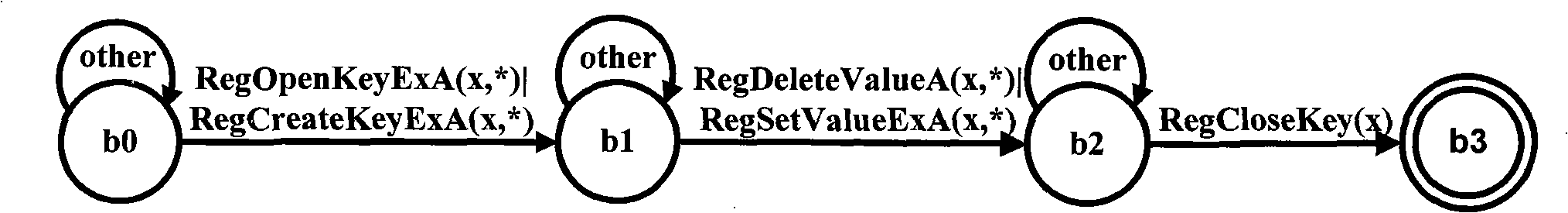Patents
Literature
364 results about "Program transformation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A program transformation is any operation that takes a computer program and generates another program. In many cases the transformed program is required to be semantically equivalent to the original, relative to a particular formal semantics and in fewer cases the transformations result in programs that semantically differ from the original in predictable ways.
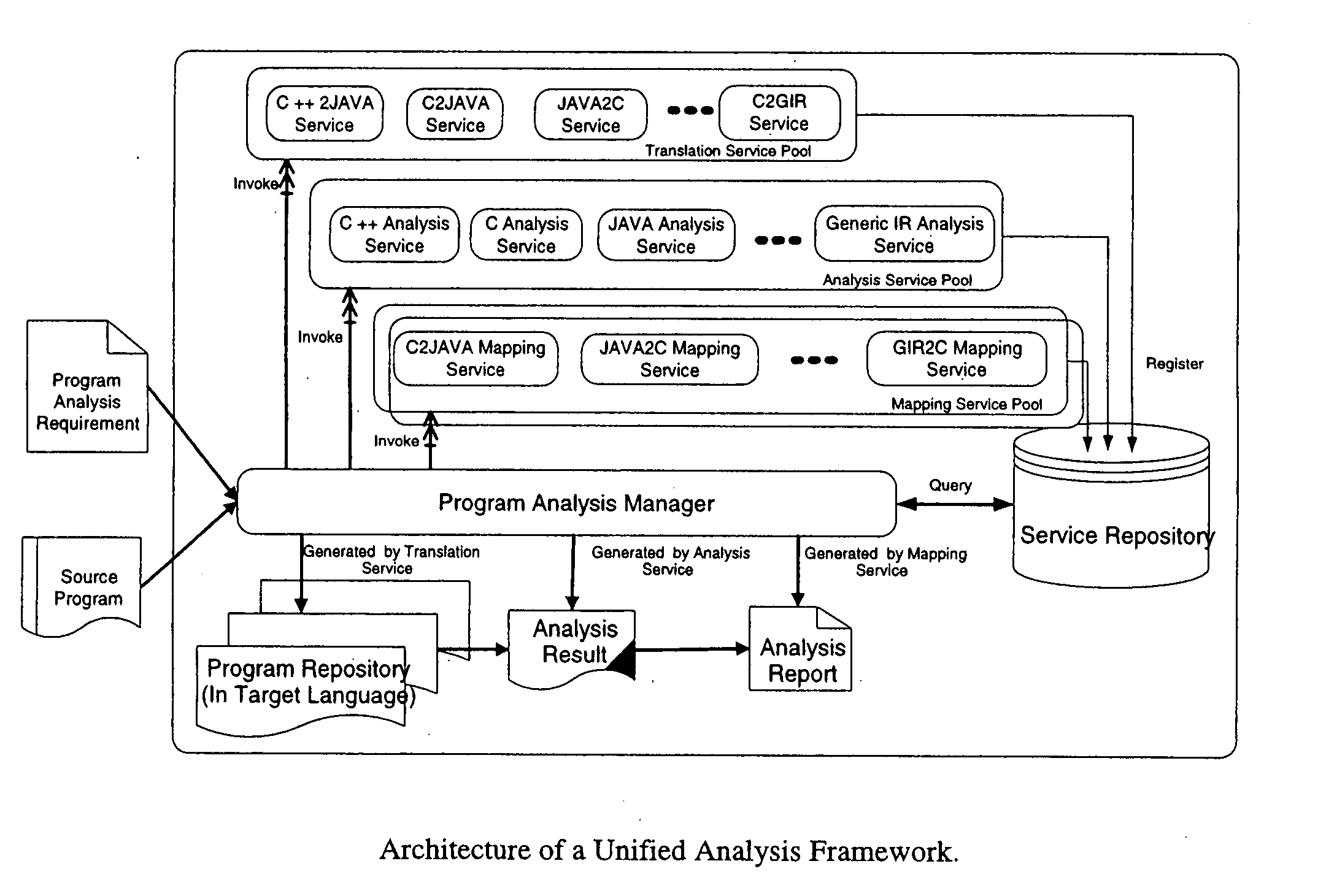
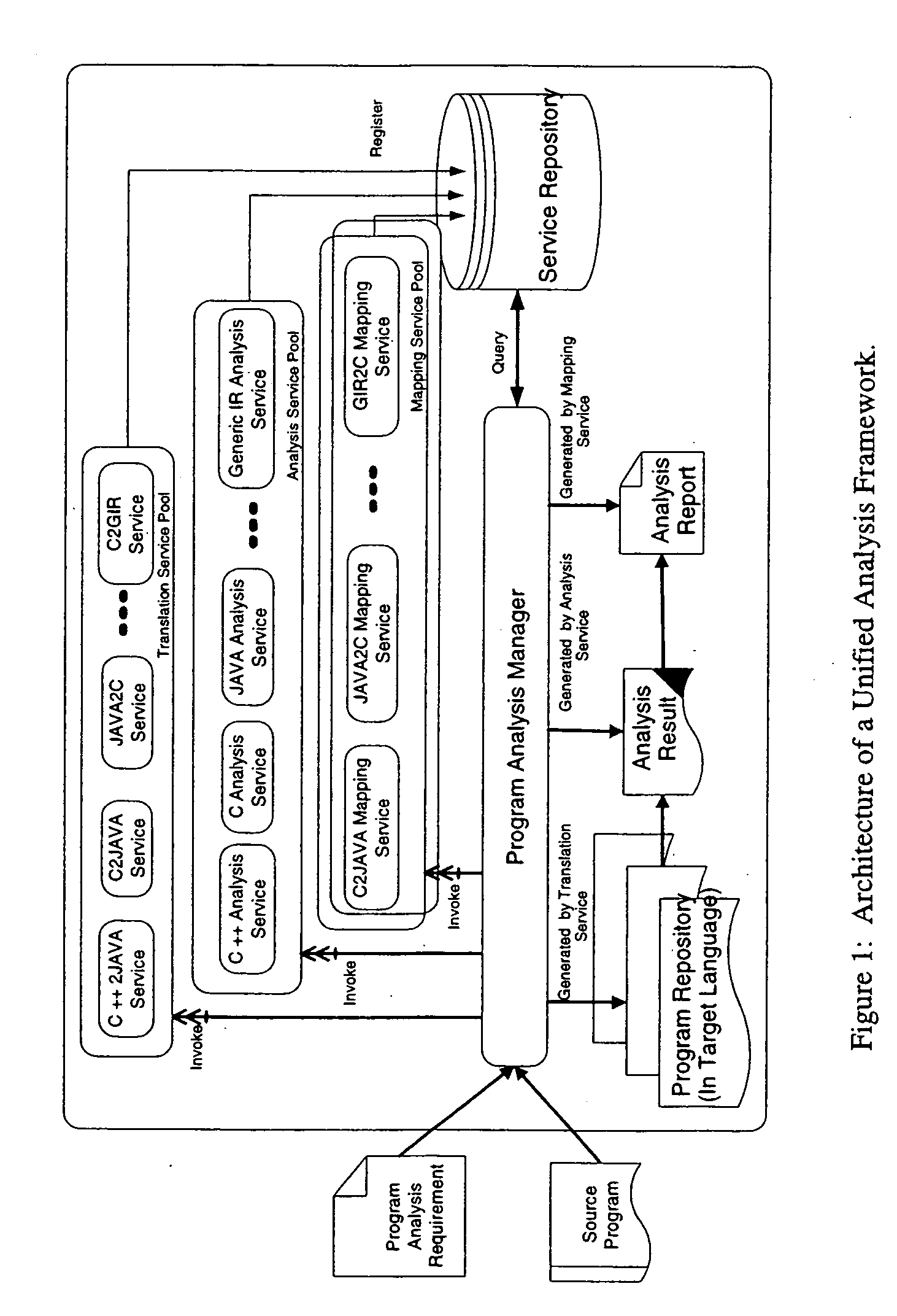
Methods and arrangements for unified program analysis
InactiveUS20060248519A1Low costMaximize returnError detection/correctionSpecific program execution arrangementsMulti languageSoftware system
A unified program analysis framework that facilitates the analysis of complex multi-language software systems, analysis reuse, and analysis comparison, by employing techniques such as program translation and automatic results mapping, is presented. The feasibility and effectiveness of such a framework are demonstrated using a sample application of the framework. The comparison yields new insights into the effectiveness of the techniques employed in both analysis tools. These encouraging results yield the observation that such a unified program analysis framework will prove to be valuable both as a testbed for examining different language analysis techniques, and as a unified toolset for broad program analysis.
Owner:IBM CORP
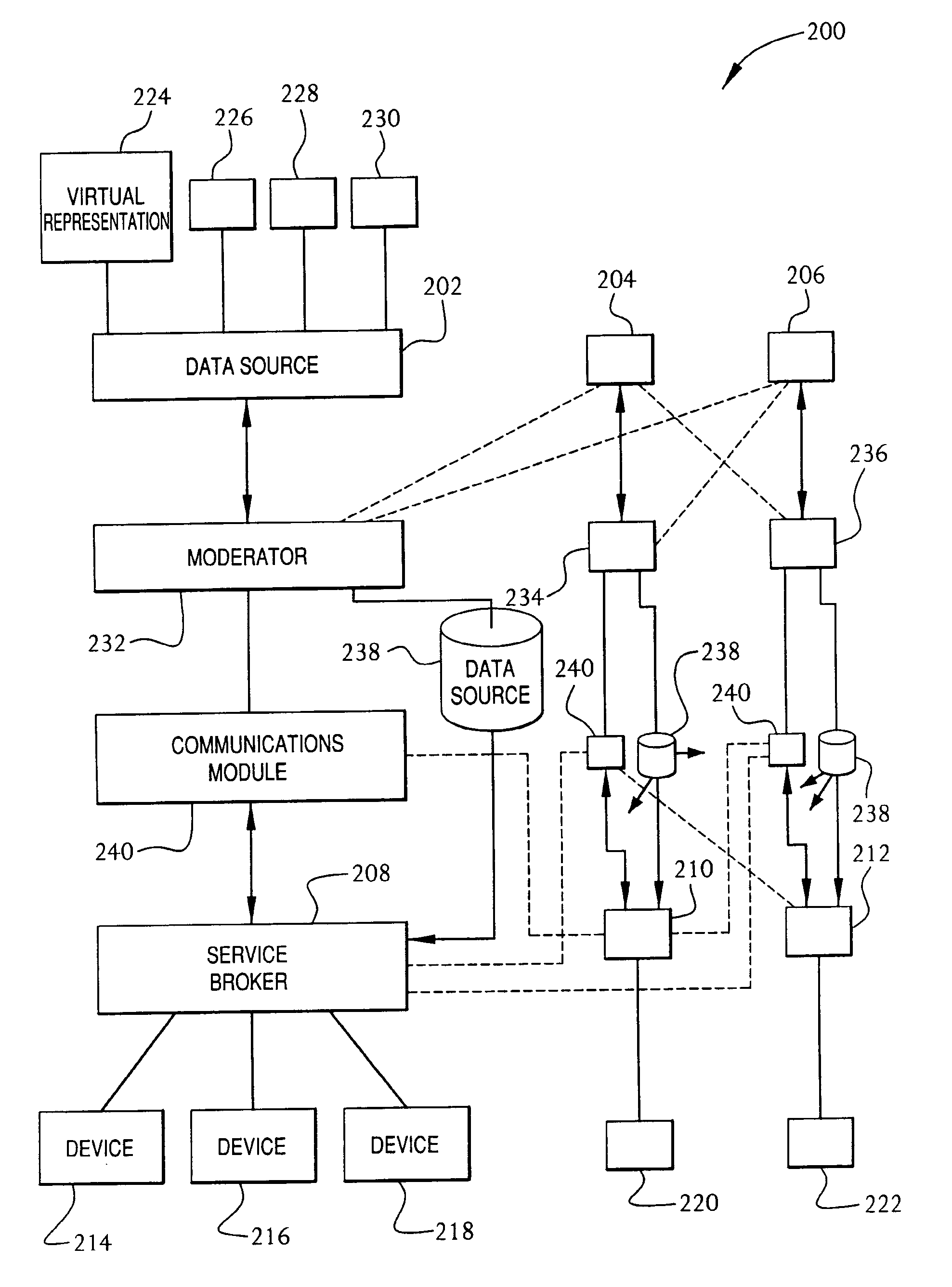
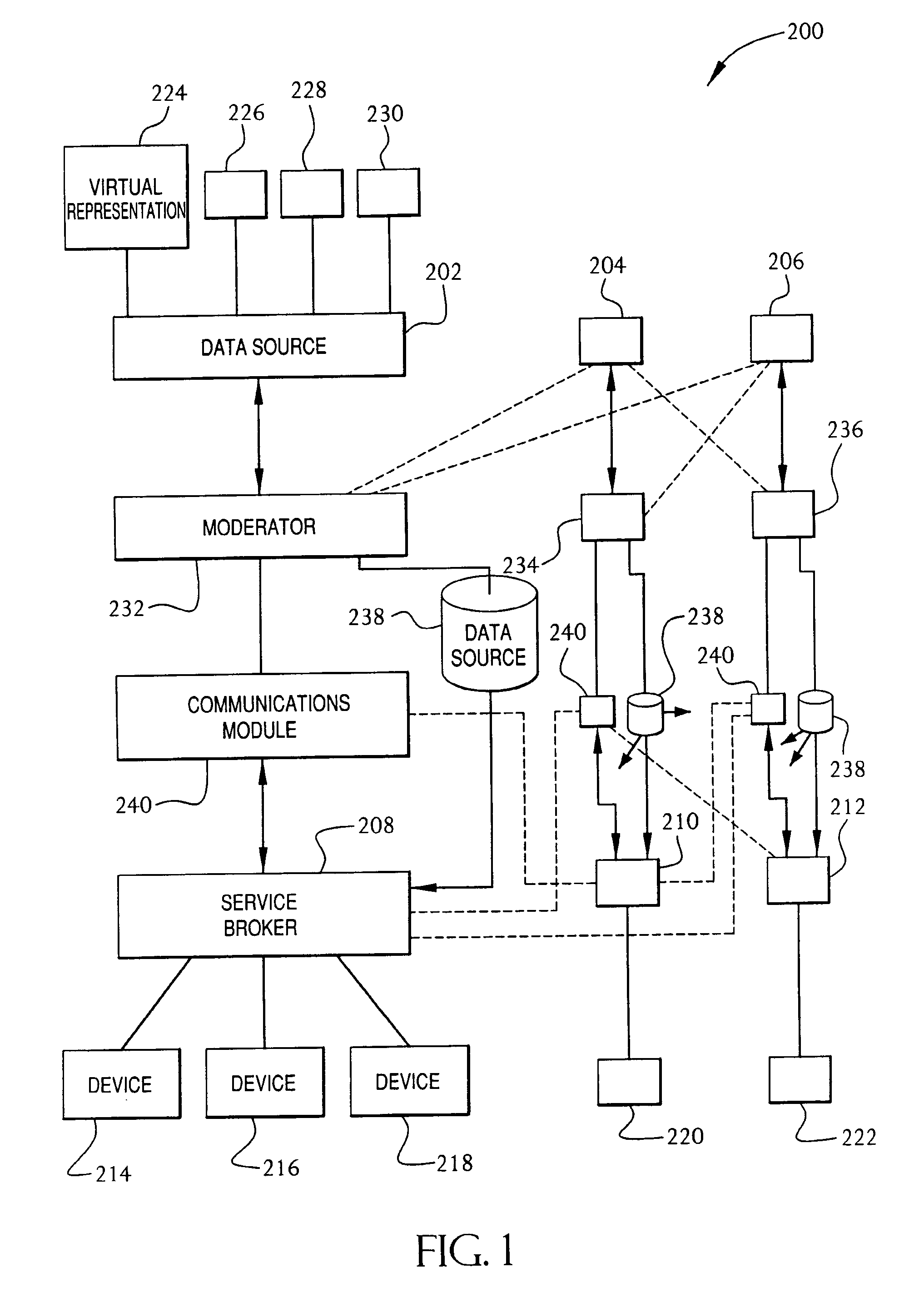
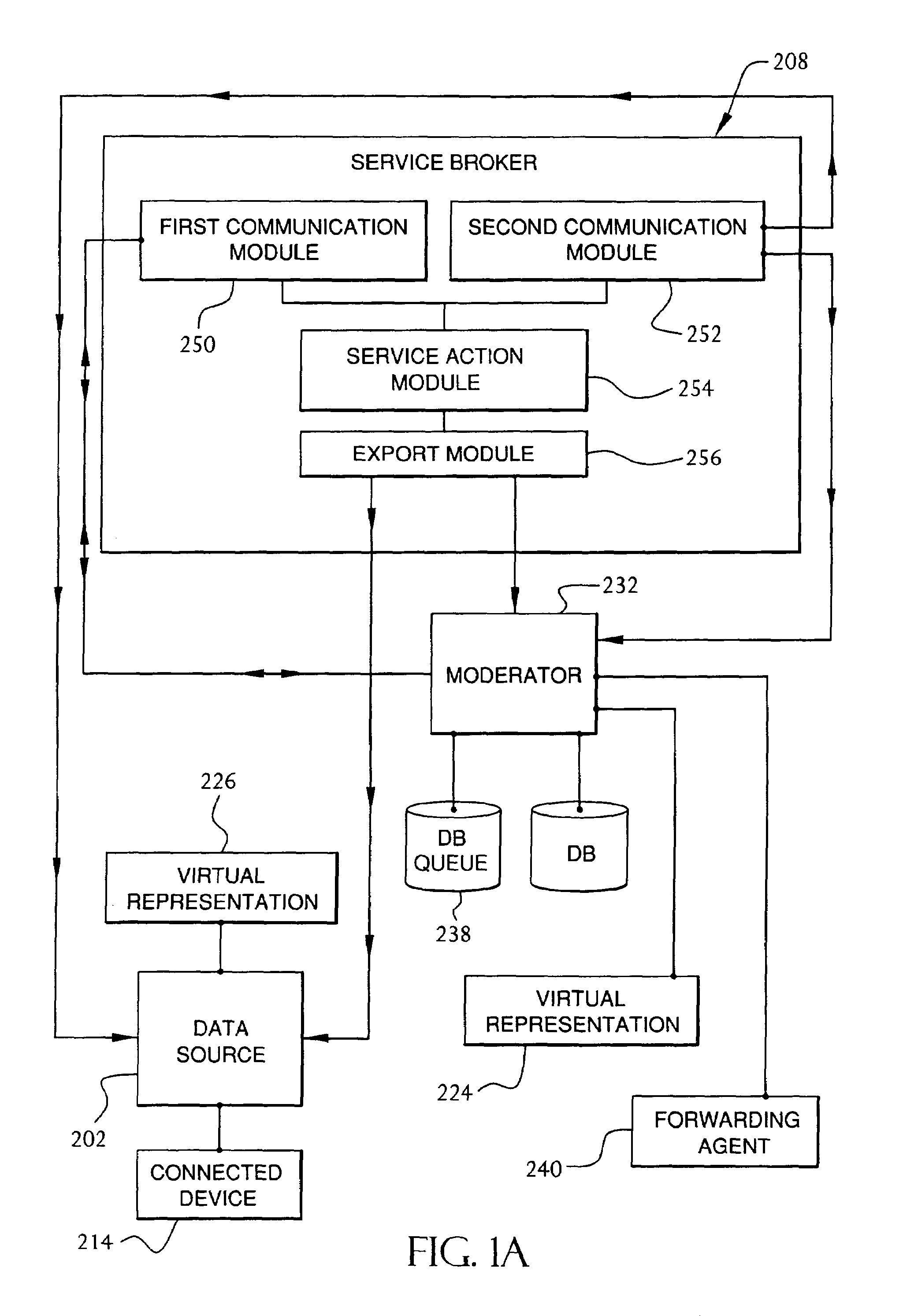
Service broker for processing data from a data network
InactiveUS7032002B1Multiple digital computer combinationsStore-and-forward switching systemsCommand languageServer appliance
A method and system for communication between server-less computing devices or clients in computers communicating over networks, such as the World Wide Web (WWW) using stateless protocols, e.g., HTTP. In this scheme, there are two classes of clients which can operate independently or can be combined in computers communicating over the network: a) clients that issue commands and request status or data, and b) clients that function as service brokers for providing services and processing commands, updating status and providing specific data—resembleing a server device but without accessible TCP / IP ports. Each service providing device is authenticated, retains a unique identity and establishes a soft state with the globally accessible server or servers. All devices and clients can compile and process a globally common command language established between all communicating network clients. The central server includes a CGI processing program and a database to retain client specific information. The server database represents a collection of queues, each having a client unique identifiable status, pending commands and / or data components. In this scheme, commands and signaling transmitted between the servers and clients utilize standard HTTP protocol semantics and HTML or standard markup language syntax. Clients encapsulate or embed information as parameters passed to HTTP CGI as a set of standard HTTP conversations. A CGI processing program converts, parses or processes each conversation and passes arguments with or without data to queues.
Owner:AT&T DIGITAL LIFE
Reconfigurable processing
ActiveUS20070198971A1Reduce signal delayReduce areaEnergy efficient ICTSoftware engineeringPathPingComputer architecture
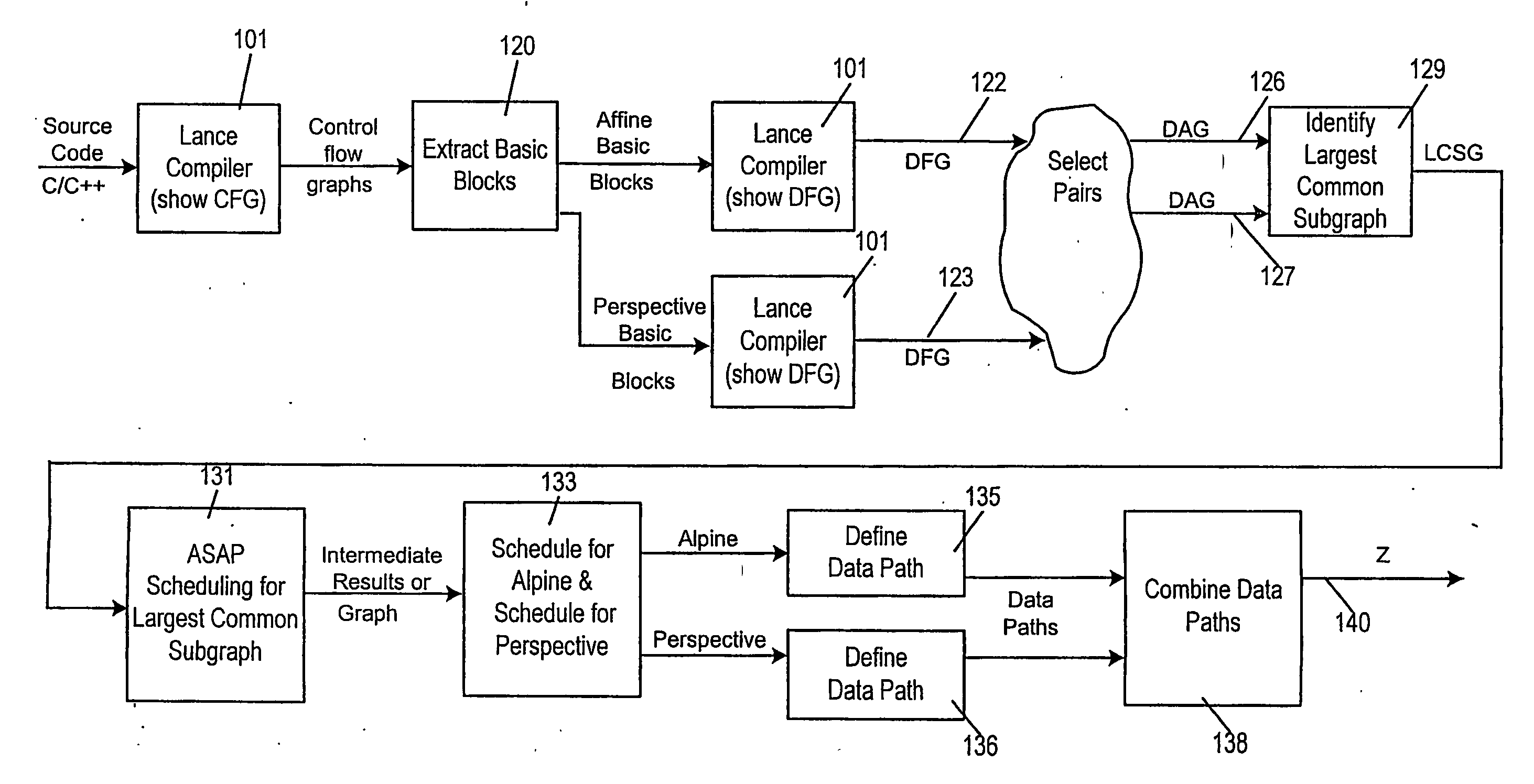
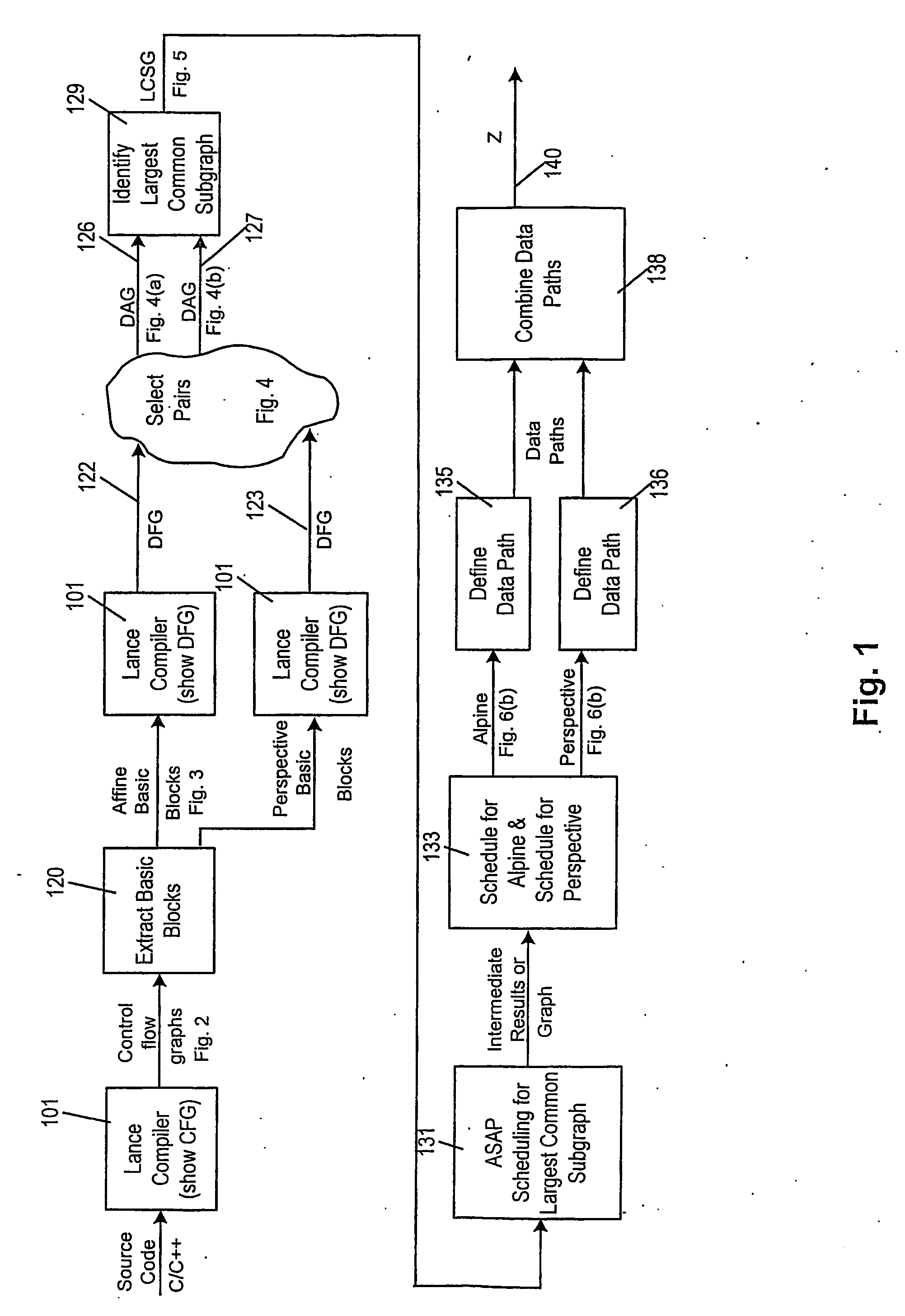
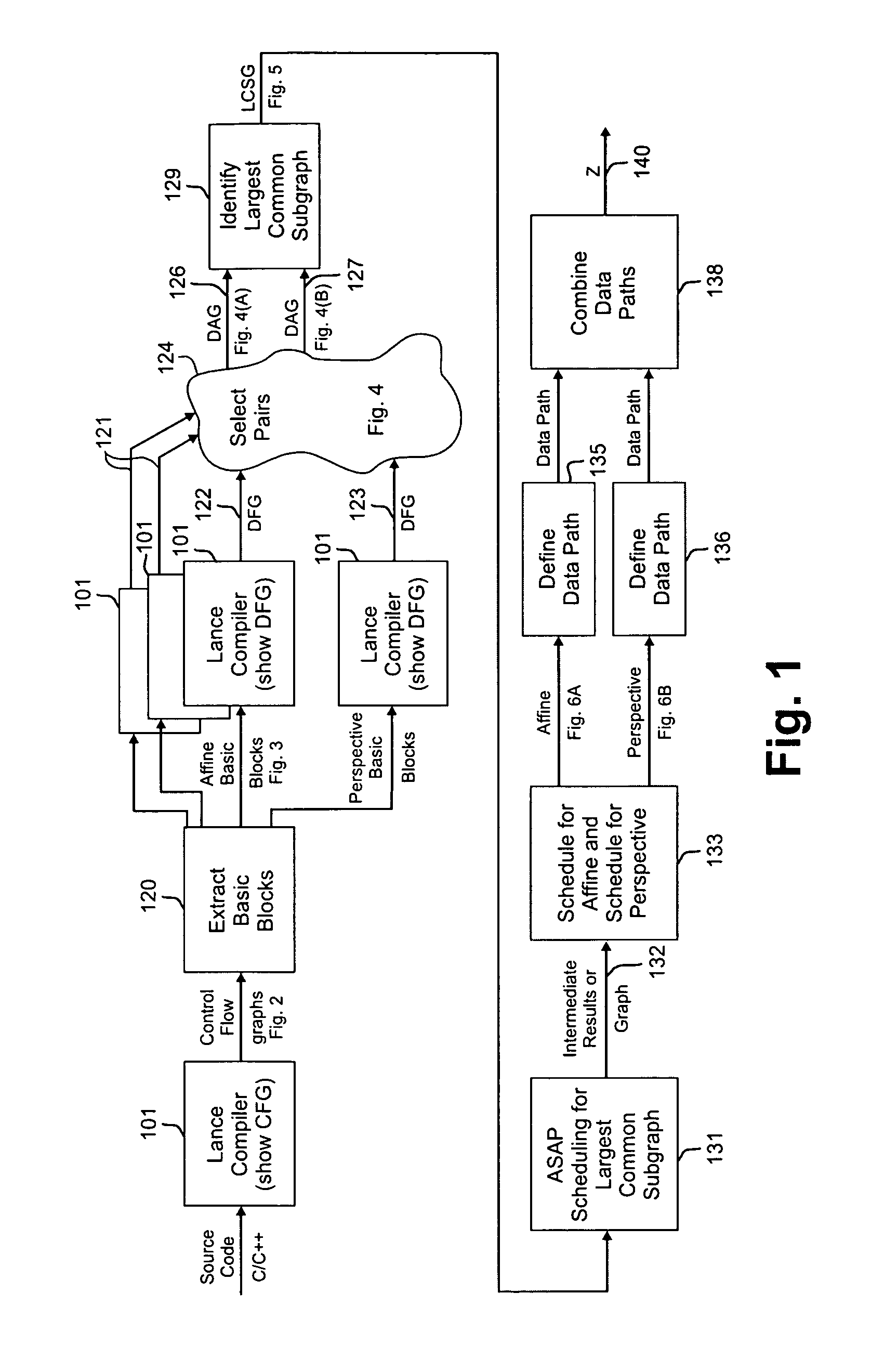
A method of producing a reconfigurable circuit device for running a computer program of moderate complexity such as multimedia processing. Code for the application is compiled into Control Flow Graphs representing distinct parts of the application to be run. From those Control Flow Graphs are extracted basic blocks. The basic blocks are converted to Data Flow Graphs by a compiler utility. From two or more Data Flow Graphs, a largest common subgraph is determined. The largest common subgraph is ASAP scheduled and substituted back into the Data Flow Graphs which also have been scheduled. The separate Data Flow Graphs containing the scheduled largest common subgraph are converted to data paths that are then combined to form code for operating the application. The largest common subgraph is effected in hardware that is shared among the parts of the application from which the Data Flow Graphs were developed. Scheduling of the overall code is effected for sequencing, providing fastest run times and the code is implemented in hardware by partitioning and placement of processing elements on a chip and design of the connective fabric for the design elements.
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
Method and system for converting a single-threaded software program into an application-specific supercomputer
ActiveUS20130125097A1Improve efficiencyLow overhead implementationMemory architecture accessing/allocationTransformation of program codeSupercomputerComputer architecture
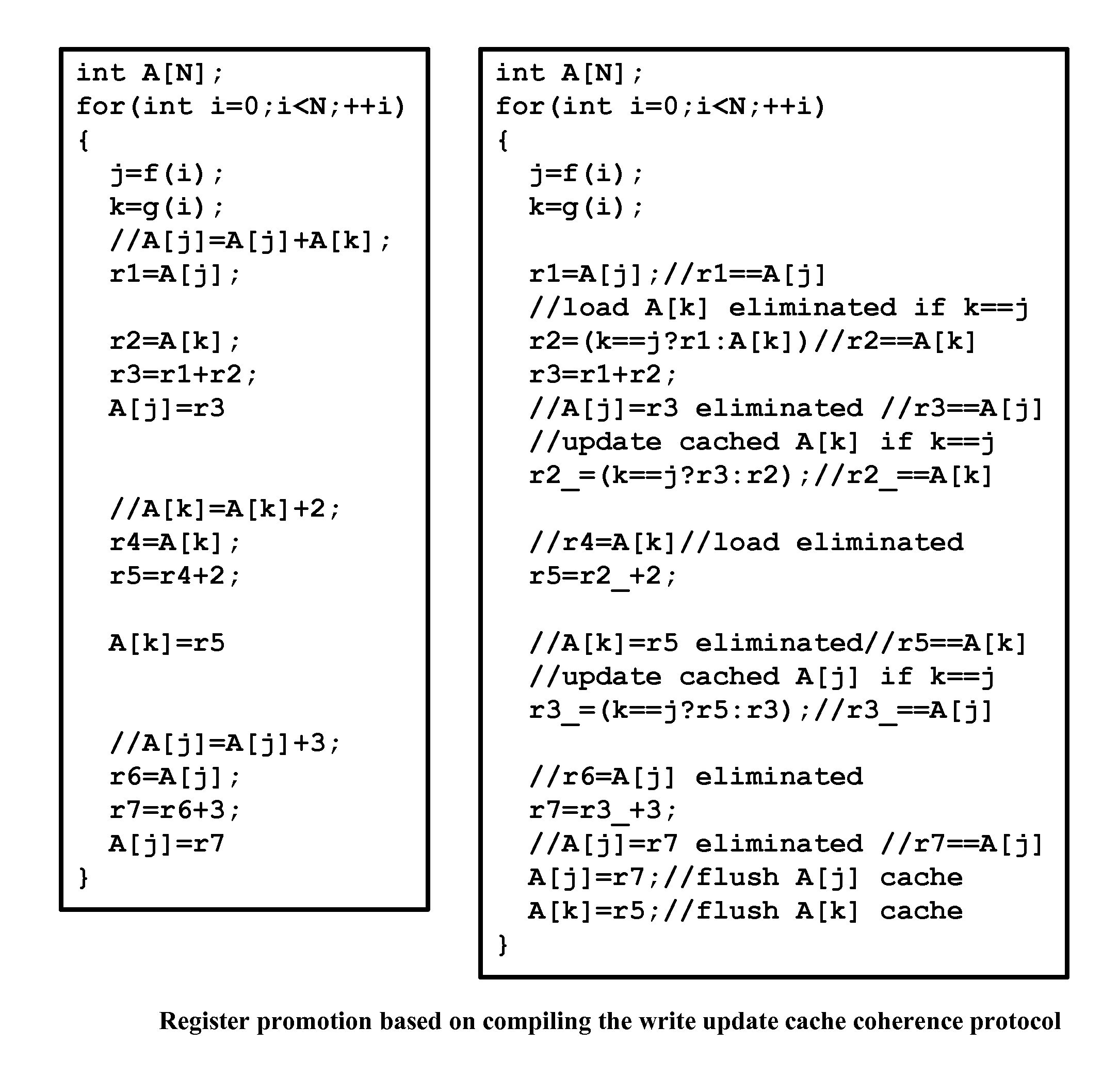
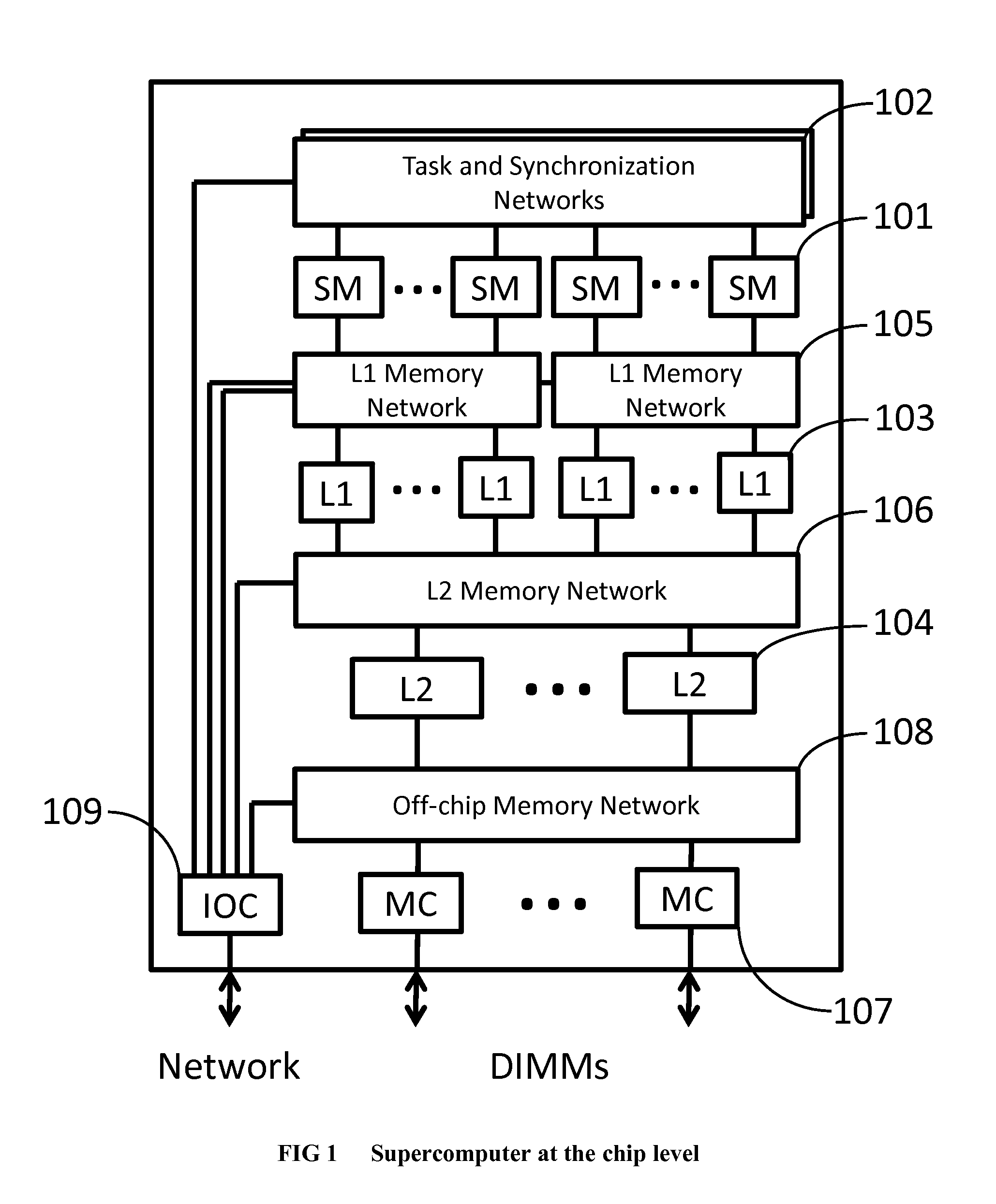
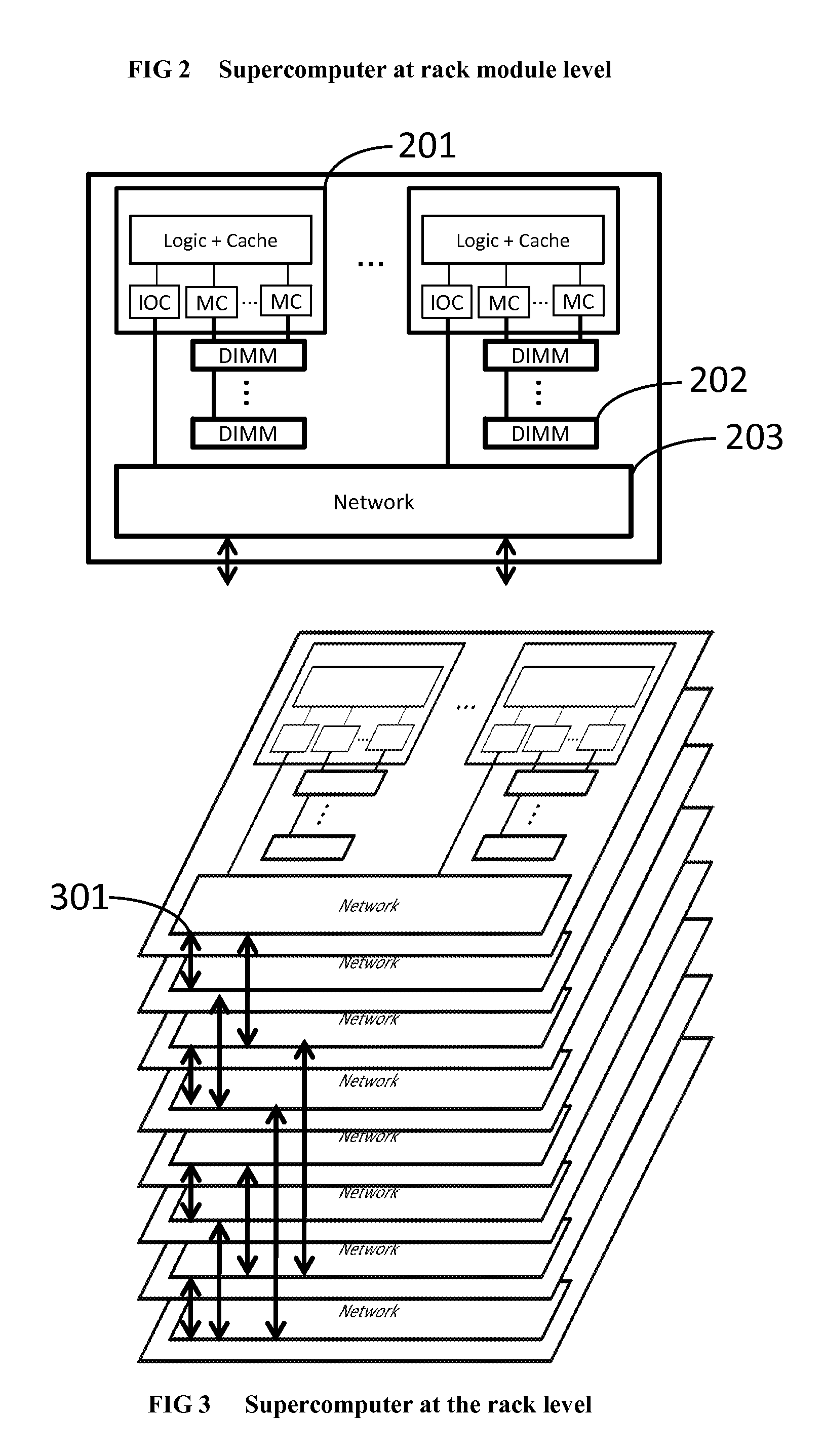
The invention comprises (i) a compilation method for automatically converting a single-threaded software program into an application-specific supercomputer, and (ii) the supercomputer system structure generated as a result of applying this method. The compilation method comprises: (a) Converting an arbitrary code fragment from the application into customized hardware whose execution is functionally equivalent to the software execution of the code fragment; and (b) Generating interfaces on the hardware and software parts of the application, which (i) Perform a software-to-hardware program state transfer at the entries of the code fragment; (ii) Perform a hardware-to-software program state transfer at the exits of the code fragment; and (iii) Maintain memory coherence between the software and hardware memories. If the resulting hardware design is large, it is divided into partitions such that each partition can fit into a single chip. Then, a single union chip is created which can realize any of the partitions.
Owner:GLOBAL SUPERCOMPUTING CORP
Reconfigurable processing
ActiveUS8281297B2Reduce the amount requiredQuick switchEnergy efficient ICTSoftware engineeringControl flowProcessing element
A method of producing a reconfigurable circuit device for running a computer program of moderate complexity such as multimedia processing. Code for the application is compiled into Control Flow Graphs representing distinct parts of the application to be run. From those Control Flow Graphs are extracted basic blocks. The basic blocks are converted to Data Flow Graphs by a compiler utility. From two or more Data Flow Graphs, a largest common subgraph is determined. The largest common subgraph is ASAP scheduled and substituted back into the Data Flow Graphs which also have been scheduled. The separate Data Flow Graphs containing the scheduled largest common subgraph are converted to data paths that are then combined to form code for operating the application. The largest common subgraph is effected in hardware that is shared among the parts of the application from which the Data Flow Graphs were developed. Scheduling of the overall code is effected for sequencing, providing fastest run times and the code is implemented in hardware by partitioning and placement of processing elements on a chip and design of the connective fabric for the design elements.
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
Method for processing data
ActiveUS7657877B2Simple programmabilityEasy and efficient connectionDetecting faulty computer hardwareRead-only memoriesParallel computingProgram transformation
A method and device for translating a program to a system including at least one first processor and a reconfigurable unit. Code portions of the program which are suitable for the reconfigurable unit are determined. The remaining code of the program is extracted and / or separated for processing by the first processor.
Owner:SCIENTIA SOL MENTIS AG
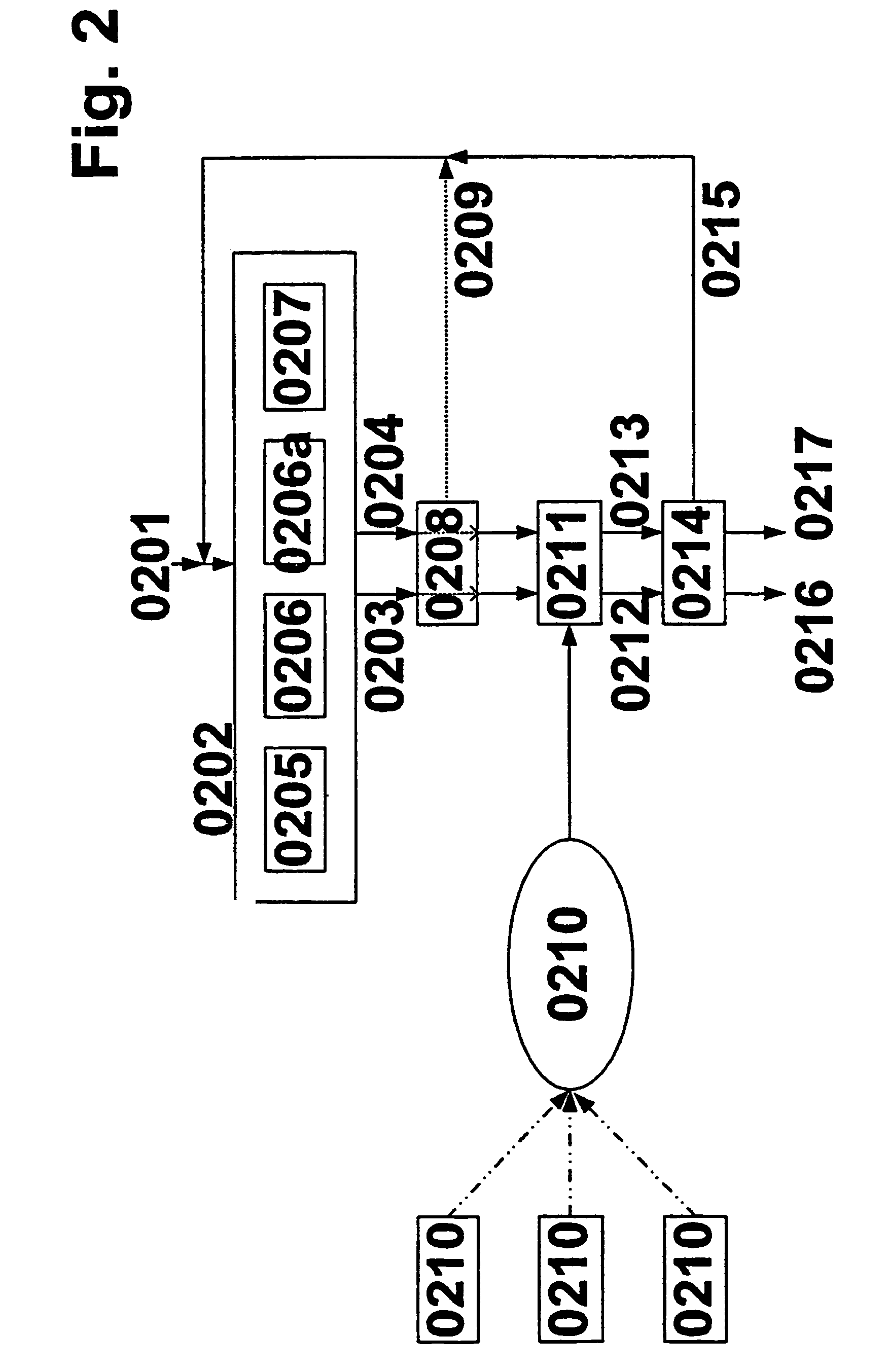
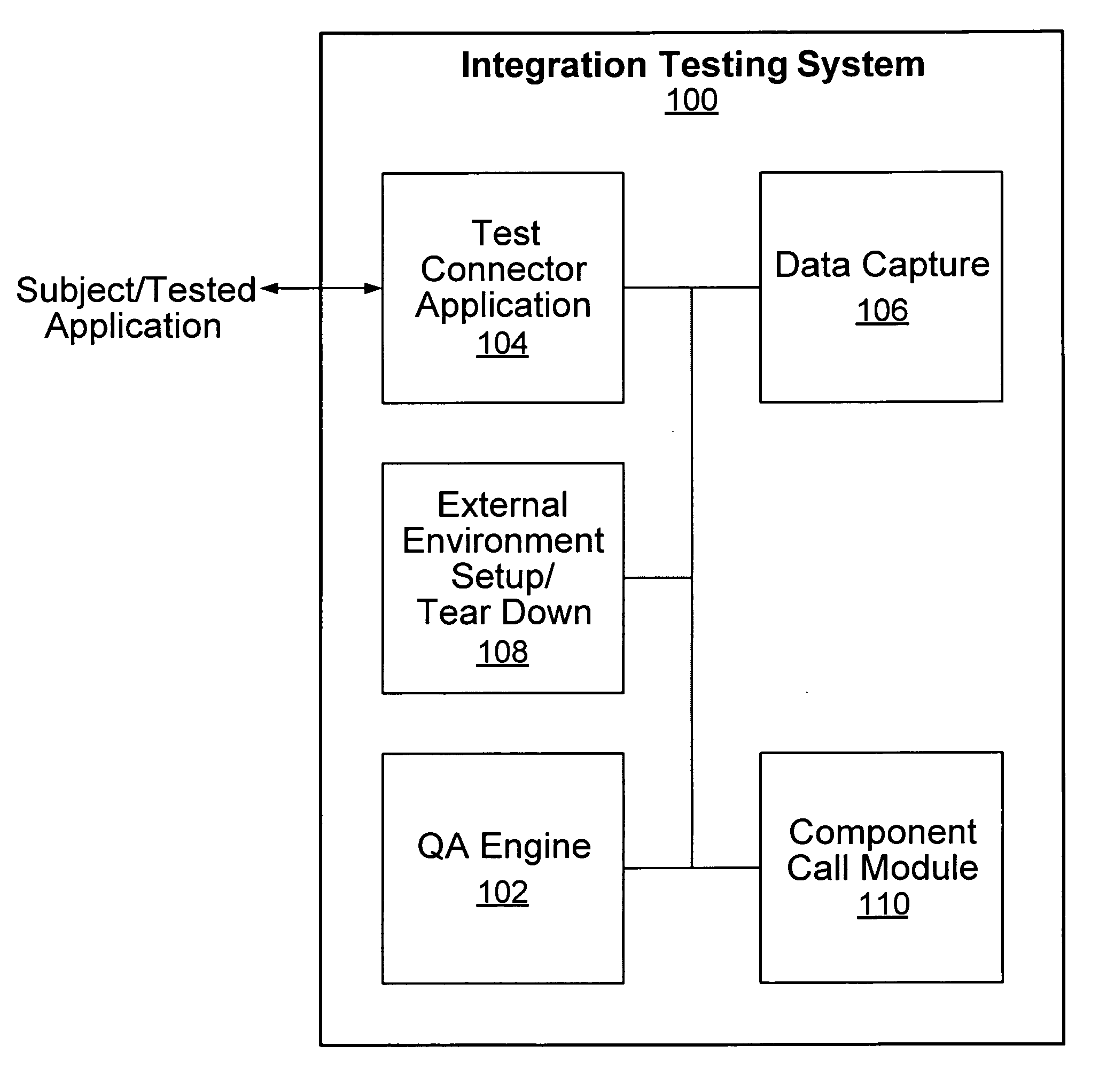
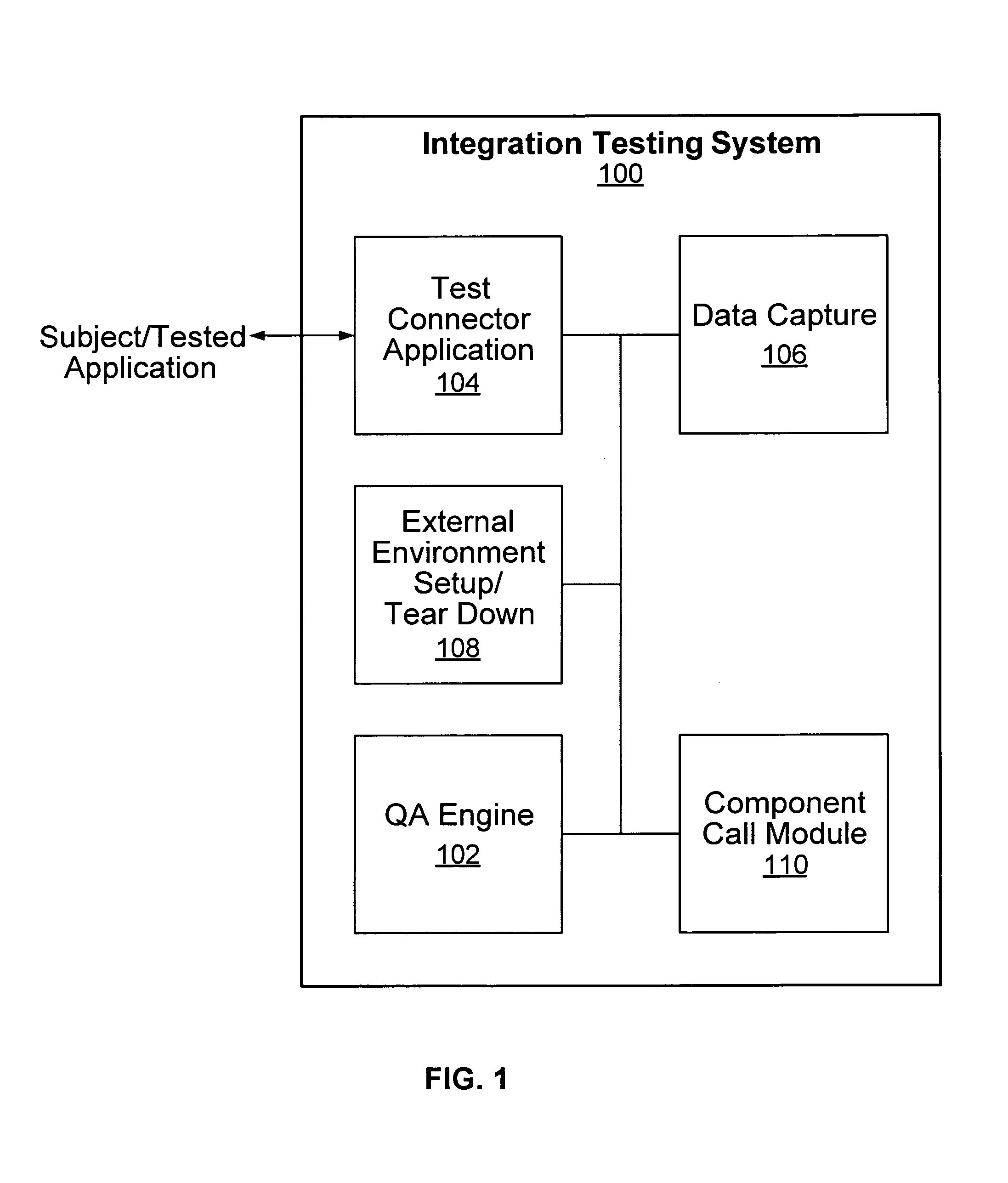
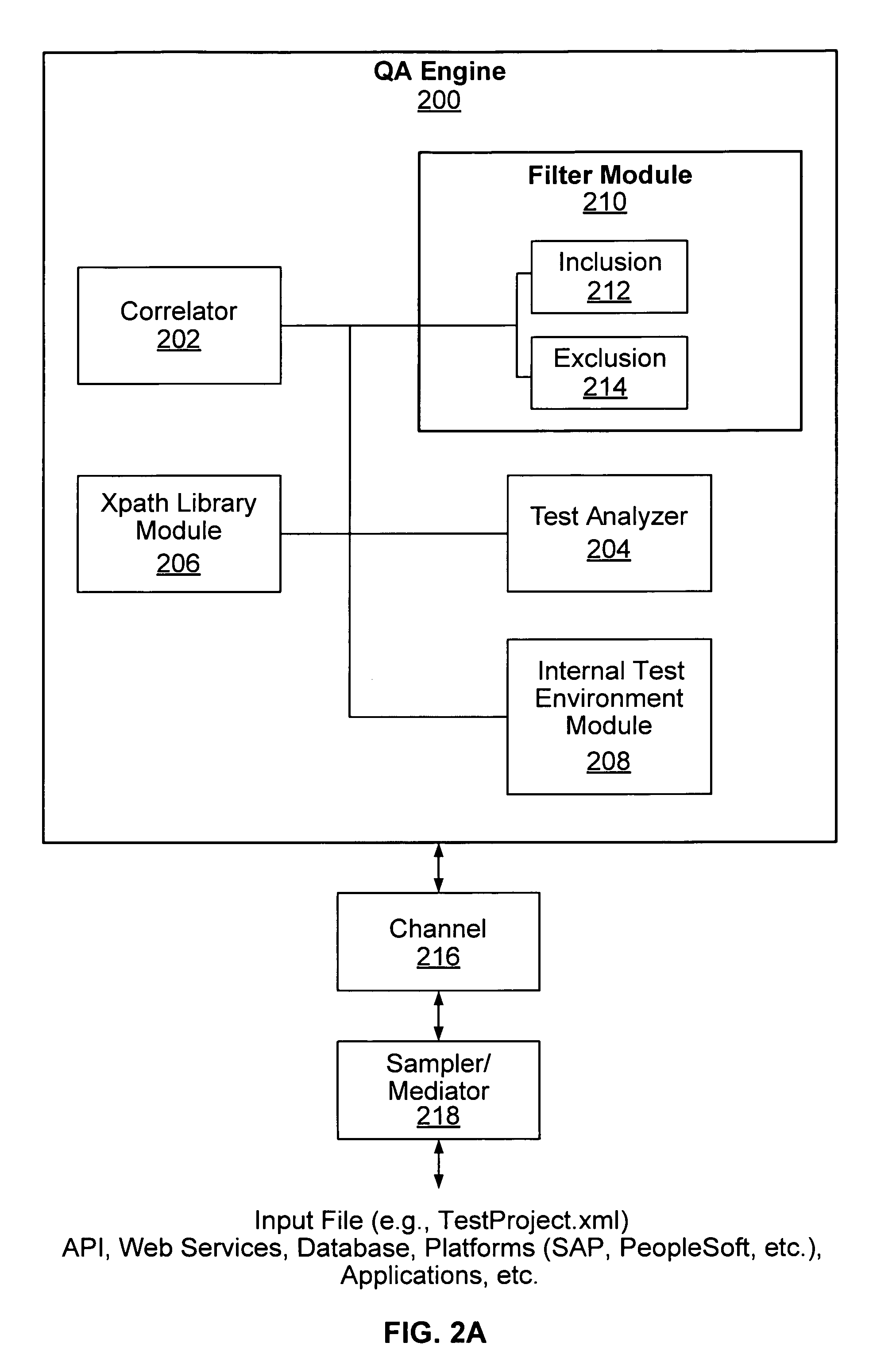
Application integration testing
Application testing is disclosed. A definition of a test to be performed on a subject application is received in a generic form not specific to the subject application. The test is performed by exchanging data with the subject application, as required to perform the test, using a test connector application associated with the subject application to do at least one of (1) convert an input data to be supplied to the subject application during the test from a generic data format not specific to the subject application into an application-specific data format associated with the subject application, if the application-specific data format is different than the generic data format and (2) normalize an output data received from the subject application in the application-specific data format into the generic data format not specific to the subject application, if the application-specific data format is different than the generic data format.
Owner:MATADOR TECH CORP
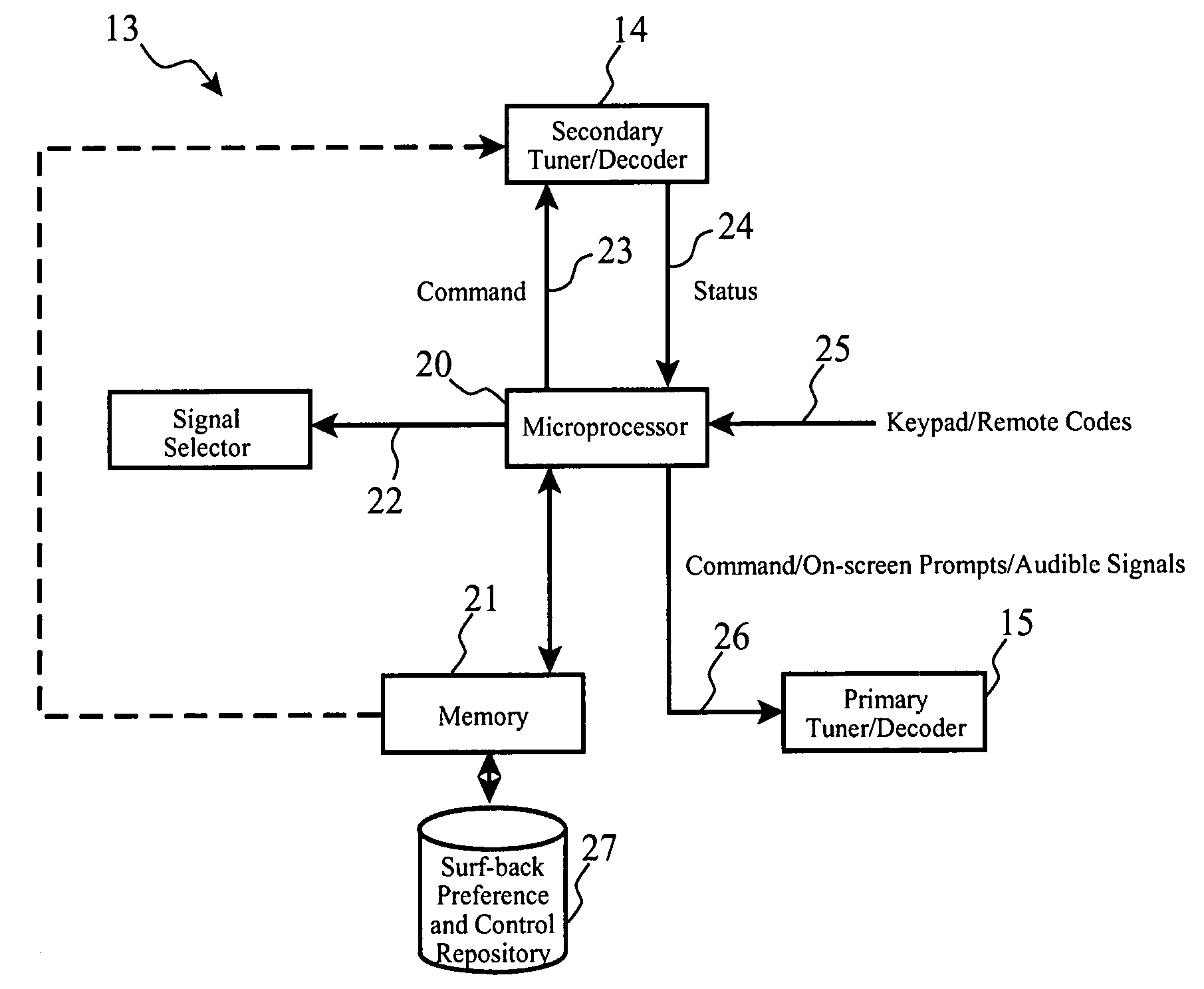
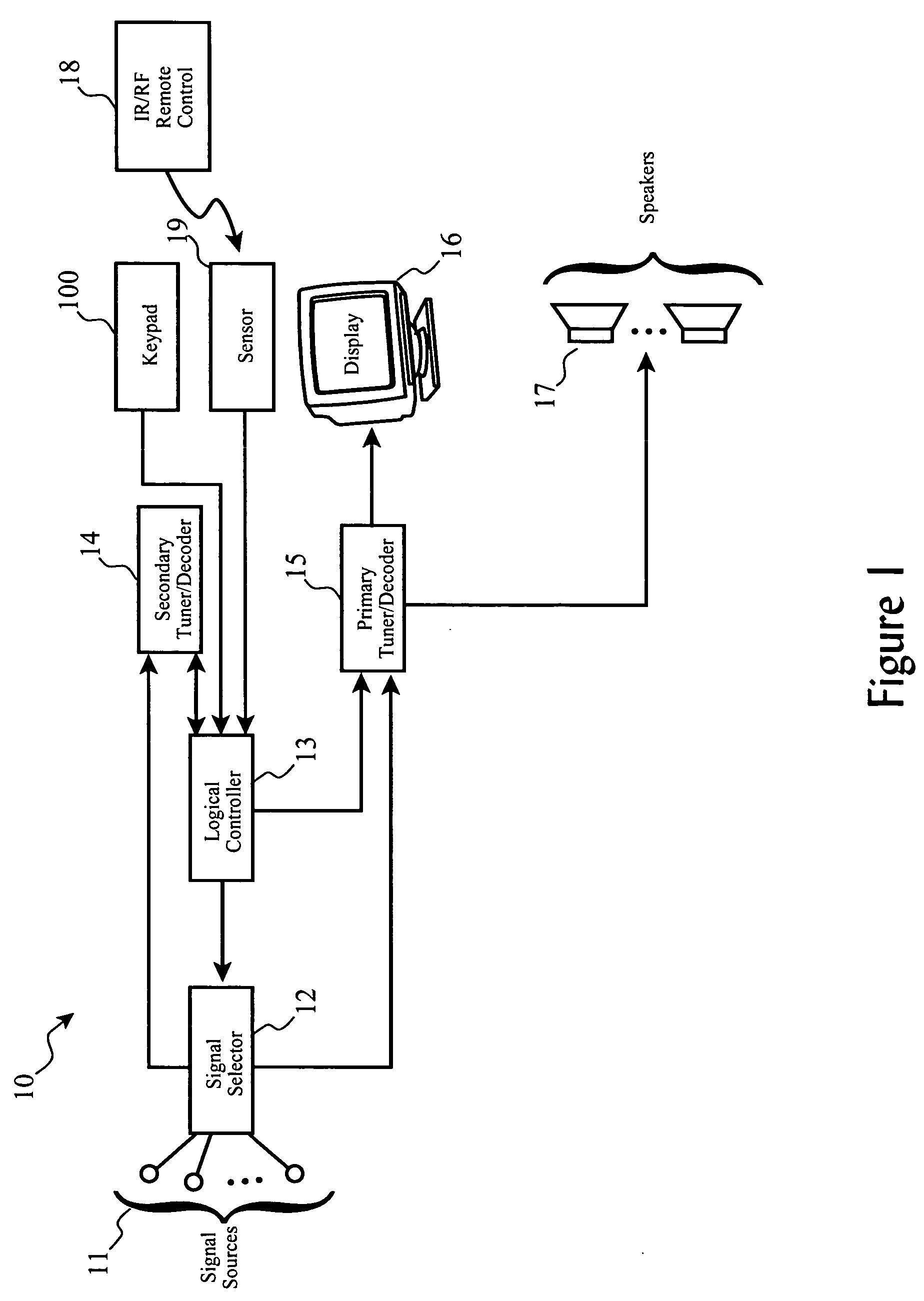
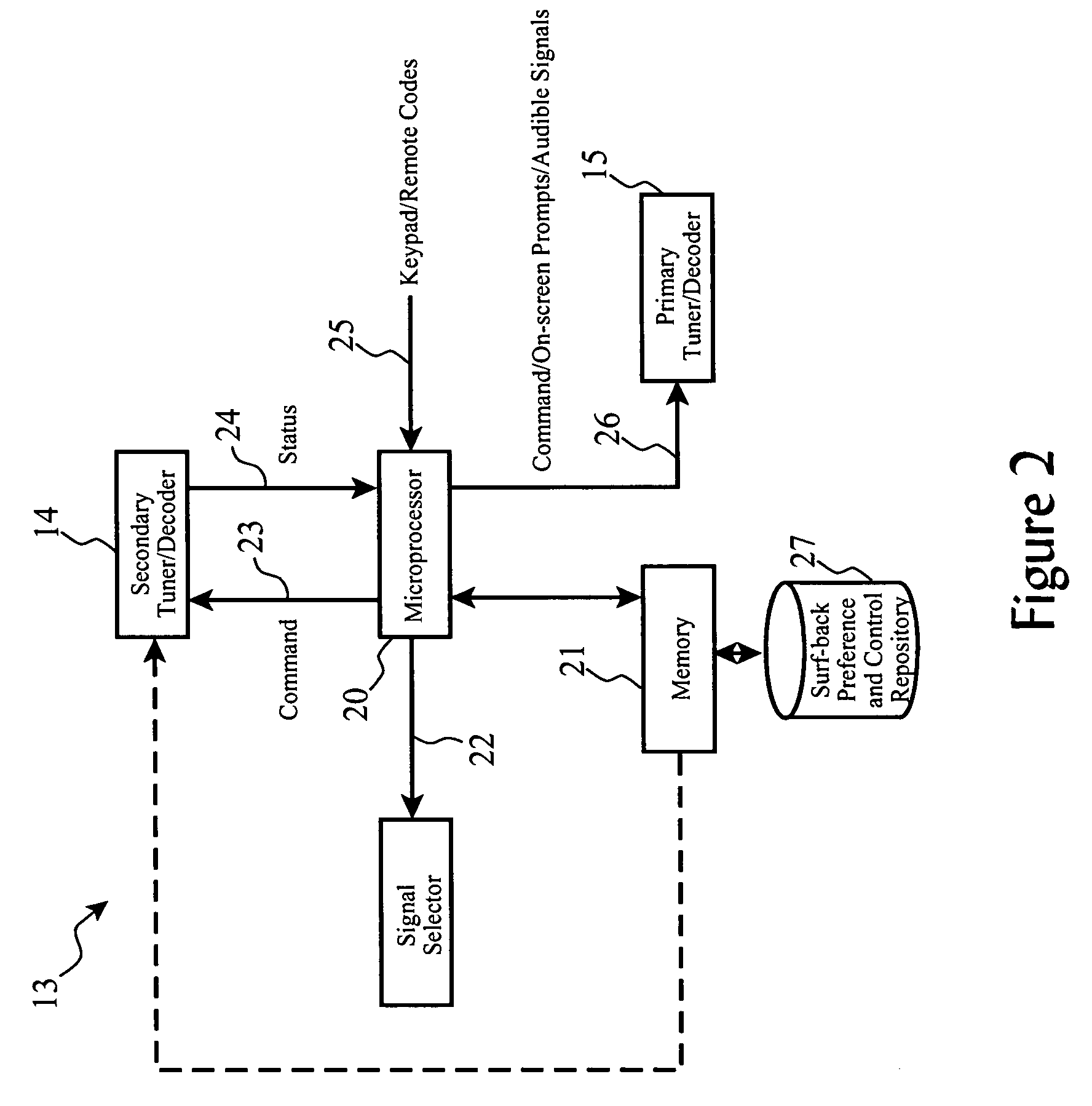
Sub-program avoidance redirection for broadcast receivers
ActiveUS20060238656A1Substantial abilityTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsBroadcastingProgram transformation
A system for automatically tuning a primary broadcast receiver using a secondary broadcast receiver to receive a first broadcast signal corresponding to a source of an origin program, one or more program transition detectors to monitor first broadcast signal tuned by the secondary broadcast receiver to determine and signal a transition from a non-original program content to origin program content while a user views or hears alternate programming from a primary broadcast receiver, and automatically tuning of the primary broadcast receiver to the first broadcast signal upon detection by the program transition detector that one or more of user-specific tune conditions have been met.
Owner:TERRACE LICENSING LLC
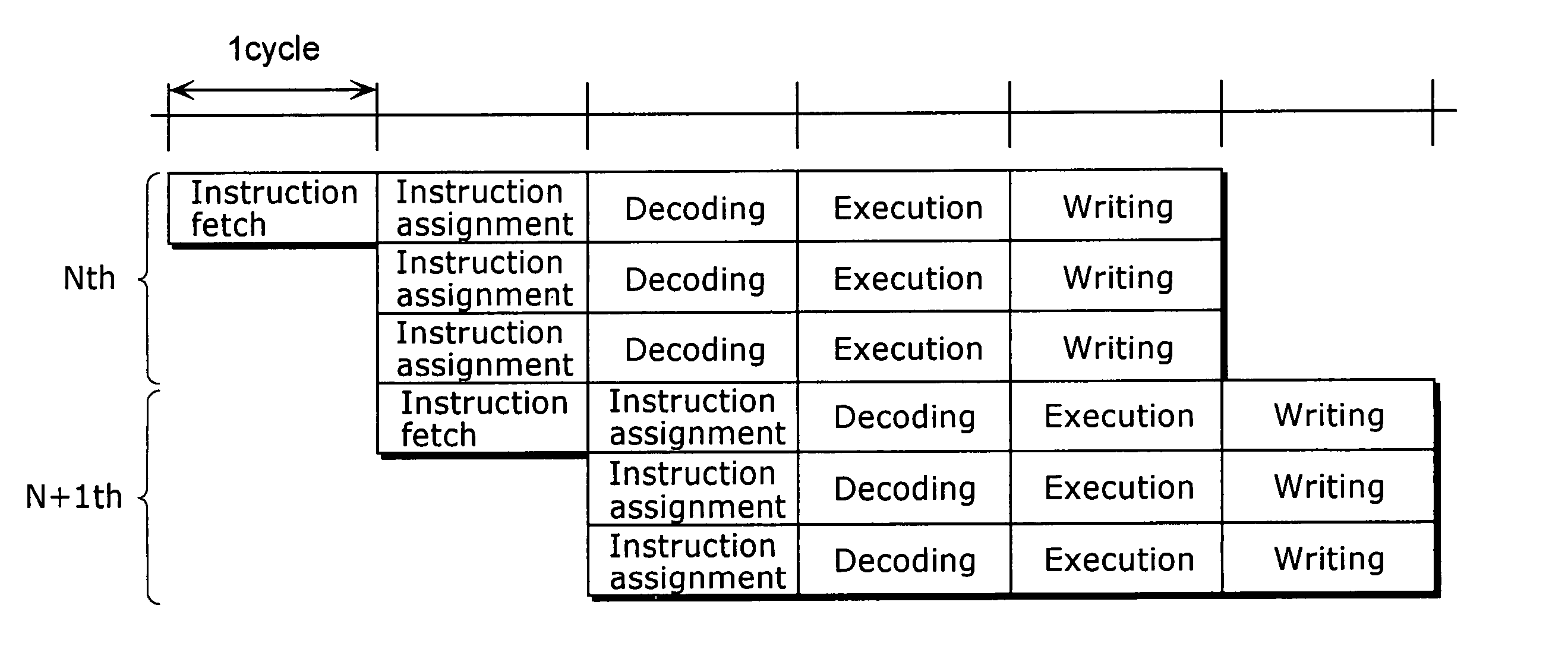
Compiler apparatus and compilation method
InactiveUS20040154006A1Avoid changeReduce power consumptionEnergy efficient ICTSoftware engineeringMachine instructionInstruction cycle
A compiler apparatus that is capable of generating instruction sequences for causing a processor with parallel processing capability to operate with lower power consumption is a compiler apparatus that translates a source program into a machine language program for the processor including a plurality of execution units which can execute instructions in parallel and a plurality of instruction issue units which issue the instructions executed respectively by the plurality of execution units, and includes: a parser unit operable to parse the source program; an intermediate code conversion unit operable to convert the parsed source program into intermediate codes; an optimization unit operable to optimize the intermediate codes so as to reduce a hamming distance between instructions placed in positions corresponding to the same instruction issue unit in consecutive instruction cycles, without changing dependency between the instructions corresponding to the intermediate codes; and a code generation unit operable to convert the optimized intermediate codes into machine language instructions.
Owner:SOCIONEXT INC
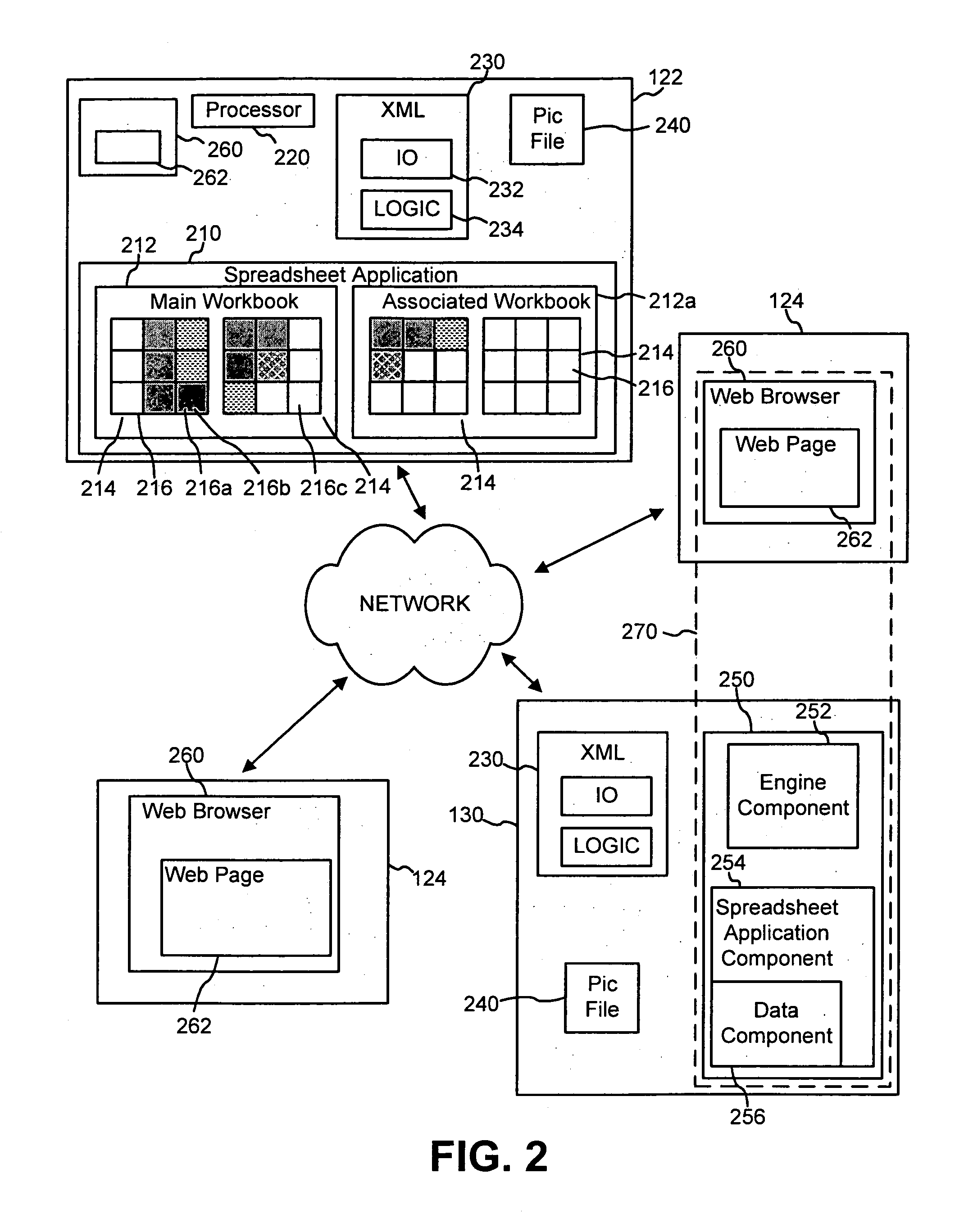
Converting spreadsheet applications to web-based applications
A networked version of a spreadsheet application can be automatically created from an existing “conventional” spreadsheet. In one implementation, a server may obtain a data file, where the data file represents a networked version of a spreadsheet application that was converted from the “conventional” application and the data file defines characteristics of the networked version of the spreadsheet application including logic and interactivity attributes of cells in the networked version of the spreadsheet application. A remote request may be received from a client to access the networked version of the spreadsheet application. In response, the server may transmit a document to the client that represents a portion of the networked version of the spreadsheet application that the interactivity attributes specify as being displayable to the client.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
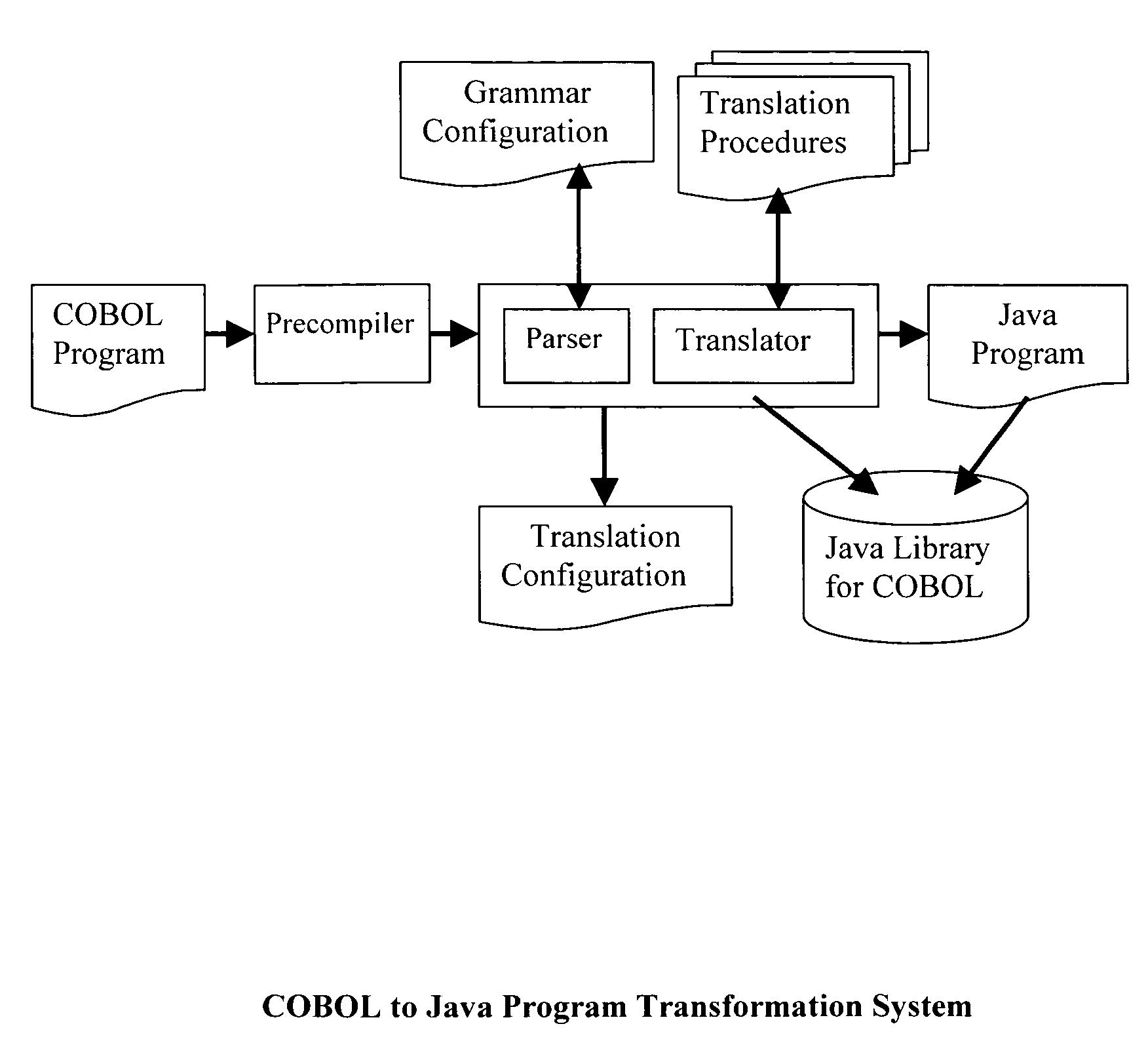
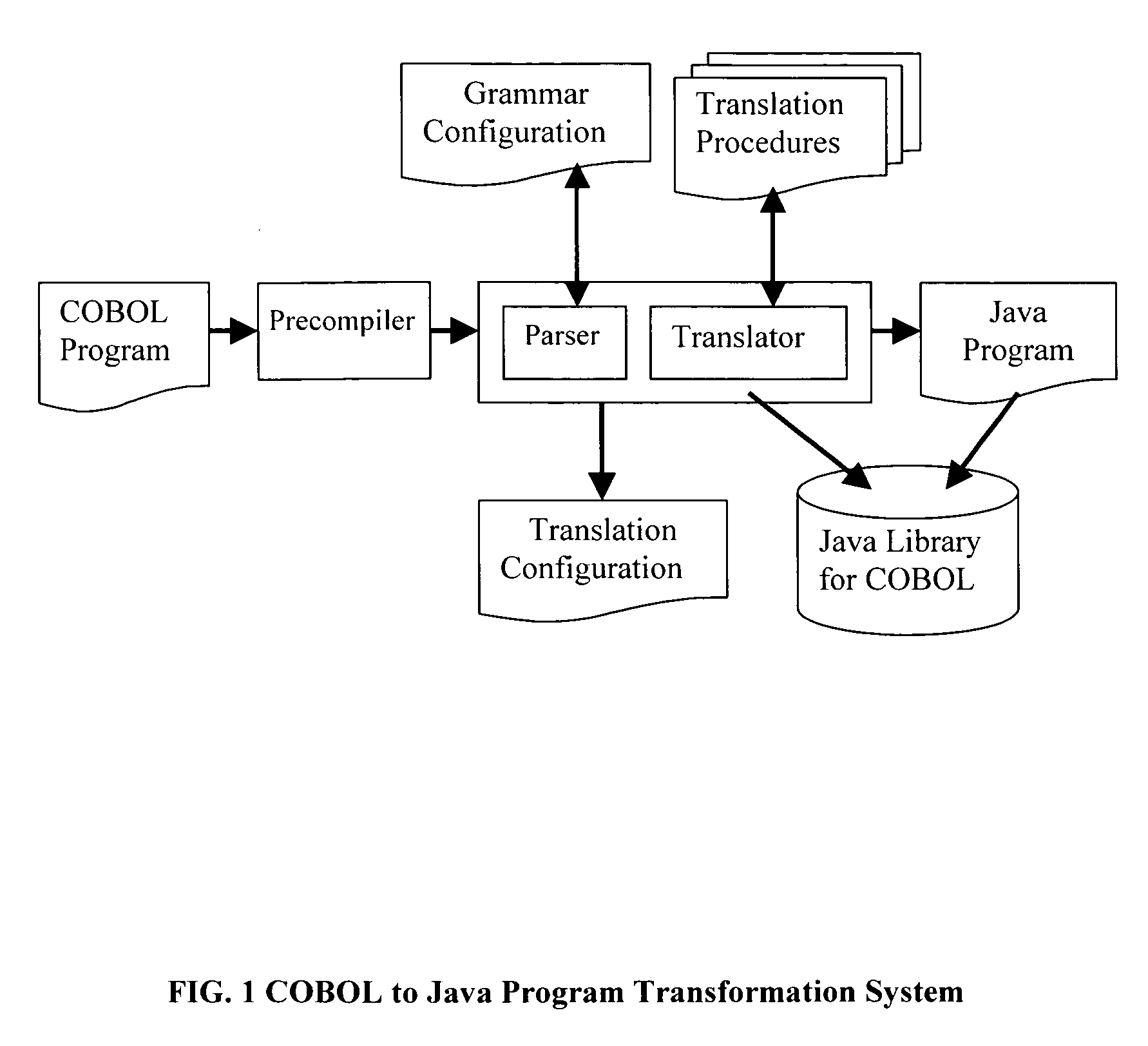
Method for program transformation and apparatus for COBOL to Java program transformation
InactiveUS20060031820A1Maintain maintainabilityImprove maintainabilityProgram controlMemory systemsTime complexityGoto
The present invention relates to a method for program transformation and an apparatus for COBOL to Java program transformation. The method consists of: (1) a new approach for statement-to-statement program transformation, facilitated by a predefined target language library, which keeps original comments, program control flow, functionality, and time complexity; (2) a new approach for goto statement elimination, which uses existing exception handling mechanism in target language and its implementation is hidden in a super class in a library; (3) a new extended BNF to distinguish different occurrences of the same term in a BNF production; (4) a new approach for embedded statement as a special marker statement and a comment, (5) in the description of the above, a program transformation specification language is defined to describe relationship between comments in two languages. (6) an apparatus, as the preferred embodiment of the method, is a COBOL to Java program transformation system Cobol2Java; a sample COBOL application and its Cobol2Java translation are given.
Owner:LI AIZHONG
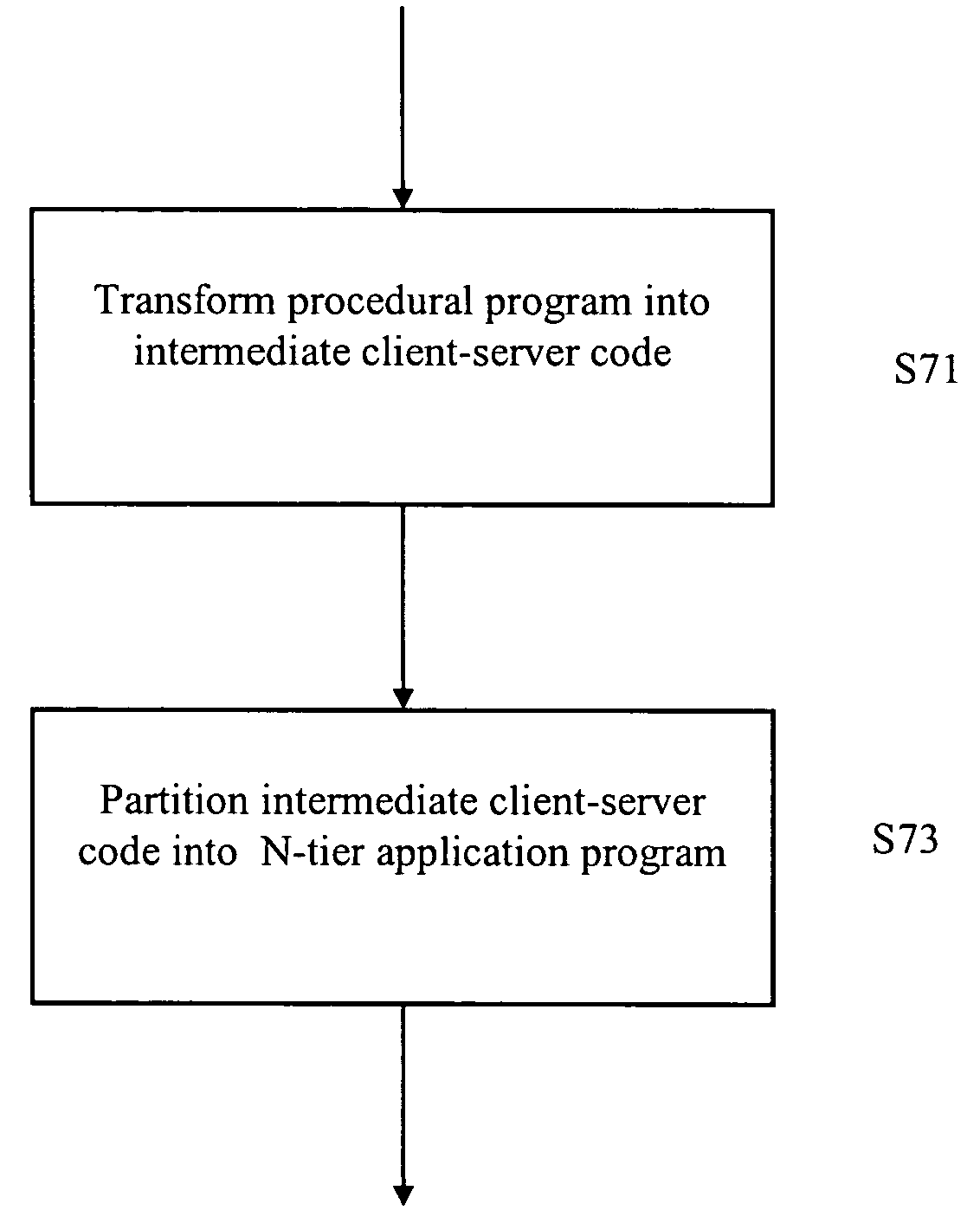
Method and apparatus for transforming legacy software applications into modern object-oriented distributed systems
A method for transforming a procedural program having procedural language code into an object-oriented distributed software program is provided. A procedural program is transformed into intermediate client-server code. The intermediate client-server code is partitioned into an N-tier application program.
Owner:CA TECH INC
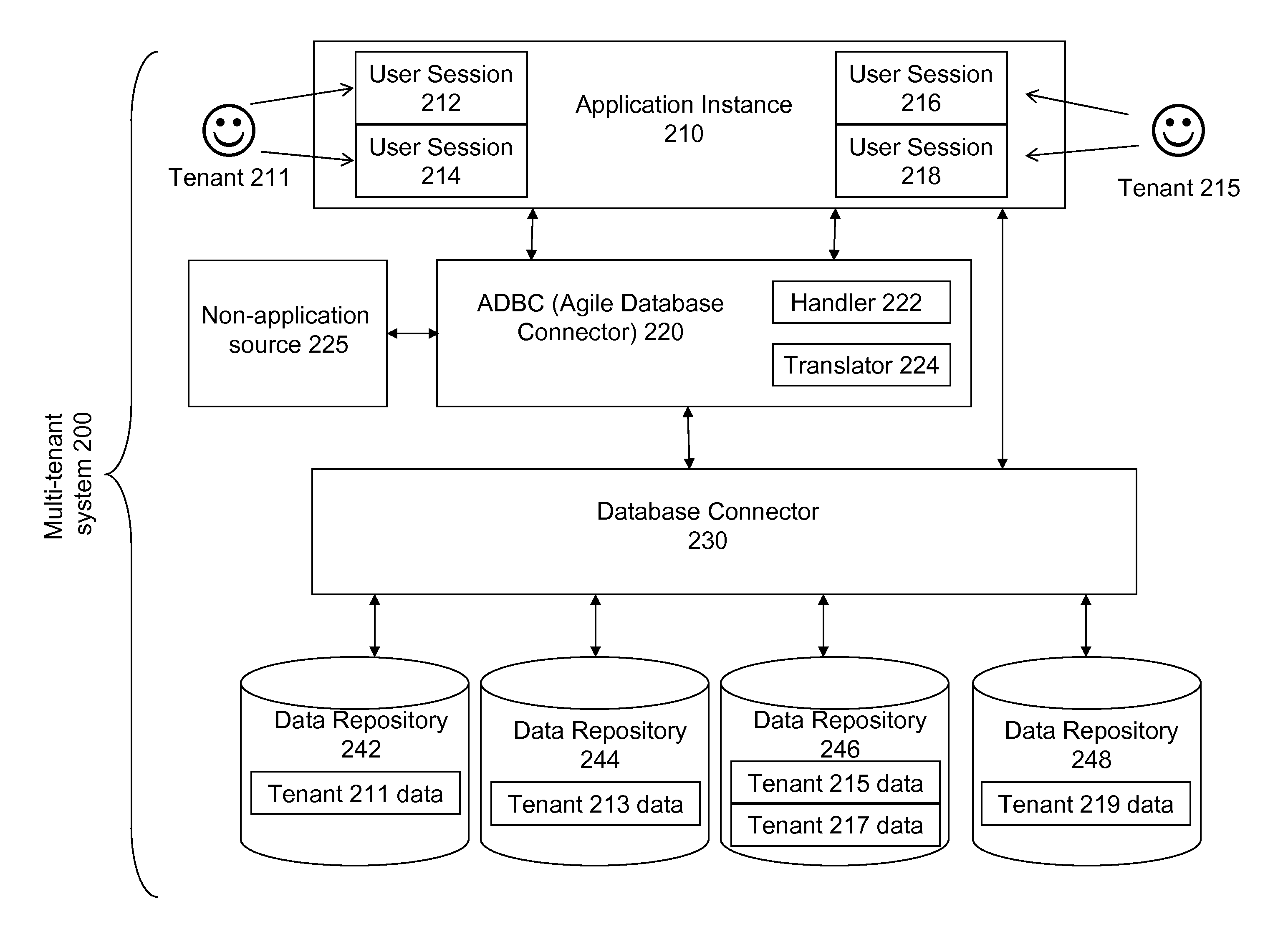
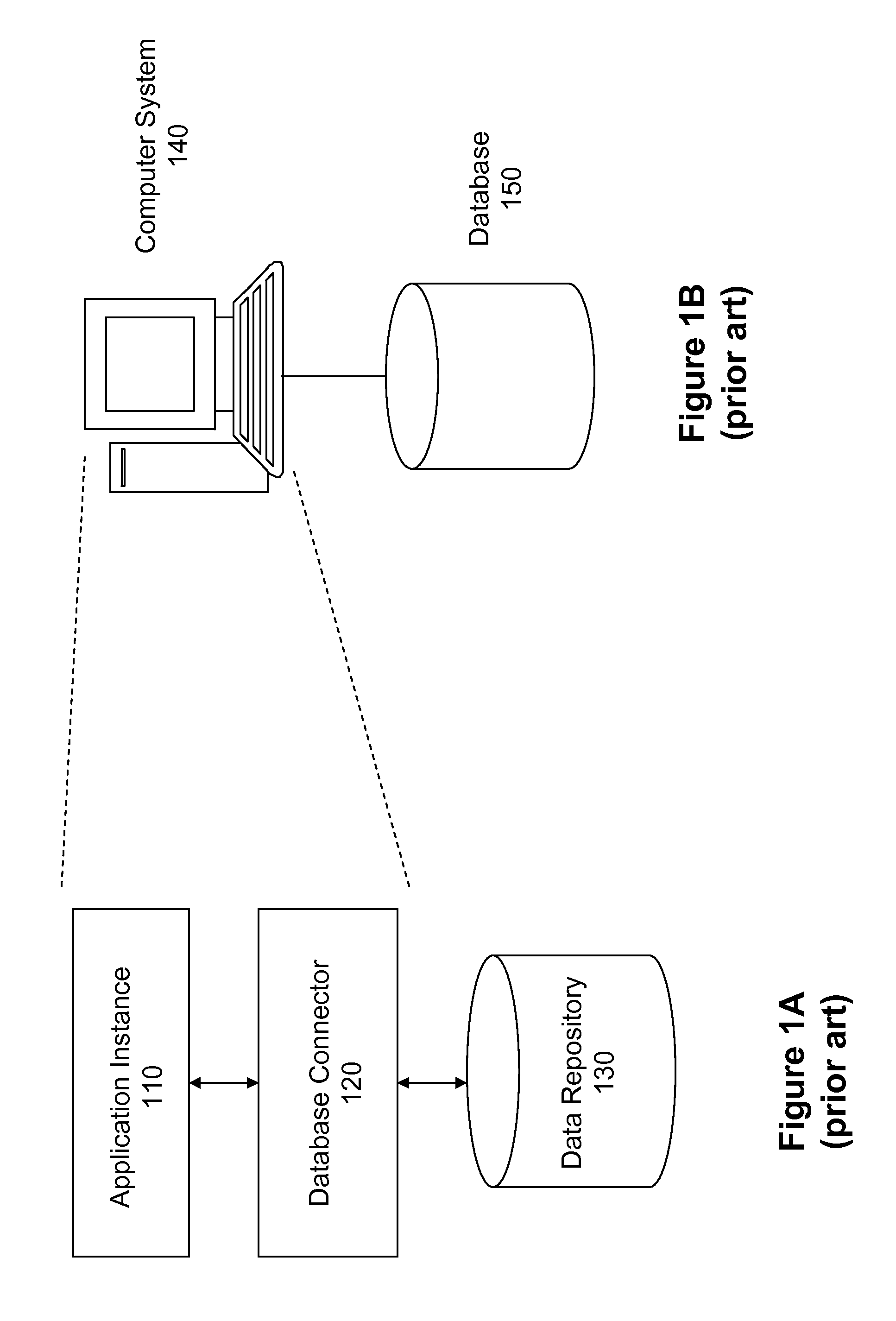
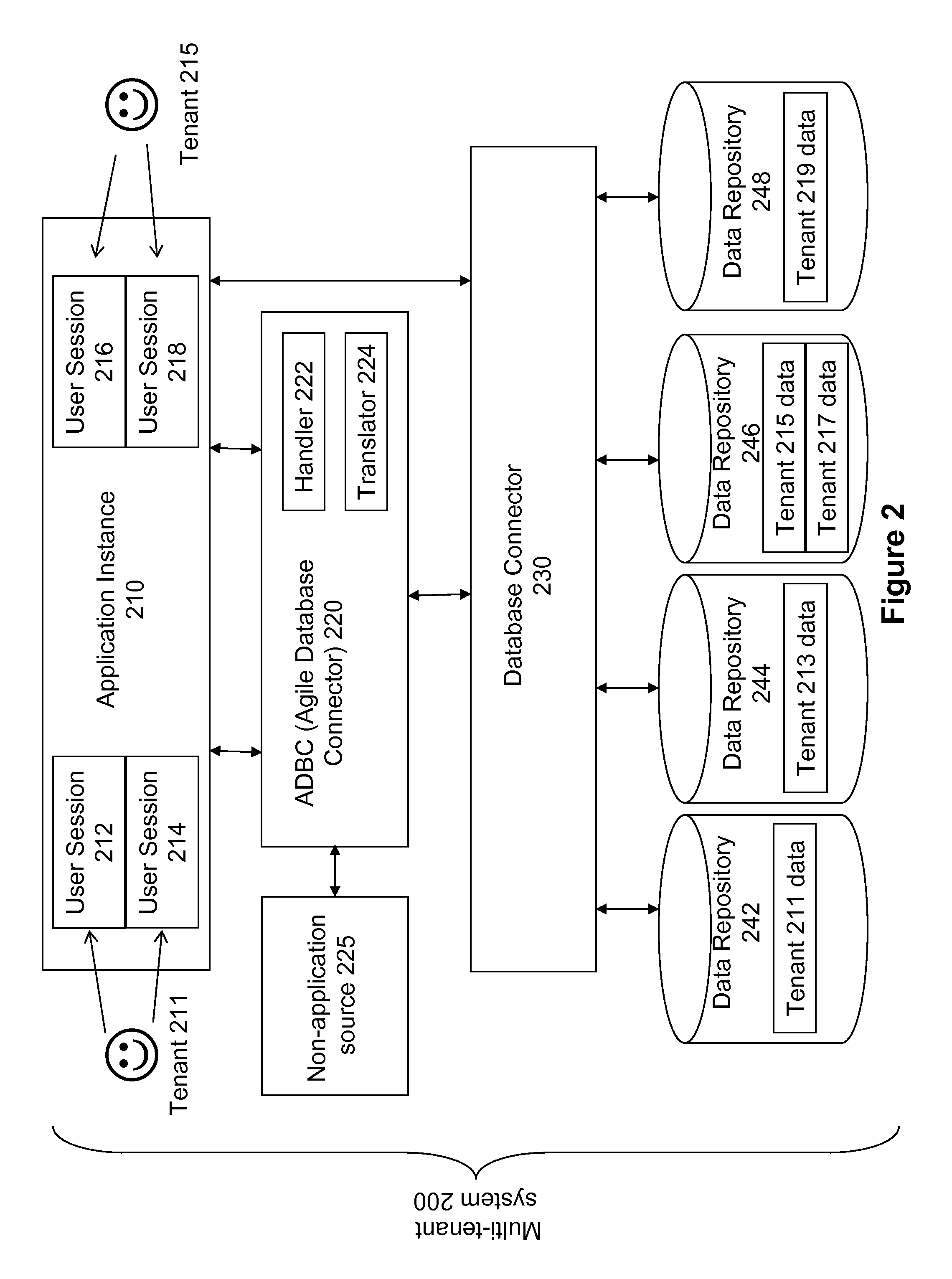
Multi-tenant agile database connector
ActiveUS8326876B1Reduce loadImprove performanceDigital data processing detailsFile access structuresData accessApplication software
A module provides an interface between a multi-tenant database and a non-tenant-specific application instance such that the application instance sends data access commands to the module as if it is communicating with a single-tenant database. The module translates the non-tenant-specific data access command from the non-tenant-aware application into a multi-tenant data access command, as needed, without needing to alter the non-tenant specific application instance in any way. In this manner, a single-tenant application could be used by multiple tenants in a multi-tenant environment.
Owner:CORENT TECH
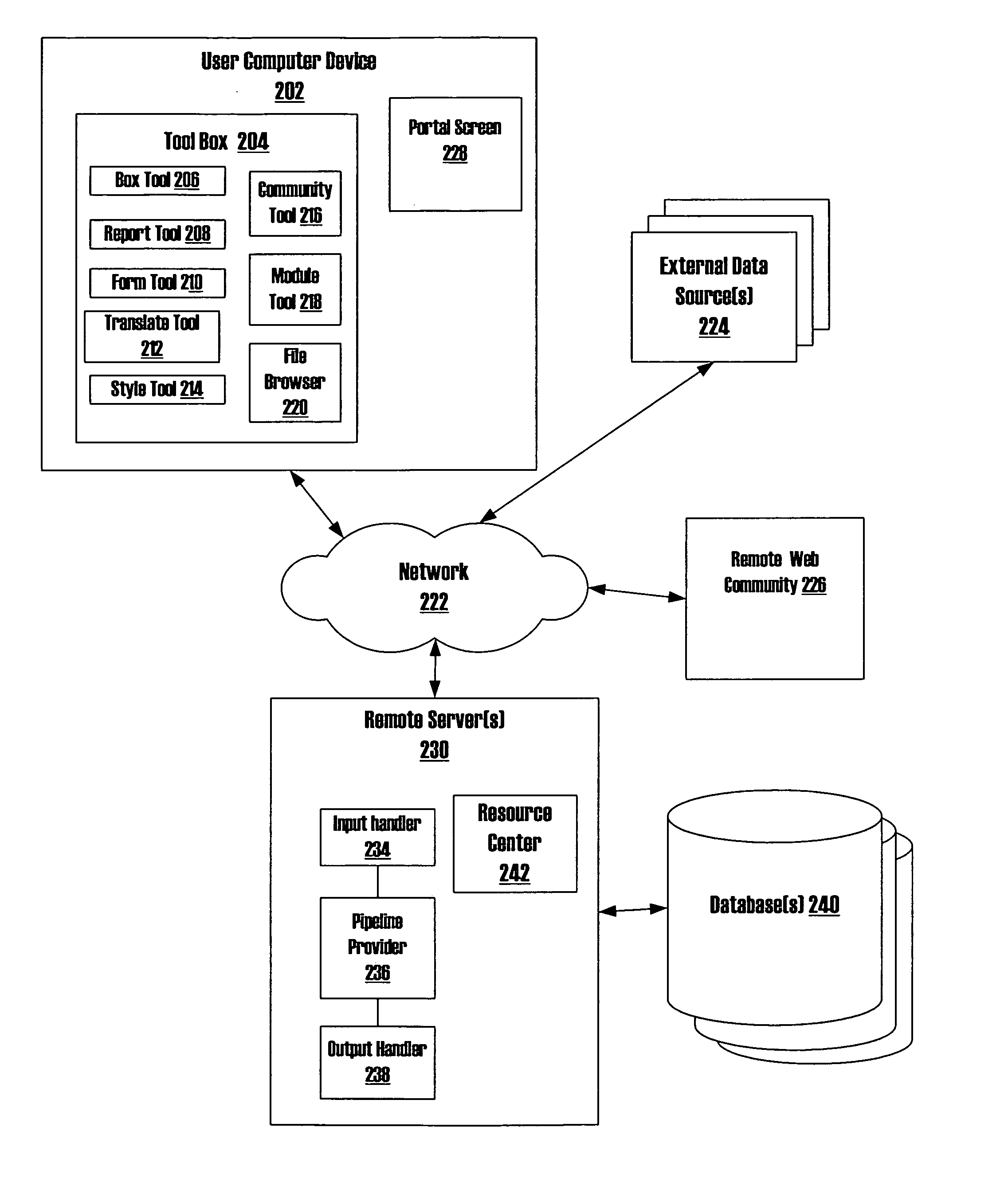
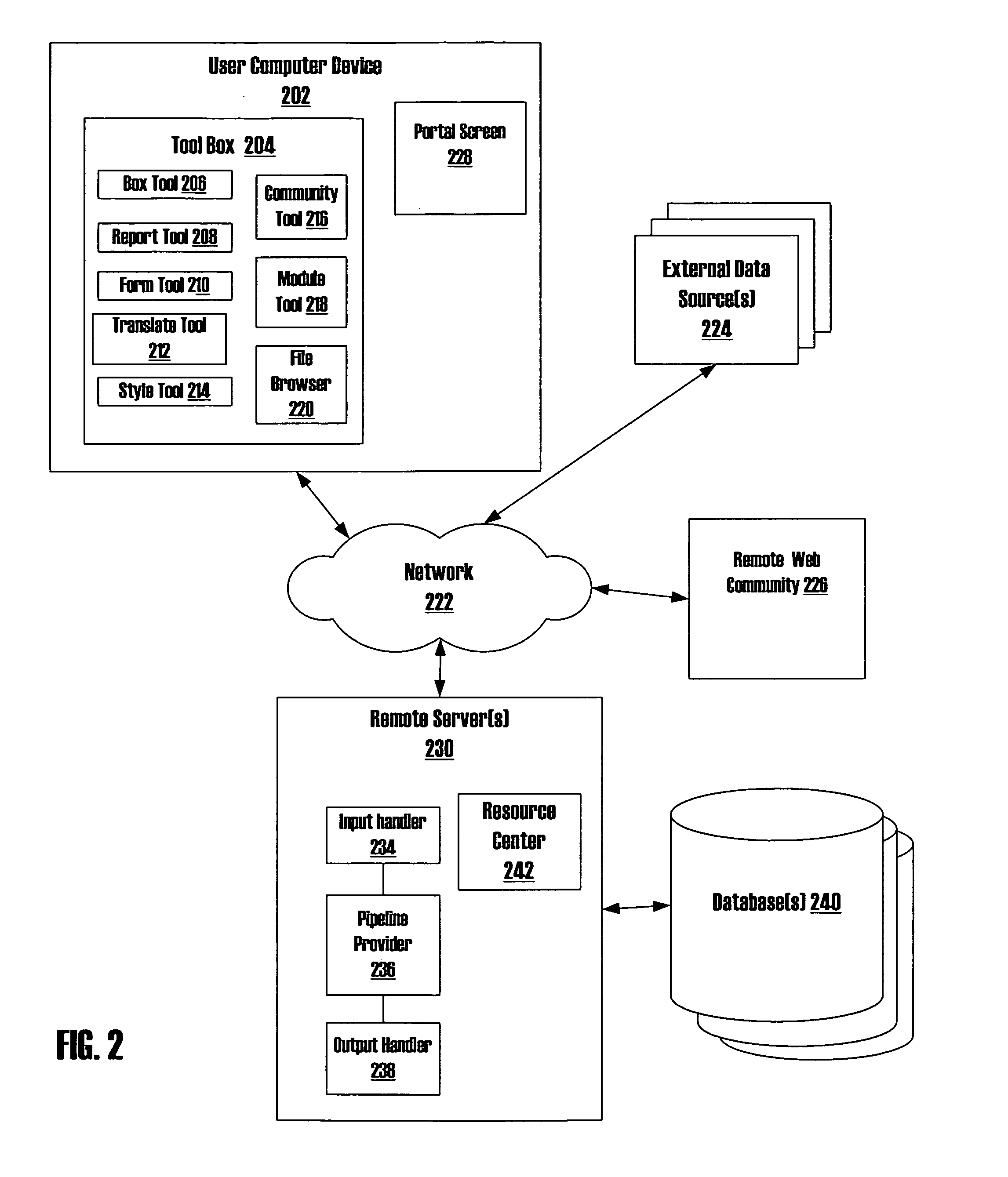
Systems and methods of transforming data for web communities and web applications
InactiveUS20070239726A1Multiple digital computer combinationsOffice automationWeb applicationData source
Systems and methods for modifying the content of portal screens associated with a web community that include one or more web communities accessible by at least one server through a network, where each web community is associated with one or more portal screens and each portal screen is associated with particular report data. Moreover, a user computer device, capable of accessing and rendering one or more portal screens, is connected to the server(s) through the network, where the server(s) may access report data. The user computer device provides access to a user interface associated with the portal screens that may provide access to a file browser for querying a remote data source through the network to locate and retrieve the report data to be associated with one or more portal screens. Additionally, several tools for altering the retrieved report data may be accessible through the user interface.
Owner:CAMPUS CRUSADE FOR CHRIST
Branch instruction conversion to multi-threaded parallel instructions
InactiveUS7010787B2Process is performedImprove performanceProgram initiation/switchingProgram synchronisationRegister allocationProcessor register
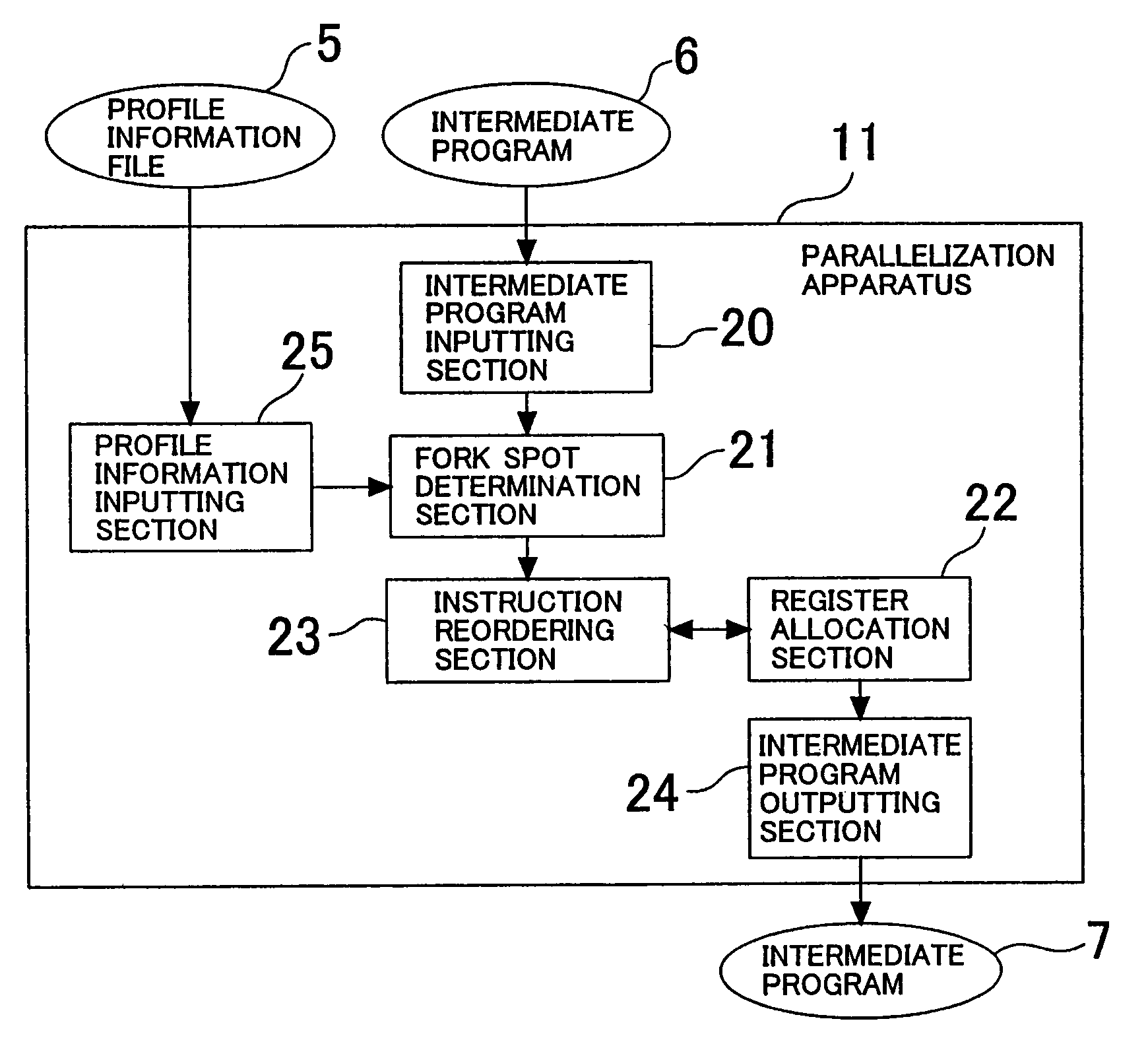
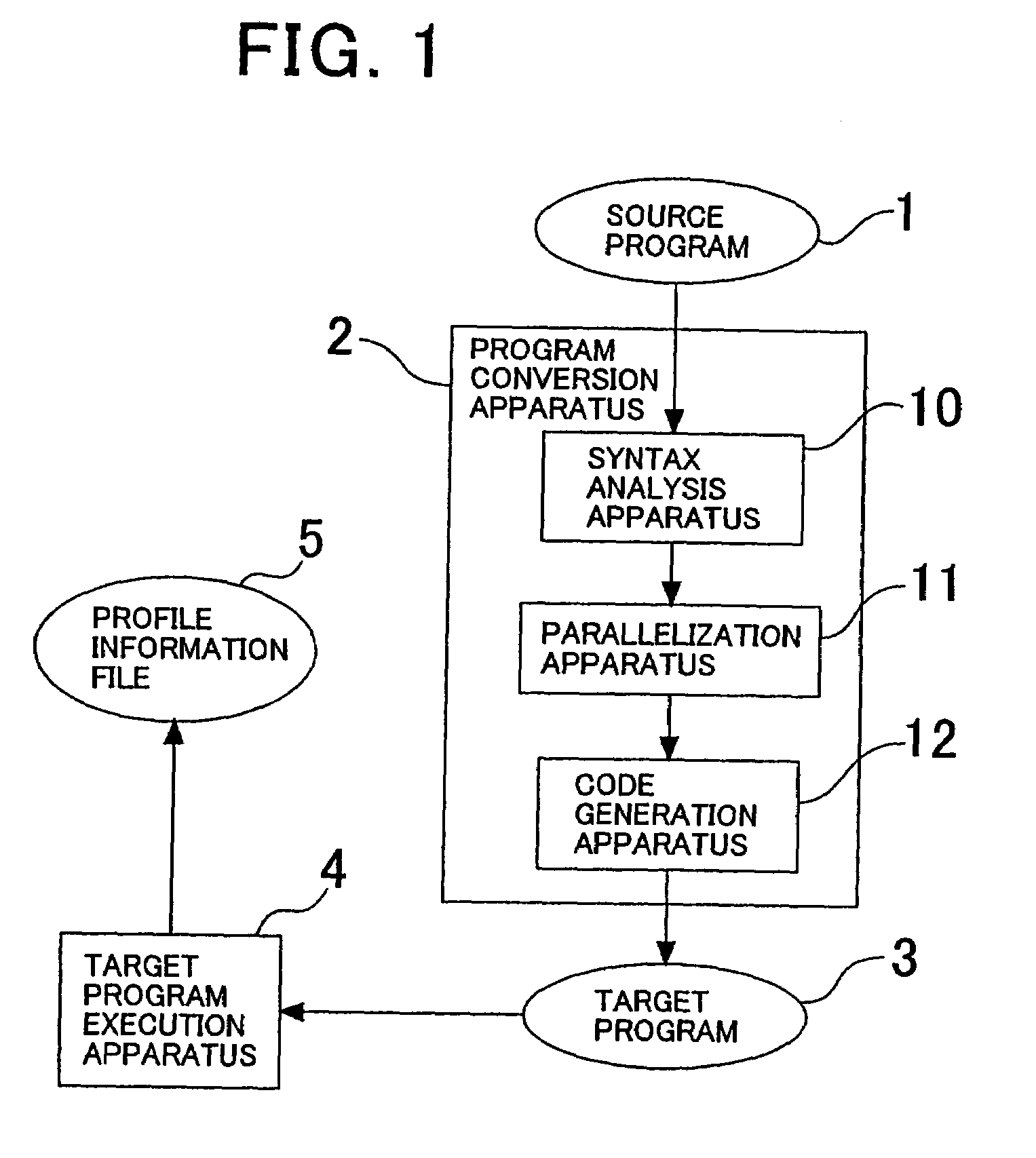
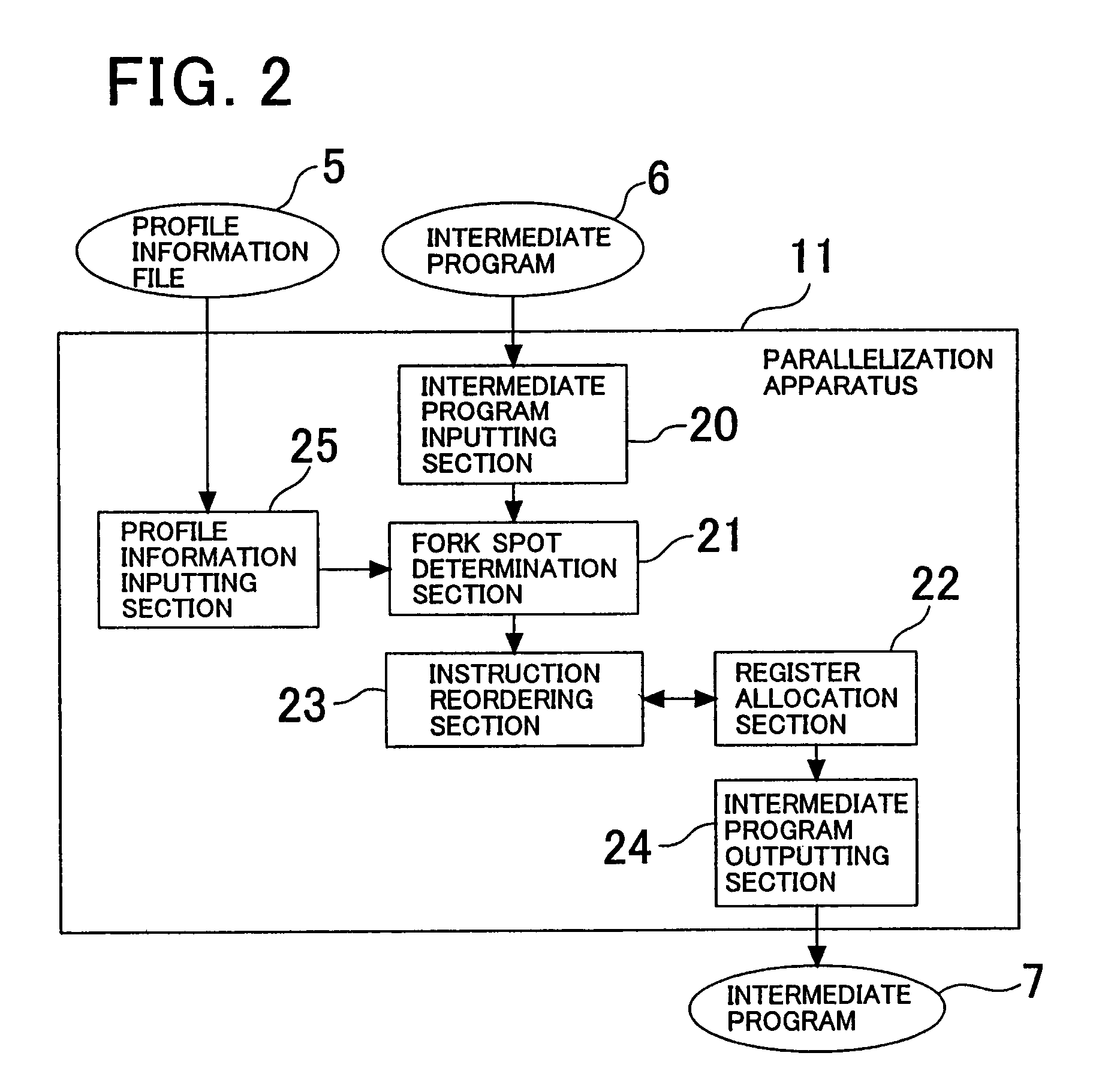
The invention provides a program conversion apparatus which performs parallelization for a multi-thread microprocessor on an intermediate program level. A parallelization apparatus of the program conversion apparatus includes a fork spot determination section, a register allocation section and an instruction reordering section. The fork spot determination section determines a fork spot and a fork system based on a result of a register allocation trial performed by the register allocation section, the number of spots at which memory data dependence is present, and branching probabilities and a data dependence occurrence frequency obtained from a profile information file. The instruction reordering section reorders instructions preceding to and succeeding the FORK instruction in accordance with the determination.
Owner:NEC CORP
Technique for dynamically restricting thread concurrency without rewriting thread code
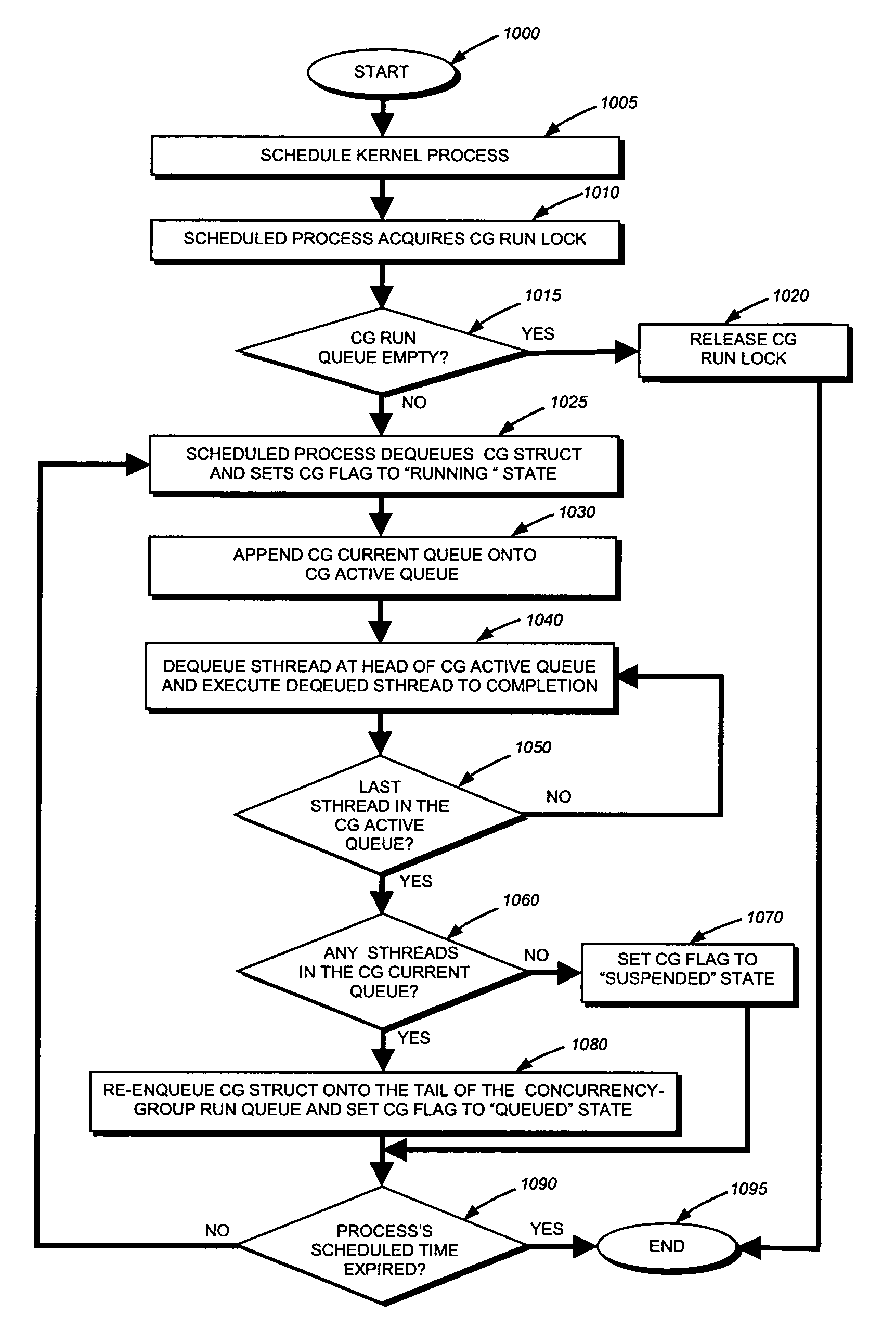
ActiveUS7373640B1Reduce decreaseEasy to scaleSoftware engineeringDigital computer detailsMulti processorParallel computing
The present invention provides a technique for converting a multi-threaded application configured to execute on a uniprocessor (UP) system to one that executes on a multiprocessor (MP) system. Unlike previous approaches, a novel scheduling technique is employed so that different UP-coded user-level threads (“sthreads”) can execute concurrently in the MP system without having to rewrite their original code. To that end, the UP-coded sthreads are organized into different concurrency groups, each of which defines a set of one or more sthreads not permitted to execute concurrently. By grouping the UP-coded sthreads in this manner, different concurrency groups can be scheduled to execute their UP-coded sthreads at substantially the same time without incorporating traditional synchronization mechanisms into the sthreads' original UP code.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
Apparatus and method for an automatic thread-partition compiler
InactiveUS20050108695A1Program initiation/switchingSoftware engineeringParallel computingTerm memory
In some embodiments, a method and apparatus for an automatic thread-partition compiler are described. In one embodiment, the method includes the transformation of a sequential application program into a plurality of application program threads. Once partitioned, the plurality of application program threads are concurrently executed as respective threads of a multi-threaded architecture. Hence, a performance improvement of the parallel multi-threaded architecture is achieved by hiding memory access latency through or by overlapping memory access with computations or with other memory accesses. Other embodiments are described and claimed.
Owner:INTEL CORP
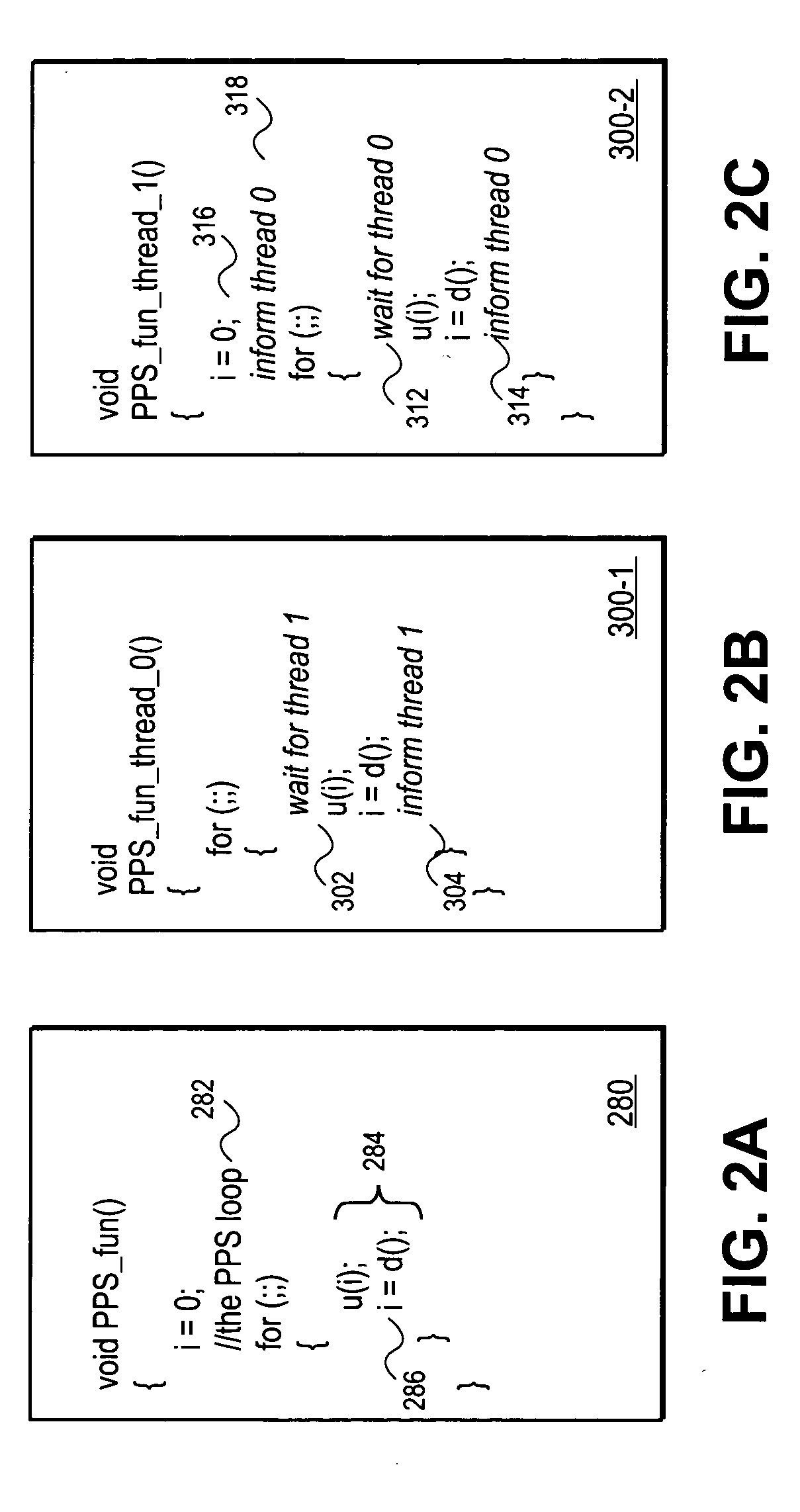
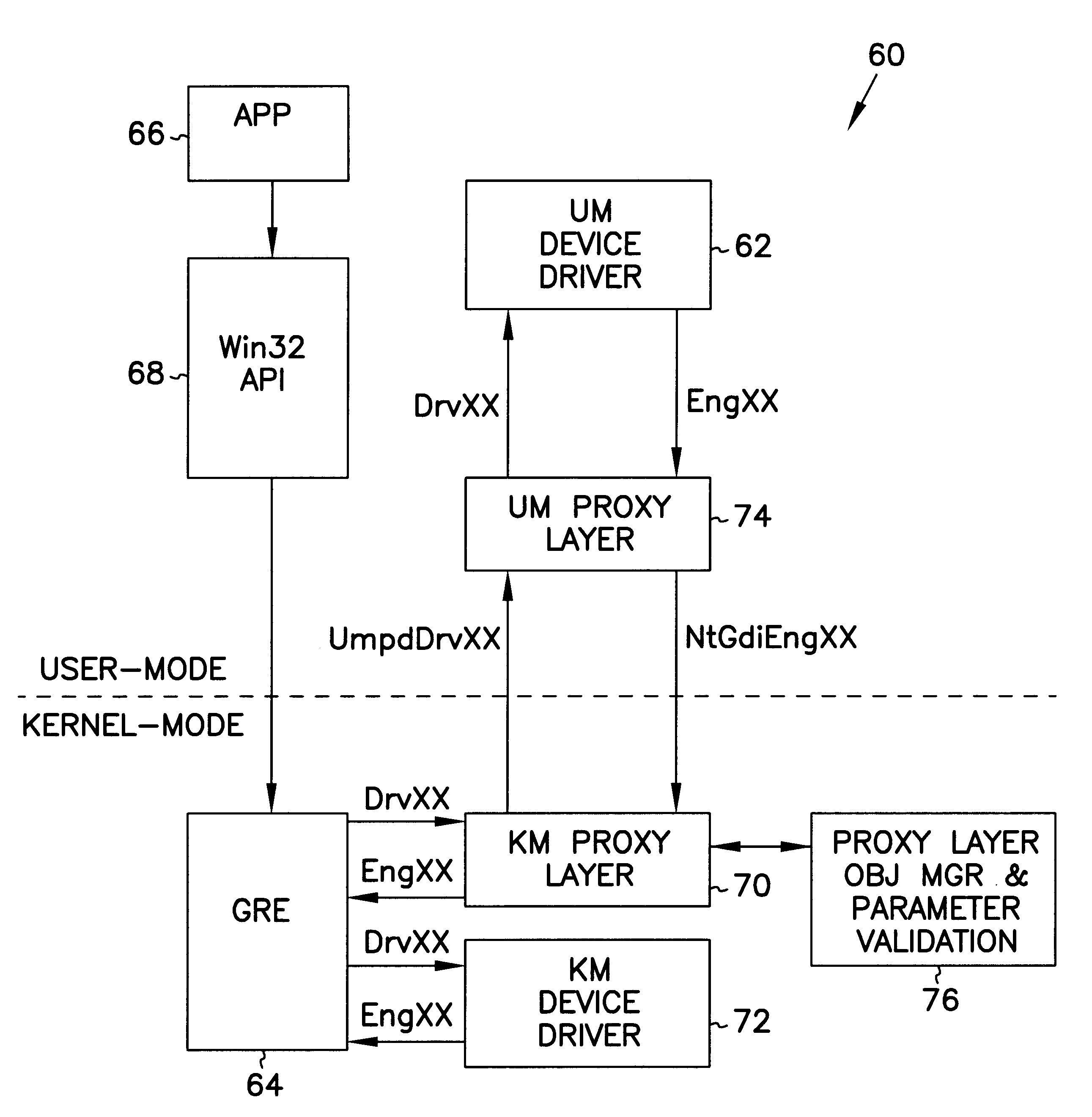
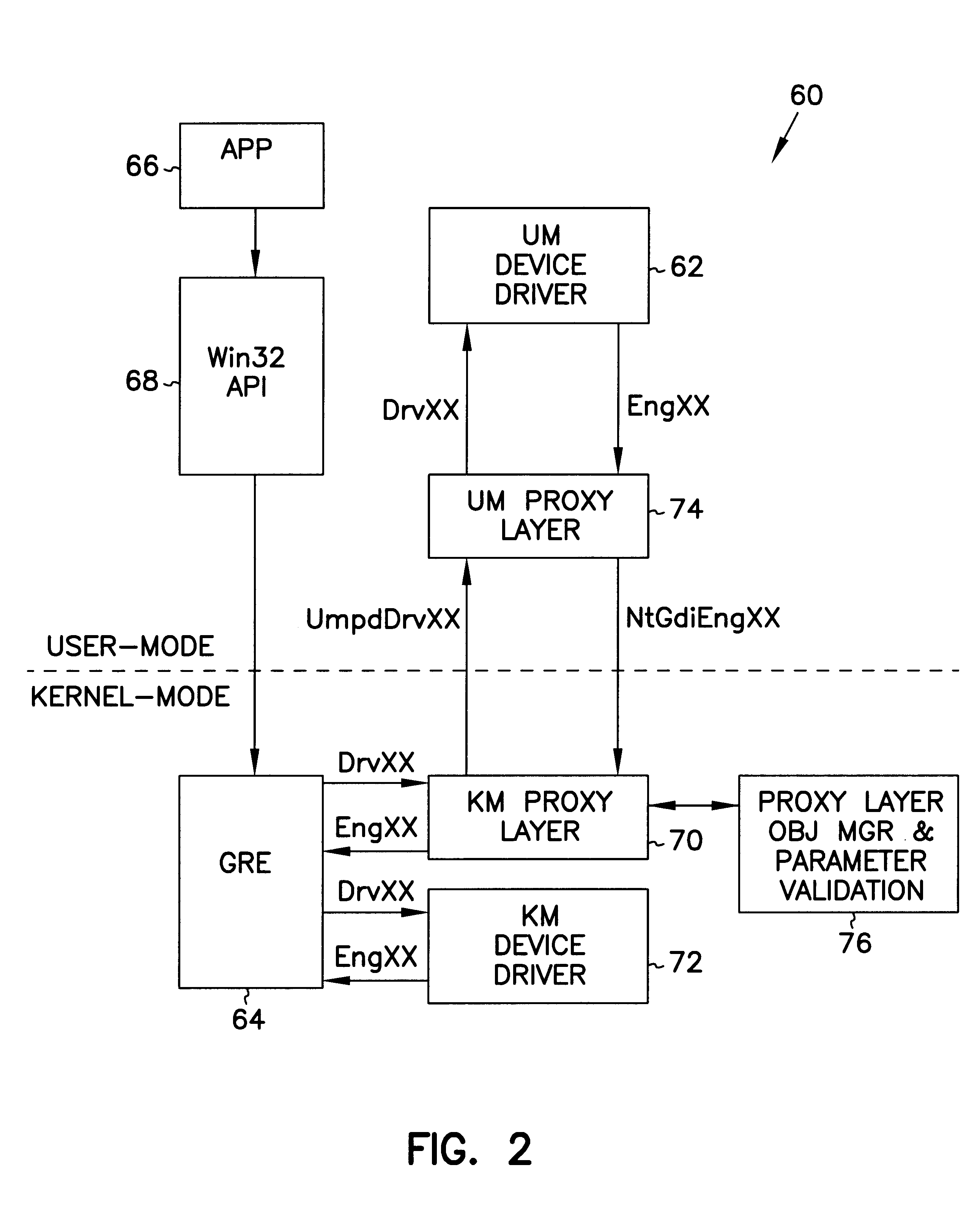
User mode device driver interface for translating source code from the user mode device driver to be executed in the kernel mode or user mode
A user mode device driver interface (UMDDI) is disclosed. The UMDDI is preferably implemented in Windows® NT® version 5.0 and similar systems. The UMDDI allows a device driver to execute in user-mode while the graphics engine (GRE) remains in kernel-mode. The UMDDI exists as a layer between the user-mode driver and GRE; from the perspective of GRE, it encapsulates the user-mode driver and makes it appear to be a normal kernel-mode driver. The UMDDI layer handles the kernel-to-user and user-to-kernel transitions, parameter validation, and management of the kernel-mode and user-mode data and objects.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
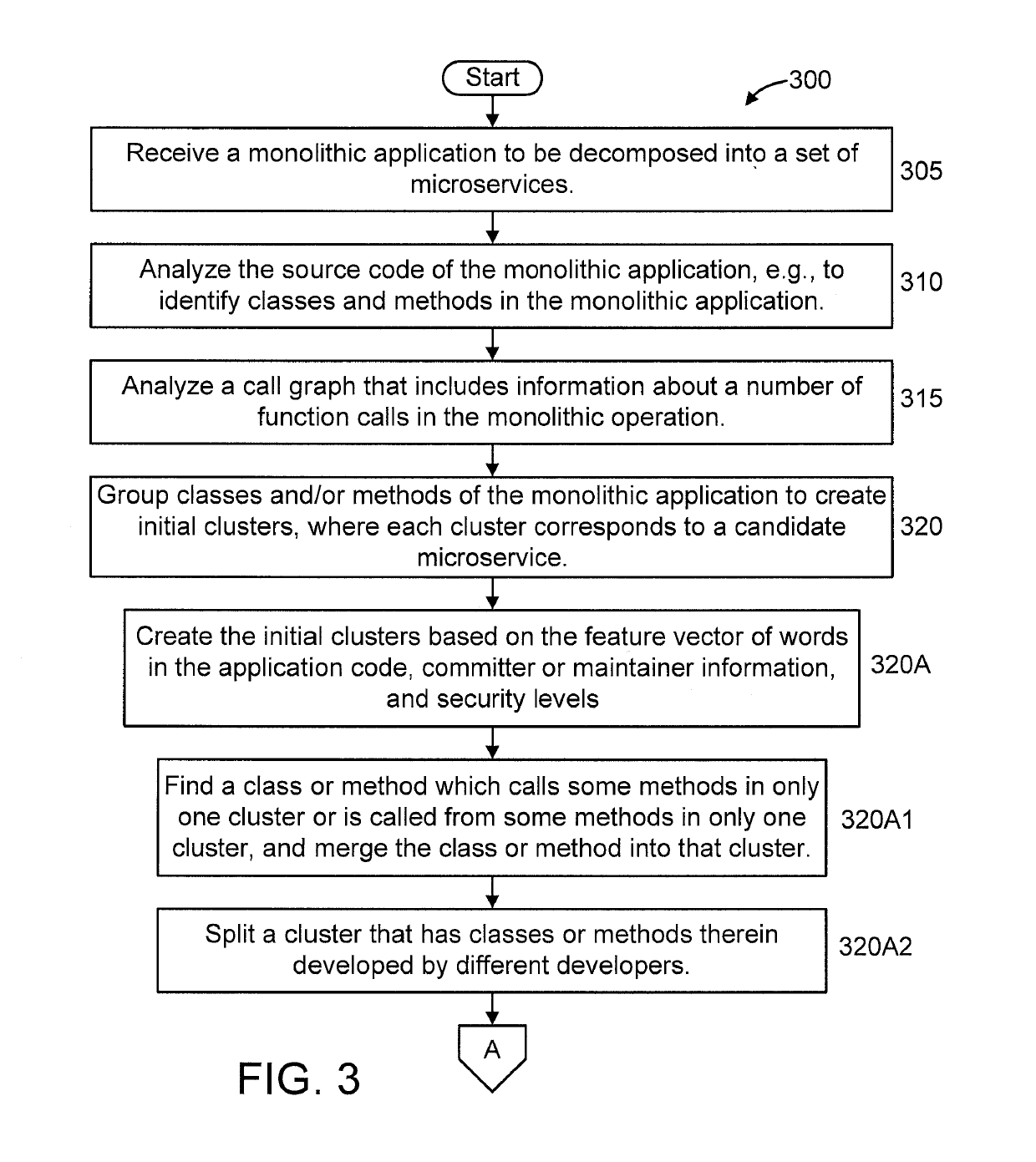
Decomposing monolithic application into microservices
A method transforms a monolithic application into microservices. The method groups application classes and methods into clusters, each corresponding to a respective microservice. The method determines a number of function calls to and from each clustered class and method. The method presents processing options for at least the one of the clustered classes and the methods that has a maximum value for the number of functions calls. The options include: create a new cluster with the at least of the classes and the methods; merge the at least one of the classes and the methods into a different cluster; duplicate the at least one of the classes and the methods into clusters having caller or callee classes or methods; and remain the at least one of the classes and the methods. The method processes the at least one of the classes and the methods based on the user selected option.
Owner:IBM CORP
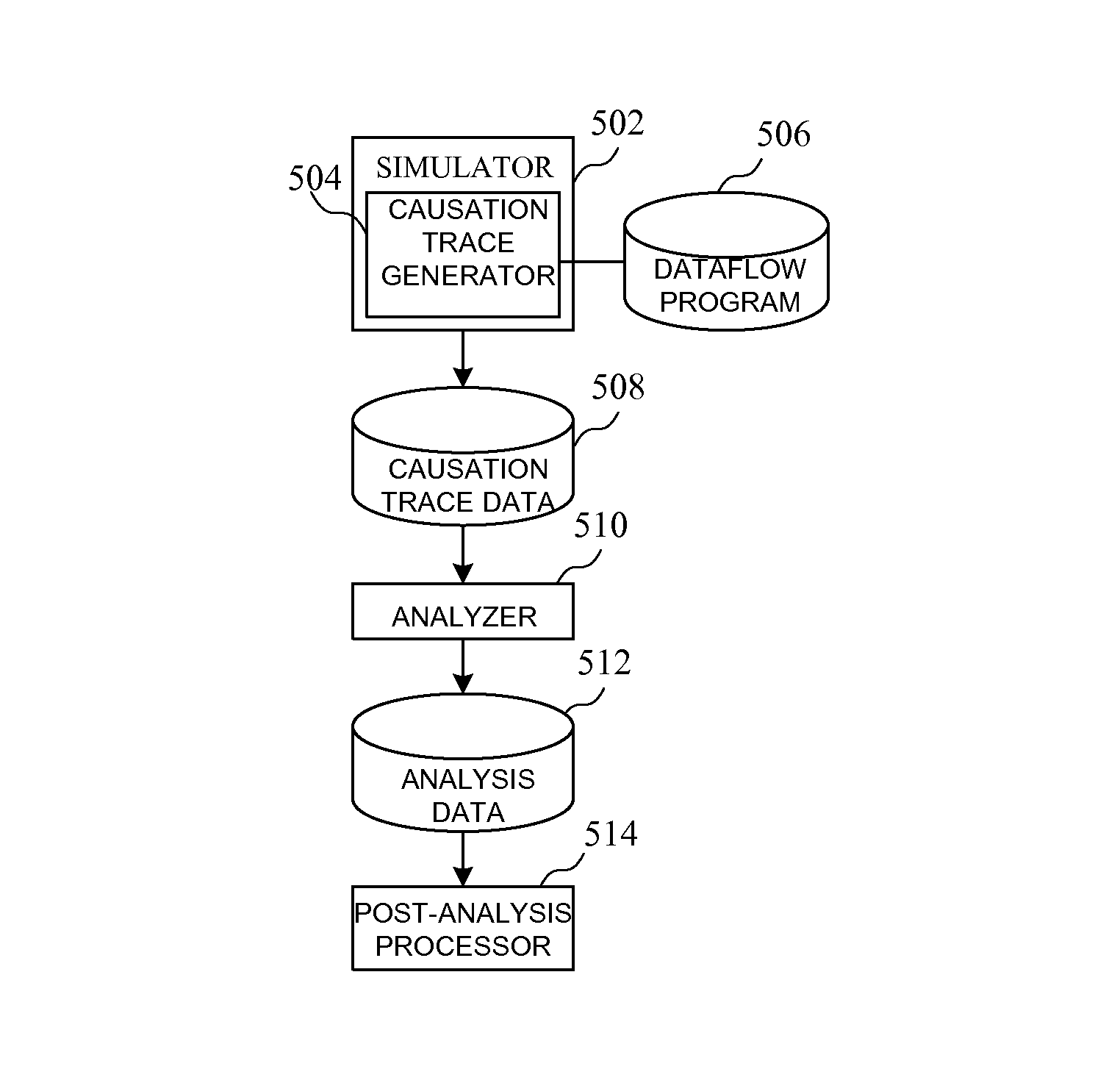
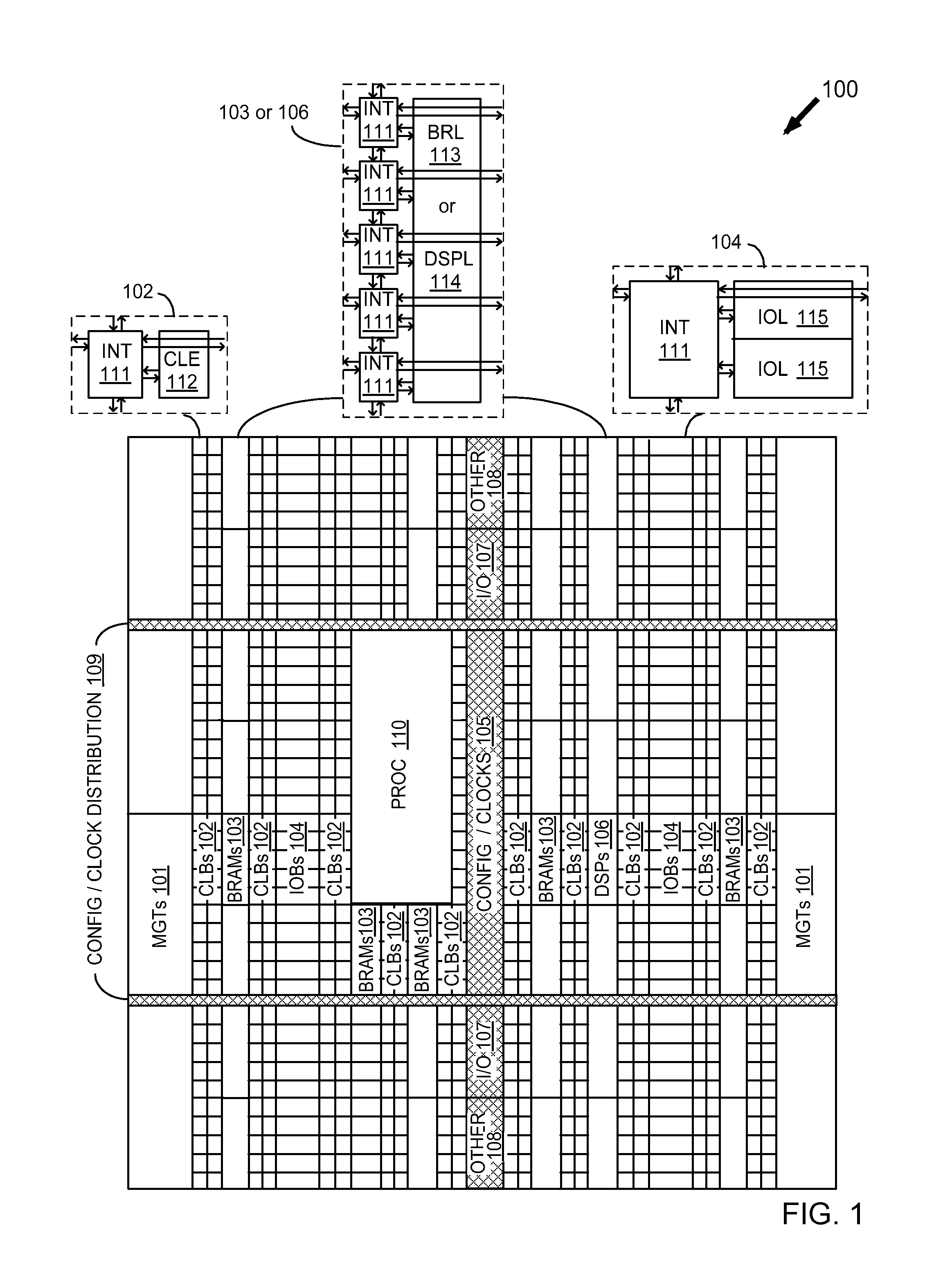
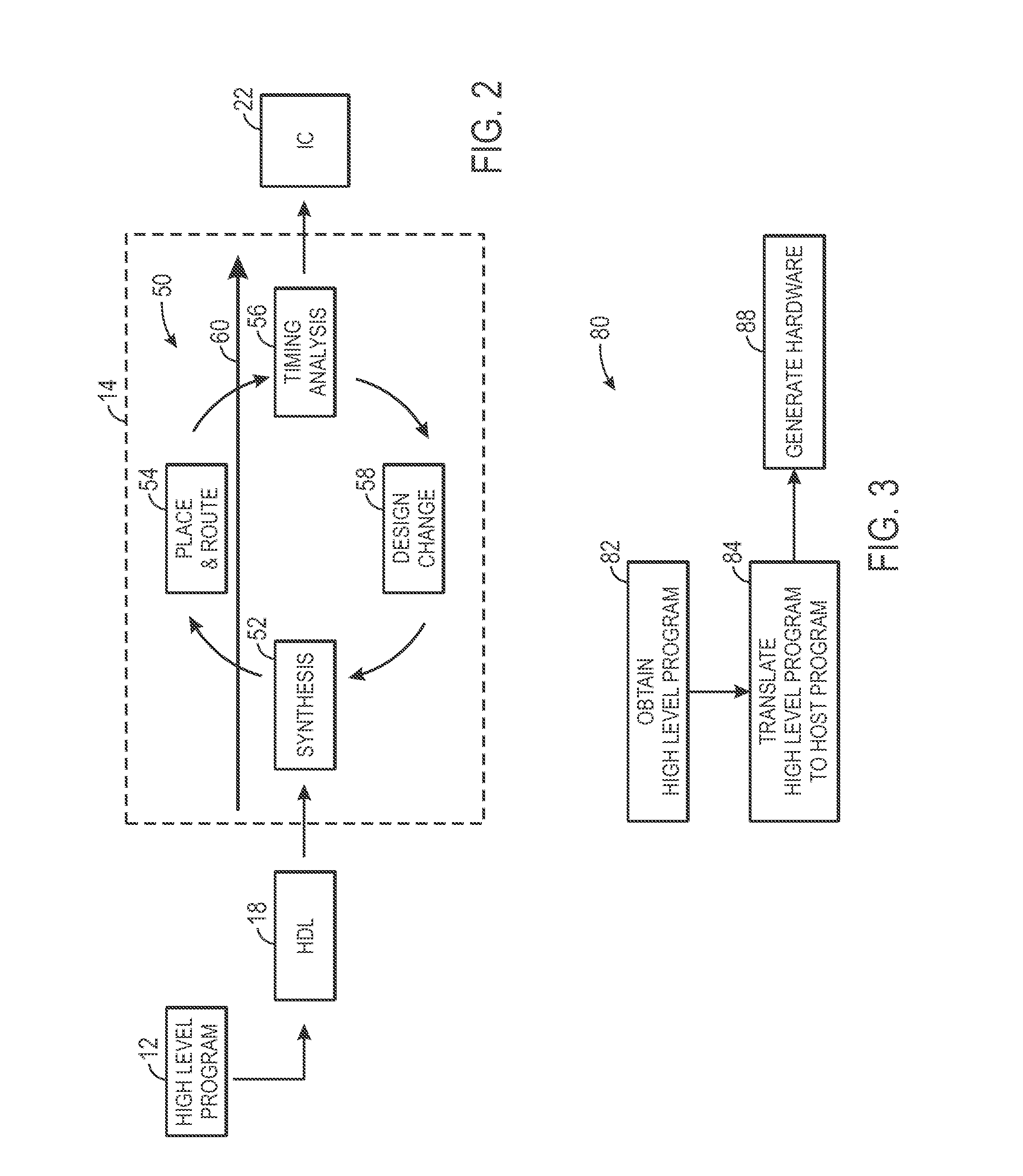
Method of evaluating an architecture for an integrated circuit device
ActiveUS8146040B1CAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationComputer architectureArchitecture of Integrated Information Systems
A method of evaluating an architecture for an integrated circuit device is disclosed. The method comprises generating a library of primitives for a predetermined architecture; transforming an original dataflow program into an intermediate format; transforming the intermediate format to a dataflow program defined in terms of the predefined library of primitives; and generating an implementation profile comprising information related to an implementation of the original dataflow program in an integrated circuit having the predetermined architecture. A method of evaluating an architecture for an integrated circuit device is also disclosed.
Owner:XILINX INC
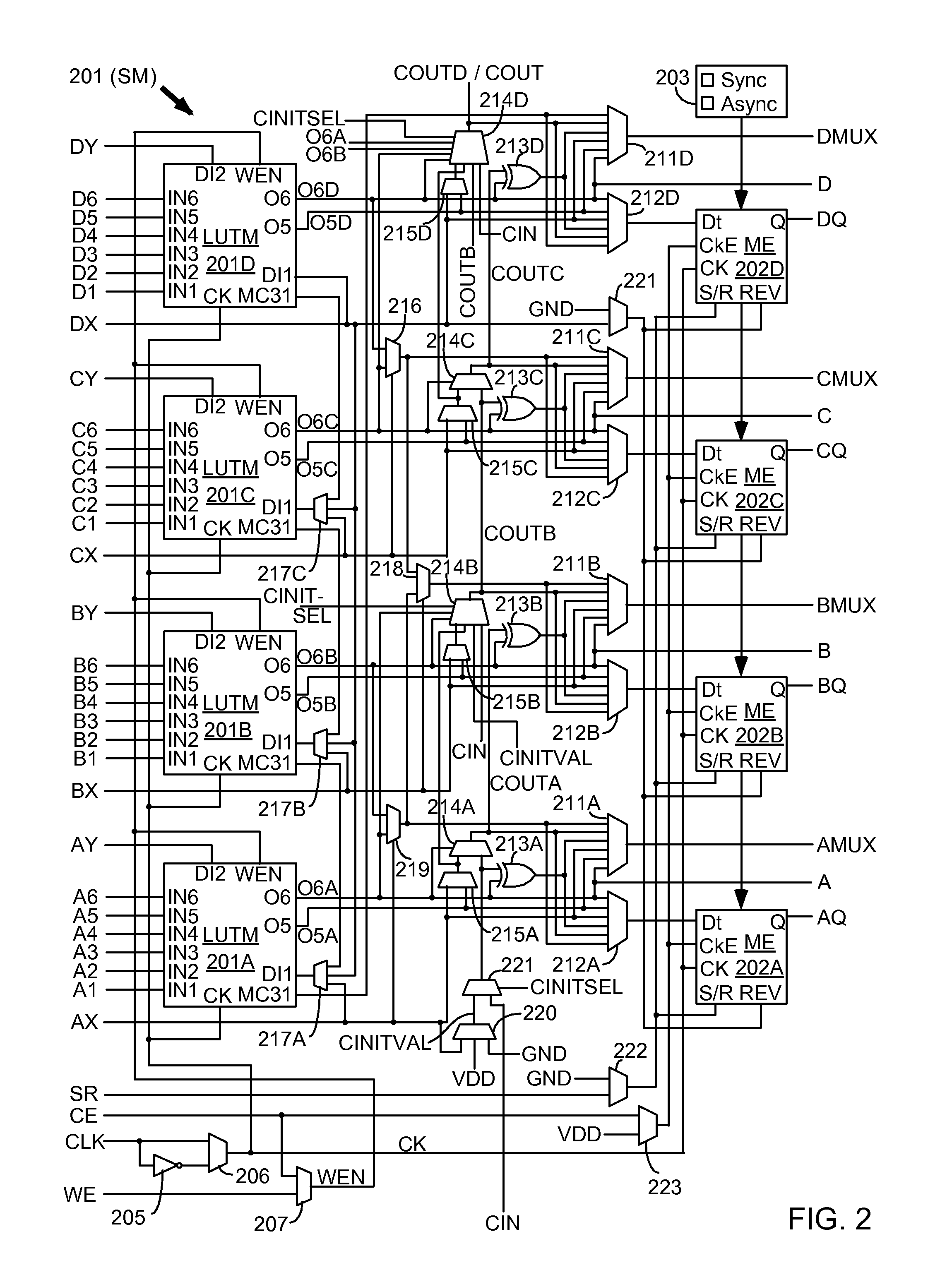
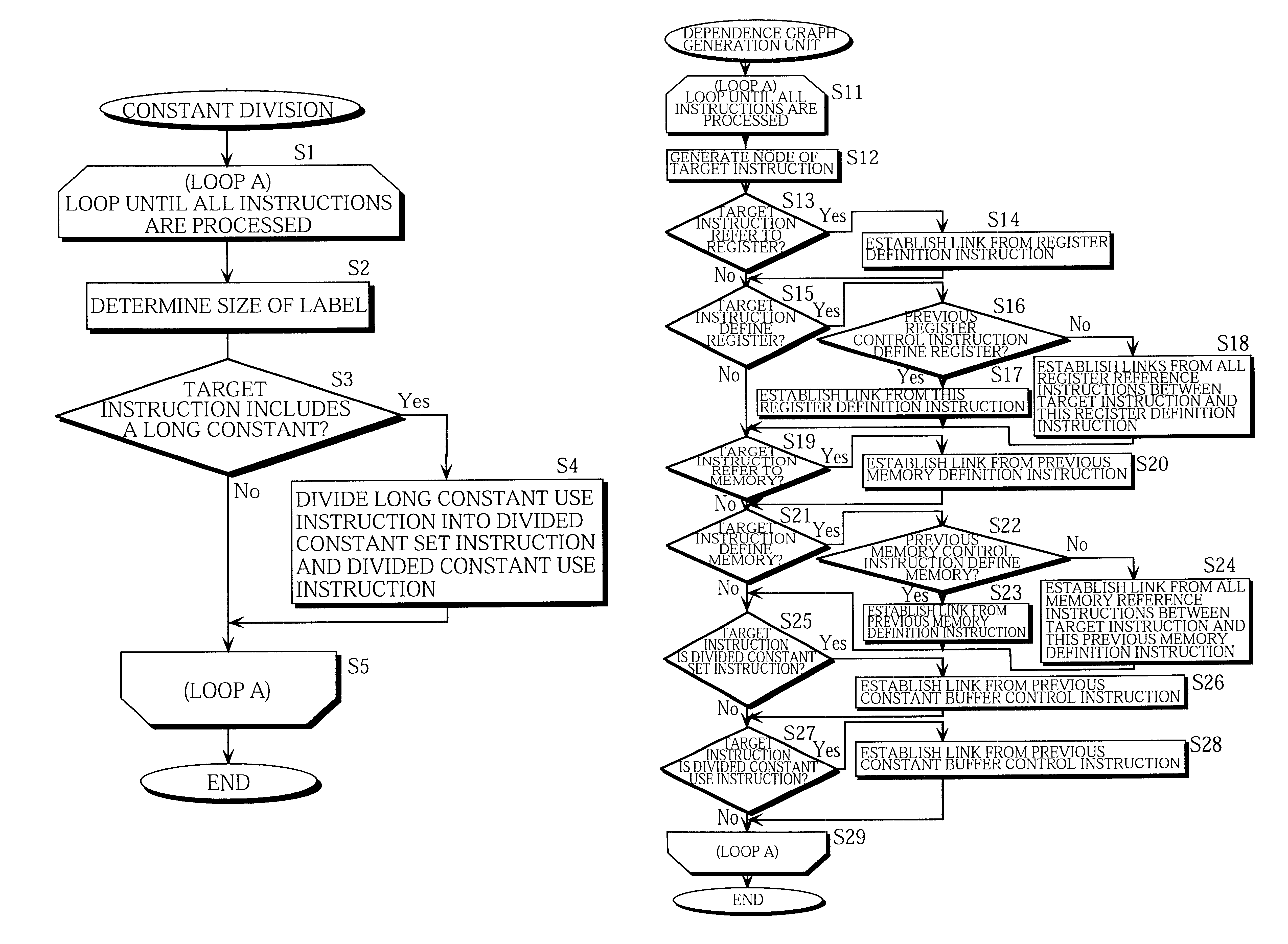
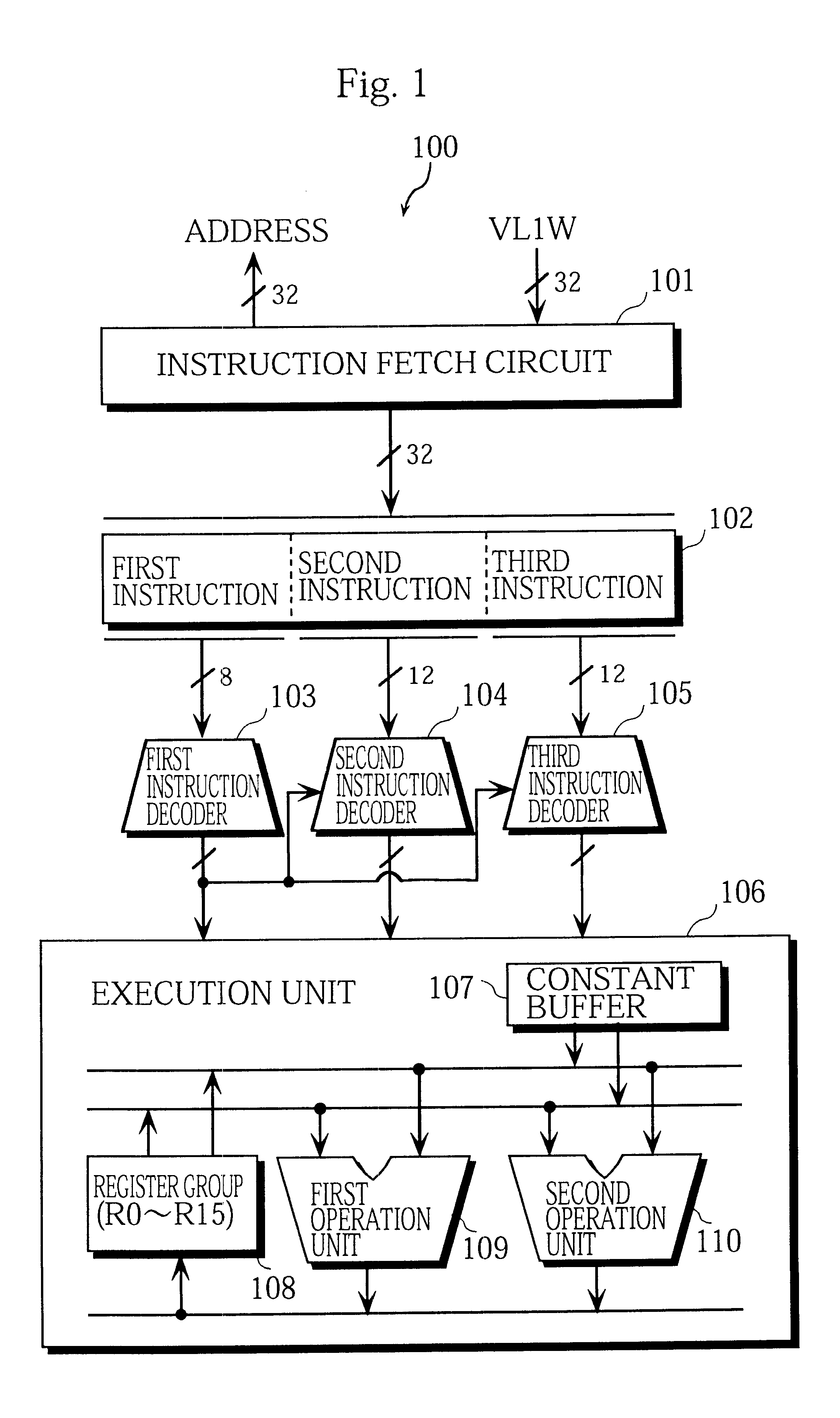
Program conversion apparatus for constant reconstructing VLIW processor
InactiveUS6367067B1Shorten the timeAvoid combiningTransformation of program codeInstruction analysisParallel computingLattice constant
A program conversion apparatus includes: the constant division unit 12 for specifying instructions in the serial assembler code 42 that use large constants which cannot be arranged within the operation fields of object VLIWs and for dividing the specified instructions into divided constant use instructions for storing pieces of the large constants into the specialized constant buffer 107 of a VLIW processor and divided constant use instructions for performing operations using the stored constants; the dependence graph generation unit 20 for generating a dependence graph based on the execution order of each instruction in the serial assembler code 42 after the division process by the constant division unit 12; and the instruction relocation unit 21 for relocating the instructions according to the dependence graph to generate parallel assembler code.
Owner:SOCIONEXT INC
Compiling system, debugging system and program development system
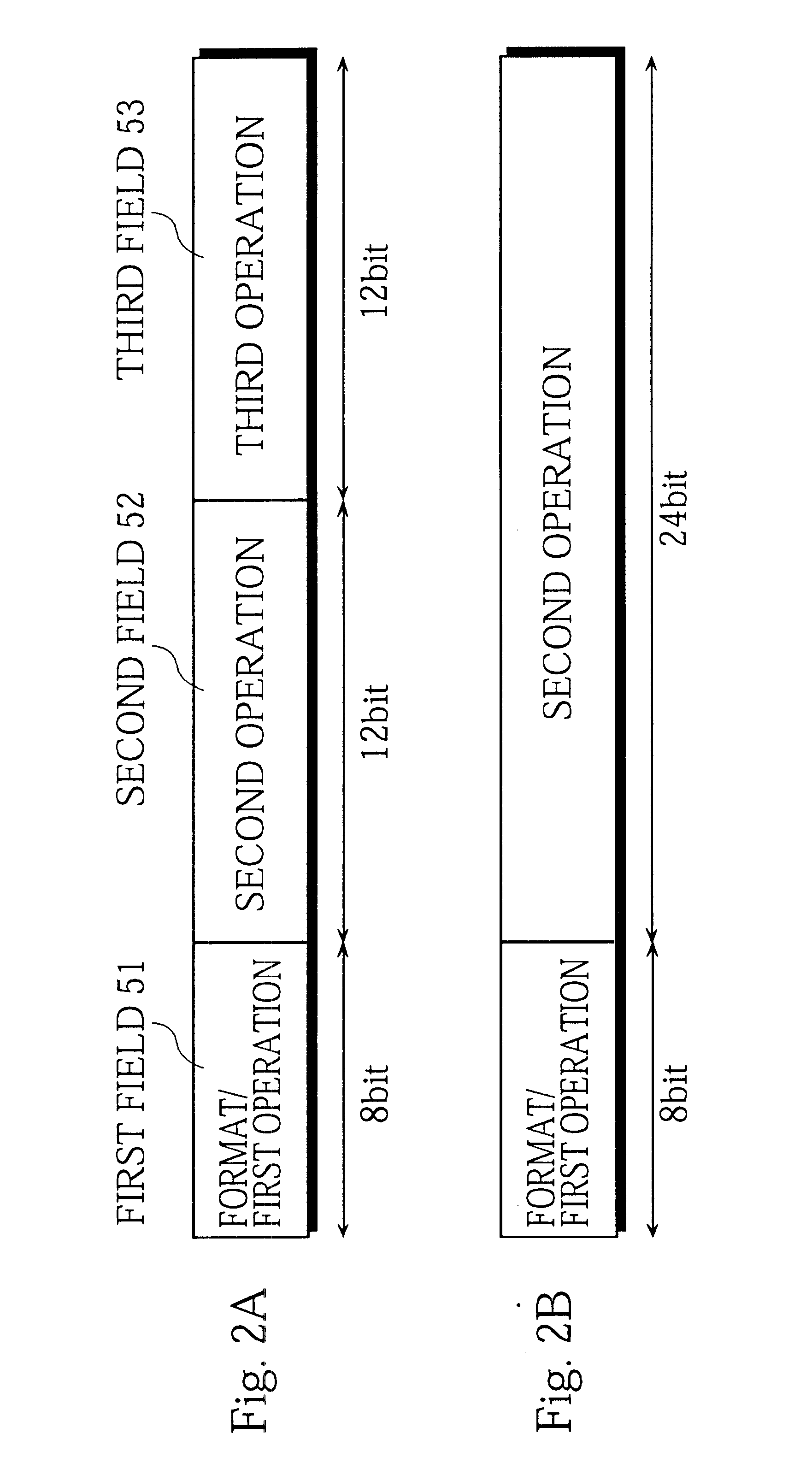
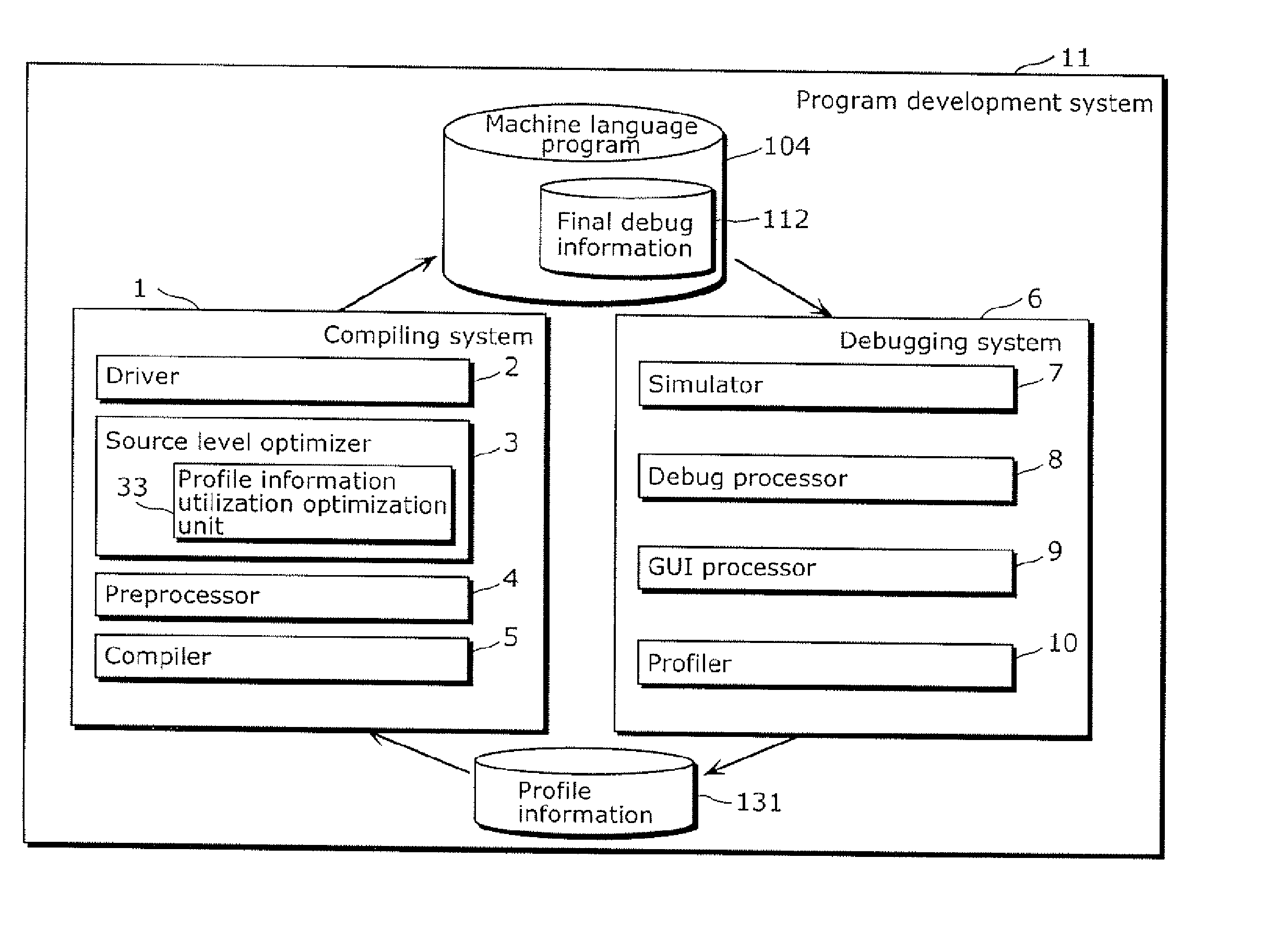
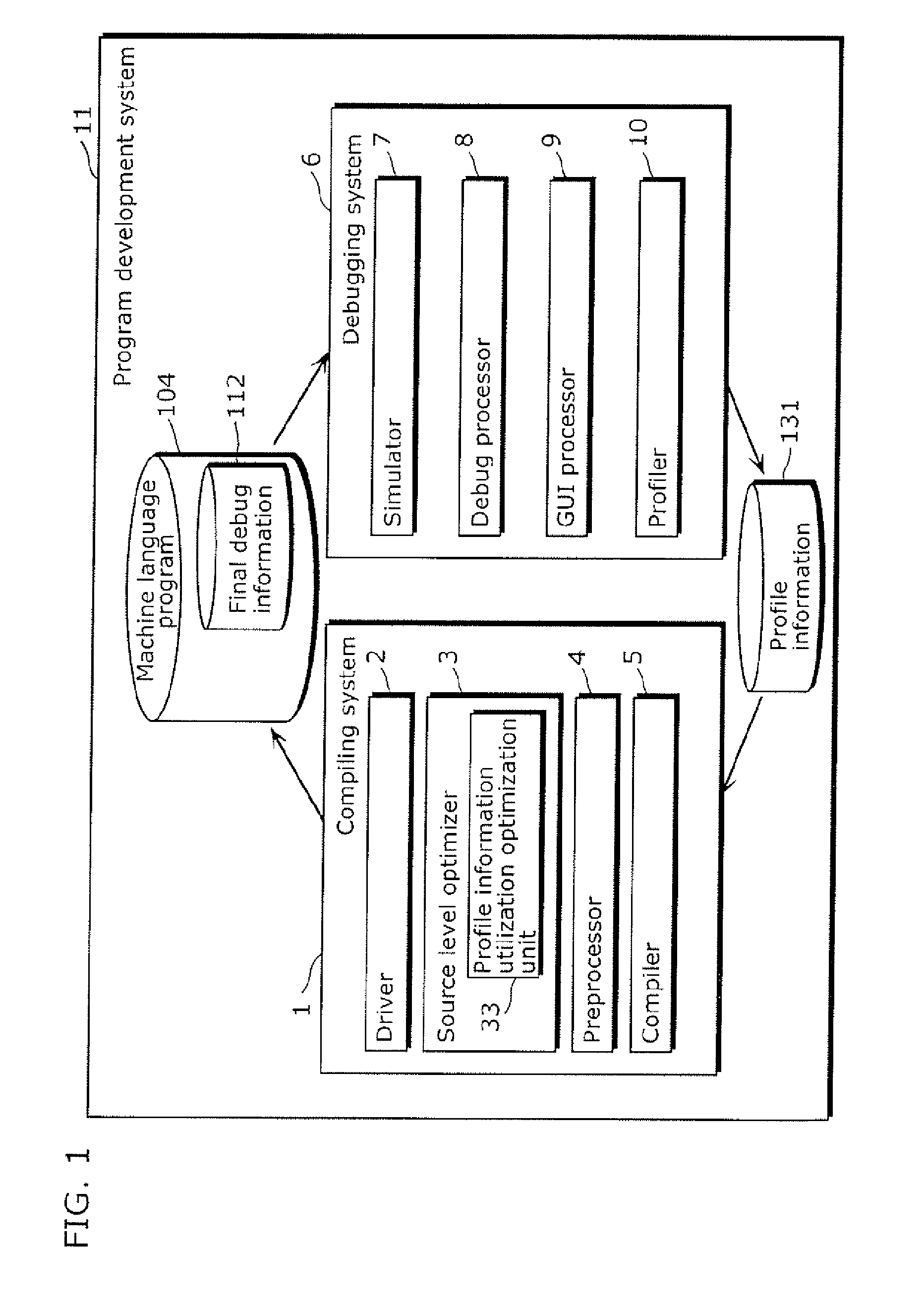
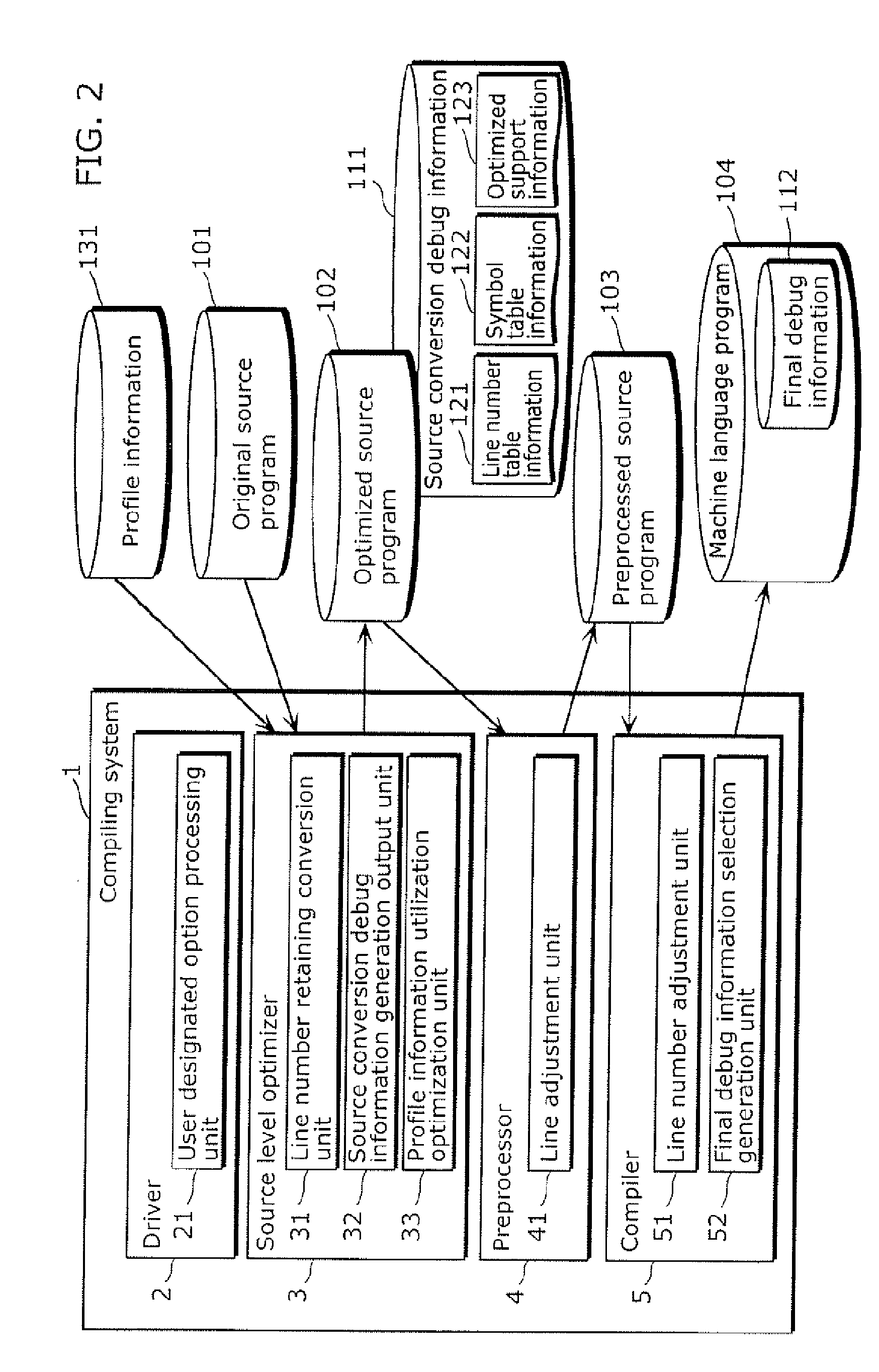
InactiveUS20070168984A1Maintain easeImprove convenienceError detection/correctionSpecific program execution arrangementsSource levelProgram compilation
A compiling system which translates a source program written in a high-level language into a machine language program, and includes a source level optimizer which converts an original source S program into an optimized source program by optimizing the original source program at the source program level, a compiler which converts the optimized source program into the machine language program, and a final debug information selection generation unit which generates final debug information which indicates a corresponding relationship between the original source program and the machine language program.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
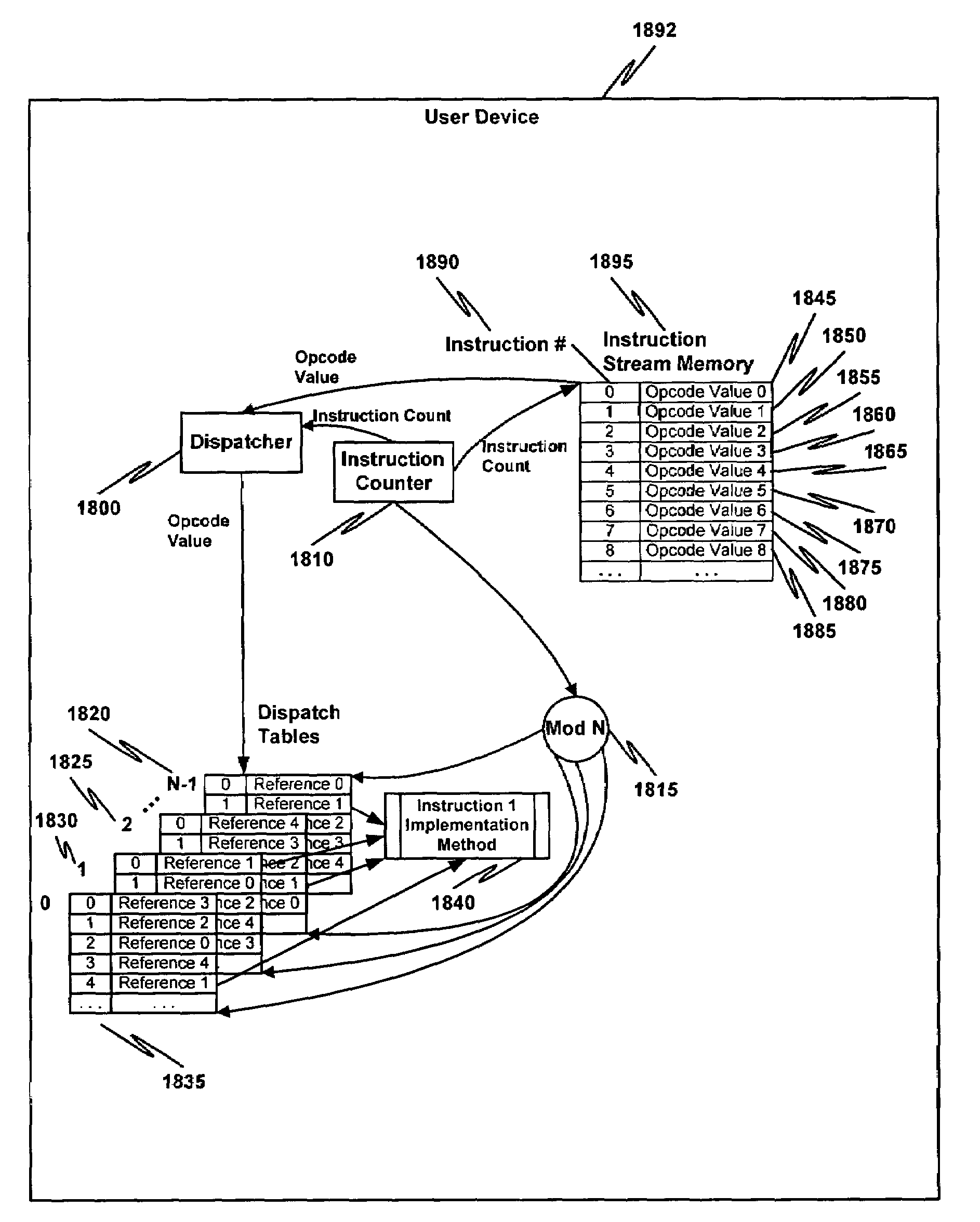
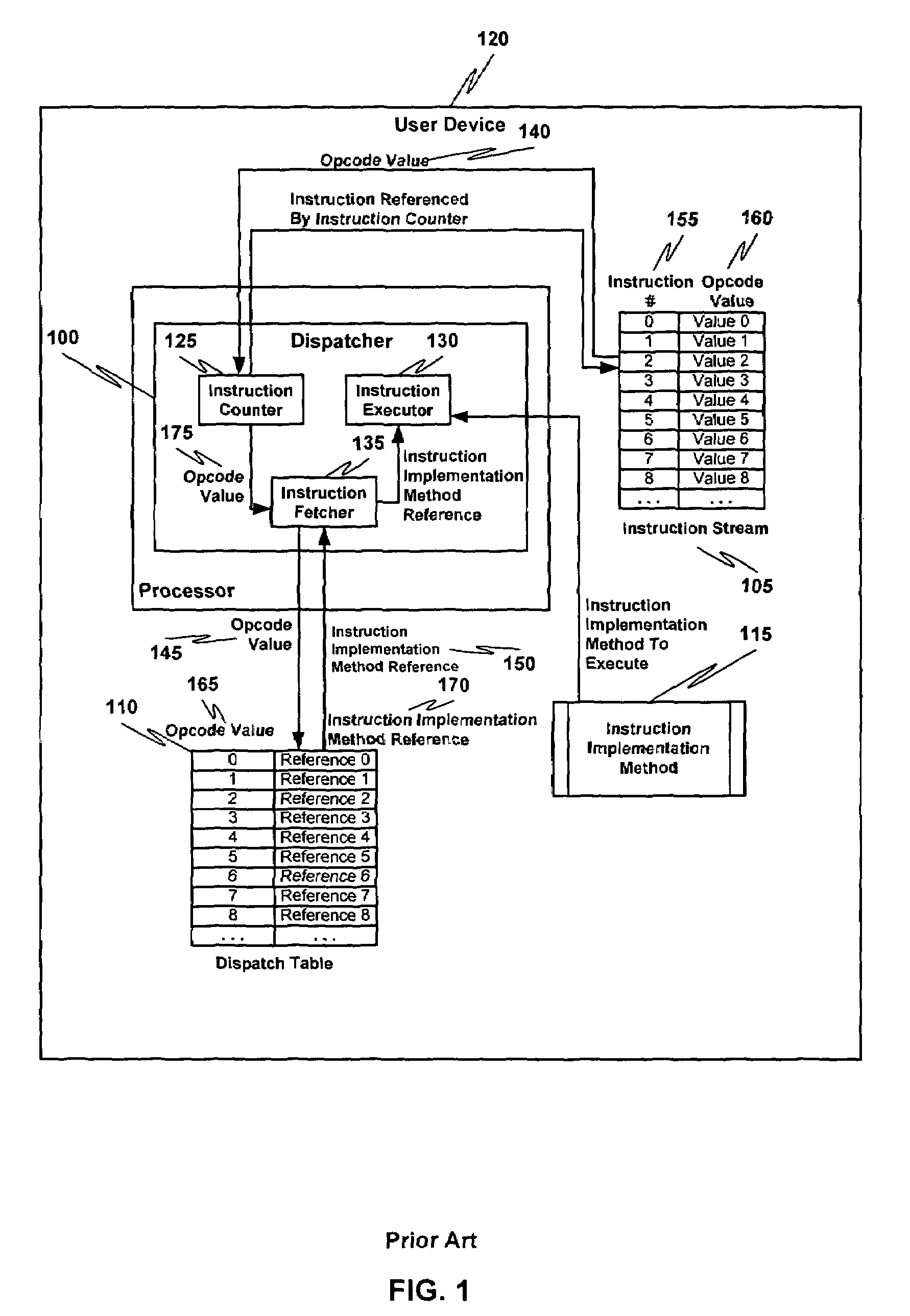
Multiple instruction dispatch tables for application program obfuscation
ActiveUS7353499B2Key distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsProgram instructionScheduling instructions
Obfuscating an application program comprises reading an application program comprising code, determining multiple dispatch tables associated with the application program, transforming the application program into application program code configured to utilize the dispatch tables during application program execution to determine the location of instruction implementation methods to be executed based at least in part on a current instruction counter value, and sending the application program code. Executing an obfuscated application program comprises receiving an obfuscated application program comprising at least one instruction opcode value encoded using one of multiple instruction set opcode value encoding schemes, receiving an application program instruction corresponding to a current instruction counter value, selecting an instruction dispatch table based at least in part on the current instruction counter value, and executing the application program instruction using the selected instruction dispatch table.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
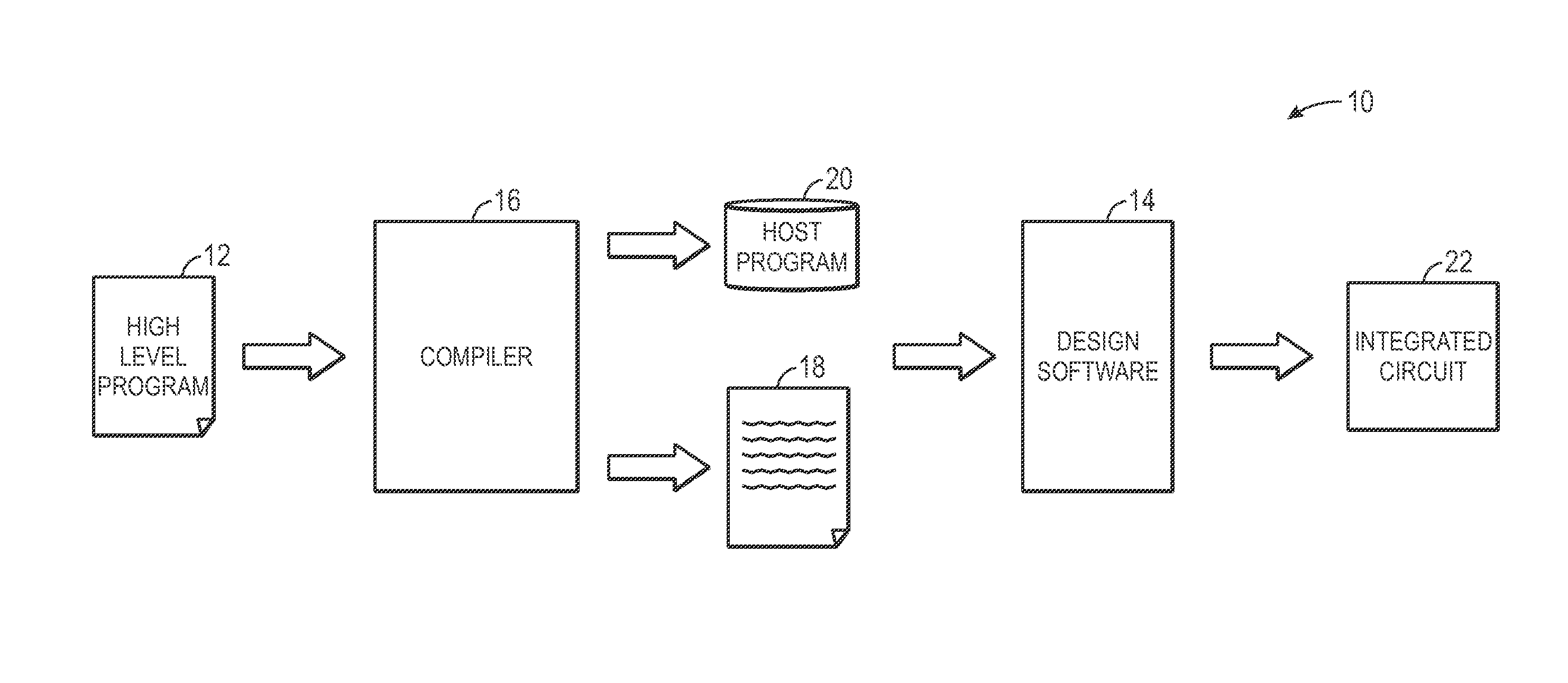
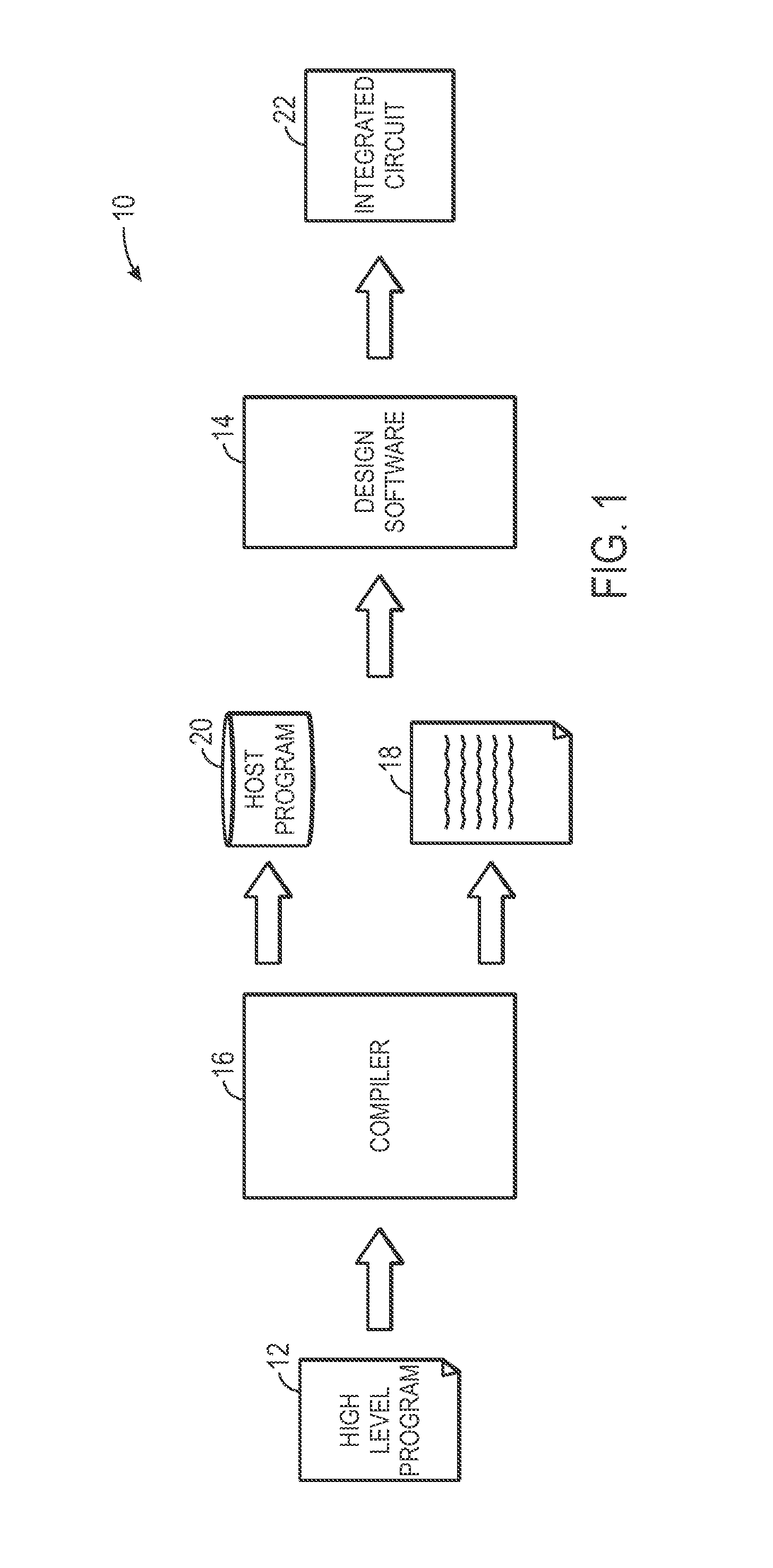
Opencl compilation
ActiveUS20130346953A1Increases compile timeLess timeCAD circuit designProgram controlComputer architectureProgrammable logic device
Systems and methods for increasing speed and reducing processing power of a compile process of programmable logic of an integrated circuit (IC) are provided. For example, in one embodiment, a method includes obtaining a high level program, comprising computer-readable instructions for implementation on programmable logic of an integrated circuit (IC); translating the high level program into low level code representative of functional components needed to execute functionalities of the high level program; generating a host program comprising computer-readable instructions for implementing the low level code based upon the high level program; obtaining modifications to the high level program; determining whether the modifications can be implemented by a new host program utilizing the low level code; and generating the new host program to implement the modifications, when the modifications can be implemented by the new host program utilizing the low level code.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
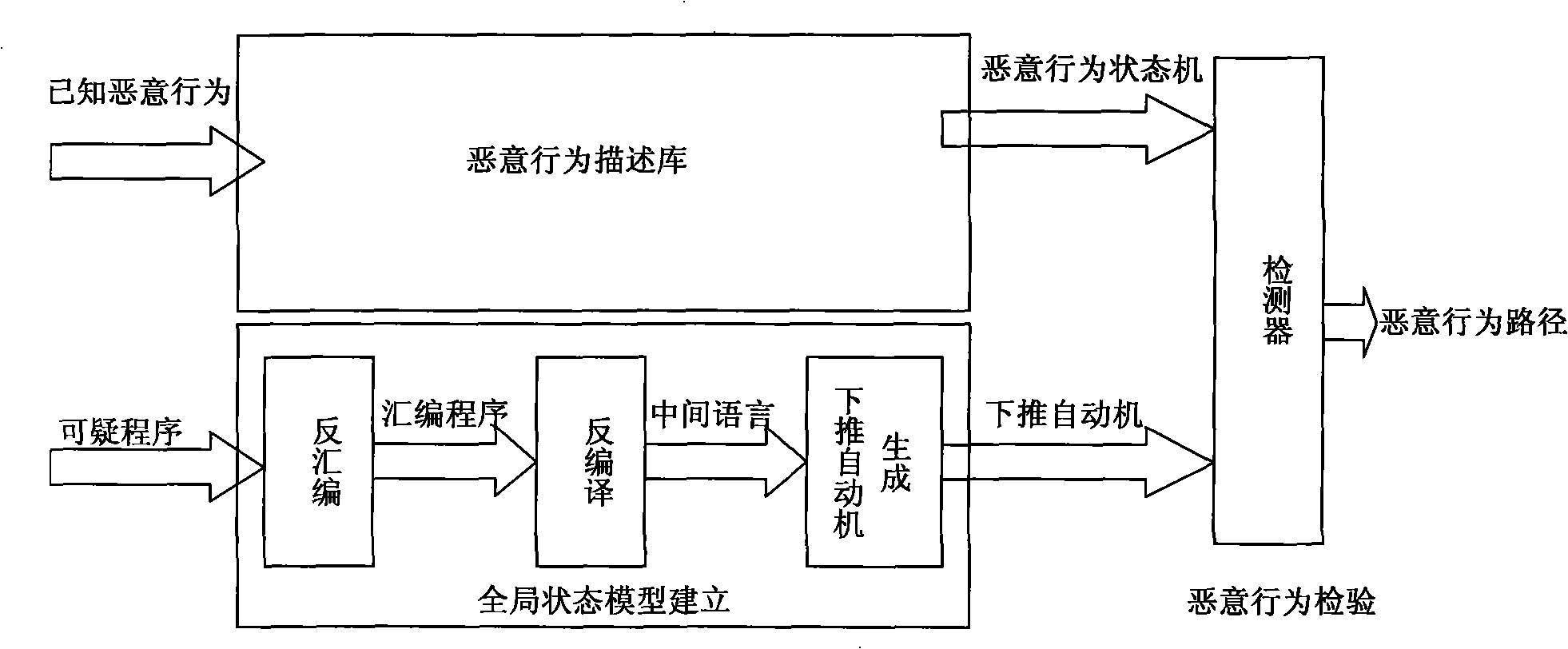
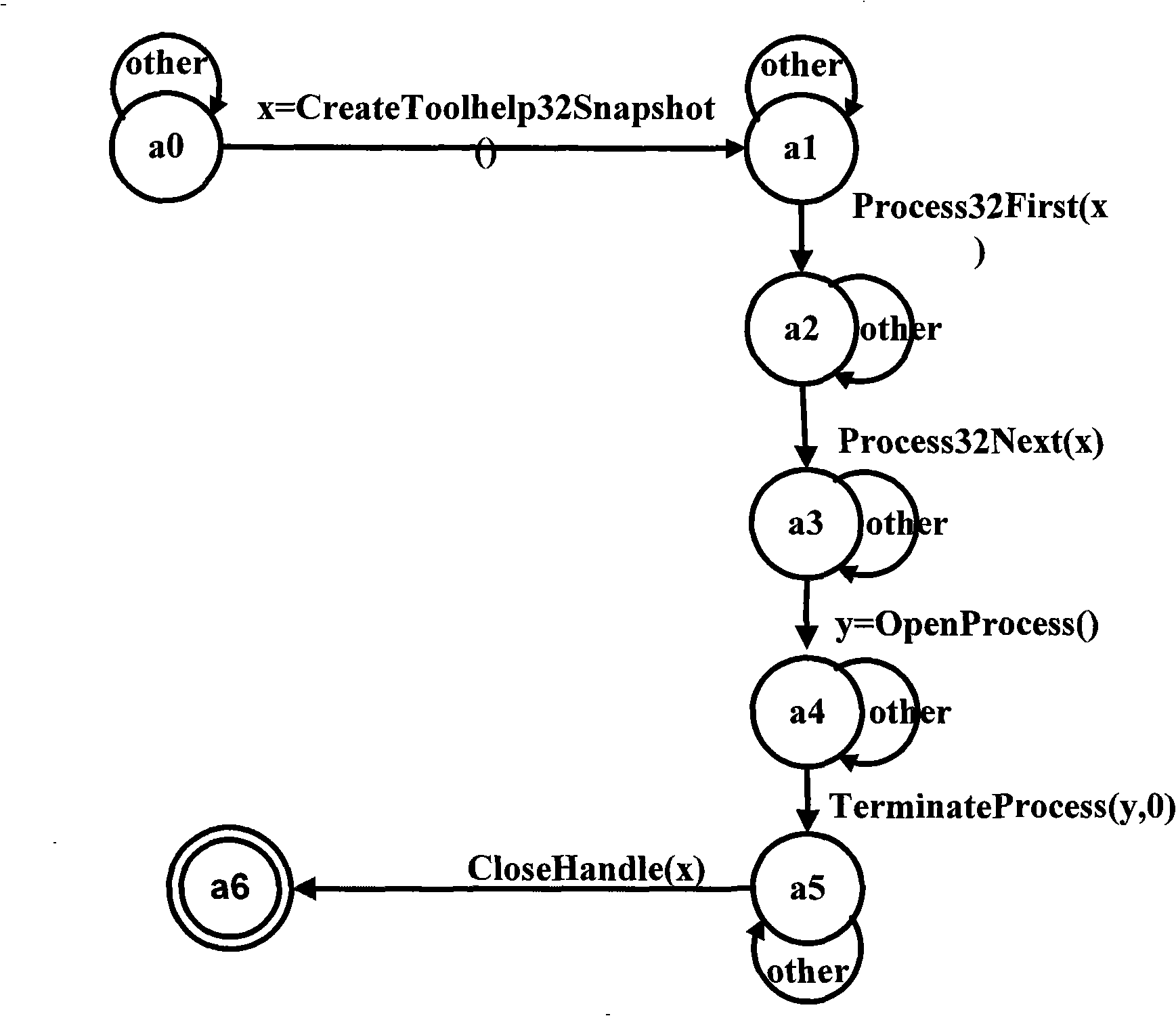
Malicious code detection method
InactiveCN101266550ALess malicious behaviorPlatform integrity maintainanceProgram controlPushdown automatonThe Internet
The invention discloses a malicious code examination method based on the semanteme, which may completely portray aggressive behaviors based on the function call, effectively distinguishes malicious behaviors in the binary suspicious procedure, and belongs to the Internet safety technology domain. The method of the invention includes: a) to obtain the finite state automata of the known malicious code; b) to obtain the push down automata of the binary suspicious procedure to be examined; c) to use a model inspection method to inspect whether an input character string which can be simultaneously received exists between the push down automata and the finite state automata or not, if yes, the suspicious procedure to be examined is judged as the malicious procedure. The invention uses the finite state automata to describe the malicious behaviors, combines the existing tool and the method to convert the suspicious program to be the push down automata, then uses the existing model inspection method to examine whether the malicious code is contained in the suspicious procedure or not. And the malicious code examination in the Internet safety technology domain can be effectively used.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
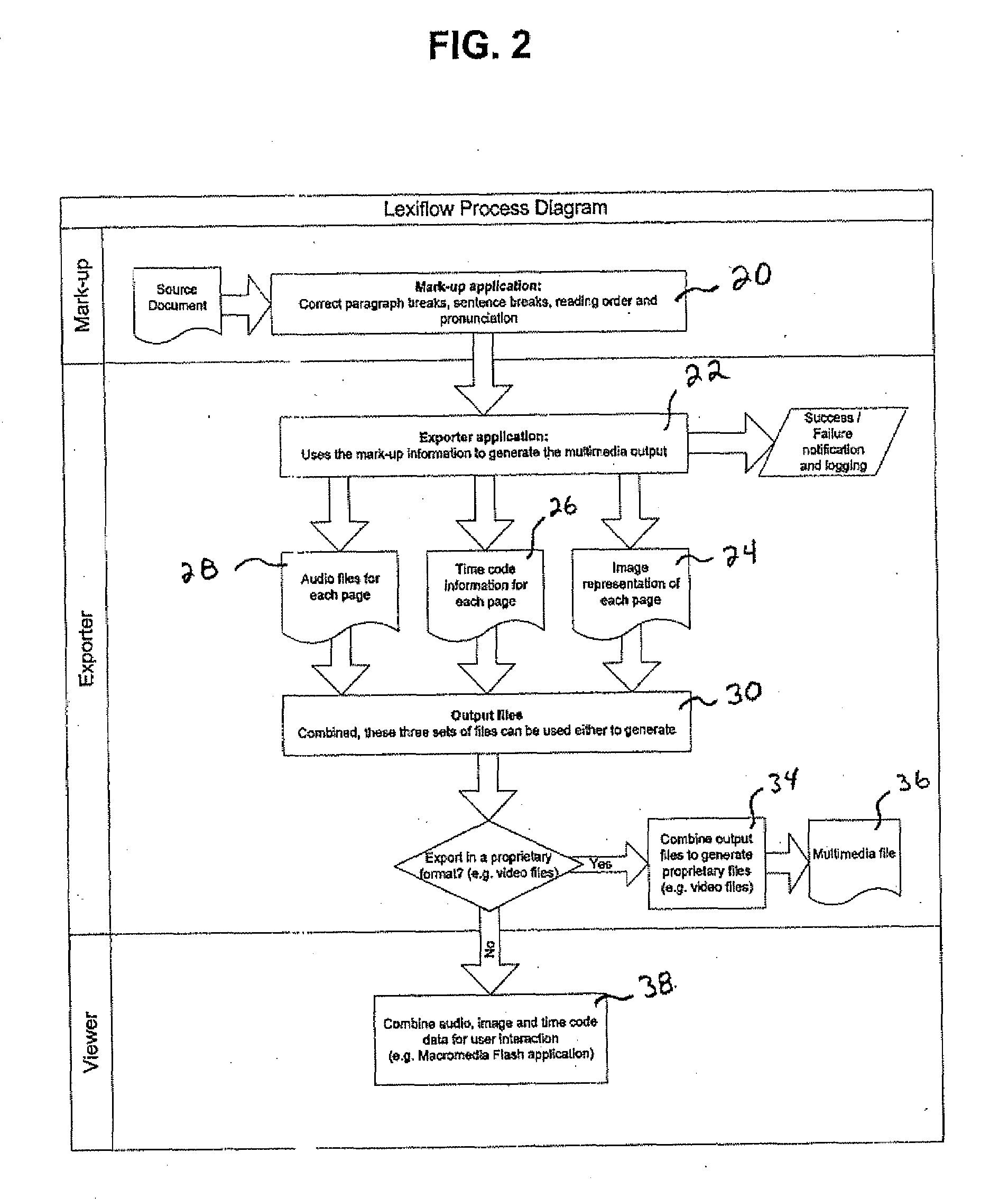
System and method for converting electronic text to a digital multimedia electronic book
InactiveUS20090202226A1Television system detailsColor television signals processingElectronic bookDocumentation
A system and method for converting an existing digital source document into a speech-enabled output document and synchronized highlighting of spoken text with the minimum of interaction from a publisher. A mark-up application is provided to correct reading errors that may be found in the source document. An exporter application can be provided to convert the source document and corrections from the mark-up application to an output format. A viewer application can be provided to view the output and to allow user interactions with the output.
Owner:TEXTHELP SYST
Virtual storage for removable storage media
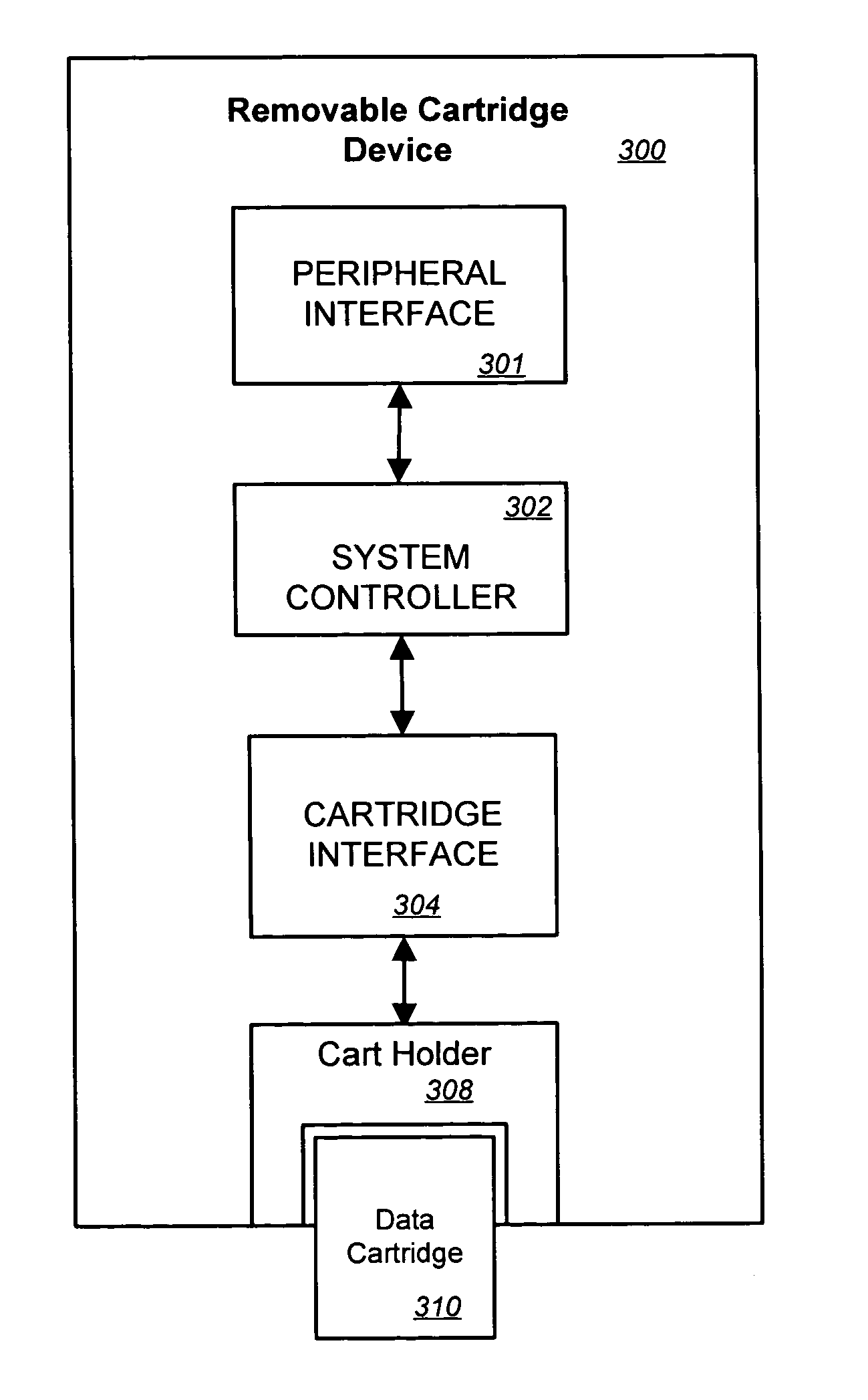
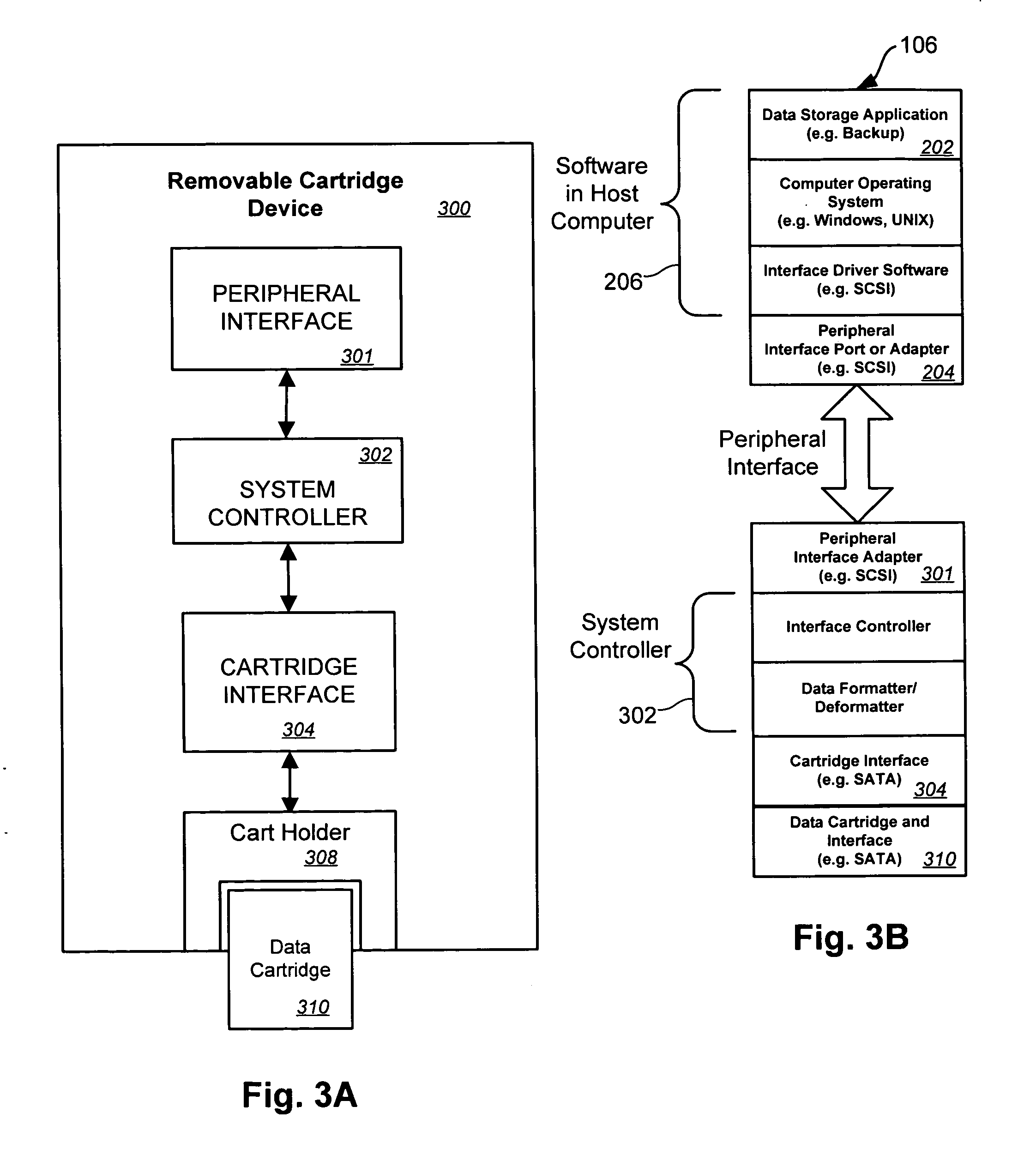
InactiveUS20060010285A1Memory systemsInput/output processes for data processingInterface circuitsProgram transformation
According to the invention, a storage system for emulating a first interface command set different from a second interface command set of a second interface is disclosed. The storage system includes an interface connector, an interface circuit, an interface driver, and a cartridge controller. The interface connector is configured to removably couple with a storage cartridge, which includes the second interface and uses the second interface command set. The interface circuit is coupled to the interface connector. The interface driver manages operation of the interface circuit. The cartridge controller uses the first interface command set and is logically coupled to the interface driver. The cartridge controller software translates the first interface command set for the interface driver. The first interface command set is for tape drives.
Owner:VENTURE LENDING & LEASING IV +1
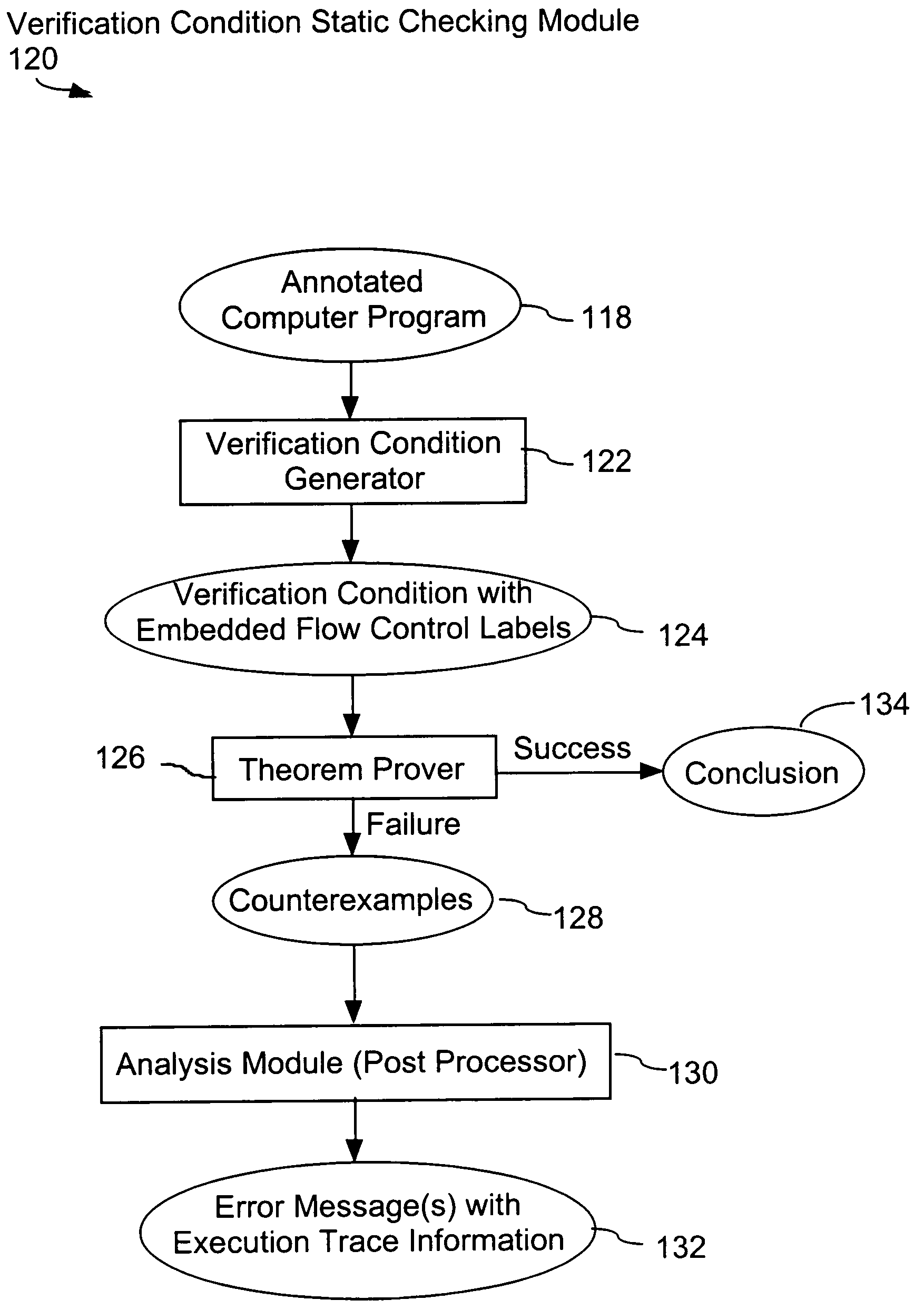
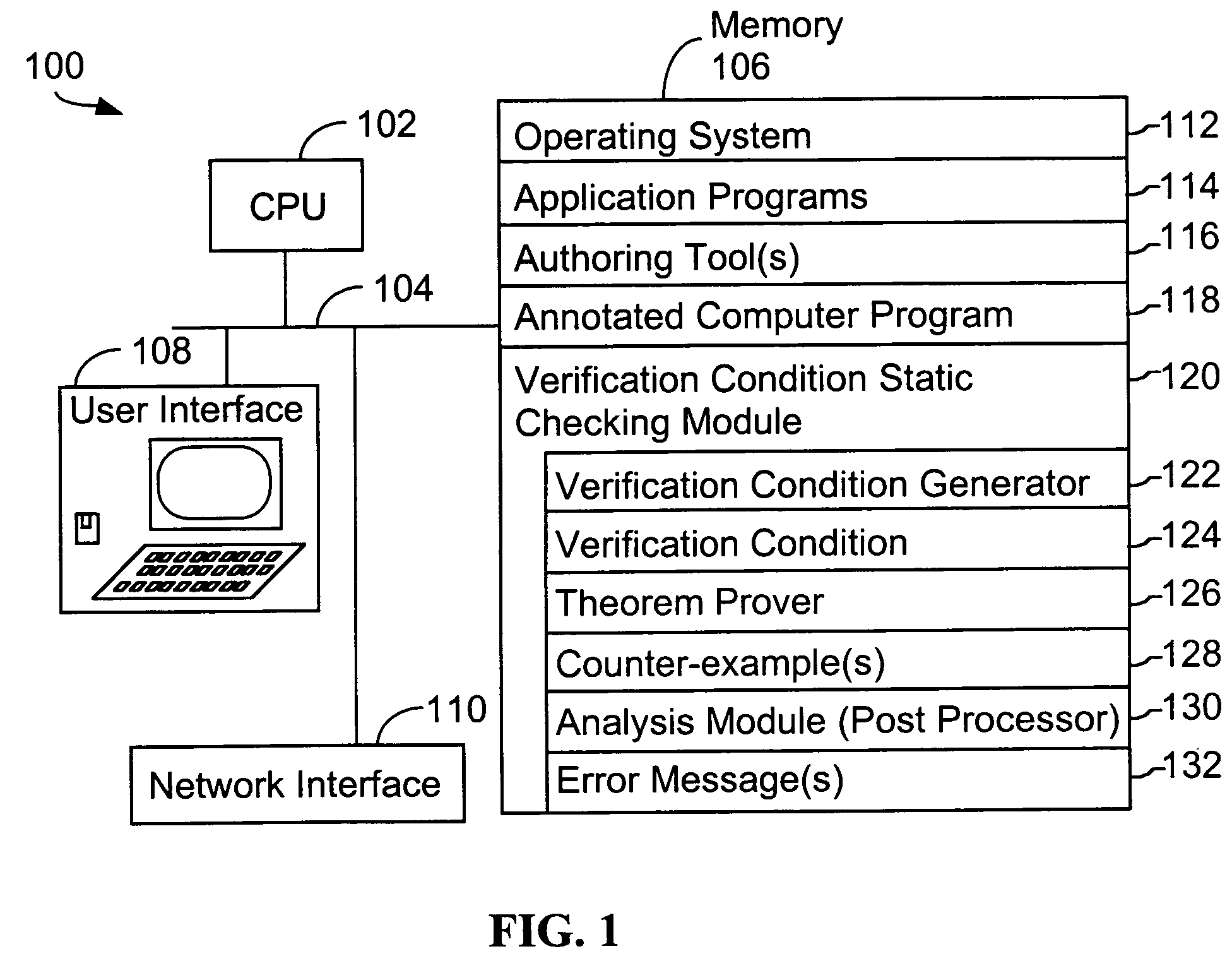
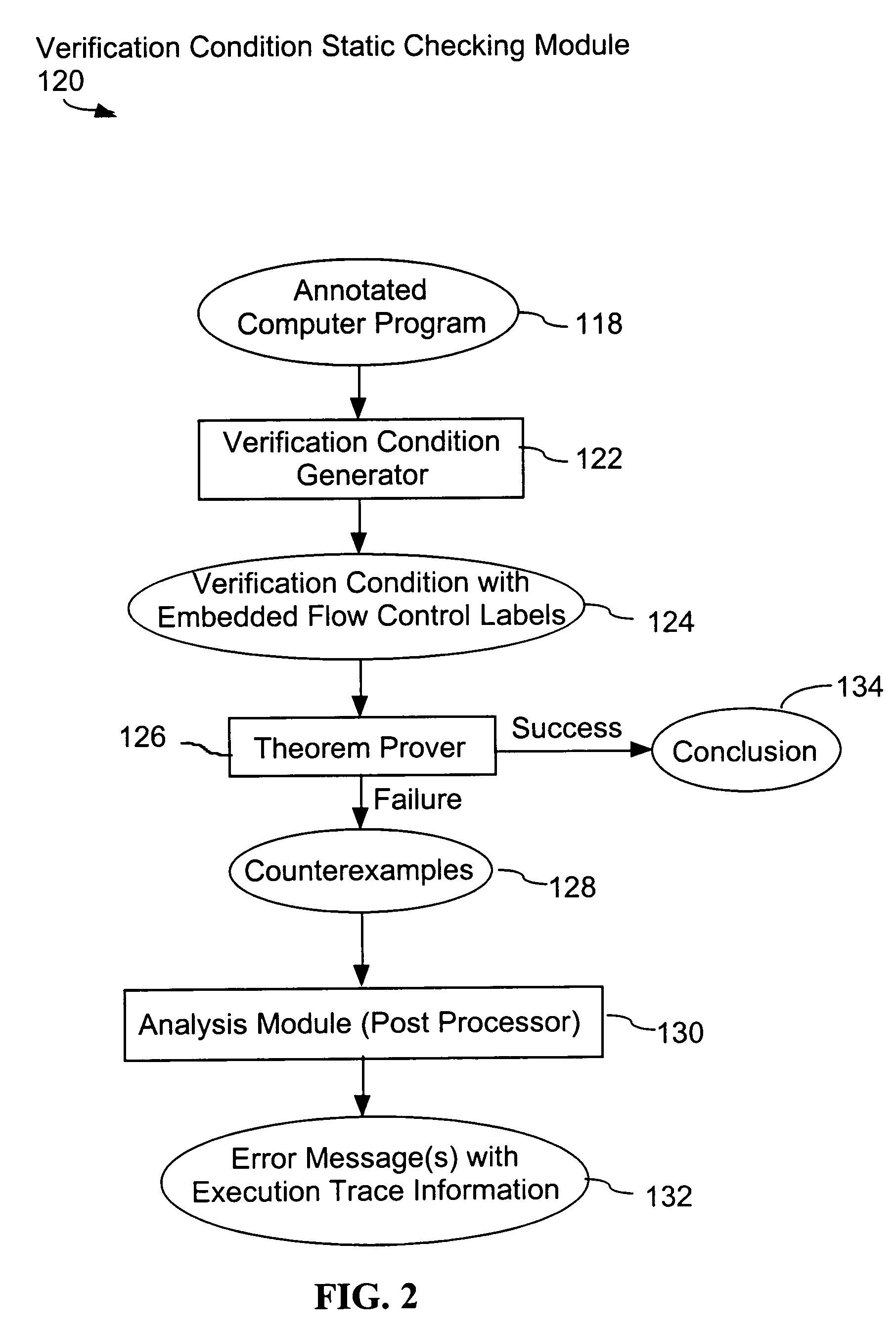
System and method for verifying computer program correctness and providing recoverable execution trace information
In a system for statically analyzing a specified computer, a verification condition generator converts the program into a logical equation, called a verification condition, and inserts program flow control labels into the sub-equations of the verification condition. The flow control labels identify conditional branch points in the specified computer program. A theorem prover is applied to the logical equation to determine truth of the logical equation, and when the truth of the logical equation cannot be proved, the theorem prover generates at least one counter-example identifying one of the conditions, one or more variable values inconsistent with that condition, and any of the flow control labels for conditional branch points of the program associated with the identified variable values. A post processing module converts each counter-example into an error message that includes a program trace when the counter-example identifies one or more of the flow control labels.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
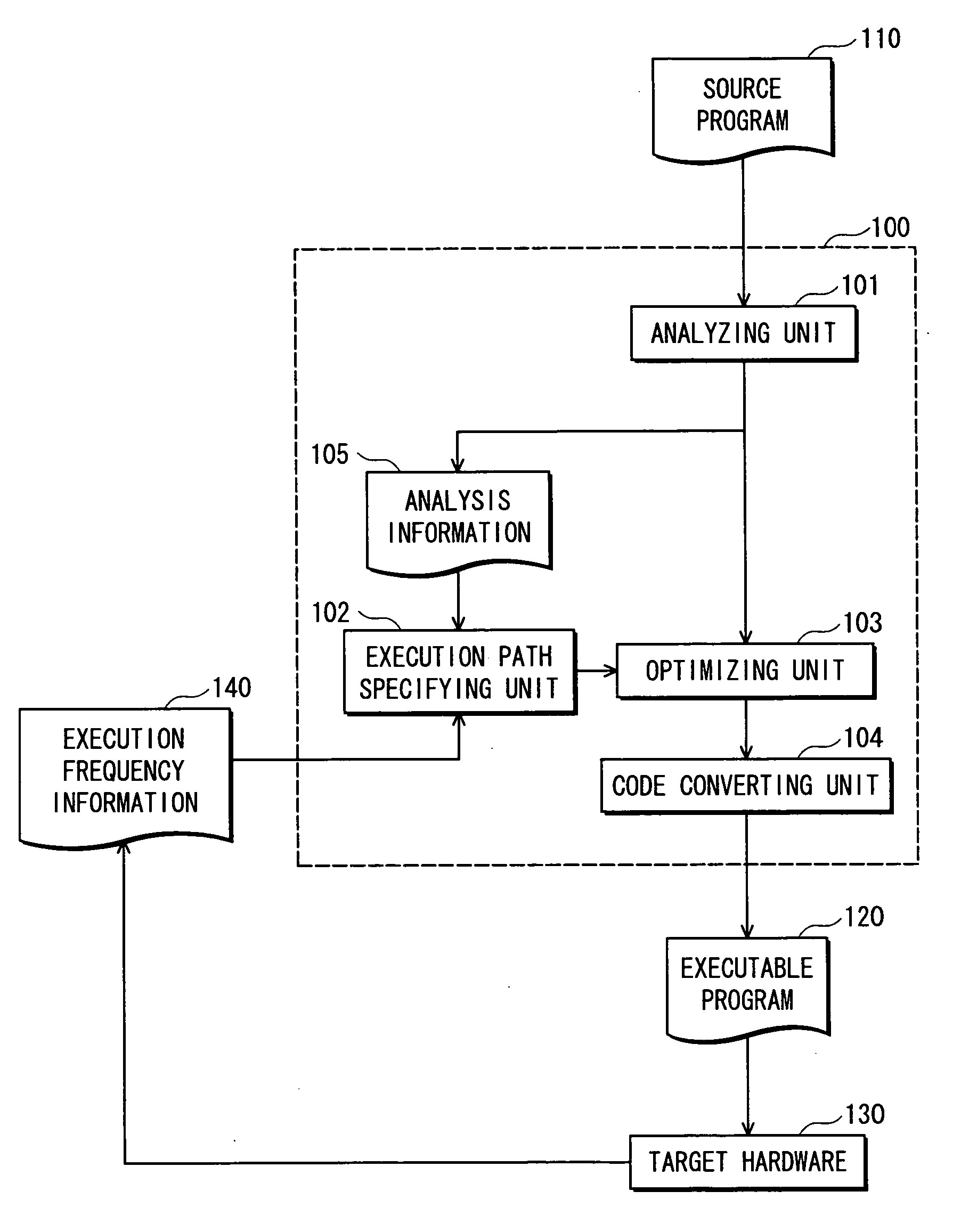
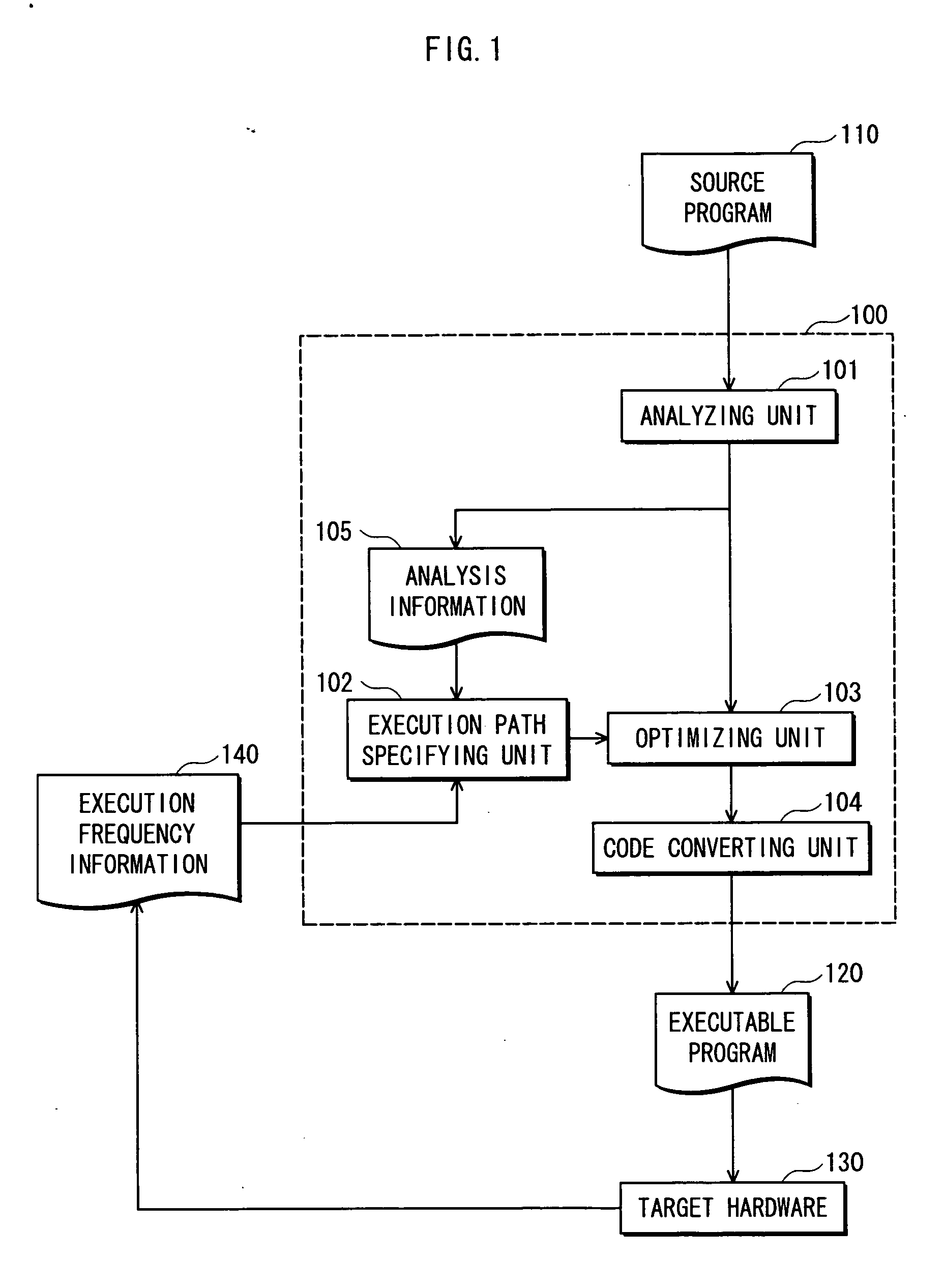
Program conversion device, program conversion and execution device, program conversion method, and program conversion and execution method
InactiveUS20060130012A1Run fastImprove execution performanceSoftware engineeringProgram controlParallel computingComputer generation
To provide a compiler device that generates an executable program for a computer capable of executing two or more instructions in parallel, without using compensation code in trace scheduling. The compiler device generates the executable program that causes the computer to concurrently execute code which is a substantially direct translation of the source program, and code generated by optimizing a sequence of instructions of a most frequent execution path in the source program.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
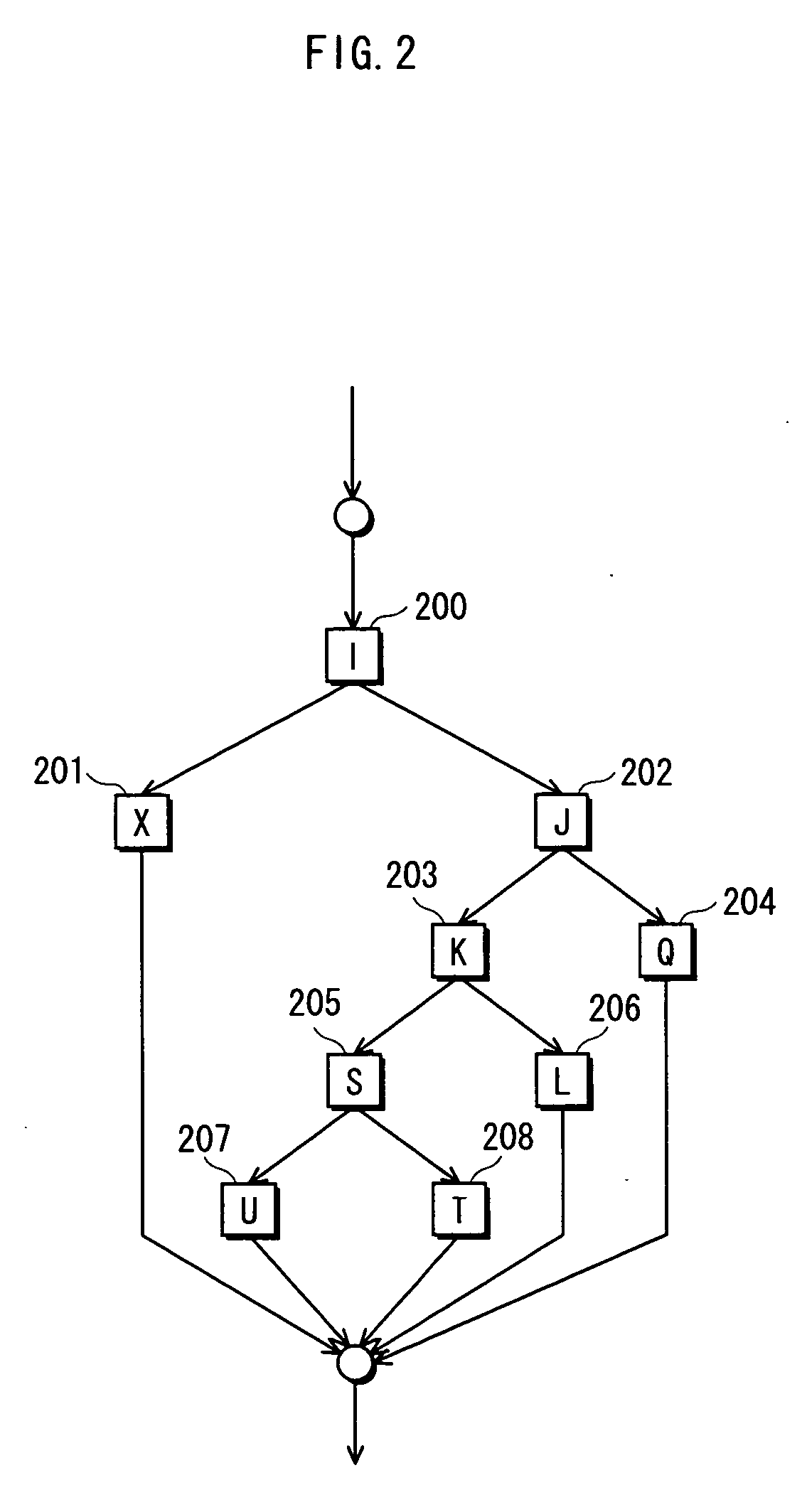
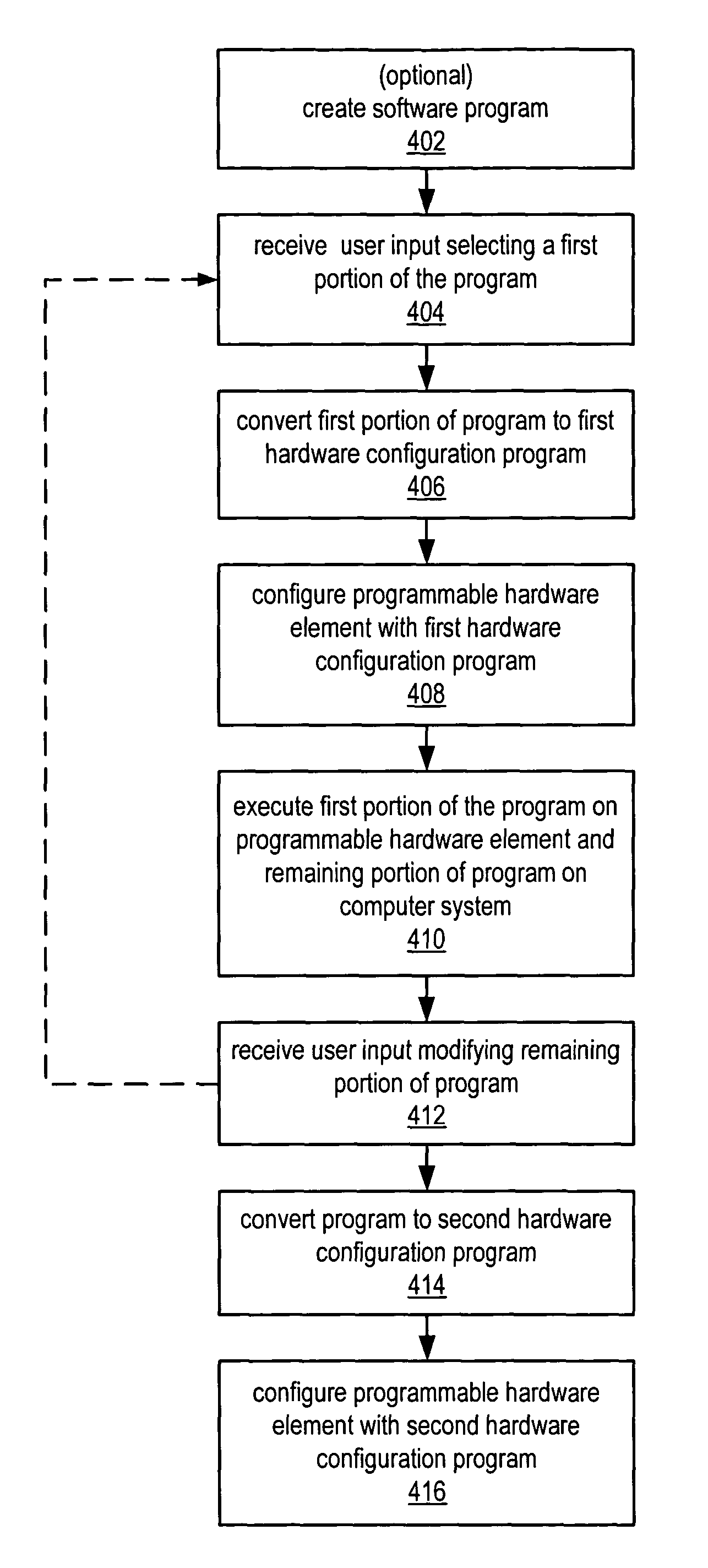
Emulation of a programmable hardware element
ActiveUS20050034102A1Shorten the timeImprove performanceError detection/correctionSpecific program execution arrangementsUser inputParallel computing
System and method for debugging a program intended for execution on a programmable hardware element (PHE) to perform a function. A first portion of the program is converted into a first hardware configuration program (HCP) deployable on the PHE, where a remaining portion is to be debugged by a user. The PHE is configured with the first HCP, and the program executed, including the PHE executing the first portion of the program, and the computer system executing the remaining portion, which is then analyzed and debugged in response to being executed, and user input received modifying the remaining portion to debug the remaining portion. The method is repeated, where in each iteration the first portion is a successively larger portion of the program. After being debugged, the program is converted into a second HCP deployable on the PHE to perform the function, and the PHE configured with the second HCP.
Owner:NATIONAL INSTRUMENTS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com