Patents
Literature
46 results about "K matrix" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
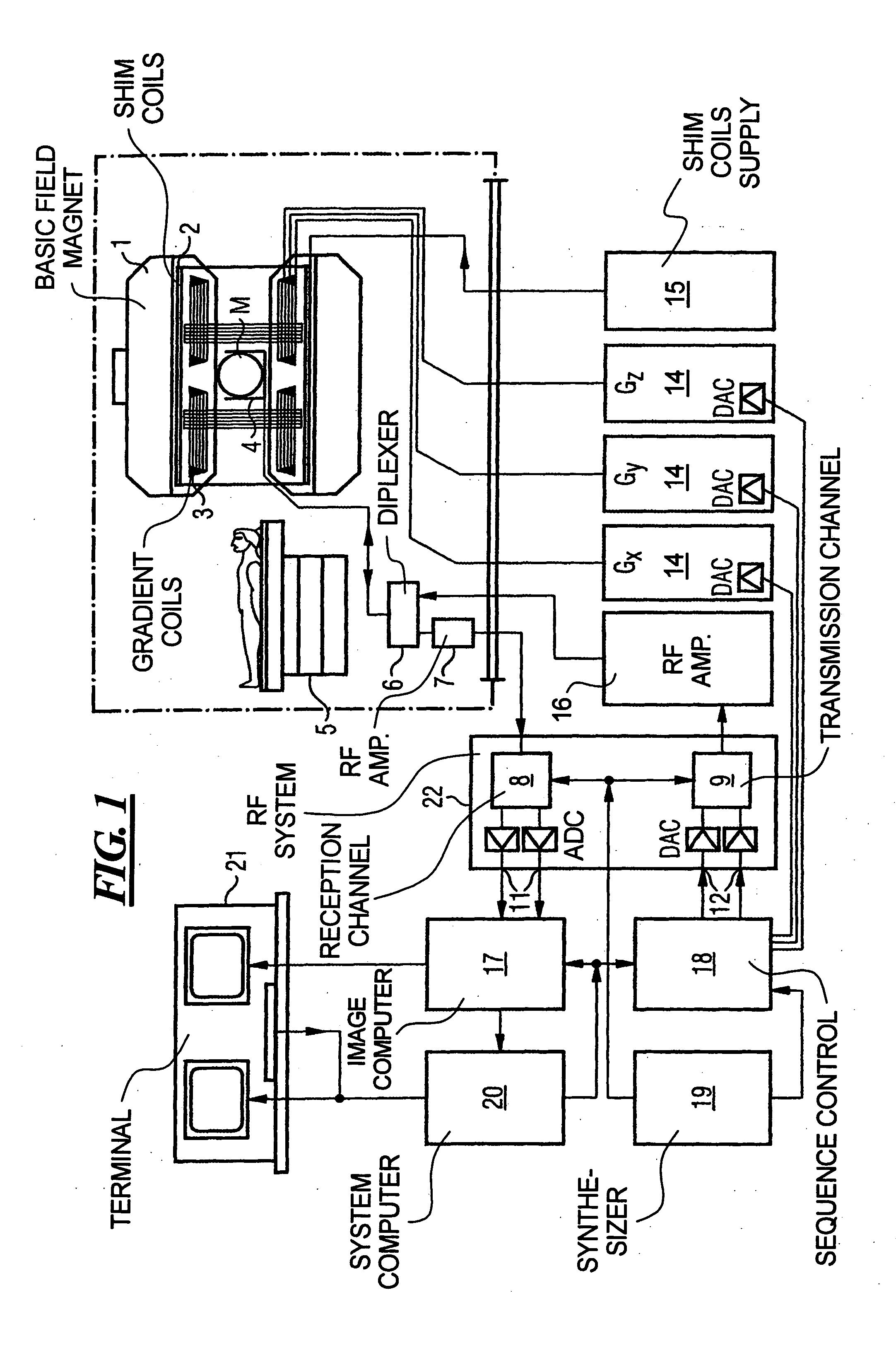
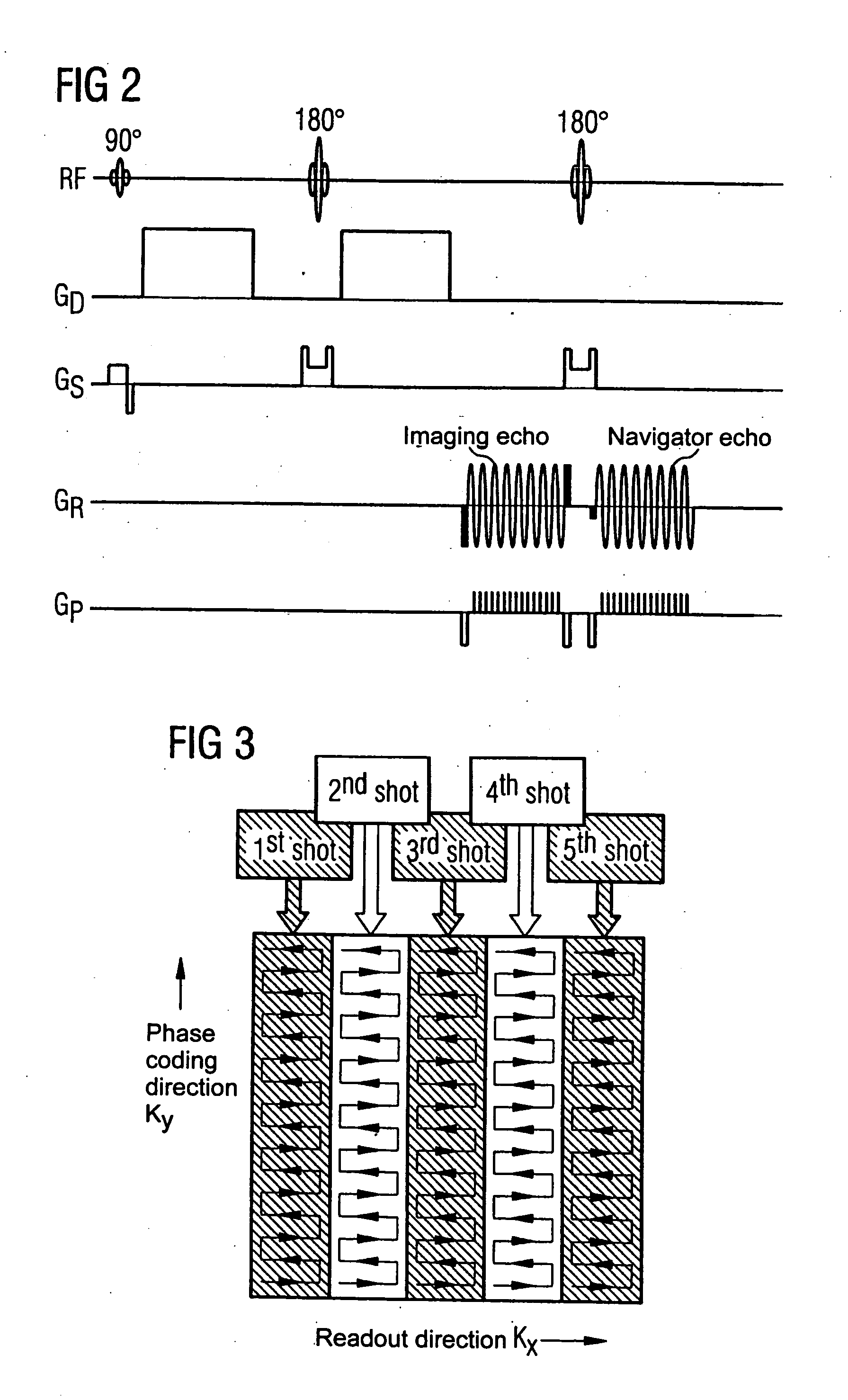
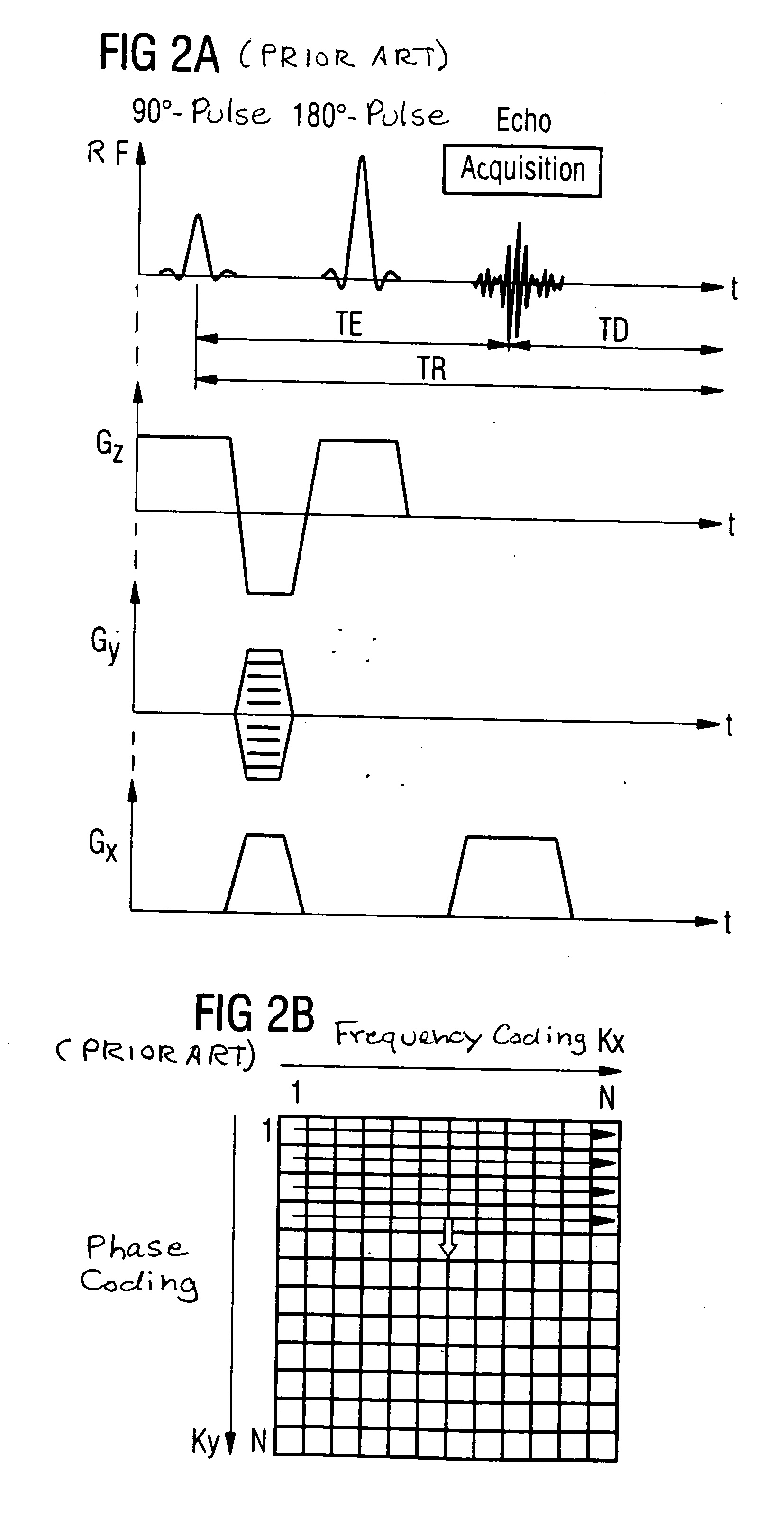
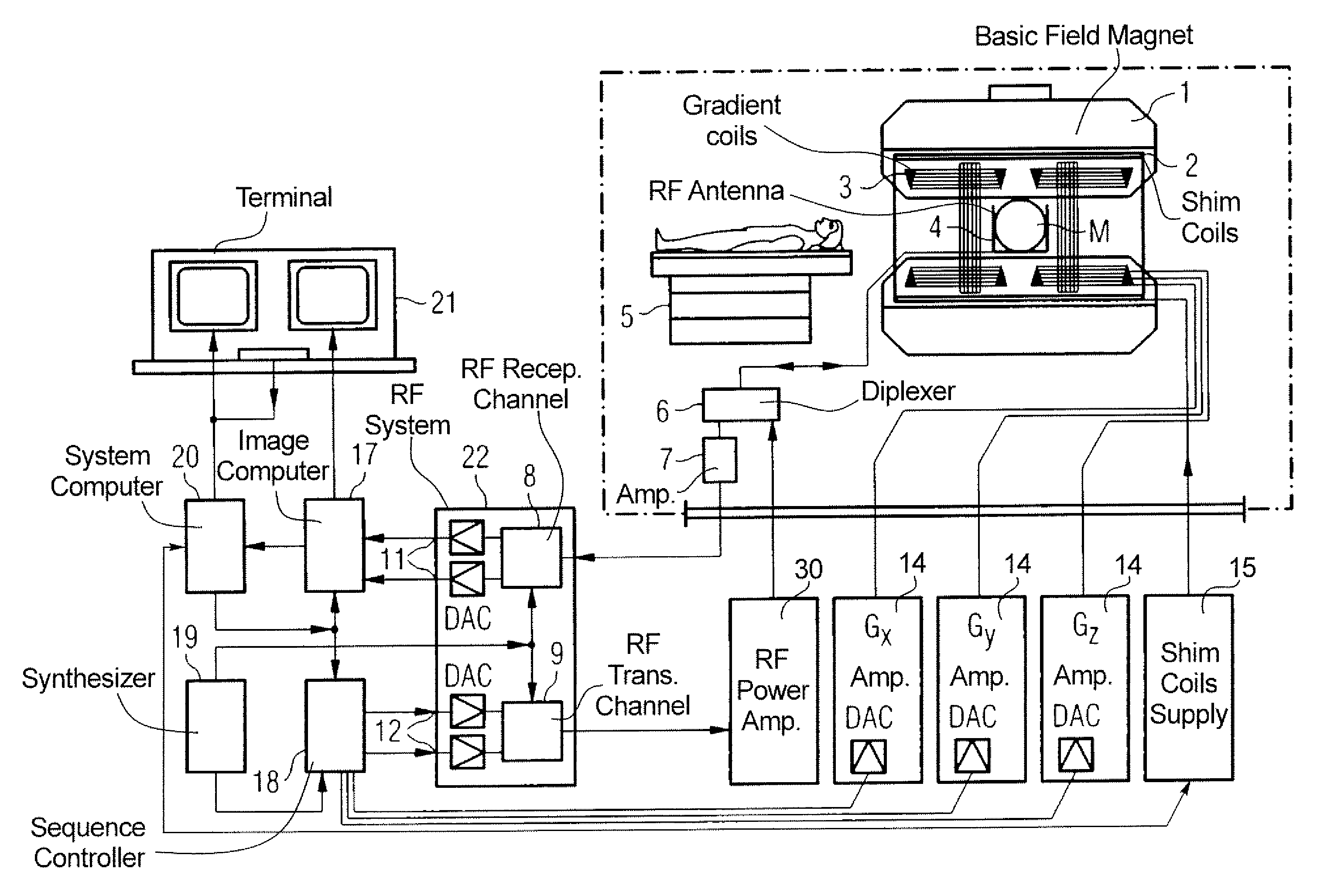
Movement-corrected multi-shot method for diffusion-weighted imaging in magnetic resonance tomography
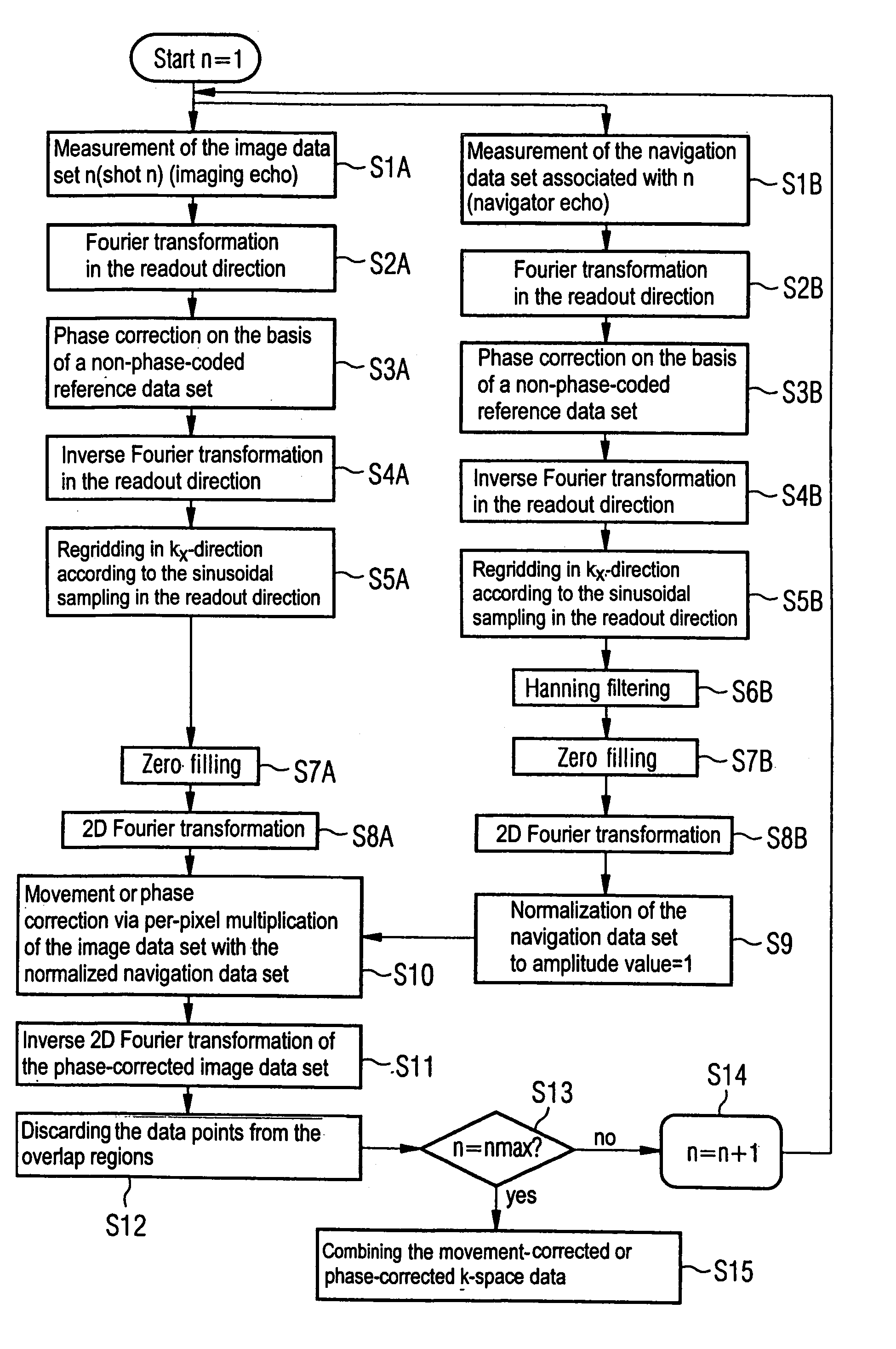
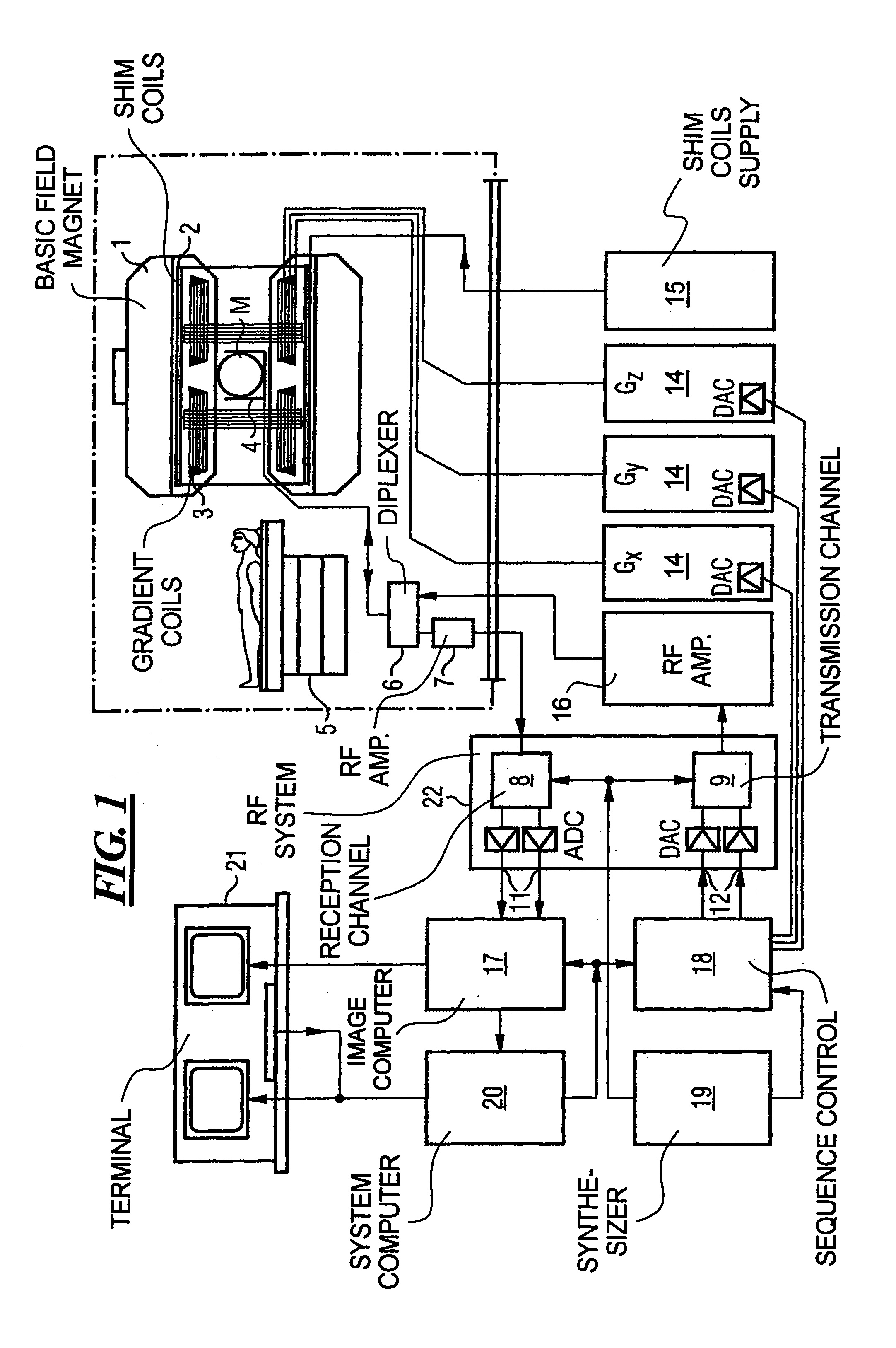
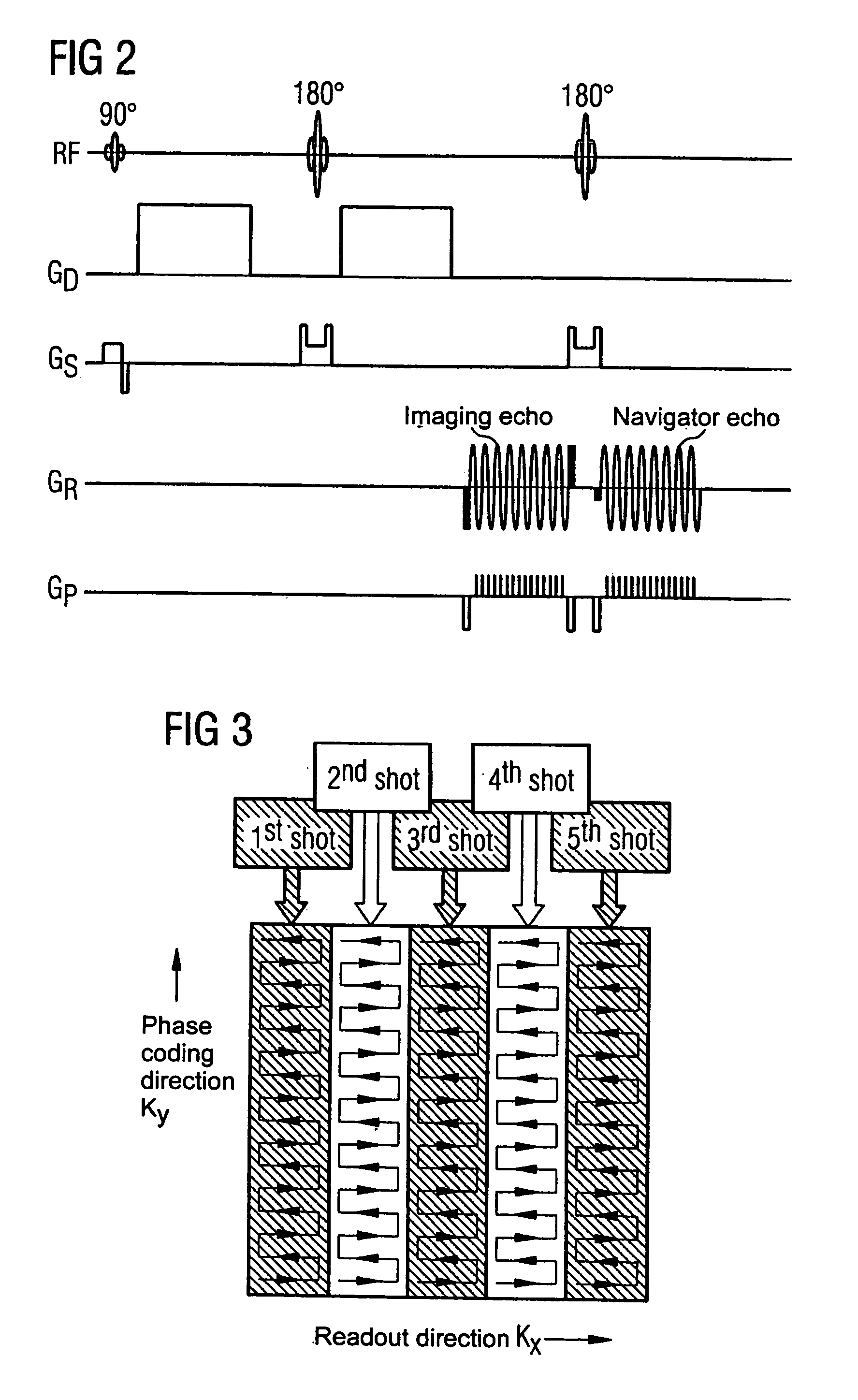
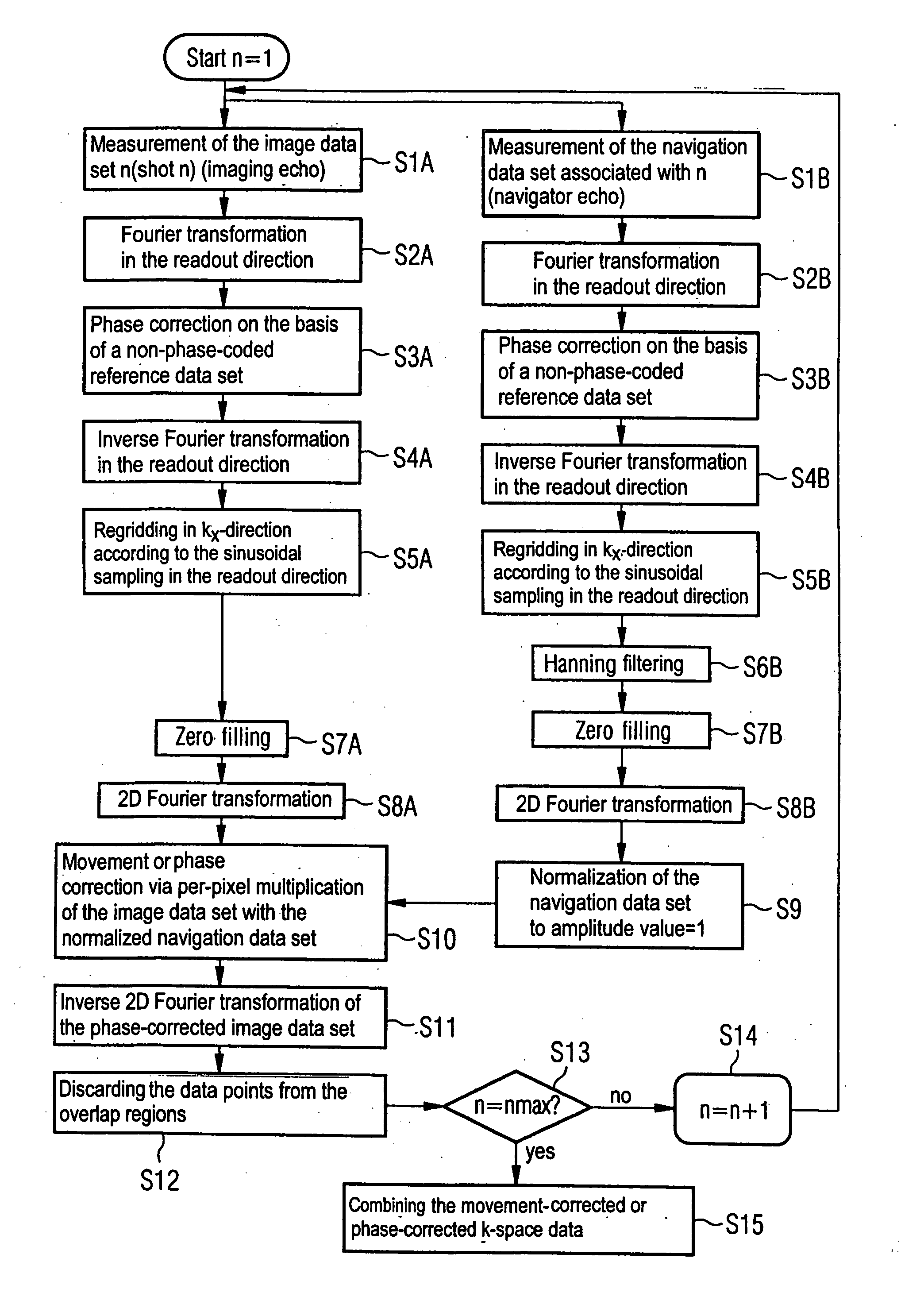
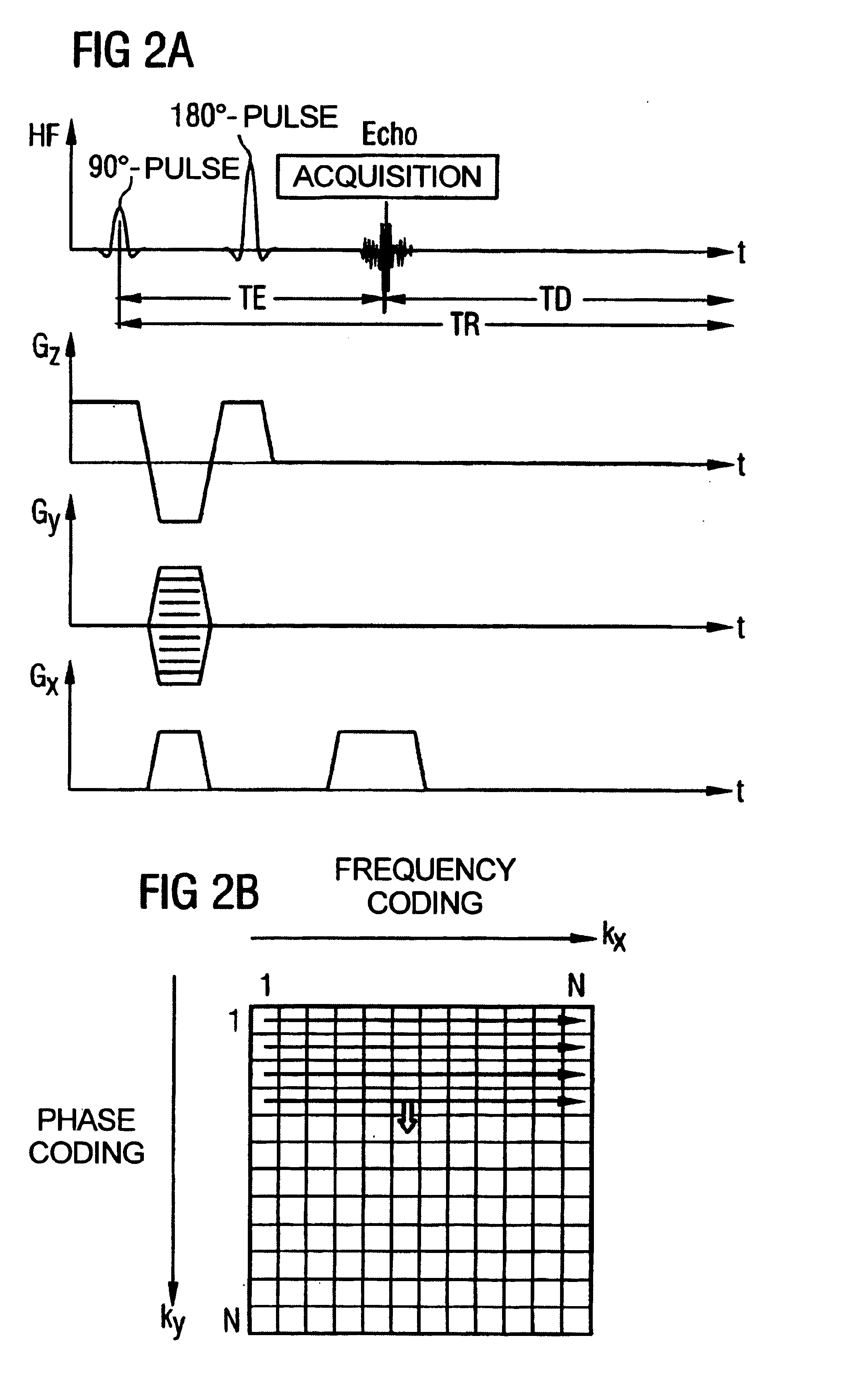
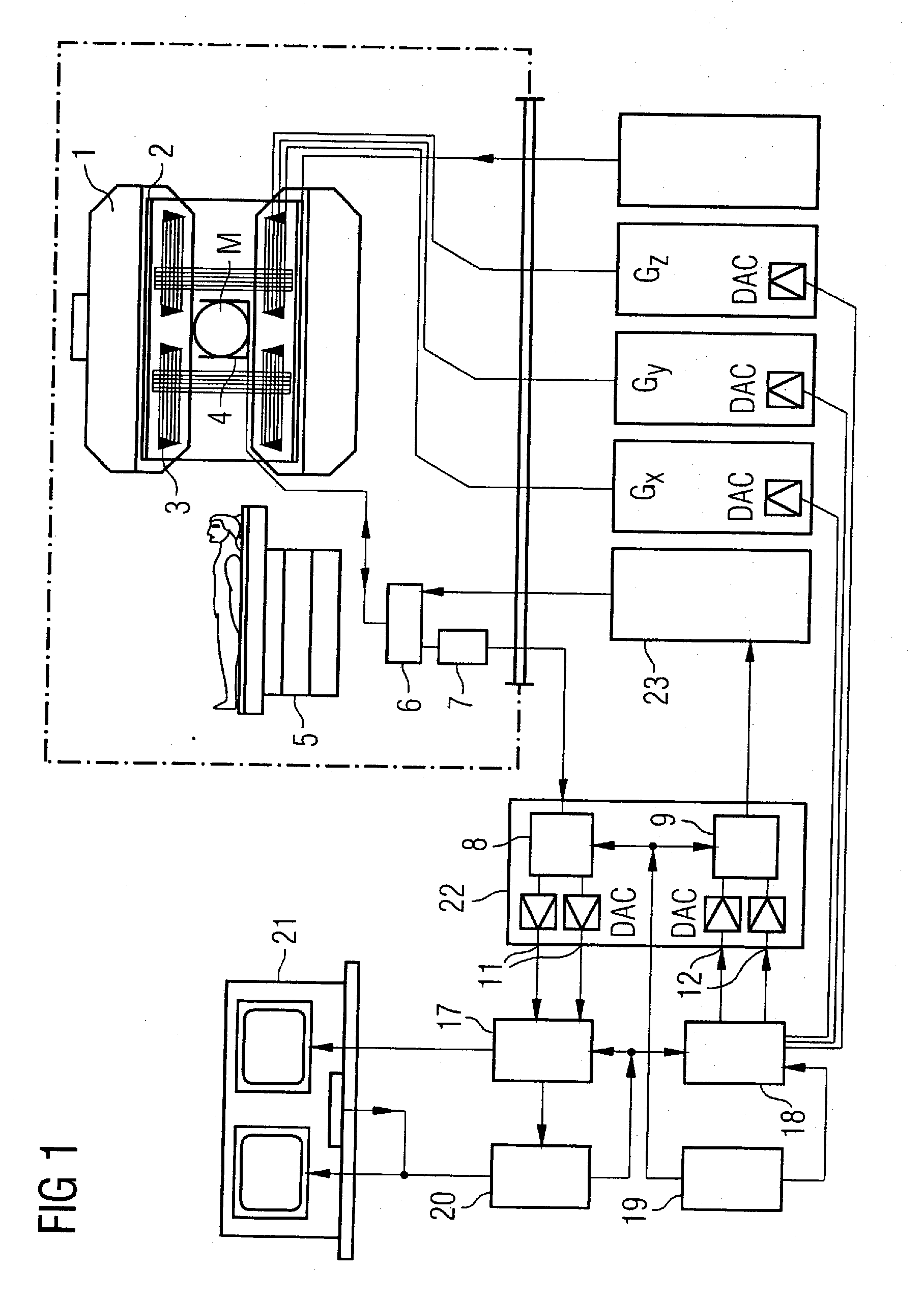
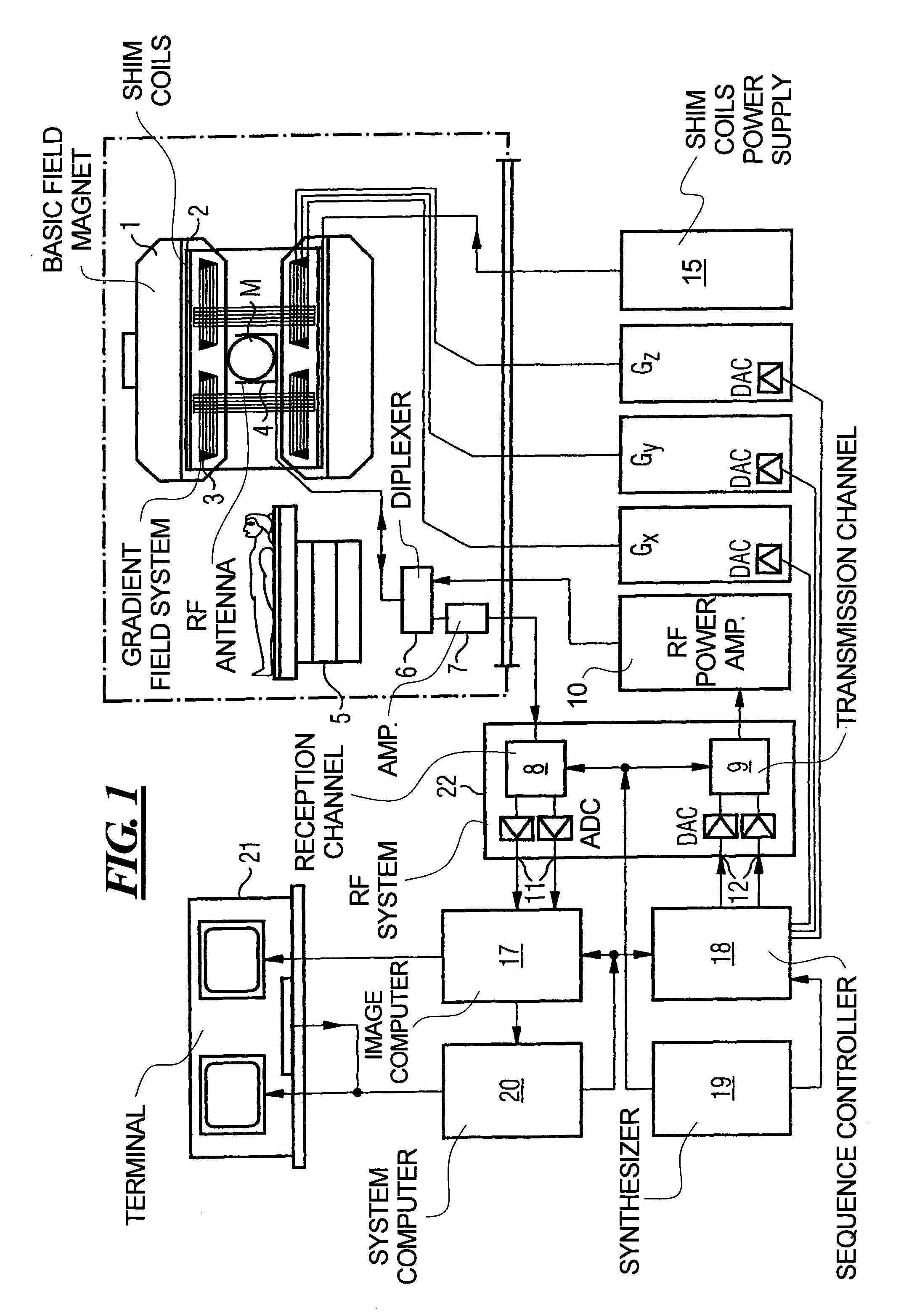
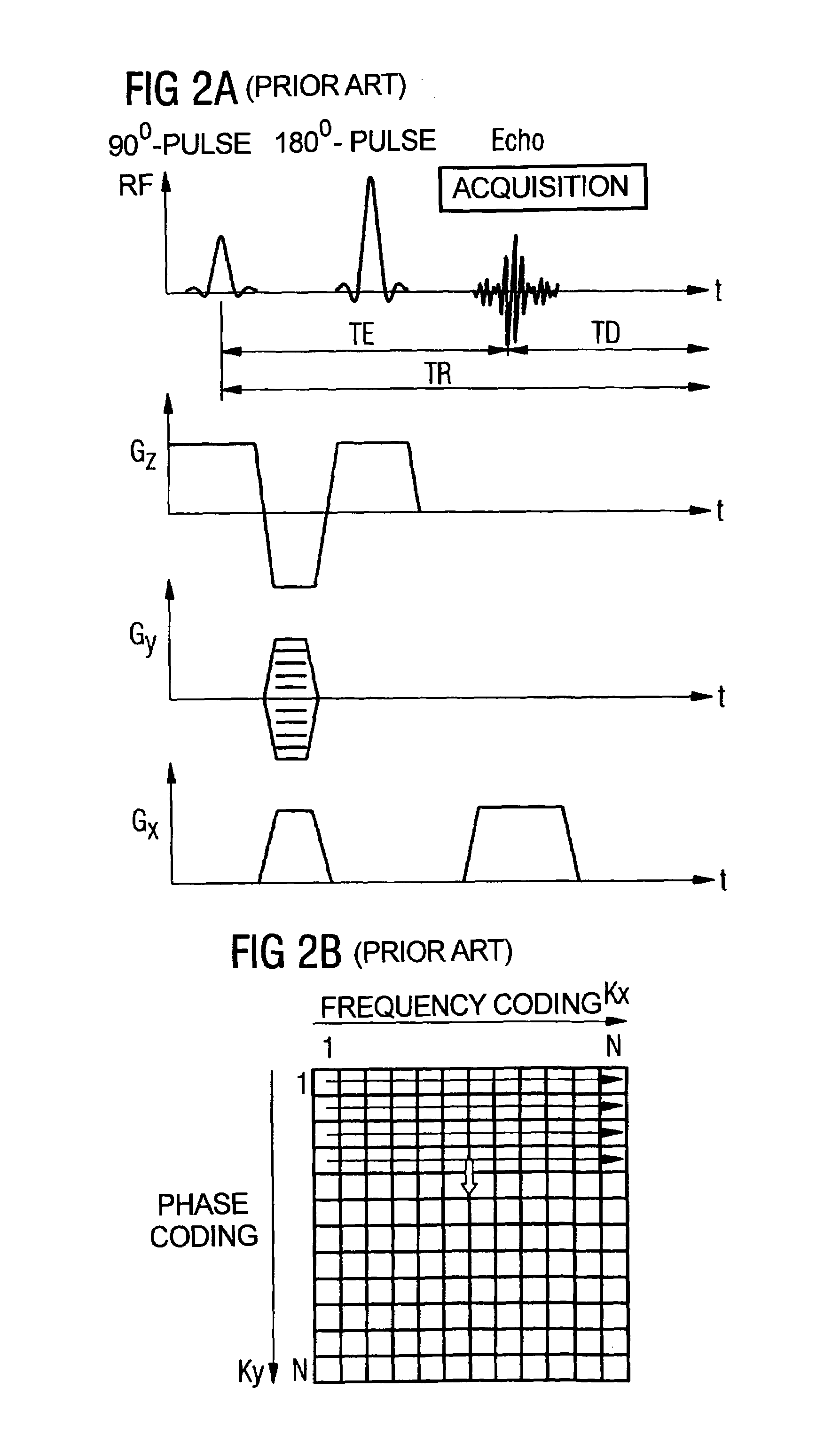
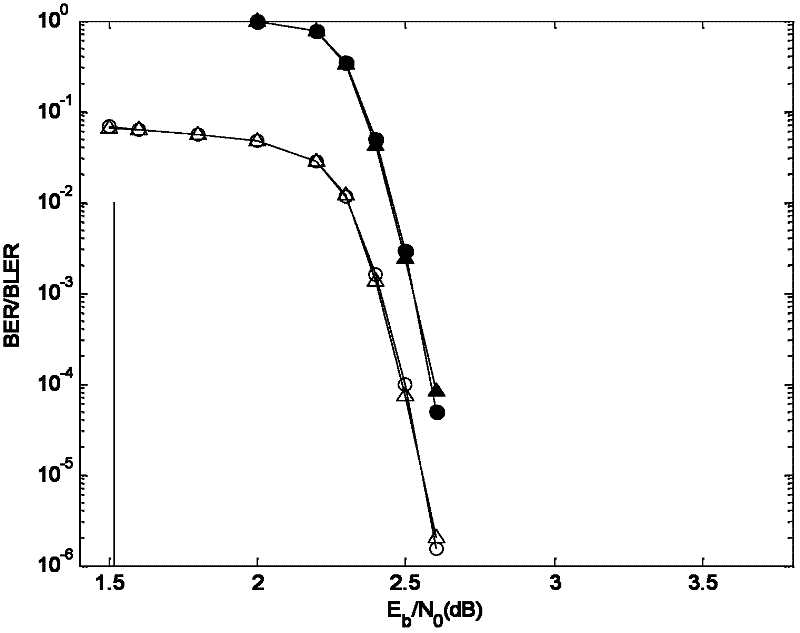
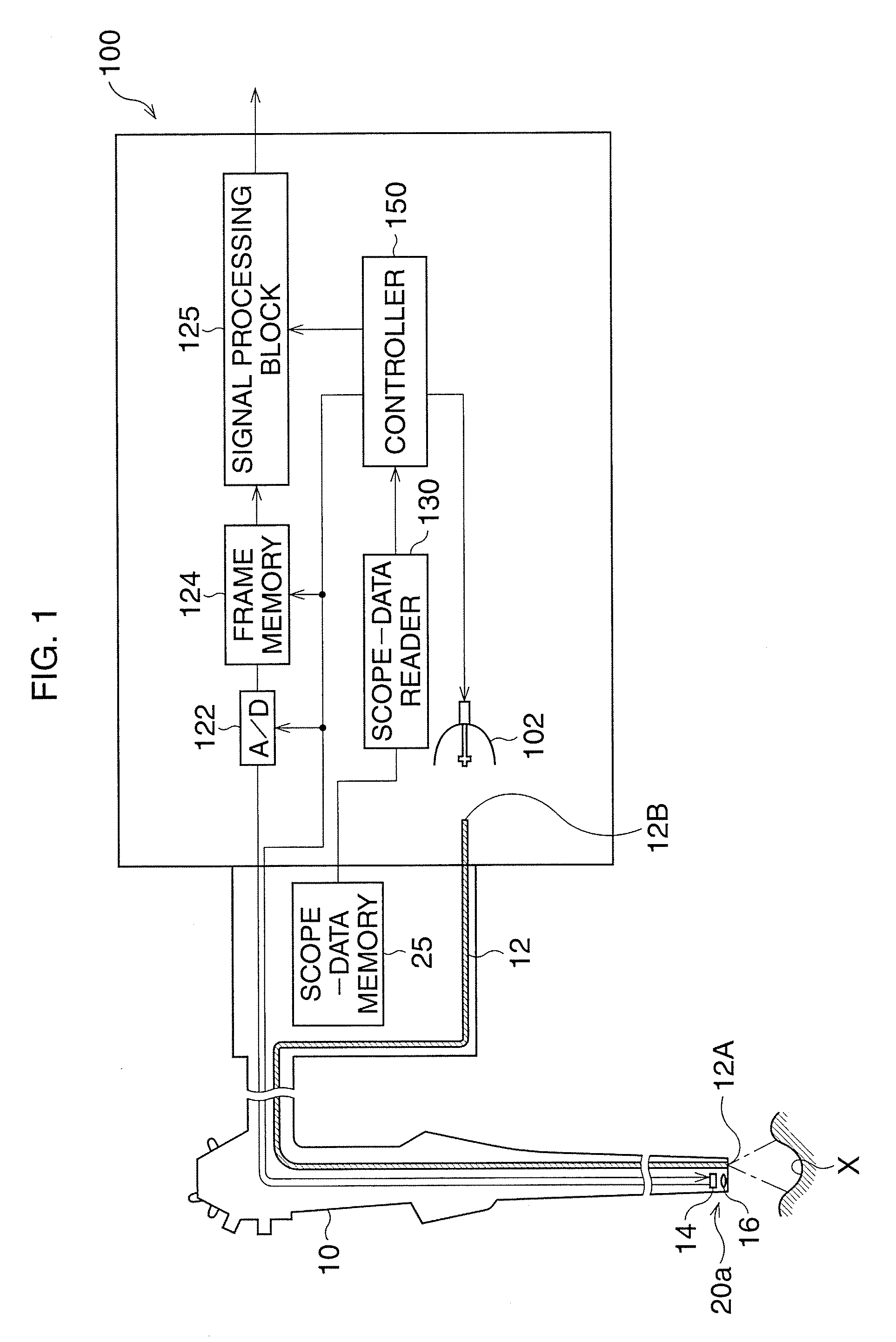
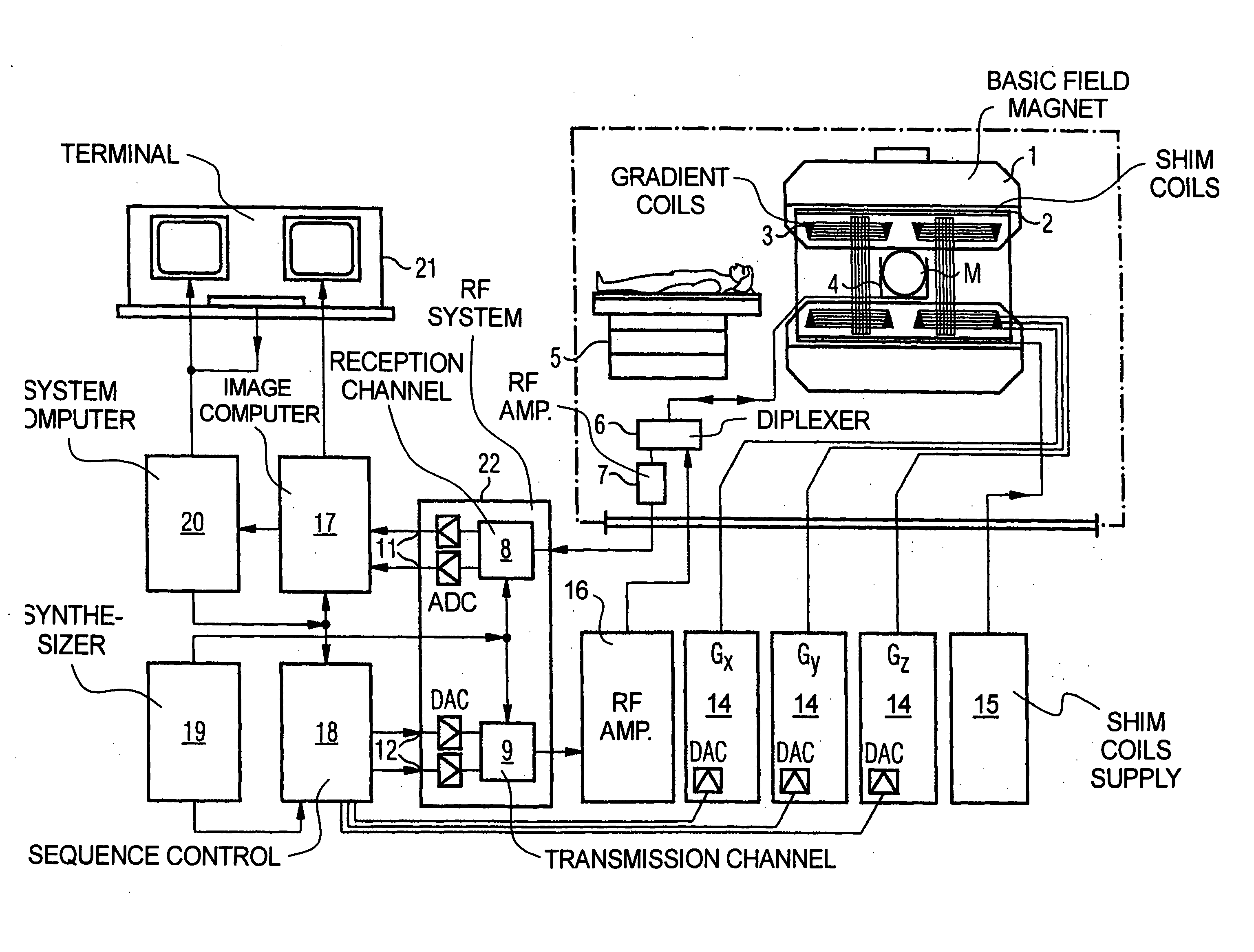
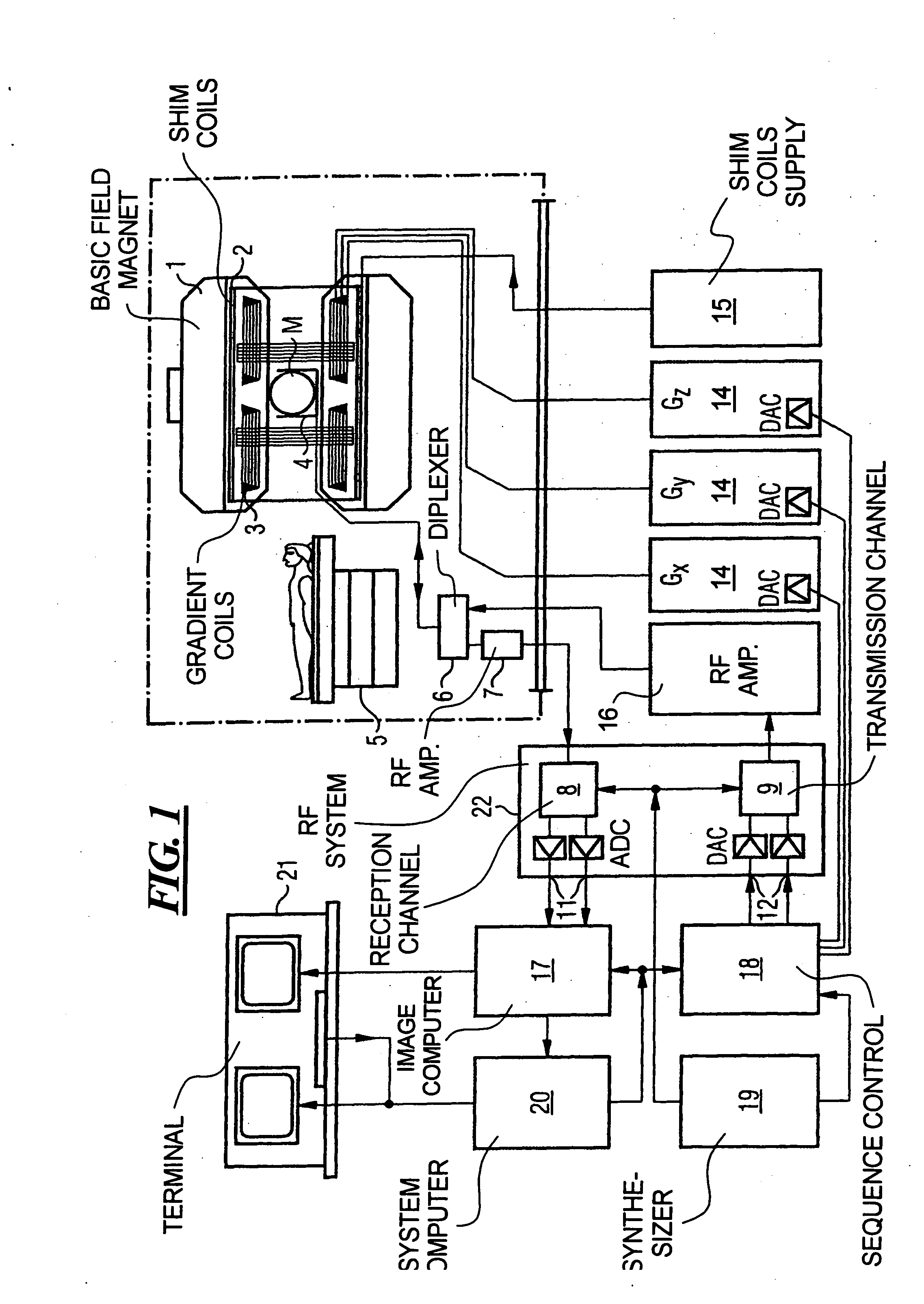
In a multi-shot method for diffusion-weighted imaging in magnetic resonance tomography, the sampling of the k-matrix in the readout direction ensues in segments, and immediately after acquisition of an image data set by readout of one segment by means of echo signals, a navigation data set is acquired by readout of the middle region of the k-matrix at virtually the same time. A movement-corrected diffusion-weighted MRT image is generated by combining of the image data sets with the corresponding navigation data sets and subsequent Fourier transformation.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Movement-corrected multi-shot method for diffusion-weighted imaging in magnetic resonance tomography
In a multi-shot method for diffusion-weighted imaging in magnetic resonance tomography, the sampling of the k-matrix in the readout direction ensues in segments, and immediately after acquisition of an image data set by readout of one segment by means of echo signals, a navigation data set is acquired by readout of the middle region of the k-matrix at virtually the same time. A movement-corrected diffusion-weighted MRT image is generated by combining of the image data sets with the corresponding navigation data sets and subsequent Fourier transformation.
Owner:SIEMENS HEATHCARE GMBH
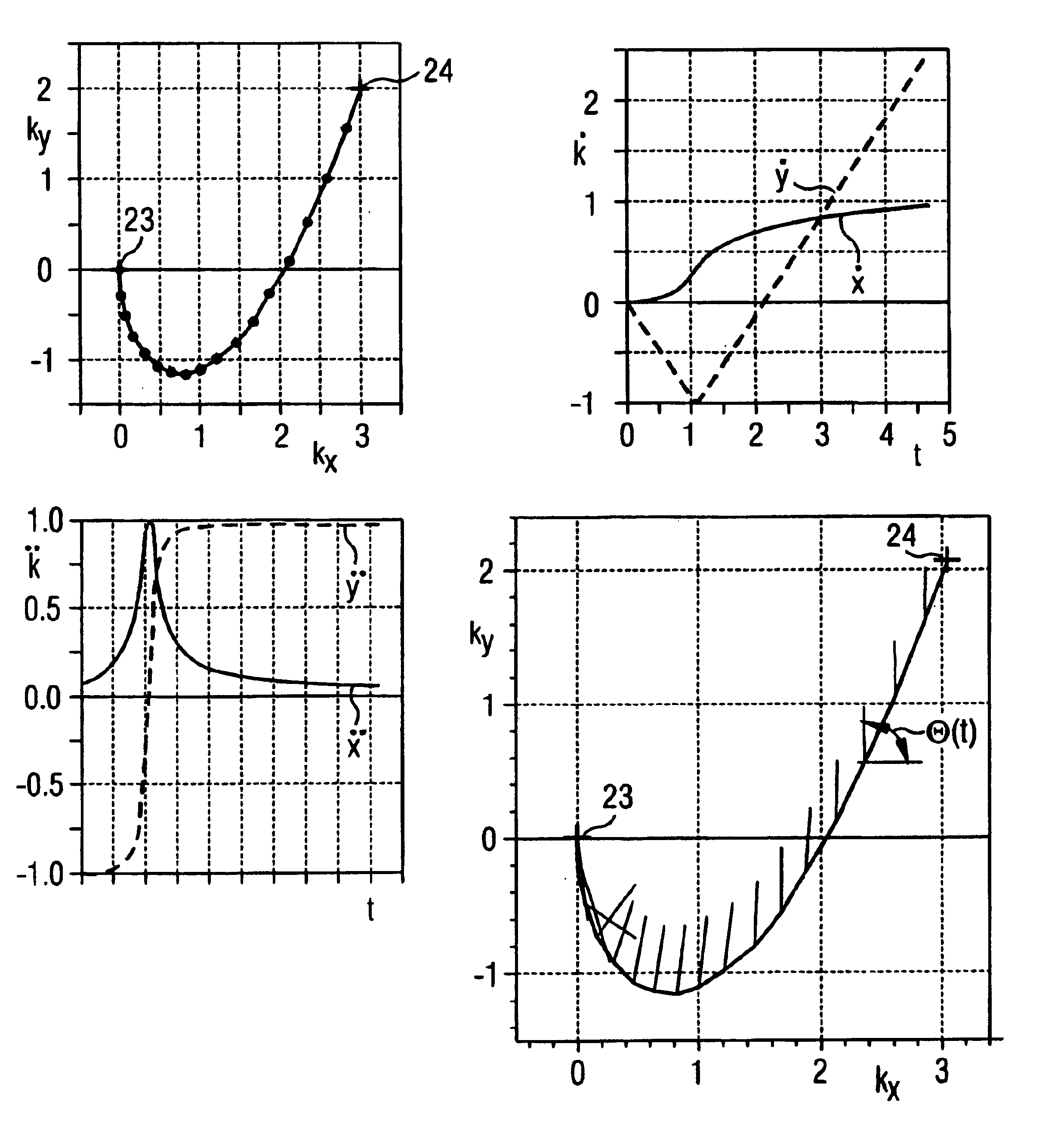
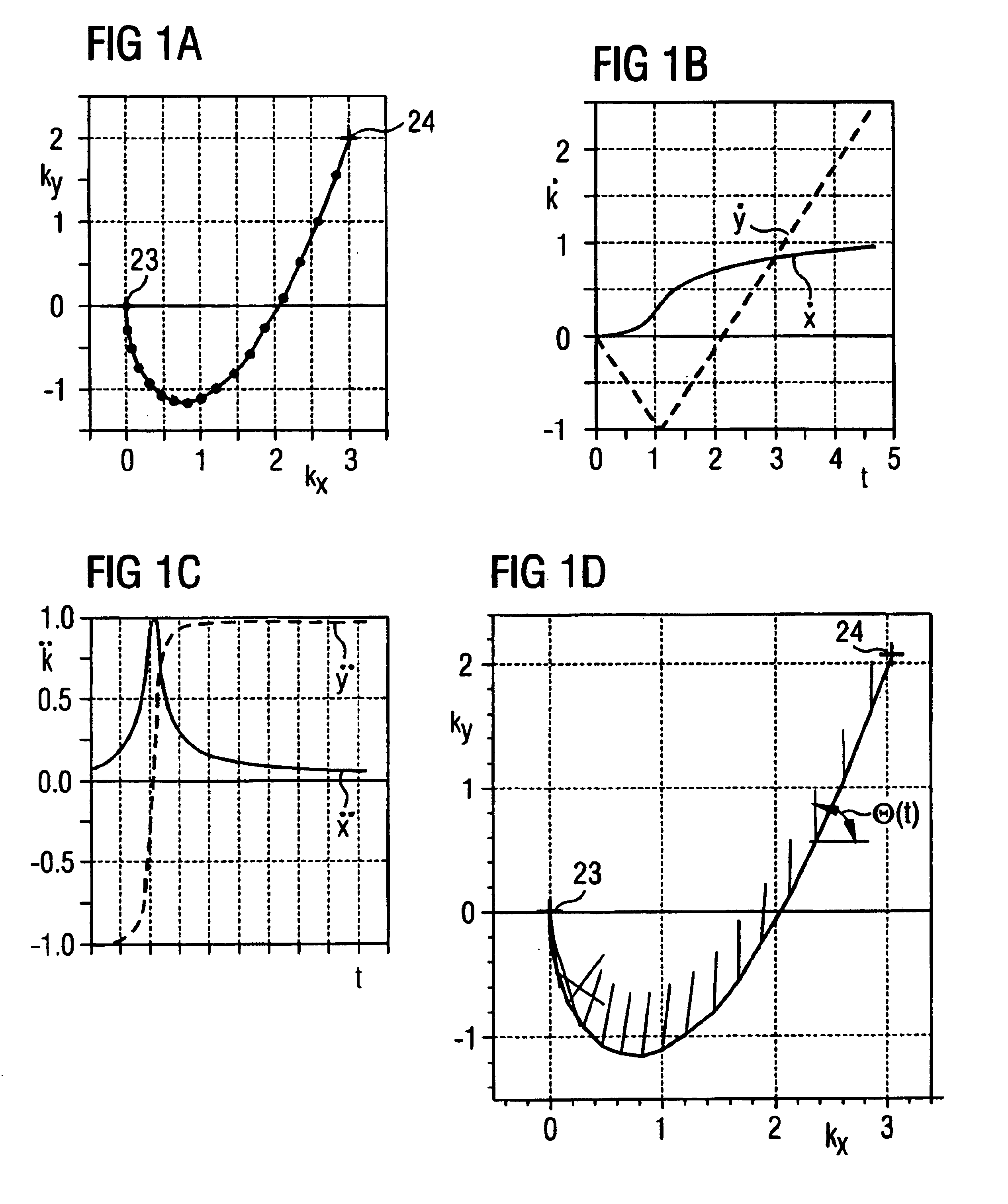
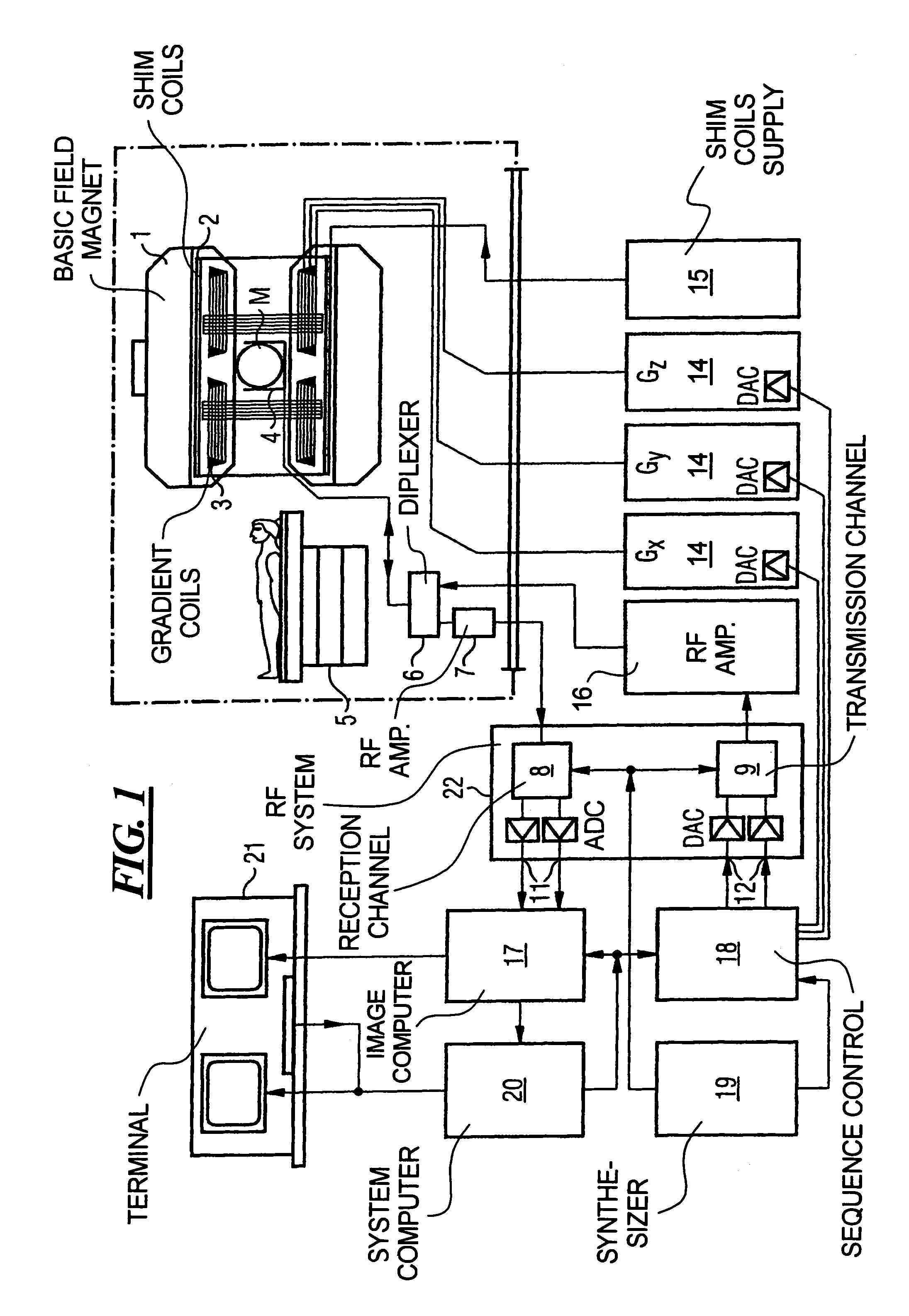
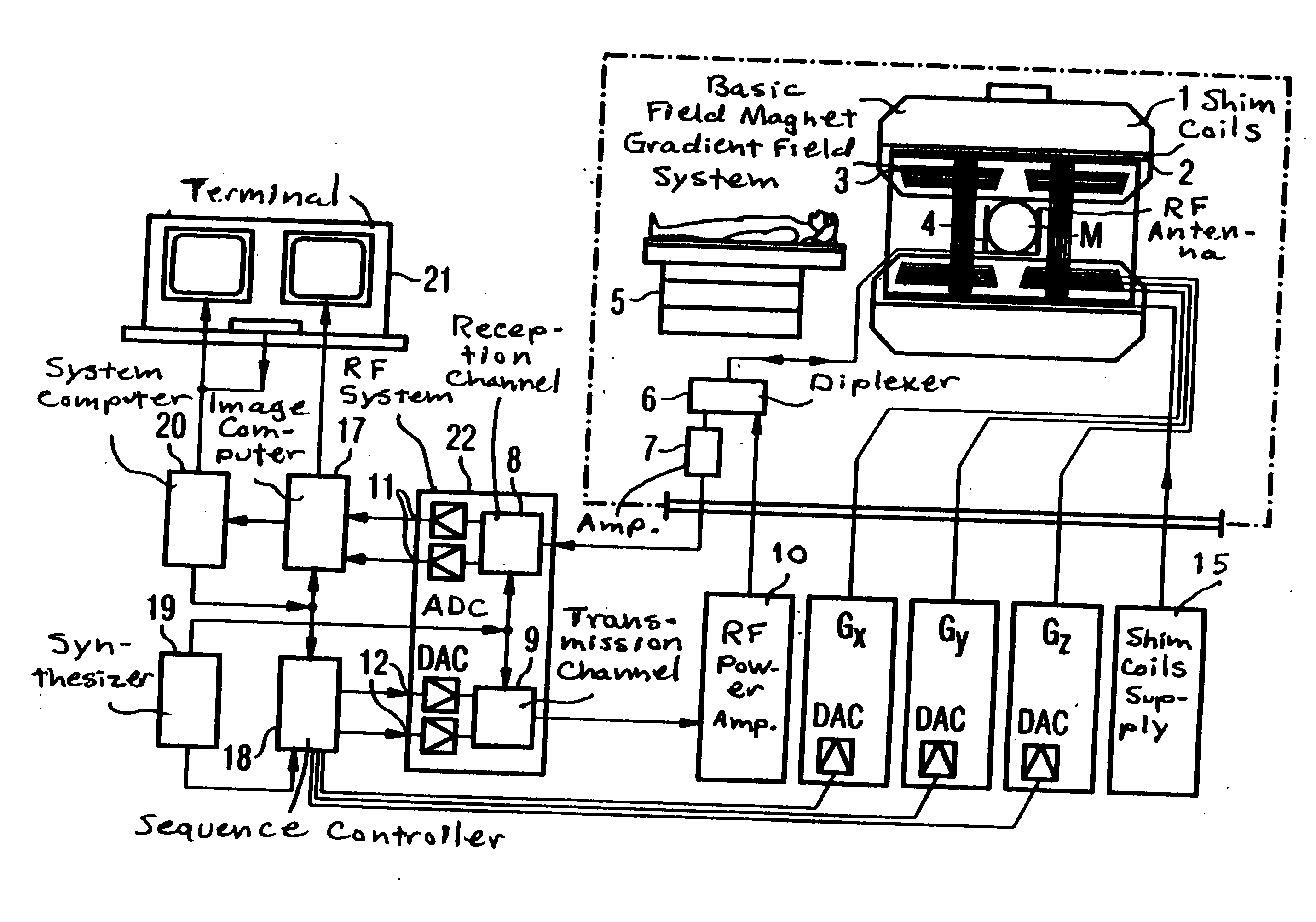
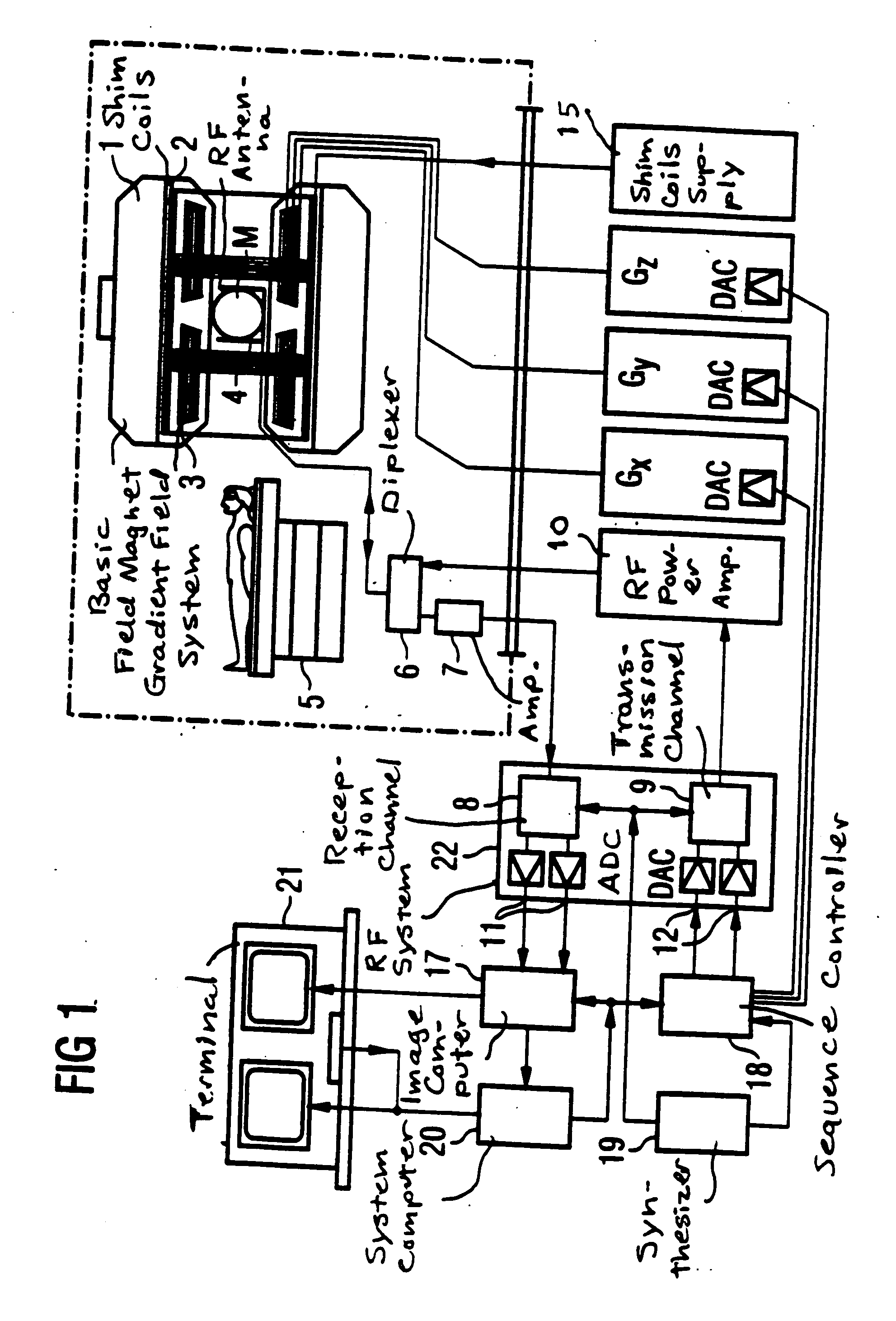
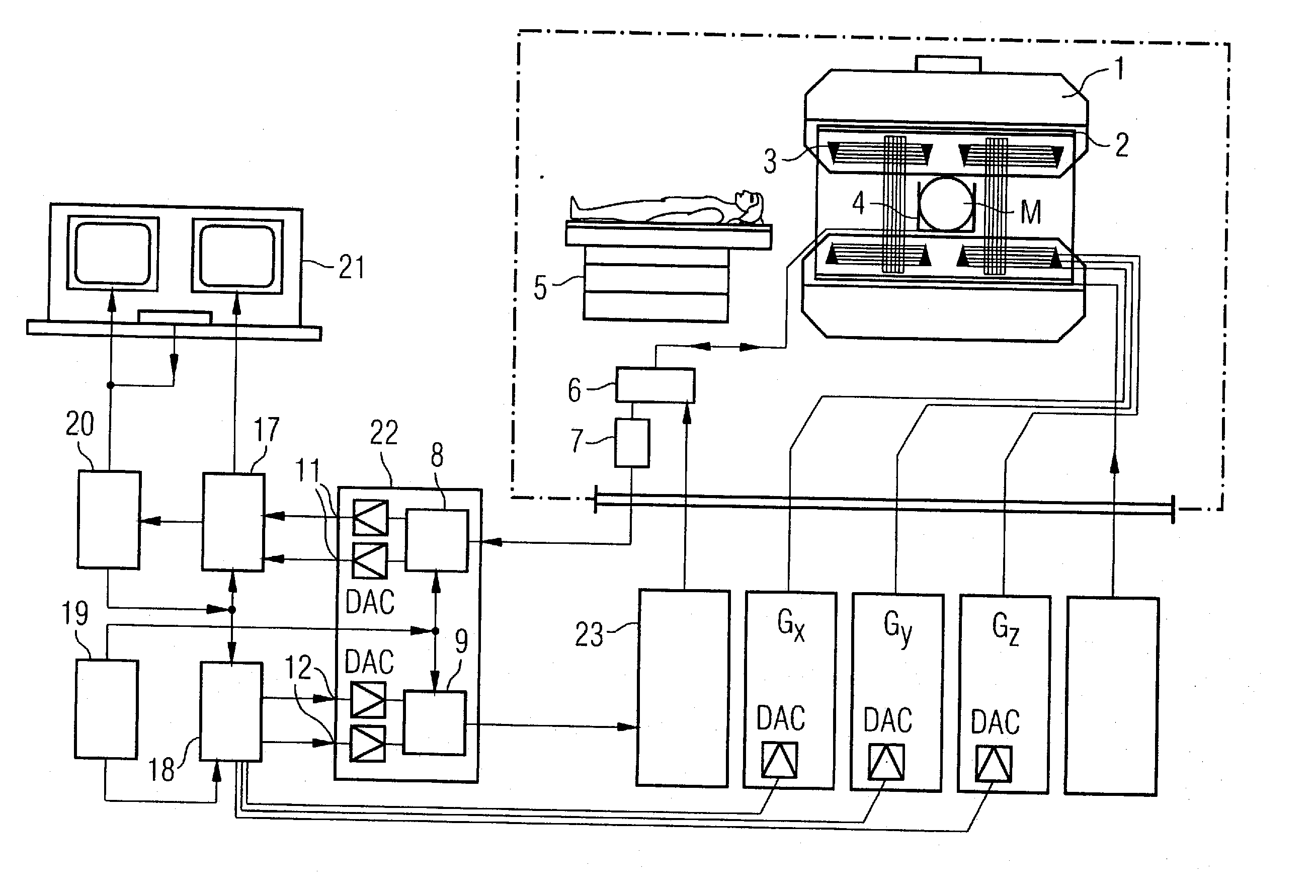
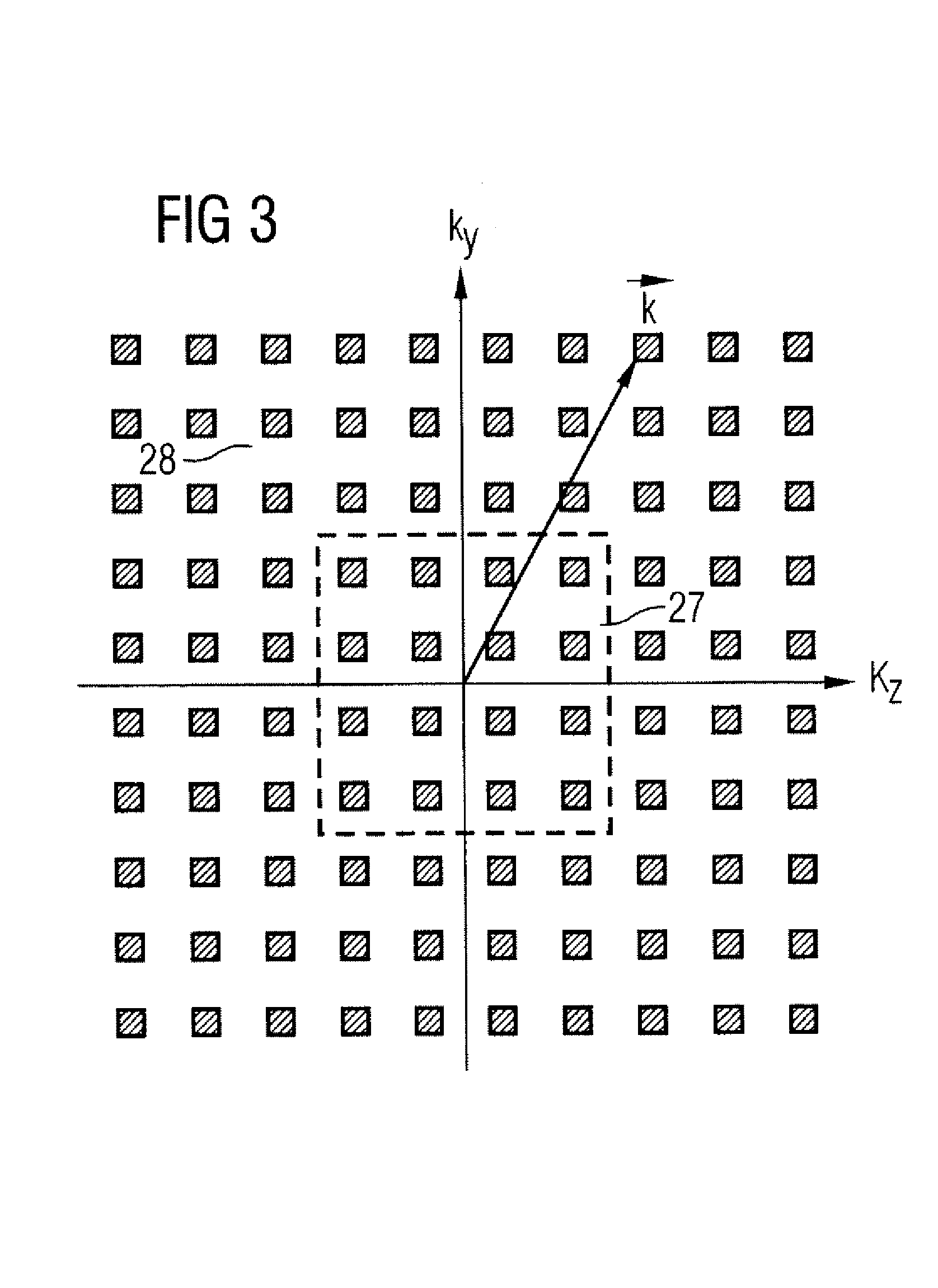
Method for optimizing the k-space trajectories in the location encoding of a magnetic resonance tomography apparatus
InactiveUS6937015B2Optimally fast samplingDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsSequence controlResonance
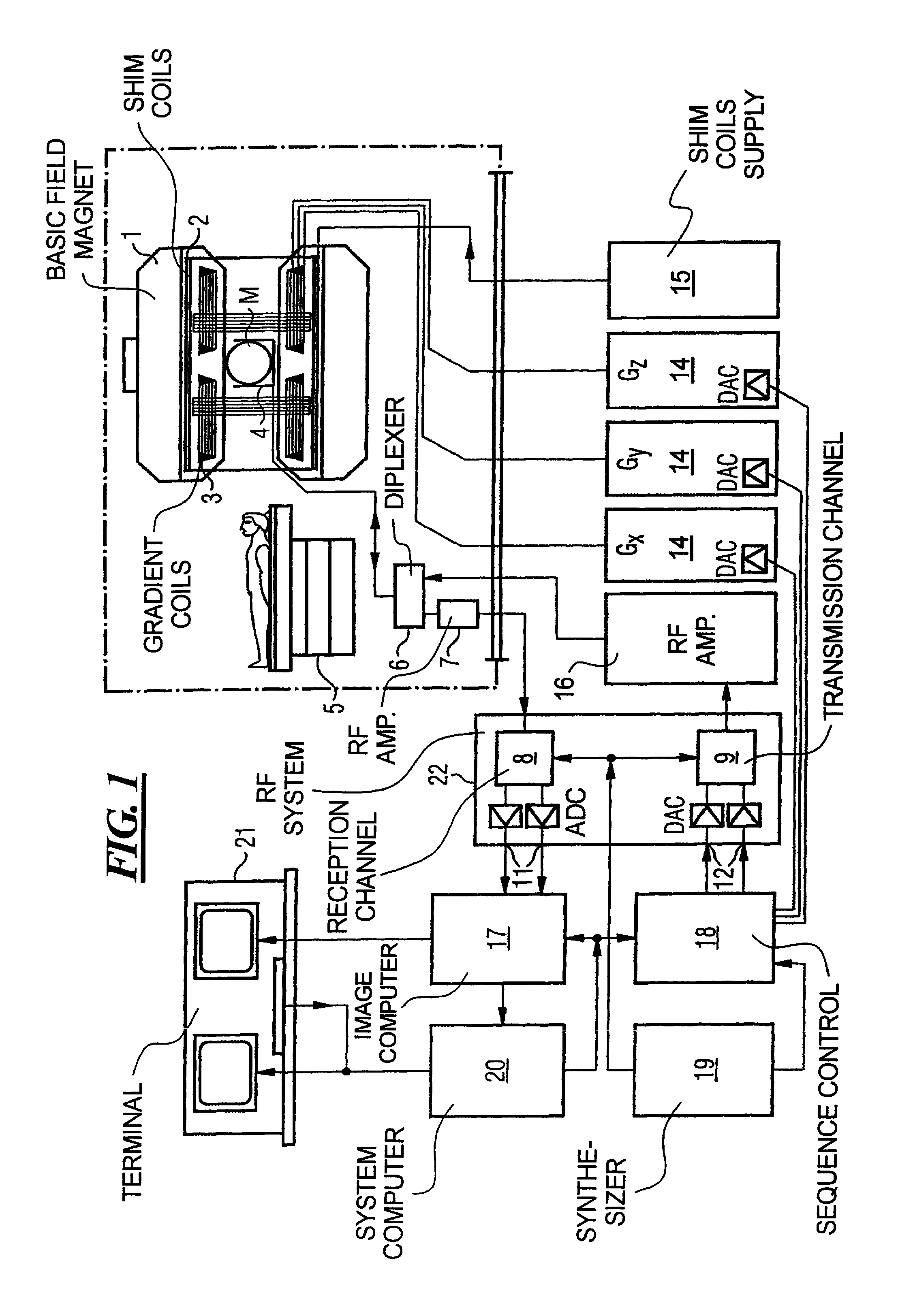
In a method and apparatus for calculating the sampling path of the k-matrix under given boundary conditions for the examination of a subject by means of a magnetic resonance tomography apparatus having a gradient amplifier with appertaining gradient coils, an input-display terminal, a sequence controller and a system computer as well as an analog-to-digital converter, boundary conditions are entered into the sequence controller or into the system computer via the input-display terminal, the sampling path of the k-matrix is calculated taking the boundary conditions into consideration by the sequence controller or the system computer, and the gradient current curves are determined by the sequence controller or the system computer that lead to a sampling along the previously calculated sampling path when applied to the corresponding gradient coils with utilization of the ADC.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method of constructing parity-check matrix of LDPC code and encoding method and encoding apparatus based on the method
InactiveUS20120173949A1Improve performanceImplementation complexity can be reducedError preventionCode conversionExpansion factorParity-check matrix
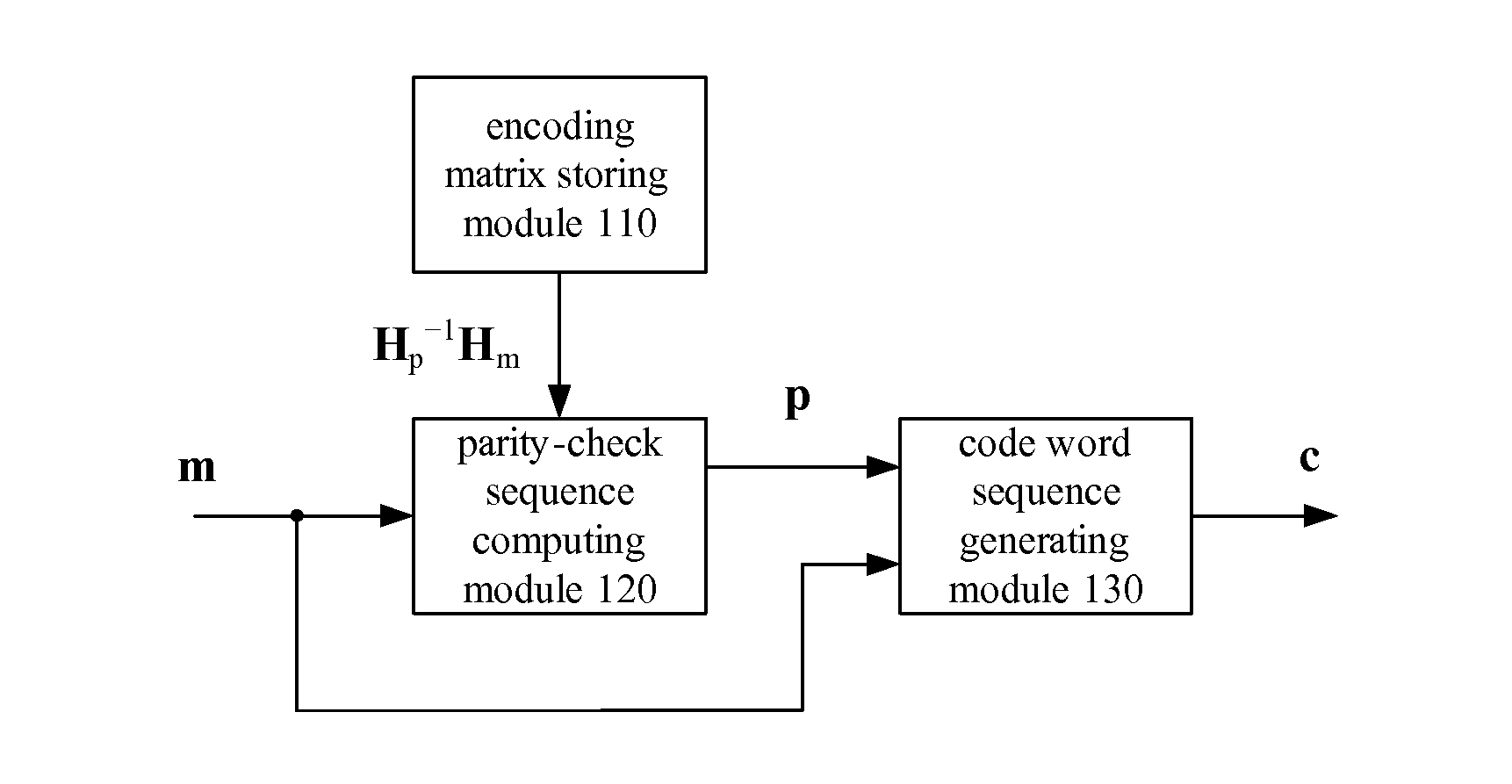
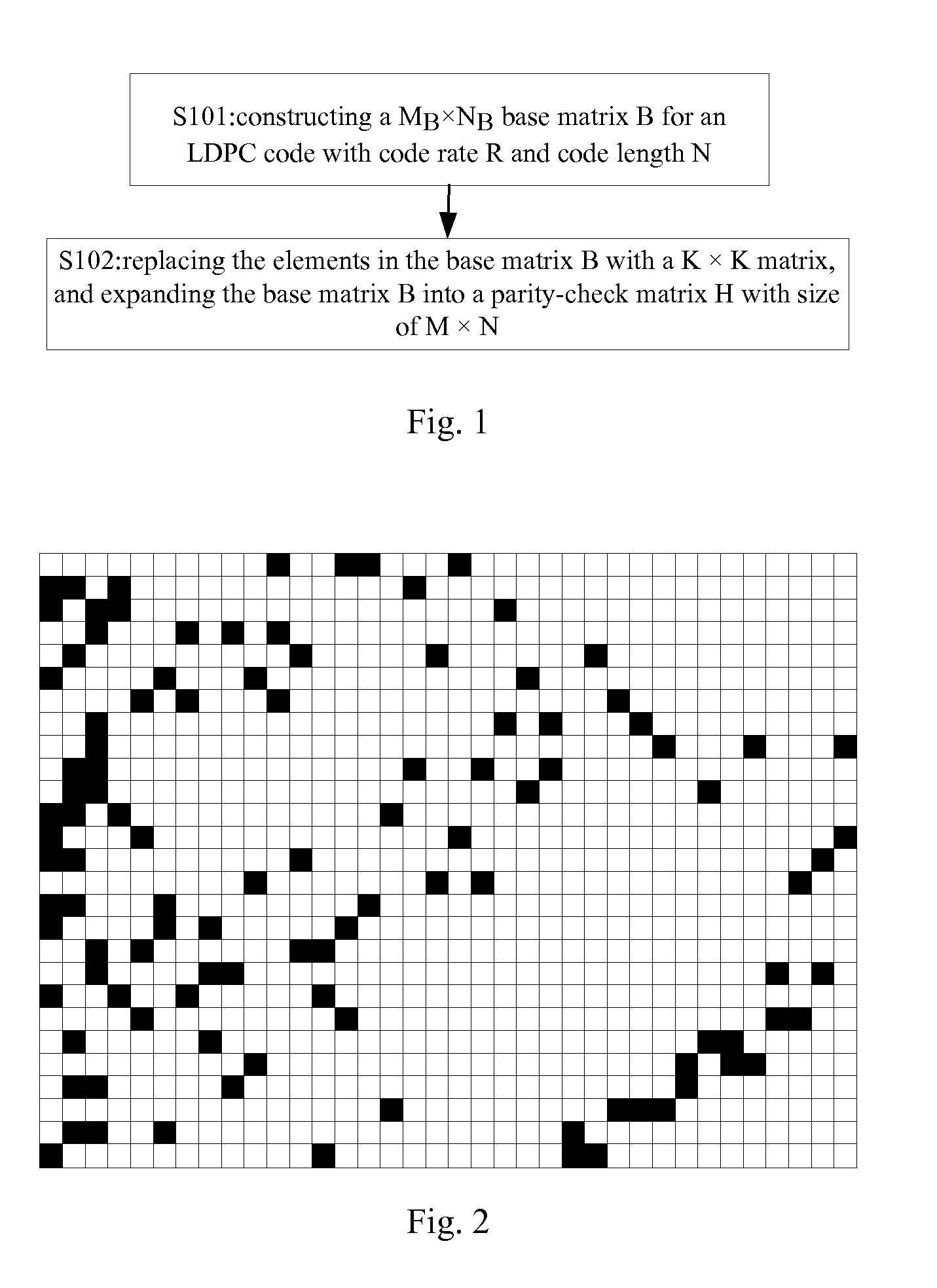
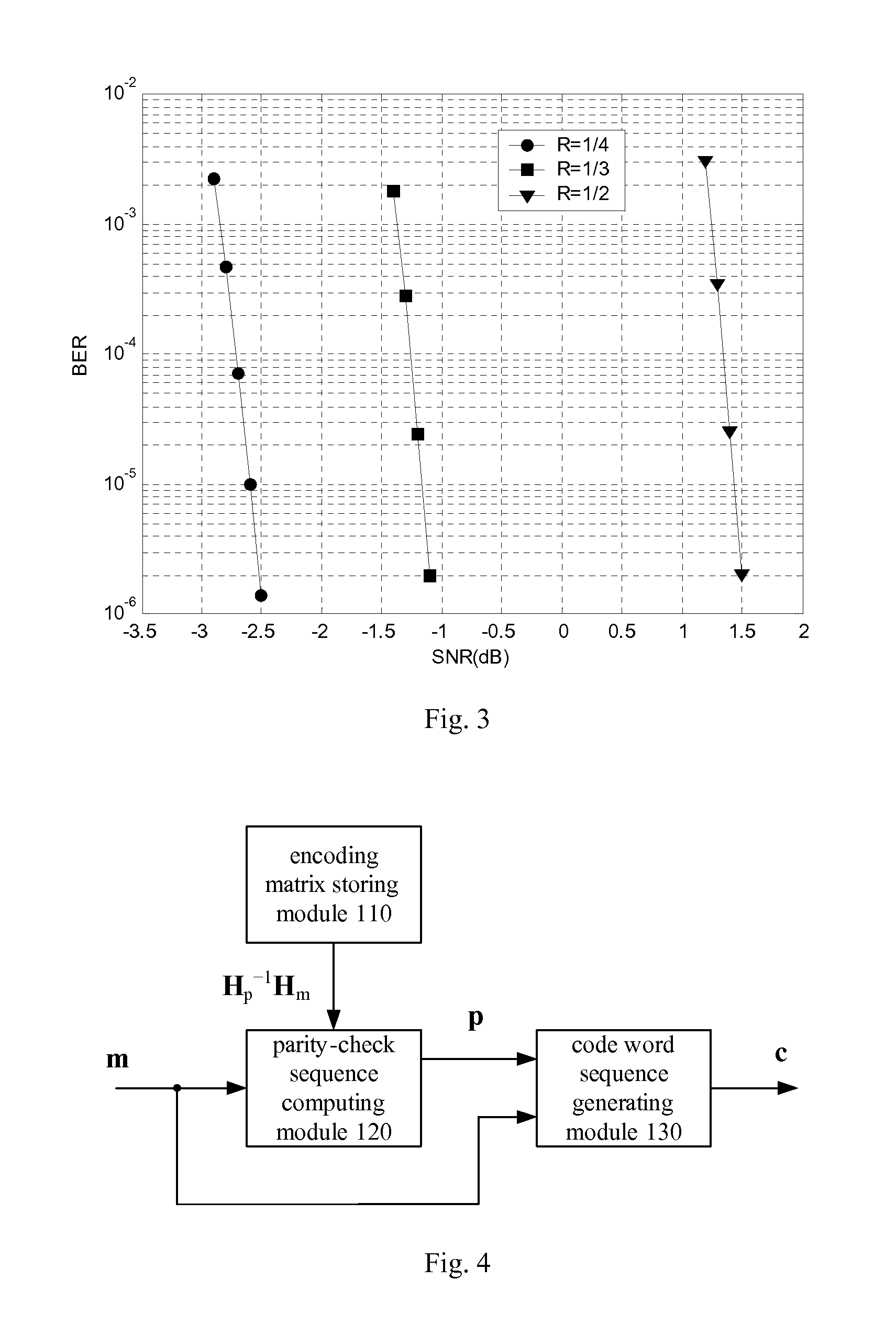
The embodiments of the present invention provide a method of constructing parity-check matrix of LDPC code. The method comprises the following steps of: constructing a MB×NB base matrix B for an LDPC code with code rate R and code length N, wherein MB=M / K, NB=N / K, M=N (1−R), K is the expansion factor of the base matrix, Kεφ, and φ is the set of the common factors of M and N; and replacing the elements of the base matrix B with a K×K matrix, and expanding the base matrix B into a parity-check matrix H with size of M×N for the encoding or decoding of the LDPC code. An encoding method and apparatus of LDPC code are also provided by the embodiments of the present invention. The technical solutions provided by the embodiments of the present invention can construct LDPC codes with good performance, solve the storage problem of the parity-check matrix, and effectively reduce the implementation complexity of the encoding apparatus.
Owner:TIMI TECH
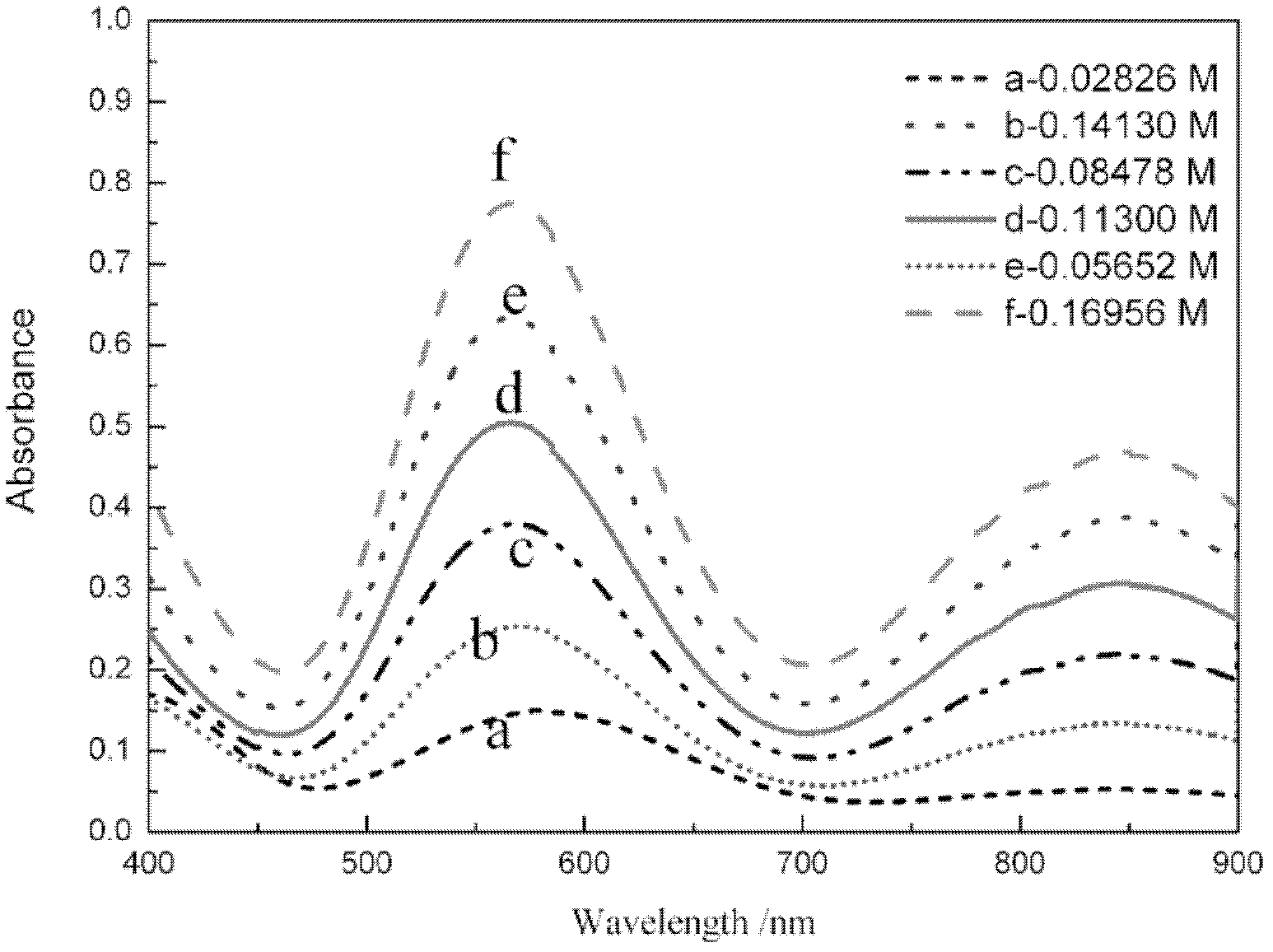
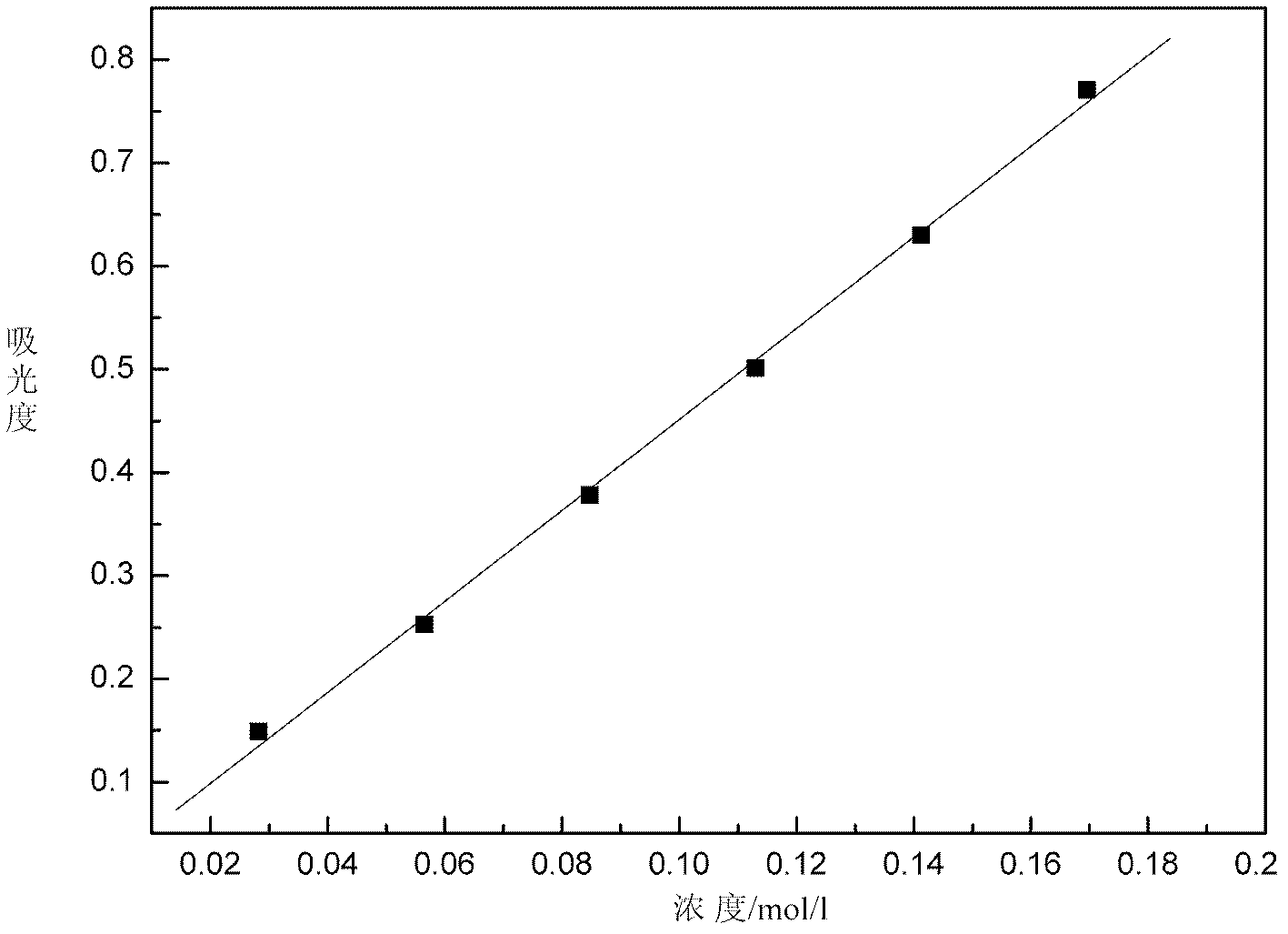
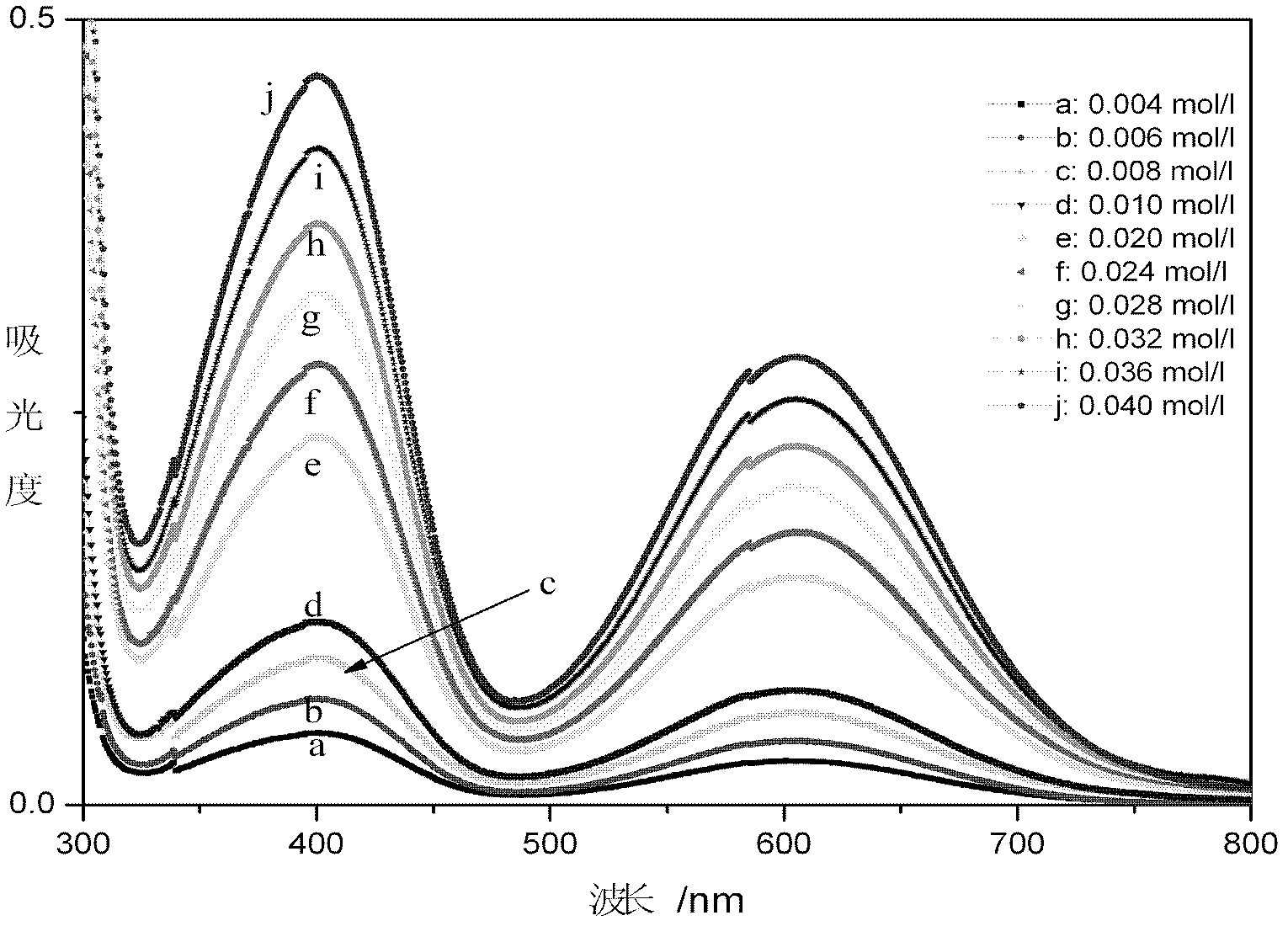
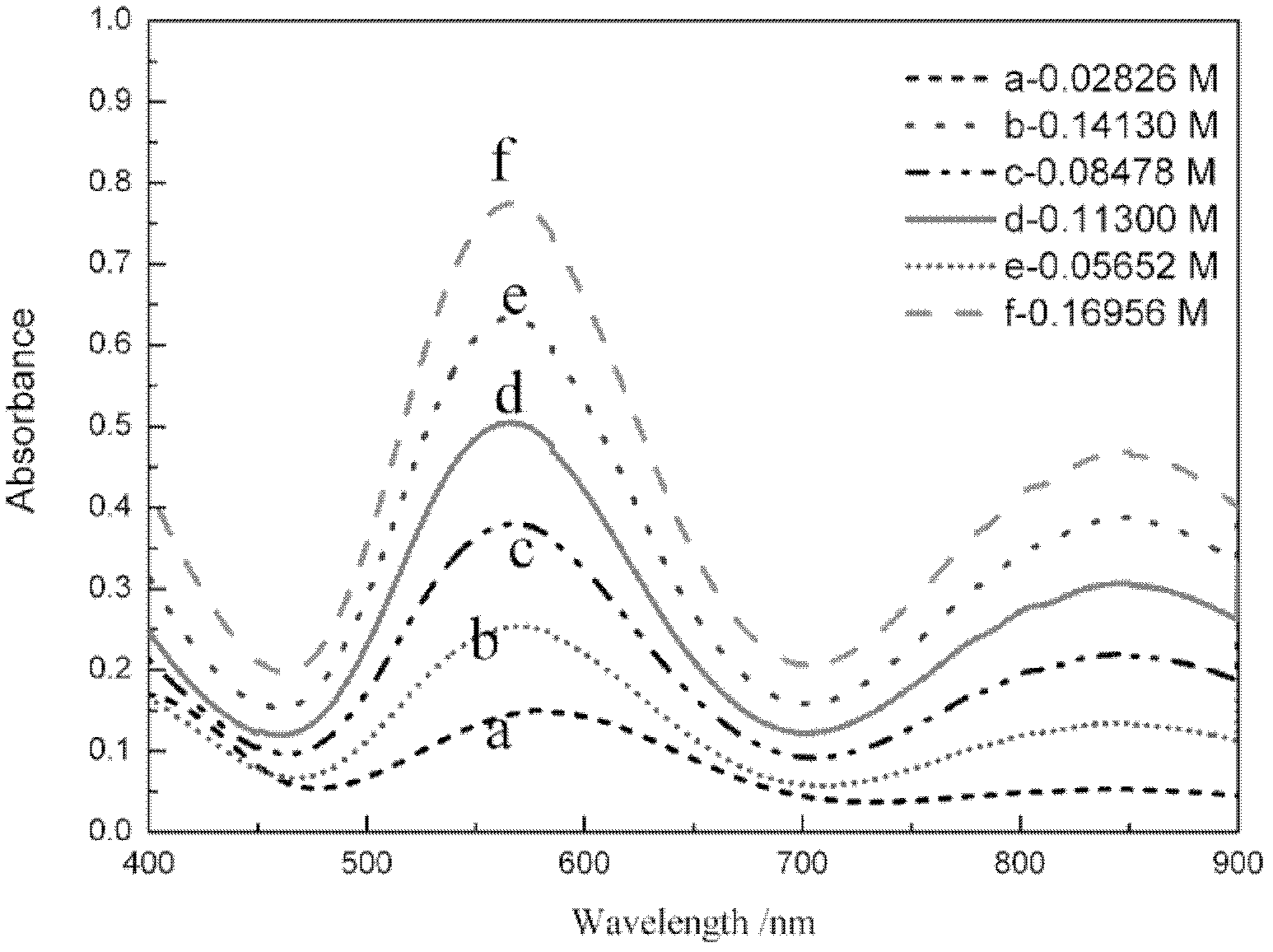
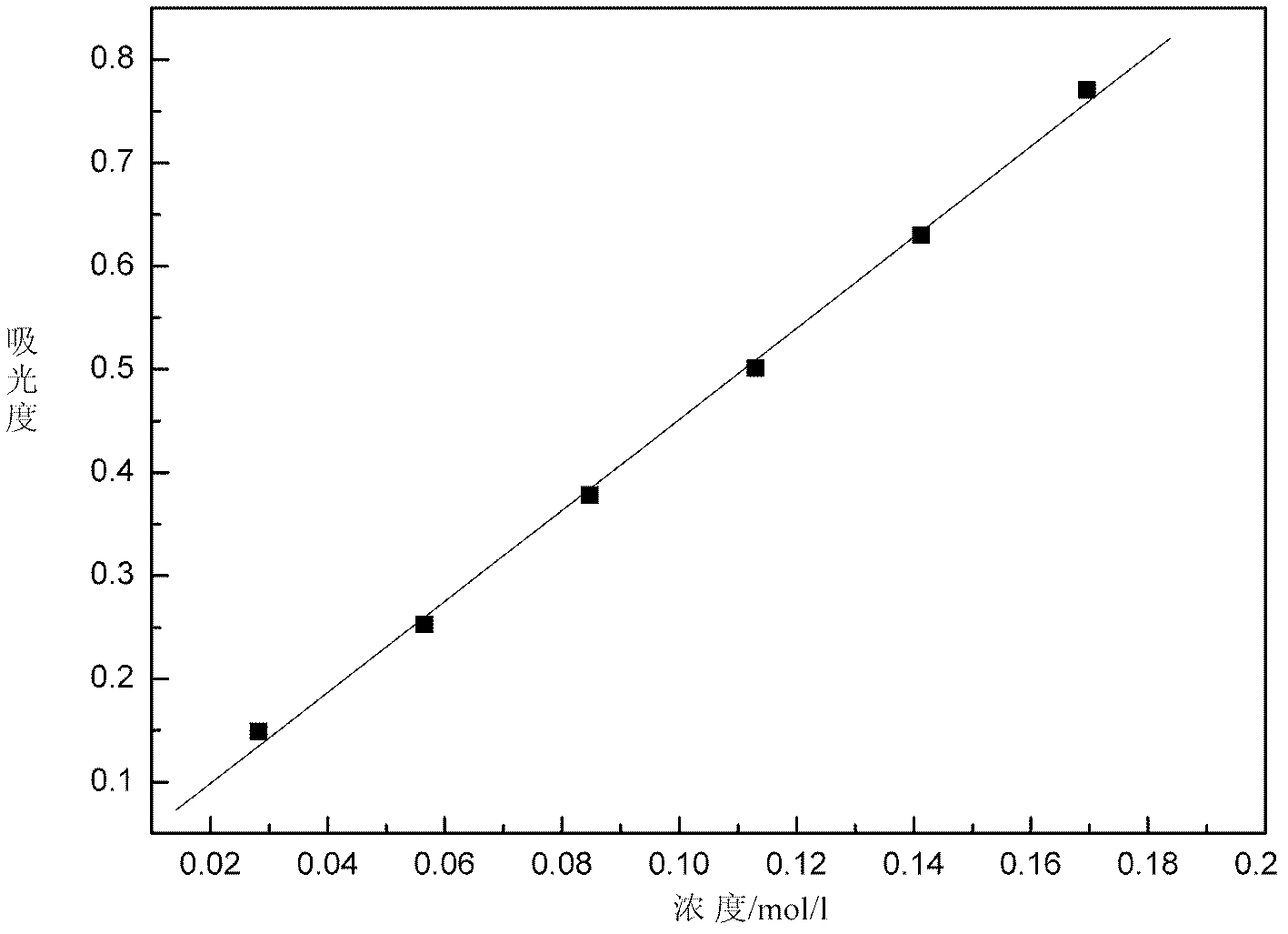
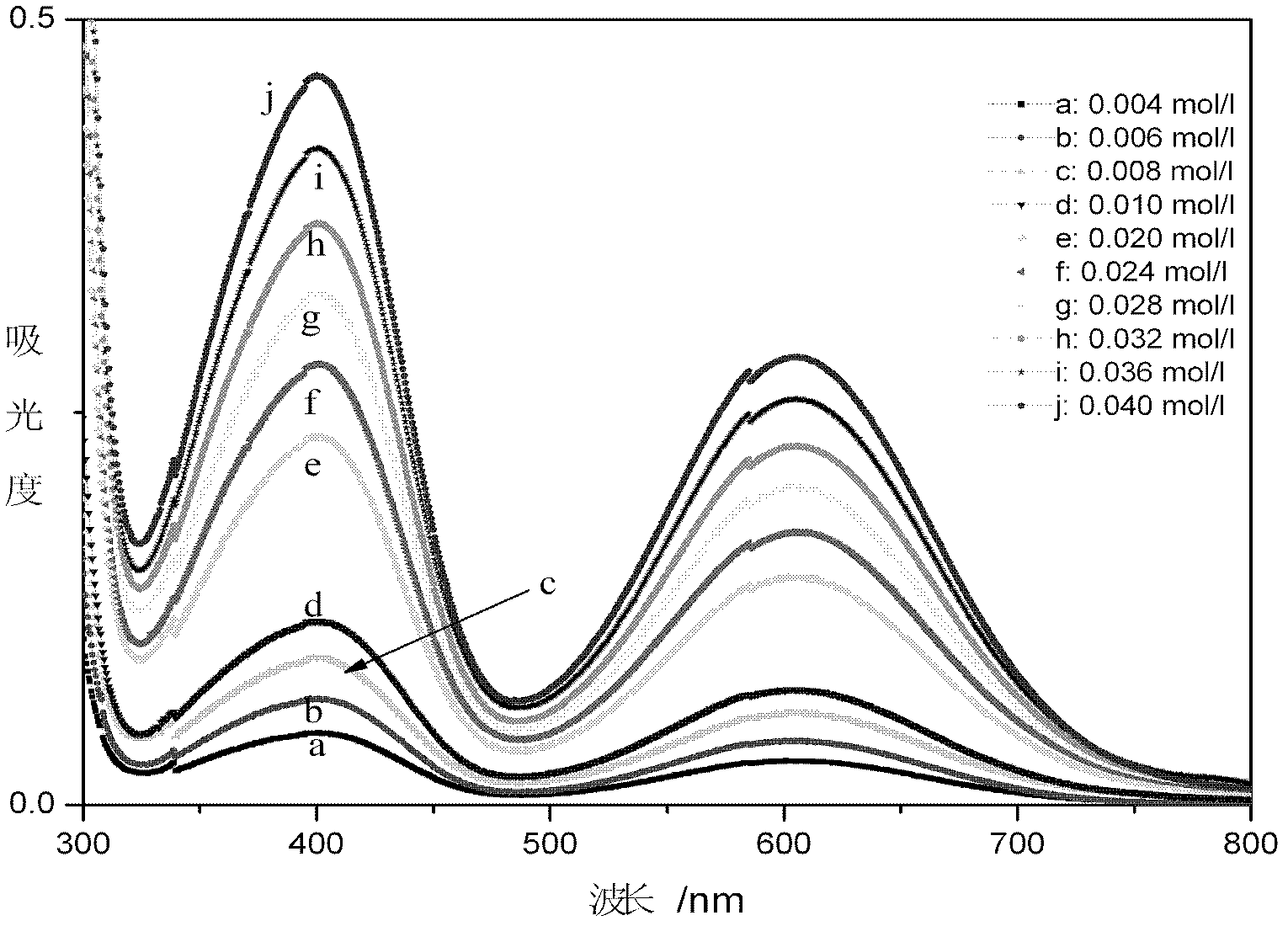
Method for online detection of concentration of electrolyte of vanadium battery
InactiveCN102621085AOnline rapid monitoring of valence changesQuickly monitor valence changesColor/spectral properties measurementsVanadium redox batteryAbsorbance
The invention relates to a method for online detection of the concentration of electrolyte of an all vanadium redox flow battery. A divalent vanadium V (II) system, a trivalent vanadium V (III) system and a tetravalent vanadium V (IV) system are analyzed by the aid of ultraviolet and visible spectrophotometry, a divalent vanadium V (II) and trivalent vanadium V (III) mixed system and a trivalent vanadium V (III) and tetravalent vanadium V (IV) mixed system are analyzed by the aid of a K matrix method, and a curve equation of the concentration of the vanadium with various valence states and absorbance in the systems is deduced. The concentration of vanadium ions with various valence states in a test sample can be rapidly detected only by substituting absorbance data of the test sample with unknown concentration in the electrolyte of the vanadium battery into the absorbance-concentration curve equation measured and deduced by the method, and accuracy of the method is proved as compared with a national standard method. The method has a huge application prospect in terms of dynamically monitoring valence changes of the electrolyte of the vanadium ions and simultaneously, qualitatively and quantitatively checking the vanadium electrolyte with mixed valence states.
Owner:HUNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
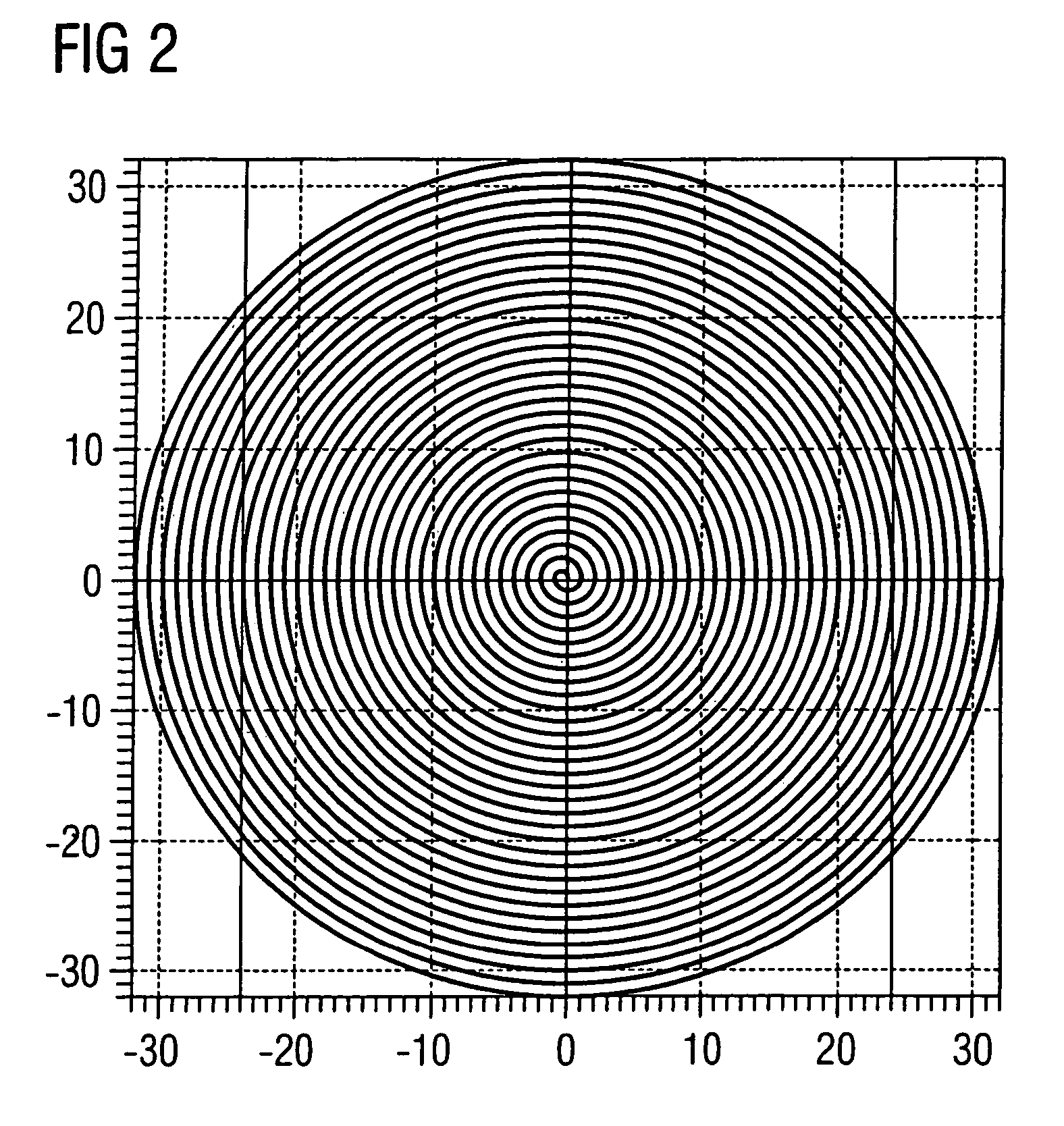
Method and apparatus for accelerated spiral-coded imaging in magnetic resonance tomography
InactiveUS7265545B2Shorten the durationMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionResonanceTomography
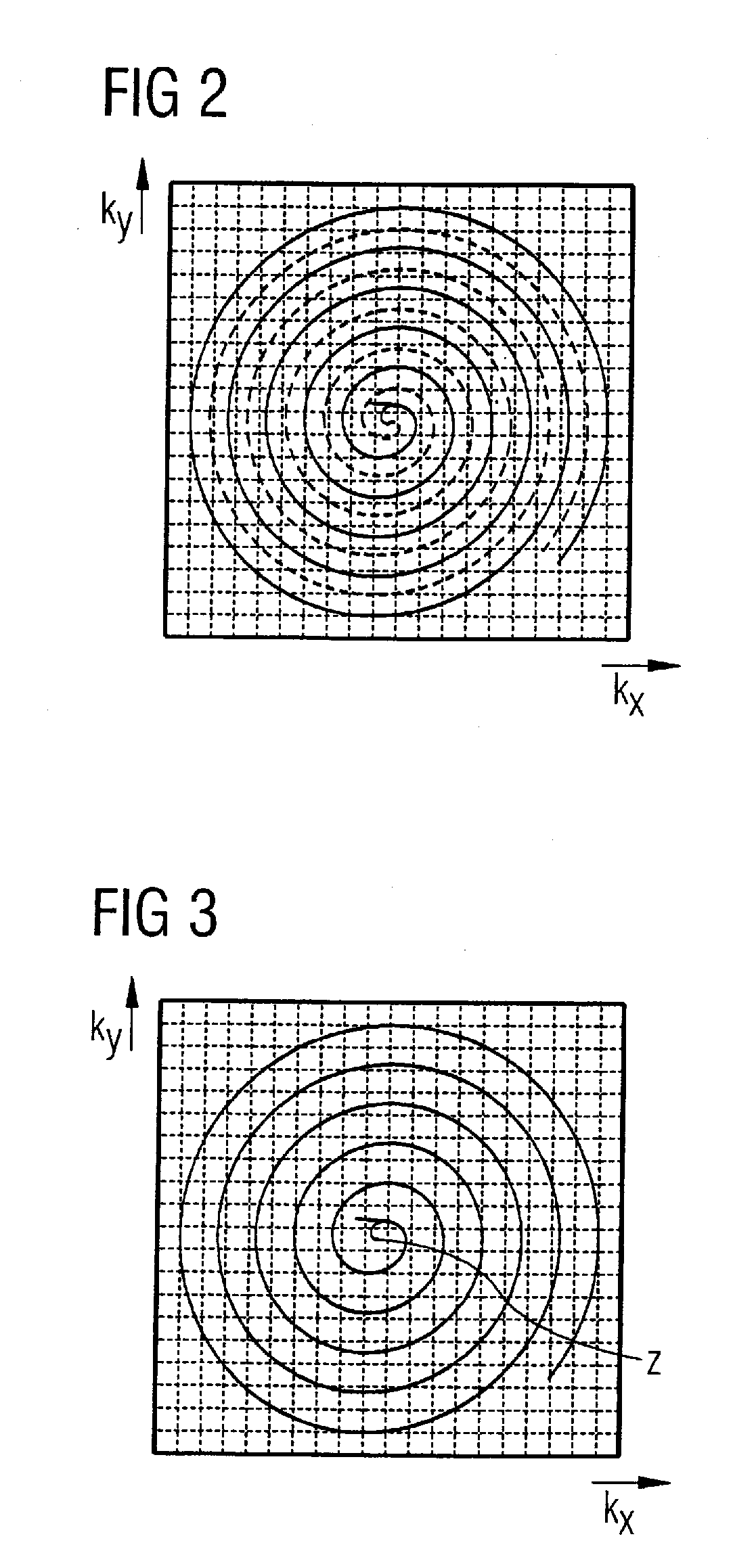
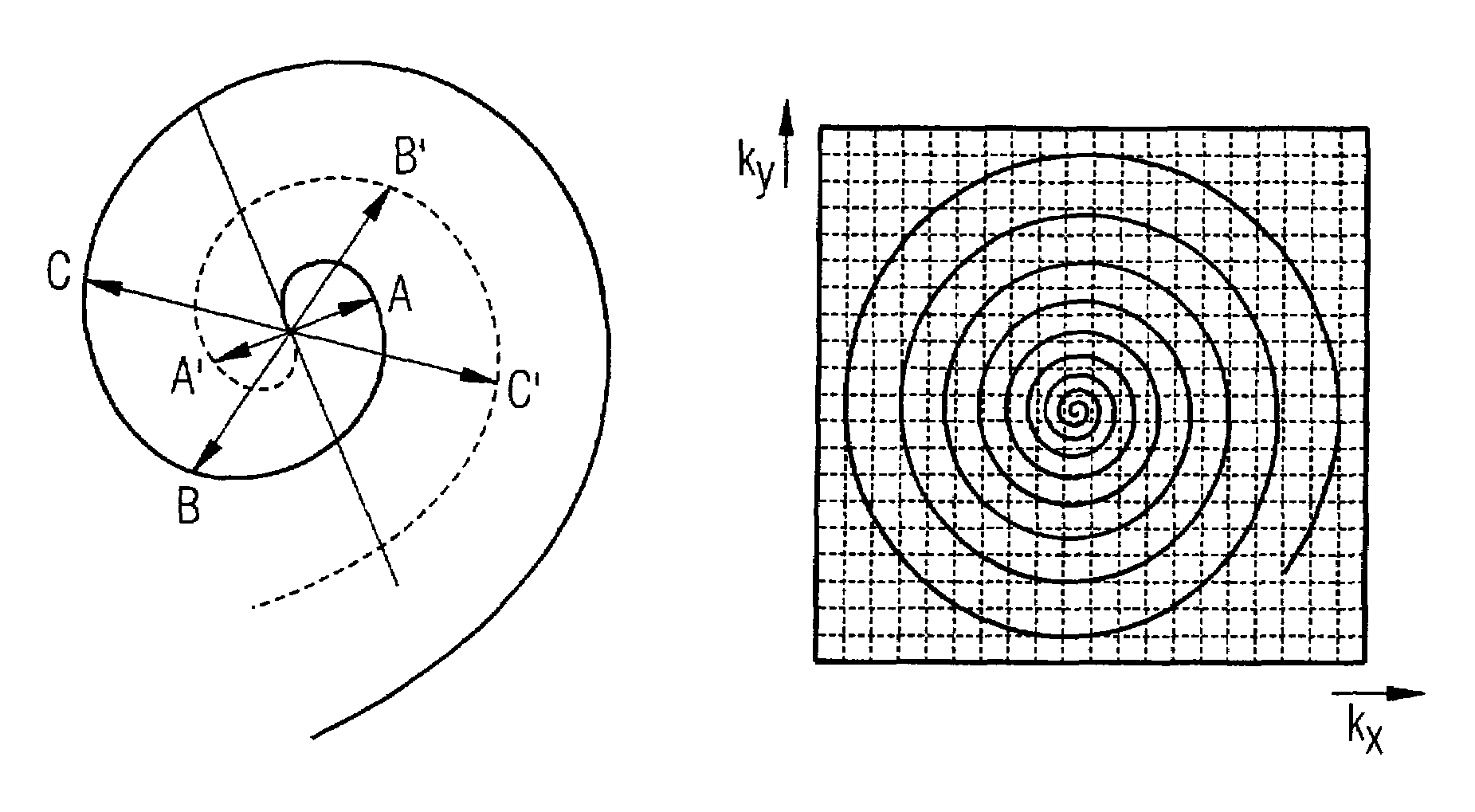
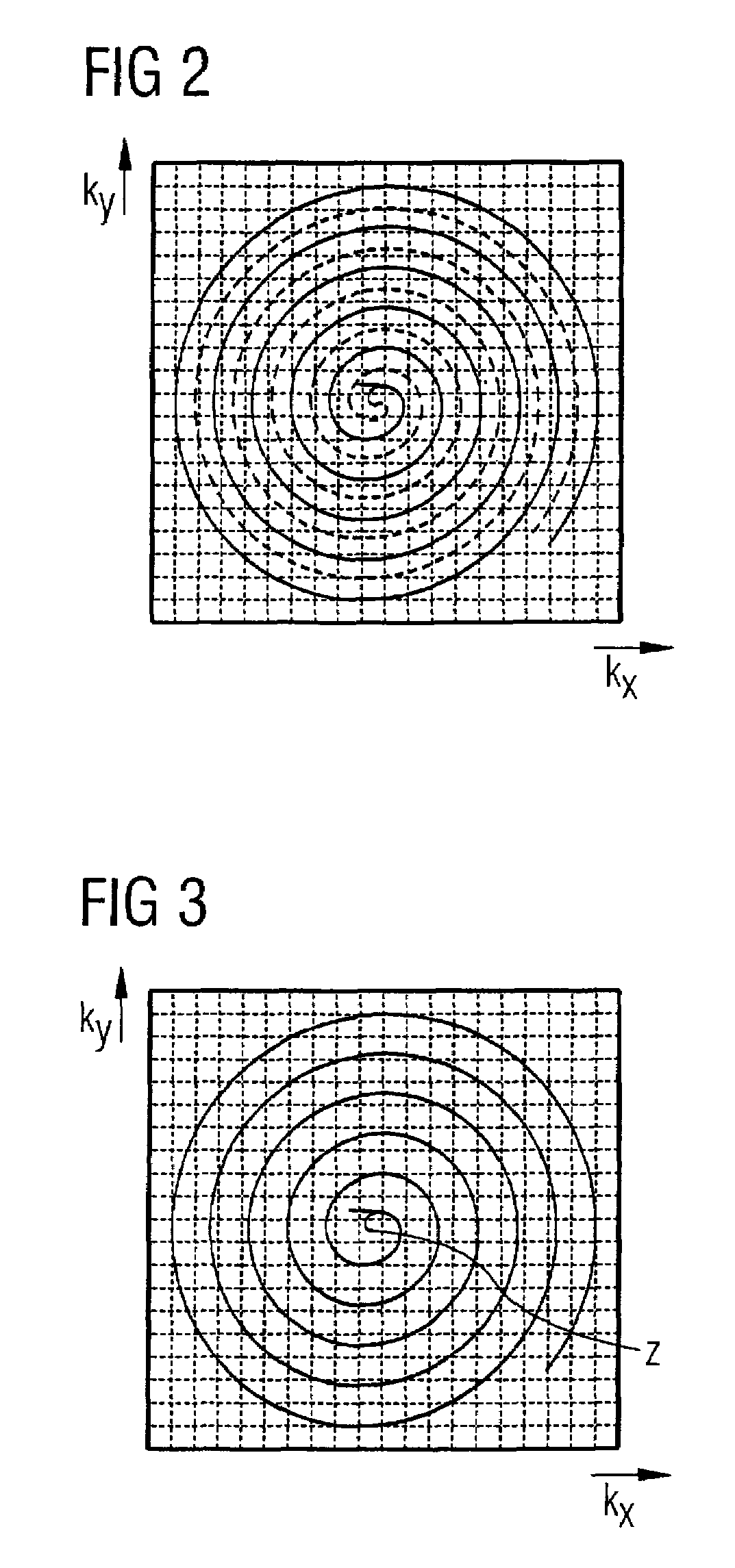
In a method and apparatus for accelerated spiral-coded imaging (scanning k-space with a spiral trajectory) in magnetic resonance tomography, the user-defined sequence forming the basis of the spiral scanning is modified such that the k-matrix forming the basis of the sequence is scanned only in a sub-region, the sub-region being defined by a symmetrical shortening on both sides of the k-space matrix in a first direction as well as by a one-sided shortening of the k-space matrix in a second direction orthogonal to the first direction.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
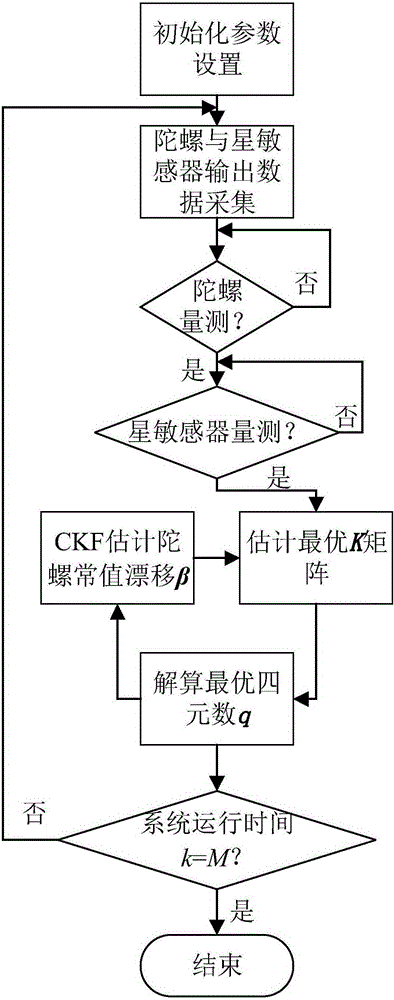
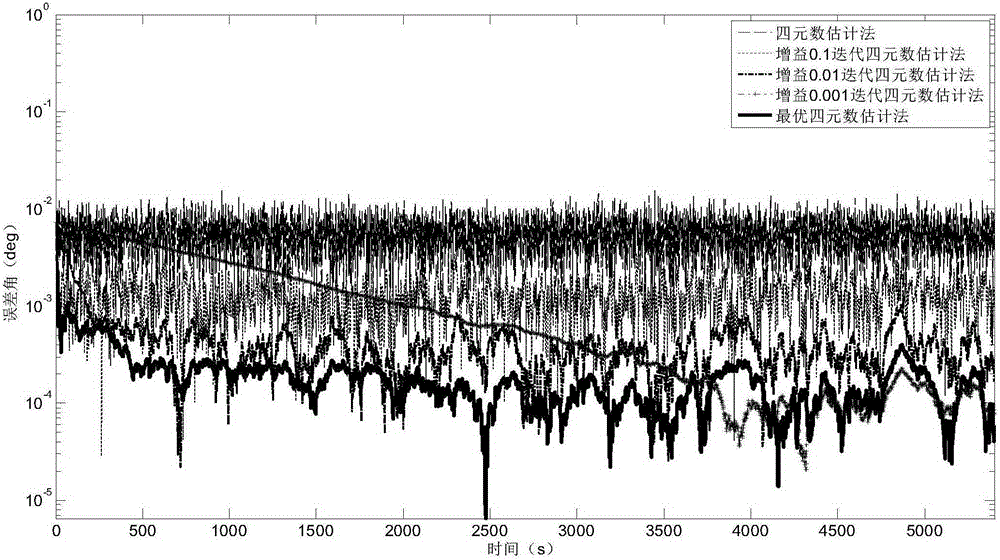
Interactive filtering method for satellite attitude determination
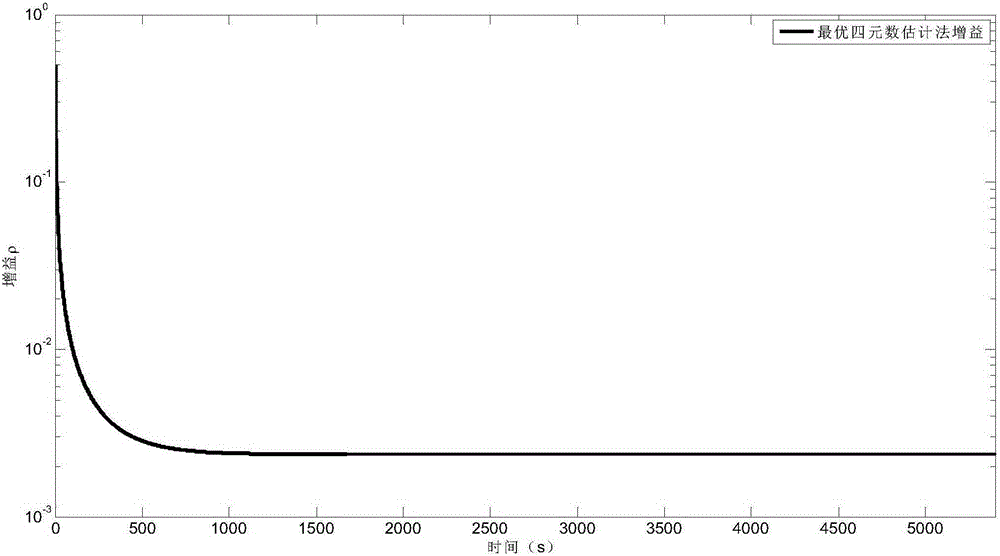
ActiveCN105300384AAvoid calculationEasy to calculateInstruments for comonautical navigationGyroscopeQuaternion
The invention discloses an interactive filtering method for satellite attitude determination, and aims to overcome the defect that constant gyro drifts cannot be estimated by utilizing the optimal-REQUEST algorithm and improve the algorithm applicability. The method comprises the following steps: step 1, acquiring sensor measurement data, including gyroscope data and star sensor data; step 2, building a state space model of a satellite attitude estimation system, as well as building an attitude K matrix; step 3, according to the state space model, the state estimate of the known moment k, and a gyro measurement value, estimating constant gyro drifts at the moment k+1 by utilizing the CKF algorithm and the optimal quaternion at the moment k, and then compensating the gyro measurement value; step 4, according to the compensated gyro measurement value, carrying out time update and measurement update by utilizing the optimal-REQUEST algorithm, so as to obtain the optimal K matrix at the moment k+1; the remaining steps of obtaining the optimal quaternion at the moment k+1. The interactive filtering method is beneficial to improvement of the estimation precision.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
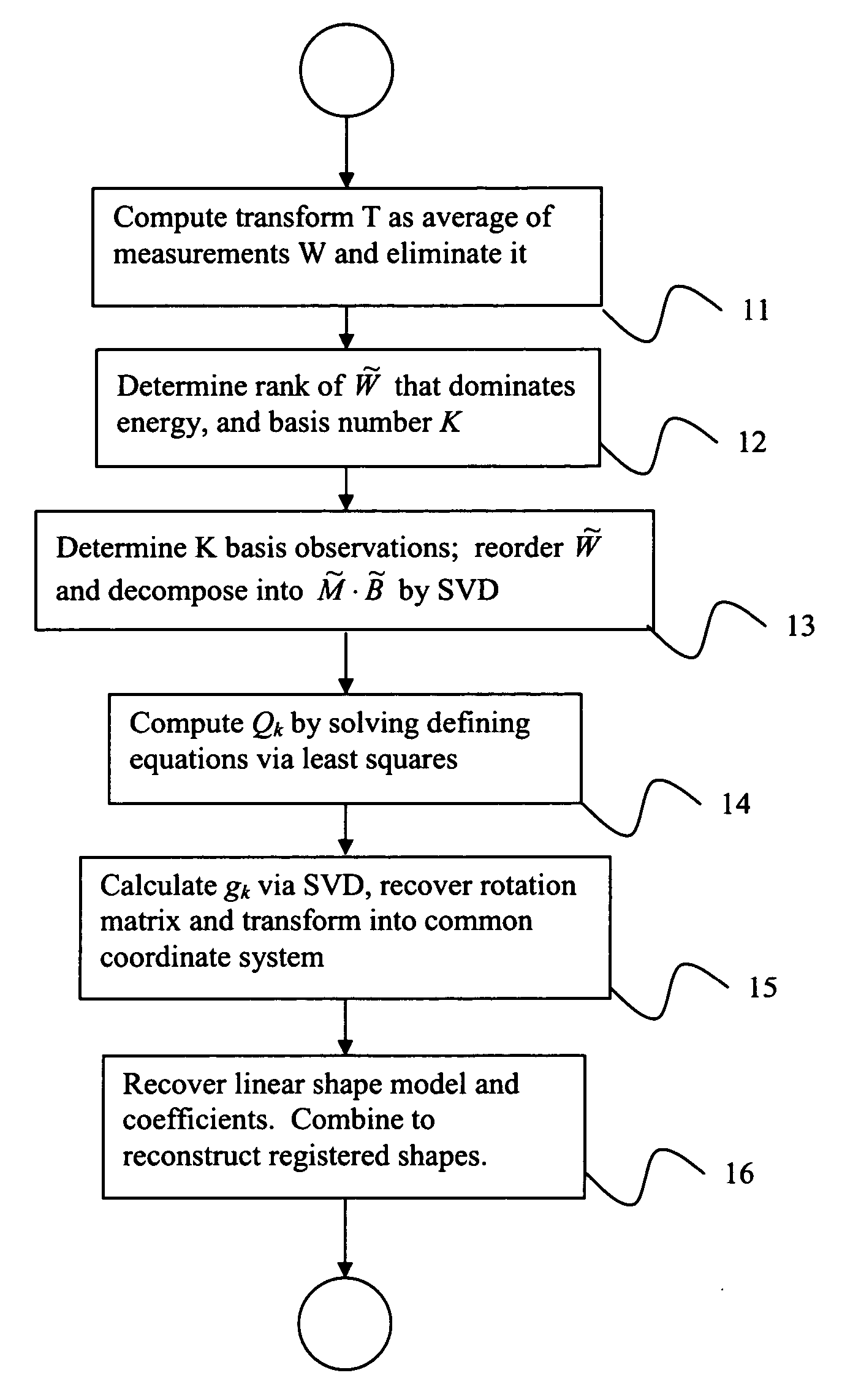
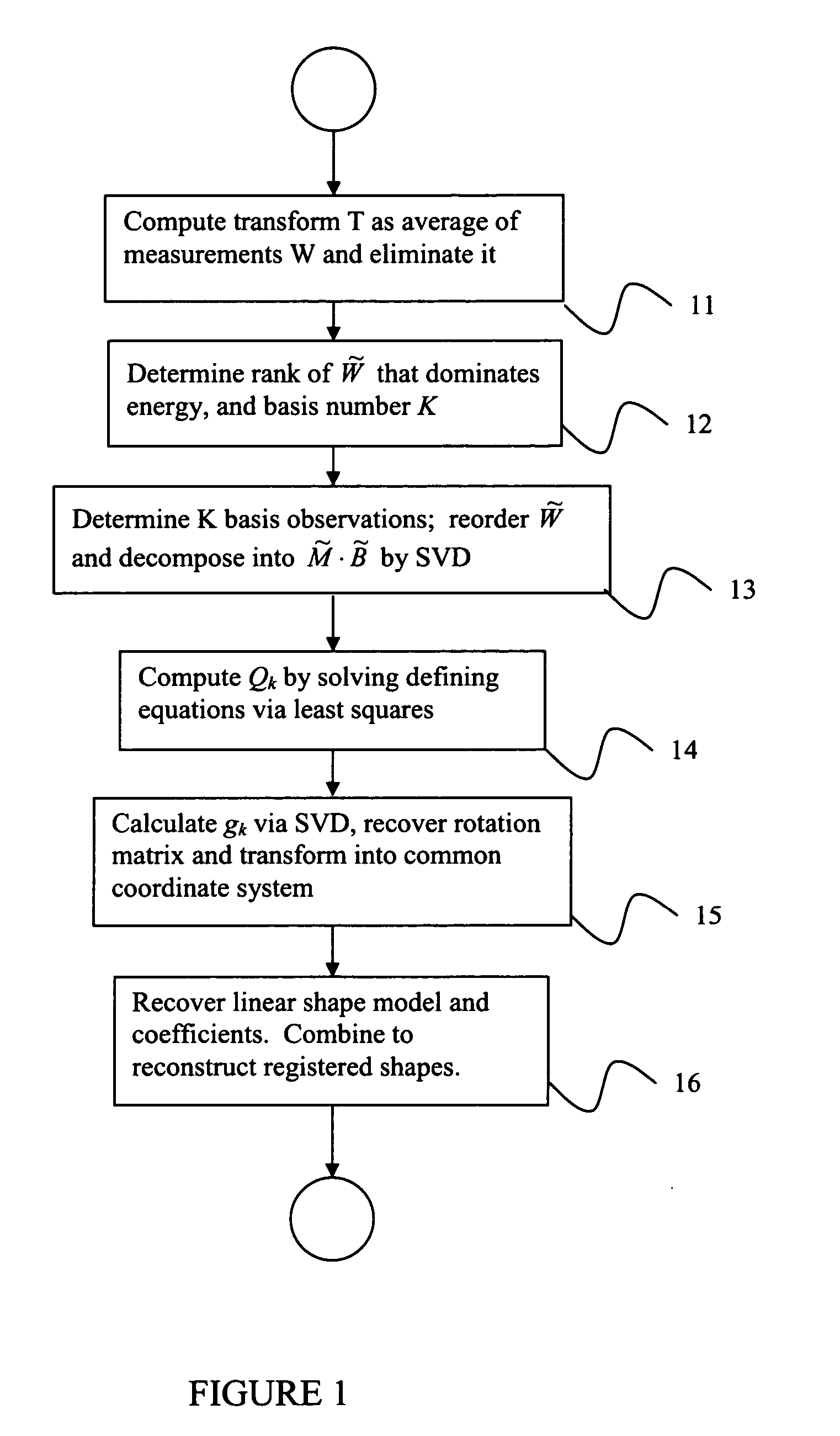
System and method for registration and modeling of deformable shapes by direct factorization
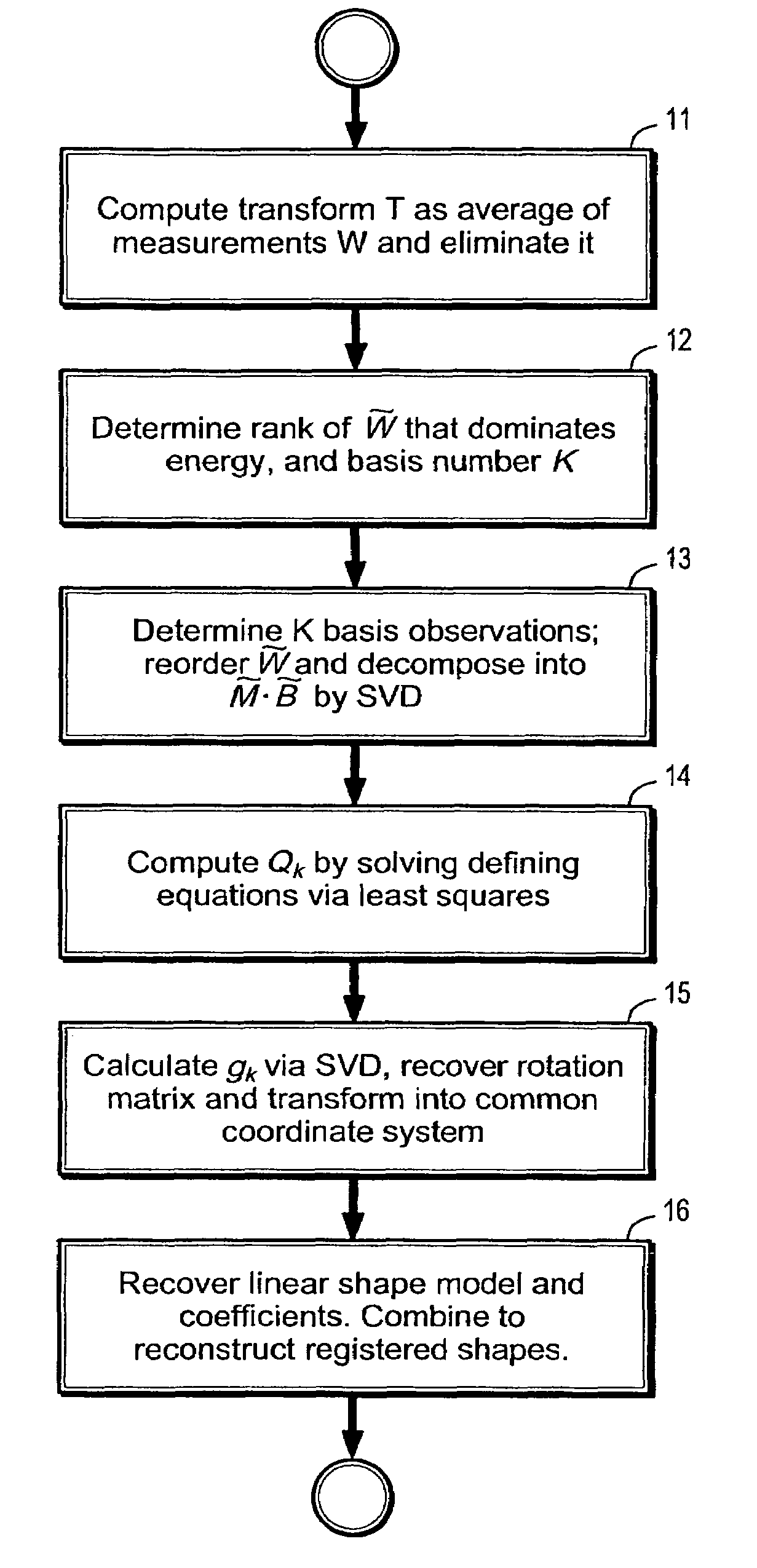
A method of registering and modeling a deformable shape in a digitized image is provided, comprising the steps of providing a measurement matrix W of N measurements of P points of a D-dimensional deformable shape, determining a basis number K for the N measurements, wherein K<N, and selecting K measurements of said measurement matrix W as a basis set, decomposing said measurement matrix W into a matrix product Mx∃B, wherein M is a proposed scaled rotation matrix and B is a proposed basis matrix, computing a matrix Qk defined by MiQkMjT={ID×D,i=j=k0D×D,(i,j)∈Φ,where Φ stands for {(i, j)|i=1, . . . , K; j=1, . . . , N, iγk}, which represents an ambiguity matrix transforming the proposed scaled rotation matrix and the proposed basis matrix into a true scaled rotation matrix and a true basis matrix; decomposing the matrix Qk into gkgkT, for k=1, . . . , K, wherein gk is a column of a D∃K % D∃K matrix G; and recovering the true scaled rotation matrix from Mx∃G and the true basis matrix from G−1x∃B.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Face recognition and movement track judging methods under high noise
InactiveCN107153820AMake sure the target is reliableReduce the possibility of misjudgmentCharacter and pattern recognitionFeature extractionK matrix
The invention discloses face recognition and movement track judging methods under high noise. The face recognition method comprises an image acquisition step, a feature extraction step, a feature comparison step, and a judgment step. In the image acquisition step, images of a video stream are acquired at intervals. In the feature comparison step, extracted features are compared with features stored in a face library, corresponding result vectors <id1, id2,...,idk > and <score1, score2,...,scorek> (respectively representing the IDs of most similar k persons in the face library and the similarity thereof) of faces are obtained, and two m*k matrixes are obtained for each image, wherein m is the number of persons in the frame of image. In the judgment step, a candidate person set is obtained according to images decoded from the same video stream and the number of times each ID appears in the comparison results, and a suspect ID is determined according to the number of times each ID in the candidate person set appears in images decoded from different video streams and the similarity. The method is of high detection reliability and low misjudgment rate under the condition of high noise.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
MRI method and apparatus with elimination of the ambiguity artifact
InactiveUS20050001619A1Avoid it happening againMagnetic measurementsNon-surgical orthopedic devicesAmbiguityFourier transform on finite groups
In a method for magnetic resonance imaging, by combined switching of radio-frequency excitation pulses, slice selection gradient pulses, phase-coding gradient pulses and readout gradient pulses, a matrix in the k-space is scanned row-by-row and transformed using a Fourier transformation into a matrix in the spatial domain, with the polarity of the slice selection gradient being inverted during the scanning of the k-matrix, allowing elimination of the ambiguity artifact.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Method and apparatus for accelerated spiral-coded imaging in magnetic resonance tomography
InactiveUS20080021303A1Shorten readout durationShorten the durationMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringComplete dataResonance
In a method and apparatus for accelerated spiral-coded imaging in magnetic resonance tomography using spiral-shaped k-space sampling, the underlying k-matrix is under-sampled such that an additional spiral is obtained by point mirroring of the measured values at the center of the k-matrix. This additional spiral forms a complete data set of the k-matrix together with the first spiral for imaging the output information.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
MRI method and apparatus with elimination of the ambiguity artifact
InactiveUS7109711B2Avoid it happening againMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringAmbiguityFourier transform on finite groups
In a method for magnetic resonance imaging, by combined switching of radio-frequency excitation pulses, slice selection gradient pulses, phase-coding gradient pulses and readout gradient pulses, a matrix in the k-space is scanned row-by-row and transformed using a Fourier transformation into a matrix in the spatial domain, with the polarity of the slice selection gradient being inverted during the scanning of the k-matrix, allowing elimination of the ambiguity artifact.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
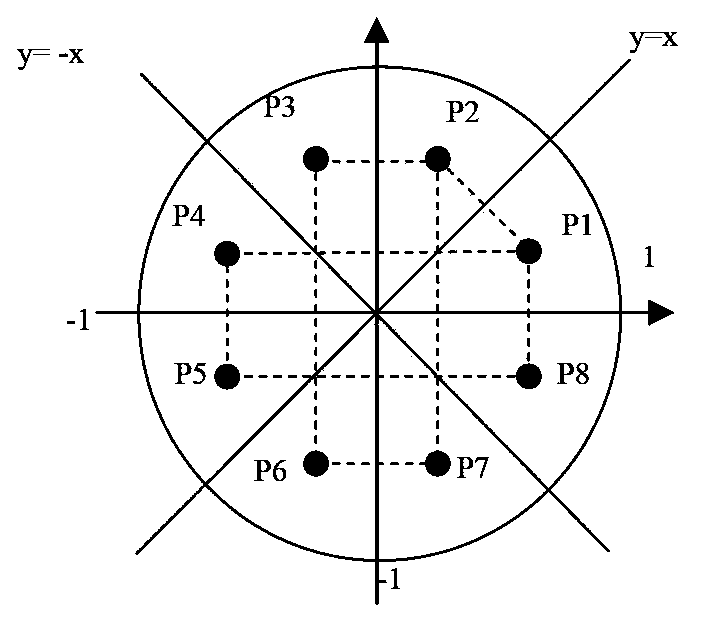
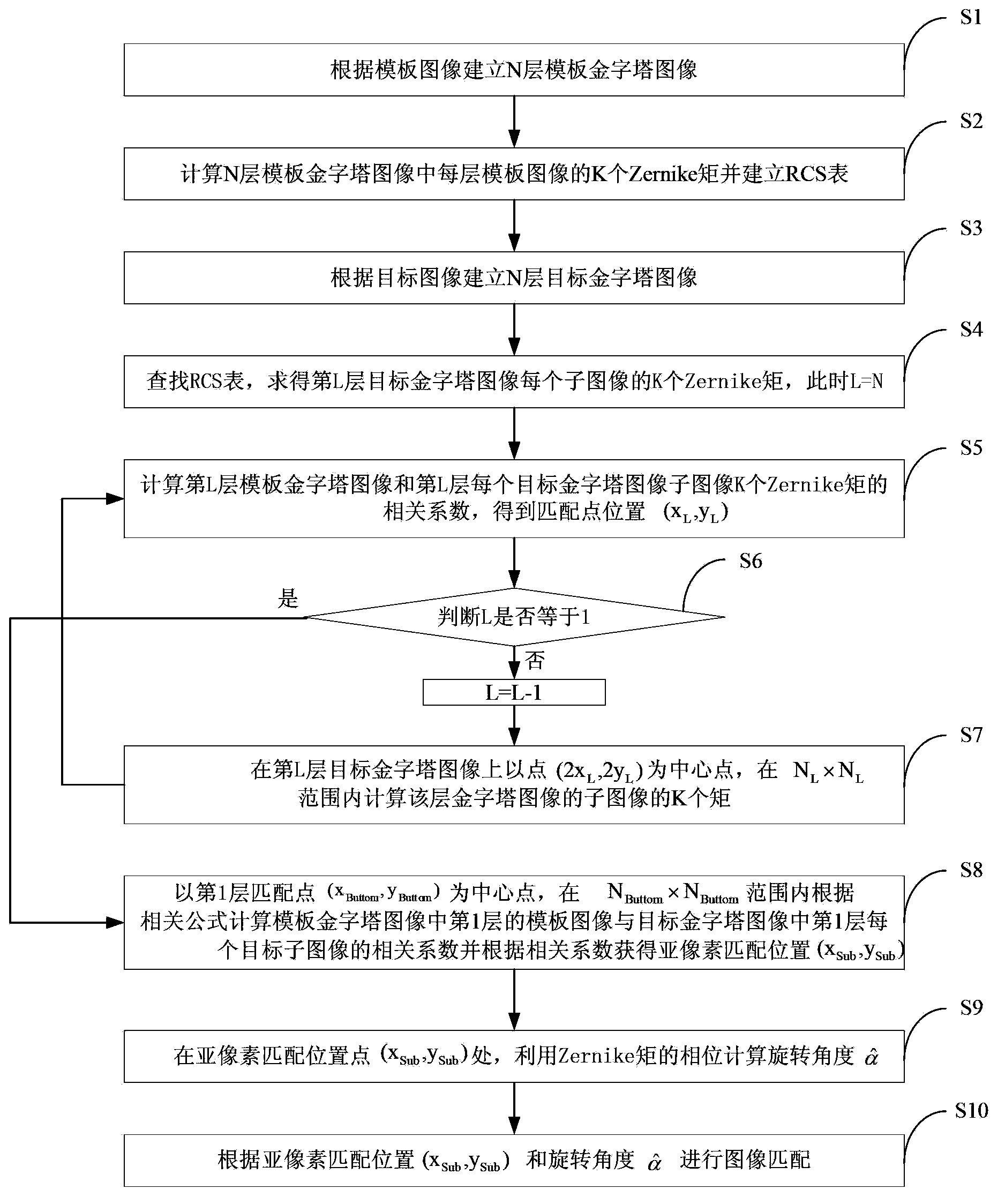
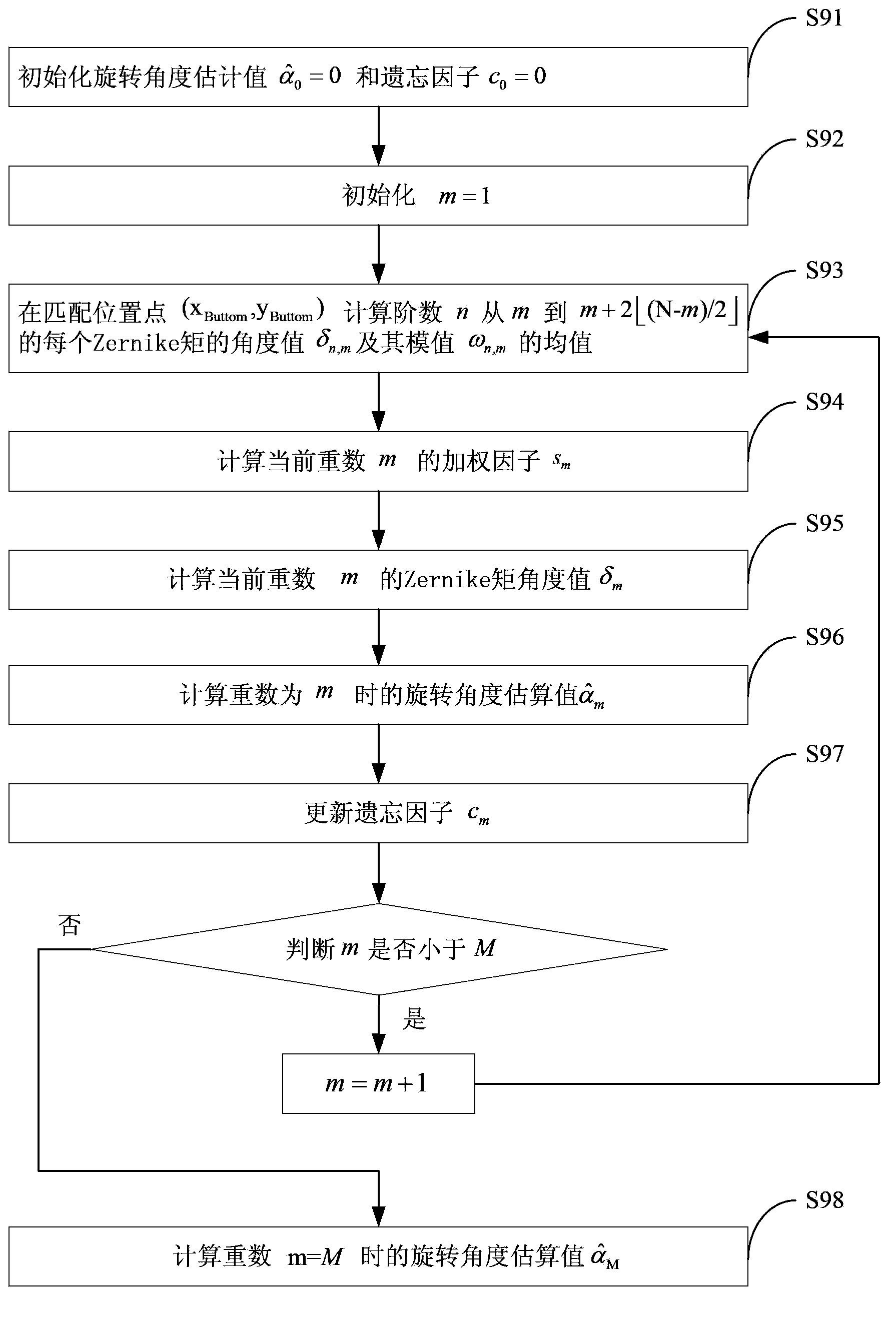
Image matching method based on Zernike matrix
The invention discloses an image matching method based on a Zernike matrix. The method comprises the following steps: S1, establishing N layers of template pyramid images; S2, calculating K matrixes of each layer of template images in the N layers of template pyramid images, and establishing an RCS table; S3, establishing N layers of object pyramid images; S4, calculating K matrixes of each object sub-image of the L-th layer of the N layers of the object pyramid images through searching the RCS table; S5, calculating correlation coefficients of K matrixes of the L-th layer of the template pyramid images and the sub-image of each object pyramid image in the L-th layer, and obtaining a matching point position (x<L>,y<L>) of the L-th layer of the object pyramid images; and S6, determining whether L is equal to 1, if so, entering S8, and if not, L=L-1, and entering S7; S7, calculating K matrixes of each object sub-image in the L-th layer within a scope of N<L>*N<L> by taking a point with the coordinates (2 x<L>,2y<L>) as a center in the L-th layer, and returning to S5; S8, calculating the correlation coefficients within a scope of N<Buttom>*N<Buttom> by taking a matching point with the coordinates (x<Buttom>,y<Buttom>) in the first layer as a center point, and obtaining a sub-pixel matching position with the coordinates (x,y); and S9, at the sub-pixel matching position with the coordinates (x,y), according to phase, calculating an image rotation angle alpha<^>.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
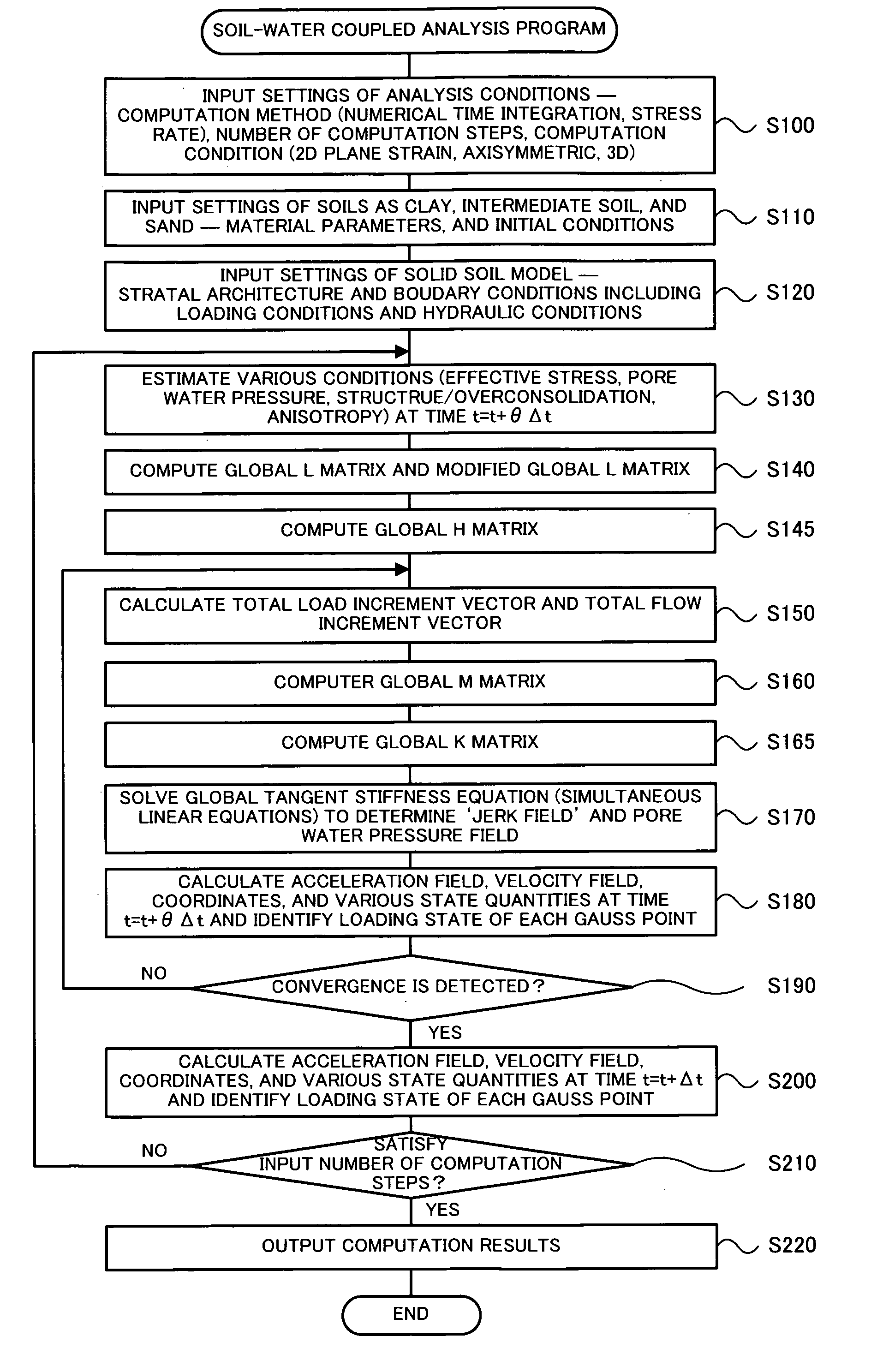
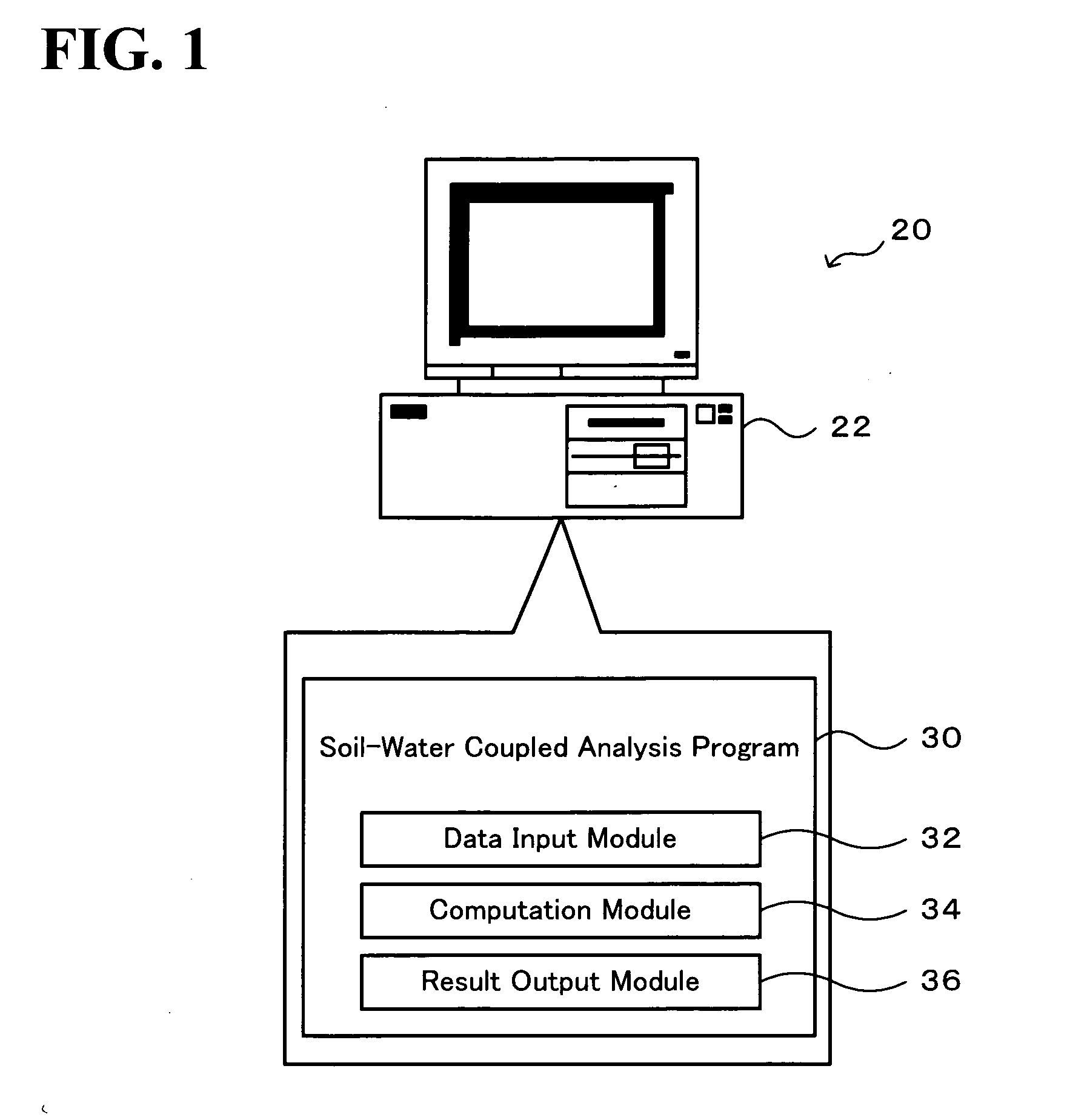
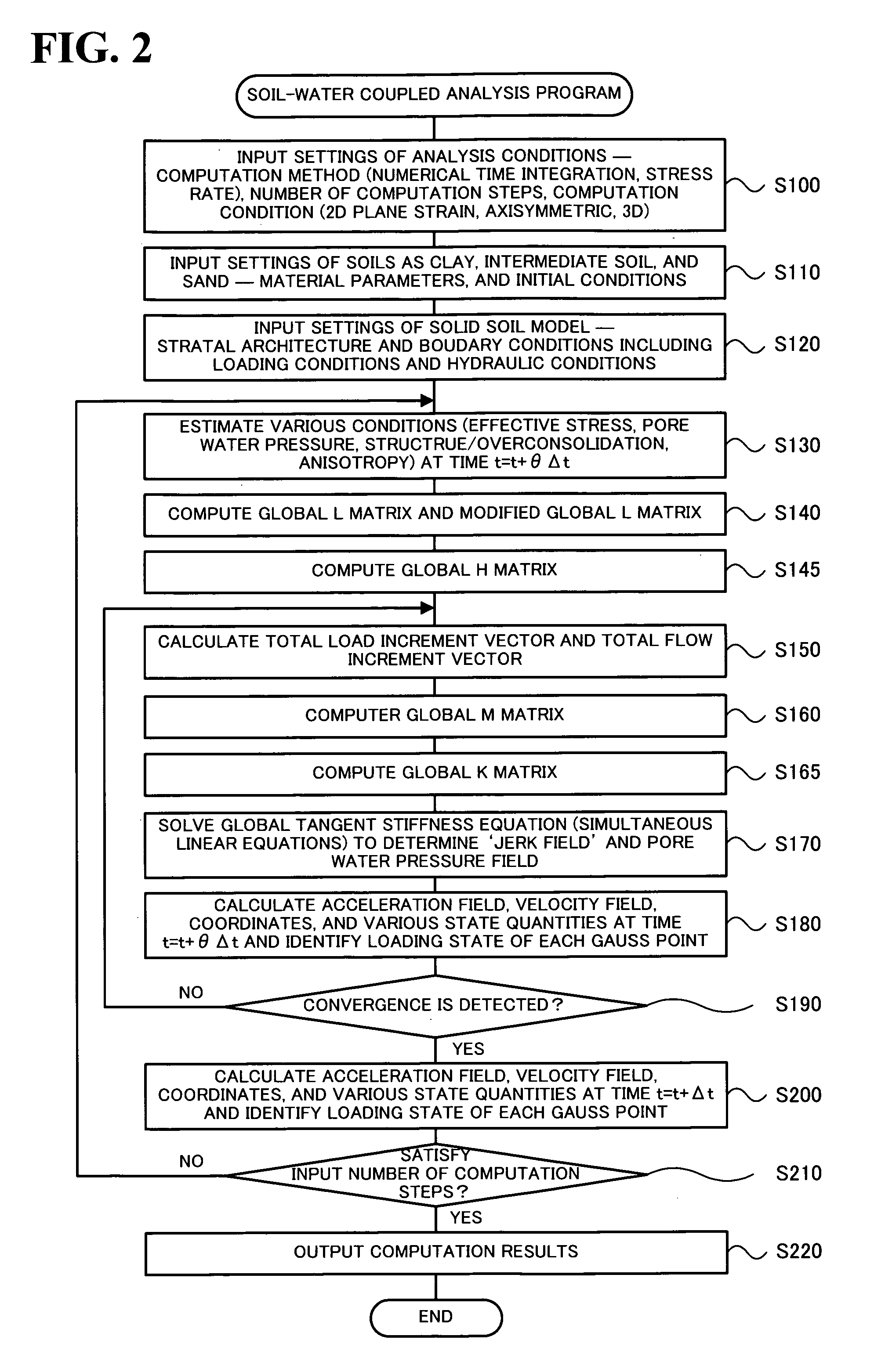
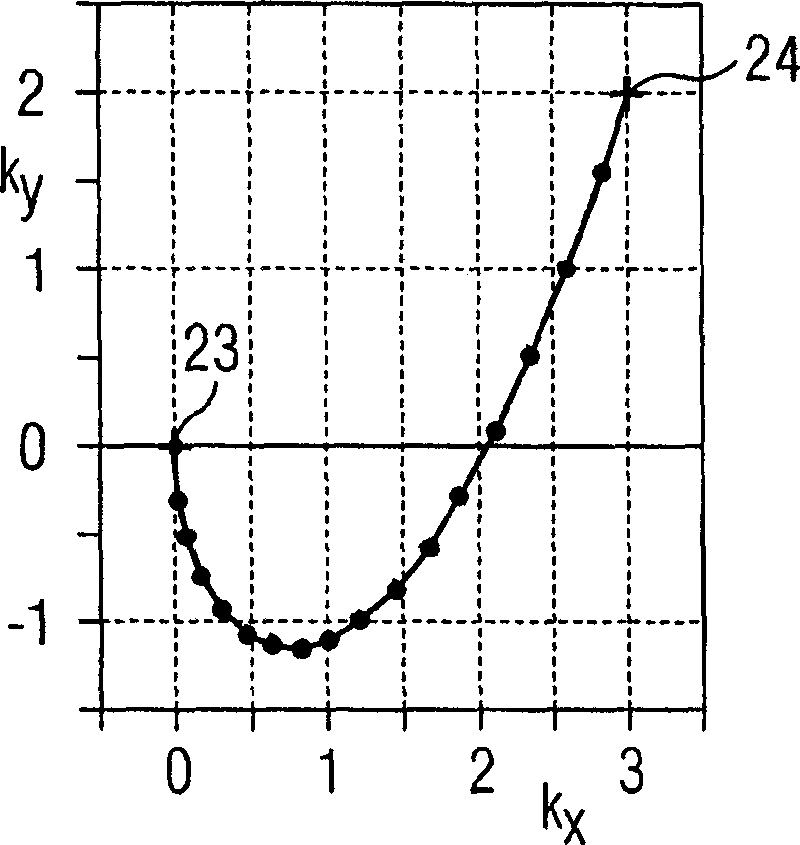
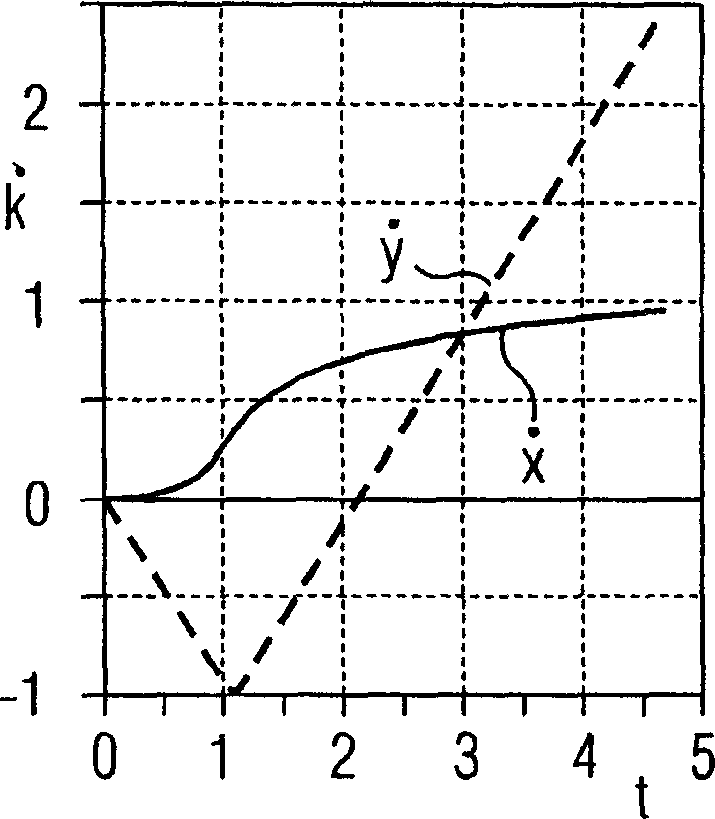
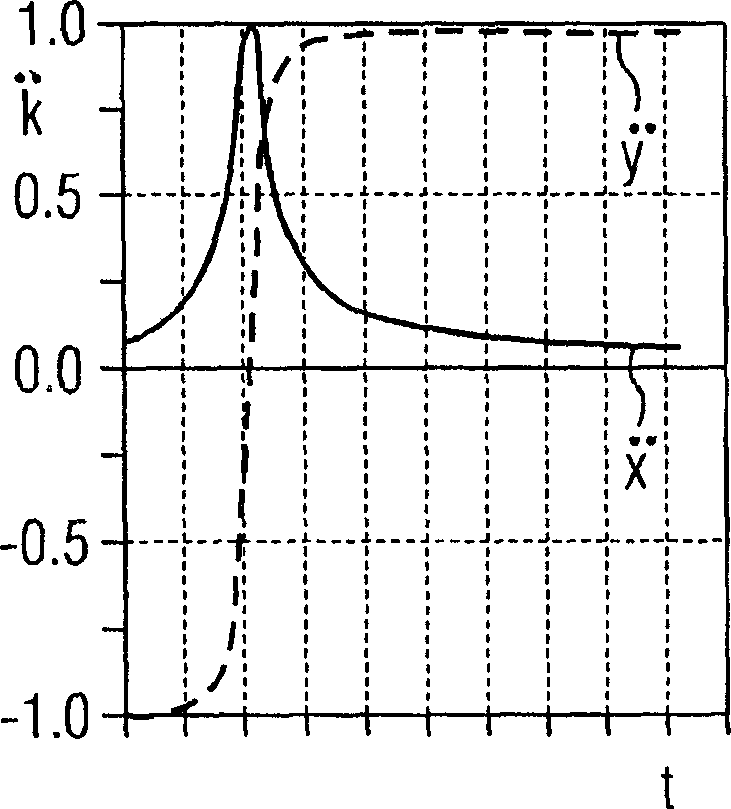
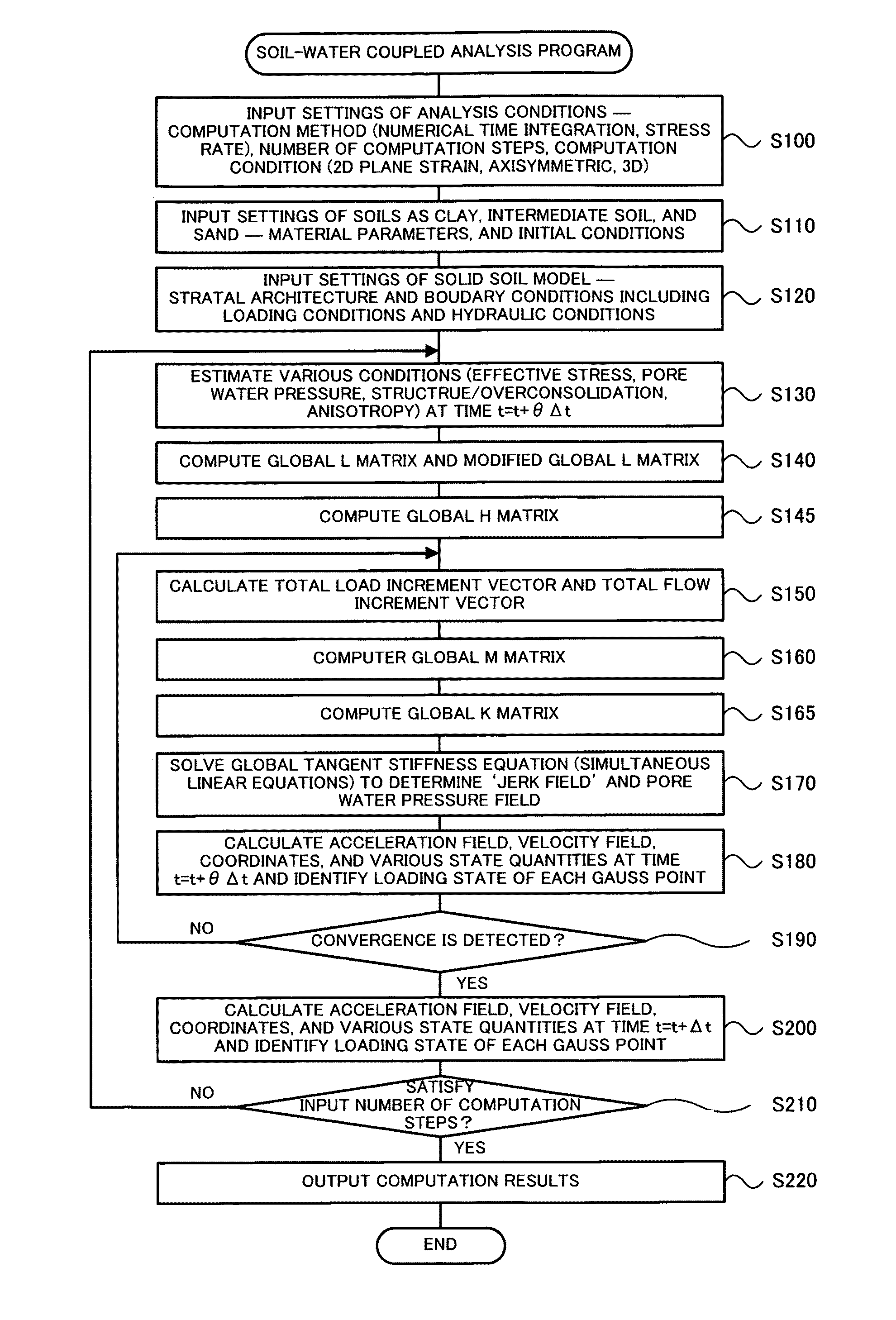
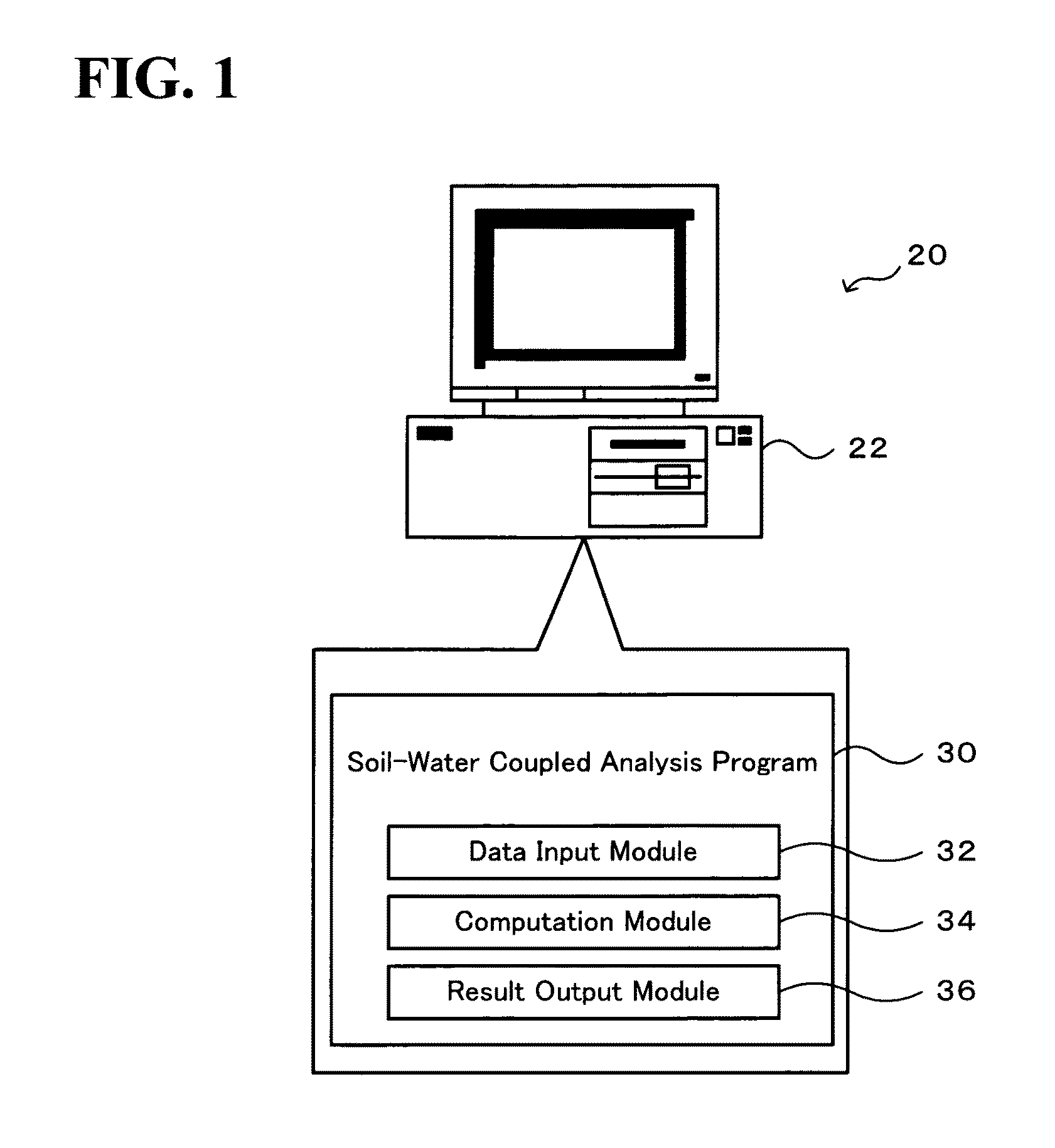
Soil-Water Coupled Analyzer and Soil-Water Coupled Analysis Method
InactiveUS20090164179A1Easy to calculateForecastingComputation using non-denominational number representationSoil skeletonH matrix
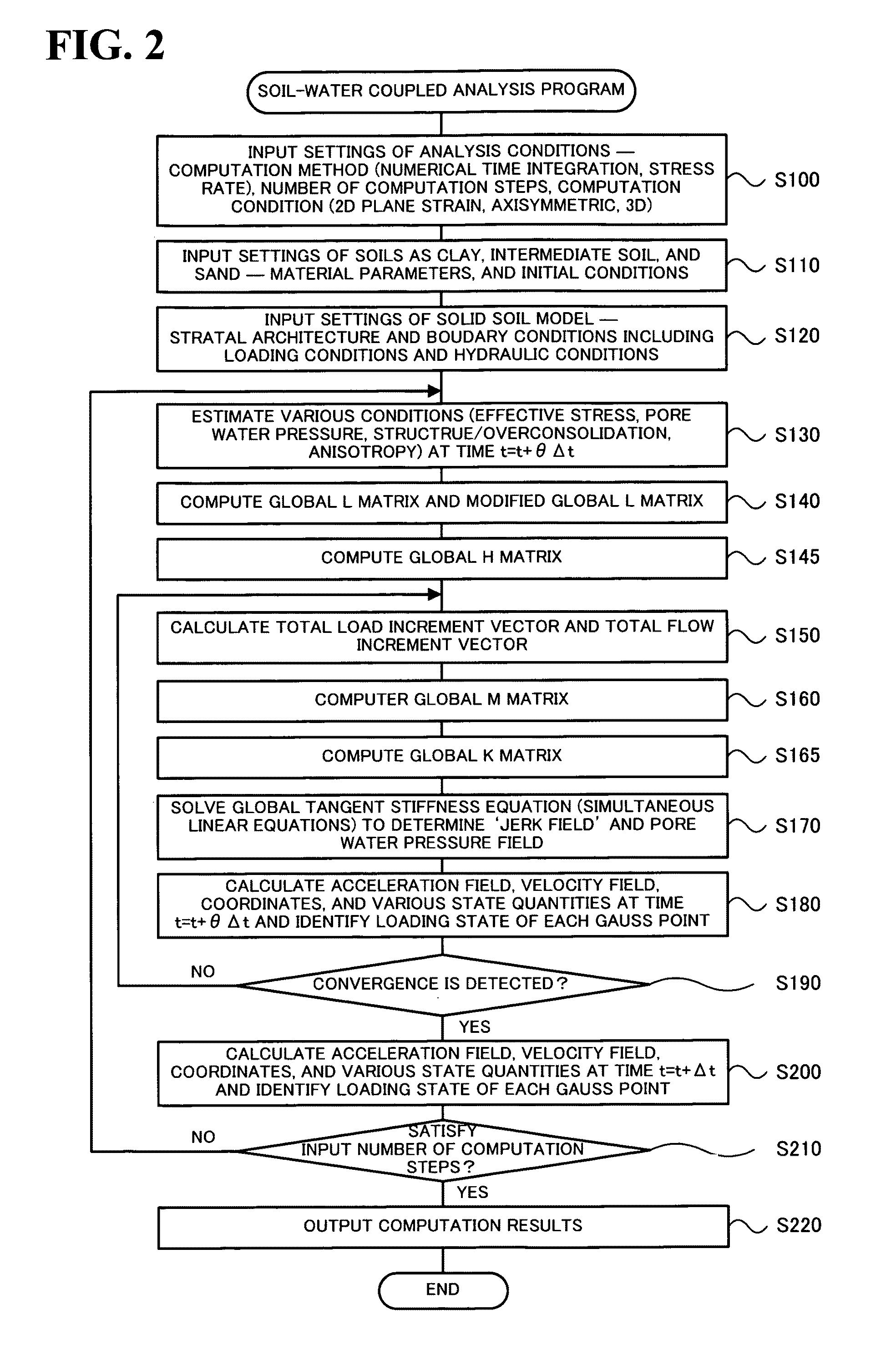
The soil-water coupled analysis program of the invention computes a global L matrix and a modified global L matrix regarding a volume change rate of a soil skeleton over time, a global H matrix regarding a water permeability of soil, a global M matrix regarding a mass, and a global K matrix regarding a tangent stiffness of the soil skeleton, based on input settings of soils, such as clay, intermediate soil, and sand, to respective elements of a soil foundation, input settings of a solid soil model, and input settings of analysis conditions (steps S140 to S165). The soil-water coupled analysis program formulates a global tangent stiffness equation (simultaneous linear equations) using all these computed matrixes and determines an unknown ‘jerk field’ and a ‘pore water pressure field’ under given boundary conditions, for example, a given deformation condition and a given stress rate condition (step S170). This enables highly-accurate dynamic and static analyses in soil foundations of various soils from sand to intermediate soils and clay.
Owner:NAGOYA UNIVERSITY
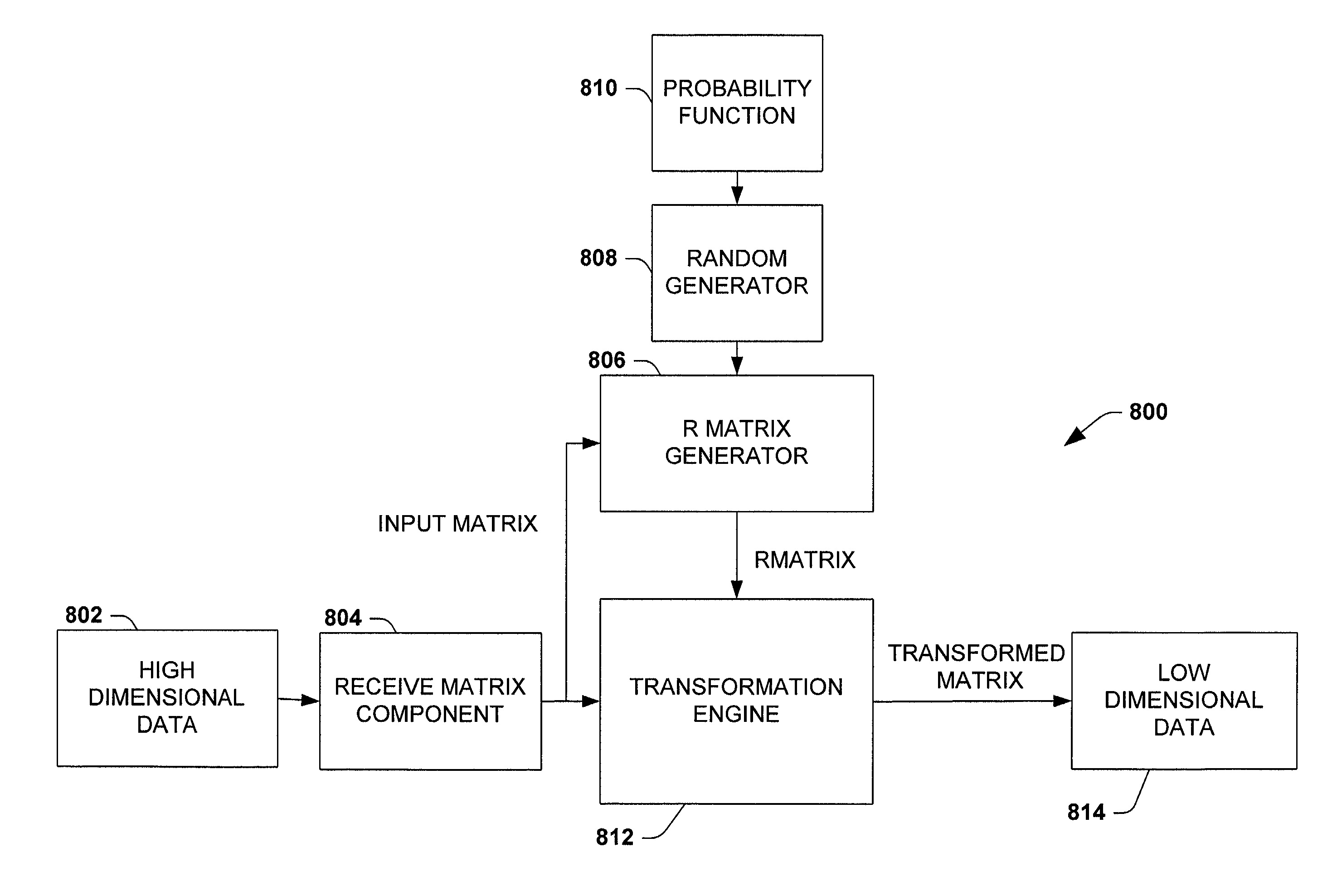
System and method adapted to facilitate dimensional transform
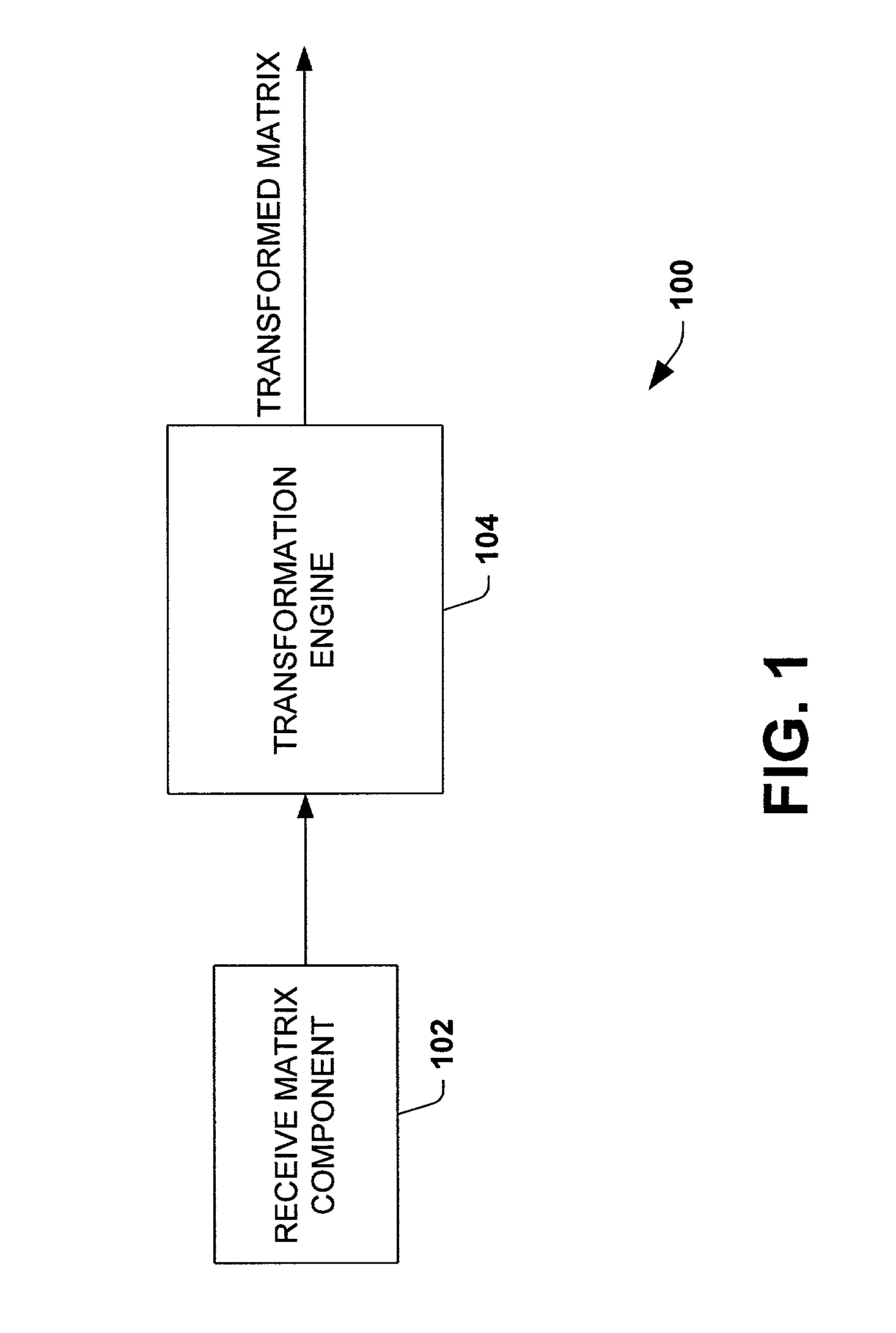
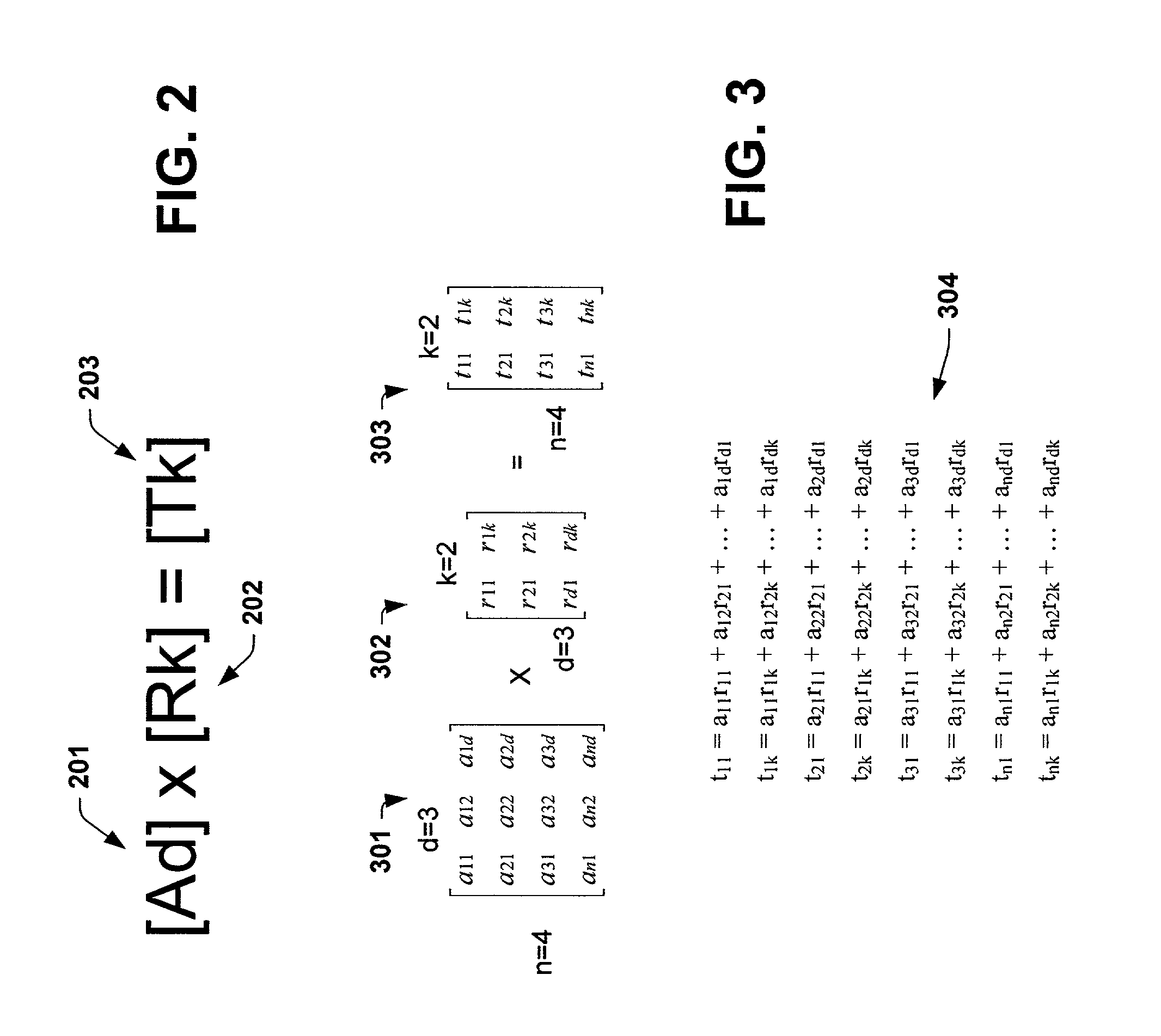
InactiveUS7043514B1Facilitates mapping and transformingReduce variationCharacter and pattern recognitionComplex mathematical operationsHat matrixData compression
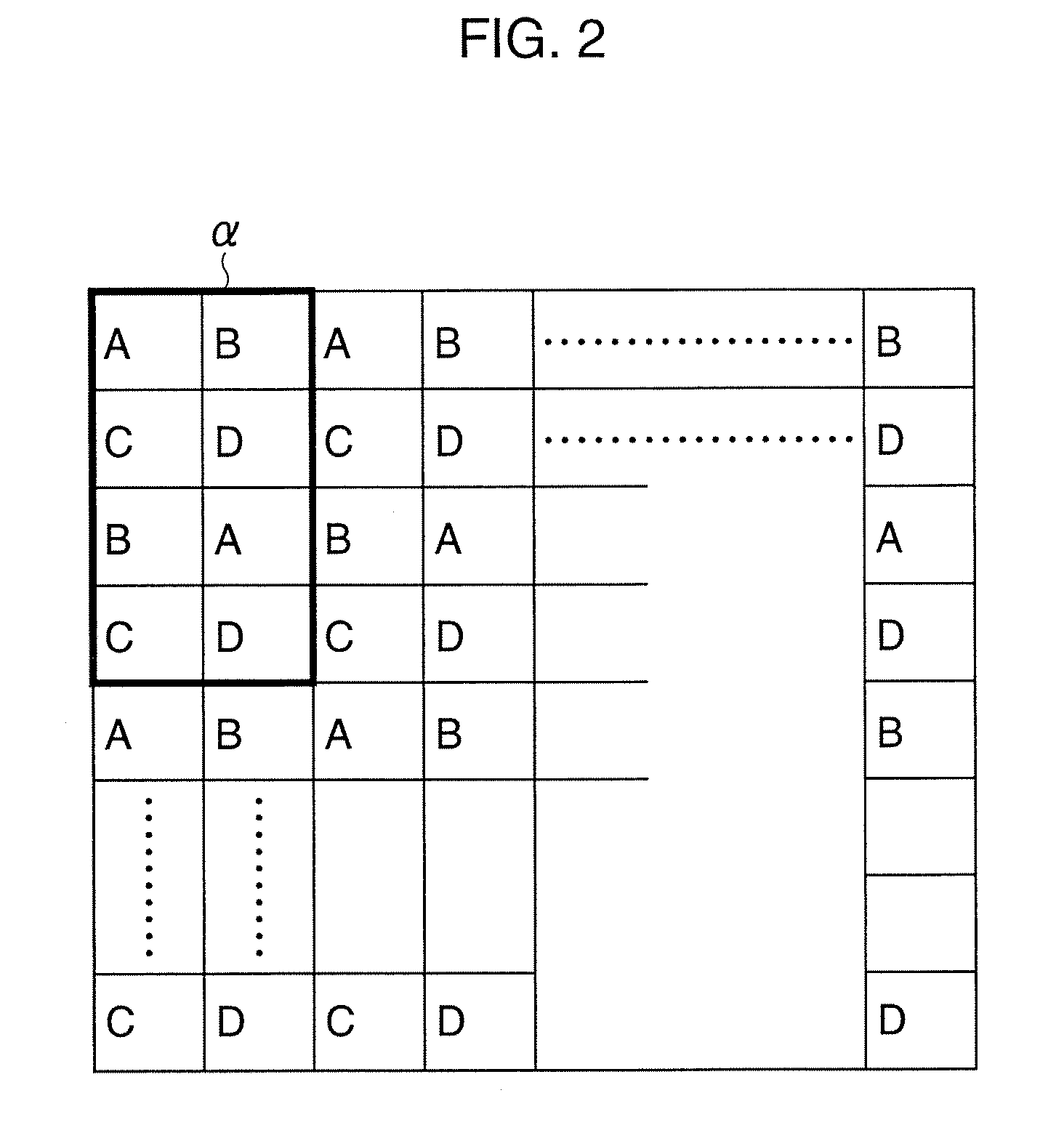
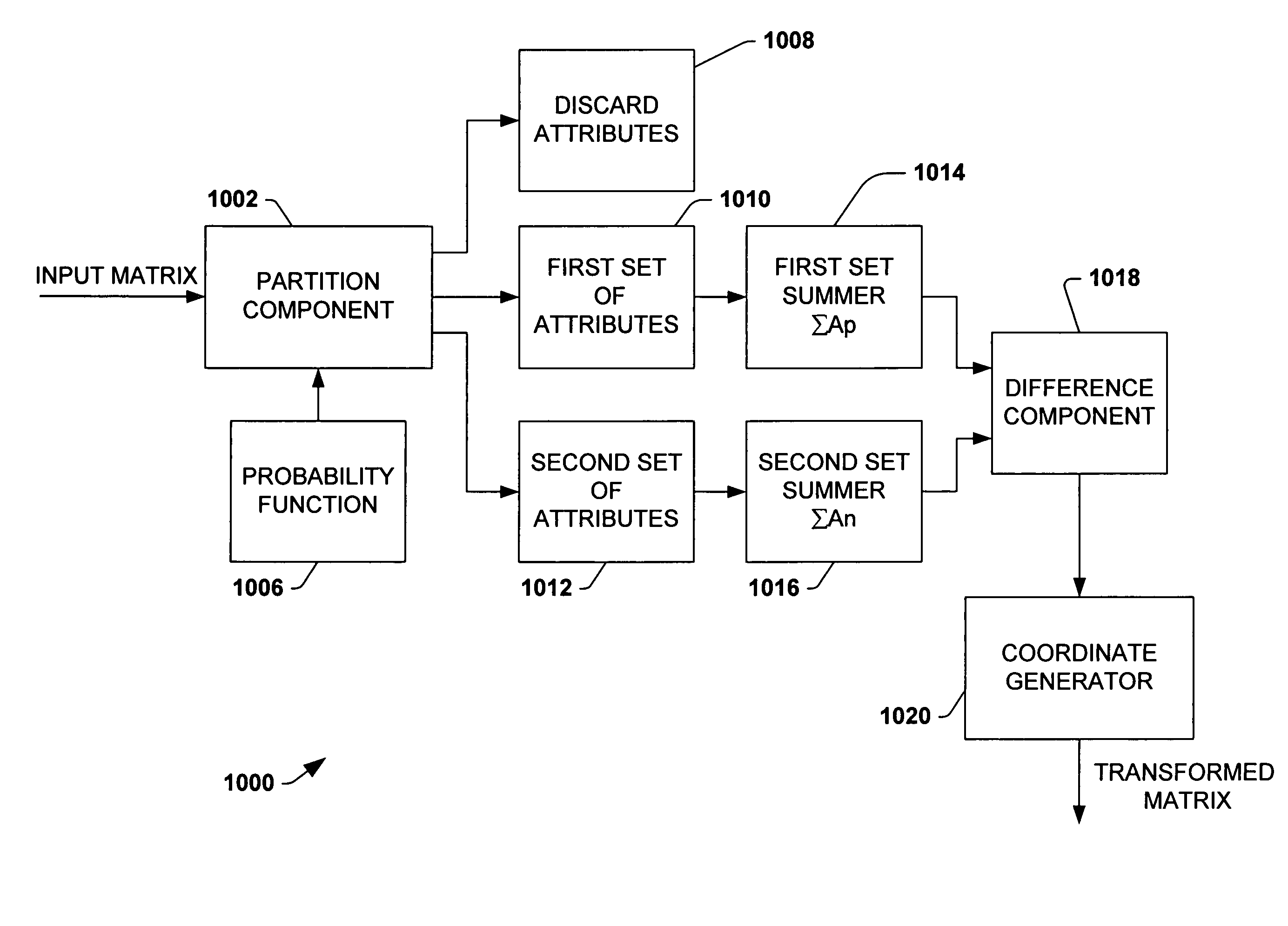
Systems and methods that facilitate dimensional transformations of data points are disclosed. In particular, the subject invention provides for a system and methodology that simplifies dimensional transformations while mitigating variations of a distance property between pairs of points. A set of n data points in d dimensional space is represented as an n×d input matrix, where d also corresponds to the number of attributes per data point. A transformed matrix represents the n data points in a lower dimensionality k after being mapped. The transformed matrix is an n×k matrix, where k is the number of attributes per data point and is less than d. The transformed matrix is obtained by multiplying the input matrix by a suitable projection matrix. The projection matrix is generated by randomly populating the entries of the matrix with binary or ternary values according to a probability distribution. Unlike previous methods, the projection matrix is formed without obtaining an independent sample from a Gaussian distribution for each entry in the projection matrix, without applying a linear algebraic technique to generate the projection matrix and without employing arbitrary floating point numbers. Processes and / or algorithms can utilize the reduced transformed matrix instead of the larger input matrix to facilitate computational efficiency and data compression.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method for constructing quasi-cyclic low-density check code based on Euclidean geometry (EG)
InactiveCN102412845AImprove error correction performanceAvoid iterative decoding performance impactError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsLow densityBroadcasting
The invention discloses a method for constructing quasi-cyclic low-density check codes based on Euclidean geometry (EG). The method comprises the following steps of: I, selecting Euclidean geometry EG (m, ps) to construct K sparse matrixes; II, constructing a matrix H by taking K matrixes as sub-matrixes; III, constructing a sub-array H (gamma, rho) of an array H for given code parameters: rho is more than or equal to row weight 1 and less than or equal to K, and gamma is more than or equal to line weight 1 and less than or equal to ps; IV, performing random arrangement to obtain a sparse matrix, wherein T is less than an optional threshold (gamma !) (pho-1) and more than or equal to 104, performing random arrangement for T times to obtain T sparse matrixes, and calculating the quantity of loops 6 in a corresponding Tenna figure; and V, selecting a matrix of which the quantity of loops 6 is smallest for serving as a check matrix of LDPC (Low Density Parity Check) codes to finish the construction of codes. The obtained LDPC codes are (2550, 1553), (5100, 4103), (15345, 11286). In the method, QC-LDPC (Quasi-Cyclic-Low Density Parity Check) codes not containing loops 4 are constructed by using the structural characteristics of EG, and QC-LDPC codes with least loops 6, superior loop distribution and excellent error correcting performance can be selected; and the method is suitable for China digital sound broadcasting.
Owner:桂林市思奇通信设备有限公司
Method and apparatus for accelerated spiral-coded imaging in magnetic resonance tomography
InactiveUS7719270B2Shorten the durationImage can be preventedMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringComplete dataData set
In a method and apparatus for accelerated spiral-coded imaging in magnetic resonance tomography using spiral-shaped k-space sampling, the underlying k-matrix is under-sampled such that an additional spiral is obtained by point mirroring of the measured values at the center of the k-matrix. This additional spiral forms a complete data set of the k-matrix together with the first spiral for imaging the output information.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
System and method for registration and modeling of deformable shapes by direct factorization
InactiveUS7460733B2Image analysisAcquiring/recognising microscopic objectsBasis setComputational physics
A method of registering and modeling a deformable shape in a digitized image is provided, comprising the steps of providing a measurement matrix W of N measurements of P points of a D-dimensional deformable shape, determining a basis number K for the N measurements, wherein K<N, and selecting K measurements of said measurement matrix W as a basis set, decomposing said measurement matrix W into a matrix product M×∃B, wherein M is a proposed scaled rotation matrix and B is a proposed basis matrix, computing a matrix Qk defined byMiQkMjT={ID×D,i=j=k0D×D,(i,j)∈Φ,where Φ stands for {(i, j)|i=1, . . . , K; j=1, . . . , N, iγk}, which represents an ambiguity matrix transforming the proposed scaled rotation matrix and the proposed basis matrix into a true scaled rotation matrix and a true basis matrix; decomposing the matrix Qk into gkgkT, for k=1, . . . , K, wherein gk is a column of a D∃K%D∃K matrix G; and recovering the true scaled rotation matrix from M×∃G and the true basis matrix from G−1×∃B.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Image signal processing device and method of image signal processing
InactiveUS20070126897A1Television system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsK matrixSolid-state
A device, for processing each pixel signal output from a solid-state imaging device, has a determination processor and an interpolation processor. Each pixel is defined as a center pixel of a k×k matrix. The interpolation processor presumes which pixels have the same color as one another in the k×k matrix, according to the plurality of pixel-array patterns, and conducts a pixel interpolation in each case of presumed color arrangement according to the plurality of pixel-array patterns, so as to generate signal groups of presumed interpolation signals of the center pixel. The determination processor determines a pixel-array pattern in the k×k matrix to be a pattern selected from the plurality of pixel-array patterns. One of the signal groups that is generated according to the determined pixel-array pattern is selected as interpolation signals of the center pixel.
Owner:HOYA CORP
System and method adapted to facilitate dimensional transform
InactiveUS7318078B1Facilitates mapping and transformingReduce variationDigital data processing detailsDigital computer detailsData compressionHat matrix
Systems and methods that facilitate dimensional transformations of data points are disclosed. In particular, the subject invention provides for a system and methodology that simplifies dimensional transformations while mitigating variations of a distance property between pairs of points. A set of n data points in d dimensional space is represented as an n×d input matrix, where d also corresponds to the number of attributes per data point. A transformed matrix represents the n data points in a lower dimensionality k after being mapped. The transformed matrix is an n×k matrix, where k is the number of attributes per data point and is less than d. The transformed matrix is obtained by multiplying the input matrix by a suitable projection matrix. The projection matrix is generated by randomly populating the entries of the matrix with binary or ternary values according to a probability distribution. Unlike previous methods, the projection matrix is formed without obtaining an independent sample from a Gaussian distribution for each entry in the projection matrix, without applying a linear algebraic technique to generate the projection matrix and without employing arbitrary floating point numbers. Processes and / or algorithms can utilize the reduced transformed matrix instead of the larger input matrix to facilitate computational efficiency and data compression.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Channel coding/decoding apparatus and method for a CDMA mobile communication system
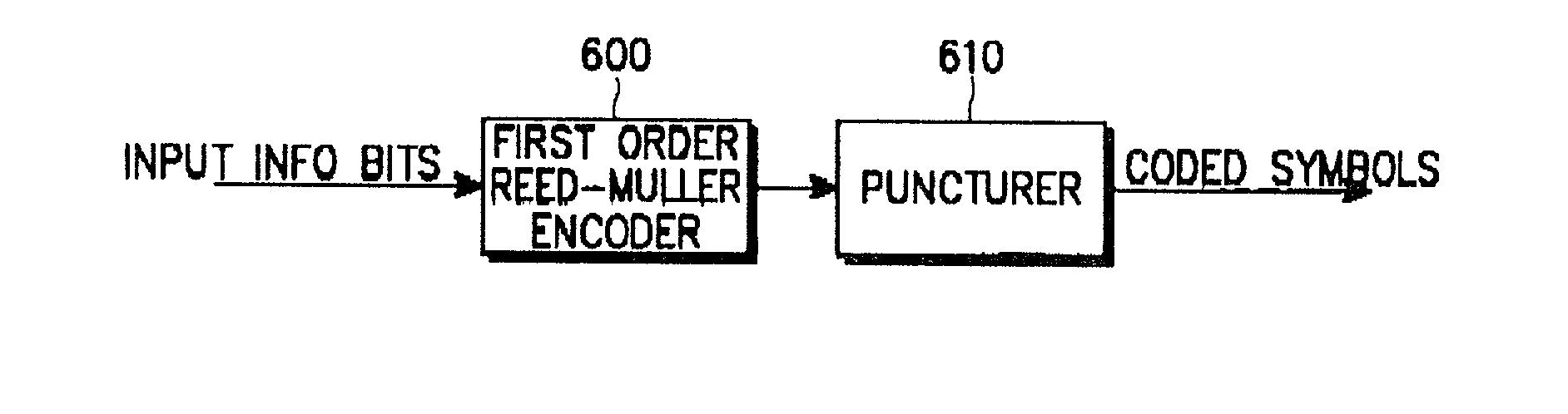
InactiveUS7050417B2Correction capabilityImprove reliabilityReed-muller codesError preventionReed–Muller codeAlgorithm
Disclosed is a method for generating (2k−2t) first order Reed-Muller codes from 2k first order Reed-Muller codes based on k input information bits. The method comprises selecting t linearly independent kth order vectors; generating 2t linear combinations by linearly combining the t selected vectors; calculating 2t puncturing positions corresponding to the 2t linear combinations; selecting one k×k matrix out of a plurality of k×k matrixes having k×k inverse matrixes; calculating 2t new puncturing positions by multiplying each of the 2t puncturing positions by the selecting k×k matrix; and generating (2k−2t) first order Reed-Muller codes by puncturing the 2t new puncturing positions from the 2k first order Reed-Muller codes.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for optimizing the K-space trajectories in the location encoding of a magnetic resonance tomography apparatus
InactiveCN1449720AWill not cause overloadQuick scanMagnetic property measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringSequence controlResonance
The present invention relates to a method for calculating the scanning path of the k-matrix, under given boundary conditions for the examination of a subject by means of a magnetic resonance tomography apparatus having a gradient amplifier with appertaining gradient coils, an input-display terminal, a sequence controller and a system computer as well as an analog-to-digital converter. The method has the following steps: entering the boundary conditions into the sequence controller or into the system computer via the input-display terminal; calculating the sampling path of the k-matrix taking the boundary conditions into consideration by the sequence controller or the system computer; and determining the gradient current curves by the sequence controller or the system computer that lead to a scanning along the previously calculated scanning path when applied to the corresponding gradient coils with utilization of the ADC.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Soil-water coupled analyzer and soil-water coupled analysis method
InactiveUS7966165B2Easy to calculateForecastingComputation using non-denominational number representationSoil skeletonH matrix
Owner:NAGOYA UNIVERSITY
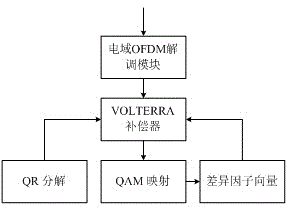
Nonlinear damage compensation method based on VOLTERRA model in OFDM-PON (orthogonal frequency division multiplexing-passive optical network) system
InactiveCN104158787AIncreased complexityImprove interferenceMultiple carrier systemsQR decompositionInterference resistance
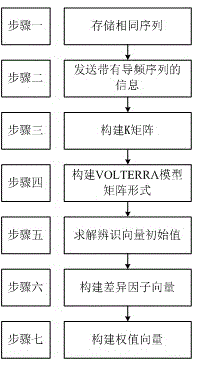
The invention discloses a nonlinear damage compensation method based on a VOLTERRA model in an OFDM-PON (orthogonal frequency division multiplexing-passive optical network) system. The method comprises the steps as follows: (1), similar sequences are stored to a database from a transmitting terminal and a receiving terminal; (2), information containing a pilot frequency sequence is transmitted and extracted at the receiving terminal; (3), a K matrix is established according to model characteristics; (4), a VOLTERRA model matrix form is established; (5), an initial value of an identification vector is resolved; (6), a constellation diagram is analyzed to establish a difference factor vector; and (7), a new weight vector is established continuously. With the adoption of the method, various types of nonlinear damage in the OFDM-PON system are identified according to the VOLTERRA model, the resolving complexity is reduced by adopting QR for decomposing matrix dimension, self-adaptive correction processing is performed on identification coefficient vectors, and nonlinear interference resistance and reliability of the system are improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
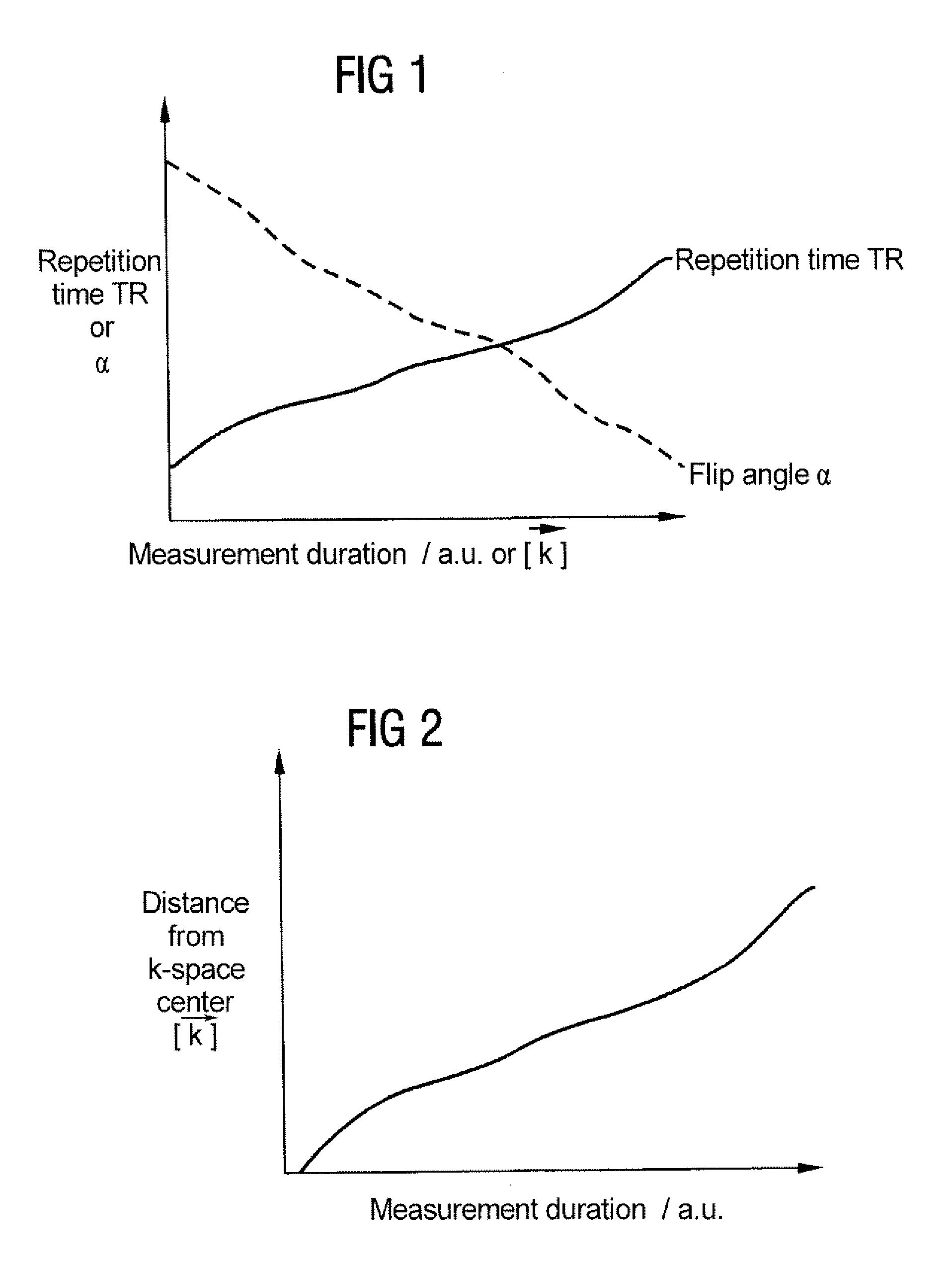
Method and apparatus for improving the vessel/tissue contrast in time-of-flight angiography of a magnetic resonance tomography measurement
InactiveUS7206628B2Increase contrastMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurement pointRadio frequency
In a method and apparatus for improving the vessel / tissue contrast in time-of-flight angiography with a magnetic resonance tomography measurement, a sequence of radiofrequency excitation pulses is generated that each have a flip angle and a temporal spacing in the sequence defined by a repetition time, gradient pulses are generated with gradient coils such that, using an analog-to-digital converter, the magnetic resonance response signals are sampled in the frequency domain (k-space) in a slice referred to as a k-matrix, the k-matrix is sampled such that the respective distances of the measuring points from the center of the k-matrix are continuously increased (or decreased), and the repetition time is varied during the sampling, and / or the flip angle is varied during the sampling.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Method and apparatus for accelerated spiral-coded imaging in magnetic resonance tomography
InactiveUS20060158185A1Reduce readout durationShorten the durationMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionResonanceTomography
In a method and apparatus for accelerated spiral-coded imaging (scanning k-space with a spiral trajectory) in magnetic resonance tomography, the user-defined sequence forming the basis of the spiral scanning is modified such that the k-matrix forming the basis of the sequence is scanned only in a sub-region, the sub-region being defined by a symmetrical shortening on both sides of the k-space matrix in a first direction as well as by a one-sided shortening of the k-space matrix in a second direction orthogonal to the first direction.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
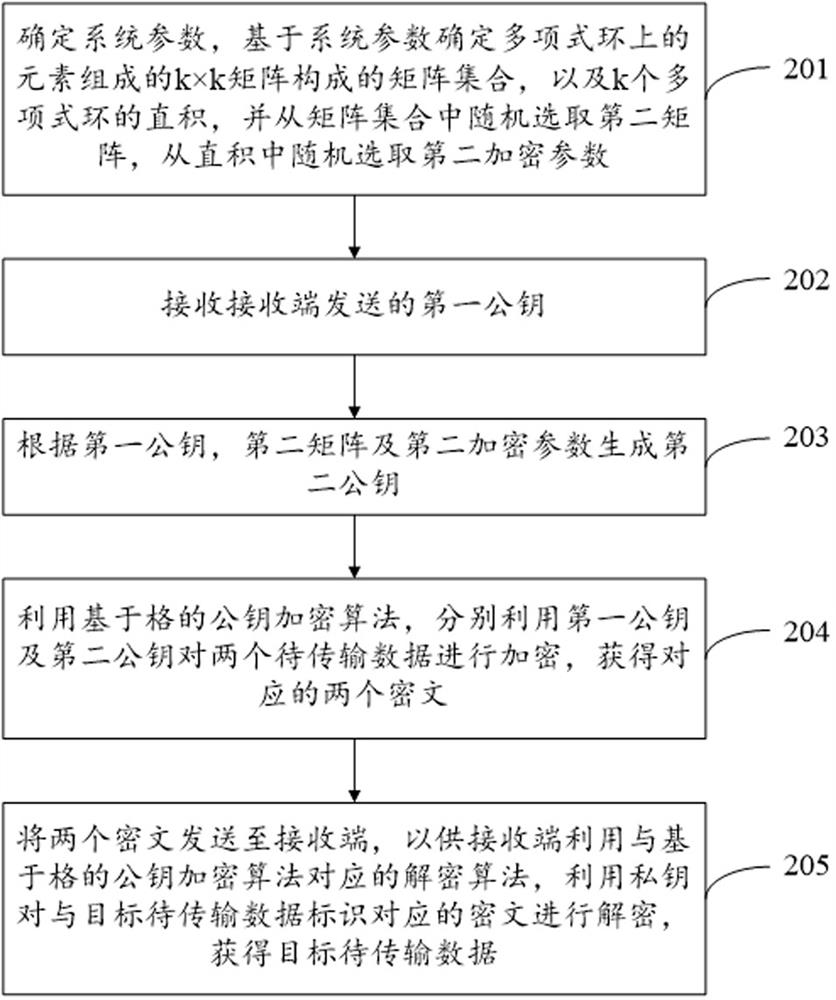
Data processing method, device and system and computer readable storage medium
ActiveCN114095170AImprove securityDefend against quantum attacksKey distribution for secure communicationAlgorithmCiphertext
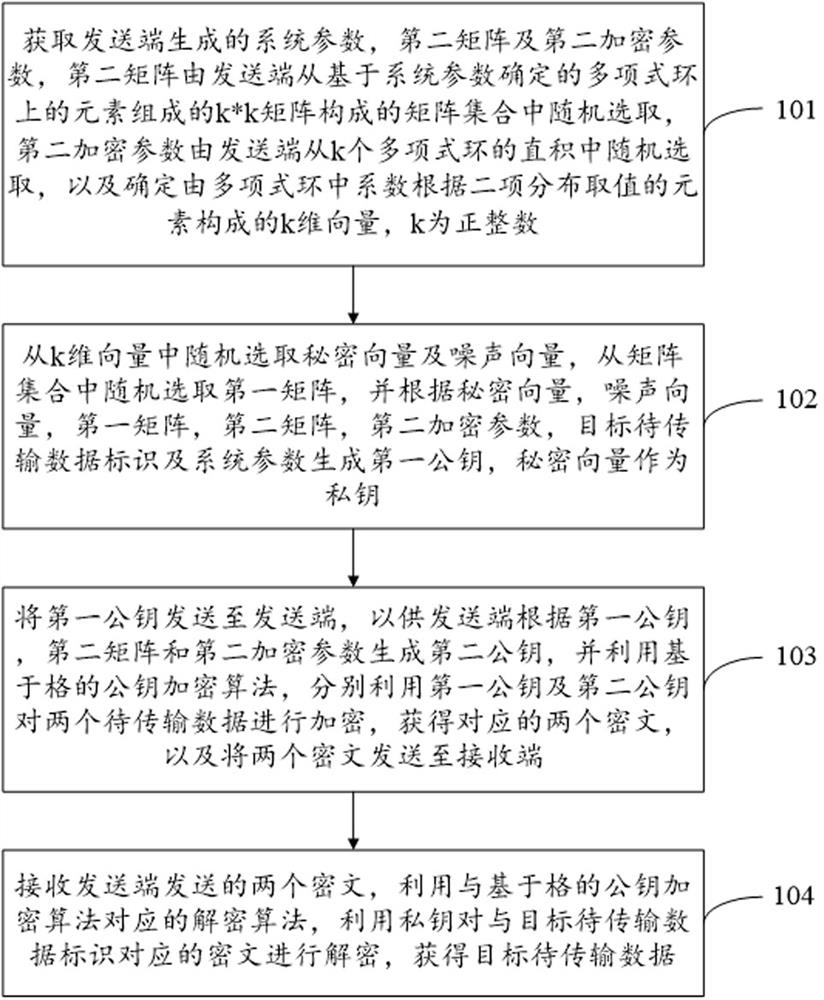
The embodiment of the invention provides a data processing method, device and system and a computer readable storage medium. The method comprises the steps that: a system parameter, a second matrix and a second encryption parameter are obtained, a matrix set composed of a k * k matrix composed of elements on a polynomial ring is determined, and a k-dimensional vector is composed of elements of which coefficients are valued according to binomial distribution in the polynomial ring; a secret vector and a noise vector are randomly selected from the k-dimensional vector, a first matrix is randomly selected from the matrix set, a first public key is generated according to the secret vector, the noise vector, the first matrix, the second matrix, the second encryption parameter, a target to-be-transmitted data identifier and the system parameter, and the secret vector is taken as a private key; the first public key is sent to a sending end, so that the sending end generates a second public key, and to-be-transmitted data is encrypted by using a lattice-based public key encryption algorithm and the public key; and the ciphertext corresponding to the target to-be-transmitted data identifier is decrypted by using an decryption algorithm and the private key, so that the security of accidental transmission of the data is improved.
Owner:北京信安世纪科技股份有限公司
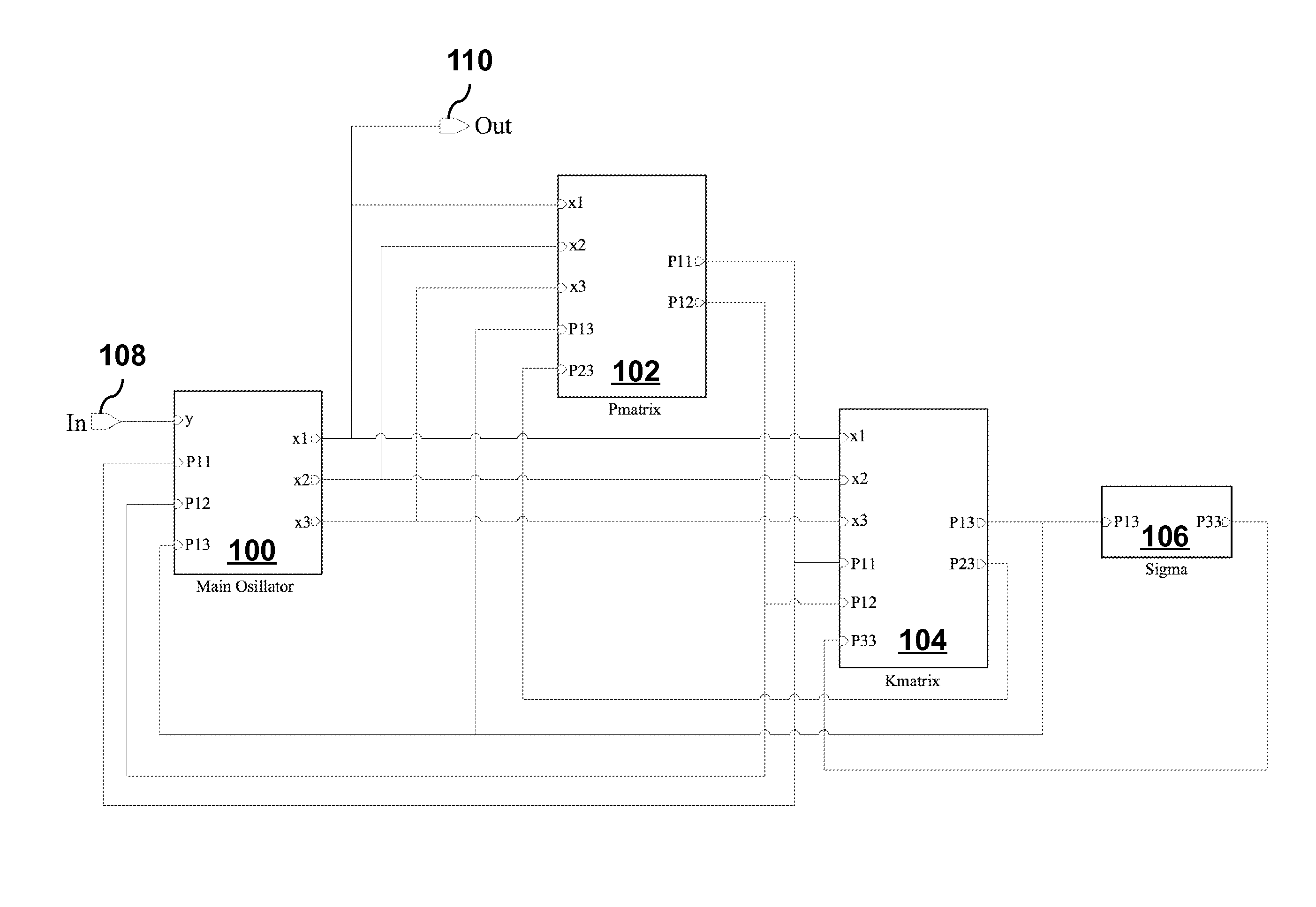
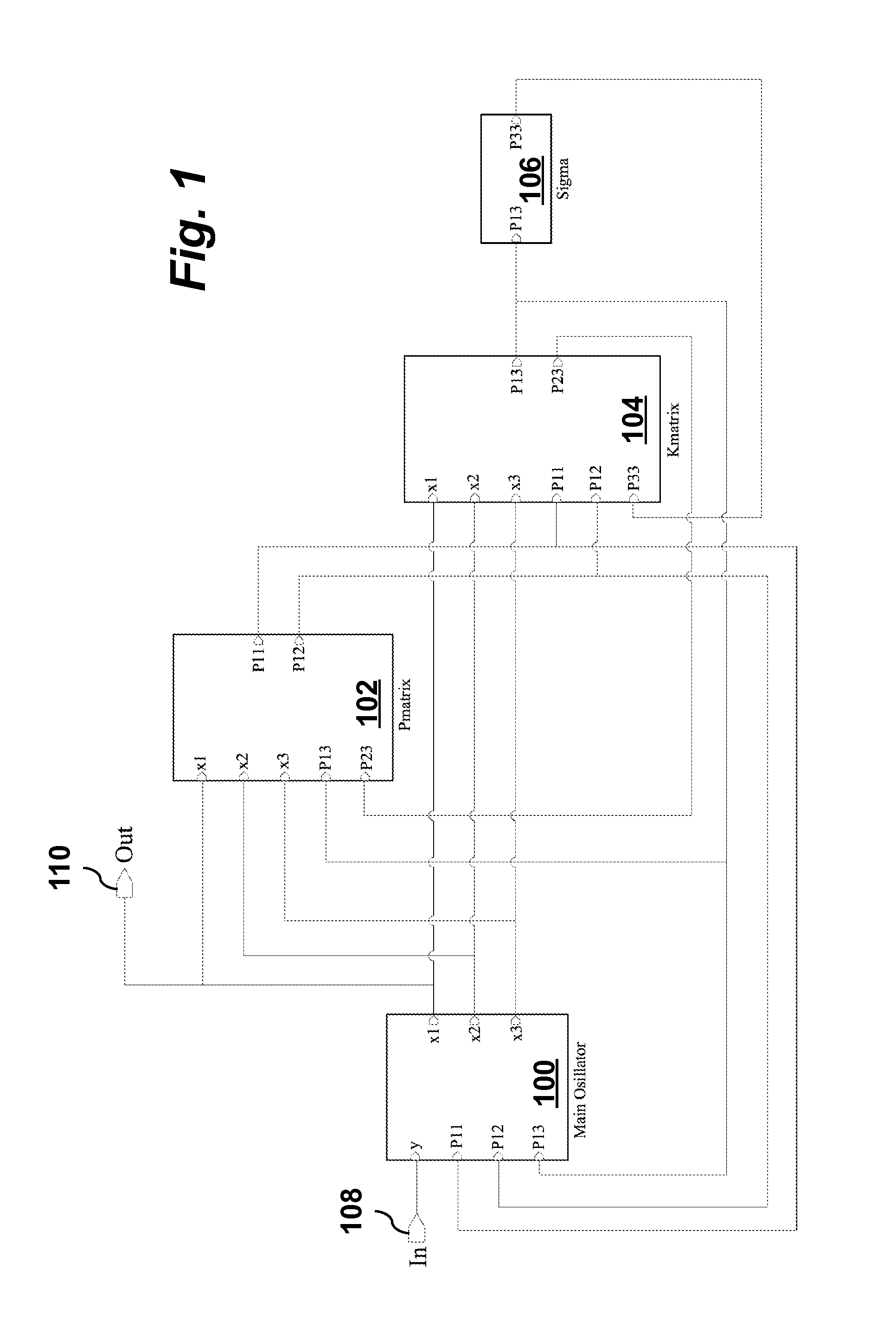
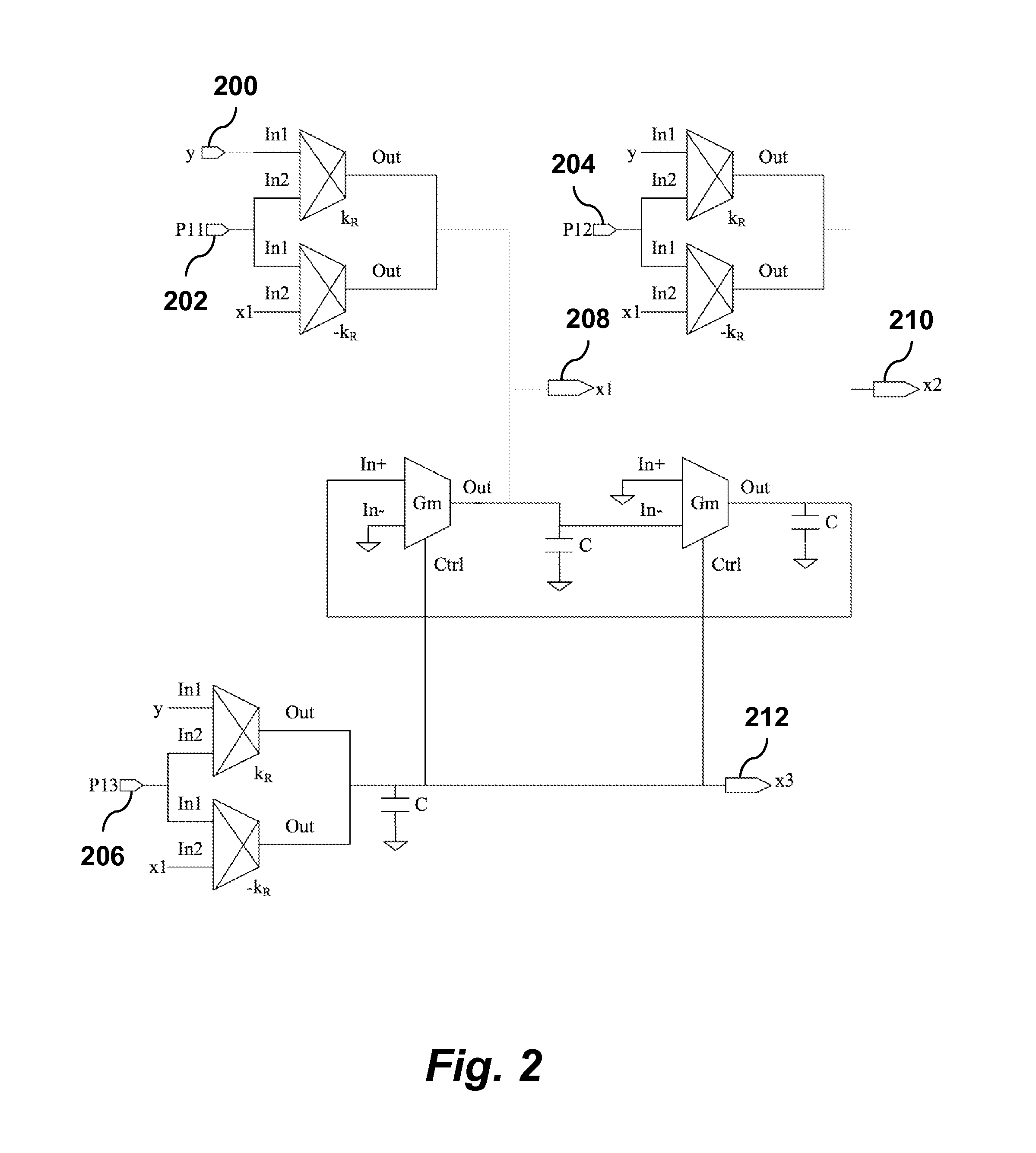
Fast Frequency Estimator
ActiveUS20160006446A1Improve performanceInfinite acquisition rangePulse automatic controlFrequency measurement arrangementKaiman filterIntegrator
In one aspect, the invention provides a method implemented by an analog hardware circuit for fast frequency estimation. The analog circuit may be implemented a main oscillator circuit block [100], a P matrix circuit block [102], a K matrix circuit block[104], and a sigma integrator circuit block [106]. From input signals [108] having unknown frequency, amplitude and phase, the analog hardware circuit generates estimates of state variables x, x2, x3 of a model oscillator, and outputs a sinusoidal estimate [110] of the model oscillator signal. The analog hardware circuit generates the estimates by implementing in continuous time an extended Kalman filter that relates a generating frequency co of the model oscillator to x3 by an affine transformation ω=ω0+£x3, where k is a slope of a frequency error estimate and coo is a best estimate input signal frequency.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method for online detection of concentration of electrolyte of vanadium battery
InactiveCN102621085BImprove accuracyHigh precisionColor/spectral properties measurementsVanadium redox batteryAbsorbance
The invention relates to a method for online detection of the concentration of electrolyte of an all vanadium redox flow battery. A divalent vanadium V (II) system, a trivalent vanadium V (III) system and a tetravalent vanadium V (IV) system are analyzed by the aid of ultraviolet and visible spectrophotometry, a divalent vanadium V (II) and trivalent vanadium V (III) mixed system and a trivalent vanadium V (III) and tetravalent vanadium V (IV) mixed system are analyzed by the aid of a K matrix method, and a curve equation of the concentration of the vanadium with various valence states and absorbance in the systems is deduced. The concentration of vanadium ions with various valence states in a test sample can be rapidly detected only by substituting absorbance data of the test sample with unknown concentration in the electrolyte of the vanadium battery into the absorbance-concentration curve equation measured and deduced by the method, and accuracy of the method is proved as compared with a national standard method. The method has a huge application prospect in terms of dynamically monitoring valence changes of the electrolyte of the vanadium ions and simultaneously, qualitatively and quantitatively checking the vanadium electrolyte with mixed valence states.
Owner:HUNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
An adaptive matrix multiplication optimization method based on Godson 3b
The invention discloses an adaptive matrix multiplication optimization method based on Loongson 3B. First, the multiplication matrix and the multiplied matrix of Loongson 3B are divided into two sub-matrices according to the principle that the size of the block is not larger than the second-level cache. The direct cache memory accessor prefetches the multiplication matrix whose column length is M and whose width is K to the high-speed buffer, and at the same time copies the multiplied matrix whose column length is K and whose width is N to the secondary high-speed buffer, and uses direct register access The device prefetches the multiplication matrix with column length l and width h and the multiplied matrix with length h and width g from the secondary high-speed buffer to the register, uses the multiply-add instruction to complete the multiply-add operation, and collects the module through the memory access state Obtain information and make adaptive adjustments to the block parameters M, K, N, l, h, and g to obtain new block parameters, thereby realizing efficient adaptive optimization of matrix multiplication operations on the Loongson 3B platform.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com