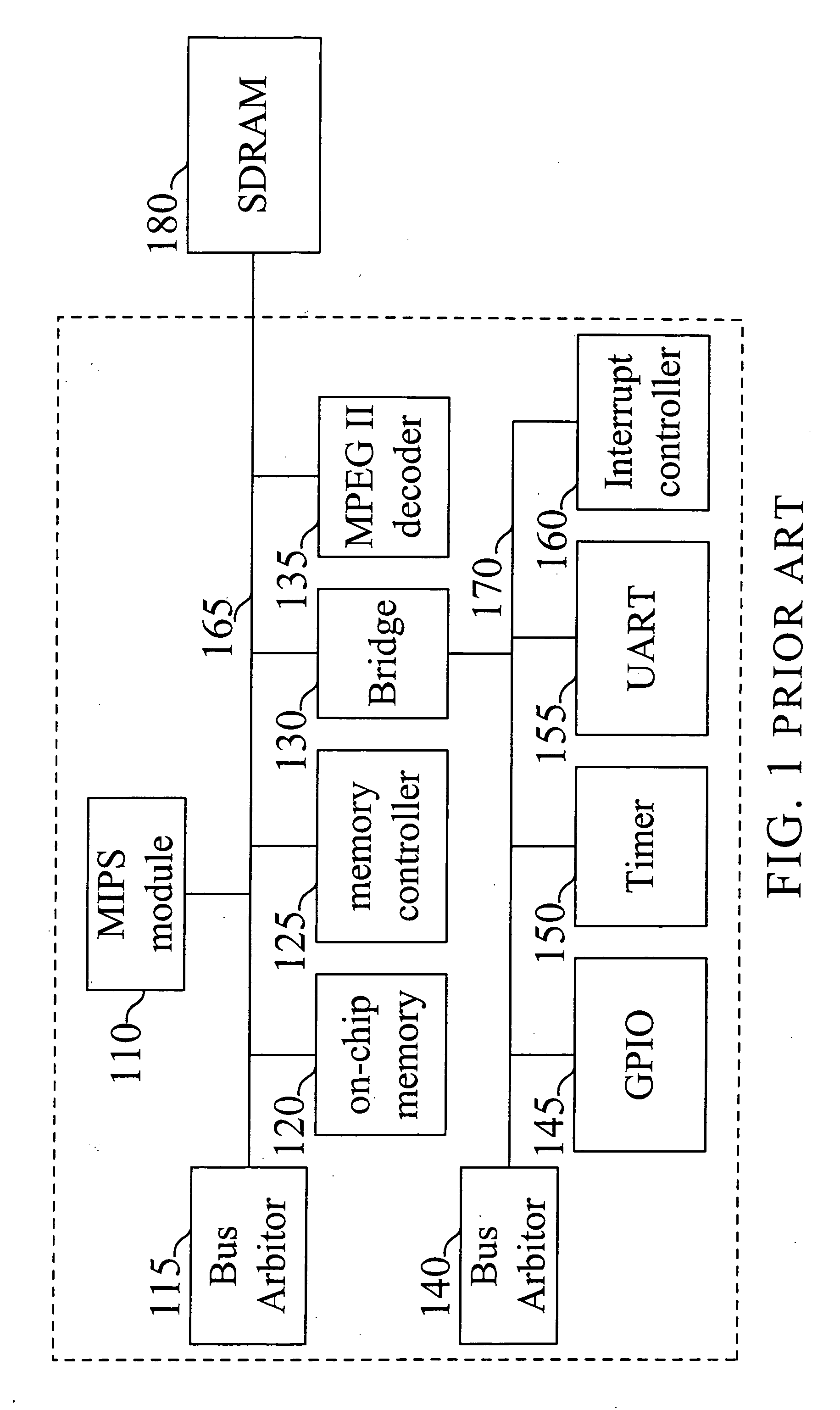
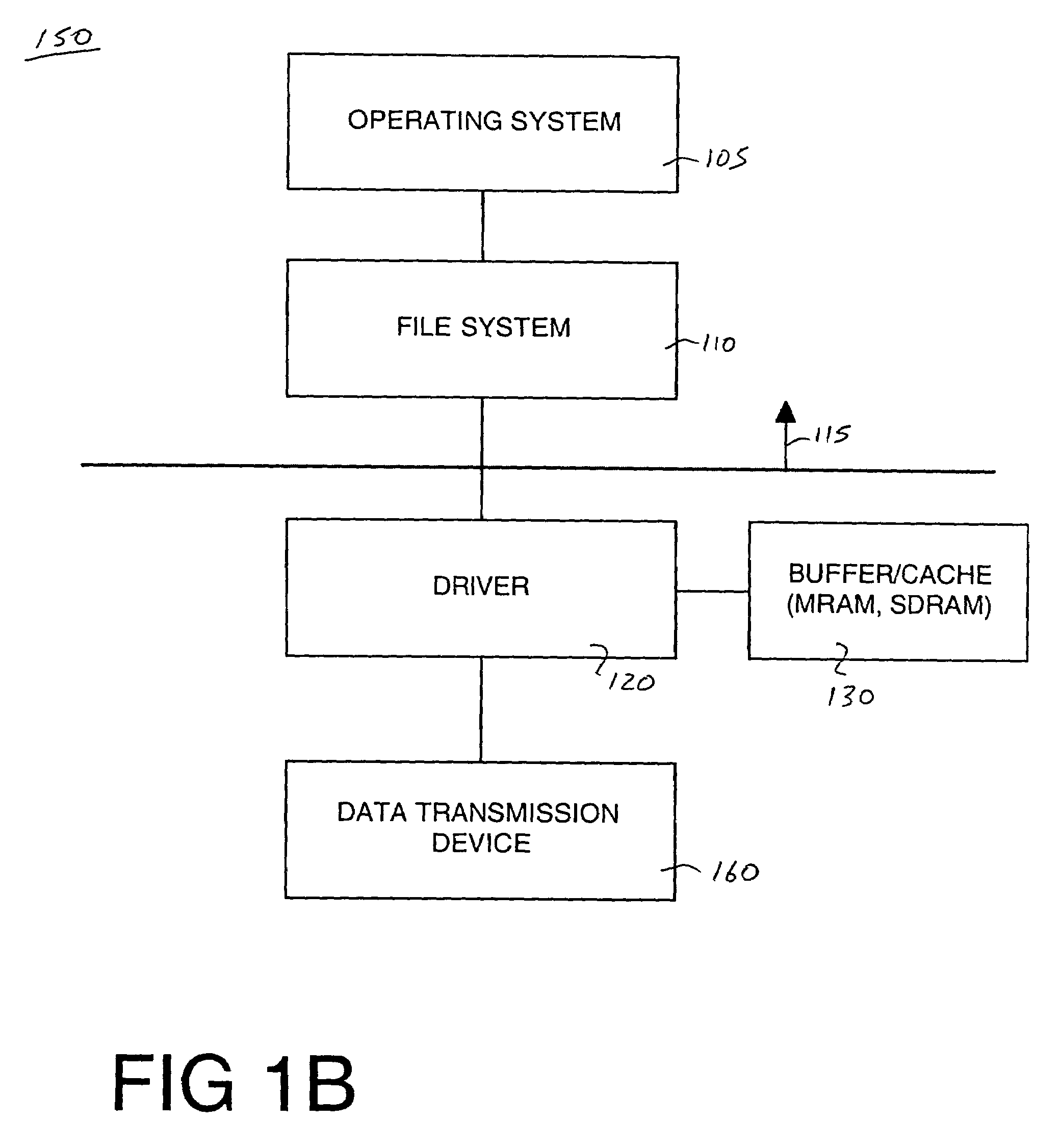
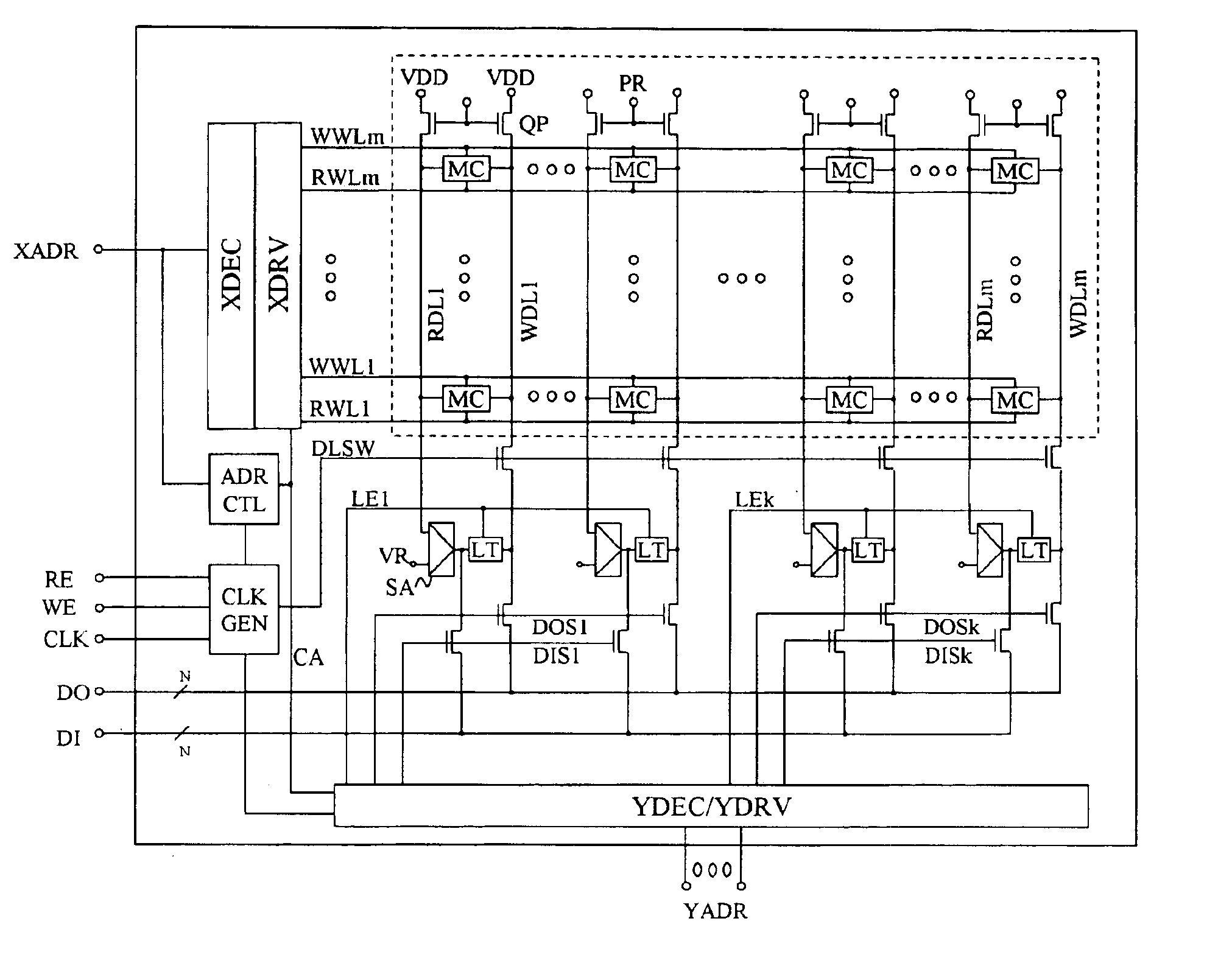
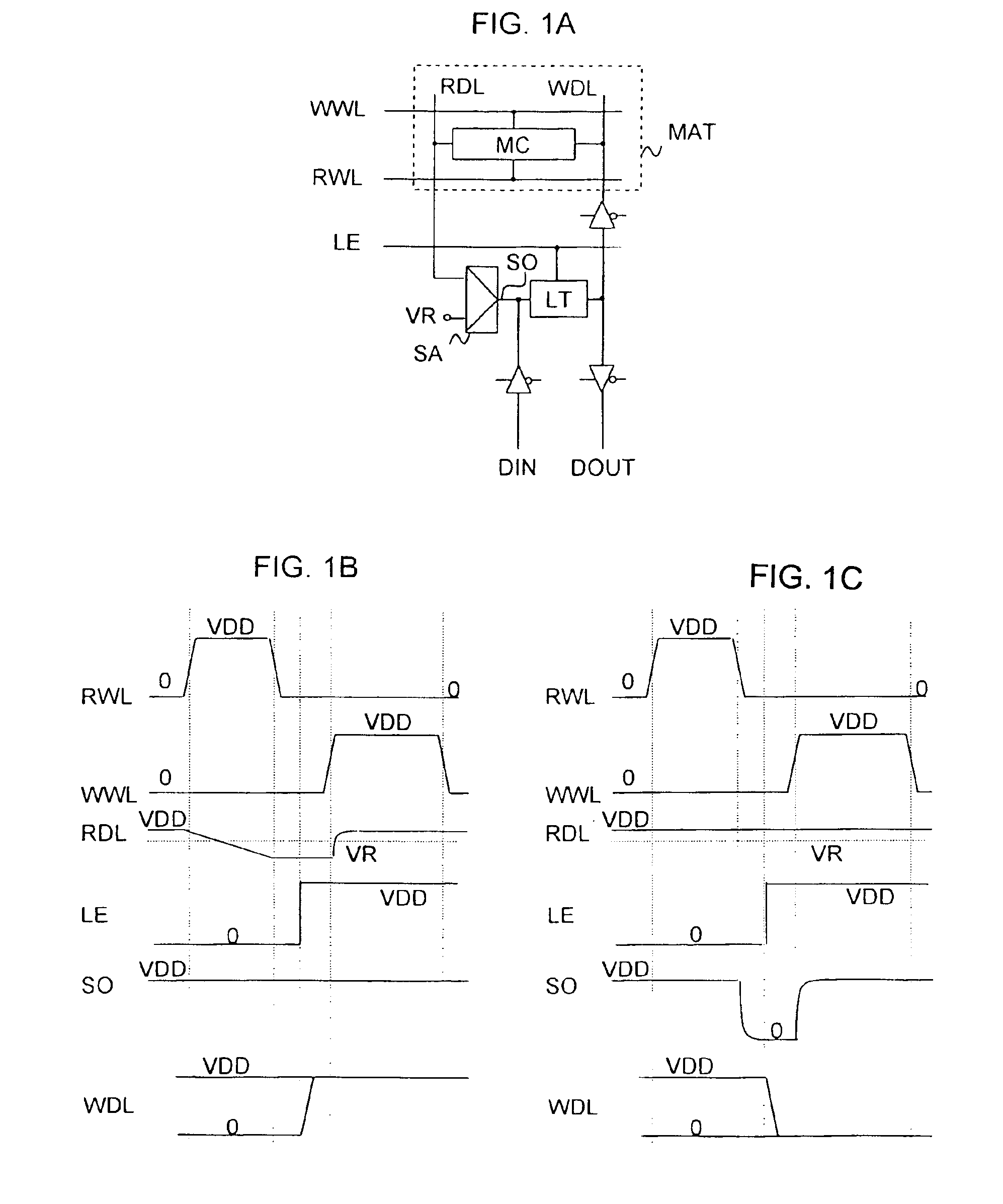
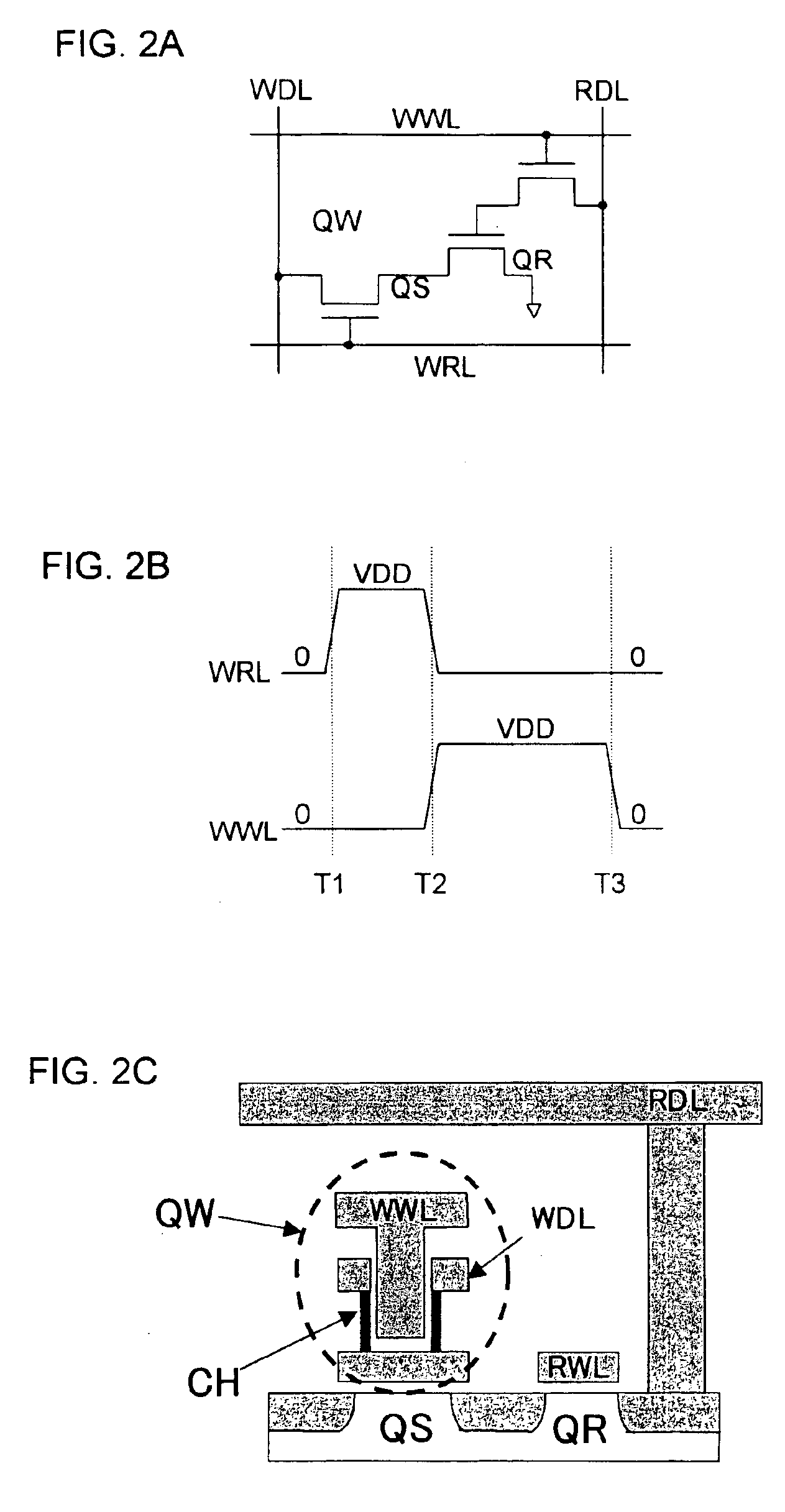
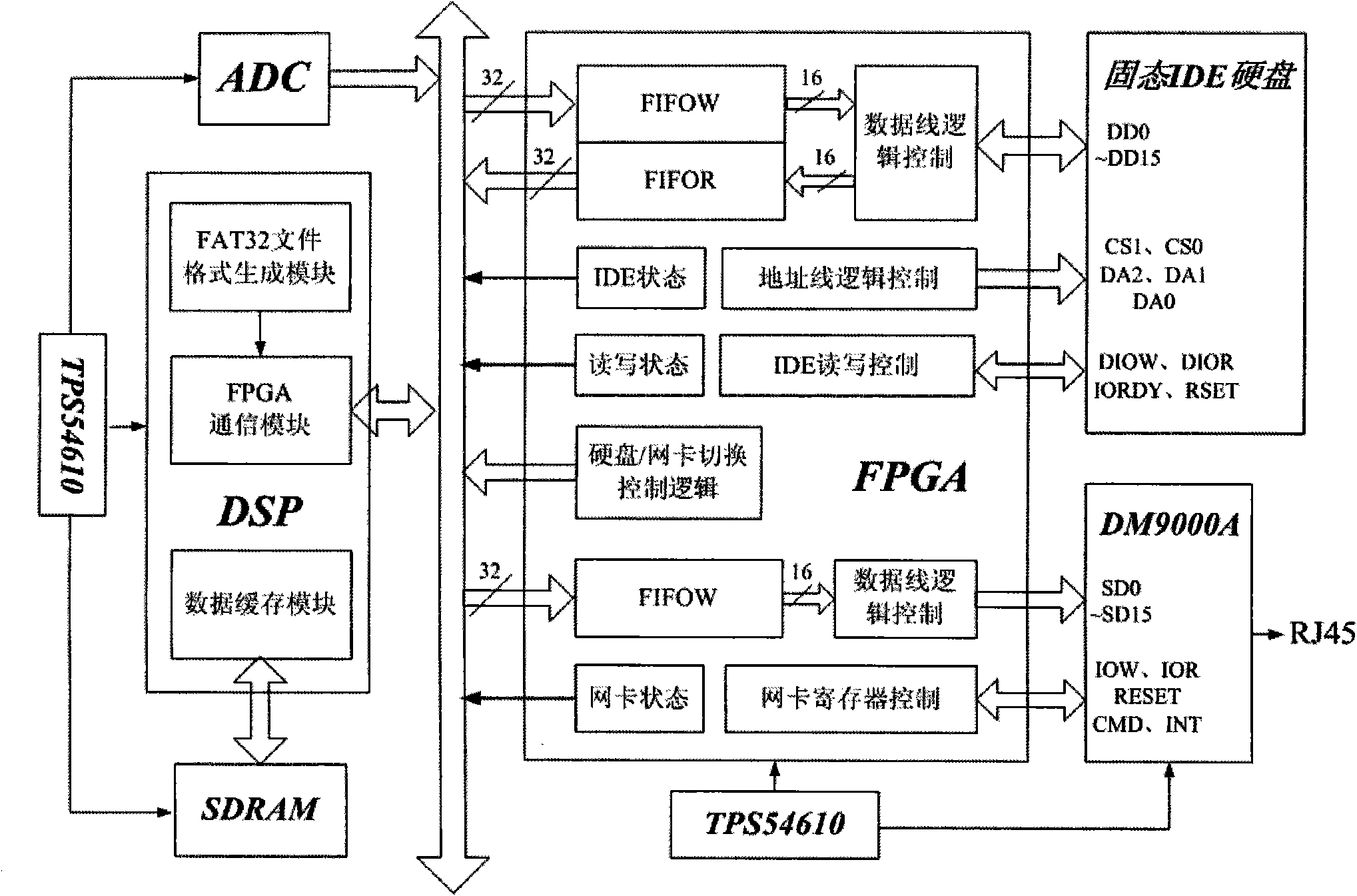
Patents
Literature
766 results about "Synchronous dynamic random-access memory" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
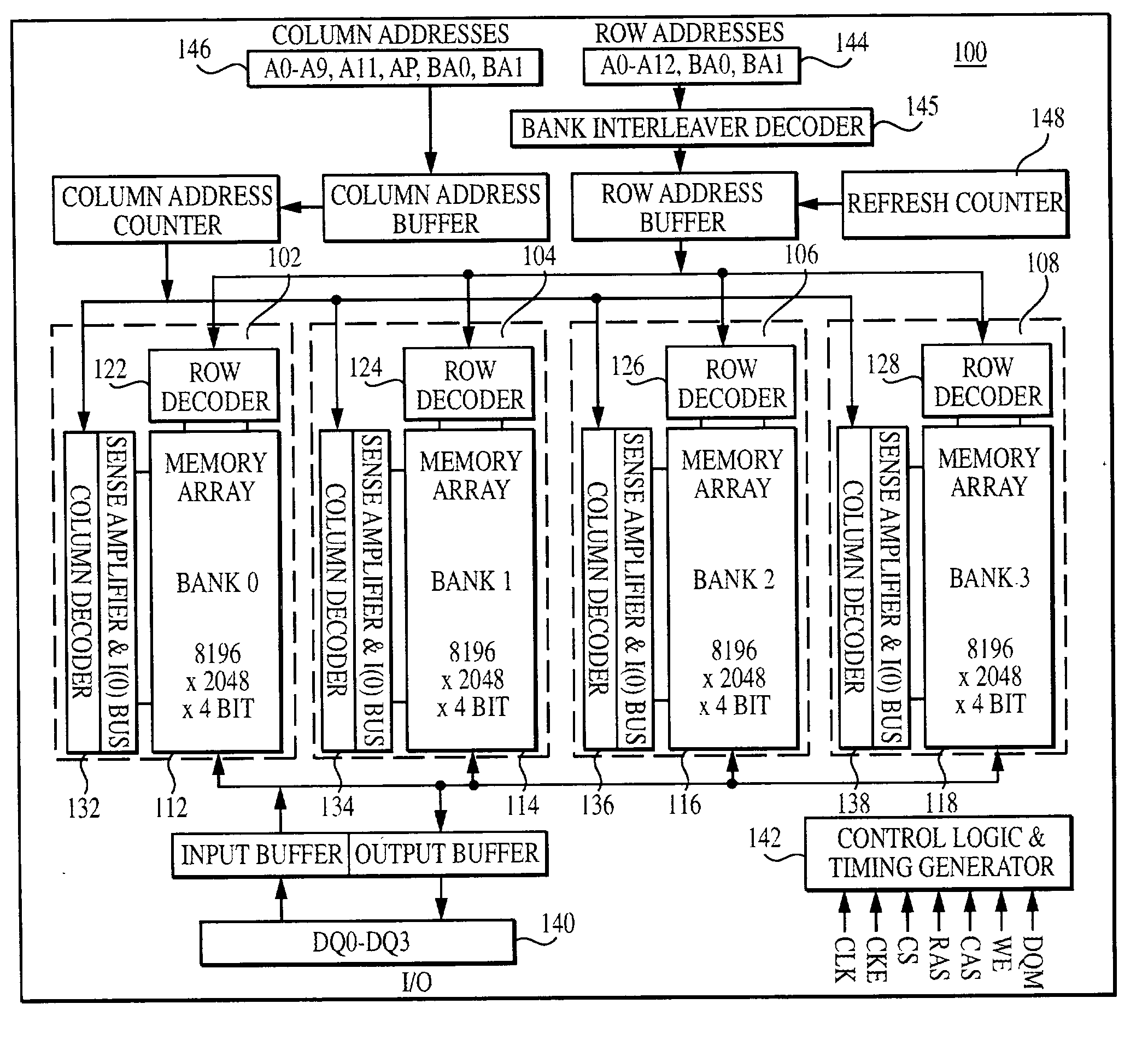
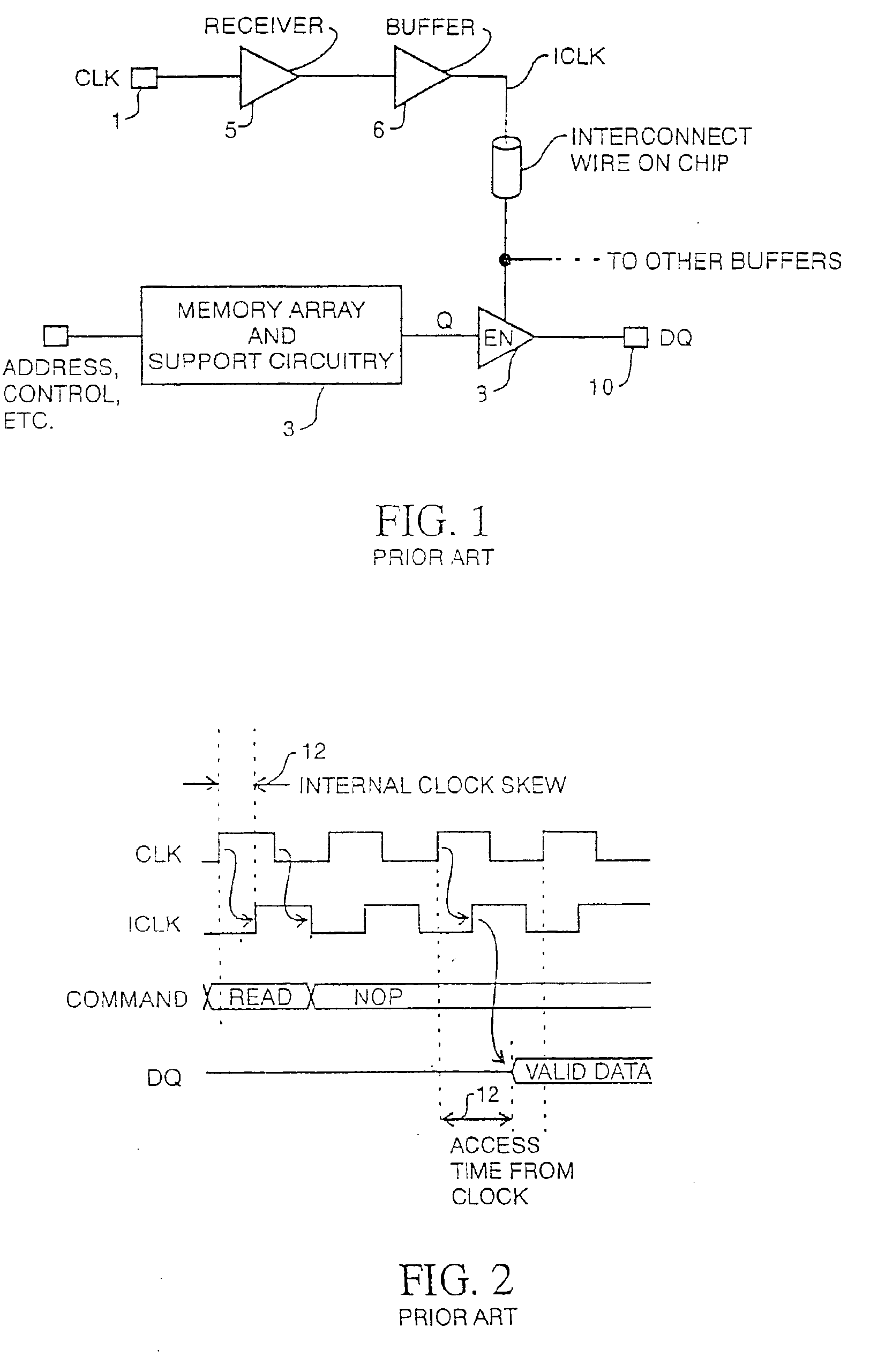
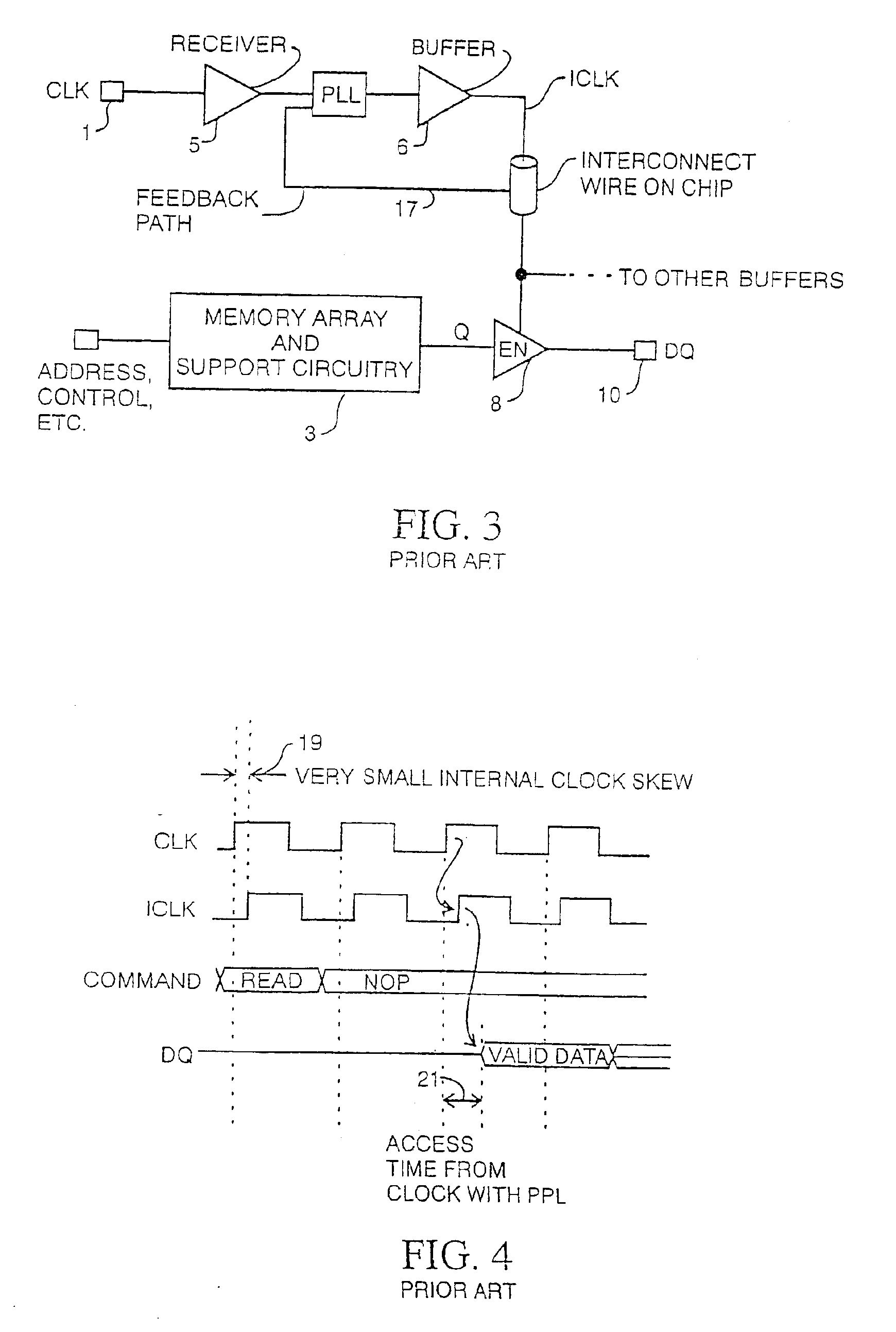
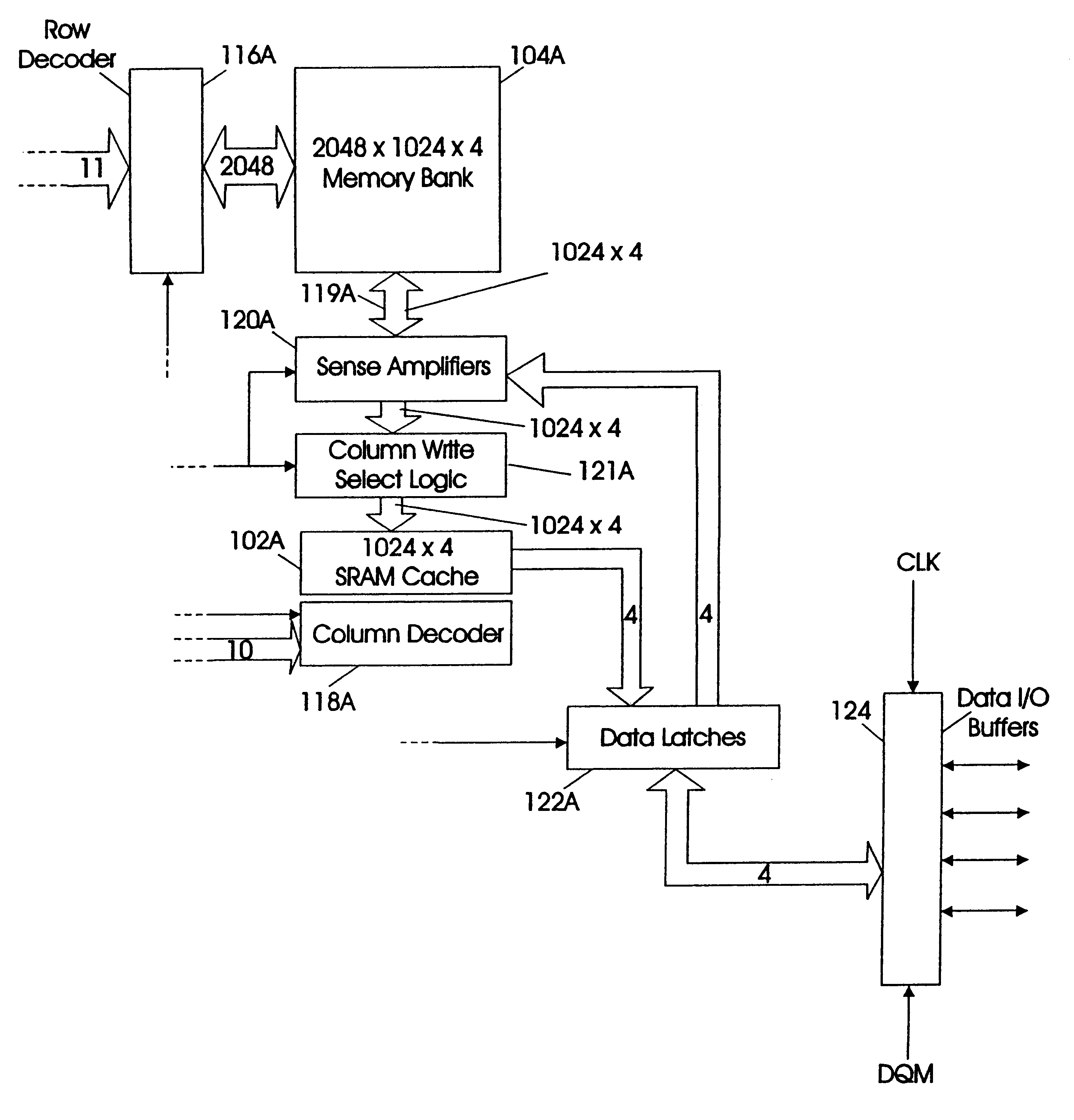
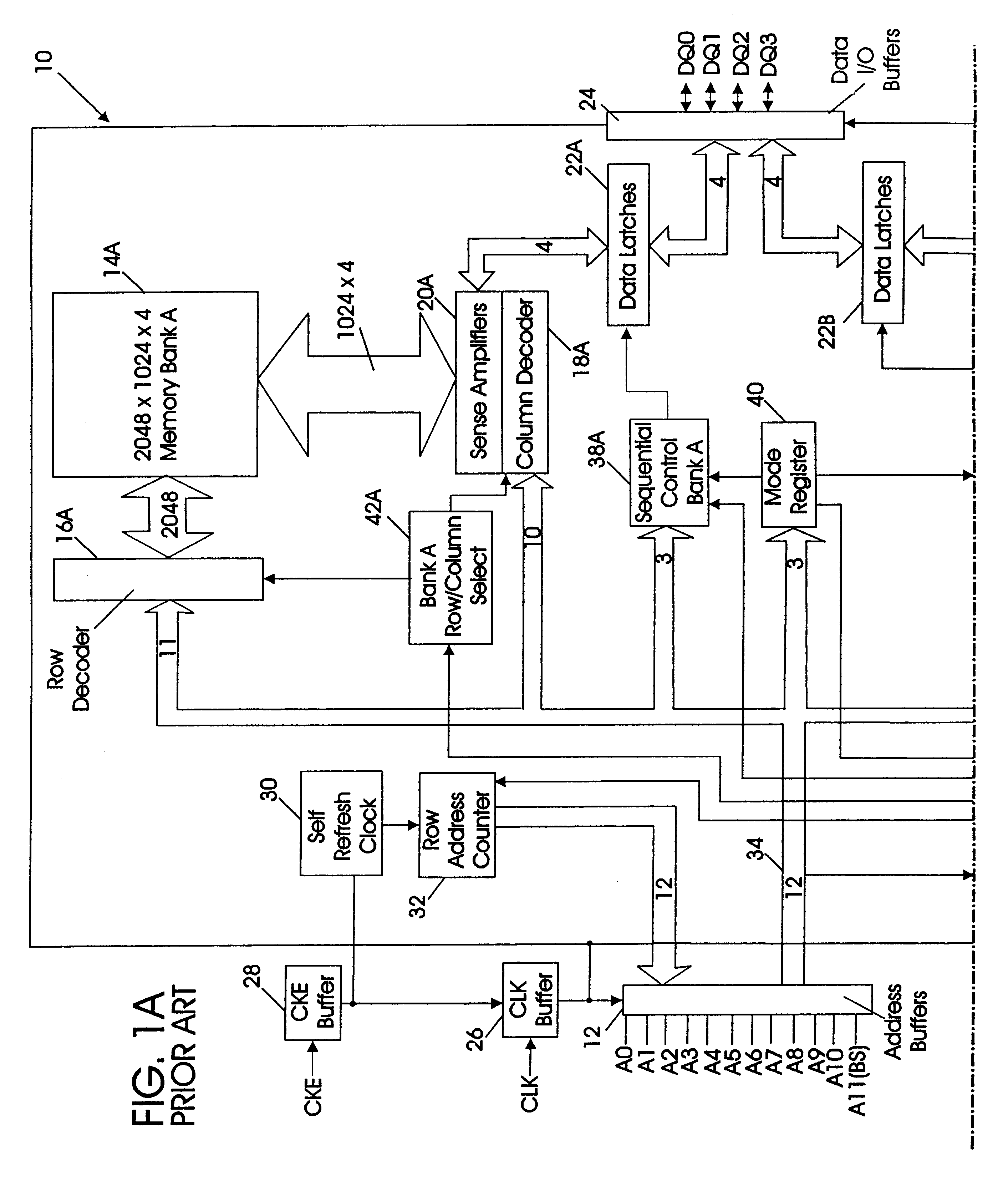
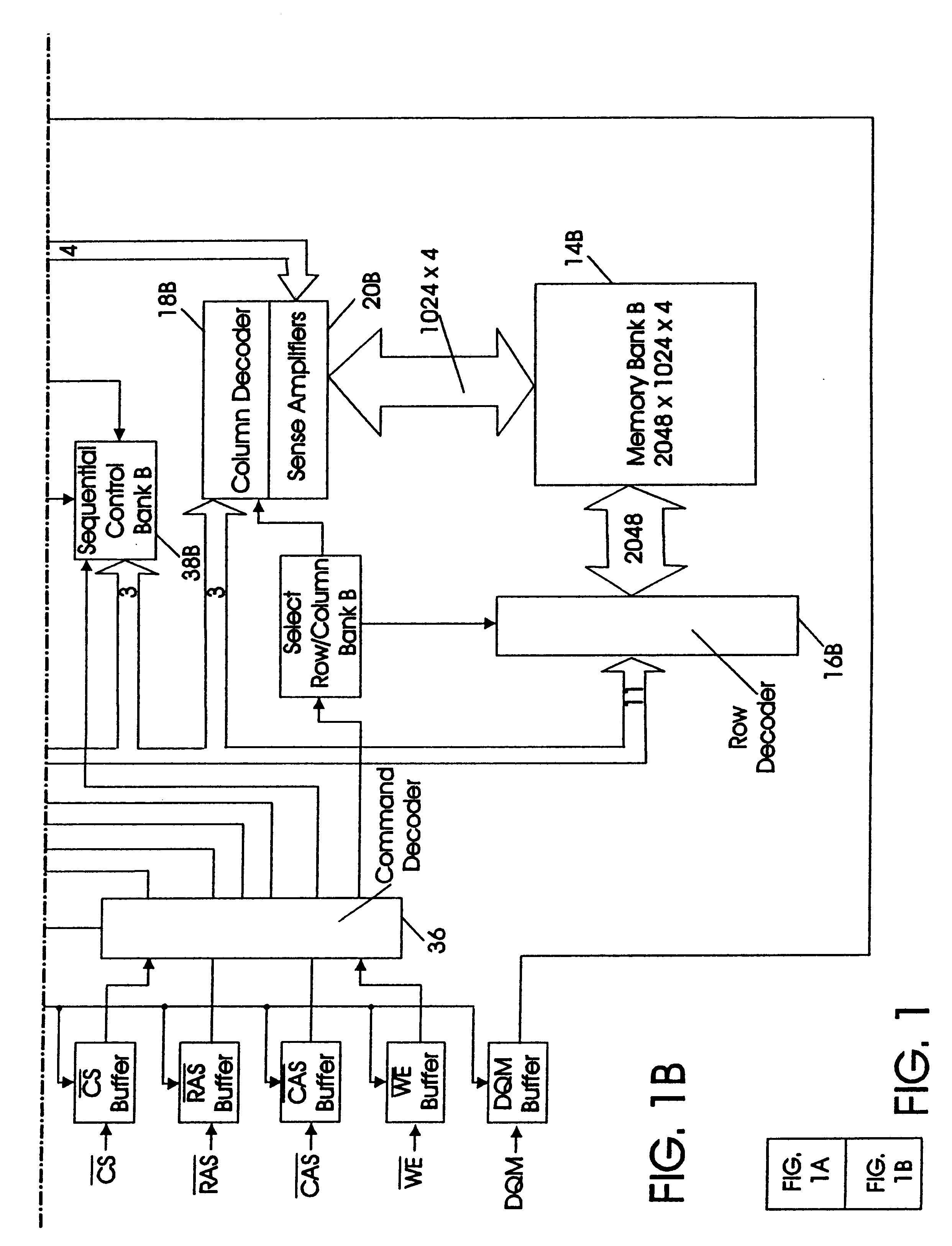
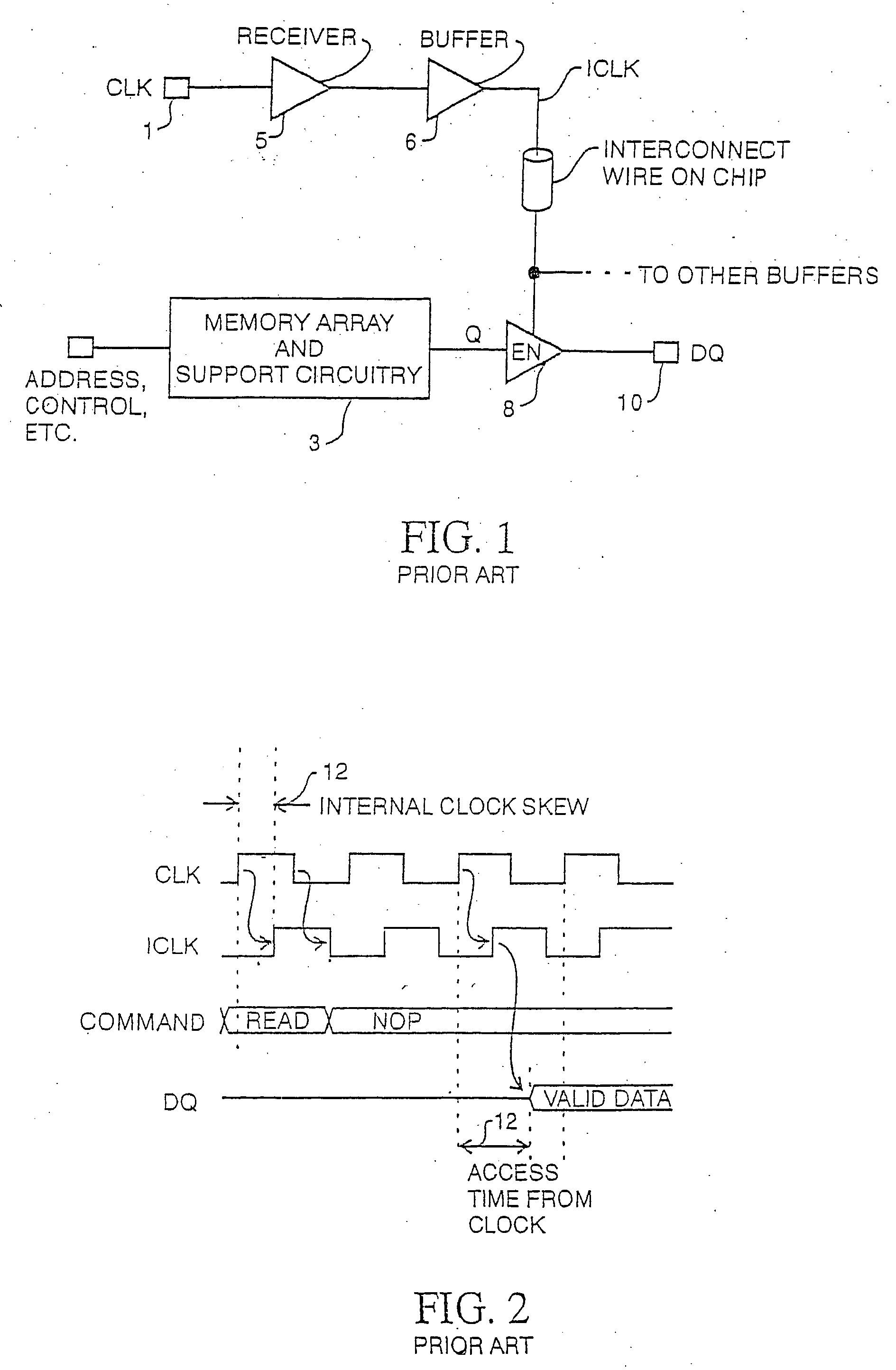
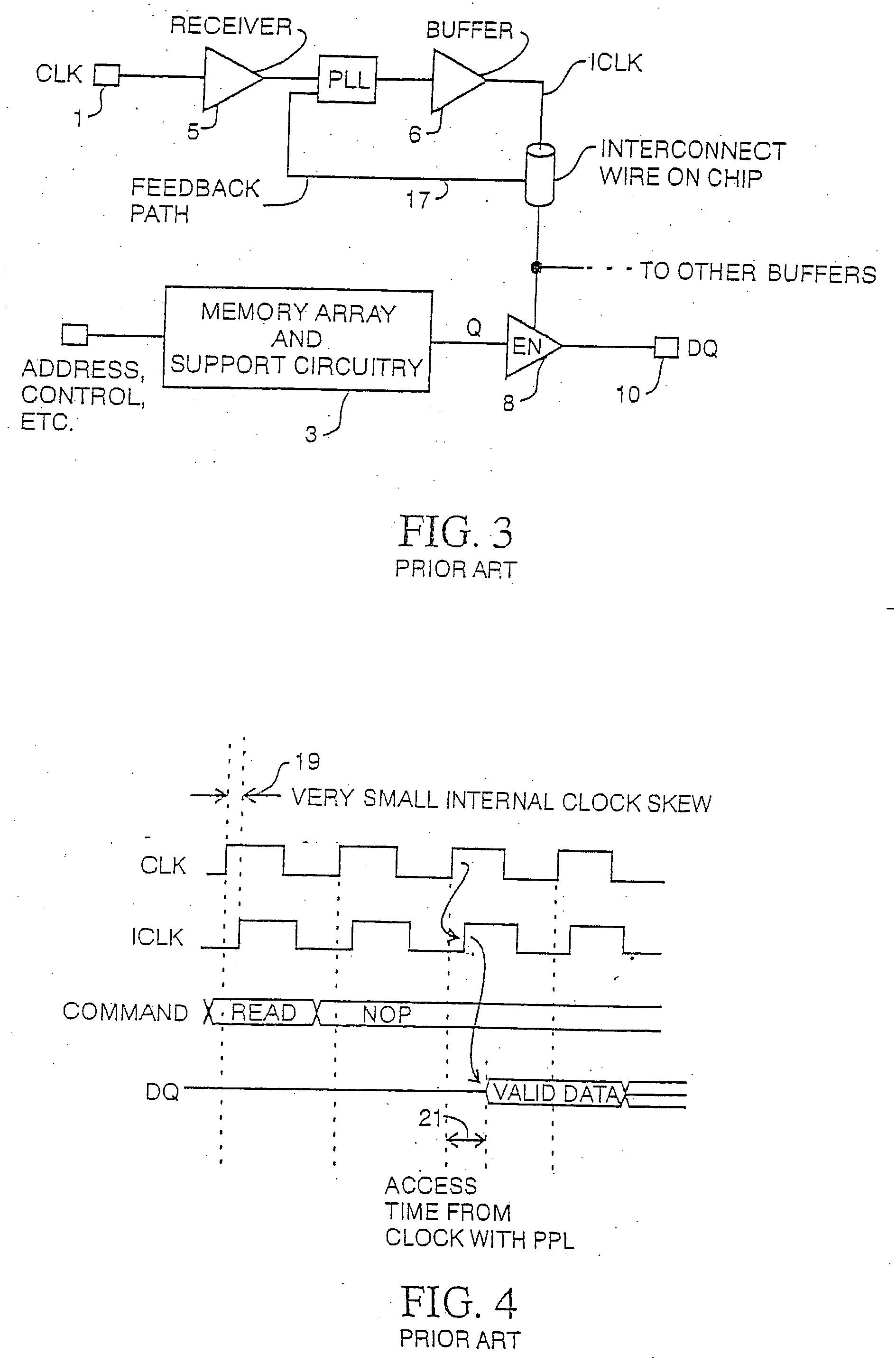
Synchronous dynamic random-access memory (SDRAM) is any dynamic random-access memory (DRAM) where the operation of its external pin interface is coordinated by an externally supplied clock signal. DRAM integrated circuits (ICs) produced from the early 1970s to early 1990s used an asynchronous interface, in which input control signals have a direct effect on internal functions only delayed by the trip across its semiconductor pathways. SDRAM has a synchronous interface, whereby changes on control inputs are recognised after a rising edge of its clock input. In SDRAM families standardized by JEDEC, the clock signal controls the stepping of an internal finite state machine that responds to incoming commands. These commands can be pipelined to improve performance, with previously started operations completing while new commands are received. The memory is divided into several equally sized but independent sections called banks, allowing the device to operate on a memory access command in each bank simultaneously and speed up access in an interleaved fashion. This allows SDRAMs to achieve greater concurrency and higher data transfer rates than asynchronous DRAMs could.
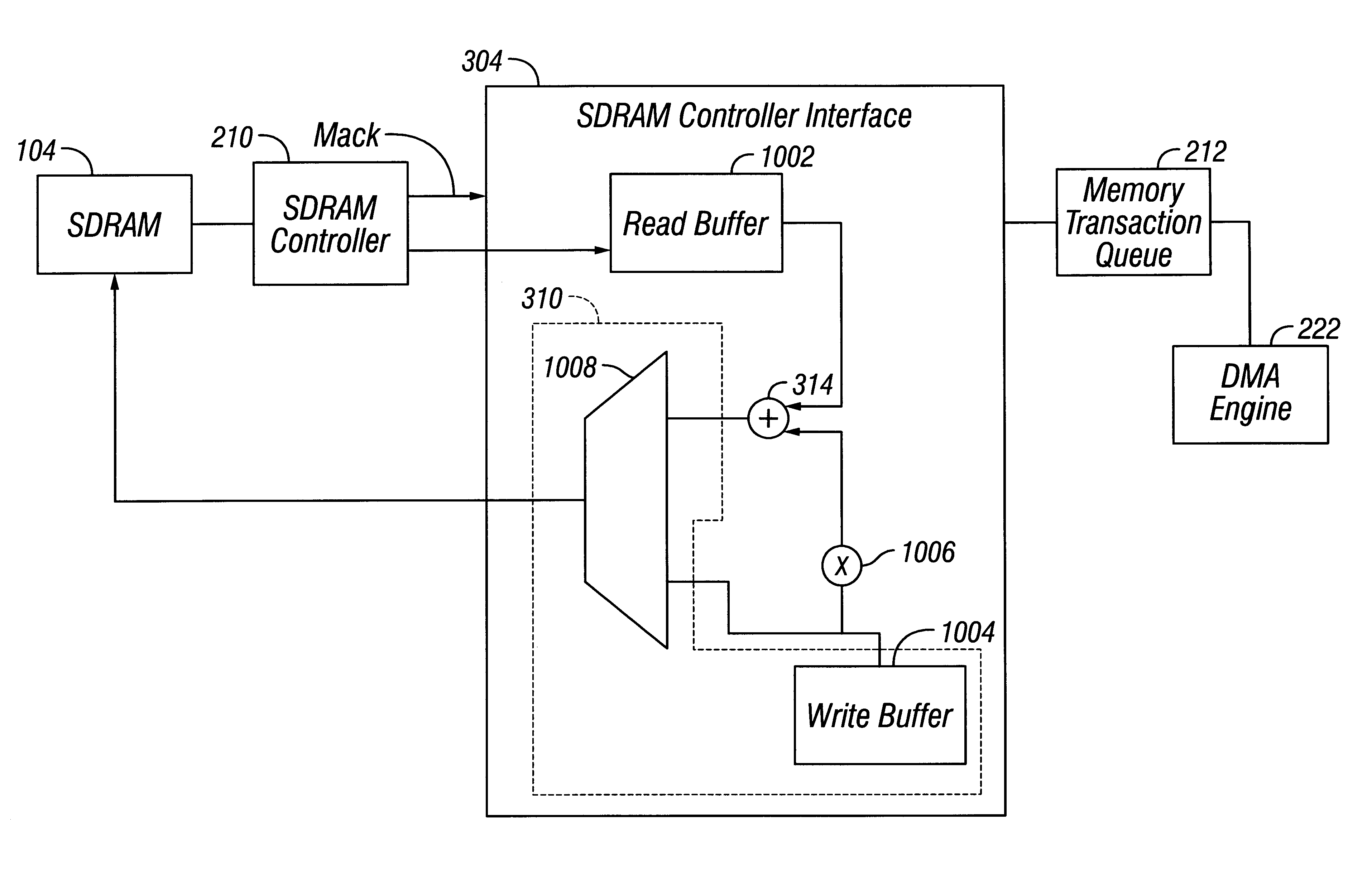
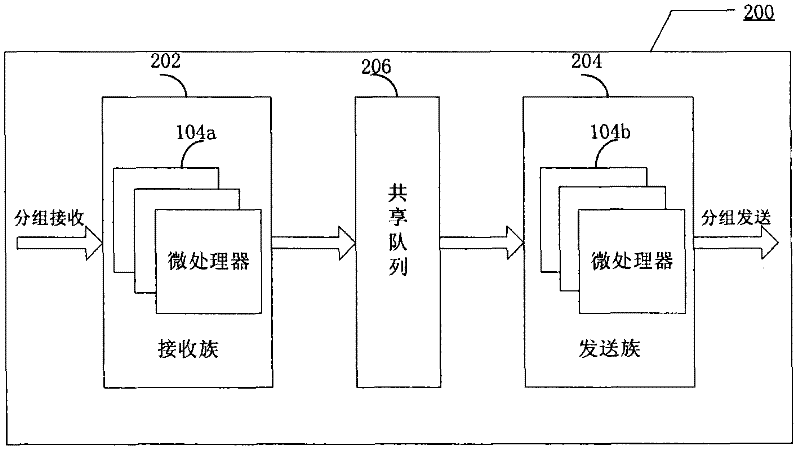
Raid XOR operations to synchronous DRAM using a read buffer and pipelining of synchronous DRAM burst read data
A memory interface controller includes a read buffer to pipeline data from a synchronous dynamic random access memory (DRAM) in response to a plurality of consecutive SDRAM burst read requests, a write buffer to store write data, an exclusive or (XOR) engine to XOR the write data with the data from the read buffer, and a write interface to write resulting data from XORing the write data and the data from the read buffer to the synchronous DRAM. Data is pipelined in the read buffer by repeatedly issuing an SDRAM burst read request before data is transferred out of the synchronous DRAM in response to a previous SDRAM burst read request until a desired amount of data is stored in the read buffer. The memory interface controller thus can perform an external read-modify-write cycle for the synchronous DRAM. The synchronous DRAM can serve as a RAID (Redundant Array s of Inexpensive Disks) memory.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
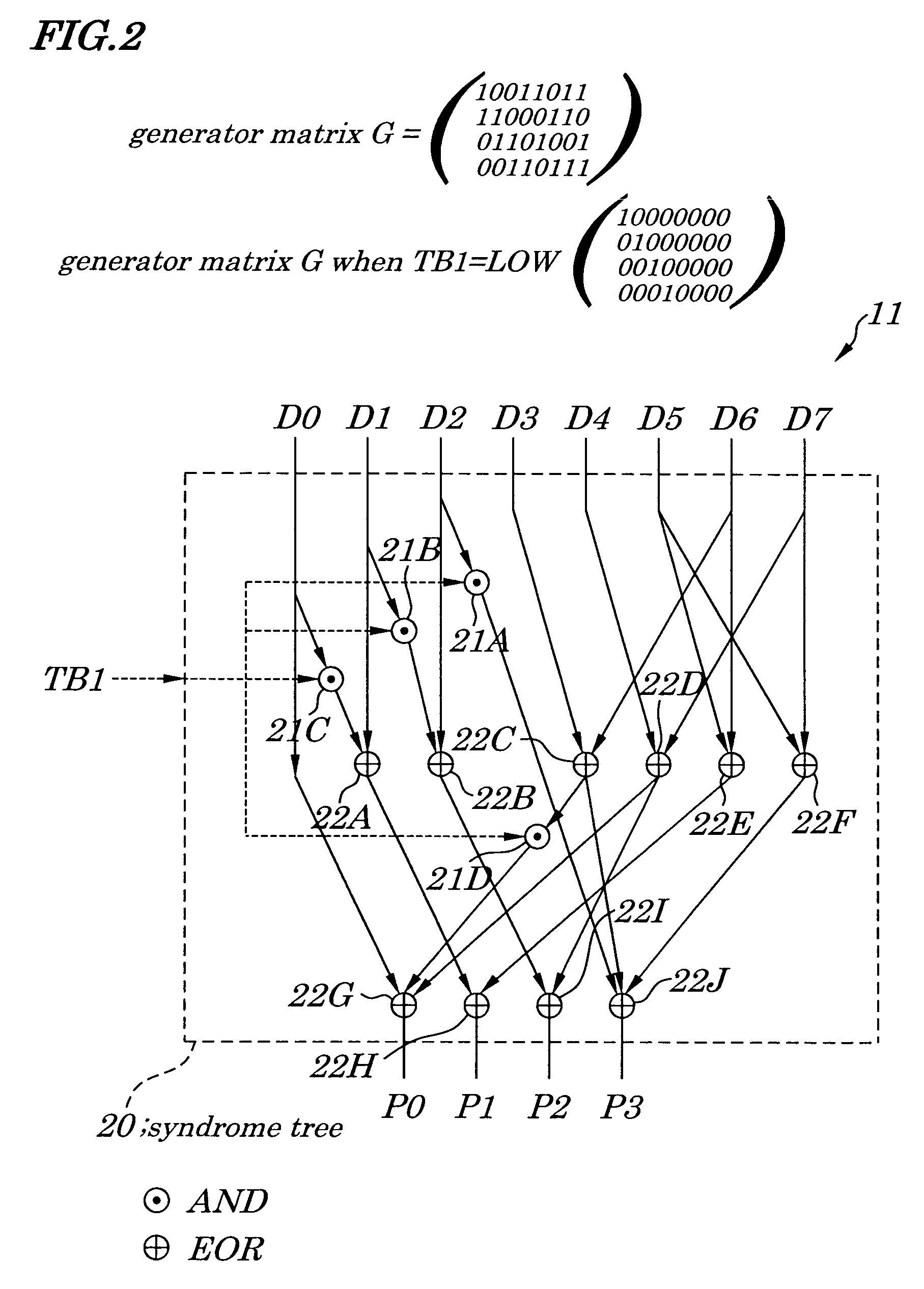
Combined command set
InactiveUS20030217223A1Memory adressing/allocation/relocationDigital storageStatic random-access memoryMemory bank
A circuit and method of operation for combining commands in a DRAM (dynamic random access memory) are revealed. The method applies to DRAMs having a plurality of memory banks or arrays. The method combines commands to rows on different memory banks, and the method also combines row and column commands on different memory banks. The method eliminates steps in a sequence of commands, and may significantly increase speed of input / output to a DRAM.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
Memory hub with internal cache and/or memory access prediction
InactiveUS7133972B2Memory adressing/allocation/relocationMultiple digital computer combinationsRandom access memoryMemory interface
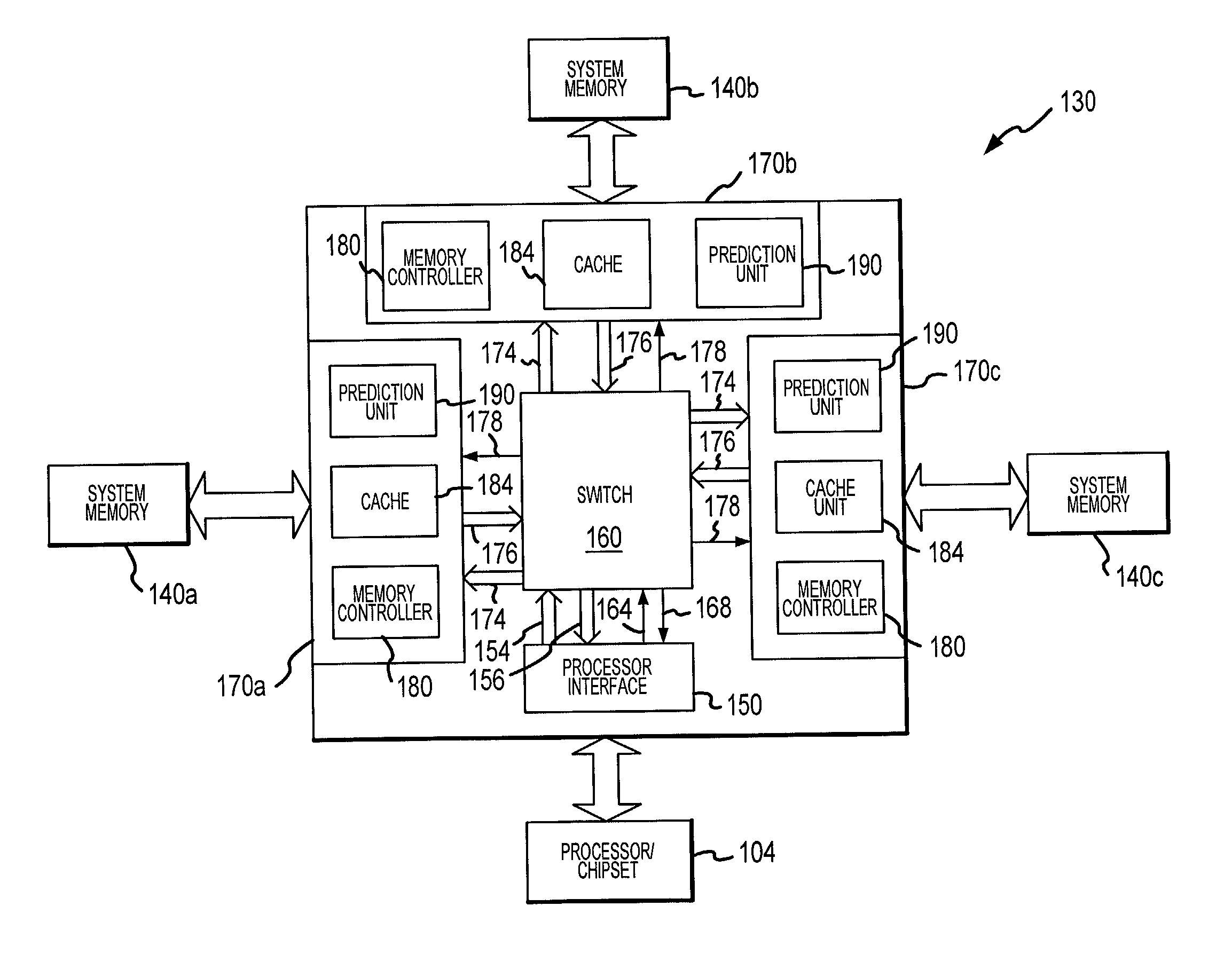
A computer system includes a memory hub for coupling a processor to a plurality of synchronous dynamic random access memory (“SDRAM”) devices. The memory hub includes a processor interface coupled to the processor and a plurality of memory interfaces coupled to respective SDRAM devices. The processor interface is coupled to the memory interfaces by a switch. Each of the memory interfaces includes a memory controller, a cache memory, and a prediction unit. The cache memory stores data recently read from or written to the respective SDRAM device so that it can be subsequently read by processor with relatively little latency. The prediction unit prefetches data from an address from which a read access is likely based on a previously accessed address.
Owner:ROUND ROCK RES LLC
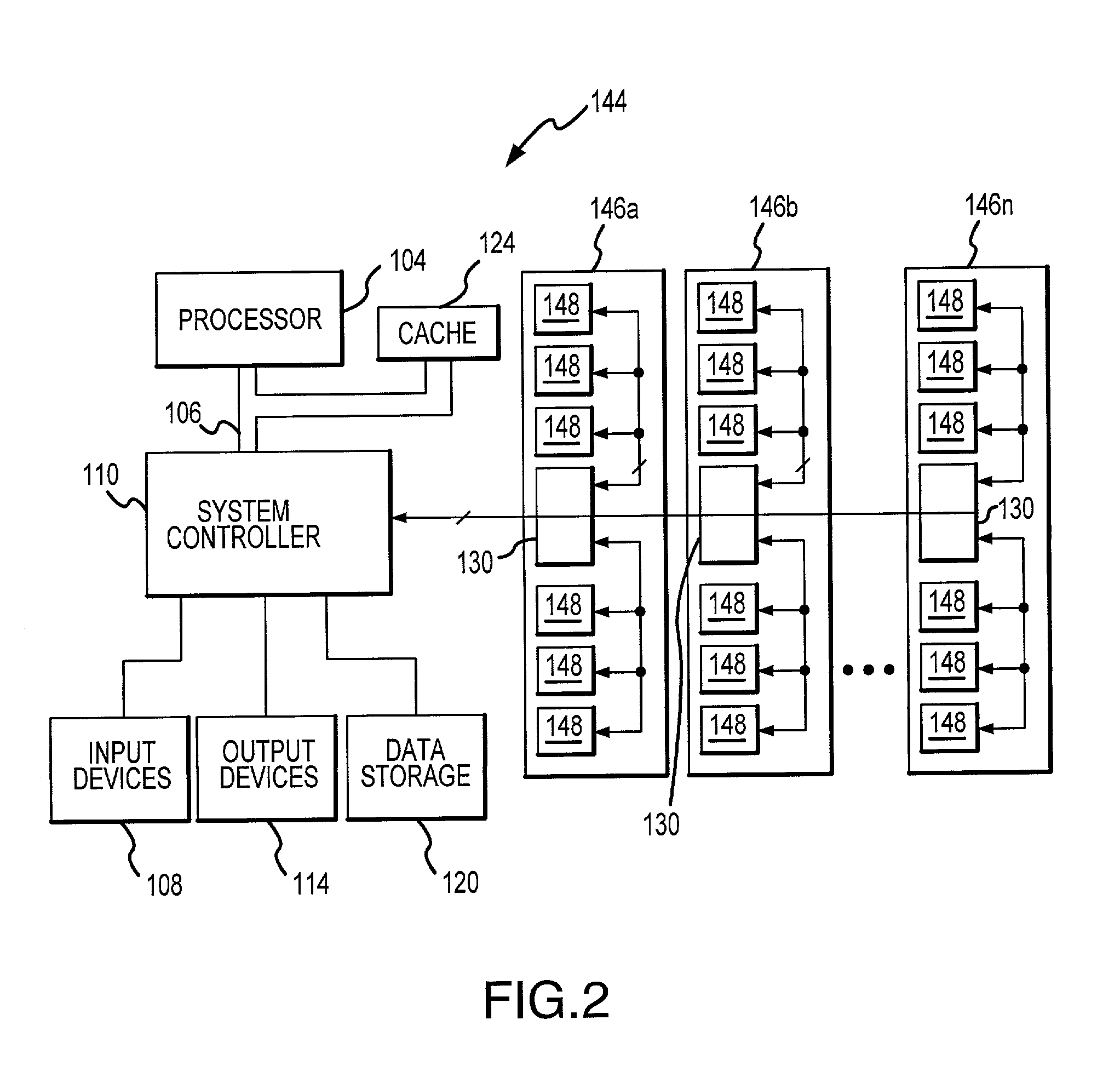
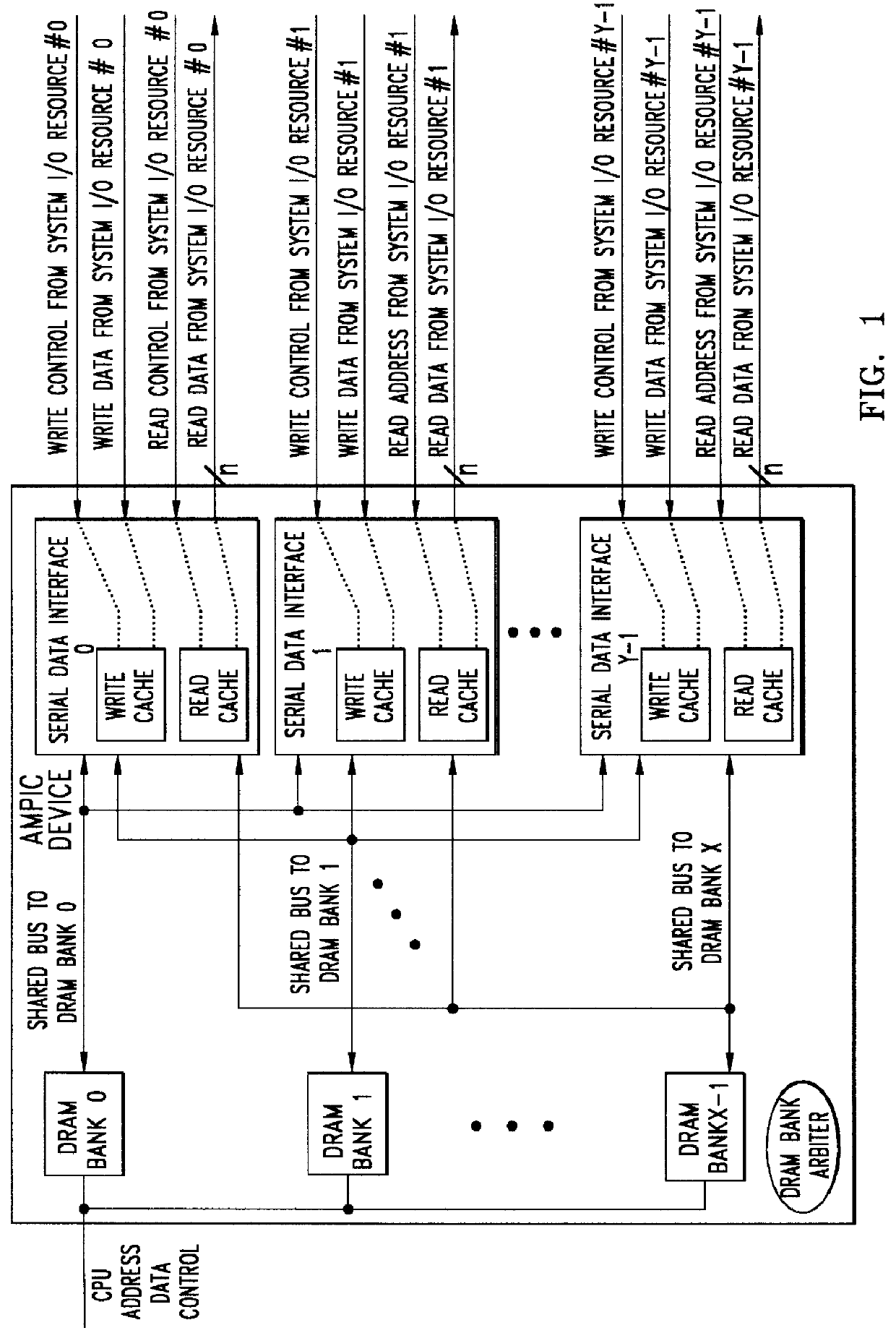
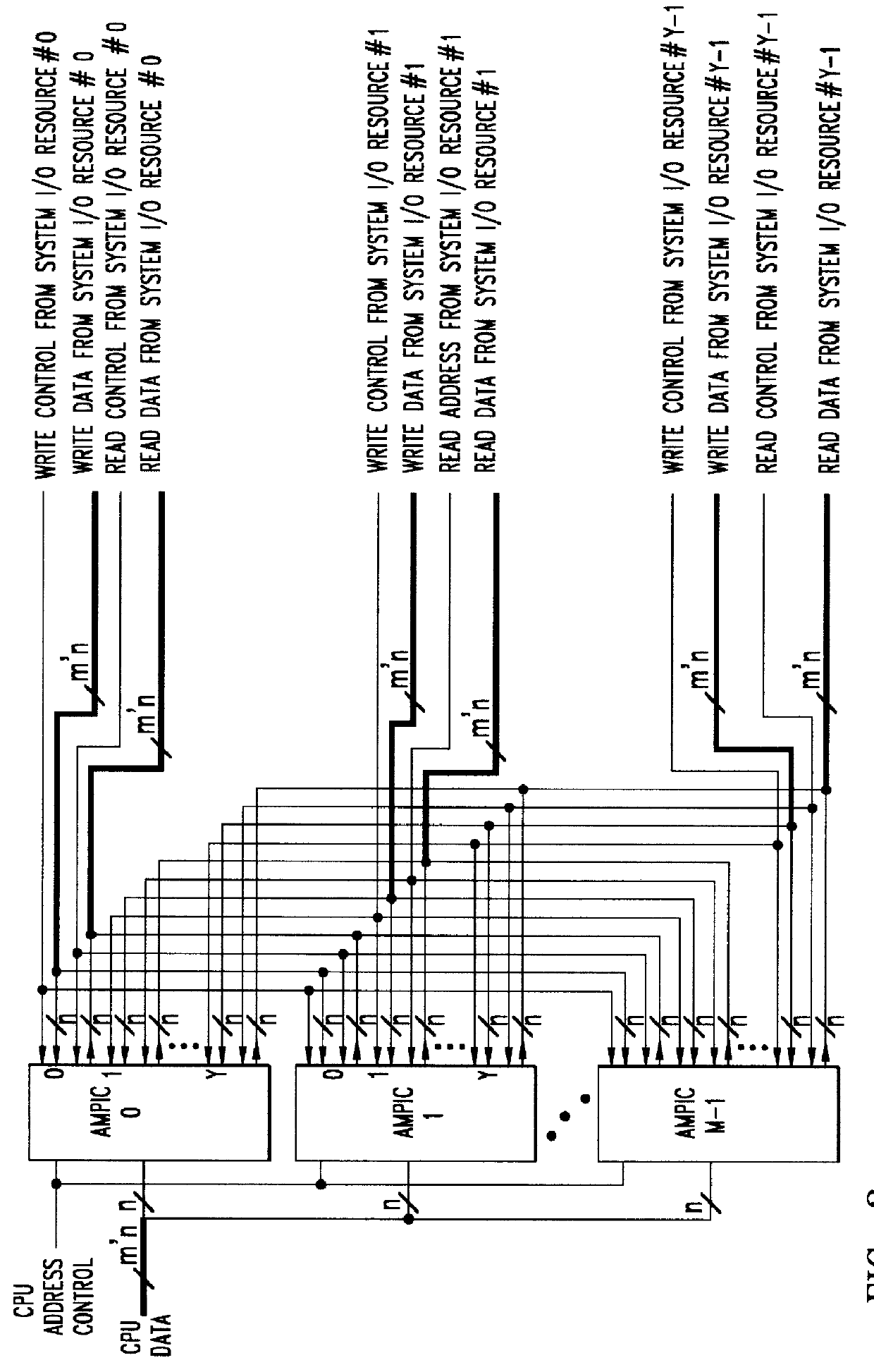
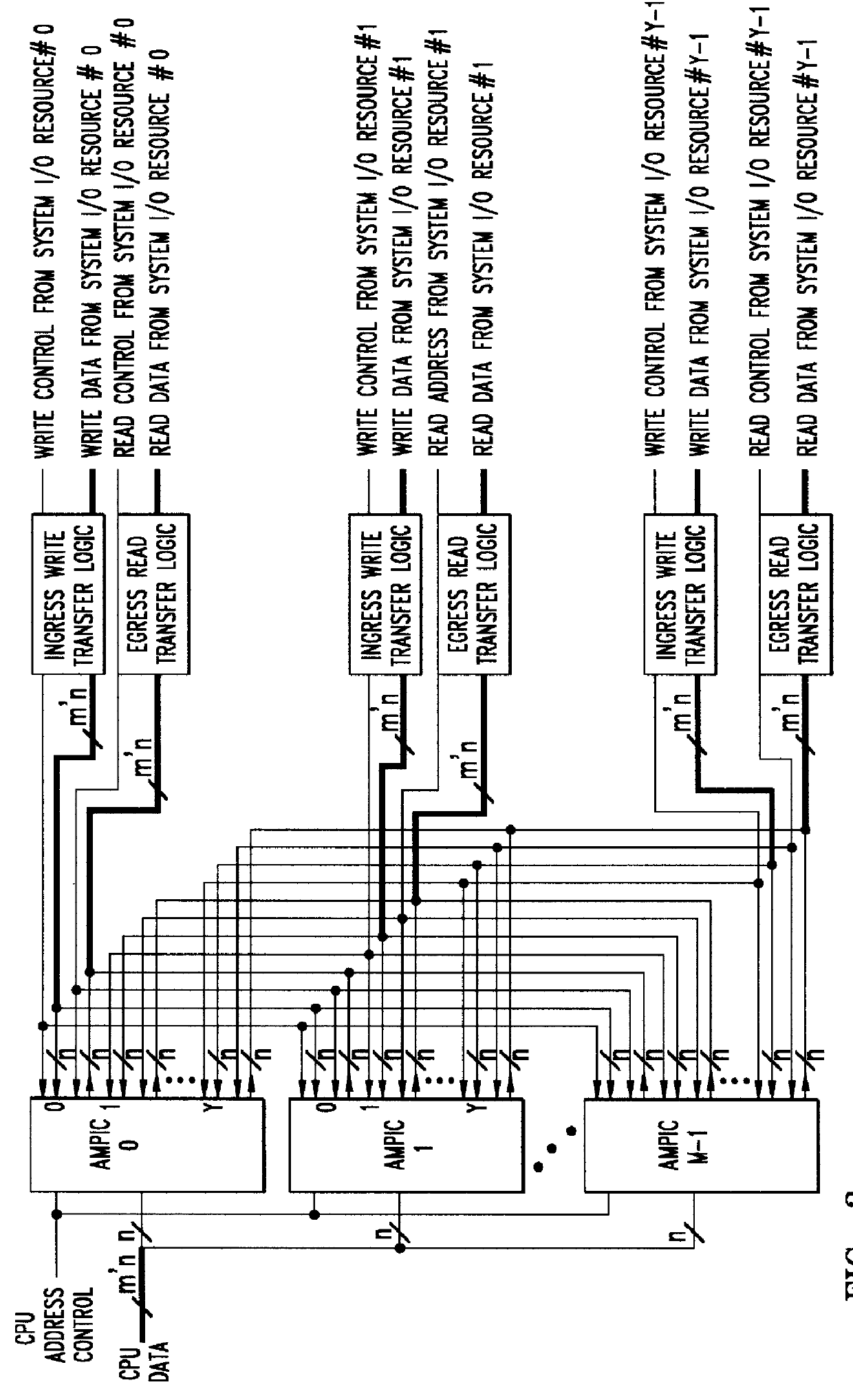
Method of and apparatus for validating data read out of a multi port internally cached dynamic random access memory (AMPIC DRAM)
InactiveUS6085290AEliminates race conditionMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationData validationStatic random-access memory
An apparatus for and method of enhancing the performance of a multi-port internal cached DRAM (AMPIC DRAM) by providing an internal method of data validation within the AMPIC memories themselves to guarantee that only valid requested data is returned from them, or properly marked invalid data. A modified technique for identifying bad data that has been read out of AMPIC memory devices in the system.
Owner:NEXABIT NETWORKS +1
System and method for using dynamic random access memory and flash memory
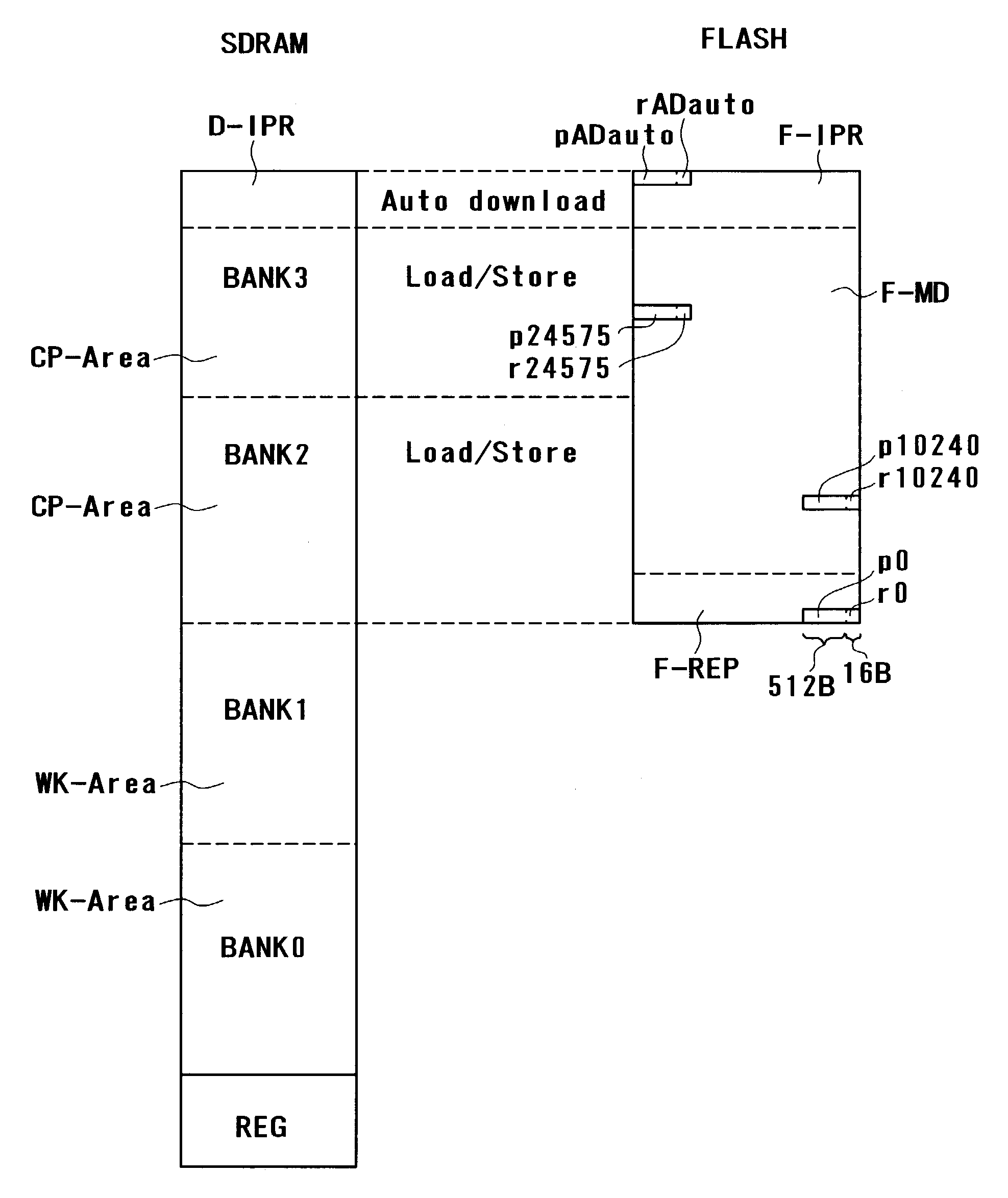
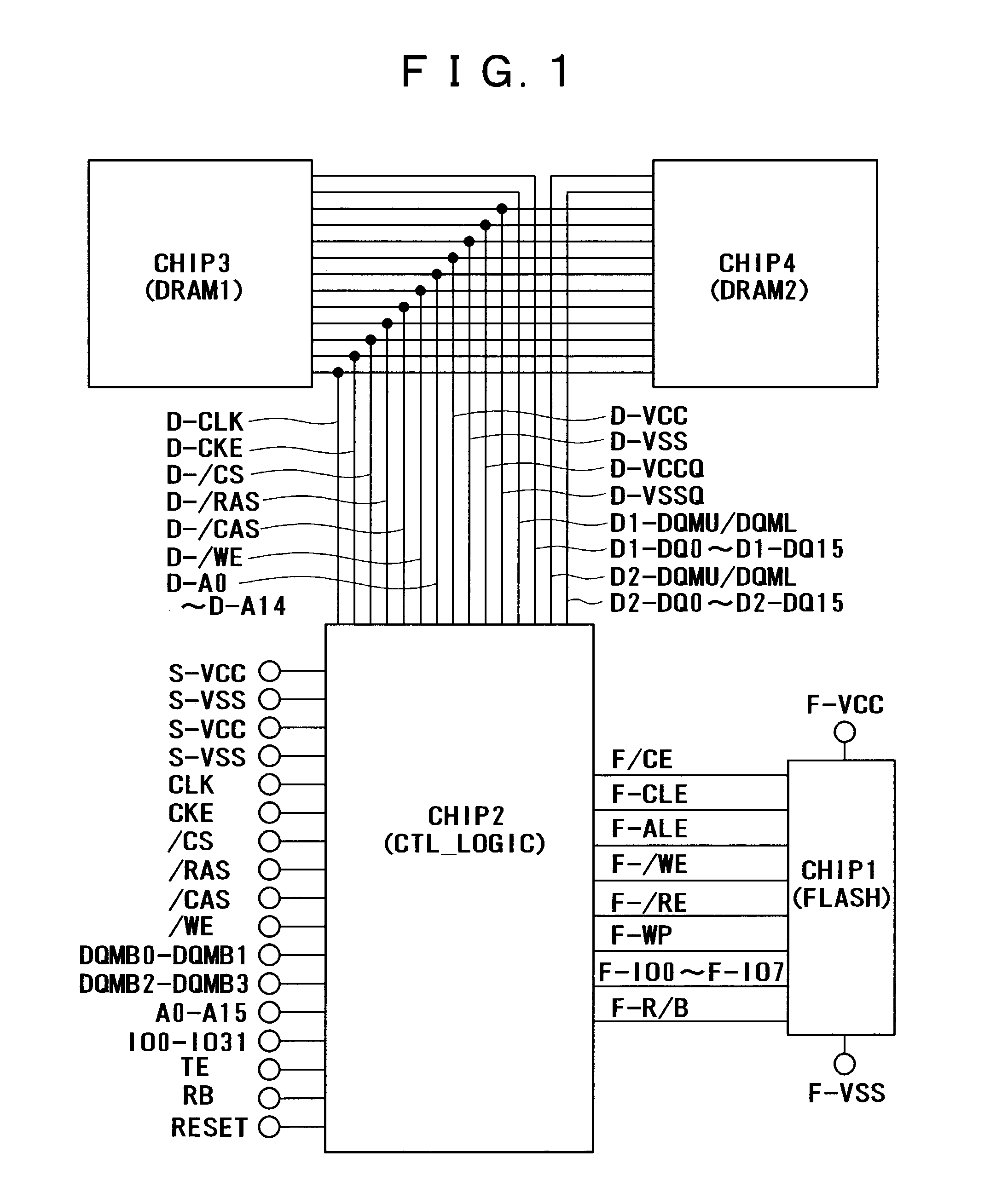
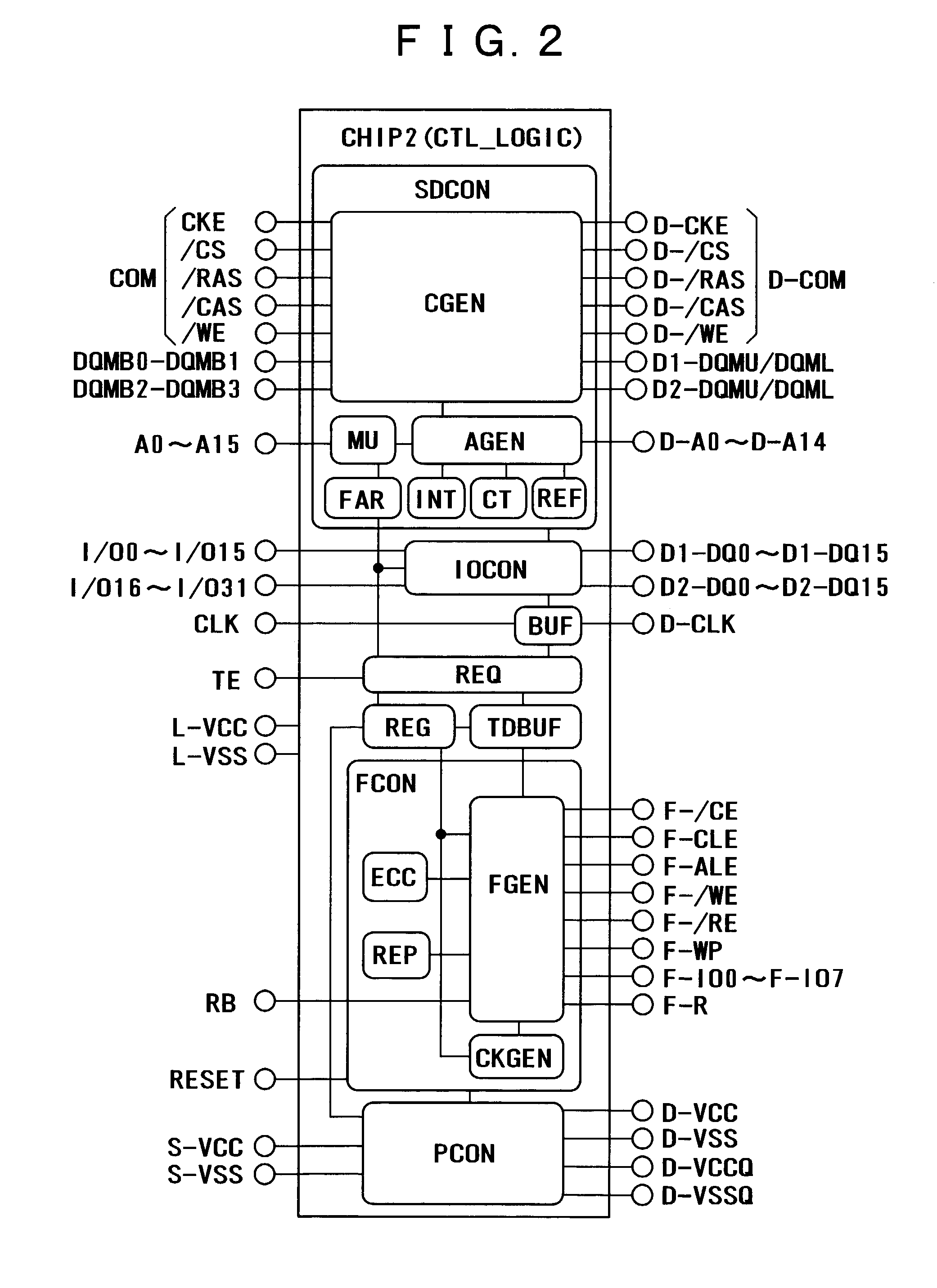
InactiveUS7136978B2Increase storage capacityIncrease speedEnergy efficient ICTMemory loss protectionRandom access memorySynchronous dynamic random-access memory
A system and method are provided for using dynamic random access memory and flash memory. In one example, the memory system comprises a nonvolatile memory; synchronous dynamic random access memories; circuits including a control circuit which is coupled with the nonvolatile memory and the synchronous dynamic random access memories, and controls accesses to the nonvolatile memory and the synchronous dynamic random access memories; and a plurality of input / output terminals coupled with the circuits, wherein in data transfer from the nonvolatile memory to the synchronous dynamic random access memories, error corrected data is transferred.
Owner:HITACHI ULSI SYST CO LTD +1
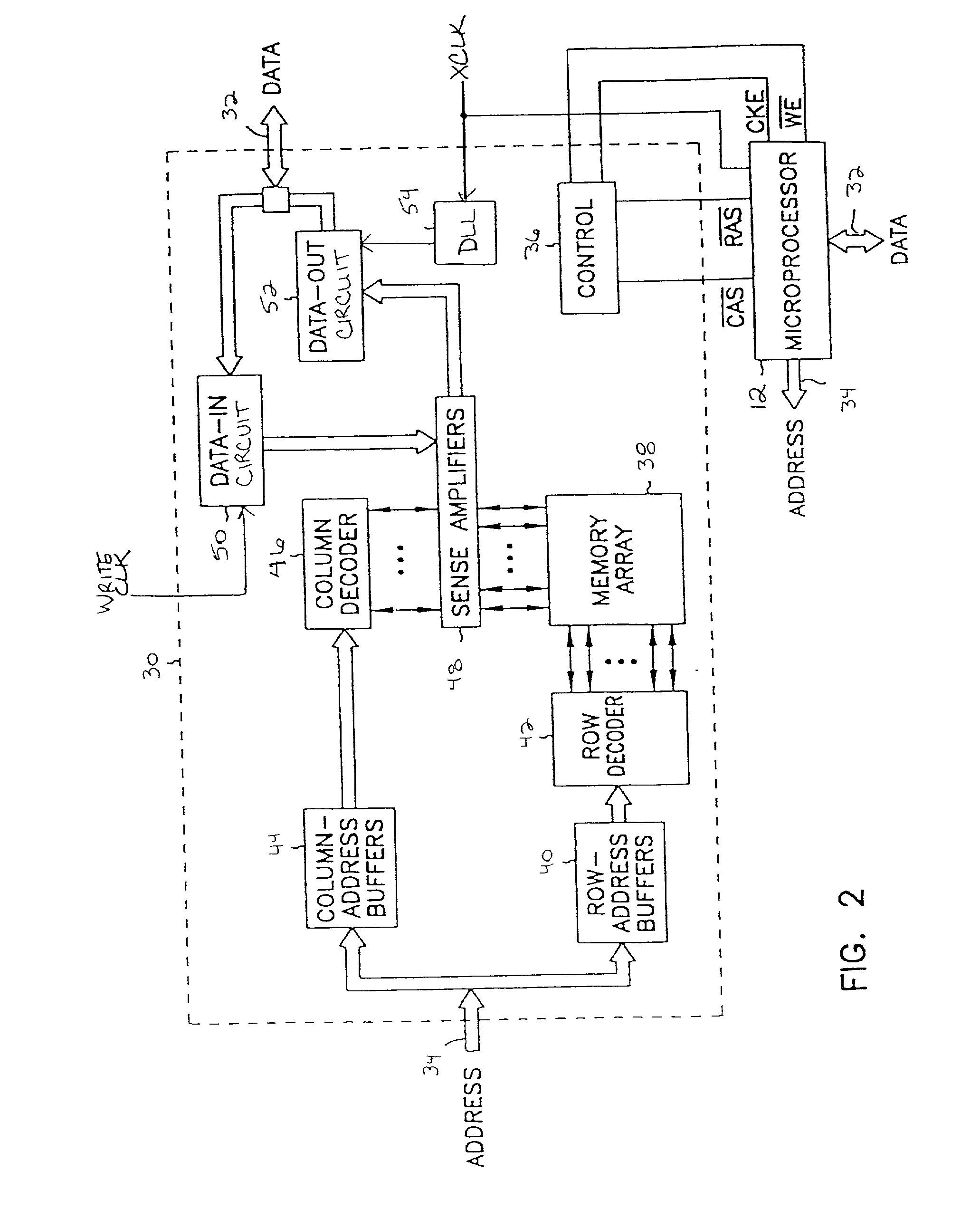
Delay locked loop implementation in a synchronous dynamic random access memory
InactiveUS6992950B2High operating requirementsLess standby current and start-up timePulse automatic controlSingle output arrangementsRandom access memoryDelay-locked loop
Owner:CONVERSANT INTPROP MANAGEMENT INC
Cached synchronous DRAM architecture having a mode register programmable cache policy
InactiveUS6289413B1Memory adressing/allocation/relocationDigital storageBit lineAudio power amplifier
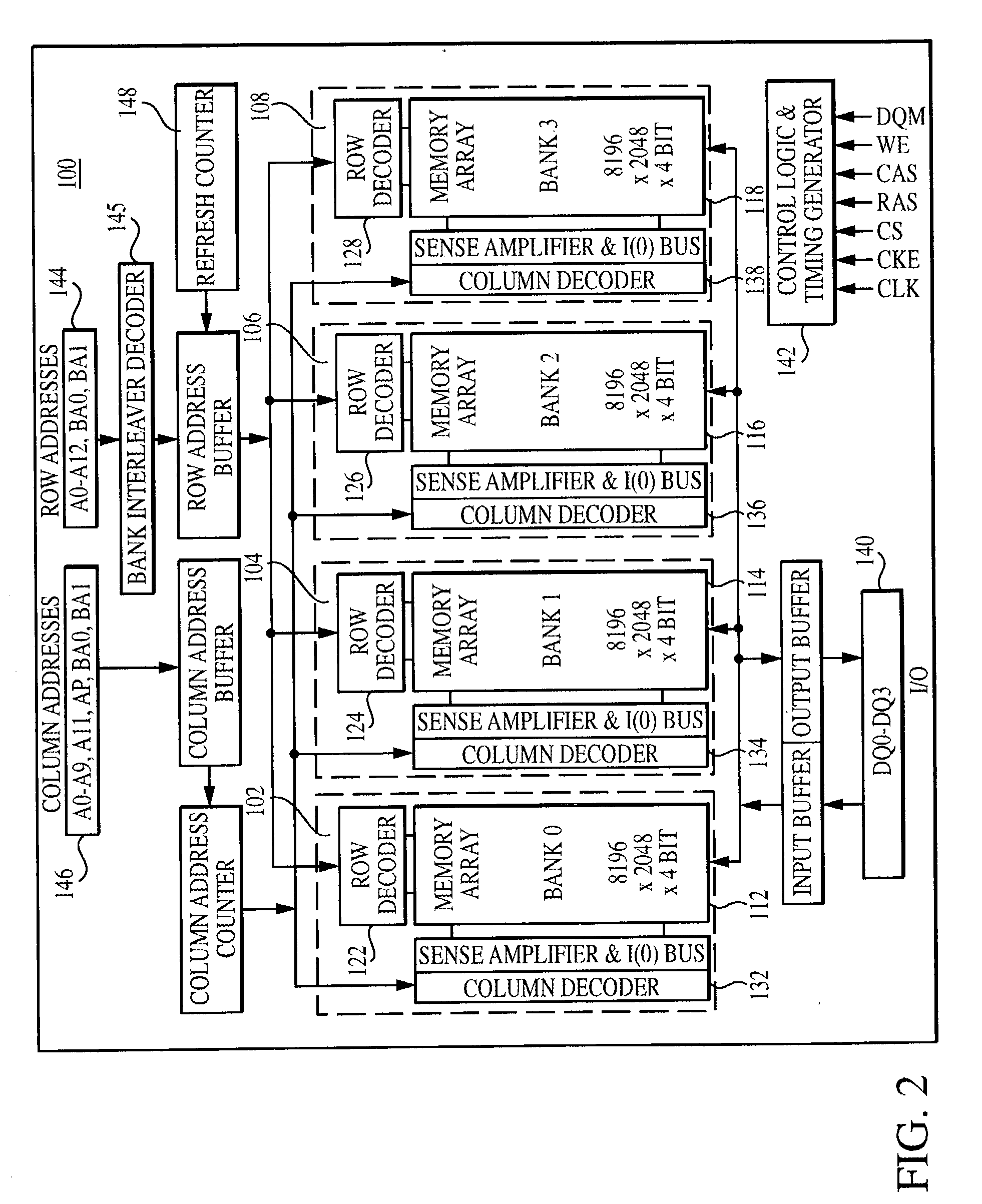
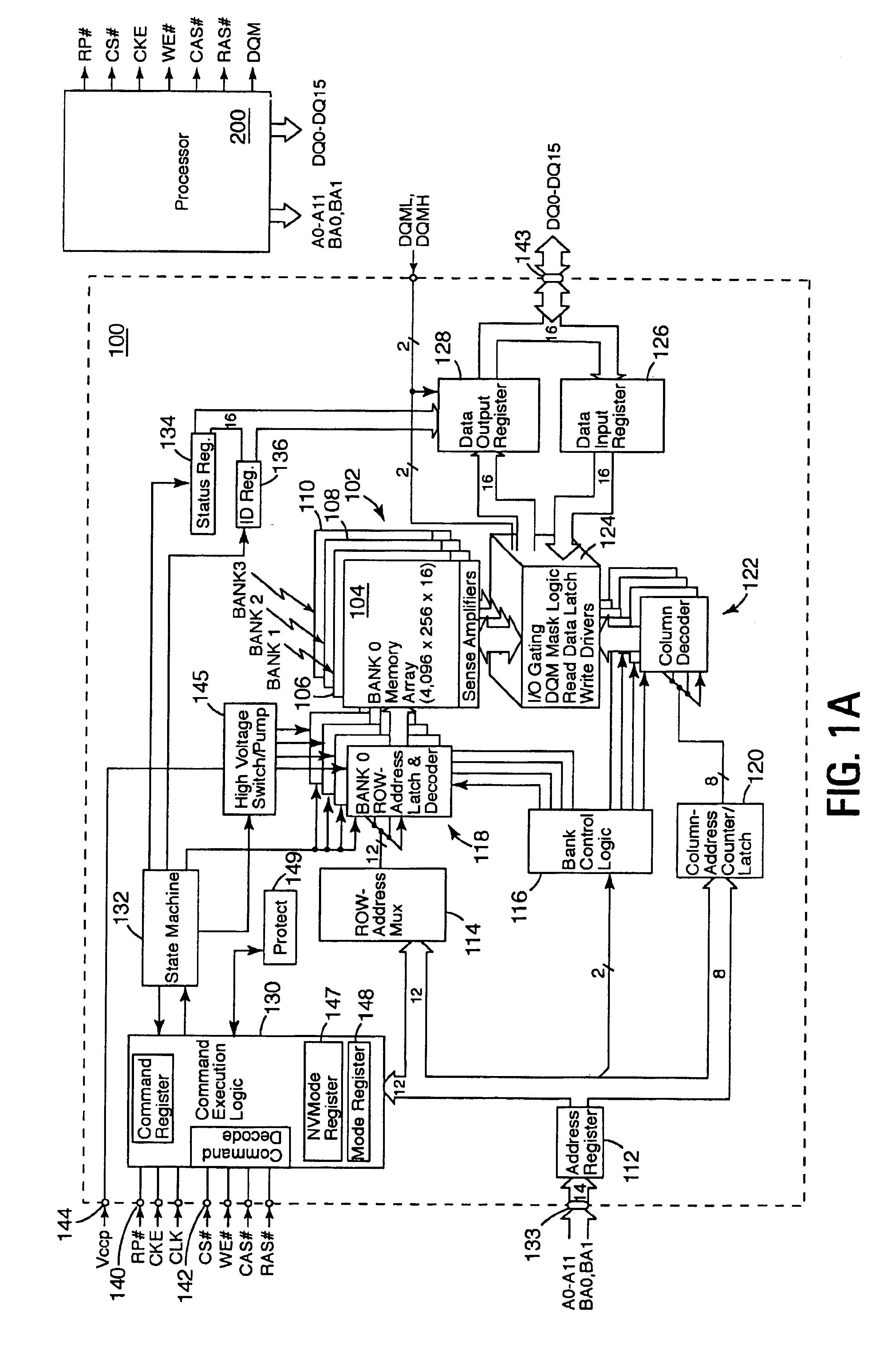
A cached synchronous dynamic random access memory (cached SDRAM) device having a multi-bank architecture and a programmable caching policy includes a synchronous dynamic random access memory (SDRAM) bank, a synchronous static randomly addressable row register, a select logic gating circuit, and mode register for programming of the cached SDRAM to operate in a Write Transfer mode corresponding to a Normal Operation mode of a standard SDRAM during a Write cycle, and to operate in a No Write Transfer mode according to an alternate operation mode during a Write cycle, thereby operating under a first and a second caching policy, respectively. The SDRAM includes a row decoder for selecting a row of data in a memory bank array, sense amplifiers for latching the row of data selected by the row decoder, and a synchronous column selector for selecting a desired column of the row of data. The row register stores a row of data latched by the sense amplifiers and the select logic gating circuit, disposed between the sense amplifiers and the row register, selectively gates the row of data present on the bit lines to the row register in accordance to particular synchronous memory operations being performed.
Owner:IBM CORP +2
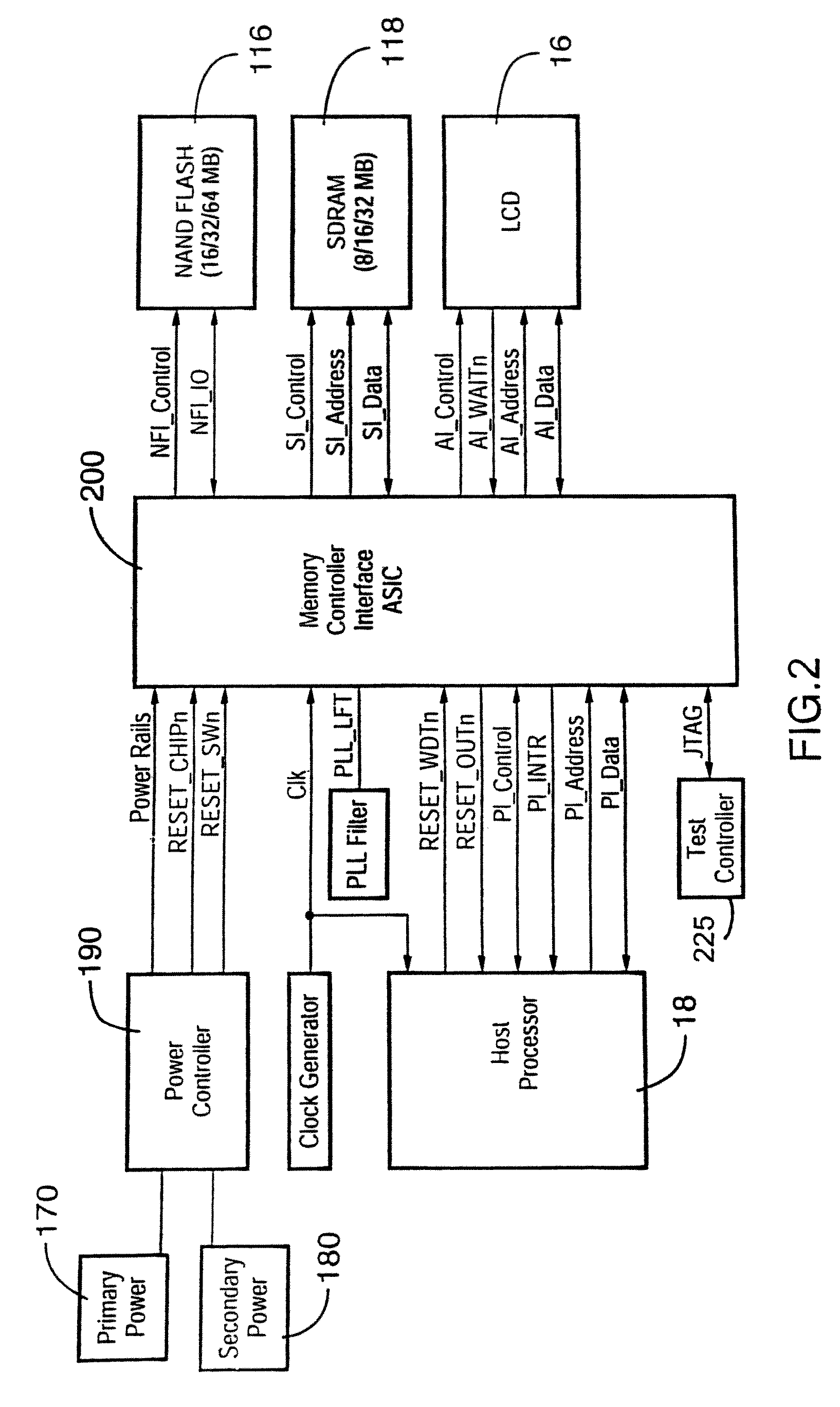
Memory controller interface
ActiveUS7610433B2Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory loss protectionStatic random-access memoryMemory interface
A memory interface controller and method to allow a processor designed and configured to operate with NOR flash and static random access memory (SRAM) memory devices to instead operate using NAND flash and synchronous dynamic random access memory (SDRAM). The system accomplishes this by caching sectors out of NAND flash into SDRAM, where the data can be randomly accessed by the processor as though it were accessing data from NOR flash / SRAM. Sectors containing data required by the processor are read out of NAND flash and written into SDRAM, where the data can be randomly accessed by the processor.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
Synchronous flash memory emulating the pin configuration of SDRAM
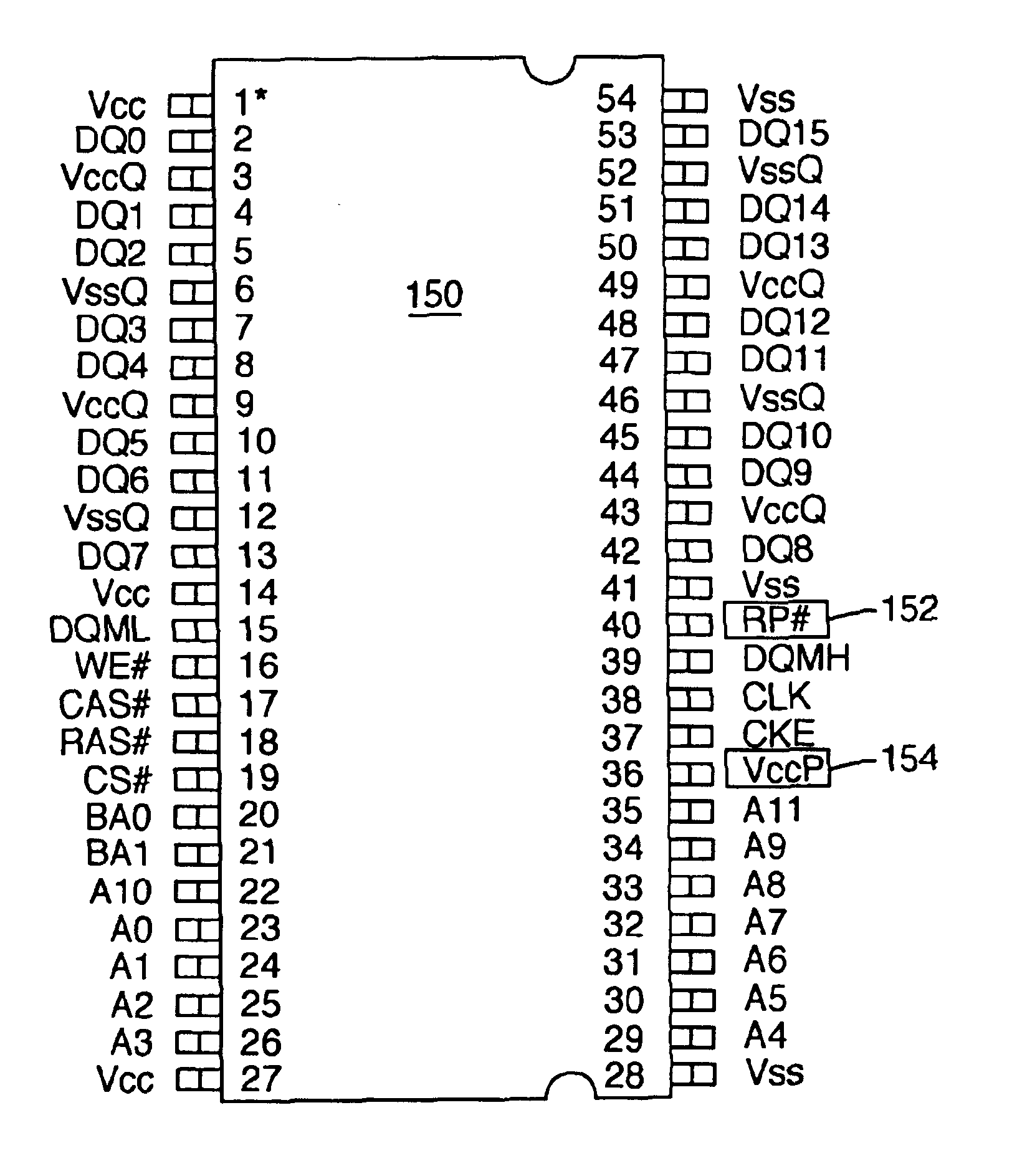
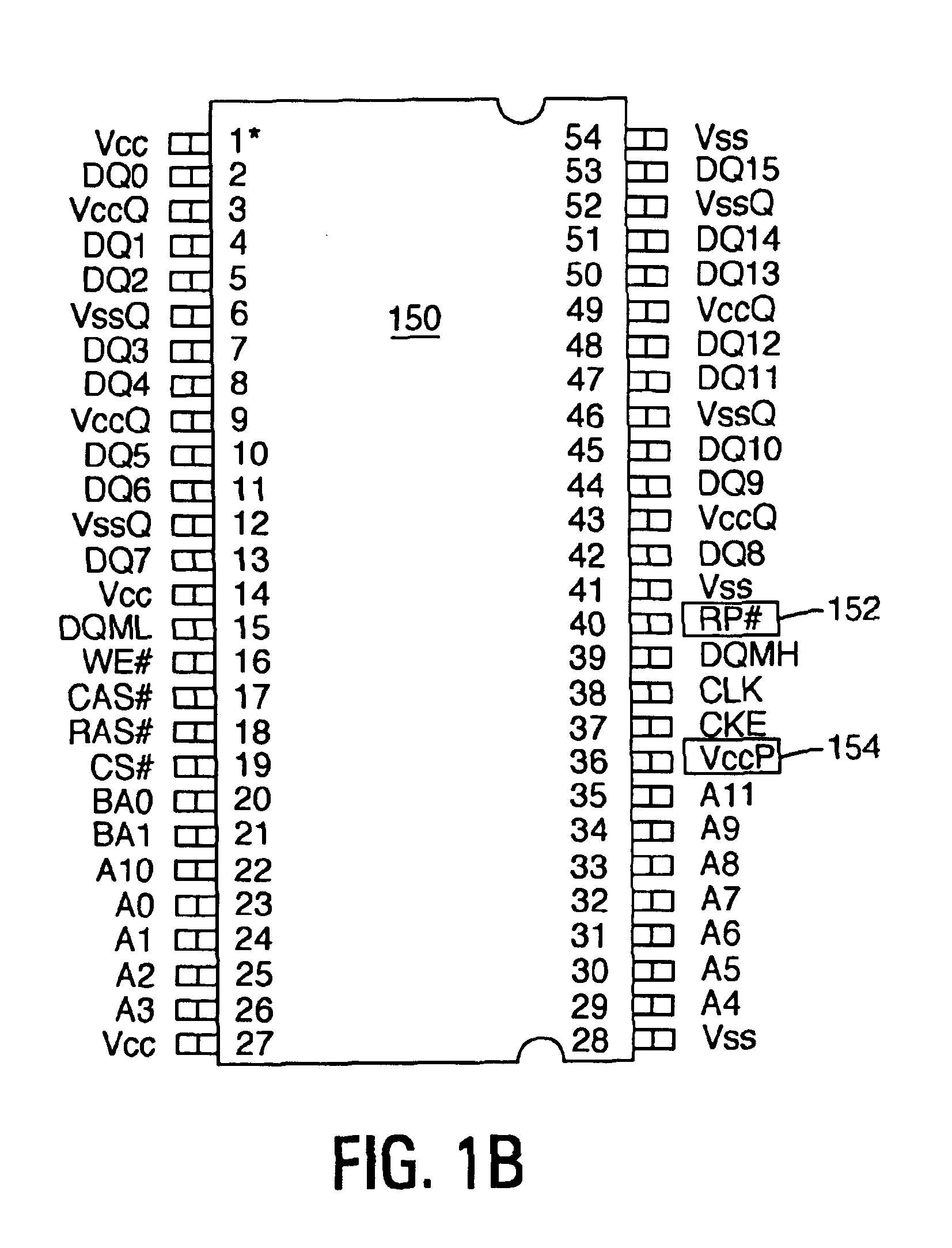
InactiveUS6892270B2Improves operation of systemImprove operationRead-only memoriesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRandom access memoryComputerized system
A computer system comprises a memory controller and a synchronous non-volatile memory device coupled to the memory controller via a main memory bus. The synchronous non-volatile memory device has external interconnects arranged in a manner that corresponds to interconnects of a synchronous dynamic random access memory device. The synchronous flash memory device, however, comprises a reset connection, and a Vccp power supply connection correspond to first and second no-connect (NC) interconnect pins of the synchronous dynamic random access memory. In one embodiment, the synchronous non-volatile memory device has a command interface comprising a write enable connection (WE#) to receive a write enable signal, a column address strobe connection (CAS#) to receive a column address strobe signal, a row address strobe connection (RAS#) to receive a row address strobe signal, and a chip select connection (CS#) to receive a chip select signal.
Owner:ROUND ROCK RES LLC
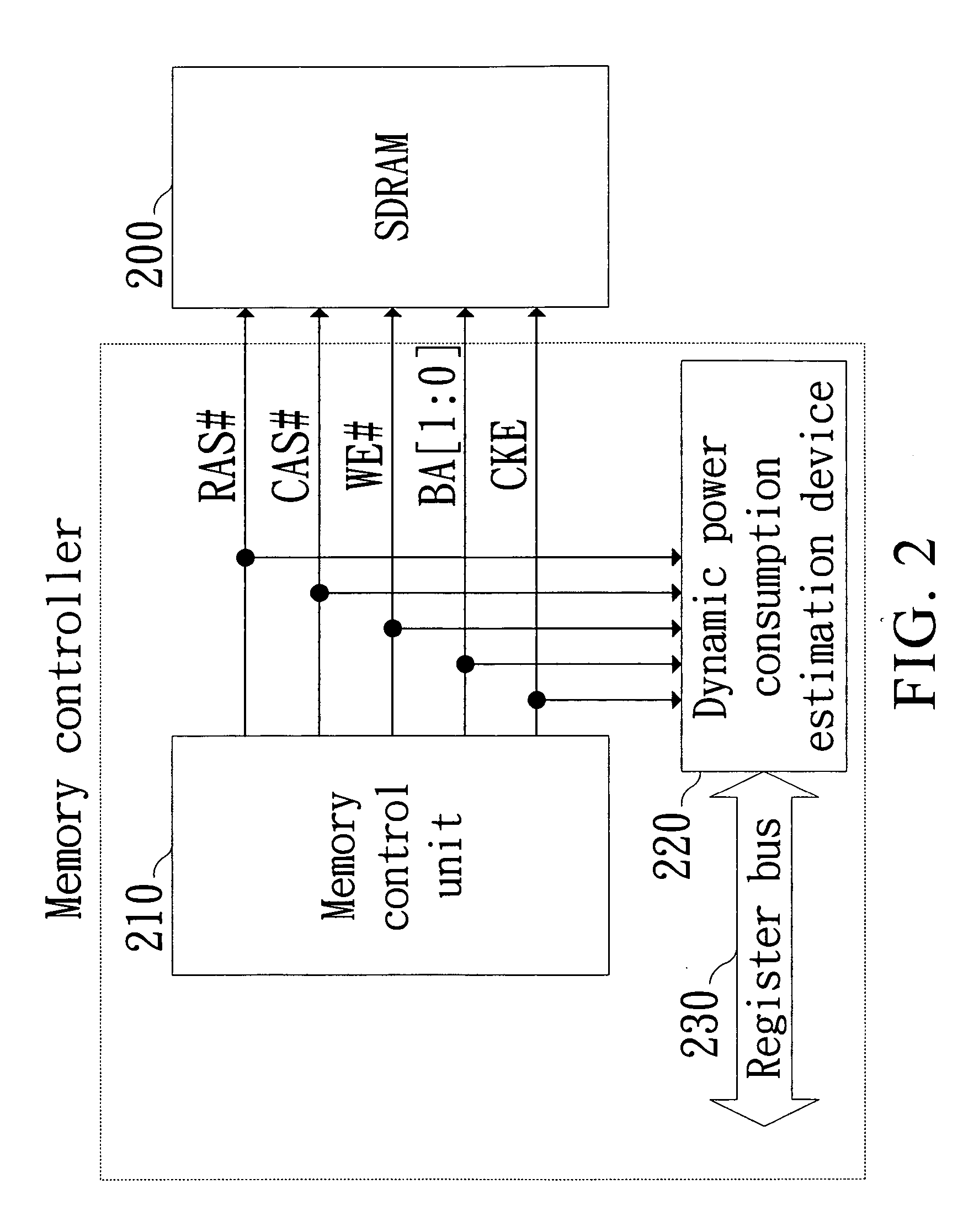
Memory controller capable of estimating memory power consumption
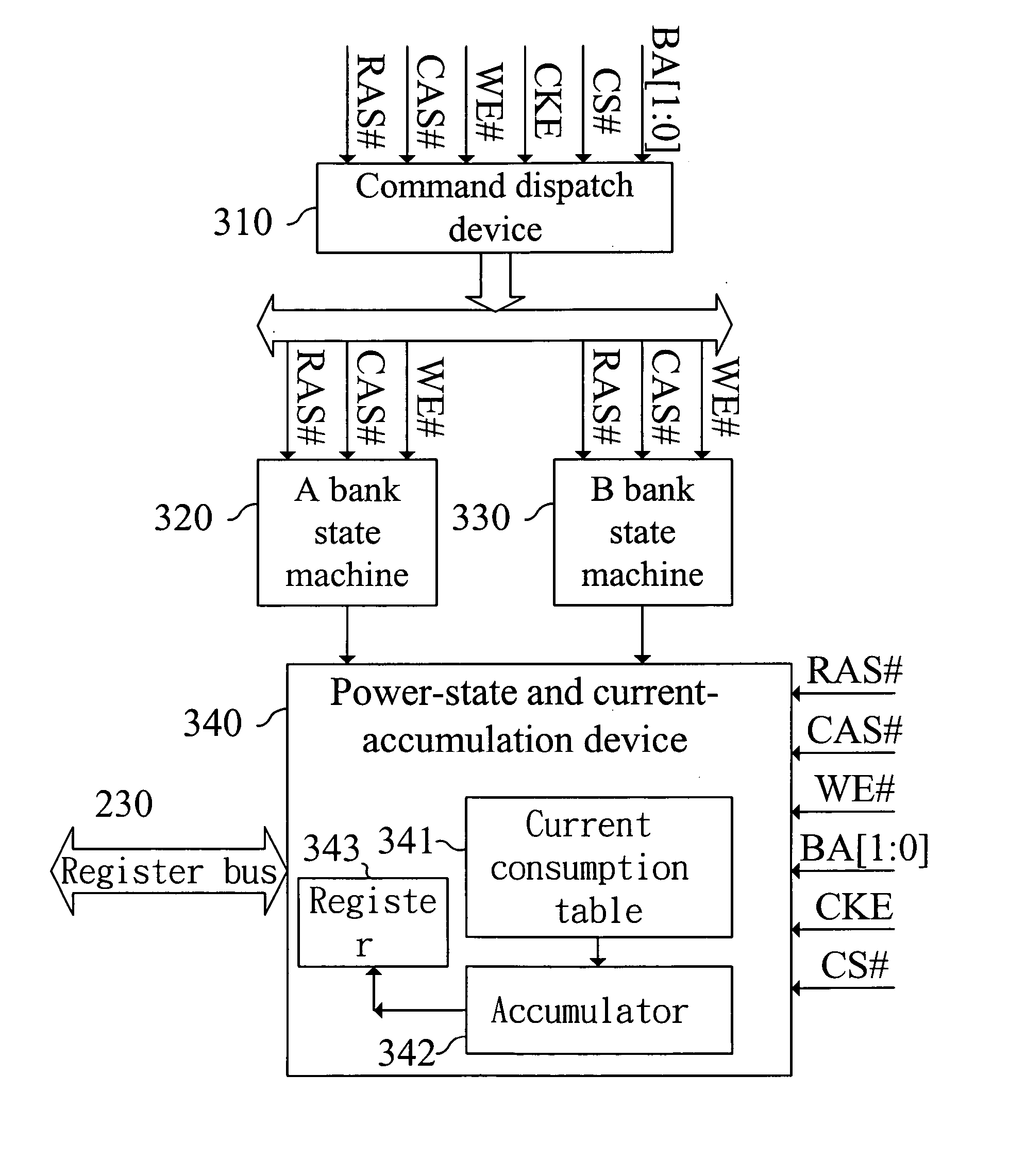
ActiveUS20050152212A1Accurate estimateDigital data processing detailsHardware monitoringControl signalRandom access memory
A memory controller capable of estimating memory power consumption includes a memory control unit, a command dispatch device, plural bank state machines and a power-state and current-accumulation device. The memory control unit generates control signals based on a memory access command sent by a system for accessing a synchronous dynamic random access memory (SDRAM). The command dispatch device synchronously receives the control signals sent by the controller to the SDRAM. The plural bank state machines are connected to the command dispatch device to receive the control signals dispatched by the command dispatch device and accordingly determine whether to transfer its internal state or not. The power-state and current-accumulation device determines on which state the SDRAM is in accordance with states of the plural band state machines, thereby computing current consumption of the SDRAM.
Owner:SUNPLUS TECH CO LTD
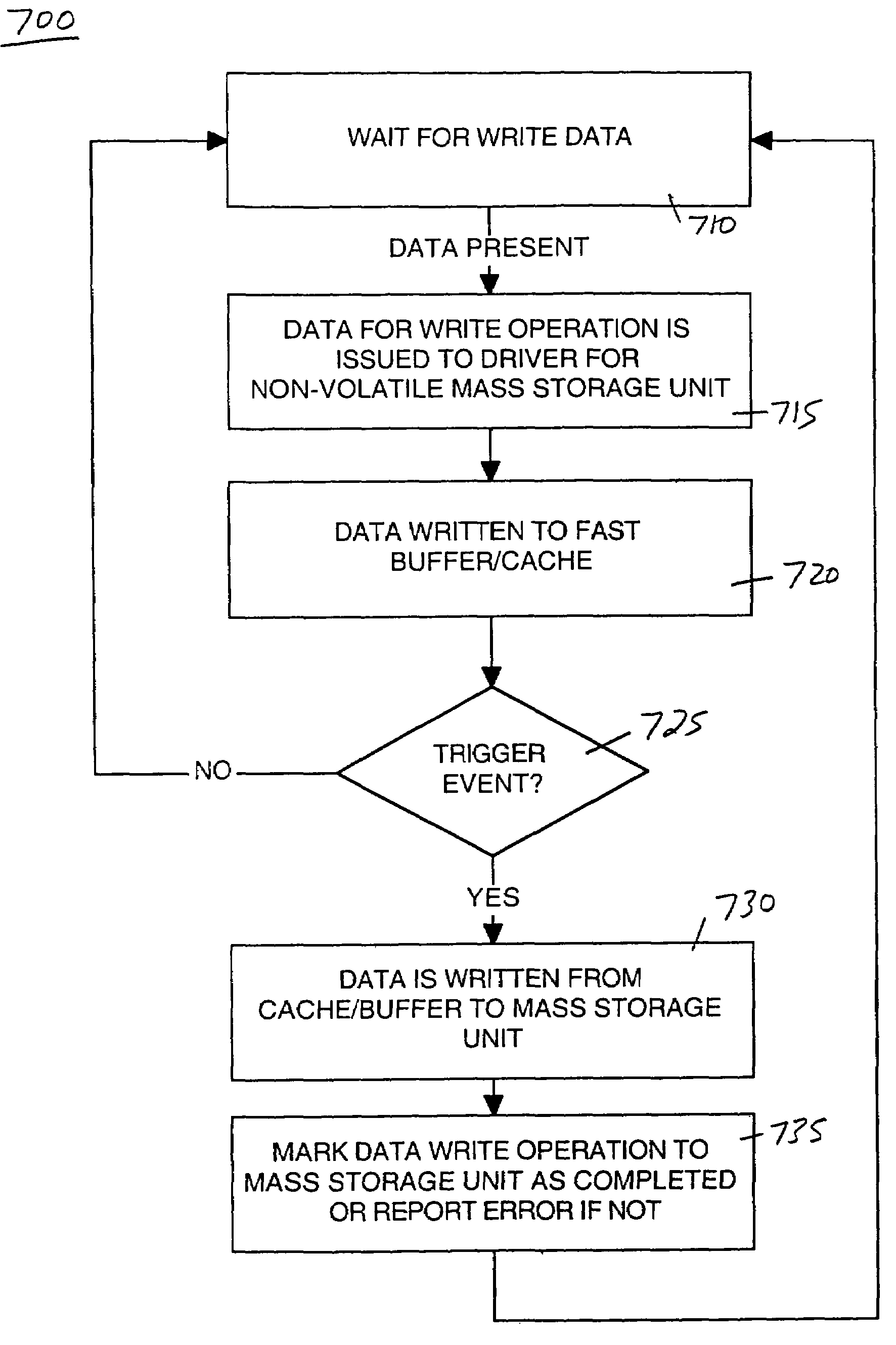
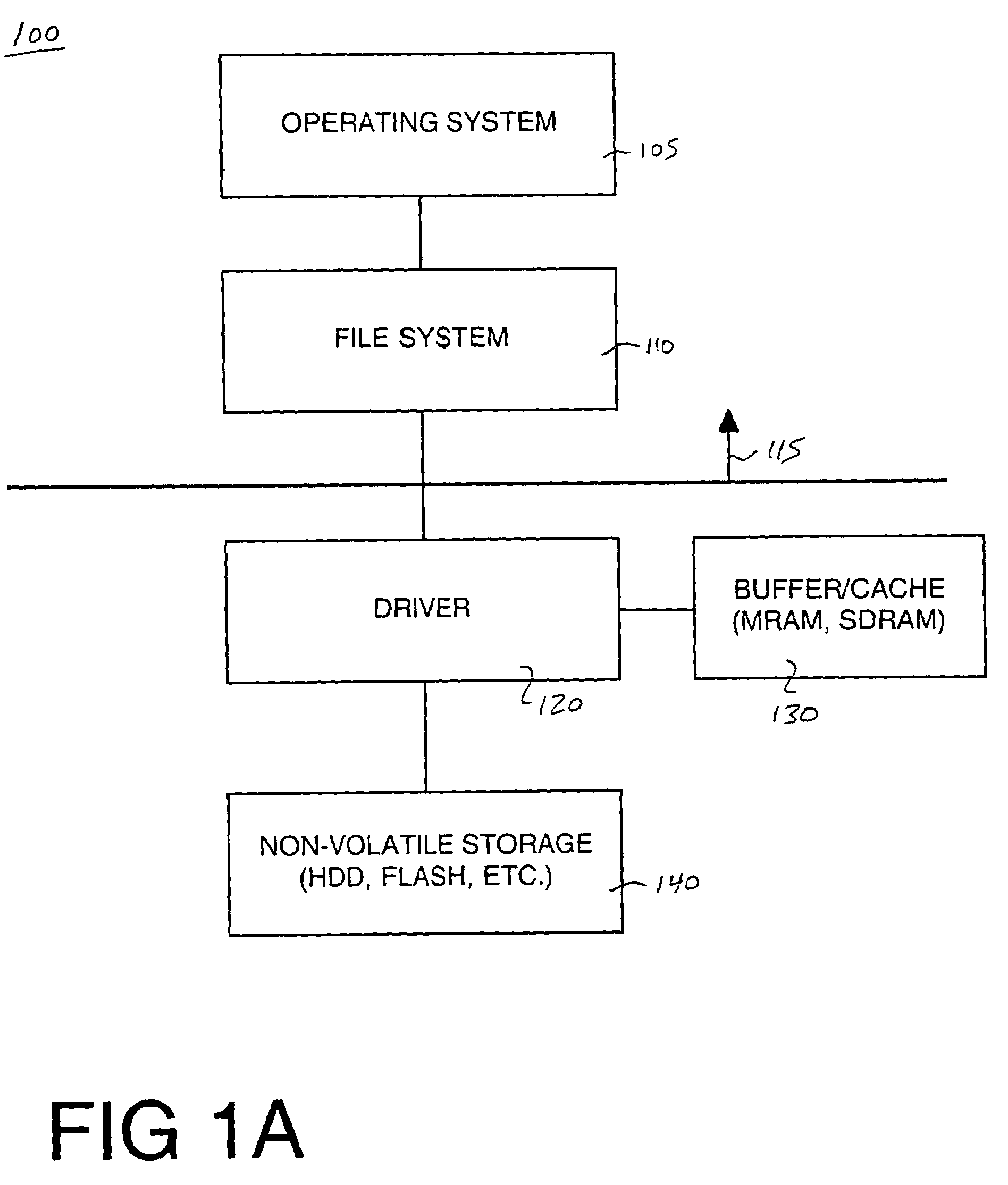
System and method for improving data integrity and memory performance using non-volatile media
A system and computer system for improving data integrity and memory performance using non-volatile media. A system includes a non-volatile mass storage unit, e.g., a flash memory device and / or a hard drive unit for instance. A memory device is used as a high speed data buffer and / or cache for the non-volatile storage unit. The memory device may be non-volatile, e.g., magnetic random access memory (MRAM) or volatile memory, e.g., synchronous dynamic random access memory (SDRAM). By buffering and / or caching the write data, fewer accesses are required to the mass storage device thereby increasing system performance. Additionally, mechanical and electrical degradation of the mass storage device is reduced. Certain trigger events can be programmed to cause data from the memory device to be written to the mass storage device. In one embodiment, the write buffer contents are preserved across reset or power loss events. In one embodiment, the mass storage unit may be a data transport layer, e.g., Ethernet, USB, Bluetooth, etc.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
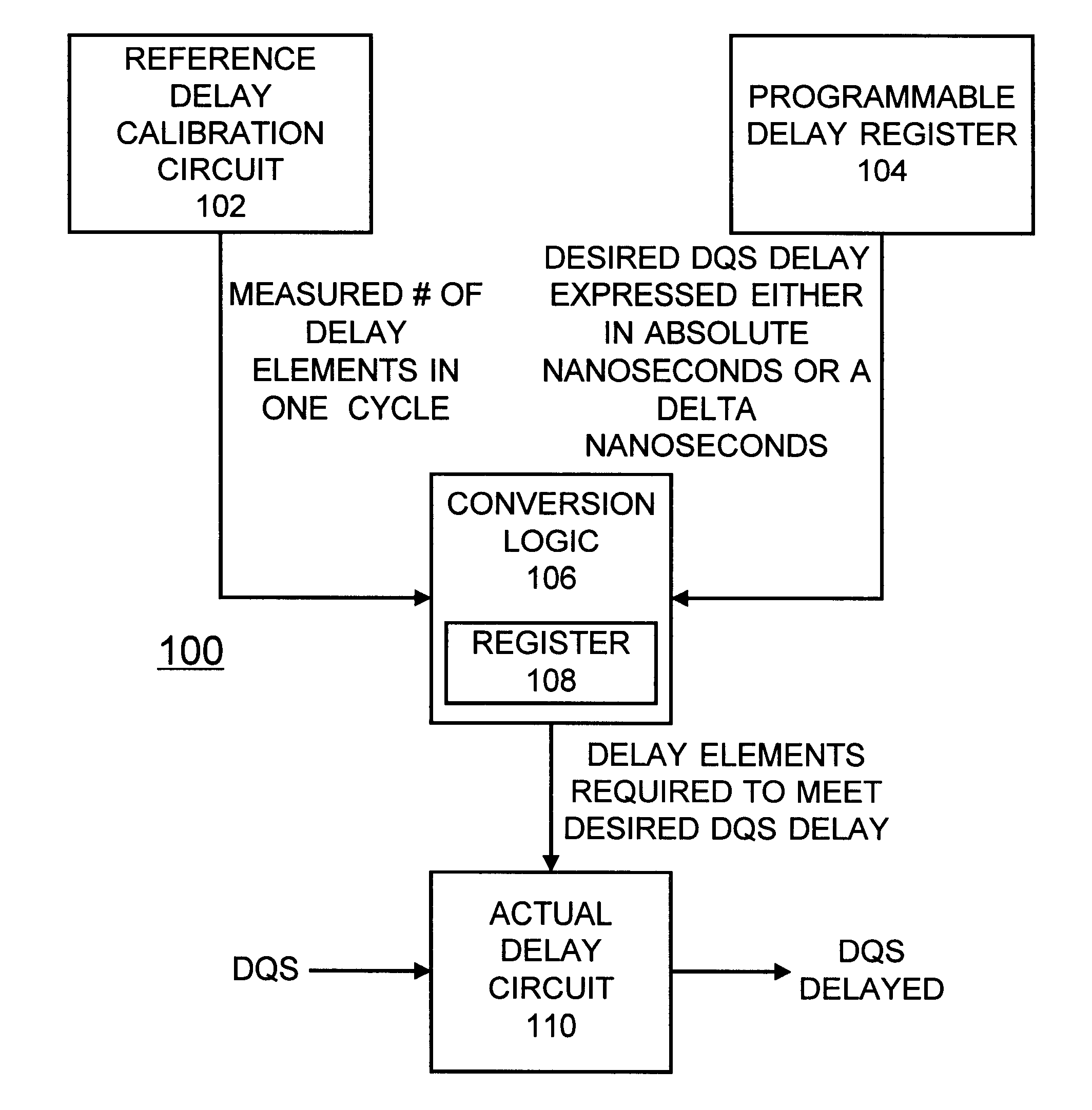
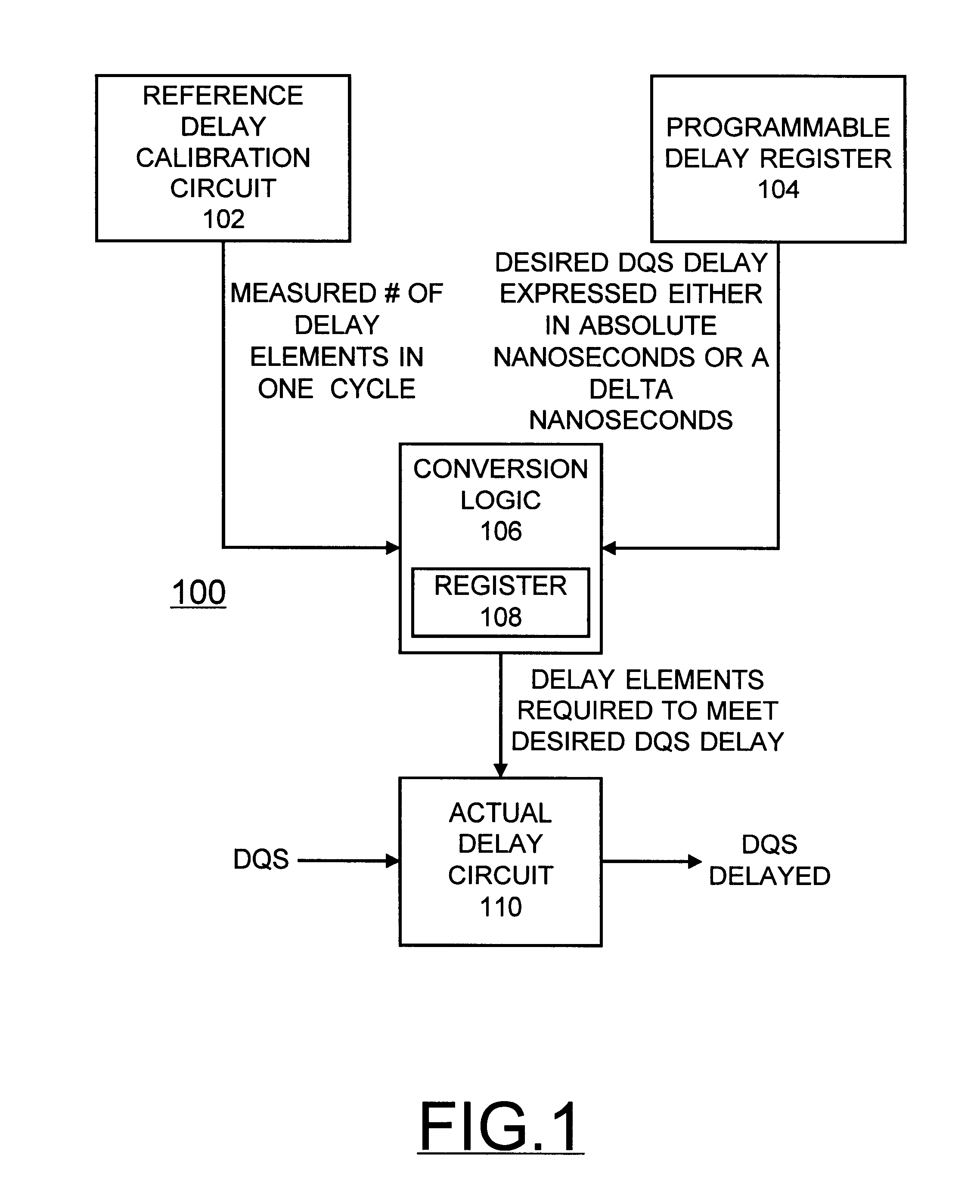
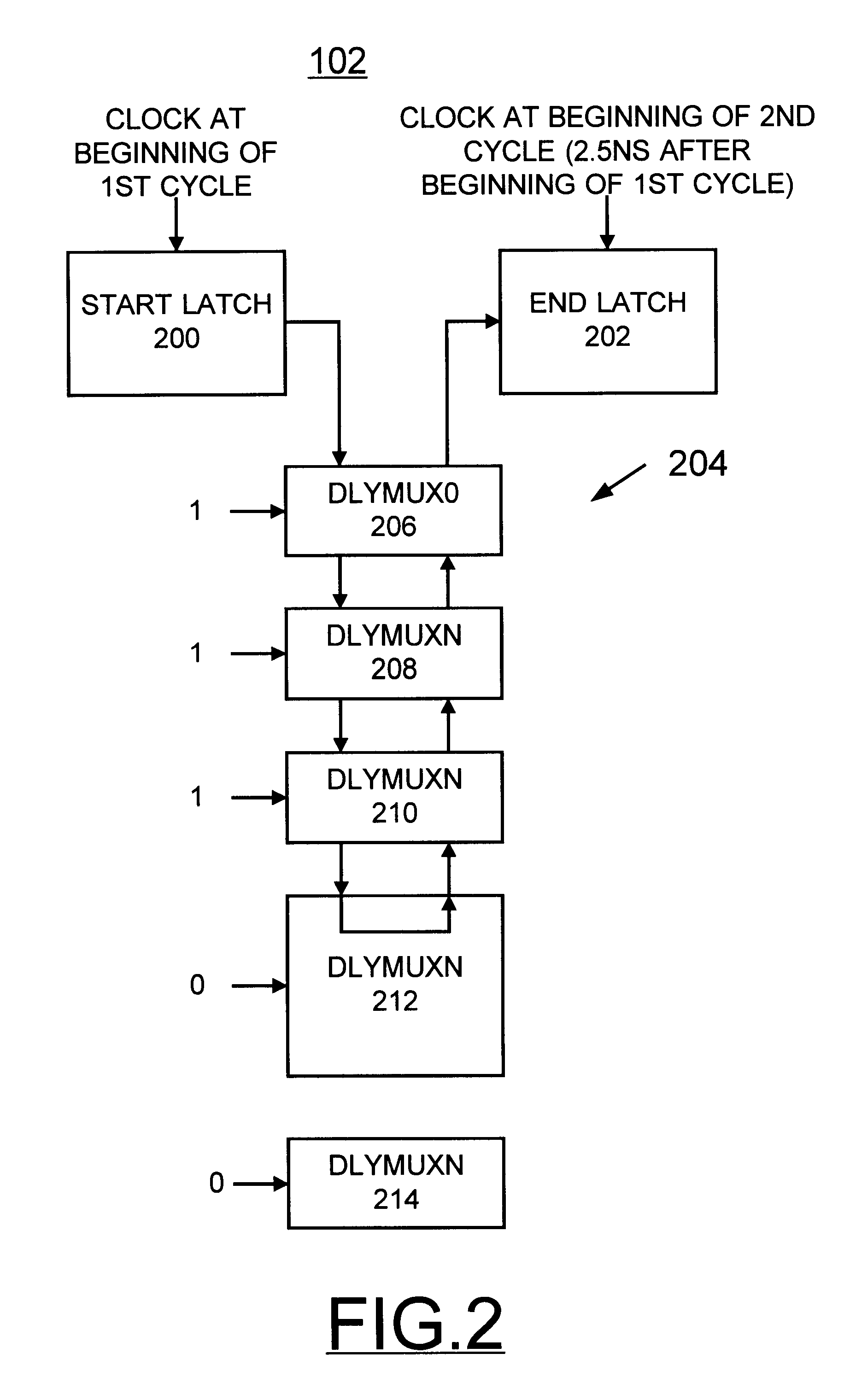
Programmable compensated delay for DDR SDRAM interface using programmable delay loop for reference calibration
A programmable compensated delay for a double data rate (DDR) synchronous dynamic random access memory (SDRAM) interface is provided. A programmable compensated delay apparatus includes a reference delay calibration circuit for providing a measured number of delay elements in one cycle. A programmable delay register provides a desired delay value. A conversion logic is coupled to the reference delay calibration circuit and the programmable delay register for receiving both the measured number of delay elements in one cycle and the desired delay value. The conversion logic provides a number of required delay elements. A delay circuit is coupled to the conversion logic for receiving the number of required delay elements and providing the desired delay. A SDRAM control logic provides a refresh start signal to the reference delay calibration circuit for updating the delay circuit during each DRAM refresh. The DQS clock strobe on the DDR SDRAM is applied to the delay circuit and is delayed by the desired delay.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
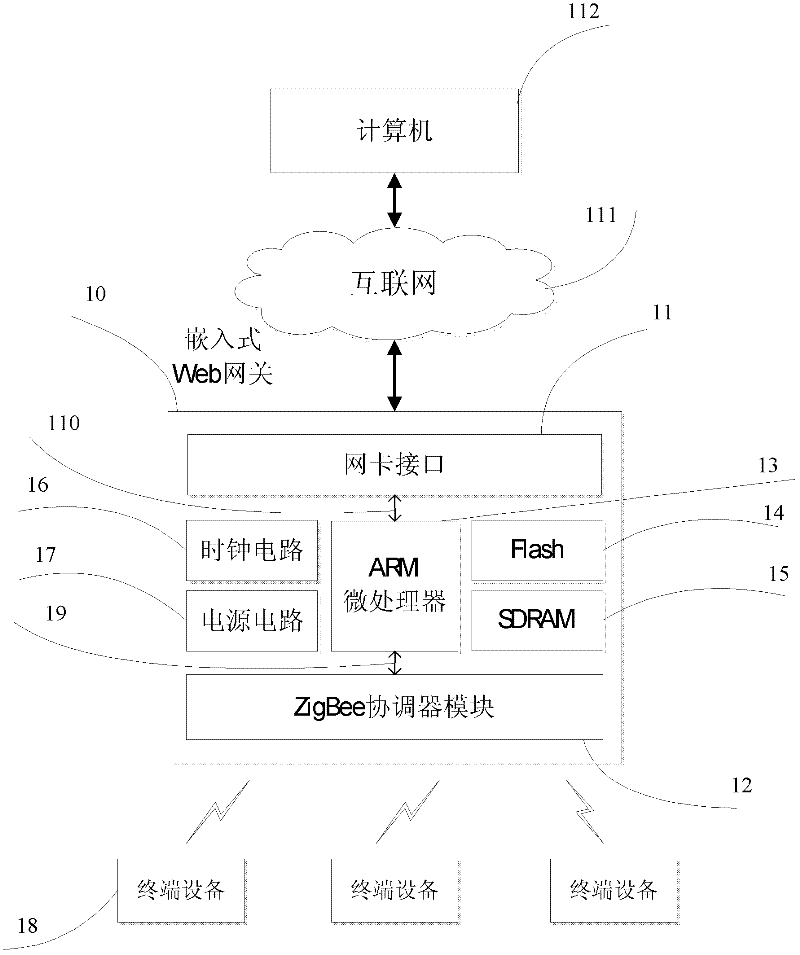
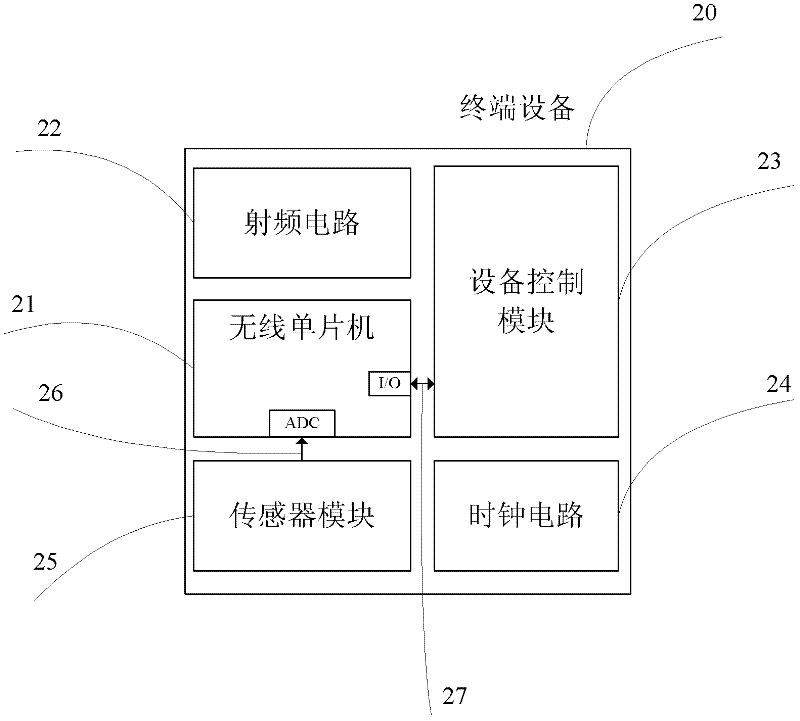
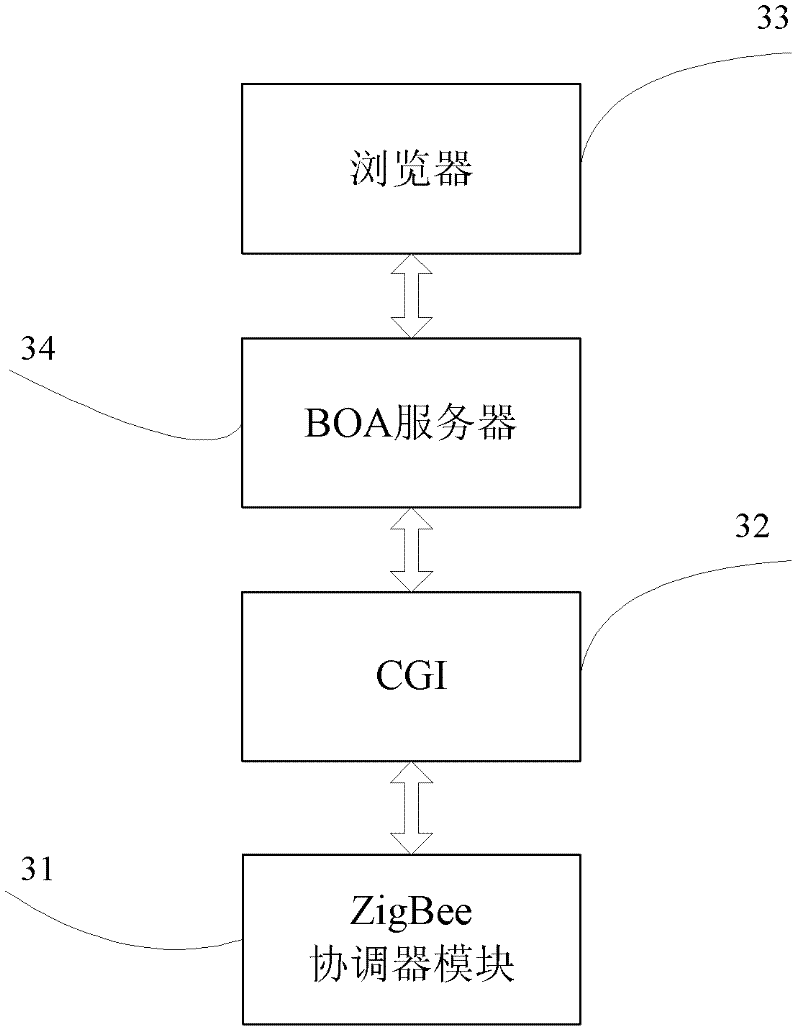
Intelligent household electric appliance system based on ZigBee and page generation and implementation method thereof
InactiveCN102238236AImprove versatilityEasy to manage centrallyProgramme controlTransmission systemsWeb serviceSynchronous dynamic random-access memory
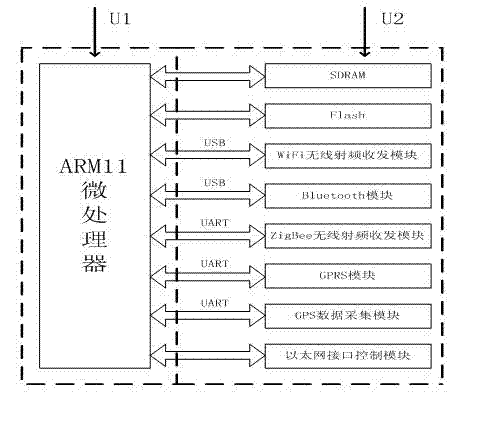
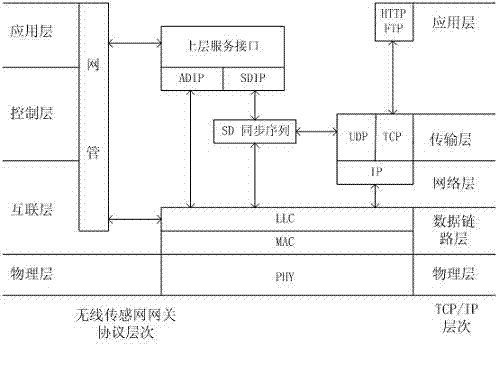
The invention provides an intelligent household electric appliance system based on ZigBee and page generation and an implementation method thereof, wherein the system comprises a computer, an embedded Web gateway and a plurality of terminal devices. The embedded Web gateway comprises an ARM (Advanced RISC Machine) microprocessor, a Flash SDRAM (synchronous dynamic random access memory), a time circuit, a power circuit, a network card interface and a ZigBee coordinator module, wherein the automatic generation of the household electric appliance control page is achieved based on the embedded Web server. The ZigBee coordinator module is wirelessly connected with the terminal devices via a ZigBee protocol for transmitting operation instructions and uploading the date of the terminal devices. The terminal devices receive the gateway instructions, execute the control instructions and unload the operation state of the devices and the environment parameter data. The computer remotely accesses the embedded Web gateway via the internet so as to obtain the household electric appliance control page, to manage the names of the terminal devices and to check and control the operation state of the devices and the environment parameter.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
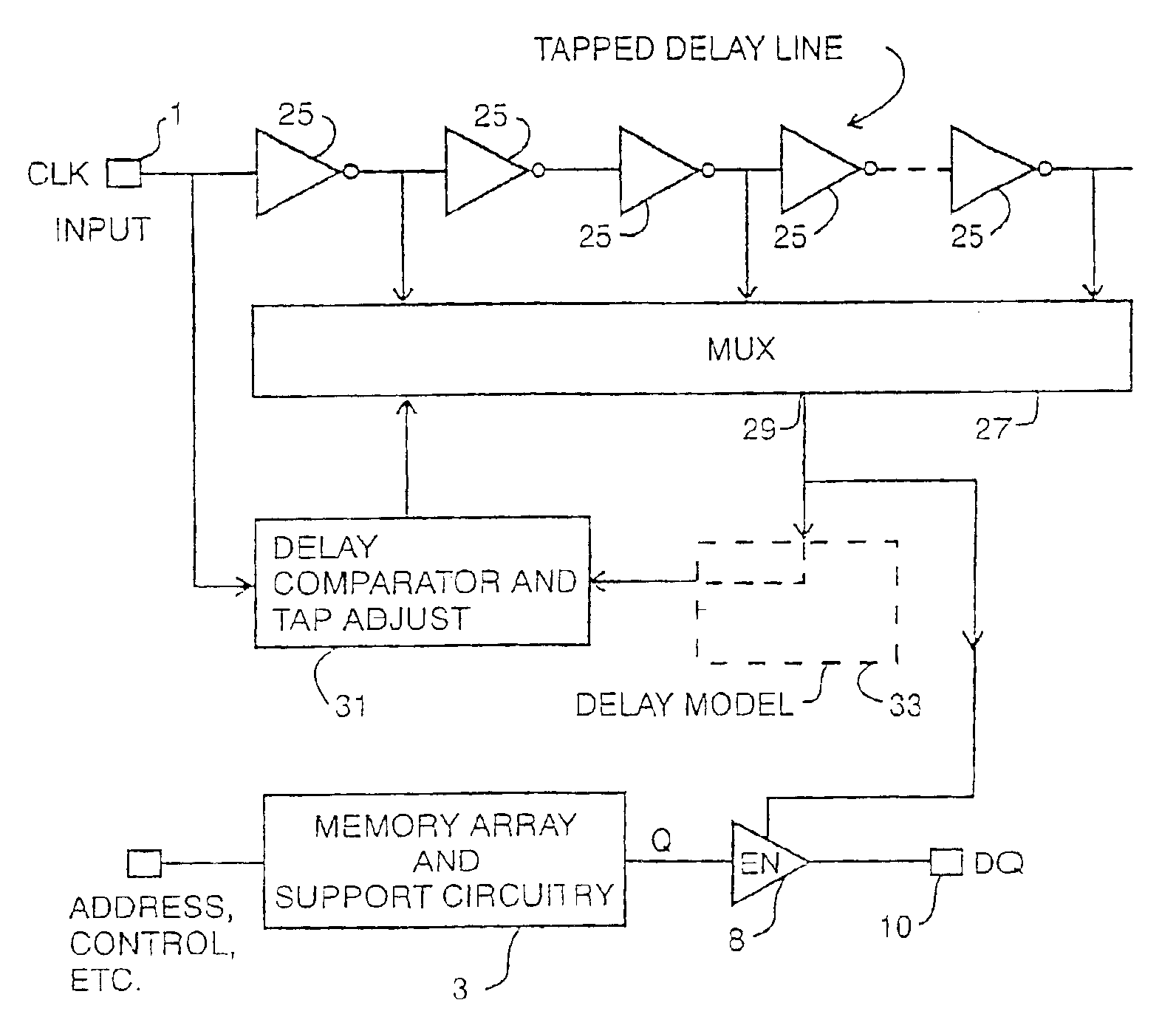
Delay locked loop implementation in a synchronous dynamic random access memory
InactiveUS20050265506A1Minimizes elapsed timeHigh clock frequency operationPulse automatic controlSingle output arrangementsRandom access memoryDelay-locked loop
A clock applying circuit for a synchronous memory is comprised or a clock input for receiving a clock input signal, apparatus connected to the synchronous memory for receiving a driving clock signal, and a tapped delay line for receiving the clock input signal and for delivering the clock driving signal to the synchronous memory in synchronism with but delayed from the clock input signal, the delay being a small fraction of the clock period or the clock input signal.
Owner:CONVERSANT INTPROP MANAGEMENT INC
Phased array radar antenna beam control device
ActiveCN102495565AImprove reliabilityMeet developmentProgramme controlWave based measurement systemsDouble data rateUniversal asynchronous receiver/transmitter
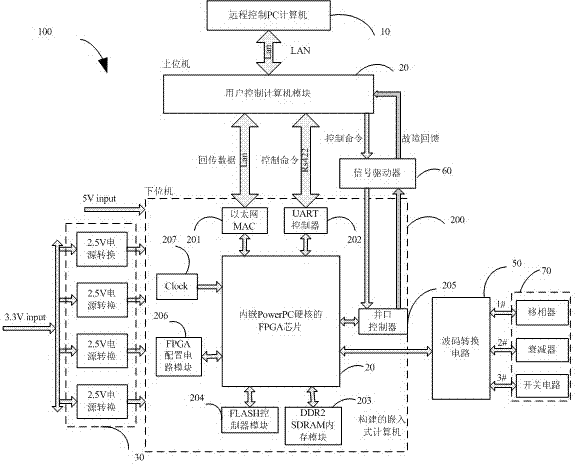
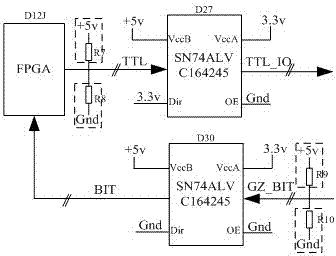
The invention relates to a phased array radar antenna beam control device. The phased array radar antenna beam control device comprises a remote control PC (Personal Computer) computer, a user control computer module, a power supply management module, a FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array) chip, a signal driver, a wave control conversion circuit and a controlled device which is electrically connected with the wave control conversion circuit, wherein the user control computer module remotely communicates with the remote control PC computer and are electrically connected with the FPGA chip, thepower supply management module and the wave control conversion circuit, respectively. The FPGA chip is embedded with a PowerPC hardcore and used for constructing an embedded computer; the embedded computer also comprises an Ethernet (Media Access Control), a UART (Universal Asynchronous Receiver Transmitter) controller, a DDR2SDRAM (Double Data Rate 2 Synchronous Dynamic Random Access Memory) memory module, a FLASH controller module, a parallel controller, a FPGA configuration circuit module and a clock generating circuit module. The phased array radar antenna beam control device provided by the invention has the advantage of high reliability.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRONIC TECH GRP CORP NO 38 RES INST
Multi-protocol multi-interface wireless sensor network gateway
InactiveCN102448202AImprove anti-interference abilityReduce power consumptionHigh level techniquesWireless communicationGeneral Packet Radio ServiceTransceiver
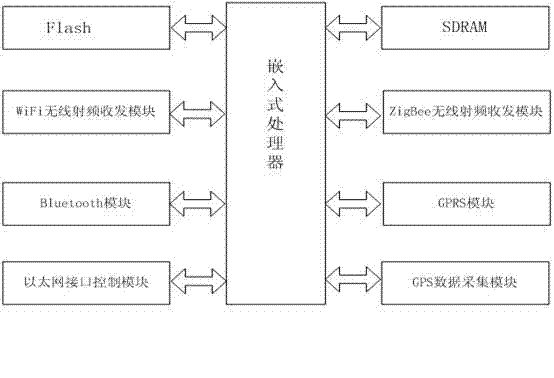
The invention discloses a multi-protocol multi-interface wireless sensor network gateway and relates to the technical field of a wireless sensor network. The gateway mainly consists of an embedded processor, an SDRAM (Synchronous Dynamic Random Access Memory), a Flash memory, a WiFi (Wireless Fidelity) wireless radio frequency transceiver module, a ZigBee wireless radio frequency transceiver module, a GPRS (General Packet Radio Service) module, a Bluetooth module, a GPS (Global Positioning System) data acquisition module and an Ethernet interface control module. A networked operating system Linux is used as an operating system of the multi-protocol multi-interface wireless sensor network gateway and can be compatible with a TCP / IP (Transmission Control Protocol / Internet Protocol) protocol IPv6 (Internet Protocol Version 6). The multi-protocol multi-interface wireless sensor network gateway has the advantages that conversion among various protocols is completed by treatment of a design protocol conversion program; the multi-protocol multi-interface wireless sensor network gateway can be used for setting up networks with various architectures, interconnecting the networks with various architectures and transmitting data; various network access schemes are provided for the wireless sensor network; the multi-protocol multi-interface wireless sensor network gateway has strong anti-interference capability, low power consumption and small volume; and portable equipment is provided for interconnection among the networks with various architectures and building of an integrated network.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
Memory device and method having separate write data and read data buses
InactiveUS20070028027A1Memory adressing/allocation/relocationDigital storageMultiplexerRandom access memory
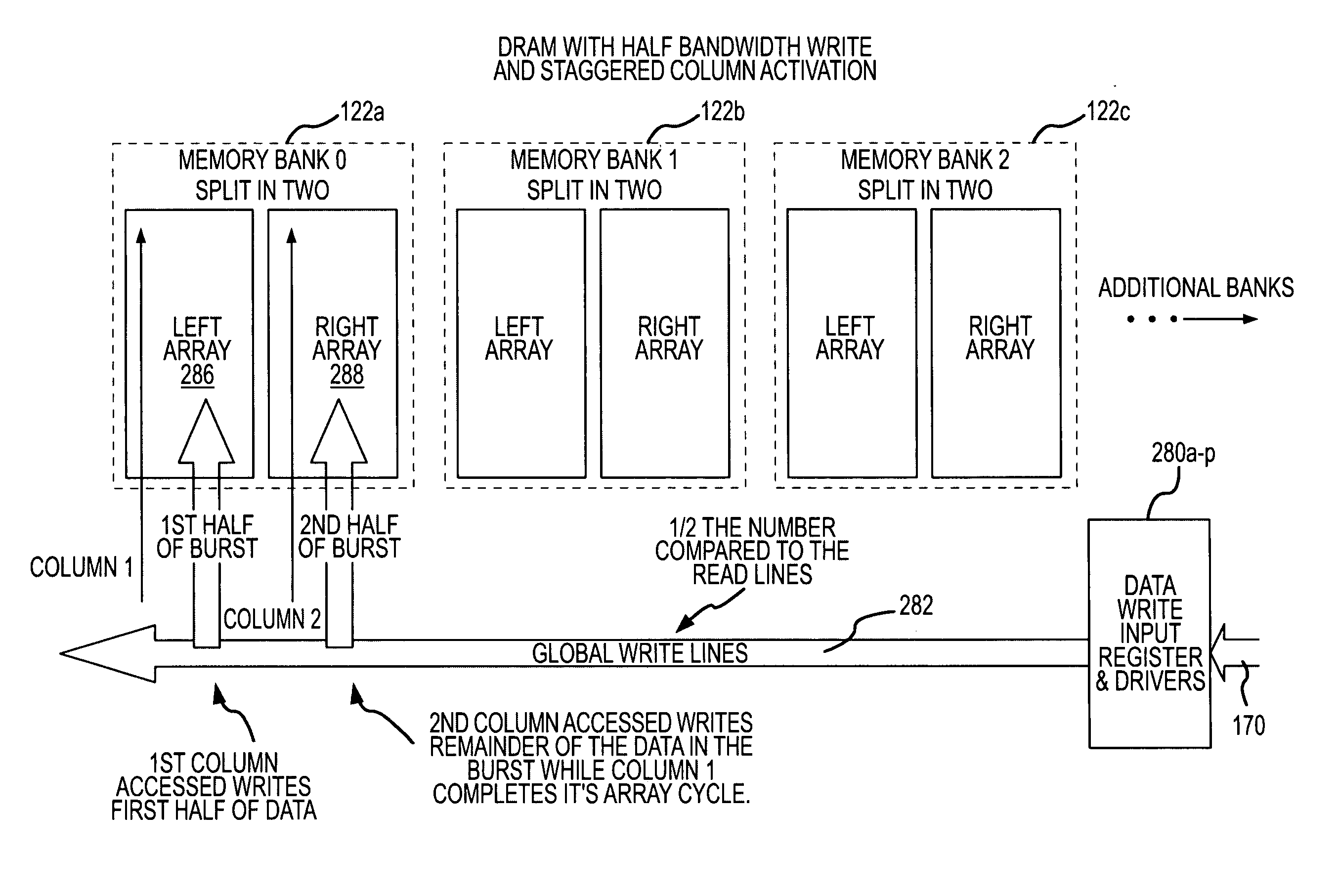
A synchronous dynamic random access memory (“SDRAM”) device includes several banks of memory cell coupled to a read data path and a write data path. The read data path includes a read latch that stores a relatively large number of read data bits received in parallel from a bank of memory cells. Groups of the stored read data bits are sequentially selected by a multiplexer and applied to a read data bus. Groups of write data bits are sequentially coupled to the SDRAM device through a write data bus that is separate from the read data bus, and they are sequentially stored in input registers. When the input registers are full, the write data bits are coupled in parallel to a bank of memory cells. The number of bits in the write data bus is preferably a submultiple of the number of bits in the read data bus.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
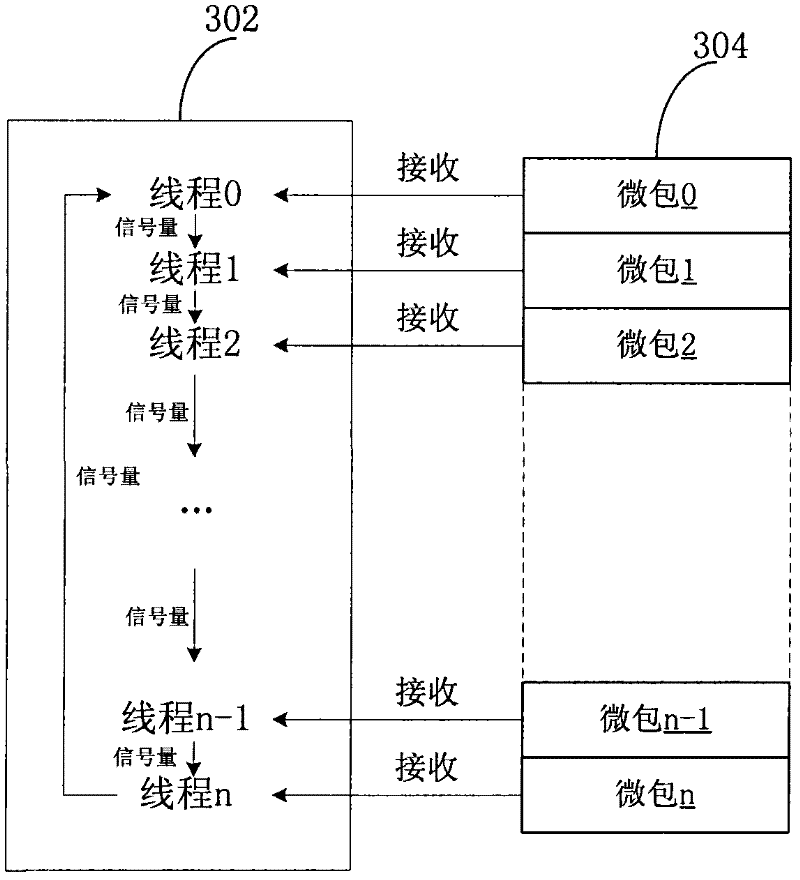
Multi-core and multi-threading processor-based functional macropipeline implementing method
InactiveCN102331923ASolve bottlenecksProcessing speedConcurrent instruction executionComputer architectureNetwork packet
The invention discloses a multi-core and multi-threading processor-based functional macropipeline implementing method. A plurality of processors are divided into different clusters, namely a receiving cluster and a transmitting cluster; the plurality of processors have parallel structures in the receiving cluster and the transmitting cluster; the receiving cluster is responsible for receiving messages, a parallel structure is adopted in the receiving cluster, and all packet receiving tasks are completed parallelly by a plurality of threadings; and the transmitting cluster is responsible for transmitting the messages, including checking whether a new data packet transmitting task is present, acquiring queue descriptor information of the current head pointer after reading a new transmitting task, transmitting a data packet from a synchronous dynamic random access memory (SDRAM) unit specified by a descriptor to a specified transmitting buffer unit and maintaining synchronous communication between the head pointer of a queue and the receiving cluster, a parallel structure is adopted in the transmitting cluster, and all packet transmitting tasks are completed parallelly by a plurality of threadings.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
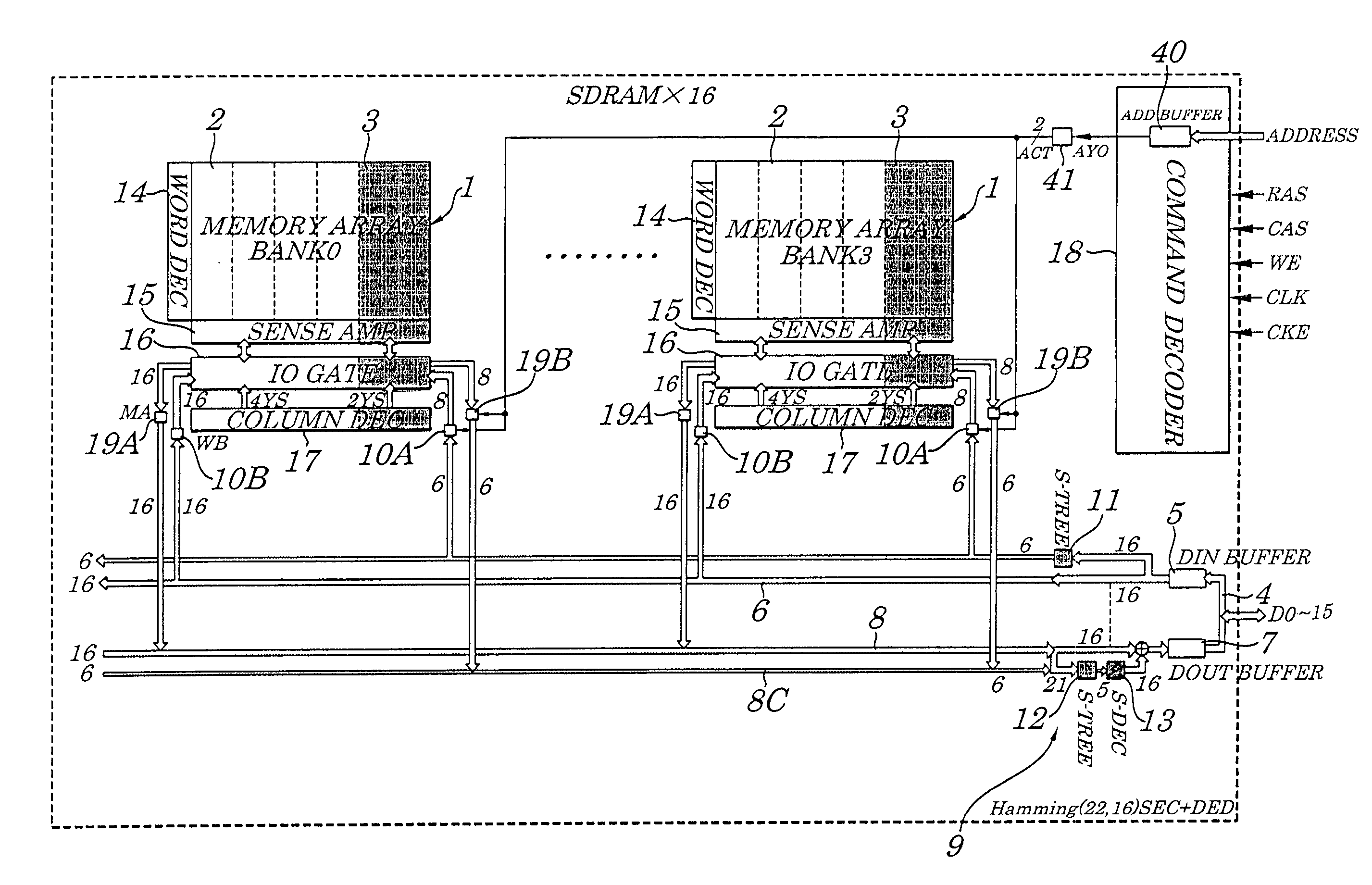
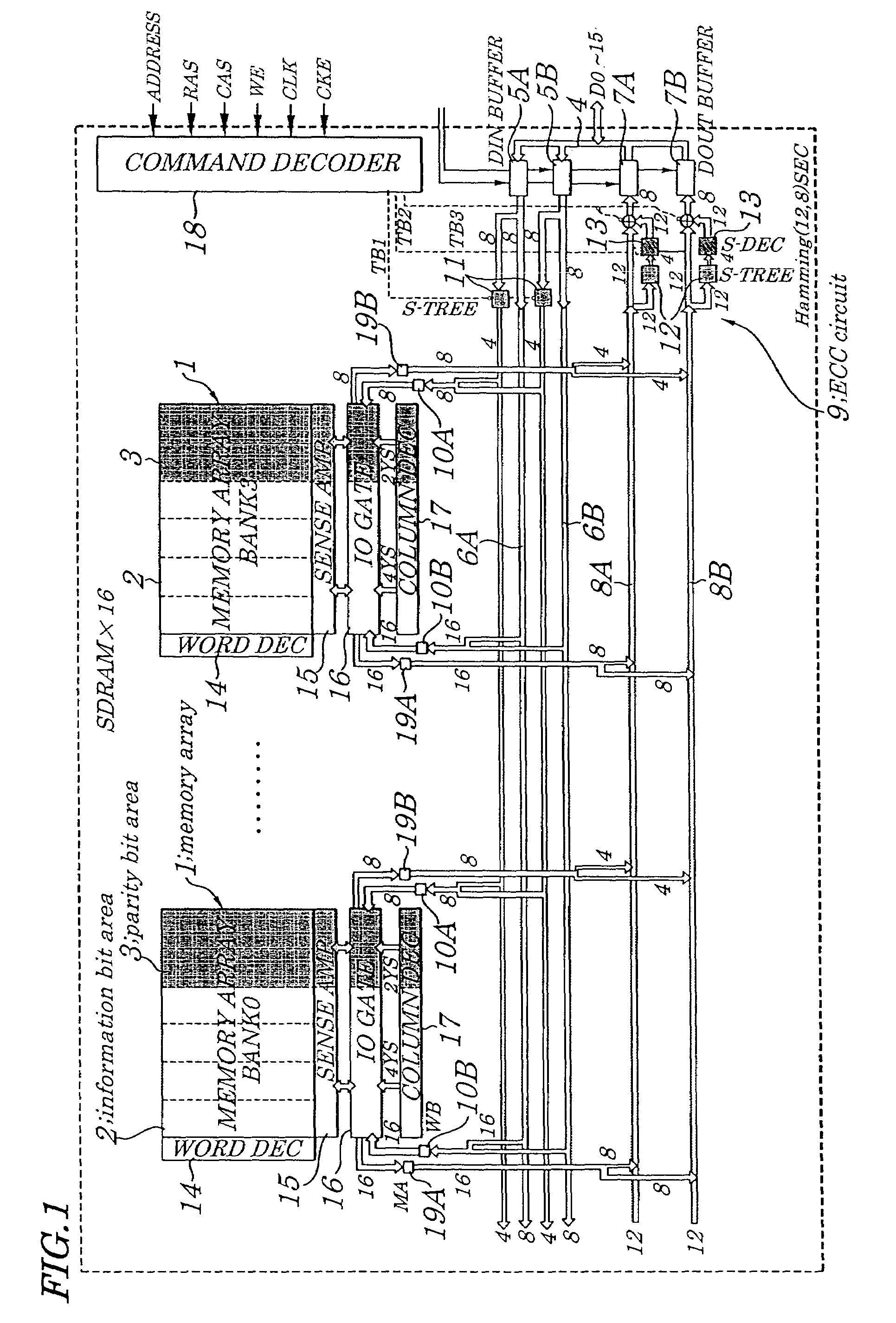
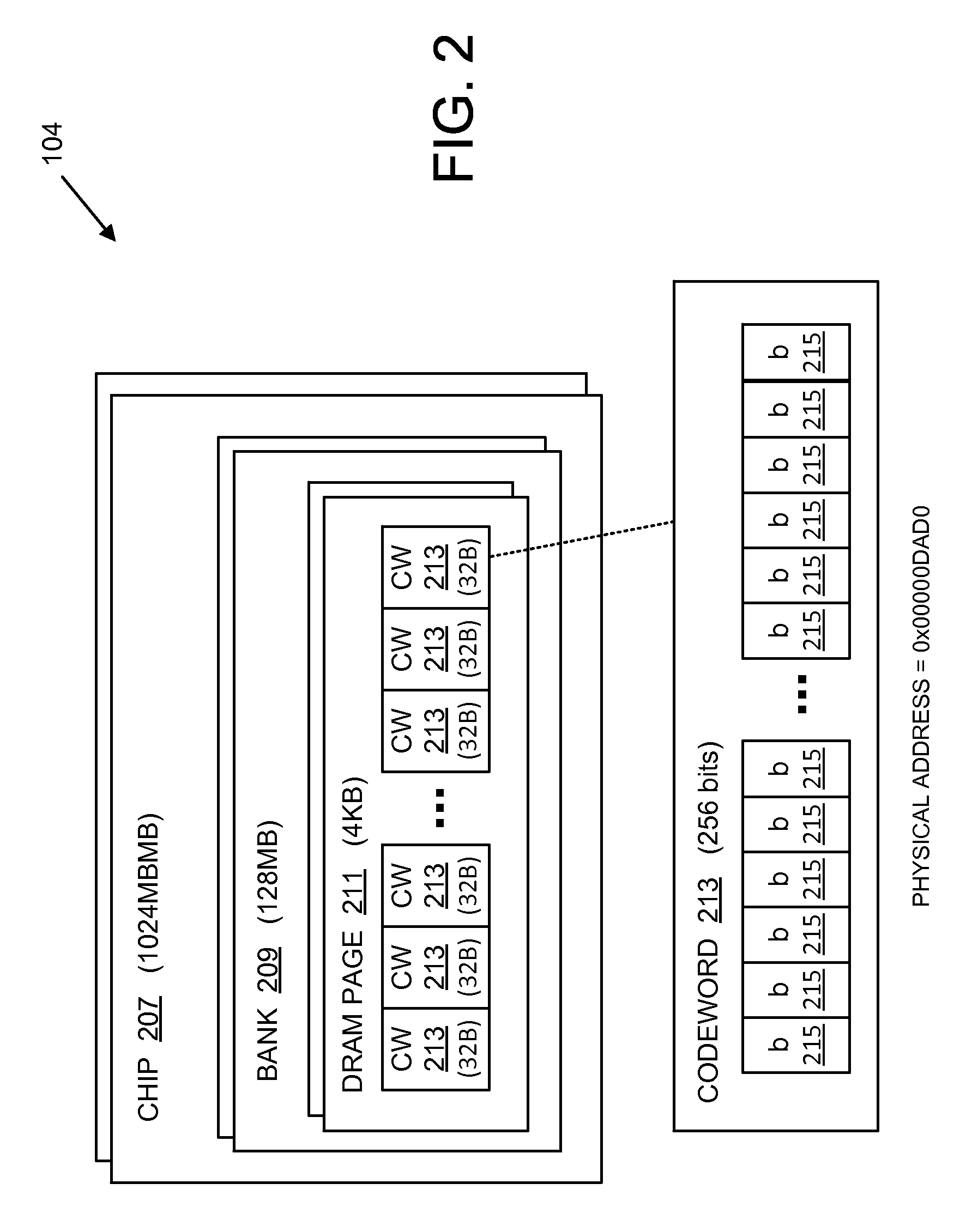
Semiconductor memory device provided with error correcting code circuitry
ActiveUS7225390B2Effective correctionReduce error rateCode conversionDigital storageHamming codeError location
A semiconductor synchronous dynamic random access memory (SDRAM) device capable of correcting bits having a low error rate in a Pause Refresh Tail distribution and of reducing a data holding current by lengthening a refresh period so that the refresh period exceeds a period for a Pause Refresh real power. The semiconductor memory device is made up of a 16-bit SDRAM having a Hamming Code and including an ECC (Error Correcting Code) circuit made up of an encoding circuit controlled by a first test signal to output a parity bit corresponding to an information bit, a decoding circuit controlled by second test signal to output an error location detecting signal indicating an error bit in codeword, and an error correcting circuit controlled by a third test signal to input an error location detecting signal and to output an error bit in a reverse manner.
Owner:LONGITUDE LICENSING LTD
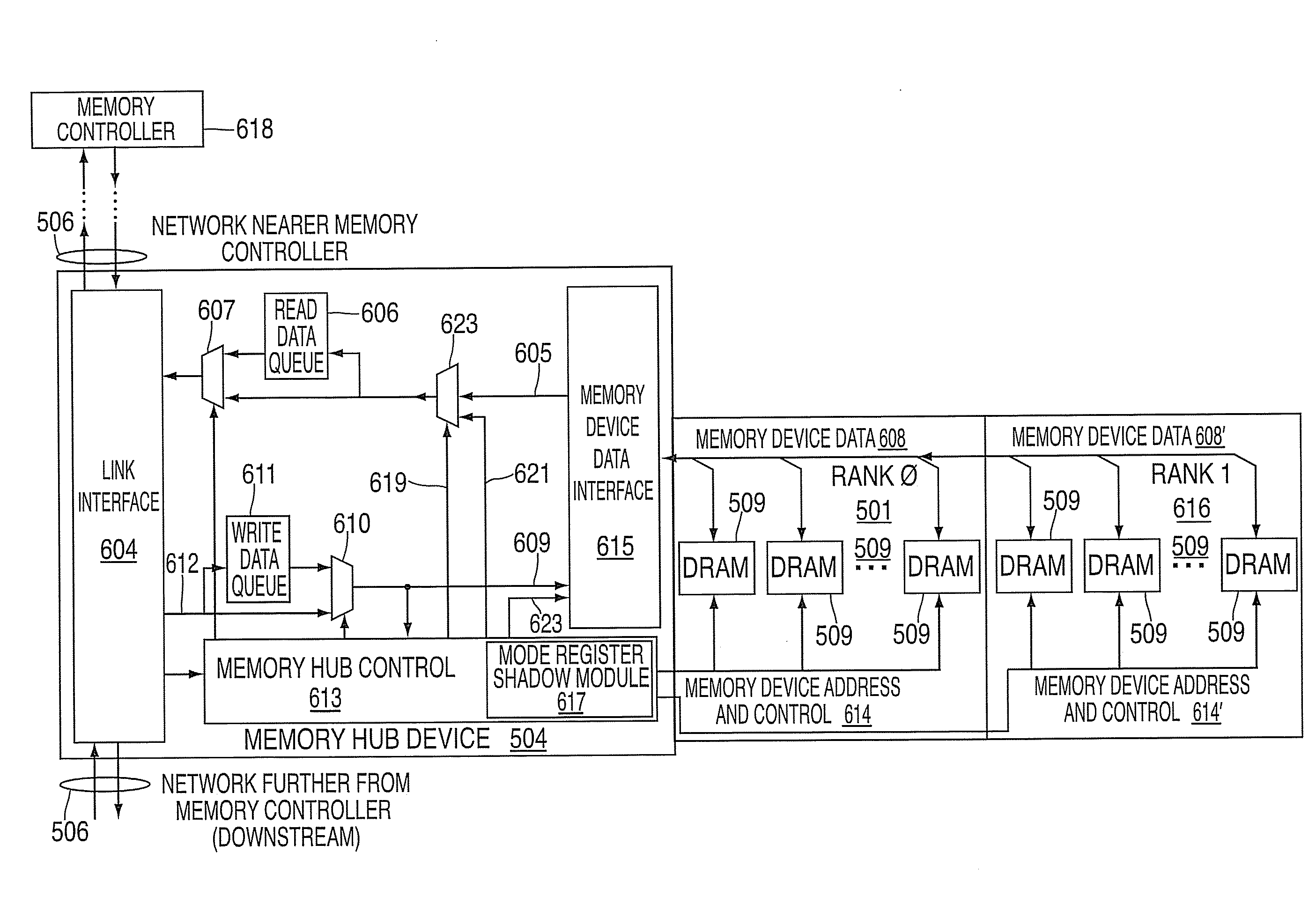
System and method for providing synchronous dynamic random access memory (SDRAM) mode register shadowing in a memory system
A system and method for providing SDRAM mode register shadowing in a memory system. A system includes a memory interface device adapted for use in a memory system. The memory interface device includes an interface to one or more ranks of memory devices, and each memory device includes one or more types of mode registers. The memory interface device also includes an interface to a memory bus for receiving commands from a memory controller. The commands include a mode register set command specifying a new mode register setting for one or more ranks of memory devices and a mode register type. The memory interface device further includes a mode register shadow module to capture settings applied to the mode registers. The module includes a shadow register for each type of mode register and a shadow log for each type of mode register. The module also includes mode register shadow logic to detect a mode register set command, to store the new mode register setting in the shadow register corresponding to the specified mode register type, and to set one or more bits in the shadow log corresponding to the specified mode register type to indicate which of the ranks of memory devices have been programmed with the new mode register setting.
Owner:IBM CORP
Semiconductor memory pipeline buffer
InactiveUS6958507B2Increase in effective access speedNegligible areaTransistorSolid-state devicesAudio power amplifierSynchronous dynamic random-access memory
A high capacity, fast access dynamic random access memory is provided. Furthermore, a pipelined write method can be realized at each array block by affixing a latch between the sense amplifier and write data line for each column. In this manner, a data write phase can occur simultaneously with the pre-read phase of the following address. Using this method, the effective access speed to the array block can be increased, yielding a fast access cache memory.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Dual-interface radar data recorder
InactiveCN101839974AReduce volumeRecord fastWave based measurement systemsData acquisitionPrinted circuit board
The invention discloses a dual-interface radar data recorder, which consists of a digital signal processor (DSP) main control module, a field programmable gate array (FPGA) interface control module, an analogue to digital converter (ADC) data acquisition module, a synchronous dynamic random access memory (SDRAM) data cache unit, a network interface chip, a solid integrated development environment (IDE) hard disc and a power supply chip. The connection relationship of the elements is that: the SDRAM data cache unit is connected with the DSP main control module for data caching; the DSP main control module and the ADC data acquisition module are both connected with the FPGA interface control module through buses to exchange data; the FPGA interface control module controls the solid IDE hard disc and the network interface chip to complete data record; and the power supply chip is responsible for supplying voltage required by the whole system. The recorder system is integrated on a printed circuit board (PCB) and conducts dual-interface functions by the coding of a DSP and an FPGA, so the use of specific chips is reduced, the area of the PCB area is reduced and the weight of the system is lightened; and the recorder has the advantages of flexible use and easy modification. The dual-interface radar data recorder has a practical value and a wide application prospect in the technical field of communication control.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
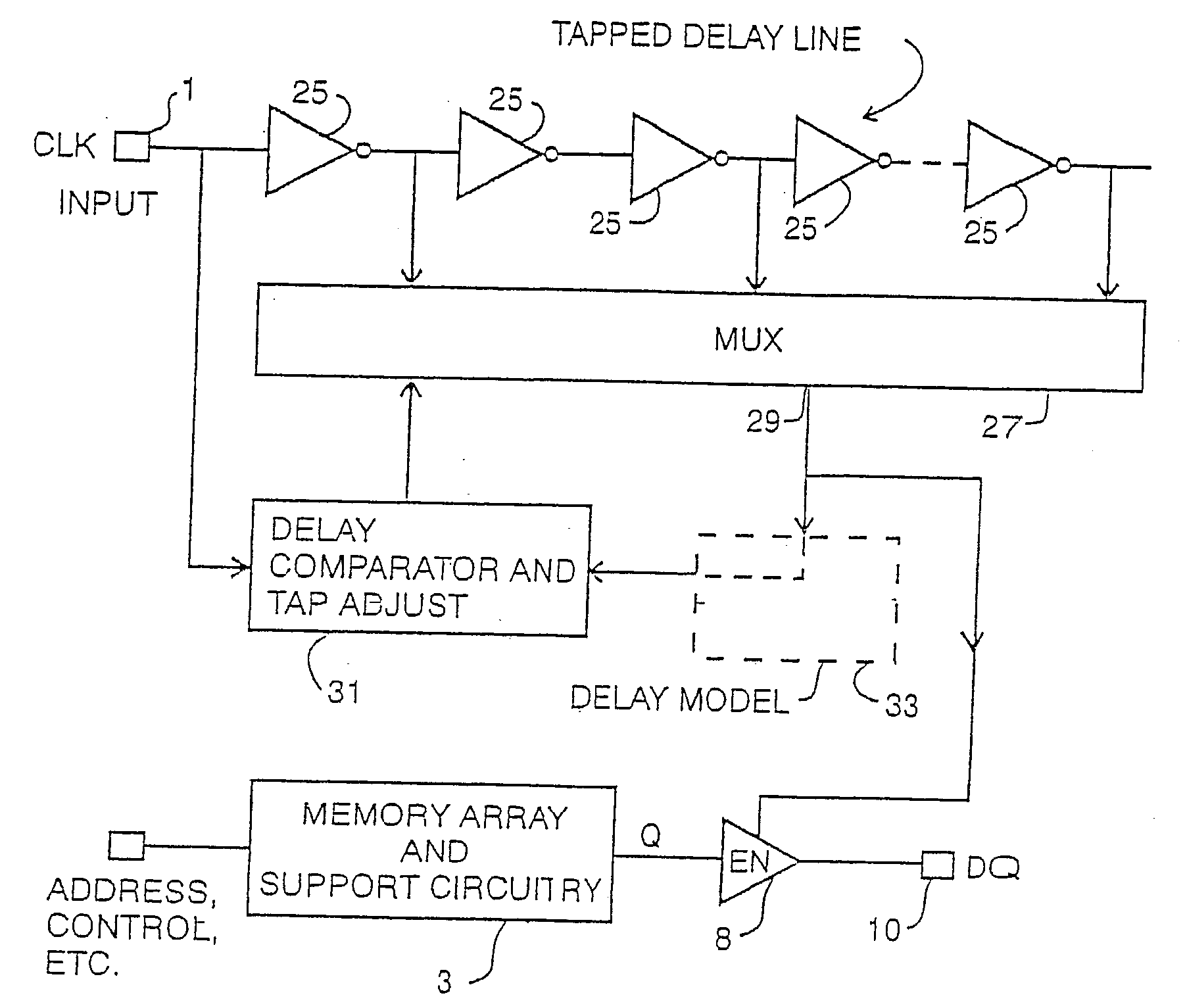
Method and apparatus for fast lock of delay lock loop
A method and apparatus to dynamically set the insertion point of a delay line control shift register based on the current cycle time. A string of delay elements equivalent to the delay elements in a delay lock loop (DLL) are laid out in the opposite direction compared to the DLL delay elements. Both strings of delay elements receive a synchronous input signal such as an external clock signal. The output clock signal of the DLL is phase-shifted relative to the external clock signal such that data removed from a device such as a synchronous dynamic random access memory (SDRAM) device is synchronous with the external clock signal. When a DLL reset command is issued, the information from the string of delay elements is captured and used to set the insertion point of the DLL to the locked or phase-equal point. This allows the DLL to quickly lock on any frequency upon reset of the DLL.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
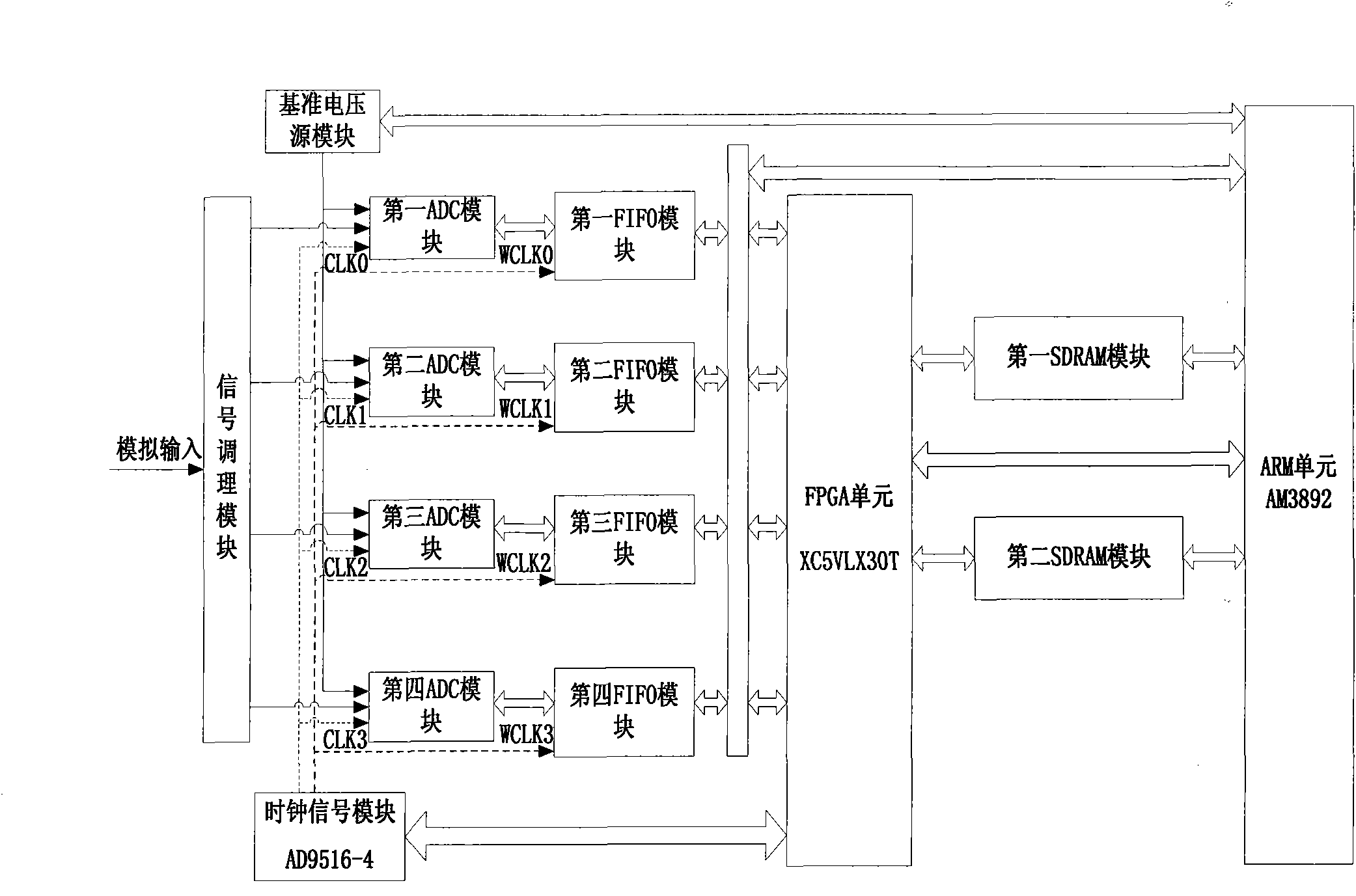
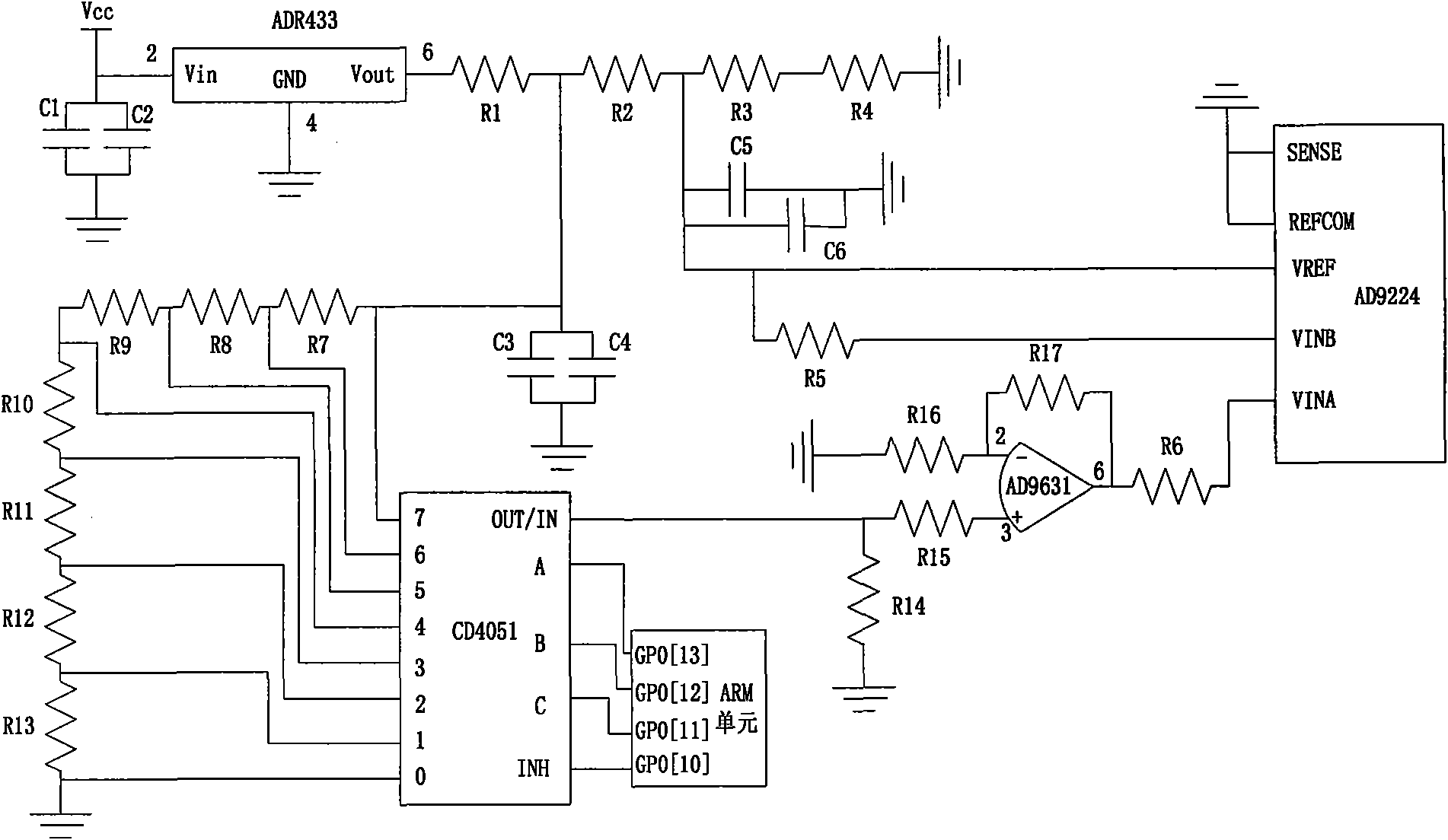
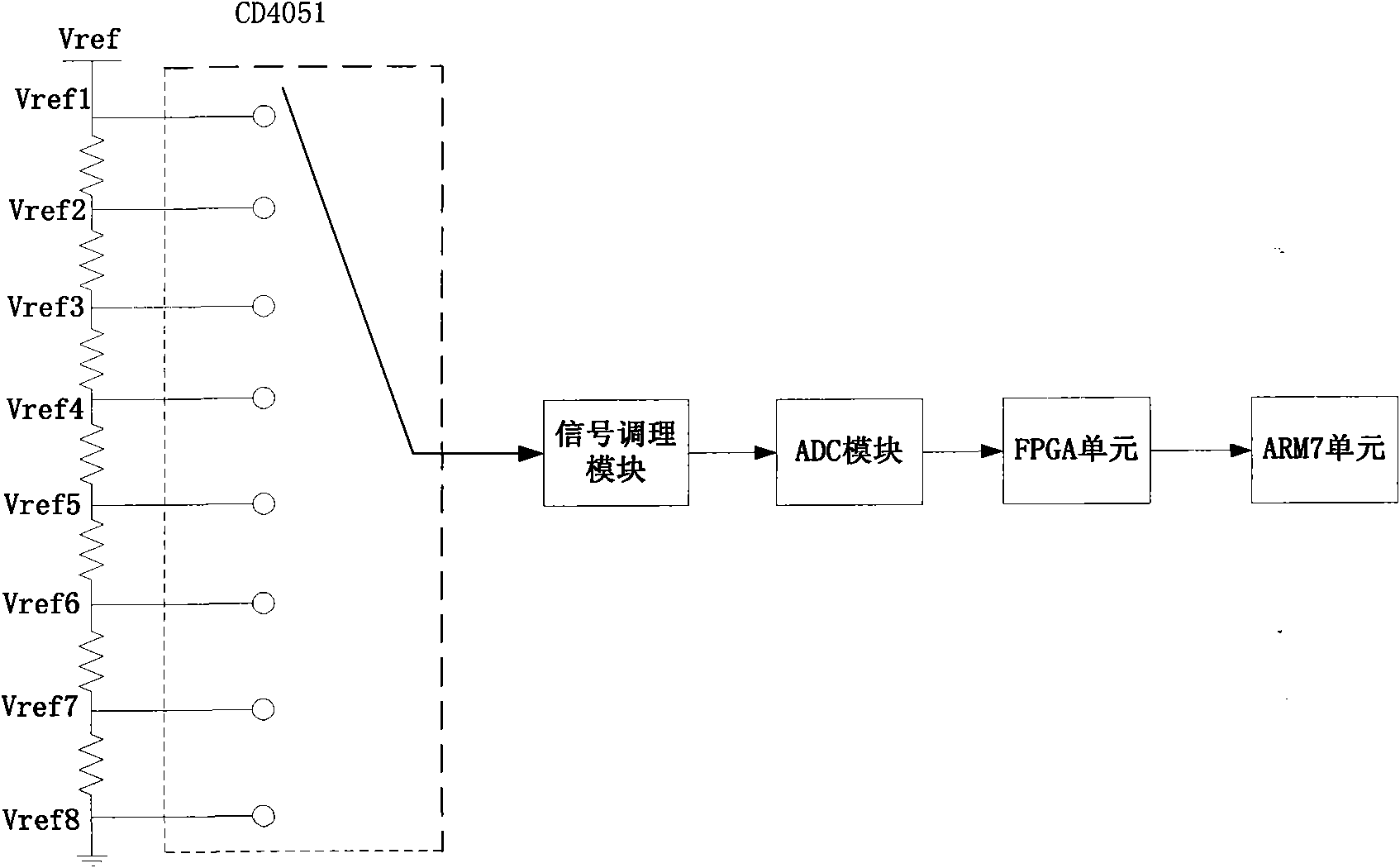
High-speed high-accuracy recorder and sampling data automatic-correction and high-order matching method thereof
InactiveCN102136841AHigh precisionReduce mismatchAnalogue/digital conversionElectric signal transmission systemsTimestampVoltage source
The invention discloses a high-speed high-accuracy recorder and a designing method thereof. The high-speed high-accuracy recorder comprises a signal conditioning module, four analogue-to-digital converter (ADC) modules, four first in first out (FIFO) modules, two synchronous dynamic random access memory (SDRAM) modules, a client-server architecture control module, a synchronous coherent clock module, a high-accuracy reference voltage source module and the like, wherein the client-server architecture control module consists of an advanced RISC machine (ARM) unit and a field programmable gate array (FPGA) unit; and the synchronous coherent clock module takes a clock chip as a core. The recorder finishes the operations of 'time-interleaved' sampling, encapsulation, caching, transmission, decapsulation combination, correction, storage, uploading and the like concurrently under the control of a concurrent time sequence logic, corrects sampling data based on an inter-ADC channel mismatchingautomatic-correction polynomial to reduce gain mismatching and offset / zero mismatching among ADC channels, reduces time mismatching among the ADC channels by using a synchronous coherent clock and a serpentine curve wire-length fine-adjustment technology, and solves the problems of associated global errors produced by data loss in the high-speed 'time-interleaved' sampling by using a high-order matching technology in which the encapsulation is performed by additional timestamp sequence numbers.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
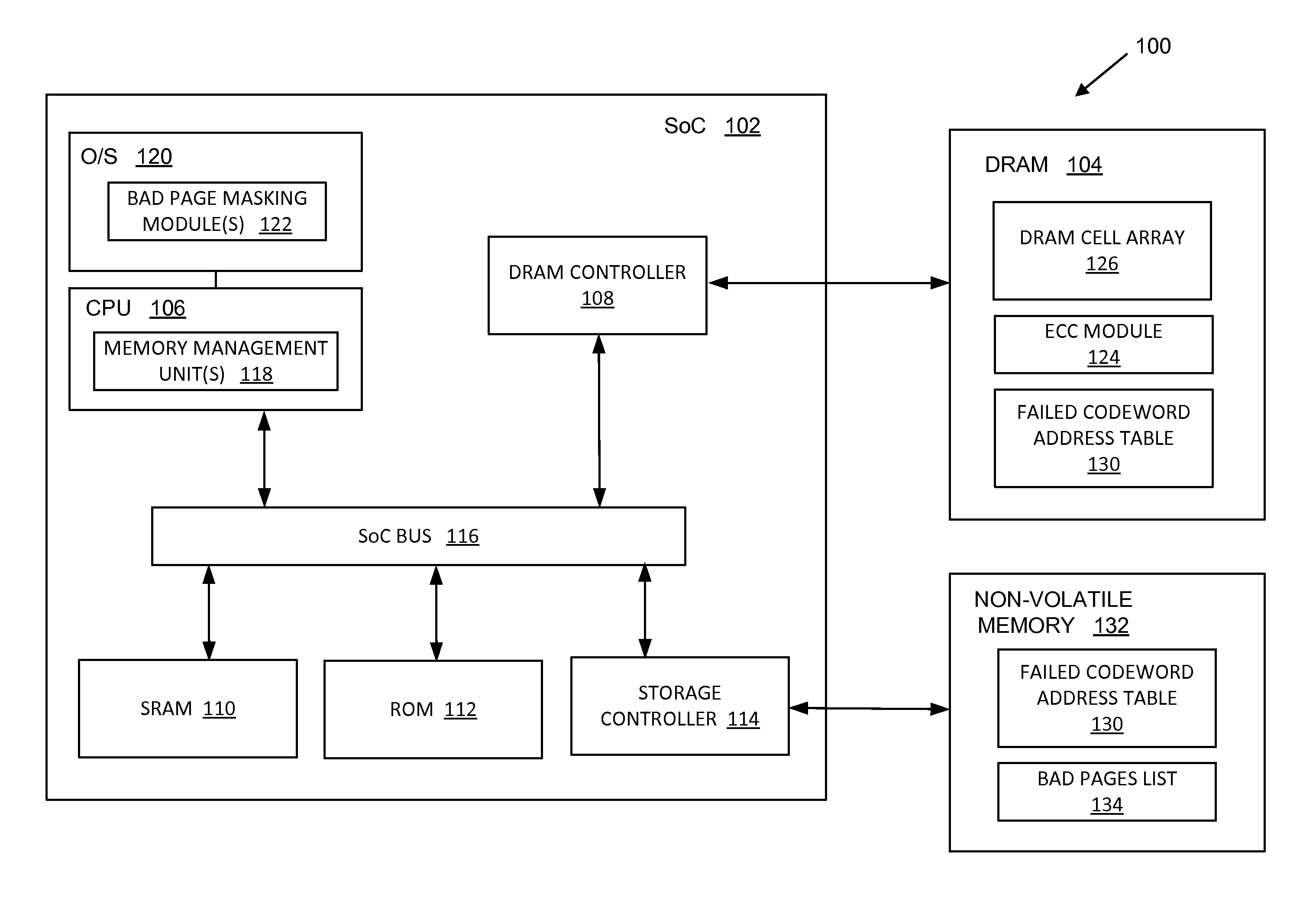
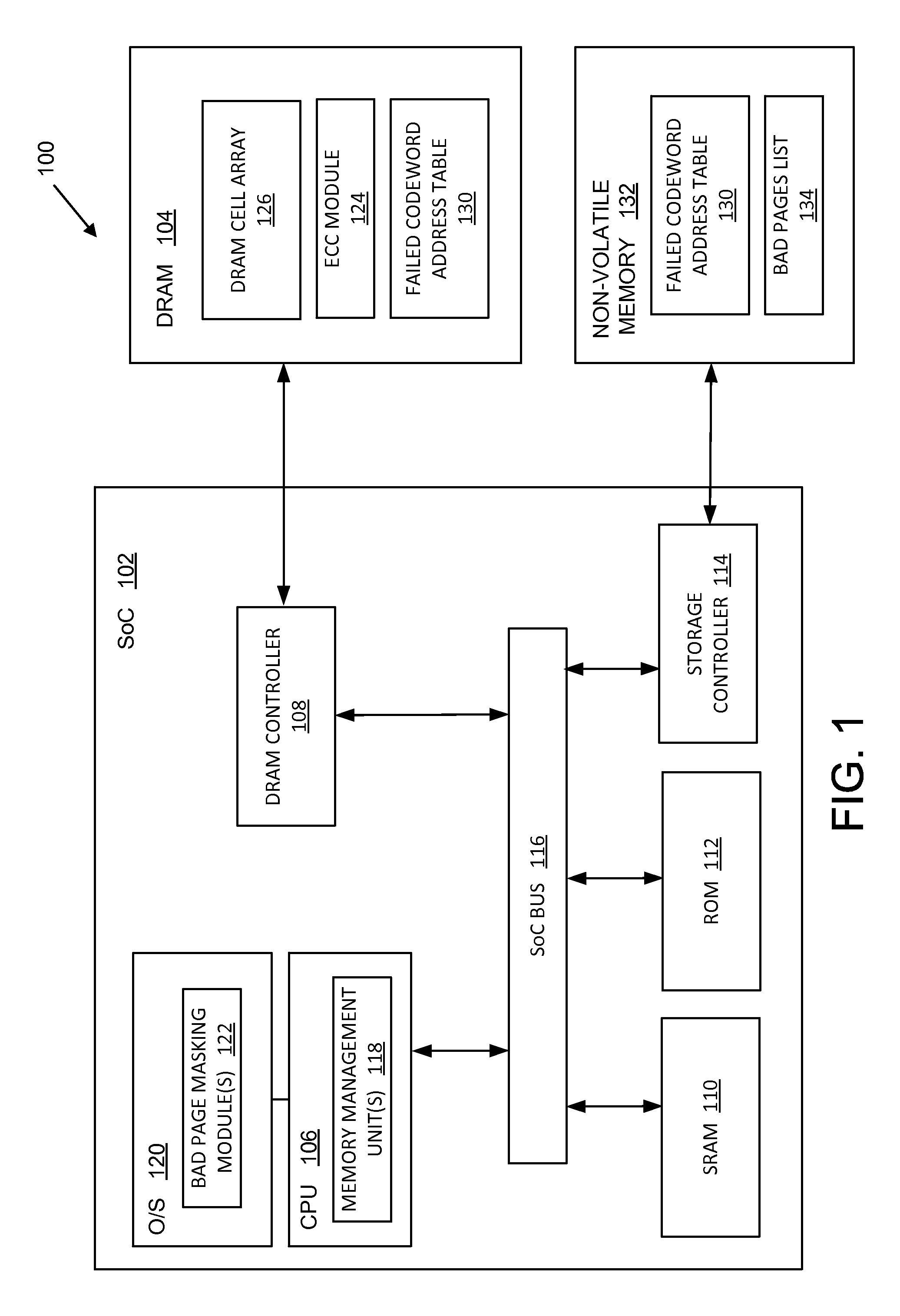
Kernel masking of DRAM defects
ActiveUS9299457B2Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationStatic random-access memoryRandom access memory
Systems, methods, and computer programs are disclosed for kernel masking dynamic random access memory (DRAM) defects. One such method comprises: detecting and correcting a single-bit error associated with a physical address in a dynamic random access memory (DRAM); receiving error data associated with the physical address from the DRAM; storing the received error data in a failed address table located in a non-volatile memory; and retiring a kernel page corresponding to the physical address if a number of errors associated with the physical address exceeds an error count threshold.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
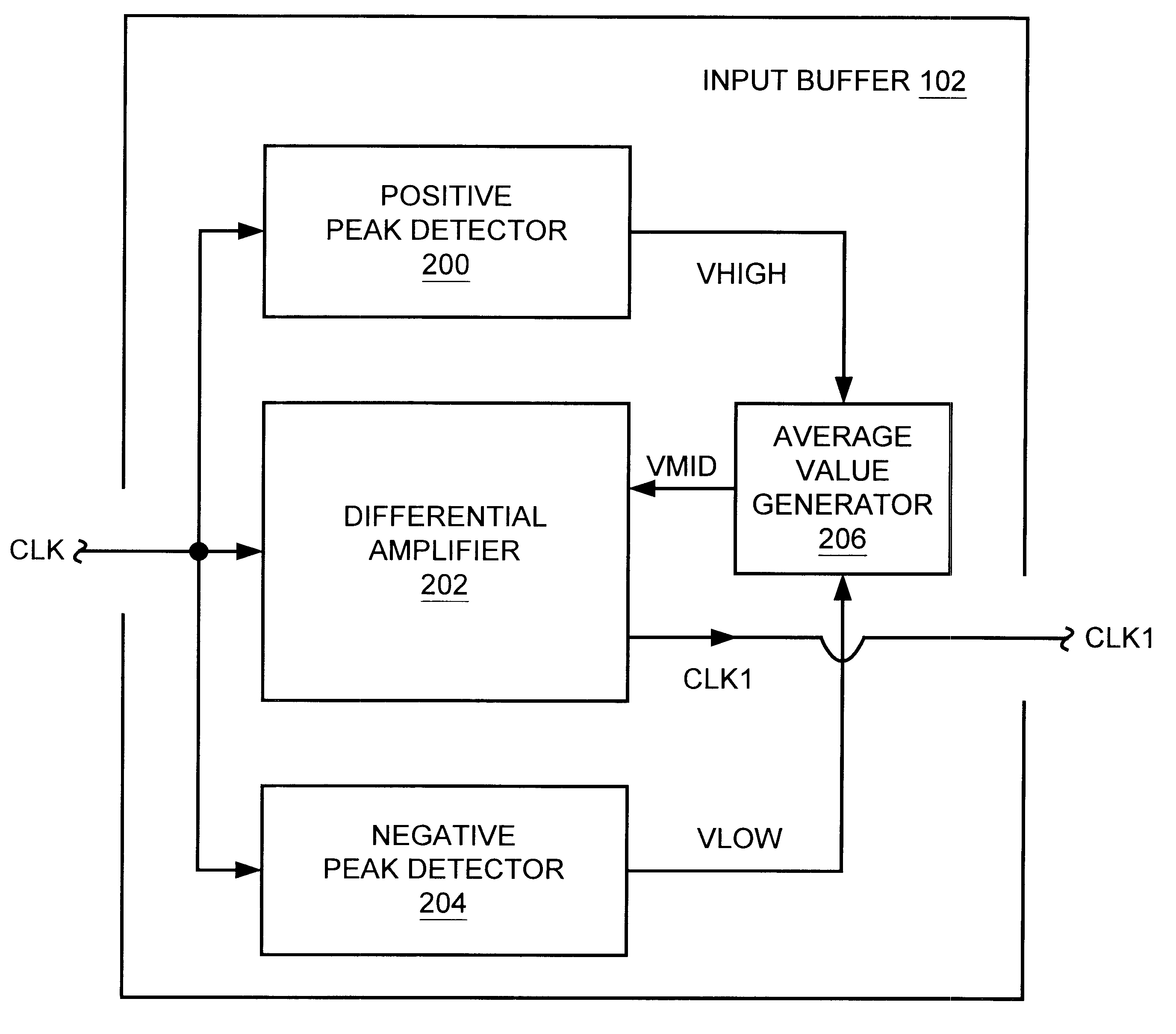
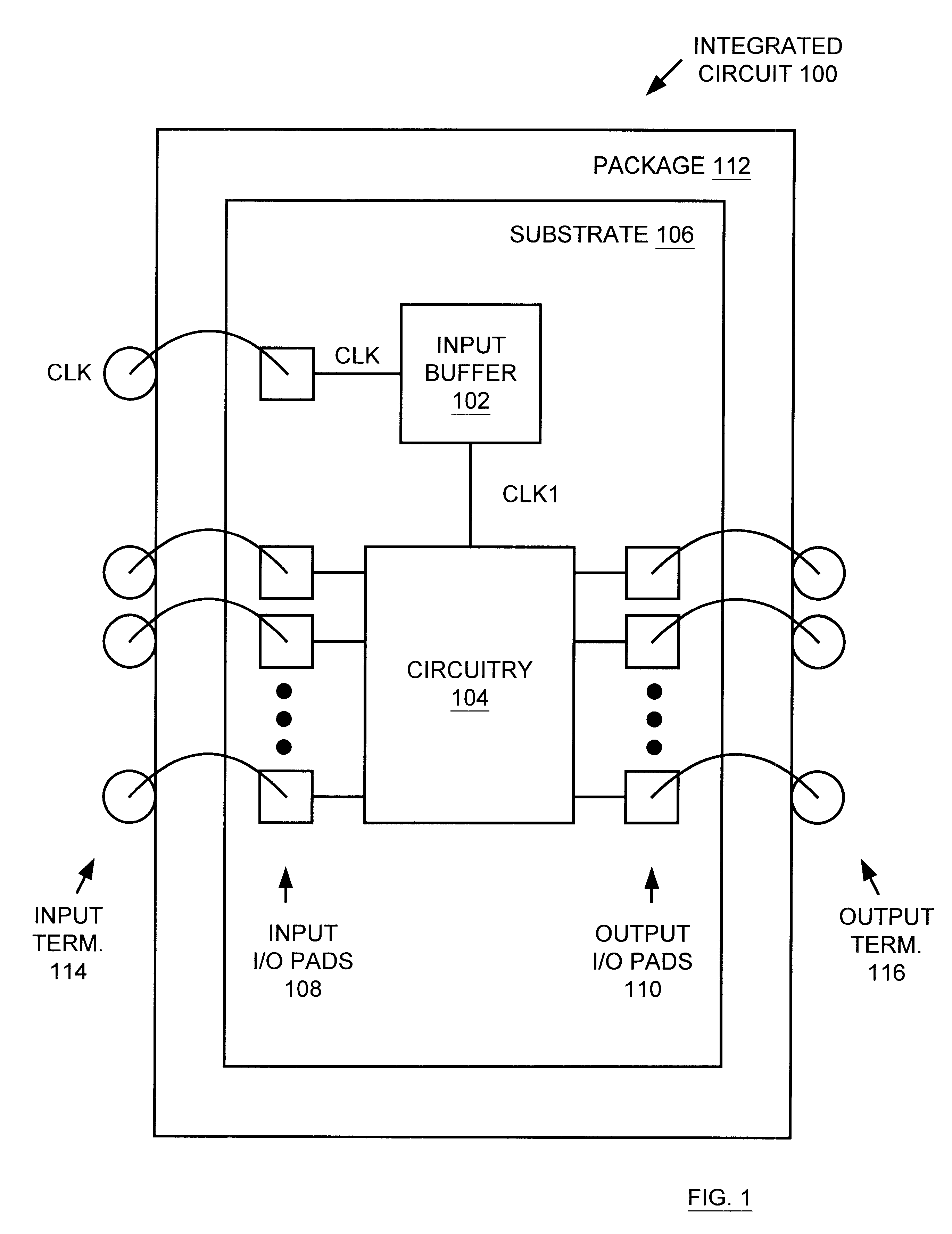
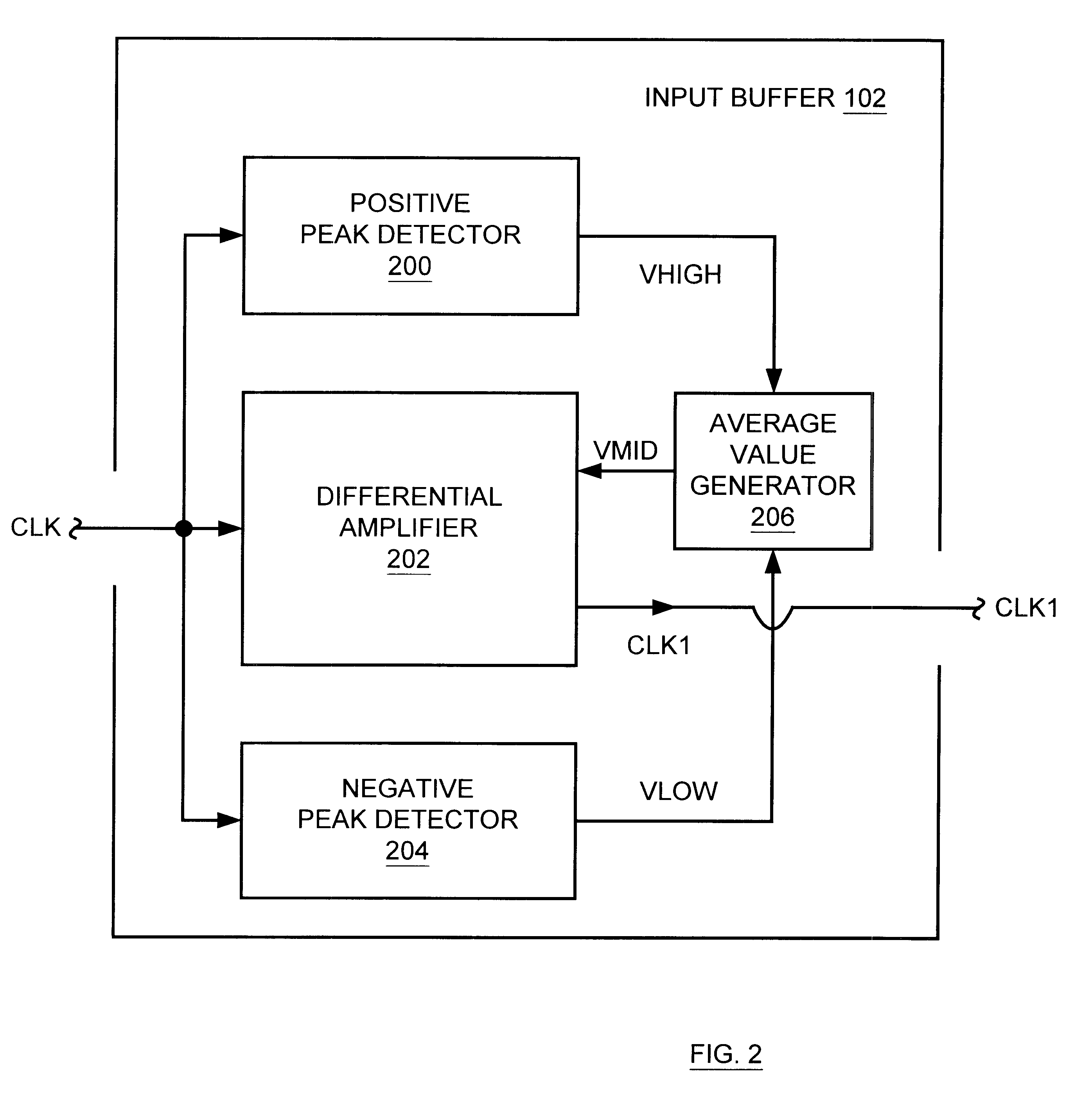
Input buffer with automatic switching point adjustment circuitry, and synchronous DRAM device including same
InactiveUS6522160B1Reliability increasing modificationsMultiple input and output pulse circuitsVoltage amplitudeDetector circuits
An input buffer is presented for buffering an input signal having a voltage magnitude which alternates between a first voltage level and a second voltage level, where the first and second voltage levels may vary over time. In one embodiment, the input buffer includes a first and second detector circuits, an average generator circuit, and a differential amplifier. The first detector circuit receives the input signal and produces a first signal having a magnitude indicative of the first voltage level. The second detector circuit receives the input signal and produces a second signal having a magnitude indicative of the second voltage level. The average generator circuit receives the first and second signals, and uses the magnitudes of the first and second signals to produce a third signal having a magnitude indicative of a third voltage level substantially mid way between the first voltage level and the second voltage level. The third voltage level defines a variable an automatically adjusted "switching point". The differential amplifier receives the input signal, the third signal, and a first and second power supply voltages. The differential amplifier amplifies a difference between the voltage magnitude of the input signal and the third voltage level in order to produce an output signal which alternates between the first and second power supply voltages. An integrated circuit is described including the input buffer coupled between one of a set of input / output pads and circuitry, wherein the circuitry may be synchronous dynamic random access memory (SDRAM) circuitry.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
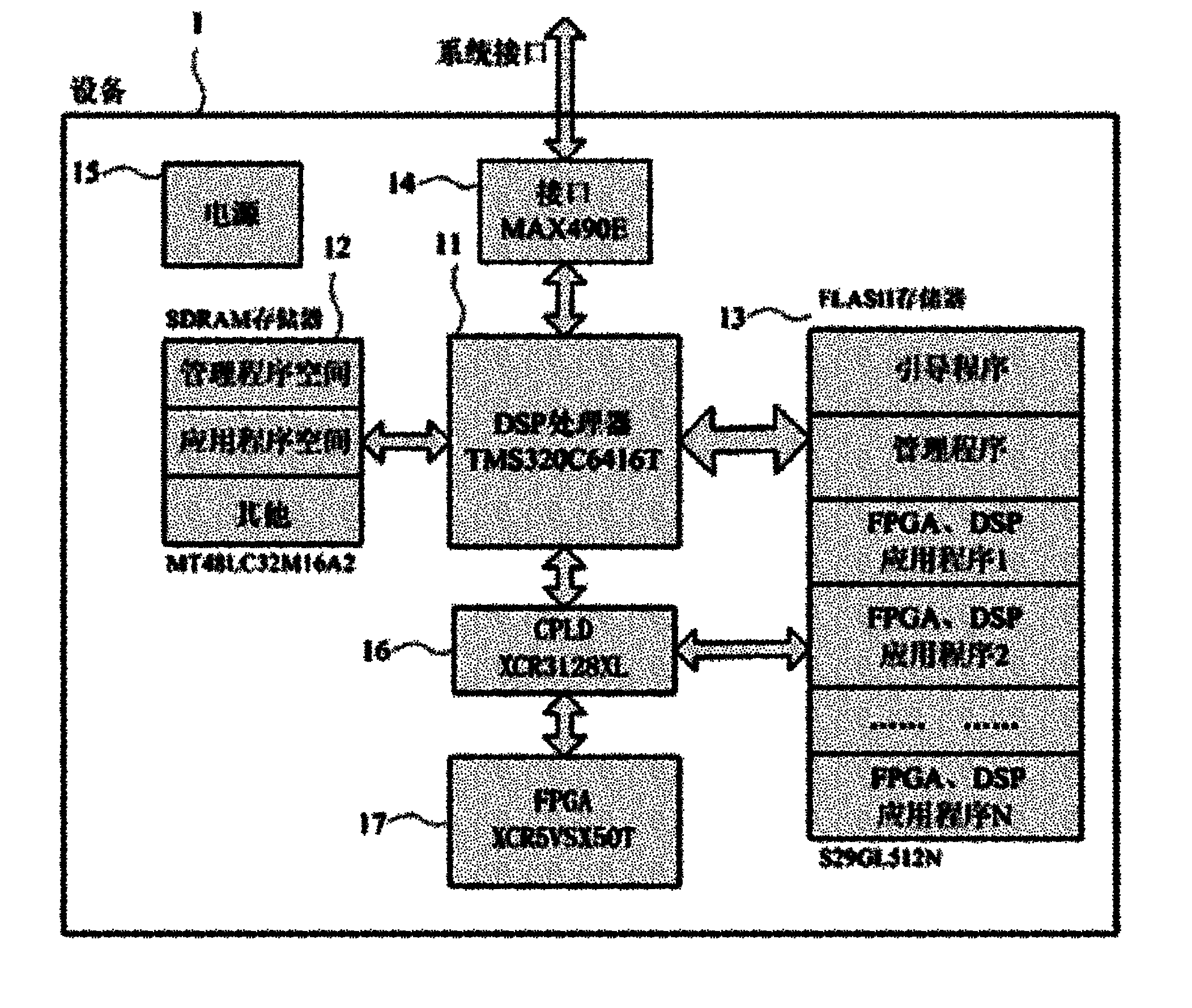
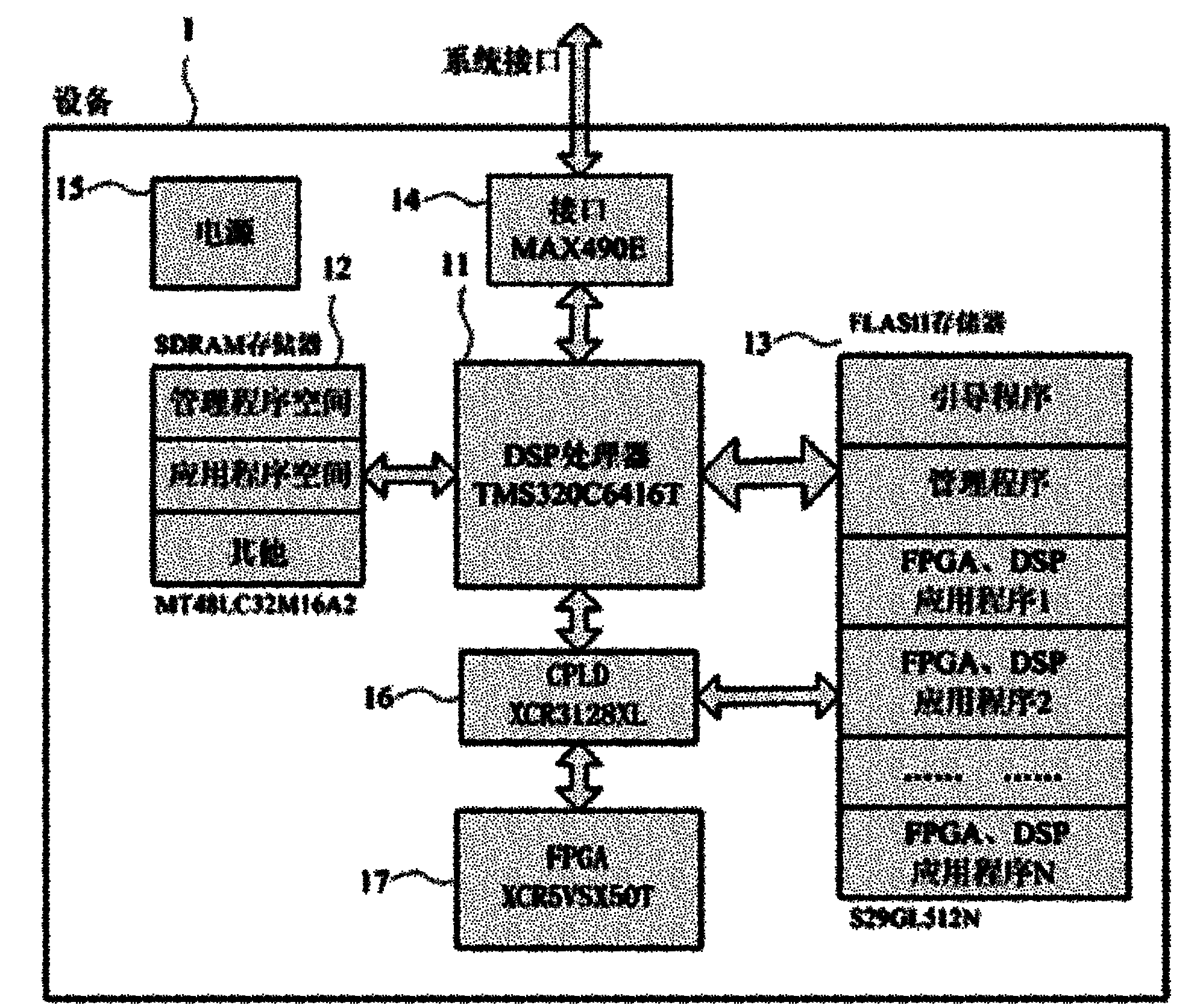
Method and system for dynamically loading processor application programs
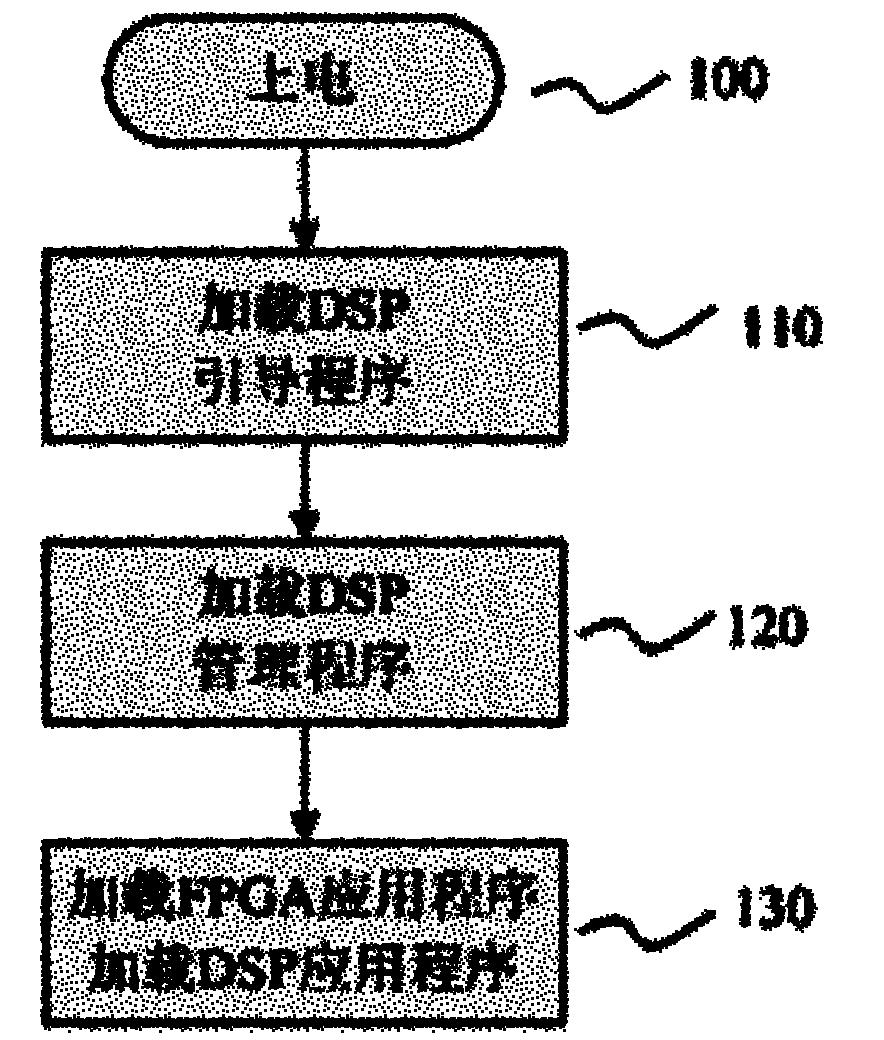
InactiveCN101901156AEasy to implementEasy to reuseProgram loading/initiatingSynchronous dynamic random-access memoryComplex programmable logic device
The invention relates to a technique for dynamically loading processor application programs and a hardware system for realizing the technique. The system mainly comprises a digital signal processor (DSP) 11, a field programmable gate array (FPGA) processor 17, a complex programmable logic device (CPLD) 16, a FLASH memory 13, a synchronous dynamic random access memory (SDRAM) 12, an interface chip14 and a power module 15, wherein fixed programs in the FLASH memory 13 comprise a DSP bootstrap program, a DSP management program and a plurality of FPGA and DSP application programs. A method for implementing the system has the characteristics that: dynamic loading and on-line updating of the FPGA application program and the DSP application program are realized by using the management program; the jump among the bootstrap program, the management program and the application programs is realized by the DSP technique so as to complete the dynamic loading function; and the FPGA is taken over bythe CPLD so as to configure a bus and the FPGA application program is loaded by combining the DSP.
Owner:SICHUAN JIUZHOU ELECTRIC GROUP
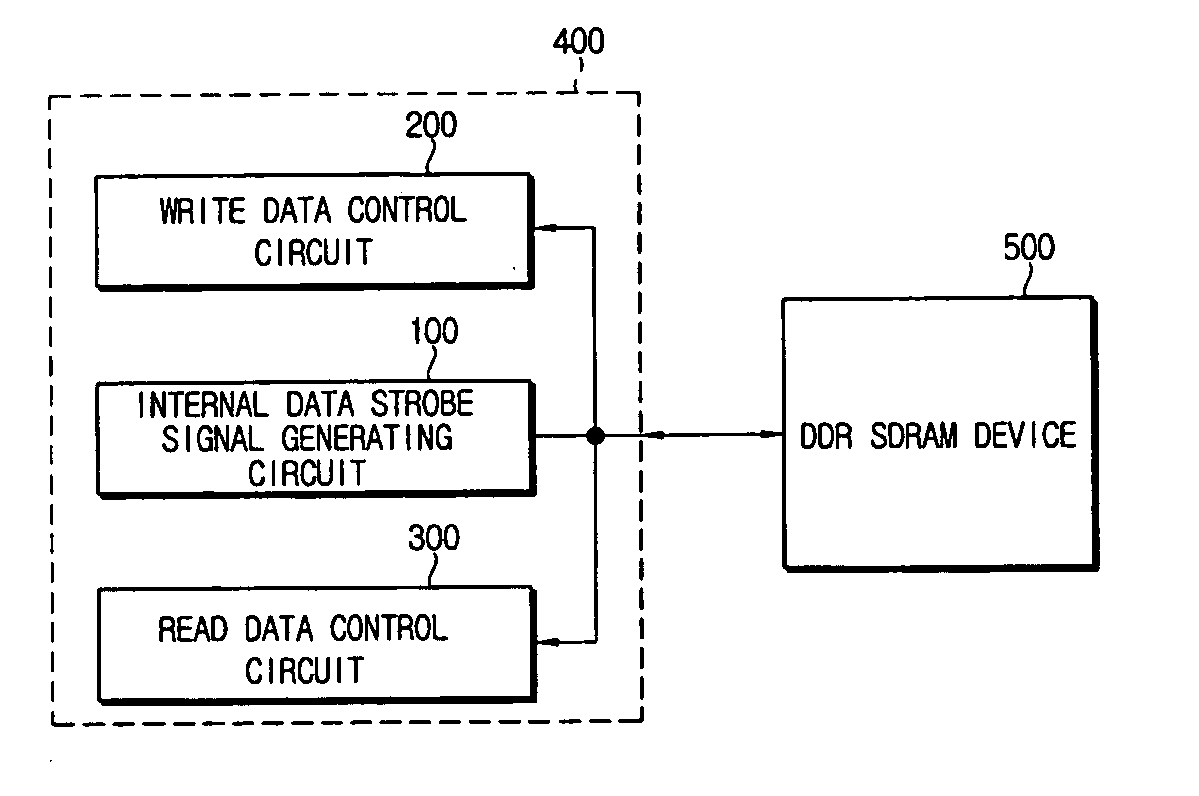
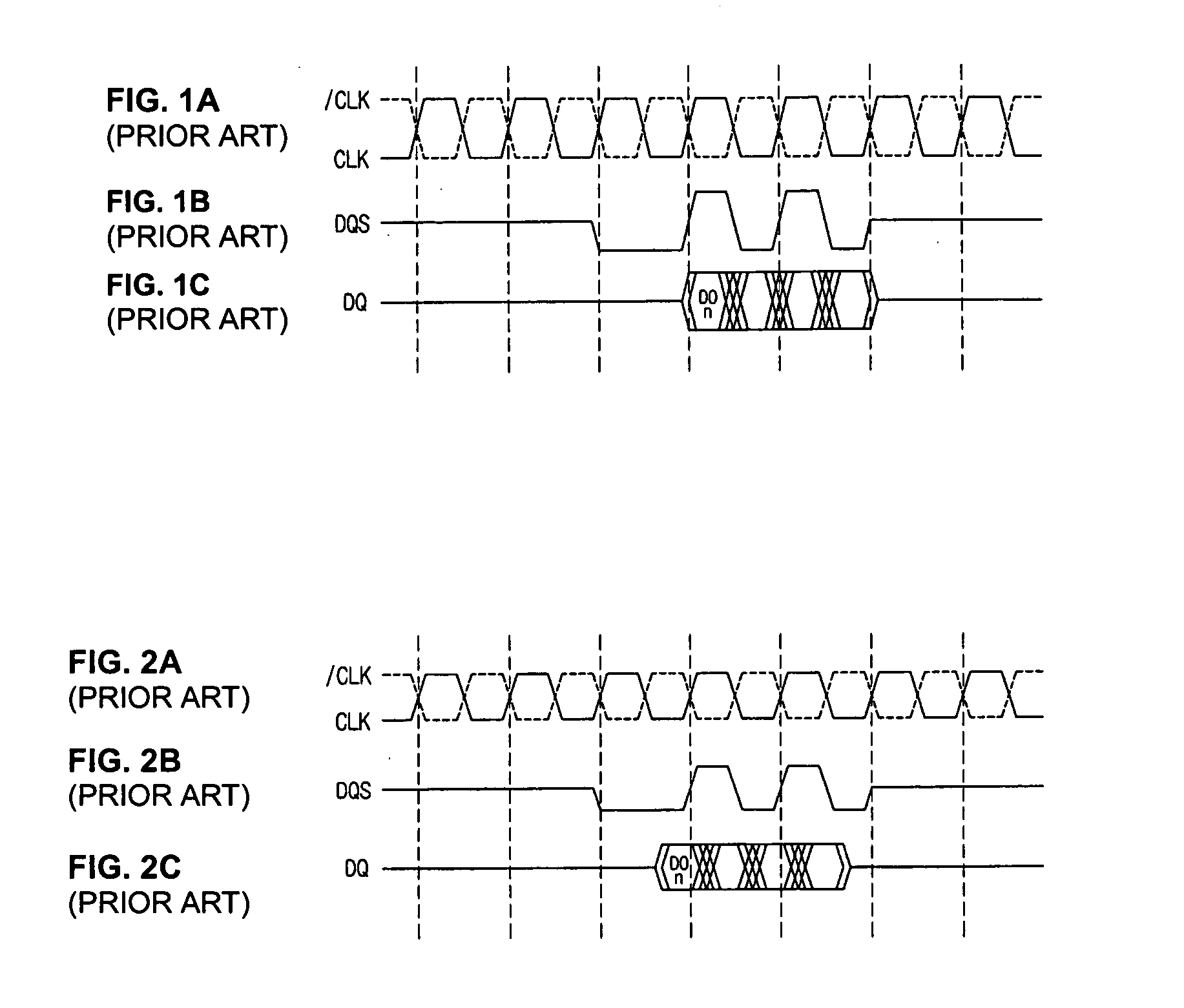
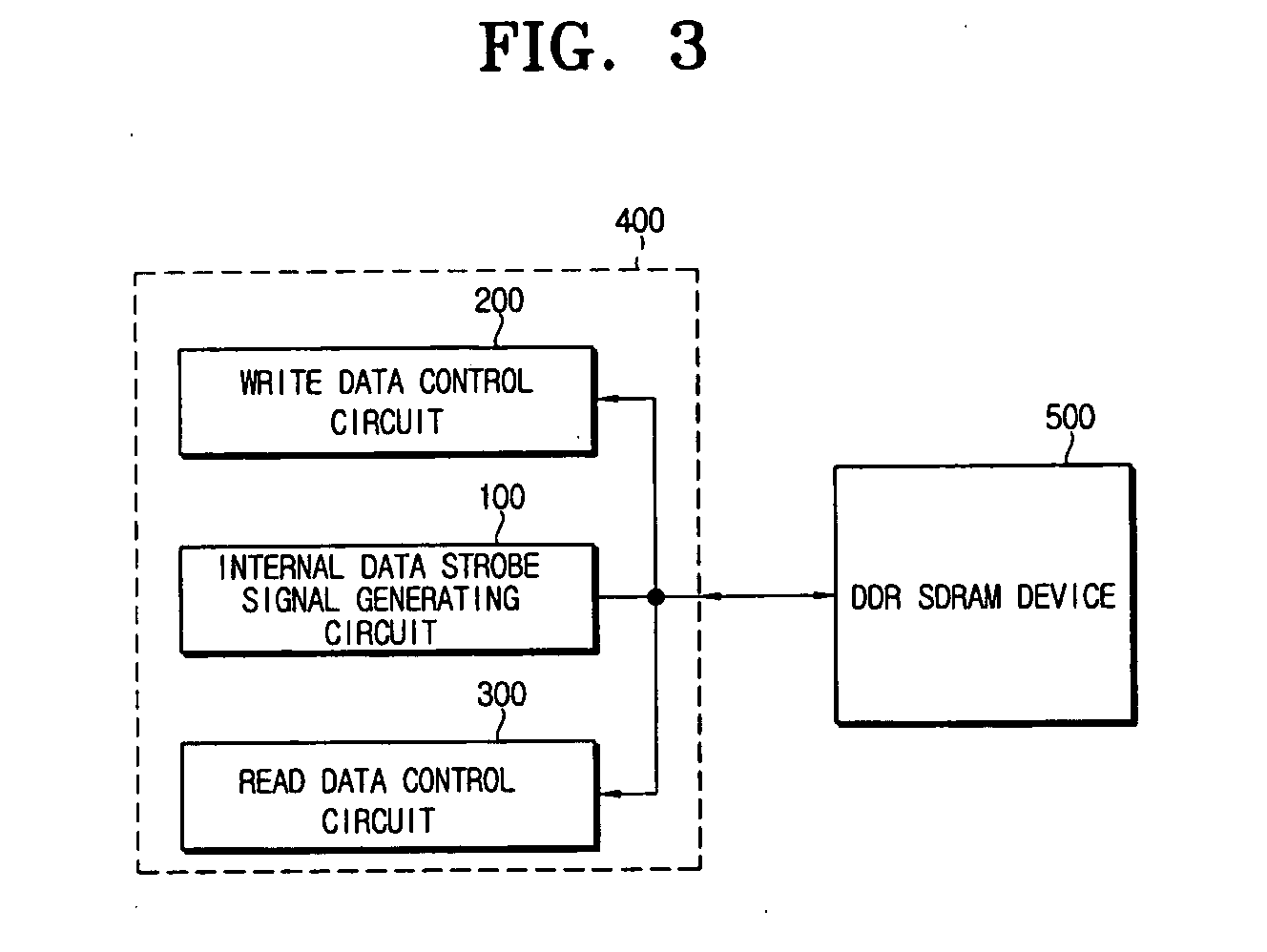
Data control circuit for DDR SDRAM controller
A data control circuit for a double data rate (DDR) synchronous dynamic random-access memory (SDRAM) that secures a stable reading / writing operation of DDR SDRAM data by generating an actively controllable internal data strobe signal. The data control circuit includes an internal data strobe signal generating circuit generating and outputting an internal data strobe signal a rising edge of which is located in a center part of valid DDR SDRAM data; a read data control circuit for receiving the internal data strobe signal, generated from the internal data strobe signal generating circuit as a clock input, dividing captured data into even data and odd data, and transmitting the even data and the odd data to a system bus; and a write data control circuit transmitting the internal data strobe signal input from the internal data strobe signal generating circuit to a DDR SDRAM device as a data strobe signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
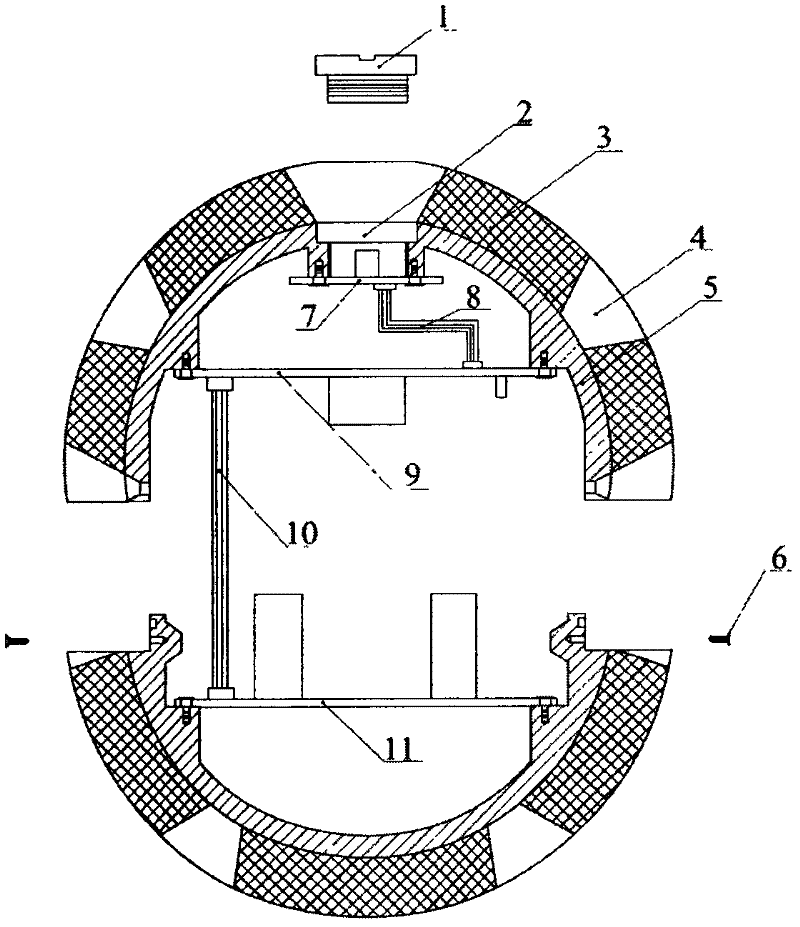
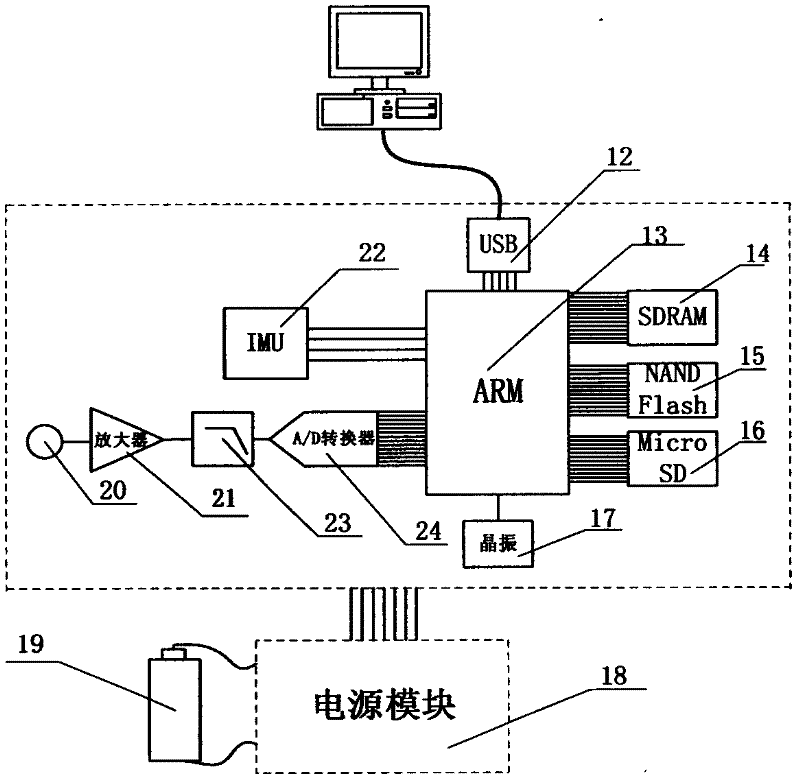
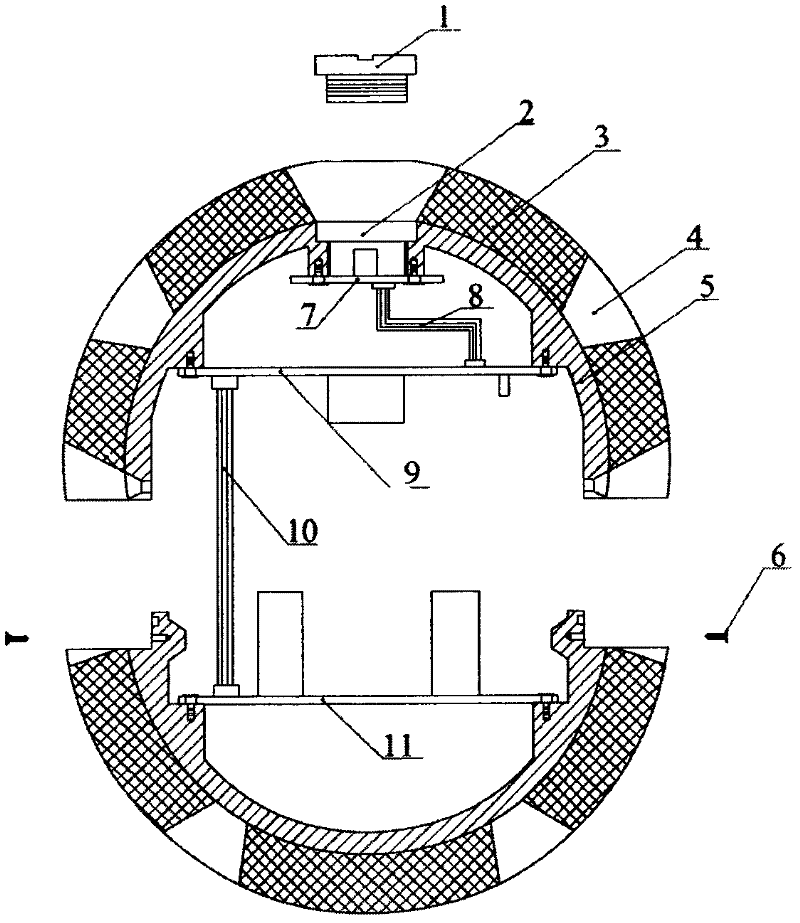
Spherical internal detector for detecting petroleum transmission pipeline leakage
InactiveCN102444786AReduce volumeHigh detection sensitivityPipeline systemsLow-pass filterAnalog-to-digital converter
The invention discloses a spherical internal detector for detecting petroleum transmission pipeline leakage. The detector comprises a spherical aluminum shell and a polyurethane foam layer outside the shell, wherein an electronic device is arranged in the aluminum shell and comprises an ARM (Advanced RISC Machines) processor, an IMU (inertia measurement unit), an A / D analog to digital converter, an SDRAM (Synchronous Dynamic random access memory) internal memory, an NAND Flash memory, a micro SD (Secure Digital) memory card, an anti-aliasing low-pass filter, a preamplifier, an electret capacitor microphone, a rechargeable lithium battery, a power supply module and a connection flat cable, wherein a digital triaxial accelerometer, a magnetometer and a gyroscope are arranged in the IMU. Theinvention has the advantages that the detector has high detection sensitivity, low preparation cost, a small size and low power consumption, is not easily blocked in a pipeline, is flexible to use and is widely applied.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
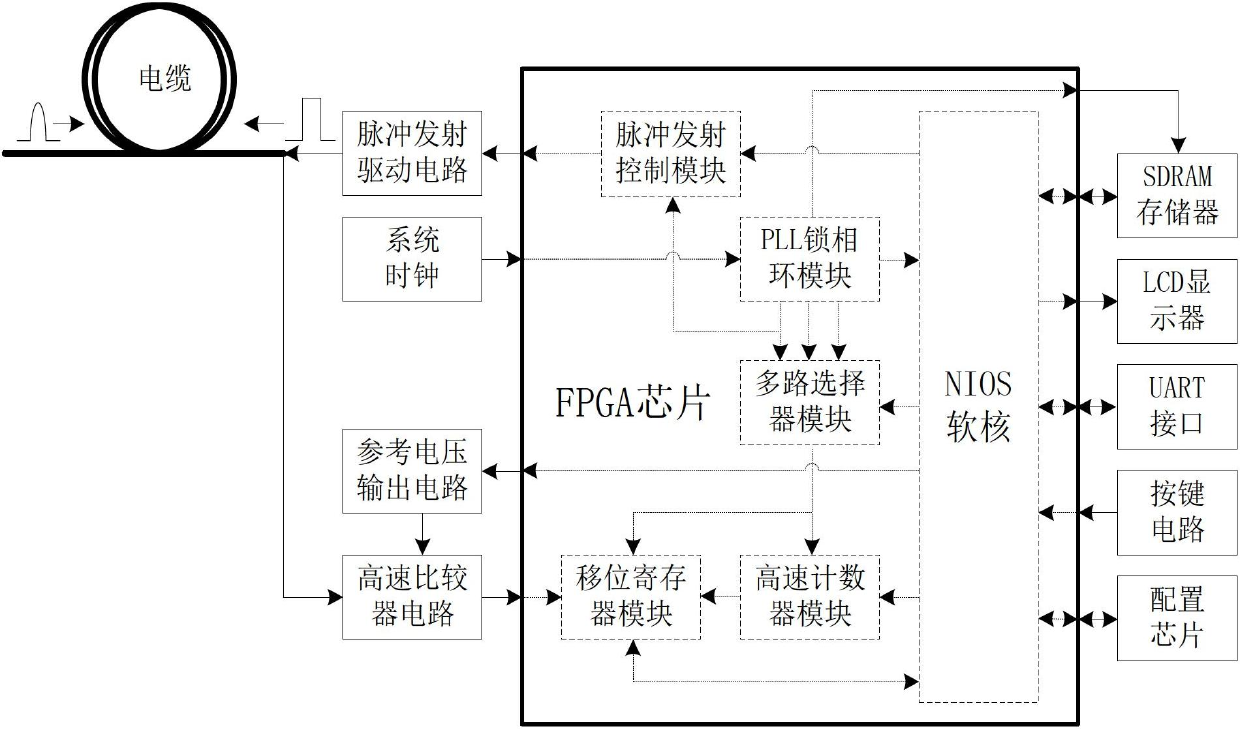
Cable fault detecting and positioning method based on waveform replication
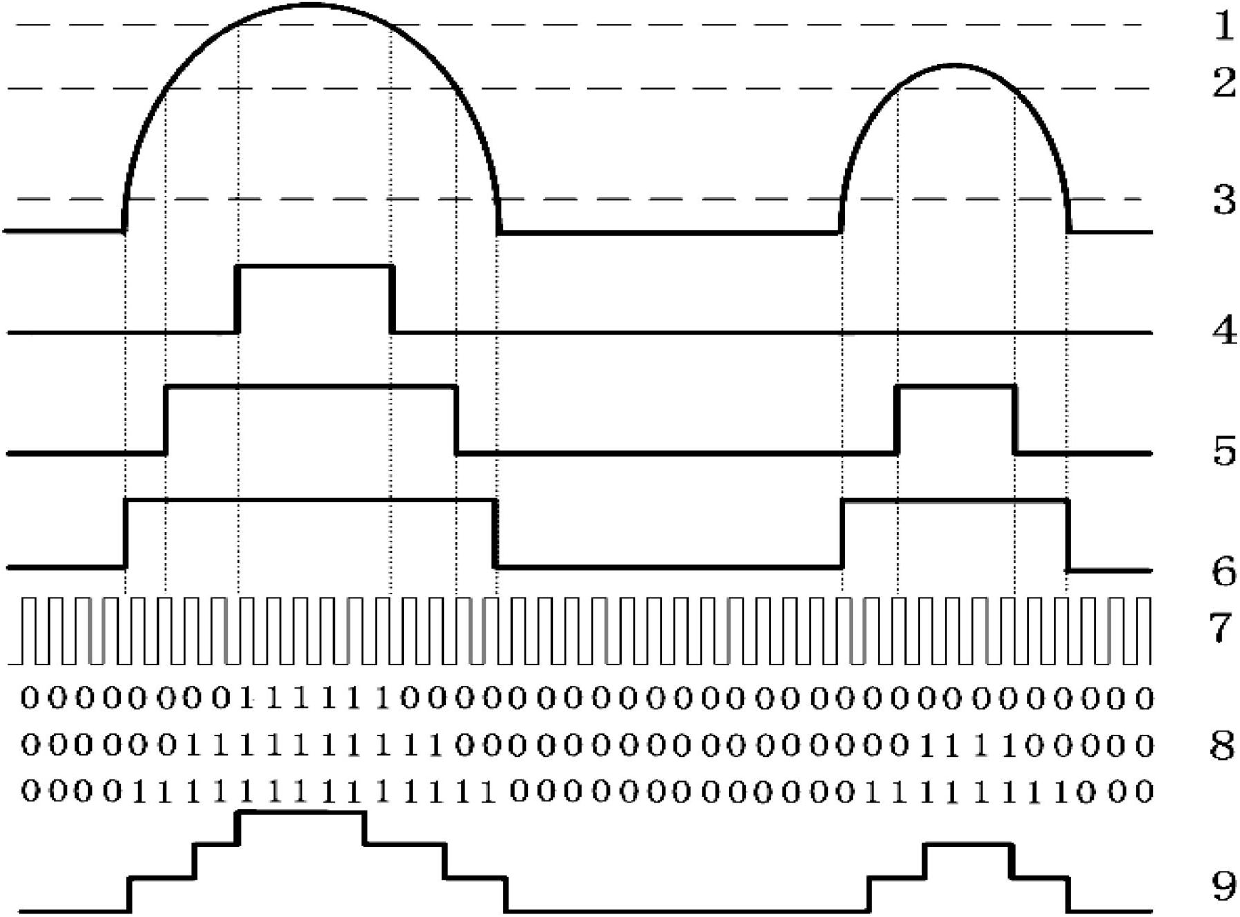
InactiveCN102680855AAdjustable increaseAdjustable sync clockFault locationShift registerLiquid-crystal display
The invention discloses a cable fault detecting and positioning method based on waveform replication. The cable fault detecting and positioning method comprises the following steps of: arranging a cable fault detecting and positioning system with an FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array) chip as a processor; outputting reference voltage to a high-speed comparator by running an embedded NIOS soft core inside the cable fault detecting and positioning system as a control core; transmitting set pulse to a detected cable by a pulse transmitting driving circuit; acquiring the comparison result of the high-speed comparator and storing the comparison result to an SDRAM (Synchronous Dynamic Random Access Memory) by a shift register module; then changing a value of reference voltage from high to low and repeating the processes of transmitting the pulse and acquiring and storing the comparison result; and finally, reading back the stored data by the NIOS soft core, carrying out waveform replication on the data; displaying the data through an LCD (Liquid Crystal Display); analyzing the replicated waveform; and judging the types of faults and calculating the position of fault points according to the conditions of echo.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com