Patents
Literature
117 results about "Channel density" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
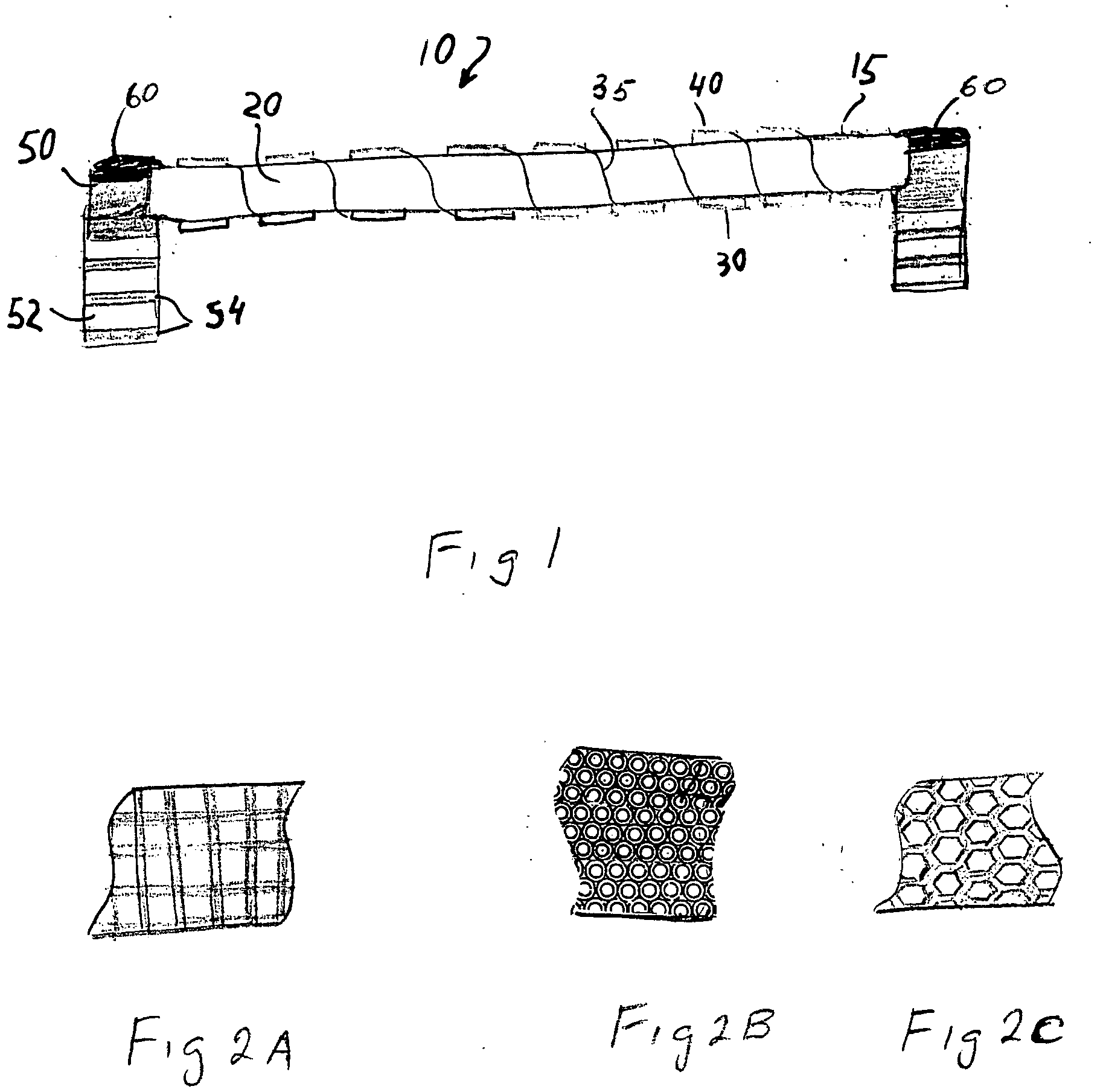
Density channel. A channel used to investigate a density current; for example, in experiments relating to the behavior of cold masses of air in the atmosphere and related frontal structures.
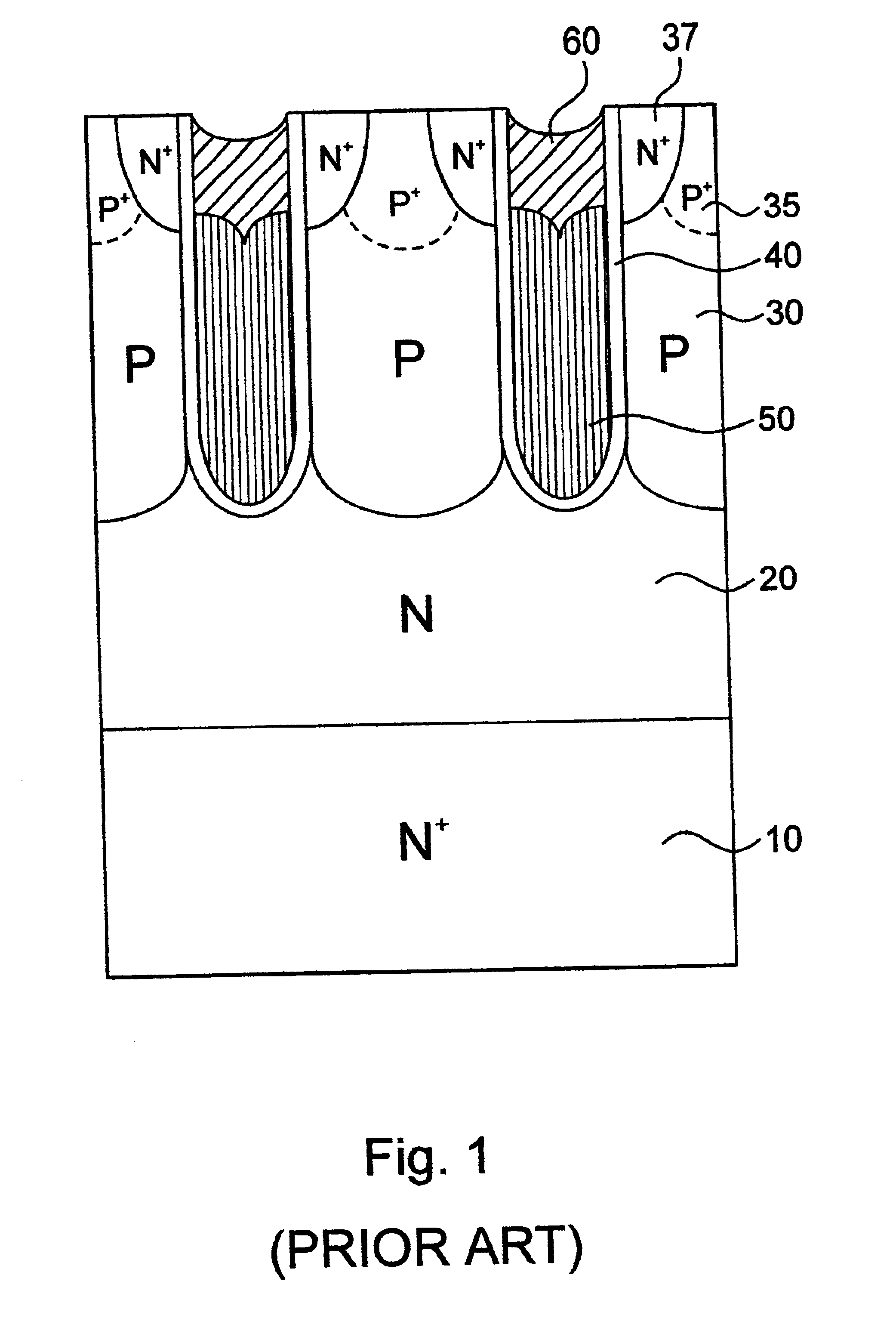
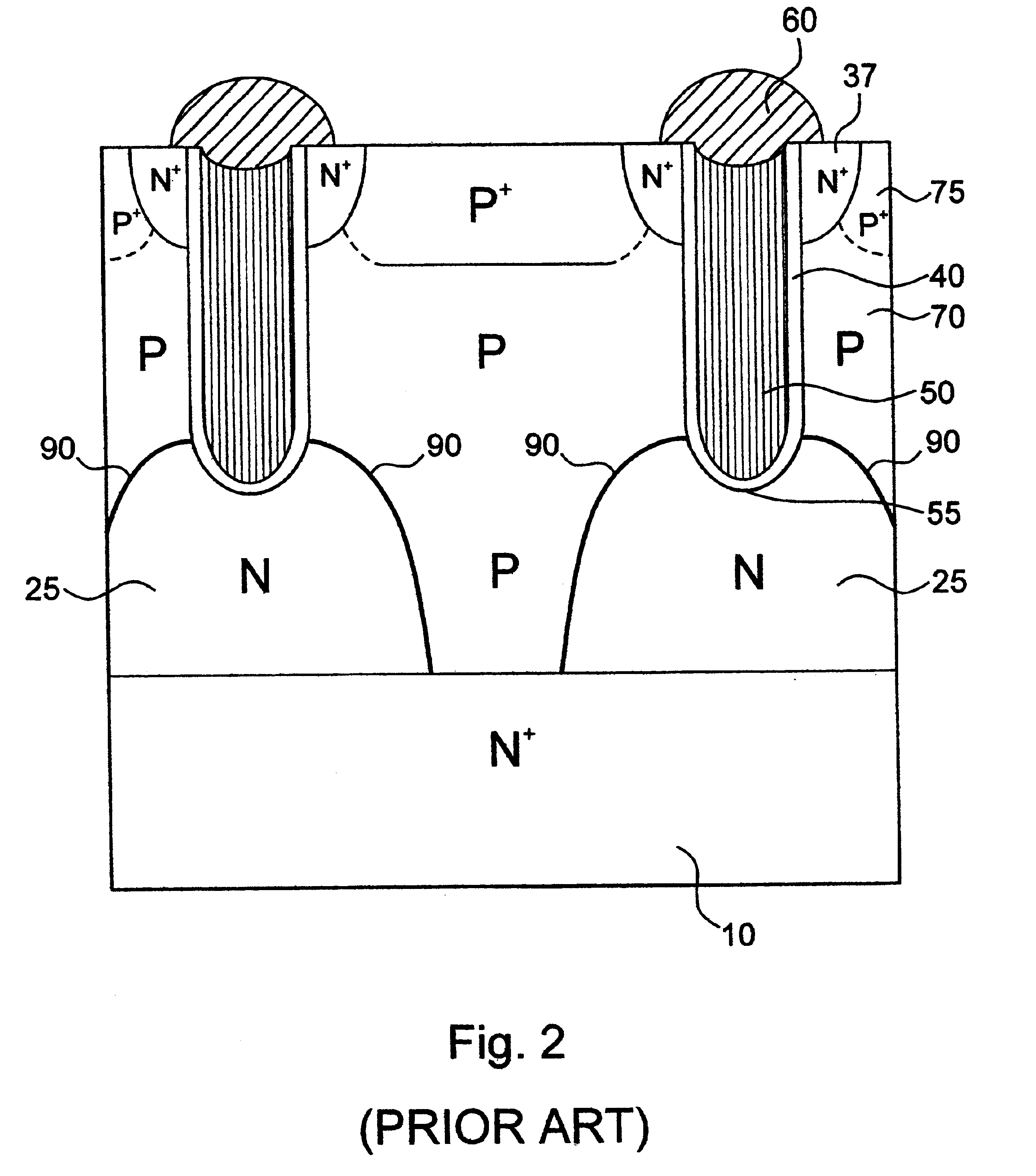
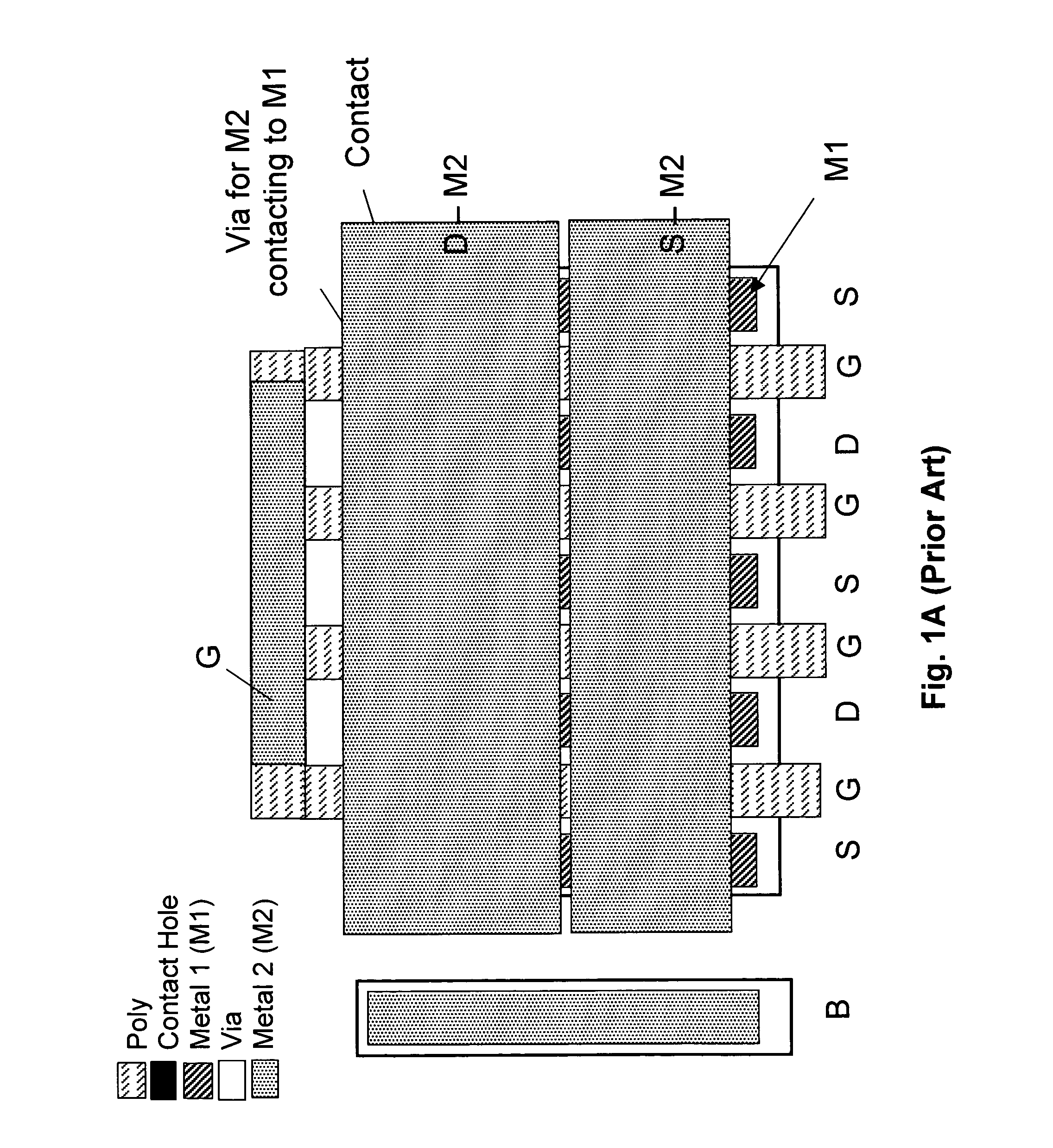
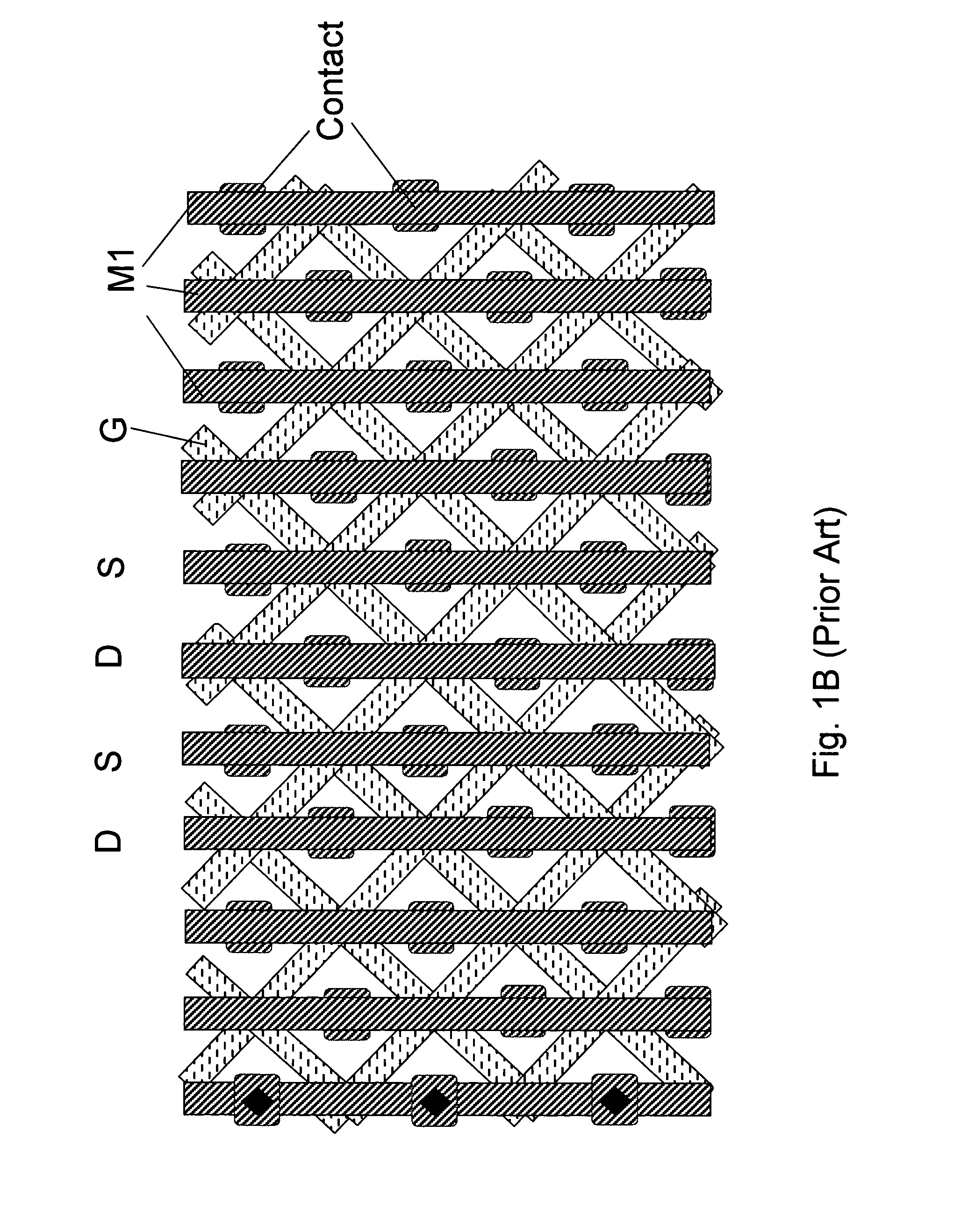
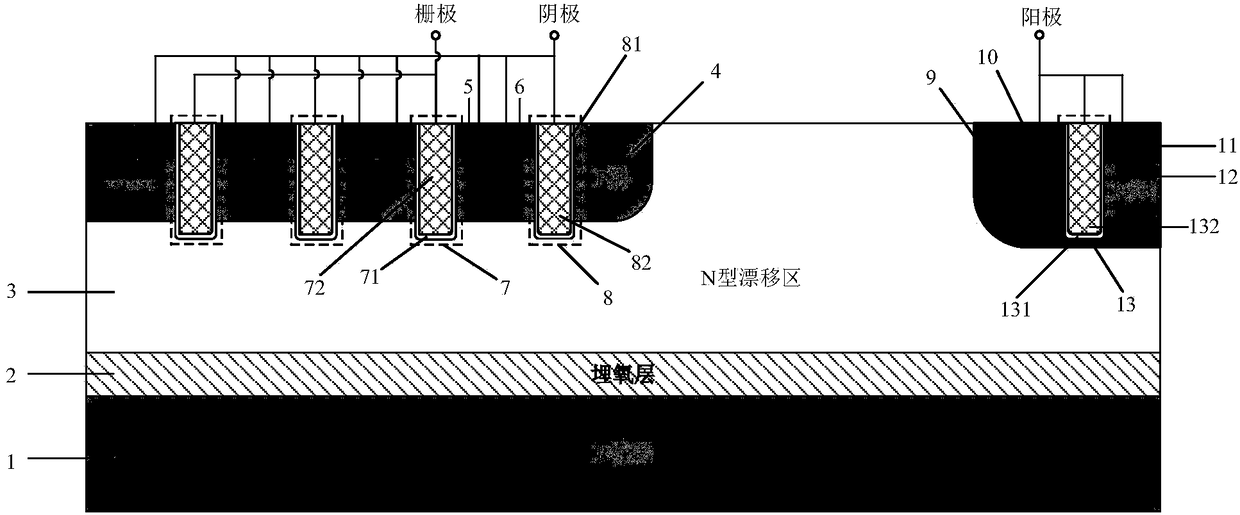
Low voltage high density trench-gated power device with uniformly doped channel and its edge termination technique
InactiveUS6784505B2Increase reverse voltageLow densityTransistorSolid-state devicesDopantChannel density
Merging together the drift regions in a low-power trench MOSFET device via a dopant implant through the bottom of the trench permits use of a very small cell pitch, resulting in a very high channel density and a uniformly doped channel and a consequent significant reduction in the channel resistance. By properly choosing the implant dose and the annealing parameters of the drift region, the channel length of the device can be closely controlled, and the channel doping may be made highly uniform. In comparison with a conventional device, the threshold voltage is reduced, the channel resistance is lowered, and the drift region on-resistance is also lowered. Implementing the merged drift regions requires incorporation of a new edge termination design, so that the PN junction formed by the P epi-layer and the N<+> substrate can be terminated at the edge of the die.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
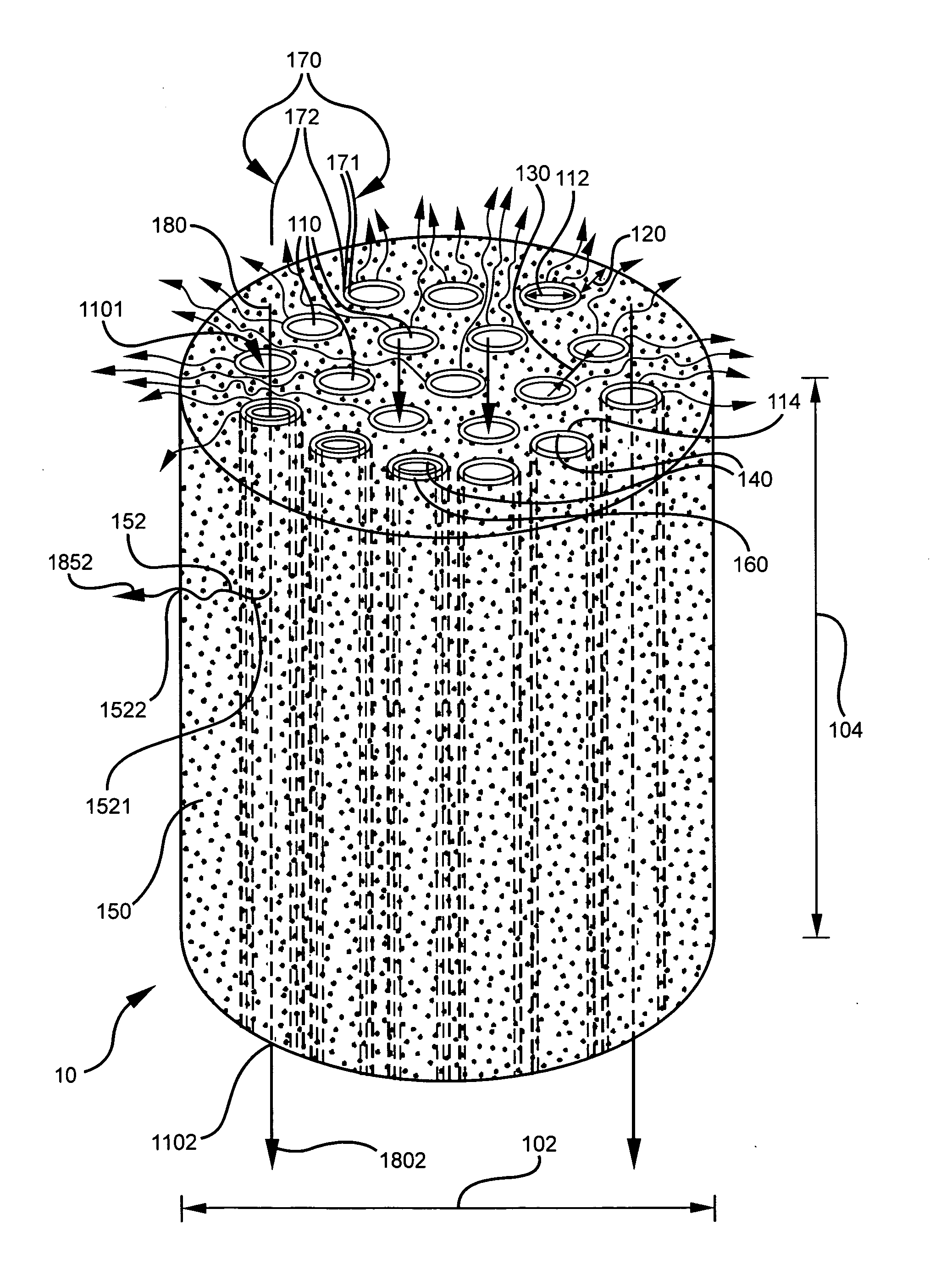
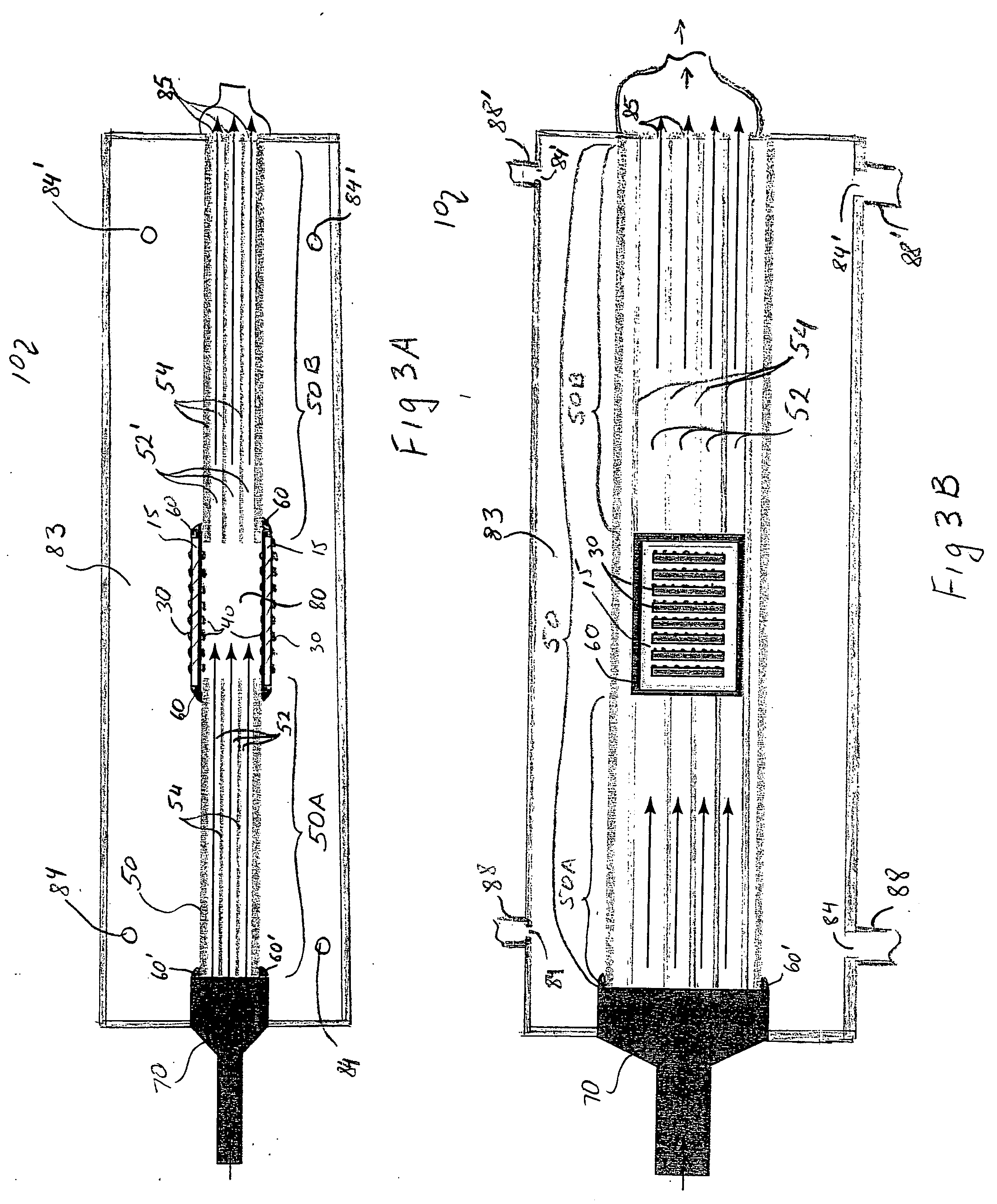
High separation area membrane module
InactiveUS20060090649A1Easy to separateReduce in quantityMembranesSemi-permeable membranesChannel densityEngineering
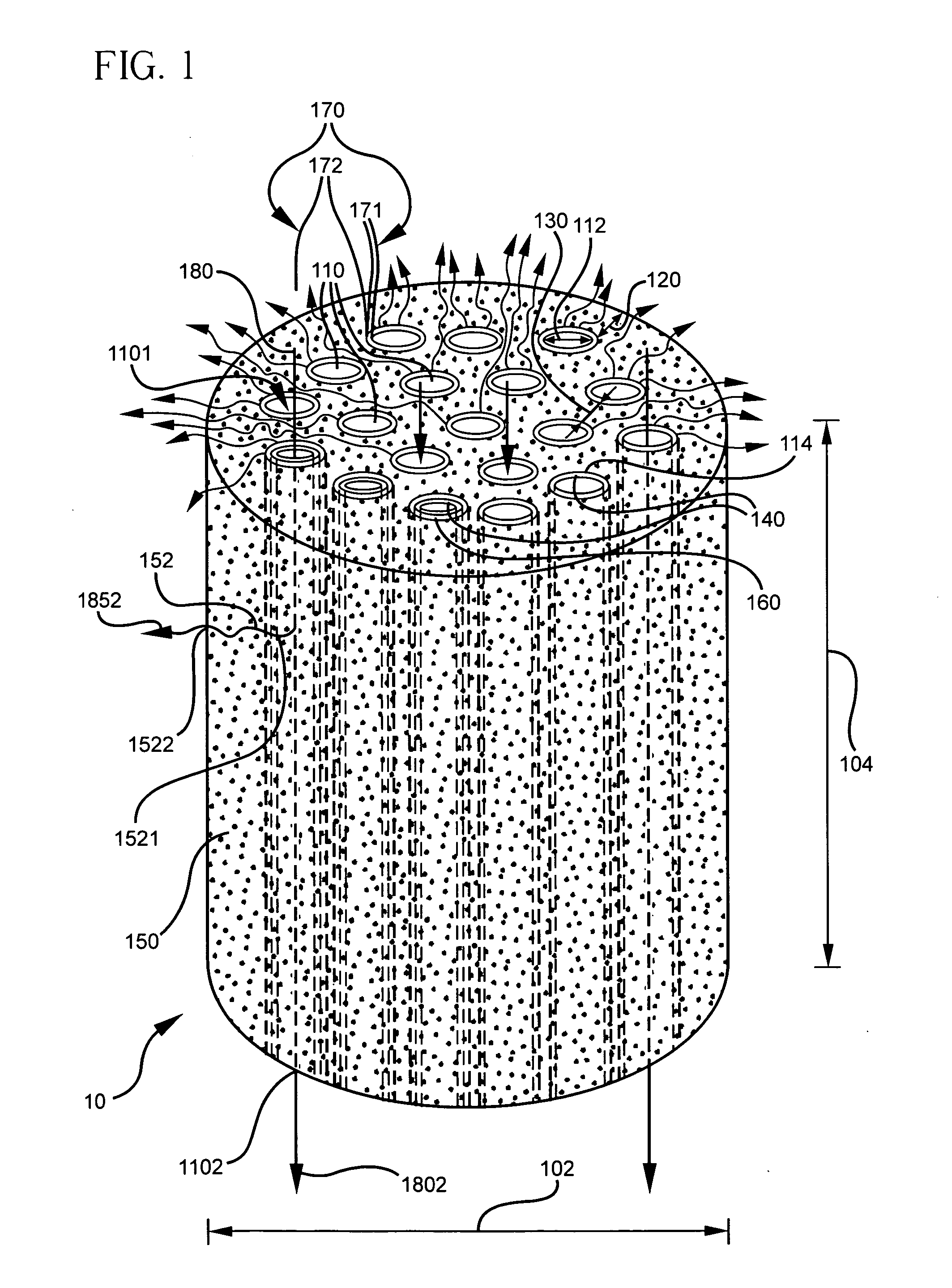
A ceramic monolithic multi-channel module support (10) has a module hydraulic diameter (102) in a range about 9 to 100 mm, an aspect ratio of the module hydraulic diameter (102) to a module length (104) greater than 1, a plurality of feed flow channels (110) distributed substantially in parallel over a module cross-section, the plurality of feed flow channels (110) having a size and shape defining a channel density in the range of about 50-800 channels / in2 (7.8-124 channels / cm2) in a module frontal area, a channel hydraulic diameter (112) in the range of about 0.5-3 mm, a rim distance (120) having a thickness greater than 1.0 mm (0.04 in), and a percent open frontal area (OFA) in the range of about 20-80%.
Owner:CORNING INC
Base station apparatus and control method for controlling channel density
InactiveUS20060189353A1Increase the number ofLow costSpatial transmit diversityConnection managementChannel densityControl channel
A base station apparatus is provided for adaptively controlling a maximal accommodation channel number per unit area (for example, the coverage area of a cell or sector) in accordance with a traffic quantity without relying upon detachment of a mobile base station and installation of a repeater. Upon inputting of a plurality of baseband signals of a user channel-multiplexed channel group, linear coupling is performed by a weight which is different per area that outputs it, thereby enabling control of the channel density. Additionally, a per-group available channel number is constantly monitored to control the weight while using threshold judgment for the available channel number as a trigger, thus achieving situation-sensitive prompt handleability.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Bidirectional parallel optical transceiver module and a method for bidirectionally communicating optical signals over an optical link
Bidirectional parallel optical transceiver modules for use in optical links and methods for communicating bidirectionally over the links are provided. The bidirectional parallel optical transceiver modules have features that ensure relatively low optical crosstalk, relatively low return loss and relatively high SNR. In addition, the modules have an in-line, zig-zag configuration that allows the modules to be compact and to have high bidirectional channel density for achieving high bandwidth.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Fuel cell device assembly and frame
An exemplary fuel cell device assembly includes: (i) an electrolyte sheet; (ii) a plurality of cathodes disposed on one side of the electrolyte sheet; (iii) a plurality of anodes disposed on another side of the electrolyte sheet; and (iv) a frame supporting the electrolyte sheet, the frame having a plurality of channels. Preferably the cross-sectional area of the frame has channel density of at least 20 / in2 and channel wall thickness of 50 mils or less.
Owner:CORNING INC
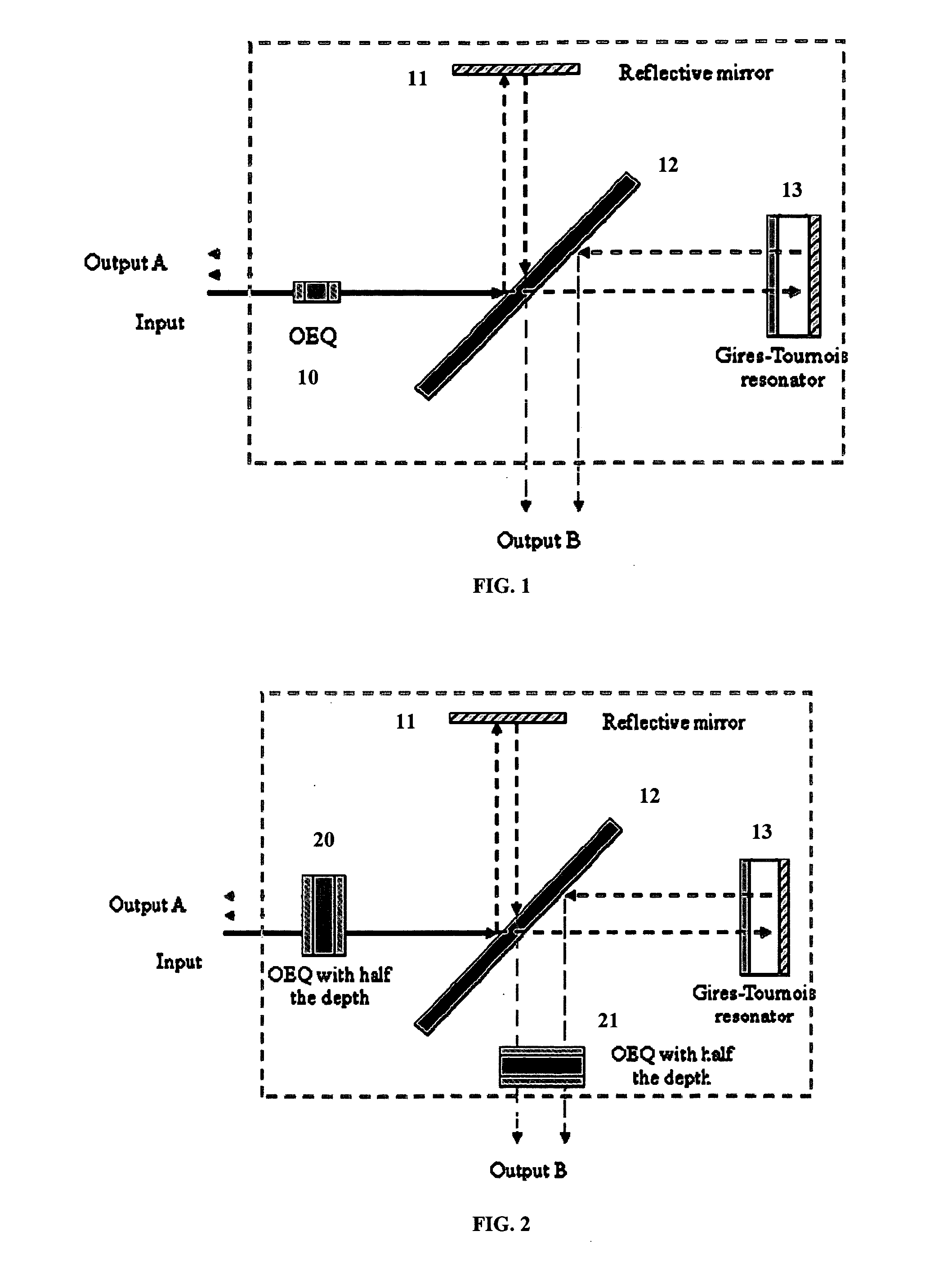
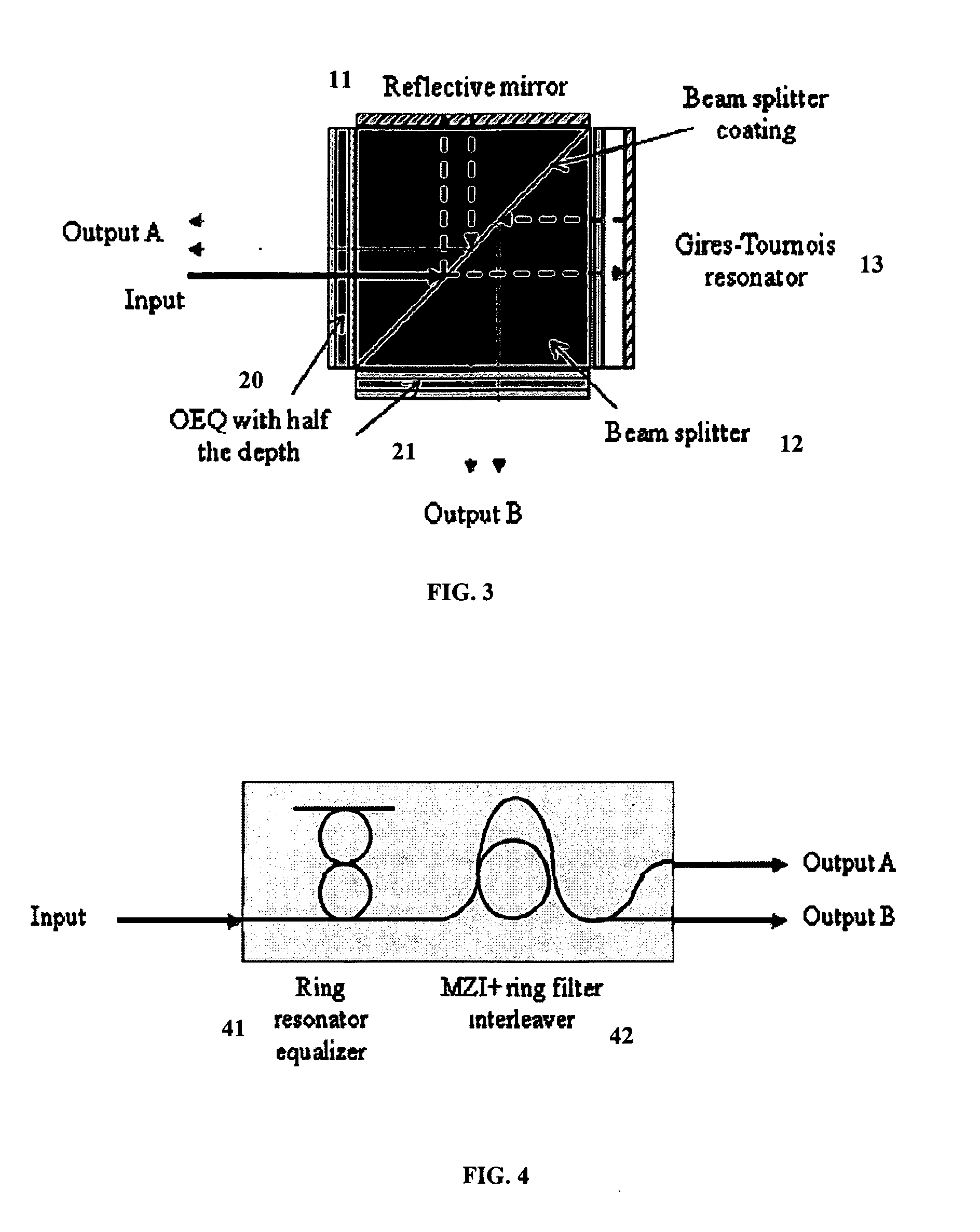
Intra-Channel Equalizing Optical Interleaver
ActiveUS20090162066A1Suppress Intersymbol InterferenceWavelength-division multiplex systemsDistortion/dispersion eliminationChannel densityIntersymbol interference
An apparatus includes an interleaver configuration for at least one of combining or separating odd and even channel groups to achieve channel density doubling; and an optical equalizer for suppressing inter symbol interference within the channels to provide intra-channel equalizing in the optical path, the equalizer being integrated into the interleaver. Preferably, optical equalizer and interleaver are integrated together as a single monolithic device, the optical equalizer includes a passband that has a dip in the channel center to achieve a raised-cosine filtering profile in the optical signal path to achieve inter-symbol interference ISI suppression, and the equalizer includes integration into the optical path of the interleaver to realize a monolithic device combining or separating odd and even channel groups to achieve channel density doubling. Preferably, also, the optical equalizer includes a first equalizer with half the depth of required ripple dips at both a first output port and an input port and a second equalizer with half the depth of required ripple dips at a second output port.
Owner:NEC CORP +1
Low voltage high density trench-gated power device with uniformly doped channel and its edge termination technique
InactiveUS20030205758A1Increase reverse voltageLow densityTransistorSolid-state devicesChannel densityLow voltage
Merging together the drift regions in a low-power trench MOSFET device via a dopant implant through the bottom of the trench permits use of a very small cell pitch, resulting in a very high channel density and a uniformly doped channel and a consequent significant reduction in the channel resistance. By properly choosing the implant dose and the annealing parameters of the drift region, the channel length of the device can be closely controlled, and the channel doping may be made highly uniform. In comparison with a conventional device, the threshold voltage is reduced, the channel resistance is lowered, and the drift region on-resistance is also lowered. Implementing the merged drift regions requires incorporation of a new edge termination design, so that the PN junction formed by the P epi-layer and the N<+> substrate can be terminated at the edge of the die.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
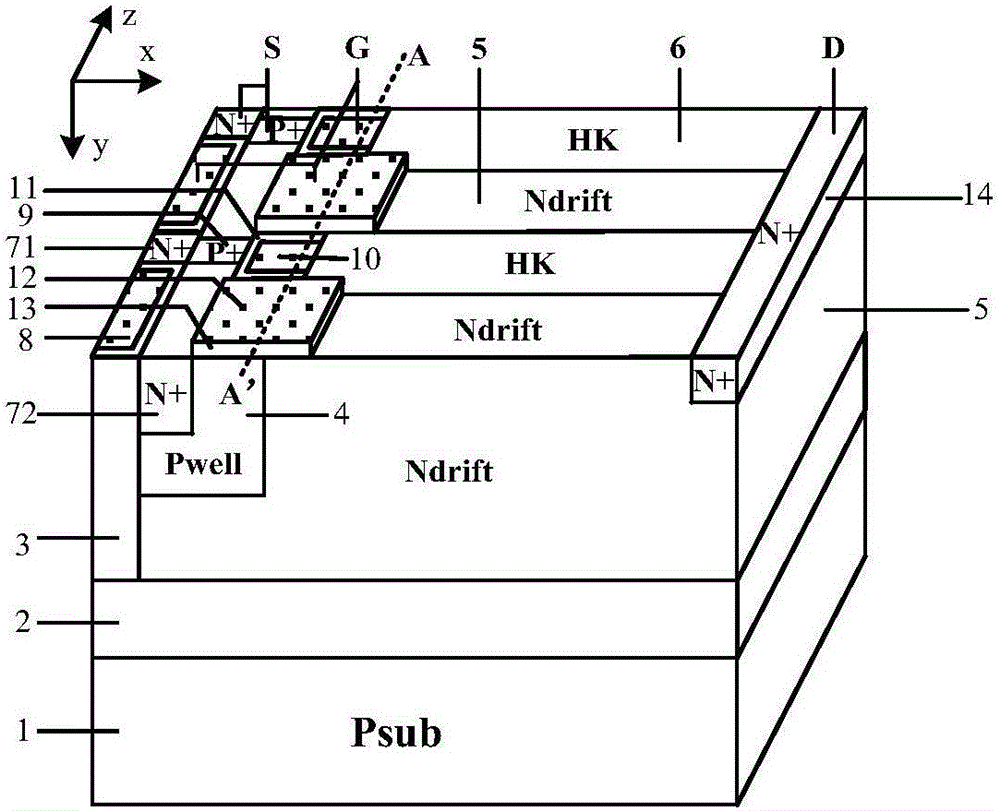
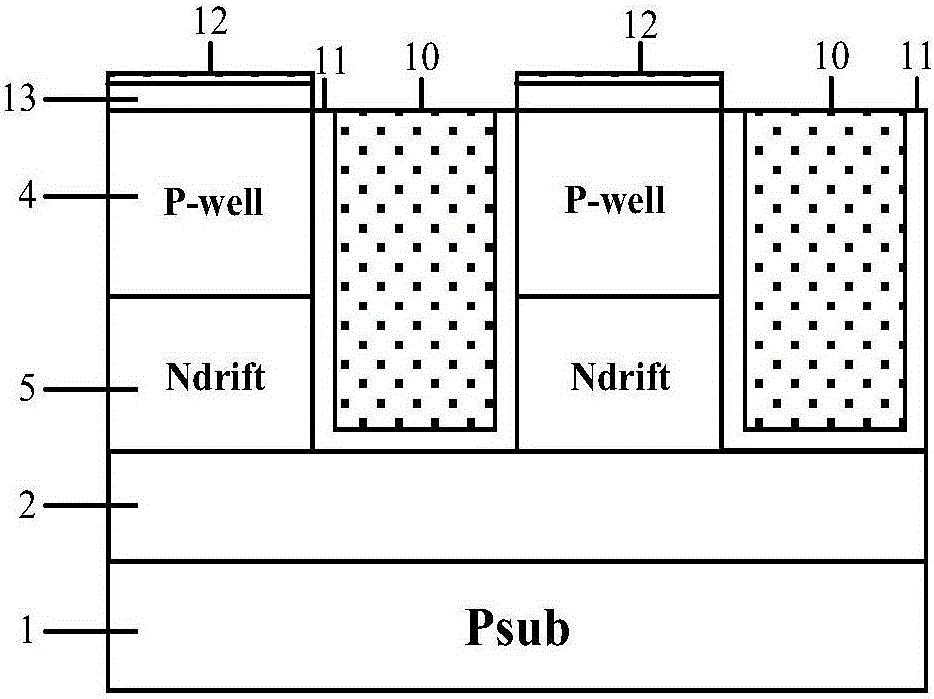
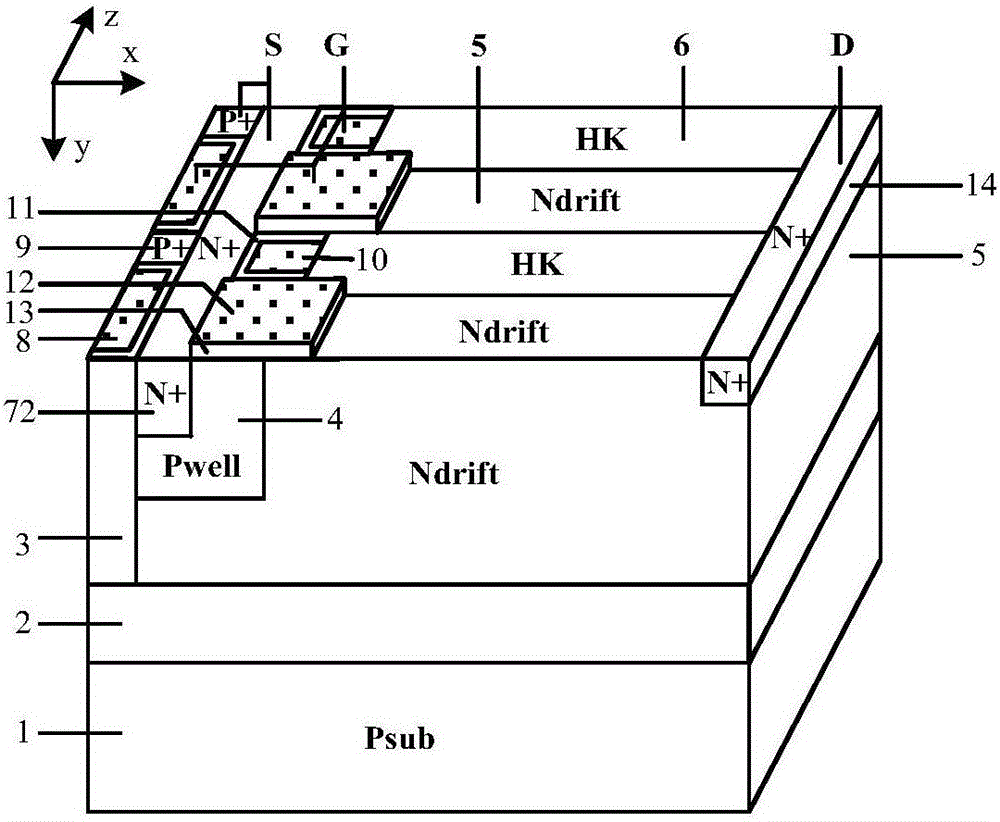
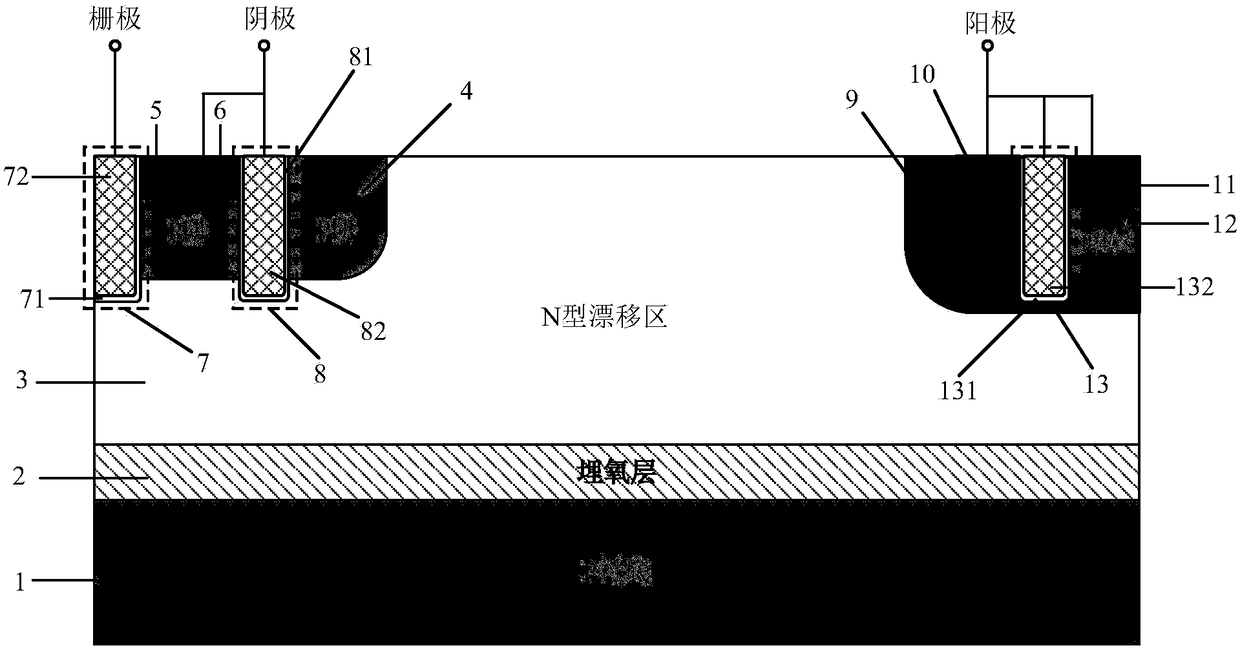
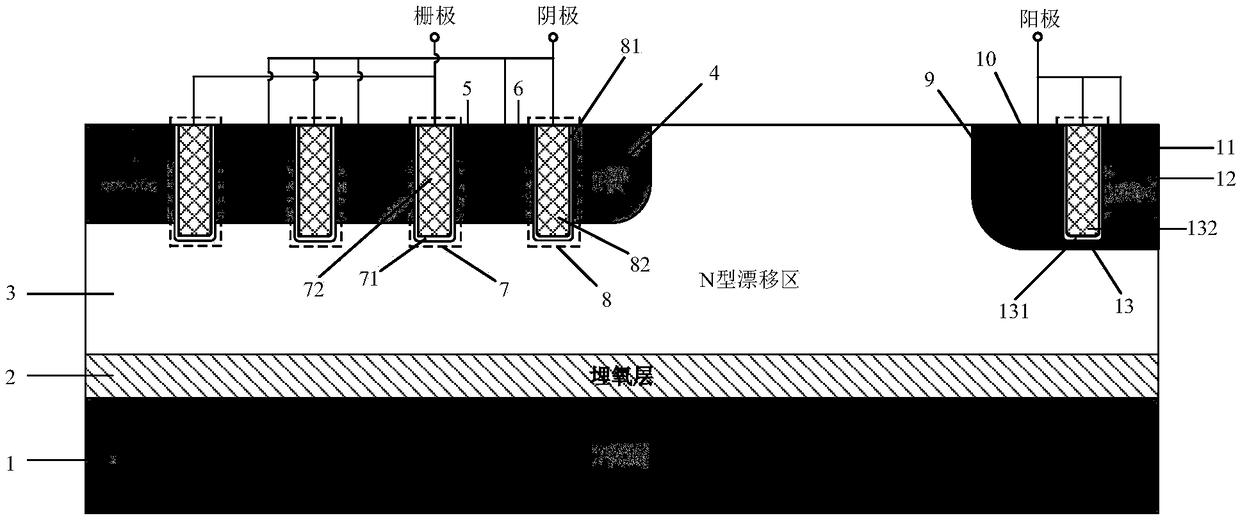
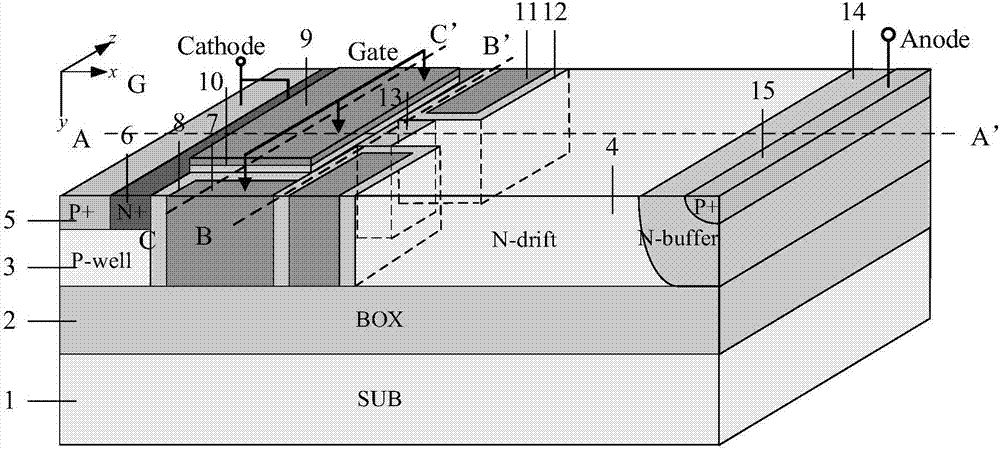
HK SOI LDMOSdevice having three-grating structure
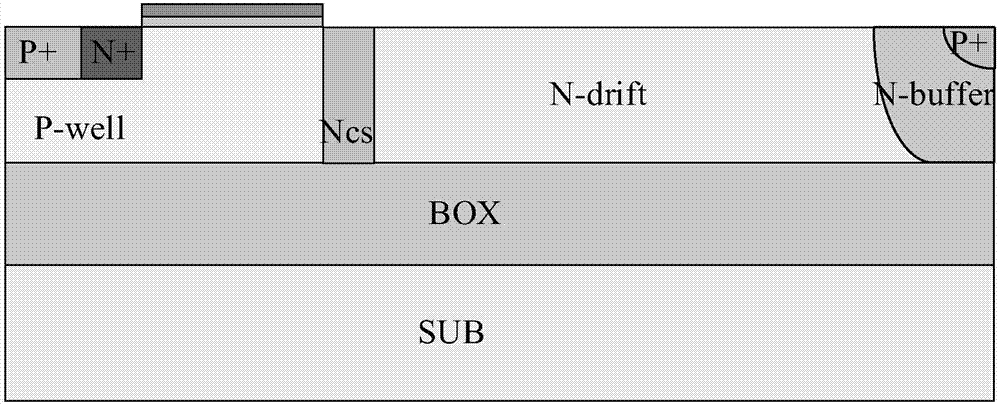
The invention belongs to a field of semiconductor technology and specifically relates to an HK SOI LDMOS (Lateral Double-Diffusion Metal Oxide Semiconductor) device. The device has the following characteristics. First, the device has three separated grating structures including a plane grate and two channel grates. In an open state, the three-grating structure an form a plurality of crosswise and longitudinal channels, thus increasing channel density, increasing current and reducing specific on-resistance. Second, high K mediums are embedded into drifting zones adjacent to a semiconductor zone and are arranged in alternation with the drifting zones. In the open state, electron accumulation layers are formed on side walls of the drifting zones adjacent to the high K mediums, so that low resistance channels are provided and the specific on-resistance is reduced. In a closed state, the high K mediums assist to drain the drifting zones, so that the drifting zone doping is improved, the electric field is improved and the specific on-resistance is reduced and the voltage holding performance is improved further. Third, an SOI structure is adopted, so that longitudinal voltage holding performance is improved, leakage current is reduced and a latch-up effect is eliminated.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Closed cell configuration to increase channel density for sub-micron planar semiconductor power device
ActiveUS7956384B2High densityIncrease channel widthTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsChannel densityEngineering
Owner:ALPHA & OMEGA SEMICON LTD
Grooved gate short circuit anode SOI LIGBT
The invention belongs to the technical field of power semiconductors and relates to a grooved gate short circuit anode SOI LIGBT. In comparison with the traditional short circuit anode LIGBT, anode grooves connected to anode potential are introduced at an anode end, and a P body area is introduced right below an N+ anode area; and grooved gates and cathode grooves connected with a cathode are introduced in a cathode area. When the device is turned off, the anode groove is connected to high potential, an NMOS in the anode area is started automatically, extraction of electrons stored in a driftarea is quickened, and the turn-off time and the turn-off energy loss are reduced; when the device is in a high-voltage high-current state, the cathode groove forms a hole bypass, and happening of latch-up effects is suppressed; when the device is conducted, under blocking of an electronic barrier in the P body area, electron current in the drift region is not easy to be collected by the N+ anode,voltage reentry effects are eliminated, and as the grooved gate structures of the cathode are in parallel connection, the channel density is increased and the conduction voltage drop is reduced. Thegrooved gate short circuit anode SOI LIGBT has the beneficial effects that in comparison with the traditional short circuit anode LIGBT, a voltage reentry phenomenon is eliminated under a smaller transverse cell size, and the conduction voltage drop is lower.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
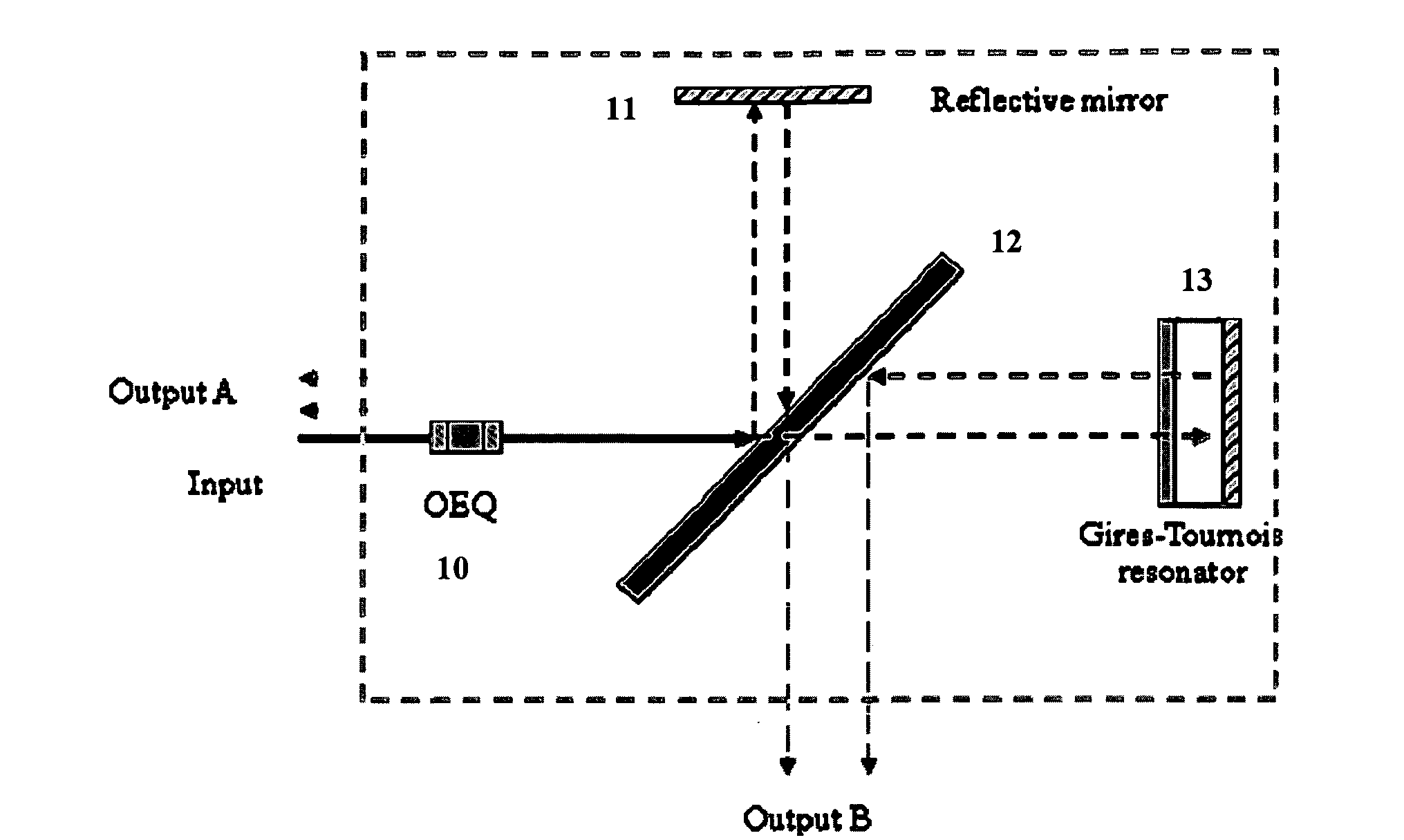
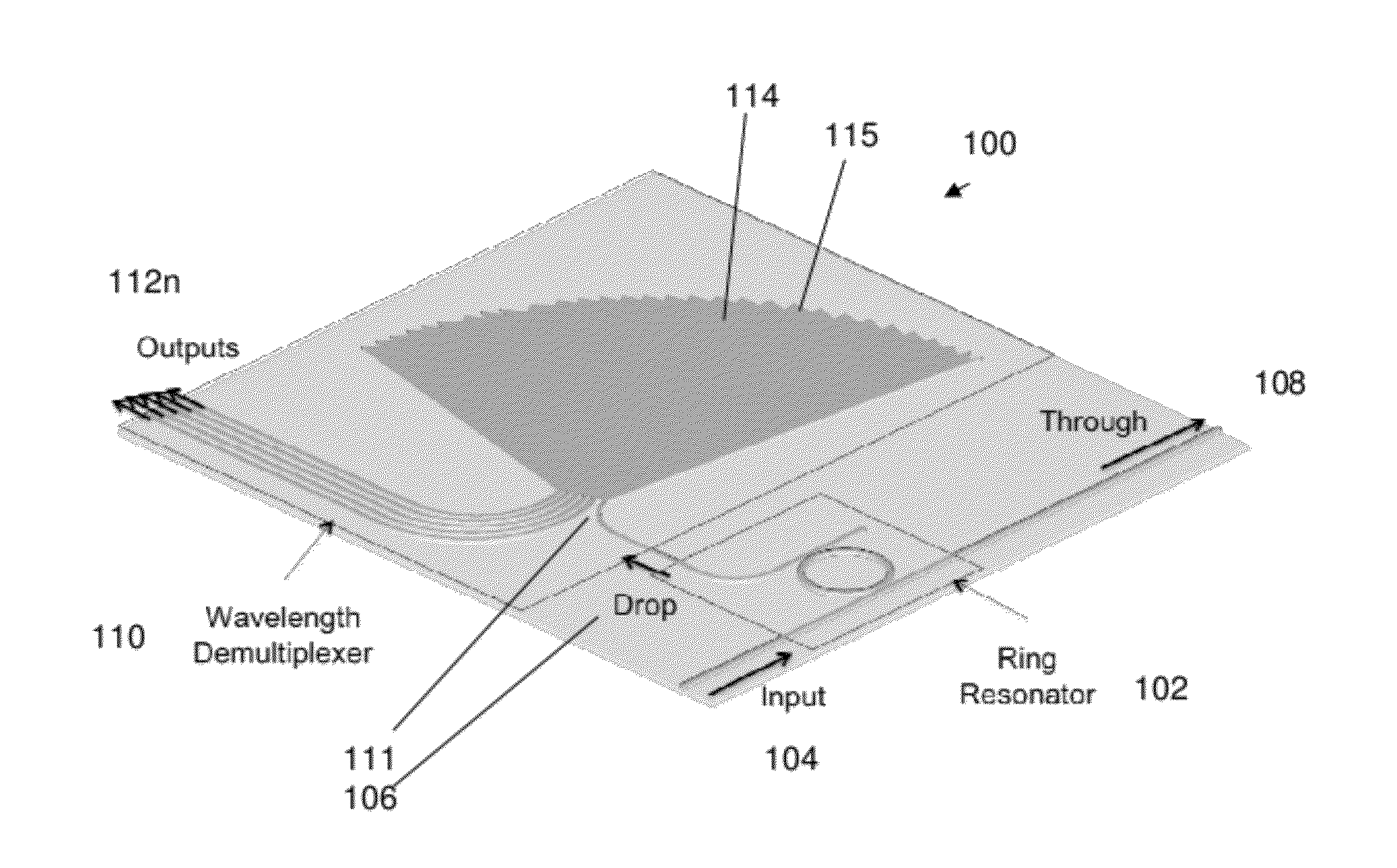
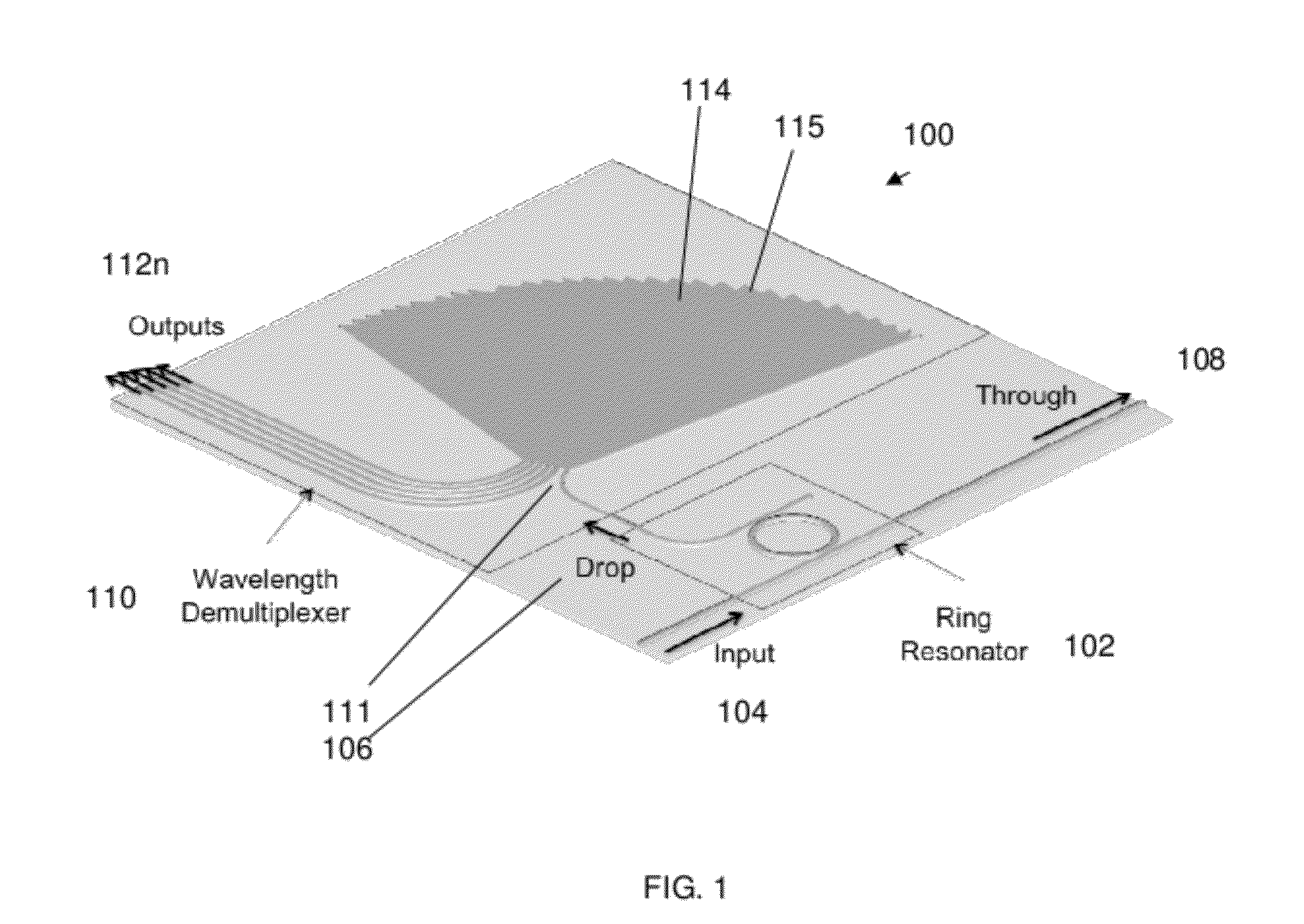
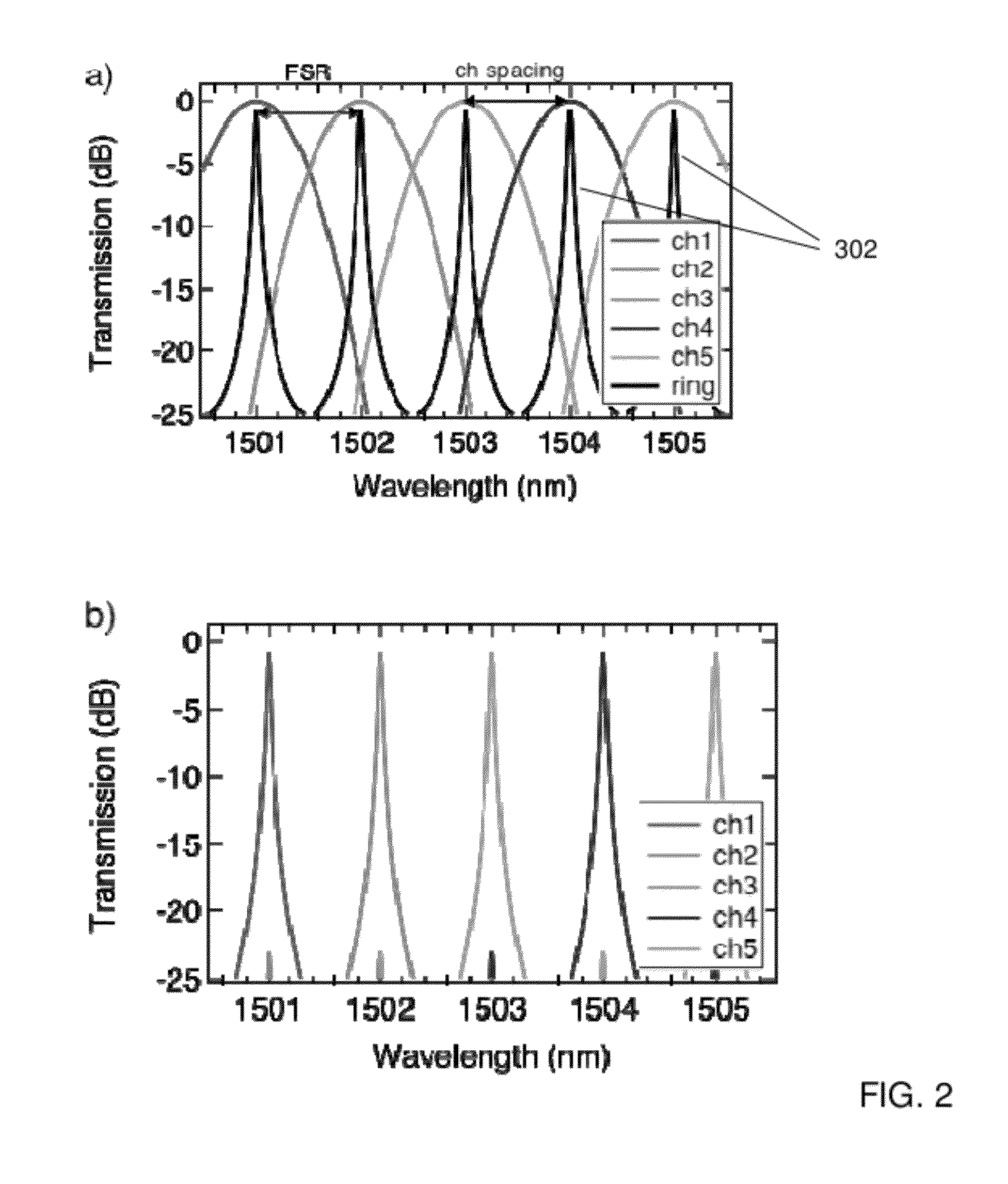
Optical apparatus, method, and applications
ActiveUS20120177060A1High resolutionEfficient solutionWavelength-division multiplex systemsTime-division multiplexResonant cavityChannel density
A high resolution, wide spectral range, optical apparatus that includes an optical resonator cavity and a wavelength demultiplexer, arrangeable in multiple configurations. A method for increasing the resolution of a wavelength demultiplexer involves inputting light into an optical resonant cavity; inputting a plurality of different resonant output wavelengths to a wavelength demultiplexer; and routing each different resonant wavelength to a different output waveguide of the demultiplexer to generate a demultiplexer output spectrum. The method further involves performing either a time serialization or a space serialization procedure to increase the channel density and fully cover the spectrum of interest.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
Closed cell configuration to increase channel density for sub-micron planar semiconductor power device
ActiveUS20070295996A1Increase channel width per unit areaIncrease the on-resistanceTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsChannel densityEngineering
A semiconductor power device supported on a semiconductor substrate that includes a plurality of transistor cells, each cell has a source and a drain region disposed on opposite sides of a gate region in the semiconductor substrate. A gate electrode is formed as an electrode layer on top of the gate region for controlling an electric current transmitted between the source and the drain regions. The gate electrode layer disposed on top of the semiconductor substrate is patterned into a wave-like shaped stripes for substantially increasing an electric current conduction area between the source and drain regions across the gate.
Owner:ALPHA & OMEGA SEMICON LTD
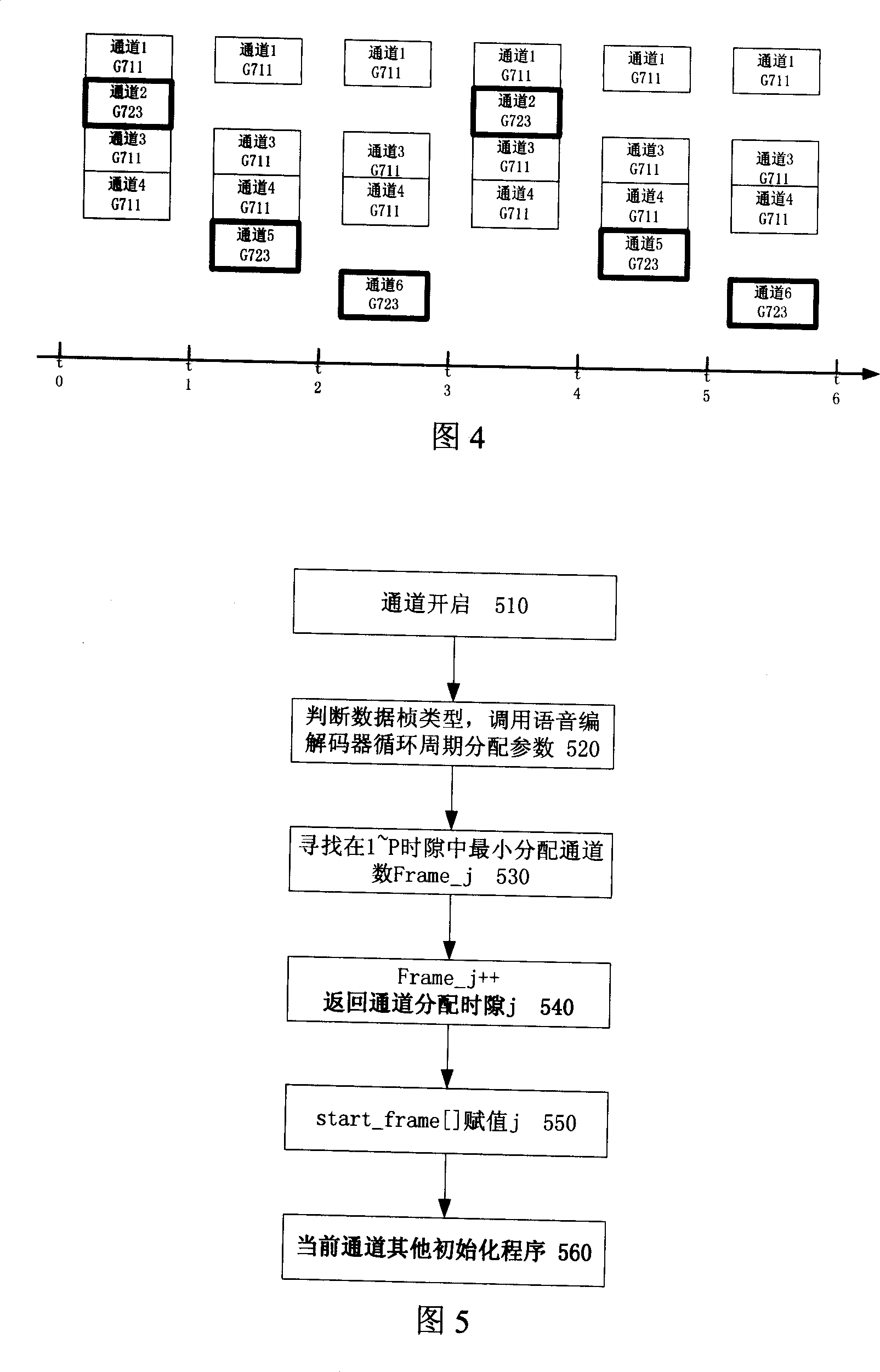
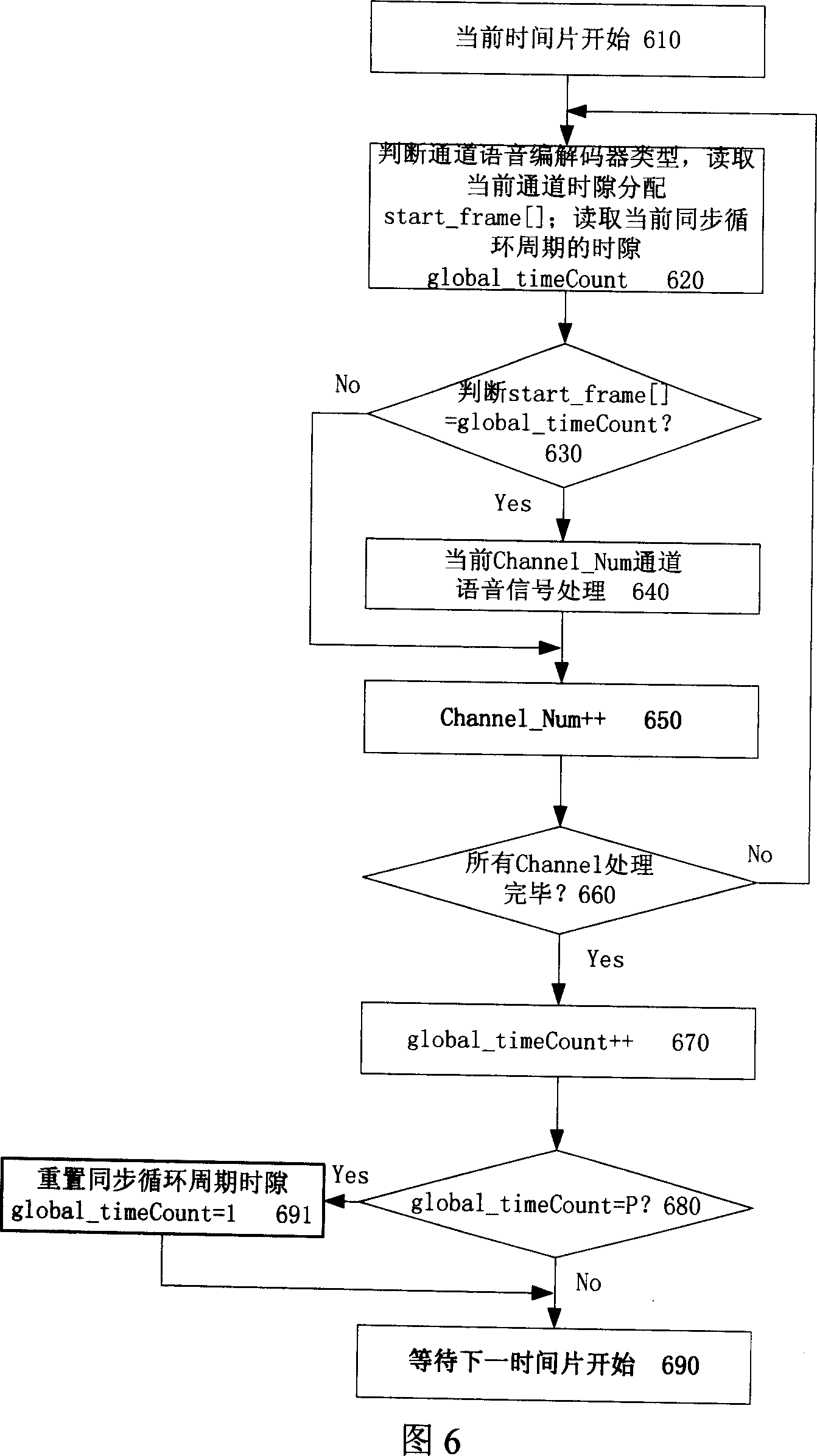
Single-chip based multi-channel multi-voice codec scheduling method
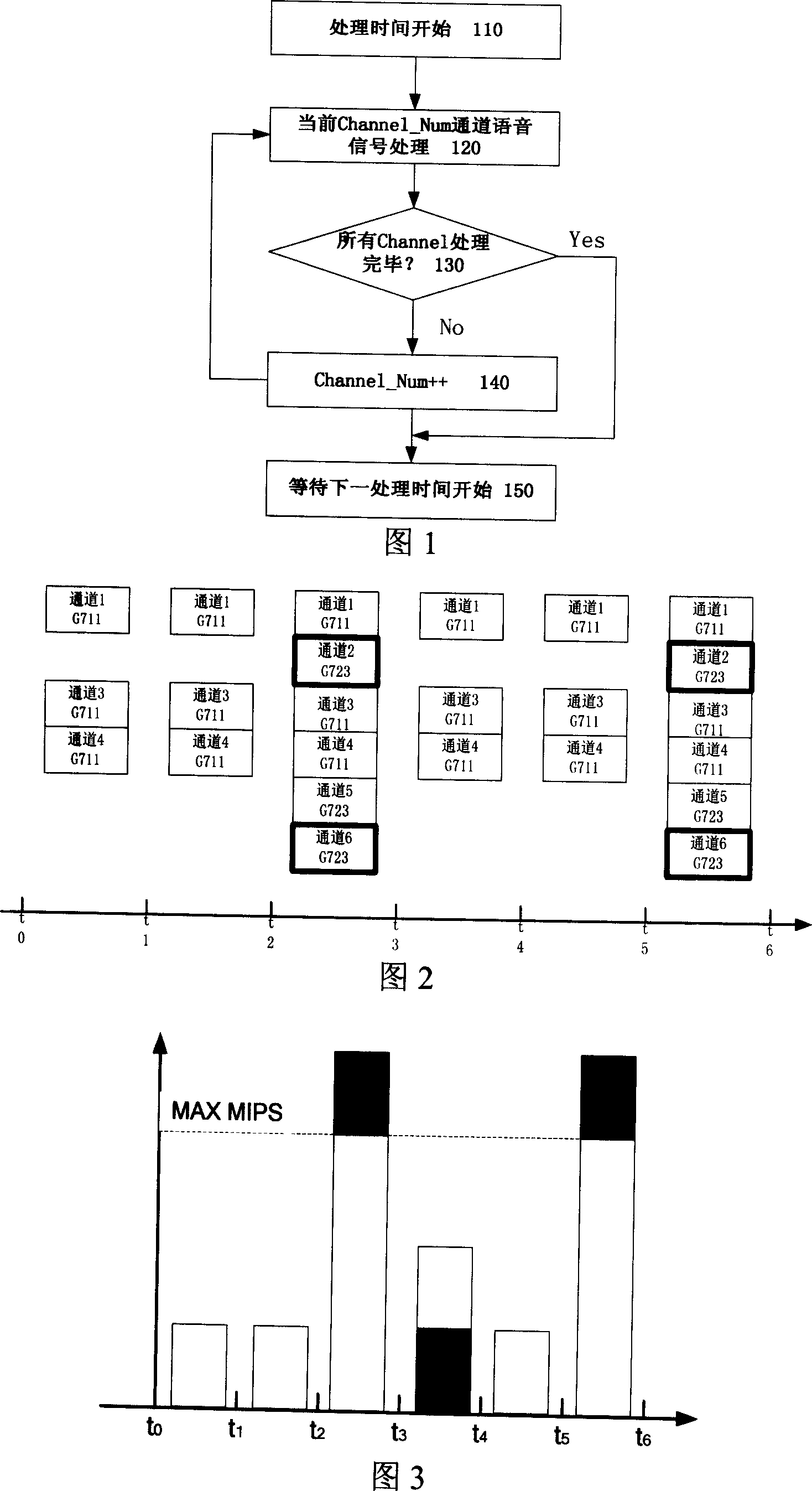
ActiveCN1971710ANo need to monitor computing load in real timeReal-time monitoring of computing loadEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesSpeech analysisProcess systemsChannel density
The invention relates to a dispatching method of multichannel and multisound codec based on the single chip. Every channel is accessed on every time slice, contains: the time of time slice is determined according to the greatest common divisor of long of processing frames of the sound codec; calculates the synchronized cycle period of the sound codec relative to the cycle count period of said time slice P; the channels of sound codec are distributed equally and called according to the time slot of cycle count period P of every sound codec. The method equally distributes the corresponding channels in the cycle count period P, the corresponding channels are distributed to the time slice equally, and realize the VoIP sound processing system channel density, any sound codec combination can be realized, and it's no need to monitor the operation load of DSP chip timely and solve the operation capability bottleneck brought by the deployment of the traditional sound codec and the complex extent.
Owner:ZTE CORP
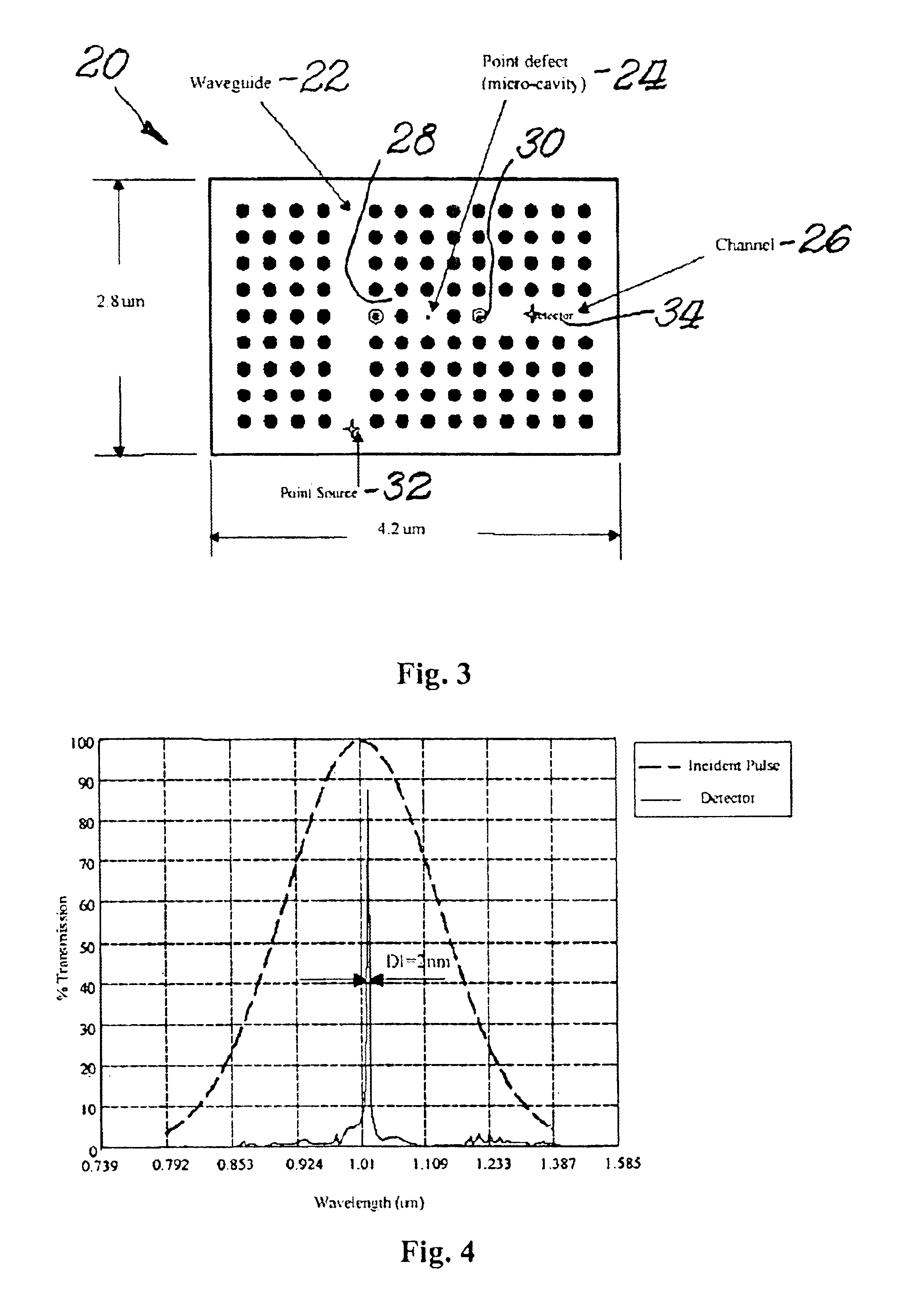
Multi-channel wavelength division multiplexing using photonic crystals
Described herein is a multi-channel wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) device including a two-dimensional photonic crystal. The photonic crystal consists of two primary components: (1) a waveguiding element created by line defects formed in the photonic crystal, and (2) frequency-selective elements created by high Q-value microcavities formed in the crystal. The multi-channel WDM system offers a flexible design and high channel density.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF DELAWARE
Fluid collection component comprising a film with fluid channels
In one embodiment, a device comprises a fluid transfer component having an average thickness less than 2 millimeters and comprising a polymer film with one or more polymeric materials in one or more layers; and an active region of the fluid transfer component comprising a surface area greater than 1 square meter and plurality of fluid channels defined by one or more interior surfaces within the polymeric film, each fluid channel of the plurality of fluid channels is separated spatially with the plurality of fluid channels comprising at least 1 row of fluid channels in a thickness direction of the polymeric film, wherein the plurality of fluid channels has a channel density across the active region of the fluid transfer component greater than 100 fluid channels per centimeter and the plurality of fluid channels collects a first fluid across the active region from the environment.
Owner:COLEMAN ZANE
Three-gate power LDMOS
ActiveCN106024897AIncrease the doping concentrationReduce gate-to-drain capacitanceSemiconductor devicesCapacitancePower semiconductor device
The invention belongs to the field of power semiconductor devices, and relates to a lateral three-gate power LDMOS based on a bulk silicon technology. The three-gate power LDMOS is mainly characterized by having a three-gate structure and a second conductive material electrically connected with a source or a gate or an external electrode. The three-gate power LDMOS has the main advantages that the three-gate structure increases the channel density and reduces the channel resistance, and thus, the specific on-resistance drops; the second conductive material can freely select the electrode, when the gate electrode is connected, in the positive case, electron accumulation surfaces are formed on the side surface and the bottom surface of a second groove, a multi-dimension low-resistance channel is formed, and the specific on-resistance is greatly reduced, and in the reverse case, assistant depletion of a drift region is carried out, the drift area doping concentration of the device is increased, the specific on-resistance of the device is reduced; when the source electrode is connected, gate-drain overlapping is reduced, the gate-drain capacitance of the device is reduced, and switching loss is reduced; and when the external electrode is electrically connected, multiple effects can be achieved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
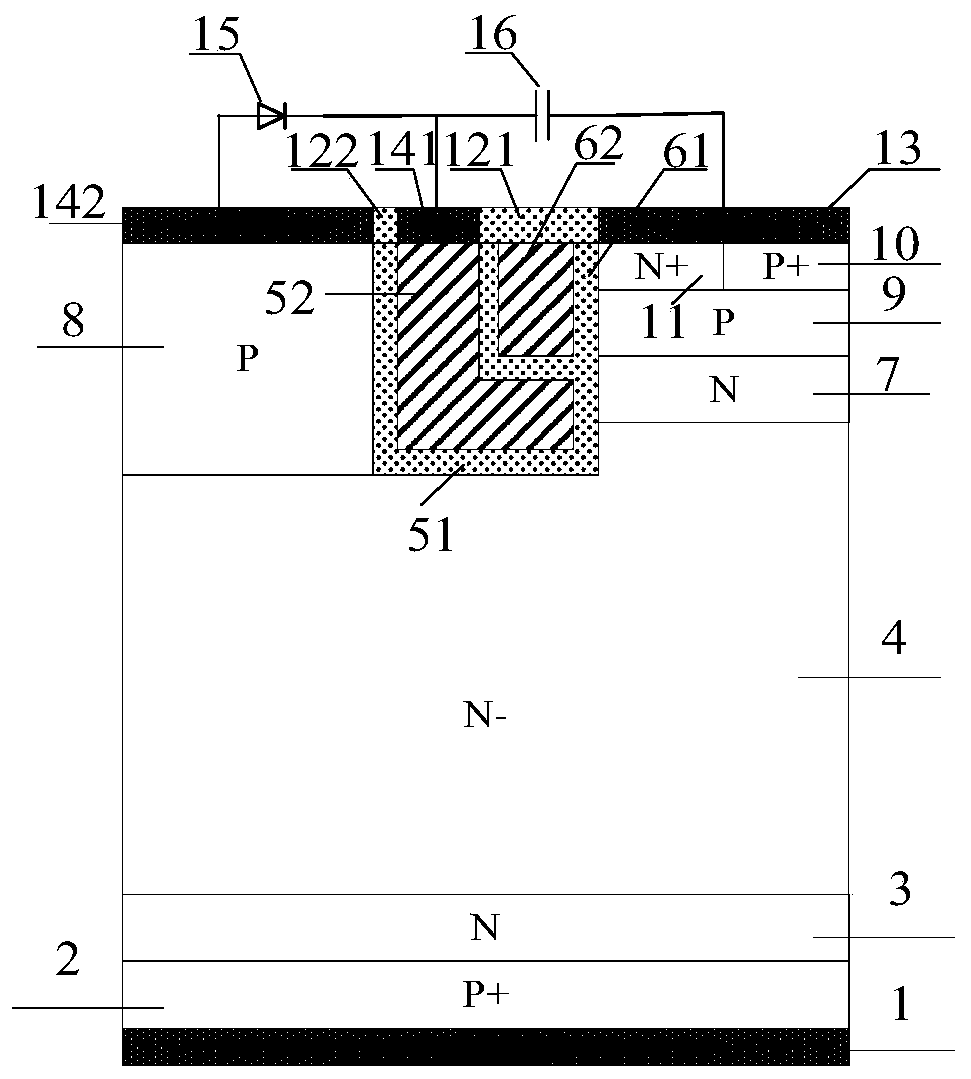
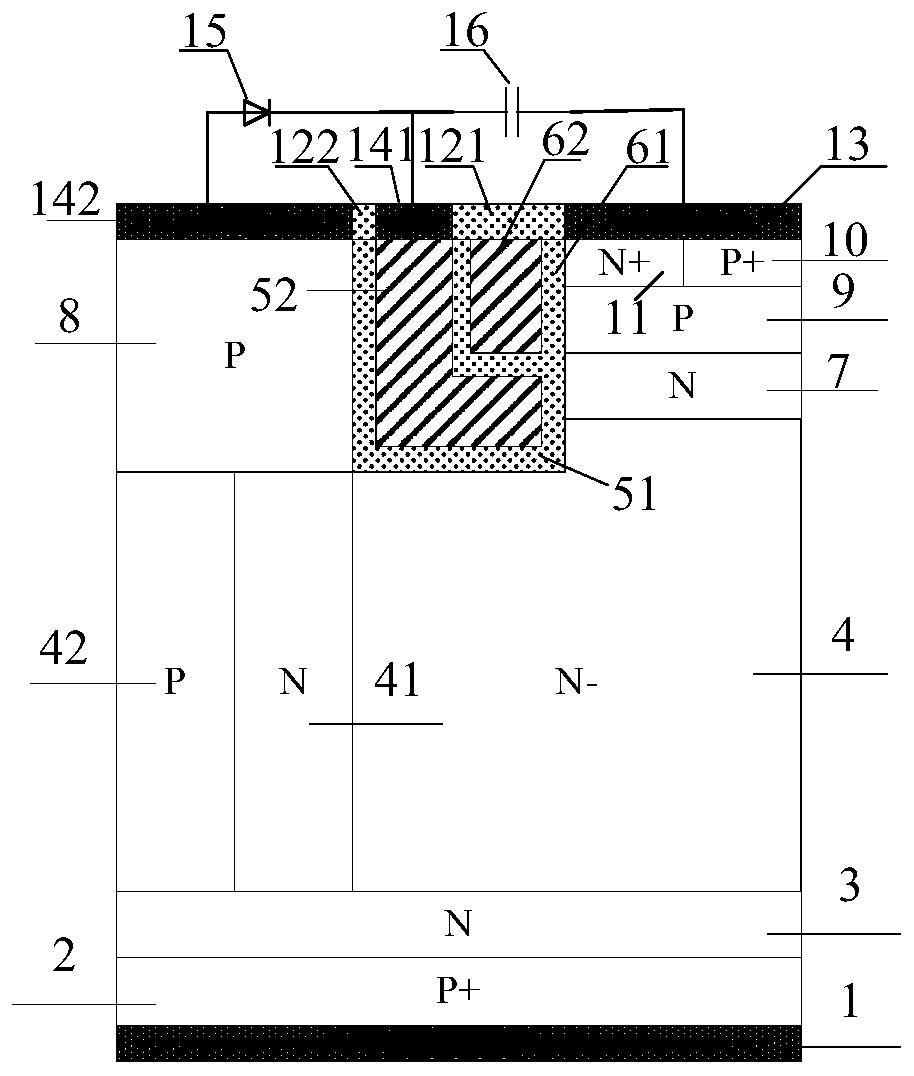
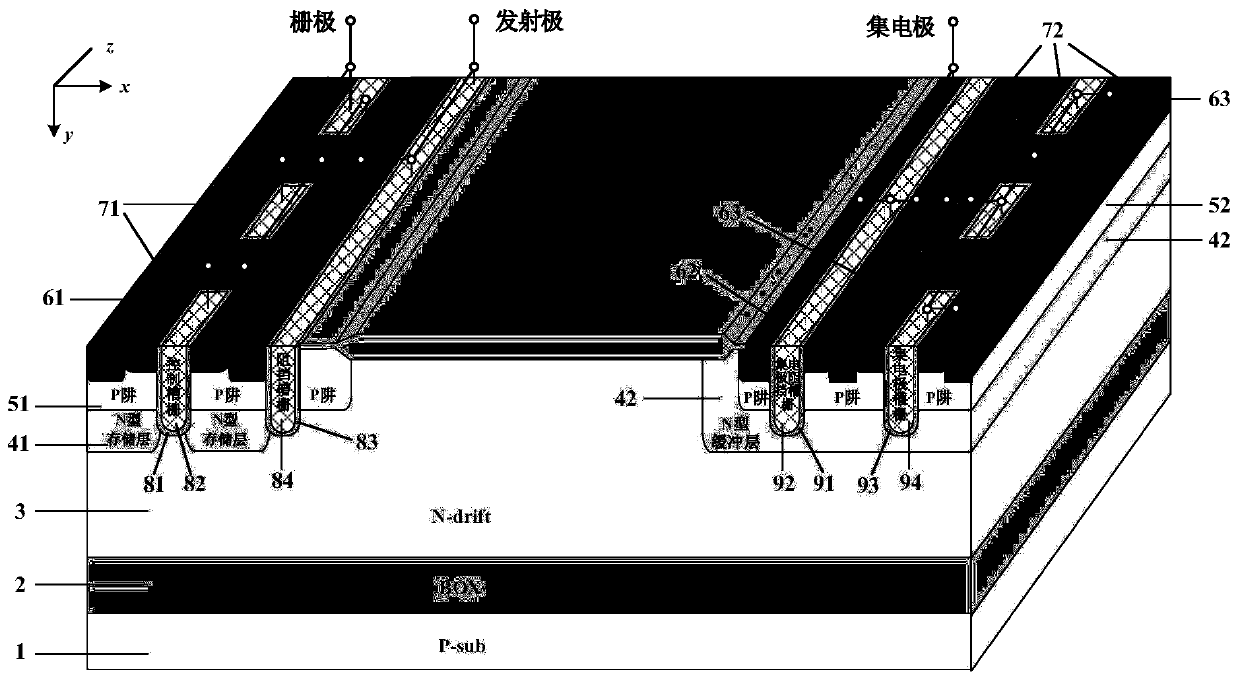
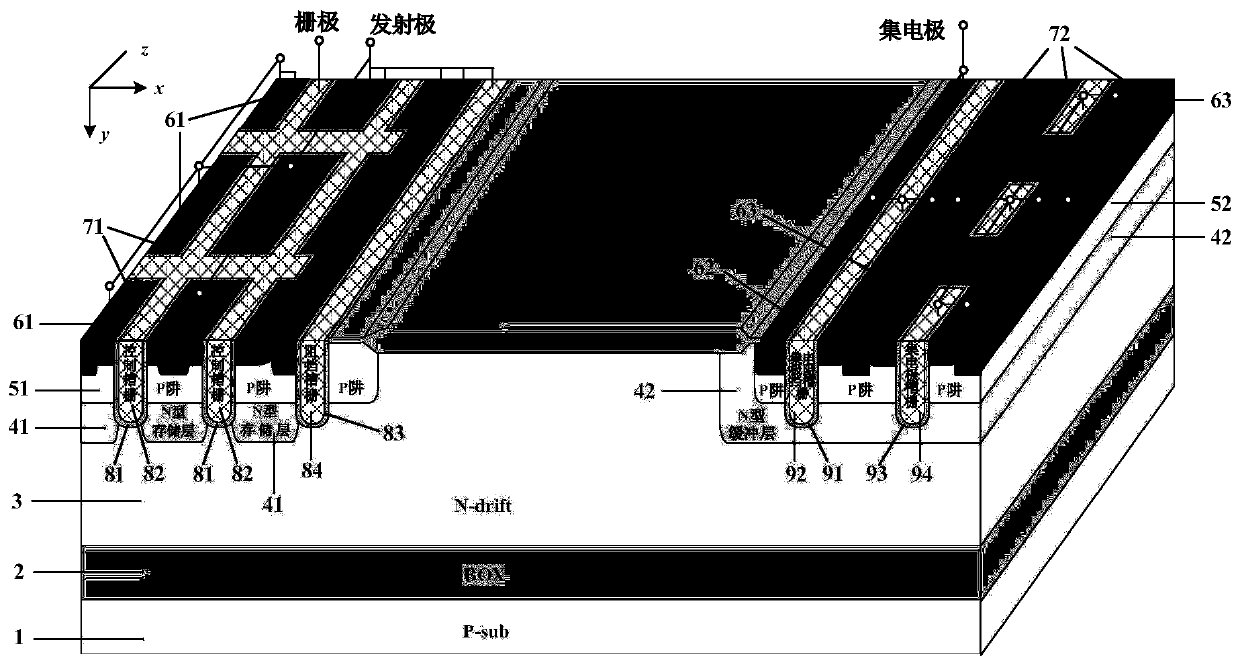
IGBT with self-biased separation gate structure
ActiveCN110491937AGuaranteed breakdown voltageFast switching speedSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesPower semiconductor deviceChannel density
The invention belongs to the technical field of power semiconductor devices, and relates to a separation gate TIGBT with a self-biased PMOS and a manufacturing method thereof. According to the invention, a PMOS structure is introduced on the basis of a traditional TIGBT; the channel density is not reduced; saturation current during forward conduction of the device is effectively improved, the short-circuit safety working capability of the device is improved, and meanwhile, an extra current discharge path provided by the PMOS structure accelerates the hole extraction speed of the device in a blocking state, so that the switching speed of the device is increased, and the switching loss of the device is reduced. Meanwhile, for the TIGBT with an N-type charge storage layer, a P-type buried layer can shield the influence of the N-type charge storage layer on the breakdown characteristic of the device; therefore, the doping concentration of the N-type charge storage layer can be improved tofurther improve the carrier distribution during forward conduction of the device, the conductivity modulation capability of a drift region is improved, and the compromise relationship between the forward conduction voltage drop Vce (on) and the turn-off loss Eoff of the device is further improved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
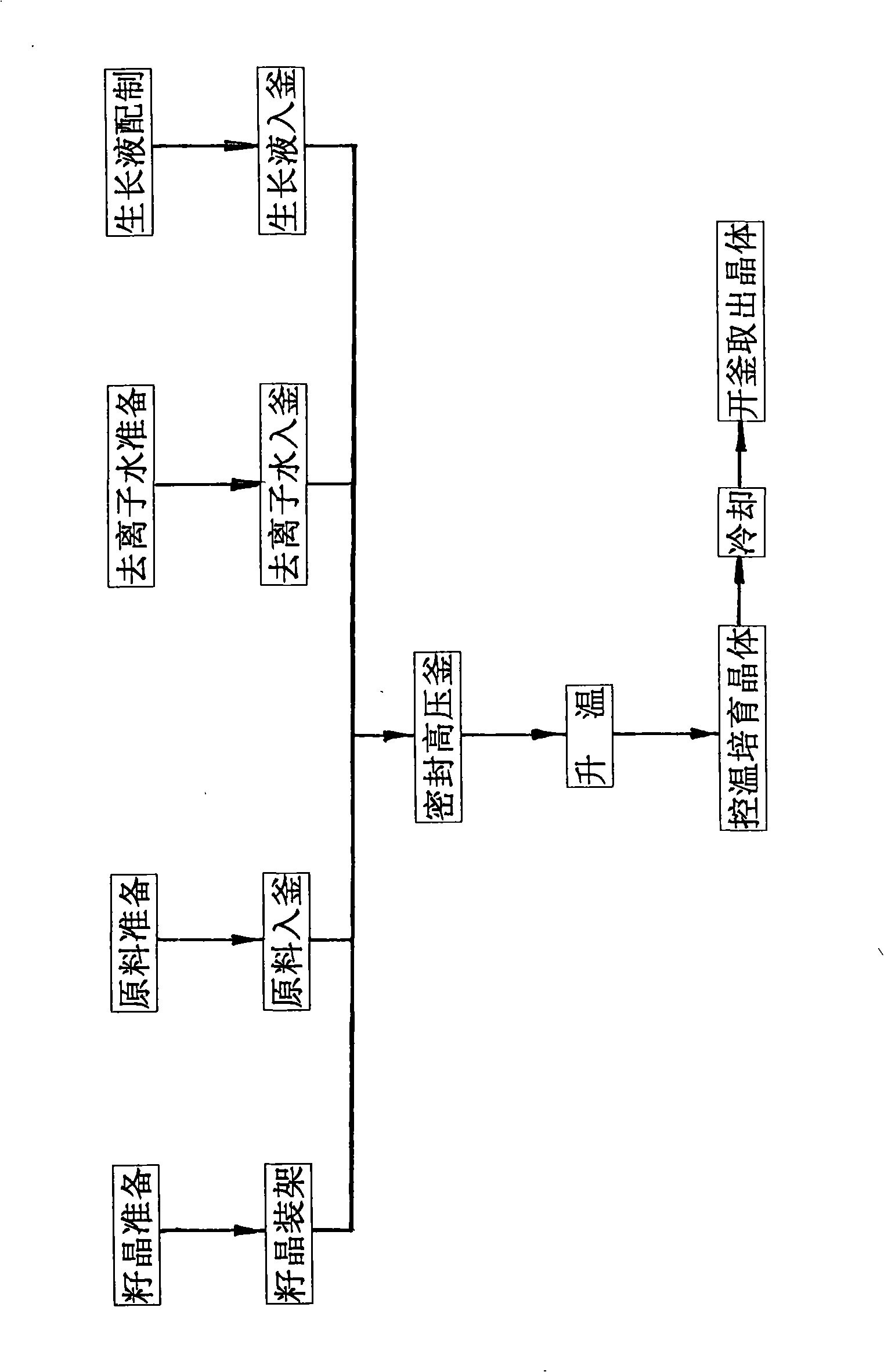
Optical-level quartz crystal temperature-variable temperature difference method growth technique
InactiveCN101319375AGuaranteed pulse indexGuarantee indicatorPolycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsChannel densityGrowth promoting
The invention discloses an optical level quartz crystal temperature-changing temperature differential method growth technology, comprising the following steps that: firstly, raw materials of seed crystal and quartzite are washed, deionized water and a growth-promoting media are prepared, and a high-pressure autoclave is washed by ionized water and is drained off by a membrane pump; secondly, a raw material basket holding the quartzite is put in the washed autoclave, the prepared grow-promoting media and a seed crystal bracket hung with the seed crystal are poured into the autoclave, the liquid level is measured, and the autoclave opening is sealed; thirdly, a temperature control system is started, the high-pressure autoclave is heated, the parameters of temperature, pressure and time of the sealed high-pressure autoclave are adjusted so that the quartz crystal is grown and formed. The optical level quartz crystal temperature-changing temperature differential method growth technology is characterized by determining the lineage grade of the seed crystal, the a equivalent concentration of the grow-promoting media, the parameter of a filling degree of the autoclave, the temperature changing and differential parameter and the pressure parameter of the heated high-pressure autoclave. According to the quartz crystal produced by the technology, the lineage index is more than the grade A, the etch channel density is less than 10 strips per centimeter<2>, the value of Q is more than or equal to 3.0x10<6>, an inclusion is higher than the Ia type, the optical uniformity delta n is less than or equal to 5x10<-6>, and the spectrum transmission ratio is more than 95 percent when the wavelength is between 800 and 2, 500 nanometers.
Owner:刘盛浦
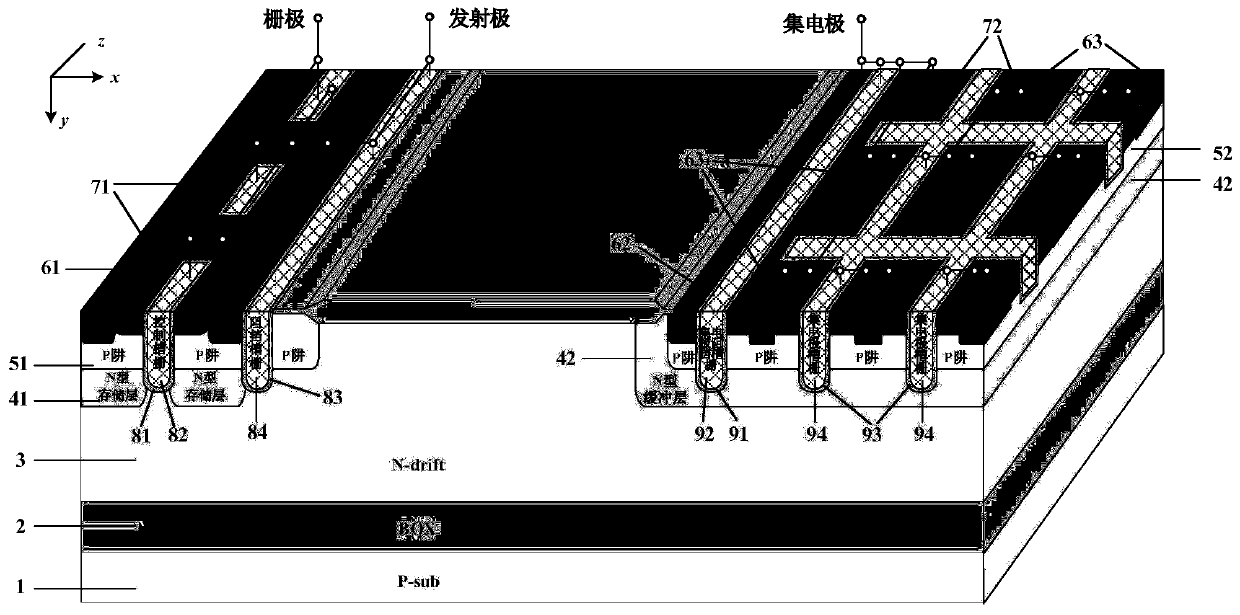
Groove type SOI LIGBT comprising carrier storage layer
ActiveCN106920842AReduce conduction voltage dropImprove pressure resistanceSemiconductor devicesHigh concentrationChannel density
The invention belongs to the field of power semiconductor technology and relates to a groove type SOI LIGBT comprising a carrier storage layer. The groove type SOI LIGBT relative to a structure in the prior art comprises the following characteristics: 1, the groove type SOI LIGBT comprises the carrier storage layer in high concentration which blocks a hole in forward conduction, the concentration of the hole near an interface is increased, according to an electroneutrality principle, more electrons is injected to a drift region, the conductivity modulation effect is enhanced, and the forward conduction voltage drop of a device is reduced, simultaneously, a medium groove is introduced, the medium groove physically block a cathode to collect the hole and acts on further reduction of forward conduction voltage drop, and more importantly, the medium groove can assistant to drain the carrier storage layer in forward blocking, so that the device maintains high pressure resistance in the condition of high concentration carrier storage layer; 2. the groove type SOI LIGBT adopts tri-gate structure, and the channel density is improved; 3. tri-gate structure and the medium groove can be manufactured simultaneously without extra processing steps.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA +1
Data processing apparatus and method for d=2 optical channels
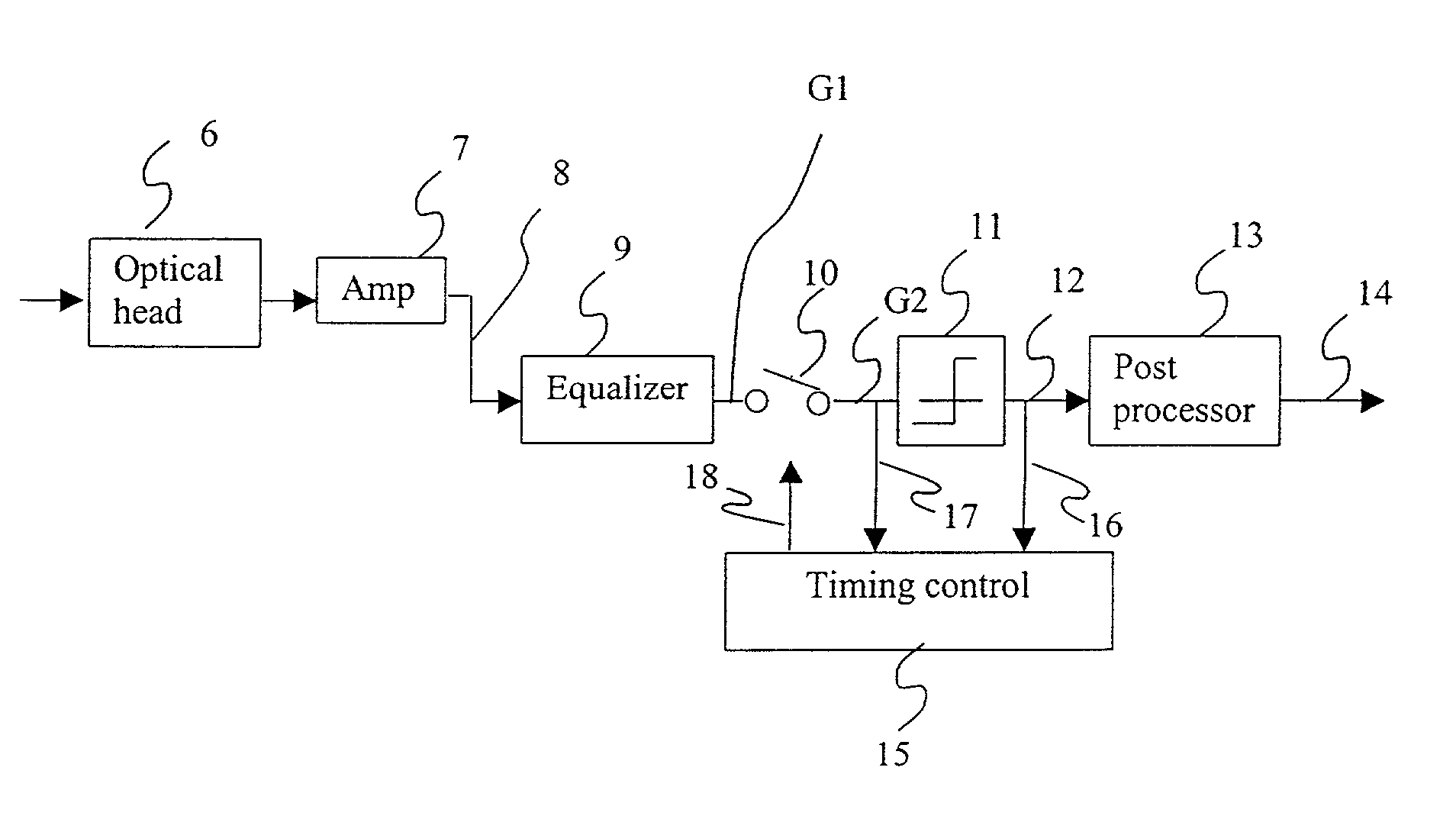
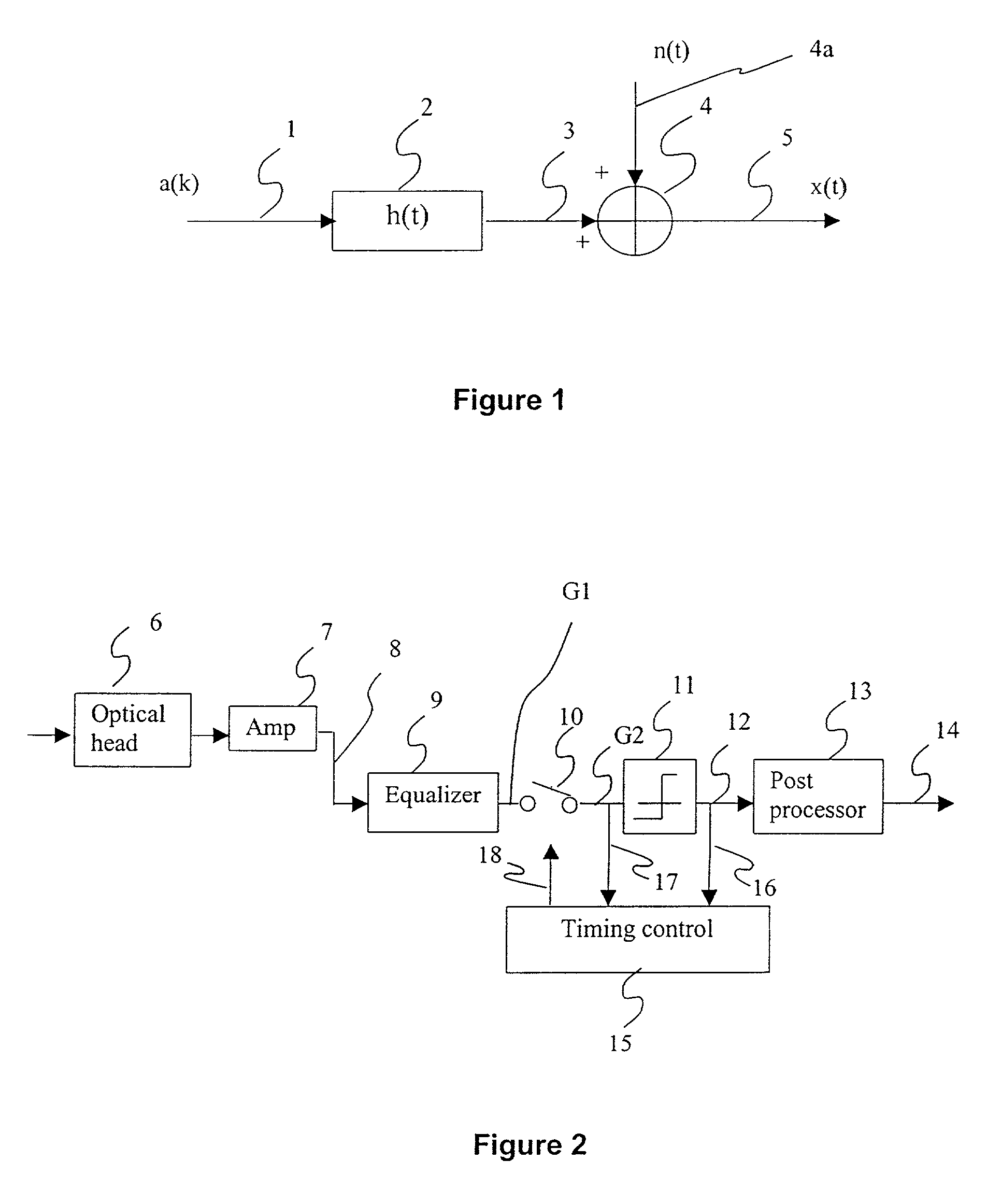
InactiveUS7079467B2Reliable detectionEasy to detectTelevision system detailsError preventionTarget ResponseChannel density
Owner:DATA STORAGE INST
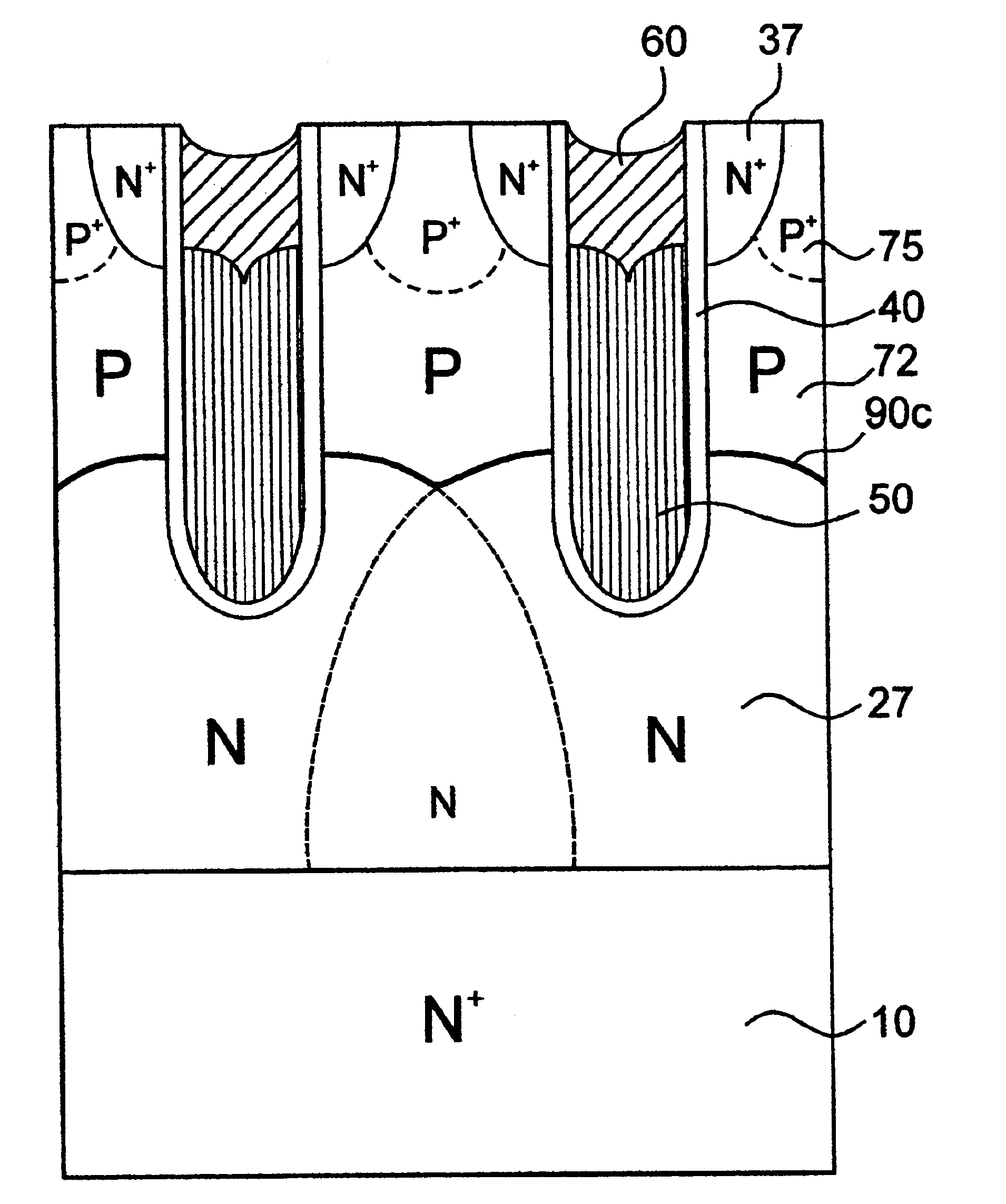
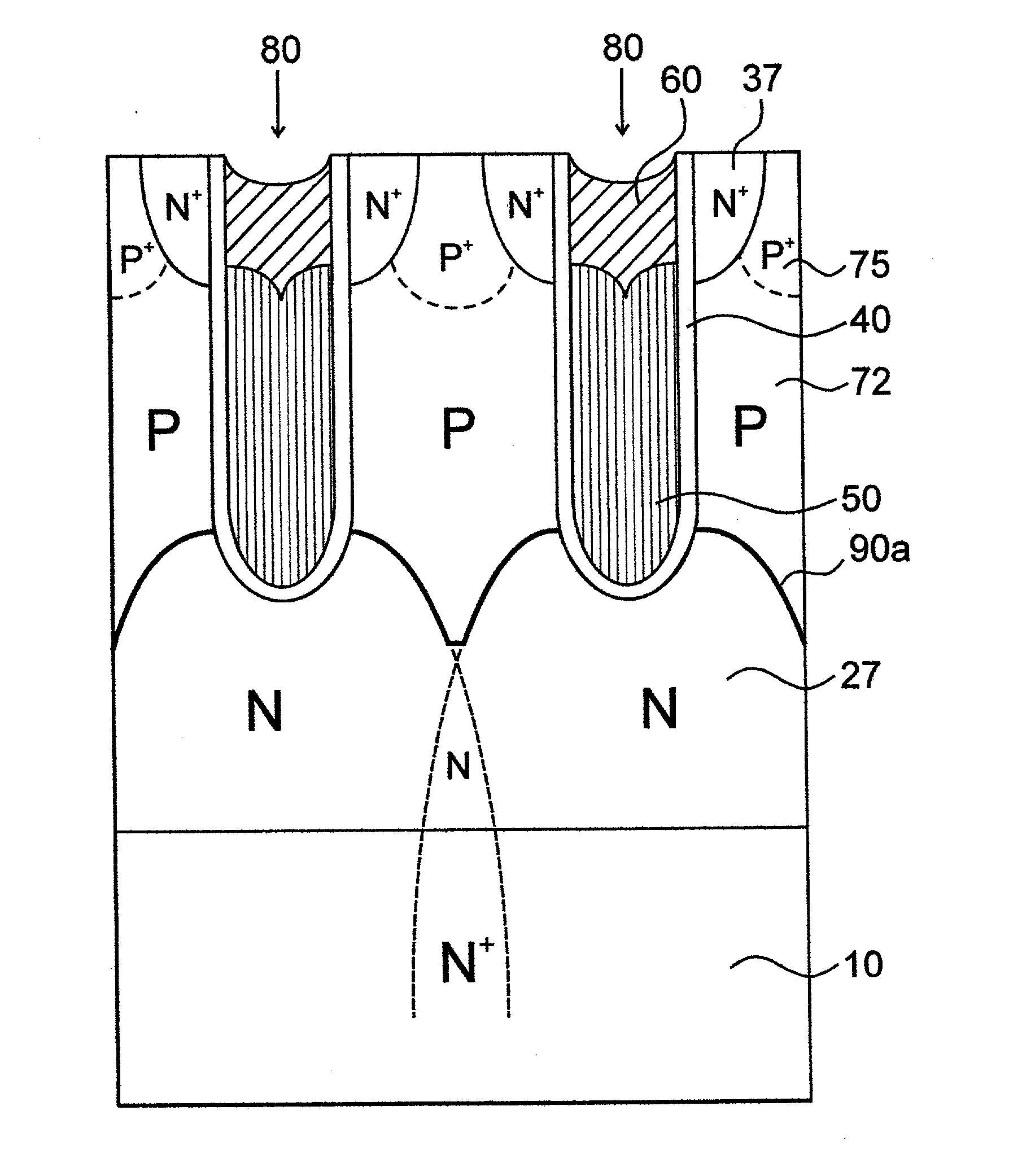
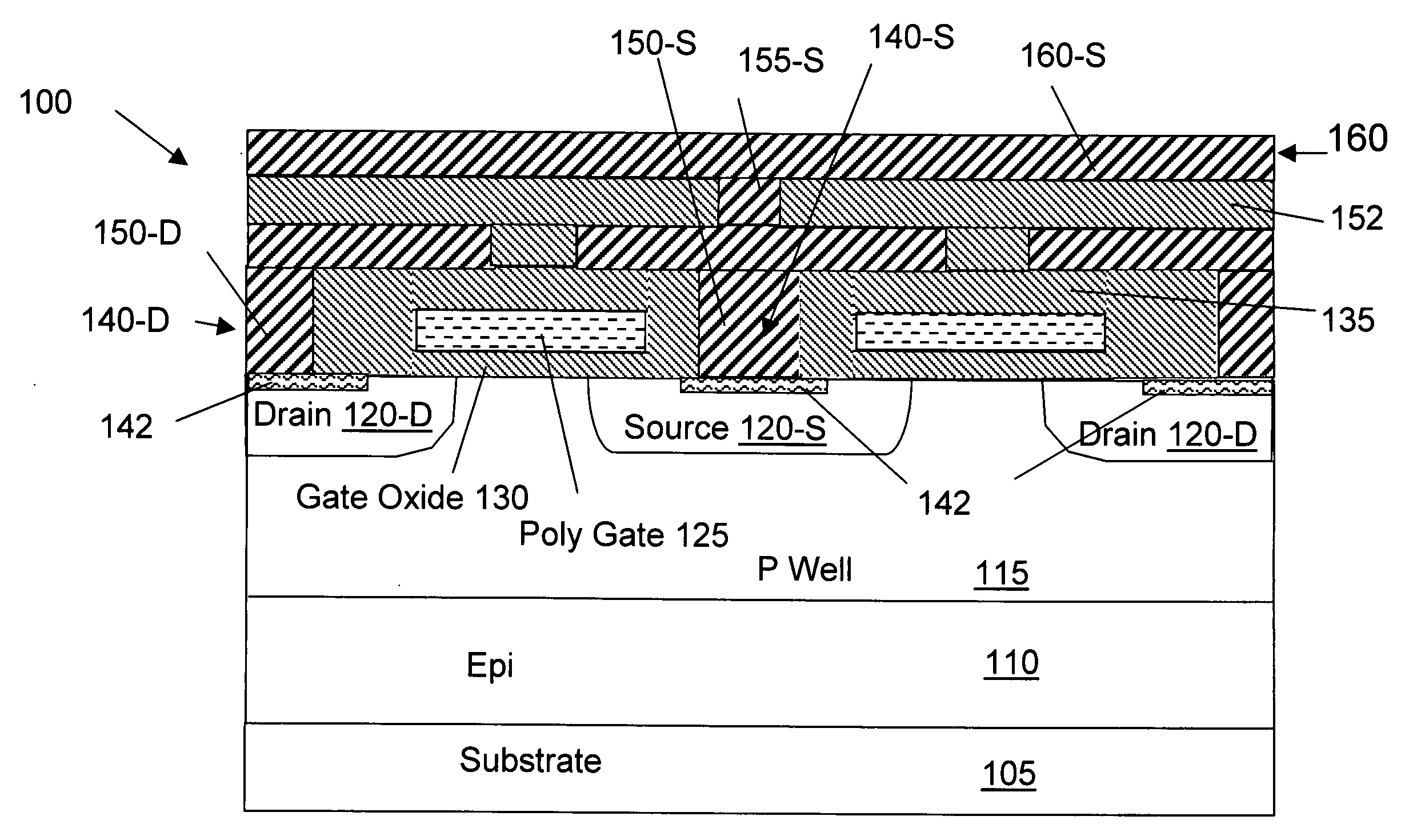
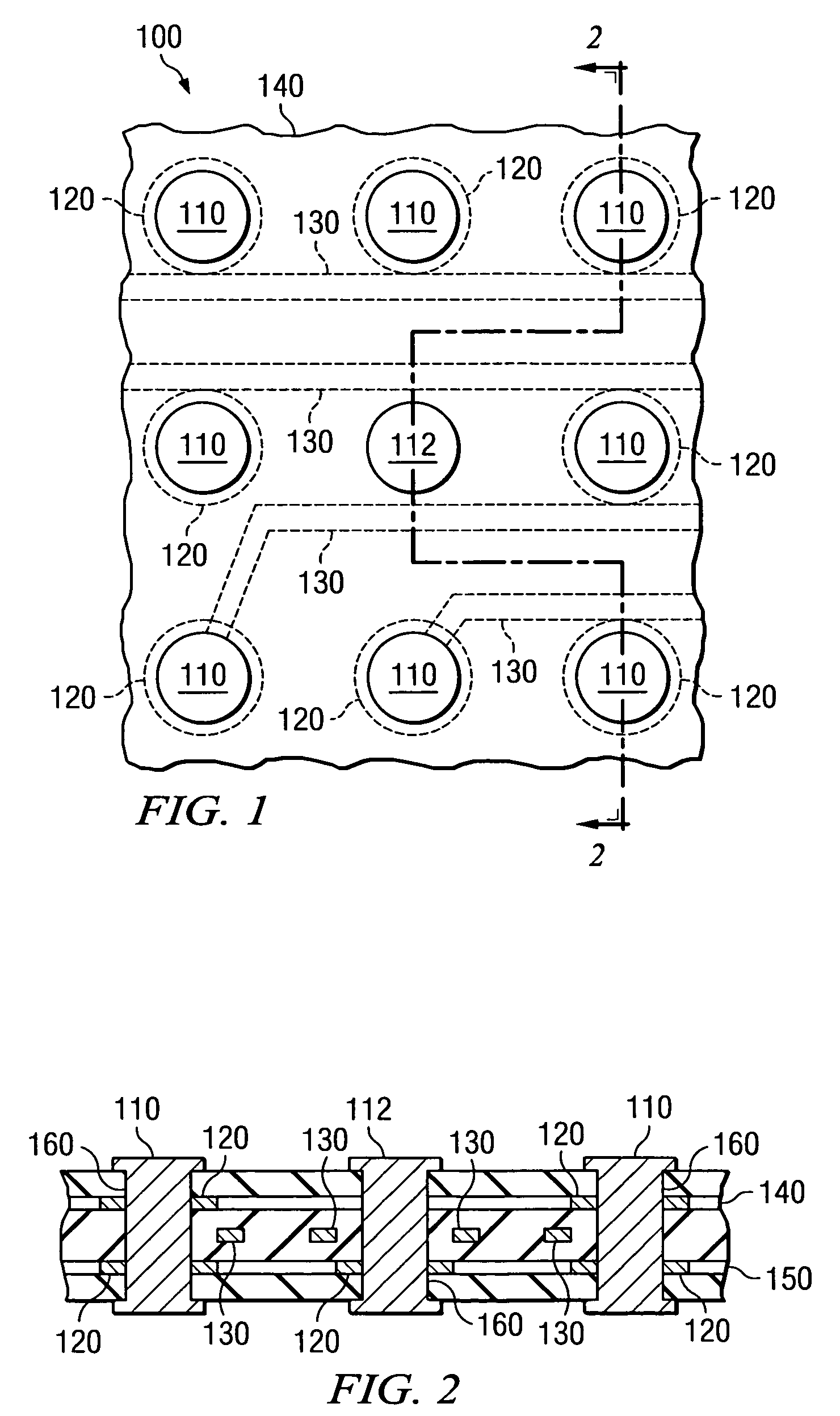
Power semiconductor device with a base region and method of manufacturing same
ActiveUS7432145B2Increase channel densitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesPower semiconductor deviceChannel density
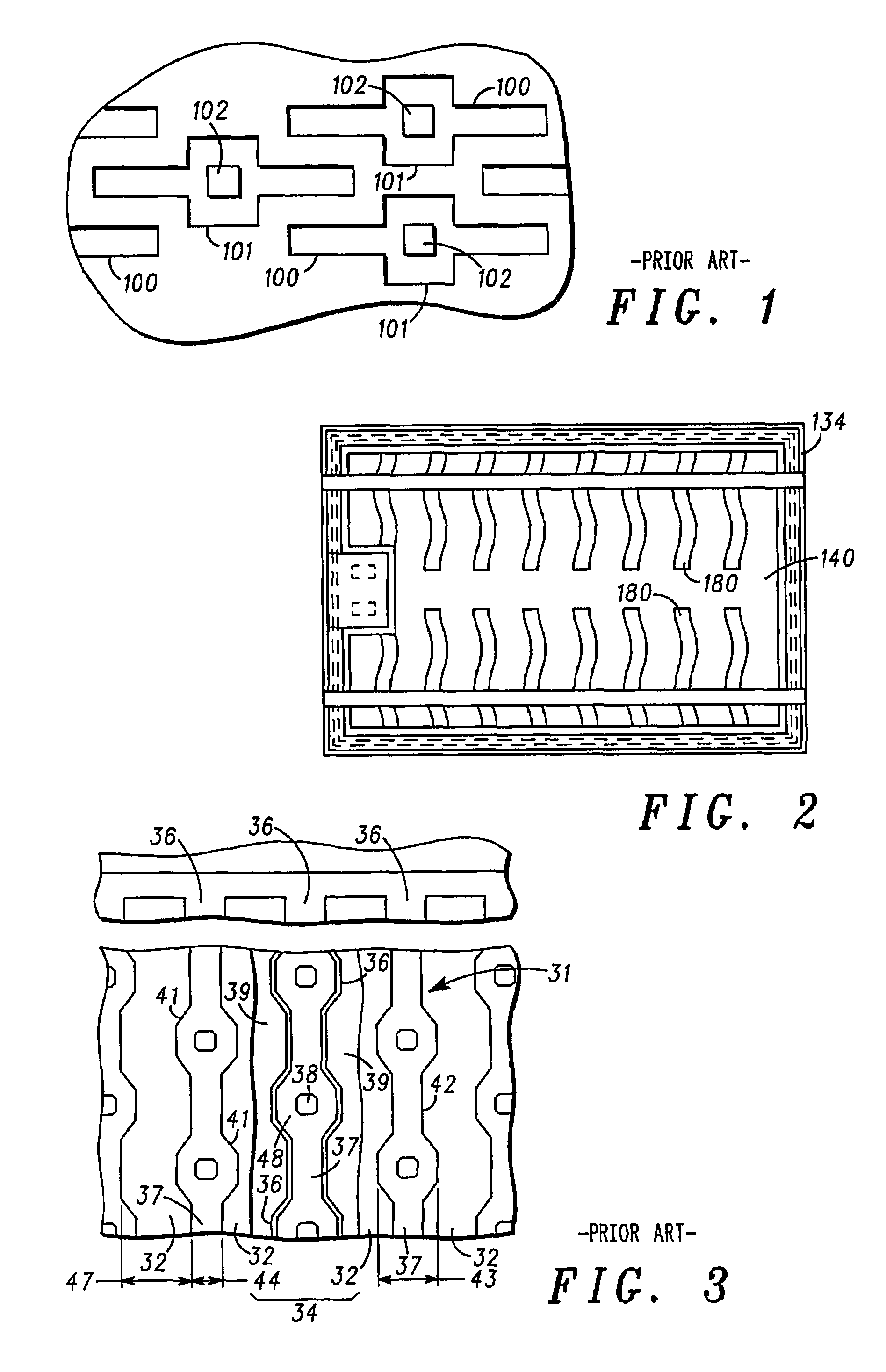
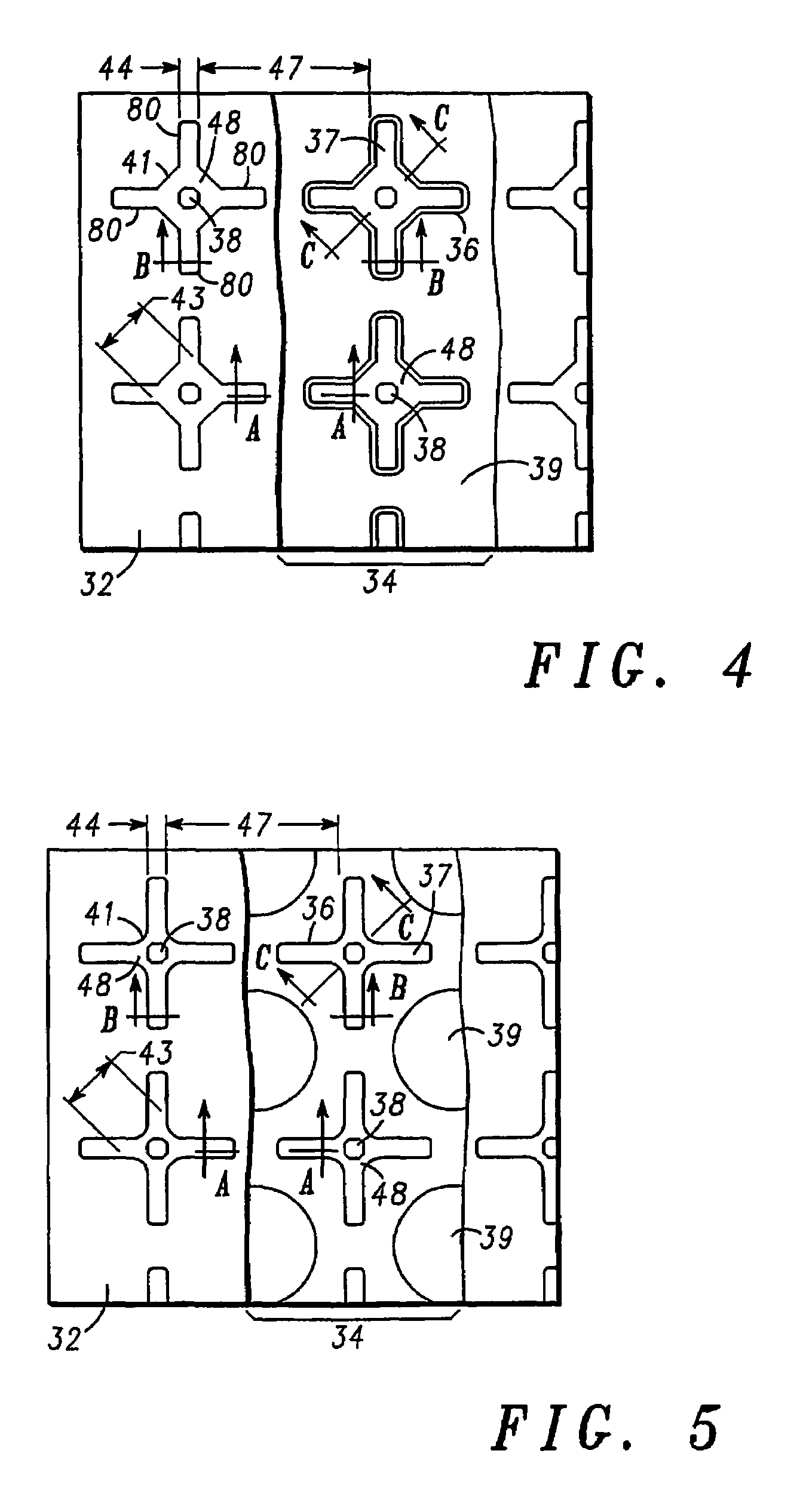
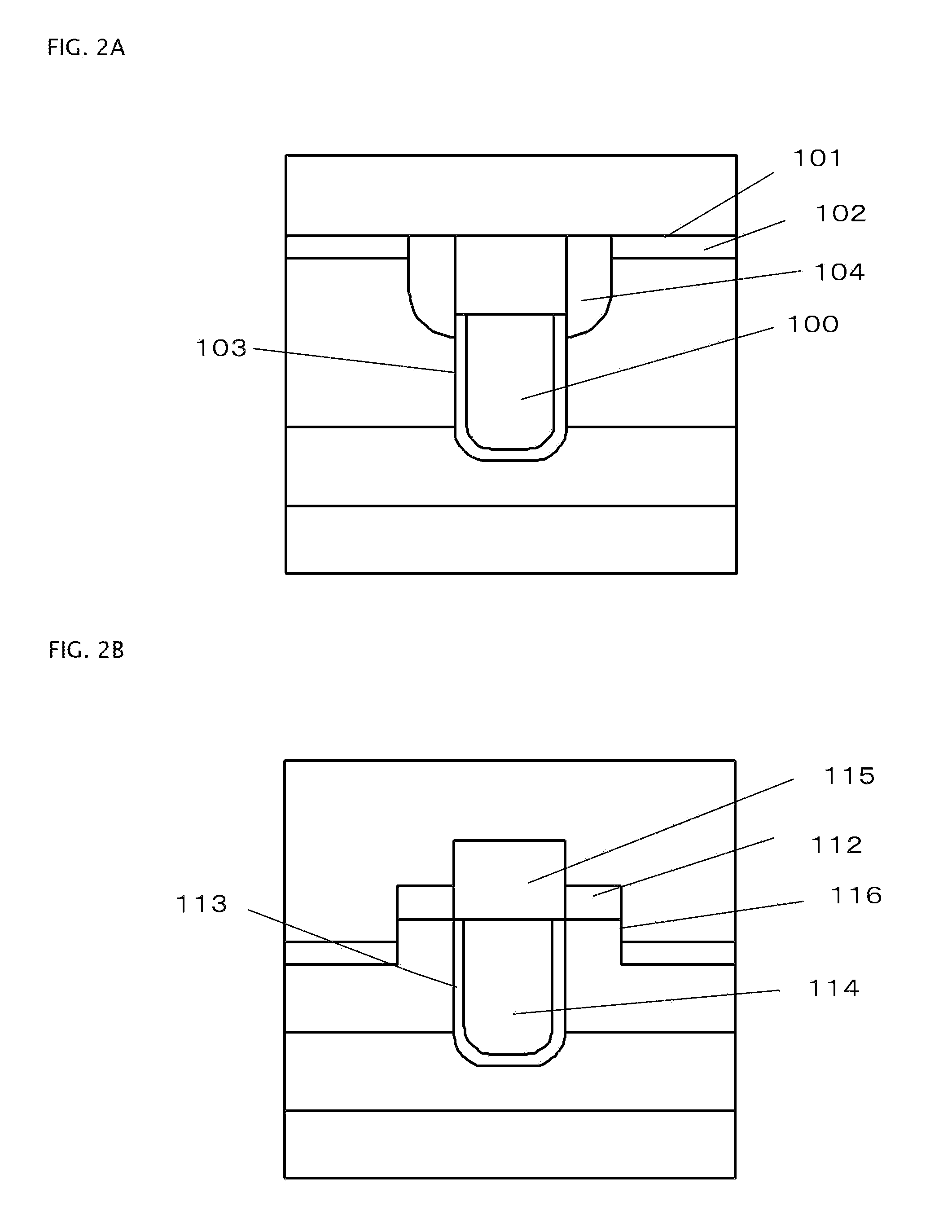
A low on-state resistance power semiconductor device has a shape and an arrangement that increase the channel density and the breakdown voltage The power semiconductor device comprises a plurality of individual cells formed on a semiconductor substrate (62). Each individual cell comprises a plurality of radially extending branches (80) having source regions (37) within base regions (36). The plurality of individual cells are arranged such that at least one branch of each cell extends towards at least one branch of an adjacent cell and wherein the base region (36) of the extending branches merge together to form a single and substantially uniformly doped base region (36) surrounding drain islands (39) at the surface of the semiconductor substrate (62).
Owner:NXP USA INC
Thin silicon-on-insulator (SOI) lateral insulator gate bipolar transistor (LIGBT) with folded groove gate
InactiveCN109887998ASimple processHigh saturation working currentSemiconductor devicesChannel densityElectron injection
The invention belongs to the technical field of a power semiconductor, and particularly relates to a thin silicon-on-insulator (SOI) lateral insulator gate bipolar transistor (LIGBT) with a folded groove gate. The thin SOI LIGBT is mainly characterized in that a non-equal deep dielectric groove and the folded groove gate are employed; during positive voltage resistance, a transverse electric fieldis modulated by the non-equal deep dielectric groove, and a uniformly-doped drift region bears high voltage; during positive conduction, air is prevented from flowing to an emitter by the dielectricgroove, the hole concentration of a drift region near to the emitter is improved, electron injection improvement effect is achieved, and the conduction voltage drop of the device is reduced; the concentration of the drift region near to one side of a collector is farther lower than the concentration of the drift region at one side of the collector of a traditional thin SOI layer linear doping device, and the injection efficiency of the collector is improved; the electrical conduction modulation effect of the device is improved, the positive conduction voltage drop is reduced, the channel density of the folded groove gate is improved, and the saturation current capability of the device is greatly improved. Compared with a traditional thin SOI LIGBT structure, the thin SOI LIGBT has the beneficial effects of lower positive conduction voltage drop and higher saturation current capability, and Von-Eoff is more excellent in difference.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
High-speed and low-loss multi-trench gate high-voltage power device
ActiveCN110504308AImprove injection efficiencyImproves latch-up resistanceSemiconductor devicesChannel densityCharge carrier
The invention belongs to the technical field of power semiconductors and particularly relates to a high-speed and low-loss multi-trench gate high-voltage power device. Compared with a traditional structure, the structure of the high-speed and low-loss multi-trench gate high-voltage power device has the advantage that a plurality of trench gate structures are introduced into an emitter terminal anda collector terminal. Channels in side walls of trench gates at the collector terminal are turned off and a connection path of an N+ collector region and an N-type buffer layer is blocked during forward conduction, so that the voltage foldback effect can be eliminated. A trench gate structure at the emitter terminal can increase the channel density to reduce the resistance of a channel region, and a barrier trench gate and a carrier storage layer can effectively improve the carrier concentration of a drift region, so that the novel device can obtain lower forward conduction voltage drop. In the turn-off process, the channels in the side walls of the trench gates at the collector terminal are opened along with voltage rise of a collector, so that the N+ collector region communicates with the N-type buffer layer to form a rapid electron extraction path and turn-off of the device is accelerated to reduce the turn-off loss. Therefore, the high-speed and low-loss multi-trench gate high-voltage power device has lower forward conduction voltage drop and smaller turn-off loss and does not have the voltage foldback effect.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA +1
Shield gate power device
InactiveCN109166926AHigh densityIncreased current capabilitySemiconductor devicesCapacitancePower semiconductor device
The invention belongs to the technical field of power semiconductors, the invention aims at the problems that the cell density and the current capability of the conventional shielded gate power deviceare limited, A mask gate power device By arranging one or more TMOS cell structures between the conventional shielded gate cell structures, the channel density is increased under the same chip area,so that the cell density and current capability of the shielded gate MOS are improved while the gate drain capacitance is lower, the breakdown voltage is higher, and the on-resistance is lower.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Fast readout method and switched capacitor array circuitry for waveform digitizing
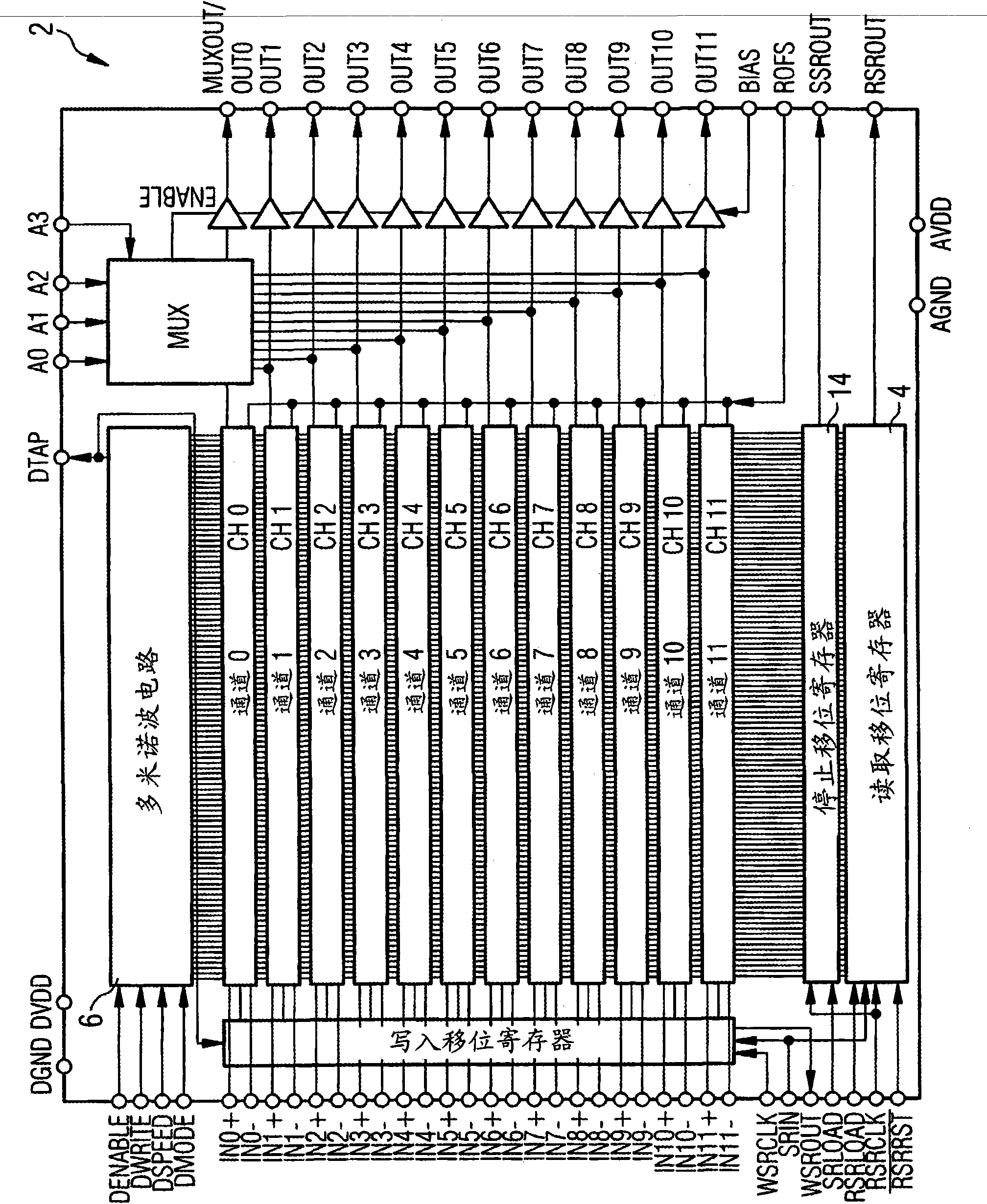
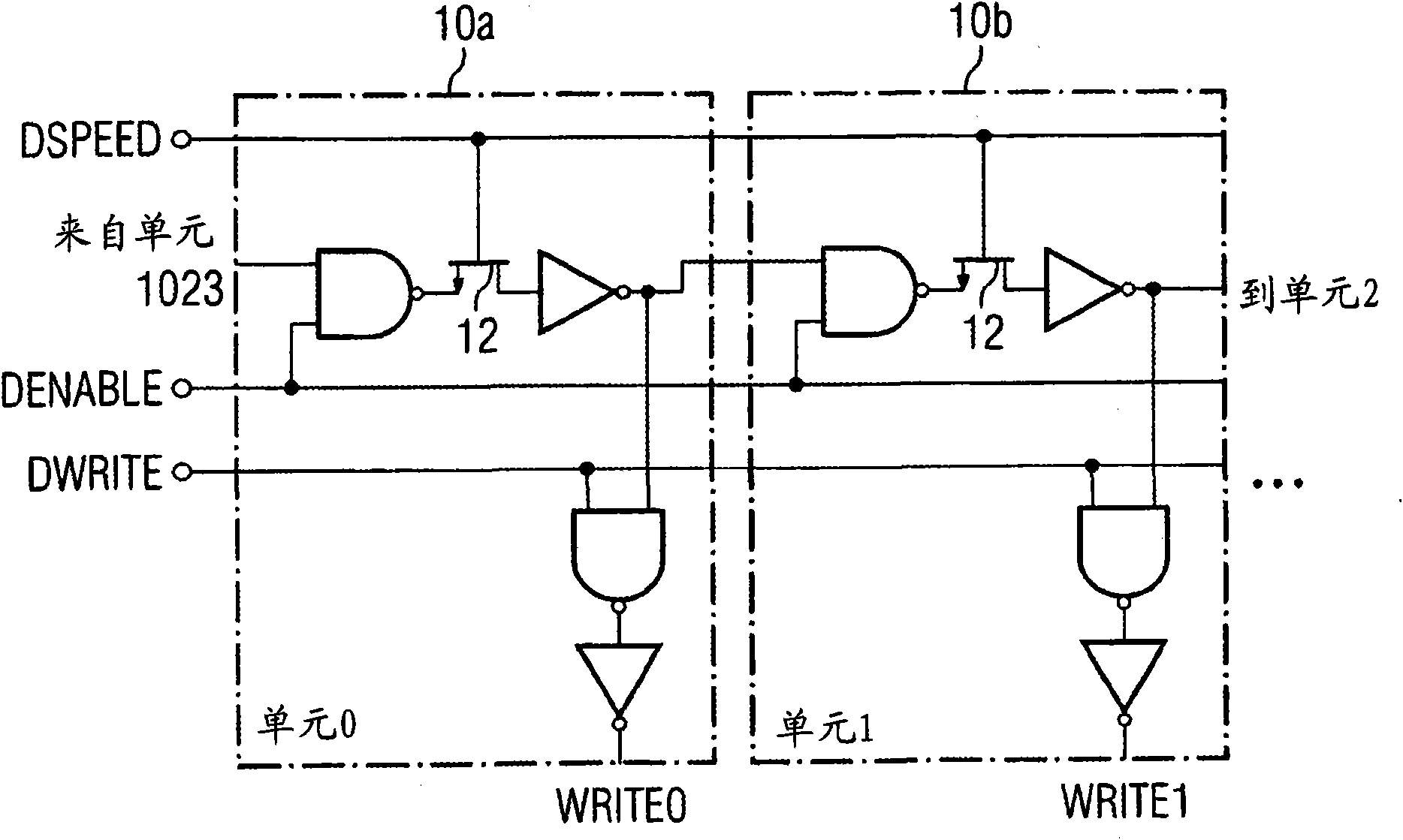
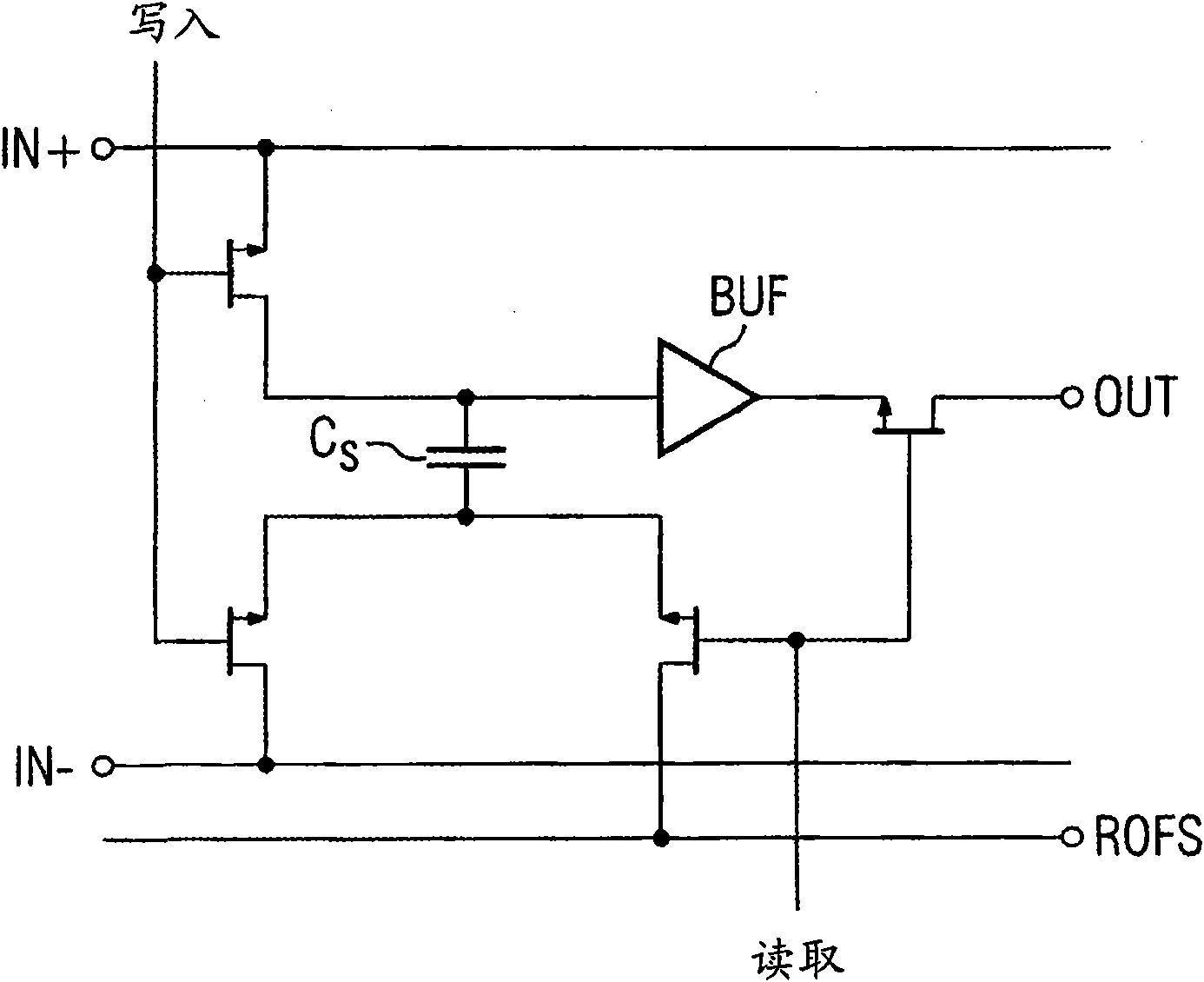
The present invention represents a technique to reduce the readout time of switched capacitor array (SCA) circuitries. A possible implementation is a SCA chip capable of sampling 12 differential input channels at a sampling speed of 10 MSPS to 5 GSPS. The analog waveform can be stored in 1024 sampling cells per channel, and can be read out after sampling via a shift register clocked at 33 MHz for external digitization. The write signal for the sampling ceils is generated by a chain of inverters (domino principle) generated on the chip. The domino wave is running continuously until stopped by a trigger. A read shift register clocks the contents of the sampling cells either to a multiplexed or to individual outputs, where it can be digitized with an external ADC. It is possible to read out only a part of the waveform for reducing the digitization time. The high channel density, high analog bandwidth of 450 MHz, and low noise of 0.35 mV (after offset calibration) makes this chip ideally suited for low power, high speed, high precision waveform digitizing. Fabricated on an advanced CMOS process in a radiation hard design, the present chip is available in a 64-lead low profile quad flat pack (LQFP) and a 64-pin quad flat non-leaded package (QFN).
Owner:PAUL SCHERRER INSTITUT
System and method for increasing wiring channels/density under dense via fields
InactiveUS20060219427A1Increasing wiring channels/densityMaximizing signal line wiringSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPrinted circuit aspectsChannel densityEngineering
A system and method for increasing the wiring channels / density under dense via fields of a circuit board are provided. With the system and method, the power / ground lines for the circuit board are designed to be provided in an orthogonal or diagonal pattern. The land grid array (LGA) / ball grid array (BGA) makes contact only on the surface pads of the printed circuit board with no plated through holes / vias underneath these surface pads. This opens up wiring channels, which previously used to be occupied by plated through holes and anti-pads, that can now be used for maximizing signal line wiring routing.
Owner:IBM CORP
High-performance optical fiber interconnection system
ActiveCN113009654ARealize multiplexingReduce design iteration cyclesFibre transmissionCoupling light guidesMultiplexingChannel density
Owner:WINGCOMM CO LTD
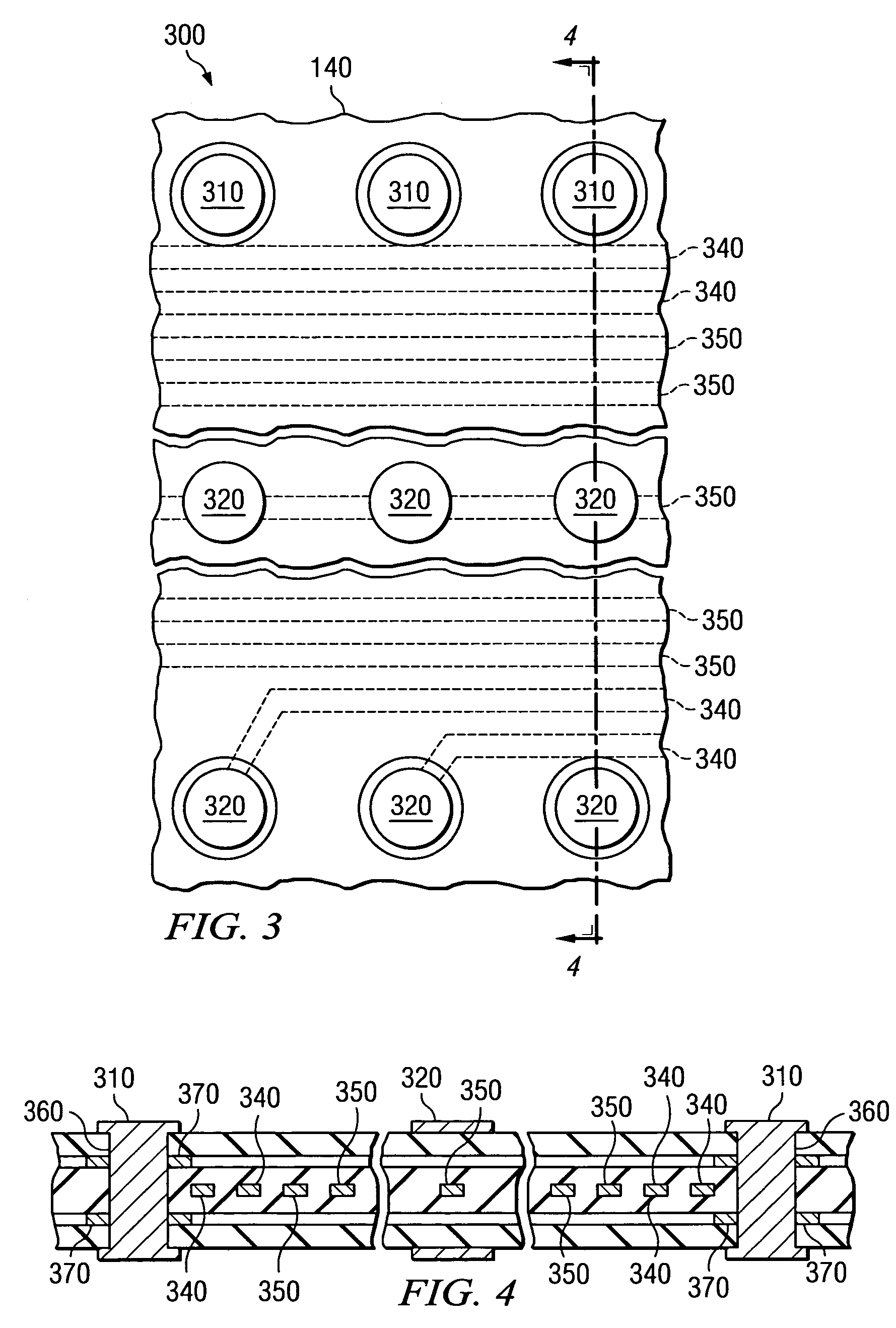
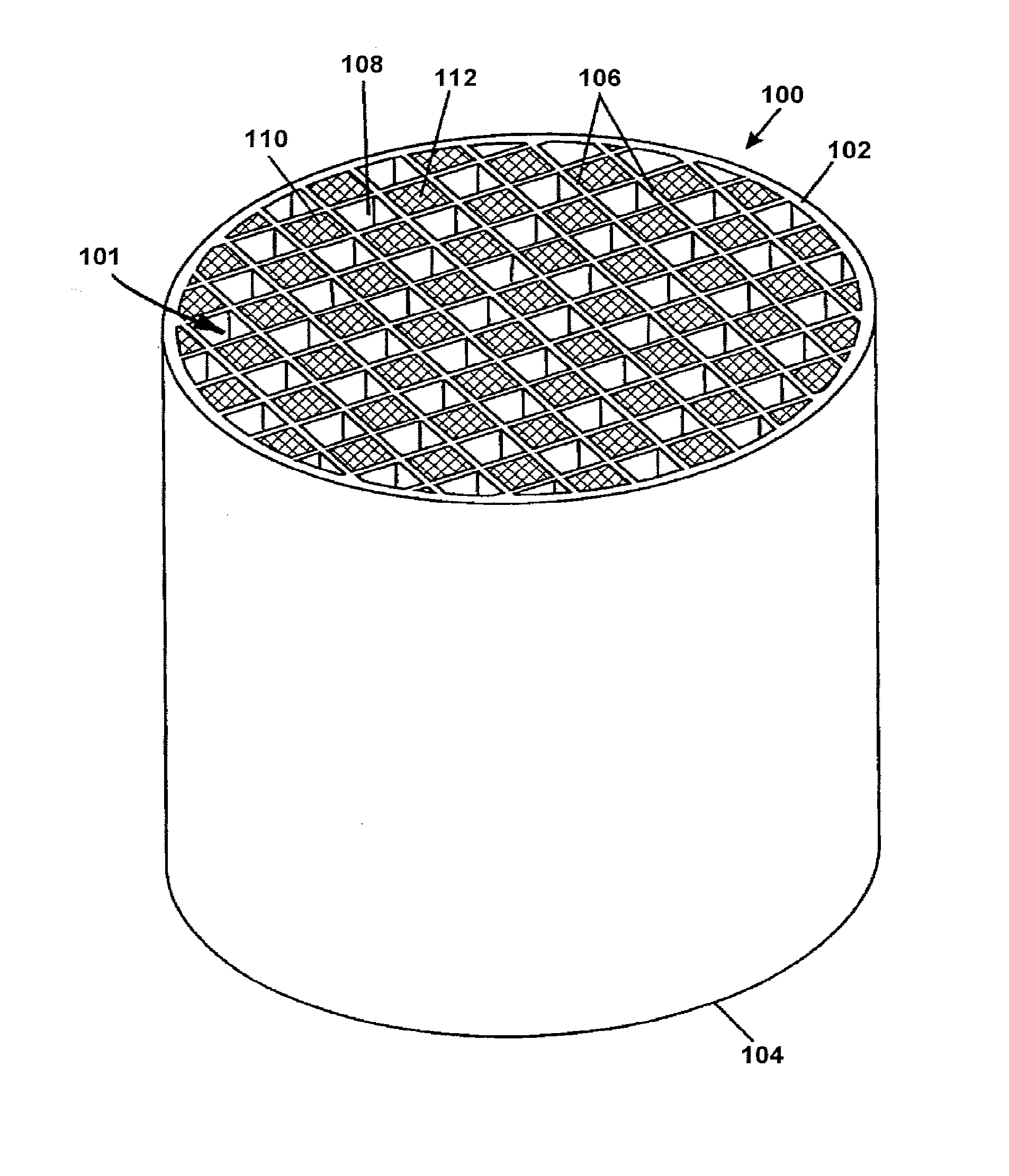
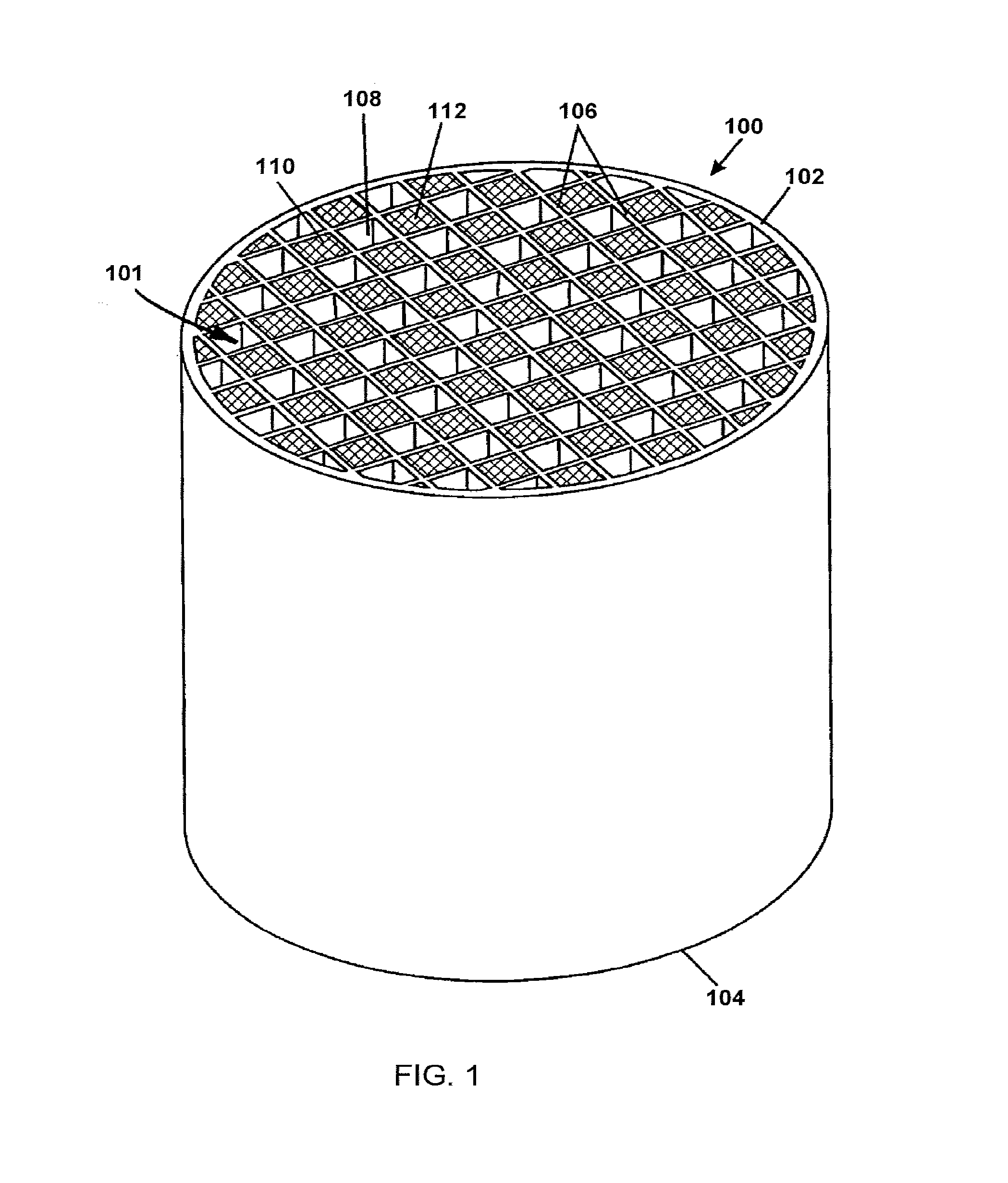
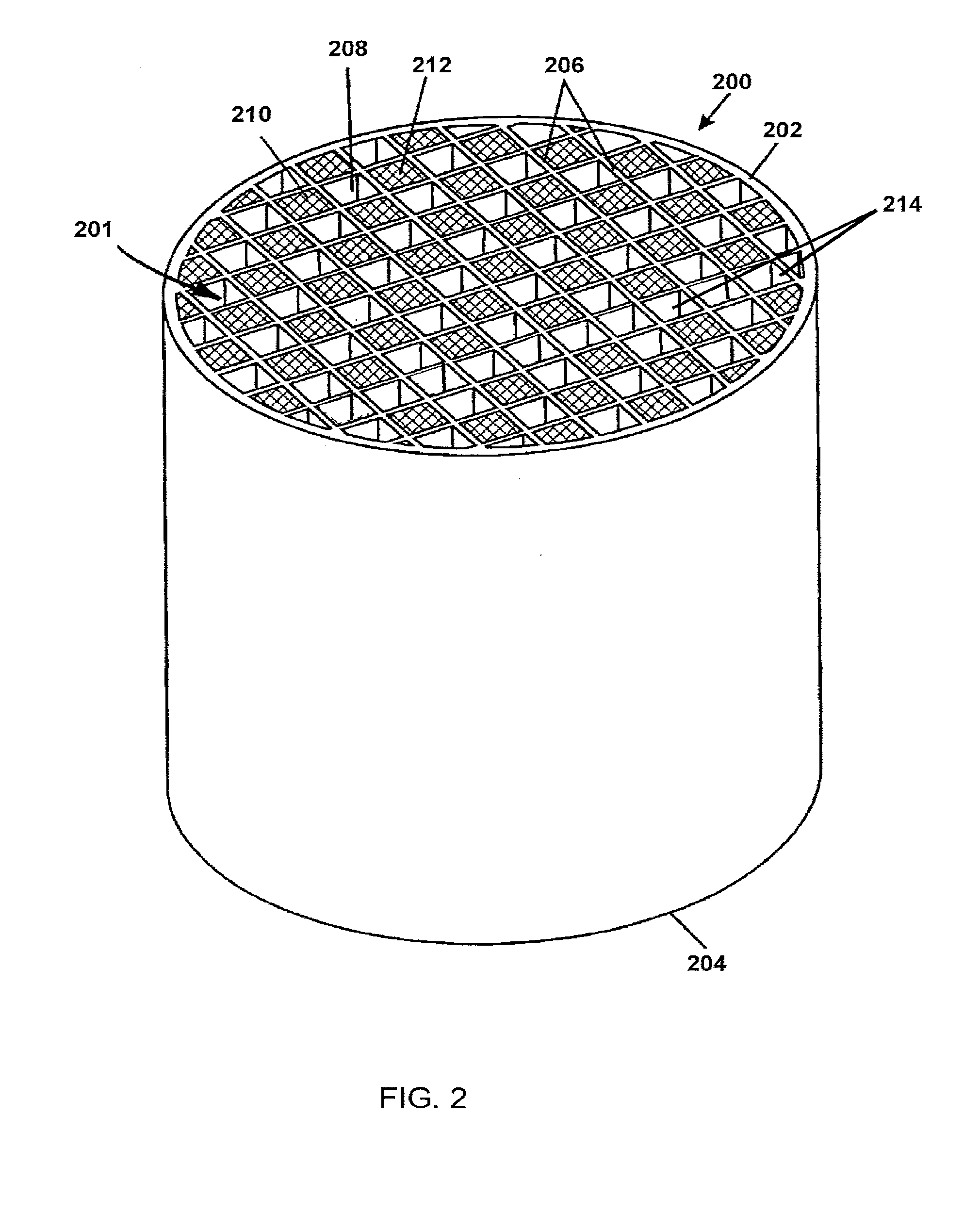
Porous ceramic honeycomb articles and methods for making the same
A porous ceramic honeycomb article comprising a honeycomb body formed from cordierite ceramic, wherein the honeycomb body has a porosity P %≧55% and a cell channel density CD ≧150 cpsi. The porous channel walls have a wall thickness T, wherein (11+(300−CD)*0.03)≧T≧(8+(300−CD)*0.02), a median pore size ≦20 microns, and a pore size distribution with a d-factor of ≦0.35. The honeycomb body has a specific pore volume of VP≦0.22. The porous ceramic honeycomb article exhibits a coated pressure drop increase of ≦8 kPa at a flow rate of 26.5 cubic feet per minute when coated with 100 g / L of a washcoat catalyst and loaded with 5 g / L of soot.
Owner:CORNING INC
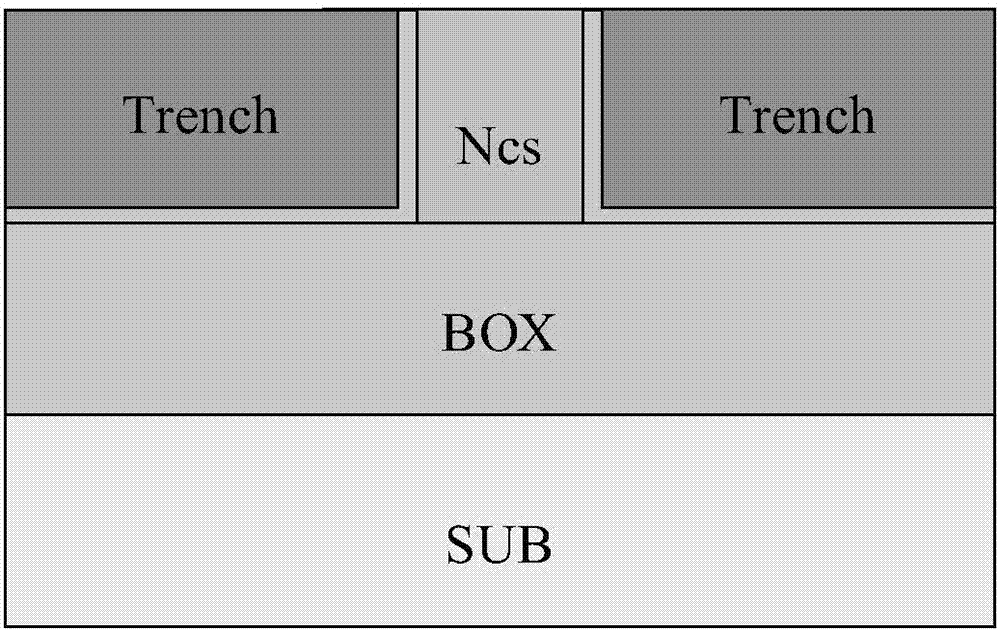
Trench gate semiconductor device and the method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20110156137A1Increase channel densityReduce parasitic resistanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesChannel densityBody contact
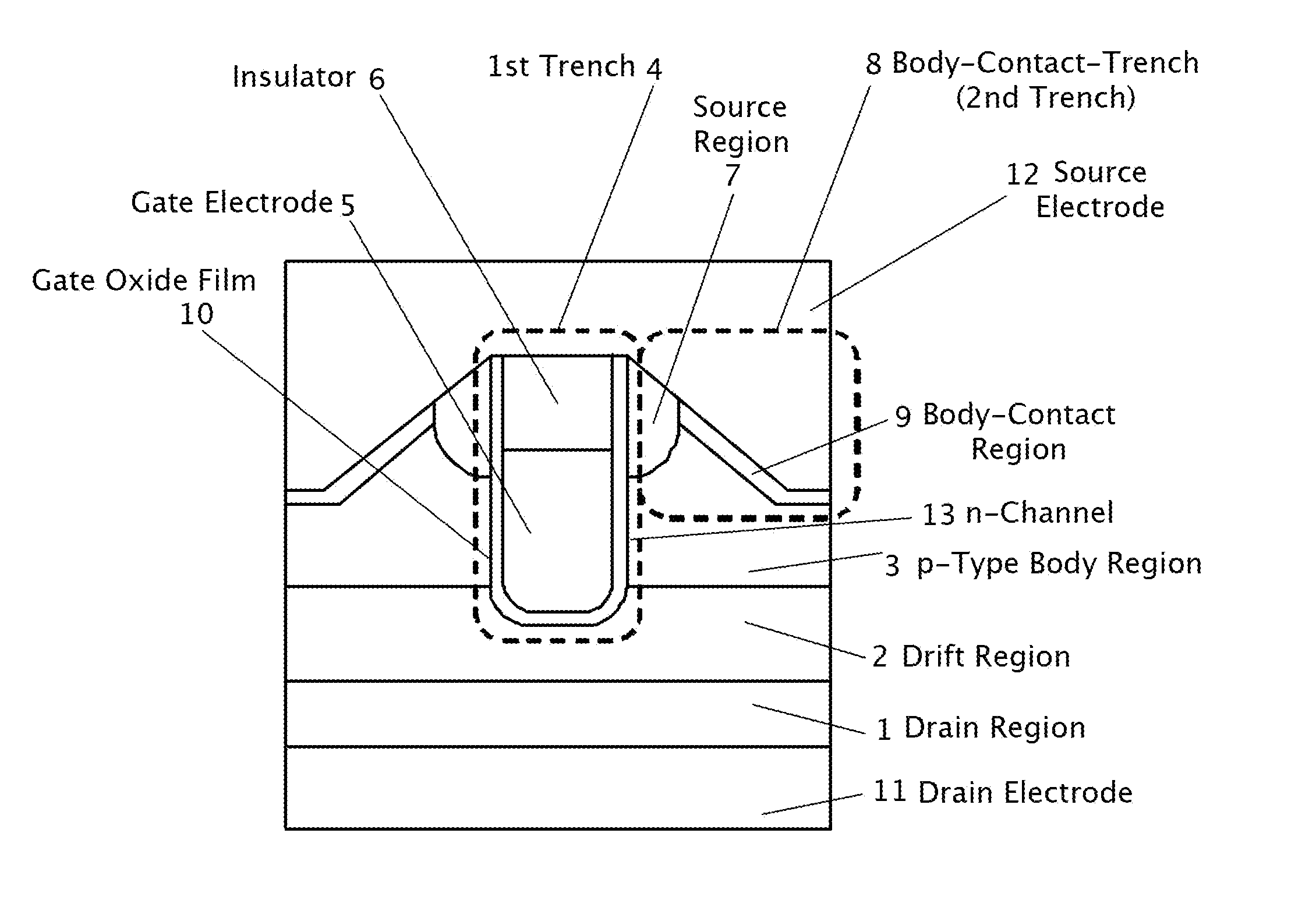
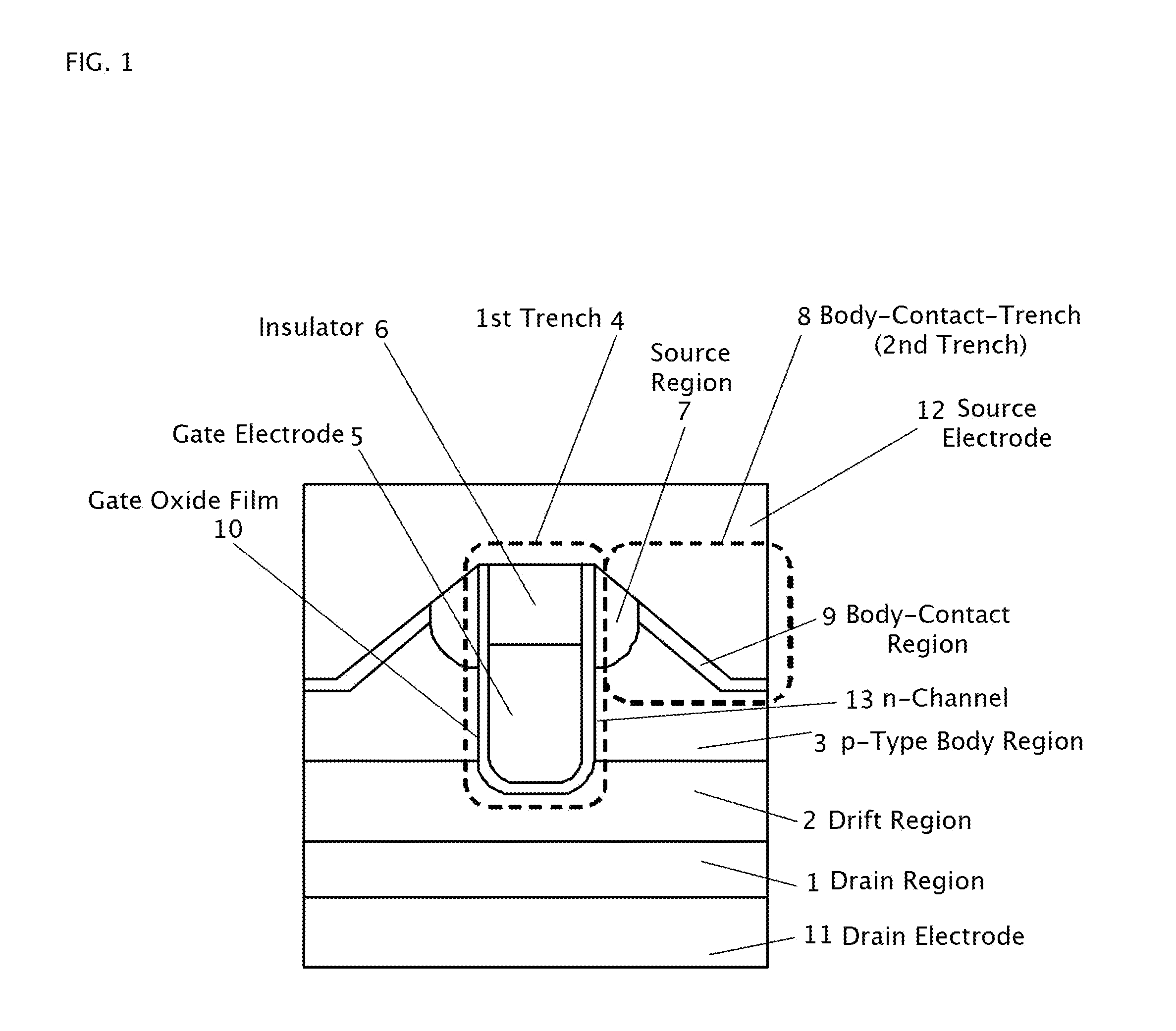
A trench gate semiconductor device is disclosed which has a trench gate structure including an insulator in the upper portion of a first trench, the insulator being on a gate electrode; a source region having a lower end surface positioned lower than the upper surface of the gate electrode; a second trench in the surface portion of a semiconductor substrate between the first trenches, the second trench having a slanted inner surface providing the second trench with the widest trench width at its opening and a bottom plane positioned lower than the lower end surface of the source region, the slanted inner surface being in contact with the source region; and a p-type body-contact region in contact with the slanted inner surface of the second trench. The trench gate semiconductor device and its manufacturing method facilitate increasing the channel density and lowering the body resistance of the parasitic BJT.
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC CO LTD
Silicon carbide power device and preparation method thereof
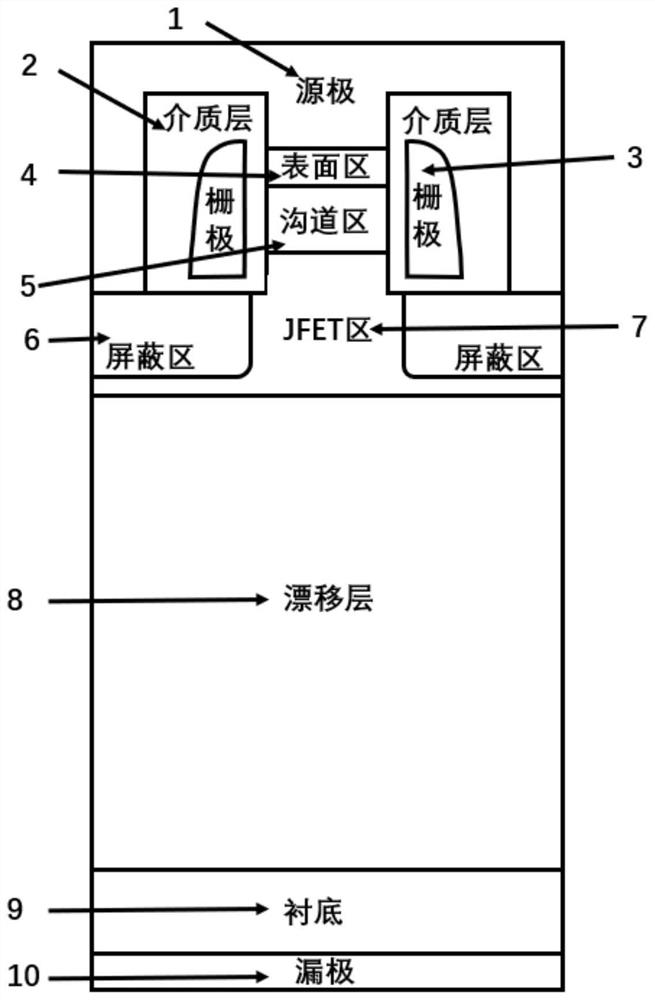
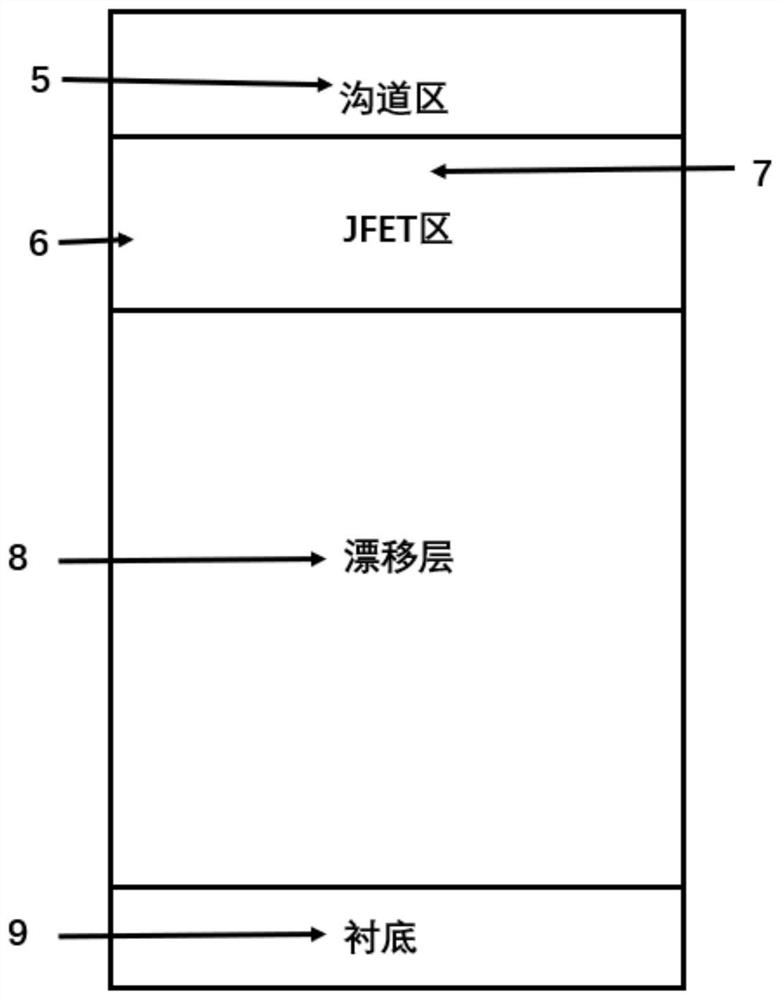
PendingCN114284358AEasy to manufactureSolve lossSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesMOSFETCarbide silicon
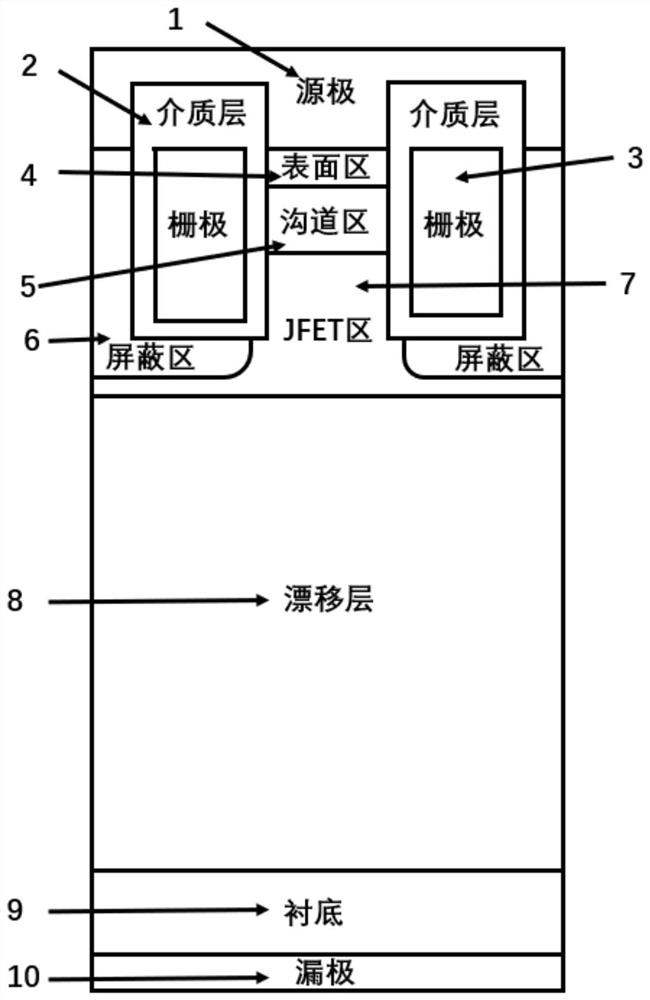
The invention discloses a silicon carbide power device and a preparation method thereof. The device is a silicon carbide MOSFET of a longitudinal structure and comprises a drain electrode, an N + type silicon carbide substrate, an N-type drift layer, an N type JFET region and a channel region which are sequentially arranged from bottom to top, the N type JFET region and the channel region form a fin-type structure, and the two sides of the N type JFET region and the channel region are each provided with a gate structure; a P-type shielding region is arranged at the bottom of the gate structure, or the P-type shielding region surrounds the bottom of the gate structure and is far away from the outer side of the fin-type structure; an N + type surface region is arranged on the channel region, and a source electrode in ohmic contact with the N + type surface region and the surface of a part of the P type shielding region is arranged on the N + type surface region; and the drain electrode is in ohmic contact with the lower surface of the N + type silicon carbide substrate. According to the silicon carbide power device, the well grounded P-type shielding region is manufactured to shield the gate dielectric layer, and meanwhile, the low-doped depletion channel region which does not need to be grounded is introduced, so that the channel mobility and the channel density are further improved, and the on resistance of the device is reduced.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com