Patents
Literature
49 results about "Memory coherence" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
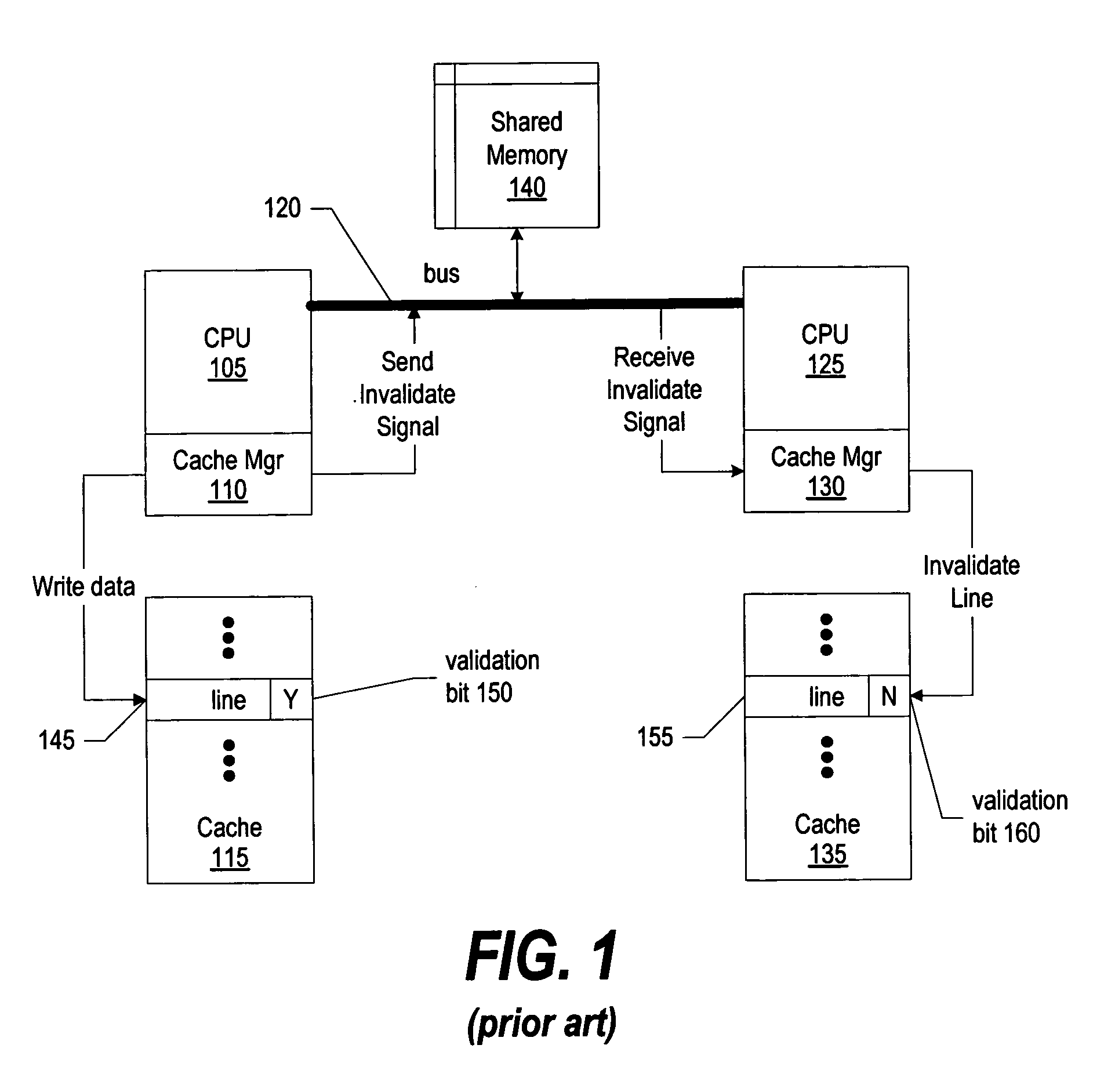
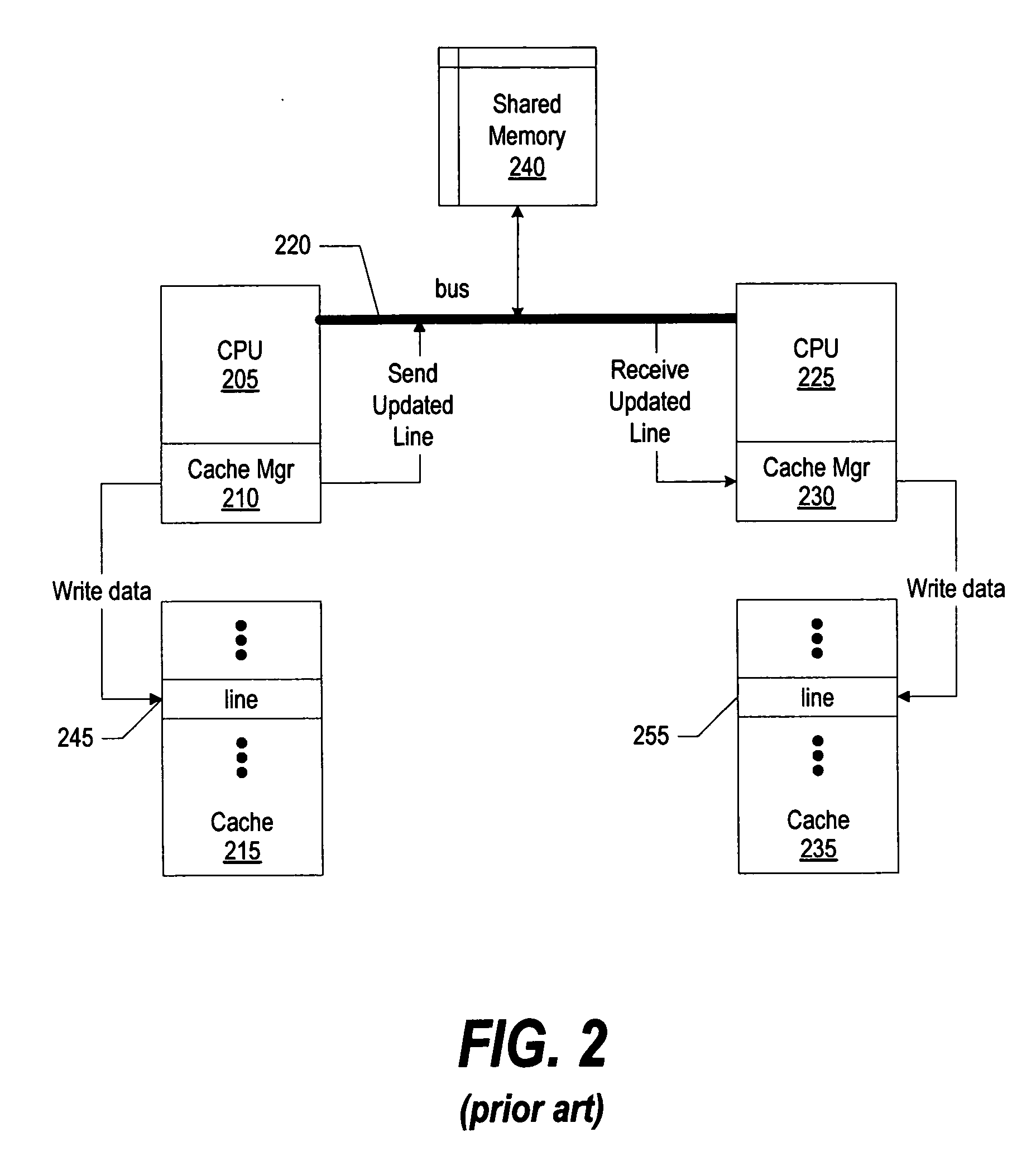
Memory coherence is an issue that affects the design of computer systems in which two or more processors or cores share a common area of memory. In a uniprocessor system (whereby, in today's terms, there exists only one core), there is only one processing element doing all the work and therefore only one processing element that can read or write from/to a given memory location. As a result, when a value is changed, all subsequent read operations of the corresponding memory location will see the updated value, even if it is cached.
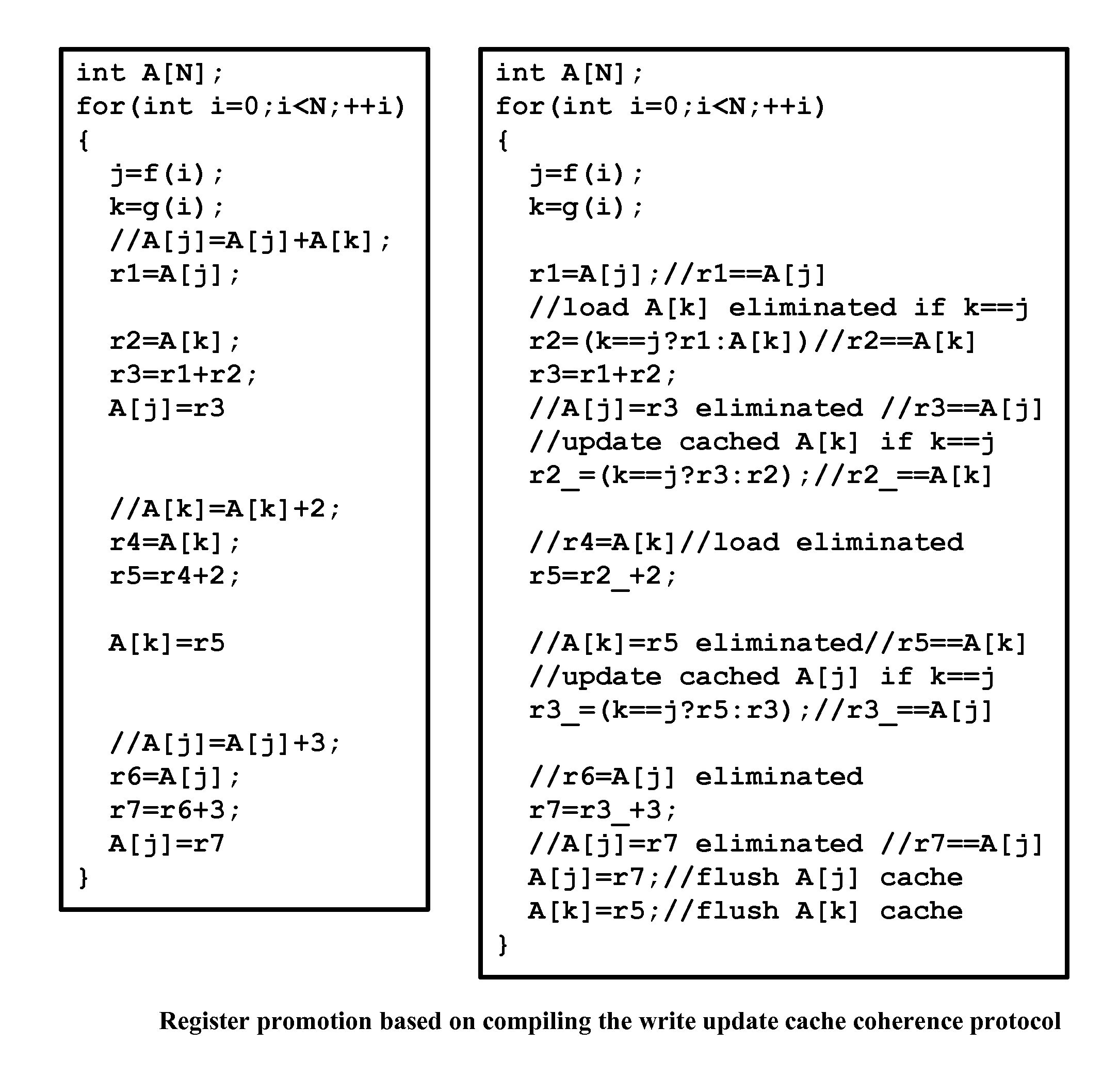
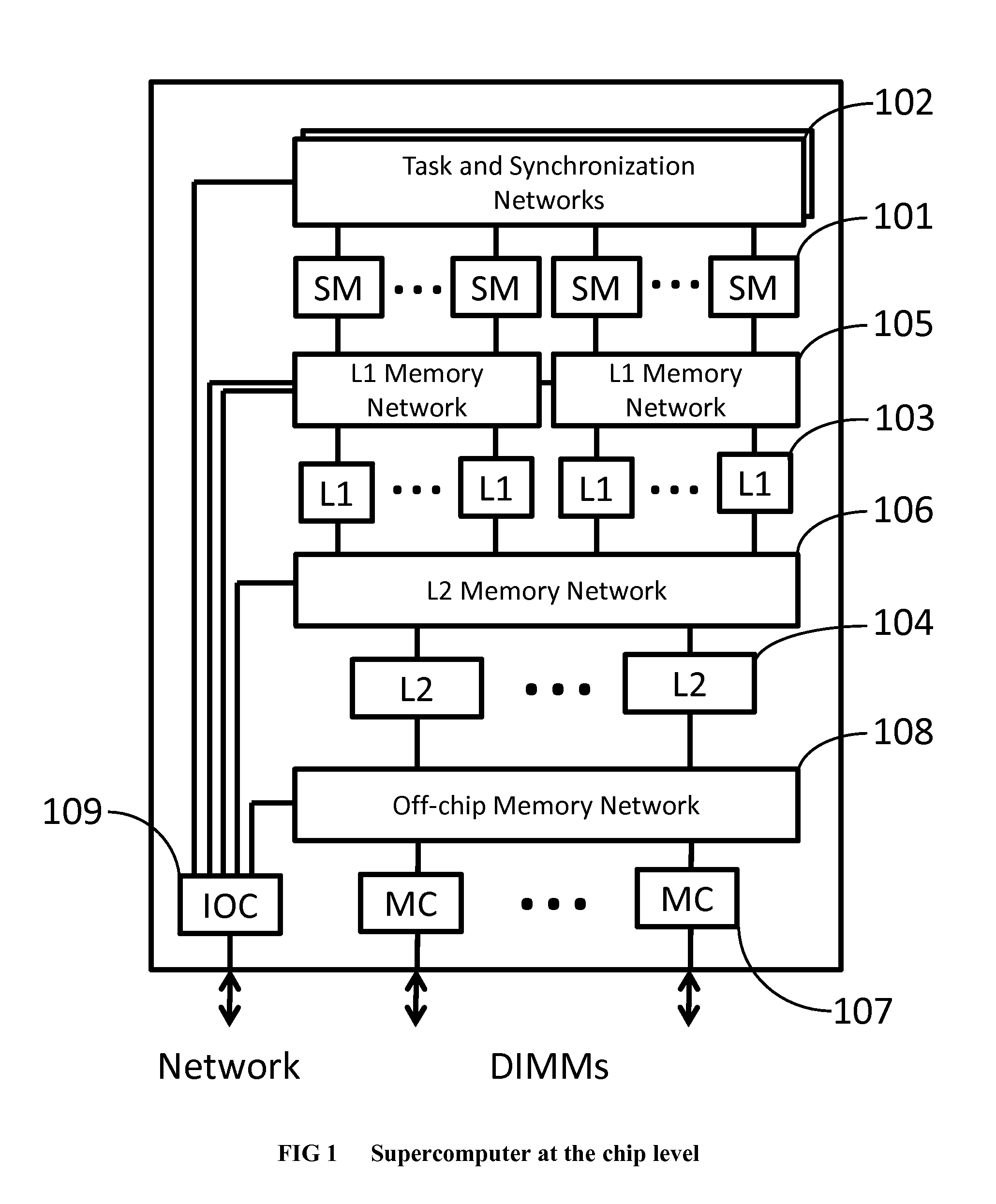
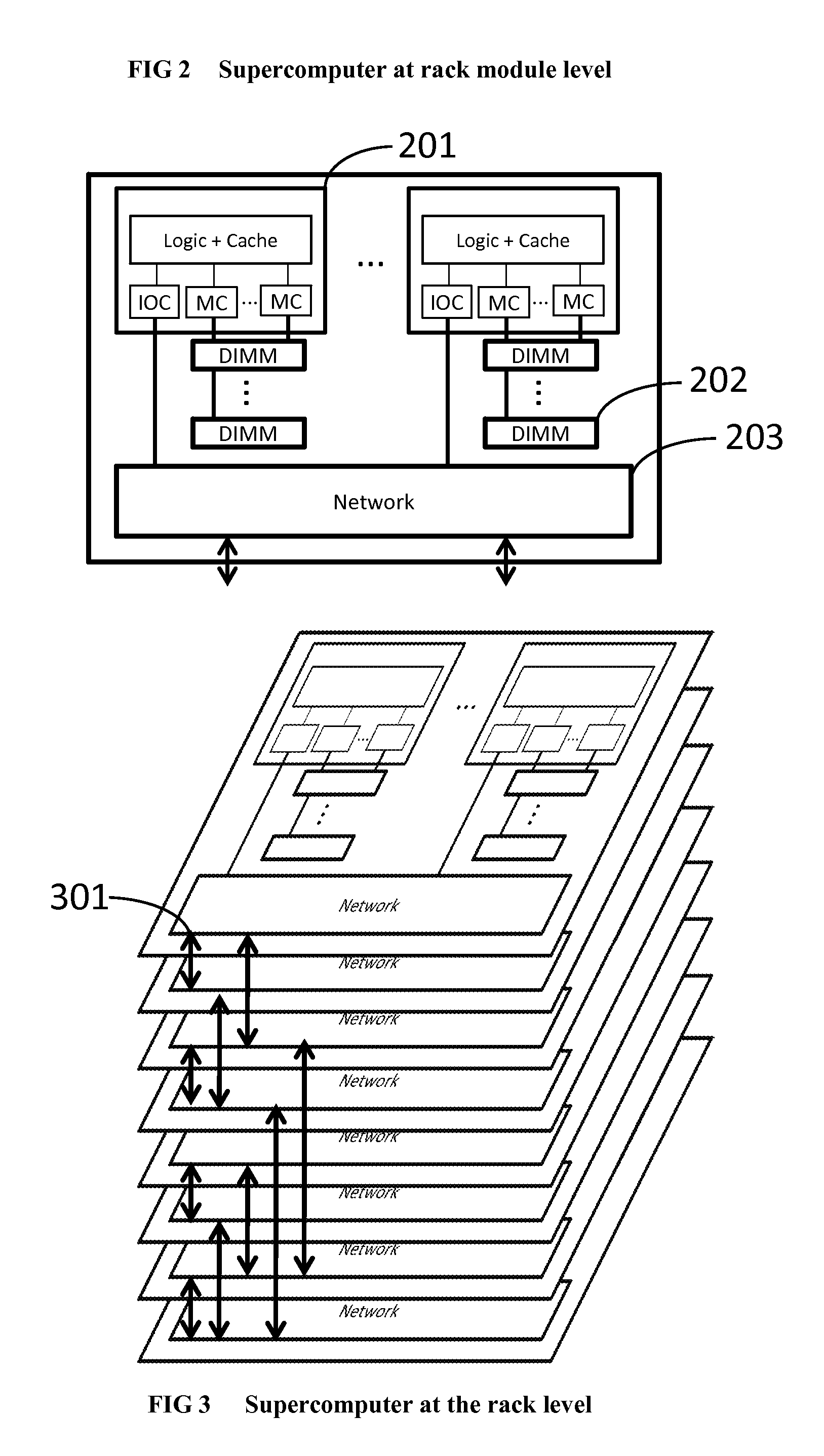
Method and system for converting a single-threaded software program into an application-specific supercomputer
ActiveUS20130125097A1Improve efficiencyLow overhead implementationMemory architecture accessing/allocationTransformation of program codeSupercomputerComputer architecture
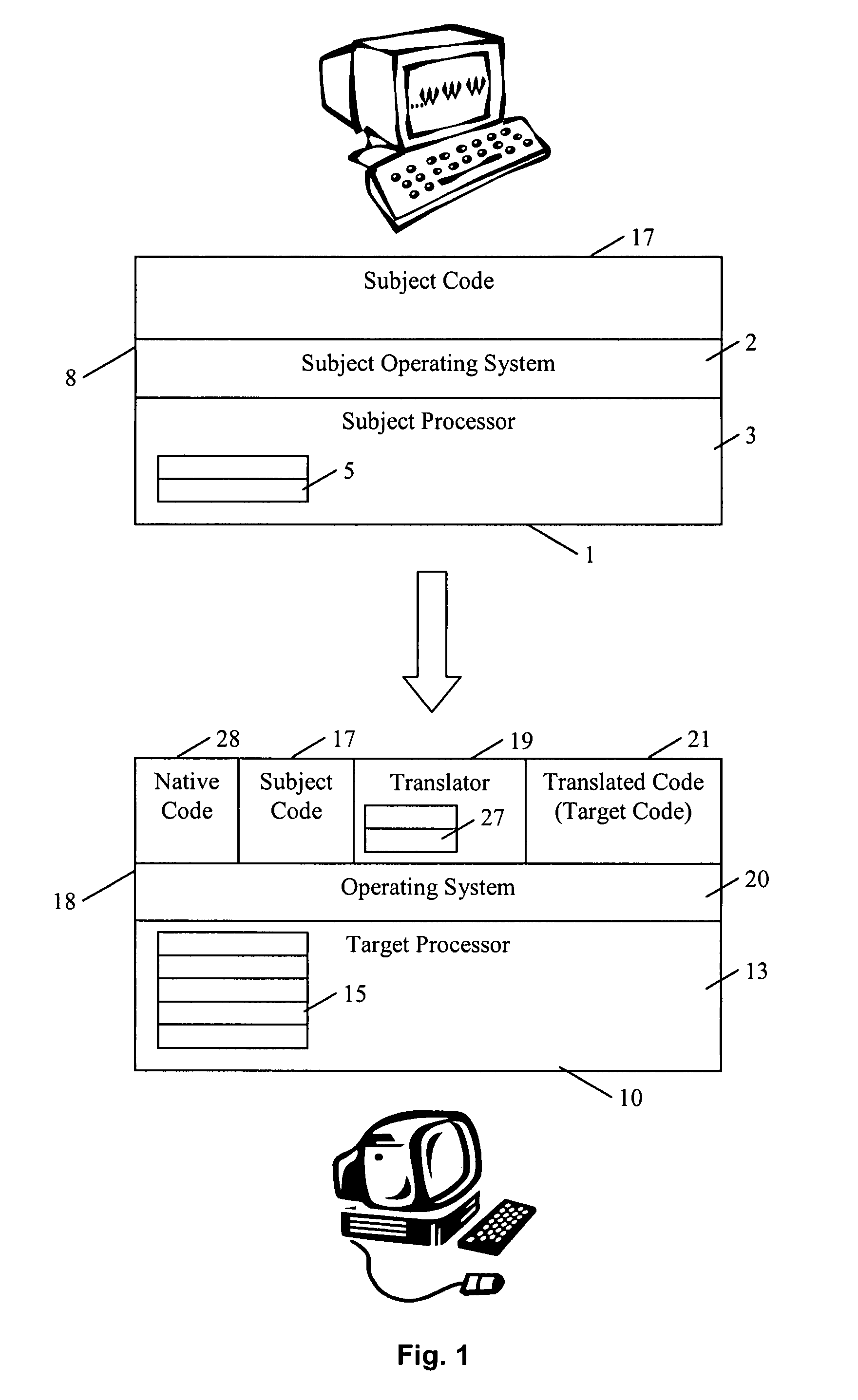
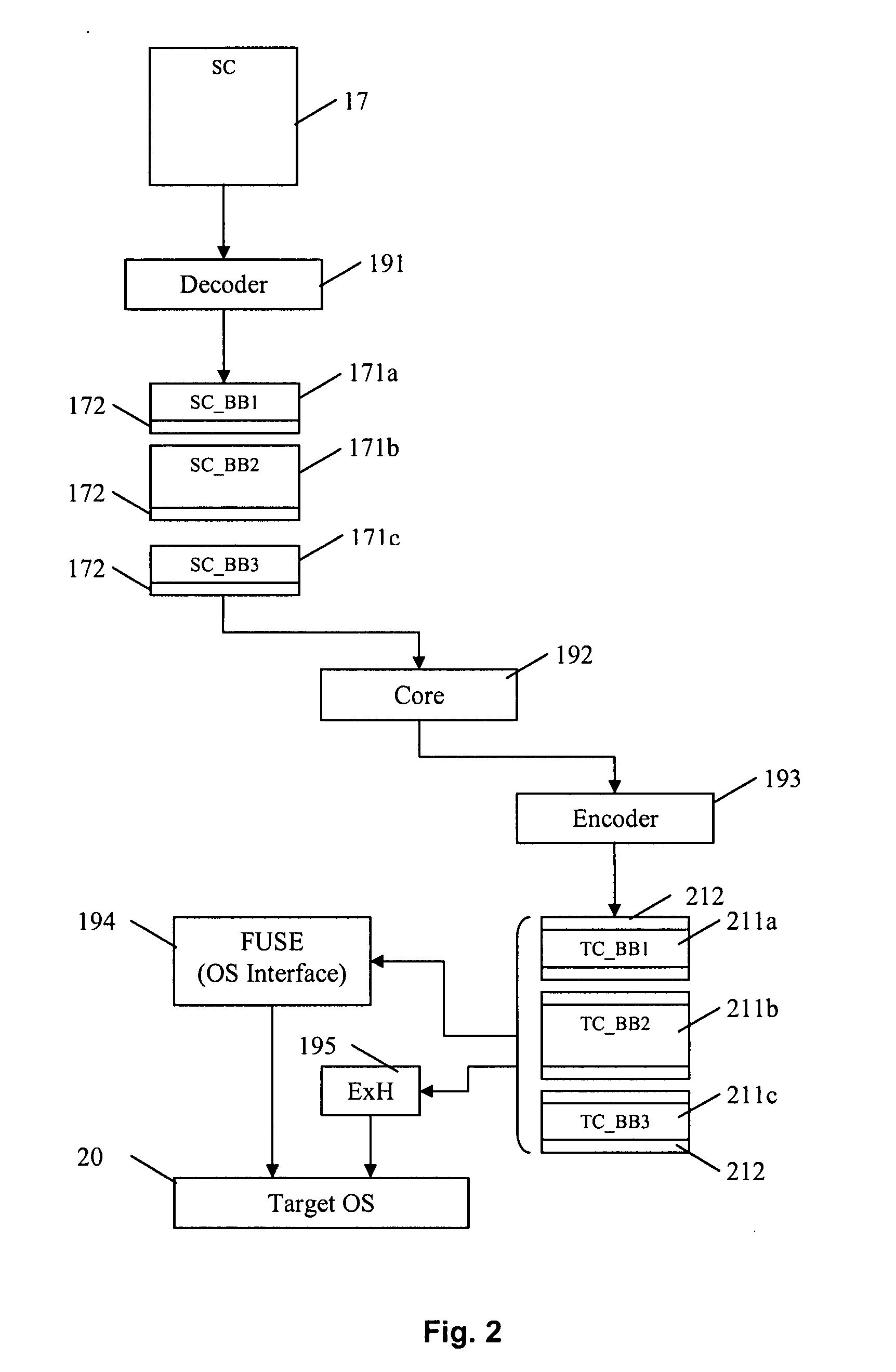
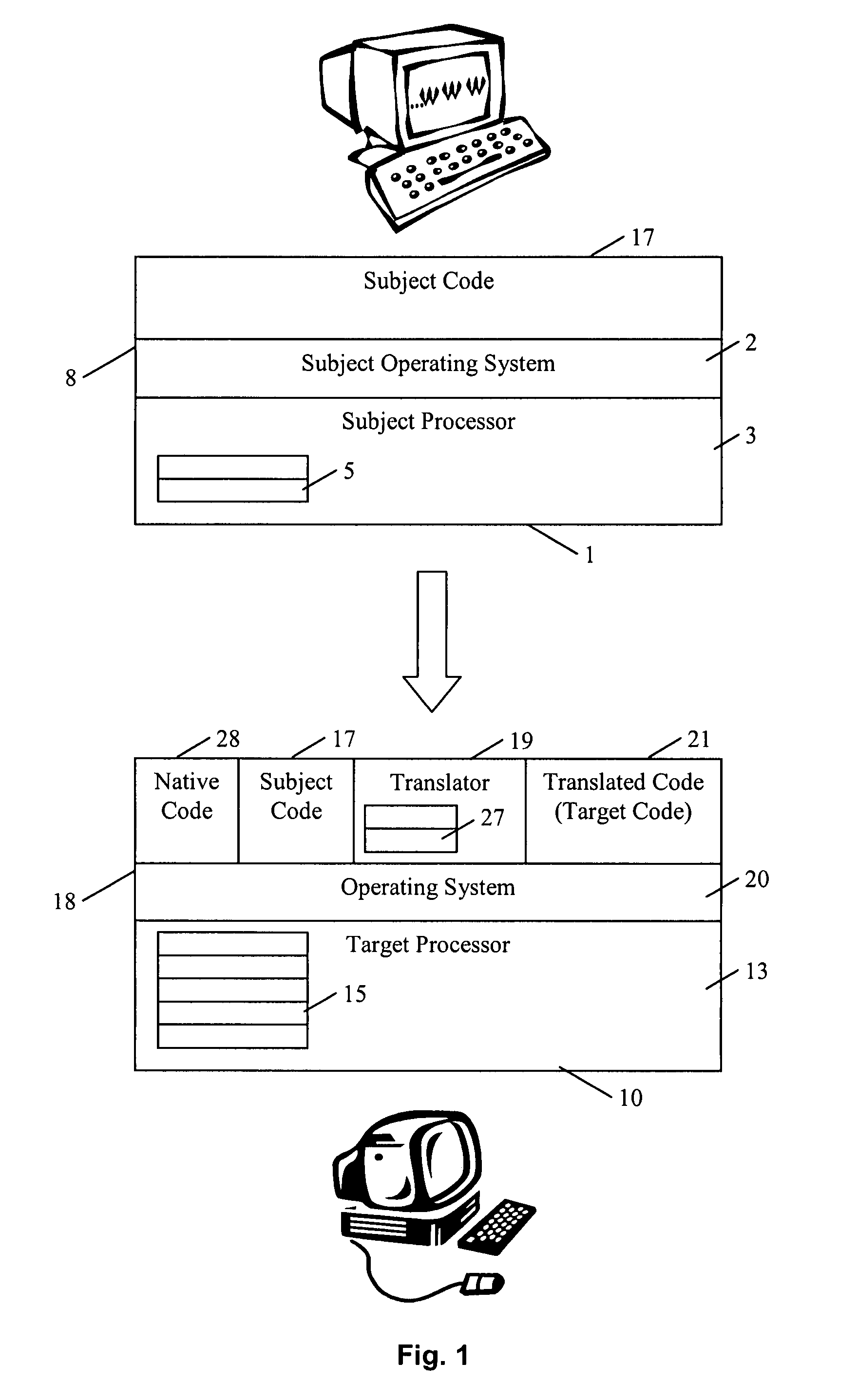
The invention comprises (i) a compilation method for automatically converting a single-threaded software program into an application-specific supercomputer, and (ii) the supercomputer system structure generated as a result of applying this method. The compilation method comprises: (a) Converting an arbitrary code fragment from the application into customized hardware whose execution is functionally equivalent to the software execution of the code fragment; and (b) Generating interfaces on the hardware and software parts of the application, which (i) Perform a software-to-hardware program state transfer at the entries of the code fragment; (ii) Perform a hardware-to-software program state transfer at the exits of the code fragment; and (iii) Maintain memory coherence between the software and hardware memories. If the resulting hardware design is large, it is divided into partitions such that each partition can fit into a single chip. Then, a single union chip is created which can realize any of the partitions.
Owner:GLOBAL SUPERCOMPUTING CORP
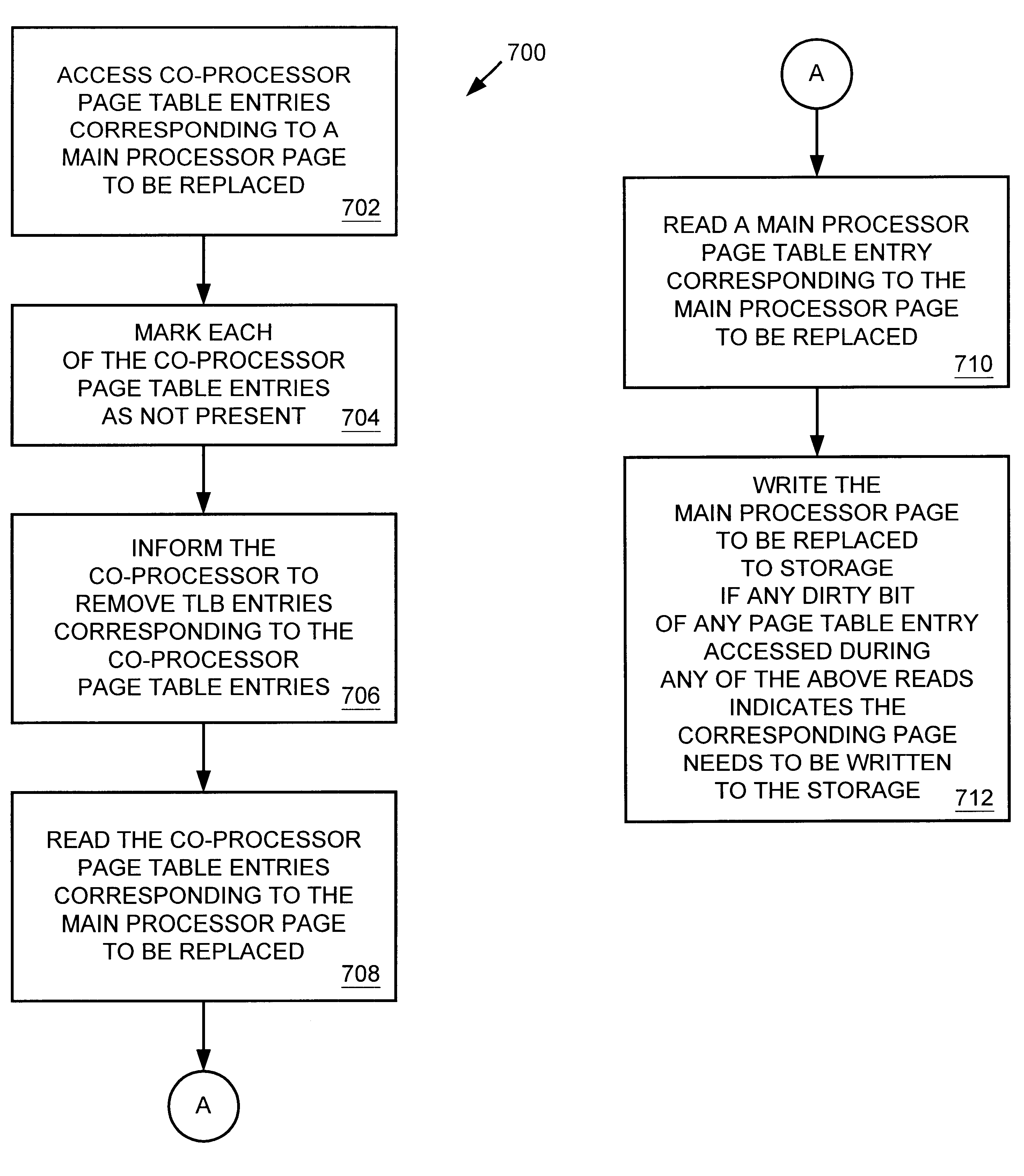
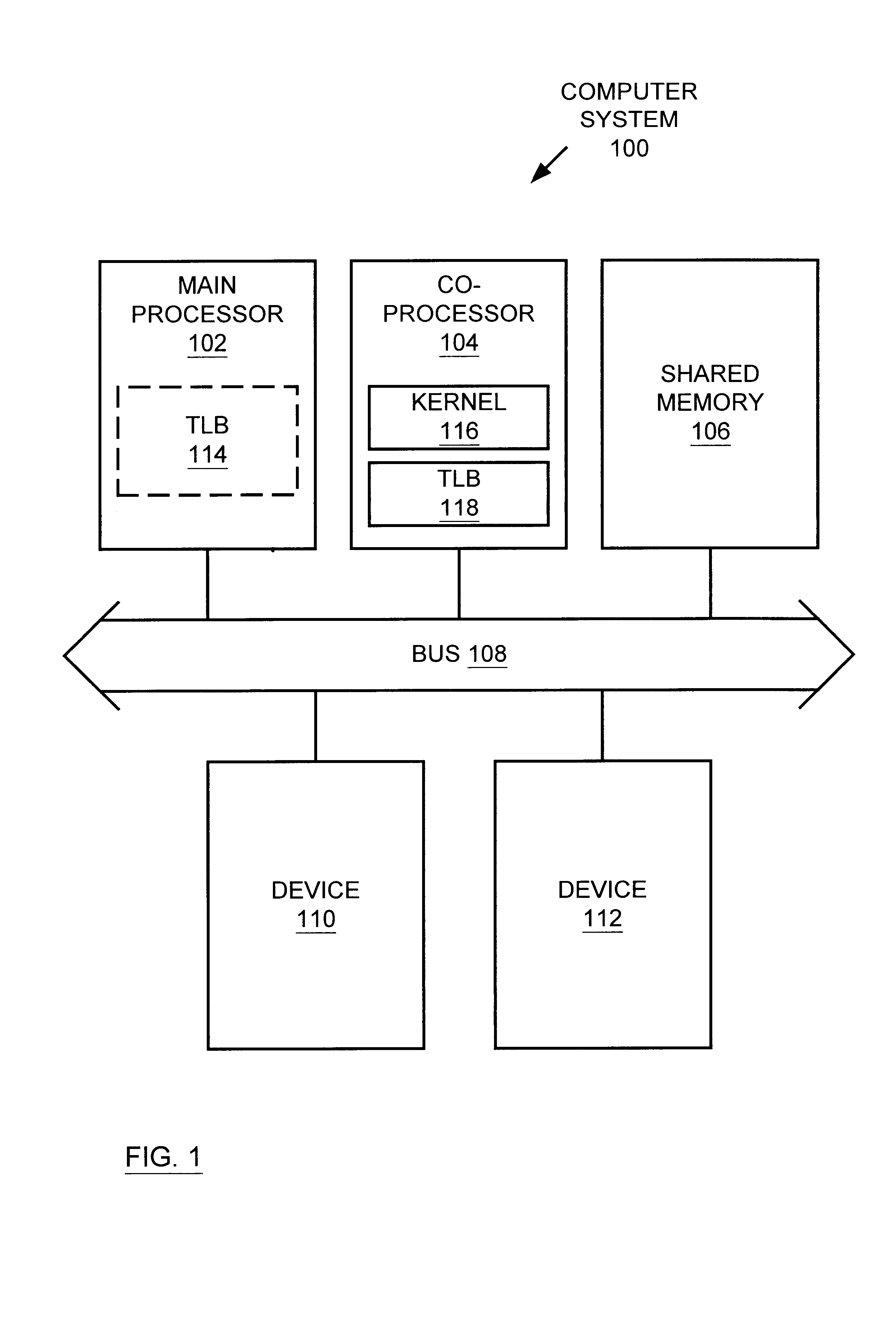
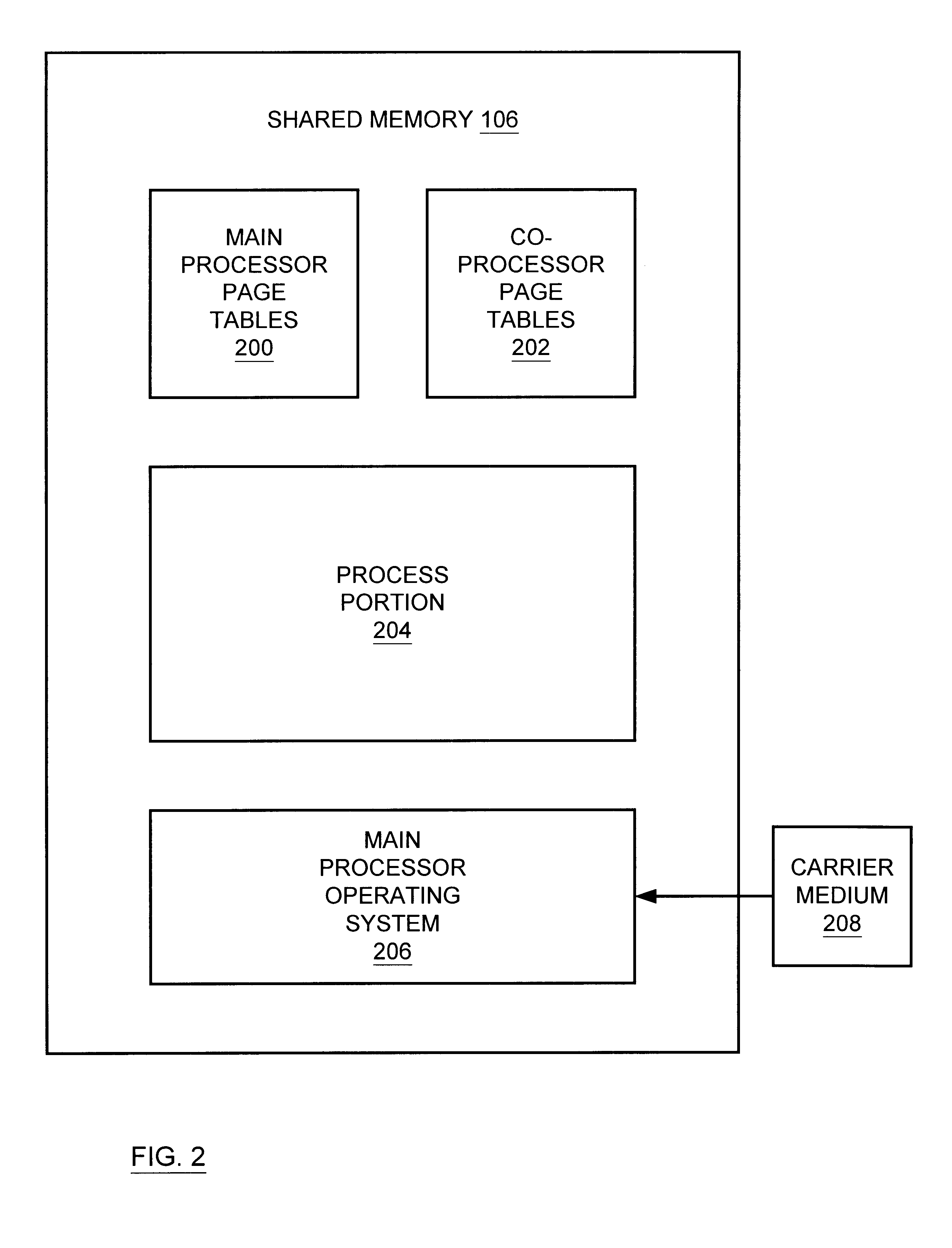
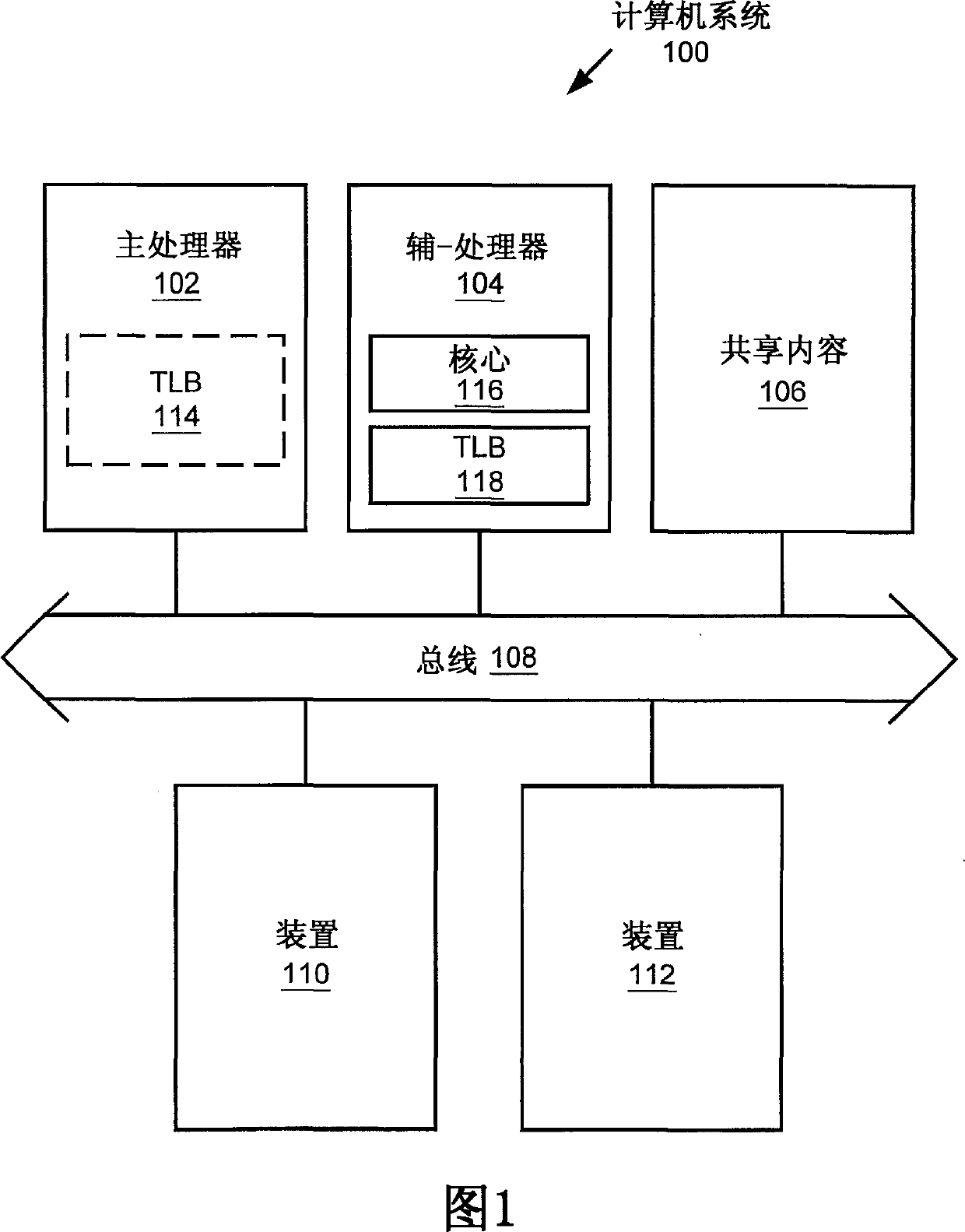
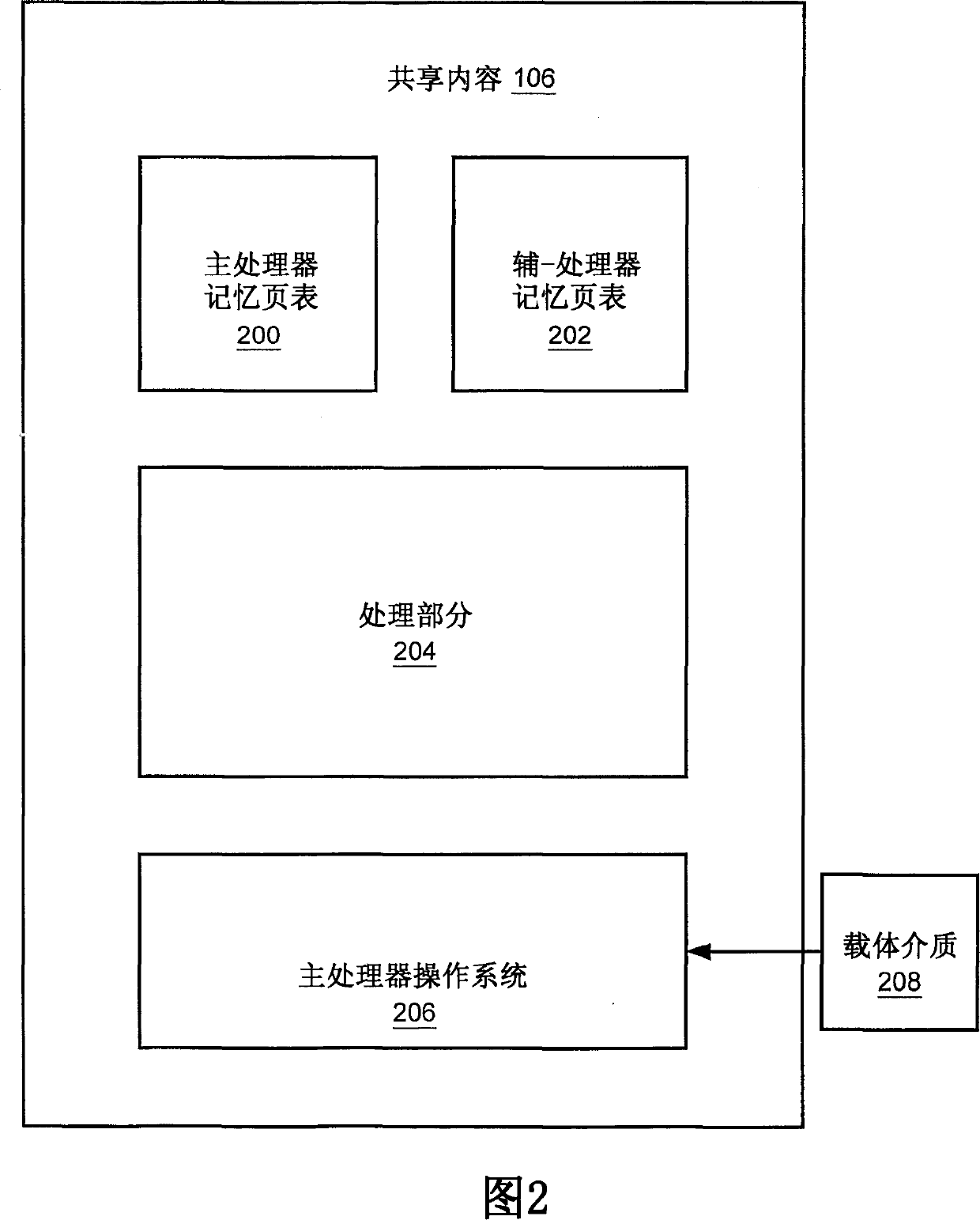
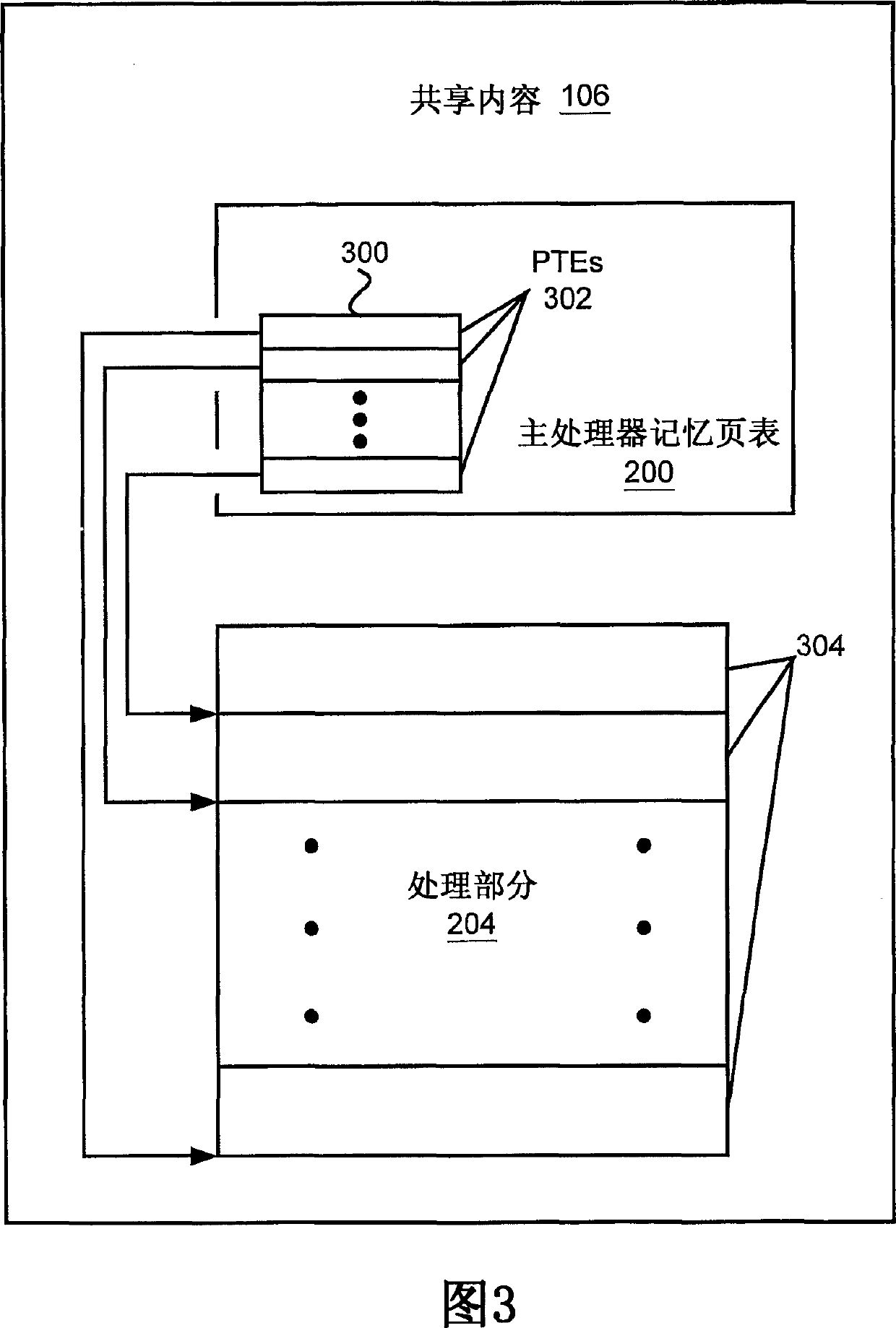
Multiprocessor system implementing virtual memory using a shared memory, and a page replacement method for maintaining paged memory coherence
InactiveUS6684305B1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationVirtual memoryComputer architecture
A computer system including a first processor, a second processor in communication with the first processor, a memory coupled to the first and second processors (i.e., a shared memory) and including multiple memory locations, and a storage device coupled to the first processor. The first and second processors implement virtual memory using the memory. The first processor maintains a first set of page tables and a second set of page tables in the memory. The first processor uses the first set of page tables to access the memory locations within the memory. The second processor uses the second set of page tables, maintained by the first processor, to access the memory locations within the memory. A virtual memory page replacement method is described for use in the computer system, wherein the virtual memory page replacement method is designed to help maintain paged memory coherence within the multiprocessor computer system.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
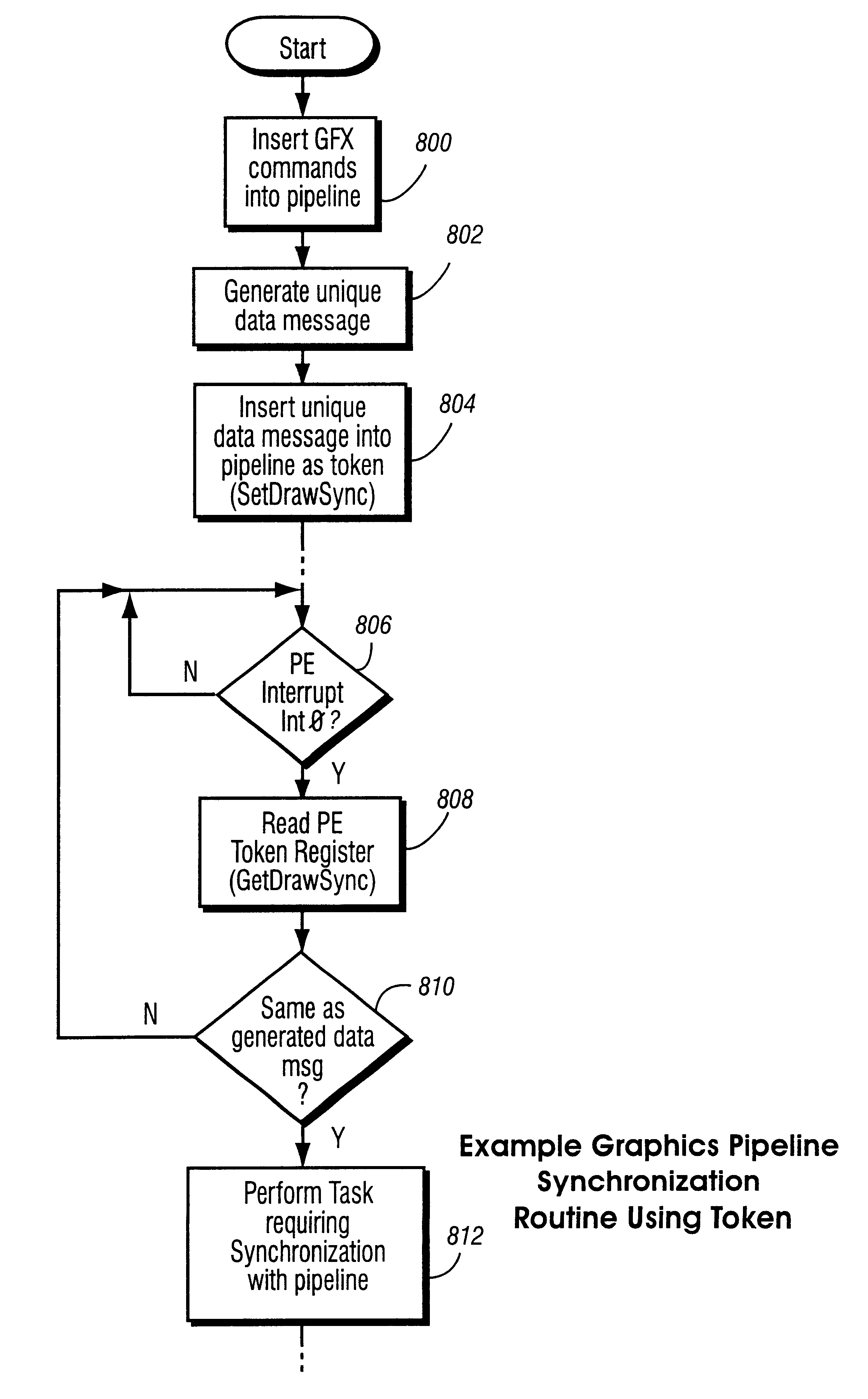
Graphics pipeline token synchronization
InactiveUS6867781B1Problem is complicatedMultiple digital computer combinationsProcessor architectures/configurationGraphicsGraphic system
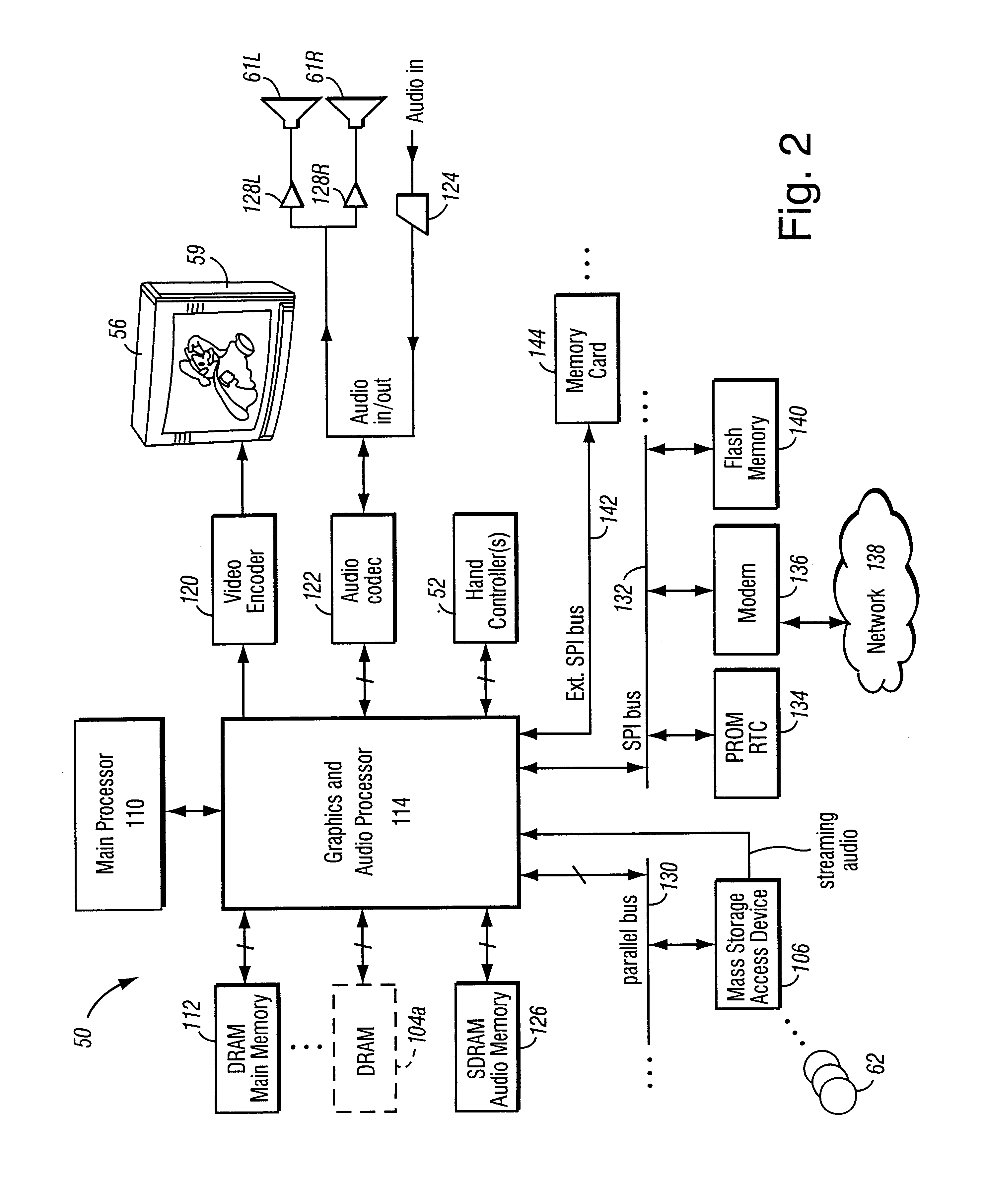
A graphics system including a custom graphics and audio processor produces exciting 2D and 3D graphics and surround sound. The system includes a graphics and audio processor including a 3D graphics pipeline and an audio digital signal processor. The graphics pipeline processes graphics commands at different rates depending upon the type of operation being performed. This makes it difficult to synchronize pipeline operations with external operations (e.g., a graphics processor with a main processor). To solve this problem, a synchronization token including a programmable data message is inserted into a graphics command stream sent to a graphics pipeline. At a predetermined point near the bottom of the pipeline, the token is captured and a signal is generated indicated the token has arrived. The graphics command producer can look at the captured token to determine which of multiple possible tokens has been captured, and can use the information to synchronize a task with the graphics pipeline. Applications include maintaining memory coherence in memory shared between the 3D graphics pipeline and a graphics command producer.
Owner:NINTENDO CO LTD
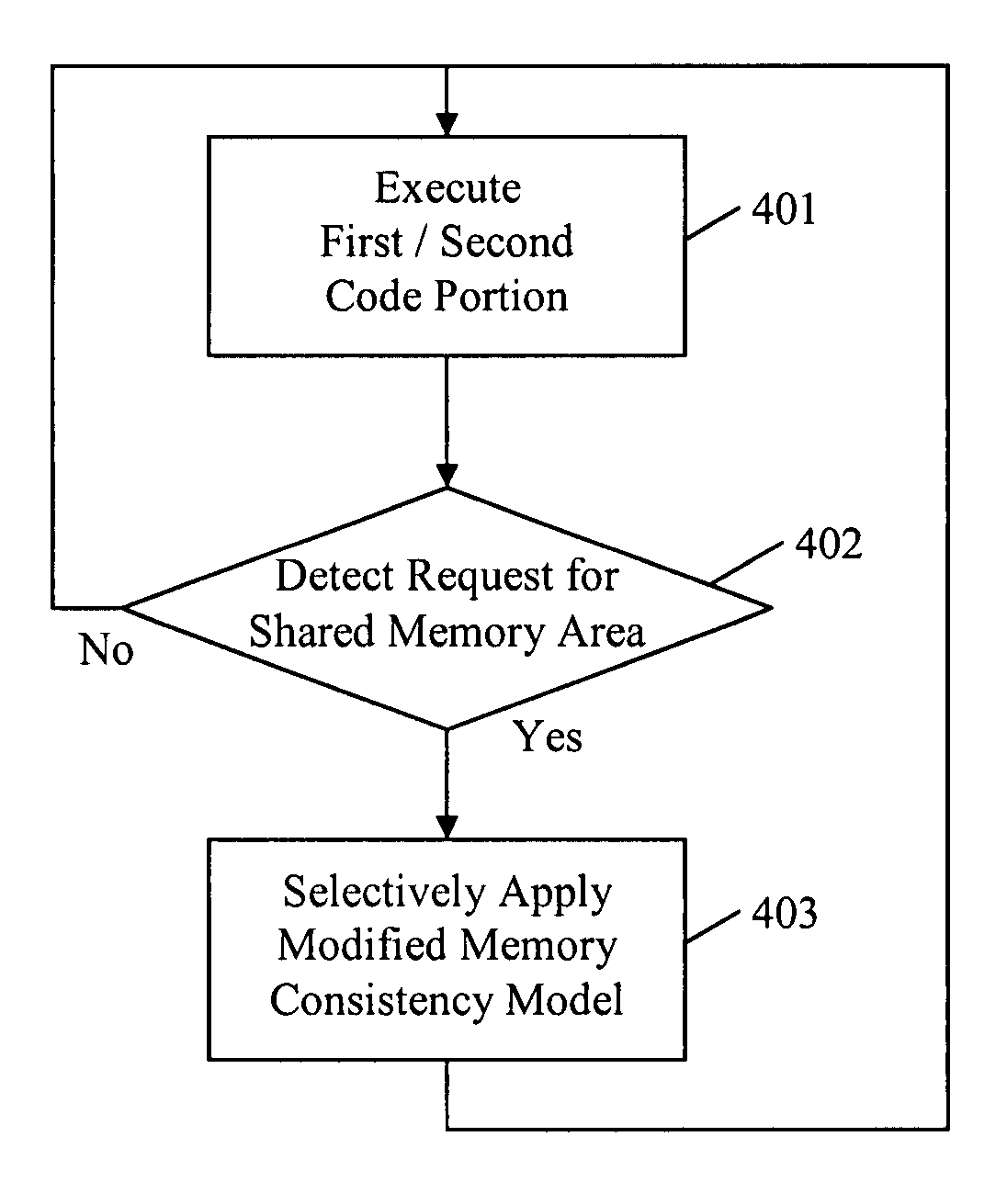
Memory consistency protection in a multiprocessor computing system
InactiveUS20080140971A1Low-cost and effectiveImproved memory consistencyResource allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationMulti processorObject code
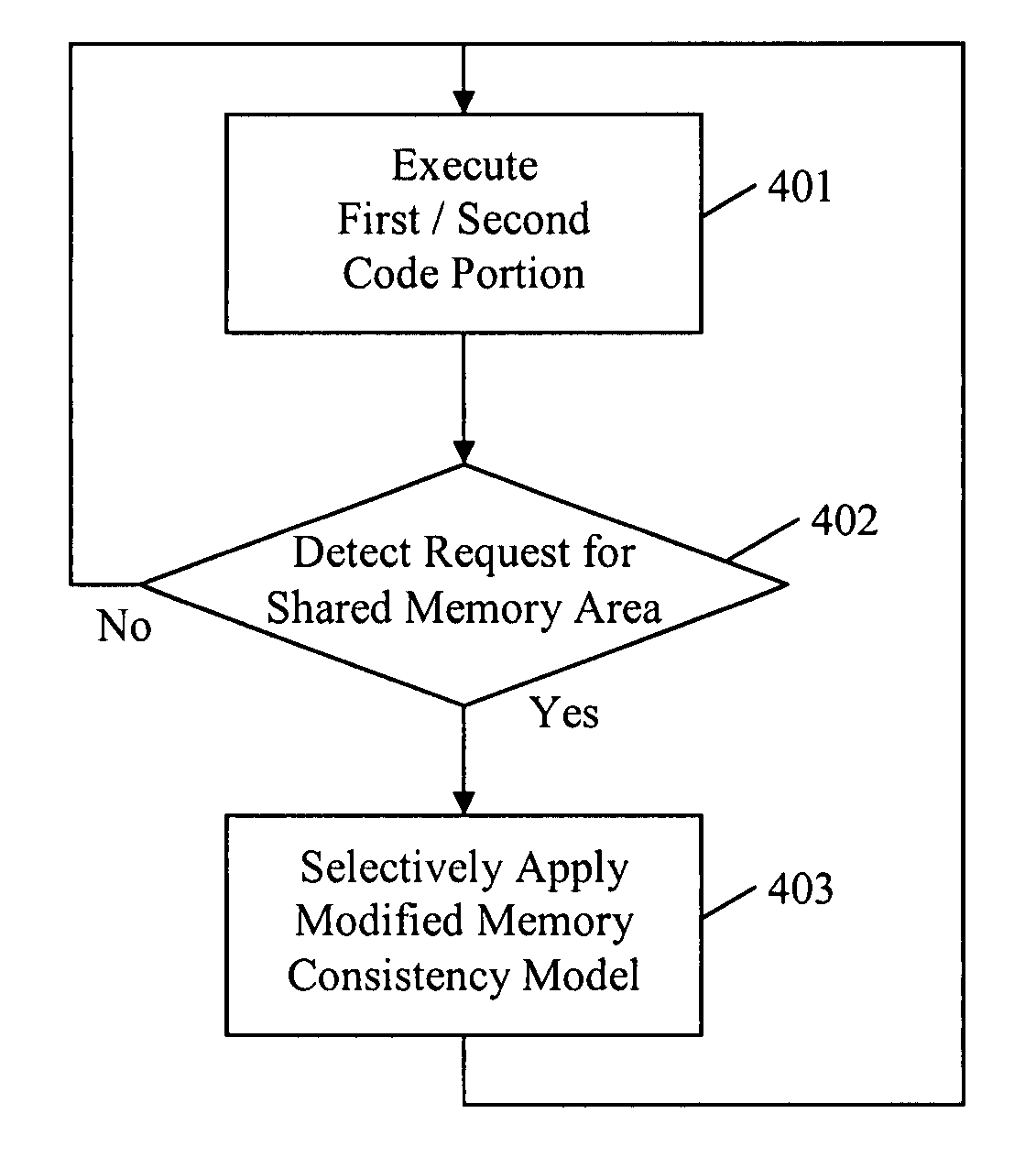
A method and apparatus to protect memory consistency in a multiprocessor computing system are described, in particular relating to program code conversion such as dynamic binary translation. The exemplary system provides a memory, processors and a controller / translator unit (CTU) arranged to convert subject code into at least first and second target code portions executable on the processors. The CTU comprises an address space allocation unit to provide virtual address space regions and direct the target code portions to access the memory therethough; a shared memory detection unit to detect a request to access a shared memory area, accessible by both target code portions, and to identify at least one group of instructions in the first target code portion which access the shared memory area; and a memory protection unit to selectively apply memory consistency protection in relation to accesses to the shared memory area by the identified group of instructions.
Owner:IBM CORP
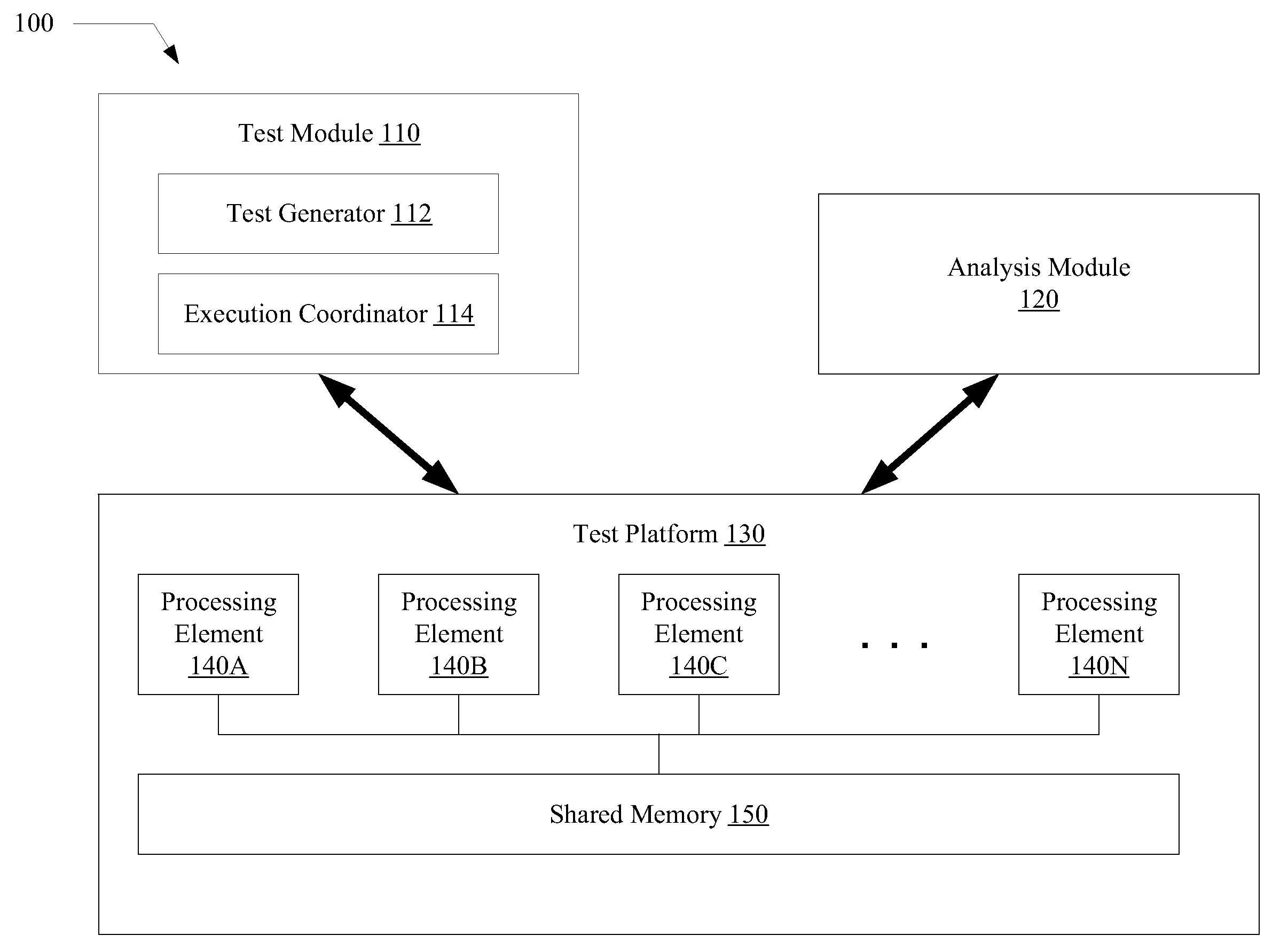
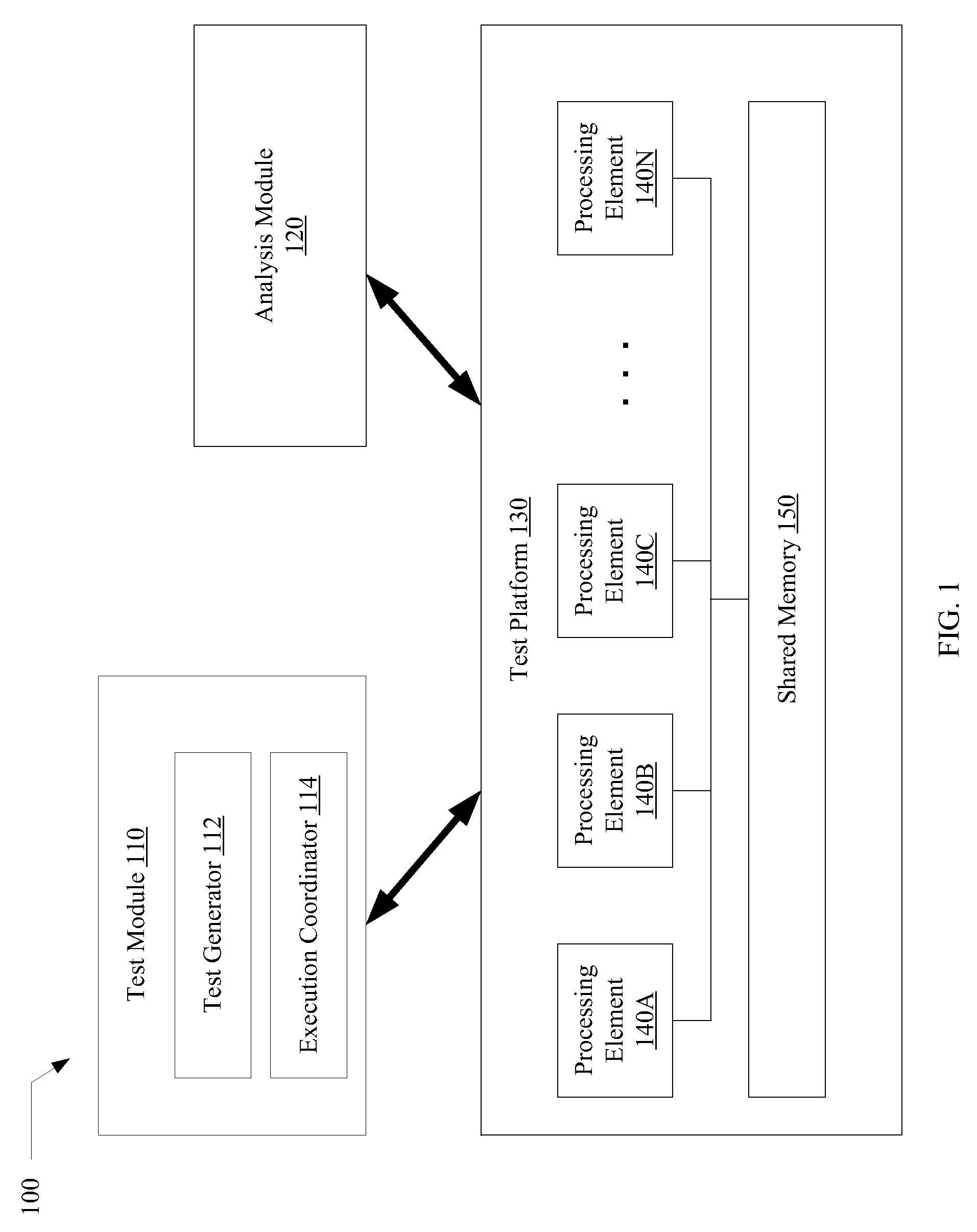
Verification of memory consistency and transactional memory
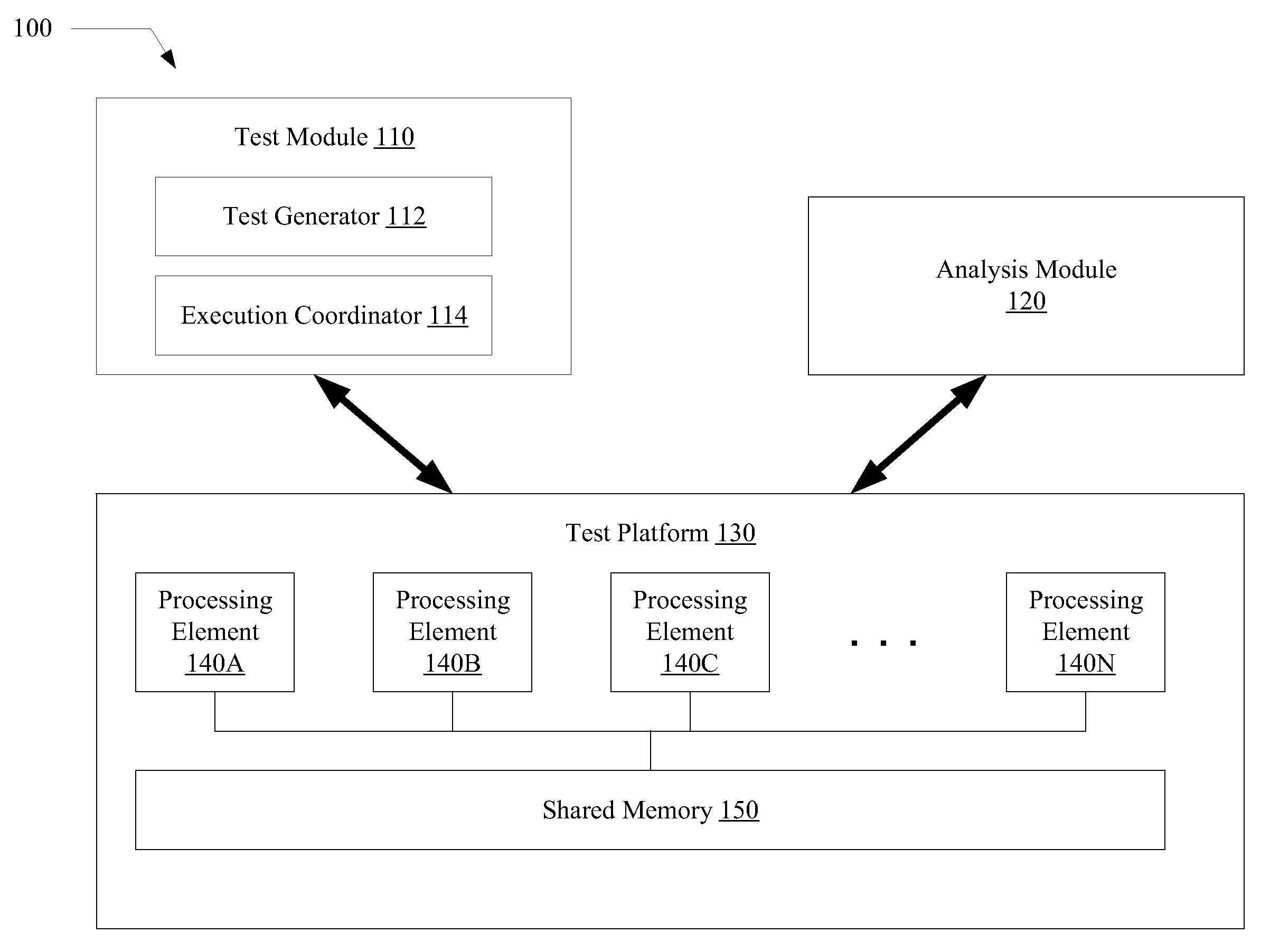
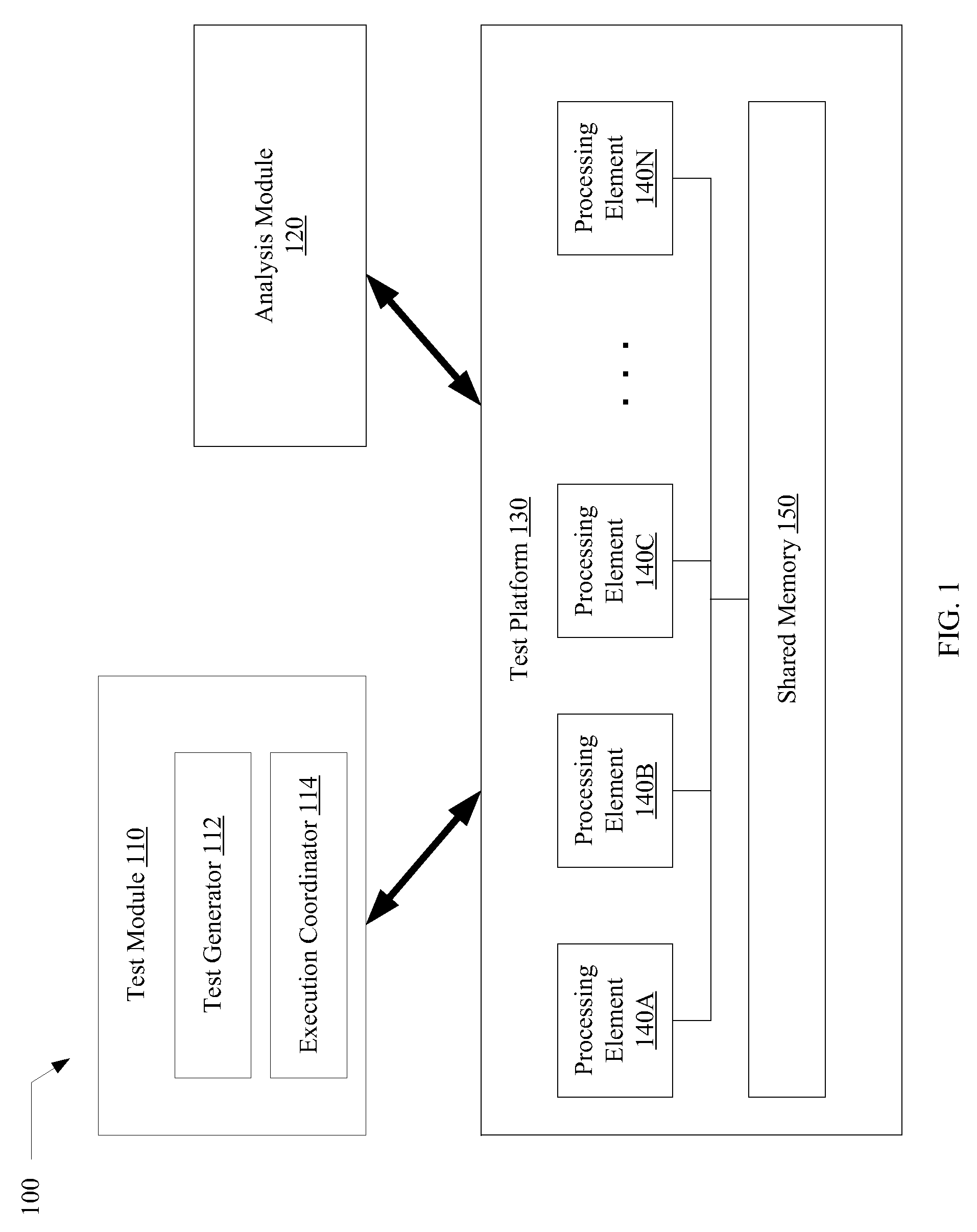
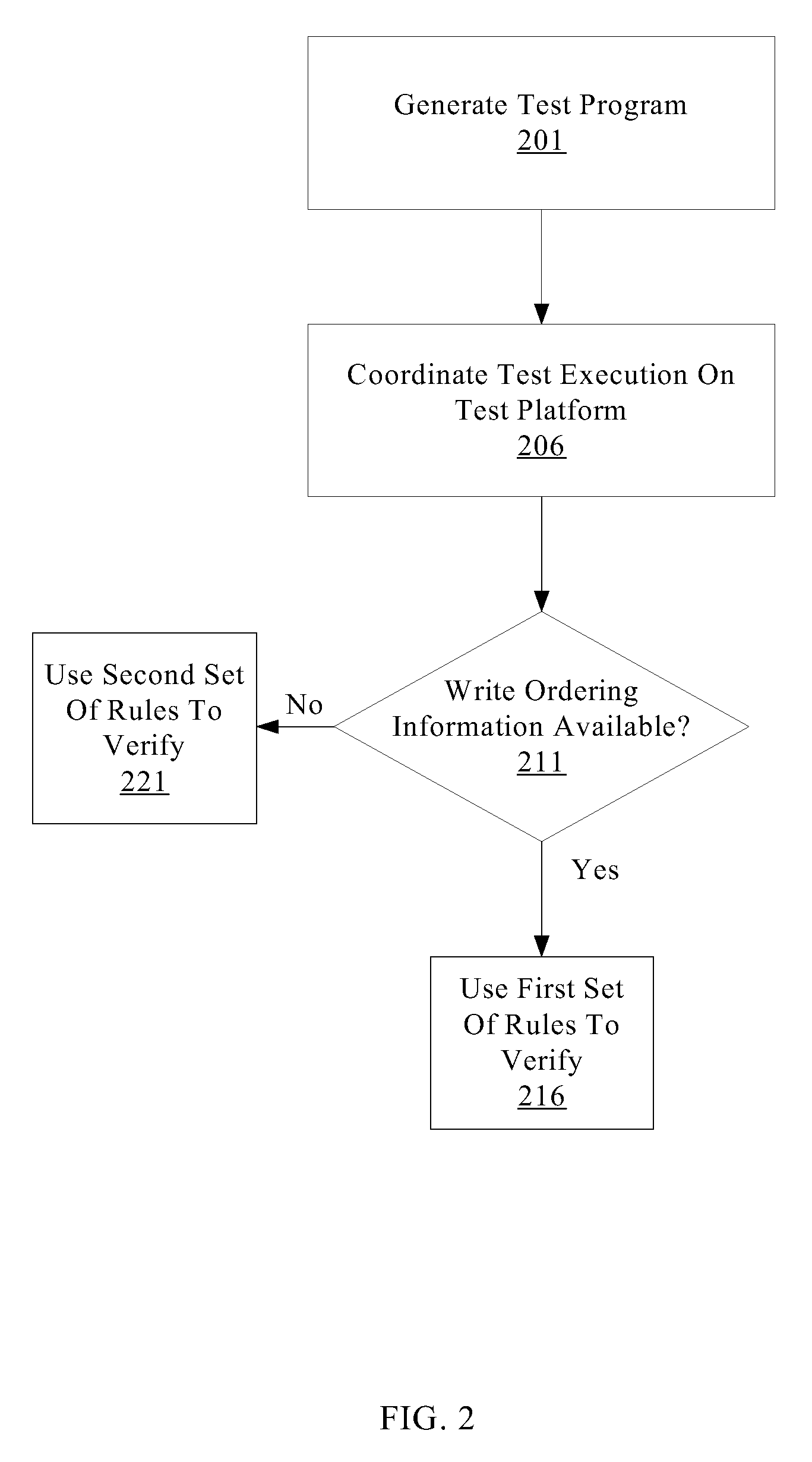
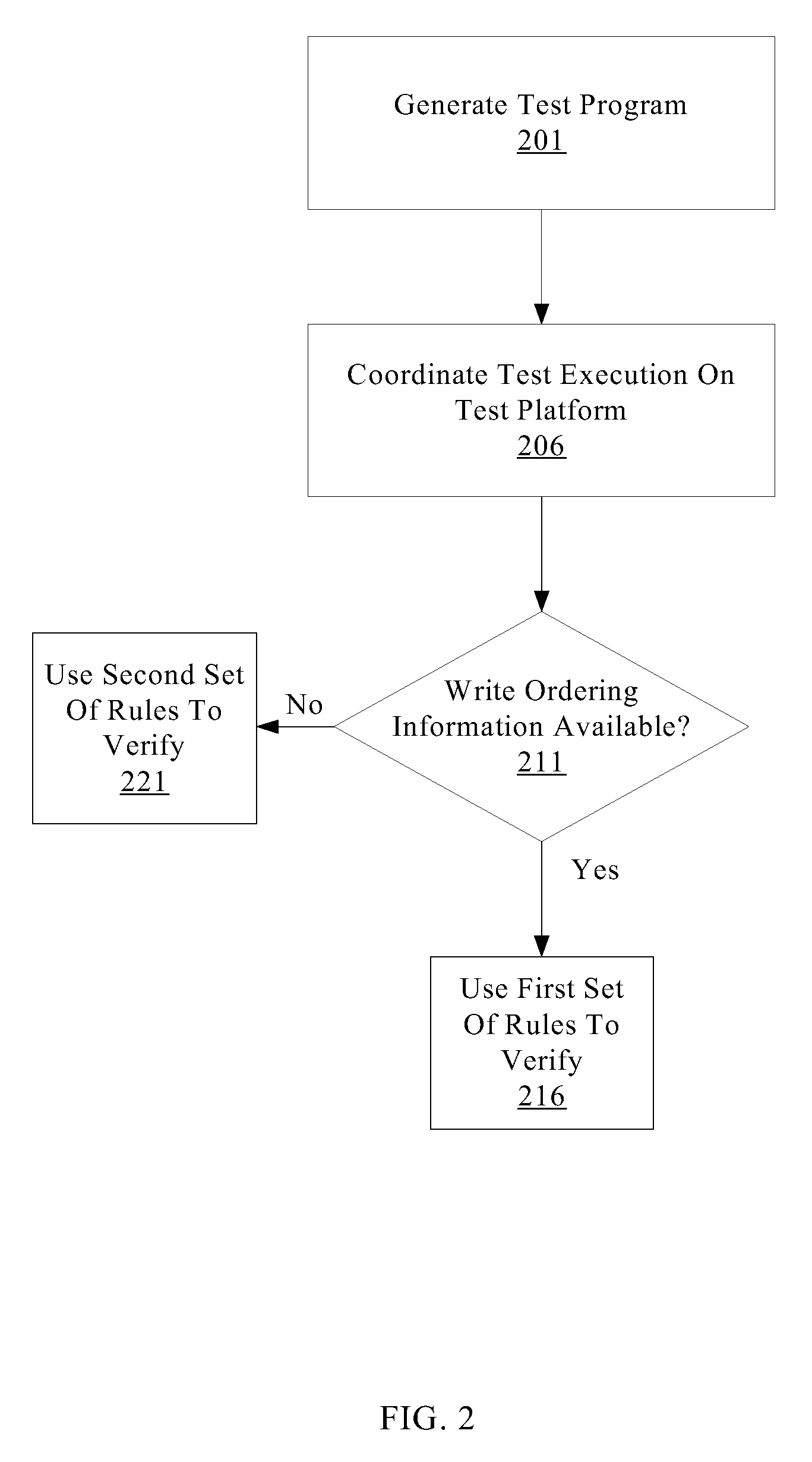
A system for efficiently verifying compliance with a memory consistency model includes a test module and an analysis module. The test module may coordinate an execution of a multithreaded test program on a test platform. If the test platform provides an indication of the order in which writes from multiple processing elements are performed at shared memory locations, the analysis module may use a first set of rules to verify that the results of the execution correspond to a valid ordering of events according to a memory consistency model. If the test platform does not provide an indication of write ordering, the analysis module may use a second set of rules to verify compliance with the memory consistency model. Further, a backtracking search may be performed to find a valid ordering if such ordering exists or show that none exists and, hence, confirm whether or not the results comply with the given memory consistency model.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Method and system for converting a single-threaded software program into an application-specific supercomputer
ActiveUS8966457B2Reduce expensesReduce overheadMemory architecture accessing/allocationTransformation of program codeSupercomputerComputer architecture
The invention comprises (i) a compilation method for automatically converting a single-threaded software program into an application-specific supercomputer, and (ii) the supercomputer system structure generated as a result of applying this method. The compilation method comprises: (a) Converting an arbitrary code fragment from the application into customized hardware whose execution is functionally equivalent to the software execution of the code fragment; and (b) Generating interfaces on the hardware and software parts of the application, which (i) Perform a software-to-hardware program state transfer at the entries of the code fragment; (ii) Perform a hardware-to-software program state transfer at the exits of the code fragment; and (iii) Maintain memory coherence between the software and hardware memories. If the resulting hardware design is large, it is divided into partitions such that each partition can fit into a single chip. Then, a single union chip is created which can realize any of the partitions.
Owner:GLOBAL SUPERCOMPUTING CORP
Verification of memory consistency and transactional memory
ActiveUS20080288834A1Efficiently verifying complianceError detection/correctionStatic storageProcessing elementTest platform
A system for efficiently verifying compliance with a memory consistency model includes a test module and an analysis module. The test module may coordinate an execution of a multithreaded test program on a test platform. If the test platform provides an indication of the order in which writes from multiple processing elements are performed at shared memory locations, the analysis module may use a first set of rules to verify that the results of the execution correspond to a valid ordering of events according to a memory consistency model. If the test platform does not provide an indication of write ordering, the analysis module may use a second set of rules to verify compliance with the memory consistency model. Further, a backtracking search may be performed to find a valid ordering if such ordering exists or show that none exists and, hence, confirm whether or not the results comply with the given memory consistency model.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
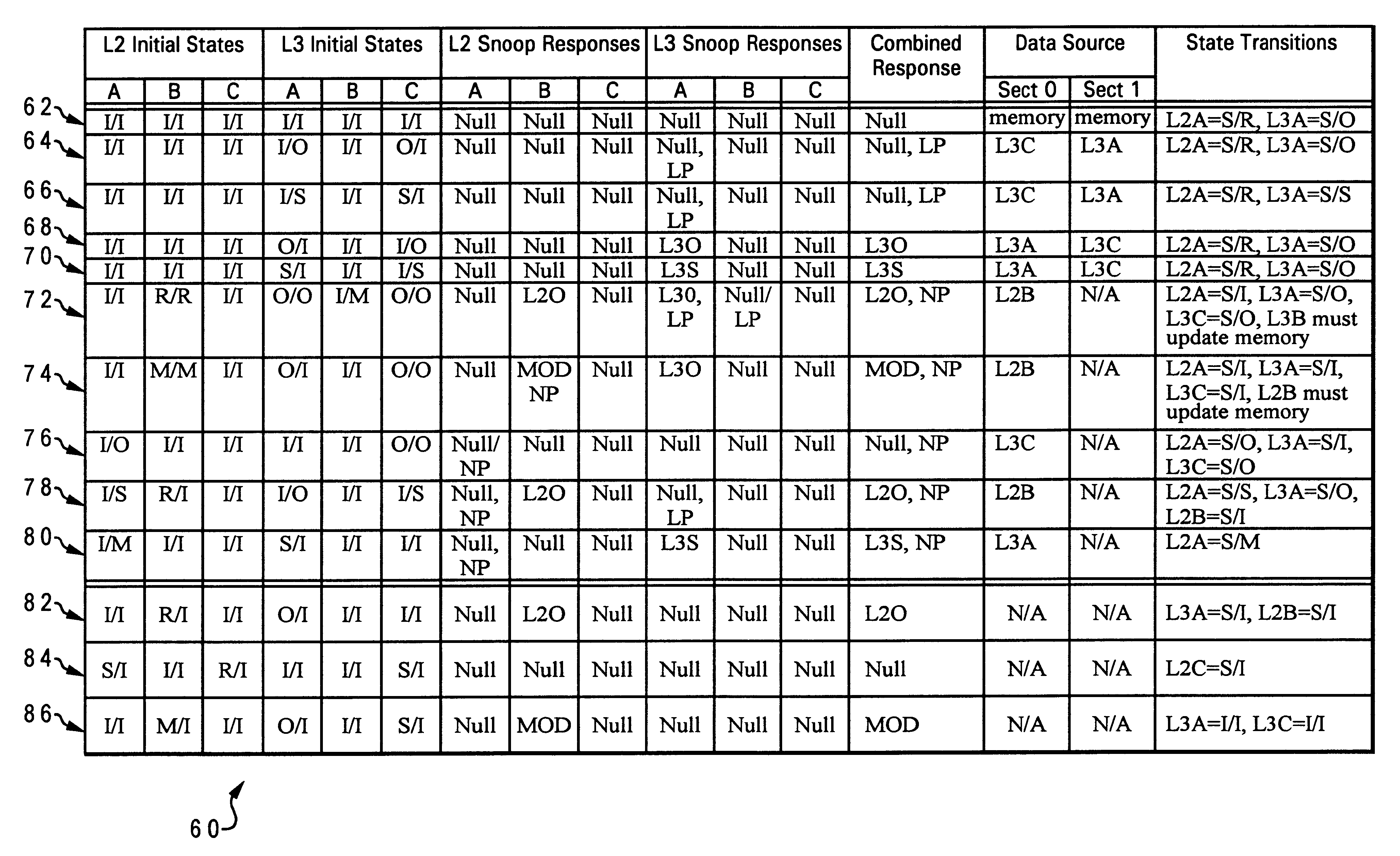
Multiprocessor system bus protocol for O state memory-consistent data
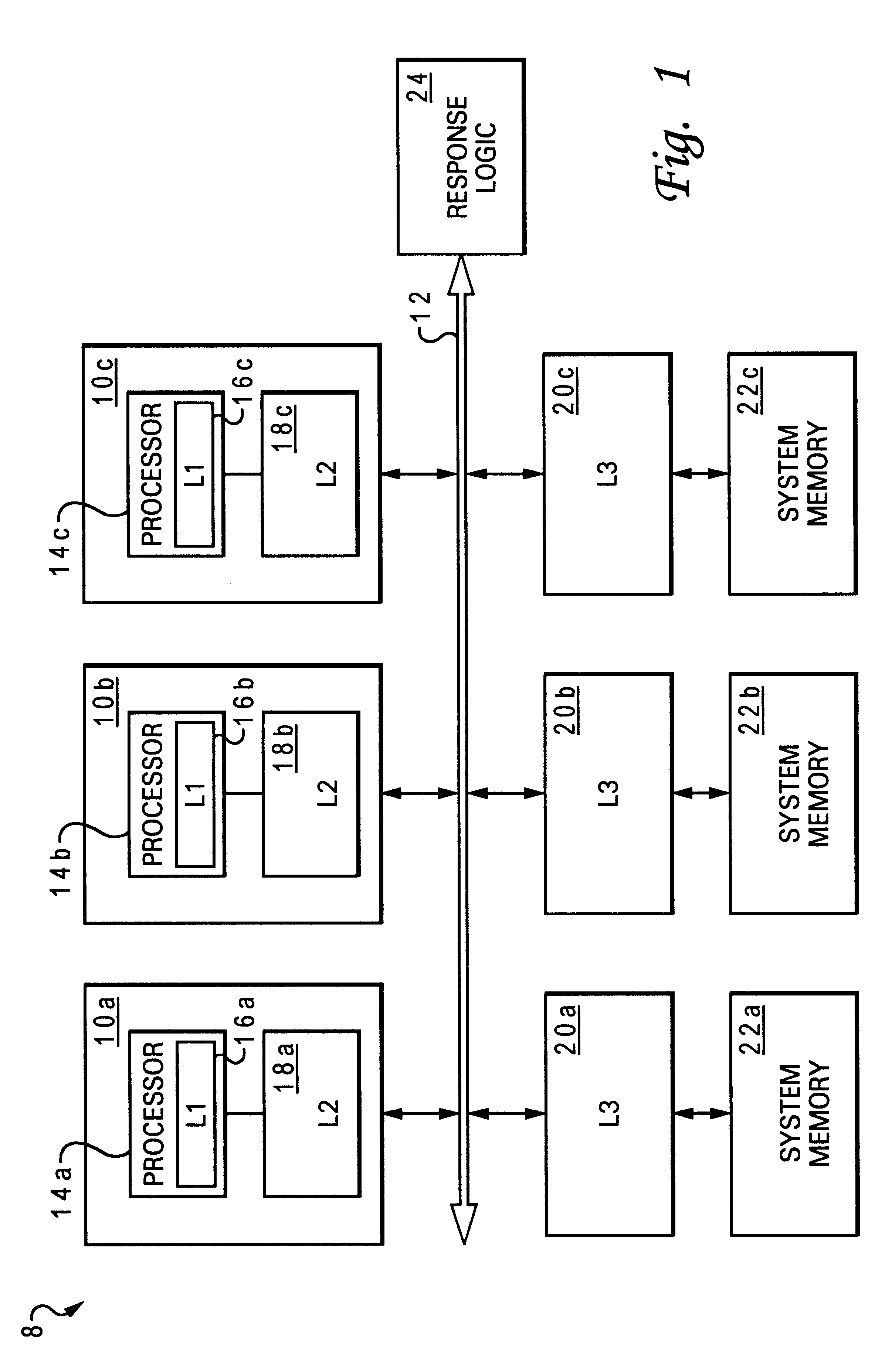
InactiveUS6405290B1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationData processing systemMemory address
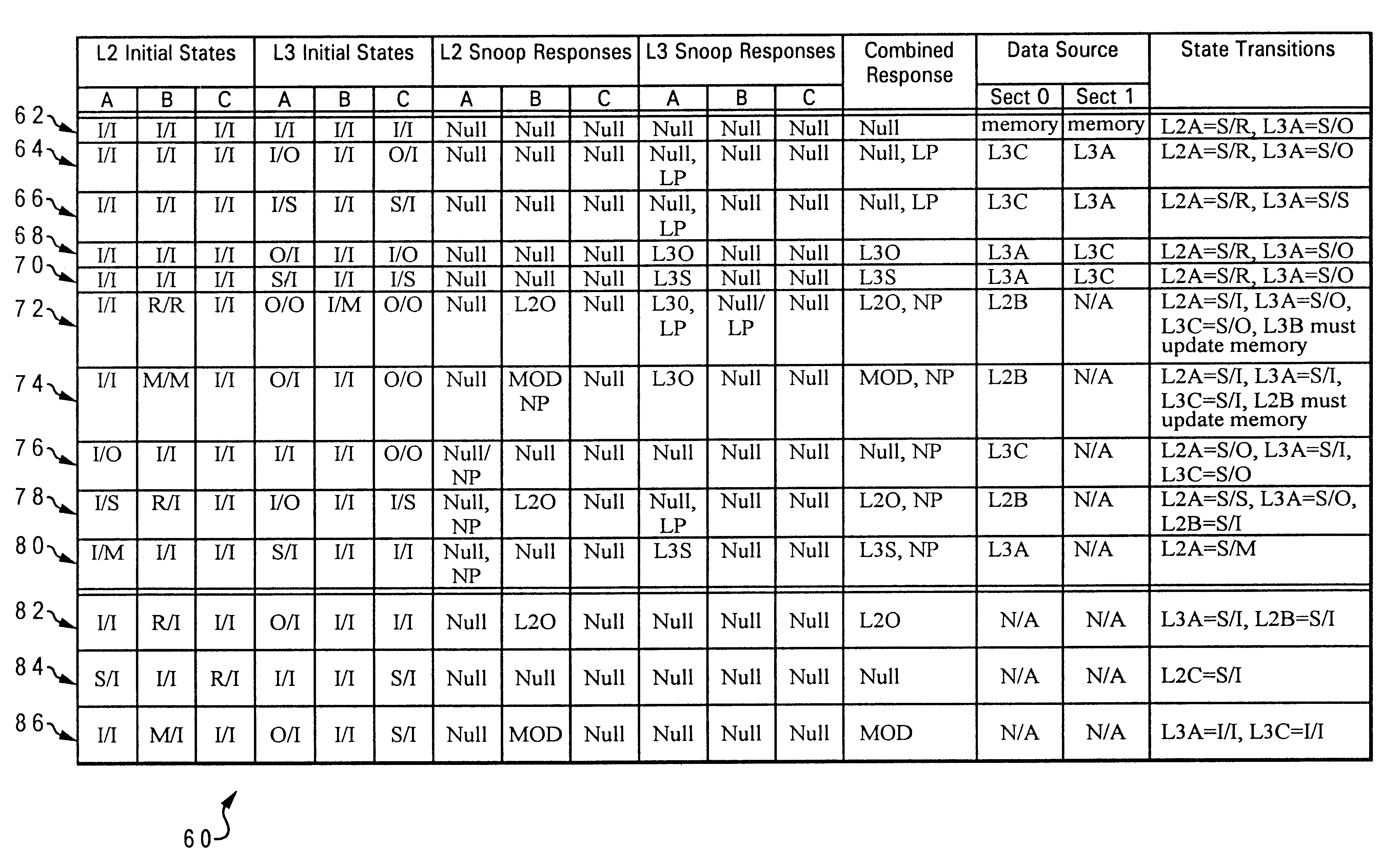
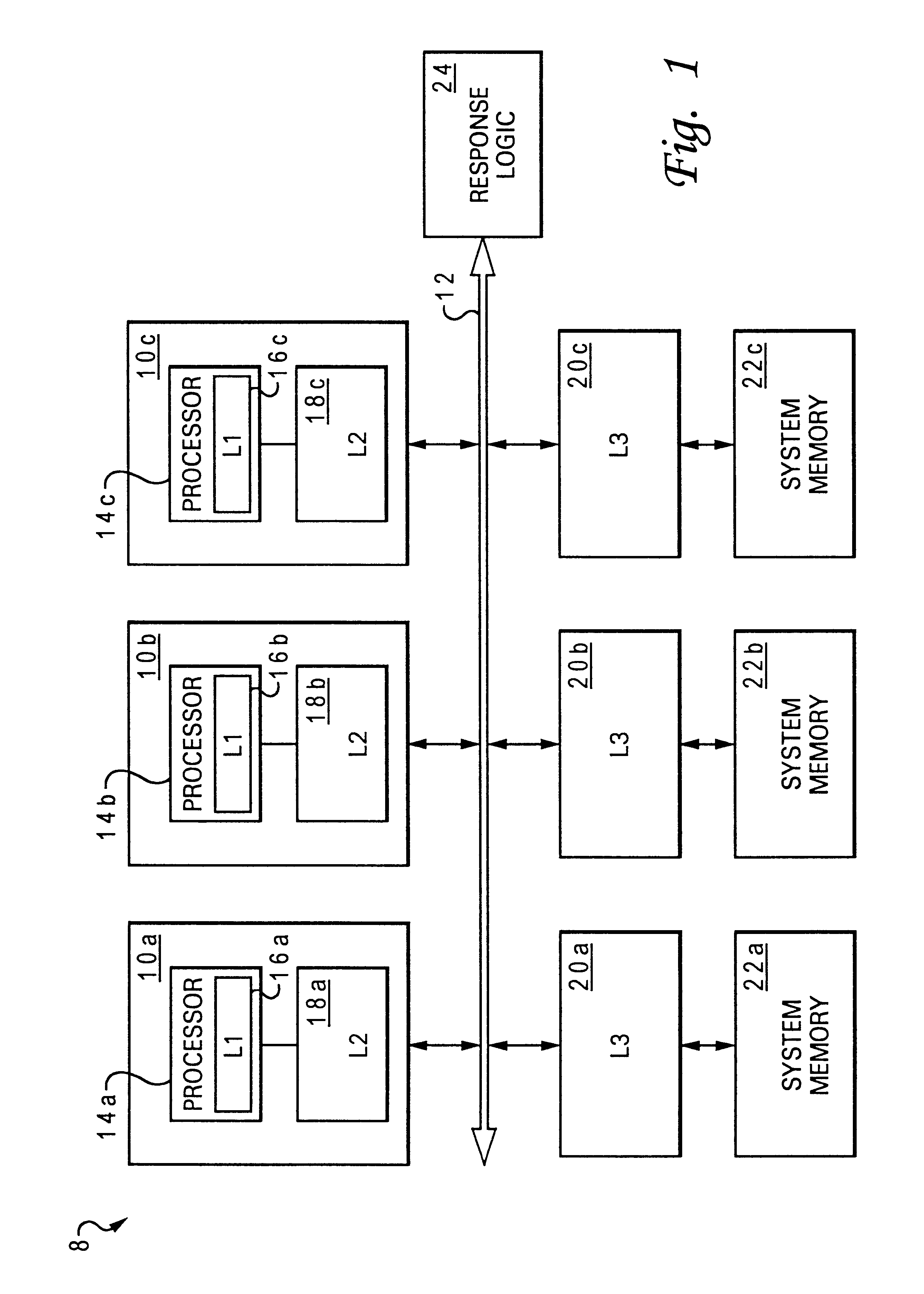
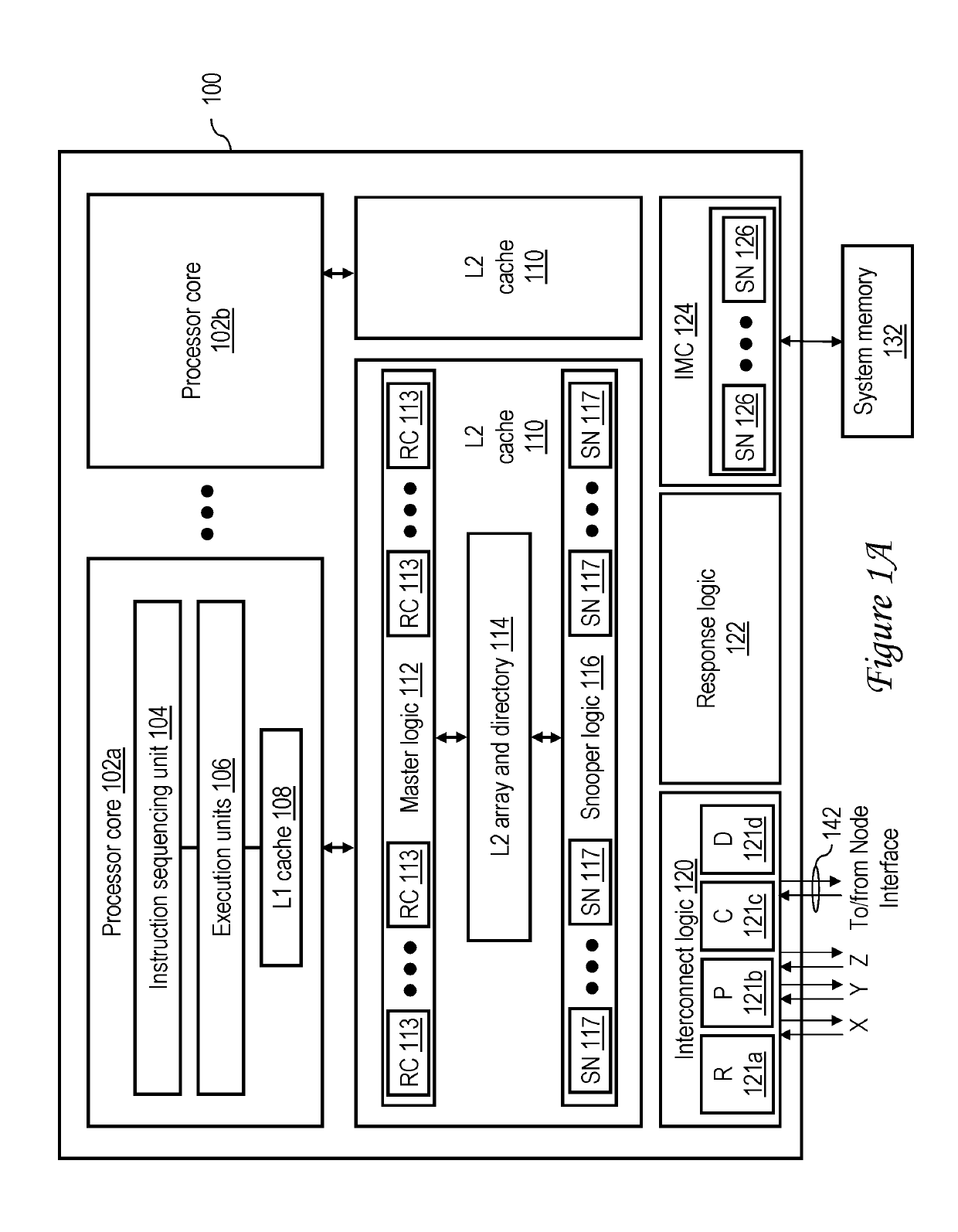
A data processing system includes an interconnect, a system memory and a number of snoopers coupled to the interconnect, and response logic. In response to a requesting snooper issuing a data request on the interconnect specifying a memory address, the snoopers provide snoop responses. The response logic compiles the snoop responses to obtain a combined response including an indication of a demand-source snooper that will source requested data associated with the memory address to the requesting snooper and an indication of whether additional non-requested data will be supplied to the requesting snooper. This combined response is then transmitted to the snoopers on the interconnect to direct the provision of the requested data, and possibly unrequested prefetch data, to the requesting snooper.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method and apparatus to concurrently boot multiple processors in a non-uniform-memory-access machine
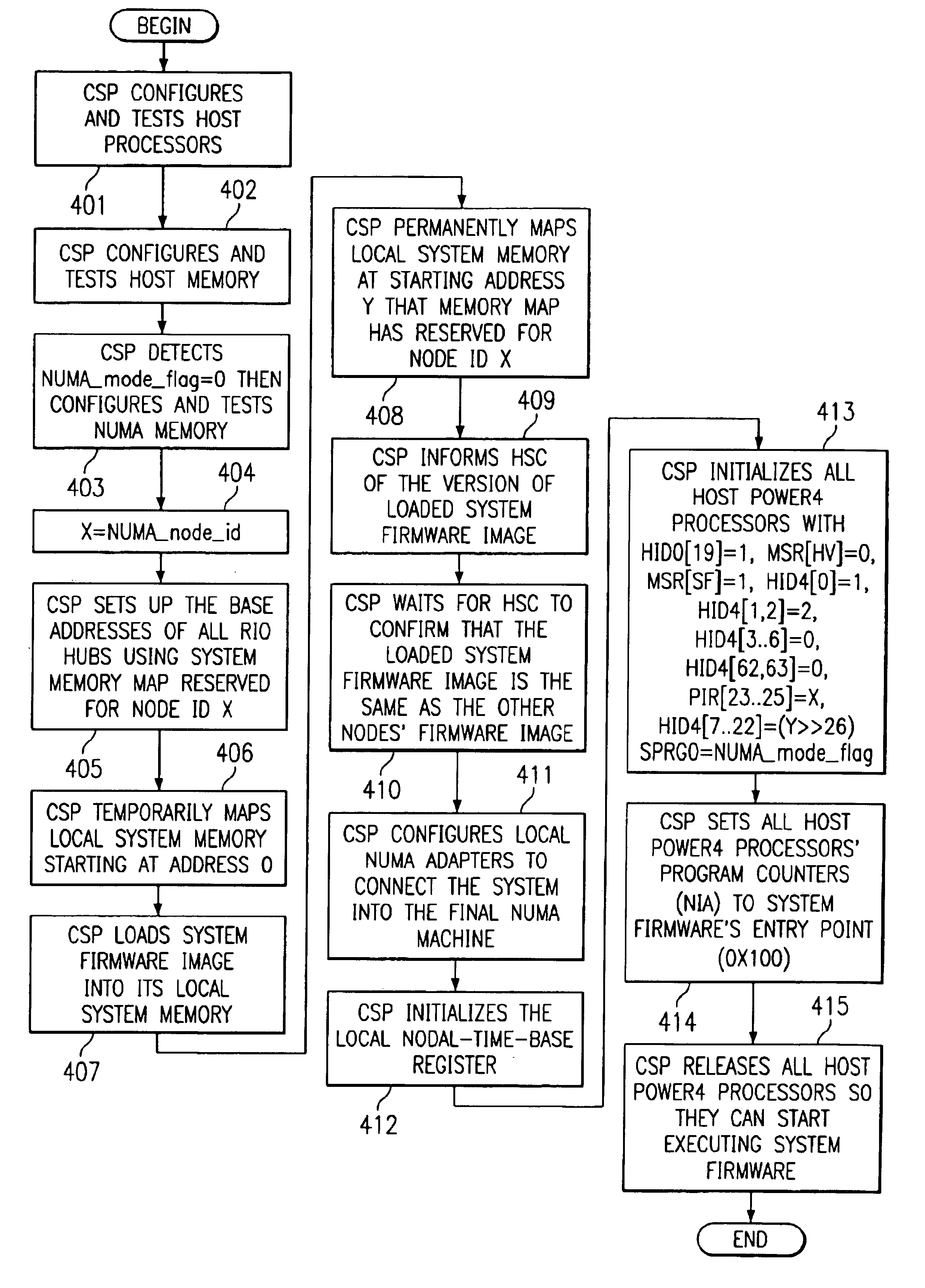
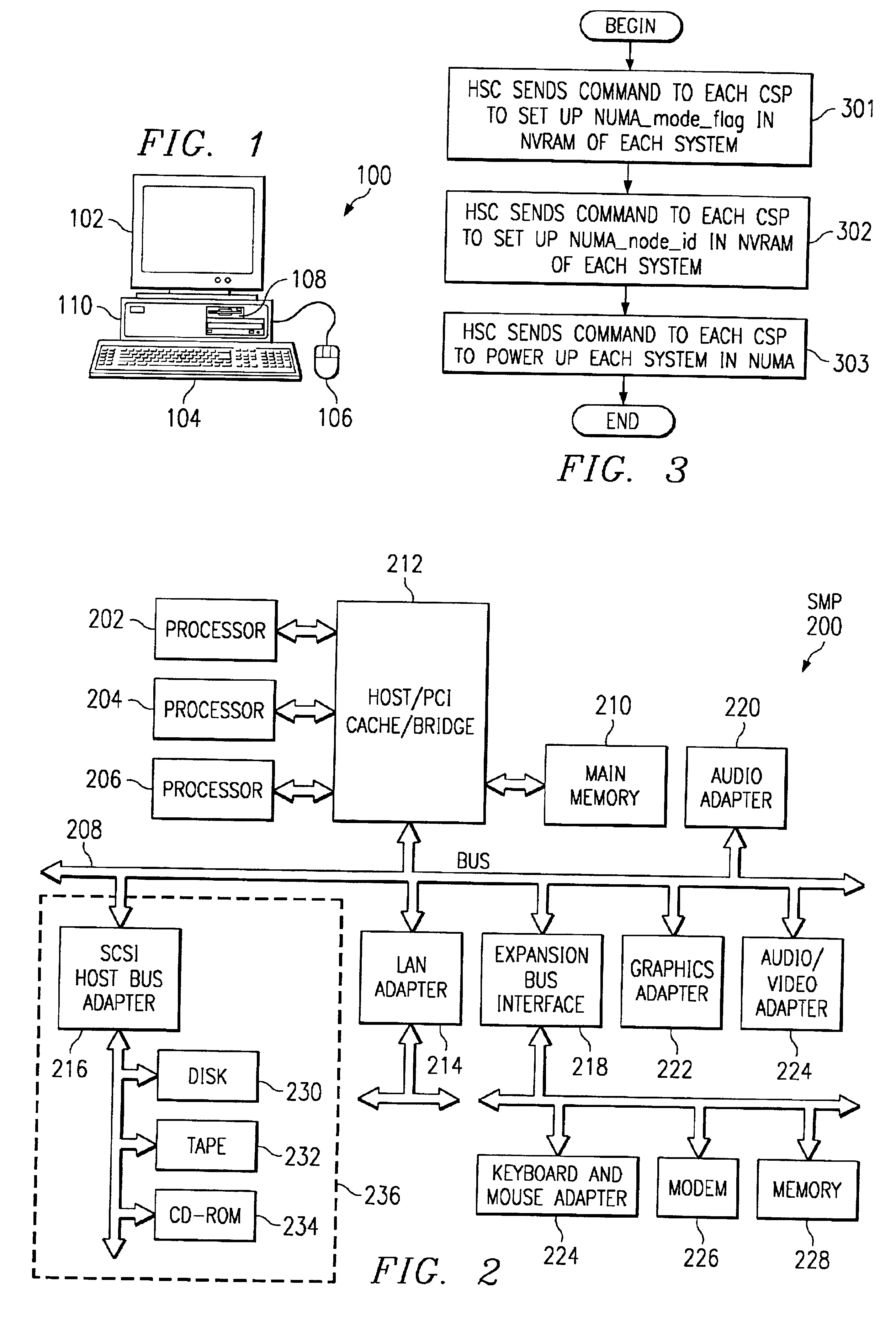
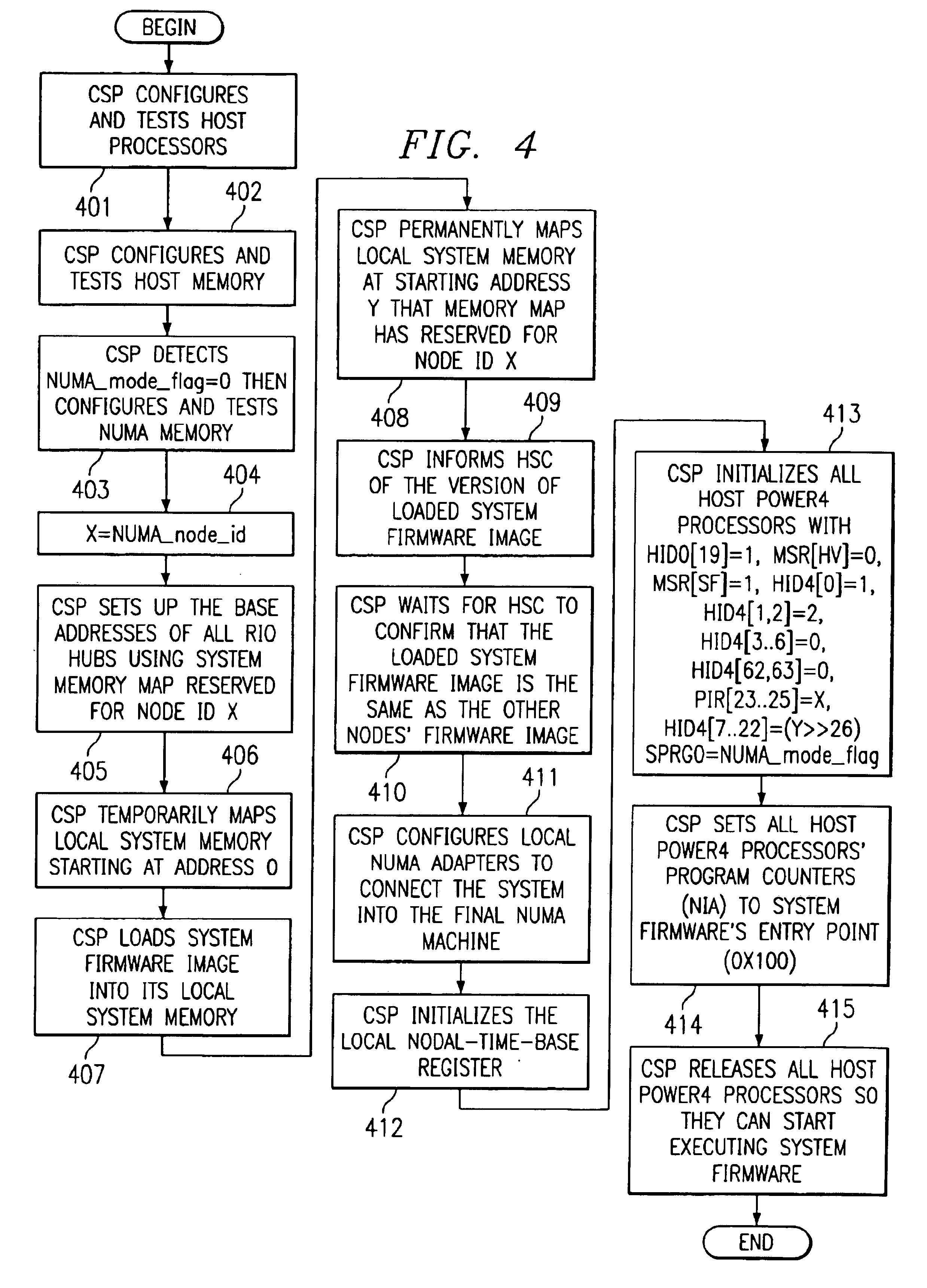
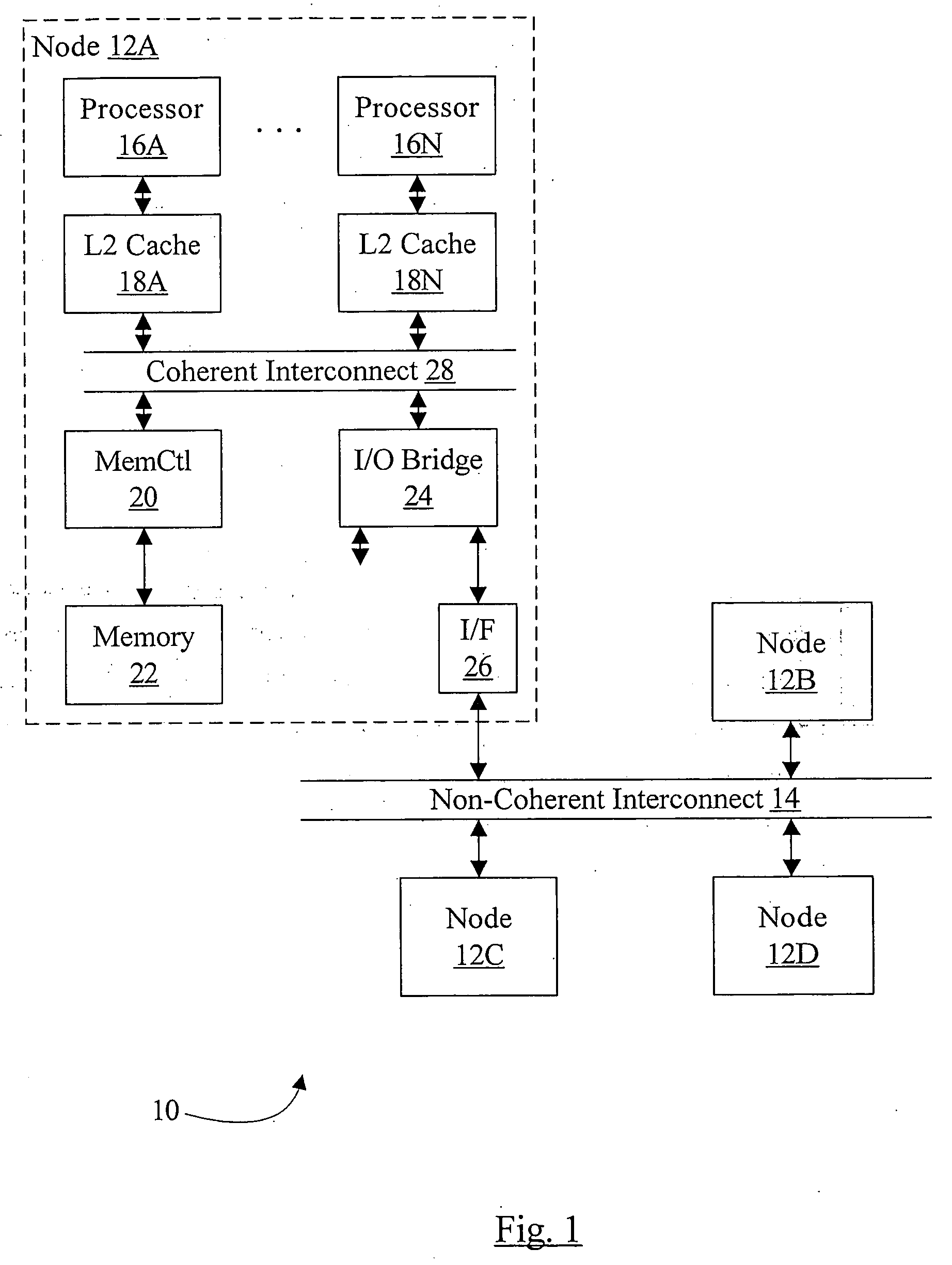
A method, apparatus and program for booting a non-uniform-memory-access (NUMA) machine are provided. The invention comprises configuring a plurality of standalone, symmetrical multiprocessing (SMP) systems to operate within a NUMA system. A master processor is selected within each SMP; the other processors in the SMP are designated as NUMA slave processors. A NUMA master processor is then chosen from the SMP master processors; the other SMP master processors are designated as NUMA slave processors. A unique NUMA ID is assigned to each SMP that will be part of the NUMA system. The SMPs are then booted in NUMA mode in one-pass with memory coherency established right at the beginning of the execution of the system firmware.
Owner:IBM CORP
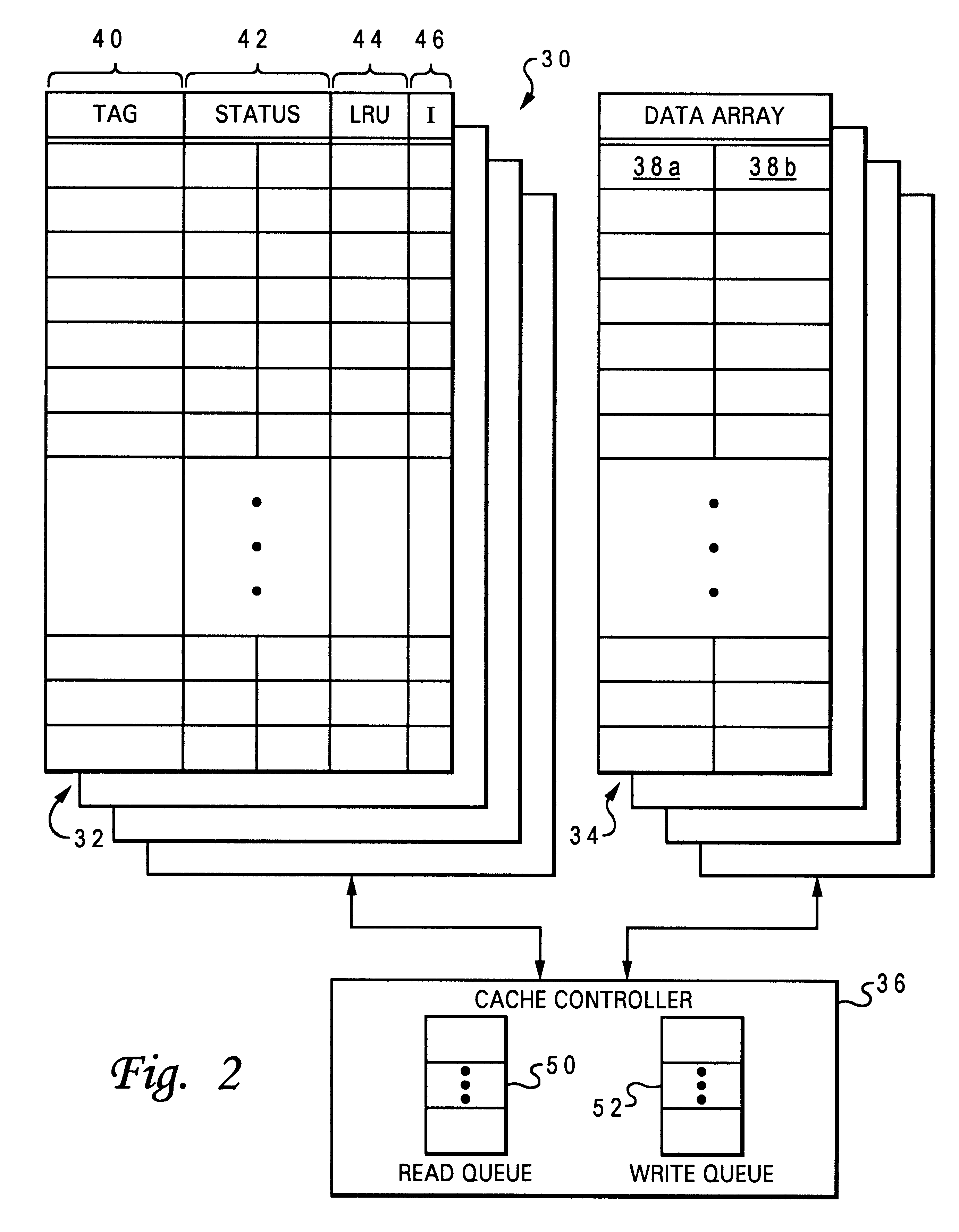
Method of cache management for dynamically disabling O state memory-consistent data
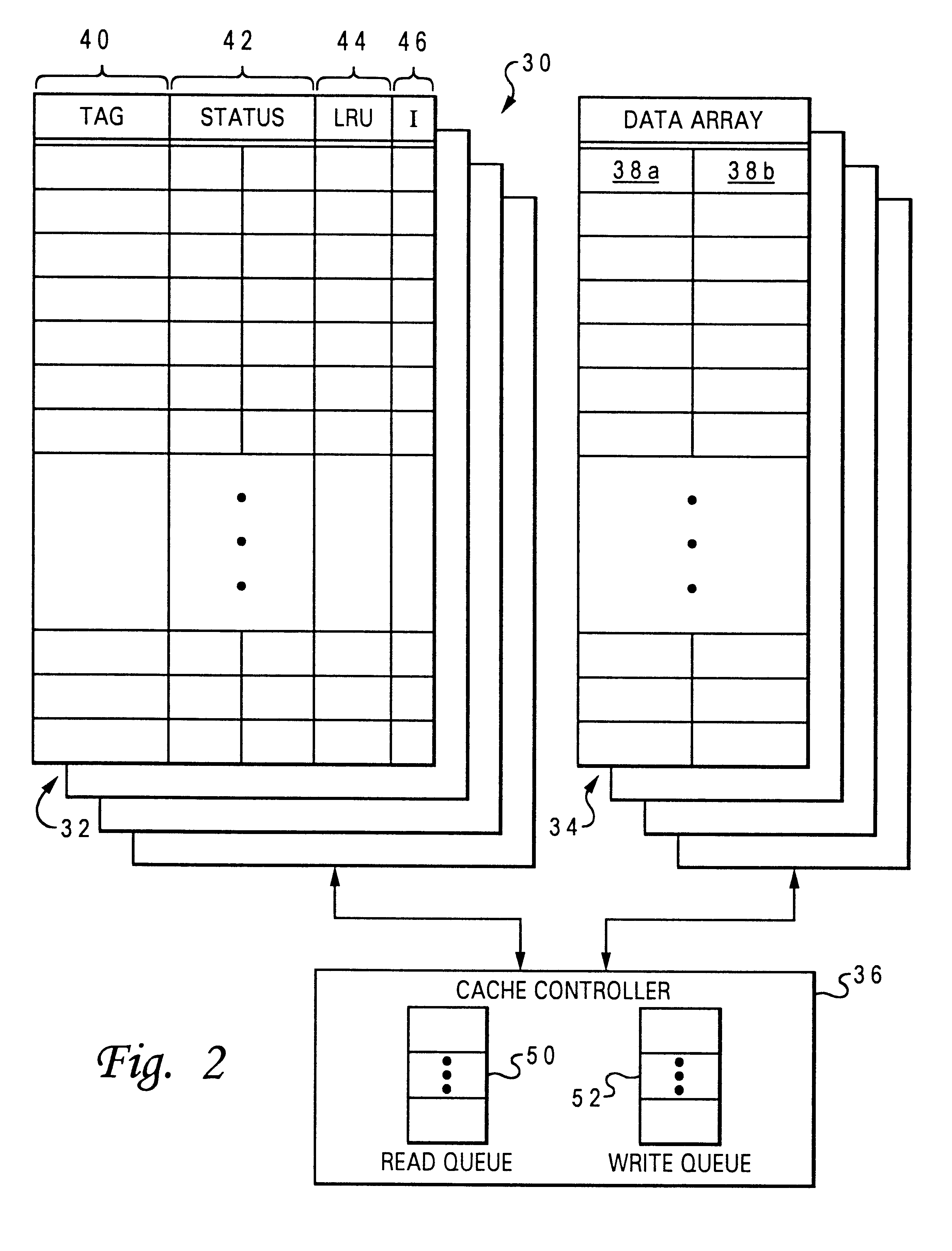
A multiprocessor data processing system includes an interconnect, a plurality of processing units coupled to the interconnect, and at least one system memory and a plurality of caches coupled to the plurality of processing units. A cache suitable for use in such a data processing system includes data storage containing multiple granules of data and a number of state fields associated with the granules of data. Each state field has a plurality of possible states including an O state indicating that an associated granule is consistent with corresponding data in the memory and has unknown coherency with respect to peer caches in the data processing system. The cache updates the state field from the O state to another of the plurality of states in response to a snooped transaction on the interconnect.
Owner:IBM CORP
Memory coherency in graphics command streams and shaders
ActiveUS20110063313A1Simple technologyCathode-ray tube indicatorsProcessor architectures/configurationDelayed MemoryParallel computing
One embodiment of the present invention sets forth a technique for performing a computer-implemented method that controls memory access operations. A stream of graphics commands includes at least one memory barrier command. Each memory barrier command in the stream of graphics command delays memory access operations scheduled for any command specified after the memory barrier command until all memory access operations scheduled for commands specified prior to the memory barrier command have completely executed.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
System and method for handling storage consistency conflict
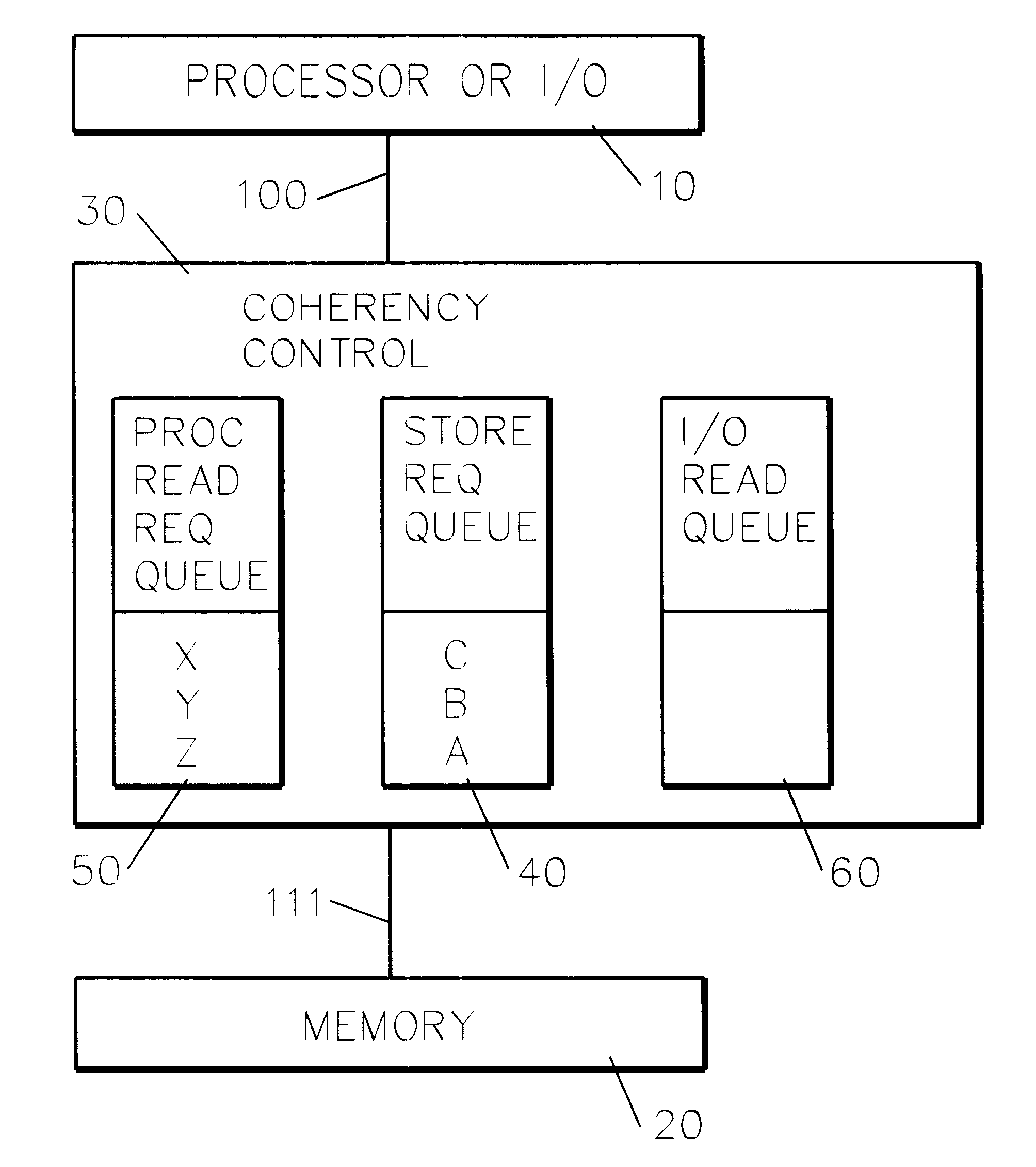
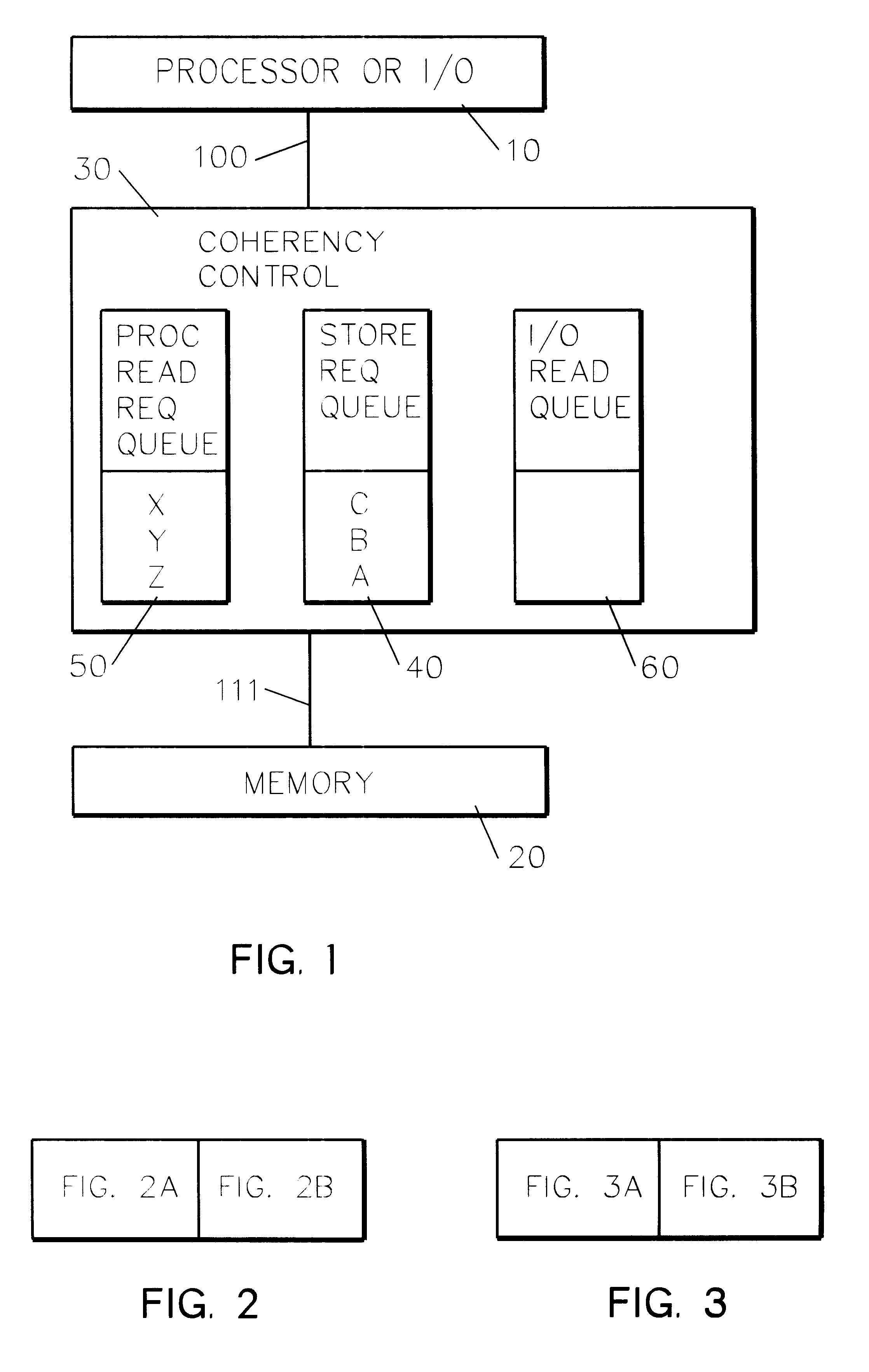
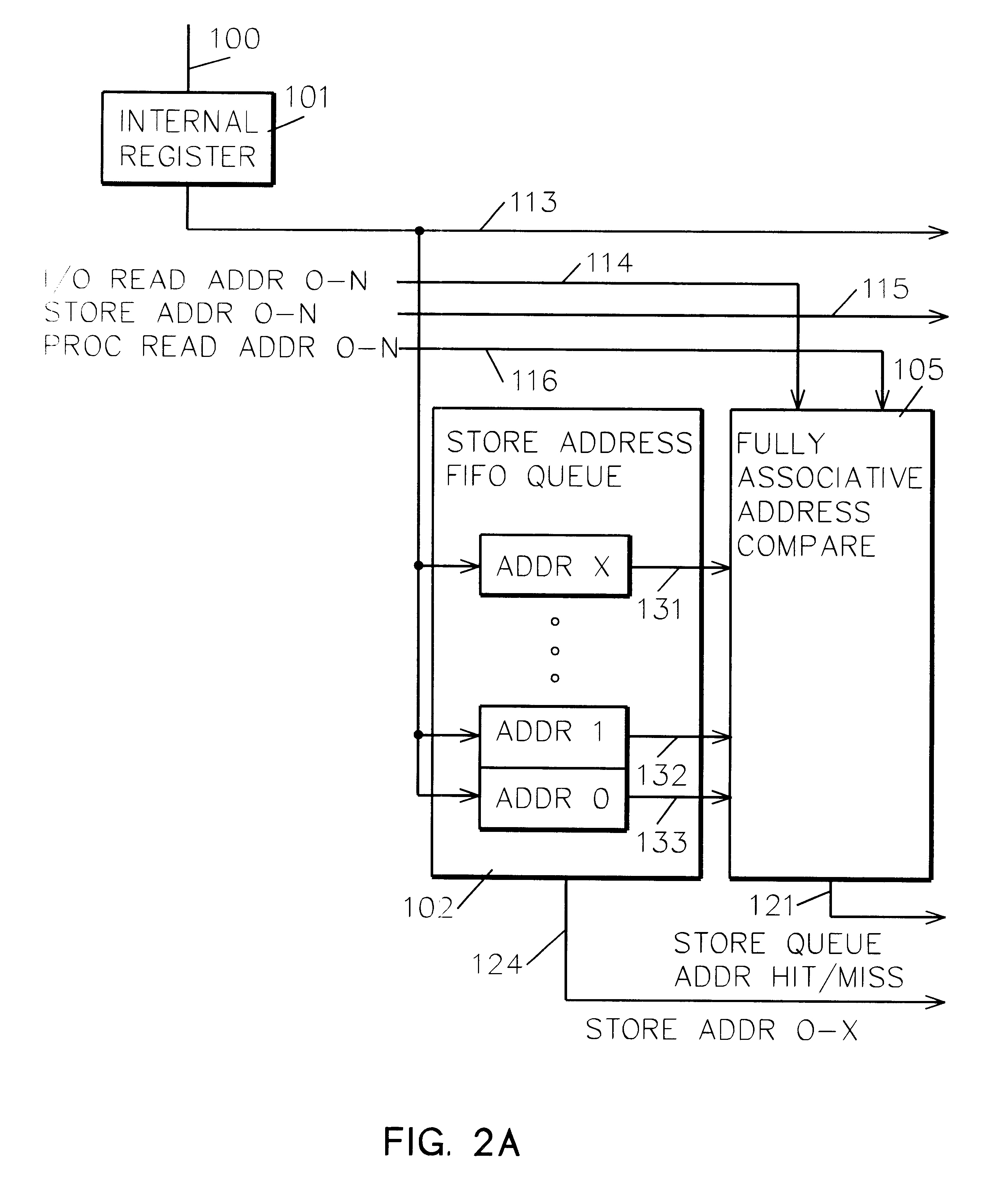
InactiveUS6237067B1Reduce complexityReduced likelihoodMemory systemsInput/output processes for data processingMemory addressOperating system
A memory coherency controller. Responsive to a request including a request type and request memory address, relevant queues are examined for queued addresses matching the request memory address. Responsive to a request memory address matching at least one of the queued addresses, the request is rejected. Following a retry latency, the request is retried. When the address of a read request matches queued address in a store queue, at least one request in the store queue is prioritized higher than all other queued requests.
Owner:IBM CORP
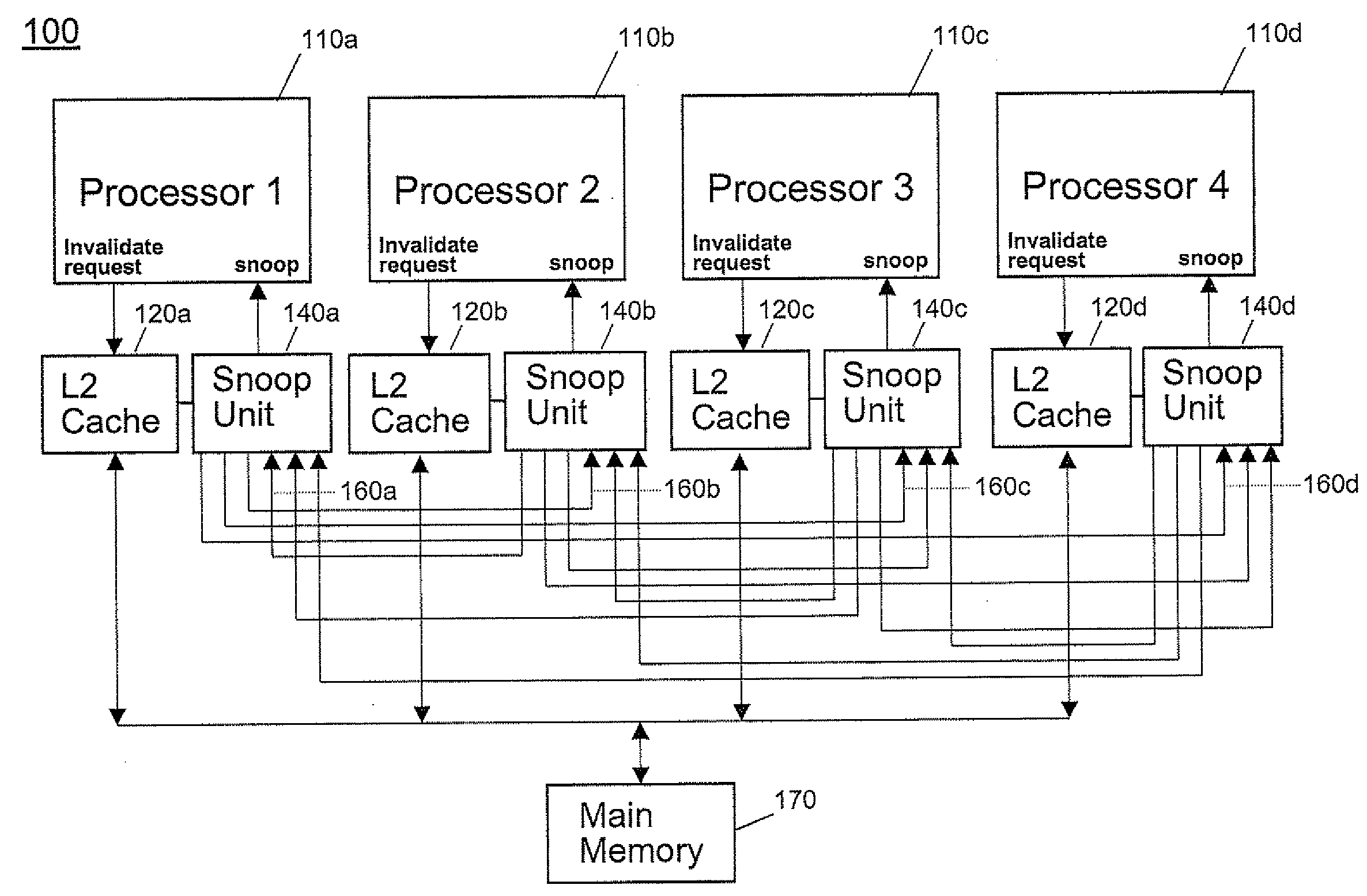
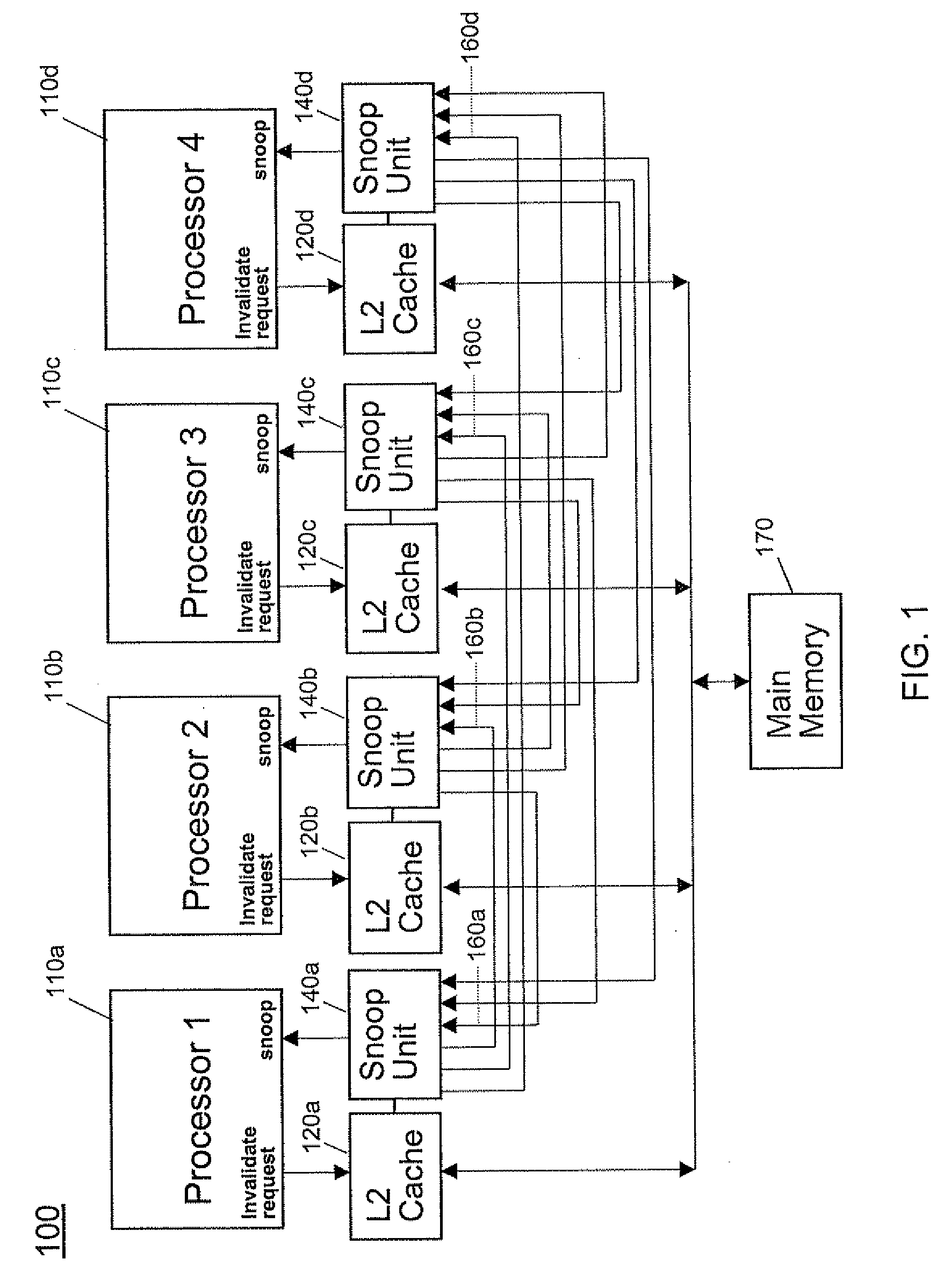
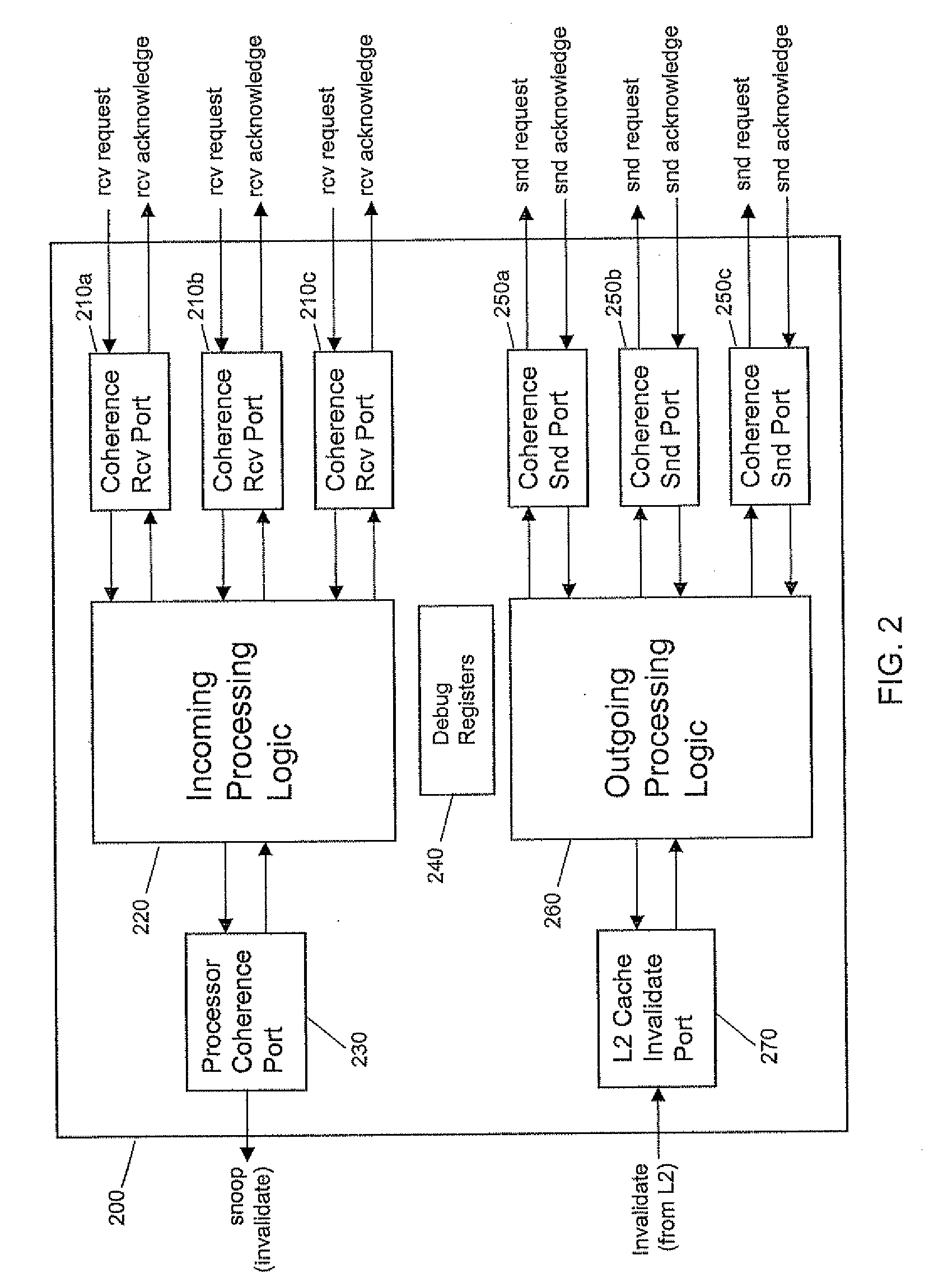
Method and apparatus for single-stepping coherence events in a multiprocessor system under software control
InactiveUS20090007119A1Simple techniqueSimple methodError detection/correctionDigital computer detailsMulti processorParallel computing
An apparatus and method are disclosed for single-stepping coherence events in a multiprocessor system under software control in order to monitor the behavior of a memory coherence mechanism. Single-stepping coherence events in a multiprocessor system is made possible by adding one or more step registers. By accessing these step registers, one or more coherence requests are processed by the multiprocessor system. The step registers determine if the snoop unit will operate by proceeding in a normal execution mode, or operate in a single-step mode.
Owner:IBM CORP
Building a wavecache
InactiveUS7490218B2Improves code schedulingGranularity is very broadSingle instruction multiple data multiprocessorsProgram synchronisationControl flowApplication software
A microarchitecture and instruction set that supports multiple, simultaneously executing threads. The approach is disclosed in regard to its applicability in connection with a recently developed microarchitecture called “WaveScalar.” WaveScalar is a compiler that breaks a control flow graph for a program into pieces called waves having instructions that are partially ordered (i.e., a wave contains no back-edges), and for which control enters at a single point. Certain aspects of the present approach are also generally applicable to executing multiple threads on a more conventional microarchitecture. In one aspect of this approach, instructions are provided that enable and disable wave-ordered memory. Additional memory access instructions bypass wave-ordered memory, exposing additional parallelism. Also, a lightweight, interthread synchronization is employed that models hardware queue locks. Finally, a simple fence instruction is used to allow applications to handle relaxed memory consistency.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
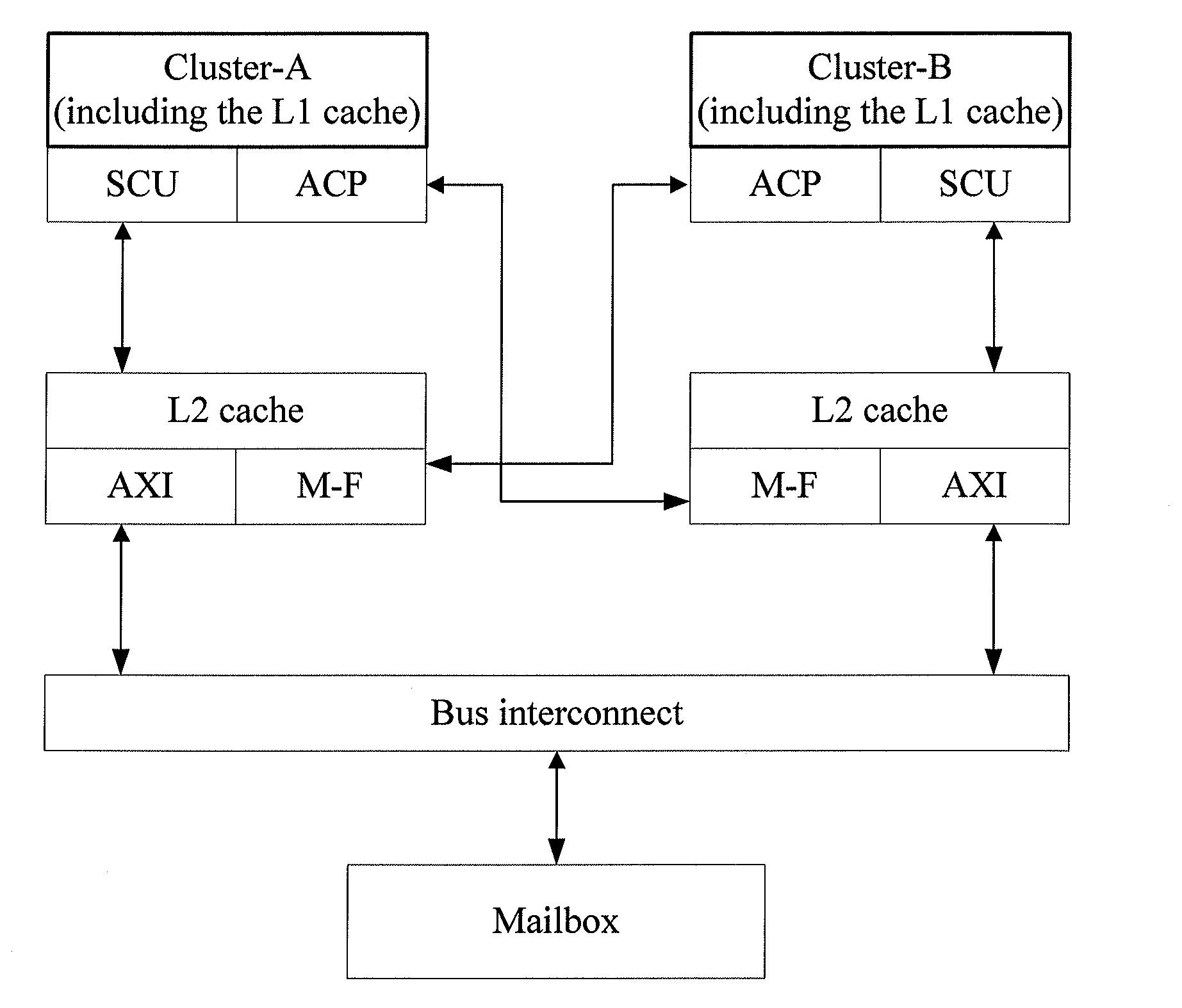
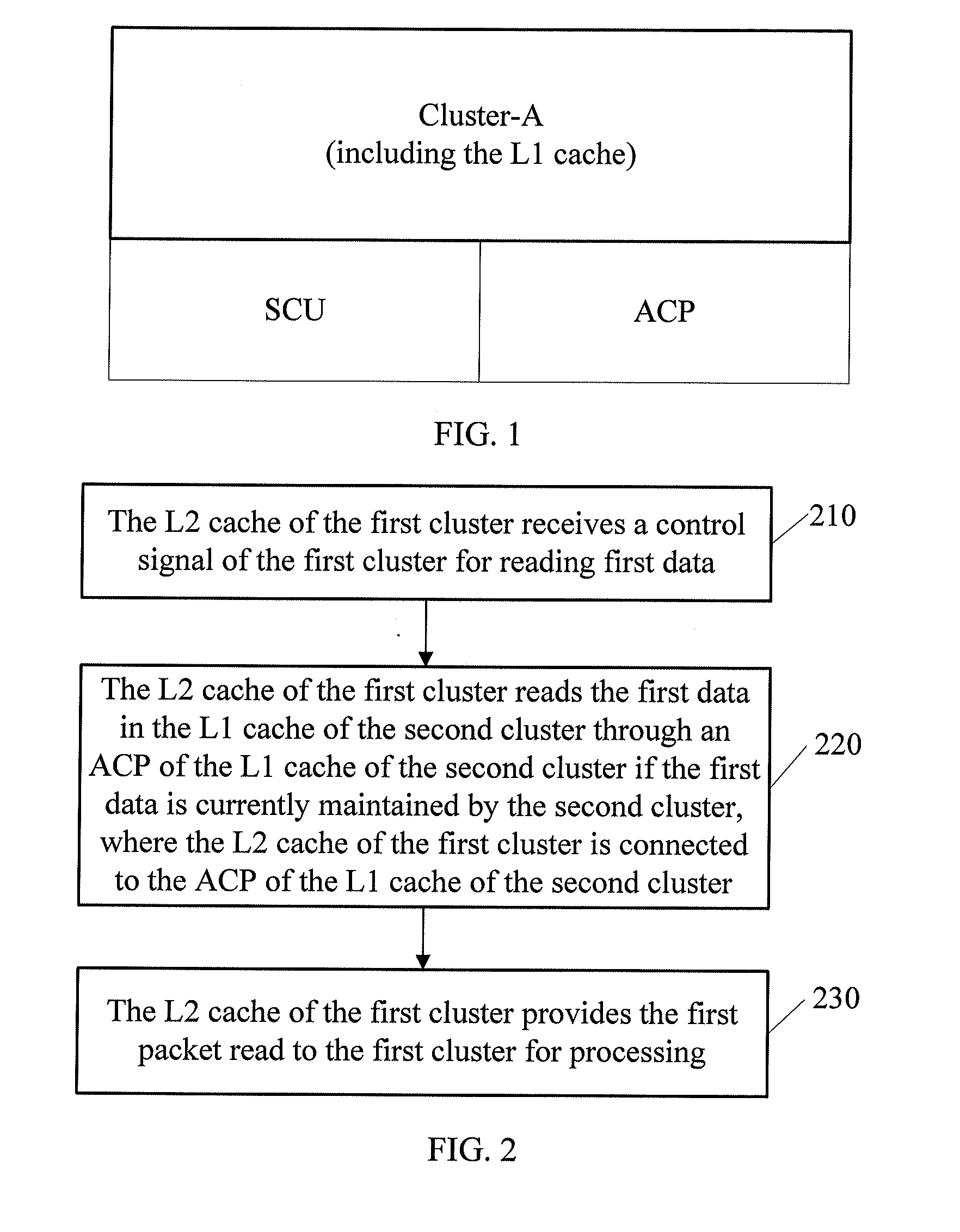
Method and apparatus for implementing multi-processor memory coherency
ActiveUS20120079209A1Ensuring validityEnabling collaborationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationDigital computer detailsMulti processorControl signal
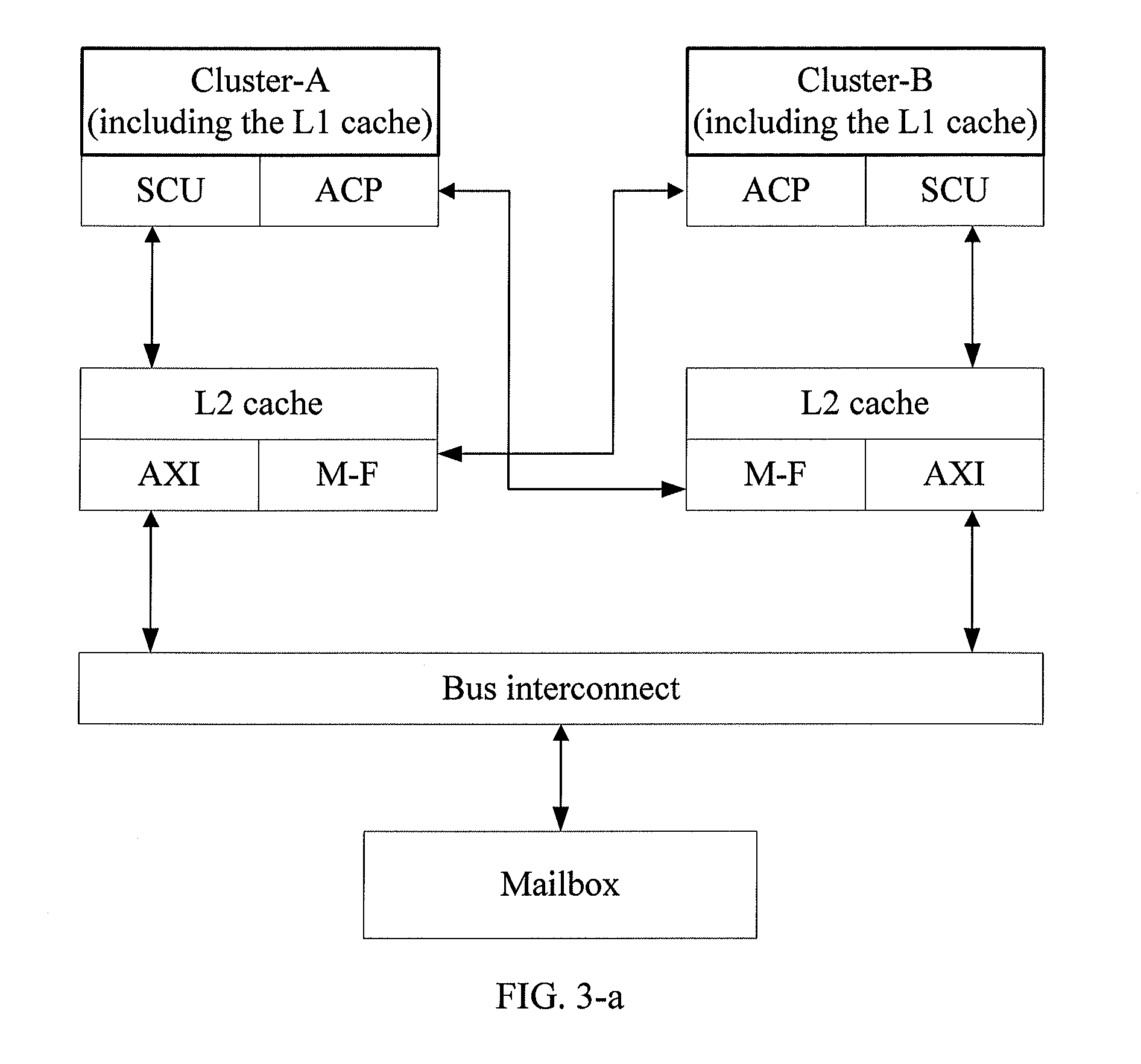
A method and an apparatus for implementing multi-processor memory coherency are disclosed. The method includes: a Level-2 (L2) cache of a first cluster receives a control signal of the first cluster for reading first data; the L2 cache of the first cluster reads the first data in a Level-1 (L1) cache of a second cluster through an Accelerator Coherency Port (ACP) of the L1 cache of the second cluster if the first data is currently maintained by the second cluster, where the L2 cache of the first cluster is connected to the ACP of the L1 cache of the second cluster; and the L2 cache of the first cluster provides the first data read to the first cluster for processing. The technical solution under the present invention implements memory coherency between clusters in the ARM Cortex-A9 architecture.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
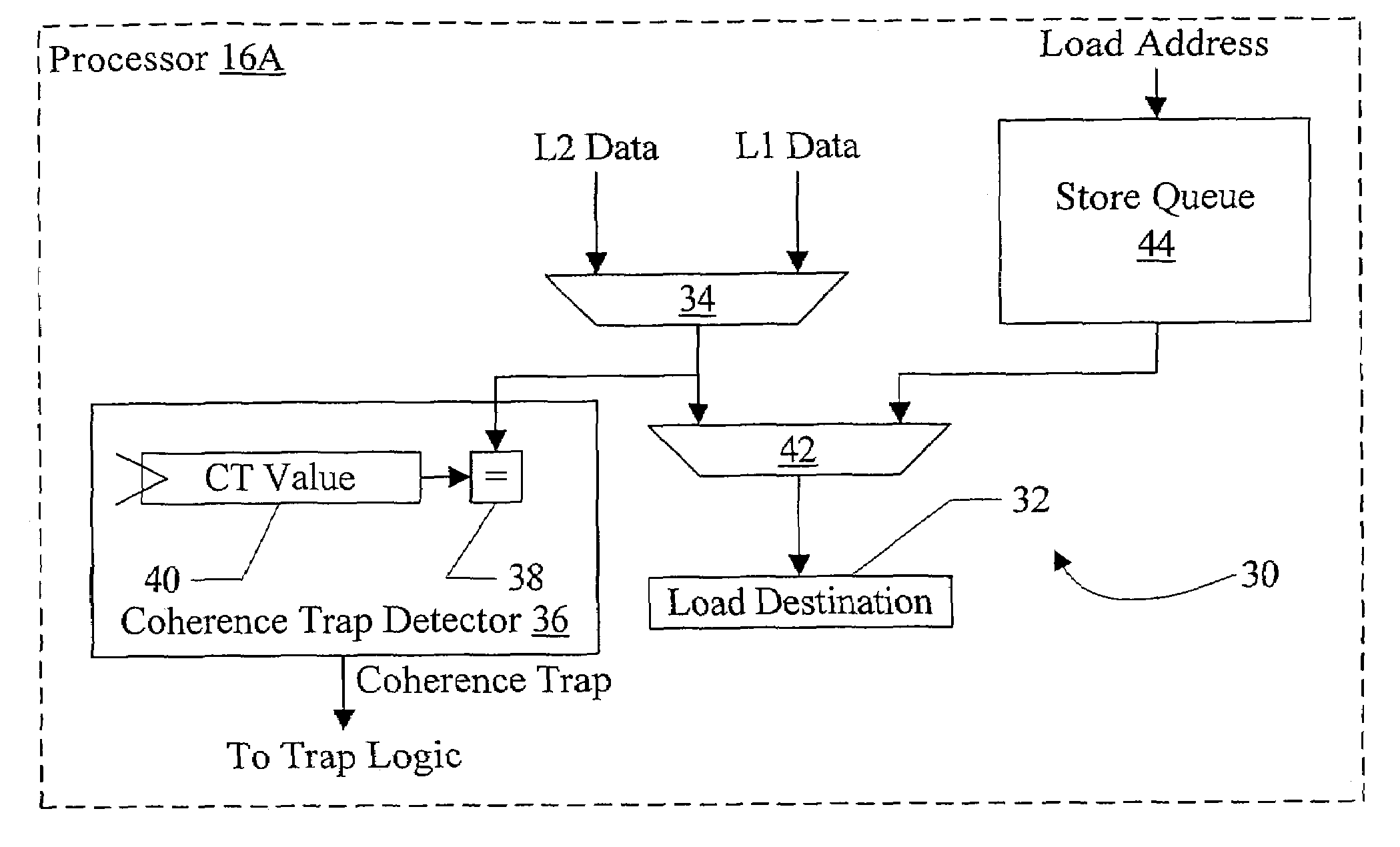
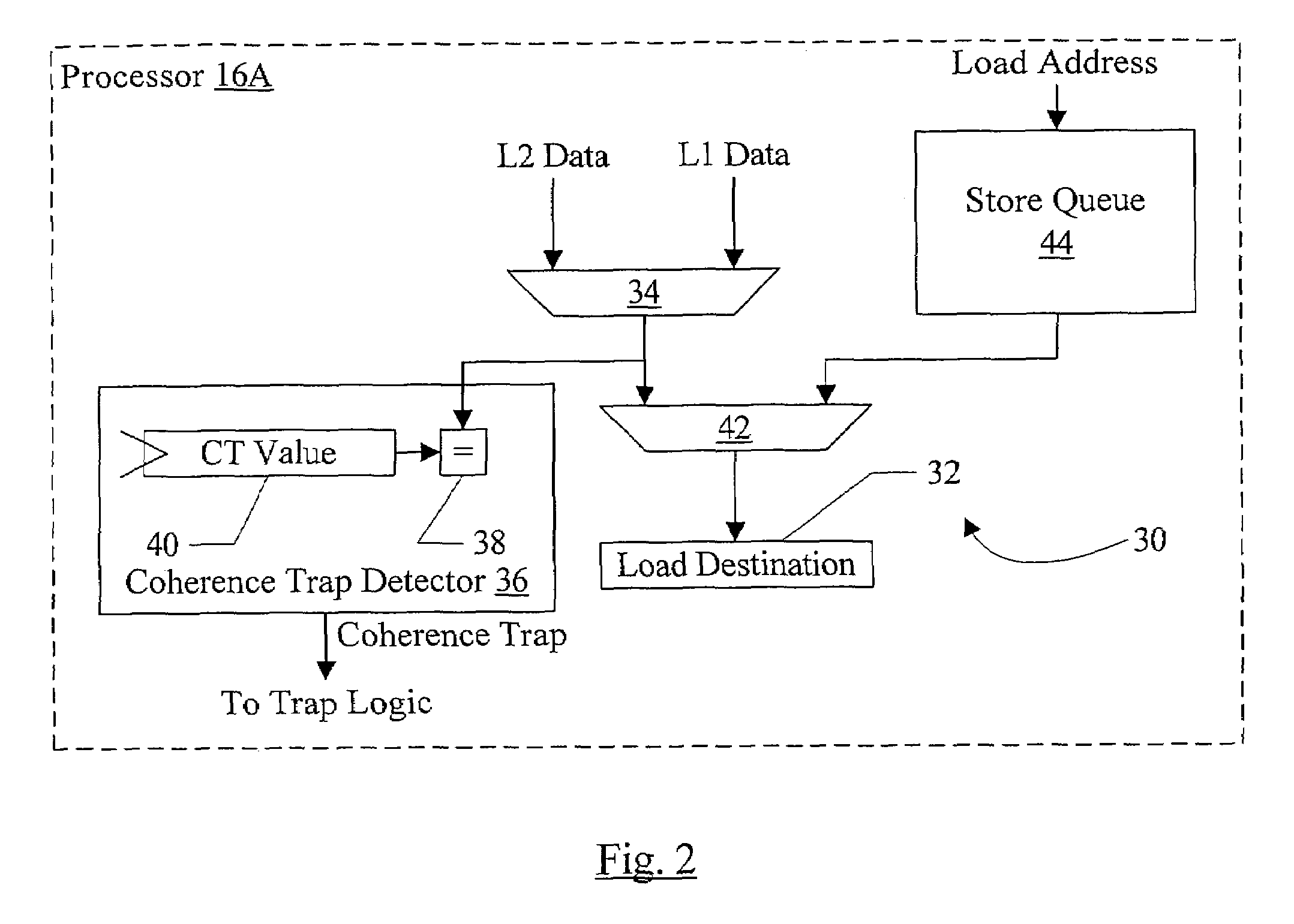
Value-based memory coherence support
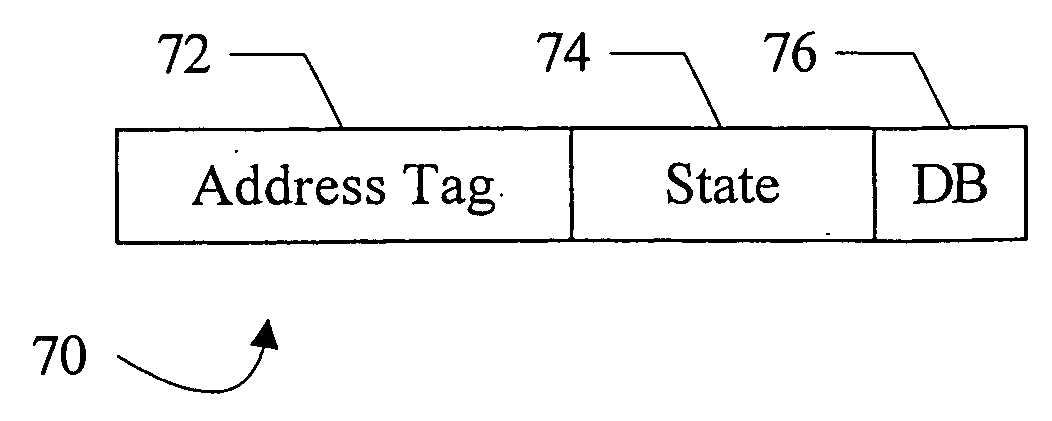
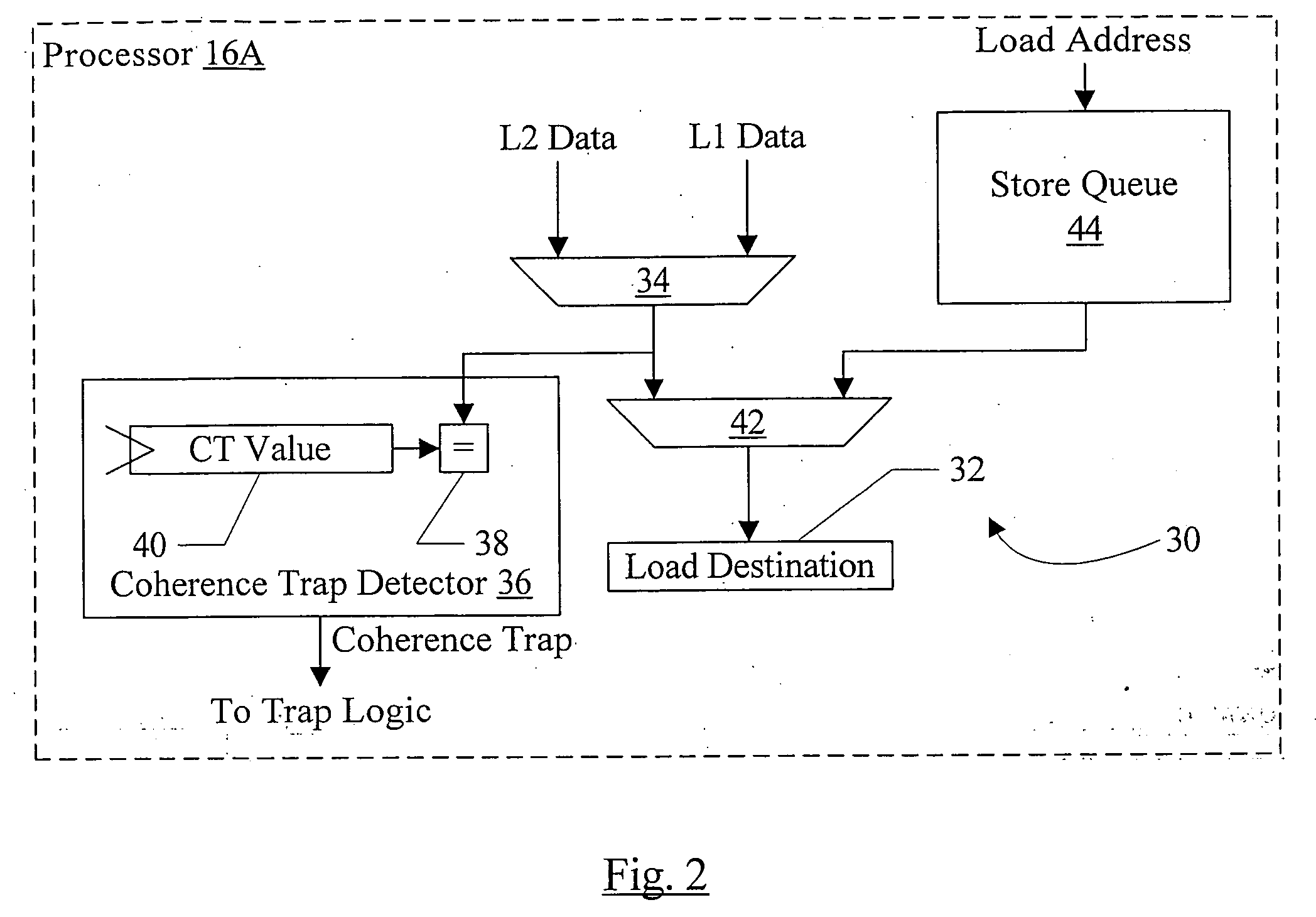
In one embodiment, a processor comprises a coherence trap unit and a trap logic coupled to the coherence trap unit. The coherence trap unit is also coupled to receive data accessed in response to the processor executing a memory operation. The coherence trap unit is configured to detect that the data matches a designated value indicating that a coherence trap is to be initiated to coherently perform the memory operation. The trap logic is configured to trap to a designated software routine responsive to the coherence trap unit detecting the designated value. In some embodiments, a cache tag in a cache may track whether or not the corresponding cache line has the designated value, and the cache tag may be used to trigger a trap in response to an access to the corresponding cache line.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Multiprocessor system implementing virtual memory using a shared memory, and a page replacement method for maintaining paged memory coherence
InactiveCN1524228AMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationVirtual memoryComputer architecture
A computer system (100) including a first processor (102), a second processor (104) in communication with the first processor (102), a memory (106) (i.e., a shared memory) coupled to the first processor (102) and the second processor (104), and a storage device (110 or 112) coupled to the first processor (102). The first processor (102) and the second processor (104) implement virtual memory using the memory (106). The first processor (102) maintains a first and second set of page tables in the memory (106). The first processor (102) uses the first set of page tables to access the memory locations witching the memory (106). The second processor (104) uses the second set of page tables, maintained by the first processor (102), to access the memory locations within the memory. A virtual memory page replacement method is also described for use in the computer system (100).
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC MALTA
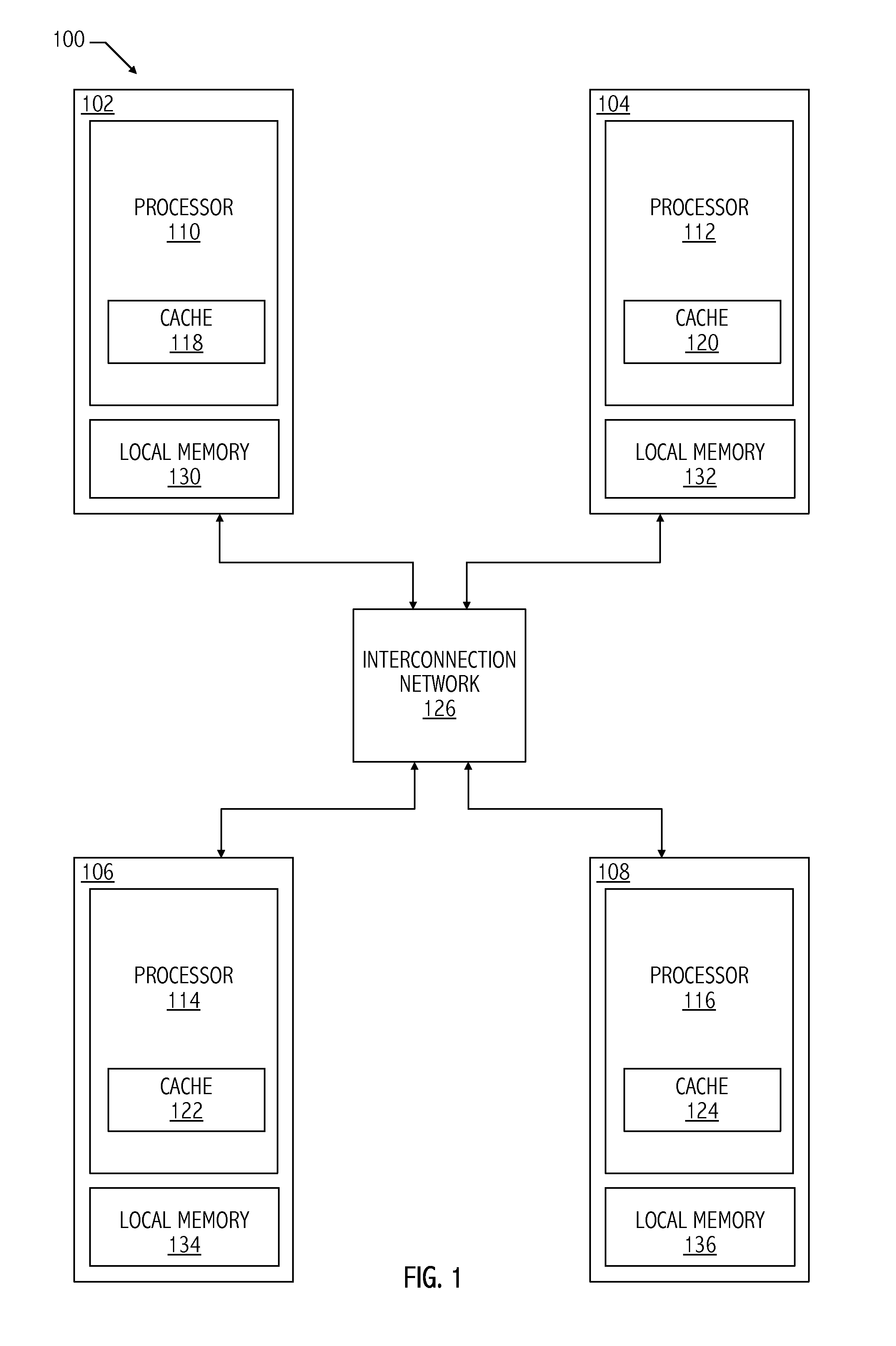
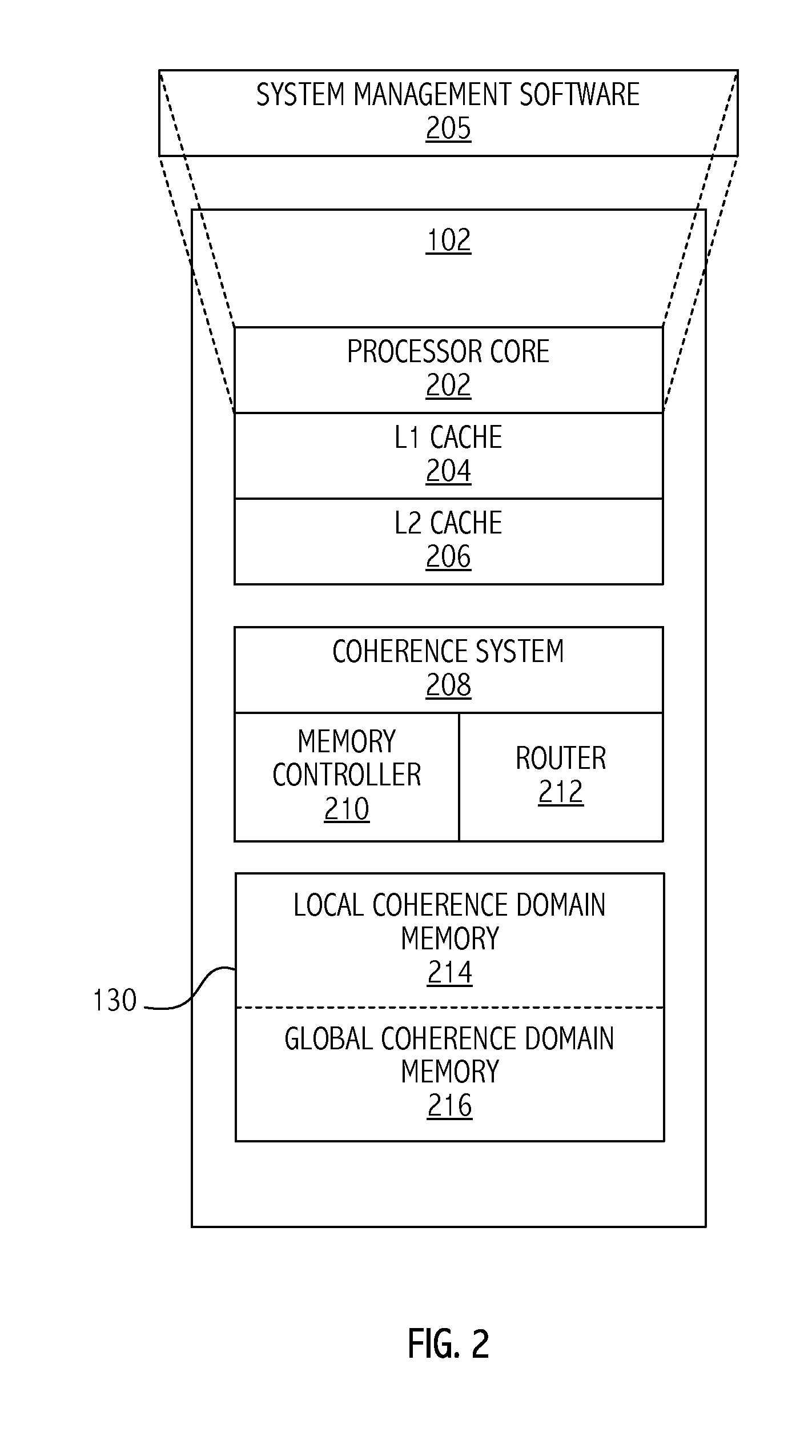
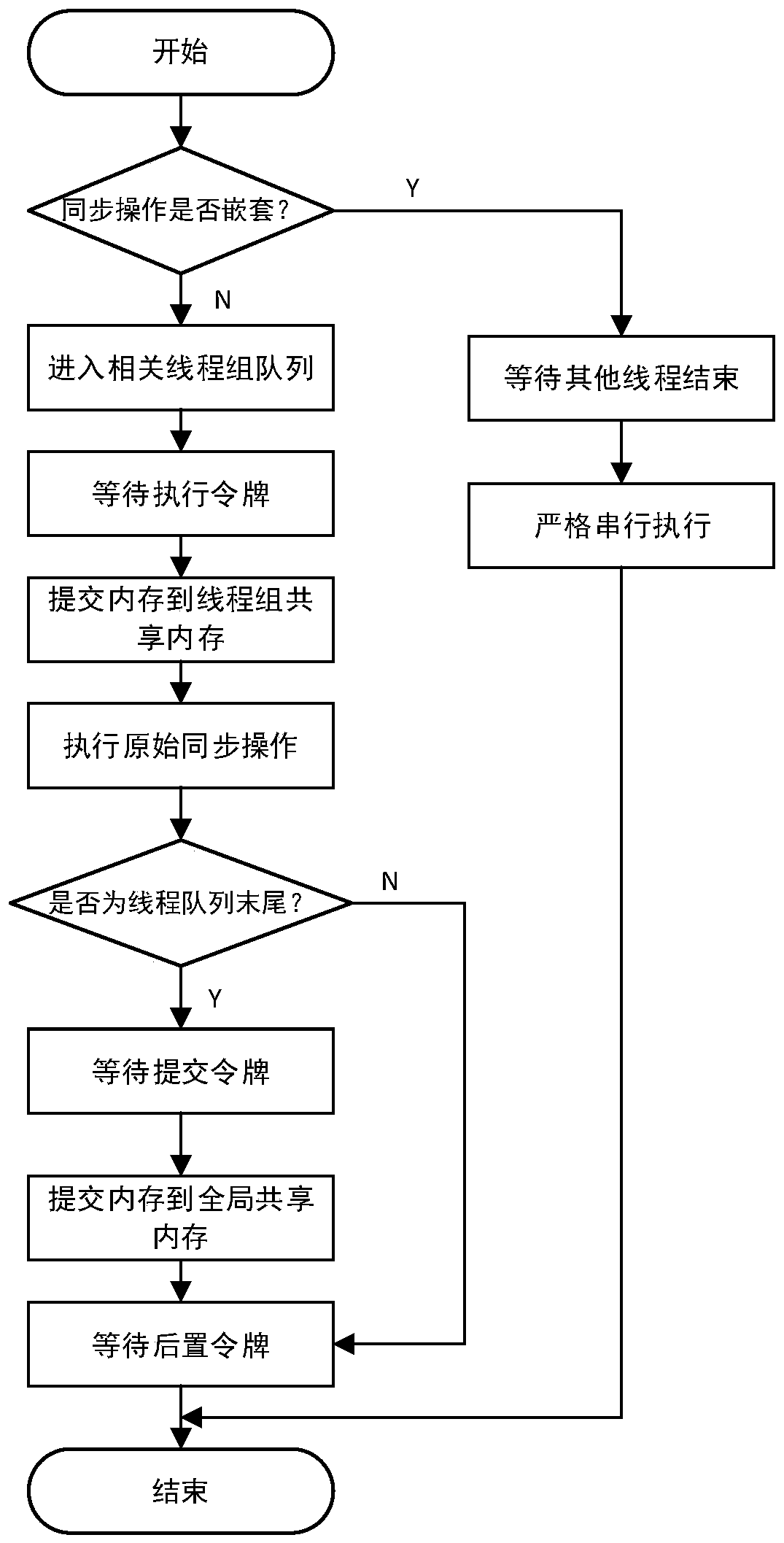
Coherence domain support for multi-tenant environment
A method includes bypassing a global coherence operation that maintains global memory coherence between a plurality of local memories associated with a plurality of corresponding processors. The bypassing is in response to an address of a memory request being associated with a local memory coherence domain. The method includes accessing a memory location associated with the local memory coherence domain according to the memory request in response to the address being associated with the local memory coherence domain.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
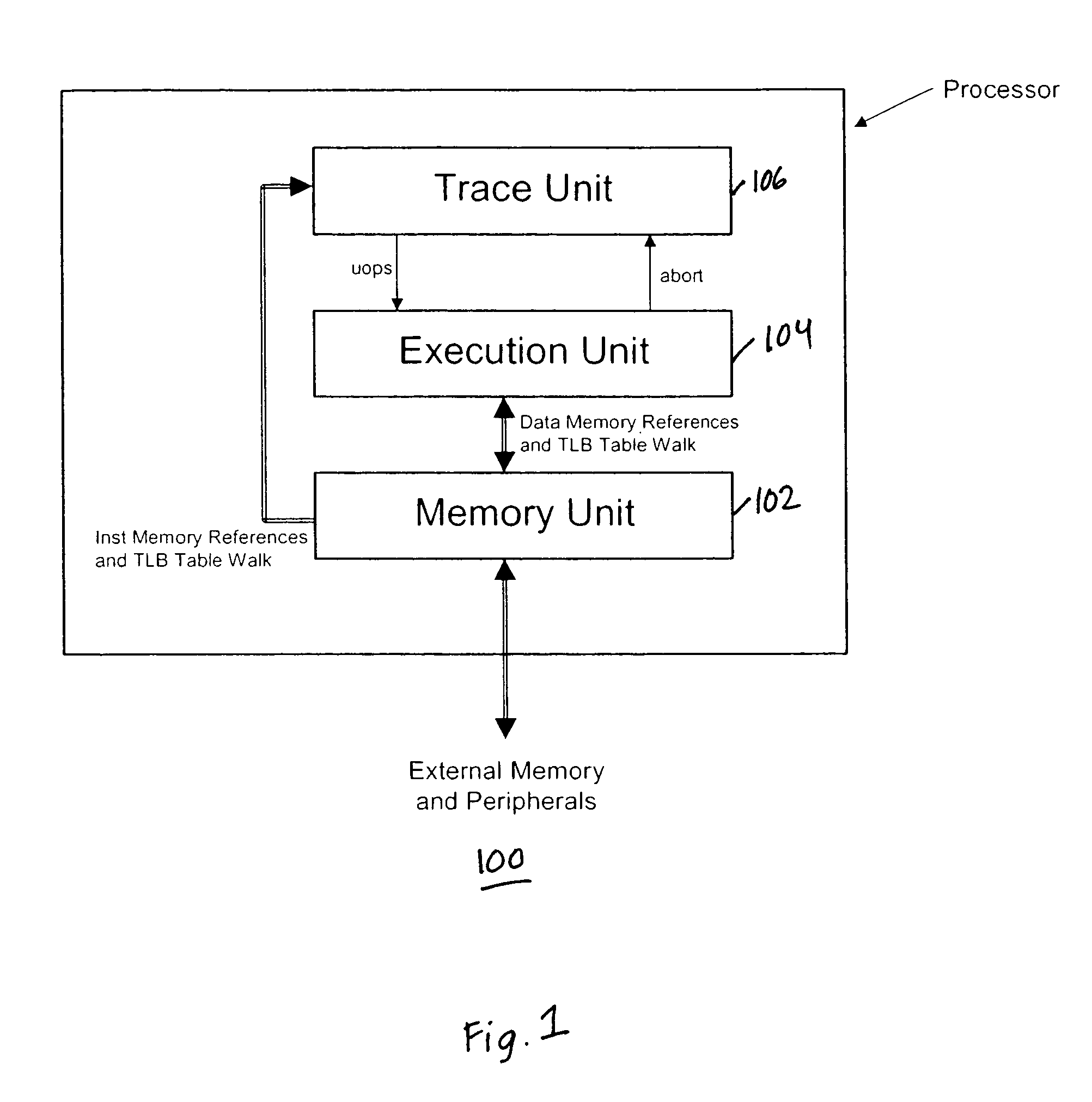
Maintaining memory coherency with a trace cache
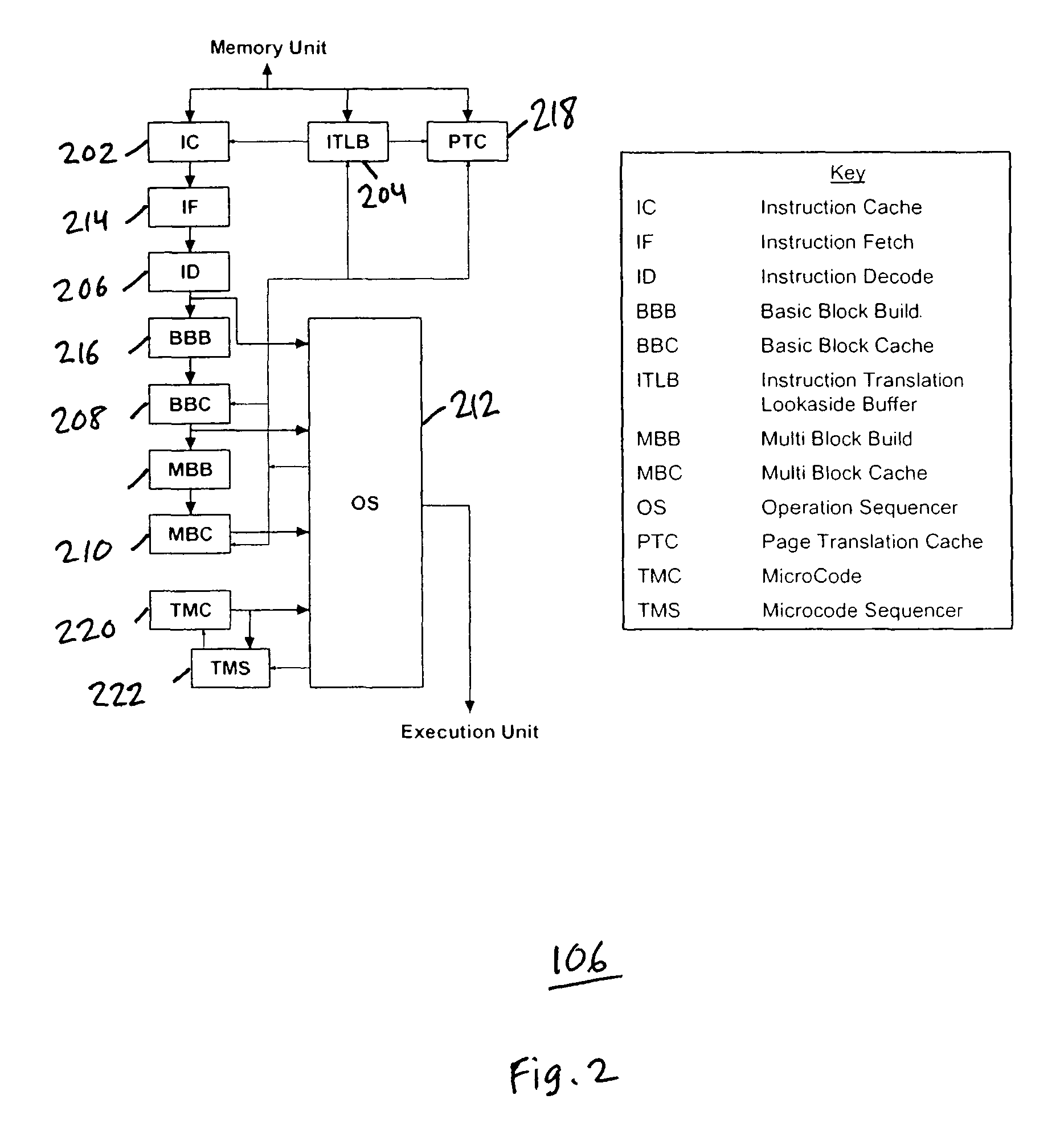
ActiveUS7747822B1Energy efficient ICTMemory adressing/allocation/relocationPower efficientCache invalidation
A method and system for maintaining memory coherence in a trace cache is disclosed. The method and system comprises monitoring a plurality of entries in a trace cache. The method and system includes selectively invalidating at least one trace cache entry based upon detection of a modification of the at least one trace cache entry.If modifications are detected, then corresponding trace cache entries are selectively invalidated (rather than invalidating the entire trace cache). Thus trace cache coherency is maintained with respect to memory in a performance and power-efficient manner. The monitoring further accounts for situations where more than one trace cache entry is dependent on a single cache line, such that modifications to the single cache line result in invalidations of a plurality of trace cache entries.
Owner:SUN MICROSYSTEMS INC
Memory consistency protection in a multiprocessor computing system
InactiveUS7895407B2Low-cost and effectiveImprove consistencyResource allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationMulti processorObject code
A method and apparatus to protect memory consistency in a multiprocessor computing system are described, in particular relating to program code conversion such as dynamic binary translation. The exemplary system provides a memory, processors and a controller / translator unit (CTU) arranged to convert subject code into at least first and second target code portions executable on the processors. The CTU comprises an address space allocation unit to provide virtual address space regions and direct the target code portions to access the memory therethough; a shared memory detection unit to detect a request to access a shared memory area, accessible by both target code portions, and to identify at least one group of instructions in the first target code portion which access the shared memory area; and a memory protection unit to selectively apply memory consistency protection in relation to accesses to the shared memory area by the identified group of instructions.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
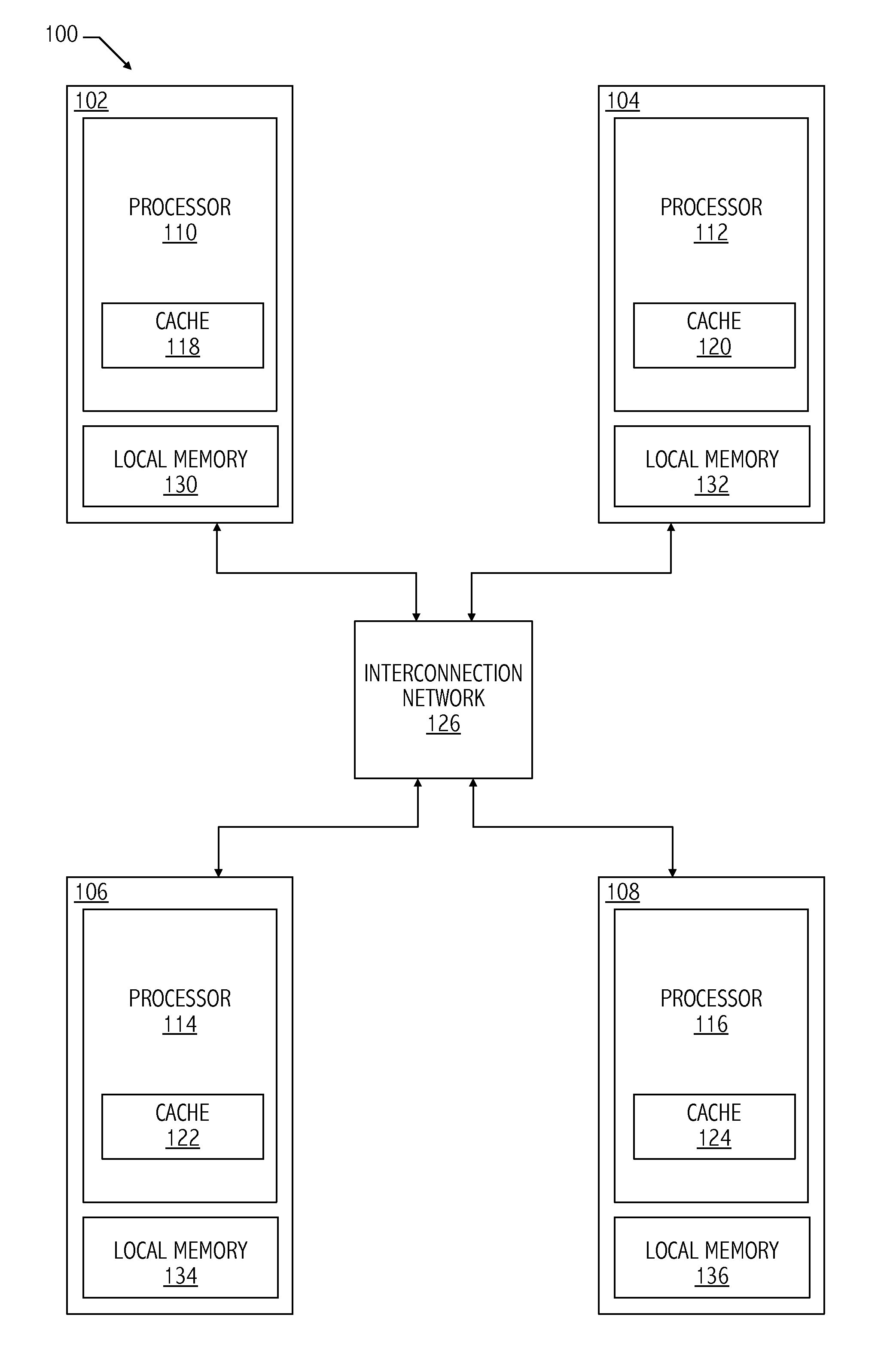
Hybrid cache coherence using fine-grained hardware message passing
ActiveUS7895400B2Light weightModerate overheadMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationHybrid systemMulti processor
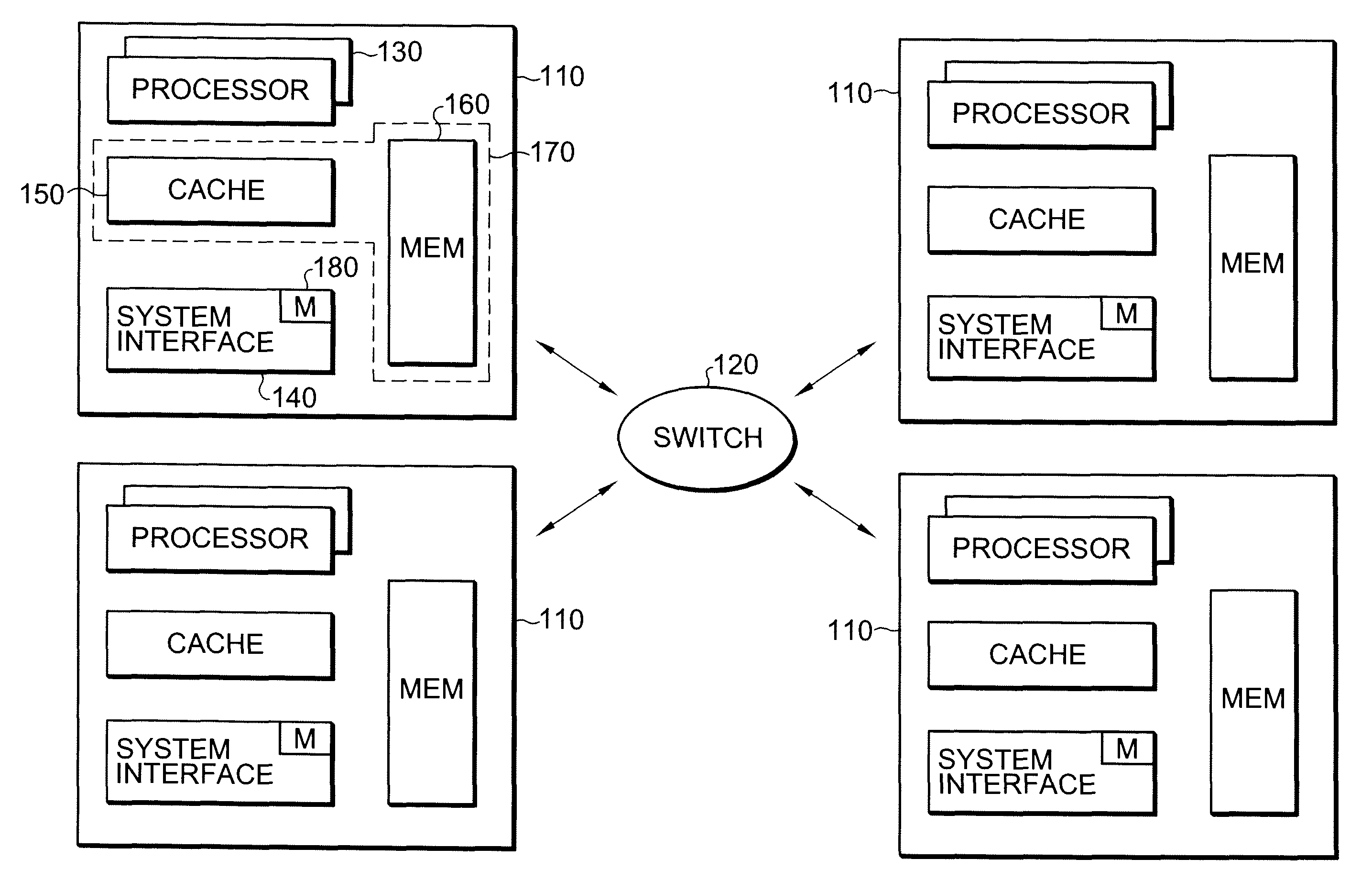
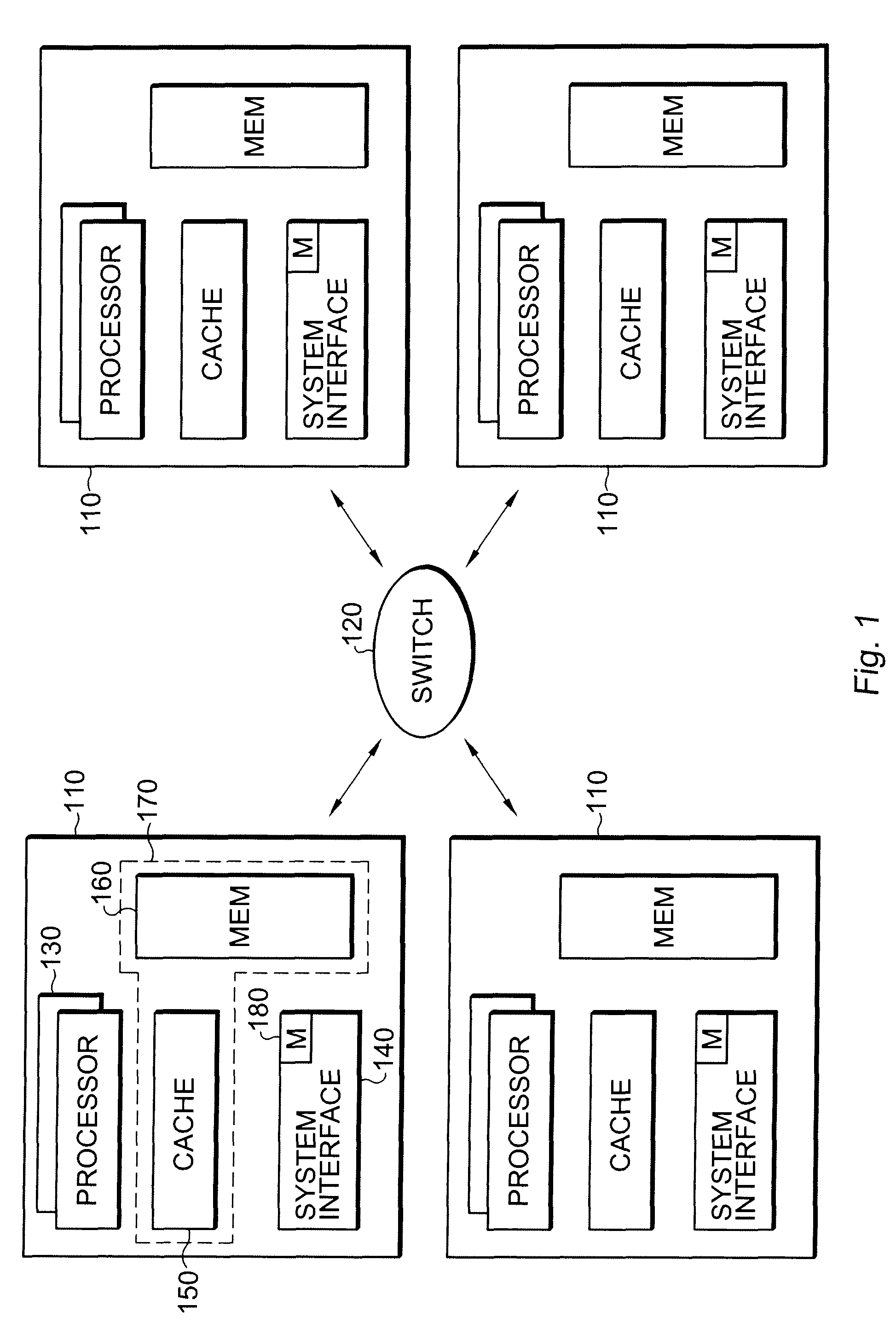
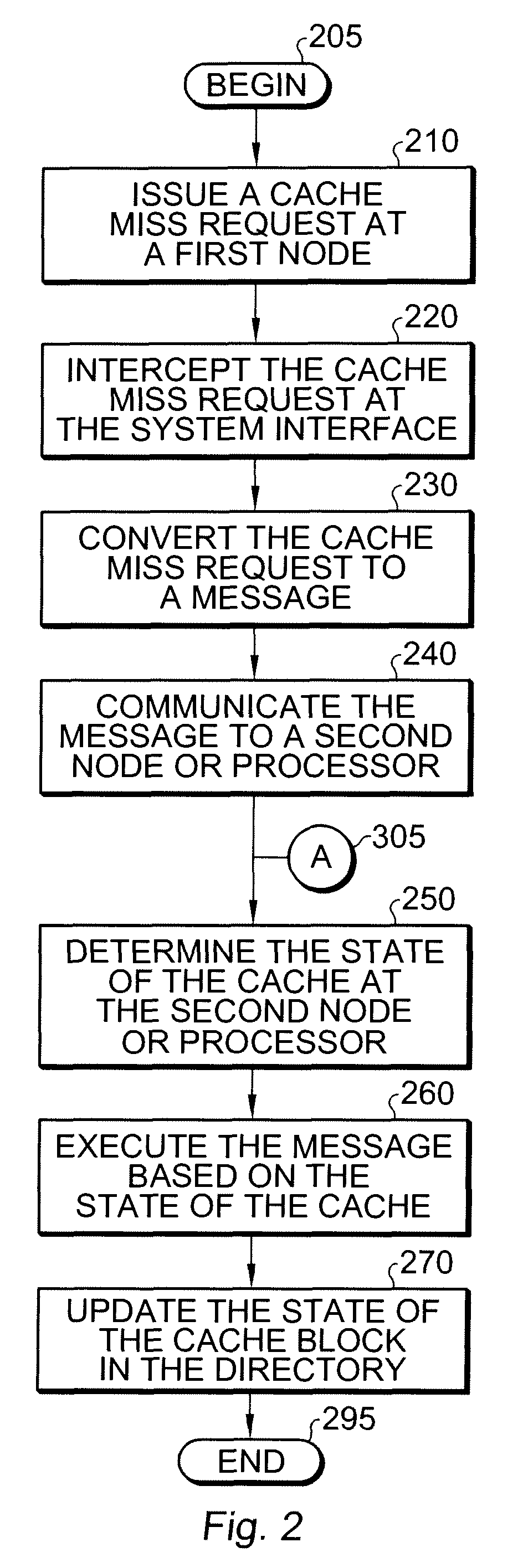
Multiprocessor systems conducting operations utilizing global shared memory must ensure that the memory is coherent. A hybrid system that combines hardware memory transactions with that of direct messaging provides memory coherence with minimal overhead requirement or bandwidth demands. Memory access transactions are intercepted and converted to direct messages which are then communicated to a target and / or remote node. Thereafter the message invokes a software handler which implements the cache coherence protocol. The handler uses additional messages to invalidate or fetch data in other caches, as well as to return data to the requesting processor. These additional messages are converted to appropriate hardware transactions by the destination system interface hardware.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
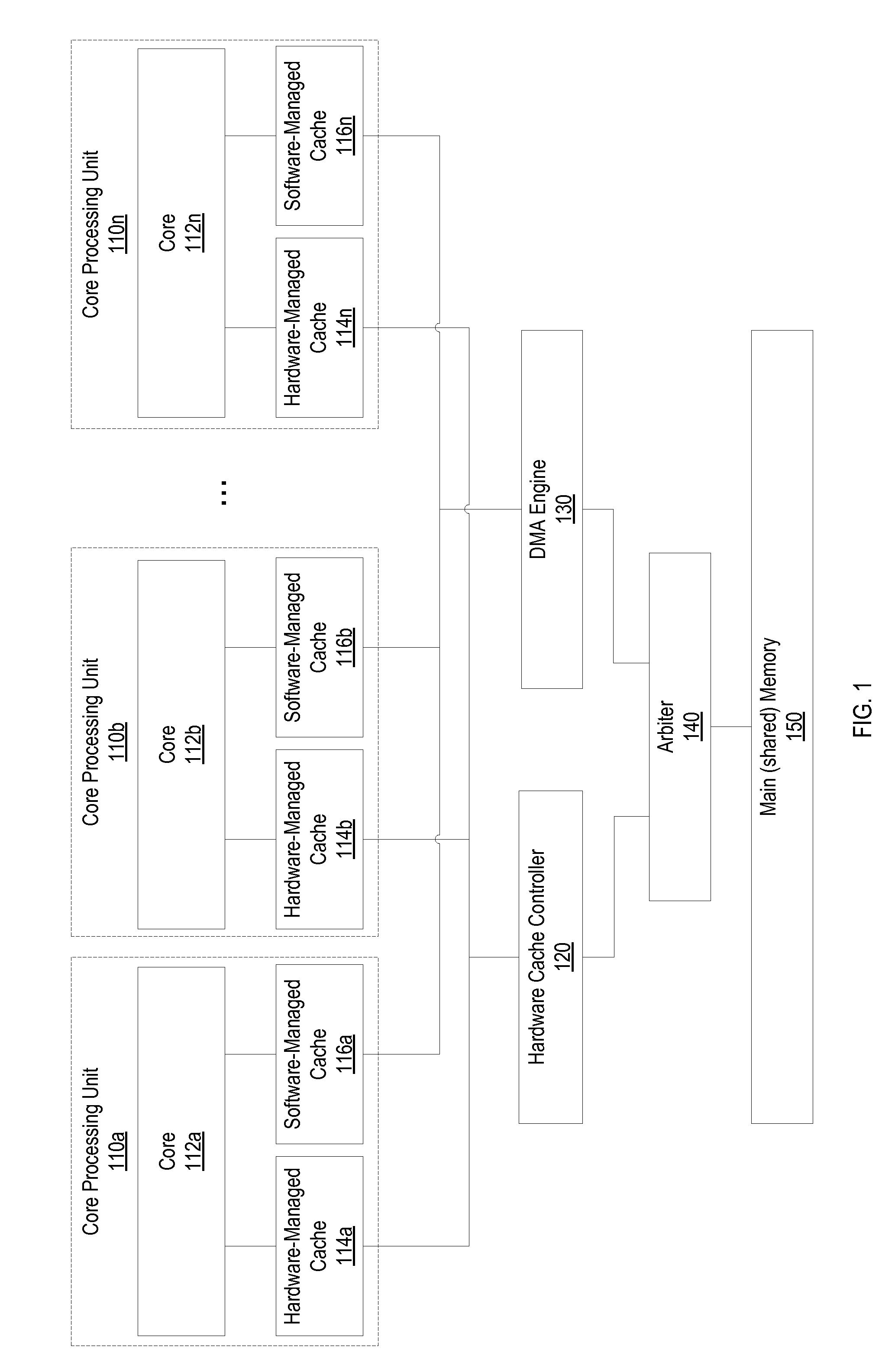
Memory coherence in a multi-core, multi-level, heterogeneous computer architecture
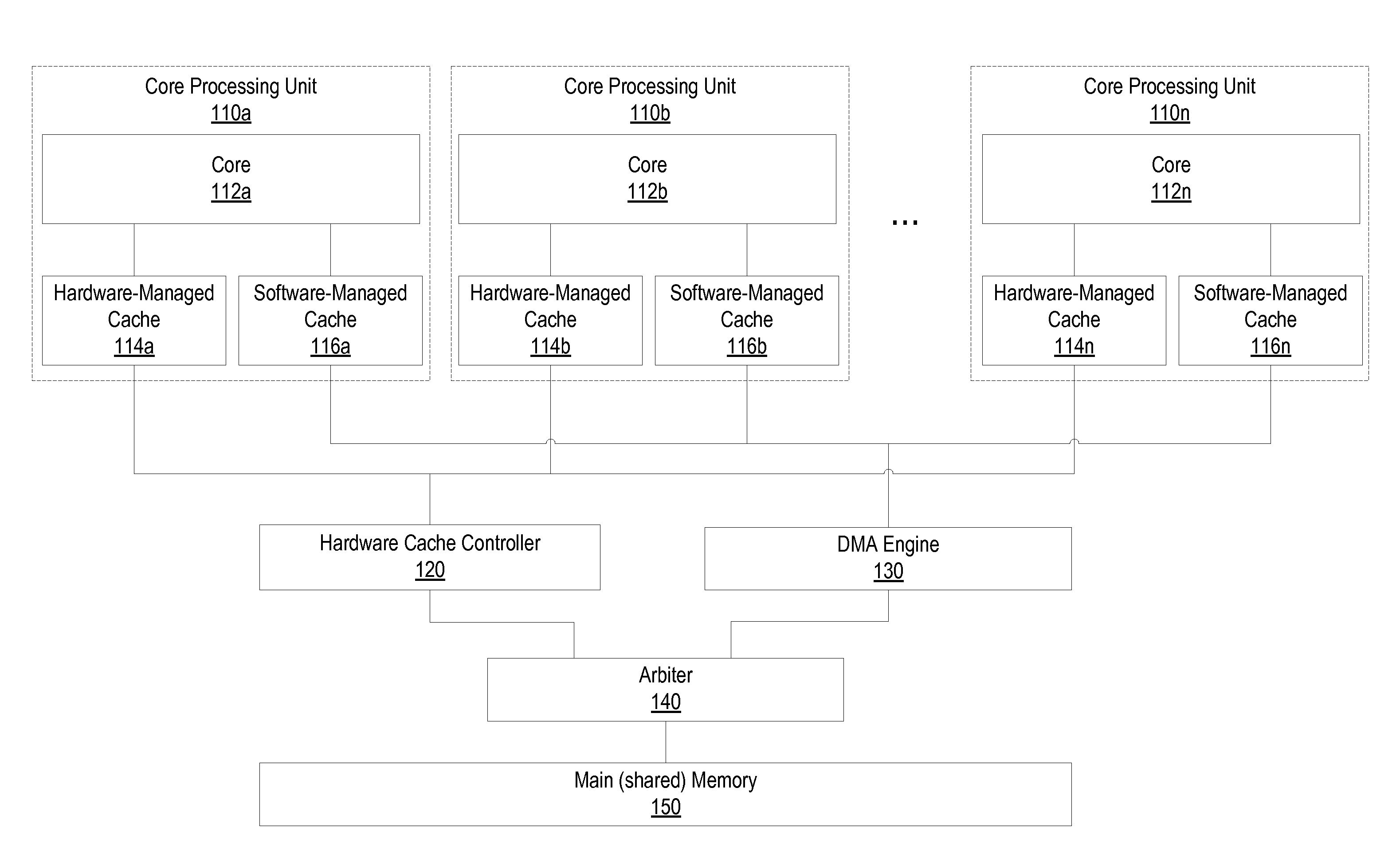
ActiveUS20160328326A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationMemory architectureMulticore systems
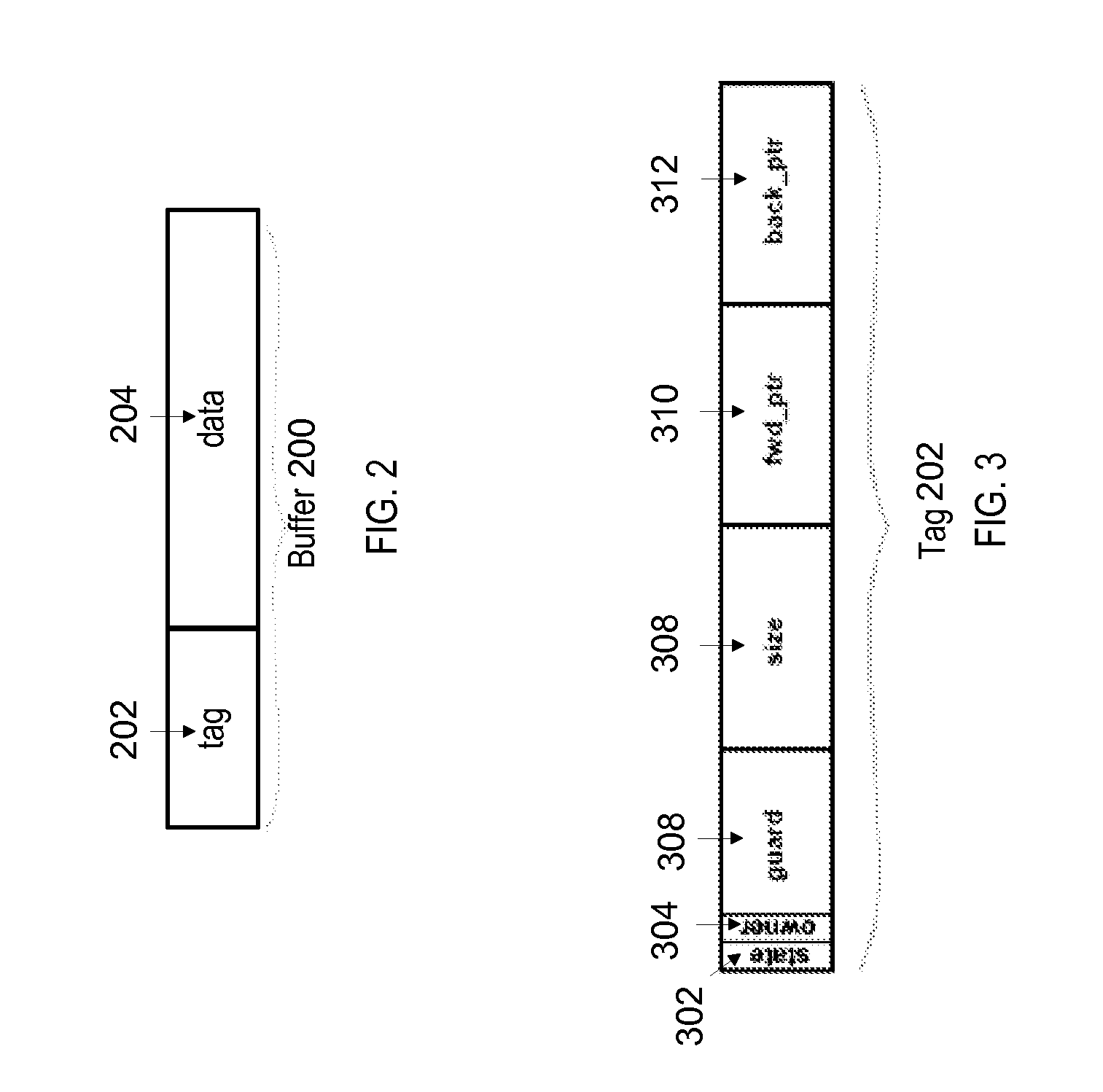
Techniques are described for memory coherence in a multi-core system with a heterogeneous memory architecture comprising one or more hardware-managed caches and one or more software-managed caches. According to one embodiment, a set of one or more buffers are allocated in memory, and each respective buffer is associated with a respective metadata tag. The metadata tag may be used to store metadata that identifies a state associated with the respective buffer. The multi-core system may enforce coherence for the one or more hardware-managed caches and the one or more software-managed caches based on the metadata stored in the metadata tag for each respective buffer in the set of one or more buffers. The multi-core system may read the metadata to determine whether a particular buffer is in a hardware-managed or a software-managed cacheable state. Based on the current state of the particular buffer, the multi-core system may perform coherence operations.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
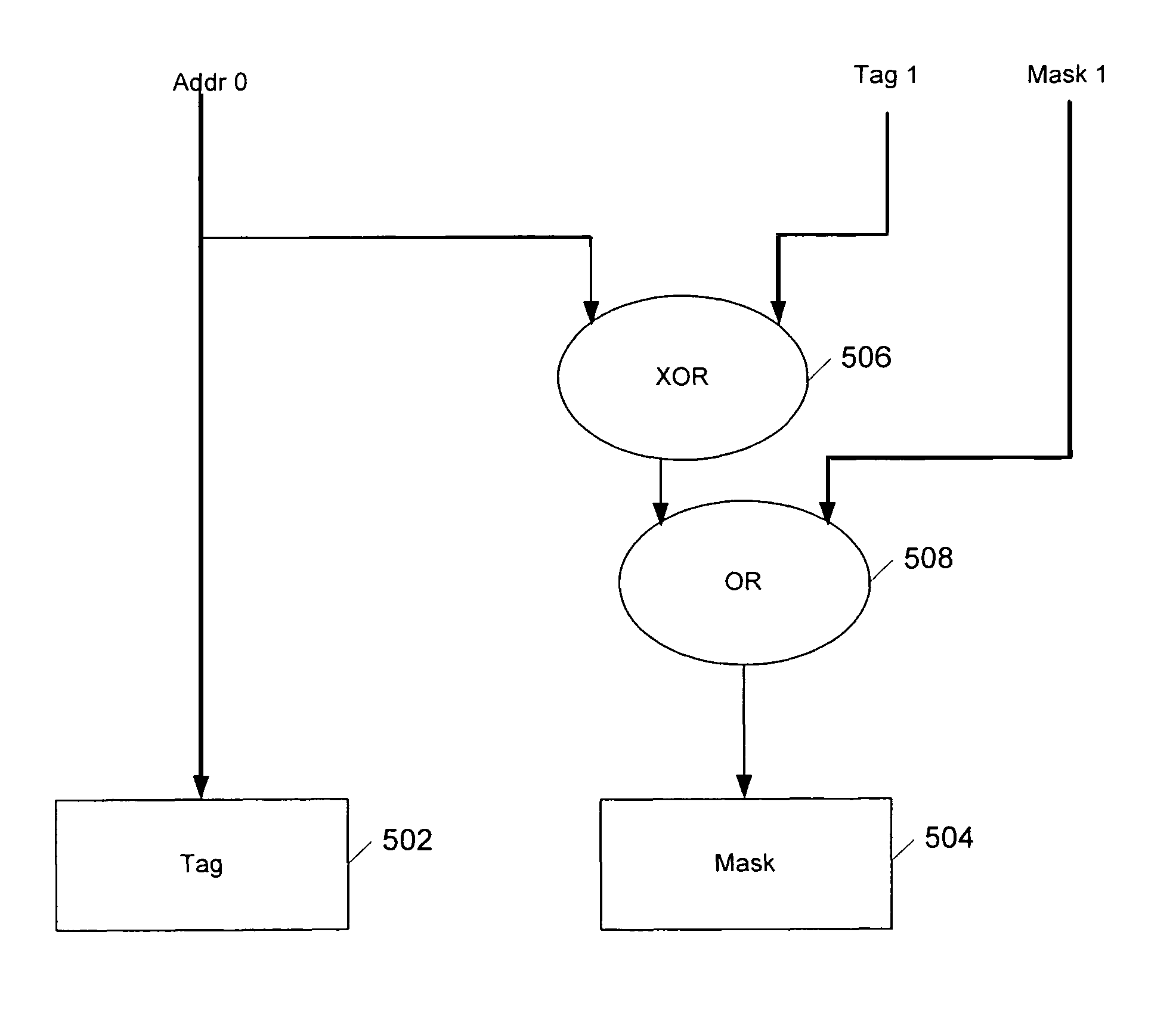
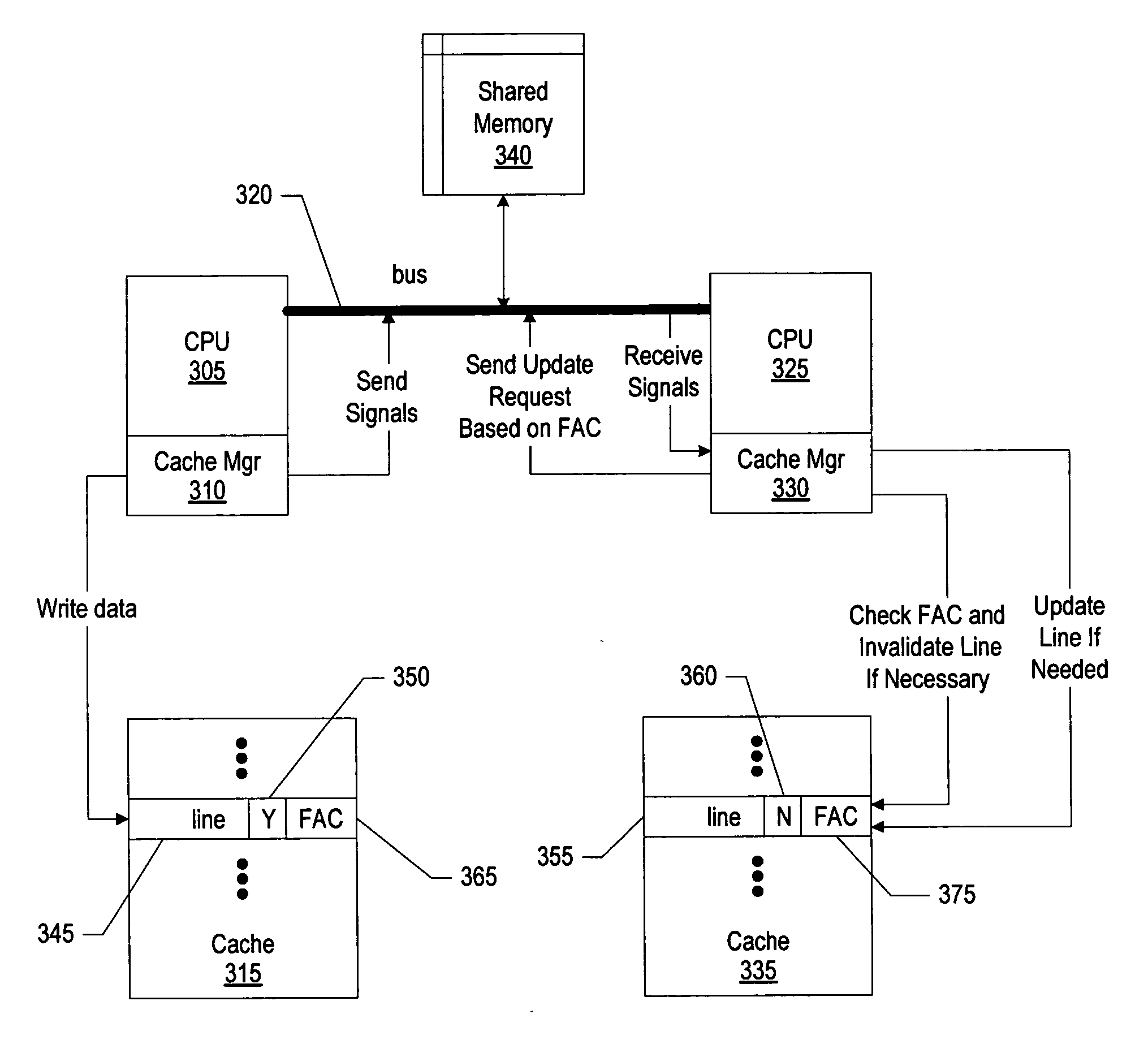
System and method for memory coherence protocol enhancement using cache line access frequencies
InactiveUS20070101068A1Improve efficiencyDecrease cache missMemory systemsMulti processorParallel computing
A memory coherence protocol is provided for using cache line access frequencies to dynamically switch from an invalidation protocol to an update protocol. A frequency access count (FAC) is associated with each line of data in a memory area, such as each cache line in a private cache corresponding to a CPU in a multiprocessor system. Each time the line is accessed, the FAC associated with the line is incremented. When the CPU, or process, receives an invalidate signal for a particular line, the CPU checks the FAC for the line. If the CPU, or process, determines that it is a frequent accessor of a particular line that has been modified by another CPU, or process, the CPU sends an update request in order to obtain the modified data. If the CPU is not a frequent accessor of a line that has been modified, the line is simply invalidated in the CPU's memory area. By dynamically switching from an invalidate protocol to an update protocol, based on cache line access frequencies, efficiency is maintained while cache misses are minimized. Preferably, all FACs are periodically reset in order to ensure that the most recent cache line access data in considered.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Coherence protocol providing speculative coherence response to directory probe
ActiveUS20190188138A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory systemsData processing systemParallel computing
A data processing system includes first and second processing nodes and response logic coupled by an interconnect fabric. A first coherence participant in the first processing node is configured to issue a memory access request specifying a target memory block, and a second coherence participant in the second processing node is configured to issue a probe request regarding a memory region tracked in a memory coherence directory. The first coherence participant is configured to, responsive to receiving the probe request after the memory access request and before receiving a systemwide coherence response for the memory access request, detect an address collision between the probe request and the memory access request and, responsive thereto, transmit a speculative coherence response. The response logic is configured to, responsive to the speculative coherence response, provide a systemwide coherence response for the probe request that prevents the probe request from succeeding.
Owner:IBM CORP
Value-based memory coherence support
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
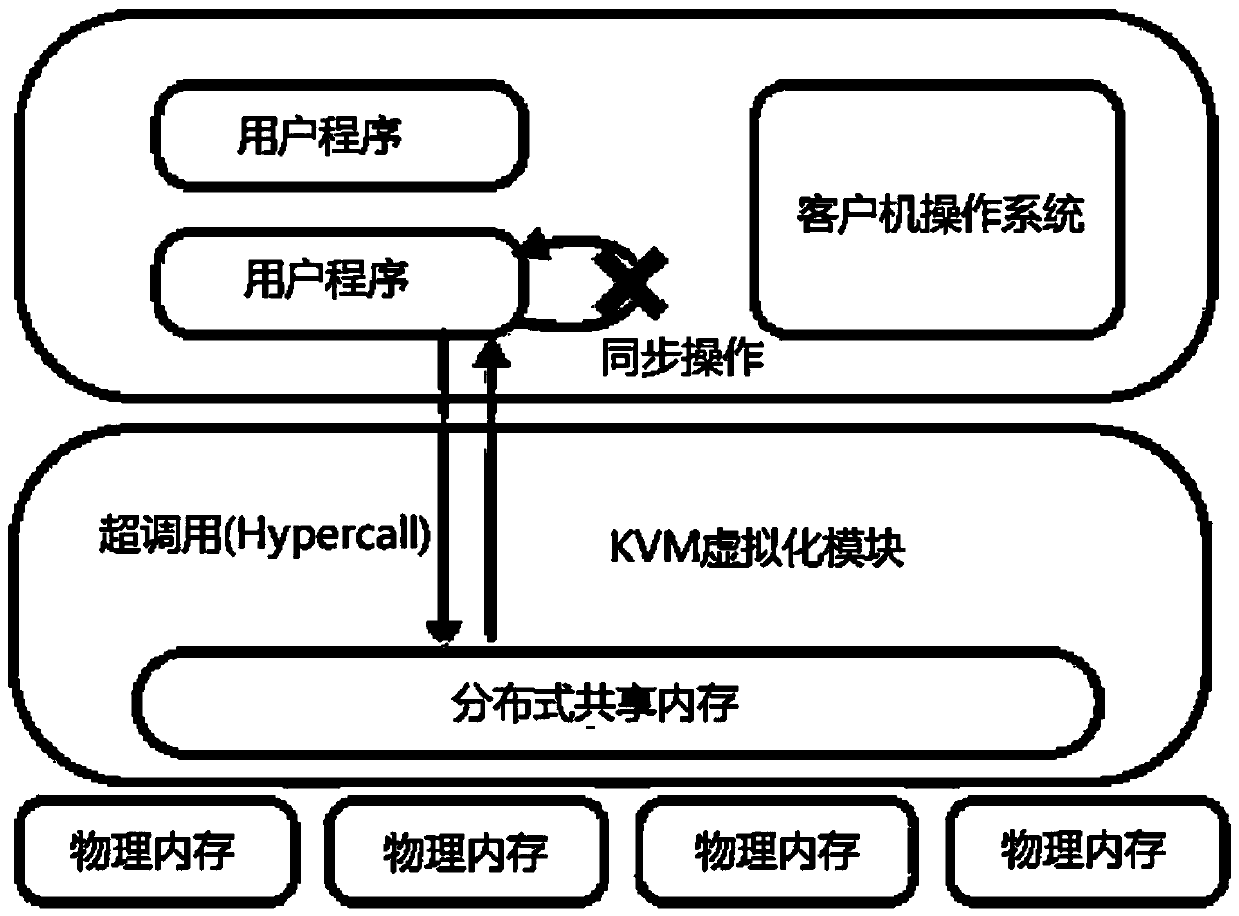
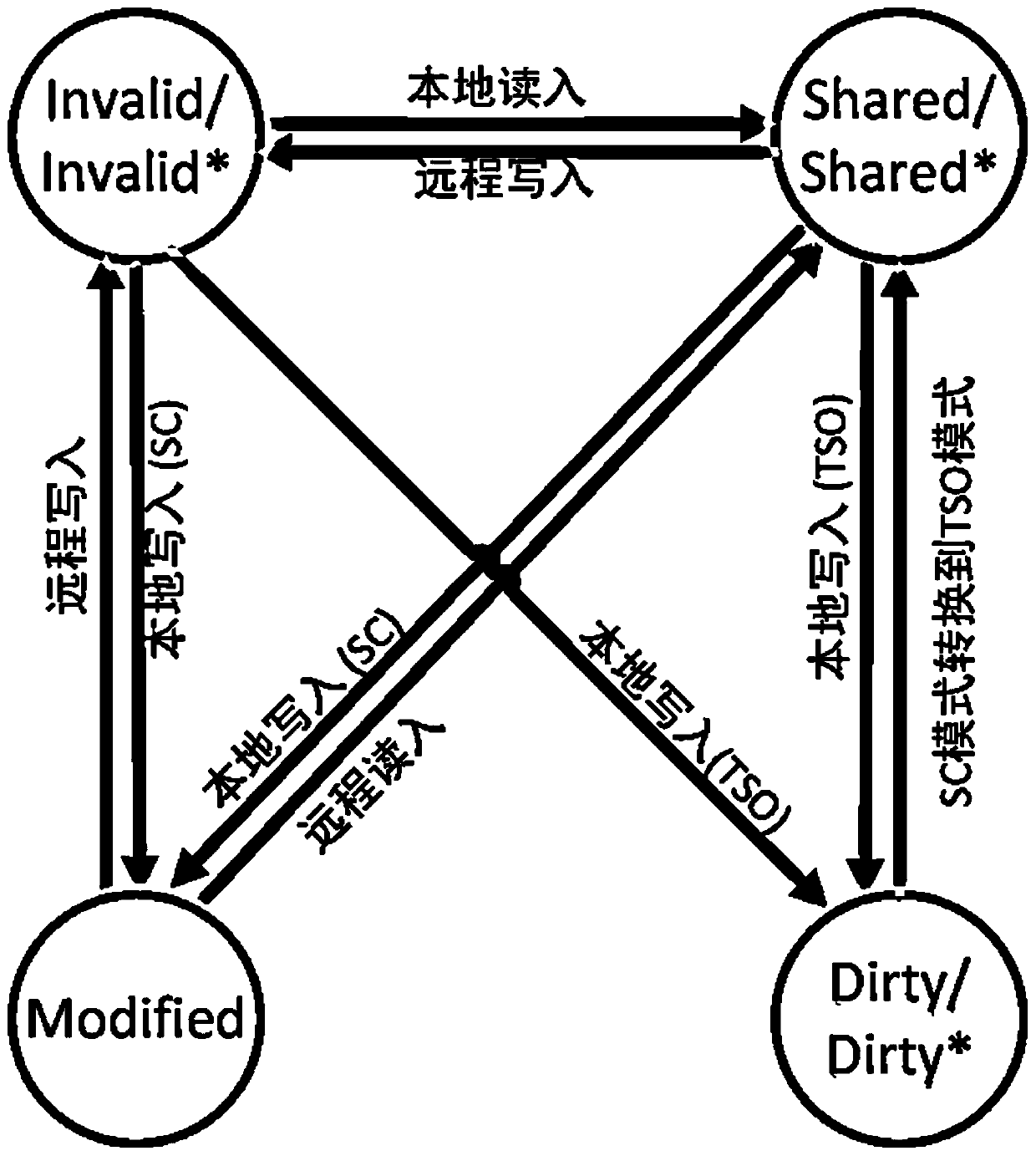
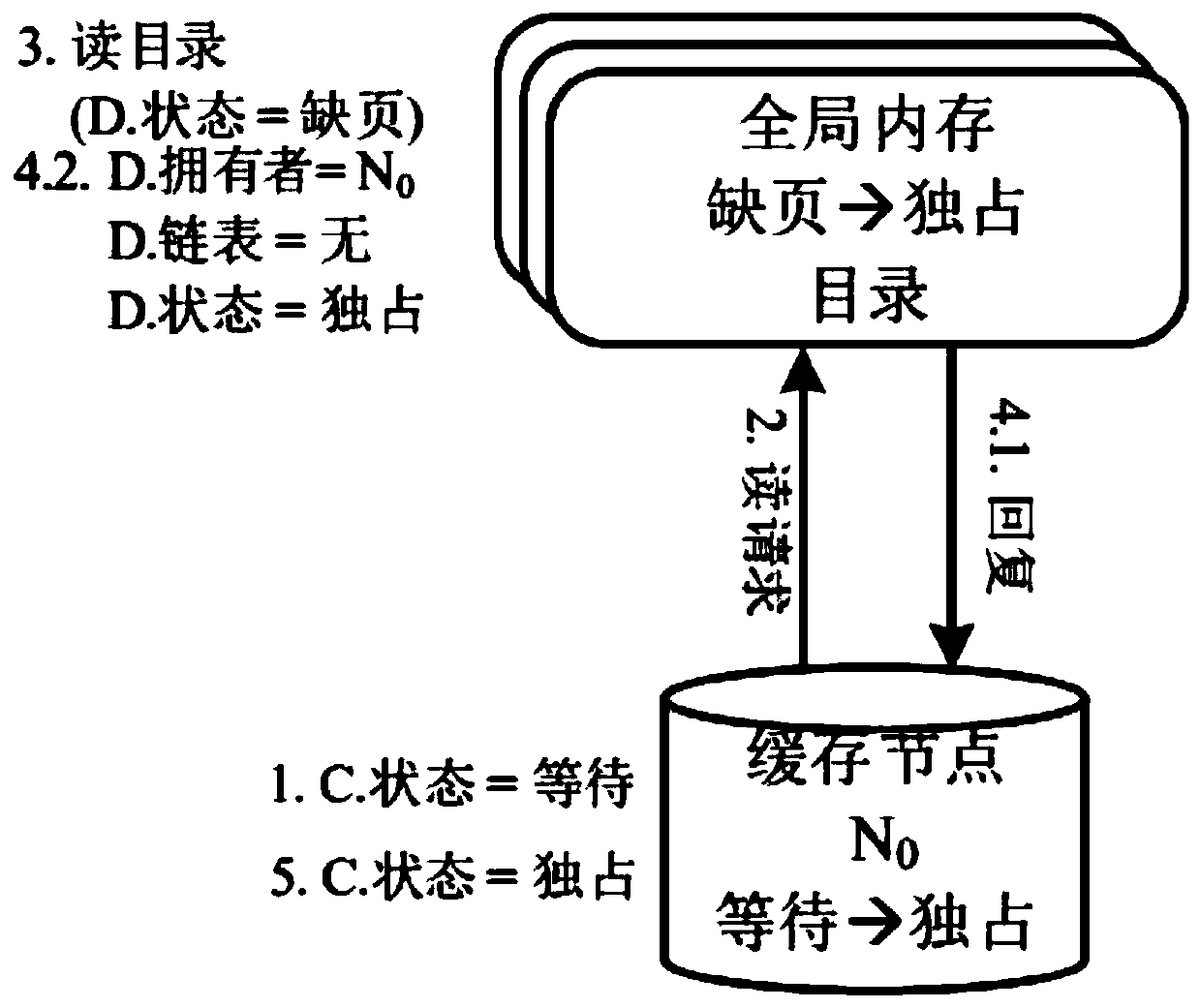
Distributed virtual machine self-adaptive memory consistency protocol, design method thereof and terminal
ActiveCN110569105AImprove performanceFlexible switchingEnergy efficient computingSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationSelf adaptiveDistributed computing
The invention provides a design method of a distributed virtual machine self-adaptive memory consistency protocol, which comprises the following steps of: intercepting synchronous operation: aiming atdifferent applications, flexibly switching a vCPU (Virtual Central Processing Unit) of a client in a sequential consistency mode and a TSO (Transport Storage and Offloading) mode; the state description of the synchronization protocol: on the basis of the original memory consistency protocol, adding Dirty and a corresponding atomic operation state, and realizing state transition. Meanwhile, the invention provides a distributed virtual machine self-adaptive memory consistency protocol obtained based on the design method and a terminal used for executing the design method. According to the method, on the basis of the distributed virtual machine, the distributed shared memory can obtain better performance. According to the method, the memory synchronization protocol of the distributed virtualmachine is flexibly switched in order consistency and x86-TSO; for different application scenarios and restrictions, the adaptive consistency protocol relaxes the original sequence consistency to x86-TSO, so that the performance of the distributed shared memory is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Memory Consistency in Graphics Memory Hierarchy with Relaxed Ordering
ActiveUS20180181489A1Facilitate mid-render computeReduce power consumptionMemory architecture accessing/allocationImage memory managementMemory hierarchySequence memory
Techniques are disclosed relating to memory consistency in a memory hierarchy with relaxed ordering. In some embodiments, an apparatus includes a first level cache that is shared by a plurality of shader processing elements and a second level cache that is shared by the shader processing elements and at least a texture processing unit. In some embodiments, the apparatus is configured to execute operations specified by graphics instructions that include (1) an attribute of the operation that specifies a type of memory consistency to be imposed for the operation and (2) scope information for the attribute that specifies whether the memory consistency specified by the attribute should be enforced at the first level cache or the second level cache. In some embodiments, the apparatus is configured to determine whether to sequence memory accesses at the first level cache and the second level cache based on the attribute and the scope.
Owner:APPLE INC
Providing memory consistency in an emulated processing environment
ActiveUS20080243468A1Reduce overheadEfficiently provideProgram synchronisationUnauthorized memory use protectionParallel computingSerialization
Memory consistency is provided in an emulated processing environment. A processor architected with a weak memory consistency emulates an architecture having a firm memory consistency. This memory consistency is provided without requiring serialization instructions or special hardware.
Owner:IBM CORP
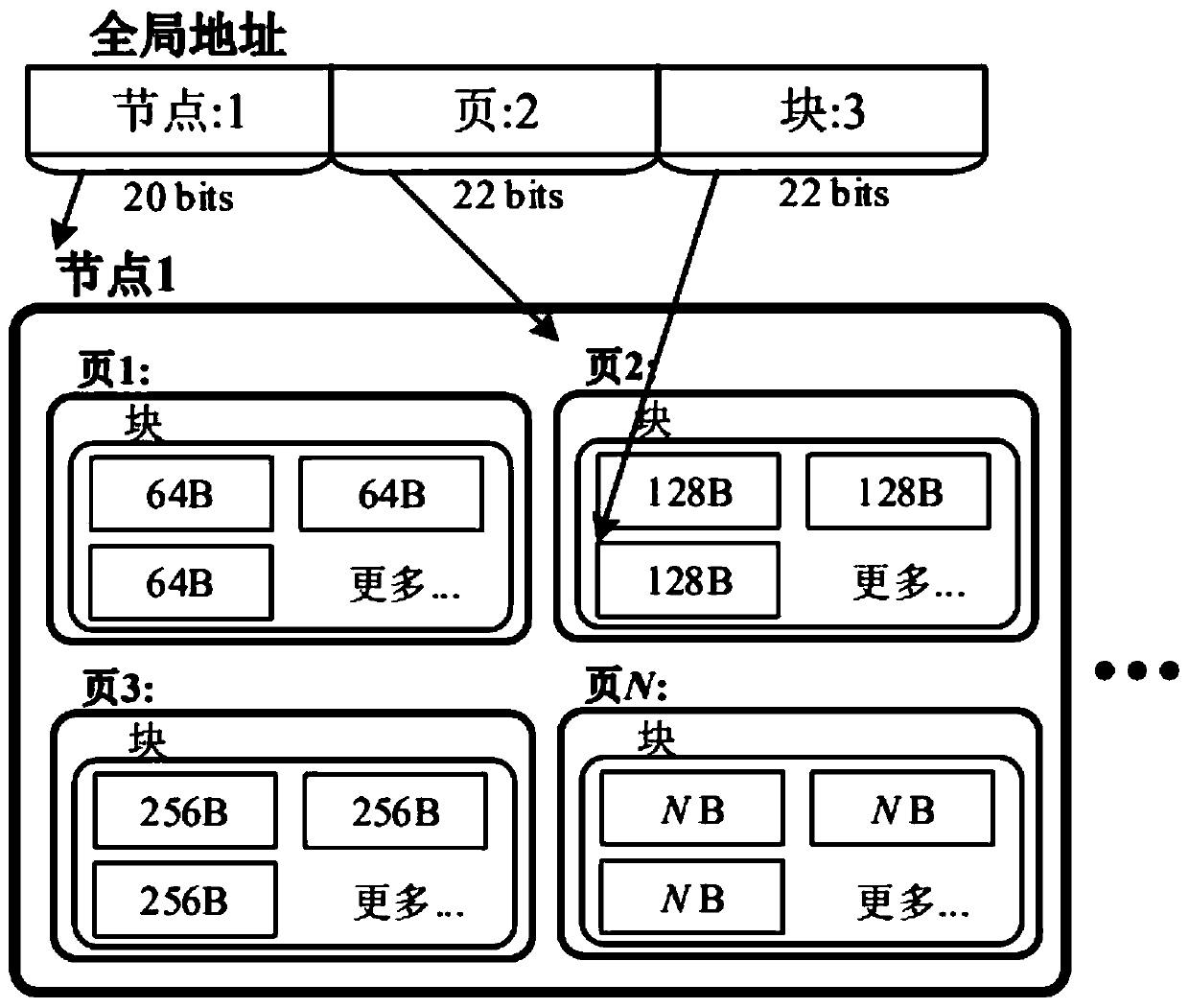
Distributed memory management method based on network and page granularity management
ActiveCN111273860AImprove throughputFix cache invalidationInput/output to record carriersMemory adressing/allocation/relocationDistributed memoryCache invalidation
The invention discloses a distributed memory management method based on network and page granularity management. The method is characterized in that a node, page and block memory management method isadopted for a global address; partial memories from different nodes are packaged in a global page-based memory (GPM), and data transmission under page granularity is supported, memory management is performed based on the updated memory consistency protocol, so that the data on the local cache page is consistent with the data on the GPM, and a high-level application program deployed in the PDMM transparently accesses the GPM, thereby realizing low-delay and high-throughput inter-node access. Compared with the prior art, the inter-node access delay with low delay and high throughput is achieved,the method is simple and convenient to use, the problem that cache is invalid due to write operation in data intensive work is effectively solved, and the performance of the PDMM is superior to thatof other products of the same type.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
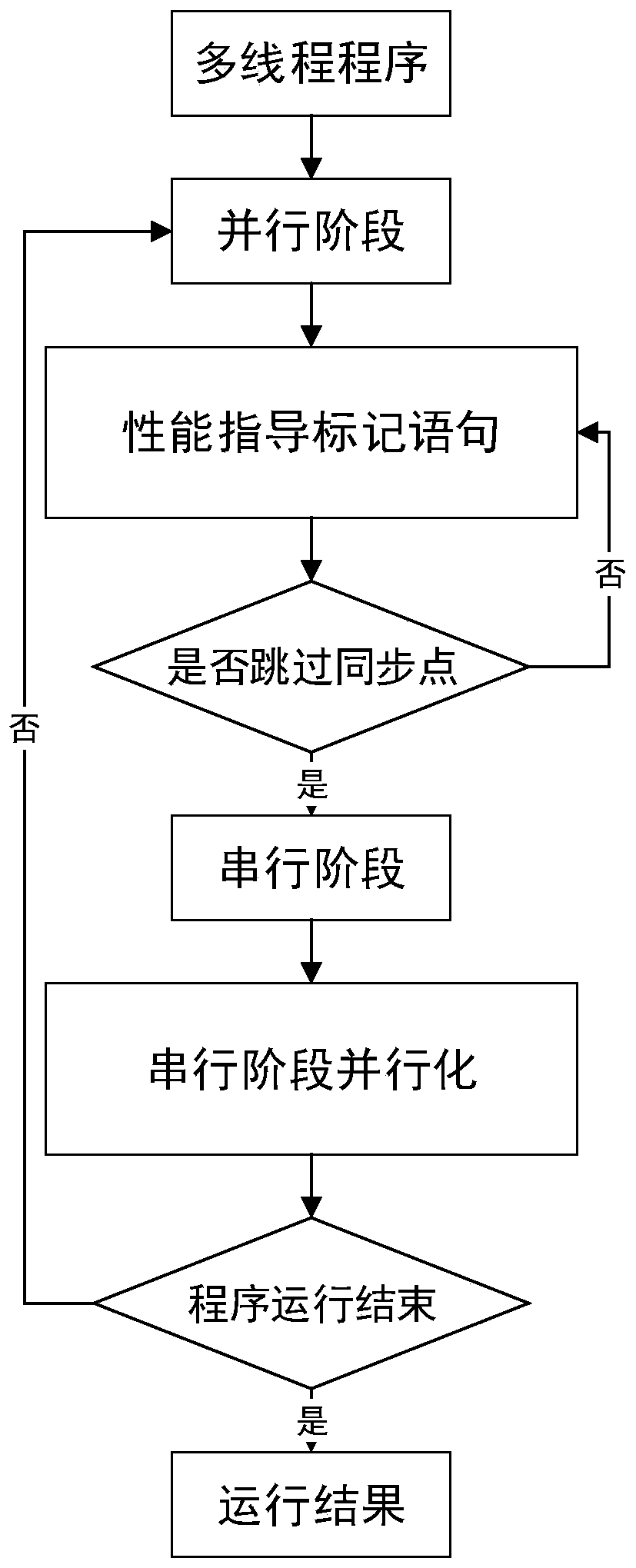
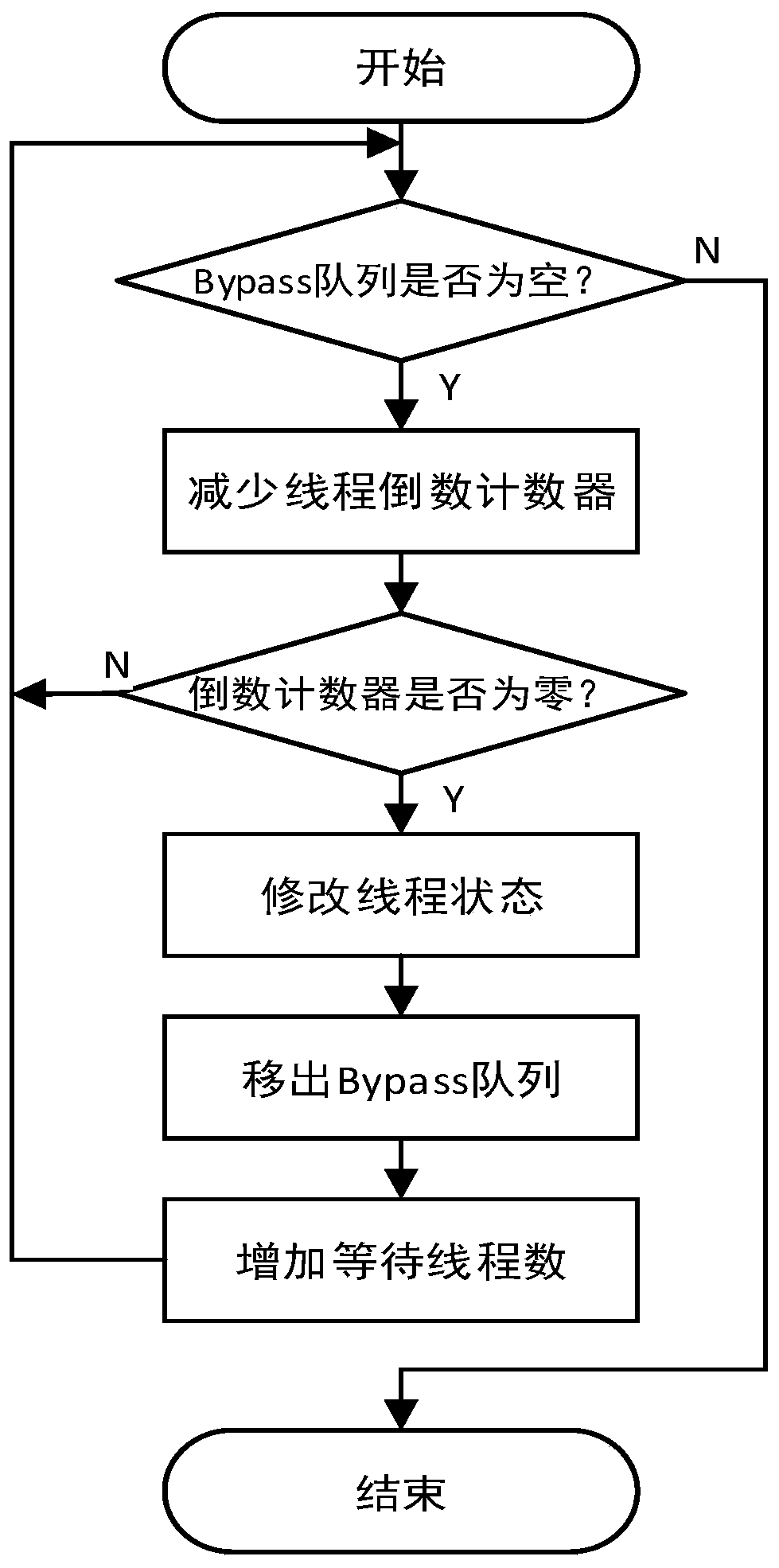
Multi-thread deterministic execution method based on weak memory consistency
ActiveCN110083445AImprove parallelismImprove performanceProgram initiation/switchingProgram synchronisationDeterministic methodConsistency model
The invention provides a multi-thread deterministic execution method based on weak memory consistency. A weak memory consistency model, a serial stage thread parallelization module and a performance guidance marking module are included. According to the method, a TSO weak memory consistency concept is used, and a two-point innovative technology is provided and comprises a serial phase part threadparallelization technology and a performance guidance marking technology for helping a long parallel distance thread to skip a synchronization point. According to the method, the problem of performance reduction caused by global synchronization of an existing deterministic method can be solved, the problem of load imbalance of parallel stages is effectively solved by enabling some threads with longer parallel stages to skip specified synchronization points, and the performance of the deterministic technology is greatly improved.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com