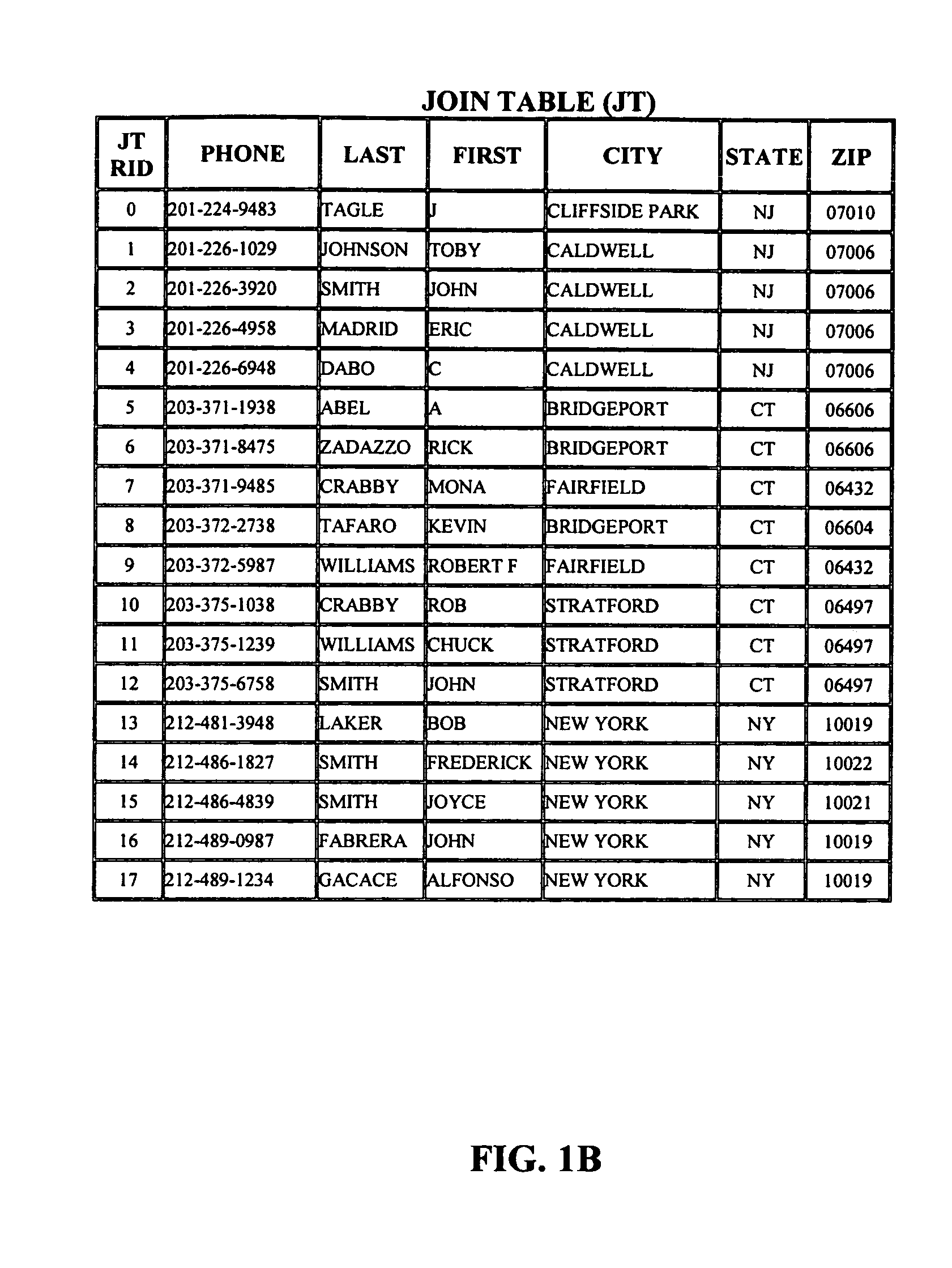
Patents
Literature
86results about How to "Significant overhead" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Interference-based routing in a wireless mesh network
ActiveUS7554998B2Low costReduce data rateEnergy efficient ICTError preventionComputer networkWireless mesh network
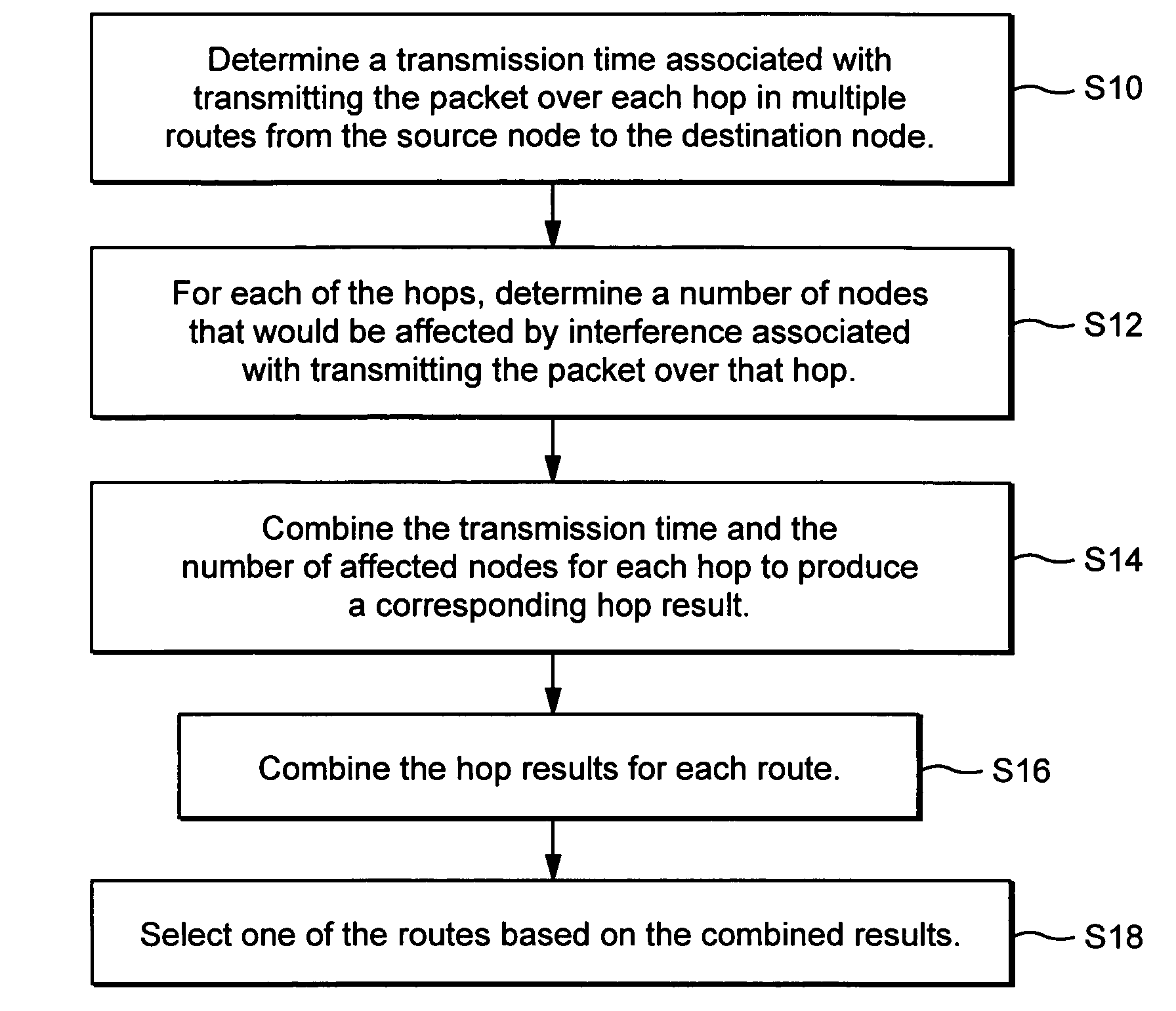
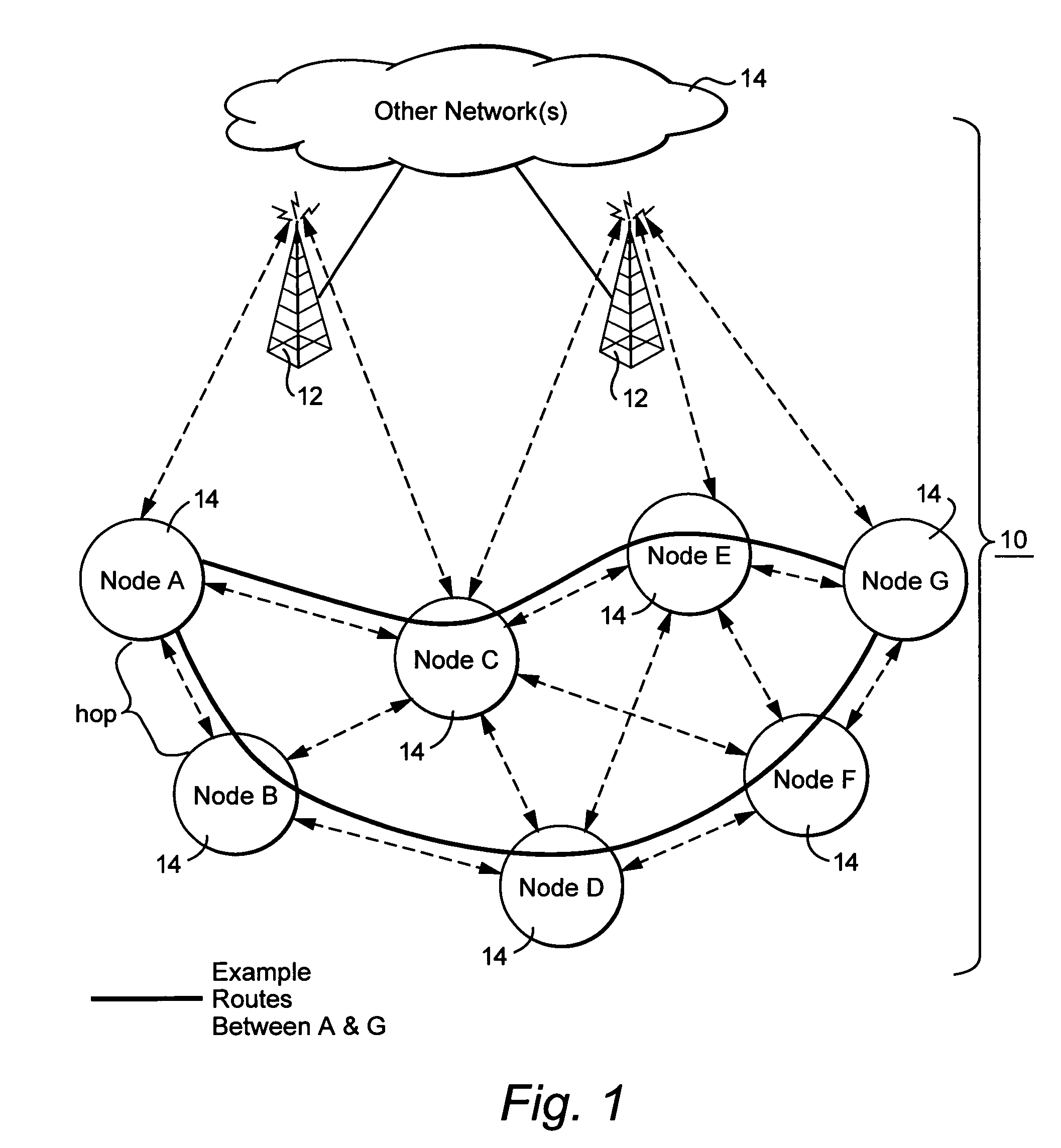
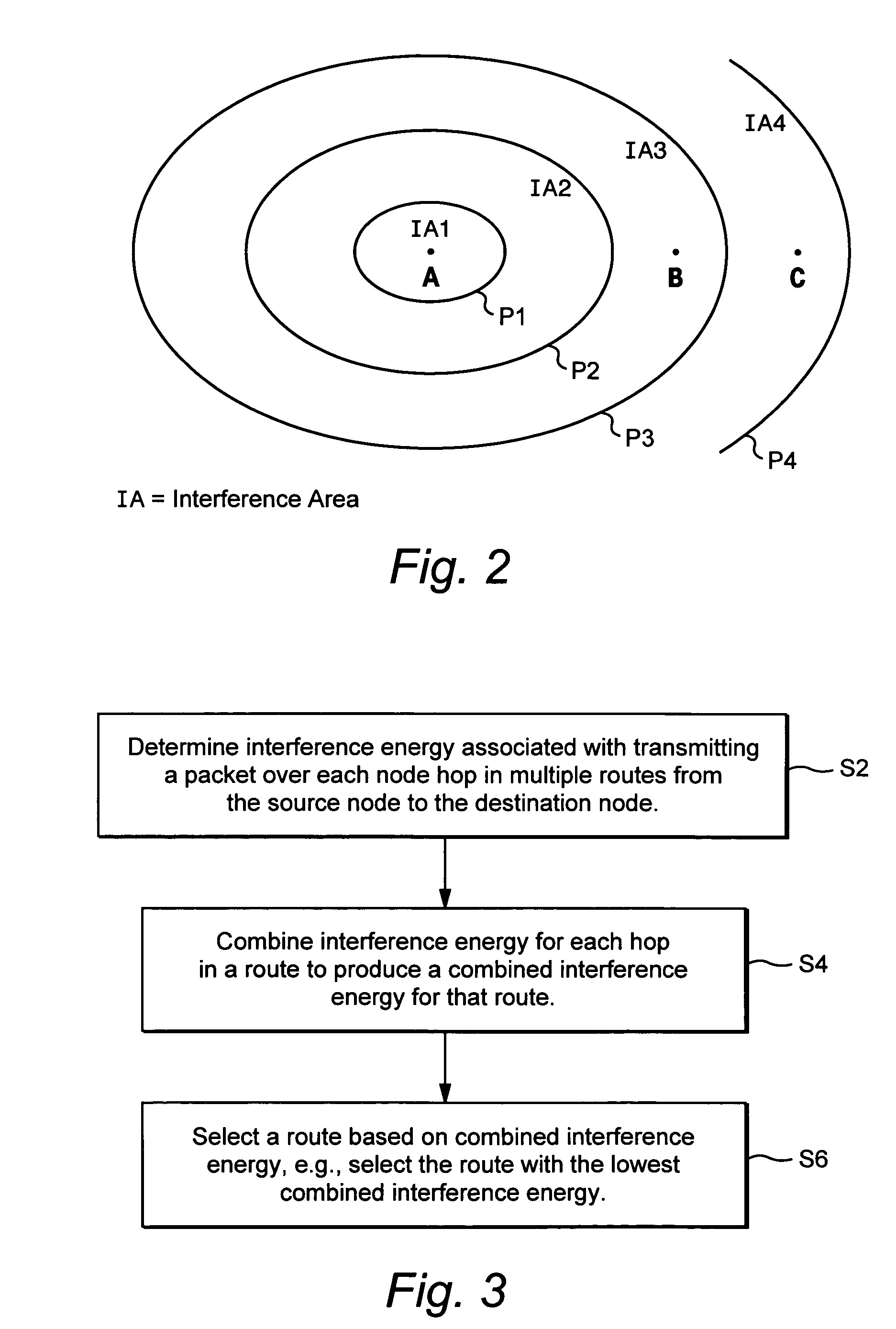
Route selection through a wireless mesh network between a source node and a destination node is based on minimizing generated interference in order to increase the capacity of the network. An interference energy associated with transmitting a packet over each hop in multiple routes from the source node to the destination node is determined. The interference energy for each hop is combined to generate a combined interference energy for each route. One of the routes is selected based on the combined interference energy determined for each route.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
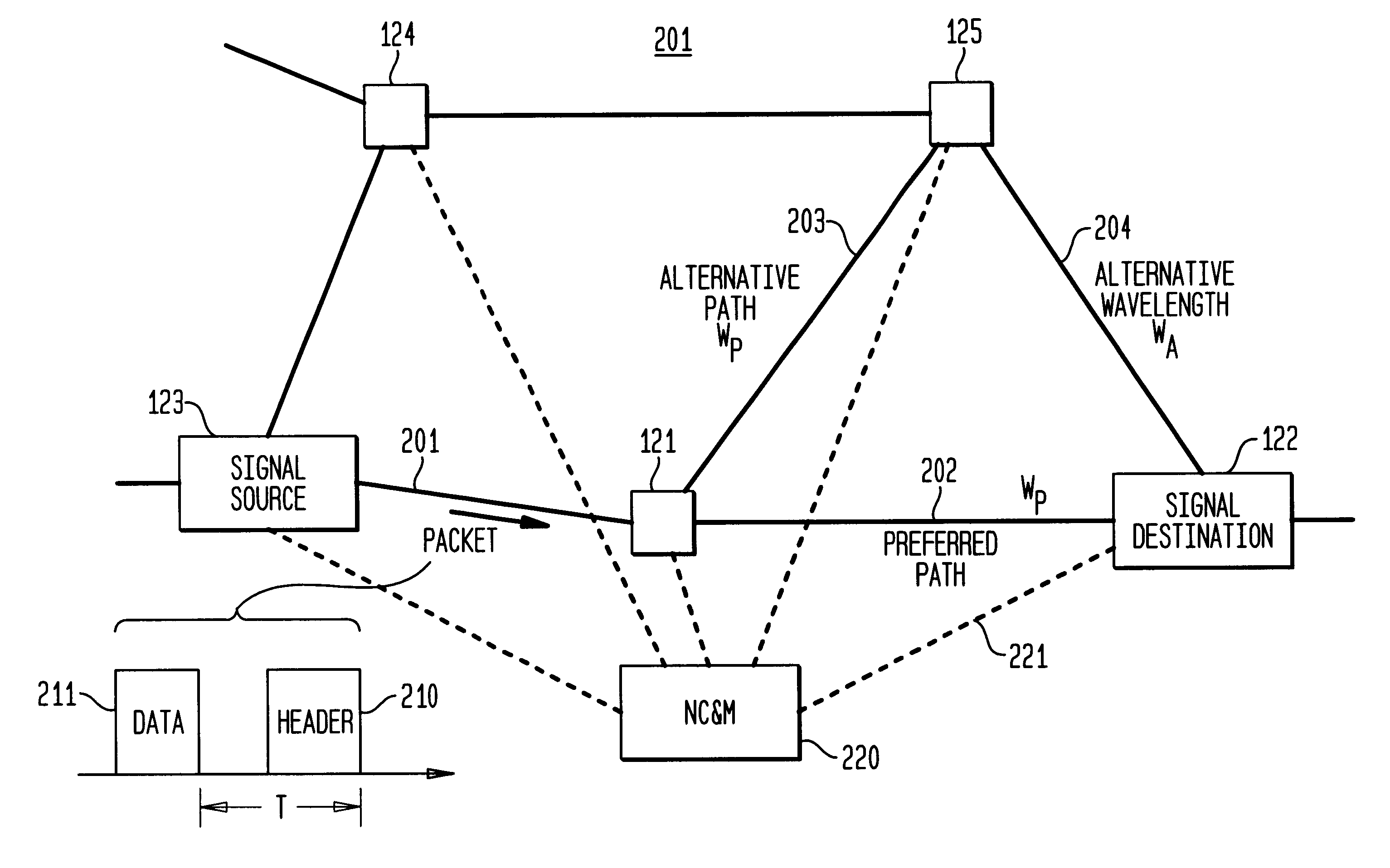
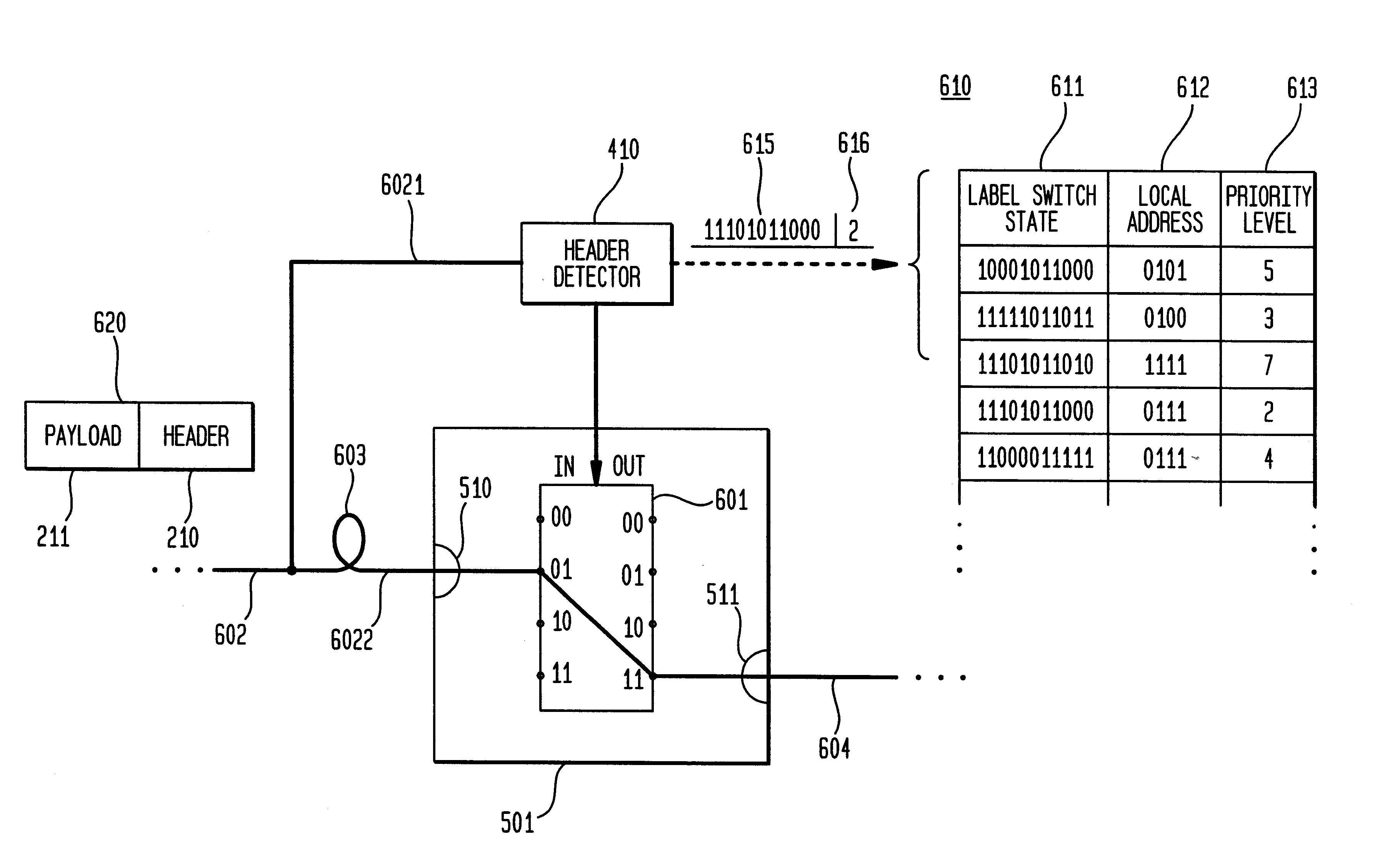
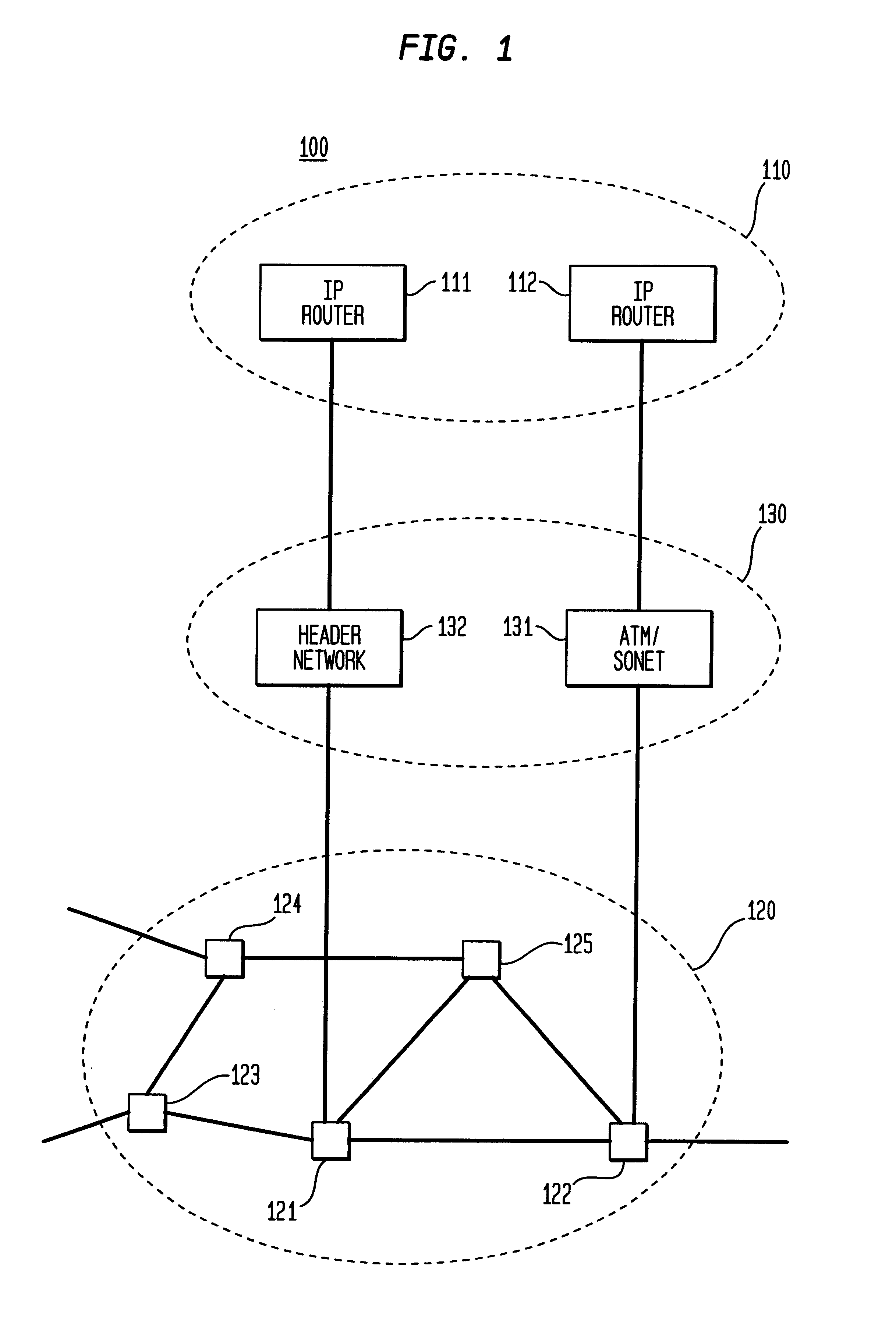
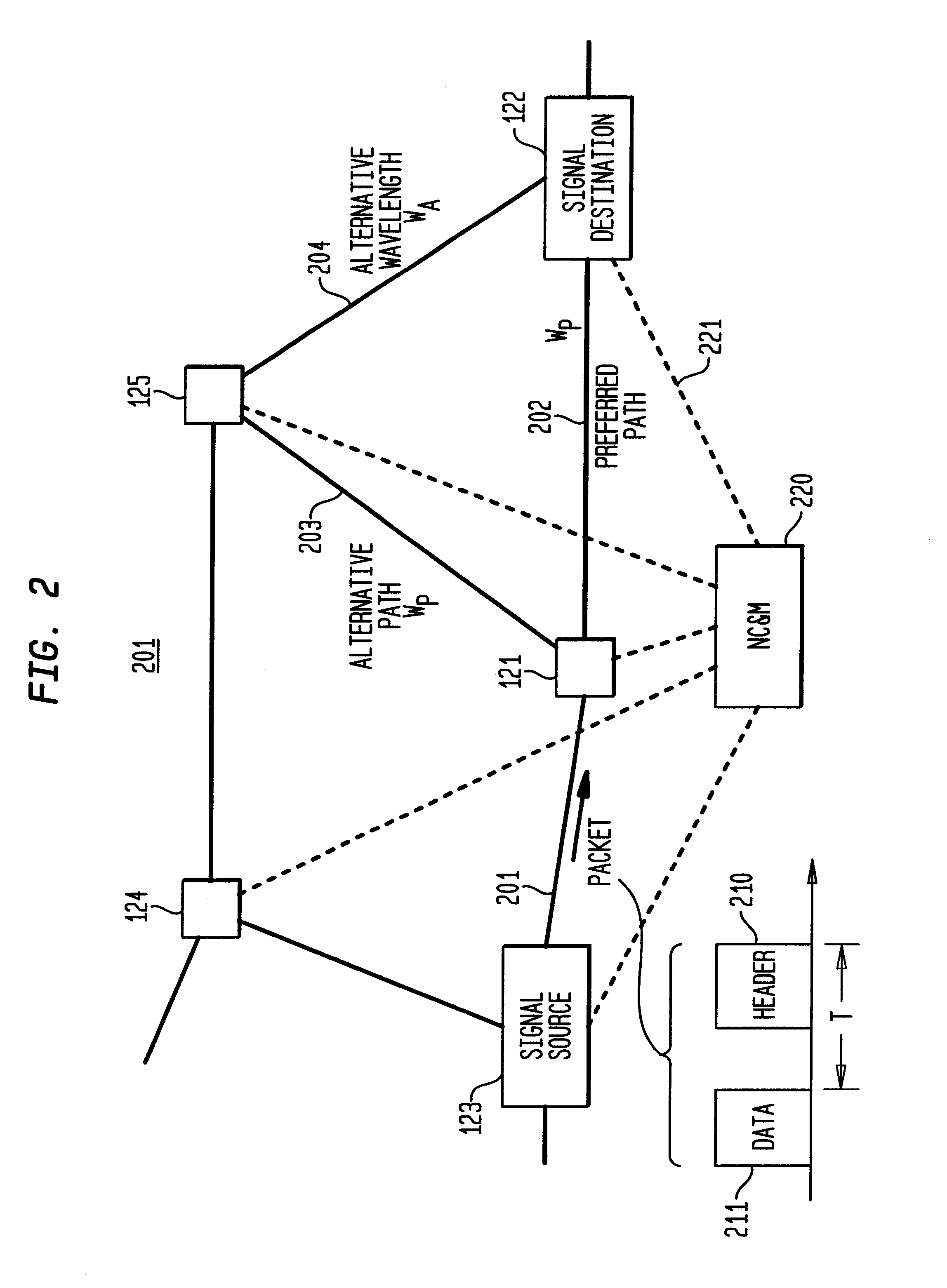
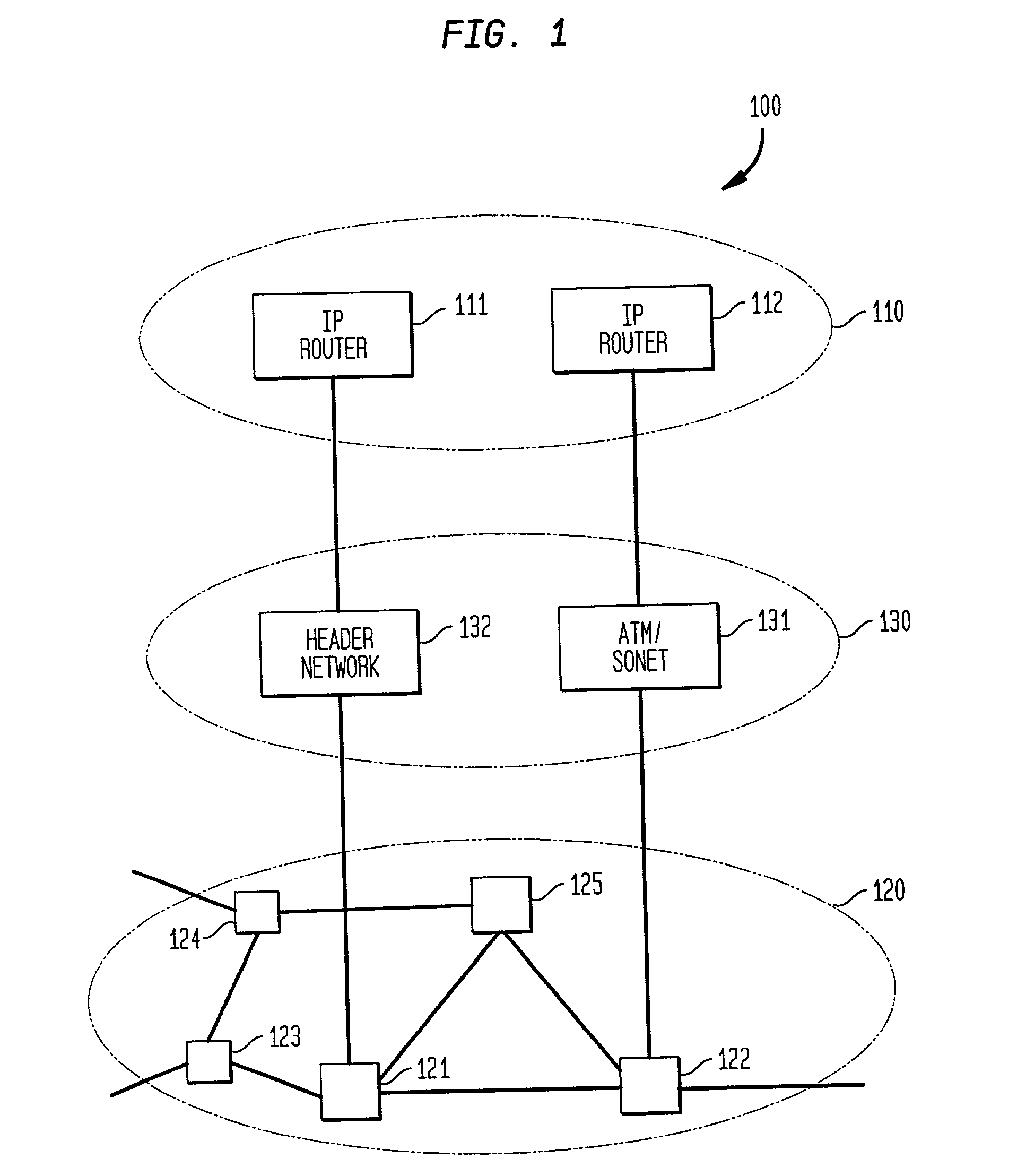
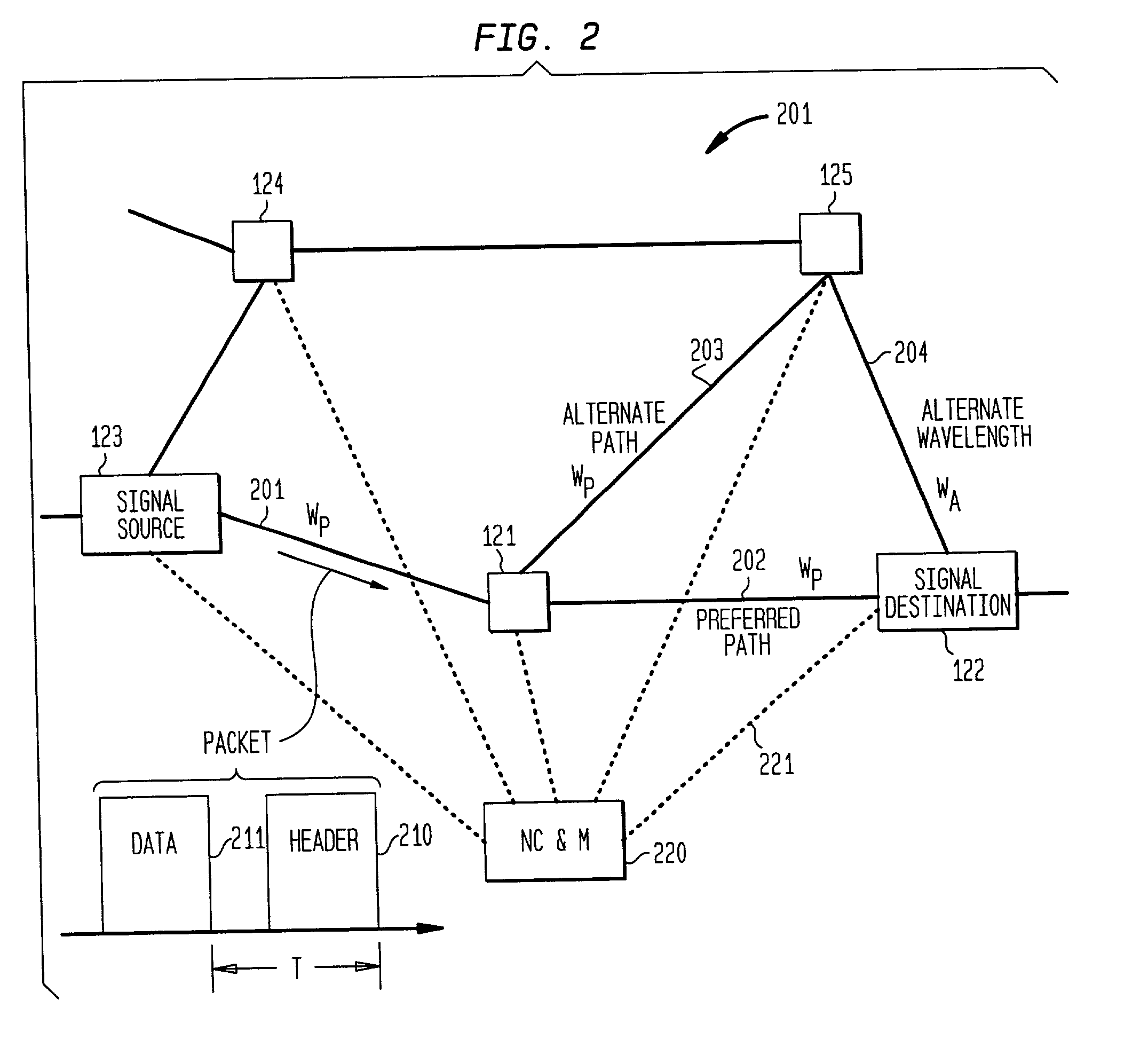
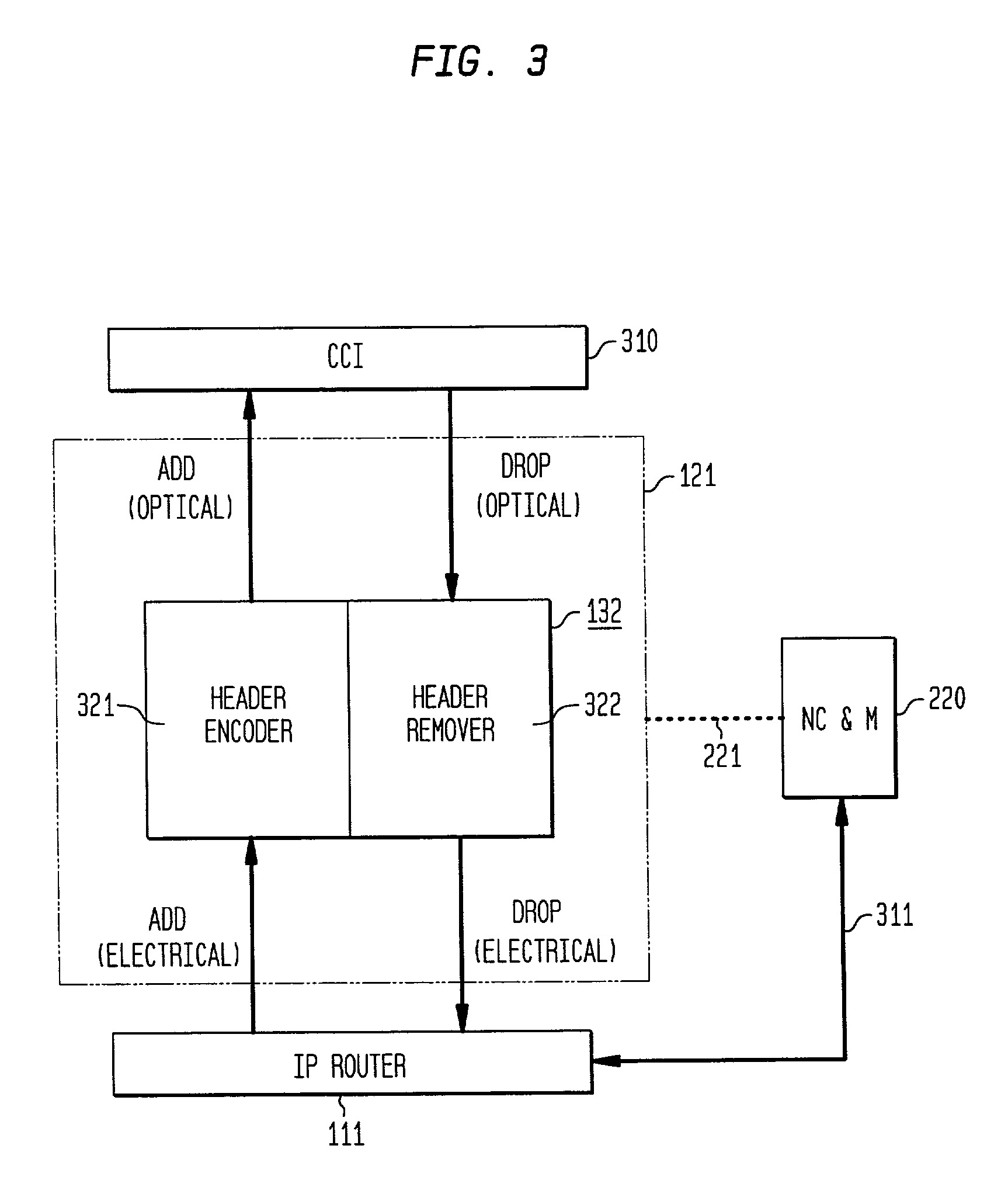
High-throughput, low-latency next generation internet networks using optical tag switching
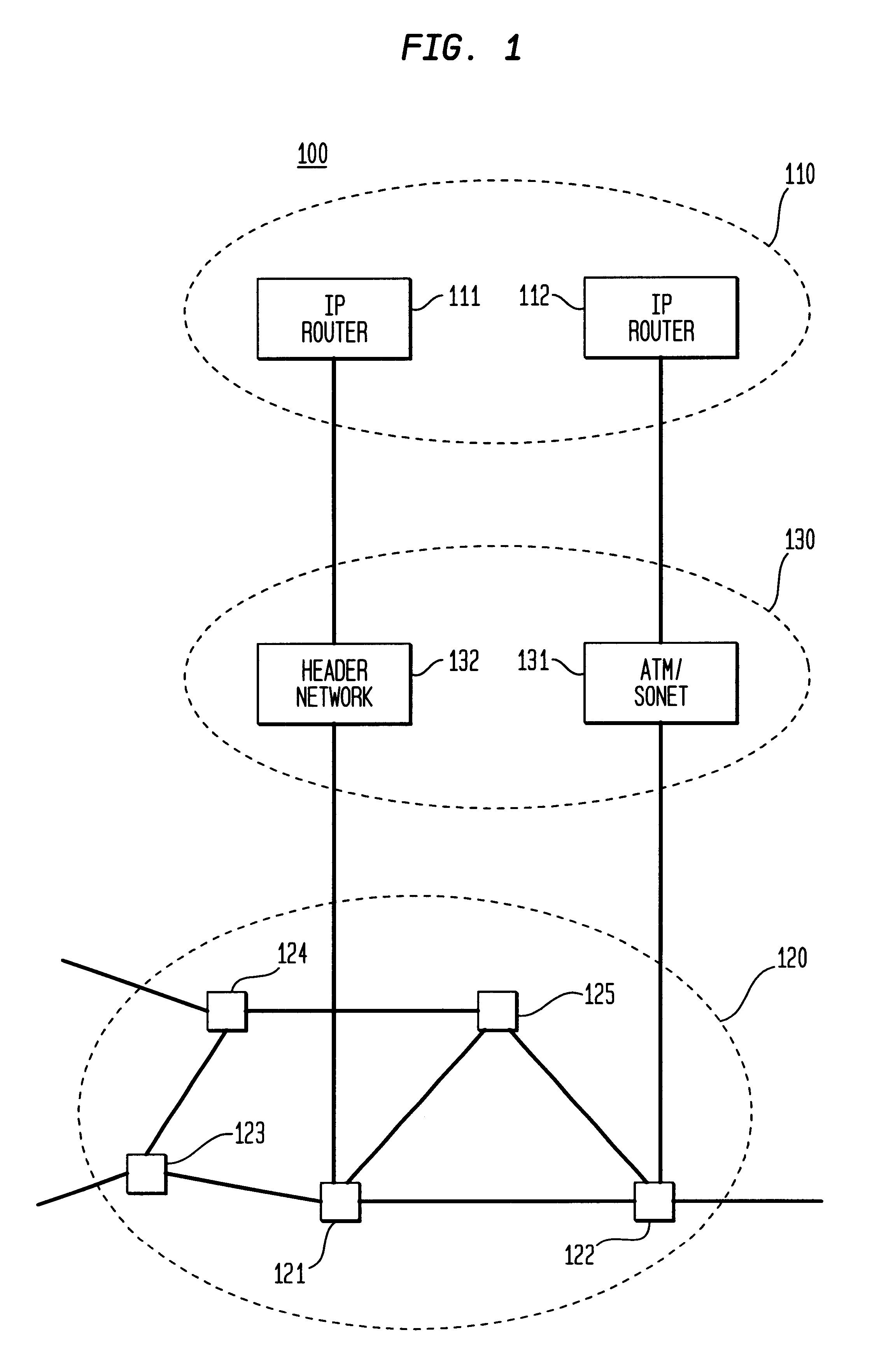
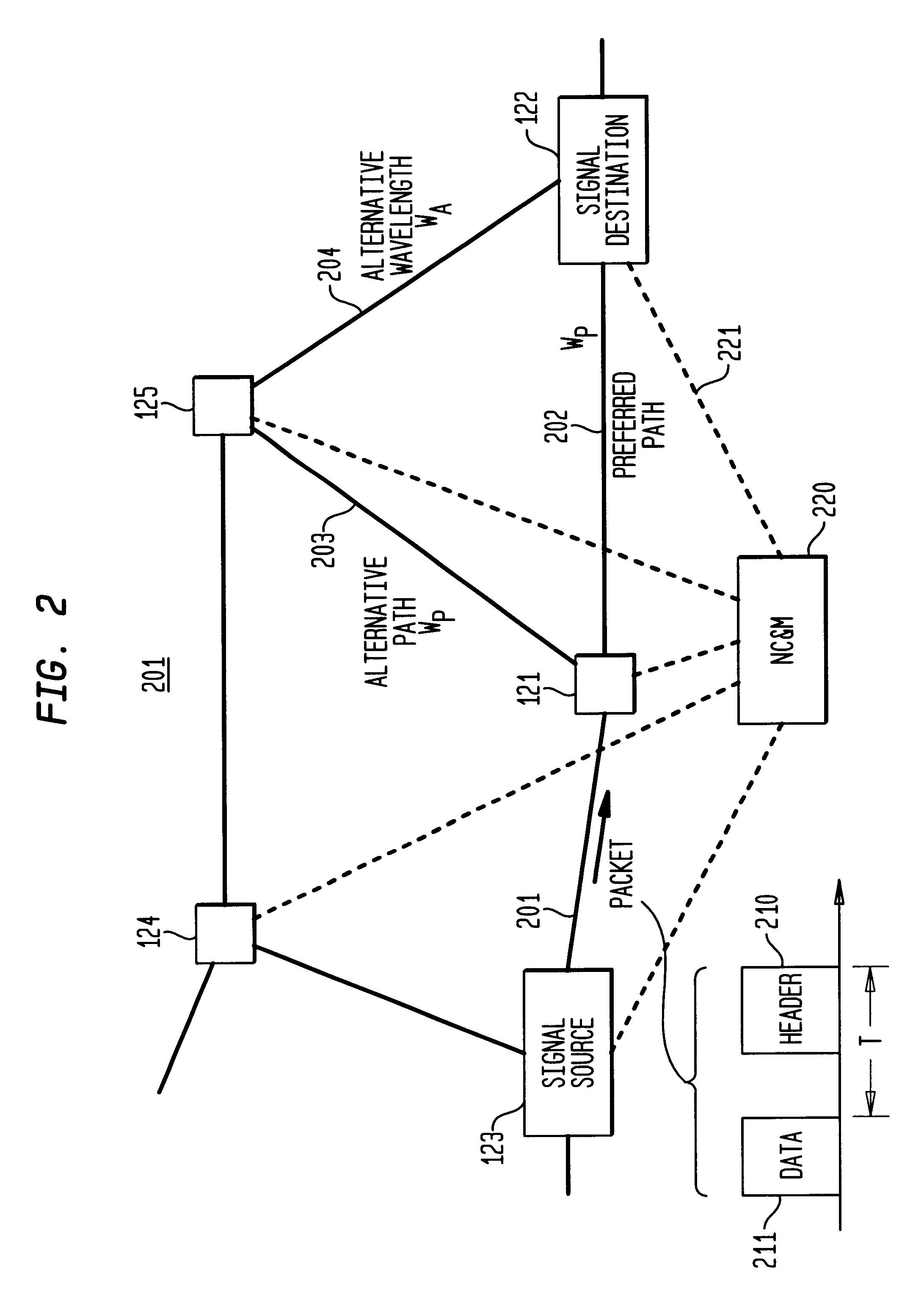
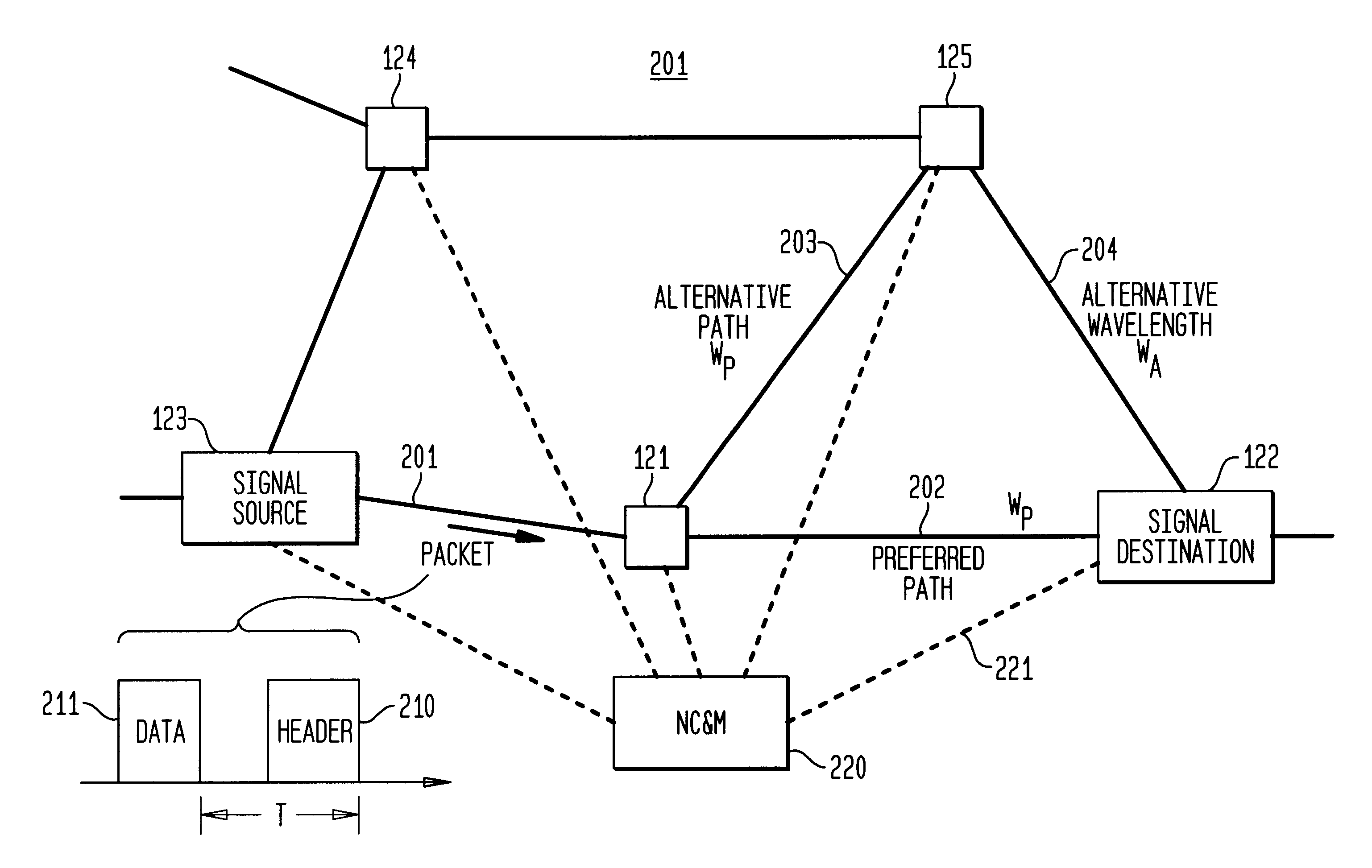
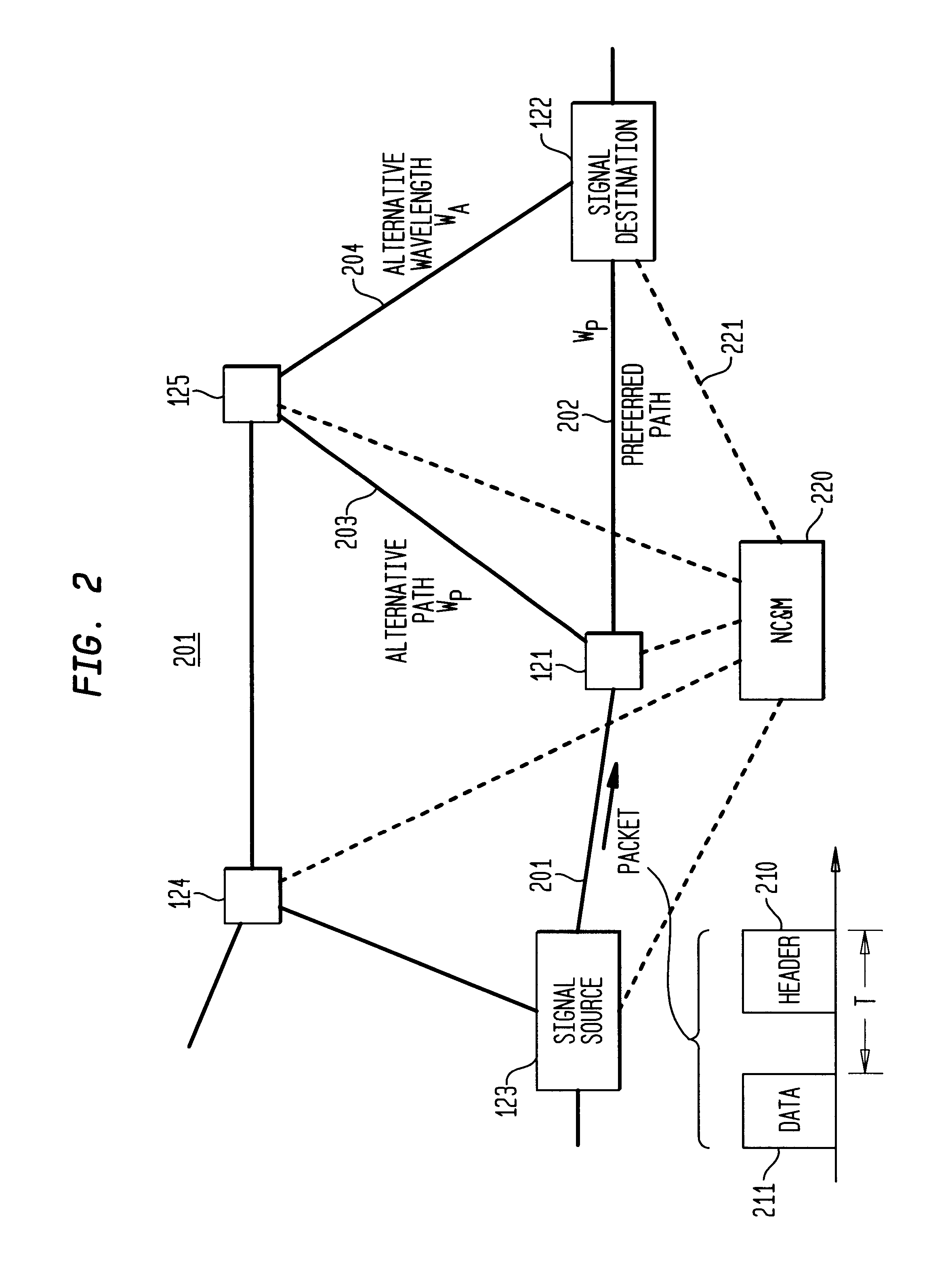
InactiveUS6111673AEfficient comprehensive utilizationSignificant overheadMultiplex system selection arrangementsLaser detailsSignal routingInternet network
An optical signaling header technique applicable to optical networks wherein packet routing information is embedded in the same channel or wavelength as the data payload so that both the header and data payload propagate through network elements with the same path and the associated delays. The header routing information has sufficiently different characteristics from the data payload so that the signaling header can be detected without being affected by the data payload, and that the signaling header can also be removed without affecting the data payload. The signal routing technique can be overlaid onto the conventional network elements in a modular manner using two types of applique modules. The first type effects header encoding and decoding at the entry and exit points of the data payload into and out of the network; the second type effects header detection at each of the network elements.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
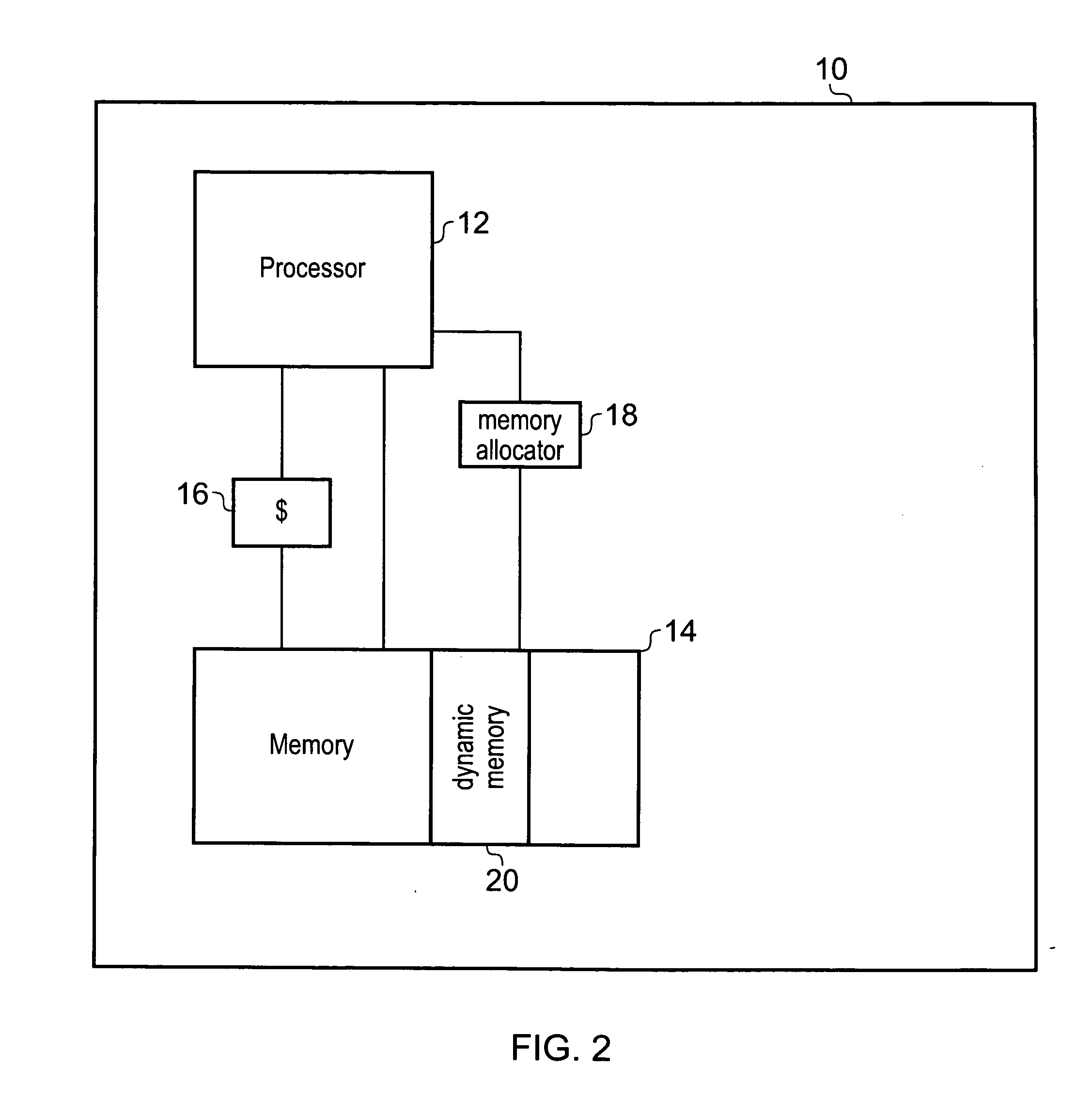
Storage device and information processing system
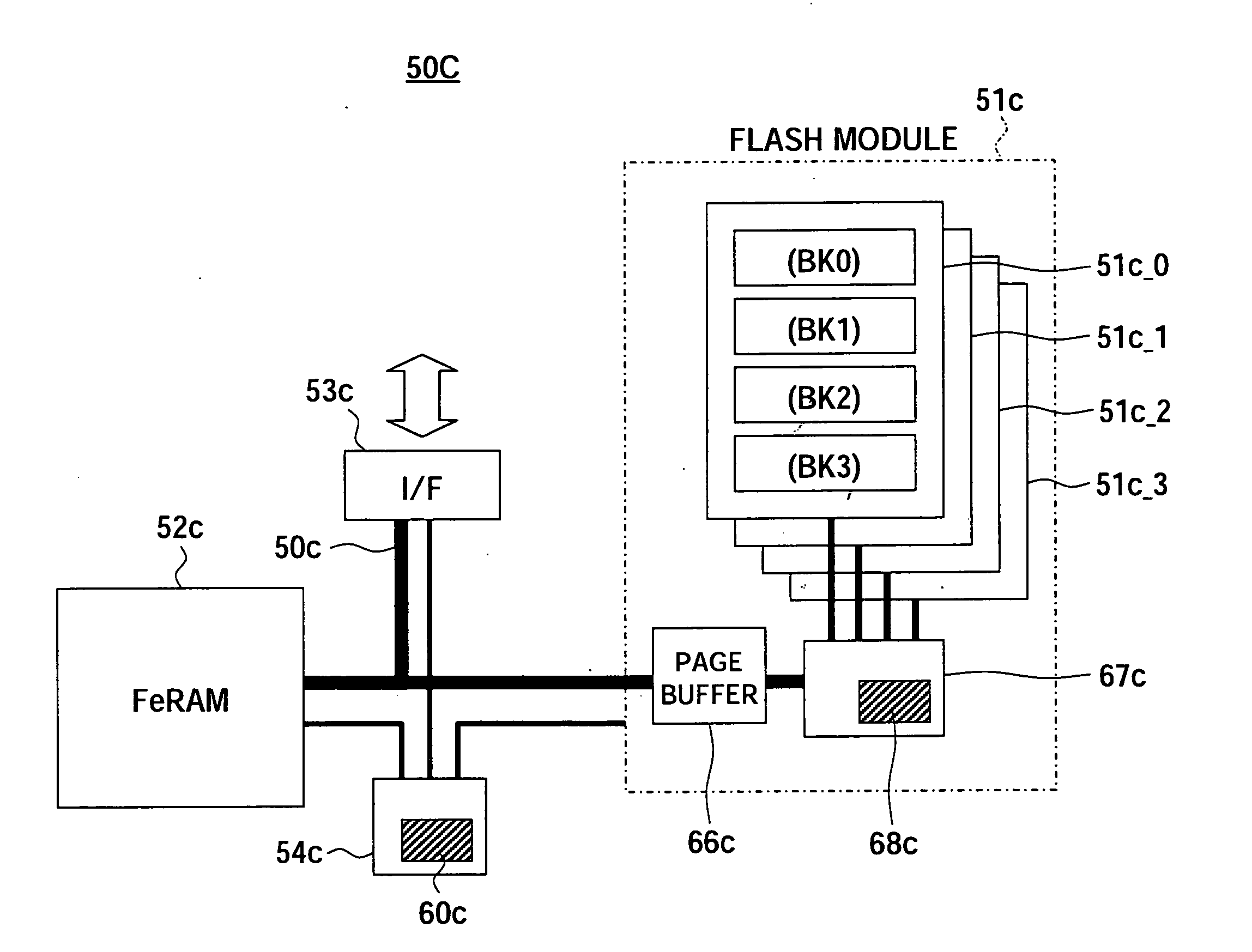
ActiveUS20060087893A1Significant overheadSolve the real problemMemory architecture accessing/allocationEnergy efficient ICTInformation handling systemControl circuit
A storage device able to make a redundant write operation of unselected data unnecessary and able to optimize an arrangement of pages to a state having a high efficiency for rewriting, wherein the storage device has a first memory unit, a second memory unit having a different access speed from the first memory, and a control circuit, wherein the control circuit has a function of timely moving the stored data in two ways between the first memory unit and the second memory unit having different access speeds in reading or rewriting.
Owner:SONY CORP
Systems, methods, and storage structures for cached databases
InactiveUS20080059492A1Improve read performanceSpace minimizationDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsData miningDisk space
Systems and methods for clustered access to as many columns as possible given a particular ongoing query mix and a constrained amount of disk space is disclosed. A compressed database is split into group of columns, each column having duplicates removed and being sorted. Then certain groups are transferred to a fast memory depending on the record of previously received queries.
Owner:TARIN STEPHEN A
System and method for synchronizing data trasnmission across a variable delay interface
InactiveUS20020089927A1Significant overheadLimitation in wireless bandwidthError prevention/detection by using return channelFrequency-division multiplex detailsSufficient timeComputerized system
A method of synchronizing data transmission between a host computer system and a transmitter across an interface with variable delay or latency. The host computer system marks transition frames between successive transmission intervals and transfers the outgoing frames across the variable interface to the transmitter. The transmitter enqueues outgoing frames into one or more FIFO transmission queue(s) and processes the enqueued frames as appropriate for the communication protocol in use. Marked frames are detected as they reach the head of the appropriate transmit queue. In particular, while bypassing is not active, the transmitter transmits unmarked frames until the end of the current interval, or until there is insufficient time in the interval to transmit another frame or until a marked frame is detected. While bypassing is not active, the transmitter terminates transmission from the transmit queue when a marked frame is detected during each interval. While bypassing is active, the transmitter discards unmarked frames without transmission until a marked frame is detected. During each interval, the transmitter activates bypassing if a marked frame has not been detected and deactivates bypassing if a marked frame is detected while bypassing is active. The transmitter enables queue mark operation if a marked frame is detected while queue mark operation is not enabled. The transmitter increments a bypass counter each time an interval ends without detecting a marked frame, and disables queue mark operation if the bypass counter reaches a predefined limit.
Owner:CONEXANT
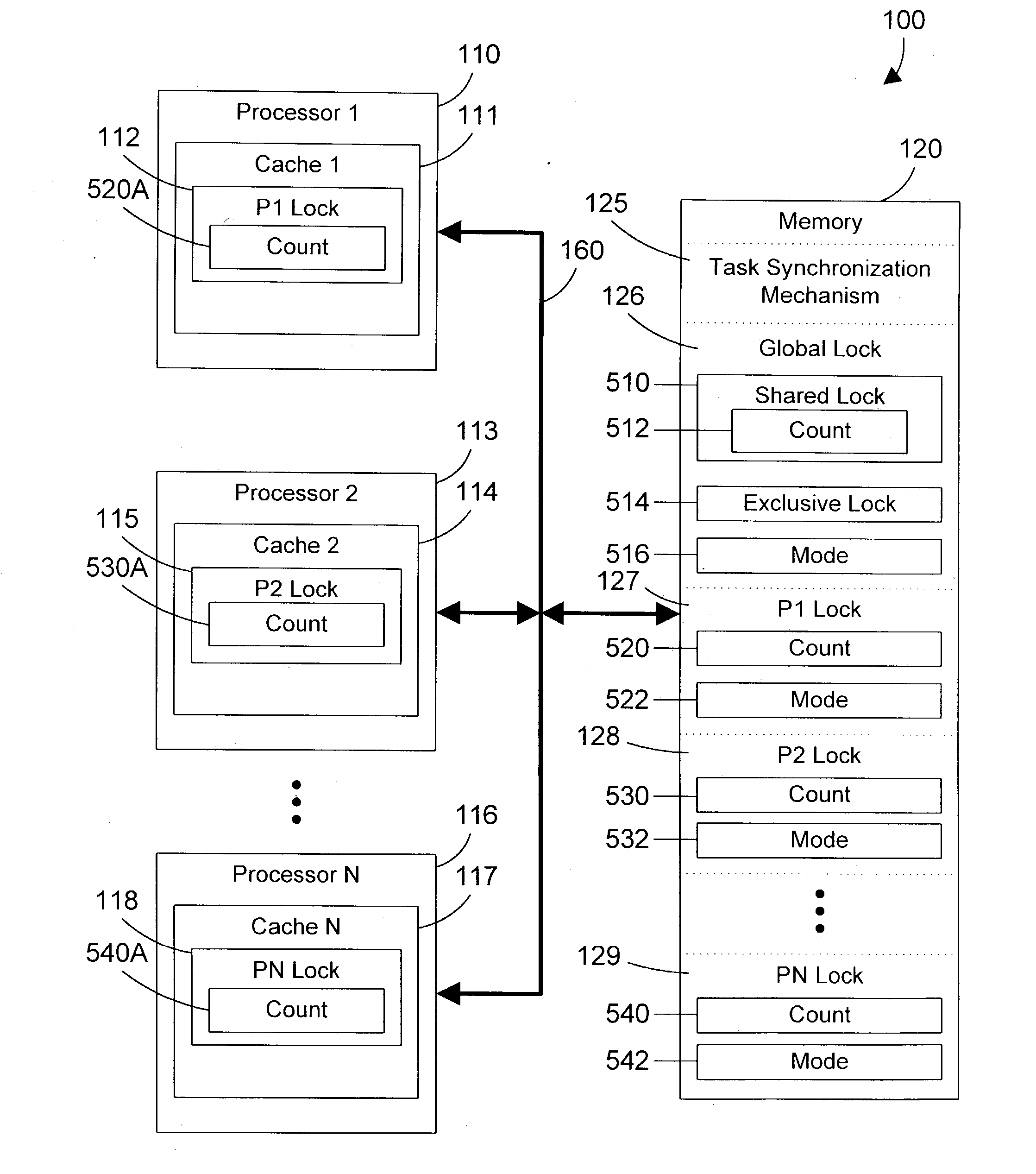
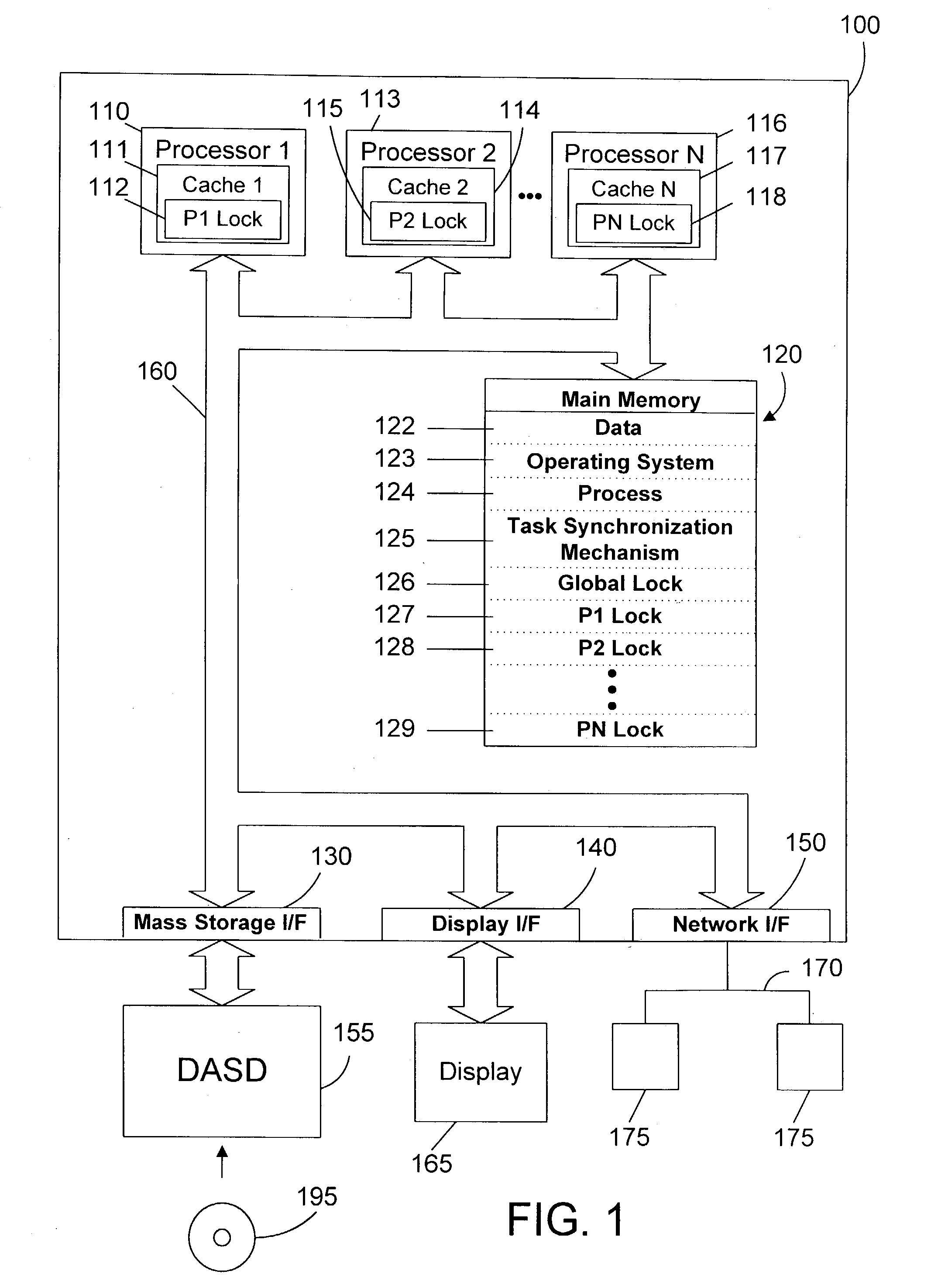
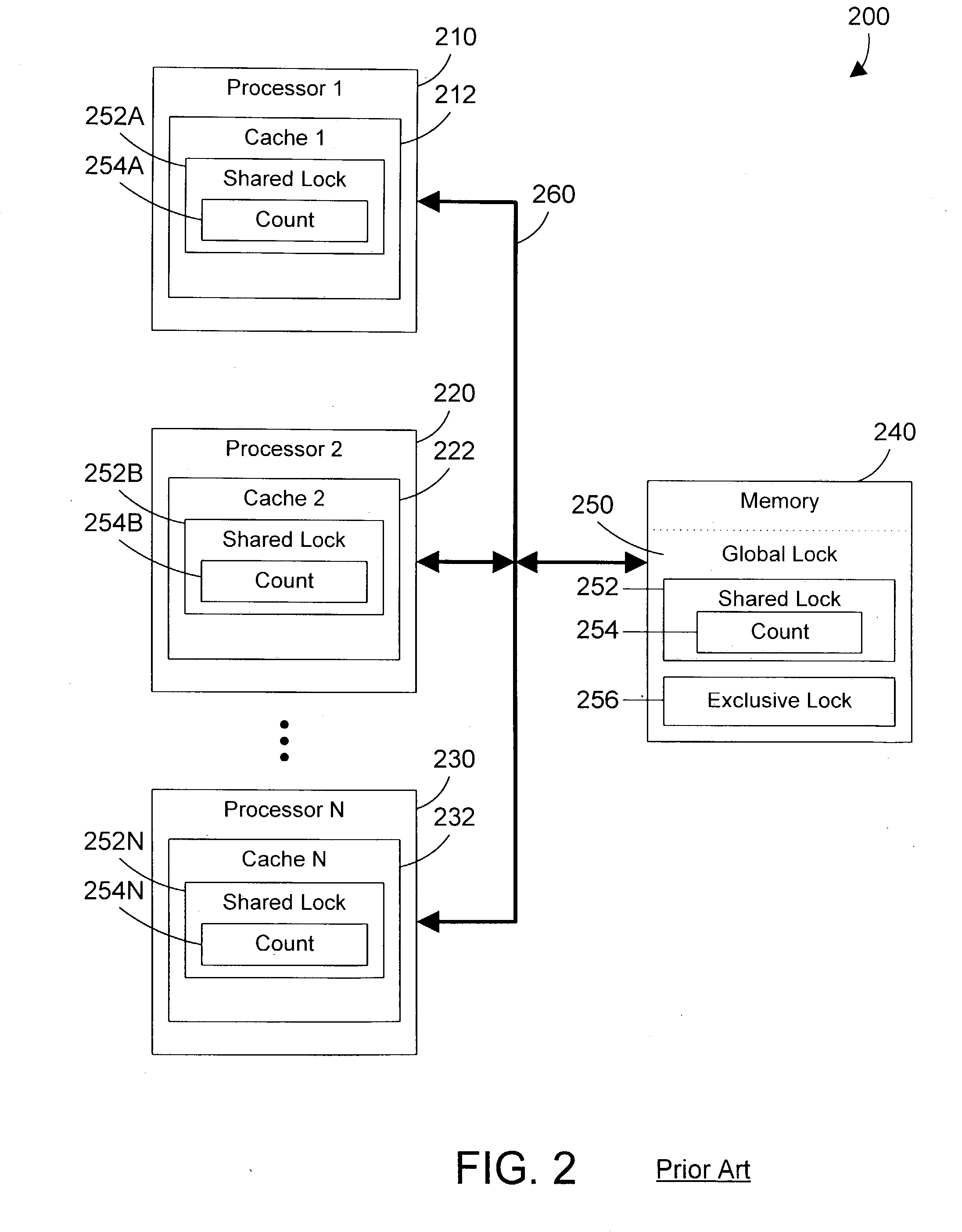
Task synchronization mechanism and method
ActiveUS20040143712A1Significant overheadSignificant performanceUnauthorized memory use protectionMultiprogramming arrangementsComputer architectureMemory bus
A task synchronization mechanism operates on a global lock that is shared between processors an on local locks that are not shared between processors. The local locks are processor-specific locks. Each processor-specific lock is dedicated to a particular processor in the system. When shared access to a resource is required, a processor updates its processor-specific lock to indicate the processor is sharing the resource. Because each processor-specific lock is dedicated to a particular processor, this eliminates a significant portion of the memory bus traffic associated with all processors reading and updating the same lock. When exclusive access to a resource is required, the requesting processor waits until the count of all processor-specific locks indicate that none of these processors have a lock on the resource. Once no processor has a lock on the resource, exclusive access to the resource may be granted. By changing from a single lock to multiple processor-specific locks, significant performance benefits are achieved by eliminating the memory bus traffic associated with caching a single lock to multiple processors.
Owner:IBM CORP
High-throughput, low-latency next generation internet networks using optical label switching and high-speed optical header generation, detection and reinsertion
InactiveUS6545781B1Efficient comprehensive utilizationSignificant overheadMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsComputer hardwareOptical IP Switching
An optical signaling header technique applicable to optical networks wherein packet routing information is embedded in the same channel or wavelength as the data payload so that both the header and data payload propagate through network elements with the same path and the associated delays. The header routing information has sufficiently different characteristics from the data payload so that the signaling header can be detected without being affected by the data payload, and that the signaling header can also be removed without affecting the data payload. The signal routing technique can overlaid onto the conventional network elements in a modular manner using two types of applique modules. The first type effects header encoding and decoding at the entry and exit points of the data payload into and out of the network; the second type effects header detection at each of the network elements.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
System and method for standardizing accounting of consumables
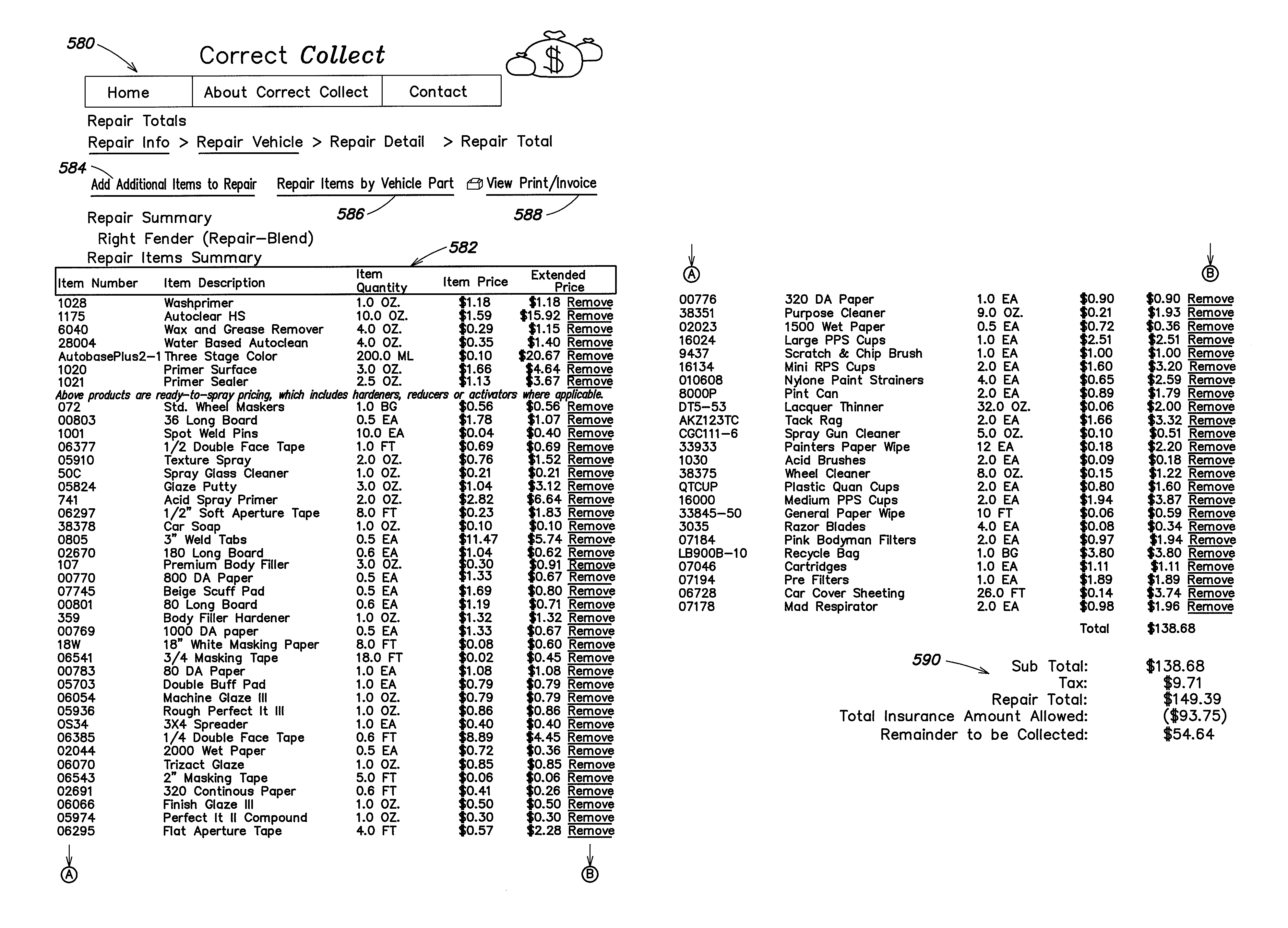
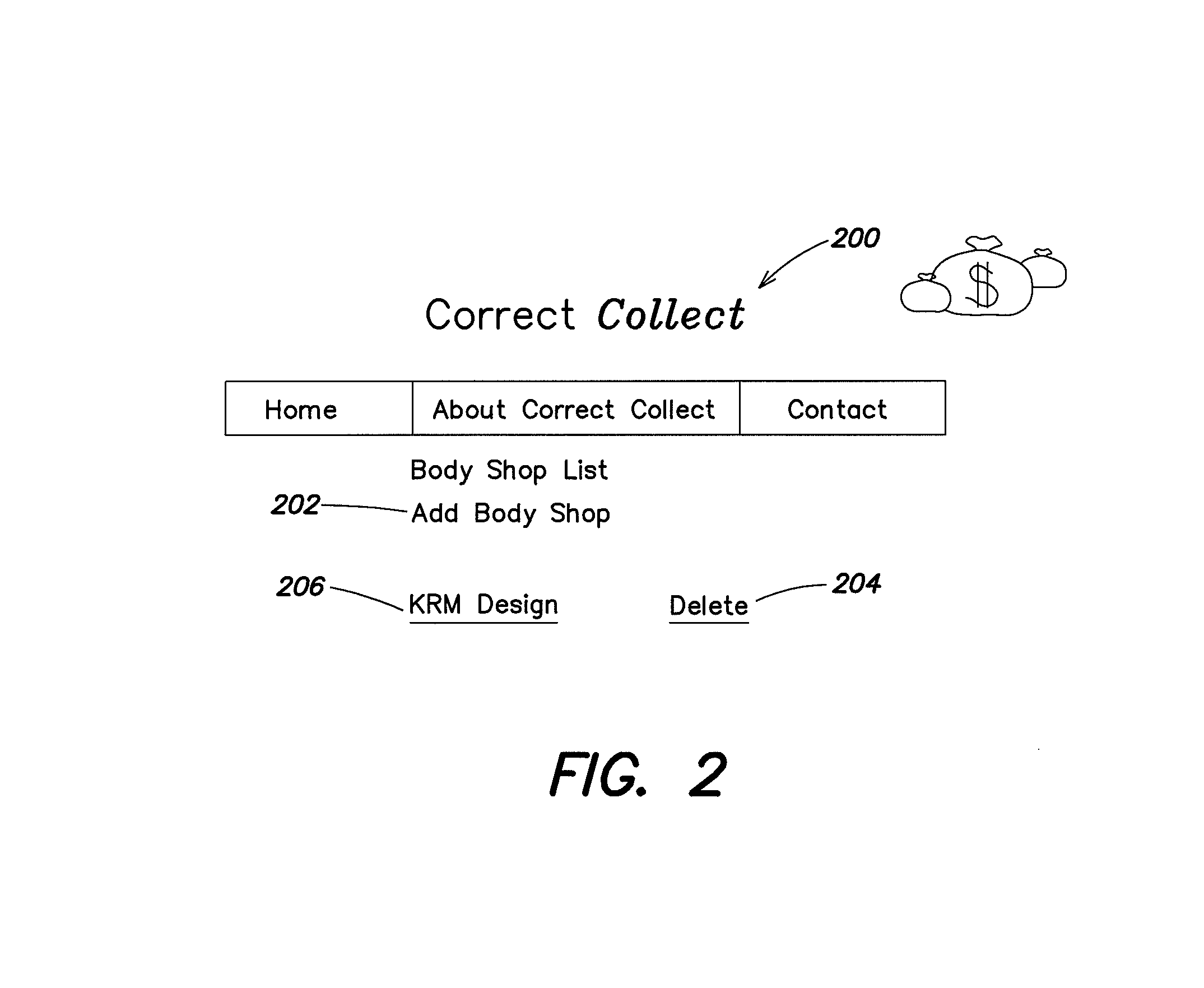
InactiveUS8364563B2Good flexibilitySignificant overheadComplete banking machinesHand manipulated computer devicesService provisionProviding material
According to one aspect, the system for standardizing accounting of consumables provides material lists of consumables used in particular repairs. The development of the material lists takes place through tracking of consumables used during the repair of various parts of different types of automotive vehicles. The size, shape, time, and material for repair may vary by make and model of vehicle, as well as the characteristics associated with each make and model. Once a materials list for a reasonable repair is assembled, the process is repeated for each vehicle make, model, and part to be repaired. The end result is a material list template for each part that a body shop repairs. In one embodiment, a wholesaler maintains and provides access to a system for standardizing accounting to body shops. The interface is customized for each body shop, so that specific materials will be provided on the material list for a repair. In another embodiment, user selectable options provide brand selection for the materials used in a particular repair. Providing brand selections and / or restricting selection of brand may provide an incentive for material purchases into specific brands. According to another aspect, maintaining material lists for each any every part of each model and make of vehicle represents significant overhead for any service provider. Creating standardized automobile objects for use in conjunction with a system for standardizing accounting of consumables provides for easier maintenance and greater flexibility to updates.
Owner:CAR PARTS COLOR SYST
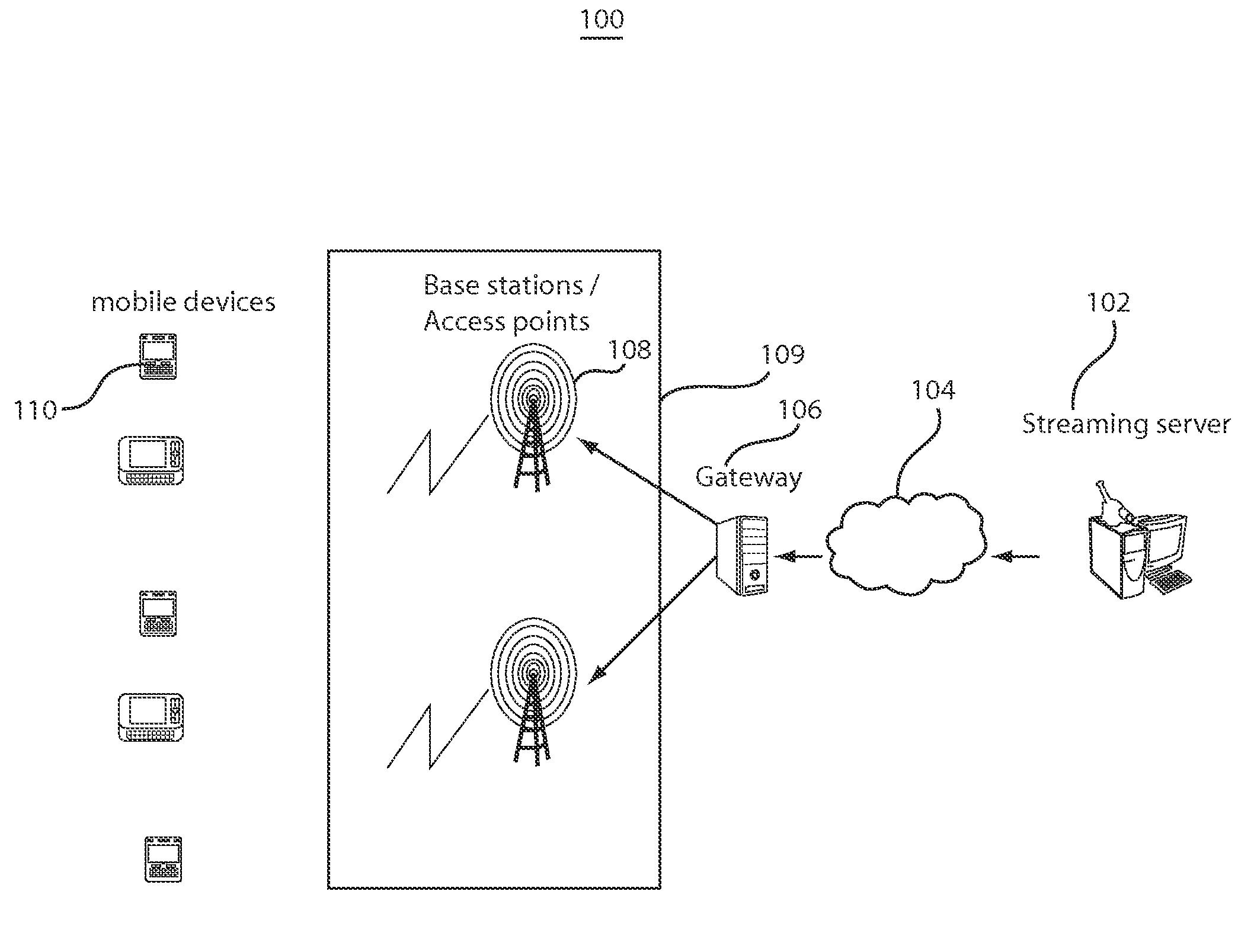
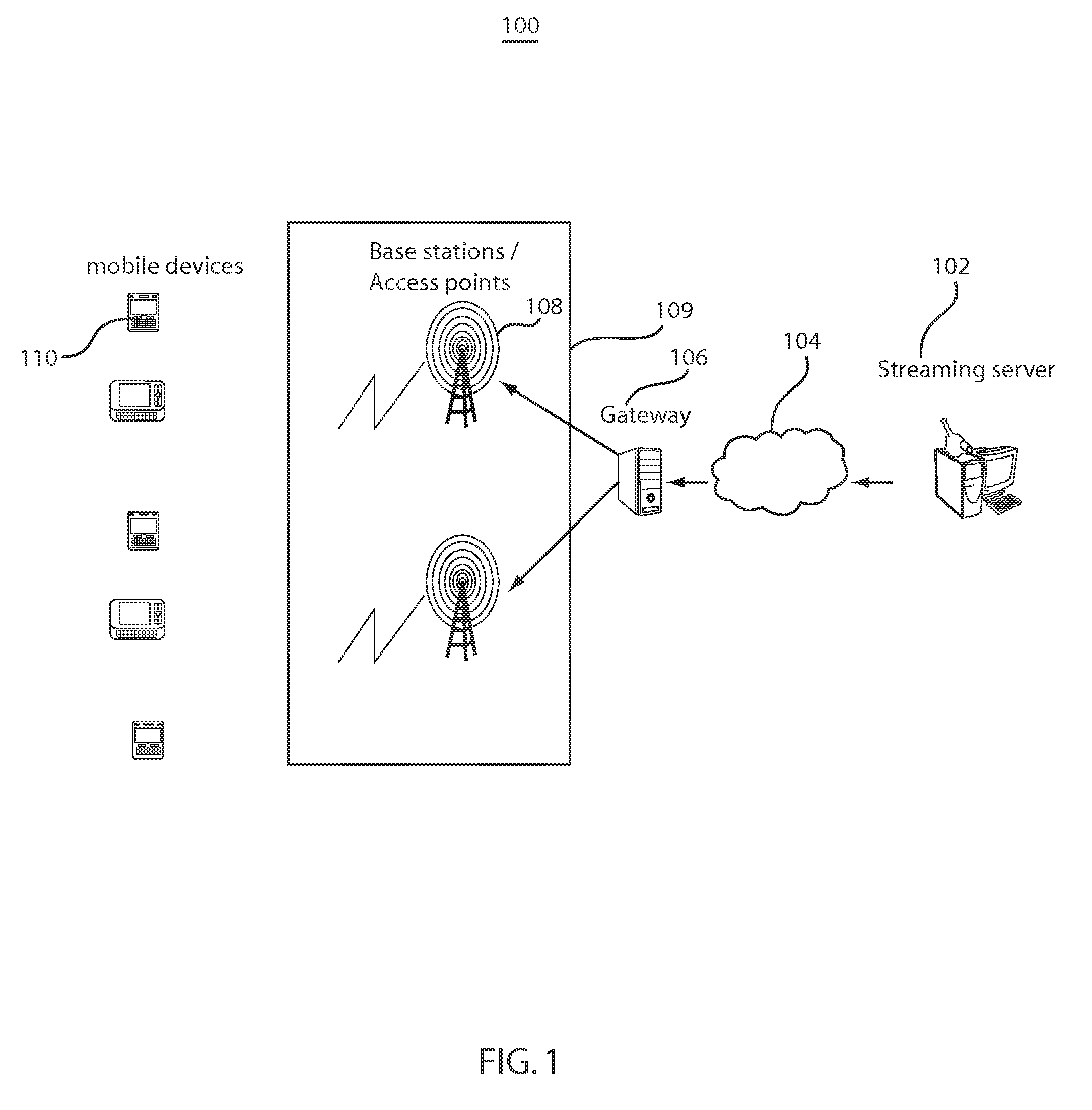
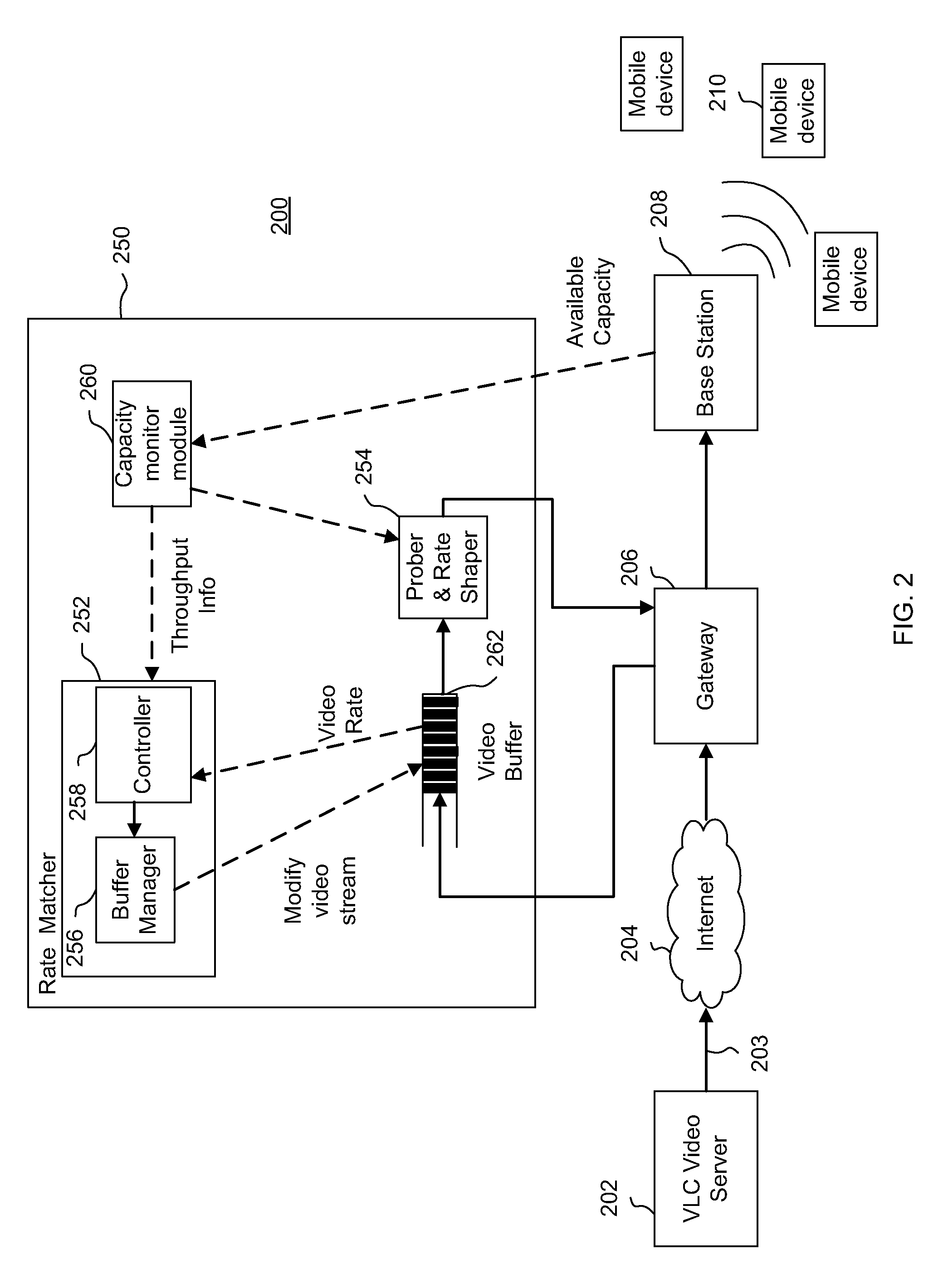
Methods and systems for rate matching and rate shaping in a wireless network
ActiveUS20100189063A1Accurate estimateSignificant overheadNetwork traffic/resource managementDigital video signal modificationRate shapingWireless data
Rate matching and rate shaping methods and systems for managing data traffic on wireless channels are disclosed. Rate matching embodiments dynamically determine downlink video data transmission rates based on frame decoding deadlines and frame sizes. In addition, if the channel capacity cannot support the video data transmission rate, the rate matcher can adjust the video stream accordingly so that it is supportable by the channel capacity. In turn, rate shaping implementations can tailor the transmission rate shaping based on the state of the wireless data channel. Shaper operations can be specifically adapted to a saturated state of the wireless channel, to an unsaturated state of the wireless channel and to transitions between the unsaturated and saturated states.
Owner:NEC CORP
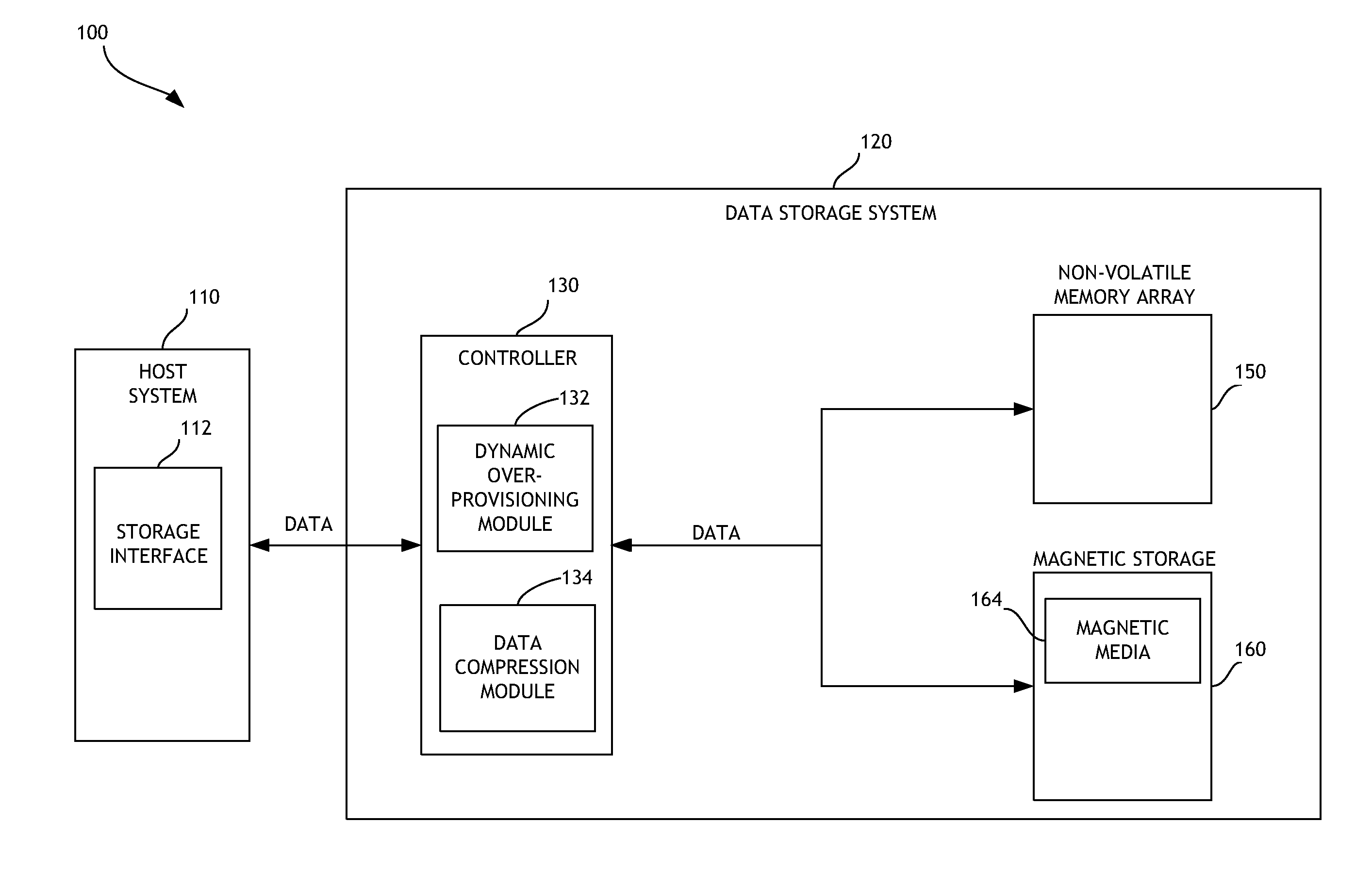
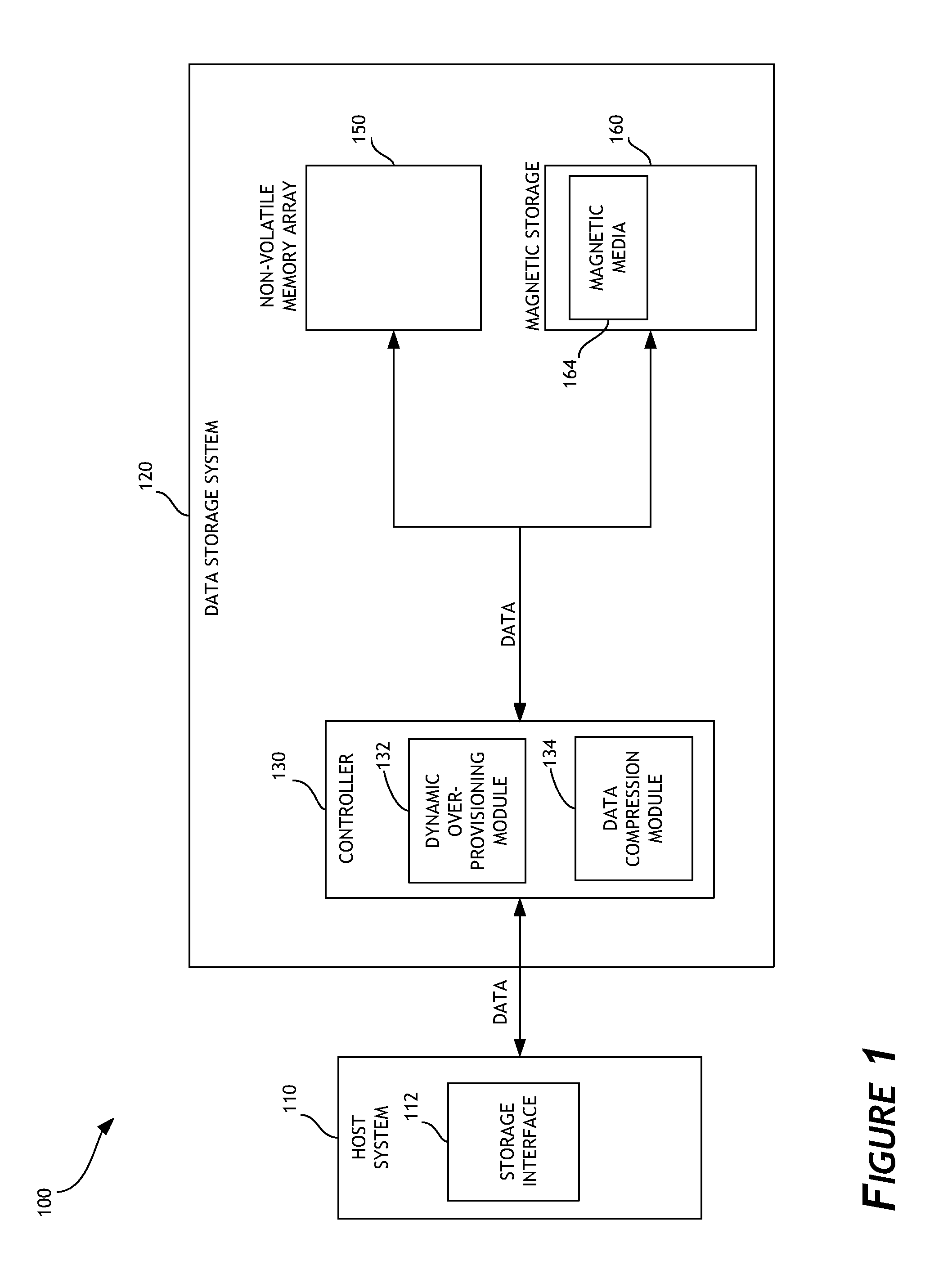
Dynamic overprovisioning for data storage systems
ActiveUS20140181369A1Improve efficiencyIncreased longevityMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationWrite amplificationCache hit rate
Disclosed embodiments are directed to systems and methods for dynamic overprovisioning for data storage systems. In one embodiment, a data storage system can reserve a portion of memory, such as non-volatile solid-state memory, for overprovisioning. Depending on various overprovisioning factors, recovered storage space due to compressing user data can be allocated for storing user data and / or overprovisioning. Utilizing the disclosed dynamic overprovisioning systems and methods can result is more efficient utilization of cache memory, reduction of write amplification, increase in a cache hit rate, and the like. Improved data storage system performance and increased endurance and longevity can thereby be attained.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Allocating and deallocating portions of memory
ActiveUS20130088501A1Reduce in quantityShorten the timeMemory adressing/allocation/relocationParallel computing
Owner:ARM LTD
High-throughput, low-latency next generation internet networks using optical label switching and high-speed optical header generation, detection and reinsertion
InactiveUS6580537B1Efficient comprehensive utilizationSignificant overheadMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsComputer hardwareOptical IP Switching
An optical signaling header technique applicable to optical networks wherein packet routing information is embedded in the same channel or wavelength as the data payload so that both the header and data payload propagate through network elements with the same path and the associated delays. The header routing information has sufficiently different characteristics from the data payload so that the signaling header can be detected without being affected by the data payload, and that the signaling header can also be removed without affecting the data payload. The signal routing technique can overlaid onto the conventional network elements in a modular manner using two types of applique modules. The first type effects header encoding and decoding at the entry and exit points of the data payload into and out of the network; the second type effects header detection at each of the network elements.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
High-throughput, low-latency next generation internet networks using optical label switching and high-speed optical header generation, detection and reinsertion
InactiveUS6525850B1Efficient comprehensive utilizationSignificant overheadMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsComputer hardwareOptical IP Switching
An optical signaling header technique applicable to optical networks wherein packet routing information is embedded in the same channel or wavelength as the data payload so that both the header and data payload propagate through network elements with the same path and the associated delays. The header routing information has sufficiently different characteristics from the data payload so that the signaling header can be detected without being affected by the data payload, and that the signaling header can also be removed without affecting the data payload. The signal routing technique can overlaid onto the conventional network elements in a modular manner using two types of applique modules. The first type effects header encoding and decoding at the entry and exit points of the data payload into and out of the network; the second type effects header detection at each of the network elements.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
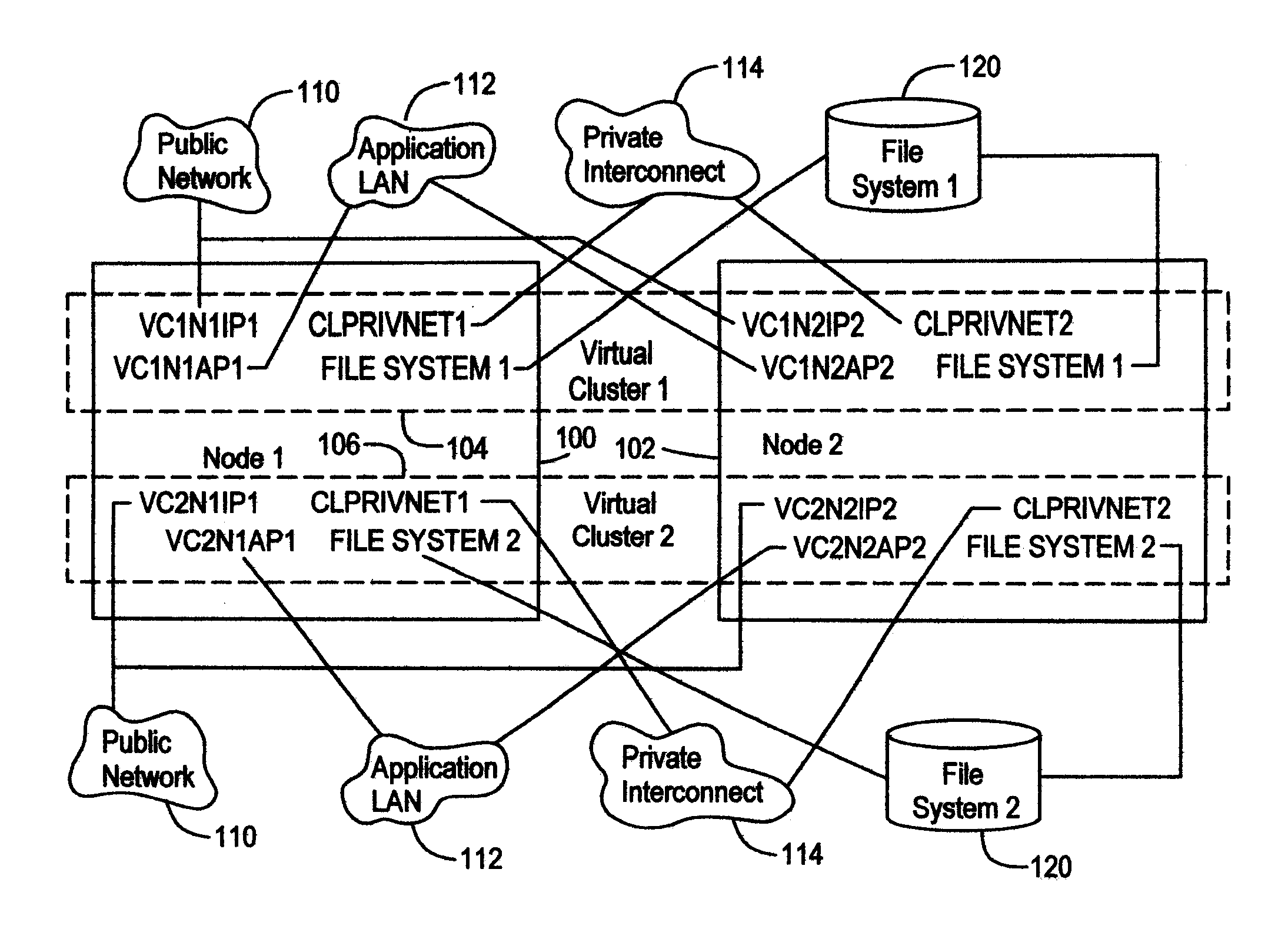
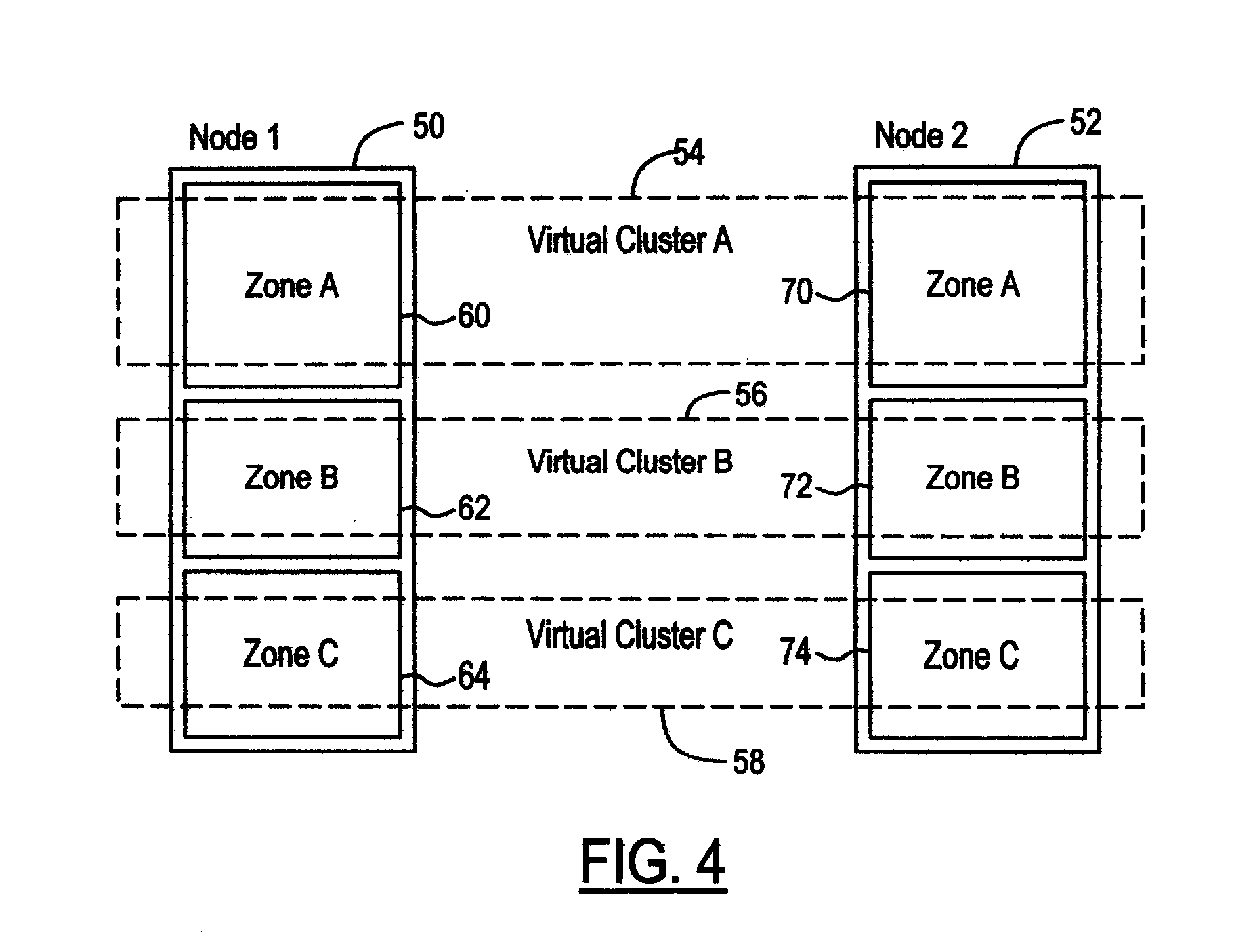
Virtual cluster based upon operating system virtualization
ActiveUS20090089406A1Significant overheadSignificant burdenDigital computer detailsSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationVirtualizationApplication software
Virtual clusters are based upon virtual operating systems. The physical cluster includes a plurality of physical server nodes. Each physical server node includes a plurality of physical resources and a virtualizing subsystem. The virtualizing subsystem is capable of creating separate environments that logically isolate applications from each other. The separate environments are virtual operating systems. A virtual operating system is configured on each physical server node by defining properties of the virtual operating system. A virtual cluster is composed of a plurality of virtual operating systems that are on a plurality of physical server nodes. A cluster application runs on the virtual cluster. The virtual cluster presents the plurality of virtual operating systems that compose the virtual cluster to the cluster application such that the cluster application is isolated from any other virtual operating systems that compose other virtual clusters on the plurality of physical server nodes.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
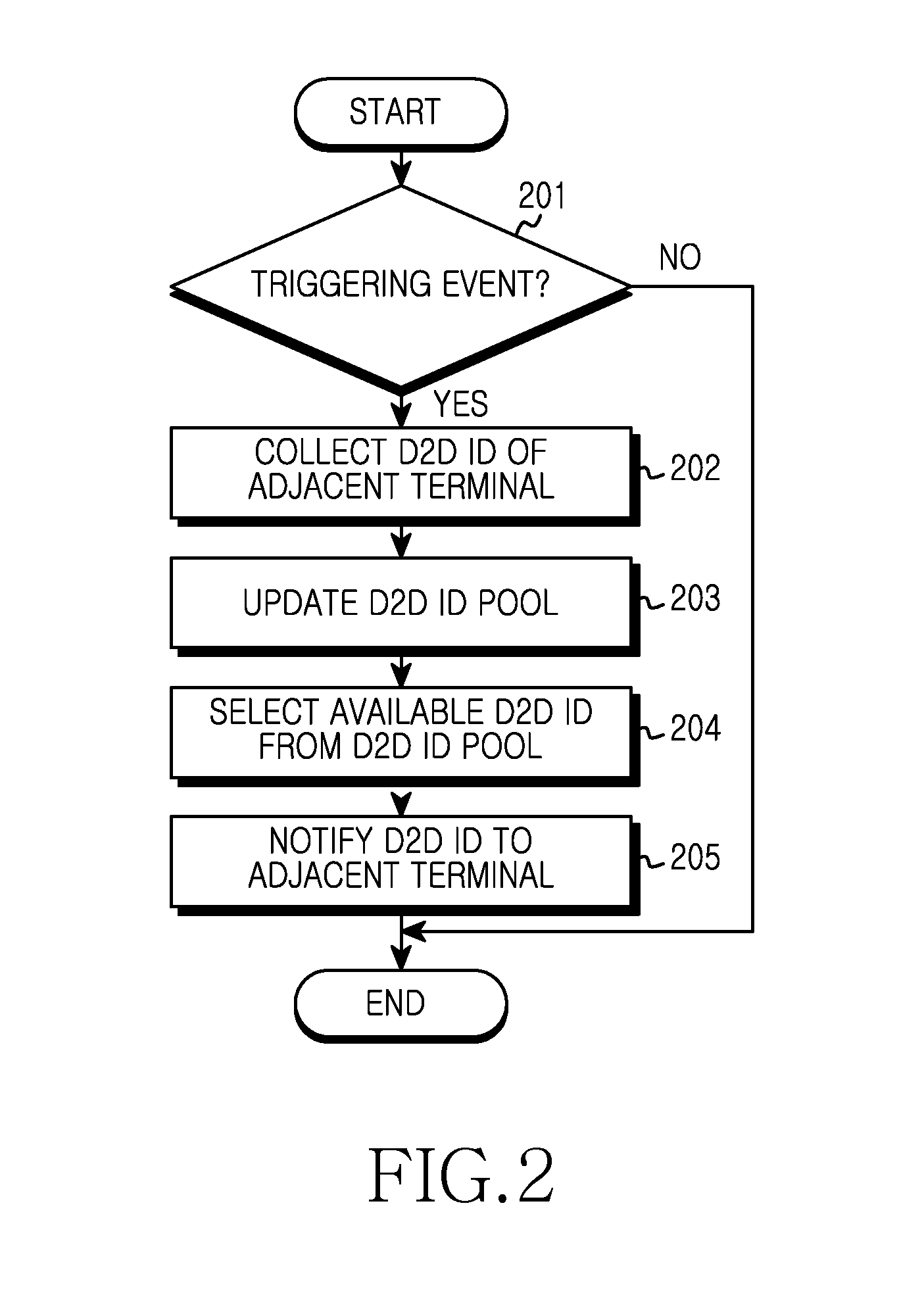
Apparatus and method for allocating d2d id of user terminal in ad-hoc network
ActiveUS20130040677A1Avoid collisionSignificant overheadNetwork topologiesRadio transmissionReal-time computingDevice to device
An apparatus and a method for allocating a Device-to-Device (D2D) IDentity (ID) of a user terminal in an ad-hoc network are provided. The method includes determining that a first D2D ID allocated to the user terminal is duplicated with a second D2D ID allocated to at least one other terminal located within a predefined range from the user terminal, determining whether the user terminal is in communication, when the first D2D ID is duplicated with the second D2D ID, and changing the first D2D ID into a third D2D ID with reference to a D2D ID pool so that the first D2D ID is not duplicated with the second D2D ID, when the user terminal is not in communication.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
High-throughput, low-latency next generation internet networks using optical label switching and high-speed optical header generation, detection and reinsertion
InactiveUS20010017723A1Efficient comprehensive utilizationSignificant overheadMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division optical multiplex systemsComputer hardwareWavelength
An optical signaling header technique applicable to optical networks wherein packet routing information is embedded in the same channel or wavelength as the data payload so that both the single-sideband modulated header and data payload propagate through network elements with the same path and the associated delays. The header routing information has sufficiently different characteristics from the data payload so that the signaling header can be detected without being affected by the data payload, and that the signaling header can also be removed without affecting the data payload. The signal routing technique can overlaid onto the conventional network elements in a modular manner using two types of applique modules. The first type effects header encoding and decoding at the entry and exit points of the data payload into and out of the network; the second type effects header detection at each of the network elements.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Thread suspension system and method using trapping instructions
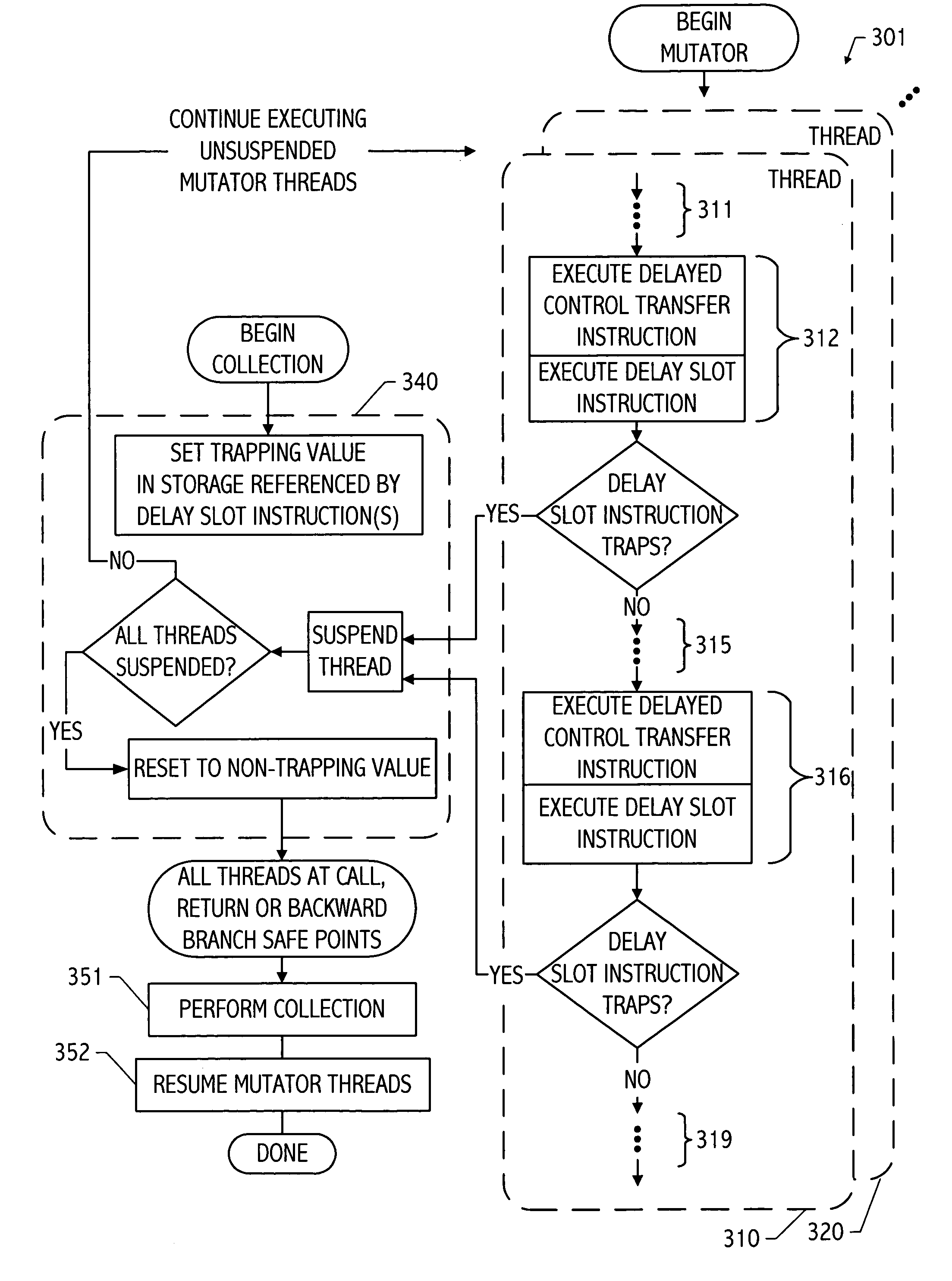
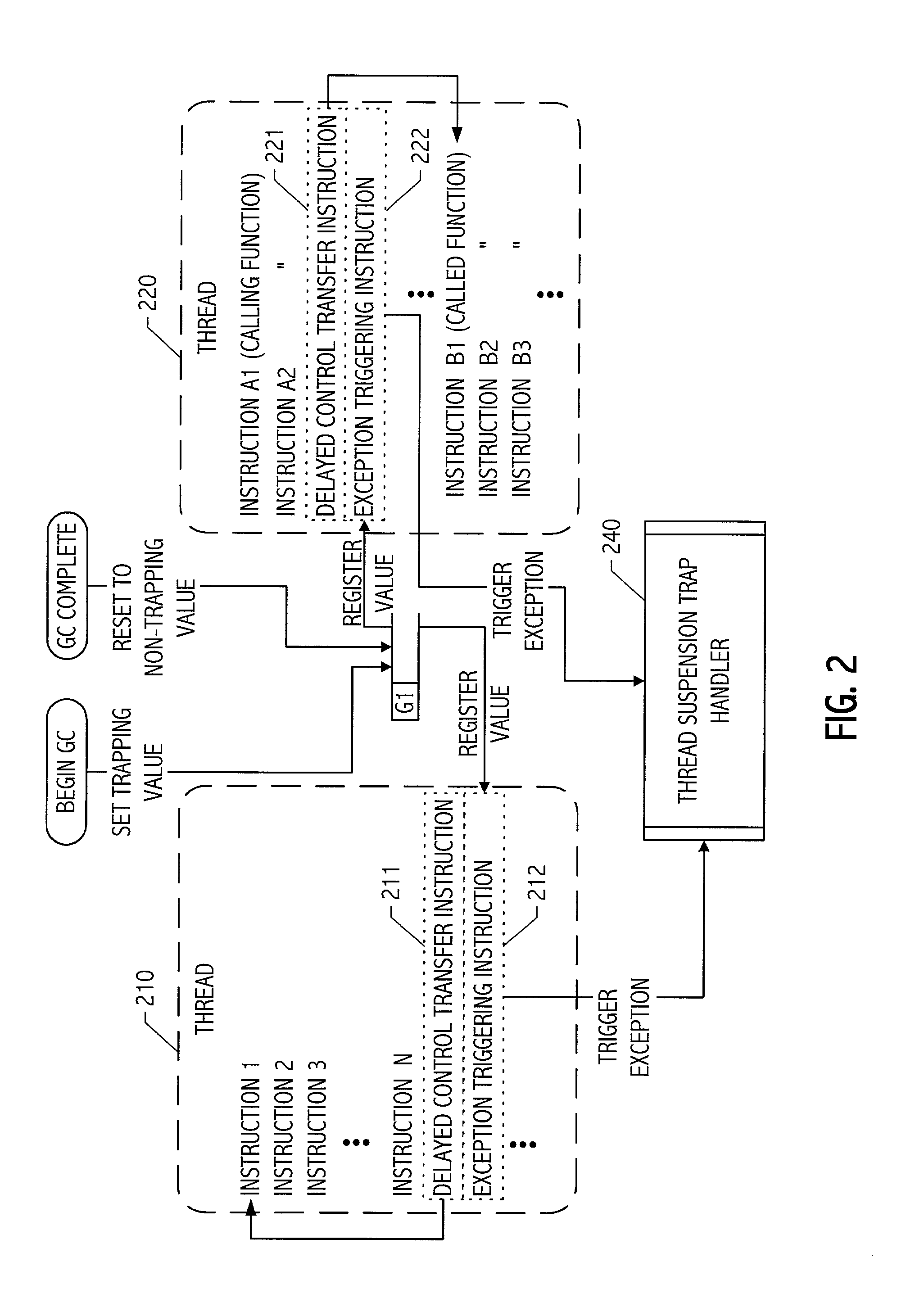
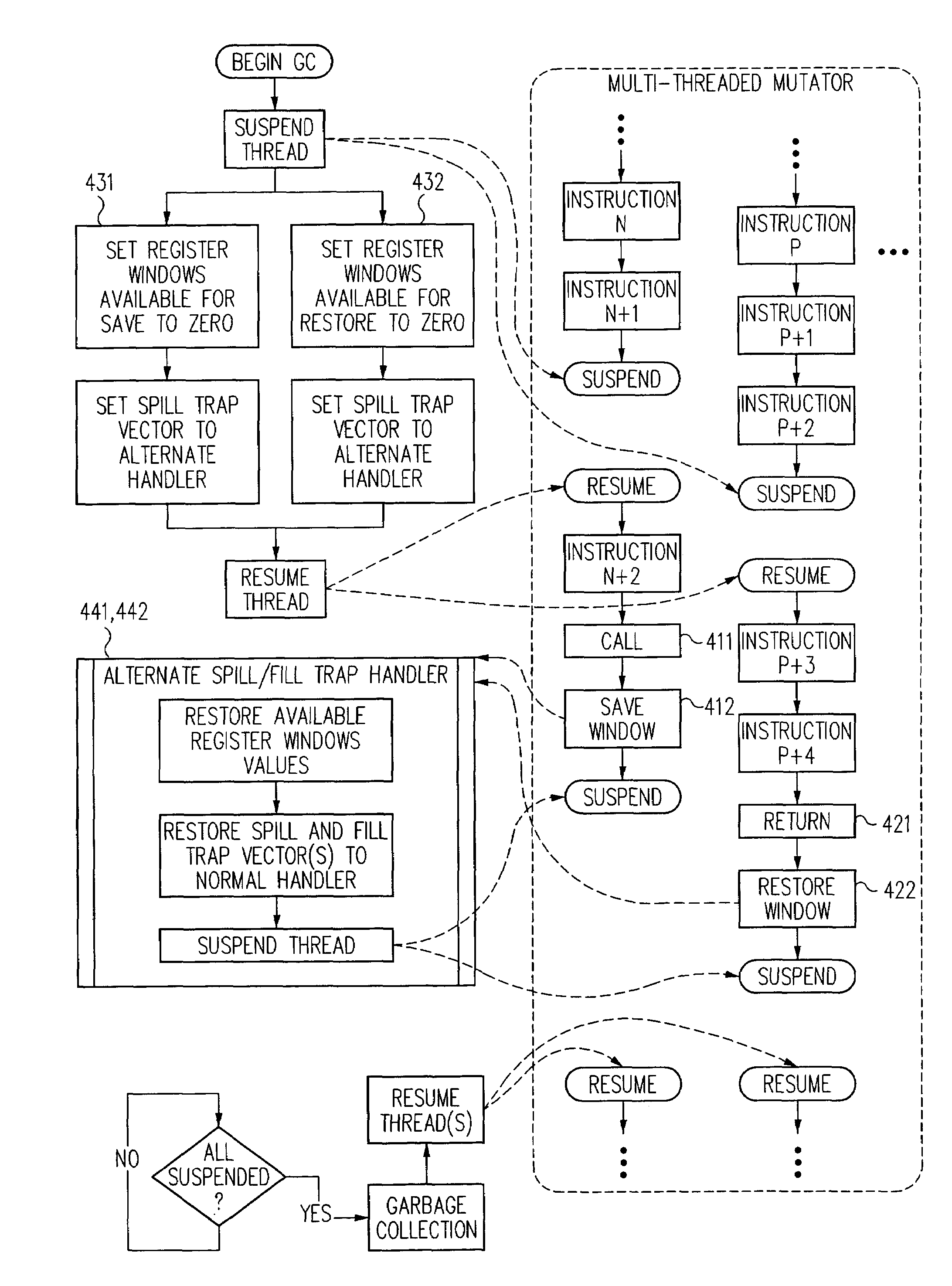
InactiveUS7013454B2Lower latencyNegligible overheadData processing applicationsProgram initiation/switchingTrappingWaste collection
By encoding an exception triggering value in storage referenced by an instruction in an otherwise unused slot (e.g., the delay slot of a delayed control transfer instruction or an unused instruction position in a VLIW-based architecture) coinciding with a safe point, an efficient coordination mechanism can be provided for multi-threaded code. Because the mechanism(s) impose negligible overhead when not employed and can be engaged in response to an event (e.g., a start garbage collection event), safe points can be defined at call, return and / or backward branch points throughout mutator code to reduce the latency between the event and suspension of all threads. Though particularly advantageous for thread suspension to perform garbage collection at safe points, the techniques described herein are more generally applicable to program suspension at coordination points coinciding with calls, returns, branches or calls, returns and branches therein.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Method for processing uplink signal, base station, and user equipment
InactiveUS20120039182A1Significant overheadFrequency-division multiplex detailsTransmission systemsComputer scienceUser equipment
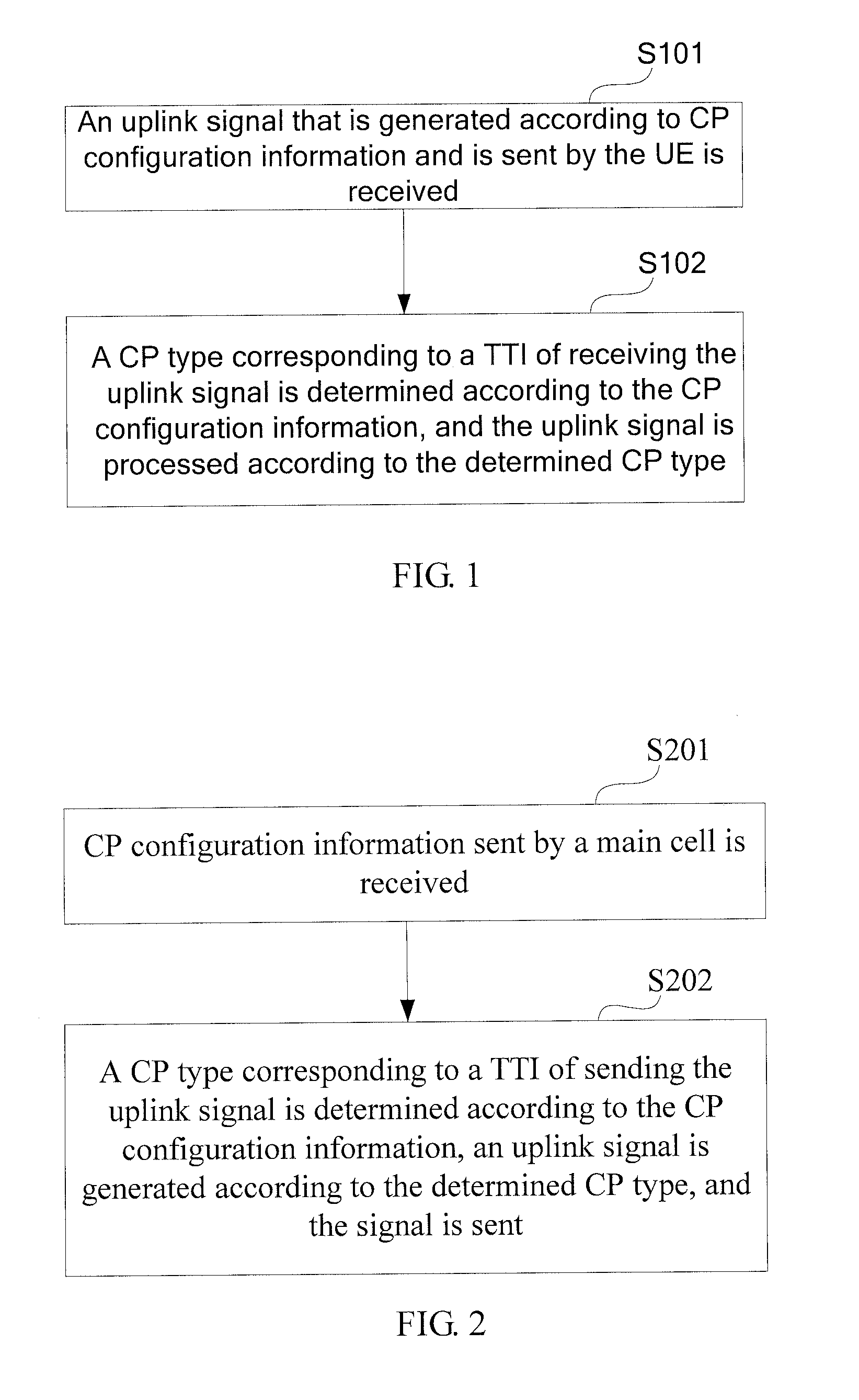
A method for processing an uplink signal, a BS, and a UE are provided. The method includes: receiving an uplink signal that is generated according to CP configuration information and is sent by a UE, where the CP configuration information is used to identify a mapping relationship between a TTI and a CP type that is used by the uplink signal; and determining, according to the CP configuration information, a CP type corresponding to a TTI of receiving the uplink signal, and processing the uplink signal according to the determined CP type. The UE can use different CP types in the case of different TTIs. Therefore, the technical solutions provided in embodiments of the present invention provide support for solving the uplink delay without introducing too large overhead.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Handover of a mobile station
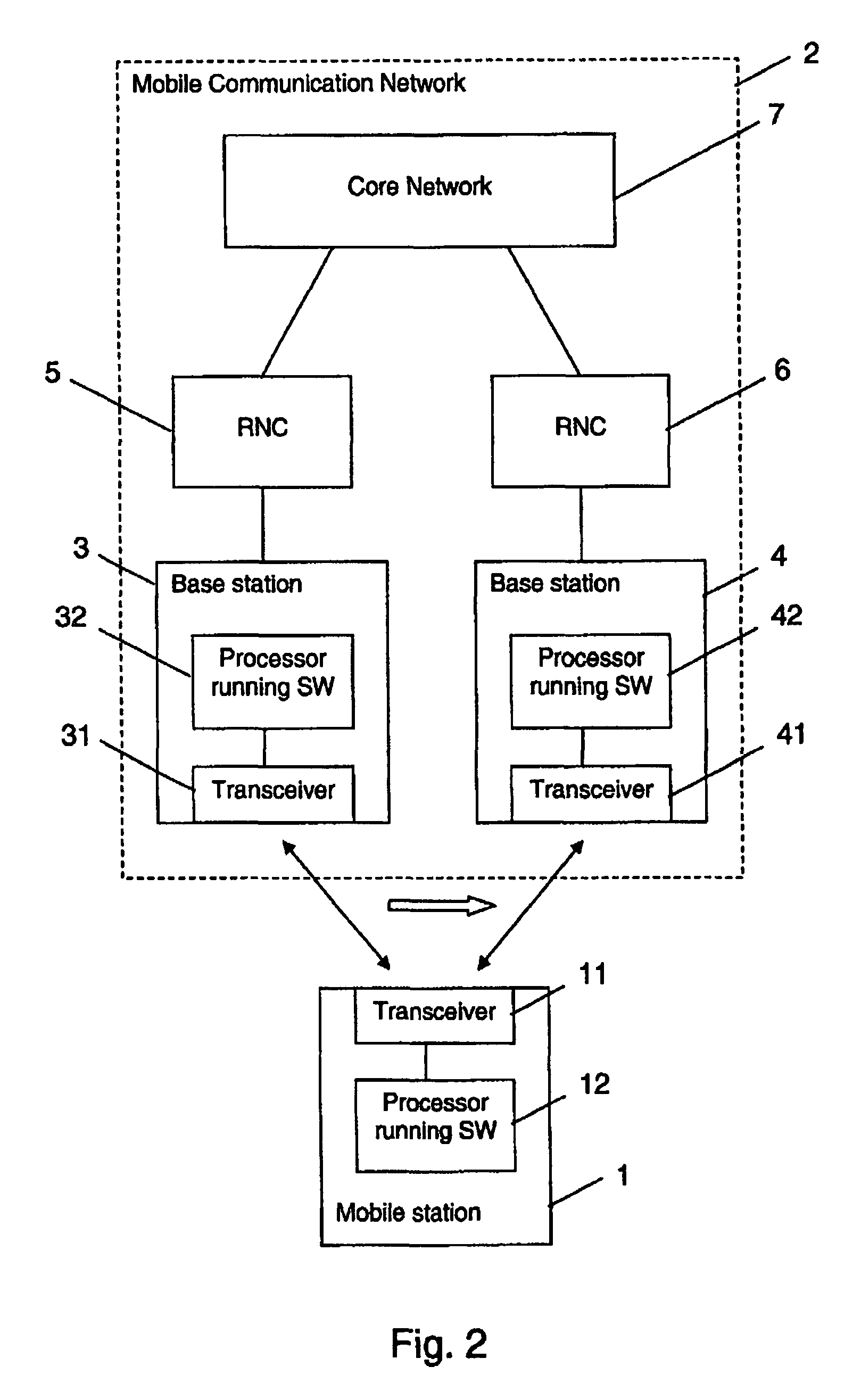
InactiveUS7916697B2Relieve pressureMinimize the numberWireless commuication servicesData switching networksCommunications systemMobile station
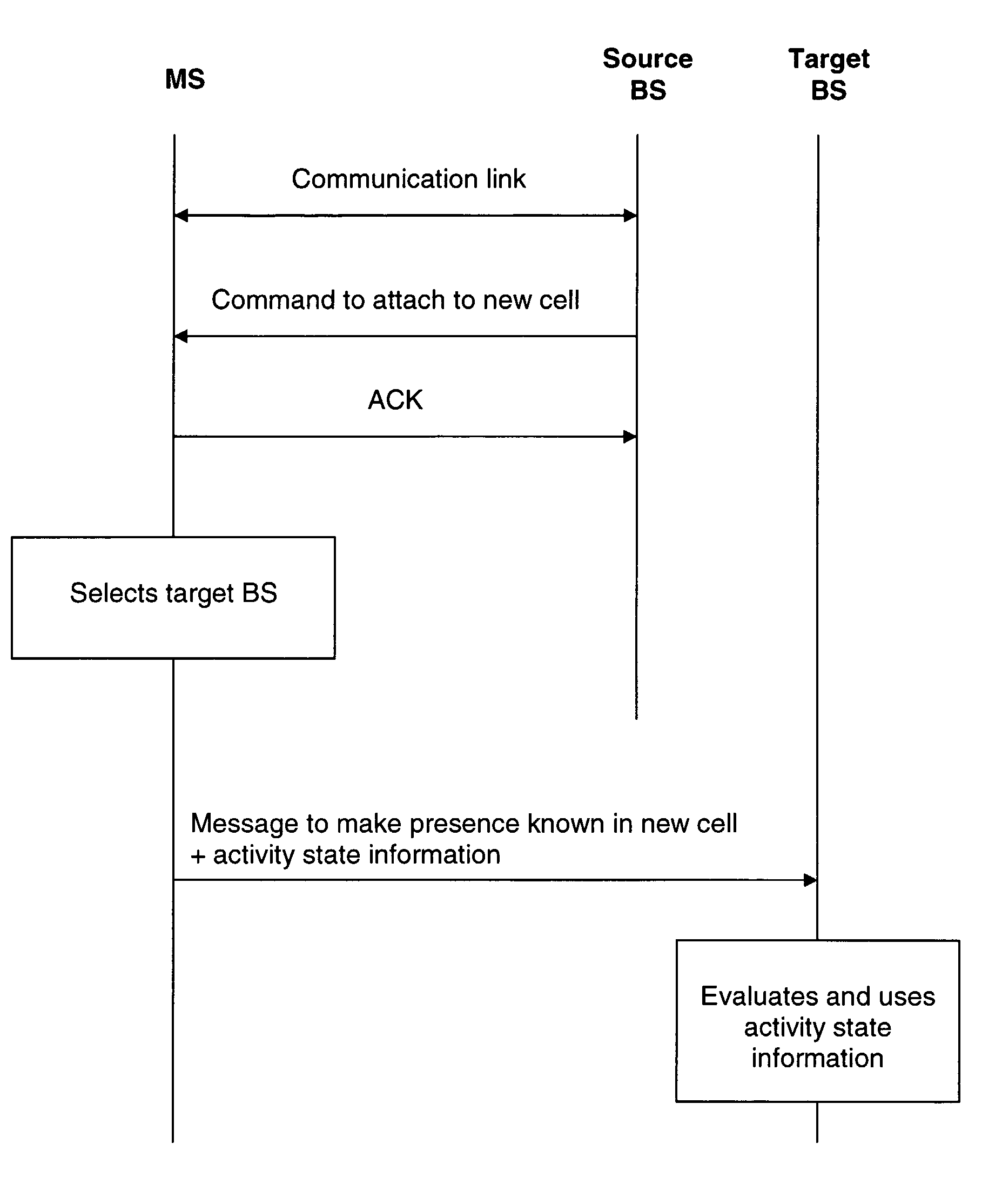
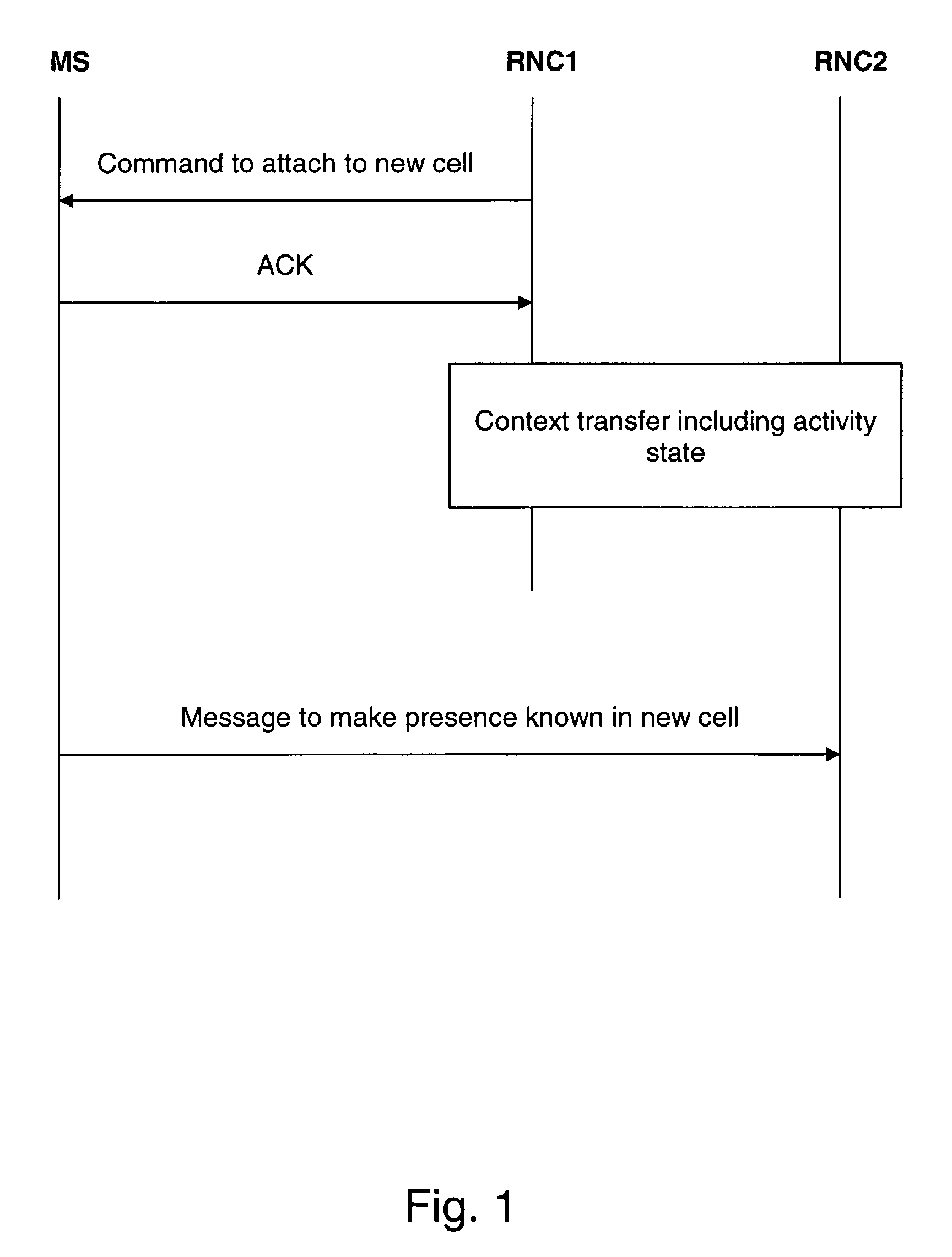
The invention relates to a method for supporting a handover of a mobile station 1 from a first radio access unit 3, 8 of a wireless communication network 2 to a second radio access unit 4, 9 of a wireless communication network 2. In order to improve a context transfer in the case of a handover of the mobile station 1, the mobile station 1 transmits information about its activity state to the second radio access unit 4, 9 when it is to be handed over to the second radio access unit 4, 9. The invention relates equally to such a mobile station, to such a second radio access unit, to a wireless communication system comprising such a mobile station and such a second radio access unit, and to a software code causing the transfer of information at the mobile station.
Owner:NOKIA TECH OY
Femtocell architecture in support of voice and data communications
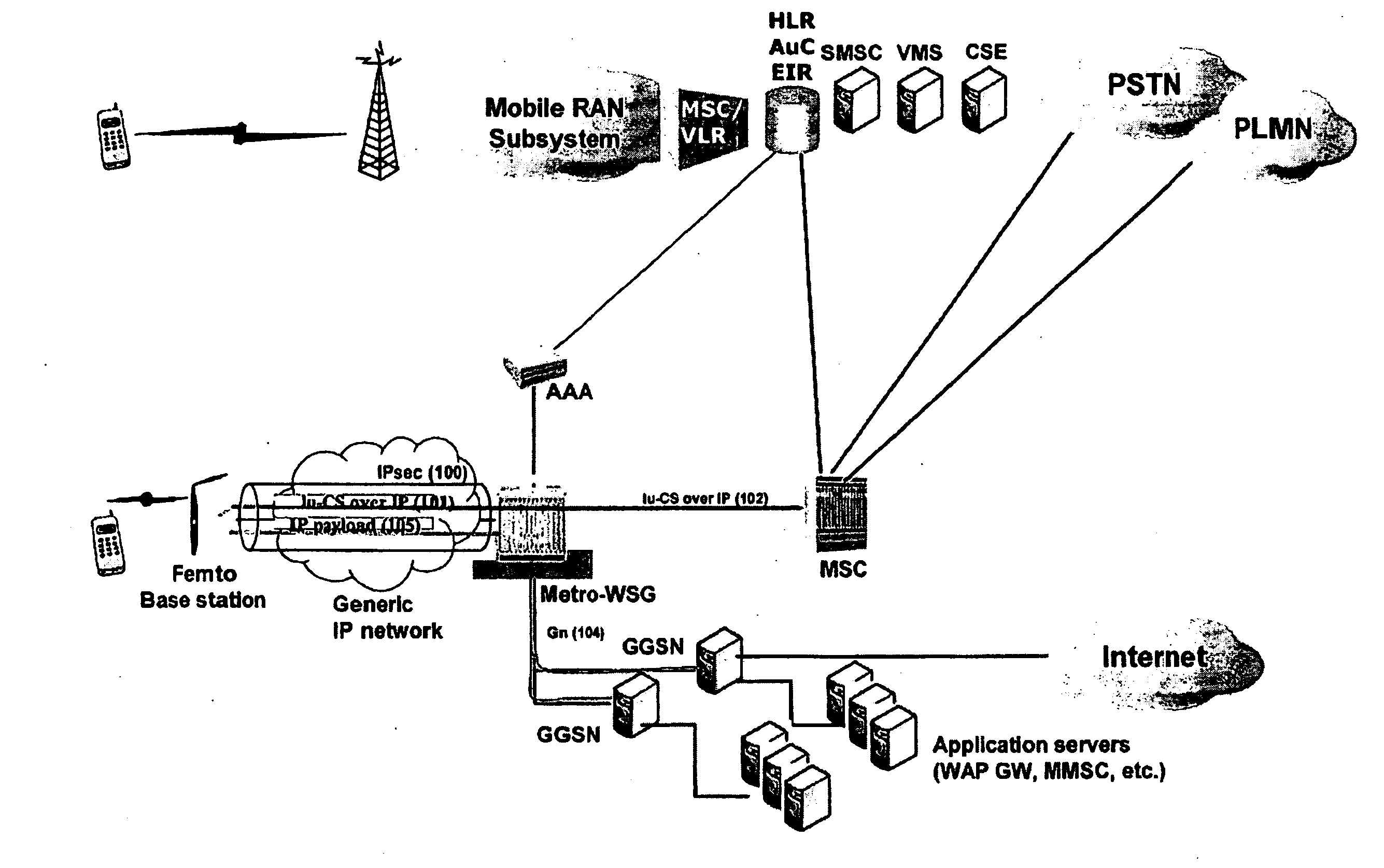
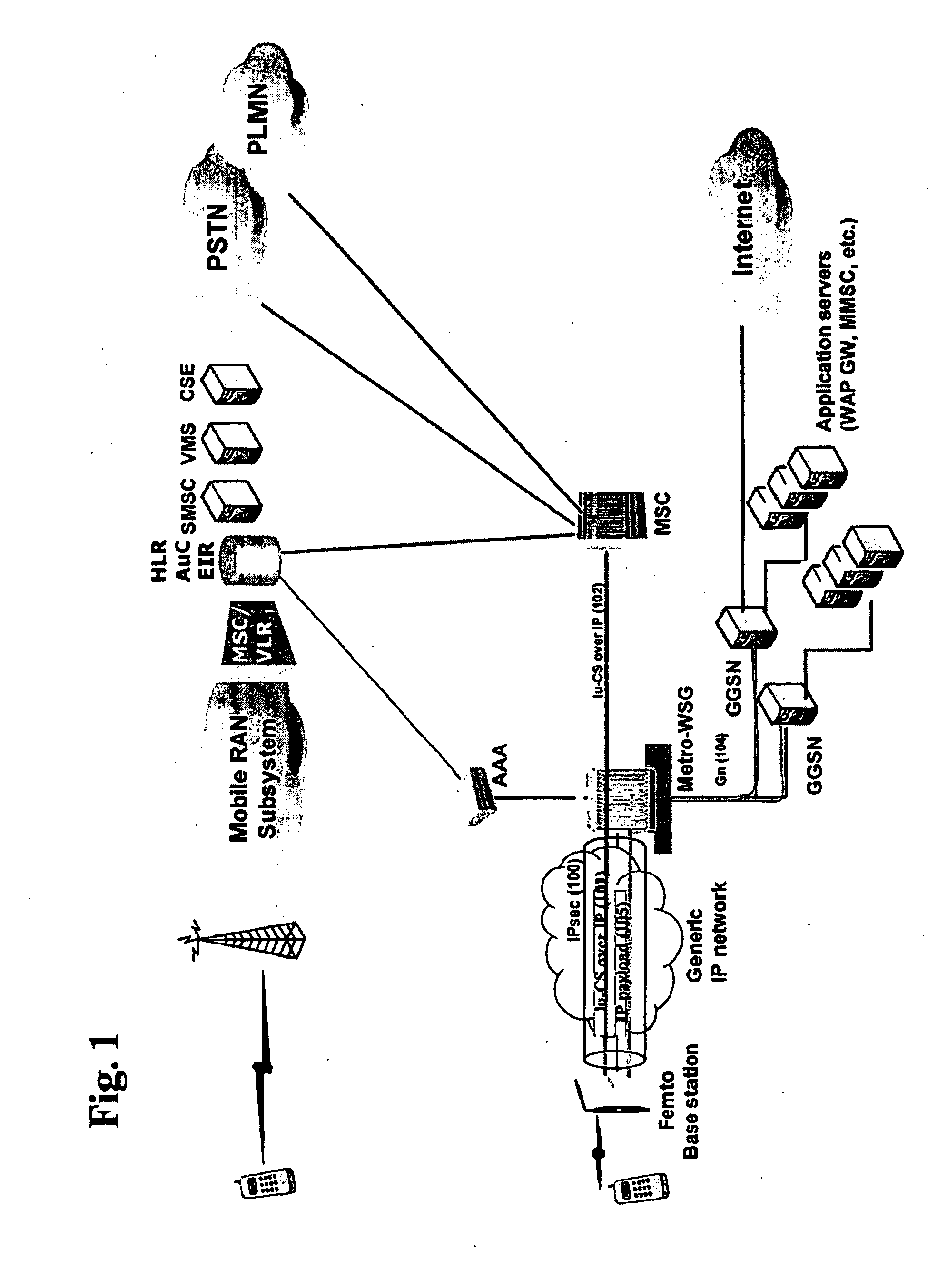
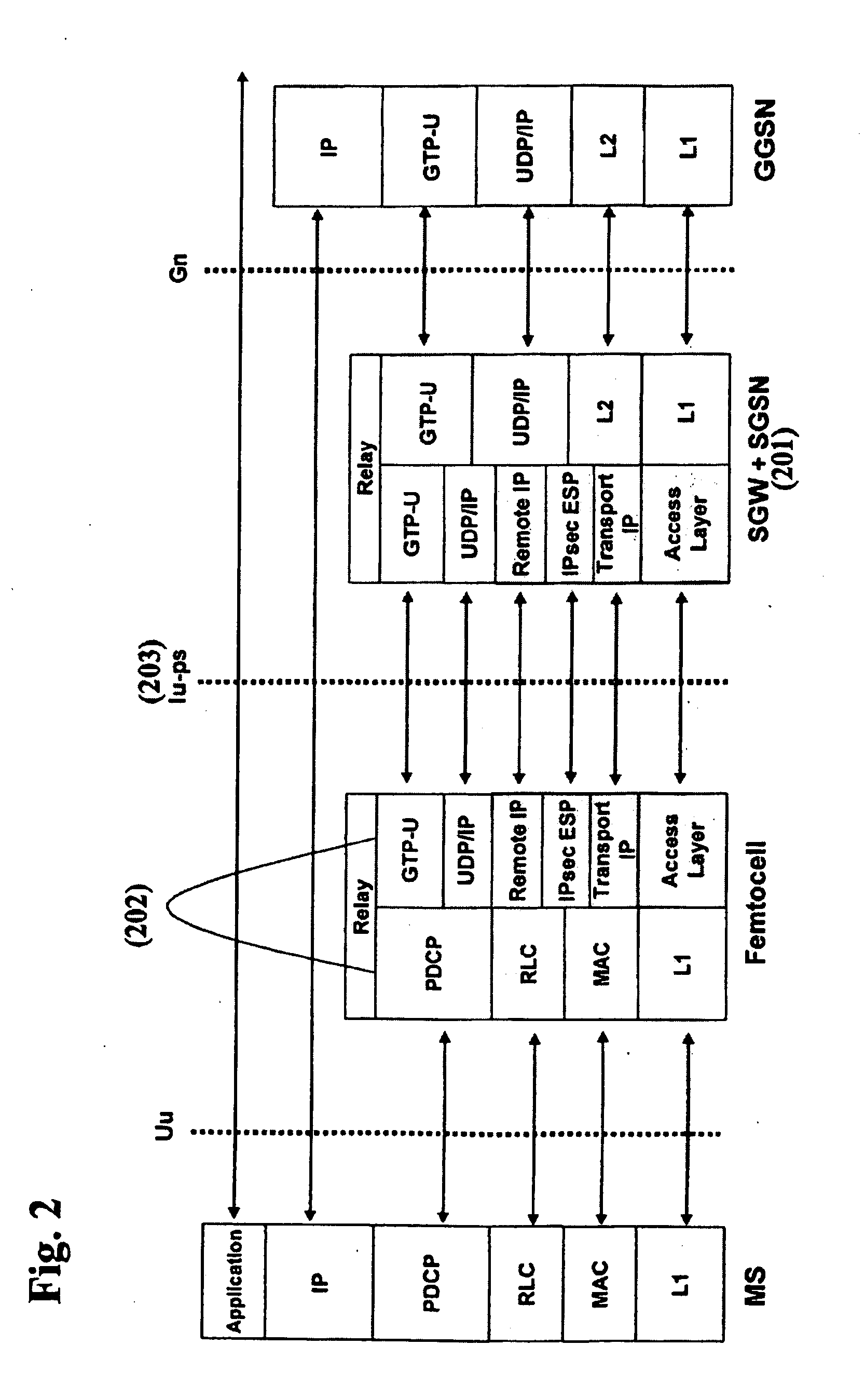
ActiveUS20090135795A1Significant overheadEasy to handleNetwork topologiesWireless commuication servicesThird generationVoice traffic
Methods and systems for providing voice and date services in a femtocell wireless network. The proposed approach integrates IWLAN architecture into femtocell architecture by introducing a gateway to serve both IWLAN and femtocell users. The proposed approach handles the voice and data in a different way so that it enhances the data handling efficiency while re-using existing MSC investment. The proposed approach carries the data traffic from a femtocell base station to the gateway in native IP packet, instead of encapsulating them in 3G data, thus enhancing the efficiency and performance for the data traffic. The data traffic can then be sent to GGSN or directly to packet data network. The approach tunnels voice traffic to MSC through the gateway as in conventional Iu-CS approach.
Owner:BISON PATENT LICENSING LLC
Method for searching a tree structure
InactiveUS20100082664A1Significant overheadLow scalabilityDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsTheoretical computer scienceTree architecture
A method, apparatus, and computer readable article of manufacture for tracing, on the basis of a key, an index created using a tree structure to access data. The method includes: searching the tree structure to reach a target node that can be associated with the key without acquiring a lock on the root node and on an internal node; setting the target node as a current node when the target node is a leaf node; moving the search to a node at a lower layer when the target node is an internal node by tracing an edge in the tree structure to reach a leaf node and setting the leaf node as the current node; and associating the key with the leaf node specified as the current node by acquiring a lock on the leaf node specified as the current node, thereby accessing the data.
Owner:IBM CORP
Dynamic authentication and initialization method
InactiveUS7428637B1Not require large overheadSimple deceptionKey distribution for secure communicationUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionAuthentication serverClient-side
A method for authentication of a first client in communication with a second client via an authentication server is disclosed, such that the first client and the second client are authenticated to each other, and the authentication server is authenticated to both the first client and the second client. The ability of a client and an authentication server to generate a one-time-use key unique to the client for a given request, is used as the basis for authentication. The flow of requests and responses coupled with each client's unique one-time-use key, such as a one time use account number used to encrypt messages, results in all three entities, the two clients and the authentication server, mutually authenticating each other. The method effectively prohibits a “man-in-the-middle” attack, wherein an unauthorized entity tries to assume the roll of one of the two clients, or the authentication server.
Owner:BILLMAN RICHARD E +1
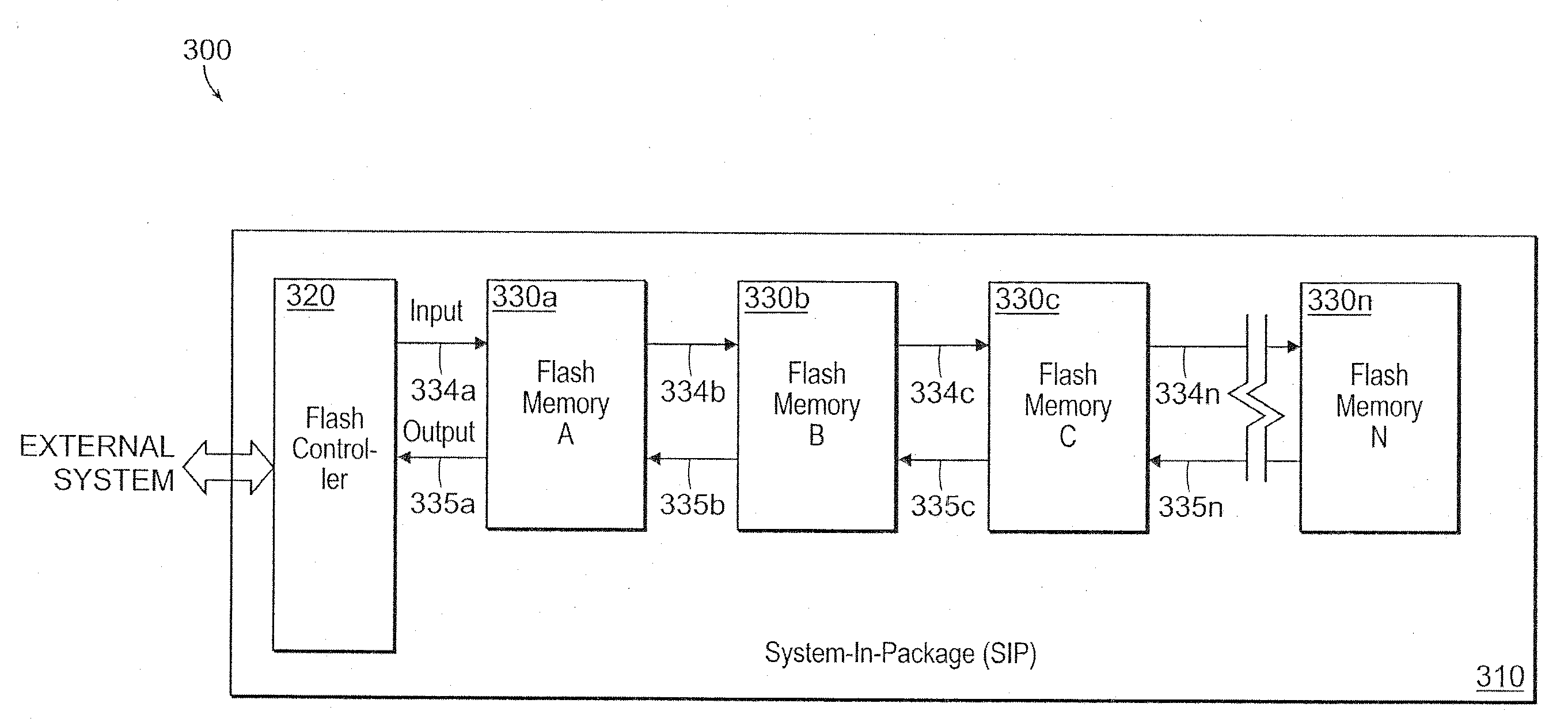
Nonvolatile memory system
InactiveUS20100030951A1Increase memory capacitySignificant overheadSolid-state devicesMemory adressing/allocation/relocationFlash memory controllerMemory controller
Owner:CONVERSANT INTPROP MANAGEMENT INC
Video image color encoding
InactiveUS6301389B1Significant overheadLow efficiencyColor television with pulse code modulationCode conversionDigital videoVideo image
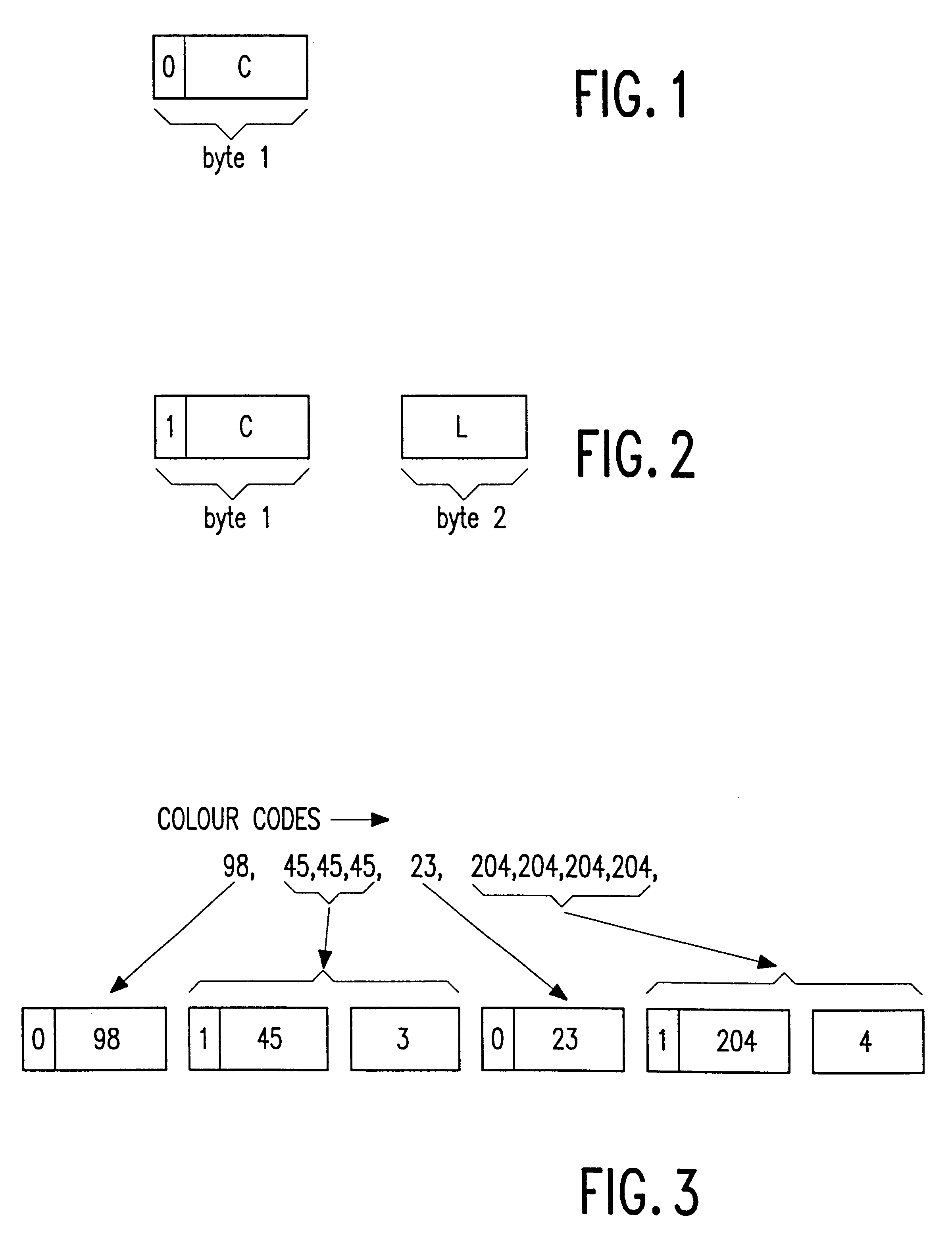
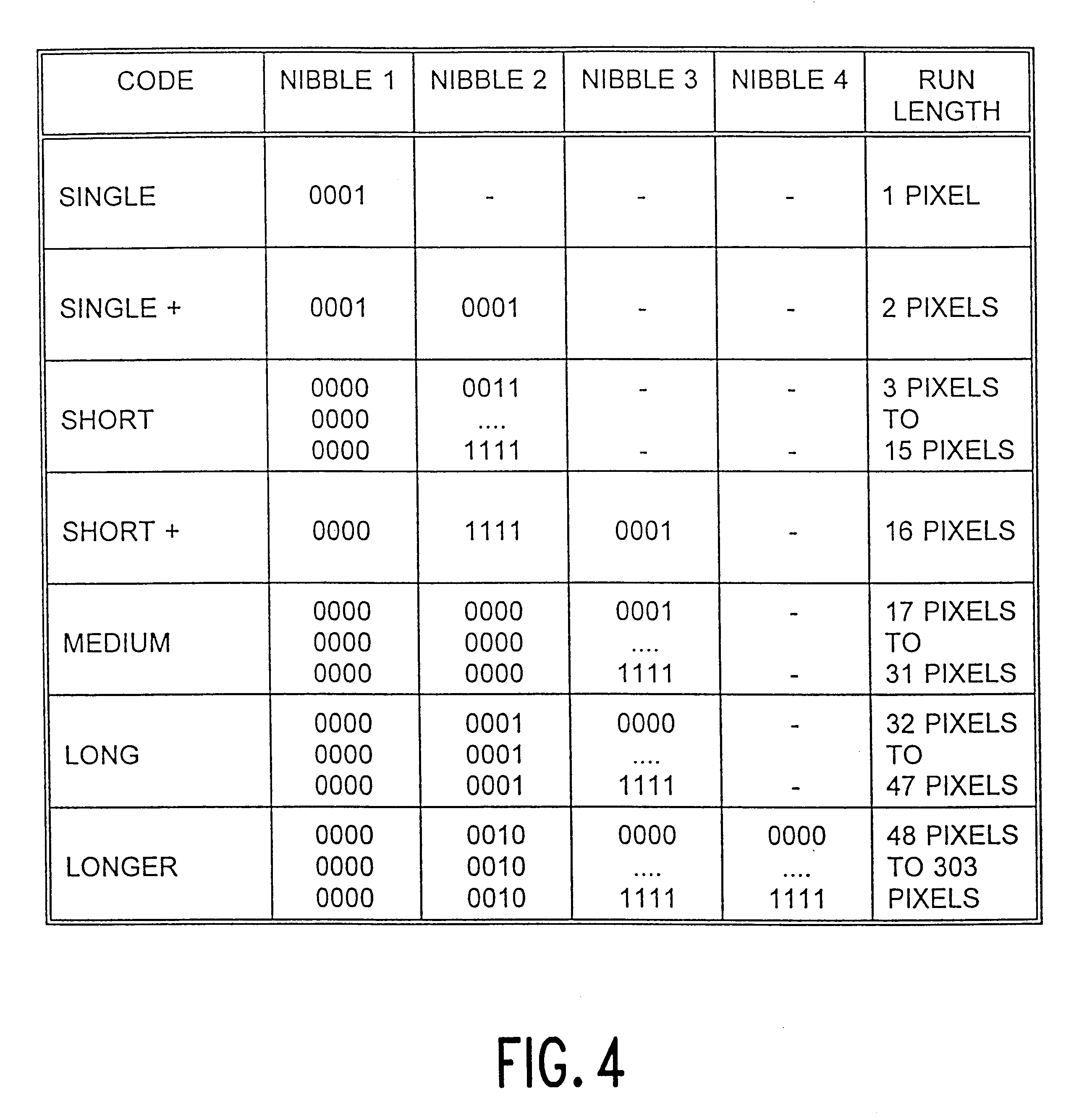
A method is described of encoding pixel color values for a digital video image frame in which each different color within the image is assigned a color value. A predominant color is identified for the image frame and, in a first embodiment (FIG. 5), each pixel having a color other than the predominant color is separately coded as its respective color value (0010 to 1111), with runs of three or more successive pixels of the predominant color being run-length encoded. A further code (0000 0011 cccc), similar in arrangement to that indicating a run, is provided to allow a change in the specified predominant color during the course of a frame. In a further embodiment, runs of all colors are run-length encoded but with a shorter coding scheme for runs of the predominant color or, in a still further embodiment, a small range of predominant colors. A principle use for these coding schemes is to improve efficiency of coding for certain classes of image material.
Owner:U S PHILIPS CORP
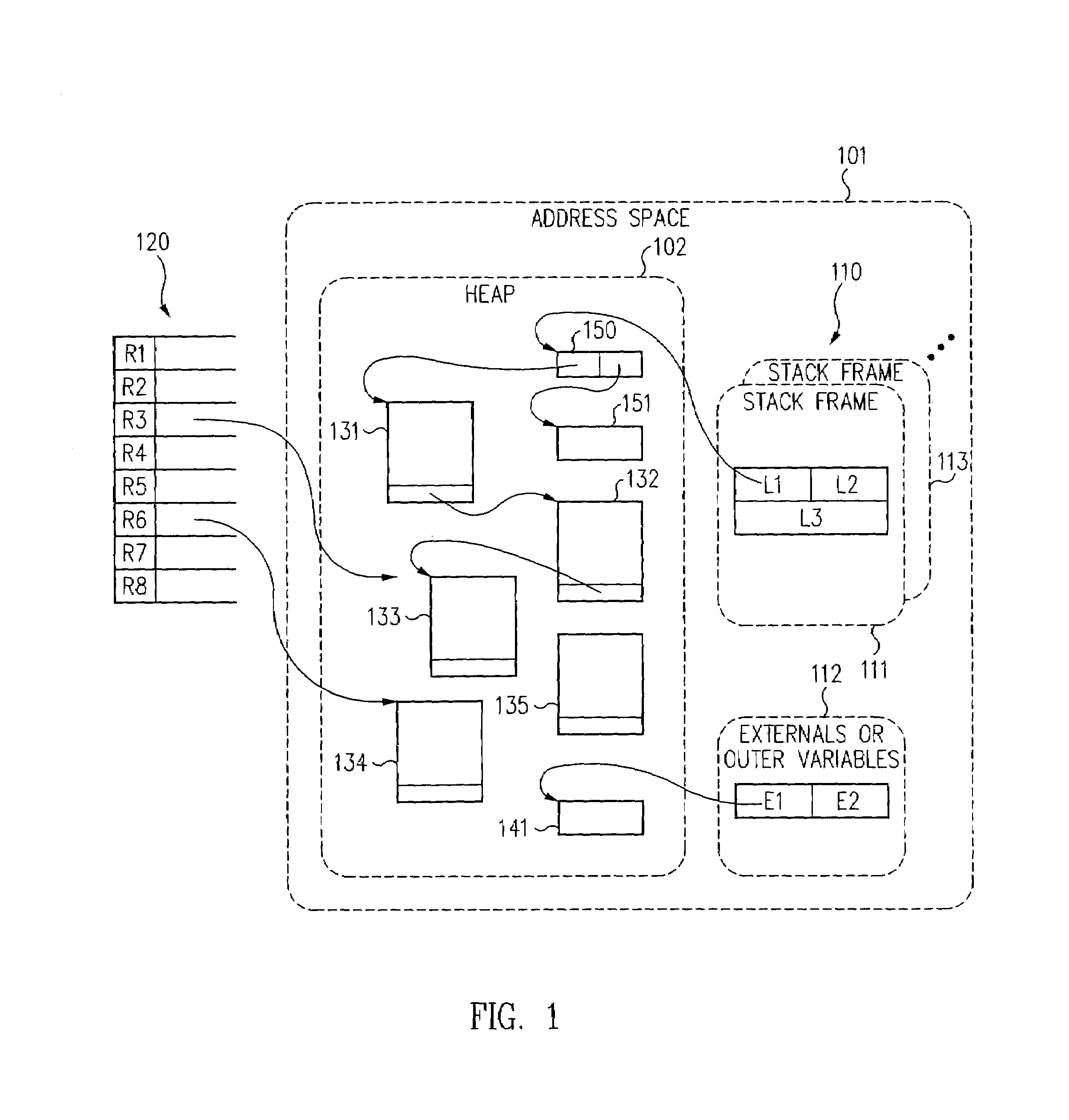
Thread suspension and method in a multi-threaded environment
InactiveUS7376940B1Negligible overheadLower latencyMemory adressing/allocation/relocationDigital computer detailsOperating system
Mechanisms can be used to facilitate suspension of a mutator thread (or mutator threads) while imposing negligible overhead on the mutator computation during periods when thread suspension is not requested. Mechanisms are provided to spill values from a fixed set of resources to a secondary store and to fill values from the secondary store into the fixed set in correspondence with function call triggered overflows and function return triggered underflows. In some configurations, modified spill and / or fill mechanism(s) are used to suspend threads at safe points coinciding with call and / or return sites. Because the modified spill and / or fill mechanism(s) impose negligible overhead when not employed and can be engaged in response to an event (e.g., a start garbage collection event), safe points can be defined at call and / or return points throughout mutator code to reduce the latency between the event and suspension of threads.
Owner:SUN MICROSYSTEMS INC
Apparatus and method for renewal-based resource allocation in a broadband wireless access communication system
ActiveUS20080102848A1Quantity minimizationReduce resource consumptionNetwork traffic/resource managementTransmission path divisionCommunications systemBroadband
An apparatus and method for renewal-based resource allocation in a Broadband Wireless Access (BWA) system are provided. A Base Station (BS) allocates resources to a Mobile Station (MS) by resource allocation information. It is determined whether the MS requires continuous resource allocation or whether the MS does not have transmission data temporarily, when a resource allocation duration for downlink resources allocated to the MS has expired. One of resource allocation termination, resource allocation renewal, and temporary resource lending to another MS is performed according to the determination. Information for updating the resource allocation information is transmitted to the MS.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Increased packet scheduling throughput and efficiency using über batching
ActiveUS20180302328A1Improve network efficiencyImprove efficiencyData switching networksCritical periodPacket scheduling
Described embodiments improve the performance of a computer network via selectively forwarding packets to bypass quality of service (QoS) processing, avoiding processing delays during critical periods of high demand, increasing throughput and efficiency may be increased by sacrificing a small amount of QoS accuracy. QoS processing may be applied to a subset of packets of a flow or connection, referred to herein as “lazy” processing or lazy byte batching. Packets that bypass QoS processing may be immediately forwarded with the same QoS settings as packets of the flow for which QoS processing is applied, resulting in tremendous overhead savings with only minimal decline in accuracy. In case of backlog, packets may be collected together into an aggregated or ‘uber’ packet, with QoS processing applied based on a virtual size of the aggregated packet.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
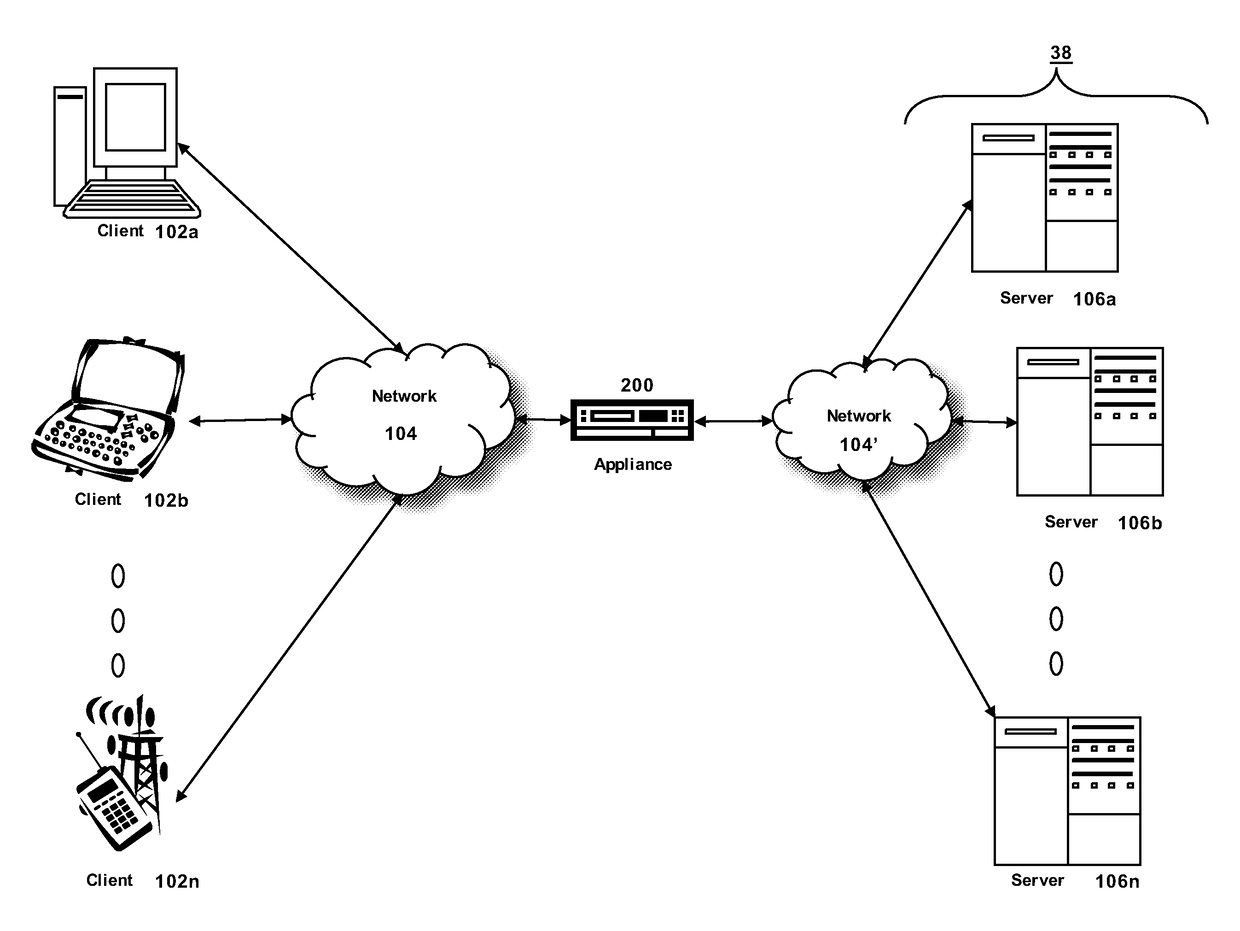
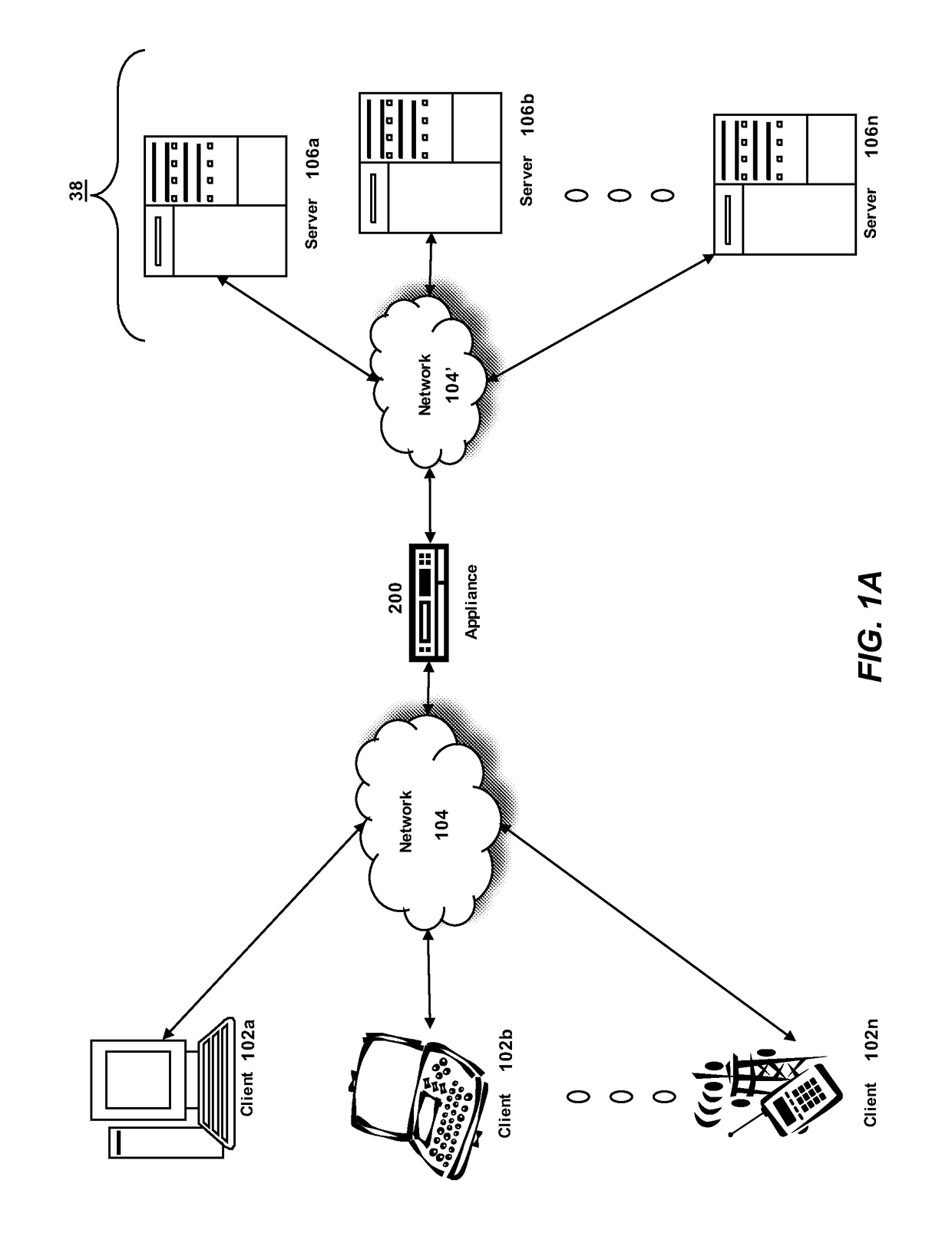
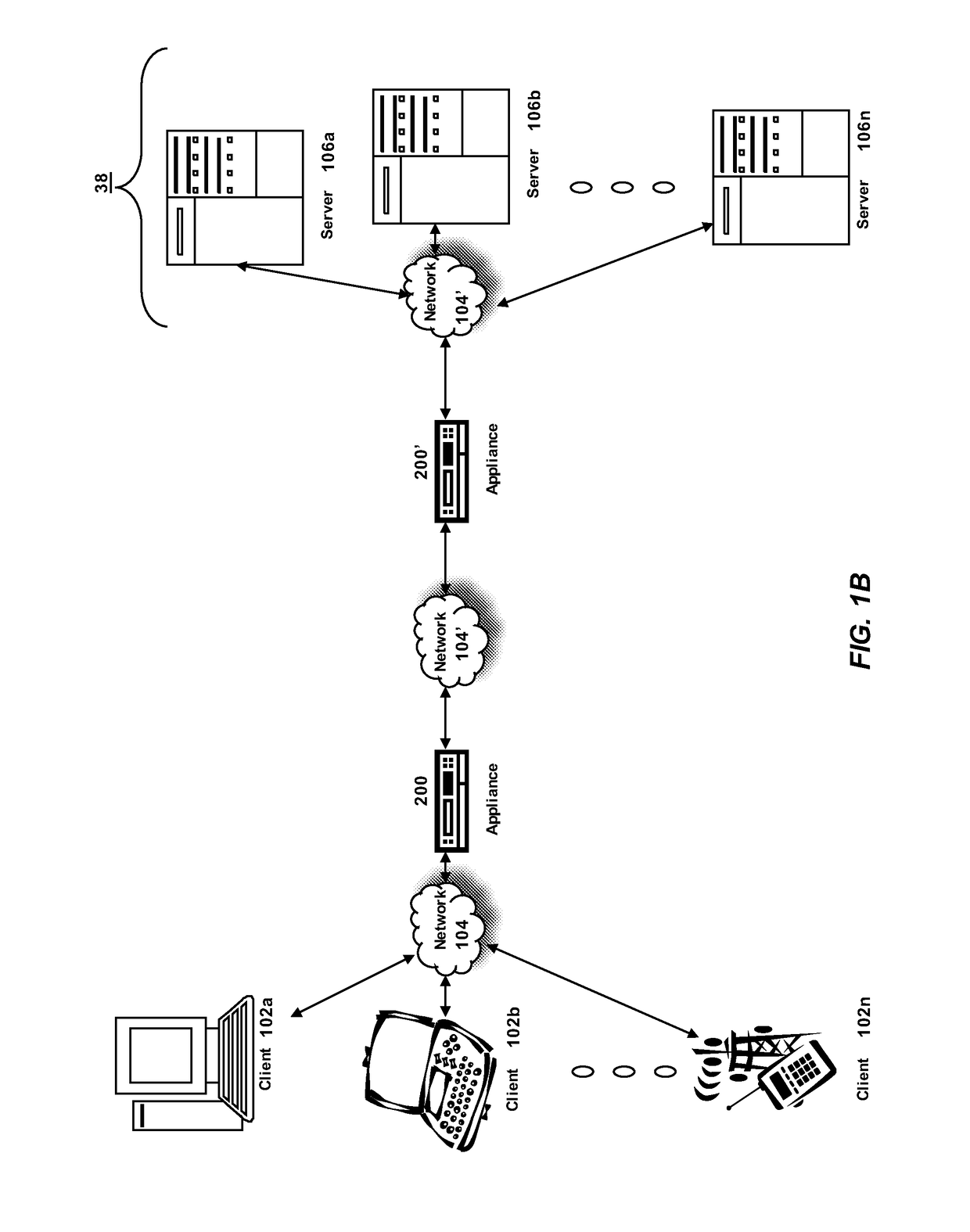
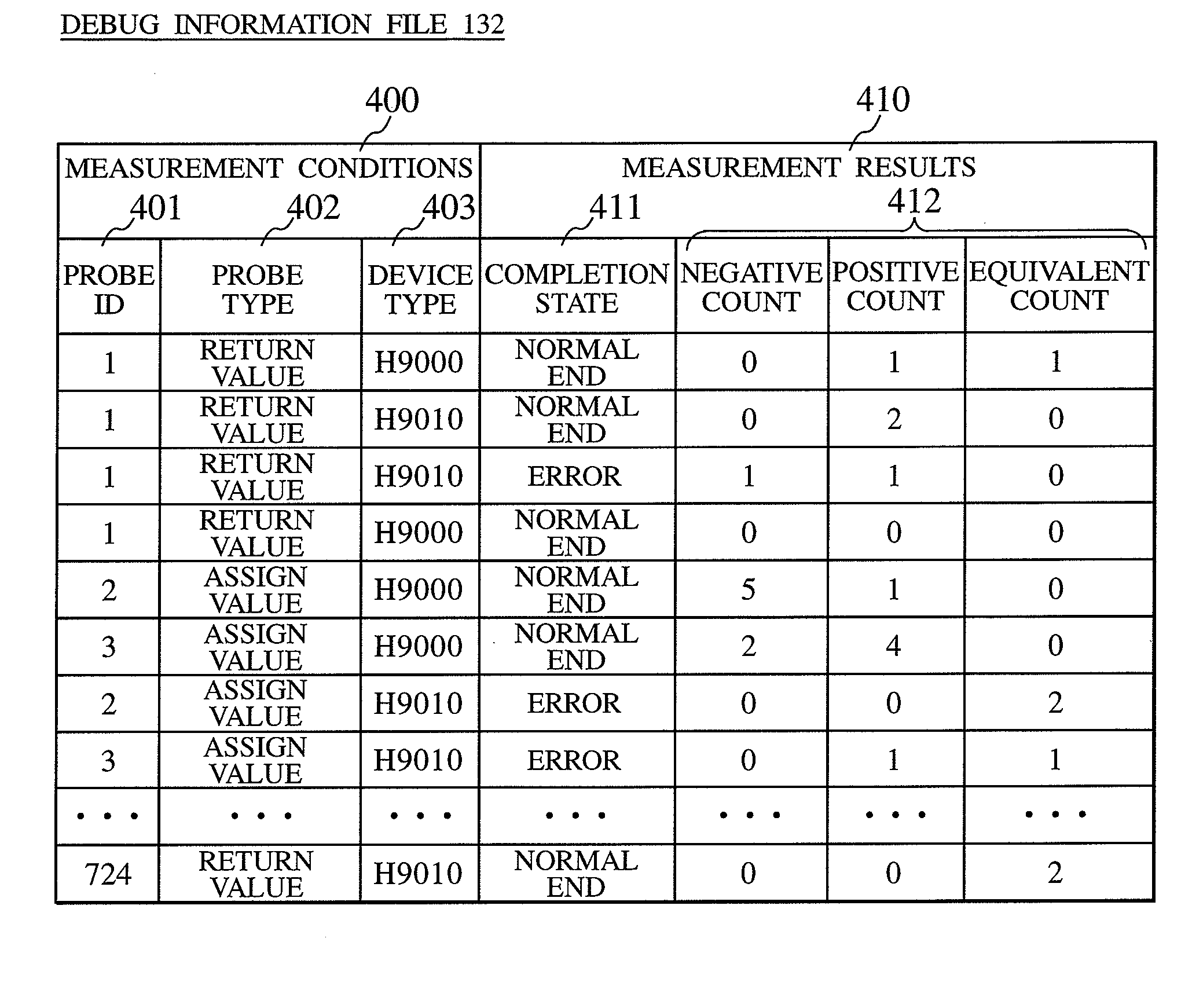
Debug information collection method and debug information collection system
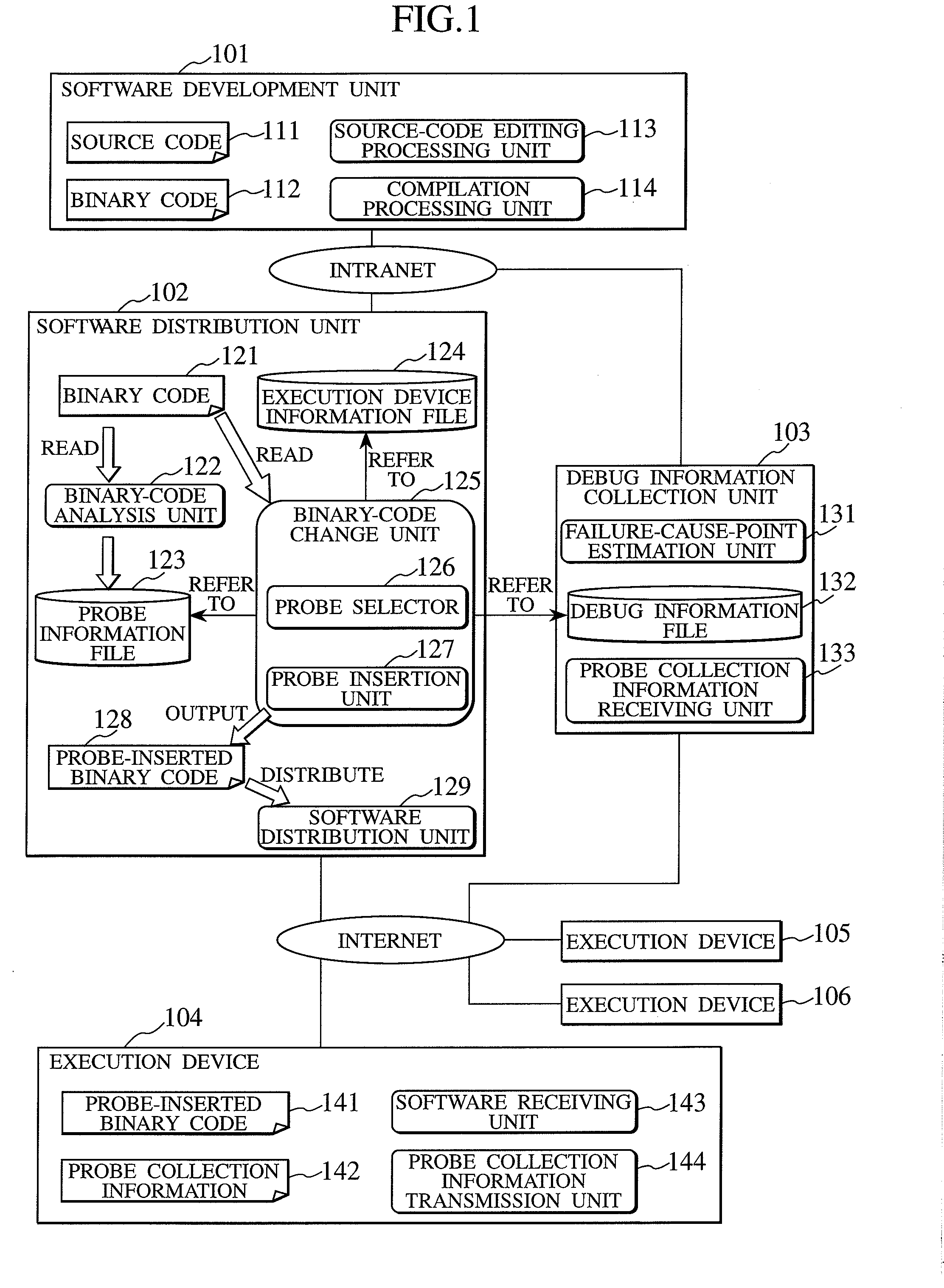
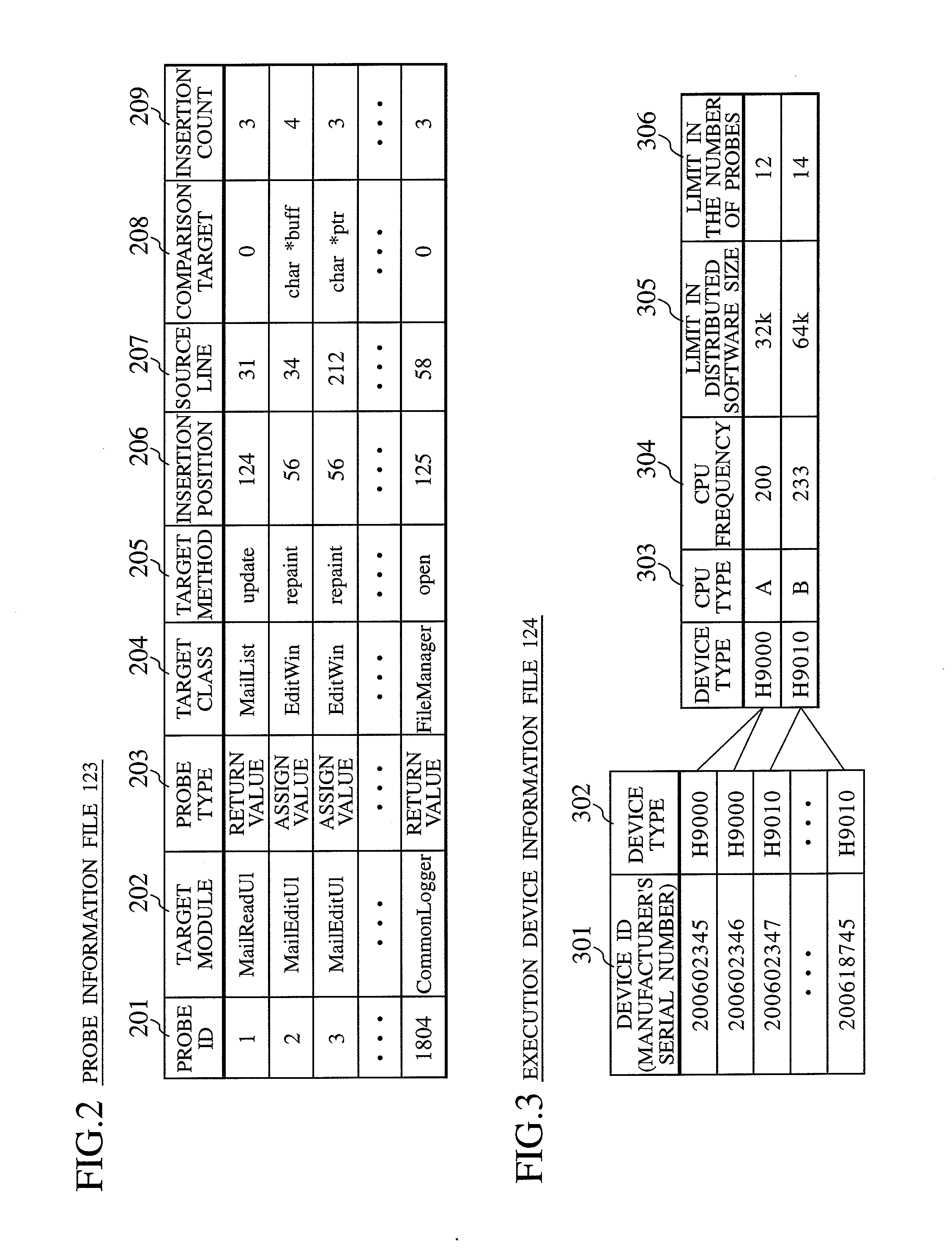
InactiveUS20080141224A1Reduce loadSpeed up failure-cause analysisHardware monitoringSoftware testing/debuggingSoftware distributionCollection system
In a software distribution unit, a binary-code analysis unit determines a total set of insertion positions at which probes can be inserted into software. A binary-code change unit determines the population of insertion positions of probes to be inserted into the software and the number of insertion positions of probes to be inserted on a device basis. Then, the binary-code change unit selects, from the population, insertion positions of probes as many as the determined number of insertion positions and inserts the probes into the software at the selected insertion positions. A software distribution unit distributes, to the device, the software into which the probes are inserted. As a result, it is possible to reduce both a load on the device side and a load on the software developer side at the same time and to acquire uniform debug information without deviations.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Method and circuit arrangement for accessing slave units in a system on chip in a controlled manner
InactiveUS20160004647A1Simple wayIncrease overheadMemory architecture accessing/allocationUnauthorized memory use protectionControl mannerNetworks on chip
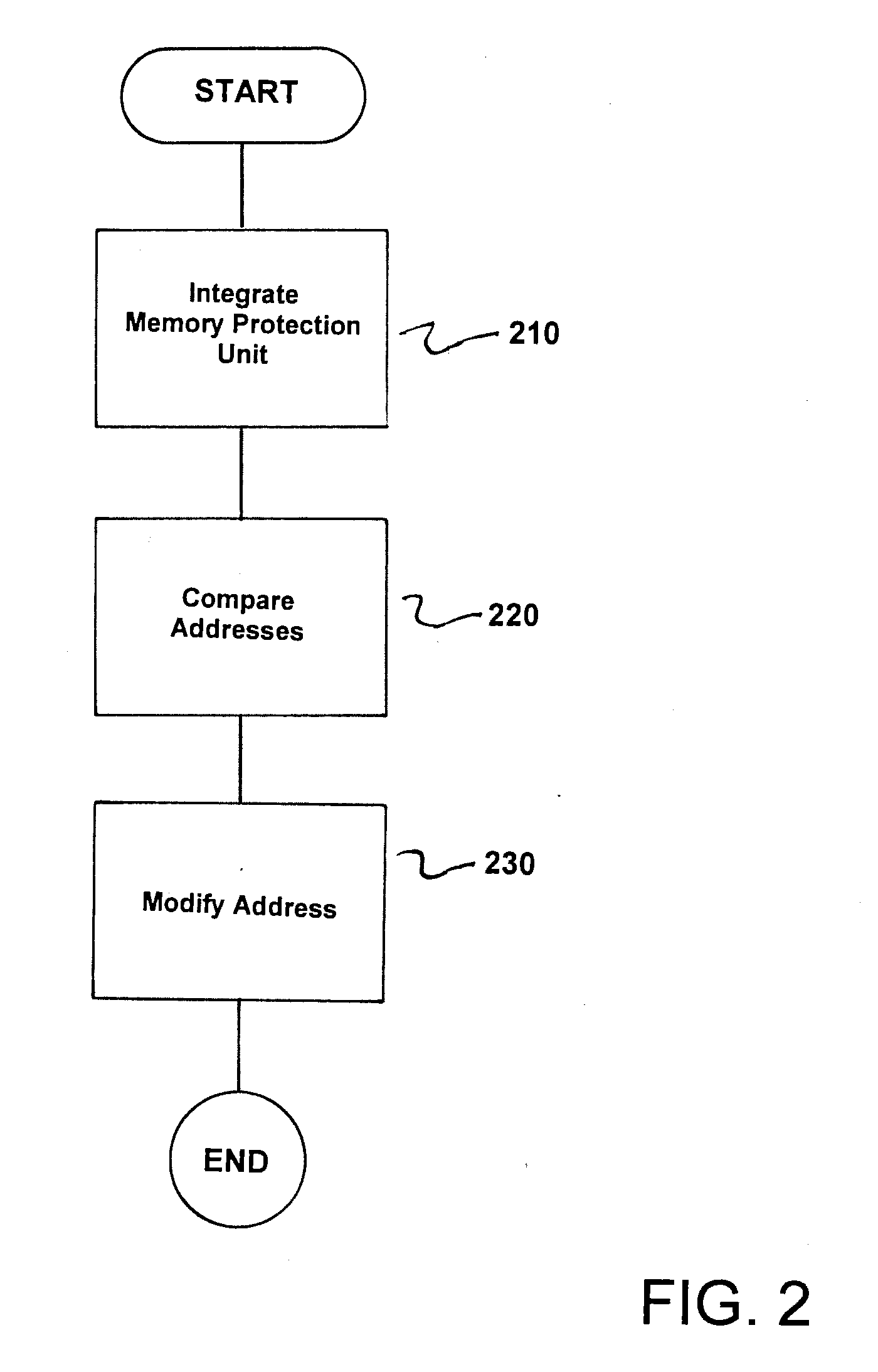
A circuit arrangement and method for accessing slave units in a system on chip in a controlled manner, wherein an access of a master unit of the system on chip to one of the slave units is performed via a network-on-chip bus system using an access address, where a memory protection unit is integrated between the at least one master unit and the network-on-chip bus system, and access authorization of the master unit to a slave unit is checked by the memory protection unit by comparing the access address with specified address sections, and when an unauthorized access of the master unit to a slave unit is identified, the access address is modified by the memory protection unit such that the unauthorized access is terminated in the network-on-chip bus system.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Hybrid cache coherence using fine-grained hardware message passing
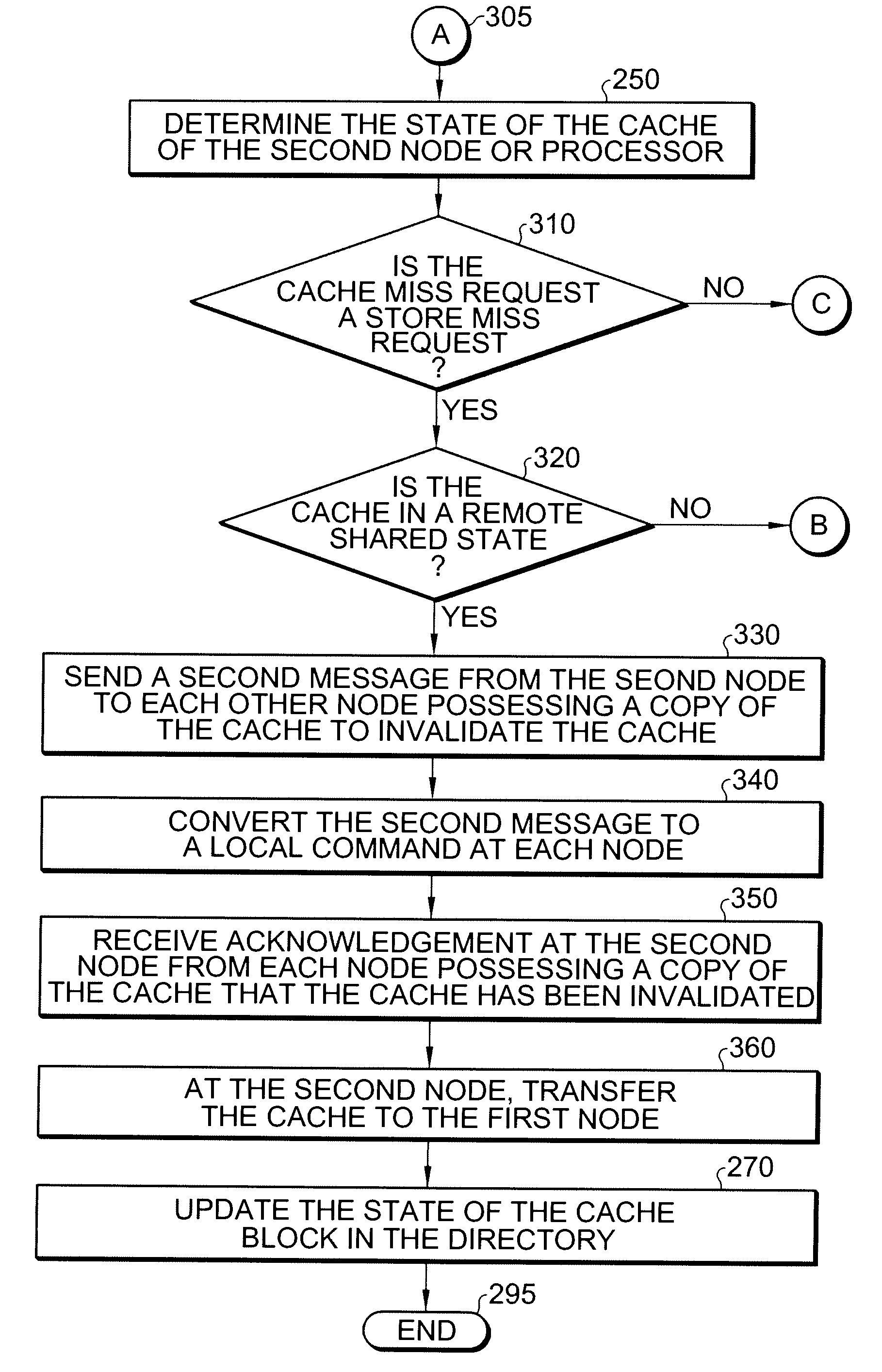
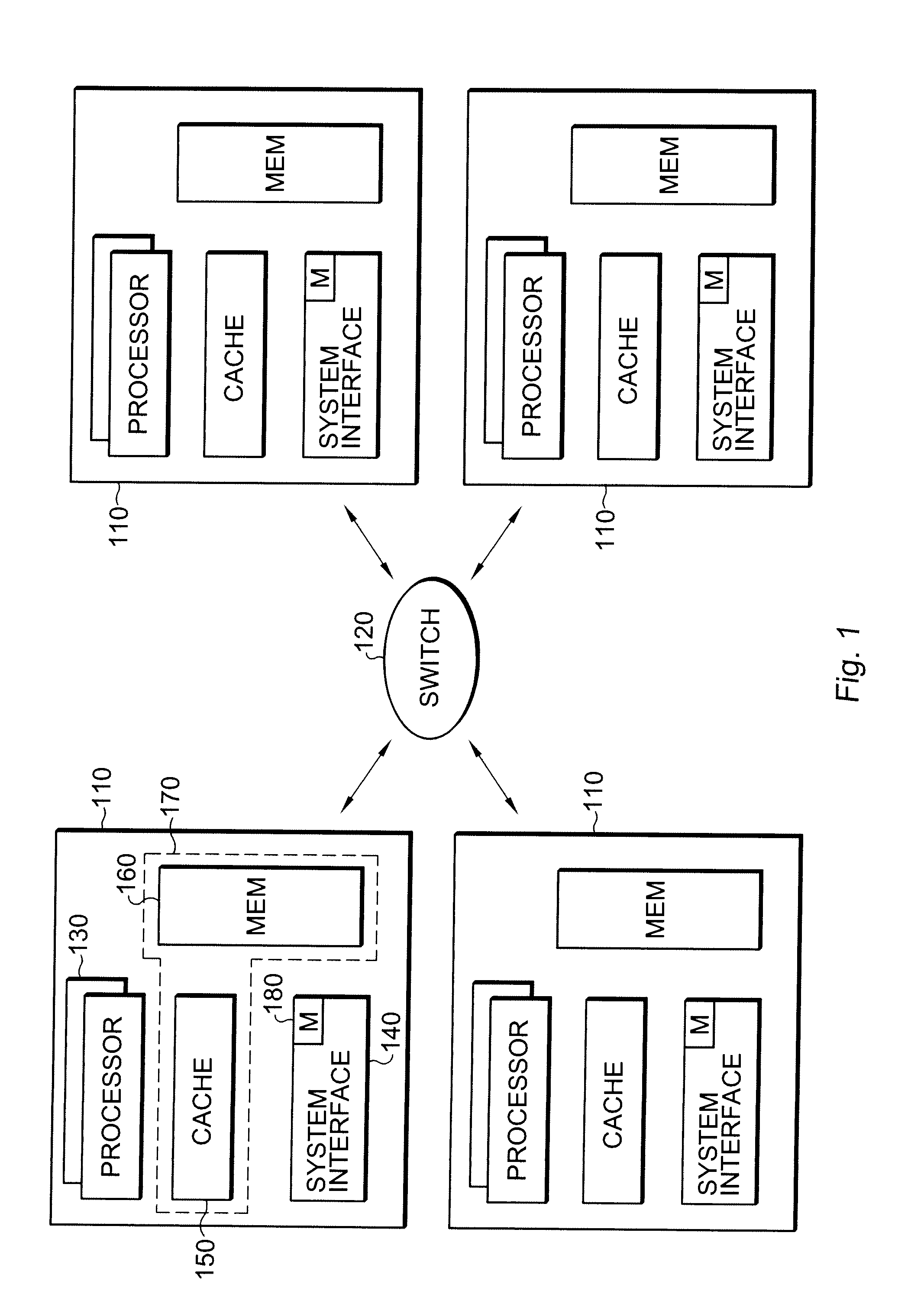
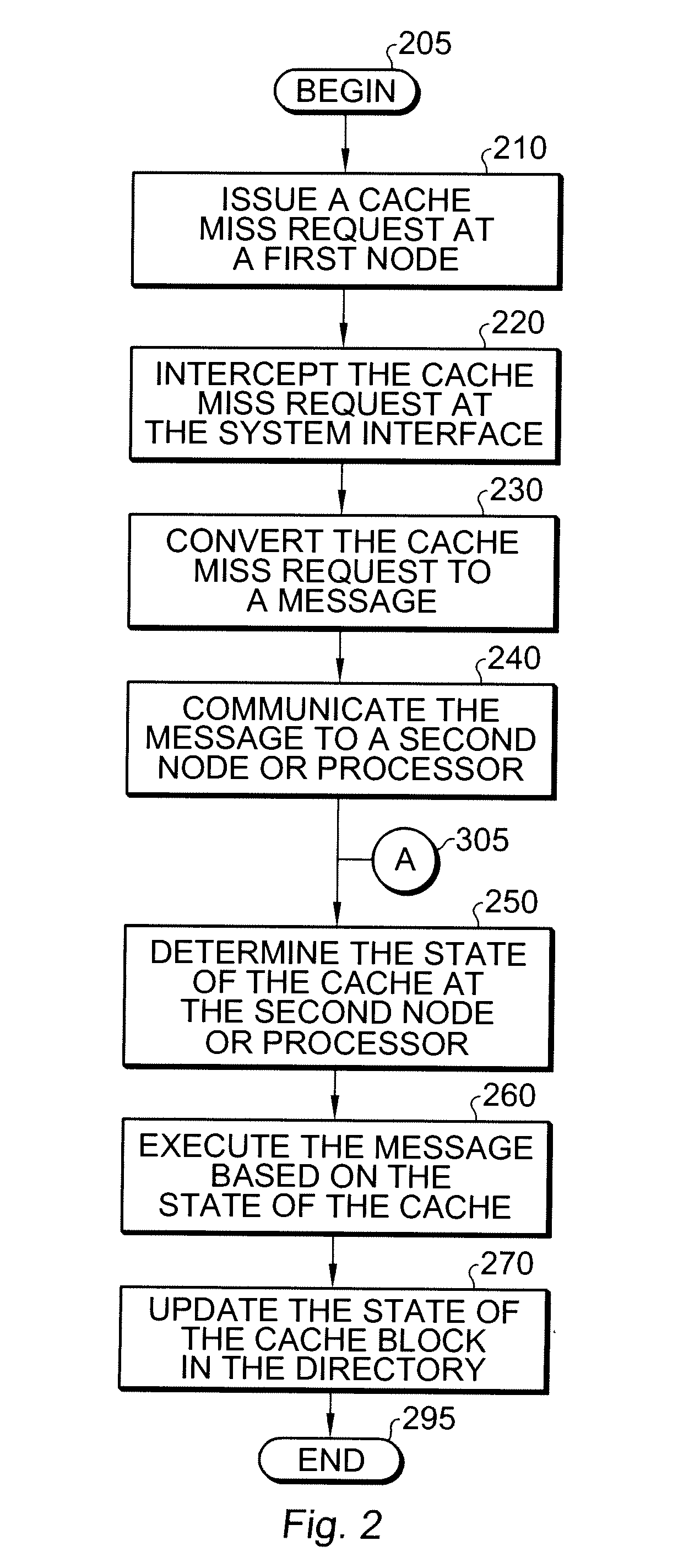
ActiveUS20090089511A1Light weightCost-effectiveMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationGoal systemMessage passing
Multiprocessor systems conducting operations utilizing global shared memory must ensure that the memory is coherent. A hybrid system that combines hardware memory transactions with that of direct messaging provides memory coherence with minimal overhead requirement or bandwidth demands. Memory access transactions are intercepted and converted to direct messages which are then communicated to a target and / or remote node. Thereafter the message invokes a software handler which implements the cache coherence protocol. The handler uses additional messages to invalidate or fetch data in other caches, as well as to return data to the requesting processor. These additional messages are converted to appropriate hardware transactions by the destination system interface hardware.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com