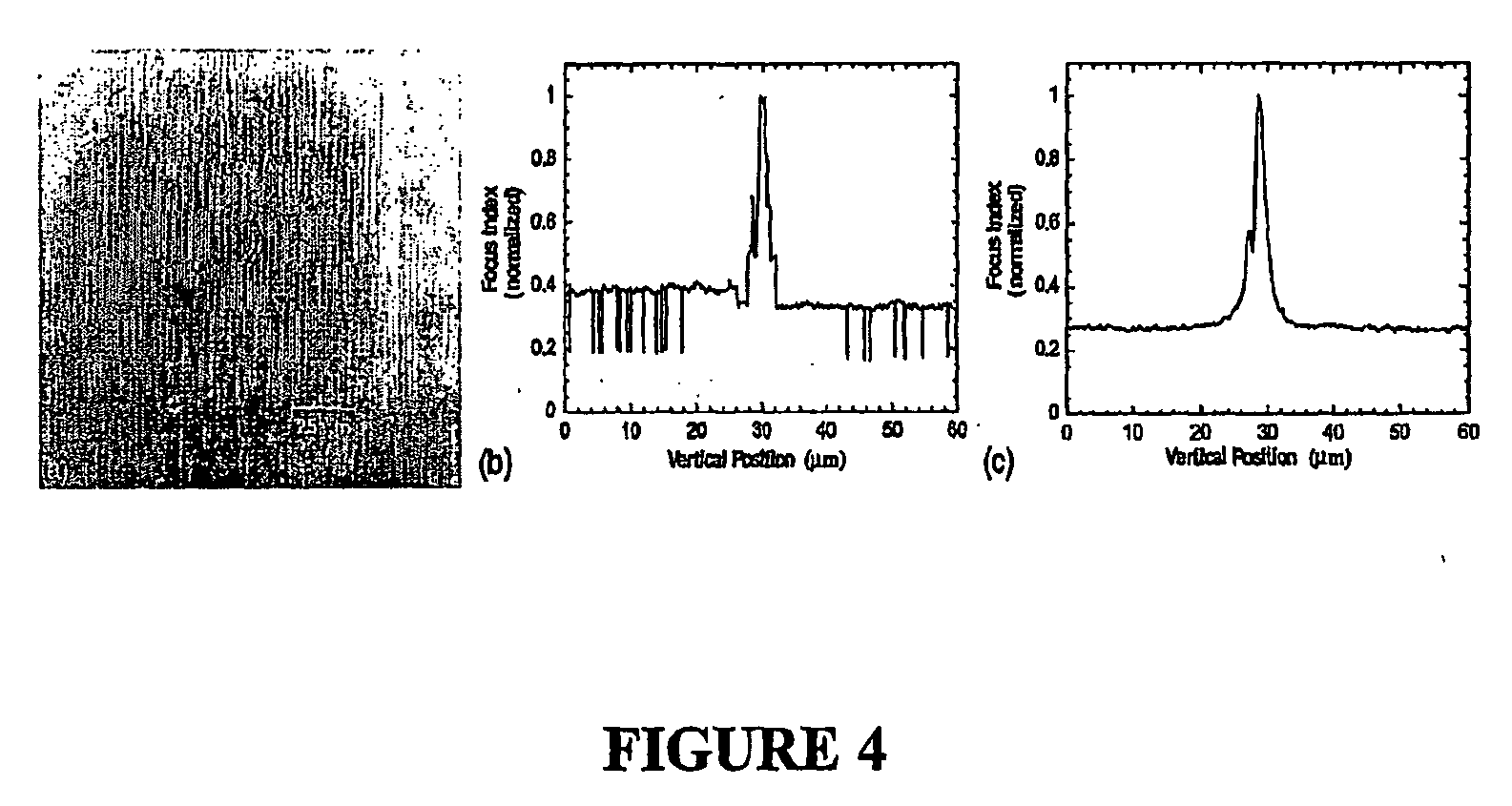
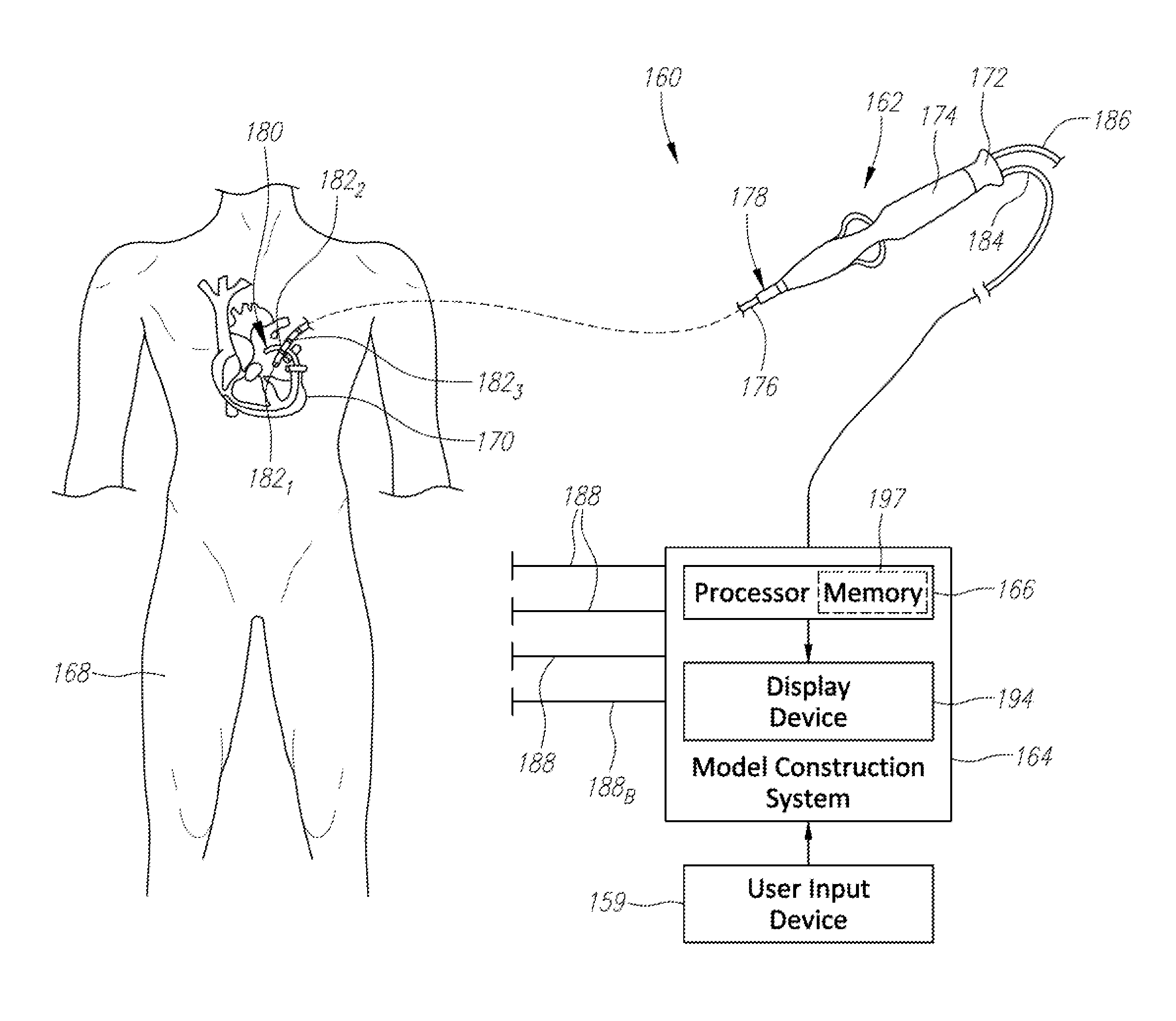
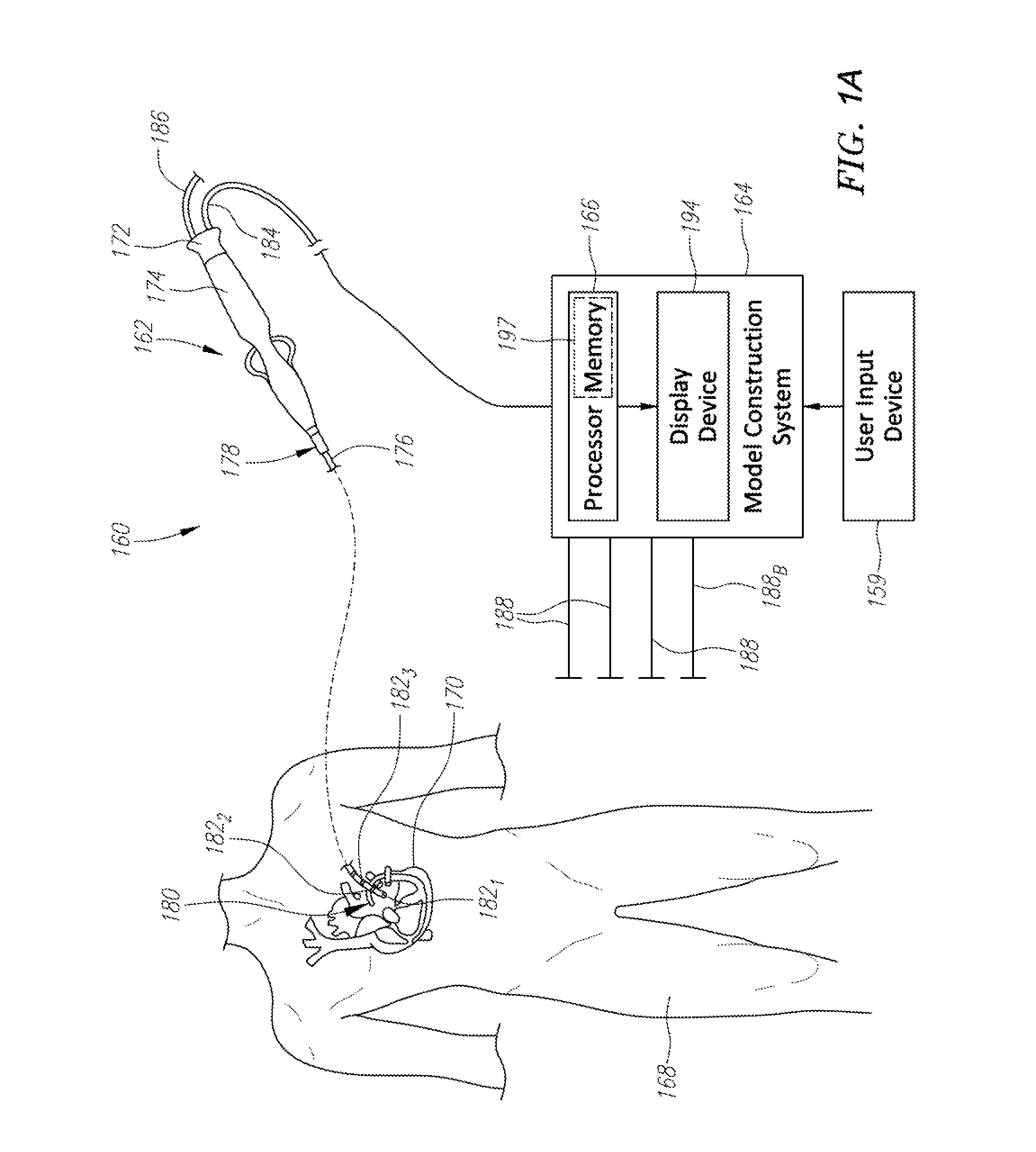
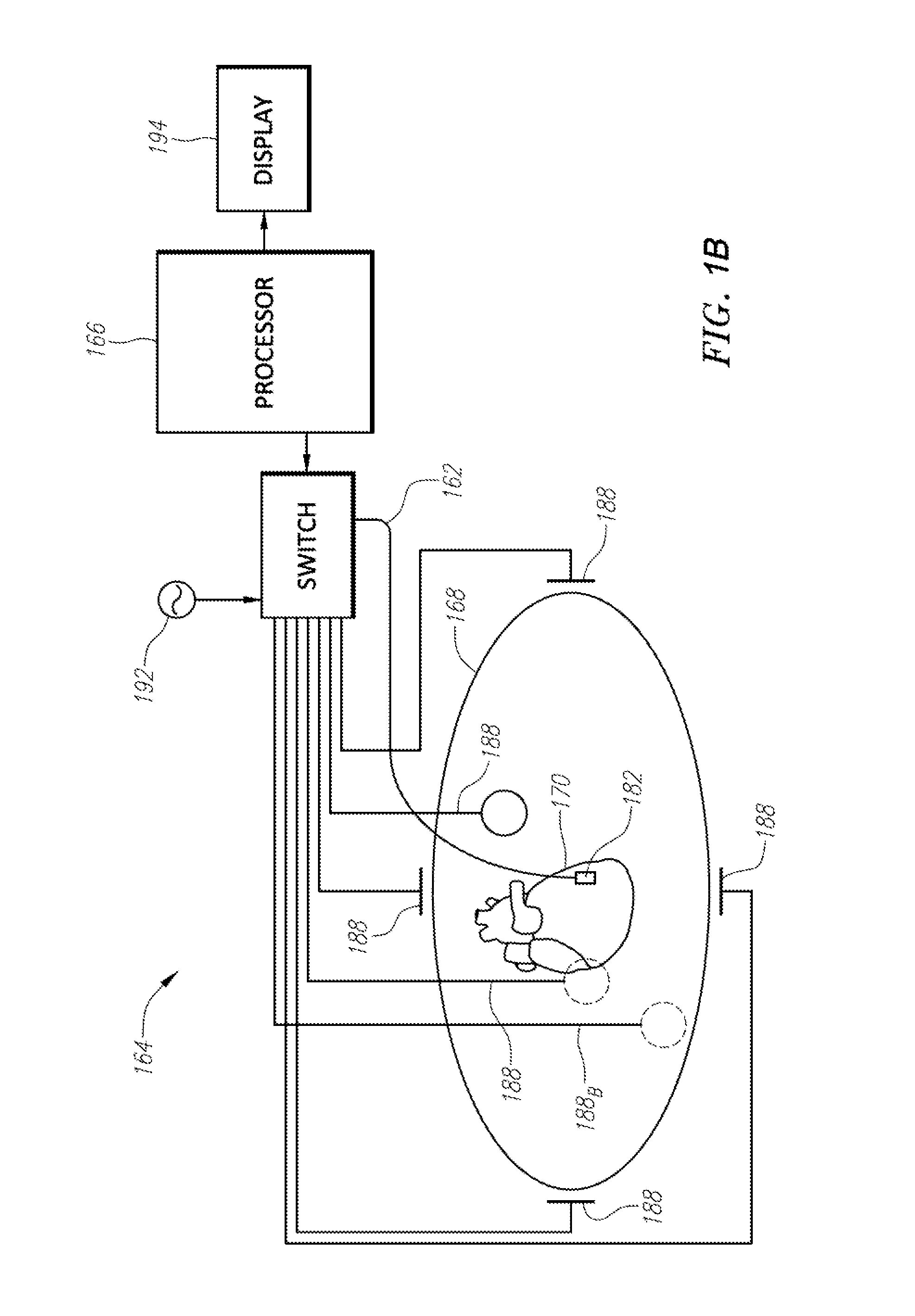
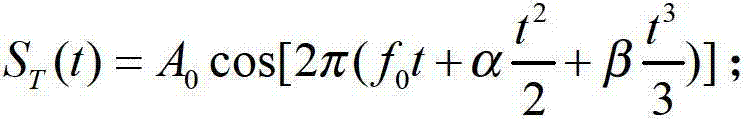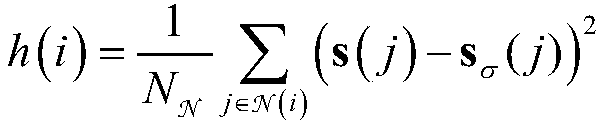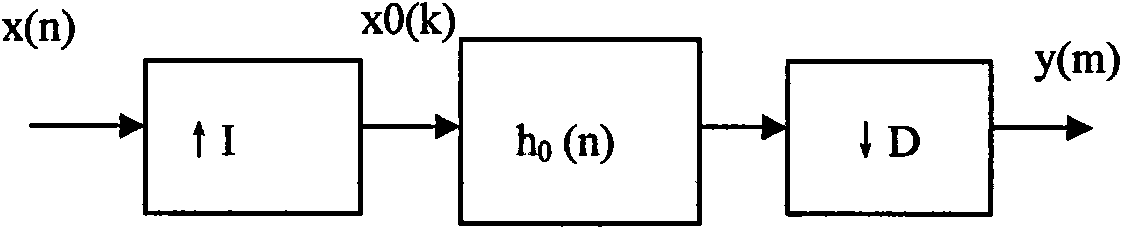Patents
Literature
89 results about "Fraction number" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The top number in a fraction is called the numerator and the bottom number is called the denominator. The denominator shows the whole amount, while the numerator gives you a portion of the whole. Fractions can be reduced when both the numerator and the denominator can be divided by the same number.
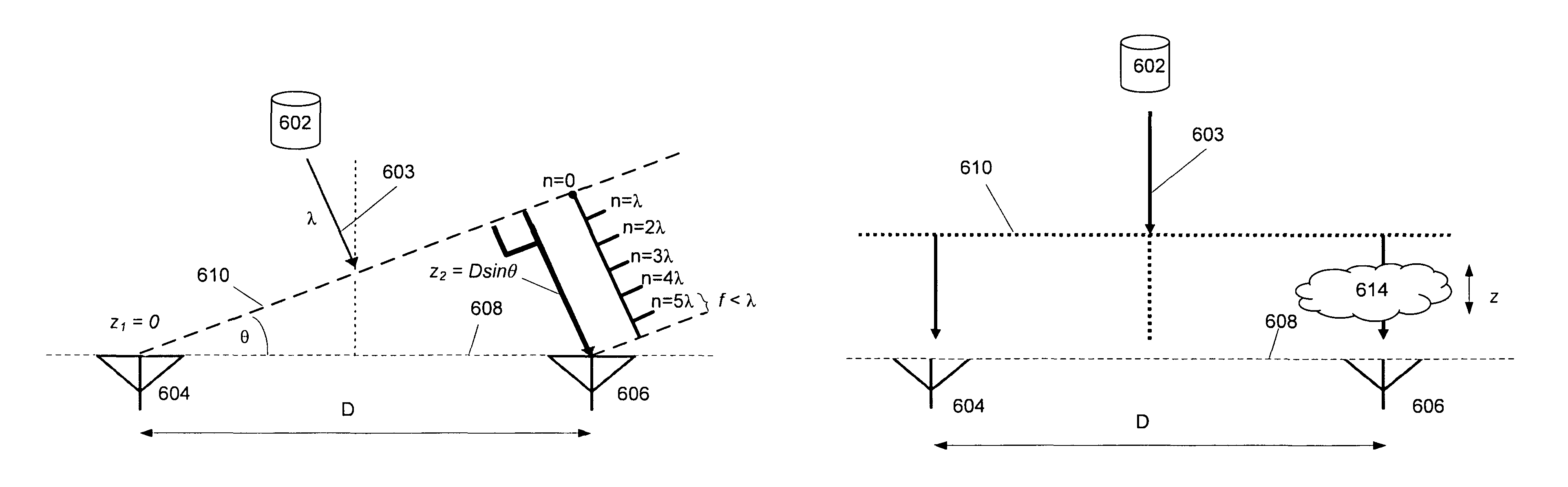
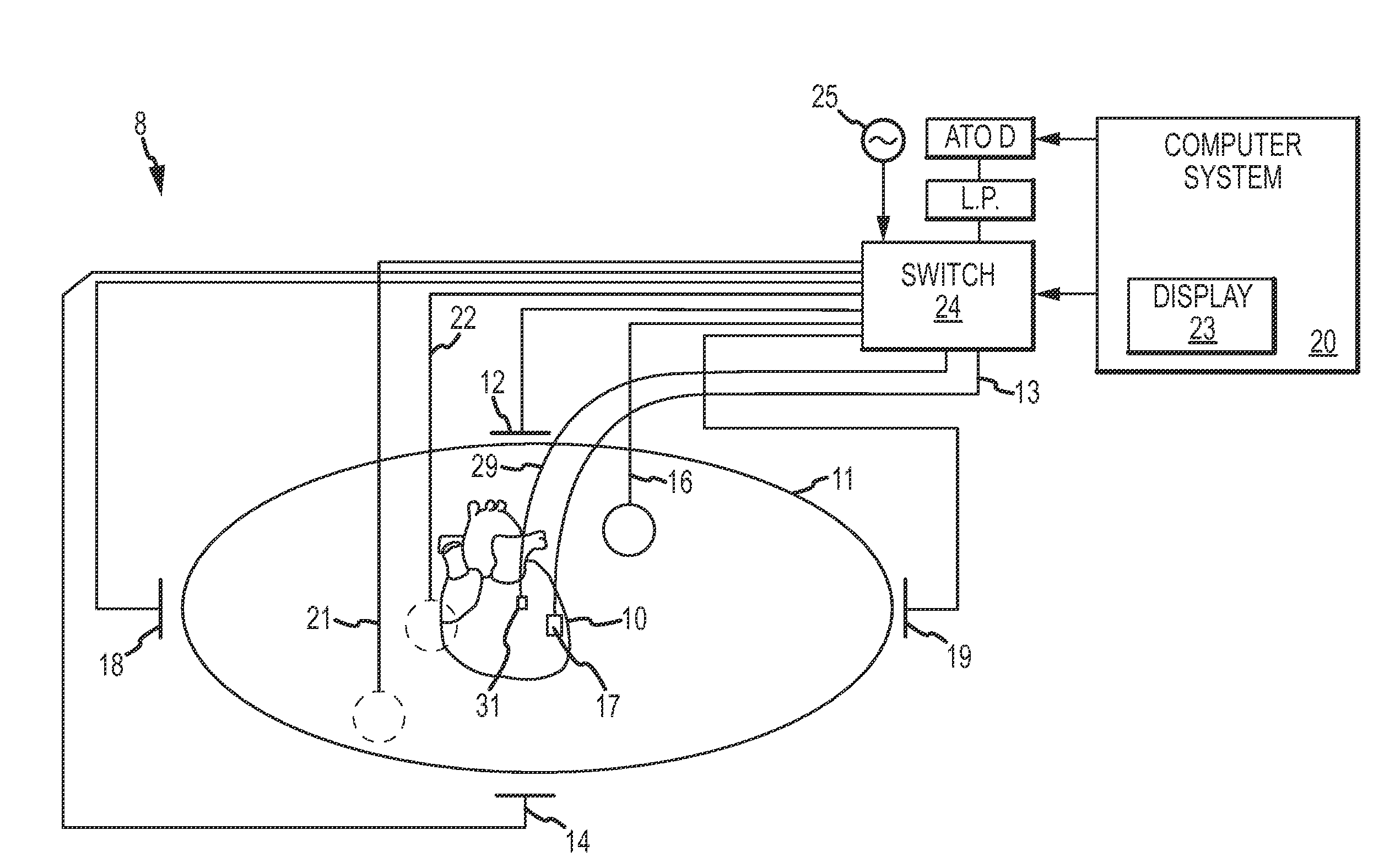
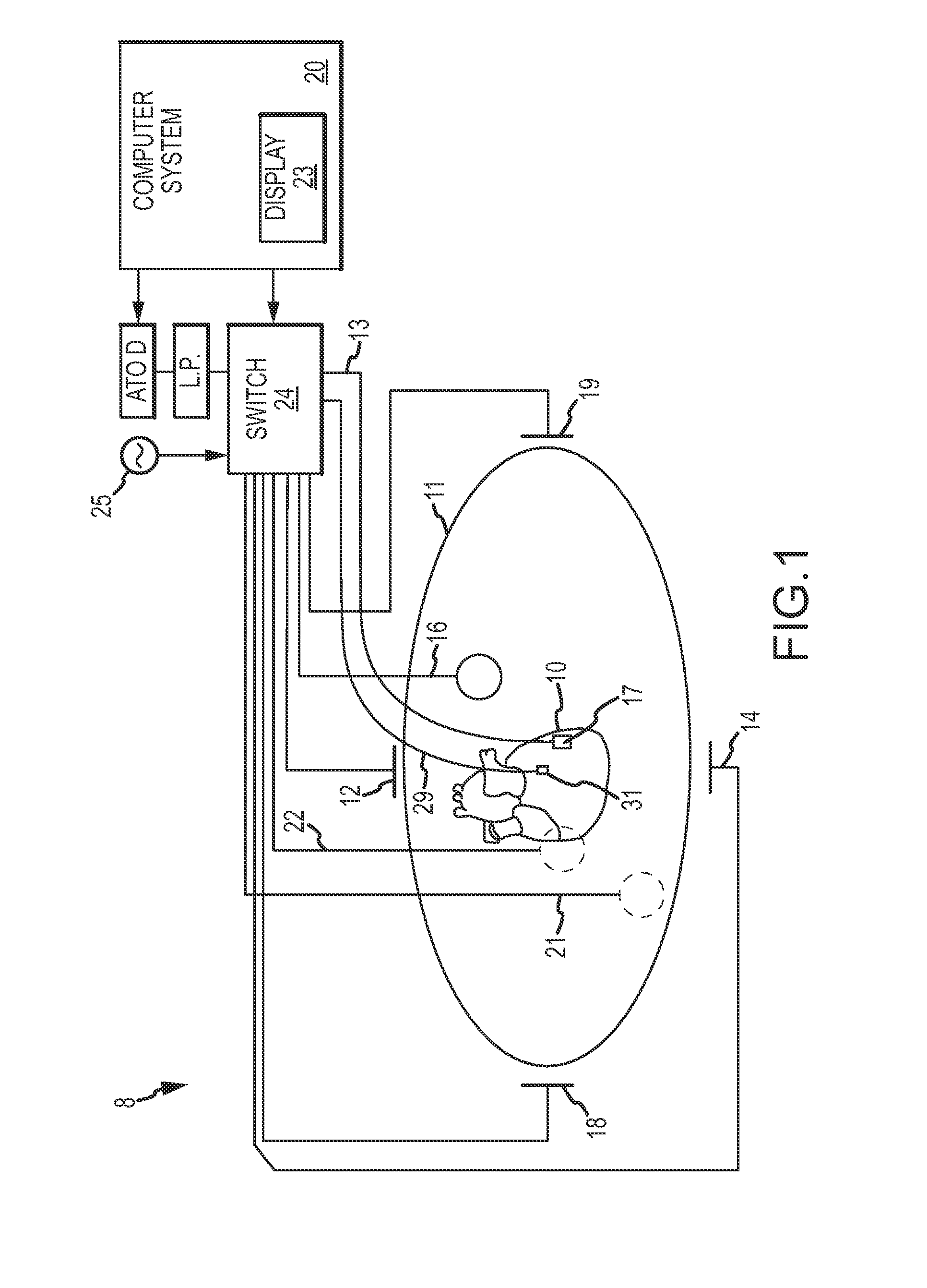
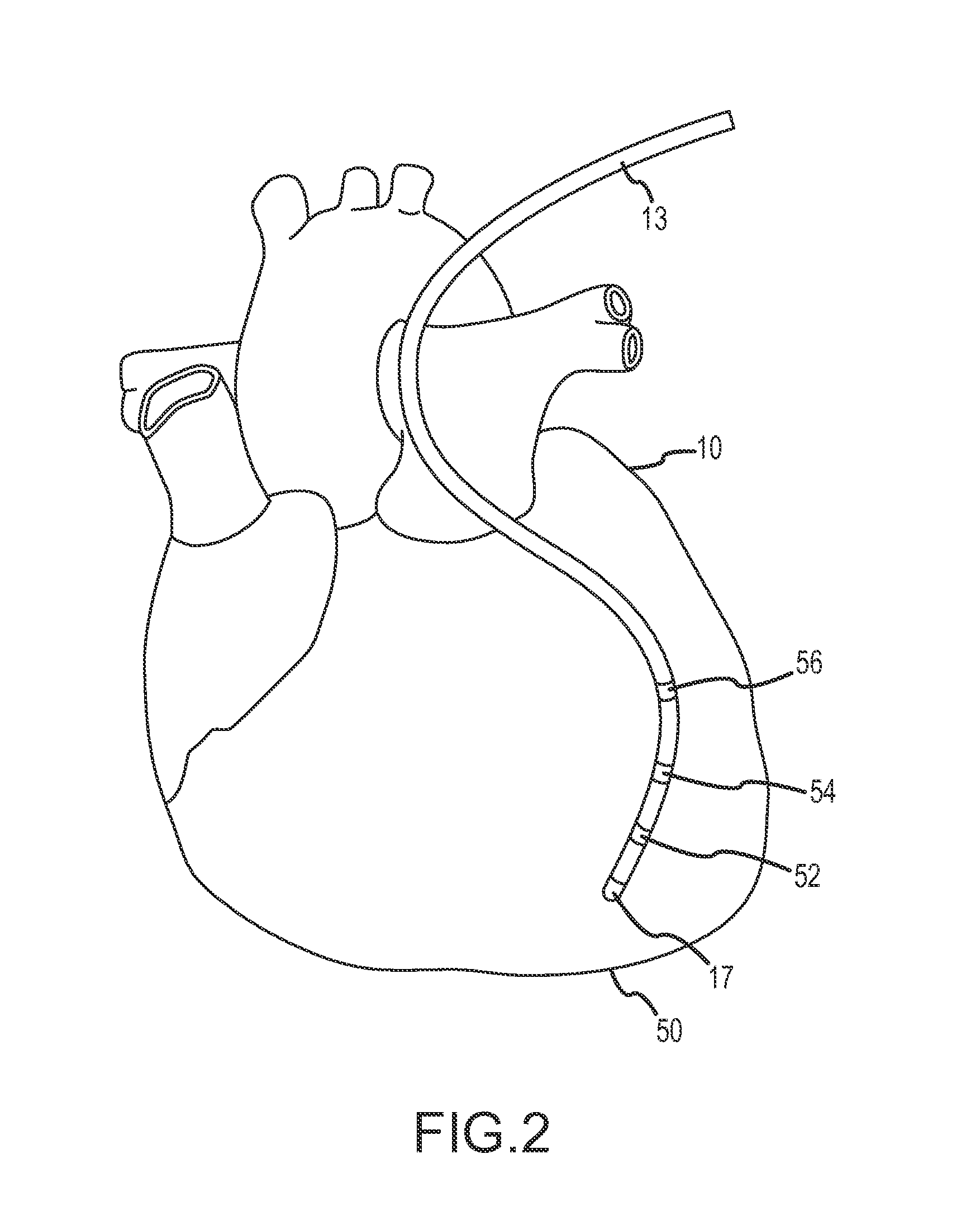
Systems and methods for compensating for transmission phasing errors in a communications system using a receive signal
Owner:HARRIS CORP
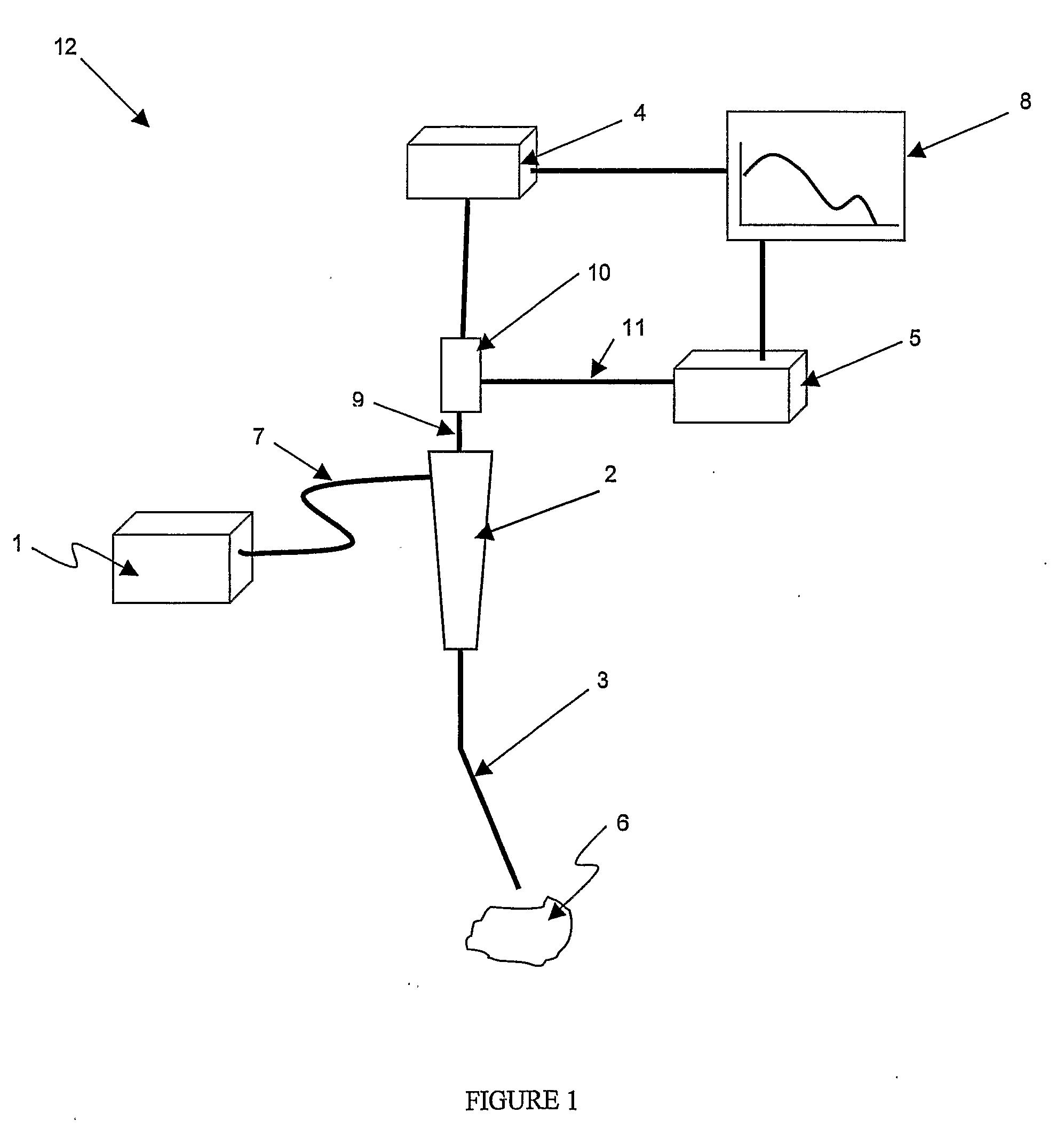
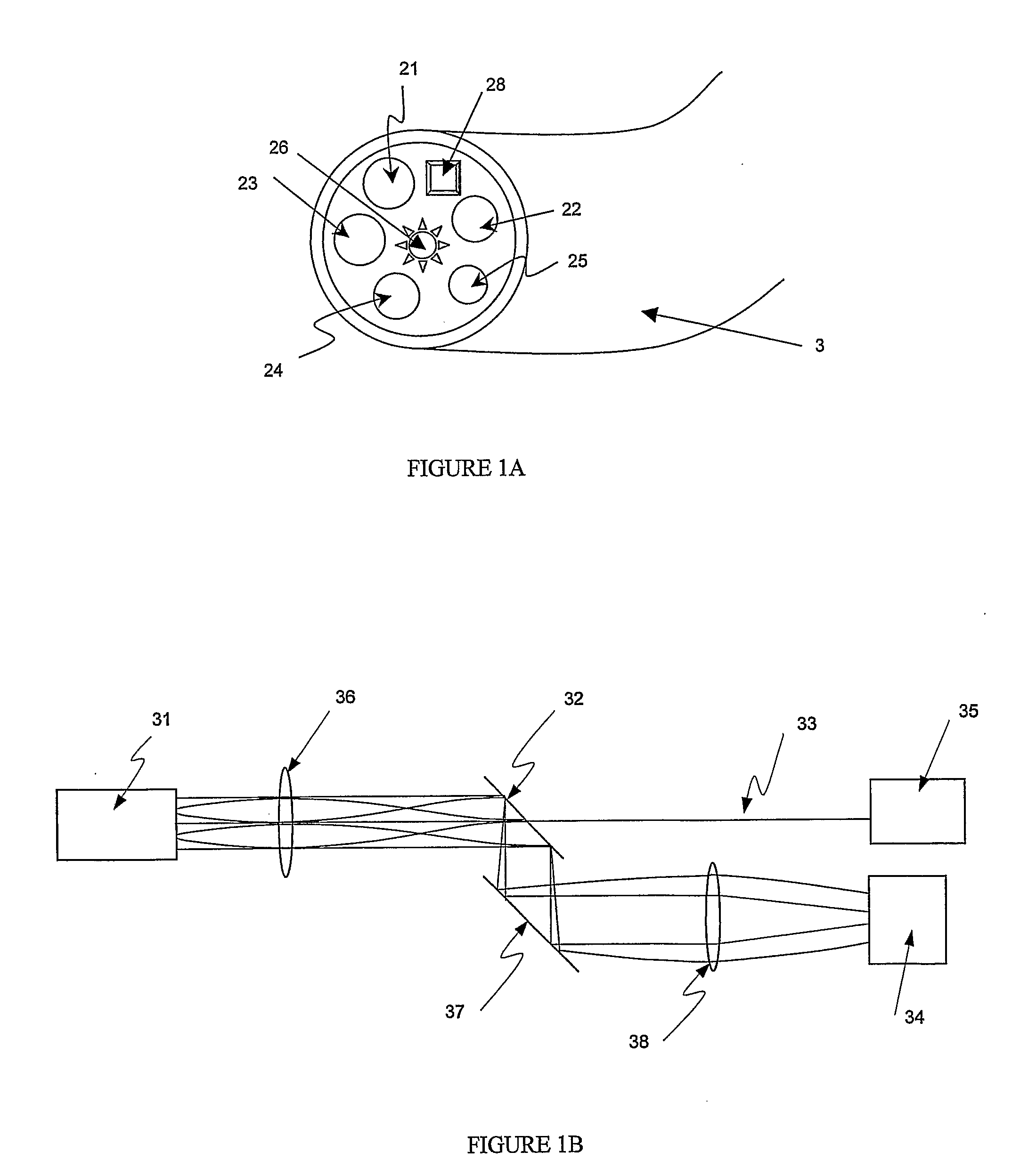
Method and apparatus for measuring cancerous changes from reflectance spectral measurements obtained during endoscopic imaging
The present invention provides a new method and device for disease detection, more particularly cancer detection, from the analysis of diffuse reflectance spectra measured in vivo during endoscopic imaging. The measured diffuse reflectance spectra are analyzed using a specially developed light-transport model and numerical method to derive quantitative parameters related to tissue physiology and morphology. The method also corrects the effects of the specular reflection and the varying distance between endoscope tip and tissue surface on the clinical reflectance measurements. The model allows us to obtain the absorption coefficient (μa) and further to derive the tissue micro-vascular blood volume fraction and the tissue blood oxygen saturation parameters. It also allows us to obtain the scattering coefficients (μs and g) and further to derive the tissue micro-particles volume fraction and size distribution parameters.
Owner:PERCEPTRONIX MEDICAL +1
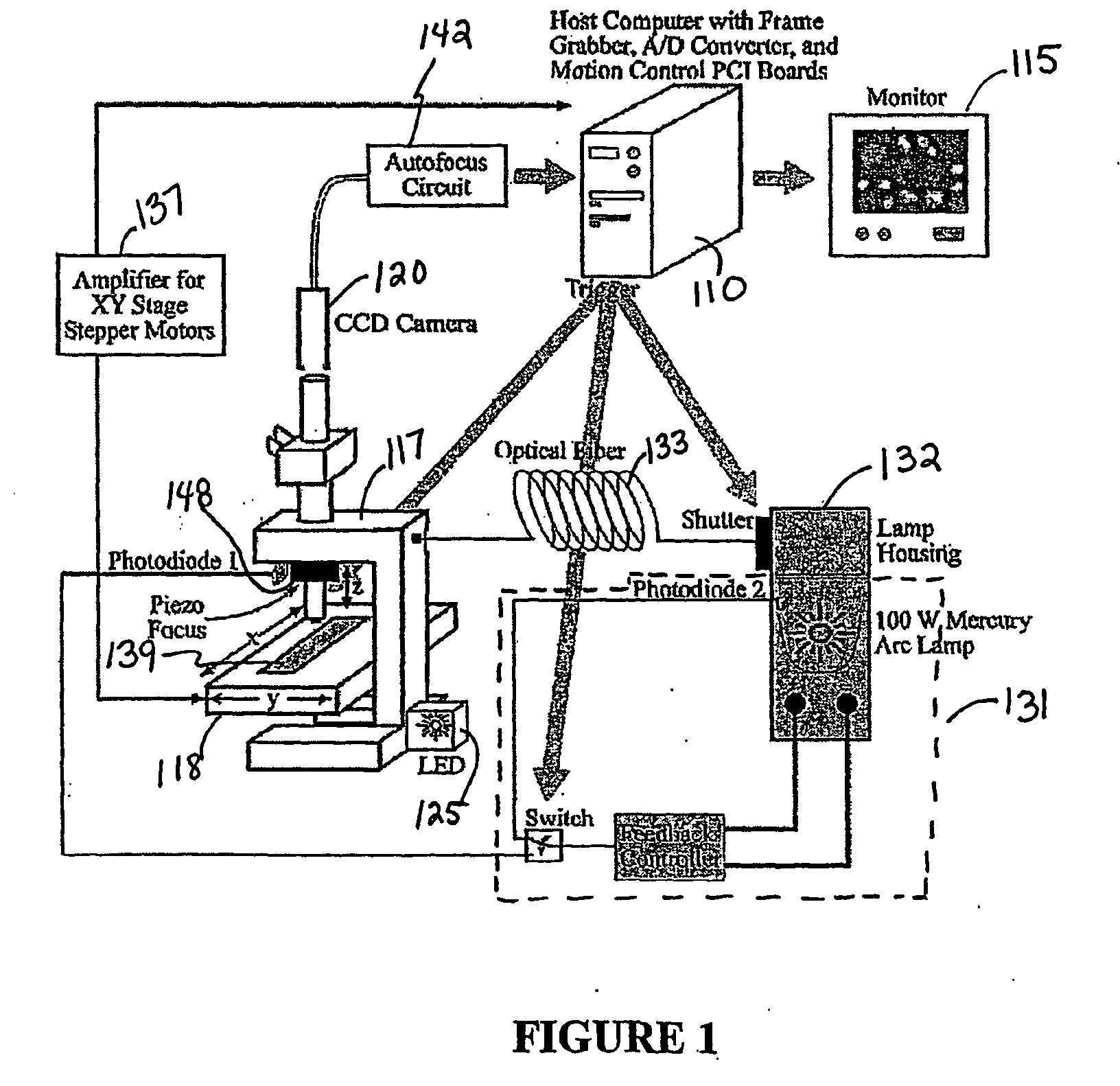
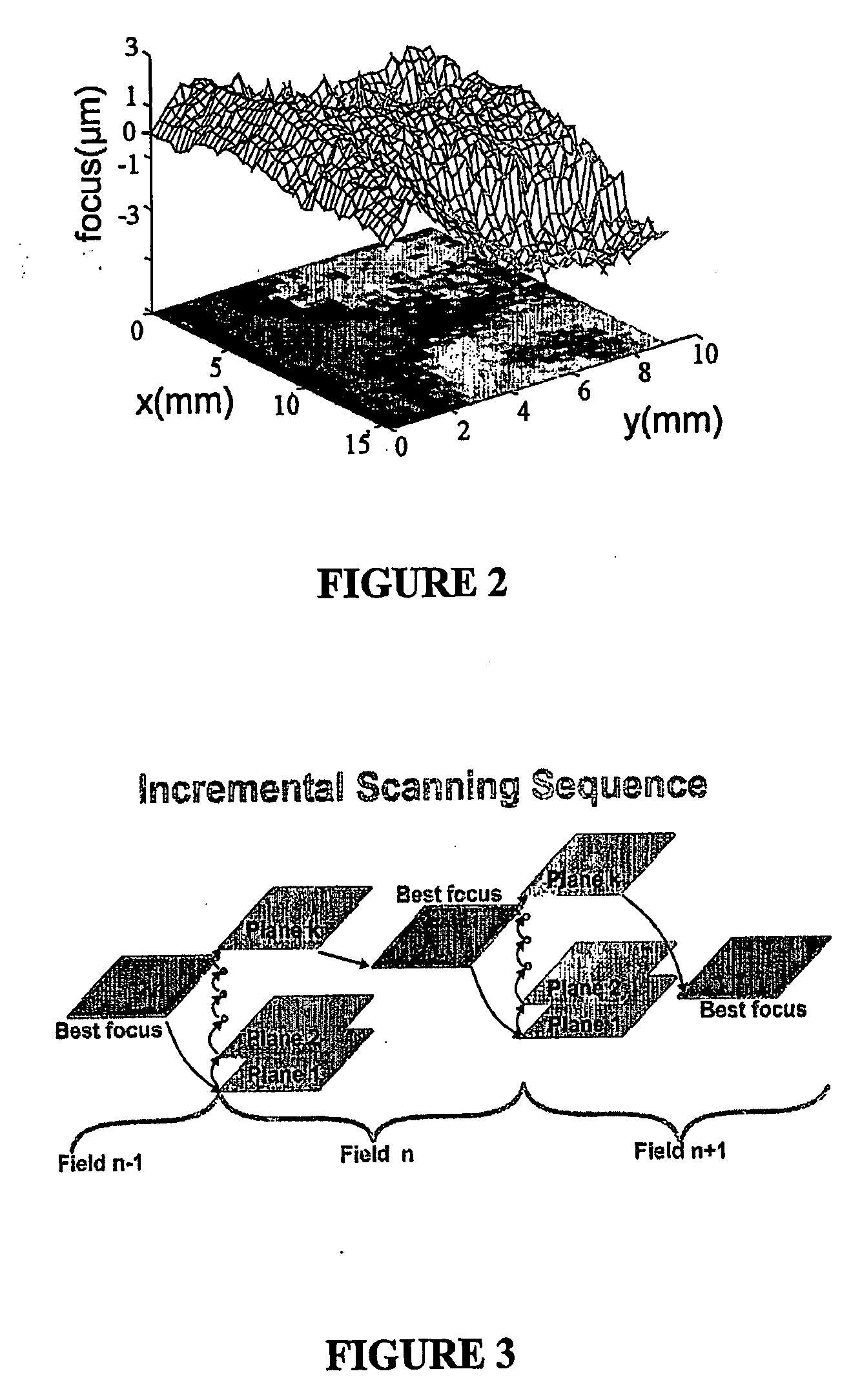
System and method for automatic color segmentation and minimum significant response for measurement of fractional localized intensity of cellular compartments
ActiveUS20070016373A1Improve throughputInteraction is complexBioreactor/fermenter combinationsImage enhancementSystems approachesComputer science
A system, a method, and a programmed device for measurement of translocational activity among cellular compartments process magnified images of cellular material exposed to an agent by segmenting and compartmentalizing the images and then measuring fractional localized intensity of two or more components in the segmented, compartmentalized image. The measured fractional localized intensities are compared to determine translocation of cellular material among the measured components caused by the agent.
Owner:VALA SCI
Systems and methods for orientation independent sensing
A system and method for obtaining an OIS coordinate frame comprising an electronic control unit configured to determine a local 3D electric field loop, create a zero mean version of E(t) over a depolarization interval, compute an Ė value at each of a plurality of time intervals, compute an initial estimate of ŵ from a cross product of E and the Ė value for each of the plurality of time intervals, average the initial estimate of ŵ from each of the plurality of time for a best estimate of ŵ, determine a plurality of â(θ) values and using the corresponding {circumflex over (n)}(θ) values, compute a composite match score, and choose at least one best value for â and a best value for {circumflex over (n)}.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL CARDILOGY DIV INC
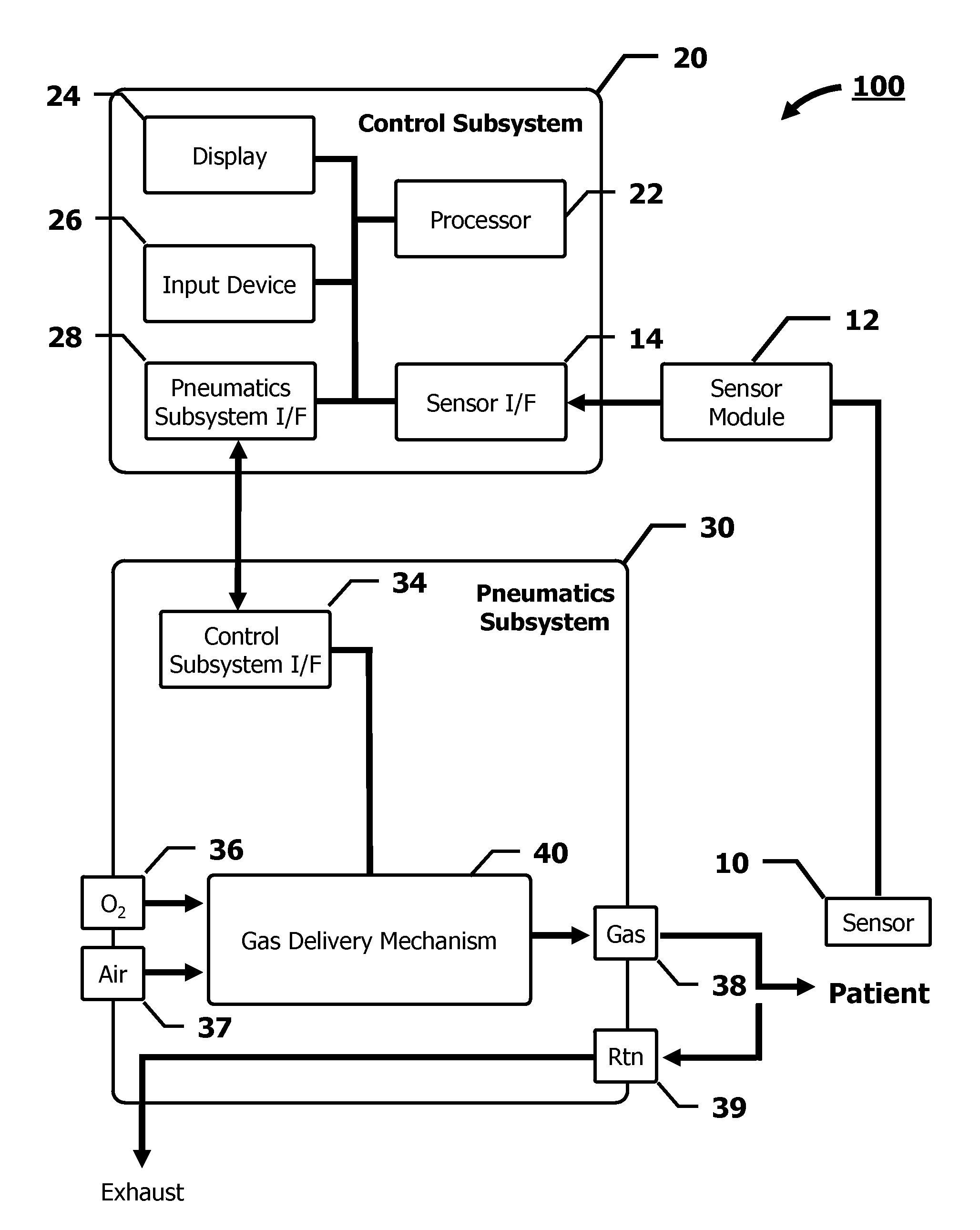
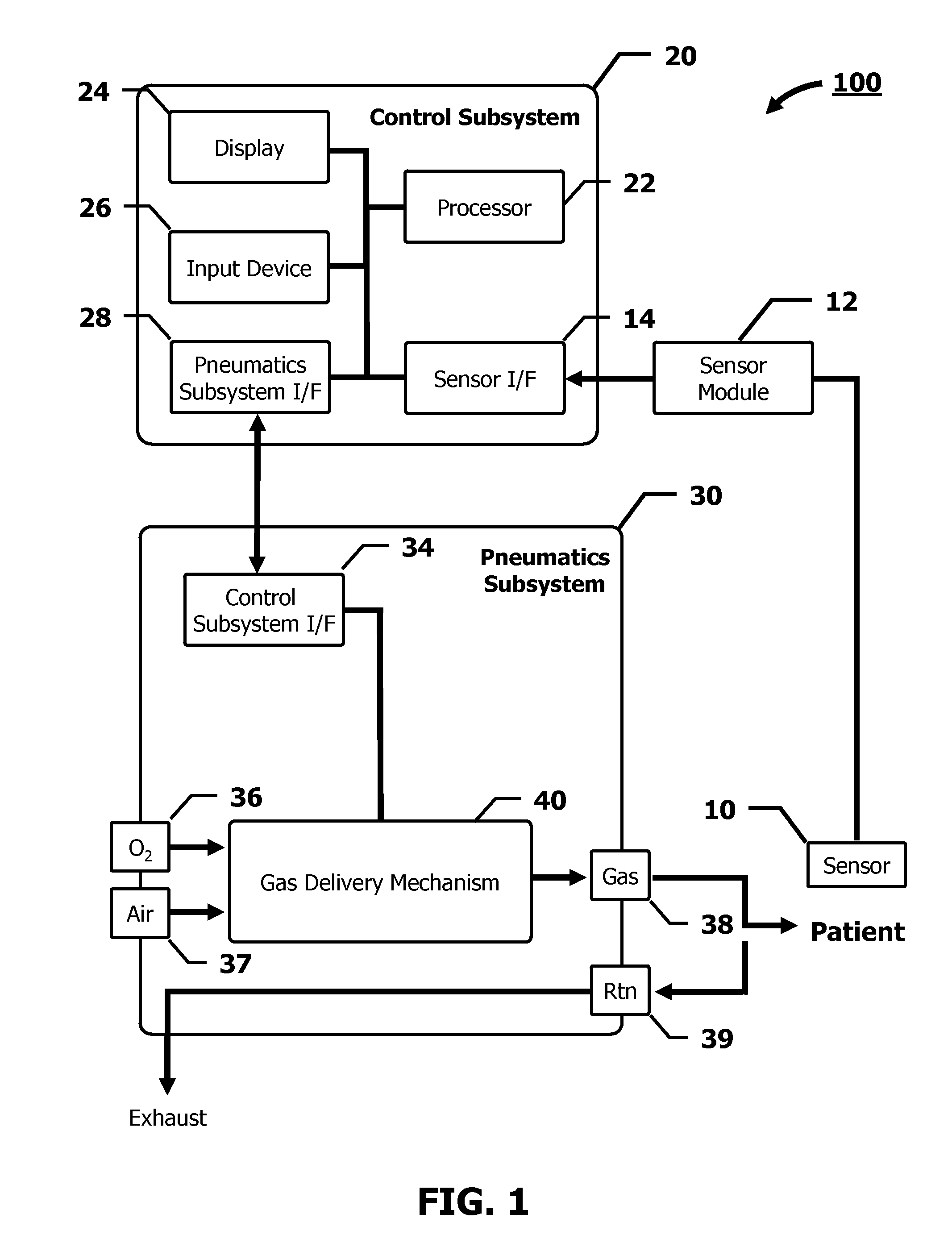
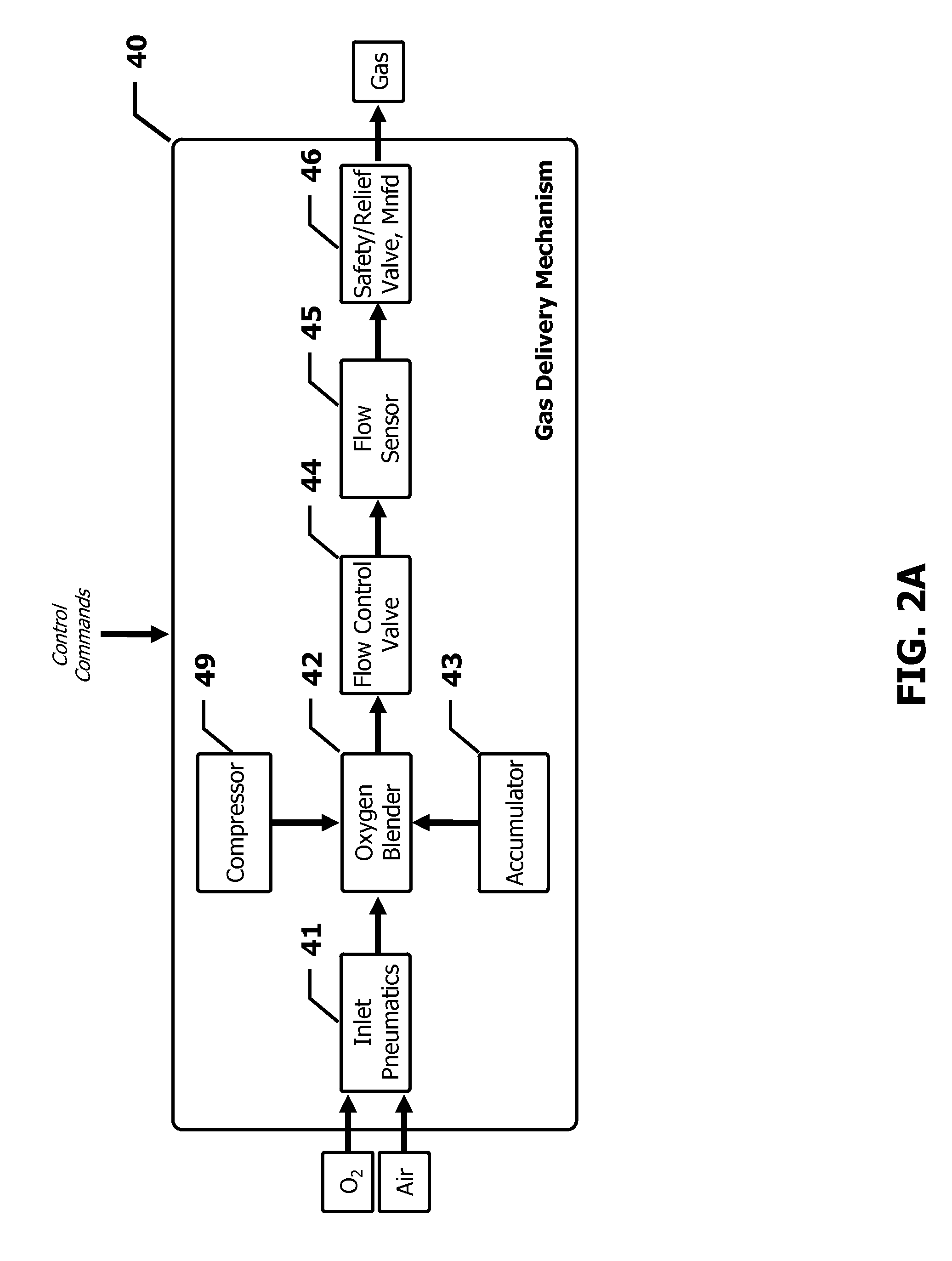
Automated Oxygen Delivery Method
InactiveUS20100224192A1Simple methodRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesOxygen deliveryIntensive care medicine
The present invention advantageously provides a method of automatically delivering oxygen to a patient. A desired concentration of oxygen in a bloodstream of a patient is received from a user. Data, including a measurement of the amount of oxygen in the bloodstream of the patient, as well as status information associated with the measurement, is received from a sensor. The measured data are determined to be valid or invalid based on the measurement value and the status information, and, based on this determination, a delivered fraction of inspired oxygen is delivered to the patient. If the measured data are determined to be valid, then the delivered fraction of inspired oxygen is based on the desired oxygen concentration and the measured data. On the other hand, if the measured data are determined to be invalid, then the delivered fraction of inspired oxygen is set to a predetermined value.
Owner:CAREFUSION
Residual map segmentation method for multi-leaf collimator-intensity modulated radiotherapy
InactiveUS6853705B2Handling using diaphragms/collimetersX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyIntensity modulate radiotherapyMulti leaf collimator
In a method for sequentially generating segment fields for use in delivering intensity modulated radiotherapy an input continuous intensity map is generated. A segment field is generated directly from the input intensity map. A residual continuous intensity map is generated that is based on the respective photon fluence contributions from the input intensity map and a fractionally intensity map corresponding to the segment field. These steps are repeated for a number of iterations to generate a like number of additional segment fields and residual maps derived therefrom. In each iteration, the residual map generated in the previous iteration is used as the input intensity map.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
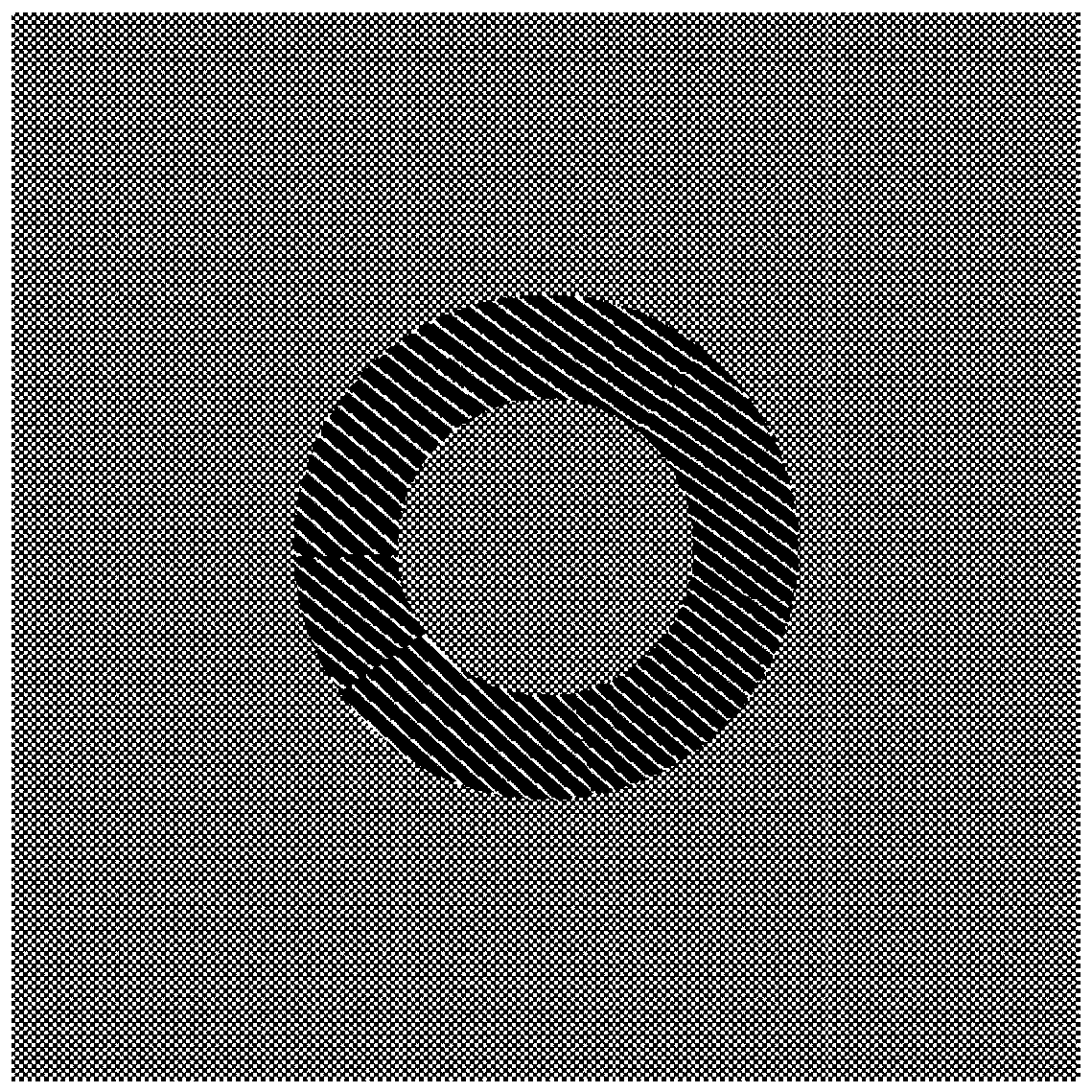
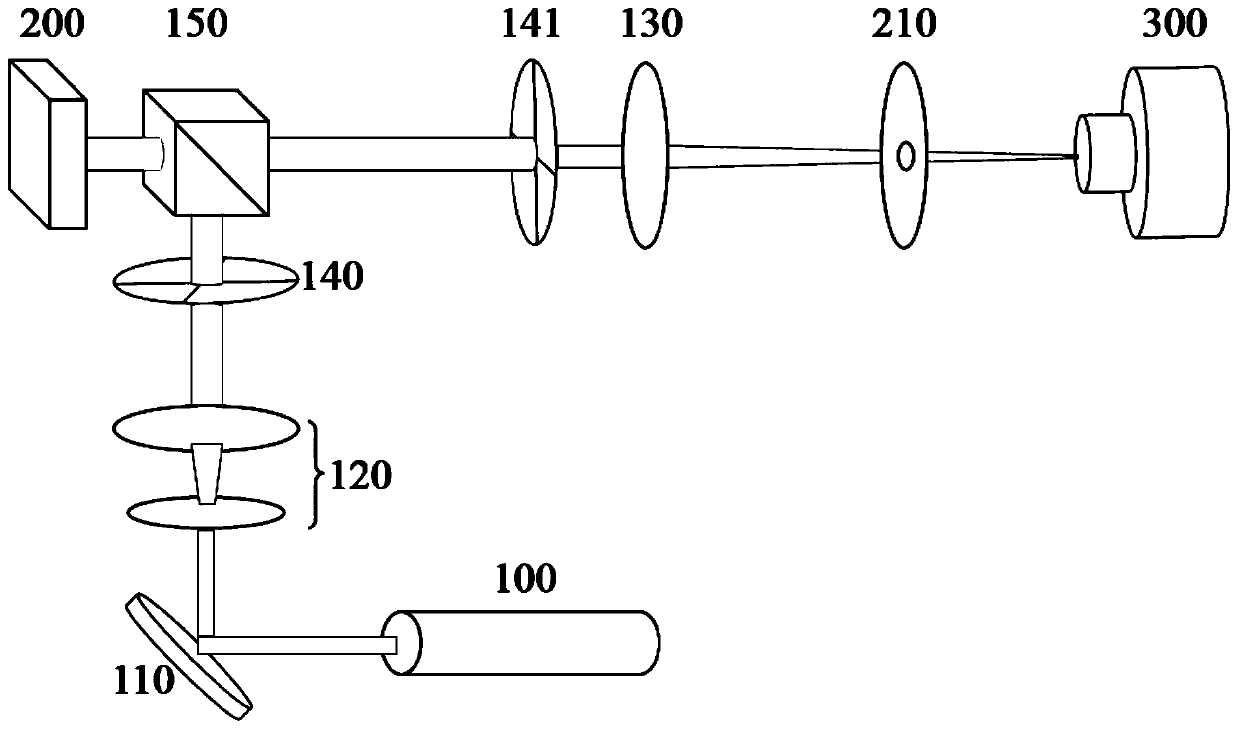
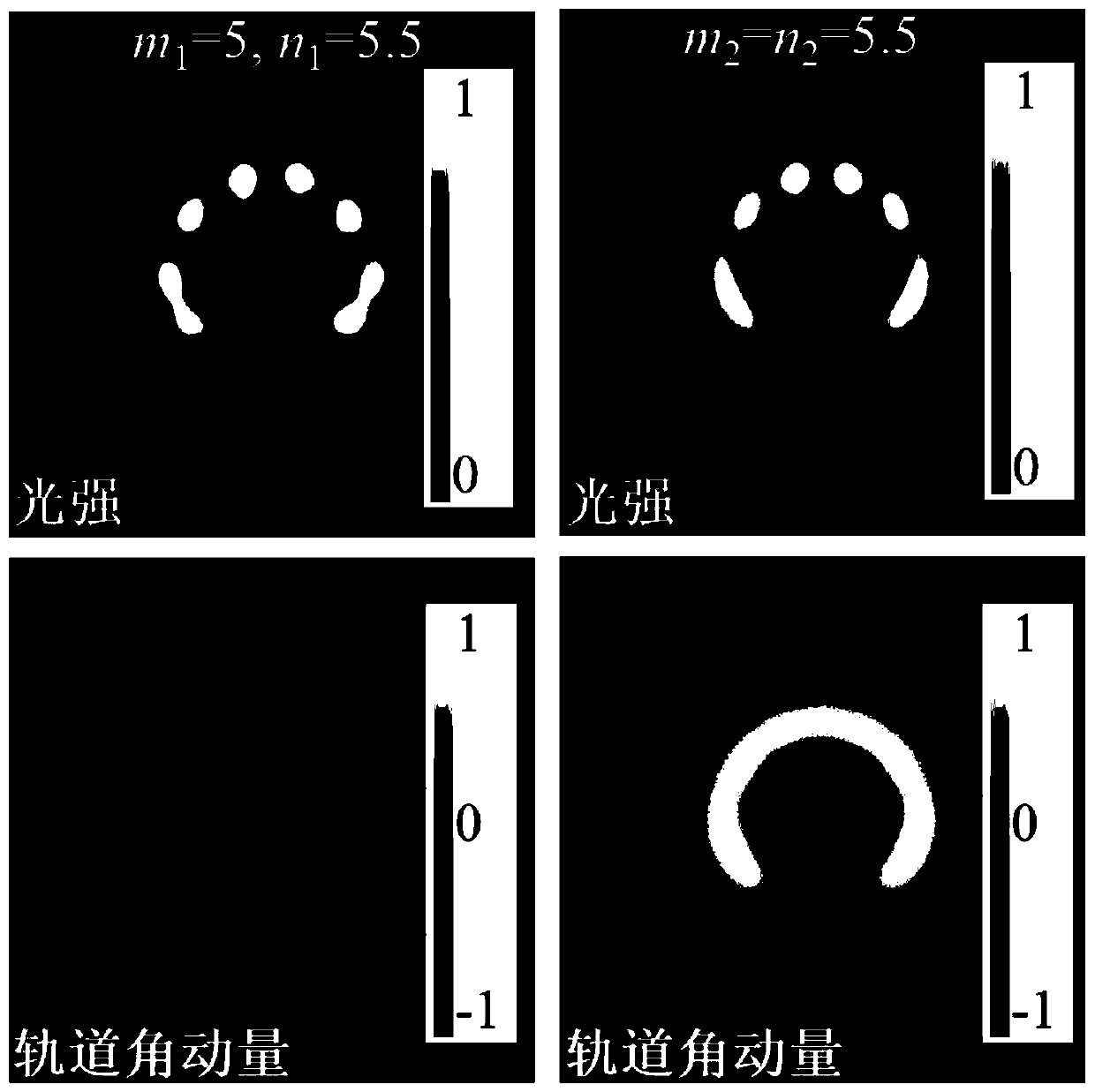
Device for measuring fractional-order optical vortex topology charge values and measuring method thereof
Provided are a device for measuring fractional-order optical vortex topology charge values and a measuring method thereof. The measuring method comprises the steps of writing generated calculating holographic images into a spatial light modulator through a computer holographic technique, acquiring wrapped phase images of vortex light beams through Michelson interference light paths and a four-step phase shifting technique, analyzing distribution of real phases theta of the vortex light beams through a phase image unwrapping algorithm, and calculating according to the topology charge definition of m=theta / 2pi to obtain topology charge values m of any fractional-order accuracy. The device and method achieve the measurement of any step (0.1 step) of topology charge values of the fractional-order vortex light beams, can correct measurement of topology charge values of vortex light beams from existing half-integer step (0.5 step) to any step and can be widely applied to measurement of topology charge values in the fields of bose-einstein condensation, quantum communication, information coding and transmission, particle confinement, optical tweezers, optical wrenches and the like.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Holographic projection method
ActiveCN102749793ABreak through the limitation of imaging distanceProjectorsGrismSpatial light modulator
The invention discloses a holographic projection method which comprises the following steps of: (10) laying projection devices: successively laying a phase spatial light modulator, a beam splitting prism, a lens and a screen, laying a mono-color laser and a polarizing film on the same side of the beam splitting prism, and connecting the phase spatial light modulator with a computer; (20) measuring the distance of an imaging face; (30) measuring and calculating the relationship between the focal length of the lens and the distance of the imaging face; (40) after determining the order of fractional Fourier transformation in the system, and carrying out iteration by using the fractional Fourier transformation formula and the inverse transformation formula to obtain the phase of a two-dimensional image; and (50) transmitting the phase hologram to the phase spatial light modulator via the computer, and projecting the phase hologram onto the screen in the specific location by using the phase spatial light modulator. With the holographic projection method, the holographic reconstructed two-dimensional image can be projected onto any plane behind the lens, and the focal length of the lens does not need to be changed to control the distance of imaging.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
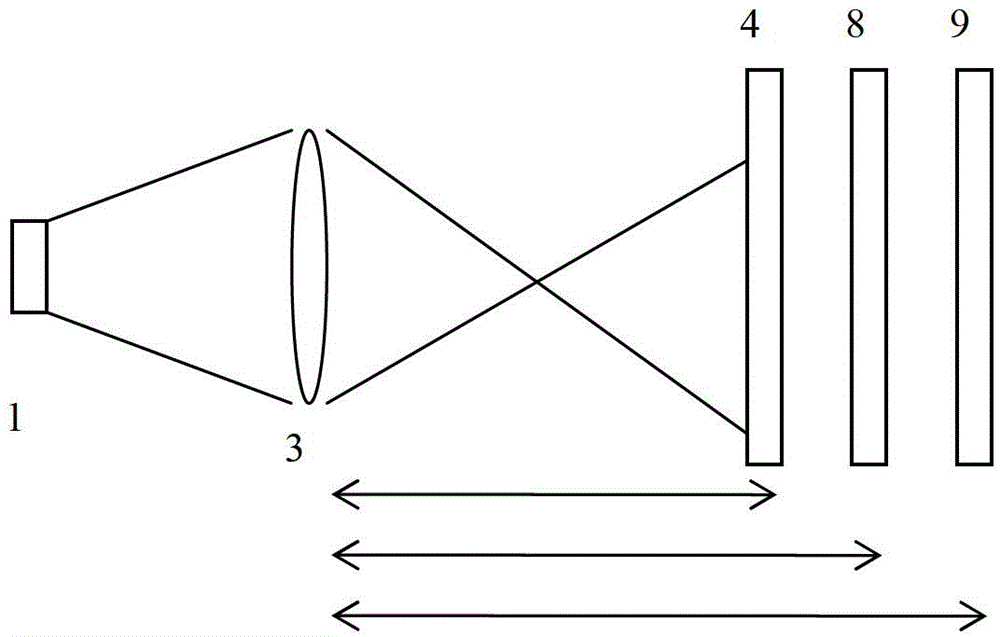
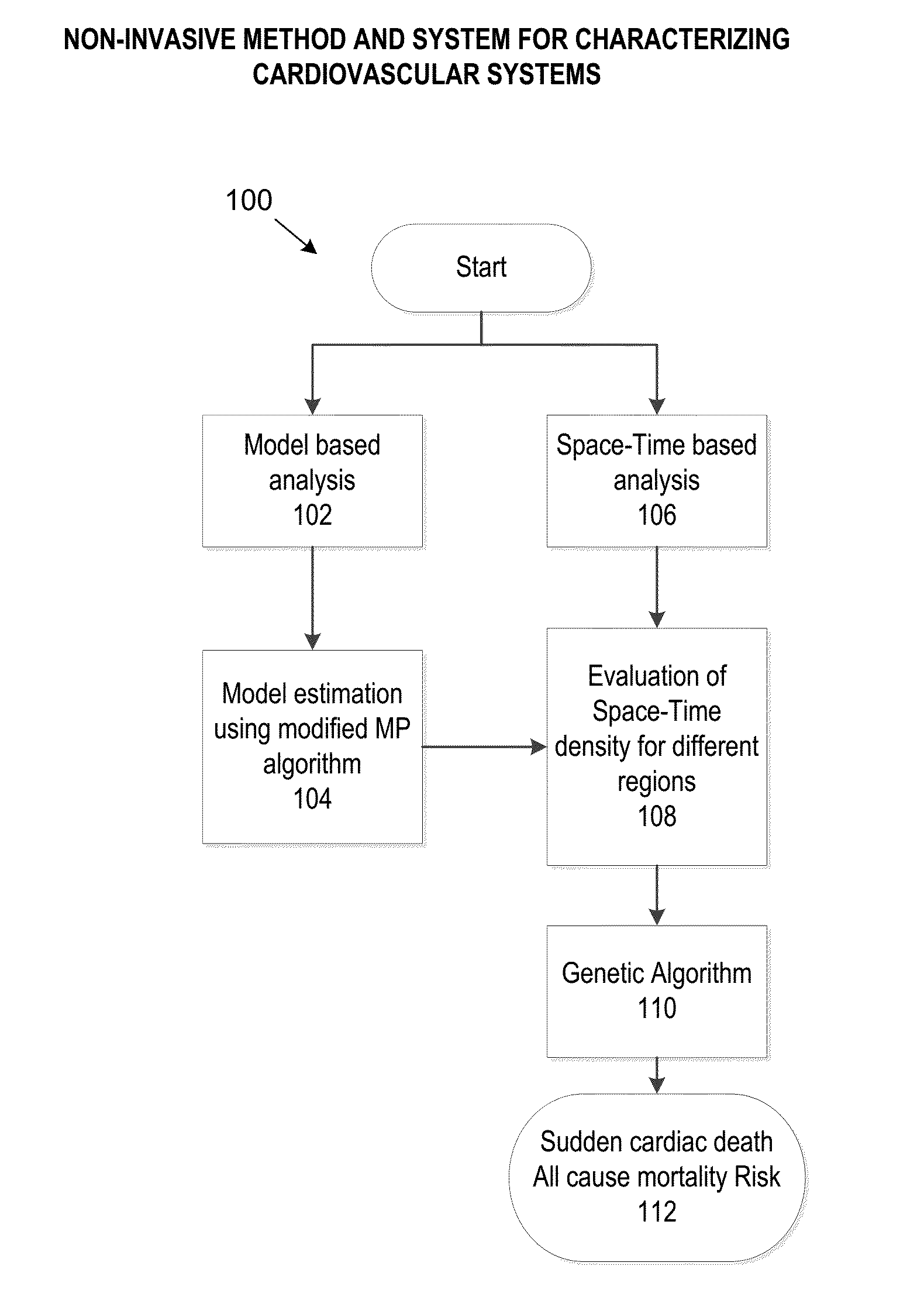
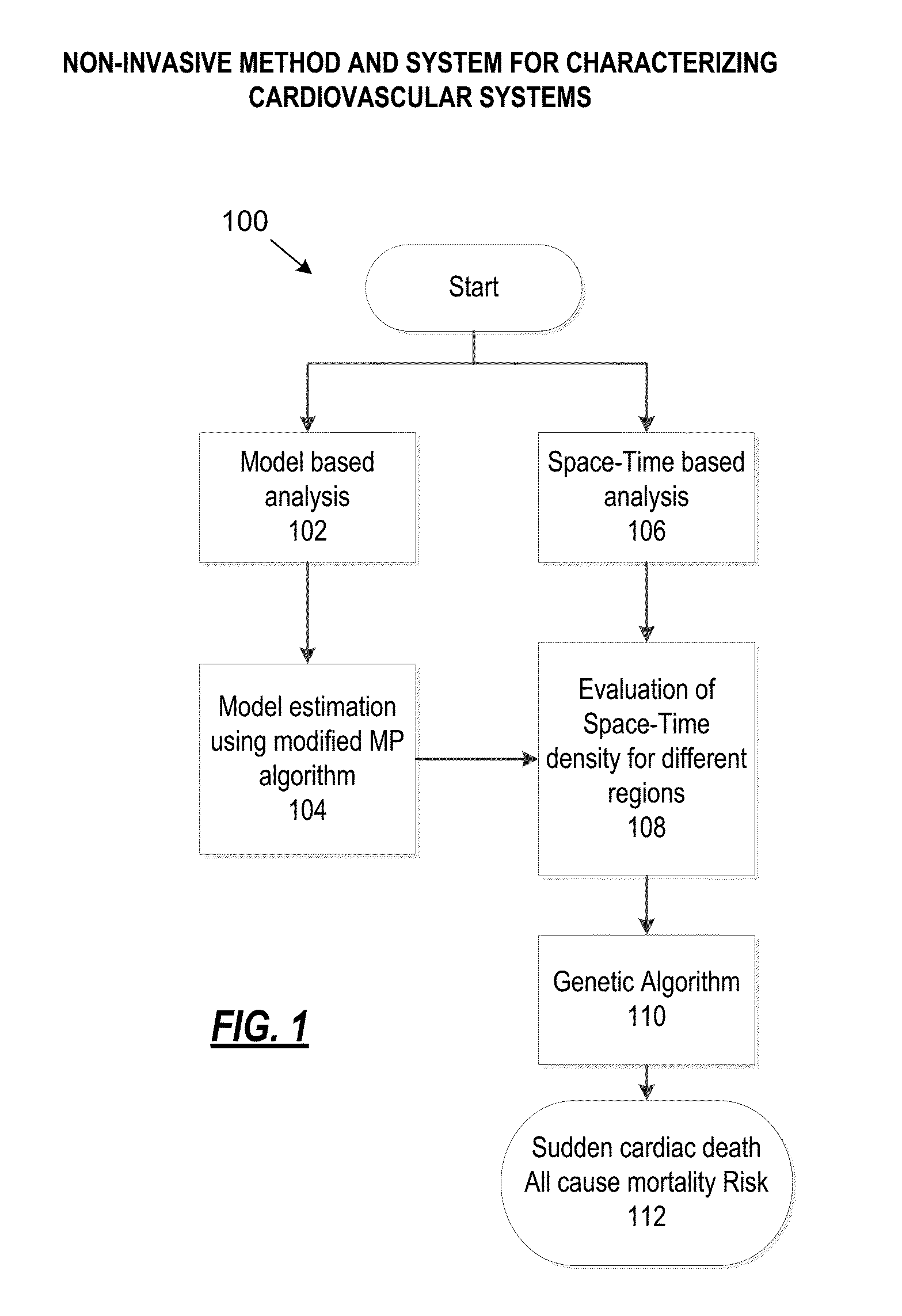
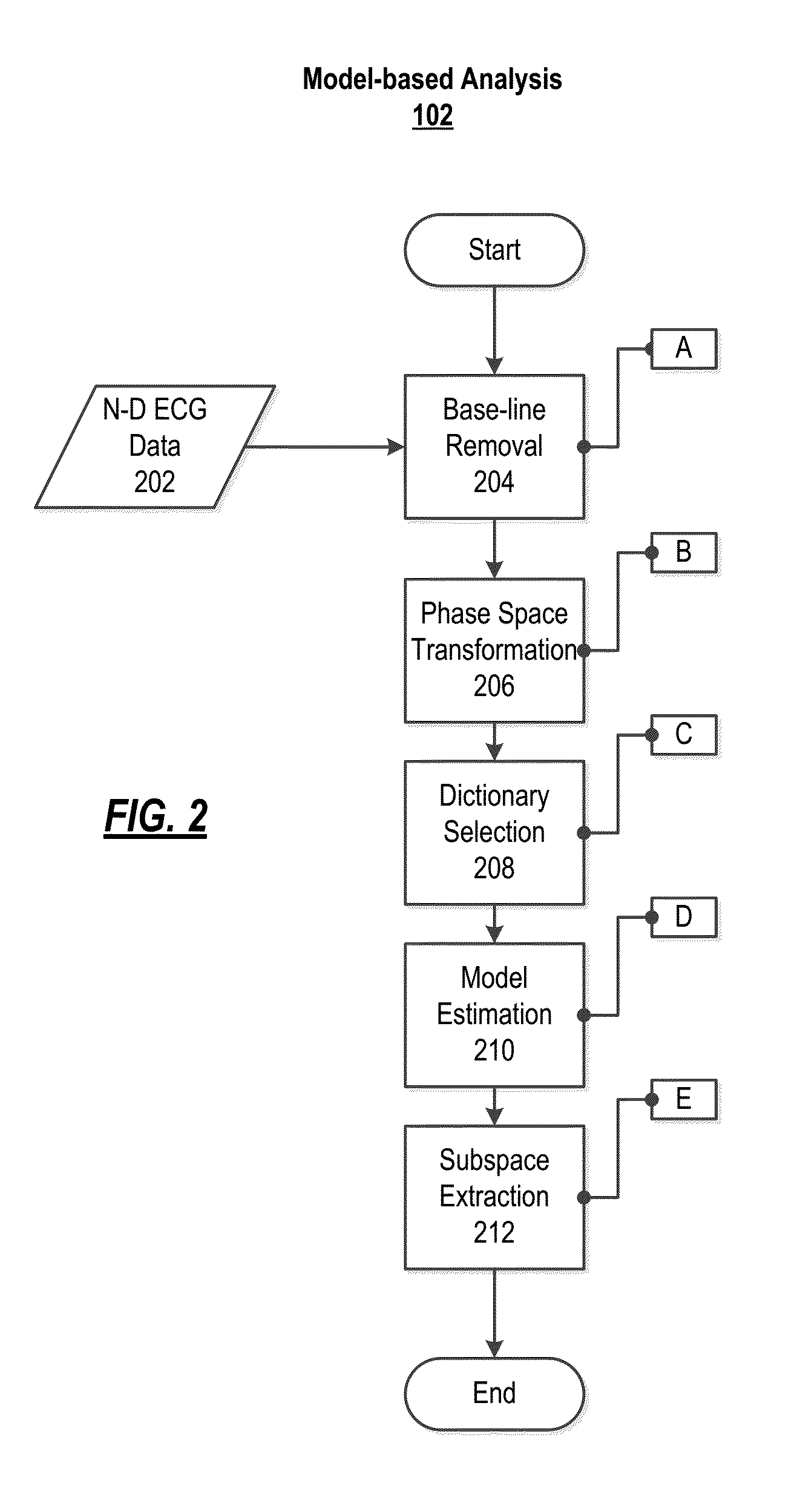
Method and system for characterizing cardiovascular systems from single channel data
ActiveUS20150216426A1Cumbersome to executeBroaden applicationMedical simulationElectrocardiographyDiseaseCardiac defects
Methods to identify and risk stratify disease states, cardiac structural defects, functional cardiac deficiencies induced by teratogens and other toxic agents, pathological substrates, conduction delays and defects, and ejection fraction using single channel biological data obtained from the subject. A modified Matching Pursuit (MP) algorithm may be used to find a noiseless model of the data that is sparse and does not assume periodicity of the signal. After the model is derived, various metrics and subspaces are extracted to characterize the cardiac system. In another method, space-time domain is divided into a number of regions (which is largely determined by the signal length), the density of the signal is computed in each region and input to a learning algorithm to associate them to the desired cardiac dysfunction indicator target.
Owner:ANALYTICS FOR LIFE
Non-linear software correction method of linear frequency modulated continuous wave radar
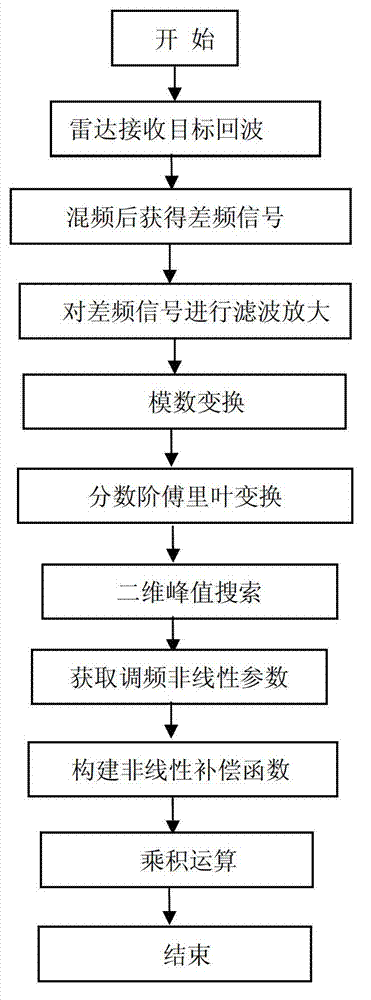
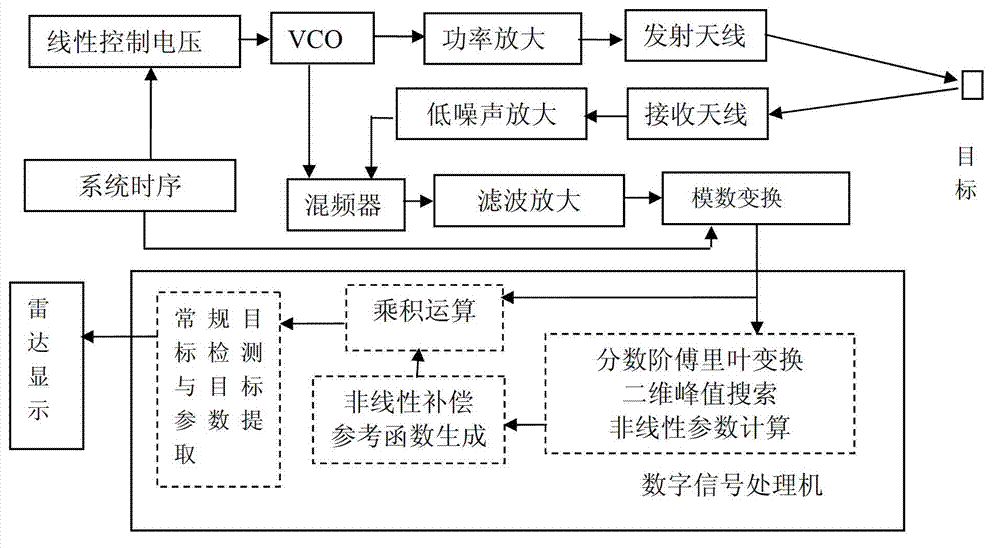
InactiveCN102901954AEasy to detectHigh precisionWave based measurement systemsPeak valueCorrection method
The invention provides a non-linear software correction method of a linear frequency modulated continuous wave radar, belonging to the technical field of signal treatment and detection. The non-linear software correction method particularly comprises the following steps of: in a linear frequency modulated continuous wave radar receiver, carrying out analogue-to-digital conversion on amplified and filtered video echo receiving signals into digital signals; secondly, carrying out fractional order Fourier transform analysis on the digital echo signals; carrying out peak value search on a fractional order Fourier transform result in two dimensions of an order quantity and a transform frequency domain, wherein the fractional order and the frequency which correspond to a peak value show main and target time delay of non-linear frequency modulation; and calculating to obtain a frequency modulated non-linear parameter until the treatment process of the method can be completed. With the adoption of the method provided by the invention, the frequency modulated non-linear parameter can be obtained for establishing a non-linear correction reference function. The non-linear influence in the echo signals can be effectively removed by convolving the reference function and the radar echo signals.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF TECH & EDUCATION TEACHER DEV CENT OF CHINA VOCATIONAL TRAINING & GUIDANCE
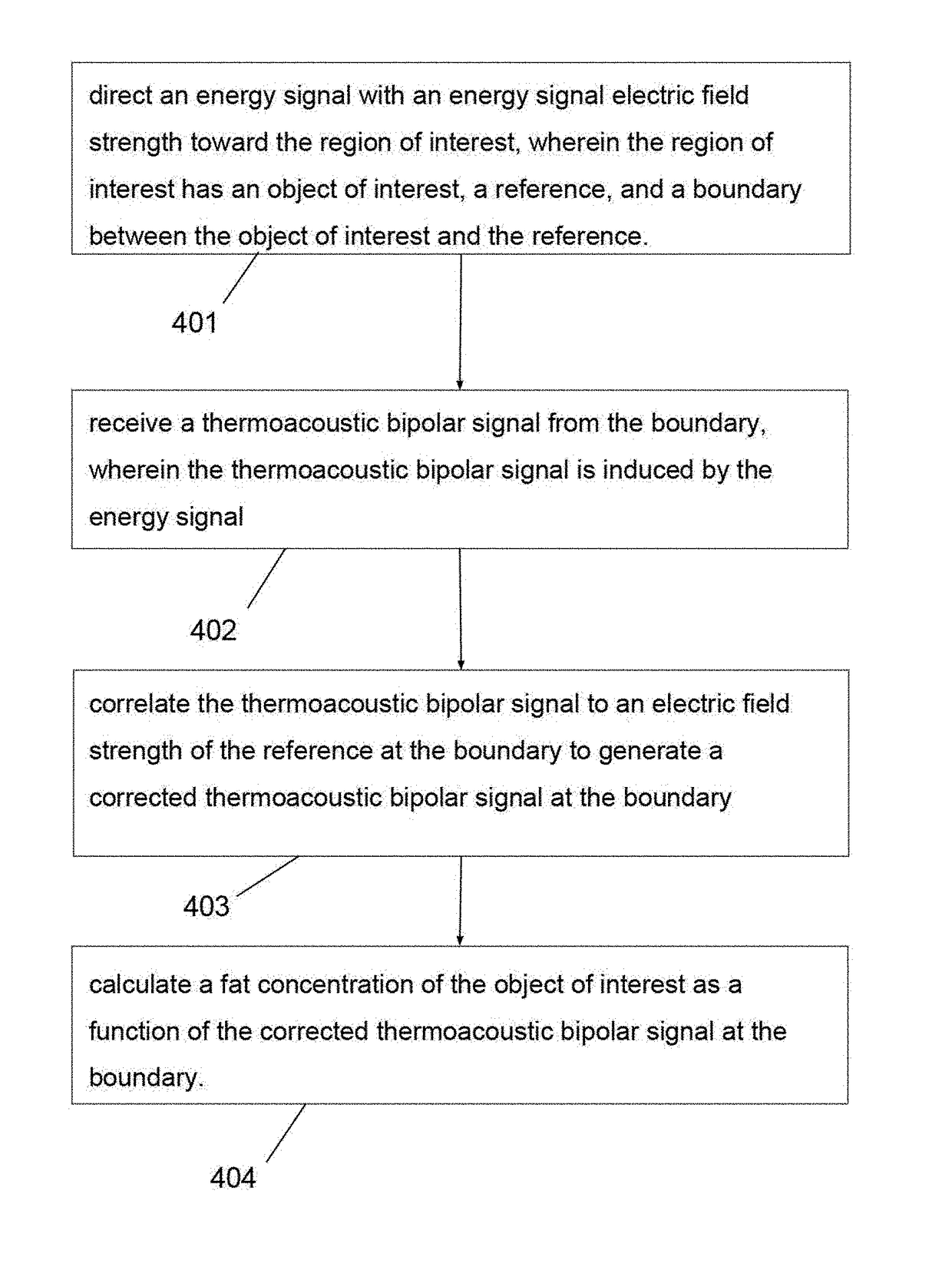
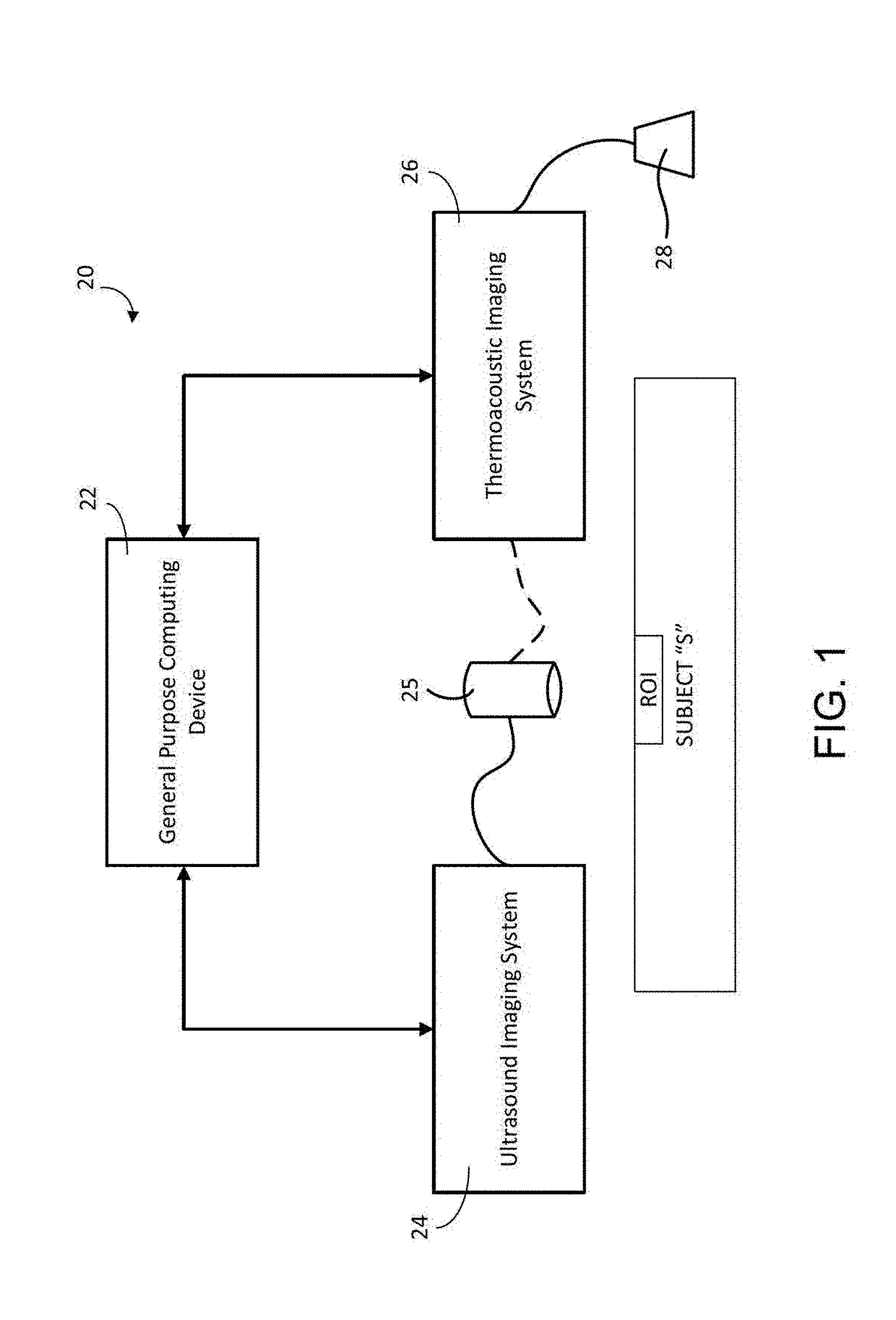
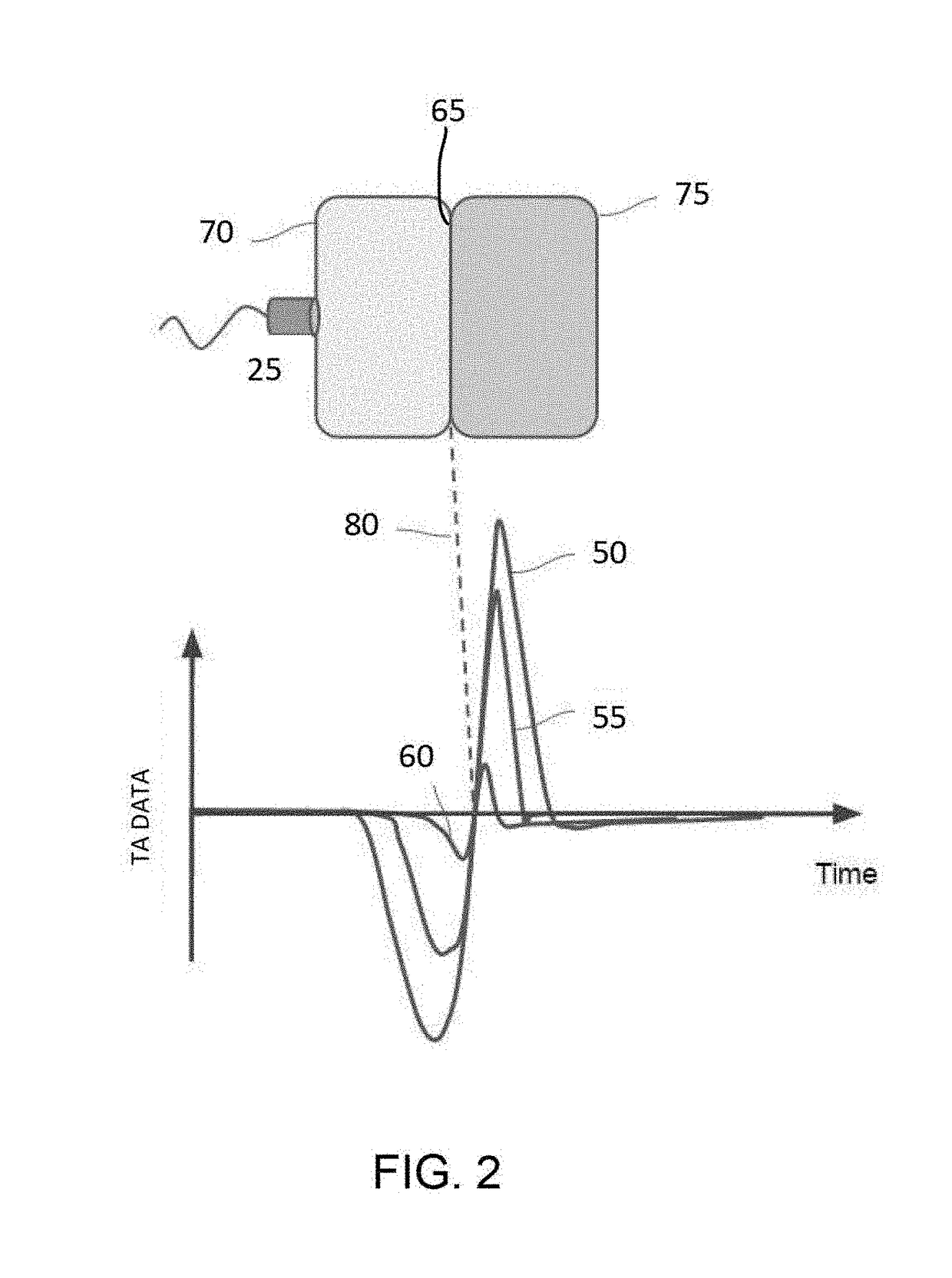
Method and system for estimating fractional fat content of an object
ActiveUS9888879B1Organ movement/changes detectionDiagnostic recording/measuringUltrasonic sensorBipolar signal
A method and system for estimating fractional fat content of an object of interest. An energy emitter is used to direct an energy signal with an energy signal electric field strength toward the region of interest, wherein the region of interest has an object of interest, a reference, and a boundary between the object of interest and the reference. Next, a thermoacoustic or ultrasonic transducer is used to receive a thermoacoustic bipolar signal from the boundary, wherein the thermoacoustic bipolar signal is induced by the energy signal. Finally, a machine is used to accept data from the energy emitter and thermoacoustic or ultrasonic transducer, correlate the thermoacoustic bipolar signal to an electric field strength of the reference at the boundary to generate a corrected thermoacoustic bipolar signal at the boundary, and calculate a fat concentration of the object of interest as a function of the corrected thermoacoustic bipolar signal at the boundary.
Owner:ENDRA LIFE SCI INC
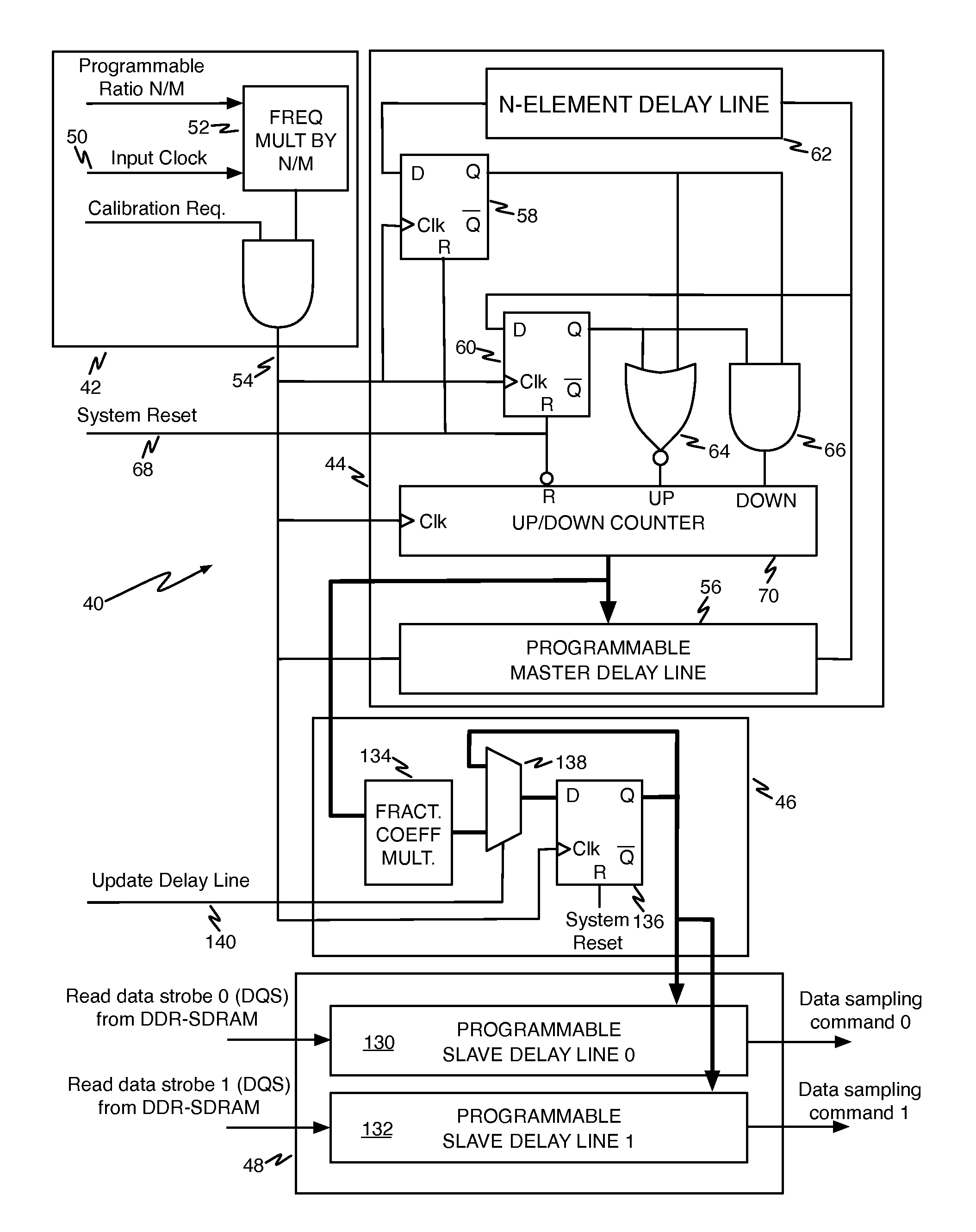
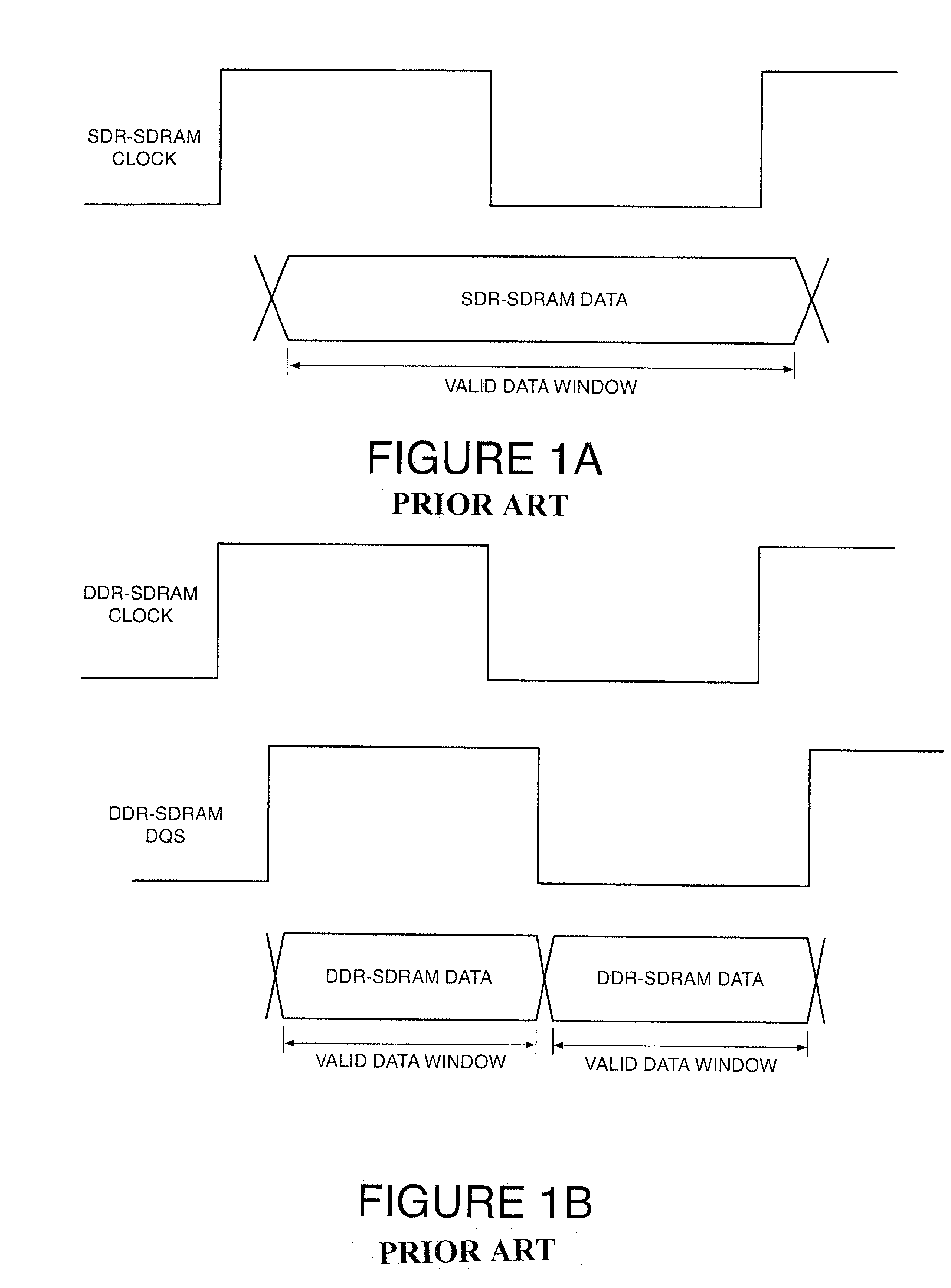
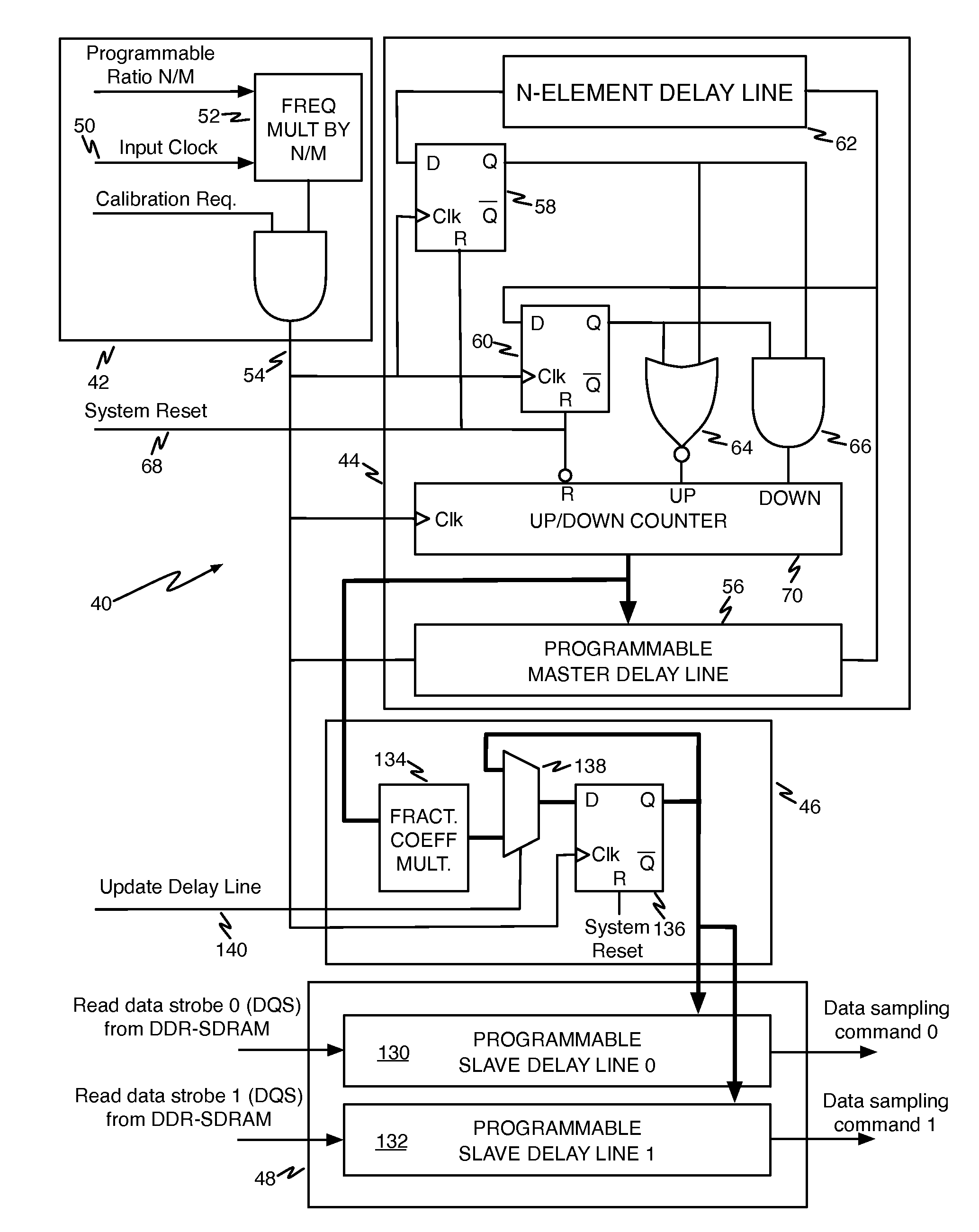
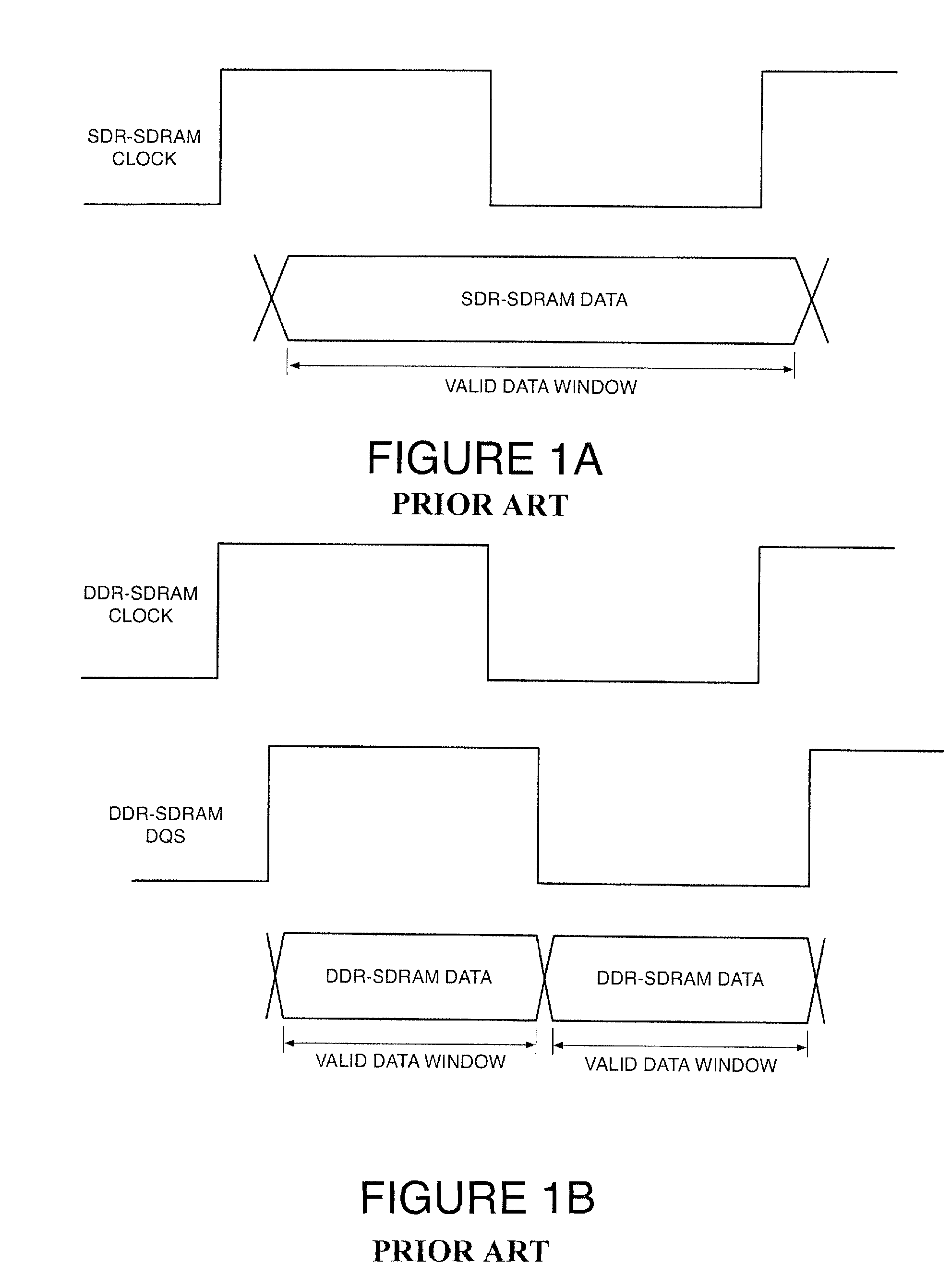
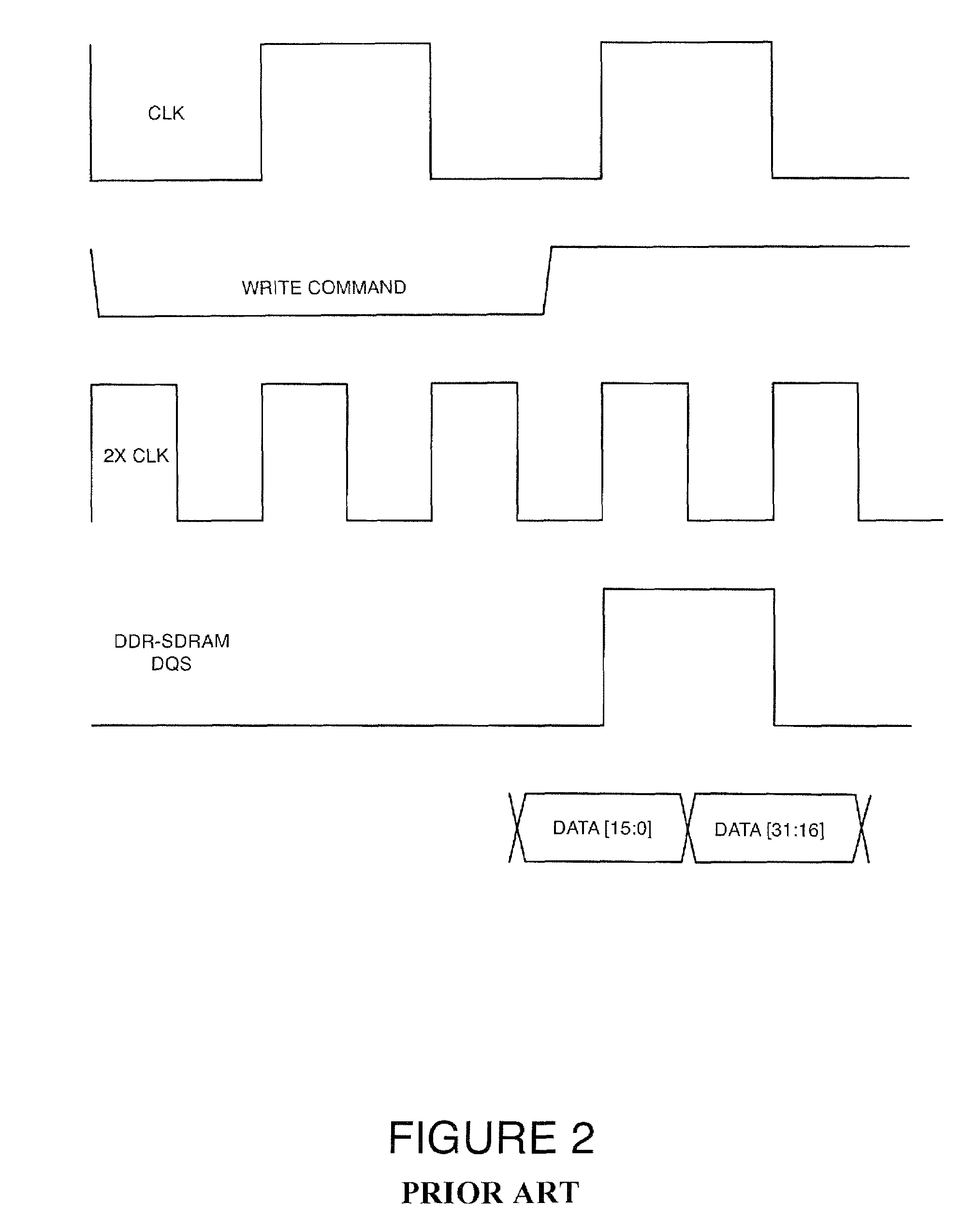
Circuits to delay a signal from ddr-sdram memory device including an automatic phase error correction
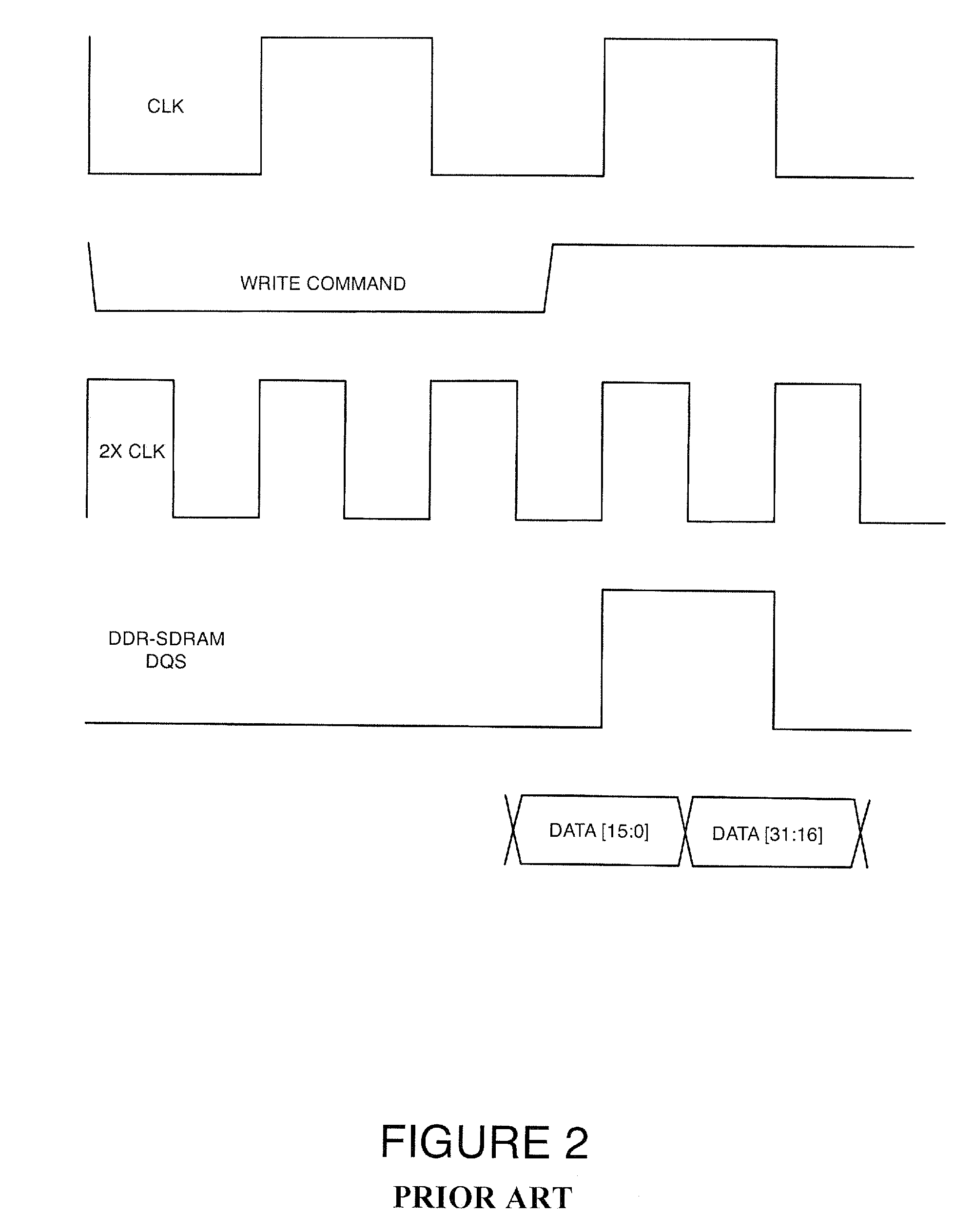
A method for delaying a control signal, includes receiving a clock signal, determining a number of delay elements required to generate a first delay equal to a target amount of the period of the clock signal, receiving a data signal having an edge generated at the same time as an edge of the control signal, determining a fraction number equal to the number of delay elements needed to generate a second delay for the data signal or the control signal to align their edges, divided by the number of cascaded delay elements necessary to provide a delay equal to the target amount of the period of the clock signal, multiplied by the number of delay elements to generate the first delay, and delaying the control signal by the number of cascaded delay elements to relaize said first delay altered by the fraction number of delay elements.
Owner:ATMEL CORP
System and method for diagnosing pathologic heart conditions
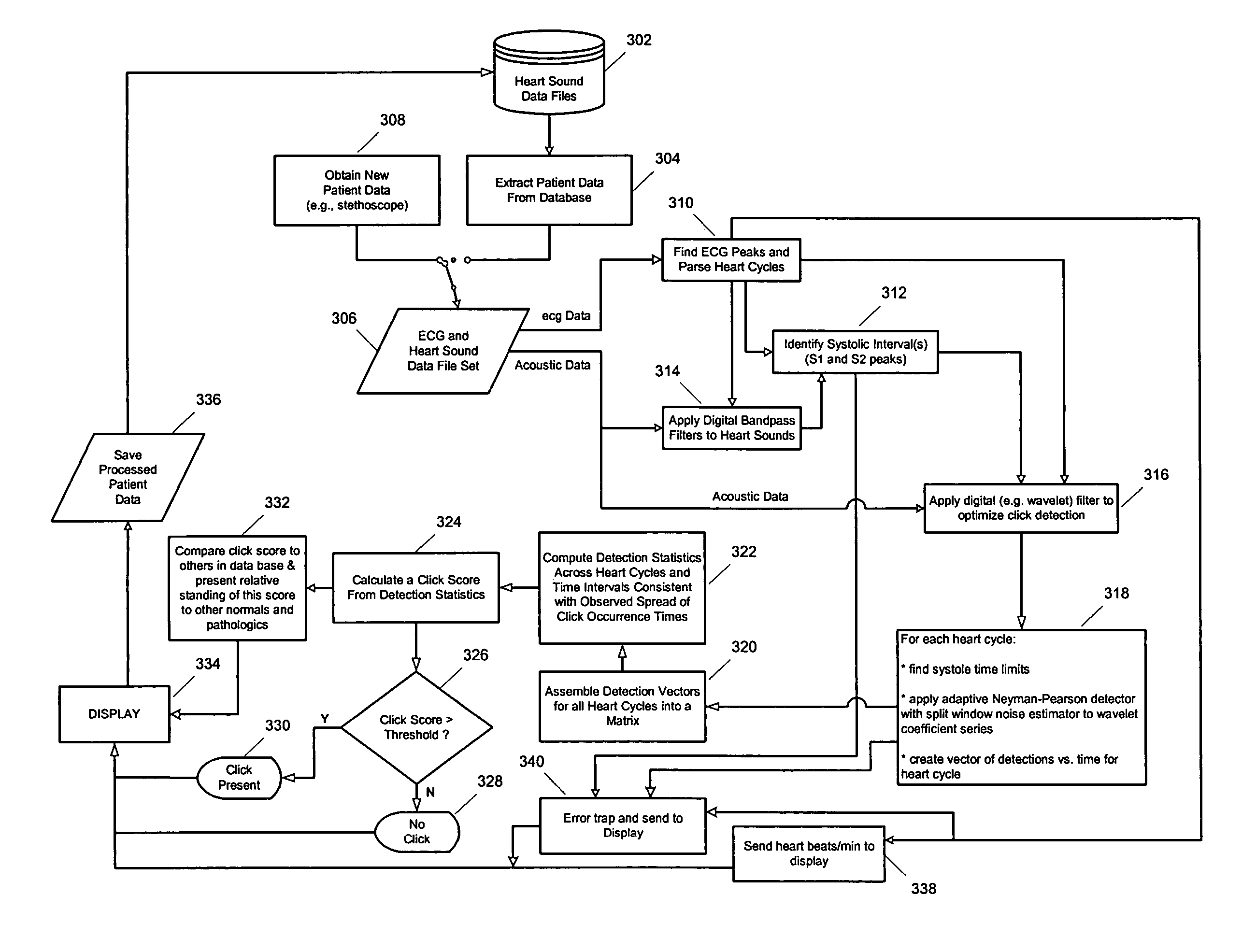
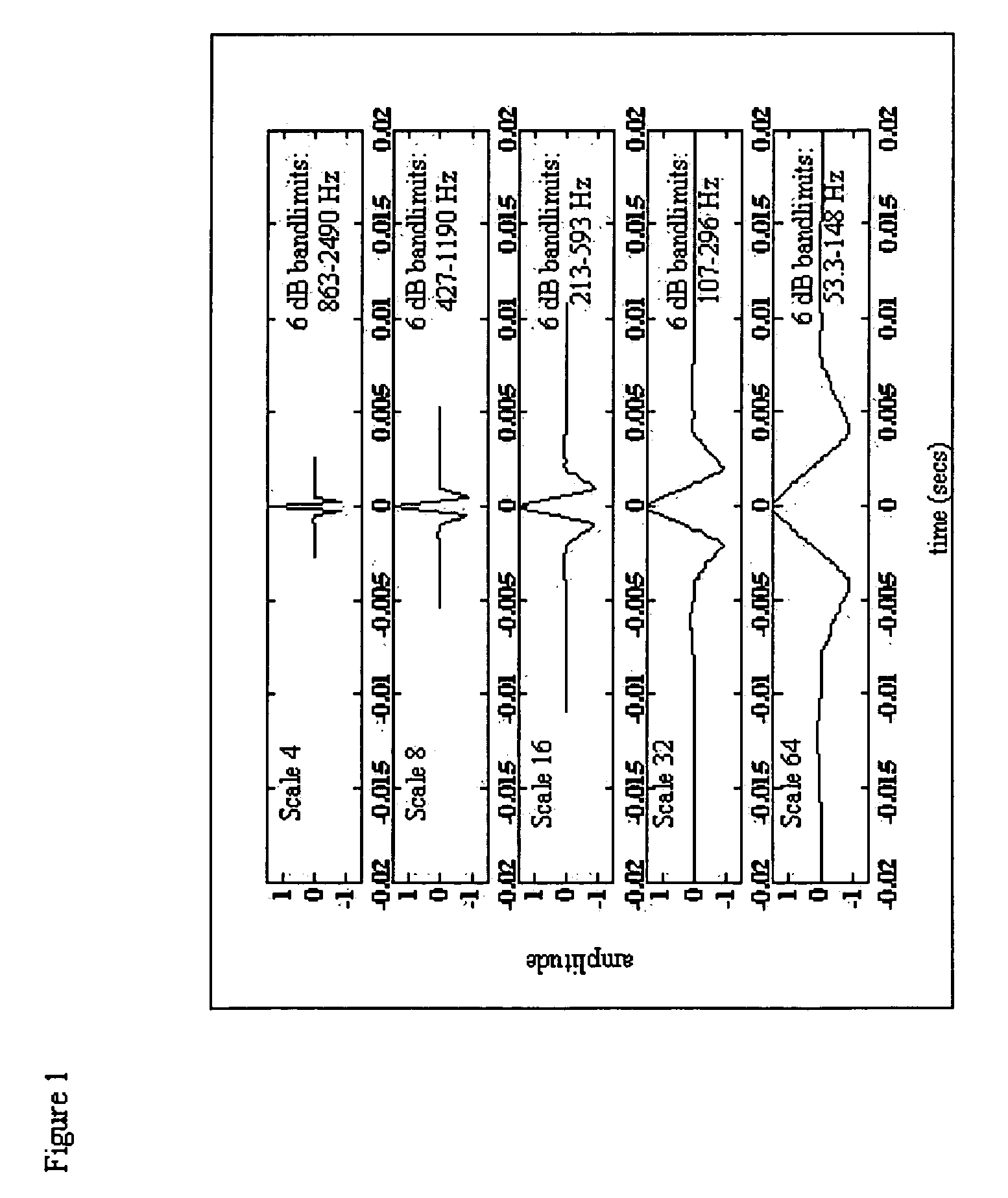
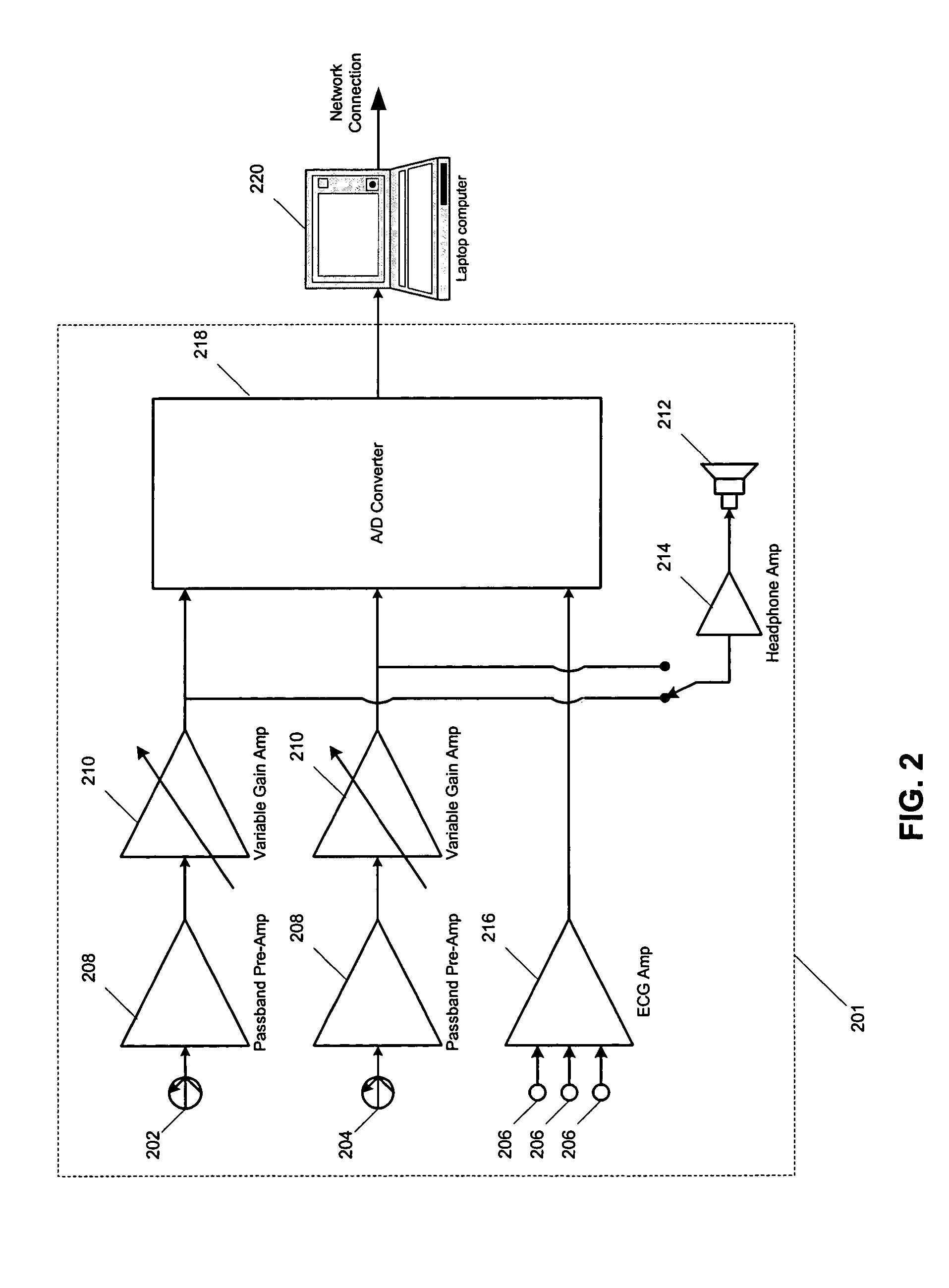
A method of diagnosing pathologic heart conditions in which a time series of heart sounds is filtered and parsed into a sequence of individual heart cycles. A systolic interval as well as systolic sub-intervals are identified for each heart cycle. The systolic intervals and ECG peaks are then digitally filtered to optimize for click detection. For each heartcycle, systole time limits are determined, a time series of the transform at specific wavelet scales are input to a Neyman-Pearson “constant false alarm rate” (CFAR) detector to identify anomalously high wavelet coefficients, and a vector of detections vs. time is created. The series of anomalously high detections (one series for each heart cycle) are then assembled into a matrix and convolved with an averaging vector yielding detection statistics across heart cycles and time intervals consistent with an observed spread of click occurrence times. A click score is then determined as the maximum element of the vector formed by the median wavelet coefficient amplitude across heart cycles squared at each time sample multiplied element-wise by the vector formed by the sum across heart cycles of the number of detections at each time sample. The click score is compared to a threshold value set by a desired probability of detection vs. a probability of false alarm tradeoff. If the click score is less than the threshold then a “no click” indicator is displayed. If the click score is greater than the threshold then a “click present” indicator is displayed.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
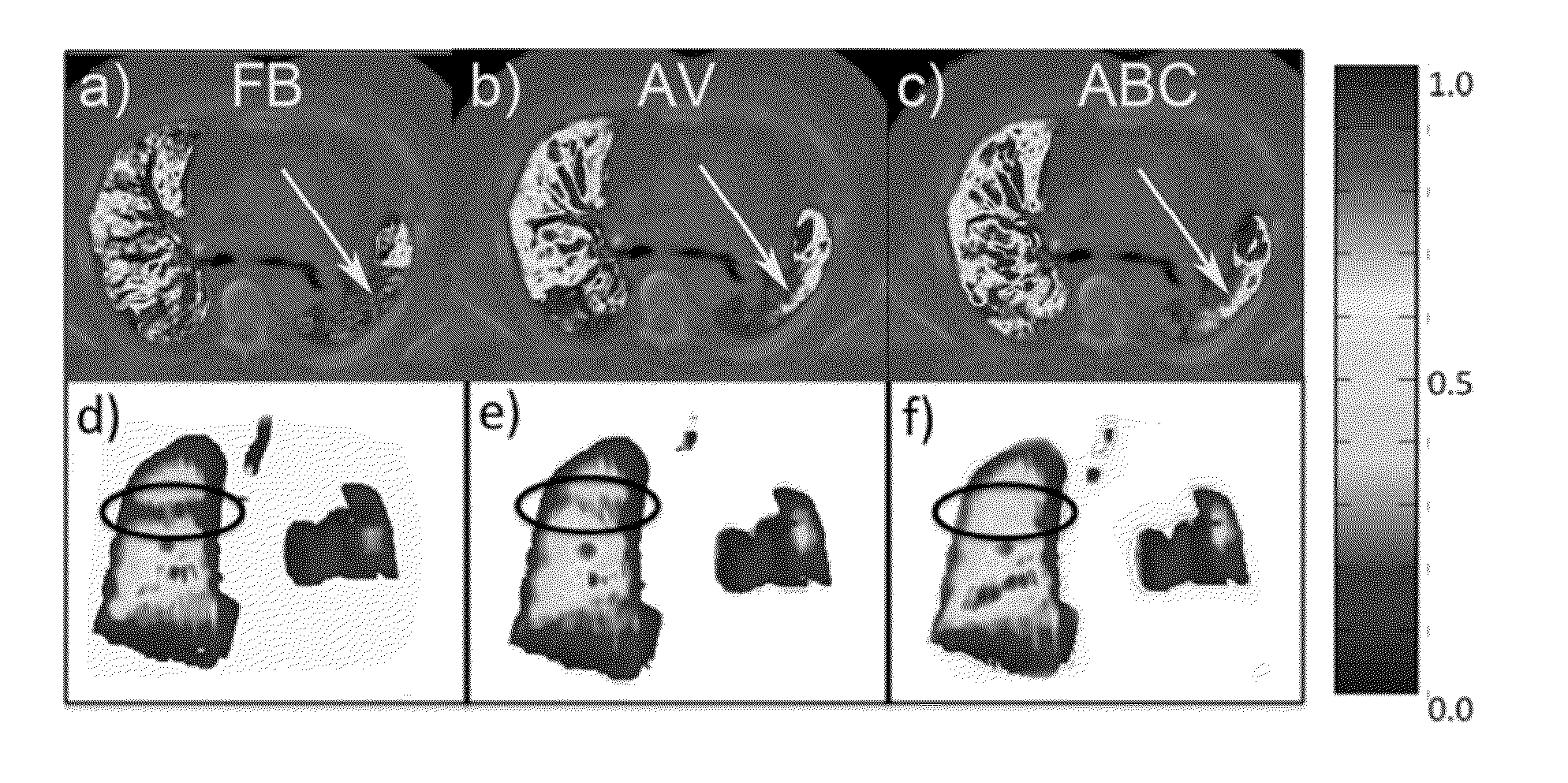
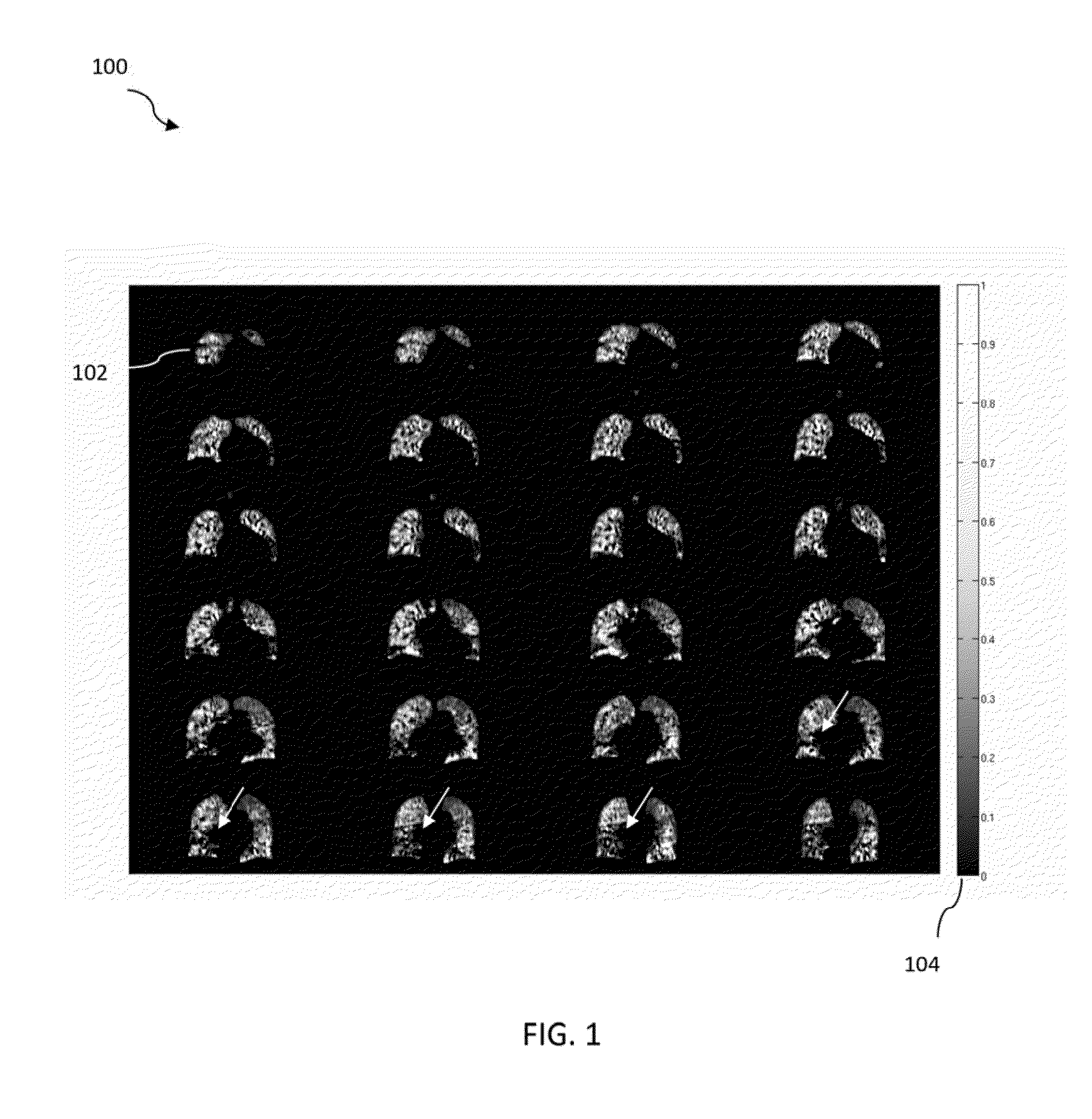
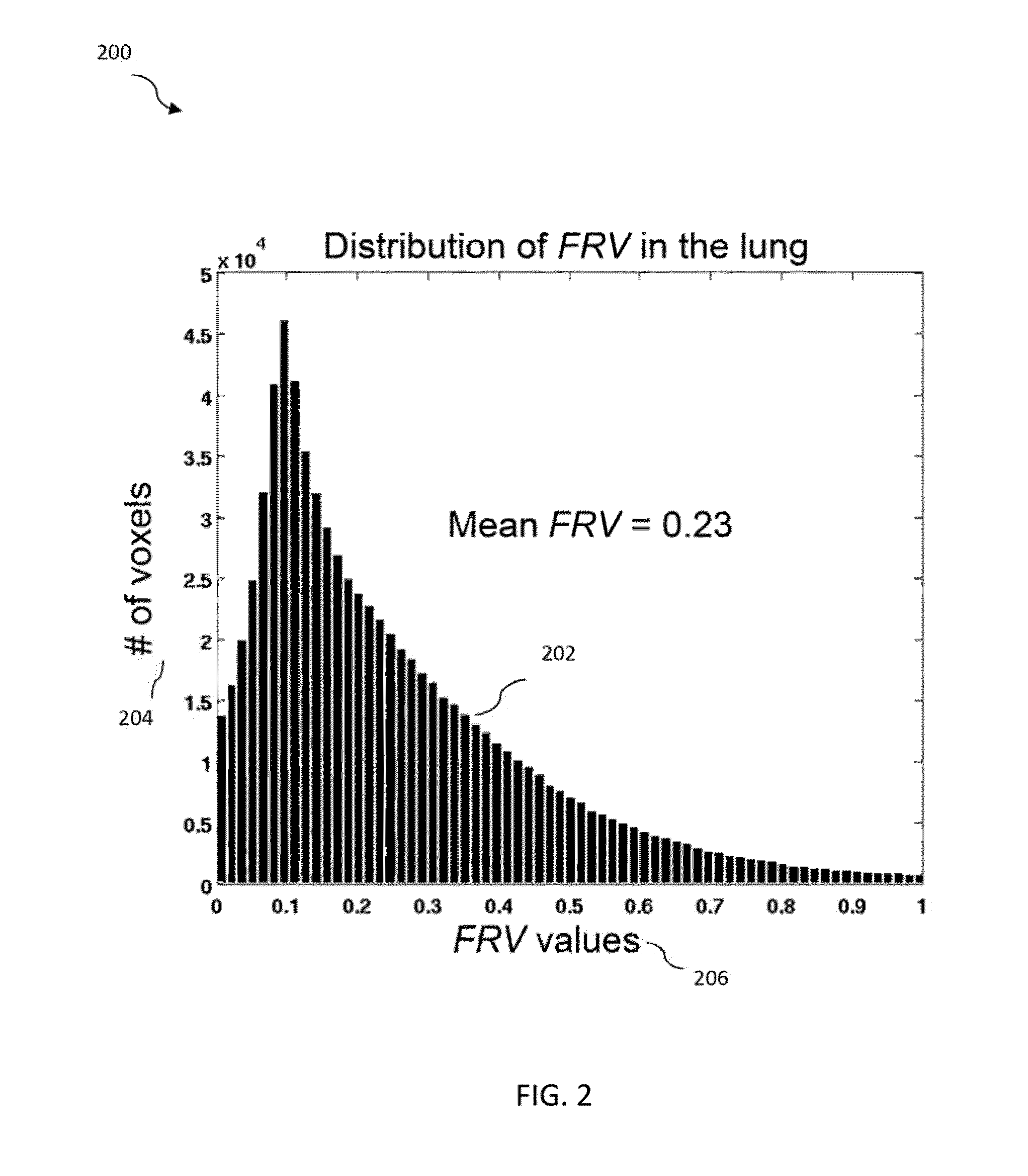
Quantitative evaluation of fractional regional ventilation using four-dimensional computed tomography
InactiveUS20130303899A1Noise minimizationHealth-index calculationDiagnostic recording/measuringVoxelRadiology
Methods and systems for determining fractional regional ventilation are disclosed. A method includes obtaining first and second lung image data indicative of a first phase and a second phase of a respiratory cycle, respectively, determining an apparent mass ratio k based on the first lung image data and the second lung image data, determining first and second spatially matched lung image data, each including N voxels, based on the first lung image data and the second lung image data, and determining at least one fractional regional ventilation value (FRV value), in accordance with a first equation FRV(n)=(k·ρ2_n−ρ1_n) / ρ1_n. The value of n is a voxel index, ρ1_n is indicative of a density of a voxel n of the first spatially matched lung image data, and ρ2_n is indicative of a density of a voxel n of the second spatially matched lung image data.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
Circuits to delay a signal from DDR-SDRAM memory device including an automatic phase error correction
A method for delaying a control signal, includes receiving a clock signal, determining a number of delay elements required to generate a first delay equal to a target amount of the period of the clock signal, receiving a data signal having an edge generated at the same time as an edge of the control signal, determining a fraction number equal to the number of delay elements needed to generate a second delay for the data signal or the control signal to align their edges, divided by the number of cascaded delay elements necessary to provide a delay equal to the target amount of the period of the clock signal, multiplied by the number of delay elements to generate the first delay, and delaying the control signal by the number of cascaded delay elements to realize said first delay altered by the fraction number of delay elements.
Owner:ATMEL CORP
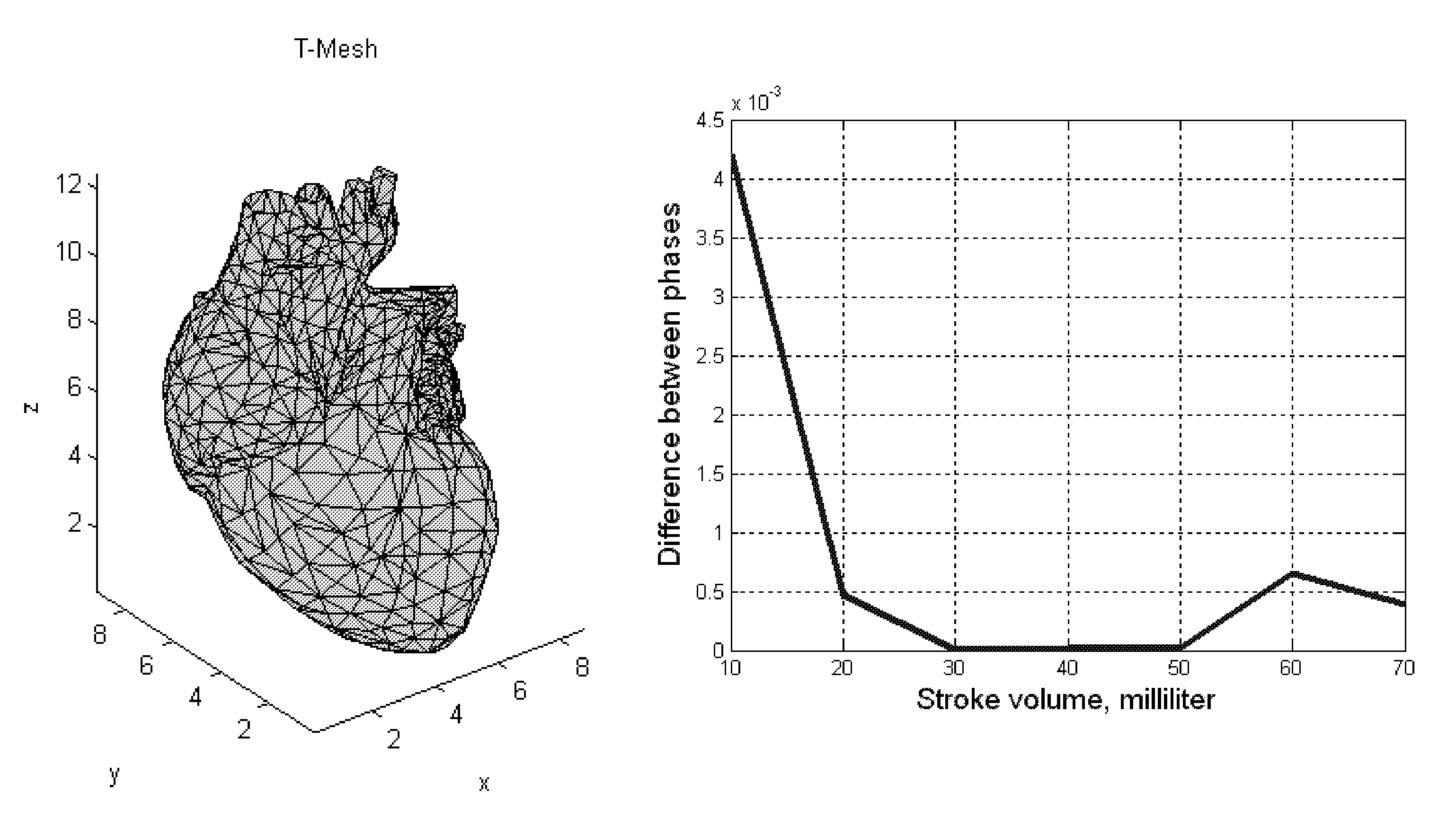
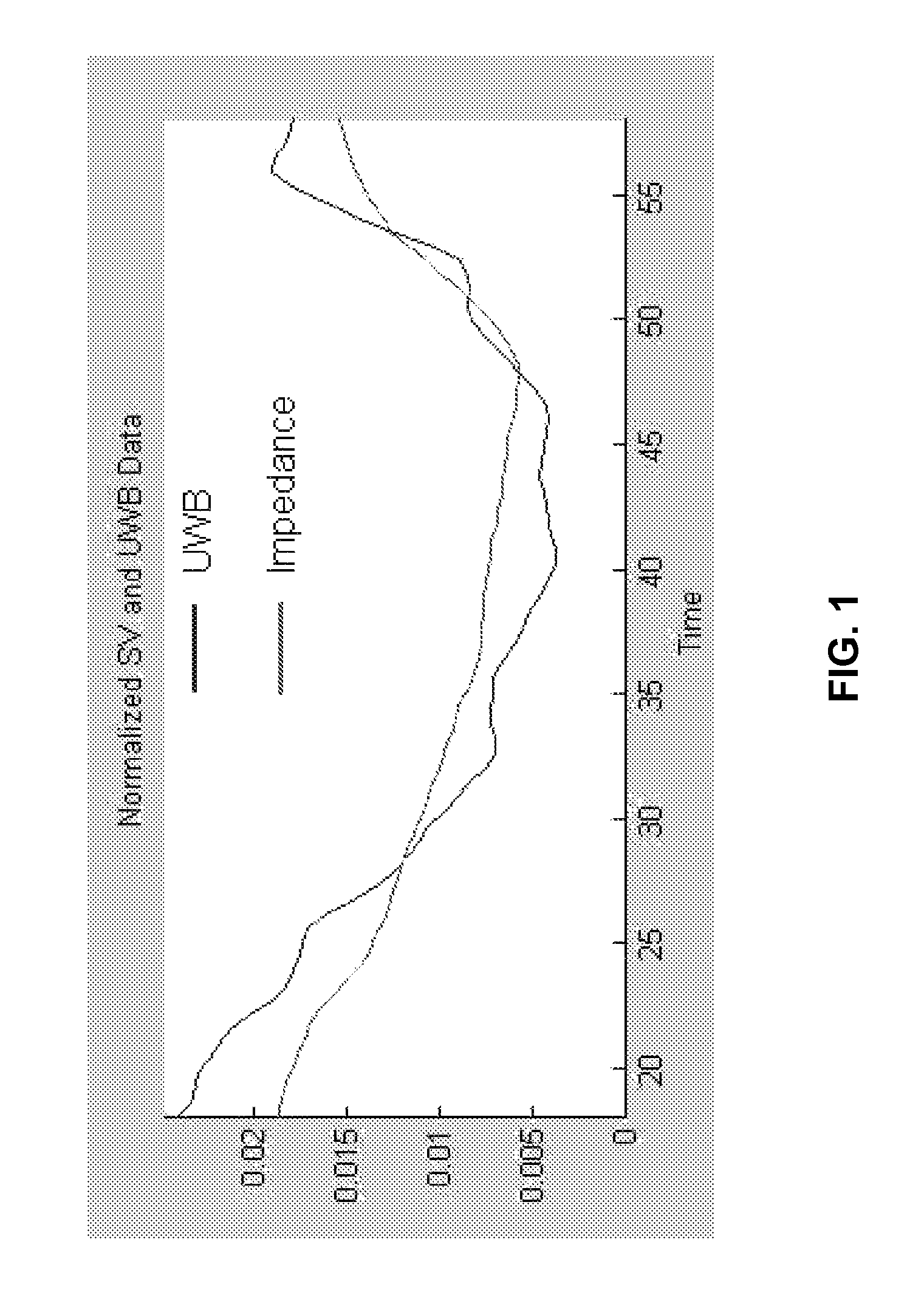
System and method for non-invasive instantaneous and continuous measurement of cardiac chamber volume
ActiveUS8463361B2Easy to monitorUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryContinuous measurementRadar systems
A system and method for non-invasive and continuous measurement of cardiac chamber volume and derivative parameters including stroke volume, cardiac output and ejection fraction comprising an ultrawideband radar system having a transmitting and receiving antenna for applying ultrawideband radio signals to a target area of a subject's anatomy wherein the receiving antenna collects and transmits signal returns from the target area which are then delivered to a data processing unit, such as an integrated processor or PDA, having software and hardware used to process the signal returns to produce a value for cardiac stroke volume and changes in cardiac stroke volume supporting multiple diagnostic requirements for emergency response and medical personnel whether located in the battlefield, at a disaster site or at a hospital or other treatment facility.
Owner:LIFEWAVE BIOMEDICAL
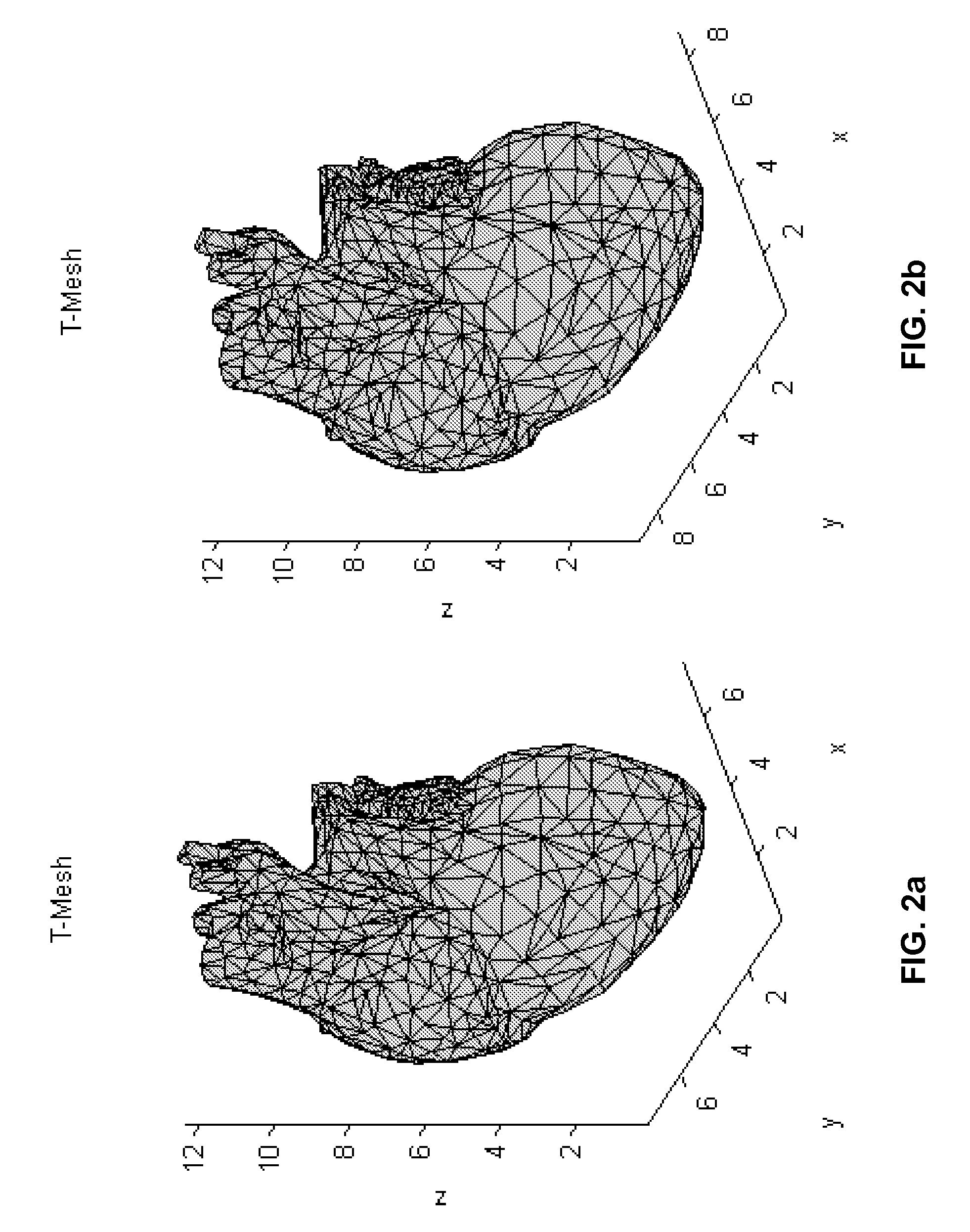
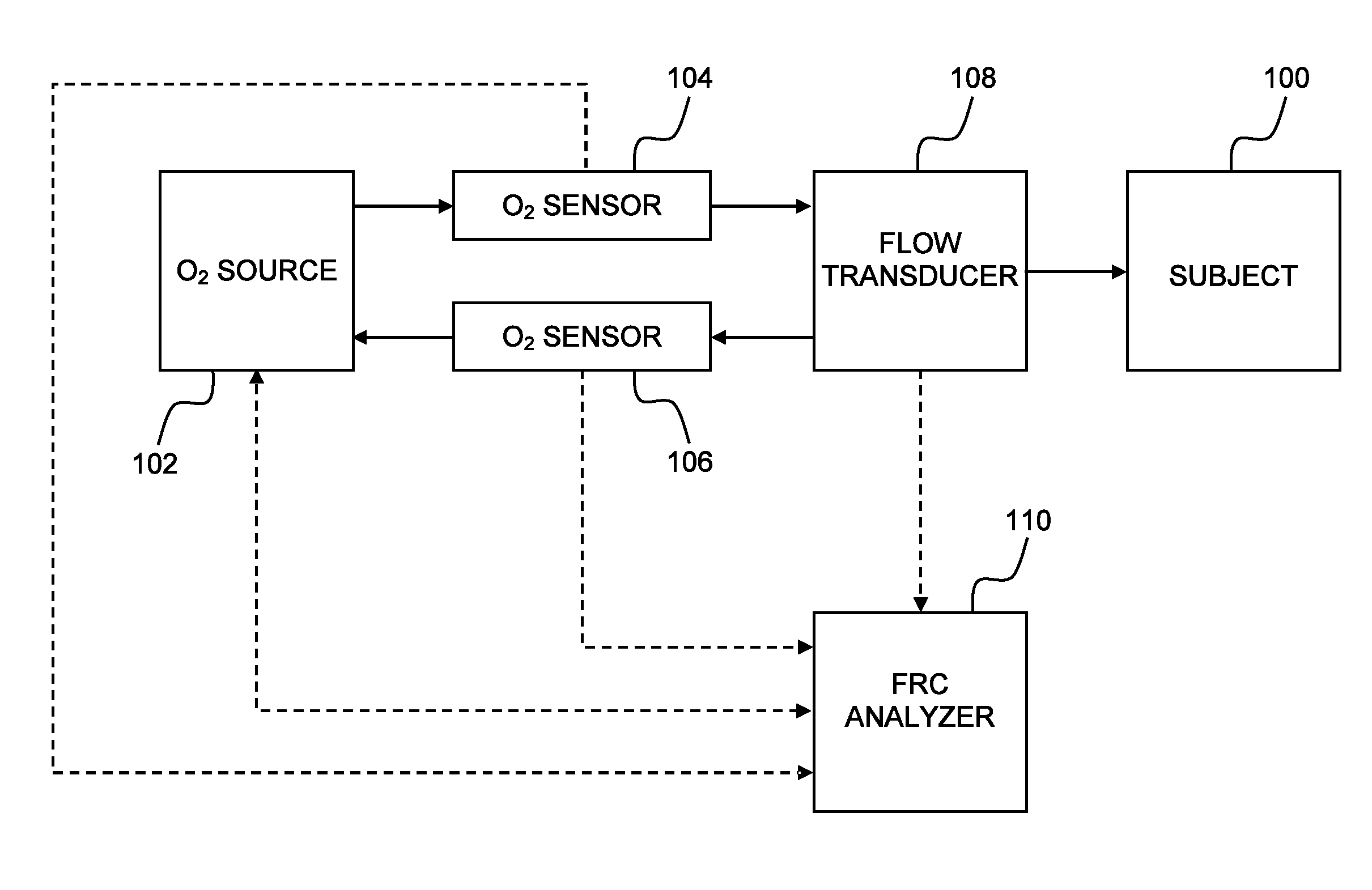
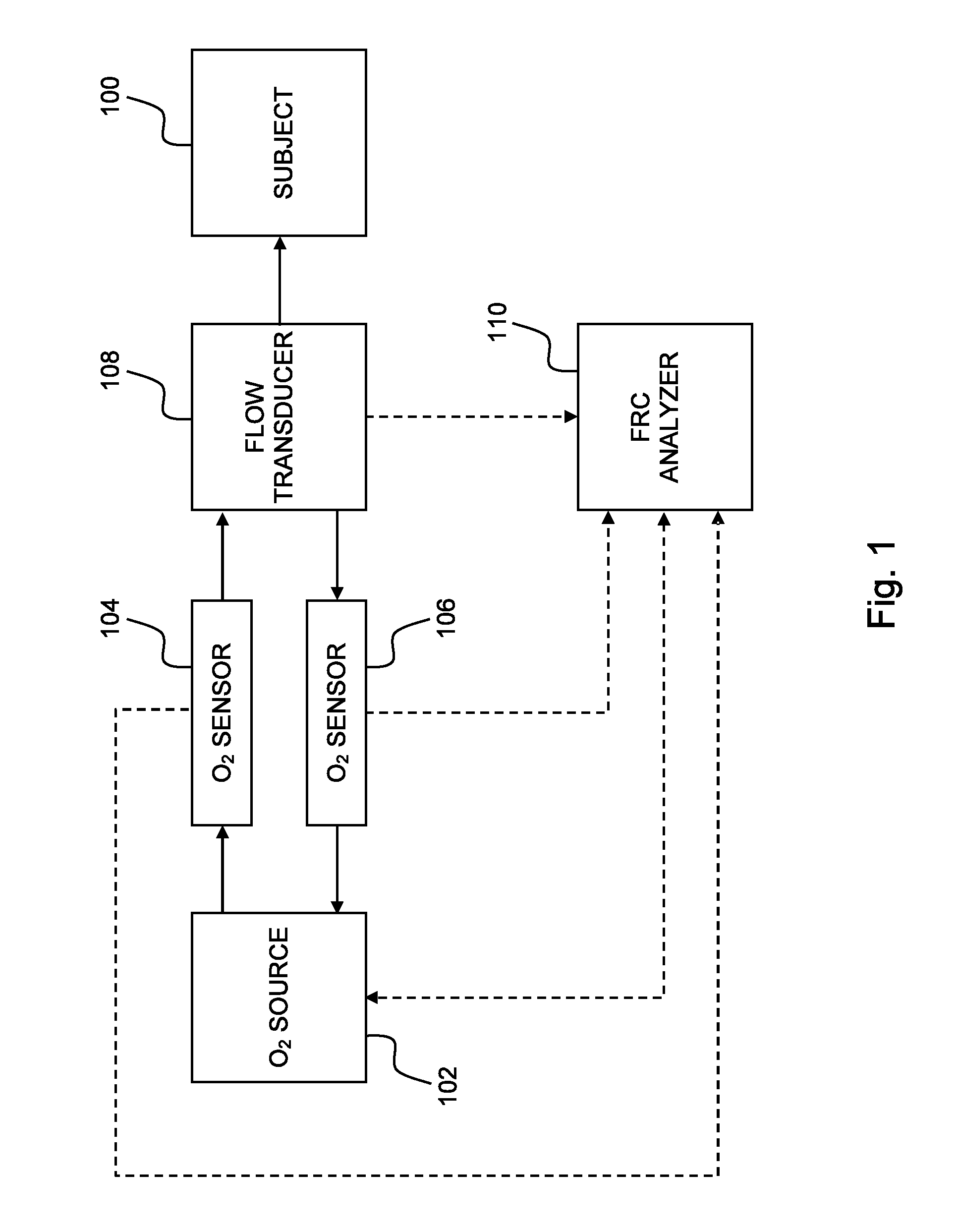
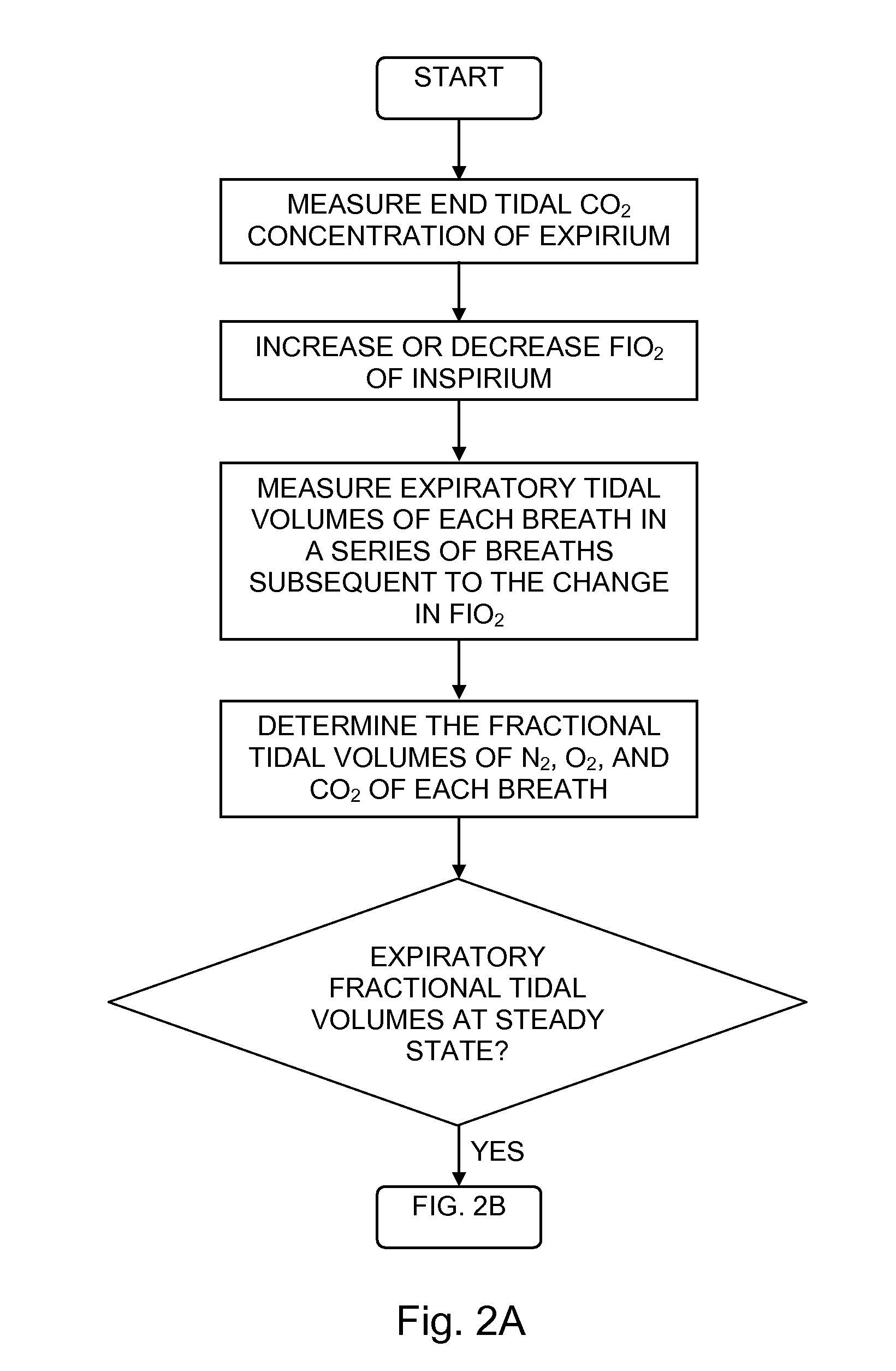
Determining functional residual lung capacity
InactiveUS20110112424A1RespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesAbsolute differenceIntensive care medicine
Determining functional residual lung capacity (FRC) by changing a subject's inspirium FiO2 by a predetermined amount, and a) for each breath in a series of breaths subsequent to changing the FiO2, determining expiratory tidal volume, determining expiratory fractional N2 tidal volume, multiplying the expiratory tidal volume by an absolute difference between the expiratory fractional N2 tidal volume of the breath and that of an immediately preceding breath for a first multiplication result, dividing the first multiplication result by the sum of the differences for a first division result, and multiplying the fractional N2 tidal volume by the sum of the first division results of the breaths for a second multiplication result, and b) dividing the sum of the second multiplication results of the breaths by the absolute difference between the fractional N2 tidal volume of the first and last breaths to produce a measurement of the subject's FRC.
Owner:KESSELMAN YITZHAK +1
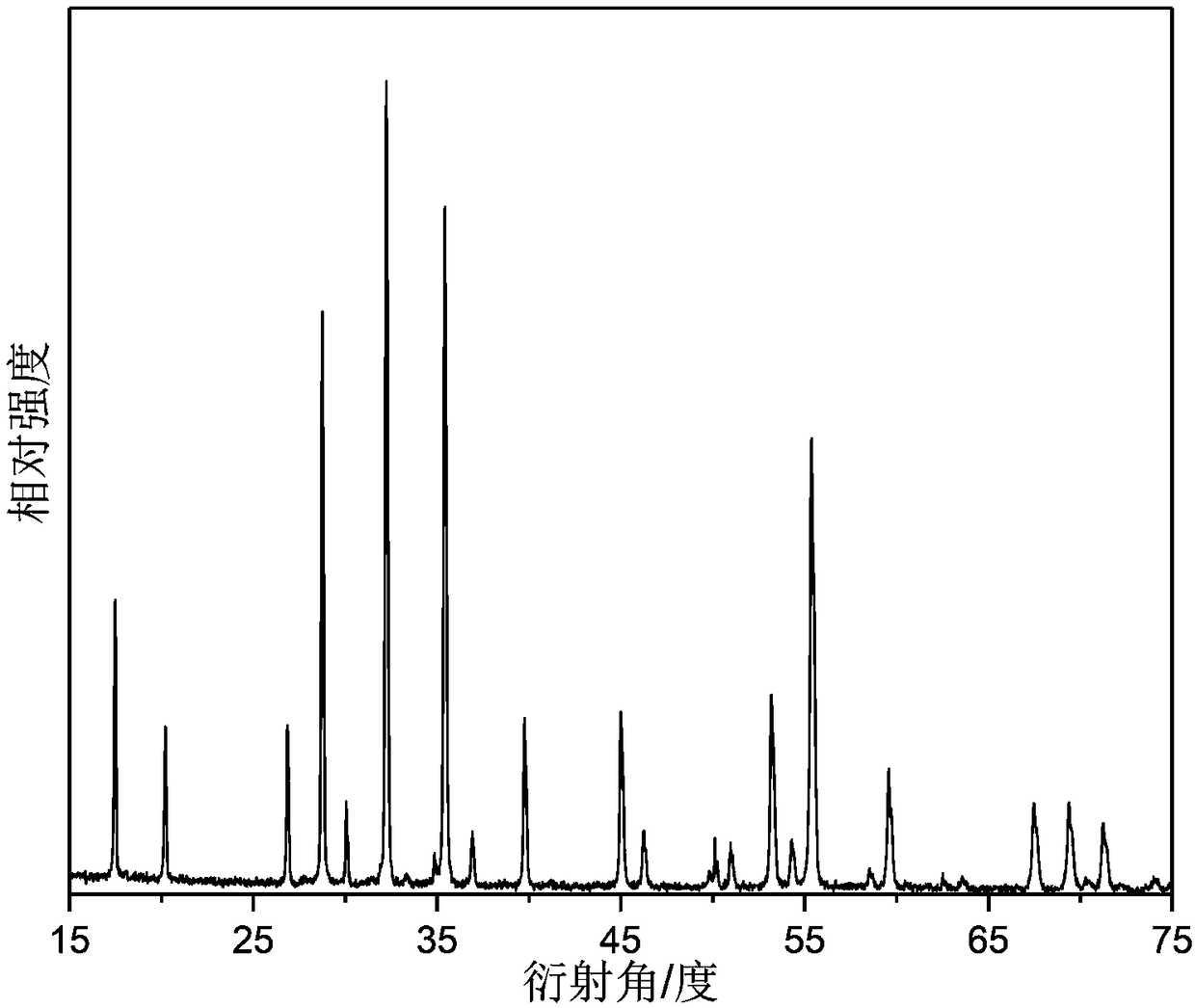
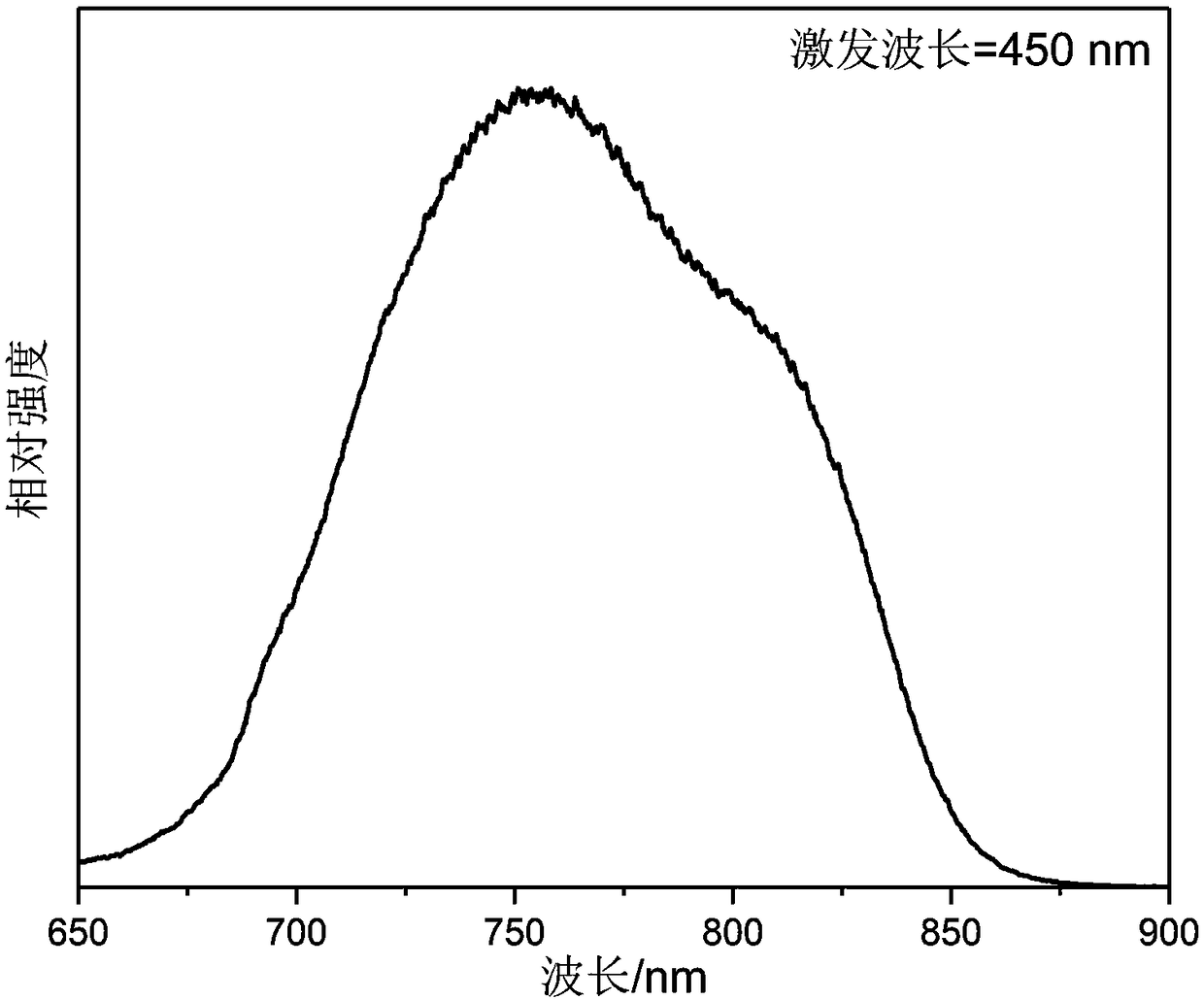
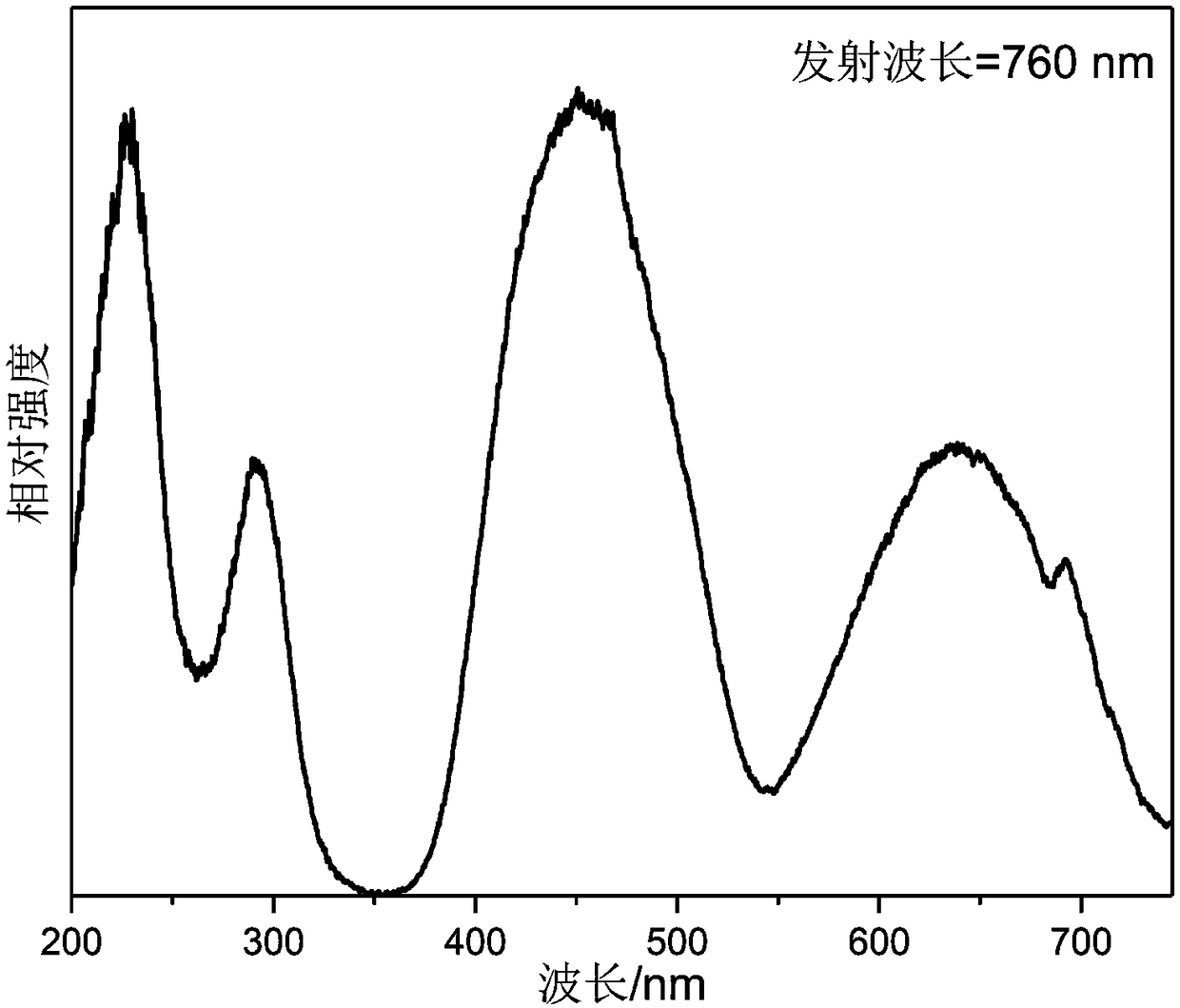
Near-infrared fluorescent powder with broadband emission characteristics, and preparation method and applications thereof
ActiveCN108424770APromote absorptionValence stableLuminescent compositionsSemiconductor devicesBroadbandTomography
The invention discloses a near-infrared fluorescent powder with broadband emission characteristics, and a preparation method and applications thereof, and belongs to the technical field of luminescentmaterial. The near-infrared fluorescent powder with broadband emission characteristics is suitable for near ultraviolet light and blue light chip excitation. The general chemical formula of the near-infrared fluorescent powder is Ca<2+x>Ln<1-x-y>Zr<2-x>Al<3>O<12>:xCr<3+>, yCe<3+>, and Cr<3+> is taken as a luminescence center, wherein Ln is used for representing one or a plurality of ions selectedfrom Y<3+>, Lu<3+>, and Gd<3+>, x and y are used for representing molar fractions, 0<x<=0.15, and 0<=y<=0.1. The near-infrared fluorescent powder can be taken as a light conversion material of near ultraviolet light LED chips or blue light LED chips, can be used for preparation of broadband near-infrared light sources, and is capable of satisfying requirements of blood oxygen detection or coherence tomography on infrared light sources with broadband emission characteristics.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Methods for fat quantification with correction for noise bias
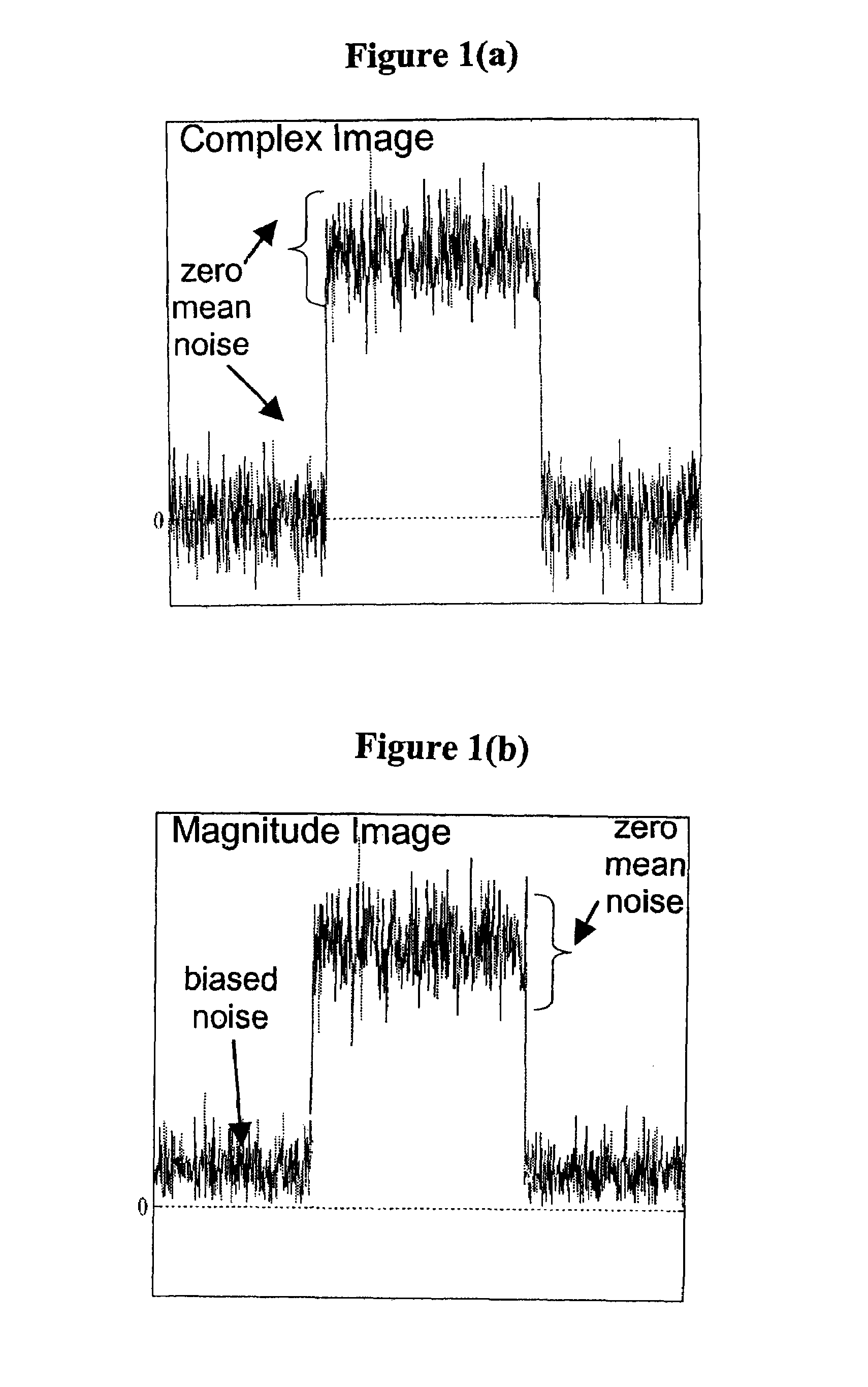
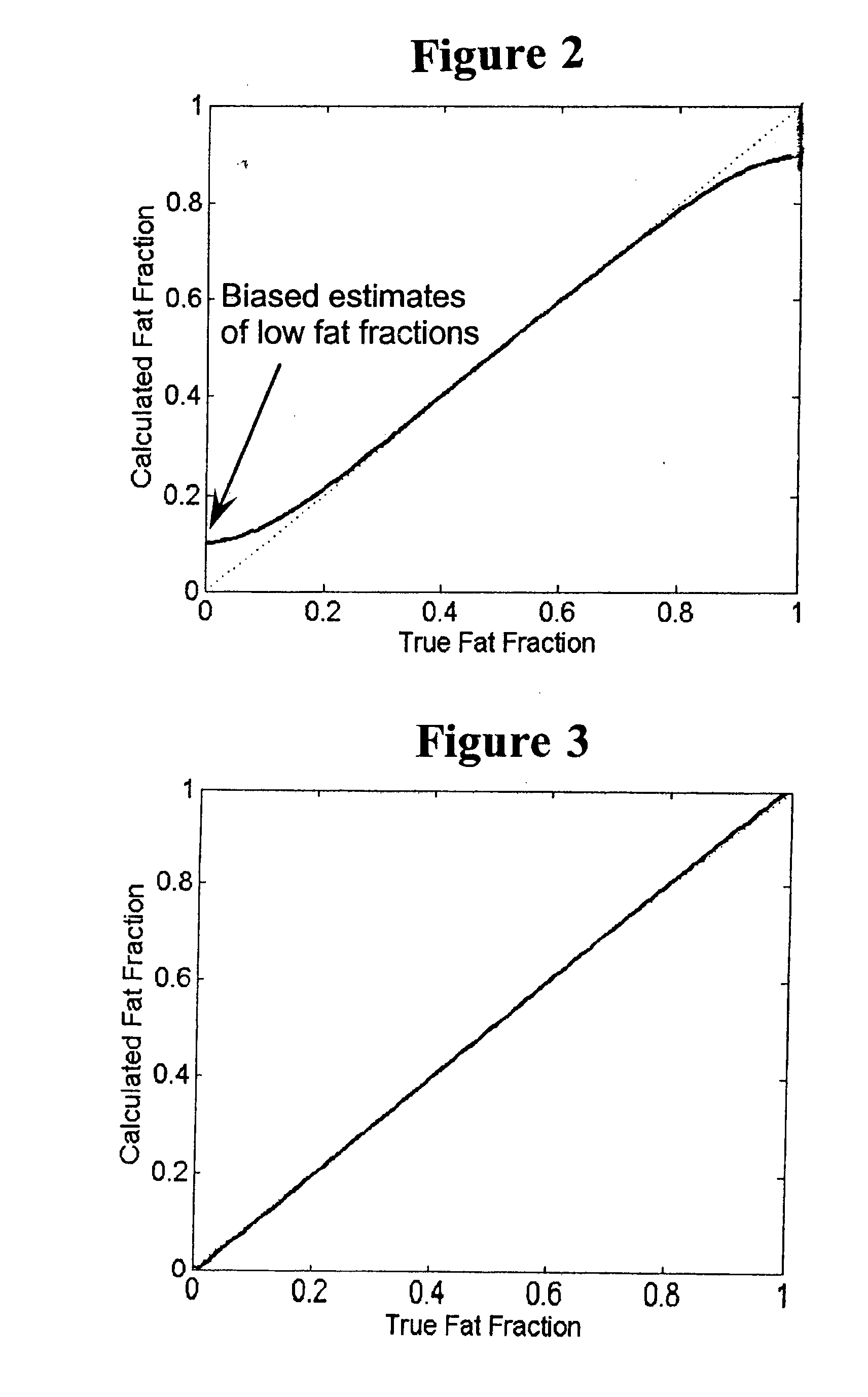
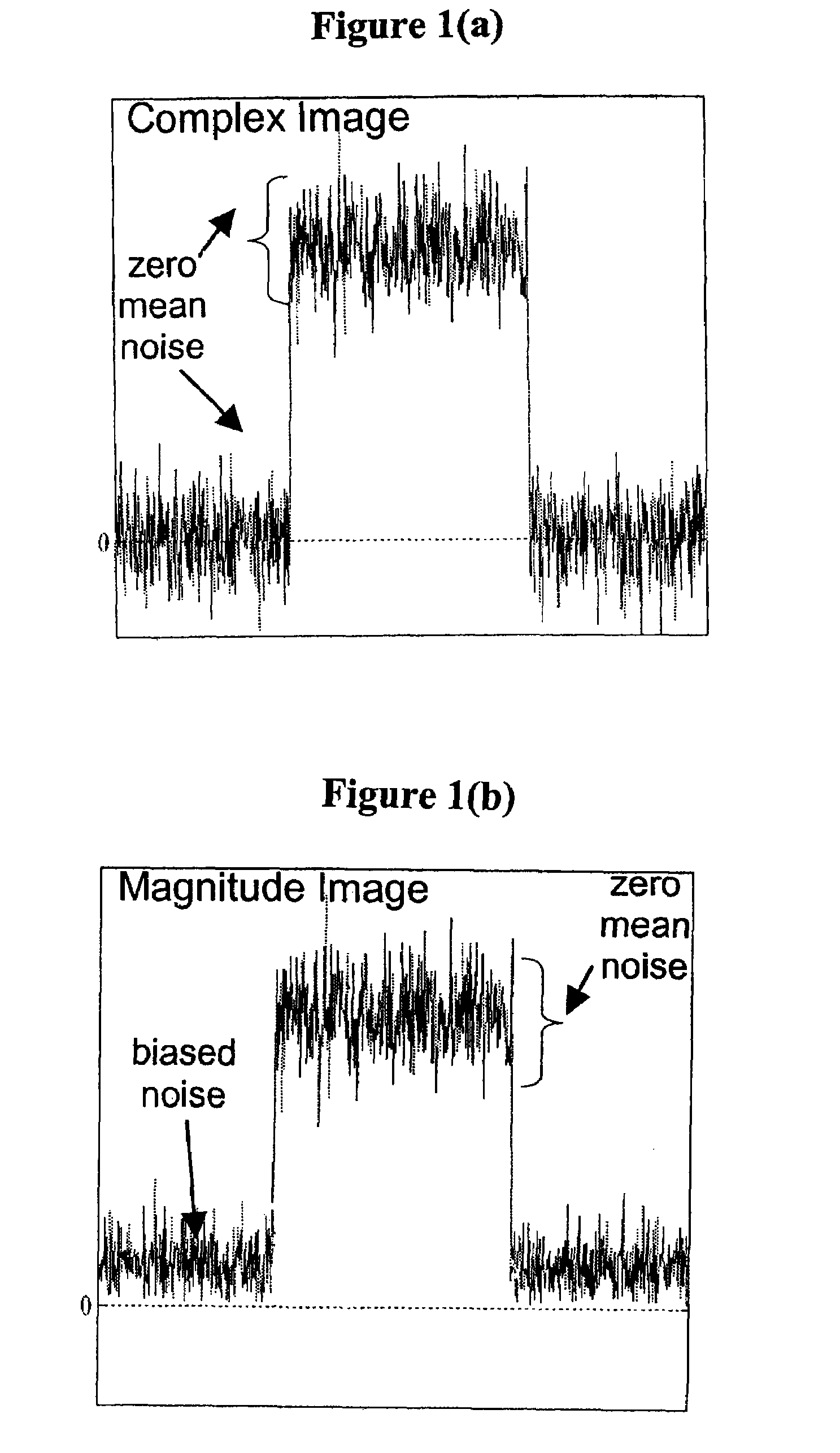
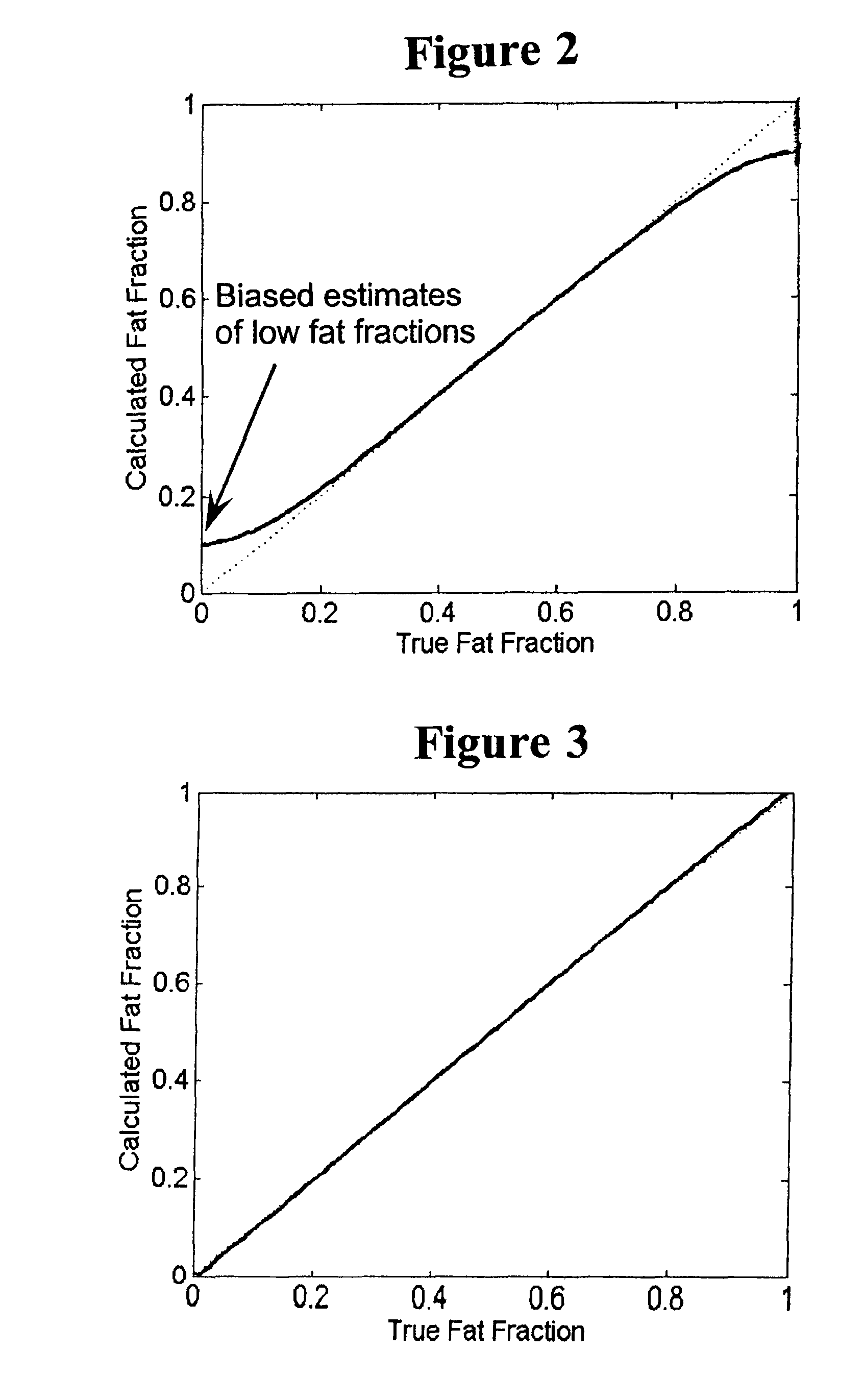
ActiveUS20090112081A1Accurate calculationImprove image signal-to-noise ratioMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringData setVoxel
Methods are disclosed for calculating a fat fraction corrected for noise bias of one or more voxels of interest using a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) system. A plurality of image data sets are obtained each corresponding to NMR k-space data acquired using a pulse sequence with an individual associated echo time tn. A system of linear equations is formed relating image signal values to a desired decomposed calculated data vector having a component such as a water and fat combination having zero mean noise, or having a real fat component and a real water component. A fat fraction is calculated from at least one component of the decomposed calculated data vector. In another embodiment, the system of linear equations is normalized and can directly estimate a fat fraction or a water fraction having reduced noise bias.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO +1
Method for identifying malignancies in barrett's esophagus using white light endoscopy
A method is described for computing a statistically significant difference between dysplasia and Barrett's esophagus (both with and without inflammatory component) using a discriminate function with diffuse reflectance measurements performed at a minimum of four different wavelengths of 485, 513, 598, and 629 nm. The discriminate function found depends both on local blood fraction volume THB and oxygenation SO2. A pull-back approach of spectral data acquisition is disclosed which takes into account tissue motility in esophagus and measurement geometry peculiarities. The pull-back approach provides a significant improvement of measurement reproducibility and reduction of data deviation by 75-100%, resulting in a better discrimination between different histological groups.
Owner:NOVADAG TECH INC
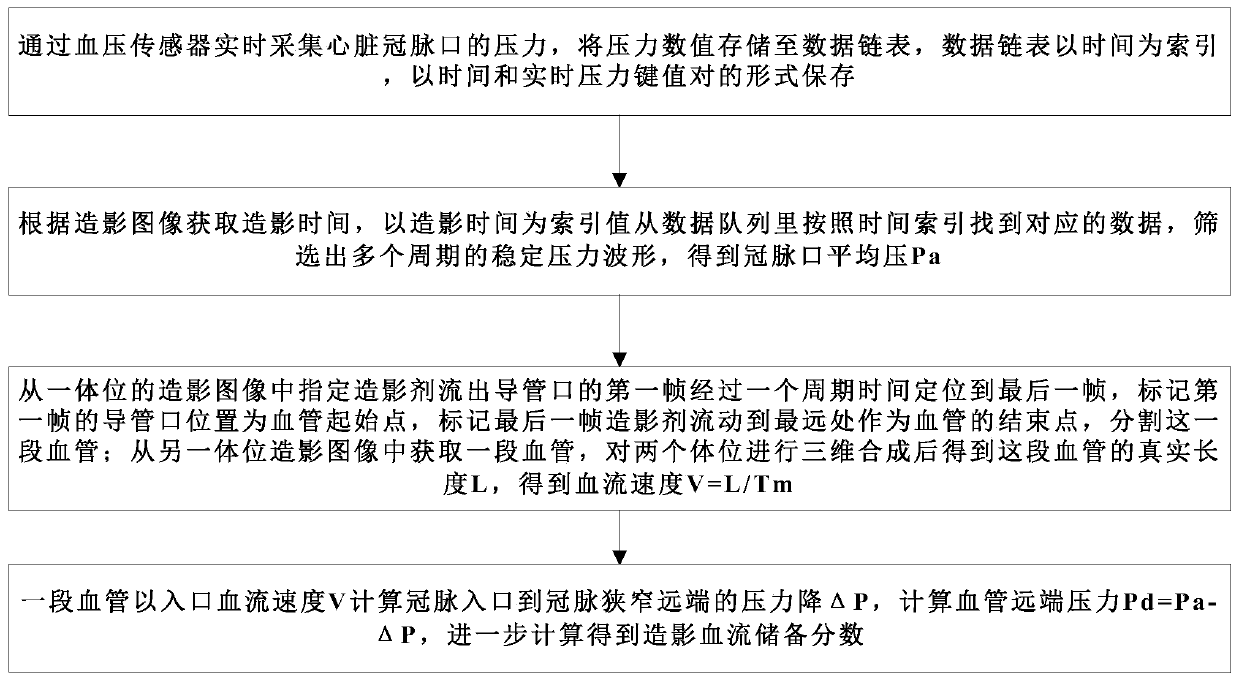
Method for calculating fractional flow reserve based on pressure sensor and contrast image
ActiveCN109805949AImprove accuracyStable pressure valueImage enhancementImage analysisCardiac cycleBlood vessel
The invention discloses a method for calculating fractional flow reserve based on a pressure sensor and a contrast image. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring pressure of a heart coronary mouth in real time through a blood pressure sensor; storing a pressure numerical value to a data link list; storing the data link list by using time as an index in a form of time and real-time pressure key value pairs; acquiring the contrast time according to contrast images and searching corresponding data from a data queue according to the time index by using the contrast time as an index value, and screening out stable pressure waveform in multiple periods so as to acquire average pressure Pa; acquiring the length of a section of blood vessel from the contrast images of two body positions so as to acquire blood flow velocity; calculating pressure drop delta P at the section of the blood vessel at the inlet blood flow velocity V; calculating far-end pressure Pd of the blood vessel tofurther calculate the contrast fractional flow reserve. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the stable pressure value after injection of contrast agent can be accurately acquired; theaverage blood flow velocity of one cardiac cycle can be accurately acquired through the pressure waveform and the contrast images, so that the accuracy of FFR (Fractional Flow Reserve) can be greatlyimproved.
Owner:SUZHOU RAINMED MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Systems and methods for orientation independent sensing
A system and method for obtaining an OIS coordinate frame comprising an electronic control unit configured to determine a local 3D electric field loop, create a zero mean version of E(t) over a depolarization interval, compute an Ė value at each of a plurality of time intervals, compute an initial estimate of ŵ from a cross product of E and the Ė value for each of the plurality of time intervals, average the initial estimate of ŵ from each of the plurality of time for a best estimate of ŵ, determine a plurality of â(θ) values and using the corresponding {circumflex over (n)}(θ) values, compute a composite match score, and choose at least one best value for â and a best value for {circumflex over (n)}.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL CARDILOGY DIV INC
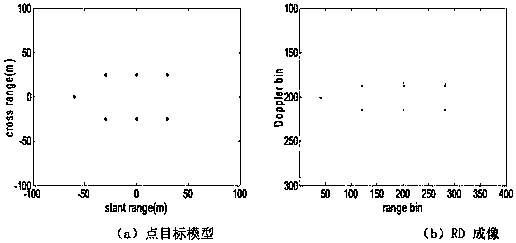
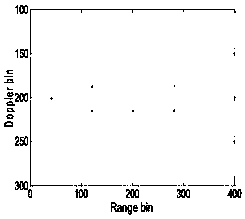
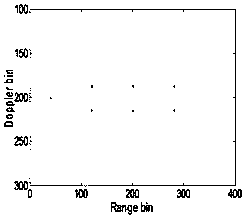
Ship target ISAR imaging method based on fractional Fourier transform
ActiveCN108107430AAccurate estimateEliminate couplingRadio wave reradiation/reflectionTime delaysFourier transform on finite groups
The invention provides a ship target ISAR imaging method based on fractional Fourier transform. The ship target ISAR imaging method comprises the steps of: acquiring a radar echo signal of a scattering point of a ship target in each distance unit; modeling the acquired radar echo signals in the distance units into multi-component secondary frequency modulation signals through pulse compression andmotion compensation; determining estimated parameters of scattering point echo signals in the distance units according to the secondary frequency modulation signals; updating radar echo signals in the distance units by adopting the estimated parameters of the scattering point echo signals in the distance units; and acquiring an ISAR image of a ship target by utilizing the updated radar echo signals. The ship target ISAR imaging method adopts a symmetrical correlation function, fractional Fourier transform and multi-product processing for the radar echo signals in sequence, avoids the couplingof time and time delay, estimates a quadratic term phase coefficient and a cubic term phase coefficient with high precision, adopts a range-instantaneous-Doppler imaging technology combining with parameter estimation, and obtains a high-quality and high-precision ISAR image of a moving target.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY +1
Methods and Systems for Filtering Respiration Noise from Localization Data
A method of filtering respiration noise from a localization signal includes acquiring a localization signal from at least one position measurement sensor within a localization field and acquiring an acceleration signal for at least one localization field generator (e.g., a patch electrode). A displacement signal for the field generator is calculated, for example by integrating the acceleration signal twice, and transformed into the frequency domain in order to calculate a fractional power indicative of patient respiration. The fractional power can then be compared to a threshold value, and the localization signal can be filtered if the fractional power exceeds the threshold value. Alternatively, the acquired acceleration signal can be used to gate collection of data points from the localization signal.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
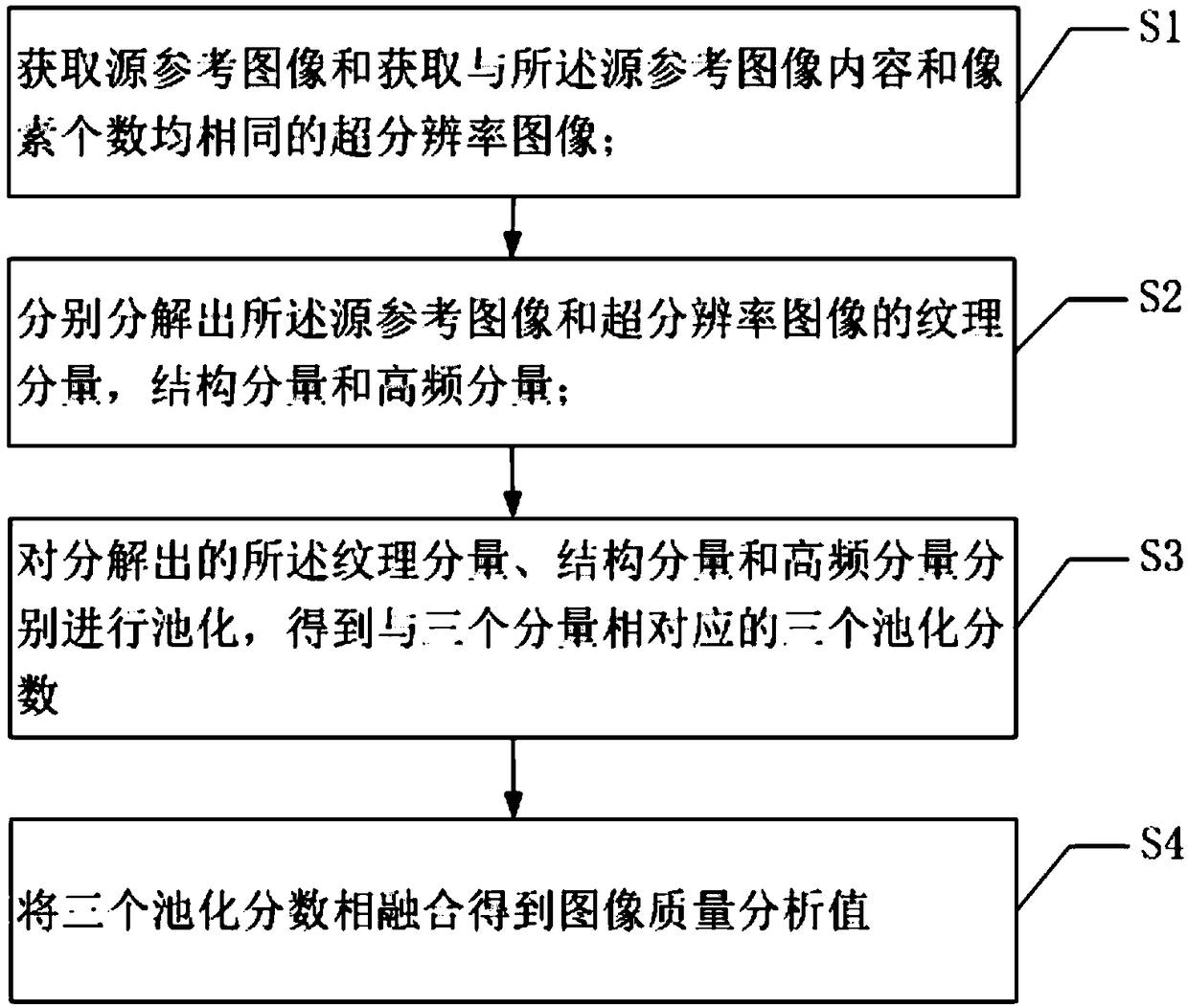
An image quality analysis method and a system of a super-resolution image
ActiveCN109410177AObjective experimental data is superiorImage enhancementImage analysisImaging qualityReference image
The invention provides an image quality analysis method and a system of a super-resolution image. The method includes obtaining a source reference image and a super-resolution image with the same content and number of pixels as the source reference image; decomposing the texture component, the structure component and the high frequency component of the source reference image and the super-resolution image respectively; pooling the decomposed texture components, structural components and high frequency components to obtain three pooling fractions corresponding to the three components; three pooling fractions are fused to get the image quality analysis value. The analysis of the invention on the super-resolution image is more objective and accurate than the existing image quality analysis method, and provides important application value for the analysis of the super-resolution image quality obtained after the reconstruction of the low-resolution image in the monitoring field, the satellite image and the medical image.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
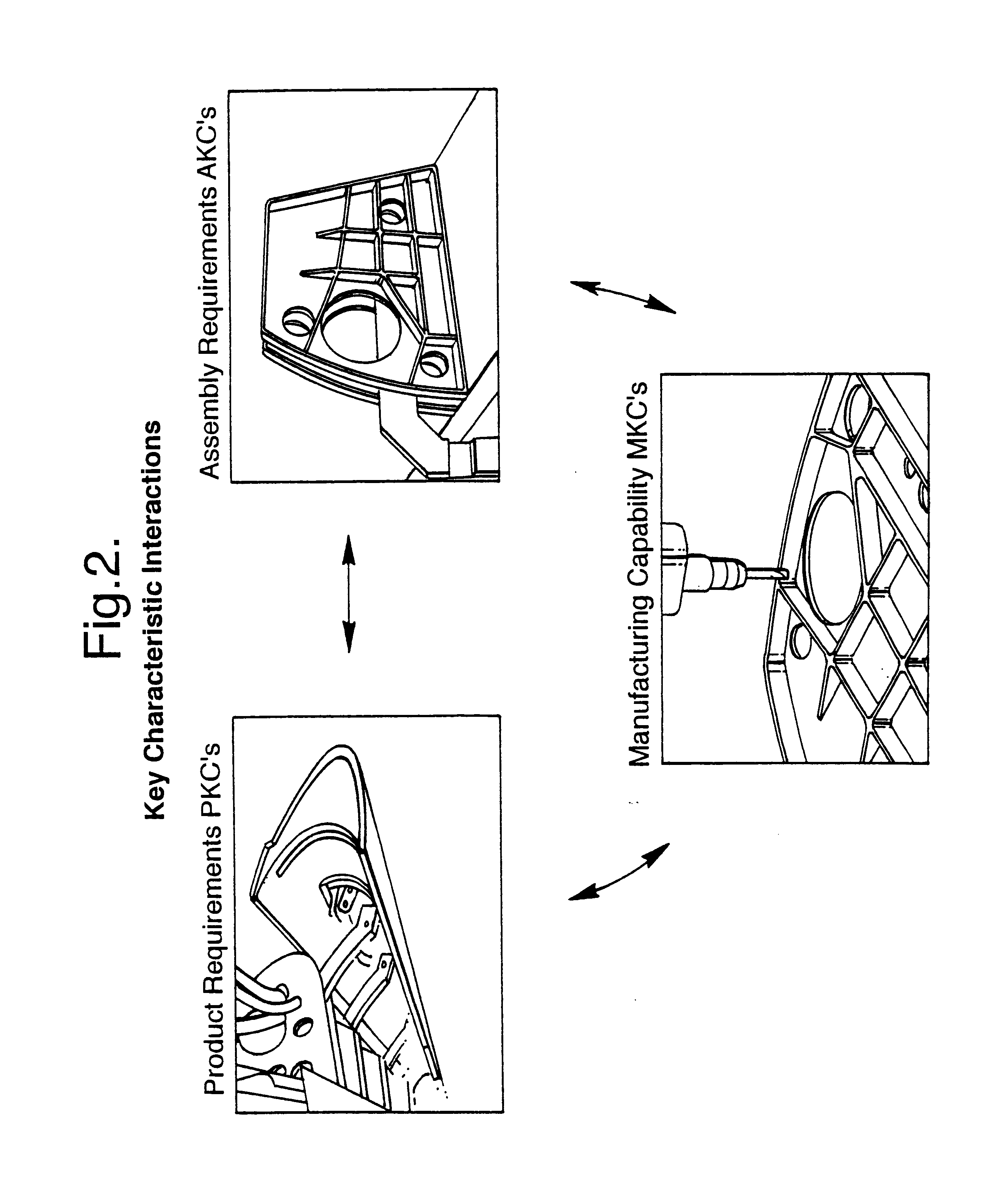
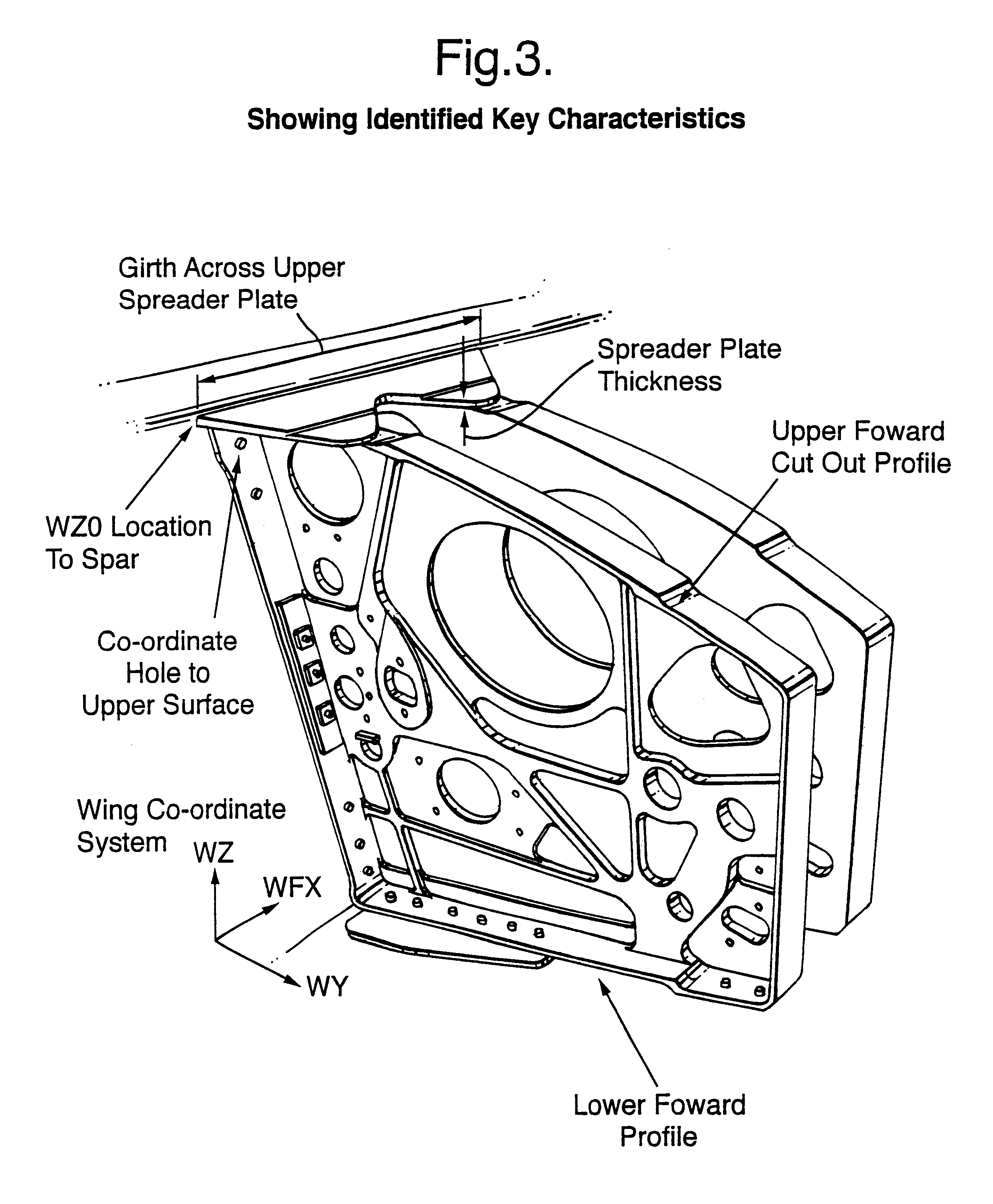
Feature based assembly
A method of design and manufacture of an assembly of components including selecting KCs of the type, Product KCs, Assembly KCs or Manufacturing KCs is provided. The method includes the steps of identifying potential KCs and carrying out a risk assessment for variation of the potential KCs based upon four values, namely probability of failure or variation; the severity of the variation; the detectability of the variation, and the repairability of the variation. Scores attributed to each said value may then be multiplied together to produce the risk assessment. Once the KCs have been selected, a process of feature identification and classification for the KC may be carried out, followed by establishment of assembly precedence of features for the KC.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS LTD +1
Methods for fat quantification with correction for noise bias
ActiveUS8000769B2Improve image signal-to-noise ratioExcessive signal averagingMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringData setVoxel
Methods are disclosed for calculating a fat fraction corrected for noise bias of one or more voxels of interest using a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) system. A plurality of image data sets are obtained each corresponding to NMR k-space data acquired using a pulse sequence with an individual associated echo time tn. A system of linear equations is formed relating image signal values to a desired decomposed calculated data vector having a component such as a water and fat combination having zero mean noise, or having a real fat component and a real water component. A fat fraction is calculated from at least one component of the decomposed calculated data vector. In another embodiment, the system of linear equations is normalized and can directly estimate a fat fraction or a water fraction having reduced noise bias.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO +1
Phase mask plate of integer-order vortex beam with fractional-order vortex profile and optical path system
ActiveCN109870890ARealize continuous controlAchieve continuous changeOptical elementsGratingSpatial light modulator
The invention provides a phase mask plate of an integer-order vortex beam with a fractional-order vortex profile. A generated novel vortex beam simultaneously has the topological charge of the integer-order vortex and the light intensity profile of the fractional-order vortex. The phase mask plate generates a vortex beam by inputting the phase mask plate into a reflection type spatial light modulator, wherein the transmission rate function expression of the phase mask plate is a formula which is as shown in the specification, wherein A (x, y) is an amplitude modulation function and is used forchanging the profile of the incident coherent light field so as to improve the quality of the vortex beam and avoid the interference of a phase modulation signal and an amplitude modulation signal; ang (.) is an angle-solving function of an imaginary number; rem (.) is a complementary function; m is the topological charge value of the beam, and n is a phase step factor, wherein n is greater thanm; the phase step can be compressed by changing the value of n, so that the required phase step size is generated; theta is the polar angle of a polar coordinate system; and 2 <pi>x / d is a blazed grating item, and is used for generating a blazed grating with a period of d, so that the energy is concentrated in +1 stage diffraction.
Owner:XI'AN INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
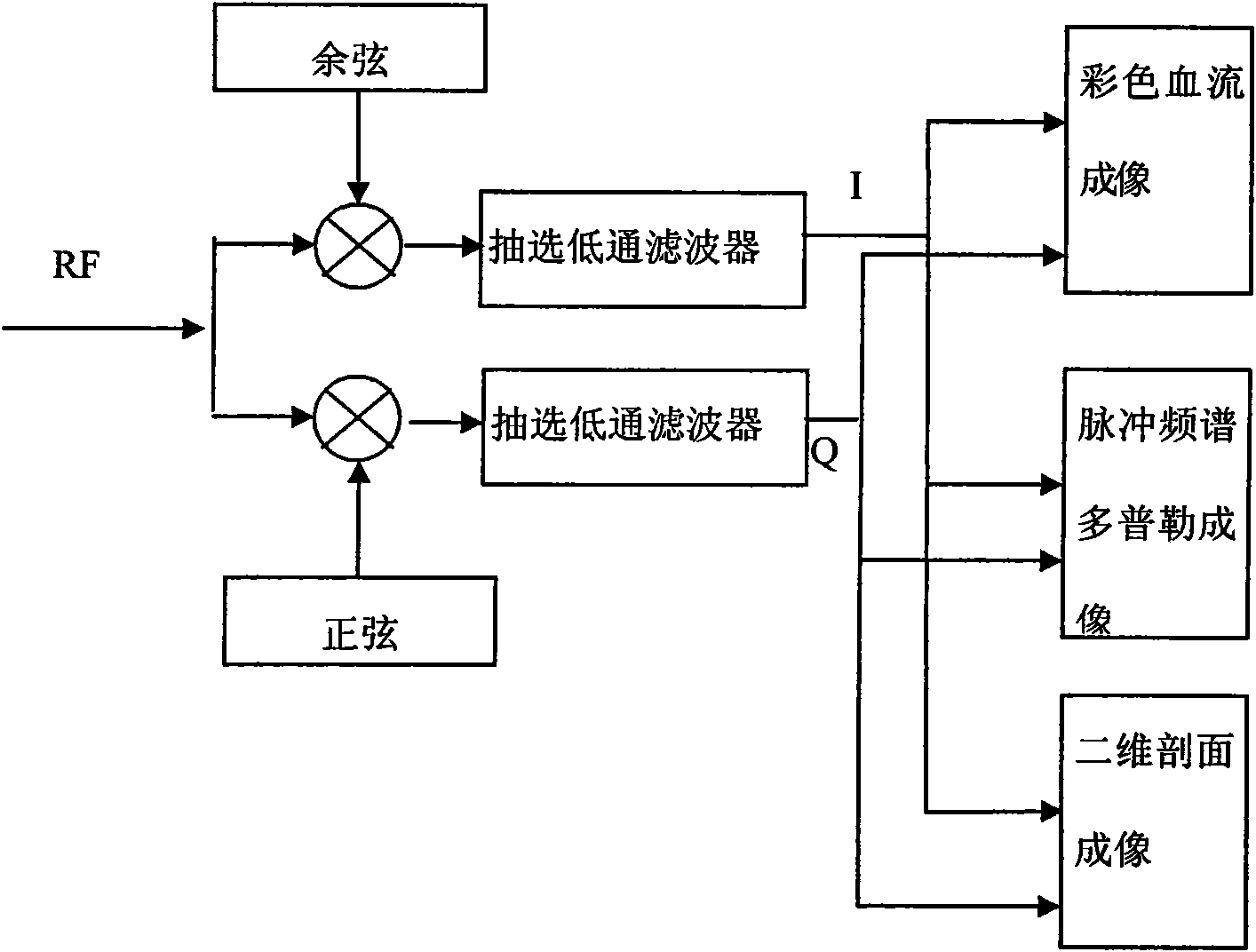
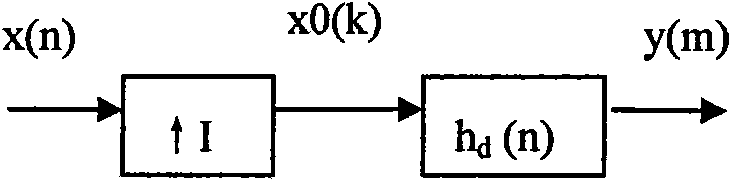
Decimating filtering method and decimating filter
ActiveCN101919706AReduce overheadSmall amount of calculationBlood flow measurement devicesInfrasonic diagnosticsUltrasonic imagingComputer science
The invention discloses a decimating filtering method and a decimating filter for ultrasonic imaging. The decimating filtering method comprises the following steps of: storing a filter coefficient; carrying out L-grade latching on an input signal, wherein L is multiplication accumulator number used during the filtering; as for each grade of latched input signals, reading the stored filter coefficient with the serial number of K from a coefficient memory for carrying out multiplication accumulating calculation with the grade latched input signals, wherein the serial number K of the read filter coefficient is formed by calculating the serial number num of the current latching-grade input signals, the serial number m of the current calculated output signal, an extracting factor D and an interpolation factor I; and accumulating L-grade latched multiplication accumulating calculation results to obtain a filtered output signal. The decimating filtering method and the decimating filter of the invention remove an interpolation inserted zero value and items of carrying out multiplication accumulating on the filter coefficient, directly carry out multiplication accumulation on the original input signal and the corresponding filter coefficient, thereby not only realizing the decimating filter of any fraction proportion but also reducing calculated amount.
Owner:SHENZHEN MINDRAY BIO MEDICAL ELECTRONICS CO LTD
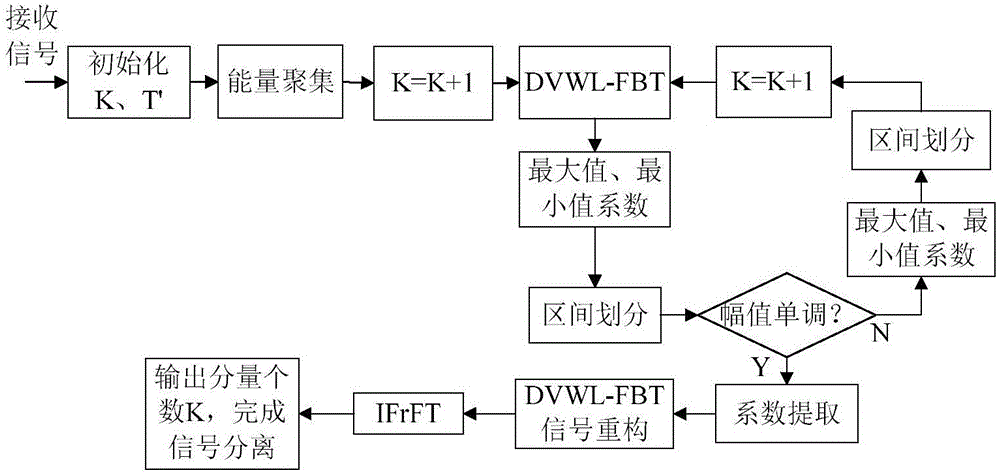
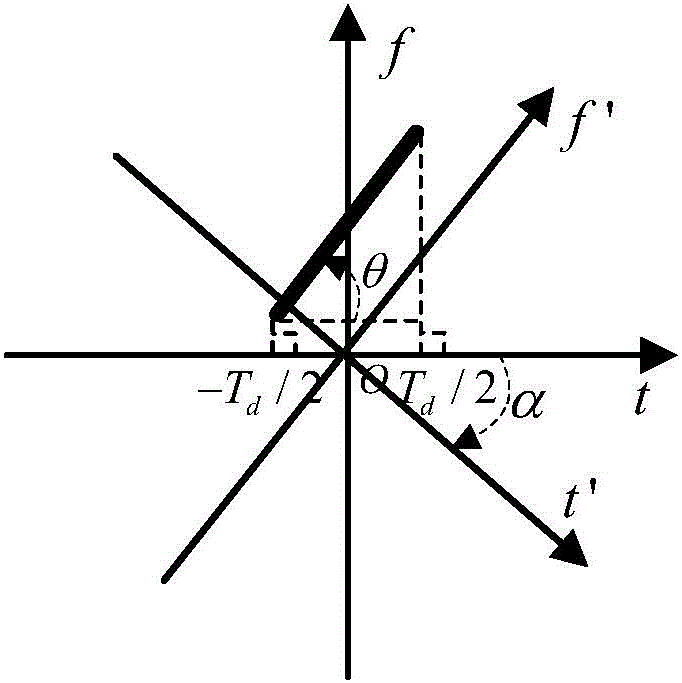
Accurate detection and separation method for multi-component LFM signal
The invention provides an acurate detection and separation method for a multi-component LFM signal. The method comprises the steps of firstly, subjecting a received signal to FrFT, searching the energy peak and the corresponding fractional fourier domain of the signal, and conducting the coarse detection on the components of the signal; secondly, subjecting the signal to DVWL-FB series expansion, determining a DVWL-FB coefficient minimum value and a DVWL-FB coefficient maximum value to obtain a coefficient interval, and continuously updating the coefficient amplitude characteristics of the interval for signal detection and correction; thirdly, extracting the DVWL-FB coefficients of a finally divided interval for signal reconstruction, and subjecting a reconstructed signal to IFrFT to obtain an original single-component signal in the time-frequency domain. The above first step and the above second step are repeated until no significant energy concentration peak occurs. Based on the method, multi-component LFM signals, similar in frequency, can be accurately detected and effectively separated. The method has obvious advantages in the aspects of signal detection accuracy, signal separation accuracy, low signal-to-noise ratio, robustness and the like.
Owner:AIR FORCE UNIV PLA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com