Patents
Literature
528 results about "Frame size" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
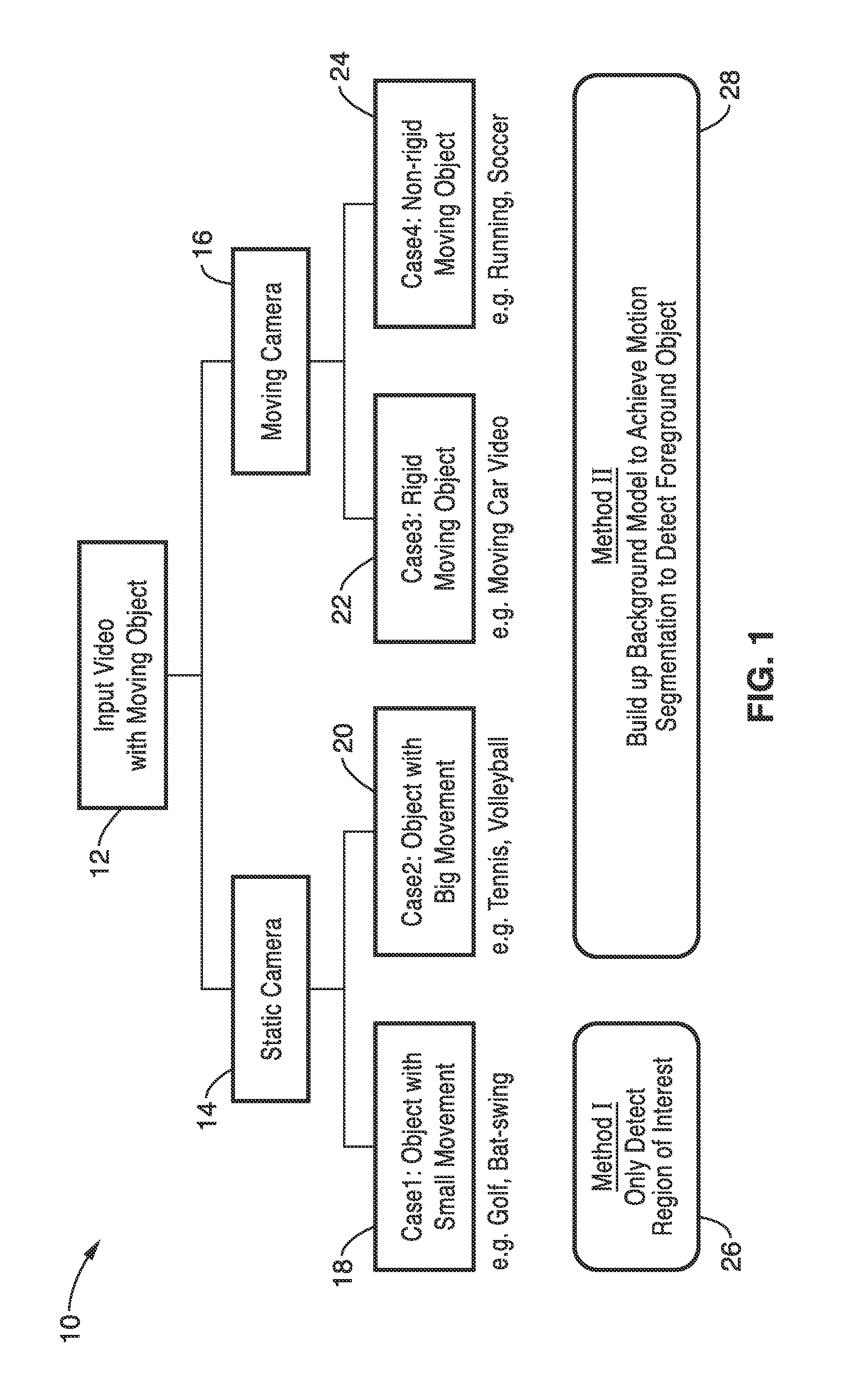
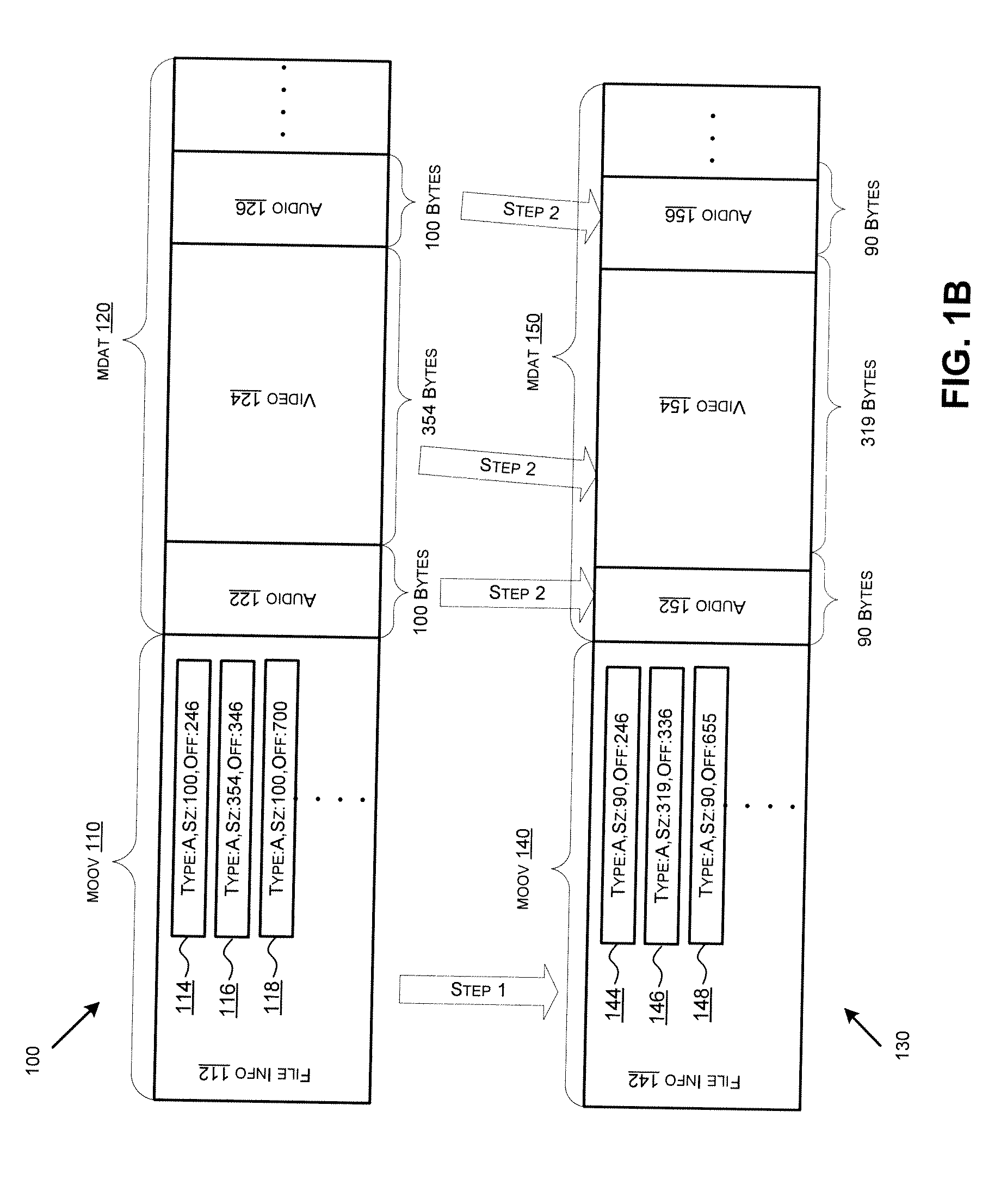
Frame size refers specifically to the width and height of the frame, so it’s expressed as 2 measurements (width x height) rather than as a ratio.
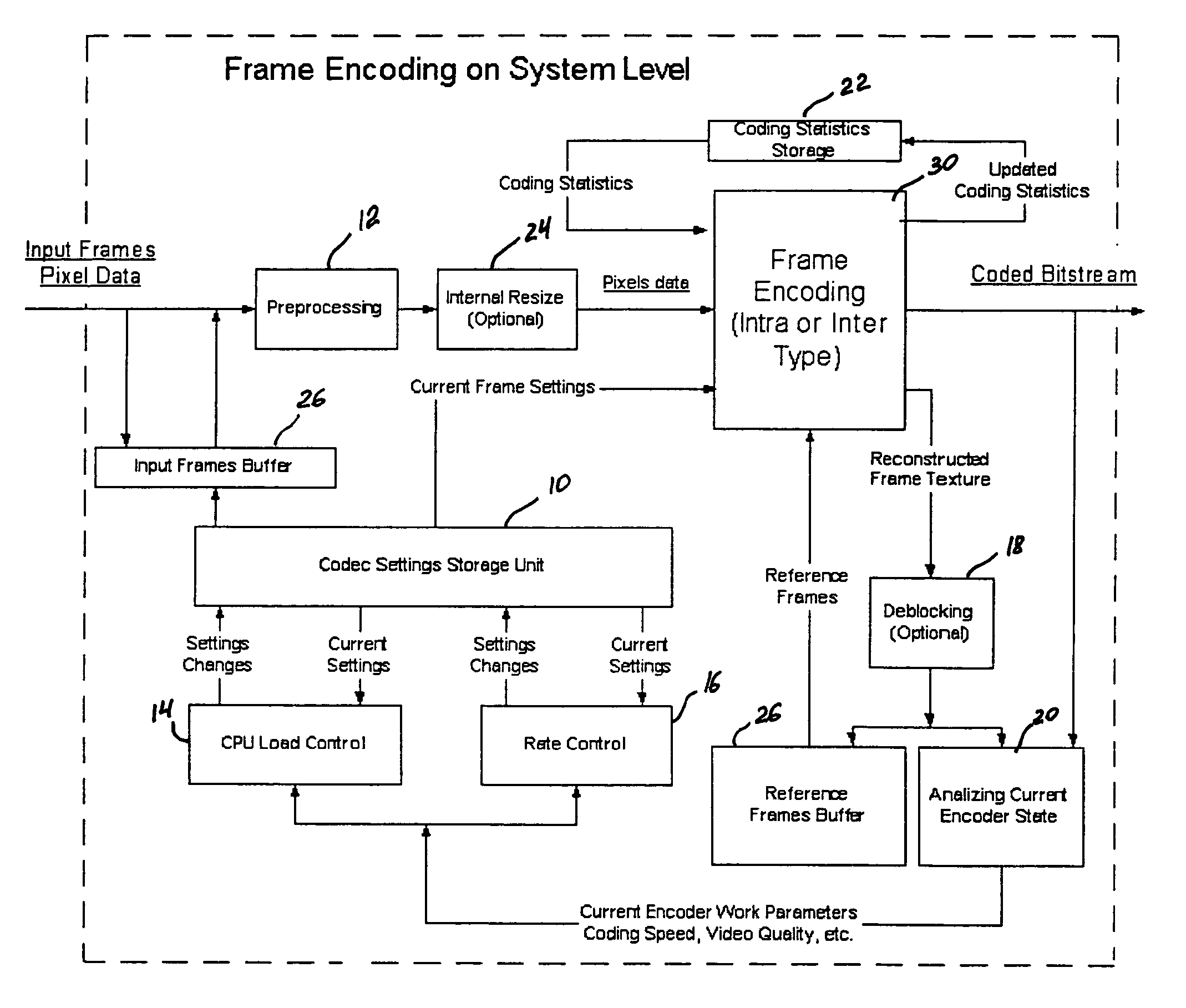
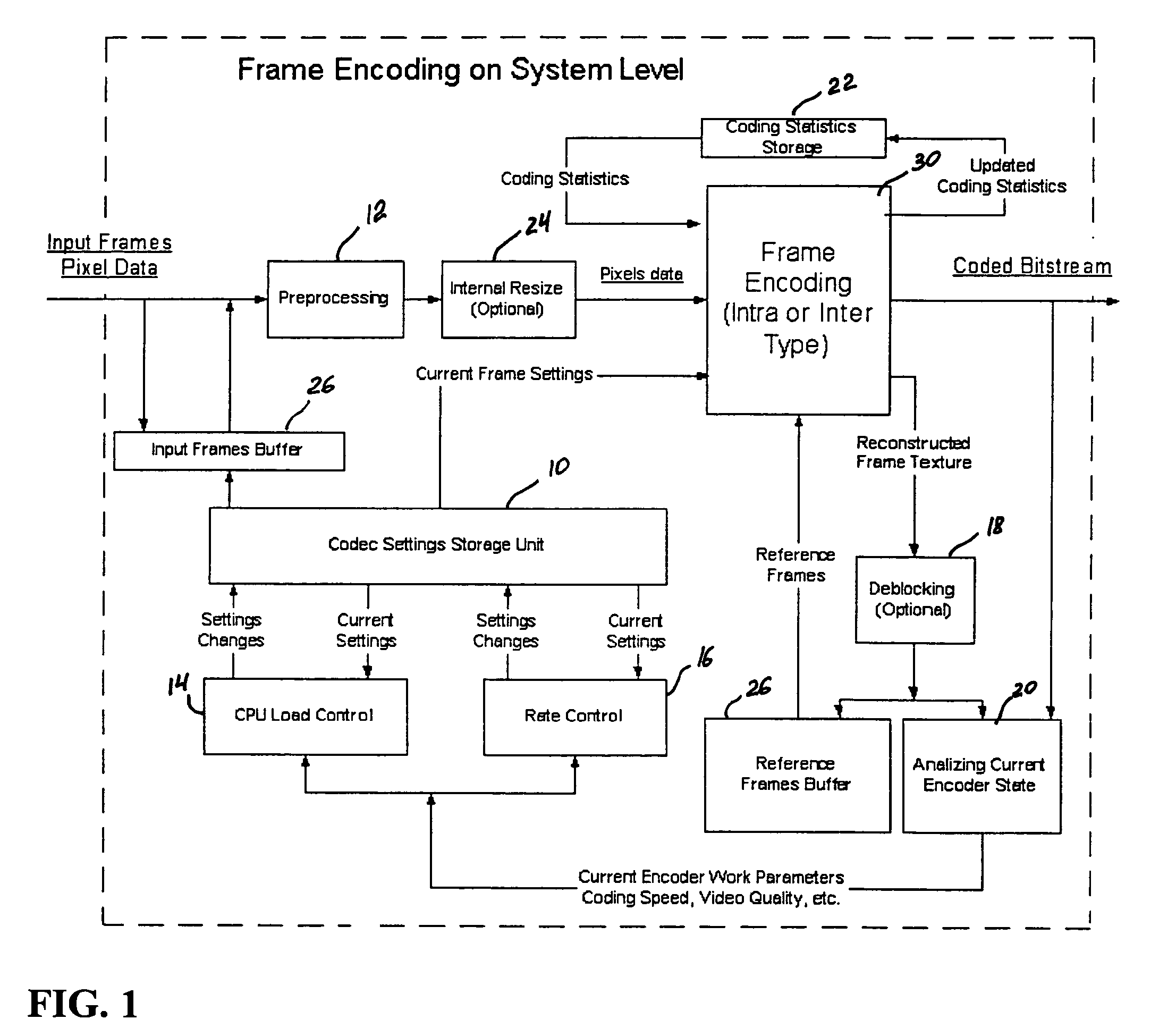
Real-time video coding/decoding
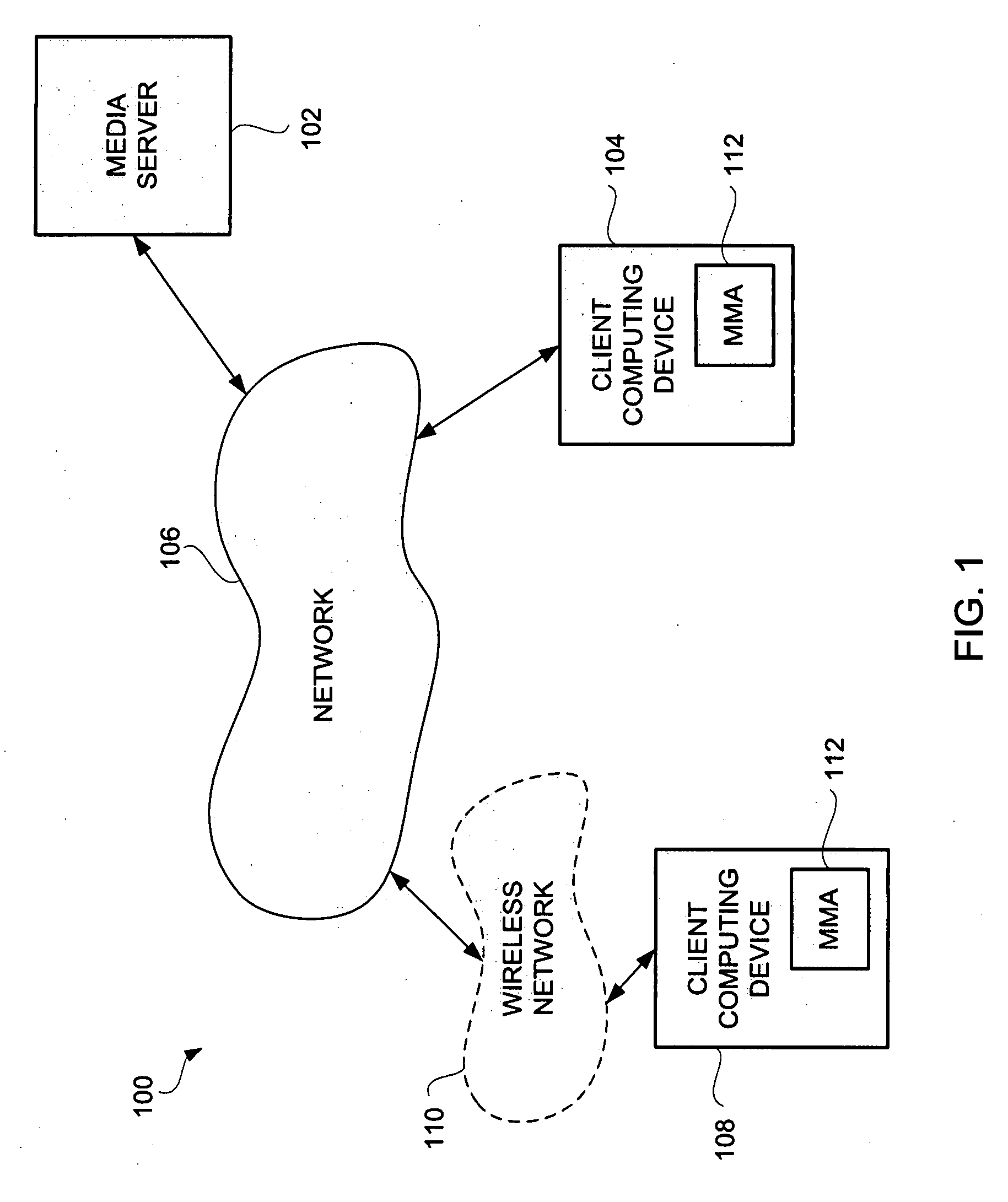
ActiveUS20050276323A1Picture reproducers using cathode ray tubesCode conversionMotion vectorDownscaling
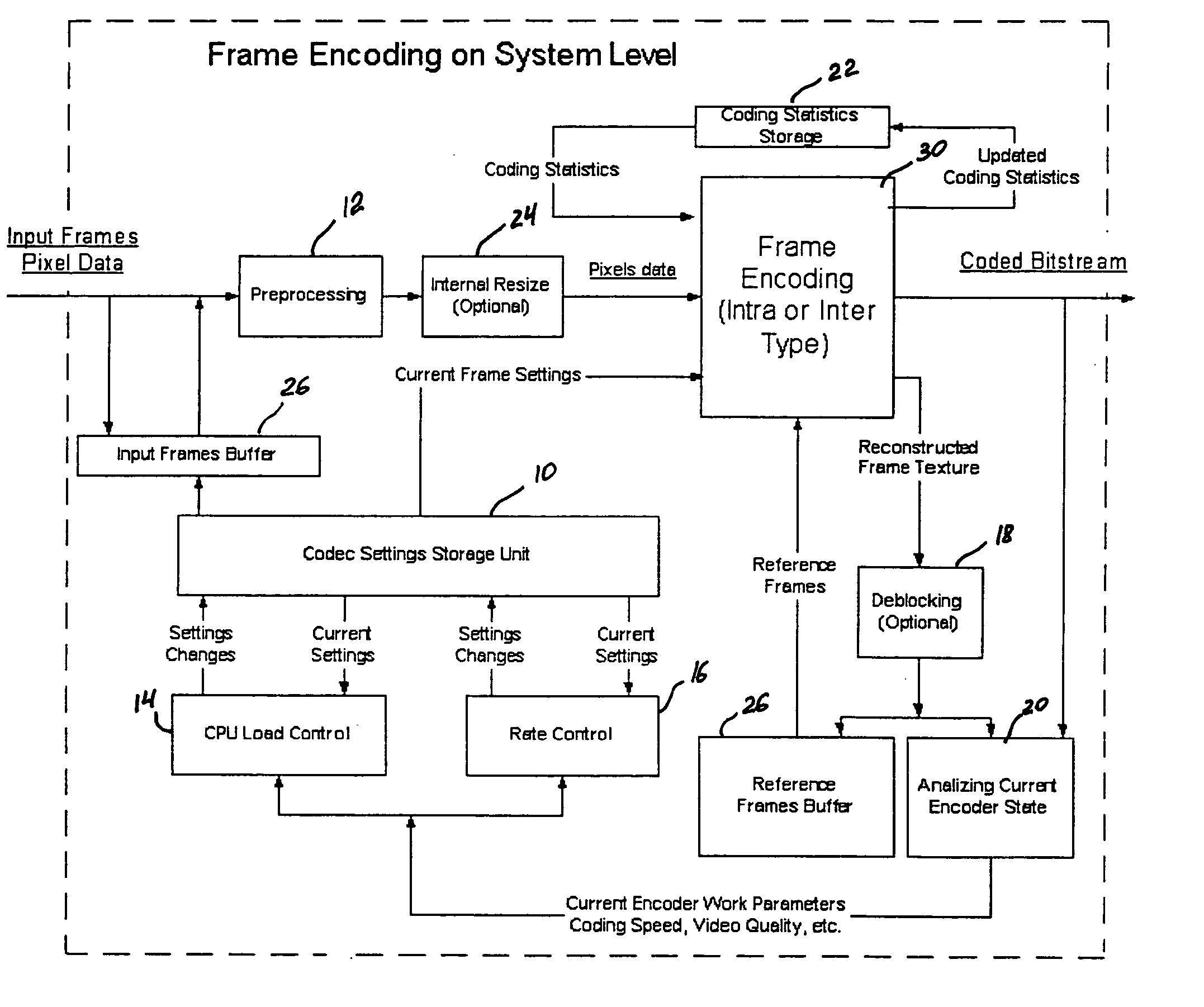
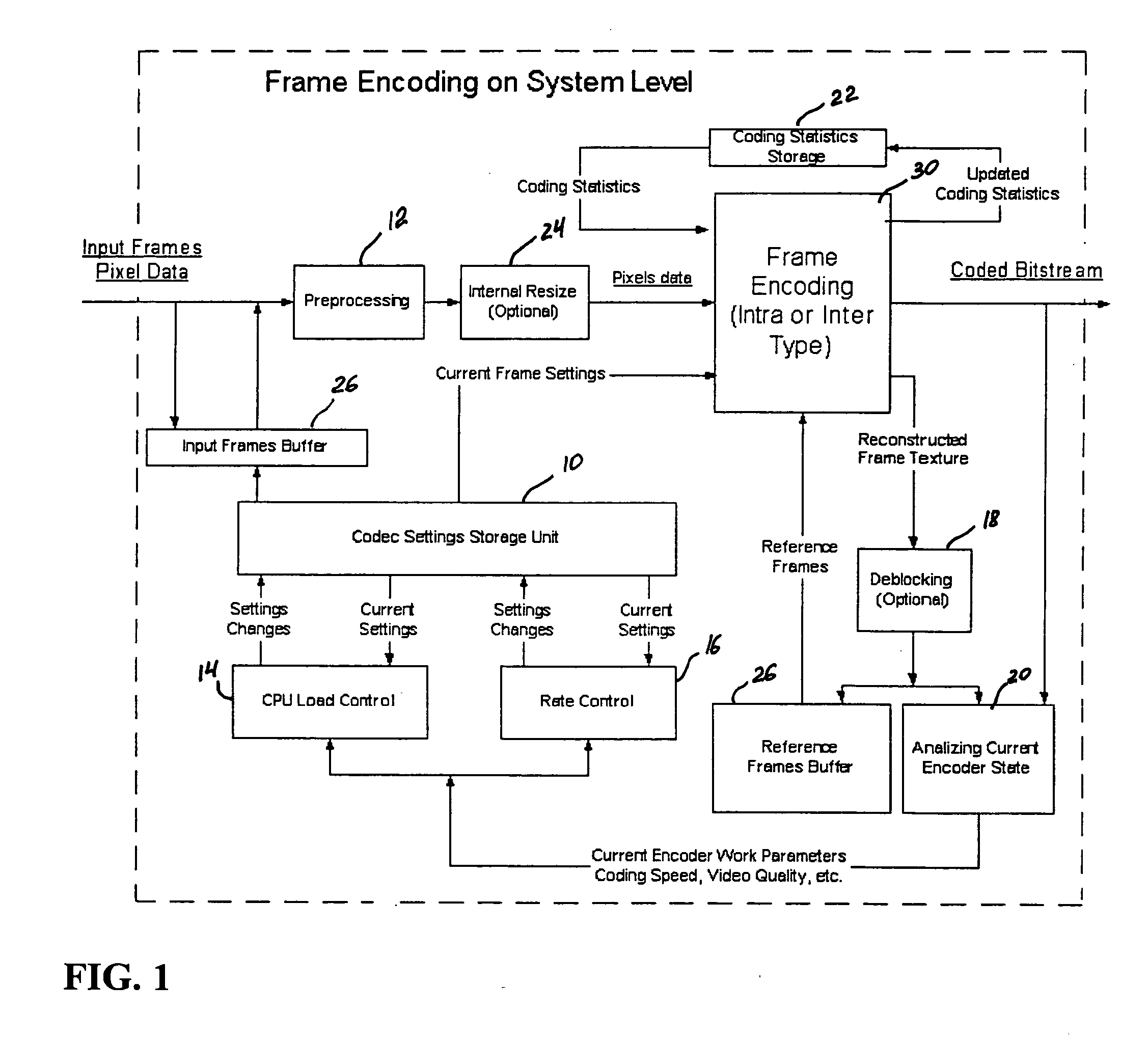
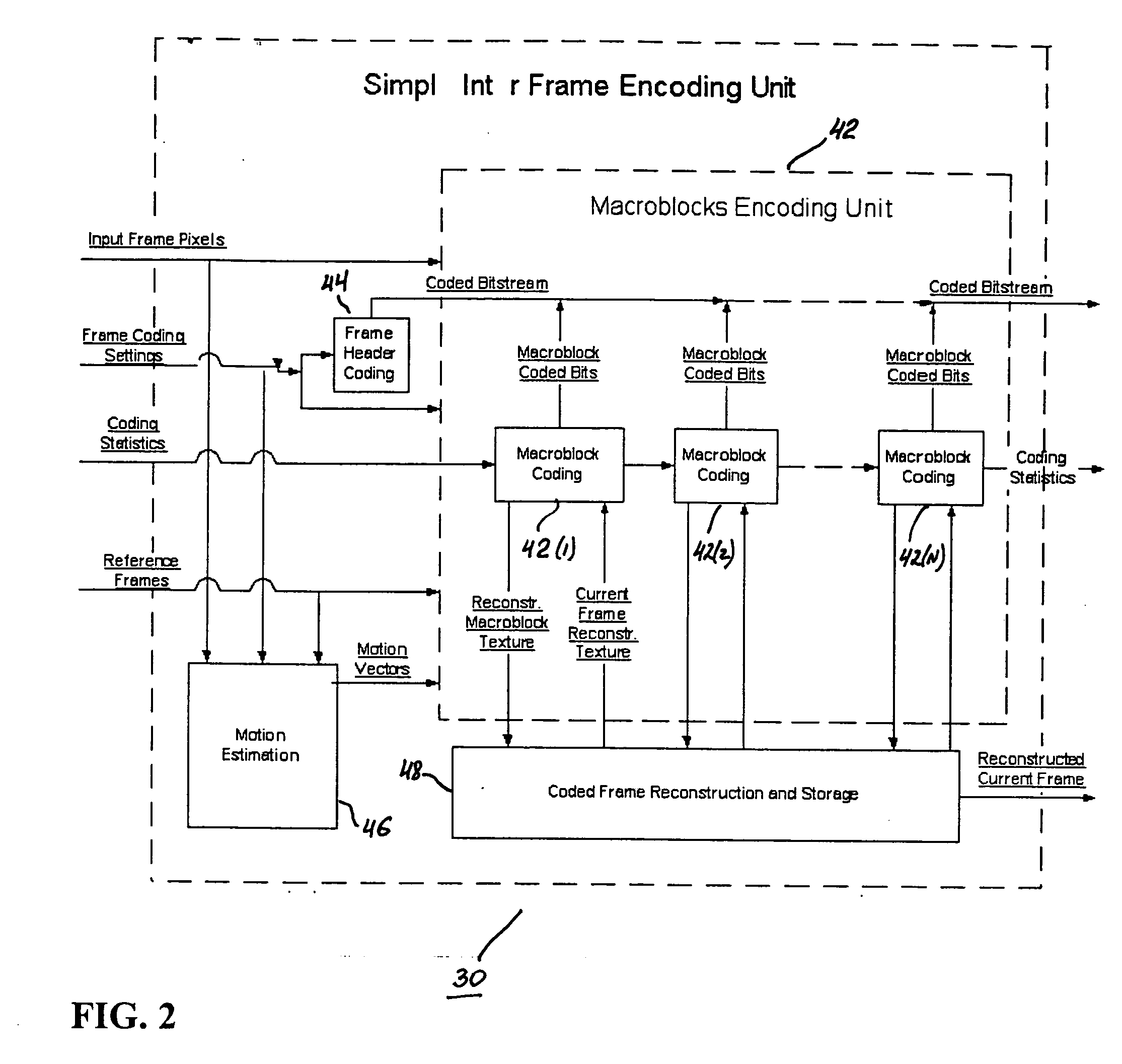
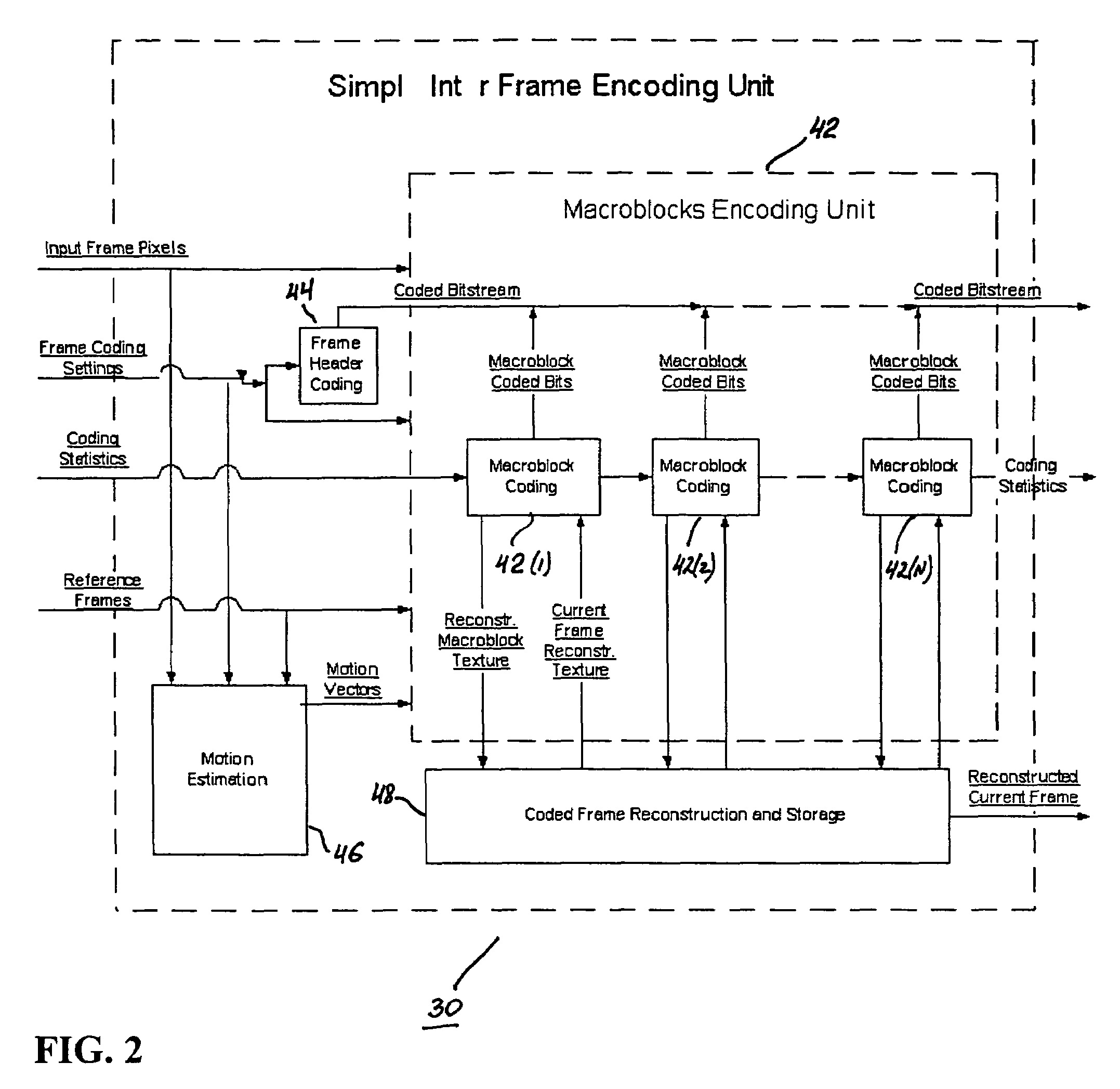
A video codec for real-time encoding / decoding of digitized video data with high compression efficiency, comprising a frame encoder receiving input frame pixels; a codec setting unit for setting and storing coding setting parameters; a CPU load controller for controlling desired frame encoding time and CPU loading; a rate controller for controlling frame size; a coding statistics memory for storing frequency tables for arithmetic coding of bitstream parameters and a reference frame buffer for storing reference frames. The frame encoder comprises a motion estimation unit, a frame head coding unit, a coded frame reconstruction and storage unit and a macroblock encoding unit. The macroblock encoding unit provides calculation of texture prediction and prediction error, transforming texture prediction error and quantization of transform coefficient, calculation of motion vector prediction and prediction error and arithmetic context modeling for motion vectors, header parameters and transform coefficients. The codec also includes a deblocking unit for processing video data to eliminate blocking effect from restored data encoded at high distortion level, which may be a part of encoder or decoder, an internal resize unit, providing matching downscaling of a frame before encoding and upscaling of decoded frame according to the coding setting parameters, and a noise suppression unit.
Owner:BEAMR IMAGING LTD
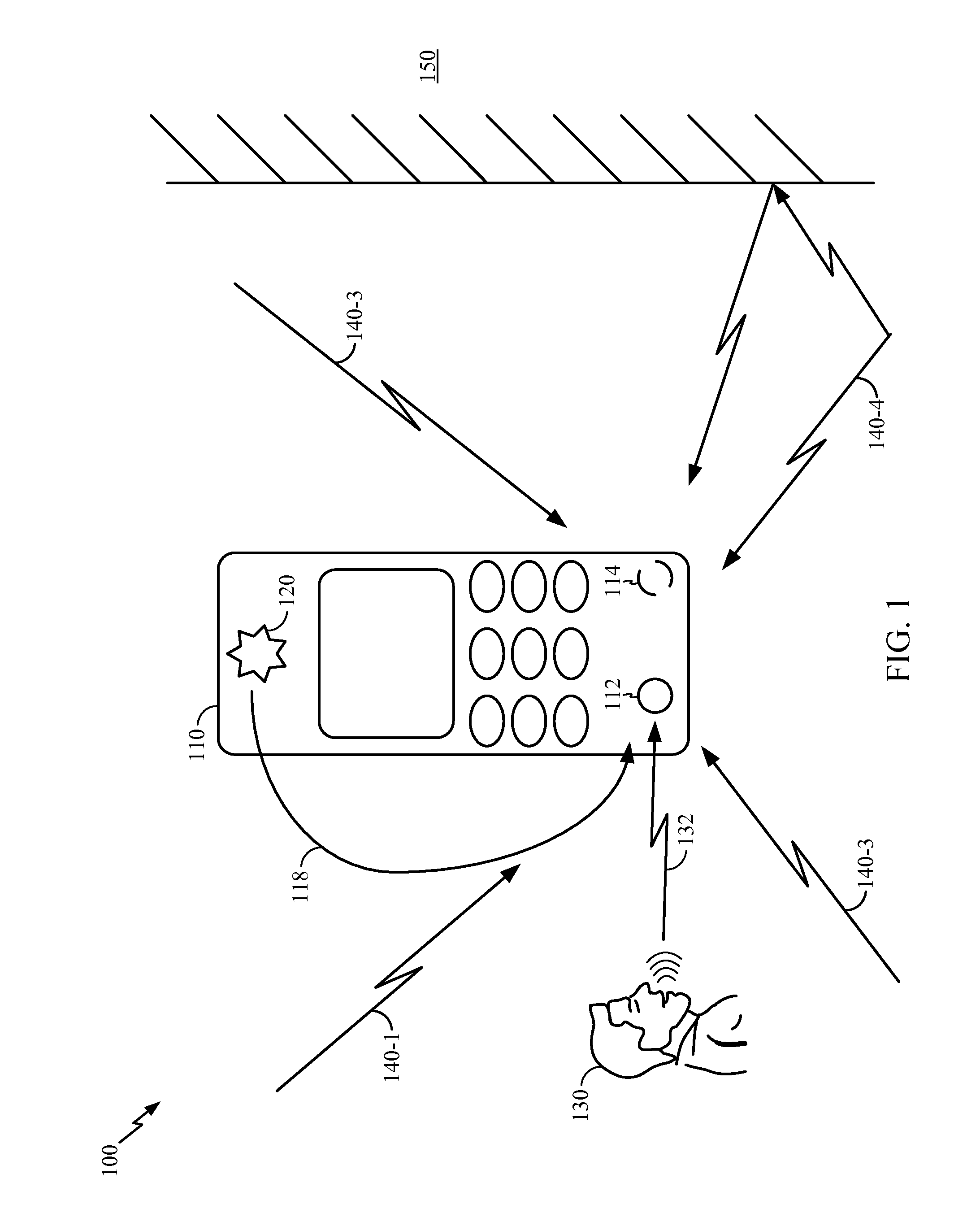
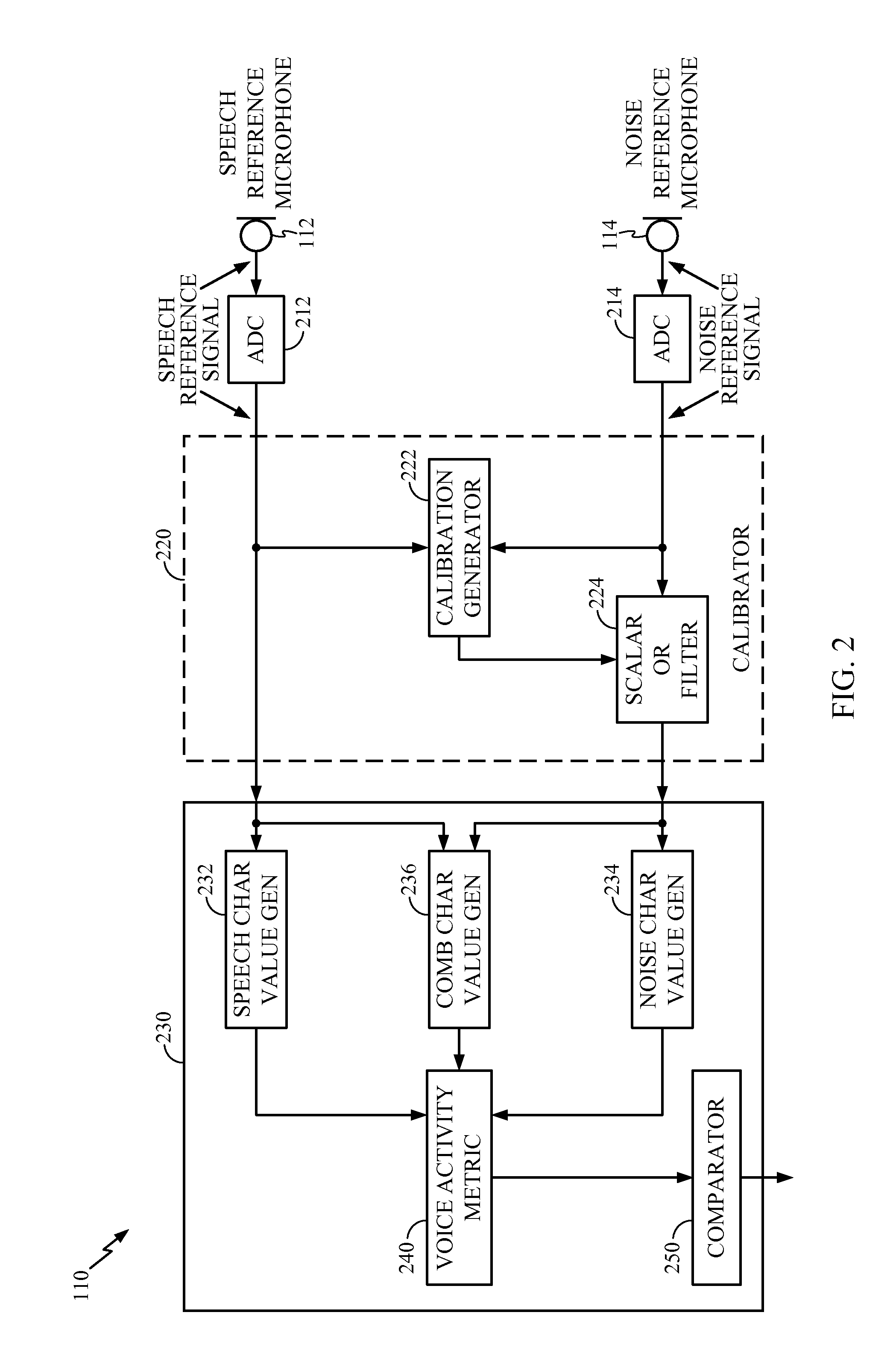
Multiple microphone voice activity detector
Voice activity detection using multiple microphones can be based on a relationship between an energy at each of a speech reference microphone and a noise reference microphone. The energy output from each of the speech reference microphone and the noise reference microphone can be determined. A speech to noise energy ratio can be determined and compared to a predetermined voice activity threshold. In another embodiment, the absolute value of the autocorrelation of the speech and noise reference signals are determined and a ratio based on autocorrelation values is determined. Ratios that exceed the predetermined threshold can indicate the presence of a voice signal. The speech and noise energies or autocorrelations can be determined using a weighted average or over a discrete frame size.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Real-time video coding/decoding
Owner:BEAMR IMAGING LTD
Universal digital framer architecture for transport of client signals of any client payload and format type
ActiveUS20050286521A1Reduce the required sizeReduce capacityError preventionTransmission systemsClient-sideByte
Client signals to be transported in a transmission network, particularly an optical transmission network, may have different payload envelope rates and are digitally mapped on the client egress side into first transport frames (also referred to as iDTF frames, or intra-node or internal digital transport frames), at the client side for intra-transport within terminal network elements (NEs) and further digitally mapped into second transport frames (also referred to as DTFs or digital transport frames) for inter-transport across the network or a link which, through byte stuffing carried out in the first transport frames so that they always have the same frame size. As a result, the system of framers provides for a DTF format to always have a uniformly universal frame rate throughout the network supporting any client signal frequency, whether a standard client payload or a proprietary client payload, as long as its rate is below payload envelope rate of the client signal. At the client signal ingress side, the signal are digitally demapped from the second transport frames (DTF format) into the first transport frames where the stuff bytes are removed and accordingly processed at an intermediate node element before further transport, or digitally demapped from the first transport frames (iDTF format) to reproduce or reassemble the client signal or signals comprising the client payload at the client payload envelope rate for reception at the client's equipment. Among various features disclosed, two predominate features are (1) a single channel or network rate for transport of all signals between network elements (NEs) and end terminal network elements and (2) the digitally wrapping of different types of payloads into N client side or first frames using stuff bytes to render each client side frame size equal to a predetermined value. Then the stuffed first frames are wrapped into line side or second frames for transport over the network at the same high speed line rate for all digitally wrapped client signals. The client side framers may be, for example, running at the lowest signal rate encountered, to digitally wrap then into parallel N client signals or digitally wrap a client signal multi-sected into N parts, where these two different client signals have different payload rates.
Owner:INFINERA CORP
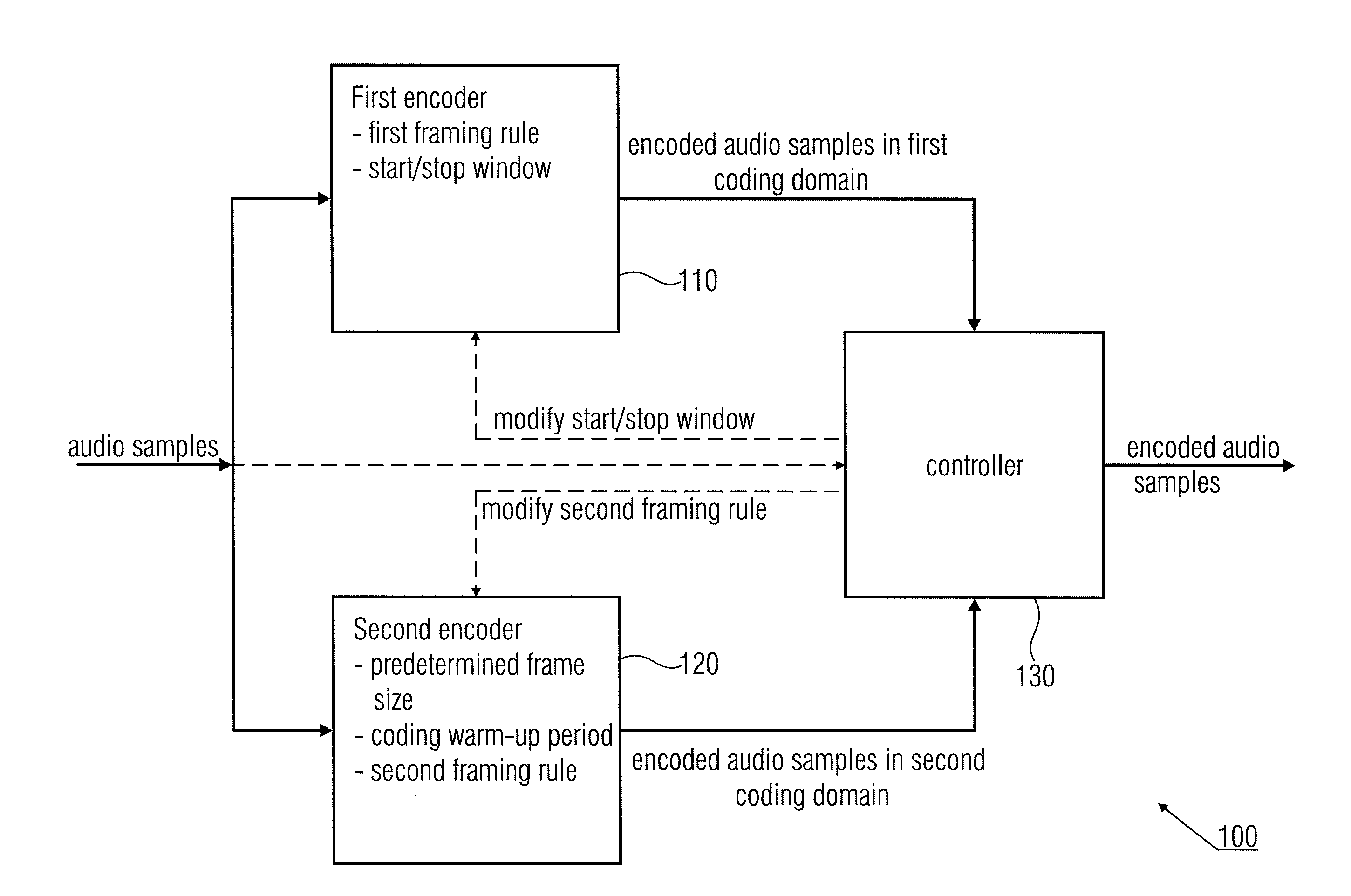
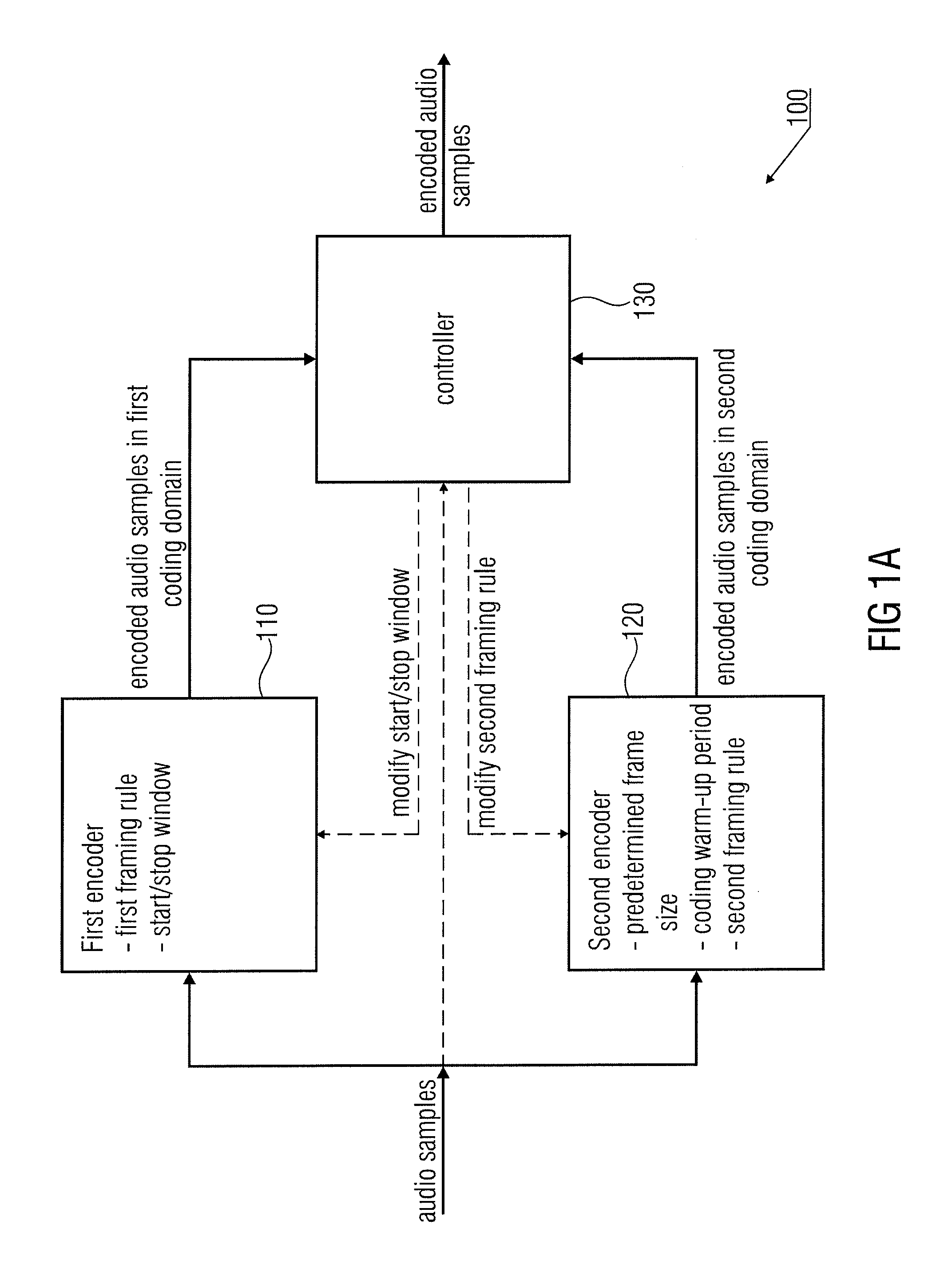
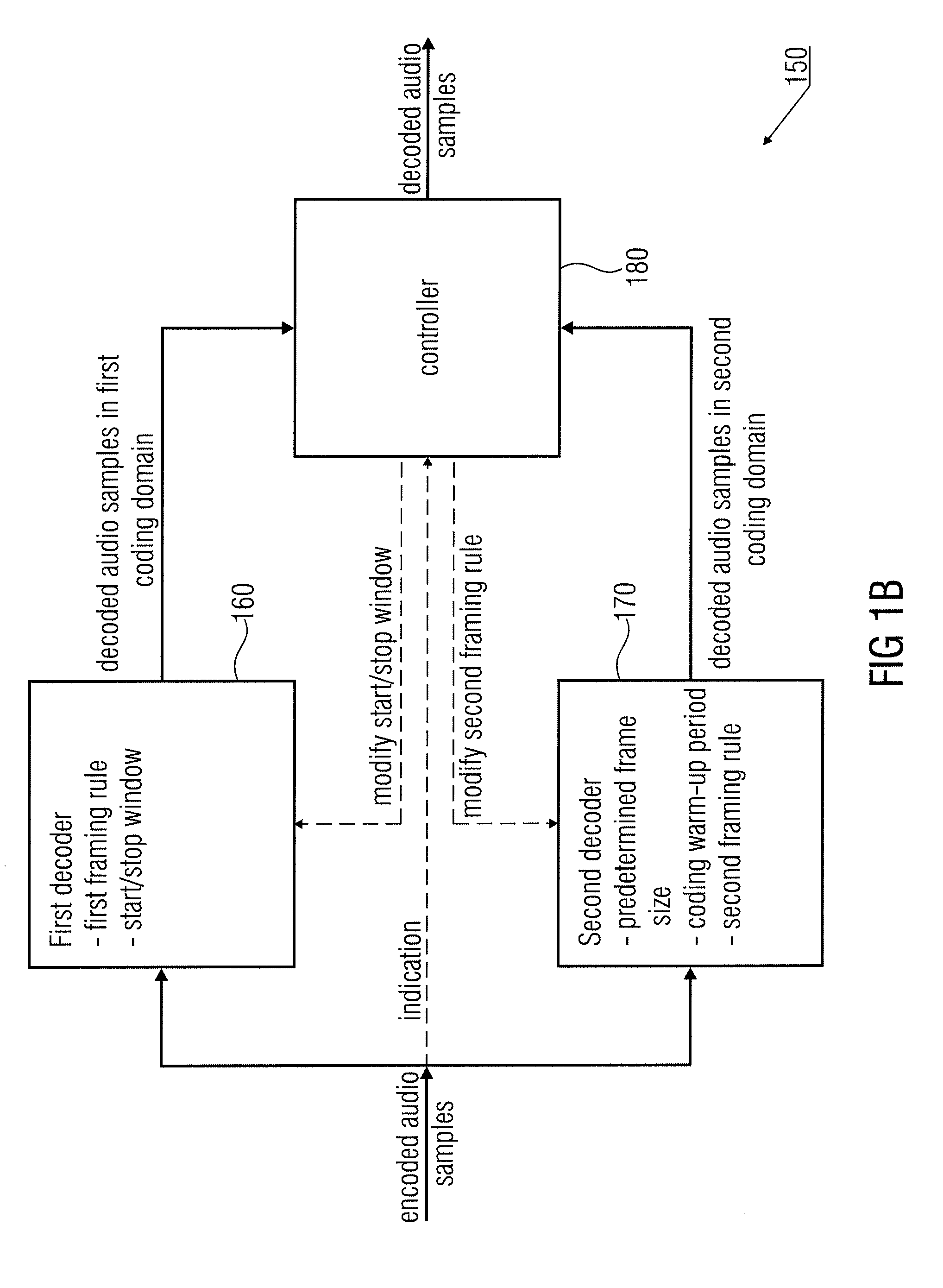
Audio Encoder and Decoder for Encoding and Decoding Audio Samples
ActiveUS20110173010A1Reduction of informationIncrease the number ofSpeech analysisTime domainEncoder
An audio encoder for encoding audio samples has a first time domain aliasing introducing encoder configured to decode audio samples in a first encoding domain and having a first framing rule, a start window and a stop window. The audio encoder further has a second encoder configured to encode samples in a second encoding domain and having a predetermined frame size number of audio samples, and a coding warm-up period number of audio samples, the second encoder having a different second framing rule, a frame of the second encoder being an encoded representation of a number of successive audio samples that is equal to the predetermined frame size number of audio samples. The audio encoder further has a controller switching from the first to the second encoder and for modifying the second framing rule or for modifying the start or the stop window of the first encoder.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV +1
Tail the motion method of generating simulated strobe motion videos and pictures using image cloning
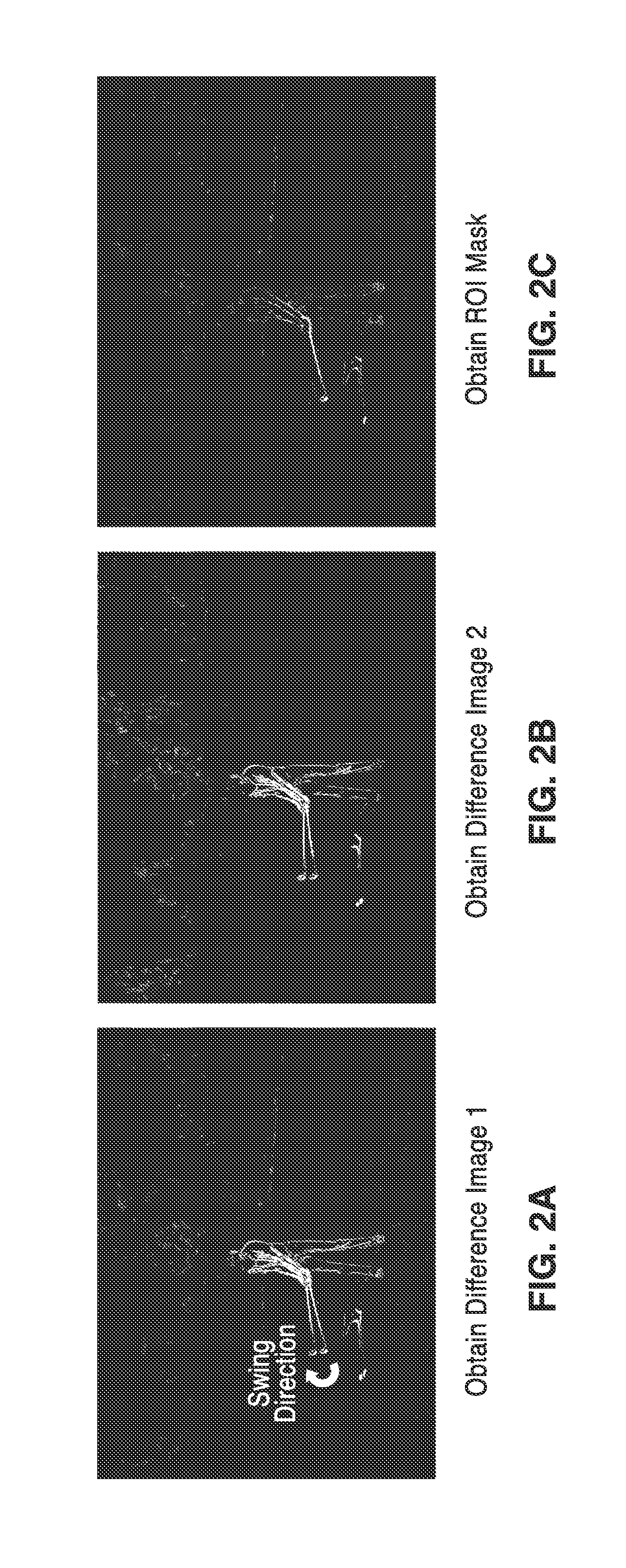
InactiveUS20120002112A1Avoid attenuationImproved cost functionTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsImage motionImage registration
The apparatus generates simulated strobe effects in the form of video or still image output in response to receipt of a video stream, and without the need of additional strobe hardware. Videos of a moving target object are categorized into one of multiple categories, from which a strobe generation process is selected. In one mode, the two categories comprise target objects with either small motion or large motions in relation to the frame size. Interoperation between image registration and cloning are utilized to produce simulated strobe motion videos or pictures. Motion segmentation is applied to the foreground object in each image frame, and a foreground mask is updated as each checkpoint is reached along the object trajectory, such as in response to time differences between checkpoints. Potential applications include special features for camcorders, digital cameras, or computer software.
Owner:SONY CORP
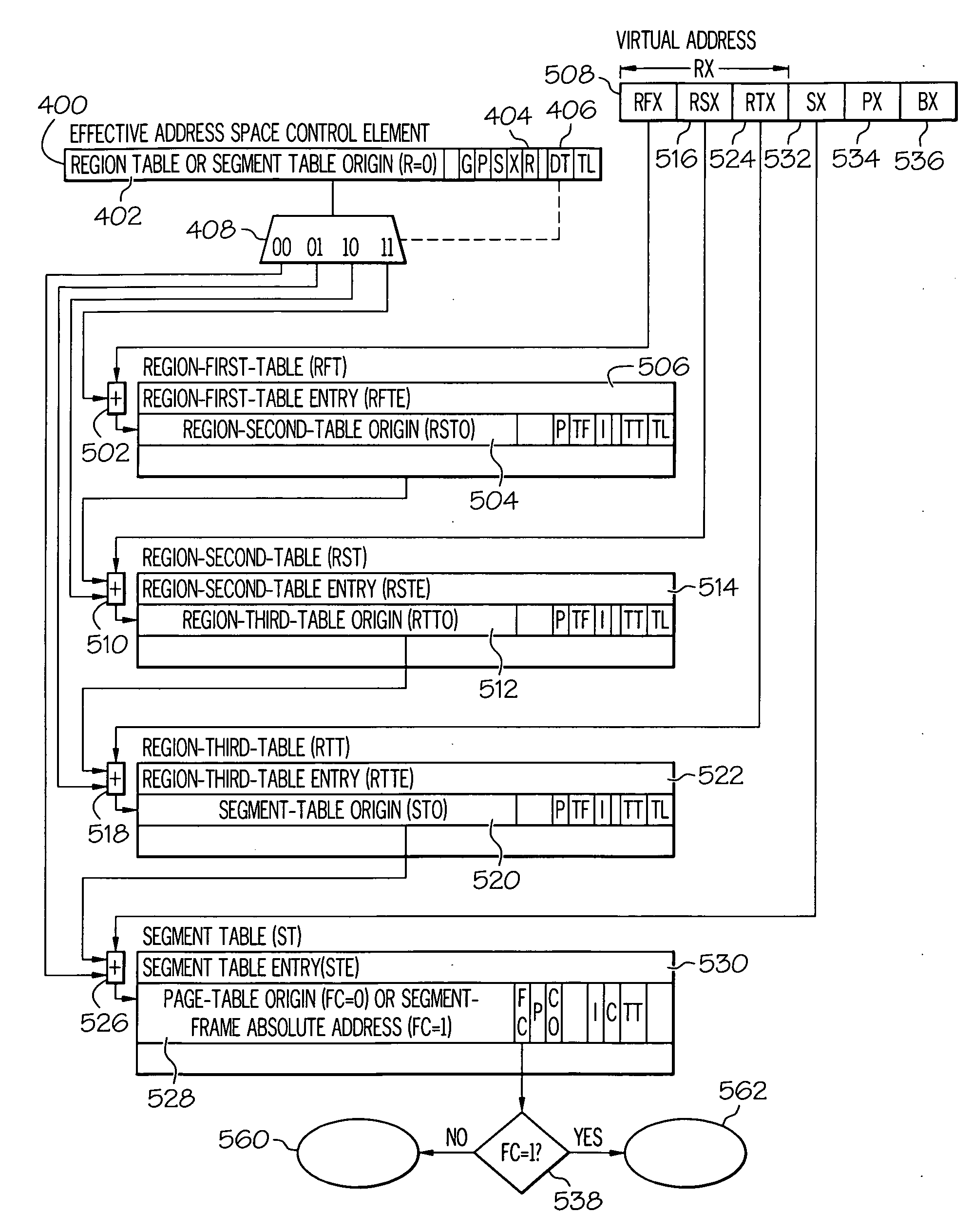
Dynamic address translation with translation exception qualifier
ActiveUS20090216992A1Small sizeMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationTranslation tableComputer science
What is provided is an enhanced dynamic address translation facility. In one embodiment, a virtual address to be translated and an initial origin address of a translation table of the hierarchy of translation tables are obtained. Dynamic address translation of the virtual address proceeds. In response to a translation interruption having occurred during dynamic address translation, bits are stored in a translation exception qualifier (TXQ) field to indicate that the exception was either a host DAT exception having occurred while running a host program or a host DAT exception having occurred while running a guest program. The TXQ is further capable of indicating that the exception was associated with a host virtual address derived from a guest page frame real address or a guest segment frame absolute address. The TXQ is further capable of indicating that a larger or smaller host frame size is preferred to back a guest frame.
Owner:IBM CORP
Hybrid platform for content delivery and transcoding
InactiveUS20130117418A1Distributed supportMultiple digital computer combinationsDigital video signal modificationTranscodingSubject matter
Owner:AKAMAI TECH INC
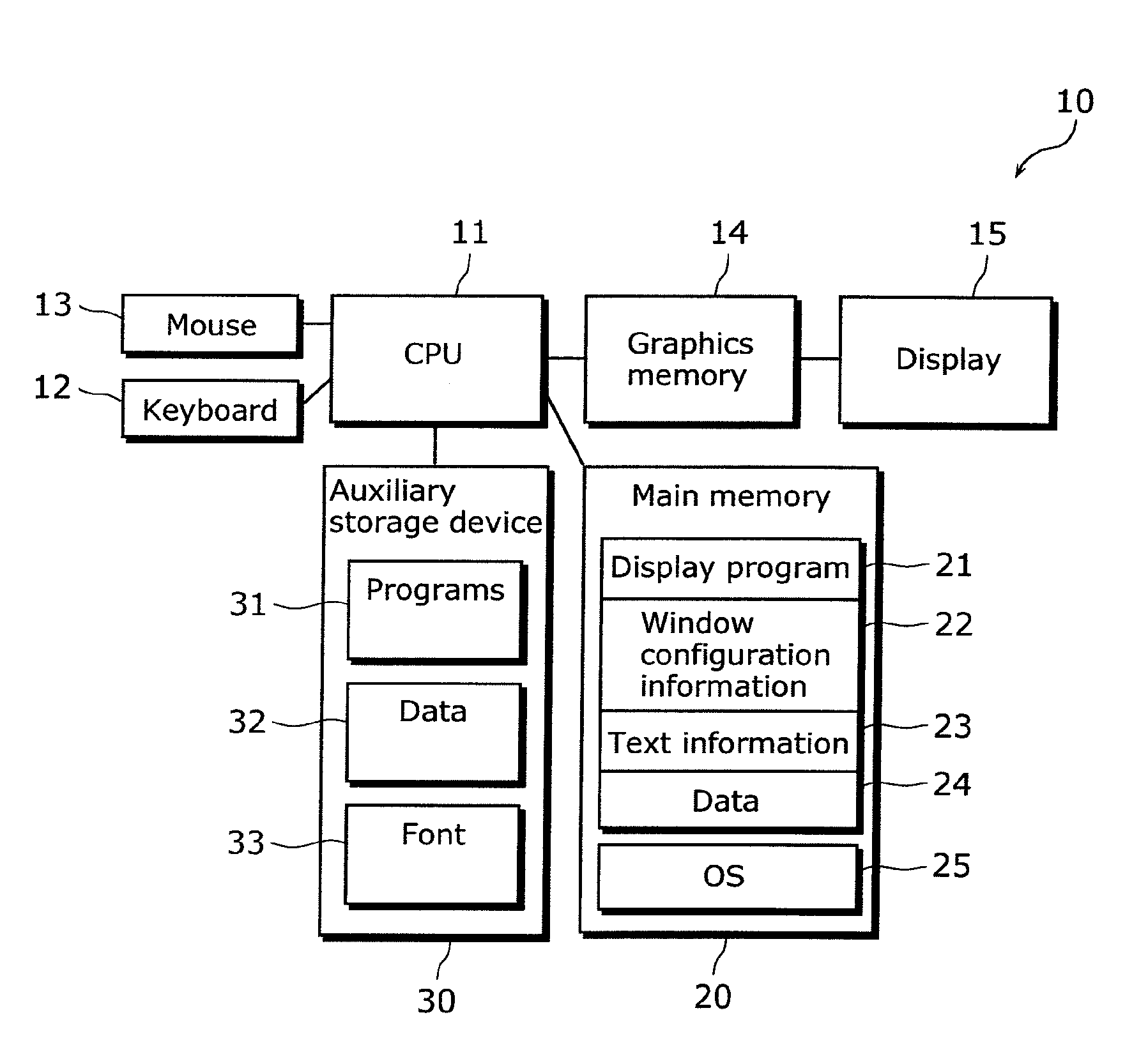
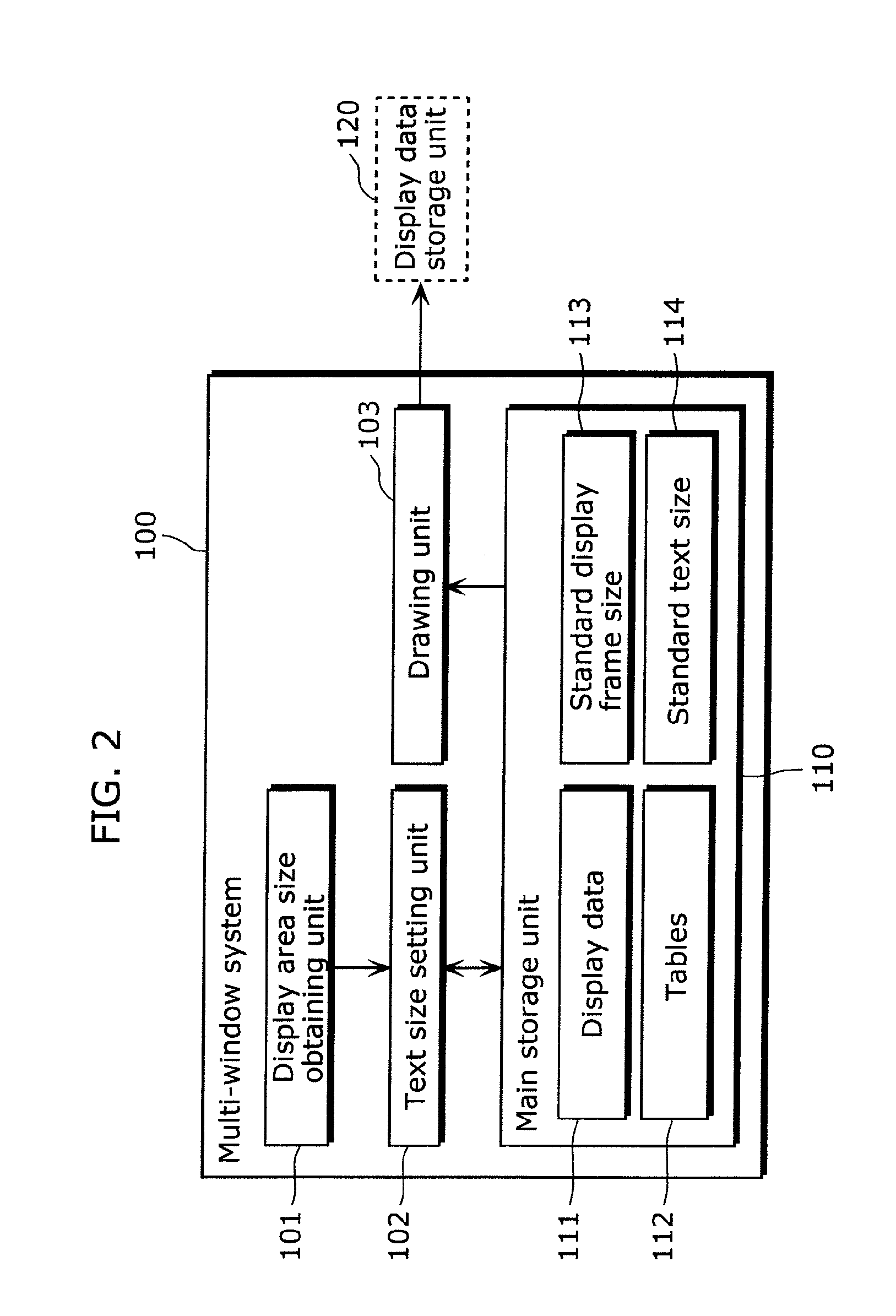
Display system, display method, program, and recording medium
ActiveUS20110025719A1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsExecution for user interfacesComputer graphics (images)Imaging data
The multi-window system includes: a main storage unit storing display data including a display frame and a display element, a standard display frame size, and a standard text size; a display area size obtaining unit obtaining a display area size; a text size setting unit determining a text size for correcting the standard text size, based on the display area size with reference to the standard display frame size, and setting the text size to the display data as the actual text size of the text to be added to the display element; and a drawing unit generating, using the display data, the image data of the display frame and the display element added with the text having the text size, and displaying the image data in the display area by storing the image data in a display data storage unit different from the main storage unit.
Owner:YANASE TAKATOSHI
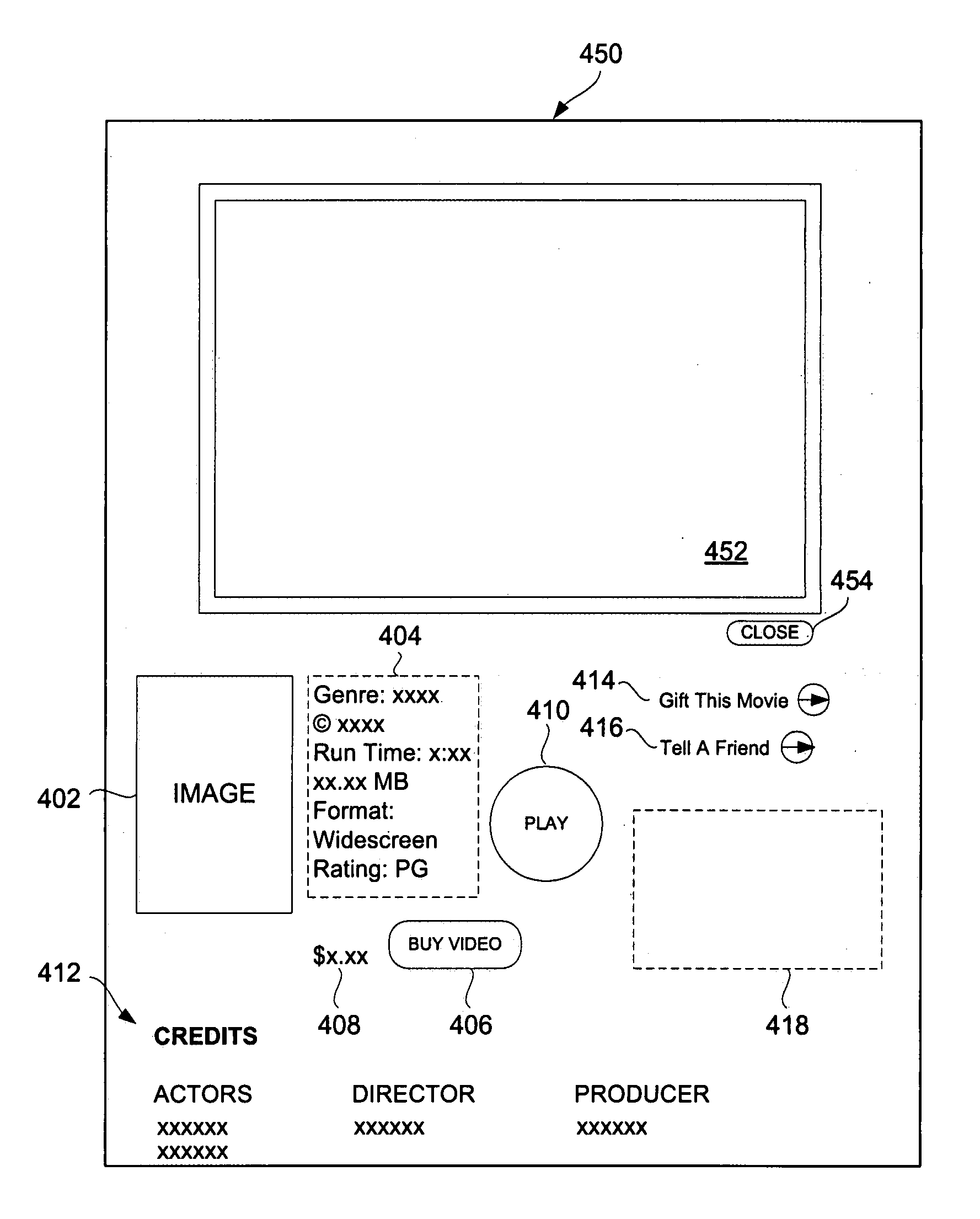
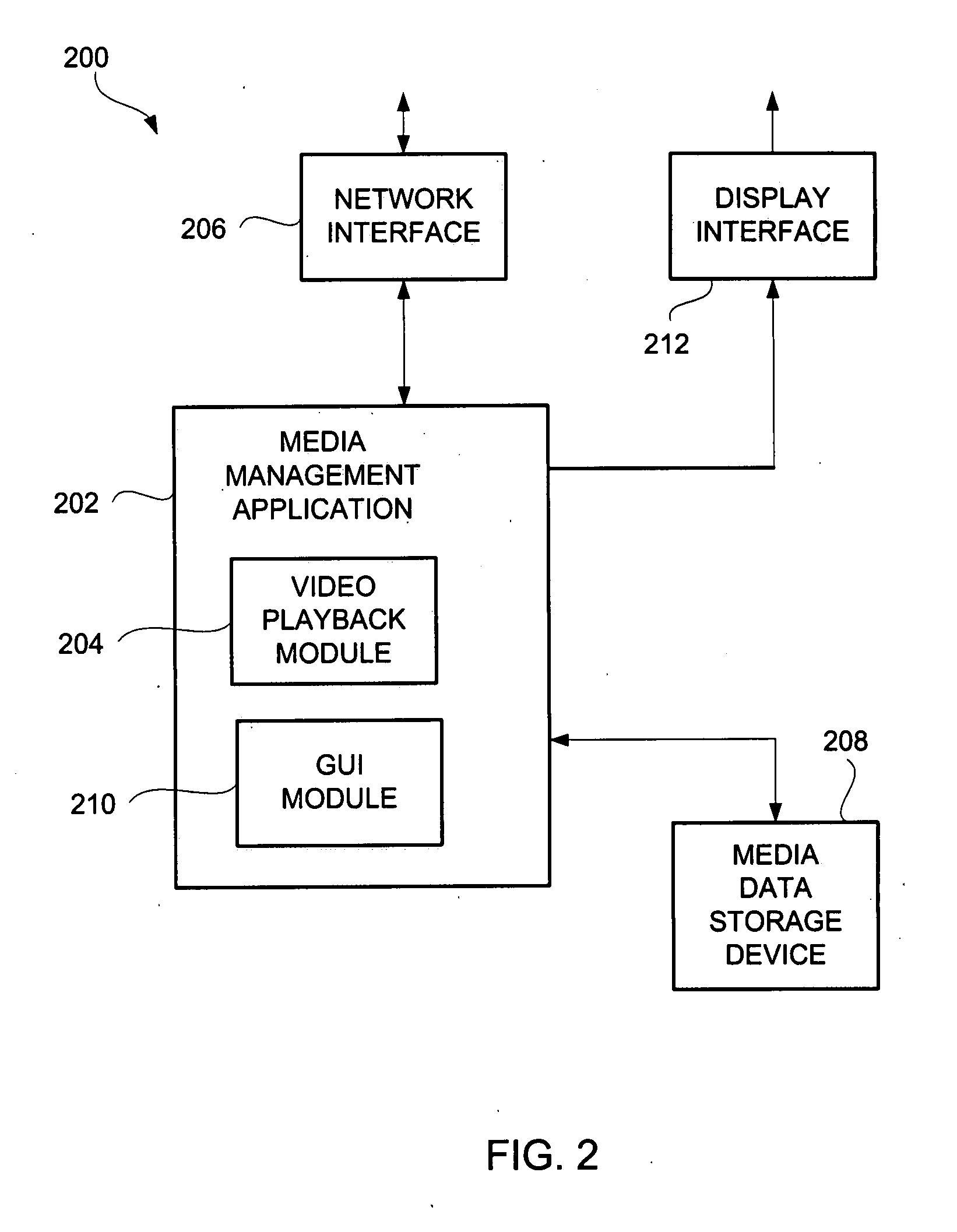
Techniques and Graphical User Interfaces for Review of Media Items
ActiveUS20080066102A1Facilitate requestTelevision system detailsColor television detailsGraphicsGraphical user interface
Improved techniques and graphical user interfaces for presenting a media item on a computing device are disclosed. In one embodiment, the media item is a video. A video information window can provide a user with information concerning the video and can enable the user to play at least a portion of the video on request. When the video is to be played, the video information window can expand to present a video playback region in which the video is provided when played. The video can be provided with high resolution and appropriate frame size.
Owner:APPLE INC
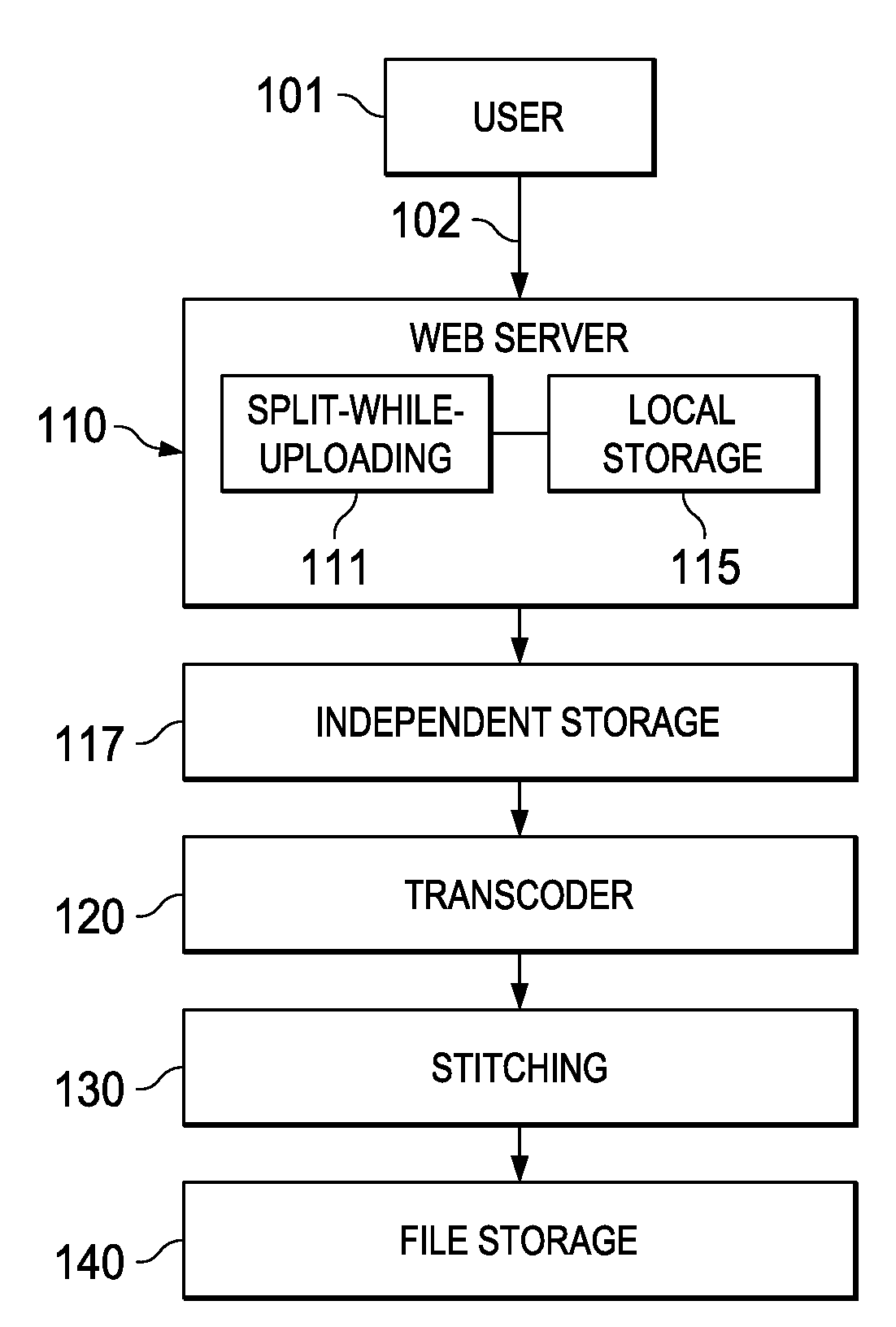
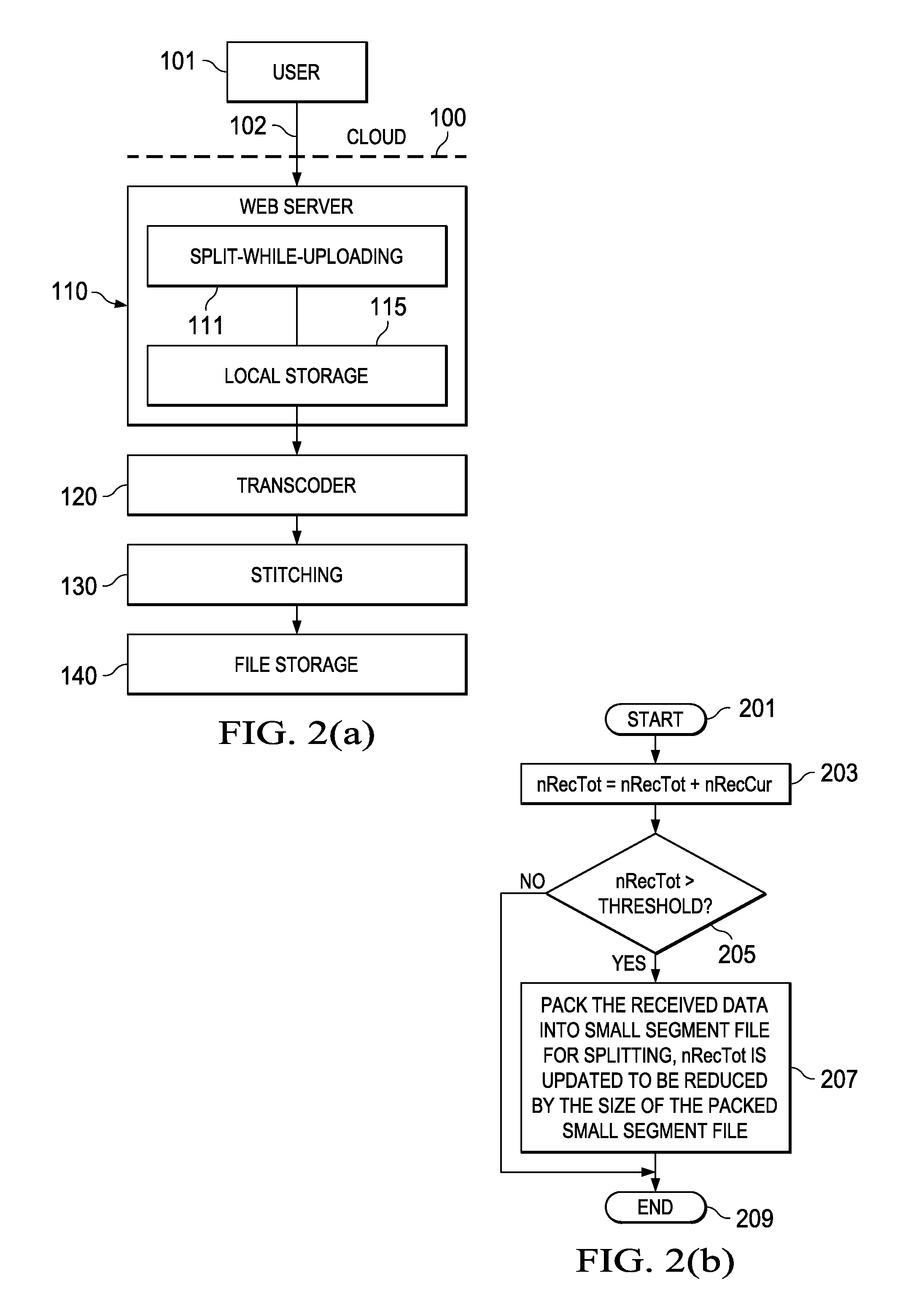
Cloud-Based Transcoding Platform Systems and Methods
InactiveUS20120102154A1Multiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionContent distributionCloud base
Methods and systems for transcoding in a cloud computing platform are disclosed. According to an embodiment, a receiver receives an uploading file by one data block at a time, and stores the received data blocks in various storage modules. Small segment files are then generated when the size of the received data blocks is larger than a threshold. A transcoder transcodes the small segment files from one format such as a bit rate or a frame size to another while the receiver is still receiving a new data block. The transcoded small segment files may be stitched together to form a stitched file, which may be stored in a storage module to be downloaded through a content distribution network (CDN). The transcoded small segment files may be passed to streaming servers for streaming over a network while the receiver is still receiving a new data block of the uploading file.
Owner:FUTUREWEI TECH INC
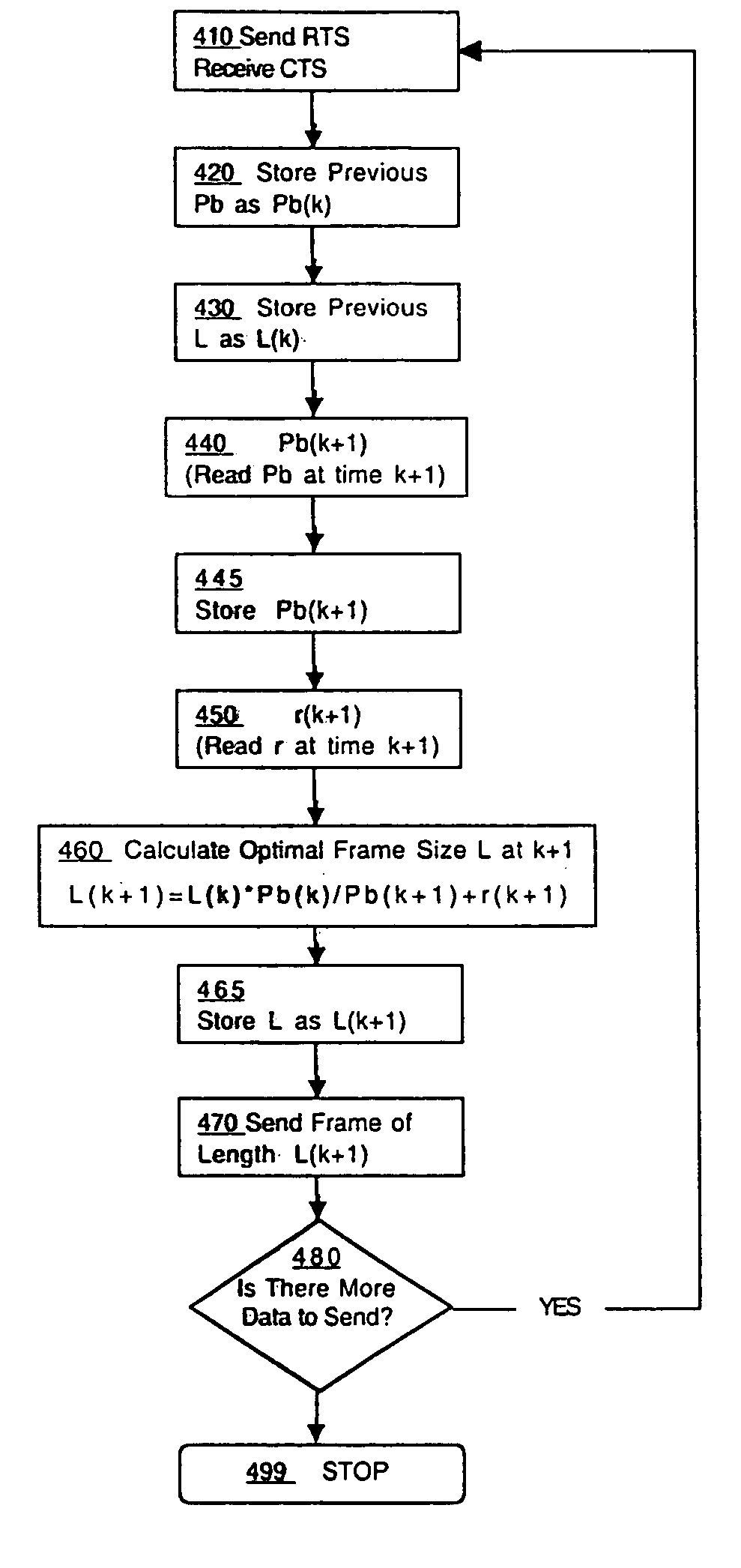
Optimum frame size predictor for wireless Local Area Network
ActiveUS7096274B1QualityNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesKaiman filterTransmission channel
The present invention relates to a method for predicting an optimum transmission frame size in a wireless computer network. The method comprises assessing transmission channel quality in the network, calculating an optimum length for the transmission frame, adjusting the length of the transmission frame to the predicted optimum length, transmitting the frame at its adjusted length and assessing the quality of the transmission of the frame. Prediction of the optimum frame size employs a Kalman filter which employs the parameters of bit error rate and random processing noise in the calculation of the predicted optimum frame length.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
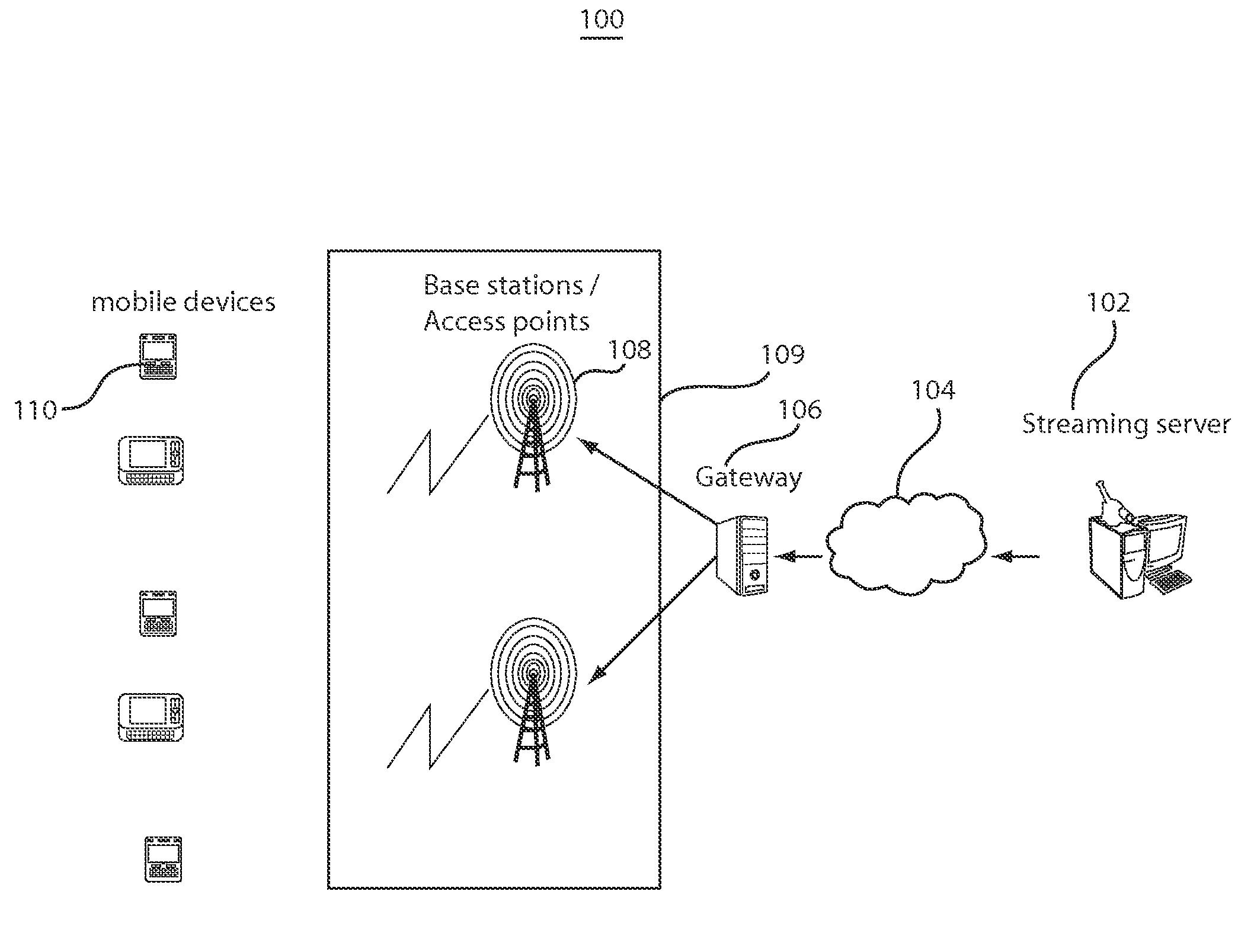
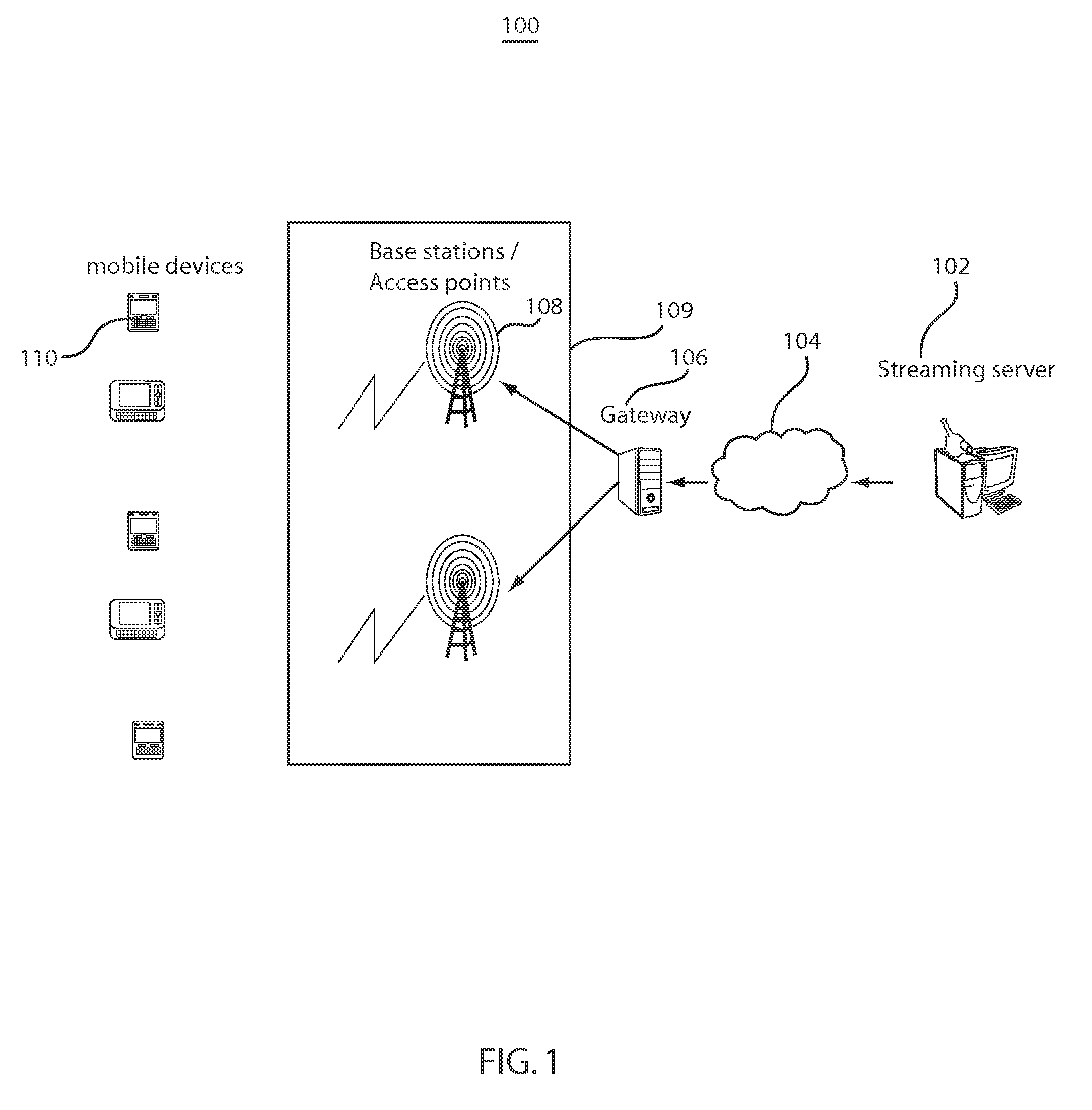
Methods and systems for rate matching and rate shaping in a wireless network
ActiveUS20100189063A1Accurate estimateSignificant overheadNetwork traffic/resource managementDigital video signal modificationRate shapingWireless data
Rate matching and rate shaping methods and systems for managing data traffic on wireless channels are disclosed. Rate matching embodiments dynamically determine downlink video data transmission rates based on frame decoding deadlines and frame sizes. In addition, if the channel capacity cannot support the video data transmission rate, the rate matcher can adjust the video stream accordingly so that it is supportable by the channel capacity. In turn, rate shaping implementations can tailor the transmission rate shaping based on the state of the wireless data channel. Shaper operations can be specifically adapted to a saturated state of the wireless channel, to an unsaturated state of the wireless channel and to transitions between the unsaturated and saturated states.
Owner:NEC CORP
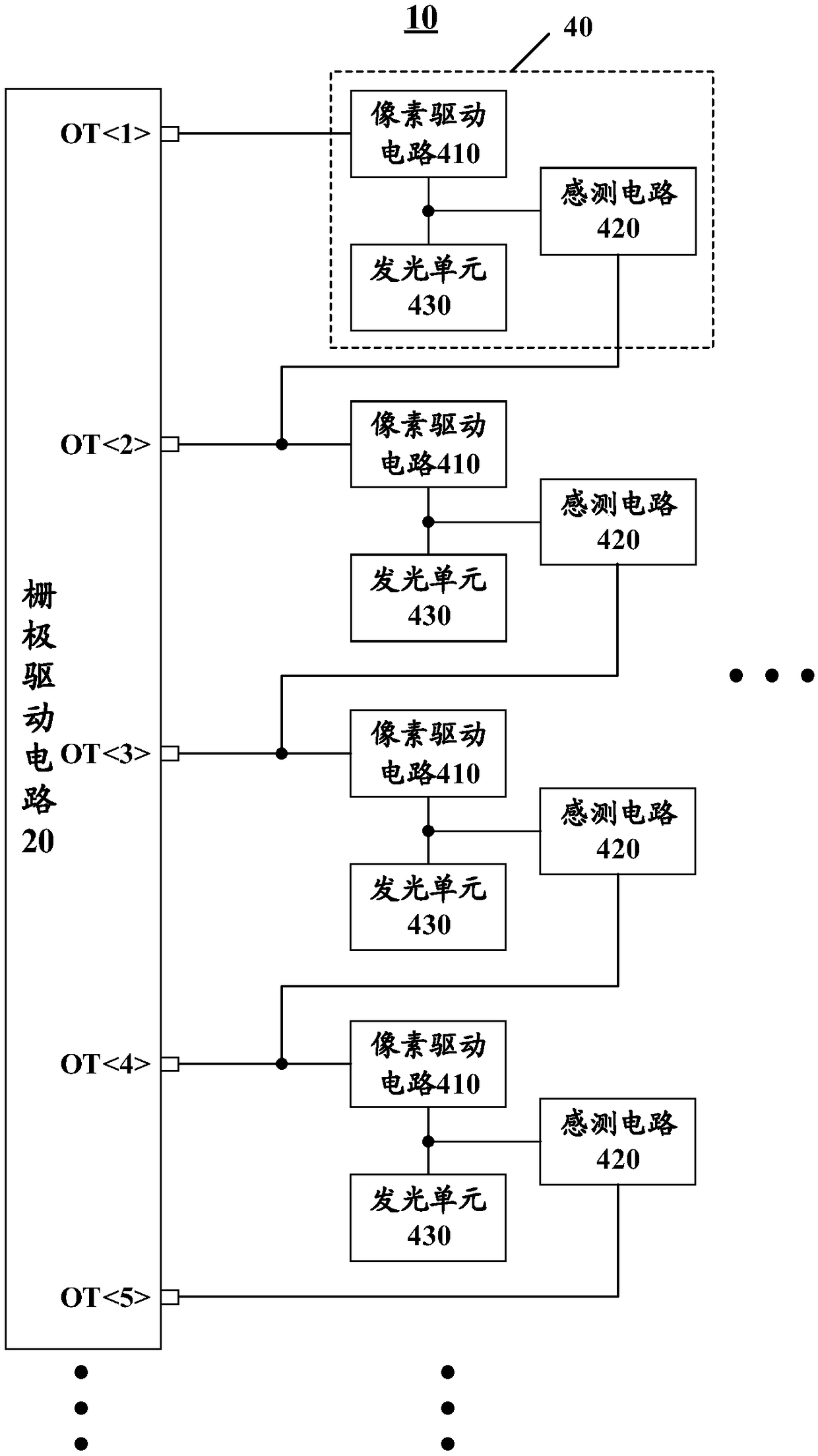
Display panel, display device, and driving method thereof
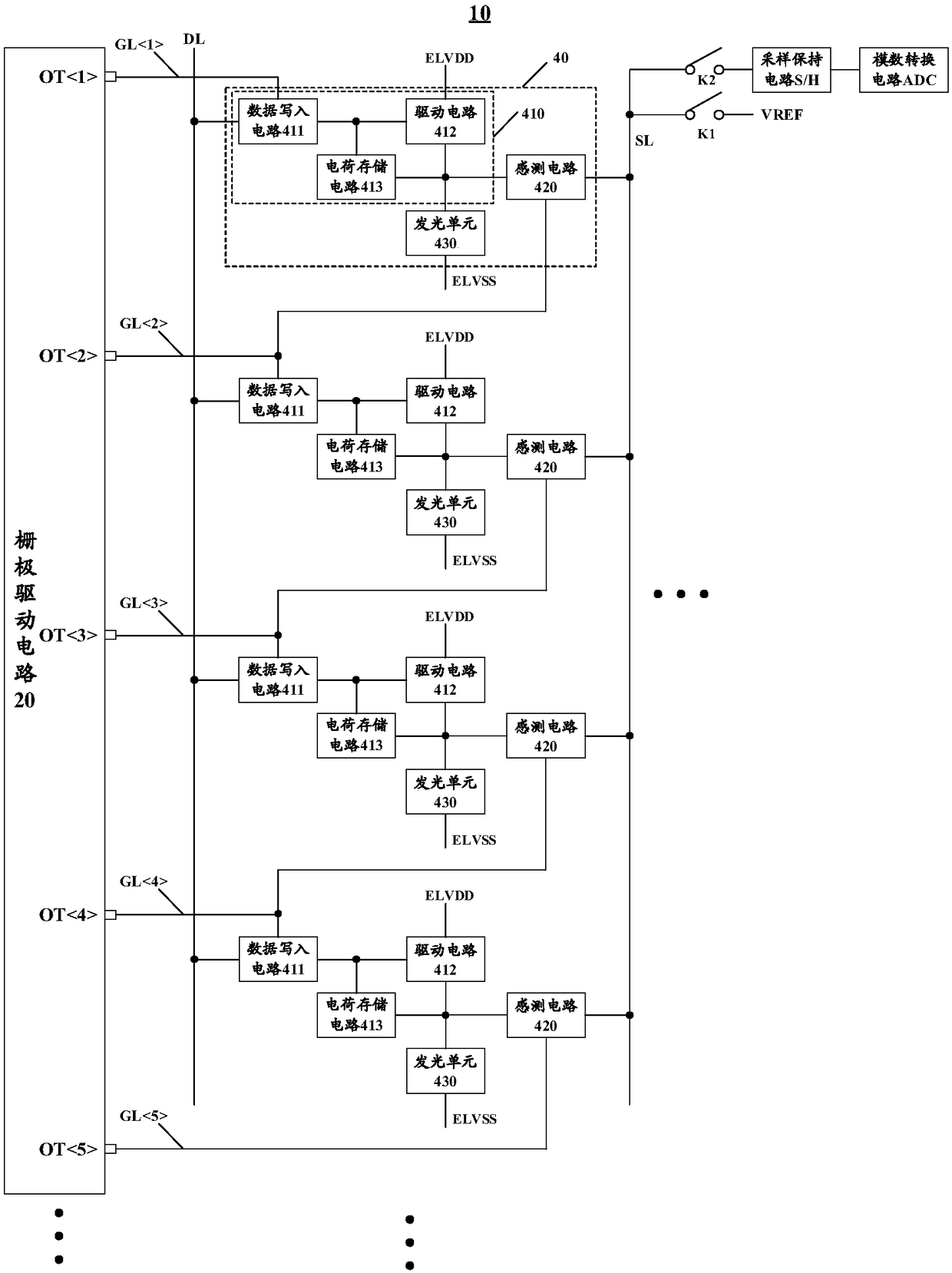
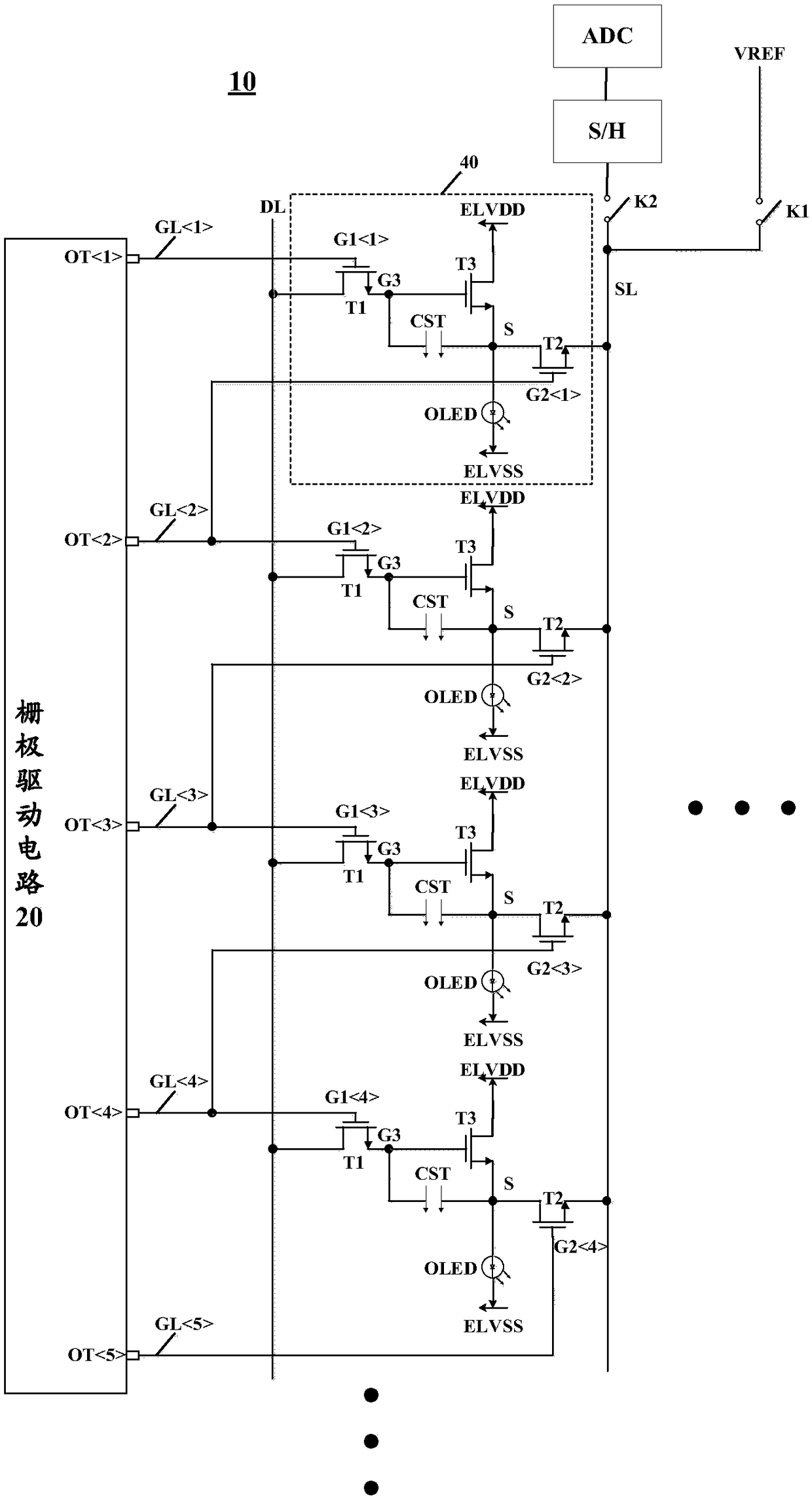
Disclosed are a display panel, a display device and a driving method thereof. The display panel includes a plurality of sub-pixel cells arranged in an array including N rows and M columns and a gate driving circuit. Each of the plurality of sub-pixel units includes a light emitting unit, a pixel driving circuit for driving the light emitting unit to emit light, and a sensing circuit for sensing the pixel driving circuit. The gate driving circuit includes N+1 sequentially arranged output terminals and is configured to output a gate scanning signal that turns N rows of sub-pixel cells of the array on line by line. The pixel driving circuit of the nth row sub-pixel unit and the nth output terminal of the gate driving circuit are connected to receive a gate scanning signal as a scan driving signal, and the sensing circuit of the nth row sub-pixel unit and the n+1 output terminal of the gate driving circuit are connected to receive a gate scanning signal as a sense driving signal. The display device using the display panel can reduce the frame size.
Owner:HEFEI BOE ZHUOYIN TECH CO LTD +1
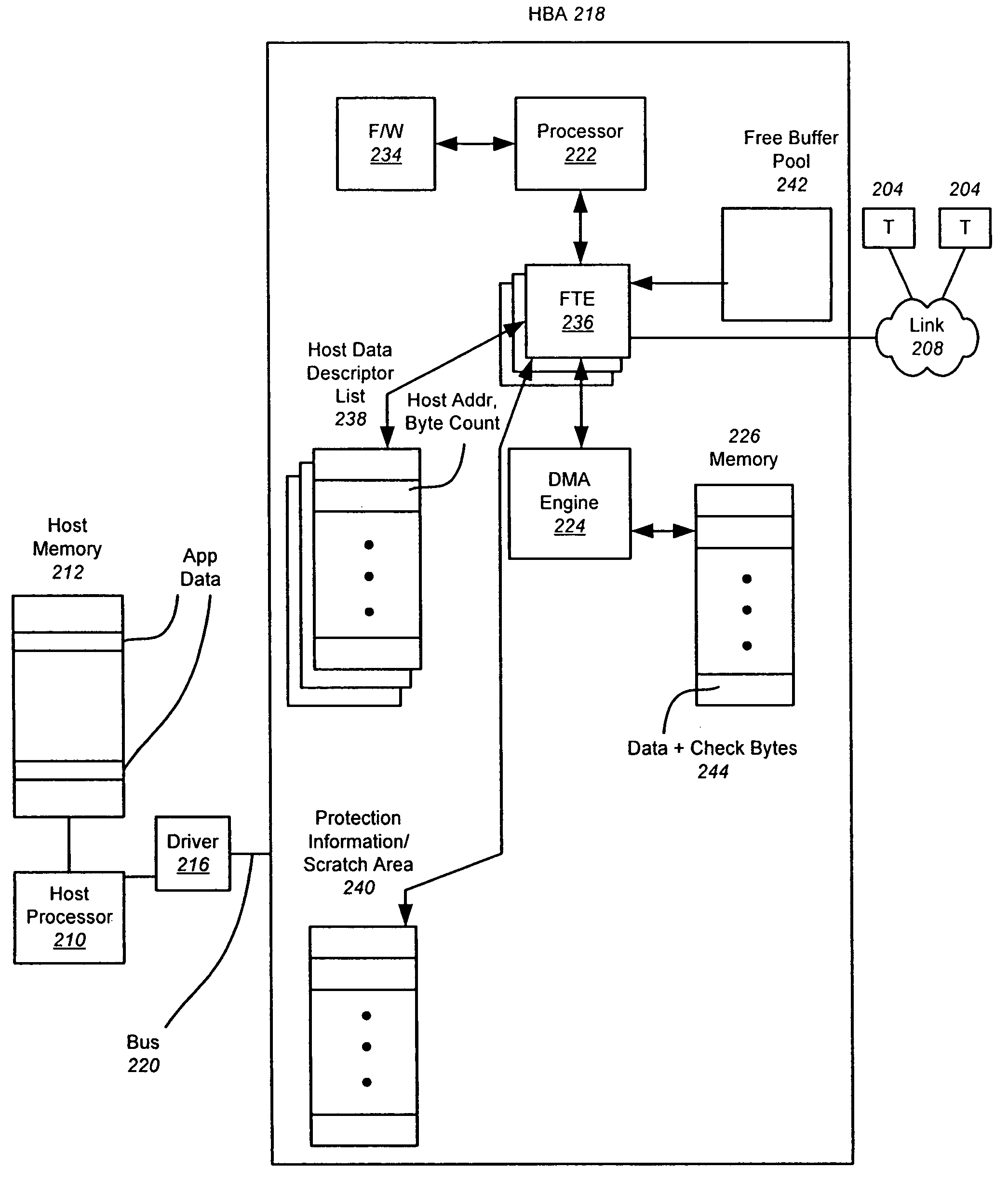
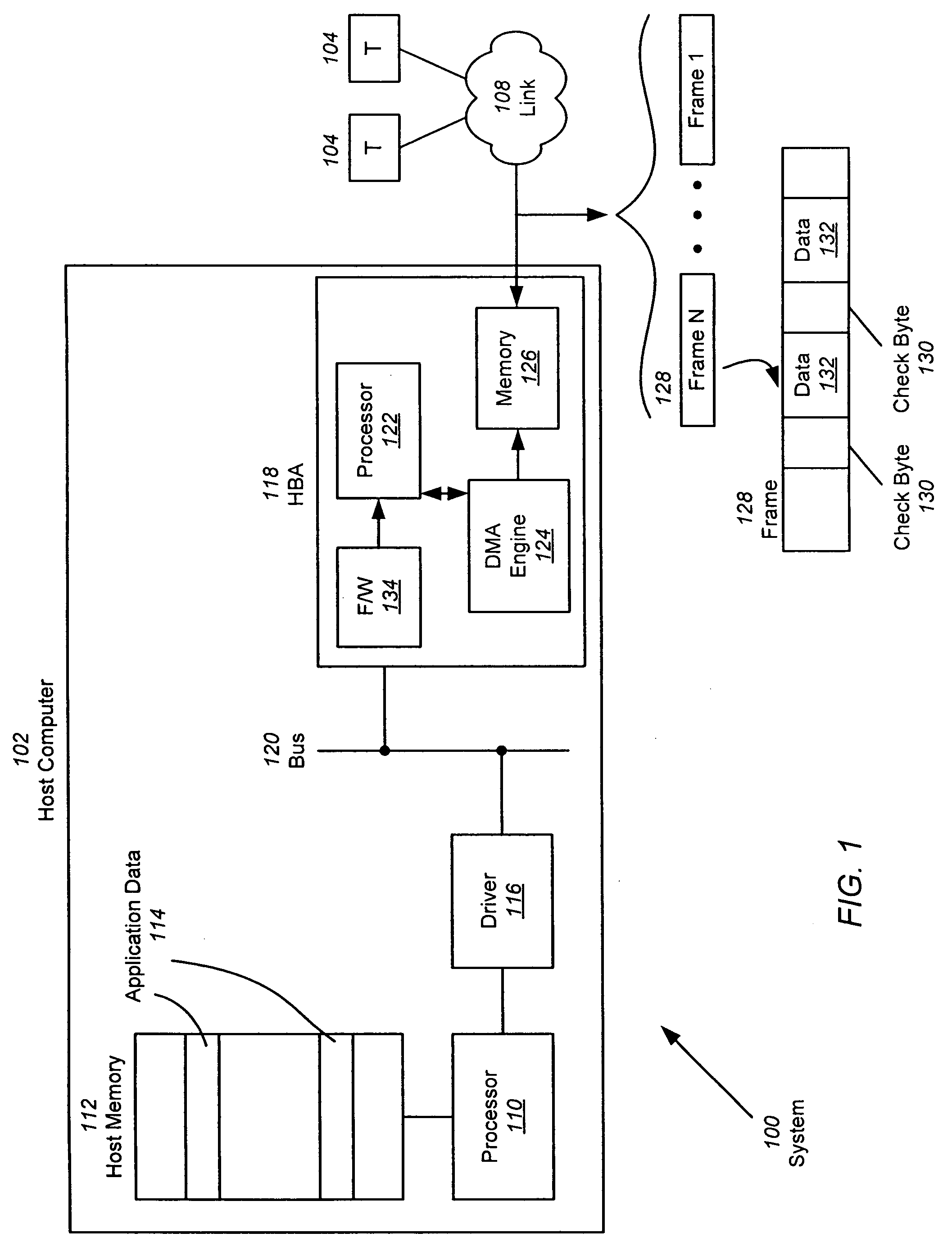
Autonomous mapping of protected data streams to Fibre channel frames
InactiveUS20080307122A1Minimize involvementPerform other taskTransmissionElectric digital data processingData streamFibre Channel
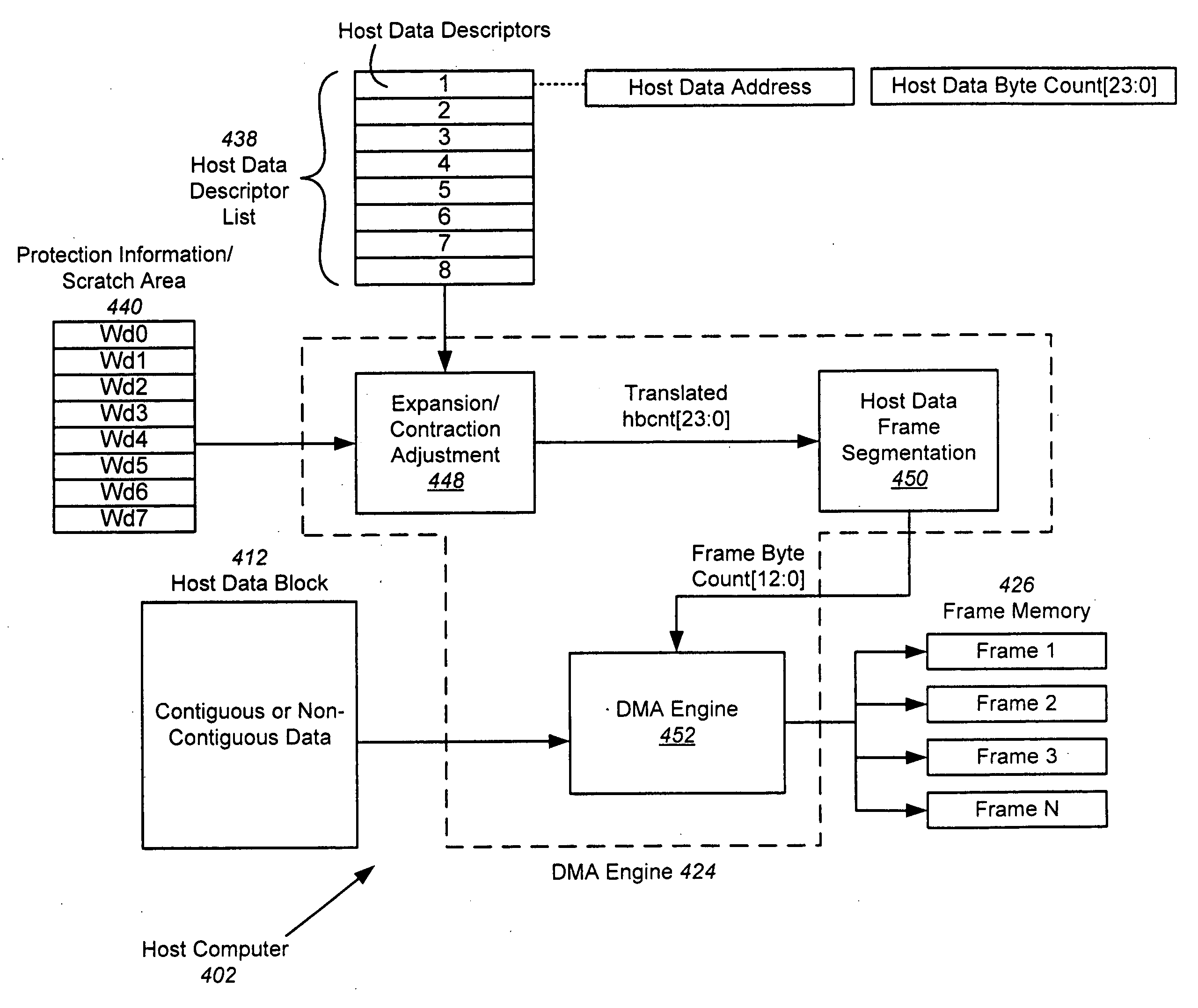
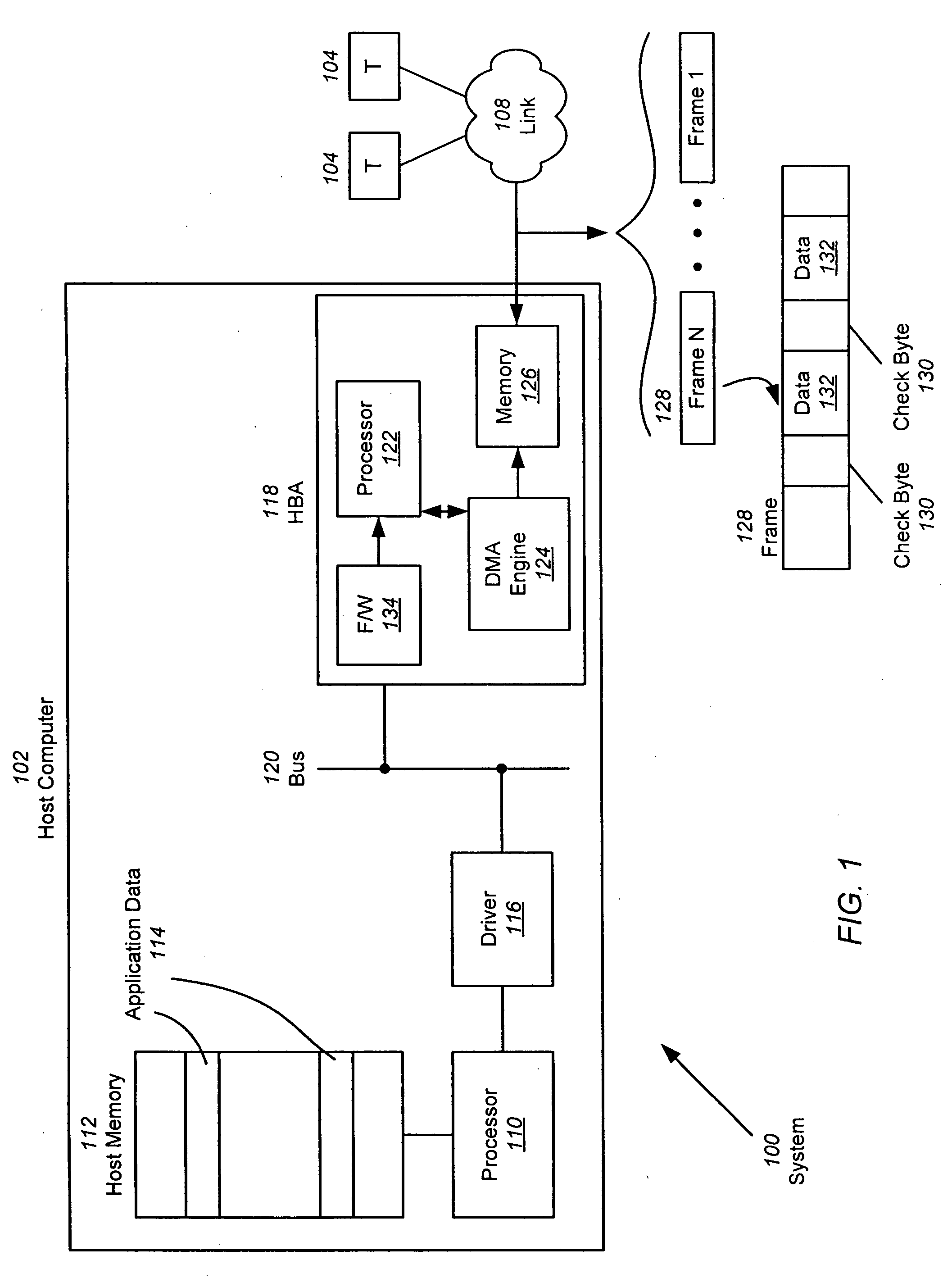
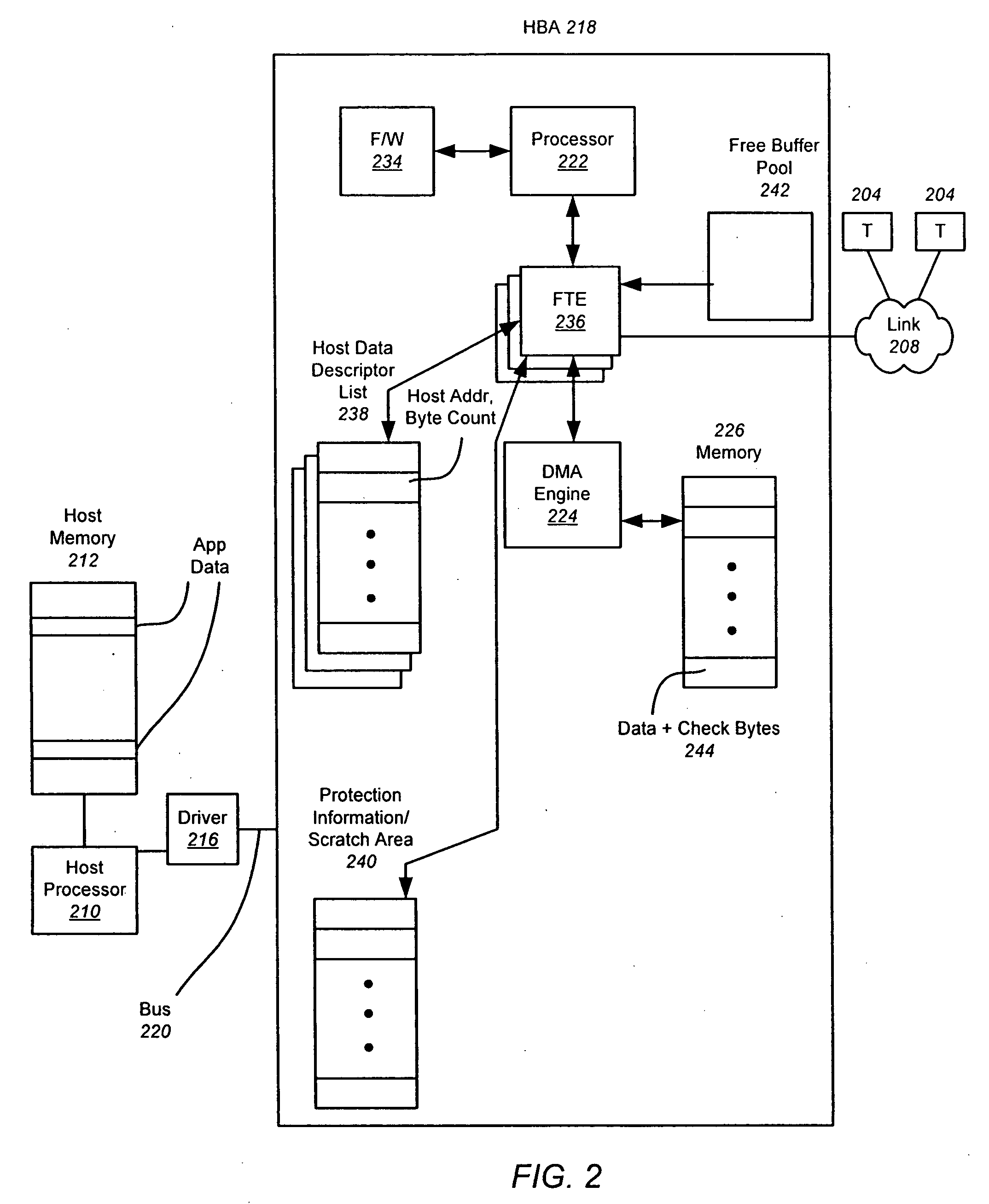
A hardware-based offload engine is disclosed for mapping protected data into frames. For a write operation, the HBA determines host addresses and the size of data to be read from those addresses. The HBA also determines the frame size and protection scheme for data to be written. A frame transmit engine reads each host descriptor in the host data descriptor list to determine the location and byte count of the data to be read. A DMA engine reads the protection information / scratch area to determine the exact data size used to fill each frame and the protection scheme, and retrieves one or more free frame buffers. Check bytes are inserted alongside the data and stored in free frame buffers. After each frame is filled, the frame transmit engine also generates and stores header information for that frame, and then combines header, data and check bytes for transmission over the network.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
System and Method for Dynamically Configured, Asymmetric Endpoint Video Exchange
InactiveUS20070271358A1Quality improvementTelevision conference systemsDigital computer detailsVideo qualityBit rate
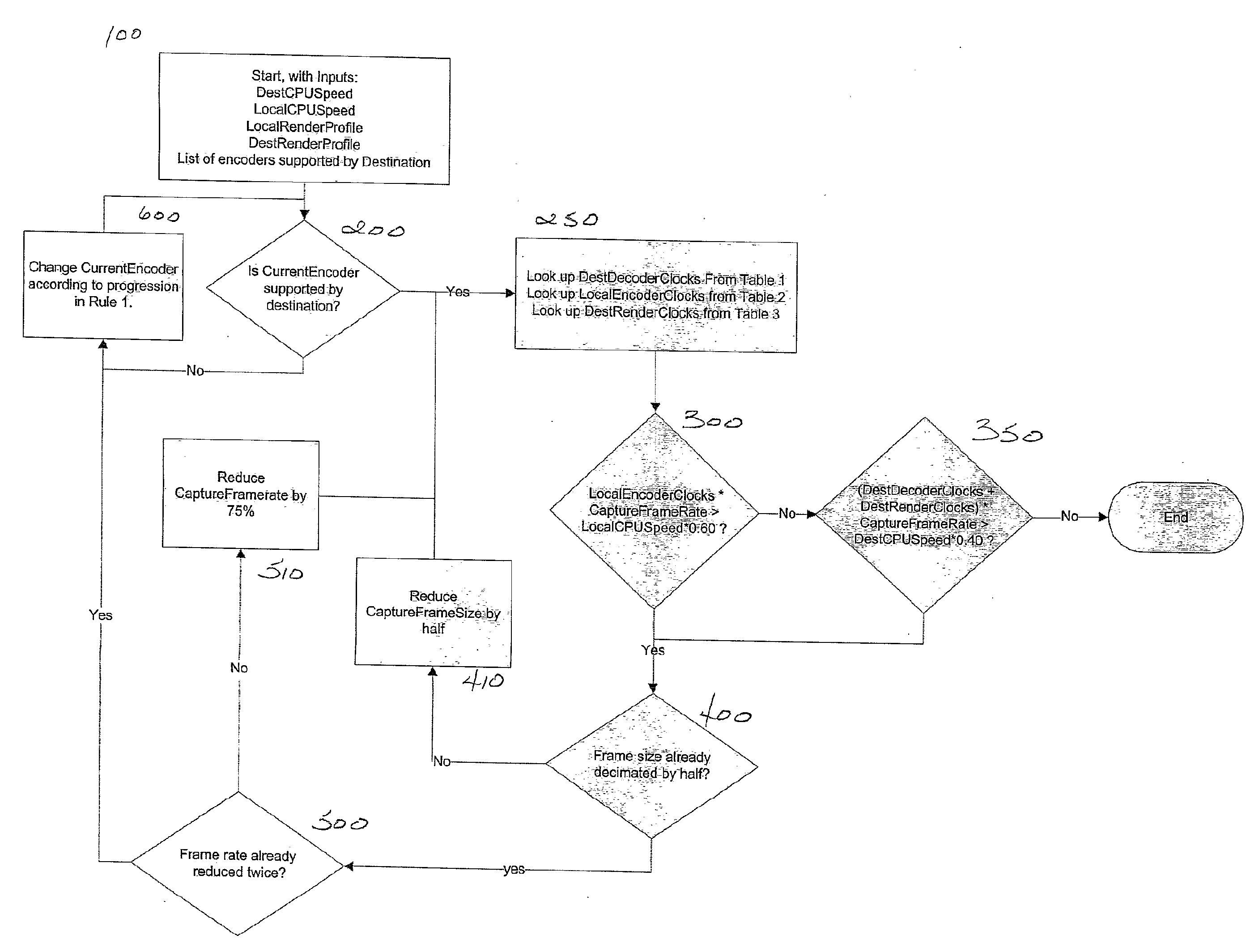
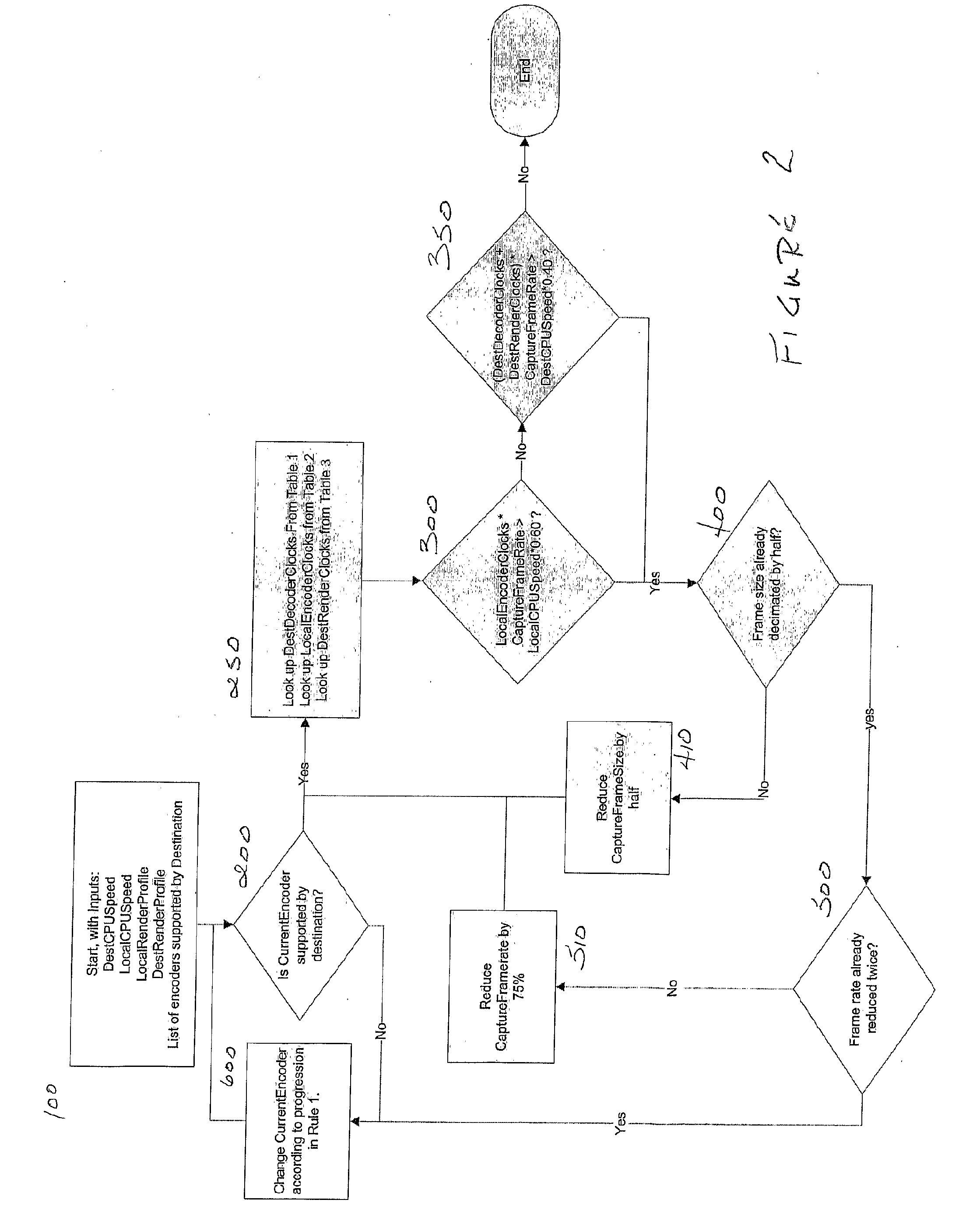
Provided herein are exemplary embodiments of a system for and method of initially and dynamically allocating the available resources that affect video quality in an asymmetric endpoint network so as to provide an enhanced quality of video exchange. Relevant variables that may be dynamically configured to allocate resources include, but are not limited to, frame size, frame rate, choice of codec (e.g., MPEG4, H263, H263+, H264), codec bit rate and size of rendering window (which may or not be identical to the frame size).
Owner:SPINELLA IP HLDG
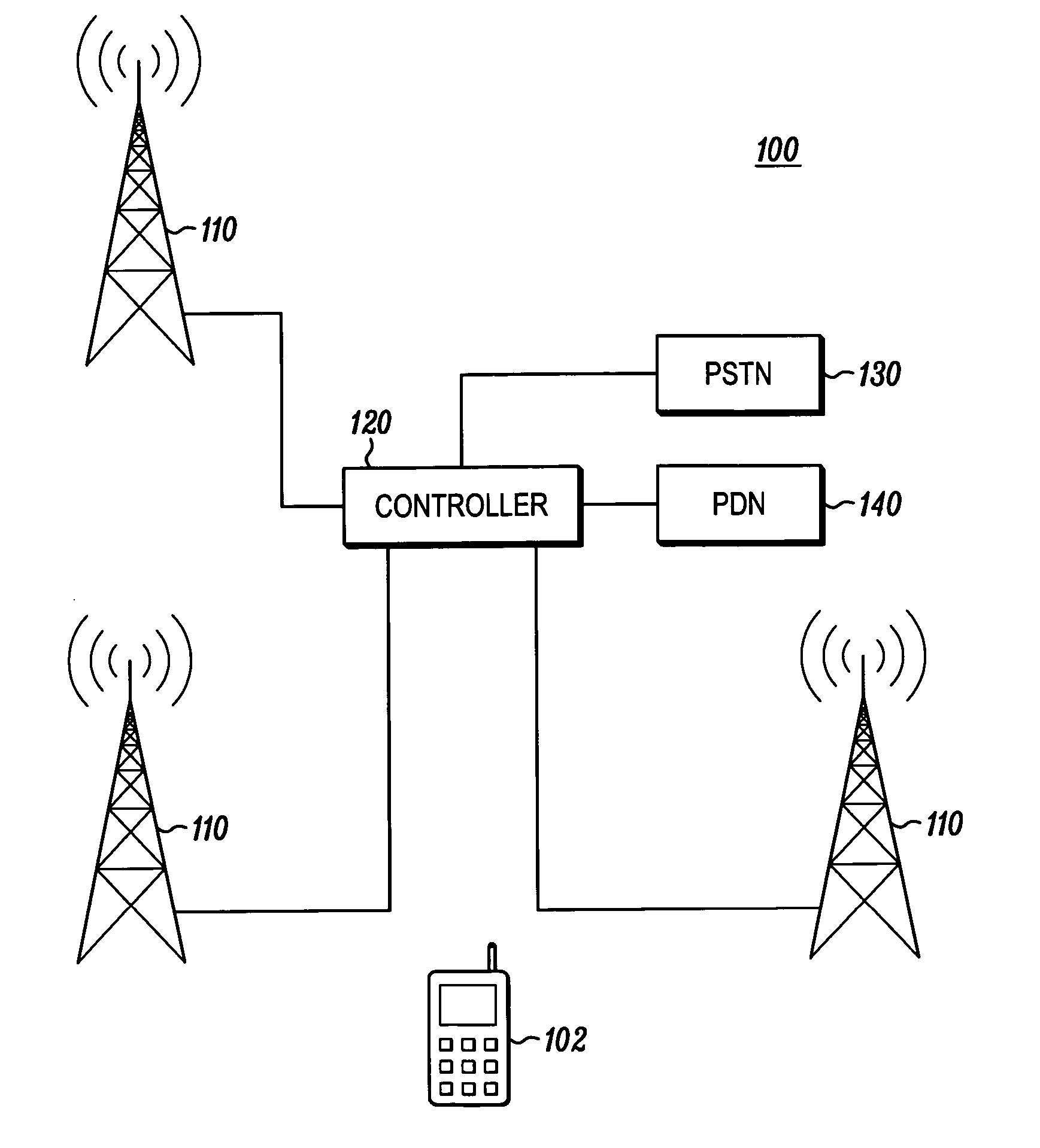
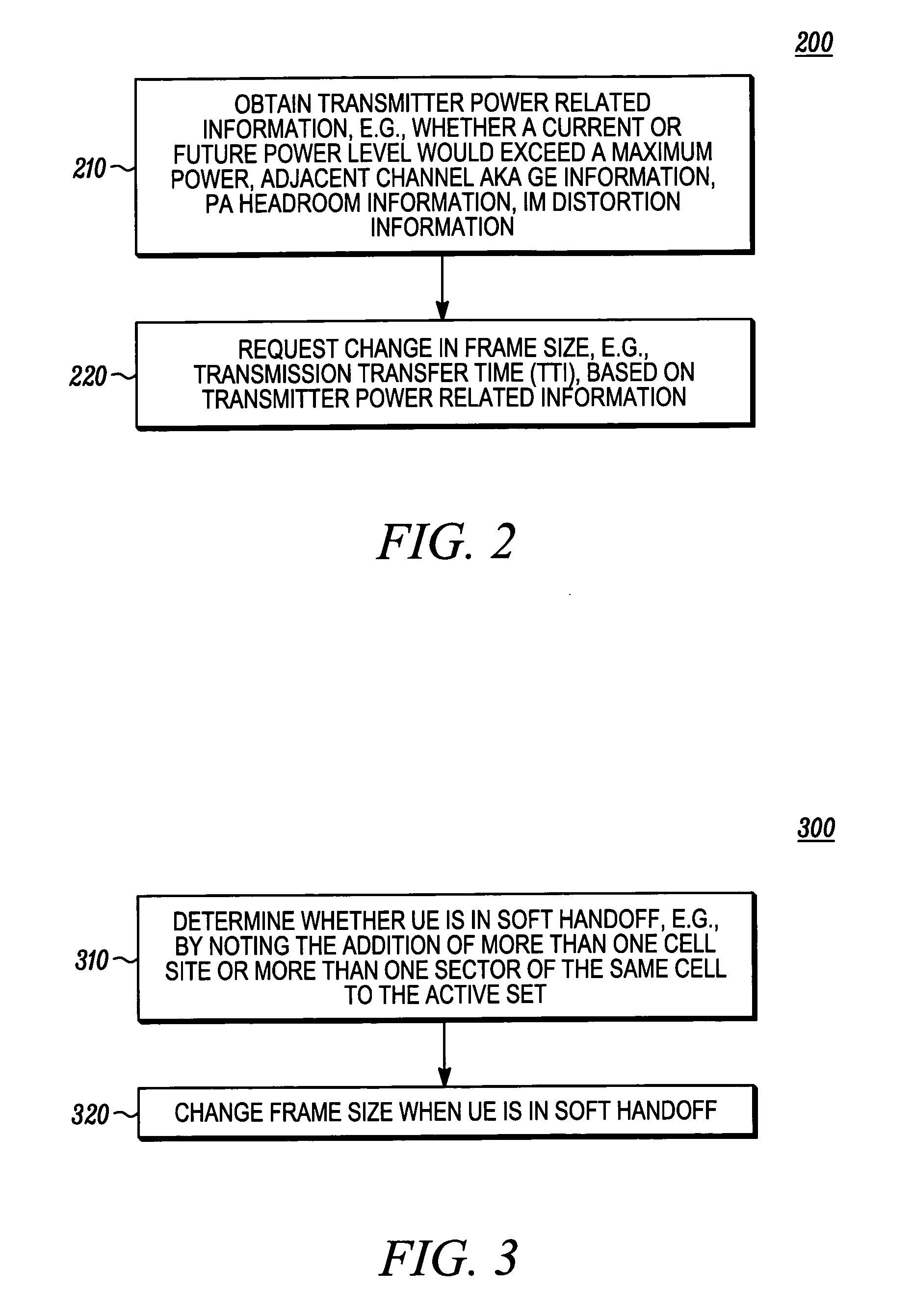
Wireless transmitter configuration
A method in a mobile wireless communication transmitter, the method including obtaining (200) transmitter power related information, for example, transmitter headroom information and transmitter inter-modulation distortion information, and requesting (210) a change in transmitter channel configuration, for example, frame size, based on the transmitter power related information obtained. In another embodiment, the channel configuration is changed based on whether the transmitter is in soft handoff.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Method and system for dynamic aggregation in a wireless network
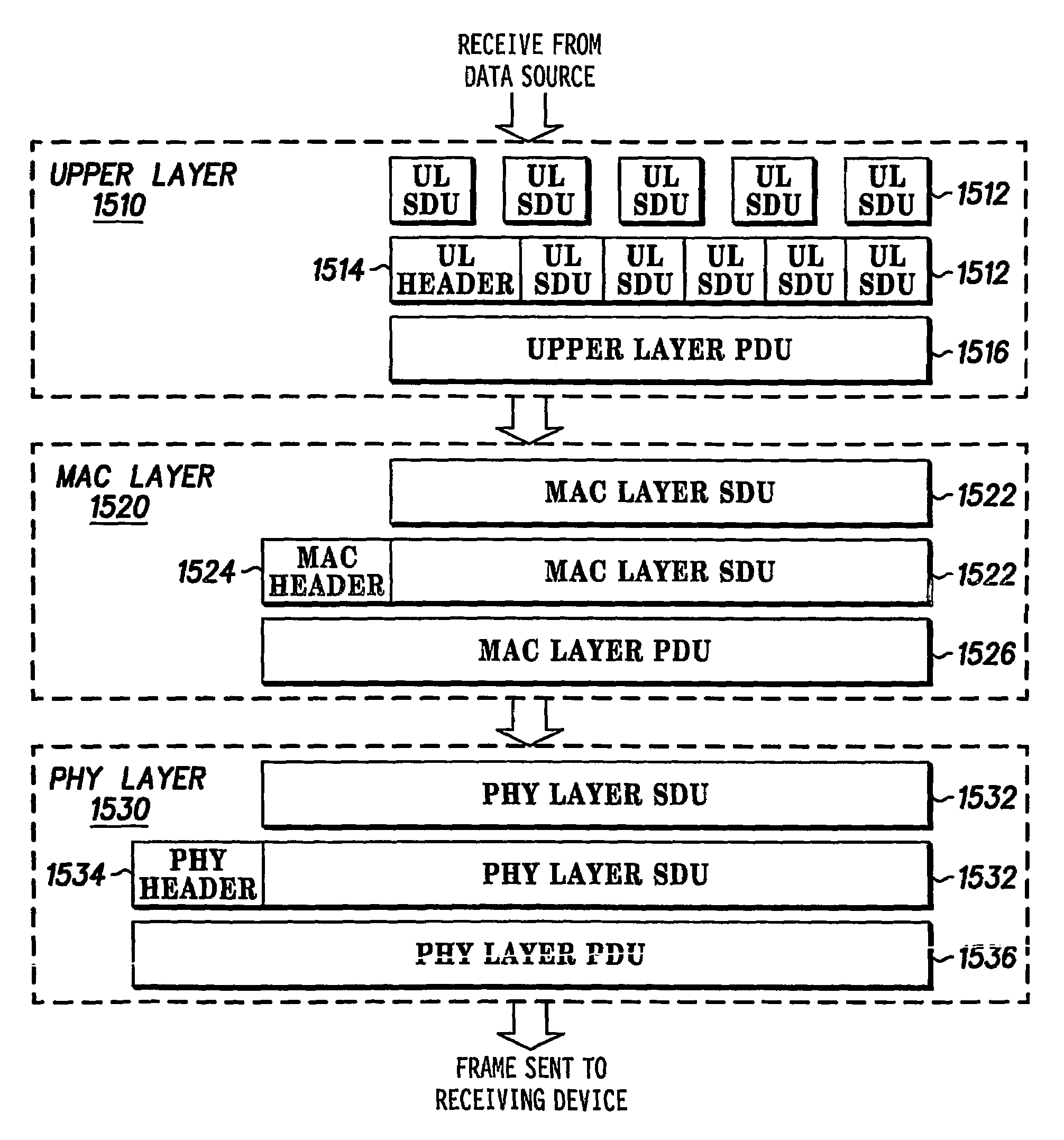
A method is provided for dynamically controlling aggregation in an ultrawide bandwidth wireless device. In this method, a device receives a plurality of intermediate service data units at an intermediate layer, aggregates at least two of the plurality off intermediate service data units to form an intermediate protocol data unit, and sends the intermediate protocol data unit to a physical layer. The physical layer generates a data frame based on the intermediate protocol data unit and information corresponding to the physical layer, and transmits the data frame in a data stream. The device selects an intermediate size criteria for the intermediate protocol data unit based on a desired frame size criteria for the data frame. The aggregating of the at least two of the plurality of intermediate layer service data units is performed such that an actual intermediate layer protocol data unit size corresponds to the intermediate size criteria.
Owner:NORTH STAR INNOVATIONS
Variable length data encapsulation and encoding
ActiveUS20070126612A1Eliminate needImprove packaging efficiencyColor television with pulse code modulationError preventionComputer hardwareCoding block
Systems, apparatus, and methods of encoding variable length data for efficient transport over a wireless channel. A wireless terminal can determine a frame size to encode, and can encode and transmit the frame data as one or more encoded blocks selected from a family of block sizes. Each block size can correspond to a particular encoder rate. The frame is parsed into a number of segments having a block size selected from the family of block sizes. The block sizes are selected to maximize the spectral efficiency of the frame. Each segment is then encoded with an encoder corresponding to the block size and having a coding rate that is configured to provide a substantially equal energy per symbol for all of the blocks. The encoded blocks are then aggregated and the smallest block zero padded. The aggregate of encoded blocks can be transported in one or more bursts.
Owner:VIASAT INC
Video Rate Control for Video Coding Standards
ActiveUS20100080292A1Quality improvementColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionVideo rateVideo encoding
A method and device for improving rate controlling in video coding of sequences including a series of Inter frames separated by Intra frames, when a decoding delay is considered, comprise for each Inter frame of the series: computing a target frame size, computing a maximum buffer level related to a position of each Inter frame relative to a previous Intra frame and an upcoming Intra frame, and optimizing a transmission buffer level in response to the computed target frame size and the computed maximum buffer level.
Owner:MASIMO CORP
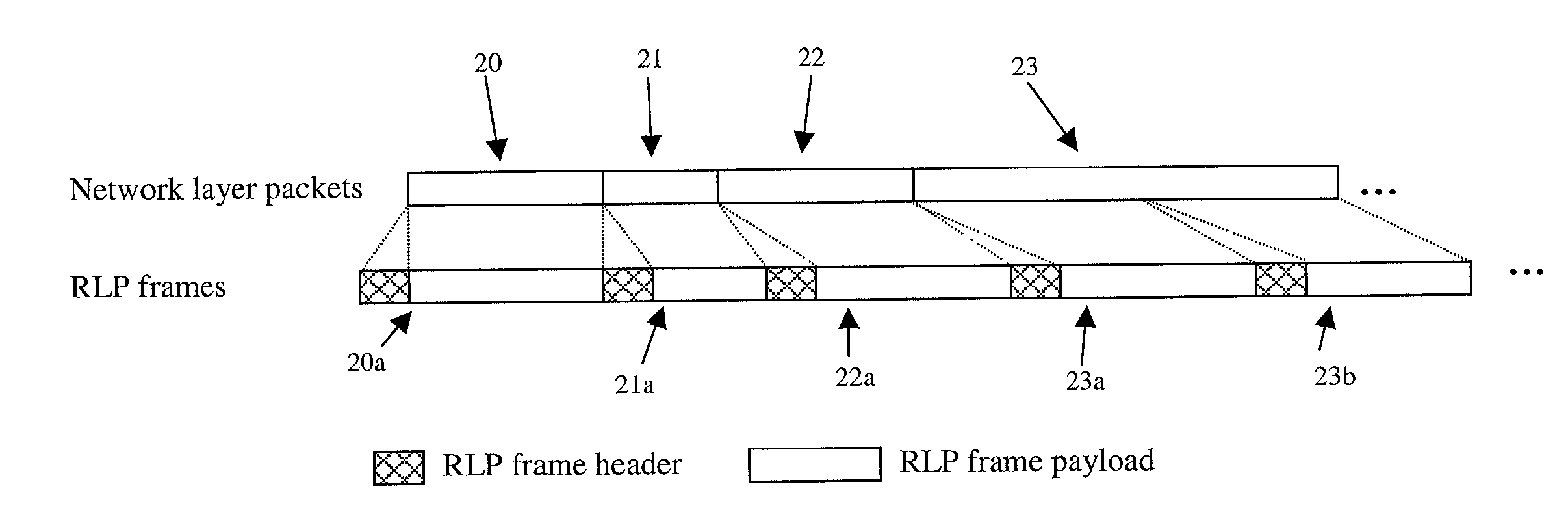
Network layer protocol aware link layer
InactiveUS7085291B2Enhances conventional RLP designResolution problemError prevention/detection by using return channelNetwork traffic/resource managementAccess networkWireless mesh network
An enhanced radio link protocol (RLP) in a wireless access network that is network aware is disclosed. The RLP increases radio link quality by various ARQ mechanisms. The RLP framing structure is included that supports and enables at least network layer packet boundary detection, dynamic and adaptive ARO schemes for QoS support on a per-packet basis, and a flexible RLP frame structure for fast adaptation to physical layer channel rate / RLP frame sizes. Optional uses include supporting negative acknowledgment (NAK) based ARQ.
Owner:APPLE INC
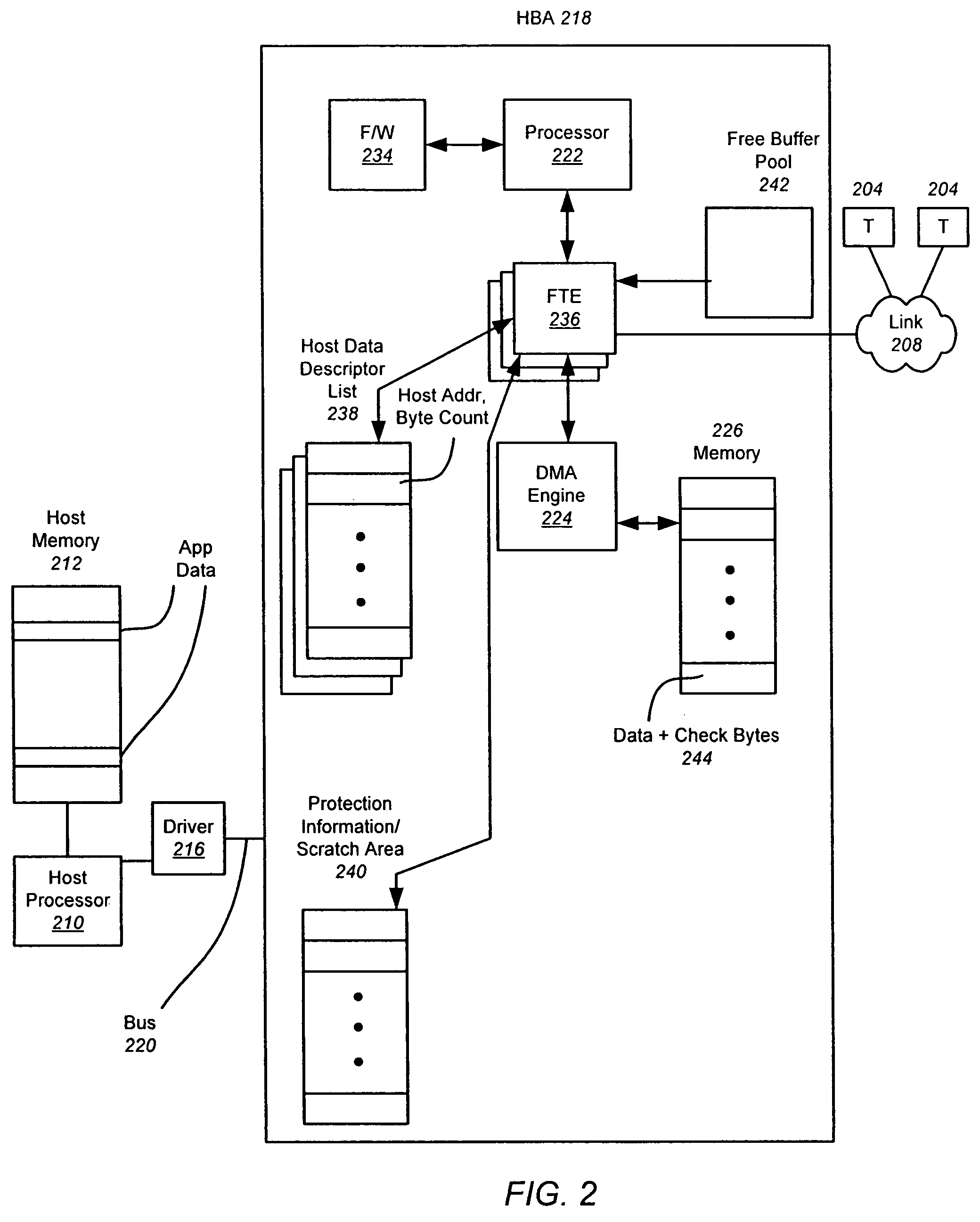
Autonomous mapping of protected data streams to fibre channel frames
InactiveUS7765336B2Minimize involvementPerform other taskTransmissionInput/output processes for data processingData streamFibre Channel
A hardware-based offload engine is disclosed for mapping protected data into frames. For a write operation, the HBA determines host addresses and the size of data to be read from those addresses. The HBA also determines the frame size and protection scheme for data to be written. A frame transmit engine reads each host descriptor in the host data descriptor list to determine the location and byte count of the data to be read. A DMA engine reads the protection information / scratch area to determine the exact data size used to fill each frame and the protection scheme, and retrieves one or more free frame buffers. Check bytes are inserted alongside the data and stored in free frame buffers. After each frame is filled, the frame transmit engine also generates and stores header information for that frame, and then combines header, data and check bytes for transmission over the network.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
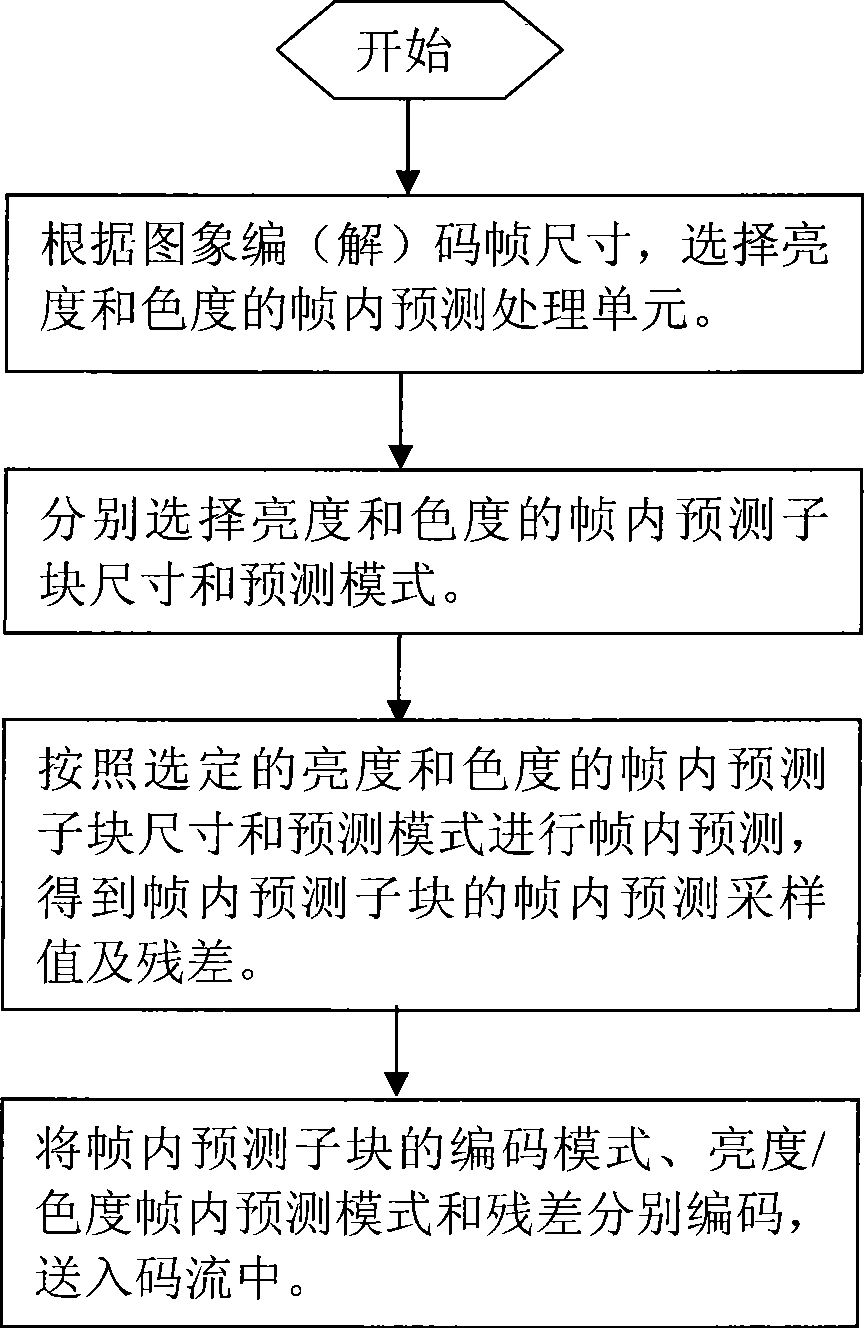
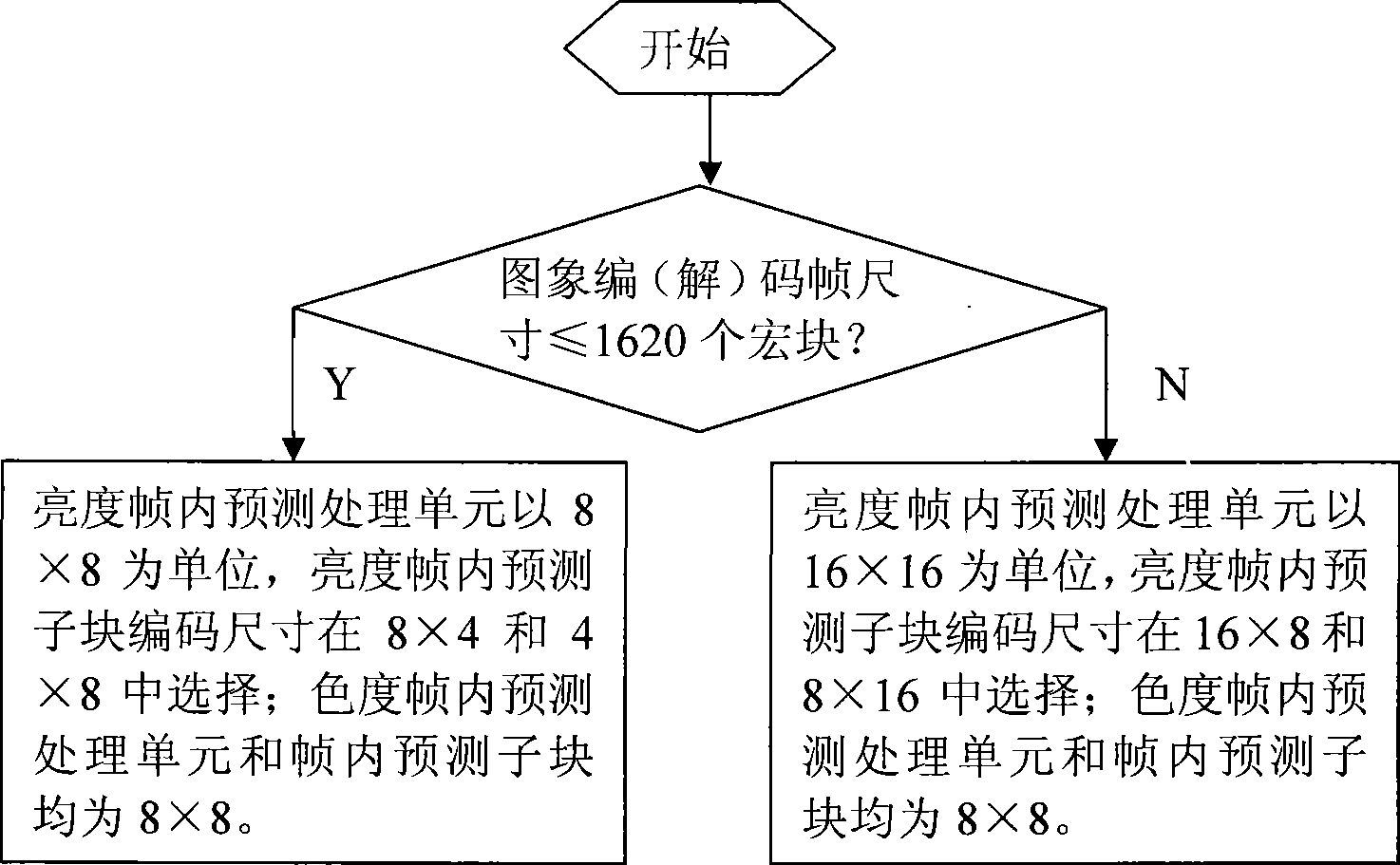
Intra-frame prediction method
ActiveCN101394565AImprove encoding and compression efficiencySave stream bandwidthTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationImaging qualityAlgorithm
The invention relates to an intra-frame prediction method, which increase the intra-frame prediction compression efficiency and comprises the following steps: (1) a brightness intra-frame prediction processing unit and a chroma intra-frame prediction processing unit are selected according to the image coding (decoding) frame size; (2) the sizes and the prediction modes of a brightness intra-frame prediction subblock and a chroma intra-frame prediction subblock are selected respectively; (3) the intra-frame prediction is performed according the selected sizes and the prediction modes of the brightness intra-frame prediction subblock and the chroma intra-frame prediction subblock to obtain an intra-frame prediction sampling value and a residual error of the intra-frame prediction subblocks; and (4) the coding mode of the intra-frame prediction subblocks, the brightness intra-frame prediction mode as well as the chroma intra-frame prediction mode and the residual error are coded respectively and then are sent to a code stream. The classification of the intra-frame prediction method is mainly aimed at the circumstances that the sizes of the intra-frame prediction subblocks are 4*8, 8*4, 8*16 and 16*8, and five optional prediction modes are matched, so that 3 percent to 5 percent of code stream bandwidth is saved under the condition that the image quality is identical, and the image encoding compression efficiency is increased; and the effect of simplifying the computational complexity can be also achieved due to the selection of partial prediction modes.
Owner:CHENGDU JIUZHOU ELECTRONIC INFORMATION SYSTEM CO LTD
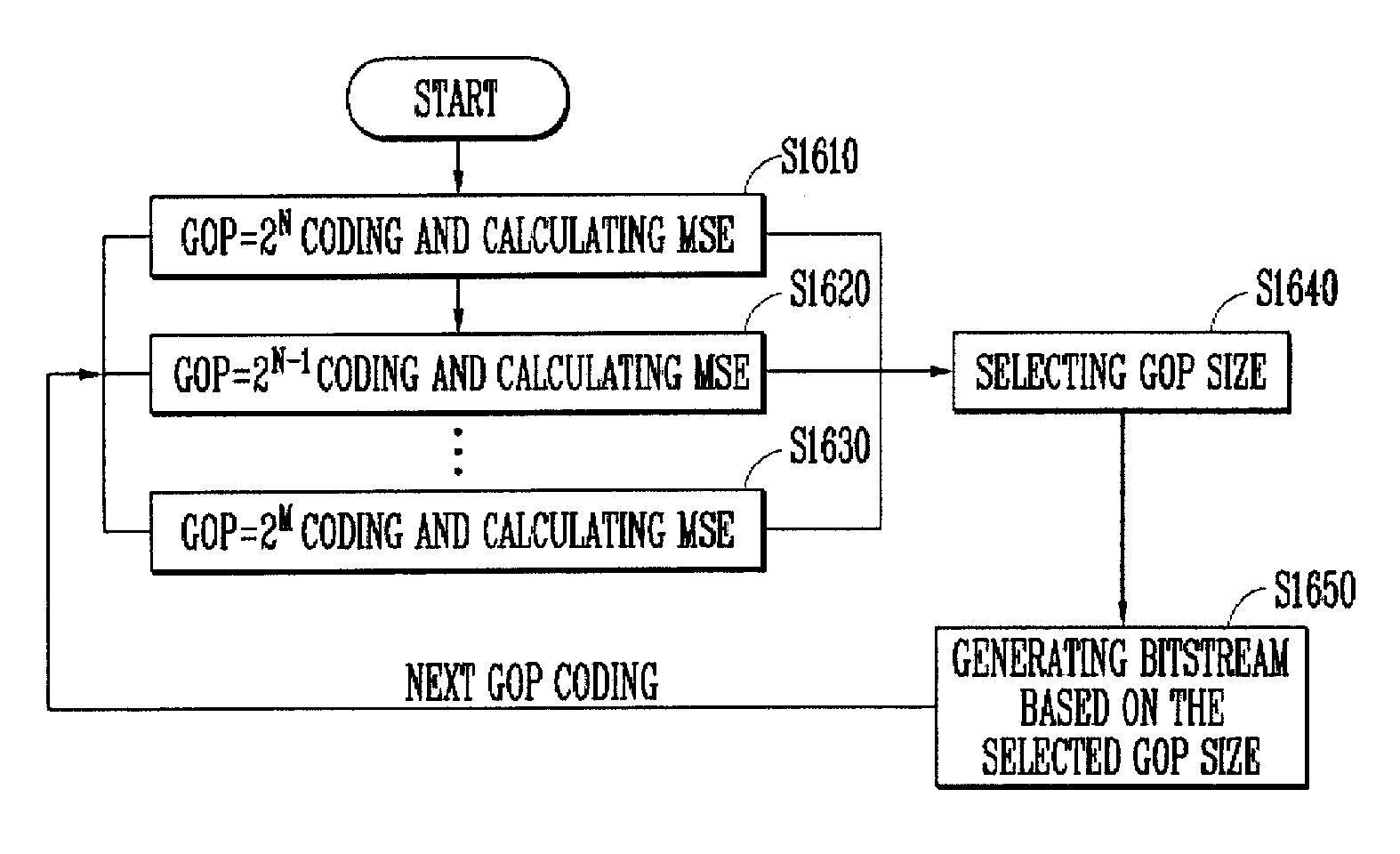
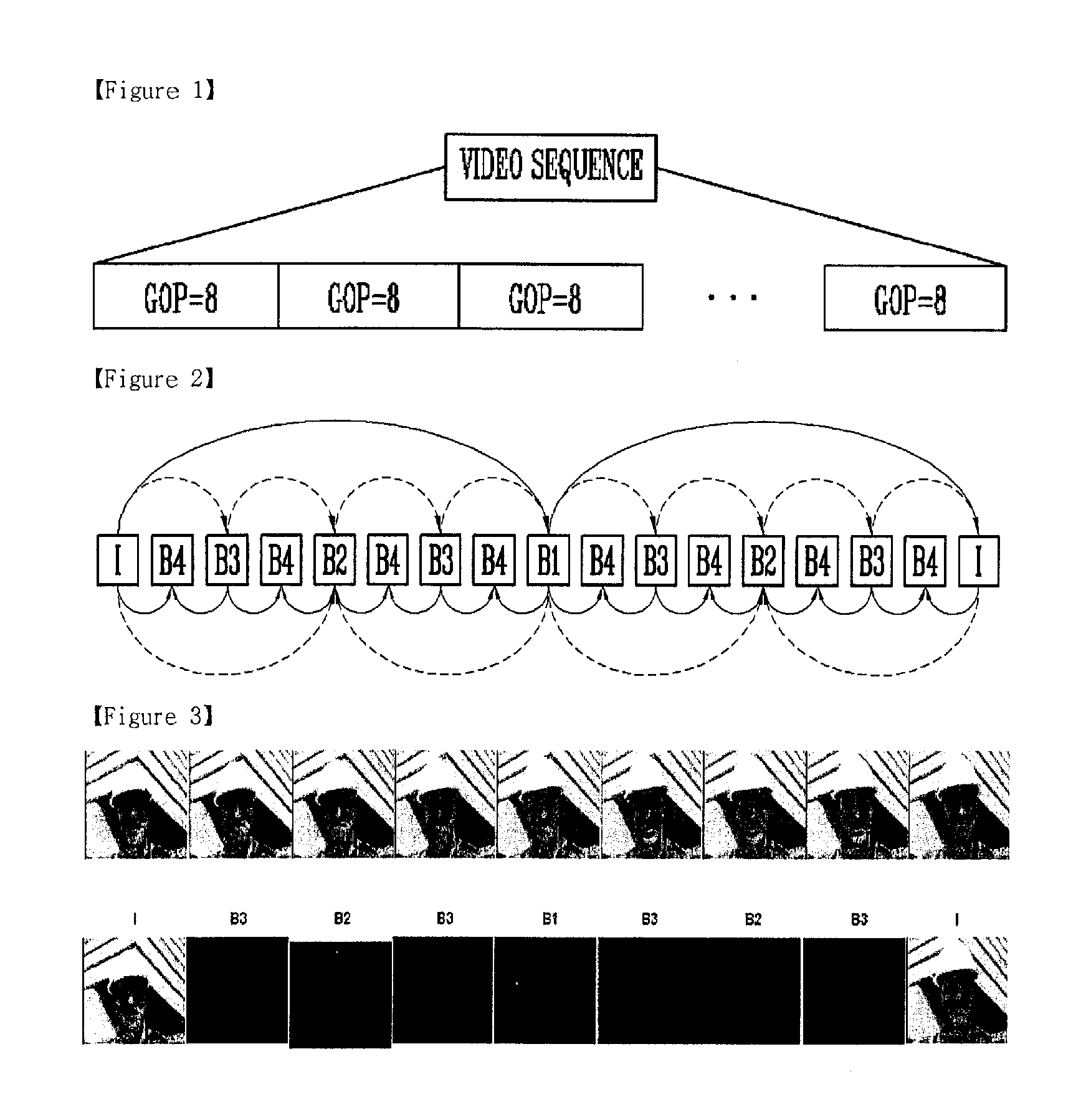
Method for Encoding/Decoding a Video Sequence Based on Hierarchical B-Picture Using Adaptively-Adjusted Gop Stucture
ActiveUS20070247549A1Improve coding efficiencyImprove efficiencyPulse modulation television signal transmissionPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPattern recognitionBase code
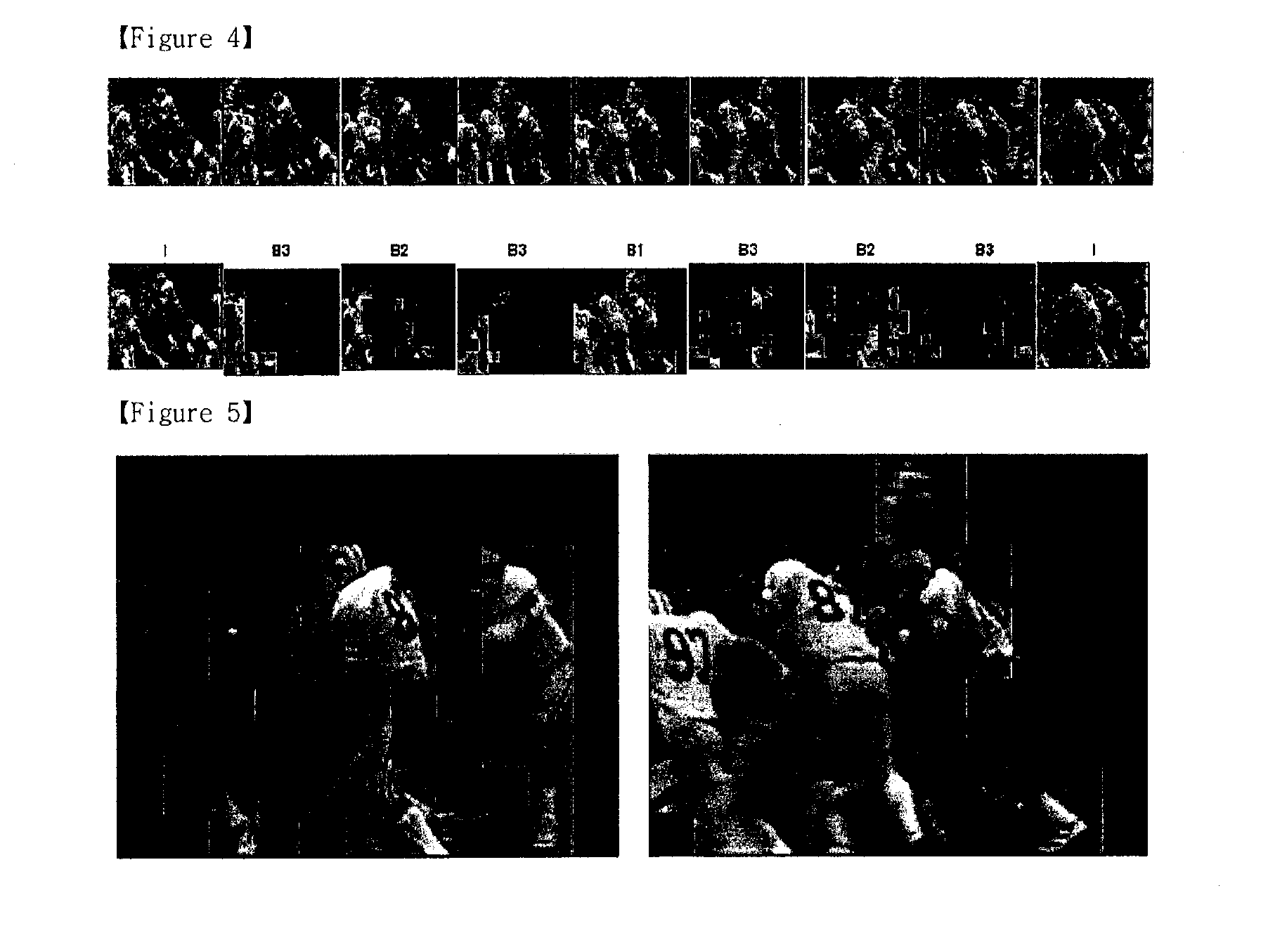
Provided is a method for performing hierarchical B picture-based coding on a video sequence using the structure of adaptively divided group of pictures (GOP). The method includes the steps of, for each predefined 2N frame-sized group of pictures (GOP) of the video sequence, (a) encoding the 2N frame-sized GOP of the video sequence based on each of the different GOP sizes from the maximum size, 2N, to the minimum size, 2M (M is an integer between 1 and N) and obtaining different values between frames reconstructed after the encoding is performed and frames after the hierarchical B-picture prediction is performed, based on each of the different GOP sizes; (b) selecting at least one sub-GOP based on the difference values obtained by encoding the 2N frame-sized GOP of the video sequence based on each of the different GOP sizes; and (c) generating a bitstream by encoding the 2N-frame-sized GOP based on the at least one selected sub-GOP. Thereby, the hierarchical B picture-based video coding is performed by adaptively dividing the GOP size based on performance and thereby obtains high coding efficiency.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST +1
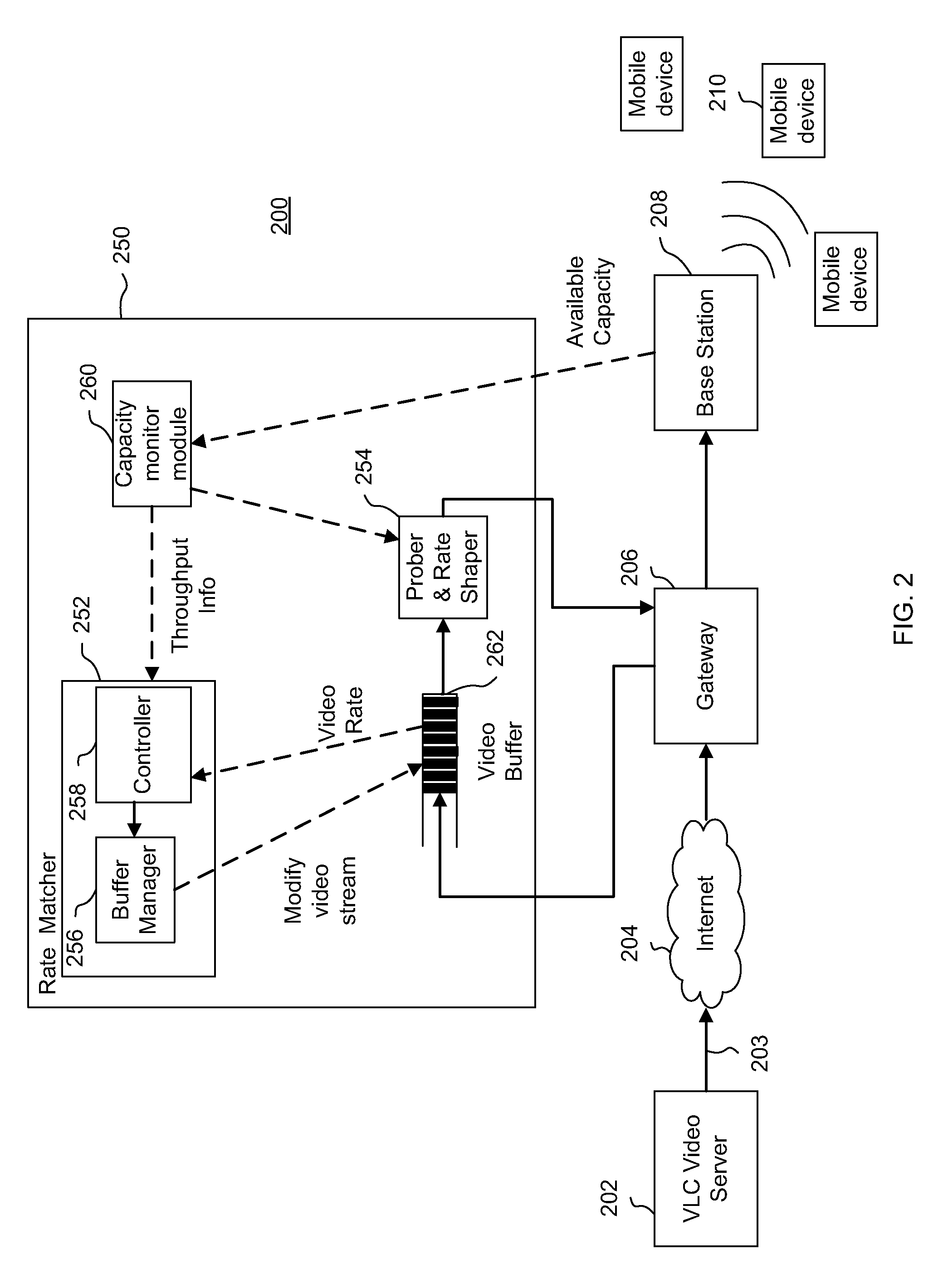
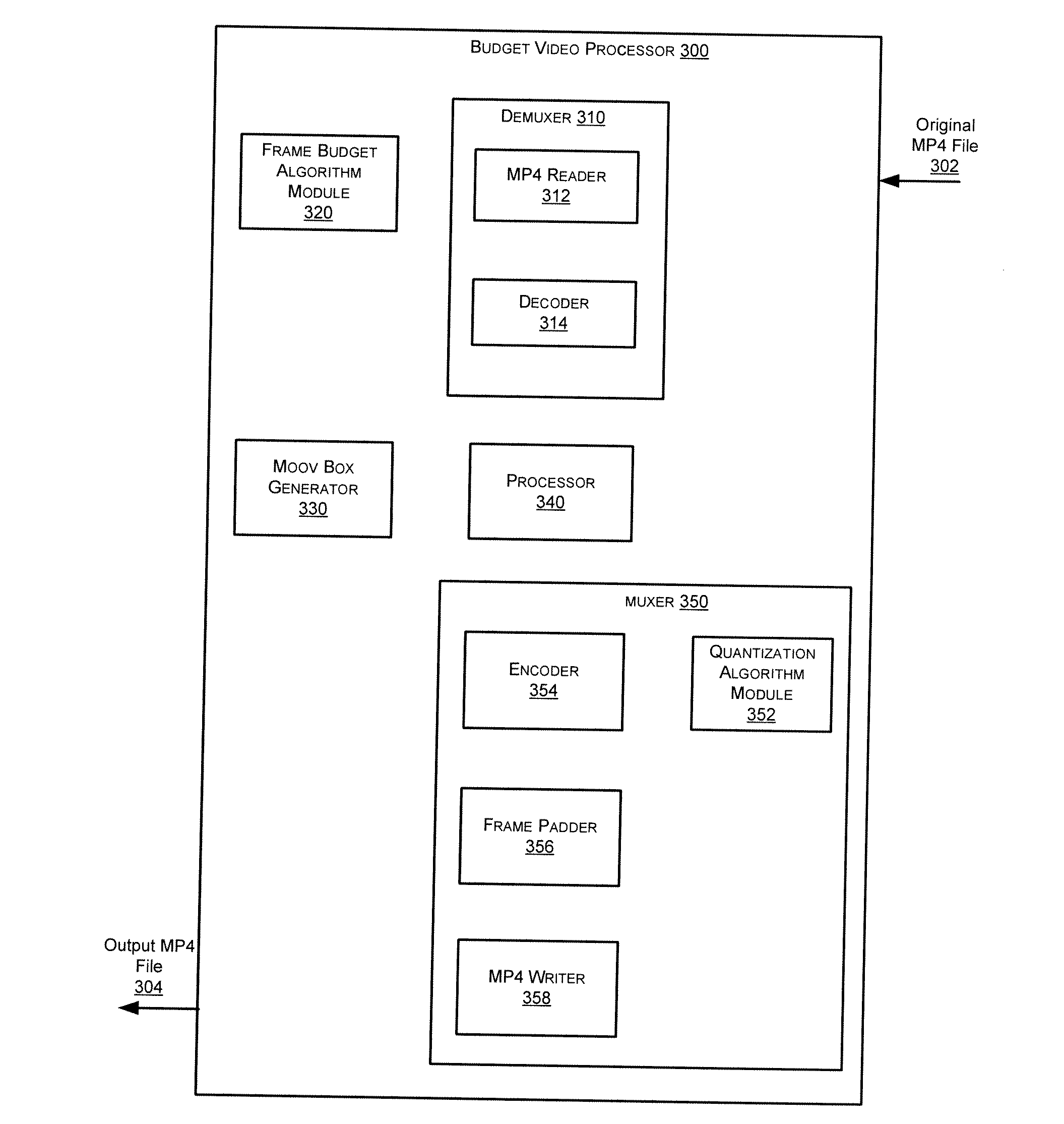
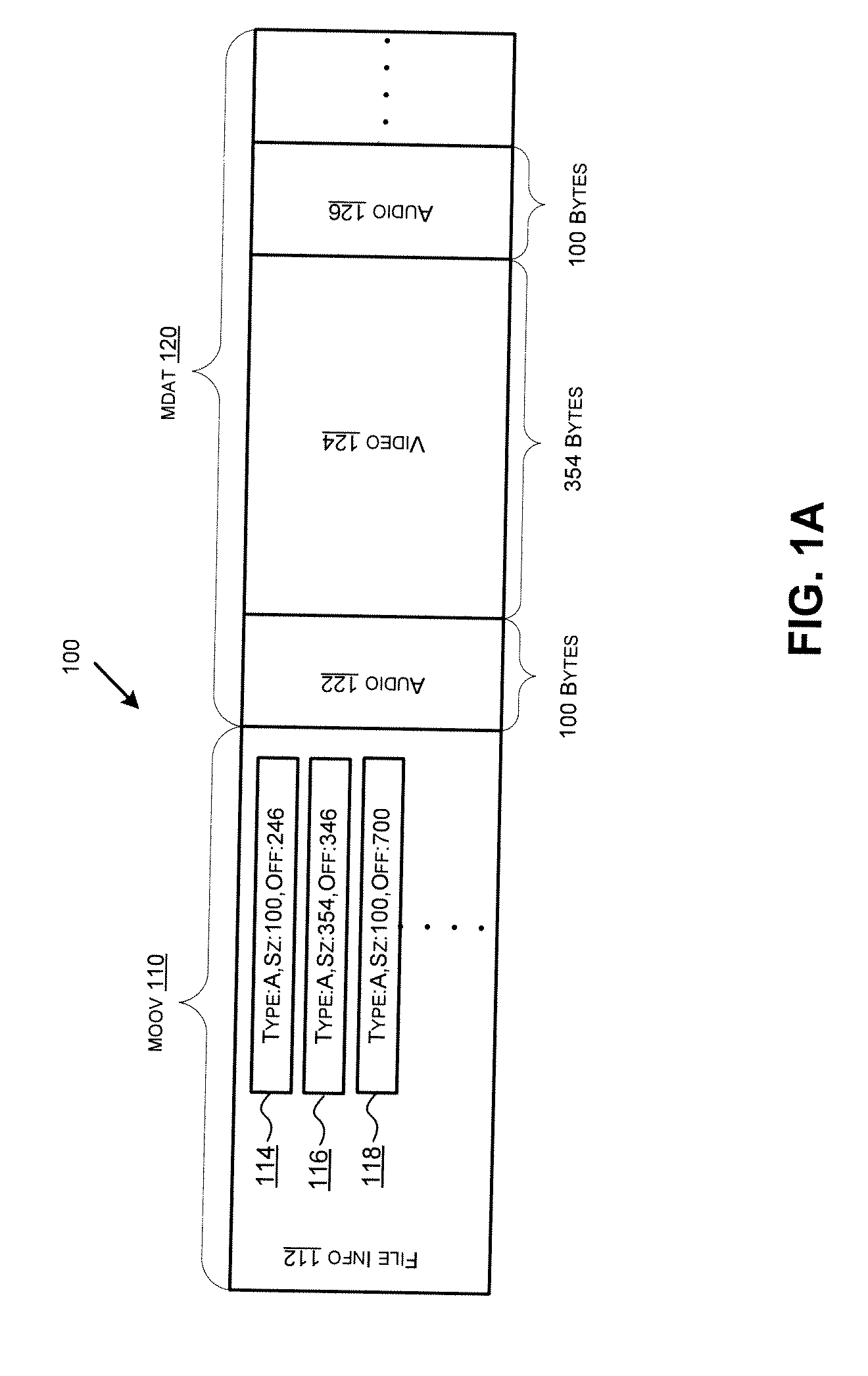
Budget encoding
ActiveUS20110090953A1Picture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningReal-time computingFrame size
A method includes receiving streaming media data having a media frame and a frame index referencing the media frame; allocating a frame budget for an output media frame by estimating a frame size of the output media frame based on the frame index; generating the output media frame in real-time by processing the media frame based on first processing parameters and, if the allocated frame budget is greater than a frame size of the processed media frame, padding the processed media frame; and providing the output media frame.
Owner:OPTIMORPHIX INC
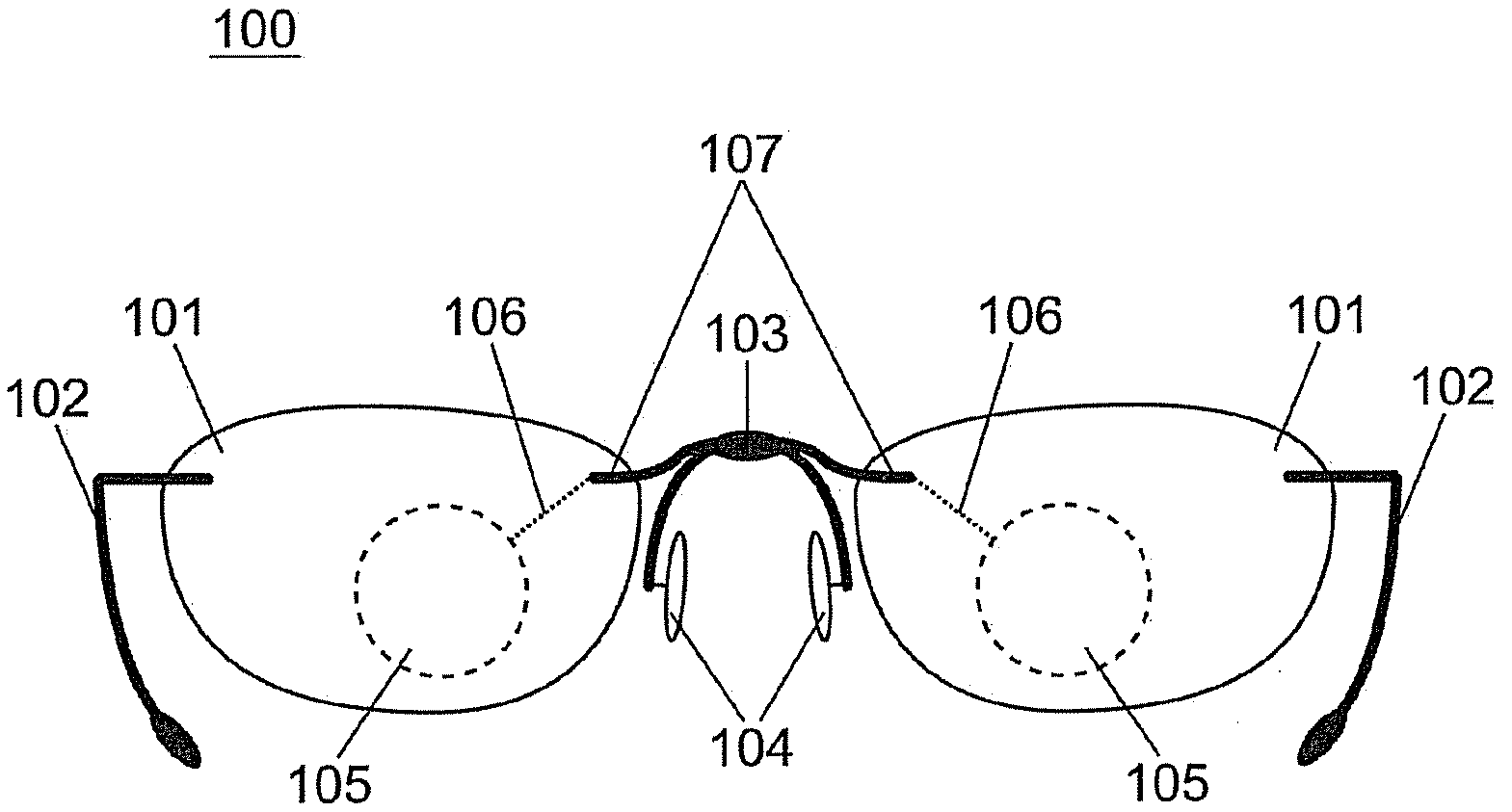
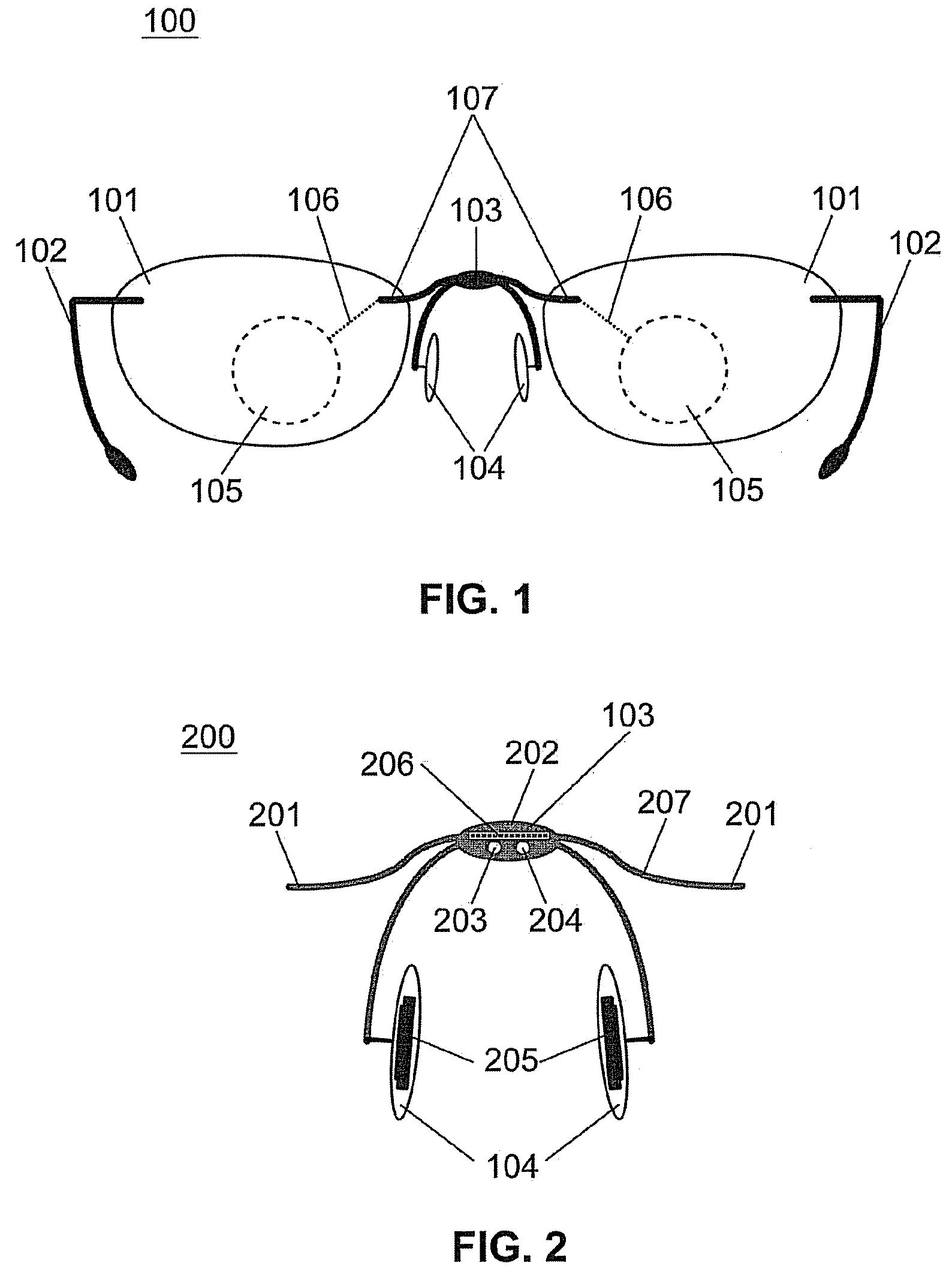
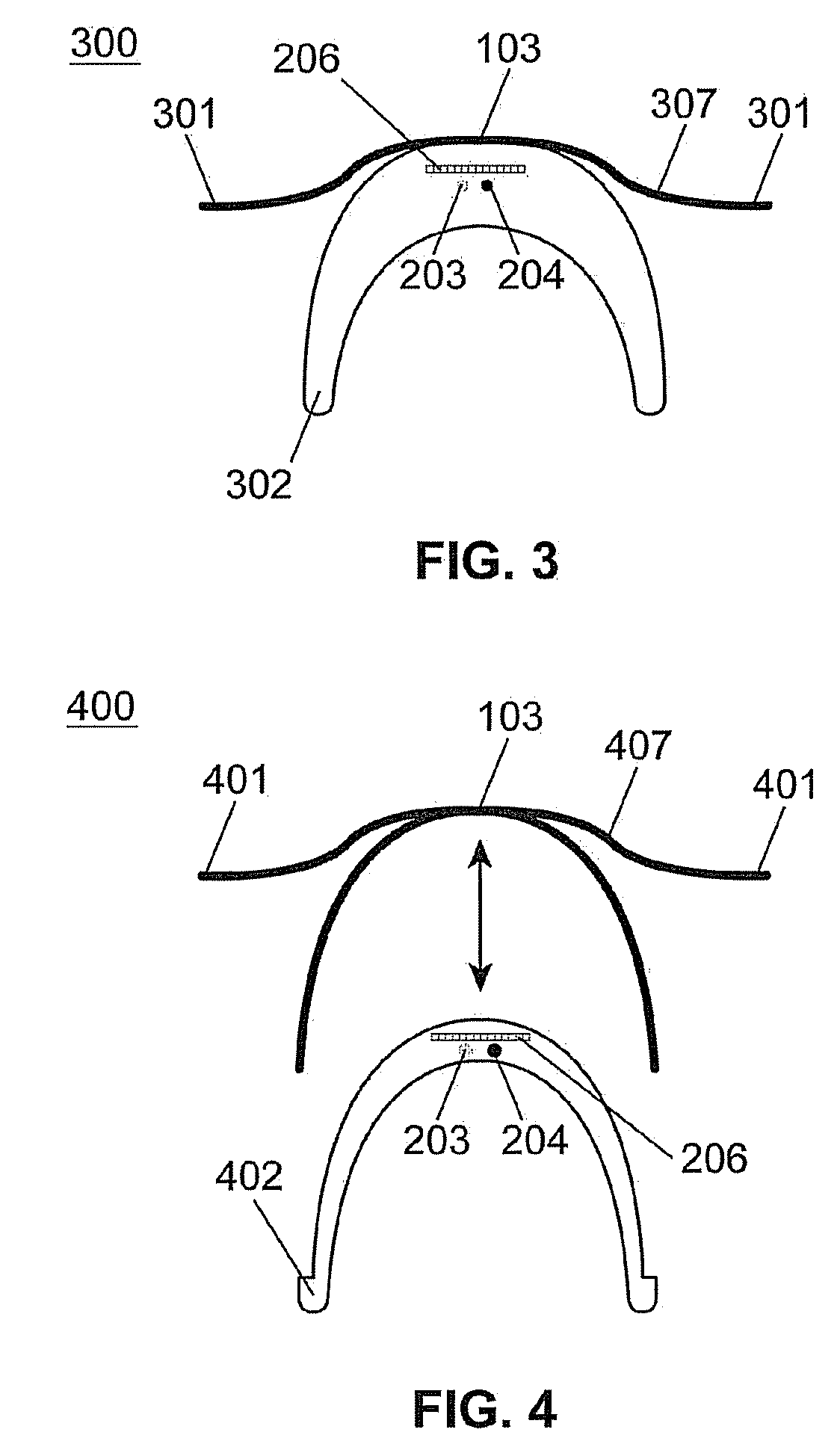
Spectacle frame bridge housing electronics for electro-active spectacle lenses
A nose bridge for a fashion spectacle lens frame adapted for housing electro-active lenses is presented. The nose bridge may include a body which may further include electronic components. The nose bridge may further include a connecting element for connecting the electronic components with the electro-active lenses for altering optical properties of the electro-active lenses. The nose bridge may be adapted to fit a variety of frame sizes, shapes, and styles as well as lenses of a variety of sizes and shapes.
Owner:DUSTON DWIGHT P +4
Method and system for video quality assessment
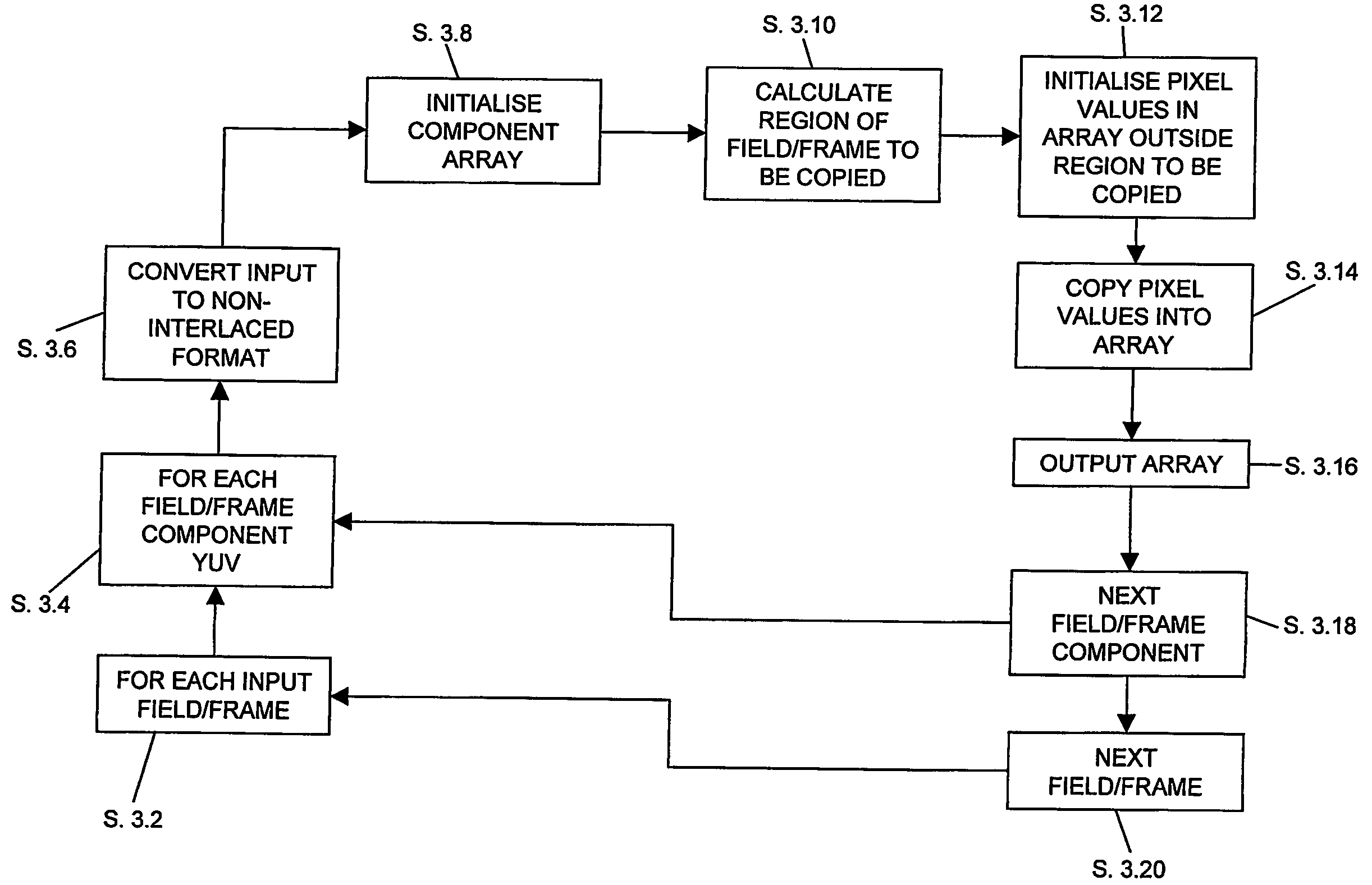
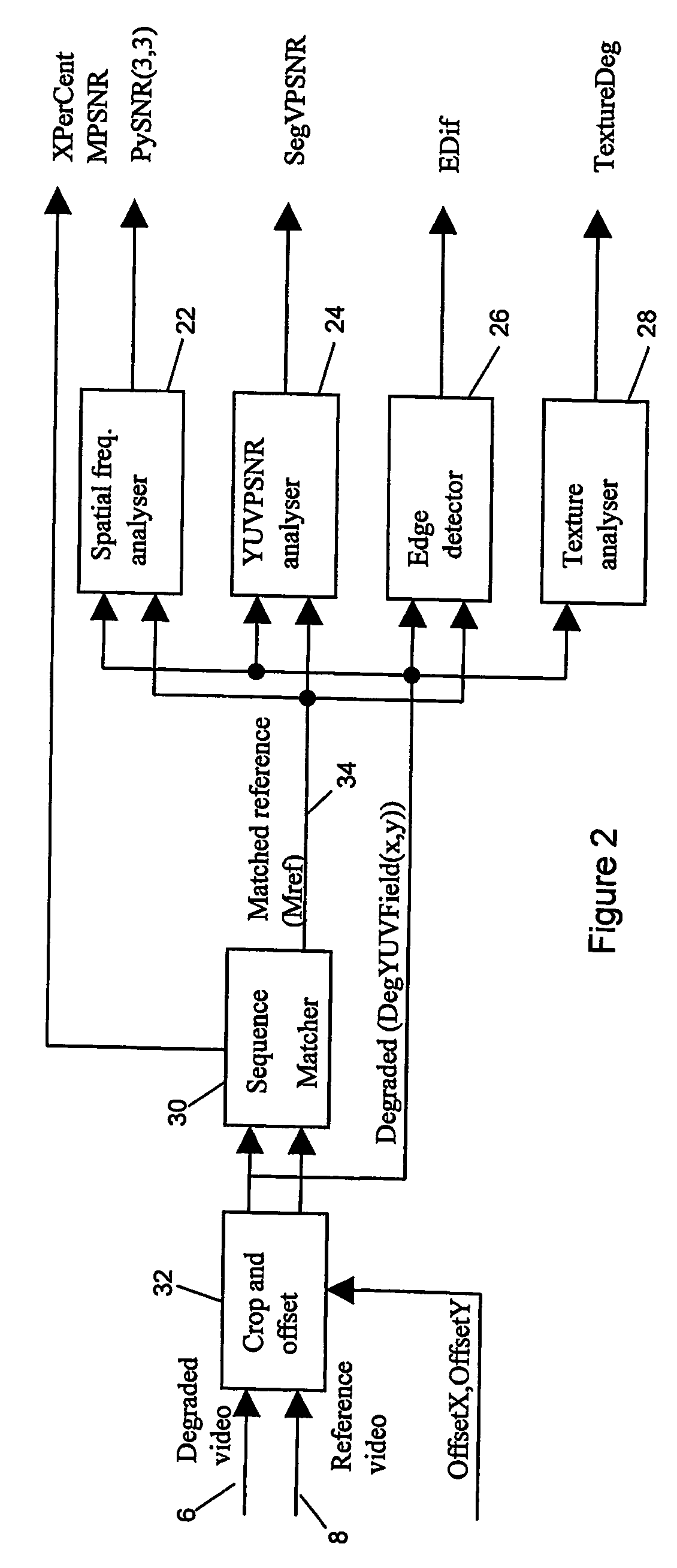
ActiveUS20060152585A1Reduce adverse effectsEffective trackingImage analysisNoise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementVideo qualityTest sequence
A method and system for automated video quality assessment which reduces the adverse effects of sub-field / frame misalignments between the reference and test sequences. More particularly, the invention provides for misalignments down to a sub-field / frame level to be handled by individually matching sub-field / frame elements of a test video field / frame with sub-field / frame elements from a reference video field / frame. The use of a matching element size that is significantly smaller than the video field / frame size enables transient sub-field / frame misalignments to be effectively tracked.
Owner:BRITISH TELECOMM PLC
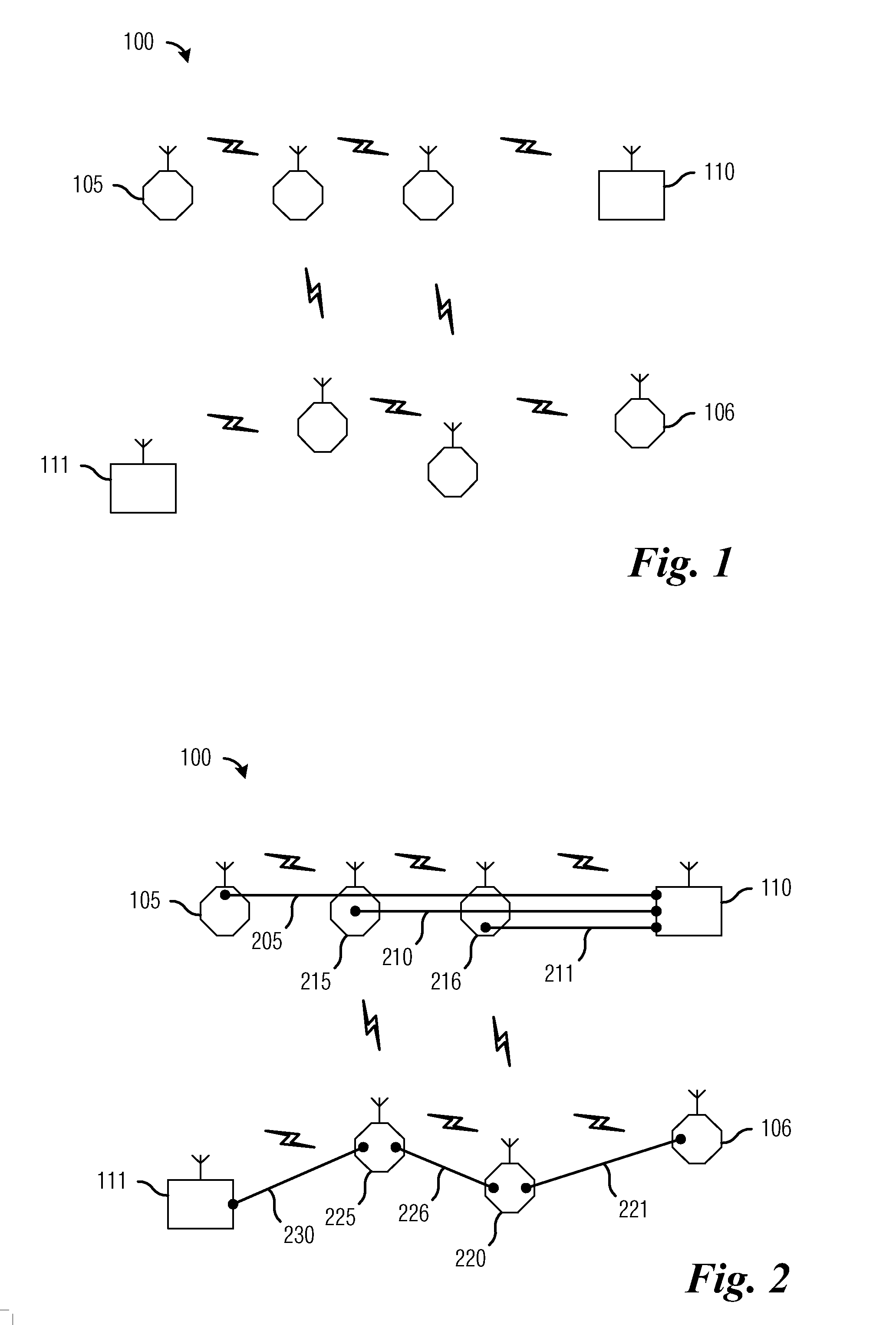
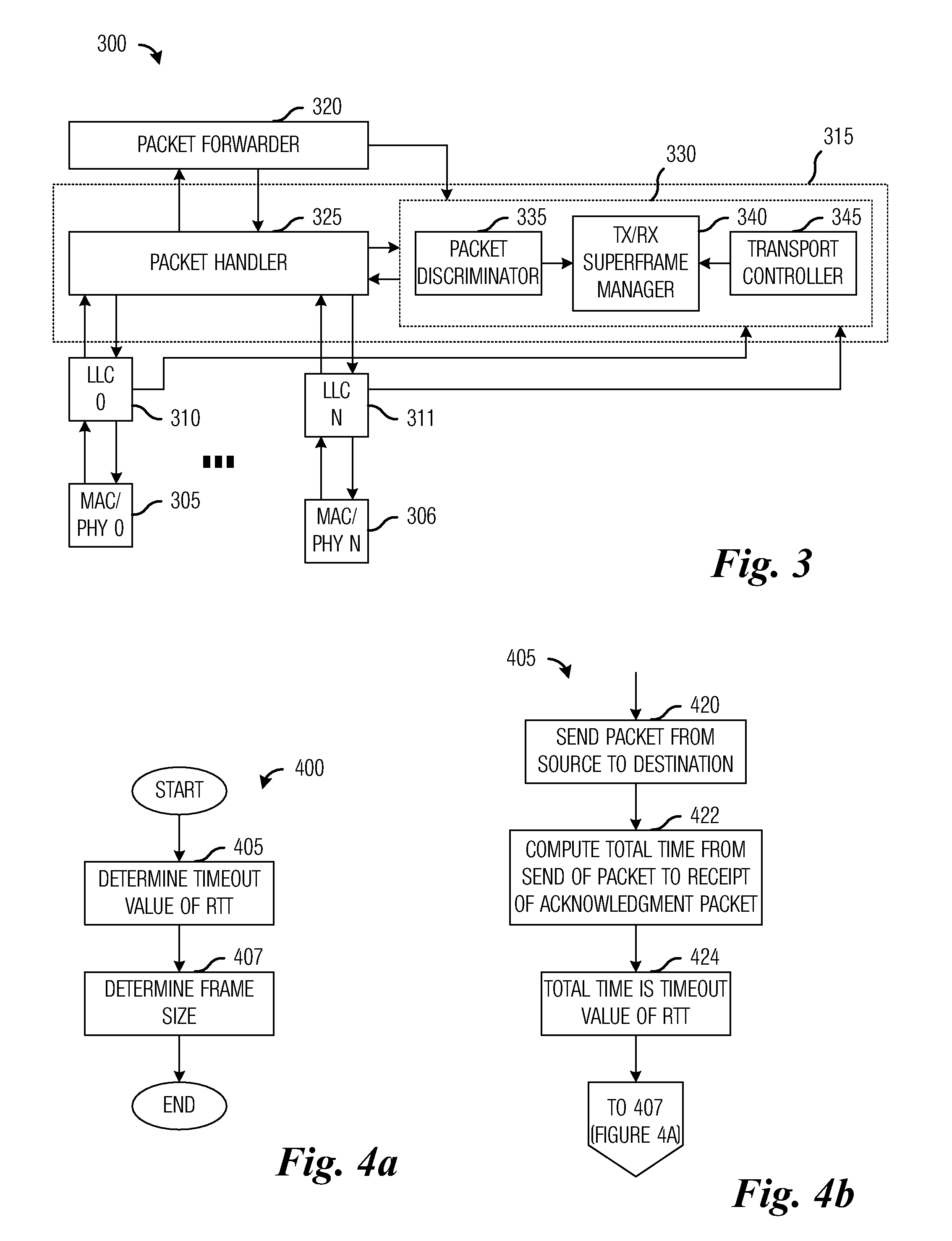
System and Method for Adaptive Frame Size Management in a Wireless Multihop Network
InactiveUS20070195820A1Reduce probabilityImprove performanceTransmission systemsNetwork traffic/resource managementTimerReal-time computing
A system and method for adaptively managing frame size in a wireless multihop network (100) is disclosed. In one embodiment, a packet is transmitted from a source to a destination (420). A acknowledgement packet (422) is received and a successful acknowledgement packet counter is incremented if the acknowledgement packet arrives prior to a time-out of a timer (444). A frame size is increased if the successful acknowledgement packet counter reaches a specified value (446, 448). If the acknowledgement packet arrives after the time-out of the timer, the successful acknowledgement packet counter (460) is reset and the frame size (462) is decreased. These procedures can be repeated until the frame size is greater than or equal to a maximum frame size (450) or less than or equal to a minimum frame size (464).
Owner:BLACKBERRY LTD
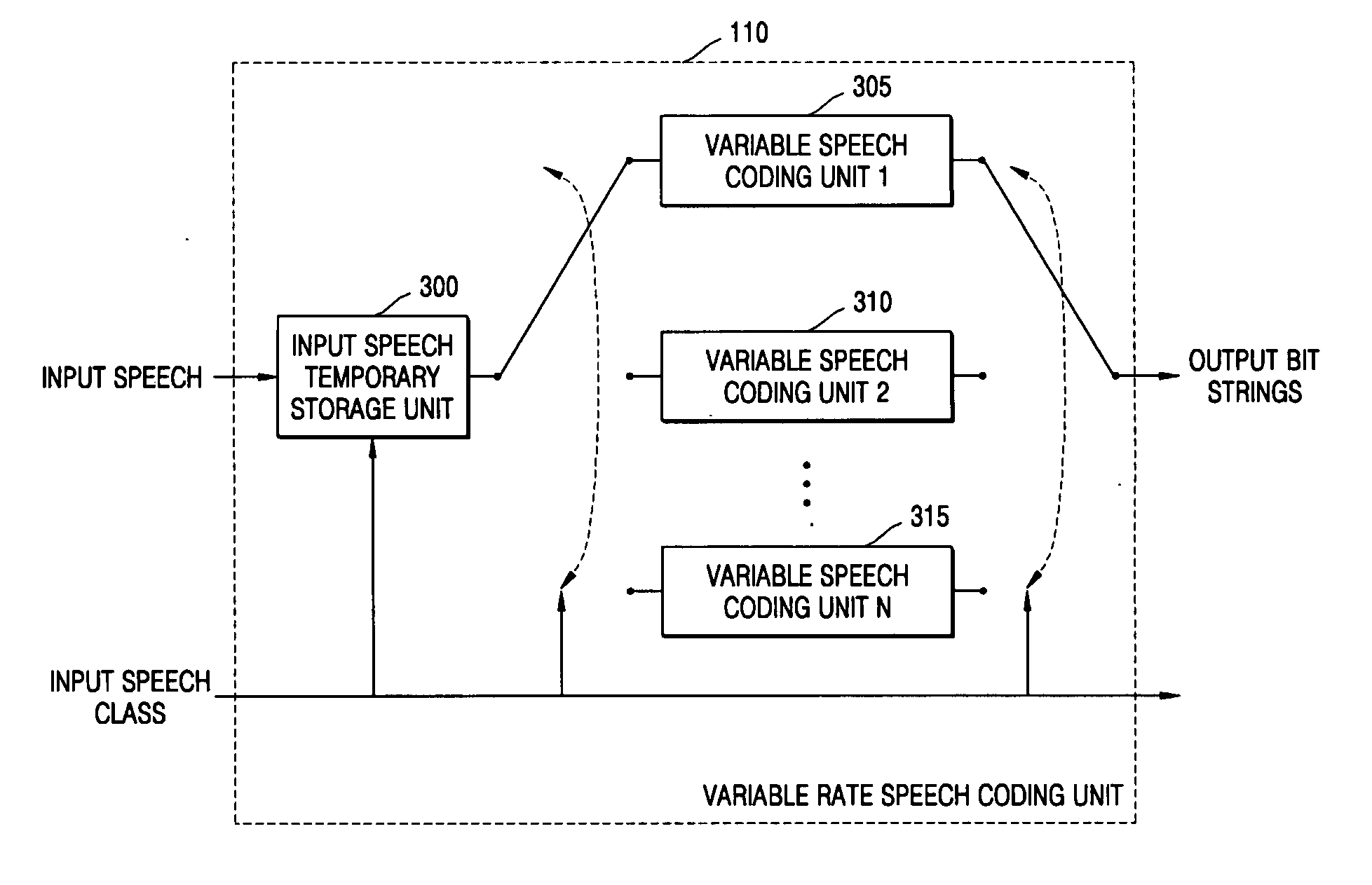
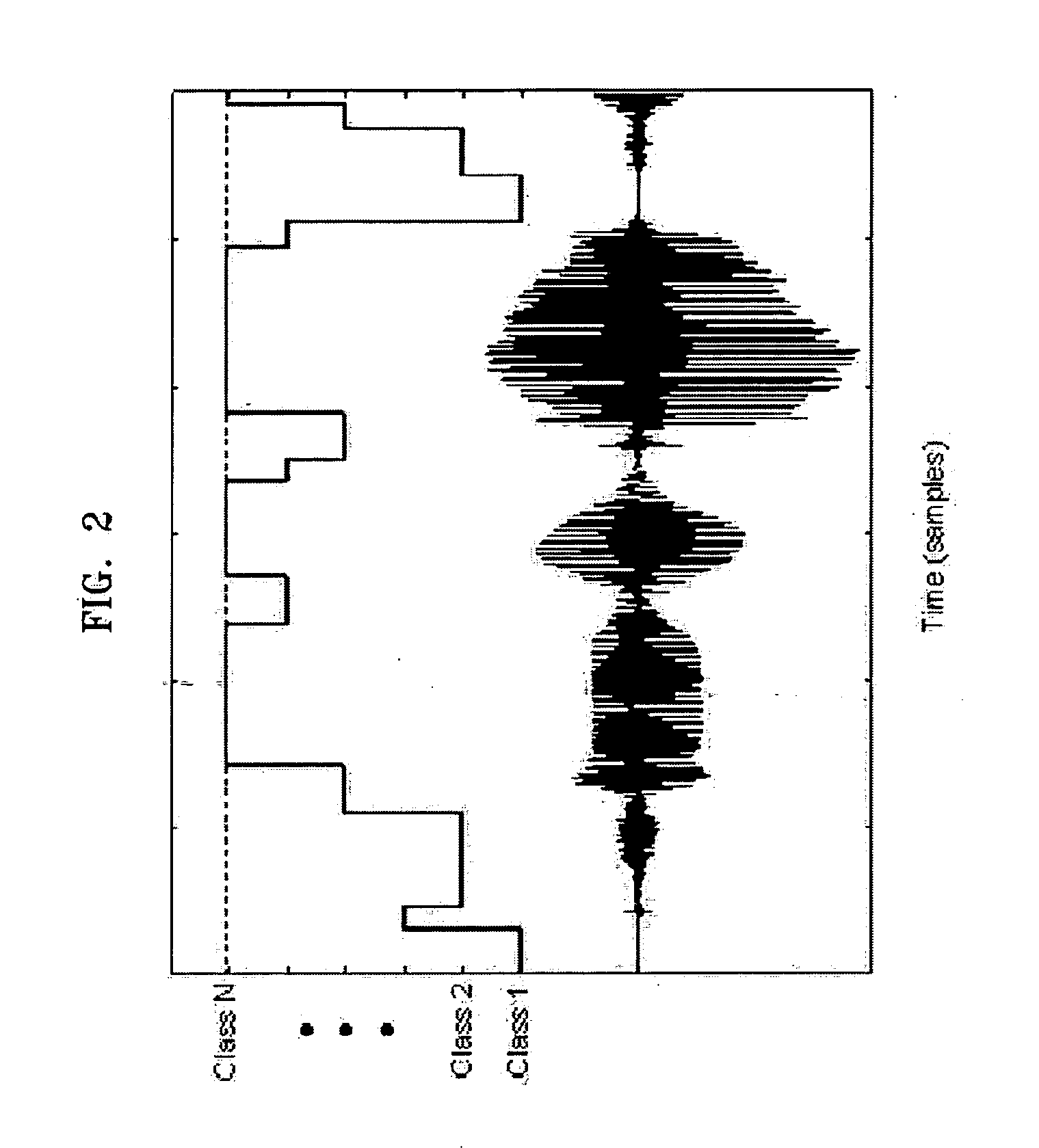
Variable-frame speech coding/decoding apparatus and method
InactiveUS20050143979A1Improve performanceImprove service qualitySpeech analysisSpeech codeNetwork conditions
There is provided a speech coding / decoding apparatus and method, in which the input speech signals are classified into several classes in accordance with characteristics of the input speech signals and the input speech signals are coded using frame sizes, quantizer structures, and bit assignment methods corresponding to the determined classes, or in which the frame sizes can be adjusted in accordance with network conditions or codec type of a counter part. Therefore, by optimally adjusting the frame size, the quantizer structure, and the bit assignment method in accordance with the characteristics of input speech, it is possible to improve the performance of the speech coding apparatus, and by adjusting the frame size in accordance with the speech codec type of a counter part, it is also possible to reduce the total end-to-end delay.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST +1
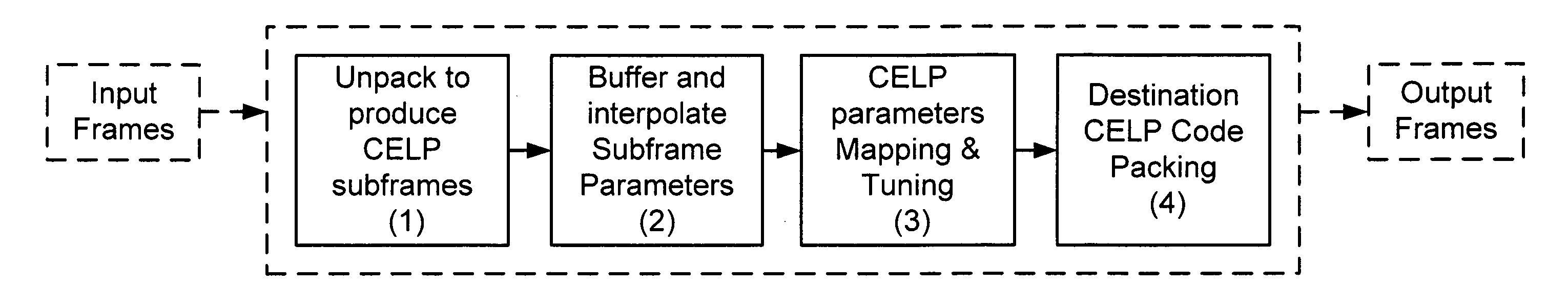
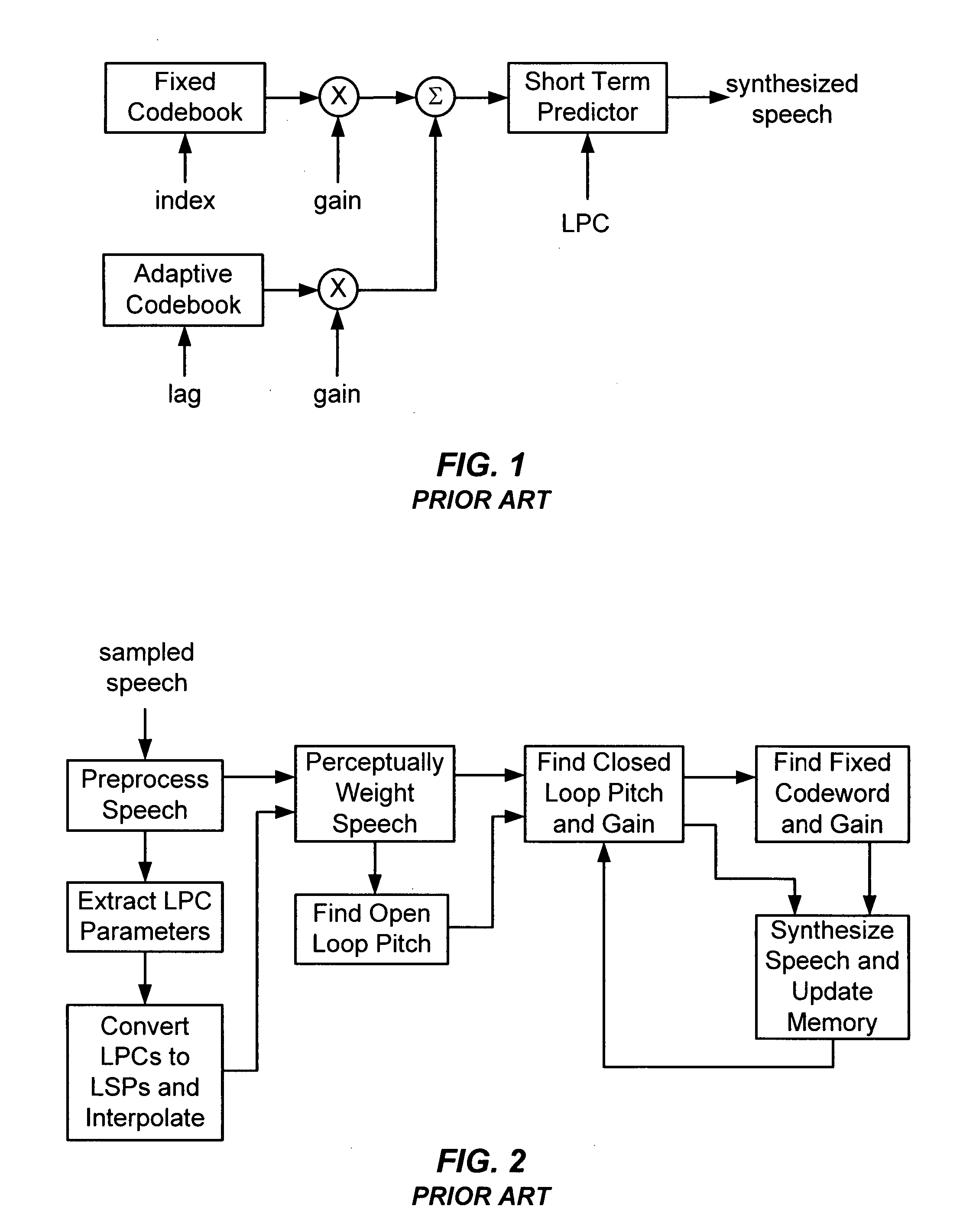
Transcoding method and system between CELP-based speech codes with externally provided status
InactiveUS20080077401A1Computational complexity is reducedReduce the amount requiredSpeech analysisSpeech codeComputer science
A method for transcoding a CELP based compressed voice bitstream from source codec to destination codec. The method includes processing a source codec input CELP bitstream to unpack at least one or more CELP parameters from the input CELP bitstream and interpolating one or more of the plurality of unpacked CELP parameters from a source codec format to a destination codec format if a difference of one or more of a plurality of destination codec parameters including a frame size, a subframe size, and / or sampling rate of the destination codec format and one or more of a plurality of source codec parameters including a frame size, a subframe size, or sampling rate of the source codec format exist. The method includes encoding the one or more CELP parameters for the destination codec and processing a destination CELP bitstream by at least packing the one or more CELP parameters for the destination codec.
Owner:DILITHIUM NETWORKS PTY LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com