Patents
Literature
165 results about "Instruction cycle" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
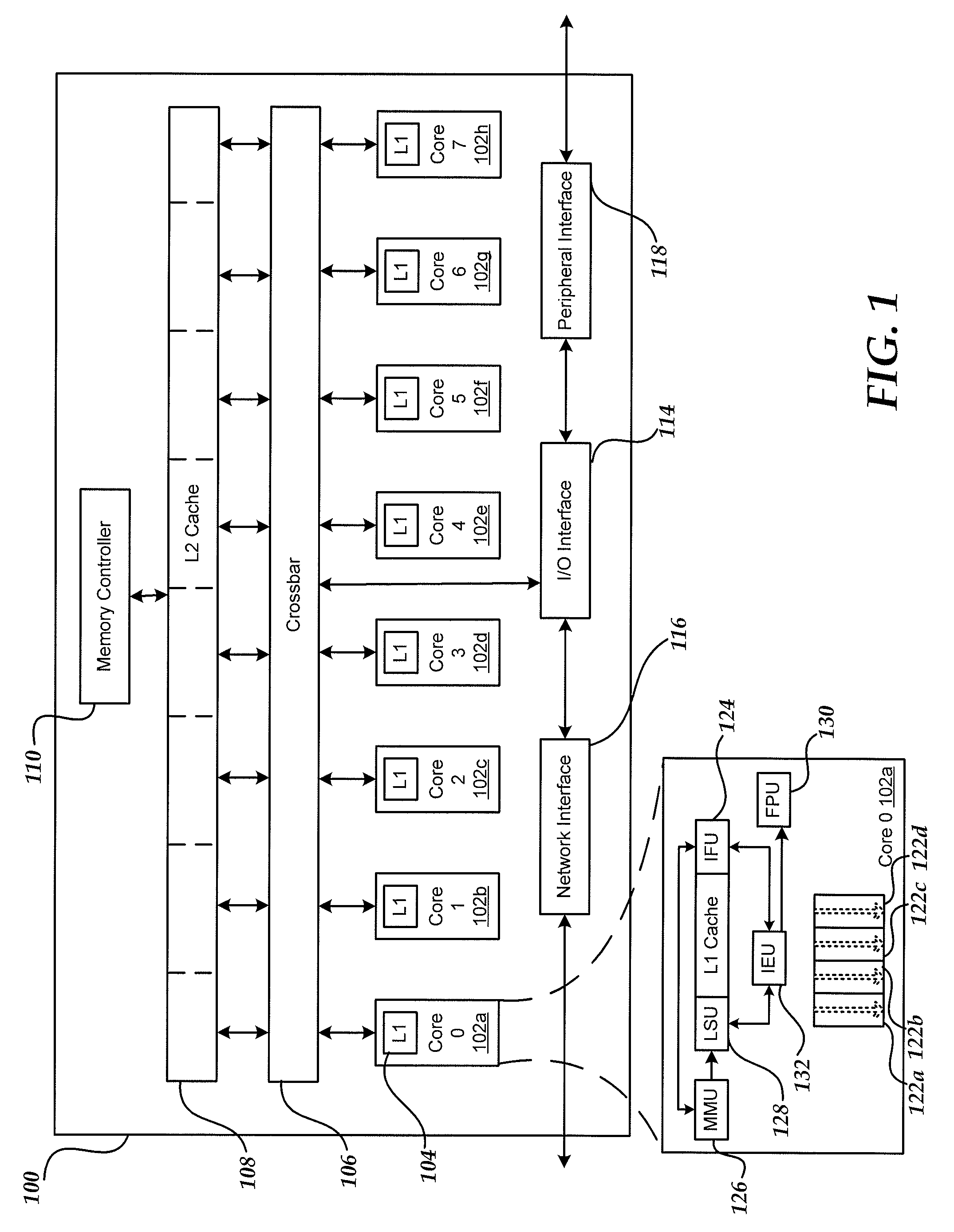
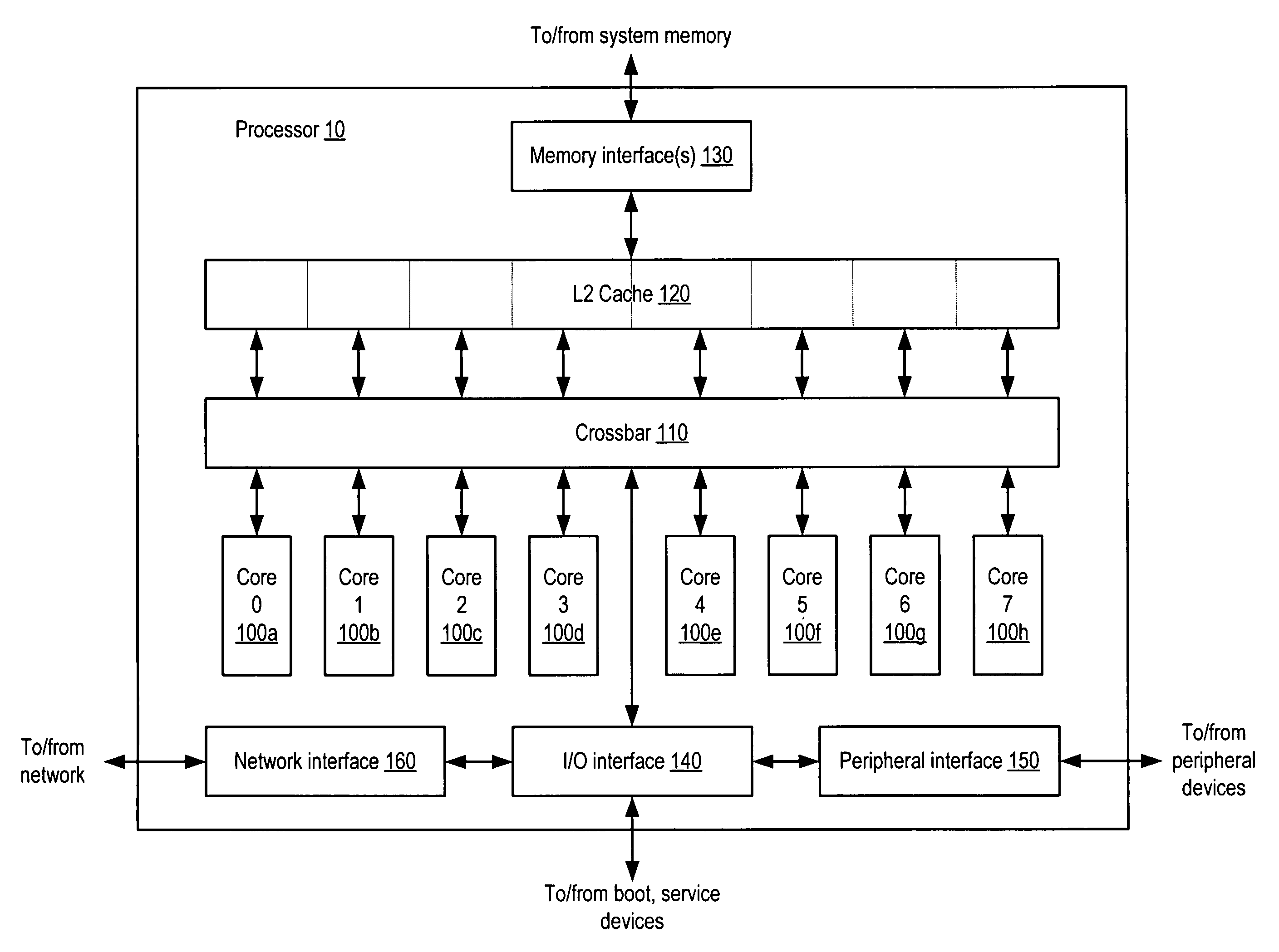
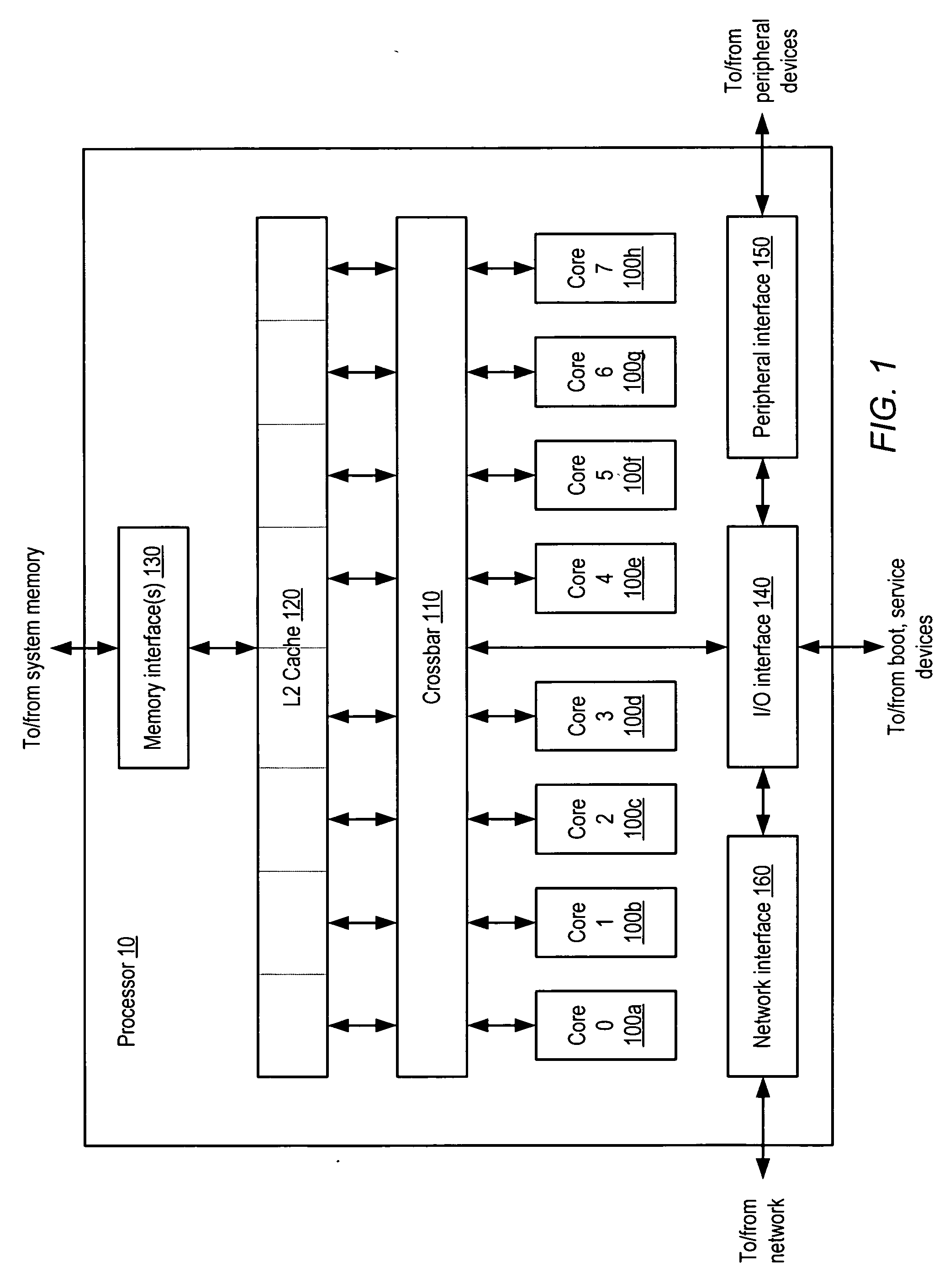
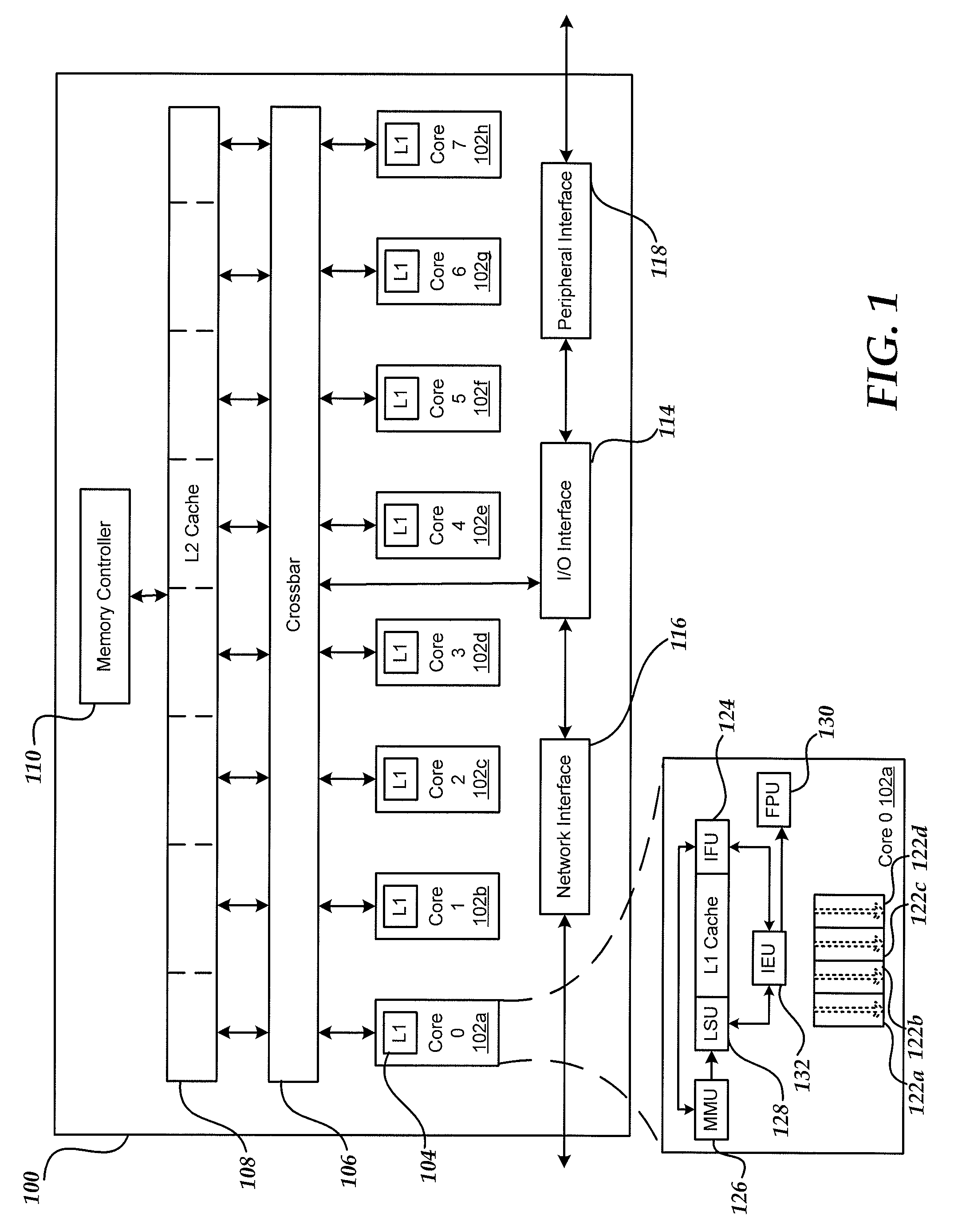
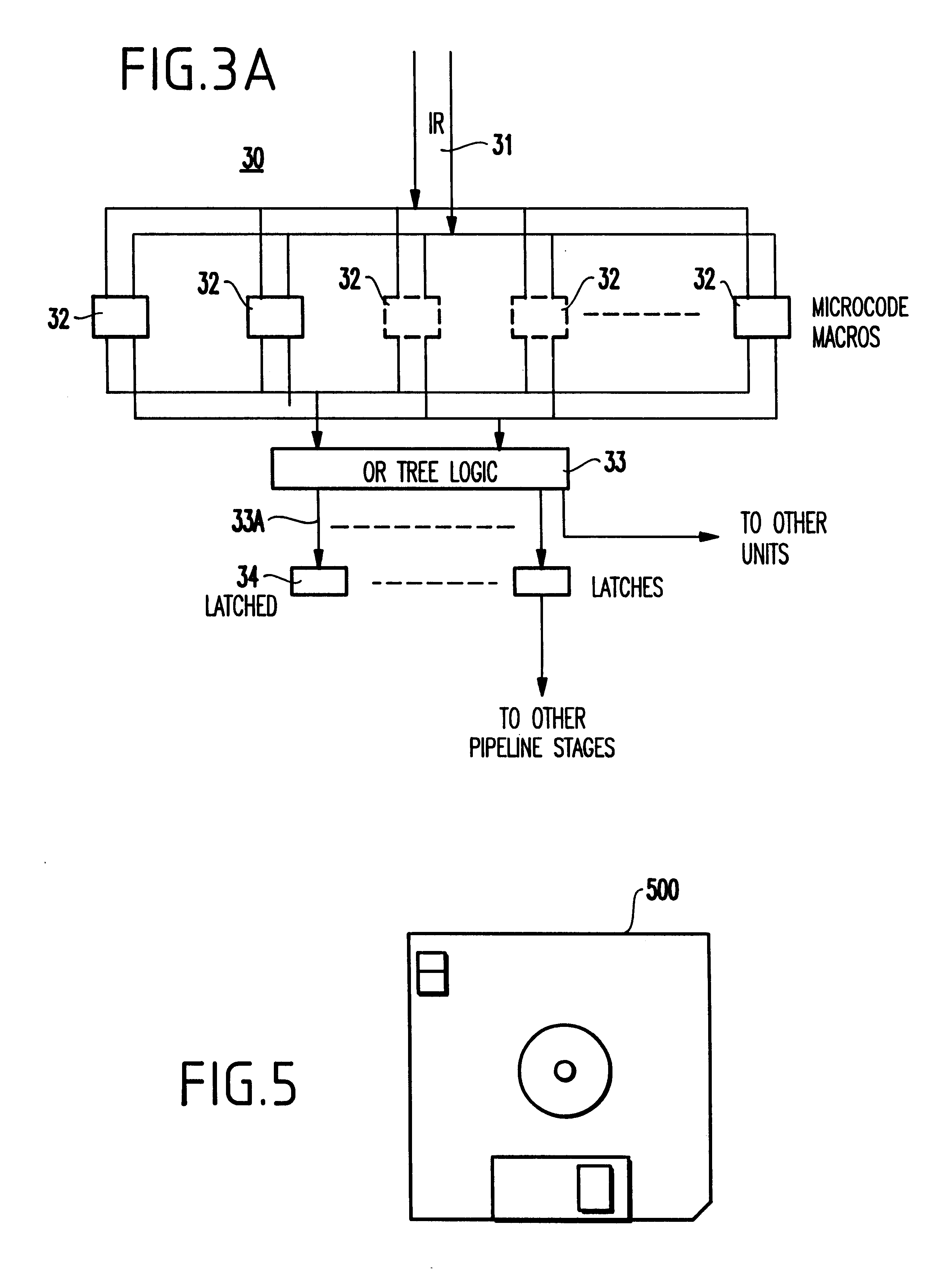
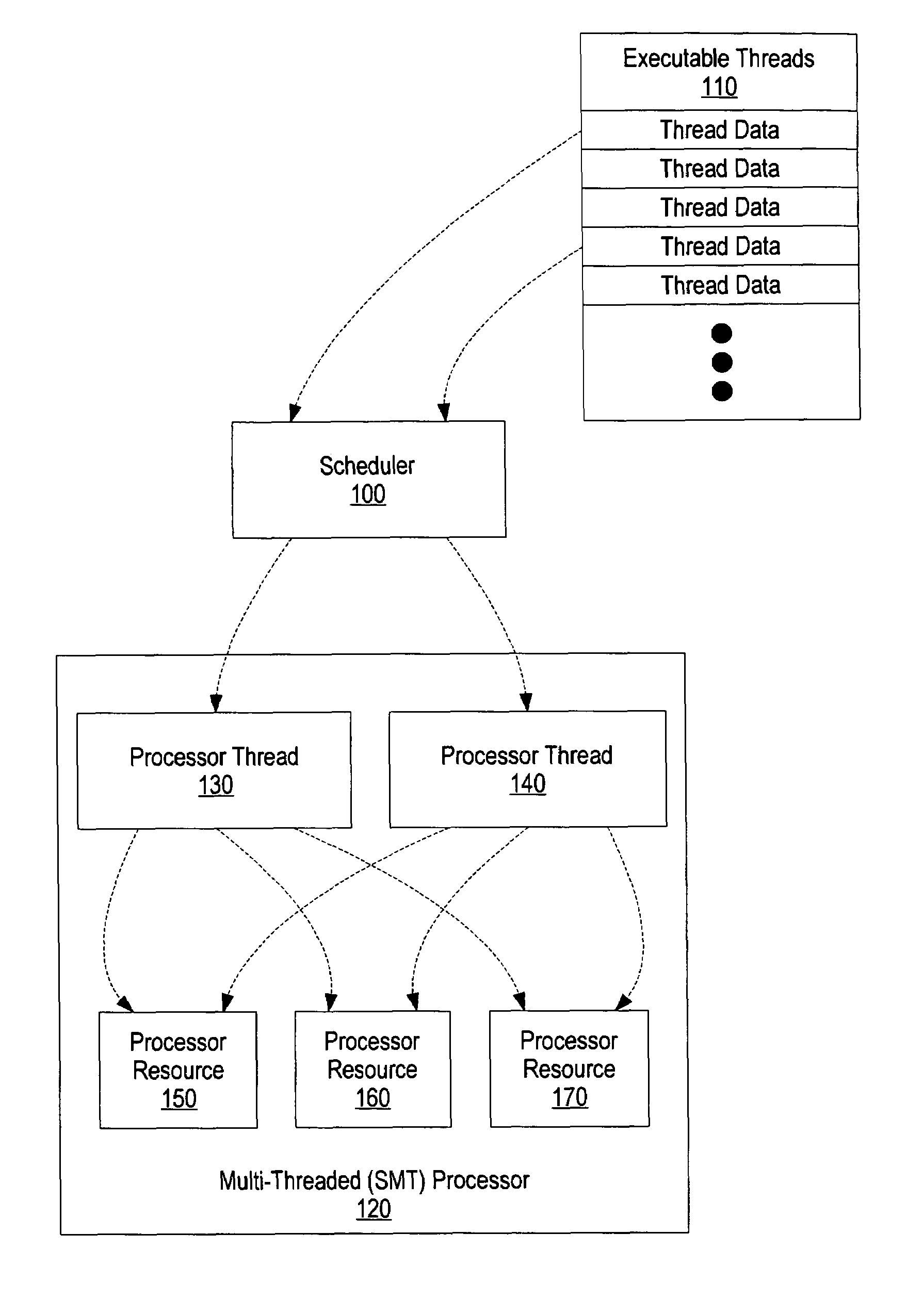
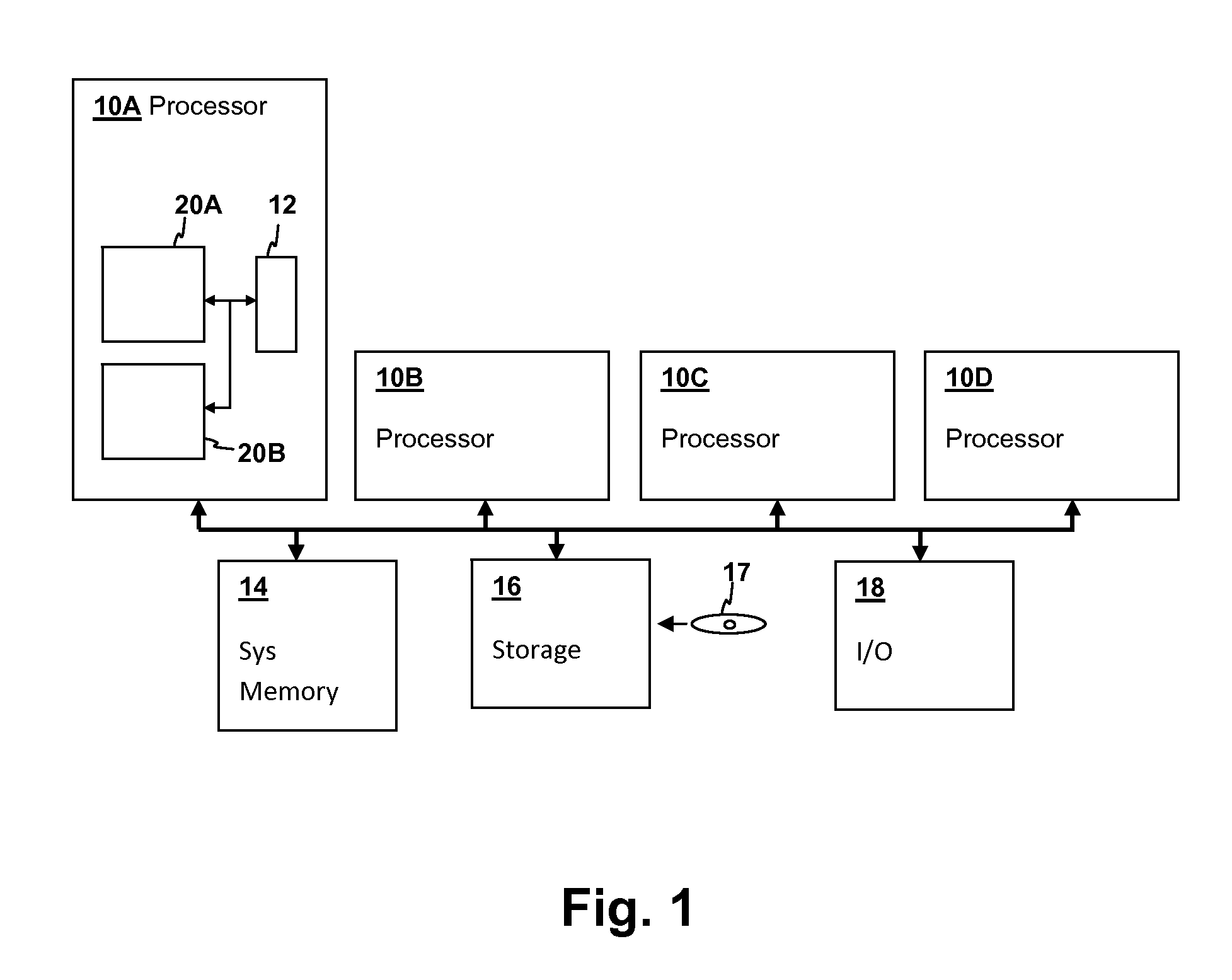
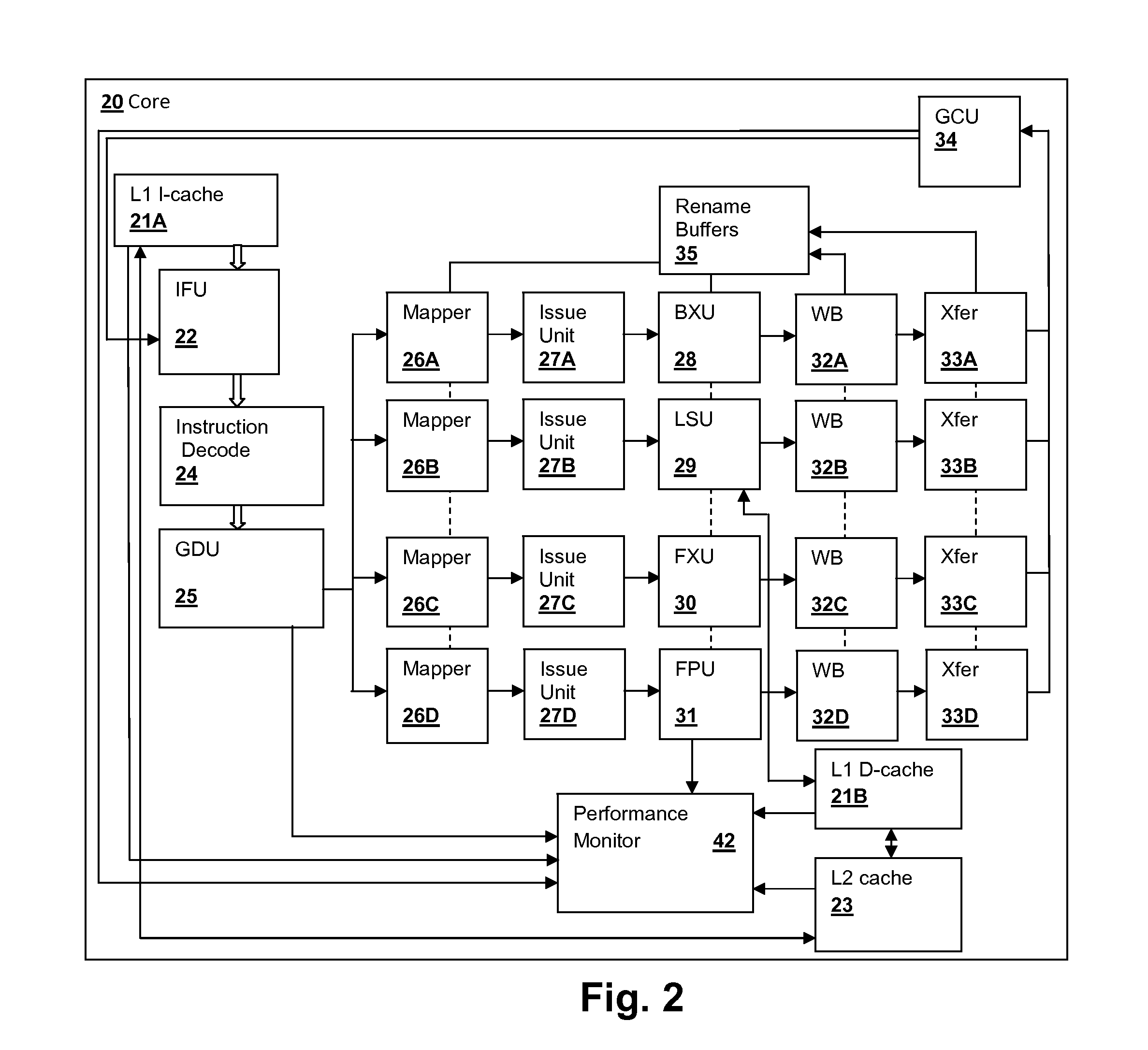
The instruction cycle (also known as the fetch–decode–execute cycle or simply the fetch-execute cycle) is the cycle which the central processing unit (CPU) follows from boot-up until the computer has shut down in order to process instructions. It is composed of three main stages: the fetch stage, the decode stage, and the execute stage.
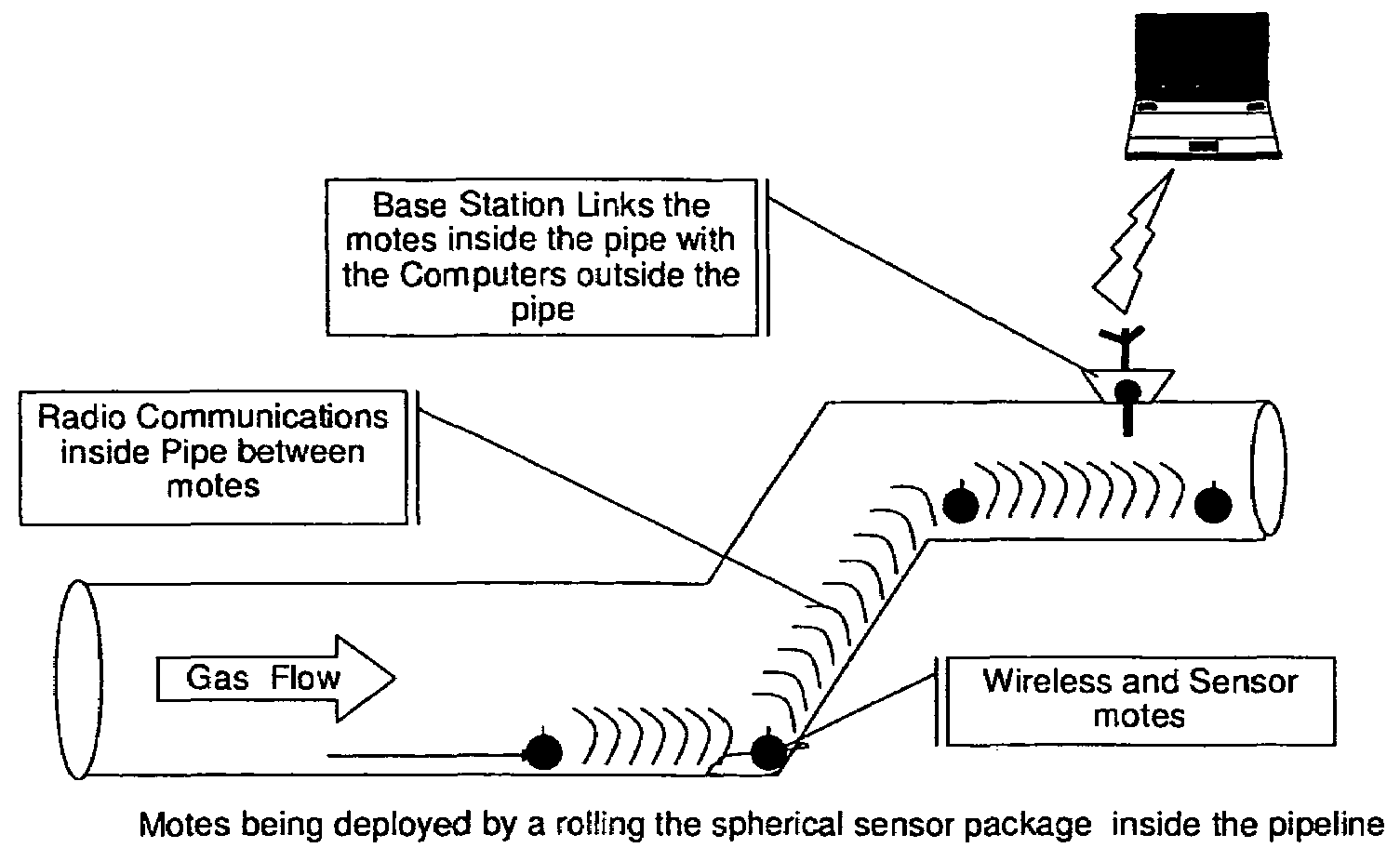
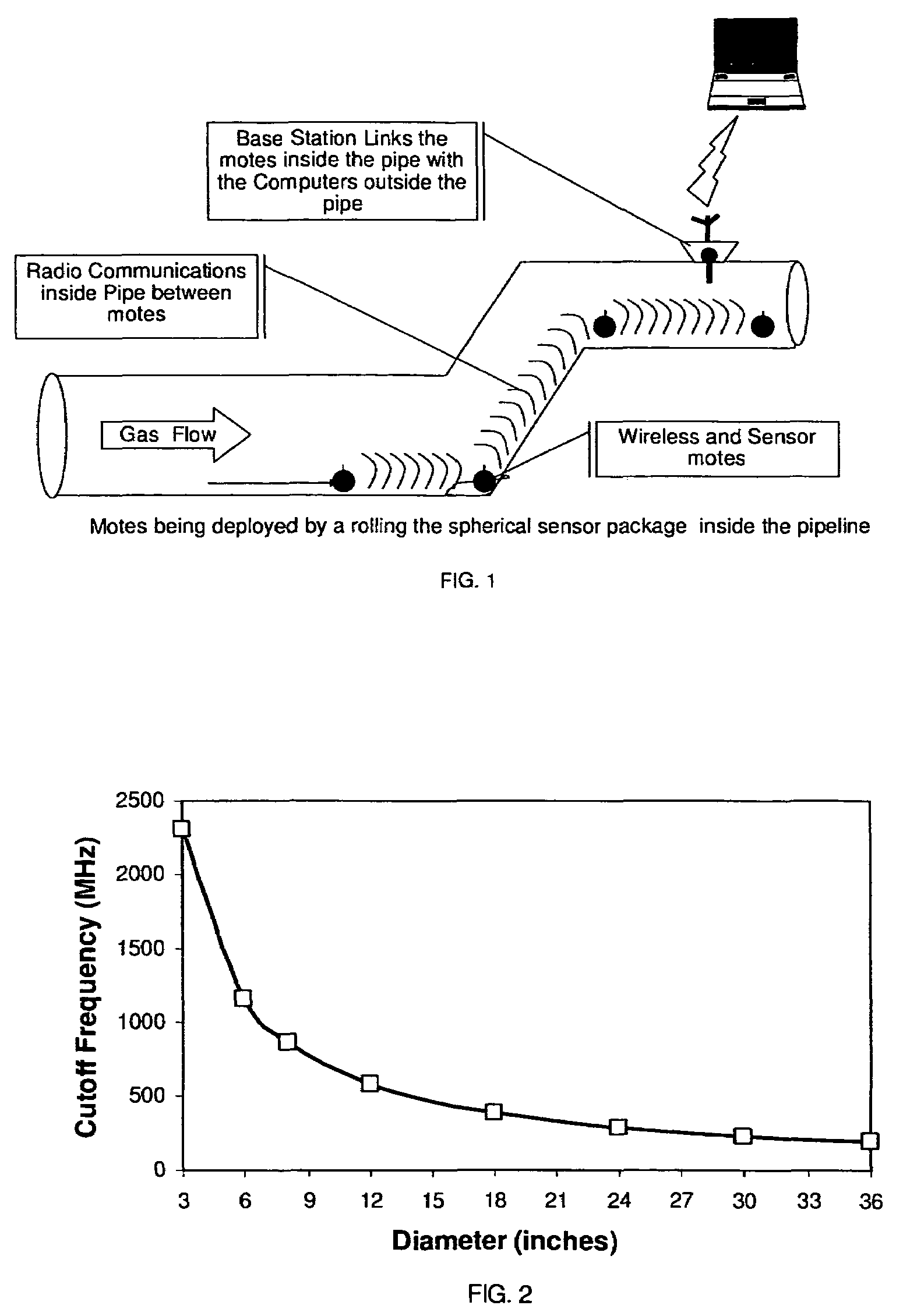
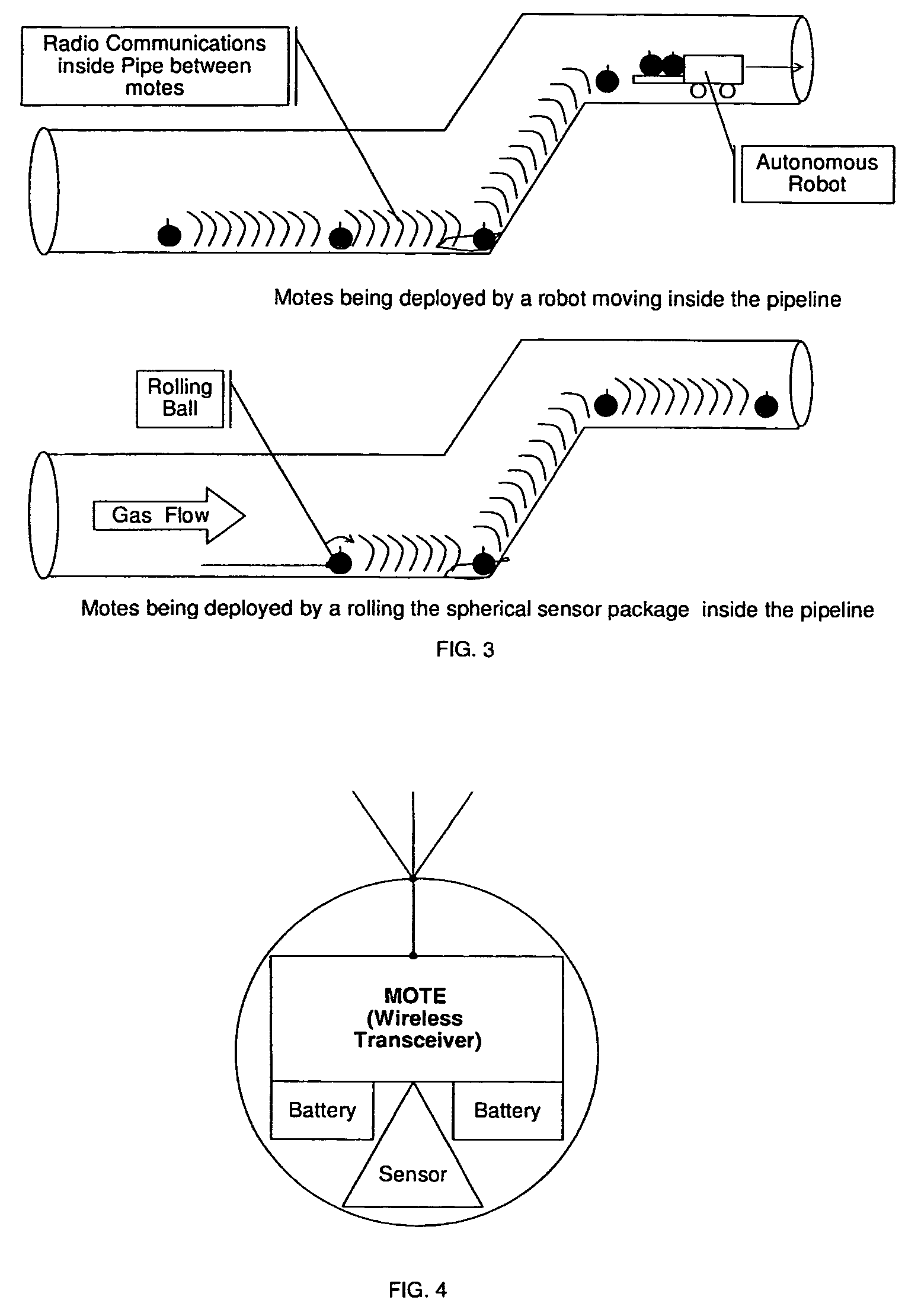
Remote monitoring of pipelines using wireless sensor network
InactiveUS7526944B2Low powerLow costVehicle testingDetection of fluid at leakage pointWireless transceiverWireless mesh network
A wireless sensor network is installed inside pipelines using sensors and wireless transceivers that are small, low-cost, and rugged. The objective is monitoring the pipeline and recommending maintenance and repair at specific locations in the pipeline. Maintenance includes detection of internal corrosion using sensors that can result in leaks. Furthermore detection of leaks for prevention of catastrophic failures as a result of damage, such as third party mechanical damage. After establishing the wireless sensor network, the network is activated so the sensors can make measurements periodically or continuously using instructions transmitted via a base station. The sensor data from the various sensors are transmitted inside the pipe and extracted to access points in the pipeline to a remote computer that stores the data within the computer. The sensed information can be used for monitoring as well as analysis using a recommendation engine to provide maintenance and repair alerts.
Owner:SOUTHWEST RES INST
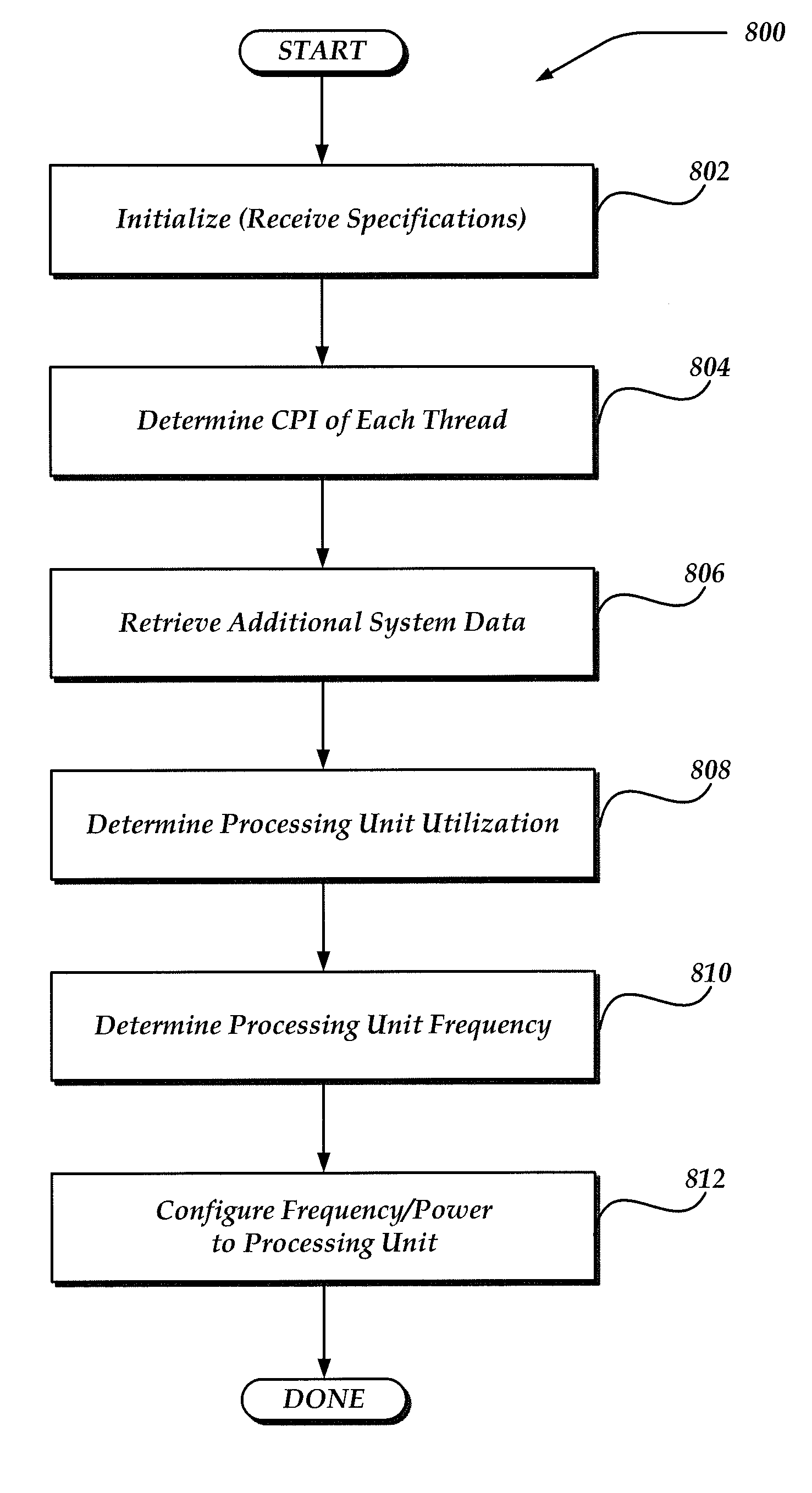
Use of cpi power management in computer systems
A device, system, and method are directed towards managing power consumption in a computer system with one or more processing units, each processing unit executing one or more threads. Threads are characterized based on a cycles per instruction (CPI) characteristic of the thread. A clock frequency of each processing unit may be configured based on the CPI of each thread assigned to the processing unit. In a system wherein higher clock frequencies consume greater amounts of power, the CPI may be used to determine a desirable clock frequency. The CPI of each thread may also be used to assign threads to each processing unit, so that threads having similar characteristics are grouped together. Techniques for assigning threads and configuring processor frequency may be combined to affect performance and power consumption. Various specifications or factors may also be considered when scheduling threads or determining processor frequencies.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
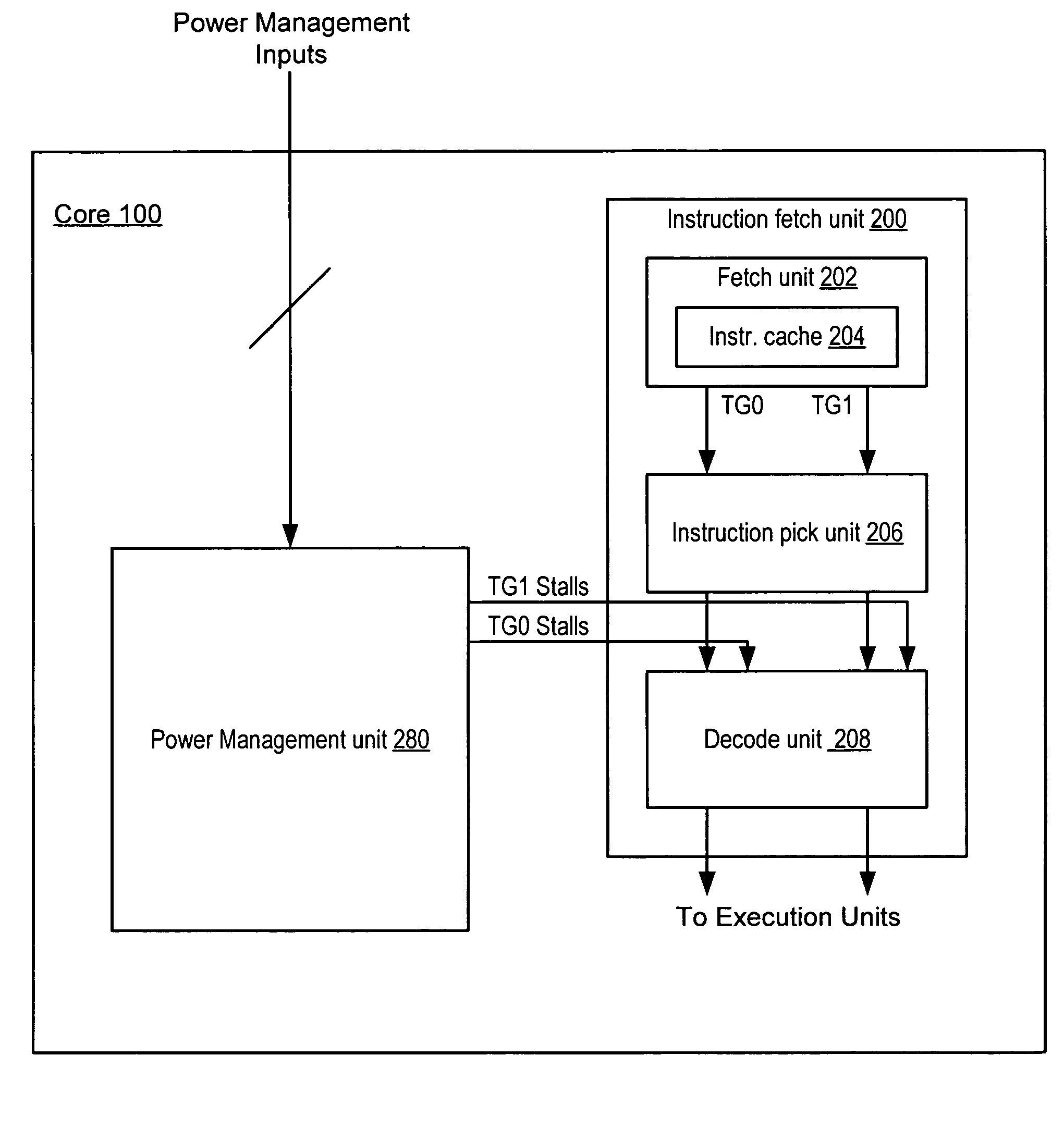
Method and appratus for power throttling in a multi-thread processor
ActiveUS20060020831A1Save powerRegister arrangementsVolume/mass flow measurementControl powerParallel computing
A method and apparatus for controlling power consumption in a processor. In one embodiment, a processor includes a pipeline. The pipeline includes logic for fetching instructions, issuing instructions, and executing instructions. The processor also includes a power management unit. The power management unit is configured to input M stalls into the pipeline every N instruction cycles (where M and N are integer value and wherein M is less than N).
Owner:SUN MICROSYSTEMS INC
Compiler apparatus and compilation method
InactiveUS20040154006A1Avoid changeReduce power consumptionEnergy efficient ICTSoftware engineeringMachine instructionInstruction cycle
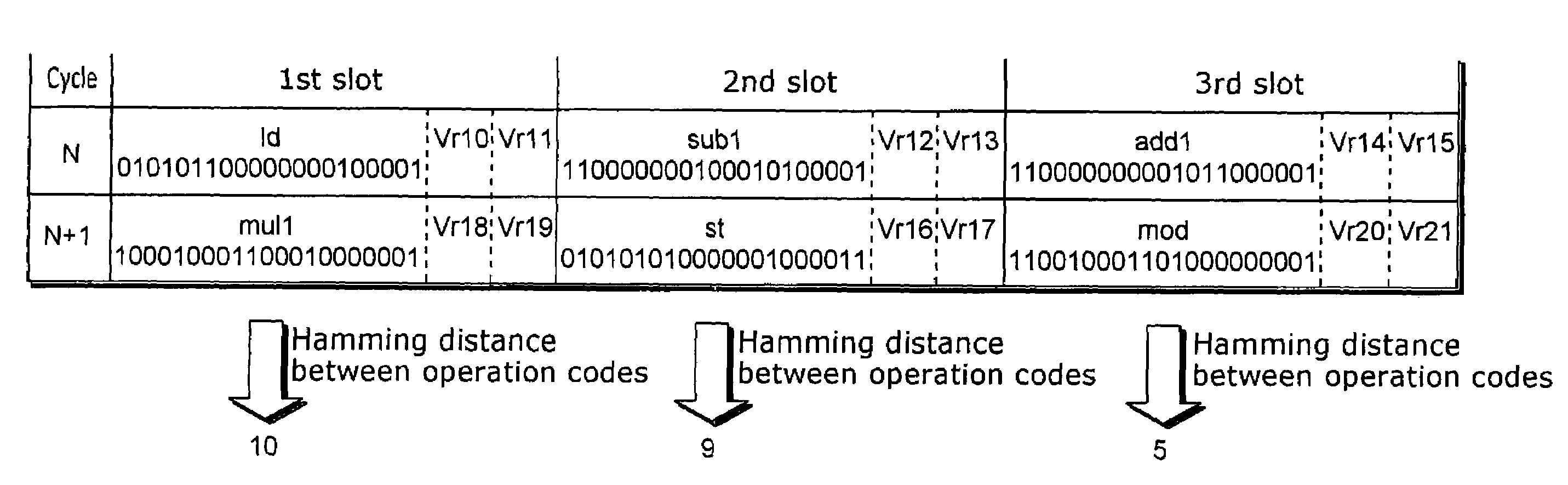
A compiler apparatus that is capable of generating instruction sequences for causing a processor with parallel processing capability to operate with lower power consumption is a compiler apparatus that translates a source program into a machine language program for the processor including a plurality of execution units which can execute instructions in parallel and a plurality of instruction issue units which issue the instructions executed respectively by the plurality of execution units, and includes: a parser unit operable to parse the source program; an intermediate code conversion unit operable to convert the parsed source program into intermediate codes; an optimization unit operable to optimize the intermediate codes so as to reduce a hamming distance between instructions placed in positions corresponding to the same instruction issue unit in consecutive instruction cycles, without changing dependency between the instructions corresponding to the intermediate codes; and a code generation unit operable to convert the optimized intermediate codes into machine language instructions.
Owner:SOCIONEXT INC
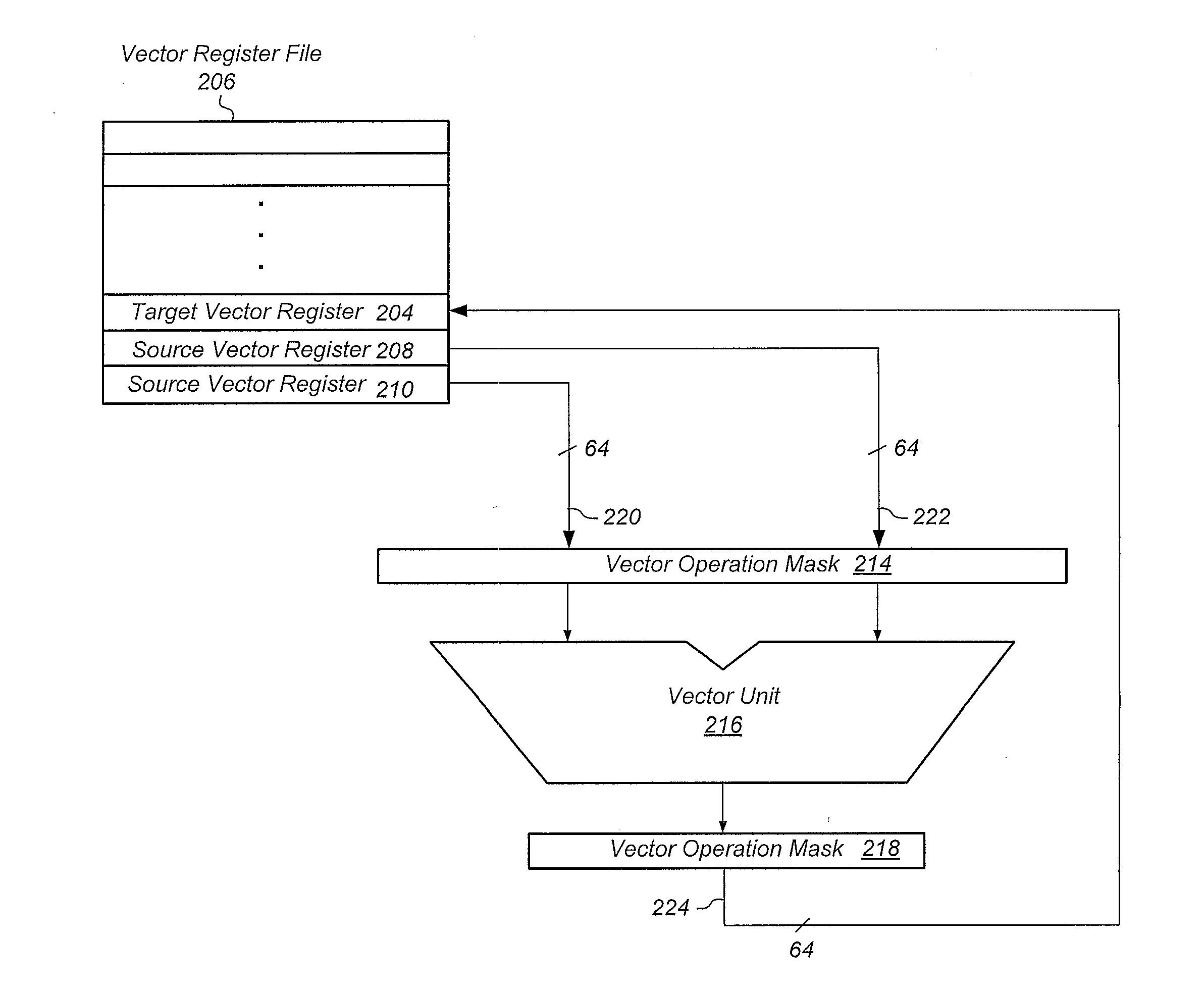
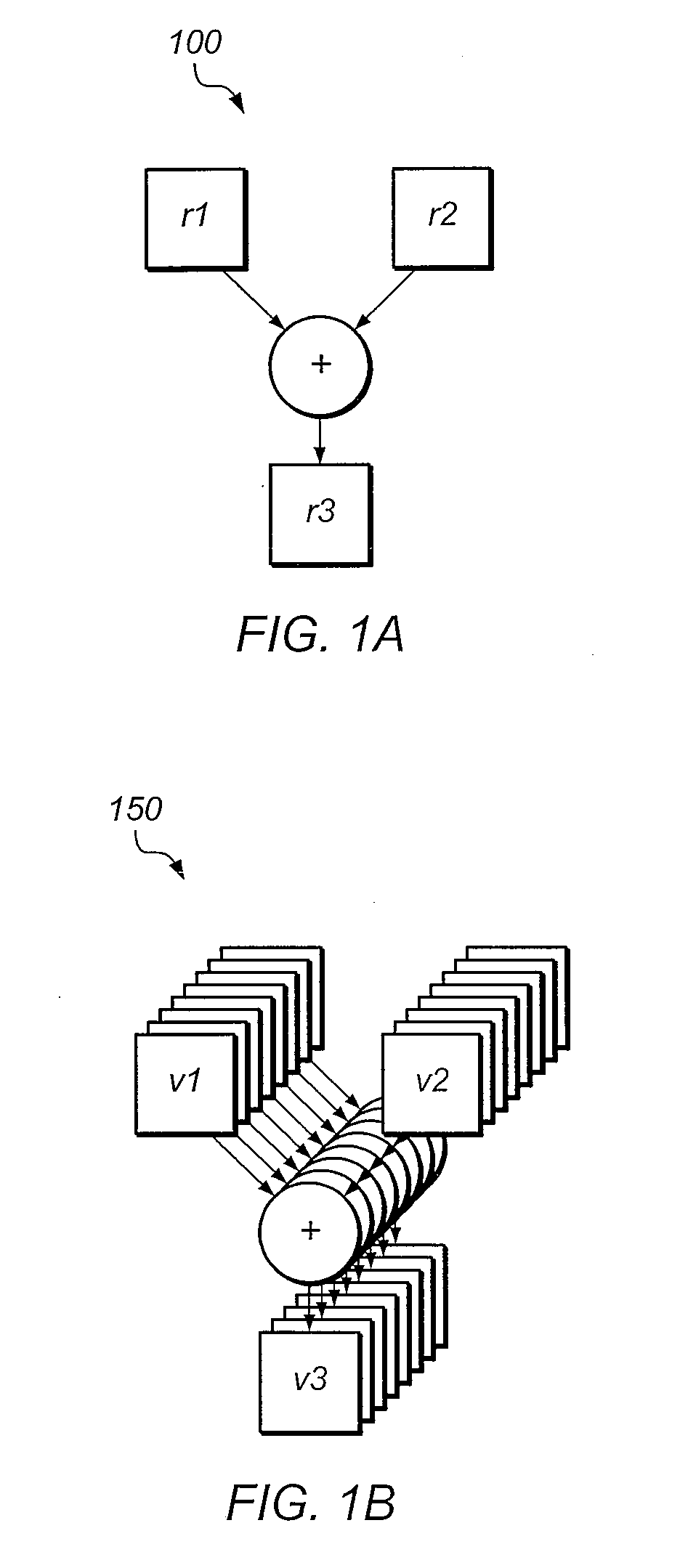
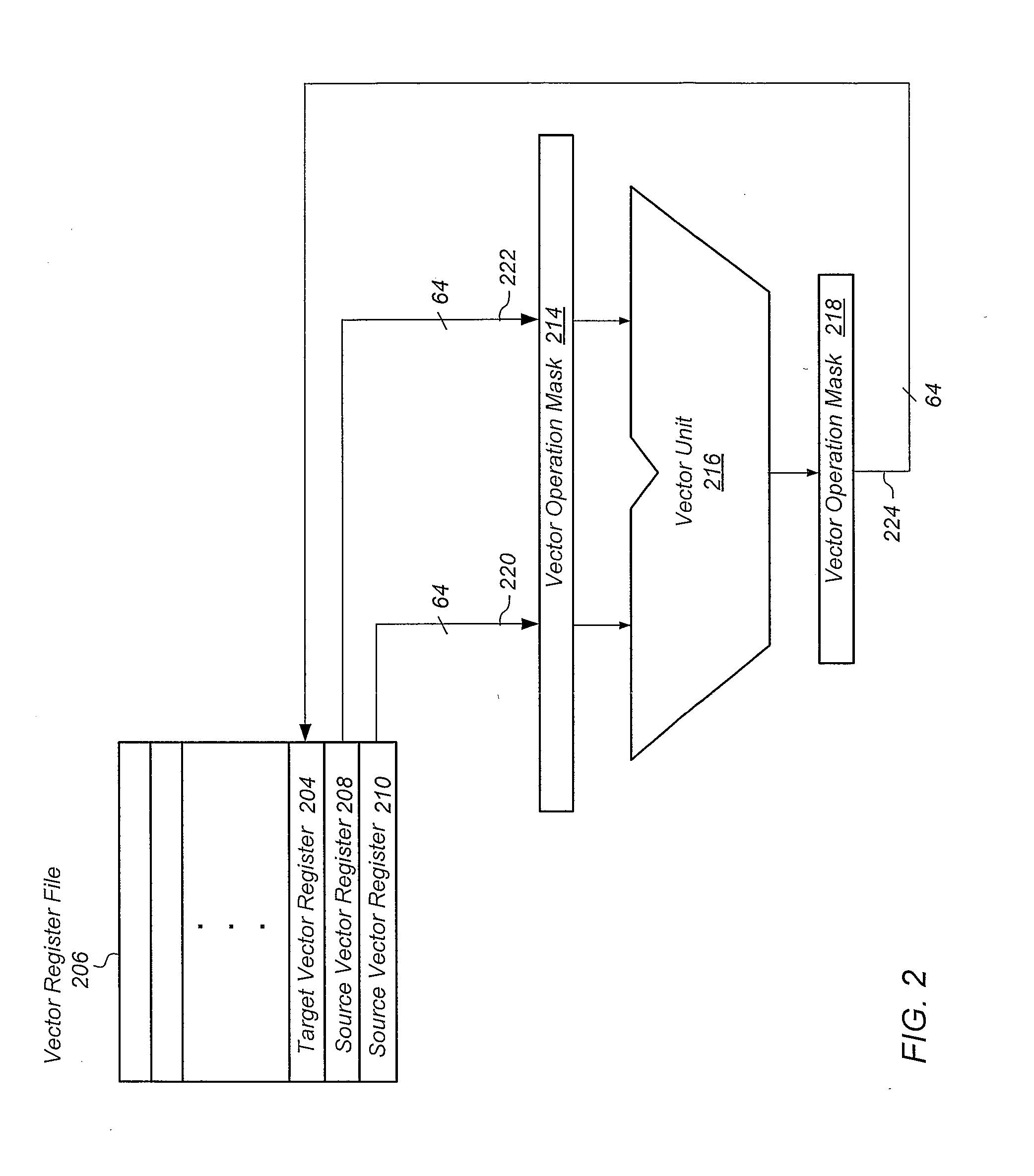
Apparatus and method of single-instruction, multiple-data vector operation masking
InactiveUS20120216011A1Reduce power consumptionGeneral purpose stored program computerMachine execution arrangementsInstruction cyclePartial filling
An apparatus, method, and medium for performing a vector operation on portions of one or more source vector registers. A vector unit performs an operation on the source vector registers and only stores results in the target vector register for elements which are selected by the vector operation mask. The vector operation mask can be read by the vector unit or loaded into the vector unit for each instruction cycle. The vector operation mask allows the vector unit to be used with partially filled source vector registers and eliminates the need for scalar operations to be performed on vector data.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
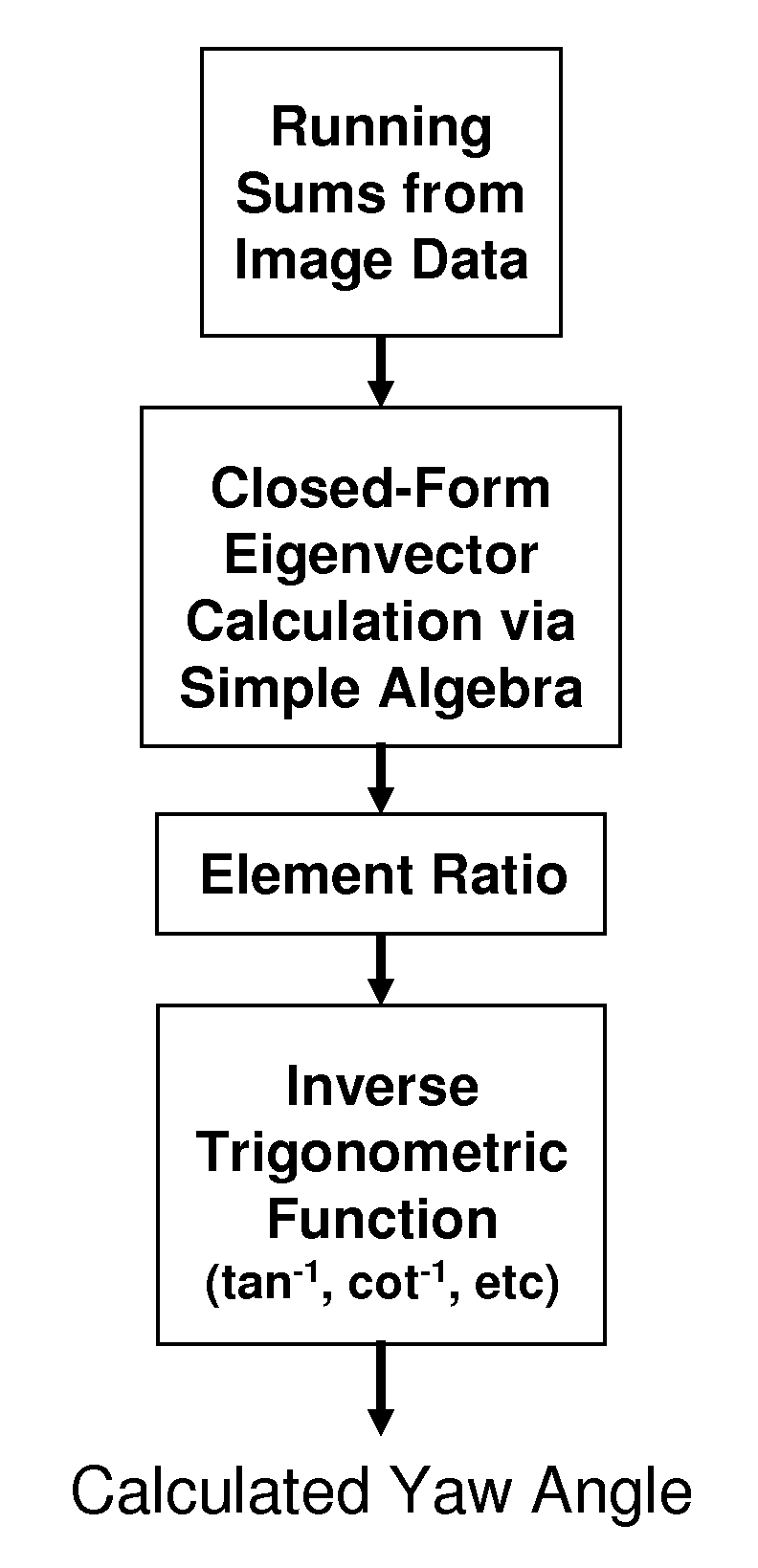
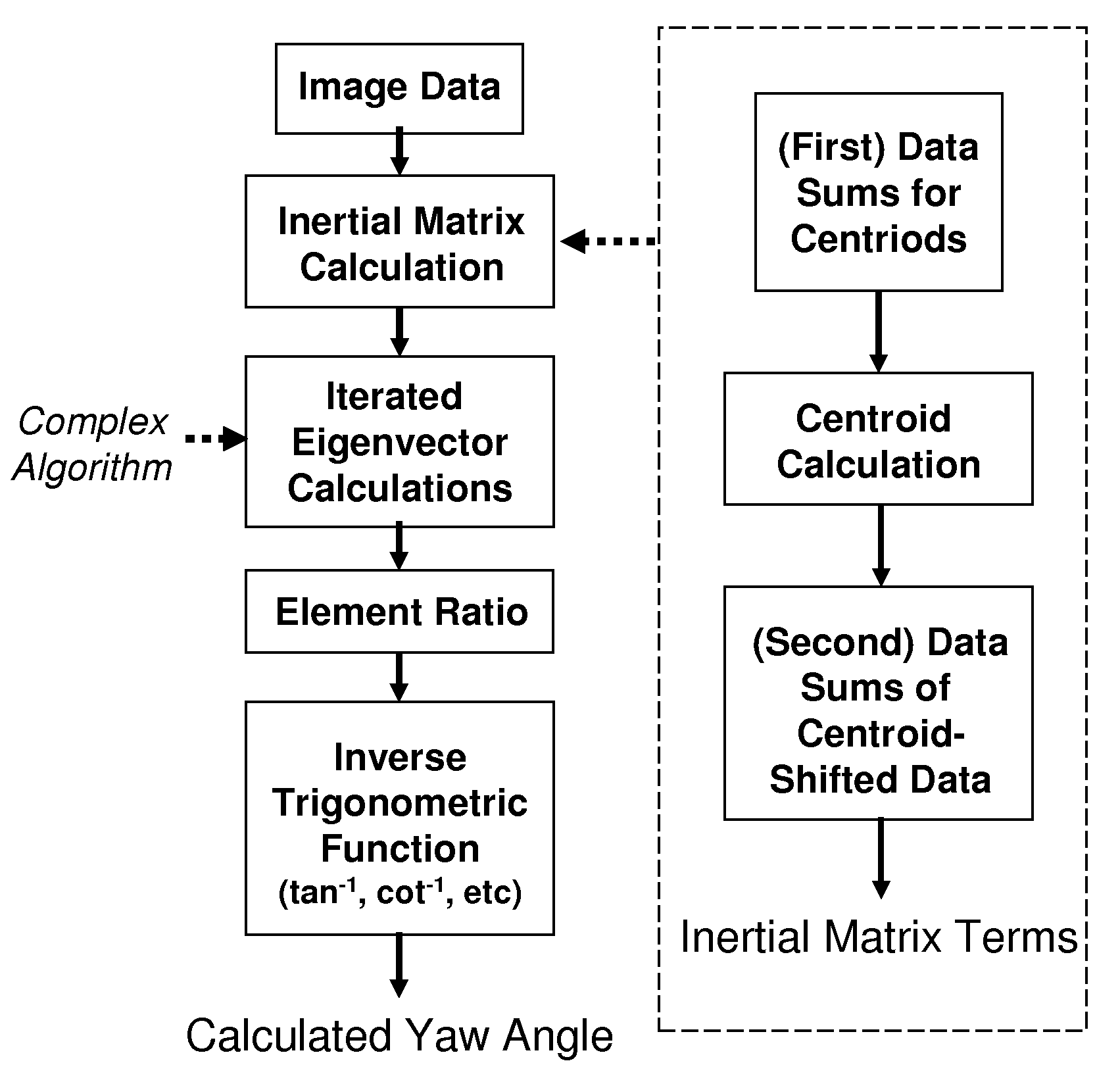
High-performance closed-form single-scan calculation of oblong-shape rotation angles from binary images of arbitrary size using running sums
A method for performing a high-performance closed-form single-scan calculation of oblong-shape rotation angles from binary images of arbitrary size on a processor using running sums is disclosed. Running sums are calculated and stored throughout each scan, and the results are obtained in closed form by simple post-scan computation. An algorithmic embodiment may execute on one or more hardware processors with limited or constrained computation power, available instruction cycles, available memory, etc. Exemplary hardware processors are found in one or more CPUs of a desktop, laptop, tablet, or handheld computing device, and may be an embedded processor or a signal processor chip. The resulting method may be used for touch or optical user interfaces, real-time image recognition, real-time machine vision, and other purposes.
Owner:NRI R&D PATENT LICENSING LLC
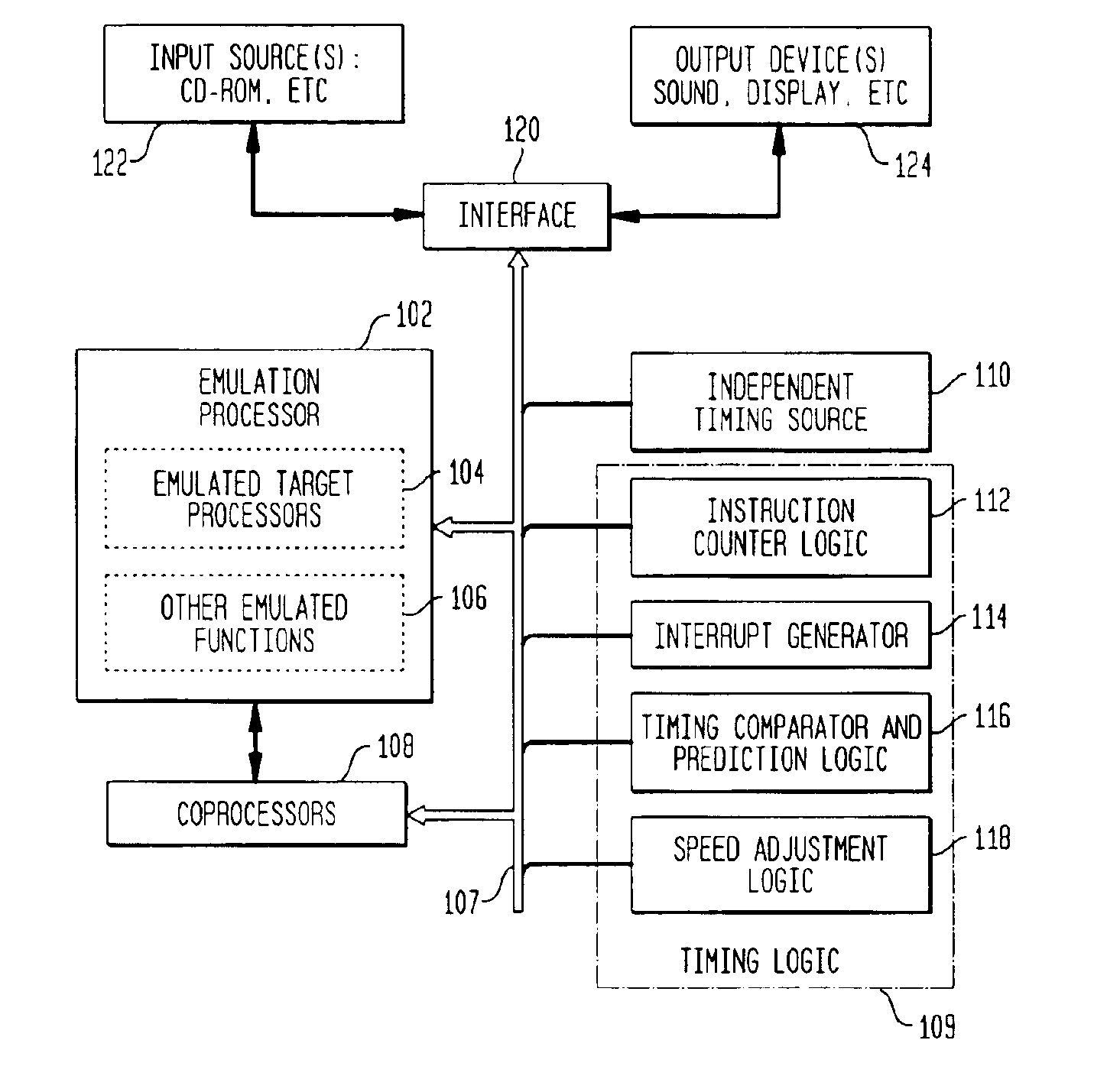
Method of measuring performance of an emulator and for adjusting emulator operation in response thereto
InactiveUS6882968B1Consistent and accurate outputHardware monitoringGenerating/distributing signalsParallel computingHosting environment
A method which simulates the operating speed of an emulated target system with a consistent rate of instruction execution on a plurality of host systems with varied and variable instruction execution speeds. An arbitrary “time quantum” is selected as a referent and is multiplied by the target's speed of instruction cycle execution to determine the quantity of instructions the target system executes in the specified time period. When non-native code is executed on the host system, a counter is used to track the number of instructions executed and to interrupt when that target quantity is reached. A processor-activity-independent timing source is queried to determine the time elapsed; that measurement is then compared to the original “time quantum.” The resulting ratio is a timing reference that is independent of the operating speed characteristics of any particular host system. This reference is used to predict the operational speed of the host system and to adjust factors in the host computer and emulation process to more accurately match the target system before executing the next block of instructions and repeating the process. In certain embodiments, the time quantum is dynamically adjusted to avoid sampling frequencies, which may conflict or resonate with timing frequencies of other system activities or to place a greater or lesser load on the host system. This process results in more consistent, accurate simulation of the target system's speed on a variety of host system configurations, within the limitations and flexibility of the host environment.
Owner:SONY COMPUTER ENTERTAINMENT INC
Changing a codec or MAC size without affecting the encryption key in PacketCable communication
ActiveUS7127604B2Synchronising transmission/receiving encryption devicesError detection/correctionComputer hardwareRC4
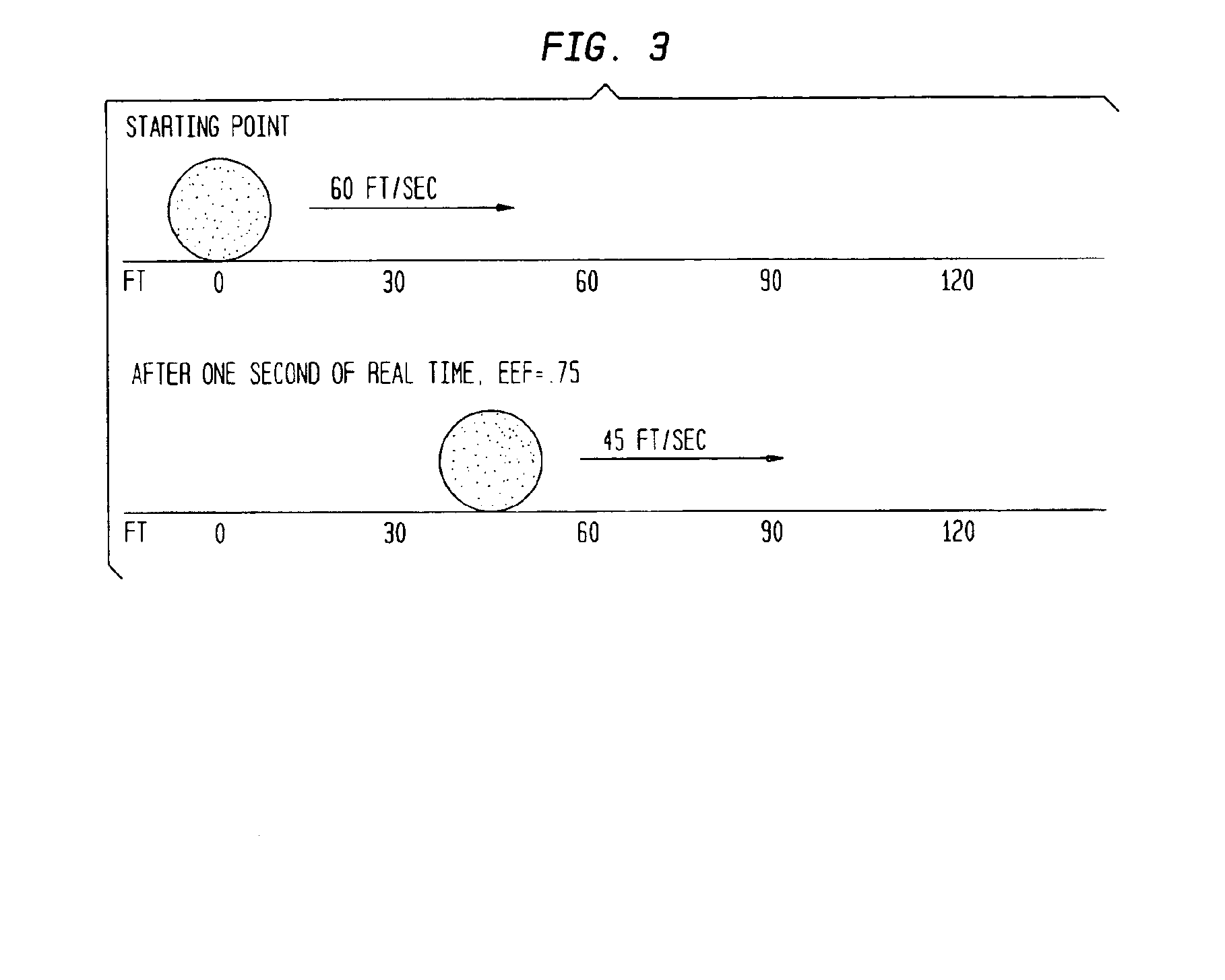
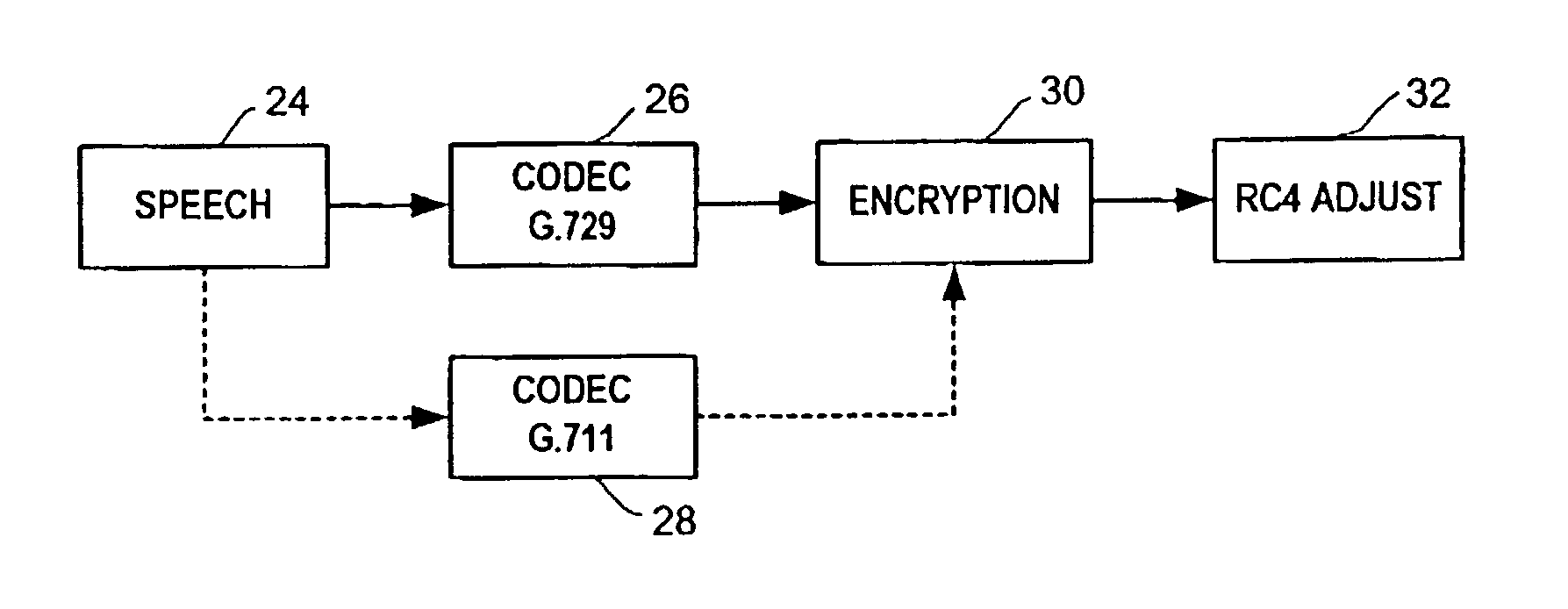
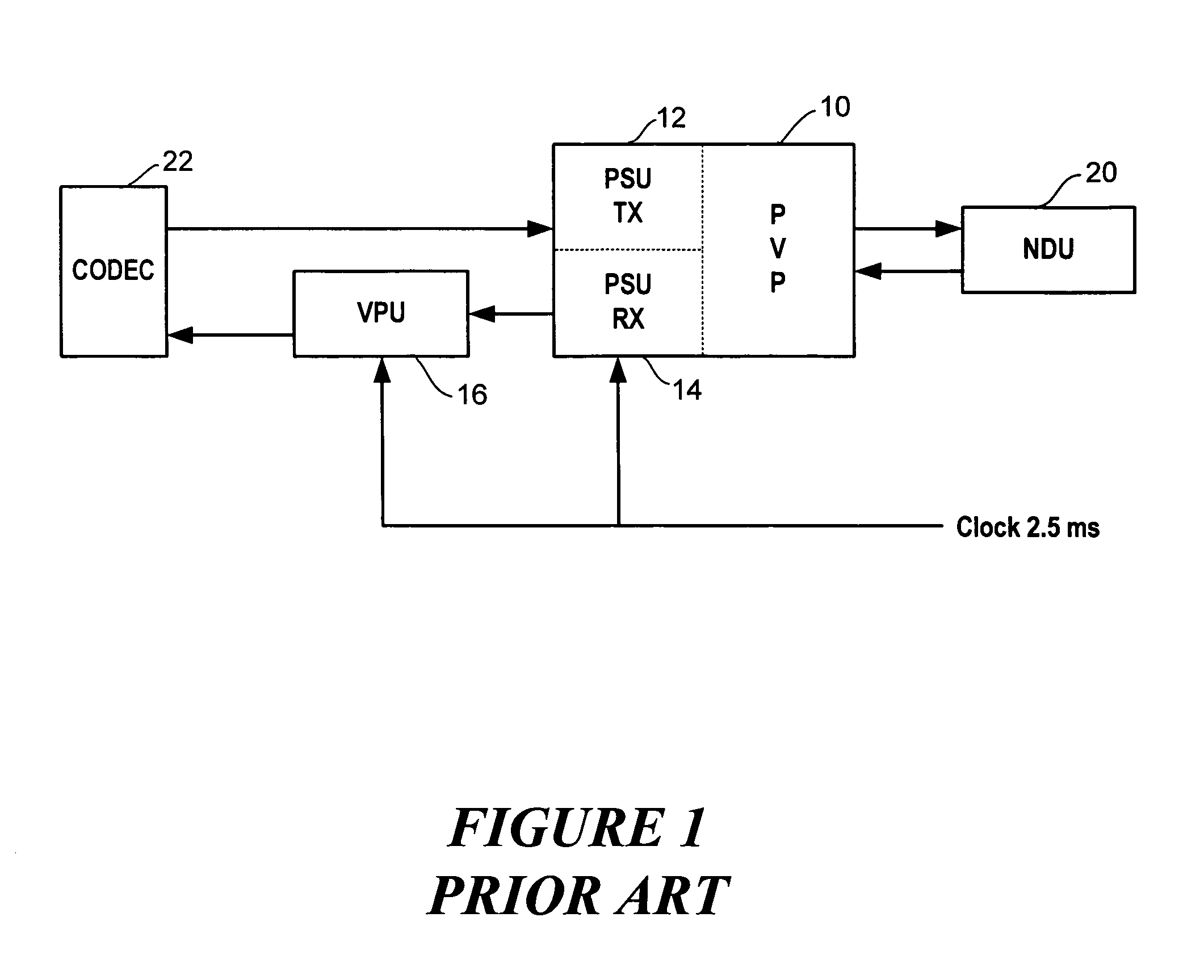
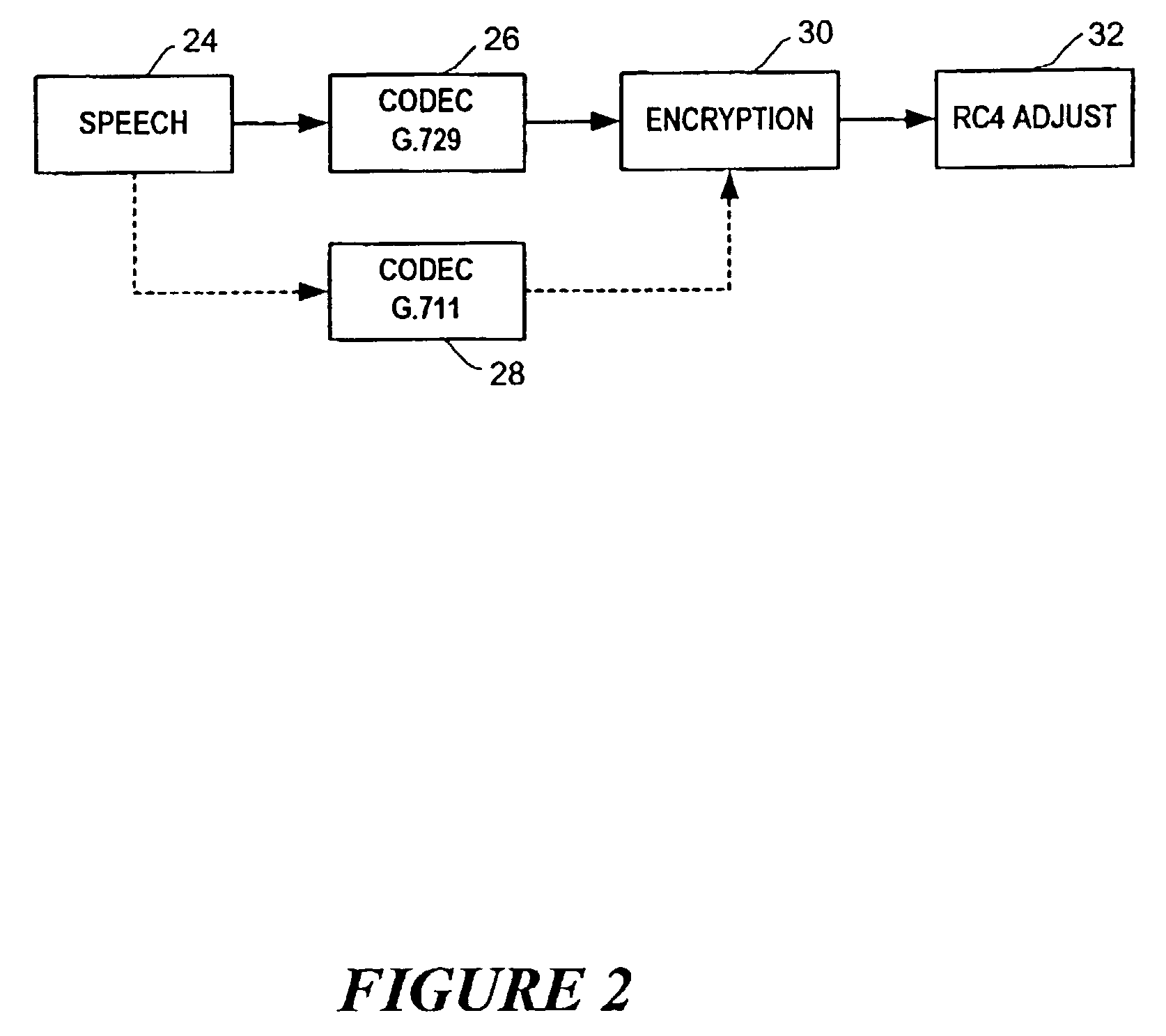
A technique is described to change the codec or MAC (message authentication code) size in a packet security unit for PacketCable communications during realtime voice transmissions is described. An algorithm that provides fast RC4 key advancing to prevent MIPS (millions of instruction cycles per second) overflow is used to perform codec or MAC size changes. The invention is performed without changing the keying material, where the sender and receiver must continue the RC4 encryption process from its state prior to the codec or MAC size change. A sender needs to preserve continuity of the timestamp across a codec change, since the timestamp reflects realtime. Changing the codec or MAC size is likely to change the frame parameters. To preserve continuity of the RC4 state and the timestamp across the codec / MAC size change, the sender TX and receiver RX generates a new frame number. The new frame number is applied to the first frame generated by the new codec or MAC size.
Owner:TELOGY NETWORKS
Adaptive cache compression system
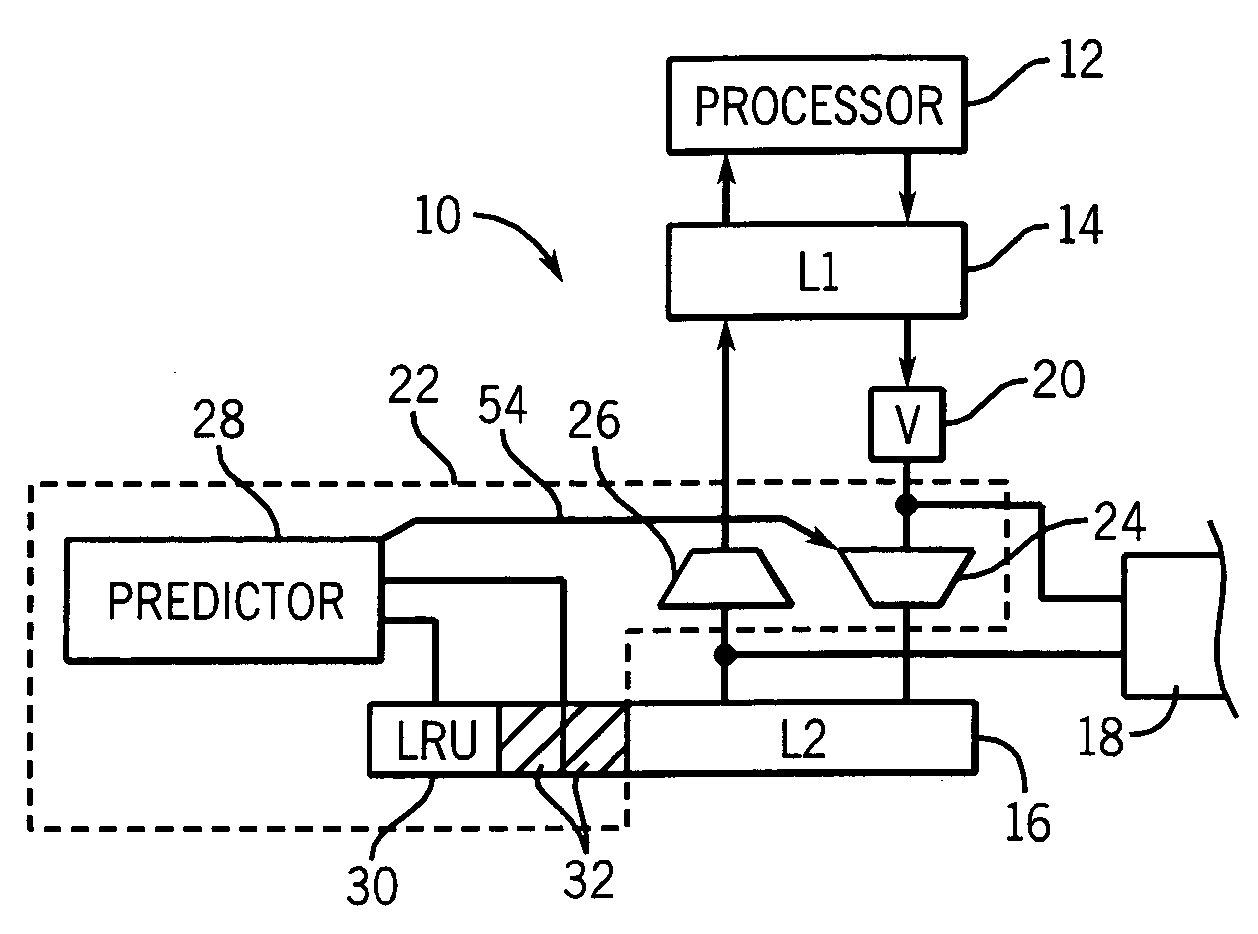
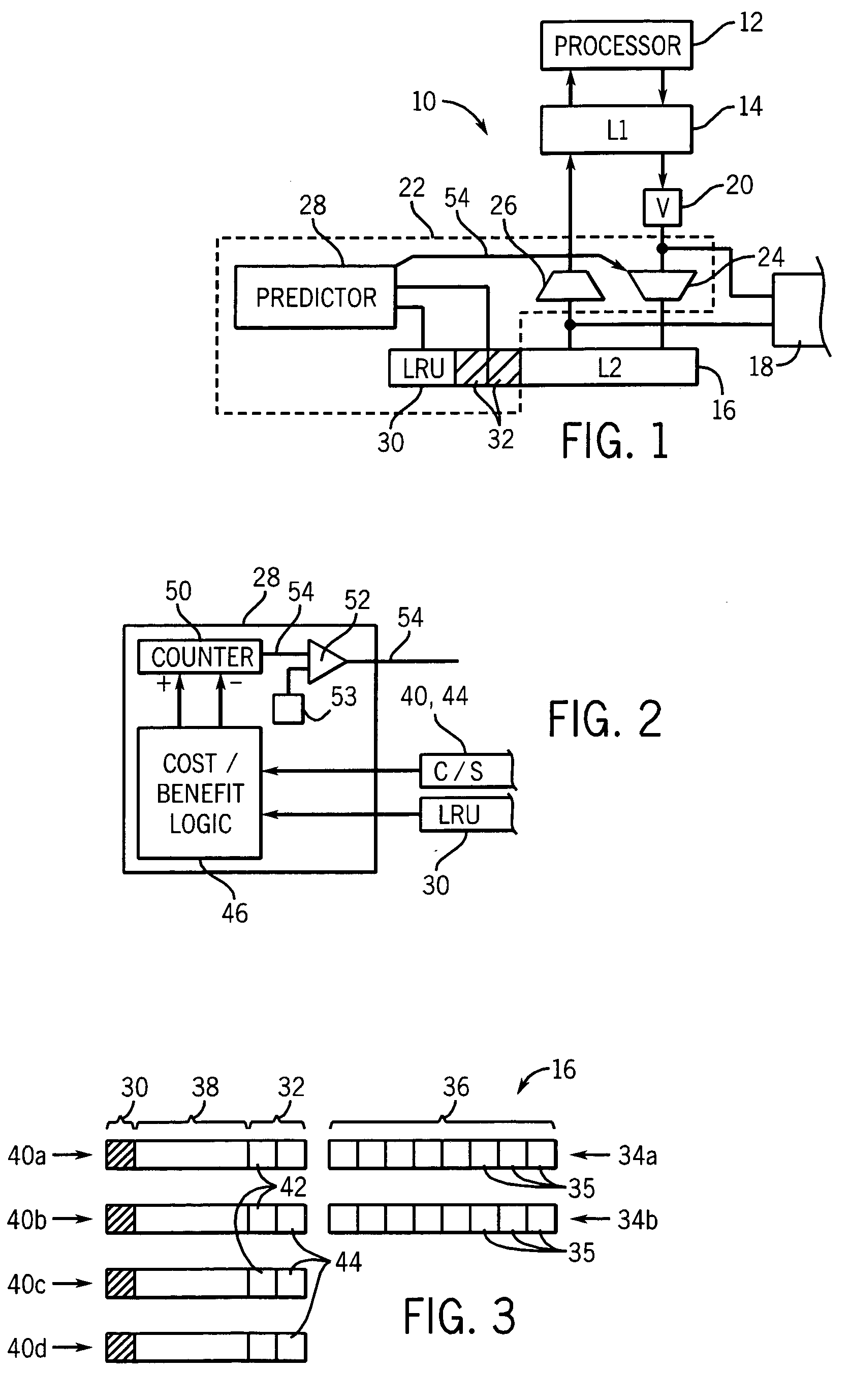
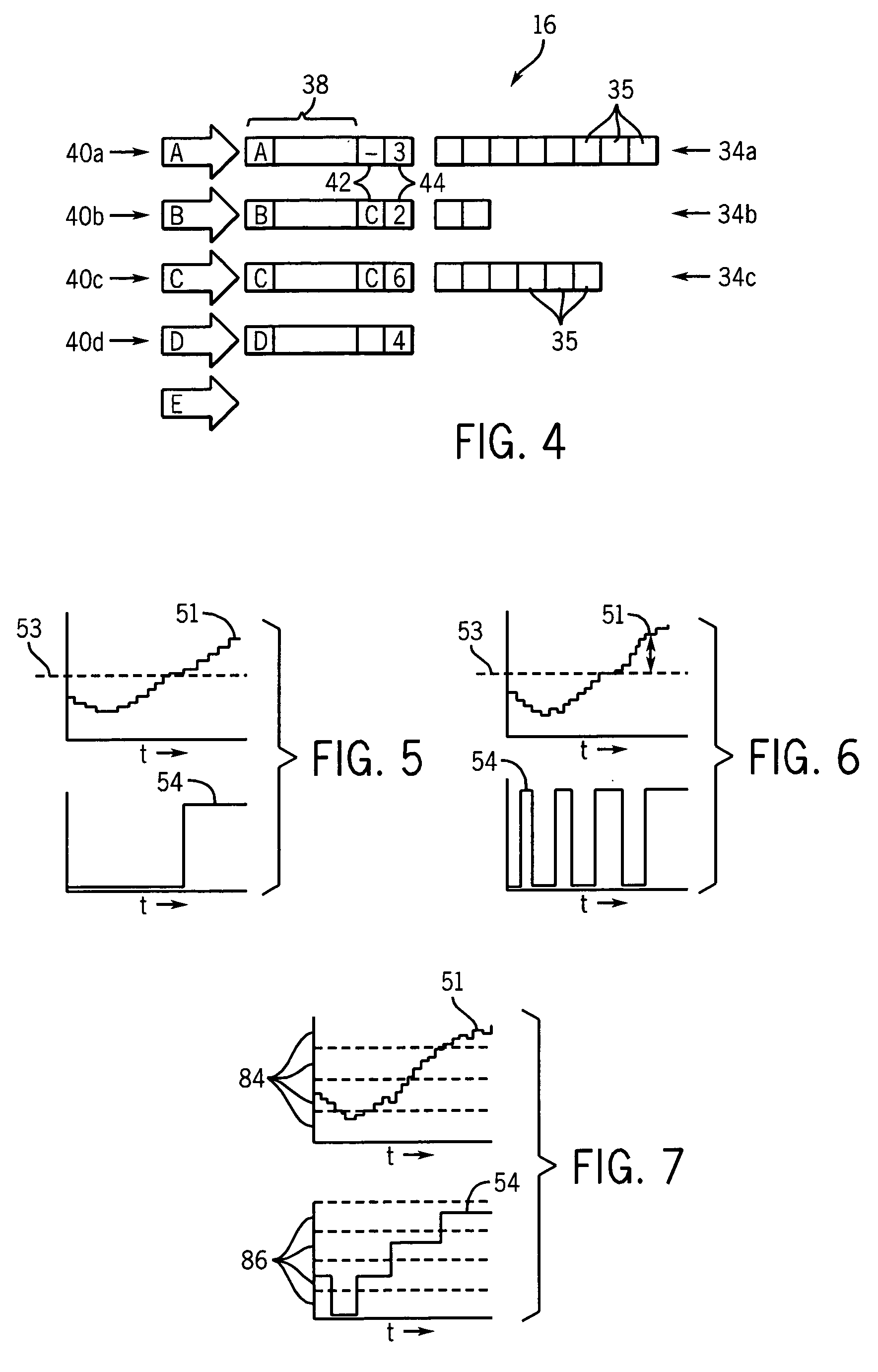
ActiveUS20060101206A1Simple methodStable controlMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory systemsParallel computingInstruction cycle
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
High-performance closed-form single-scan calculation of oblong-shape rotation angles from binary images of arbitrary size using running sums
A method for performing a high-performance closed-form single-scan calculation of oblong-shape rotation angles from binary images of arbitrary size on a processor using running sums is disclosed. Running sums are calculated and stored throughout each scan, and the results are obtained in closed form by simple post-scan computation. An algorithmic embodiment may execute on one or more hardware processors with limited or constrained computation power, available instruction cycles, available memory, etc. Exemplary hardware processors are found in one or more CPUs of a desktop, laptop, tablet, or handheld computing device, and may be an embedded processor or a signal processor chip. The resulting method may be used for touch or optical user interfaces, real-time image recognition, real-time machine vision, and other purposes.
Owner:NRI R&D PATENT LICENSING LLC
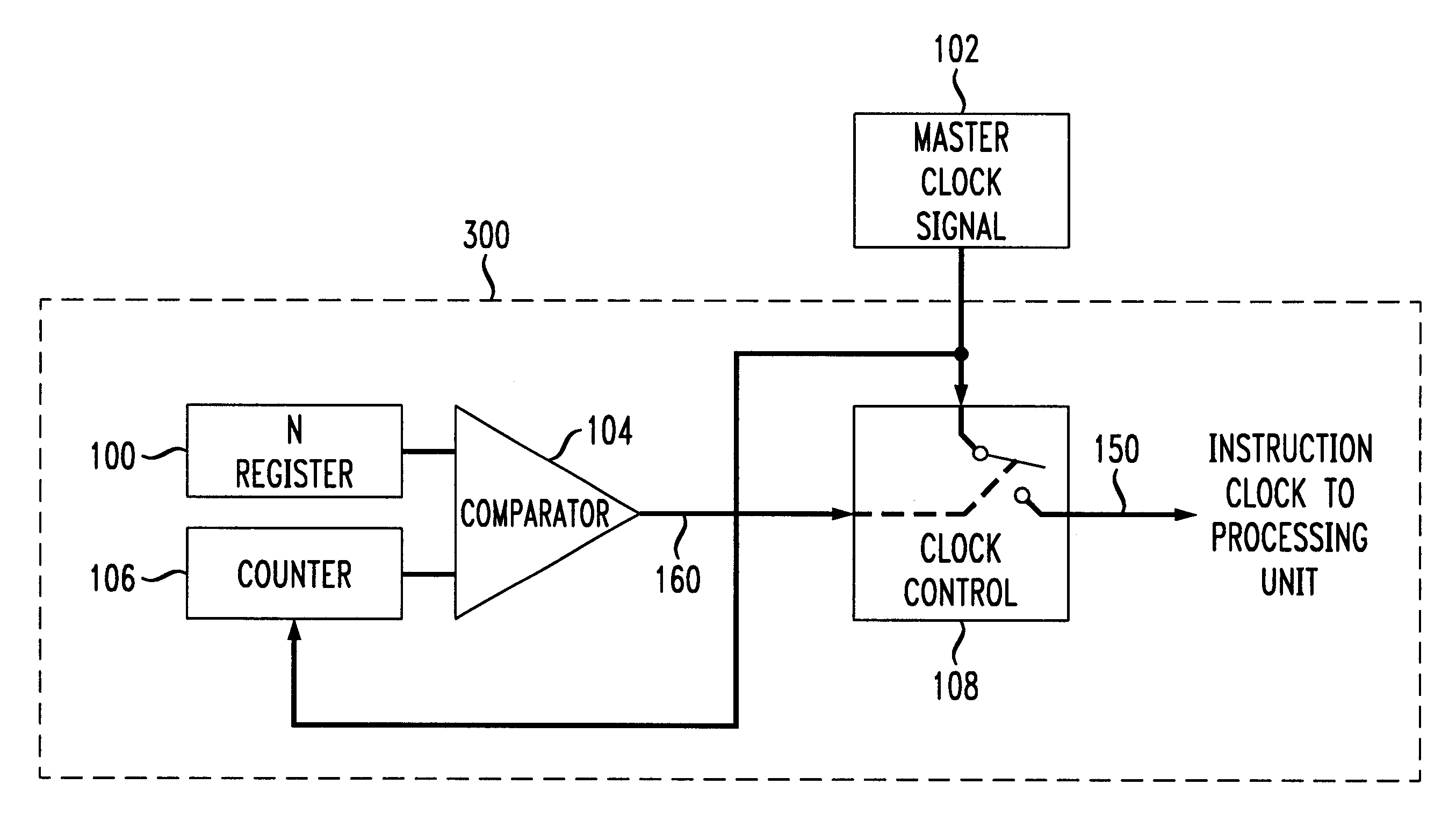
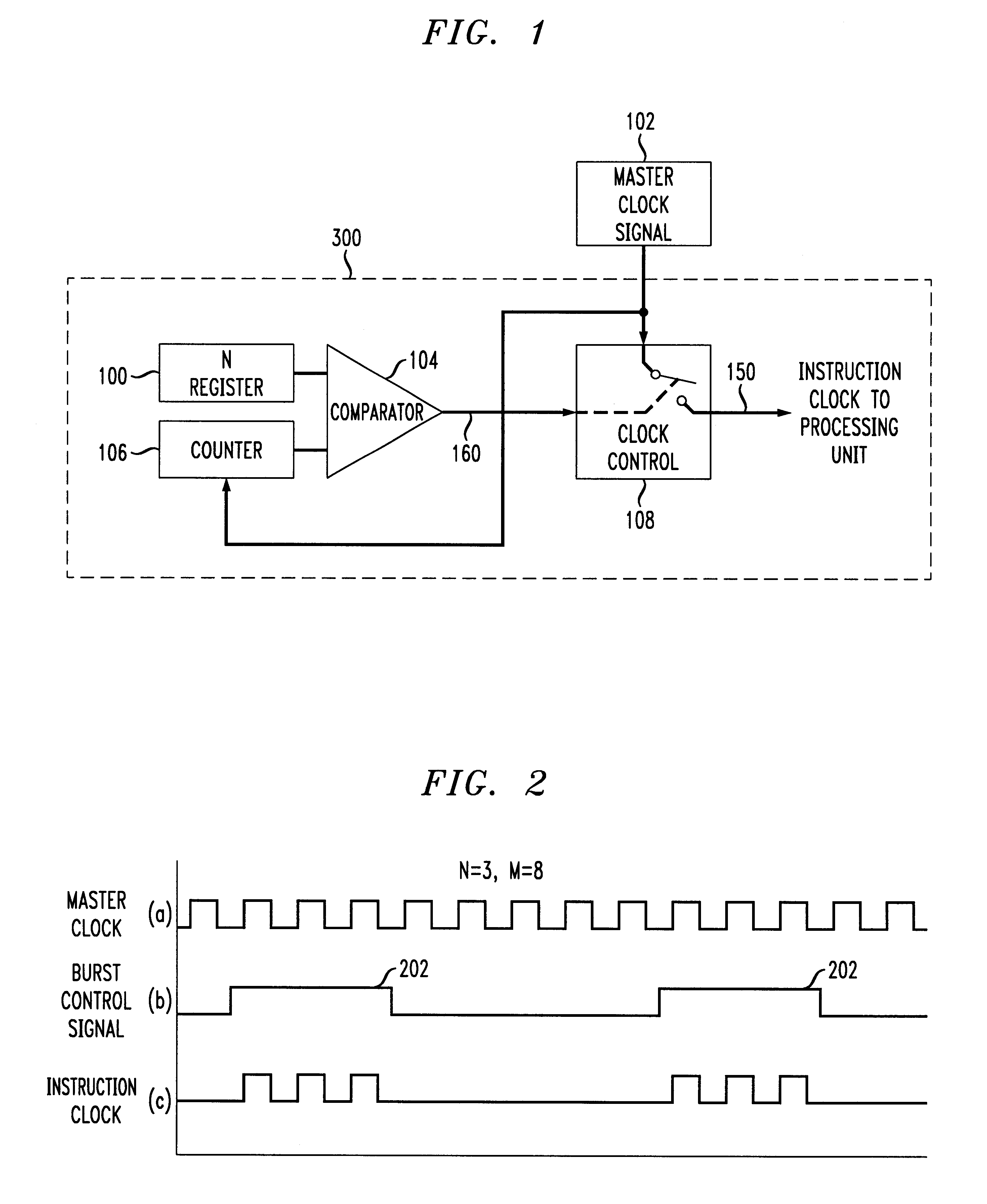
Processor powerdown operation using intermittent bursts of instruction clock
InactiveUS6275948B1Reduce power consumptionReceiver initialisationEnergy efficient ICTPower modeControl signal
An instruction clock of a processing unit in a low power mode in accordance with the principles of the present invention is qualified with a burst mode control signal. The burst mode control signal is allowed to start and stop the instruction flow of the relevant processing unit. In the disclosed embodiment, a master clock signal is qualified by a clock control circuit to provide bursts of an instruction clock signal to the relevant processing unit. To operate the burst instruction cycle control unit, a user pre-programs a burst length, into a register to set the length of the burst of instruction cycles to the relevant processing unit. A maximum counter value in a counter sets the period of the instruction cycle bursts provided to the relevant processing unit. As long as the current value of the counter is less than or equal to the pre-programmed burst length, the burst control signal allows a clock controller to pass a master clock signal or other relevant clock signal as an instruction clock signal to the relevant processing unit. The low power burst mode and thus the power savings is adjustable according to the combined values of burst length and maximum counter value.
Owner:AGERE SYST INC
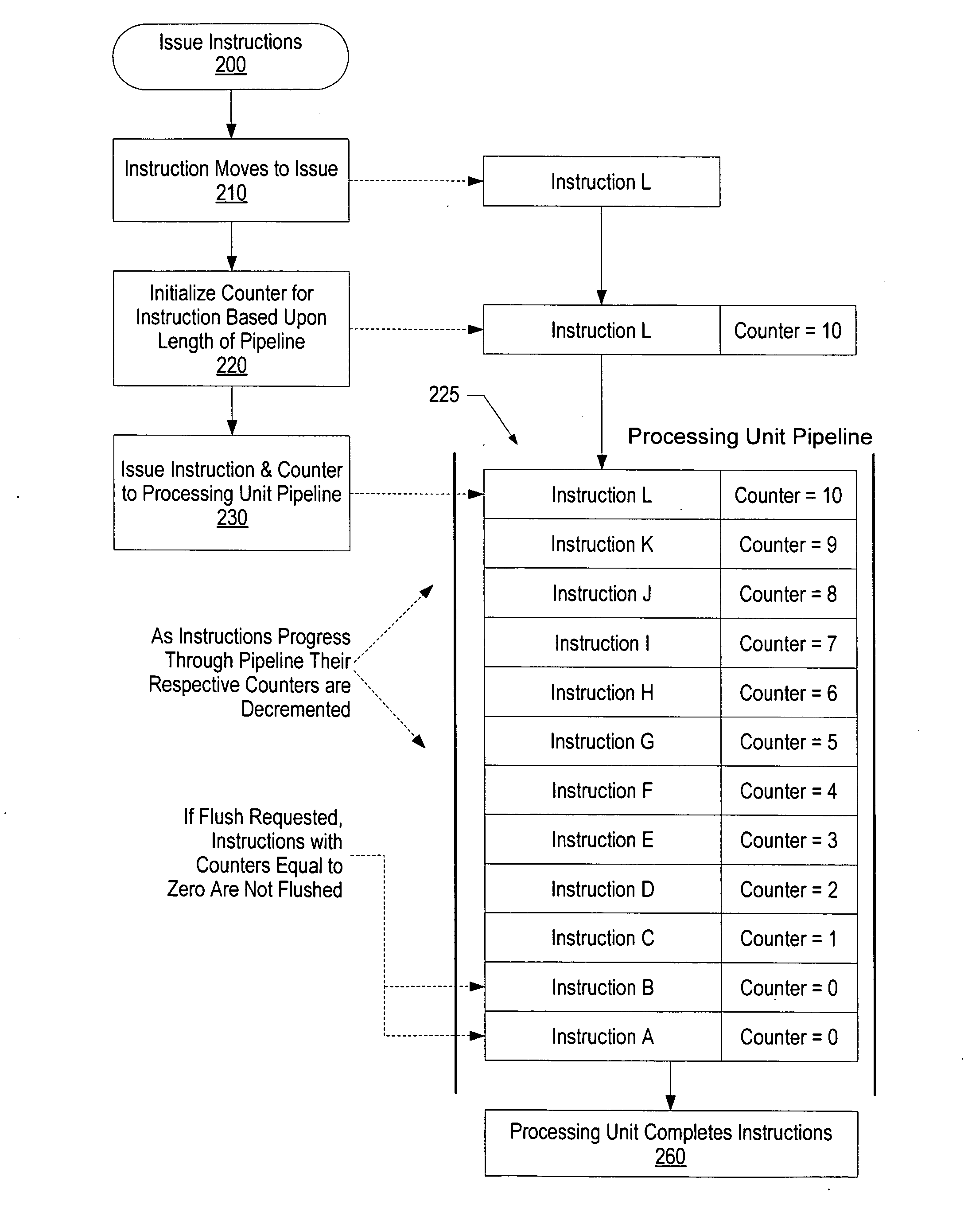
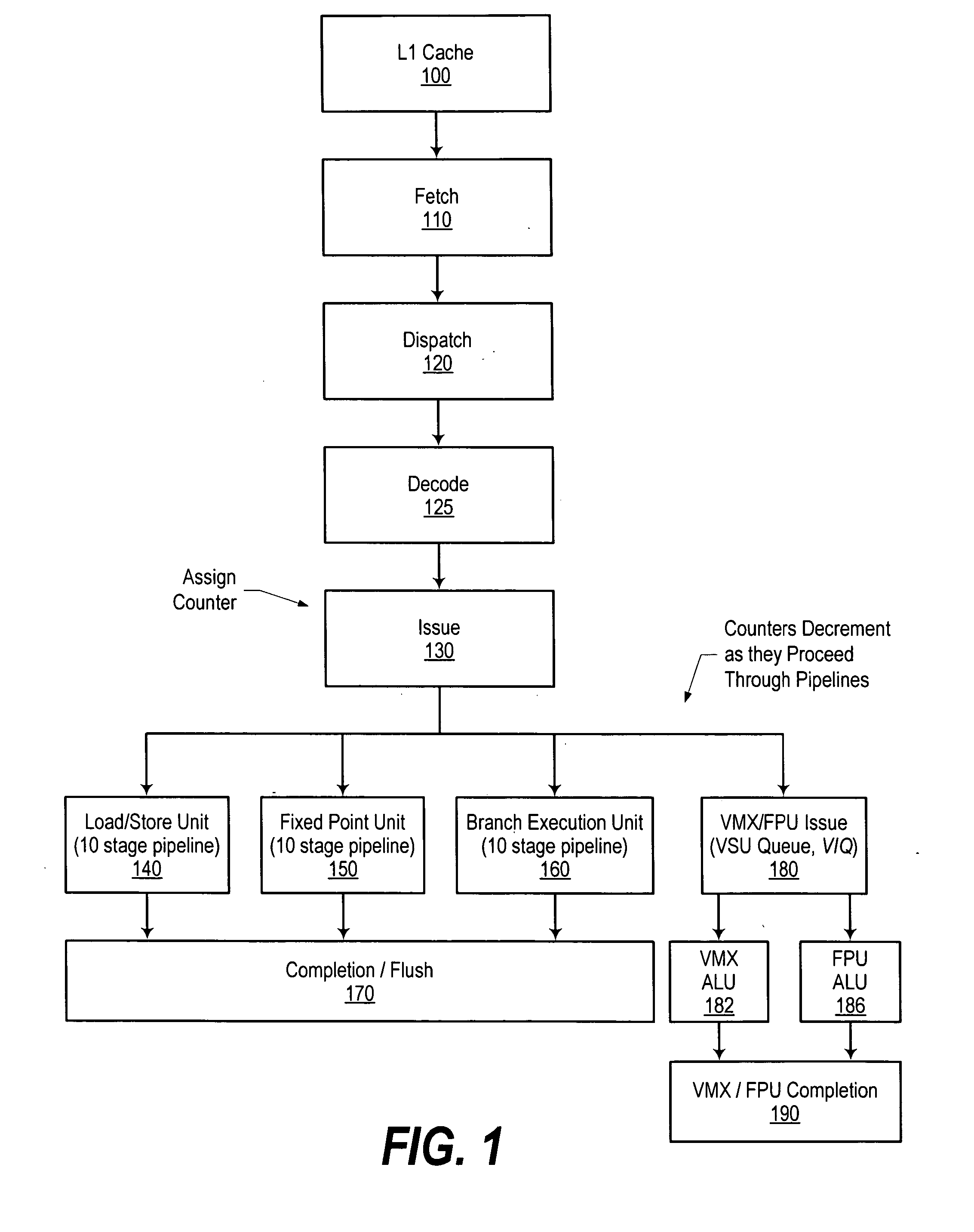
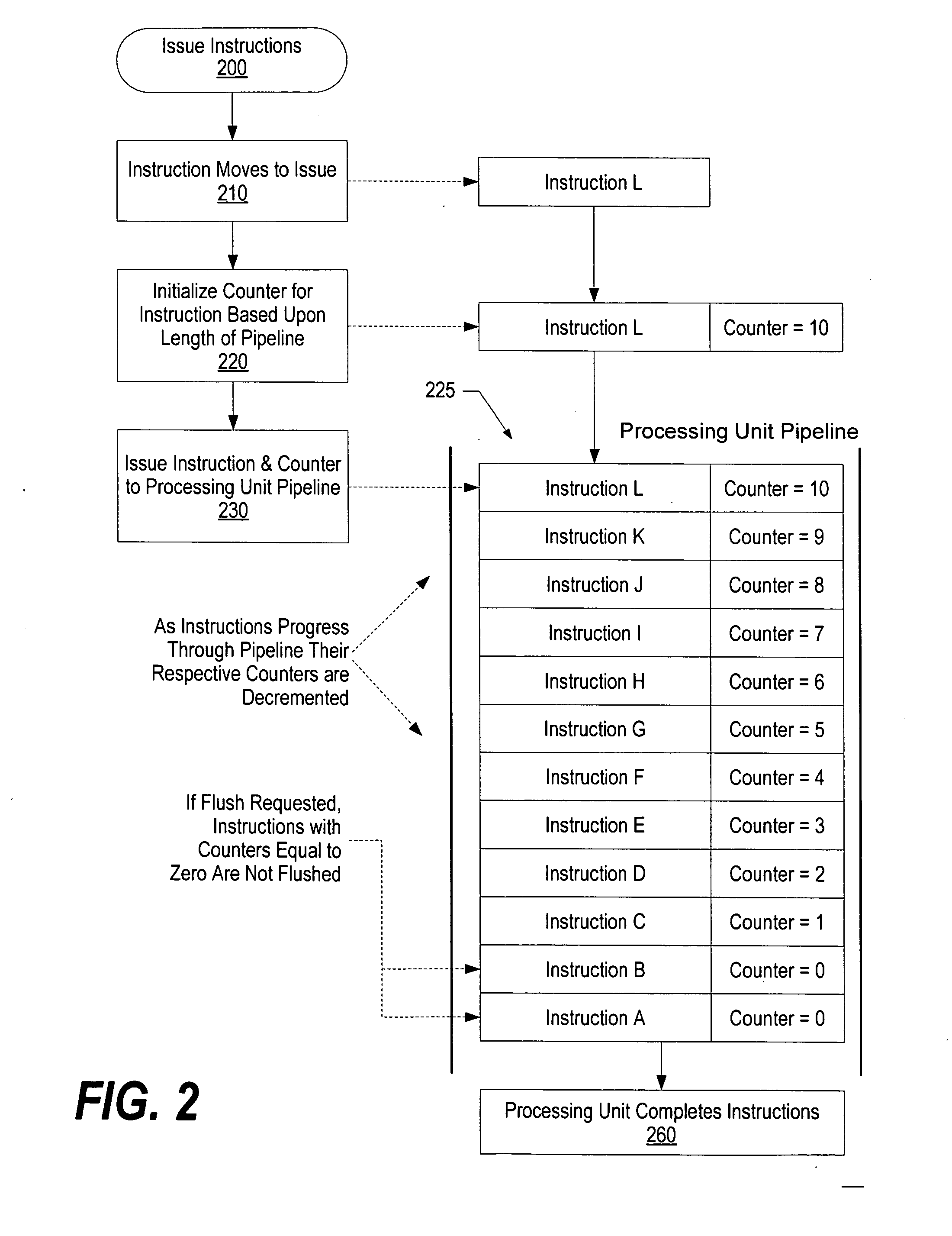
System and method for time-of-life counter design for handling instruction flushes from a queue
InactiveUS20070083742A1Effectively and efficiently flushedEfficient identificationDigital computer detailsSpecific program execution arrangementsParallel computingInstruction cycle
A system and method for tracking the order of issued instructions using a counter is presented. In one embodiment, a saturating, decrementing counter is used. The counter is initialized to a value that corresponds to the processor's commit point. Instructions are issued from a first issue queue to one or more execution units and one or more second issue queues. After being issued by the first issue queue, the counter associated with each instruction is decremented during each instruction cycle until the instruction is executed by one of the execution units. Once the counter reaches zero it will be completed by the execution unit. If a flush condition occurs, instructions with counters equal to zero are maintained (i.e., not flushed or invalidated), while other instructions in the pipeline are invalidated based upon their counter values.
Owner:GERHARDT DIANA R
Frequency scaling of processing unit based on aggregate thread CPI metric
A device, system, and method are directed towards managing power consumption in a computer system with one or more processing units, each processing unit executing one or more threads. Threads are characterized based on a cycles per instruction (CPI) characteristic of the thread. A clock frequency of each processing unit may be configured based on the CPI of each thread assigned to the processing unit. In a system wherein higher clock frequencies consume greater amounts of power, the CPI may be used to determine a desirable clock frequency. The CPI of each thread may also be used to assign threads to each processing unit, so that threads having similar characteristics are grouped together. Techniques for assigning threads and configuring processor frequency may be combined to affect performance and power consumption. Various specifications or factors may also be considered when scheduling threads or determining processor frequencies.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
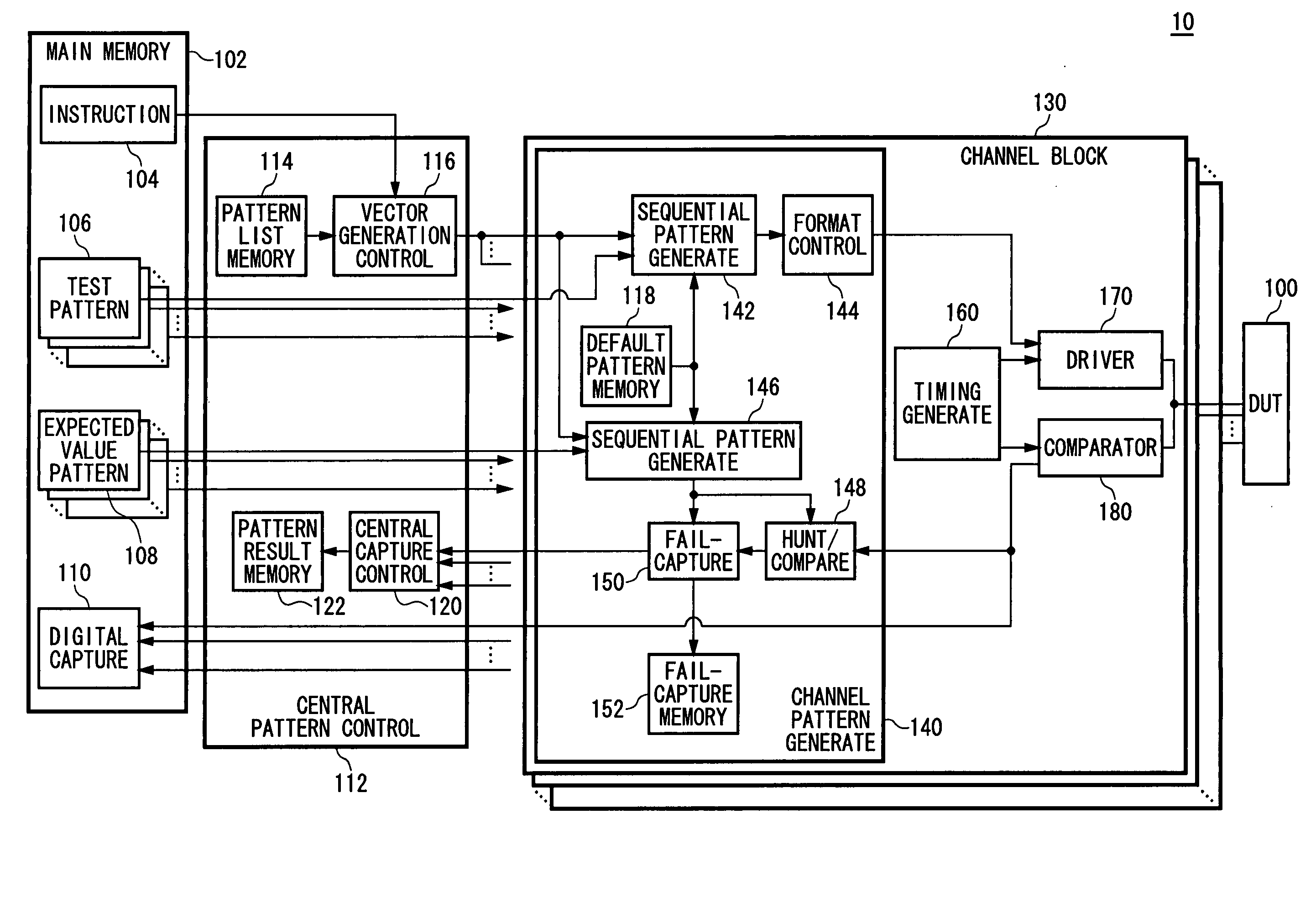
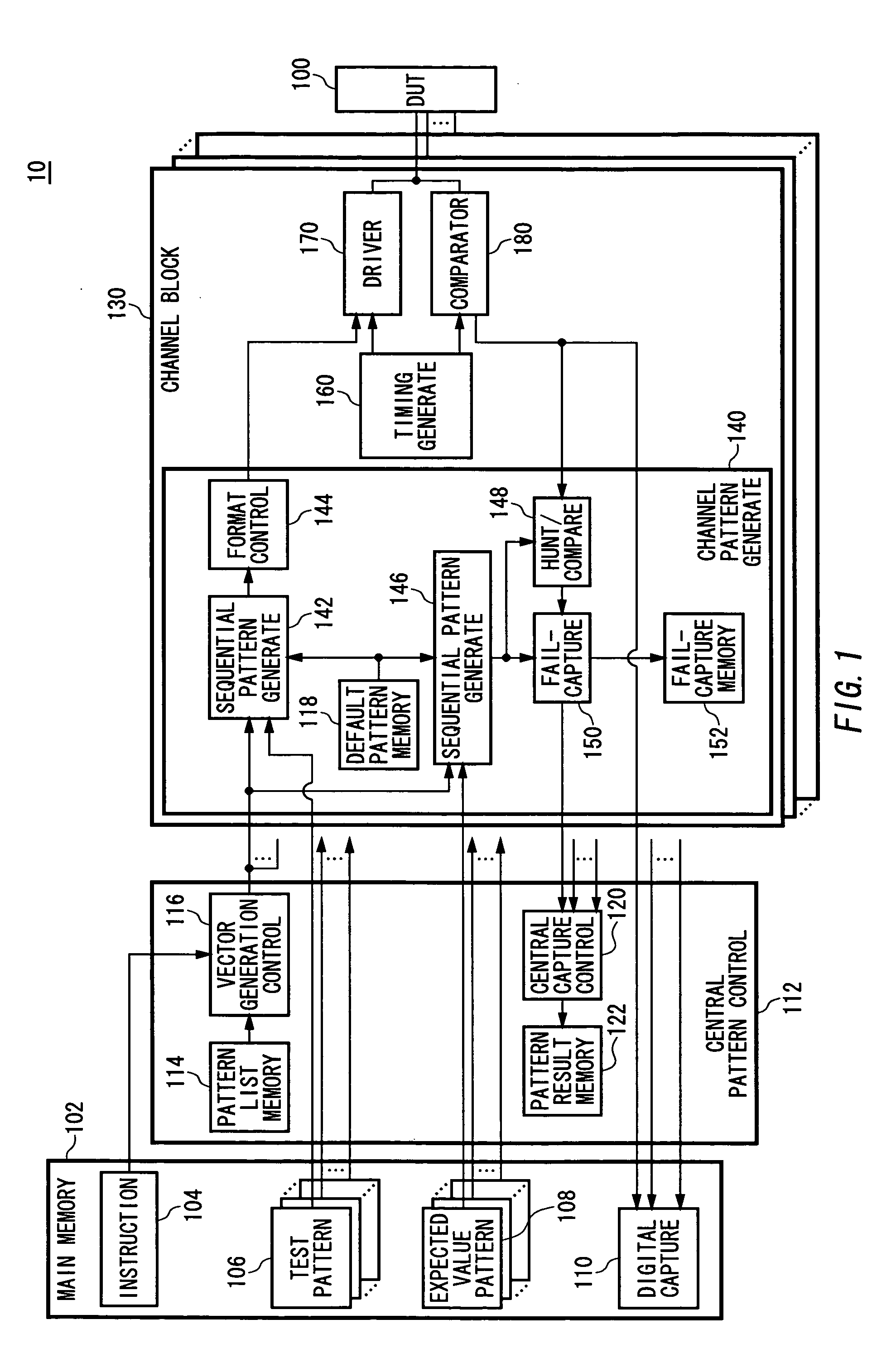
Test apparatus and test method
InactiveUS20060161829A1Electronic circuit testingError detection/correctionProgramming languagePattern sequence
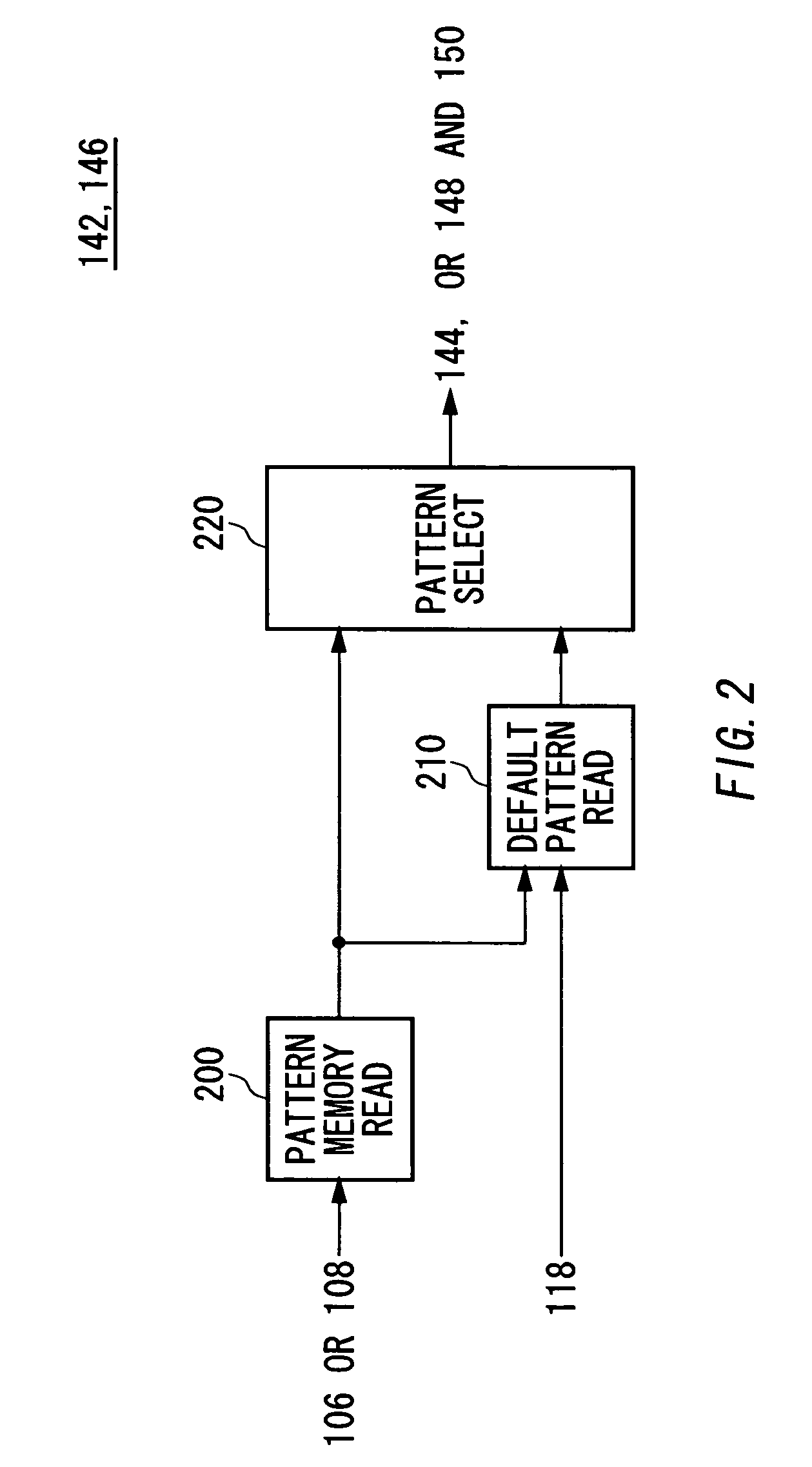
A test apparatus includes: an instruction execution unit for sequentially executing instructions in a test program for a DUT in each instruction cycle; a default pattern memory for storing default pattern sequence to be associated with default pattern identification information for identifying that default pattern sequence, the default pattern sequence being a preset one of a plurality of test pattern sequence sets, each formed by a plurality of test patterns to be sequentially output to a terminal of the DUT during an instruction cycle period; a test pattern memory for storing, for each instruction, test pattern sequence output in an instruction cycle period for executing that instruction or the default pattern identification information that is output in the instruction cycle period; a test pattern memory read unit for, in a case of executing one instruction, reading the test pattern sequence or the default pattern identification information that is stored and is associated with that instruction in the test pattern memory; a default pattern read unit for, when the test pattern memory read unit read the default pattern identification information, reading the default pattern sequence that is stored and is associated with the default pattern identification information in the default pattern memory; and a test pattern output unit for outputting the test pattern sequence read by the test pattern memory to correspond to the one instruction, or the default pattern sequence read by the default pattern read unit to a terminal of the DUT during an instruction cycle period for executing that instruction.
Owner:ADVANTEST CORP
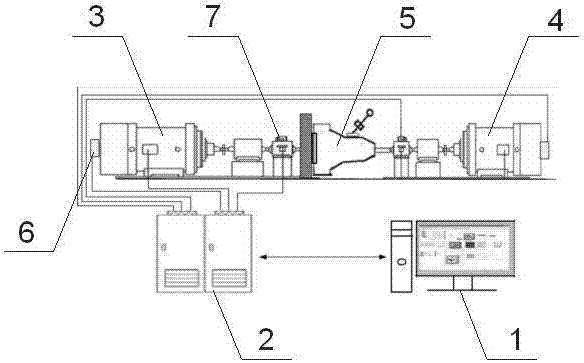
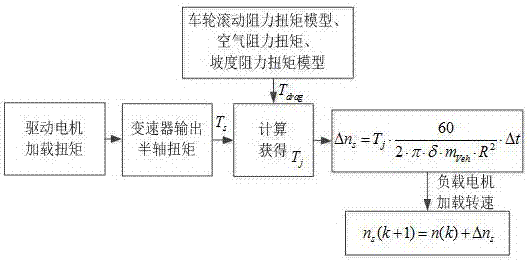
Acceleration inertia electric simulation control method for test bench of automobile transmission system
ActiveCN106895981AImprove accuracyThe effect of reducing control accuracyVehicle testingMachine gearing/transmission testingAerodynamic dragRolling resistance
The invention discloses an acceleration inertia electric simulation control method for a test bench of an automobile transmission system. The method includes the steps of 1) according to inherent parameters of an engine, establishing an engine "throttle opening-speed-torque" model; 2) loading a torque type to a drive motor, and then acquiring the speed and torque of an output half shaft of a transmission; 3) respectively establishing a wheel rolling resistance torque model, a slope resistance torque model and an air resistance torque model during the driving process of an automobile; 4) obtaining the following shown in the description; 5) for a sufficiently small test instruction cycle, obtaining ns(k+1)=ns(k)+<delta>ns, and loading the speed ns(k+1) onto a load motor; and 6) repeating the steps 2) to 6) to complete the automobile acceleration inertia electric simulation. The method can be used to accurately simulate the dynamic condition of the automobile, so as to effectively improve the accuracy of the automobile transmission system test.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF TECH +1
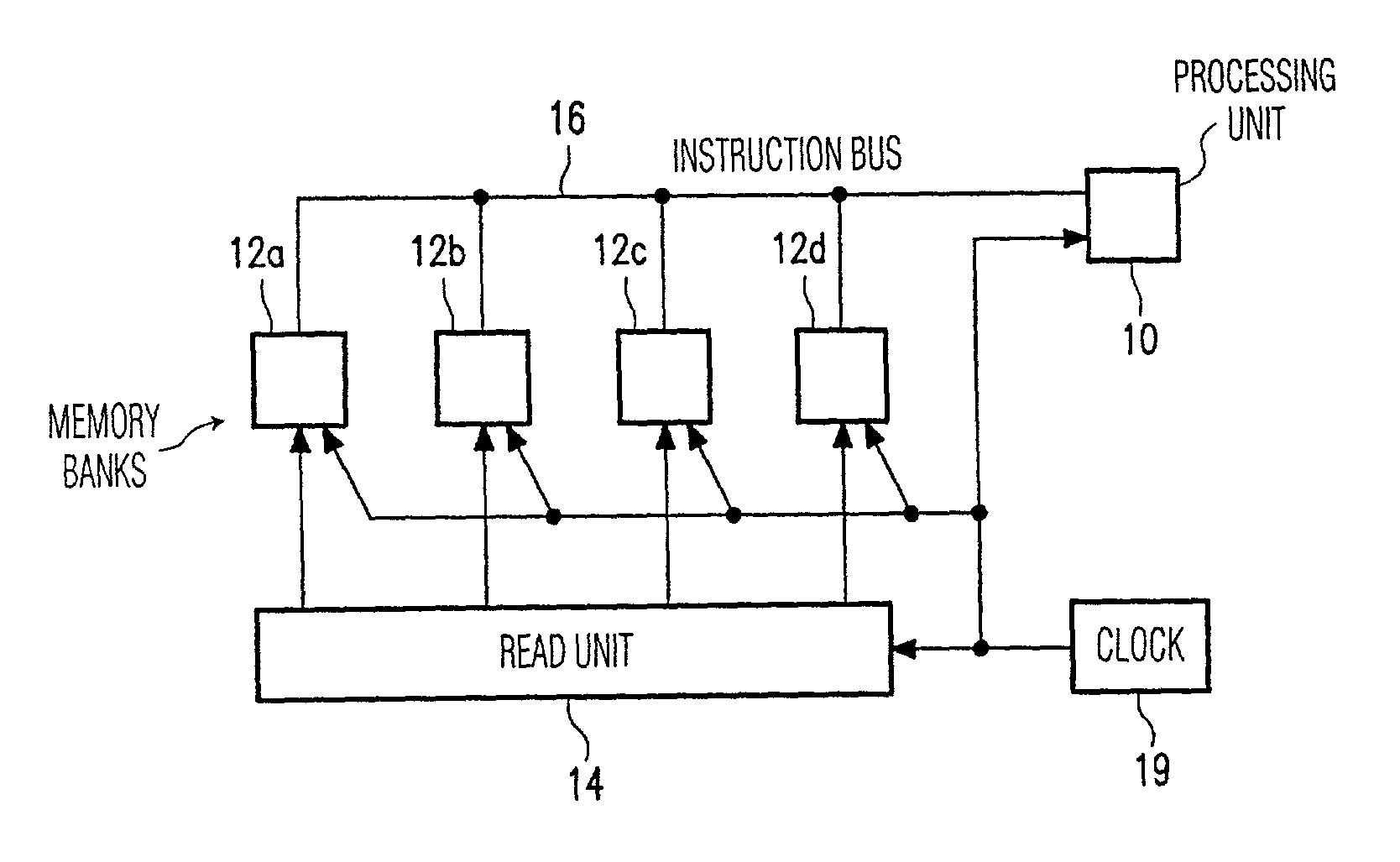
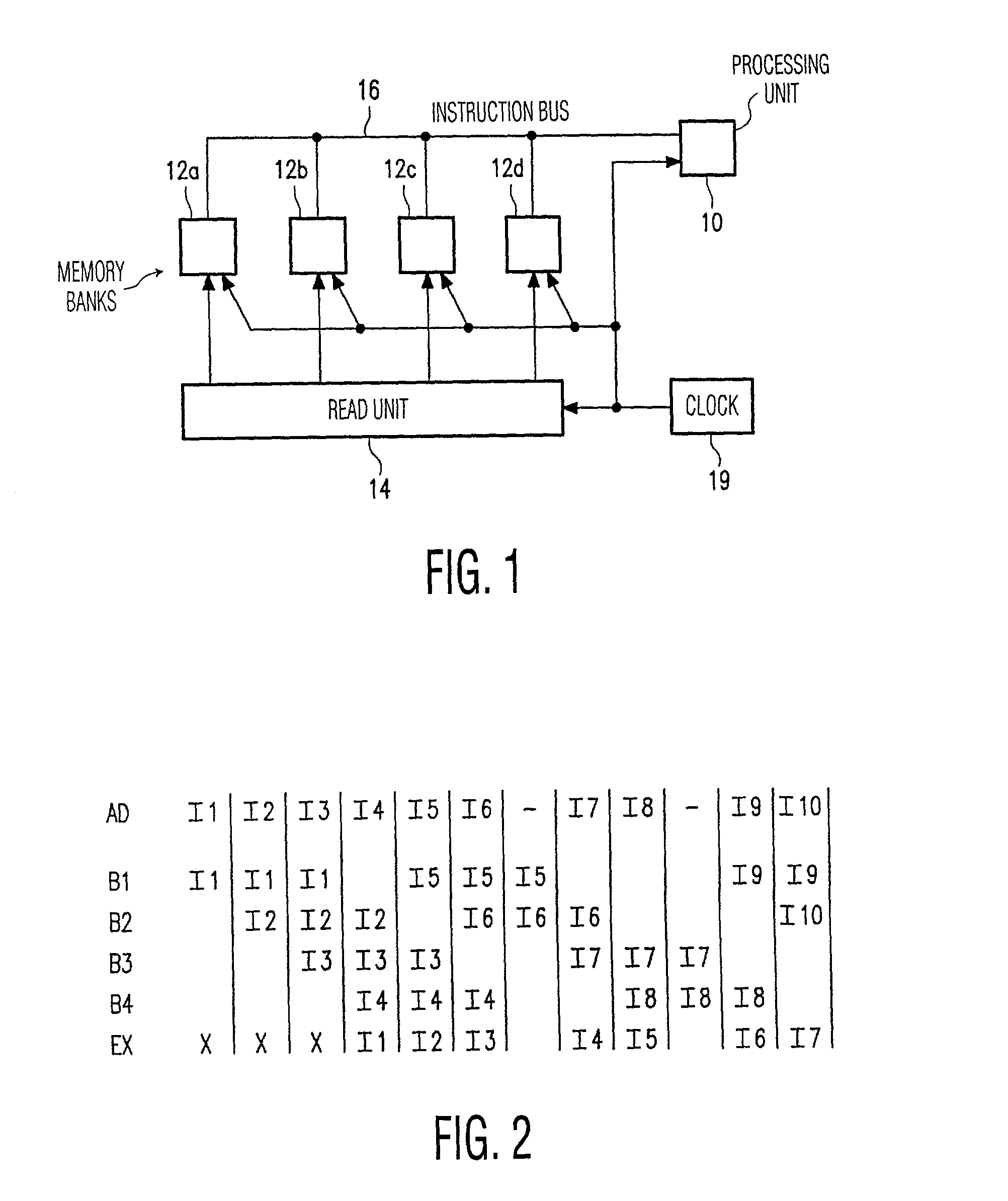
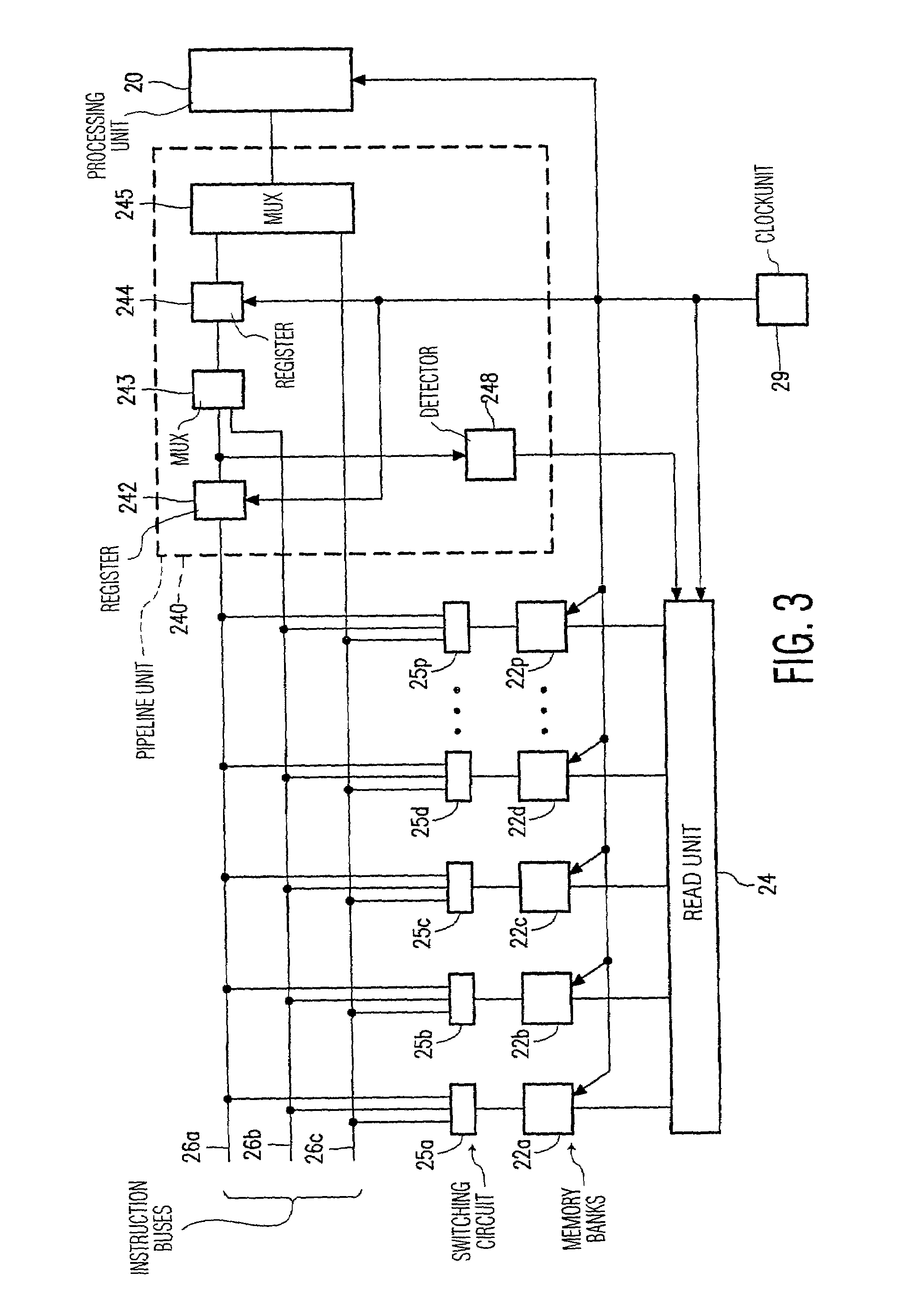
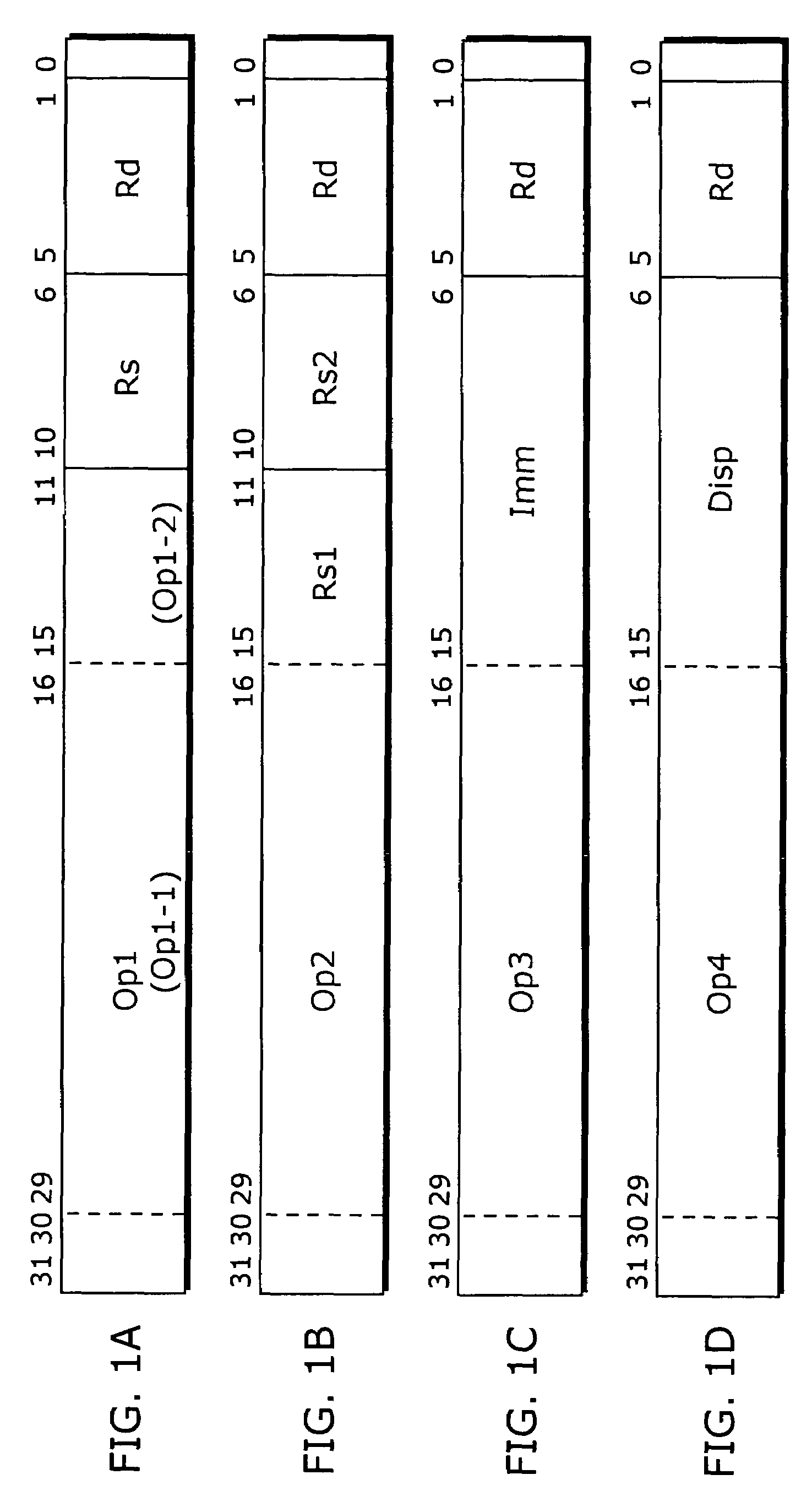
Processor architecture with independently addressable memory banks for storing instructions to be executed
InactiveUS7124282B2Solve excessive overheadReduce riskMemory adressing/allocation/relocationDigital computer detailsInstruction unitMemory bank
Instructions for a processing unit are stored in a number of memory banks, successive instructions being stored in successive, different memory banks. Whenever execution of an instruction is started, the reading of one instruction which will be executed more than one instruction cycle later is also started. Consequently, a plurality of instructions are read in parallel from different memory banks. After the reading of an instruction, and before starting the execution of the instruction, the instruction passes through a pipeline in which the processing device detects whether the relevant instruction is a branch instruction. If this is so, the processing unit starts the reading in parallel of a number of instructions as from a branch target instruction. If it appears at a later stage that the branch is taken, said number of instructions is loaded into the pipeline in parallel.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and apparatus for power throttling in a multi-thread processor
A method and apparatus for controlling power consumption in a processor. In one embodiment, a processor includes a pipeline. The pipeline includes logic for fetching instructions, issuing instructions, and executing instructions. The processor also includes a power management unit. The power management unit is configured to input M stalls into the pipeline every N instruction cycles (where M and N are integer value and wherein M is less than N).
Owner:SUN MICROSYSTEMS INC
Symbolic Execution of Instructions on In-Order Processors
InactiveUS20080168260A1Digital computer detailsMemory systemsProcessing InstructionInstruction cycle
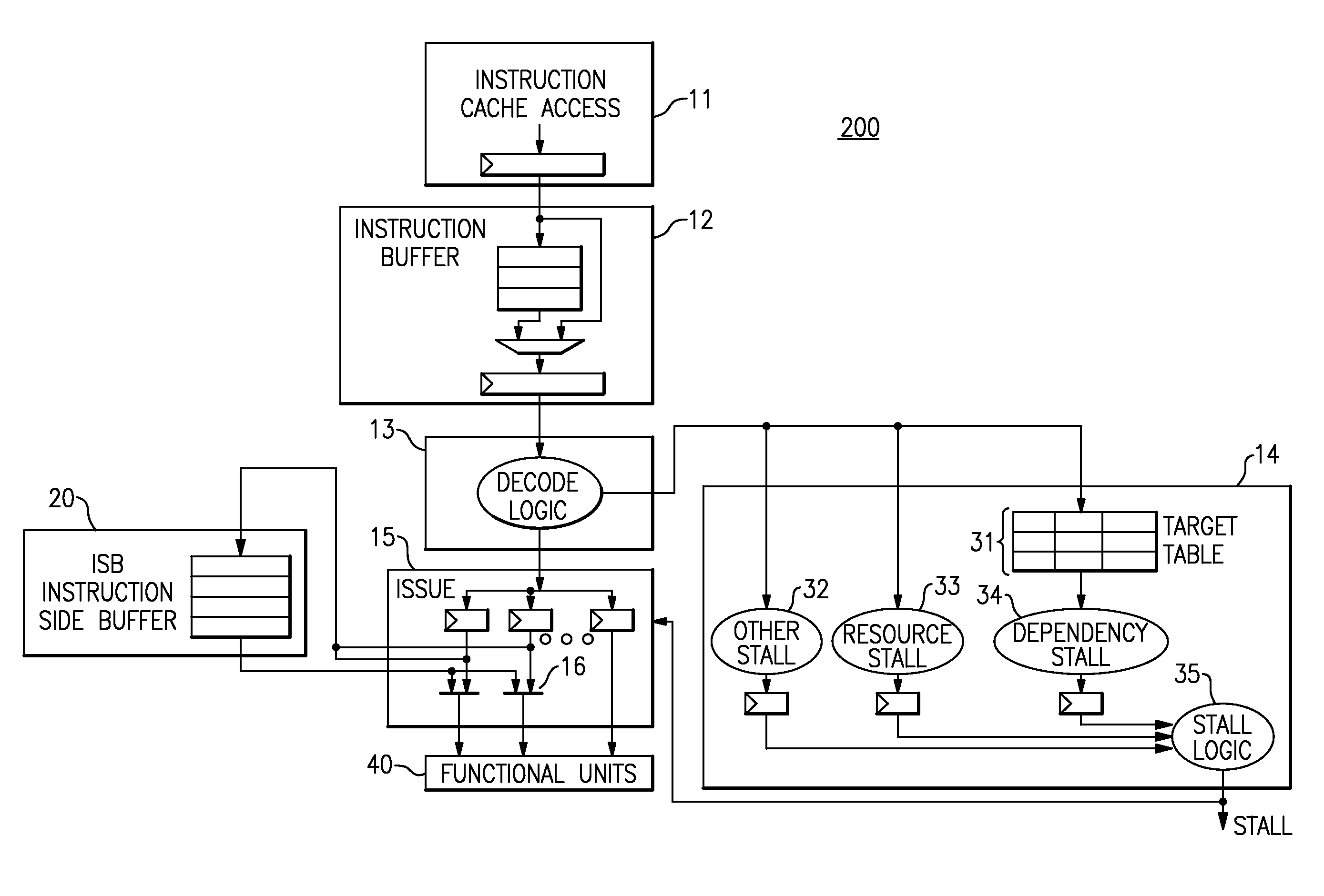
A method is provided for processing instructions by a processor, in which instructions are queued in an instruction pipeline in a queued order. A first instruction is identified from the queued instructions in the instruction pipeline, the first instruction being identified as having a dependency which is satisfiable within a number of instruction cycles after a current instruction in the instruction pipeline is issued. The first instruction is placed in a side buffer and at least one second instruction is issued from the remaining queued instructions while the first instruction remains in the side buffer. Then, the first instruction is issued from the side buffer after issuing the at least one second instruction in the queued order when the dependency of the first instruction has cleared and after the number of instruction cycles have passed.
Owner:IBM CORP
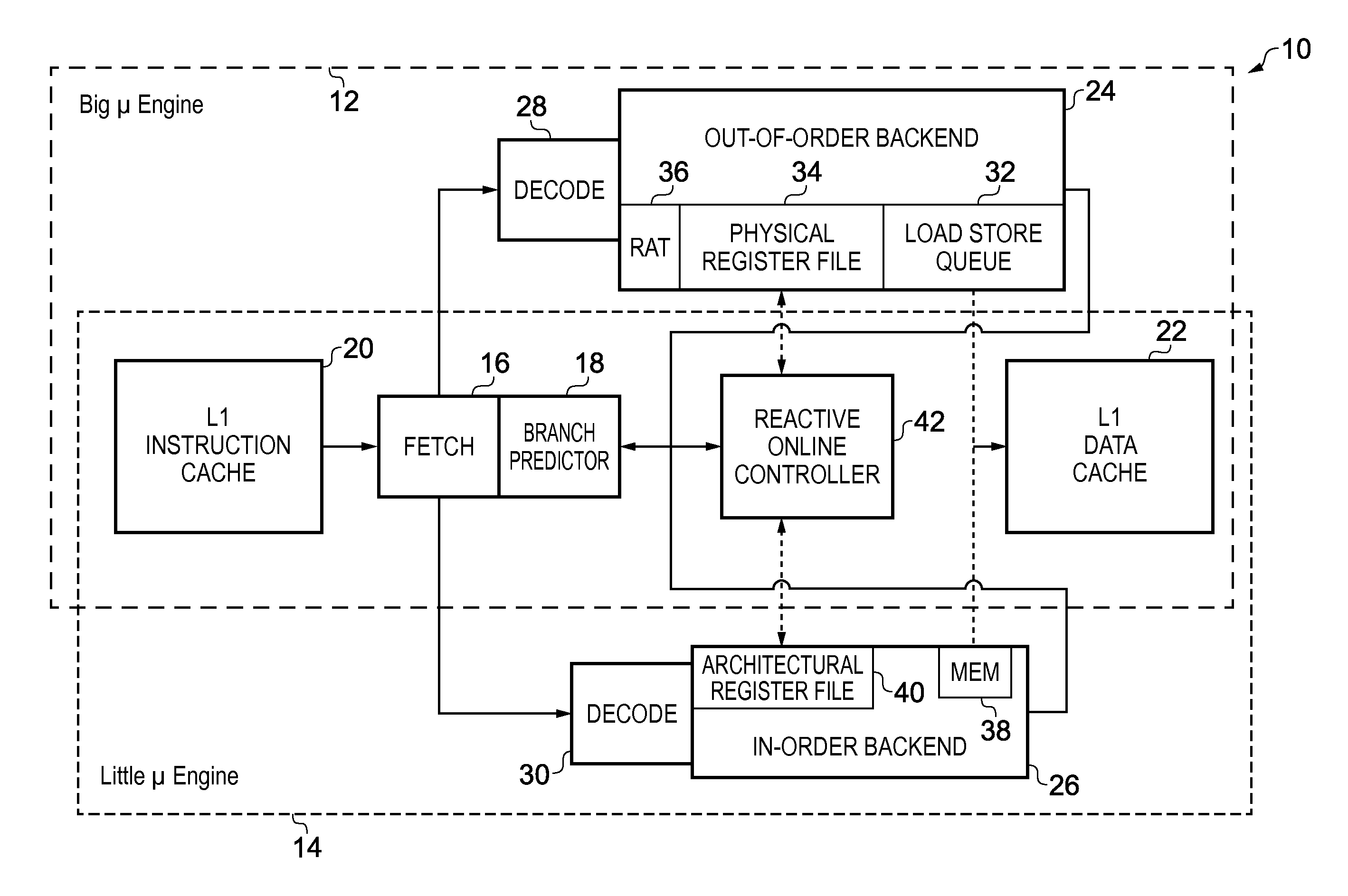
Heterogeneity within a processor core
ActiveUS20150121048A1Reduce probabilityHigh energy consumptionDigital computer detailsPower supply for data processingProgram instructionInstruction cycle
A processor core includes a front end, and first and second back ends, the front end including a fetch engine configured to retrieve the sequence of data processing instructions for both the first back end and the second back end from a memory, and the first and second back ends are each configured to execute the sequence of program instructions. The core operates in a first mode in which the first back end is active and receives the sequence of data processing instructions from the fetch engine and the second back end is inactive, and a second mode in which the first back end is inactive and the second back end is active and receives the sequence of data processing instructions from the fetch engine, where the cycles-per-instruction rate is lower and energy consumption is higher for the first mode than the second mode.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Device and method for executing a program, and method for storing a program
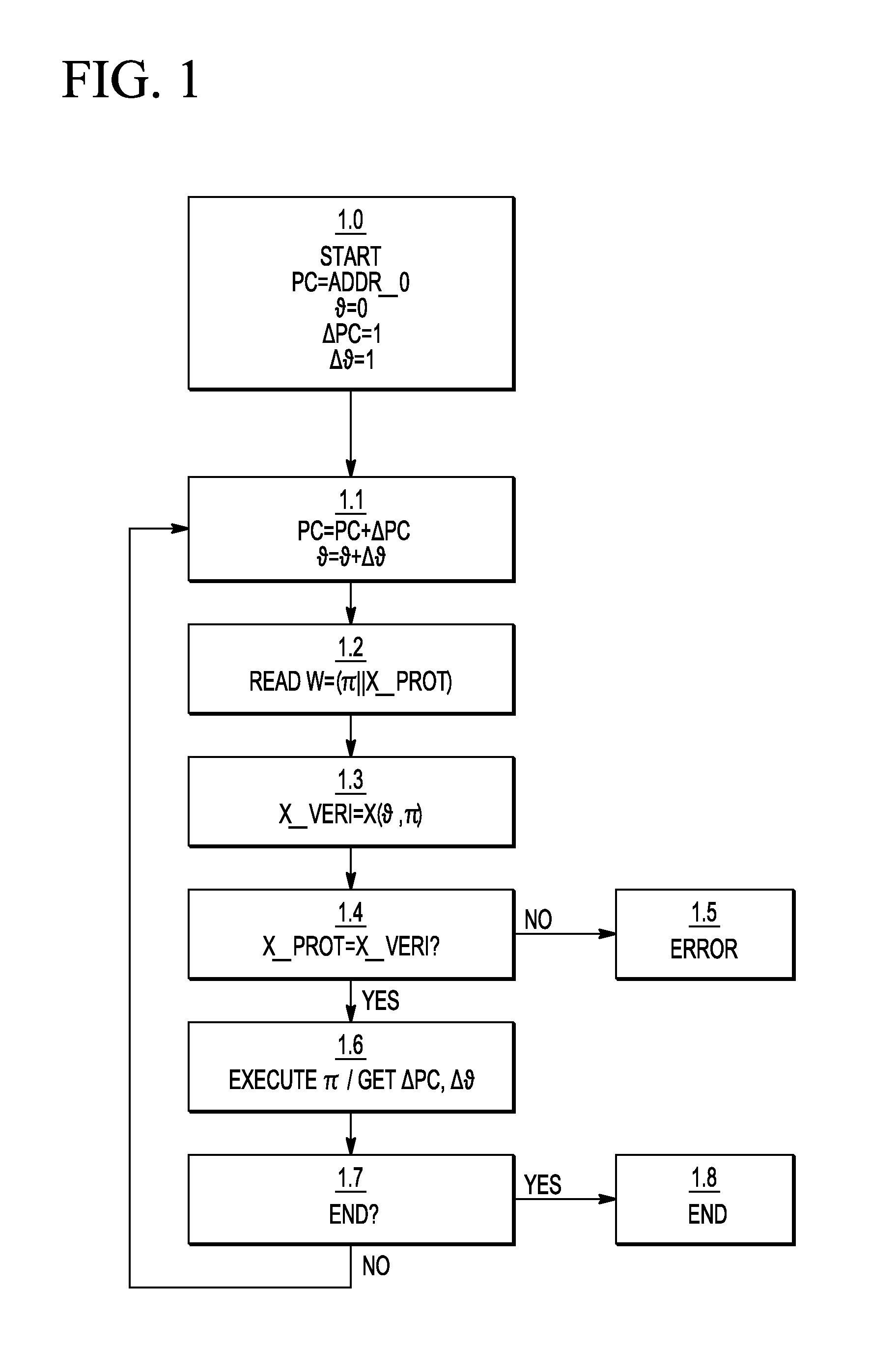
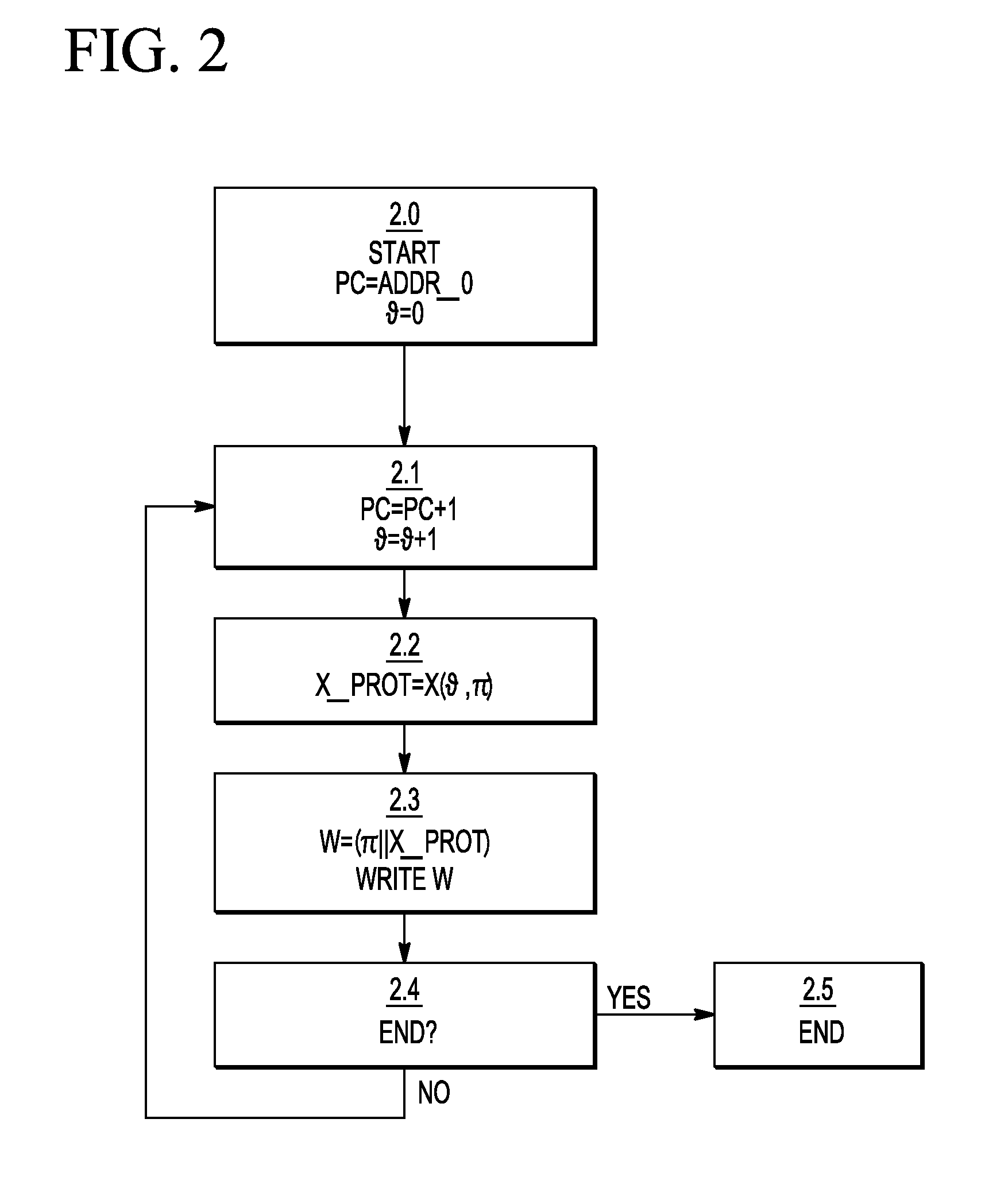
A device and a method for executing a program, and a method for storing a program are described. The method of executing a program includes a sequence of instruction cycles, wherein each instruction cycle comprises: updating the program counter value; reading a data word from a memory location identified by the updated program counter value, wherein the data word comprises an instruction and a protection signature; determining a verification signature by applying a signature function associated with the program counter value to the instruction; executing the instruction if the verification signature and the protection signature are consistent with each other; and initiating an error action if they are inconsistent with each other. A method for storing a program on a data carrier is also described.
Owner:NXP USA INC
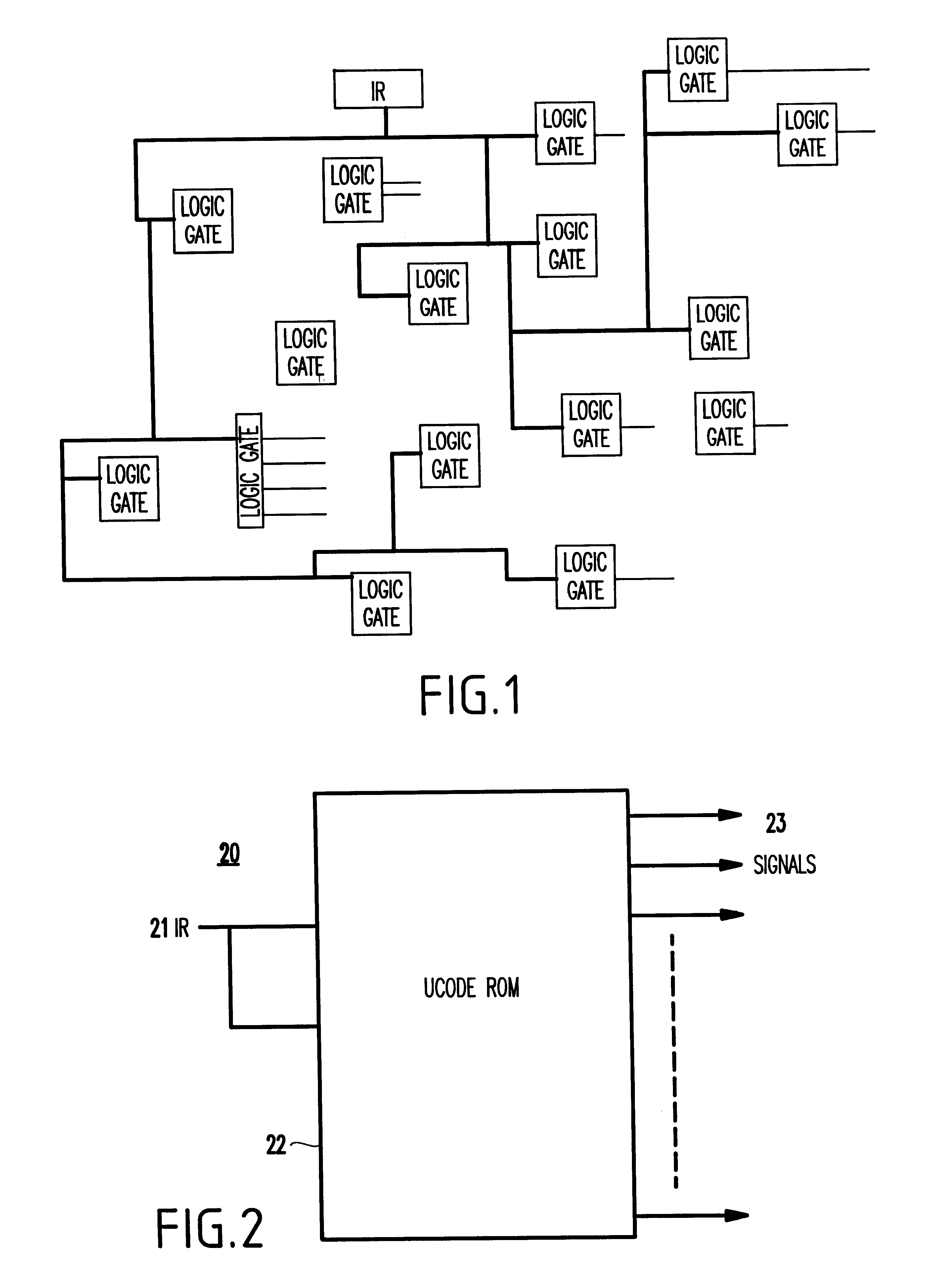
Microprocessor including controller for reduced power consumption during decoding of instructions by microcode units
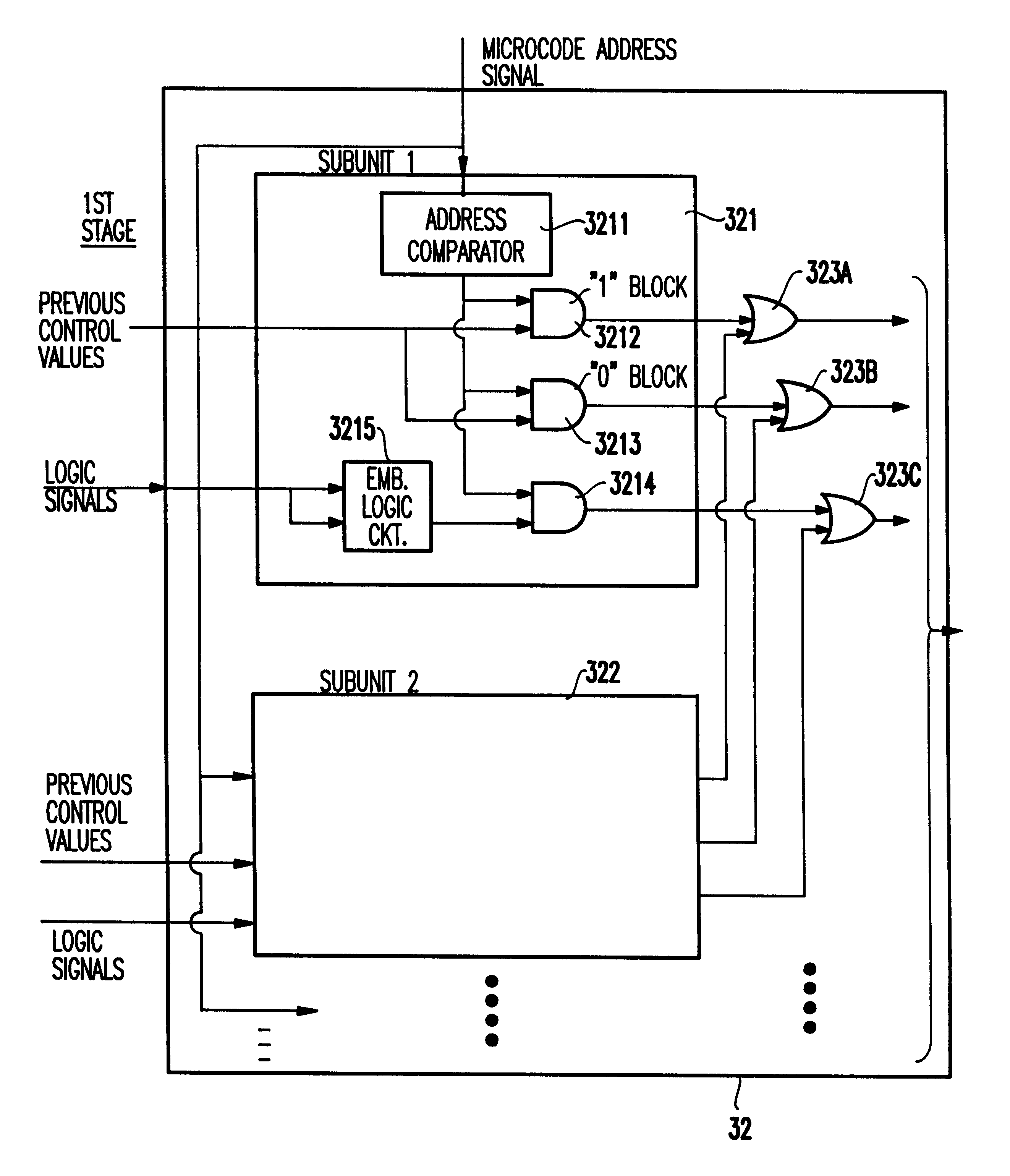
A microprocessor for a portable computer, for reducing power consumption, includes a plurality of microcode units, the microcode units for outputting control signals, for each of a plurality of instructions, requires by the microprocessor for executing the instructions. A unit is provided for maintaining selected control signals to values the same as in an immediately previous instruction cycles. Further, there is a unit for passing a control variable to one of the microcode units. Power conservation is provided during the decoding of instructions by the microcode unit by maintaining control signals during the execution of an instruction at the values / levels determined during the decode of a preceding instruction if it is not necessary to change the level of the control signals to execute the instruction.
Owner:IBM CORP
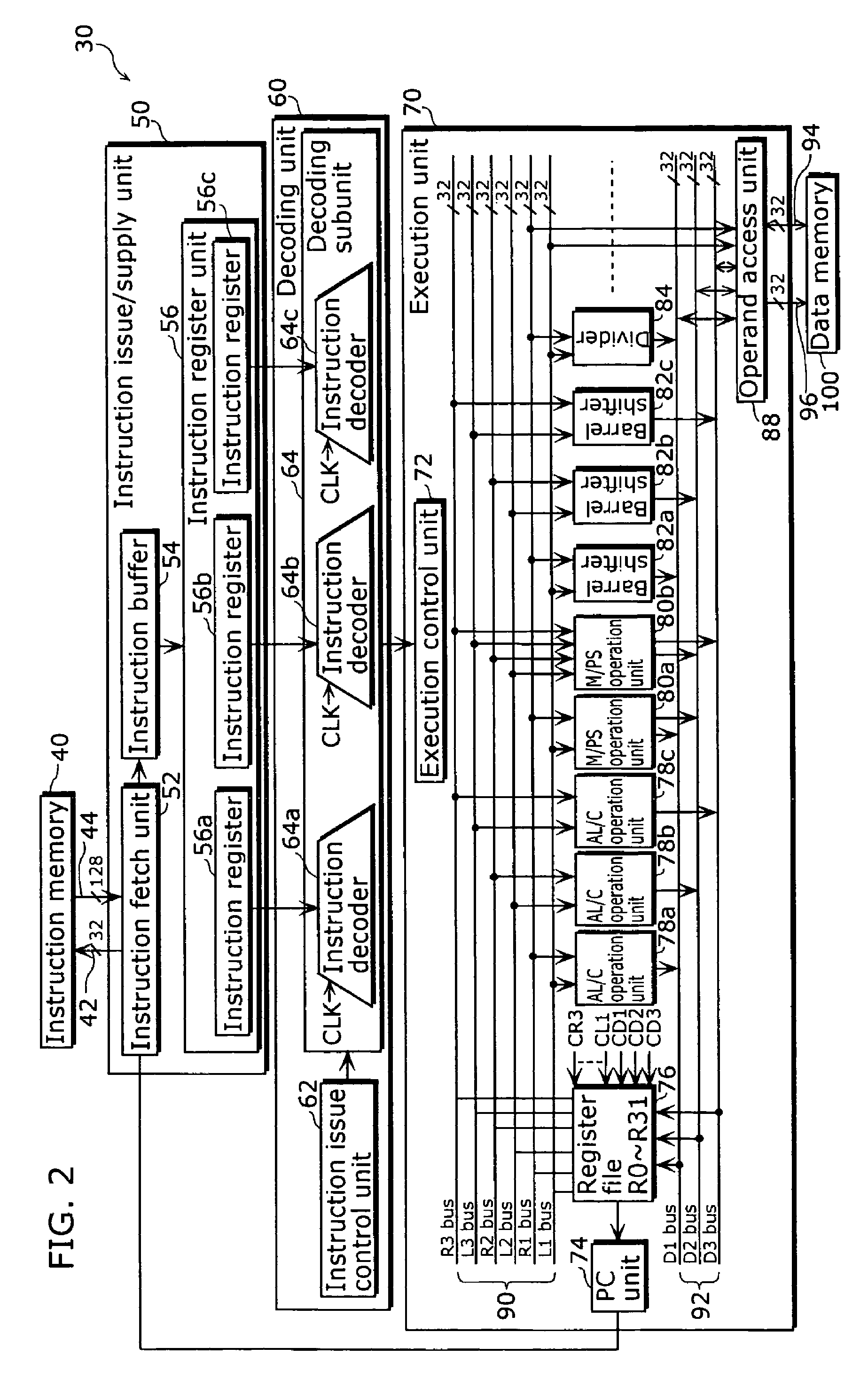
A four-stage assembly line RISC-V processor with a rapid data bypass structure
PendingCN109918130AReduce messagingSimple control logicMachine execution arrangementsInstruction memoryControl signal
The invention provides a four-stage assembly line RISC-V processor with a rapid data bypass structure. The processor has a four-stage pipeline structure, when the operation except the non-Load instruction is executed, the direct bypass is carried out, and the effective data pipeline is changed into three stages, so that the operation speed is increased. Compared with a traditional four-level assembly line, the structure reduces the instruction period of most instructions and the frequency of occurrence of data danger, and greatly improves the performance of the processor. And the four-stage pipeline structure comprises an instruction fetching module, a decoding module, an execution module and a write-back module. The fetch module can generate a PC of a next instruction according to the instruction fetched from the instruction memory in the current period and an external control signal; The decoding module is used for extracting an operation code, a function code, a source register, a destination register and an immediate of the instruction, and taking a value from the general register; The execution module is responsible for executing various arithmetic operations; And the write-back module is used for recording the information of the memory access instruction and writing the data read from the memory into the general register.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
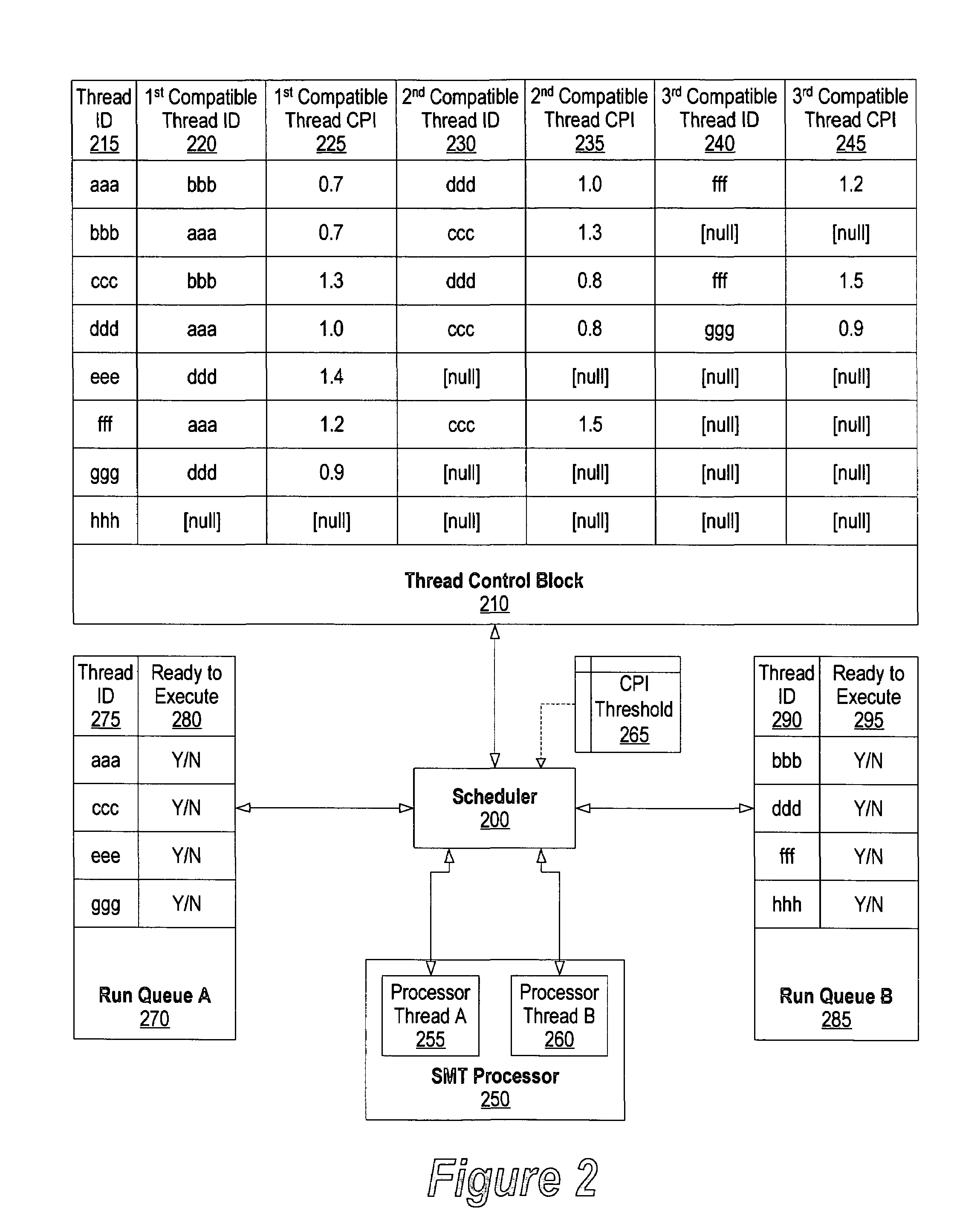
System and method for scheduling compatible threads in a simultaneous multi-threading processor using cycle per instruction value occurred during identified time interval
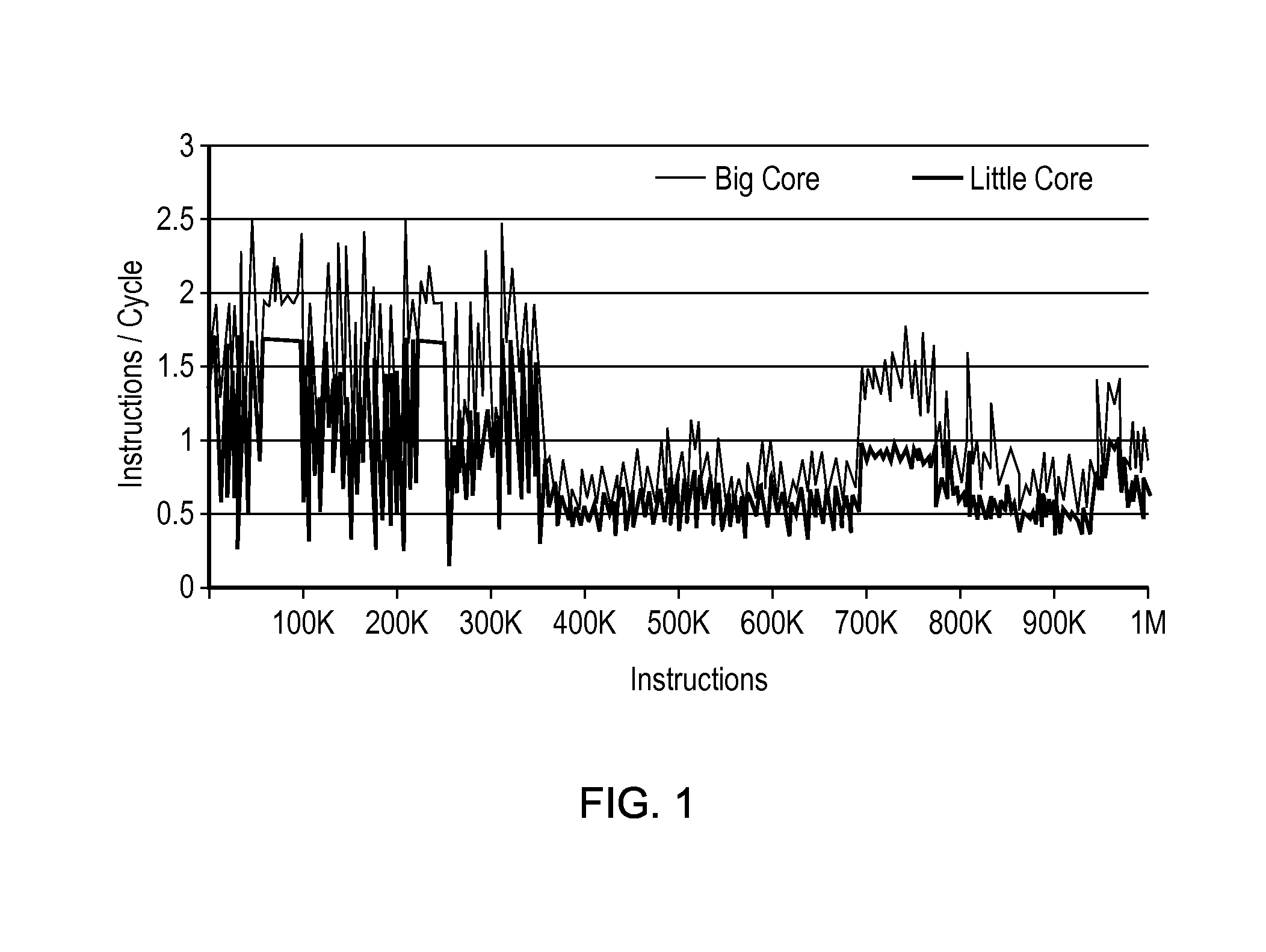
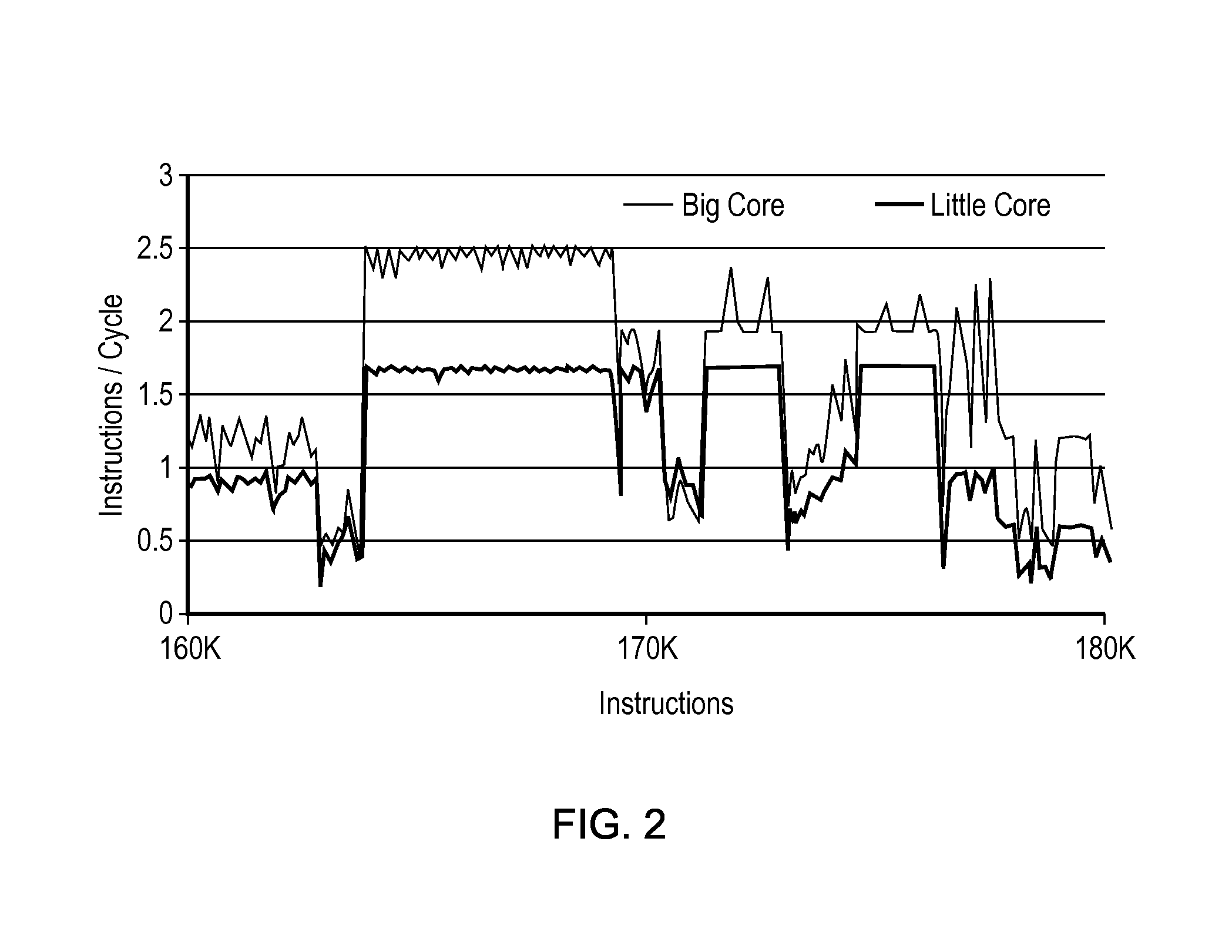
ActiveUS7360218B2Improve performanceDigital computer detailsMultiprogramming arrangementsComputer compatibilityInstruction cycle
A system and method for identifying compatible threads in a Simultaneous Multithreading (SMT) processor environment is provided by calculating a performance metric, such as cycles per instruction (CPI), that occurs when two threads are running on the SMT processor. The CPI that is achieved when both threads were executing on the SMT processor is determined. If the CPI that was achieved is better than the compatibility threshold, then information indicating the compatibility is recorded. When a thread is about to complete, the scheduler looks at the run queue from which the completing thread belongs to dispatch another thread. The scheduler identifies a thread that is (1) compatible with the thread that is still running on the SMT processor (i.e., the thread that is not about to complete), and (2) ready to execute. The CPI data is continually updated so that threads that are compatible with one another are continually identified.
Owner:META PLATFORMS INC
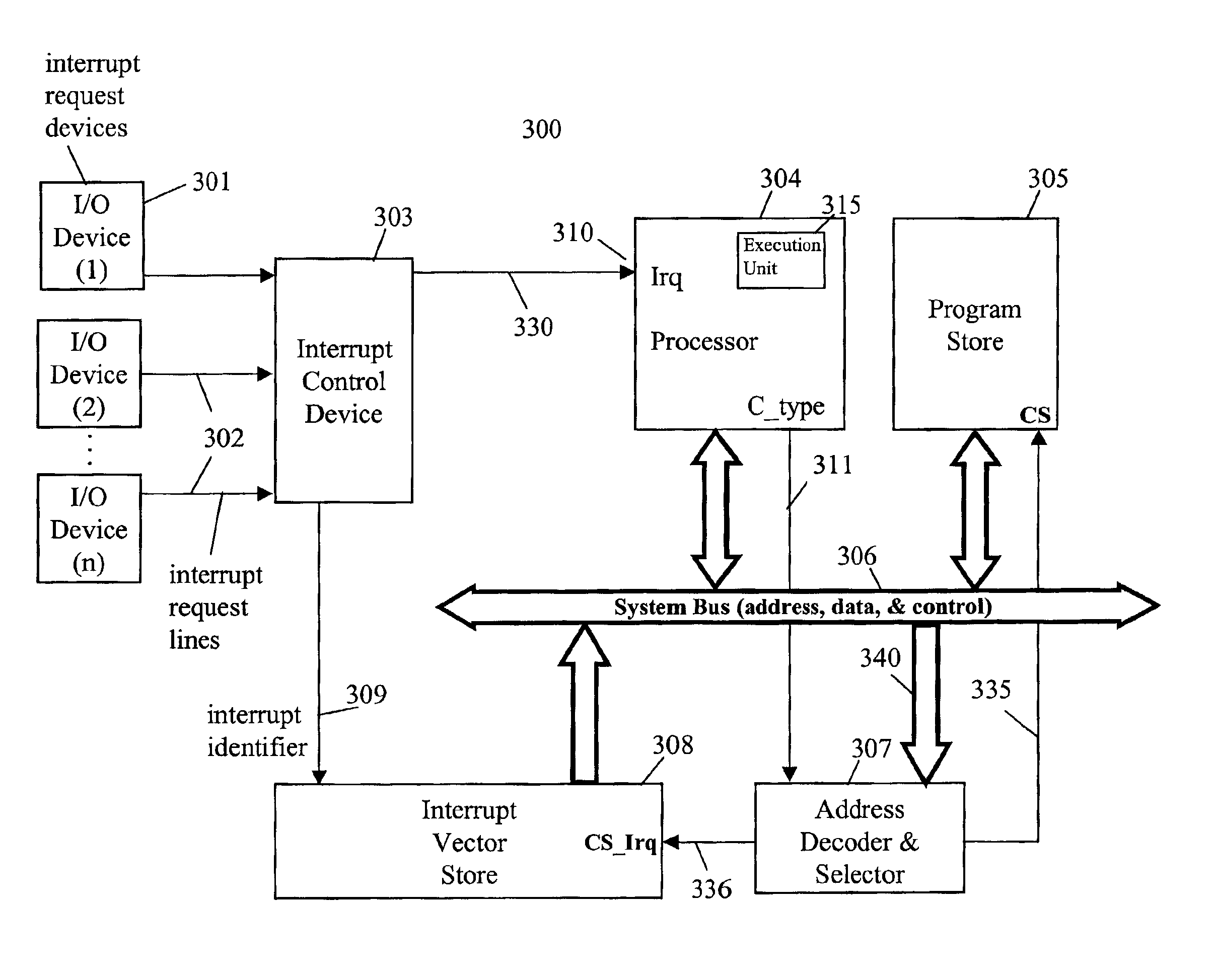
Pre-stored vector interrupt handling system and method
InactiveUS6889279B2Reduced interrupt-processing latencySave overheadProgram initiation/switchingNext instruction address formationChip selectInstruction cycle
A pre-stored vector interrupt handling system for rapidly processing interrupt requests from input / output (I / O) devices in processor-based systems includes selection logic and an interrupt vector store to quickly deliver a branch instruction from the interrupt vector store directly to the execution unit of a processor. The interrupt vector store is either pre-loaded with a table of the processor's branch instructions during system initialization or implemented in ROM. During normal operation, when an interrupt is received, a master interrupt signal is issued to the processor, which asserts an instruction cycle mode signal to external chip select logic. The chip select logic deselects the program store and selects the interrupt vector store. An interrupt vector from the vector store is loaded onto the data bus and then directly into the execution unit of the processor.
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
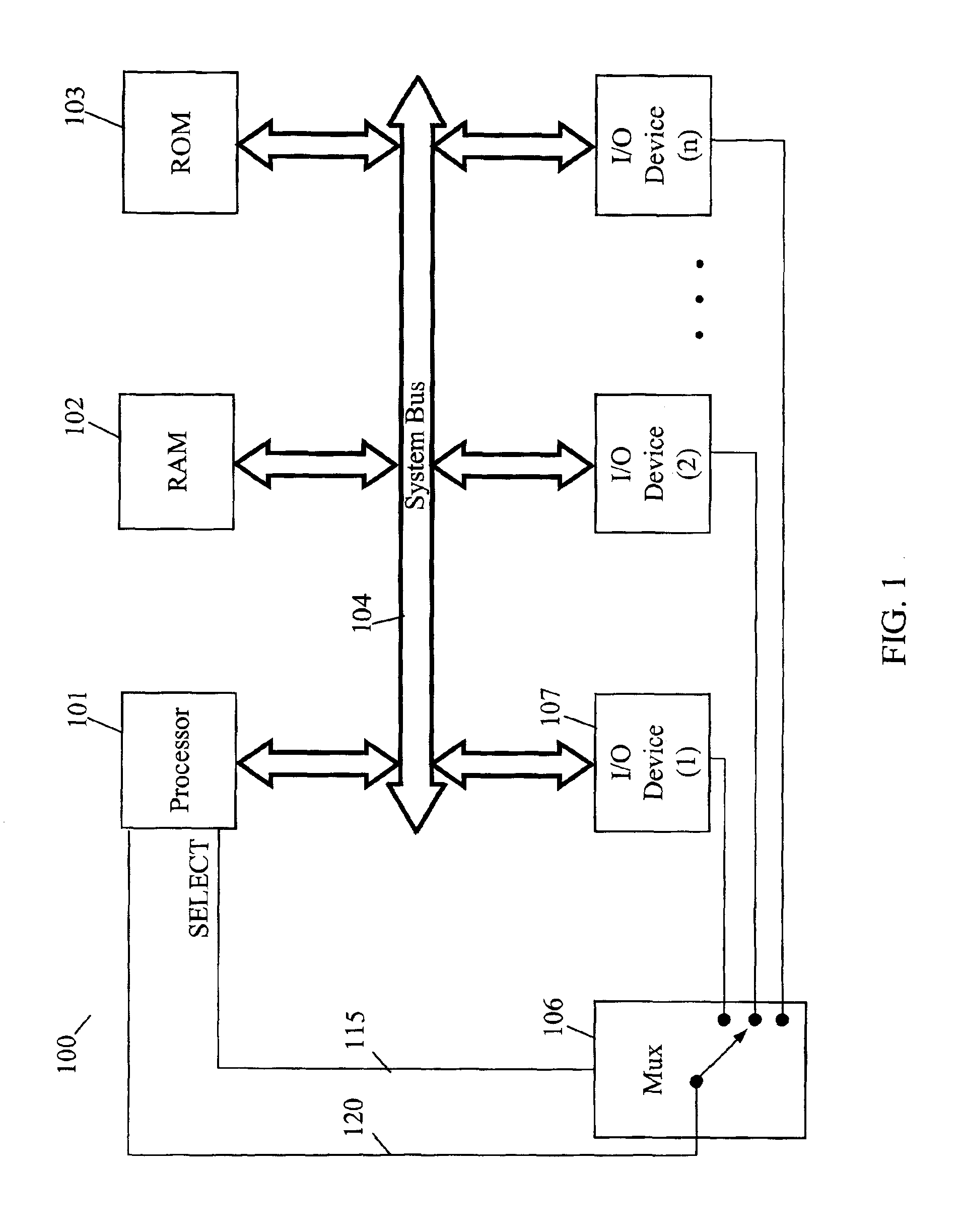
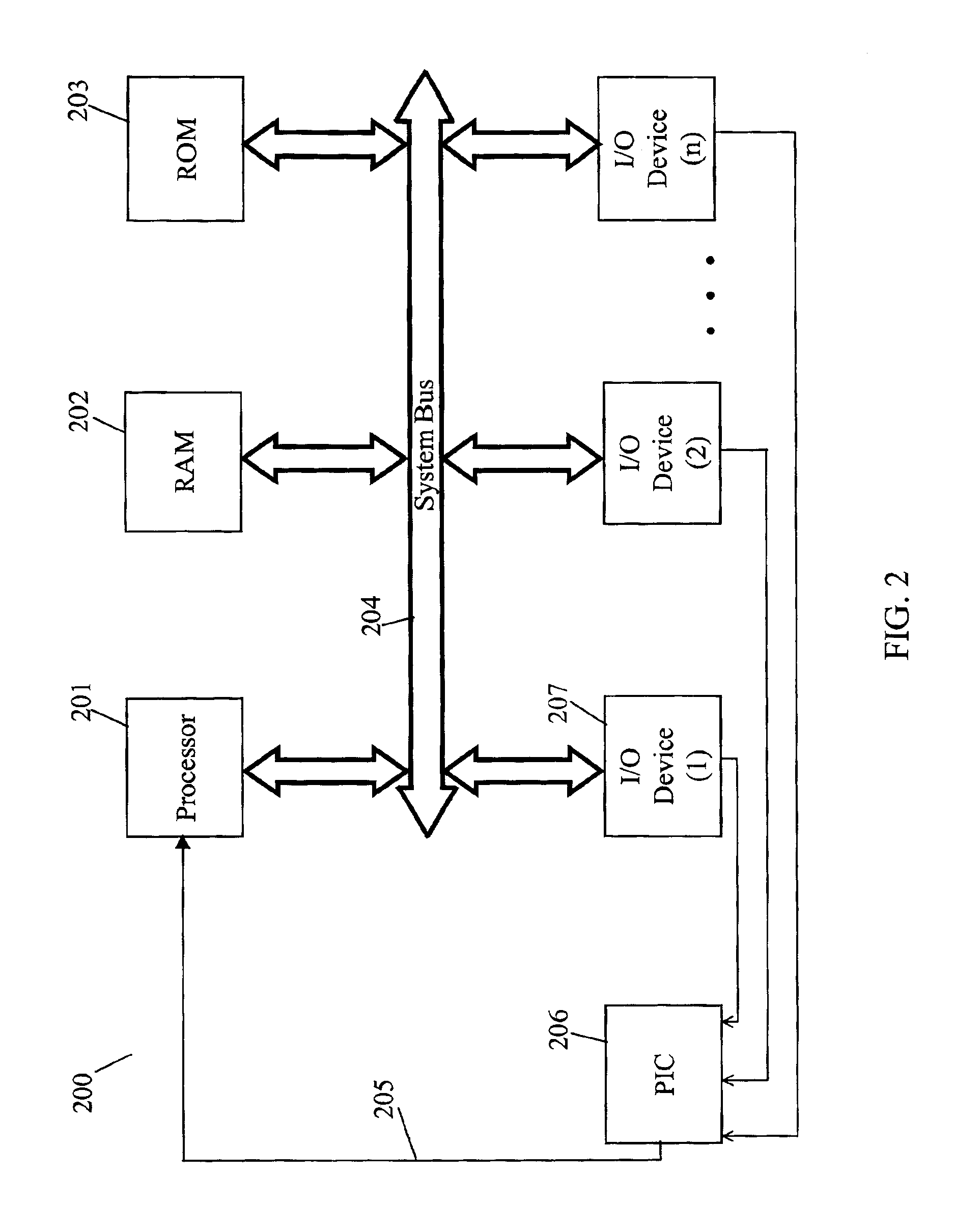
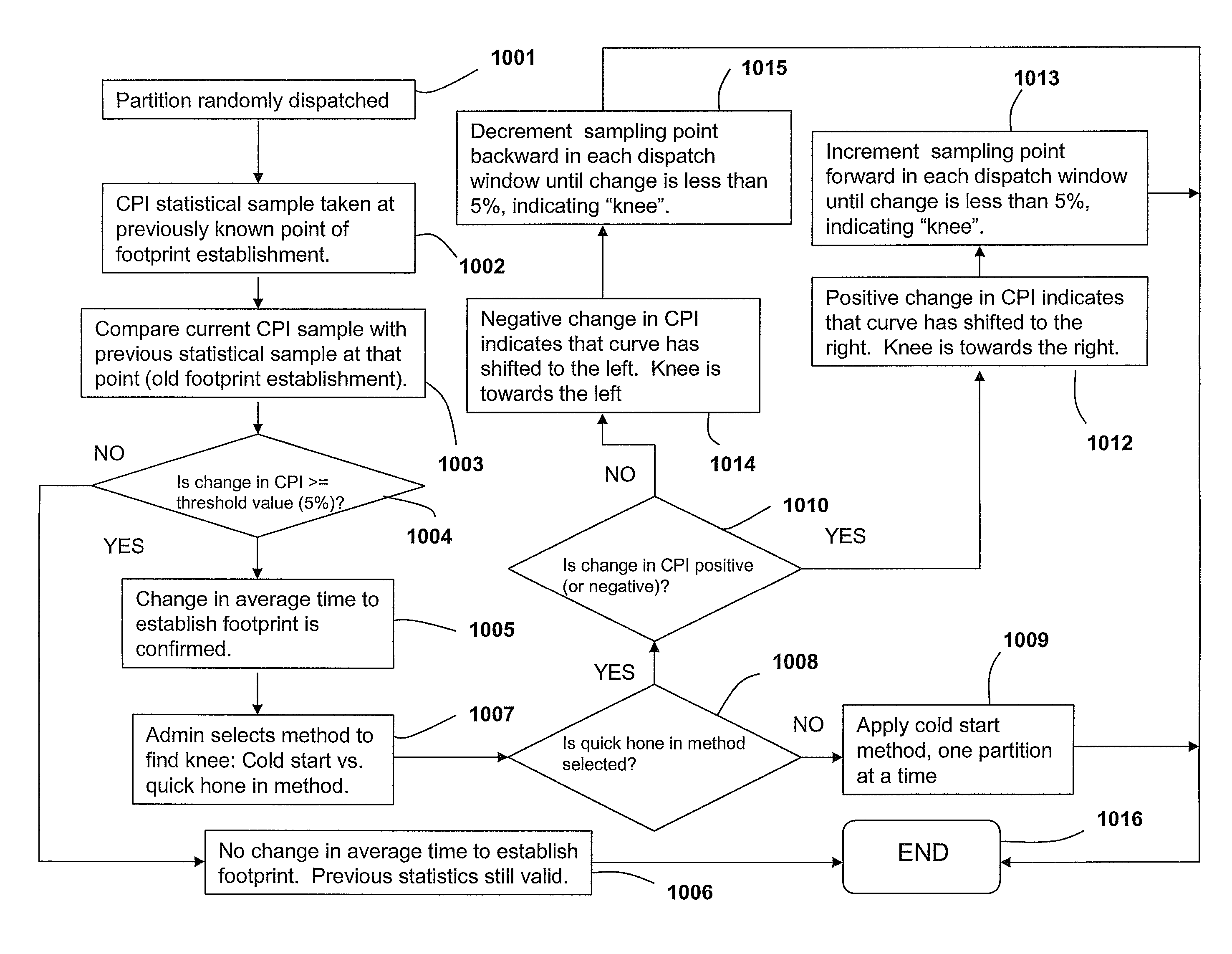
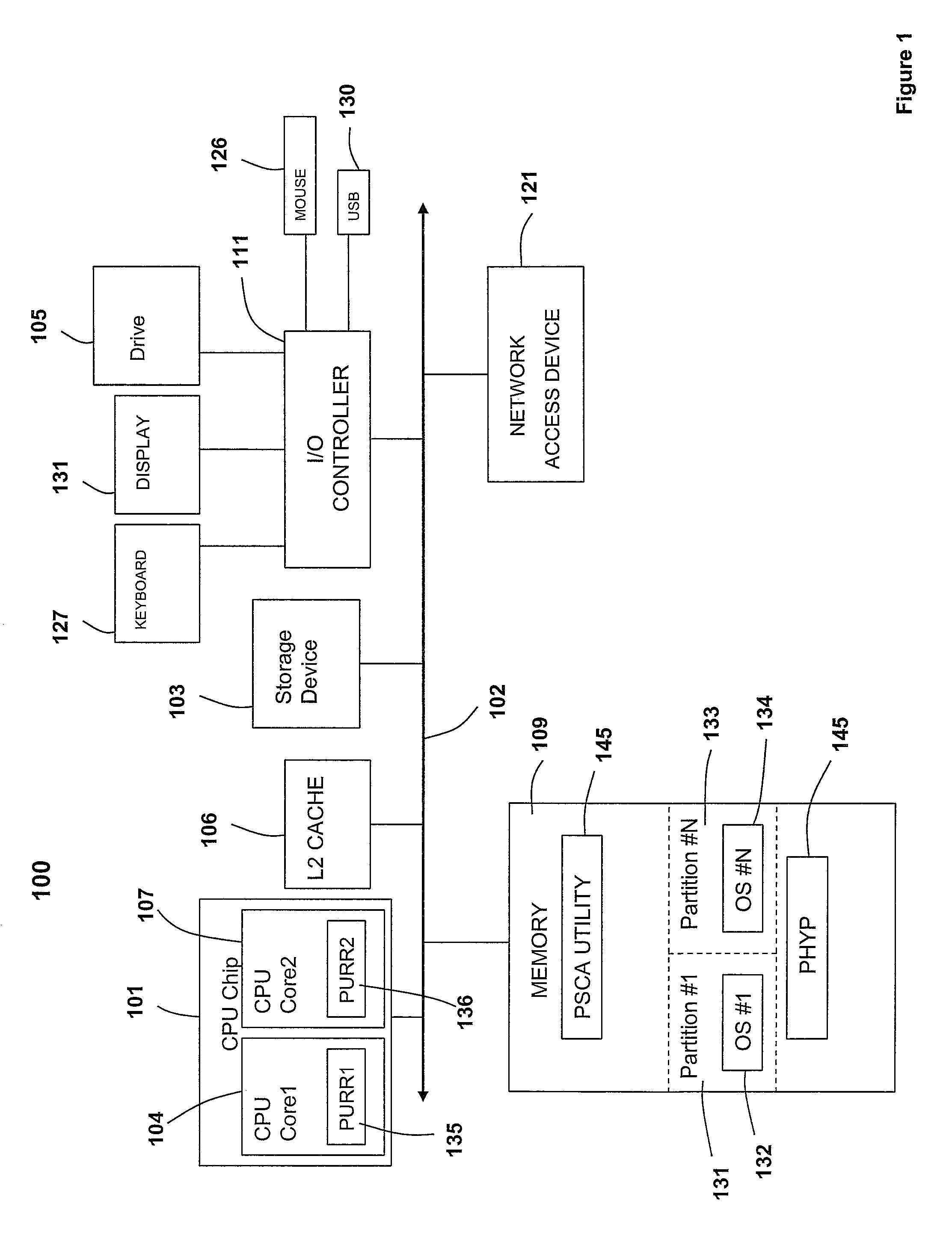
Capturing hardware statistics for partitions to enable dispatching and scheduling efficiency
InactiveUS8219995B2Error detection/correctionMultiprogramming arrangementsProcessor registerDecision taking
A method, system and computer program product enables the granular collection and utilization of hardware statistical samples for the efficient scheduling and allocation of data processing resources. In particular, a Partition Statistics Capture and Analysis (PSCA) utility utilizes special purpose registers to collect statistical samples, such as: (1) instructions completed; (2) Level2 (L2) cache misses; (3) cycles per instruction (CPI); and / or (4) other statistics selected based on the programming of the PSCA utility. Further, these statistical samples are utilized for the several purposes, including: (1) determining how long (time) the footprint of a partition takes to become established during the “cold start” period, i.e., during system instantiation; (2) detecting movement of the CPI curve in order to determine the (shifted) location of the onset of steady state (i.e., the knee) on the CPI curve; and (3) utilizing the statistical samples to guide dispatch decisions and make tuning recommendations.
Owner:IBM CORP
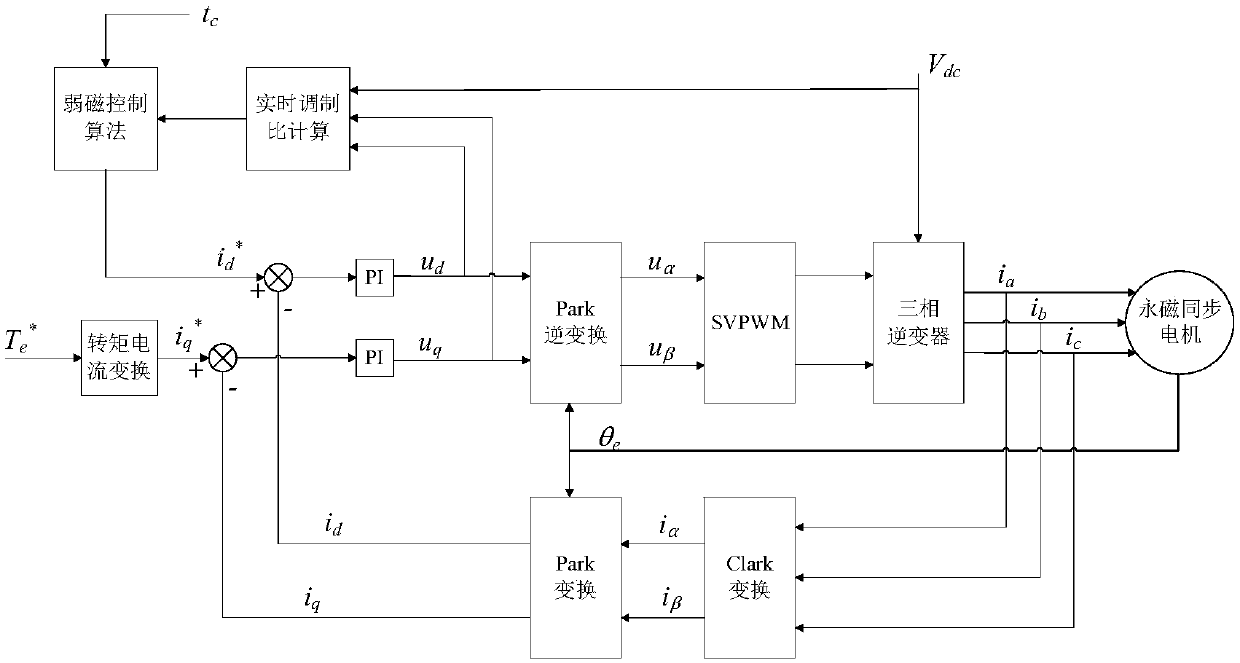
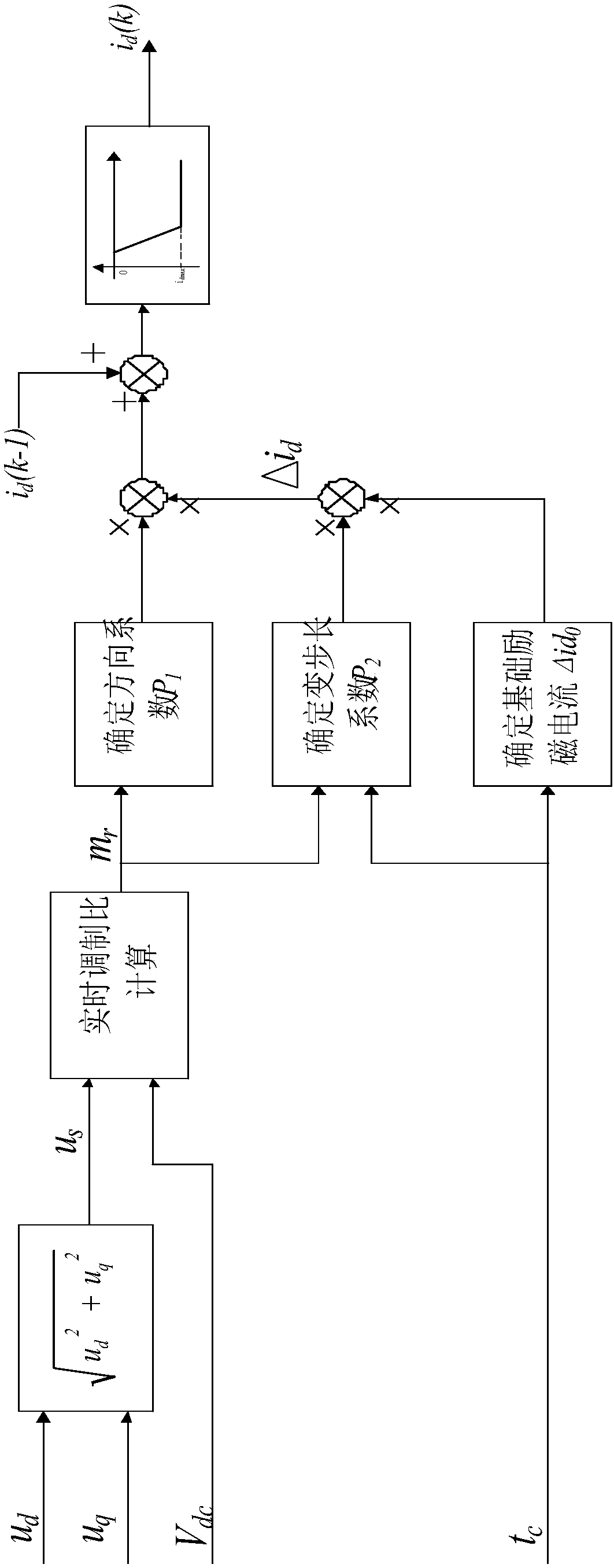
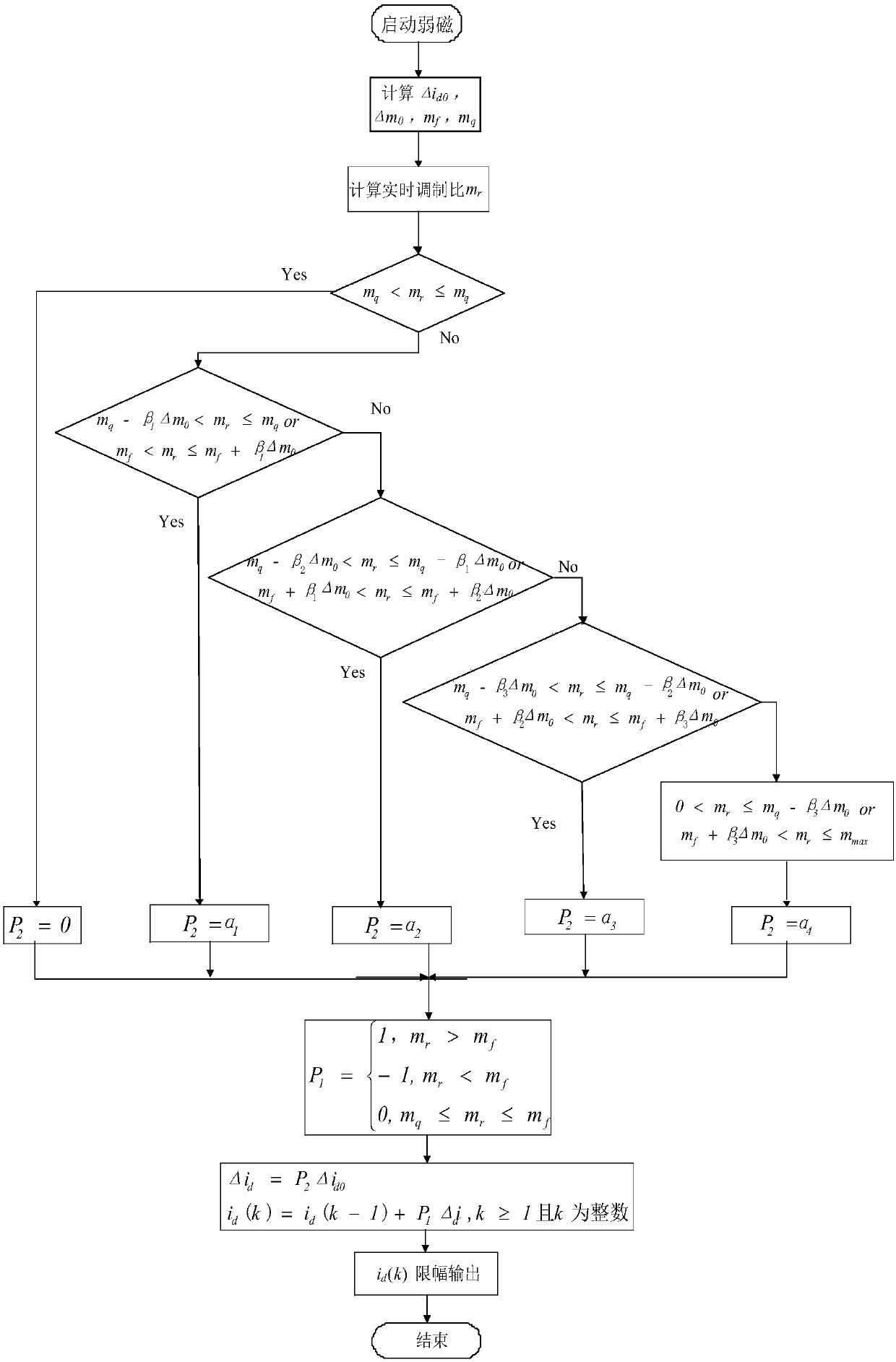
Method for adaptive field-weakening control of permanent magnet synchronous motor
ActiveCN107592047AAvoid the influence of field weakening effectAchieve the effect of adaptive switching of field weakening controlElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlHysteresisExcitation current
The present invention discloses a method for adaptive field-weakening control of a permanent magnet synchronous motor. The objective of the invention is to mainly solve the problems that a current field-weakening method depends too much on motor parameters and computation load of an algorithm is large in the prior art. The method provided by the invention, according to specific application conditions of a permanent magnet synchronous motor, calculates a real-time modulation ratio mr, a switching point modulation ratio mf, an exit field-weakening point modulation ratio mq and a modulation hysteresis width [Delta]m0, and determines a basic excitation current value [Delta]id0, a direction coefficient P1 and a field current difference coefficient P2, and a current instruction cycle instructionexcitation current is calculated through a formula. Through the above scheme, an influence of working conditions on field-weakening points is avoided, and field-weakening switching points are automatically switched according to a real-time modulation ratio so as to realize stable field-weakening switching of a permanent magnet synchronous motor with different conditions such as different rotatingspeeds and voltages and have a high practical value and a promotion value.
Owner:深圳市富鑫产业科技有限公司
Compiler apparatus and method of optimizing a source program by reducing a hamming distance between two instructions
InactiveUS7386844B2Reduce power consumptionEnergy efficient ICTSoftware engineeringCode generationInstruction cycle
A compiler apparatus is capable of generating instruction sequences causing a processor to operate with lower power consumption. The compiler apparatus translates a source program into a machine language program for a processor including execution units which can execute instructions in parallel, and including instruction issue units which issue the instructions executed, respectively, by the execution units. The compiler apparatus includes a parser unit operable to parse the source program, an intermediate code conversion unit operable to convert the parsed source program into intermediate codes, an optimization unit operable to optimize the intermediate codes to reduce a hamming distance between instructions from the same instruction issue unit in consecutive instruction cycles, and includes a code generation unit operable to convert the optimized intermediate codes into machine language instructions.
Owner:SOCIONEXT INC
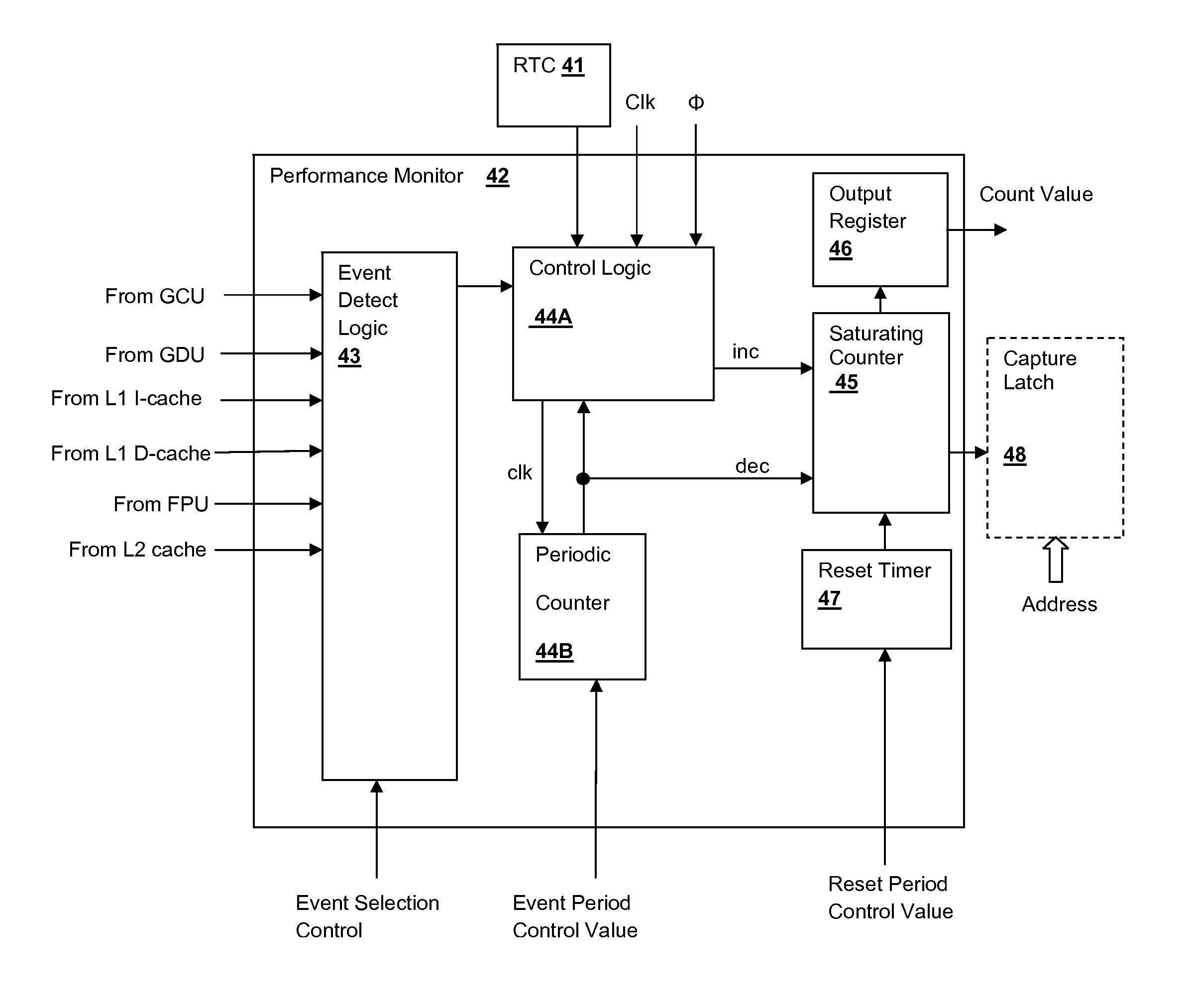
Processor core having a saturating event counter for making performance measurements
A performance monitor including a saturating counter provides a relative measure of event frequency without requiring a minimum polling rate or periodic reset to avoid or account for counter overflow. The saturating counter is incremented upon detection of an event and decremented if an event is not detected within a predetermined period. The period of detecting may be programmable and may be determined by real time clock, processor or instruction cycles. Multiple event types may be selected from for detection and input to a single counter, or alternatively multiple event counters may be provided for various event types. The saturating counter may additionally be periodically reset in a selected operating mode, in combination with the decrementing action performed on the counter.
Owner:IBM CORP
A method for optimizing the operation of an electro-thermal coupling integrate energy system
ActiveCN109190785ARun accuratelyGuaranteed comfortForecastingIntegrated energy systemImage resolution
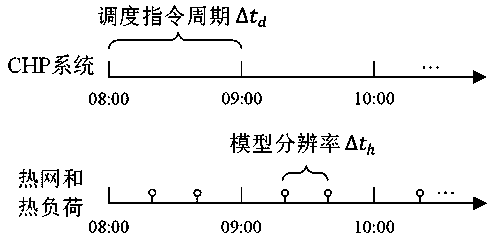
A method for optimizing the operation of an electro-thermal coupling integrate energy system is disclosed. An objective function and constraint conditions of the operation optimization of the electro-thermal coupled integrated energy system are established, so as to establish the operation optimization model of the electro-thermal coupling comprehensive energy system, then the simulation model ofheat network and heat load state is established, taking the temperature of heat medium injected into the heating network in the operation optimization result as the input to calculate the actual stateof the heating network and heat load, at last, the operation optimization flow of the electrothermal couple integrated energy system is established, the results of simulation model are compared withthose of optimization model, and error values are judged. As the error exceeds the allowable range, the resolution of the heating network and the heat load model is reduced and the above steps are repeated, otherwise, the method stops, thereby determining the appropriate resolution of the heat network and the heat load model. The method can fully consider the slow dynamic process of the change ofthe heat network and the heat load state in the dispatching instruction cycle, and effectively ensures the user comfort while realizing the efficient and economical operation of the system.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Apparatus and method for realizing digital predistortion
InactiveCN101257283AReduce computing timeAchieve fast and accurateNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsAudio power amplifierEngineering
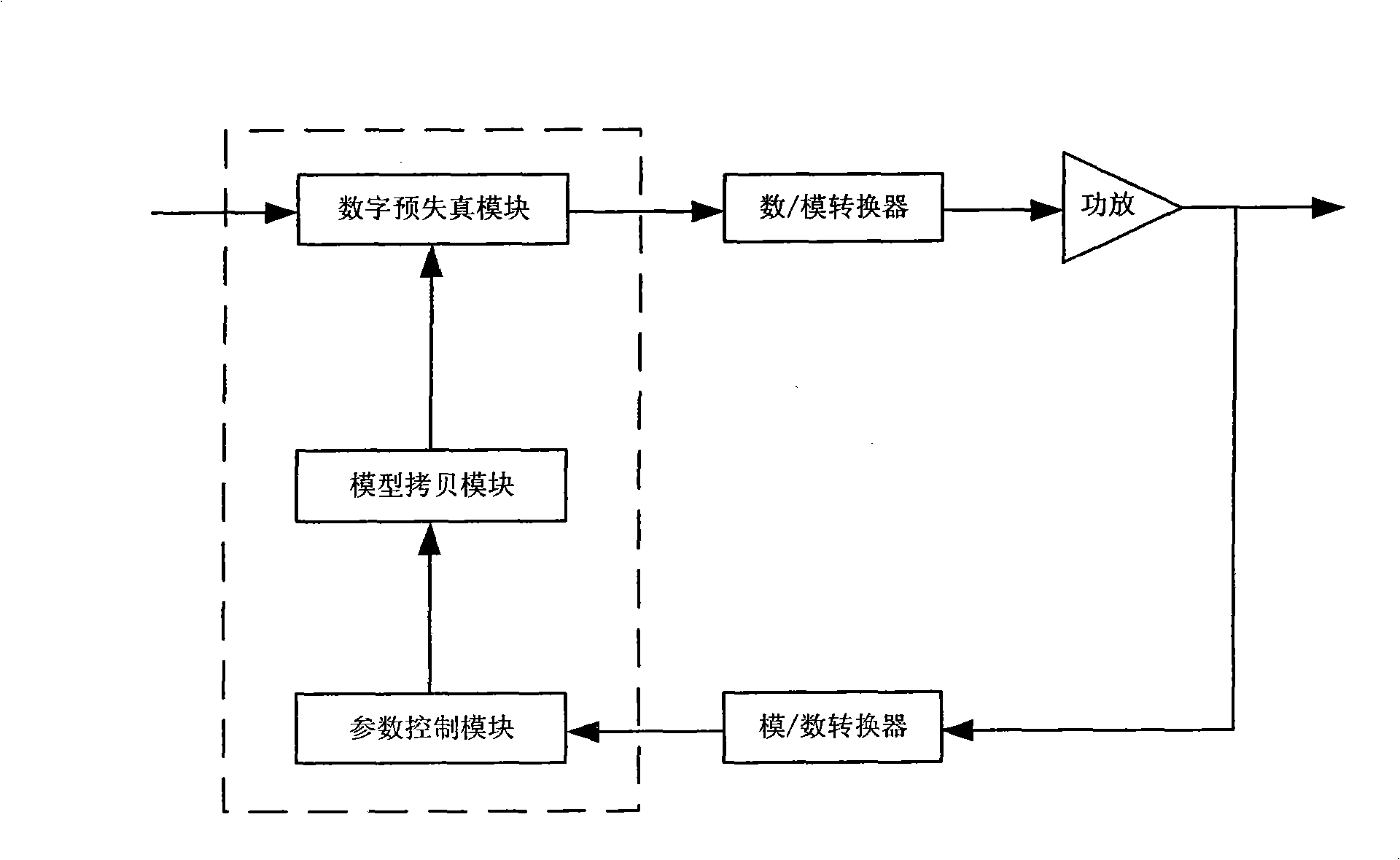
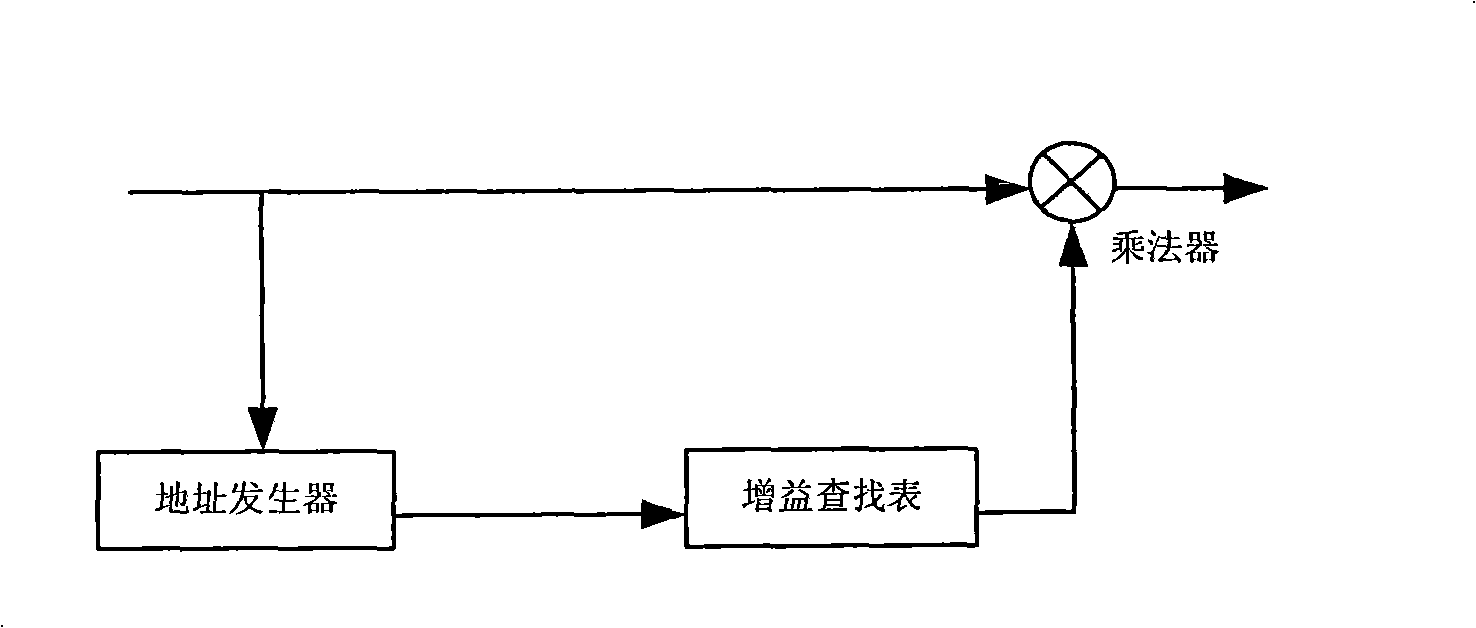
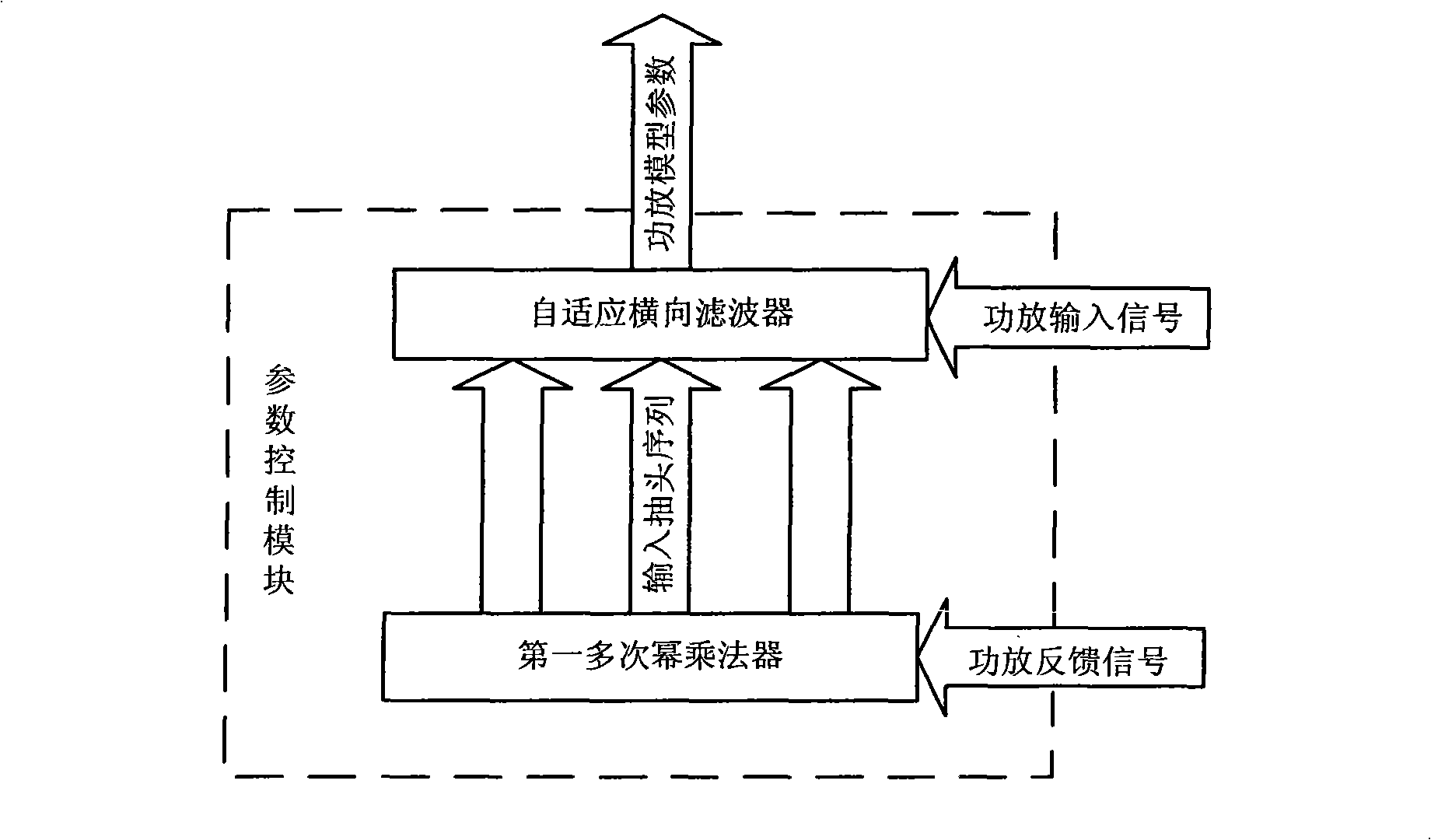
The invention discloses an apparatus and method for implementing digital predistortion, wherein the method includes utilizing programmable logic structure to realize the following steps: S1. a parameter control module utilizes power amplifier incoming signals and power amplifier feedback signals of a power amplifier to synchronously calculate and renovate all power amplifier model parameters in the memorization multinomial model; S2. a model copy module assigns the value of the power amplifier model parameter to the corresponding model parameters a digital predistortion module; S3. the digital predistortion module carries out a predistortion process to the incoming signals according to model parameters. The inventive apparatus and method utilizes parallel arithmetic advantage of the programmable logic structure, thereby realizing the calculation of all model parameters in an instruction cycle, reducing computing time, improving predistortion process efficiency, and quickly and accurately realizing the digital predistortion process.
Owner:郭颖 +5
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com