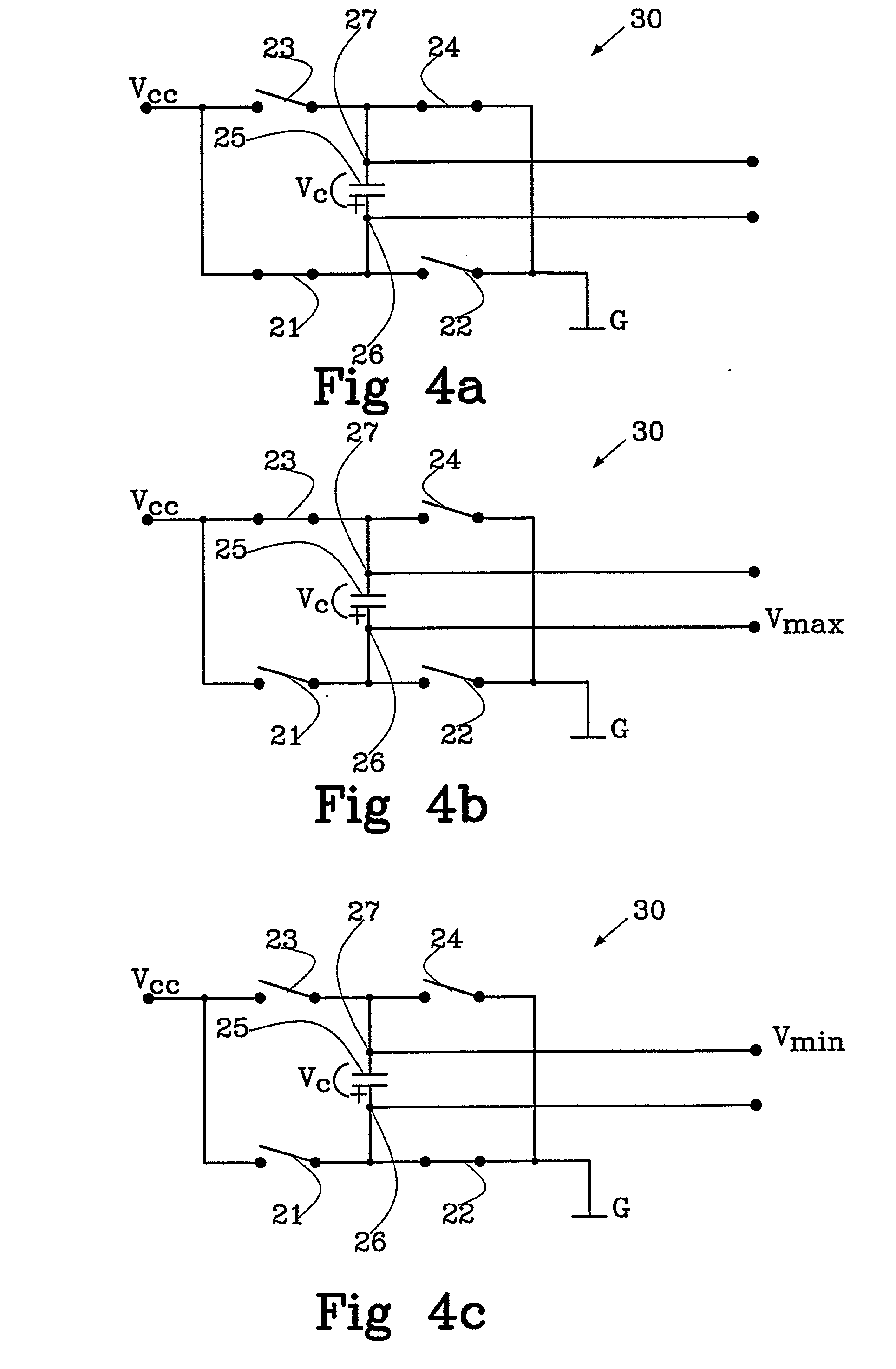
Patents
Literature
198results about "Switching accelaration modifications" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
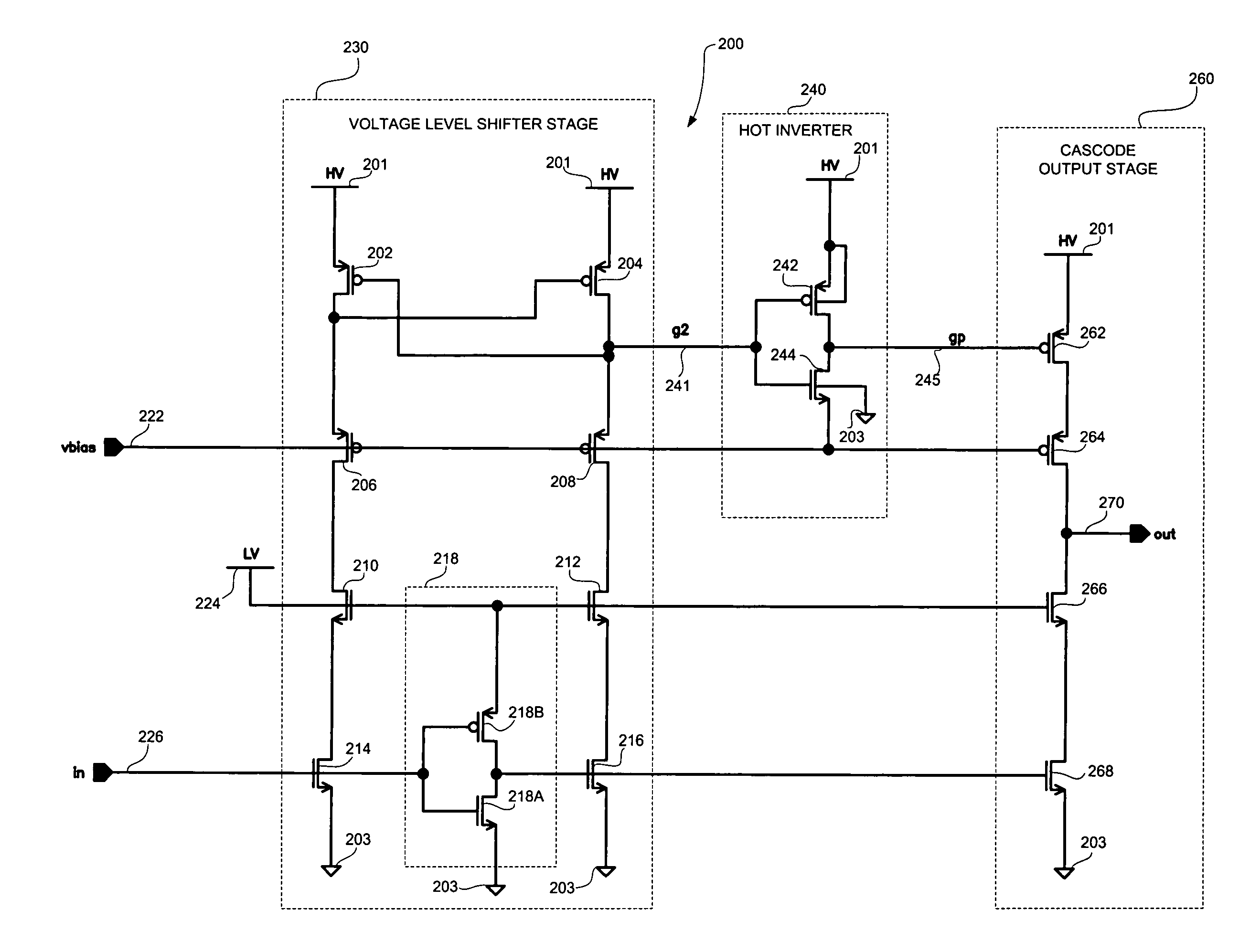
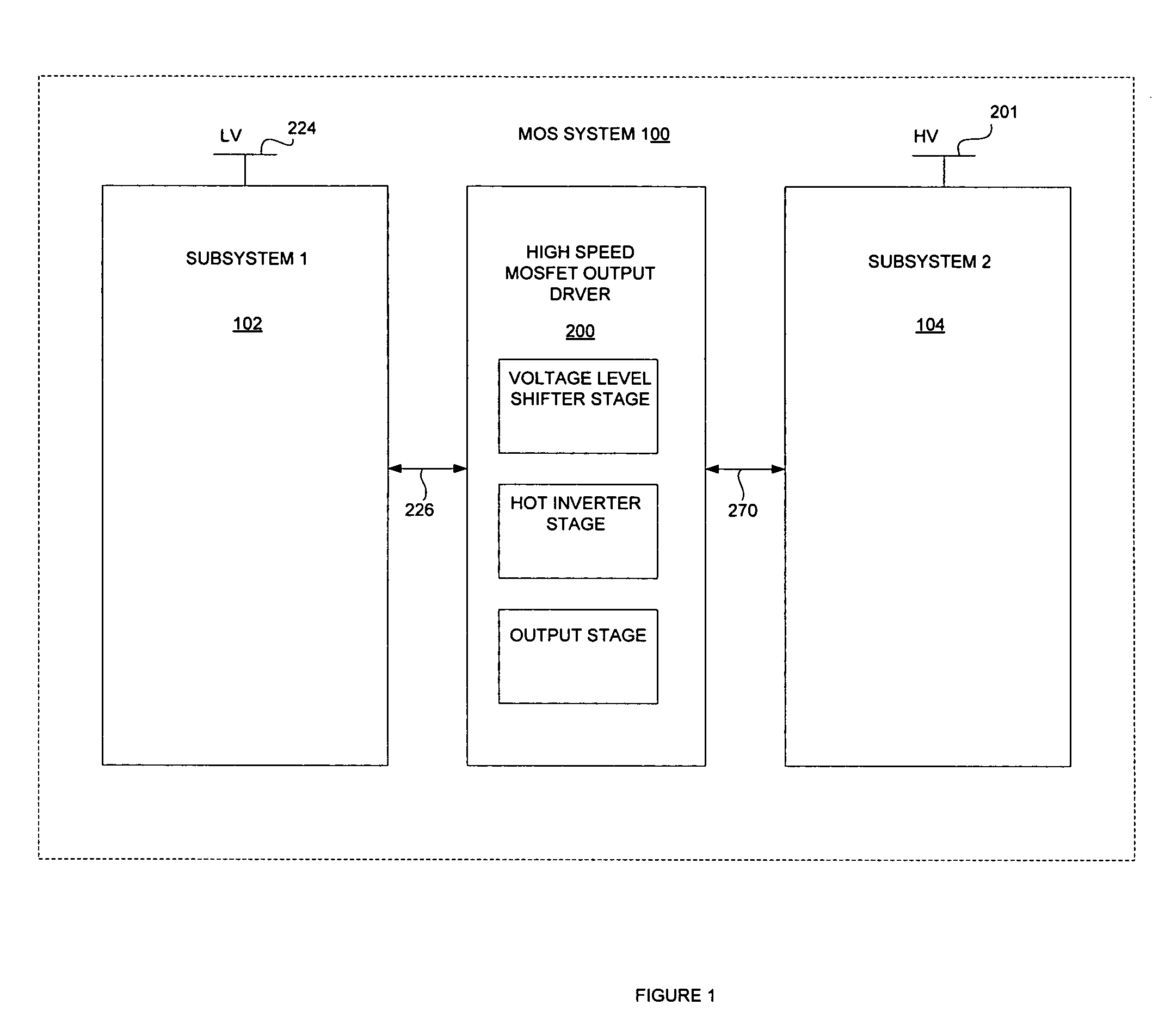
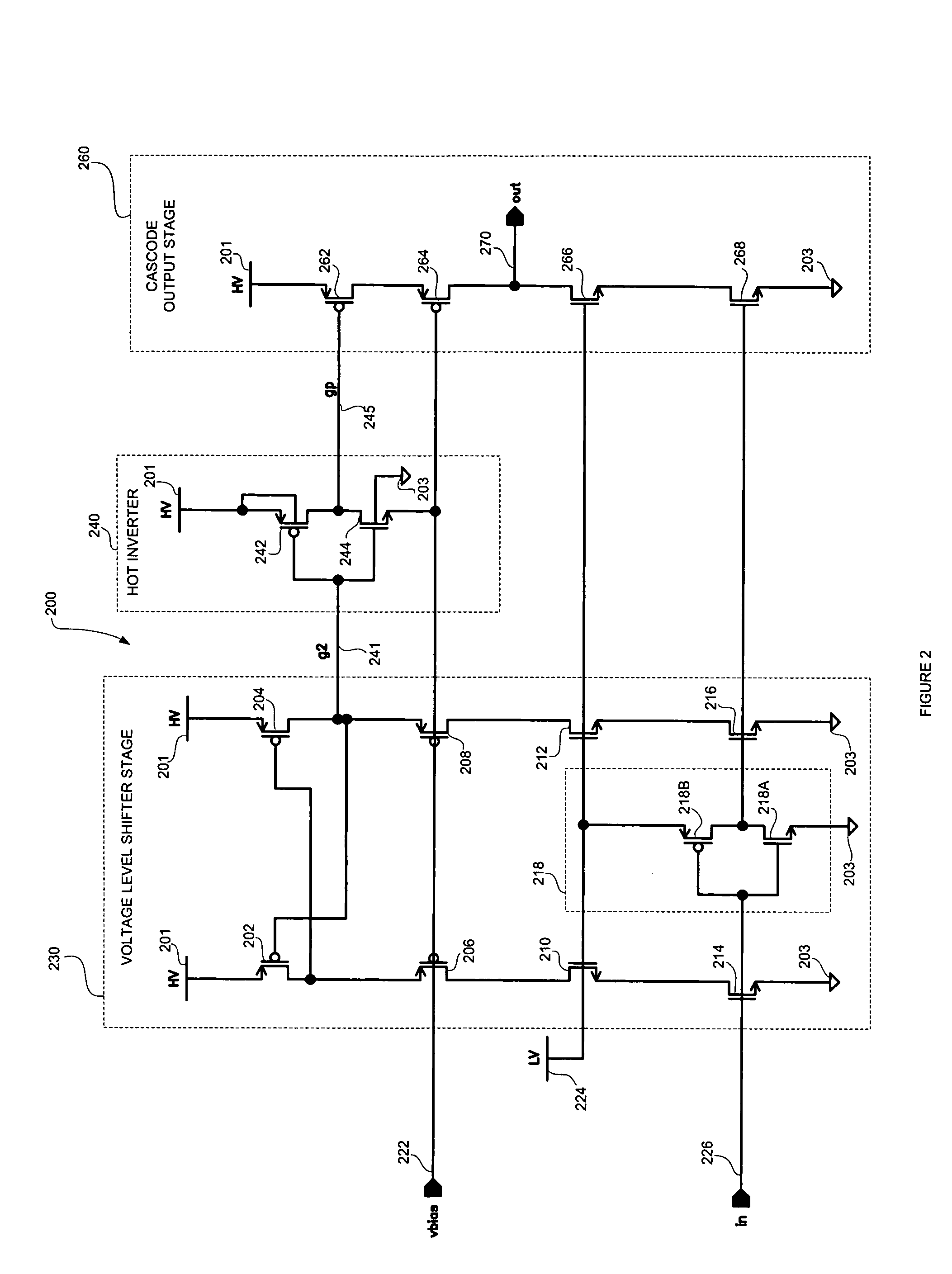
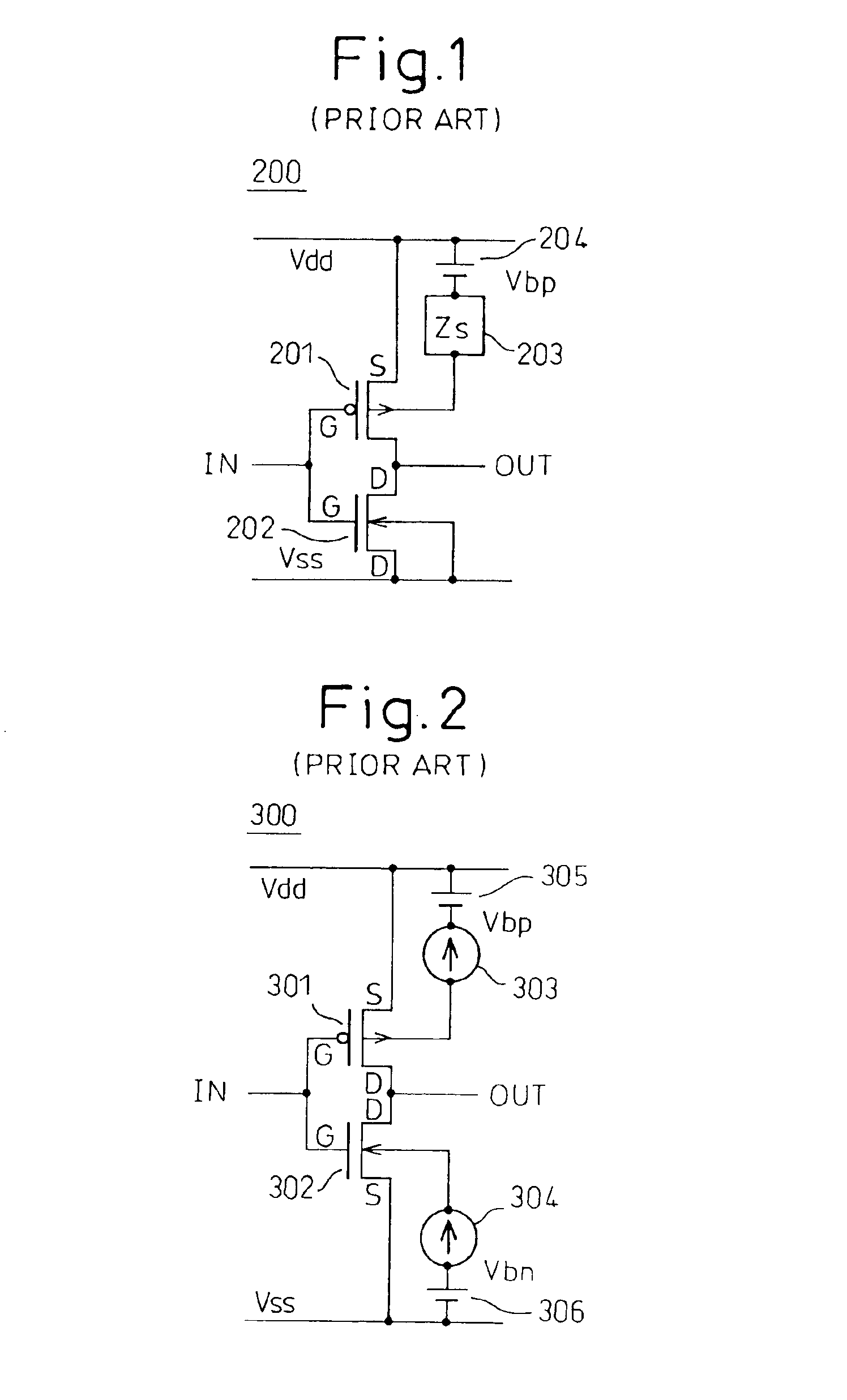
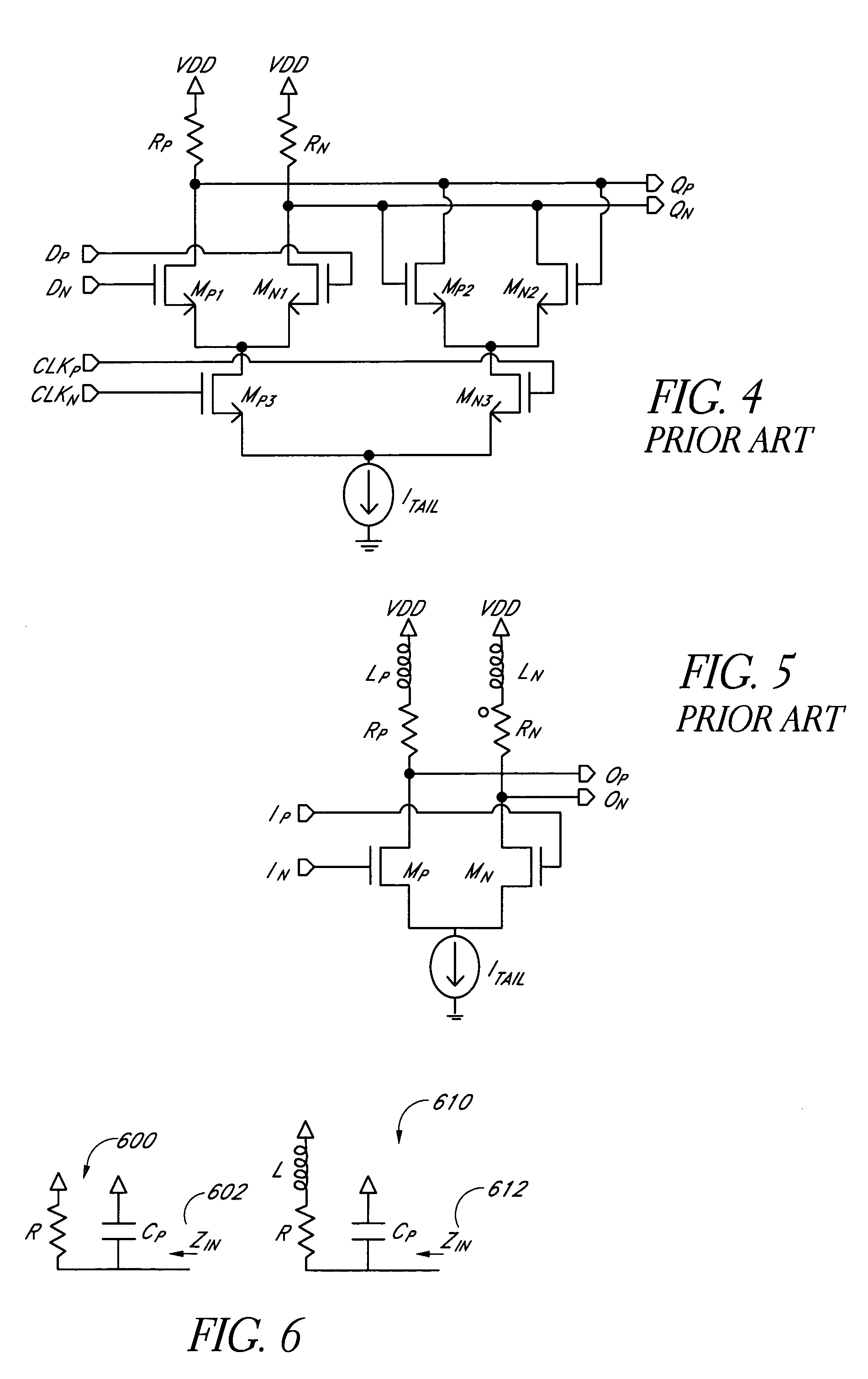
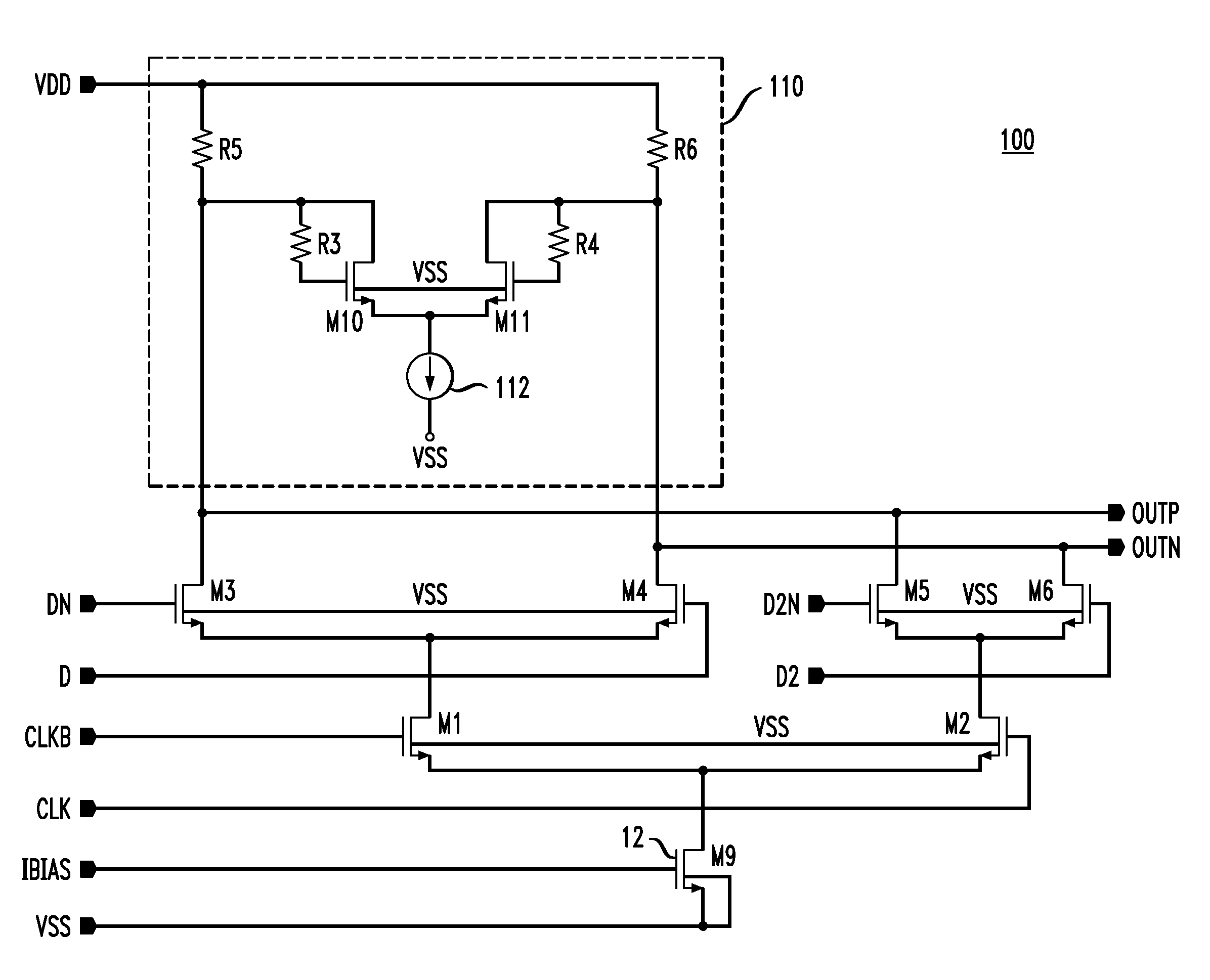
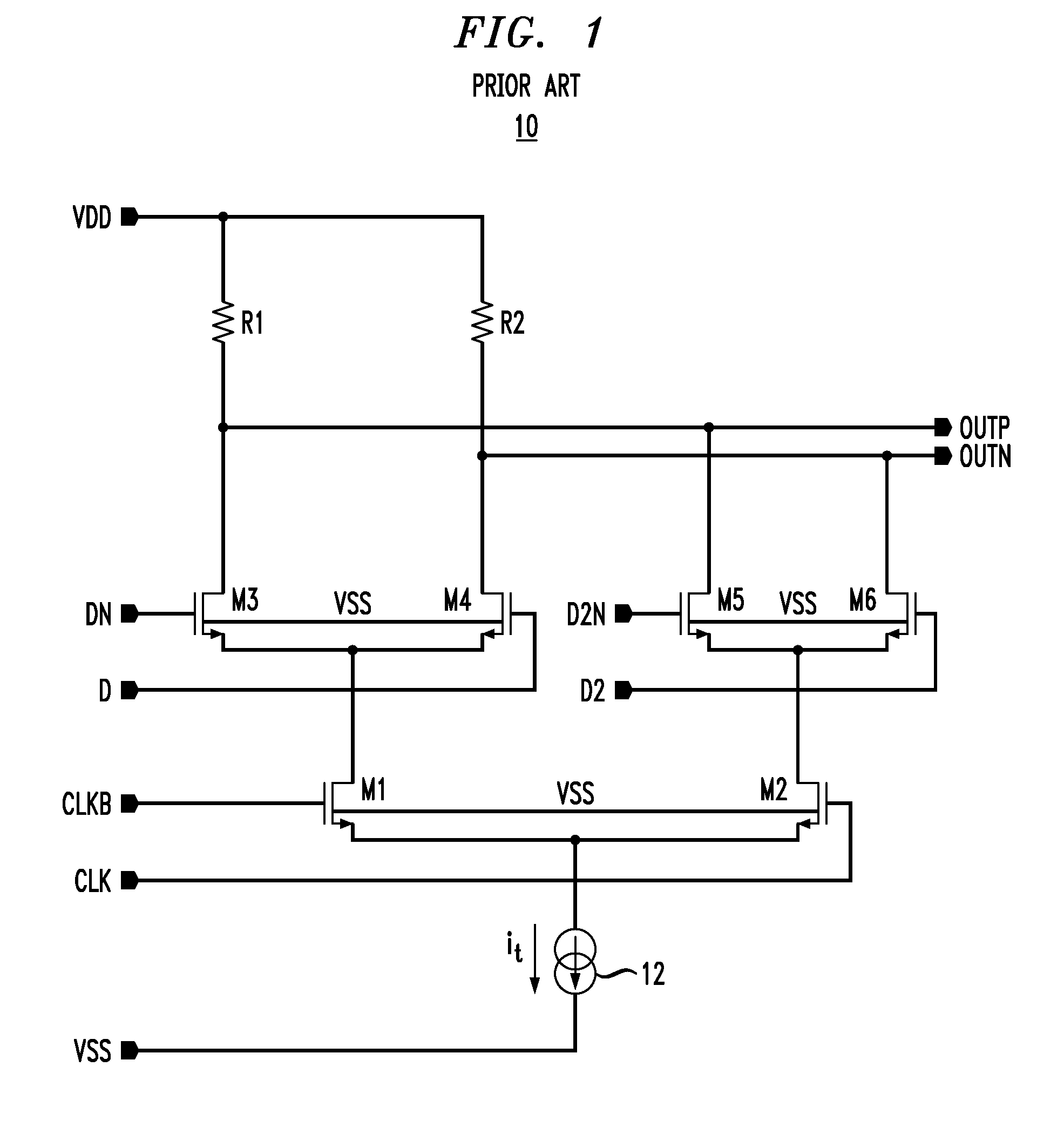
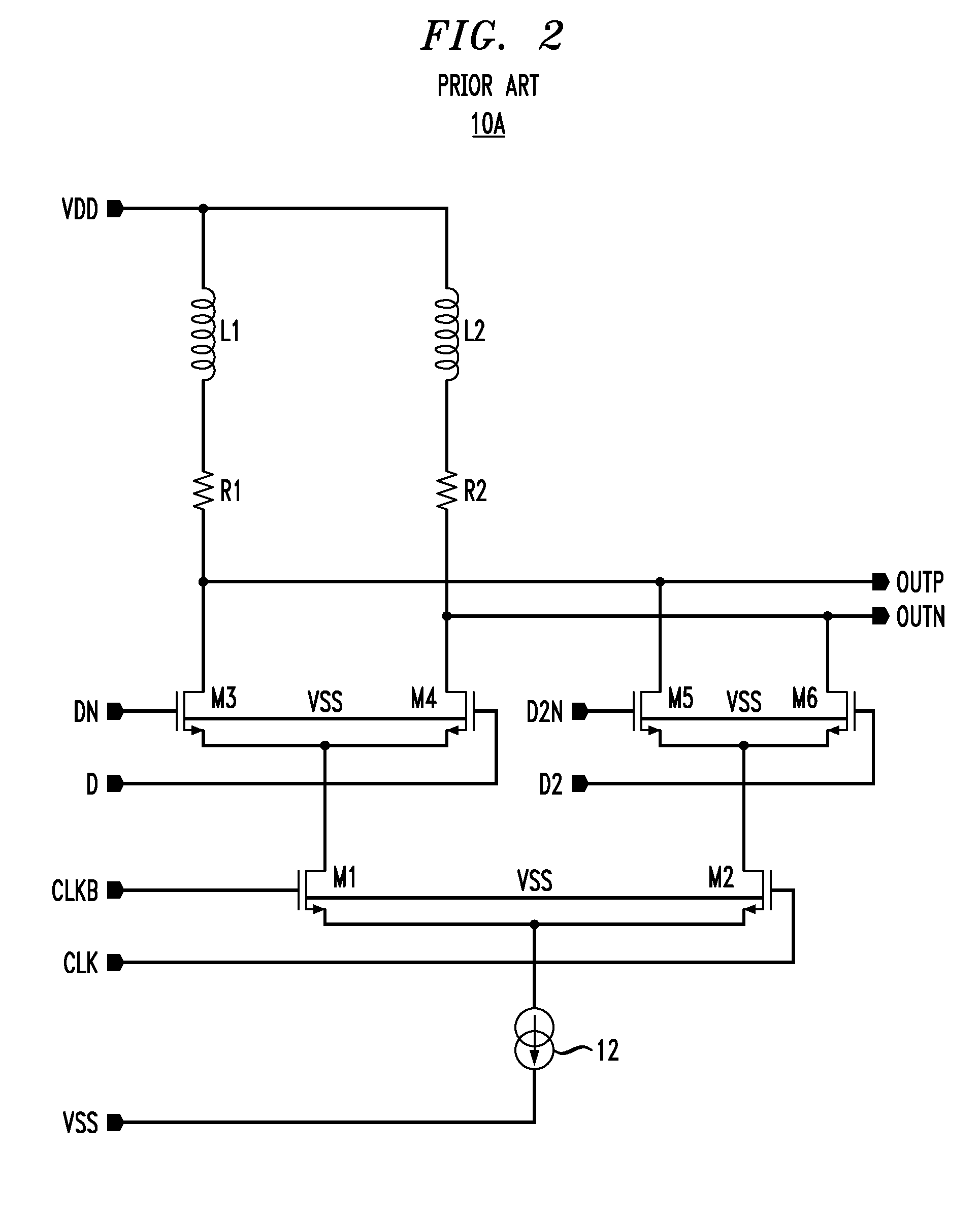
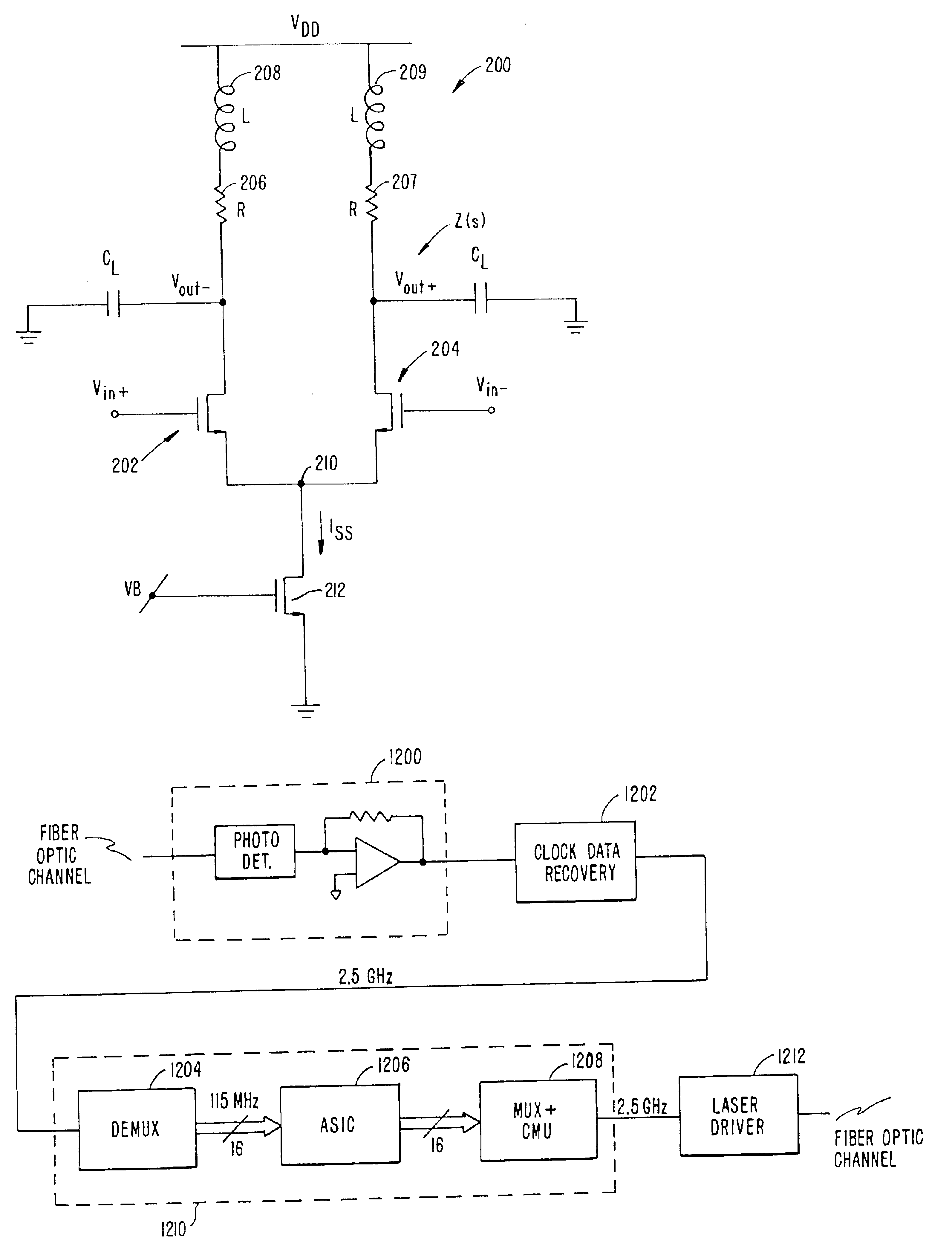
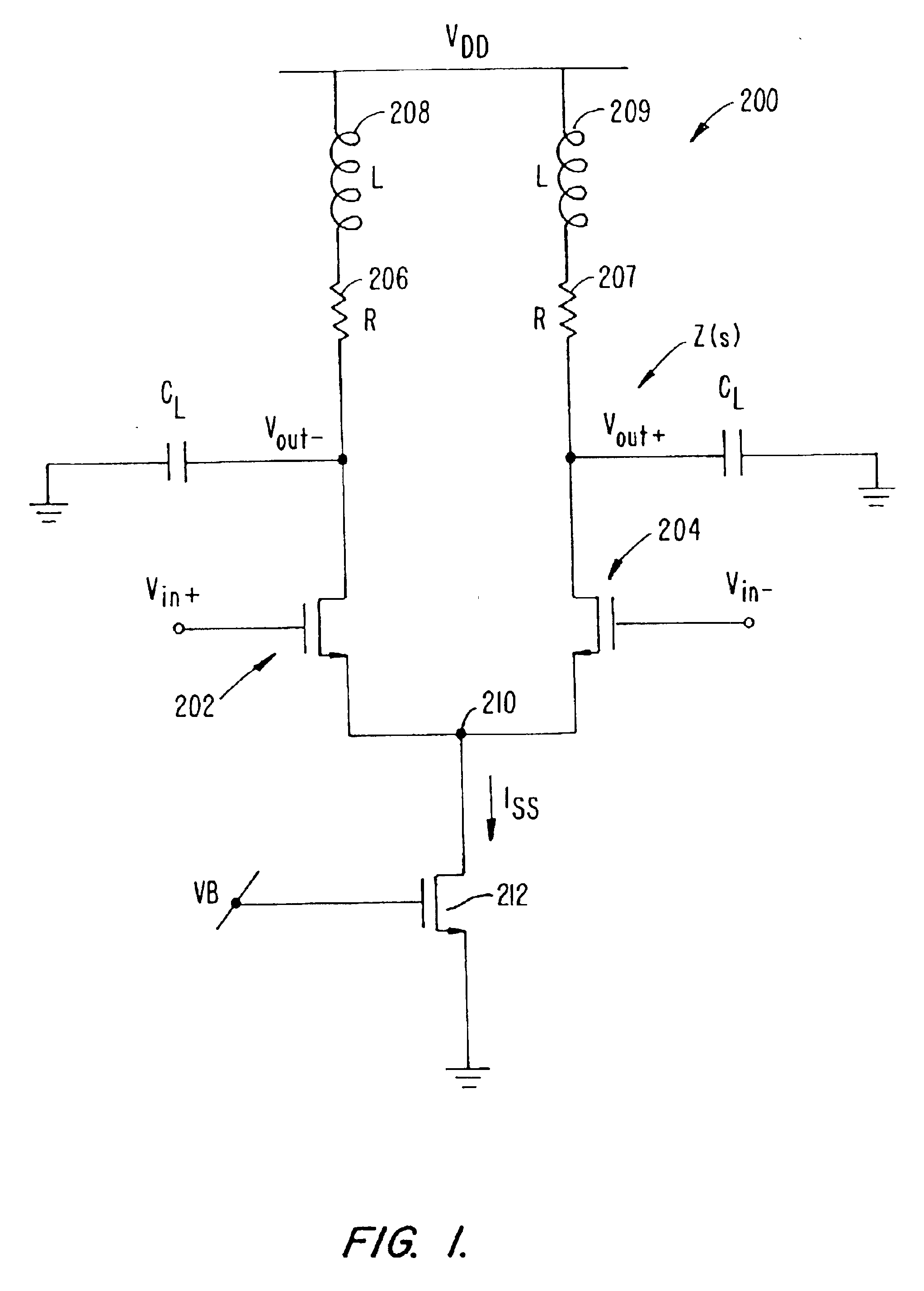
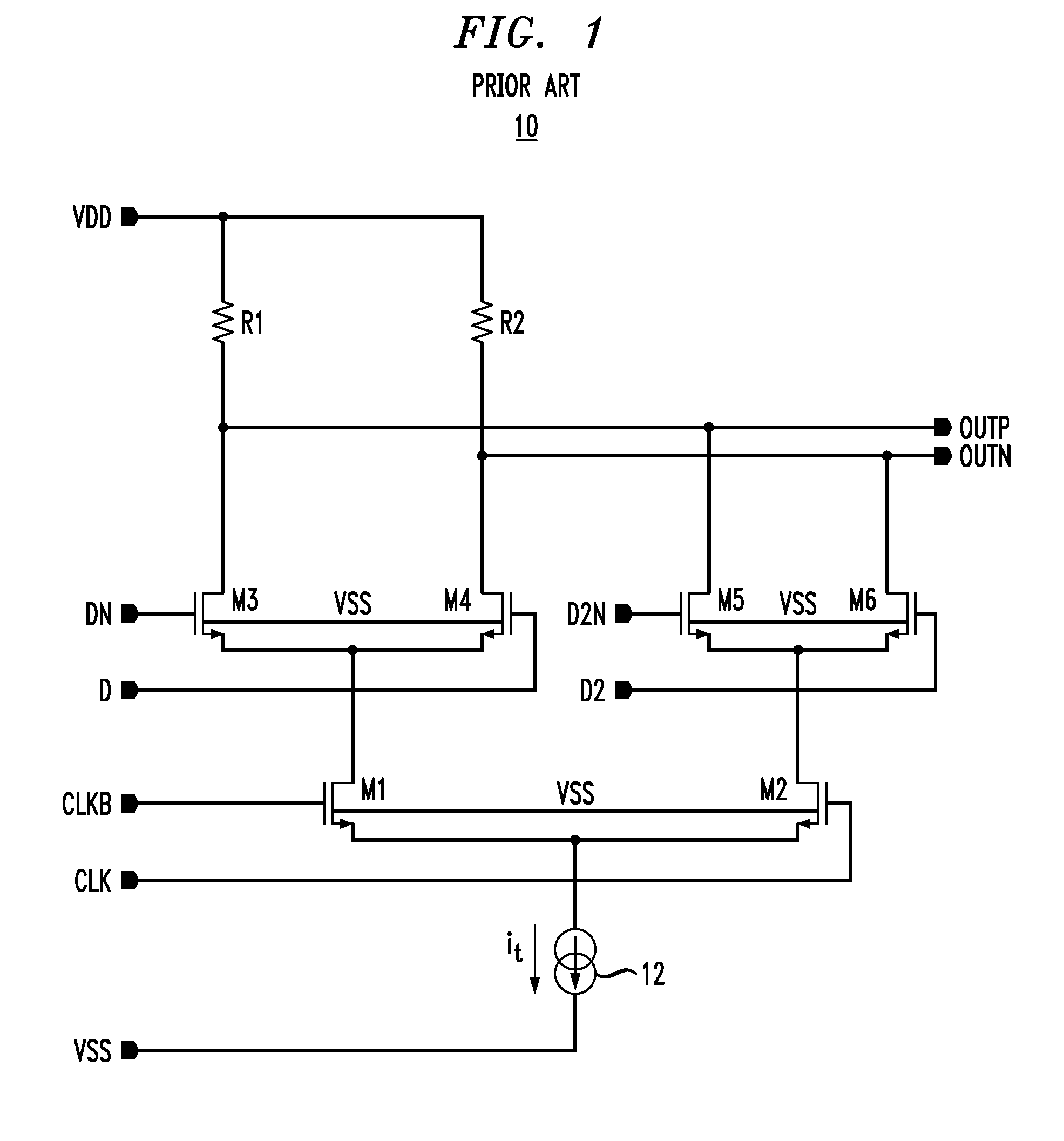
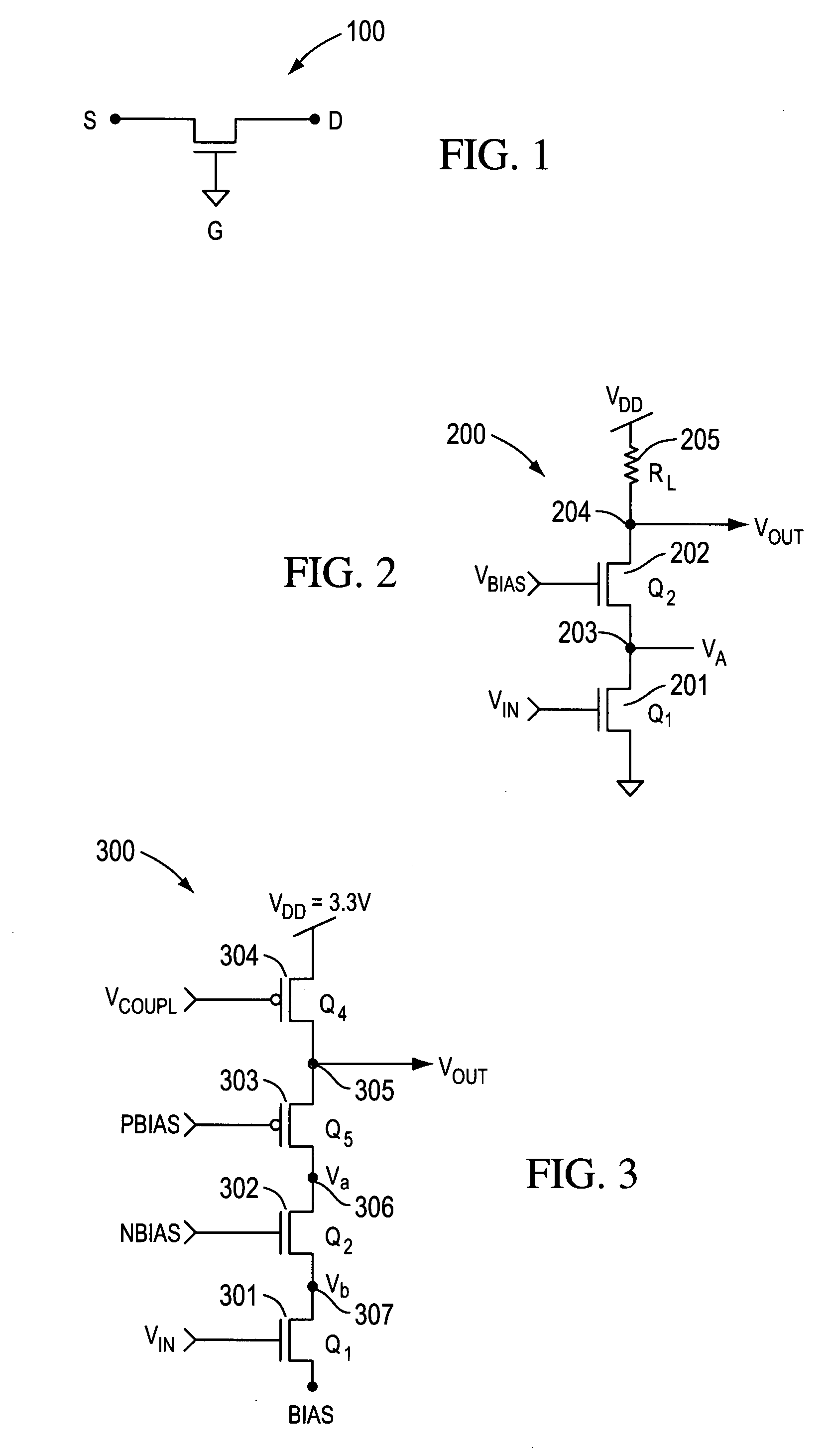
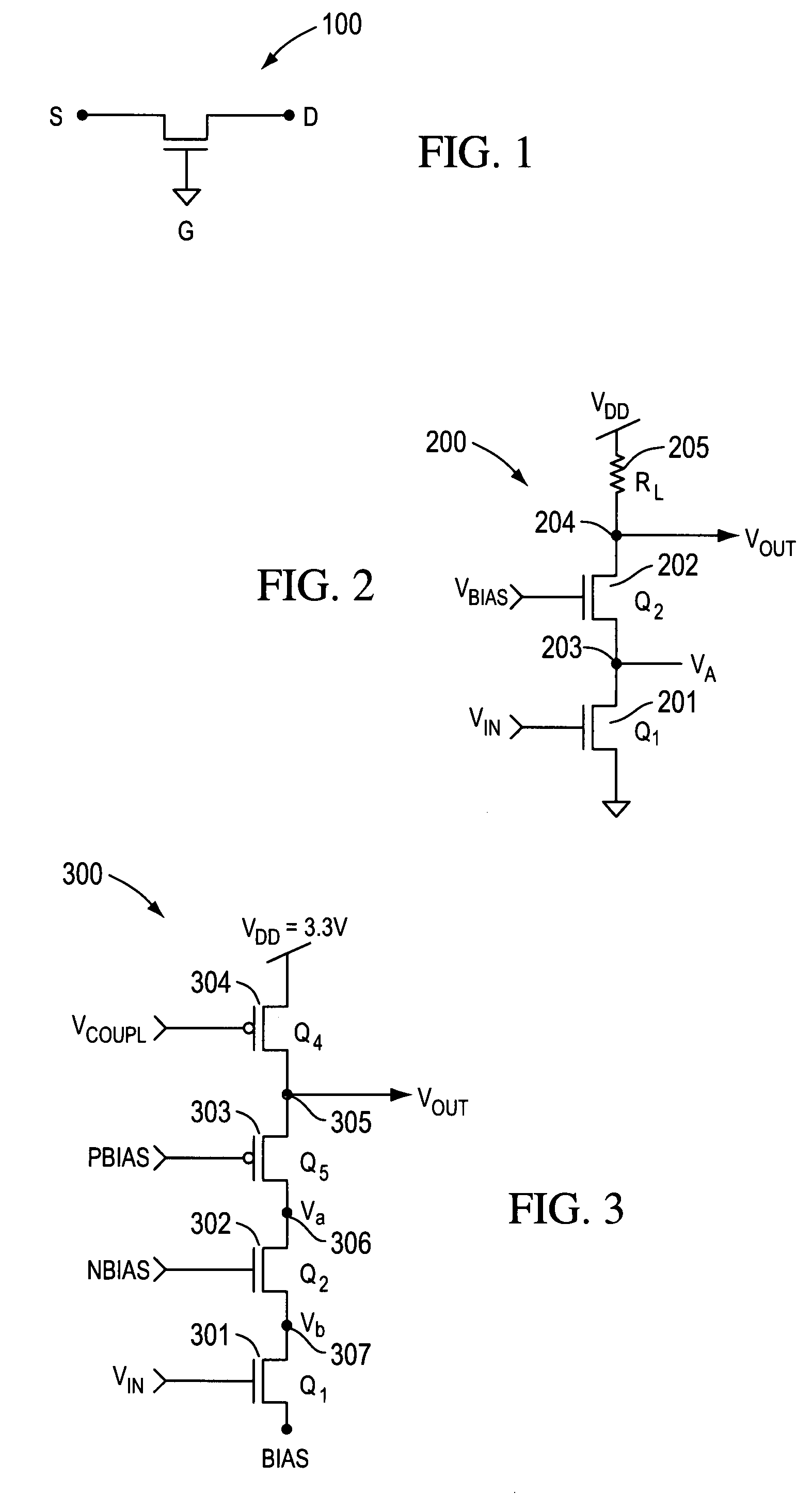
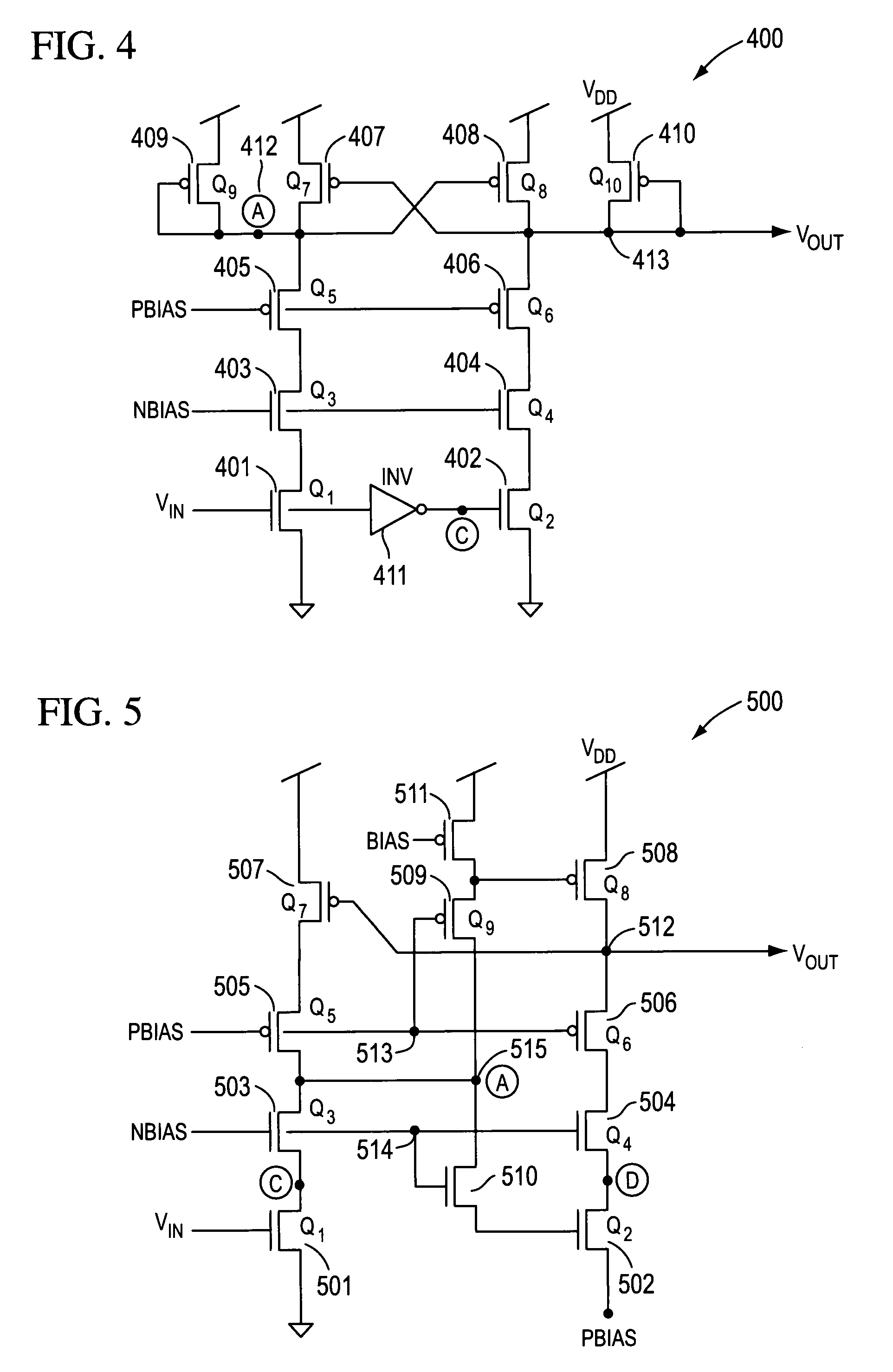
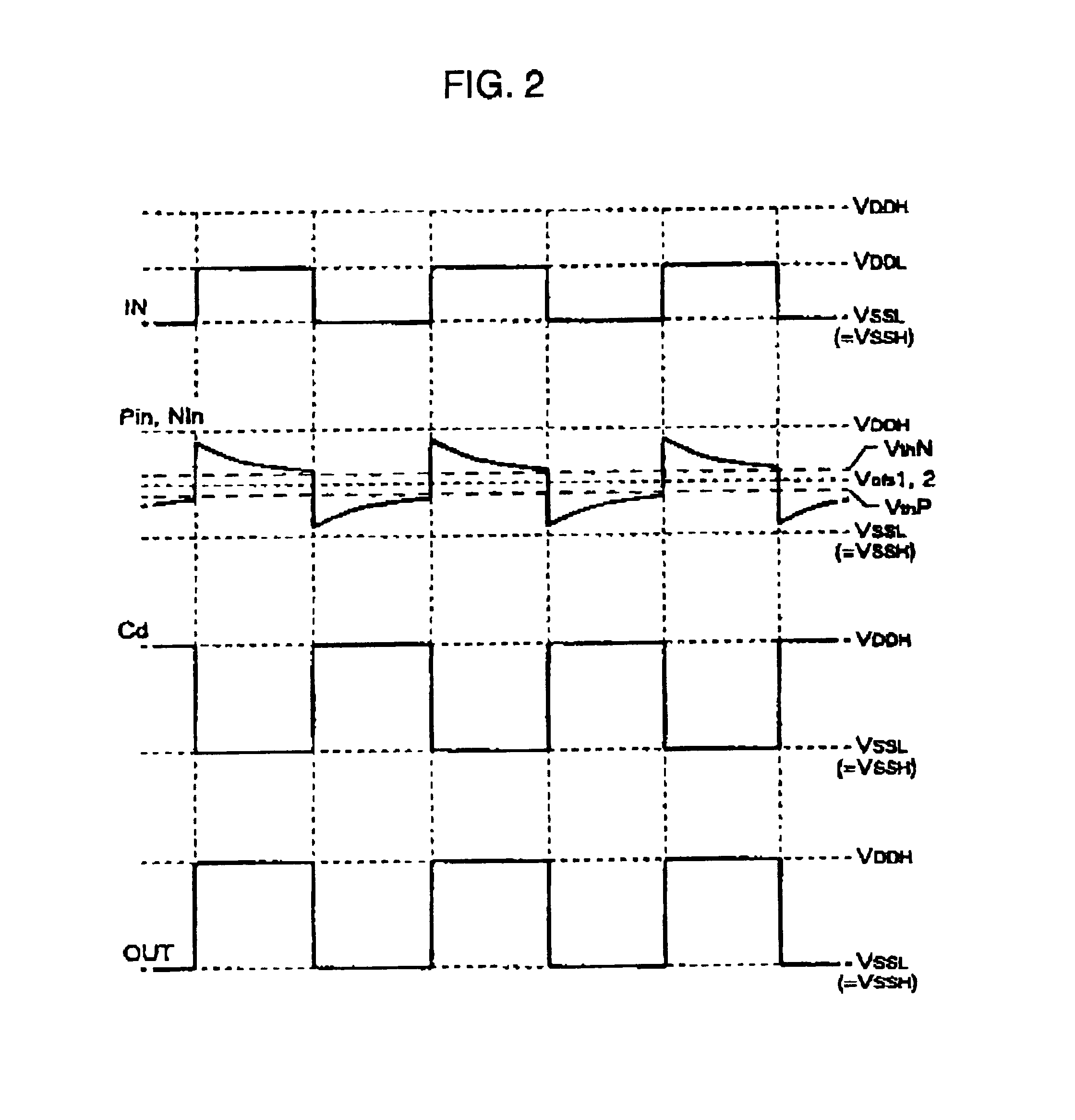
High speed MOSFET output driver
ActiveUS7227400B1High voltage gainReducing minimum voltage levelSwitching accelaration modificationsPulse automatic controlMOSFETEngineering
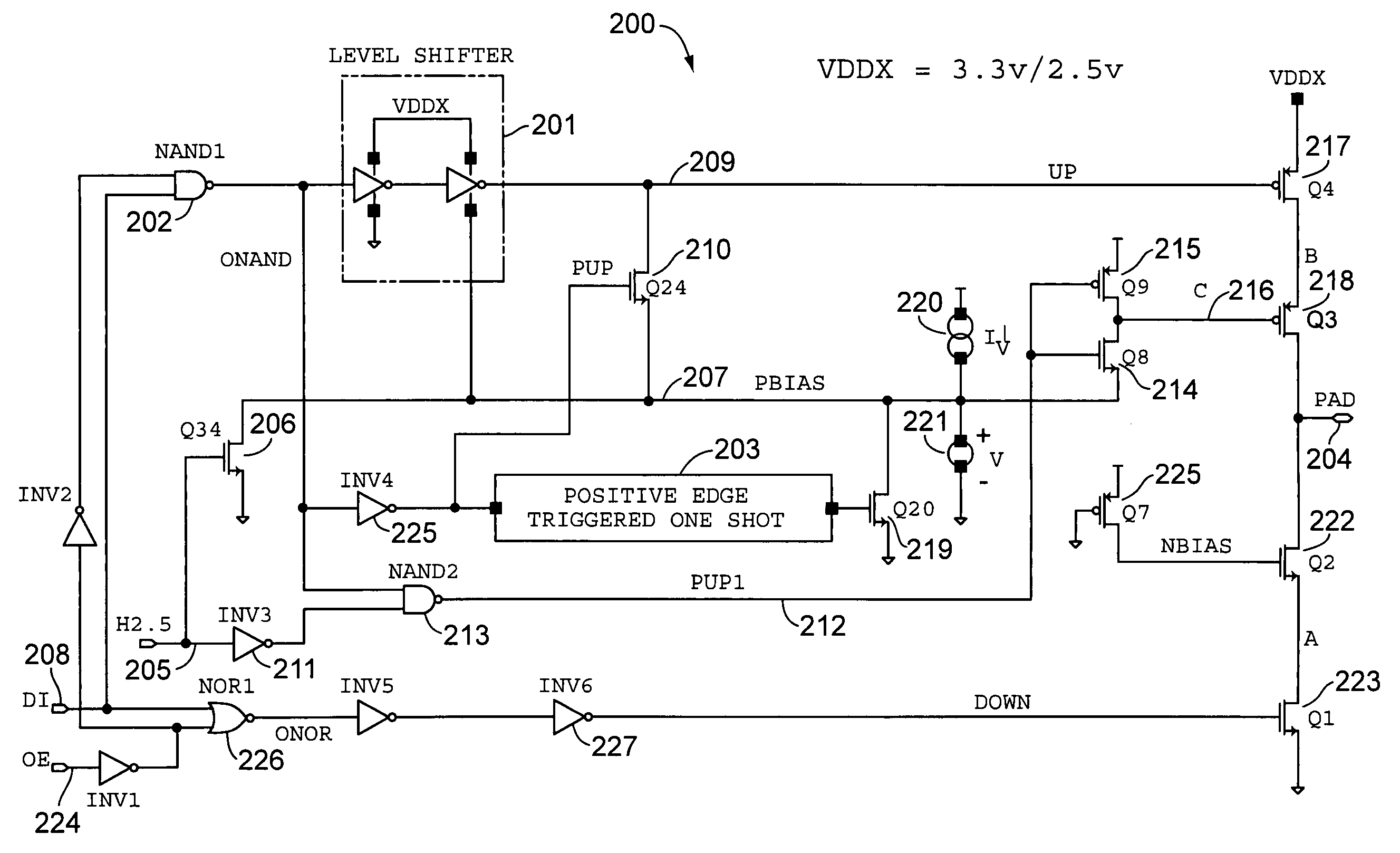
A high speed MOSFET output driver is disclosed that includes a voltage level shifter stage operable to transition an input signal at a first voltage level to an output signal at a second voltage level, an output stage operable to drive high voltage output load, and a hot inverter, biased between the second voltage level and the bias voltage such that the voltage gain of the output signal is increased and at the same time the minimum voltage level of the output signal introduced to the output stage is decreased, improving the control and the transition time of the output signal and allowing all components of the high speed MOSFET output driver of the present invention to be fabricated using a single thin gate oxide process.
Owner:INTEGRATED DEVICE TECH INC
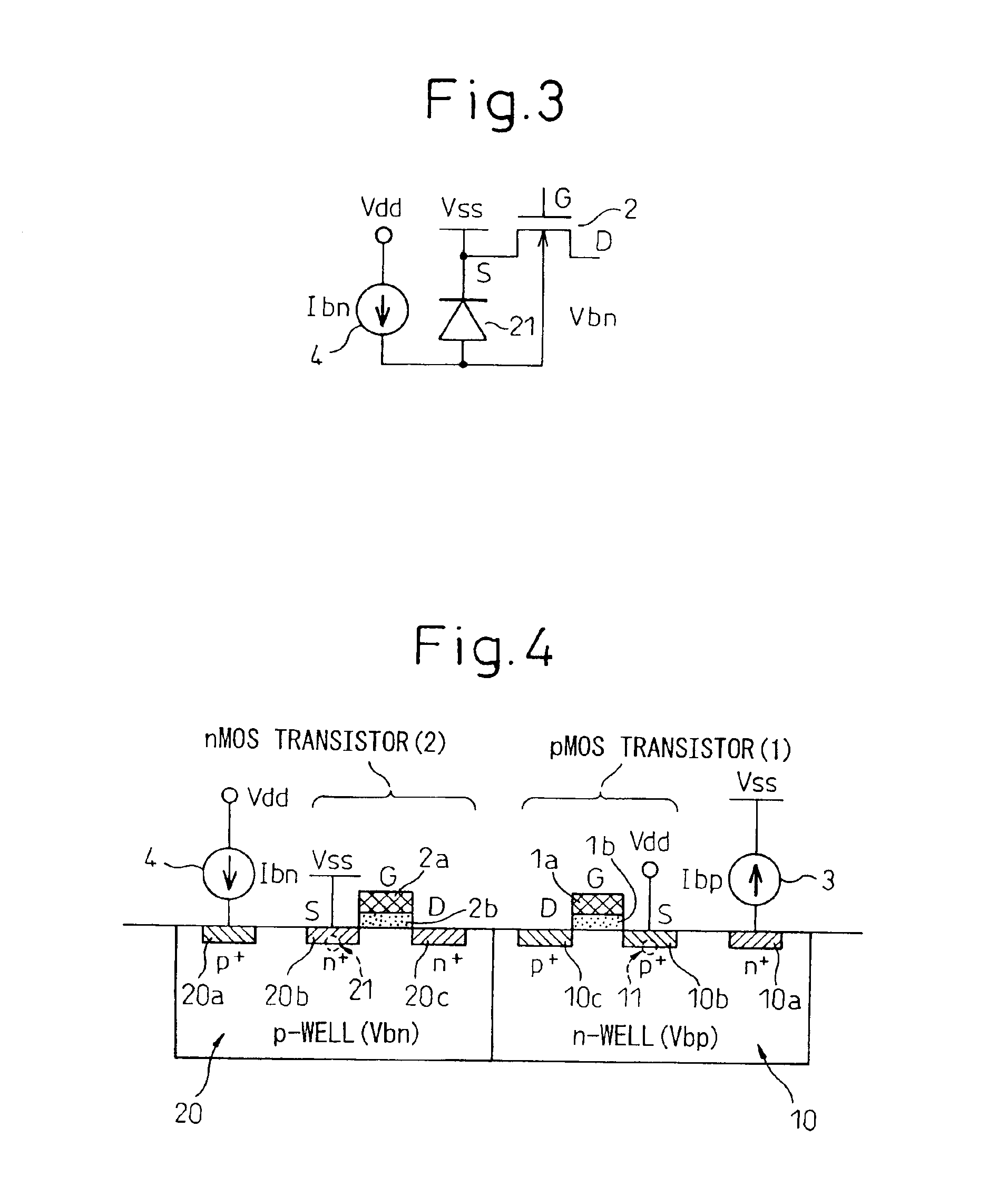
Semiconductor integrated circuit device having body biasing circuit for generating forward well bias voltage of suitable level by using simple circuitry
InactiveUS6864539B2Simple circuitTransistorSwitching accelaration modificationsSemiconductorSimple circuit
A semiconductor integrated circuit device has a MISFET and a body biasing circuit. The MISFET has a source electrode and a drain electrode of a first conductivity type and a gate electrode, and the MISFET is formed in a well of a second conductivity type. The body biasing circuit generates a voltage in the well by passing a prescribed current in a forward direction into a diode which is formed from the well and the source electrode of the MISFET.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Systems and methods for actively-peaked current-mode logic
ActiveUS7202706B1Minimal costLess cost-effectiveSwitching accelaration modificationsLogic circuits characterised by logic functionElectrical resistance and conductanceLogic cell
Owner:MICROSEMI STORAGE SOLUTIONS
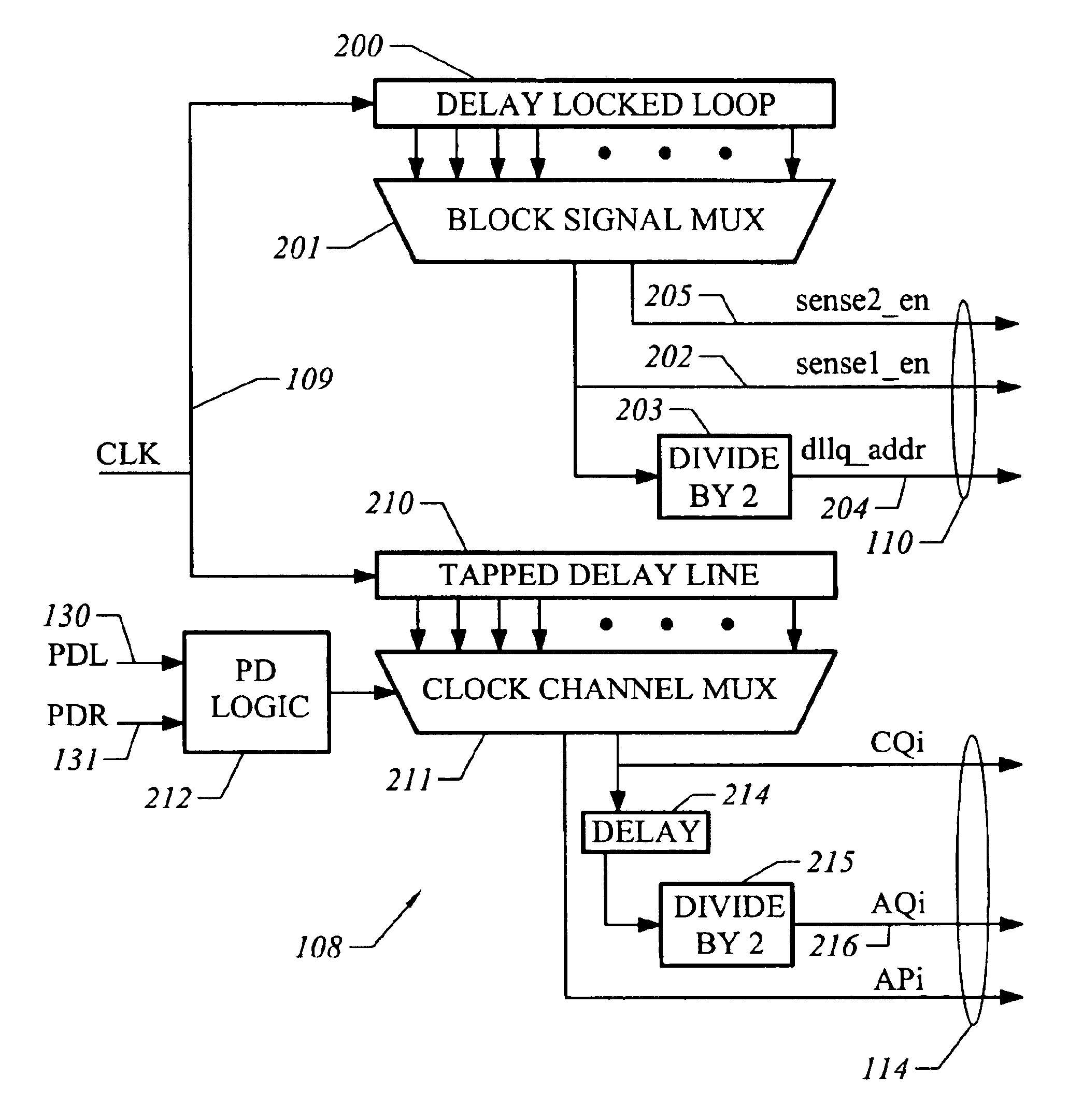
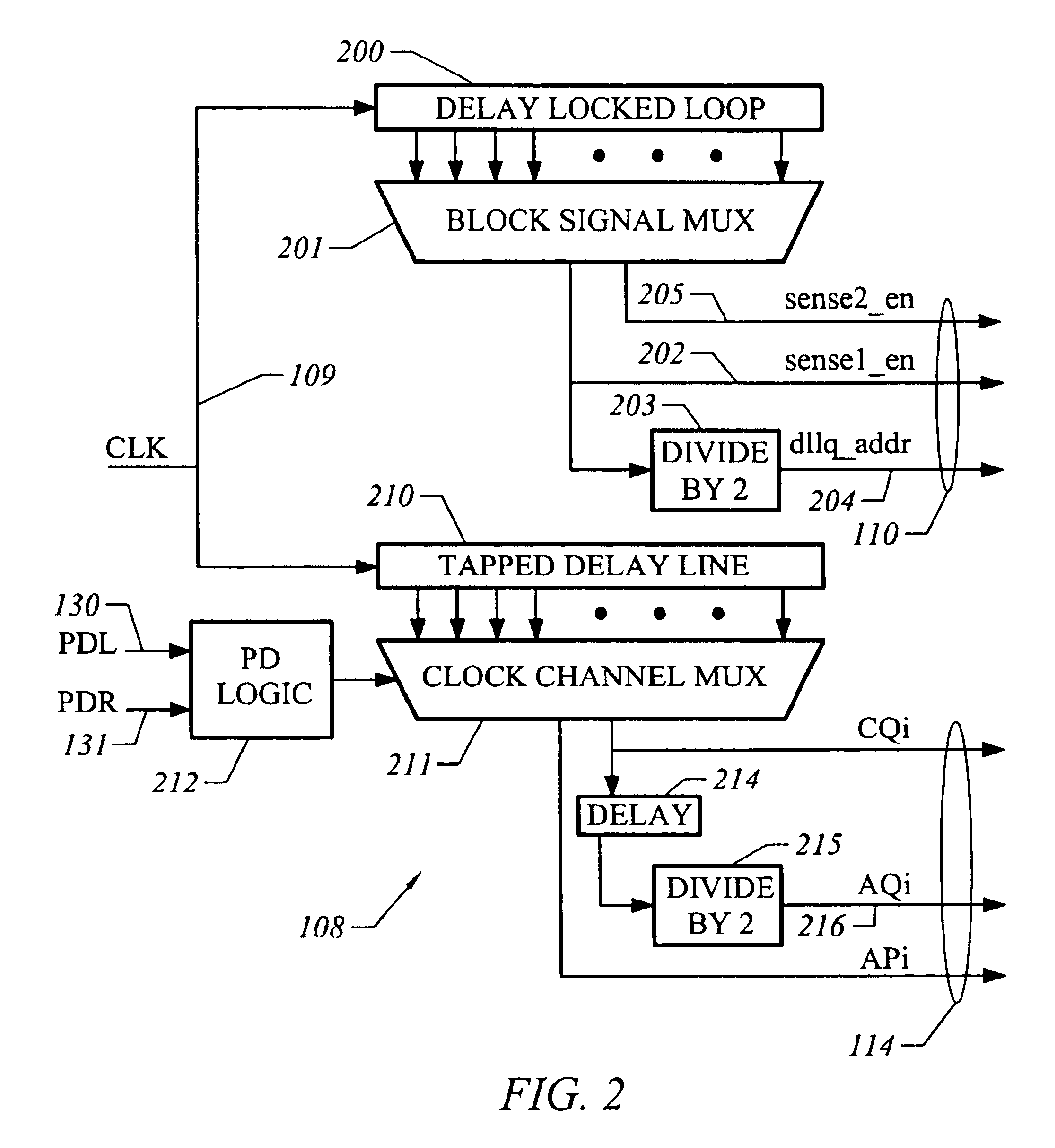
Delay line and output clock generator using same
InactiveUS6891774B1Avoid failureImprove performanceSwitching accelaration modificationsPulse automatic controlMultiplexingShift register
A delay line for an adjustable, high speed clock generator is based on two-stage multiplexing, in which for all pairs of adjacent taps, a change from a current tap to an adjacent tap in the pair is executed by switching only one of the first stage and second stage multiplexers. Control signals are generated for the first and second stage multiplexers by logic based on bidirectional shift registers. The delay line is suitable for generation of an output clock having an adjustable phase, allowing for smooth, glitch-free adjustment over a large range of phases.
Owner:T RAM ASSIGNMENT FOR THE BENEFIT OF CREDITORS LLC +1
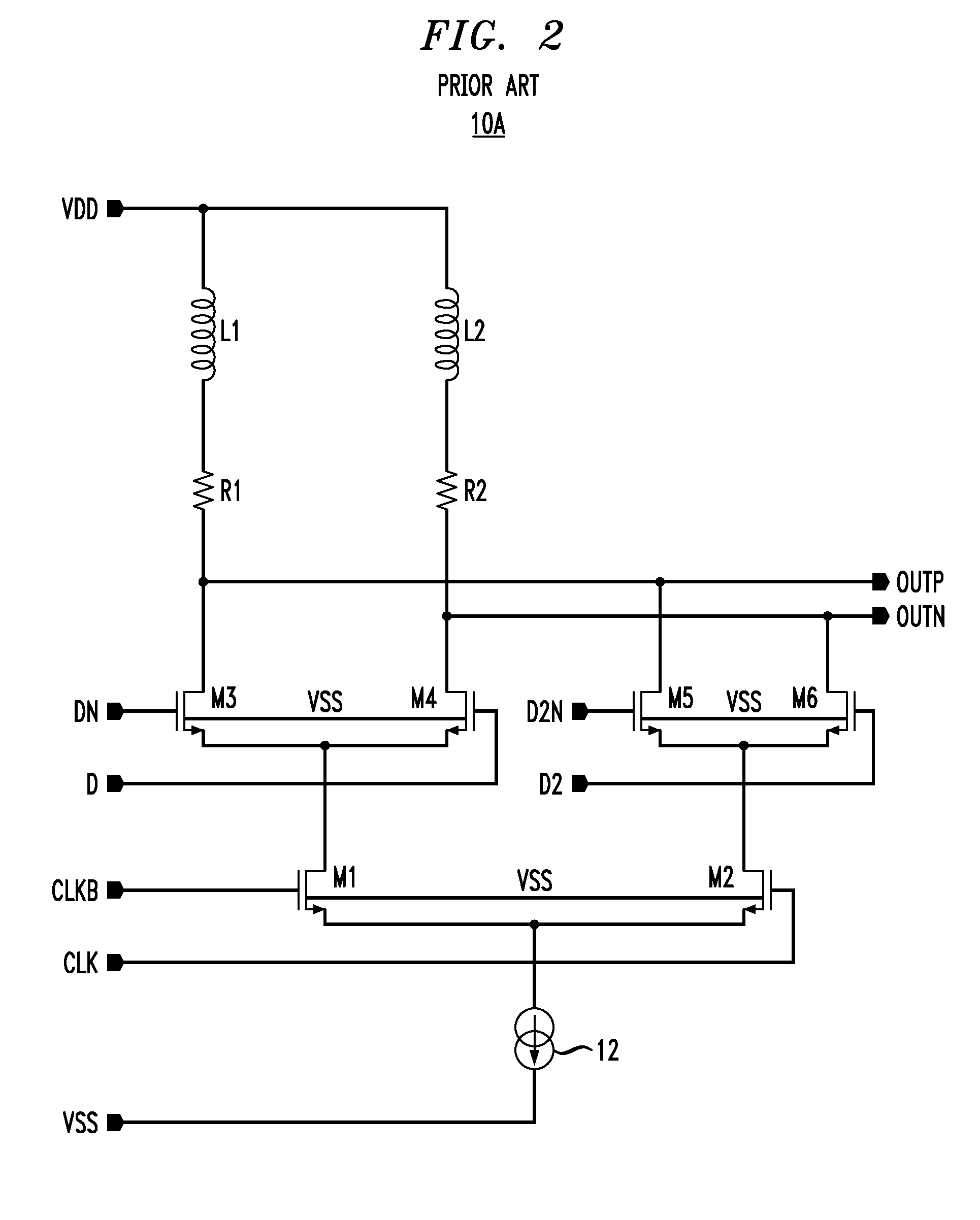
High-speed CML circuit design
ActiveUS7560957B2Switching accelaration modificationsReliability increasing modificationsInductorEngineering
A current mode logic digital circuit is provided comprising a logic circuit component having at least one data input node and at least one output node. A load is coupled between a power supply node and the output node. The load comprises a folded active inductor coupled to the output node.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Systems and methods for actively-peaked current-mode logic
ActiveUS7288971B1Reduce power consumptionReduce areaSwitching accelaration modificationsLogic circuits characterised by logic functionElectrical resistance and conductanceLogic cell
A method and apparatus for creating high speed logic circuits in a CMOS environment using current steering logic cells with actively-peaked NMOS or PMOS loads and the biasing of these logic cells is disclosed. The logic cells can include, for example, buffers, AND gates, OR gates, flip-flops, and latches. The current steering cells with actively-peaked loads can provide benefits such as reduced power consumption, smaller area, and higher speed performance over conventional devices. This performance boost is preferably achieved using NMOS followers with resistively degenerated gates to create frequency peaked transfer function of current-mode logic cells. These logic cells with actively-peaked loads can advantageously be used in circuits in which relatively good power area and performance are desired for state machine logic, parallel to serial conversions, serial to parallel conversions, and the like.
Owner:MICROSEMI STORAGE SOLUTIONS
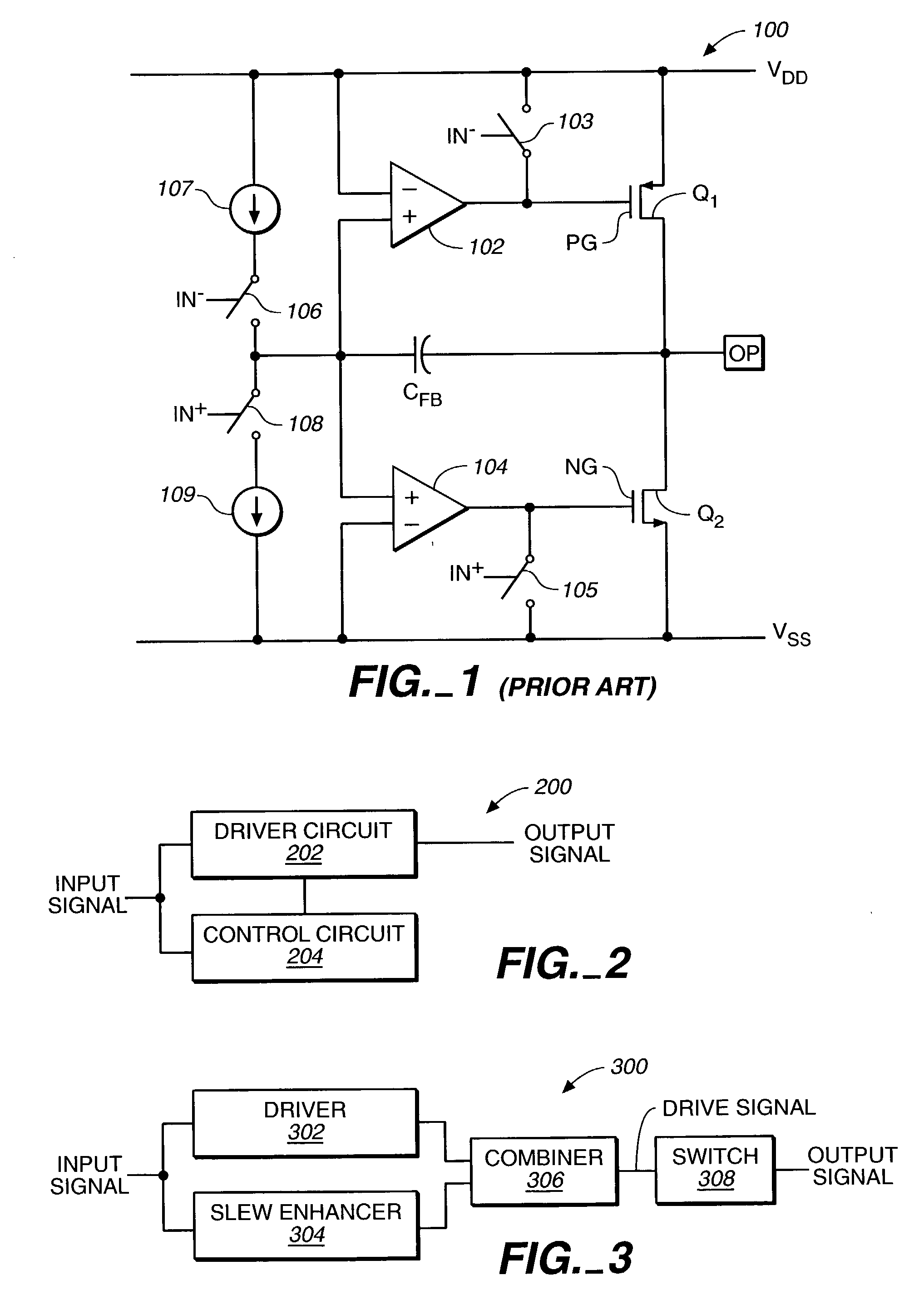
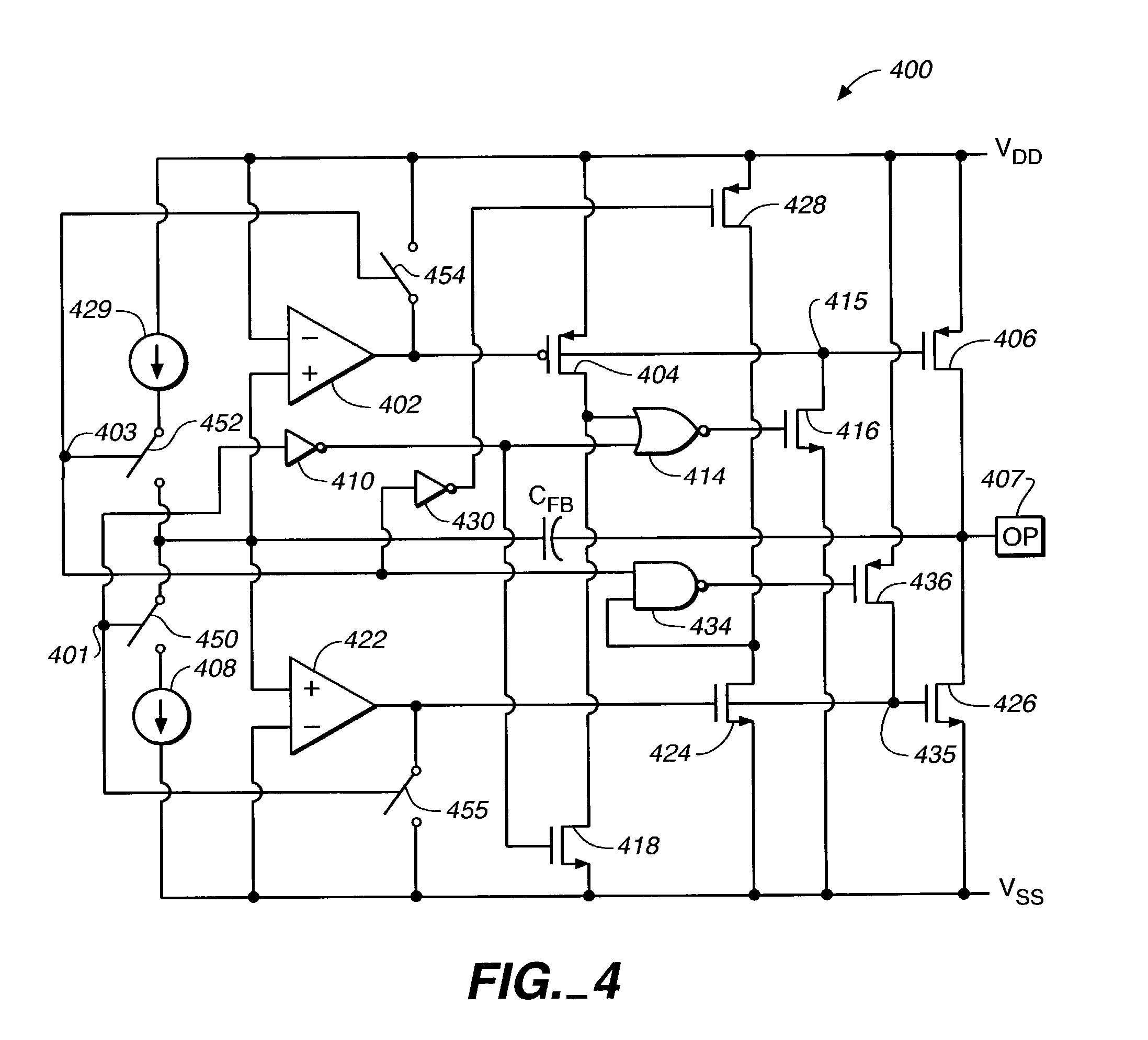
Method and apparatus for slew control of an output signal
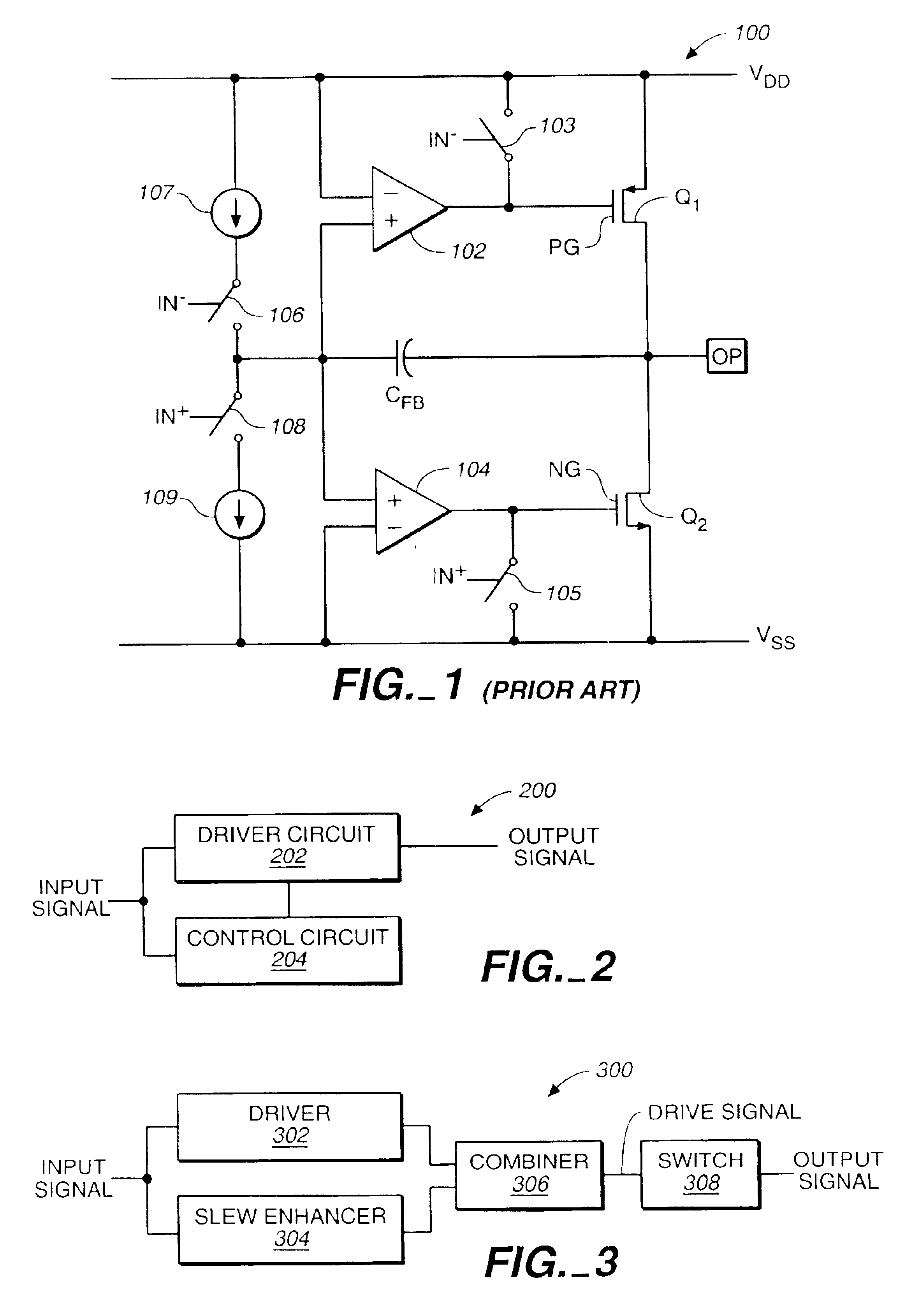
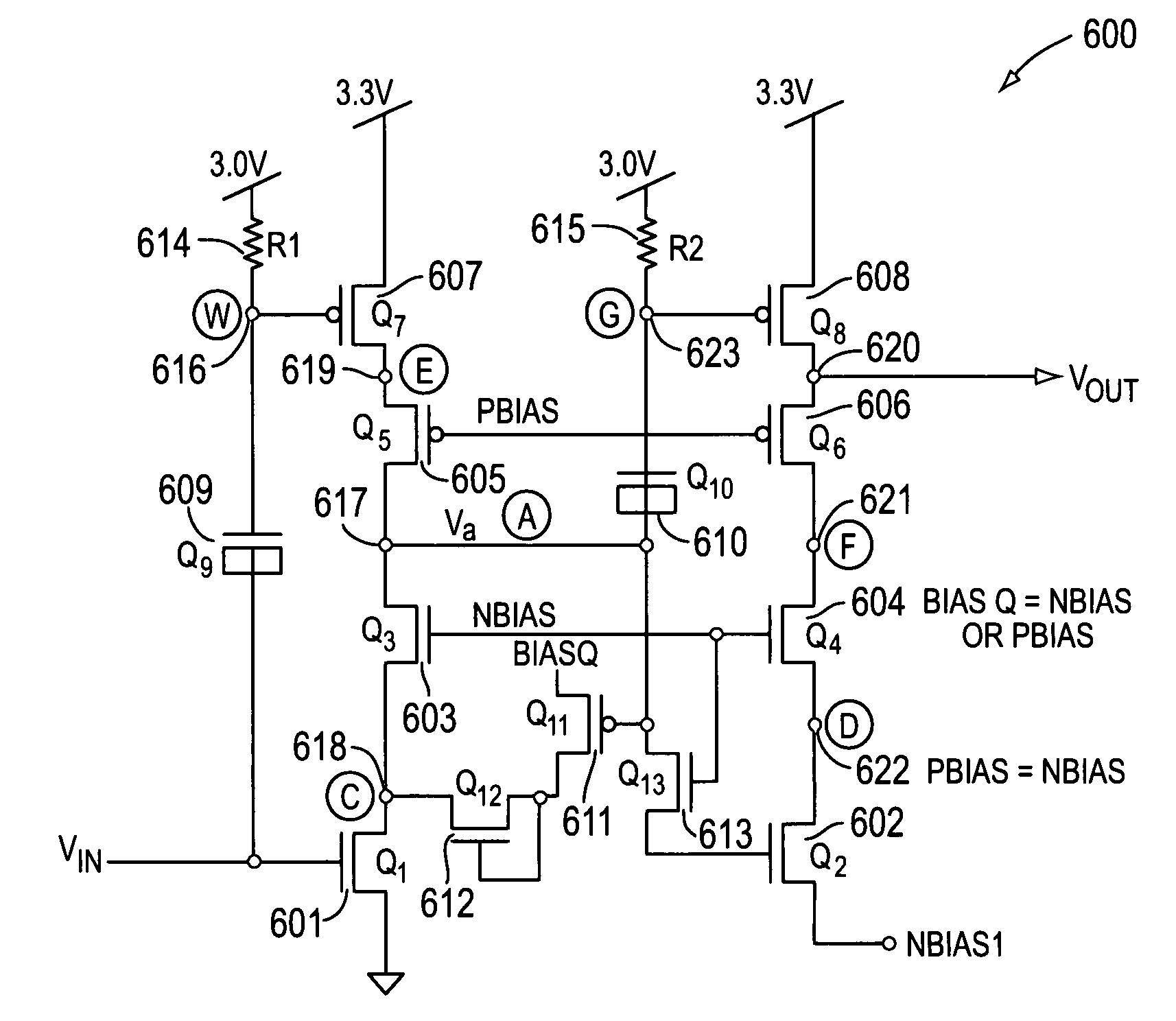
InactiveUS6842058B2Enhanced slew controlStable maintenanceSwitching accelaration modificationsReliability increasing modificationsAudio power amplifierEngineering
Systems and methods for enhancing slew control of output signals. An output driver receives an input signal and controllably increases the gain of that signal to provide a high quality output signal for use by an electronic device coupled thereto. The output driver includes an operational amplifier that maintains stability of the output signal through a feedback of the output signal. A control circuit supplies a signal to the output driver such that the driver to improve the shape of the output signal as the input signal is applied. After the operational amplifier regains control, the control circuit disengages. One embodiment of the present invention may be particularly useful as a USB output driver.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
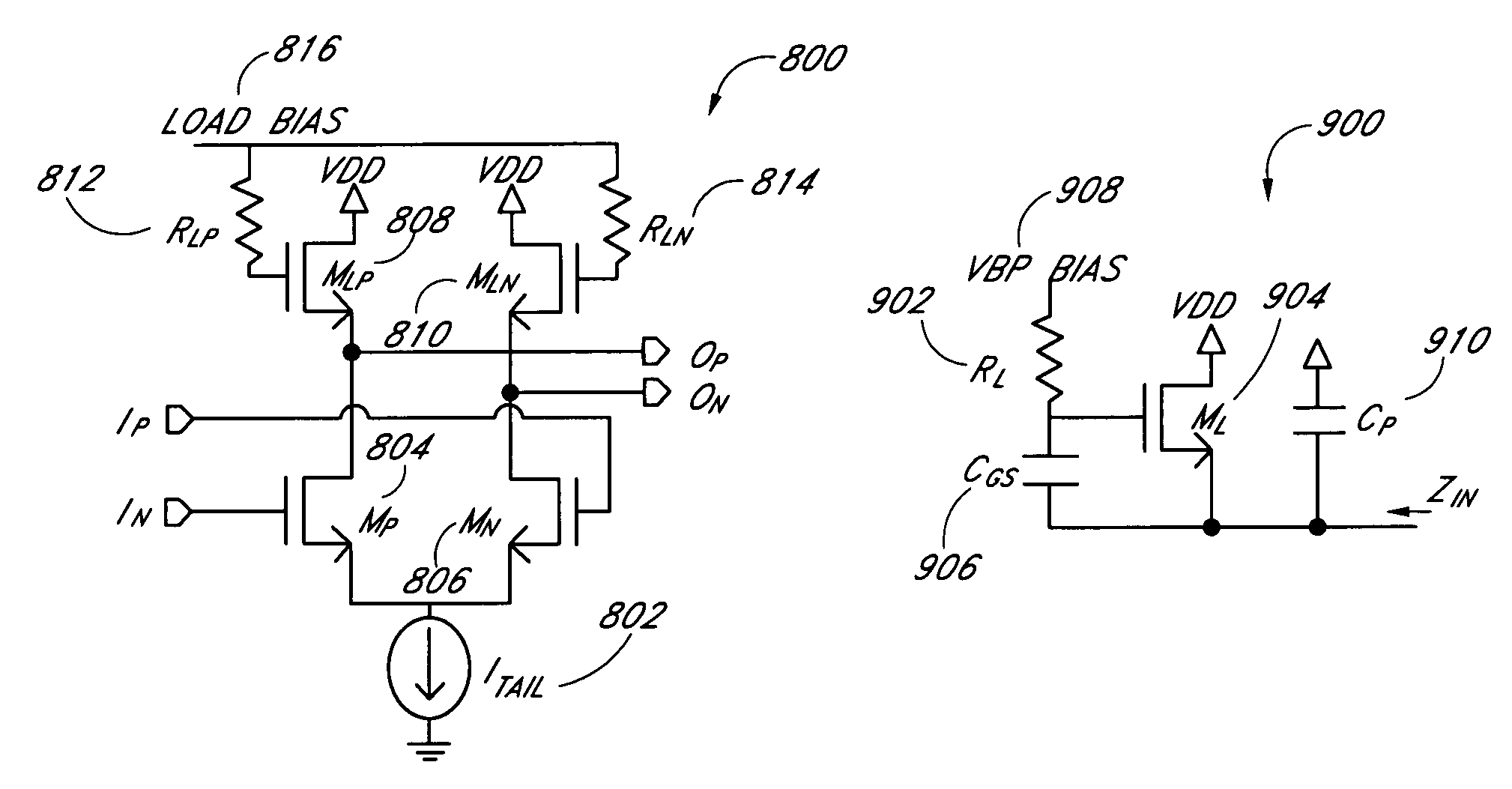
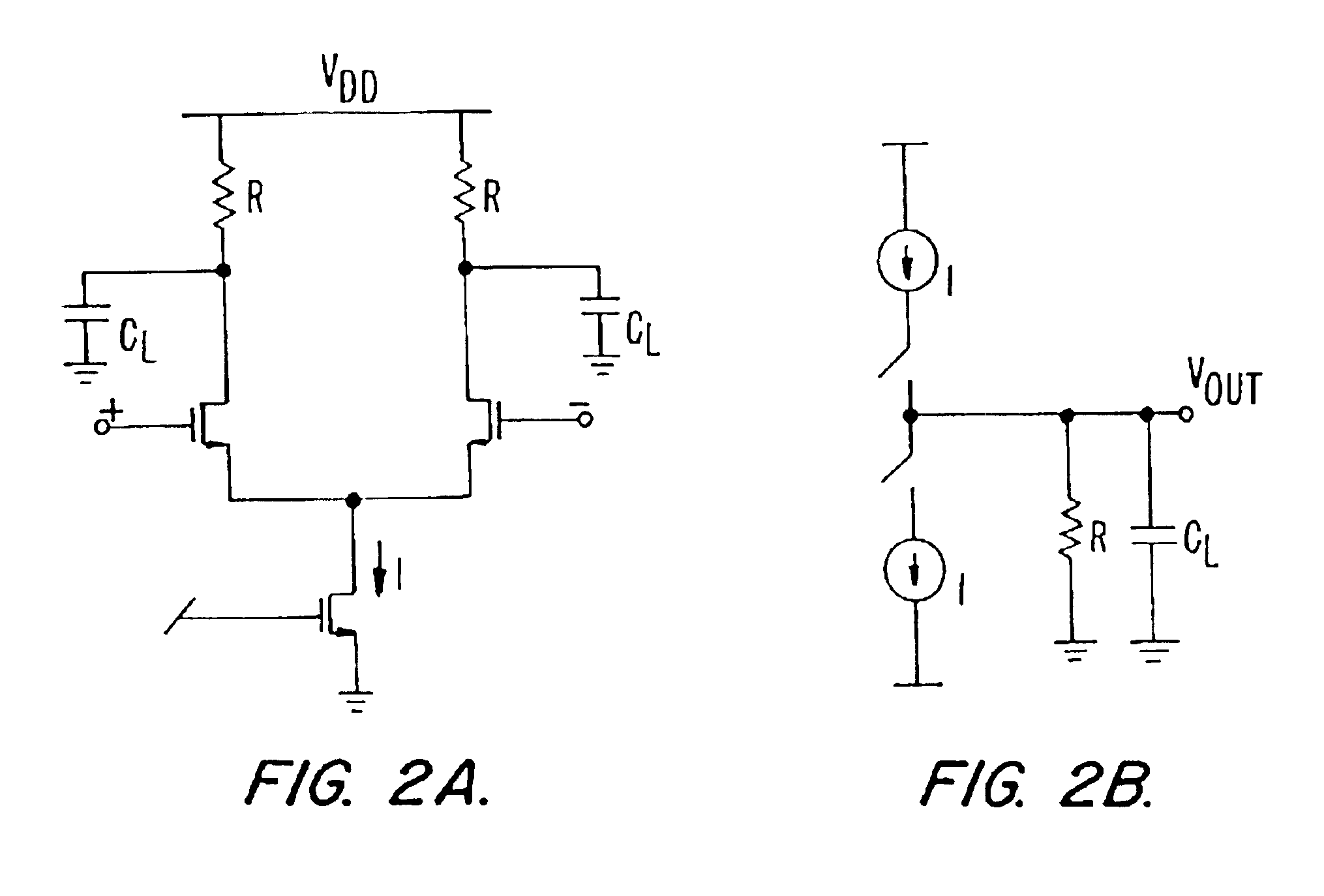
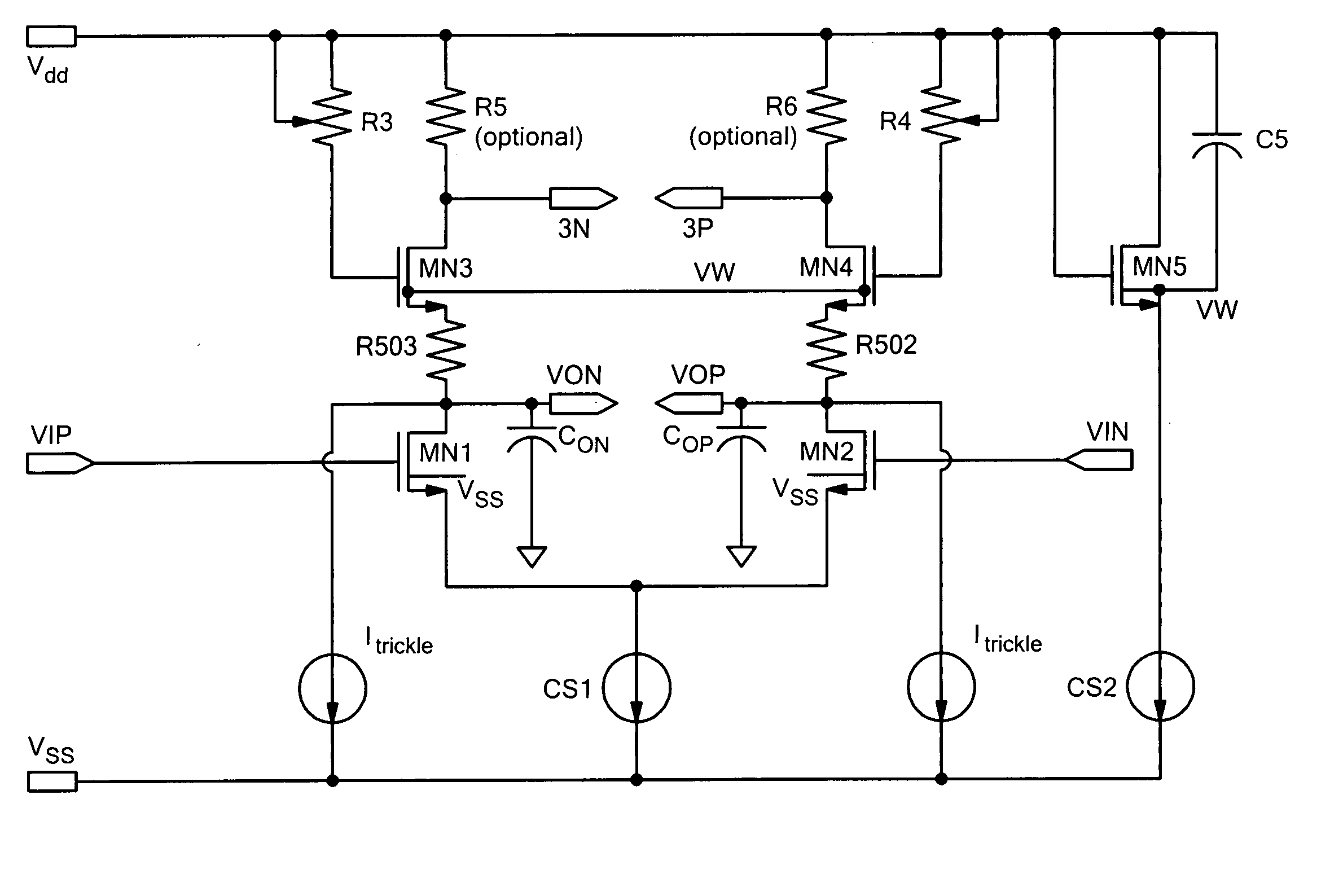
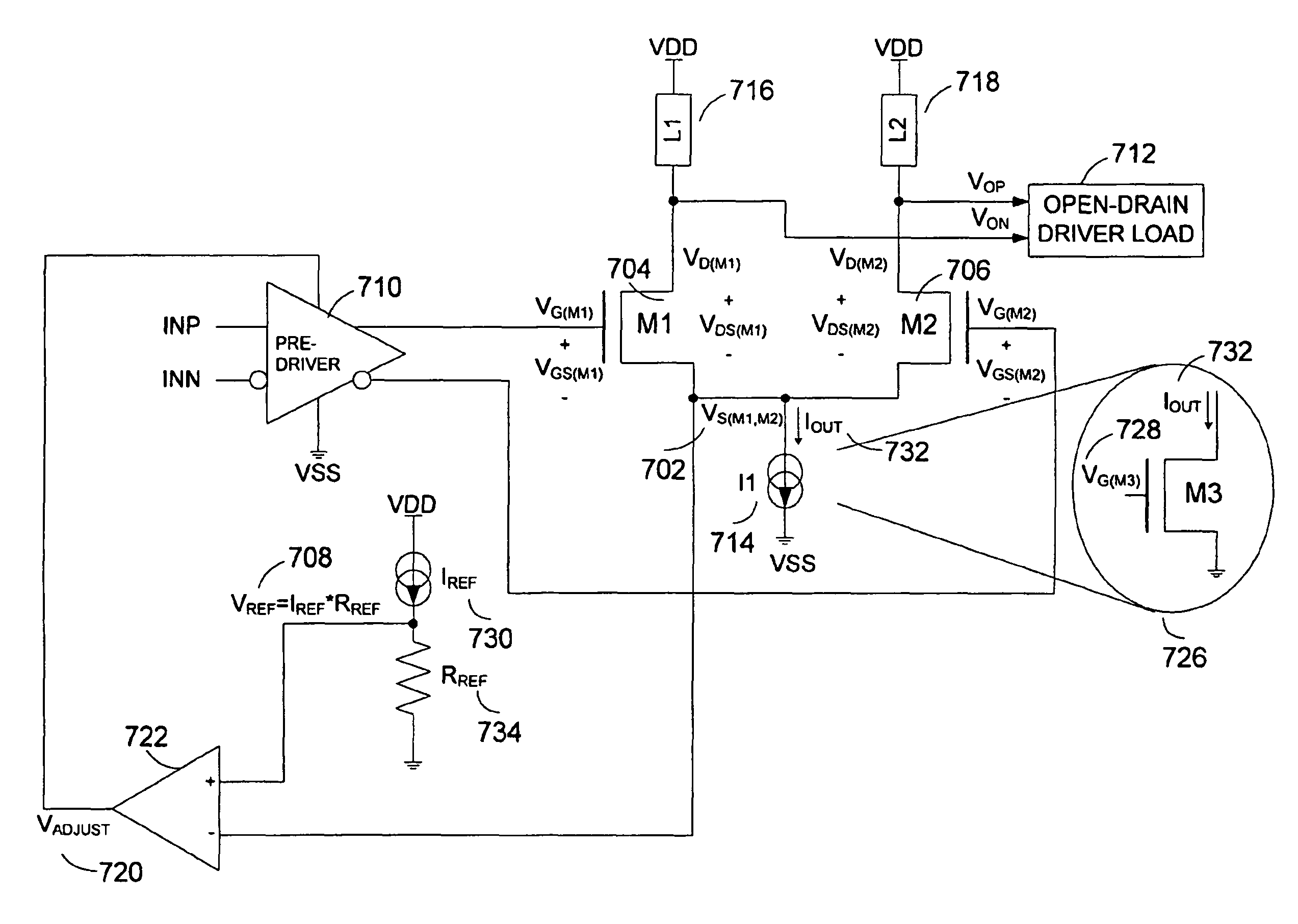
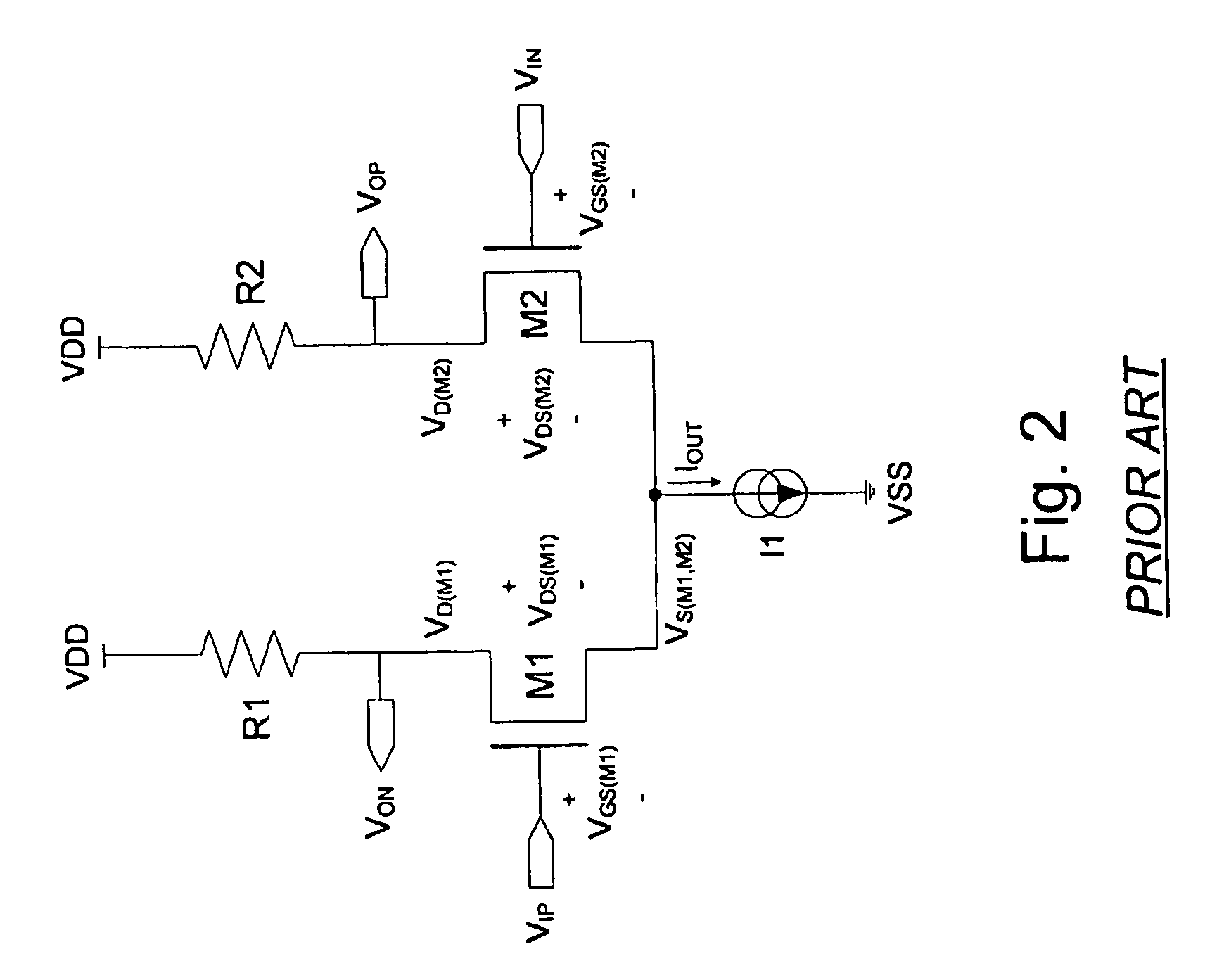
Active biasing in metal oxide semiconductor (MOS) differential pairs
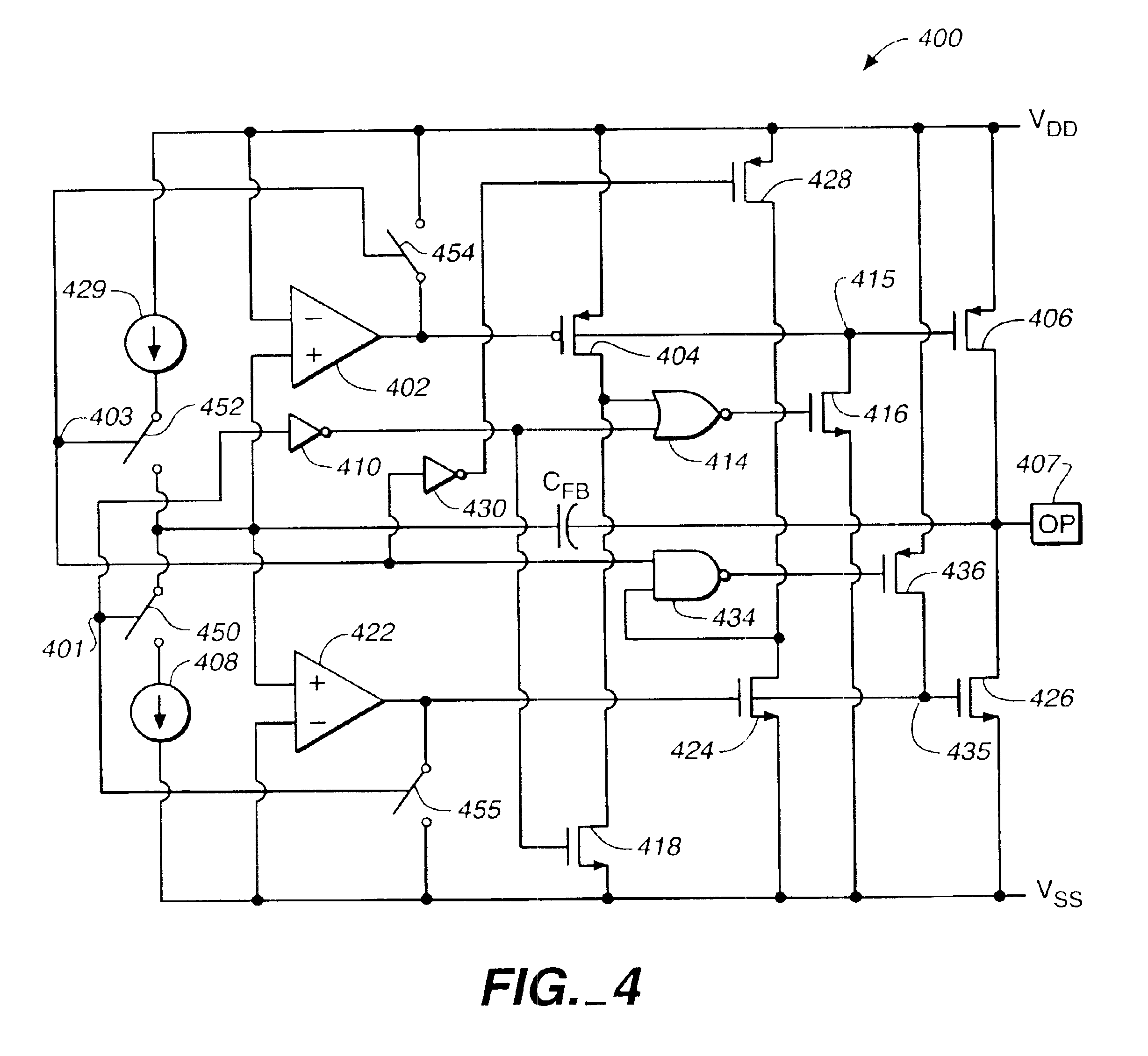
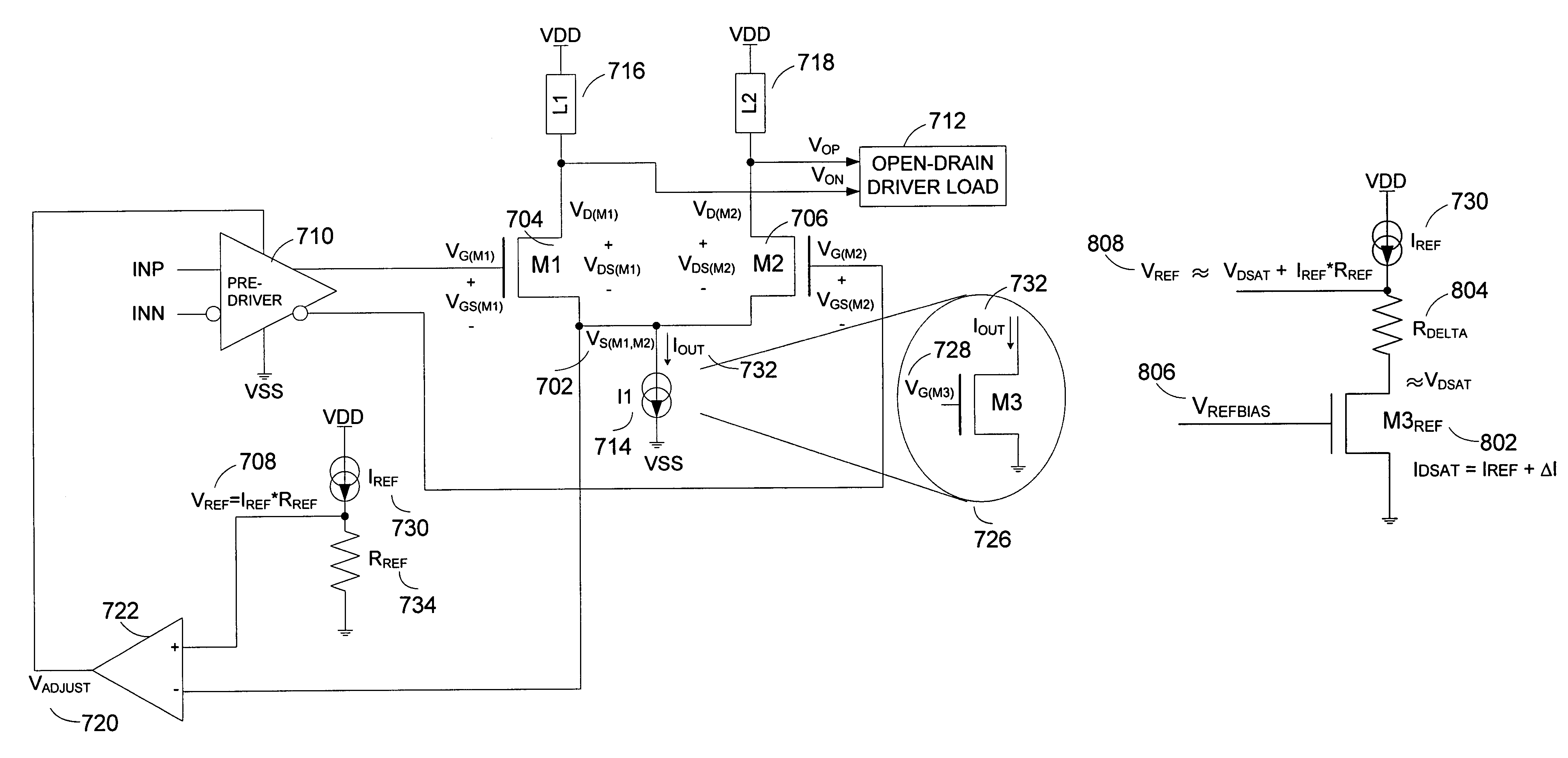
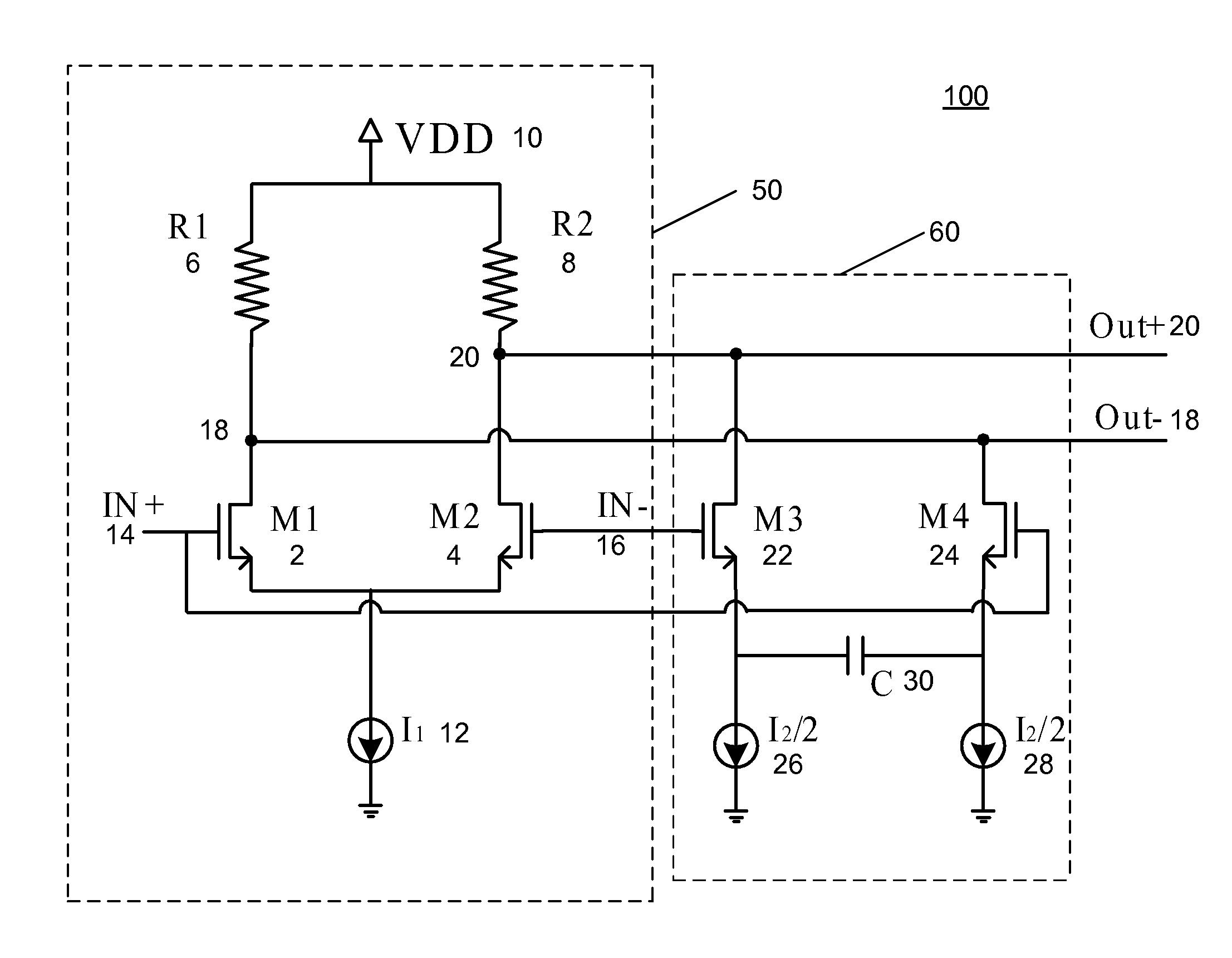
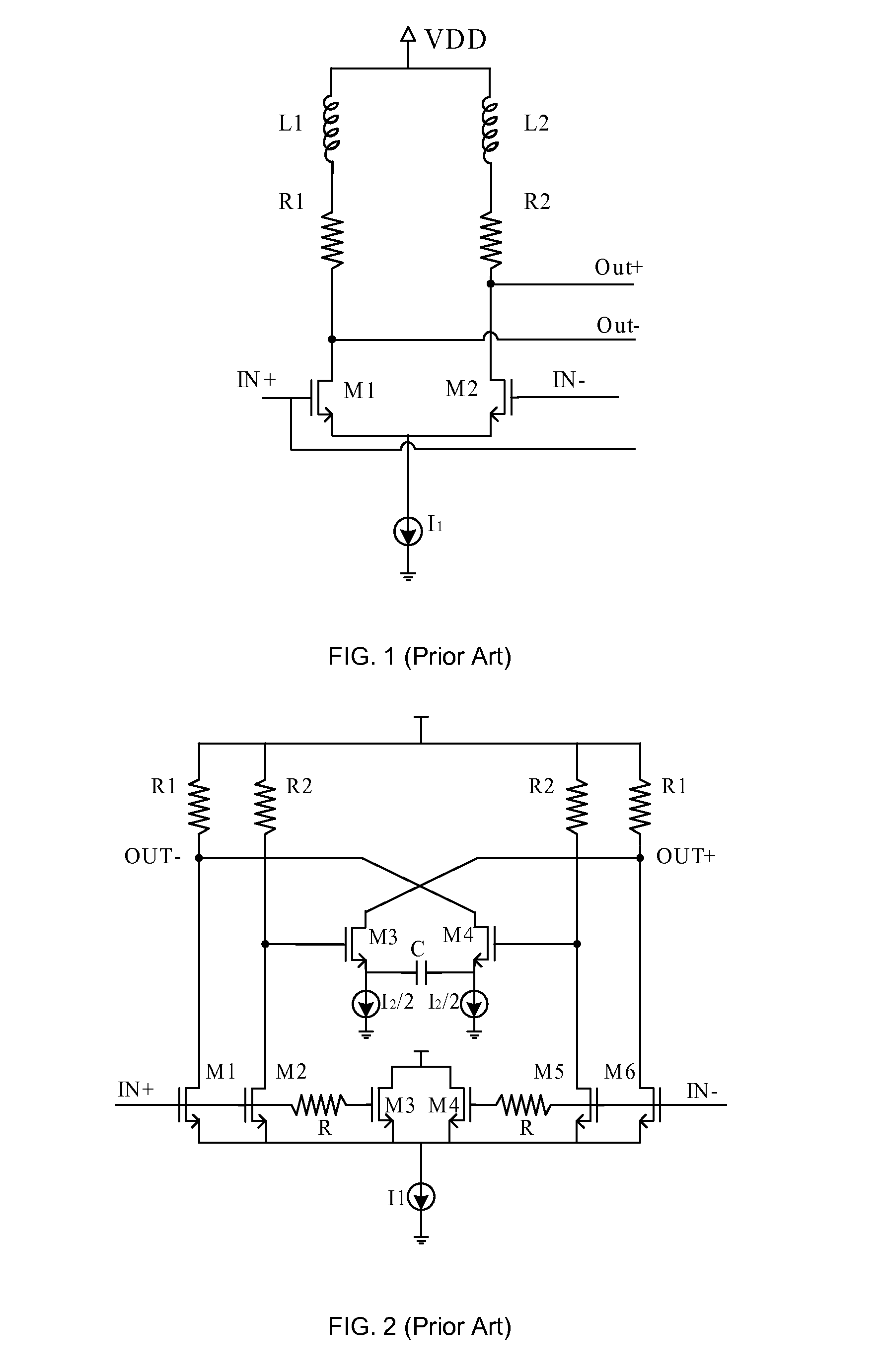
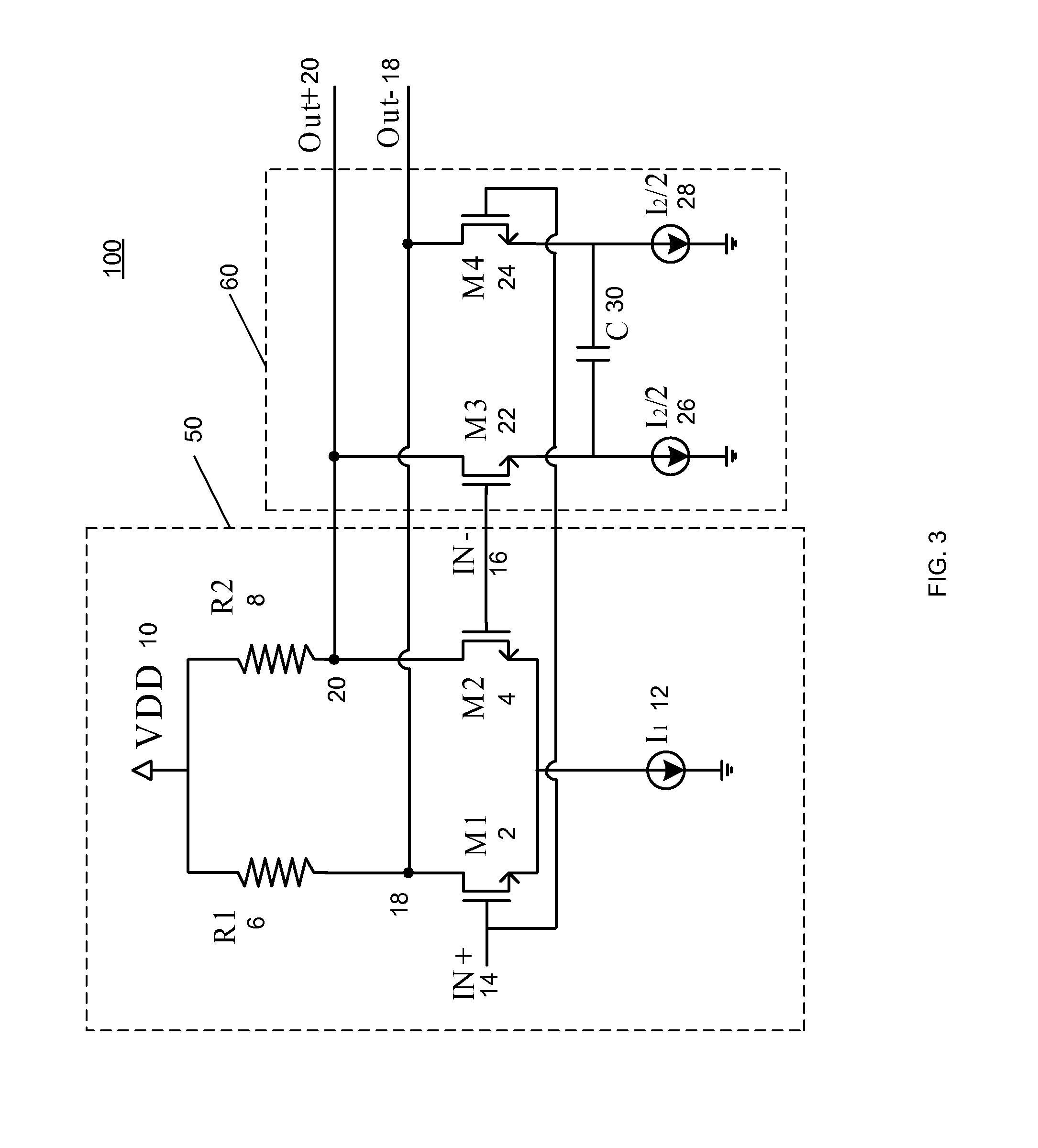
Apparatus and methods advantageously maintain transistors of open-drain differential pairs biased in the saturation region when “active,” rather in than the triode or linear region. The biasing techniques are effective over a broad range of process, voltage, and temperature (PVT) variations. By controlling a high voltage level used to drive the gate of a transistor of the differential pair, the biasing of the transistor in the saturation region is maintained. In one embodiment, the low voltage level used to cut off the transistor of the differential pair is also controlled. These techniques advantageously permit differential drivers to exhibit relatively large output swings, relatively high edge rates, relatively high return loss, and relatively good efficiency.
Owner:MICROSEMI STORAGE SOLUTIONS
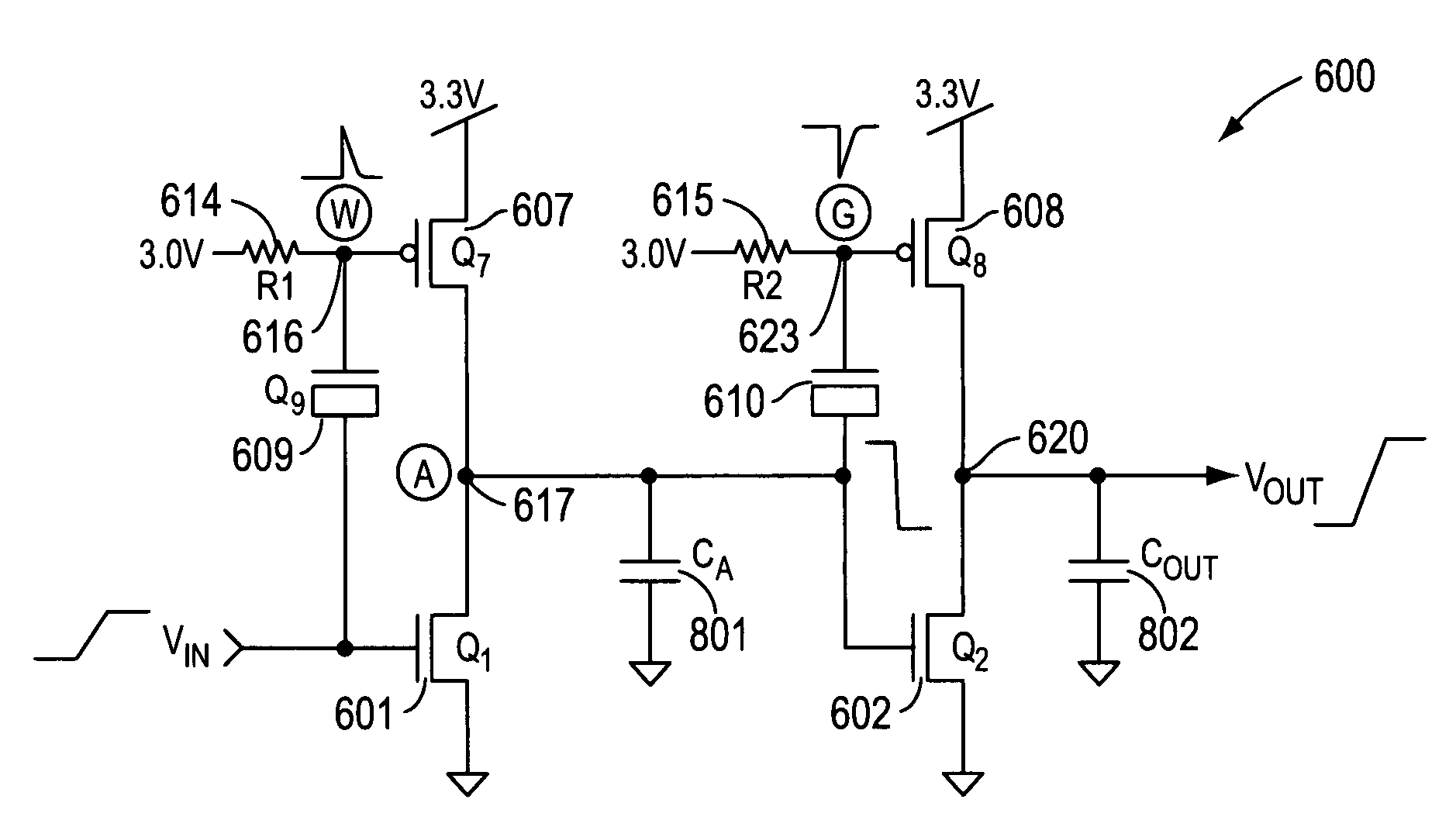
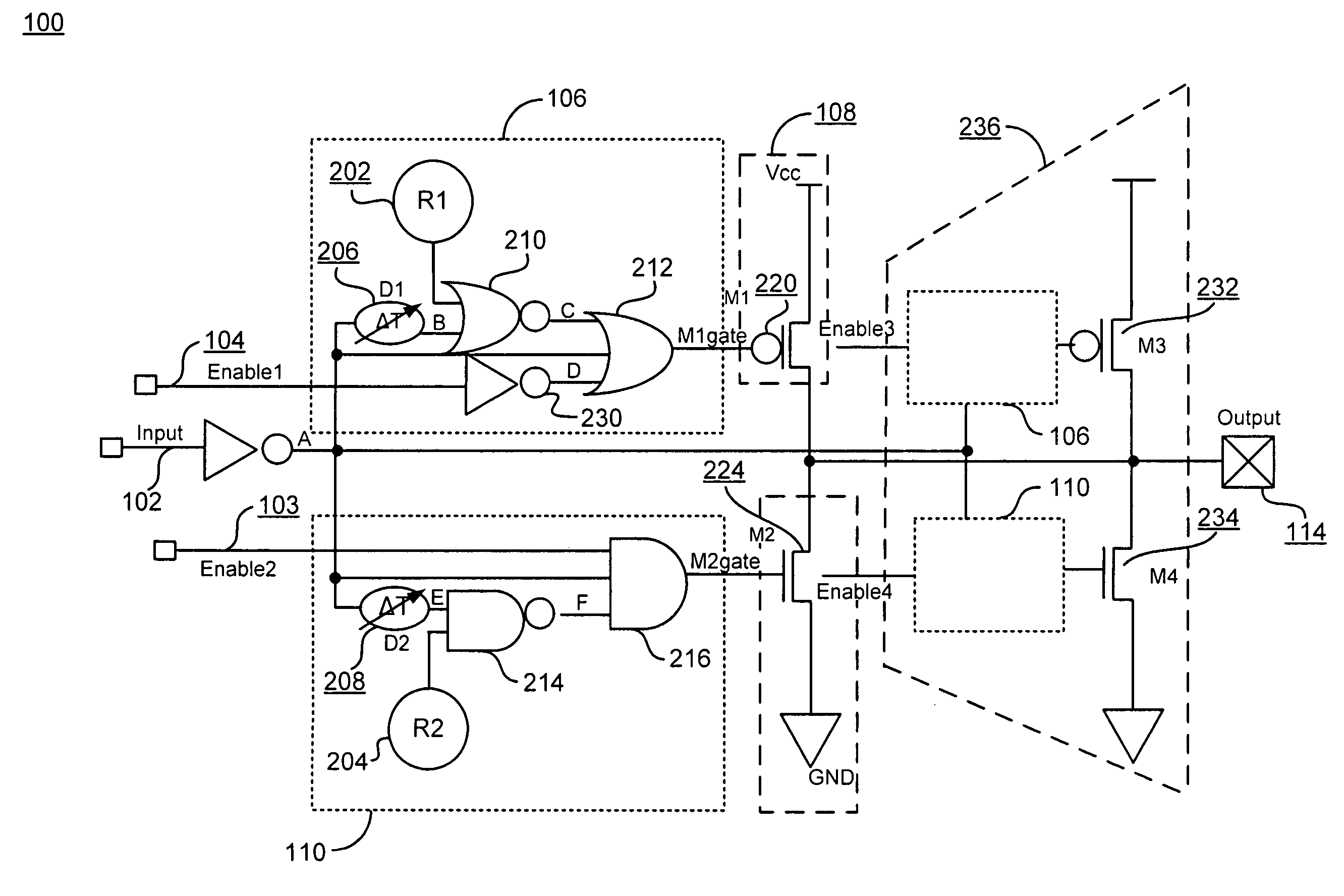
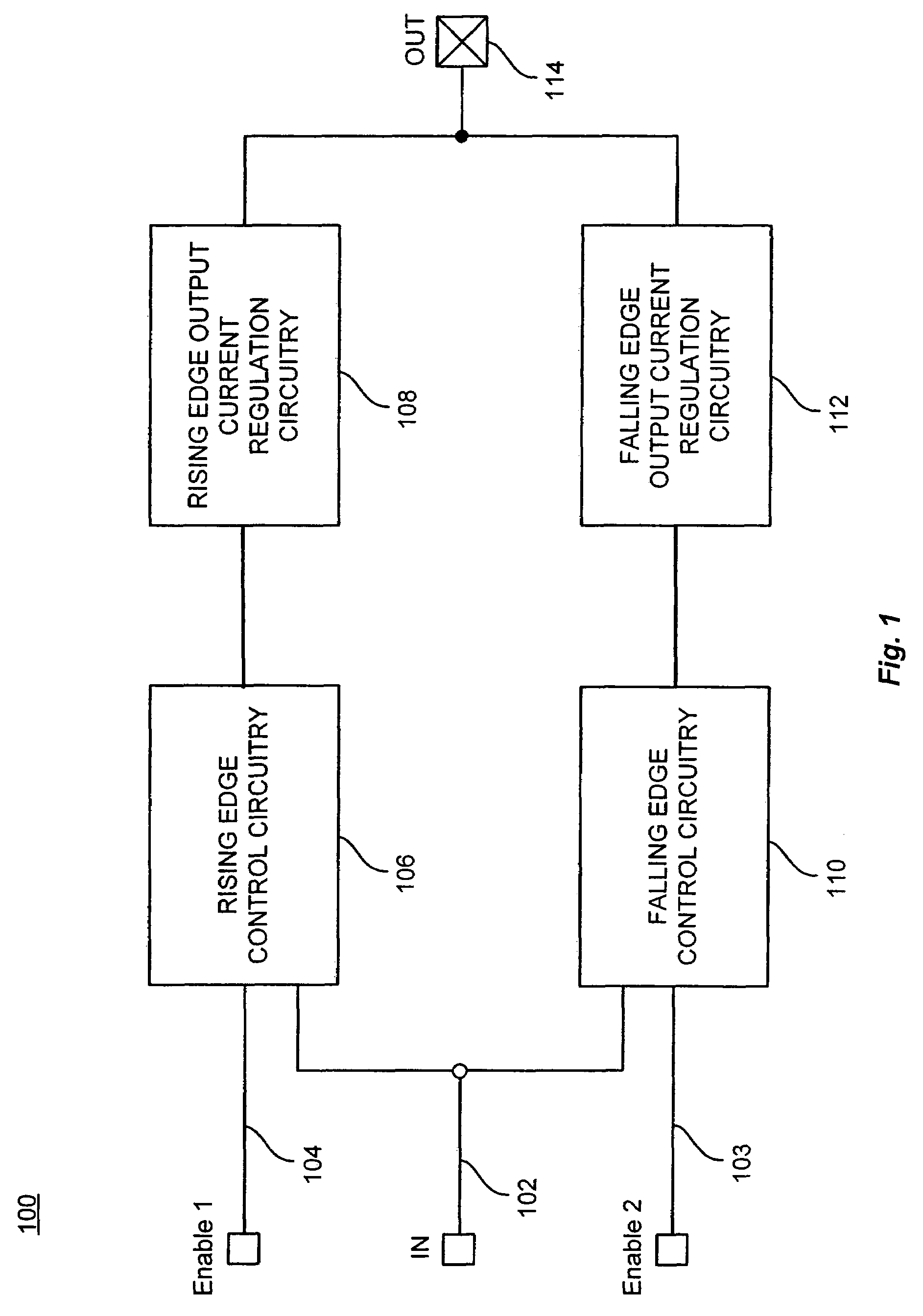
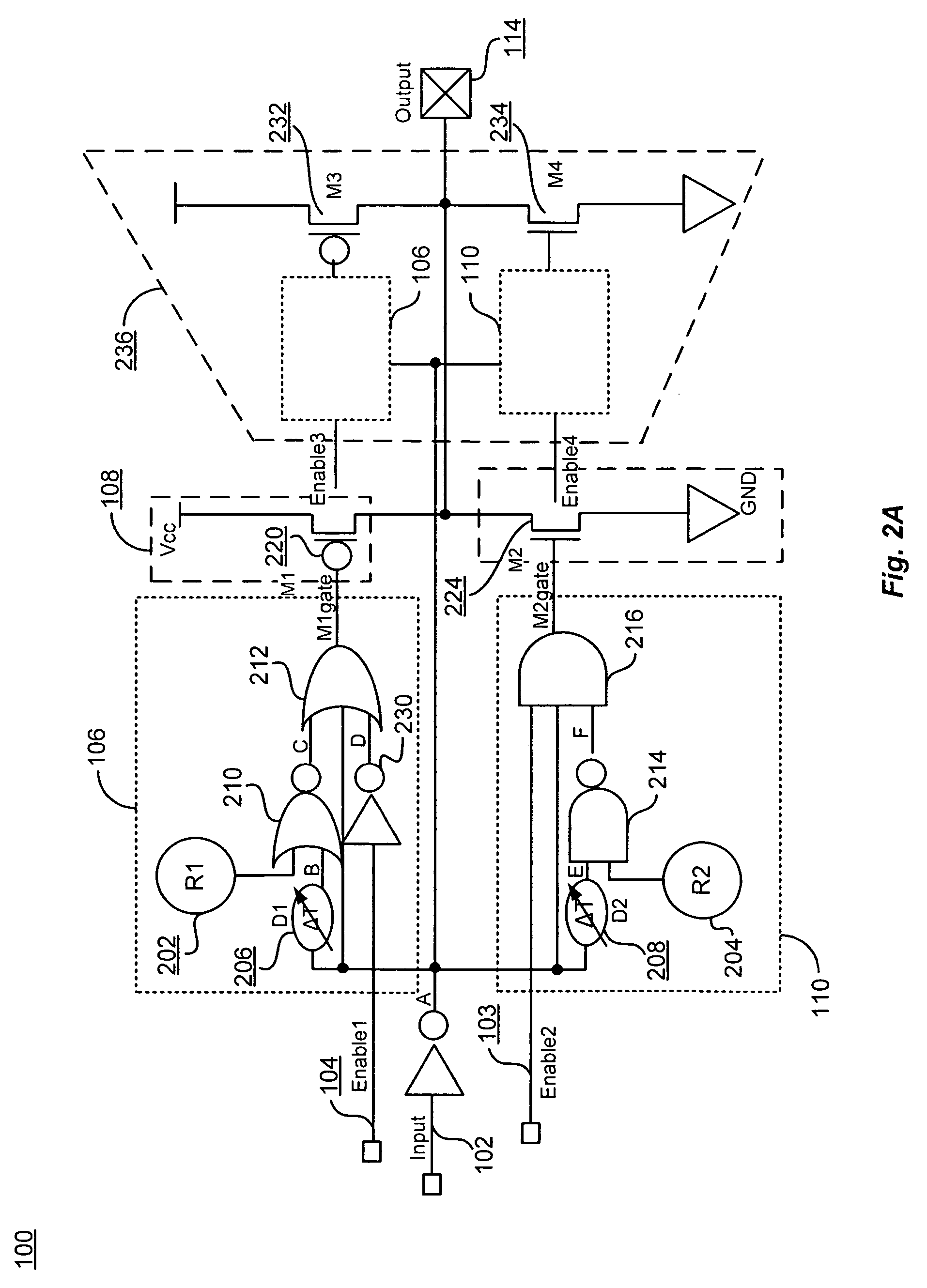
Driving circuit that eliminates effects of ambient temperature variations and increases driving capacity
ActiveUS7508242B2Eliminate the effects ofIncrease delay timeTransistorSwitching accelaration modificationsCMOSDriving circuit
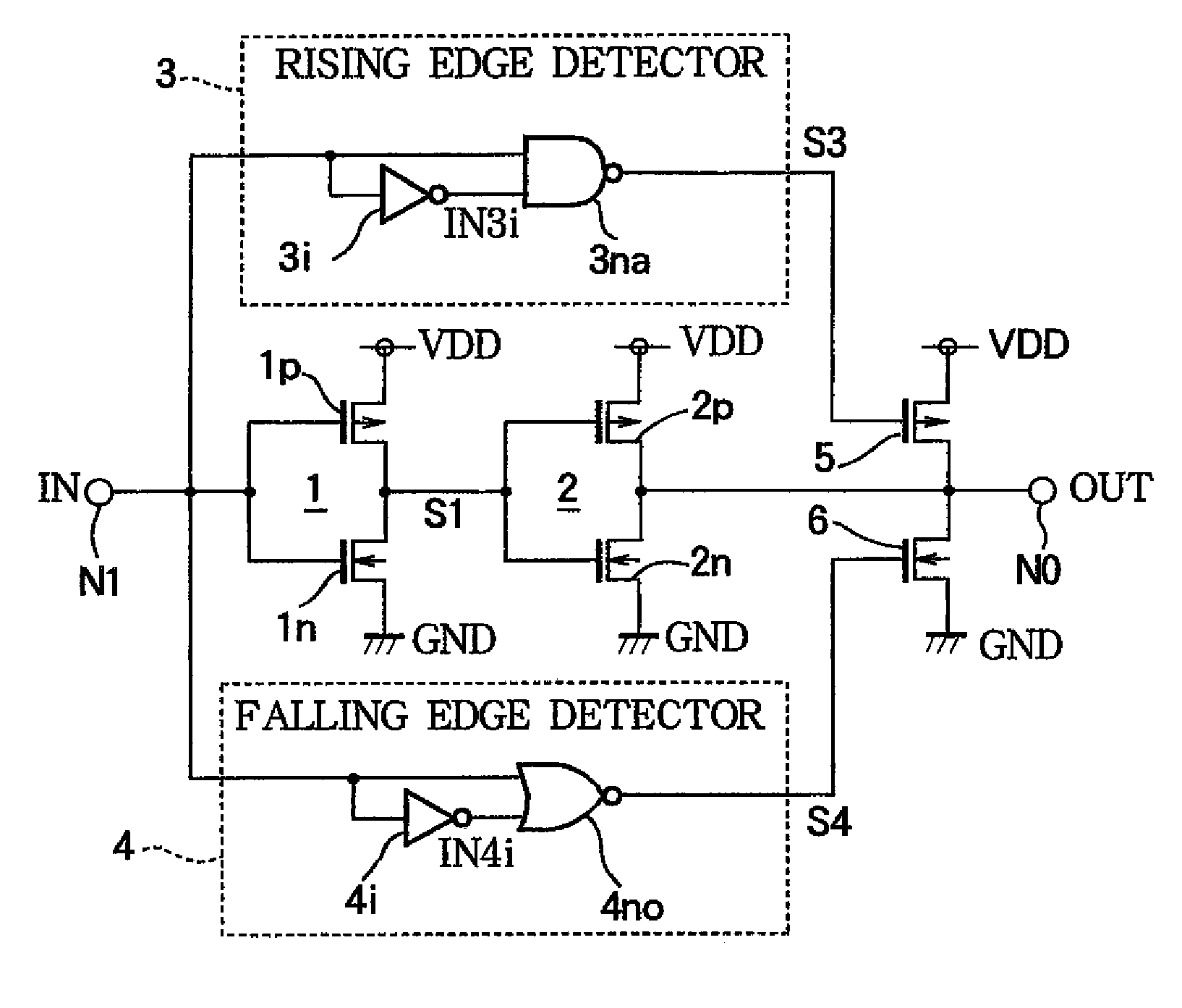
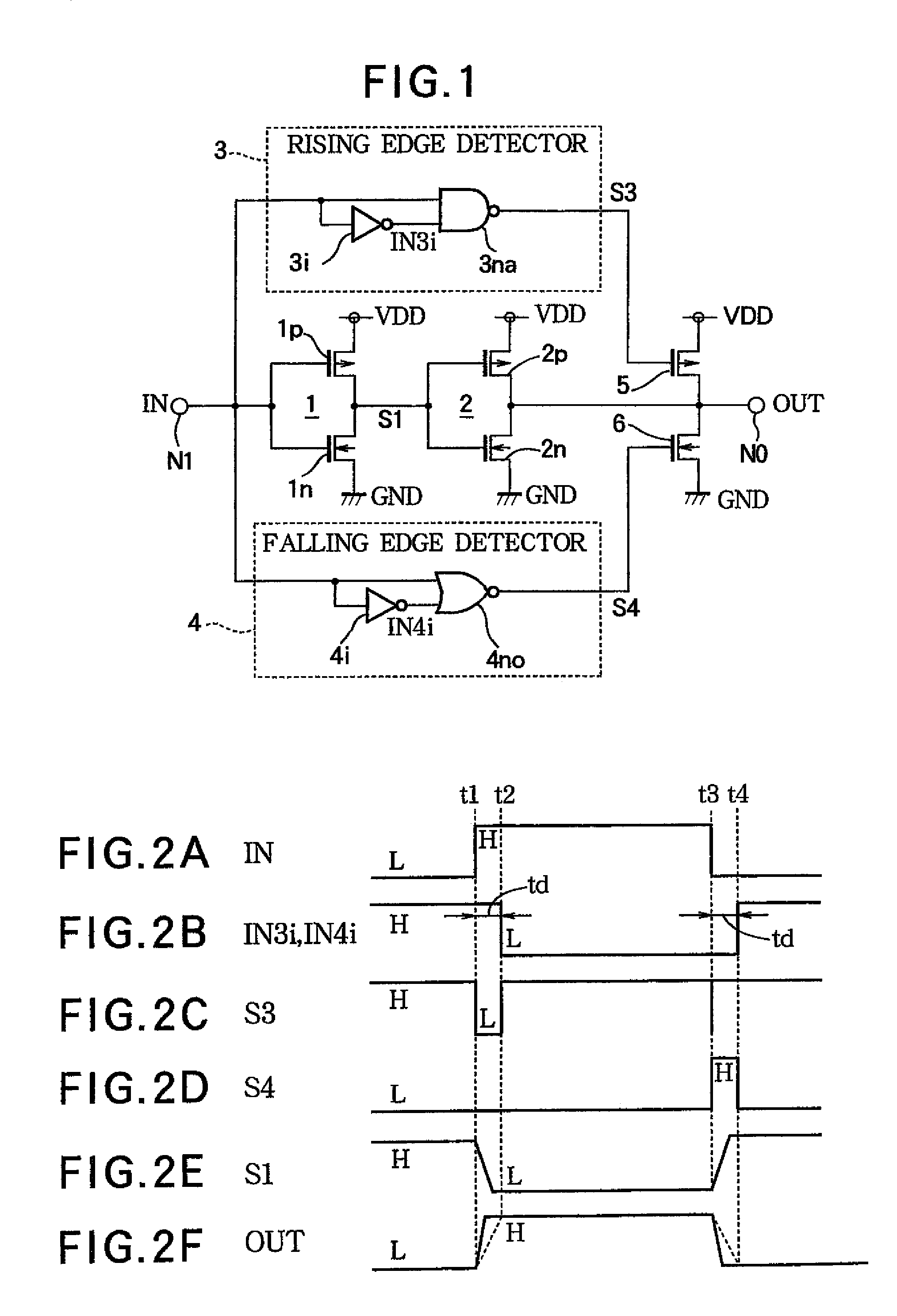
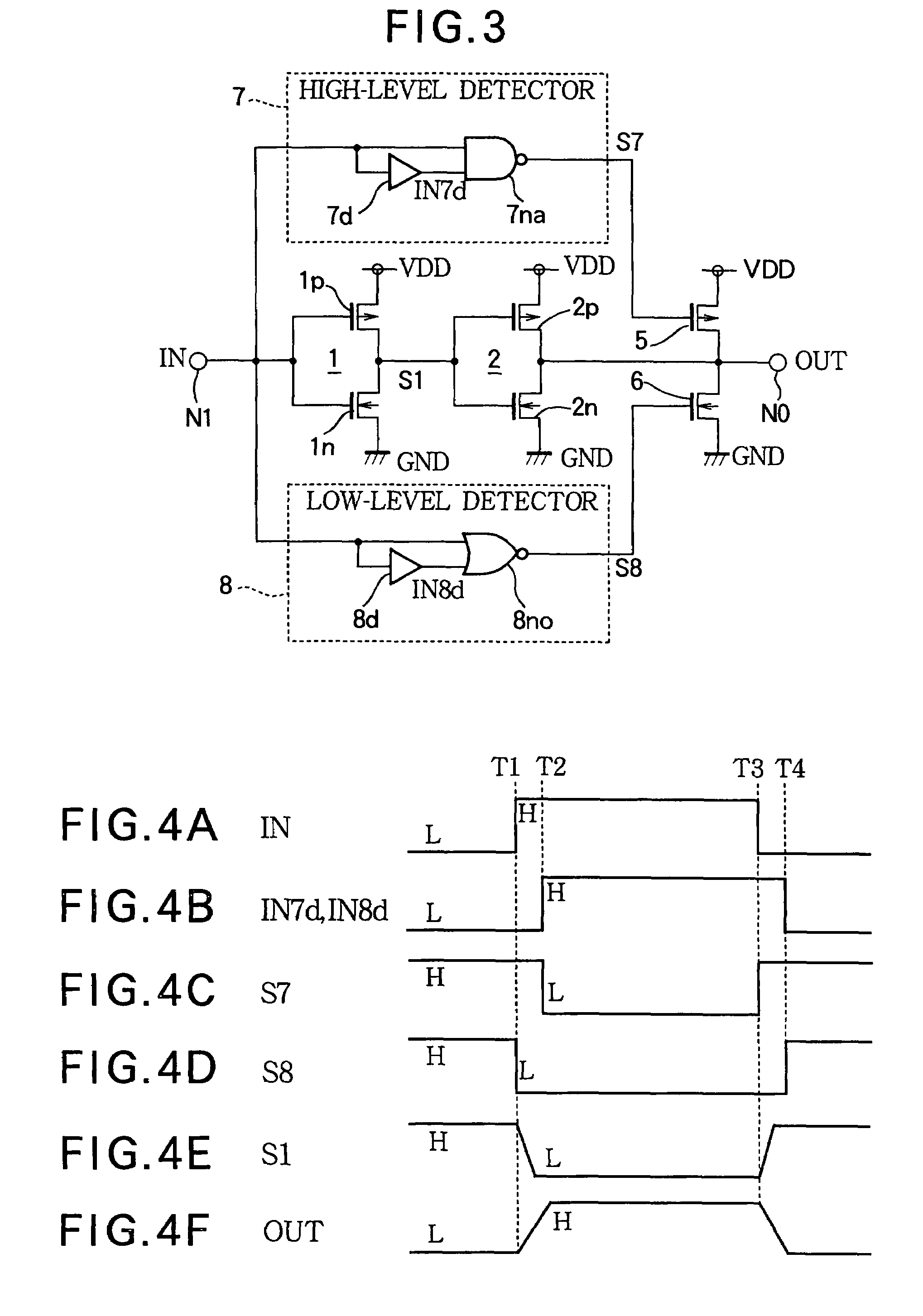
In addition to two-stage CMOS inverters inverting and amplifying the input signal, a rising edge detector detects the rising edge of the input signal, and outputs a rising edge detection signal having a pulse width corresponding to ambient temperature, a PMOS drives the output node to the power supply potential according to the rising edge detection signal, a falling edge detector detects the falling edge of the input signal and outputs a falling edge detection signal having a pulse width corresponding to ambient temperature, and an NMOS drives the output node to ground potential according to the falling edge detection signal. When ambient temperature rises, and delay time of the inverters are thereby increased, pulse widths of the rising and falling edge detection signals are increased. The additional driving restrains delay time variation in a driving circuit due to ambient temperature change.
Owner:LAPIS SEMICON CO LTD
Output drive circuit that accommodates variable supply voltages
ActiveUS7224195B2Increase charging rateSwitching accelaration modificationsLogic circuits coupling/interface using field-effect transistorsDriver circuitEngineering
In accordance with the invention, a driver circuit is described that permits a single thin gate oxide process to be utilized where a dual oxide process may normally be necessary. Circuits employing only thin gate oxide devices are used as the design basis for a single product with a single set of tooling and manufacturing process to operate within the same timing specifications for a core voltage output drive as well as for a higher system drive.
Owner:INTEGRATED DEVICE TECH INC
Line driver
InactiveUS20010028271A1Reduce power consumptionStable voltageSwitching accelaration modificationsPower consumption reductionCapacitor voltageEngineering
The invention relates to a line driver supplied with a power supply voltage from a power supply and an amplifying method. According to the invention the following steps are performed: using whole or part of the power supply voltage to generate the output voltage if the input voltage is within the predefined range; loading at least one capacitor with at least one capacitor voltage; and using whole or part of the capacitor voltage in addition to whole or part of the power supply voltage to generate the output voltage if the input voltage is outside the predefined range.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Interface controller using JTAG scan chain
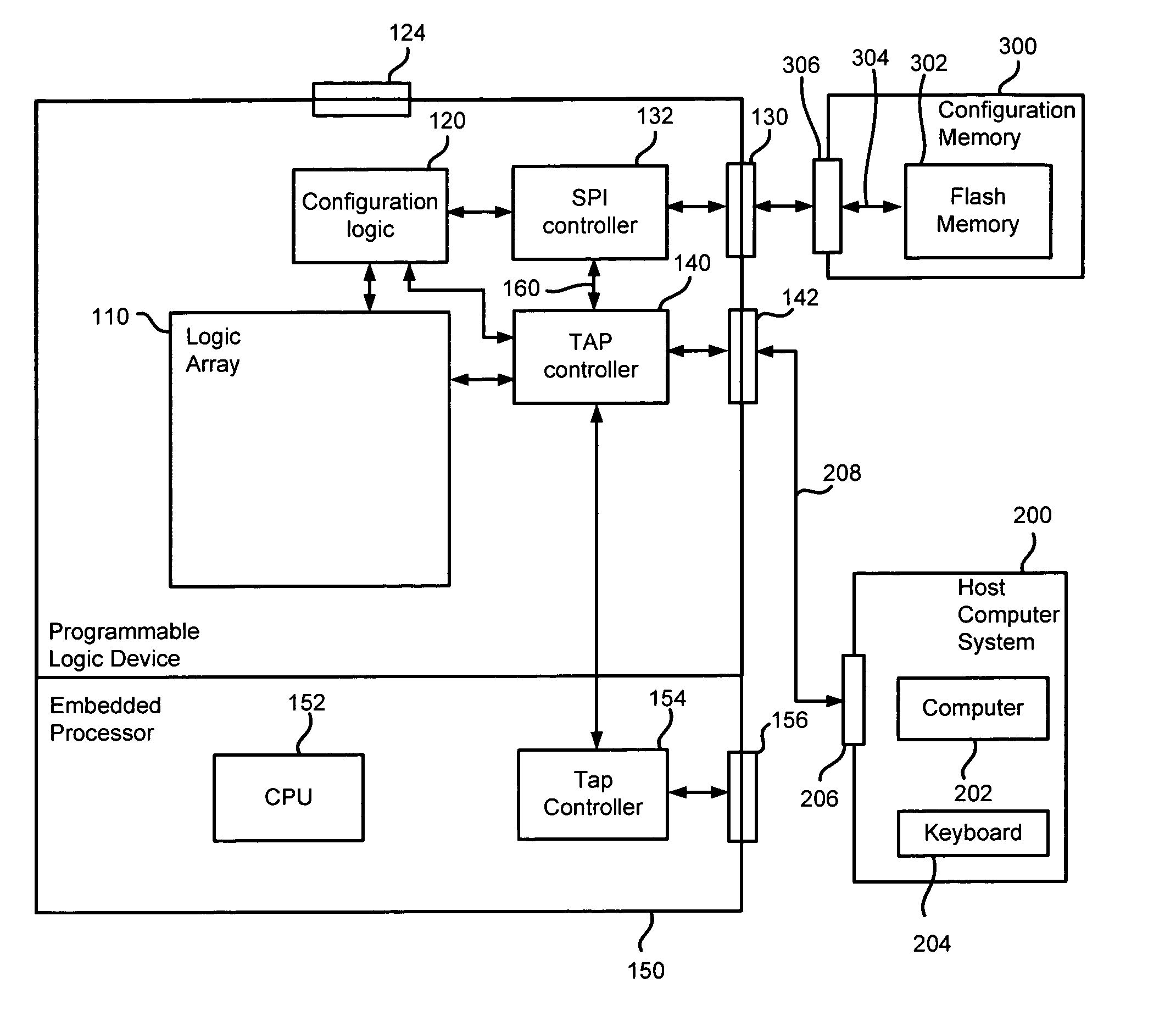
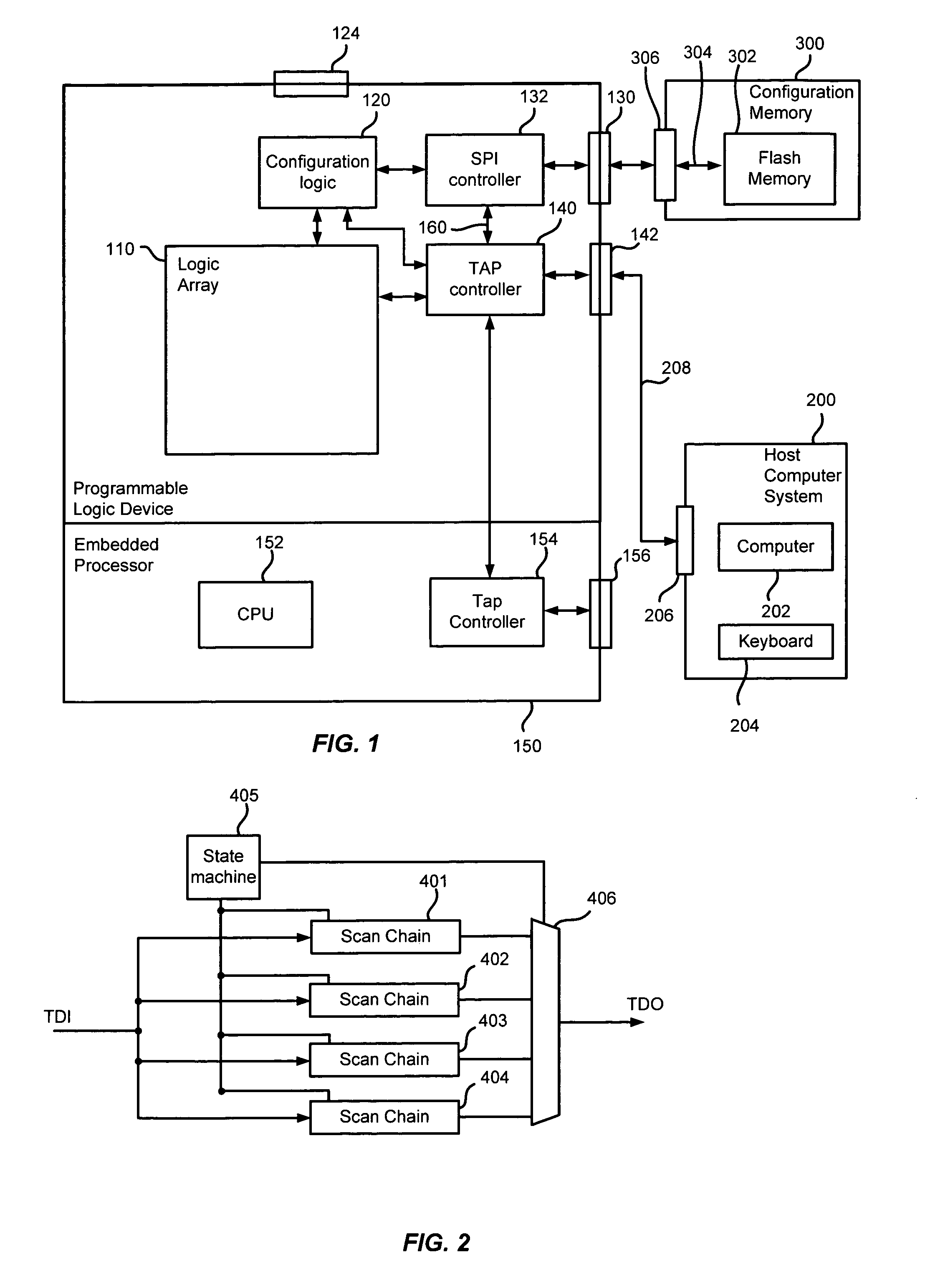
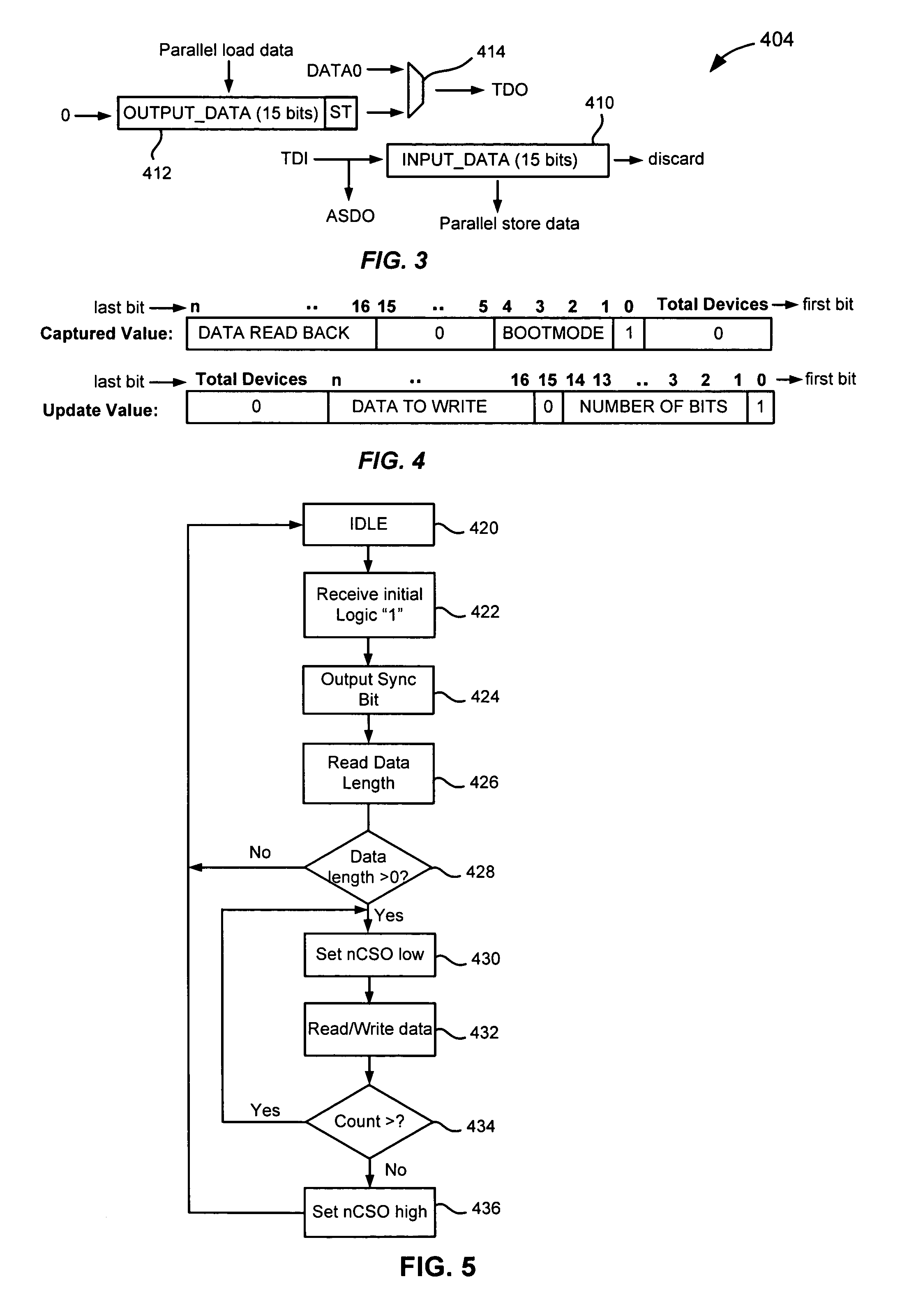
ActiveUS7078929B1Reduce the possibility of damageEasy to updateSwitching accelaration modificationsElectronic circuit testingProgrammable logic deviceData shipping
In a programmable logic device system, including a programmable logic device, a configuration memory device, for storing configuration information, and a host computer system, for generating updated configuration information, the programmable logic device has a JTAG port, for connection to said host computer system, for receiving said updated configuration information, a JTAG port controller, operatively connected to the first JTAG port, and an SPI interface, for connection to said configuration memory device. The JTAG port controller comprises a scan chain, for controlling said SPI interface on the basis of information received from said host computer system. This allows a user of the host computer system to transfer updated configuration data to the configuration memory device by means of a connection from the host computer system to the JTAG port of the programmable logic device. Since the user will in any event require a connection from the host computer system to the JTAG port of the programmable logic device to allow testing of the device, this will avoid the need for the user to continually switch connections on the programmable logic device.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
Semiconductor device incorporating internal power supply for compensating for deviation in operating condition and fabrication process conditions
InactiveUS6970391B2Improve stabilityImprove reliabilitySwitching accelaration modificationsReliability increasing modificationsPower semiconductor deviceSemiconductor chip
A semiconductor integrated circuit comprises a semiconductor chip, a power supply terminal provided on the semiconductor chip for receiving a voltage from an external power supply source, an internal circuit provided on the semiconductor chip, a power supply circuit provided on the semiconductor chip for transforming an external power supply voltage received from the power supply terminal for supplying a source voltage resulting from the voltage transformation to the internal circuit, and a control circuit provided on the semiconductor chip for controlling the power supply circuit, wherein the control circuit includes external power supply voltage detecting means and / or temperature detecting means and responds to the signal from the external power supply voltage detecting means and / or the temperature detecting means by changing the power supply voltage to the internal circuit to thereby maintain the operating speed of the internal circuit to be constant.
Owner:RENESAS TECH CORP
Method and apparatus for slew control of an output signal
InactiveUS20040090253A1Easy to shapeSwitching accelaration modificationsReliability increasing modificationsAudio power amplifierEngineering
Systems and methods for enhancing slew control of output signals. An output driver receives an input signal and controllably increases the gain of that signal to provide a high quality output signal for use by an electronic device coupled thereto. The output driver includes an operational amplifier that maintains stability of the output signal through a feedback of the output signal. A control circuit supplies a signal to the output driver such that the driver to improve the shape of the output signal as the input signal is applied. After the operational amplifier regains control, the control circuit disengages. One embodiment of the present invention may be particularly useful as a USB output driver.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Semiconductor integrated circuit device
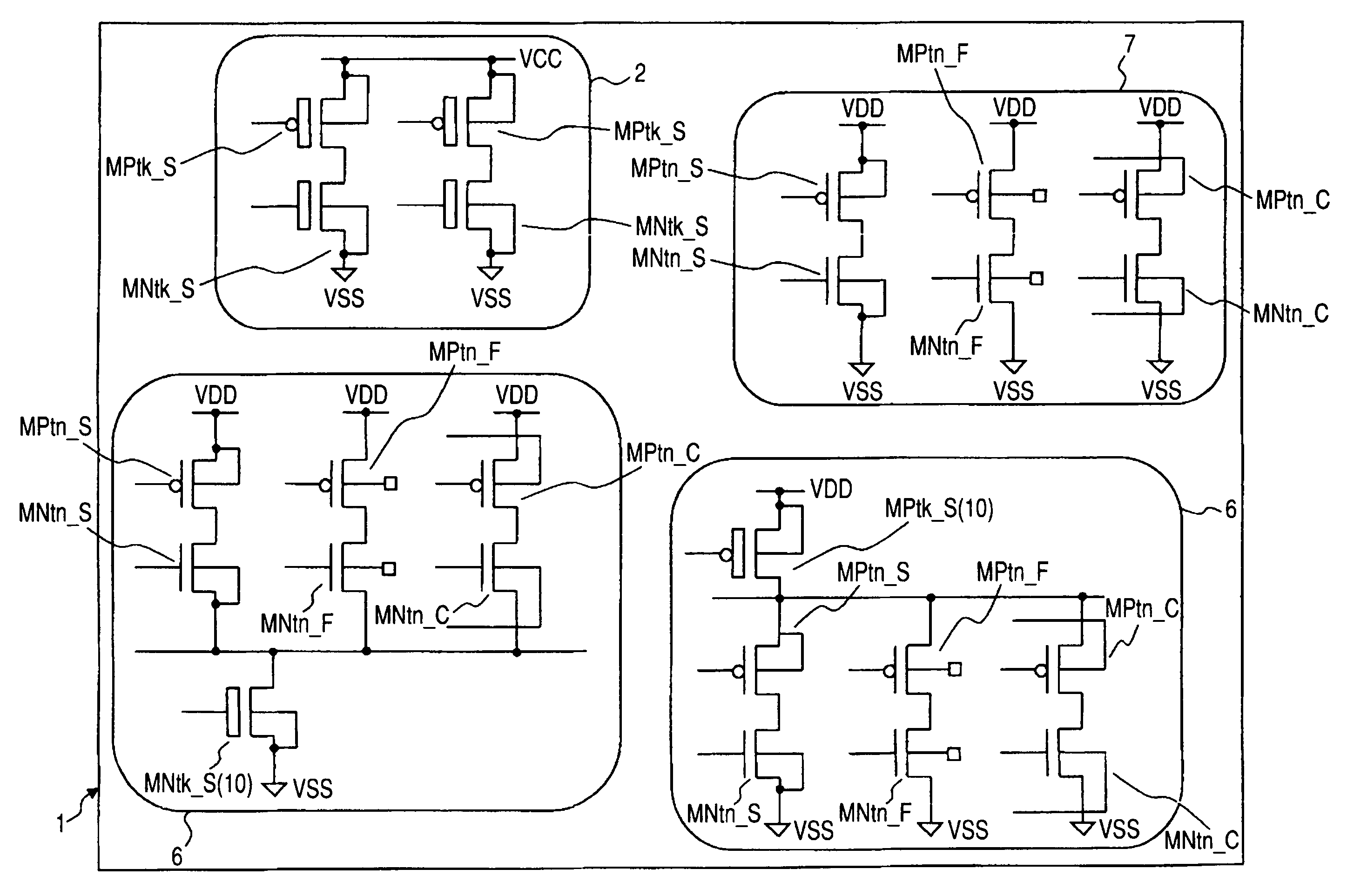
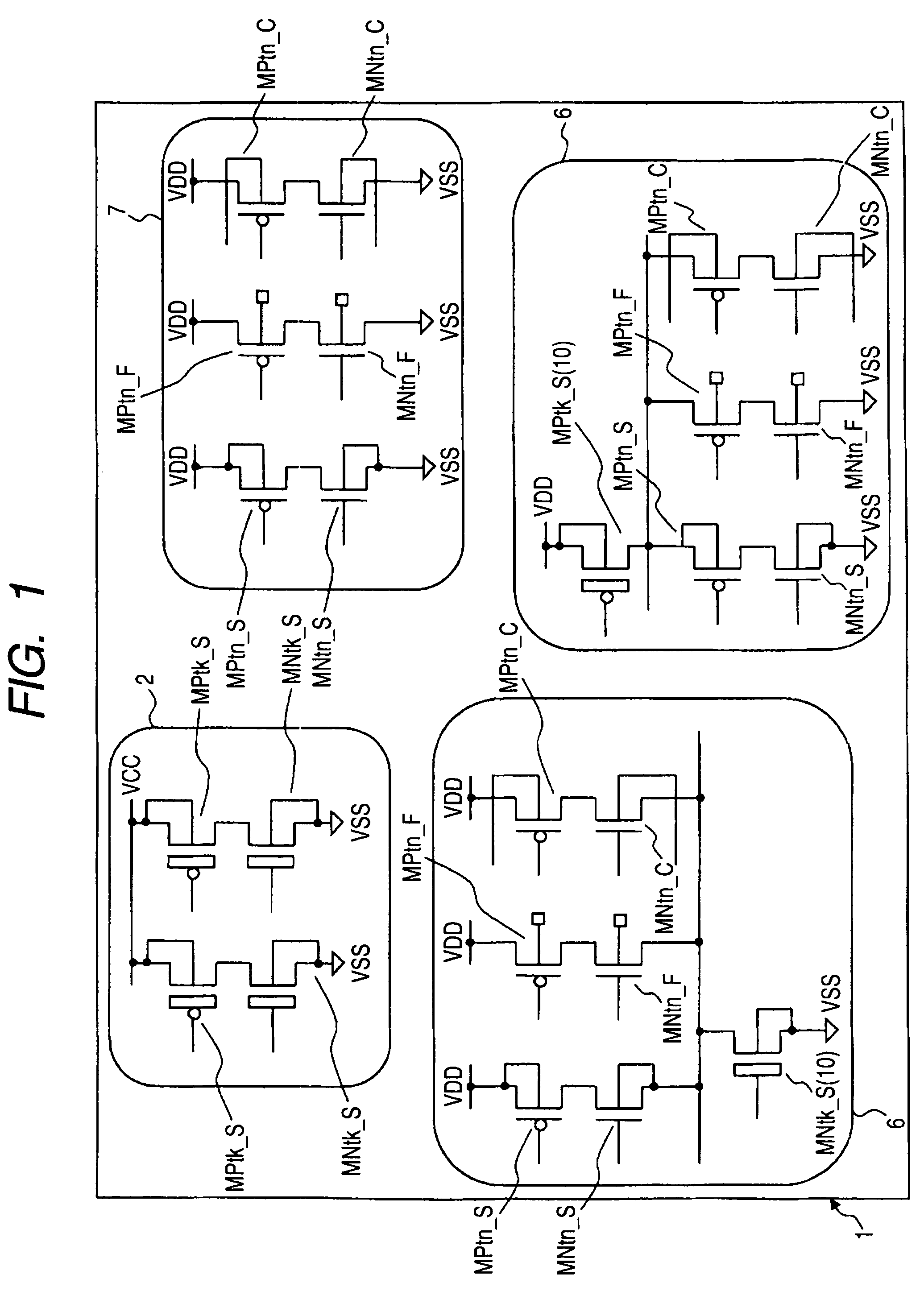
InactiveUS7612604B2Improve speed performancePower consumption performanceTransistorSwitching accelaration modificationsControl systemOperation mode
A body bias control system allows for independent design of a functional module, thereby reducing the burden of designing the module. The body bias control system provides a switch circuit having an area in which the body bias is controlled independently of its outside portion, for controlling the supply of body bias in the vicinity of the area. Preferably three types of switches are provided for switching the body bias to suitable levels for a standby mode, a mode of normal operation and a mode of high-speed operation.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP +1
Input buffer having dual paths
InactiveUS6459307B2Switching accelaration modificationsElectronic switchingComputer scienceSignal processing
An input buffer of the present invention has dual paths for increasing input signal processing speed by using two input buffers having input characteristics that differ from each other. The input buffer includes an input terminal receiving an external input signal; and first and second input buffers, both coupled to the input terminal for transferring an external input signal. The output signal of the second input buffer is blocked when the first input buffer transfers the external input signal, and the output signal of the first input buffer is blocked when the second input buffer transfers the external input signal.
Owner:HYUNDAI ELECTRONICS IND CO LTD
Current-controlled CMOS circuits with inductive broadbanding
InactiveUS6909309B2High speedHigh bandwidthSwitching accelaration modificationsParallel/series conversionUltra high speedTransceiver
Various circuit techniques for implementing ultra high speed circuits use current-controlled CMOS (C3MOS) logic with inductive broadbanding fabricated in conventional CMOS process technology. Optimum balance between power consumption and speed for each circuit application is achieve by combining high speed C3MOS logic with inductive broadbanding / C3MOS logic with low power conventional CMOS logic. The combined C3MOS logic with inductive broadbanding / C3MOS / CMOS logic allows greater integration of circuits such as high speed transceivers used in fiber optic communication systems.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
High-speed cml circuit design
ActiveUS20070018694A1Switching accelaration modificationsReliability increasing modificationsInductorLogic circuitry
A current mode logic digital circuit is provided comprising a logic circuit component having at least one data input node and at least one output node. A load is coupled between a power supply node and the output node. The load comprises a folded active inductor coupled to the output node.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Semiconductor integrated circuit
InactiveUS20070176233A1Operation of circuitReduce power consumptionSwitching accelaration modificationsReliability increasing modificationsLow voltageActive state
A plurality of MOS transistors each having an SOI structure includes, in mixed form, those brought into body floating and whose body voltages are fixed and variably set. When a high-speed operation is expected in a logic circuit in which operating power is relatively a low voltage and a switching operation is principally performed, body floating may be adopted. Body voltage fixing may be adopted in an analog system circuit that essentially dislikes a kink phenomenon of a current-voltage characteristic. Body bias variable control may be adopted in a logic circuit that requires the speedup of operation in an active state and needs low power consumption in a standby state. Providing in mixed form the transistors which are subjected to the body floating and the body voltage fixing and which are variably controlled in body voltage, makes it easier to adopt an accurate body bias according to a circuit function and a circuit configuration in terms of the speedup of operation and the low power consumption.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Semiconductor integrated circuit capable of realizing logic functions
InactiveUS6194914B1Switching accelaration modificationsLogic circuits characterised by logic functionGate arrayEngineering
A semiconductor integrated circuit is constructed with composite pass-transistor logic circuits serving as elementary circuit units each including a plurality of pass-transistor logic trees and a multiple-input logic gate. A wide variety of logical operations, even complex opearations, can be efficiently expressed using the composite pass-transistor logic circuit, and the resultant logic circuit can operate at a high speed. Thus, the semiconductor integrated circuit of the present invention can realize various logic functions required for various users in an efficient fashion. The present invention is particularly useful when applied to a field-programmable gate array integrated circuit, since complex logical operations can be expressed in a simple and efficient fashion by the composite pass-transistor logic circuits. The gate array integrated circuit obtained in accordance with the present invention can operate at a high speed with low power consumption. The present invention also discloses a basic cell suitable for use in an integrated circuit in the form of a gate array, and more particularly, a programmable logic block for use in a field programmable gate array integrated circuit.
Owner:KAWASAKI MICROELECTRONICS
Semiconductor integrated circuit
InactiveUS7714606B2Meet high-speed operationReduce power consumptionSwitching accelaration modificationsReliability increasing modificationsLow voltageEngineering
A plurality of MOS transistors each having an SOI structure includes, in mixed form, those brought into body floating and whose body voltages are fixed and variably set. When a high-speed operation is expected in a logic circuit in which operating power is relatively a low voltage and a switching operation is principally performed, body floating may be adopted. Body voltage fixing may be adopted in an analog system circuit that essentially dislikes a kink phenomenon of a current-voltage characteristic. Body bias variable control may be adopted in a logic circuit that requires the speedup of operation in an active state and needs low power consumption in a standby state. Providing in mixed form the transistors which are subjected to the body floating and the body voltage fixing and which are variably controlled in body voltage, makes it easier to adopt an accurate body bias according to a circuit function and a circuit configuration in terms of the speedup of operation and the low power consumption.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
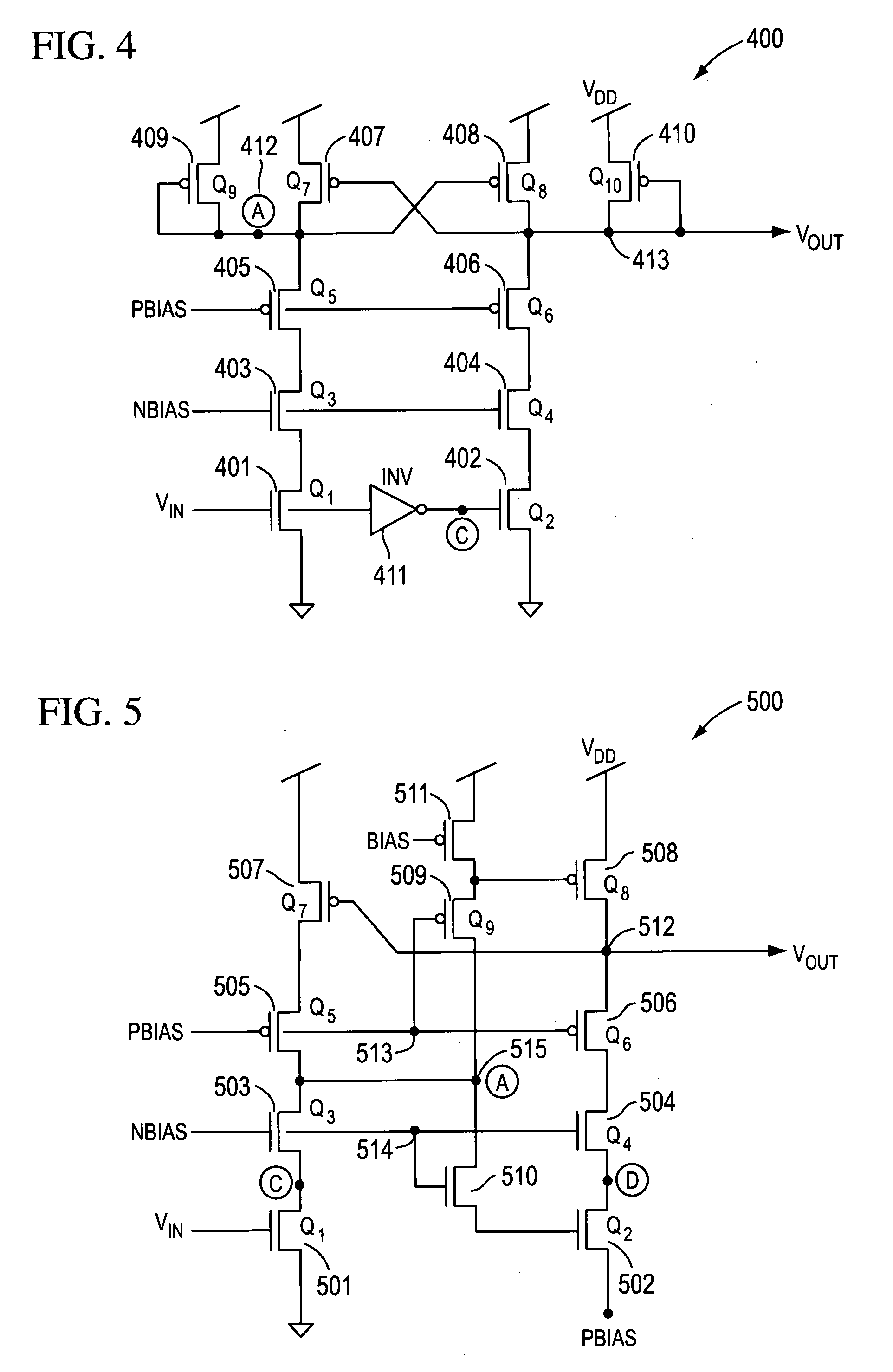
High-performance level shifter
InactiveUS20080204109A1Fast switching timePower reduction in field effect transistorsSwitching accelaration modificationsLevel shiftingLevel converter
A level shifter is presented that allows fast switching while requiring low power. In accordance with some embodiments of the invention, the level shifter is a two stage level shifting circuit with p-channel and n-channel transistors biased so as to limit the potential between the source to gate or drain to gate of any of the transistors. Pull-up transistors are placed in a transition state so that spikes resulting from an increasing or decreasing input voltage turn on or off the pull up transistors to assist in the switching.
Owner:INTEGRATED DEVICE TECH INC
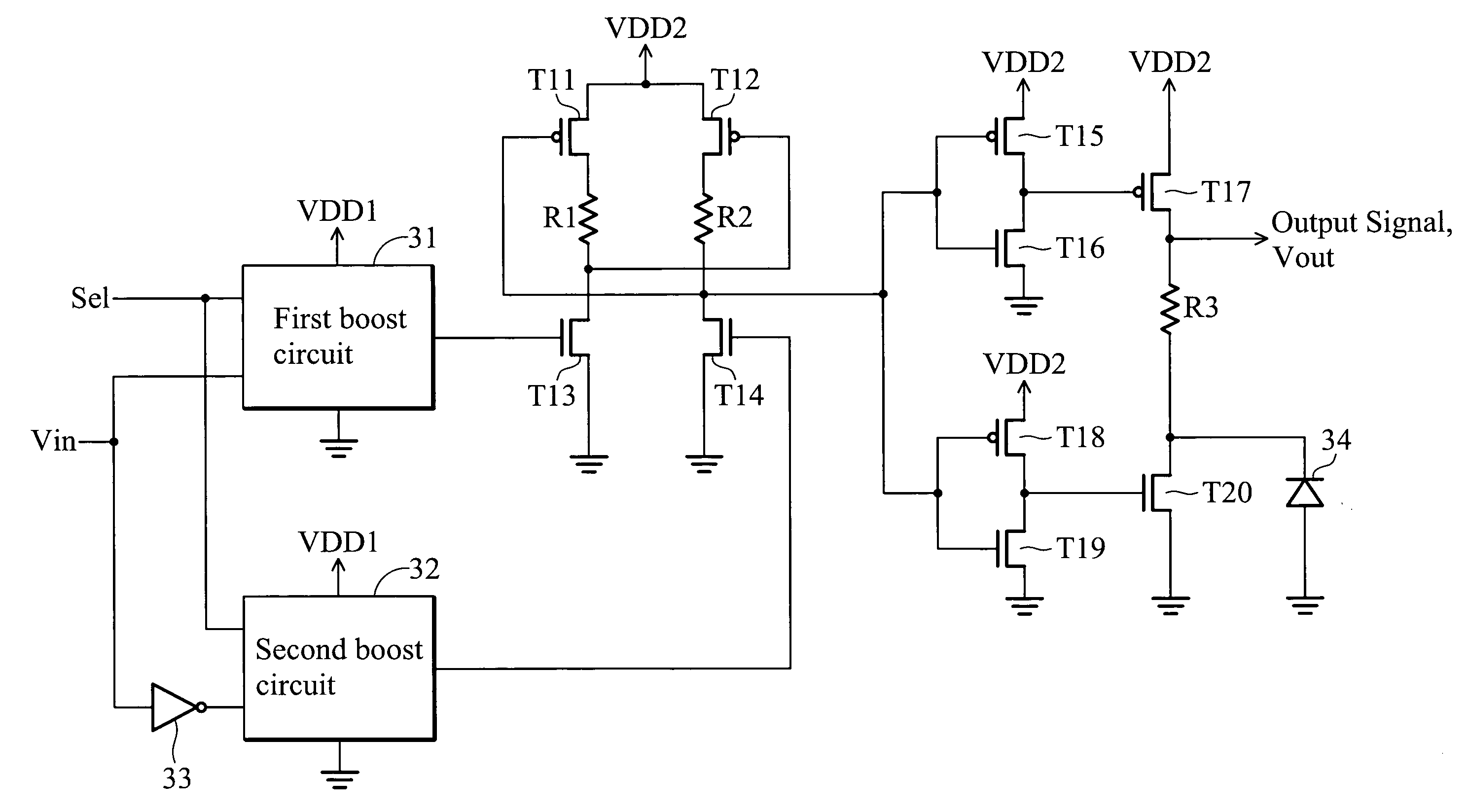
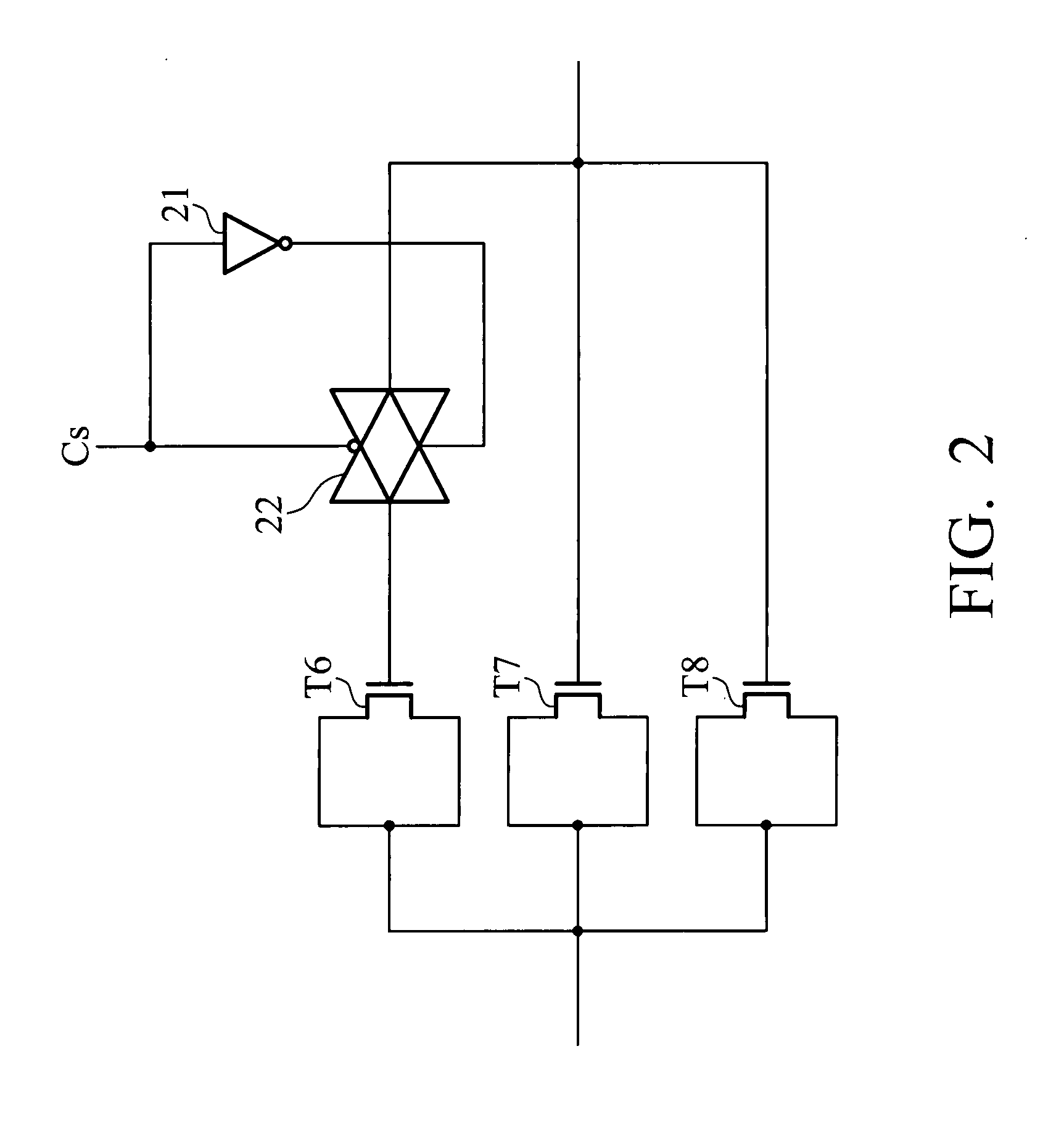
Boost circuit and level shifter
InactiveUS20080136487A1Switching accelaration modificationsPulse automatic controlControl signalLevel converter
A level shifter including a first boost circuit, an inverter, a second boost circuit and a level shift circuit is disclosed. The first boost circuit receives an input signal, and a first amplification factor for the input signal is determined based on a control signal. The inverter receives the input signal to generate an inverted input signal. The second boost circuit is coupled to an output terminal of the inverter to receive the inverted input signal, and a second amplification factor for the inverted input signal is determined based on the control signal. The level shift circuit has a first input terminal and a second input terminal respectively coupled to output terminals of the first boost circuit and second boost circuit to change the voltage level of output signals from the first boost circuit and second boost circuit to a first voltage level.
Owner:PRINCETON TECH CORP
High-speed, low-power level shifter for mixed signal-level environments
InactiveUS7554379B2Fast switching timePower reduction in field effect transistorsSwitching accelaration modificationsLevel shiftingEngineering
Owner:INTEGRATED DEVICE TECH INC
Programmable current booster for faster edge-rate output in high speed applications
InactiveUS7026847B2Maximum flexibilityFaster rising and falling edge ratesSwitching accelaration modificationsPower reduction by control/clock signalHigh velocityAc current
An AC current booster for high speed, high frequency applications having a single-ended output embodiment and a differential output embodiment. The embodiments of the present invention allow bifurcated control of the AC switching rate and the DC state of a given output signal, in order to achieve faster rising and falling edge rates without an undesirable increase in output voltage swing.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
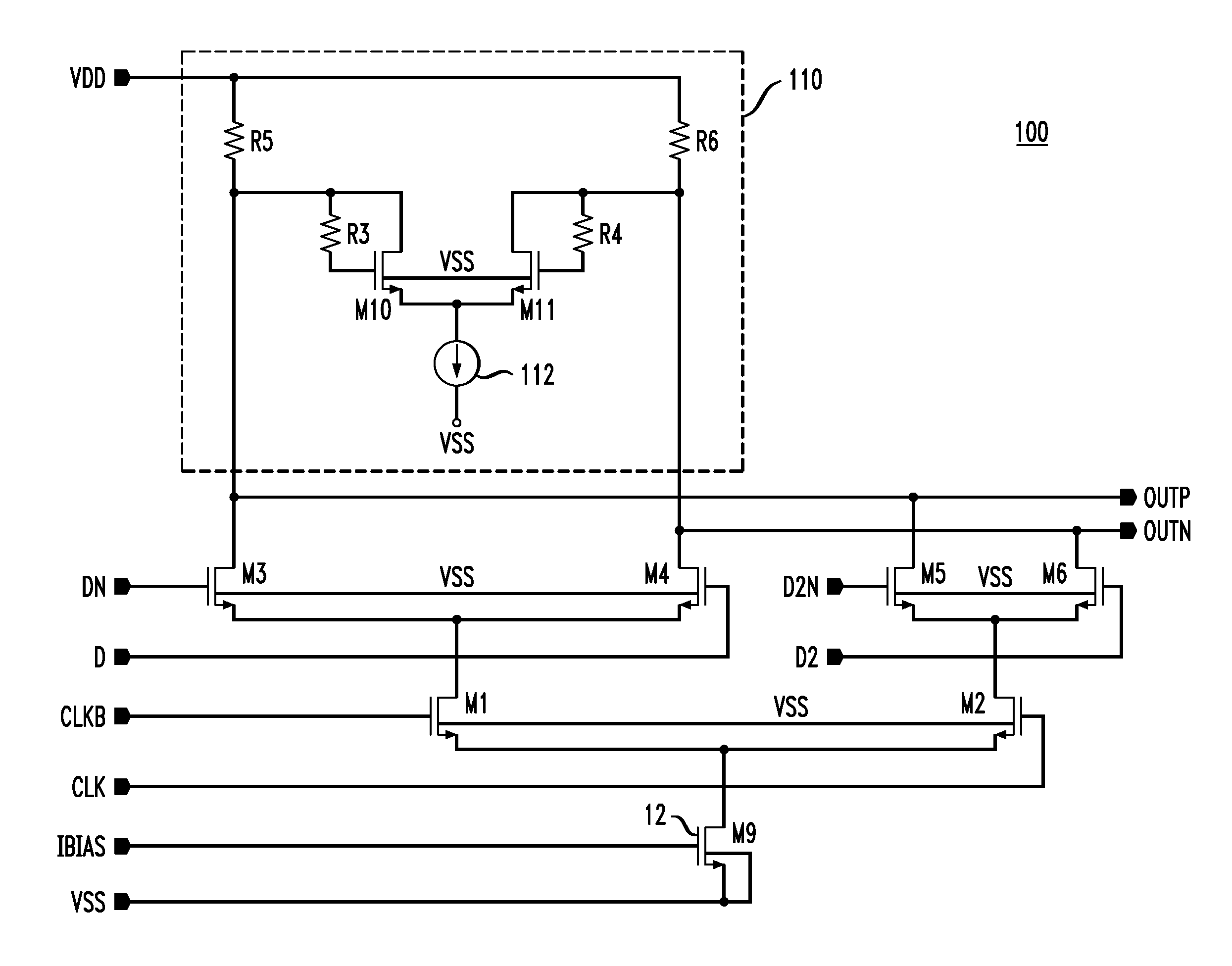
High-speed differential logic buffer
ActiveUS20060061391A1Shortened fall timeShorten rise timeSwitching accelaration modificationsLogic circuits characterised by logic functionLoad circuitActive devices
A circuit for a high speed digital buffer has an active load circuit connected to an output of the digital buffer. The active load circuit loads the buffer output with an active inductance to reduce the RC time constant at the buffer output. The active load circuit may be based on two active devices connected to the buffer output so as to form a differential cascode circuit.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Level shifter and electro-optical apparatus incorporating the same
InactiveUS6714046B2Reduce potential differenceReduce power consumptionSwitching accelaration modificationsStatic indicating devicesEngineeringVoltage reference
The invention simplifies the configuration of a level shifter and to allow fast operation. A level shifter includes a capacitor, to a first end of which a low-amplitude logic signal is input; first TFTs to apply an offset voltage to a second end of the capacitor; a capacitor, to a first end of which the low-amplitude logic signal is input; third TFTs to apply an offset voltage to a second end of the capacitor; and second TFTs connected in series between a supply line of a power supply voltage for a high-amplitude logic signal and a supply line of a reference voltage therefor, a node therebetween serving as an output terminal. A threshold voltage of one of the second TFTs is set to be not higher than the offset voltage applied by the first TFTs , and an offset voltage of the other of the second TFTs is set to be higher than or equal to the offset voltage applied by the third TFTs.
Owner:TCL CHINA STAR OPTOELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
Active biasing in metal oxide semiconductor (MOS) differential pairs
Apparatus and methods advantageously maintain transistors of open-drain differential pairs biased in the saturation region when “active,” rather in than the triode or linear region. The biasing techniques are effective over a broad range of process, voltage, and temperature (PVT) variations. By controlling a high voltage level used to drive the gate of a transistor of the differential pair, the biasing of the transistor in the saturation region is maintained. In one embodiment, the low voltage level used to cut off the transistor of the differential pair is also controlled. These techniques advantageously permit differential drivers to exhibit relatively large output swings, relatively high edge rates, relatively high return loss, and relatively good efficiency.
Owner:MICROSEMI STORAGE SOLUTIONS
Actively Compensated Buffering for High Speed Current Mode Logic Data Path
InactiveUS20080024172A1Switching accelaration modificationsLogic circuits characterised by logic functionLoad resistanceDatapath
An actively compensated CML circuit includes a CML buffer circuit and a bandwidth expansion circuit. The CML buffer circuit includes a first MOS transistor and a second MOS transistor in a differential pair configuration. A first load resistor is coupled to a first MOS transistor drain at a first output terminal and a second load resistor is coupled to a second MOS transistor drain at a second output terminal. The bandwidth expansion circuit is coupled to the CML buffer circuit in a source follower configuration. The bandwidth expansion circuit includes a third MOS transistor and a fourth MOS transistor. A capacitor is coupled across a third MOS transistor source and a fourth MOS transistor source. The fourth MOS transistor and the third MOS transistor generate a high pass function at the first output terminal and the second output terminal.
Owner:PARADE TECH
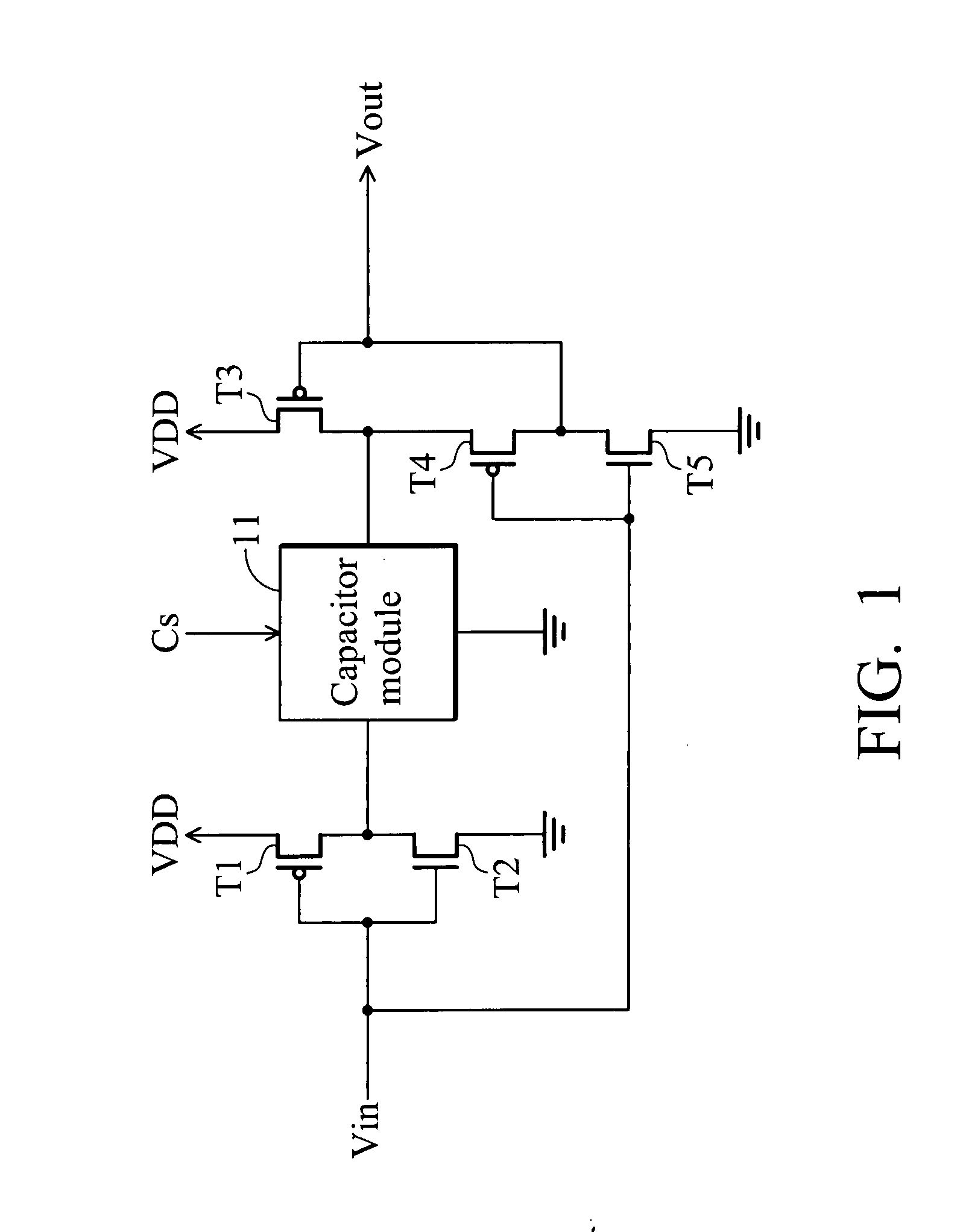
Bulk input differential logic circuit
InactiveUS6838909B2Guaranteed high speed operationReduce in quantitySwitching accelaration modificationsExclusive-OR circuitsSense amplifierLogic circuitry
A bulk input differential logic circuit. The circuit outputs a large signal high enough to assert a logic High and Low by variations of the threshold voltage controlled by the bulk input signal and amplification of the sense amplifier. A boost circuit is disposed on the bulk input terminal, which may receive multiple bulk input signals. This makes it possible to use fewer circuit elements and smaller circuit area for a complicated logic operation.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Popular searches
Electric pulse generator Reliability increase in field effect transistors Semiconductor/solid-state device details Solid-state devices Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing Electric pulse generator details Logic circuit coupling/interface arrangements Single output arrangements Digital storage Line-transmission
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com