Tunable add/drop optical filter
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
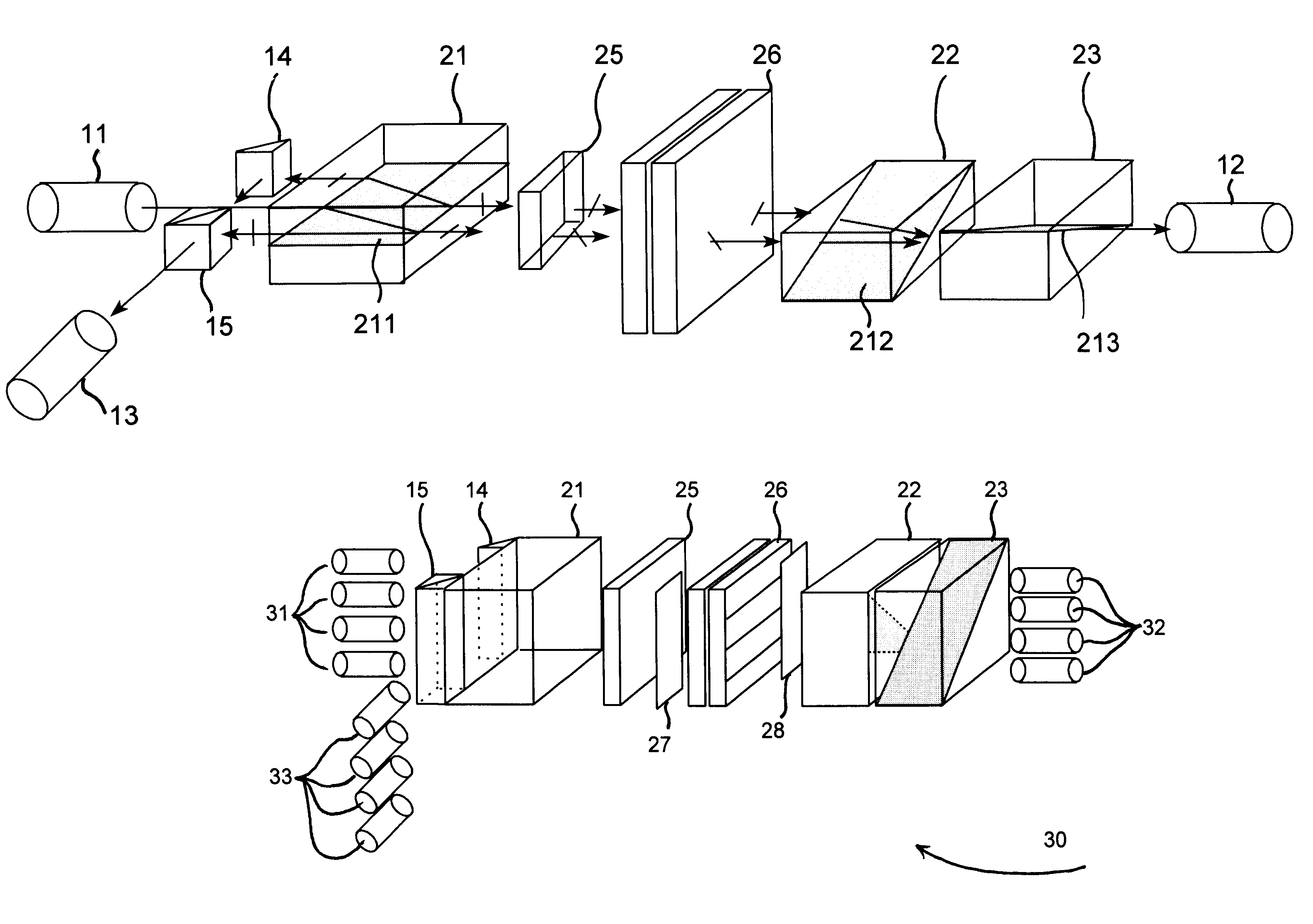
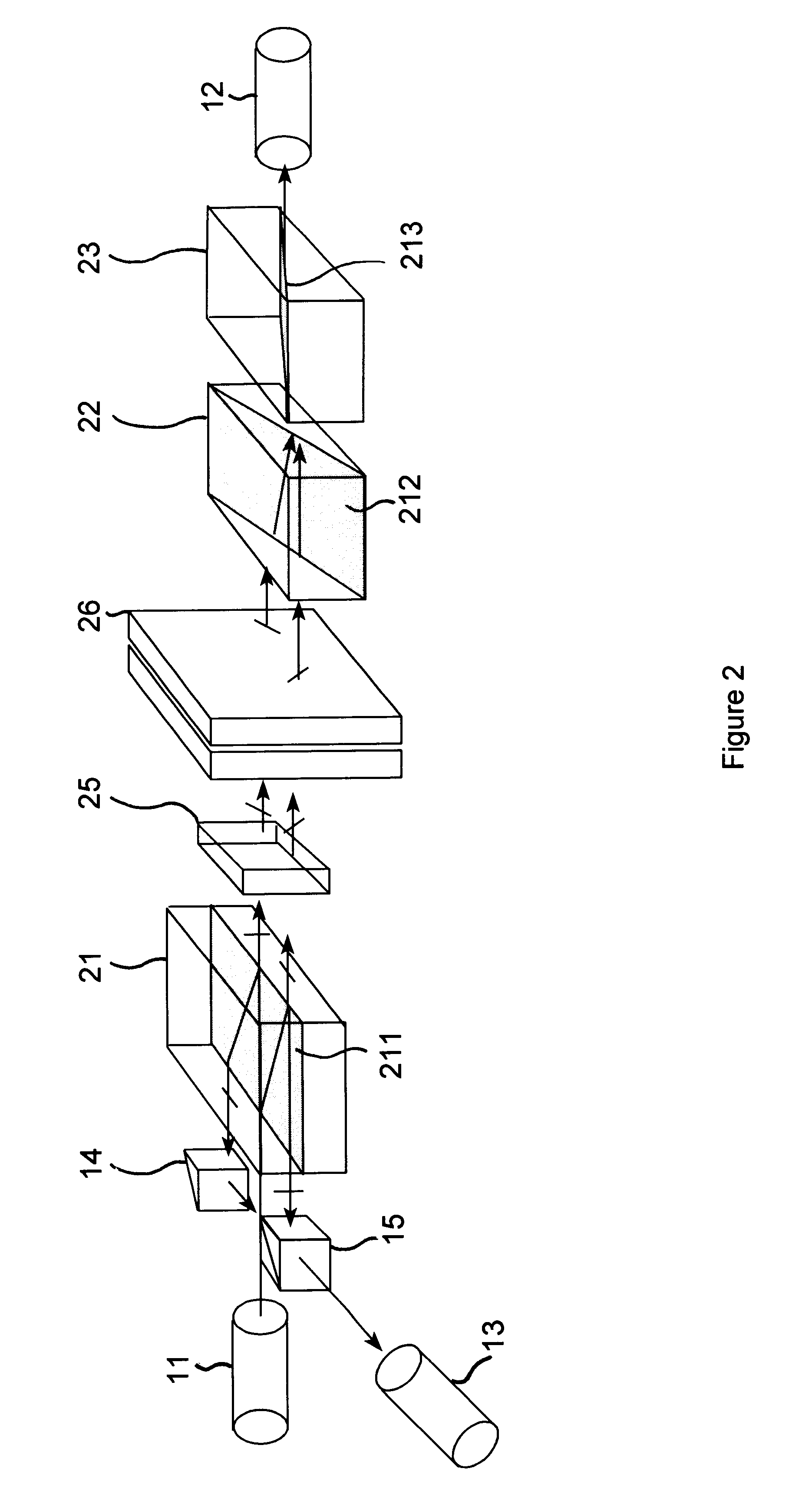
An example of the tunable add / drop filter can be realized by using a liquid-crystal Fabry-Perot tunable filter as shown in FIG. 4. A pair of halfwave plates are inserted in front of and behind of the liquid crystal filter. A halfwave plate satisfies the equation .DELTA.nd=.lambda. / 2, where .DELTA.n and d are the birefringence and thickness of the wave plate, and .lambda. is the light wavelength. The first wave plate 27 is added into the light path 800 to change the polarization of the decomposed input light to match the 45.degree. optic axis of the filter 99. The second halfwave plate 28, which is placed on the opposite side of the filter, rotates the extra-ordinary light wave into ordinary in light paths 801. The two then .[.recombines.]. .Iadd.recombine .Iaddend.by the birefringent elements 22 and 23. The rest of the operations are explained in the previous embodiment.
Due to the spatial-light-modulation capability (2-Dimensional) of a liquid-crystal Fabry-Perot filter, a multiple-...
example 2
When a fixed filter, for example the interference filter, is used in this invention a high throughput passive add / drop filter is realized. Here, the add / drop channel is pre-defined by the interference filter. However, only such a wavelength can go in and out of the ports.
example 3
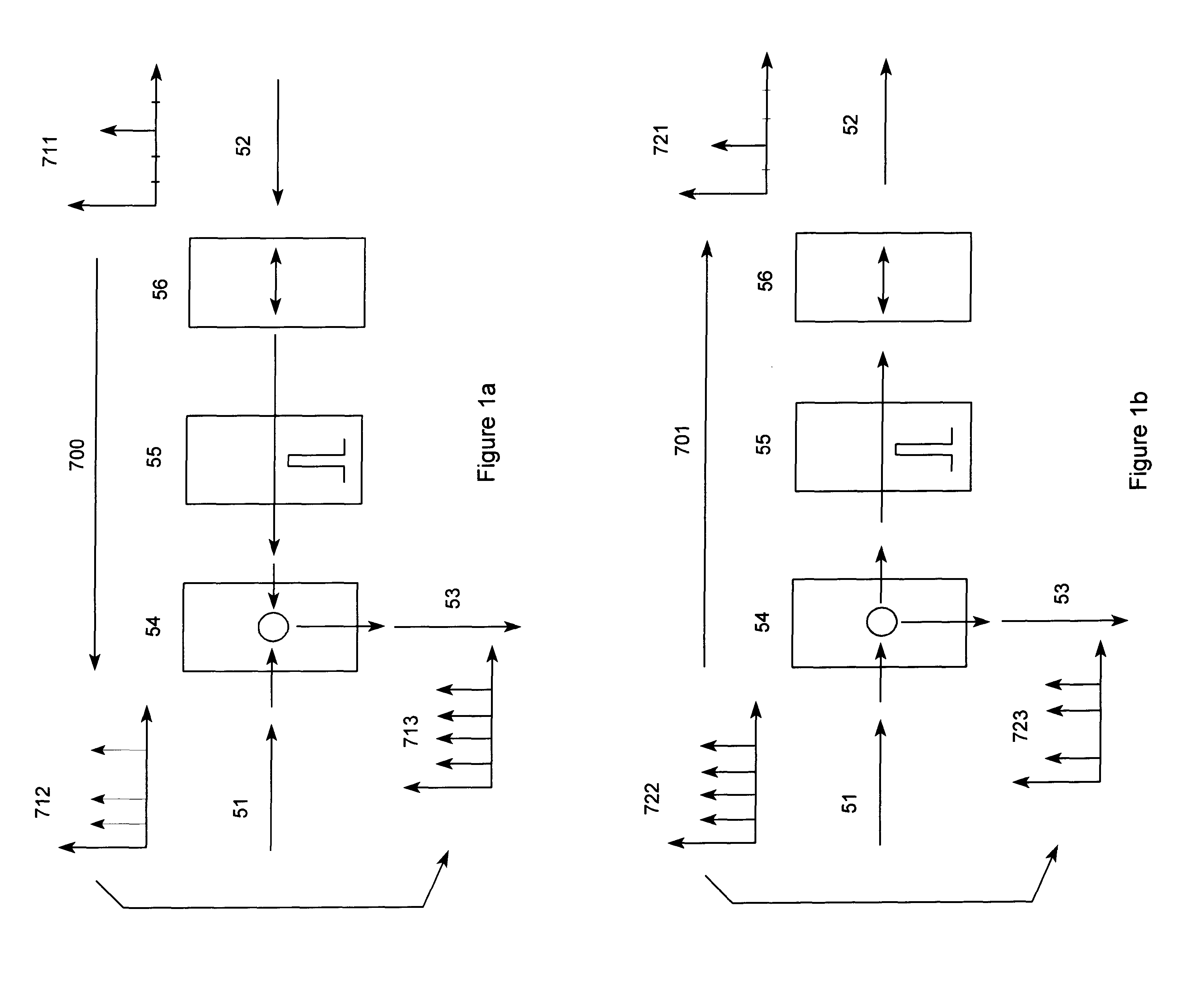
When an 1.times.2 optical switch is added onto the add / drop port, as shown in FIG. 6a, the three-port add / drop filter becomes a four-port add / drop filter with it's input- and output-port separated.(See FIG. 6b) Two of .[.this.]. .Iadd.these .Iaddend.add / drop filters 811 can be further interconnected to form a wavelength-space switching node for multi-layered WDM systems. In FIG. 6c, one of the add / drop .[.port.]. .Iadd.ports .Iaddend.823 of .[.the.]. .Iadd.each of the .Iaddend.add / drop .[.filter 811 is linked to the each other.]. .Iadd.filters 811 are linked together.Iaddend.. The channels between the two WDM systems 801 and 802 can then be shared through this interconnected optical node. Furthermore, because of the reciprocal nature of this add / drop filter at the add / drop .[.port.]. .Iadd.ports .Iaddend.821 and 822, optical channels can still be loaded up and down from the its WDM network 801 and 802, respectively. This greatly .[.increase.]. .Iadd.increases .Iaddend.the flexibilit...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com