Patents
Literature
887results about "Reliability increase in field effect transistors" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
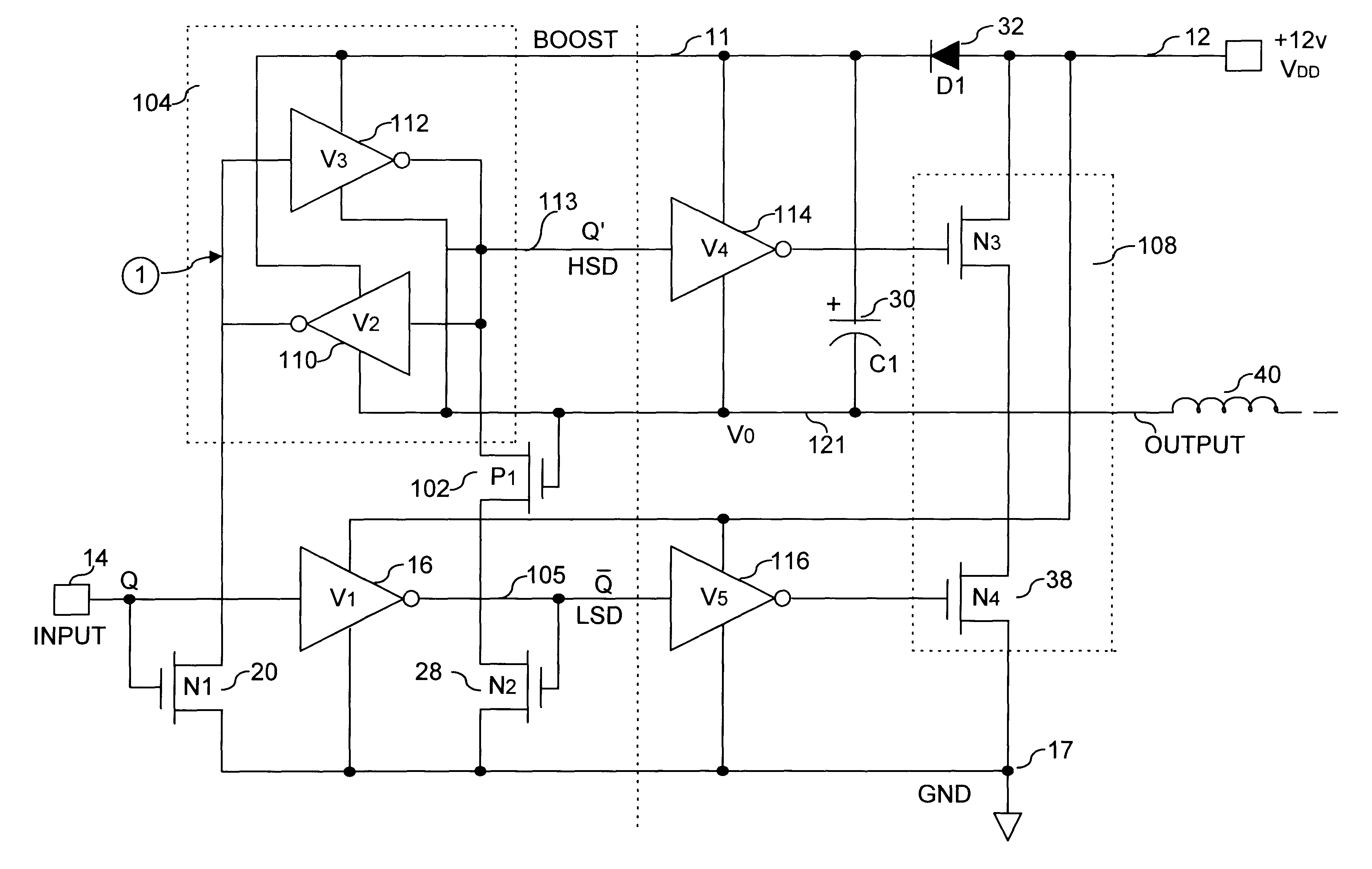
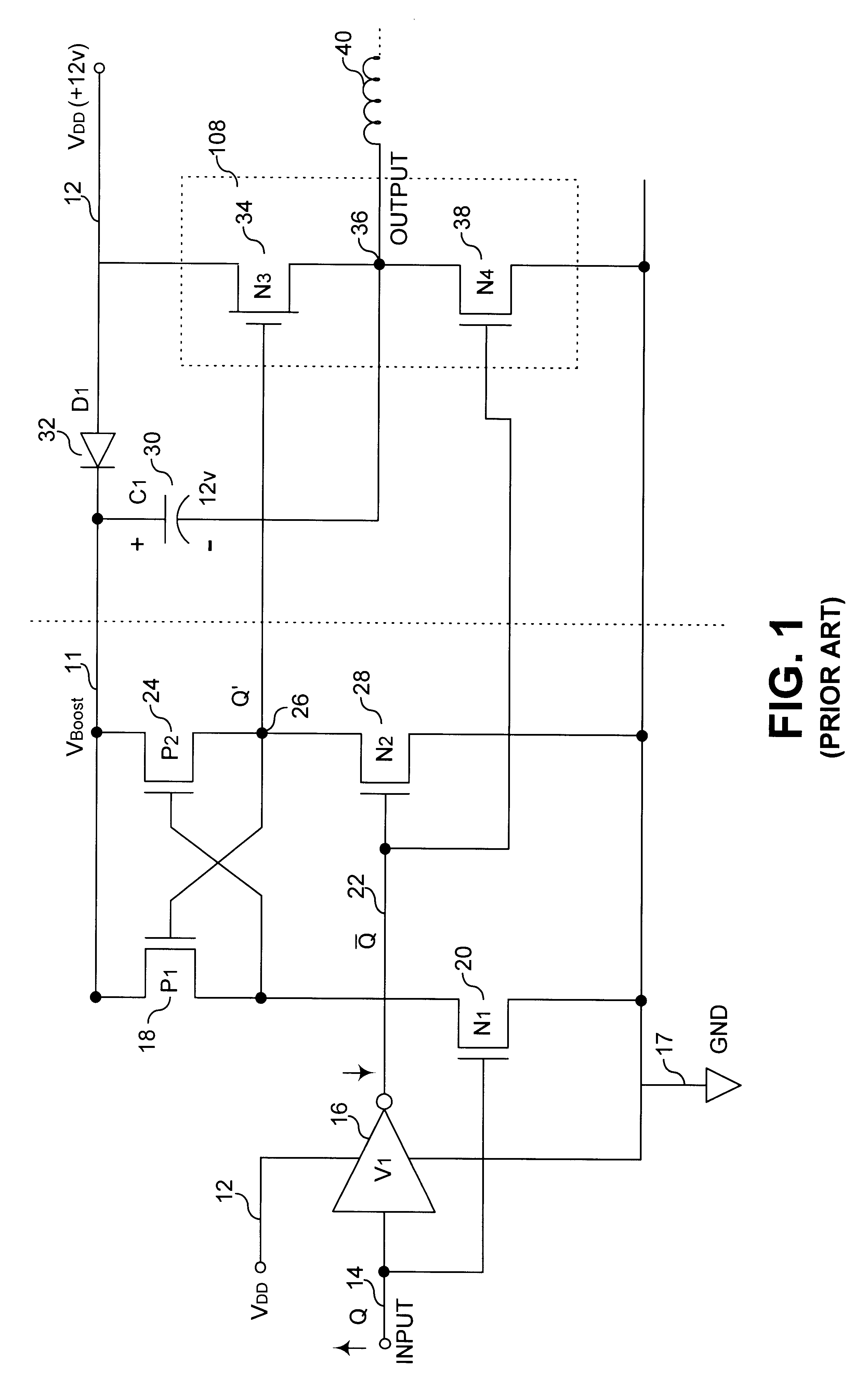
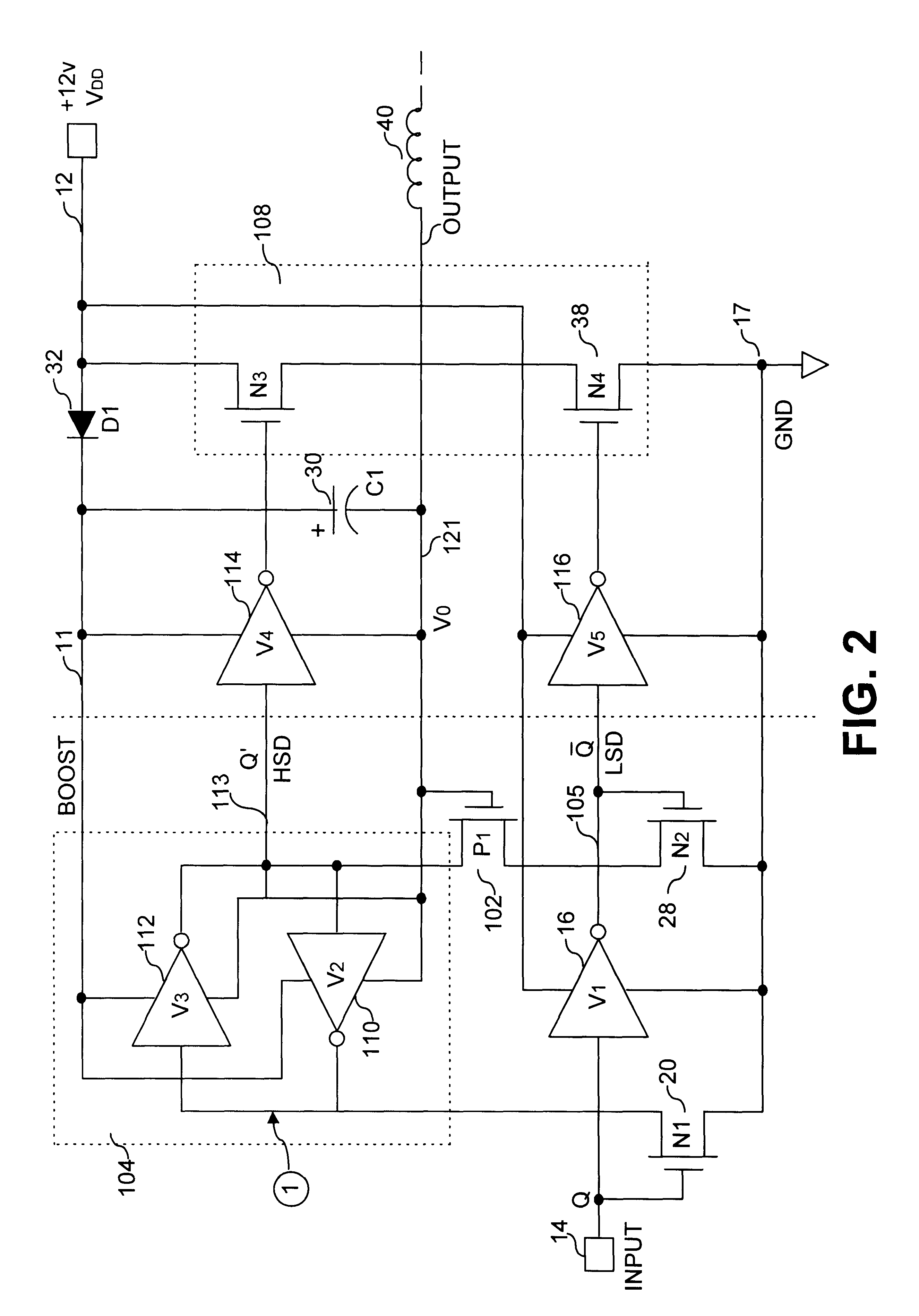
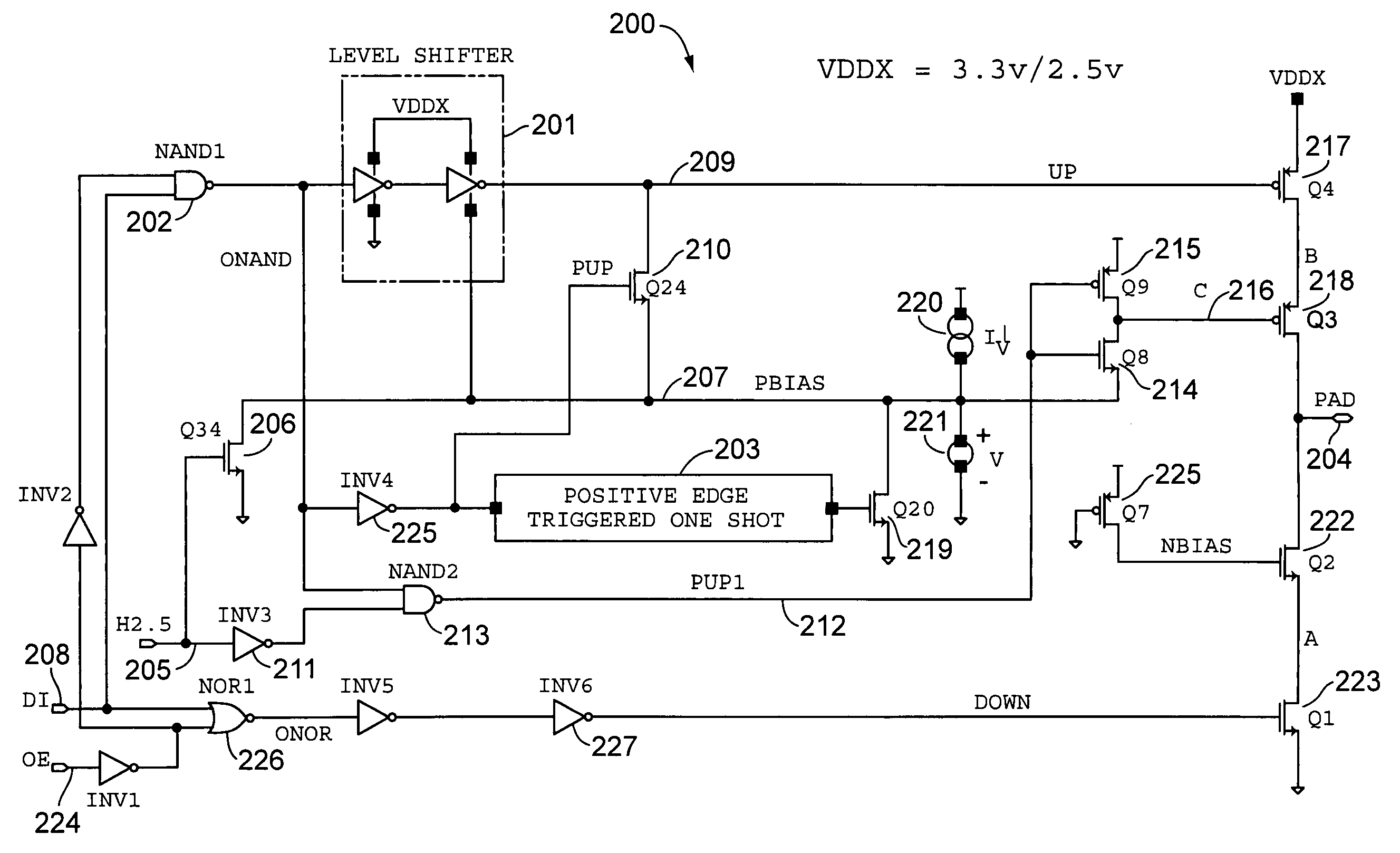
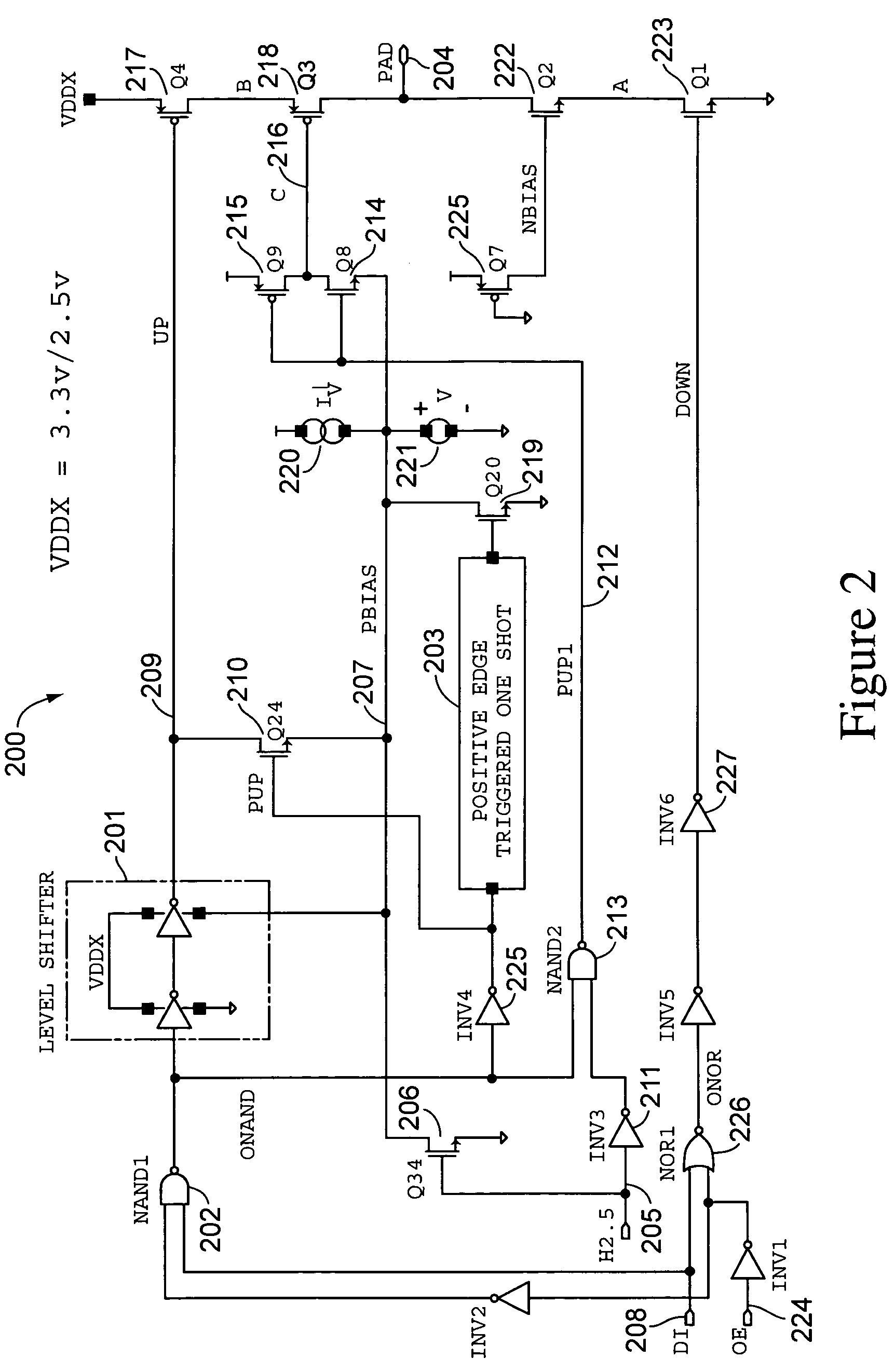
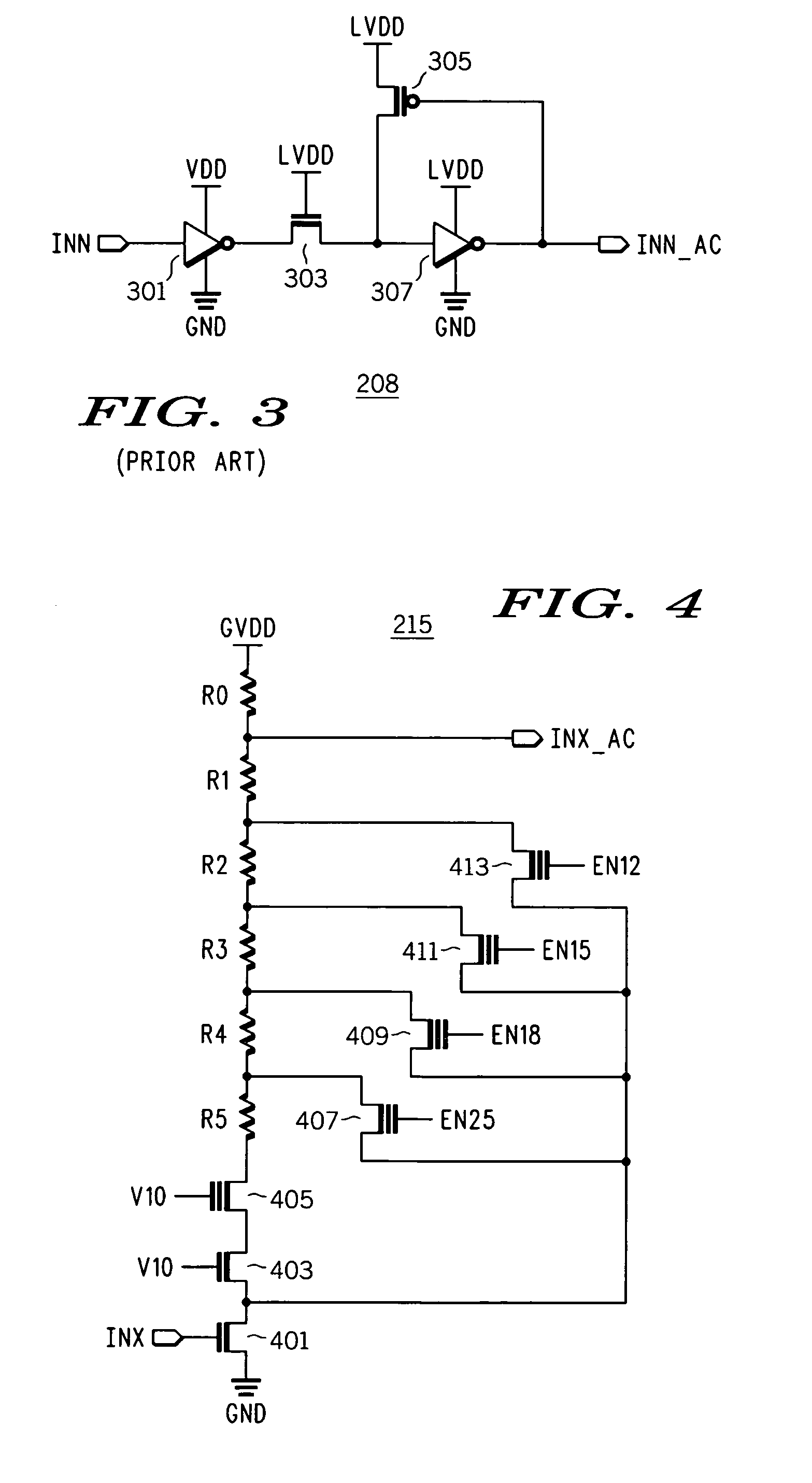
Clamped cascode level shifter circuit
InactiveUS6201429B1Preventing continuous current conductionHysteretic SwitchingPower reduction in field effect transistorsPulse automatic controlCascodeEngineering
An improved level shifter circuit that toggles a "flying Flip-Flop" comprising a cross-coupled inverter pair with control devices driven out of phase through a pair of cascode transistors. The cross-coupled inverter pair provides pull-up to the positive rail, clamping to a High Side-Common (HSC), and providing Hysteretic Switching. The cascode transistors restrict the pull-down of the control devices, thereby preventing continuous current conduction.
Owner:AME
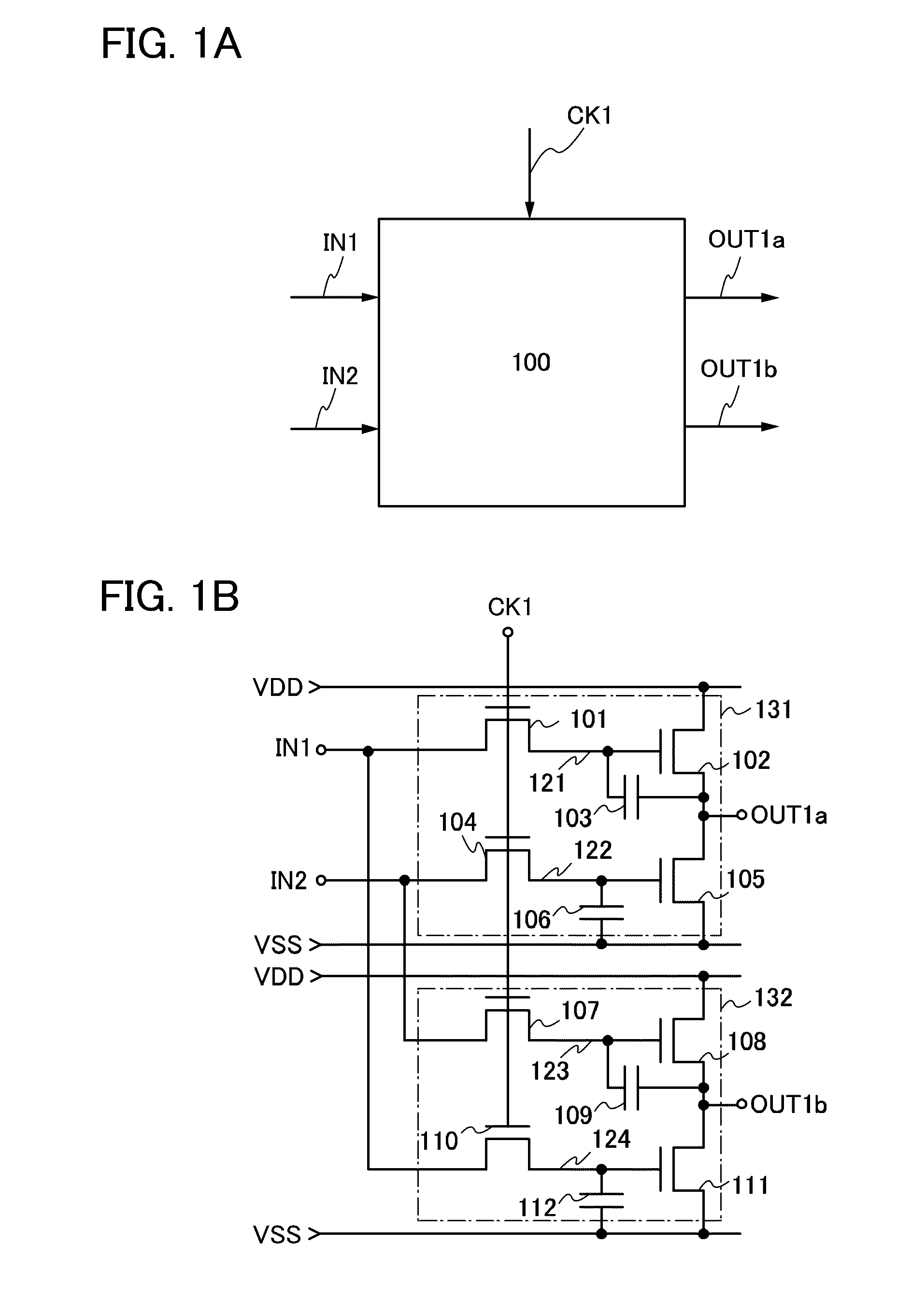
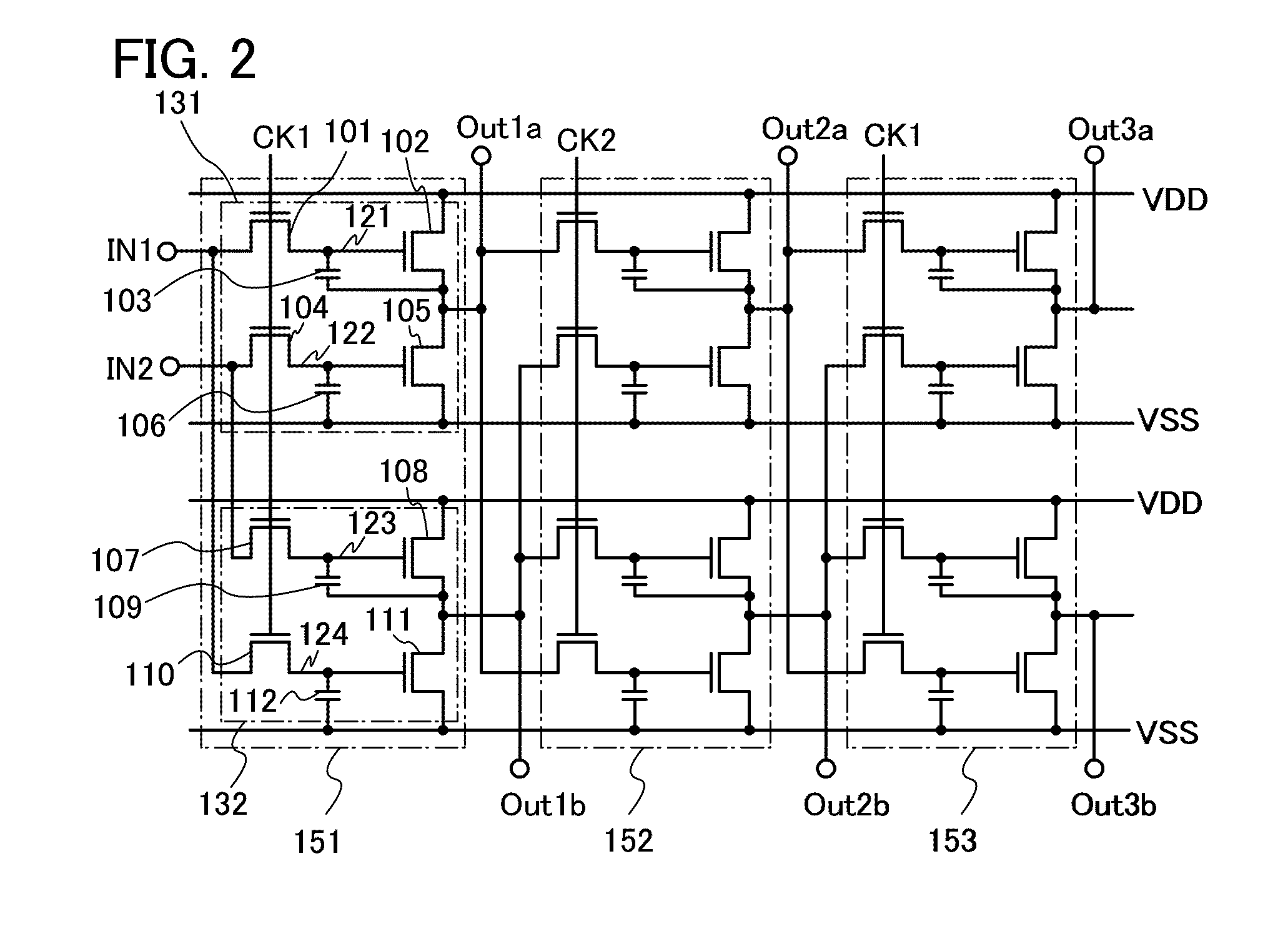
Logic circuit and semiconductor device
ActiveUS20110090184A1Reduce leakage currentTotal current dropSolid-state devicesElectronic switchingMicrometerChannel width
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
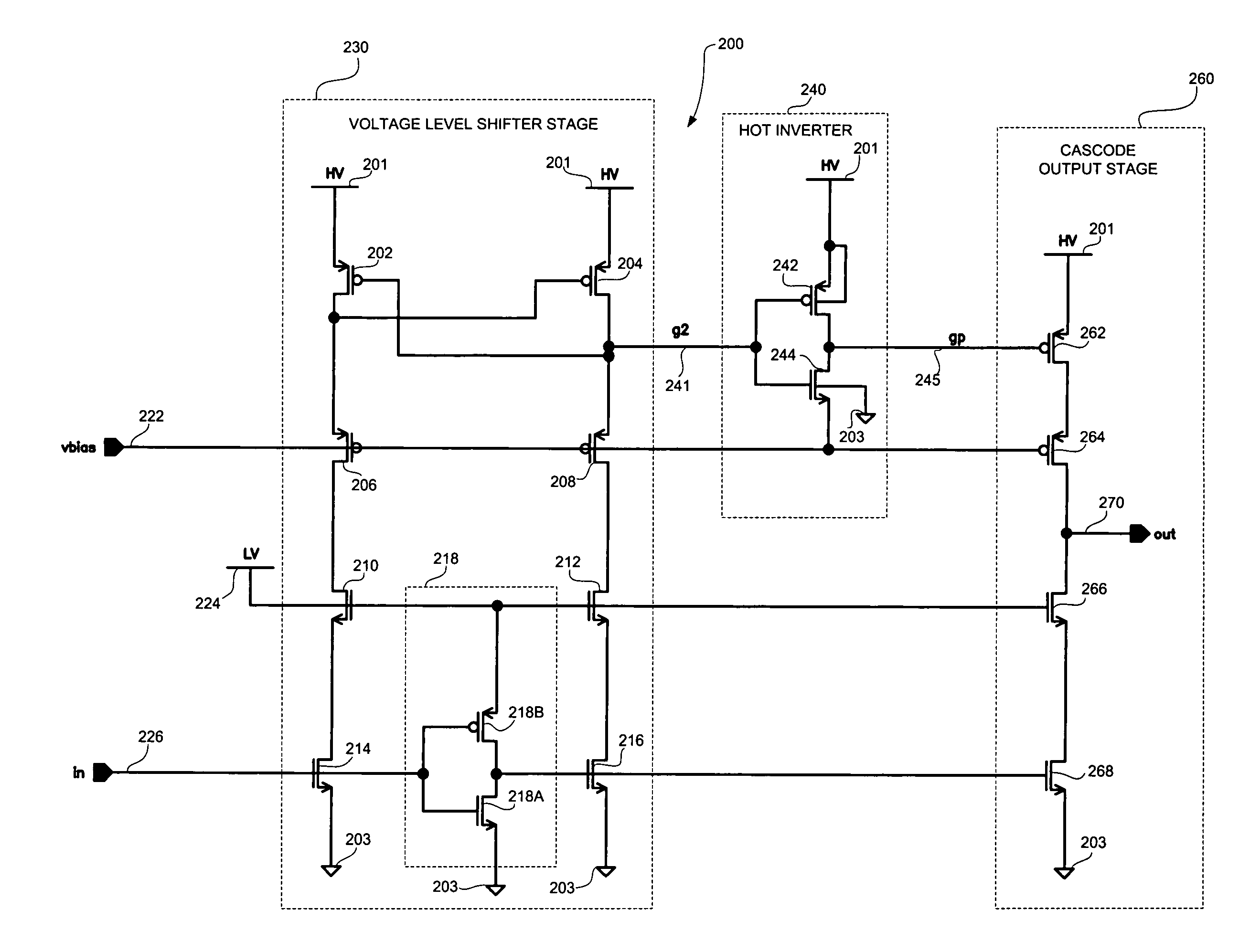
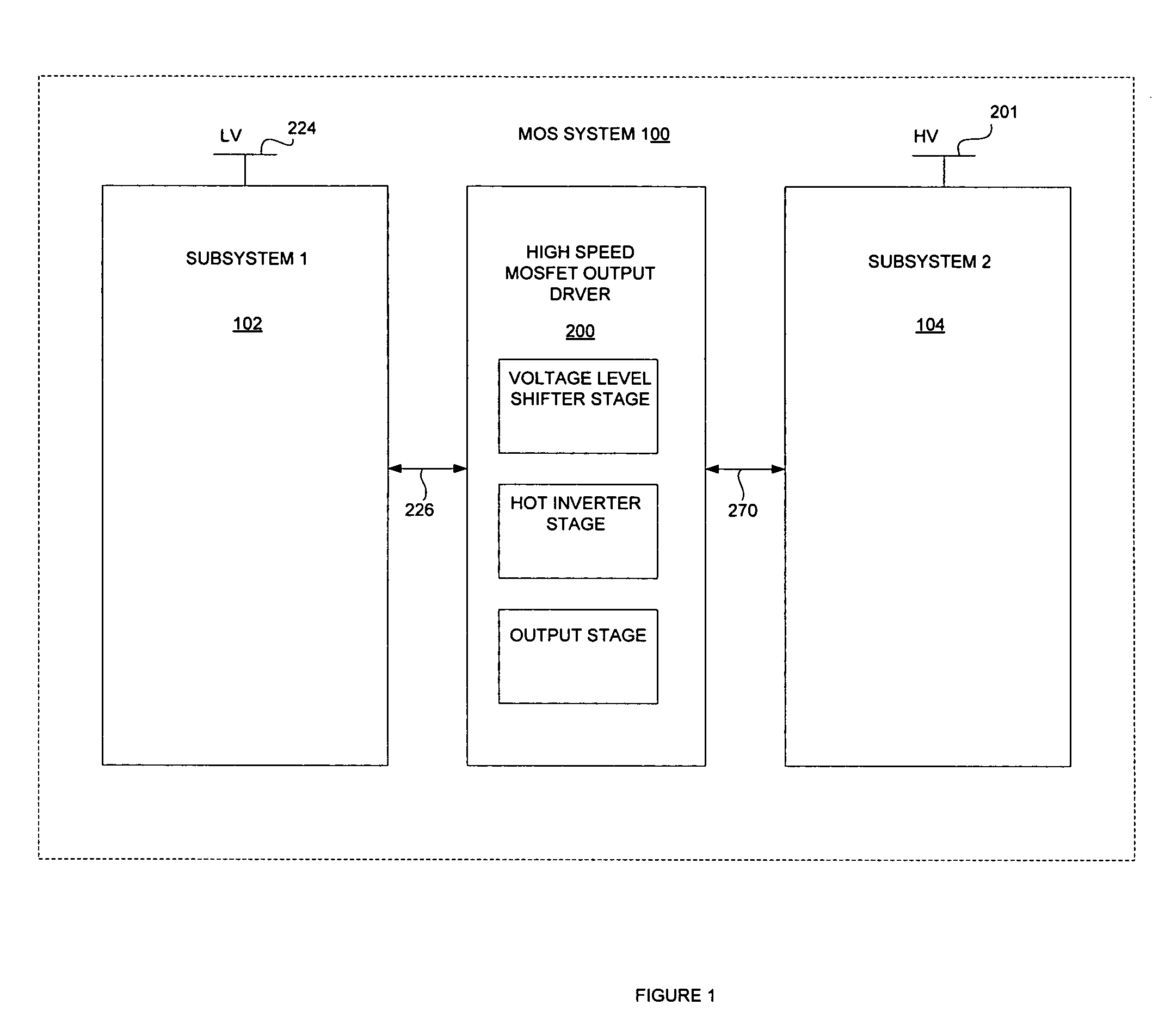
High speed MOSFET output driver
ActiveUS7227400B1High voltage gainReducing minimum voltage levelSwitching accelaration modificationsPulse automatic controlMOSFETEngineering
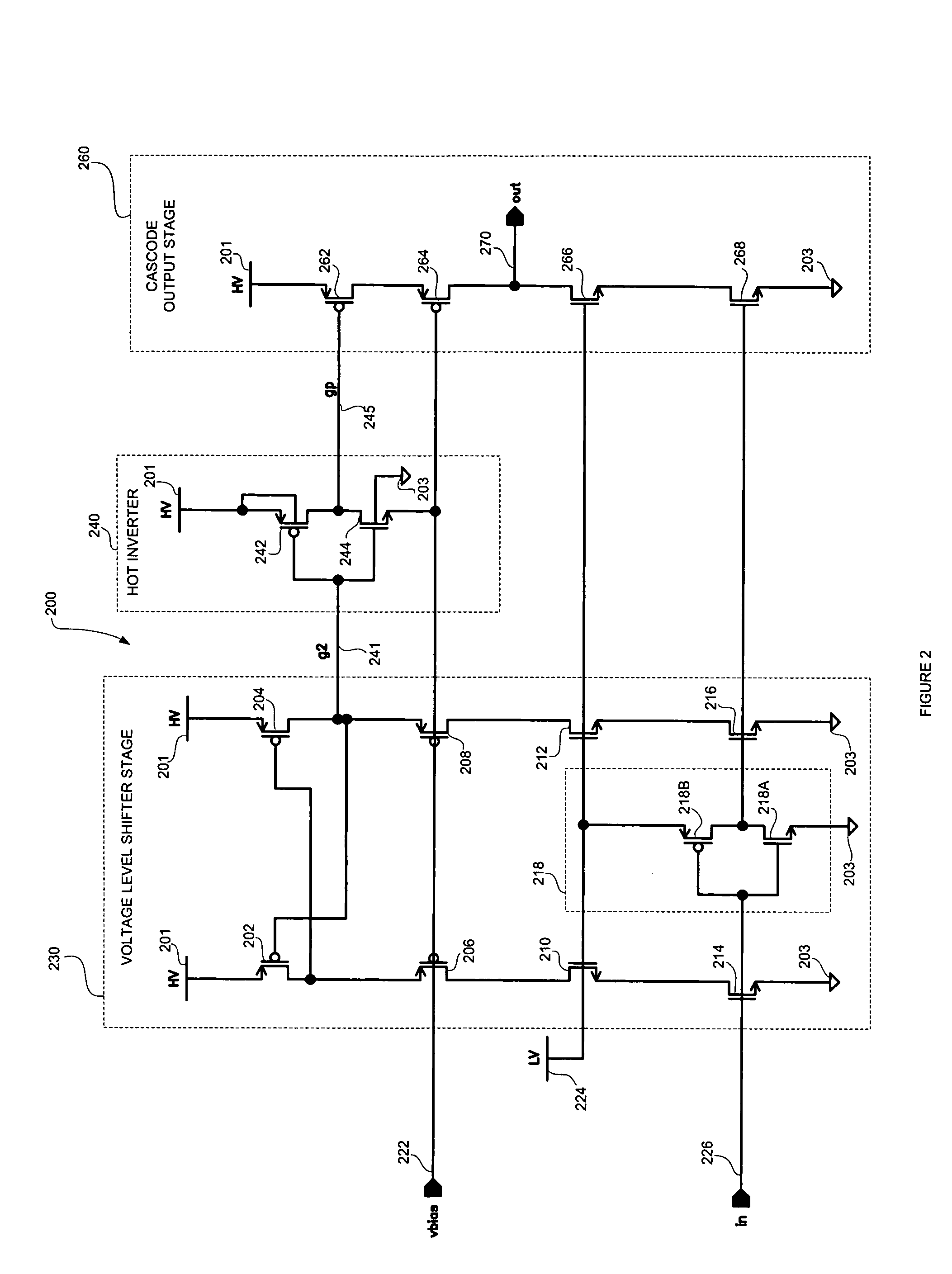
A high speed MOSFET output driver is disclosed that includes a voltage level shifter stage operable to transition an input signal at a first voltage level to an output signal at a second voltage level, an output stage operable to drive high voltage output load, and a hot inverter, biased between the second voltage level and the bias voltage such that the voltage gain of the output signal is increased and at the same time the minimum voltage level of the output signal introduced to the output stage is decreased, improving the control and the transition time of the output signal and allowing all components of the high speed MOSFET output driver of the present invention to be fabricated using a single thin gate oxide process.
Owner:INTEGRATED DEVICE TECH INC
Substrate bias circuit and method for biasing a substrate
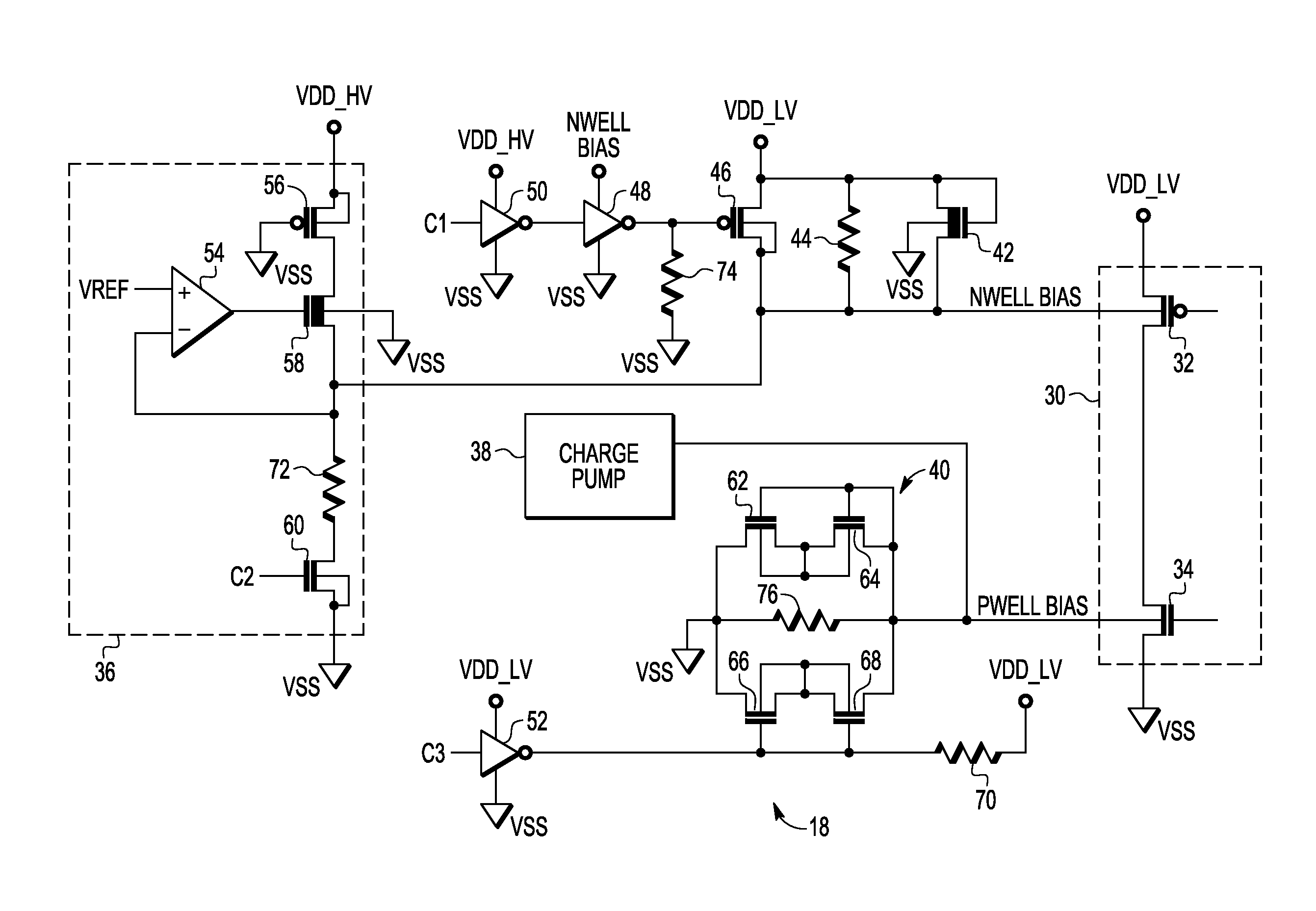
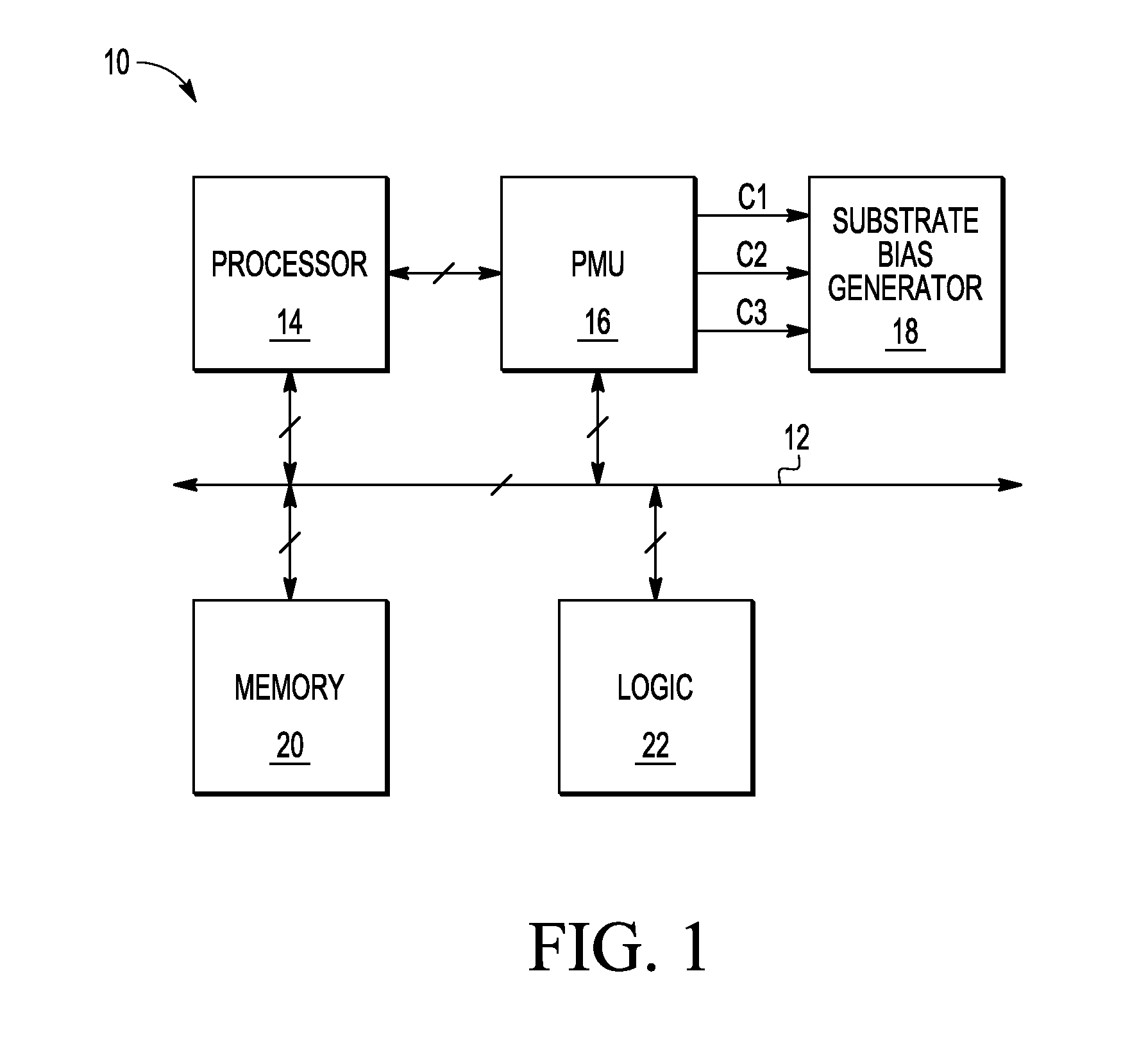
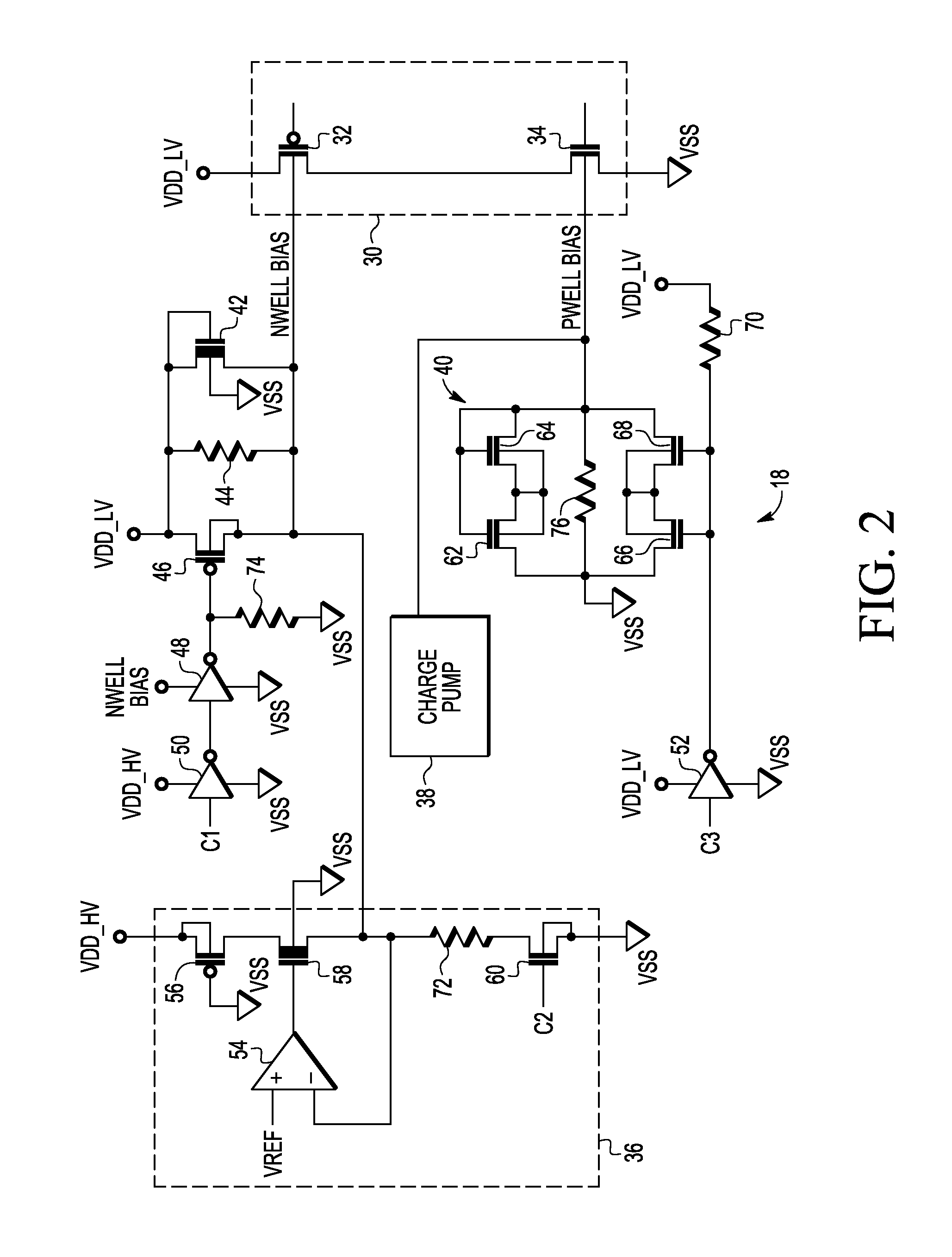
A substrate bias circuit and method for biasing a substrate are provided. A substrate bias circuit includes a first voltage source, a second voltage source, a diode coupled between the first voltage source and the second voltage source, and a plurality of transistors, each transistor in the plurality of transistors having a substrate terminal. In one example, the first voltage source supplies, via the diode, the substrate terminal of a first transistor of the plurality of transistors during a power-up, and the second voltage source supplies the substrate terminal of the first transistor after the power-up.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Voltage level shifter
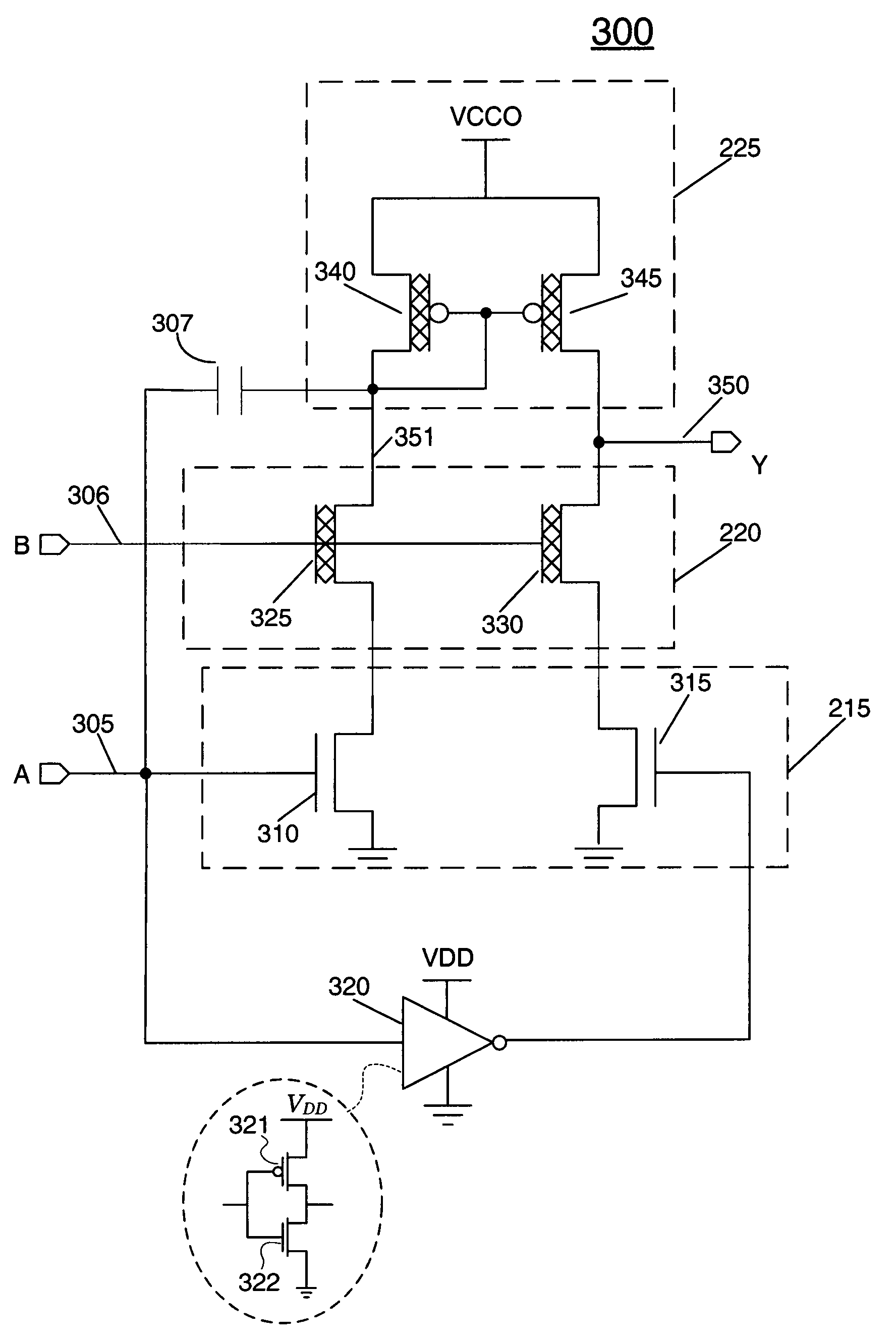
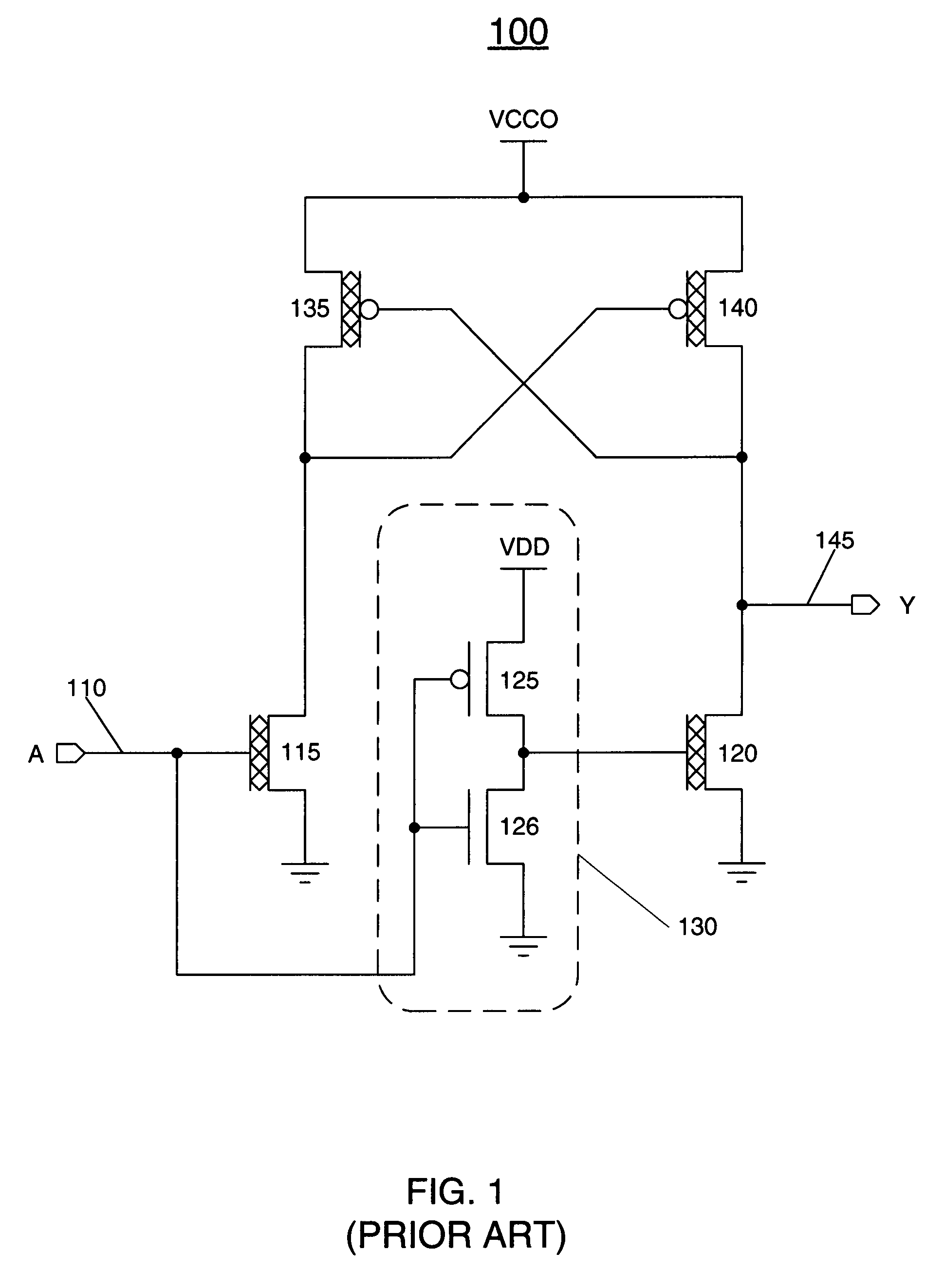
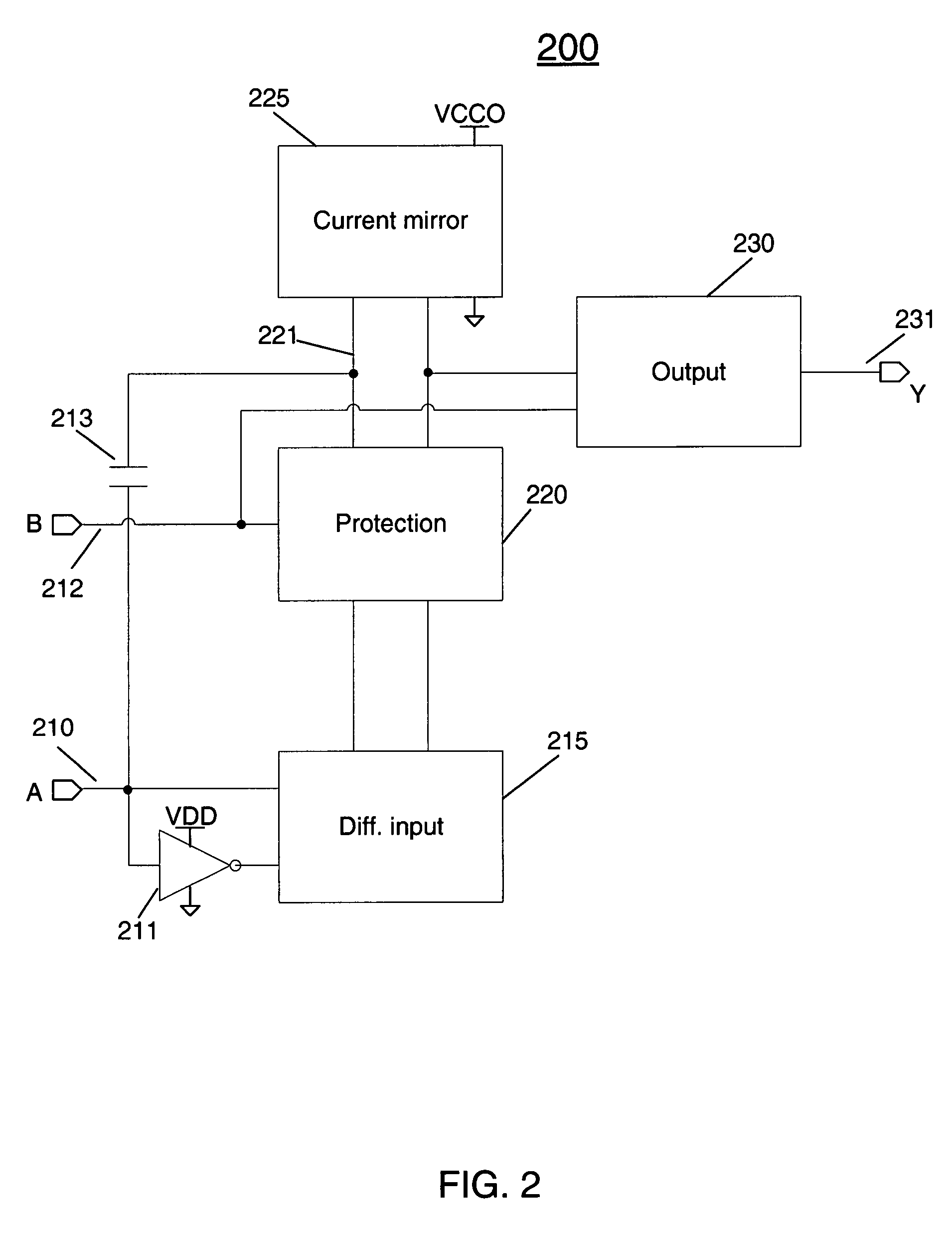
ActiveUS7468615B1Maintain performanceHigh frequencyPulse automatic controlReliability increase in field effect transistorsVoltage rangeCurrent mirror
A high-speed, area-efficient level shifter includes transistors having a variety of oxide thicknesses. The level shifter has a protection circuit stage, and a current mirror stage that allows the level shifter to perform over a wide voltage range at a high frequency. The level shifter maintains rise time, fall time, and duty cycle over a wide range of input and output voltage levels.
Owner:XILINX INC
Digital output buffer for multiple voltage system
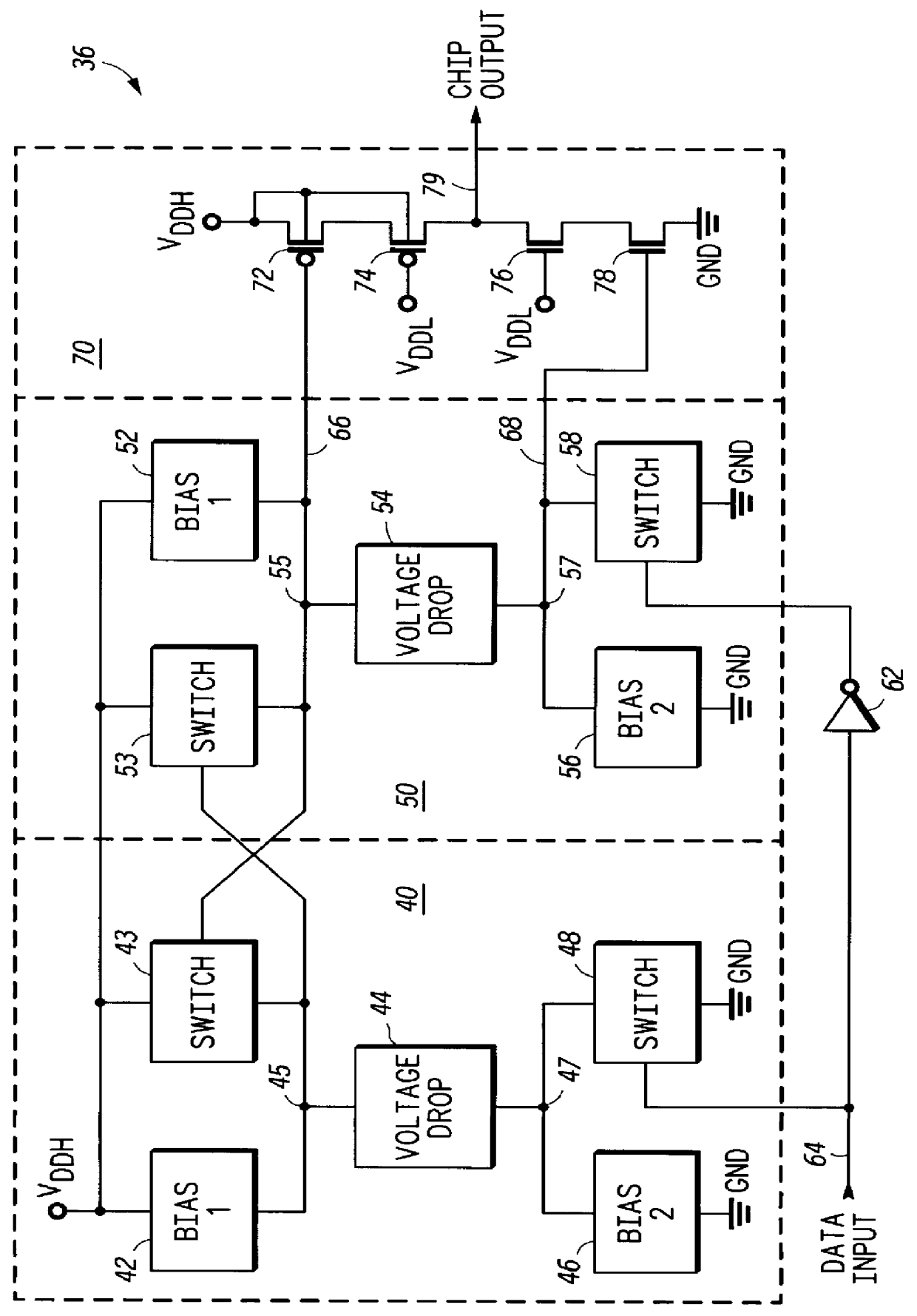
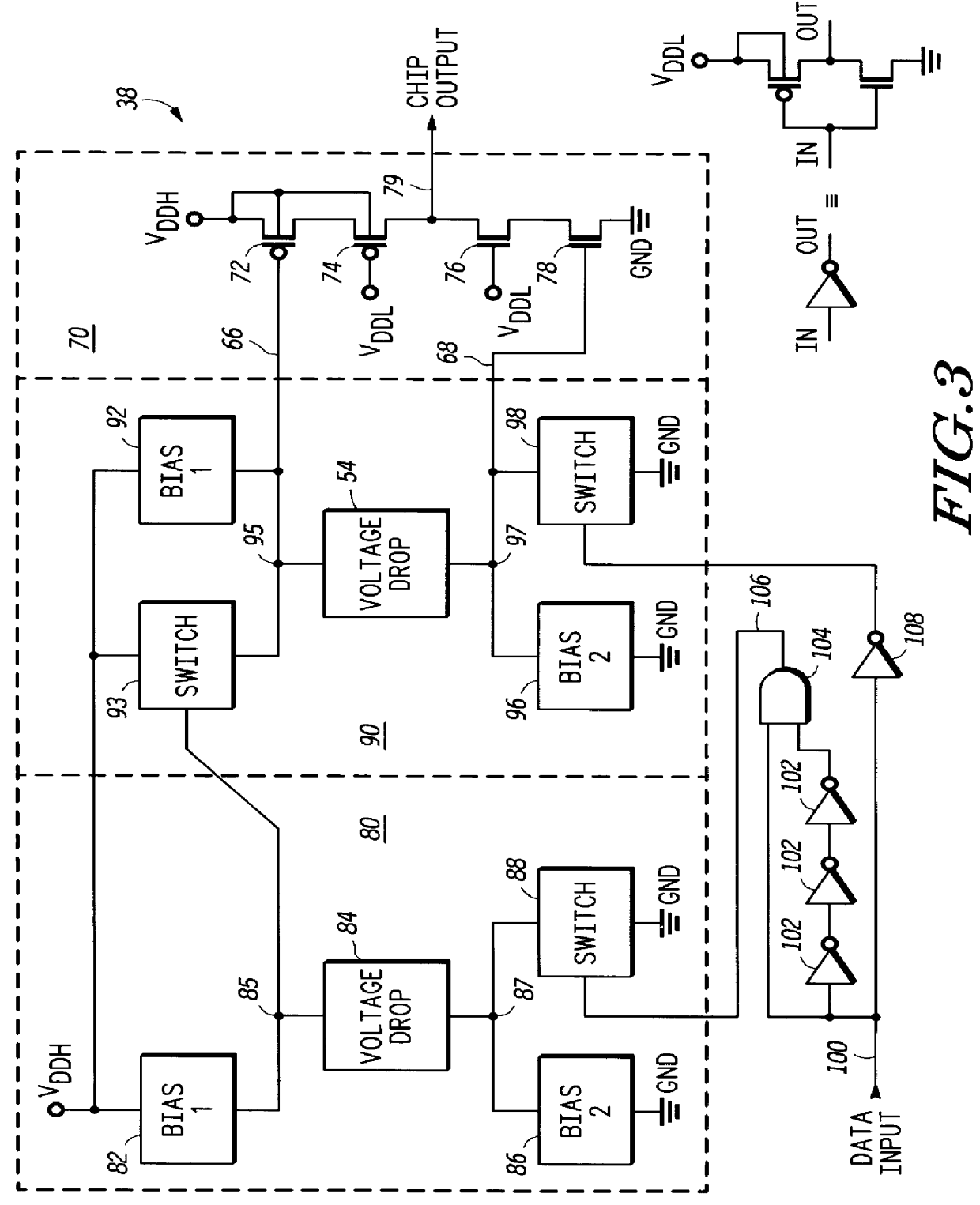
An output buffer translates digital input signals which toggle between ground and V.sub.DDL to signals which toggle between ground and V.sub.DDH. The technology dielectric breakdown voltage limit is less than the magnitude of V.sub.DDH, such that use of a traditional output stage would subject transistors' dielectrics to voltages which exceed their dielectric breakdown limit, and would thus be damaged. Predrive circuits (40, 50) control output stage (70) transistors' (72, 78) gates, and voltage dropping circuits control output stage (70) transistors (74, 76). These control signals are generated specifically to maximize output stage transistor drive strengths, thereby minimizing output stage size. Output buffer functions when V.sub.DDL =V.sub.DDH, and its performance is V.sub.DDL independent. Temperature compensation is incorporated into the output buffer by deliberately offsetting temperature effects on output stage transistor drive strengths. Desired performance and temperature compensation are accomplished without subjecting any dielectrics to voltages which exceed the technology dielectric breakdown limit.
Owner:NXP USA INC
ESD Protection using a Capacitivly-Coupled Clamp for Protecting Low-Voltage Core Transistors from High-Voltage Outputs
ActiveUS20100315748A1TransistorReliability increase in field effect transistorsCapacitanceLow voltage
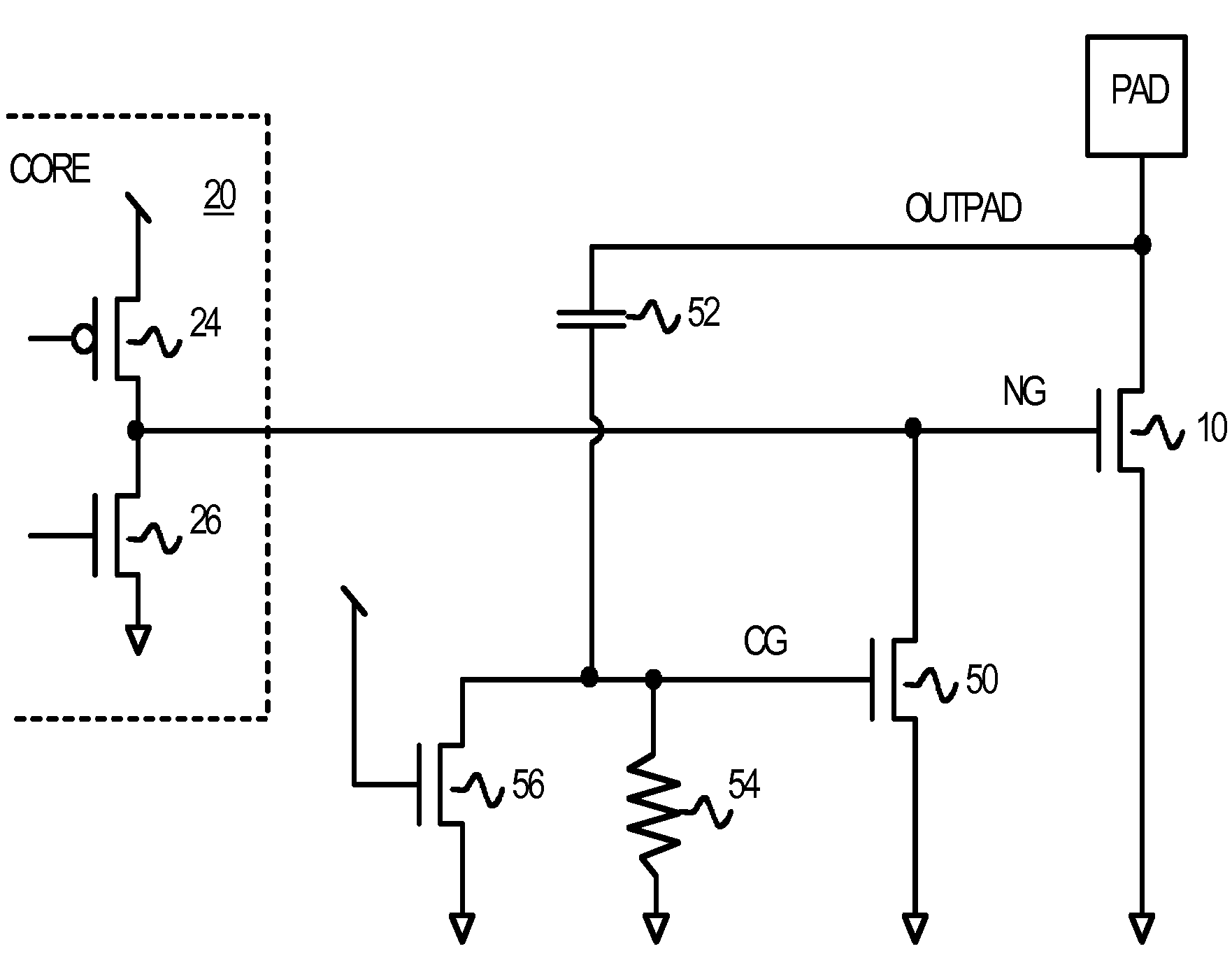
An electro-static-discharge (ESD) protection circuit protects core transistors. An internal node to the gate of an n-channel output transistor connects to the drain of an n-channel gate-grounding transistor to ground. The gate of the gate-grounding transistor is a coupled-gate node that is coupled by an ESD coupling capacitor to the output and to ground by an n-channel disabling transistor and a leaker resistor. The gate of the n-channel disabling transistor is connected to power and disables the ESD protection circuit when powered. An ESD pulse applied to the output is coupled through the ESD coupling capacitor to pulse high the coupled-gate node and turn on the gate-grounding transistor to ground the gate of the n-channel output transistor, which breaks down to shunt ESD current. The ESD pulse is prevented from coupling through a parasitic Miller capacitor of the n-channel output transistor by the gate-grounding transistor.
Owner:HONG KONG APPLIED SCI & TECH RES INST
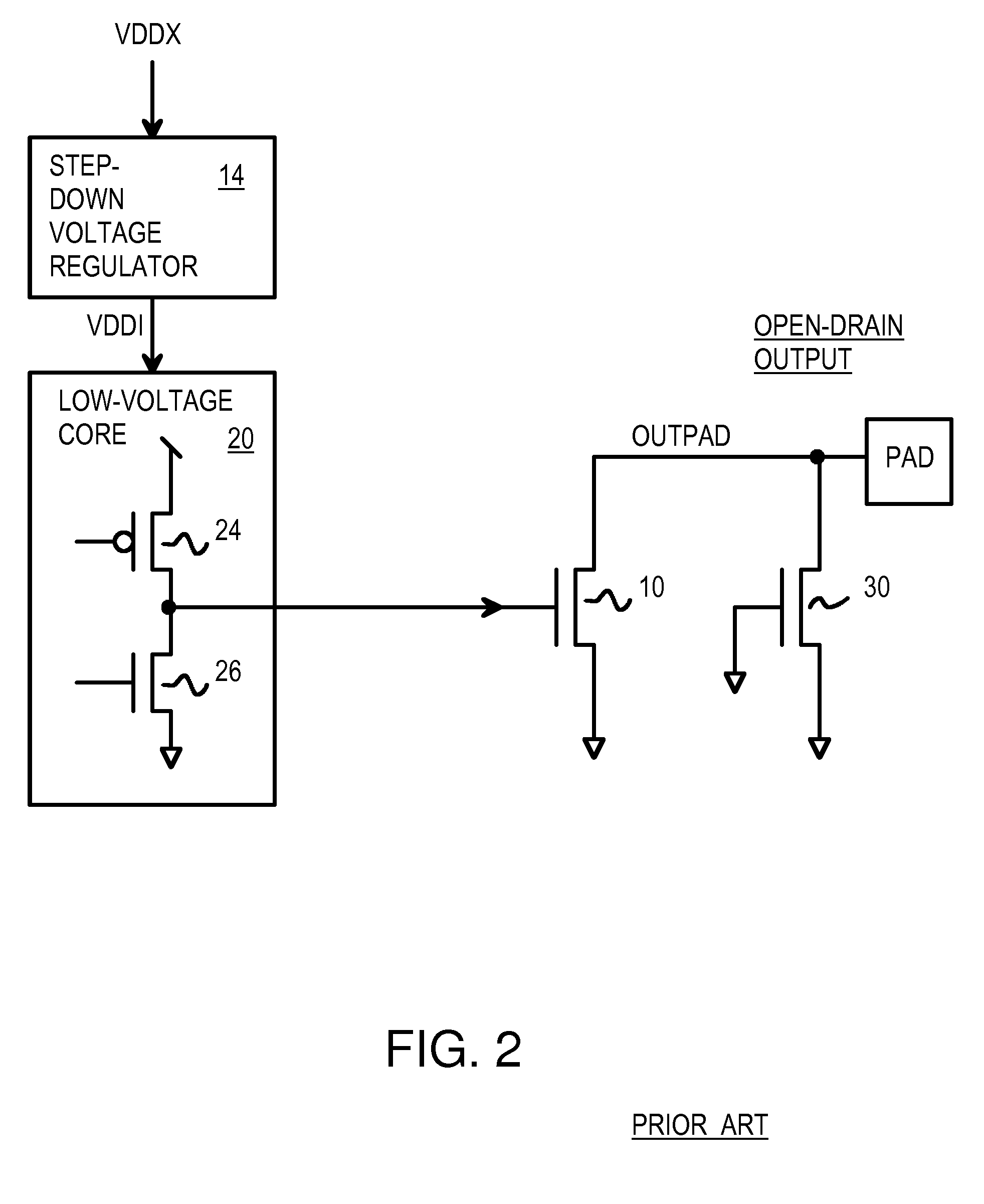
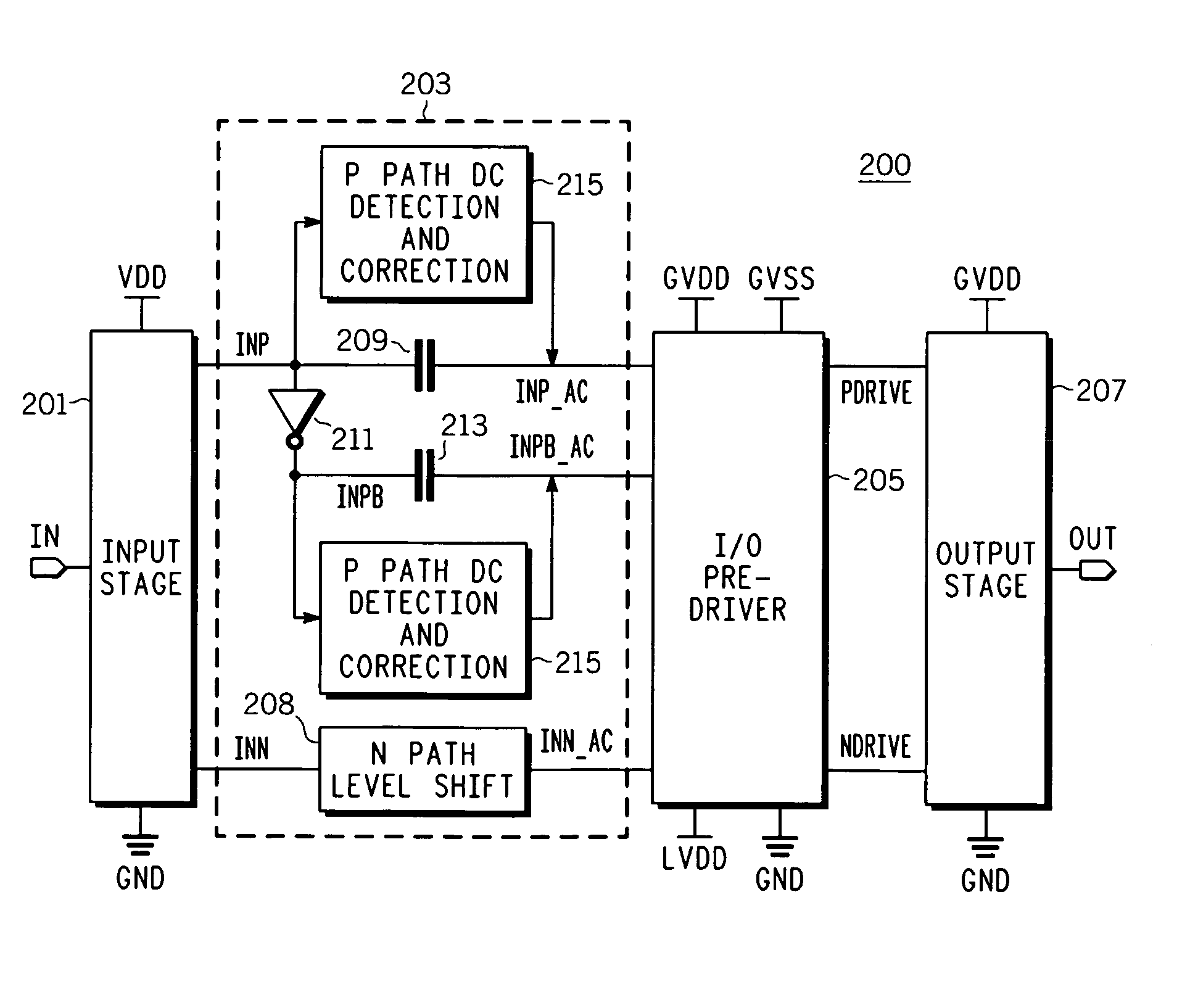
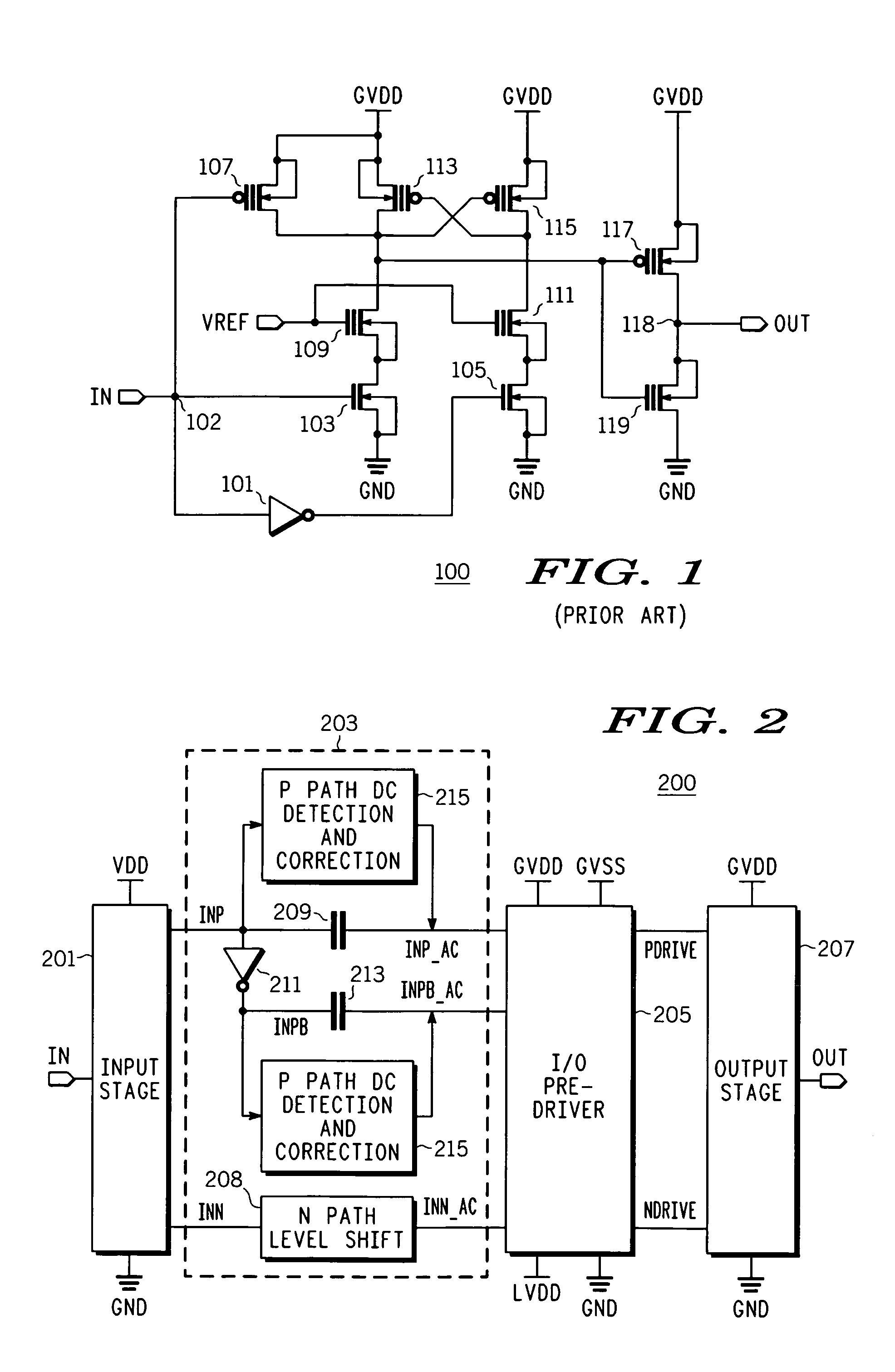
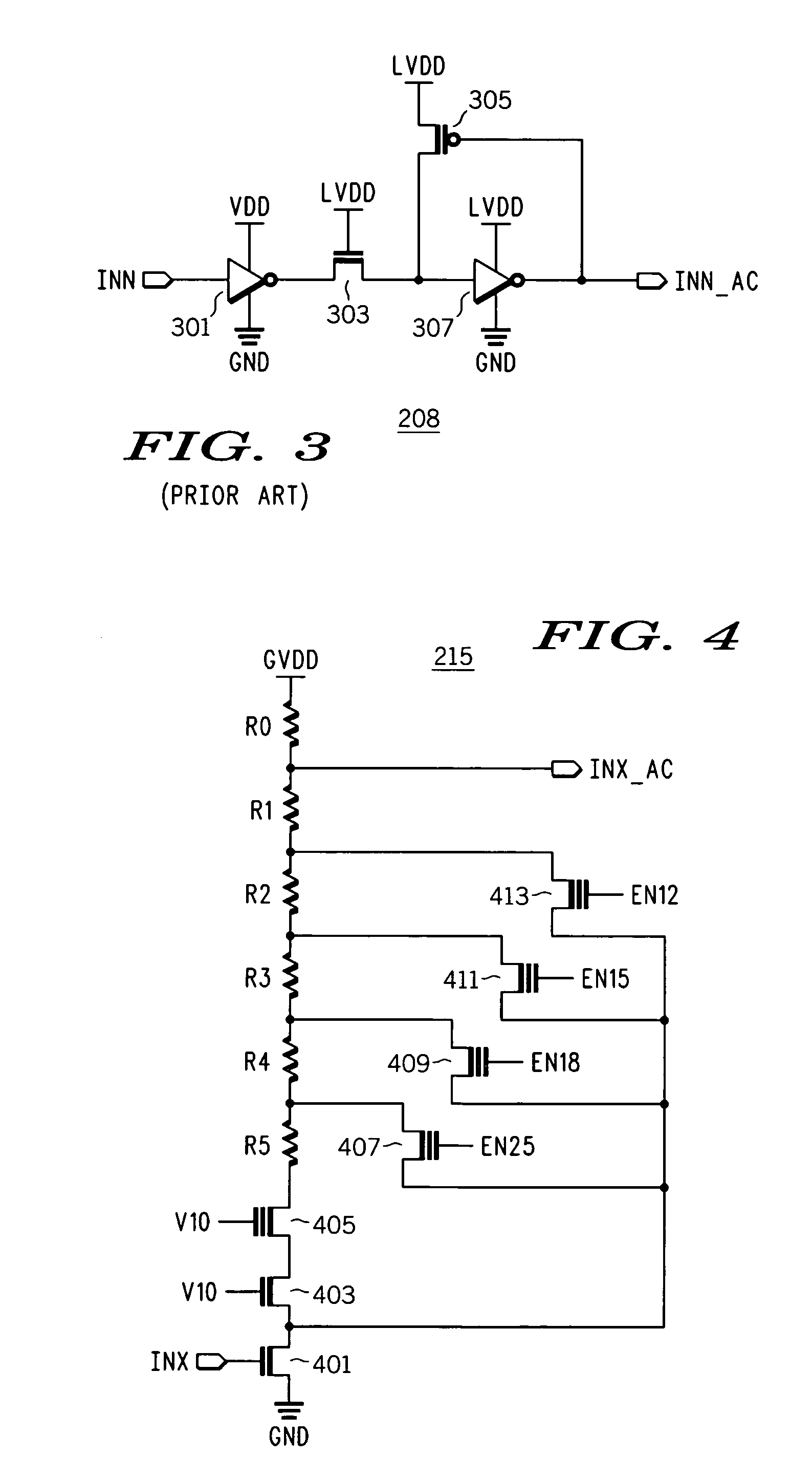
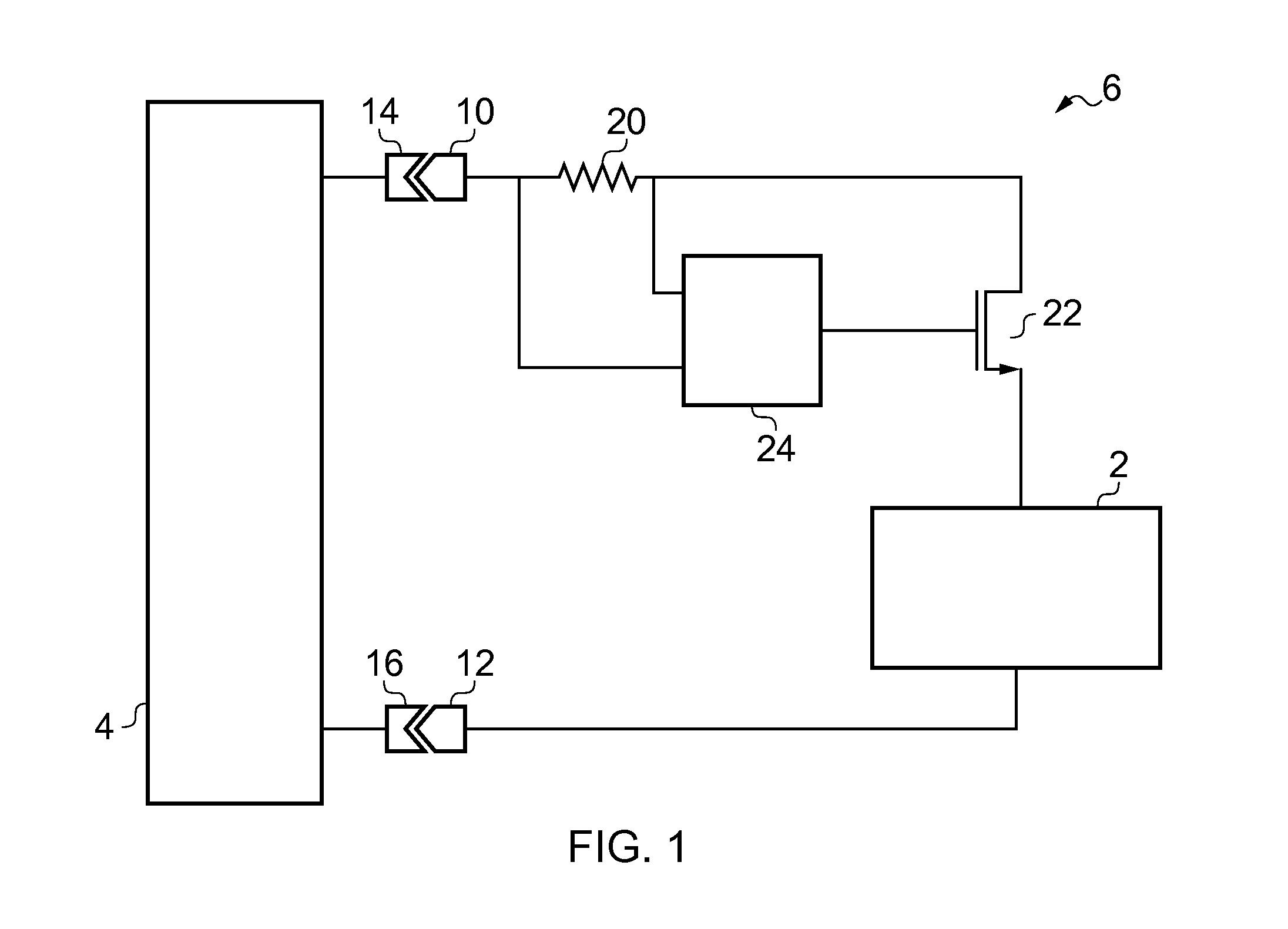
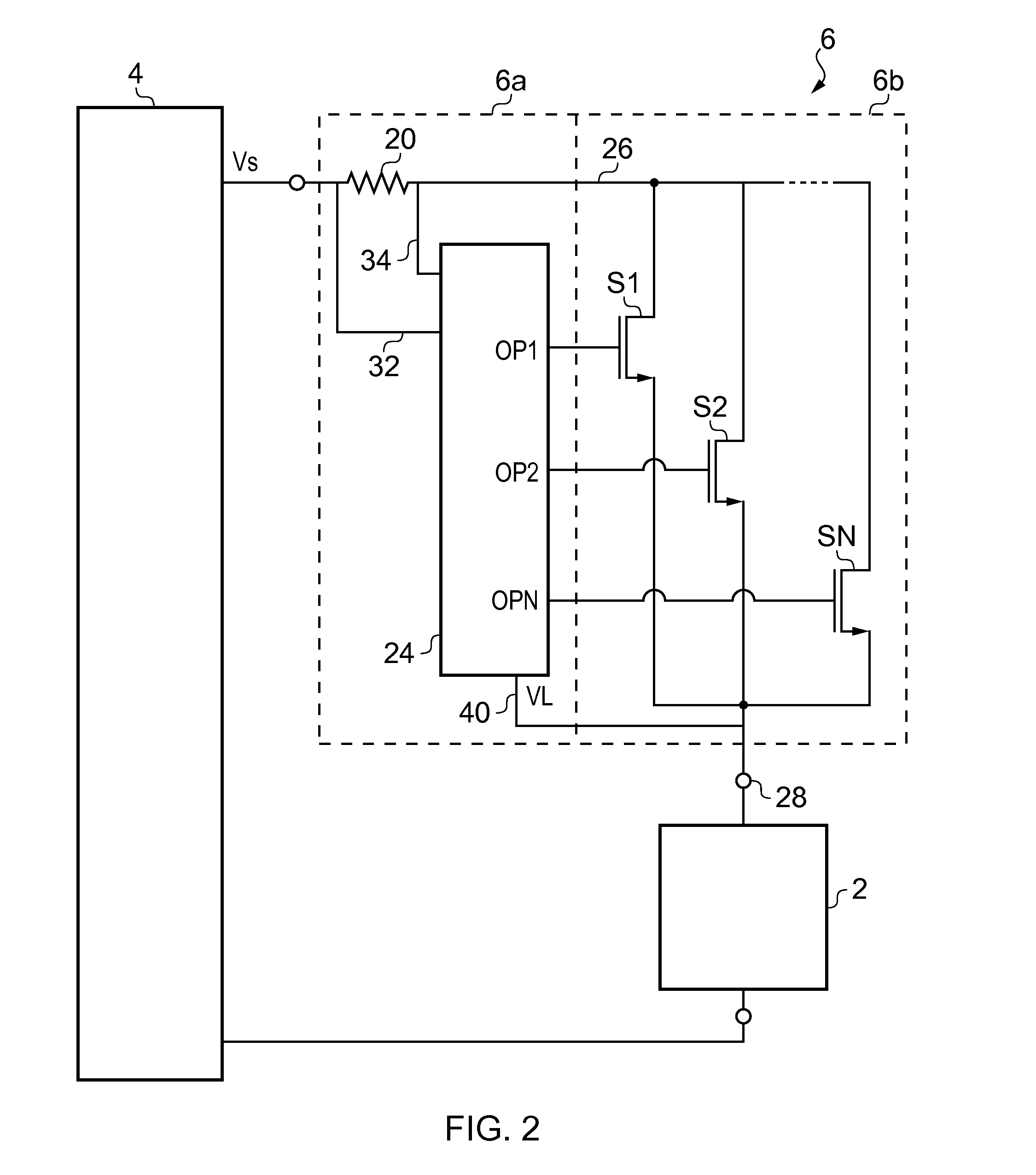
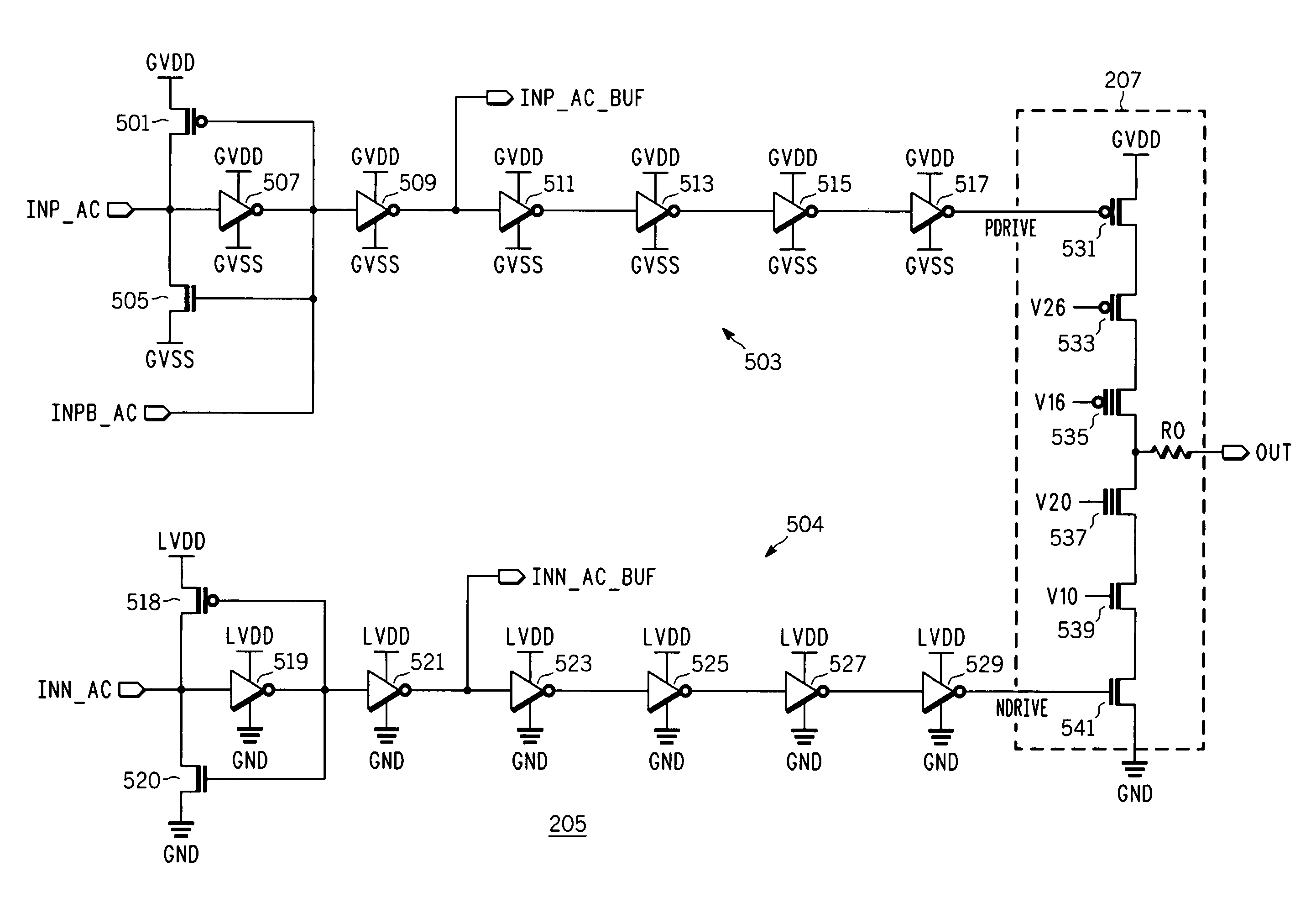
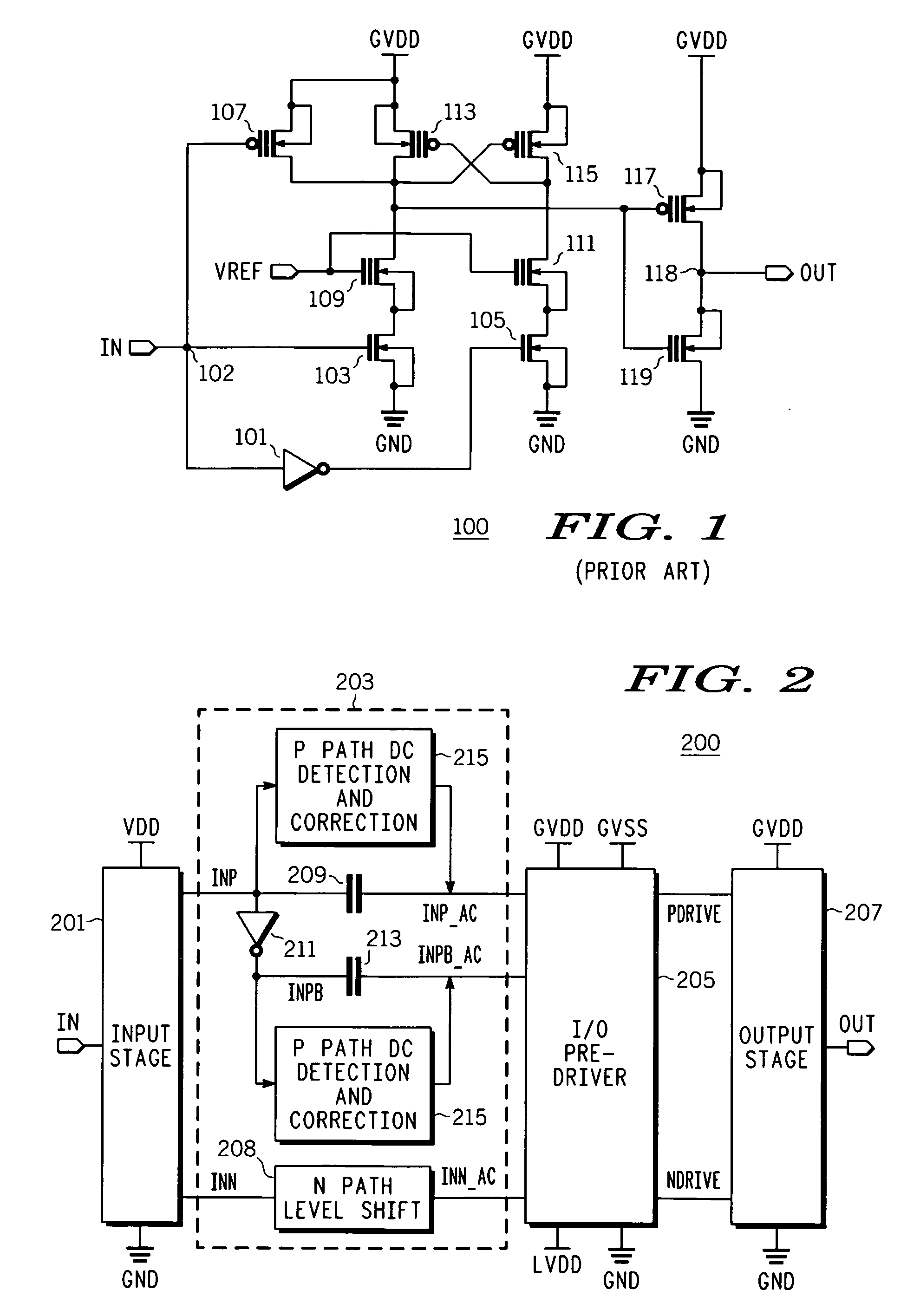
High speed output buffer with AC-coupled level shift and DC level detection and correction
InactiveUS7183817B2Pulse automatic controlReliability increase in field effect transistorsDriver circuitVoltage range
A high speed output buffer including an input circuit providing first and second signals within a first voltage range having a first common mode voltage, an AC interface receiving the first and second signals and providing first and second preliminary drive signals, a detection and correction circuit that corrects a state of the first preliminary drive signal AC coupled to the first signal, first and second drive circuits receiving the preliminary drive signals and providing first and second drive signals, where the first drive circuit operates within a second voltage range having a greater common mode voltage and where the second drive circuit operates within a third voltage range, and an output that switches an output node within a voltage range that is greater than a maximum voltage range. The first, second and third voltage ranges are each within the maximum voltage range suitable for thin-gate devices.
Owner:NORTH STAR INNOVATIONS
Suppressing the leakage current in an integrated circuit
InactiveUS6864708B2Lower levelPower reduction by control/clock signalSolid-state devicesDrain currentGate oxide
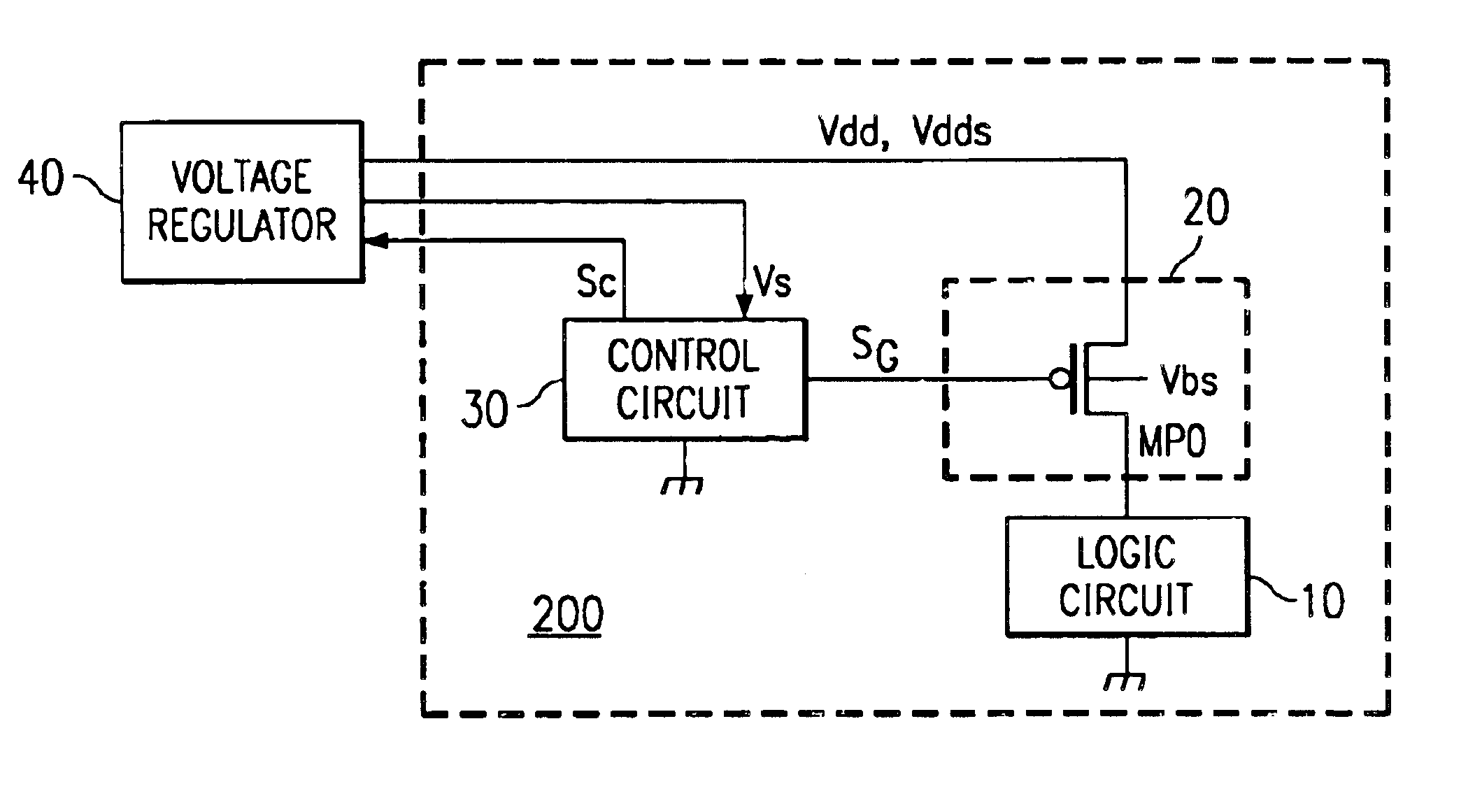
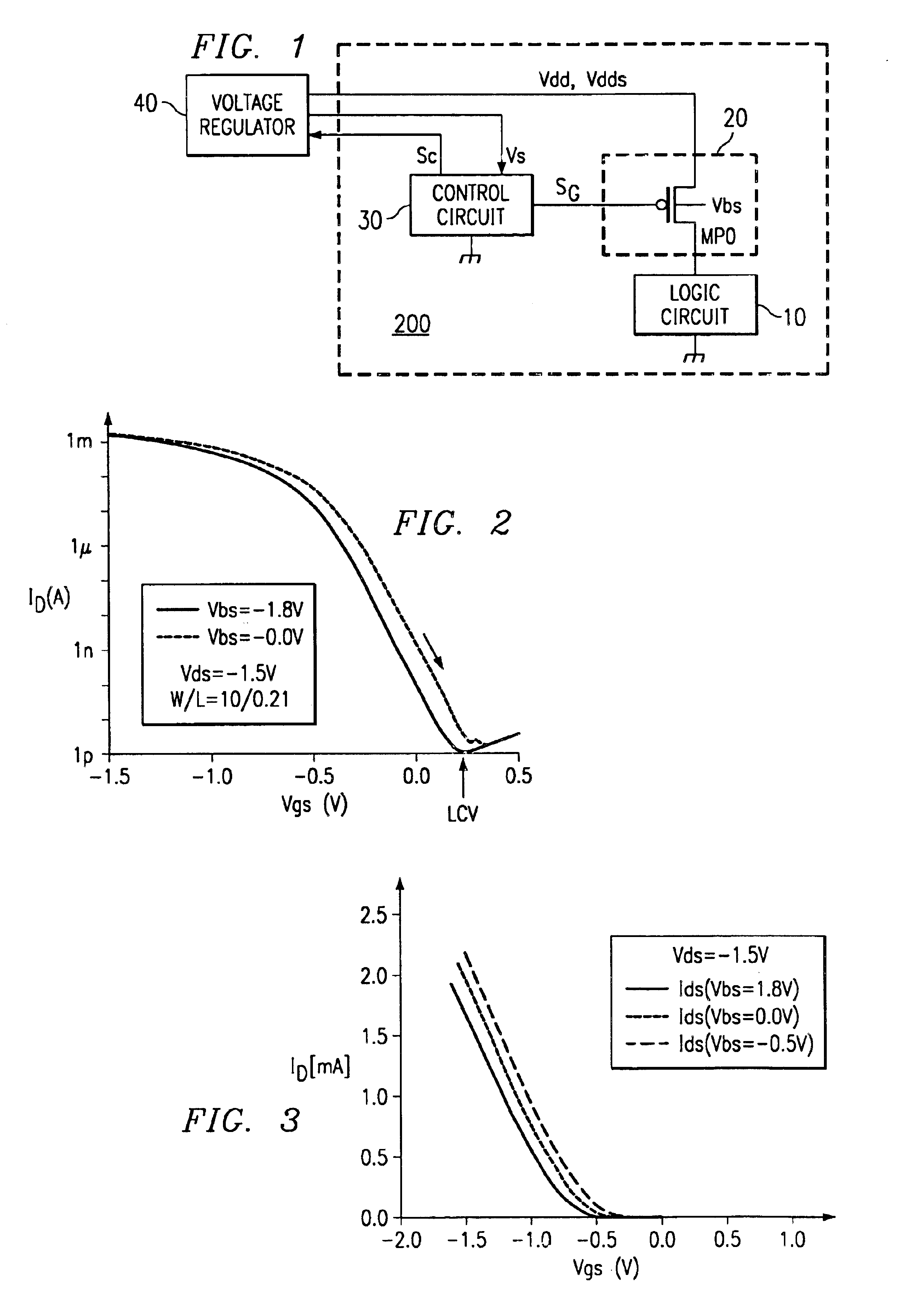
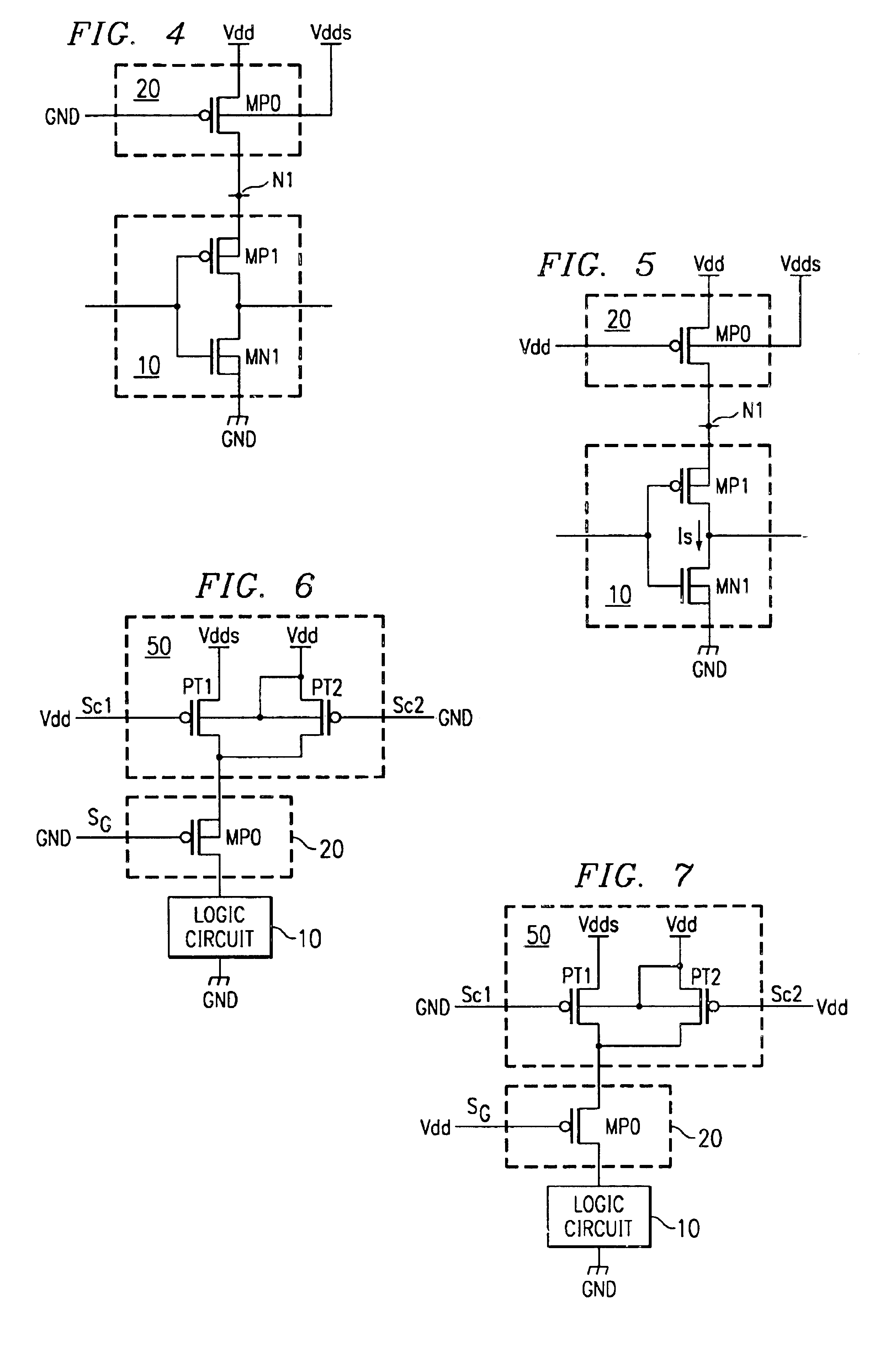
A semiconductor integrated circuit wherein the circuit area can be minimized, and defects can be detected reliably during a standby status while maintaining the reliability of a gate oxide film. Switching circuit 20 is provided between logic circuit 10 and source voltage Vdd supply terminal. While in an operating status, 0 V voltage is applied to the gate of transistor MP0 of switching circuit 20, and bias voltage VB equal to or slightly lower than source voltage Vdd is applied to its channel region in order to reduce the threshold voltage of transistor MP0 and increase its current driving capability. While in a standby status, a voltage equal to source voltage Vdd is applied to the gate of transistor MP0, a voltage lower than the source voltage is applied to the source, and bulk bias voltage VB equal to or higher than source voltage Vdd is applied to the channel region in order to minimize the drain current of transistor MP0, so that current path of logic circuit 10 is cut off, and the occurrence of leakage current is suppressed.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Pass gate input buffer for a mixed voltage environment
InactiveUS6031393AReliability increase in field effect transistorsLogic circuit coupling/interface arrangementsEngineeringVoltage source
An input buffer to interface among devices on a main circuit board is described. The input buffer includes a first transistor coupled between a first terminal and an input terminal of an inverter. The first transistor has an enable terminal adapted to be coupled to a first voltage supply. A second transistor that is coupled between the first terminal and the input terminal is also included. The input buffer further includes a control circuit to enable the second transistor. The control circuit is coupled to the first terminal, an enable terminal of the second transistor, the input terminal, and an output terminal of the inverter. A method for buffering signals among devices on a main circuit board comprises receiving a first signal in a first state from a first device. A first portion of the first signal is transmitted through a first transistor. A second portion of the first signal is transmitted through a second transistor. A second signal is generated by applying the first signal to the enable terminals of the third and fourth transistors. The second signal is then transmitted to a second device.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Semiconductor integrated circuit and manufacturing method therefor
InactiveUS20080143423A1Improve production yieldLittle overheadTransistorSolid-state devicesCMOSControl switch
The present invention is directed to realize high manufacture yield and compensate variations in threshold voltage of a MOS transistor with small overhead. A semiconductor integrated circuit includes a CMOS circuit for processing an input signal in an active mode, a control switch, and a control memory. The control switch supplies a pMOS body bias voltage and an nMOS body bias voltage to an N well in a pMOS transistor and a P well in an nMOS transistor, respectively, in the CMOS circuit. The control memory stores control information indicating whether or not the pMOS body bias voltage and the nMOS body bias voltage are supplied from the control switch to the N well in the pMOS transistor and the P well in the nMOS transistor, respectively, in the CMOS circuit in the active mode.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Semiconductor device having impedance calibration function to data output buffer and semiconductor module having the same
ActiveUS20130088257A1Impedance can be adjustedInput/output impedence modificationLogic circuit coupling arrangementsData terminalSemiconductor
Disclosed herein is a semiconductor device that includes a first transistor unit coupled to the data terminal, and a plurality of second transistor units coupled to the calibration terminal. The first transistor unit includes a plurality of first transistors having a first conductivity type connected in parallel to each other so that an impedance of the first transistor unit is adjustable. Each of the second transistor units includes a plurality of second transistors having the first conductivity type connected in parallel to each other so that an impedance of each of the second transistor units is adjustable. The semiconductor device further includes an impedance control circuit that reflects the impedance of each of the second transistor units to the first transistor unit.
Owner:LONGITUDE LICENSING LTD
Integrated header switch with low-leakage PMOS and high-leakage NMOS transistors
ActiveUS7164291B2High currentLower unit costPower reduction in field effect transistorsElectronic switchingControl signalLow voltage
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
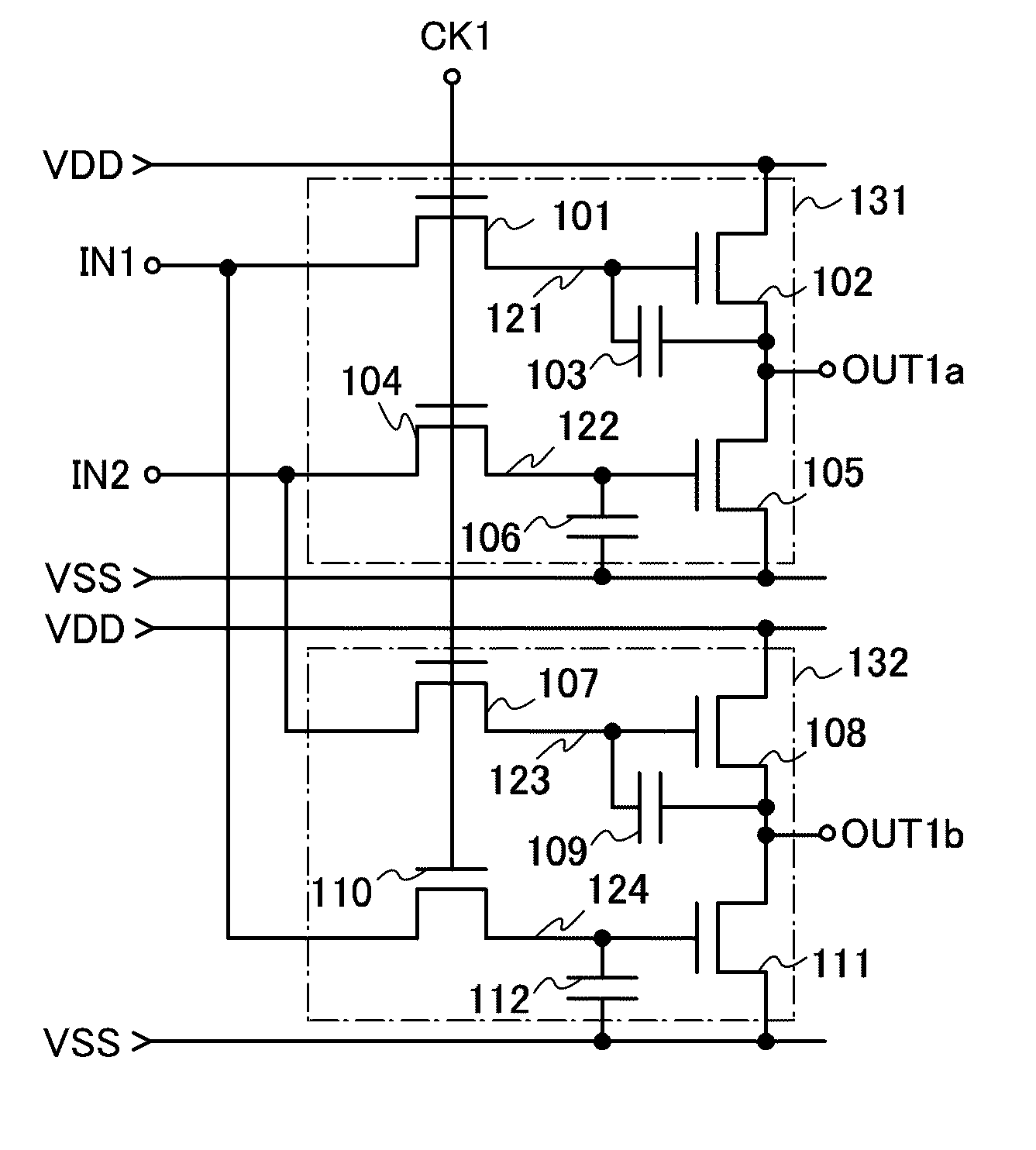
Shift register apparatus and method thereof
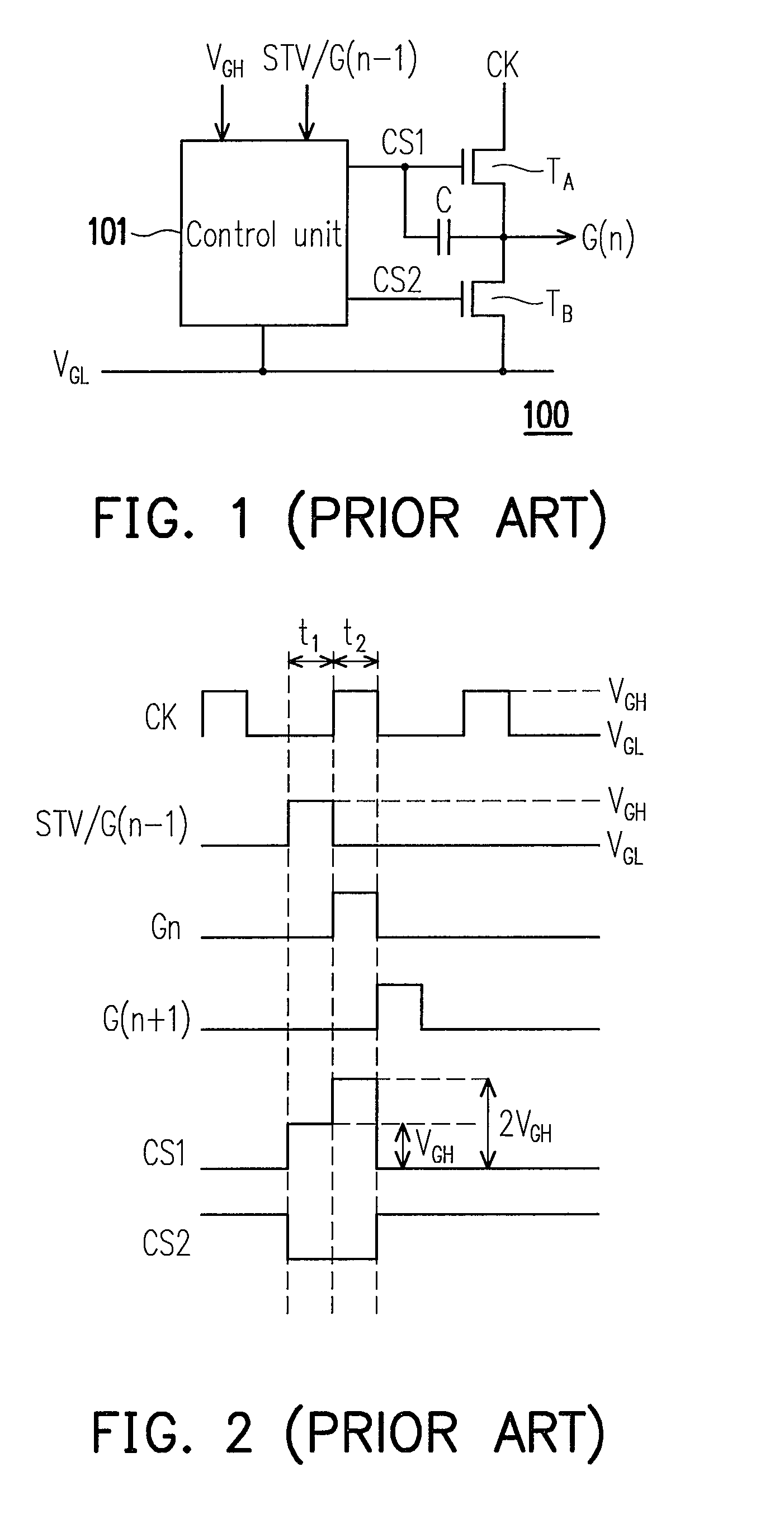
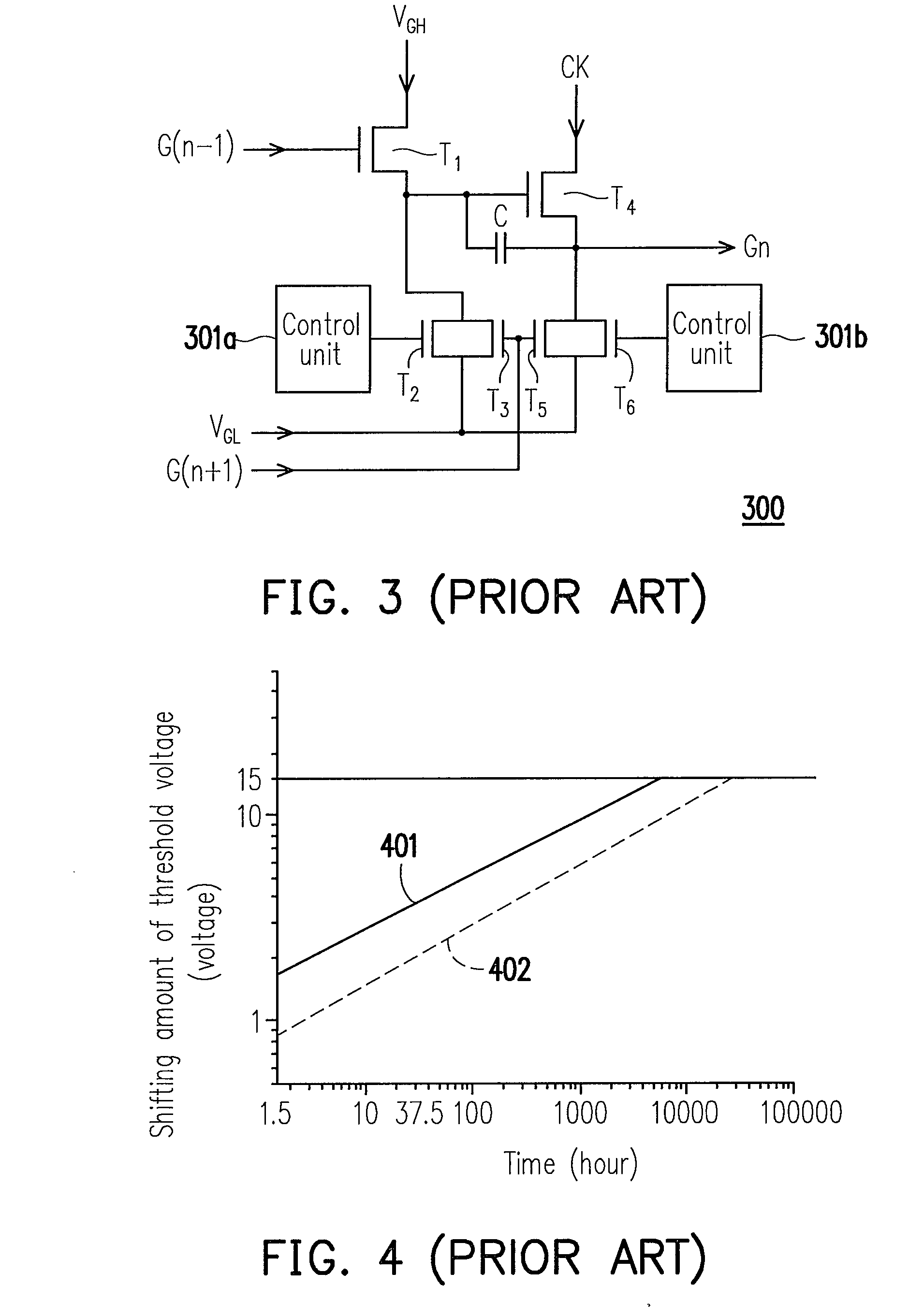
InactiveUS20100002827A1Improve use reliabilityIncrease profitStatic indicating devicesCounting chain synchronous pulse countersShift registerProcessor register
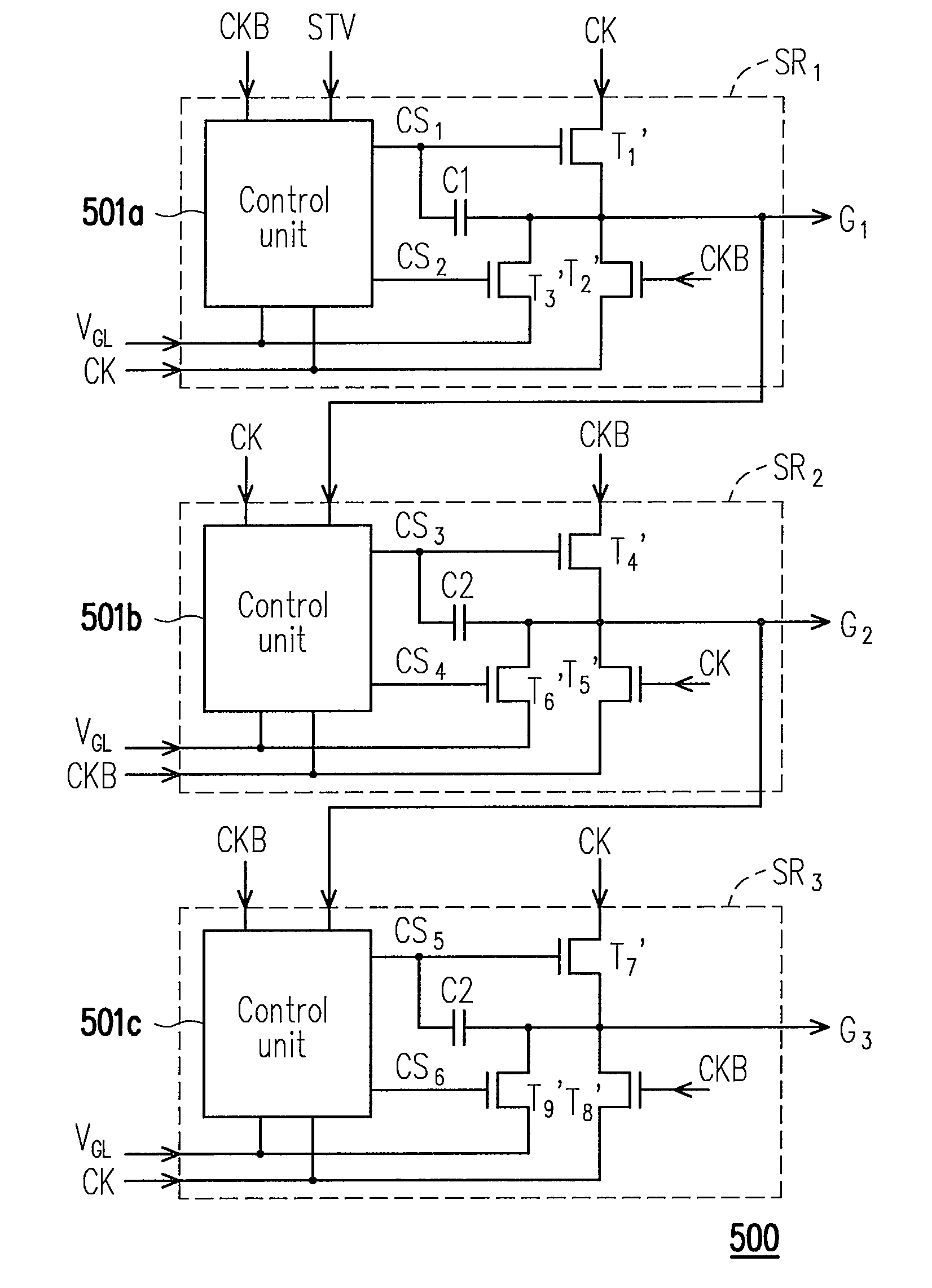
A shift register apparatus and a method thereof are provided. The technique manner submitted by the present invention utilizes two NMOS transistors for pulling down the voltage level of the scan signals output by the shift registers within the shift register apparatus to the low level gate voltage, wherein one of the NMOS transistors is controlled by a control unit, and the other NMOS transistor is controlled by a clock signal or the inverted clock signal provided to the shift registers. Therefore, shifting amount of the threshold voltage of those NMOS transistors can trend to be flat, and the reliability of those NMOS transistors can be promoted. In addition, since only one control unit is needed to dispose in each shift register so that the layout area of whole shift register apparatus can be reduced, and the panel with narrow frame size also can be achieved by the present invention.
Owner:CHUNGHWA PICTURE TUBES LTD
Differential circuit and output buffer circuit including the same
InactiveUS20080048736A1Solid-state devicesAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesEngineeringTransistor
An output buffer circuit in a multi-power system operating at a high power supply voltage and a low power supply voltage includes a pre-driver, and a main driver. The pre-driver performs a differential switching operation on first and second differential input signals to output first and second differential output signals. The main driver performs a differential switching operation on the DC-eliminated and level-shifted first and second differential output signals to output third and fourth differential output signals. The main driver includes a differential switching circuit including first and second NMOS transistors, and performs a differential switching operation on the DC-eliminated and level-shifted first and second differential output signals to output the third and fourth differential output signals, and an equalizer coupled between source electrodes of the first and second NMOS transistors, and controls a bandwidth of the third and fourth differential output signals.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Low leakage and data retention circuitry
ActiveUS7227383B2Reduce power consumptionReduce leakagePower reduction by control/clock signalLogic circuits characterised by logic functionSleep stateLow leakage
An integrated circuit includes first circuitry and sleep transistor circuitry. The first circuitry receives input signals and processes the input signals. The first circuitry also retains data in a sleep state that has low leakage. The sleep transistor circuitry is coupled to the first circuitry and receives a sleep signal that has a negative voltage. The sleep circuitry reduces power consumption of the first circuitry in the sleep state to have low leakage based on the sleep signal while retaining the data in the first circuitry.
Owner:MOSAID TECH
Integrated circuit with both clamp protection and high impedance protection from input overshoot
InactiveUS6255850B1Logic circuits characterised by logic functionReliability increase in field effect transistorsVoltage clampIntegrated circuit
An integrated circuit is provided for use with a supply voltage and which includes an input / output (I / O) circuit with an output driver with a pull-up transistor and a pull-down transistor and which includes an I / O pin connected to receive output signals from the output driver and connected to provide input signals to the integrated circuit, the protection circuit comprising: bias circuitry that imparts a bias voltage to the pull-up transistor so as to substantially prevent leakage current when a voltage applied externally to the I / O pin rises above the supply voltage; a switch connected to conduct current from the I / O pin to the supply voltage when the switch is turned on and to block current flow from the I / O pin to the supply voltage when the switch is turned off; and voltage clamp circuitry connected to clamp voltage on the I / O pin to the supply voltage when the switch is turned on; and programming circuitry which is programmable to turn the switch on and off.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
Electrostatic discharge protective circuit having rise time detector and discharge sustaining circuitry
ActiveUS20100157491A1Not to damageImprove stabilityTransistorReliability increase in field effect transistorsShunt DeviceEngineering
Methods and devices of the invention include an electrostatic discharge (ESD) protection circuit. This circuit includes rise time dependent activation circuitry capable of detecting a slew rate of an input signal and capable of determining whether the slew rate of the input signal is greater than a threshold value. For an ESD event said activation circuitry generates a trigger signal. Additionally, the activation circuitry is coupled with the ESD dissipation duration control circuitry which is further coupled with an ESD dissipation circuit. This arrangement enabling the duration control circuit to be activated by the trigger signal which responds by producing an activation signal that activates the ESD dissipation circuitry and that controls the length of time the dissipation circuit remains active. The ESD dissipation circuitry includes a shunt that redirects the ESD energy away from the protected internal circuit. The ESD dissipation duration circuitry further configured to maintain shunting of the energy for a period of time sufficient to discharge of the ESD energy without damaging the protected circuitry.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Logic circuit and semiconductor device
ActiveUS8884651B2Reduce leakage currentMalfunction can be suppressedTransistorStatic indicating devicesMicrometerChannel width
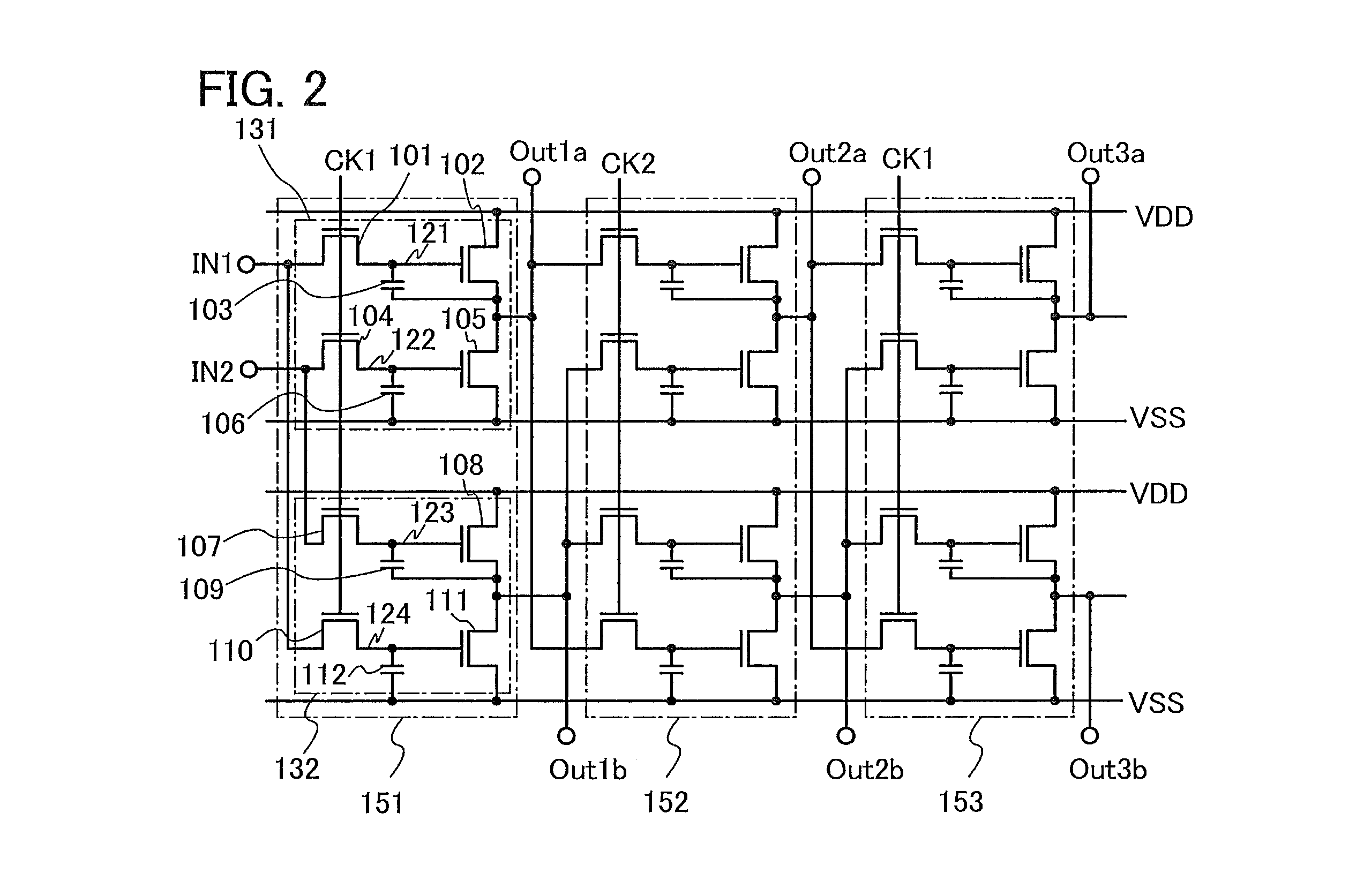
To reduce a leakage current of a transistor so that malfunction of a logic circuit can be suppressed. The logic circuit includes a transistor which includes an oxide semiconductor layer having a function of a channel formation layer and in which an off current is 1×10−13 A or less per micrometer in channel width. A first signal, a second signal, and a third signal that is a clock signal are input as input signals. A fourth signal and a fifth signal whose voltage states are set in accordance with the first to third signals which have been input are output as output signals.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Charge distribution control for secure systems
ActiveUS20140167837A1Reliability increase in field effect transistorsInternal/peripheral component protectionDistribution controlLogic cell
Advantageous analog and / or digital logic cells and methods of powering circuit blocks using the same are provided. A digital logic cell can include a charge storage device, a logic block, and connections to a power supply. The charge storage device may be a capacitor. The capacitor or other charge storage device can be disconnected from the logic block and a power supply to discharge the capacitor, and then connected to the power supply, via the power supply connections, to charge the capacitor. The capacitor can be disconnected from a ground connection of the power supply while the capacitor is discharged. After being charged via the power supply, the capacitor can also be disconnected from the power supply (including ground) and connected to the logic block to power the logic block.
Owner:CHAOLOGIX INC
Output drive circuit that accommodates variable supply voltages
ActiveUS7224195B2Increase charging rateSwitching accelaration modificationsLogic circuits coupling/interface using field-effect transistorsDriver circuitEngineering
In accordance with the invention, a driver circuit is described that permits a single thin gate oxide process to be utilized where a dual oxide process may normally be necessary. Circuits employing only thin gate oxide devices are used as the design basis for a single product with a single set of tooling and manufacturing process to operate within the same timing specifications for a core voltage output drive as well as for a higher system drive.
Owner:INTEGRATED DEVICE TECH INC
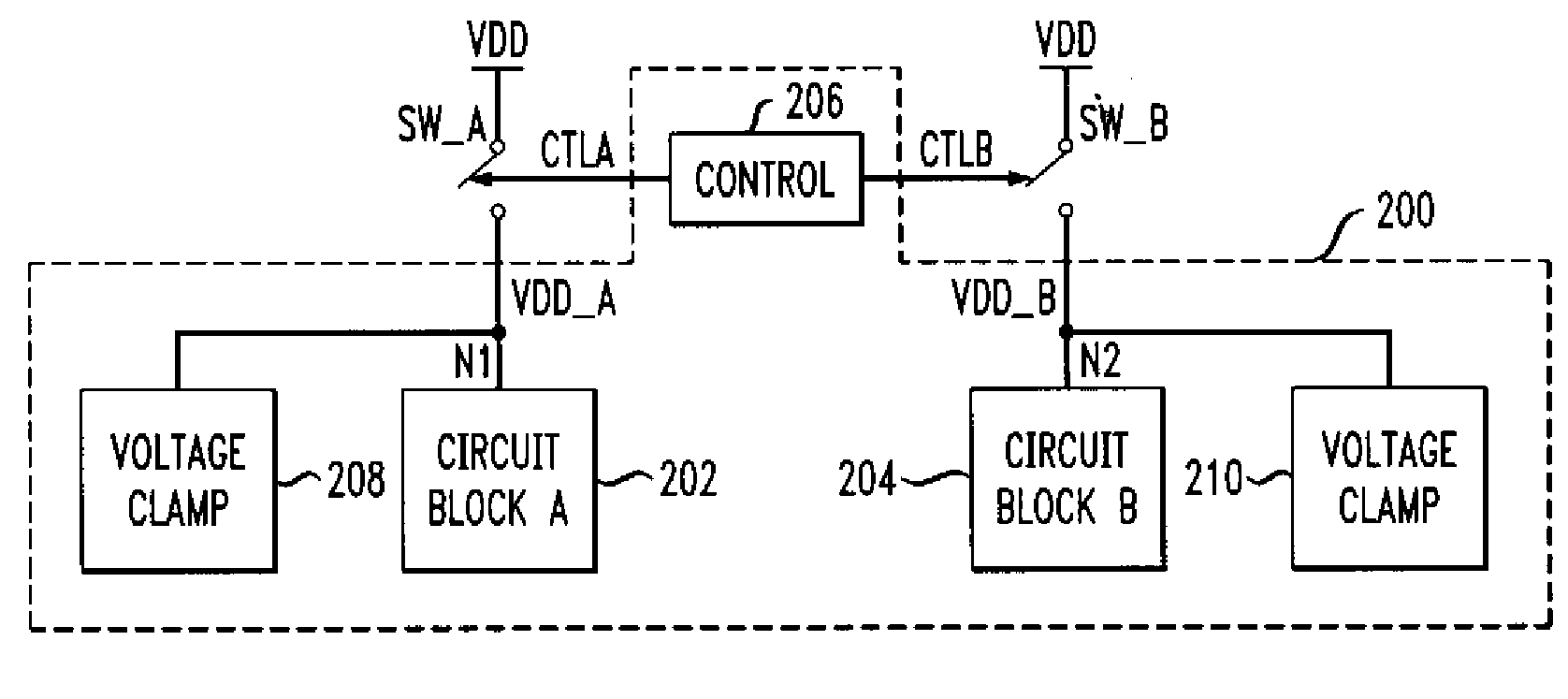
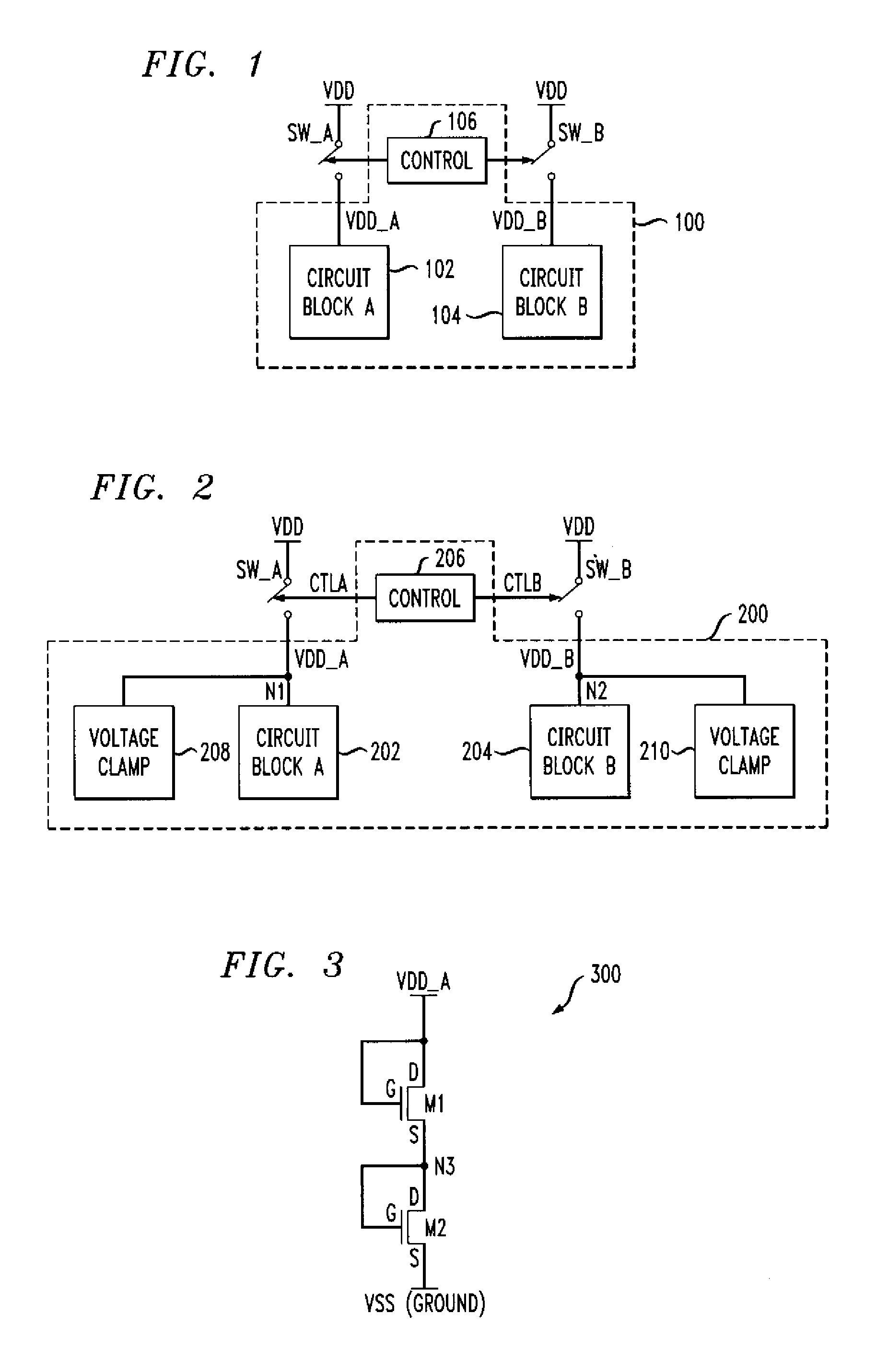
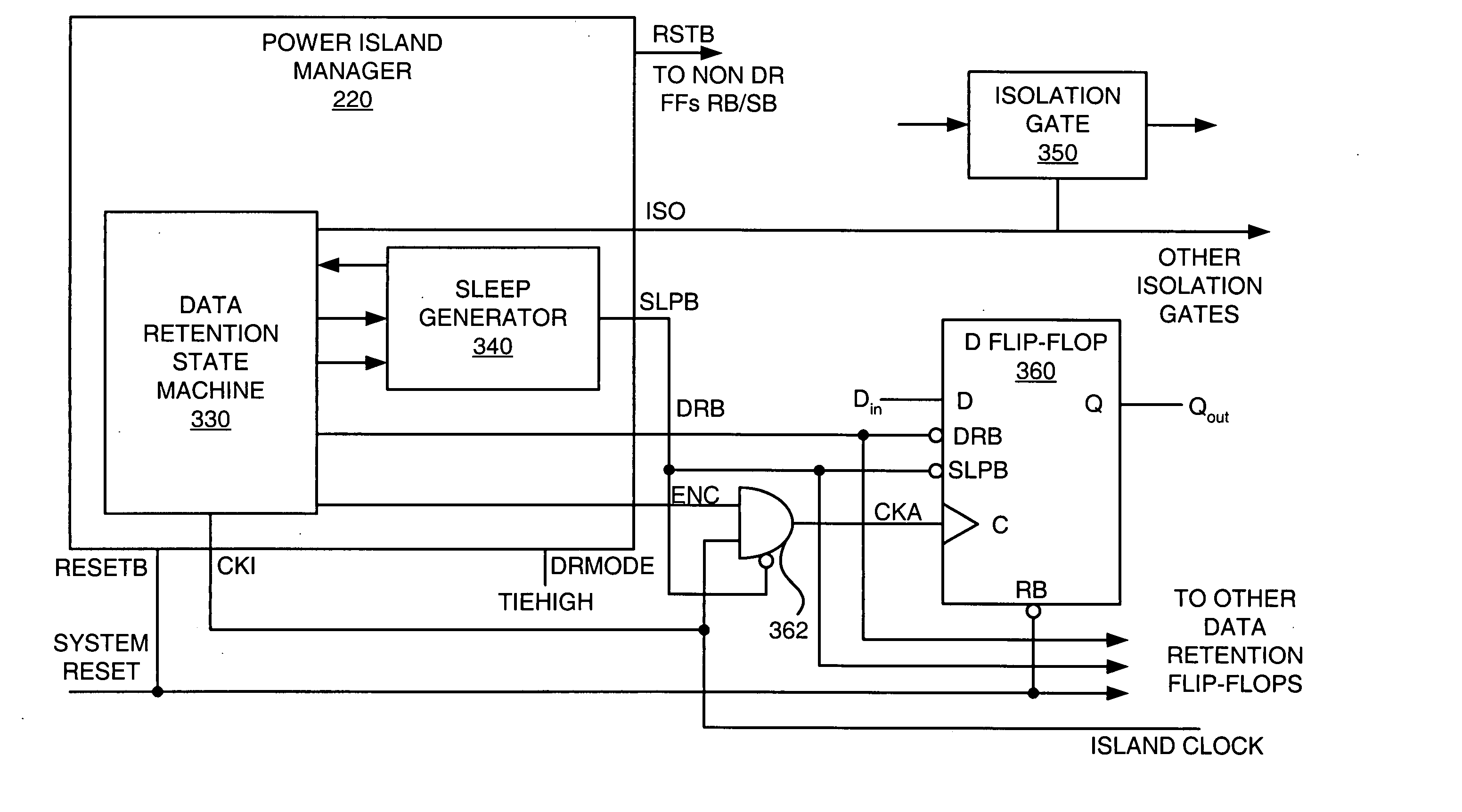
Method and Apparatus for Improving Reliability of an Integrated Circuit Having Multiple Power Domains
ActiveUS20080074171A1Reduce leakage currentIncreased riskPower reduction by control/clock signalPulse automatic controlControl signalHemt circuits
An IC having improved reliability includes at least first and second circuit blocks and at least first and second power domains, the first circuit block being connected to the first power domain and the second circuit block being connected to the second power domain. The IC further includes at least one control circuit configured to generate at least first and second control signals. The first control signal is operative to selectively connect the first power domain to a first voltage supply, and the second control signal is operative to selectively connect the second power domain to a second voltage supply. The IC includes at least first and second clamp circuits, the first clamp circuit being connected to the first power domain, the second clamp circuit being connected to the second power domain. Each of the clamp circuits is operative to prevent a voltage on a corresponding power domain from rising above a prescribed voltage level for the corresponding power domain.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
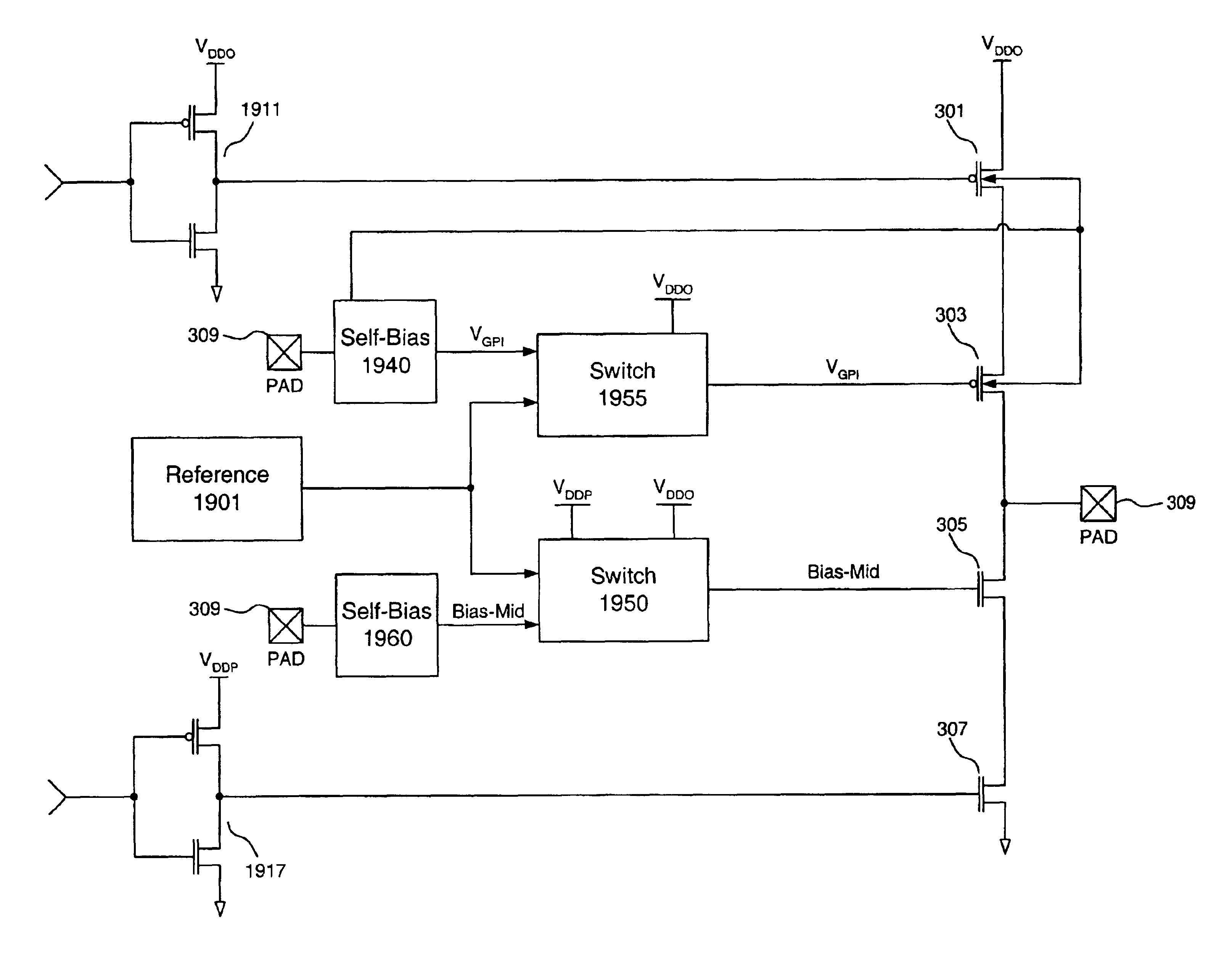
I/O circuit using low voltage transistors which can tolerate high voltages even when power supplies are powered off
InactiveUS6859074B2Pulse automatic controlReliability increase in field effect transistorsLow voltageVoltage reference
An apparatus for providing bias voltages for input / output (I / O) connections on low voltage integrated circuits. In one embodiment, the invention comprises an I / O pad, a pull-down transistor device that has a protective transistor coupled to said I / O pad, and a pull-up transistor device that has a second protective transistor, coupled to said I / O pad. A first switch coupled to the first protective transistor is responsive to a first supply voltage, a second supply voltage, and a reference voltage. Likewise, a second switch coupled to the second protective transistor is responsive to the first supply voltage and the reference voltage. A first self-bias circuit is also coupled to the first switch, wherein said the self-bias circuit uses a voltage at said I / O pad to bias the first protective transistor when both of the first and second supply voltages are powered off. Likewise, a second self-bias circuit coupled to the second switch, wherein the second self-bias circuit also uses the voltage at the I / O pad and an output of the first self bias circuit, to bias the second protective transistor when the first supply voltage is powered off.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
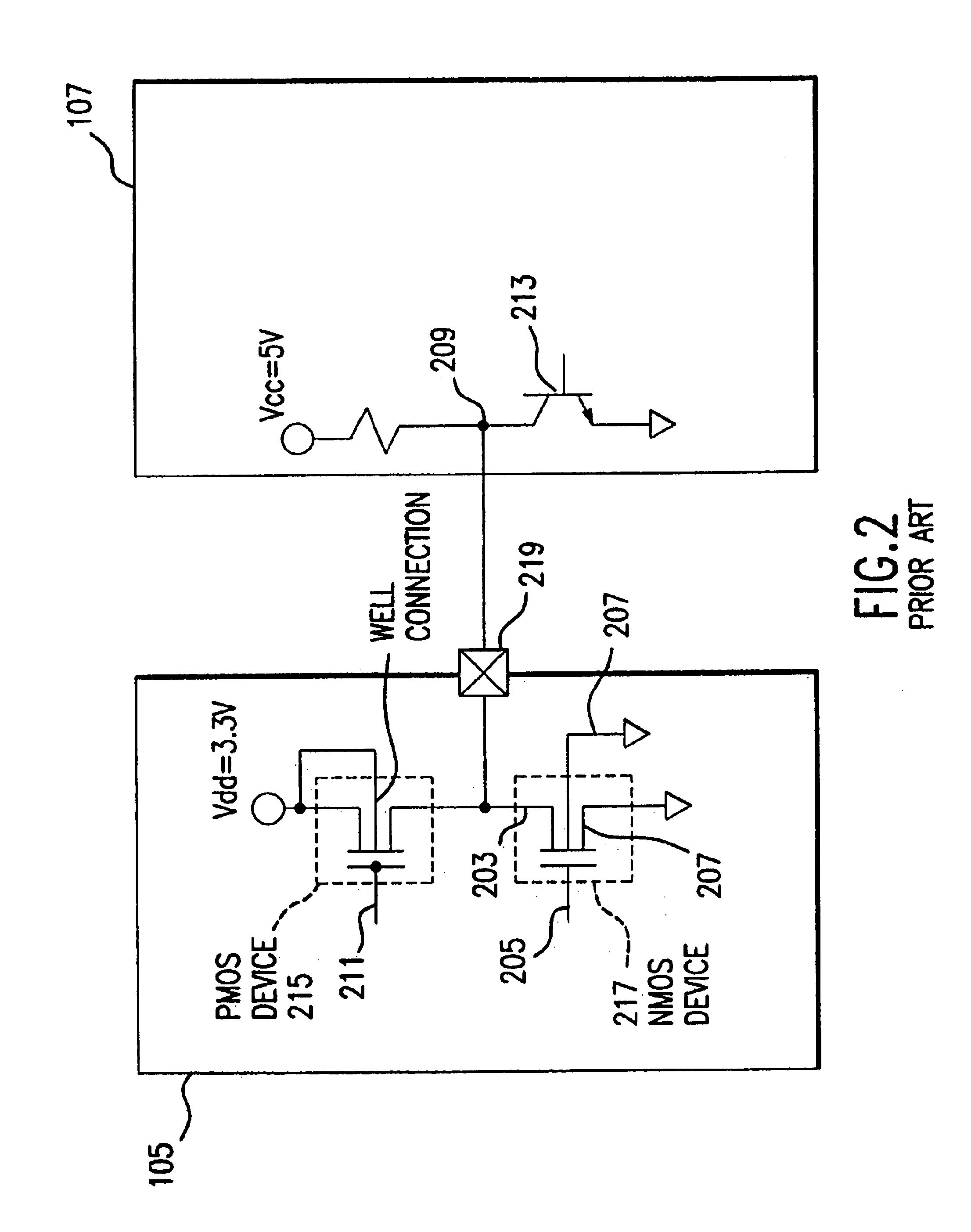
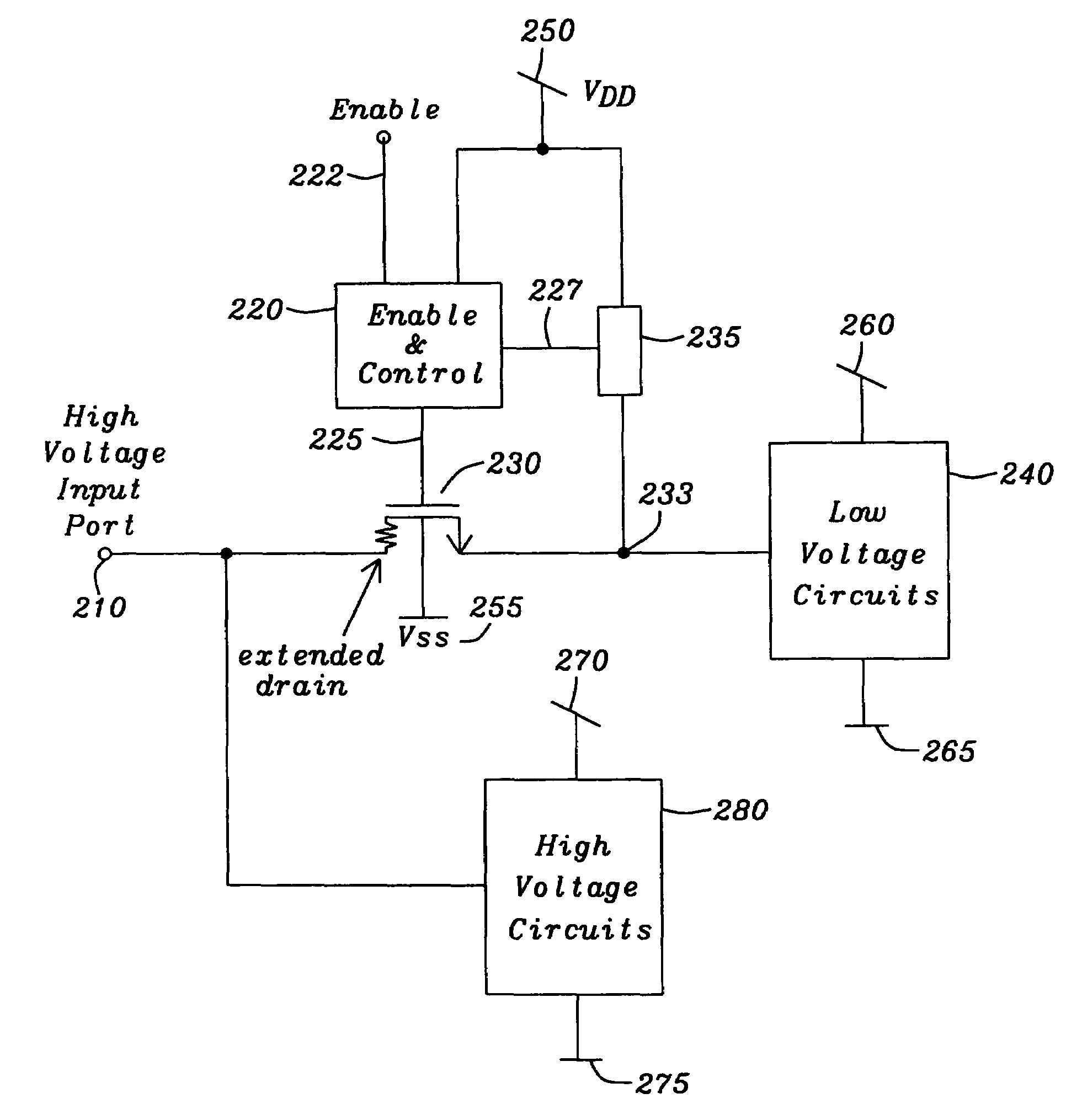
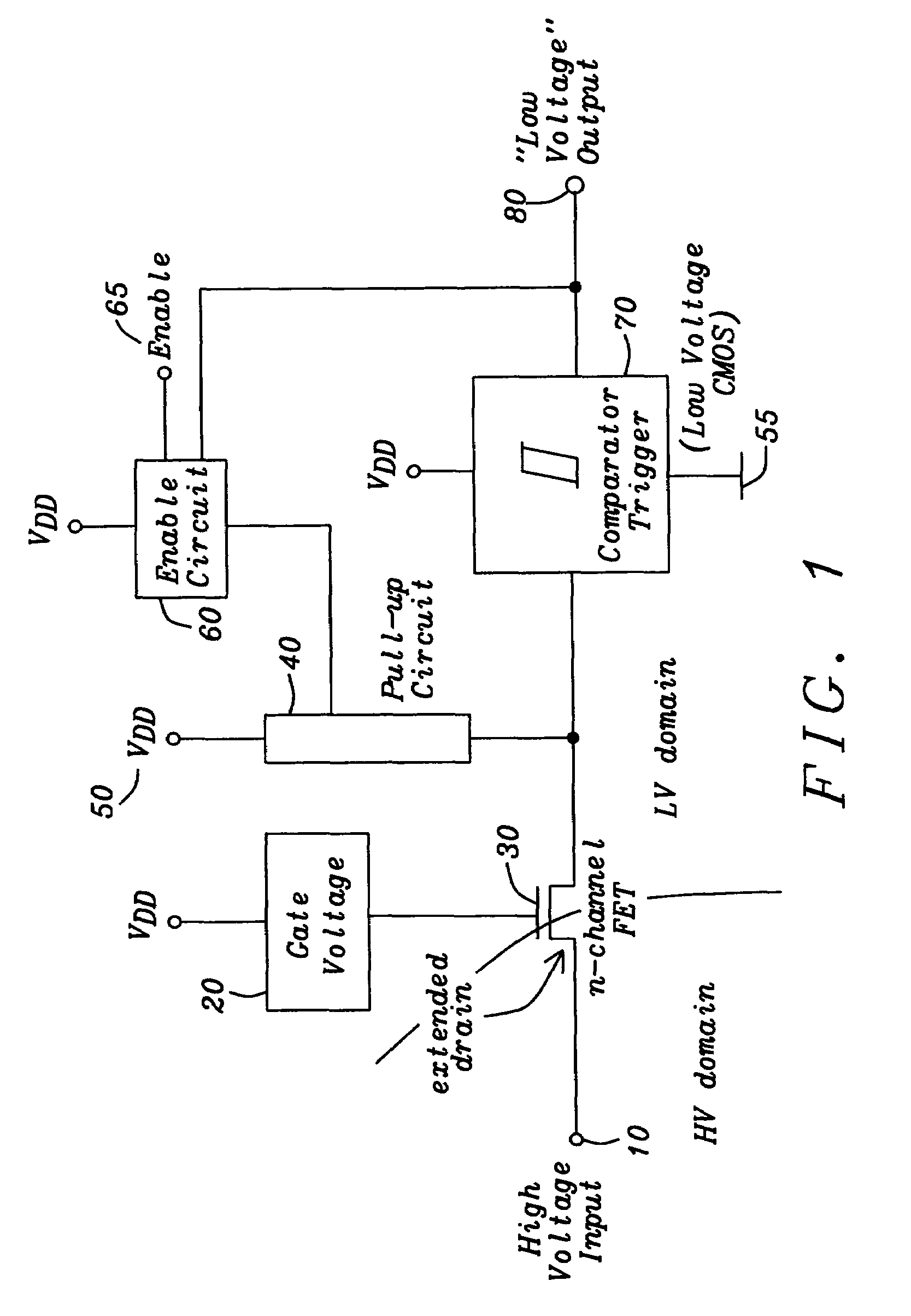
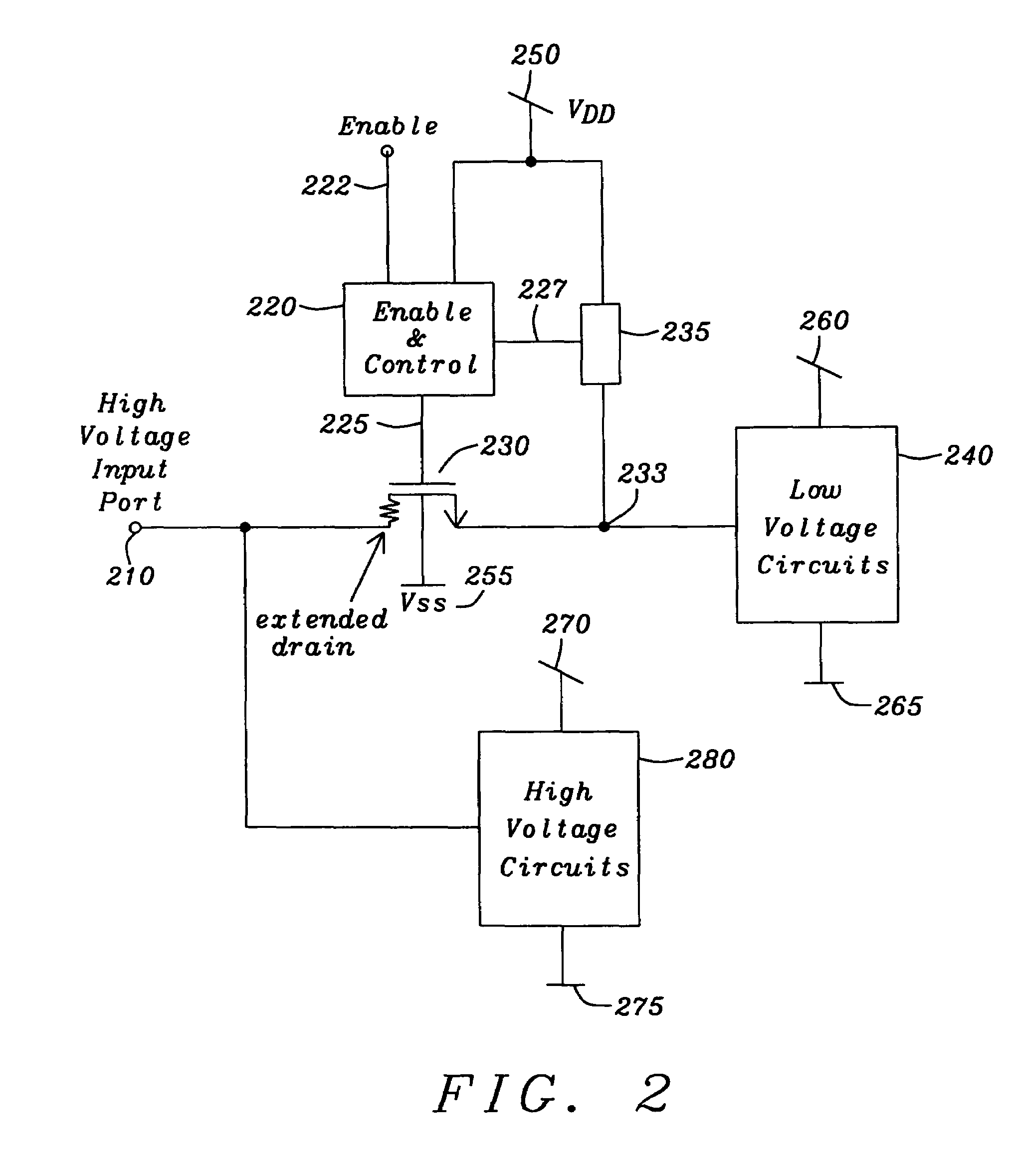
Digital CMOS-input with N-channel extended drain transistor for high-voltage protection
ActiveUS7236002B2Low costFail-safe circuitsReliability increase in field effect transistorsCMOSElectronic systems
A circuit and a method are given, to realize an electronic system for combined usage at differing voltage ranges as defined by a low-voltage range for operating standard CMOS devices and a high-voltage range exceeding said standard CMOS low-voltage operating range significantly by multiples and thus necessarily utilizing input ports with an intrinsic high-voltage protection feature. Said circuit and method are designed in order to be implemented with a very economic number of components, capable to be realized with standard modern integrated circuit technologies in CMOS technology.
Owner:DIALOG SEMICONDUCTOR GMBH
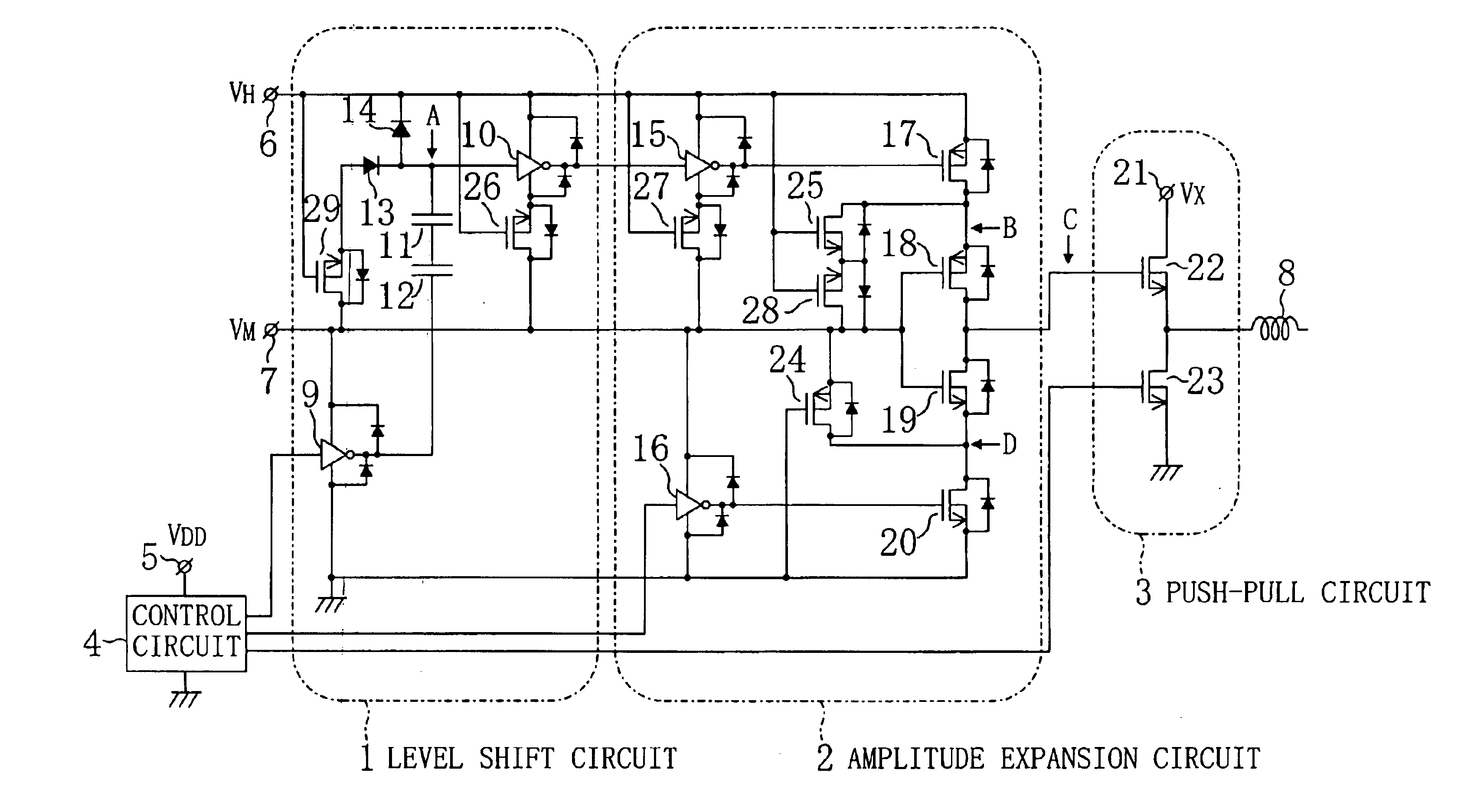
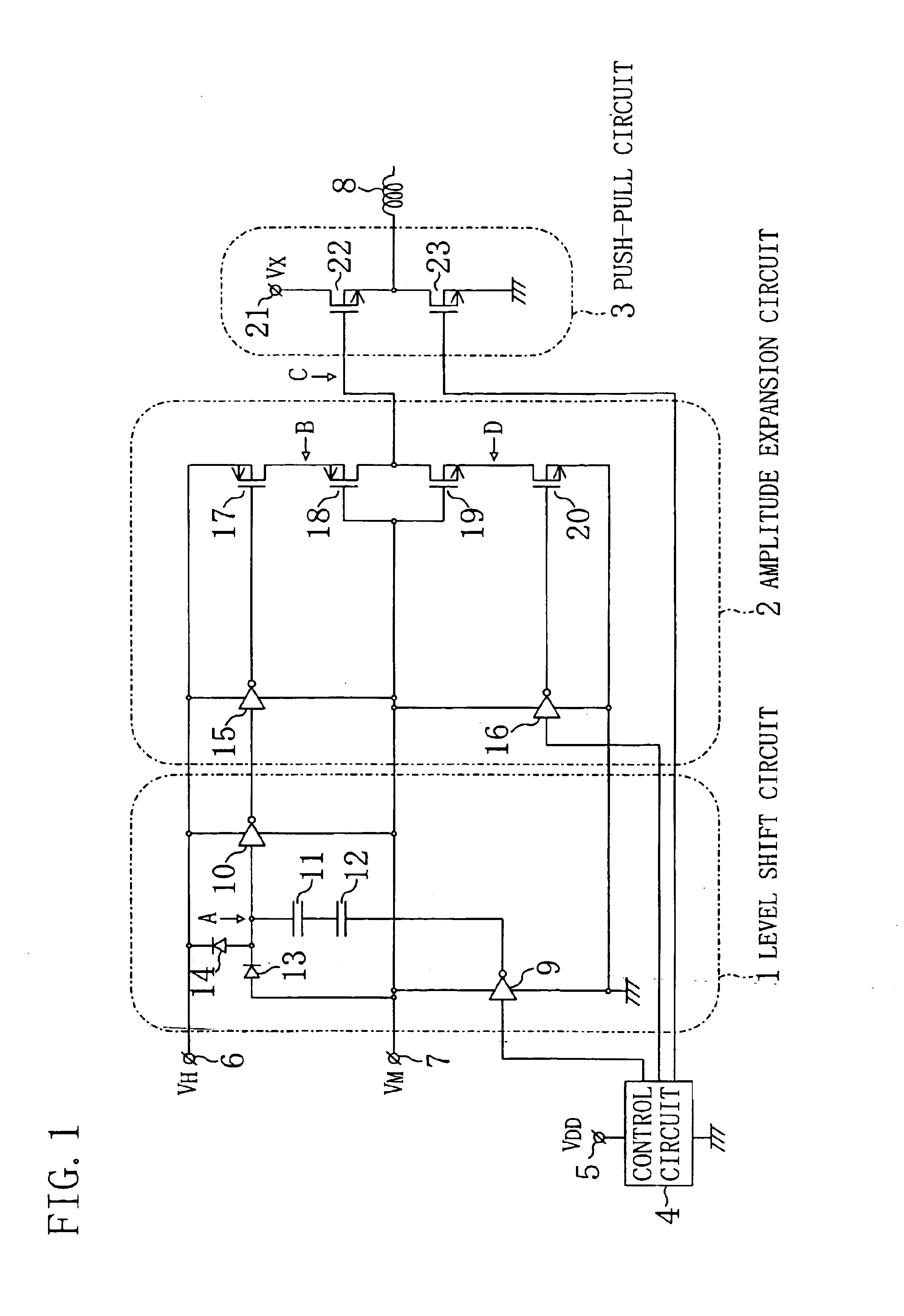
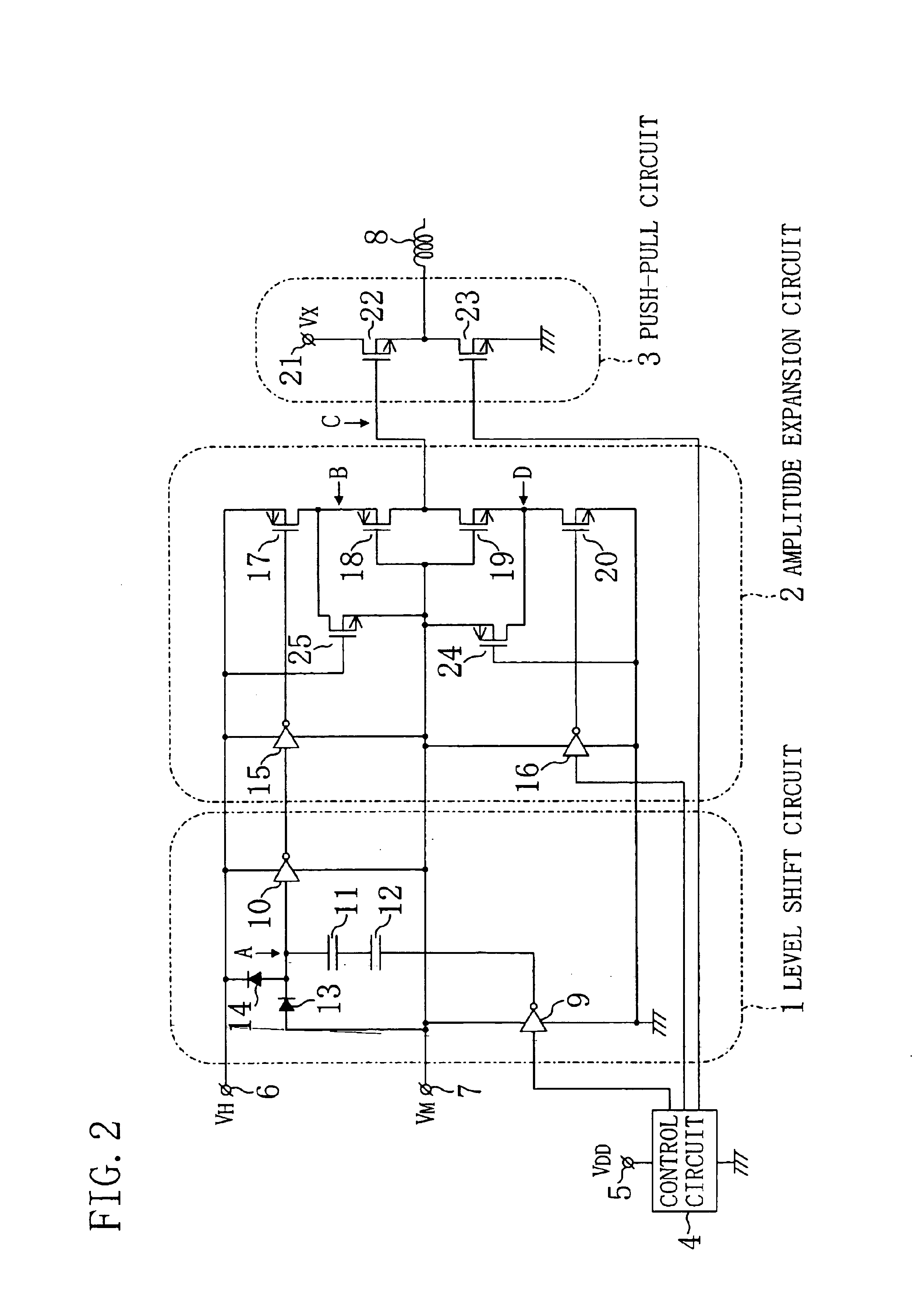
Drive circuit
The amplitude expansion circuit as a main part of a drive circuit includes: a VM DC power supply line to which a voltage VM is applied; a VH DC power supply line to which a voltage VH roughly twice as high as the voltage VM is applied; an inverter circuit receiving a pulse signal oscillating between the ground voltage and the voltage VM; another inverter circuit receiving a pulse signal oscillating between the voltage VM and the voltage VH in correspondence with the oscillation of the voltage level of the above pulse signal; a p-channel MOSFET having a gate receiving an output from the inverter circuit; another p-channel MOSFET having a gate connected to the VM DC power supply line; an n-channel MOSFET having a gate connected to the VM DC power supply line; and another n-channel MOSFET having a gate receiving an output from the other inverter circuit. A common connection node of the p-channel MOSFET and the n-channel MOSFET works as the output terminal of the amplitude expansion circuit.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Connection device
ActiveUS20130088278A1Low drain to source resistancePerform less-wellTransistorElectronic switchingElectrical and Electronics engineeringEngineering
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
High speed output buffer with AC-coupled level shift and DC level detection and correction
InactiveUS20070001716A1Pulse automatic controlReliability increase in field effect transistorsDriver circuitLevel shifting
A high speed output buffer including an input circuit providing first and second signals within a first voltage range having a first common mode voltage, an AC interface receiving the first and second signals and providing first and second preliminary drive signals, a detection and correction circuit that corrects a state of the first preliminary drive signal AC coupled to the first signal, first and second drive circuits receiving the preliminary drive signals and providing first and second drive signals, where the first drive circuit operates within a second voltage range having a greater common mode voltage and where the second drive circuit operates within a third voltage range, and an output that switches an output node within a voltage range that is greater than a maximum voltage range. The first, second and third voltage ranges are each within the maximum voltage range suitable for thin-gate devices.
Owner:NORTH STAR INNOVATIONS
Method and apparatus for protecting a circuit during a hot socket condition
InactiveUS6972593B1Increase valueReliability increase in field effect transistorsLogic circuits using specific componentsHot swappingEngineering
The hot socket detect circuit of the present invention includes a well bias circuit and three hot socket detect blocks. If the output of any of the three hot socket detect blocks is a digital high signal then the output of the hot socket detect circuit is a digital high signal. The digital high signal indicates that a hot socket condition exists.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
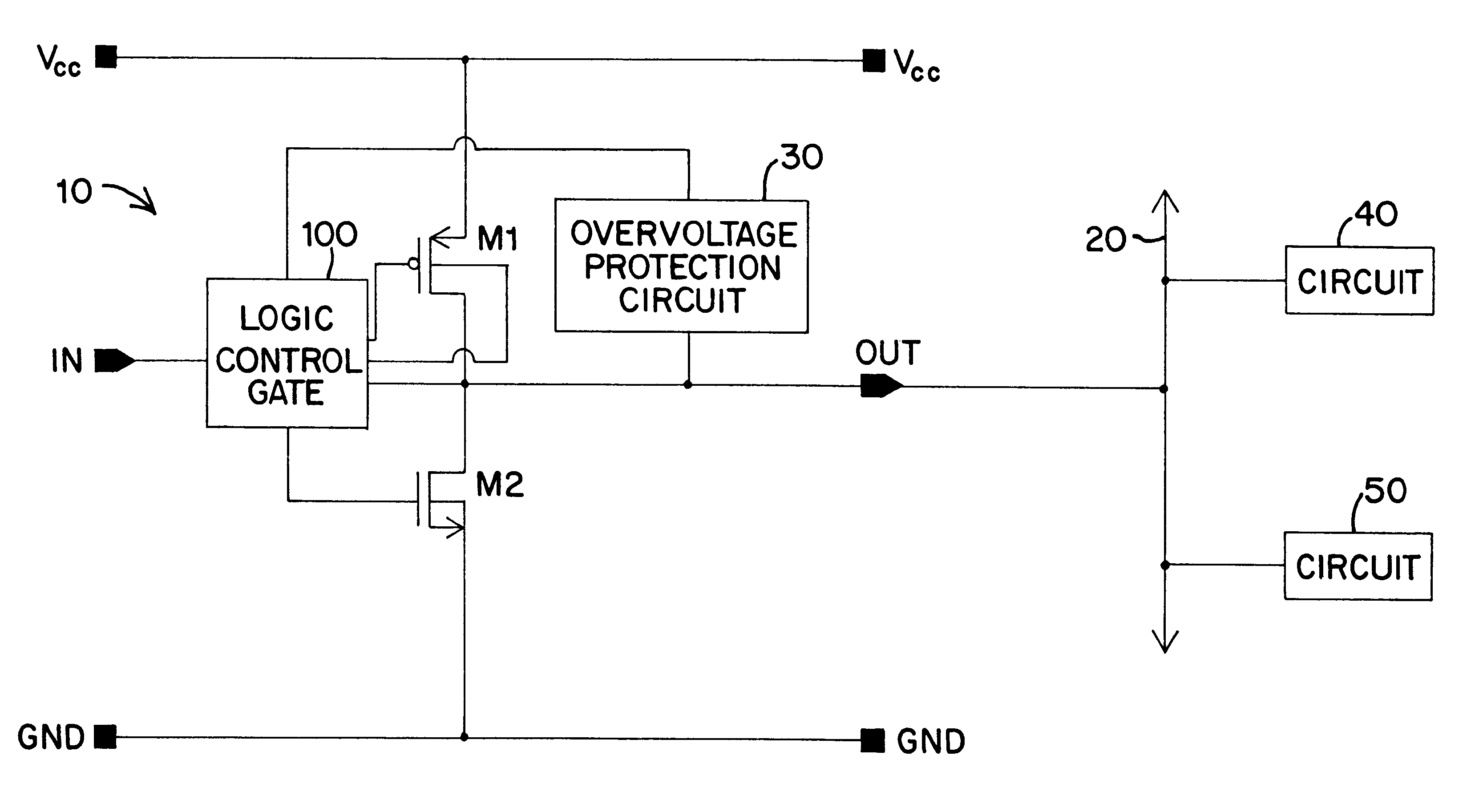
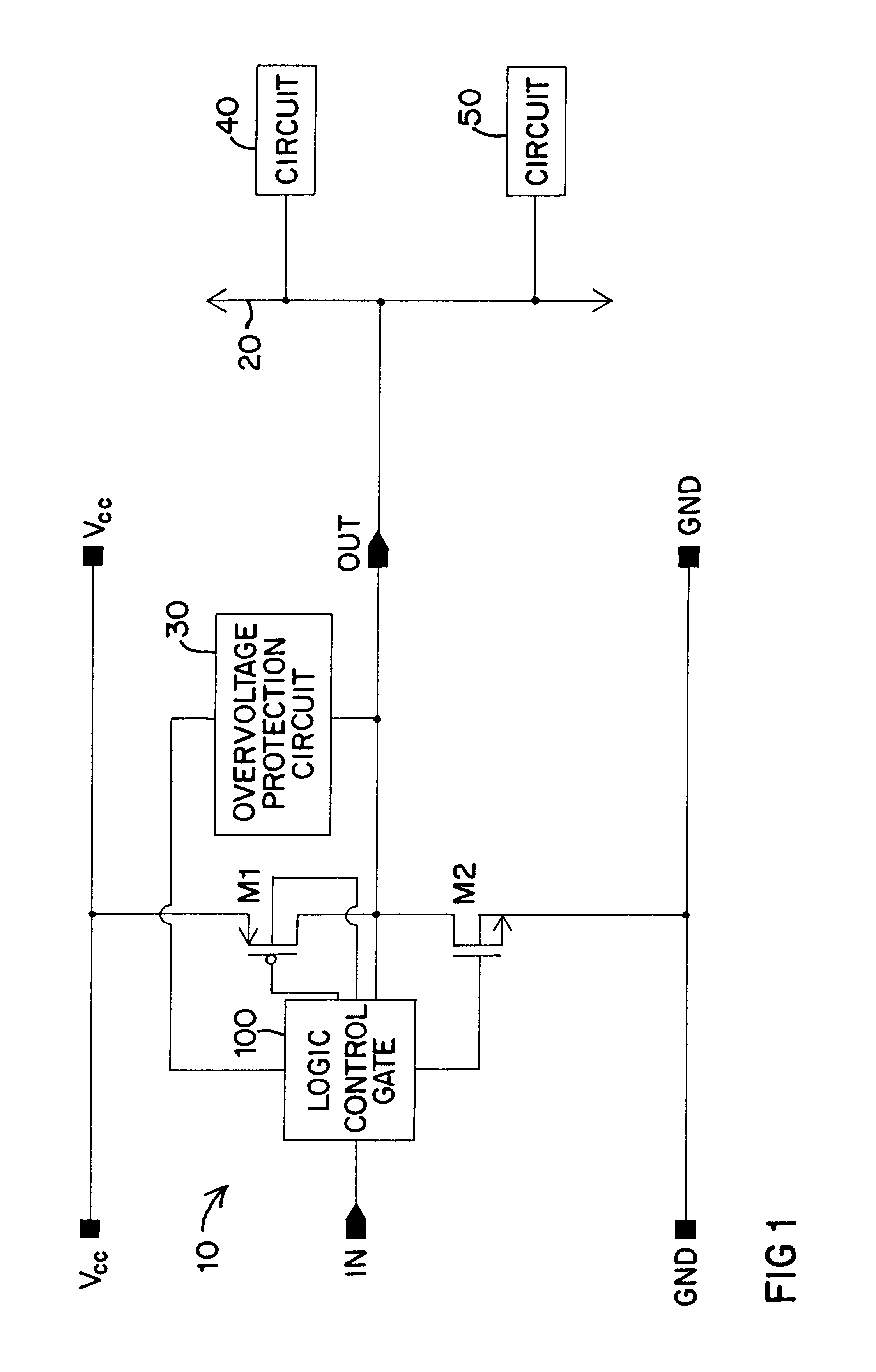
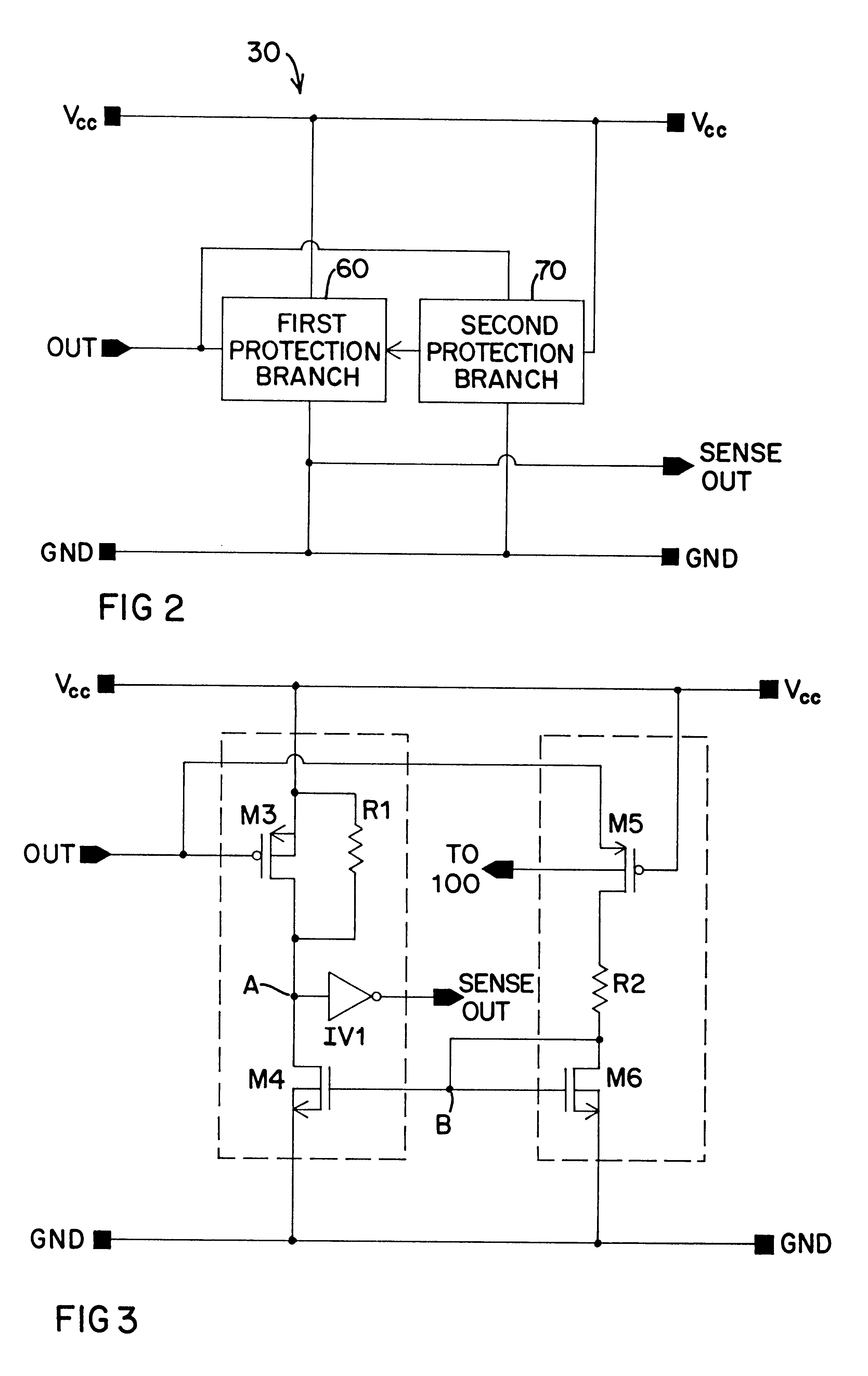
Overvoltage protection circuit with overvoltage removal sensing
InactiveUS6344958B1Ensure maintenanceMinimize impactElectronic switchingReliability increase in field effect transistorsOvervoltageEngineering
An overvoltage protection circuit arranged to sense removal of the overvoltage condition. The protection circuit blocks current passing through a pull up transistor of an output circuit to a high-potential supply rail during an overvoltage condition applied at a common bus. The protection circuit includes one protection branch controlled by the potential at the bus and powered by the high-potential supply rail of the output circuit to be protected. The protection circuit also includes a second protection branch controlled by the high-potential supply rail and powered by the potential on the bus. When an overvoltage condition occurs, the second branch is activated and regulates an output from the first protection branch. That output signal controls the control node of the pull up transistor of the output circuit to be protected. The two protection branches are configured such that removal of the overvoltage condition causes a rapid changing of the state of the output of the first protection branch so that the operating condition of the pull up transistor remains the same as it was prior to the overvoltage condition.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Low leakage and data retention circuitry
ActiveUS20050184758A1Reduce power consumptionReduce leakagePower reduction by control/clock signalLogic circuits characterised by logic functionSleep stateEngineering
An integrated circuit includes first circuitry and sleep transistor circuitry. The first circuitry receives input signals and processes the input signals. The first circuitry also retains data in a sleep state that has low leakage. The sleep transistor circuitry is coupled to the first circuitry and receives a sleep signal that has a negative voltage. The sleep circuitry reduces power consumption of the first circuitry in the sleep state to have low leakage based on the sleep signal while retaining the data in the first circuitry.
Owner:MOSAID TECH
Popular searches
Cathode-ray tube indicators Input/output processes for data processing Semiconductor devices Electric pulse generator Electric variable regulation Pulse shaping Computing operation arrangements Oscillations generators Emergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/current Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com