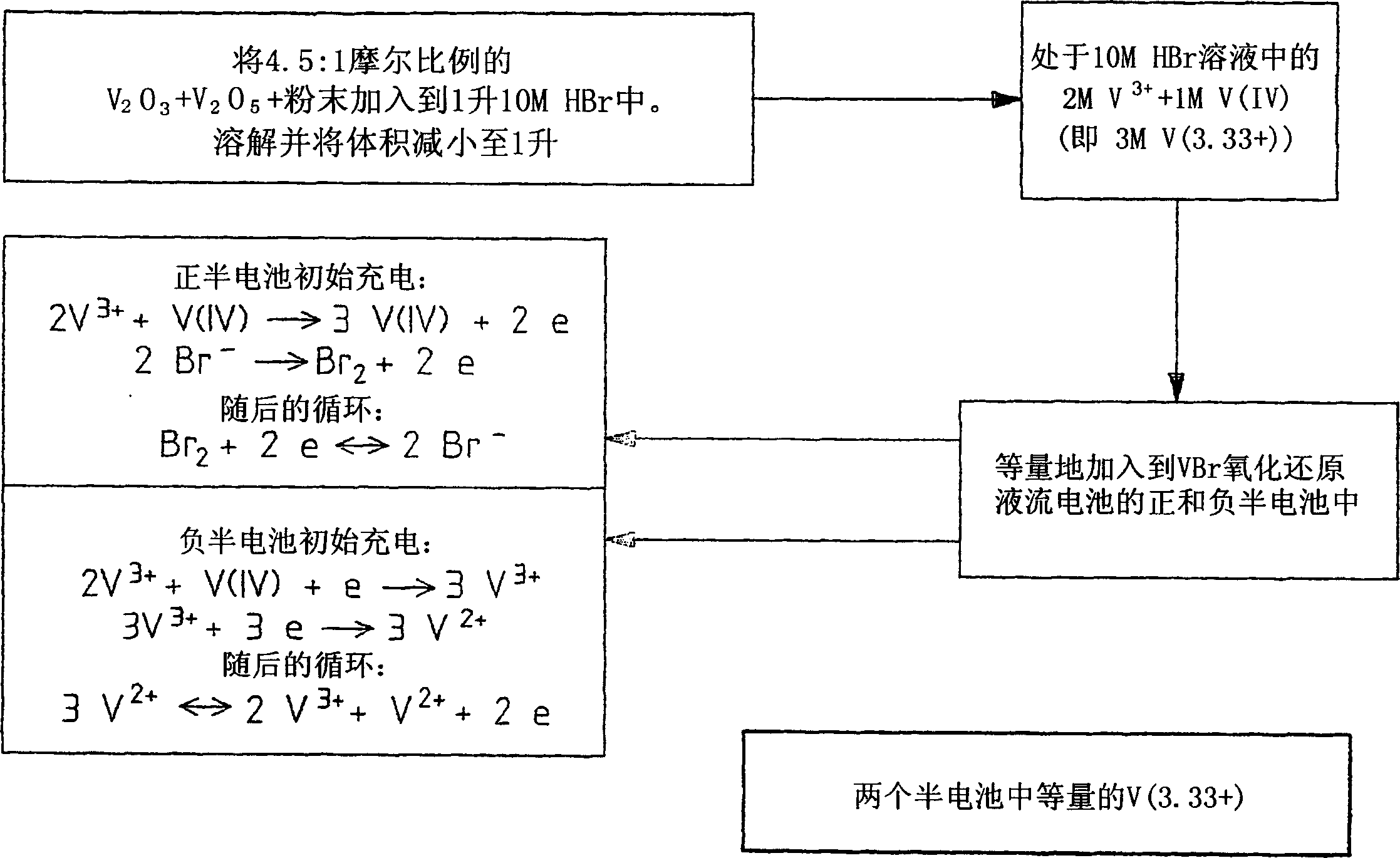
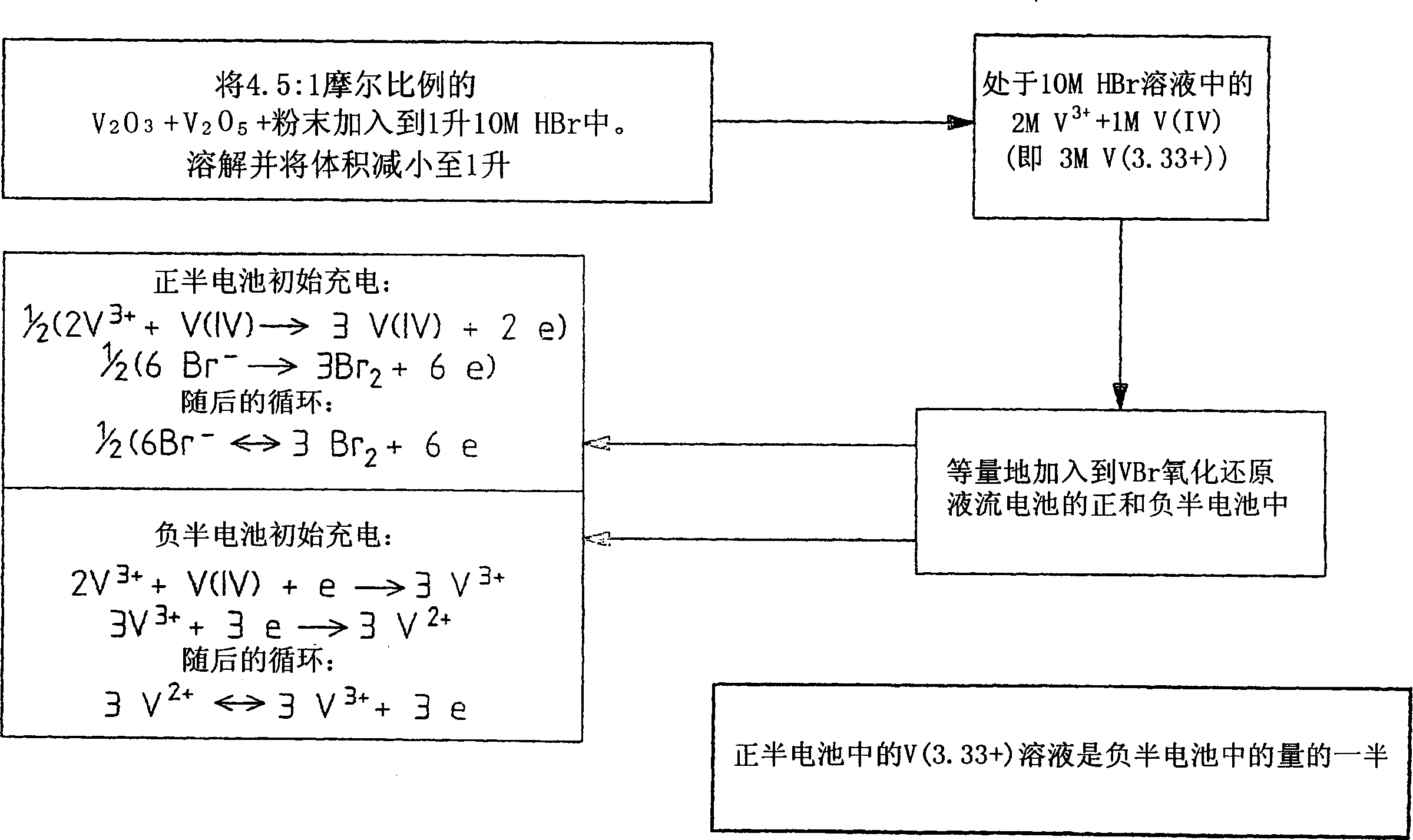
The present invention relates generally to the production of a vanadium electrolyte, including a mixture of trivalent and tetravalent vanadium ions in a sulphuric acid solution, by the reactive dissolution of vanadium trioxide and vanadium pentoxide powders, the surface area and particle size characteristics being controlled for complete reaction to produce the desired ratio of V(III) to V(IV) ions in the solution. The solution may be suitable for direct use in the vanadium redox battery, or the solution can provide an electrolyte concentrate or slurry which can be reconstituted by the addition of water or sulphuric acid prior to use in the vanadium redox battery.
Owner:UNISEARCH LTD
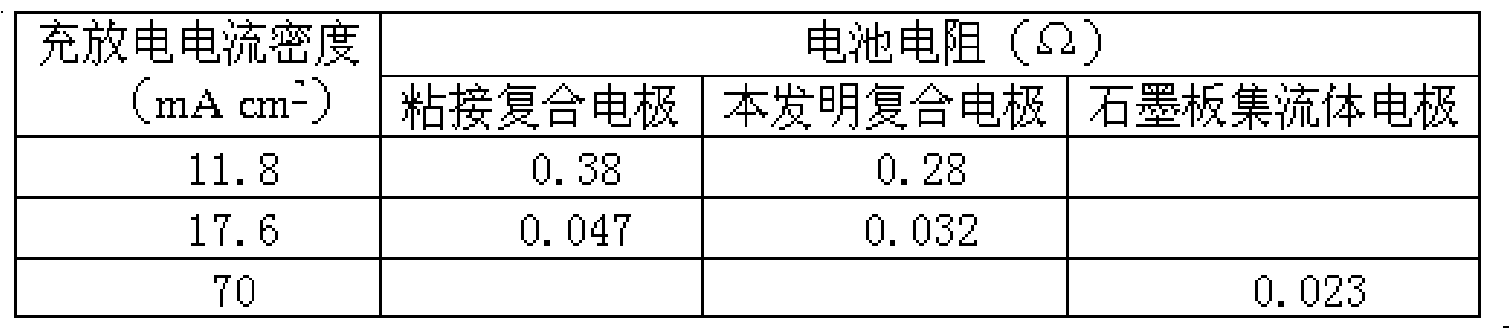
Combination electrode for all vanadium redox flow battery and preparation thereof
InactiveCN101335349AImprove mechanical propertiesImprove conductivityCell electrodesFiberVanadium redox battery
The invention relates to a composite electrode used in vanadium redox flow batteries and a preparation method thereof, pertaining to the vanadium battery manufacturing field. The composite electrode is prepared by adding three conductive fillers (conductive acetylene carbon black, conductive carbon fiber and graphite) into thermoplastic polymer to obtain a thermoplastic conductive plate which is compounded together with a graphite felt. Part of the conductive carbon fiber in the graphite felt is embedded into the surface of the conductive plate to form an interpenetrating conductive network and improve the conductivity of the whole product. Therefore, the composite electrode has excellent mechanical performance and conductivity (volume resistivity is less than or equal to 0.1omega question mark cm), integrates current collector and electrode into a whole, and effectively reduces surface resistance between the current collector and the electrode; meanwhile, during the process, no additional additive which can improve conductivity is used, thus ensuring relatively good conductivity and mechanical performance, and avoiding the falling of the additive which can improve conductivity into the electrolyte of a vanadium battery.
Owner:PANGANG GROUP VANADIUM TITANIUM & RESOURCES +3
Vanadium redox battery energy storage and power generation system incorporating and optimizing diesel engine generators
A power generation system includes a vanadium redox battery that interfaces with a control system to optimize performance and efficiency. The power generation system may include one or more wind turbine generators and one or more diesel fuel generators. The control system manages the vanadium redox battery's absorption and power generation to control system stability and system frequency. The control system further manages the operation of the wind turbine generators and diesel fuel generators to control system stability and voltage.
Owner:VRB ENERGY INC
Method for preparing vanadium redox battery negative pole electrolyte
ActiveCN101728560AImproved resistance to low temperature environmentsImprove stabilityFinal product manufactureRegenerative fuel cellsVanadium redox batteryNitrogen
The invention relates to the field of battery manufacturing, in particular to a method for preparing vanadium redox battery negative pole electrolyte, which is characterized in that industrial high purity V2O3 is adopted as raw material, proper additive and reducing agent are added into the raw material, and the vanadium redox battery negative pole electrolyte is directly prepared by a chemical method under the protection of high purity nitrogen. The method has the advantages of easily obtained raw material, low cost, simple reaction condition as well as simple and convenient operation; the prepared electrolyte is high in total vanadium concentration and good in stability, and has the using performance to be obviously improved in the low temperature environment; and the method is suitable for industrialized production.
Owner:承德新新钒钛储能科技有限公司
Vanadium redox battery and electrolyte rebalancing method thereof
ActiveCN103762377ADecrease the molar ratioReduce divalent vanadium ions in the negative electrode electrolyteReactant parameters controlElectrolyte stream managementVanadium redox batteryEngineering
The invention discloses a vanadium redox battery and an electrolyte rebalancing method thereof. The vanadium redox battery comprises a battery stack, an anode electrolyte storage tank which is connected with the battery stack to form a first circulation loop, and a cathode electrolyte storage tank which is connected with the battery stack to form a second circulation loop, wherein the vanadium redox battery also comprises a low-valence vanadium ion solution supply device used for feeding a low-valence vanadium ion solution into the anode electrolyte storage tank, low-valence vanadium ions being divalent vanadium ions and / or trivalent vanadium ions; a high-valence vanadium ion solution recovery device used for recycling extra high-valence vanadium ion solution in the anode electrolyte storage tank, high-valenceions being tetravalent vanadium ions and / or pentavalent vanadium ions. In the vanadium redox battery, the low-valence vanadium ion solution supply device can feed low-valence vanadium ions into the anode electrolyte storage tank, so as to neutralize the pentavalent vanadium ions in the vanadium ions. The high-valence vanadium ion solution recovery device can recycle the high-valence vanadium ion solution left in the anode electrolyte, so as to lower the difference between the molar quantities of vanadium ions in the anode electrolyte and the cathode electrolyte.
Owner:DONGFANG ELECTRIC (CHENGDU) HYDROGEN FUEL CELL TECH CO LTD
Methods for coupling an energy storage system to a variable energy supply system
ActiveUS7923965B2Batteries circuit arrangementsSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsElectricityVanadium redox battery
A method for coupling an energy storage system to a variable energy supply system includes providing an energy storage system including at least one Vanadium redox battery and at least one battery charge controller. The method also includes electrically coupling the at least one battery charge controller to the variable energy supply system such that the at least one battery is configured to supply a substantially consistent energy output during fluctuating energy loads of the energy supply system.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Electrode frame structure for redox flow cell
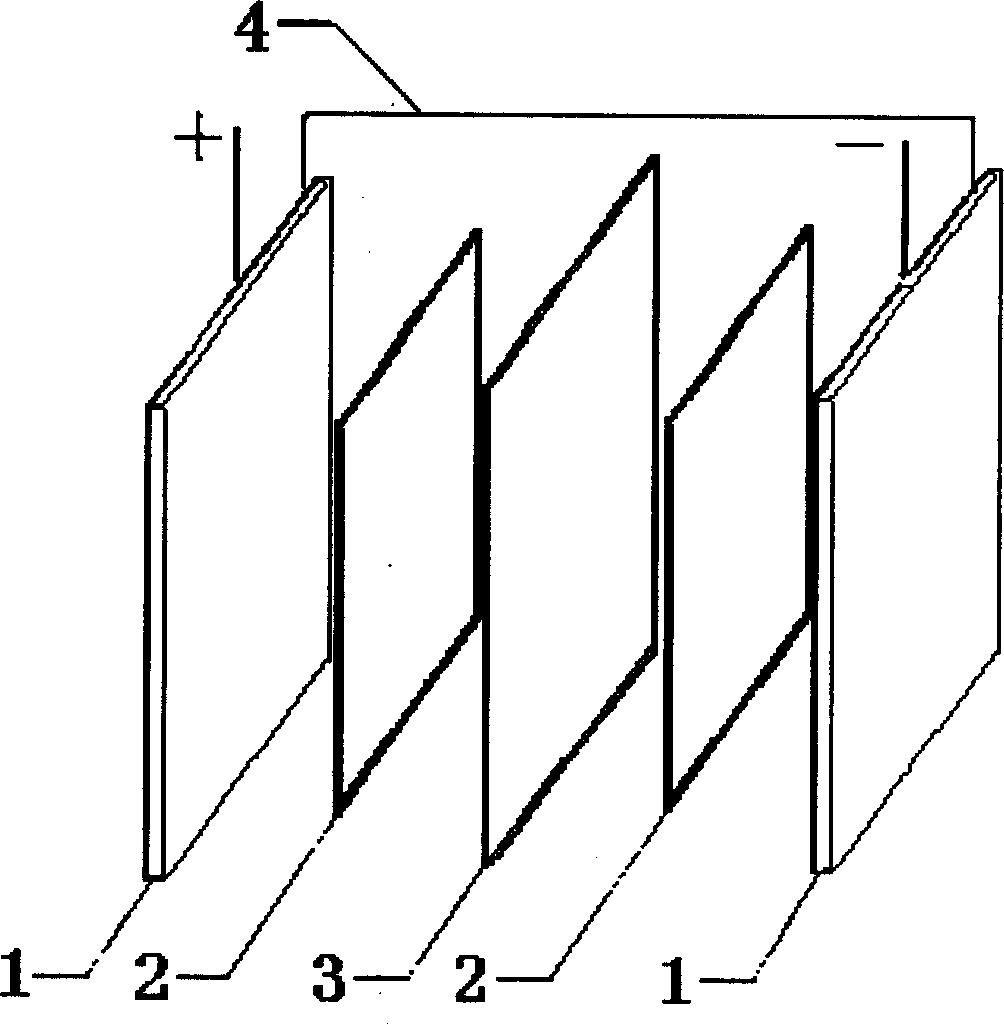
InactiveCN101667646ASimple structureLow costFuel cell detailsElectrical resistance and conductanceVanadium redox battery
The invention relates to an electrode frame for a redox flow cell, in particular to an electrode frame structure for an all-vanadium redox flow cell, which is formed by fastening two frame bodies of which the shapes and sizes are completely same; a plane where the two frame bodies are mutually fastened is a fastening surface; and the fastening surface of at least one frame body is provided with afluid channel which is fastened into a border to form an embedded-structure electrolyte inlet and outlet channel. The structure increases the resistance of an electrolyte channel branch, reduces leakage current, avoids thermogalvaniccorrosion in charging and discharging processes, and prolongs the service life of the cell (stack).
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Method for online detection of concentration of electrolyte of vanadium battery
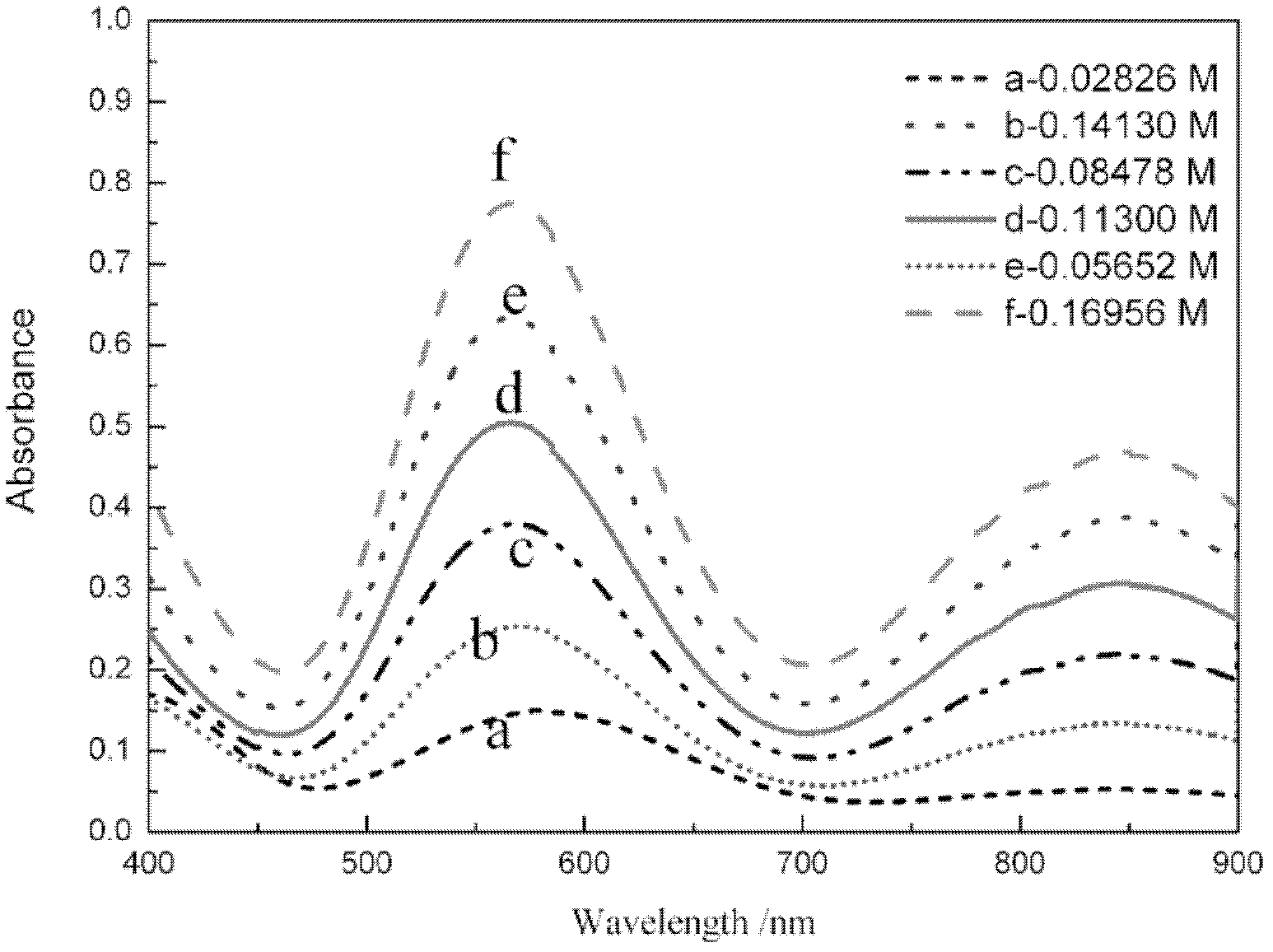
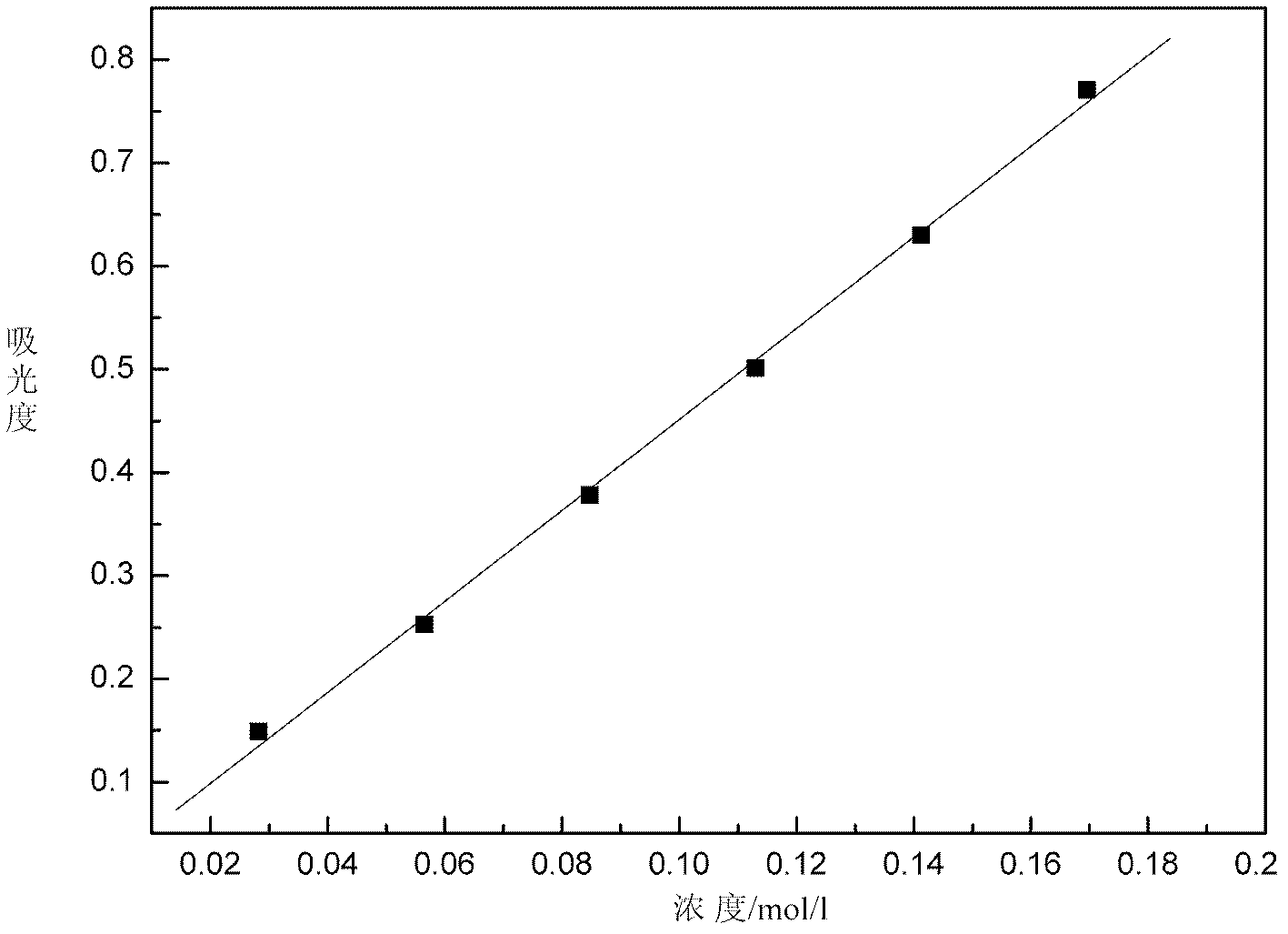
InactiveCN102621085AOnline rapid monitoring of valence changesQuickly monitor valence changesColor/spectral properties measurementsVanadium redox batteryAbsorbance
The invention relates to a method for online detection of the concentration of electrolyte of an all vanadium redox flow battery. A divalent vanadium V (II) system, a trivalent vanadium V (III) system and a tetravalent vanadium V (IV) system are analyzed by the aid of ultraviolet and visible spectrophotometry, a divalent vanadium V (II) and trivalent vanadium V (III) mixed system and a trivalent vanadium V (III) and tetravalent vanadium V (IV) mixed system are analyzed by the aid of a K matrix method, and a curve equation of the concentration of the vanadium with various valence states and absorbance in the systems is deduced. The concentration of vanadium ions with various valence states in a test sample can be rapidly detected only by substituting absorbance data of the test sample with unknown concentration in the electrolyte of the vanadium battery into the absorbance-concentration curve equation measured and deduced by the method, and accuracy of the method is proved as compared with a national standard method. The method has a huge application prospect in terms of dynamically monitoring valence changes of the electrolyte of the vanadium ions and simultaneously, qualitatively and quantitatively checking the vanadium electrolyte with mixed valence states.
Owner:HUNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Electrode material for all vanadium redox energy storage battery and application thereof
InactiveCN102867967AImprove conductivityHigh activityCell electrodesVanadium redox batteryElectricity
The invention discloses an electrode material for an all vanadium redox energy storage battery and an application thereof. The electrode comprises carbon materials as matrix, and the electrode surface is dipped or coated with an electro-catalyst. The electro-catalyst has strong acid resistance and can keep stable in the strong-acidic strong-oxidizing environment of the all vanadium flow system. The prepared electrode material has high catalytic activity to two redox couples which are VO<2+> / VO2<+> and V<2+> / V<3+>, effectively improves the reversibility of the redox couples, effectively raises the energy conversion efficiency of the Vanadium Redox Battery (VRB), and realizes the controllability of the efficiency of the all vanadium redox energy storage battery.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Novel vanadium halide redox flow battery
The present invention describes a vanadium halide redox cell prior to charging, a vanadium halide redox cell in a state of charge selected from the group below, and fully charged or partially charged vanadium halide redox cells, wherein the group Consists of zero state of charge and near zero state of charge. A vanadium halide redox cell prior to charging includes a positive half-cell having a positive half-cell solution including a halide electrolyte, a vanadium(III) halide, and a vanadium(IV) halide, and a negative half-cell having a A negative half-cell solution comprising a halide electrolyte, a vanadium(III) halide and a vanadium(IV) halide, wherein the amounts of the vanadium(III) halide, vanadium(IV) halide and halide ions in the positive and negative half-cell solutions are set to such that in the first charging step comprising charging the vanadium halide redox cell prior to charging, it is possible to prepare a vanadium halide redox cell having a state of charge selected from the group consisting of zero state of charge and With a near-zero state-of-charge composition, the vanadium halide redox cell mainly includes vanadium(IV) halide in the positive half-cell solution and V(III) halide in the negative half-cell solution. A vanadium halide redox cell at a state of charge selected from the group consisting of a positive half-cell and a negative half-cell consisting of zero and near-zero states of charge, the positive half-cell having a halide electrolyte comprising: and a positive half-cell solution of a vanadium halide mainly vanadium(IV) halide, a negative half-cell having a negative half-cell solution comprising a halide electrolyte and a vanadium halide mainly of a vanadium(III) halide, wherein the positive half-cell solution The amount of vanadium(IV) halide and the amount of vanadium(III) halide in the negative half-cell solution are set such that the vanadium halide redox cell is at a state of charge selected from the group consisting of zero state of charge and close to zero state of charge composition. A fully charged vanadium halide redox cell consists of a positive half cell with a positive half cell comprising a halide electrolyte, a polyhalide complex, a vanadium(IV) halide, and a vanadium(V) halide solution, the negative half-cell has a negative half-cell solution comprising a halide electrolyte and a vanadium(II) halide, wherein the molar concentration of vanadium(V) and polyhalide complexes: the molar concentration of vanadium(II) halide is approximately stoichiometrically balanced. A partially charged vanadium halide redox cell includes a positive half cell with a positive half cell including a halide electrolyte, a polyhalide complex, a vanadium(IV) halide, and a vanadium(V) halide solution, the negative half-cell has a negative half-cell solution comprising a halide electrolyte, a vanadium (II) halide and a vanadium (III) halide, wherein the number of moles of the polyhalide complex and the vanadium (V) halide: vanadium halide ( The moles of II) are approximately stoichiometrically balanced.
Owner:NEWSOUTH INNOVATIONS PTY LTD
Current collection plate for all vanadium redox flow battery
InactiveCN1845368AAvoid deformationReduce polarizationElectrode carriers/collectorsFuel cellsEpoxyVanadium redox battery
The structure of a collecting board for full-vanadium redox fluid cell comprises: the high-density graphite plate dipped by epoxy resin or phenol resin, and a S-shaped flow field with width rate of ridge and channel as 1:0.5~6 and the rate between the channel depth to channel width as 1:1~5. The advantages of this invention include: 1) small resistance, stable chemical property, and strong ability to bear large current charge / discharge; 2) strong rigidity and intensity; 3) smooth flow of the electrolyte, and little polarization on cell.
Owner:SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL TSINGHUA UNIV
Proton exchange composite membrane for all vanadium redox flow battery and its preparing method
InactiveCN1770503AImprove proton conductivityExcellent resistance to penetration of vanadium ionsFuel cellsVanadium redox batteryChemical stability
This invention relates to proton exchange complex film used in vanadium oxidation-reduction battery and its process method, wherein the film uses the inorganic nanometer materials polyvinylidene fluoride as base part and then introduces organic acid with sulfonic acid root through autopolymer to get aim product. The process method to make film with good proton conductivity property and good isolation vanadium ion transparency and chemical stability with simple process and low film cost. The film conducting rate can achieve 10 to 2 S / cm and the vanadium ion transparency rate is as 10 to 7 cm2 / min.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
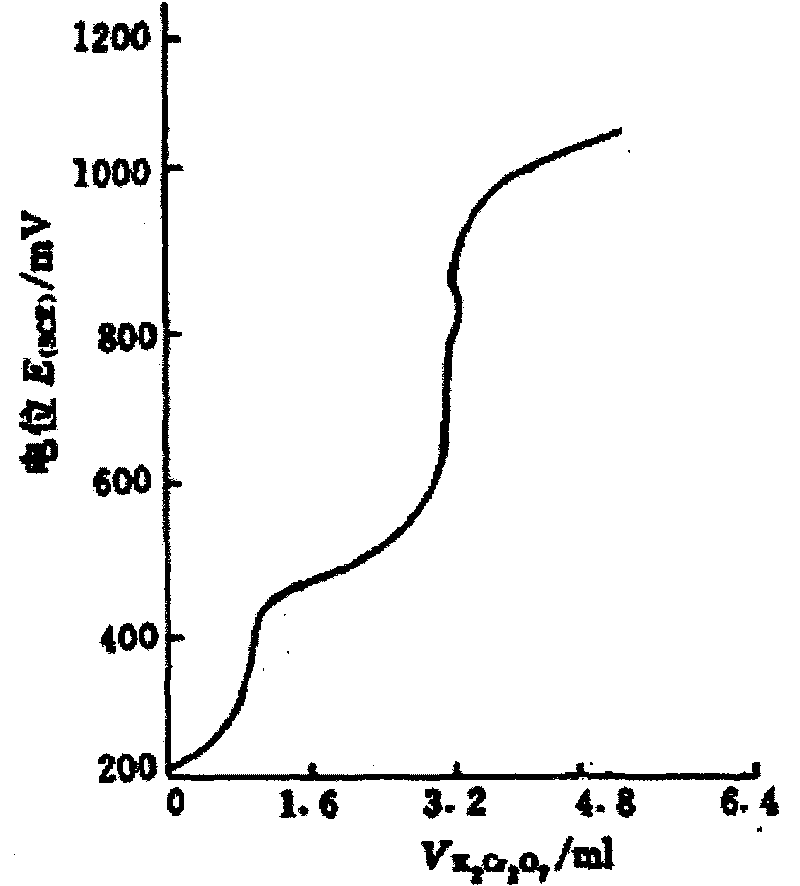
In-situ monitoring method of state of charge of anode electrolyte of vanadium battery
InactiveCN101968532ARealize in-situ monitoringRegenerative fuel cellsSecondary cellsVanadium redox batteryState of charge
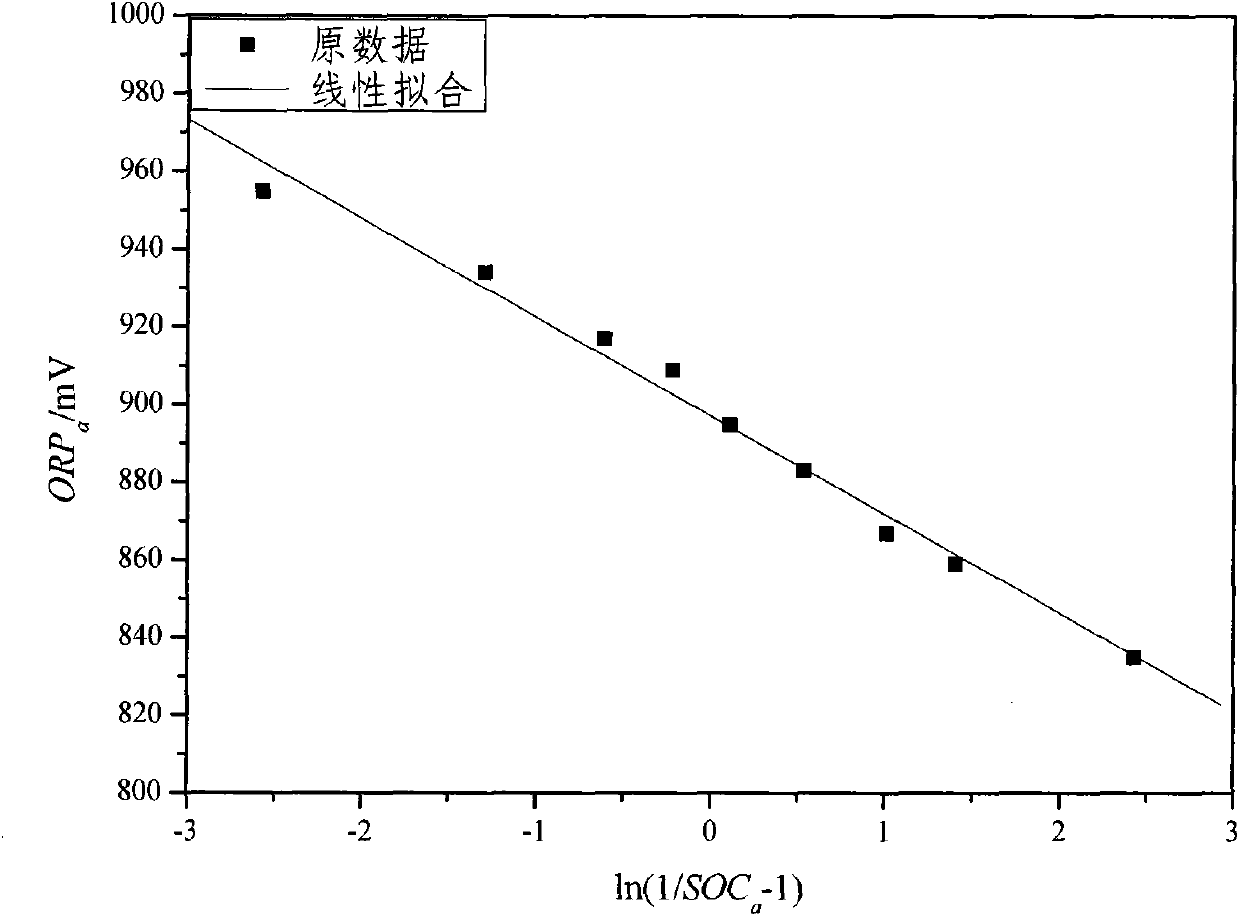
The invention relates to the monitoring technology of the state of charge (SOC) of electrolyte of a vanadium redox flow battery, in particular to an in-situ monitoring method of the SOC of the anode electrolyte of the battery. The method comprises the following steps: measuring the oxidation reduction potential value ORPa of the anode electrolyte of the vanadium redox flow battery; establishing a relation equation according to the principle that the ORPa value is in linear relation with SOCa (the SOC of the anode electrolyte) in an open interval (0,100%), and then performing temperature correction and temperature substitution on the equation to obtain an ORPa-SOCa relation equation which has universality on the temperature of the anode electrolyte; and comparing the SOCa value calculated by the equation with the SOCa value measured by a potentiometric titration method to obtain the error of less than plus or minus 1.50%, thus finally realizing in-situ monitoring of the SOC of the anode electrolyte.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
All-vanadium redox flow battery electrolytic solution preparation method
InactiveCN101192674ASimplify the assembly processSimplify the chemical processHybrid cell detailsRegenerative fuel cellsVanadium CompoundsVanadium redox battery
The invention relates to a method for preparing electrolyte for a flow battery with full vanadium oxidation reduction, which is characterized by the processes: mixing the three oxidation vanadium and the sulphuric acid with a specified volume of proportion of 1. 84, then calcining the mixture under 100 DEG C to 300DEG C in a pipe type electric stove to get vanadium compound in green color, at last dissolving the calcined product into the dilute sulfuric acid to get the vanadium electrolyte used in a vanadium battery in which 4 valence vanadium and 3 valence vanadium take 50 per cent of the total vanadium quantity. The electrolyte for a flow battery with whole vanadium oxidation reduction prepared by the method reduces the emission of SO2, simplifies the preparation work procedure and is beneficial for scale production and environment protection of the flow battery with full vanadium oxidation reduction.
Owner:PANZHIHUA UNIV
Nafion ion exchange membrane used for enhanced vanadium redox battery and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102024928AHigh mechanical strengthWork lessCell component detailsFuel cell detailsHigh current densityVanadium redox battery
The invention relates to the field of an ion exchange membrane used for a vanadium redox battery (VRB), in particular to a Nafion ion exchange membrane used for enhanced vanadium redox battery and a preparation method thereof. A Nafion ion exchange resin containing sulfonic group is taken as forming resin; the resin is dissolved into organic solvent to obtain forming solvent; and the Nafion ion exchange membrane is formed by the forming solvent; a layer of polytetrafluoroethylene mesh in the middle of the Nafion ion exchange membrane is taken as reinforcing material; or a layer of Nafion ion exchange membrane is arranged between two layers of polytetrafluoroethylene meshes. The membrane has high chemical stability and high current density, and compared with the Nafion membrane, the Nafion ion exchange membrane has higher mechanical strength, higher exchange capacity and lower cost, and the problems that the Nafion ion exchange membrane in the prior art has high exchange capacity and low mechanical strength or high mechanical strength and low exchange capacity are solved, and the Nafion ion exchange membrane is mainly applied to the vanadium redox battery (VRB).
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
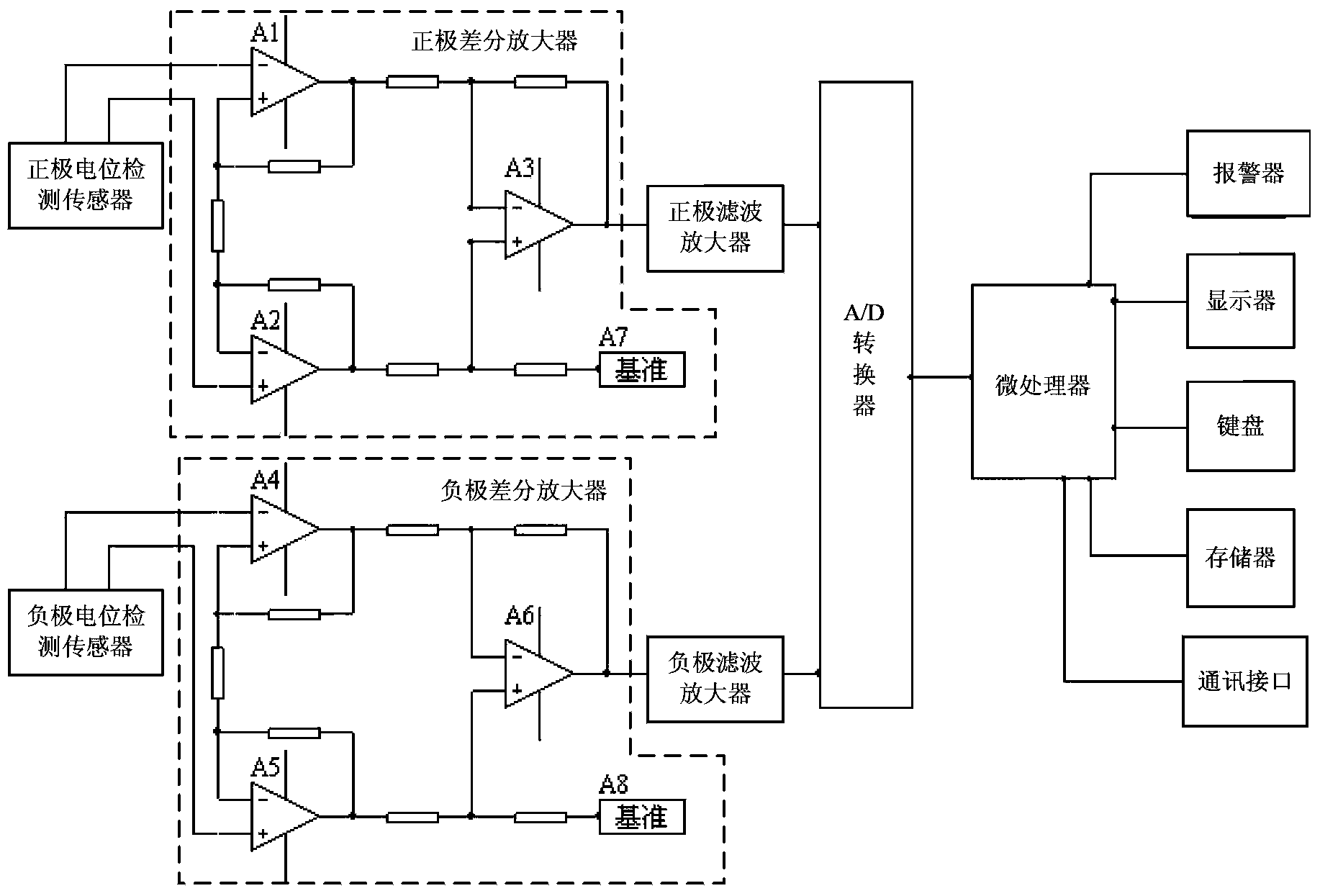
SOC (State of Charge) detection method and system for vanadium redox battery
ActiveCN104345278ASafe and stable operationReasonable designElectrical testingVanadium redox batteryElectricity
The invention discloses an SOC (State of Charge) detection method and system for a vanadium redox battery. The method comprises the following steps: measuring the positive potential of positive electrolyte and the negative potential of negative electrolyte of the vanadium redox battery; acquiring the positive potential and the negative potential, filtering and amplifying the positive potential and the negative potential, and converting the filtered and amplified positive potential and negative potential into a positive potential digital signal and a negative potential digital signal respectively; processing the positive potential digital signal and the negative potential digital signal to generate a positive SOC value and a negative SOC value respectively; displaying the positive SOC value and the negative SOC value. The SOC detection method and system for the vanadium redox battery in the embodiment of the invention are reasonable in design, are convenient in operation, are accurate in detection and are small in errors; guidance can be provided for the maintenance and management work of long-time-running vanadium electric pile electrolyte, and safe and stable running of an electric pile is ensured.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +1
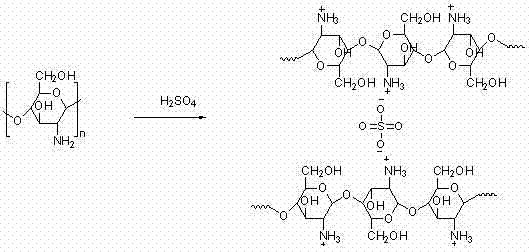
Preparation method of sulfonated polyimide/chitosan composite proton conducting film
The invention discloses a preparation method of a sulfonated polyimide / chitosan composite proton conducting film. The preparation method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: feeding 2,2'-disulfobenzidine, m-cresol and triethylamine into a reactor under the condition of nitrogen protection, and stirring until solid substances are dissolved; adding 1,4,5,8-naphthalene tetracarboxylic dianhydride, benzoic acid and 4,4'-diamido diphenyl ether, heating and reacting, and cooling to below 80 DEG C; pouring into acetone for precipitation, filtering, washing precipitate with acetone,and drying to obtain triethylamine salt type sulfonated polyimide; dissolving triethylamine salt type sulfonated polyimide in an organic solvent, casting and filming, soaking, washing and drying to obtain a protonated sulfonated polyimide film; and preparing the sulfonated polyimide / chitosan composite proton conducting film by using soaking and self-assembly chitosan solution crosslinking methods. The sulfonated polyimide / chitosan composite proton conducting film prepared by using the preparation method has good application prospect in the aspects of a full-vanadium redox liquid flow battery and a fuel battery.
Owner:SOUTHWEAT UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Preparation method for flexible inorganic/organic composite proton exchange membrane
InactiveCN102315463AHigh proton conductivityImprove heat resistanceCell component detailsFuel cell detailsVanadium redox batteryPolymer dissolution
The invention discloses a preparation method for a flexible inorganic / organic composite proton exchange membrane. The method comprises the following steps: 1, dissolving a proton conducting polymer in an organic solvent or water so as to obtain a proton conducting polymer solution; 2, mixing an inorganic proton conducting material or an inorganic proton conducting material containing organic components with the proton conducting polymer solution for mechanical ball milling so as to obtain a mixture in which the inorganic proton conducting material or the inorganic proton conducting material containing organic components disperses in the proton conducting polymer solution; 3, pouring the mixture on a substrate, and allowing the solvent to volatilize and the mixture to solidify so as to prepare the flexible inorganic / organic composite proton exchange membrane. The flexible inorganic / organic composite proton exchange membrane prepared in the invention has the characteristics of proton conducting capacity, flexibility, stable dimension, heat resistance and mechanical strength at a certain degree, and can be used in the field of fuel cells and related fields in need of proton exchange membranes like all-vanadium redox flow batteries, industrial electrolysis of chlor-alkali, super capacitors and sensors.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com