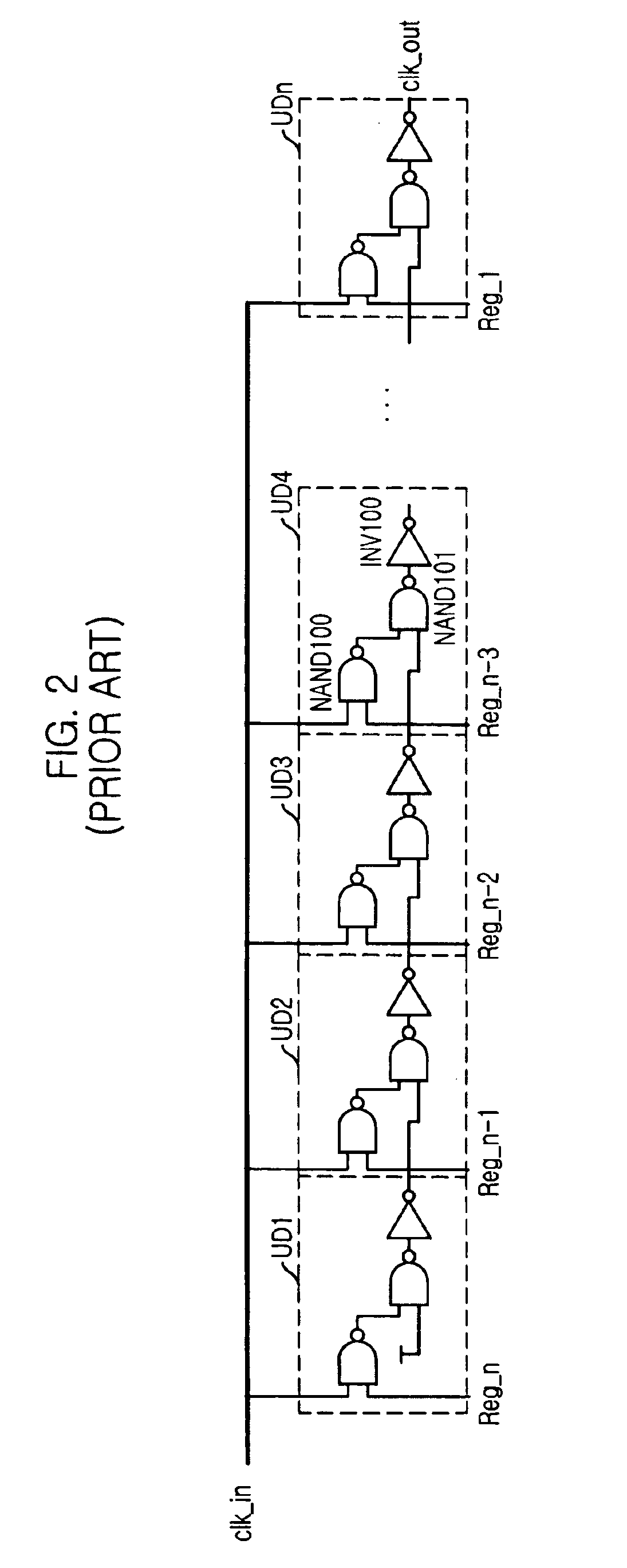
Patents
Literature
154 results about "DDR SDRAM" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
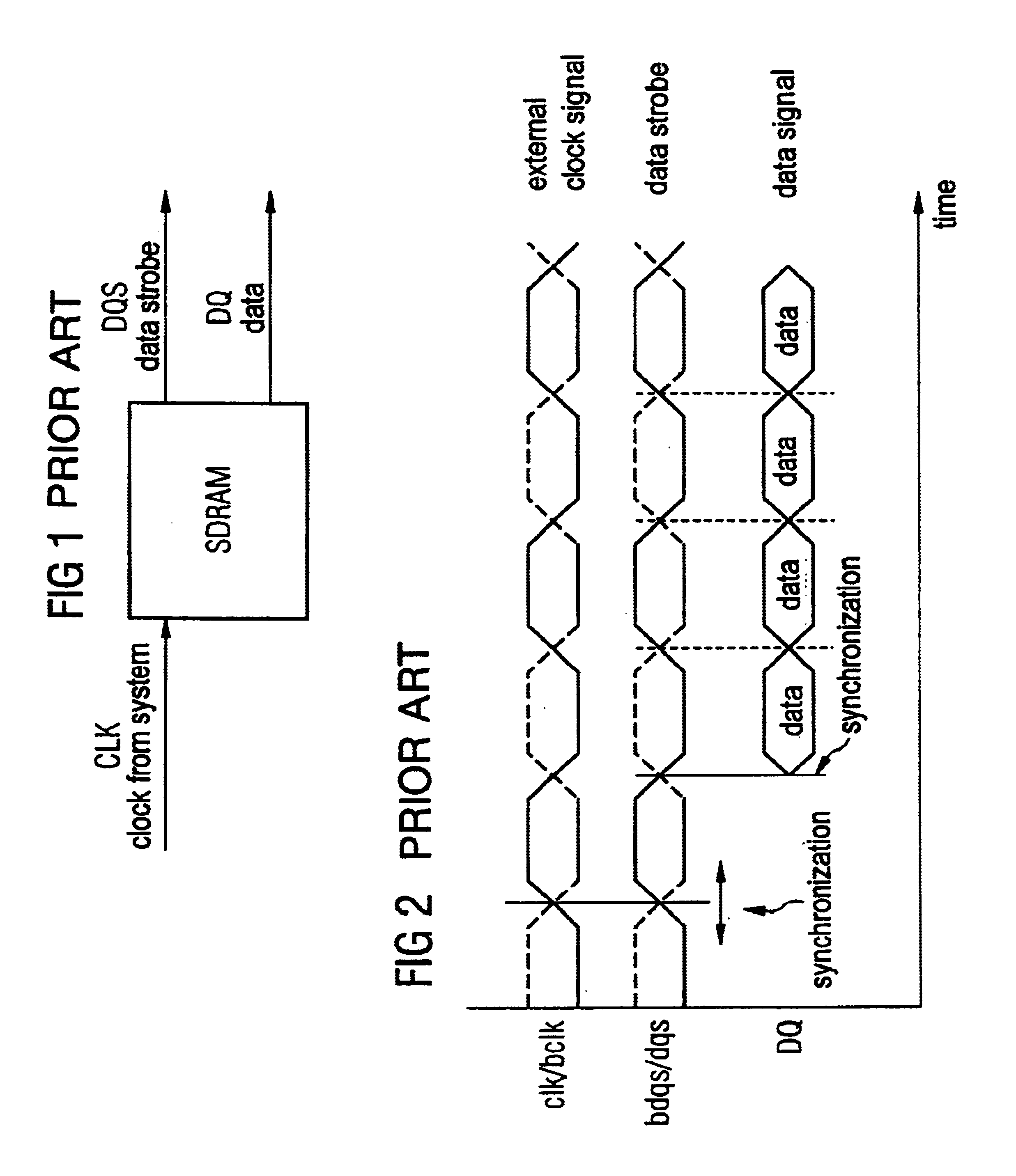
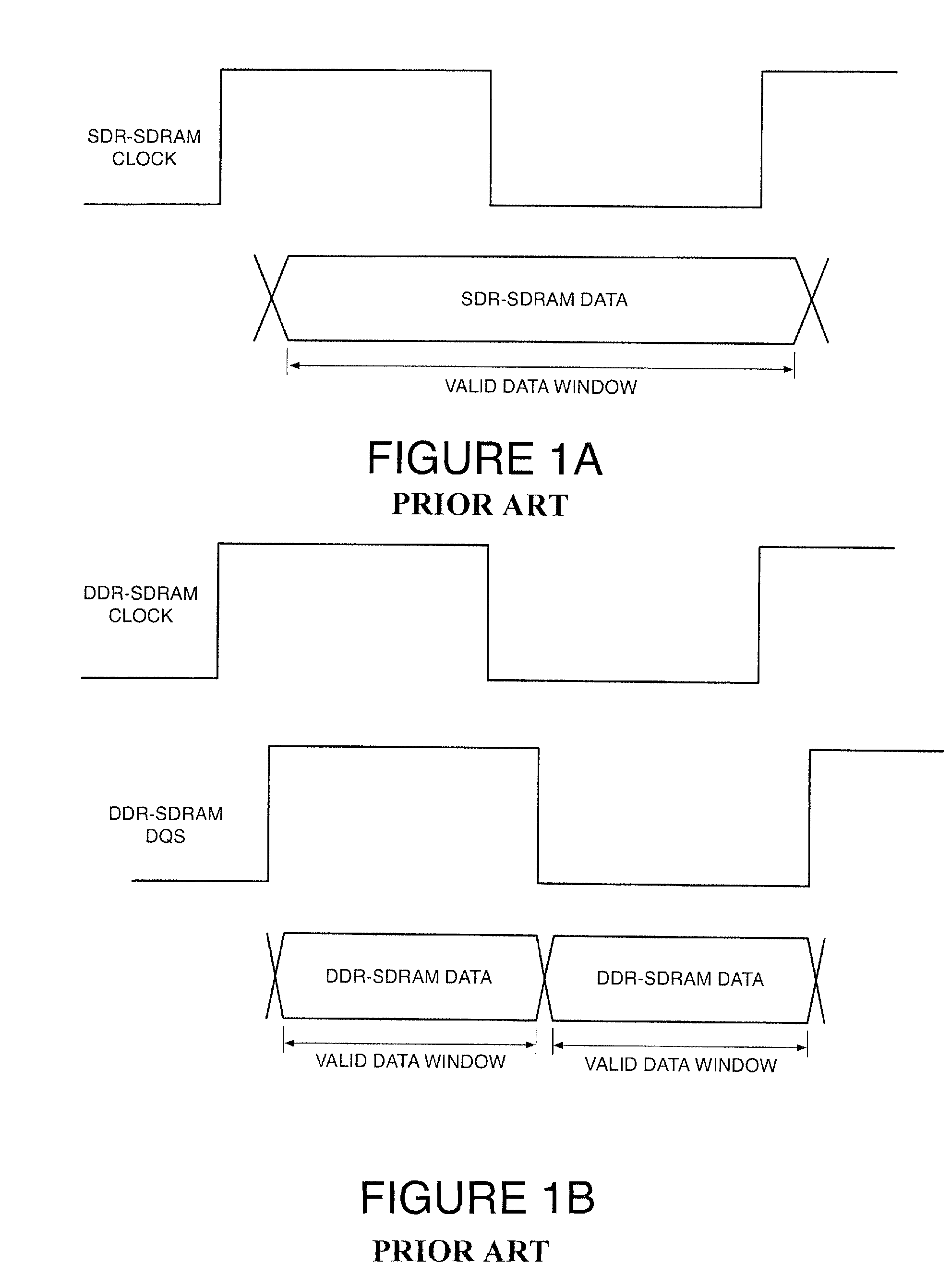
Double Data Rate Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory, officially abbreviated as DDR SDRAM, is a double data rate (DDR) synchronous dynamic random-access memory (SDRAM) class of memory integrated circuits used in computers. DDR SDRAM, also retroactively called DDR1 SDRAM, has been superseded by DDR2 SDRAM, DDR3 SDRAM and DDR4 SDRAM. None of its successors are forward or backward compatible with DDR1 SDRAM, meaning DDR2, DDR3, and DDR4 memory modules will not work in DDR1-equipped motherboards, and vice versa.
Semiconductor integrated circuit
ActiveUS20050047192A1Improve accuracyGuaranteed uptimeDigital storageGenerating/distributing signalsMemory interfaceComputer science
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
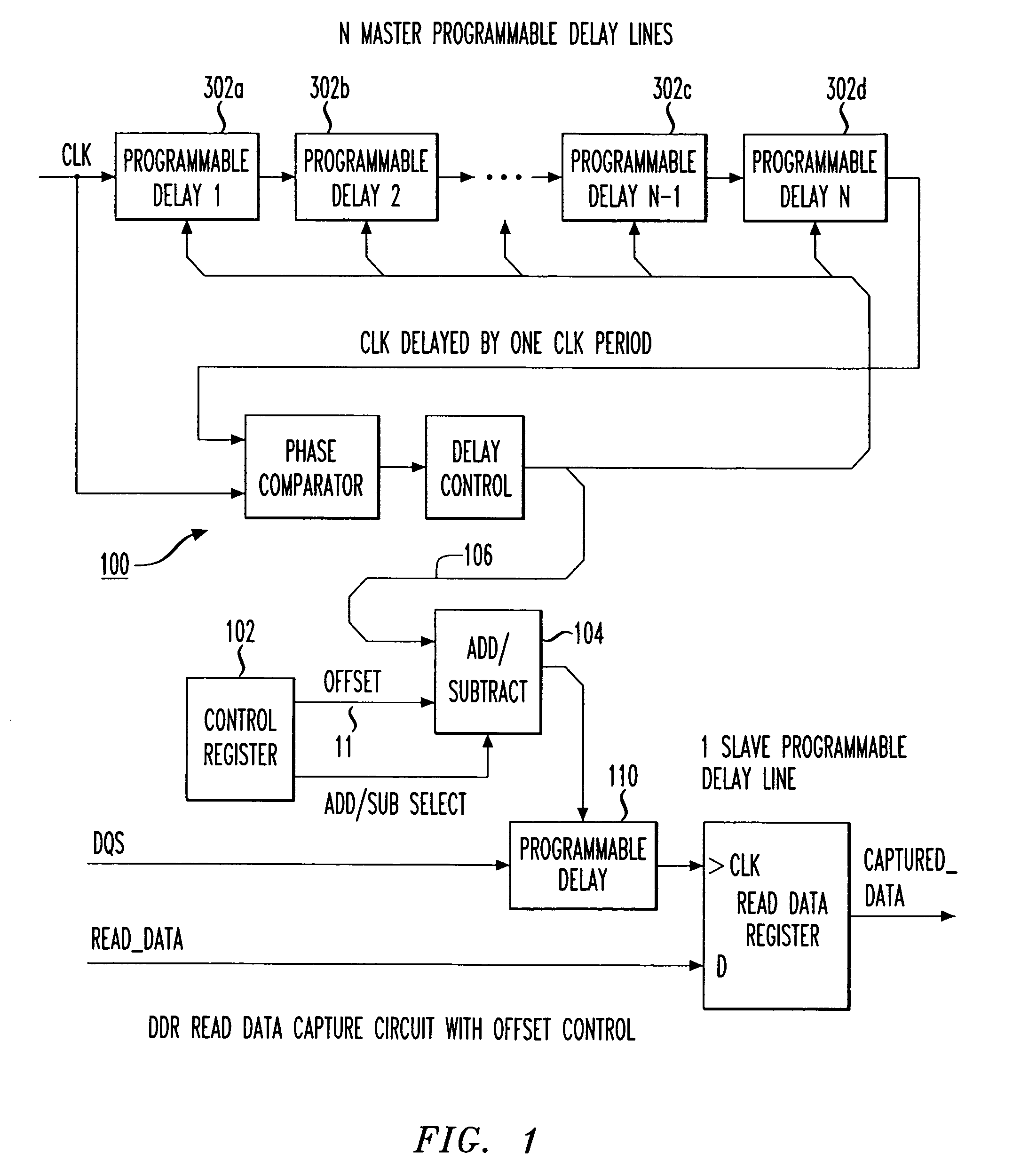
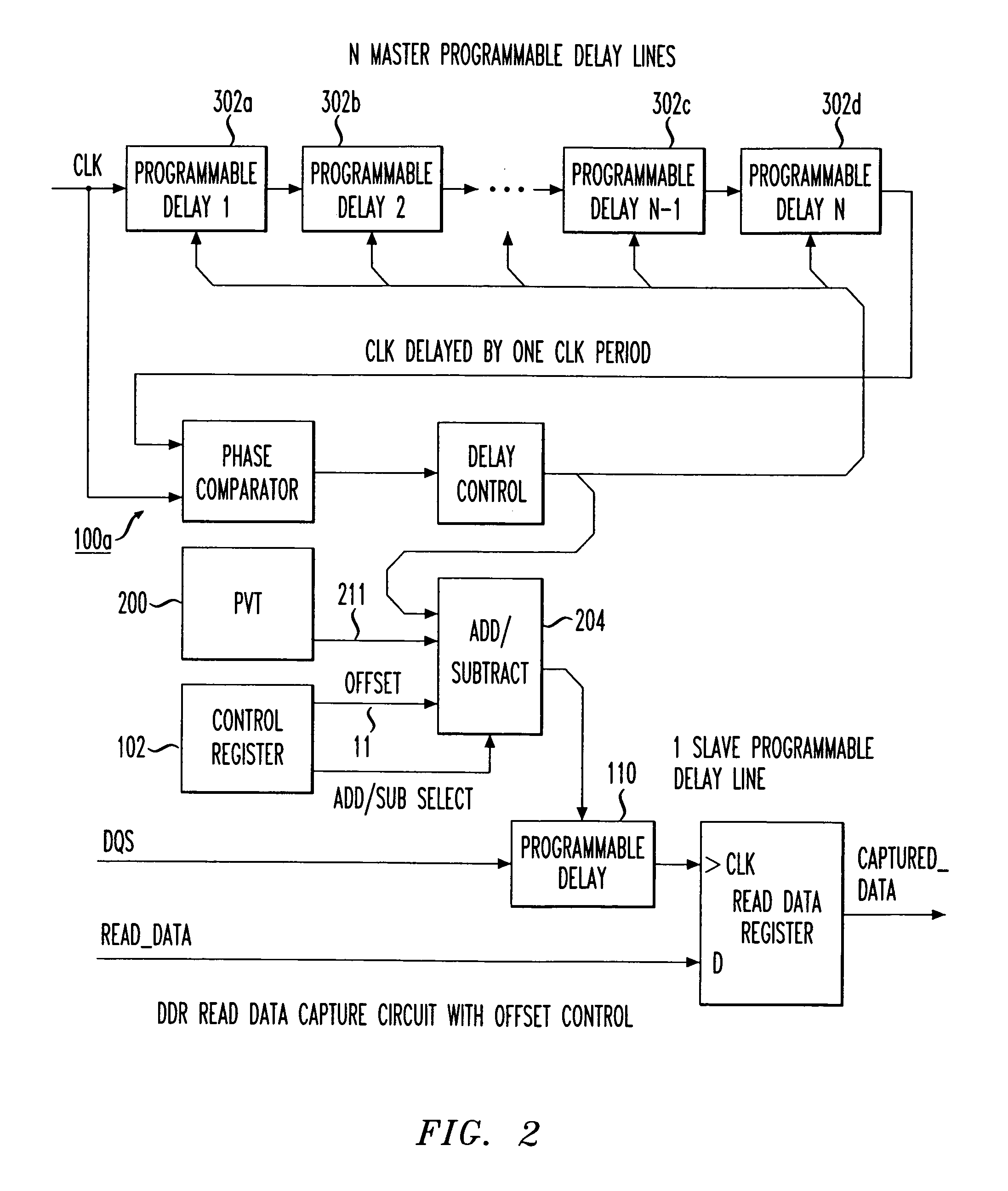
Programmable data strobe offset with DLL for double data rate (DDR) RAM memory
A double data rate (DDR) synchronous dynamic RAM (SDRAM), or DDR-SDRAM, memory controller employing a delay locked loop (DLL) circuit to delay an SDRAM data strobe (DQS) signal to the center, or ‘eye’ of the read data window. However, in distinction from conventional techniques, the initial delay determined by the DLL is fine tuned with an offset determined by a memory test. Moreover, in an additional embodiment, the delay may be further adjusted during operation to compensate for environmental conditions by a PVT (process, value, temperature) circuit.
Owner:AGERE SYST INC
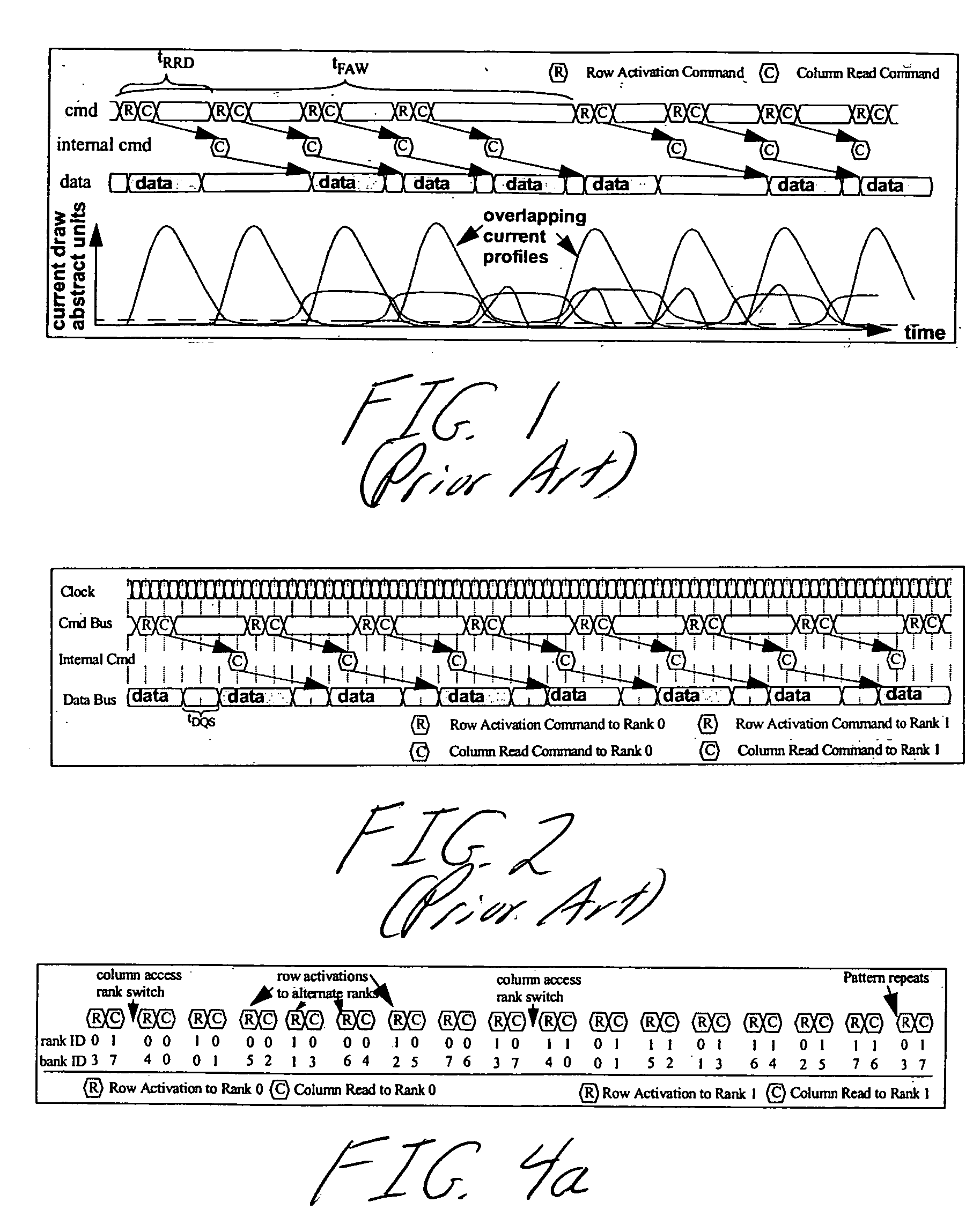
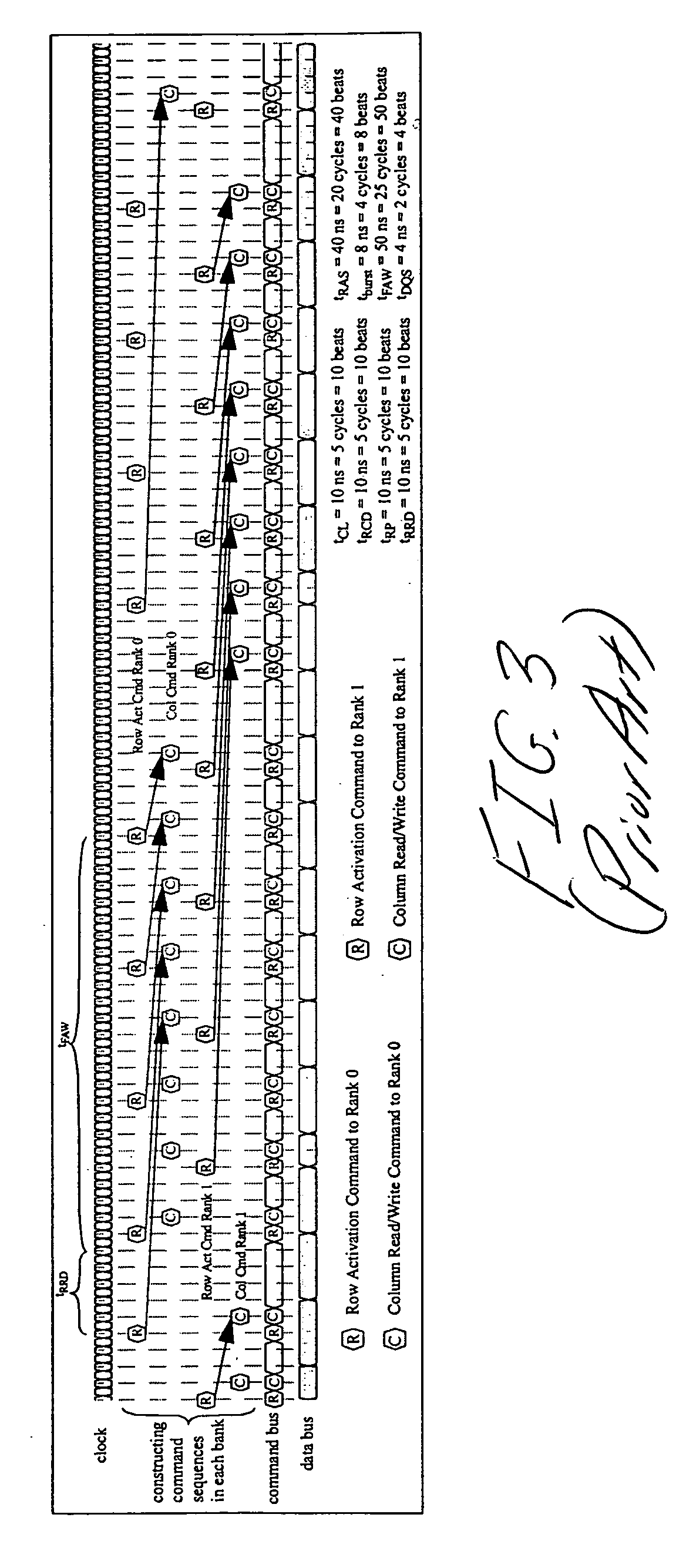
System and method for performing multi-rank command scheduling in DDR SDRAM memory systems
InactiveUS20060248261A1Better bandwidth utilizationMinimize bandwidth impactMemory adressing/allocation/relocationDigital storageMemory bankGroup scheduling
A DRAM command scheduling algorithm is presented that is designed to alleviate various constraints imposed upon high performance, high datarate, short channel DDRx SDRAM memory systems. The algorithm amortizes the overhead costs of rank-switching time and schedules around the tFAW bank activation constraint. A multi-rank DDRx memory system is also presented having at least two ranks of memory each having a number of banks and at least one memory controller configured for performing the hardware-implemented step of DRAM command scheduling for row access commands and column access commands. The step of command scheduling includes decoupling the row access commands from the column access commands; alternatively scheduling the decoupled row access commands to different ranks of memory; and group scheduling the decoupled column access commands to each bank of the number of banks of a given rank of the different ranks of memory.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
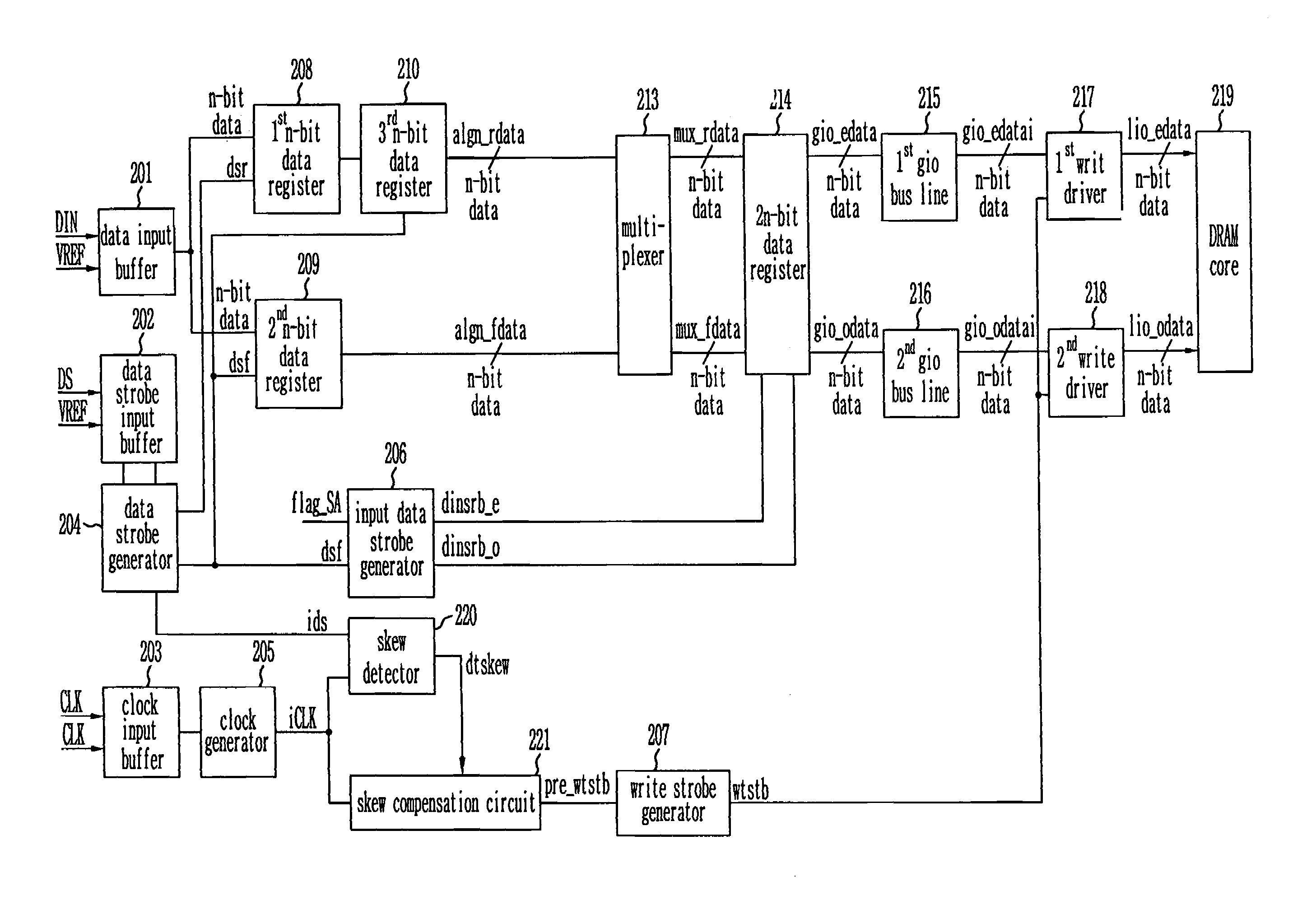
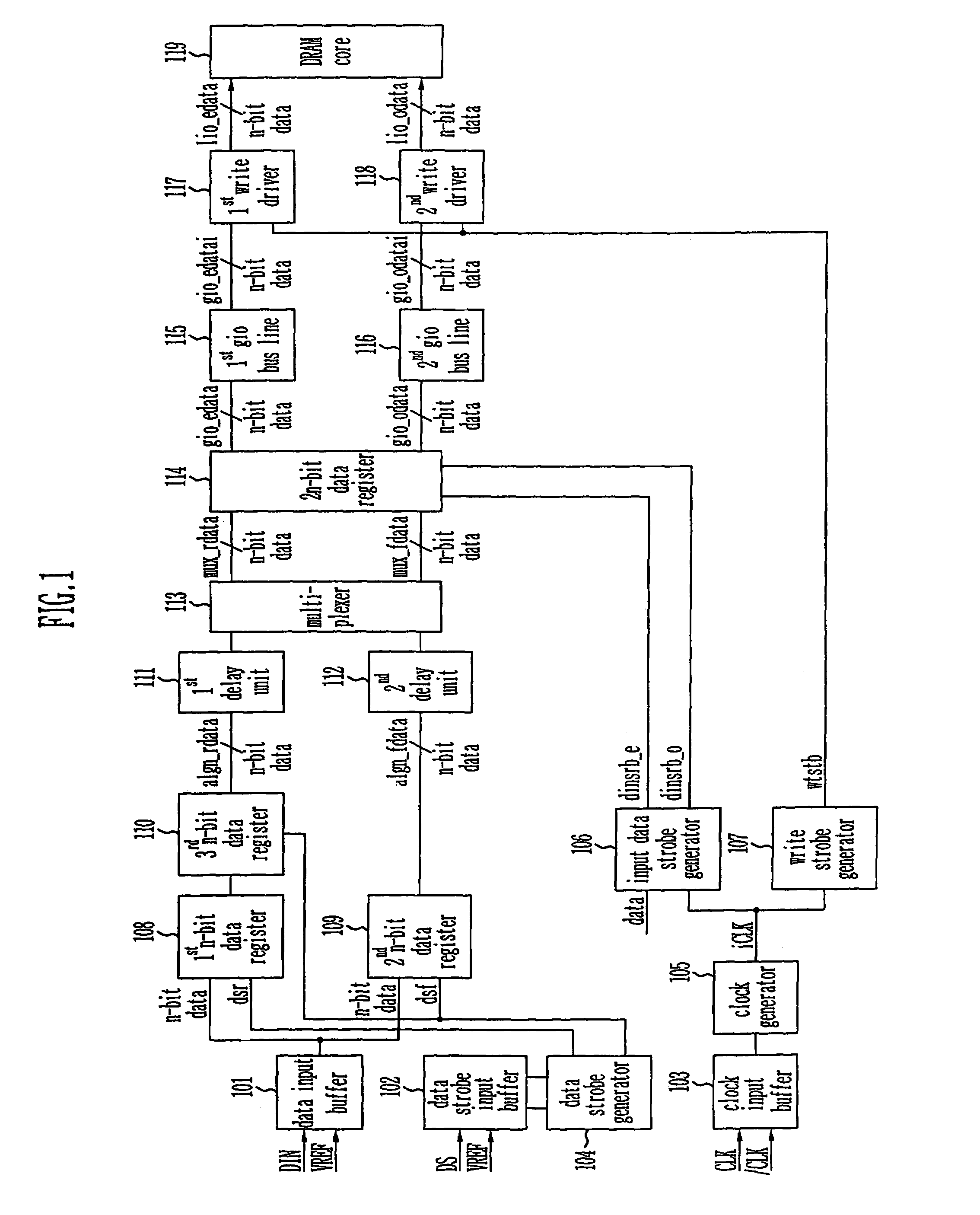
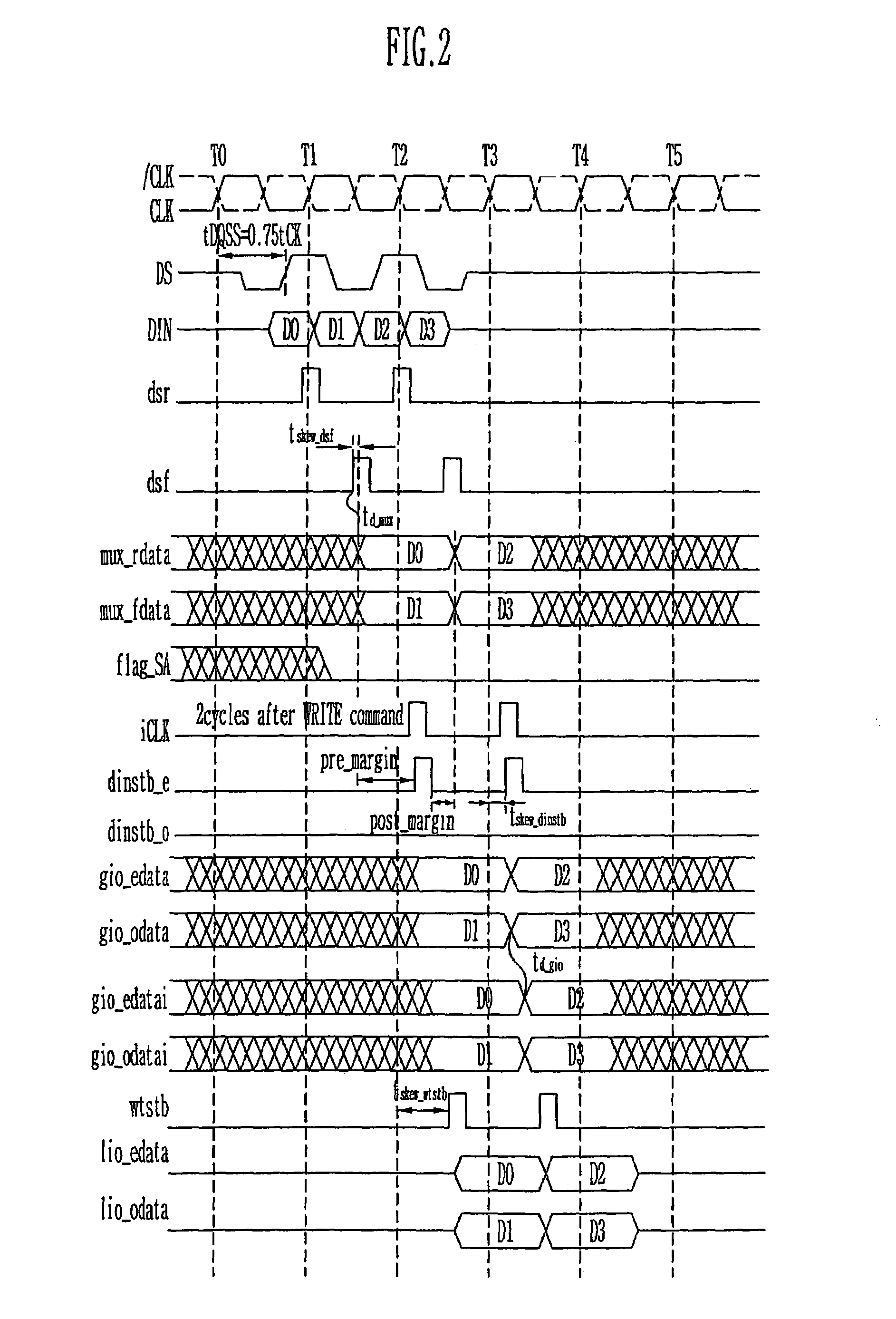
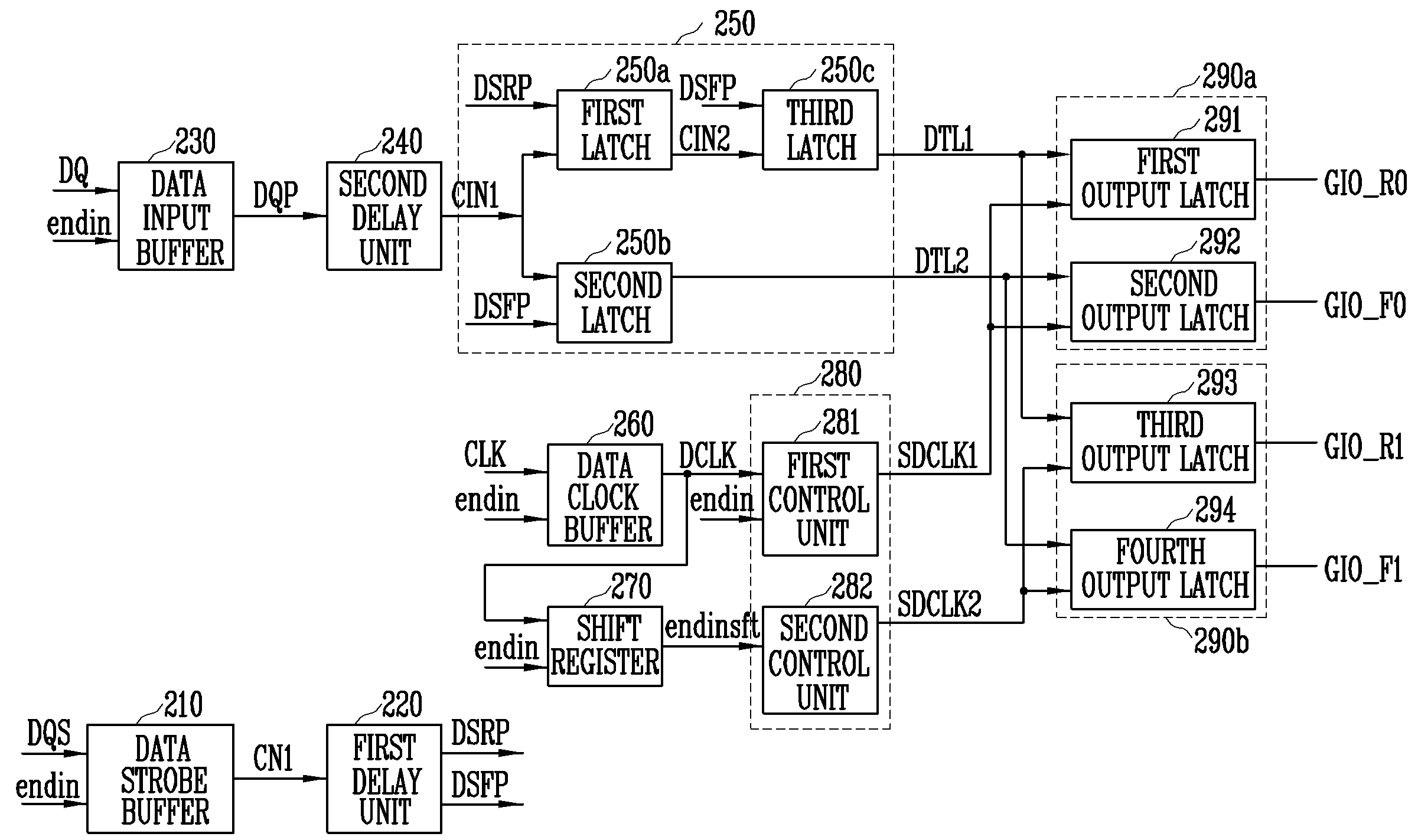
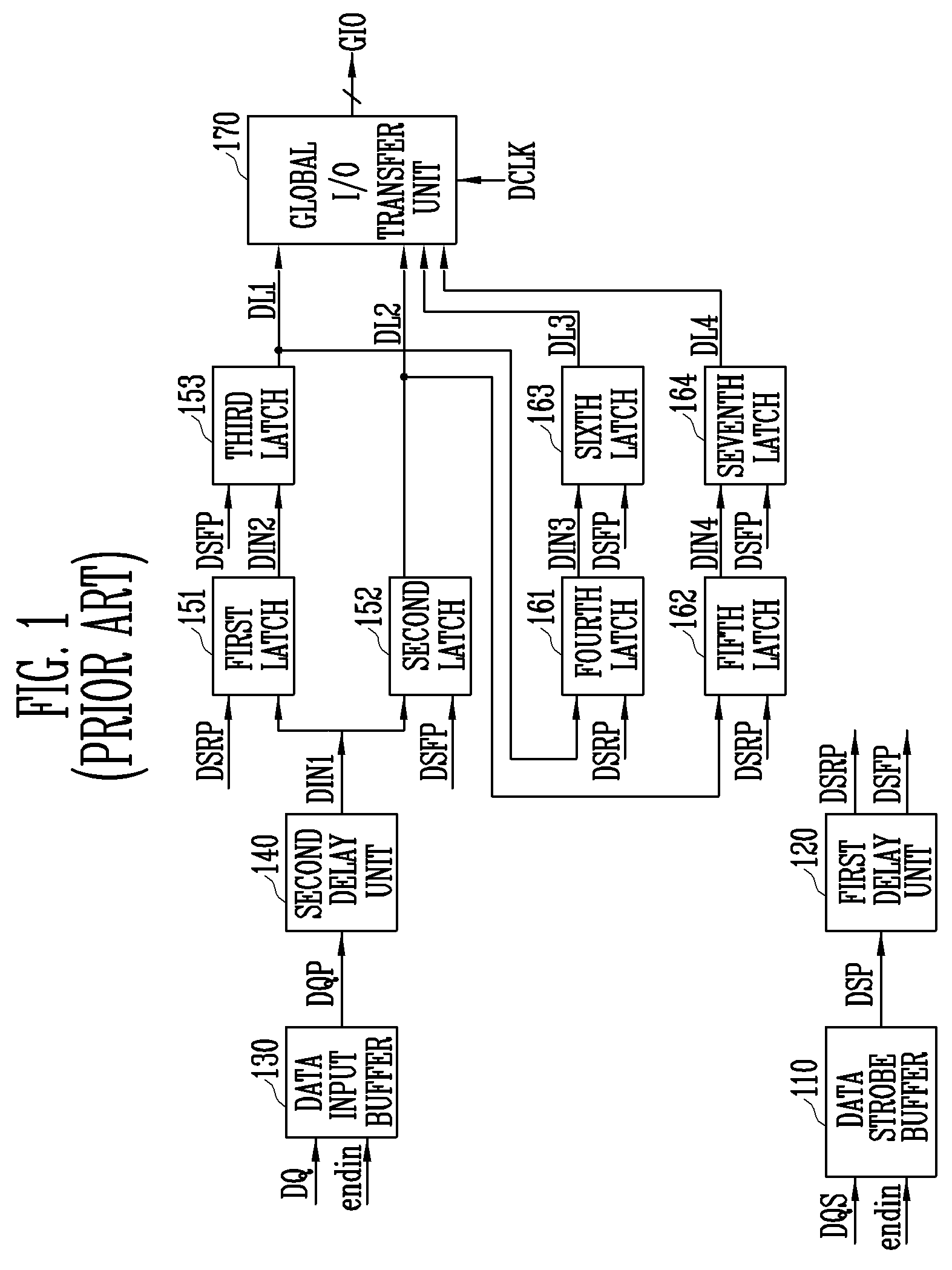
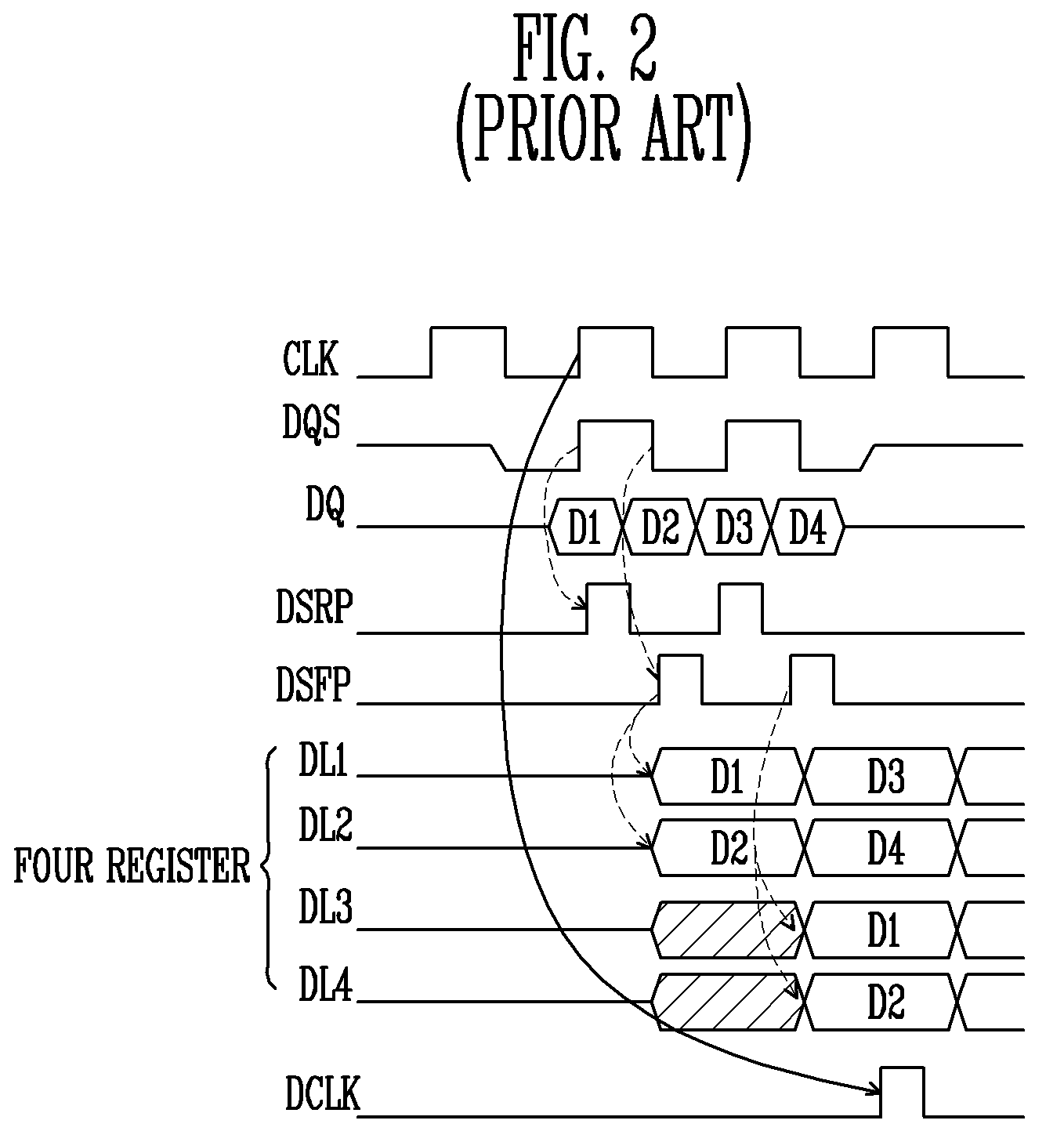
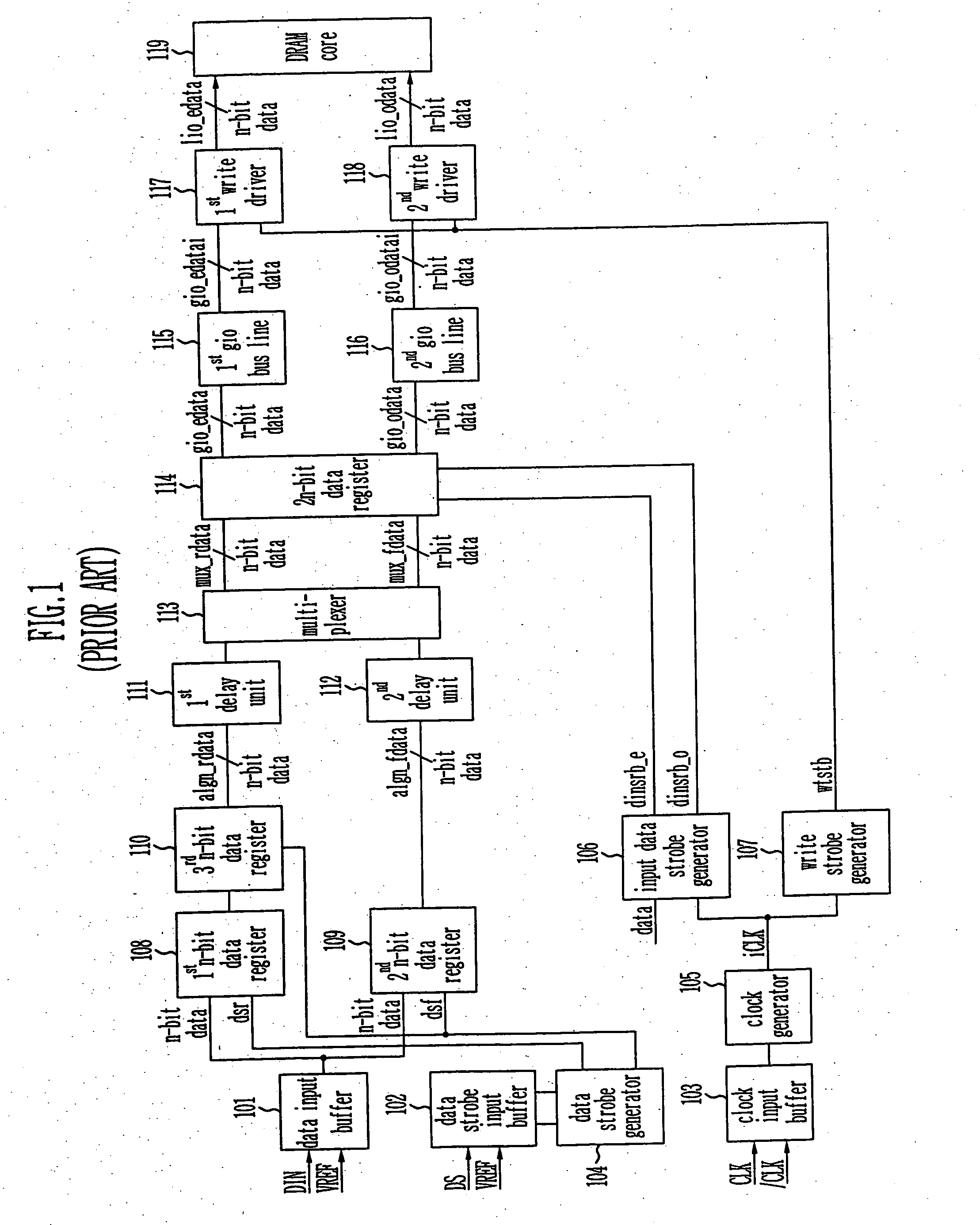
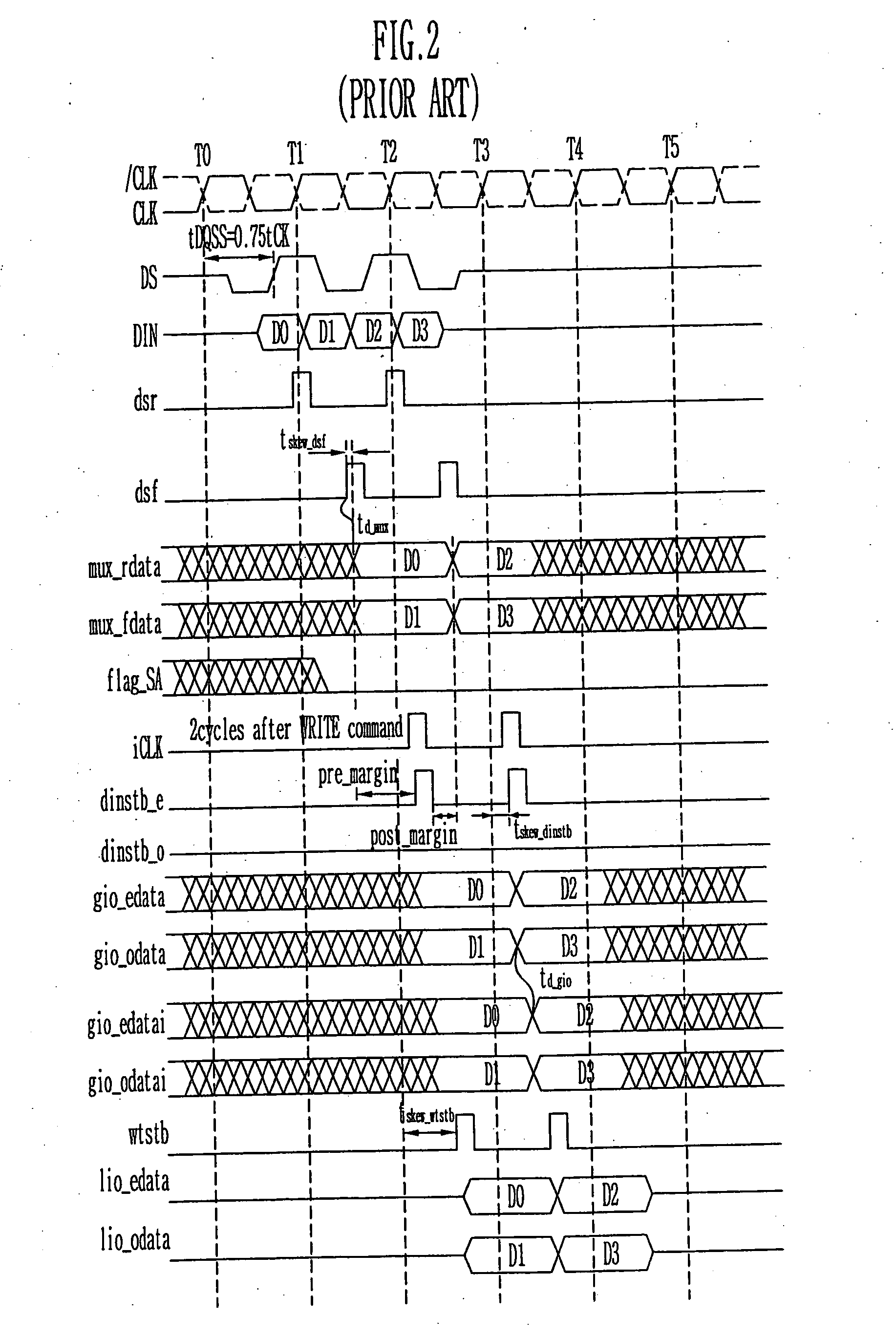
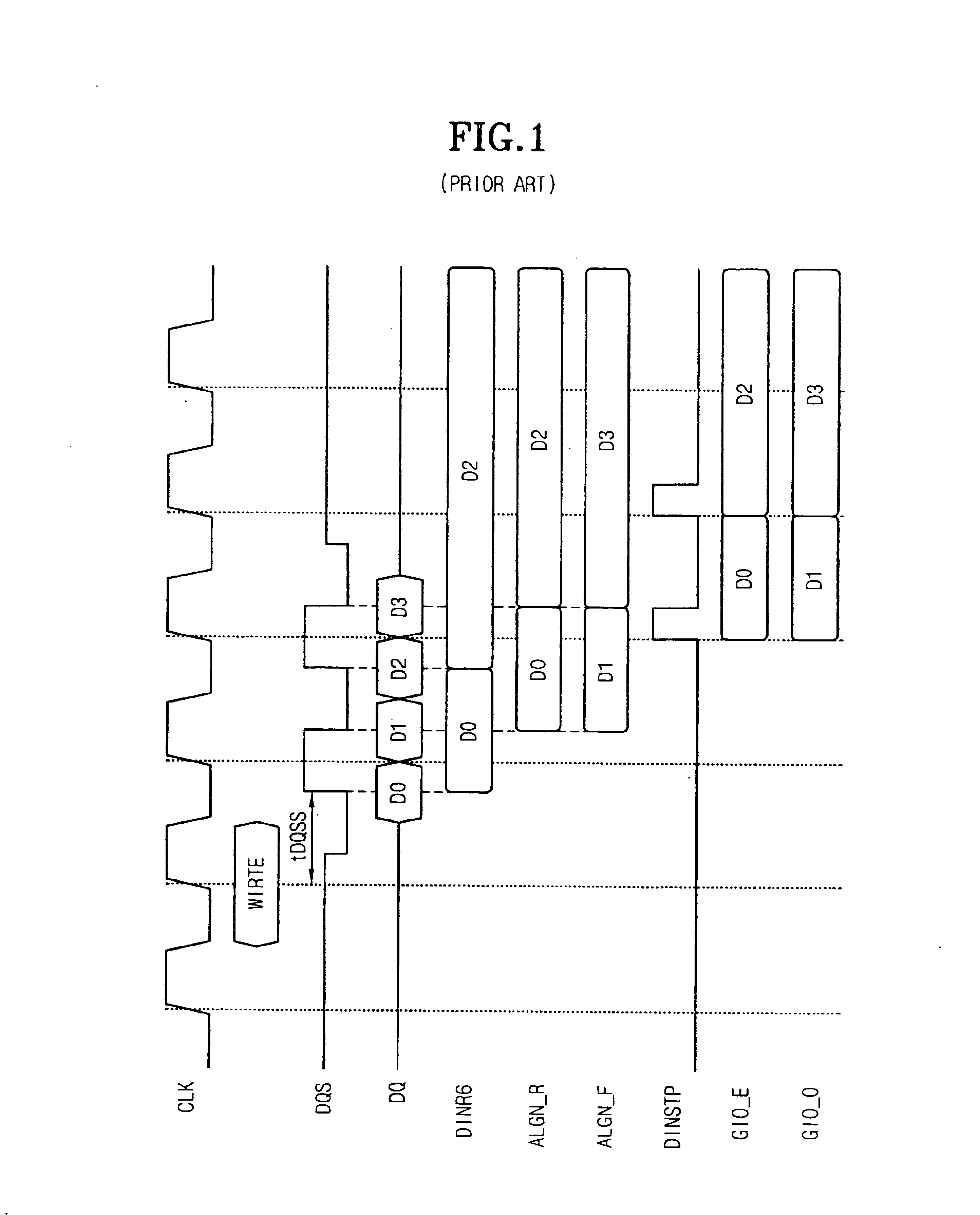
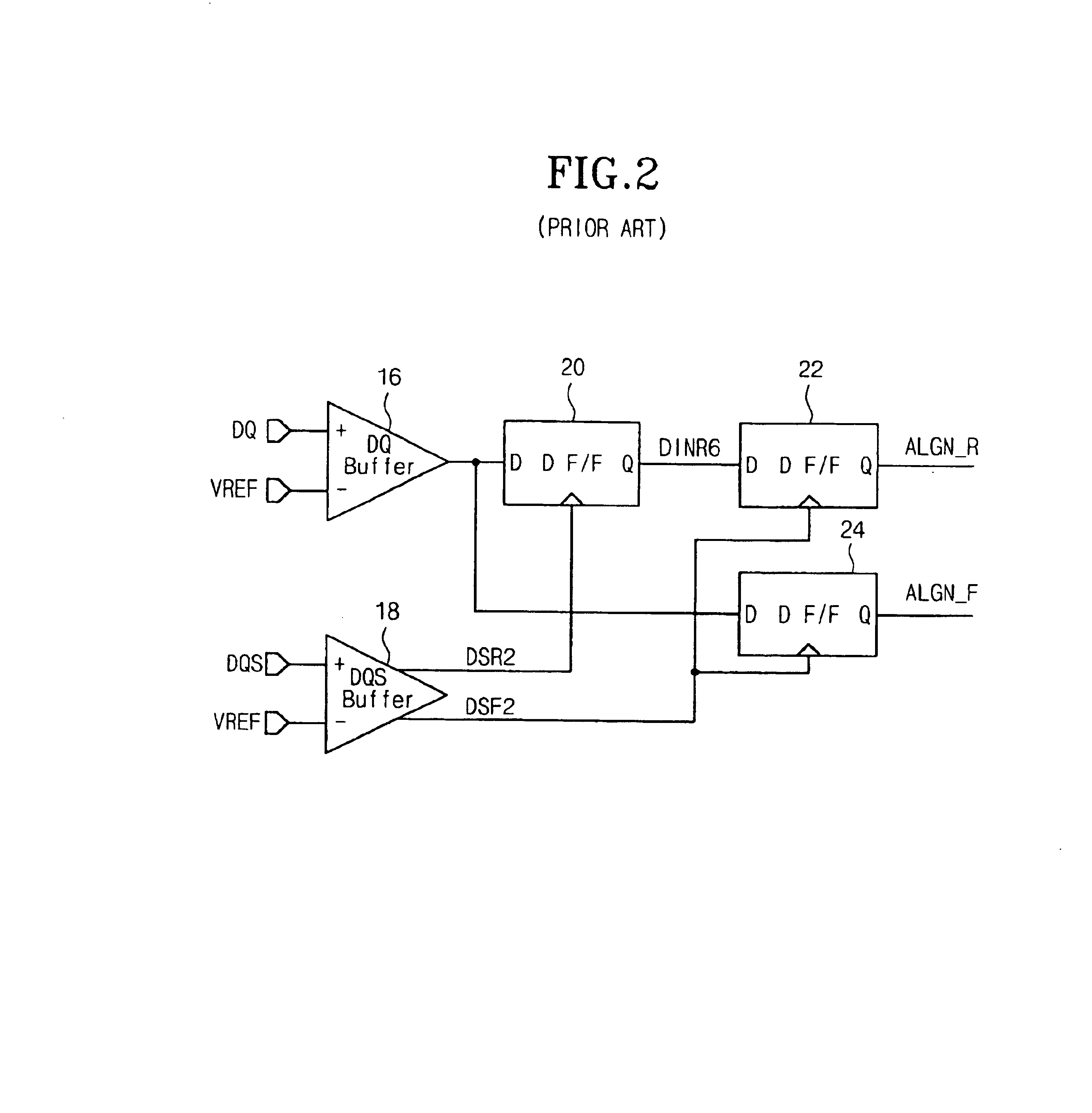
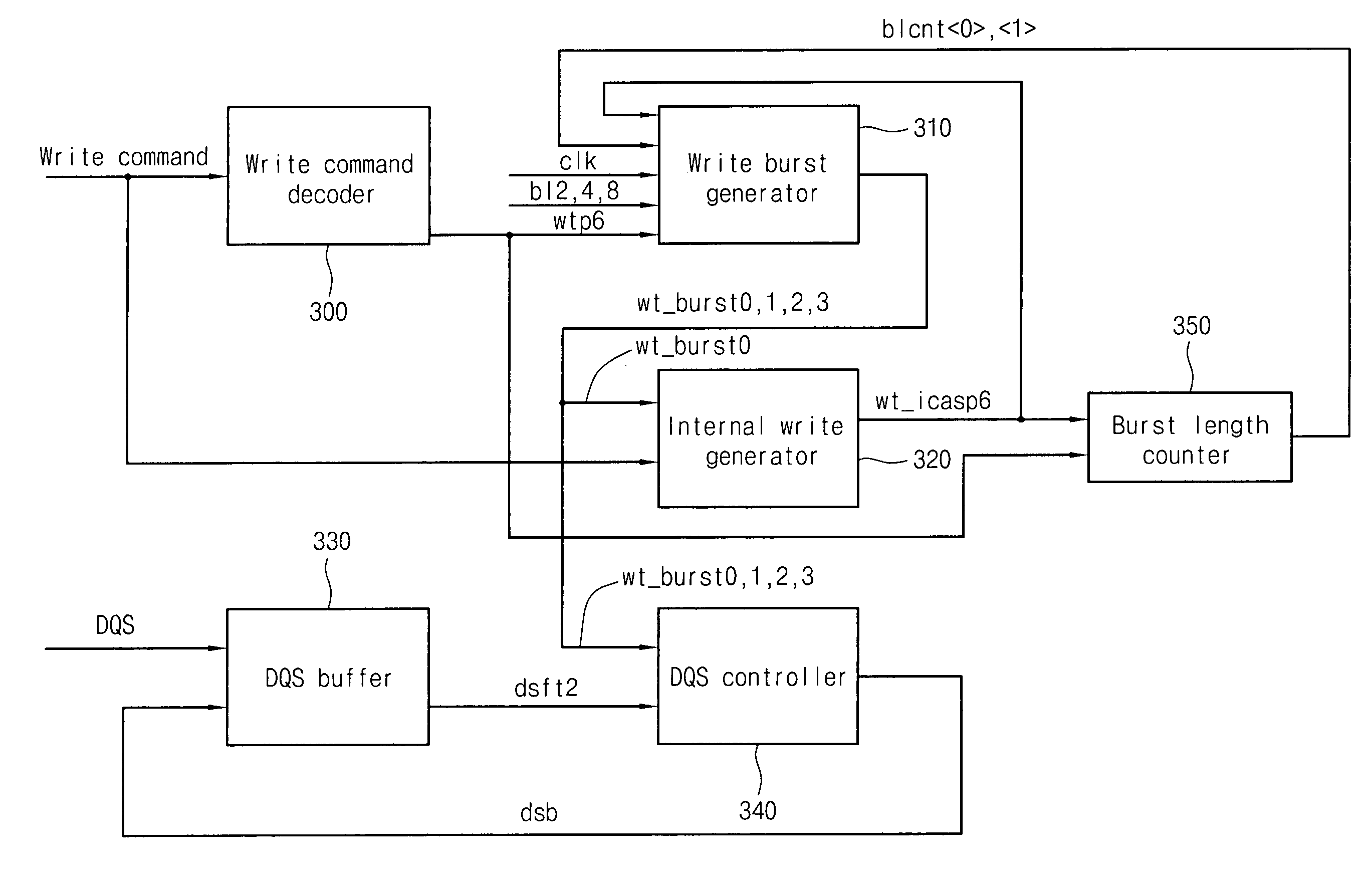
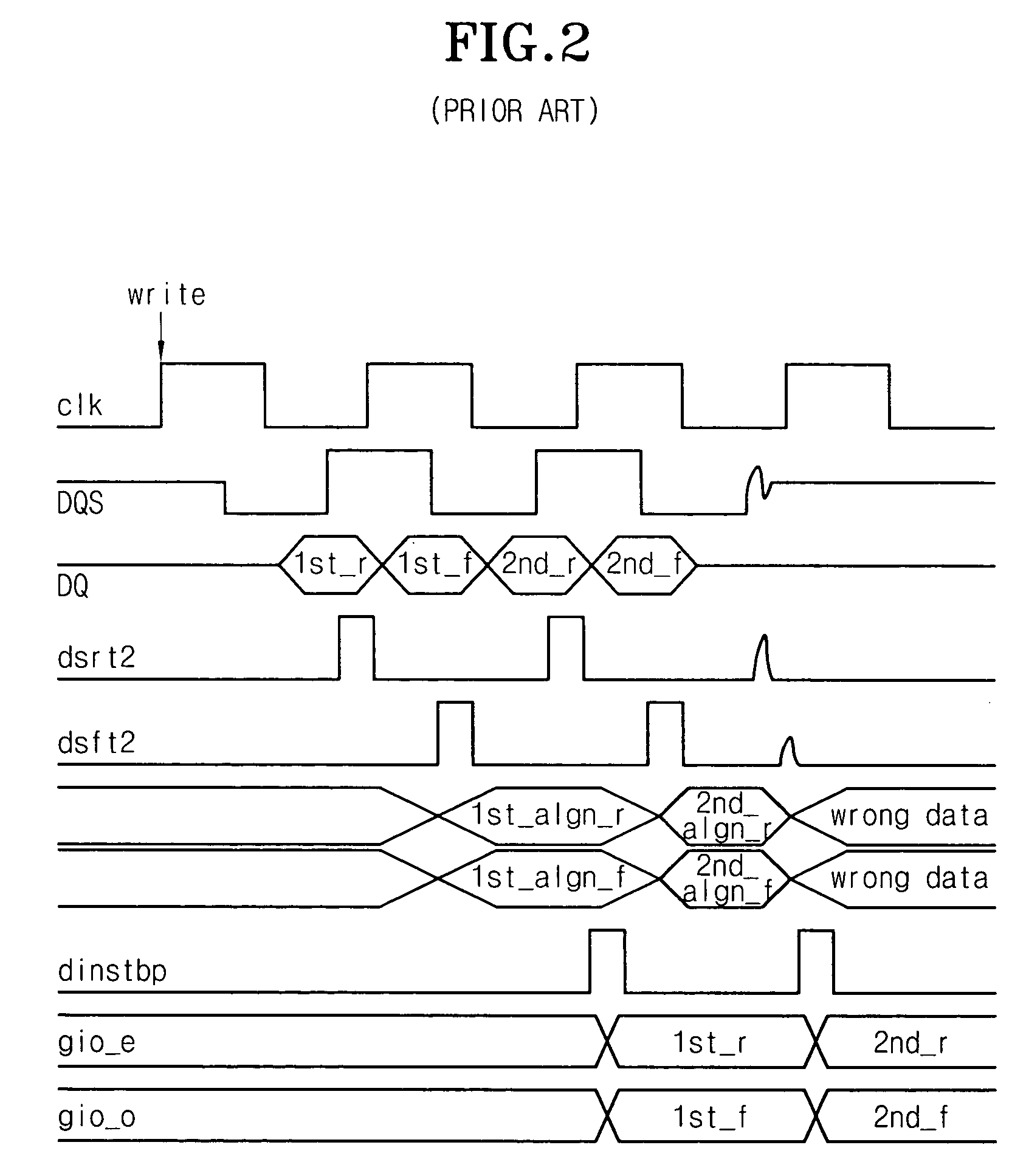
Write circuit of double data rate synchronous DRAM
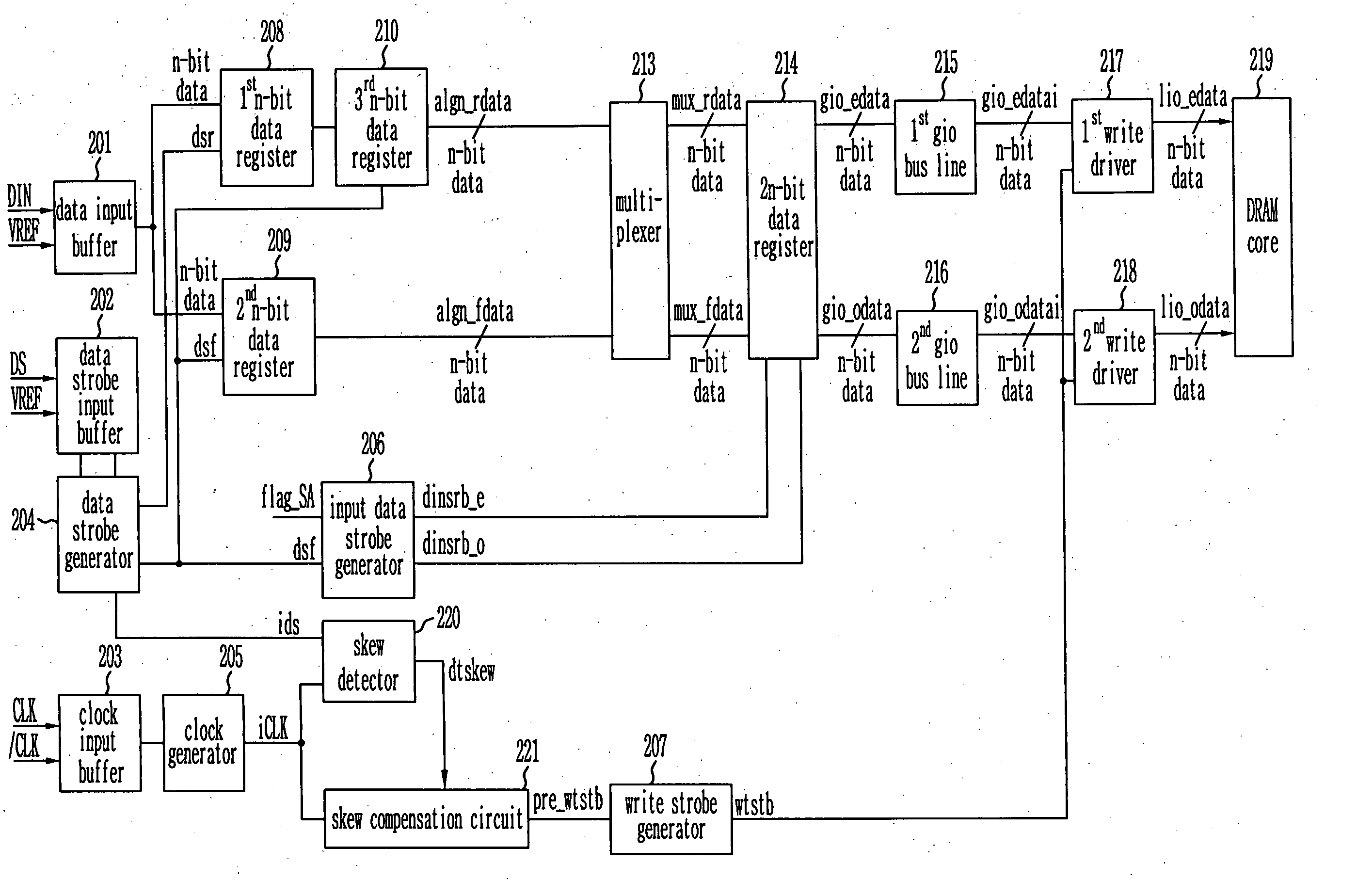
ActiveUS7042799B2Guaranteed uptimeTiming marginRead-only memoriesDigital storageTiming marginDouble data rate
Provided is a write circuit of a DDR SDRAM, in which a clock domain crossing is generated from a writing driver during a data write operation and a proper data is always transferred to a gio bus line by using the delay of an internal data strobe signal's falling for a certain amount of time as an input data strobe bar signal. Moreover, by using a skew detection circuit, it is possible to detect a skew tDQSS between a clock and a data strobe, and the skew tDQSS is automatically compensated by the skew compensation circuit. From the perspective of a timing error between the clock and the data strobe, therefore, the write operation of the DDR SDRAM has twice the timing margin (0.5tCK) compared to that of the related art. This means that a stable, high-speed write operation of the DDR SDRAM can be made possible.
Owner:MOSAID TECH
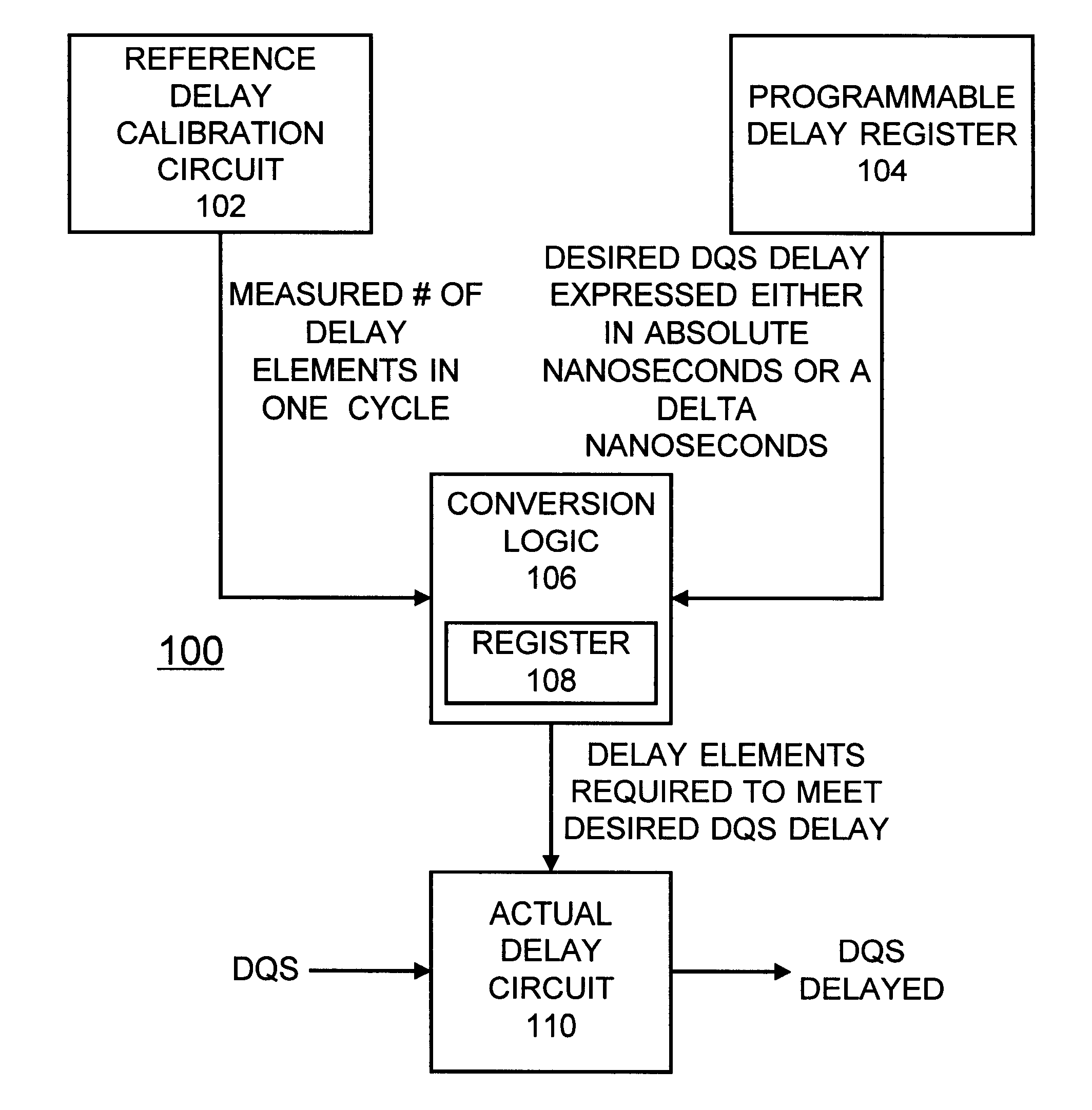
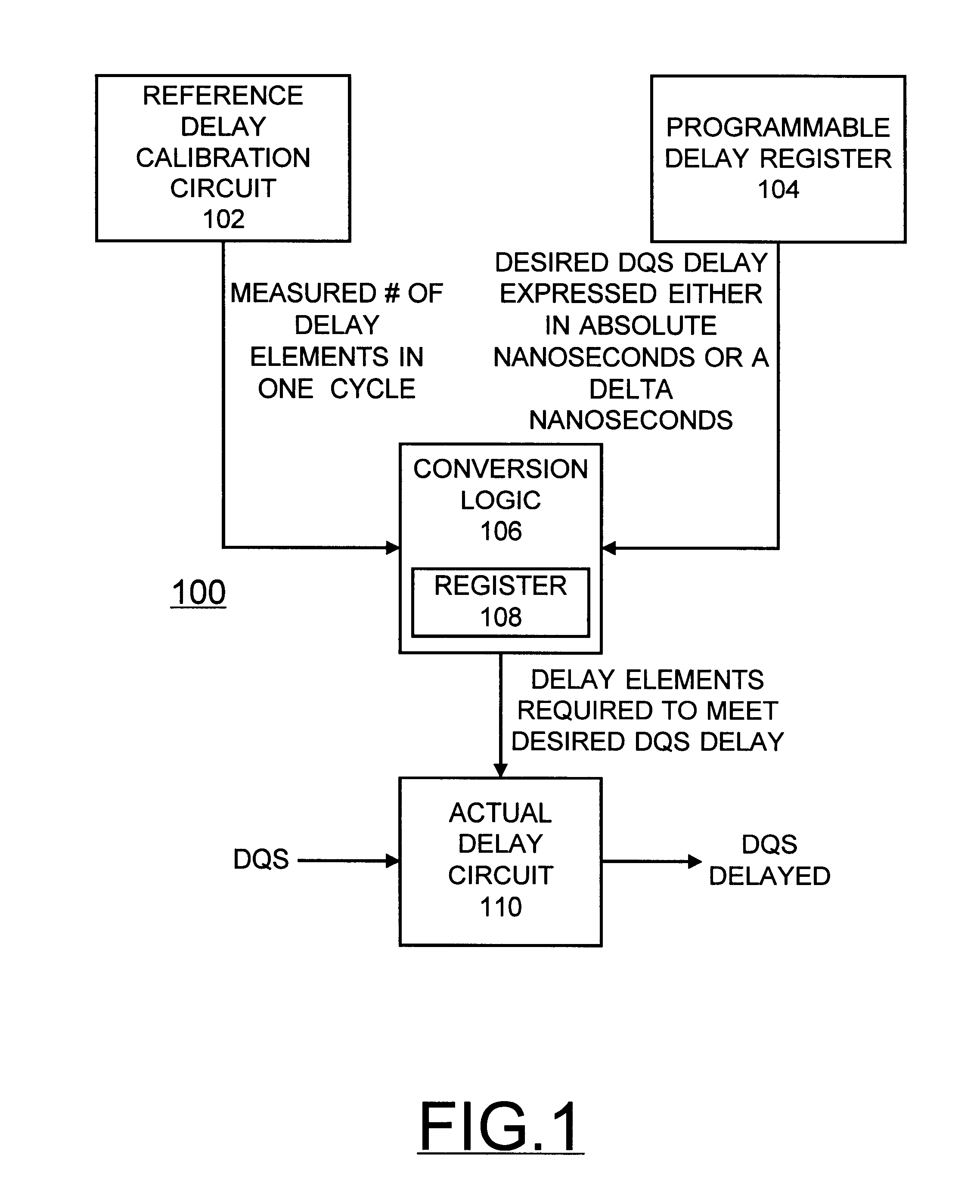
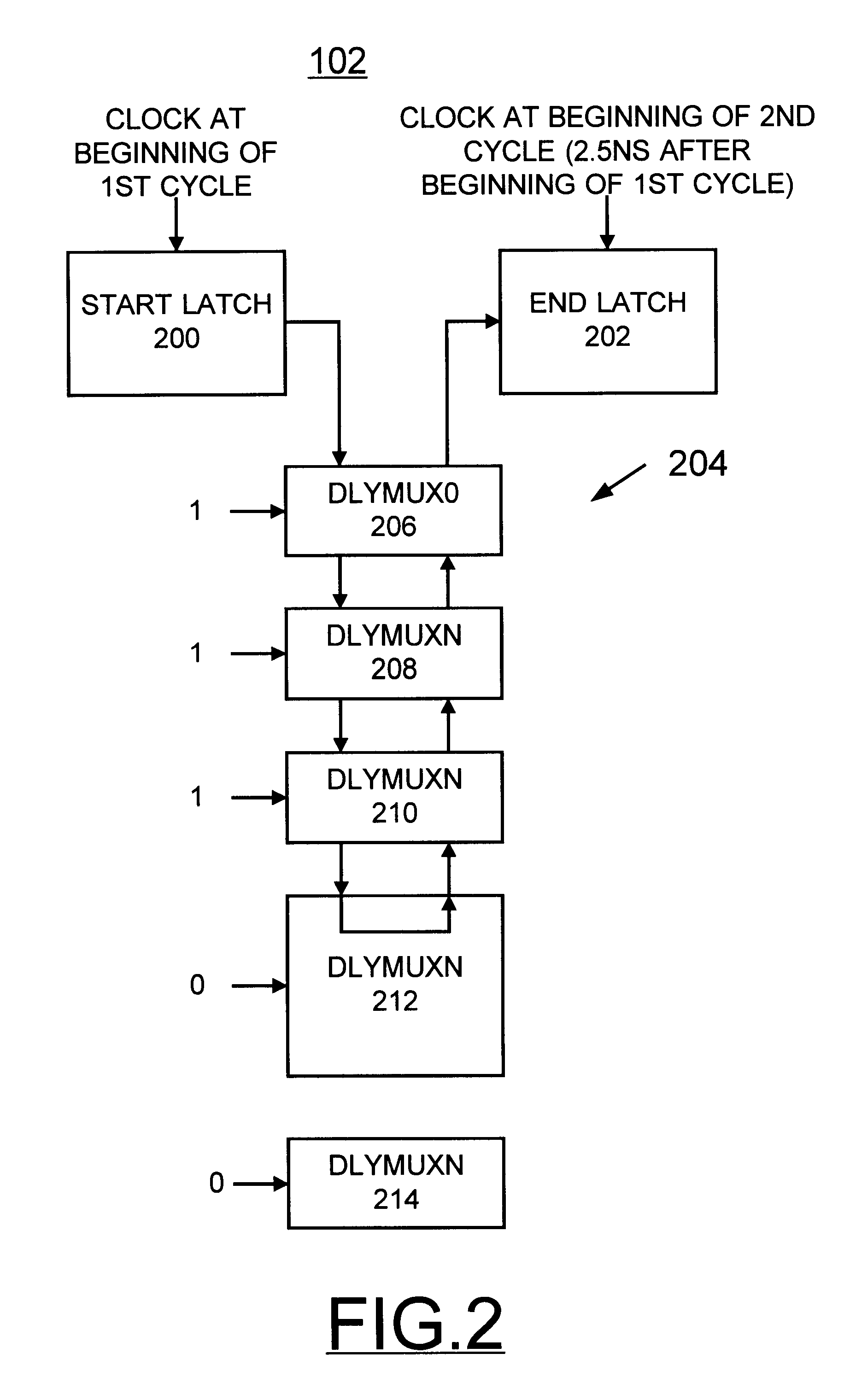
Programmable compensated delay for DDR SDRAM interface using programmable delay loop for reference calibration
A programmable compensated delay for a double data rate (DDR) synchronous dynamic random access memory (SDRAM) interface is provided. A programmable compensated delay apparatus includes a reference delay calibration circuit for providing a measured number of delay elements in one cycle. A programmable delay register provides a desired delay value. A conversion logic is coupled to the reference delay calibration circuit and the programmable delay register for receiving both the measured number of delay elements in one cycle and the desired delay value. The conversion logic provides a number of required delay elements. A delay circuit is coupled to the conversion logic for receiving the number of required delay elements and providing the desired delay. A SDRAM control logic provides a refresh start signal to the reference delay calibration circuit for updating the delay circuit during each DRAM refresh. The DQS clock strobe on the DDR SDRAM is applied to the delay circuit and is delayed by the desired delay.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Write apparatus for DDR SDRAM semiconductor memory device
A writing apparatus of a semiconductor memory device includes a pulse generator, a latch unit and an output latch unit. The pulse generator outputs a first pulse every rising edge of a data strobe pulse and a second pulse every falling edge of the data strobe pulse, respectively. The latch unit latches data input every rising edge of the first pulse, latches data input every rising edge of the second pulse and the latched data, respectively, and allocates the latched data to first and second data lines. The output latch unit latches data, which are firstly allocated to the first and second data lines, in response to a first control signal, and latches data, which are secondly allocated to the first and second data lines, in response to a second control signal.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
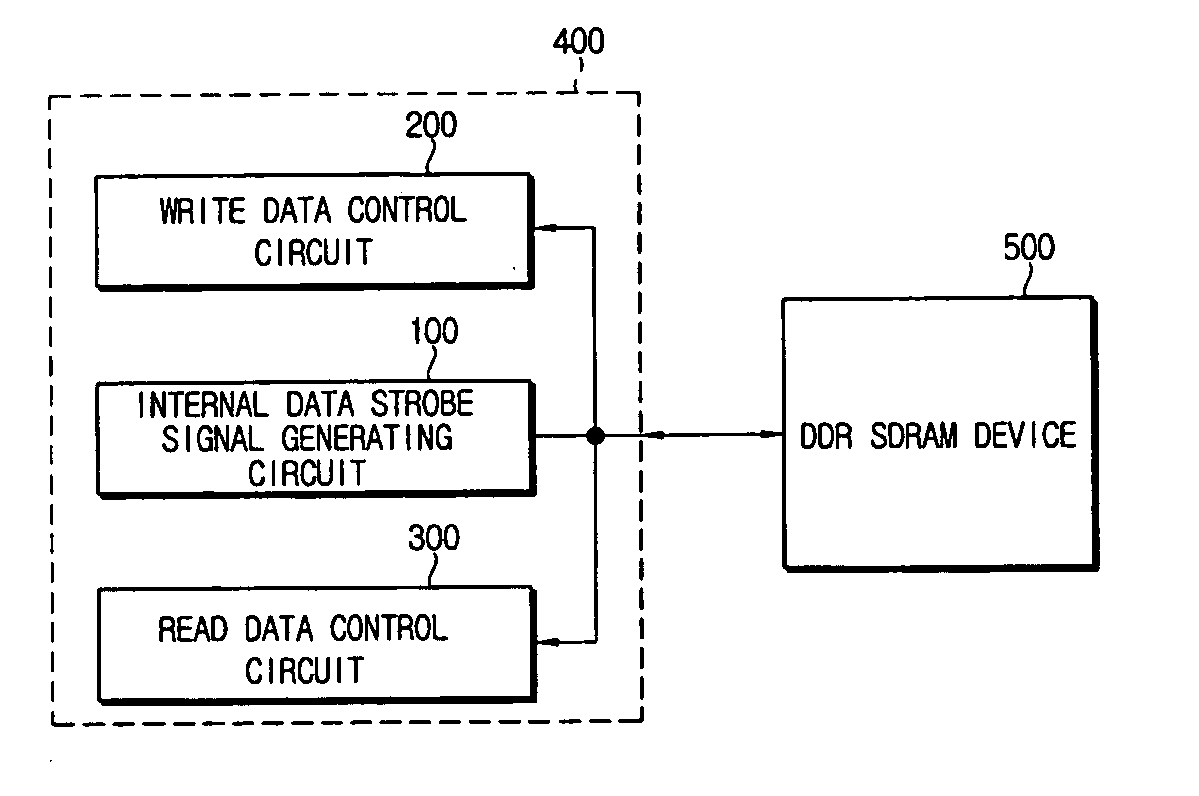
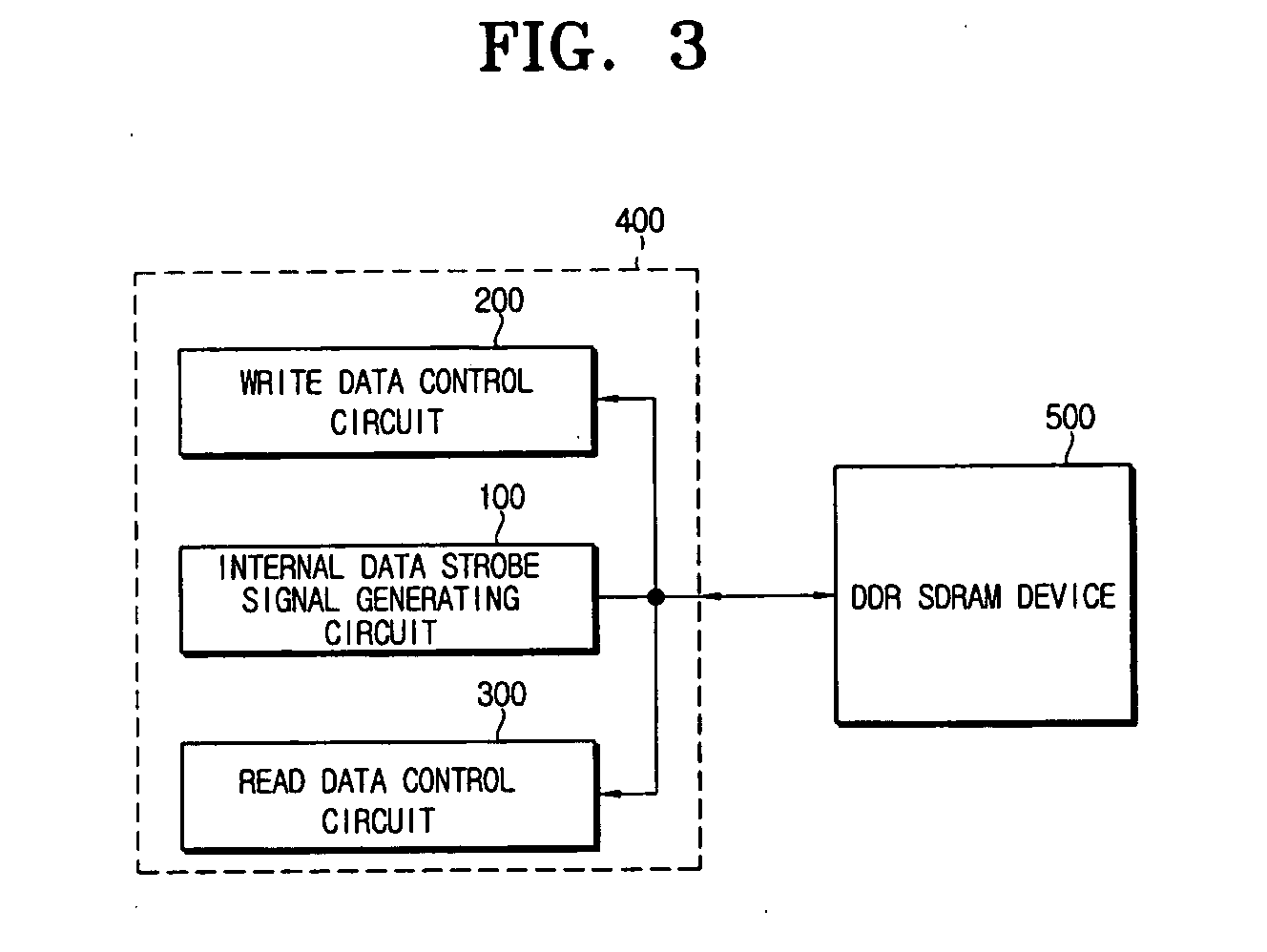
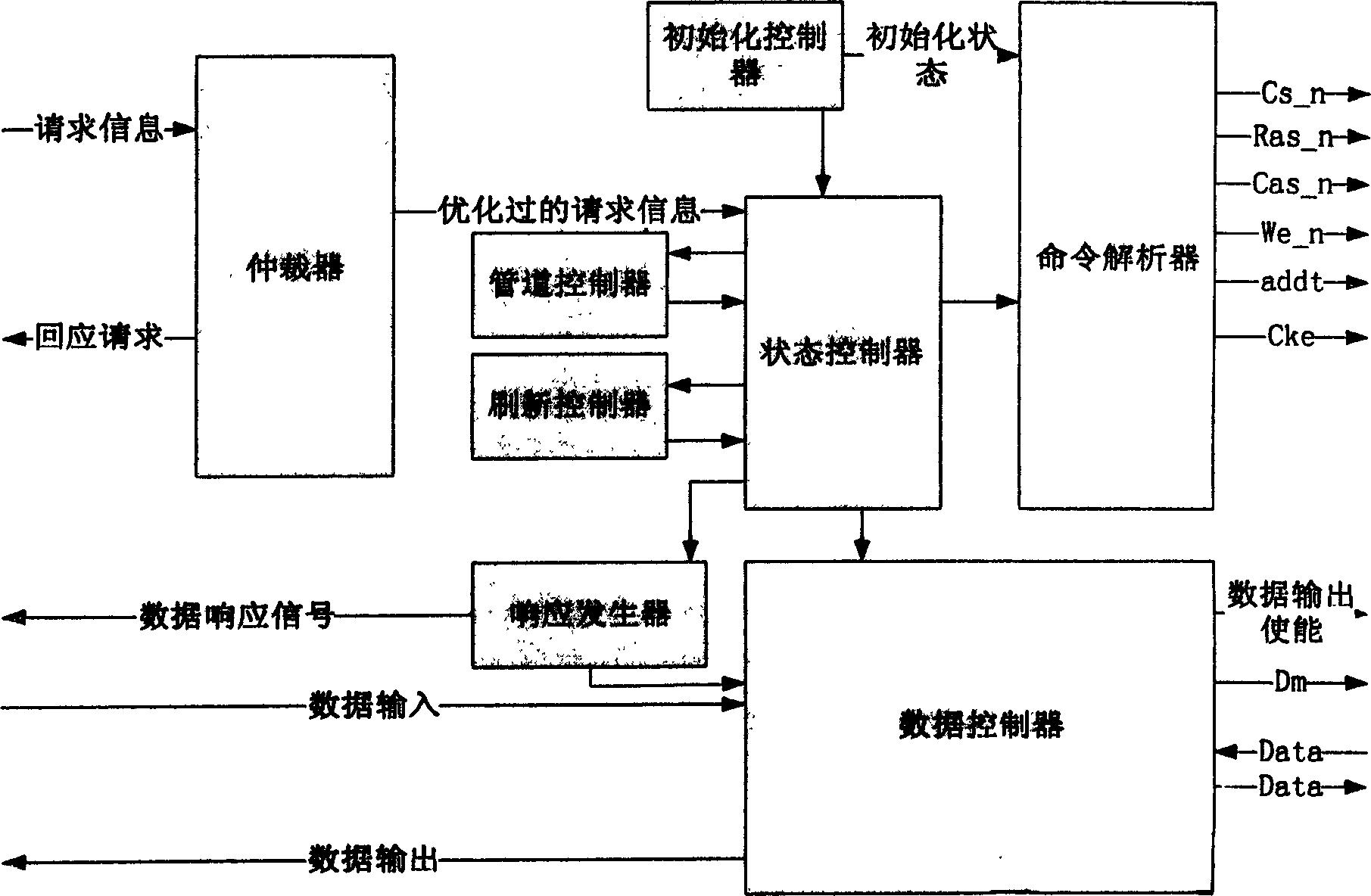
Data control circuit for DDR SDRAM controller
A data control circuit for a double data rate (DDR) synchronous dynamic random-access memory (SDRAM) that secures a stable reading / writing operation of DDR SDRAM data by generating an actively controllable internal data strobe signal. The data control circuit includes an internal data strobe signal generating circuit generating and outputting an internal data strobe signal a rising edge of which is located in a center part of valid DDR SDRAM data; a read data control circuit for receiving the internal data strobe signal, generated from the internal data strobe signal generating circuit as a clock input, dividing captured data into even data and odd data, and transmitting the even data and the odd data to a system bus; and a write data control circuit transmitting the internal data strobe signal input from the internal data strobe signal generating circuit to a DDR SDRAM device as a data strobe signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
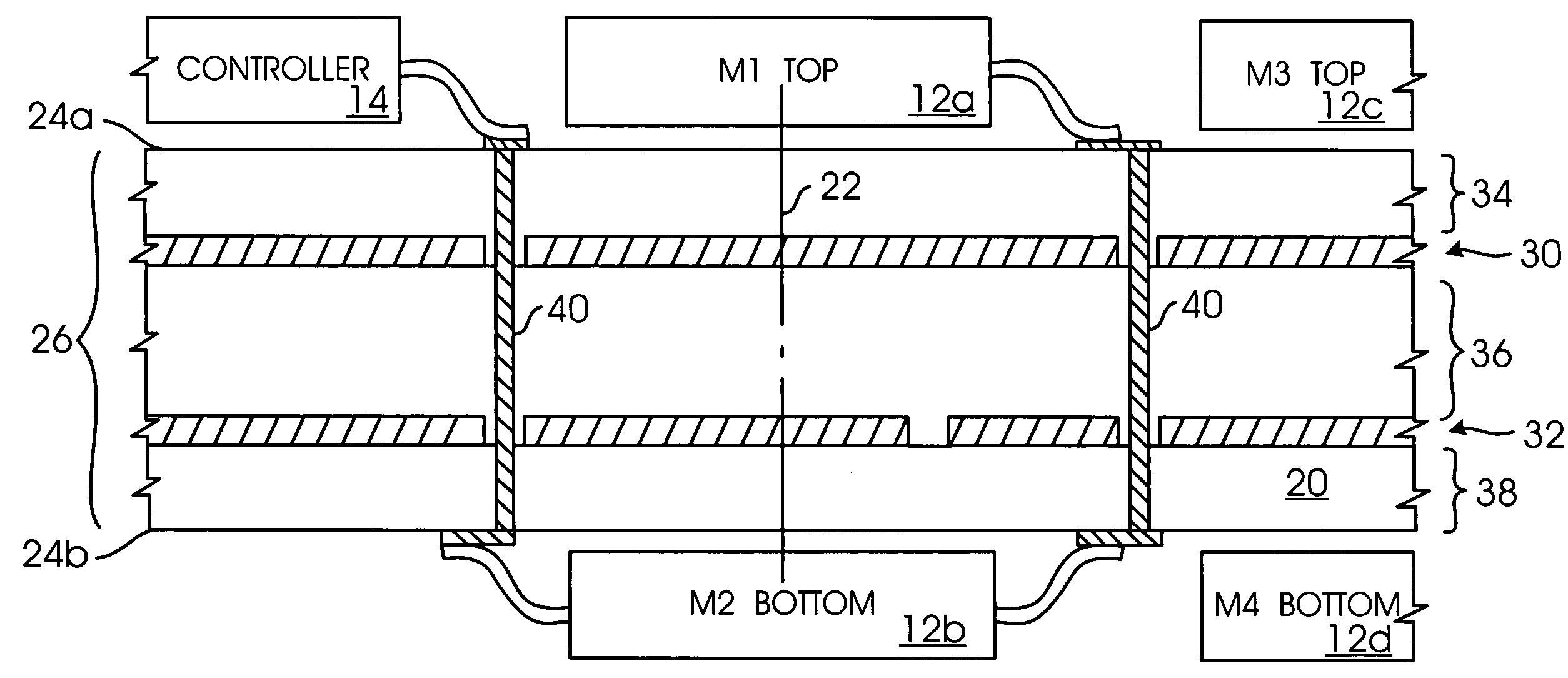
Memory module having mirrored placement of DRAM integrated circuits upon a four-layer printed circuit board
ActiveUS7023719B1Optimize routing lengthShorten the lengthFinal product manufacturePrinted circuit aspectsElectricityElectrical conductor
A memory module is provided as well as a method for forming a memory module. The memory module includes a printed circuit board having opposed first and second outside surfaces. At least one via can extend through the printed circuit board and couples a conductor on one outside surface to a conductor on another outside surface. A semiconductor memory device on one of those outside surfaces can thereby be connected to one end of the via, with another semiconductor memory device on the opposing outside surface connected to the other end of the via. Preferably, the pair of memory devices are placed on a portion of each respective outside surface so that they essentially align in mirrored fashion with each other. Accordingly, any vias which extend from the footprint of one memory device will take the shortest path to the footprint of the other memory device, with the stubs between the footprint and the via being of essentially the same length and relatively short. The printed circuit board preferably has no more than four conductive layers dielectrically spaced from each other. Two layers are reserved for the opposing outer surfaces, and two layers carrying power and ground signals are embedded within the board. The memory devices are preferably DDR SDRAMs connected to each other as well as a memory controller, each of are placed and maintained upon a single printed circuit board.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Semiconductor integrated circuit
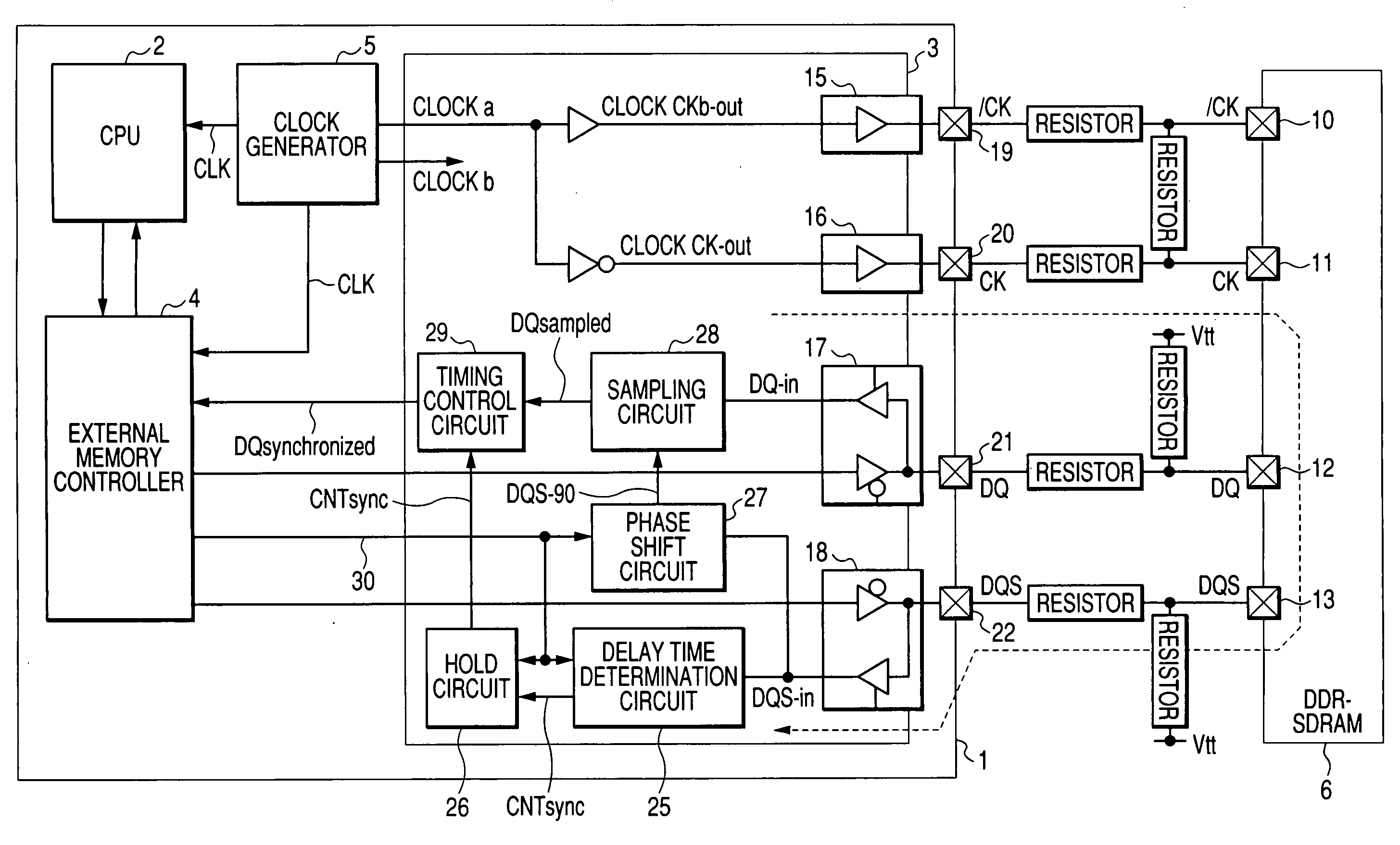
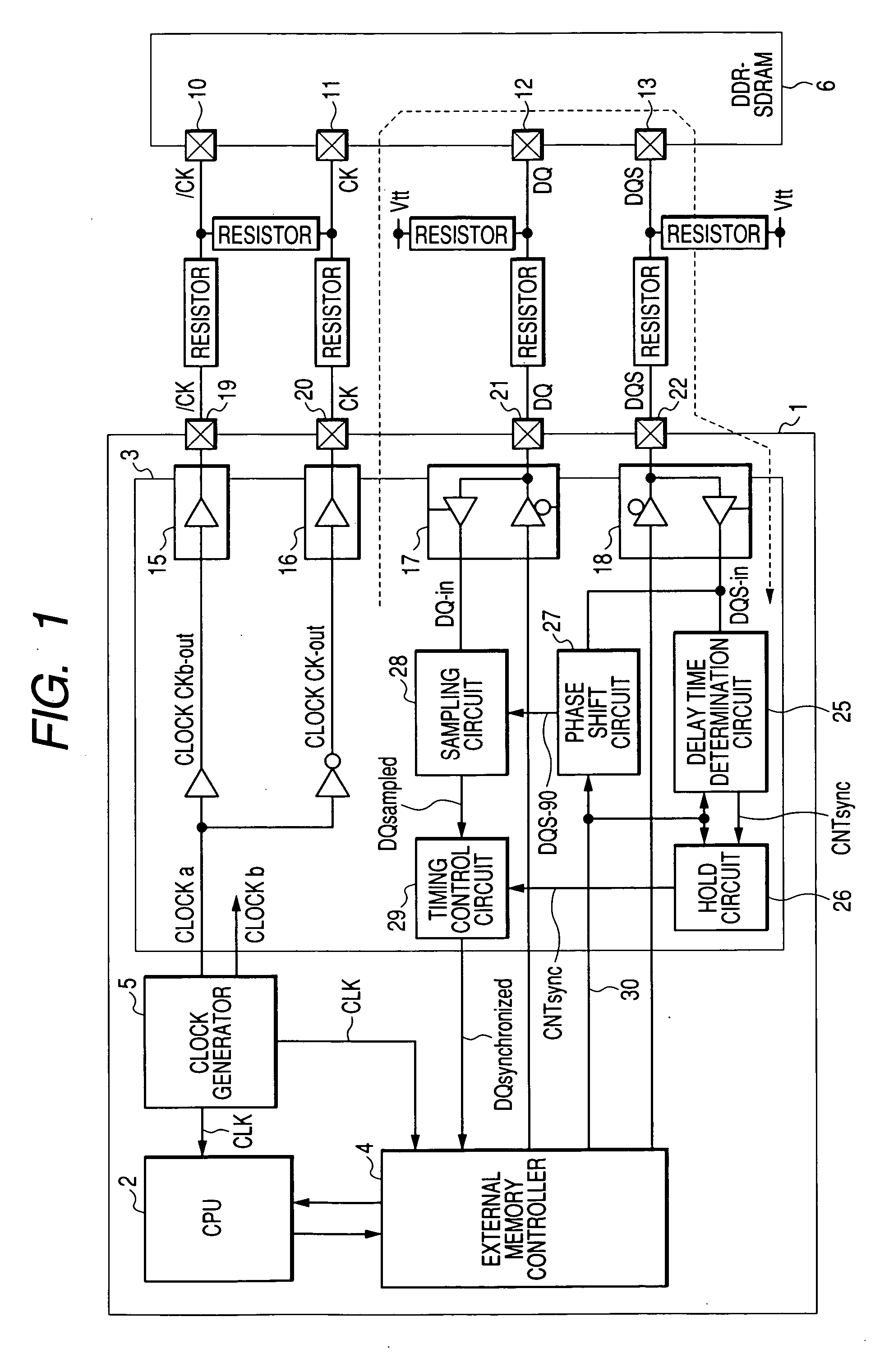
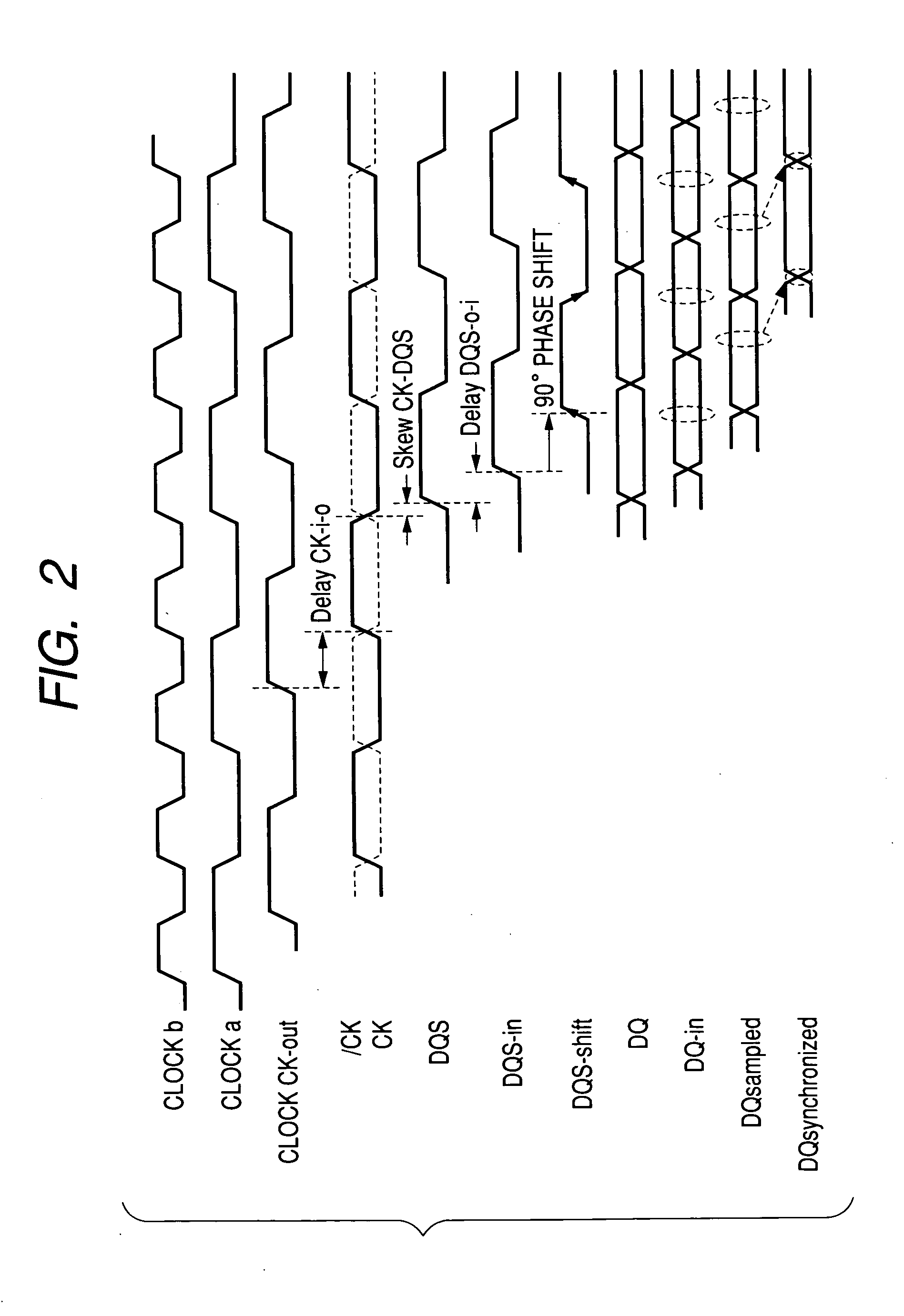
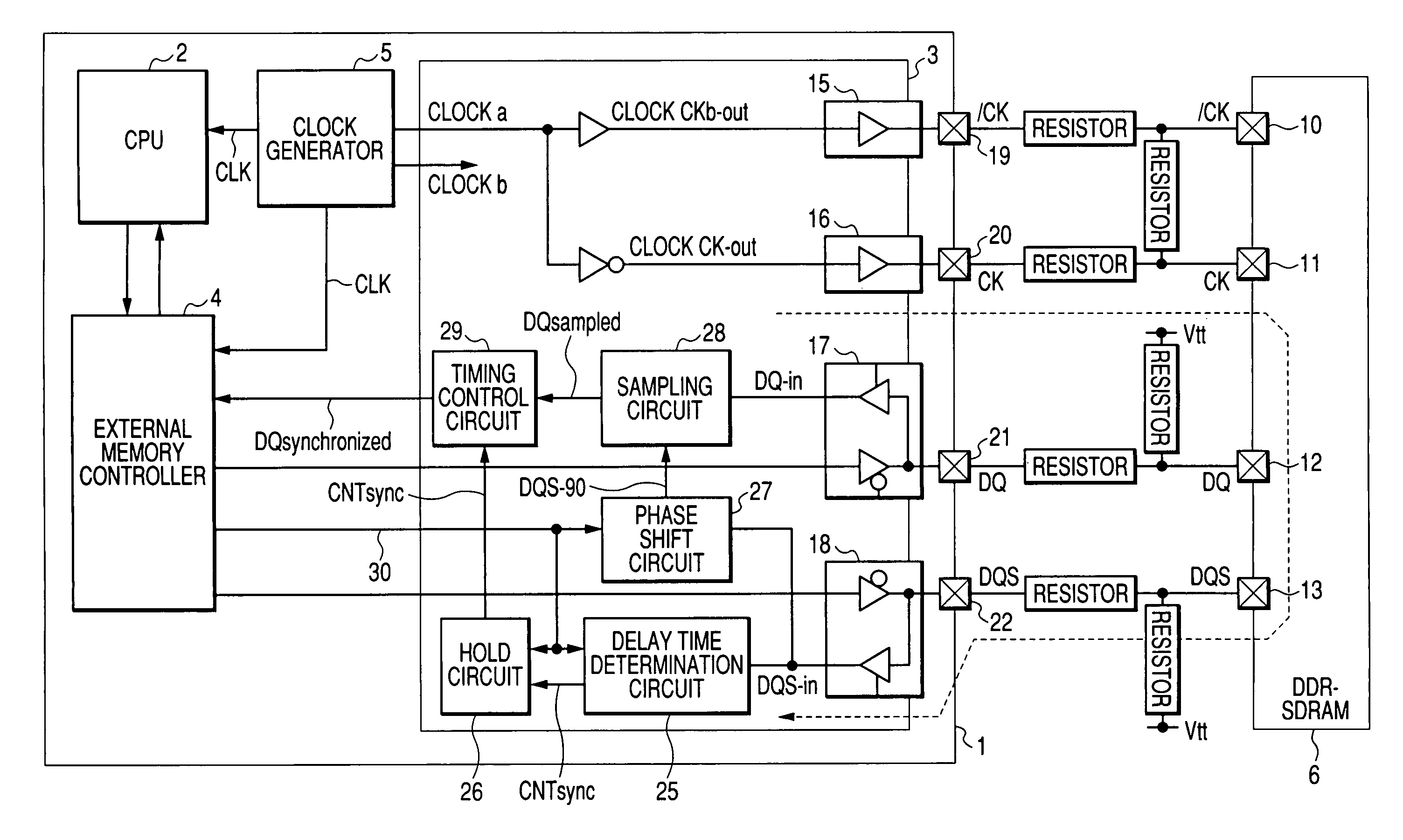
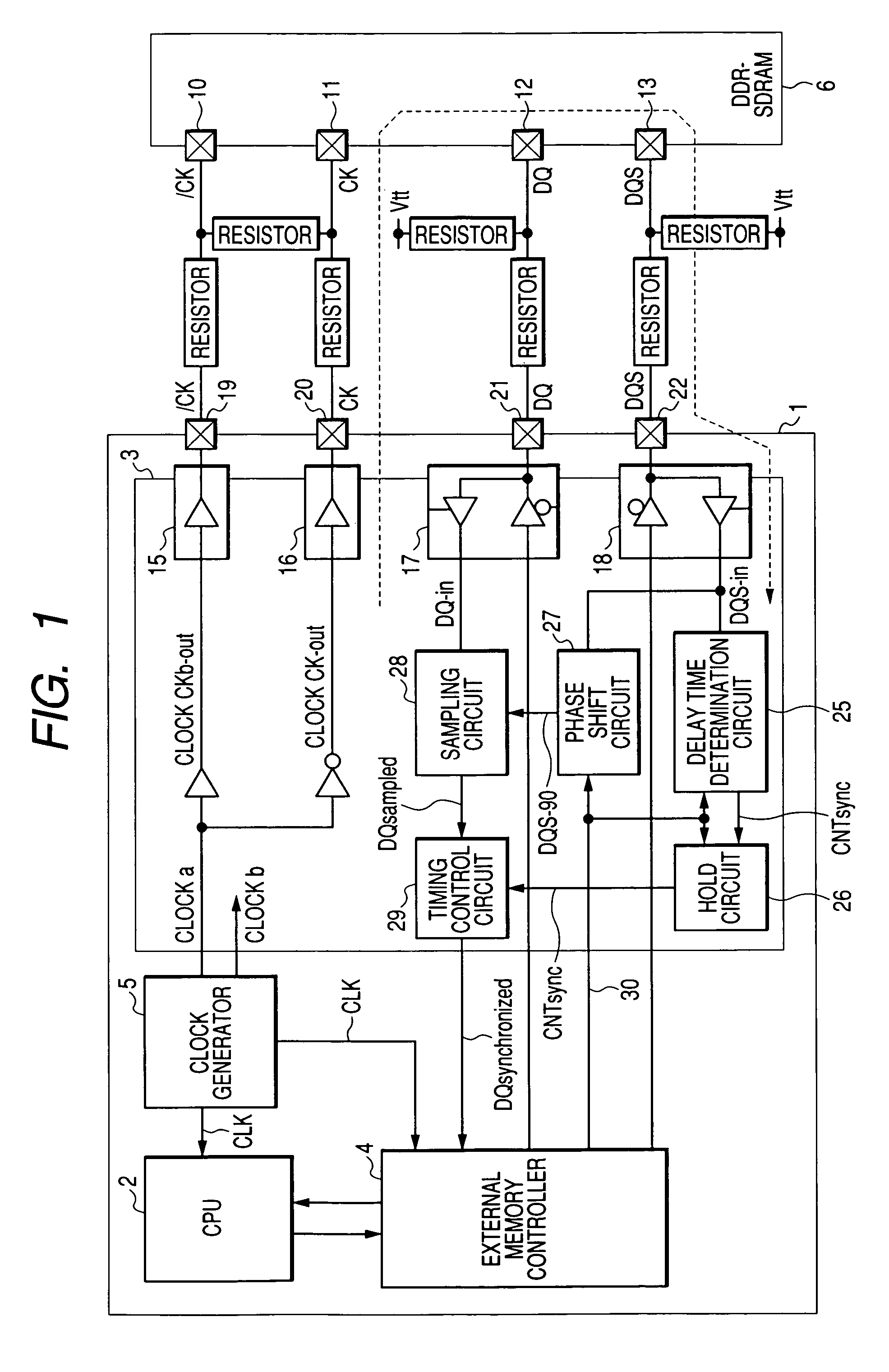
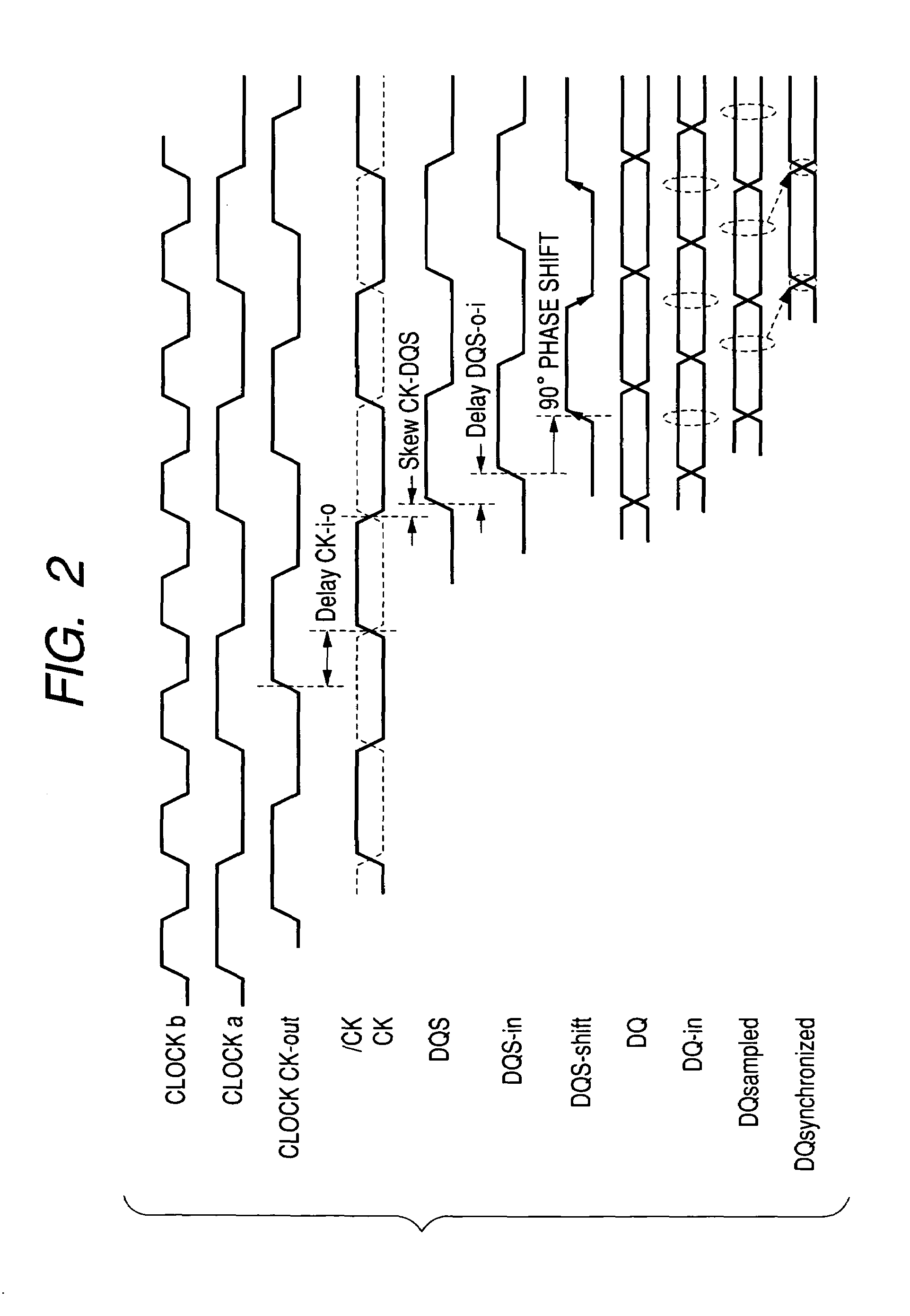
ActiveUS7412616B2Improve accuracyStablyDigital storageGenerating/distributing signalsData synchronizationMemory interface
A memory interface circuit is connectable to a DDR-SDRAM which outputs read data in synchronization with a data strobe signal together with the data strobe signal. A clock generator generates internal clock signals and memory clock signals supplied to the DDR-SDRAM. The memory interface circuit determines a delay of arrival of the data strobe signal relative to the corresponding internal clock signal by using a data strobe signal inputted in a read cycle with respect to the DDR-SDRAM, samples the arrived read data, based on a signal obtained by shifting the phase of the arrived data strobe signal, and synchronizes the sampled read data to the corresponding internal clock signal on the basis of the result of determination of the arrival delay.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Write circuit of double data rate synchronous DRAM
ActiveUS20050141331A1Stable data write operationGuaranteed uptimeRead-only memoriesDigital storageTiming marginDouble data rate
Provided is a write circuit of a DDR SDRAM, in which a clock domain crossing is generated from a writing driver during a data write operation and a proper data is always transferred to a gio bus line by using the delay of an internal data strobe signal's falling for a certain amount of time as an input data strobe bar signal. Moreover, by using a skew detection circuit, it is possible to detect a skew tDQSS between a clock and a data strobe, and the skew tDQSS is automatically compensated by the skew compensation circuit. From the perspective of a timing error between the clock and the data strobe, therefore, the write operation of the DDR SDRAM has twice the timing margin (0.5tCK) compared to that of the related art. This means that a stable, high-speed write operation of the DDR SDRAM can be made possible.
Owner:CONVERSANT INTPROP MANAGEMENT INC
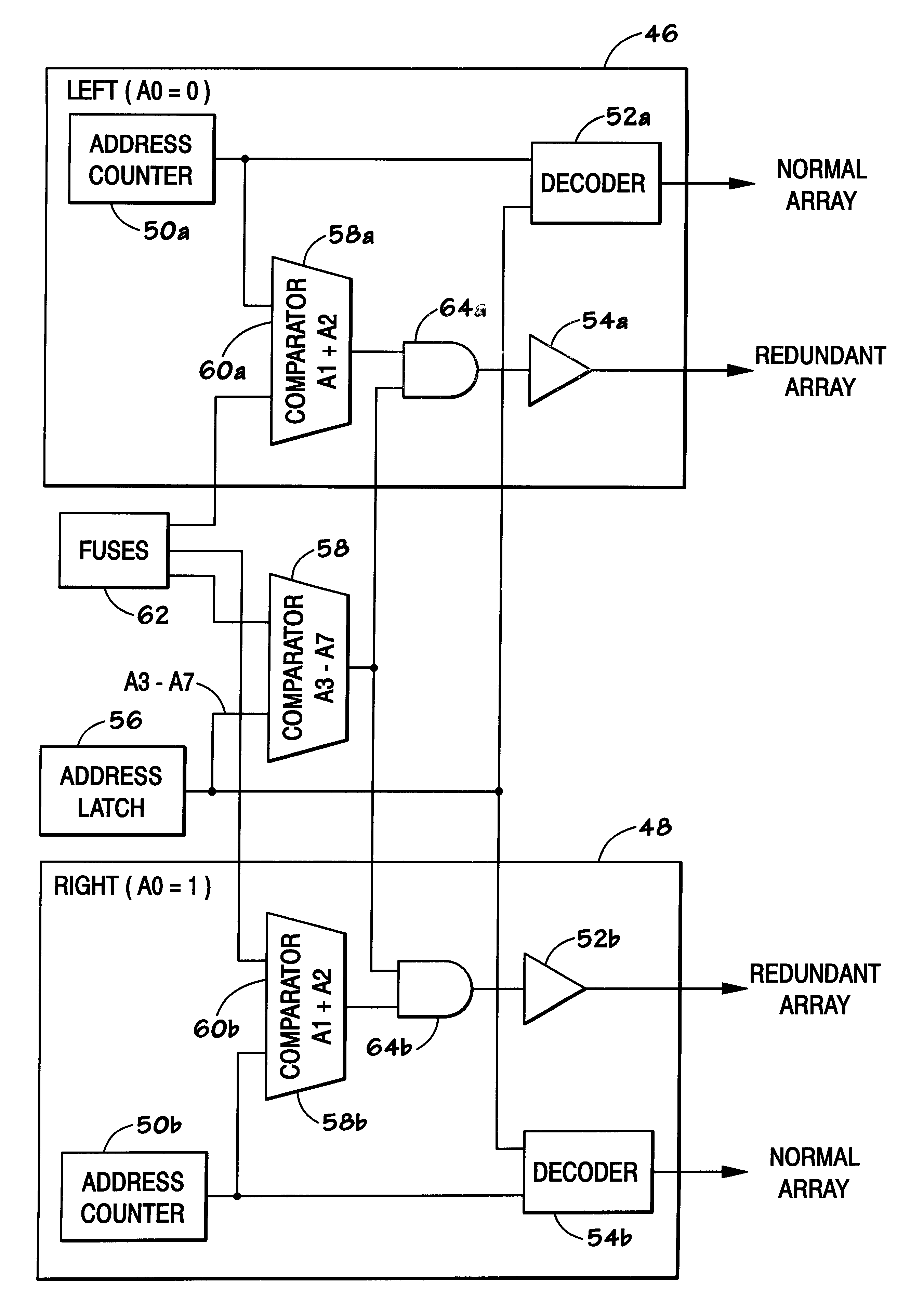
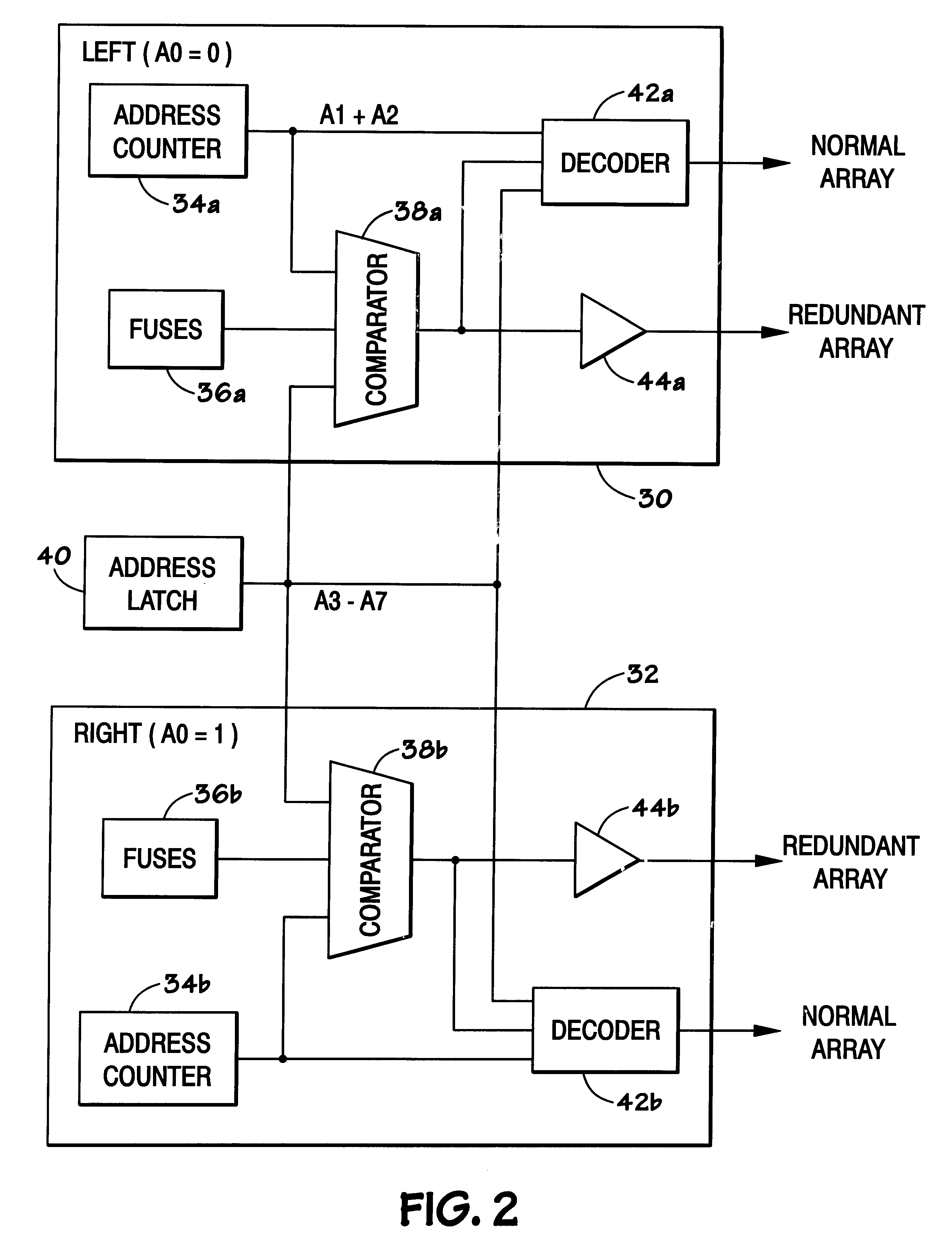
Shared redundancy for memory having column addressing
A shared redundancy prefetch scheme to provide a reduced number of fuses. DDR SDRAMs allow burst addressing at various burst lengths. DDR SDRAMs generally implement LEFT and RIGHT segment column addressing. In DDR SDRAMs which implement redundant memory arrays, fuses may be used to provide access to the redundant columns. Because burst addressing may begin with a RIGHT segment address, two different columns may be accessed on the same clock cycle. By providing a compare scheme which implements separate compare logic for the lower bits of the LEFT and RIGHT segments and compares these bits to a common fuse set used for both the LEFT and RIGHT segments, the number of fuses in the redundant DDR SDRAM scheme can be reduced.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
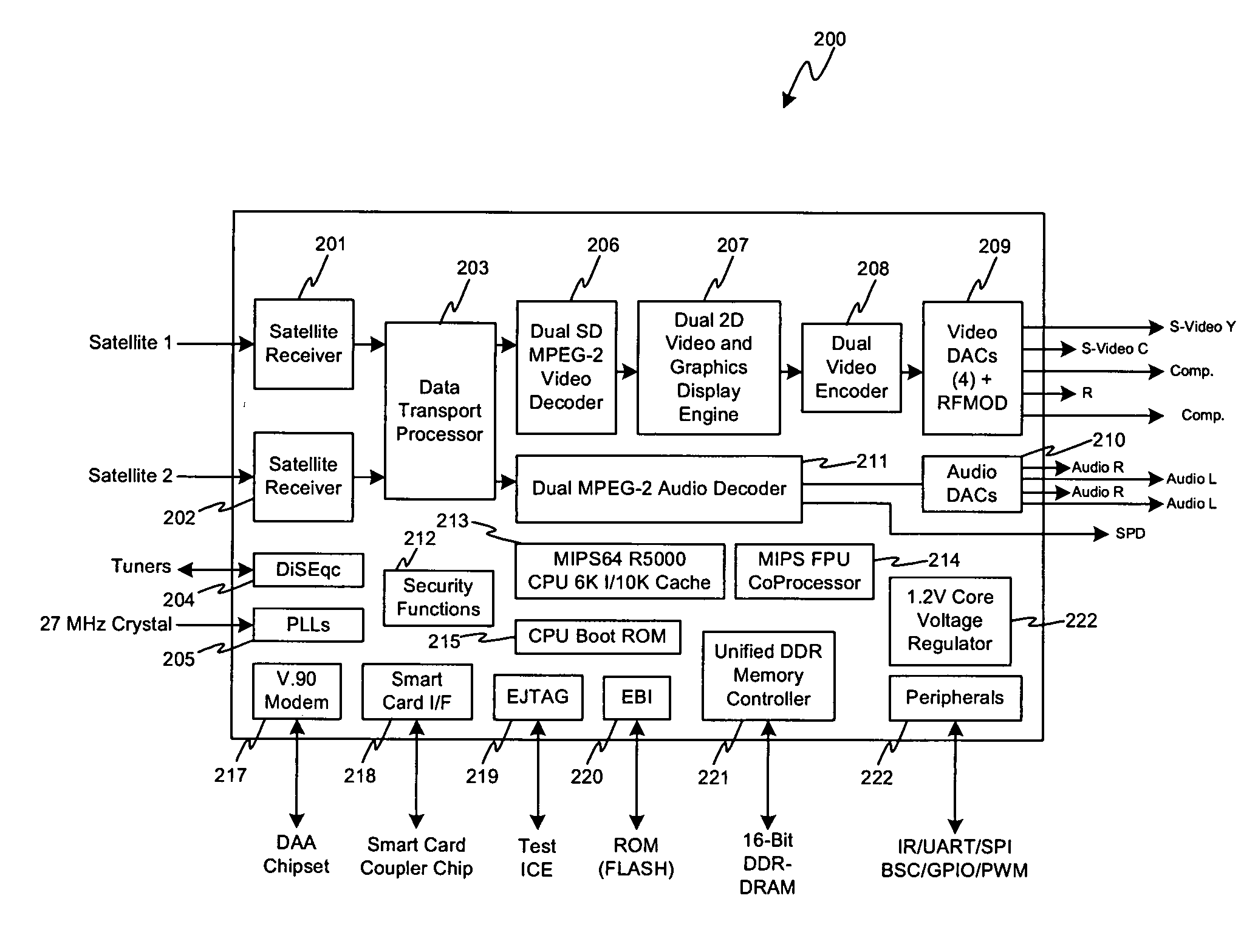
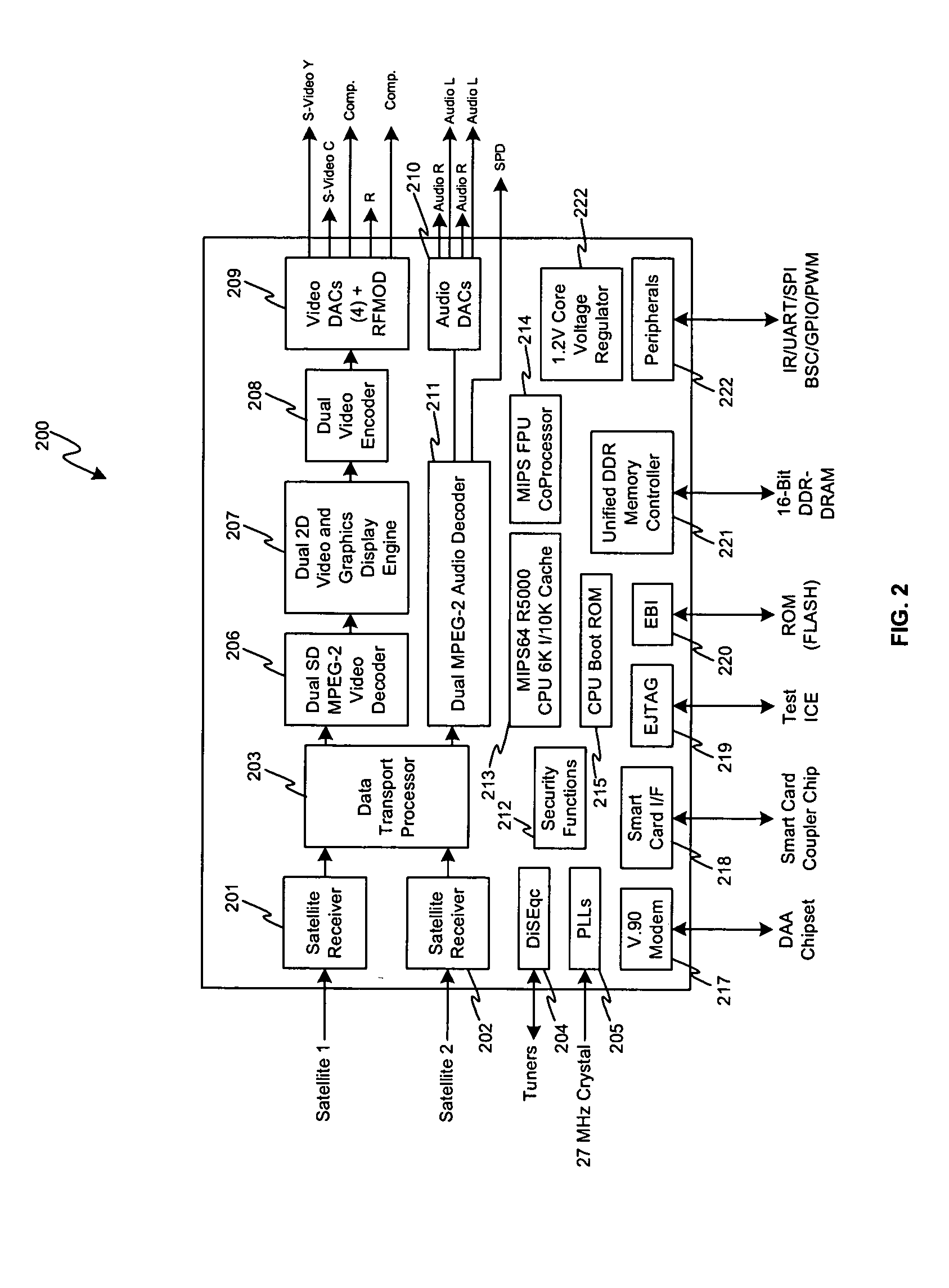
Method and system for single chip satellite set-top box system
Certain embodiments of the invention may be found in an single chip satellite set-top box solution that comprises demodulation, decoding and audio / video display functions integrated within a single chip. The single chip solution for the satellite set-top box is adapted to provide demodulation, display, and other related set-top box functions for a system that may be adapted to handle two incoming data streams modulated using an 8PSK, 8PSK-turbo or QPSK scheme, for example. Accordingly, the single chip satellite set-top box solution comprise dual 8 PSK / 8 PSK-turbo / QPSK demodulators, a MIPS CPU, a 16-bit DDR-SDRAM, graphics display capability for handling two channels, and audio / video decoders and DACs for handling two incoming channels. The single chip satellite set-top box solution may also comprise integrated peripheral support for major set top box functions including a smart card interface, IR receivers, and general purpose input / output (GP / IO) pins.
Owner:BROADCOM CORP
Processing module capable of reconstructing signals based on VPX bus
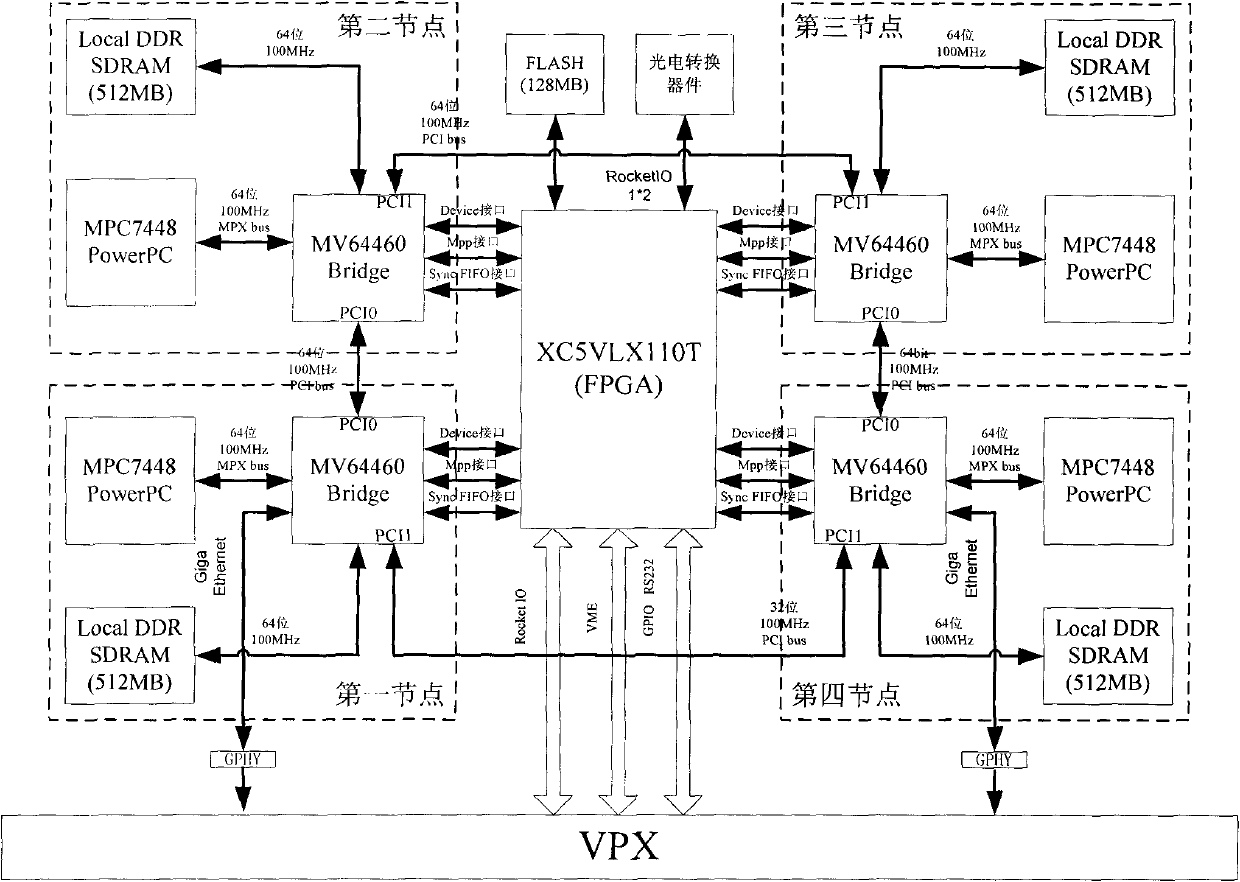
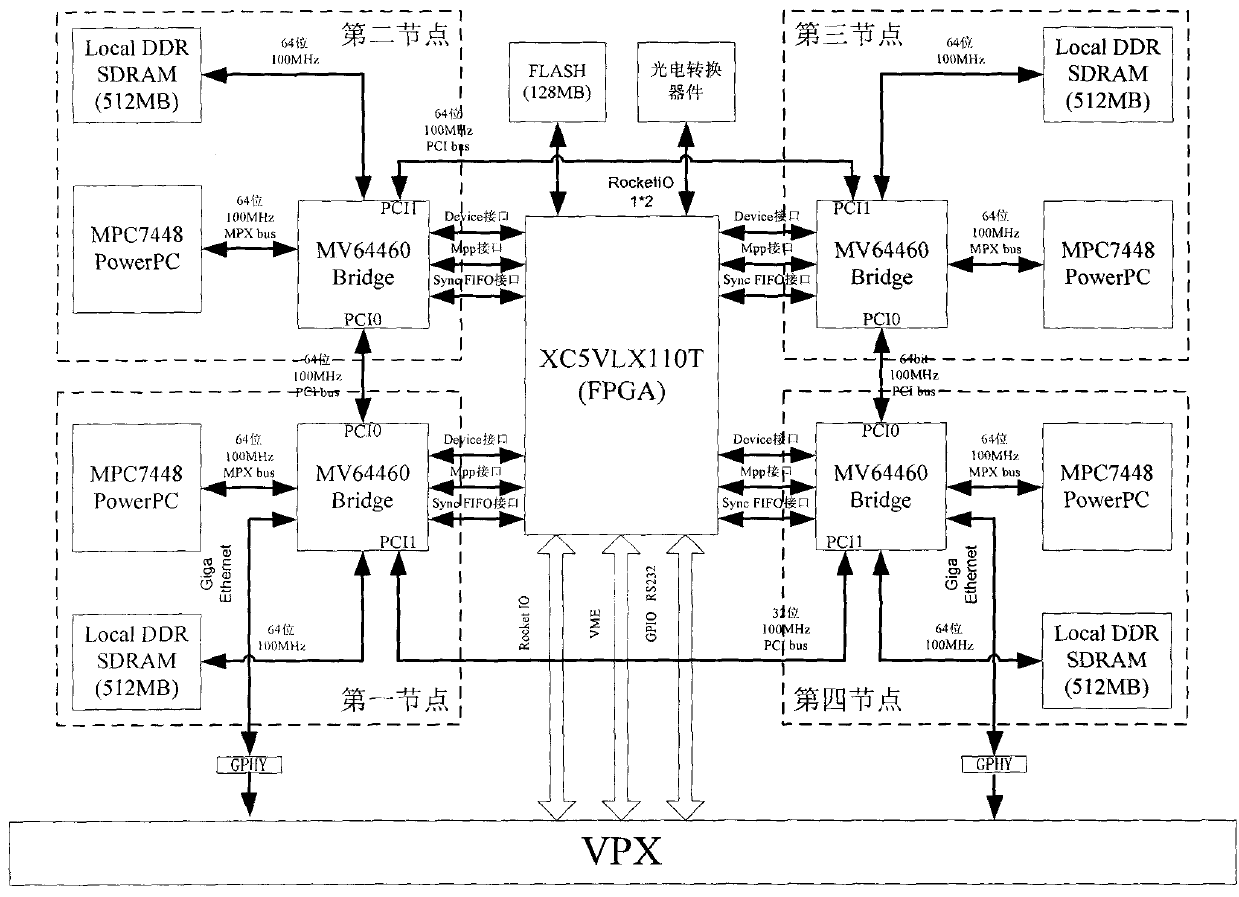
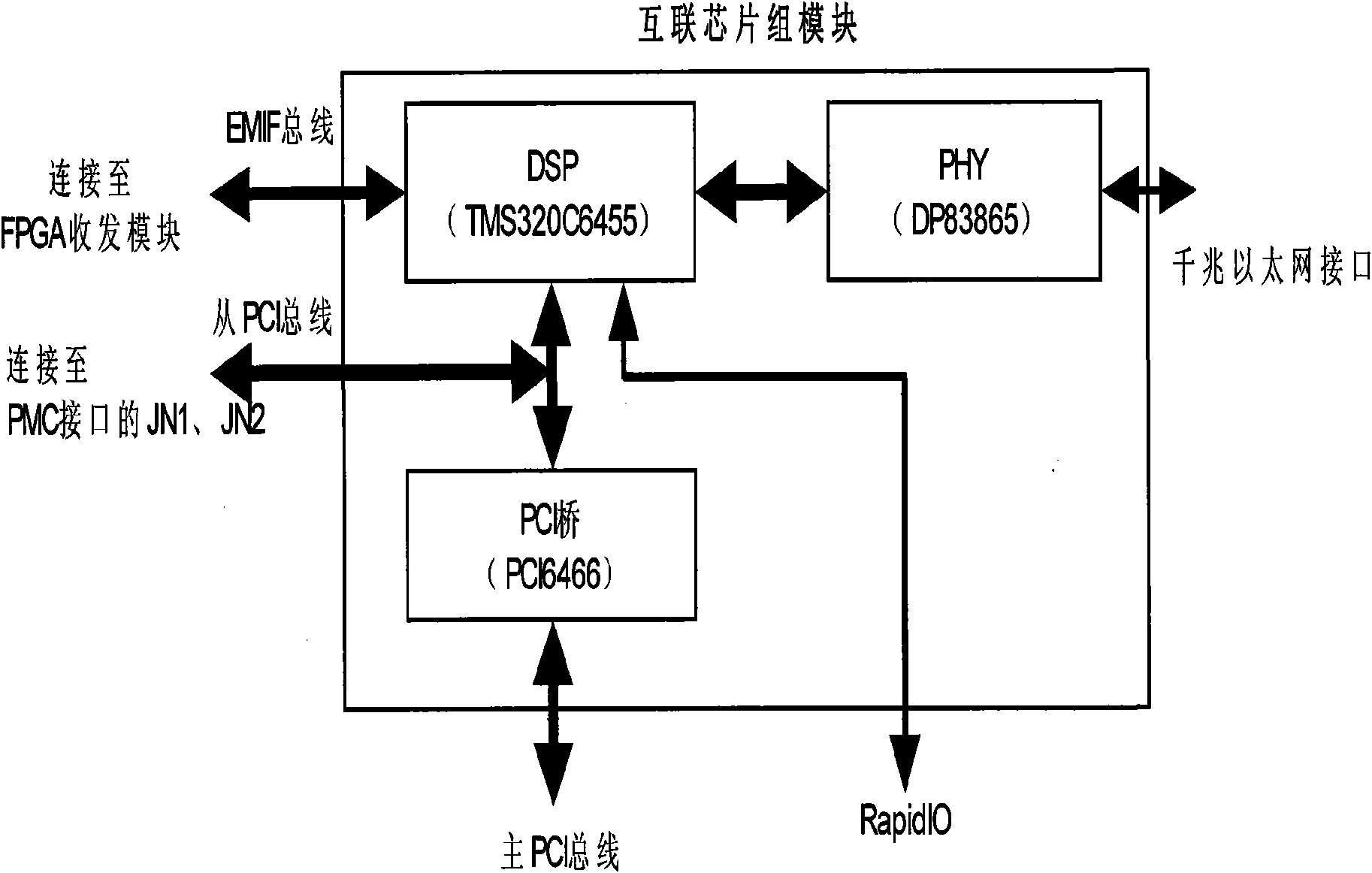
InactiveCN101794268AMeet the complexityMeet real-time requirementsElectric digital data processingDigital dataHigh density
The invention relates to a processing module capable of reconstructing signals based on a VPX bus, comprising a high-speed board card, a front panel, a radiating cover board, a module lifter, a positioning pin and a locking mechanism part. The high-speed board card comprises a VPX 6U standard high-speed printing board, a power supply circuit, an MPC7448 processor chip, an MV64460 bridging chip, a FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array) chip, a DDR SDRAM (Digital Data Receiver Synchronous Dynamic Random Access) and FLASH, a high-speed high density electric connector, an opto-electrical converter and a kilomega Ethernet interface. The high-speed board card comprises four processing nodes, each processing node comprises one MPC7448 processor chip, one MV64460 bridging chip and the DDR SDRAM; the MV64460 bridging chip is respectively connected with the MPC7448 processor chip and a storage DDR SDRAMFPGA through a CPU interface, the DDR SDRAM interface and a Device interface.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GRP CORP NO 14 RES INST +1
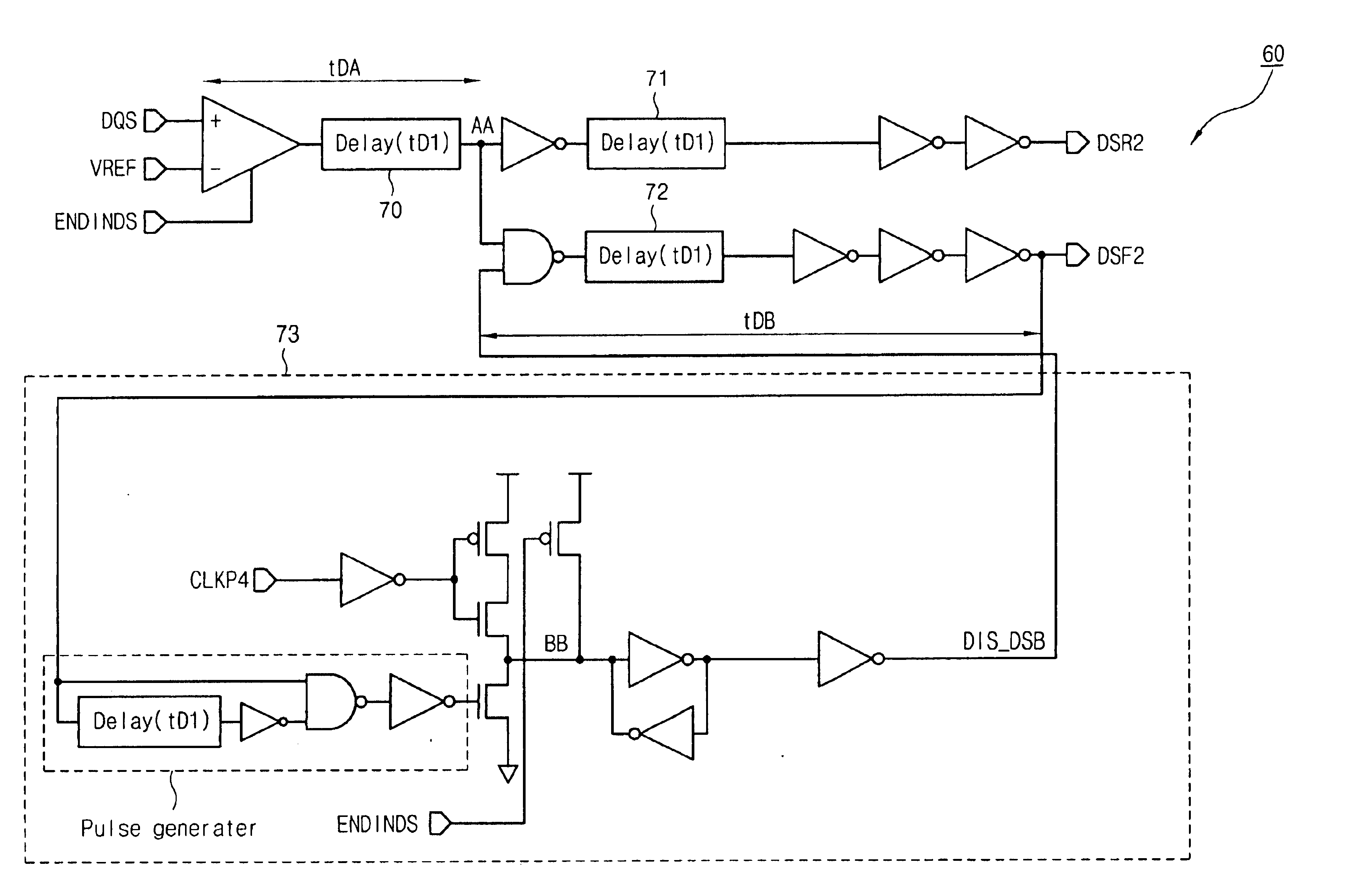
Method for masking ringing in DDR SDRAM
A method for masking a ringing in a DDR SDRAM comprises in a write mode, generating first and second synchronizing signals by means of a DQS signal inputted from an exterior circuit, in order to synchronize input data, latching data in odd sequences from among the inputted data, which are sequentially inputted, at a rising edge of the first synchronizing signal, and latching data in even sequences from among the data, which are sequentially inputted, at a rising edge of the second synchronizing signal, aligning the data in odd sequences and the data in even sequences at a falling edge of the DQS signal so that the odd and even sequenced data has the same synchronized timing, and blocking activation of the second synchronizing signal by means of a first control signal, the a first control signal being synchronized with the falling edge of the last valid DQS signal that is normally inputted, so as to enable the blocking step and thereby masking the ringing phenomenon. In the method for masking the ringing phenomenon, the point at which the DIS_DSB signal is enabled in a low state is synchronized with the last falling edge of the normal DQS signal, and therefore the DSF2 signal is disabled.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
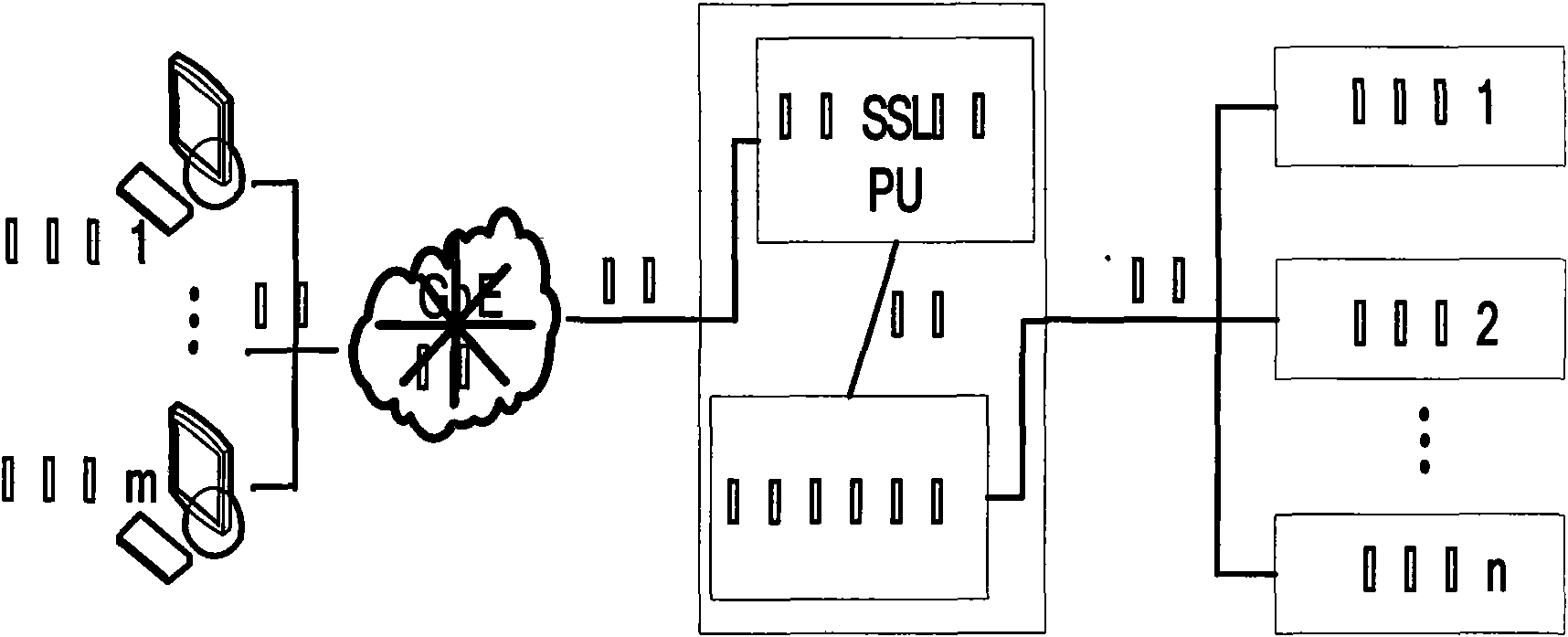
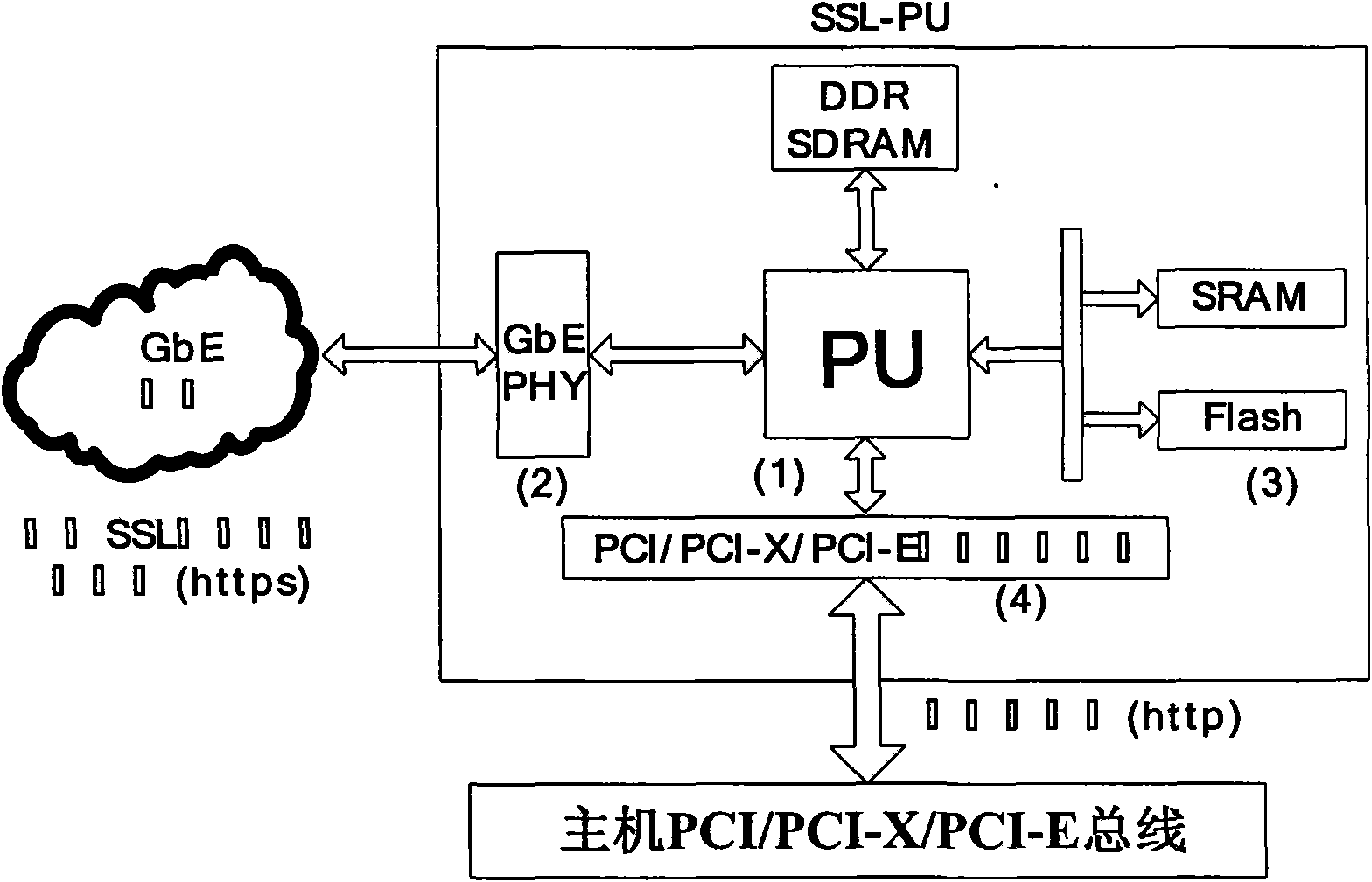
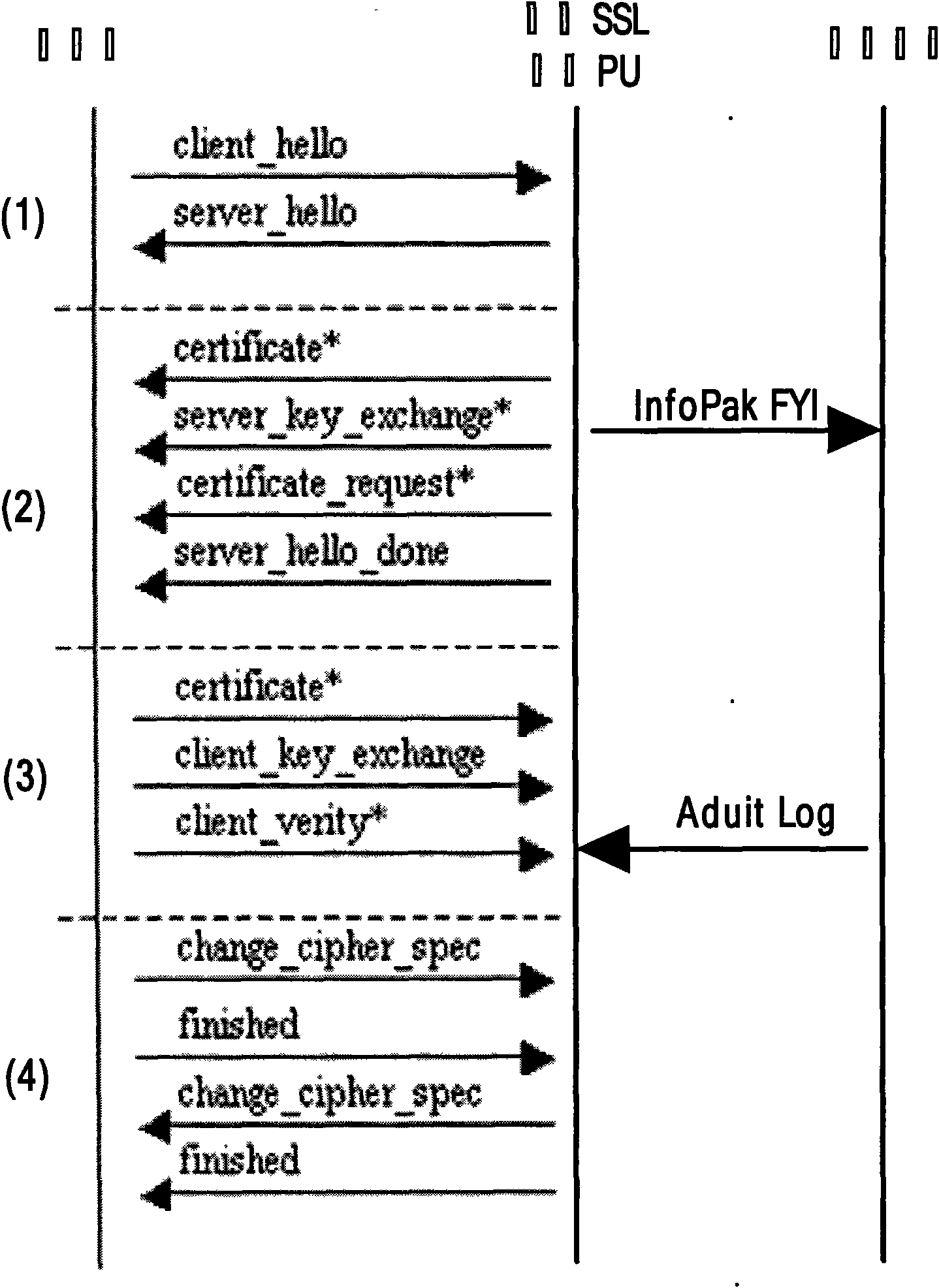
Design architecture and method for secure load balancing by utilizing SSL communication protocol
The invention discloses design architecture and a method for secure load balancing by utilizing SSL communication protocol, in particular to provide secure and reliable data communication for client and load balancing equipment by introducing SSL (Security Socket Layer) communication protocol. The invention mainly designs a processor SSL-PU based on SSL encryption, wherein, the processor SSL-PU is loaded in a load balancer and comprises a processing unit (PU), a memory cell (Flash, SRAM, DDR SDRAM, etc.), an Ethernet network controller (PCI, PCI-X, PCI-E) and GbE PHY (RJ45 interface). SSL-PU well solves the security problem caused by traditional load-balancing equipment and client clear text and the problem that traditional SSL encryption technology based on software excessively occupies system CPU and memory resources, thereby saving server bandwidth, increasing throughput and improving flexibility and availability of network; the processor well realizes the security data interaction with the client, and delivers data in the form of clear text to a load-balancing module; the load balancing module locates a request to a corresponding server according to load balancing algorithm; the server transmits data to the load balancing equipment; and the load balancer with an SSL-PU module transmits encrypted security data to the client, thereby completing secure data interactive access. The invention is particularly suitable for secure load-balancing scheduling of load balancing equipment of which the back end is a cluster system.
Owner:LANGCHAO ELECTRONIC INFORMATION IND CO LTD
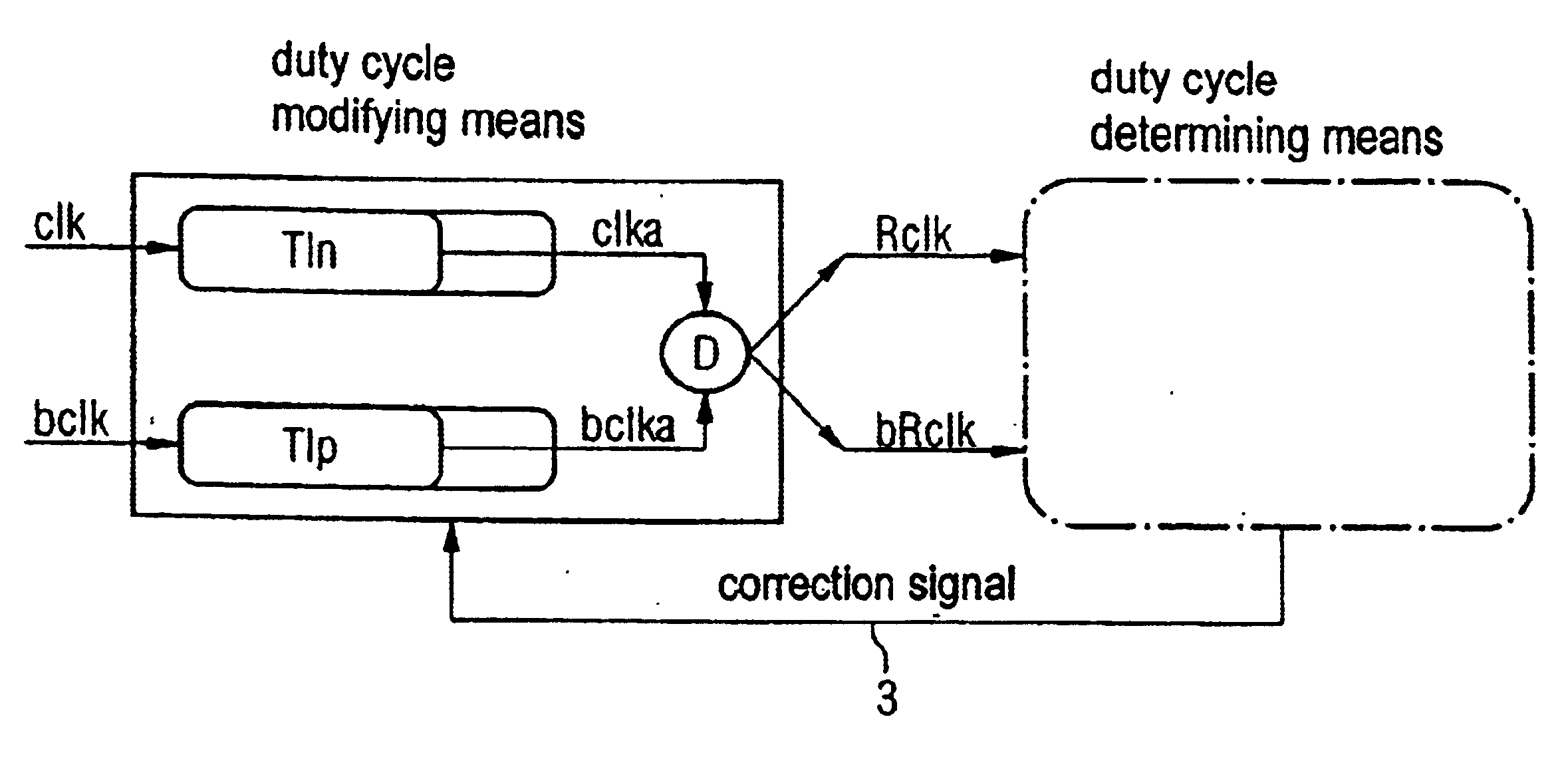
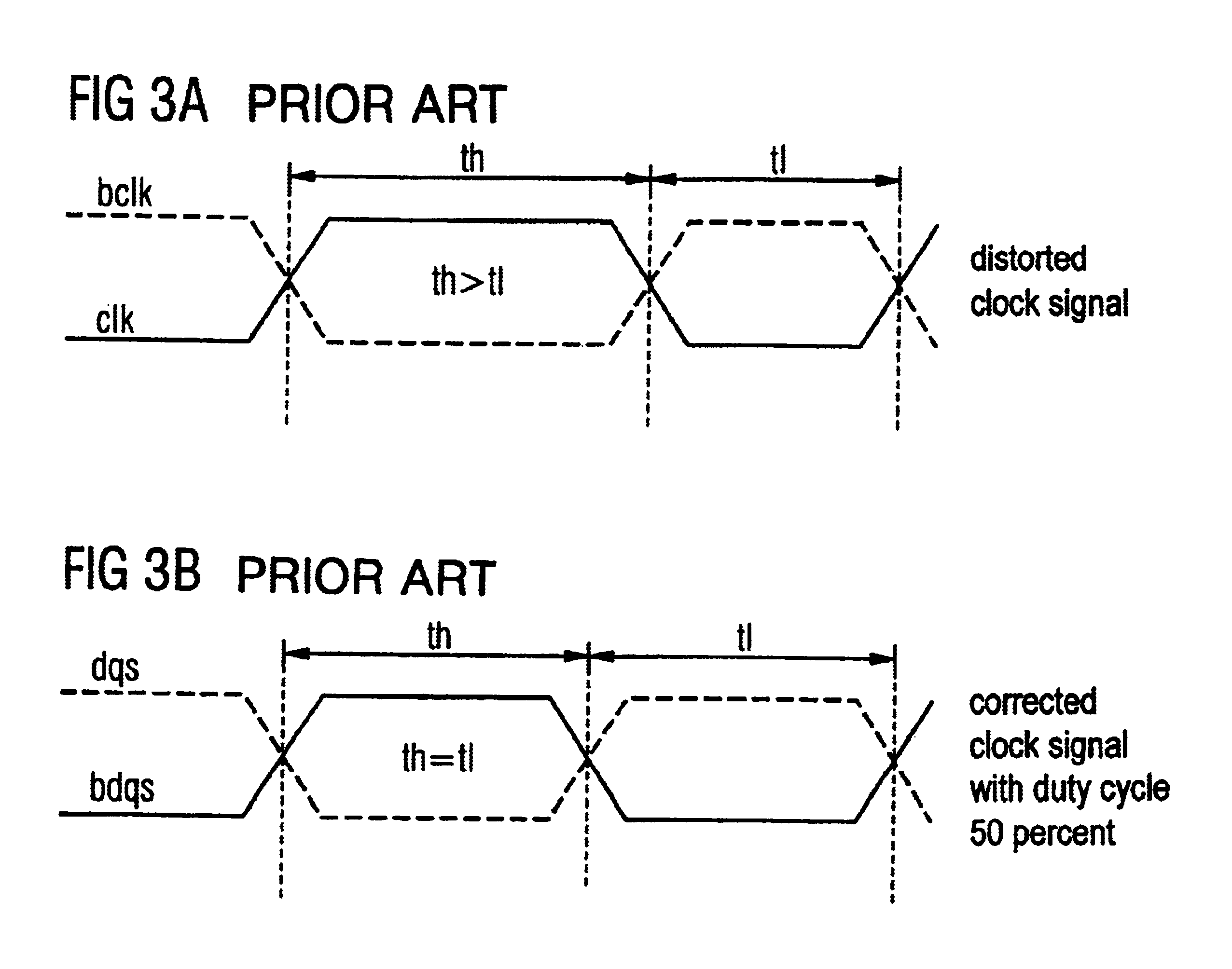
Device and method for correcting the duty cycle of a clock signal
A device for correcting the duty cycle of a clock signal with a duty cycle modifying device which receives a clock signal and a complementary clock signal, which comprises a delay device for both clock signals, and which is adapted to generate a clock signal and a complementary clock signal with corrected duty cycle. The invention also relates to a corresponding method for correcting the duty cycle of a clock signal and may preferably be used to correct the duty cycle of the system clock input in a DDR-SDRAM device in order that an ideal duty cycle of 50 percent is achieved in the memory chip during the processing thereof to a data strobe. As compared to previous similar devices and methods, the invention thus enables, with DDR-SDRAM devices, a more precise reading out of the data from the devices to the system associated with the devices.
Owner:POLARIS INNOVATIONS
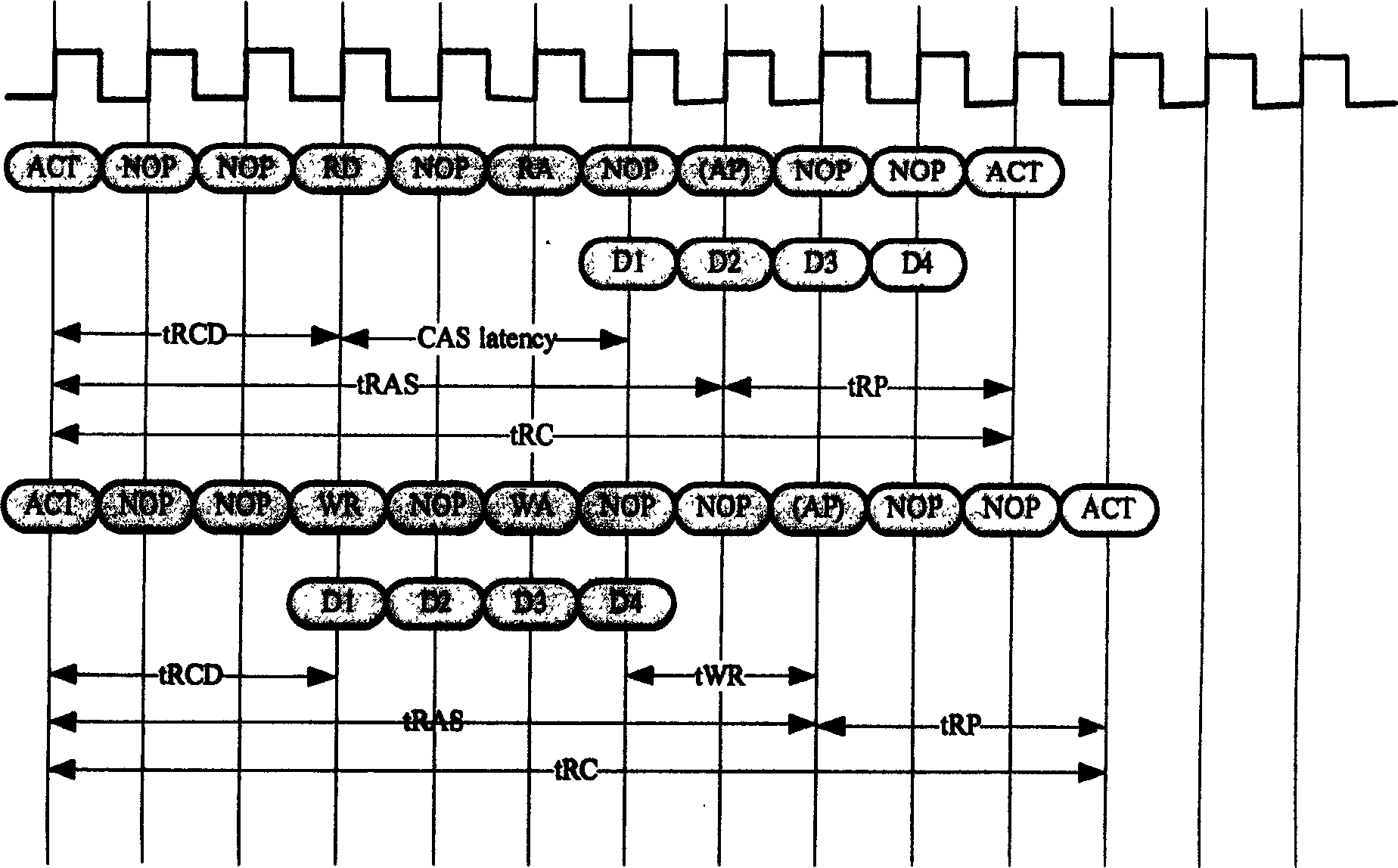
Synchronous dynamic storage controller designing method
InactiveCN1815625AIncrease profitShorten the timePulse modulation television signal transmissionDigital storageProcessor registerDynamic storage
The method includes following steps: (1) optimizing parsed address; (2) setting up first order state register and using Auto Pre-charge mode; (3) optimizing sending time for Active command; (4) dynamic controlling Refreshing time interval; (5) buffering reading / writing commands, dividing reading / writing time slices, sending reading / writing commands in concentration respectively. Advantages are: four banks in SDRAM in collaborative work to take full advantage of SDRAM ability to communicate; bandwidth use ratio reached to more than 85úÑ, realizing decoding for AVS and H.264 video in high resolution, raised reading / writing efficiency greatly, and east of implementation by hardware. Moreover, the invention is not only suitable to SDRAM and DDR SDRAM, and video decoding.
Owner:宁波中科集成电路设计中心有限公司
Method and device for masking ringing in a DDR SDRAM
A DDR SDRAM operates at a double data rate by accessing the bursts of data having a burst length in accordance with the rising and falling edges of each pulse of a DQS signal. A ringing may occur in the DQS signal causing write failures. To mask the ringing, a DQS buffer generates a first access signal at the rising edge of each DQS pulse generated in presence of the data burst. The DQS buffer also generates a second access signal at the falling edge of each DQS pulse. Each of the first and second access signals includes a finite number of pulses based on the total number of rising and falling edges of the DQS signal. Two consecutive data bursts are accessed together for a write operation for each pair of the consecutive first and second access signals. After accessing all data bursts, a mask time is calculated to disable the DQS buffer, by which the ringing is masked.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
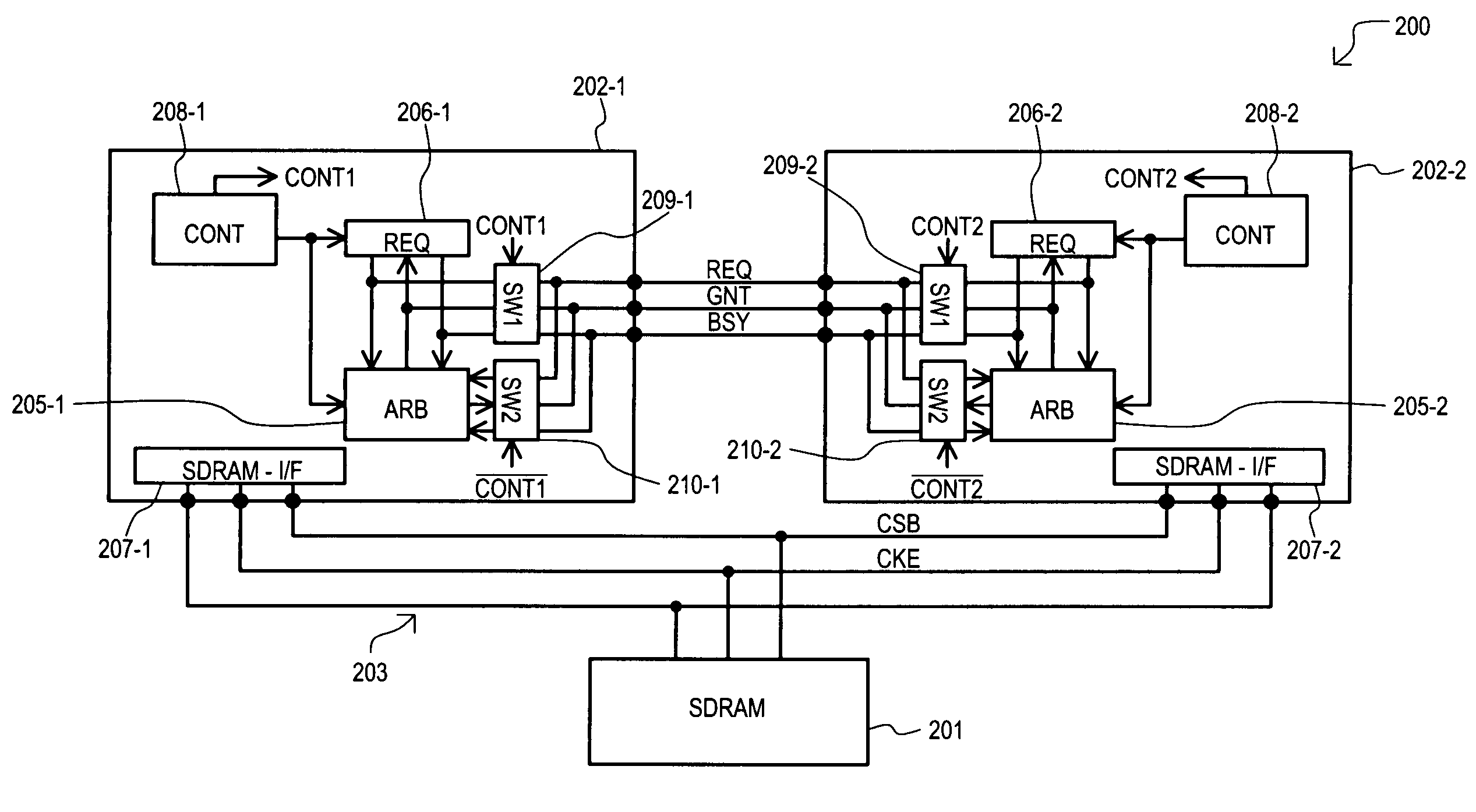
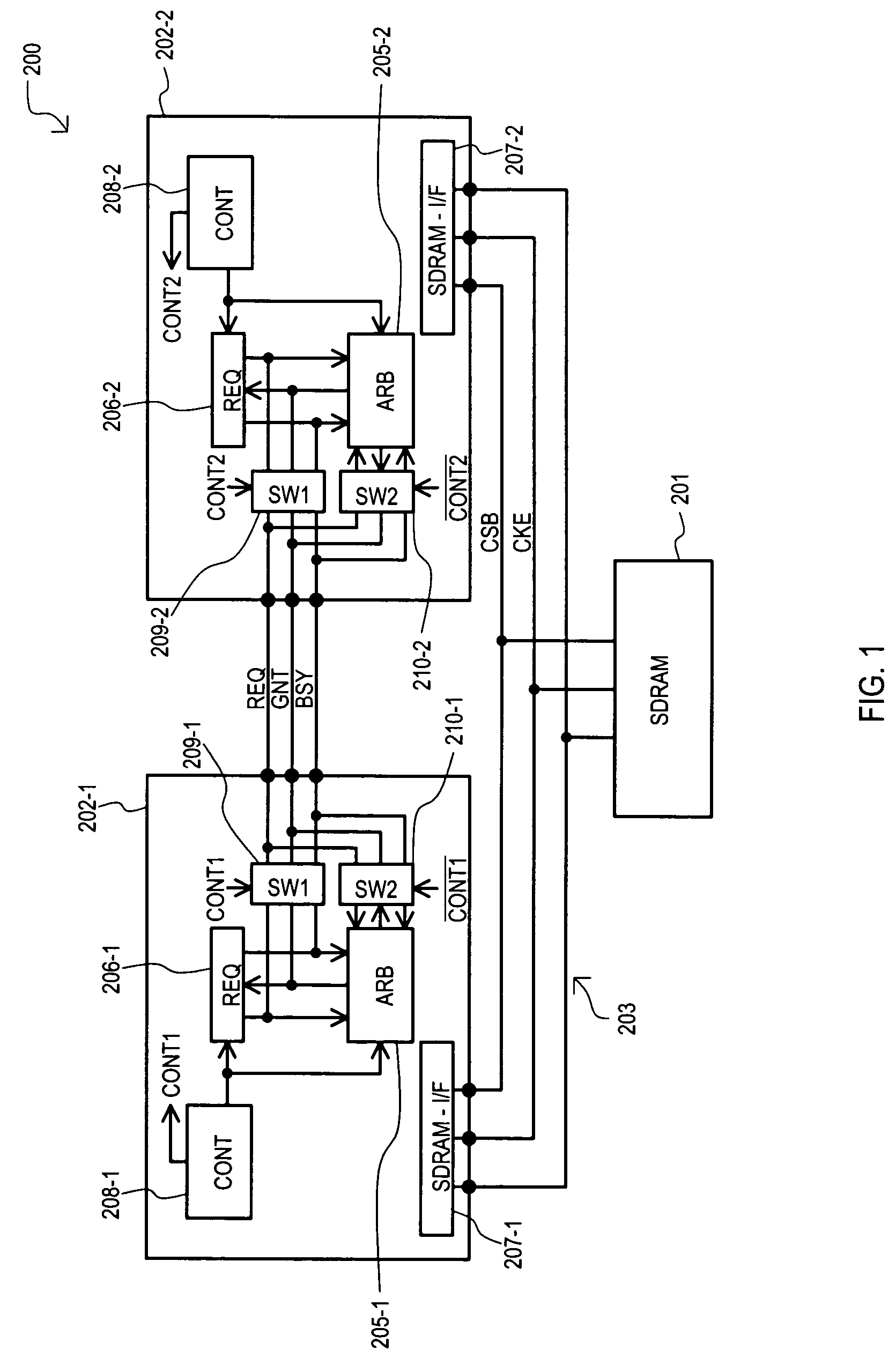
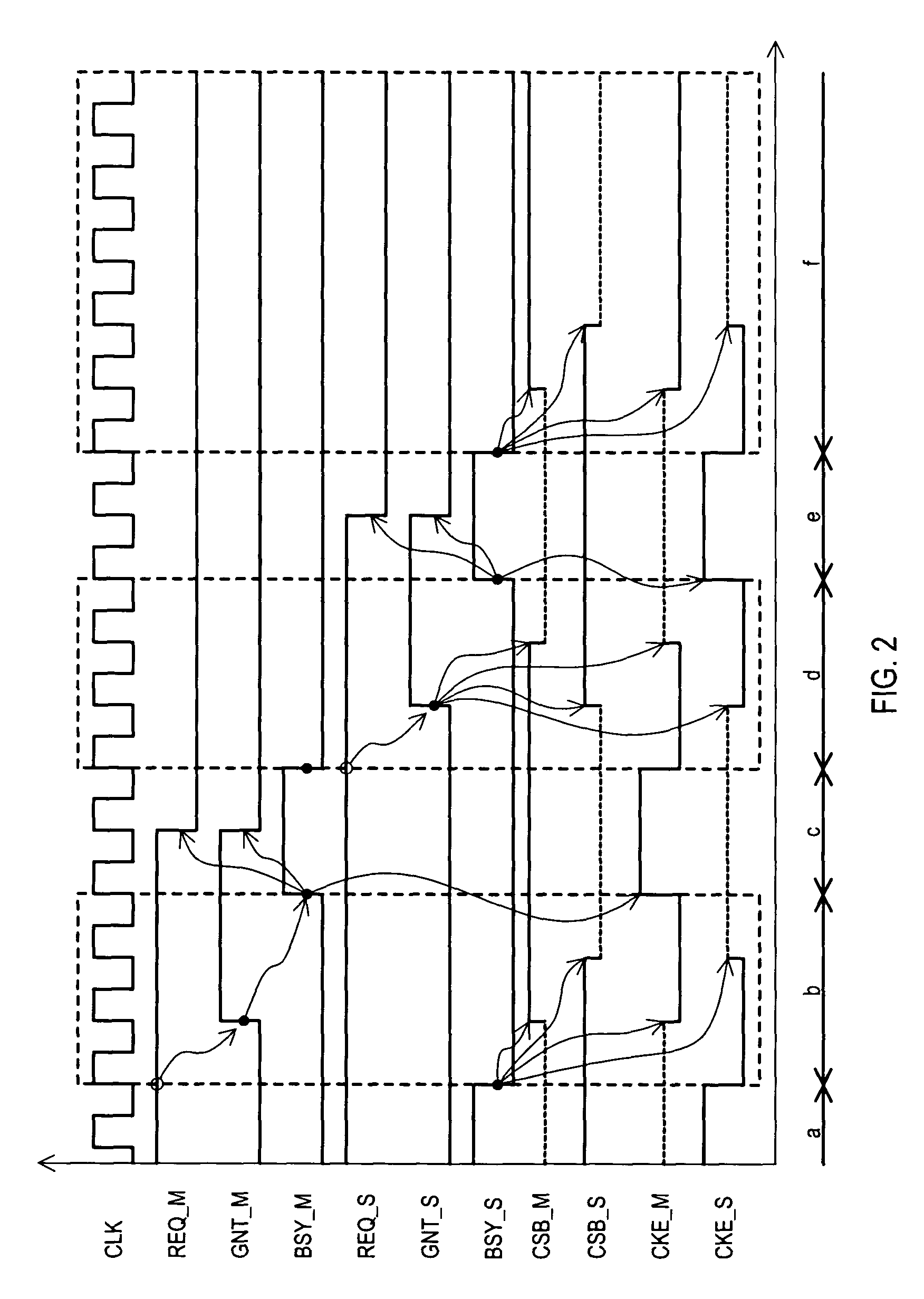
Data processing apparatus that shares a single semiconductor memory circuit among multiple data processing units
InactiveUS7254688B2Low power statePulse automatic controlGenerating/distributing signalsDouble data rateChip select
Multiple data processing circuits may share a semiconductor memory circuit, such as double-data-rate synchronous dynamic random access memory (DDR-SDRAM). A data processing circuit (202-1 or 202-2) ending control of a semiconductor memory circuit (201) supplies a clock enable signal and chip select signal at predetermined levels. A data processing circuit (202-2 or 202-1) starting control of a semiconductor memory circuit (201) supplies a clock enable signal and chip select signal at the same predetermined levels, before the data processing circuit (202-1 or 202-2) ending control stops supplying a clock enable signal and chip select signal. Therefore, a clock enable signal and chip select signal do not enter an undefined state, and malfunctions that could otherwise occur are prevented.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Motion blur image restoration system based on multi-core
InactiveCN101882302AIncrease transfer rateMeet the needs of cachingImage enhancementDigital recording/reproducingDigital dataWork distribution
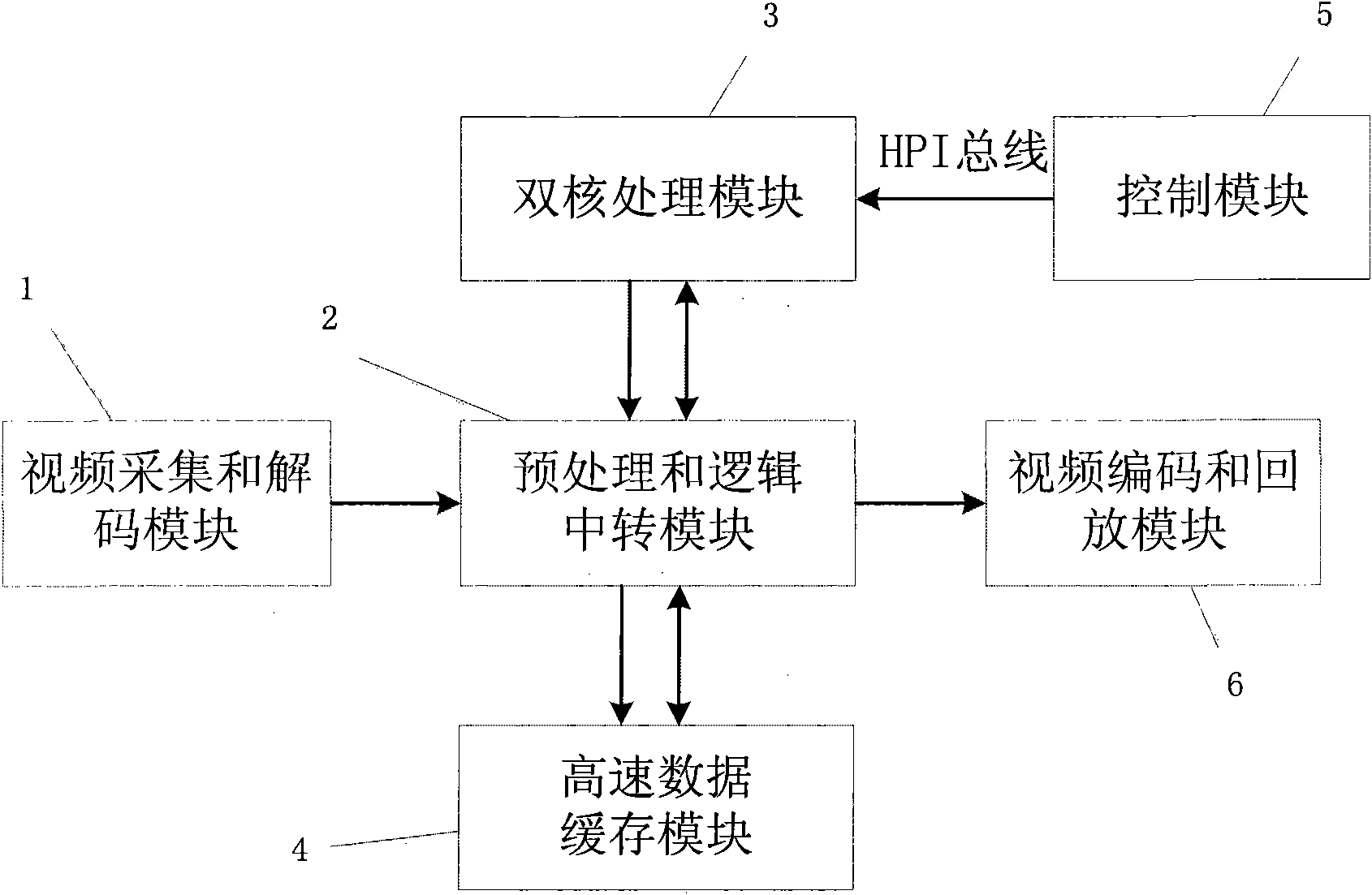
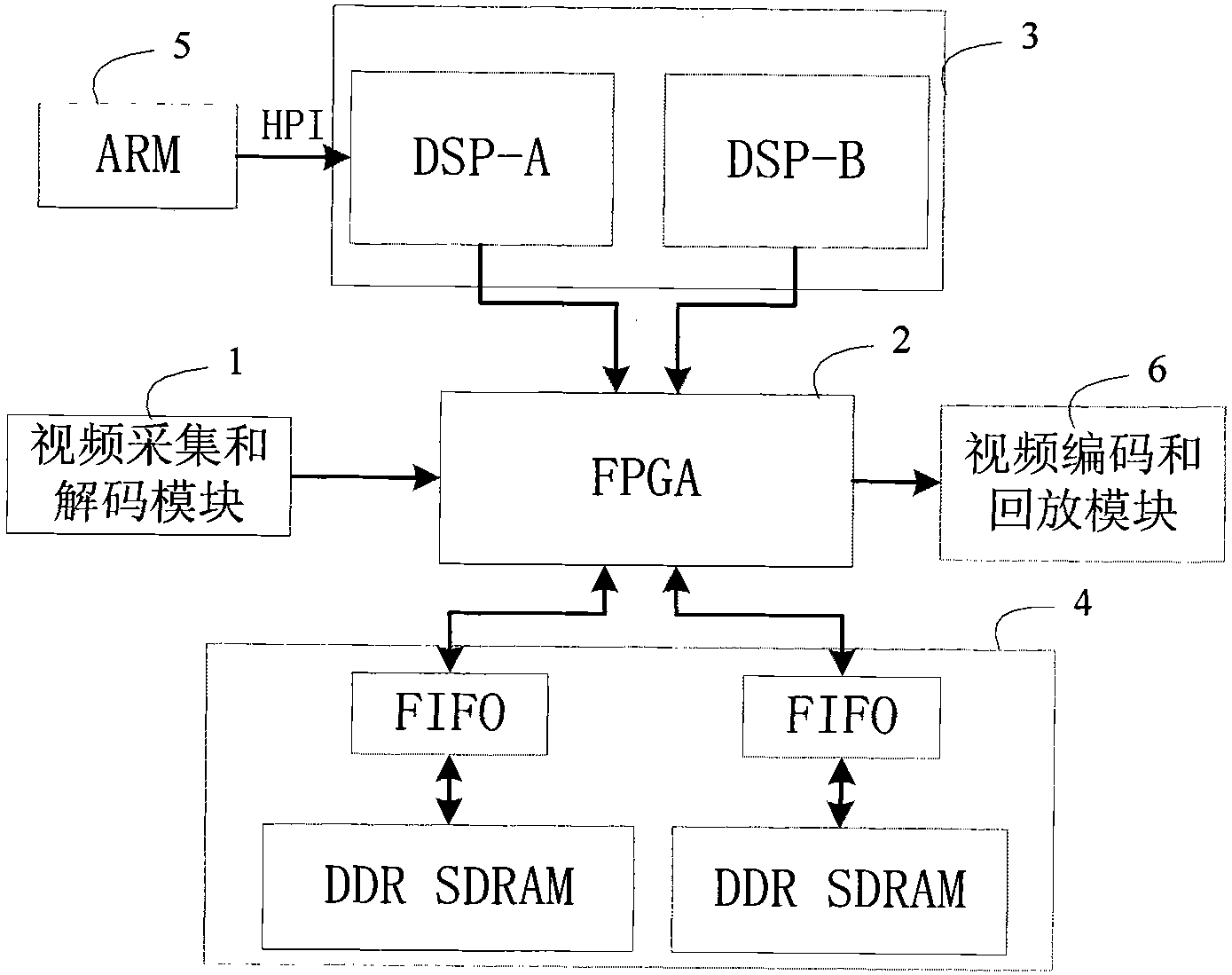
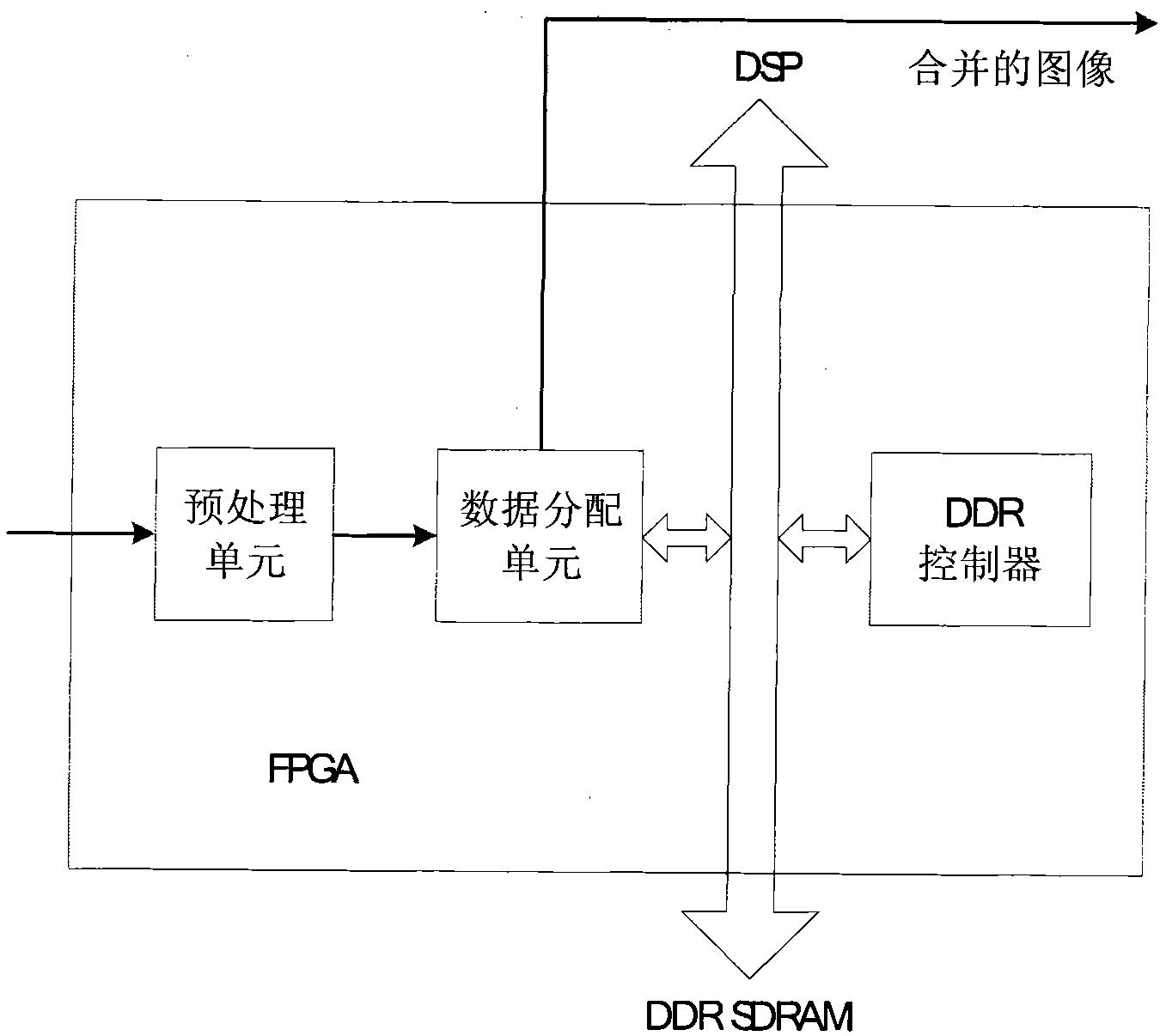
The invention discloses a motion blur image restoration system based on multi-core. In the system, a preprocessing and logic transfer module preprocesses video frames collected by a video collecting and decoding module and temporarily stores the preprocessed video frames in a high-speed data buffer module, the core calculation of a preprocessing module is finished by adopting an FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array), and the high-speed data buffer module is based on DDR SDRAM (Digital Data Receiver Synchronous Dynamic Random Access Memory). A double-core processing module reads the video frames in a high-speed data cache through the preprocessing and logic transfer module and carries out image compensation. The double-core processing module is established by adopting two DSPs (Digital Signal Processor), and video subject to parallel processing is played back in a playback module. In the system, the processing work of video is distributed to two parts, and by adopting the preprocessing of the FPGA and the high-speed reading and writing based on the DDR SDRAM data cache, the high-efficiency performance of double DSP core parallel calculation can effectively finish the tasks of image compensation and restoration.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
FPGA array processing board
InactiveCN101588175AIncrease storage capacityImprove memory depthDigital data processing detailsDigital computer detailsDigital signal processingImaging processing
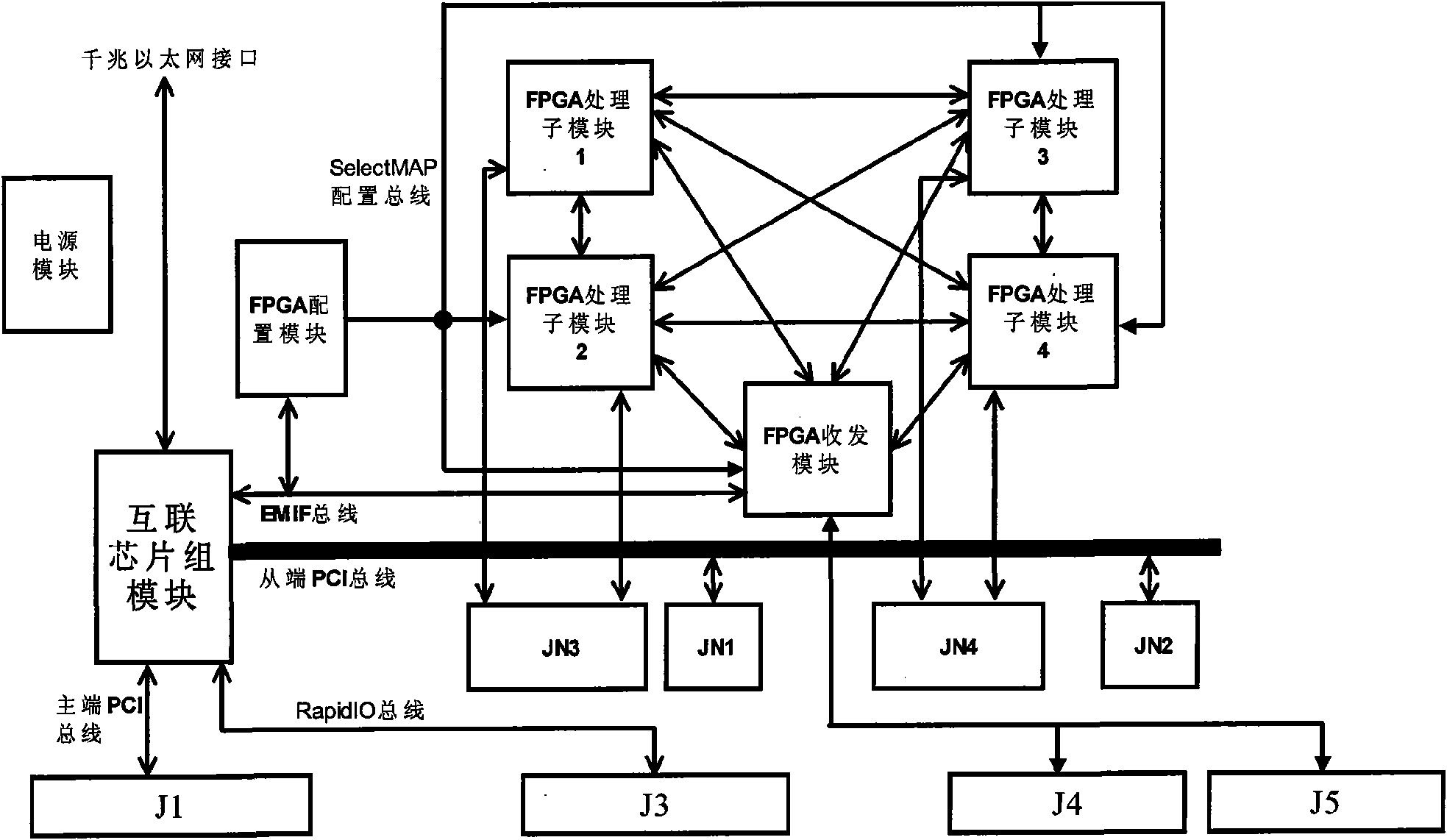
The invention relates to a FPGA signal processing board, belonging to the technical field of digital signal processing. The processing board comprises one power supply module, four FPGA processing sub modules, one FPGA transmit-receive module, one interconnect chip set module and one FPGA load application module, the FPGA processing sub module and the FPGA transmit-receive module are connected by full interconnect mode, the interconnect bandwidth between every two modules is as high as 1.6 B / s. The processing board can implement the external multiple high speed interfaces and load the DDR SDRAM with capacity of 4GB by PCI bus, Rapid IO bus and source synchronous interface, the storage bandwidth is as high as 10688 MB / s. the FPGA on the board has flexible configuring mode by adopting the DSP+CPLD+NAND configuring combination. The invention is suitable for the condition with harsh signal processing real time performance requirement, such as radar signal processing, image processing and communication base station and so on.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
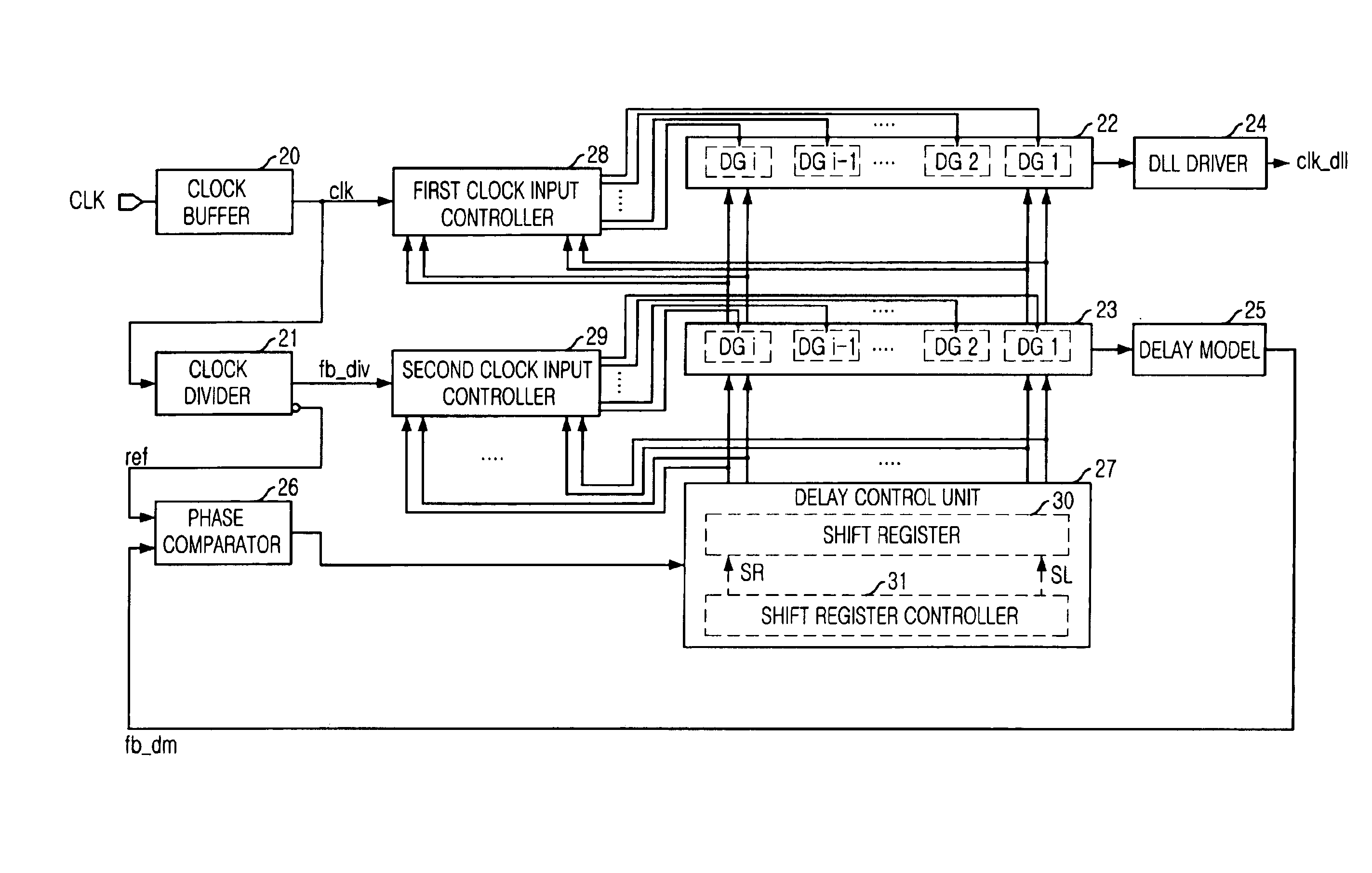
Register controlled delay locked loop with low power consumption
InactiveUS6995591B2Reduce power consumptionReduce loadPulse automatic controlSingle output arrangementsDouble data rateControl delay
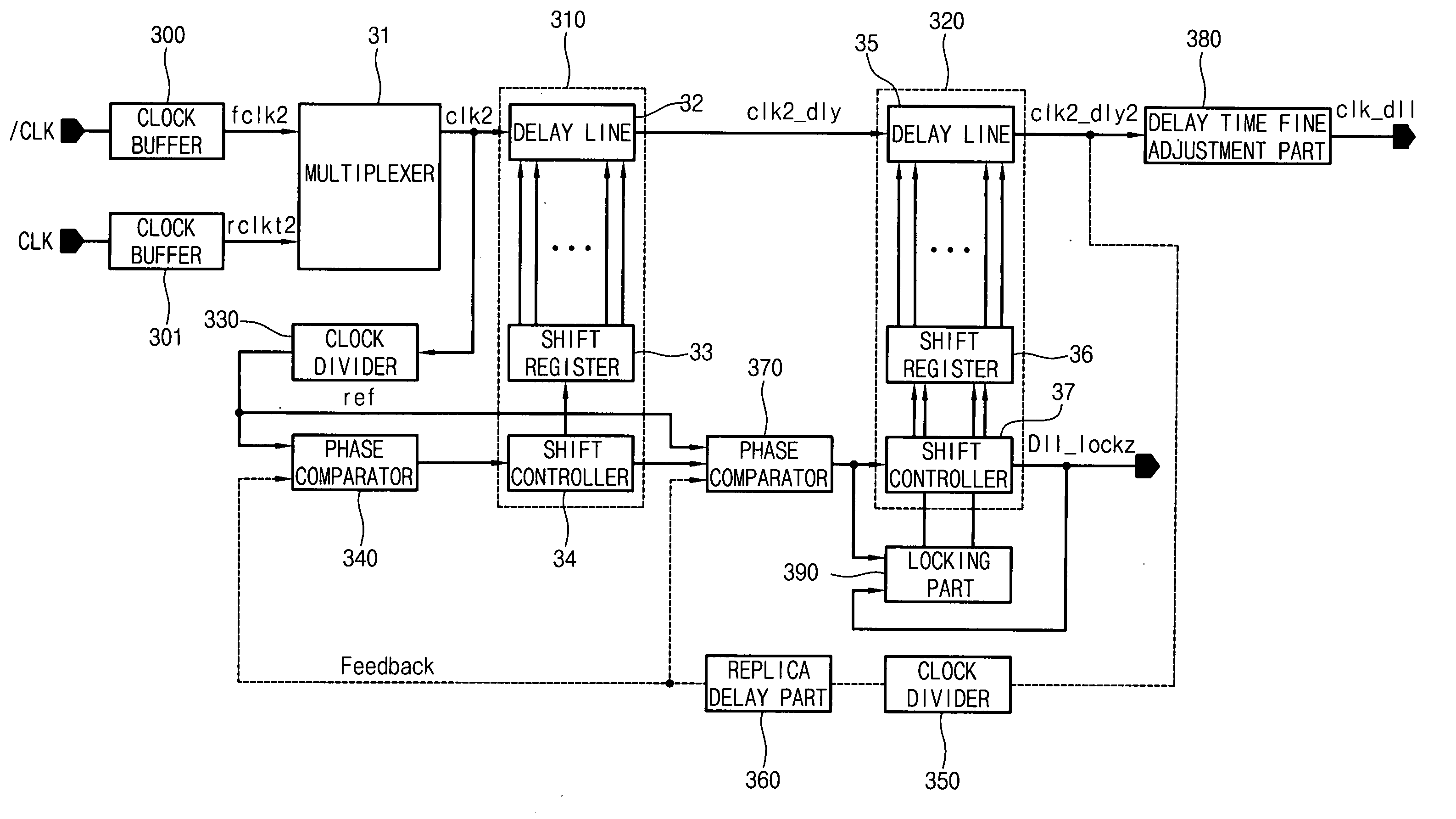
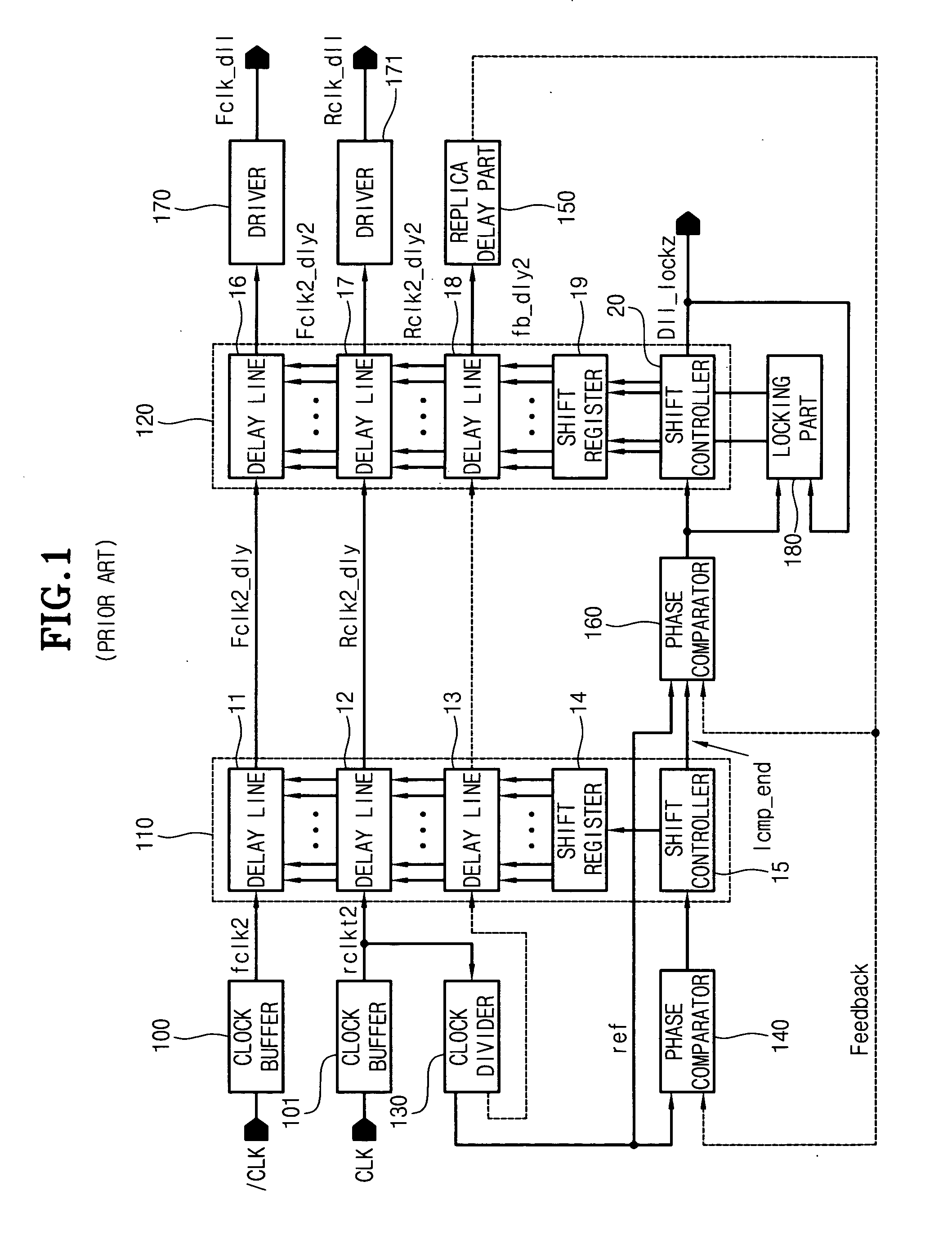
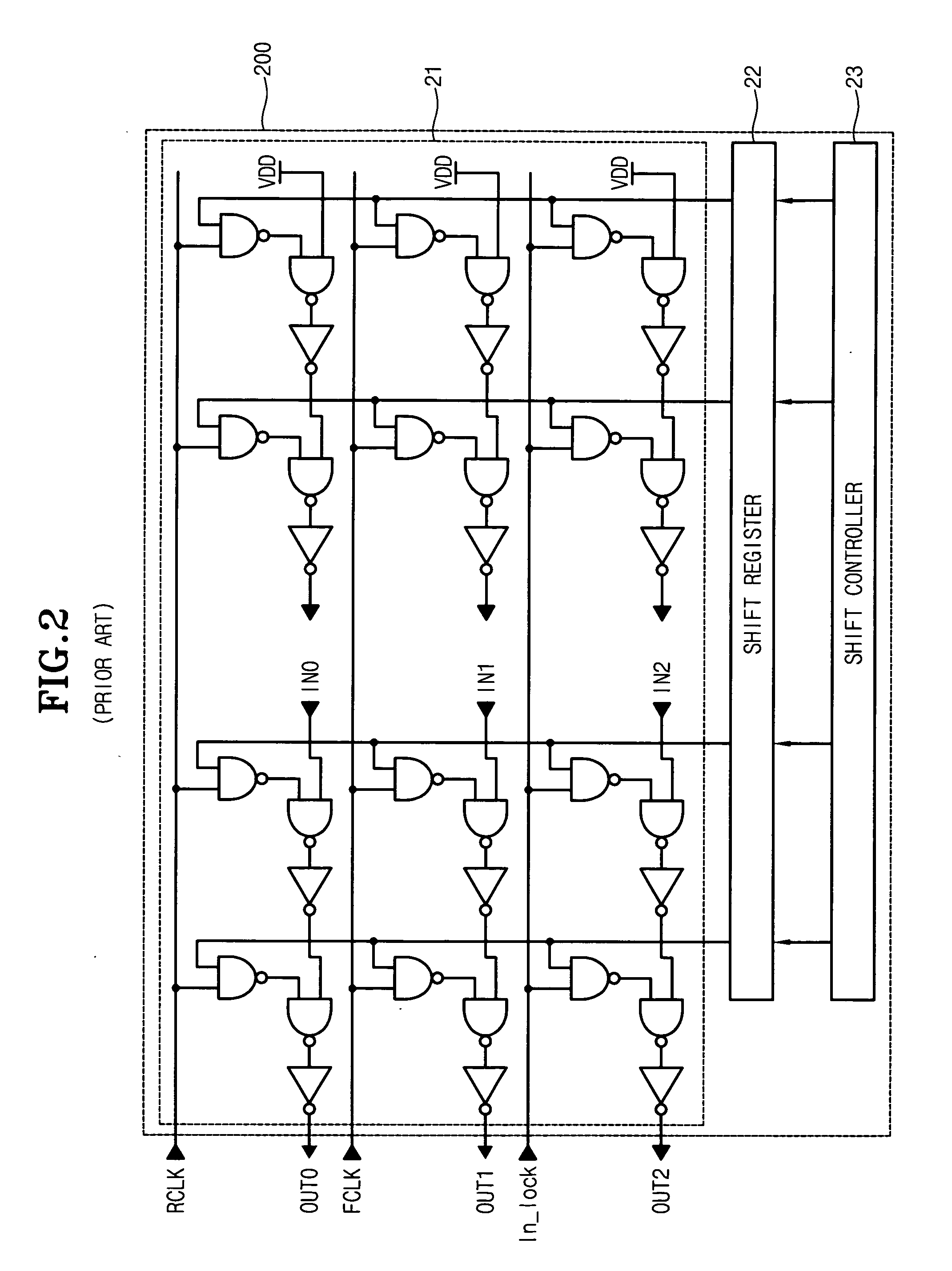
The present invention relates to a digital delay locked loop (DLL) in DDR SDRAM (Double Data Rate Synchronous DRAM). The digital delay locked loop according to the present invention includes: first and second delay lines, each of which includes a plurality of delay groups, for delaying a source clock signal and a delay monitoring signal, wherein each of the delay groups include a plurality of programmable unit delayers; a delay model receiving an output signal of the second delay line for modeling a delay component of a clock signal path; a comparator for comparing a feedback clock signal from the delay model with a reference clock signal; a delay controller for controlling an amount of delay time of the first and second delay lines in response to a comparison result of the comparator; and first and second clock input controllers, which selectively provides the source clock signal and the delay monitoring clock signal to one of delay groups in the first and second delay lines, respectively, in response to output signals of the delay controller.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
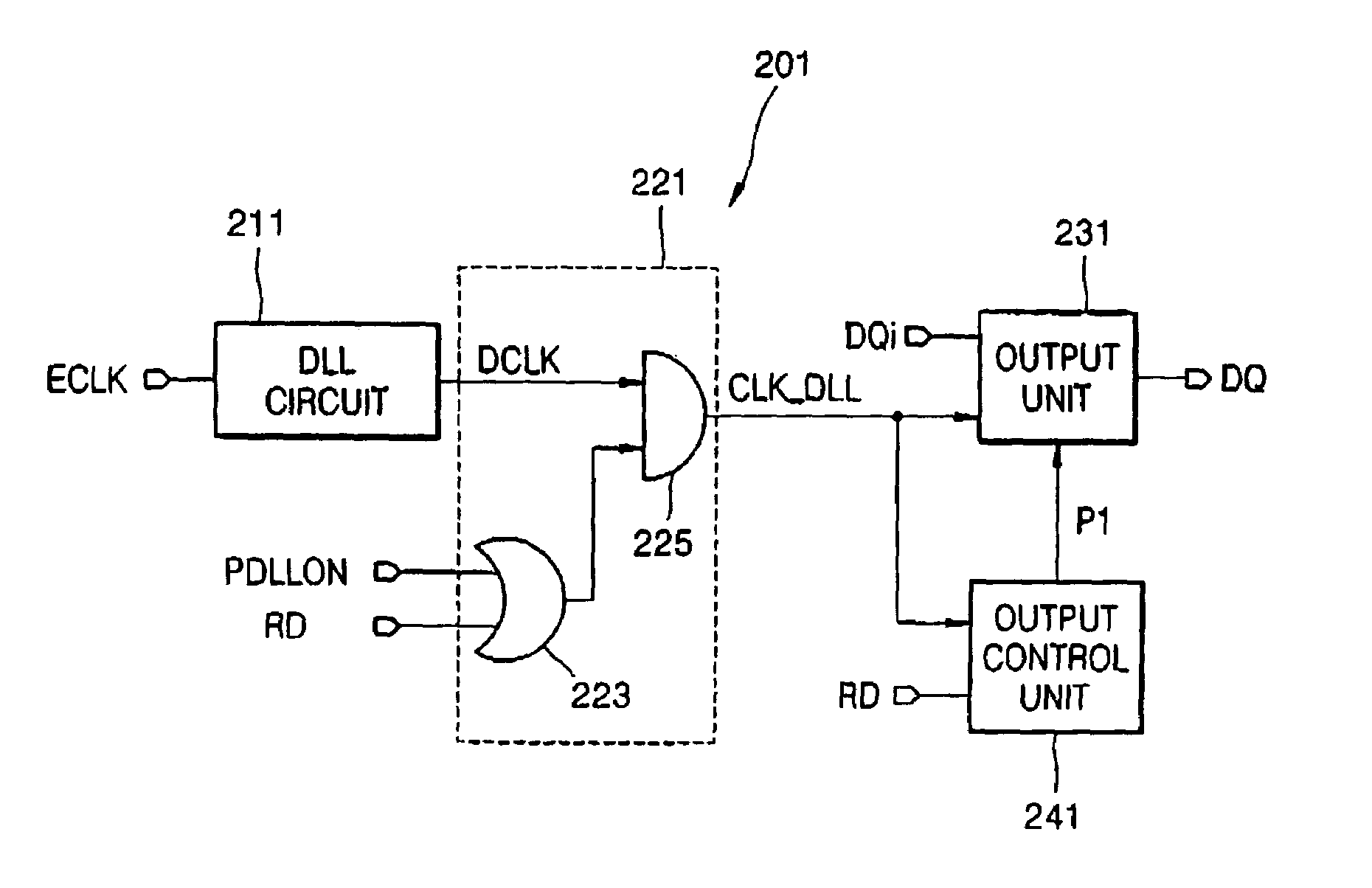
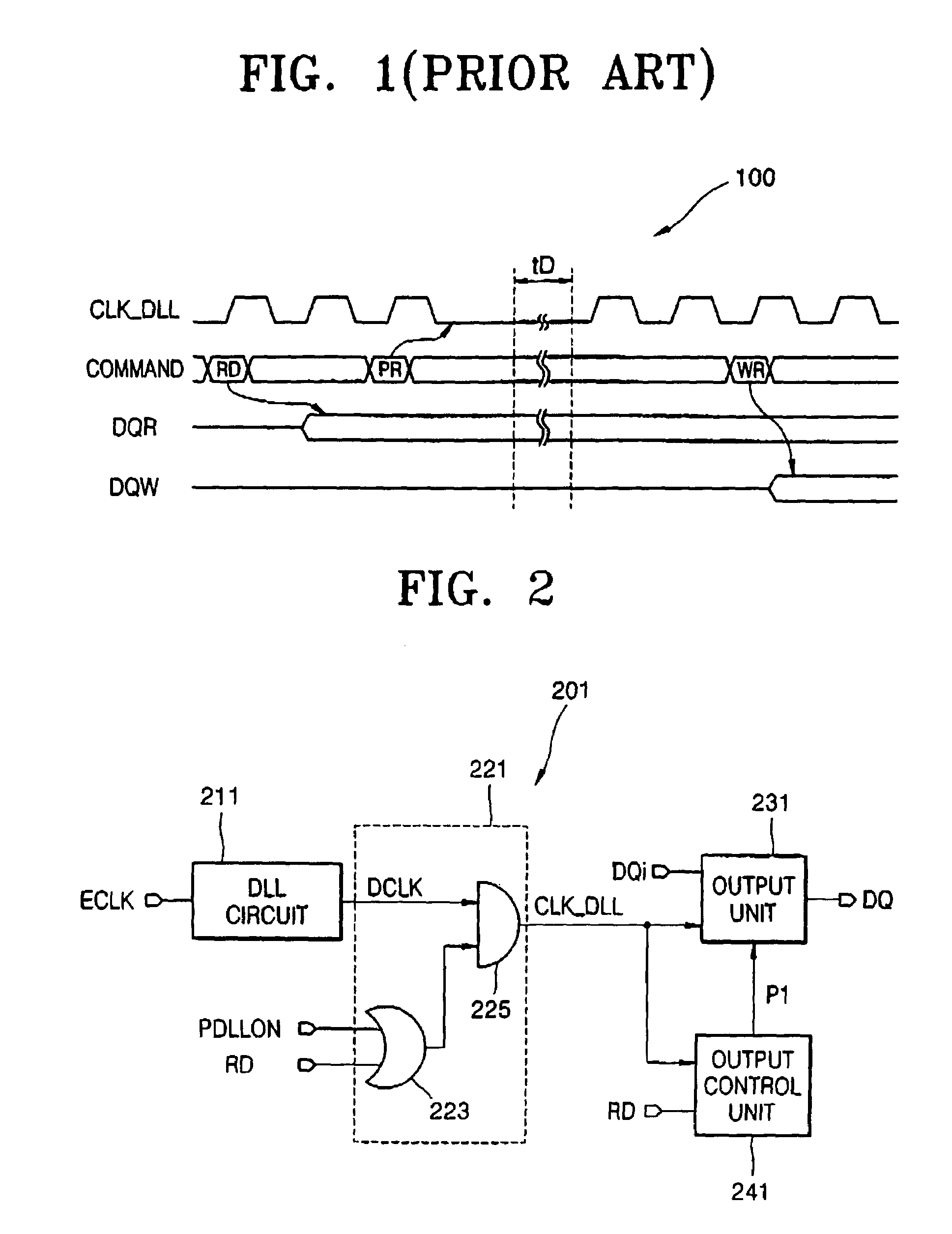
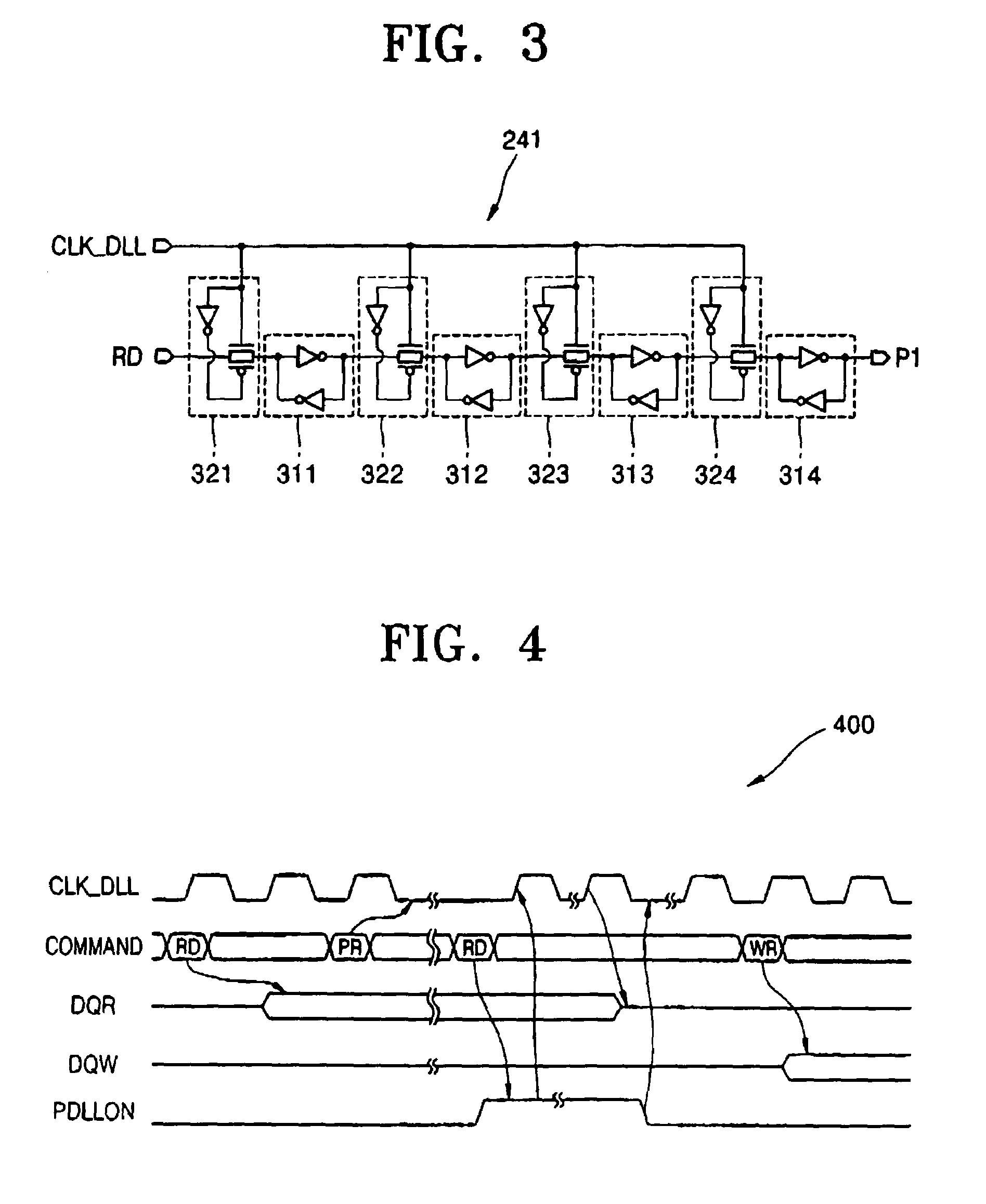
Double data rate synchronous dynamic random access memory semiconductor device
A double data rate (“DDR”) synchronous dynamic random access memory (“SDRAM”) semiconductor device is provided that prevents a conflict between data read from and data written to the DDR SDRAM semiconductor device when data is written to the DDR SDRAM semiconductor device, which includes a delay locked loop (“DLL”) circuit, a clock signal control unit, an output unit, and an output control unit, where the DLL circuit compensates for skew of an input clock signal and generates an output clock signal; the clock signal control unit receives a read signal activated when data stored in the DDR SDRAM semiconductor device is read out, a DLL locking signal activated when the DLL circuit performs a locking operation on the input clock signal, and the output clock signal, and outputs the output clock signal when either the read signal or the DLL locking signal is active; the output unit buffers data stored in the DDR SDRAM semiconductor device and outputs the data to outside of the DDR SDRAM semiconductor device in synchronization with the output clock signal output from the clock signal control unit; and the output control unit receives the output clock signal output from the clock signal control unit, and the read signal, and outputs the read signal to the output unit in synchronization with the output clock signal output from the clock signal control unit.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
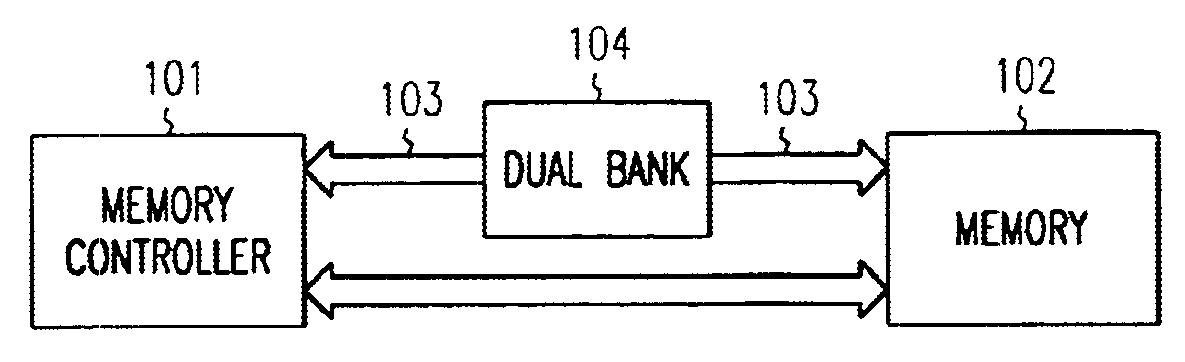
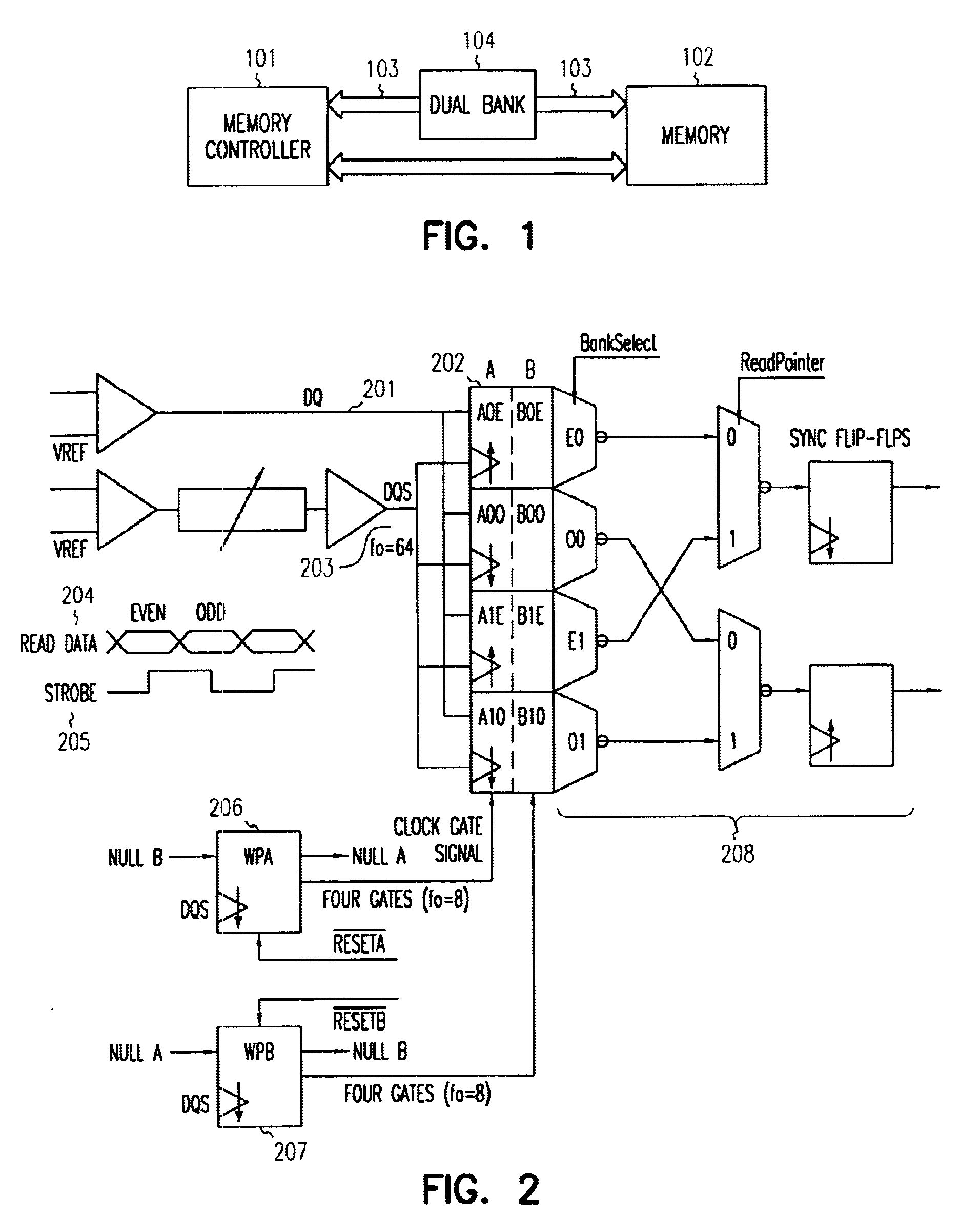
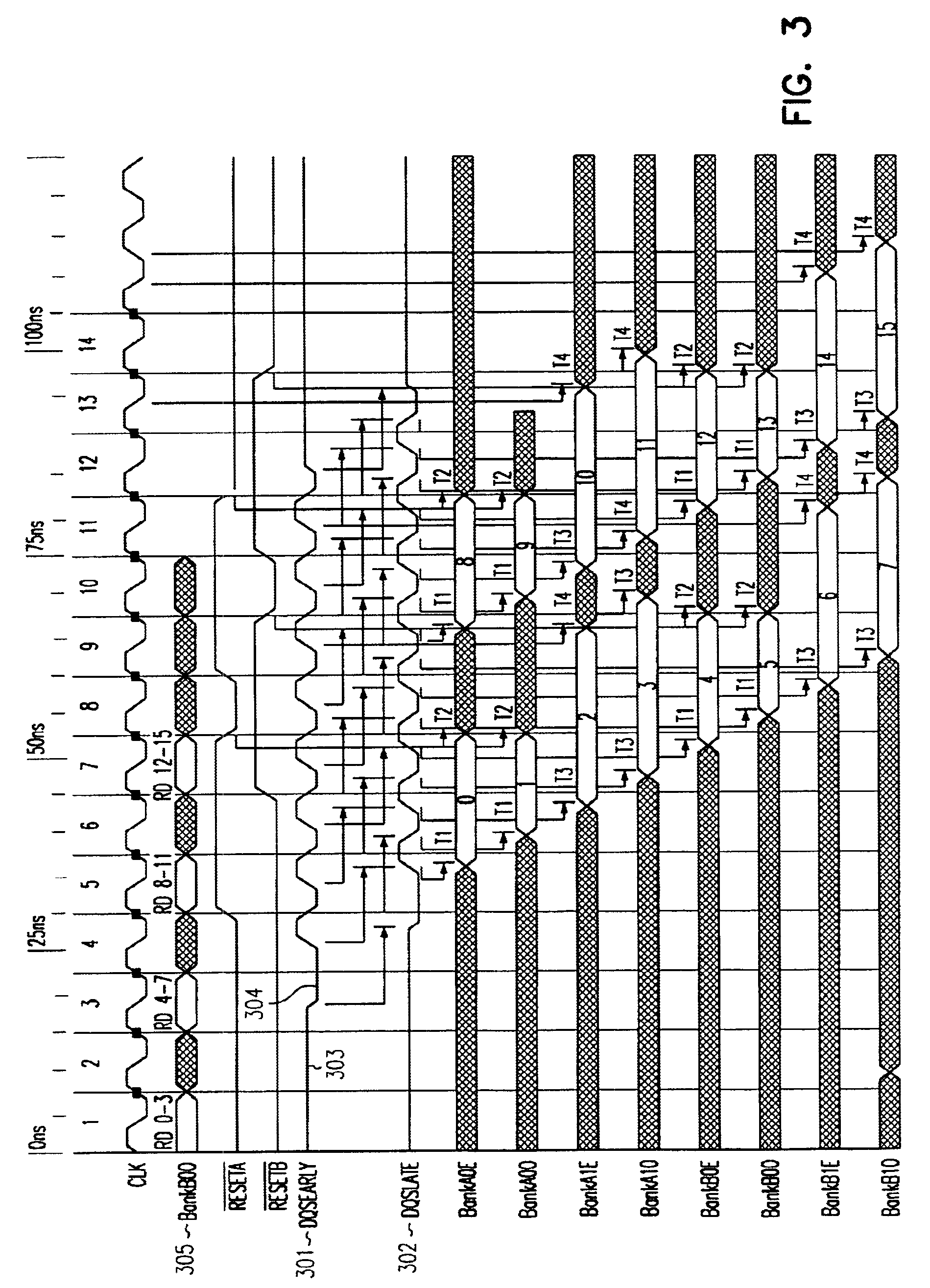
Dual-bank FIFO for synchronization of read data in DDR SDRAM
InactiveUS6920526B1Memory adressing/allocation/relocationInput/output processes for data processingComputerized systemFifo memory
The present invention comprises a dual bank FIFO memory buffer operable to buffer read data from memory and thereby compensate for specific timing problems in certain computerized systems. One embodiment of the invention includes a dual bank FIFO that comprises a first bank of memory elements operable to buffer memory data and a second bank of memory elements operable to buffer memory data. Write control address logic is operable to store selected memory data in memory elements with selected addresses within a bank of memory elements, and write control timing logic is operable to selectively grant write access to the banks of memory elements at predetermined time. Also, read control logic operable to read data stored in the first and second banks.
Owner:MORGAN STANLEY
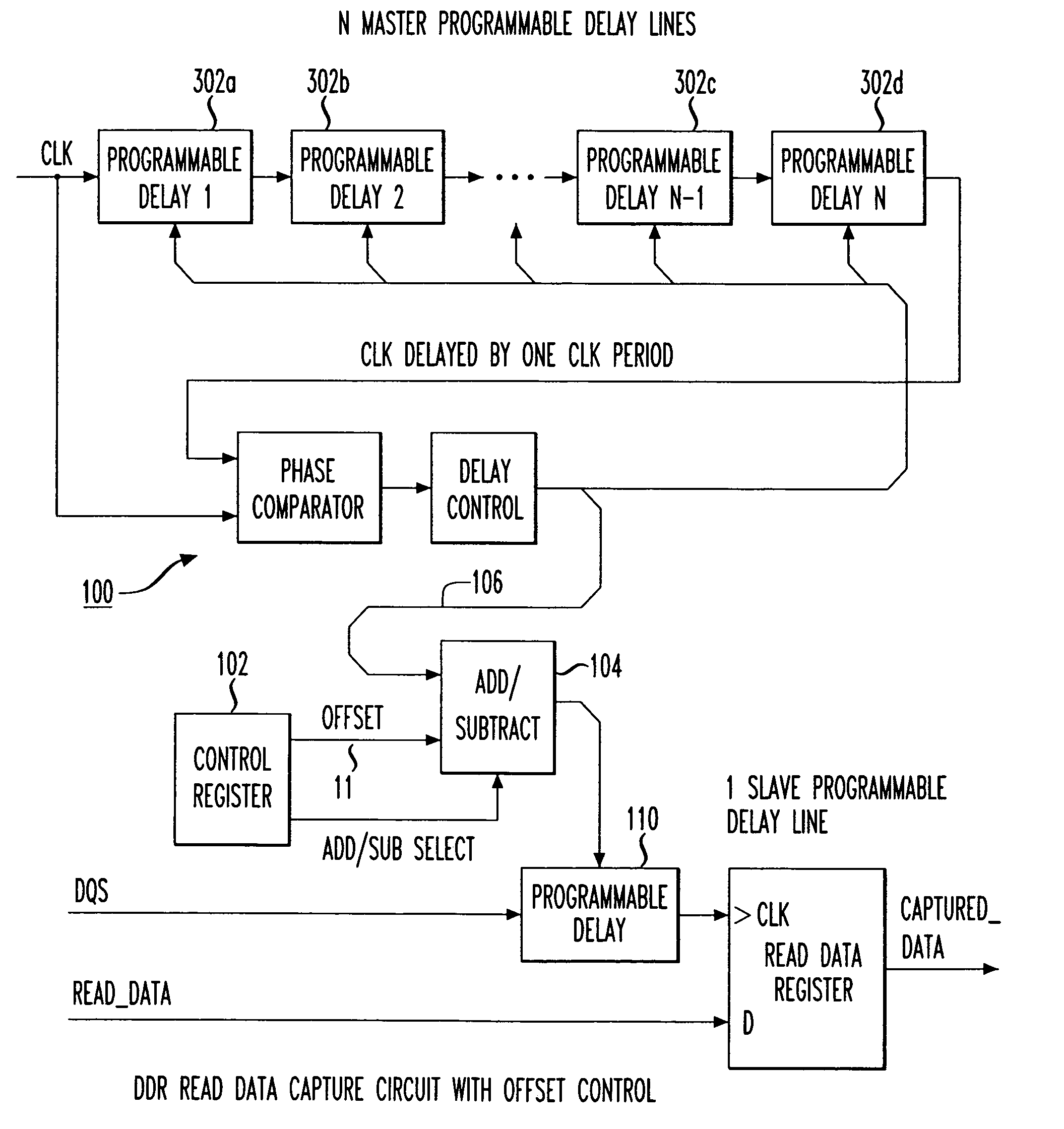
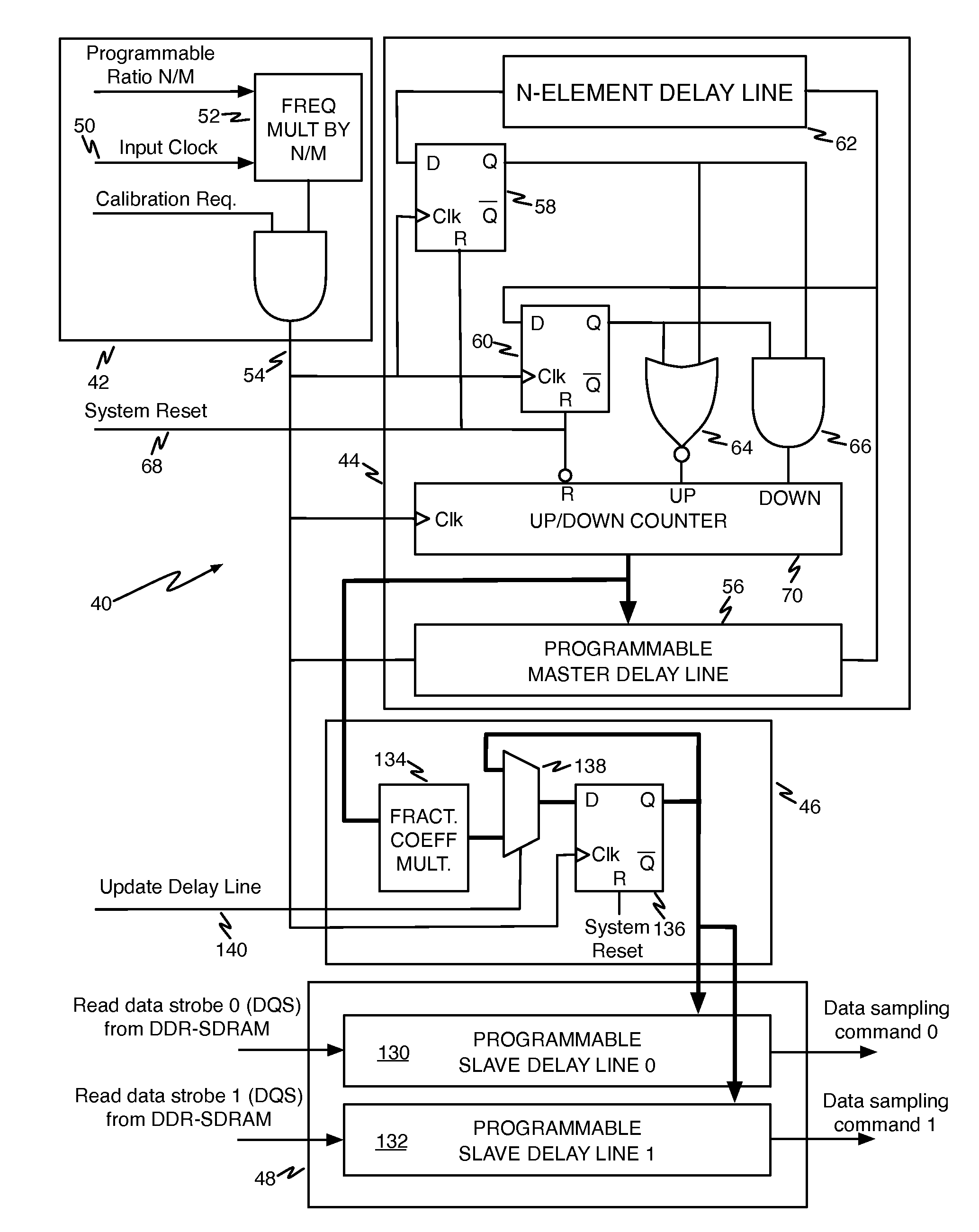
Circuits to delay a signal from DDR-SDRAM memory device including an automatic phase error correction
A method for delaying a control signal, includes receiving a clock signal, determining a number of delay elements required to generate a first delay equal to a target amount of the period of the clock signal, receiving a data signal having an edge generated at the same time as an edge of the control signal, determining a fraction number equal to the number of delay elements needed to generate a second delay for the data signal or the control signal to align their edges, divided by the number of cascaded delay elements necessary to provide a delay equal to the target amount of the period of the clock signal, multiplied by the number of delay elements to generate the first delay, and delaying the control signal by the number of cascaded delay elements to realize said first delay altered by the fraction number of delay elements.
Owner:ATMEL CORP
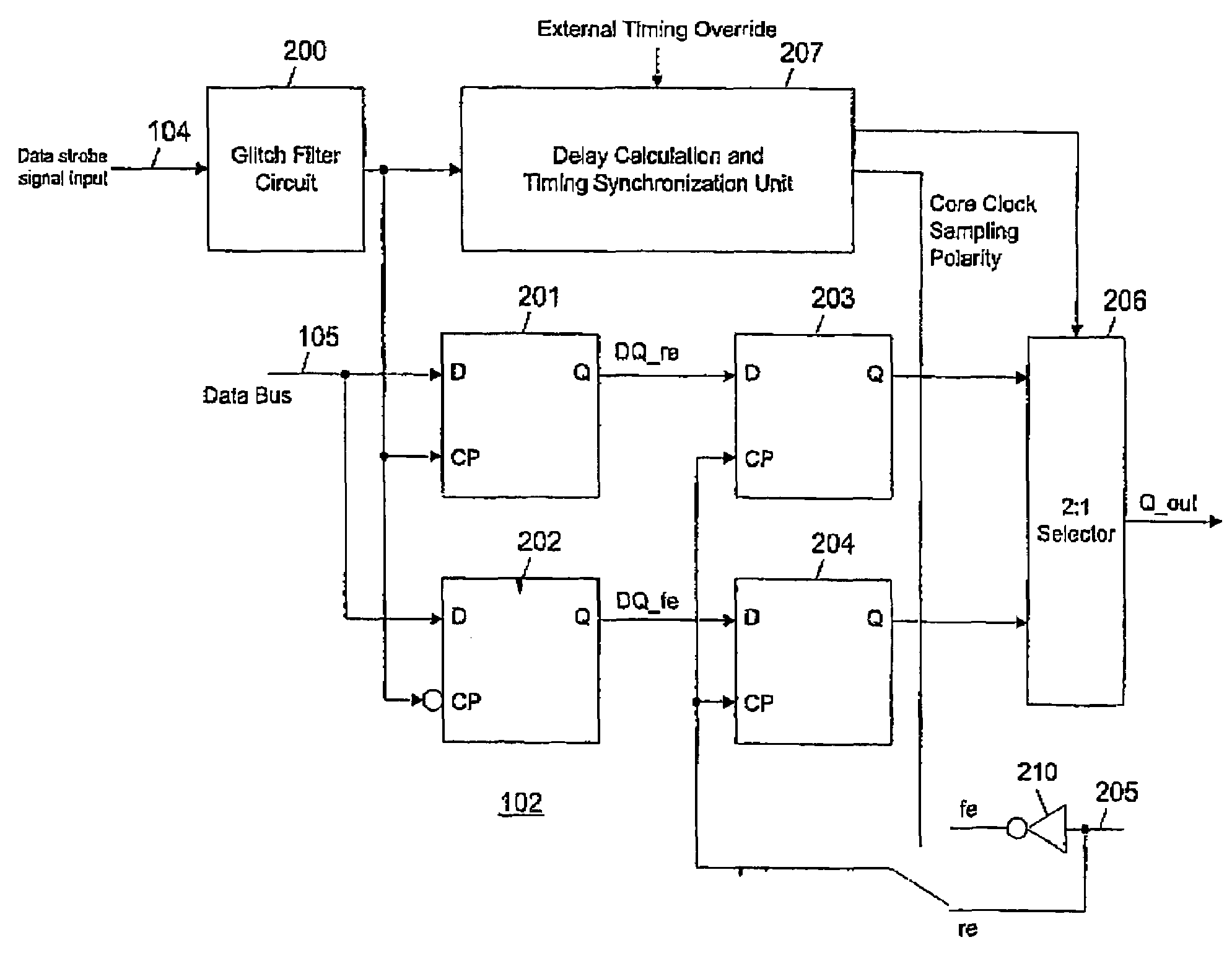
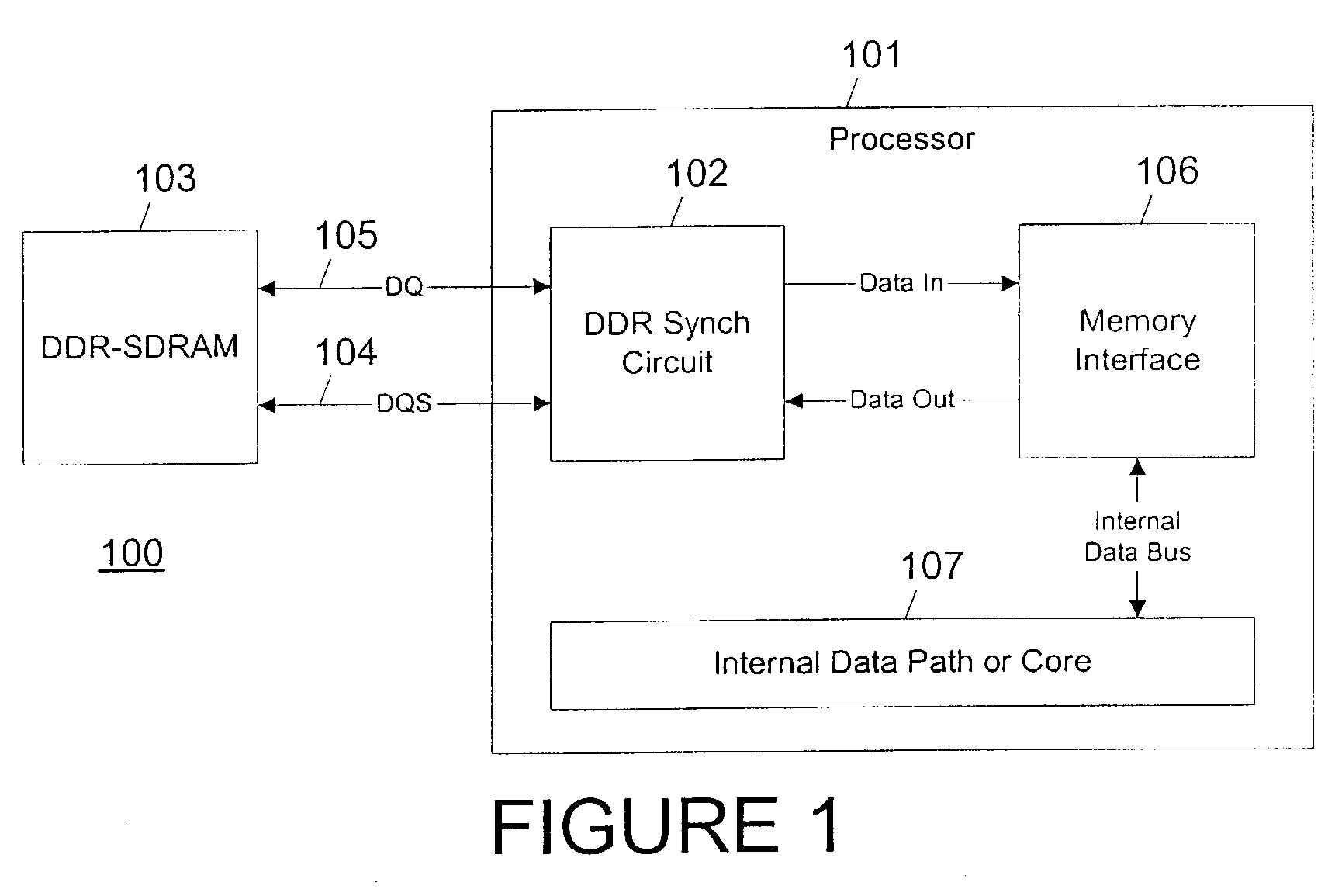
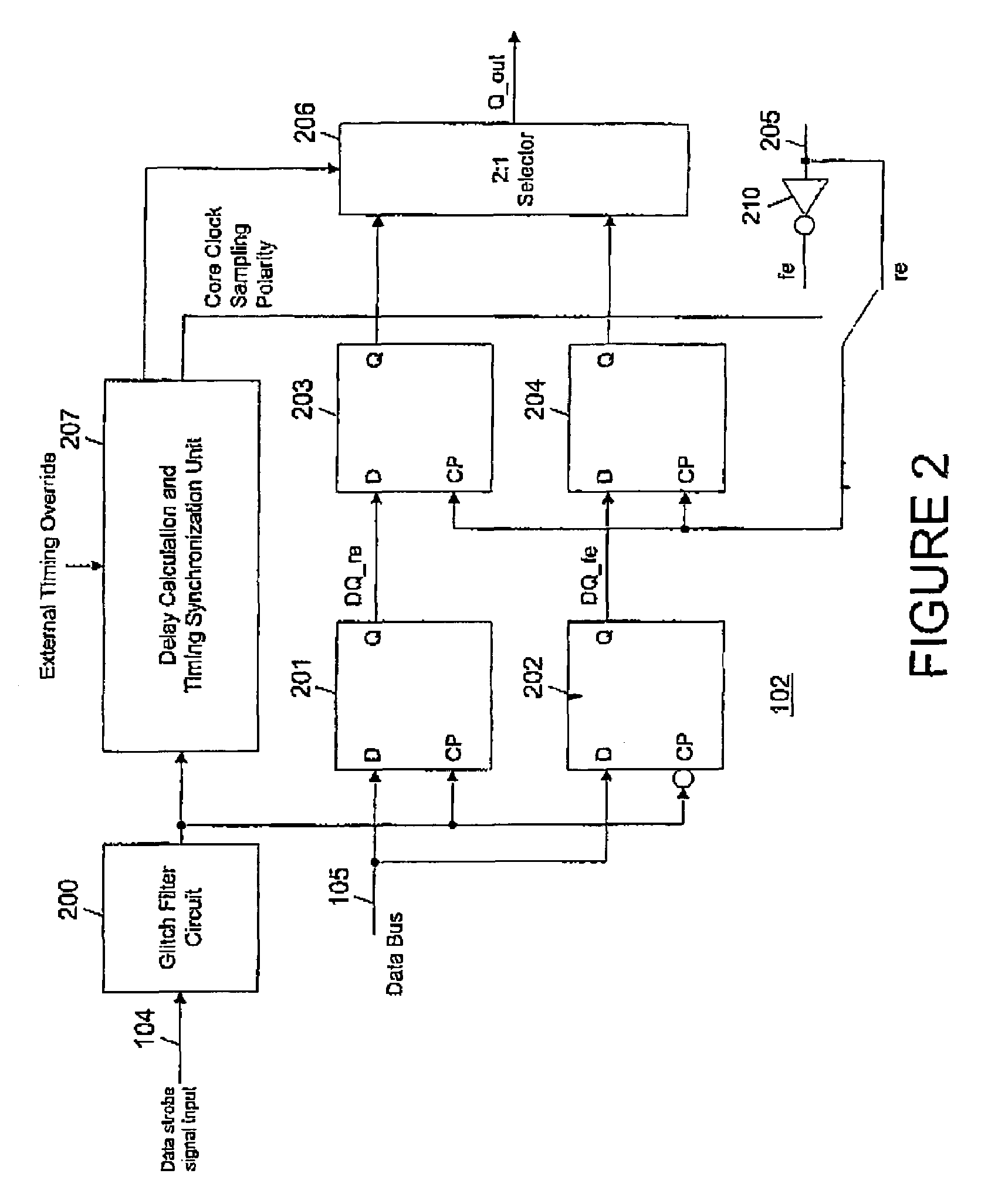
DDR on-the-fly synchronization
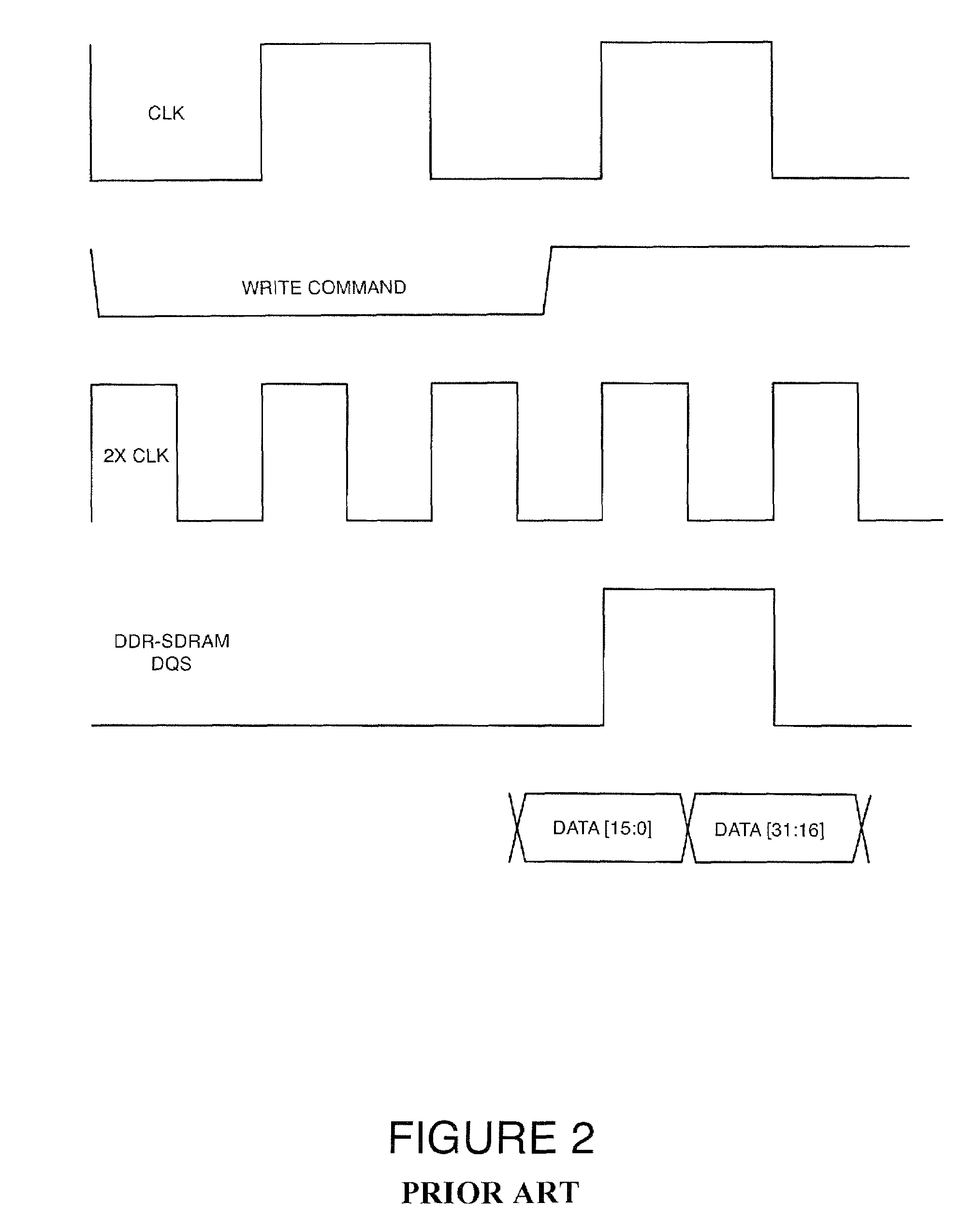
Double data rate (DDR) synchronous dynamic random access memory (SDRAM) data is sampled into a synchronization circuit on both rising and falling edges of a data strobe (DQS) signal, into separate latches. A delay calculation and timing synchronization unit determines the location of the data strobe signal relative to rising / falling edges of an internal clock, then decides which sample to transfer into the internal data path and whether to use the rising or falling internal clock edge. Every DDR-SDRAM read transaction is thus automatically synchronized without the need for predetermined delay(s), allowing a wide range of operating frequencies and frequency variations to be accommodated.
Owner:HYDAC PROCESS TECH +1
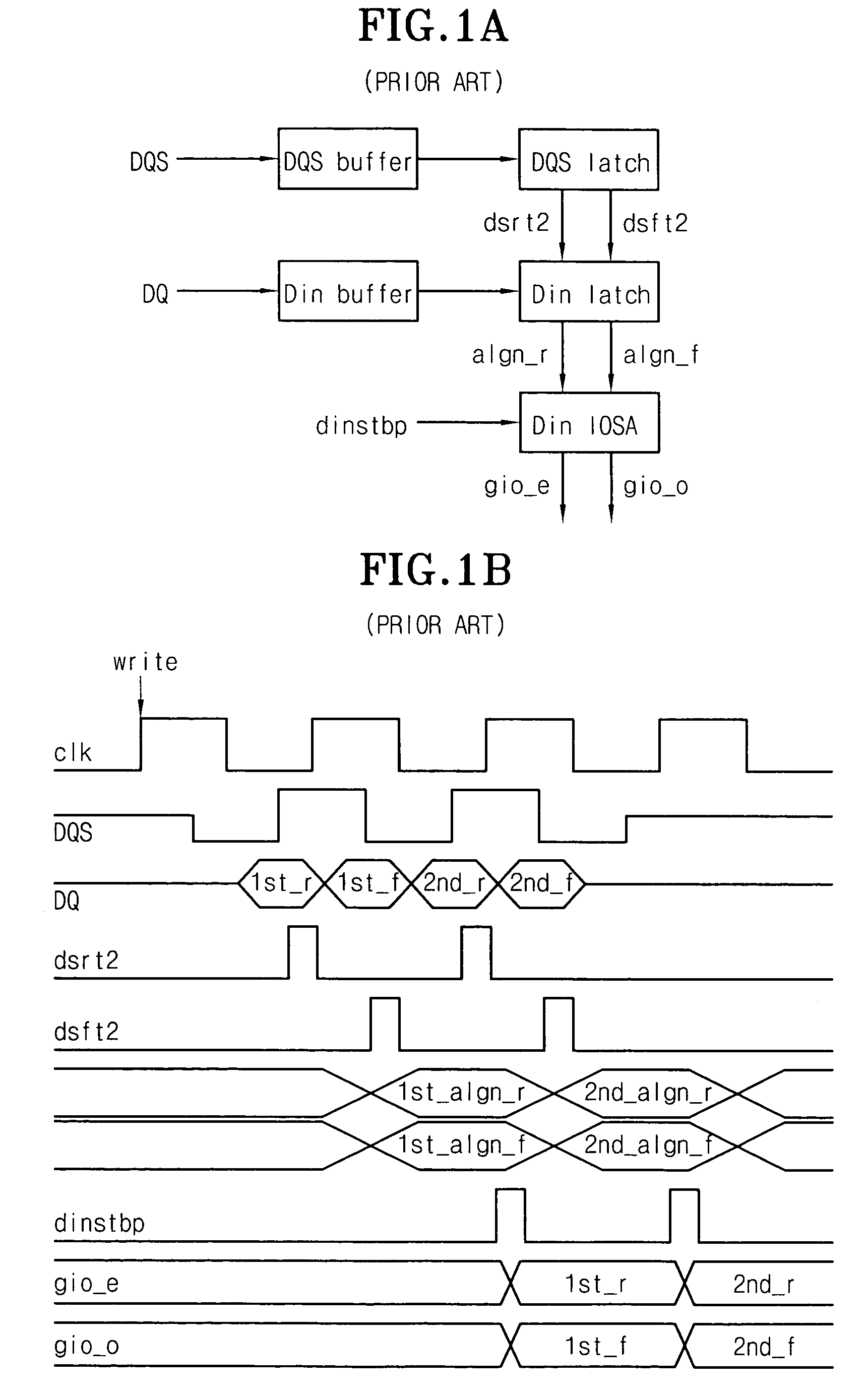
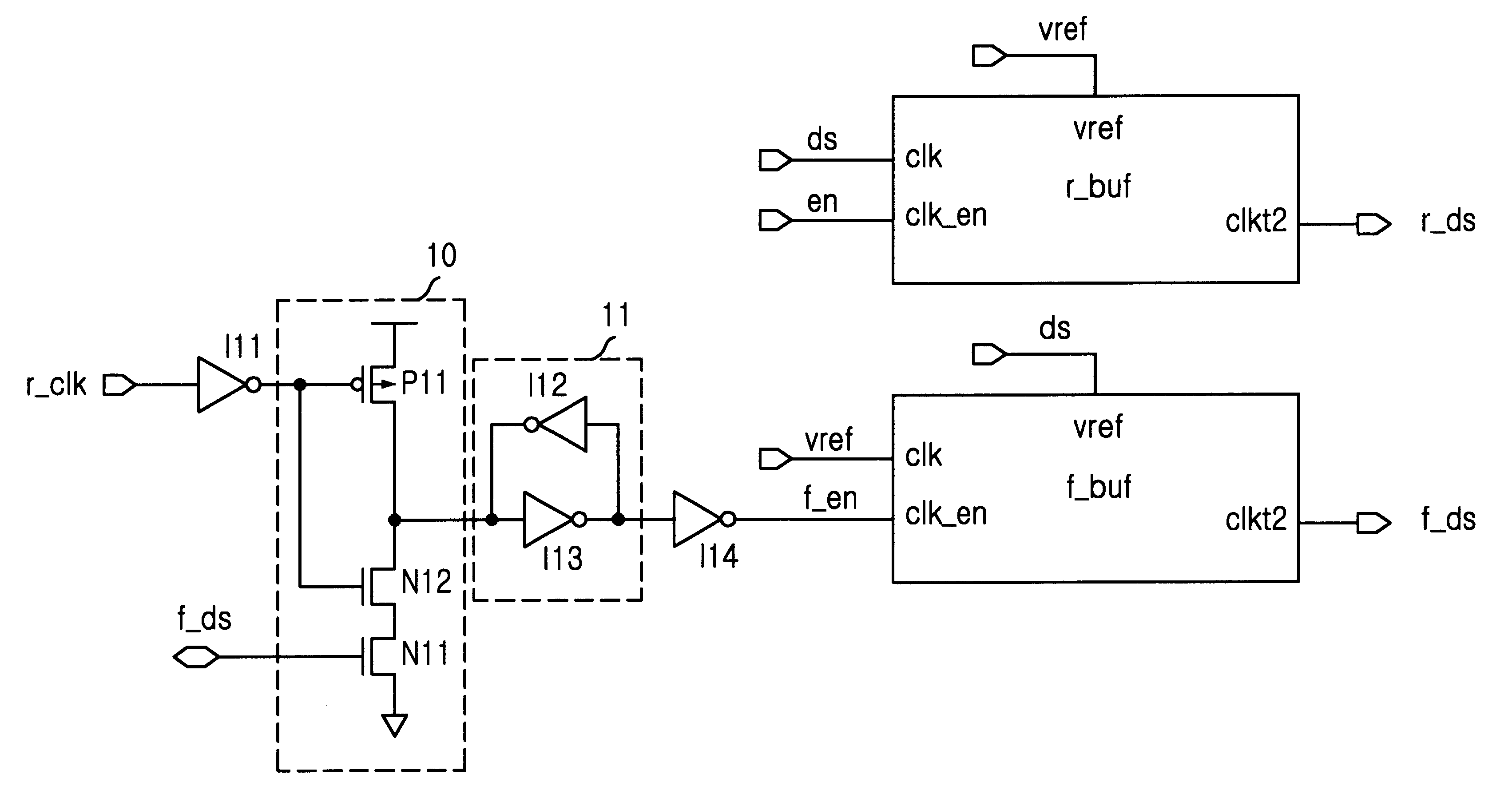
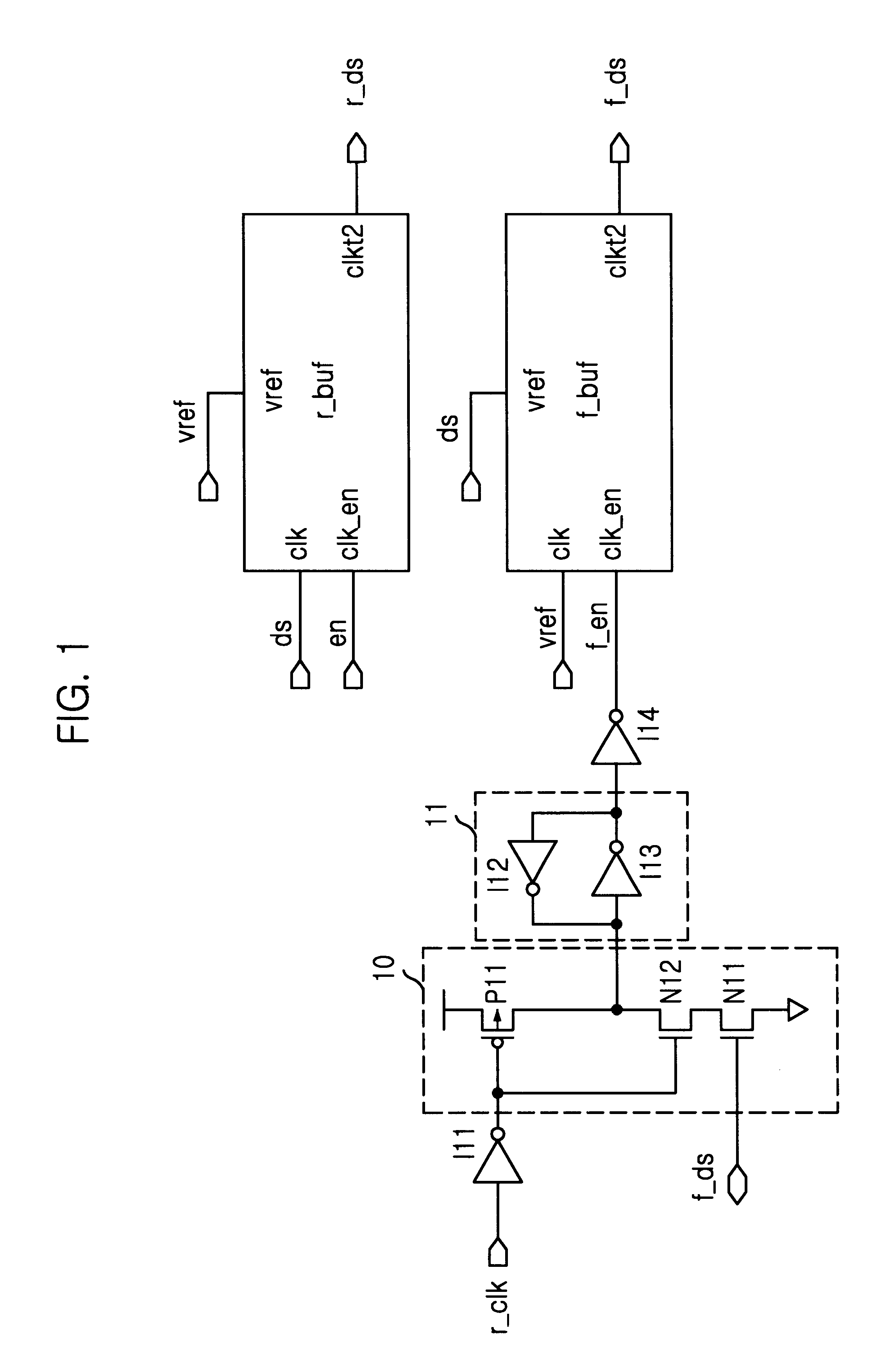
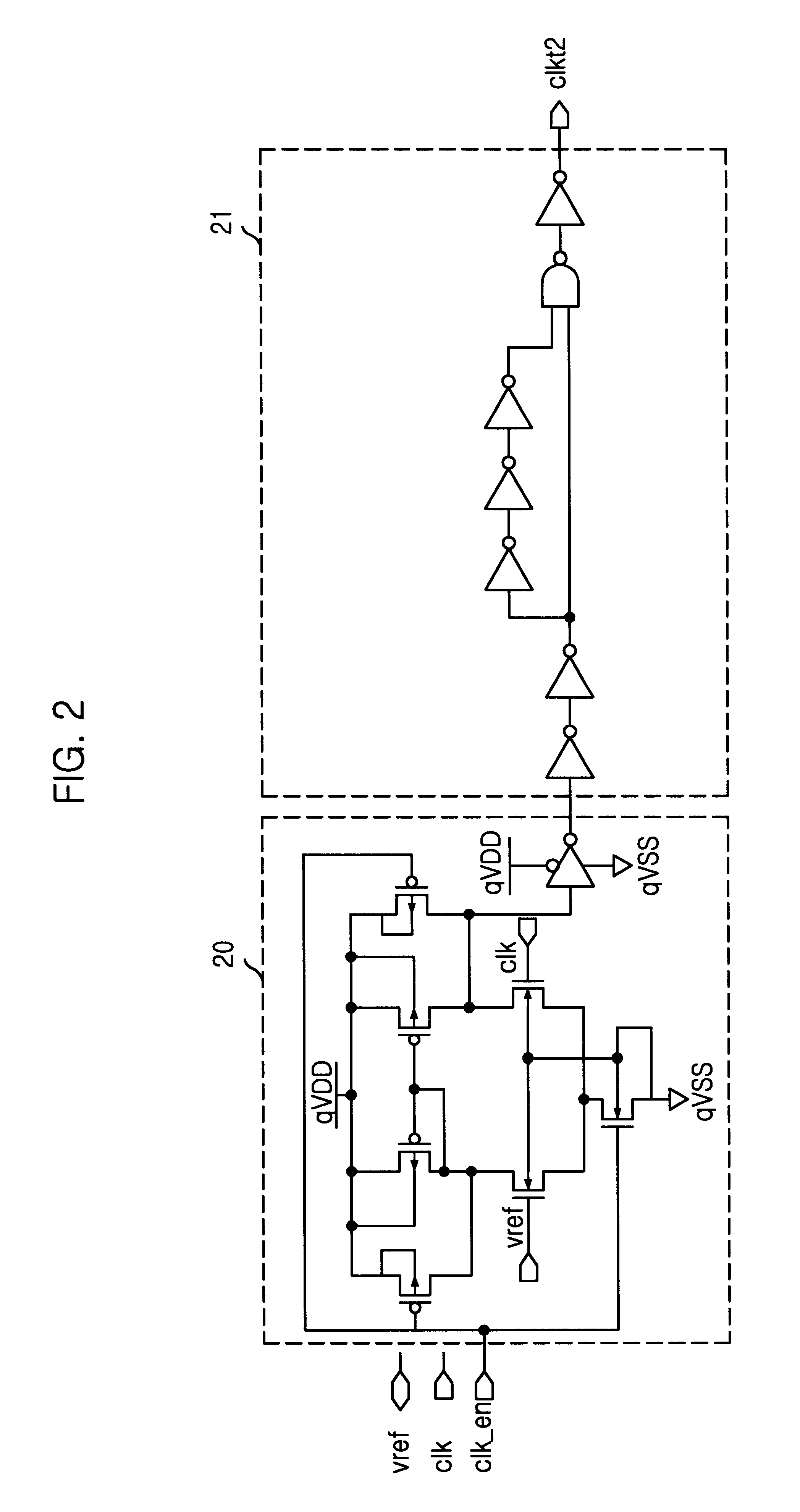
Data strobe buffer in SDRAM
A data strobe buffer in SDRAM is disclosed. The data strobe buffer for a synchronous dynamic read only memory (SDRAM), comprising: a first dynamic buffer generating a first pulse at a rising edge of a data strobe signal; a second dynamic buffer generating a second pulse at a falling edge of the data strobe signal; and a block for generating an enable signal which is enabled in a range between a rising edge of an external clock signal and a logic high state of the second pulse, and providing the second dynamic buffer with the enable signal. The data strobe buffer ensures a minimum value of tDQSS parameter in DDR SDRAM even if speed of the chip increases or operation condition of the chip becomes tight, thereby preventing the data strobe buffer from being misoperated due to the damping and the fluctuation of the data strobe signal.
Owner:HYUNDAI ELECTRONICS IND CO LTD
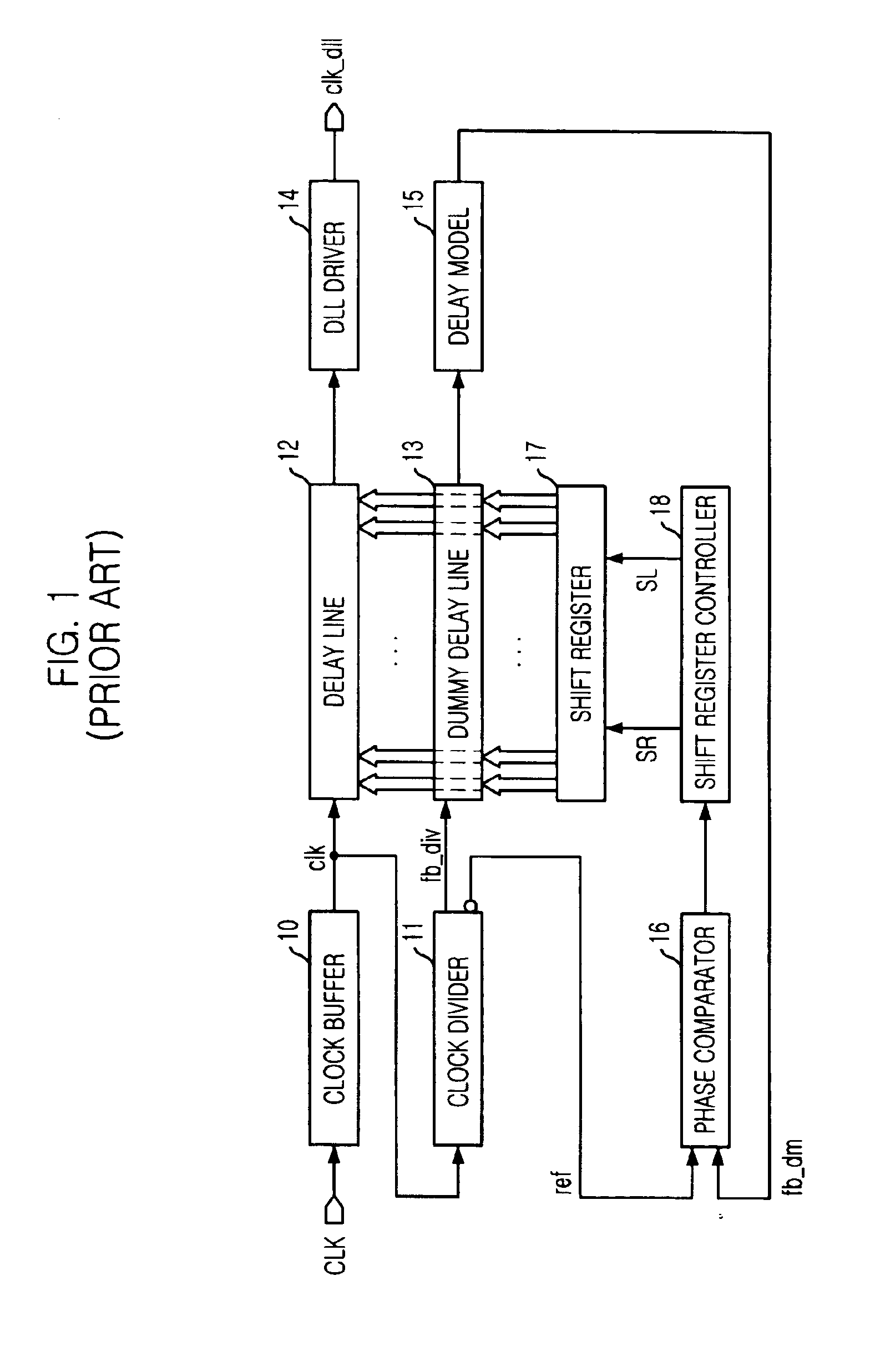
Delay locked loop circuit
InactiveUS20050242855A1Quick functionDelay line areaPulse automatic controlSpray nozzlesDelay-locked loopPhase synchronization
Disclosed is a delay locked loop circuit (DLL) used for DDR SDRAM. The DLL provides a fast locking function. In particular, the DLL detects the level of a frequency and performs the fast locking function, thereby realizing a high integrated memory device having a reduced area of a delay part used in order to synchronize a phase of an external clock signal with a phase of an internal clock.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Compact packet switching node storage architecture employing double data rate synchronous dynamic RAM
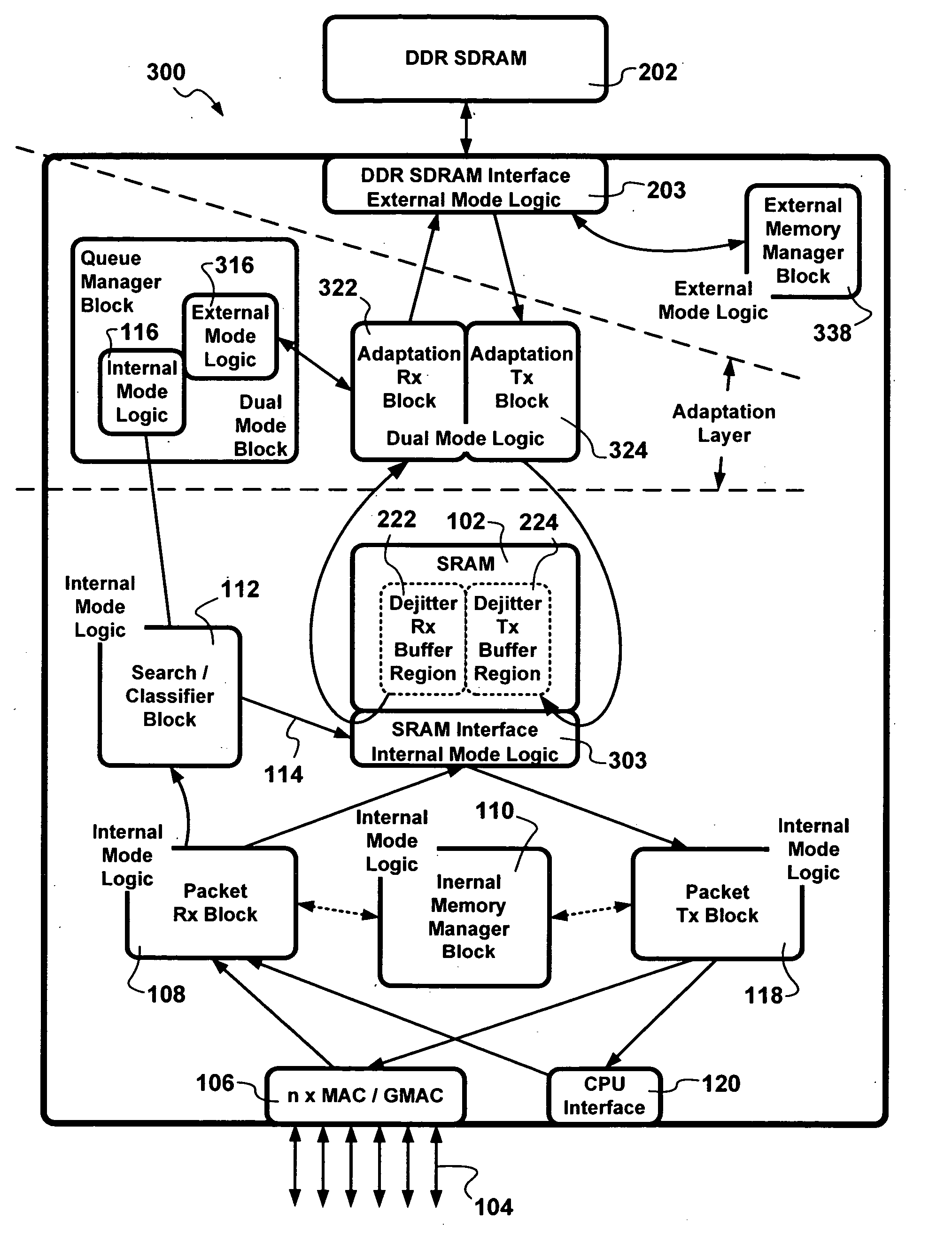
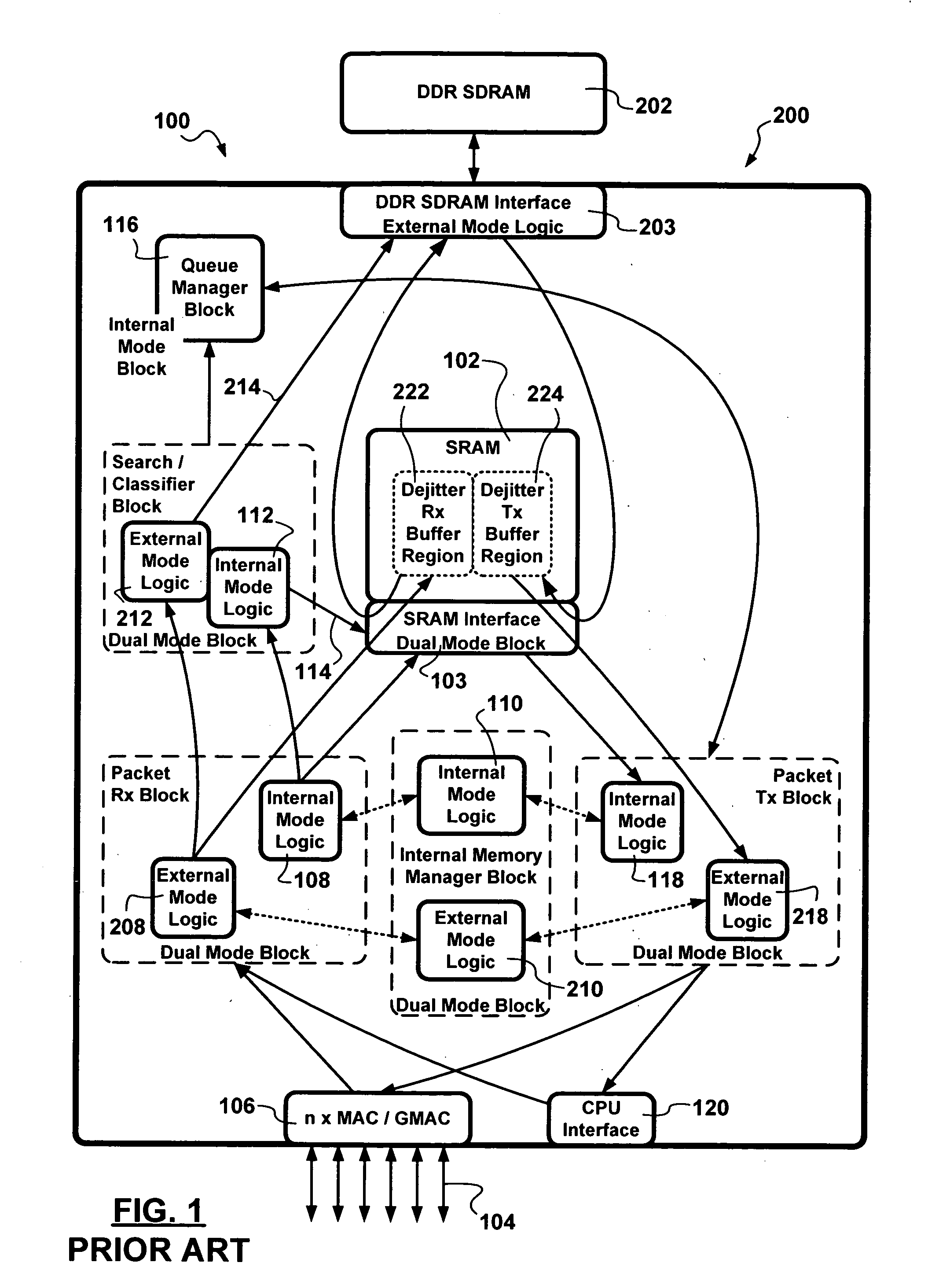
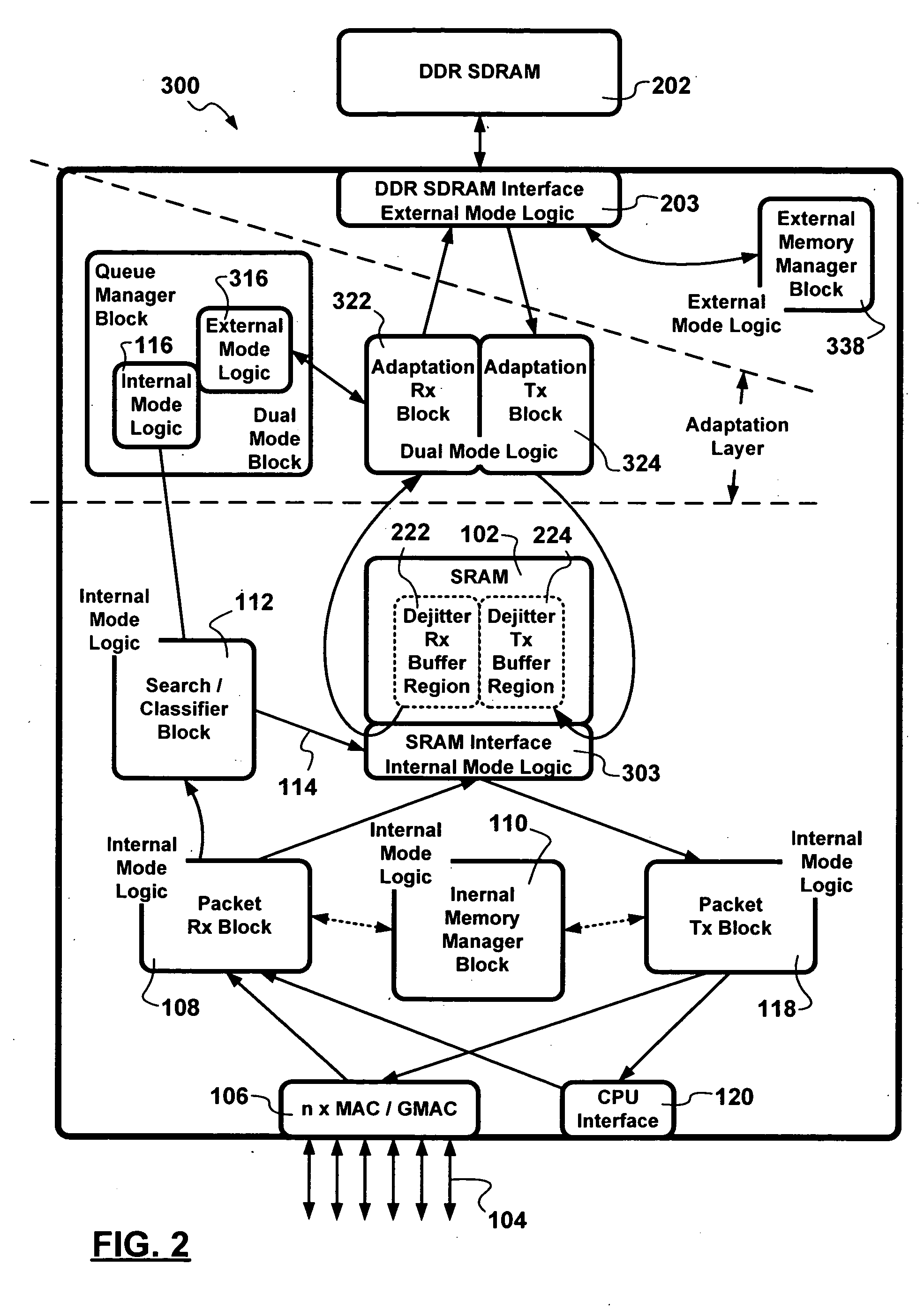
A two-chip / single-die switch architecture and a method for accessing a DDR SDRAM memory store in a switching environment are presented. The two-chip / single-die architecture includes an internal memory storage block on the single-die, an external memory storage interface to a Double Data Rate Synchronous Dynamic Random Access Memory (DDR SDRAM), an external memory manager, and a packet data transfer engine effecting packet data transfers between an internal memory store and the external DDR SDRAM memory. The packet data transfer engine operates as an adaptation layer addressing issues related to employing appropriate: addressing schemes, granule sizes, memory transfer burst sizes, access timing, etc. The packet data transfer engine includes a minimal number of dual mode operational blocks such as: a queue manager, and adaptation receive and transmit blocks. The method relates to a packet data transfer discipline addressing random memory access latencies incurred in employing DDR SDRAM, using predictive bank switching to hide random access latencies, packet length dependent variable memory write burst lengths to minimize bank switching, and performing memory read and write operations during corresponding read and write windows. Advantages are derived from the a space-efficient two-chip / single-die switching node architecture implemented with a reduced amount of dual mode logic, and also from DDR SDRAM bandwidth utilization efficiencies.
Owner:IKANOS COMMUNICATIONS
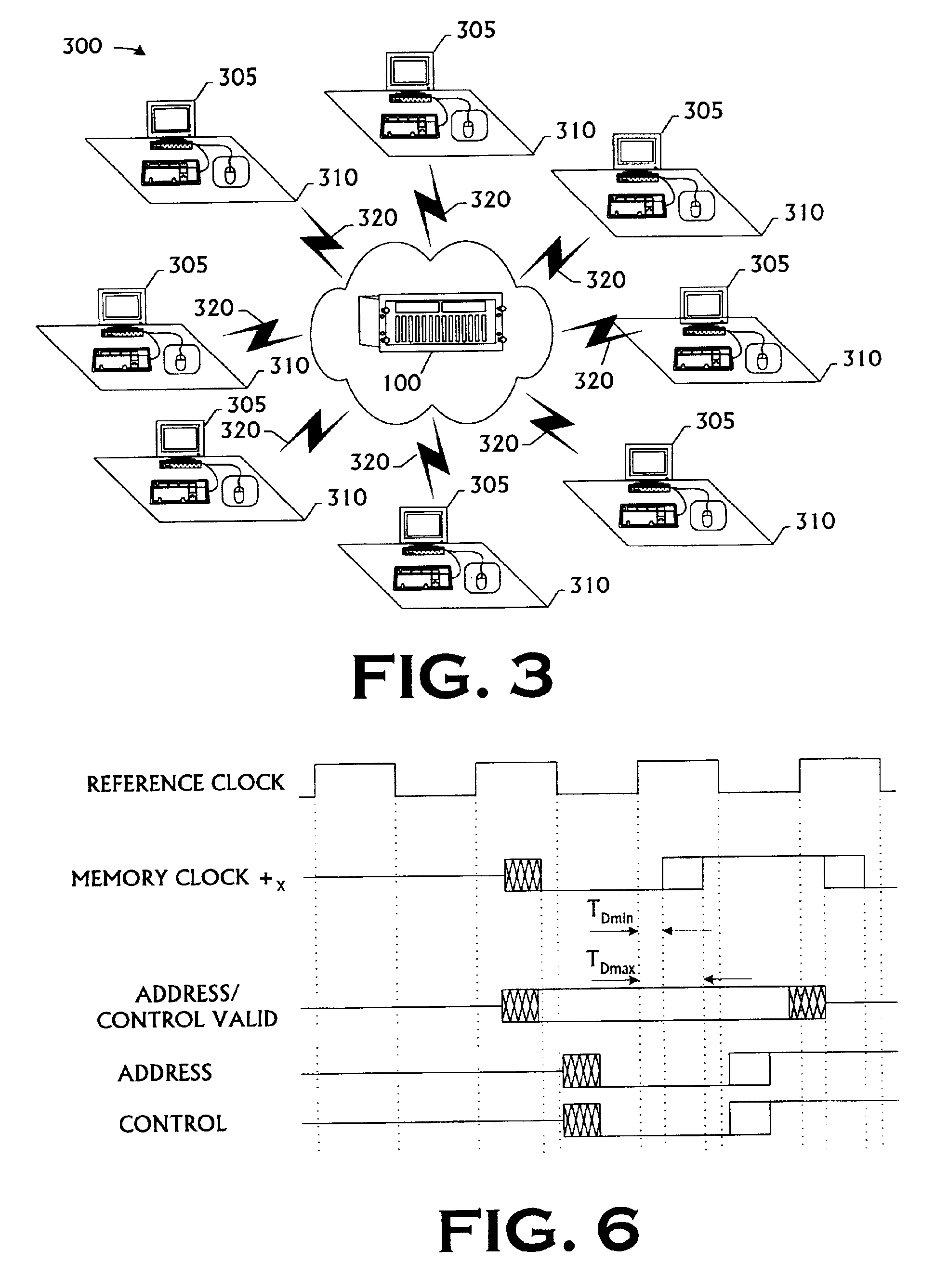
Scalable design for DDR SDRAM buses
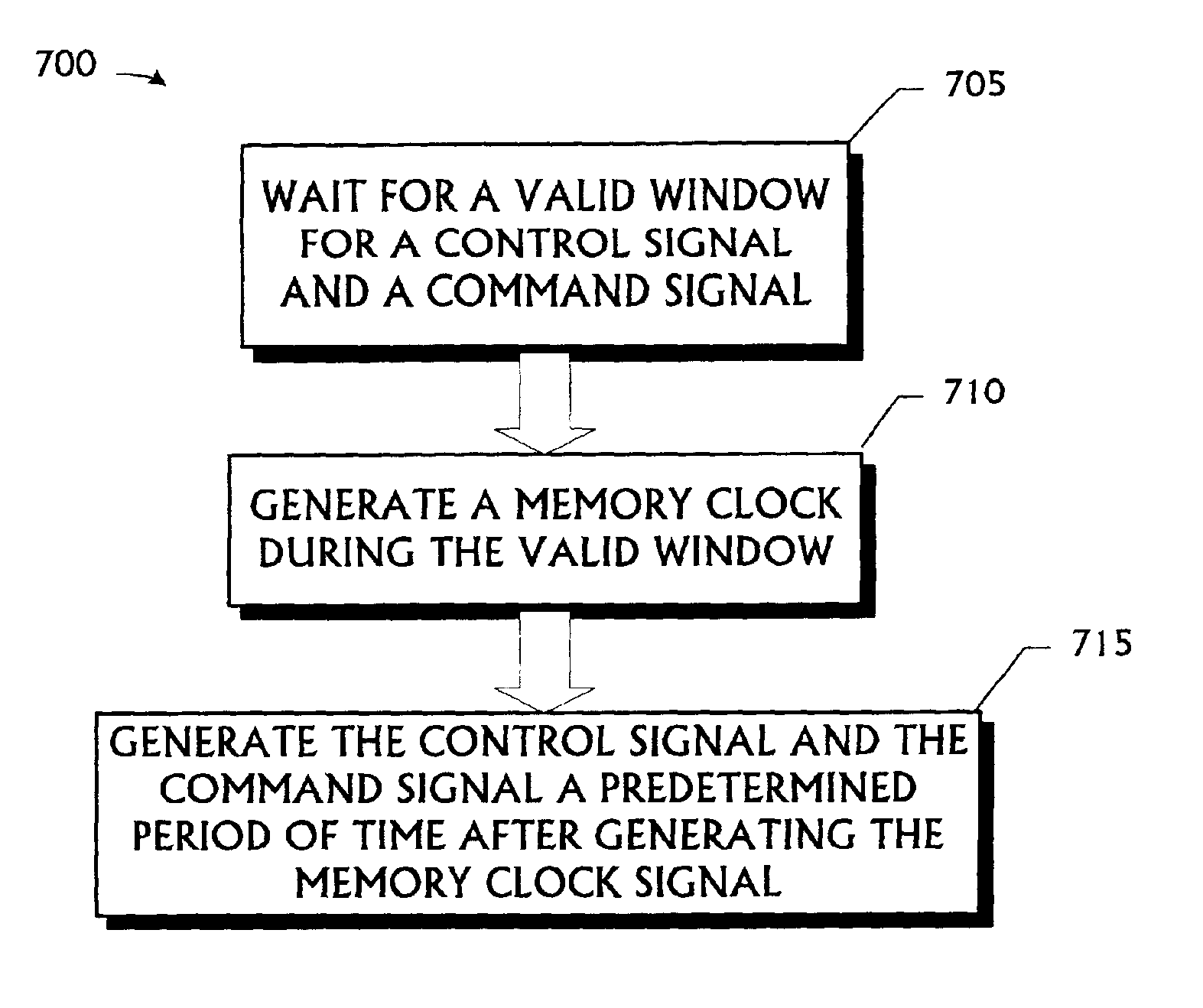
A memory subsystem and a method for use in accessing a memory system are disclosed. The memory subsystem comprising a plurality of SDRAM memory modules and a memory controller. The memory controller is capable of waiting to generate a memory clock signal for each of the SDRAM memory modules until a valid window for a control signal and an address signal; generating the memory clock signals during the valid window, and generating the control and address signals. The method comprises: waiting for a valid window for a control signal and an address signal; generating a memory clock during the valid window; and generating the control signal and the command signal a predetermined period of time after generating the memory clock signal.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com