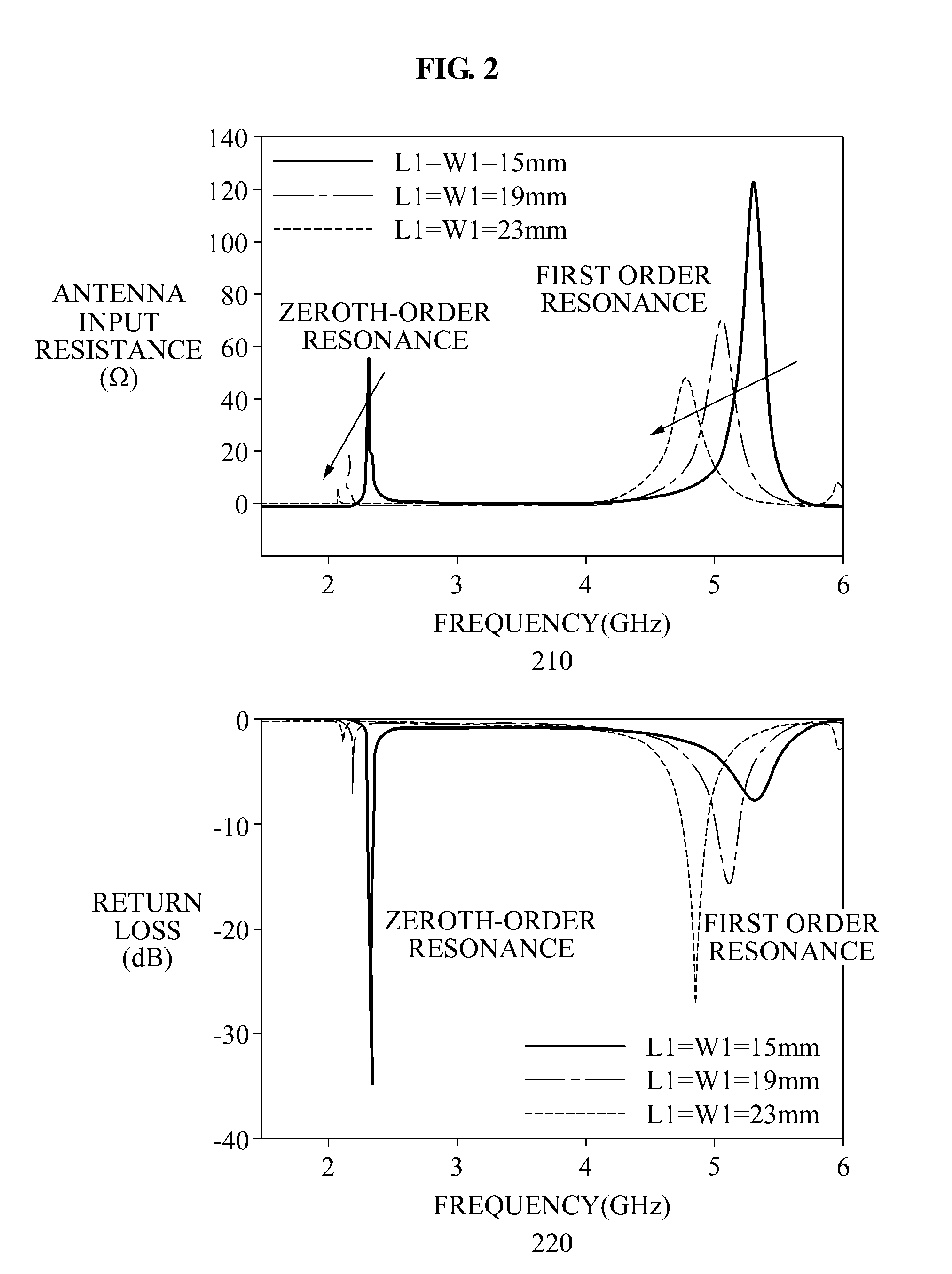
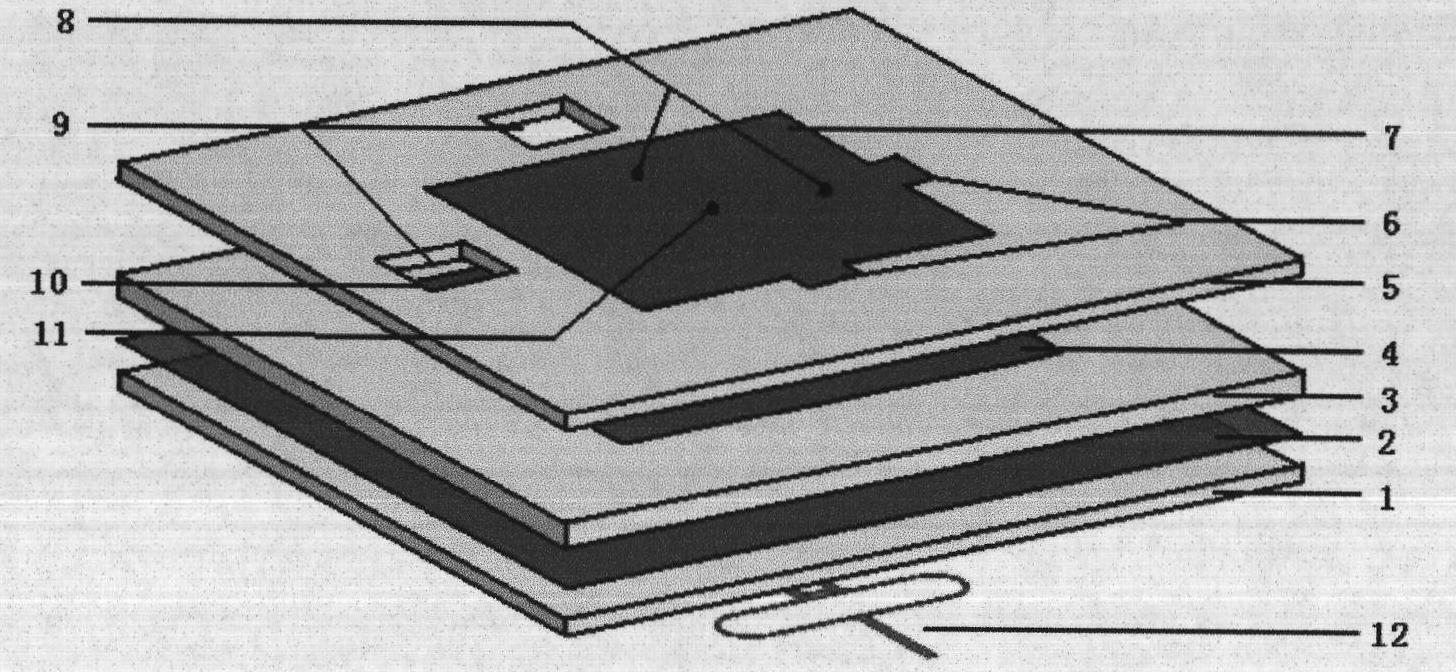
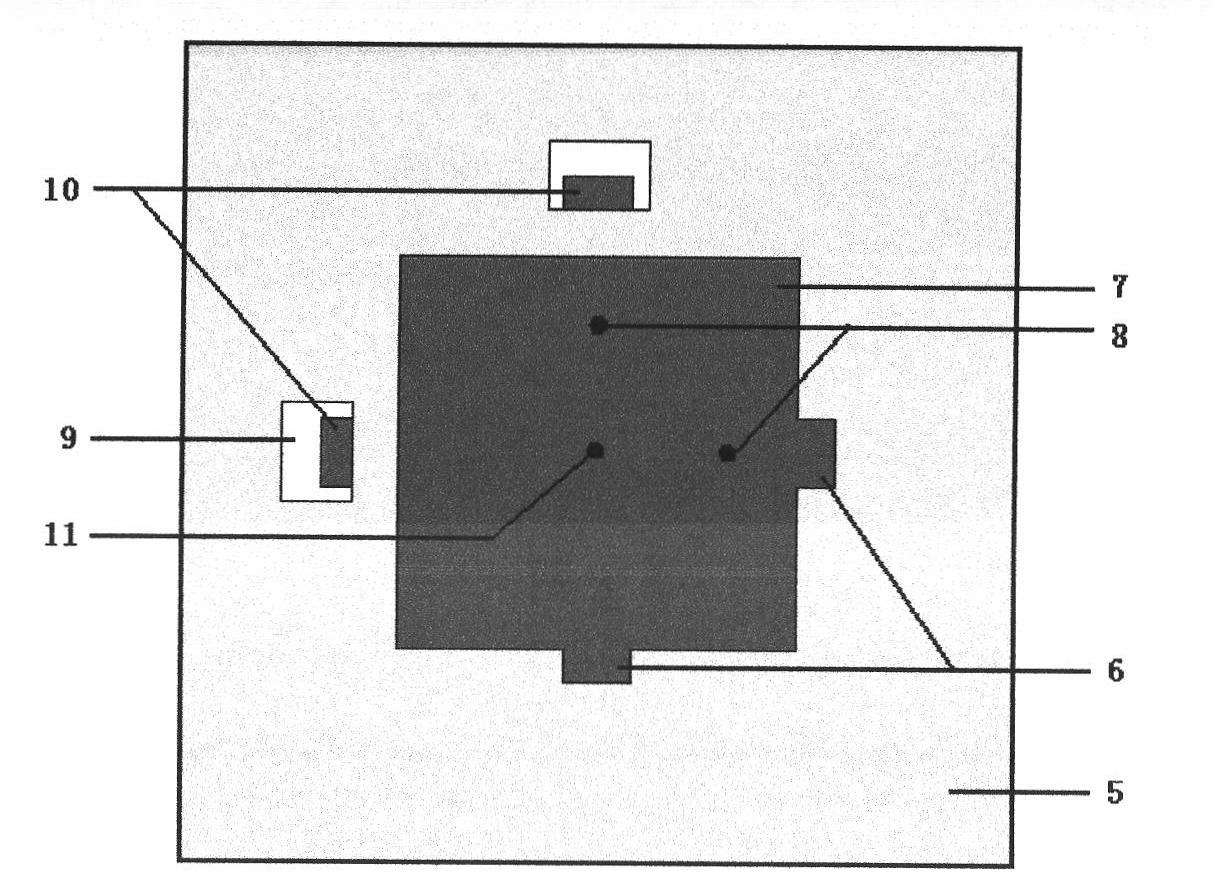
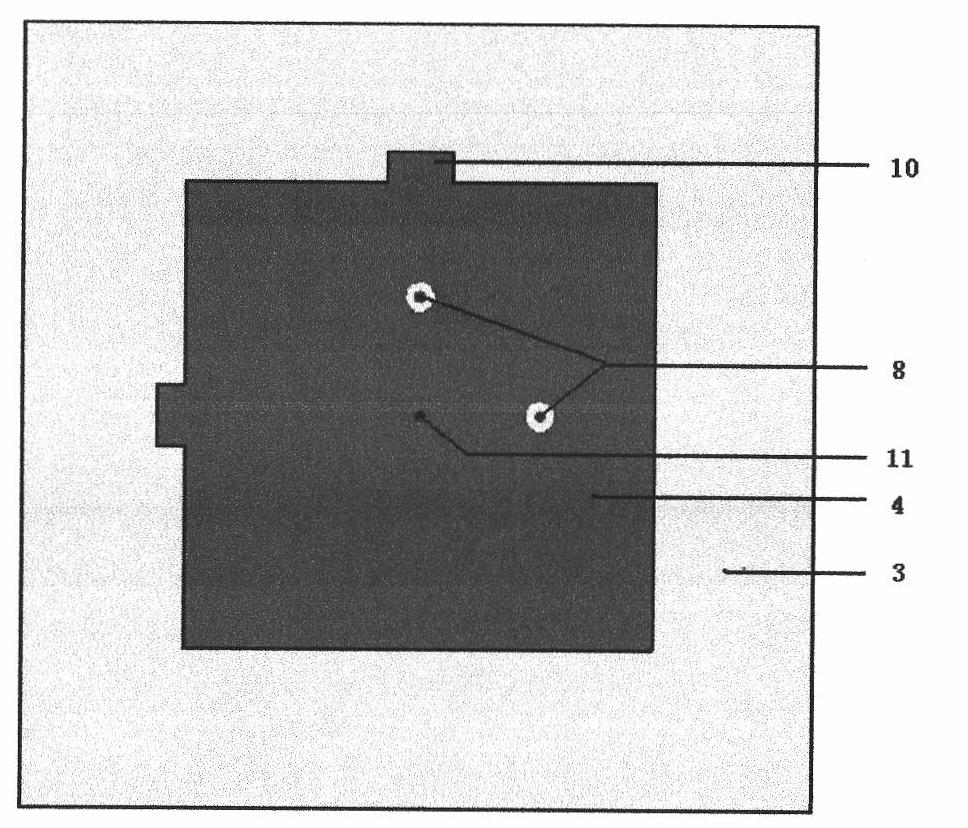
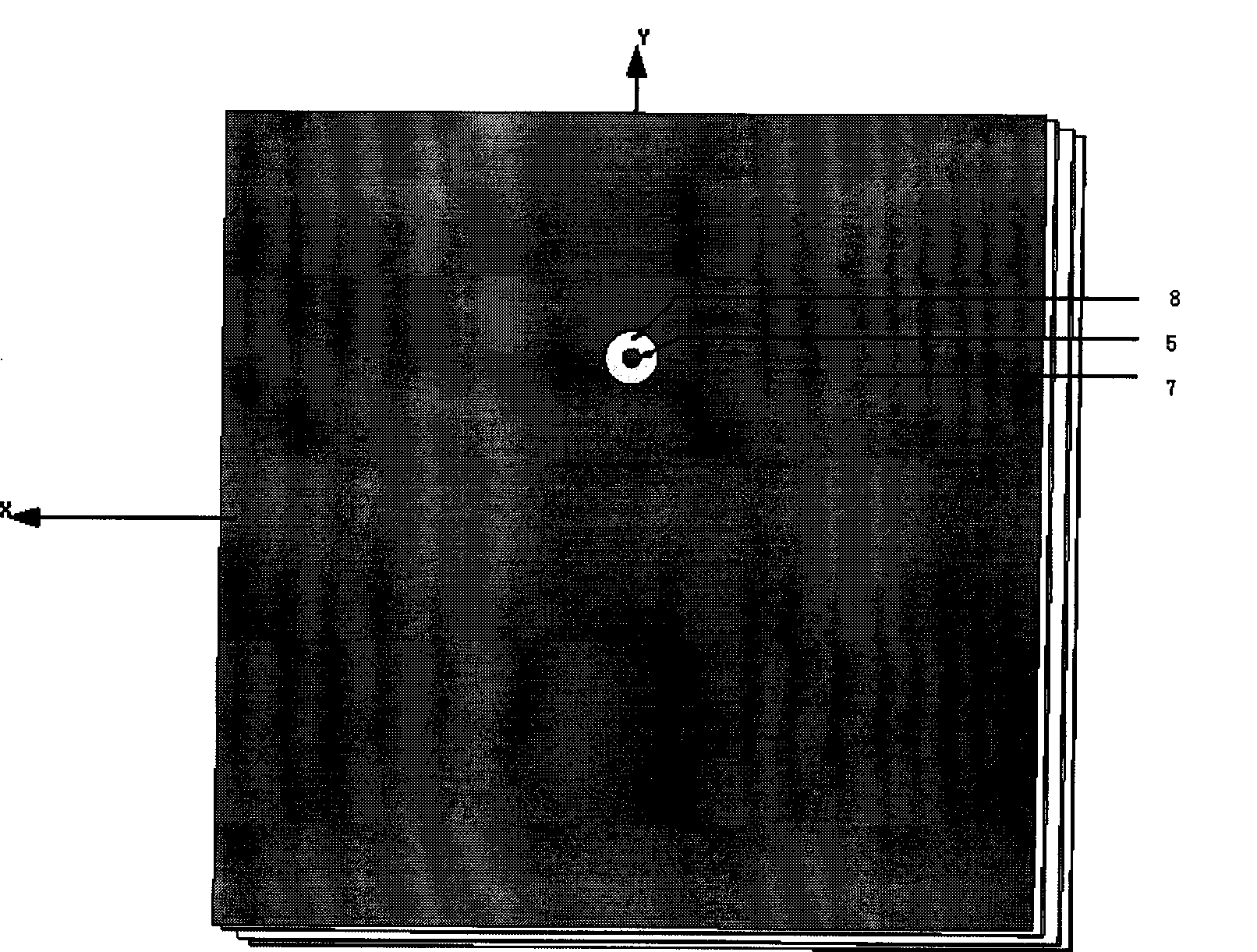
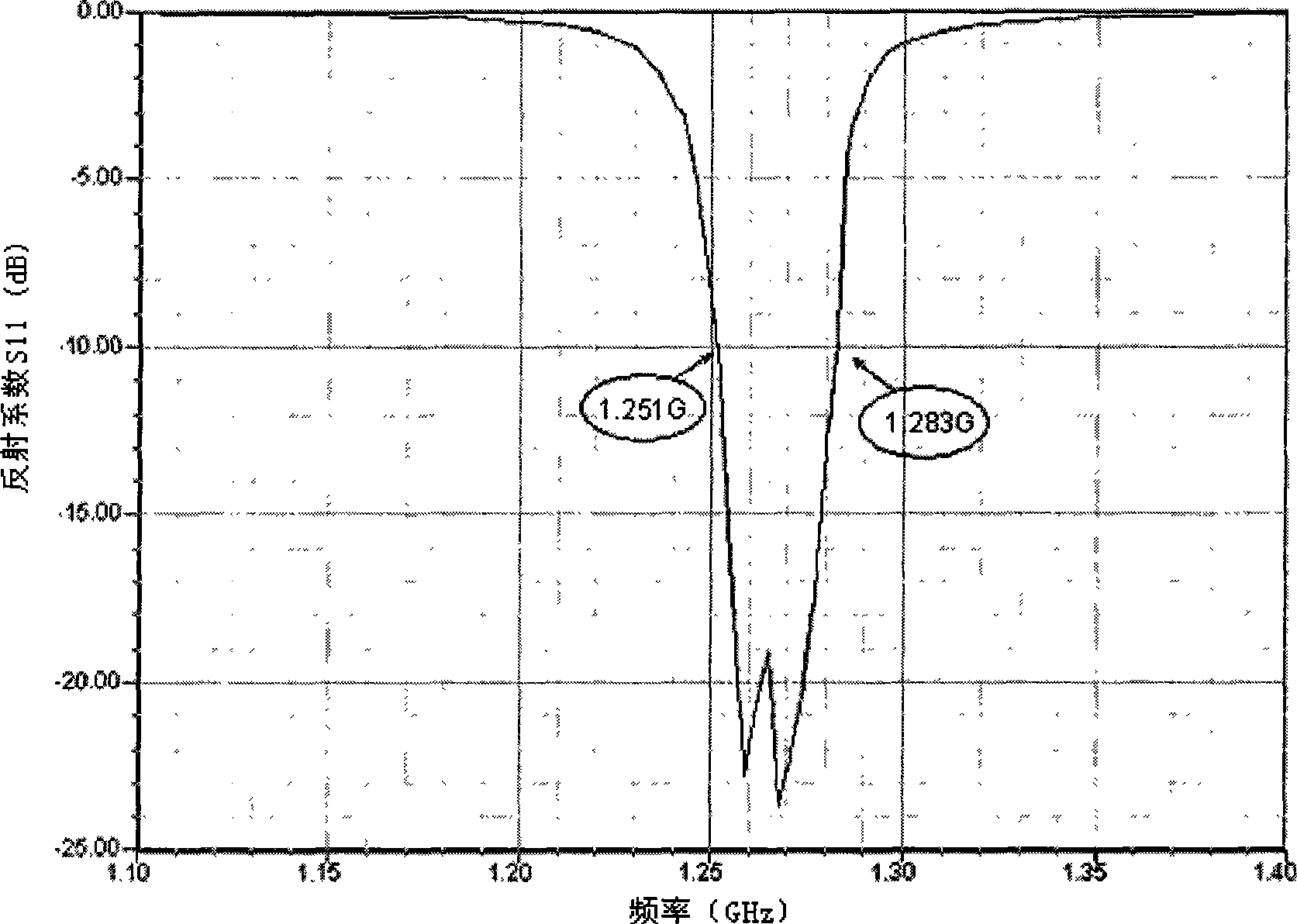
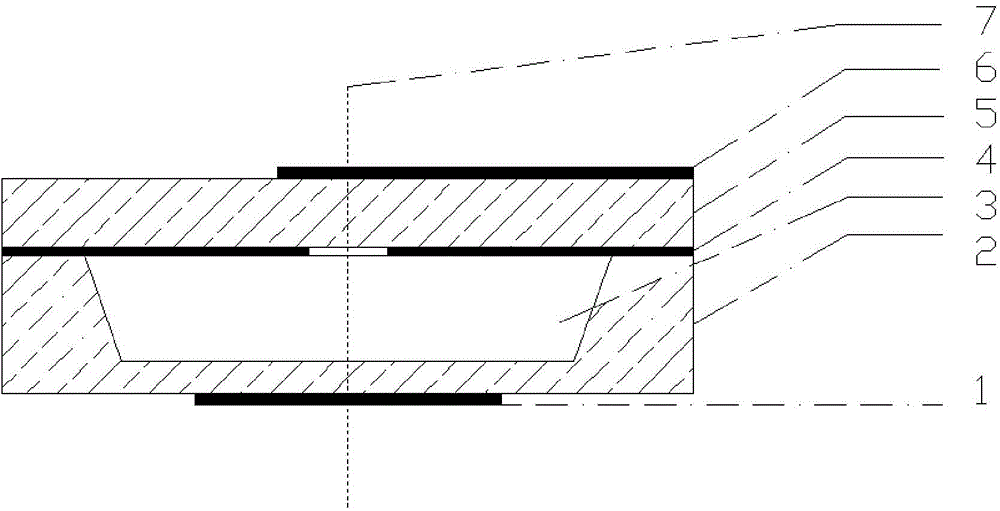
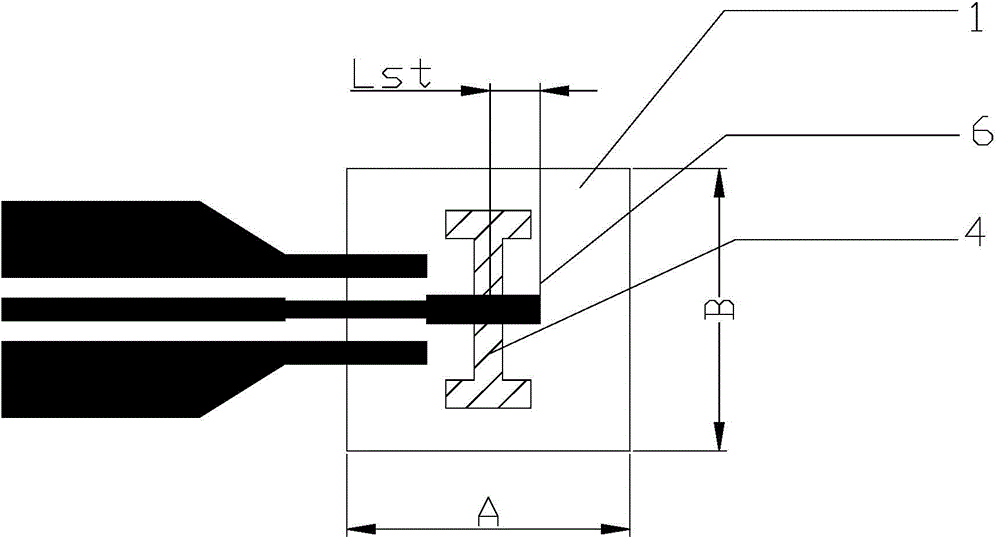
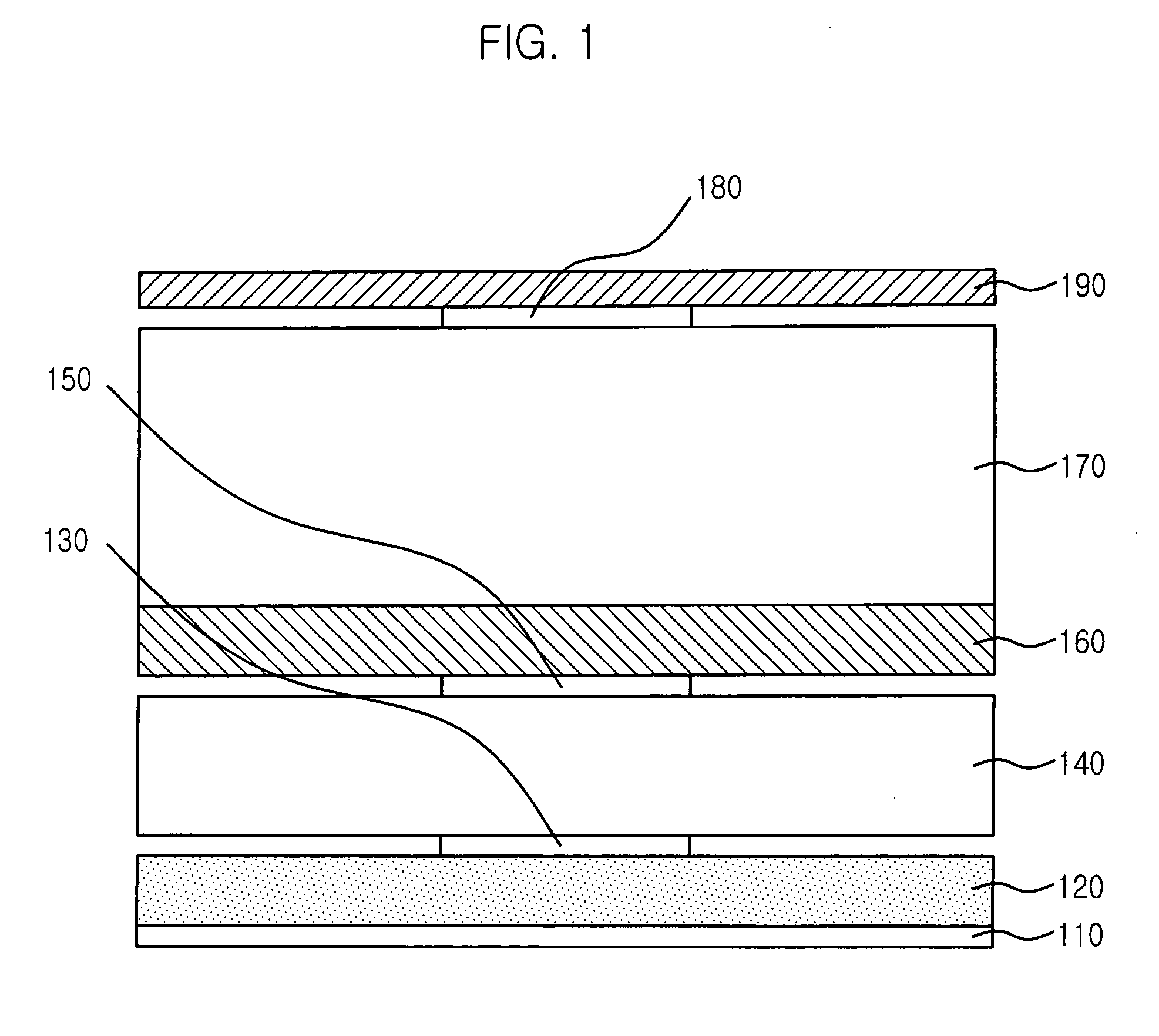
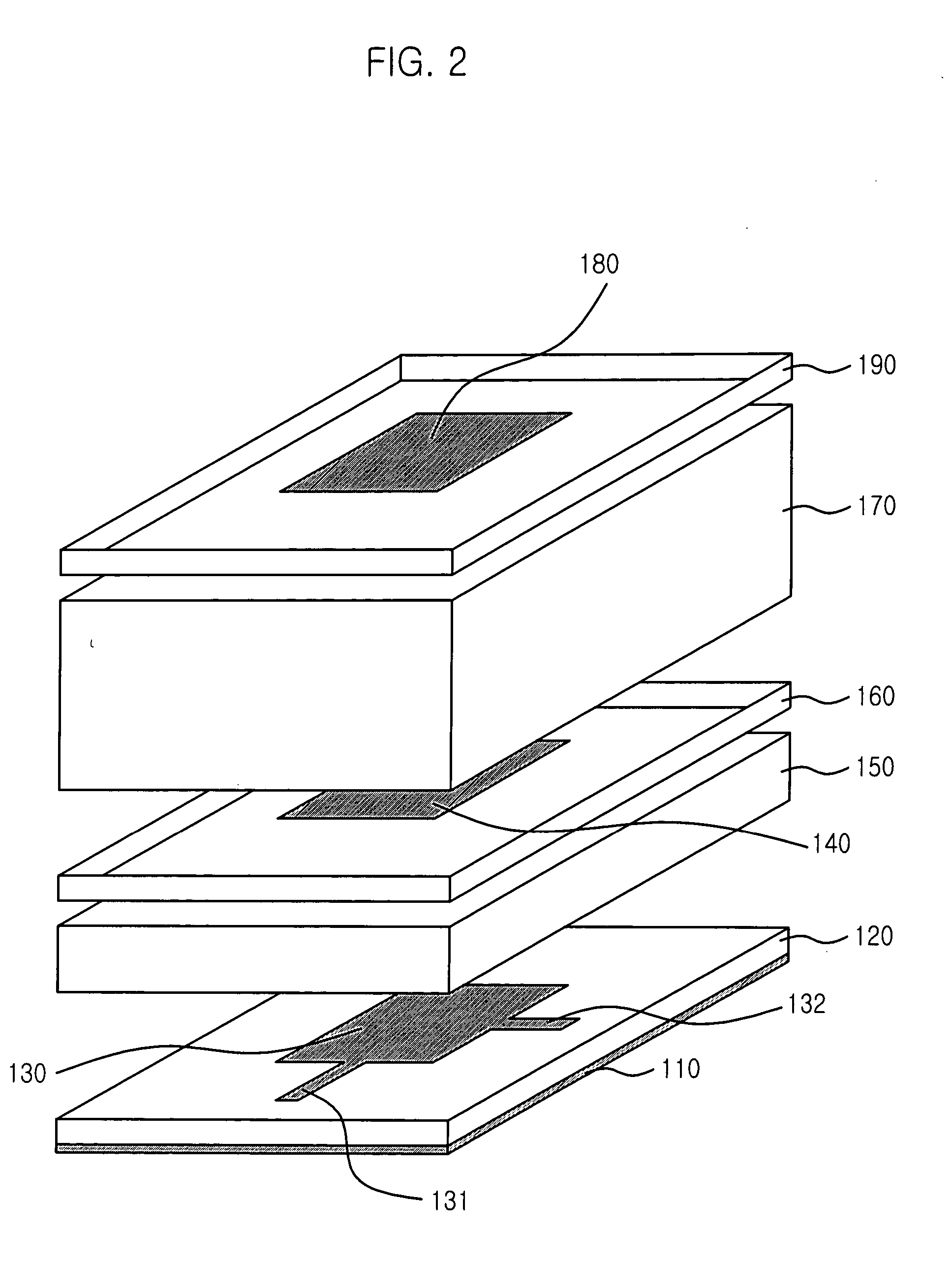
Patents
Literature
393 results about "Microstrip patch antenna" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
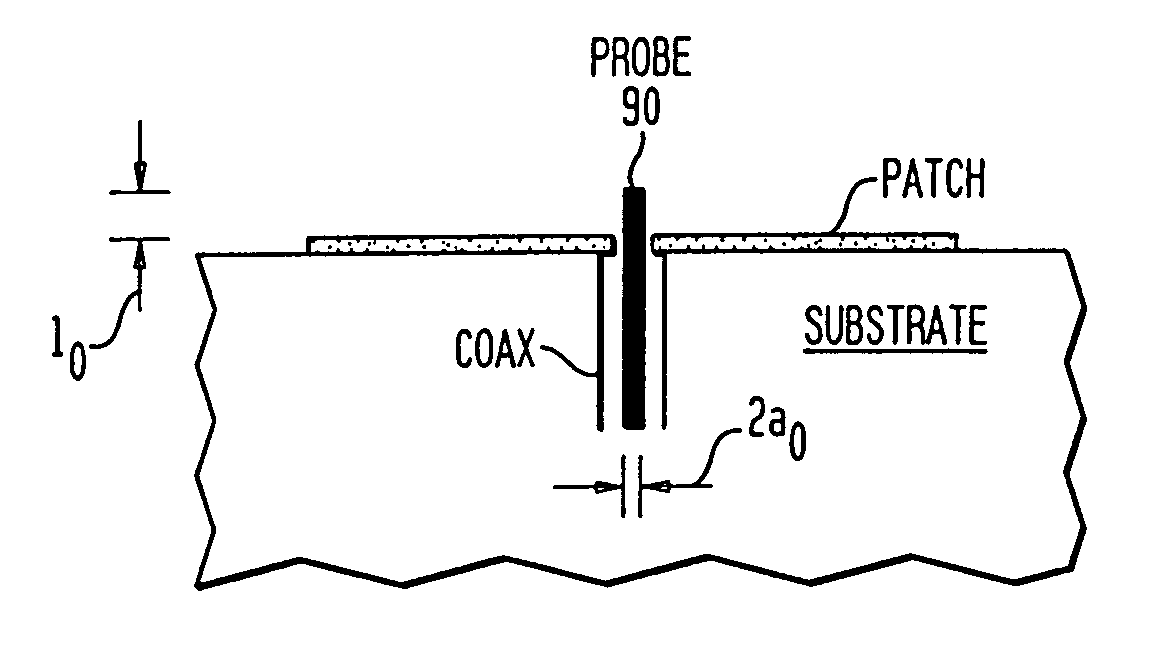
Microstrip patch antenna for high temperature environments
ActiveUS7283096B2Improve performanceImprove reliabilitySimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesMicrostrip patch antennaSpray coating
A patch antenna for operation within a high temperature environment. The patent antenna typically includes an antenna radiating element, a housing and a microwave transmission medium, such as a high temperature microwave cable. The antenna radiating element typically comprises a metallization (or solid metal) element in contact with a dielectric element. The antenna radiating element can include a dielectric window comprising a flame spray coating or a solid dielectric material placed in front of the radiating element. The antenna element is typically inserted into a housing that mechanically captures the antenna and provides a ground plane for the antenna. Orifices or passages can be added to the housing to improve high temperature performance and may direct cooling air for cooling the antenna. The high temperature microwave cable is typically inserted into the housing and attached to the antenna radiator to support the communication of electromagnetic signals between the radiator element and a receiver or transmitter device.
Owner:MEGGITT SA
Microstrip antenna for RFID device
InactiveUS20070164868A1Low costEliminate needSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsMicrostrip patch antennaAntenna design
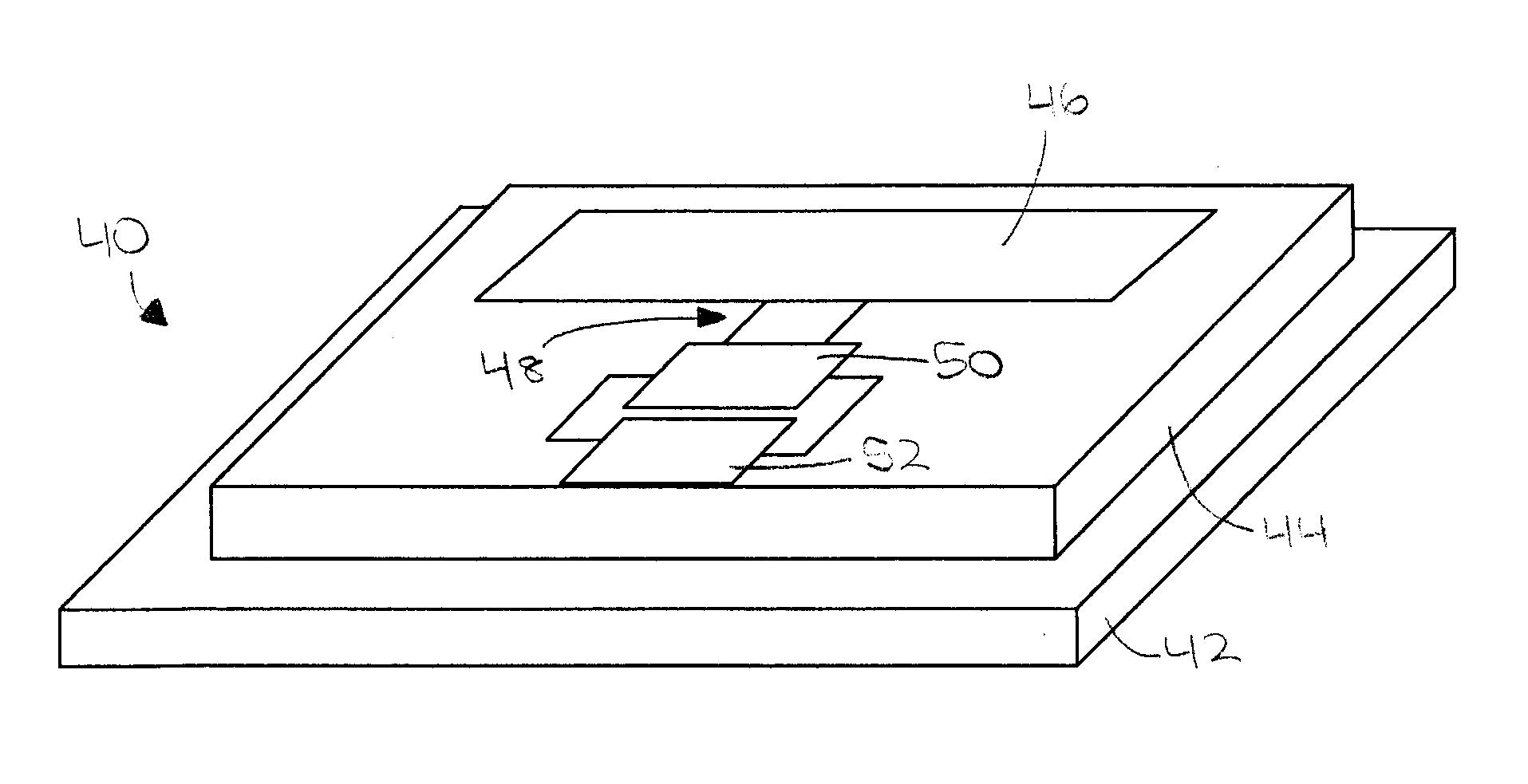
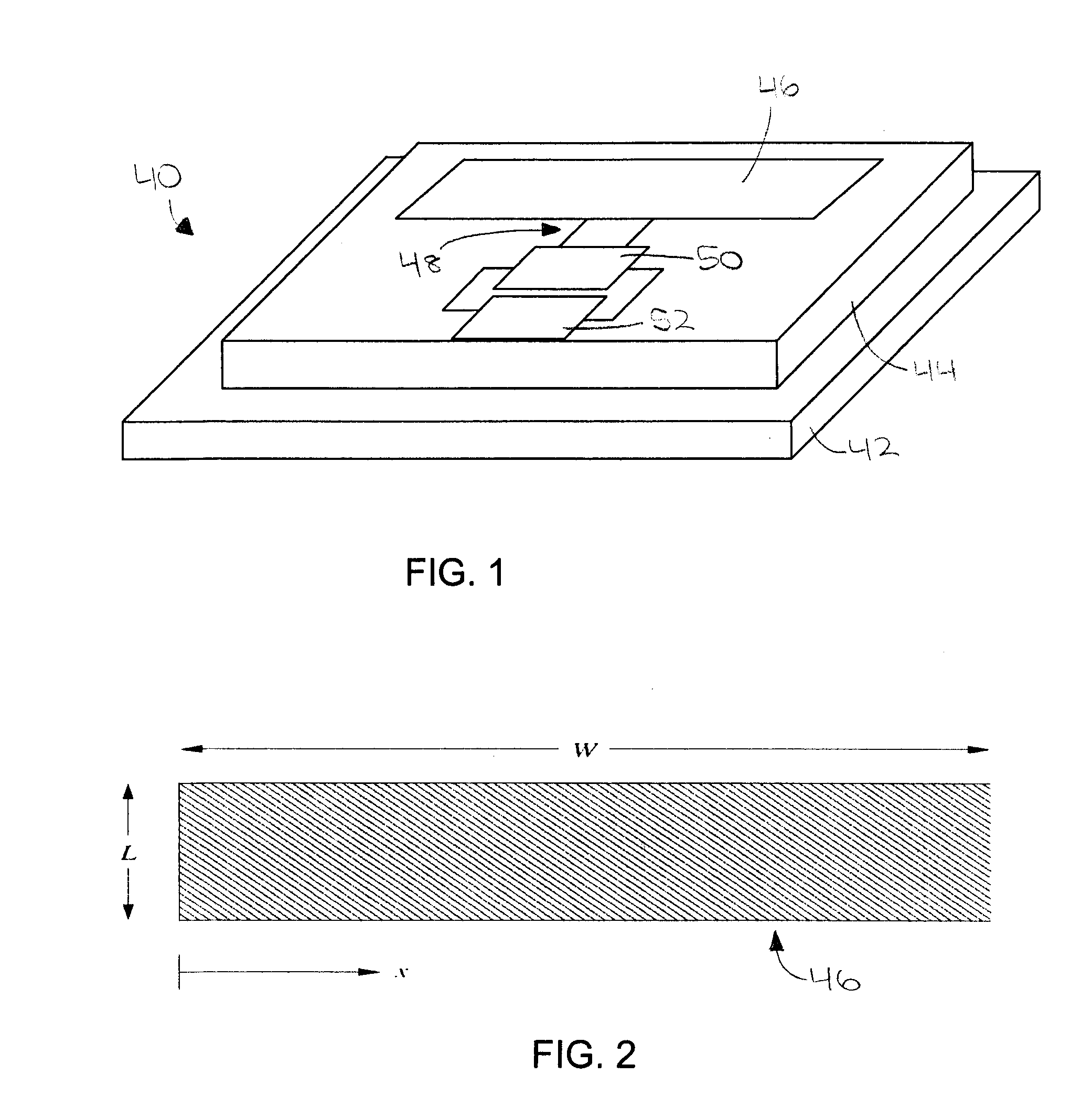
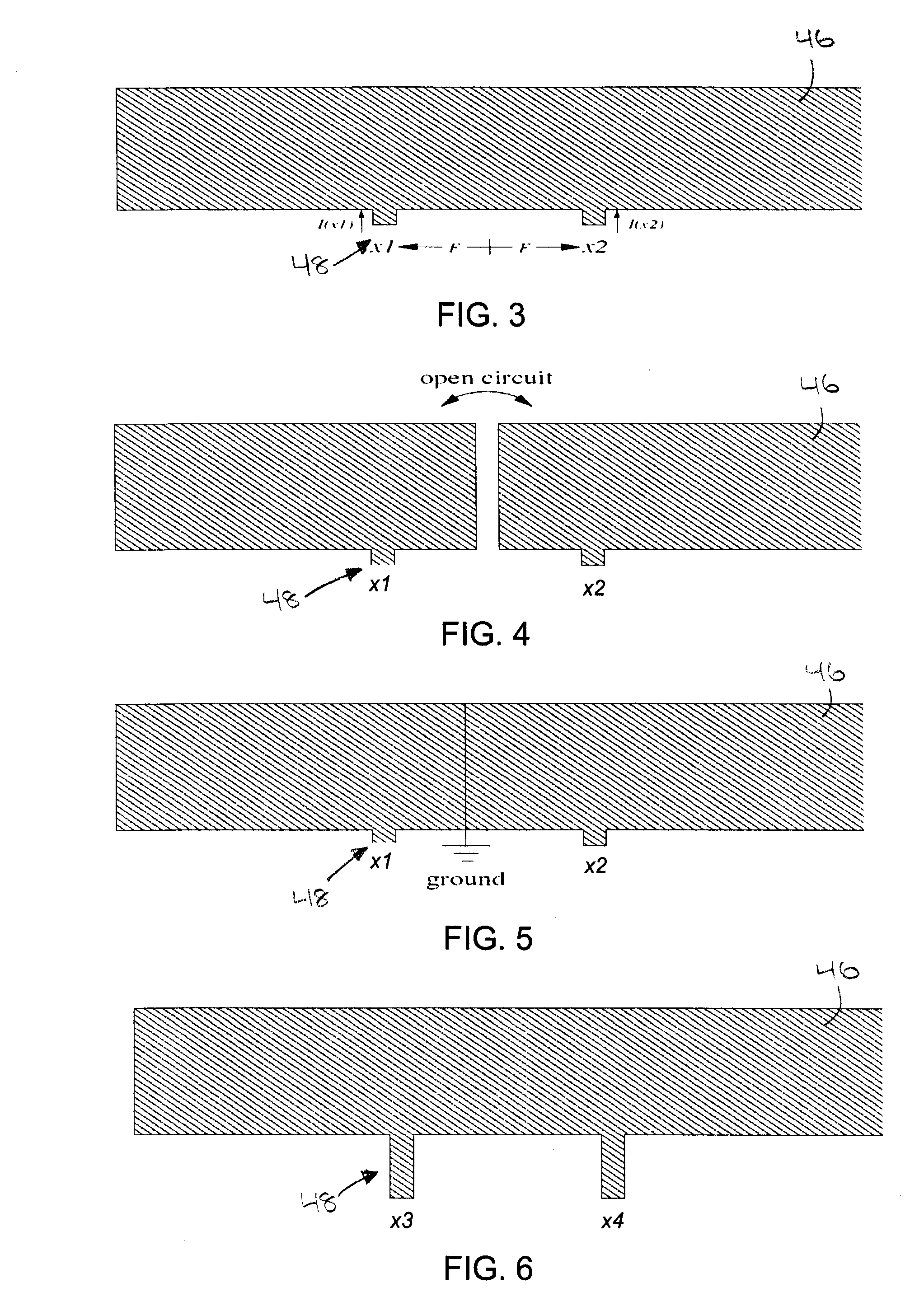
Microstrip patch antenna (46), feed structure (48), and matching circuit (50) designs for an RFID tag (10). A balanced feed design using balanced feeds coupled by a shorting stub (56) to create a virtual short between the two feeds so as to eliminate the need for physically connecting substrate to the ground plane. A dual feed structure design using a four-terminal IC can be connected to two antennas (46a,46b) resonating at different frequencies so as to provide directional and polarization diversity. A combined near / field-far / field design using a microstrip antenna providing electromagnetic coupling for far-field operation, and a looping matching circuit providing inductive coupling for near-field operation. A dual-antenna design using first and second microstrip antennas providing directional diversity when affixed to a cylindrical or conical object, and a protective superstrate (66). An annual antenna (46c) design for application to the top of a metal cylinder around a stem.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF KANSAS
Dual band electrically small tunable antenna
InactiveUS8629811B2Simultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsDual frequencyMicrostrip patch antenna
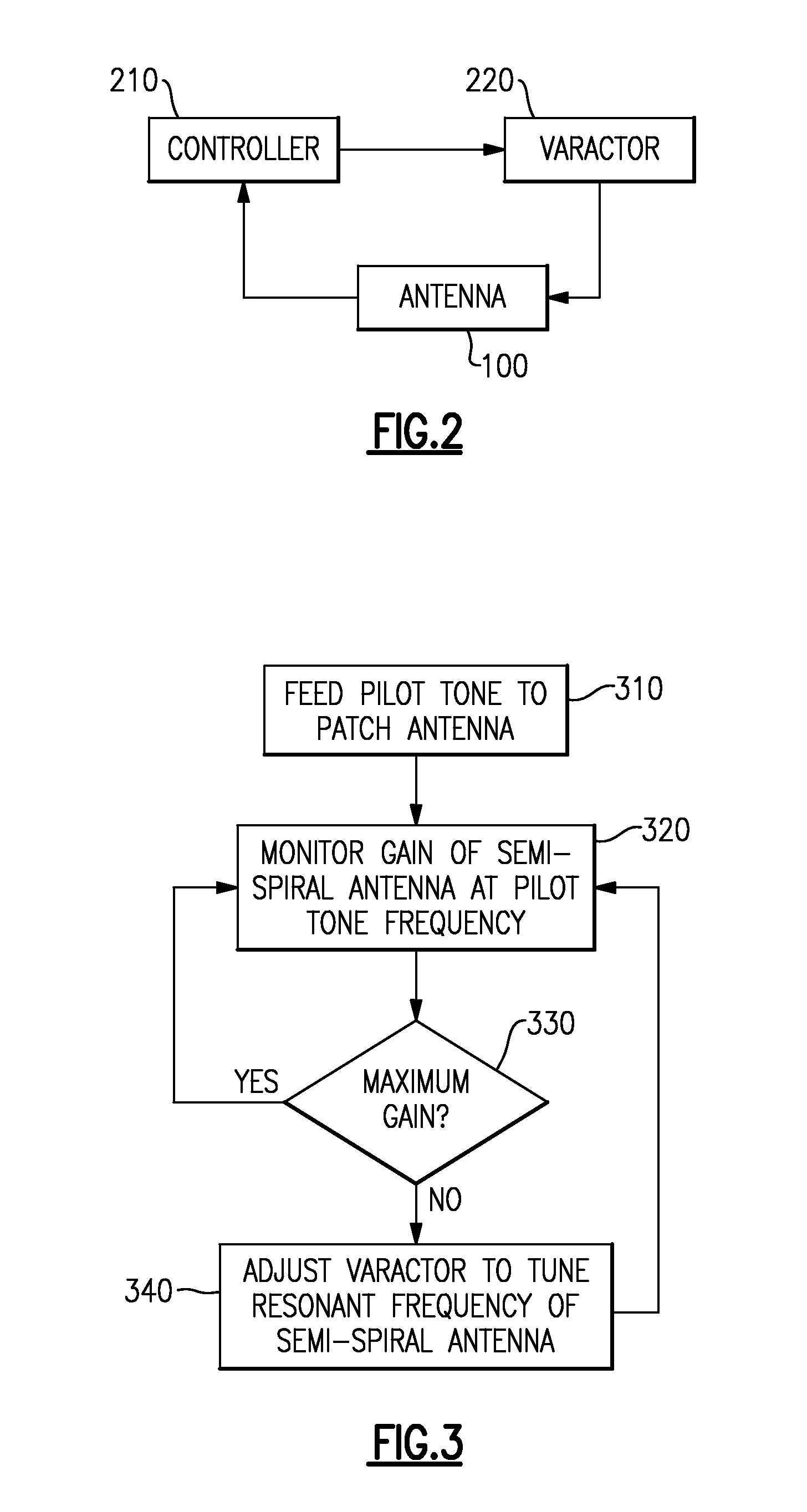
An electrically small dual-band planar tunable UHF / L-Band antenna. In one example, the dual-band antenna includes a combination of a semi-spiral antenna for the UHF frequencies and a microstrip patch antenna for the L-band frequencies.
Owner:CHARLES STARK DRAPER LABORATORY
Fractal antenna ground counterpoise, ground planes, and loading elements and microstrip patch antennas with fractal structure
InactiveUS7019695B2Lower resonance frequencyIncreased effective wavelengthSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsMicrostrip patch antennaEngineering
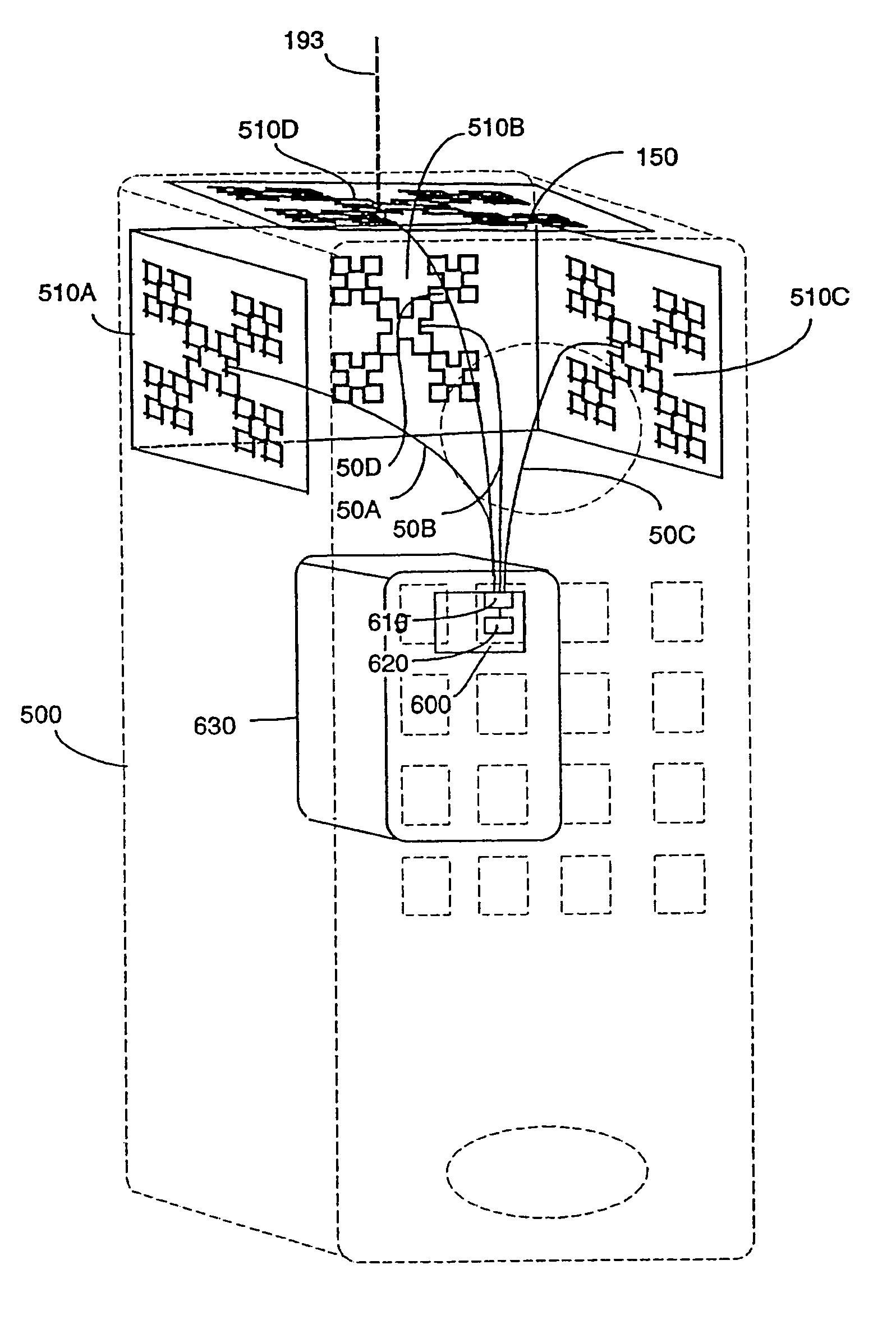
An antenna system includes a fractalized element that may be a ground counterpoise, a top-hat located load assembly, or a microstrip patch antenna having at least one element whose physical shape is at least partially defined as a first or higher iteration deterministic fractal. The resultant fractal element may rely upon an opening angle for performance, and is more compact than non-Euclidean ground counterpoise elements or the like. A vertical antenna system includes a vertical element that may also be a fractal, and a vertical antenna can include vertically spaced-apart fractal conductive and passive elements, and at least one fractal ground element. Various antenna configurations may be fabricated on opposite surfaces of a substrate, including a flexible substrate, and may be tuned by rotating elements relative to each other, and / or by varying the spaced-apart distance therebetween. Fractalized ground counterpoise elements and / or microstrip patch antenna systems may be fabricated on a flexible printed circuit substrate, and / or placed within the support mount of a cellular telephone car antenna.
Owner:FRACTAL ANTENNA SYST
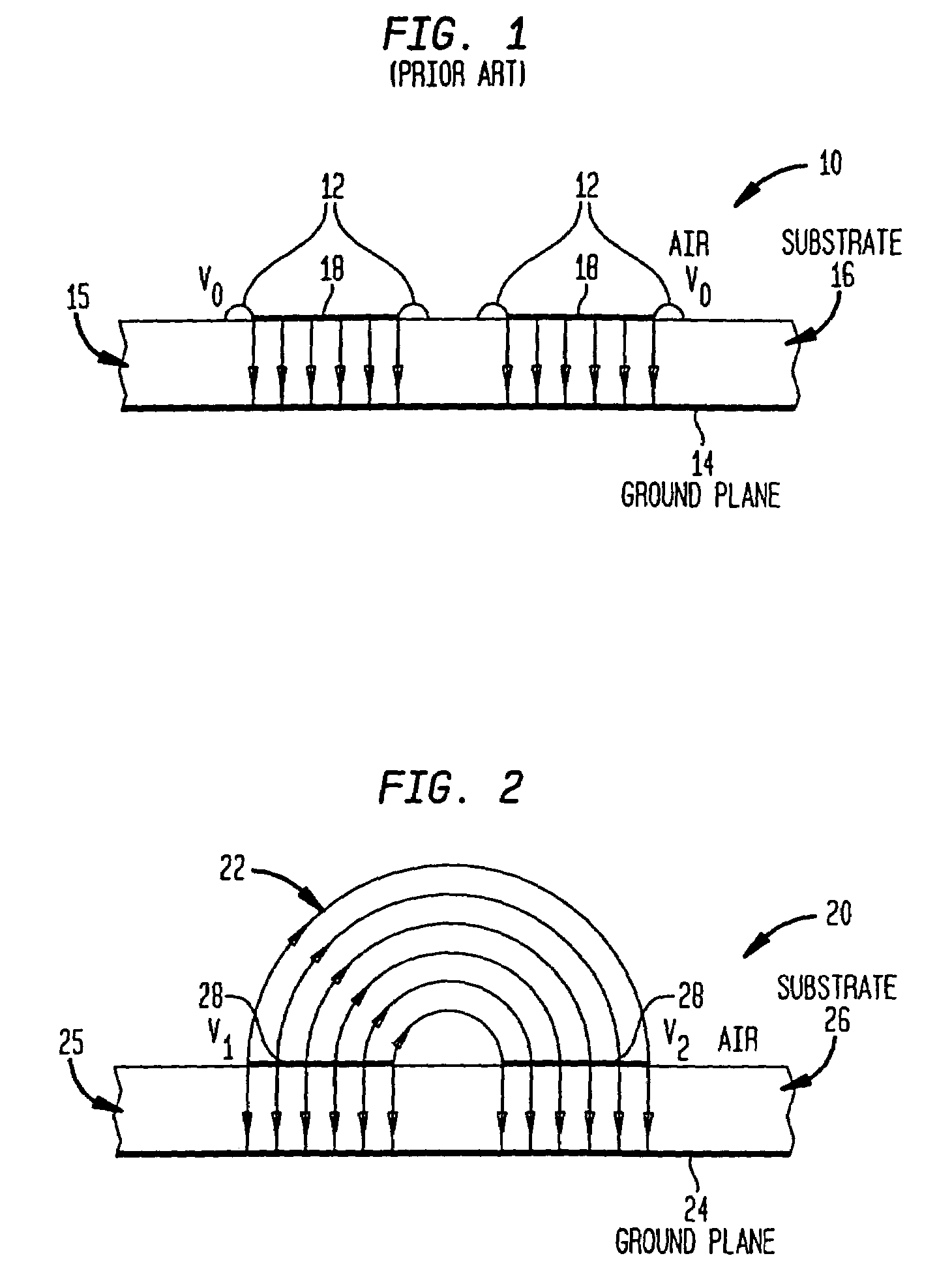
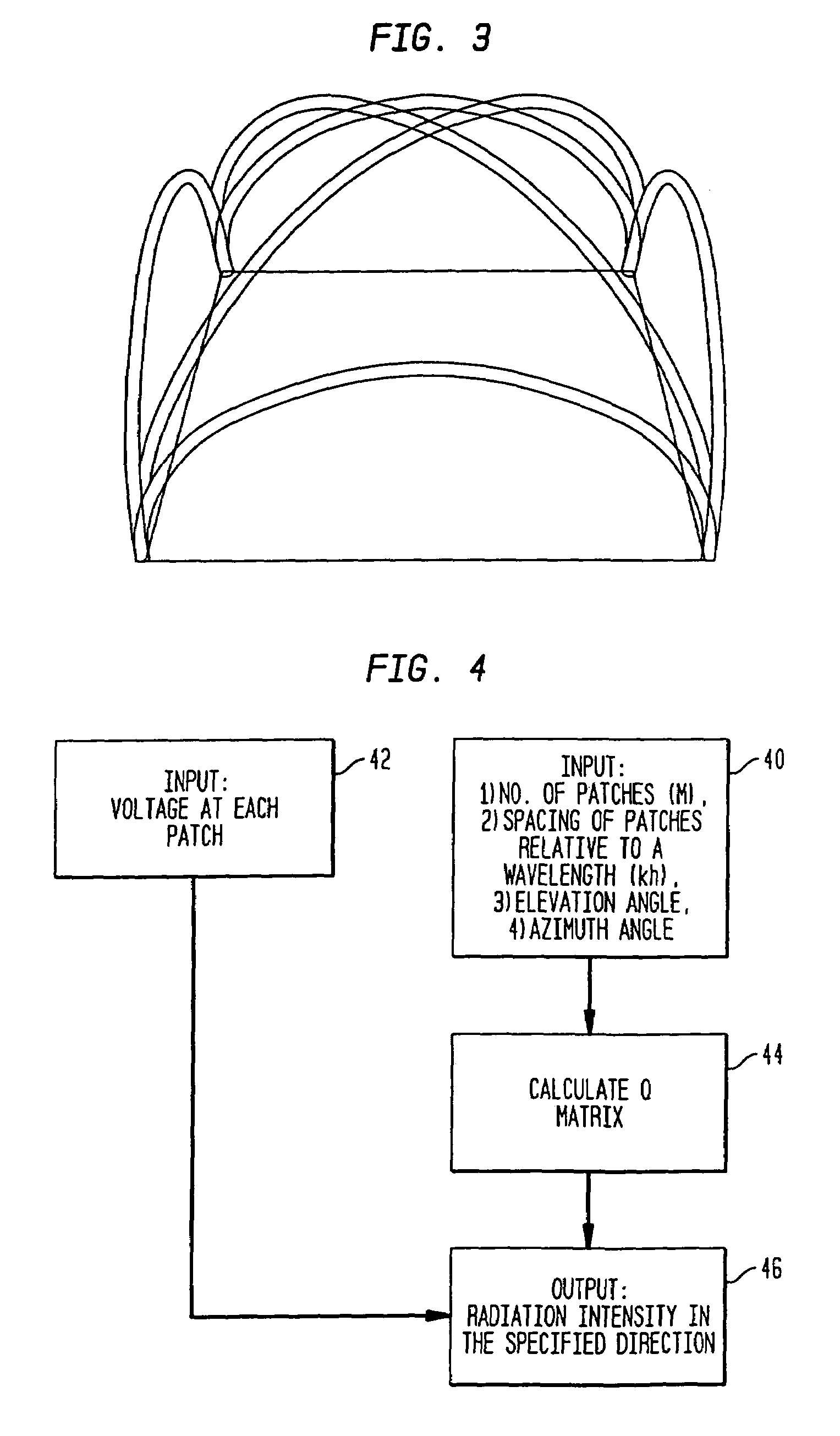
Systems and methods for providing optimized patch antenna excitation for mutually coupled patches
InactiveUS7298329B2Enhanced radiationImprove efficiencyParticular array feeding systemsSimultaneous aerial operationsMicrostrip patch antennaLight beam
An antenna array (e.g., microstrip patch antenna) operates in a manner that exploits the particular susceptibility of the mutual coupling effects between radiating elements in the array. Various differential-mode excitation schemes are provided for determining optimal differential-mode voltages or optimal differential-mode currents that are applied to the radiating elements (e.g., microstrip patches) to thereby achieve certain desirable radiation characteristics including, for example, aiming a radiated beam in a prescribed direction, steering the beam, shaping the radiated beam, and / or optimizing the gain of the antenna in a specified direction.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
System and method of using absorber-walls for mutual coupling reduction between microstrip antennas or brick wall antennas
InactiveUS7427949B2Reduce signalingReduce horizontal sizeAntenna detailsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionMicrostrip patch antennaBrick
A multi-element antenna with sufficiently small return loss and mutual coupling signals to allow the simultaneous transmission of powerful radar signals and the reception of faint target return signals. The microstrip patch antenna has radio frequency absorbing material place between neighboring antenna elements to reduce the mutual coupling leakage signals.
Owner:COBHAM DEFENSE ELECTRONICS SYST CORP
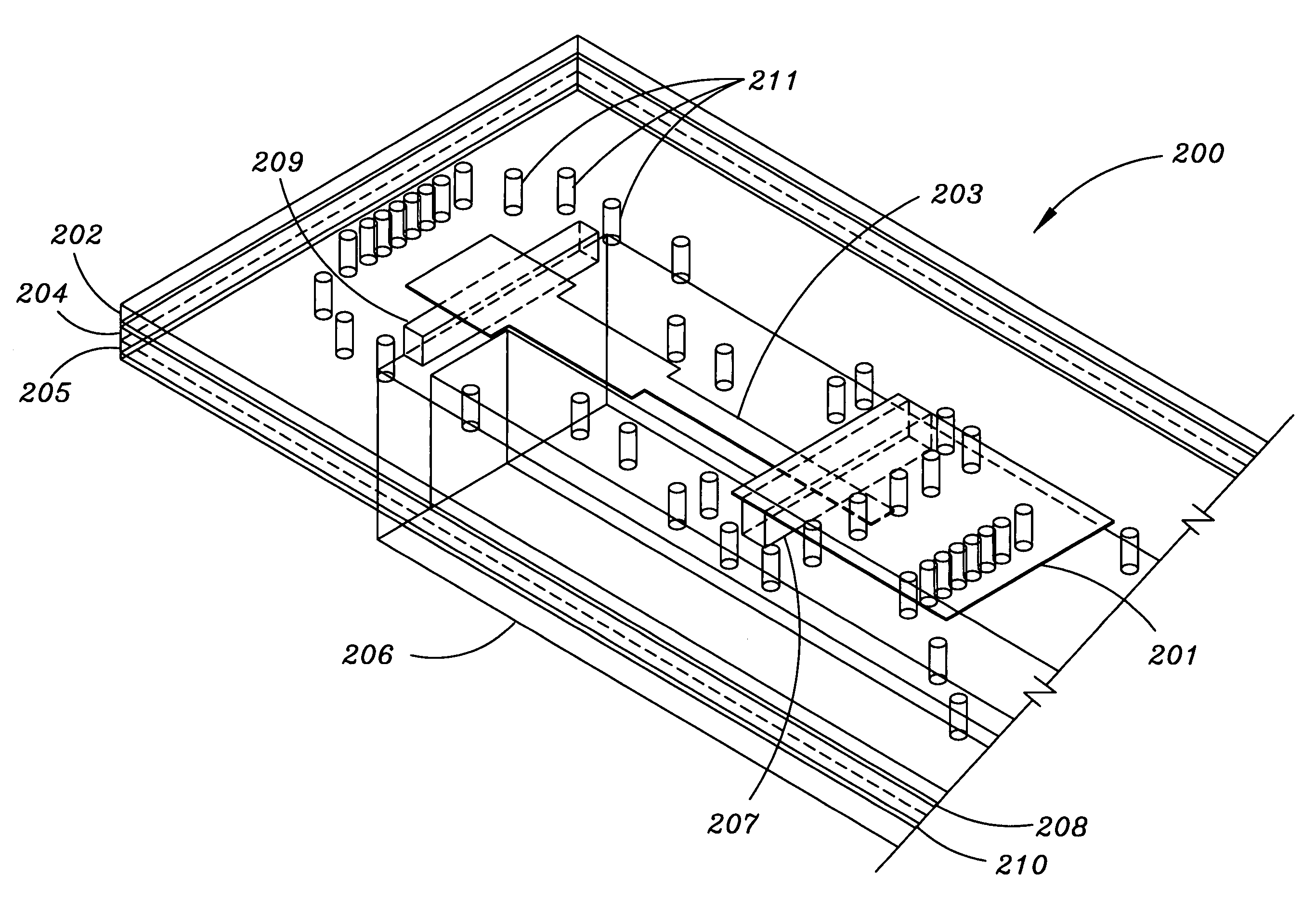
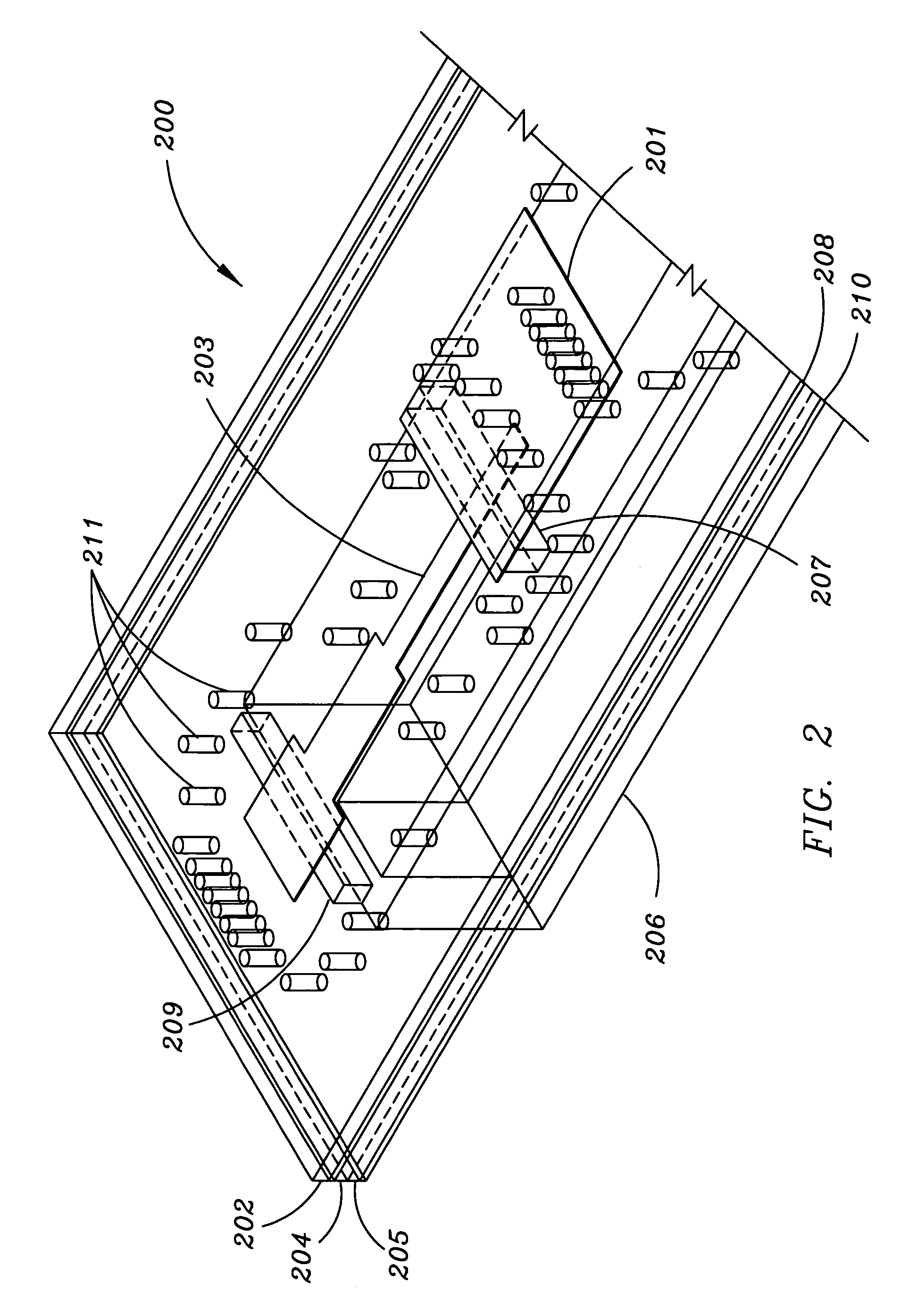
High efficiency slot fed microstrip patch antenna
InactiveUS6842140B2Small sizeLack of efficiencySimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsMicrostrip patch antennaReduced size
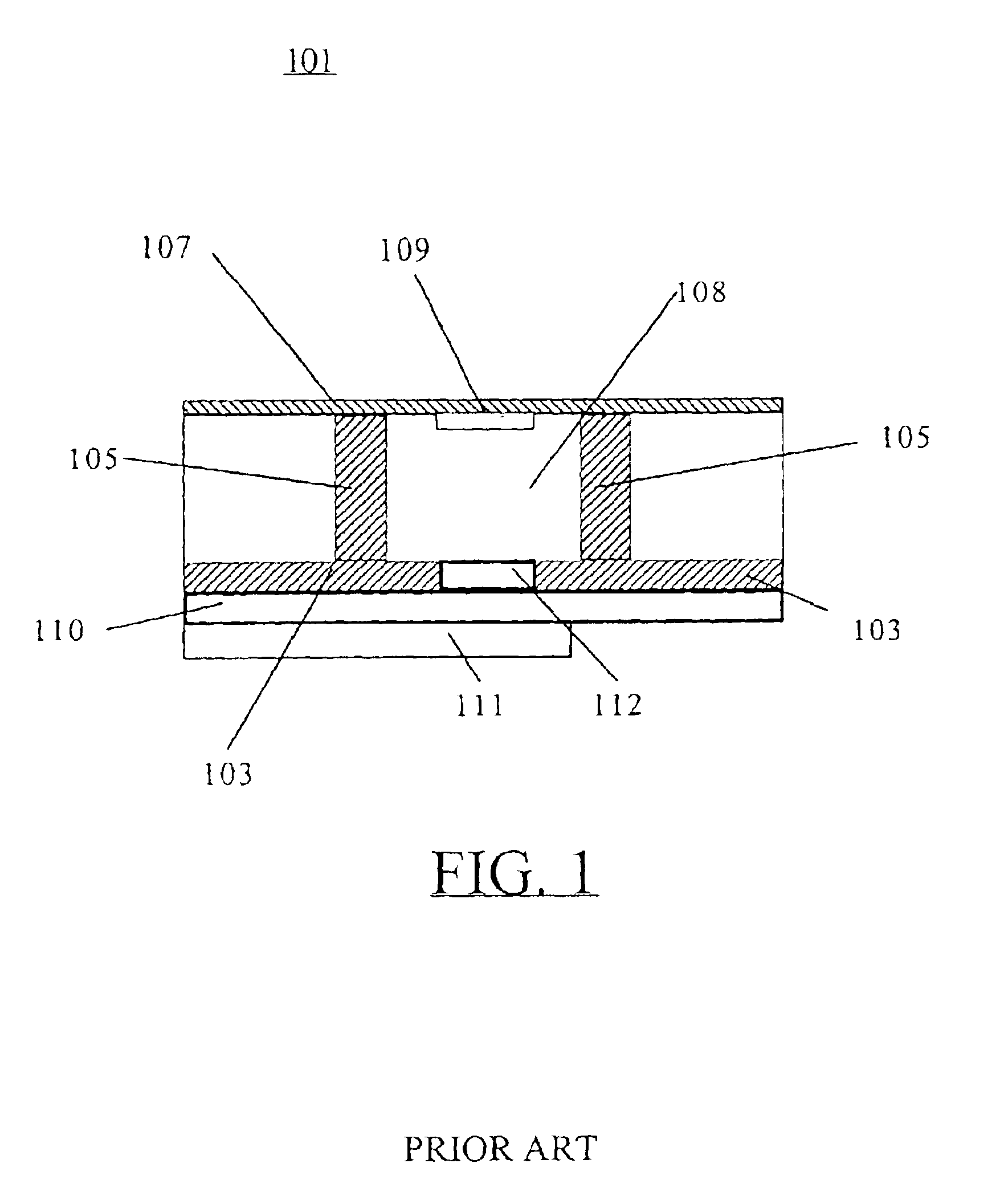
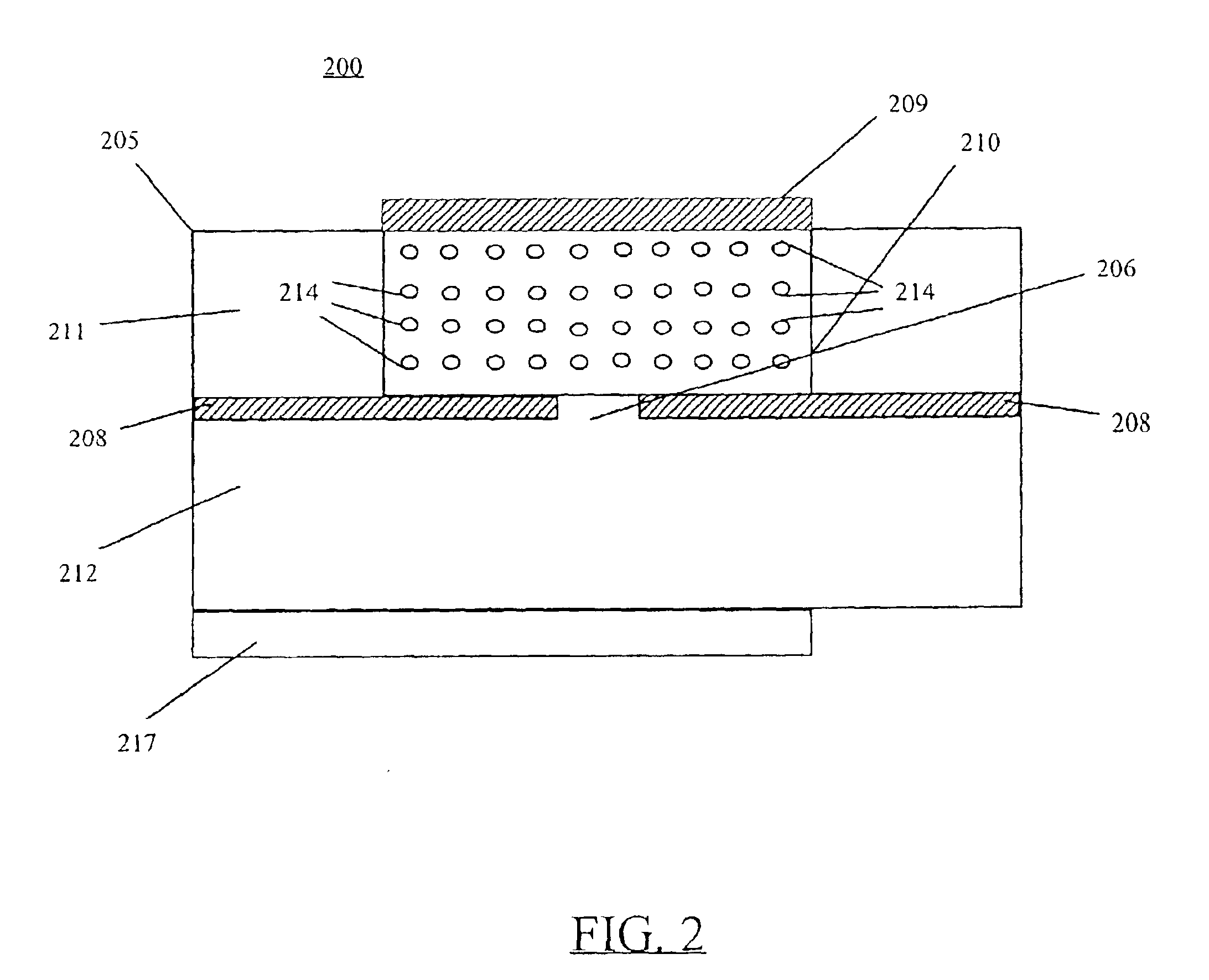
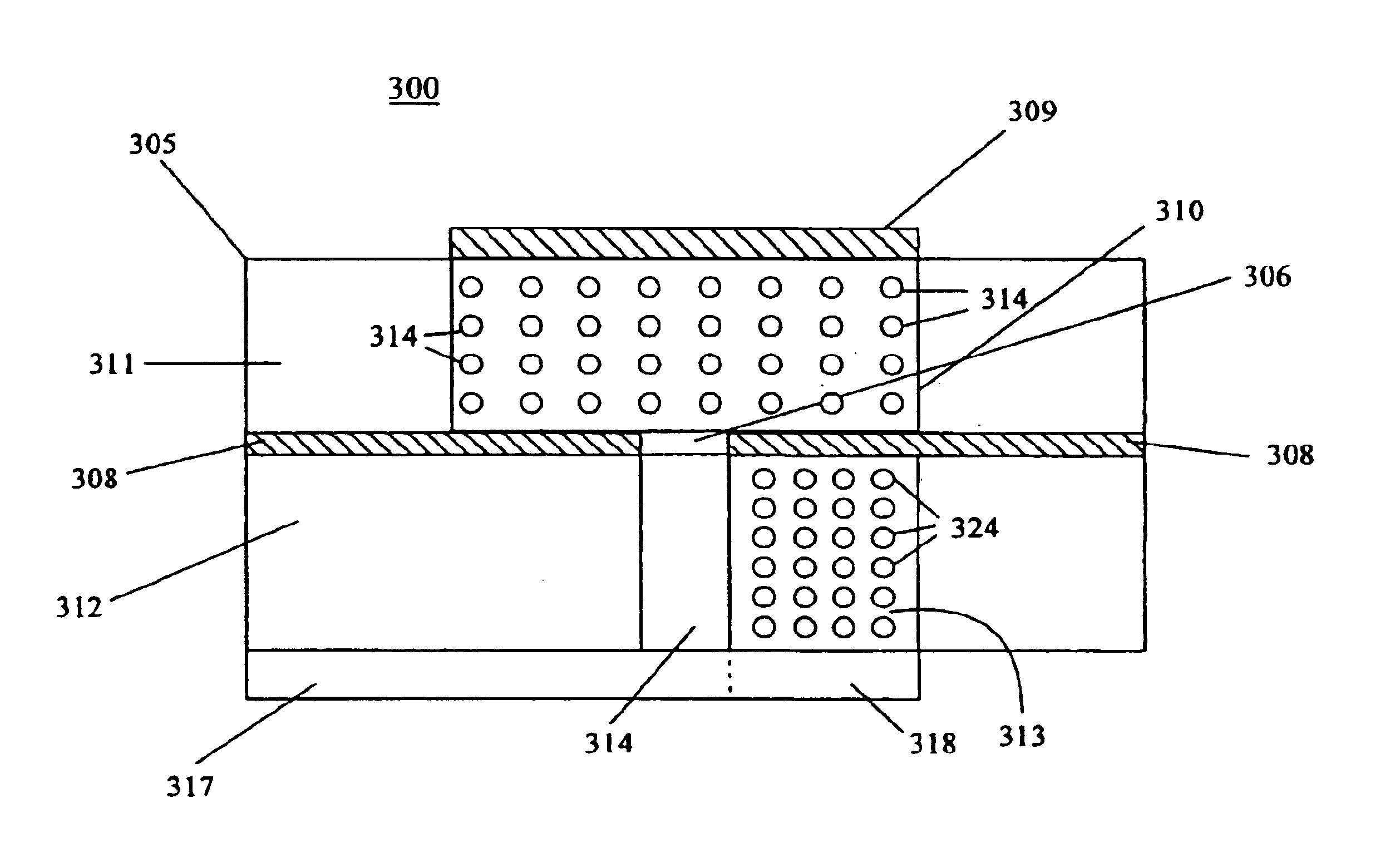
A slot fed microstrip patch antenna (200) includes an electrically conducting ground plane (208), the ground plane (208) having at least one coupling slot (206) and at least a first patch radiator (209). An antenna dielectric substrate material (205) is disposed between the ground plane (208) and the first patch radiator (209), wherein at least a portion of the antenna dielectric (210) includes magnetic particles (214). A feed dielectric substrate (212) is disposed between a feed line (217) and the ground plane (208). Magnetic particles can also be used in the feed line (217) dielectric. Patch antennas according to the invention can be of a reduced size through use of high relative permittivity dielectric substrate portions, yet still be efficient through use of dielectrics including magnetic particles which permit impedance matching of dielectric medium interfaces, such as the feed line (217) into the slot (206).
Owner:HARRIS CORP
On-line detecting and positioning device for local discharging of electrical insulated combined electrical appliance, and positioning method thereof
InactiveCN1834669AConsistent directionSuppression of interfering signalsTesting dielectric strengthFault locationMicrostrip patch antennaSensor array
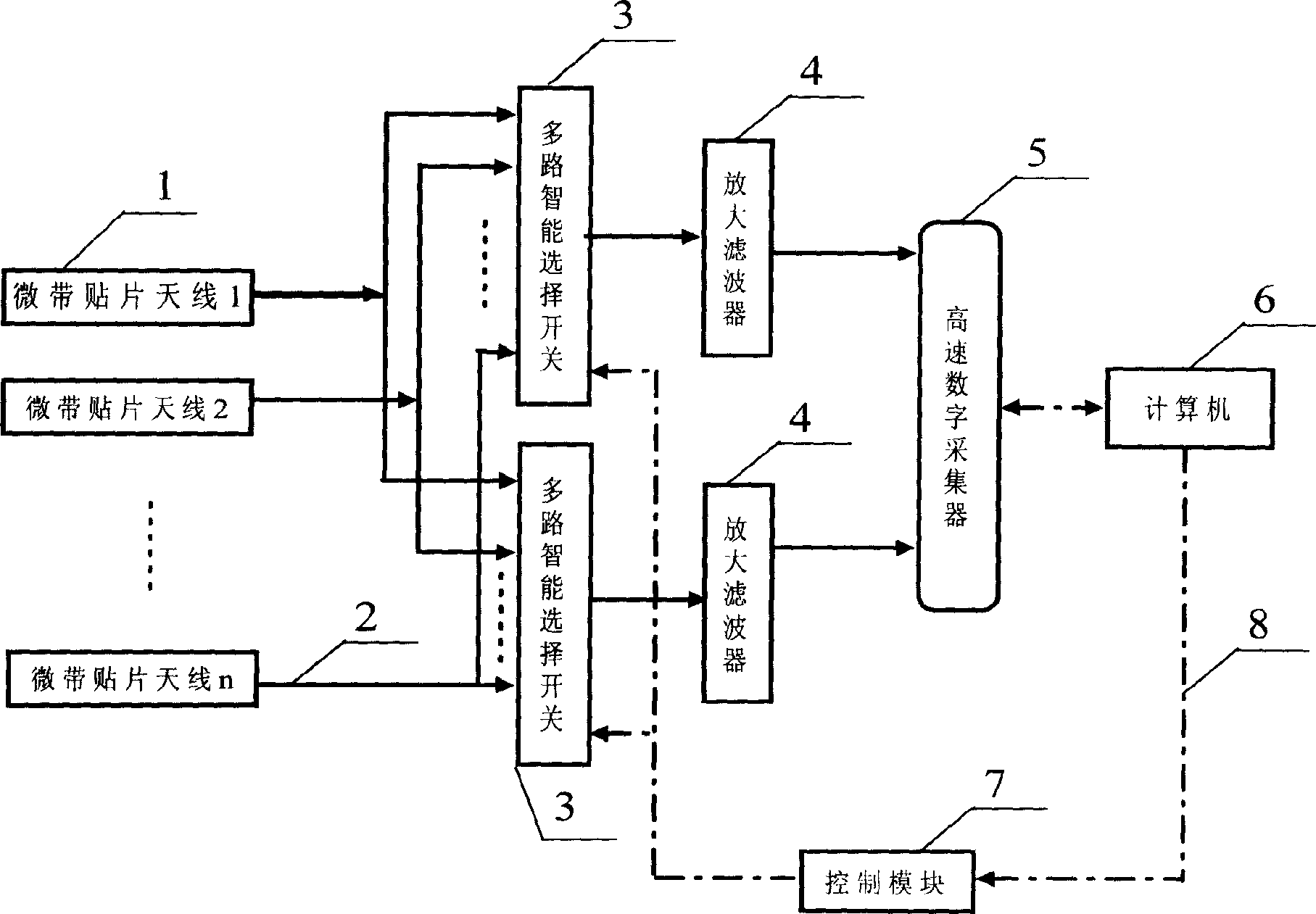
This invention relates to gas insulation combination electric apparatus partial discharge online detecting and position equipment and its position method. It belongs to electric equipment insulation detecting technique field. This invention includes sensor array consisted by microtrip patch antenna, two groups multiple intelligence selecting switch; two amplify filter, high speed digital collector, computer and control module. The array in this invention is made up by the microtrip patch antennas fixed at GIS basin type insulator, its antenna is made up by rectangular metal patch, medium board, metal platter, coaxial probe type feed line and antenna shielding case. This invention is computer program control, it can online, actual time, quickly, actually poison of GIS inner discharging. This invention can be widely used to electric generator plant booster station and electric network GIS electric substation, it can auto detecting GIS inner partial discharge, and actually poison of partial discharging defect, also it can interconnection run with electric substation and electric generator plant auto monitoring system.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
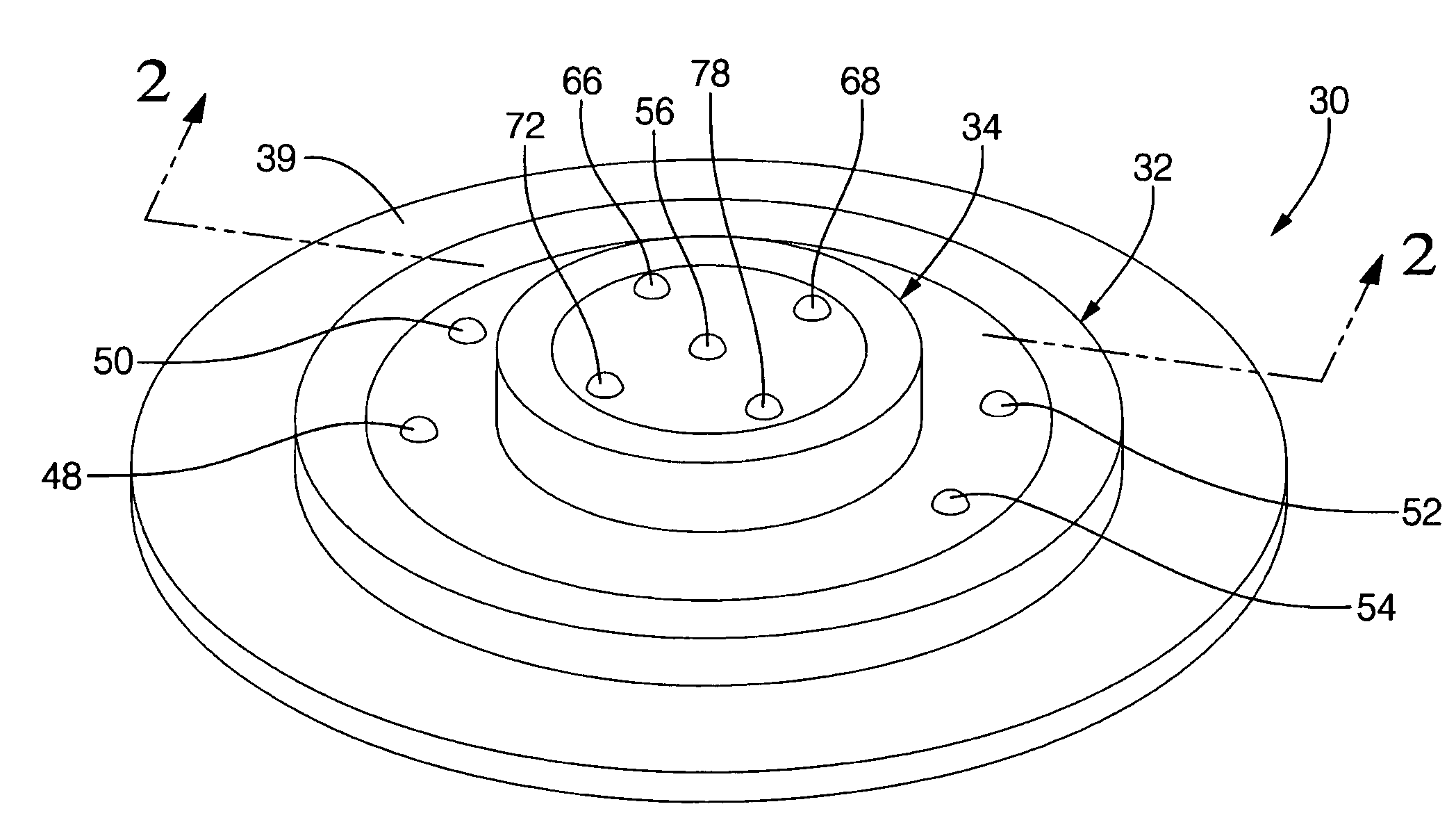
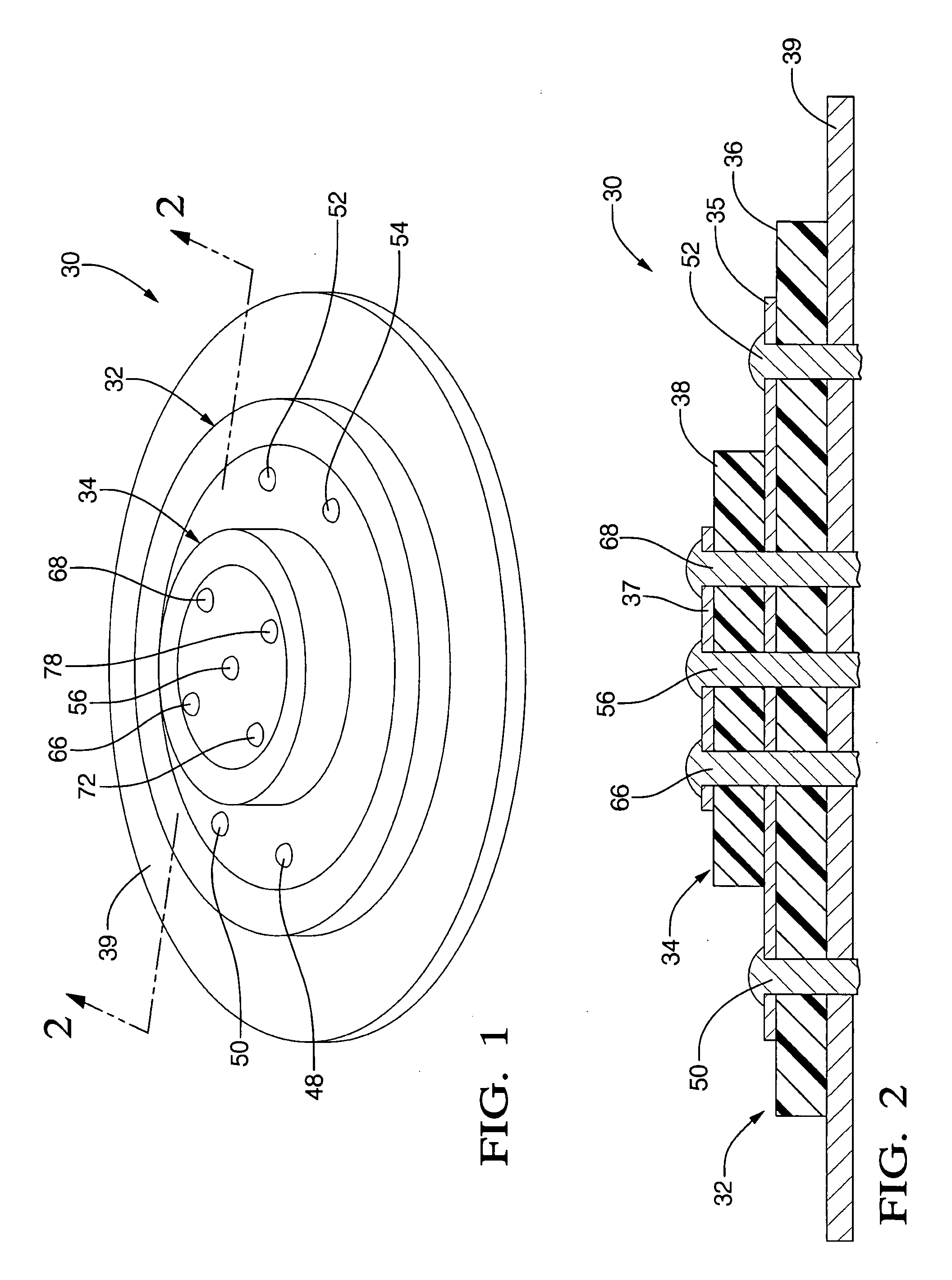
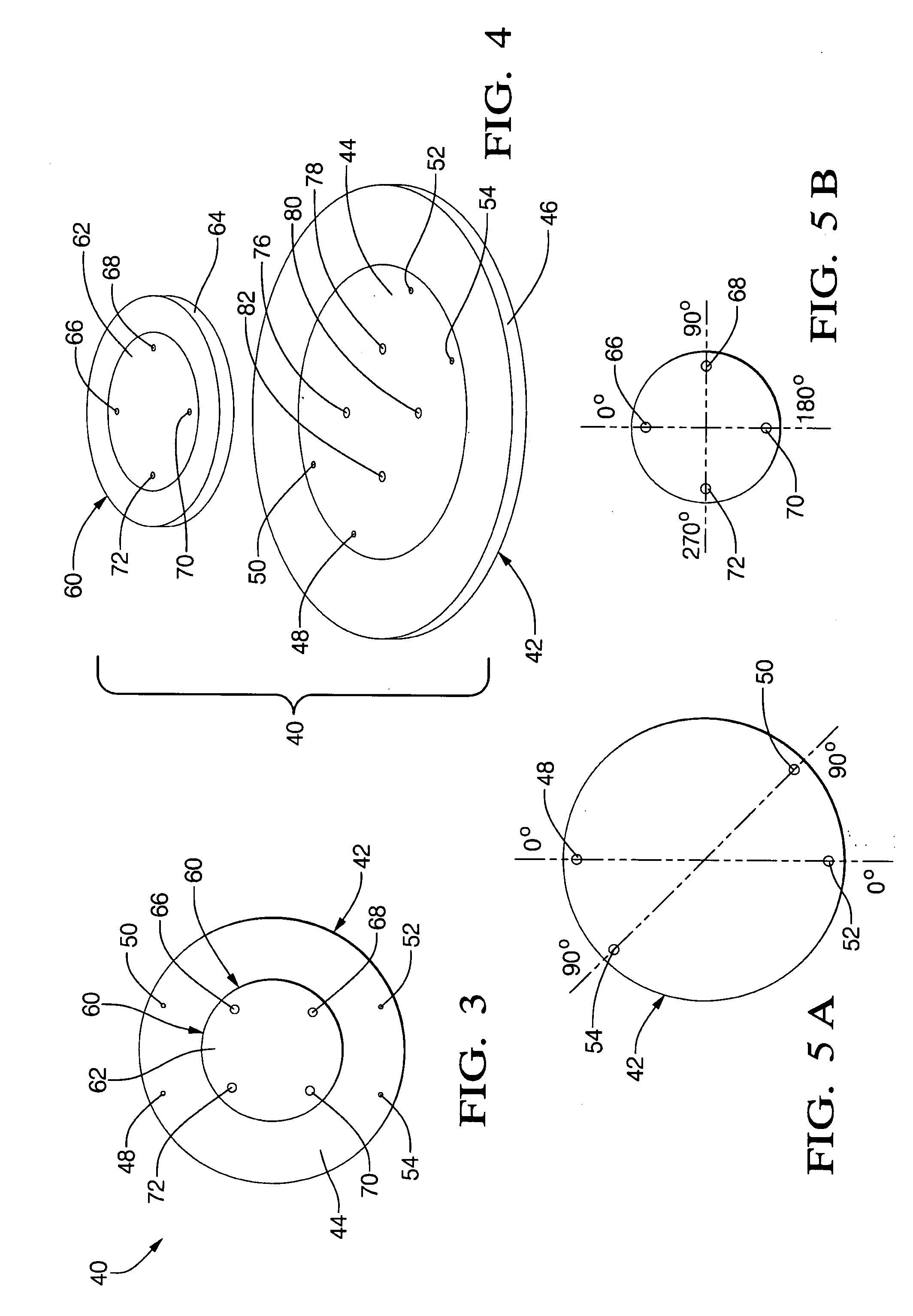
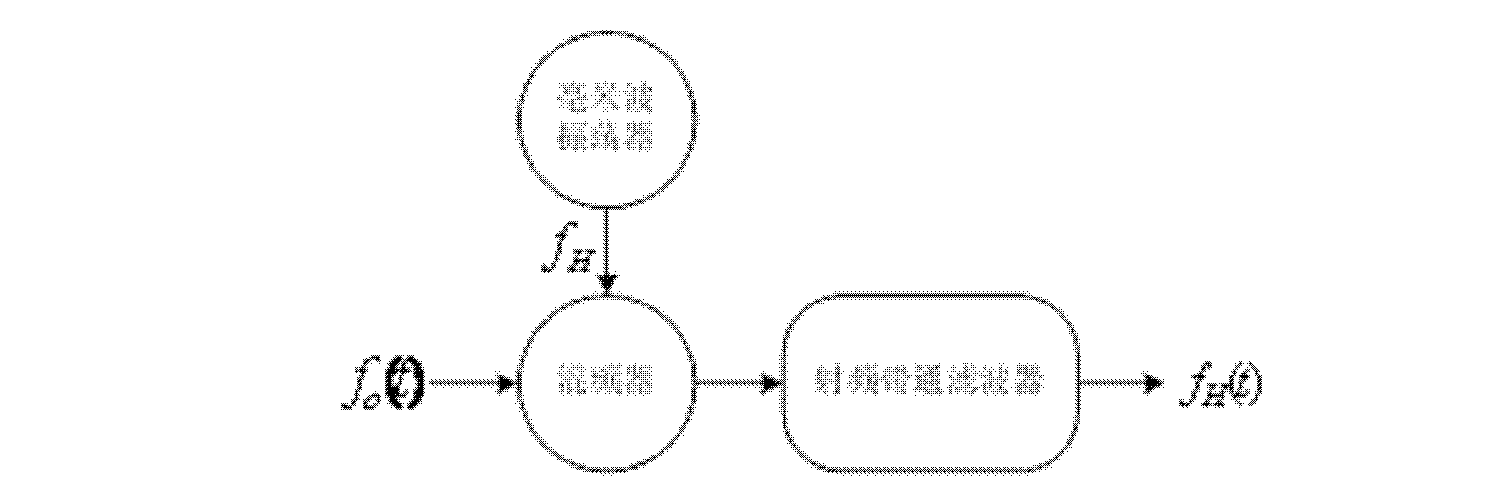
Double-sideband suppressed-carrier radar to null near-field reflections from a first interface between media layers
InactiveUS20080218400A1Increase reflectionSlitting machinesDetection using electromagnetic wavesMicrostrip patch antennaAntenna design
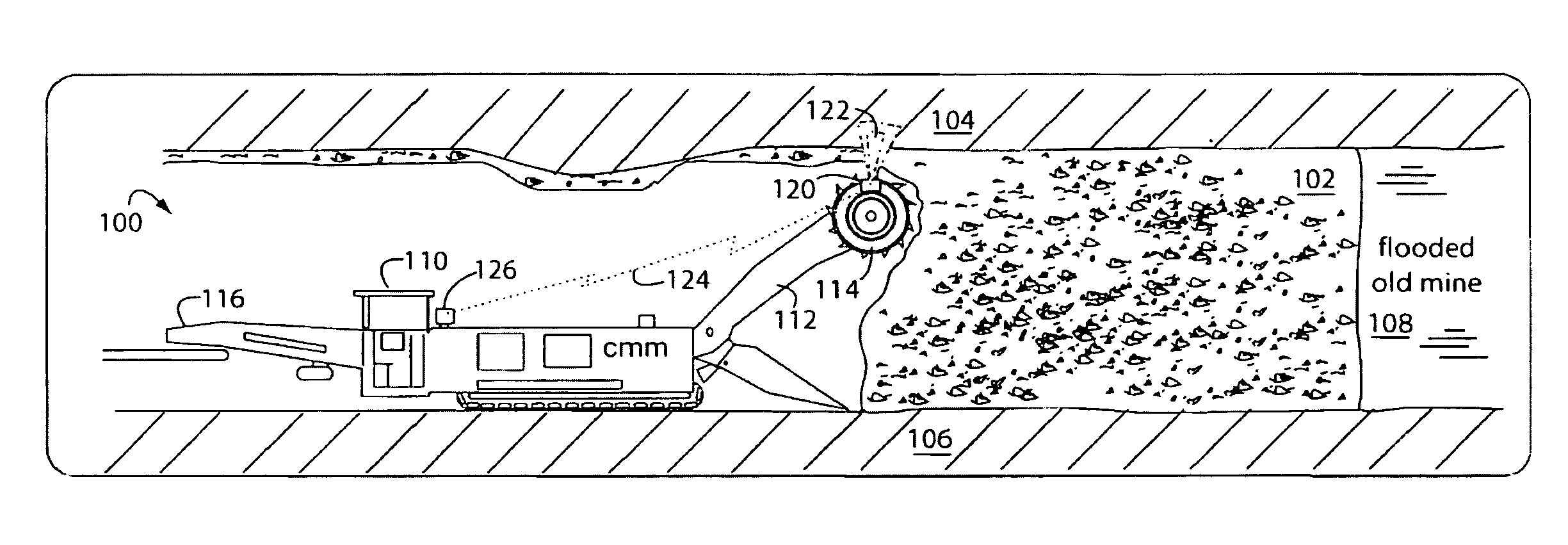
A ground-penetrating radar comprises a software-definable transmitter for launching pairs of widely separated and coherent continuous waves. Each pair is separated by a constant or variable different amount double-sideband suppressed carrier modulation such as 10 MHz, 20 MHz, and 30 MHz Processing suppresses the larger first interface reflection and emphasizes the smaller second, third, etc. reflections. Processing determines the electrical parameter of the natural medium adjacent to the antenna.The modulation process may be the variable or constant frequency difference between pairs of frequencies. If a variable frequency is used in modulation, pairs of tunable resonant microstrip patch antennas (resonant microstrip patch antenna) can be used in the antenna design. If a constant frequency difference is used in the software-defined transceiver, a wide-bandwidth antenna design is used featuring a swept or stepped-frequency continuous-wave (SFCW) radar design.The received modulation signal has a phase range that starts at 0-degrees at the transmitter antenna, which is near the first interface surface. After coherent demodulation, the first reflection is suppressed. The pair of antennas may increase suppression. Then the modulation signal phase is changed by 90-degrees and the first interface signal is measured to determine the in situ electrical parameters of the natural medium.Deep reflections at 90-degrees and 270-degrees create maximum reflection and will be illuminated with modulation signal peaks. Quadrature detection, mixing, and down-conversion result in 0-degree and 180-degree reflections effectively dropping out in demodulation.
Owner:STOLAR
Low profile hybrid phased array antenna system configuration and element
InactiveUS20050243005A1Simultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsMicrostrip patch antennaSystem configuration
A microstrip patch antenna is provided having a high gain performance with a smaller size compared to existing approaches. The antenna includes a patch having a polygon shape, such as a convex polygon, and a modified V-slot in the polygon patch including high-frequency control segments. Such an antenna has a dual band performance, such as in the Ka and Ku bands. An array of antenna elements is also described, as well as an ultra low profile phased array antenna system.
Owner:INTELWAVES TECH
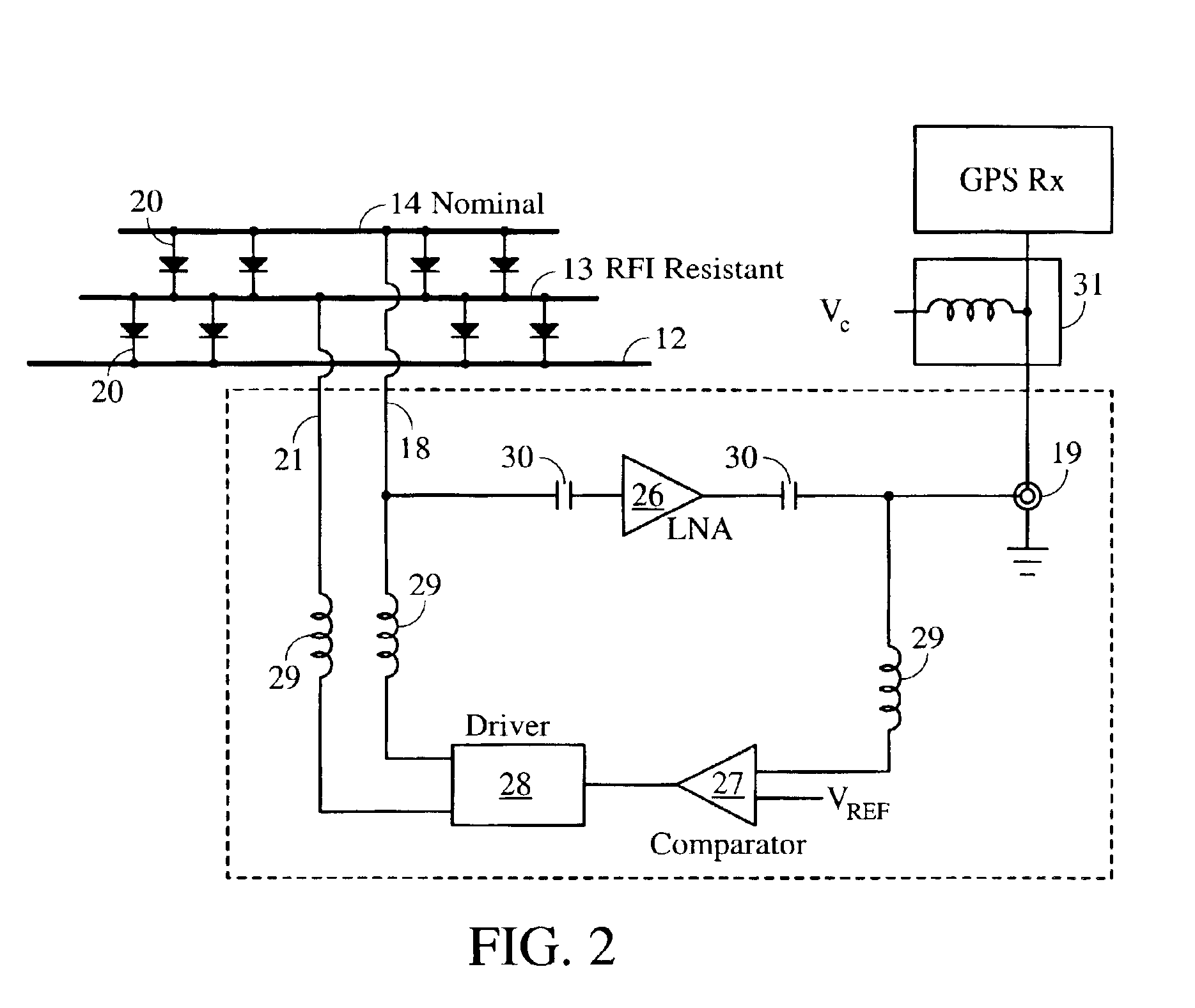
Dual-element microstrip patch antenna for mitigating radio frequency interference
InactiveUS6930639B2High sensitivityLess sensitivitySimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsMicrostrip patch antennaHorizon
Method and apparatus for reducing radio frequency interference (RFI) using a dual-element patch antenna [10]. The antenna possesses two antenna elements [13, 14] having distinct radiation patterns. Either element may be independently selected using a DC bias voltage. Diodes [20] connected to the elements serve to disable one element when the other is selected. In one selected mode, a nominal radiation pattern provides a broad, hemispherical shaped sensitivity that is designed for acquiring and tracking all navigation satellites above the horizon. This nominal radiation pattern, however, is susceptible to interference that is present near or below the horizon. The second selectable radiation pattern of the dual-element antenna has comparatively higher gain toward zenith, and lower gain at and below the horizon to mitigate interference. This combination of features is packaged in a single antenna unit that can be a direct replacement for existing antennas. The dual-element antenna unit has a low vertical profile and is suitable for mounting on high-speed moving vehicles.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Dual-polarized microstrip patch antenna structure
ActiveUS20070126641A1Improve toleranceLow profile constructionSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsMicrostrip patch antennaDielectric substrate
A dual-polarized microstrip patch antenna structure comprising: a dual microstrip feed line circuitry underneath a bottom dielectric substrate; a ground plane layer overlying the bottom dielectric substrate, the ground plane layer having coupling apertures etched to the ground plane layer; a middle metallized patch layer stacked over a middle dielectric substrate; a top metallized patch layer stacked underneath a top dielectric substrate; and an air layer between the middle dielectric substrate and the top dielectric substrate separating the middle metallized patch layer and the top metallized patch layer. The microstrip feed line circuitry is configured to utilize corner-feeding techniques for enabling diagonal modes of the patch layers, and the coupling apertures of the ground plane layer are provided with a non-resonant bow-tie shape for enabling aperture coupling between the microstrip feed line circuitry and the patch layers.
Owner:HMD GLOBAL
Fractal counterpoise, groundplane, loads and resonators
InactiveUS7215290B2Lower resonance frequencySimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsMicrostrip patch antennaPhysical shape
An antenna system includes a fractalized element that may be a ground counterpoise, a top-hat located load assembly, or a microstrip patch antenna having at least one element whose physical shape is at least partially defined as a first or higher iteration deterministic fractal. The resultant fractal element may rely upon an opening angle for performance, and is more compact than non-Euclidean ground counterpoise elements or the like. A vertical antenna system includes a vertical element that may also be a fractal, and a vertical antenna can include vertically spaced-apart fractal conductive and passive elements, and at least one fractal ground element. Various antenna configurations may be fabricated on opposite surfaces of a substrate, including a flexible substrate, and may be tuned by rotating elements relative to each other, and / or by varying the spaced-apart distance therebetween. Fractalized ground counterpoise elements and / or microstrip patch antenna systems may be fabricated on a flexible printed circuit substrate, and / or placed within the support mount of a cellular telephone car antenna.
Owner:FRACTAL ANTENNA SYST
Microstrip patch antenna and array antenna using superstrate
InactiveUS6946995B2Enhance the antenna gainSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsMicrostrip patch antennaAntenna gain
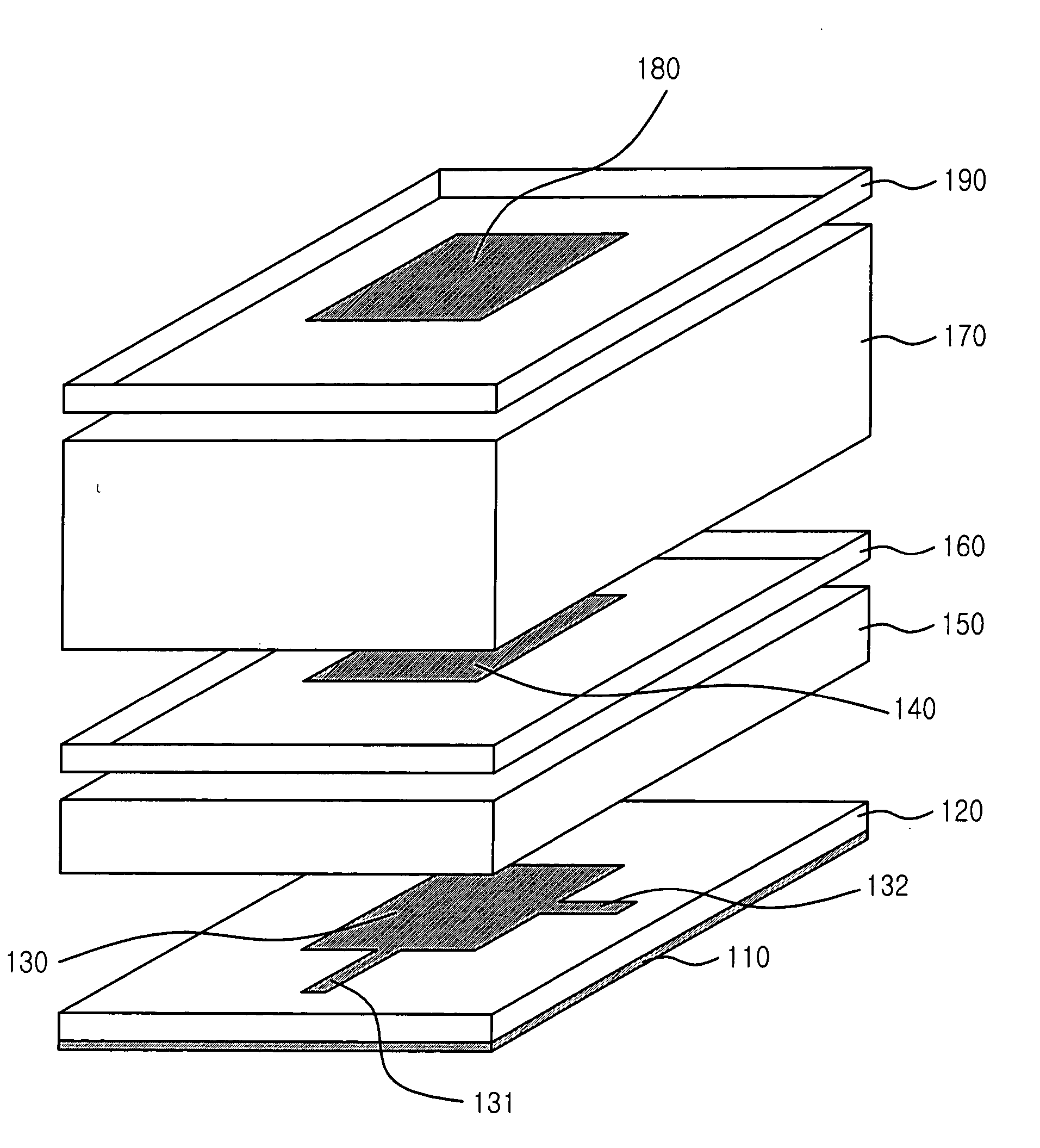
The present invention provides a microstrip patch antenna and array antenna using dielectric superstrate in order to enhance the antenna gain by stacking radiating patches and dielectric layers. The microstrip patch antenna using a dielectric superstrate for having high gain and wide bandwidth, includes: a lower patch antenna layer having a dielectric layer and a ground plane for radiating energy by exciting current by a feedline; a upper patch antenna layer having dielectric film electromagnetically coupled by the lower radiating patch; a foam layer for distancing the upper patch antenna layer from the lower patch antenna layer; and a dielectric superstrate located by being predeteremined distant from the upper patch antenna layer.
Owner:UNILOC 2017 LLC
Microstrip patch antenna including planar metamaterial and method of operating microstrip patch antenna including planar metamaterial
InactiveUS20120223869A1Wide bandwidthAntenna may be miniaturizedSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna equipments with additional functionsMicrostrip patch antennaResonance
Provided is a microstrip patch antenna in which a unit cell of a planar metamaterial may be inserted to have a miniaturized size, a wide bandwidth, or multi-resonance.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST +1
LTCC lamination double-fed circularly polarized micro-strip paster antenna
InactiveCN101859927AGood circular polarization performanceImprove stabilityRadiating elements structural formsAntenna earthingsMicrostrip patch antennaPhase difference
The invention relates to an LTCC lamination double-fed circularly polarized micro-strip paster antenna, which belongs to the technical field of antennae and particularly relates to a micro-strip paster antenna with a low section. The antenna comprises two layers of radiation metal pasters, a grounding metal layer and a feed layer, wherein the four functional layers are spaced by three layers of medium LTCC ceramic dielectric substrates, and the feed layer consists of a Wilkins-layer power divider and a 90-degree phase shift micro-strip line. The geometric centers of the two layers of radiation metal pasters and the grounding metal layer are connected with each other by metal grounding pins, and the double-fed points with 90-degree phase difference on the feed layer are connected with the upper layer of radiation metal paster via metal feed pins. Two edges of each of the two layers of radiation metal pasters are respectively provided with two rectangular frequency modulation electrodes. The invention not only can better give consideration to the performance requirements of low section, broadband and circular polarization of the micro-strip antenna, but also can appropriately regulate the frequency band of the antenna conveniently.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
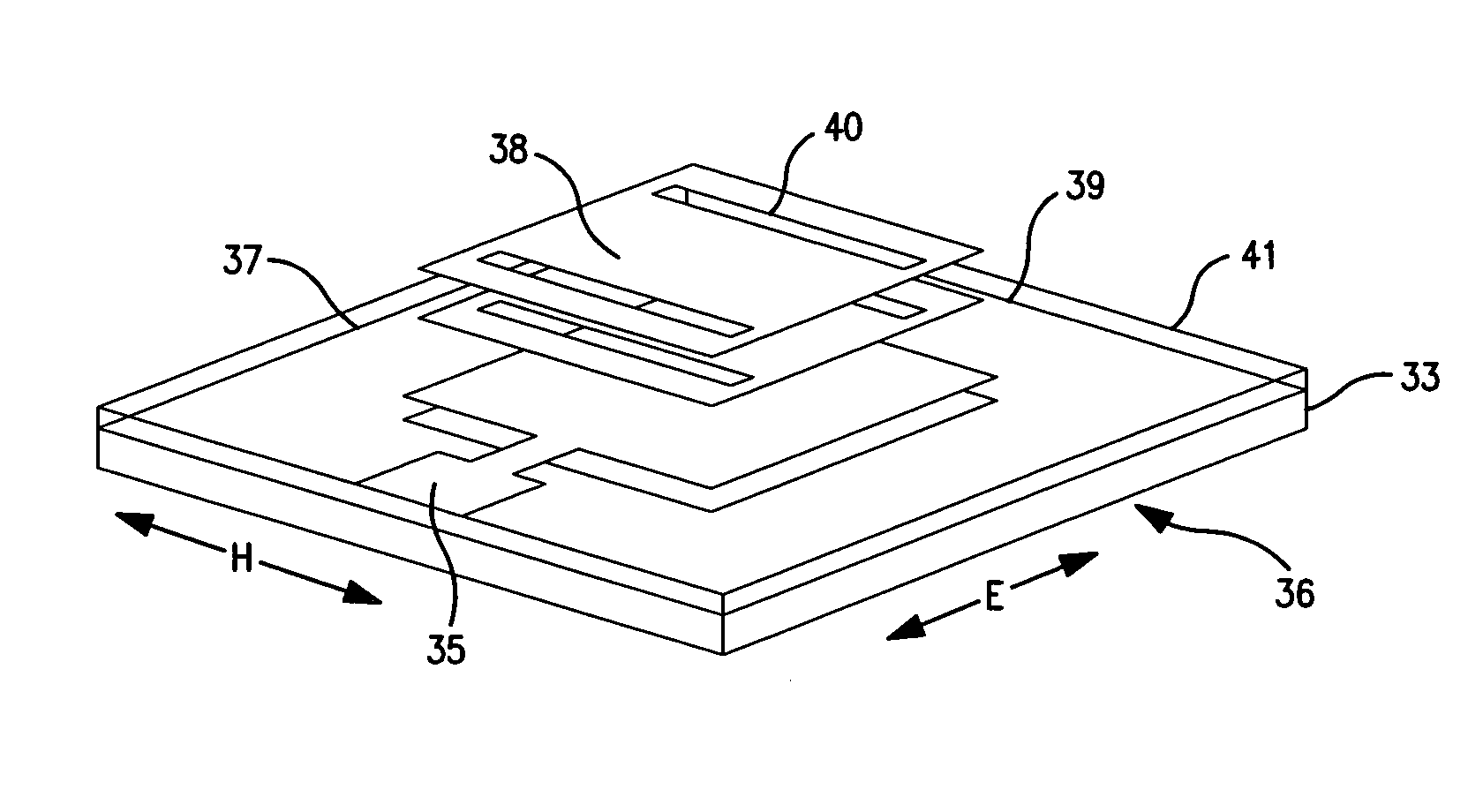
Wideband strip fed patch antenna
InactiveUS20100103049A1Reduce cross-polarized radiationHigh bandwidthAntenna arraysSimultaneous aerial operationsMicrostrip patch antennaWideband
A microstrip patch antenna comprises a patch antenna element comprising a first conductive layer; dual probe feeds separate from each other and spaced from and field coupled to the patch antenna element for transmitting or receiving RF signals, each of the dual probe feeds having a conductor segment and a deltoid shaped conductive strip orthogonal to the conductor segment; the deltoid shaped conductive strips being coplanar; and a first dielectric material layer separating the first conductive layer and the coplanar deltoid shaped conductive strips.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Probe fed patch antenna
ActiveUS20080218417A1Reduce complexityLow costSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsMicrostrip patch antennaCapacitance
A microstrip antenna configuration employs a metallic patch which is positioned on the top surface of a dielectric substrate. The dielectric substrate has the bottom surface coated with a suitable metal to form a ground plane. A hole is formed through the ground plane, through the dielectric to allow access to the bottom surface of the patch. A center conductor of a coaxial cable is directly connected to the patch. The center conductor of the coaxial cable is surrounded by a metallic housing within the substrate area. The patch forms a first plate for the capacitance while the diameter of the outer housing of the coaxial cable within the substrate is increased to form another plate on the end of the coaxial cable. The value of capacitance can be adjusted by the area of the metallic housing the relative dielectric constant of the spacing material, and the spacing between the plates. The sum of the probe inductive impedance and microstrip patch antenna input impedance using the direct probe connection is adjusted and centered at a desired design center frequency and many such frequencies can be accommodated.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Antenna using a photonic bandgap structure
InactiveUS7522105B1Reduce lossSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesMicrostrip patch antennaPhotonic bandgap
A microstrip patch antenna utilizes a microstrip patch antenna substrate formed of photonic bandgap material. One or more periodic patterns may be used therewith to produce multiple bandgaps into the photonic bandgap material. The periodic patterns may be produced by introducing periodic defects into the dielectric material substrate with drilled holes, slots, shorted vias, blind vias, buried vias, and / or plated or unplated patterns, such as plated patterns on the groundplane or on internally positioned surfaces, or on the surface adjacent the radiating elements. One or more radiating elements are used on an upper surface of said microstrip patch antenna substrate, and a groundplane is formed on a lower surface of said microstrip patch antenna substrate.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Arangements of microstrip antennas having dielectric substrates including meta-materials
InactiveUS6943731B2High dielectric constantSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsMicrostrip patch antennaDielectric substrate
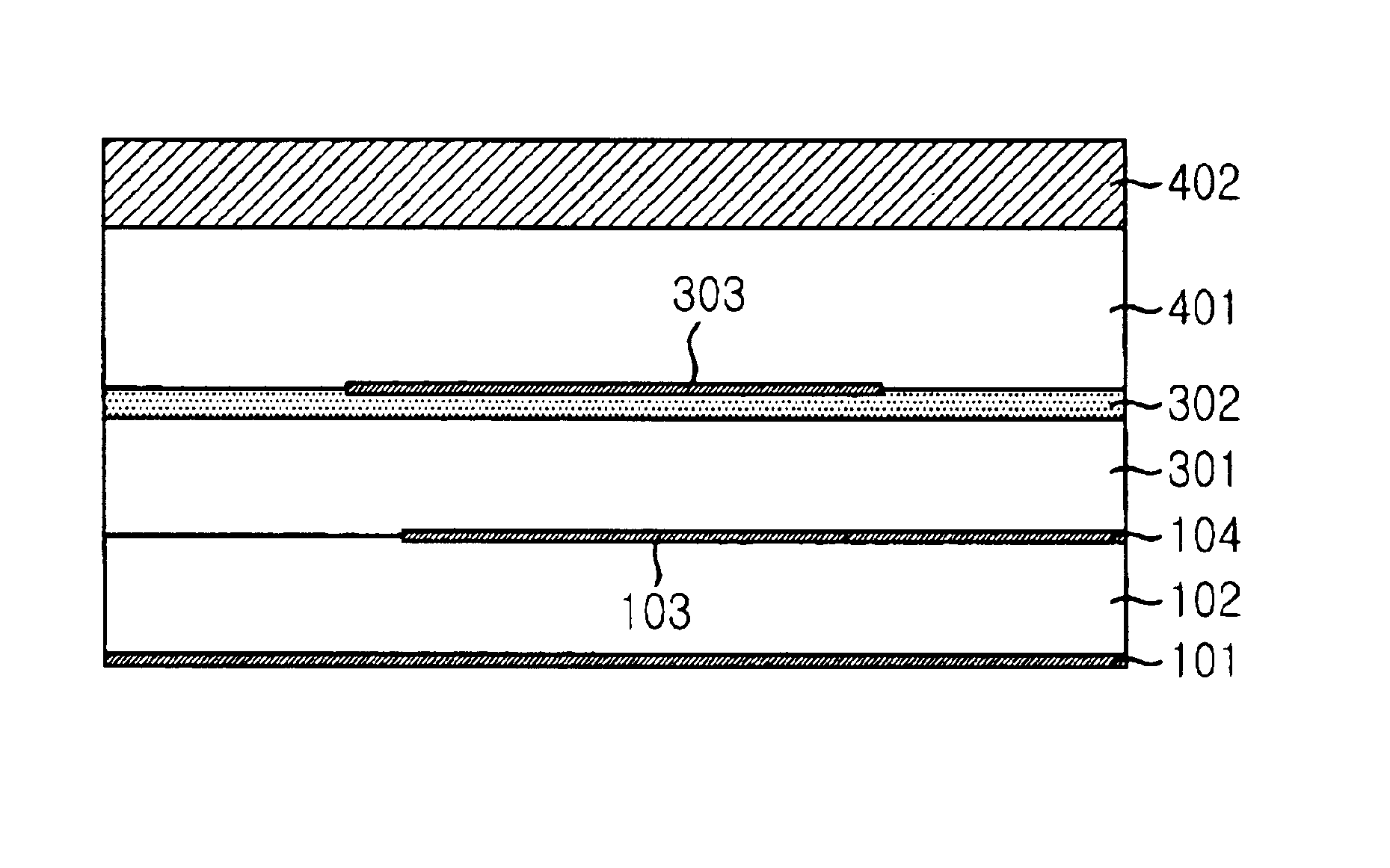
A slot fed microstrip patch antenna (300) includes a conducting ground plane (308), the conducting ground plane (308) including at least one slot (306). A dielectric material is disposed between the ground plane (308) and at least one feed line (317), wherein at least a portion of the dielectric layer (313) includes magnetic particles (324). The dielectric layer between the feed line (317) and the ground plane (308) provides regions having high relative permittivity (313) and low relative permittivity (312). At least a portion of the stub (318) is disposed on the high relative permittivity region (313).
Owner:HARRIS CORP
LTCC lamination microstrip patch antenna
InactiveCN101510630AHigh bandwidthImprove stabilityRadiating elements structural formsMicrostrip patch antennaRadio reception
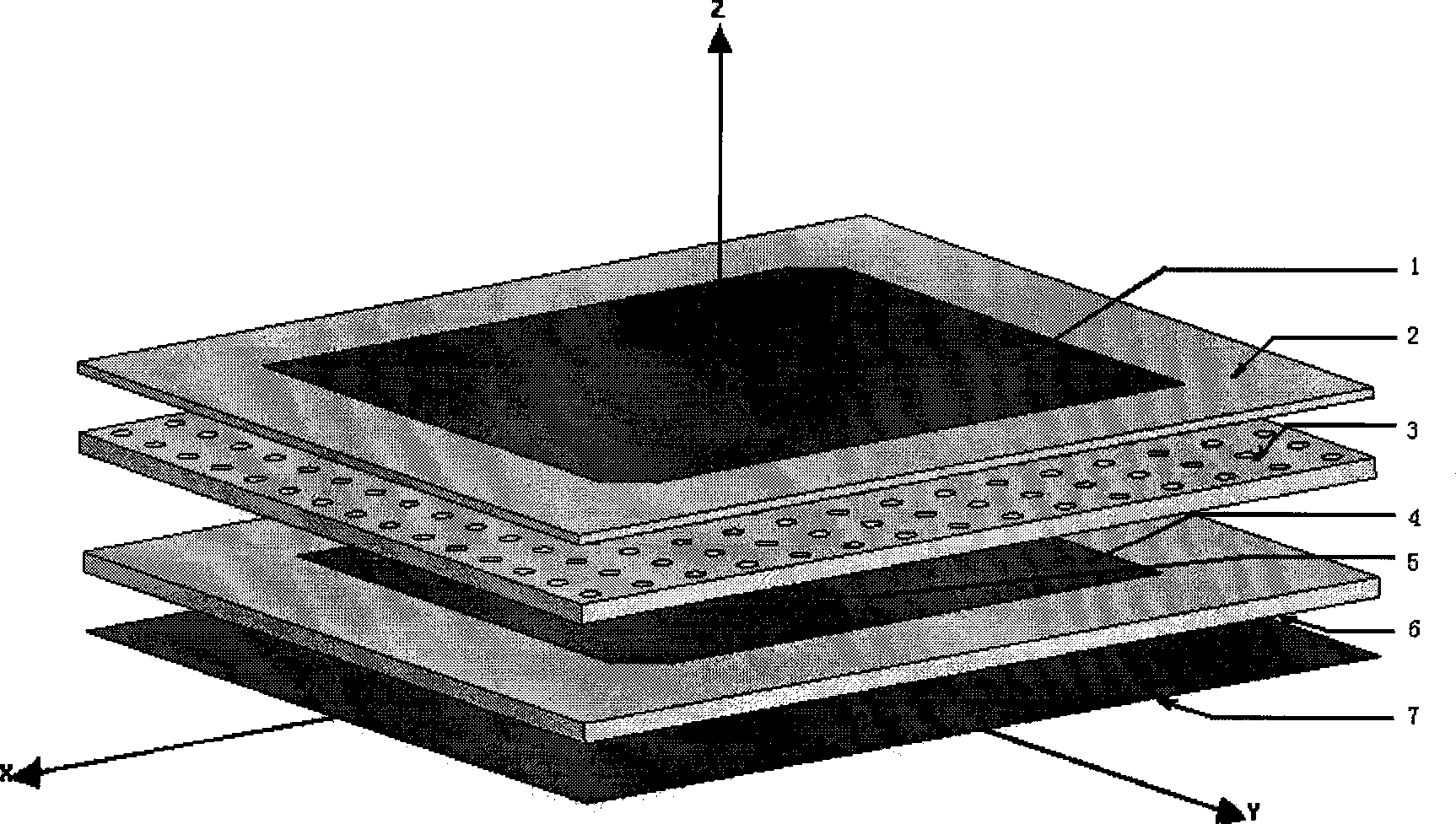
The invention discloses an LTCC-stacked microstrip patch antenna, pertains to the antenna technical field and relates to the LTCC (low temperature co-fired ceramic) technology, in particular to a low profile microstrip patch antenna applied to receiving radio. The microstrip patch antenna comprises three layers of LTCC substrates: the first layer of substrate is provided with a coaxial feeding hole, the upper surface thereof is a first radiation metal patch and the lower surface thereof is a reflection plate; the second layer of substrate is evenly provided with air holes; and the upper surface of the third layer of substrate is a second radiation metal patch. In addition, the microstrip patch antenna also comprises a coaxial feeding needle which is inserted into the coaxial feeding hole from the bottom to be connected with the first radiation metal patch on the first layer of substrate and be insulated with the reflection plate. The first, second and third layers of LTCC substrates form an integrity after passing through an LTCC stack and isostatic pressing technology from the bottom up and co-fire is carried out to the integrity at low temperature so as to form another integrity. The microstrip patch antenna can effectively widen the band width of a microstrip antenna, intensify the coupling between two radiation patches and improve the stability and reliability of the antenna.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Vertical coupled feeding structure applied to millimeter-wave microstrip antenna
InactiveCN104577316ALower effective dielectric constantWorking frequency bandwidthRadiating elements structural formsAntenna earthingsMicrostrip patch antennaCoplanar waveguide
The invention relates to a vertical coupled structure applied to a millimeter-wave microstrip antenna. The vertical coupled structure comprises microstrip patch antennae, a bottom-layer medium chip substrate, a substrate cavity forming structure, a grounding plate with a gap, a top-layer chip substrate and a coplanar waveguide adapter microstrip feeder line. The microstrip patch antennae are arranged on the bottom sides of the bottom-layer medium chip substrate and the top-layer chip substrate. The substrate cavity forming structure is formed by forming a cavity in the bottom-layer medium chip substrate. The coupling caliber of the gap is located between a bottom-layer medium chip and a top-layer chip. The coplanar waveguide adapter microstrip feeder line is arranged on the upper surface of the top-layer chip substrate. The interlayer vertical interconnection problem of the antenna and a radio-frequency circuit when working frequency is within a millimeter-wave frequency range can be solved by means of the vertical coupled structure. The vertical coupled structure has the advantages of being free of weld points and parasitic radiation and capable of obtaining an even radiation pattern, overcoming the adverse influence brought by a traditional single feed mode and design limitations and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Broadcasting receiving apparatus
InactiveUS20010055948A1Minimizing interruptionMinimum interruptionSpatial transmit diversityPolarisation/directional diversityMicrostrip patch antennaMobile vehicle
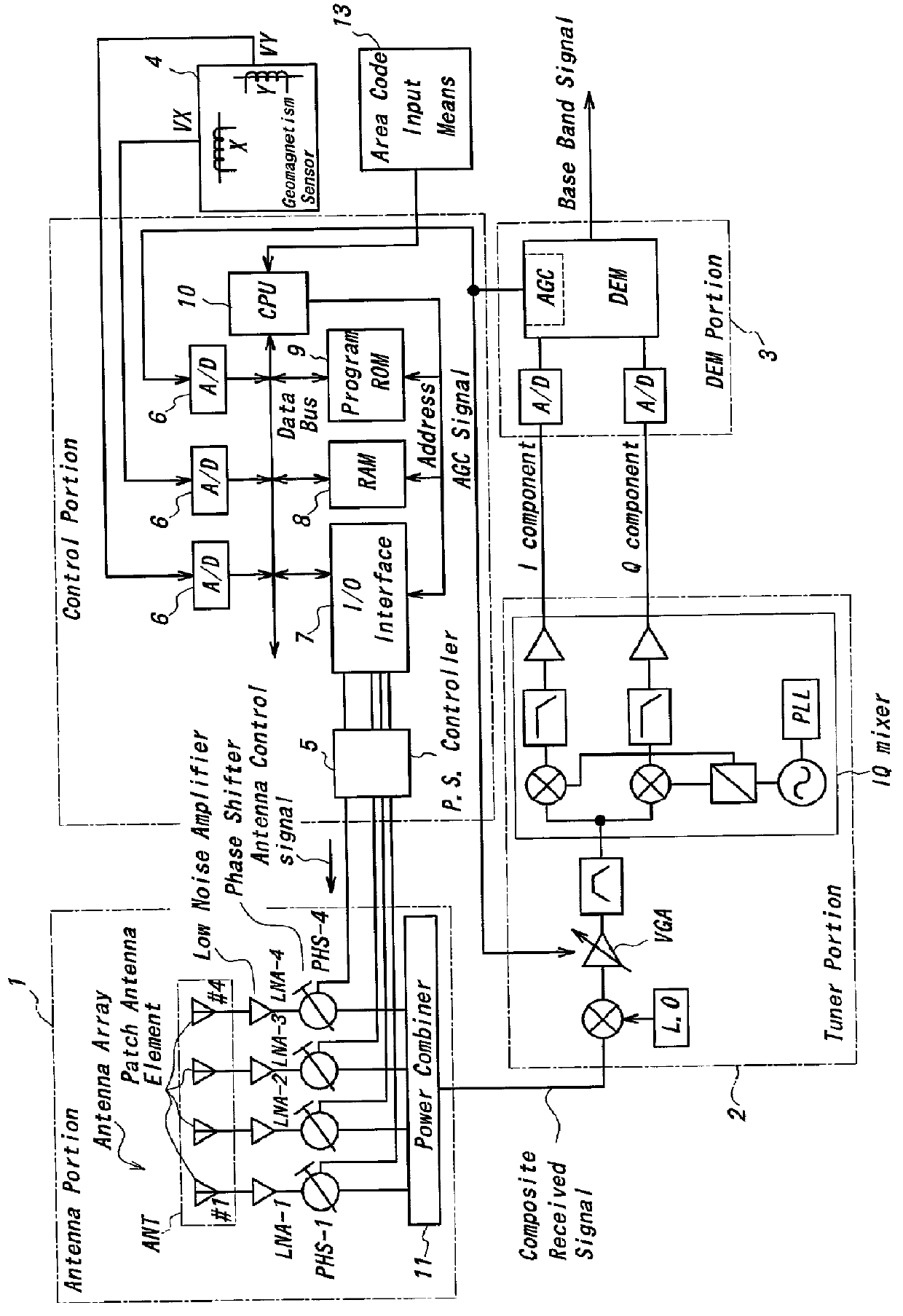
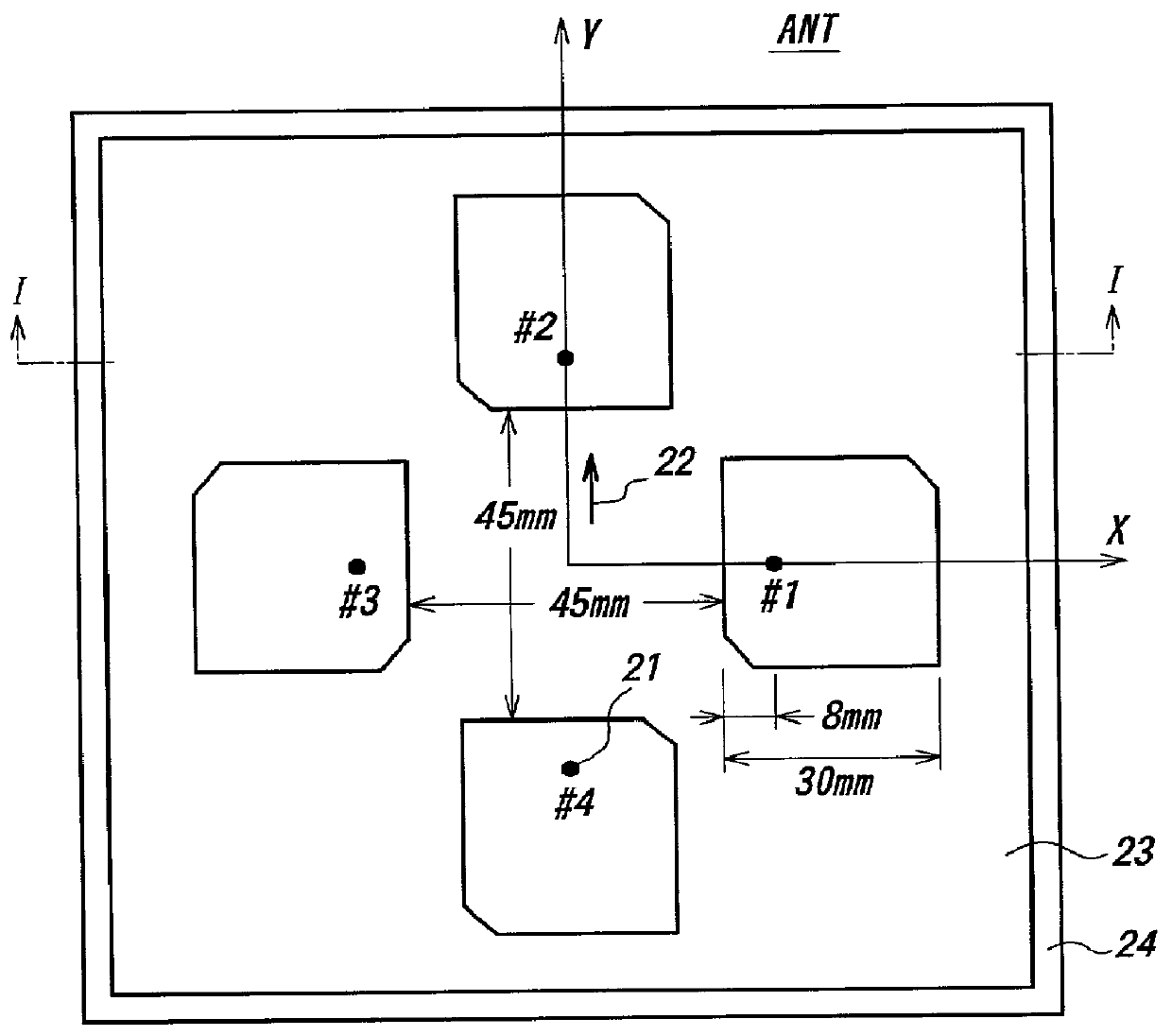
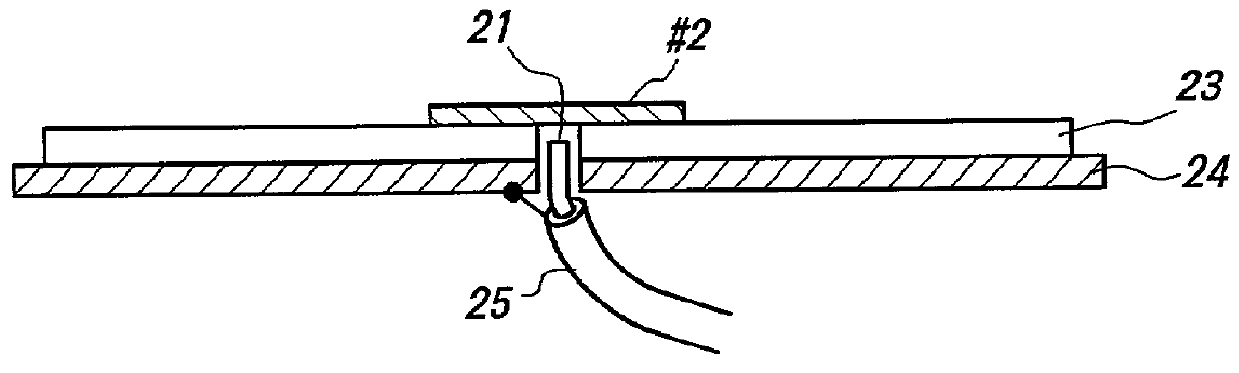
Receiving apparatus for receiving satellite broadcasting electric wave to be mounted mobile vehicle being realized at low cost and not influence by the weather etc. The apparatus is provided with an antenna of which directivity pattern can be varied, and by a geomagnetism sensor mechanically coupled with said antenna to detect present orientation of the antenna, and comprising antenna controlling means by which the directivity pattern of the antenna is directed towards objective broadcasting satellite based on said detected orientation output. When an electric wave from a gap-filler station is to be received, the antenna is controlled to become non-directivity pattern automatically. For the antenna, a microstrip patch antenna having a plurality of conductive patches arranged in a plane is used.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Dual moded stacked microstrip patch antenna
InactiveUS20090102723A1Simultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsMicrostrip patch antennaDual mode
A dual moded stacked microstrip patch antenna includes an integrated first lower antenna element having probes excited at a higher transverse magnetic order mode and a second upper antenna element with probes excited at a lower order transverse magnetic mode. Distinct probe locations and phase offset signals are supplied to each of the probes in each of the first and second antenna elements to support the higher and lower order mode of operation.
Owner:MATEYCHUK DUANE N +1
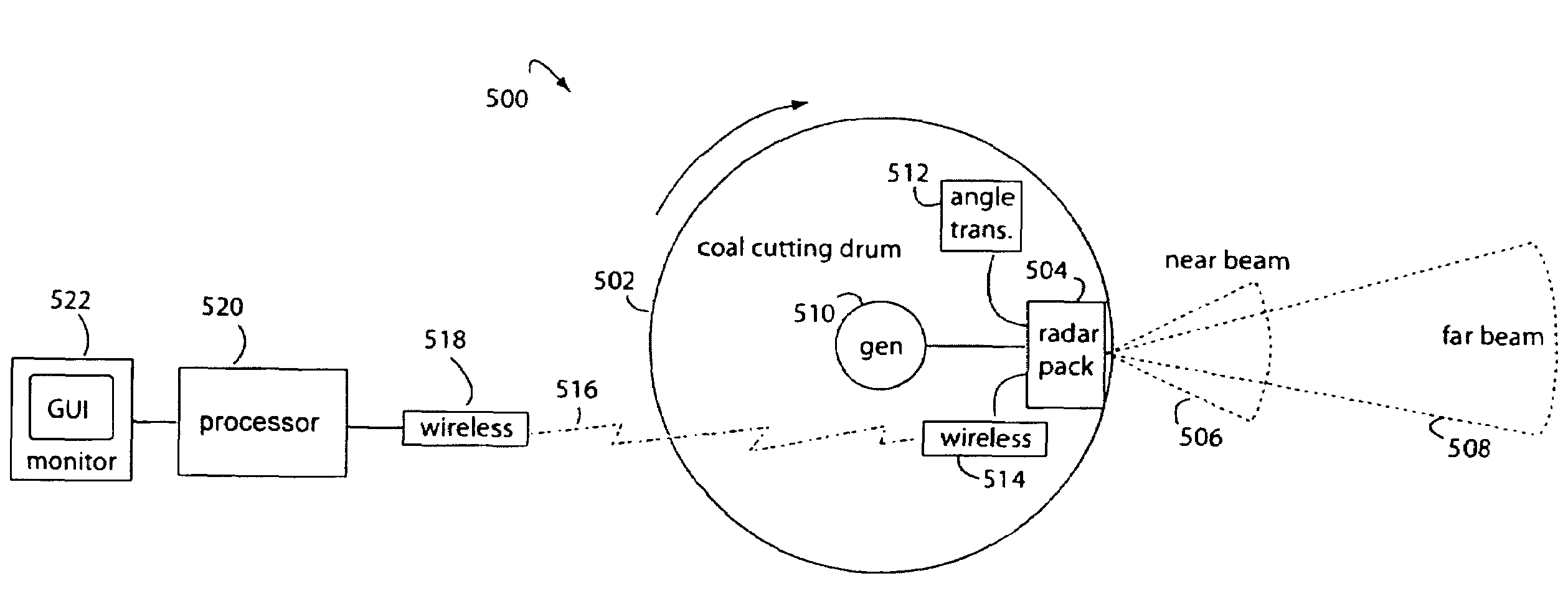
Double-sideband suppressed-carrier radar to null near-field reflections from a first interface between media layers
InactiveUS7656342B2Increase reflectionSlitting machinesDetection using electromagnetic wavesMicrostrip patch antennaAntenna design
Owner:STOLAR
Microstrip patch antenna with reconfigurable directional diagram
InactiveCN101834349AImplement beamformingImplement beam scanningRadiating elements structural formsMicrostrip patch antennaDielectric plate
The invention relates to a microstrip patch antenna with a reconfigurable directional diagram, which belongs to the technical field of antennae. The microstrip patch antenna comprises a metal ground plate on the lower surface of a dielectric plate and a radiation patch on the upper surface of the dielectric plate, wherein the radiation patch consists of a square main radiation patch unit and four appended patch units with same distances from four directions of the square main radiation patch unit; each appended patch unit consists of two rectangular patches connected by an electronic switch; and each electronic switch is respectively controlled by a switch controller. Different switch combinations control different appended patches to perform energy radiation so that a plurality of directional diagrams with multiple working modes can be realized. Meanwhile, the invention has the characteristics of little cross polarization, small size and high gain. The microstrip patch antenna is applicable to different antenna arrays to realize beam forming and scanning.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Microstrip patch antenna having high gain and wideband
ActiveUS20050054317A1High gainHigh widebandSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsMicrostrip patch antennaElectromagnetic coupling
A microstrip patch antenna having high gain and wide band is disclosed. The microstrip patch antenna includes: a first patch antenna layer for radiating a energy supplied from transmitting / receiving feeding circuit and a first radiation patch electrically coupled to the first dielectric layer and supplying the energy to a receiving feeding circuit electrically coupled with the first radiation patch, wherein the energy is supplied by electromagnetic coupling of a first parasitic patch and second parasitic patch; a second patch antenna layer for improving impedance bandwidth of energy received through the first parasitic patch arranged in between the second dielectric layer and the third dielectric layer and radiating the improved impedance bandwidth; and a third patch antenna layer for improving a gain of the energy received through the second parasitic patch arraigned in between the fourth dielectric layer and the fifth dielectric layer.
Owner:UNILOC 2017 LLC
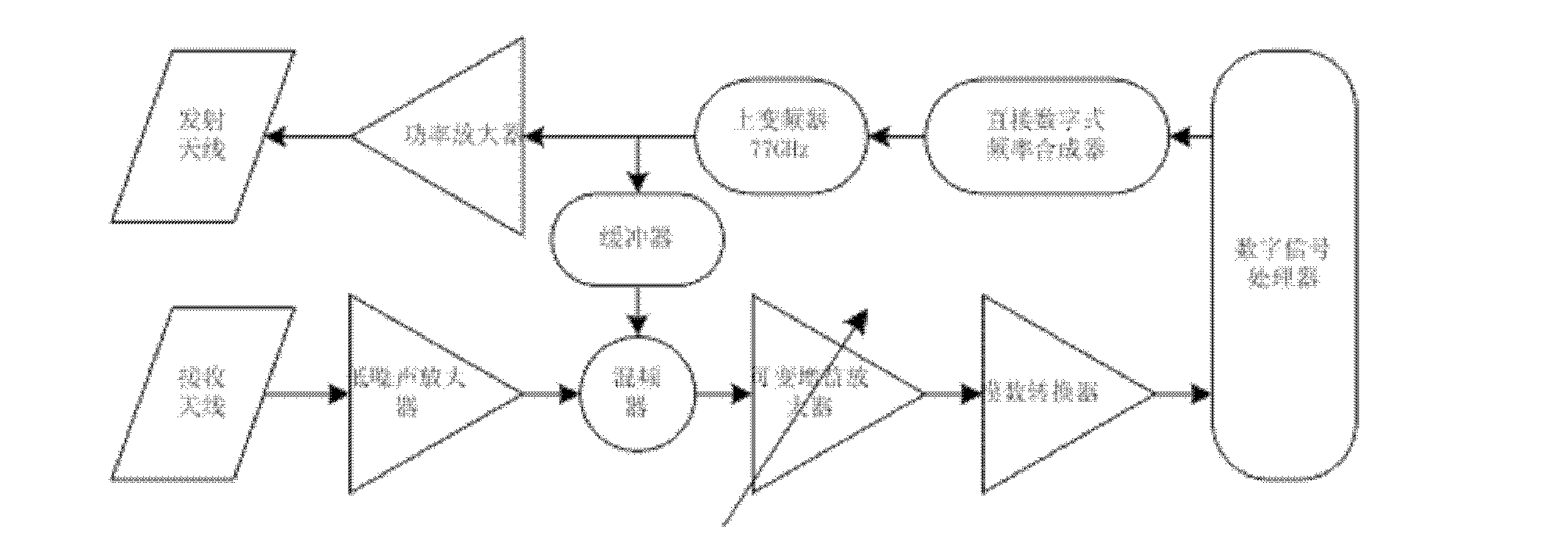
77GHz millimeter wave radio frequency device and using method thereof
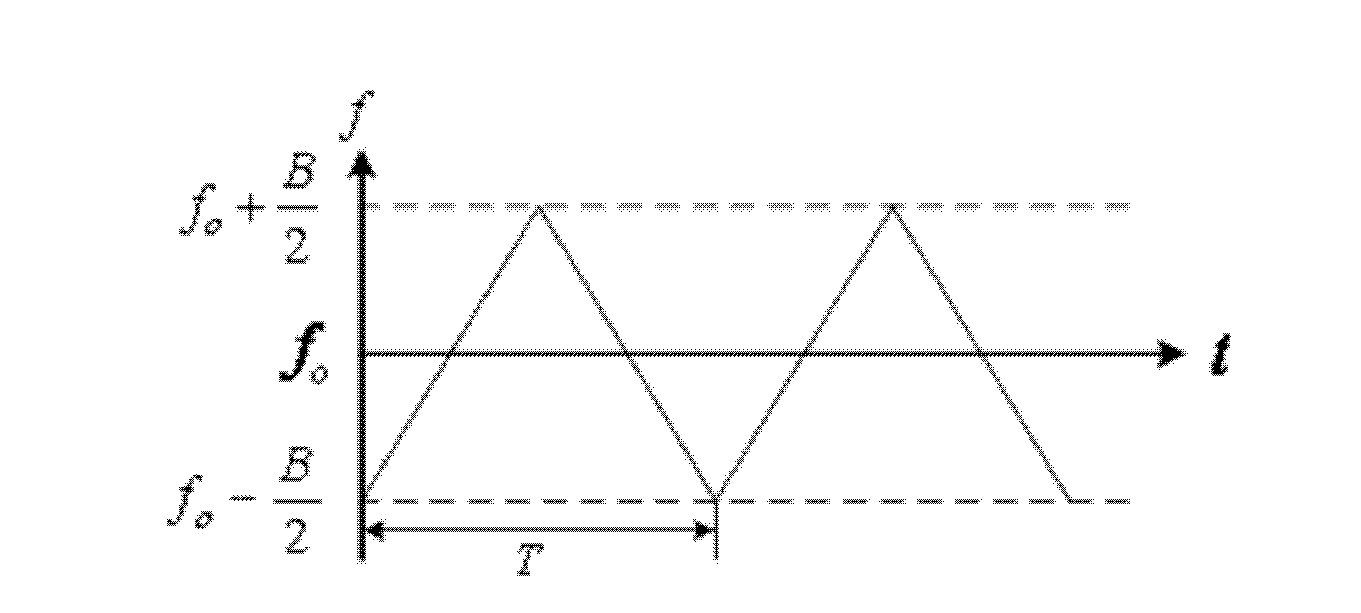
The invention provides a 77GHz millimeter wave radio frequency device and a using method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of millimeter wave radars. The 77GHz millimeter wave radio frequency device comprises a digital signal processor, a direct digital frequency synthesizer, an up-converter, a power amplifier, a buffer, a transmitting antenna, a receiving antenna, a low noise amplifier, a frequency mixer at a receiving terminal, a variable gain amplifier and a demodulating analog-to-digital converter. The 77GHz millimeter wave radio frequency device has the advantages that the 77GHz millimeter wave radio frequency device can be widely applied to millimeter wave range-and-speed measuring radar systems, and 77GHz is adopted as a working frequency band of a millimeter wave radar and combined with a phased-array antenna technology that low temperature co-fired ceramic (LTCC) is used as a substrate to manufacture each micro-strip patch antenna serving as an antenna unit; the direct digital frequency synthesizer is adopted and combined with an up-conversion technology to generate linear frequency modulated continuous waves; and a plurality of transmitter units are adopted andcombined with the phased-array antenna technology to realize horizontal scanning of millimeter wave beams.
Owner:苏州煜瑛微电子科技有限公司
Low-loss dual polarized antenna for satcom and polarimetric weather radar
The present invention is a low-loss polarized antenna for satellite communications and polarimetric weather radar. The antenna may comprise: (a) a microstrip patch antenna, (b) a waveguide, and (c) a coupling interface between the antenna and waveguide. The microstrip patch antennas may individually comprise: (i) a patch radiator having a defined area, and (ii) an associated microstrip.In a further embodiment of the invention, an antenna array is presented. The antenna array may comprise: (a) a plurality of microstrip antennas, and (b) a plurality of waveguides. The antenna array may further comprise: (c) a waveguide combiner. The microstrip patch antennas may individually comprise: (i) a patch radiator having a defined area, and (ii) an associated microstrip.In still a further embodiment of the invention, a method for the manufacturing of an antenna is presented. The method may comprise the step: (a) operably coupling a microstrip patch antenna to a waveguide.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
An LTCC stack coupled feed circularly polarized microstrip patch antenna
InactiveCN102280699AReduce coupling interferenceAdjustable resonant center frequencyRadiating elements structural formsAntenna earthingsMicrostrip patch antennaPhase shifted
The invention relates to an LTCC laminated coupling feed circularly polarized microstrip patch antenna, which belongs to the technical field of antennas. Including the feeding layer and the radiation layer dielectric substrate; the upper surface of the feeding layer dielectric substrate is a grounding metal layer with a "cross" shaped hollow area, and the lower surface has a feeding circuit and a shielding metal layer insulated from the feeding circuit; the feeding circuit Divide and phase-shift the incoming excitation signal into four branch excitation signals with equal amplitude and 90° phase difference, and couple to the radiation metal layer through the "cross" hollow area; the ground metal layer and the shielding metal layer pass through The evenly distributed metallized through holes are connected to each other; the radiation metal layer on the upper surface of the radiation layer dielectric substrate is a fractal pattern structure. The patches are formed iteratively in this way. The invention has the advantages of low profile, wide frequency band, circular polarization and miniaturization.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com