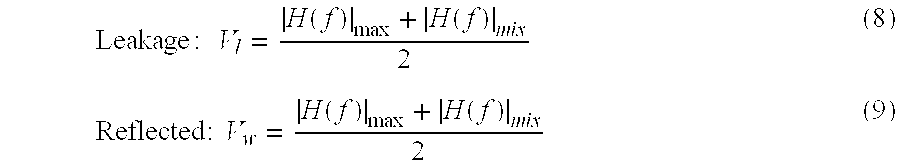Patents
Literature
1153 results about "Return loss" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
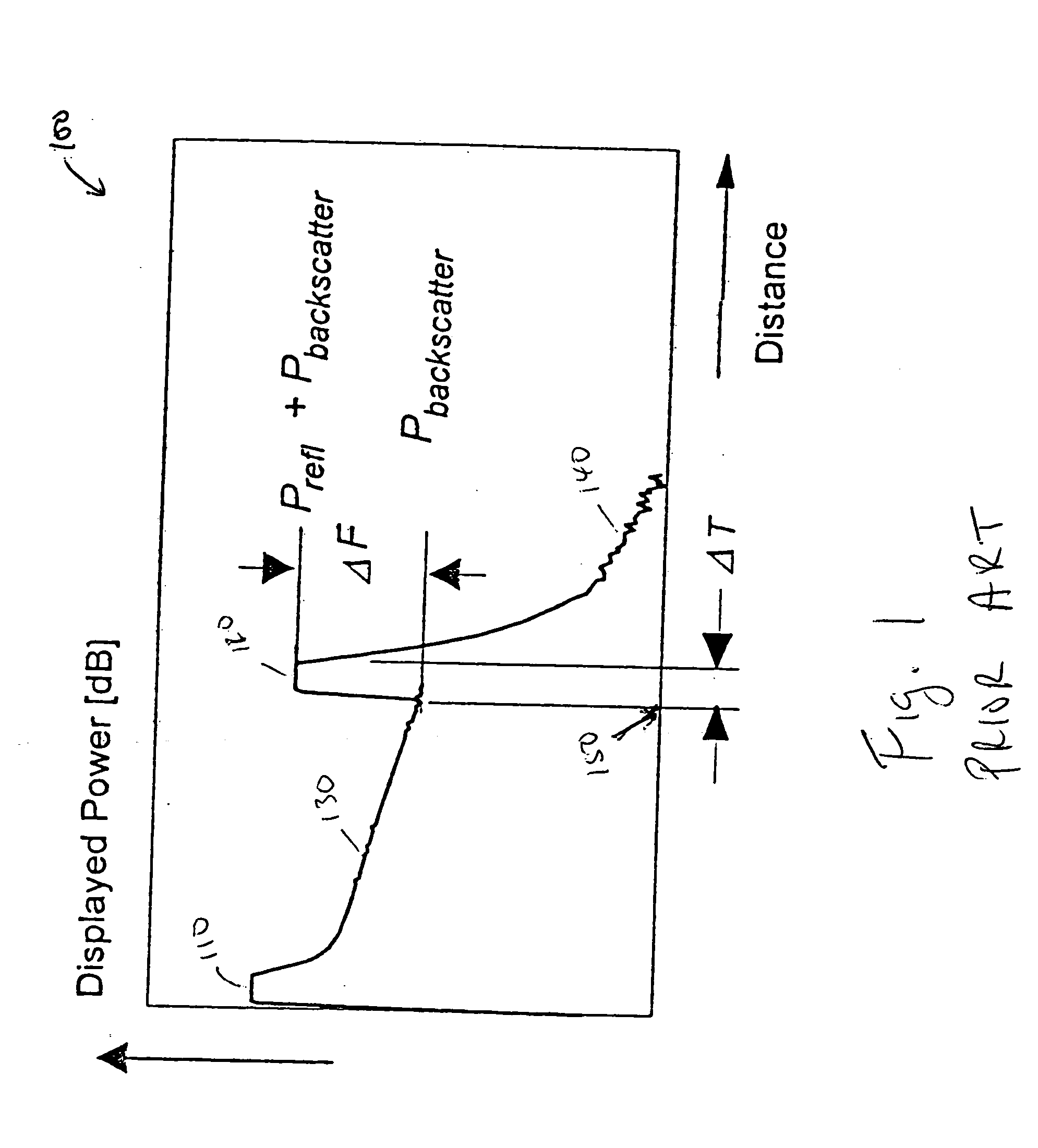
In telecommunications, return loss is the loss of power in the signal returned/reflected by a discontinuity in a transmission line or optical fiber. This discontinuity can be a mismatch with the terminating load or with a device inserted in the line. It is usually expressed as a ratio in decibels (dB); RL(dB)=10log₁₀Pi/Pᵣ where RL(dB) is the return loss in dB, Pᵢ is the incident power and Pᵣ is the reflected power.
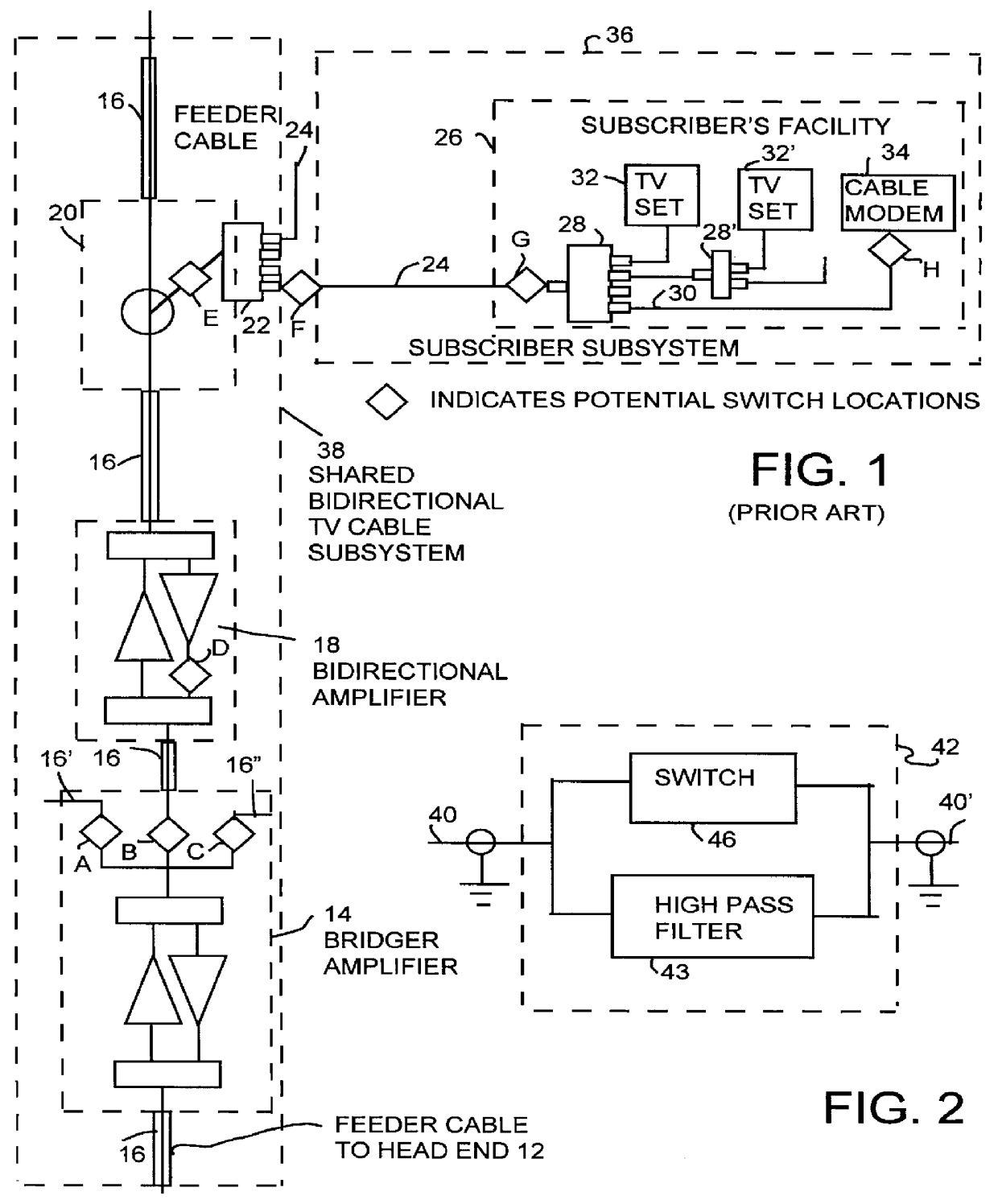
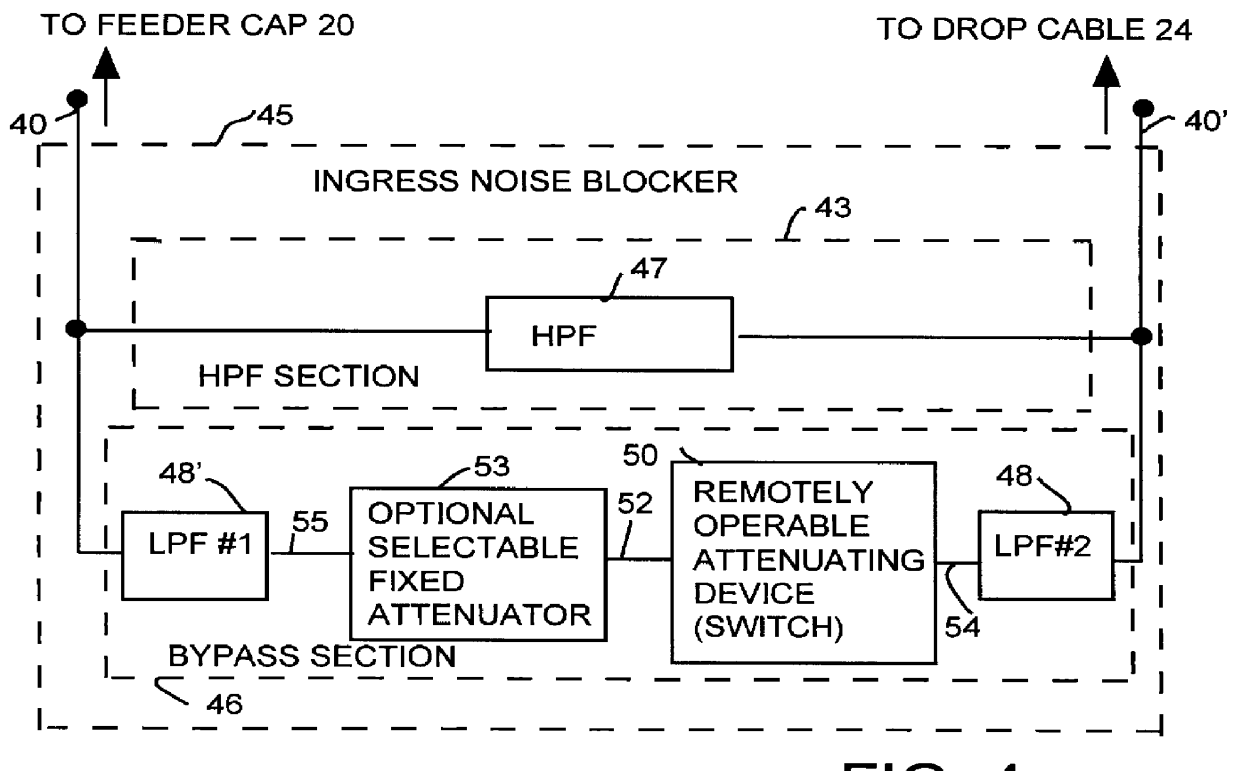
TV and data cable system ingress noise blocker
InactiveUS6094211APrevents loss of picture qualityLow costTelevision system detailsColor television detailsSignal qualityModem device
This invention permits the upstream transmission of short packets of information in a cable TV system, and blocking upstream noise at all other times, and does so without interfering with image quality of normal TV viewing. A remotely operable ingress noise blocking filter is placed at the terminating junction between a subscriber's coaxial drop cable and a corresponding feeder tap in a cable TV system. The ingress noise blocking filter contains a high pass filter to pass the normal TV band. This high pass filter is bypassed by a section containing low pass filters and a switch operated when receiving a control signal from a cable modem during those short durations the cable modem is authorized to transmit an upstream signal. Low pass filters isolate the switching elements so that switching transients cannot occur in the downstream TV band. The level of the amplitude of the downstream signal is unaffected whether the switching elements are open or closed. Further, the switching arrangement provides a relatively constant impedance, both when the switching element is on and off to provide a high return loss and avoid signal reflections and maintain signal quality. In a diagnostic mode, the location of each noise source is determined by correlating the energy measured at each a set of frequencies across the band at the headend during those periods when the cable modem is allowed to transmit versus the energy received during those periods when the same cable modem is not authorized to transmit.
Owner:ARRIS INT
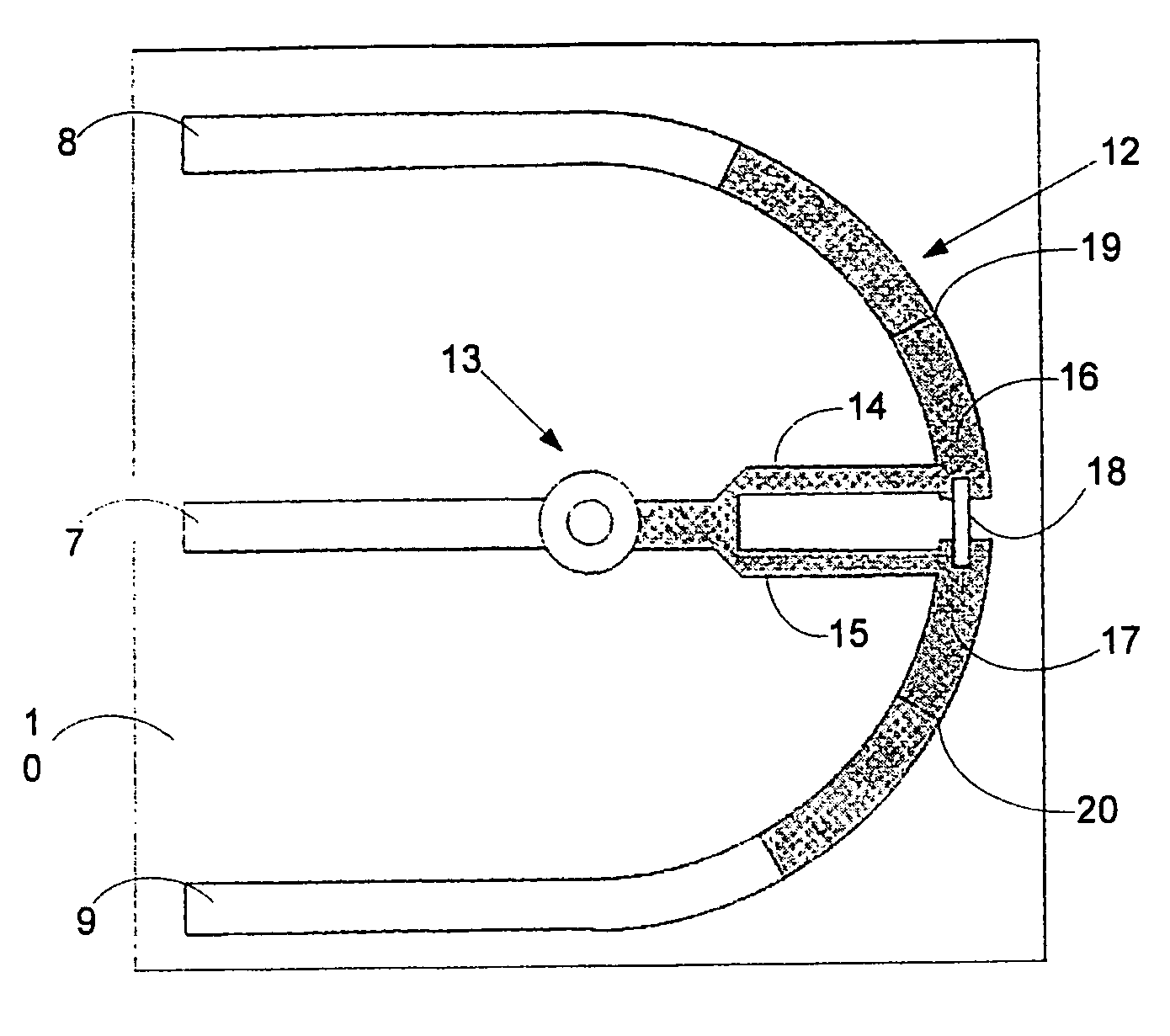
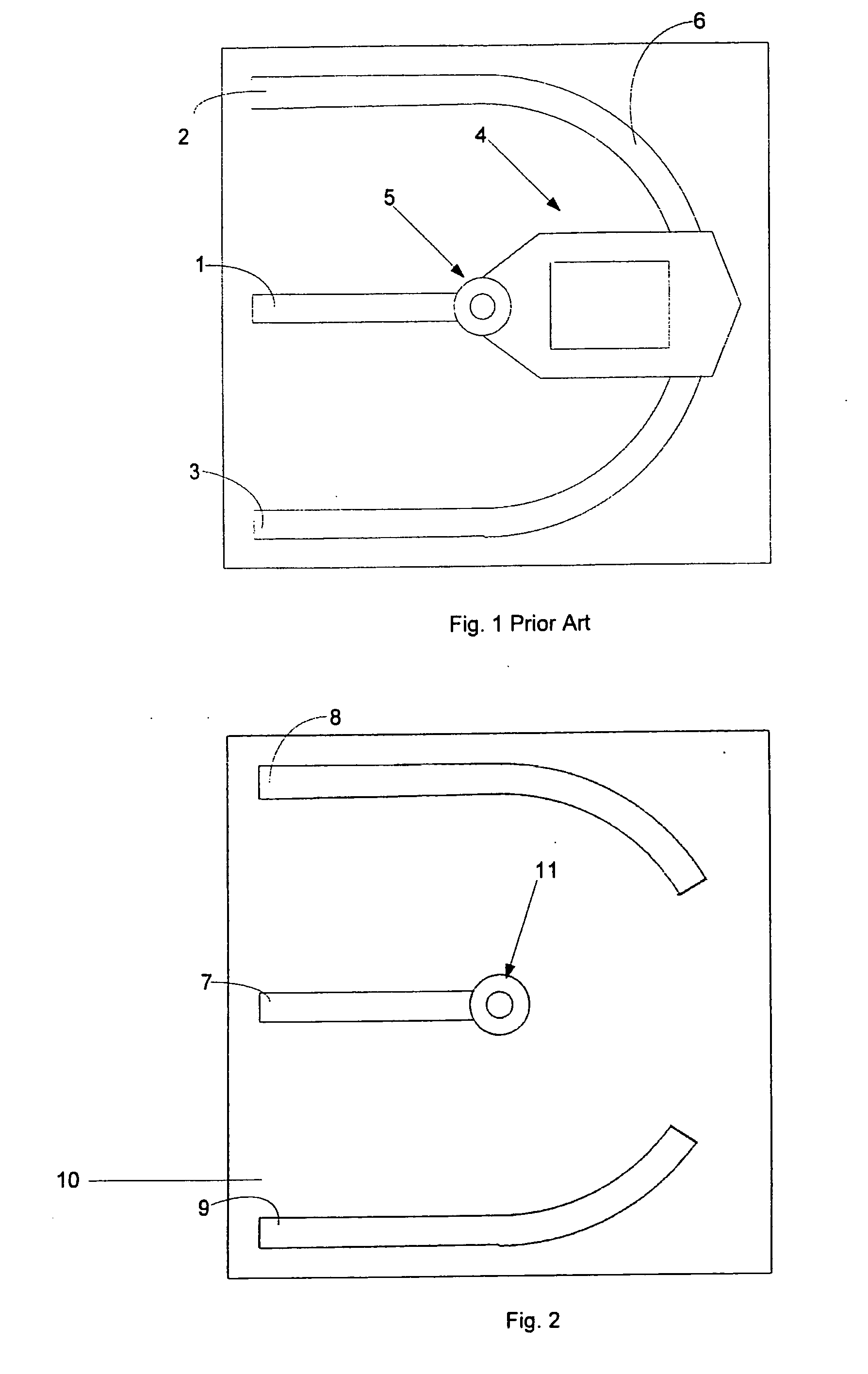
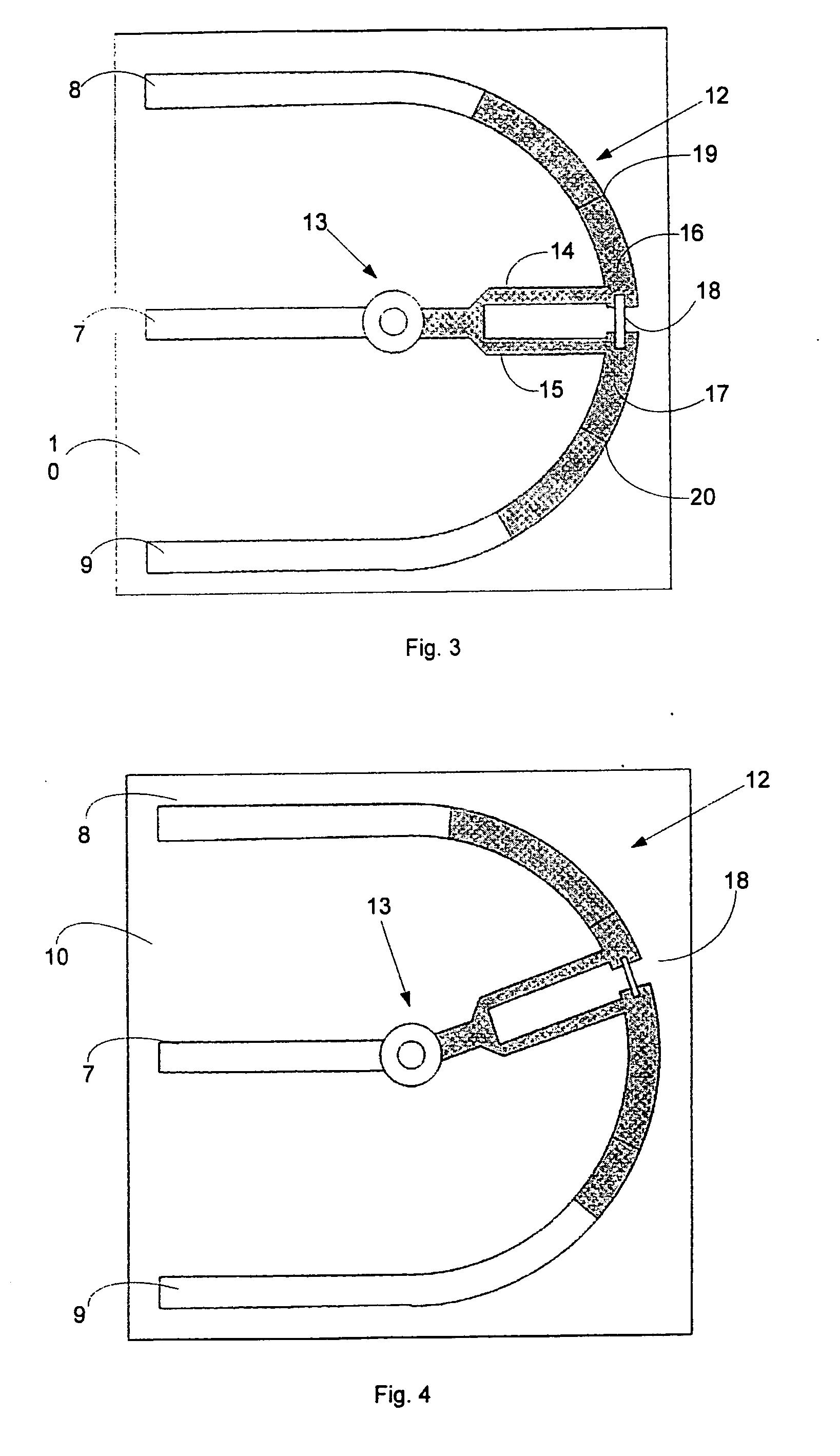
Optical fiber clamping apparatus to hold fiber cable while providing retractable distance across module unit
InactiveUS6741784B1Increase clamping forceReduce insertionFibre mechanical structuresFiberOptical Module
A fiber routing tray to hold, organize, and route fiber cables from external sources to other optical modules and optical components. The fiber routing tray mechanical device comprises a fiber entry block, fiber channel slot, retention bar with fiber clamps, fiber clamping slots, curved fiber routing fence, and a fiber exit opening. A retention bar with a contoured fiber retention clamps is used to hold fiber cables in place, provide a strain relief to a fiber cable, and distribute uniform clamping force on the fiber cable preventing insertion and return losses. Curved fiber channel slots with a preferable width help route fiber cables and prevent them from overbending. In addition, these fiber channel slots control the extension and retraction distance of the fiber cables during external fiber cable assembly. A curved fiber routing fence help route fiber cables and help prevent them from over-bending and tangling inside of the fiber reel tray. An exit opening allows fiber cables to drop below the fiber tray before the fiber cables are attached to the optical devices and optical modules.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
System and method of using absorber-walls for mutual coupling reduction between microstrip antennas or brick wall antennas
InactiveUS7427949B2Reduce signalingReduce horizontal sizeAntenna detailsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionMicrostrip patch antennaBrick
A multi-element antenna with sufficiently small return loss and mutual coupling signals to allow the simultaneous transmission of powerful radar signals and the reception of faint target return signals. The microstrip patch antenna has radio frequency absorbing material place between neighboring antenna elements to reduce the mutual coupling leakage signals.
Owner:COBHAM DEFENSE ELECTRONICS SYST CORP
Coaxial cable connector having electrical continuity member
ActiveUS20120225581A1Engagement/disengagement of coupling partsTwo pole connectionsCoaxial cableEngineering
A coaxial connector comprising a connector body; a nut, axially rotatable with respect to the connector body, the nut having a first forward end configured for threadably attaching to an interface port and a second rearward end; and a continuity member, electrically contacting the nut; wherein the connector is configured to maintain return loss below -40 dBvM when the connector is installed on the interface port, so as to be only engaged with one thread of the interface port is provided.
Owner:PPC BROADBAND INC
Method and apparatus for adaptive cancellation of responses in cabling
InactiveUS6522152B1Resistance/reactance/impedenceFault location by conductor typesSignal responseTime domain
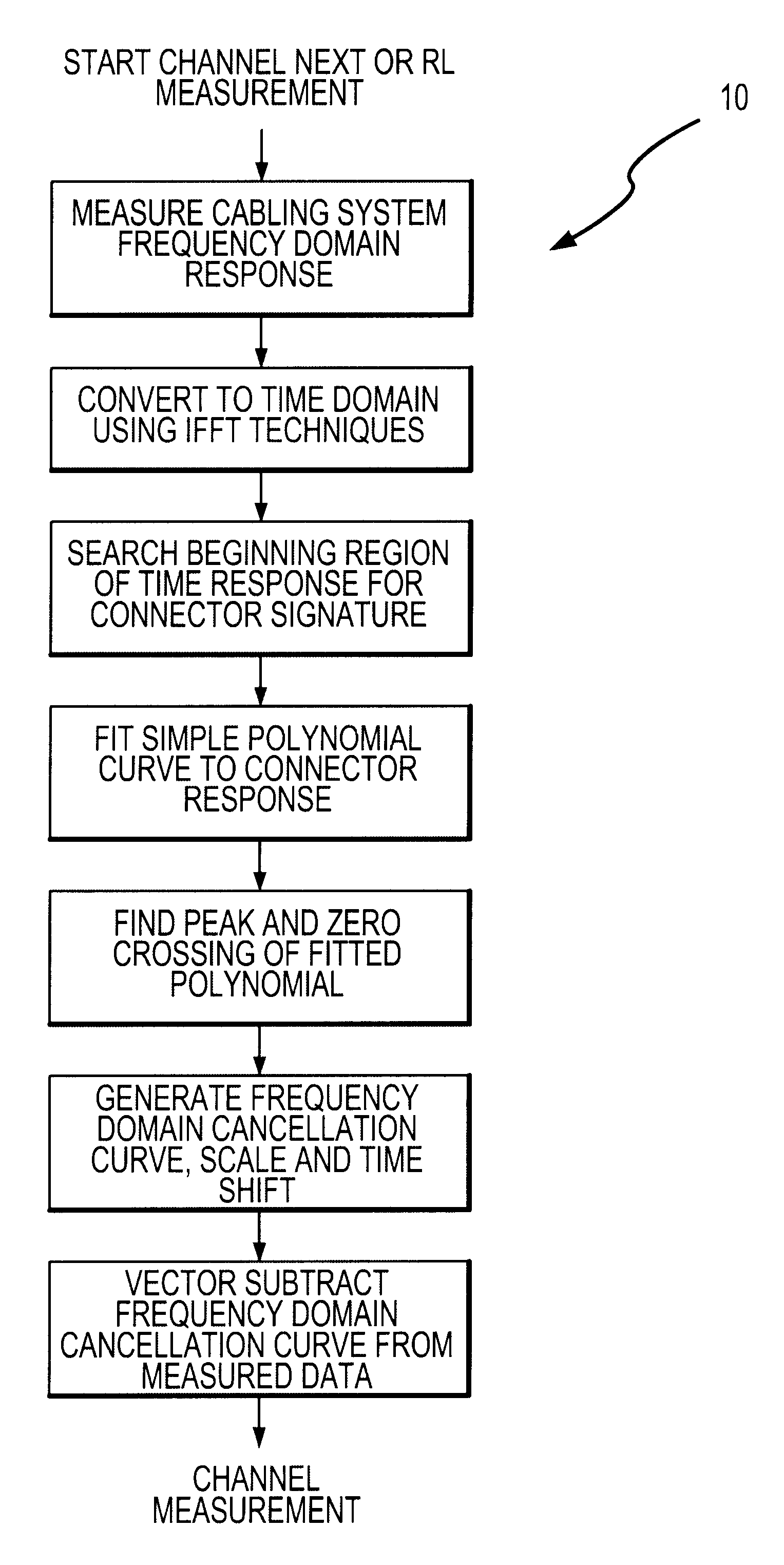
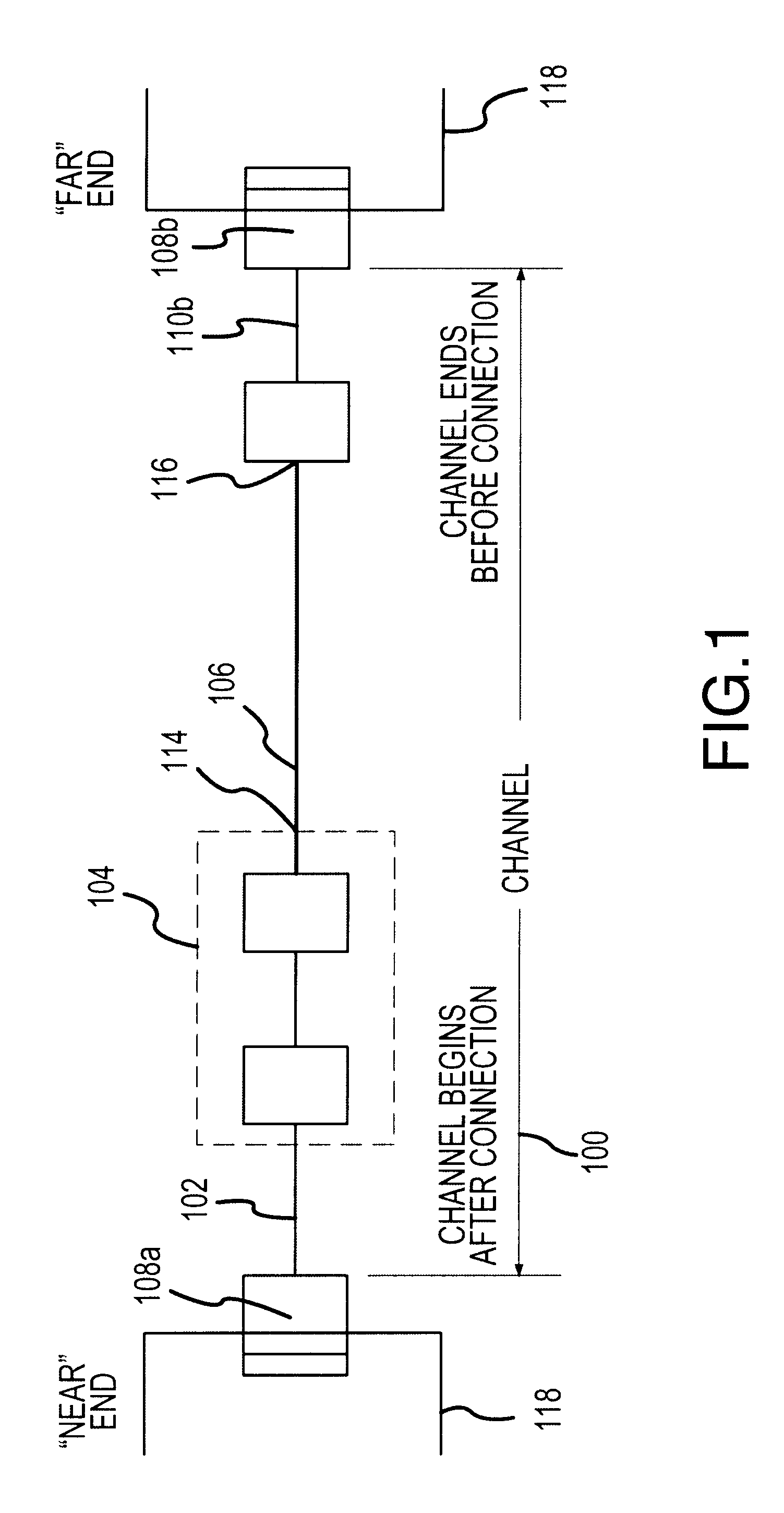
An Adaptive Vector Cancellation method which uses time domain data for an instrument connection to estimate magnitude, phase, and time position of a signal response such as NEXT or Return Loss associated with the connection. Based on the estimate of the amplitude and time of the connection response, a suitable full-bandwidth frequency response that corresponds to a point source of NEXT or Return Loss is determined. This calculated connector response is then scaled to an appropriate magnitude, phase and time shifted to the estimated position of the actual connection. The scaled / shifted response is then vectorially combined with the measured sweep data to suitably cancel the connection contribution to NEXT and / or Return Loss. Thus, the amount of NEXT or return loss existing in the user's patch cord is preserved, while the NEXT or return loss due to the instrument connection is suitably suppressed. Correction is done in the frequency domain, over the full bandwidth of the measured data.
Owner:MICROTEST
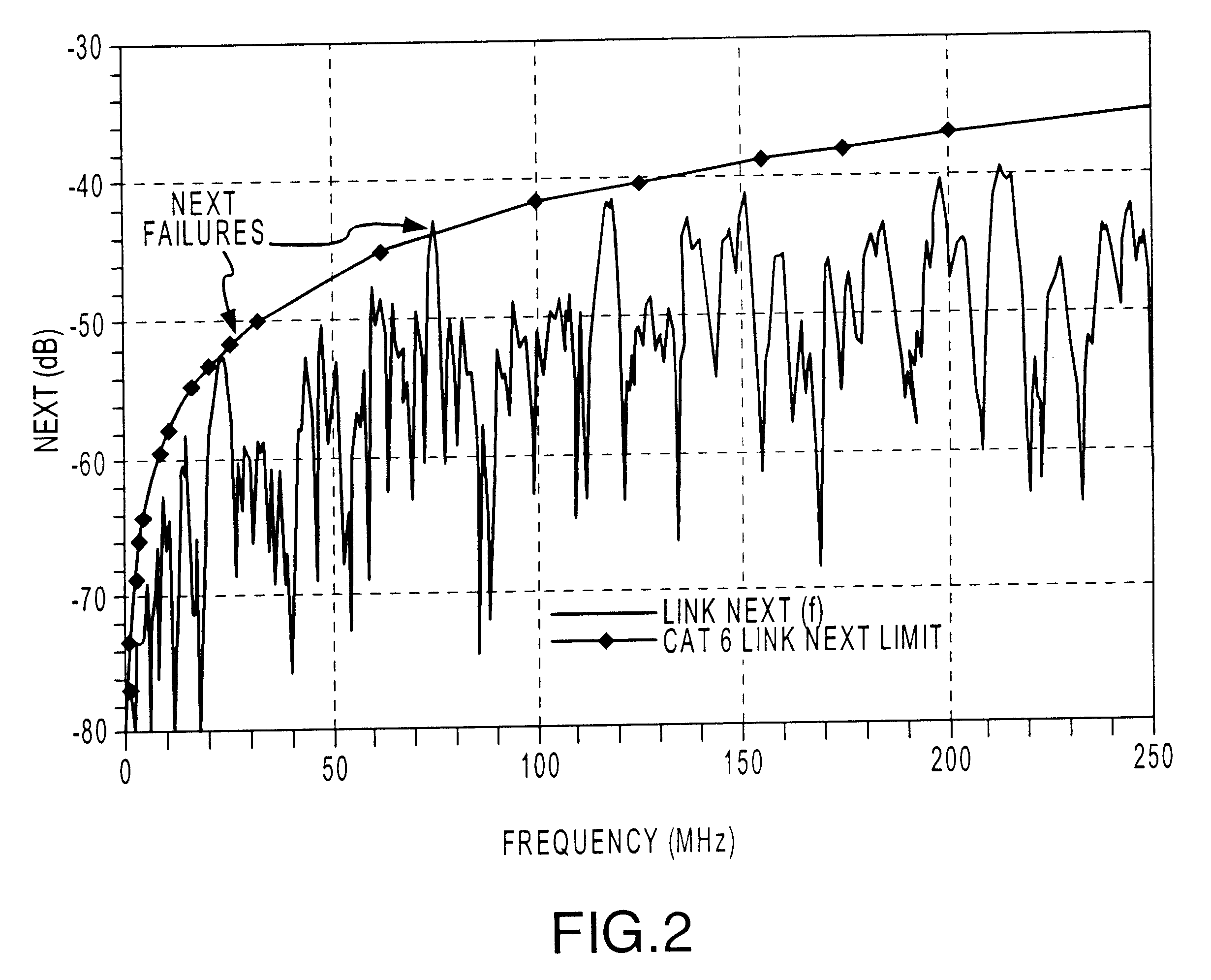
Method for diagnosing performance problems in cabling
InactiveUS6433558B1Resistance/reactance/impedenceFault location by conductor typesTime domainTime limit
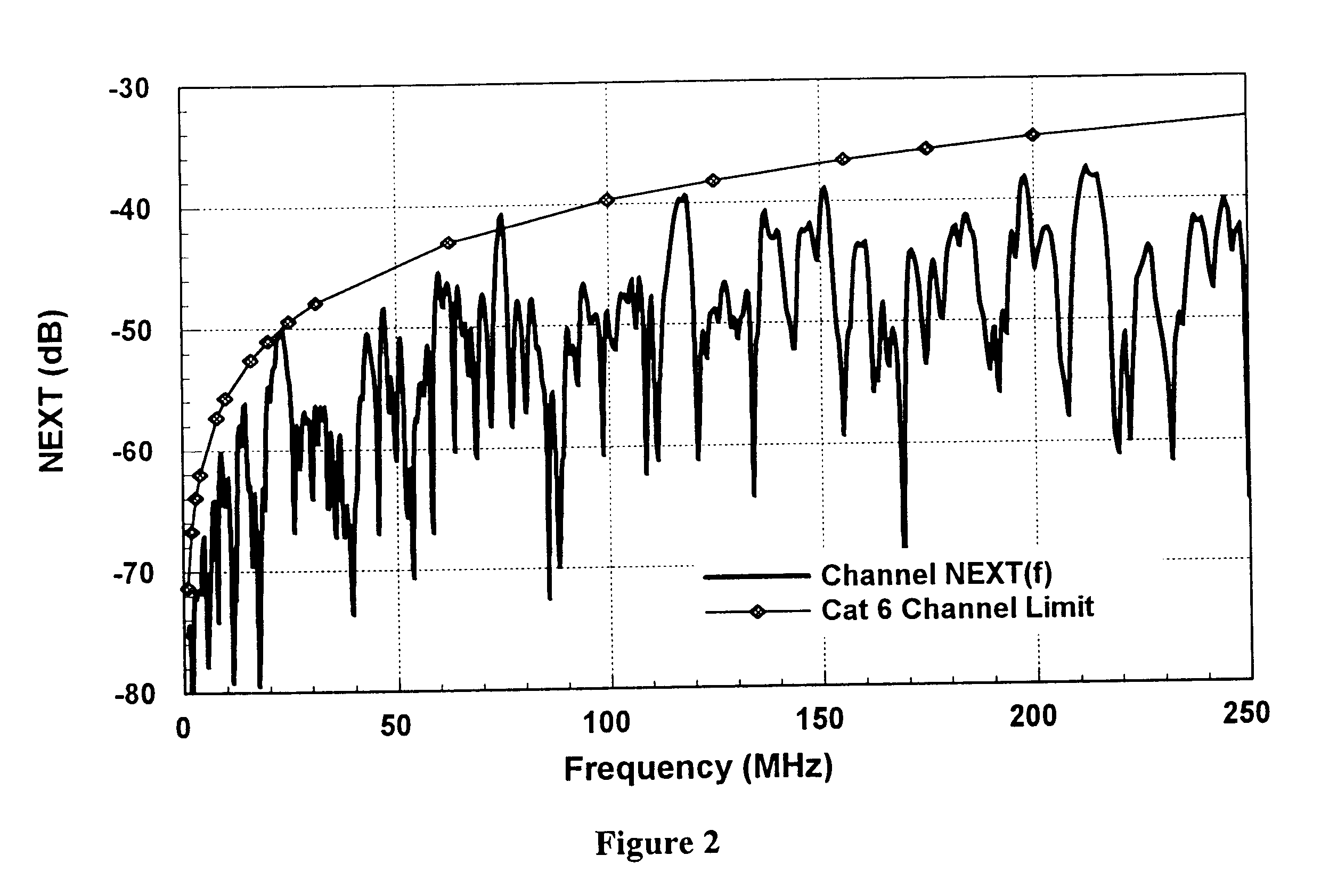
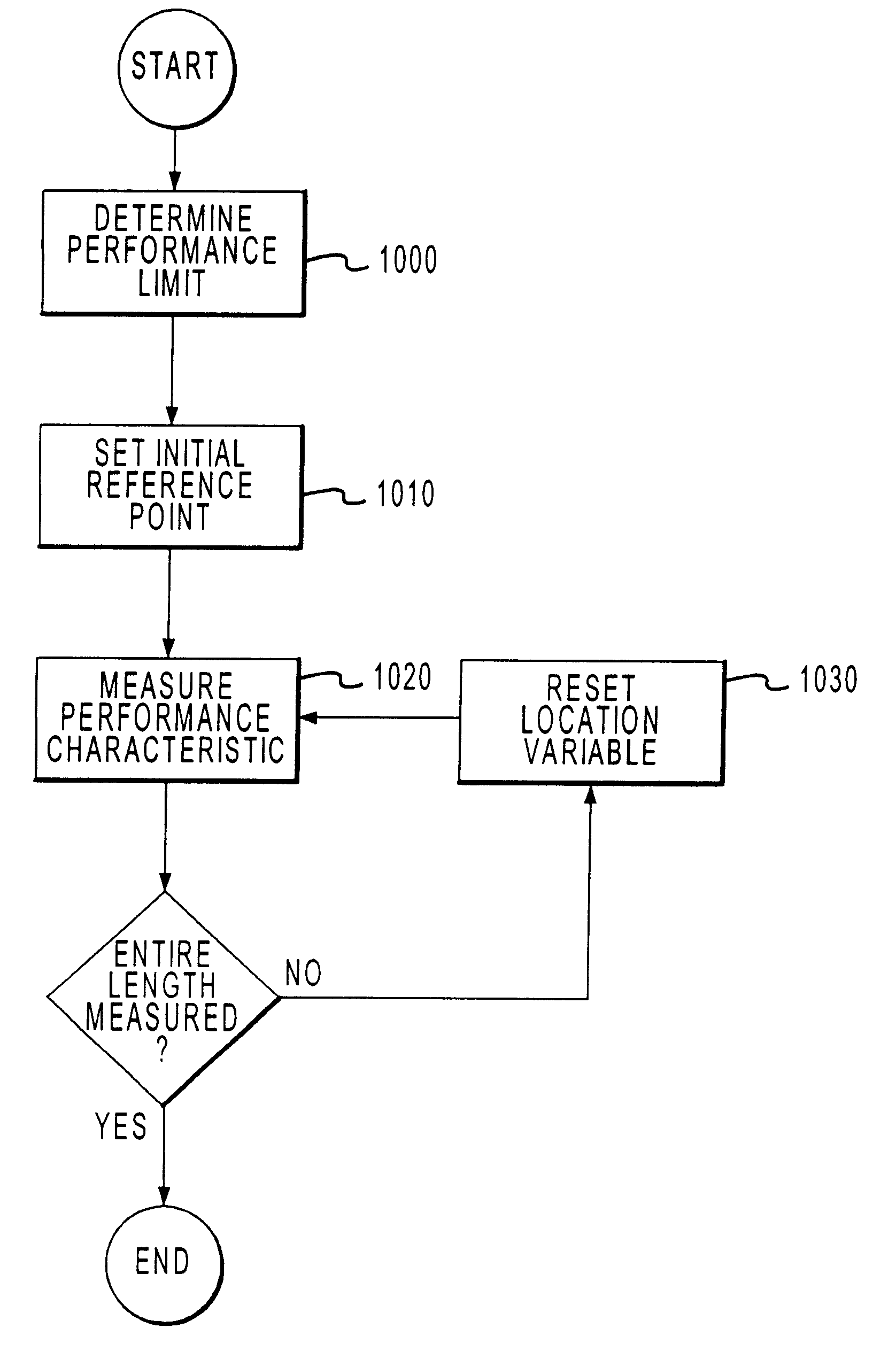
The present invention provides methods for using time domain analysis of NEXT, Return Loss and the like, in conjunction with the application of time or distance referenced limits to verify and determine compliance of the performance requirements of connections in a typical link. Time domain analysis of NEXT, Return Loss data and the like, suitably provides the performance characteristics of a link as a function of time or distance. When coupled with time or distance performance curves for connections, it can be determined if the transmission fault is at a connection or in the cable. The time limit curves for connections can be generated based on the frequency domain performance requirements for connecting hardware of a specific level of performance. The connection time limit curves thus provide an interpretation means to determine if the connection is within performance standards, allowing improved isolation of the fault condition.
Owner:MICROTEST
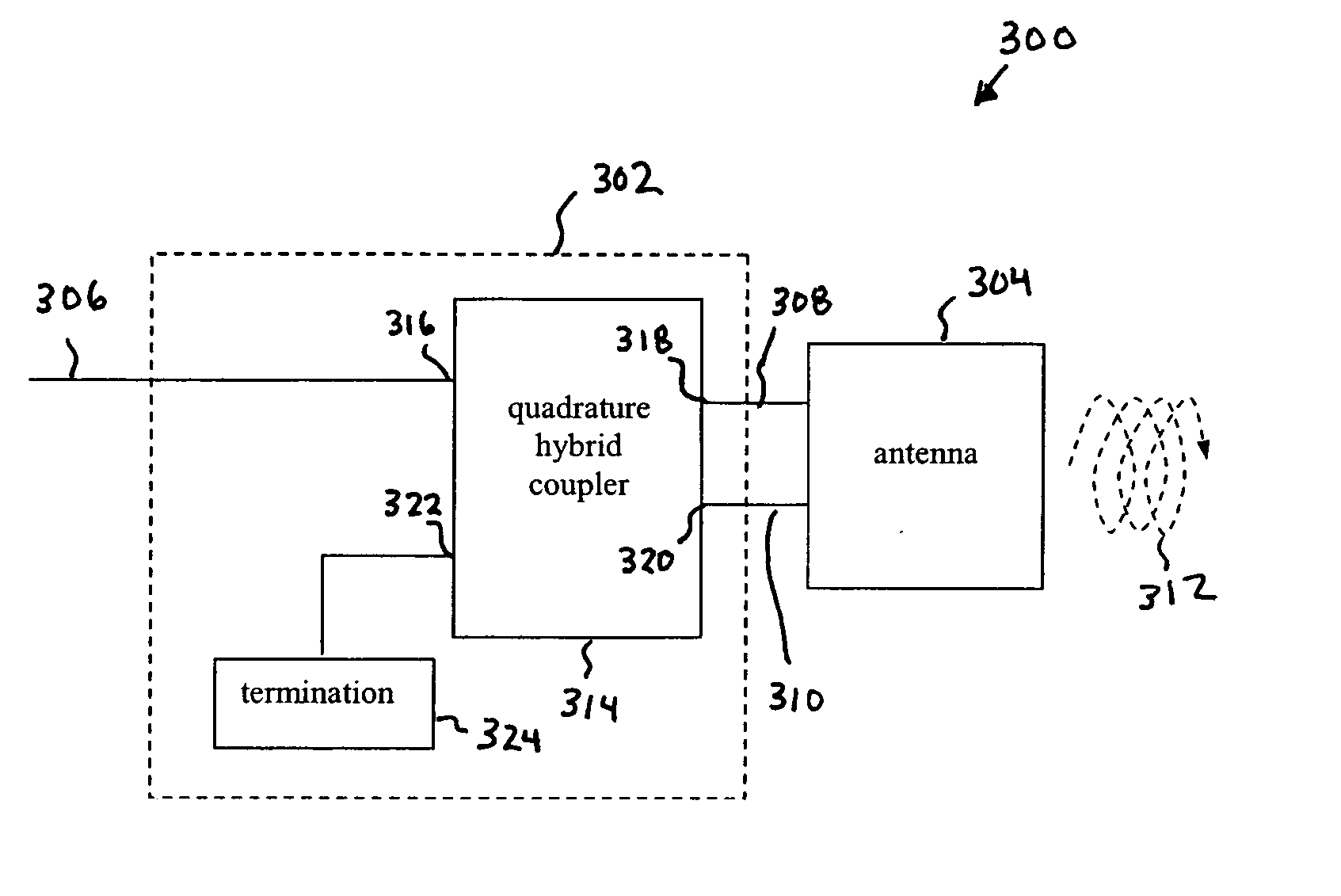
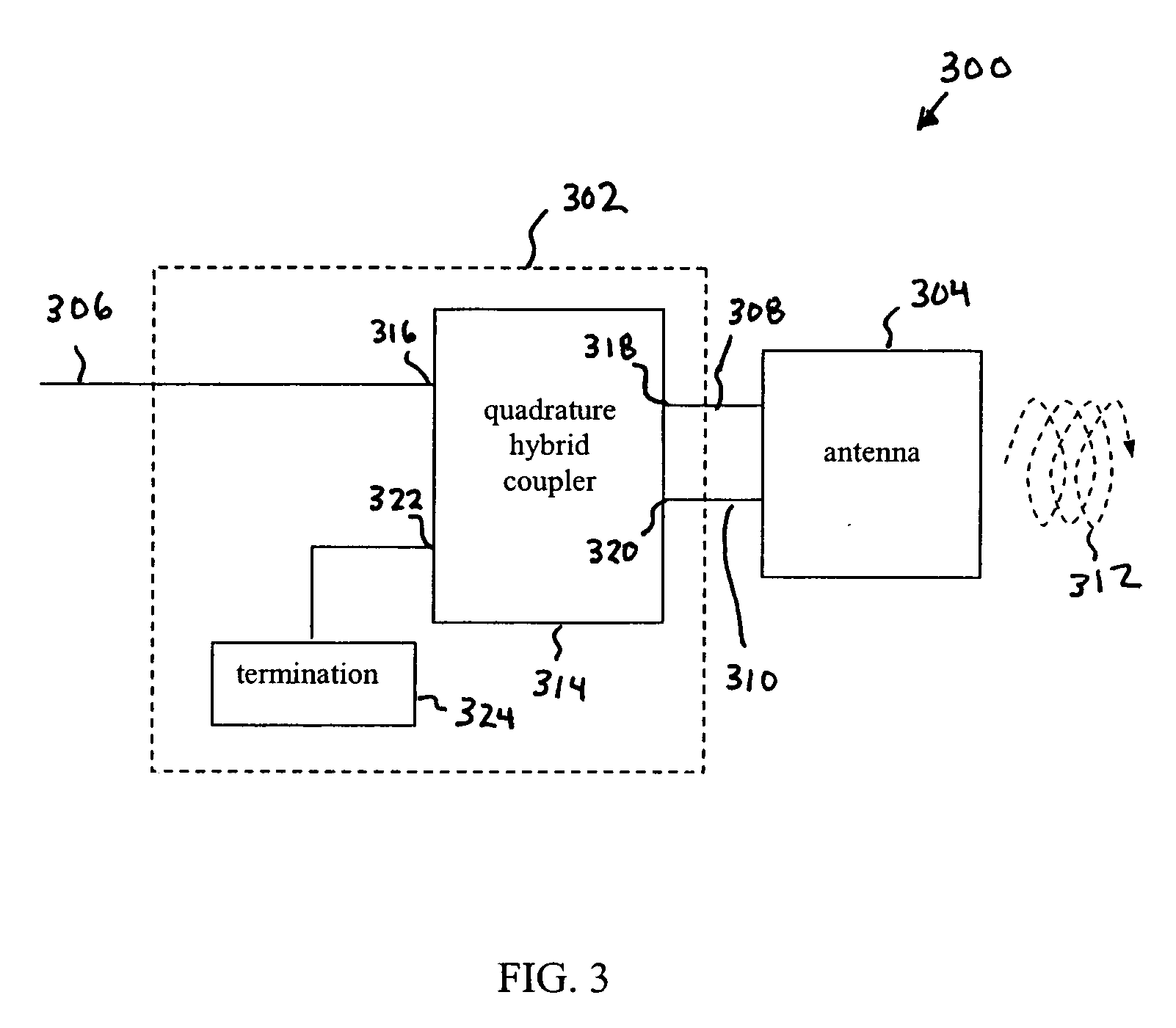
Low return loss rugged RFID antenna
ActiveUS20070096919A1Readily apparentMemory record carrier reading problemsLifting devicesHybrid couplerEngineering
Methods, systems, and apparatuses for RFID devices, such as reader antennas, are described. A reader antenna includes a quadrature hybrid coupler, a termination element, and an antenna, such as a patch antenna. The quadrature hybrid coupler has first, second, third, and fourth ports. The first port receives an input radio frequency RF signal. The second port outputs a first RF output signal. The third port outputs a second RF output signal. The second RF output signal is shifted in phase by 90 degrees relative to the first RF output signal. The fourth port is coupled to the termination element. The patch antenna has a first point coupled to the first RF output signal and a second point coupled to the second RF output signal. The patch antenna radiates a circularly polarized RF signal due to the received first and second RF output signals. The circularly polarized RF signal may be used to interrogate tags. Furthermore, the reader antenna is integrated into a ruggedized structure that provides environmental protection for the antenna, including providing shock absorption for impacts to the antenna.
Owner:SYMBOL TECH LLC
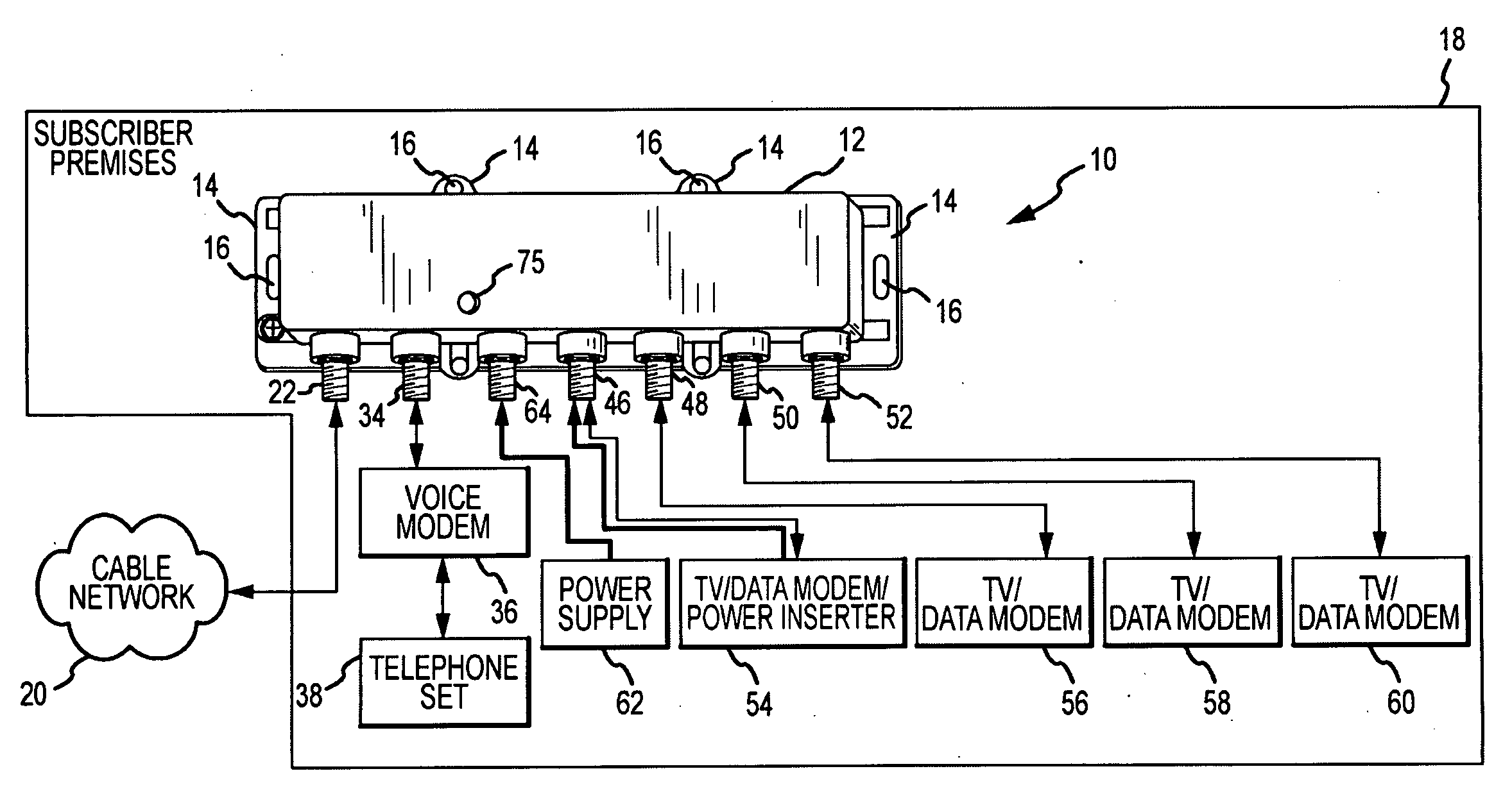
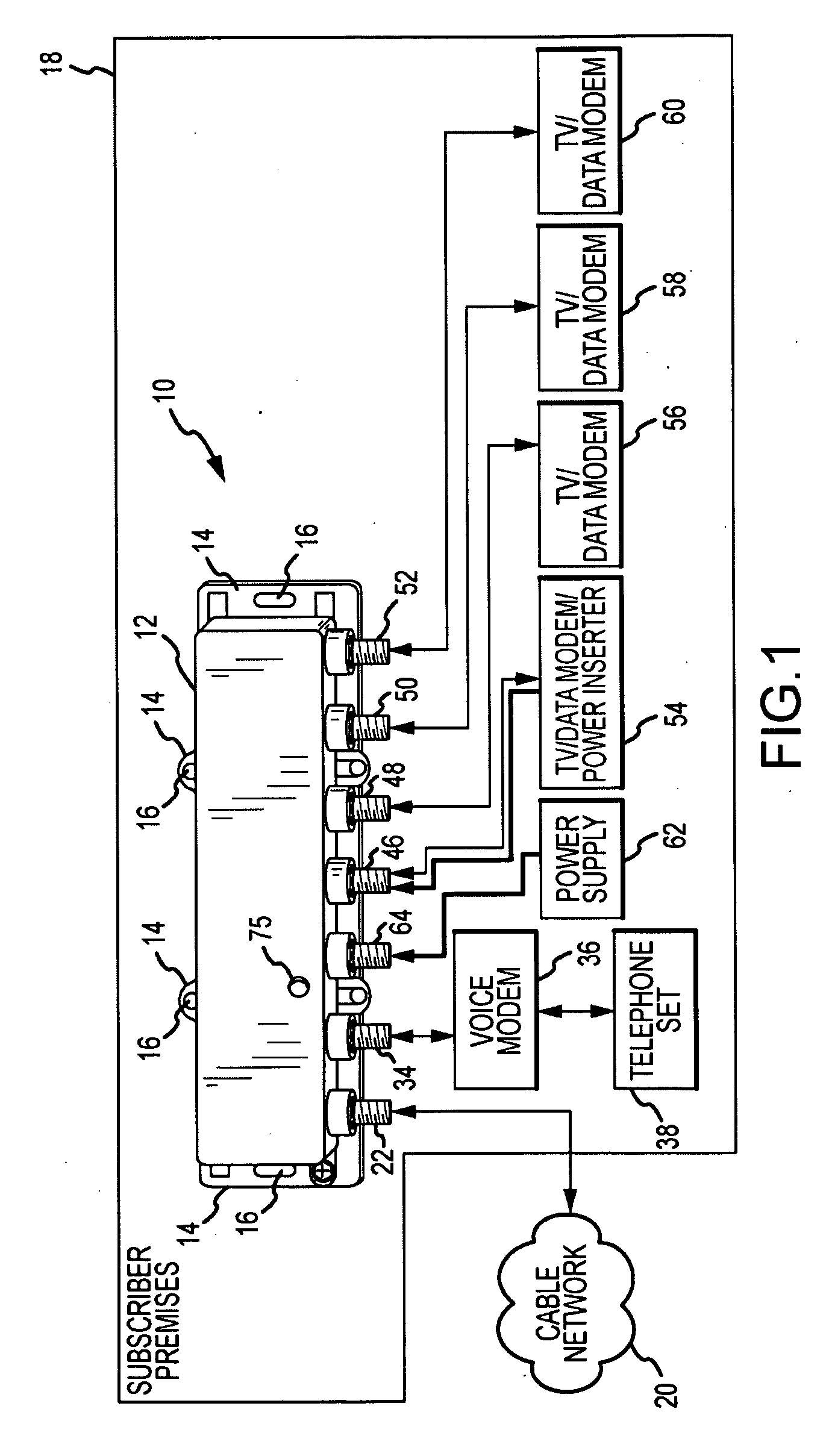
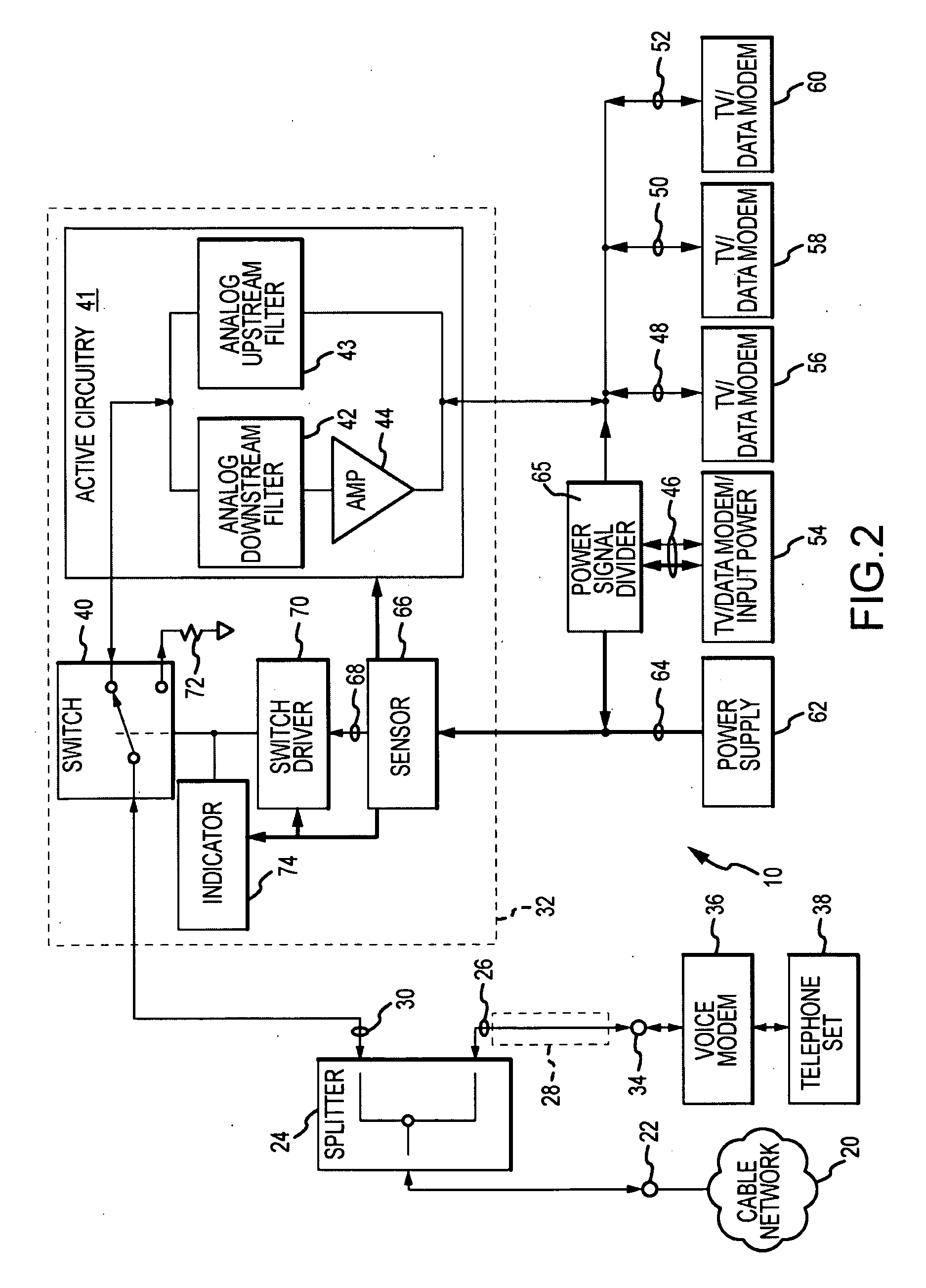
Passive-Active Terminal Adapter and Method Having Automatic Return Loss Control
ActiveUS20100017842A1Quantity minimizationPrevent and minimize signalTelevision system detailsTelephonic communicationEngineeringElectrical impedance
Return loss due to excessive signal reflection into a cable television (CATV) network from an inoperative or abnormally operative terminal adapter is minimized, to communicate enhanced passive downstream signals to passive subscriber devices such as “life-line” telephone sets. A predetermined termination impedance is substituted for an active branch circuit of the terminal adapter whenever reduced input voltage, over-current or under-current conditions exist in the terminal adapter.
Owner:PPC BROADBAND INC
Via transmission lines for multilayer printed circuit boards
ActiveUS20070205847A1Improve performanceMultiple-port networksPrinted circuit aspectsElectrical conductorEngineering
A via transmission line for a multilayer printed circuit board (PCB) in which a wave guiding channel is formed by a signal via or a number of signal vias, an assembly of ground vias surrounding the signal via or corresponding number of coupled signal vias, a set of ground plates from conductor layers of the multilayer PCB, and a clearance hole. In this via transmission line, the signal via, or the number of signal vias forms an inner conductive boundary, ground vias and ground plates from conductor layers of the multilayer PCB form an outer conductive boundary, and the clearance hole provides both isolation of the inner conductive boundary from the outer conductive boundary and high-performance broadband operation of the via transmission line by means of the predetermined clearance hole cross-sectional shape and dimensions where the cross-sectional shape of the clearance hole is defined by the arrangement of ground vias in the outer conductive boundary and dimensions of the clearance hole are determined according to a method to minimize frequency-dependent return losses caused by specific corrugations of the outer conductive boundary formed by ground plates in the wave guiding channel of the via transmission line.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP +1
Wide Angle Impedance Matching Using Metamaterials in a Phased Array Antenna System
ActiveUS20100073232A1Minimize return lossImproving Impedance MatchingAntenna arraysProtective material radiating elementsImpedance matchingConductive materials
A phased array antenna system may include a sheet of conductive material with a plurality of aperture antenna elements formed in the sheet of conductive material. Each of the plurality of aperture antenna elements is capable of sending and receiving electromagnetic energy. The phased array antenna system may also include a wide angle impedance match (WAIM) layer of material disposed over the plurality of aperture antenna elements formed in the sheet of conductive material. The WAIM layer of material includes a plurality of metamaterial particles. The plurality of metamaterial particles are selected and arranged to minimize return loss and to optimize an impedance match between the phased array antenna system and free space to permit scanning of the phased array antenna system up to a predetermined angle in elevation.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Tunable add/drop optical filter
InactiveUSRE37044E1Improve isolationMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsGratingLow voltage
In all-optical networks, optical switching and routing become the most important issues for interconnecting the transport network layers. This invention describes a novel tunable optical add / drop filter for the all-optical wavelength-division-multiplexing (WDM) network applications. This filter can add or drop part of the high transmission capacity signals of a WDM link. It can be used to decentralized access point in the access network or as small core network node to realizing branching points in the network topology. It works in both wavelength and space domains. It has the advantages of: 1) High throughput and low voltage operation; 2) Wide tuning range and therefore, high channel capacity; 3) High isolation and high directivity between input and output ports; 4) Compact device packaging is possible as compares to the conventional grating and mechanical switching type of add / drop filter; 5) Multiple ports add / drop tunable filters can be realized with this invention to interconnect multiple WDM networks. This novel add / drop filter can be used in various WDM topologies. It enhances the performance of the conventional tunable filter by re-routing the rejected wavelengths back to network, which not only save the precious optical energy, but also cut down the return loss of the device.
Owner:EZCONN
Electrical connector
InactiveUS20070032104A1Impedance stabilityReduce crosstalkCoupling for high frequencyFixed connectionsElectrical resistance and conductanceMiniaturization
An electrical connector includes, in substitution for contacts, a substrate having a plurality of signal patterns and a plurality of ground patterns on at least one surface, each of these patterns having at one end a contact portion adapted to contact a mating object and at the other end a connection portion to be connected to a cable, a housing having an inserting hole for inserting the substrate therethrough, and holding members for fixing the substrate to the housing. A capacitor and a resistance chip connected in parallel are mounted on at least one of the signal patterns. In this manner, the connector achieves its miniaturization, stability of impedance, reduction in cross talk, and better return loss level and transmission characteristics.
Owner:DDK LTD
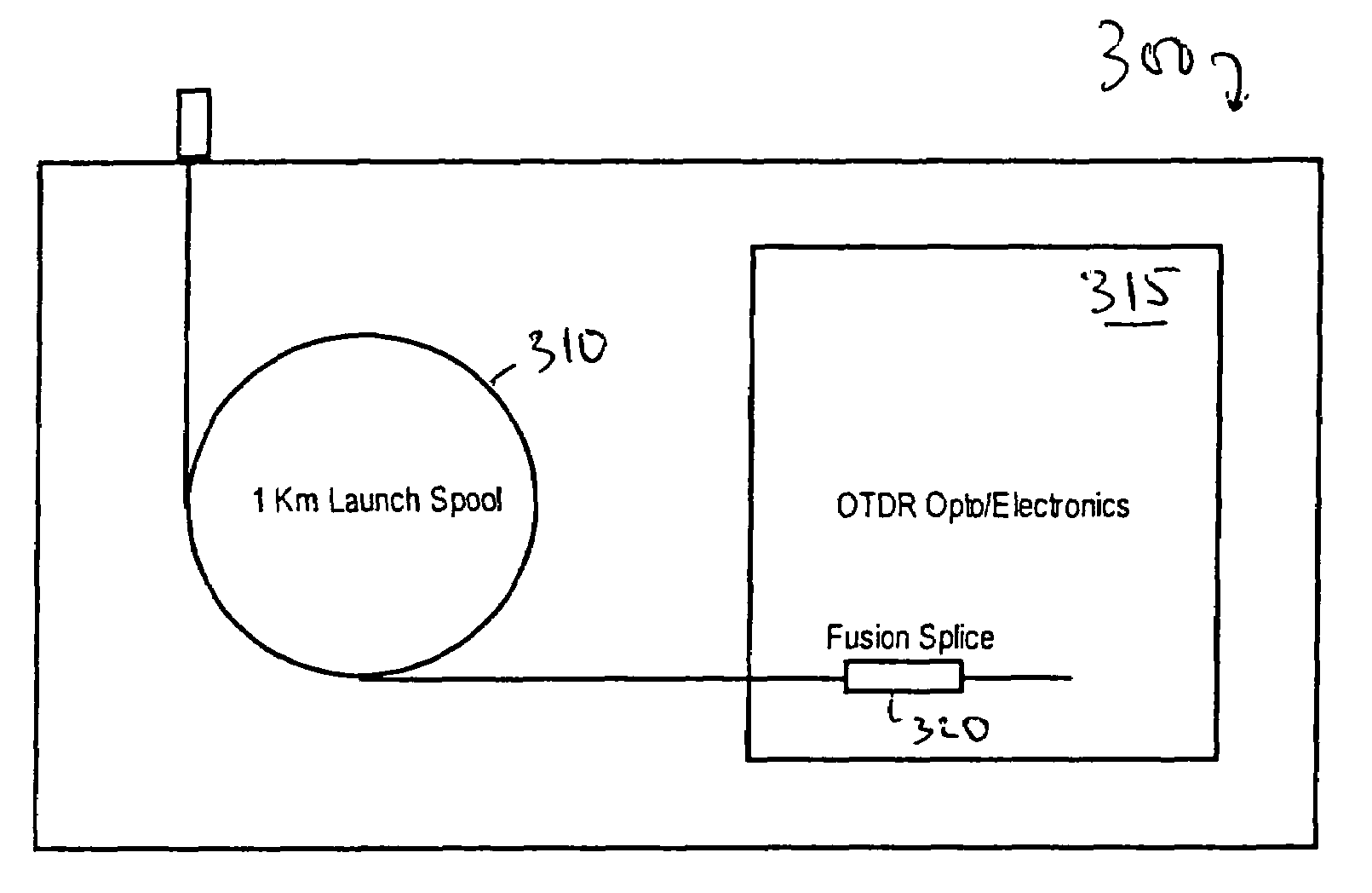
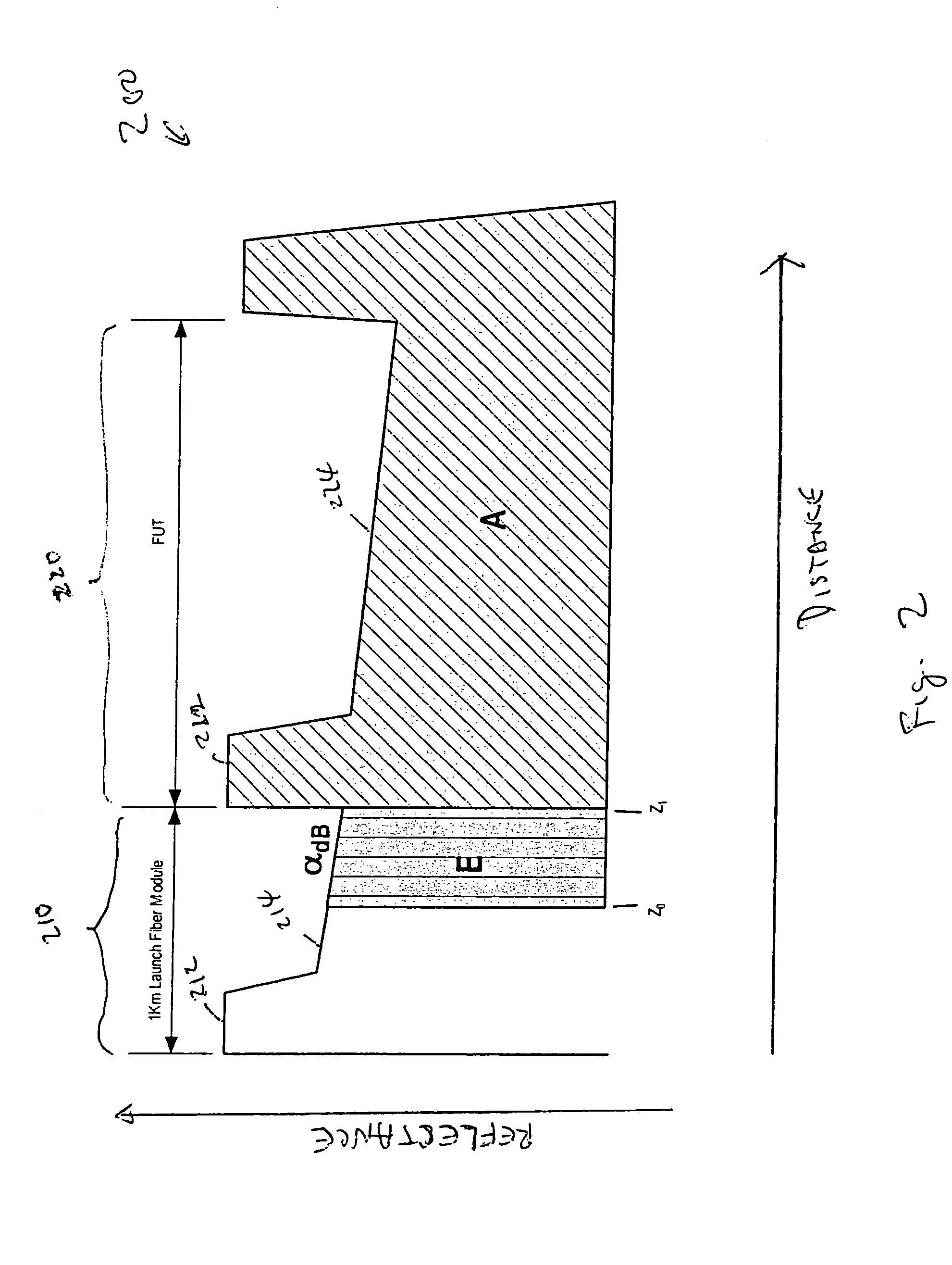
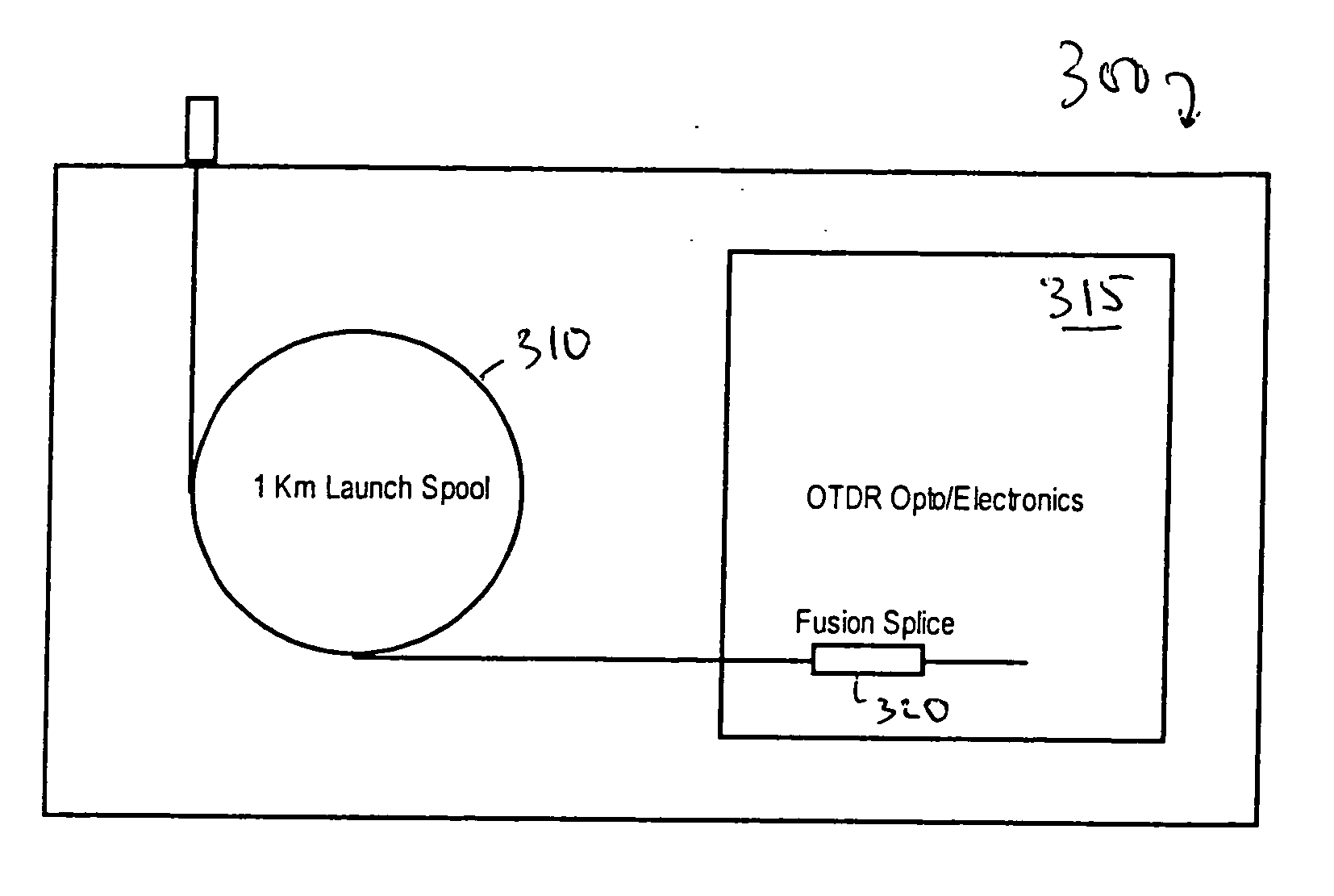
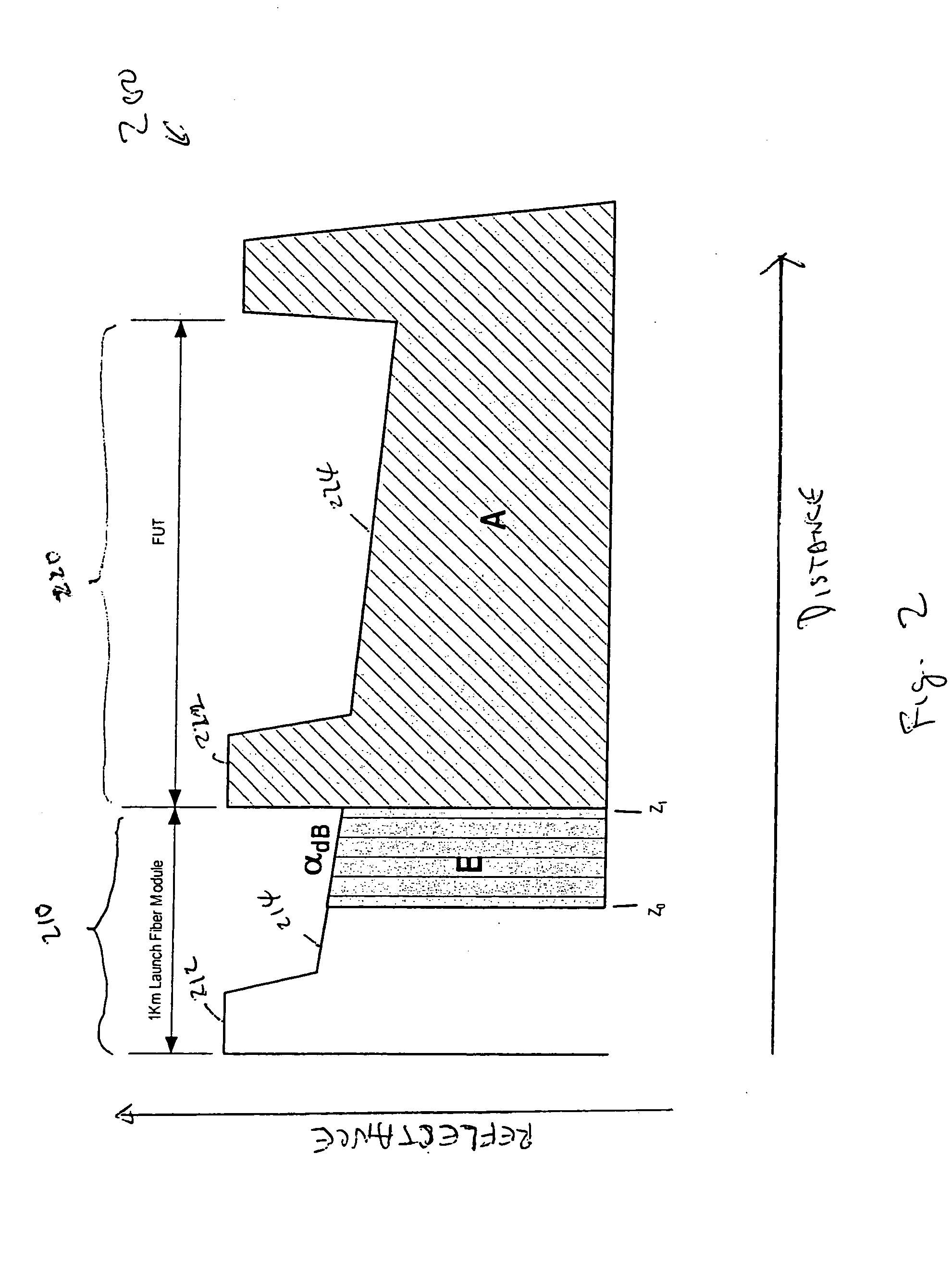
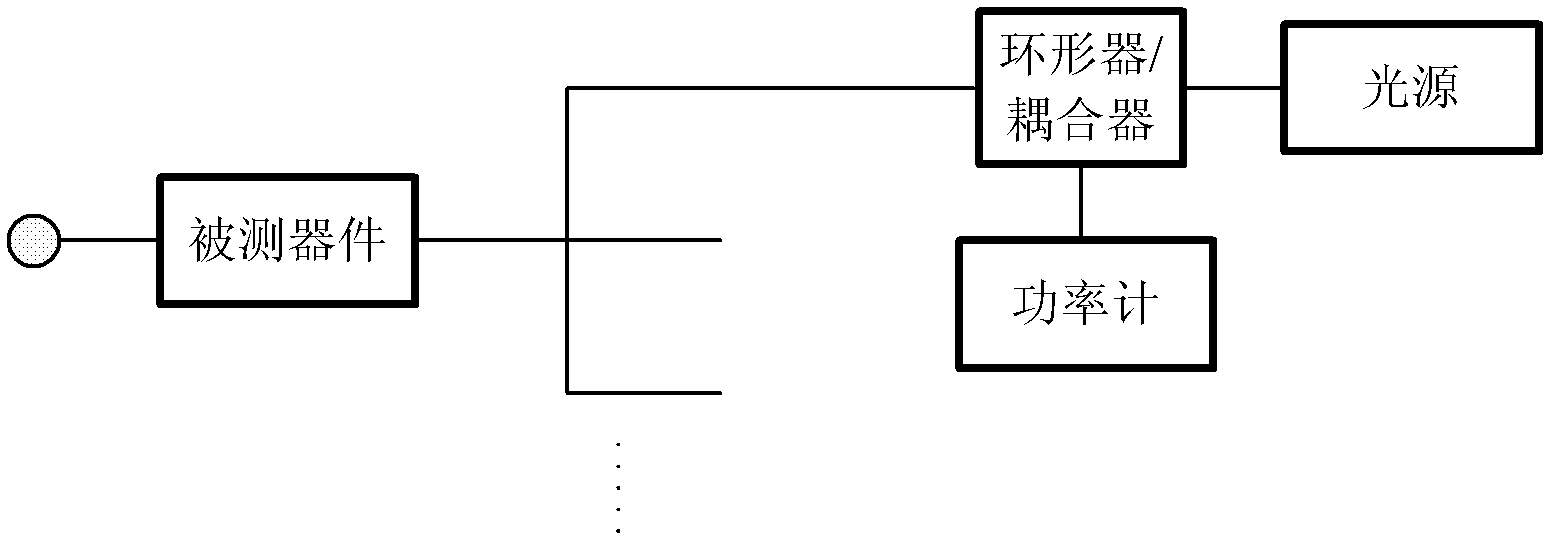
Accuracy automated optical time domain reflectometry optical return loss measurements using a "Smart" Test Fiber Module
InactiveUS7016024B2Eliminate conditionSuitable signal-to-noise ratioMaterial analysis by optical meansReflectometers detecting back-scattered light in time-domainFiberTime domain
The invention provides automated systems and methods for measuring ORL of fibers under test. A computer-based test instrument using OTDR tests fibers with the help of a STFM having predefined characteristics that are recorded in a machine-readable memory. The information recorded in the memory is accessible to the computer-based instrument and is used to calibrate a power level of an illumination source in real time using the reflectance response of the STFM. The calibrated illumination power allows the instrument to automatically determine the ORL of the fiber being tested with precision, and without requiring the intervention of an operator. The instrument also has the capability to automatically sense the presence of a test fiber, and to automatically attenuate the reflectance signal to remove a saturation condition by controlling at least one of the illumination, the detector gain, an amplifier gain, and an optional in-line optical attenuator.
Owner:NETTEST NEW YORK
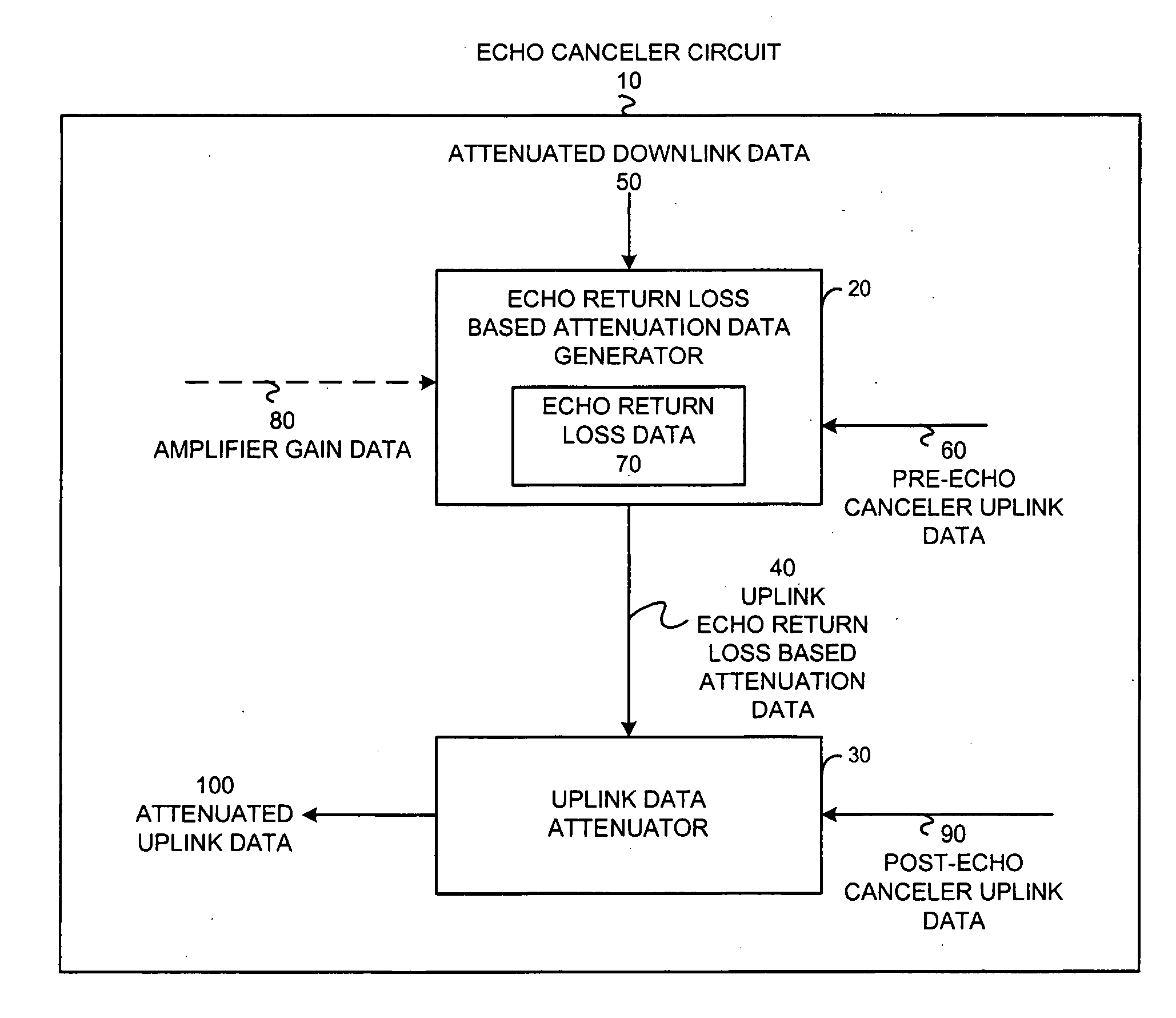
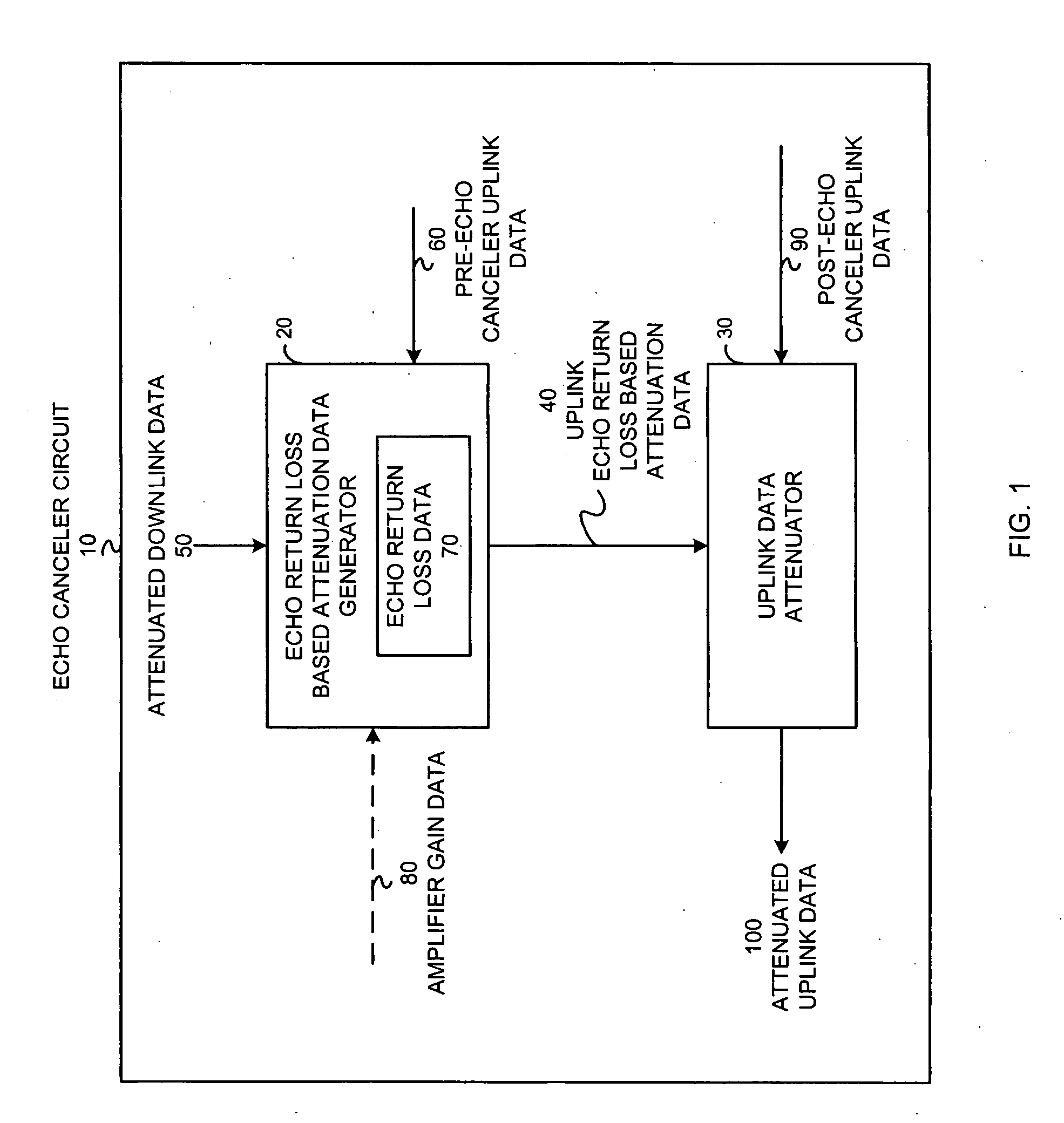
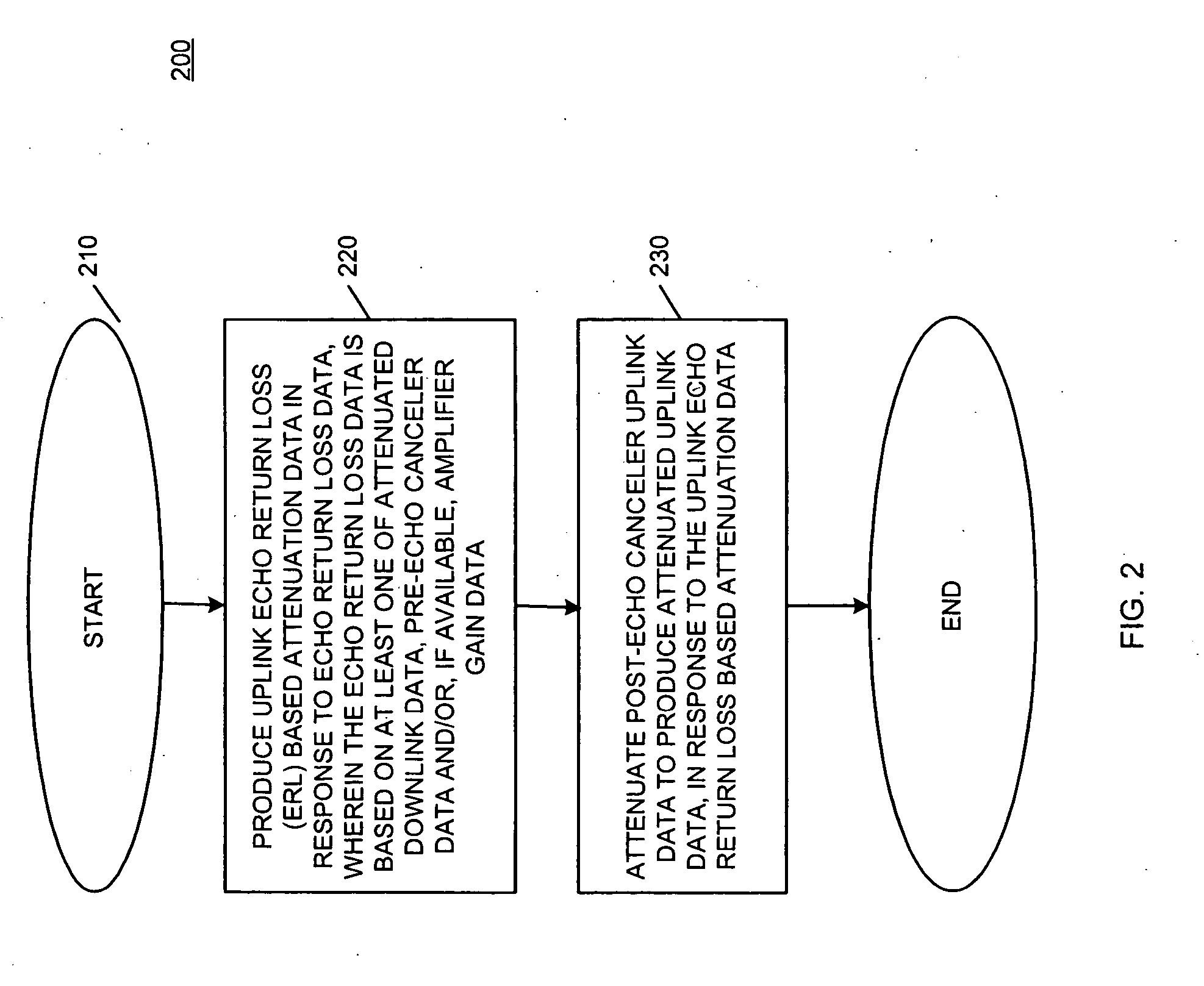
Echo canceler circuit and method
ActiveUS20050129224A1Two-way loud-speaking telephone systemsLine-transmissionUltrasound attenuationAudio power amplifier
An echo canceler circuit (10) and method attenuates at least post-echo canceler uplink data (90) to produce attenuated uplink data (100) in response to uplink echo return loss based attenuation data (40). The echo canceler circuit (10) includes an echo return loss based attenuation data generator (20) and at least an uplink data attenuator (30). The echo return loss based attenuation data generator (20) produces the uplink echo return loss based attenuation data (40) in response to echo return loss data (70). The echo return loss data (70) is based on at least one of: attenuated downlink data (50), pre-echo canceler uplink data (60), and / or amplifier gain data (80). The uplink data attenuator (30) attenuates the post-echo canceler uplink data (90) to produce attenuated uplink data (100) based on the uplink echo return loss based attenuation data (40).
Owner:CONTINENTAL AUTOMOTIVE SYST INC
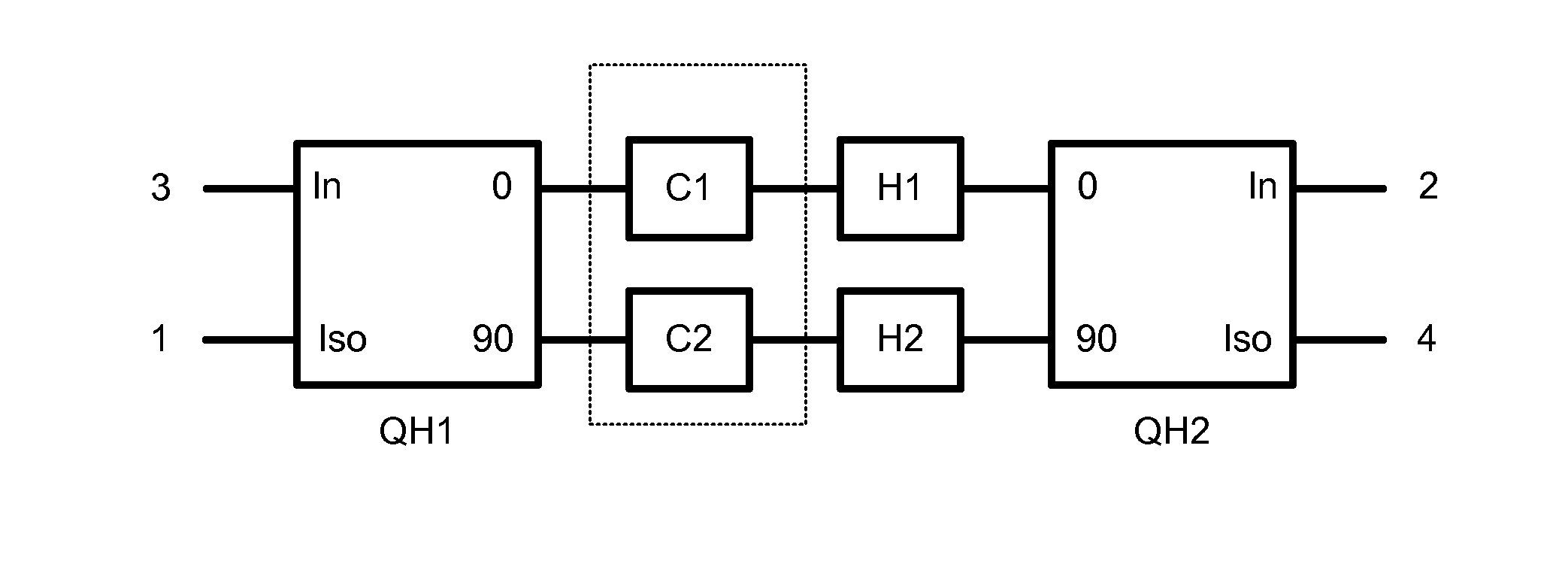
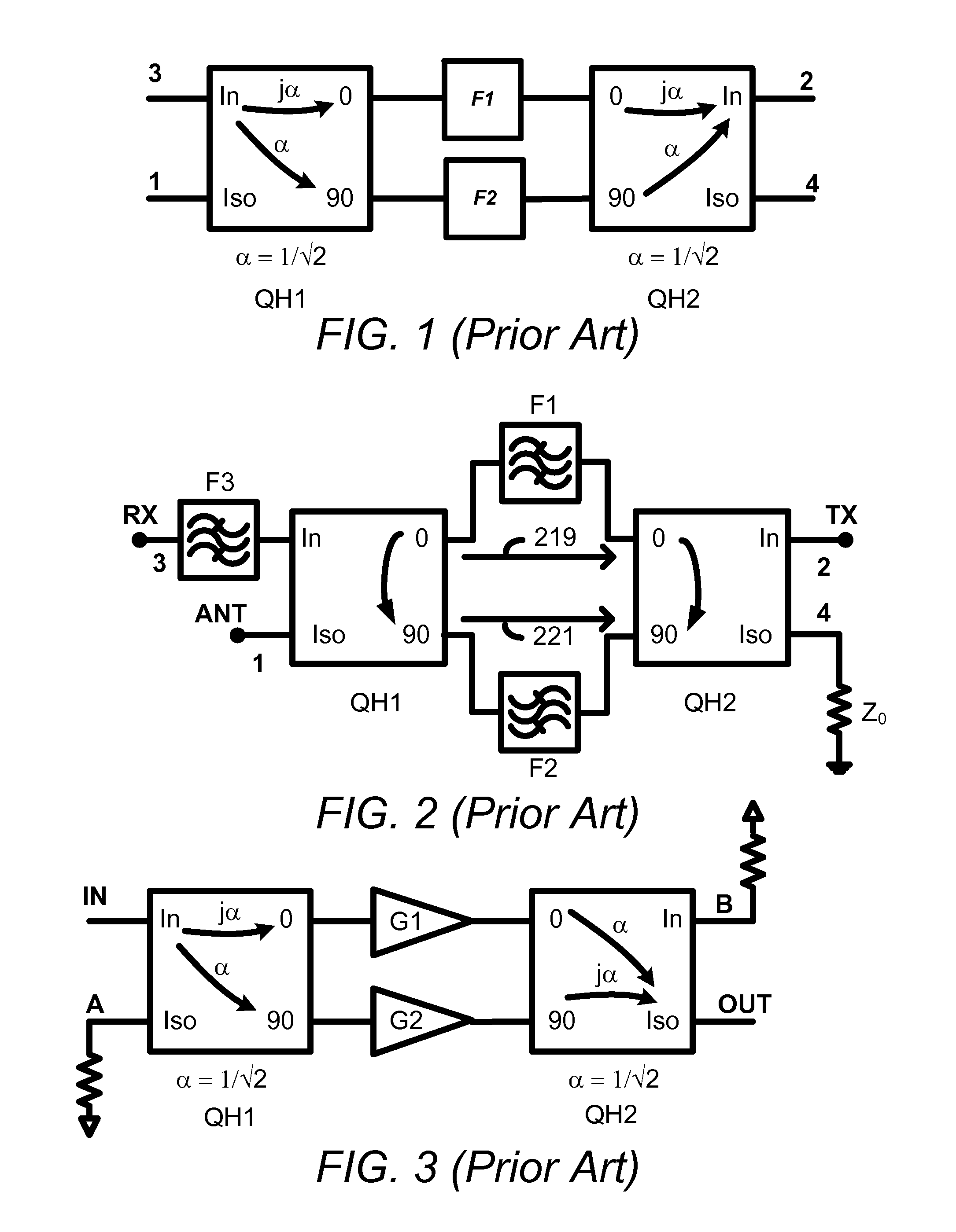
Enhancing Isolation and Impedance Matching in Hybrid-Based Cancellation Networks and Duplexers
ActiveUS20150163044A1Reduces and minimizes signal return lossIncrease and maximizes signal isolationFrequency-division multiplex detailsPower amplifiersCommunications systemAudio power amplifier
Multi-port hybrid-based cancellation networks may be used to enable simultaneous transmit and receive in one or more co-existent communication systems. A multi-port hybrid-based cancellation network may include a first and second quadrature hybrid, a first and second two-port network, and other circuitry components. The second quadrature hybrid may be distinct from the first quadrature hybrid. The first two-port network may include a first filter or a first amplifier connected between the first and the second quadrature hybrids. The second two-port network may include a second filter or a second amplifier that is distinct from but essentially the same as the first filter or the first amplifier connected between the first and the second quadrature hybrids. The other circuitry components may be connected between or connected to a connection between one of the quadrature hybrids and one of the two-port networks. These other circuitry components may have a configuration that minimizes signal return loss at least one of the ports of the multi-port hybrid-based cancellation network. They may in addition or instead have a configuration that maximizes signal isolation between at least two of the ports of the multi-port hybrid-based cancellation network.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
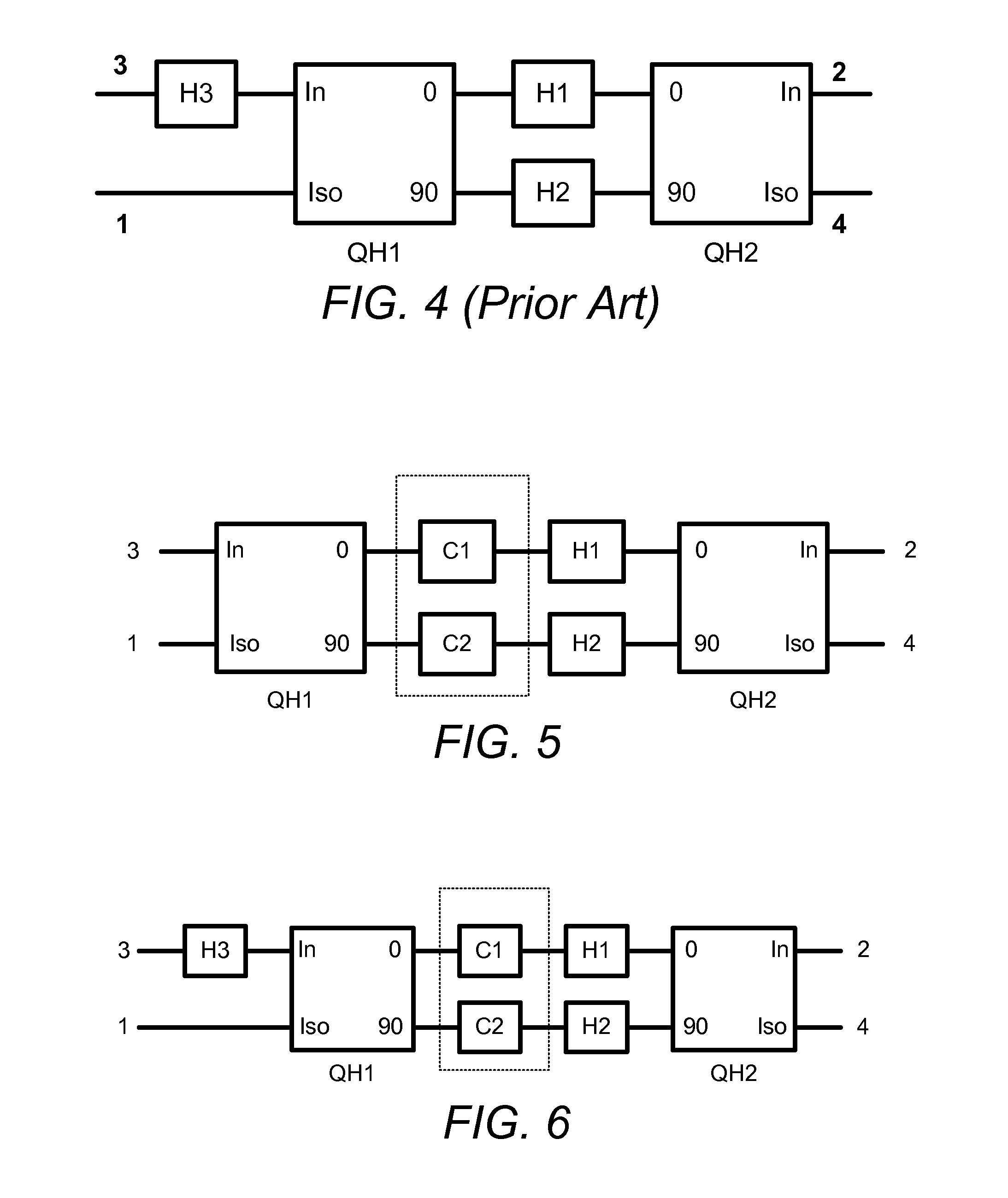
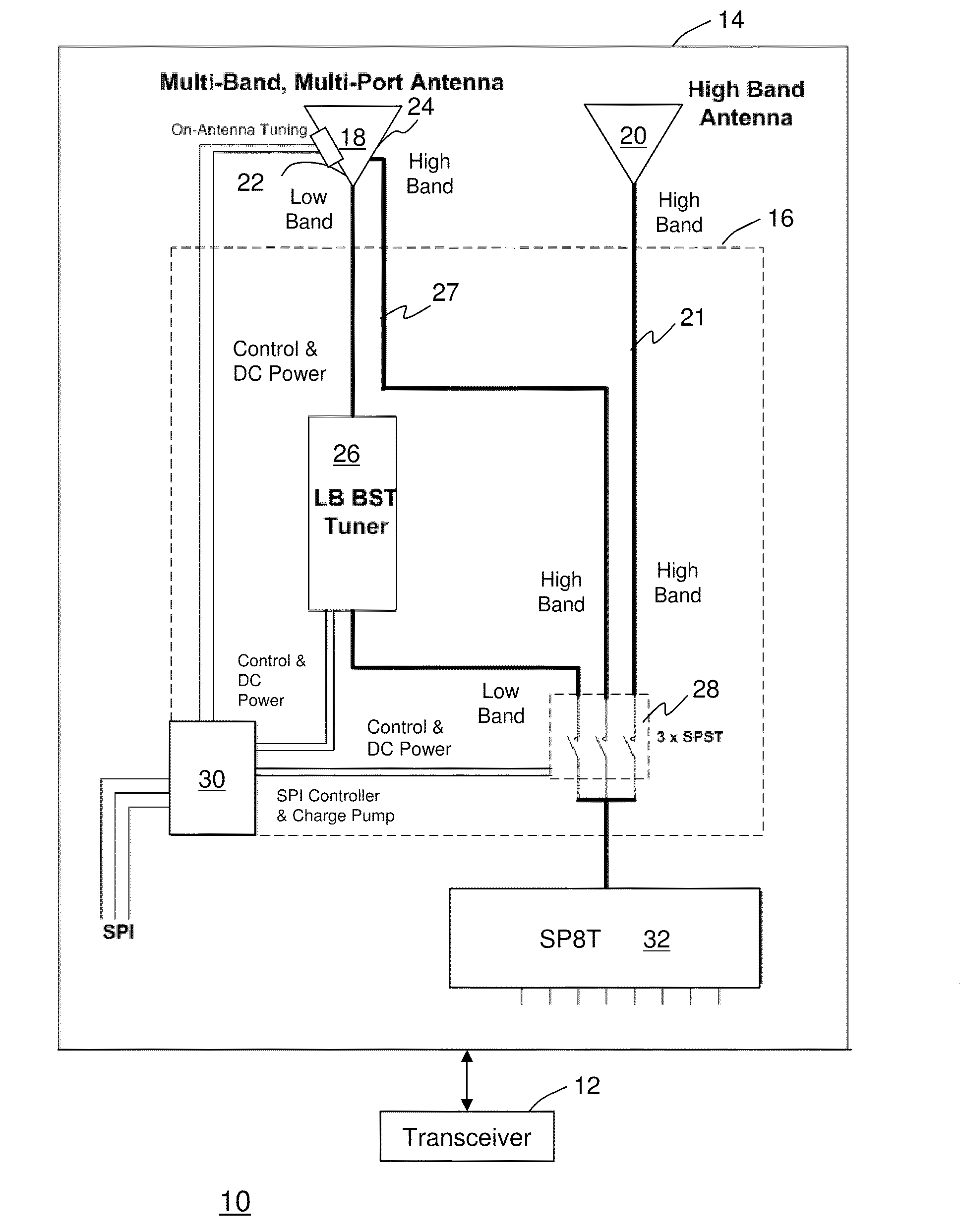
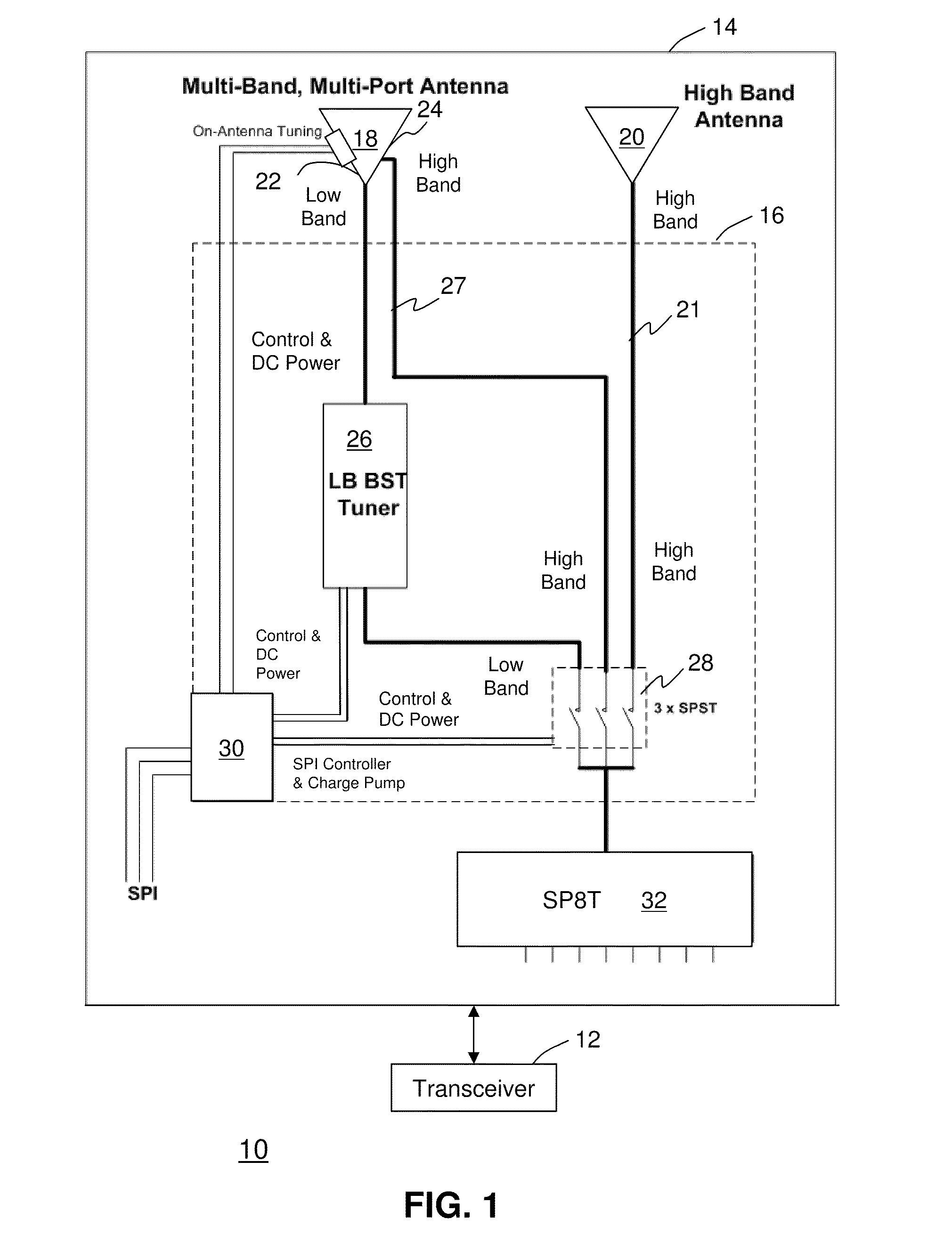
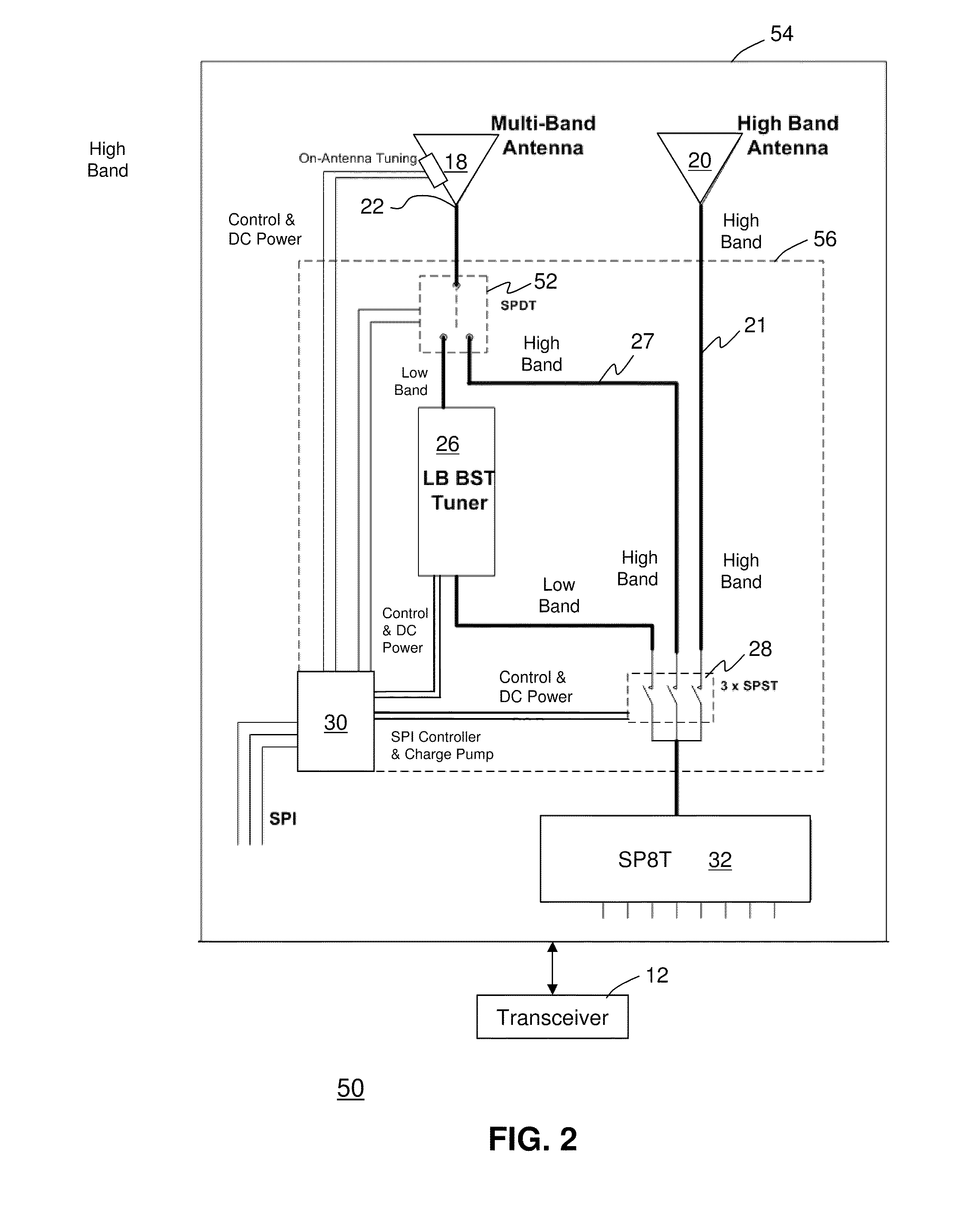
Antenna arrangement for multimode communication device
InactiveUS20110012792A1Simultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsEngineeringReturn loss
A multimode communication device (10 or 50) having an antenna arrangement (14 or 54) having a first antenna (18) operational in both low bands and high bands, a second antenna (20) operational in high bands, a tuner (26) coupled to the first antenna adapted to adjust matching elements to modify return loss to lower reflected power, a switching mechanism (28) for selecting between the first antenna and the second antenna, and a controller (30) coupled to the switching mechanism and the tuner.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
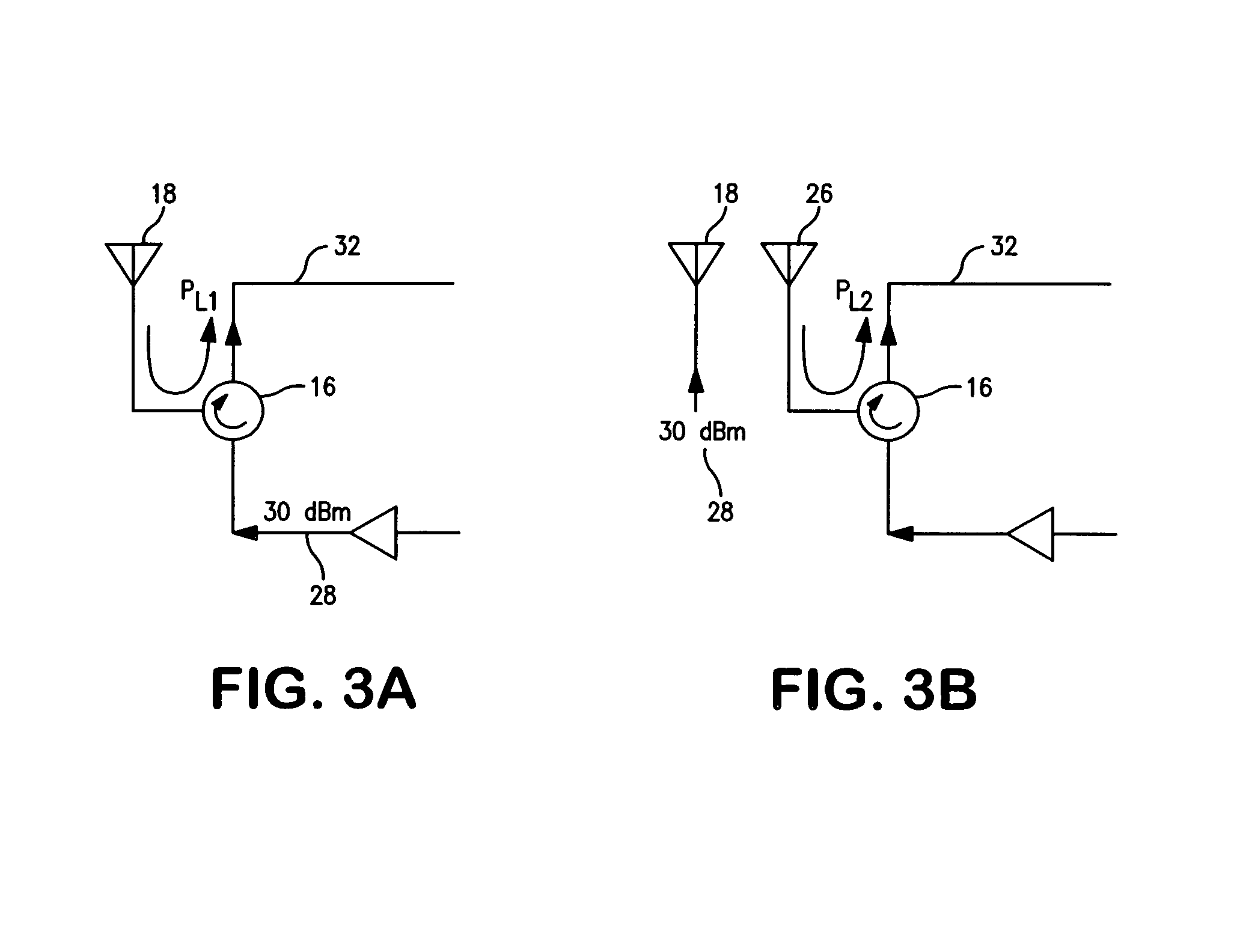
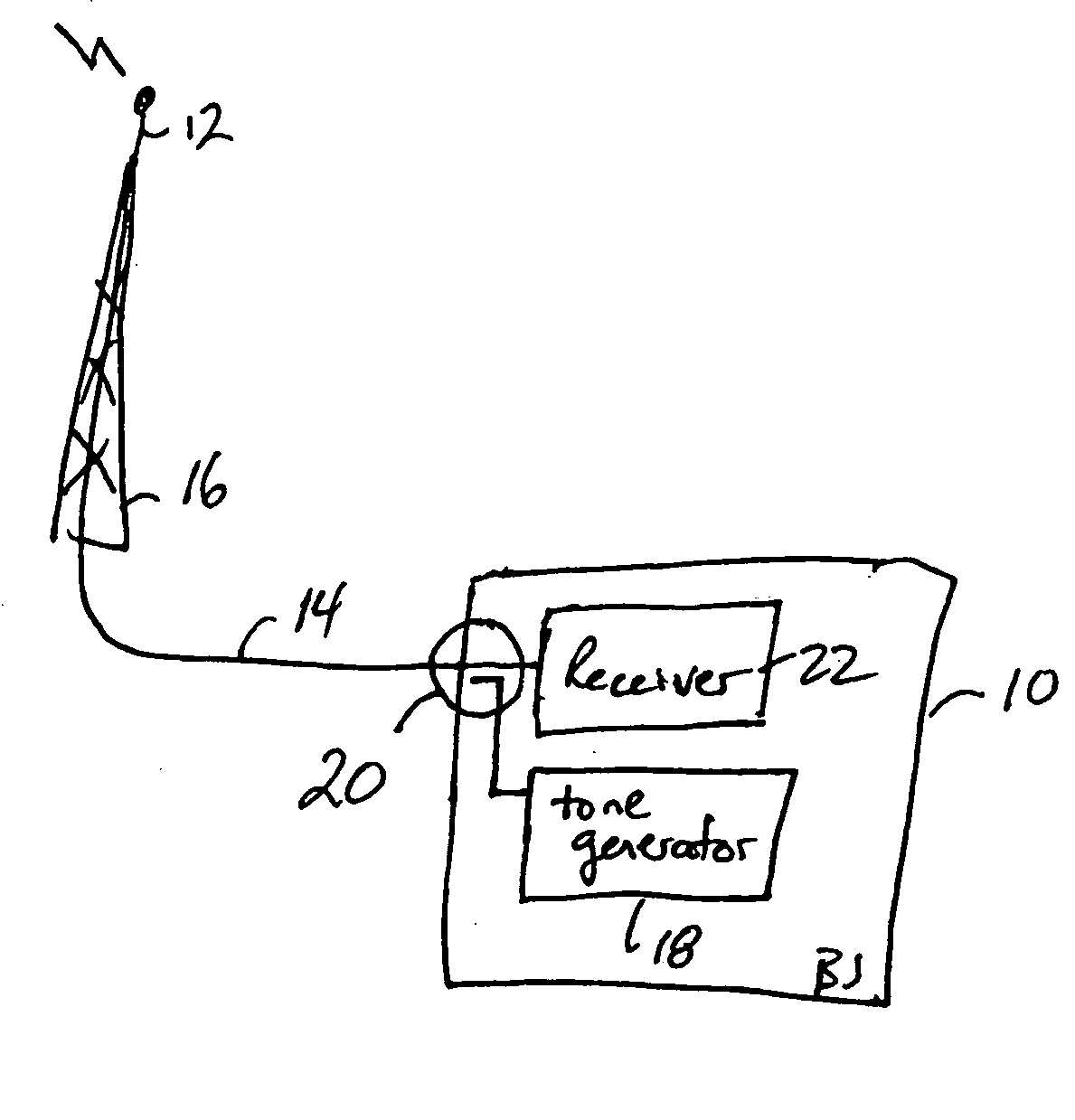
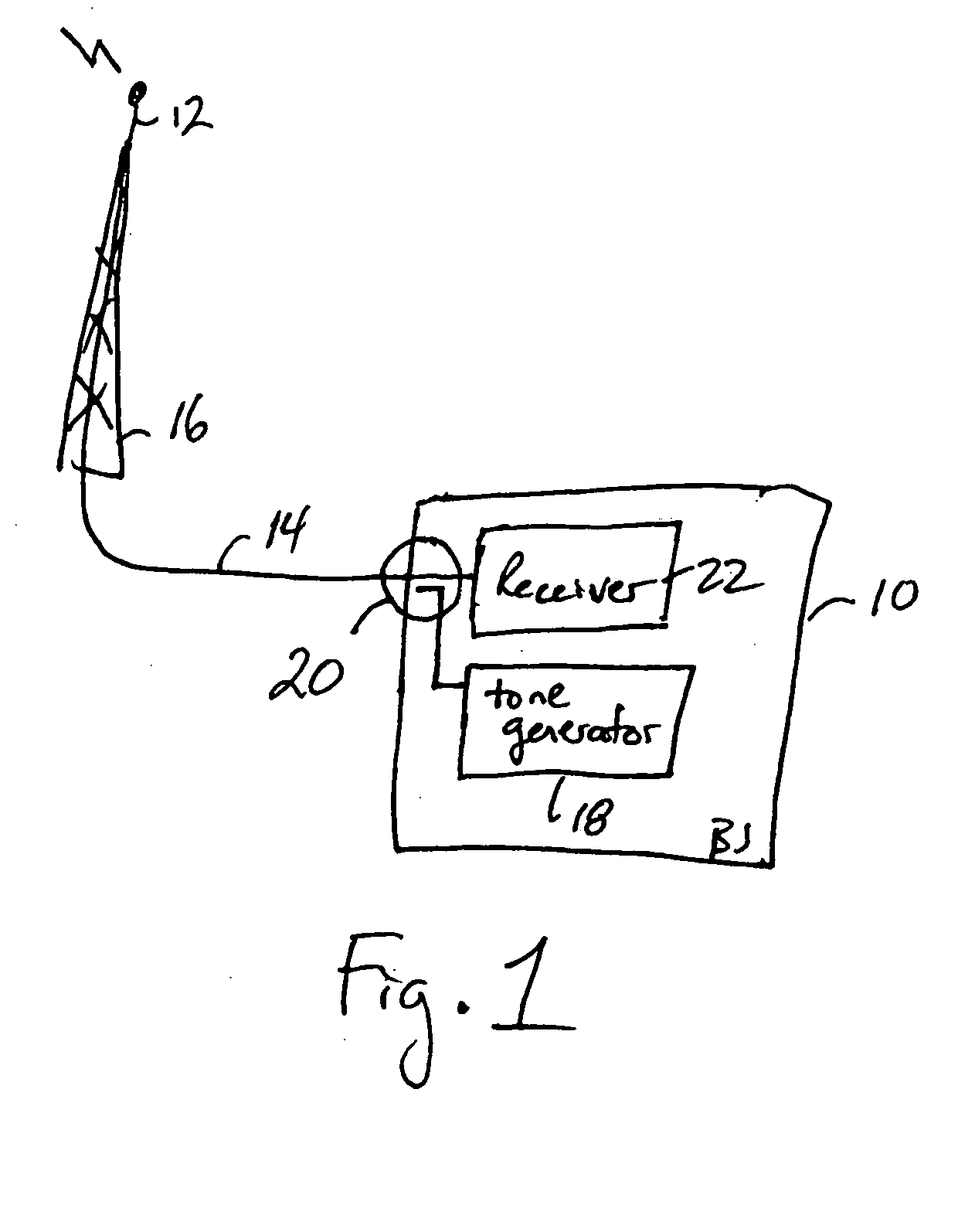
Method and apparatus for determining at least an indication of return loss of an antenna
InactiveUS20050181732A1Avoid loss of revenueAccurately determinePolarisation/directional diversityTransmission monitoringEngineeringReturn loss
A tone generator generates a test signal that a coupler injects into a cable towards an antenna. A receiver or other communication equipment, connected to the antenna via the cable, measures, across a frequency band, at least powers of a signal received at a base station from the antenna. The received signal includes a leakage signal and a reflected signal where the reflected signal is a reflected portion of the test signal and the leakage signal is a portion of the test signal leaking from the coupler away from the antenna. The communication equipment determines maximum and minimum powers of the received signal based on the measurements, and determines at least an indication of return loss of the antenna based on the determined maximum and minimum powers.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Wireless device including a multiband antenna system
ActiveUS20100109955A1Lower the volumeImprove performanceSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsGround planeImpedance matching
A wireless handheld or portable device includes an antenna system operative in a first frequency region and a higher, second frequency region that includes an antenna structure, a matching and tuning system, and an external input / output port. The antenna structure includes at least one radiating element including a connection point, a ground plane layer including at least one connection point, and at least one internal input / output port. At least one radiating element of the antenna structure protrudes beyond the ground plane layer. The antenna structure features at any of its at least one internal input / output ports when disconnected from the matching and tuning system an input return loss curve having a minimum at a frequency outside the first frequency region of operation of the antenna system. The matching and tuning system provides impedance matching to the antenna system in the first and second regions of operation of the antenna system.
Owner:IGNION SL
Reflector antenna with injection molded feed assembly
InactiveUS20050017916A1Improve wind loading characteristicMinimal degradationAntenna couplingsEngineeringInjection moulding
A reflector antenna with a self supported feed assembly that may be formed by injection molding. A waveguide portion of the feed assembly has a dielectric cone at a distal end that supports and retains a sub reflector, for example along a periphery of the sub reflector. A conductive surface coating on an internal surface of the waveguide and a bottom surface of the sub reflector creates surfaces with RF reflective and conductive properties. The return loss of the feed assembly is reduced due to a reduction of the thickness of the material forming the dielectric cone, compared to prior dielectric block designs and a soft boundary condition produced by dielectric coating of the waveguide which aids in reducing reflections to the vertex area of the reflector.
Owner:COMMSCOPE TECH LLC
Antenna System Monitor
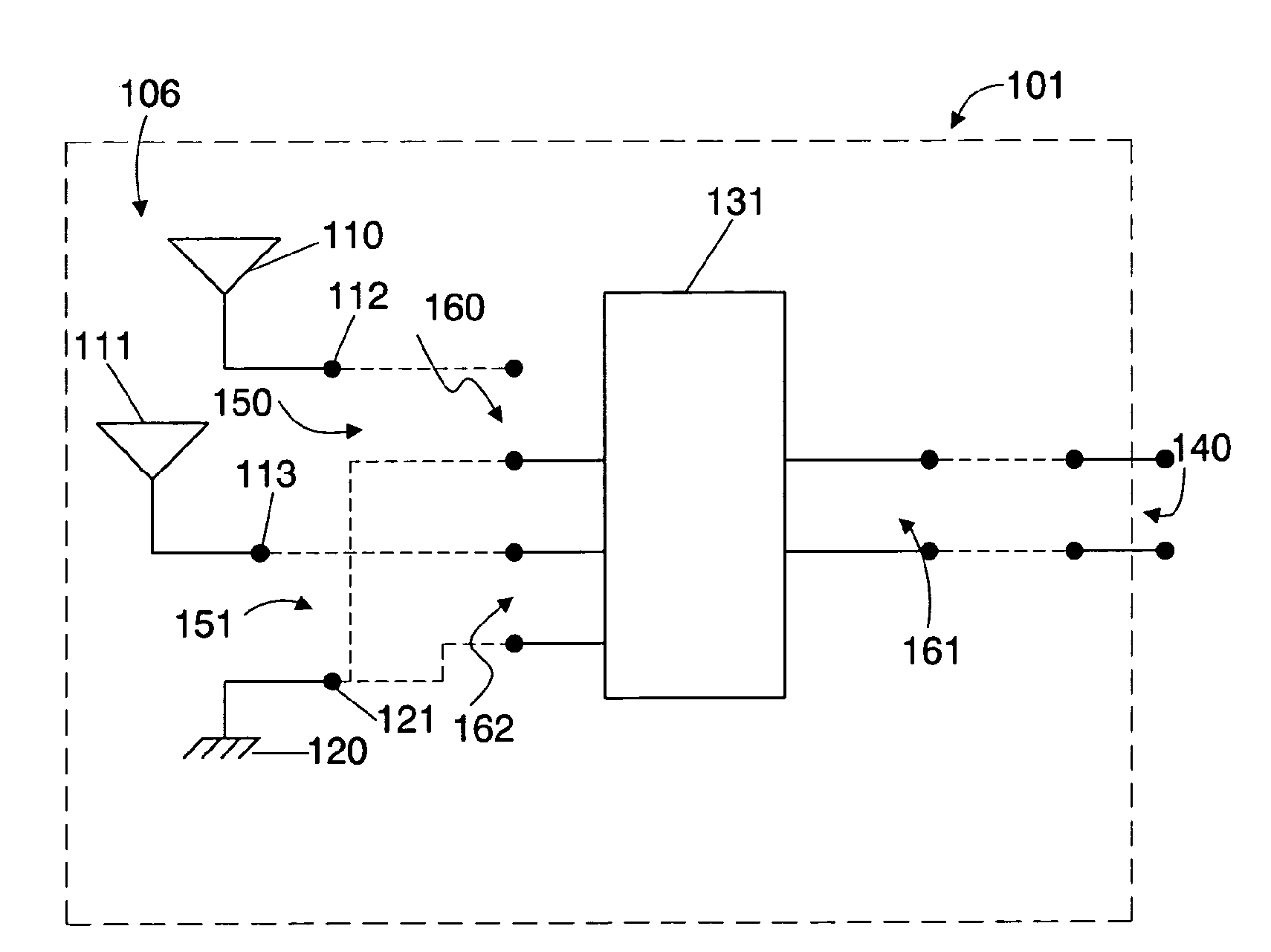
A system is disclosed for monitoring of individual frequency channels in an RF signal band by configuration of the electronic processor to operate the tunable filter to select desired channel sub bands. Measurement of forward and / or reverse-propagating fields within the selected sub-bands may be performed and corresponding power levels recorded. The records may be used to provide monitoring signals, such as measures of forward and reflected power, as well as VSWR, return loss. Indications or alarms may be activated if any of these quantities, associated with any one or more channels, falls outside a predetermined acceptable operating range.
Owner:RF IND
Accuracy automated optical time domain reflectometry optical return loss measurements using a "Smart" Test Fiber Module
InactiveUS20050259242A1Eliminate conditionSuitable signal-to-noise ratioMaterial analysis by optical meansReflectometers detecting back-scattered light in time-domainFiberTime domain
The invention provides automated systems and methods for measuring ORL of fibers under test. A computer-based test instrument using OTDR tests fibers with the help of a STFM having predefined characteristics that are recorded in a machine-readable memory. The information recorded in the memory is accessible to the computer-based instrument and is used to calibrate a power level of an illumination source in real time using the reflectance response of the STFM. The calibrated illumination power allows the instrument to automatically determine the ORL of the fiber being tested with precision, and without requiring the intervention of an operator. The instrument also has the capability to automatically sense the presence of a test fiber, and to automatically attenuate the reflectance signal to remove a saturation condition by controlling at least one of the illumination, the detector gain, an amplifier gain, and an optional in-line optical attenuator.
Owner:NETTEST NEW YORK
Reflection suppression for an optical fiber
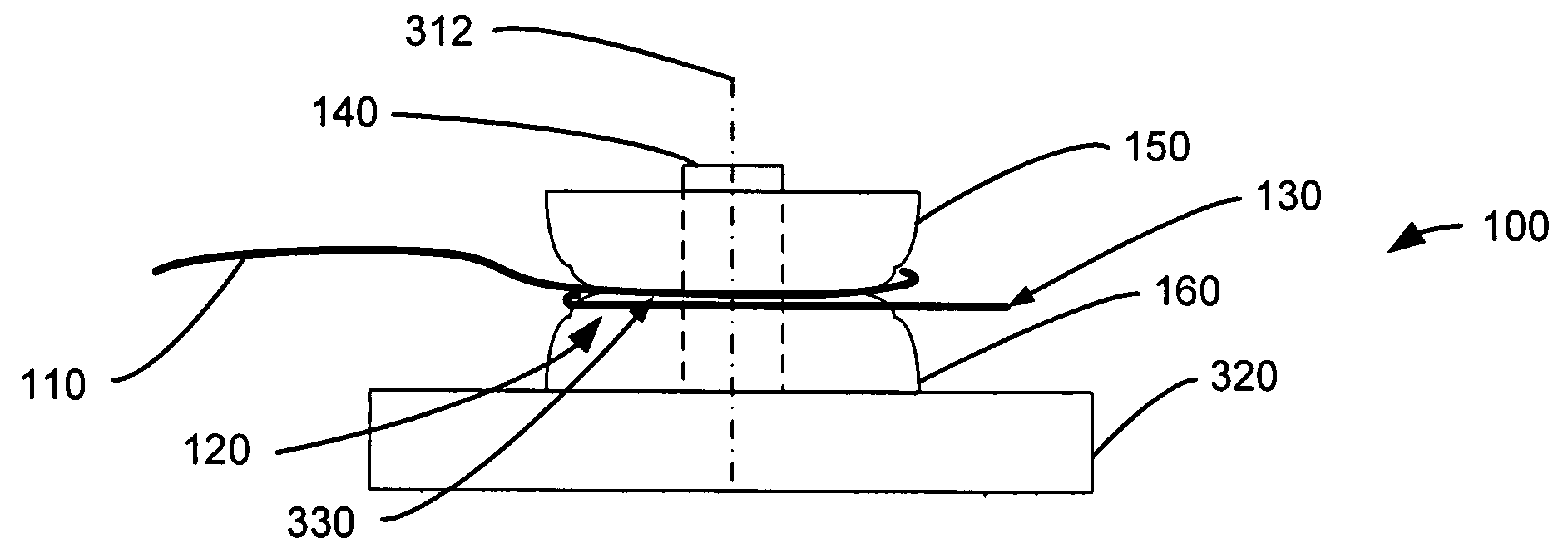
ActiveUS20050053350A1Suppresses internal reflectionSuppresses back reflectionCoupling light guidesFibre mechanical structuresEngineeringReturn loss
Forming a plurality of loops in an optical fiber around a spool adjacent to an exposed end face can suppress internal reflections from the exposed end face. The radius of the loops can attenuate light that is propagating to and from the end face by causing light to leak out of the optical fiber's core and into its cladding. The radius can be selected to control physical stress in the optical fiber and promote reliability. The radius and the number of loops can be selected to meet a return loss specification. The loops can be formed by coiling the optical fiber around a spool that includes a slot for holding the optical fiber until it is put into service.
Owner:ARRIS SOLUTIONS
Loss testing apparatus for multi-channel optical device
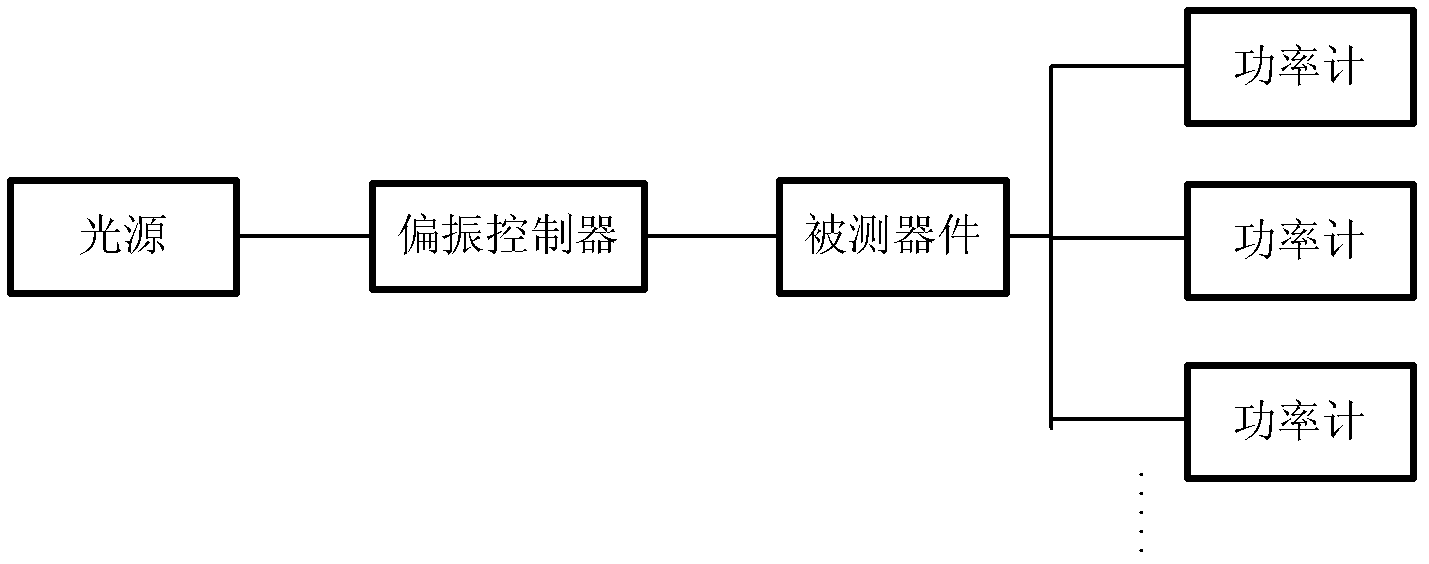
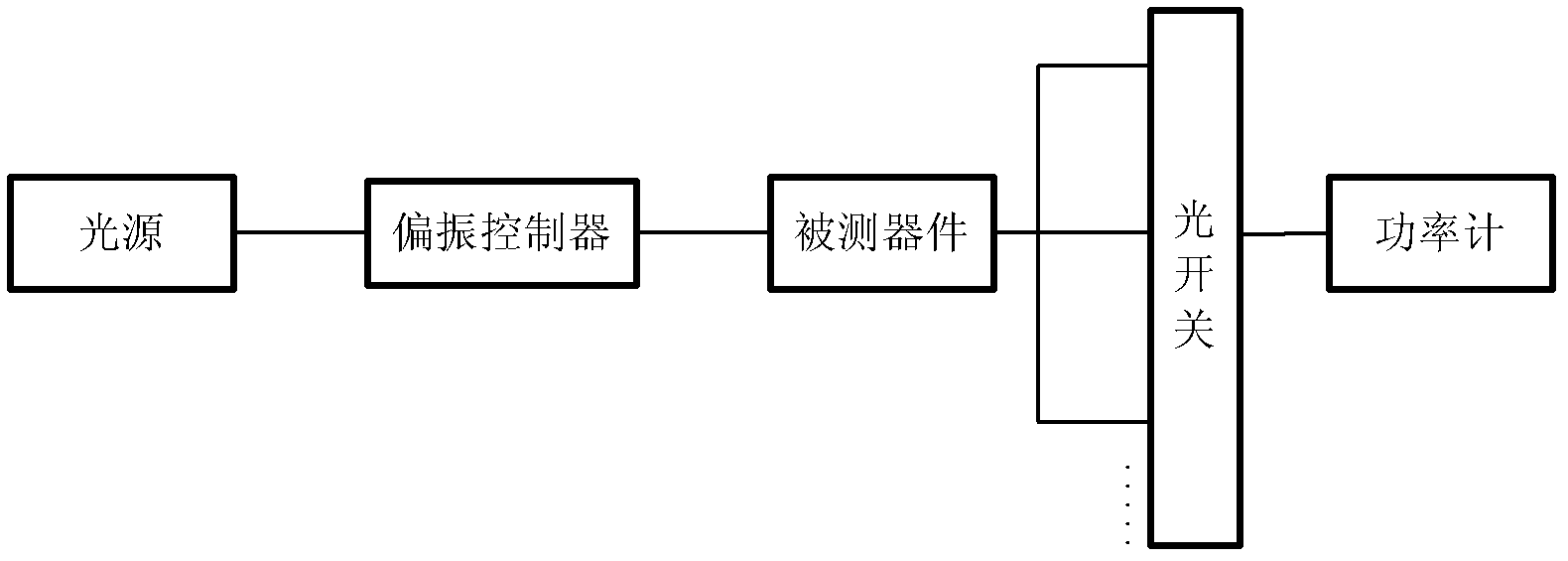
ActiveCN102201864AImprove test efficiencyAvoid unpluggingTransmission monitoring/testing/fault-measurement systemsTest efficiencyOptical power
The invention discloses a loss testing apparatus for a multi-channel optical device, which comprises an optical source module used for supplying laser of various wavelengths and stable power, an optical amplifying module used for amplifying an optical source for a return loss test and equally dividing the optical source into a plurality of channels, an optical power detecting module used for measuring the optical power and the return loss of an output end of the optical device to be measured, a polarization controller used for changing the polarization state of an input optical source, an optical source monitoring module used for detecting the stability of the optical source and testing the return loss of a public end of the device, an optical switch used for selecting one output in the laser of various wavelengths, a single chip computer and a communication module used for controlling a switching channel of the optical switch, wherein the polarization controller is used for changing the polarization state of the laser, receiving the data measured by the optical power detecting module and the optical source monitoring module and processing the data. By adopting the loss testing apparatus provided by the invention, the testing efficiency of various indexes for the multi-channel optical device can be increased to large extent.
Owner:GUANGXUN SCI & TECH WUHAN
Phase shifter, a phase shifter assembly, feed networks and antennas
A variable differential phase shifter including an isolation element providing good isolation between output ports, good return loss and reduced reflections. In one embodiment a Wilkinson divider is incorporated in the wiper arm of a wiper type variable differential phase shifter. In another embodiment a linear phase shifter incorporates a Wilkinson divider. Multistage embodiments are also disclosed. The variable differential phase shifter may be used in combination with a hybrid coupler to provide an isolated variable power divider. The variable differential phase shifter may be utilized in a variety of feed networks and antenna arrays to vary beam tilt, beam azimuth and beam width. Antennas incorporating the phase shifter exhibit low variation of half power beam width with frequency and reduced side lobes.
Owner:COMMSCOPE TECH LLC
Bidirectional parallel optical transceiver module and a method for bidirectionally communicating optical signals over an optical link
Bidirectional parallel optical transceiver modules for use in optical links and methods for communicating bidirectionally over the links are provided. The bidirectional parallel optical transceiver modules have features that ensure relatively low optical crosstalk, relatively low return loss and relatively high SNR. In addition, the modules have an in-line, zig-zag configuration that allows the modules to be compact and to have high bidirectional channel density for achieving high bandwidth.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Reflector antenna with injection molded feed assembly
InactiveUS6985120B2Improve wind loading characteristicMinimal degradationAntenna couplingsEngineeringInjection moulding
Owner:COMMSCOPE TECH LLC
Miniaturized multi-layer balun
ActiveUS7068122B2Small sizeSimple manufacturing processMultiple-port networksOne-port networksCapacitanceElectrical conductor
A miniaturized multi-layer balun includes a pair of capacitive elements, at least one section of broadside coupled lines connected in series to an unbalanced and two balanced ports through a pair of transmission lines. Each section has first and second coupled lines. A ground connection is located between two central second coupled lines, and connected to a ground. By means of a multi-layer structure and the addition of a ground connection, the balun of the invention can be fabricated with five conductor layers. This not only greatly decreases the size of the balun device, but also enhances the stability of the device. From the measured return loss and differences in magnitude and phase to the frequency response, it shows that the balun of the invention has good impedance match.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Low profile wideband multibeam integrated dual polarization antenna array with compensated mutual coupling
InactiveUS20130181880A1Suppress mutual couplingReduce mutual couplingAntenna arraysSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationElectrical impedanceMulti beam
A low profile wideband multi-beam integrated dual polarization antenna array with compensated mutual coupling effect. Instead of suppressing mutual coupling with post-element-design techniques by attempting to block the reflections between elements, an element of the array is designed using its active impedance, i.e. its impedance with mutual coupling once the element is part of the array. The active impedance is determined using various simulation techniques and the element is then designed such that its impedance is shifted in order to modify its active impedance. This technique does not reduce the mutual coupling itself but instead, compensates for the mutual coupling effect and improves the return loss of the element.
Owner:ULTRA ELECTRONICS TCS
Control method for microwave oven and microwave oven
ActiveCN105276640AImprove cooking resultsAvoid burnsDomestic stoves or rangesLighting and heating apparatusMicrowave ovenEngineering
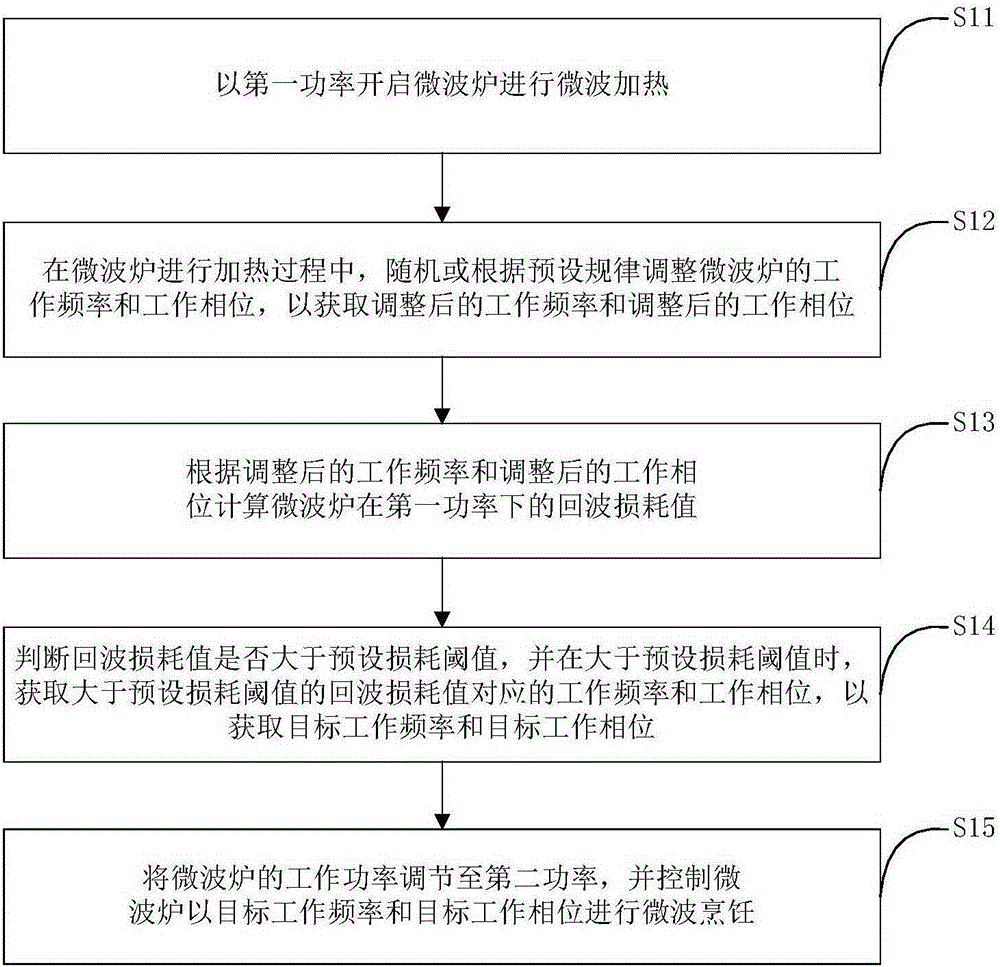
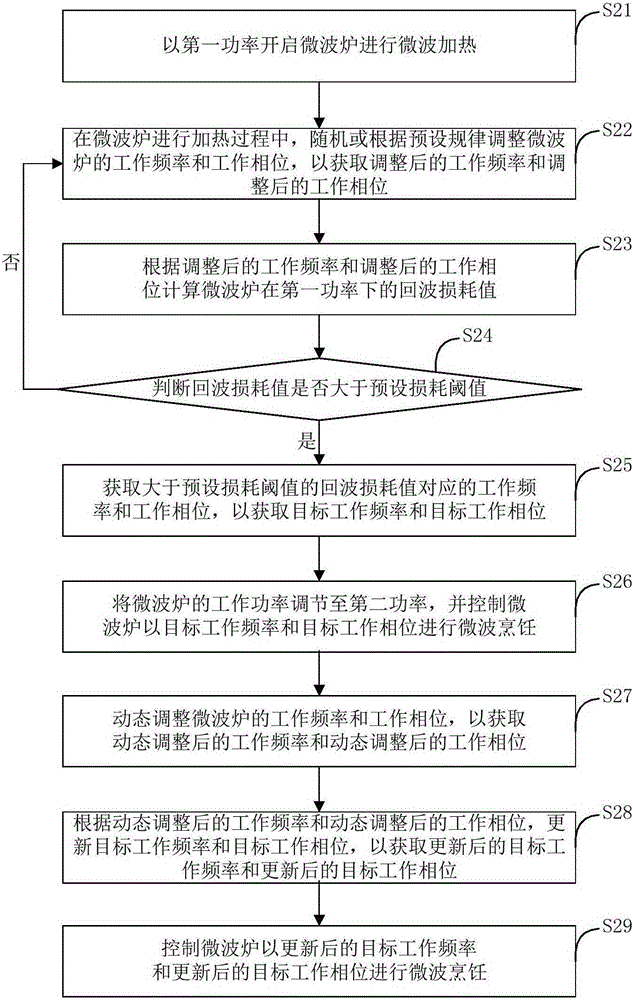
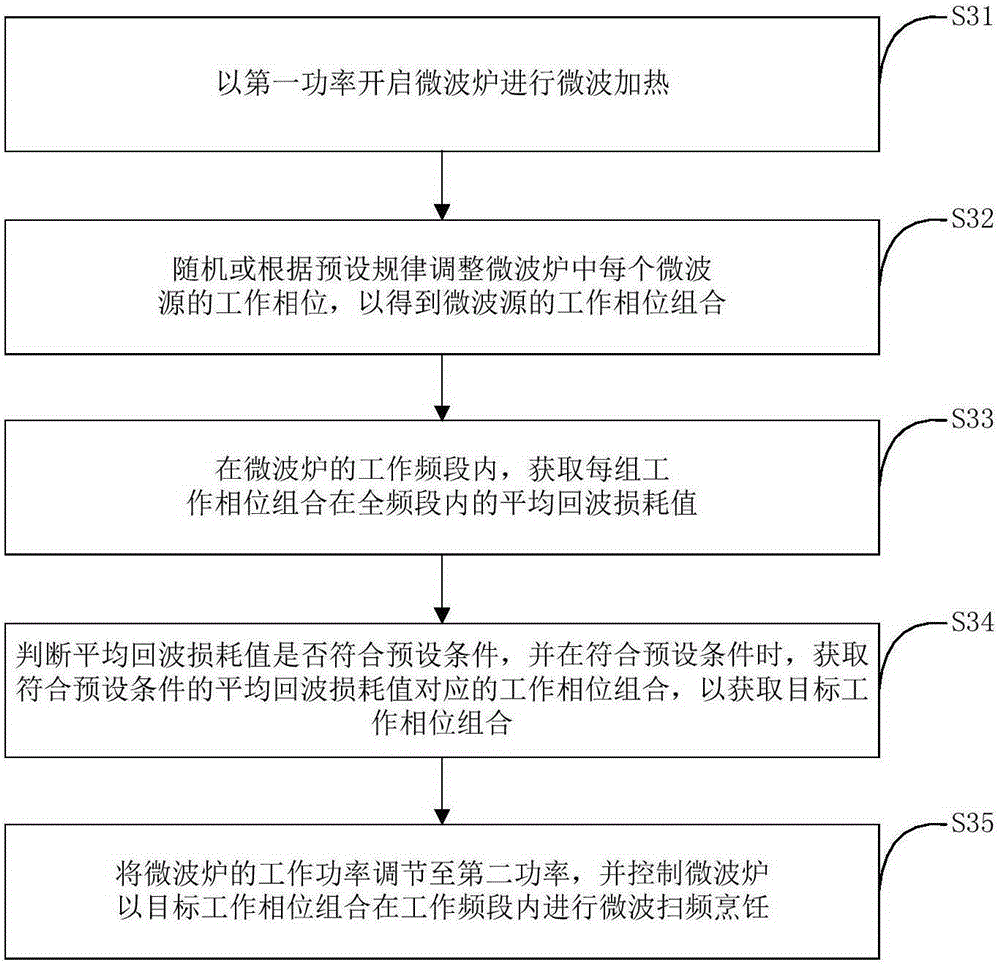
The invention discloses a control method for a microwave oven and the microwave oven. The control method for the microwave oven includes the steps that the microwave oven is started at first power to carry out microwave heating; in the heating process of the microwave oven, the work frequency and the work phase of the microwave oven are adjusted randomly or according to preset rules to obtain the adjusted work frequency and the adjusted work phase; according to the adjusted work frequency and the adjusted work phase, the return loss value of the microwave oven at the first power is calculated; whether the return loss value is larger than a preset loss threshold is judged, and when the return loss value is larger than the preset loss threshold, the work frequency and the work phase which correspond to the return loss value larger than the preset loss threshold are obtained, so that a target work frequency and a target work phase are obtained; and the work power of the microwave oven is adjusted to be second power, and the microwave oven is controlled to carry out microwave cooking at the target work frequency and the target work phase. By means of the control method and the microwave oven, microwave sources can be effectively protected, and the cooking effect of the microwave oven is improved.
Owner:GUANGDONG MIDEA KITCHEN APPLIANCES MFG CO LTD +1
Oscilloscope based return loss analyzer
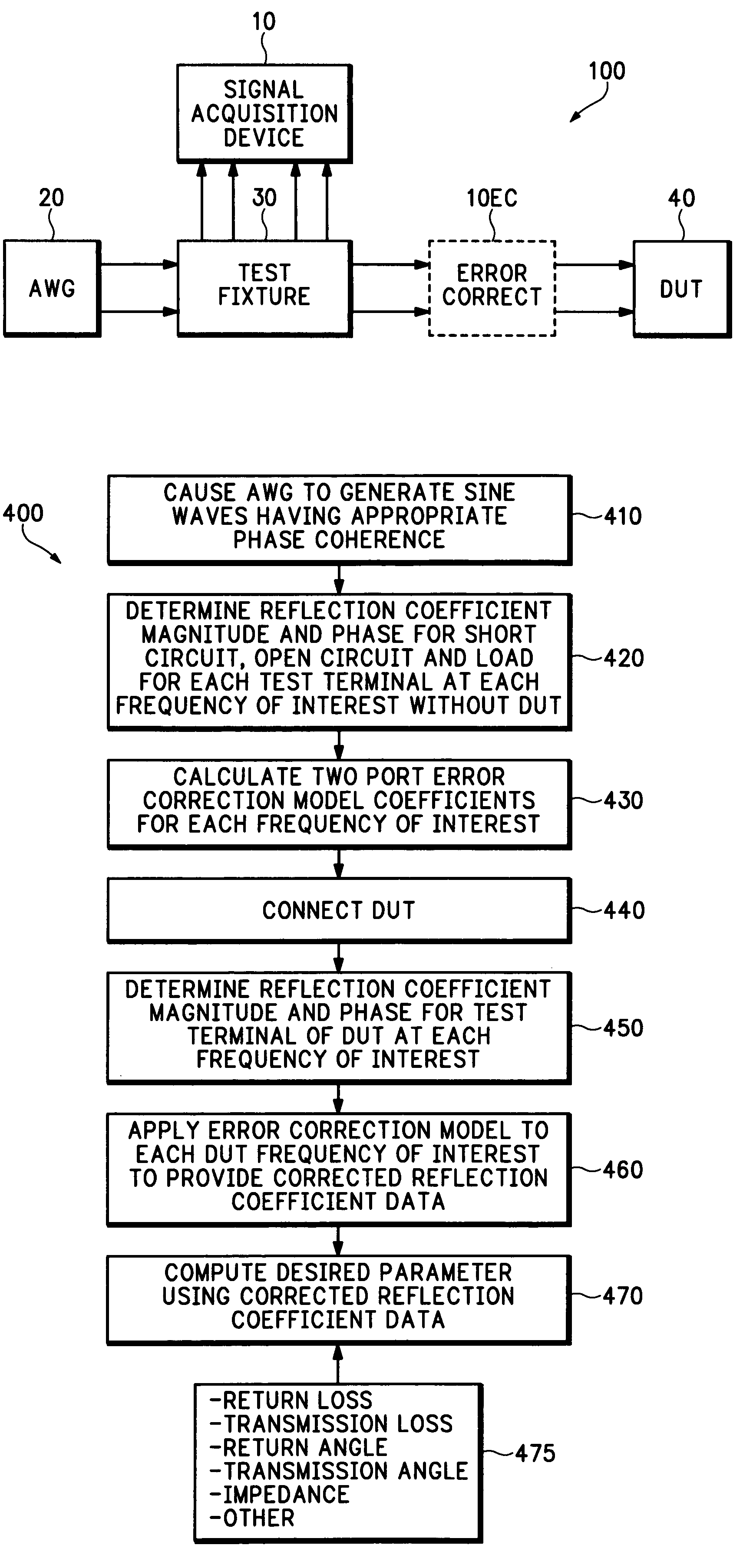
ActiveUS7271575B2Spectral/fourier analysisResistance/reactance/impedenceFrequency spectrumDifferential measurement
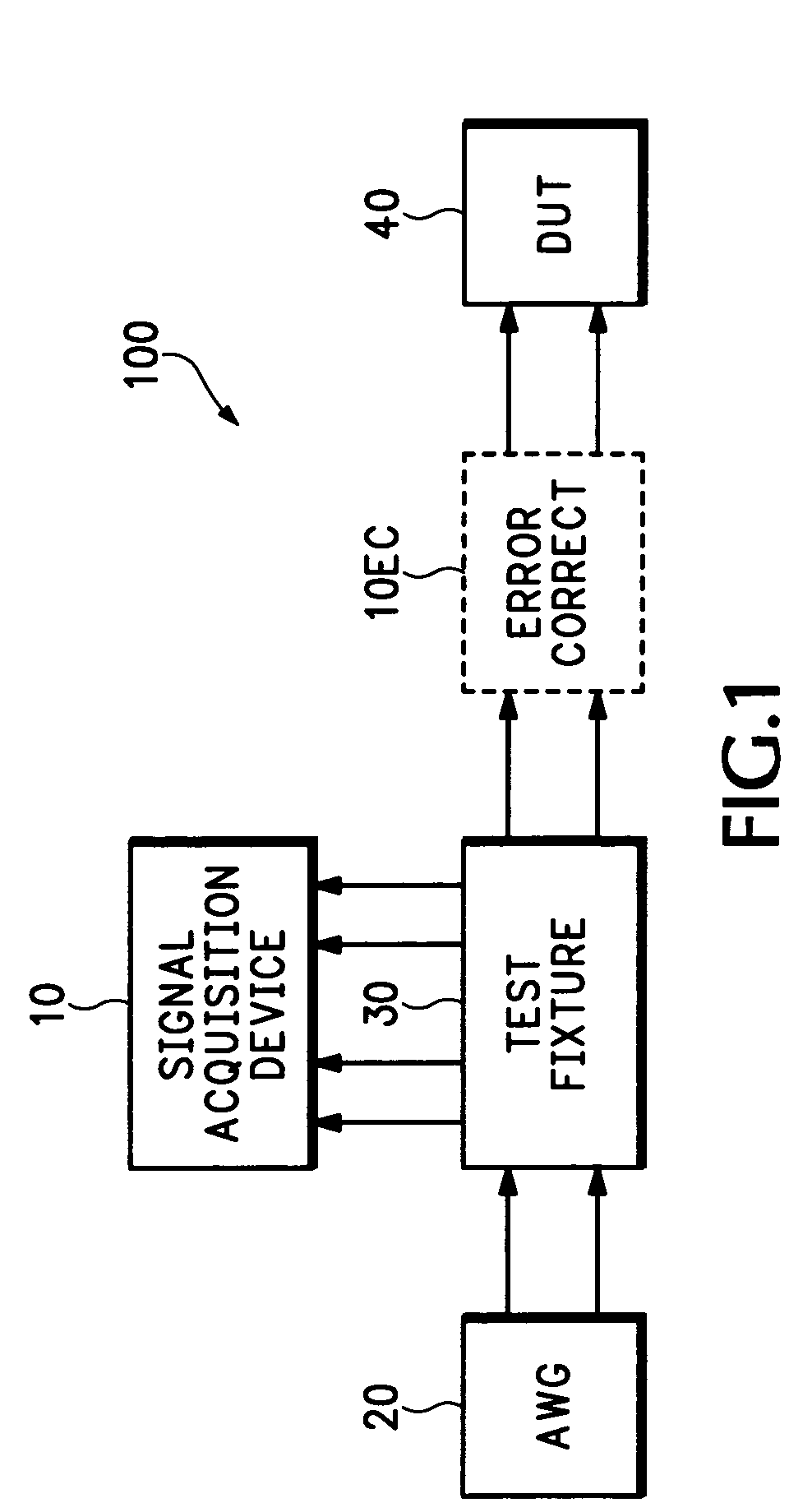
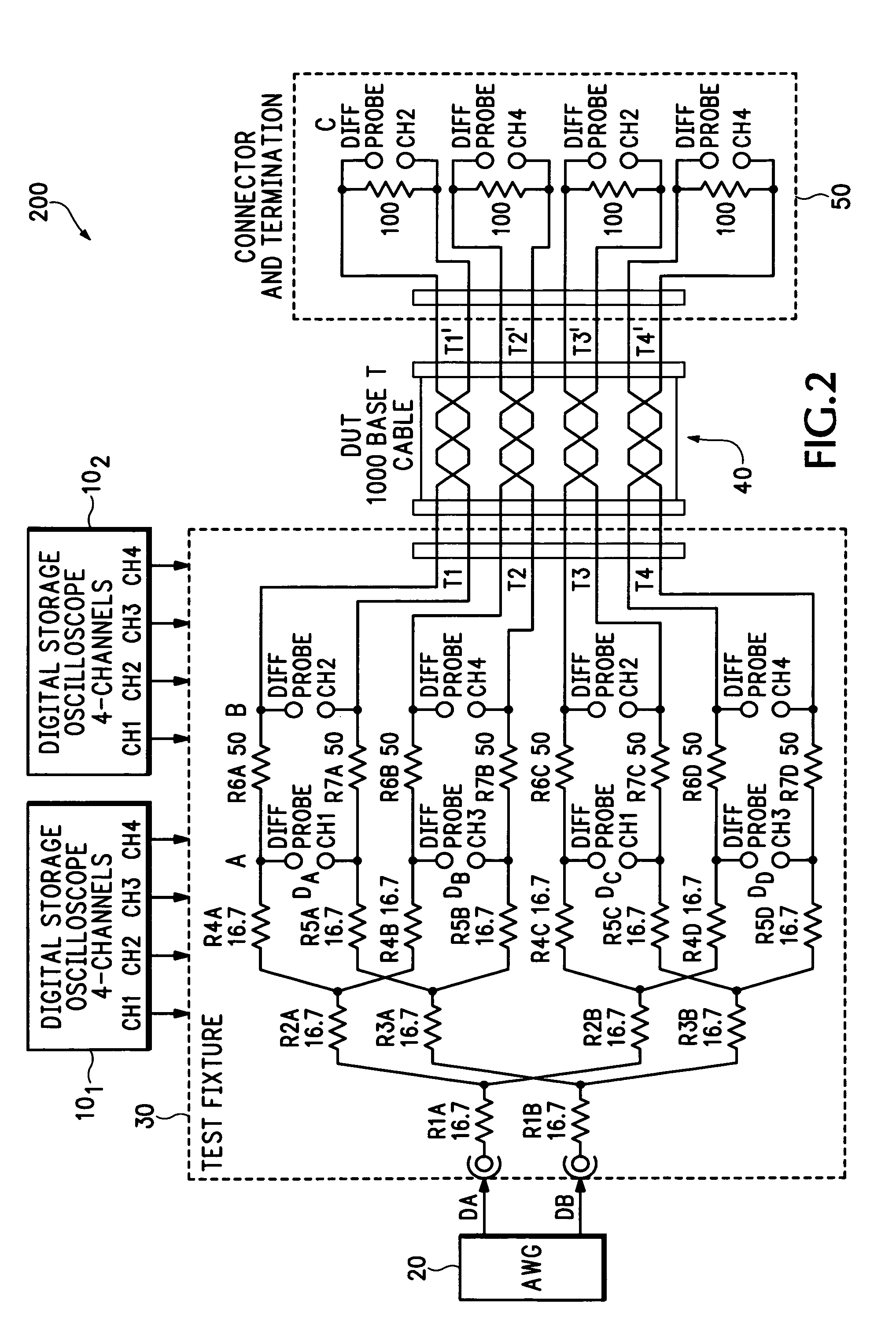
A system, apparatus and method for performing differential return loss measurements and other measurements as a function of frequency uses a digital storage oscilloscope (DSO) having spectral analysis functions. A waveform generator generates a differential test signal in the form of a series of pulses where each pulse includes spectral components associated with each of a plurality of frequencies of interest. A test fixture presents the differential test waveform to a load including at least one of a device under test (DUT), a short circuit, an open circuit and a balanced load. A signal acquisition device differentially measures the test waveform during each of the load conditions. The signal acquisition device computes an error correction parameter using measurements made during the short circuit, open circuit and balanced load conditions. The correction parameter tends to offset signal acquisition errors within measurements made during the DUT load condition.
Owner:TEKTRONIX INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com