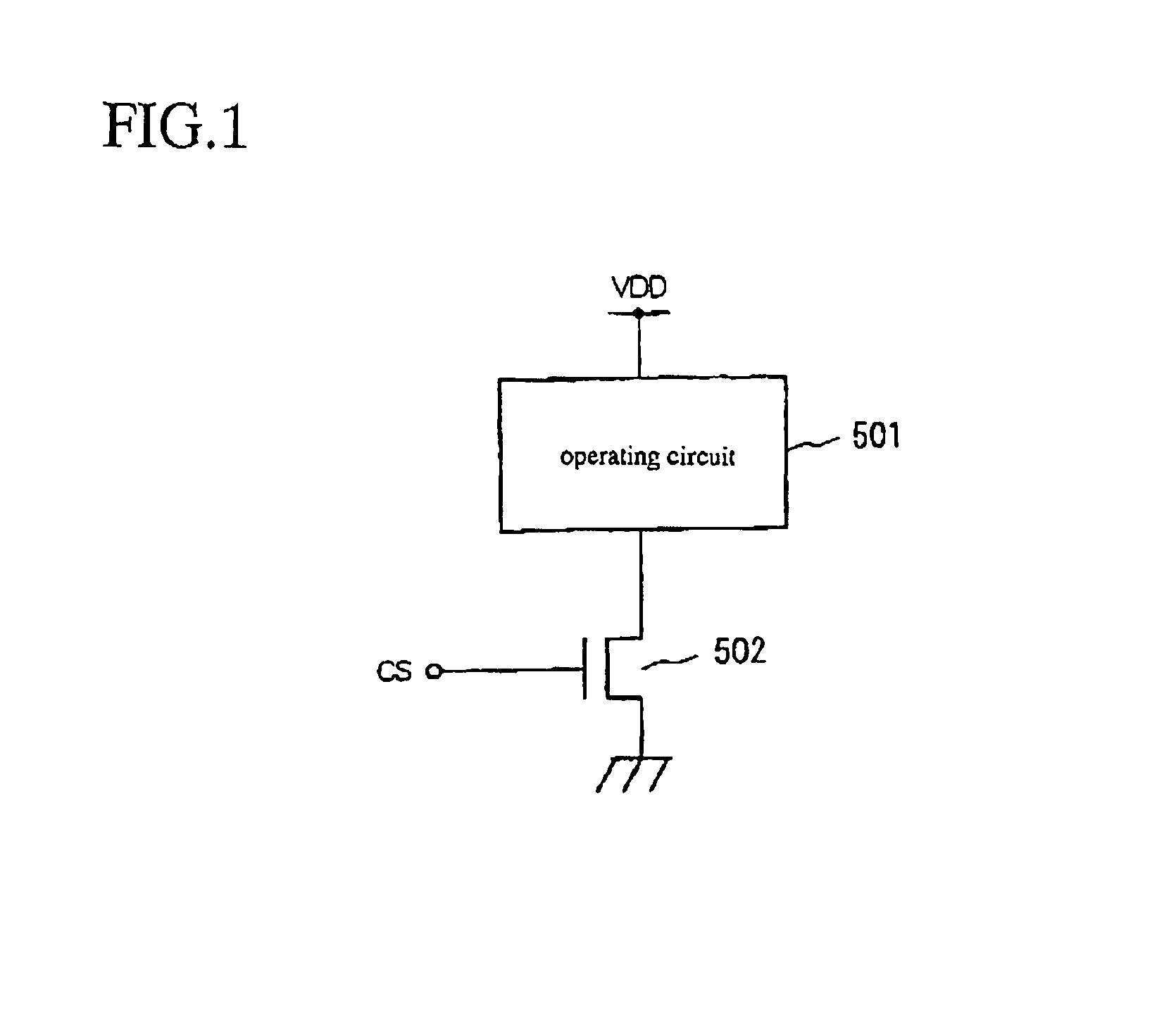
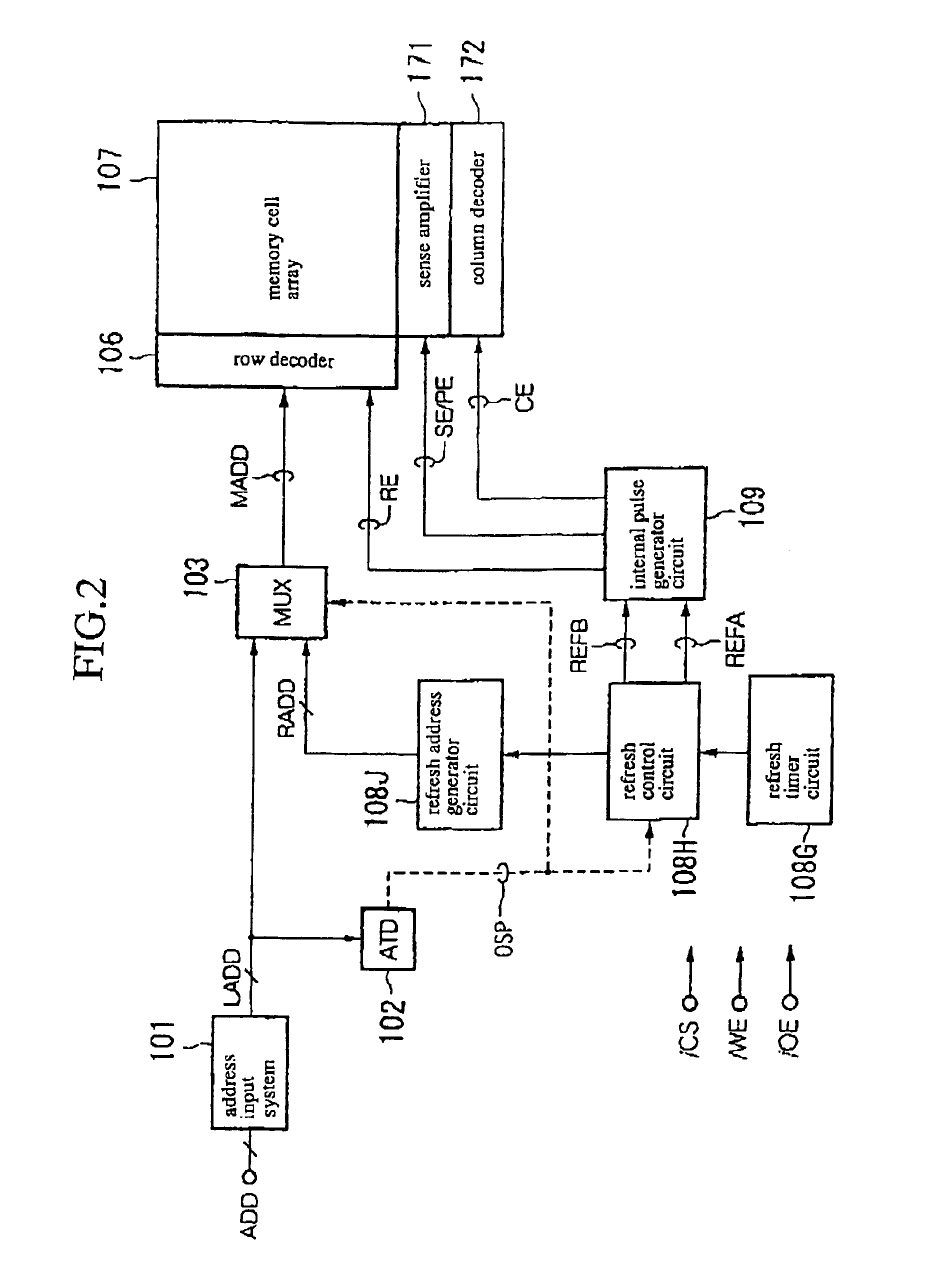
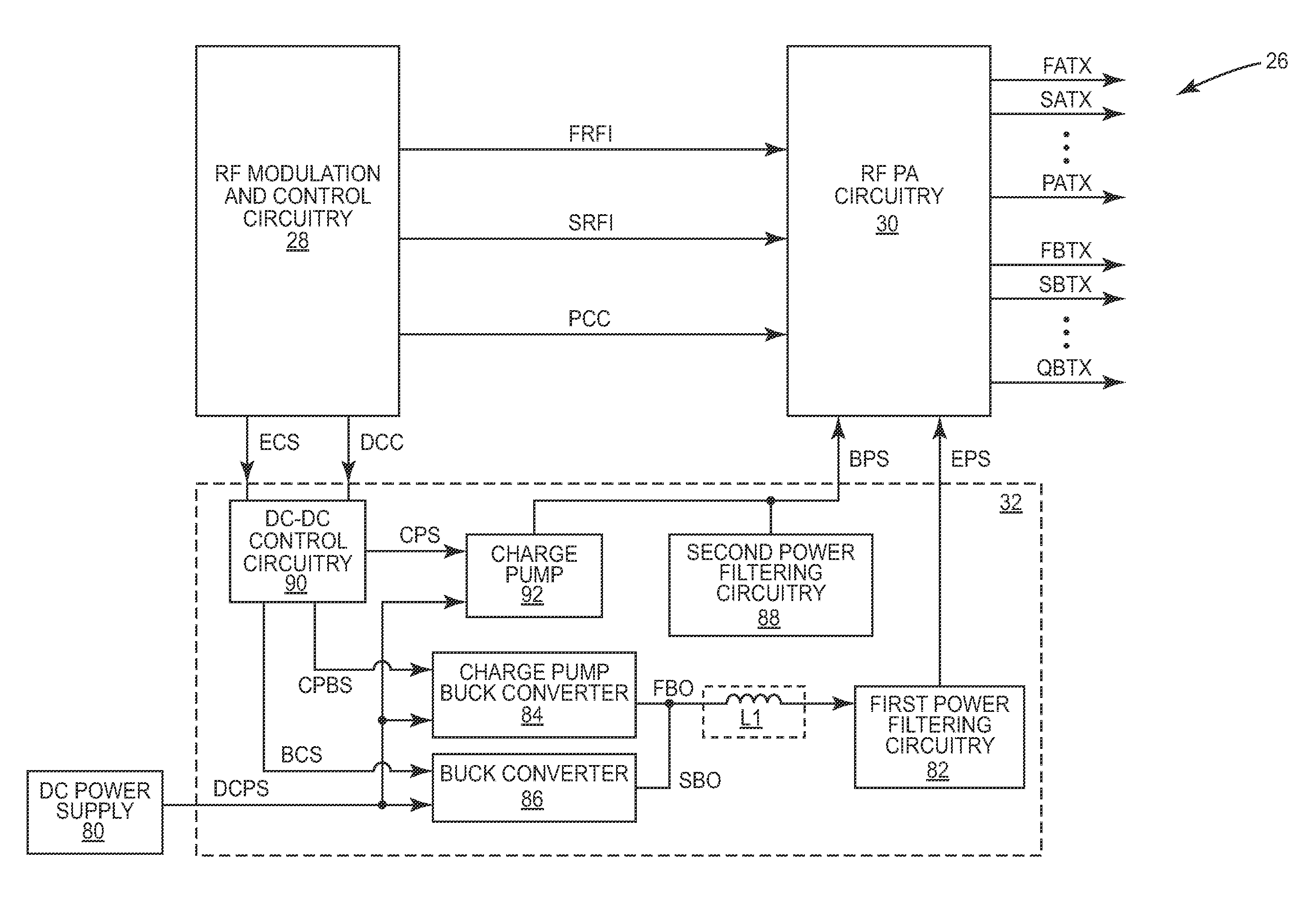
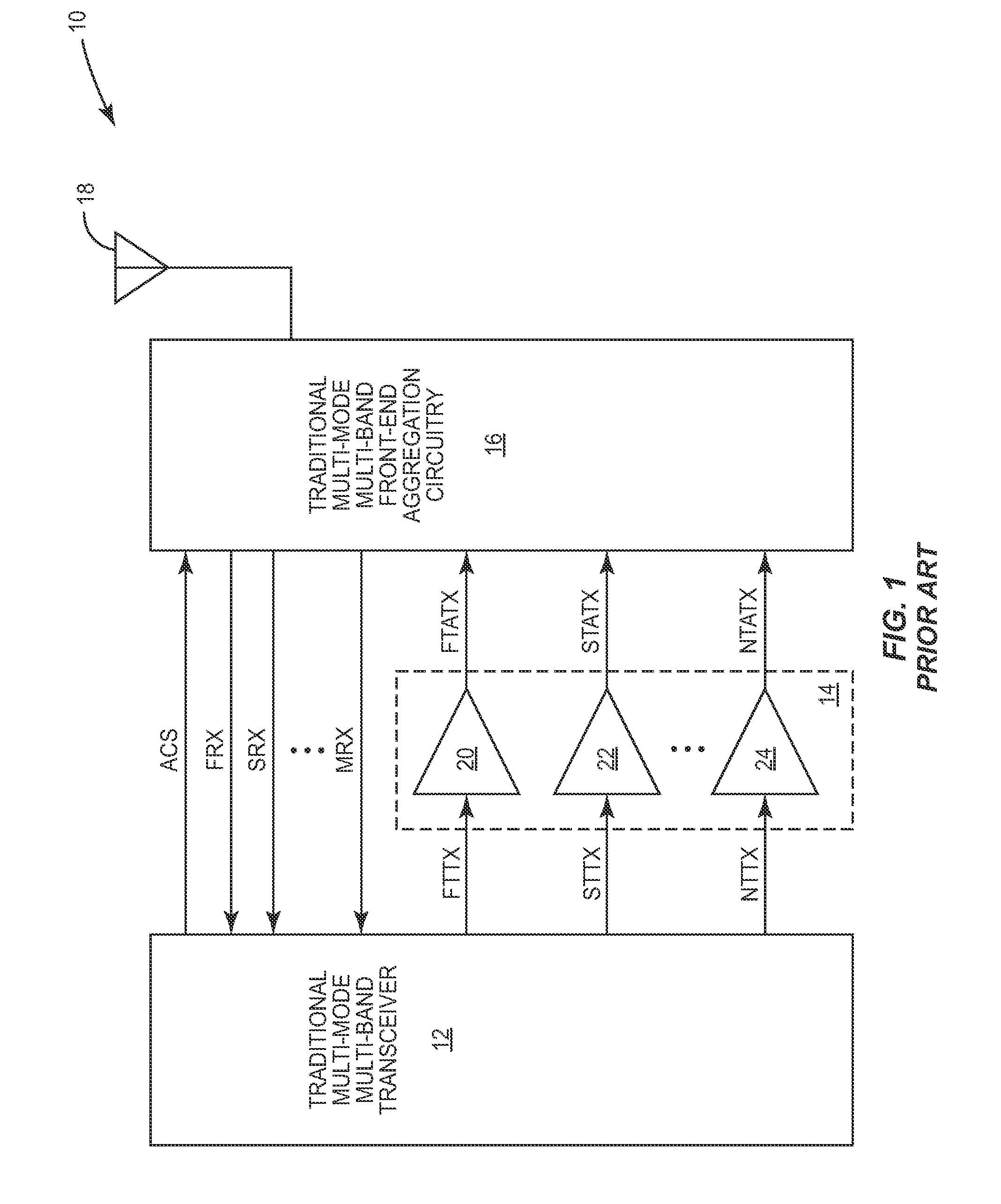
Patents
Literature
653 results about "Chip select" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Chip select (CS) or slave select (SS) is the name of a control line in digital electronics used to select one (or a set) of integrated circuits (commonly called "chips") out of several connected to the same computer bus, usually utilizing the three-state logic.
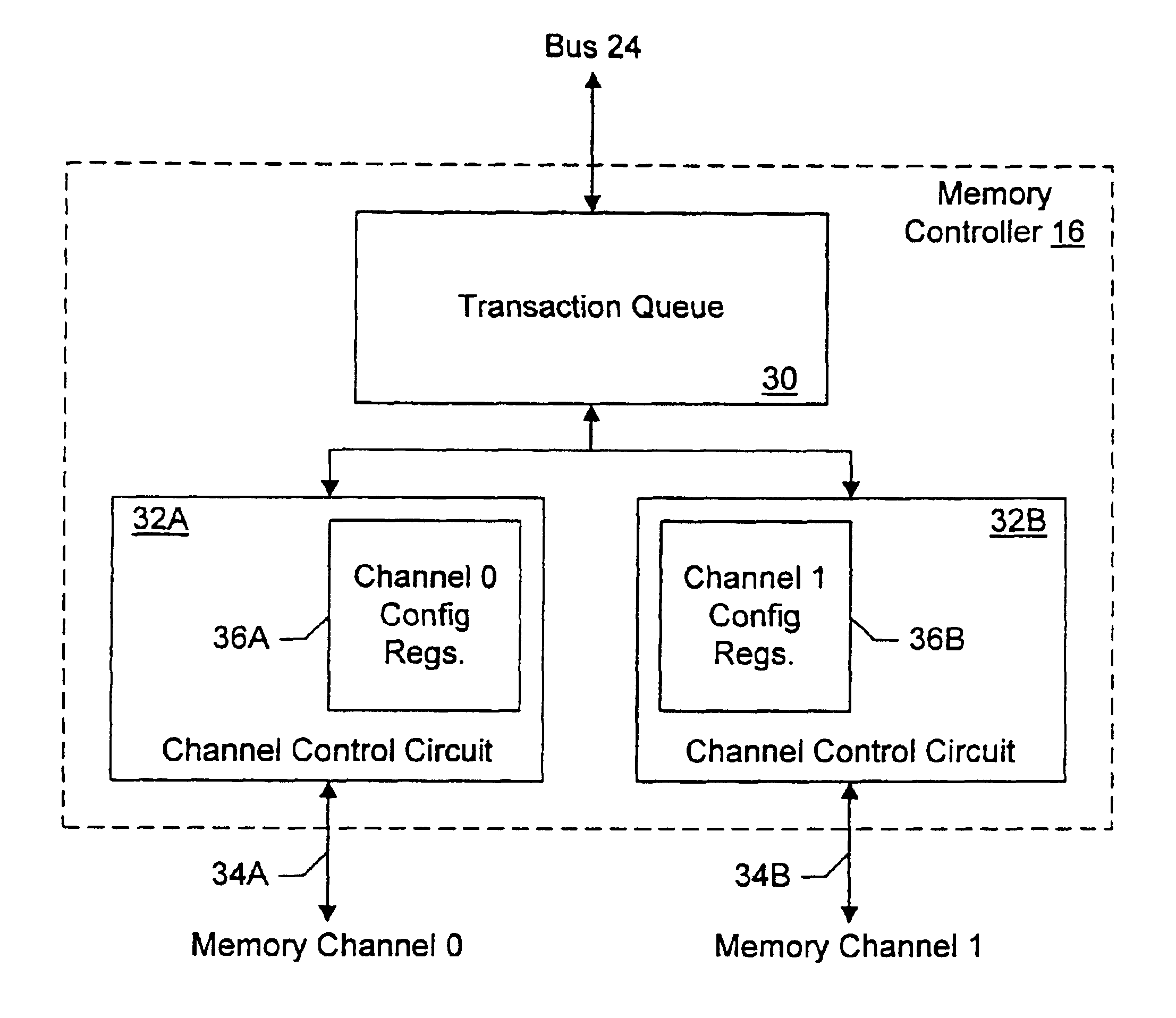
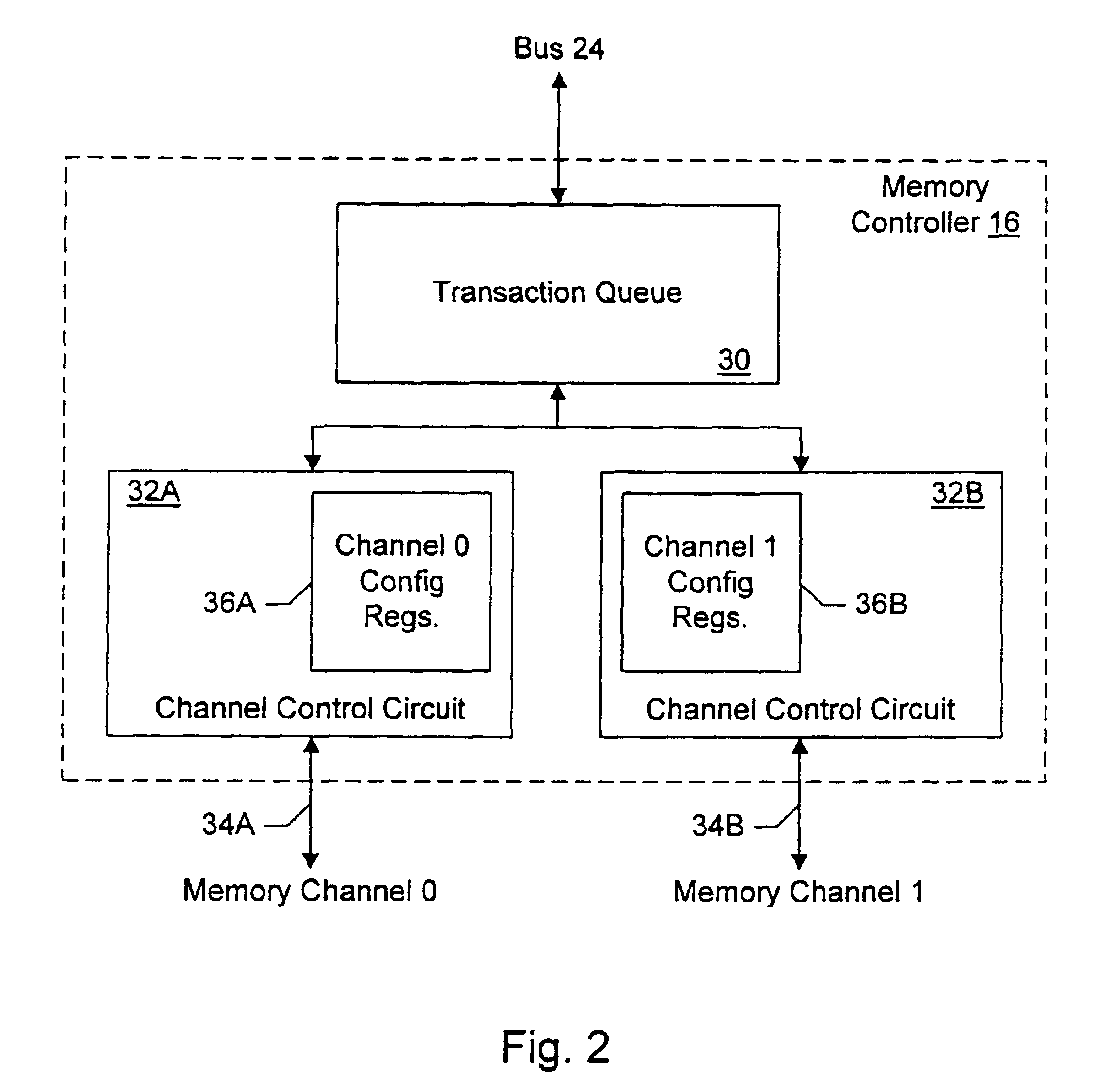
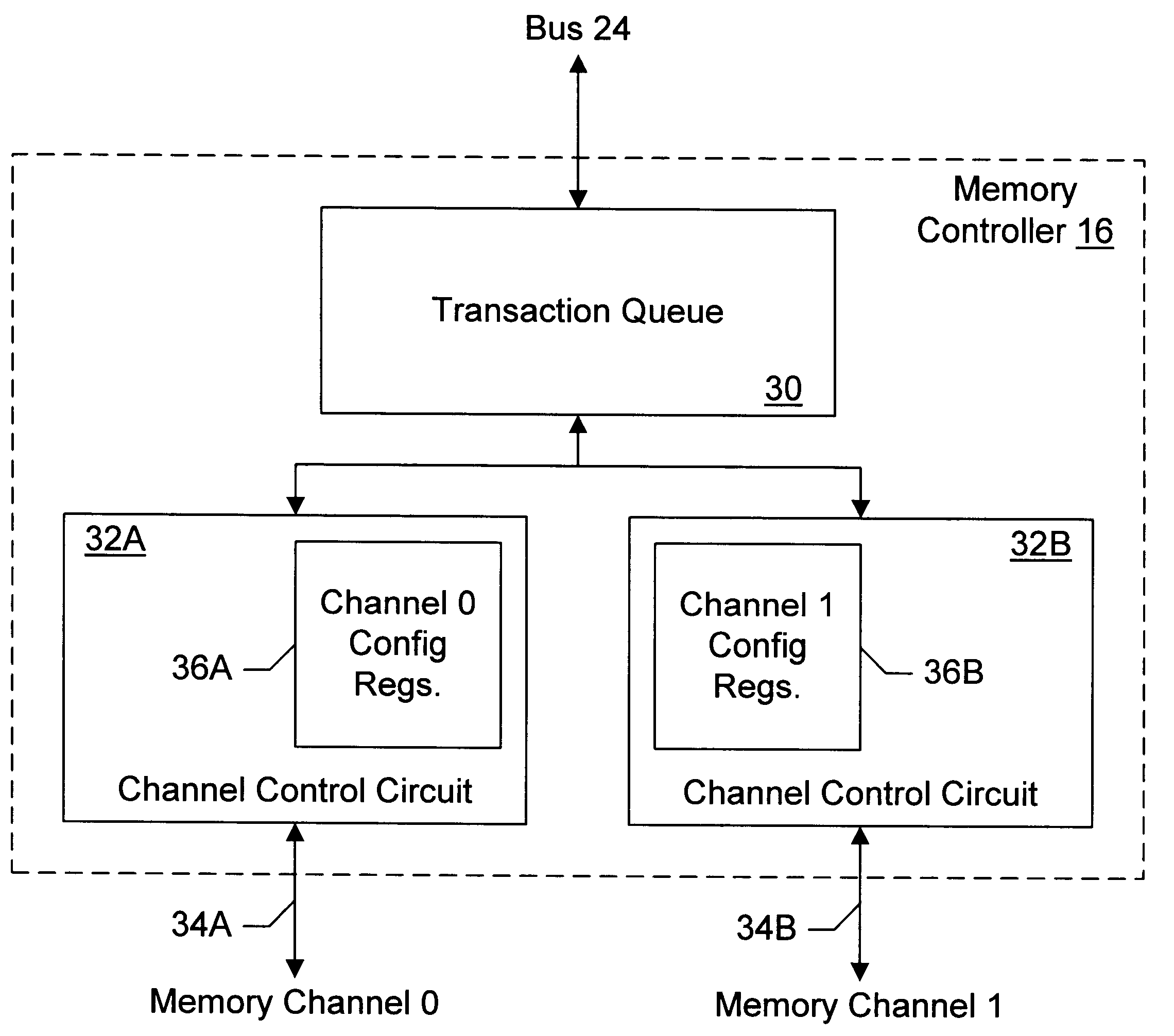
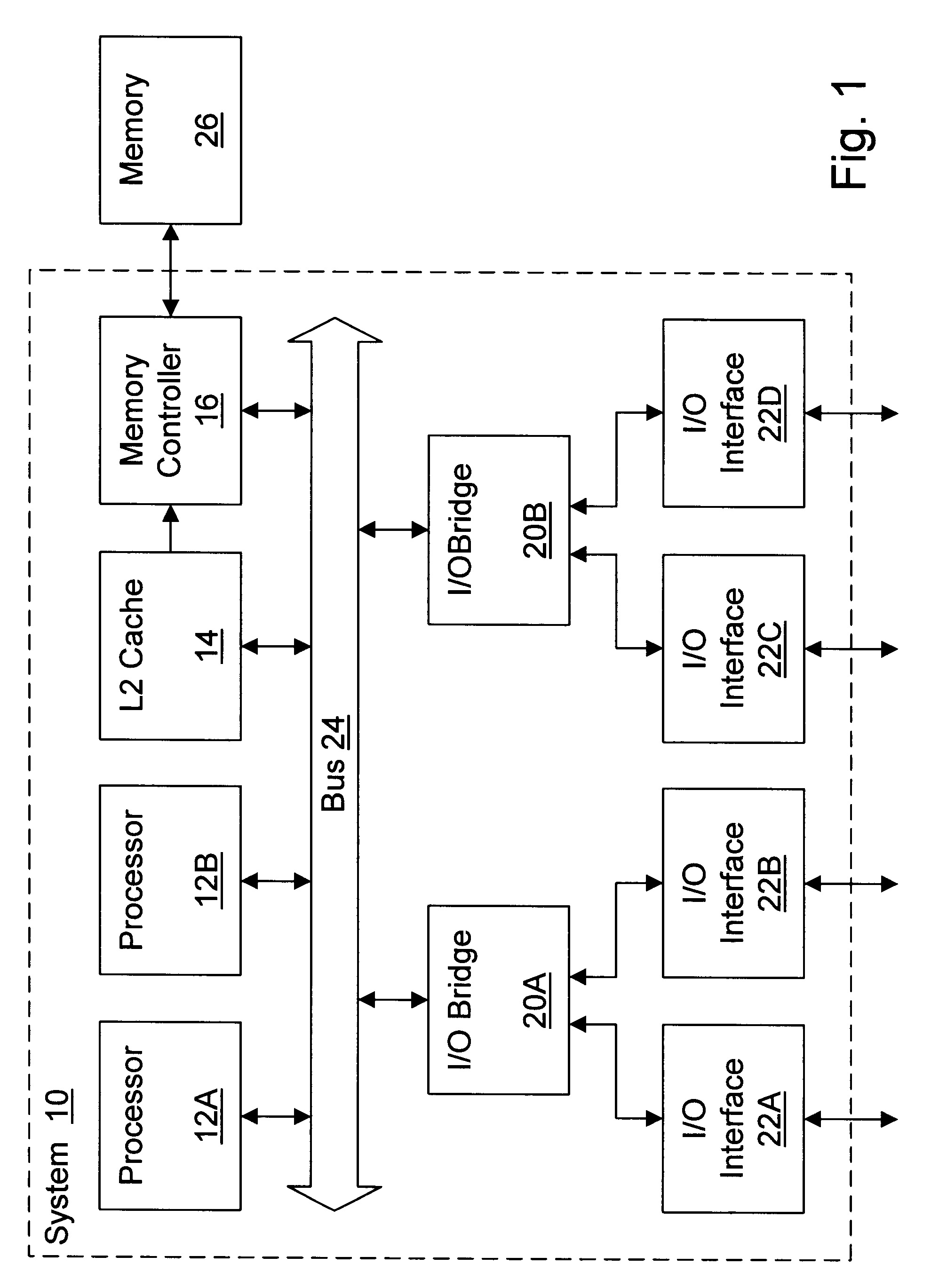
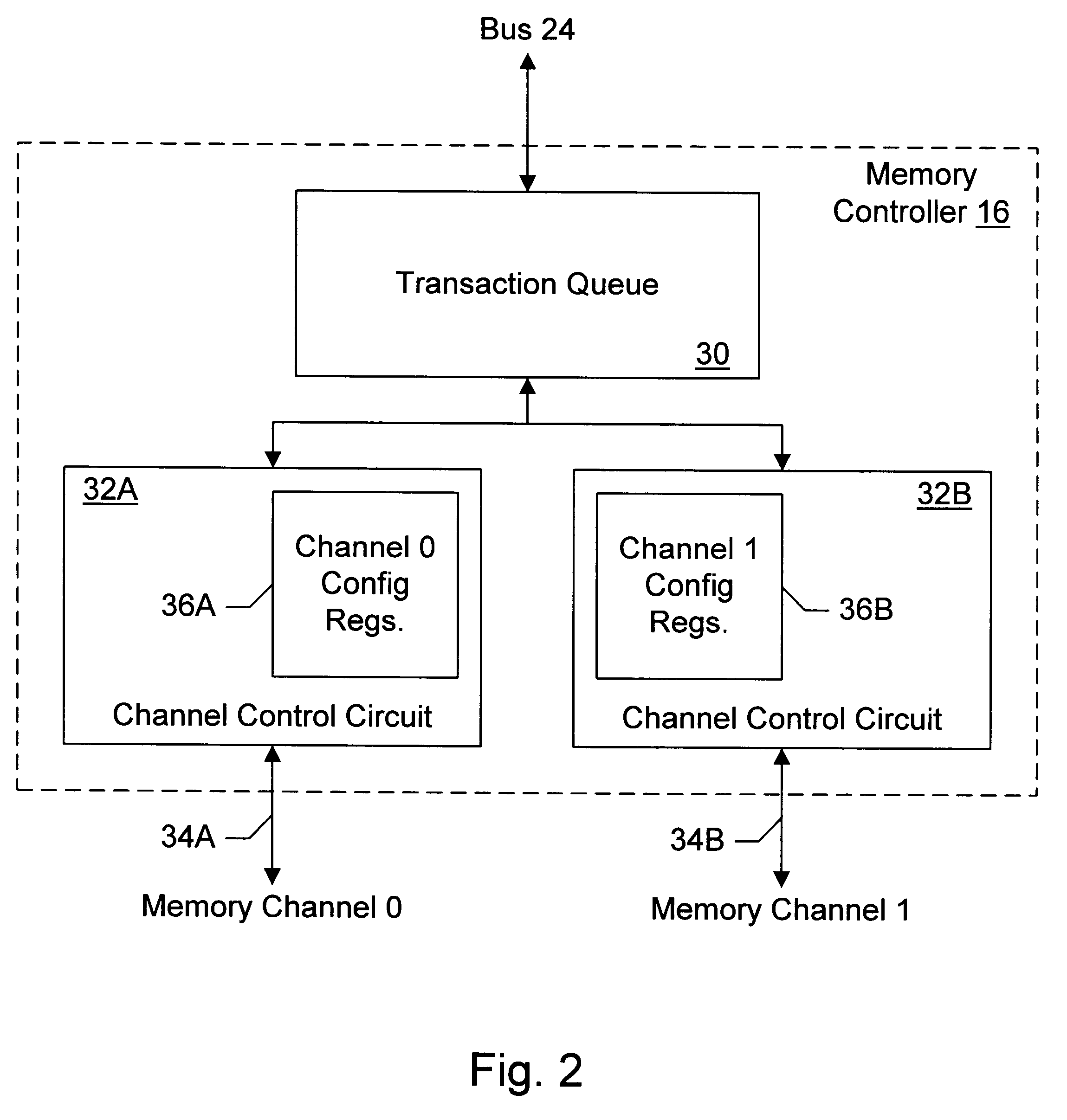
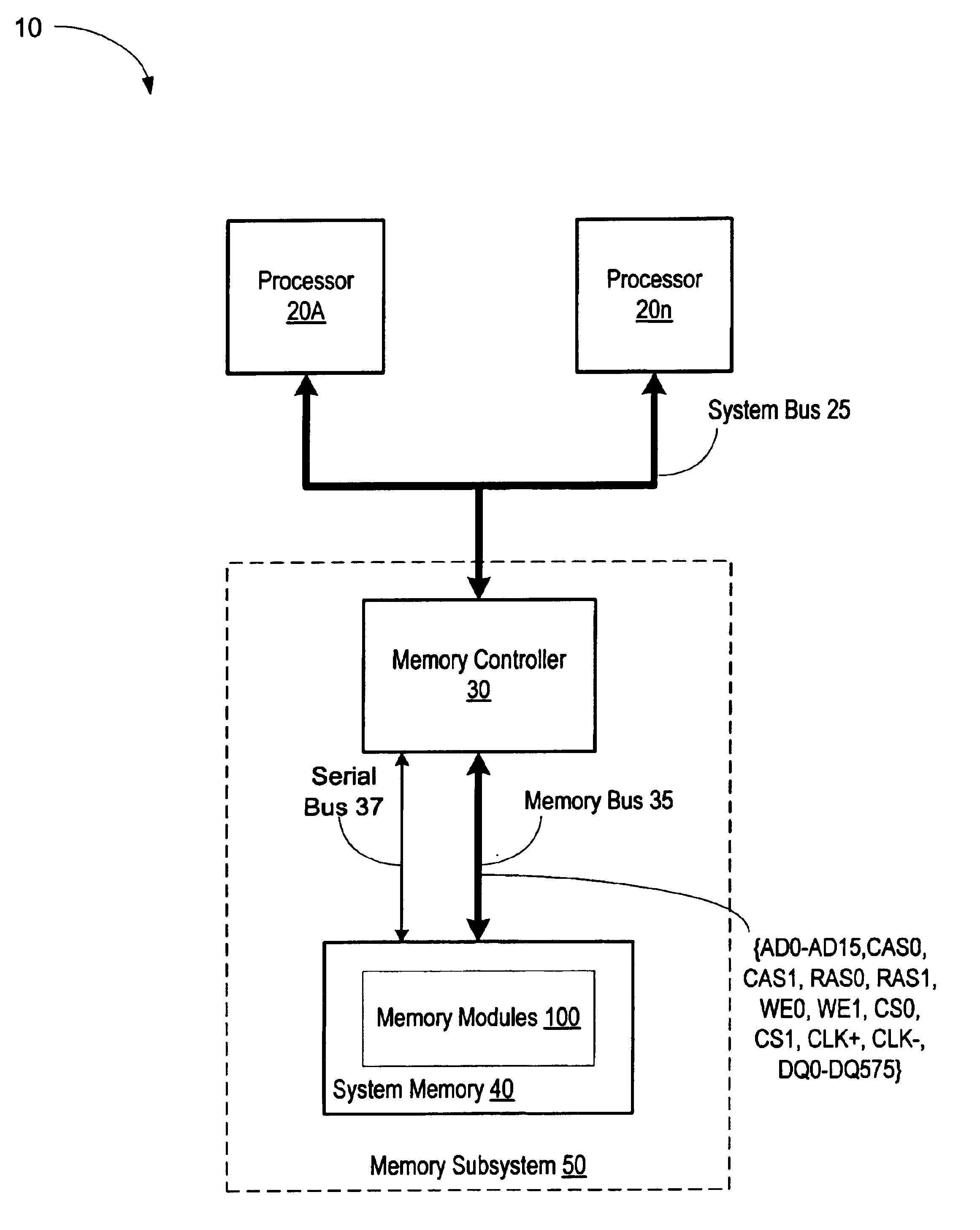
Memory controller with programmable configuration
InactiveUS6877076B1Flexible configurationOpen in timeMemory adressing/allocation/relocationMicro-instruction address formationProcessor registerParallel computing
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
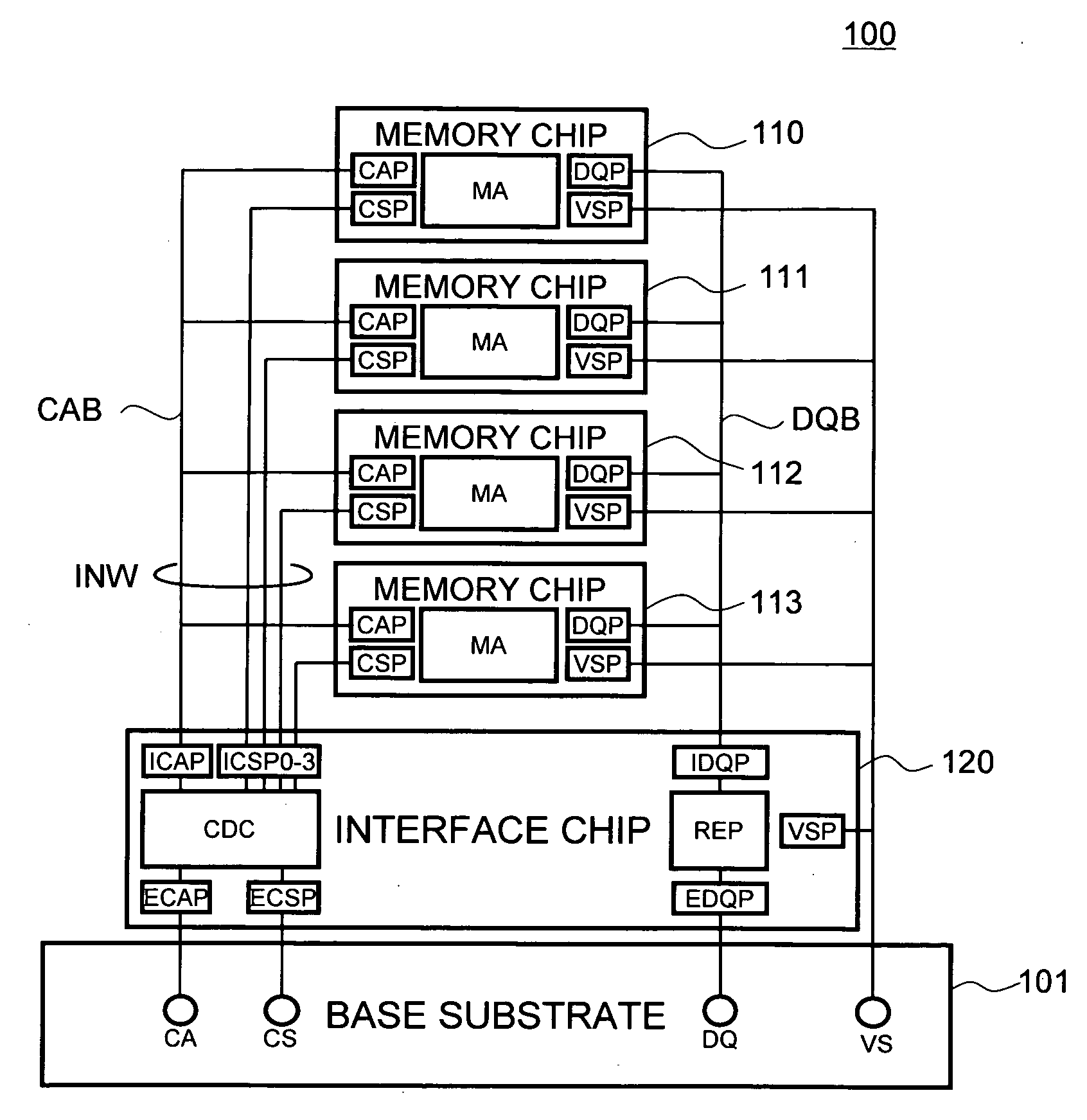
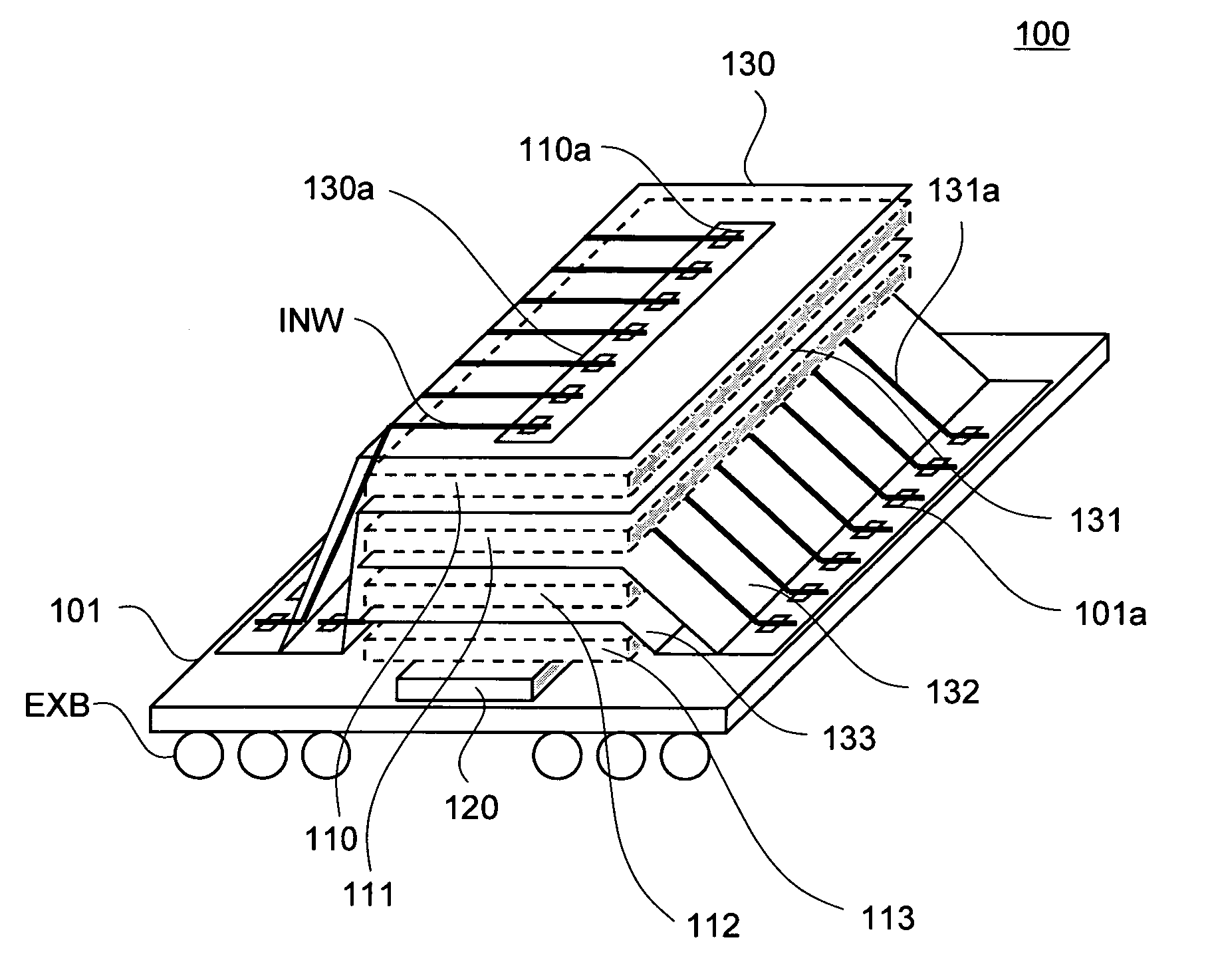
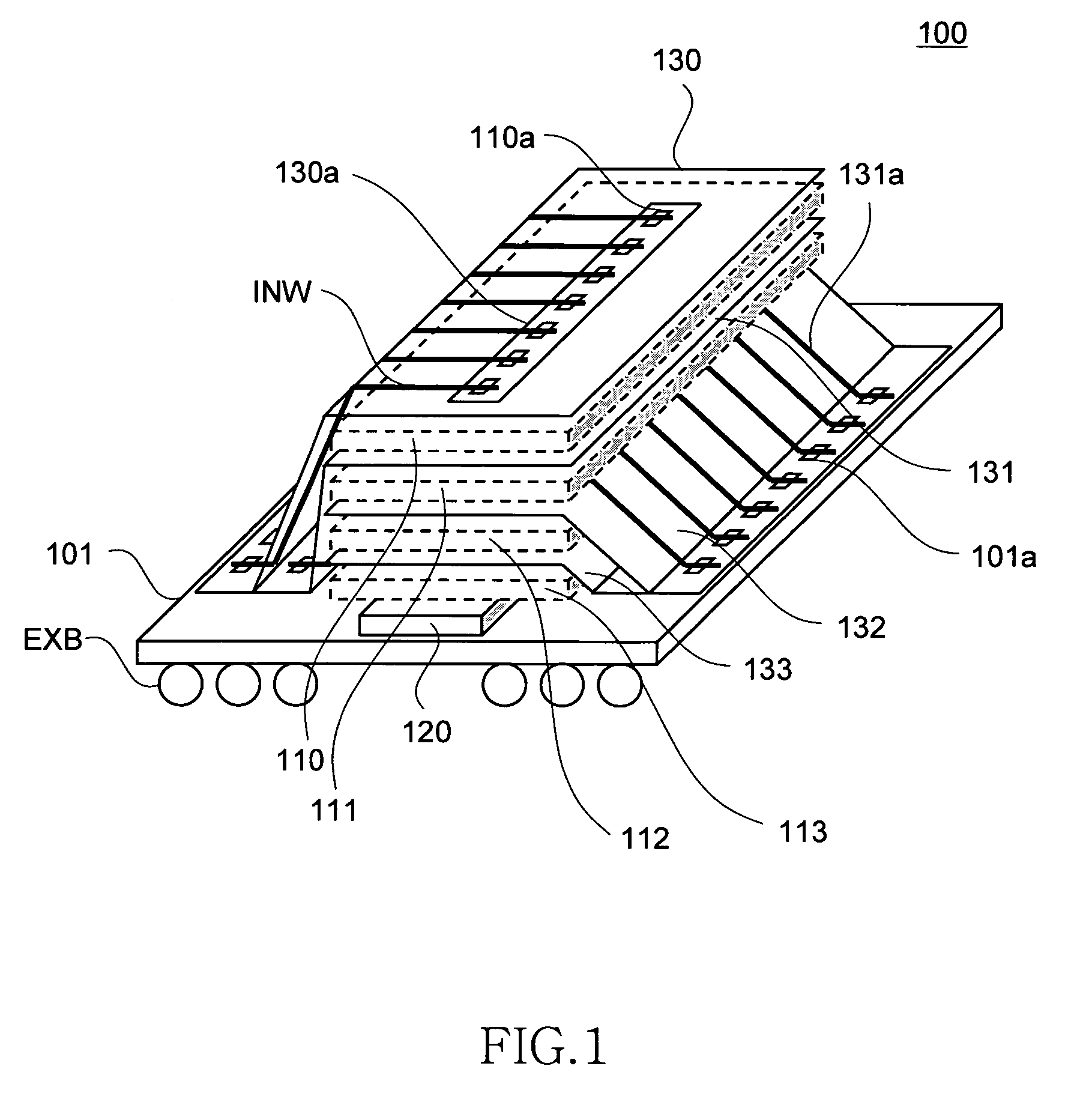
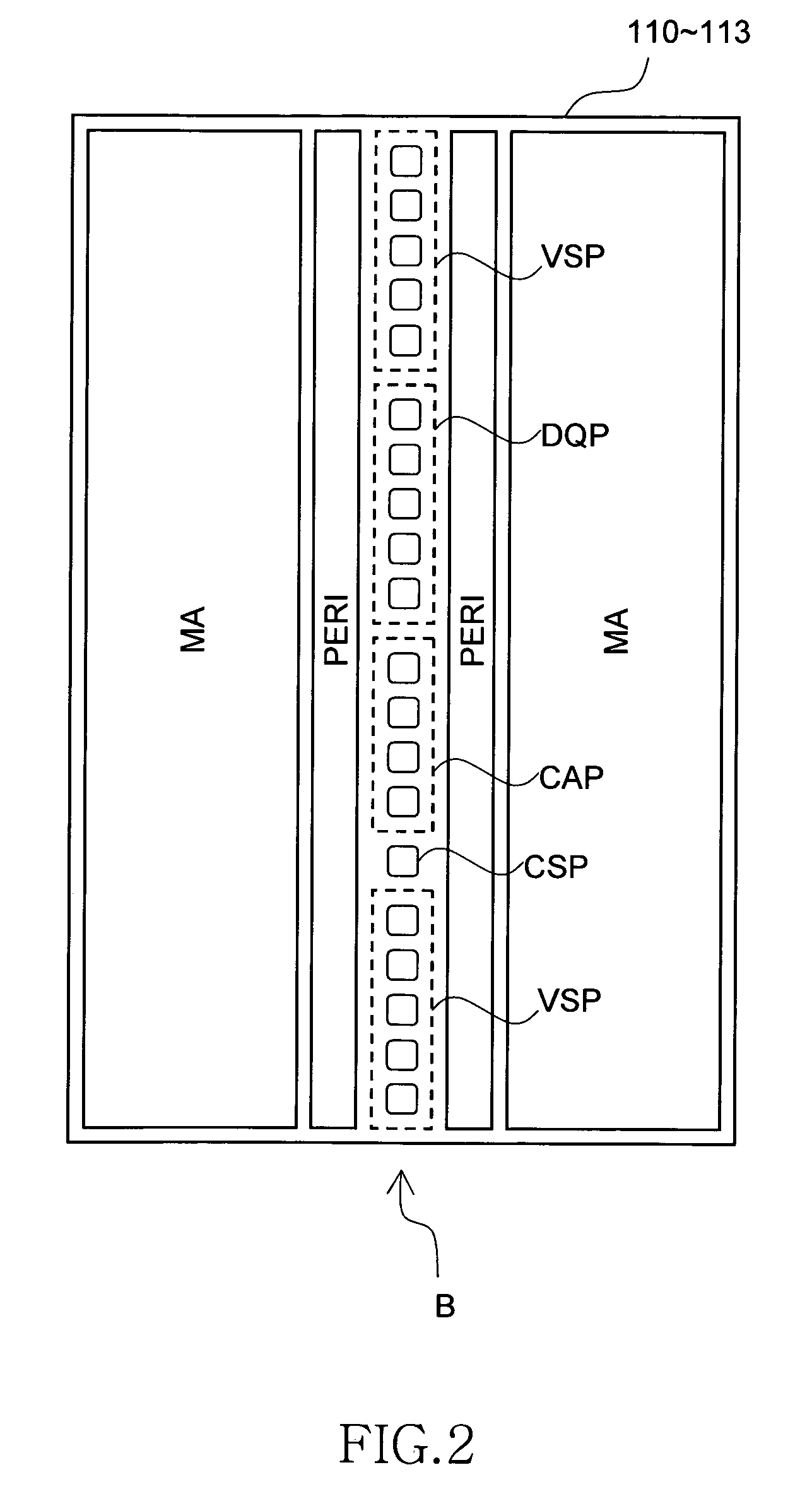
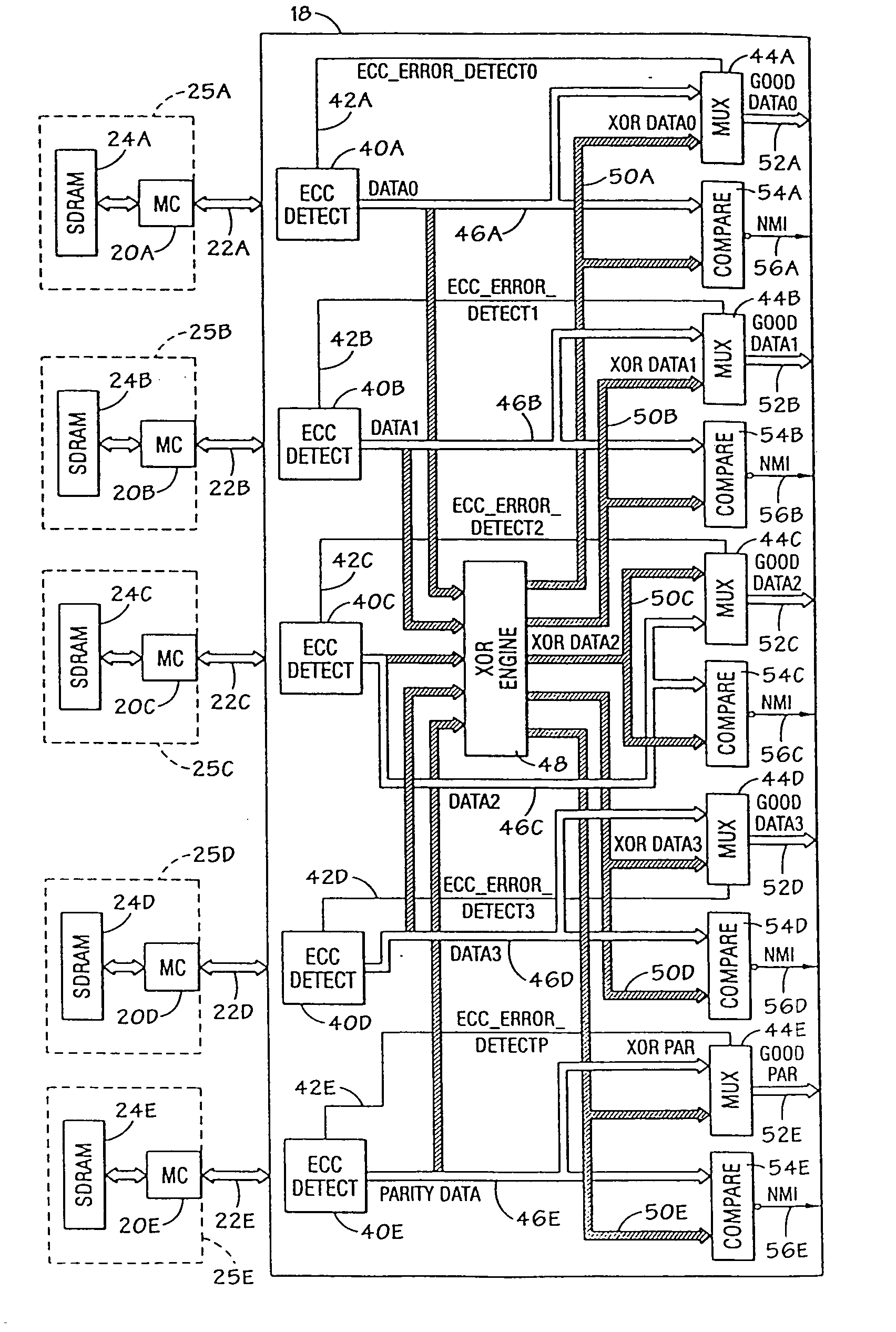
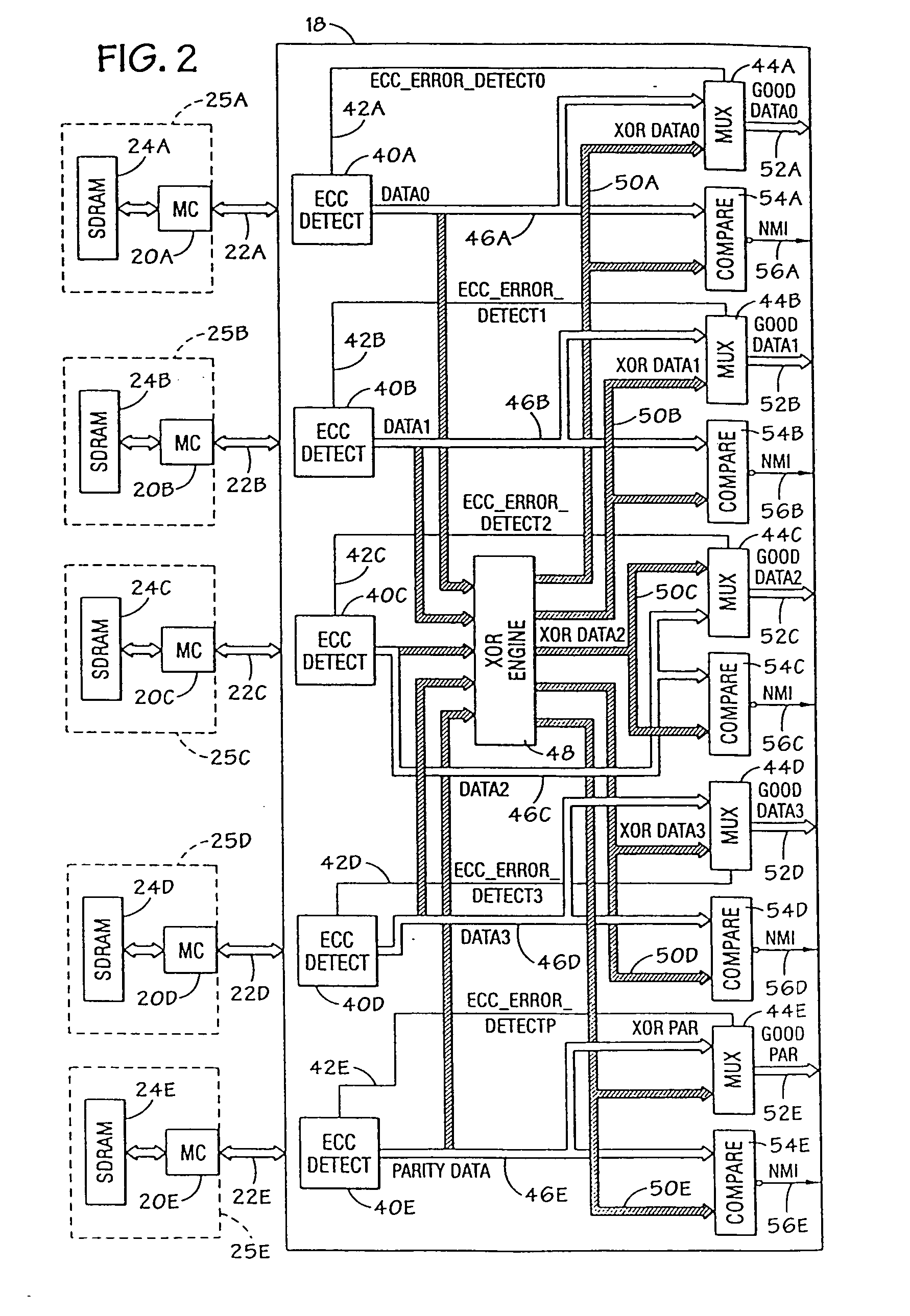
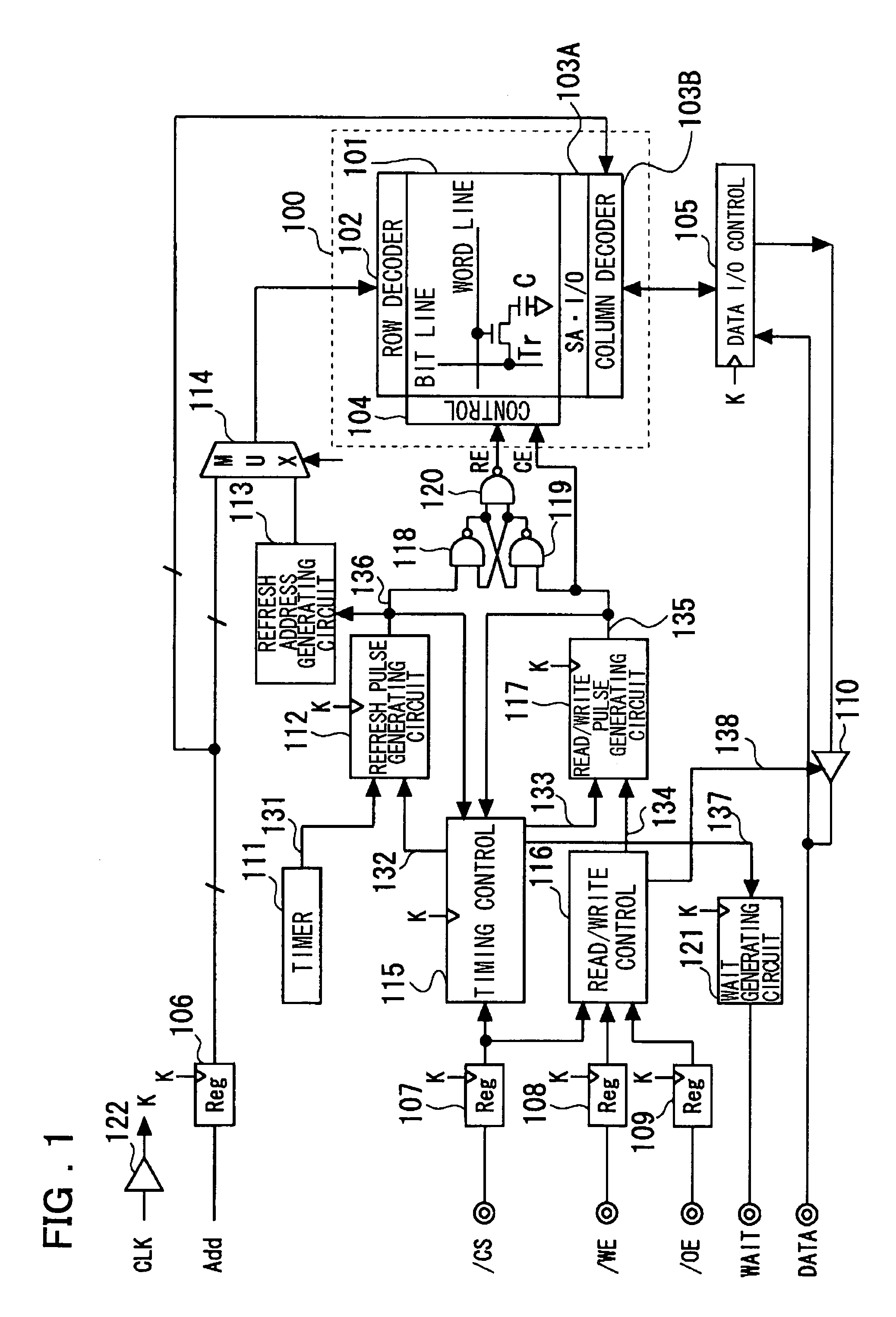
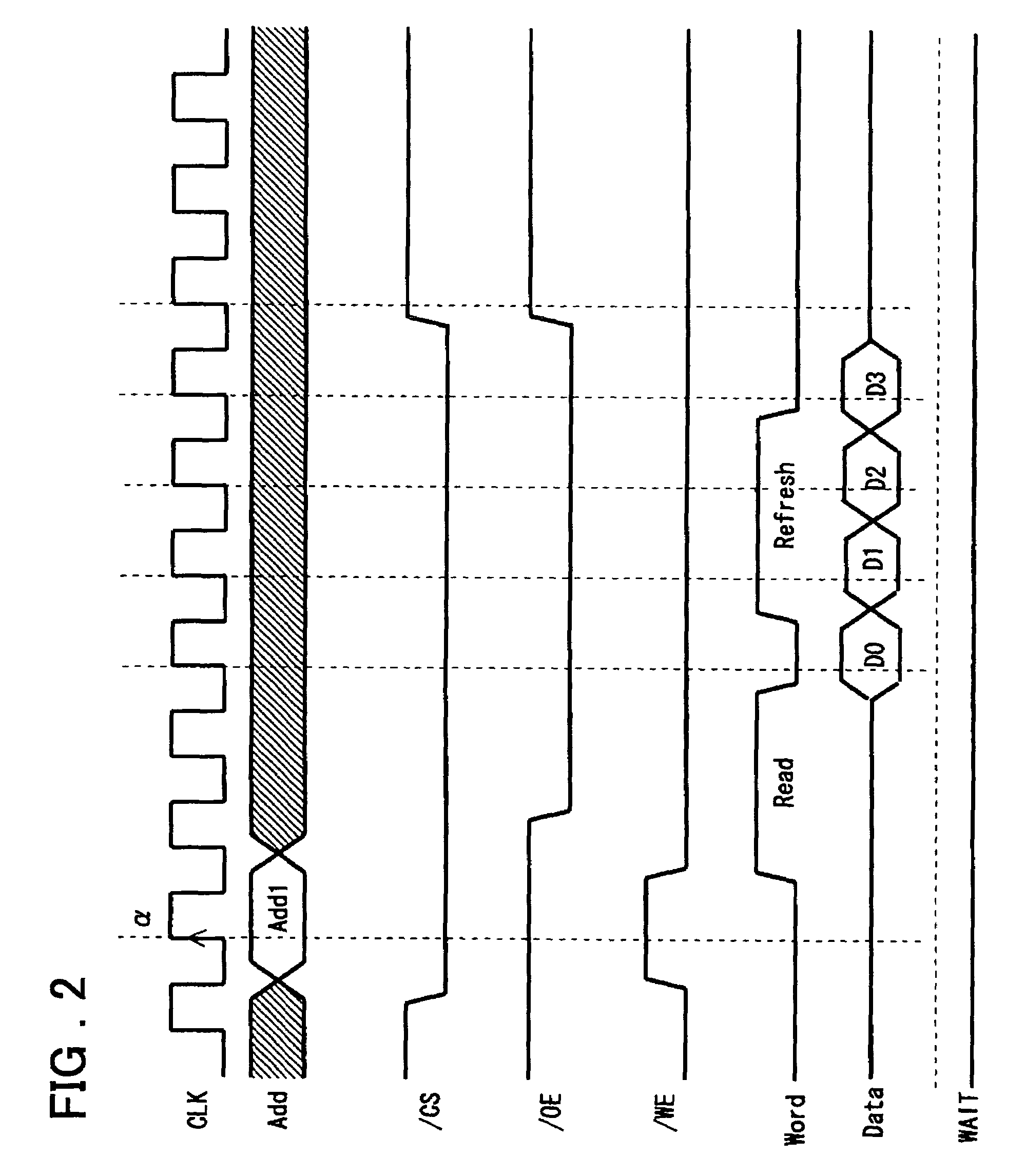
Semiconductor storage device having a plurality of stacked memory chips
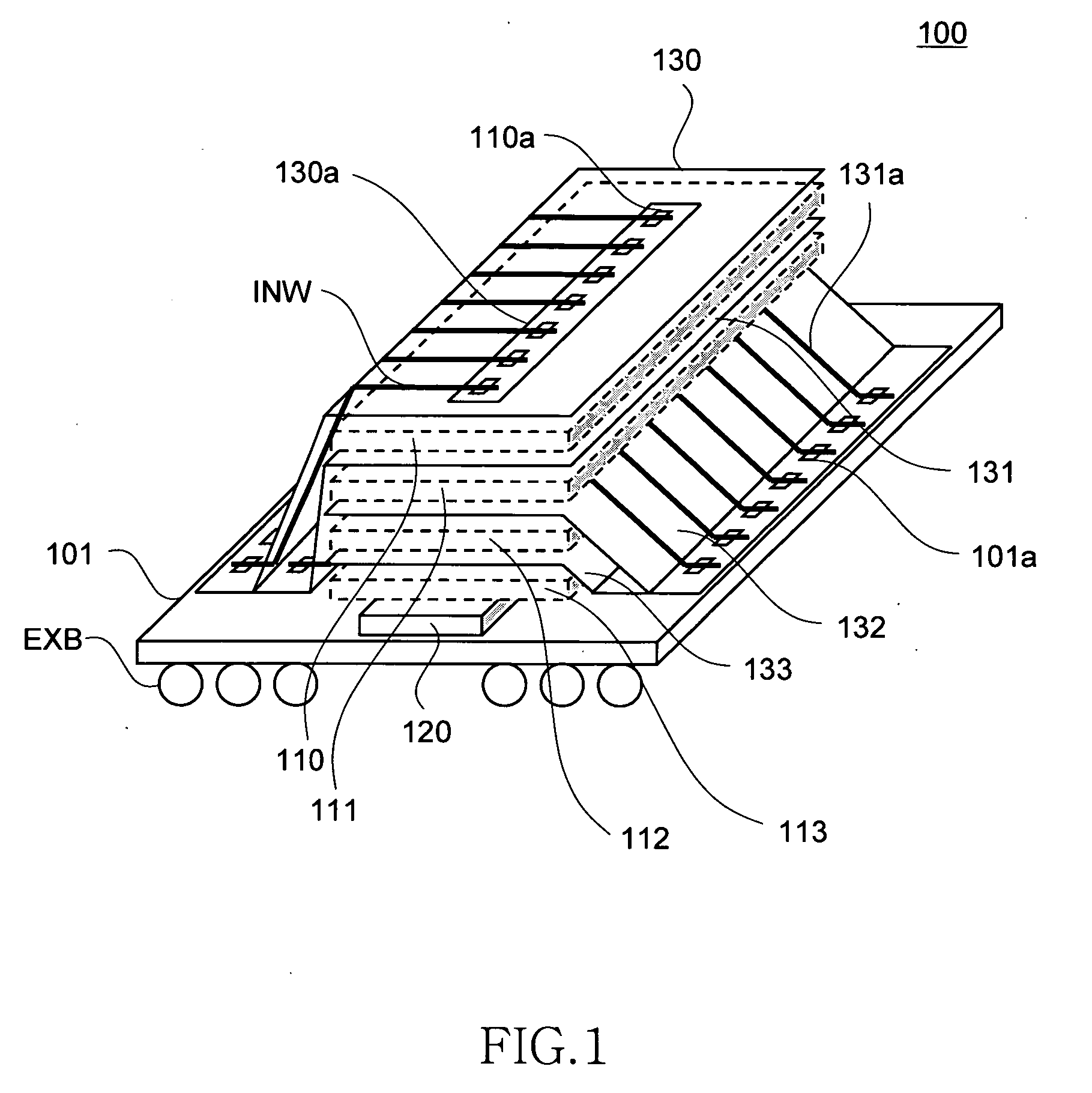
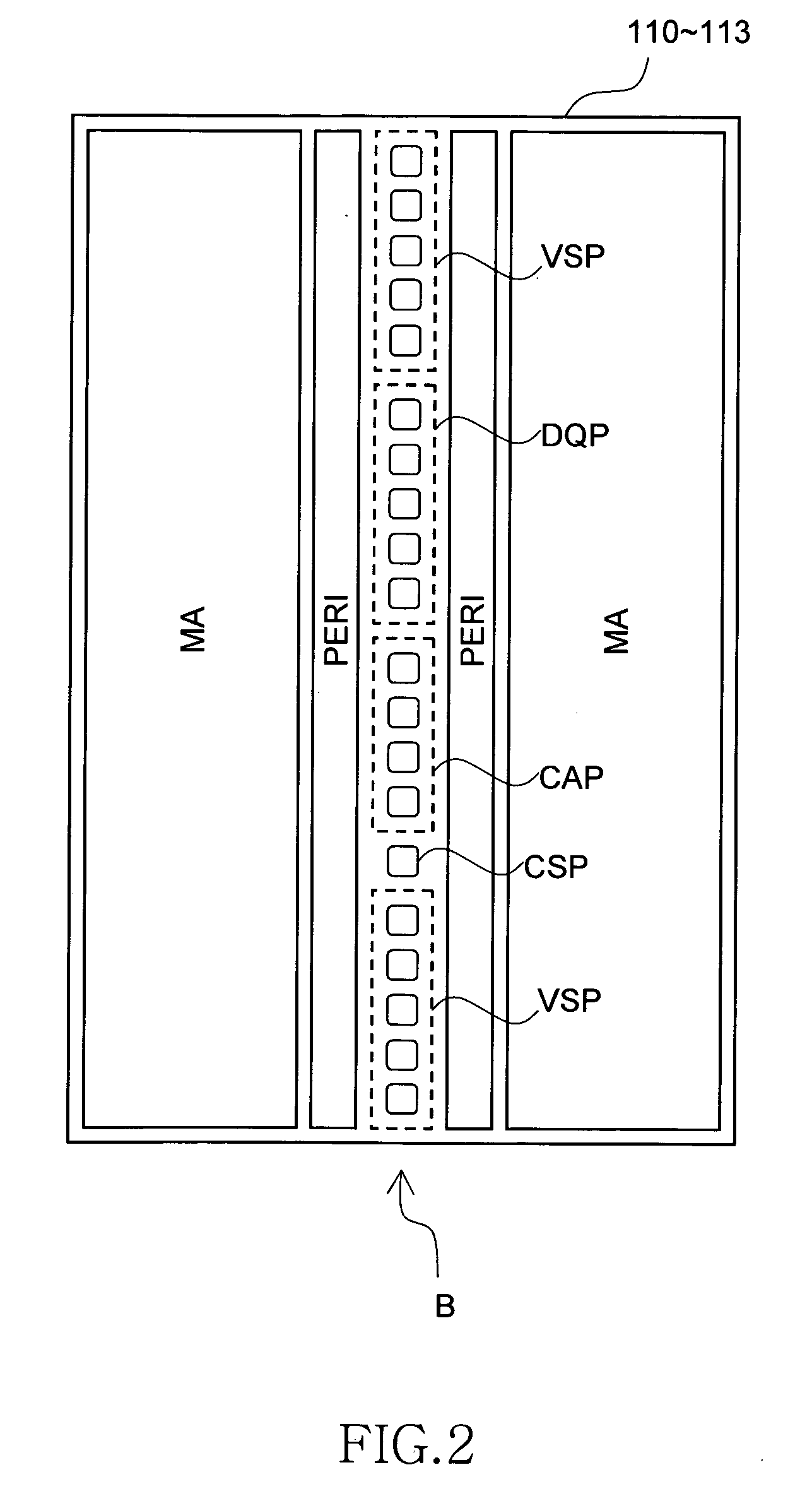
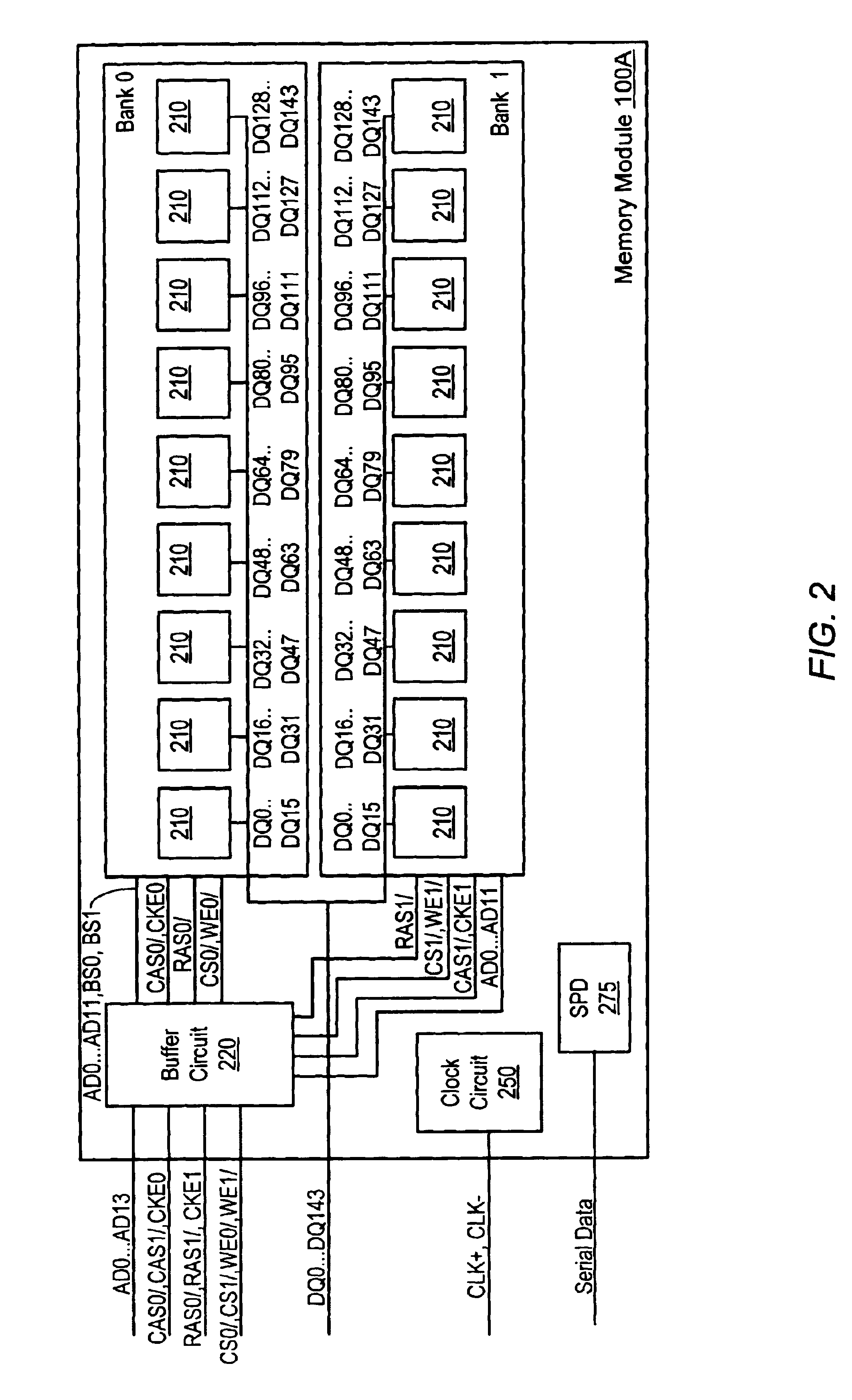
ActiveUS20060233012A1Reduce in quantityReduction in wiring capacitanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesMemory chipChip select
A semiconductor storage employs a base substrate (101) having a command / address external terminal group (CA), a data input / output external terminal group (DQ), and a single chip select external terminal (CS), and also comprises a plurality of memory chips (110) to (113) mounted on a base substrate (101), each of which can individually carry out read and write operations. The terminals (CA), (DQ), and (CS) are connected to an interface chip (120). The interface chip (120) has a chip select signal generation circuit that can individually activate a plurality of memory chips (110) to (113) on the basis of an address signal fed by way of the terminal (CA) and on the basis of a chip select signal fed by way of the terminal (CS).
Owner:LONGITUDE LICENSING LTD
Flash memory controller having reduced pinout
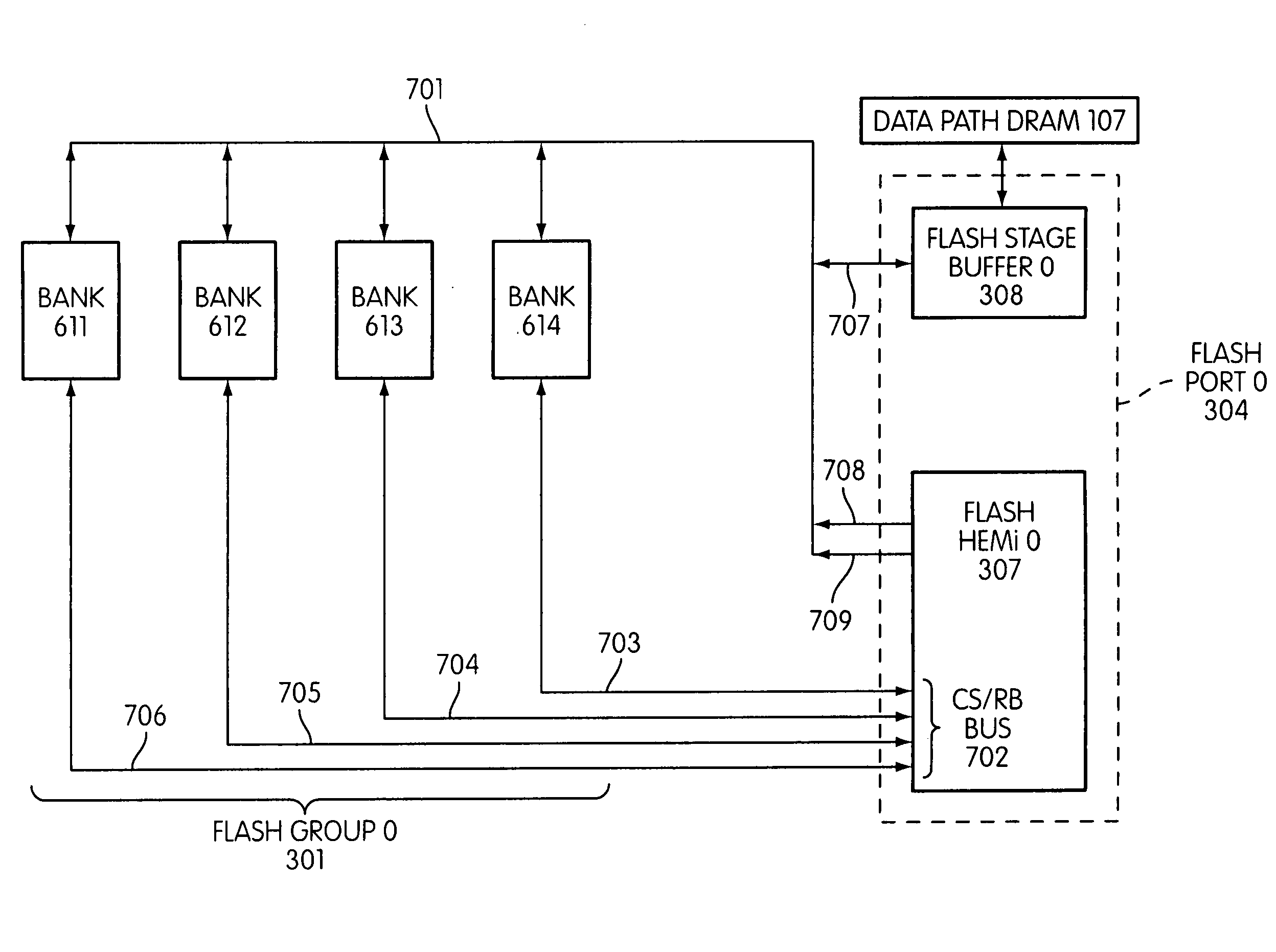
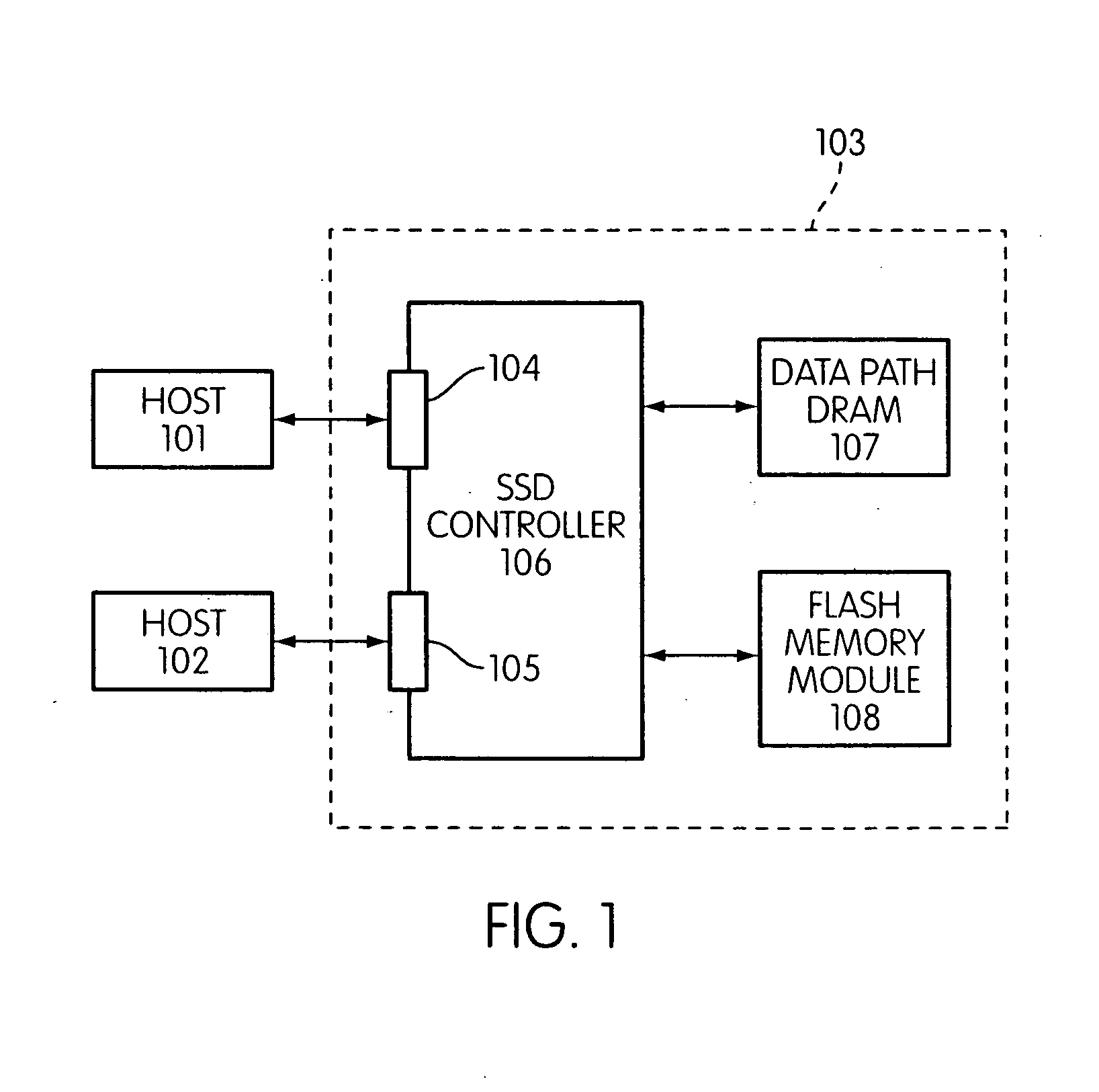
InactiveUS20090168525A1Affect performanceMaximize useMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationChip selectFlash memory controller
Disclosed is a flash memory controller connected to a flash memory module. The pin-out of the flash memory controller combines ready-busy and chip-select signals. In one embodiment, the flash memory module is made up of a set of banks, each consisting of a plurality of devices, with each bank sharing a single chip-select / ready-busy connection to the controller.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Memory controller with programmable configuration
InactiveUS6625685B1Memory adressing/allocation/relocationMicro-instruction address formationProcessor registerParallel computing
A memory controller provides programmable flexibility, via one or more configuration registers, for the configuration of the memory. The memory may be optimized for a given application by programming the configuration registers. For example, in one embodiment, the portion of the address of a memory transaction used to select a storage location for access in response to the memory transaction may be programmable. In an implementation designed for DRAM, a first portion may be programmably selected to form the row address and a second portion may be programmable selected to form the column address. Additional embodiments may further include programmable selection of the portion of the address used to select a bank. Still further, interleave modes among memory sections assigned to different chip selects and among two or more channels to memory may be programmable, in some implementations. Furthermore, the portion of the address used to select between interleaved memory sections or interleaved channels may be programmable. One particular implementation may include all of the above programmable features, which may provide a high degree of flexibility in optimizing the memory system.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Stacked packages
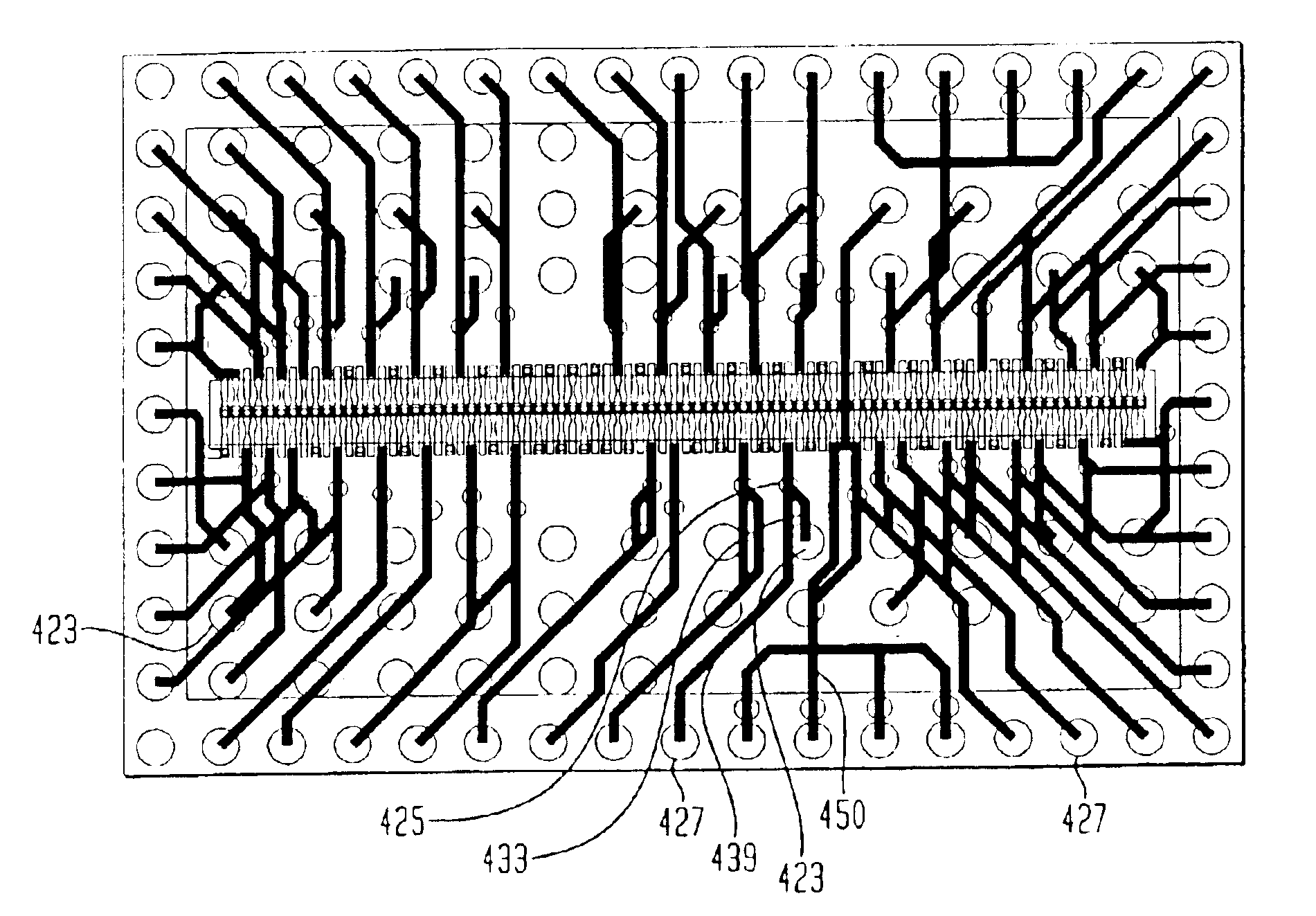
InactiveUS6977440B2Well formedSimplifying handling and stockingPrinted circuit detailsFinal product manufactureSolder ballChip select
A stacked chip assembly includes individual units having chips mounted on dielectric layers and traces on the dielectric layers interconnecting the contacts of the chips with terminals disposed in peripheral regions of the dielectric layers. At least some of the traces are multi-branched traces which connect chip select contacts to chip select terminals. The units are stacked one above the other with corresponding terminals of the different units being connected to one another by solder balls or other conductive elements so as to form vertical buses. Prior to stacking, the multi-branched traces of the individual units are selectively connected, as by forming solder bridges, so as to leave chip select contacts of chips in different units connected to different chip select terminals and thereby connect these chips to different vertical buses. The individual units desirably are thin and directly abut one another so as to provide a low-height assembly with good heat transfer from chips within the stack.
Owner:TESSERA INC
Single rank memory module for use in a two-rank memory module system
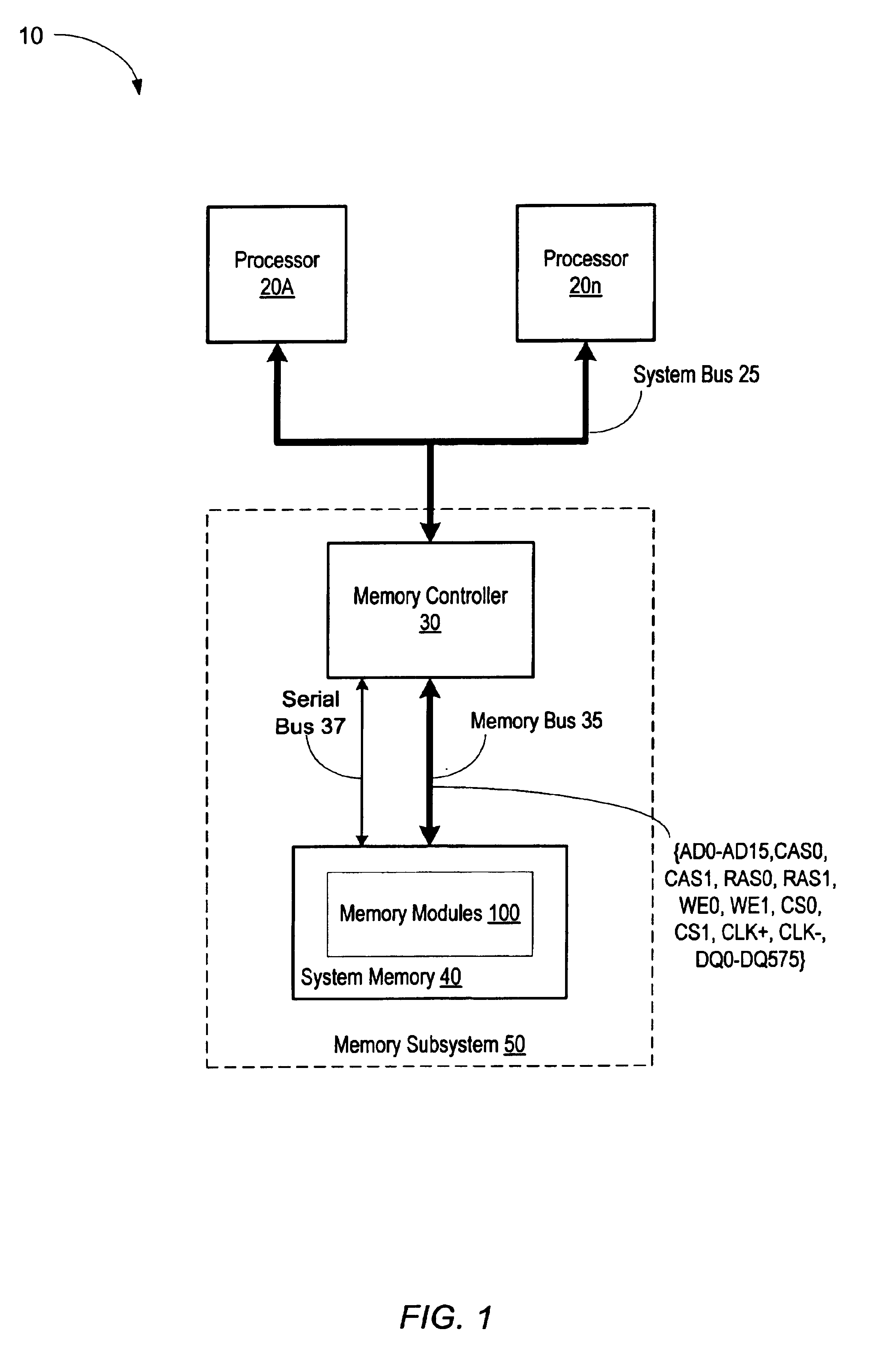
ActiveUS6961281B2Energy efficient ICTMemory adressing/allocation/relocationComputer moduleChip select
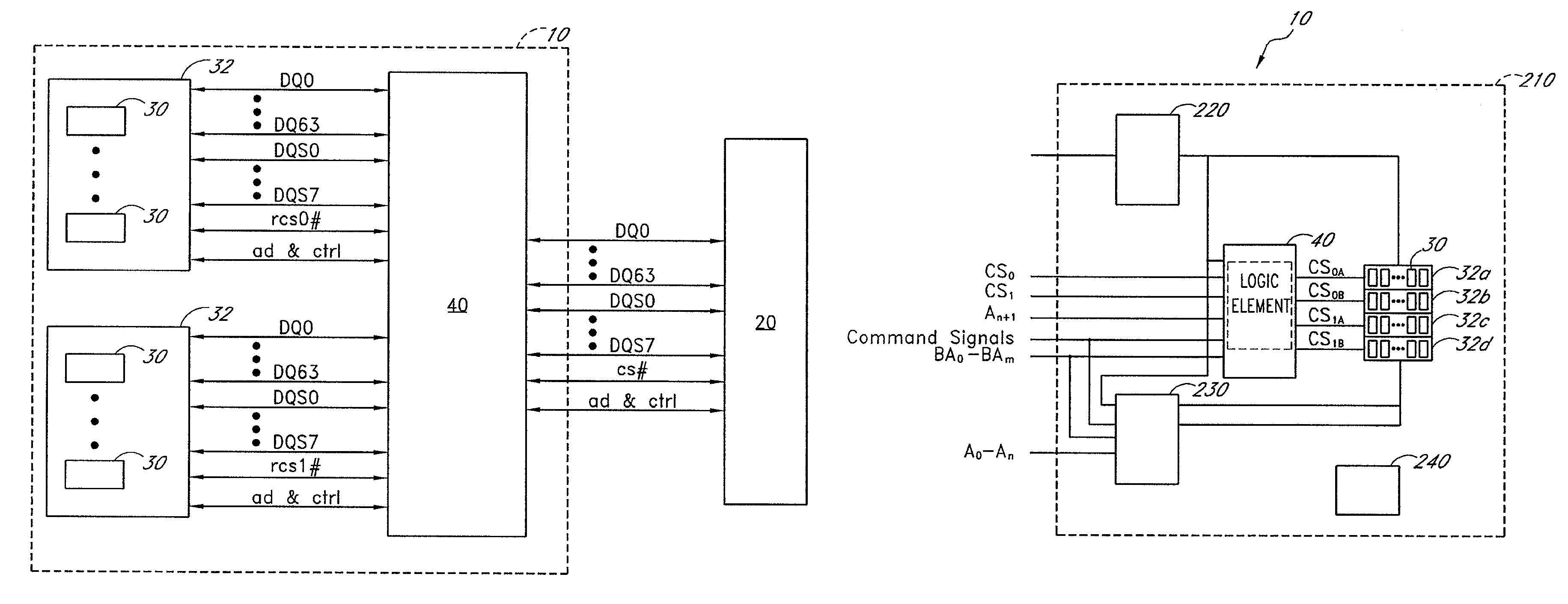
A memory module for use in a two rank memory module system includes a plurality of memory devices and a control circuit. In one embodiment, the control circuit may be configured to generate a chip select signal that is provided to each of the memory devices. The chip select signal may be dependent upon assertions of a first bank chip select signal and a second bank chip select signal received from a memory controller. The control circuit may be further configured to generate an address signal that is provided to each of the memory devices. The address signal may be asserted dependent upon which of the first bank chip select signal and the second bank chip select signal are asserted.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
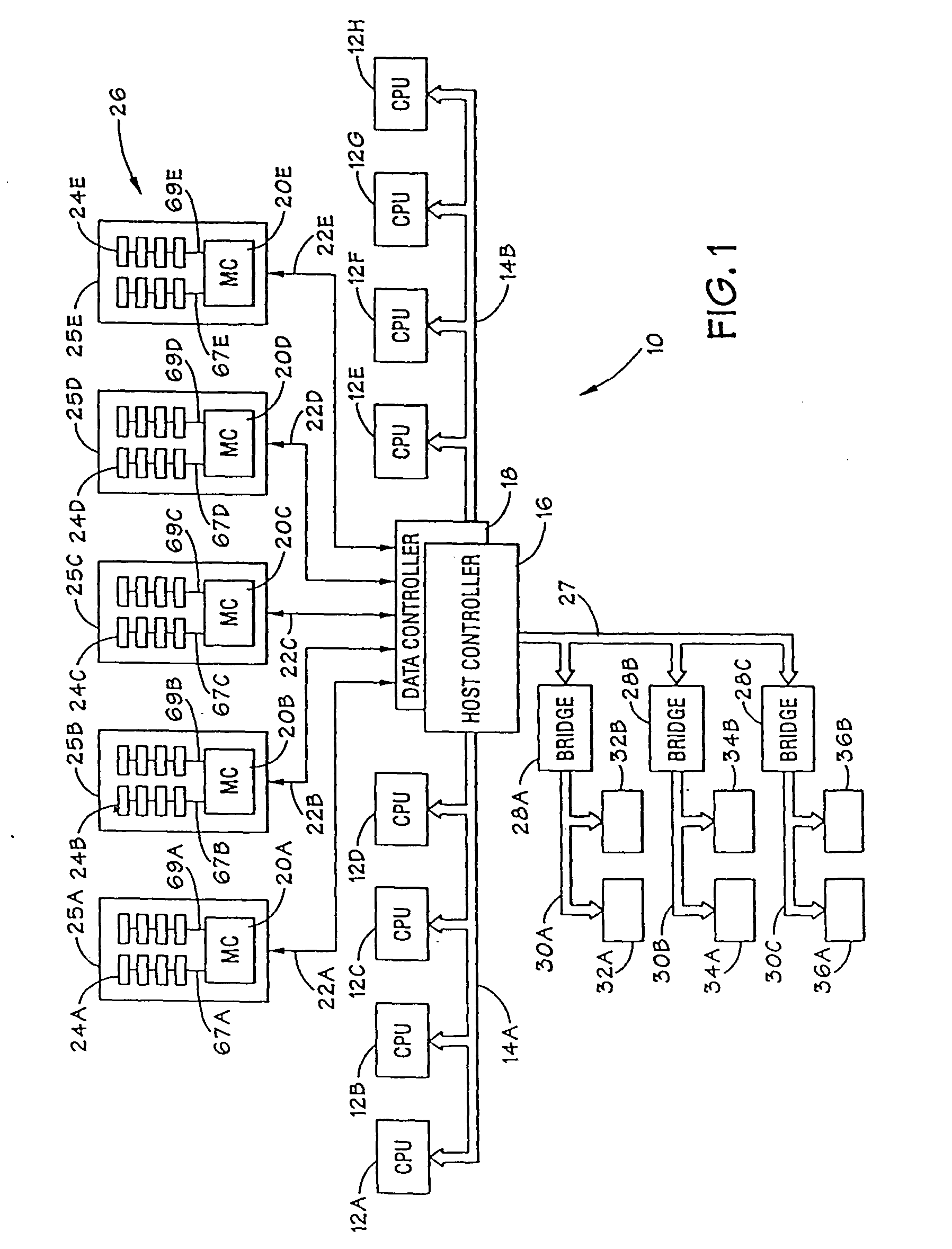
Computer system and semiconductor device on one chip including a memory and central processing unit for making interlock access to the memory
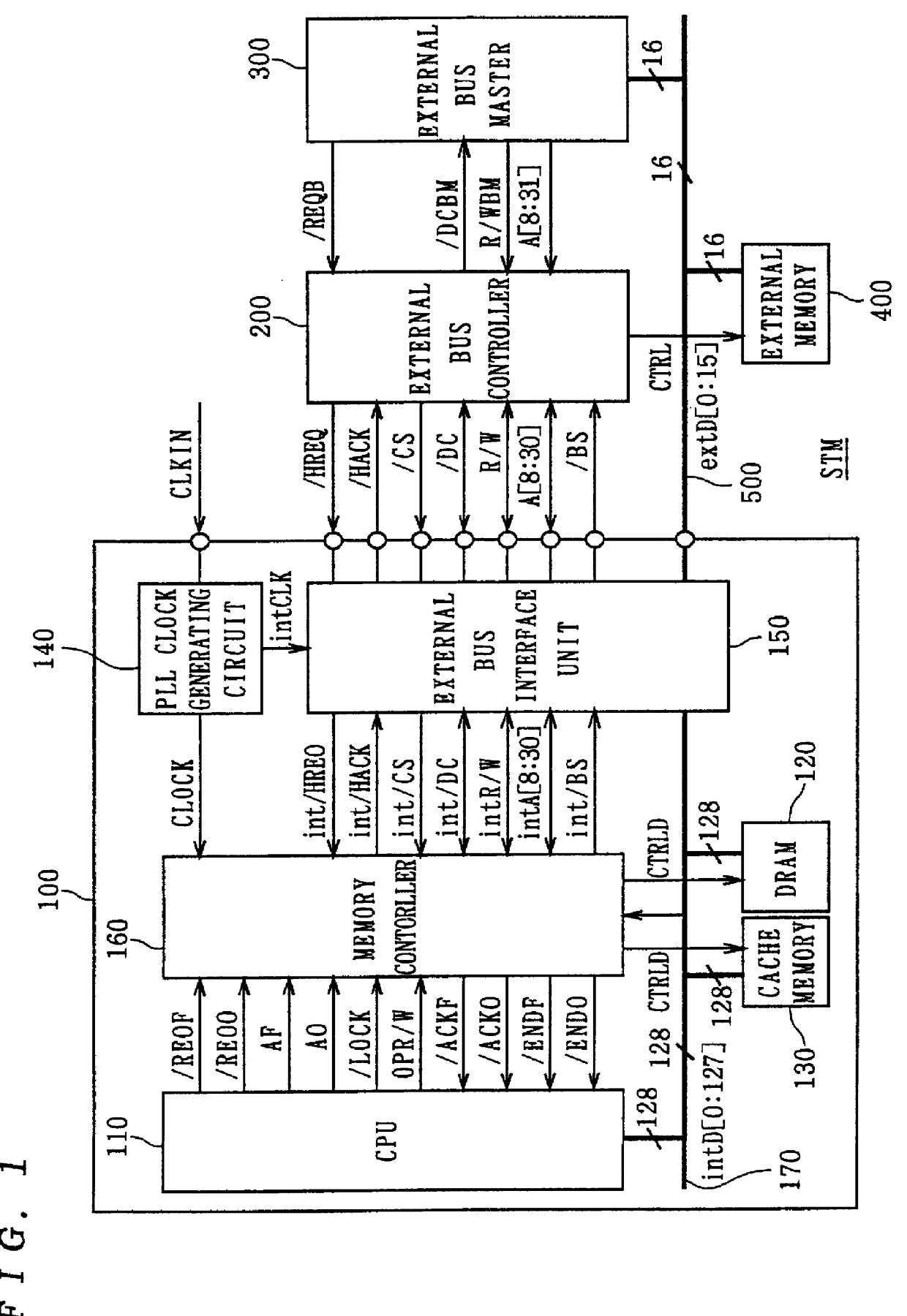
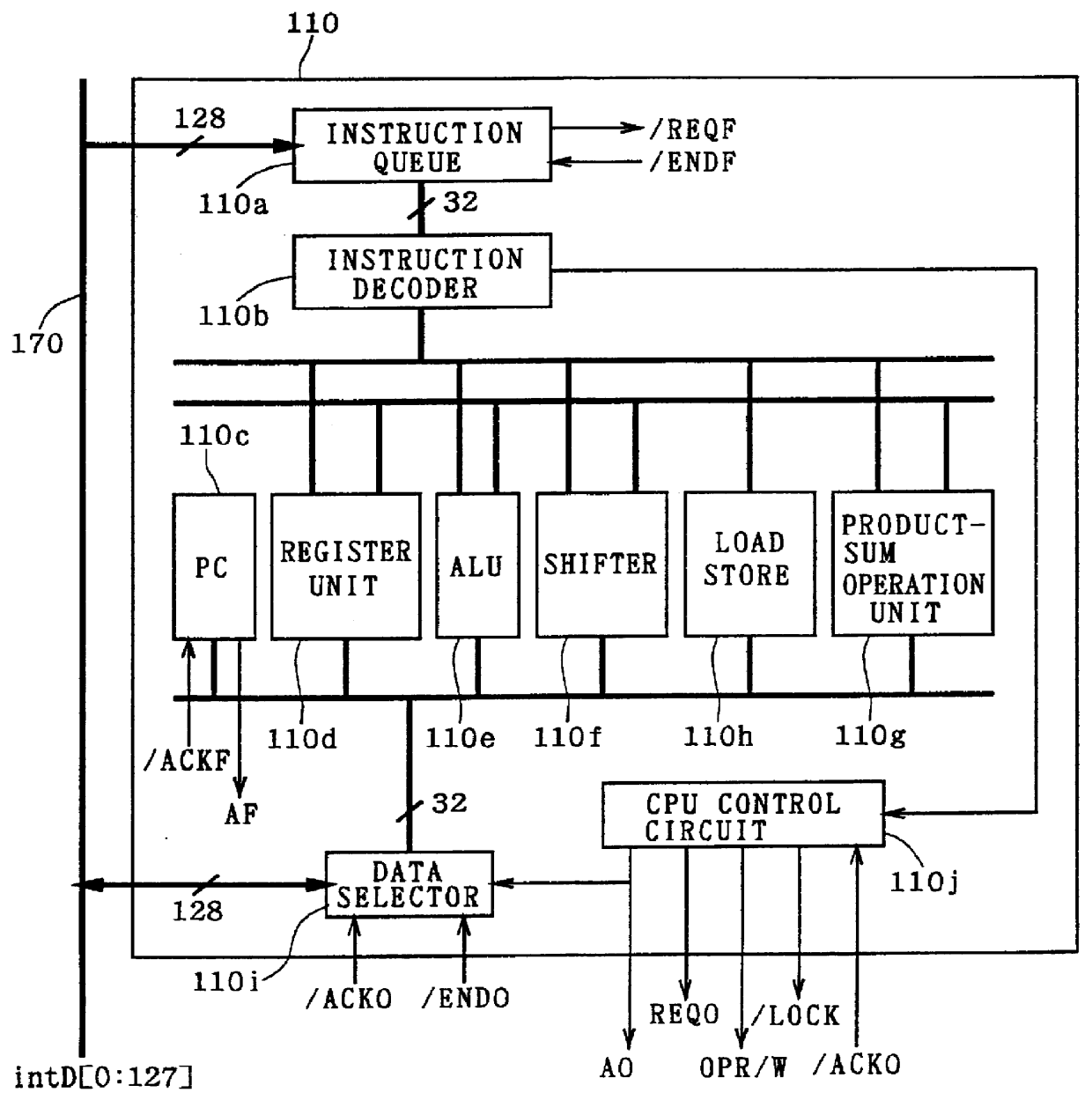
InactiveUS6101584AUnauthorized memory use protectionMultiple digital computer combinationsChip selectComputerized system
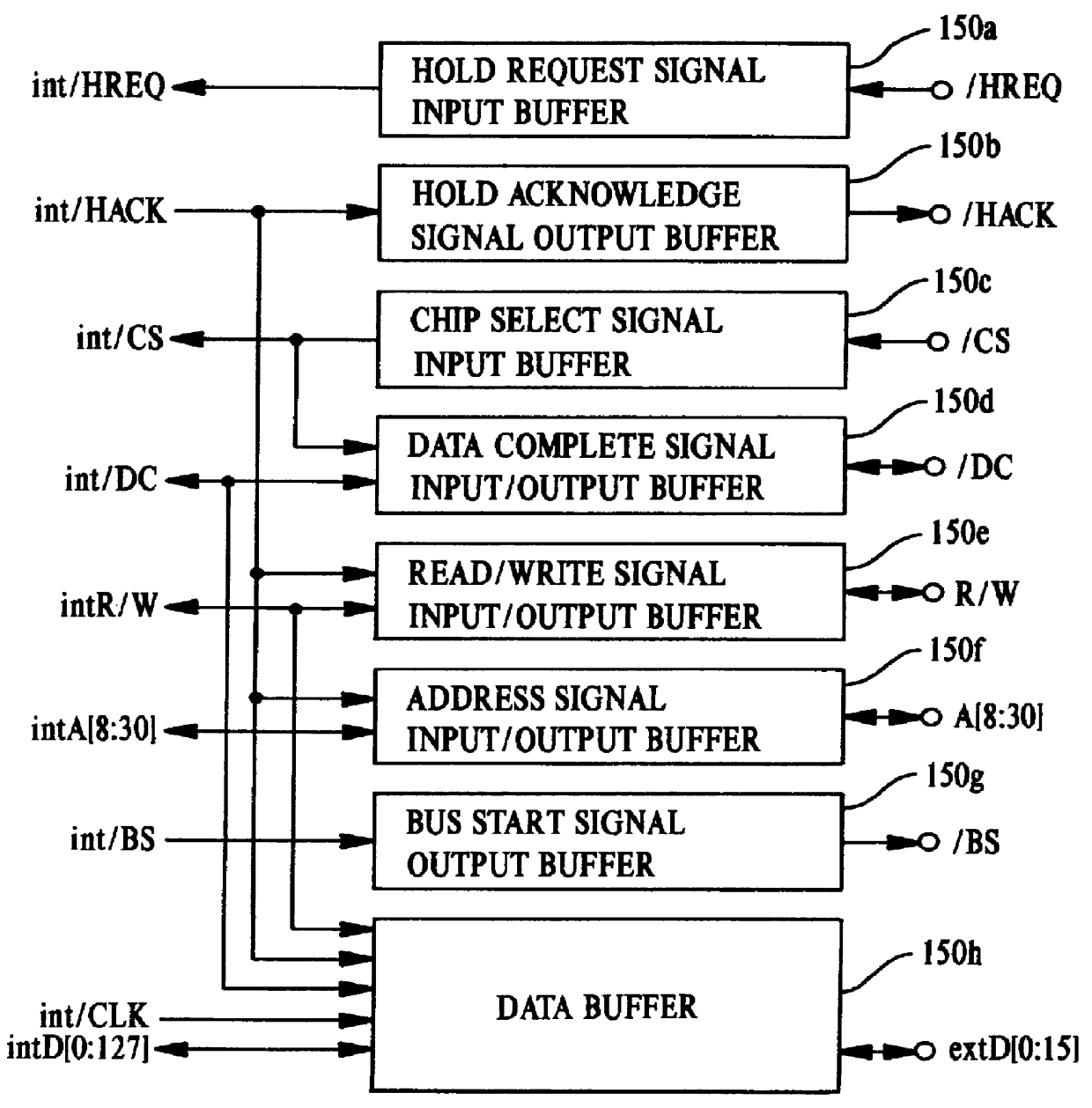
A central processing unit (CPU) having a built-in dynamic random-access memory (DRAM) with exclusive access to the DRAM when the CPU performs an interlock access to the DRAM. A memory controller prevents the DRAM from being externally accessed while the CPU is performing the interlock access. When the memory controller receives an external request for accessing the DRAM during a time when the CPU is performing an interlock access to the DRAM, the memory controller outputs a response signal indicating that external access to the DRAM is excluded or inhibited. The request signal can be a hold request signal for requesting a bus right or can be a chip select signal. The response signal can be a hold acknowledge signal or a data complete signal. The memory controller can be switched to and from first and second lock modes, where hold request and hold acknowledge signals are used during the first lock mode and chip select and data complete signals are used in the second lock mode.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
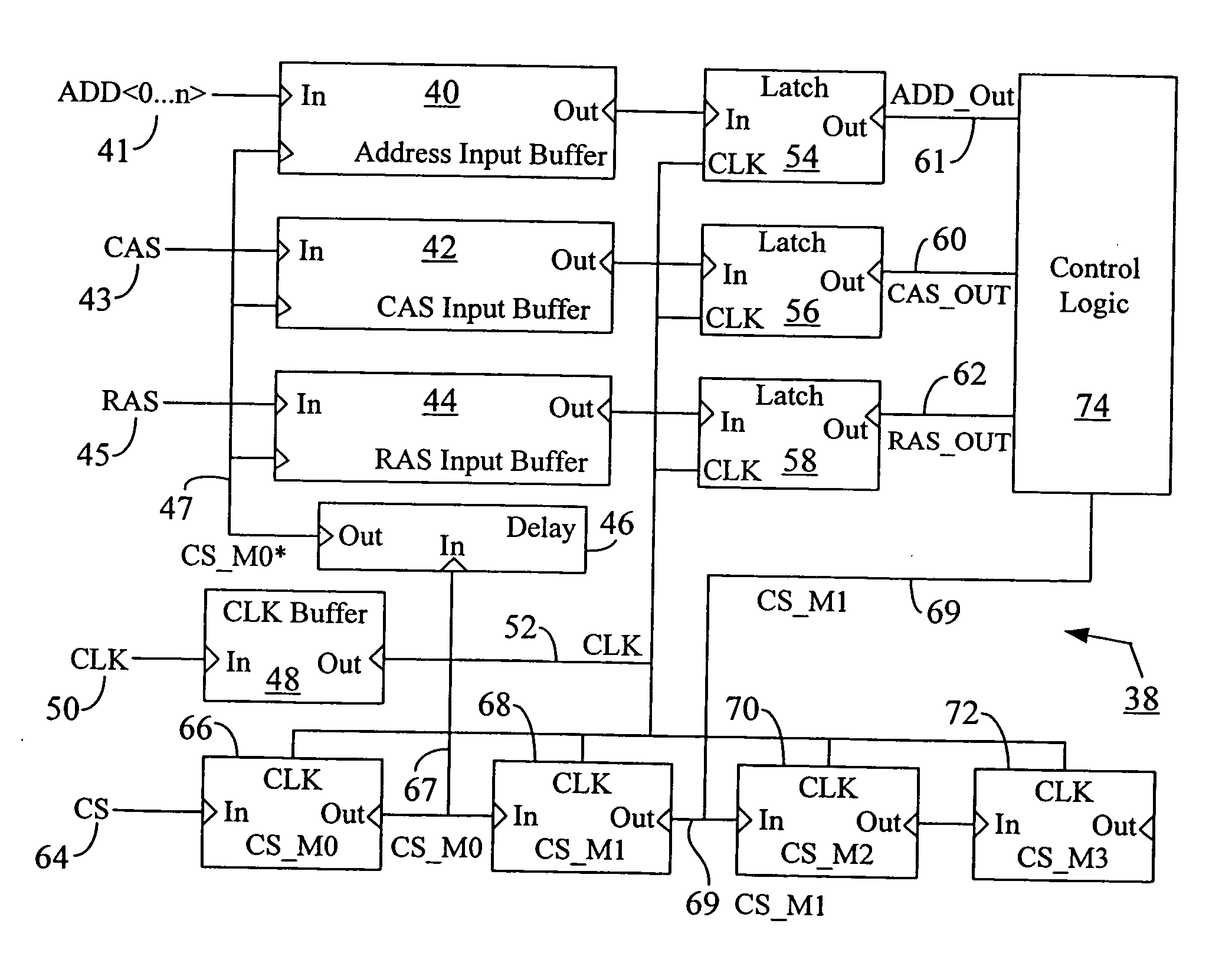
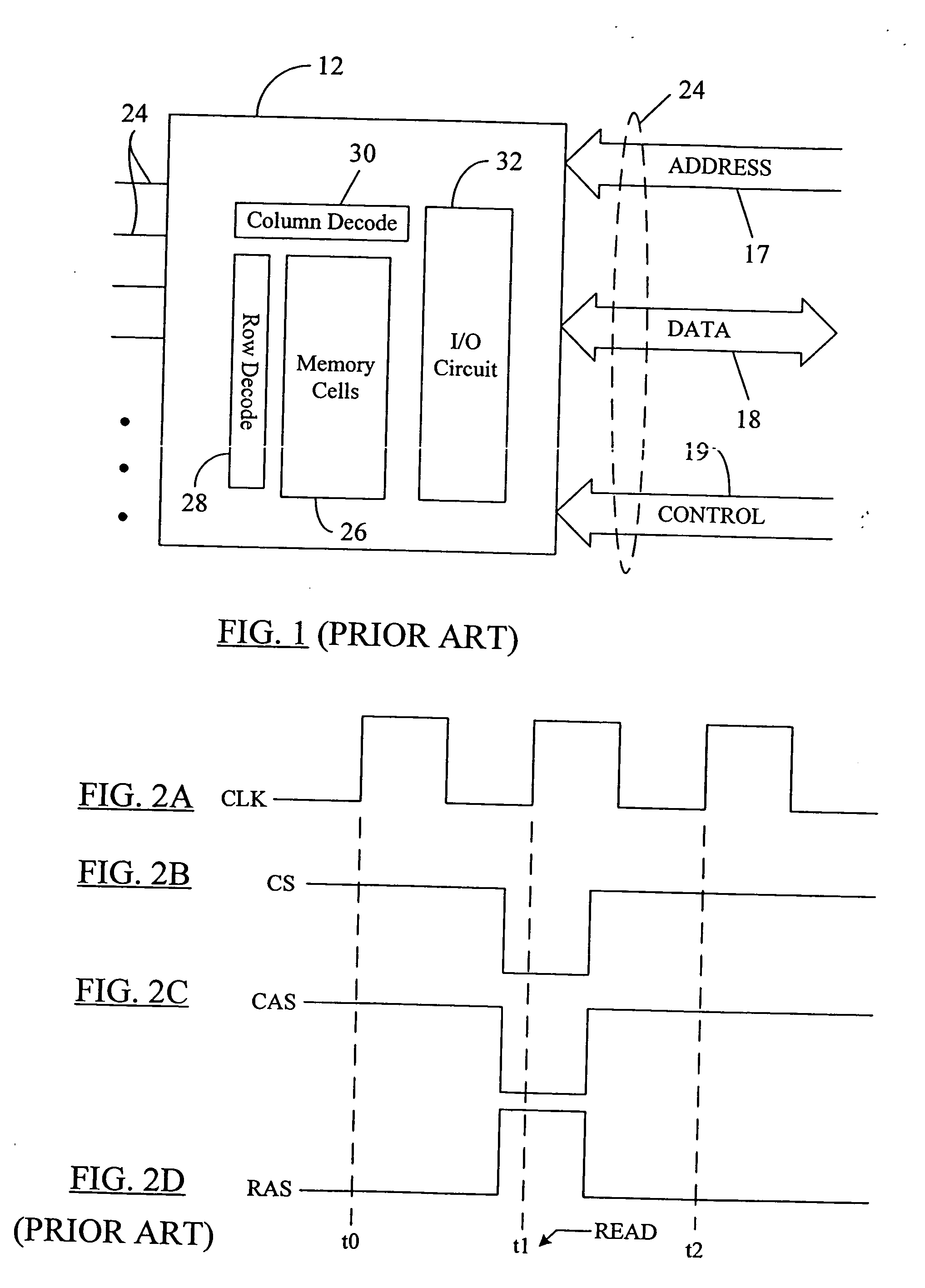
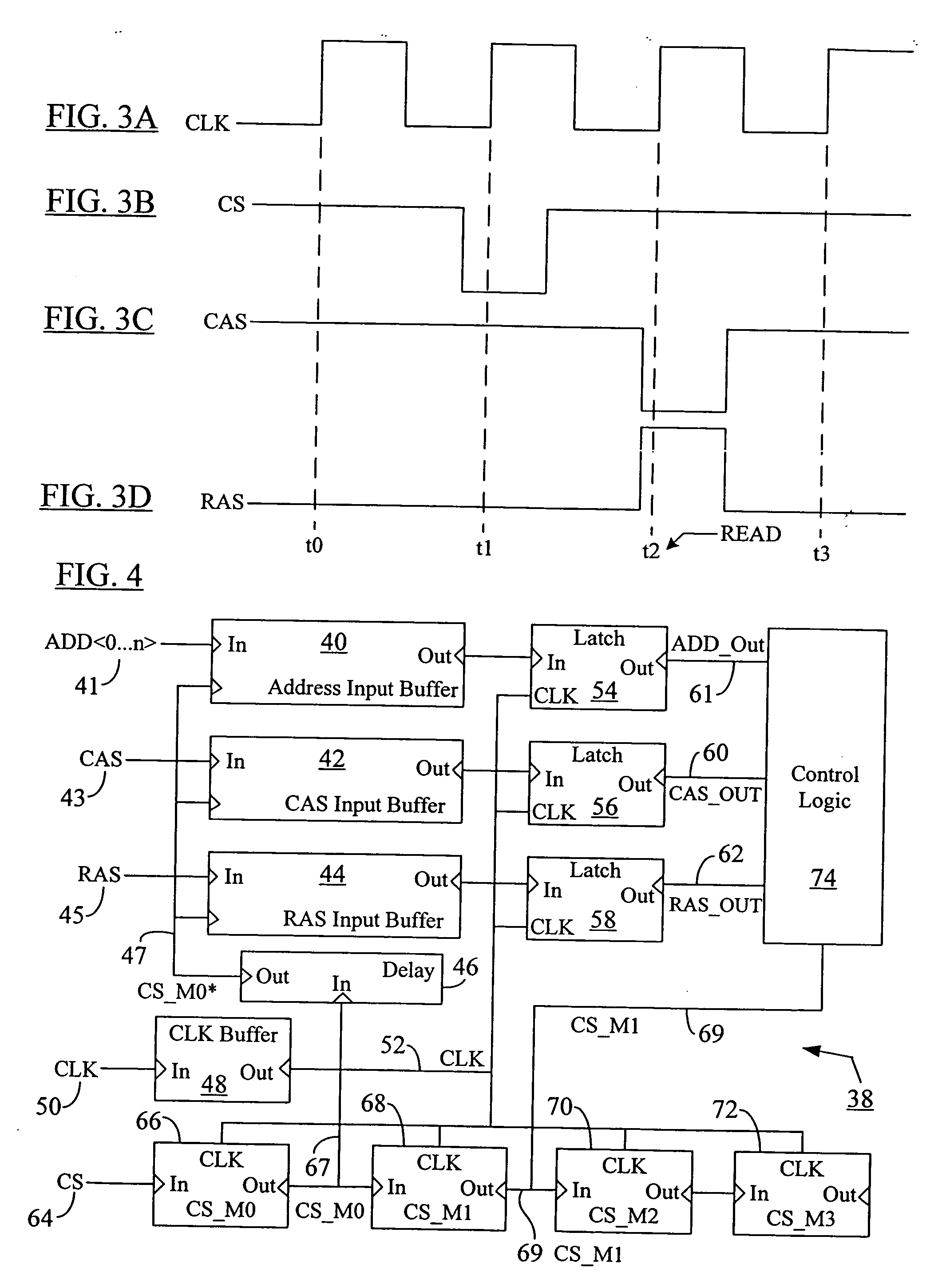
Low power chip select (CS) latency option
A system and method to reduce standby currents in input buffers in an electronic device (e.g., a memory device) is disclosed. The input buffers may be activated or deactivated by the state of a chip select (CS) signal. In case of a memory device, the active and precharge standby currents in memory input buffers may be reduced by turning off the input buffers when the CS signal is in an inactive state. A memory controller may supply the CS signal to the memory device at least one clock cycle earlier than other control signals including the RAS (row address strobe) signal, the CAS (column address strobe) signal, the WE (write enable) signal, etc. A modified I / O circuit in the memory device may internally delay the CS signal by at least one clock cycle to coincide its timing with the RAS / CAS signals for normal data access operation whereas the turning on / off of the memory input buffers may be performed by the CS signal received from the memory controller on the previous cycle. Thus, activation and deactivation of memory input buffers may be performed without forcing the memory device into power down mode and without employing complex circuits for power management. Because of the rules governing abstracts, this abstract should not be used to construe the claims.
Owner:ROUND ROCK RES LLC
Reducing the number of power and ground pins required to drive address signals to memory modules
InactiveUS20060039205A1Reduced pin countReduce in quantityEnergy efficient ICTDigital storageChip selectEngineering
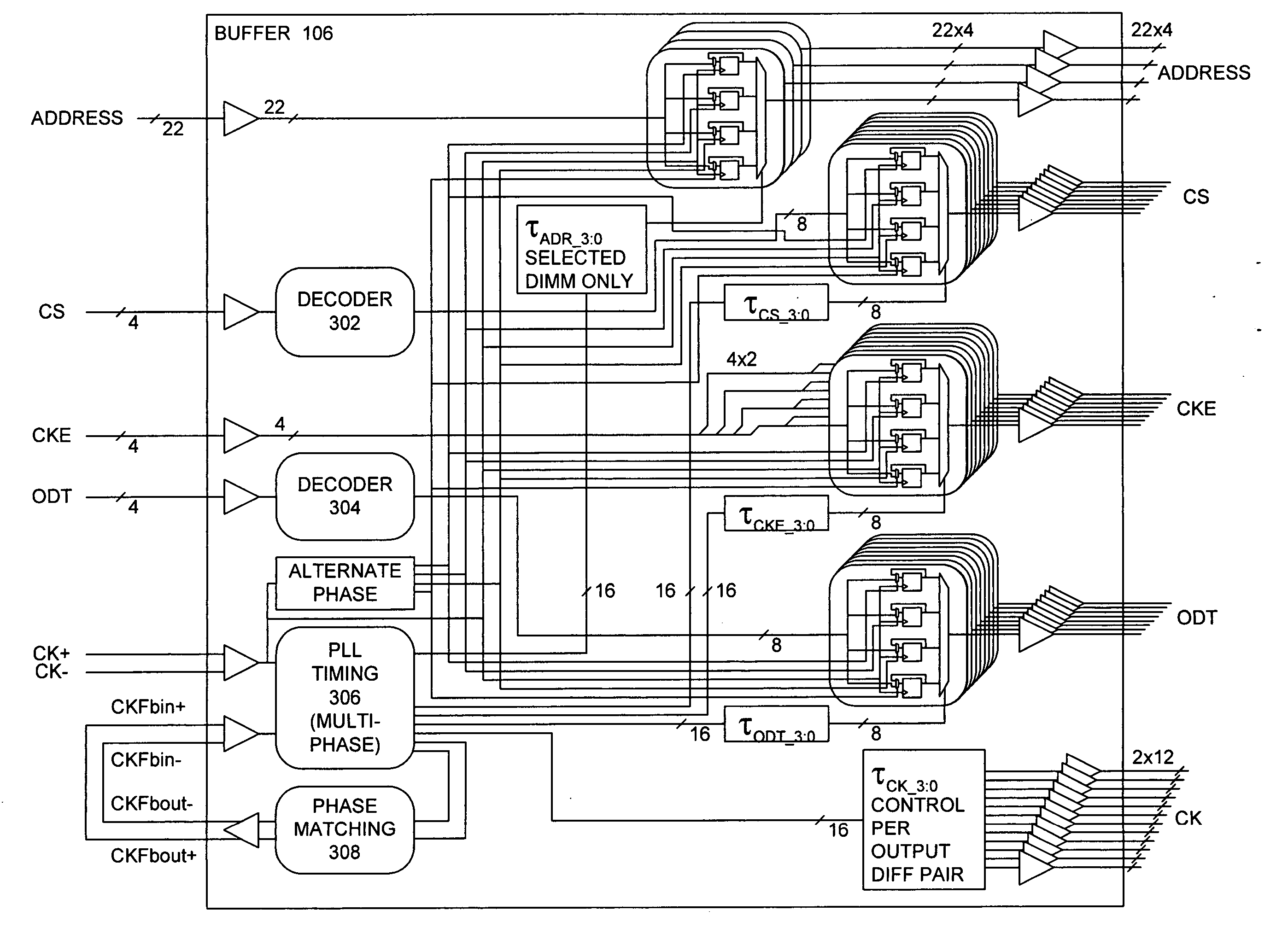
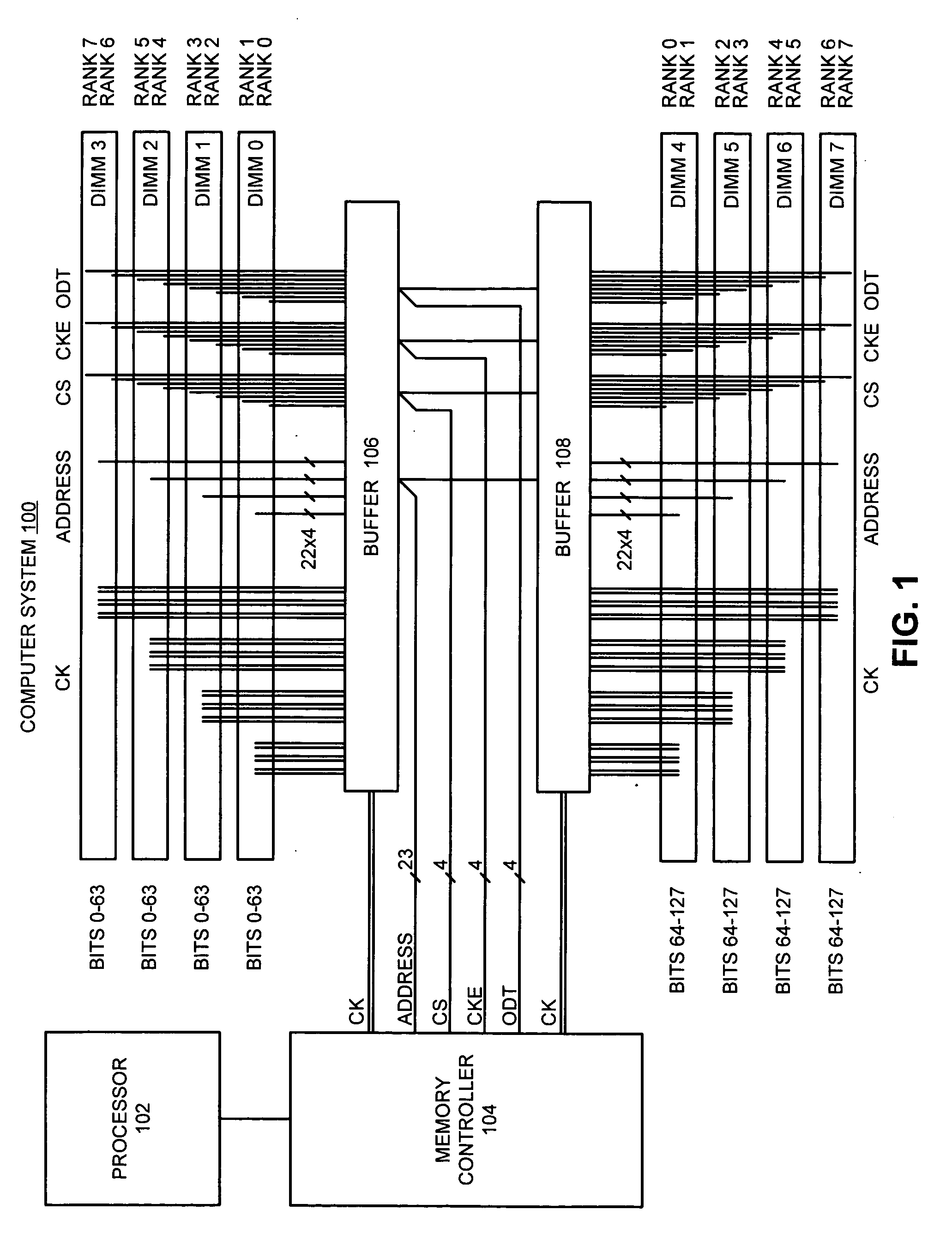
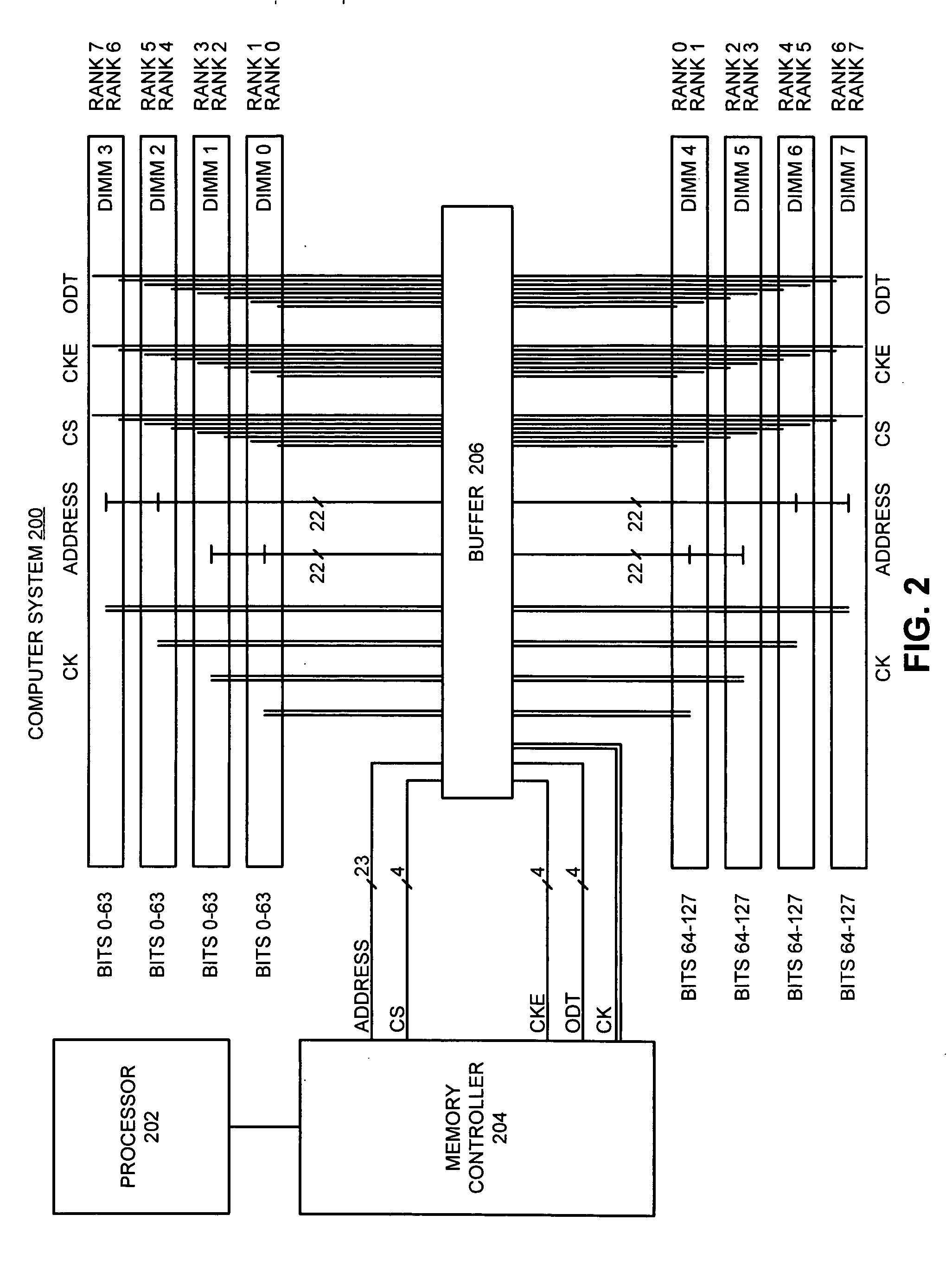
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system that reduces the number of power and ground pins required to drive address signals to system memory. During operation, the system receives address signals associated with a memory operation from a memory controller, wherein the address signals are received at a buffer chip, which is external the memory controller. The system also receives chip select signals associated with the memory operation at the buffer chip. Next, the system uses the chip select signals to identify an active subset of memory modules in the system memory, which are active during the memory operation. The system then uses address drivers on the buffer chip to drive the address signals only to the active subset of memory modules, and not to other memory modules in the system memory. In this way, the buffer chip requires fewer power and ground pins for the address drivers because the address signals are only driven to the active subset of memory modules, instead of being driven to all memory modules in the system memory.
Owner:APPLE INC
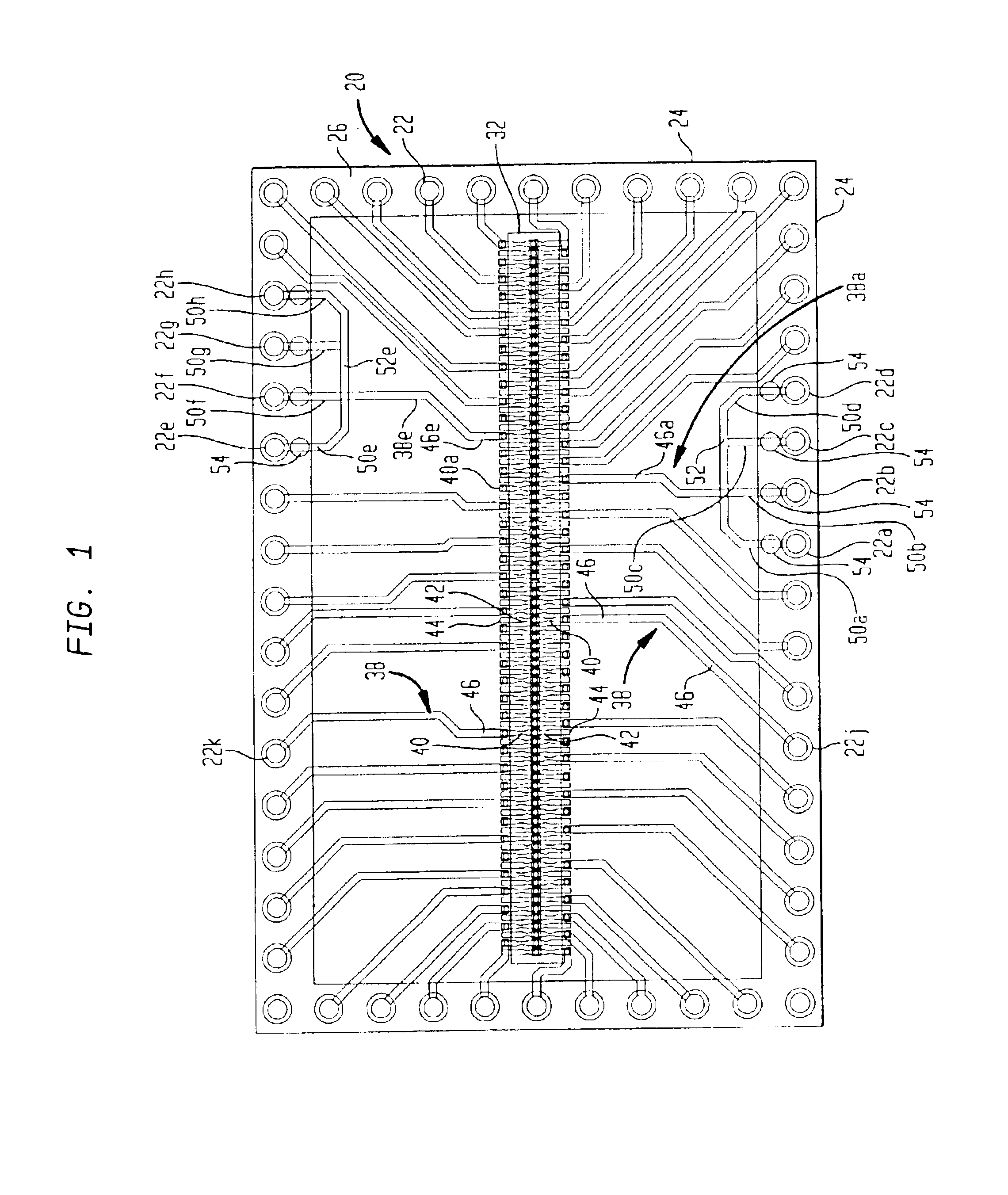
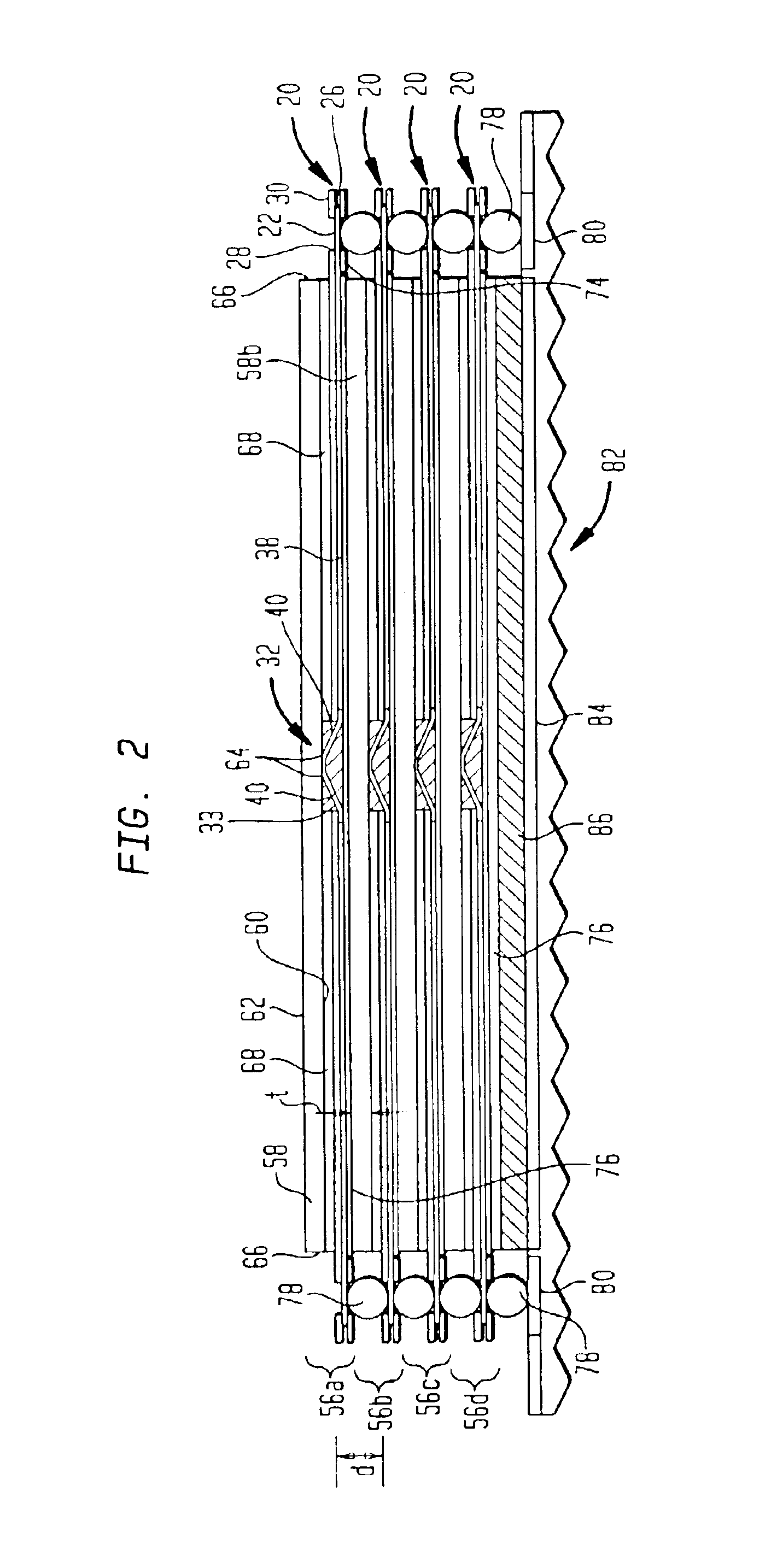
Circuit providing load isolation and memory domain translation for memory module
A circuit is configured to be mounted on a memory module connectable to a computer system so as to be electrically coupled to a plurality of memory devices on the memory module. The memory module has a first number of ranks of double-data-rate (DDR) memory devices activated by a first number of chip-select signals. The circuit is configurable to receive bank address signals, a second number of chip-select signals, and row / column address signals from the computer system. The circuit is further configurable to generate phase-locked clock signals in response to clock signals received from the computer system, to selectively isolate one or more loads of the first number of ranks from the computer system, and to translate between a system memory domain and a physical memory domain of the memory module.
Owner:NETLIST INC
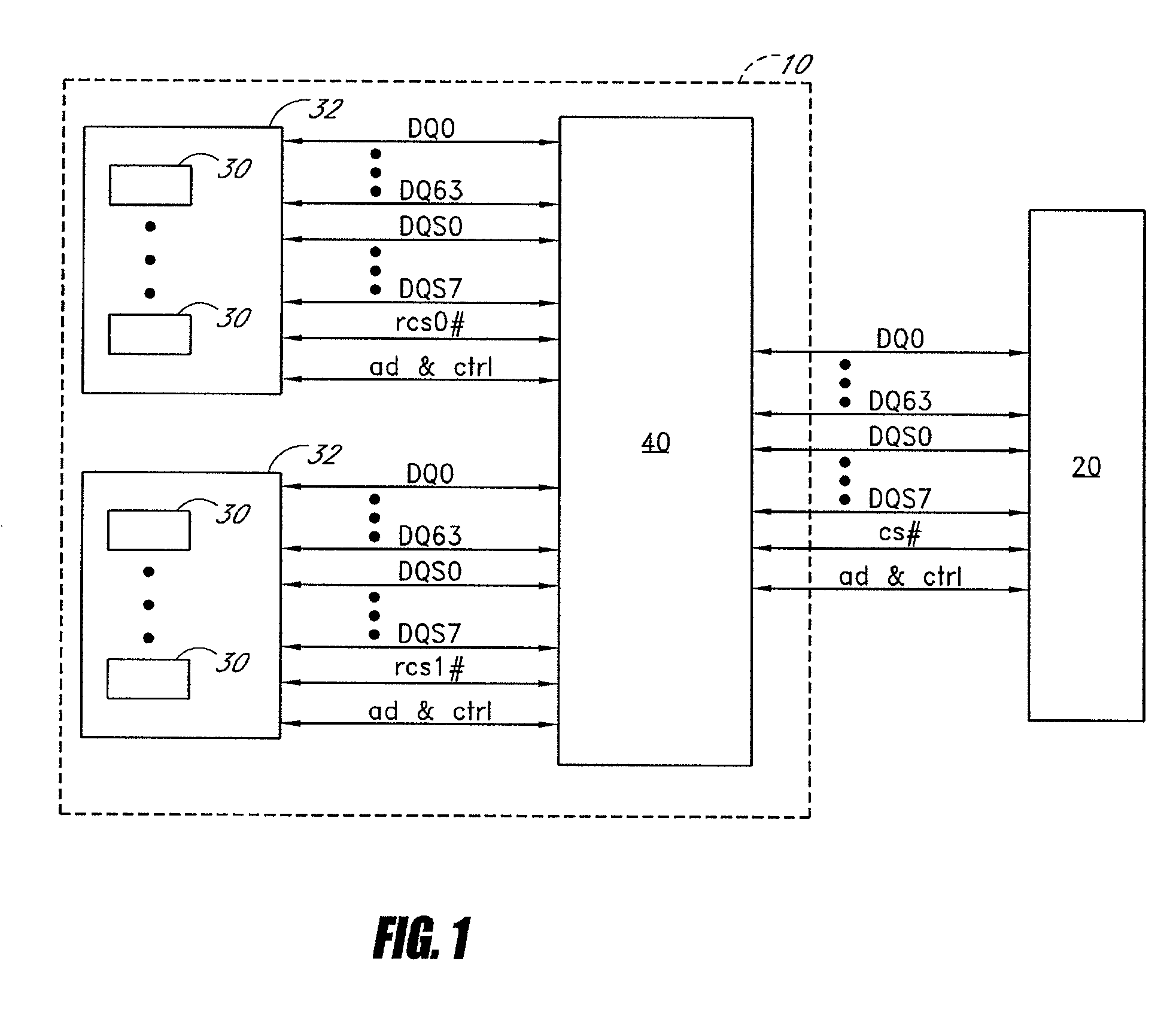
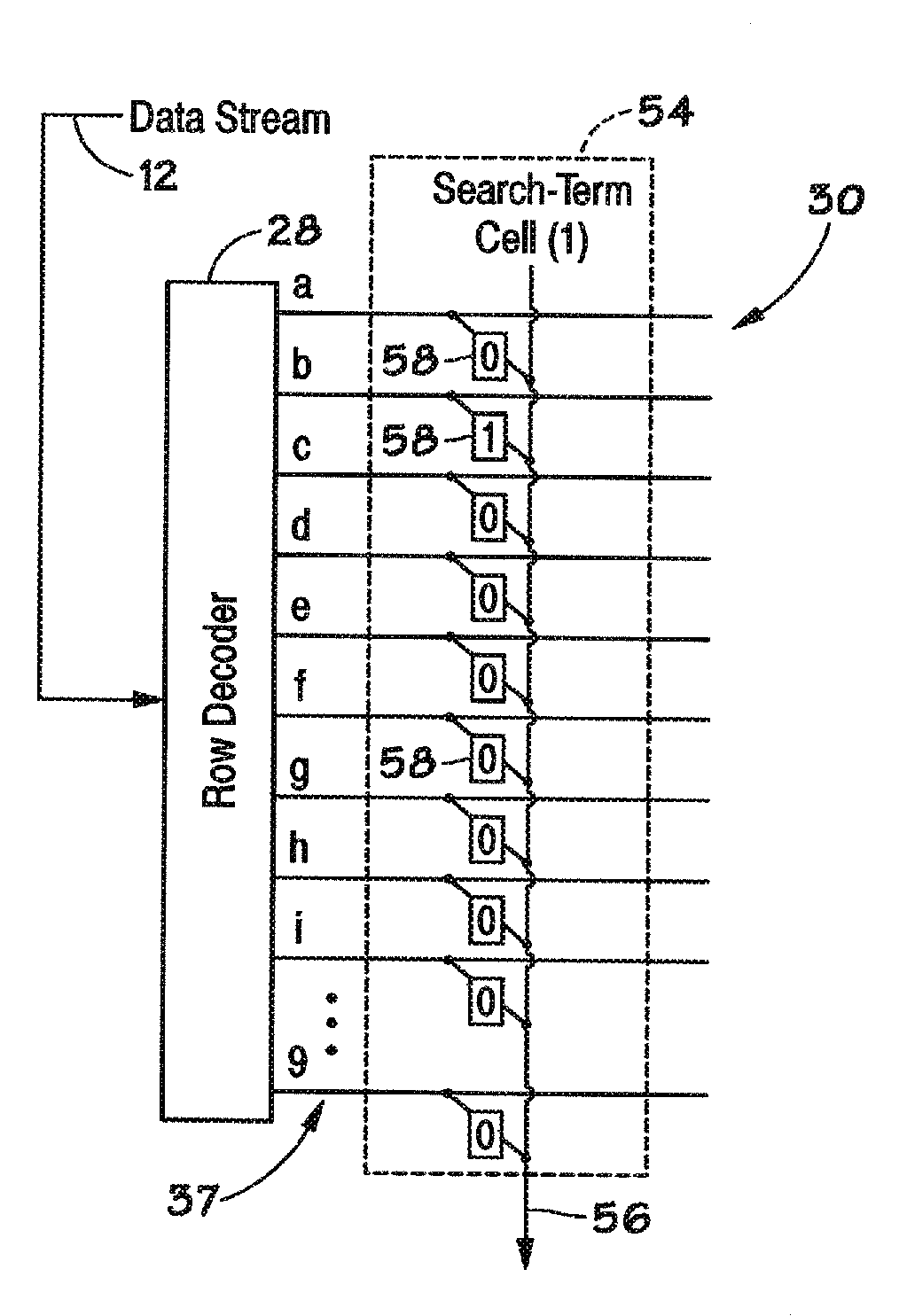
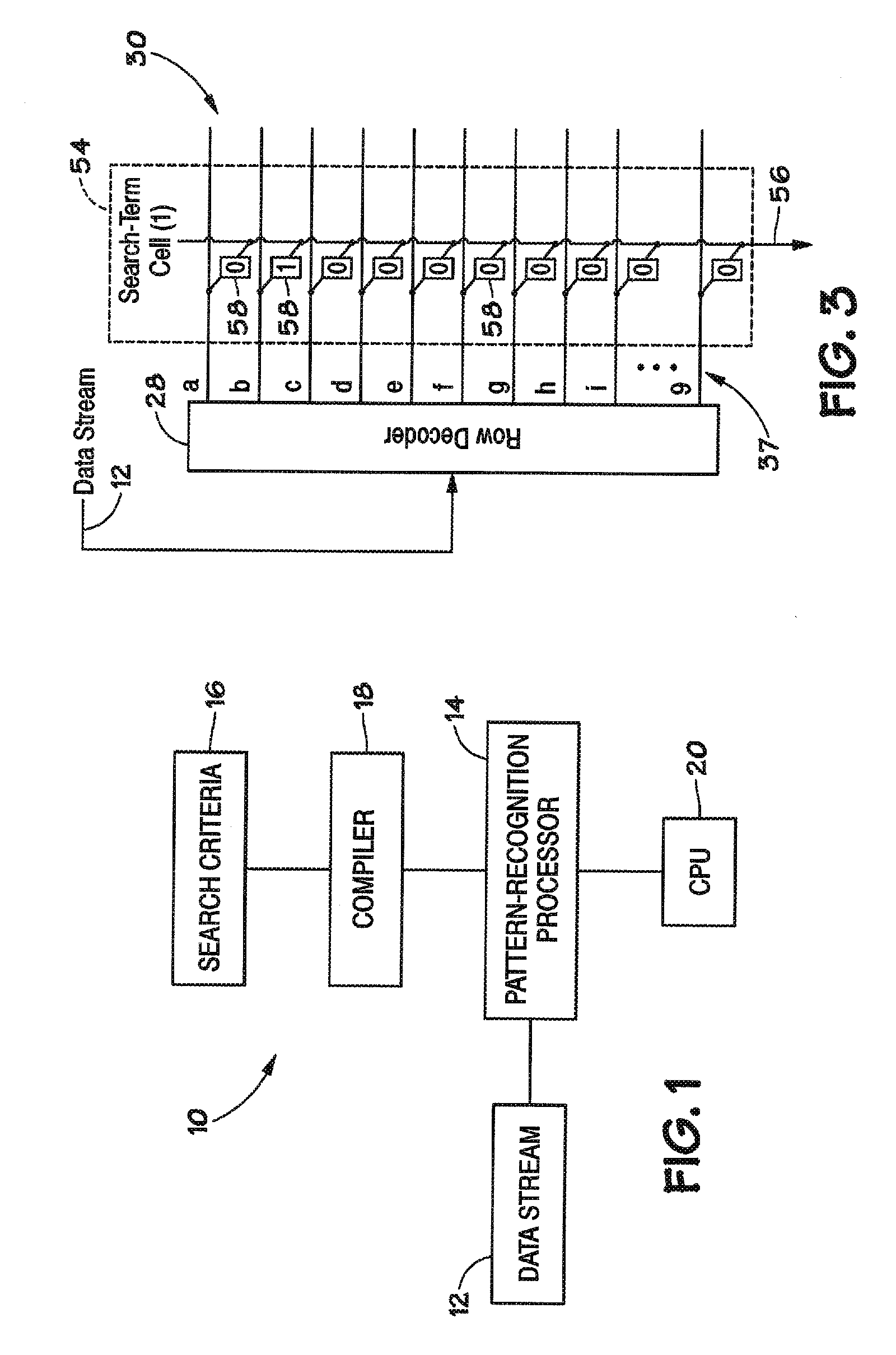
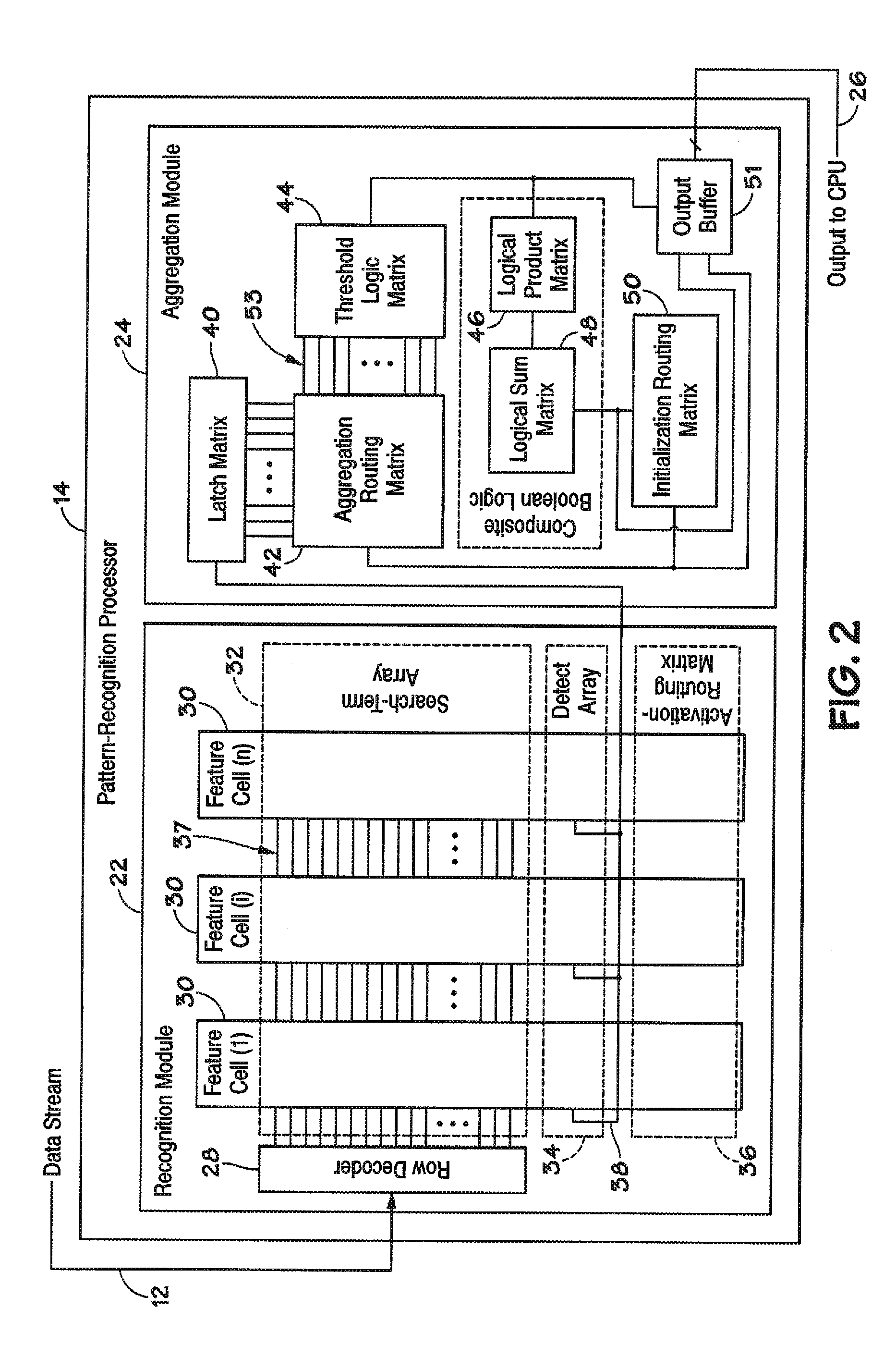
Devices, systems, and methods to synchronize parallel processing of a single data stream
ActiveUS20100138634A1Program control using stored programsGeneral purpose stored program computerData streamChip select
Disclosed are methods and devices, among which is a system that includes one or more pattern-recognition processors, such as in a pattern-recognition cluster. The pattern-recognition processors may be activated to perform a search of a data stream individually using a chip select or in parallel using a universal select signal. In this manner, the plurality of pattern-recognition processors may be enabled concurrently for synchronized processing of the data stream.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Semiconductor storage device having a plurality of stacked memory chips
ActiveUS7466577B2Reduce parasitic capacitanceAssure compatibilitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesMemory chipSemiconductor storage devices
A semiconductor storage employs a base substrate (101) having a command / address external terminal group (CA), a data input / output external terminal group (DQ), and a single chip select external terminal (CS), and also comprises a plurality of memory chips (110) to (113) mounted on a base substrate (101), each of which can individually carry out read and write operations. The terminals (CA), (DQ), and (CS) are connected to an interface chip (120). The interface chip (120) has a chip select signal generation circuit that can individually activate a plurality of memory chips (110) to (113) on the basis of an address signal fed by way of the terminal (CA) and on the basis of a chip select signal fed by way of the terminal (CS).
Owner:LONGITUDE LICENSING LTD
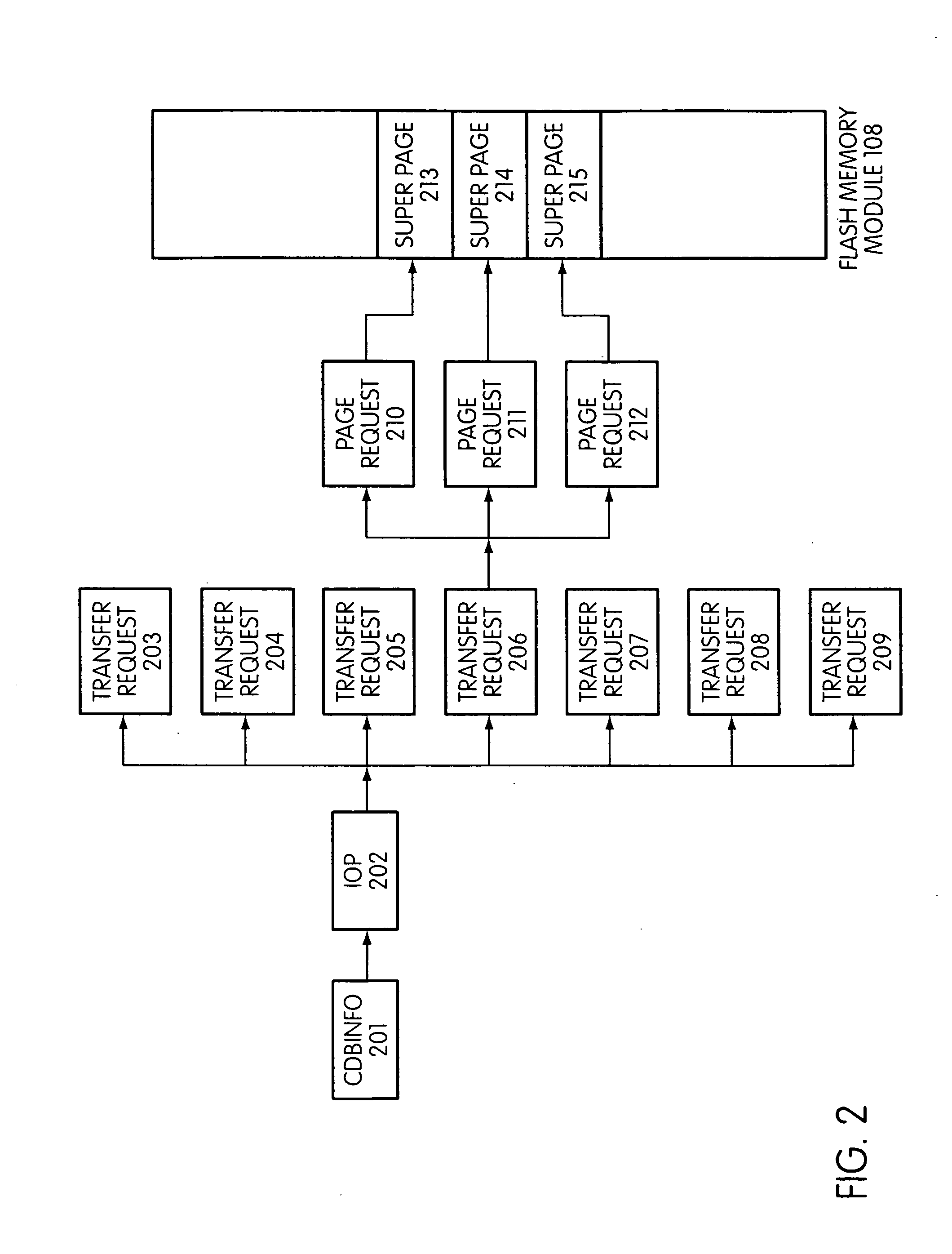
Storage control system with erase block mechanism and method of operation thereof
A method of operation of a storage control system includes: partitioning memory channels with memory devices; selecting a super device with one of the memory devices from one of the memory channels, the super device having a super chip select connected to chip selects of the memory devices; and selecting a super block associated with the super device.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Stacked packages
InactiveUS6897565B2Reduce the overall heightWell formedSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSolder ballChip select
A stacked chip assembly includes individual units having chips mounted on dielectric layers and traces on the dielectric layers interconnecting the contacts of the chips with terminals disposed in peripheral regions of the dielectric layers. At least some of the traces are multi-branched traces which connect chip select contacts to chip select terminals. The units are stacked one above the other with corresponding terminals of the different units being connected to one another by solder balls or other conductive elements so as to form vertical buses. Prior to stacking, the multi-branched traces of the individual units are selectively interrupted, as by breaking the individual branches, so as to leave chip select contacts of chips in different units connected to different chip select terminals and thereby connect these chips to different vertical buses. The individual units desirably are thin and directly abut one another so as to provide a low-height assembly with good heat transfer from chips within the stack.
Owner:TESSERA INC
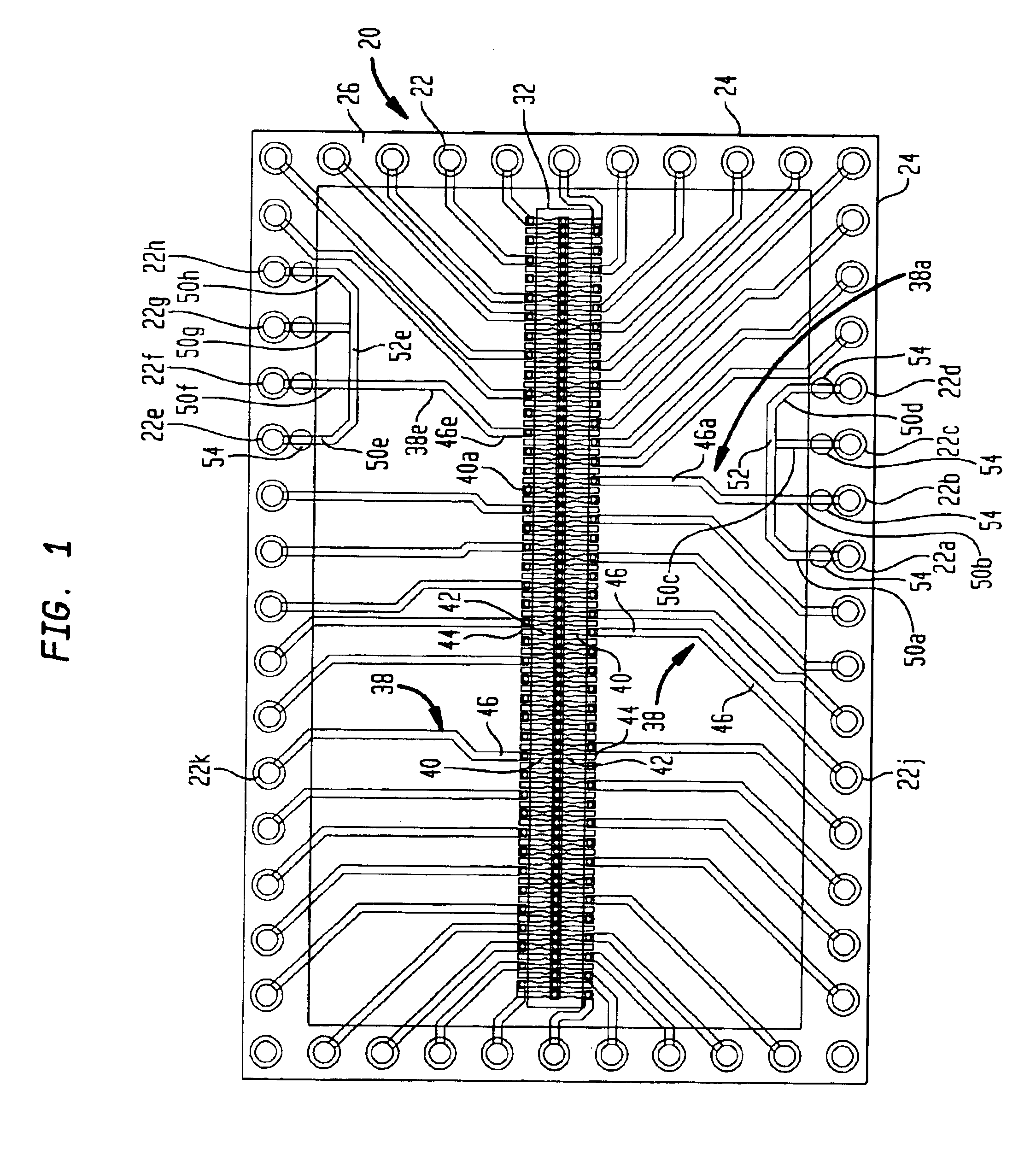
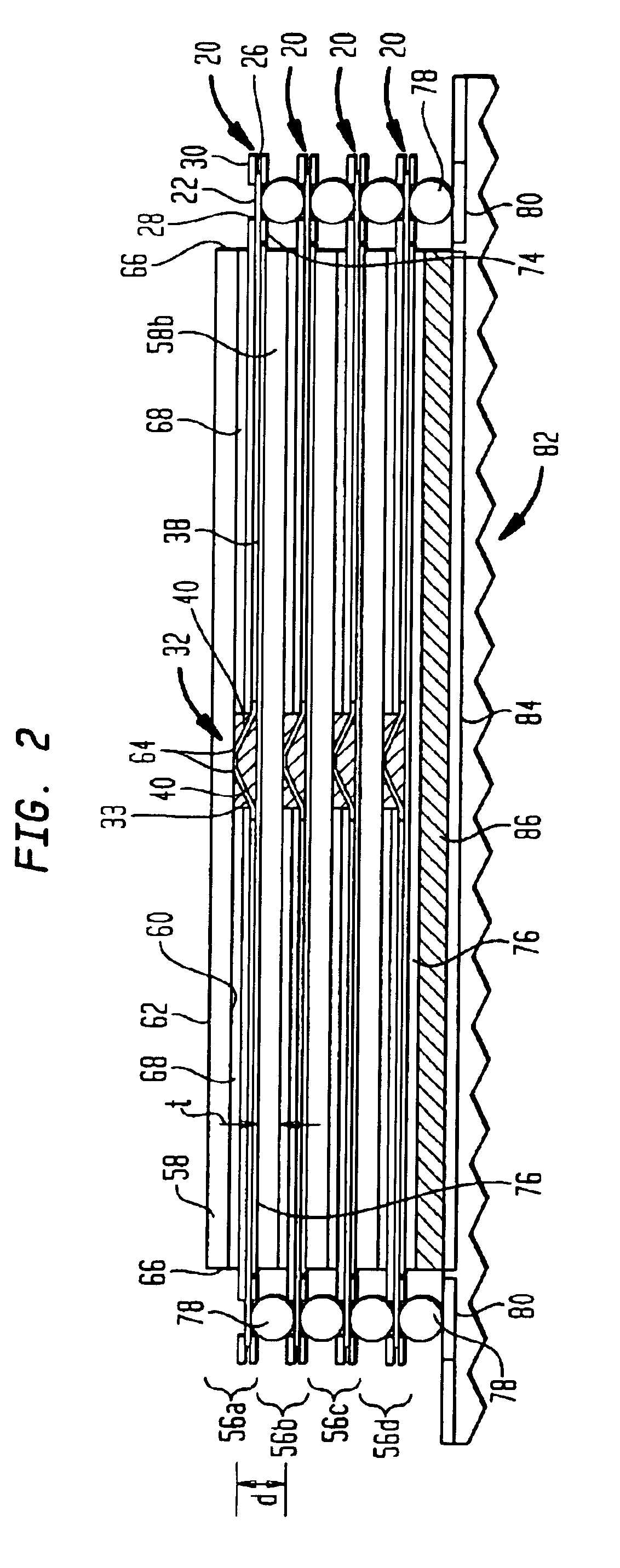
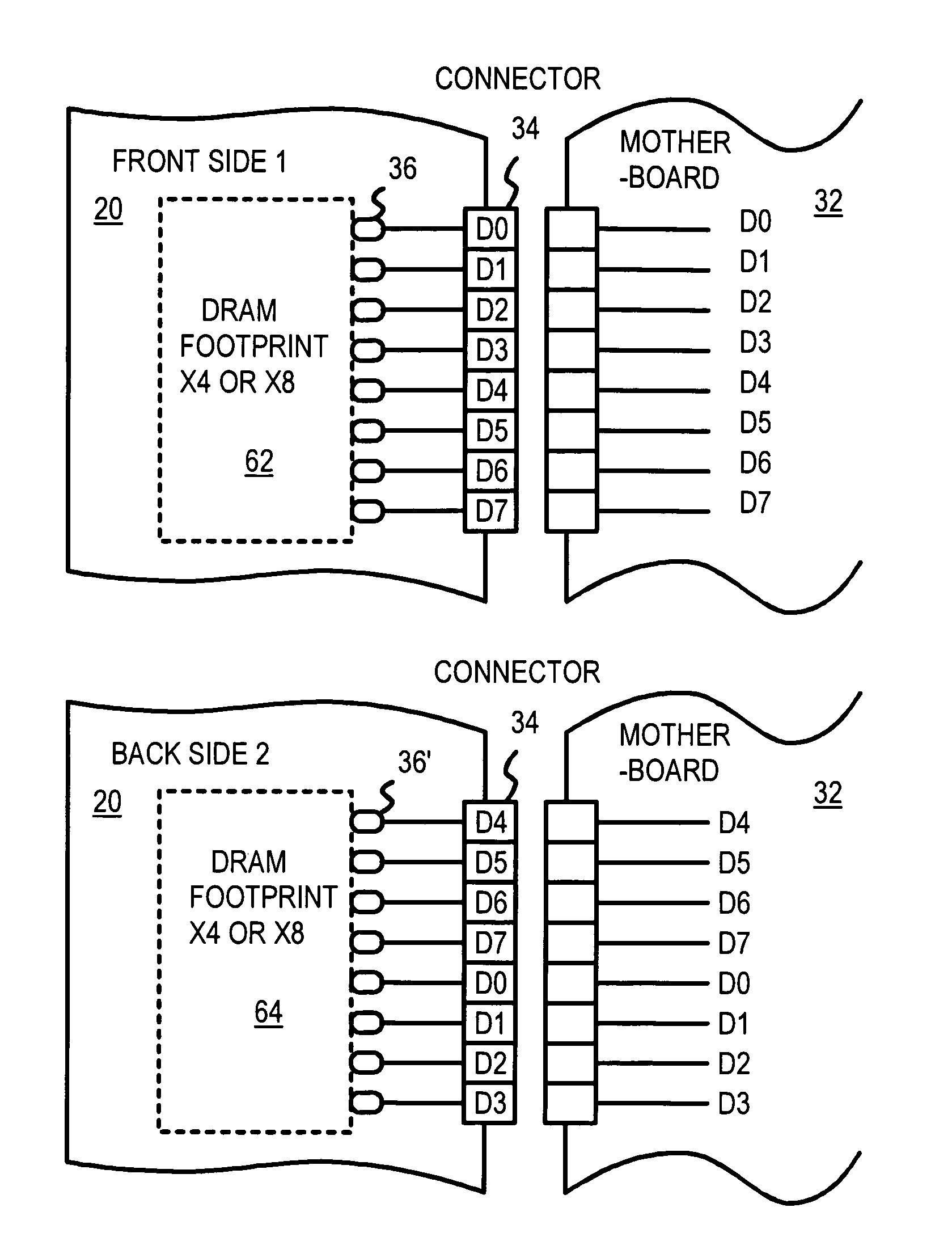
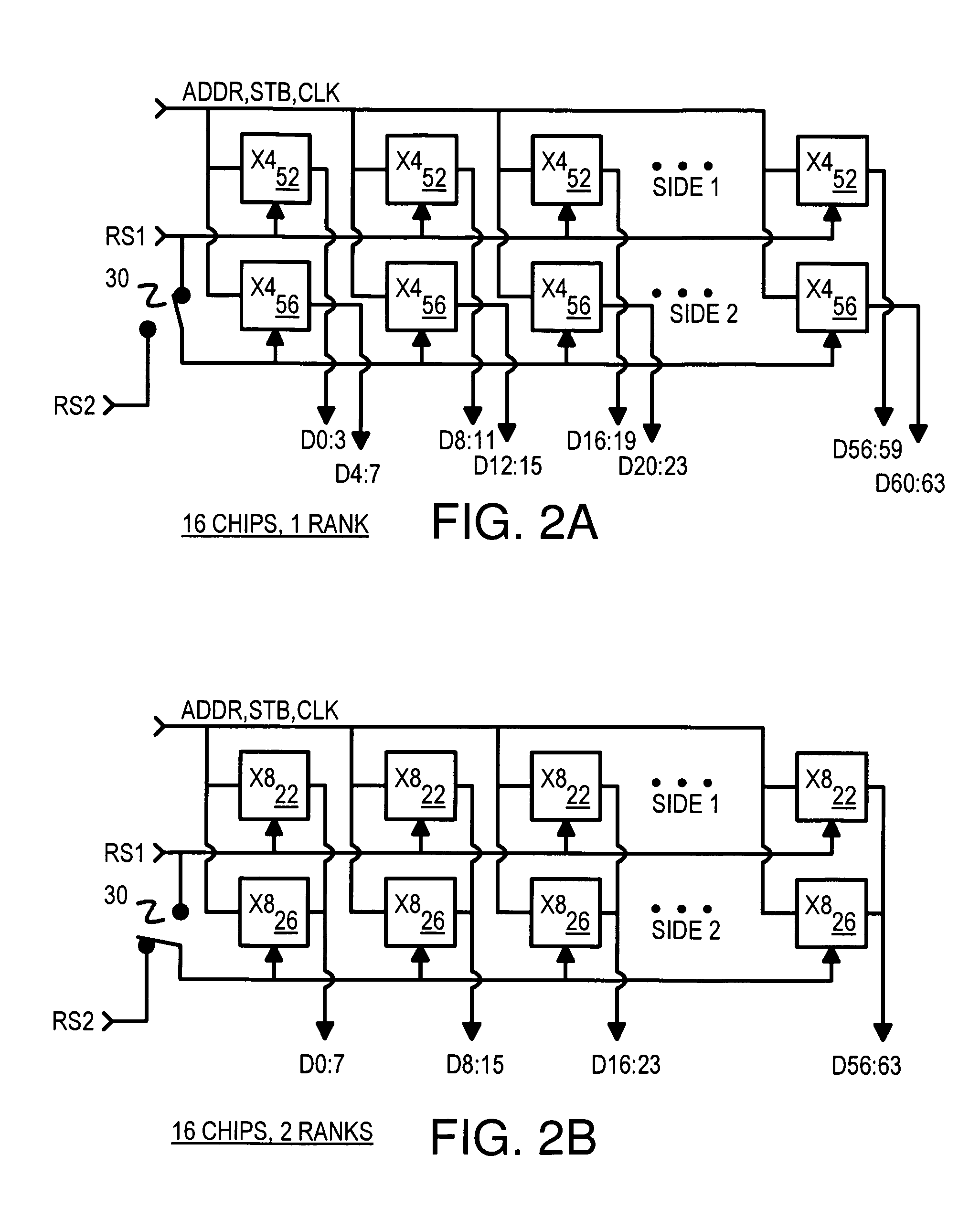
Memory-module board layout for use with memory chips of different data widths
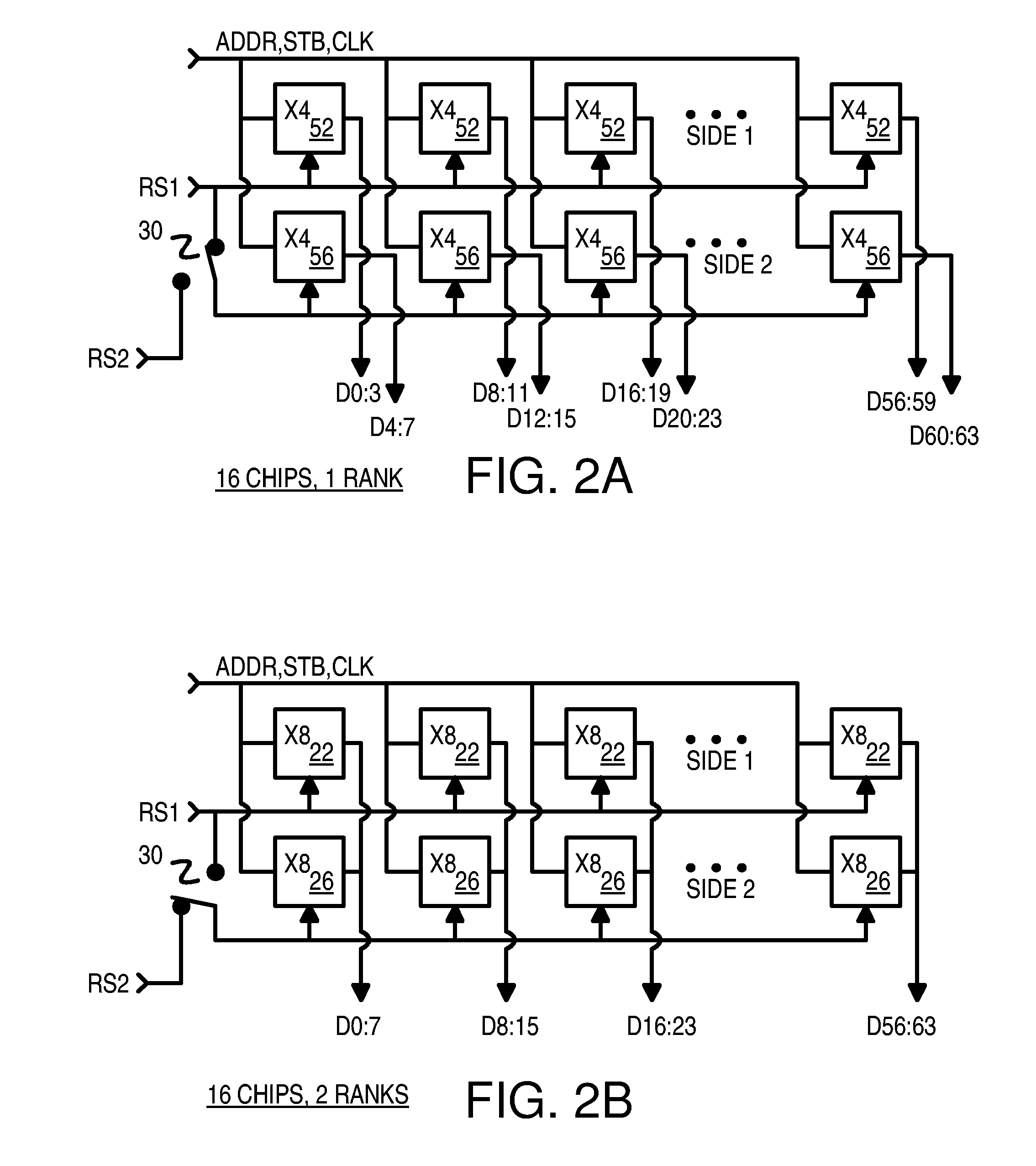
A memory module substrate printed-circuit board (PCB) has multi-type footprints and an edge connector for mating with a memory module socket on a motherboard. Two or more kinds of dynamic-random-access memory (DRAM) chips with different data I / O widths can be soldered to solder pads around the multi-type footprints. When ×4 DRAM chips with 4 data I / O pins are soldered over the multi-type footprints, the memory module has a rank-select signal that drives chip-select inputs to all DRAM chips. When ×8 DRAM chips with 8 data I / O pins are soldered over the multi-type footprints, the memory module has two rank-select signals. One rank-select drives chip-select inputs to front-side DRAM chips while the second rank-select drives chip-select inputs to back-side DRAM chips. Wiring traces on the PCB cross-over data nibbles between the solder pads and the connector to allow two ×4 chips to drive a byte driven by only one ×8 chip.
Owner:KINGSTON DIGITAL CO LTD
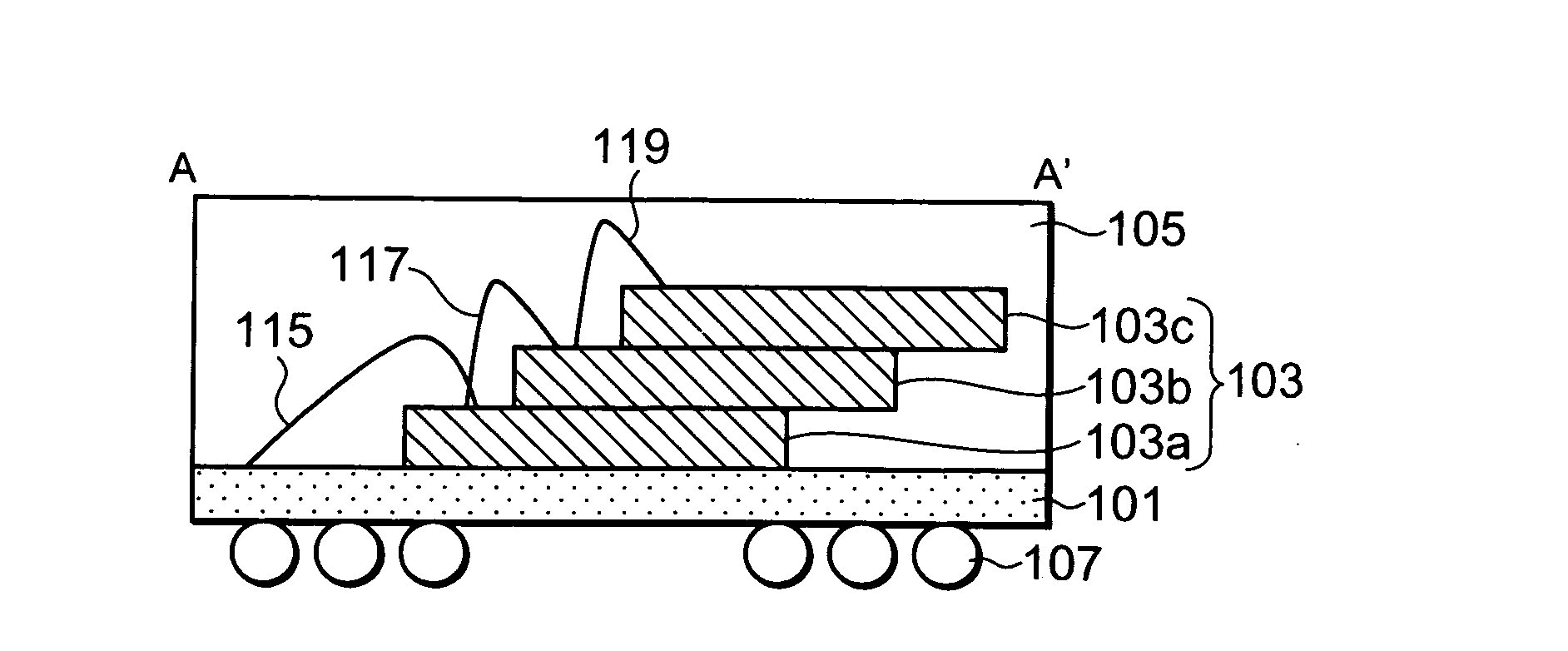
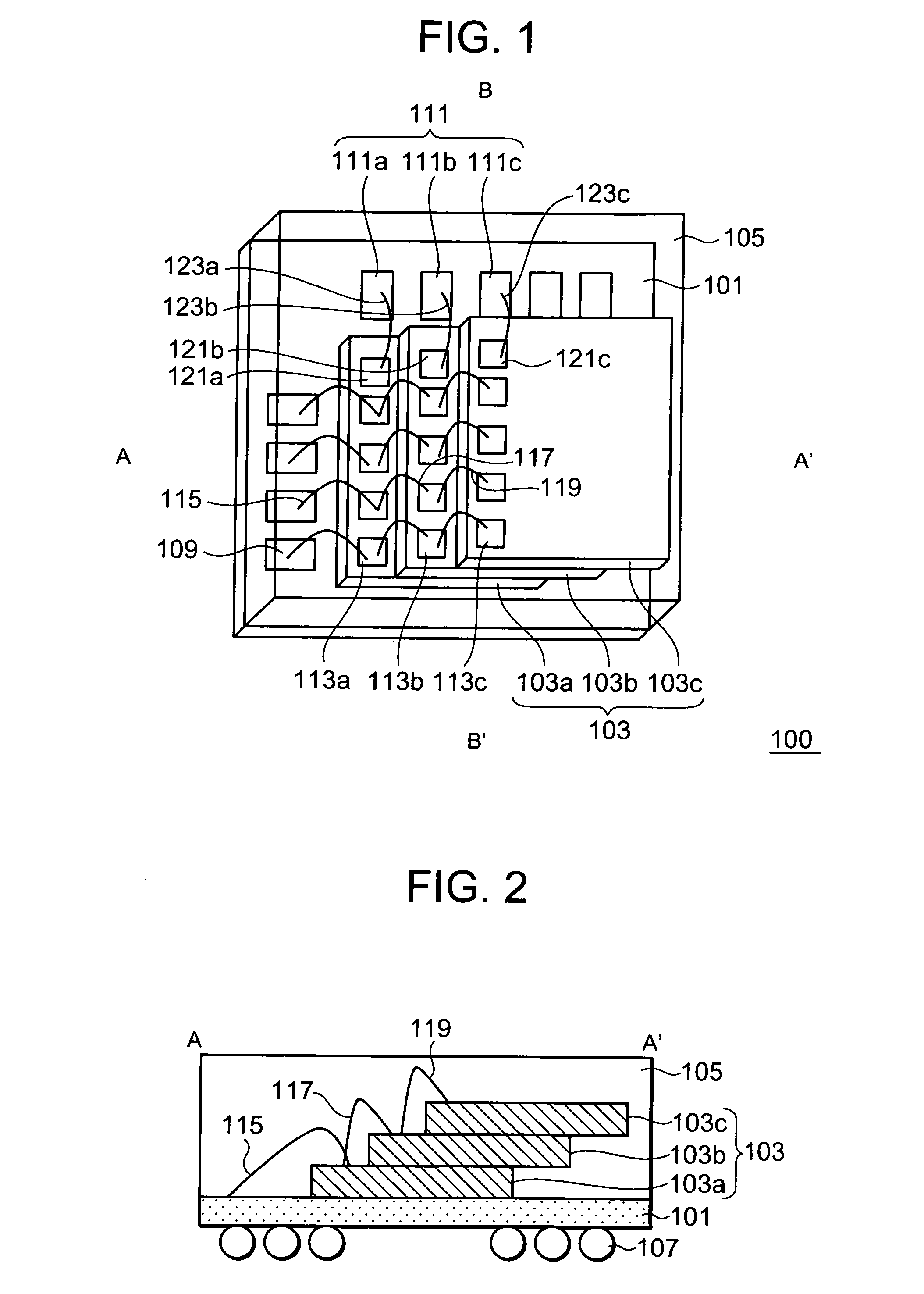
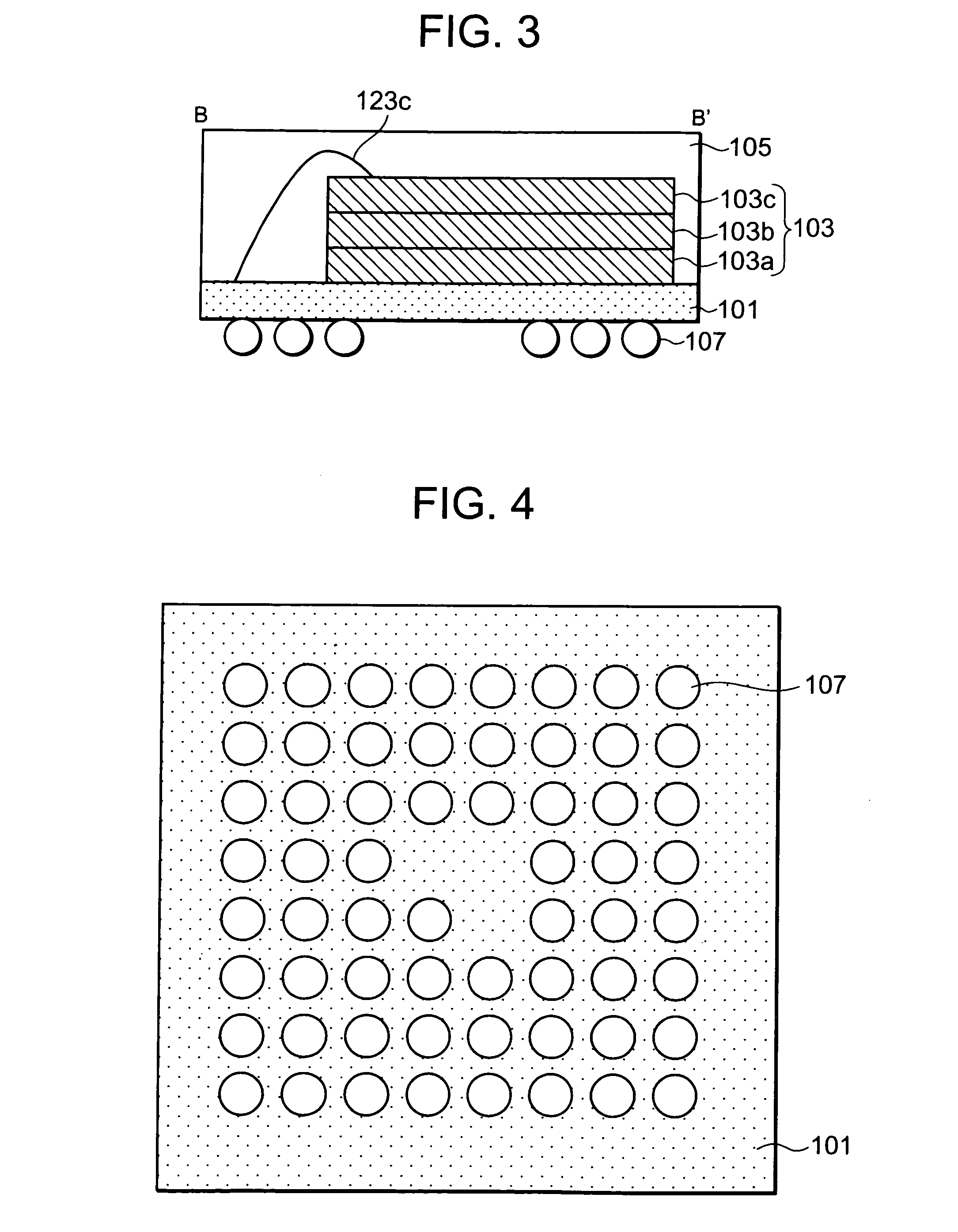
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS20080230888A1Reduce package sizeConnection distanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesMemory chipChip select
A first memory chip (103a) and a second memory chip (103b) mounted in this order on one surface of a mounting board (101) each have a rectangular planar shape and include a plurality of electrode pads formed in a single line along one side of the rectangle. An electrode pad line of the second memory chip (103b) is formed in parallel with an electrode pad line of the first memory chip (103a). A chip select pad is disposed on an end of the electrode pad line. Control pads, address pads, or data pads (113a) of the first memory chip (103a) are wire bonded to first stitches (109) formed in a single line along one side of the rectangle. A chip select pad (121a) and a chip select pad (121b) are wire bonded to second stitches (111) formed in a line along a side adjacent to a side of the chip select pad (121a). Accordingly, an increase in package area is suppressed when a plurality of memory chips are stacked.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
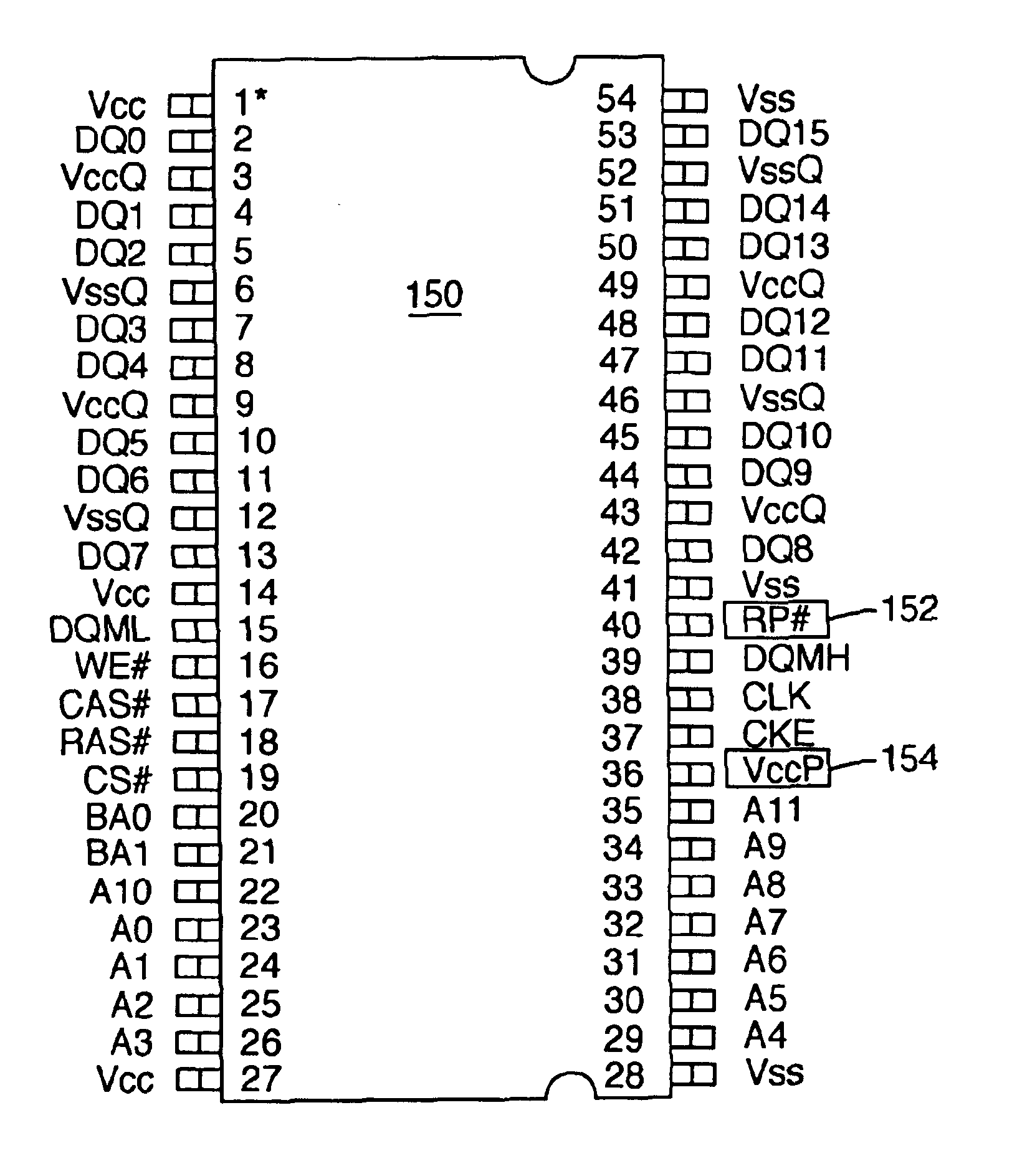
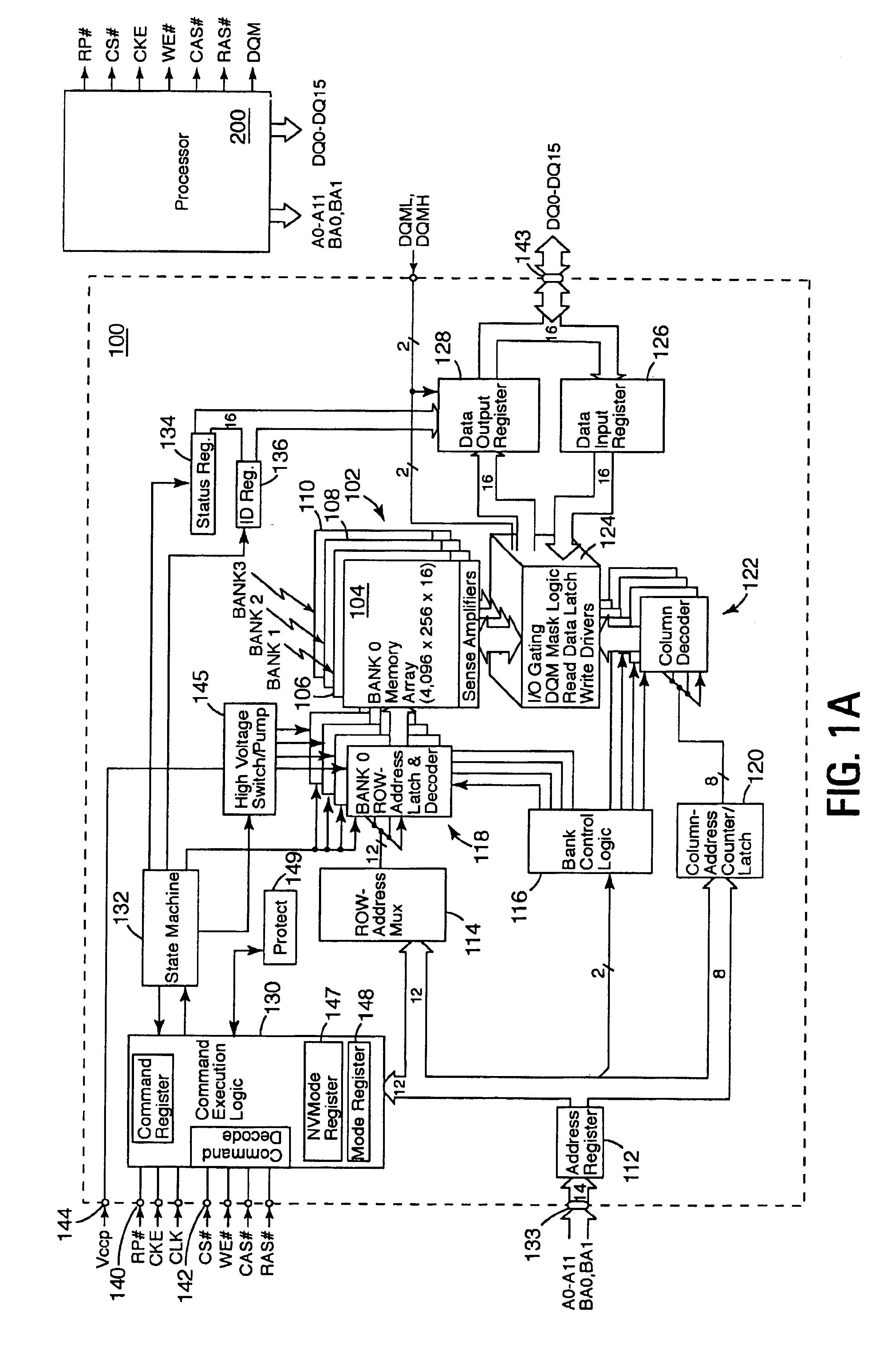
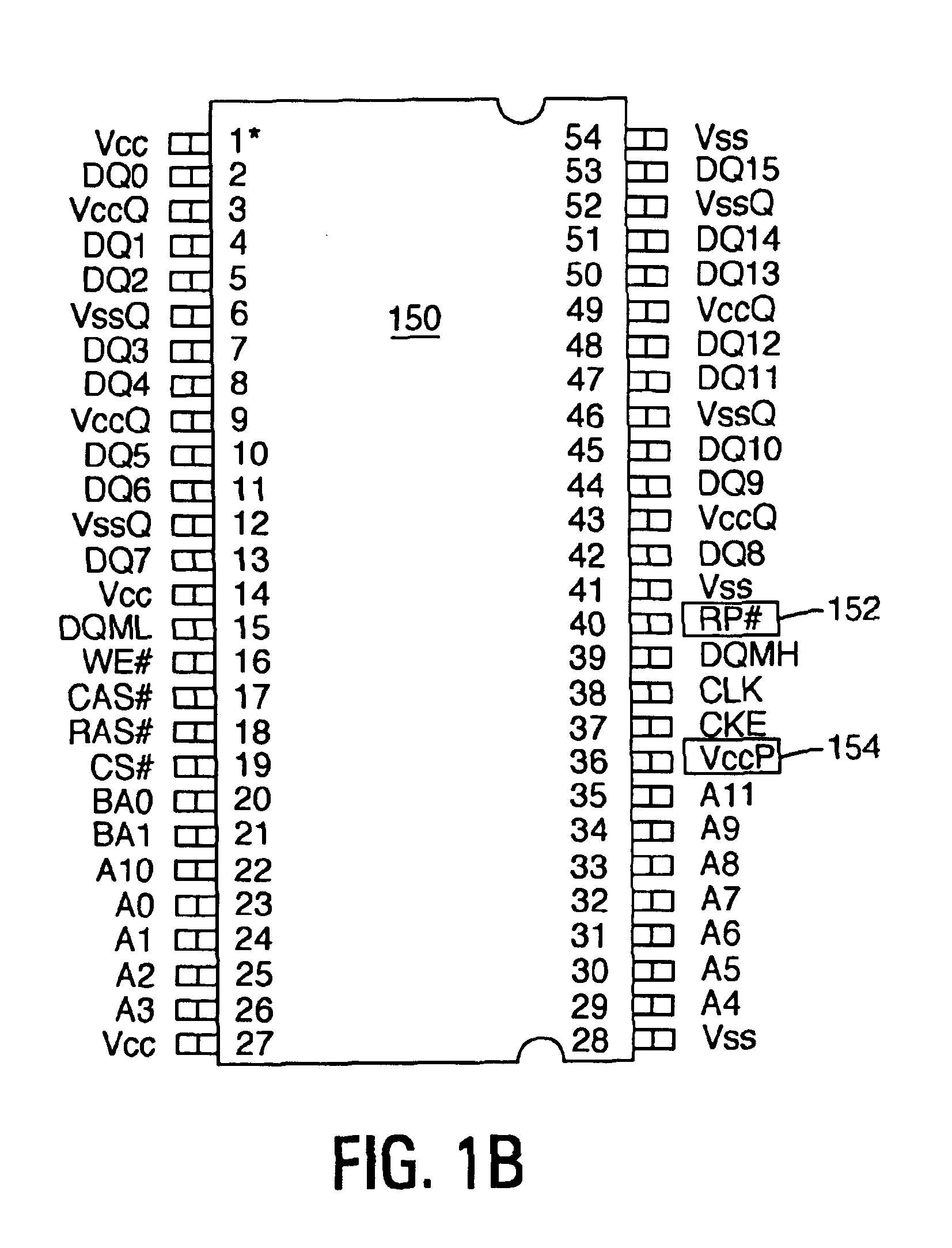
Synchronous flash memory emulating the pin configuration of SDRAM
InactiveUS6892270B2Improves operation of systemImprove operationRead-only memoriesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRandom access memoryComputerized system
A computer system comprises a memory controller and a synchronous non-volatile memory device coupled to the memory controller via a main memory bus. The synchronous non-volatile memory device has external interconnects arranged in a manner that corresponds to interconnects of a synchronous dynamic random access memory device. The synchronous flash memory device, however, comprises a reset connection, and a Vccp power supply connection correspond to first and second no-connect (NC) interconnect pins of the synchronous dynamic random access memory. In one embodiment, the synchronous non-volatile memory device has a command interface comprising a write enable connection (WE#) to receive a write enable signal, a column address strobe connection (CAS#) to receive a column address strobe signal, a row address strobe connection (RAS#) to receive a row address strobe signal, and a chip select connection (CS#) to receive a chip select signal.
Owner:ROUND ROCK RES LLC
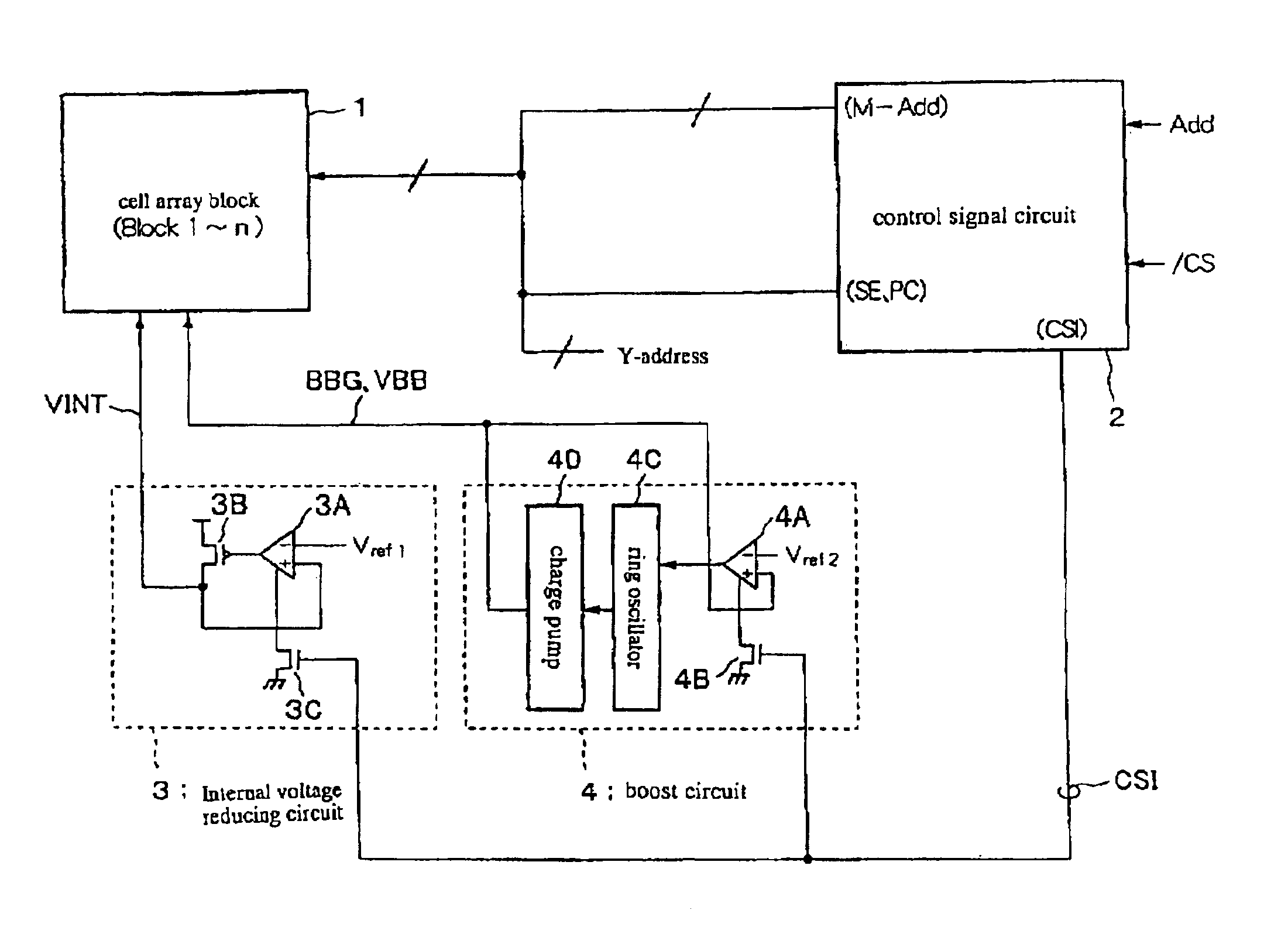
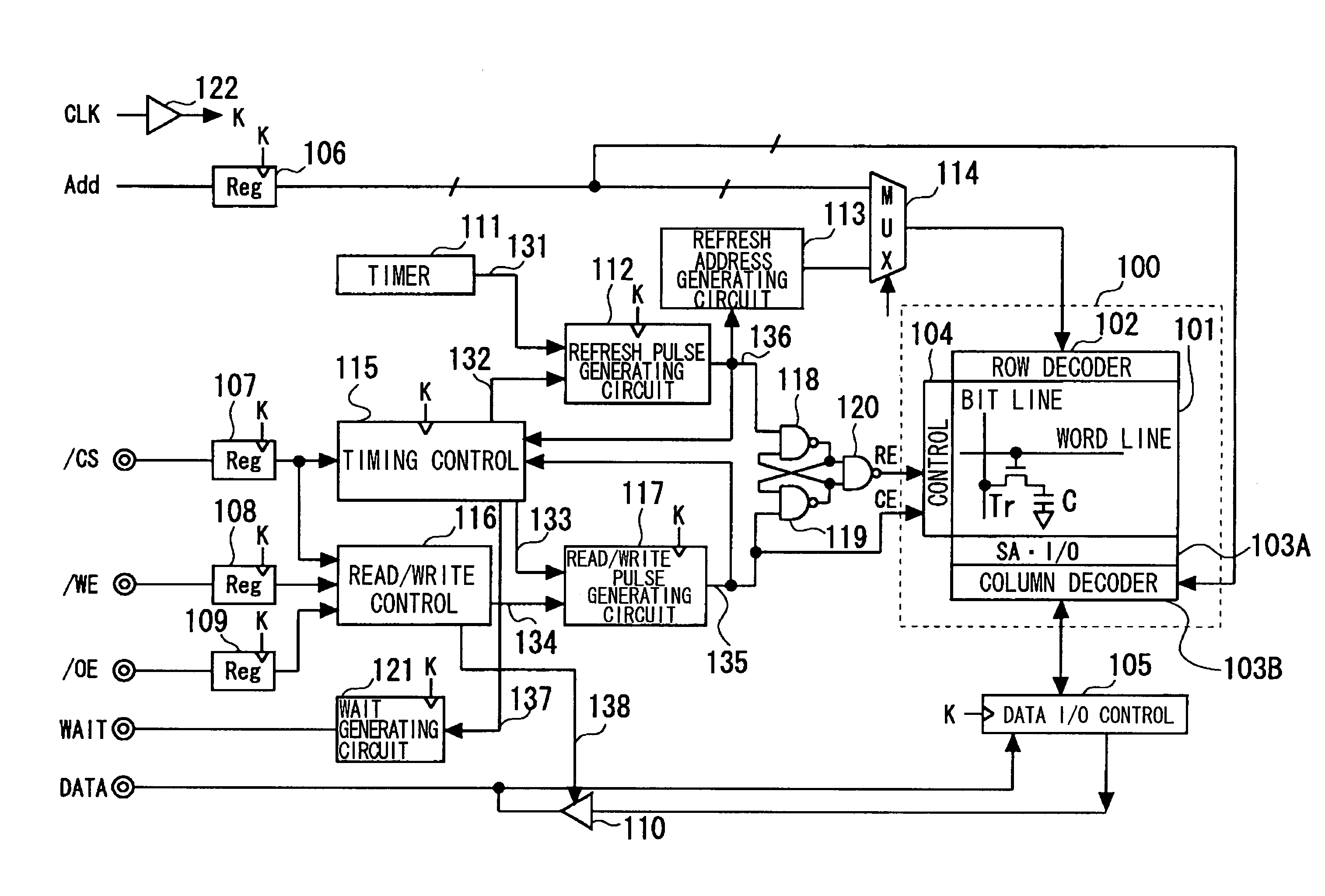
Semiconductor storage device
InactiveUS6922371B2Total current dropReduce consumptionSolid-state devicesDigital storageControl signalChip select
A semiconductor memory device is provided which effectively reduces a consumption of current of a system of circuits associated with refresh operations. A control signal circuit 2 controls n-channel transistors 3C, 4B to be in an OFF-state based on an internal chip select signal SCI in an interval time period between the refresh operations, wherein the n-channel transistors 3C, 4B are connected between the system of circuits associated with refresh operations (an internal voltage-down circuit 3 and a boost circuit 4) and the ground, so as to break down a leak path of the system of circuits associated with refresh operations for reducing the leakage of current. At a timing of starting the refresh operation by triggering a timer, the internal chip select signal SCI is transitioned to a high level for supplying a ground voltage to the internal voltage-down circuit 3 and the boost circuit 4.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Auto configurable 2/3 wire serial interface
InactiveUS20120170690A1Gated amplifiersAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsAuto-configurationSequence processing
An automatically configurable 2-wire / 3-wire serial communications interface (AC23SCI), which includes start-of-sequence (SOS) detection circuitry and sequence processing circuitry, is disclosed. When the SOS detection circuitry is coupled to a 2-wire serial communications bus, the SOS detection circuitry detects an SOS of a received sequence based on a serial data signal and a serial clock signal. When the SOS detection circuitry is coupled to a 3-wire serial communications bus, the SOS detection circuitry detects the SOS of the received sequence based on a chip select (CS) signal. The SOS detection circuitry provides an indication of detection of the SOS to the sequence processing circuitry, which initiates processing of the received sequence using the serial data signal and the serial clock signal upon the detection of the SOS. As such, the AC23SCI automatically configures itself for operation with some 2-wire and some 3-wire serial communications buses without external intervention.
Owner:QORVO US INC
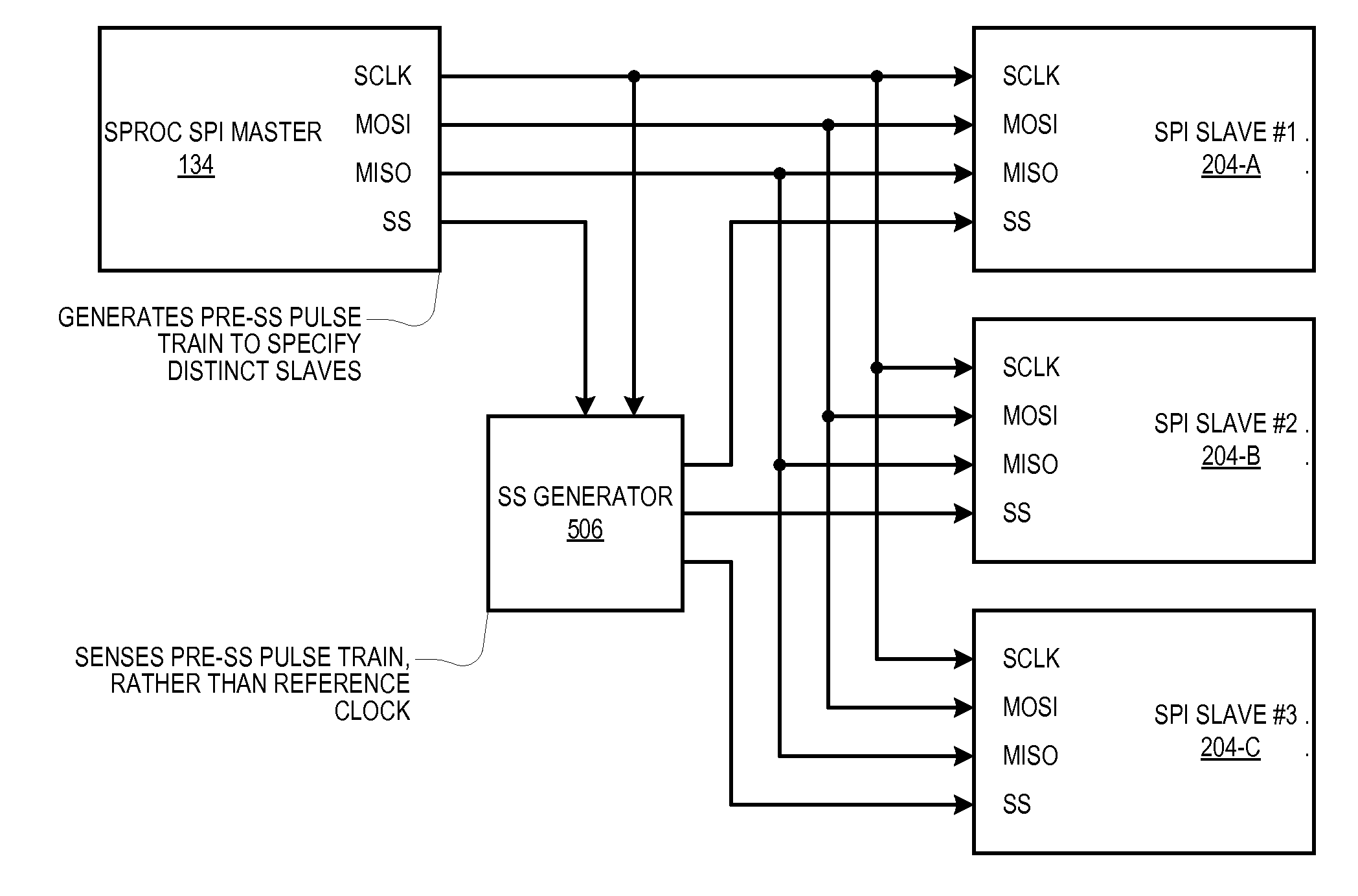
Method for generating multiple serial bus chip selects using single chip select signal and modulation of clock signal frequency
A system includes a serial bus having an electrical net for conveying a clock signal, and a master device and a plurality of slave devices coupled to the serial bus. The master device modulates a clock signal on its output on an electrical net according to first and second manners to select respective first and second of the slave devices. The first manner is distinct from the second manner. In alternate embodiments, the first and second manners are: (1) different frequencies of the clock signal; and (2) pulse trains on the clock signal with different predetermined numbers of clock edges prior to the assertion of a single slave select signal from the master device. In alternate embodiments: (1) each slave detects the first and second manners directly from the master; and (2) a distinct device detects the first and second manners from the master device and generates individual slave selects.
Owner:VIA TECH INC
Memory latency and bandwidth optimizations
InactiveUS20040073767A1Memory adressing/allocation/relocationMicro-instruction address formationRAIDComputer architecture
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Semiconductor storage device
InactiveUS7203113B2Easy loadingIncrease speedDigital storageSemiconductor storage devicesChip select
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Memory-Module Board Layout for Use With Memory Chips of Different Data Widths
ActiveUS20060267172A1Final product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsMemory chipNibble
A memory module substrate printed-circuit board (PCB) has multi-type footprints and an edge connector for mating with a memory module socket on a motherboard. Two or more kinds of dynamic-random-access memory (DRAM) chips with different data I / O widths can be soldered to solder pads around the multi-type footprints. When ×4 DRAM chips with 4 data I / O pins are soldered over the multi-type footprints, the memory module has a rank-select signal that drives chip-select inputs to all DRAM chips. When ×8 DRAM chips with 8 data I / O pins are soldered over the multi-type footprints, the memory module has two rank-select signals. One rank-select drives chip-select inputs to front-side DRAM chips while the second rank-select drives chip-select inputs to back-side DRAM chips. Wiring traces on the PCB cross-over data nibbles between the solder pads and the connector to allow two ×4 chips to drive a byte driven by only one ×8 chip.
Owner:KINGSTON DIGITAL CO LTD
Method for controlling an optic disk
InactiveUS6170043B1Shorten update timeHigh speedProgram loading/initiatingMemory systemsControl signalChip select
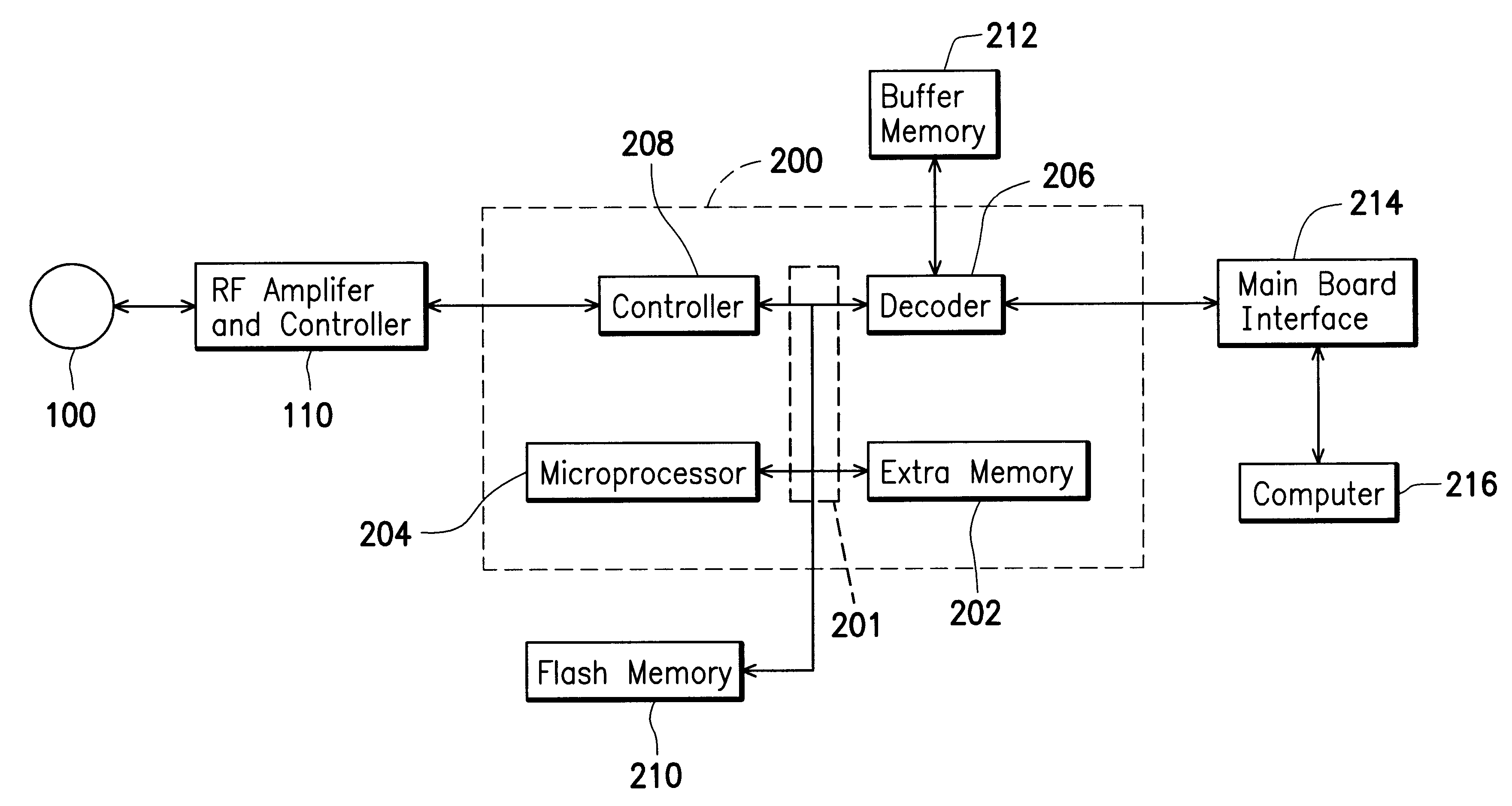
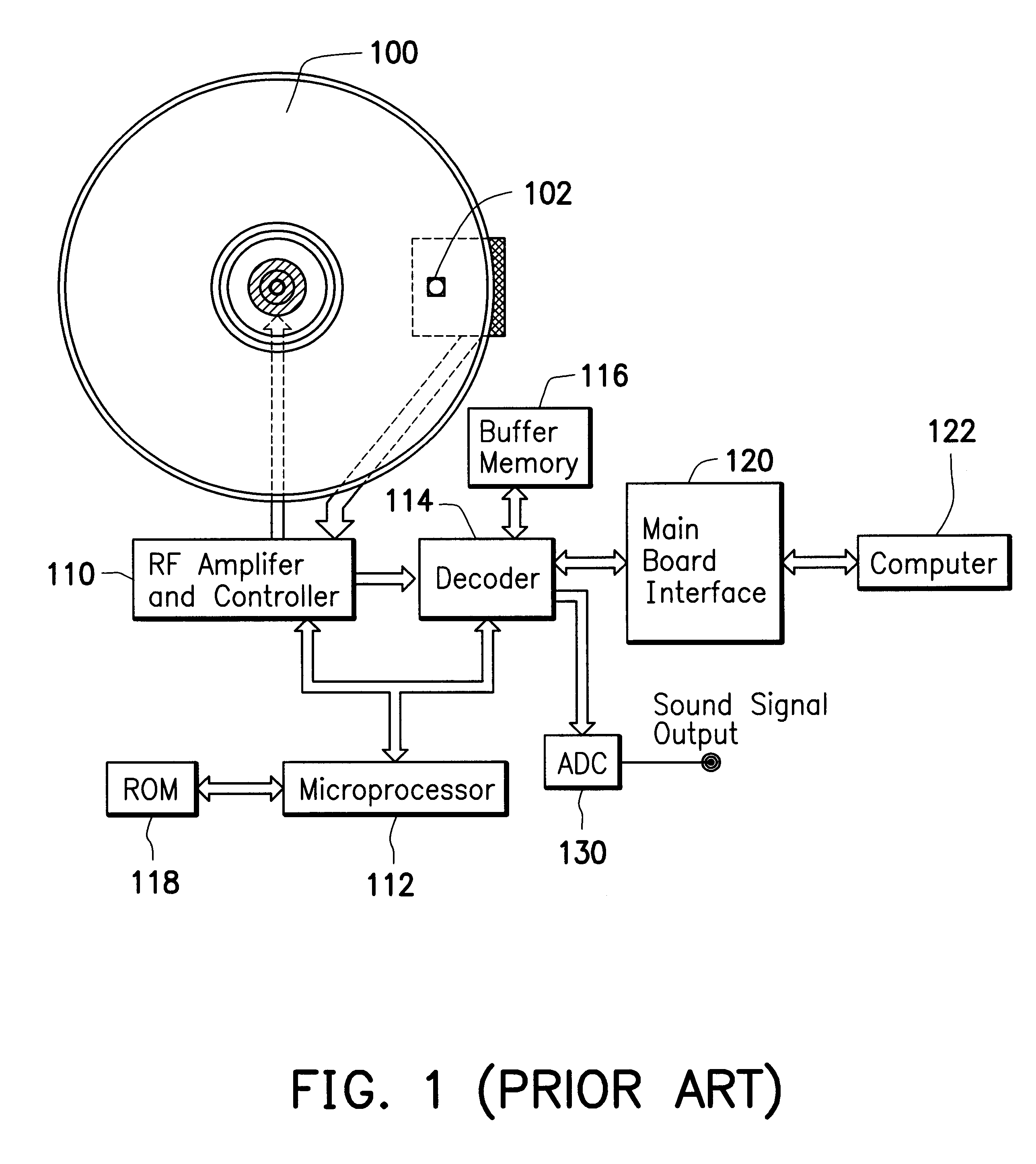
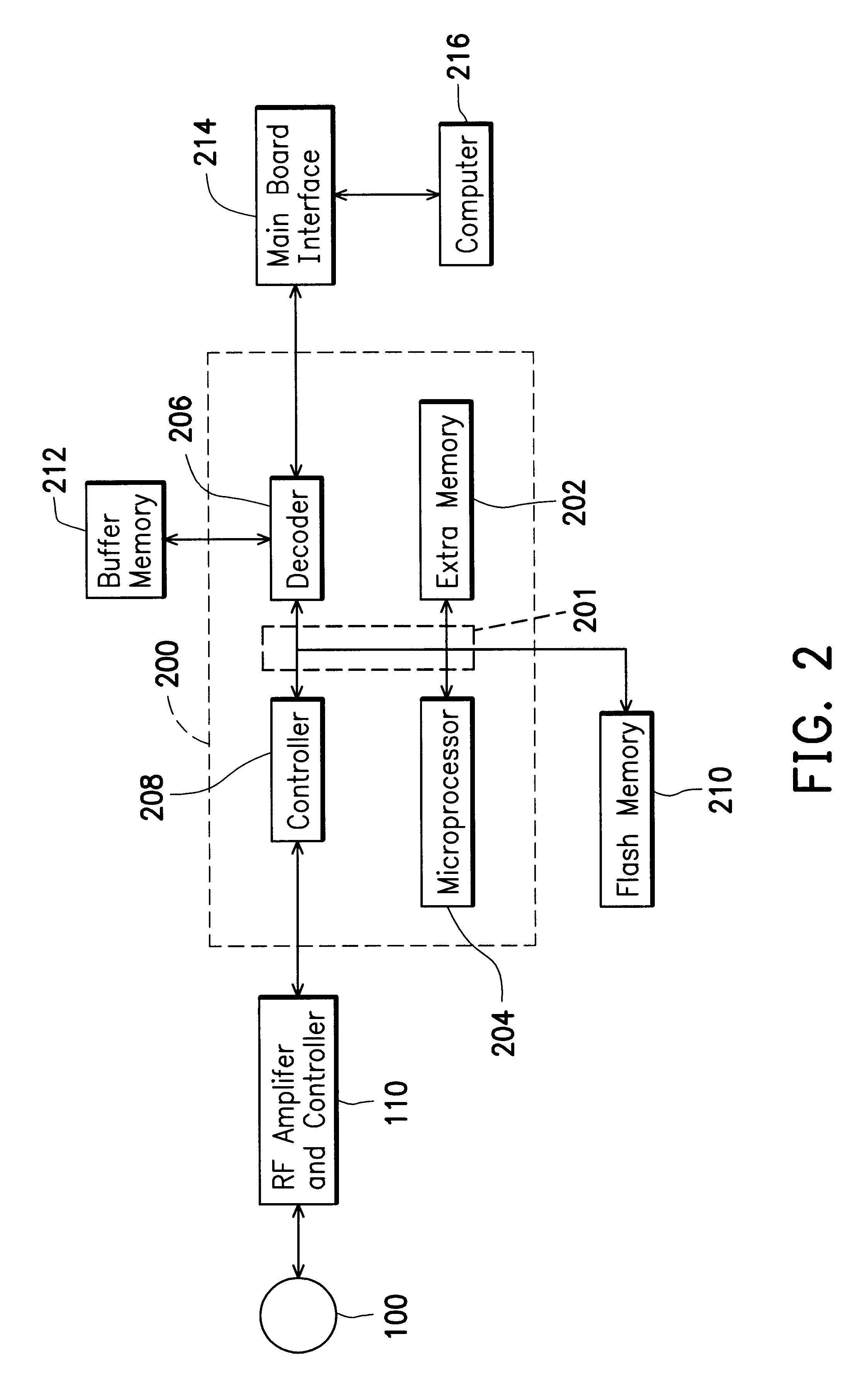
A CD-ROM control chip is provided for a use of firmware information update in the CD-ROM system. The control chip at least includes a microprocessor, a decoder, a controller, and an extra memory. The microprocessor is coupled to a data bus, and further coupled to an external ROM, which stores all firmware information. The decoder is coupled to the microprocessor through the data bus, and is also coupled to an external buffer memory and an external main board interface. The external main board interface allows the CD-ROM control chip to communicate with an external computer. The controller is coupled to the decoder, and is coupled to the microprocessor the data bus. The controller is used to receive information and control signals from an external CD. The extra memory is coupled to the microprocessor through the data bus. When the microprocessor starts to update the firmware information, it generates at least one output enabling signal, one chip selecting signal, and one writing-in signal, and sends these signals to the external ROM. The external ROM is treated as an information storing space, and the extra memory is treated as execution space used by an update program routine.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
Method for driving electro-optic displays
ActiveUS20110187689A1Reduce widthCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingChip selectDisplay device
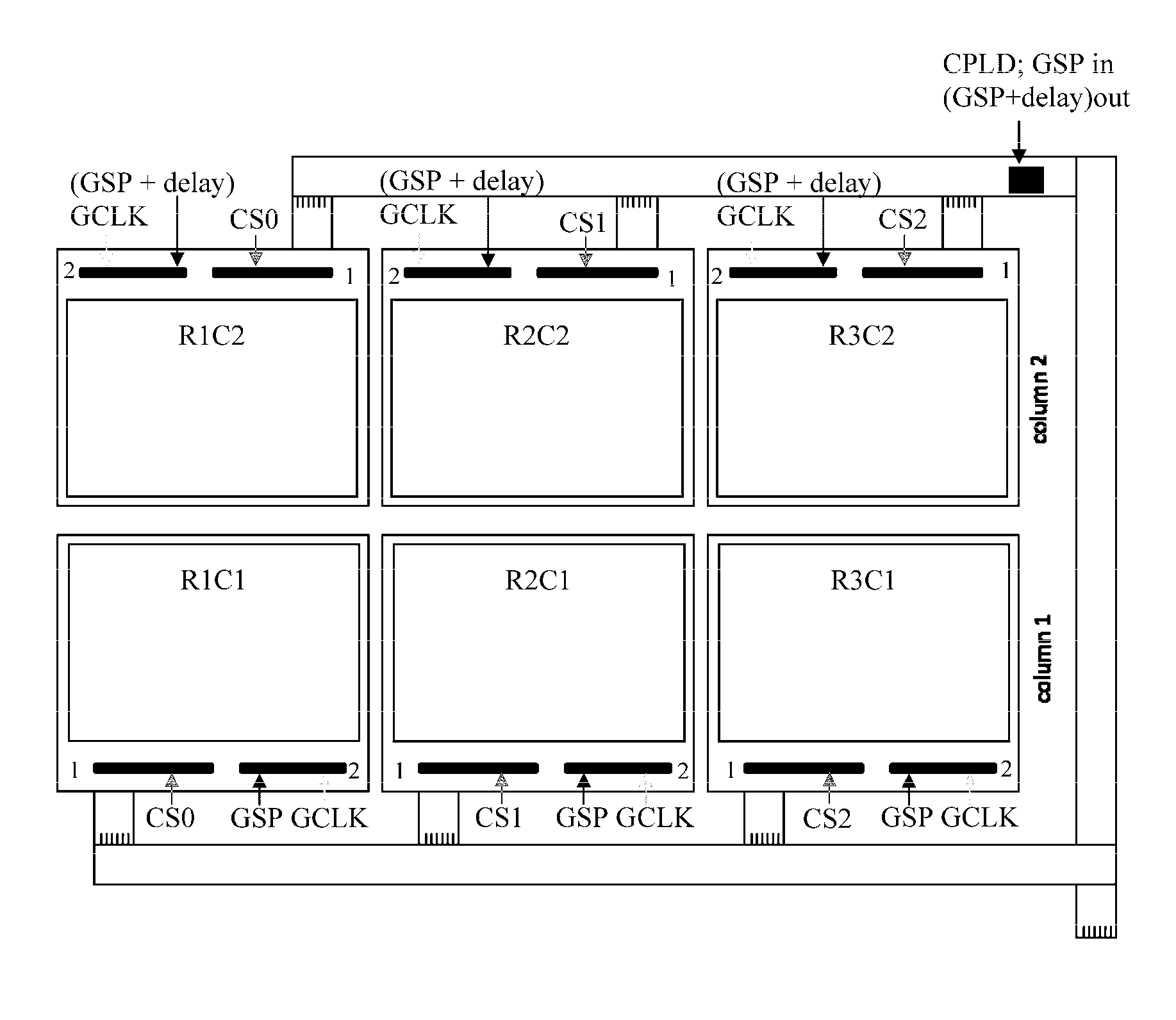
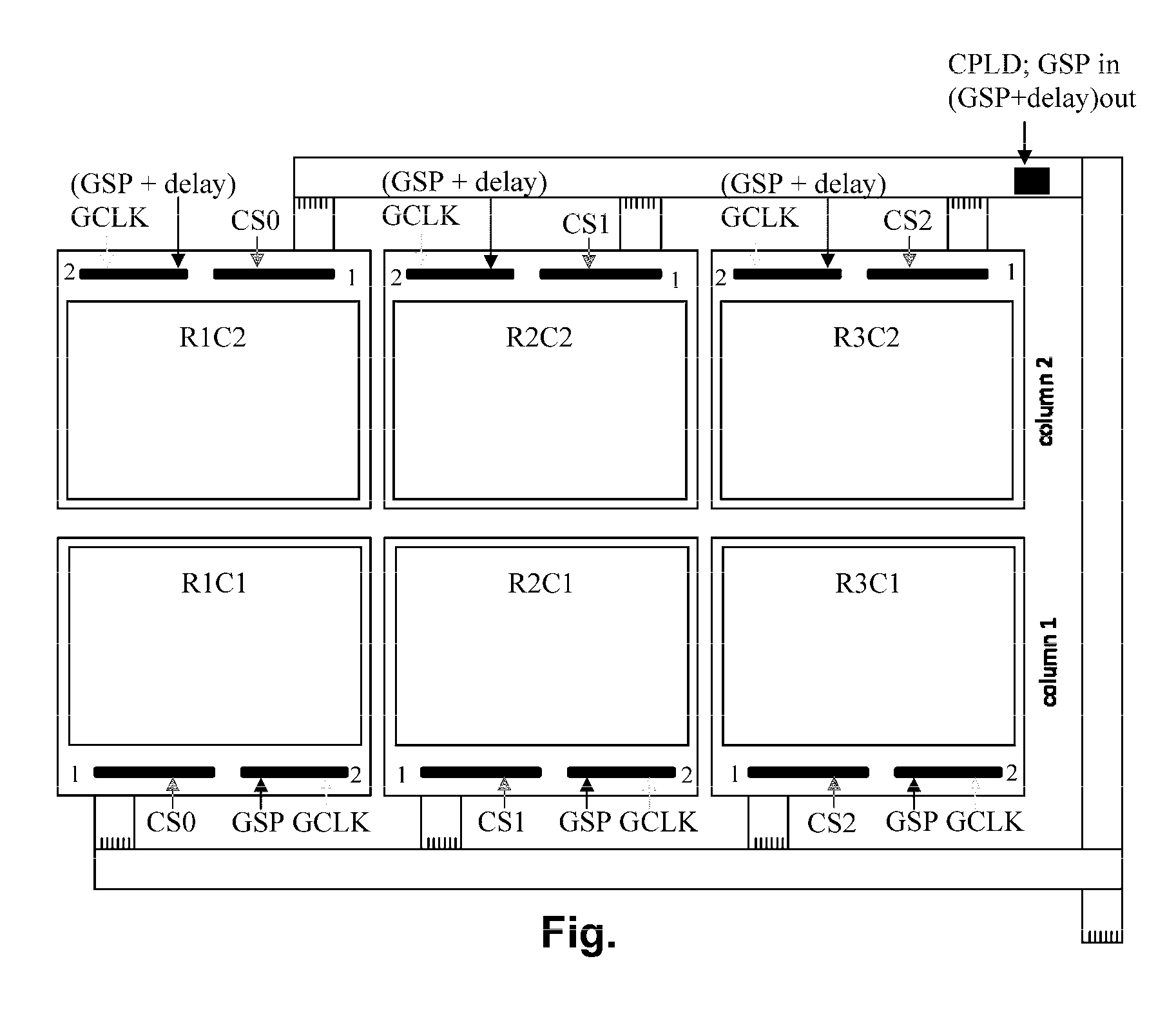
A large area display comprises multiple sub-units arranged in rows and columns. Each sub-unit has associated row and column drivers, with the column driver driving the column electrodes of all the sub-units a column. A chip select means provides a separate chip select signal to each row of sub-units, so that only one row of sub-units are scanned at a time, and all the sub-units in the selected row are scanned simultaneously. Column data are supplied to the column drivers as a linear series of column data values; and delayed Gate Start Pulse signals are fed to the column drivers in each column of sub-units after the first so that these column drivers receive the delayed Gate Start Pulse signals and apply the appropriate column data values to their associated column electrodes.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
Wafer level stacked packages with individual chip selection
ActiveUS20090039528A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringElectronic component
A method is provided for fabricating a stacked microelectronic assembly by steps including stacking and joining first and second like microelectronic substrates, each including a plurality of like microelectronic elements attached together at dicing lanes. Each microelectronic element has boundaries defined by edges including a first edge and a second edge. The first and second microelectronic substrates can be joined in different orientations, such that first edges of microelectronic elements of the first microelectronic substrate are aligned with second edges of microelectronic elements of the second microelectronic substrate. After exposing traces at the first and second edges of the microelectronic elements of the stacked microelectronic substrates, first and second leads can be formed which are connected to the exposed traces of the first and second microelectronic substrates, respectively. The second leads can be electrically isolated from the first leads.
Owner:TESSERA INC
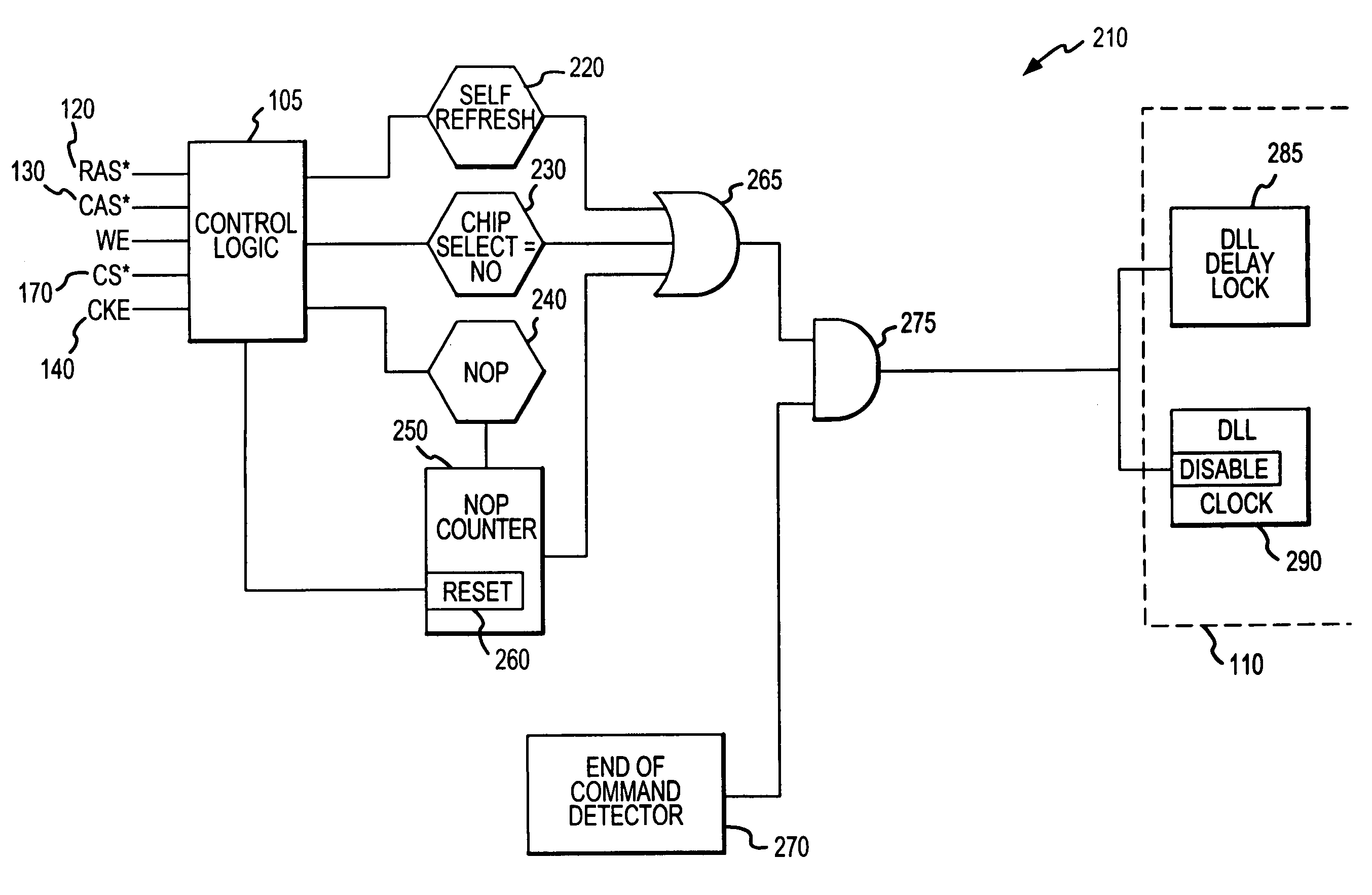
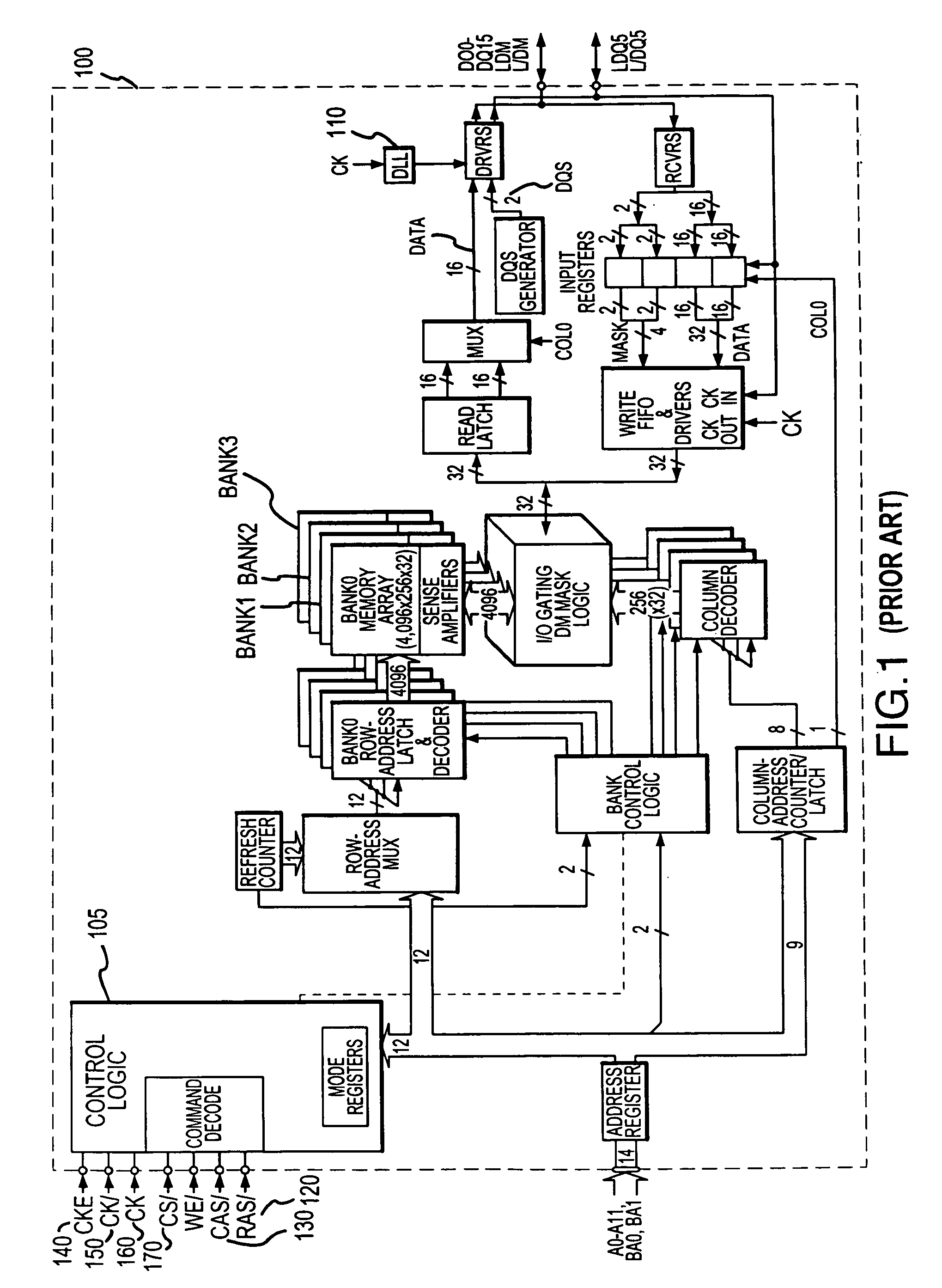
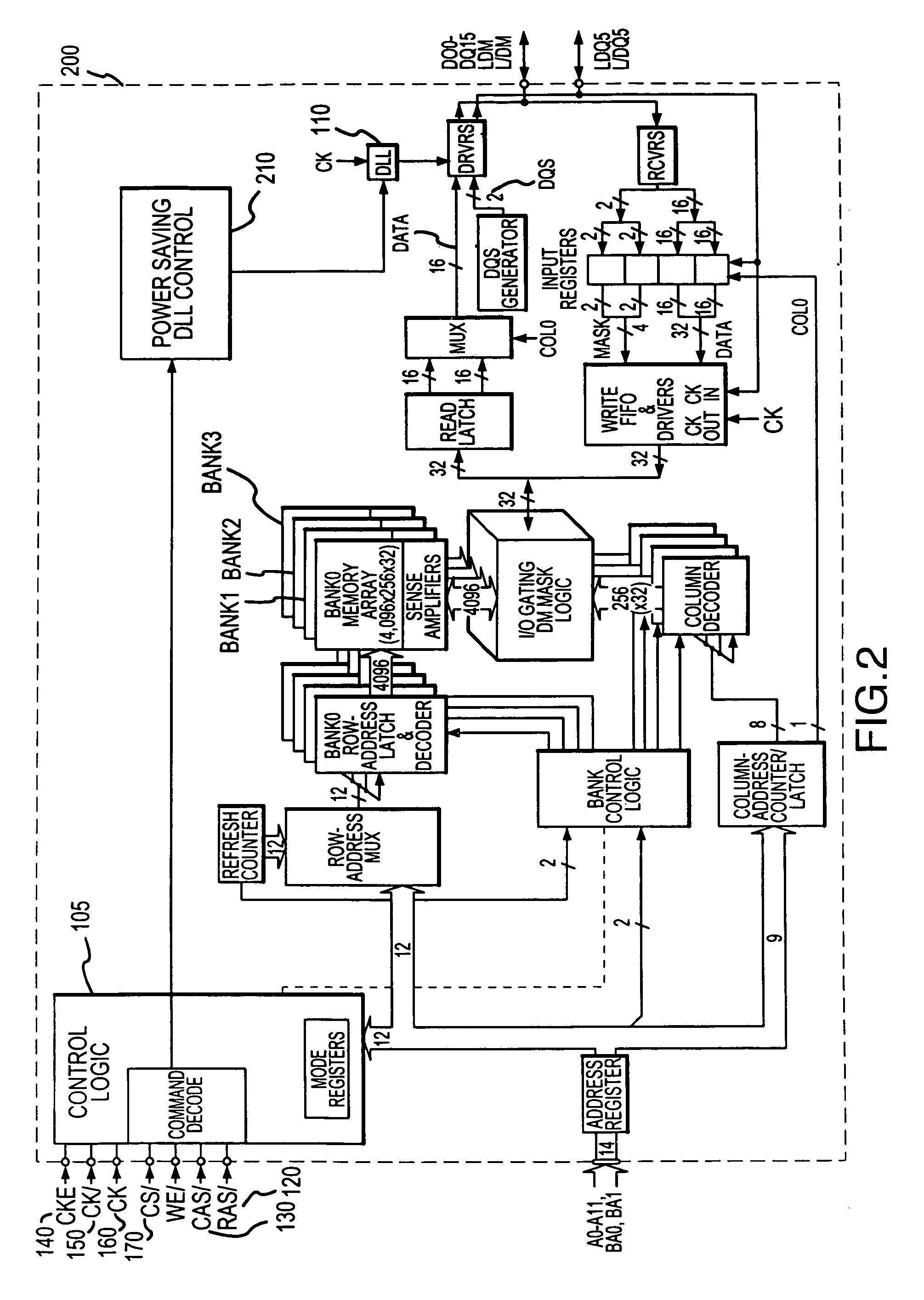
System and method for power saving delay locked loop control by selectively locking delay interval
The delay locked loop (“DLL”) delay interval can be locked to stop the DLL from wasting power in unnecessarily switching to synchronize the device with the DLL is associated to the system clock. This is achieved by adding logic sensing when a DRAM device will not imminently be called upon to output data and when the device has stabilized. Waiting for the DLL delay interval to stabilize before locking the delay interval still allows the DLL to immediately and effectively resume operations when the DLL is needed to synchronize the output of the DRAM device with the system clock. The DLL delay interval can be locked, together with the DLL clock, after the DRAM device is deselected by the chip select control line, after a number of no operation commands have been received, and / or after any command issued to the DRAM device has been completed.
Owner:ROUND ROCK RES LLC
Light emitting diode illuminating apparatus with same-type light emitting diodes
InactiveUS20100001299A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor devices for light sourcesPhosphorChip select
A light emitting diode illuminating apparatus for emitting colorful light includes a substrate, a first lighting element, a second lighting element, a third lighting element. The first, second and third lighting elements are juxtaposed at the substrate. The first lighting element includes a first LED chip, and a first filling layer encapsulating it. The first filling layer includes red phosphor generally evenly doped therein. The second lighting element includes a second LED chip and a second filling layer encapsulating it. The third lighting element includes a third LED chip and a third filling layer encapsulating it. All of the first, the second and the third LED chips are the same kind of LED chip selected from the group consisting of GaN LED chips, AlGaN LED chips and InGaN LED chips. Light emitting from the filling layers are capable of mixing to produce light of a uniform color.
Owner:ADVANCED OPTOELECTRONICS TECH
Memory module with dynamic termination using bus switches timed by memory clock and chip select
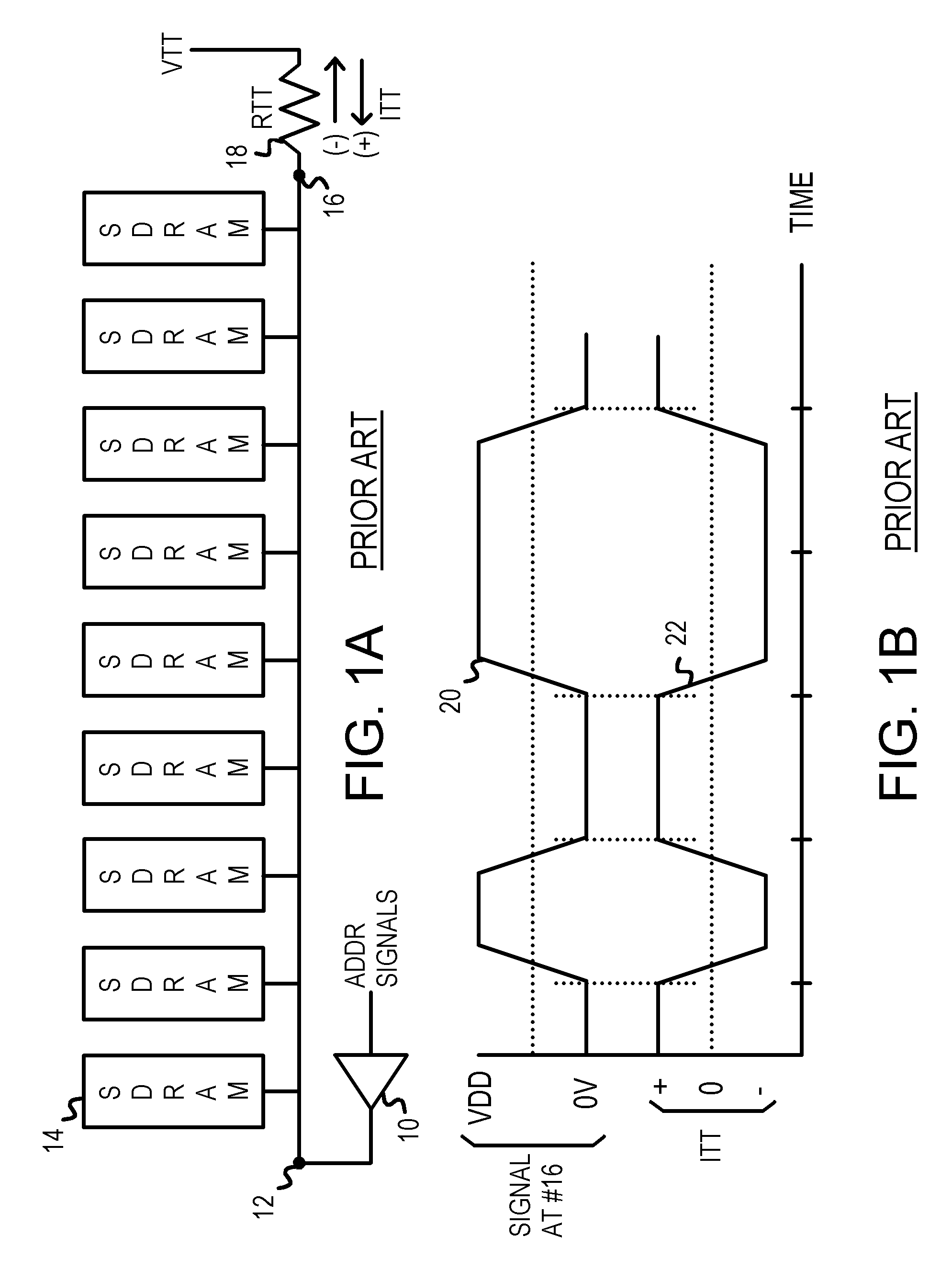
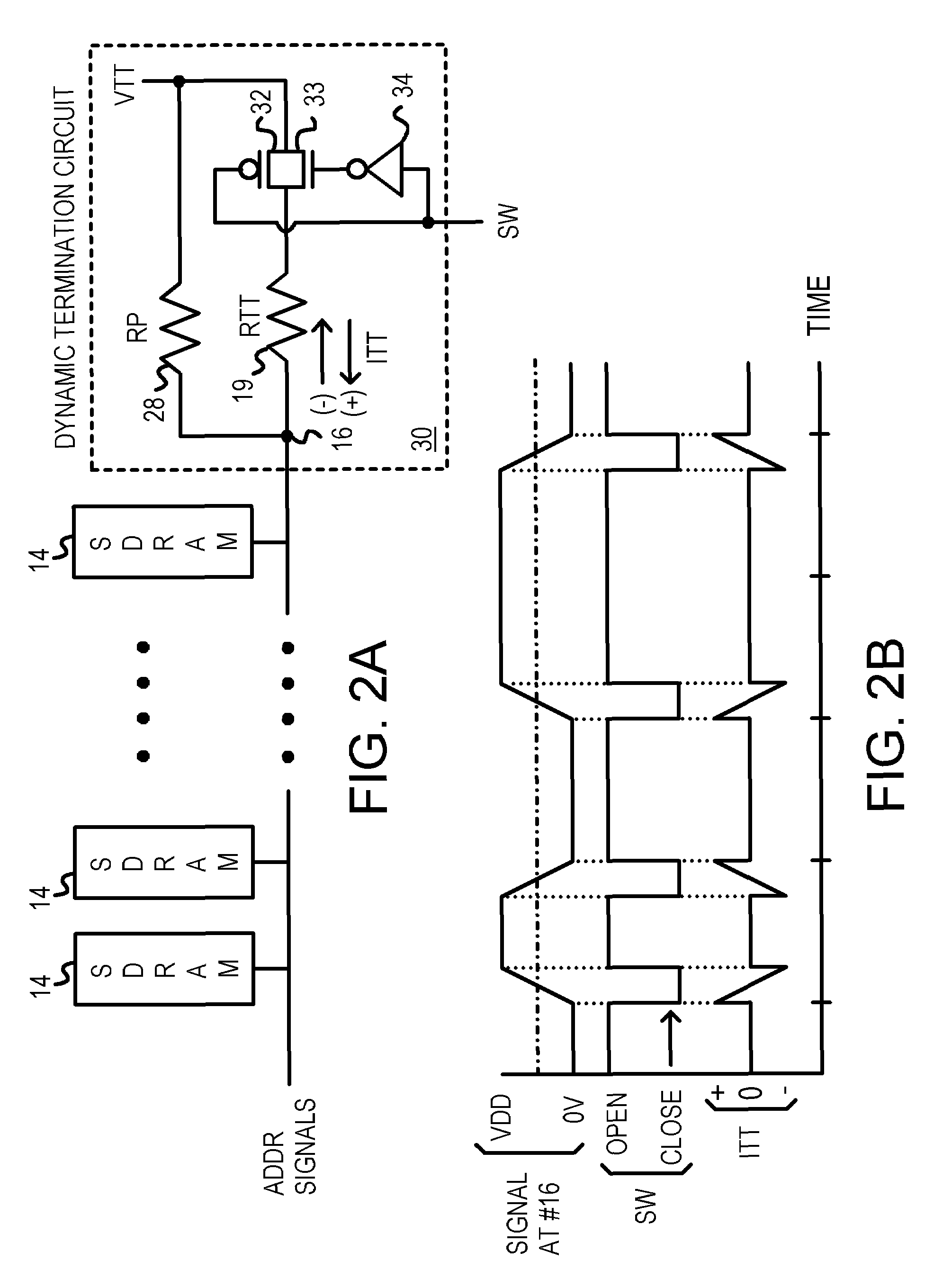
InactiveUS7068064B1Energy efficient ICTReliability increasing modificationsTransmission gateChip select
A low-power memory module has an active termination circuit at each end of critical signal traces. The dynamic termination circuit has a low-value resistor that is connected to a termination voltage by a transmission gate that is turned on by a switch signal. The switch signal is activated when the memory module is selected by a chip-select signal, and when a time window is open. The time window is generated from the clock to synchronous DRAMs on the memory module. The time window can be one-quarter of the clock period by ANDing the clock and a delayed clock that is delayed by one-quarter of a cycle. A static terminating resistor in parallel with the low-value resistor provides a much smaller terminating current that is not switched on and off. Traces can be impedance-matched at junctions to branches that each has a dynamic termination circuit at the far end.
Owner:DIODES INC
Using chip select to specify boot memory
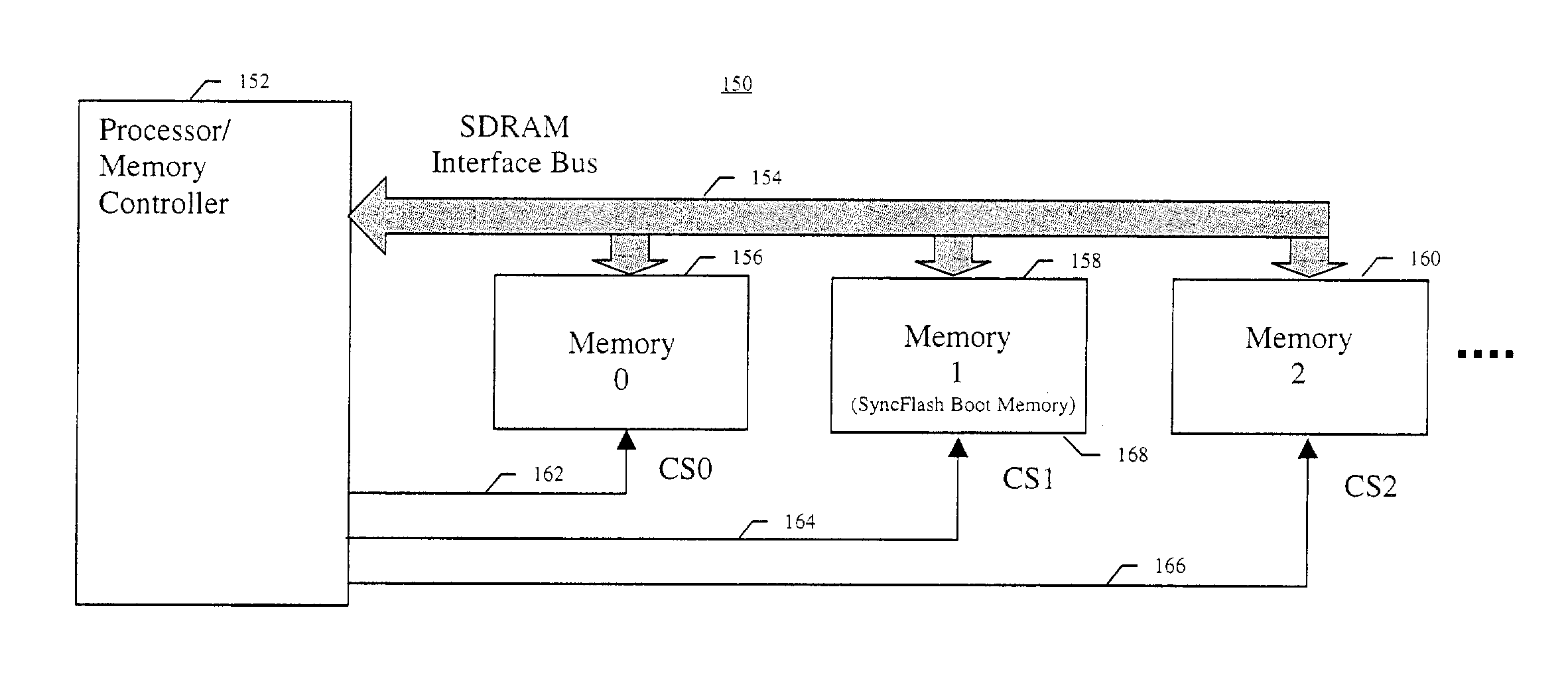
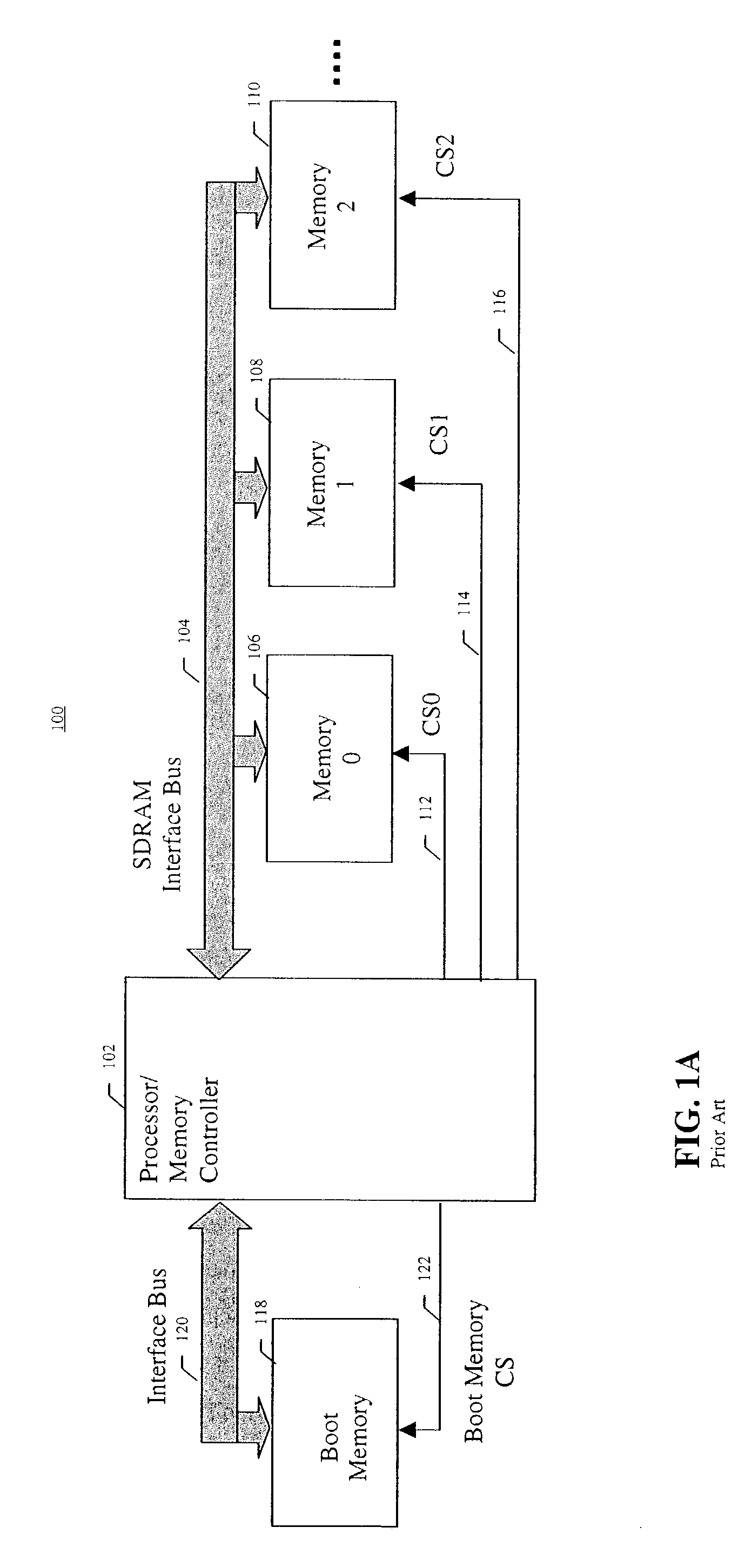
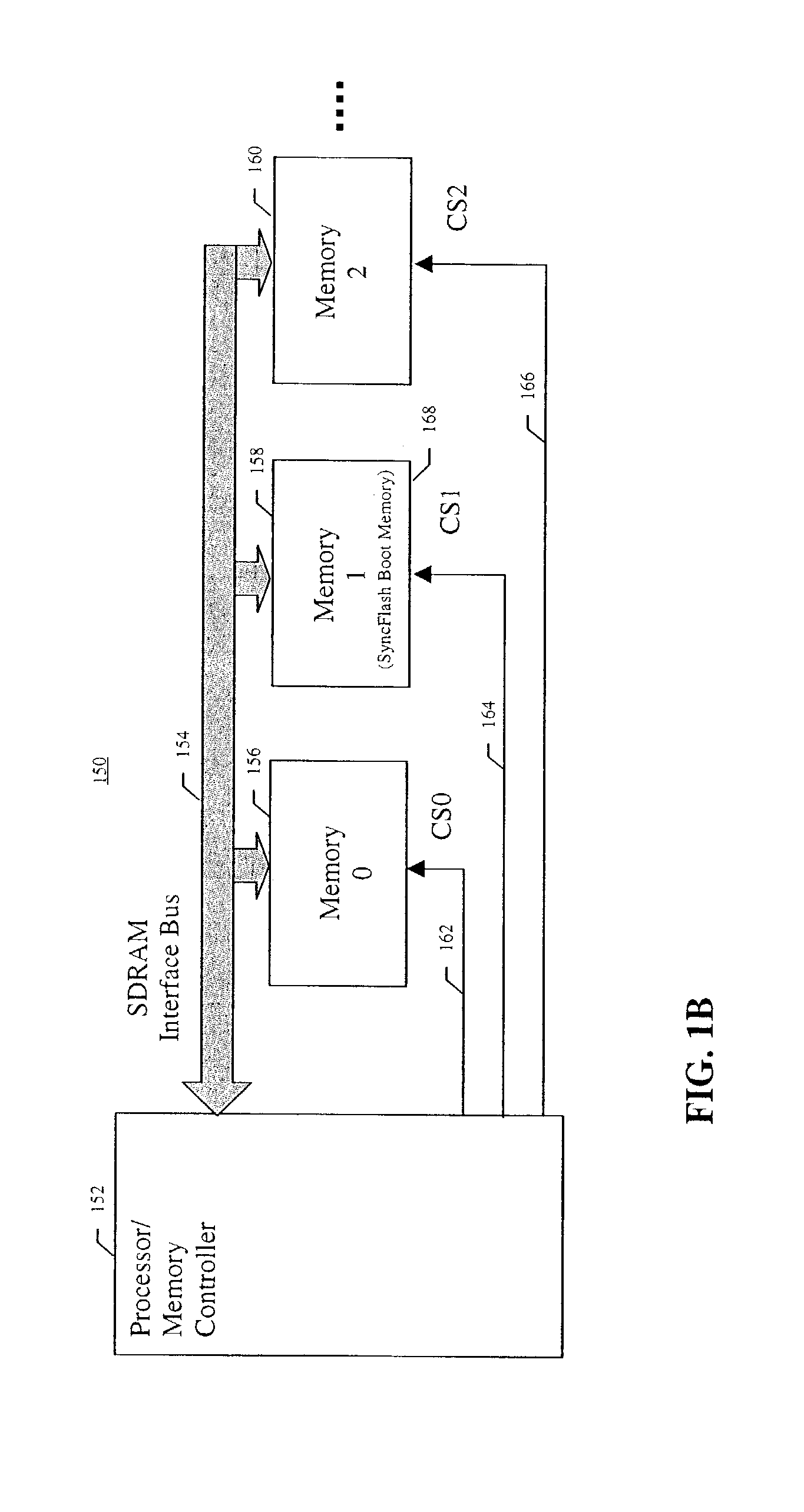
ActiveUS7272709B2Memory adressing/allocation/relocationDigital computer detailsChip selectPredictability
A synchronous Flash memory device is described that enhances initialization and boot memory device identification in synchronous memory systems. A boot memory is typically a separate device that is tied to a specific chip select line and / or address range of a system, whereas synchronous Flash memory generally can be placed in any available memory slot and assigned one of several possible chip selects and address ranges. This lack of predictability makes installing a boot memory based on a non-volatile synchronous memory device difficult. A synchronous Flash boot memory device of the detailed invention is adapted to identify itself and its chip select / address range to the memory controller at power up, reset, or upon receiving an identification request. This allows the utilization of the detailed synchronous Flash memory as a boot memory in synchronous systems where a reserved boot memory slot and / or chip select are not provided.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com