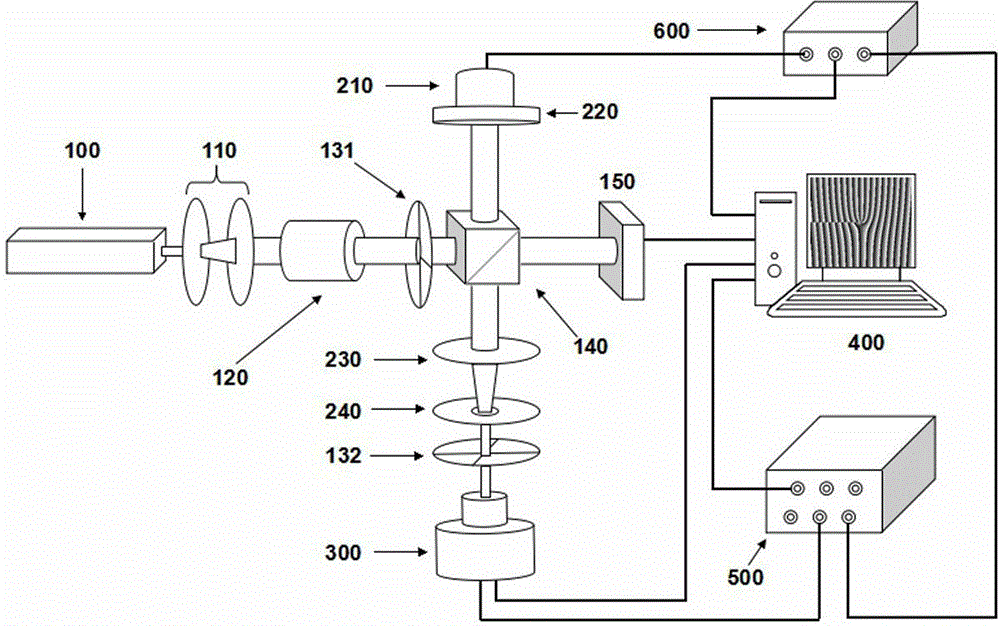
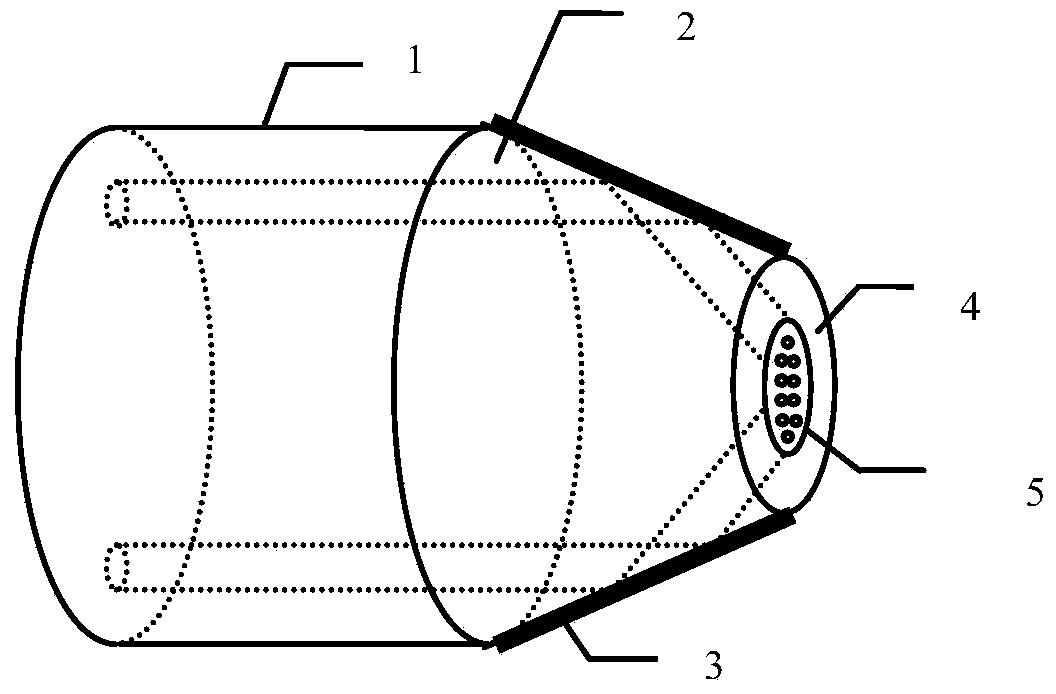
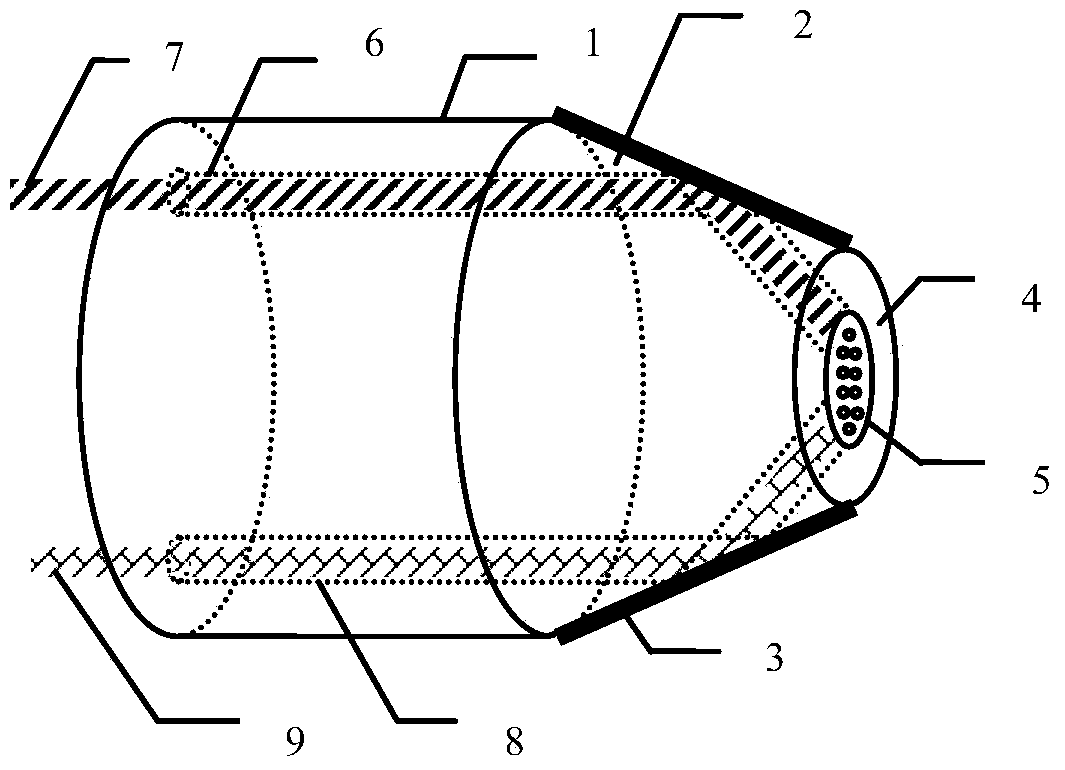
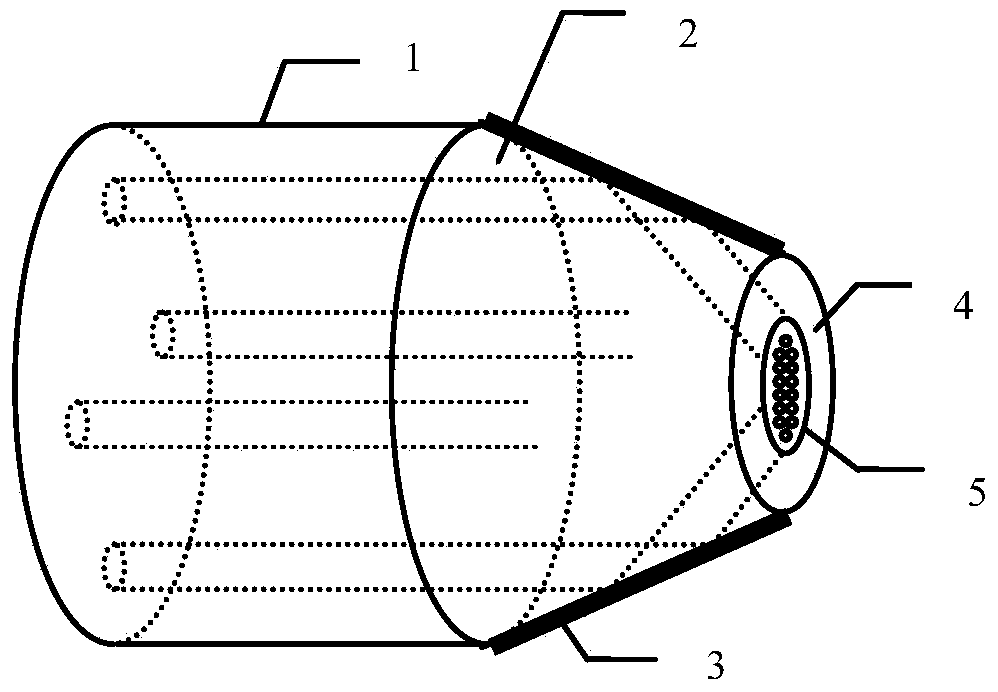
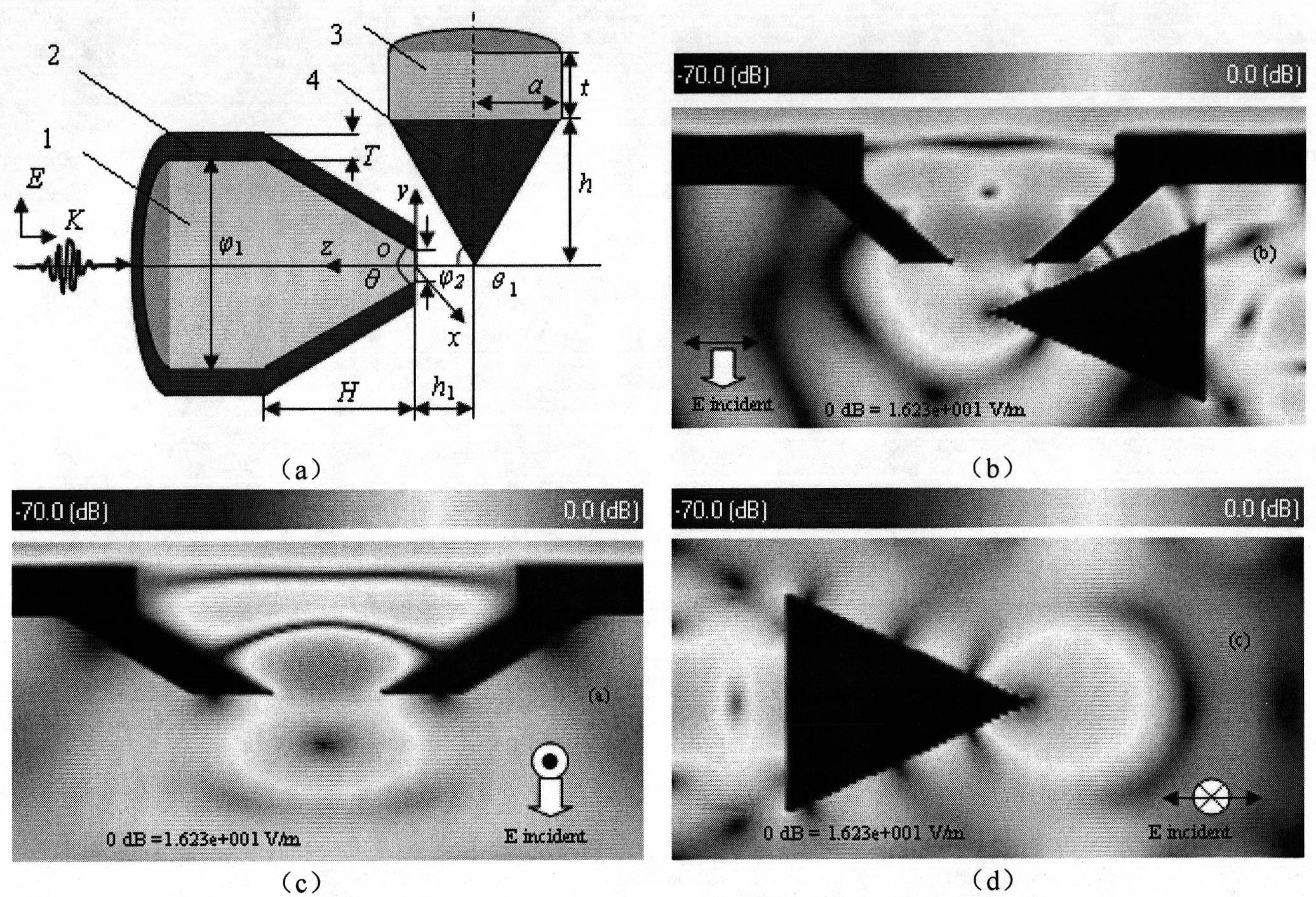
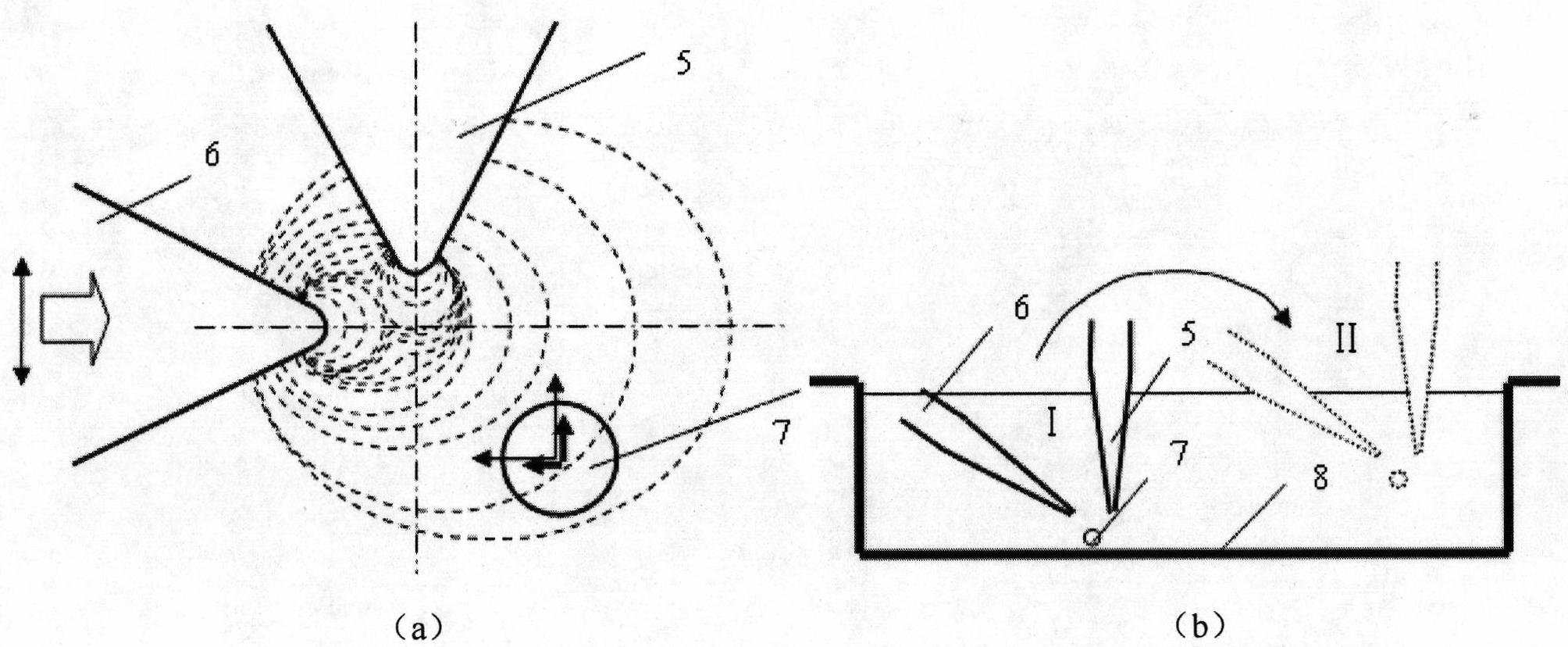
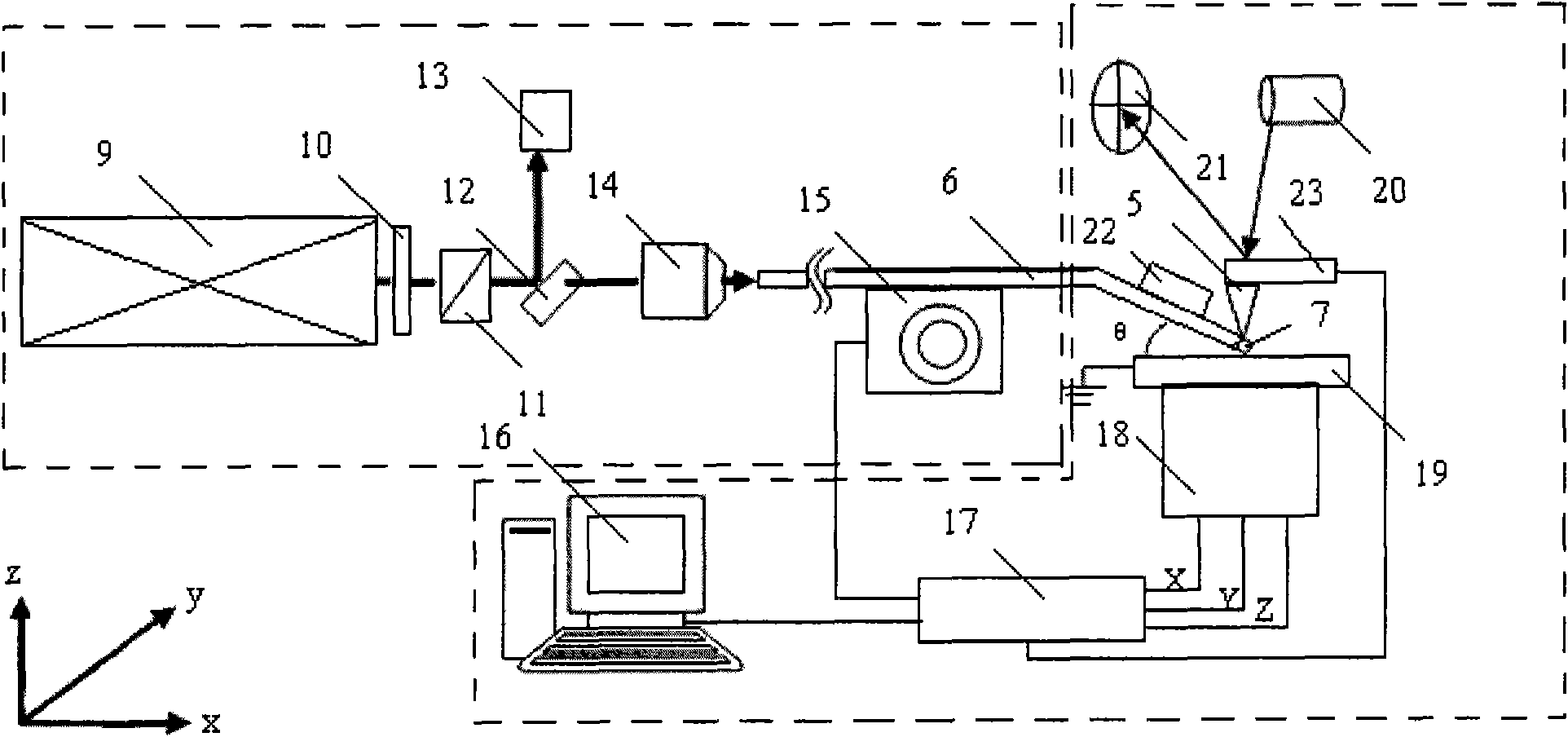
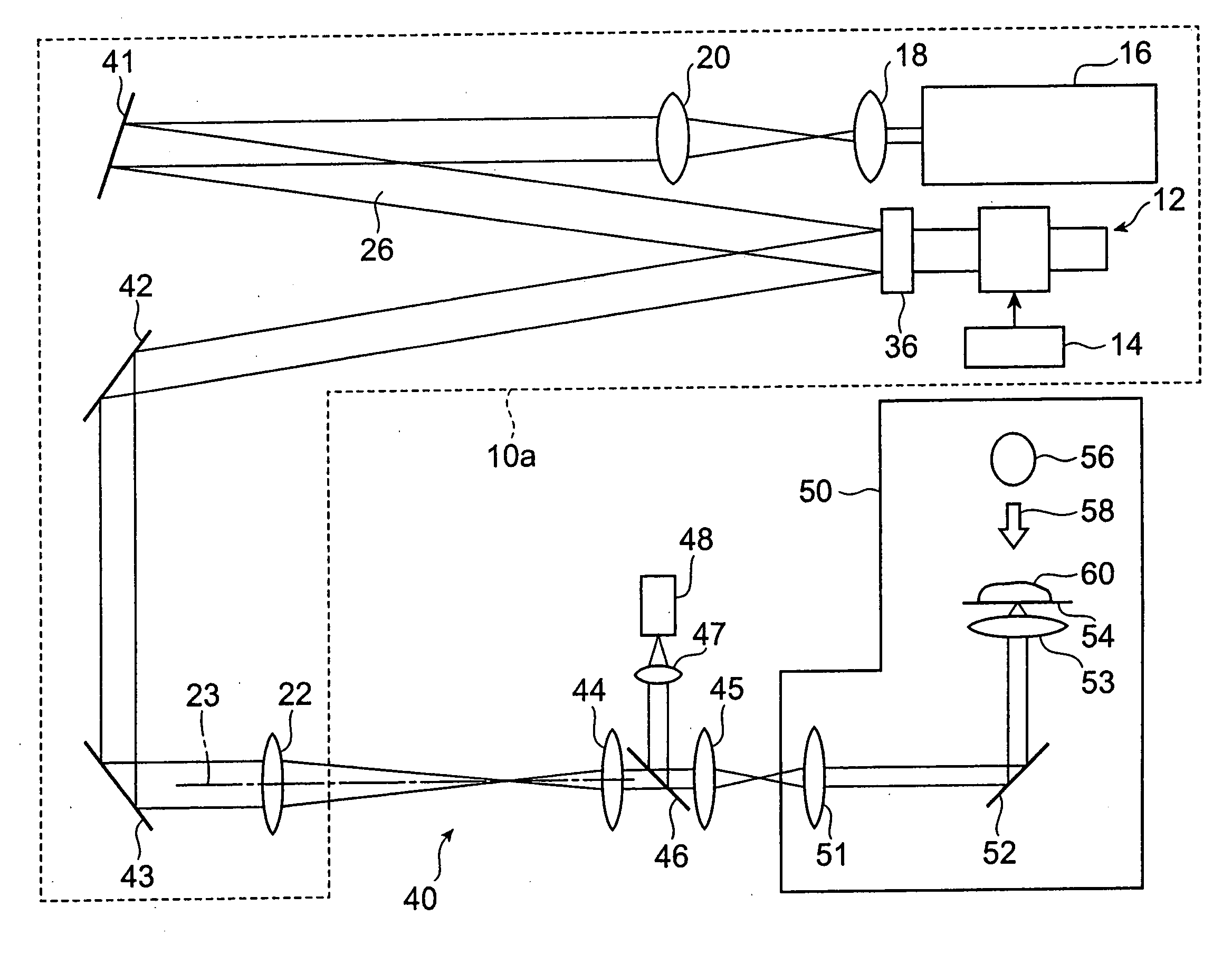
Patents
Literature
548 results about "Optical tweezers" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Optical tweezers (originally called single-beam gradient force trap) are scientific instruments that use a highly focused laser beam to provide an attractive or repulsive force (typically on the order of piconewtons), depending on the relative refractive index between particle and surrounding medium; these forces can be used to physically hold and move microscopic objects, in a manner similar to tweezers. They are able to trap and manipulate small particles, whose size is typically in microns, including dielectric and absorbing particles. Optical tweezers have been particularly successful in studying a variety of biological systems in recent years.
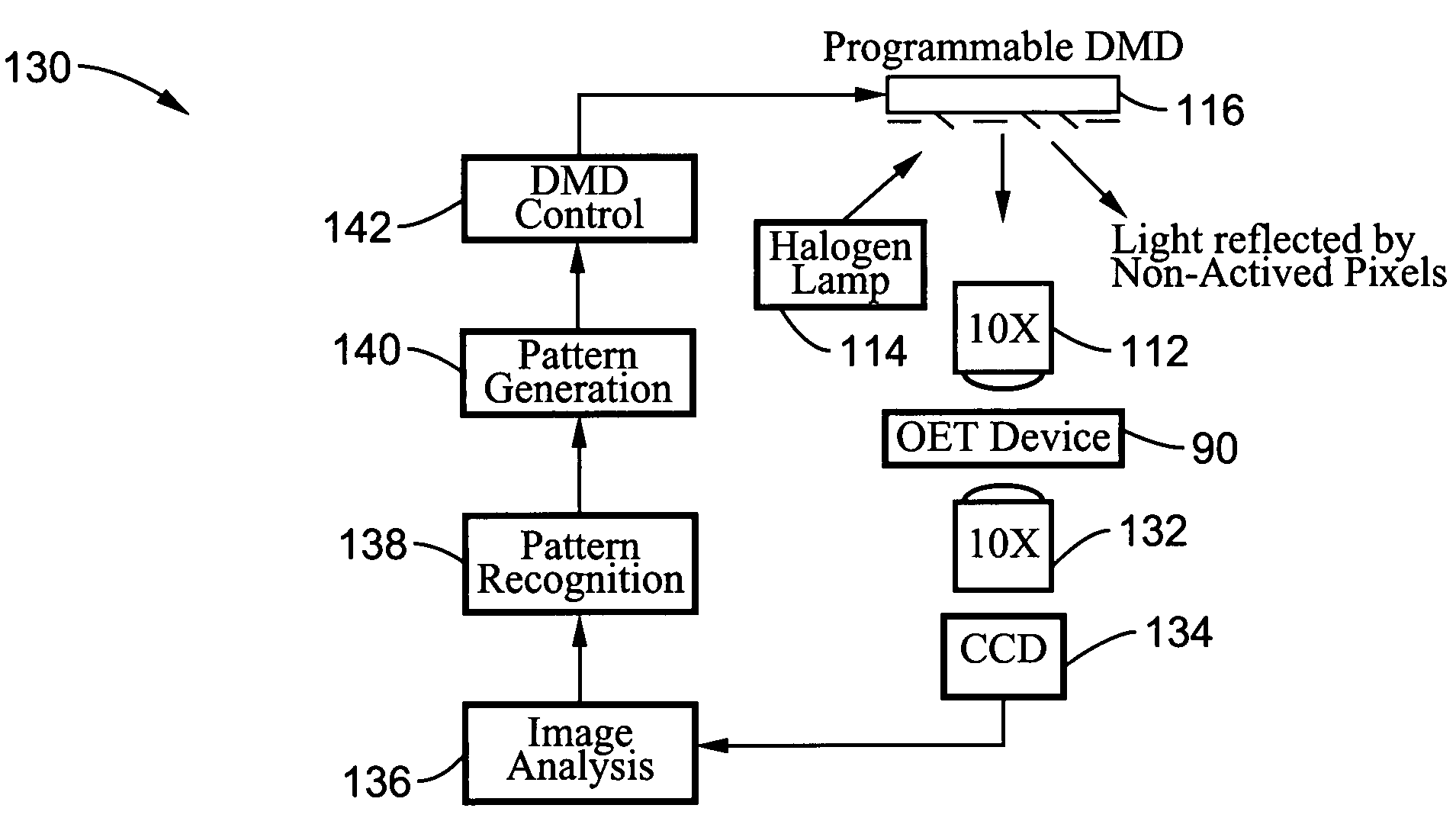
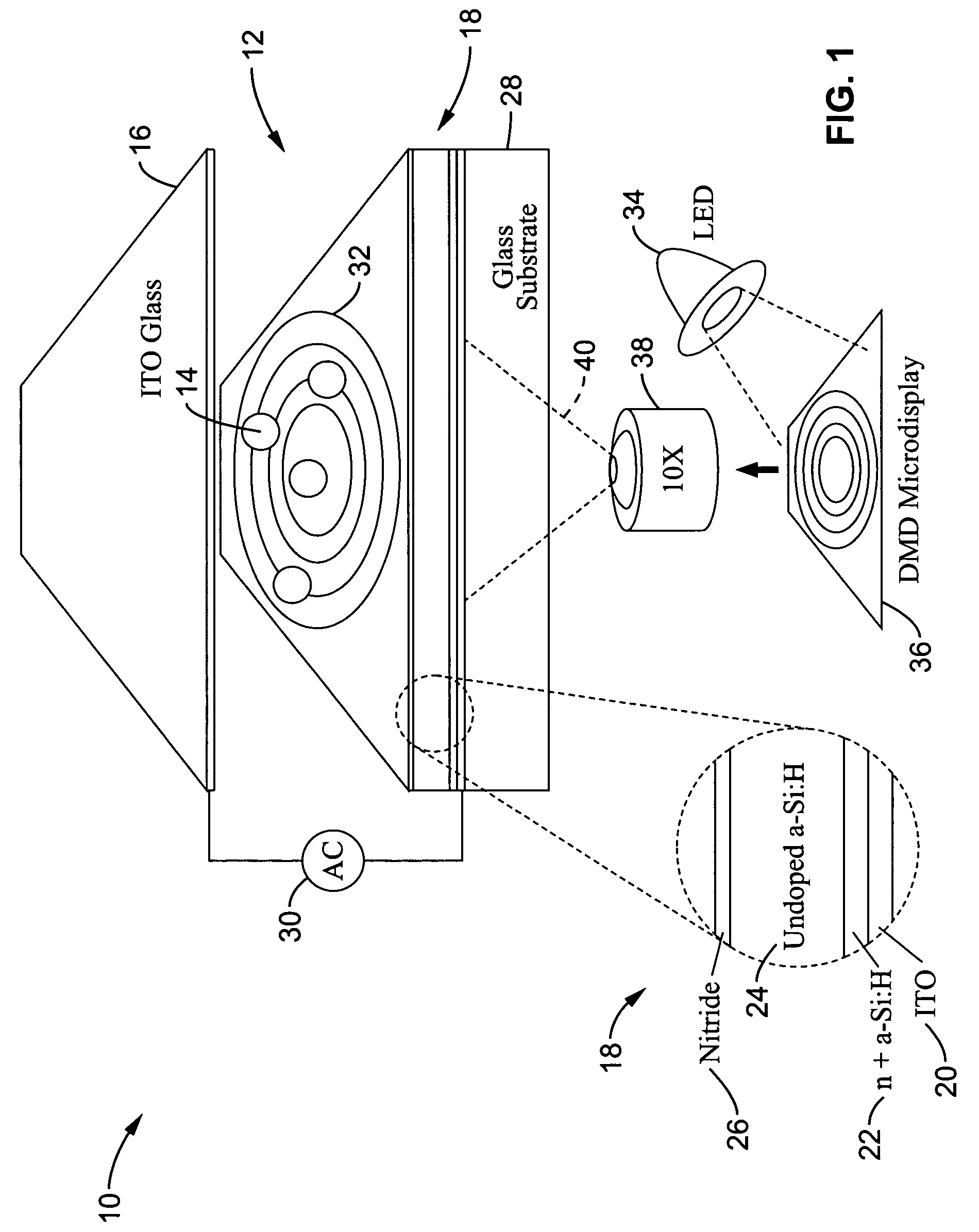
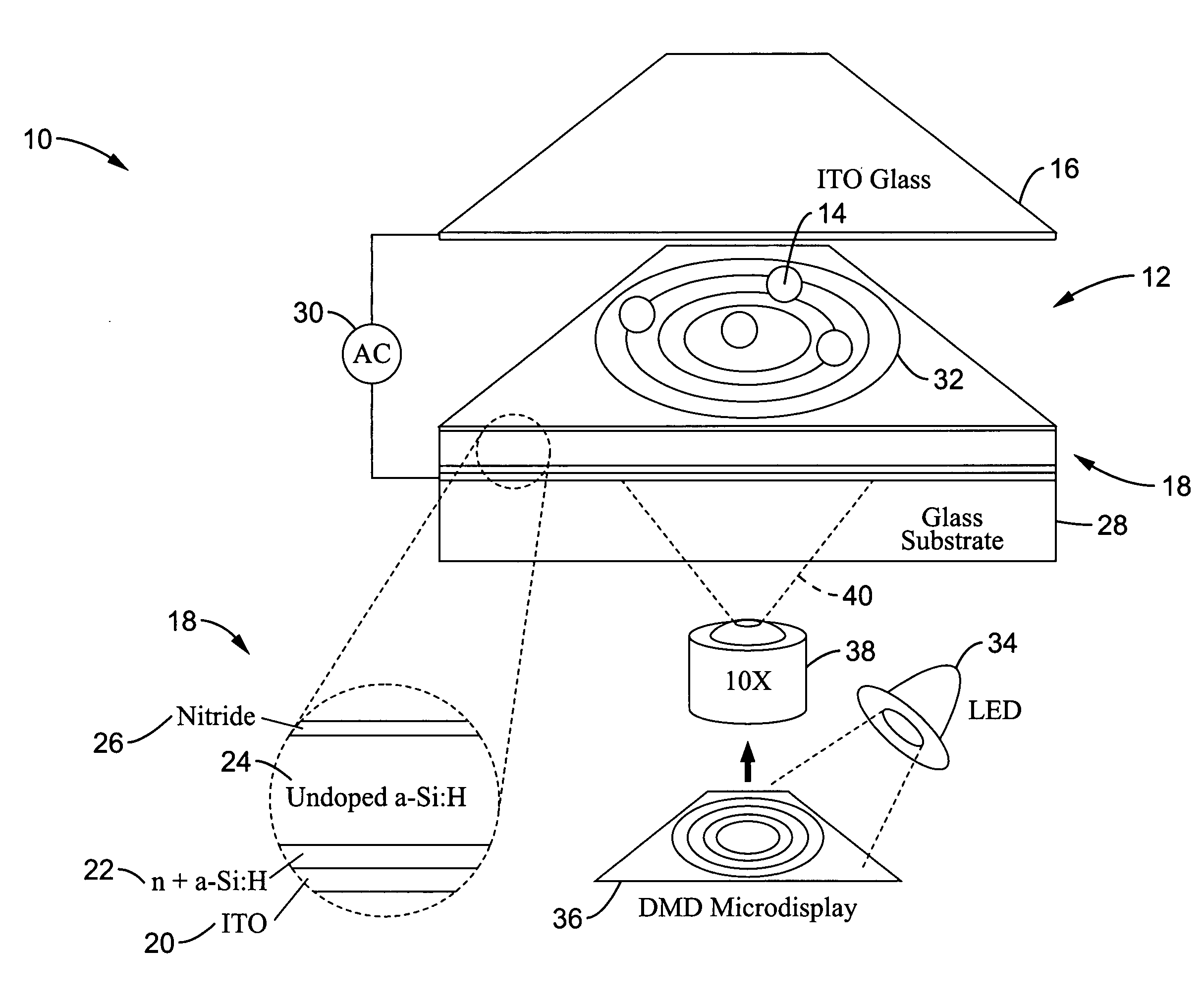
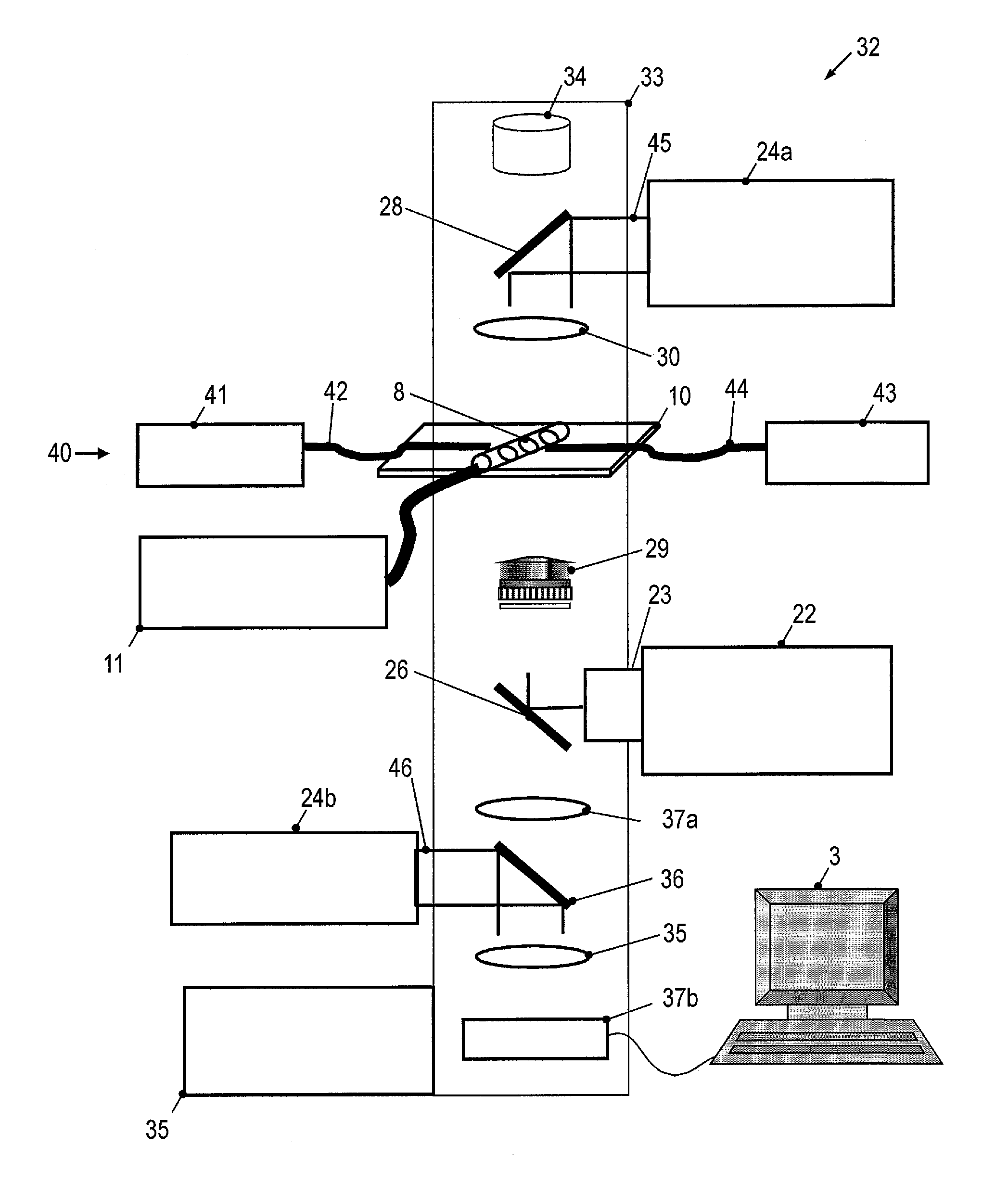
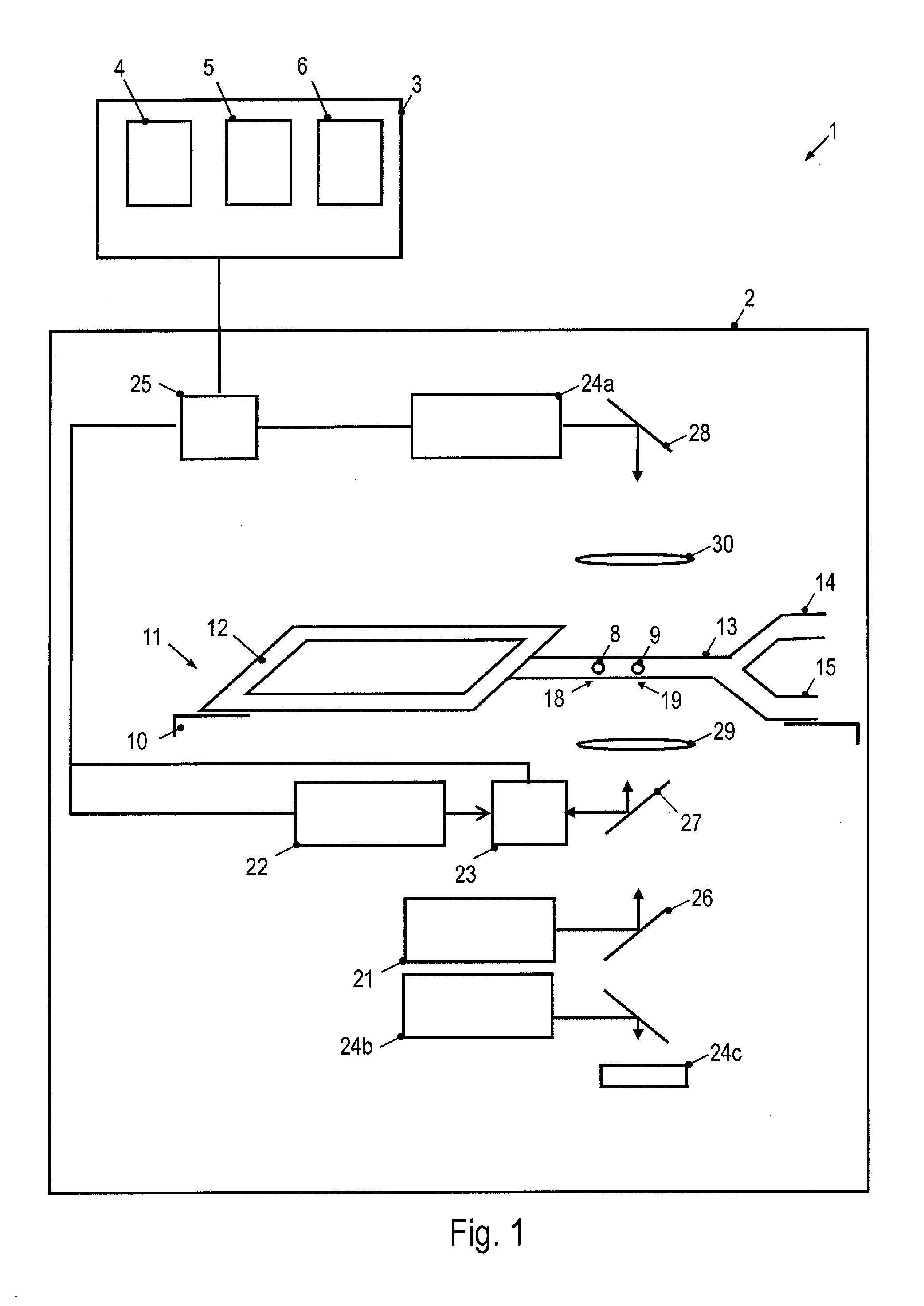
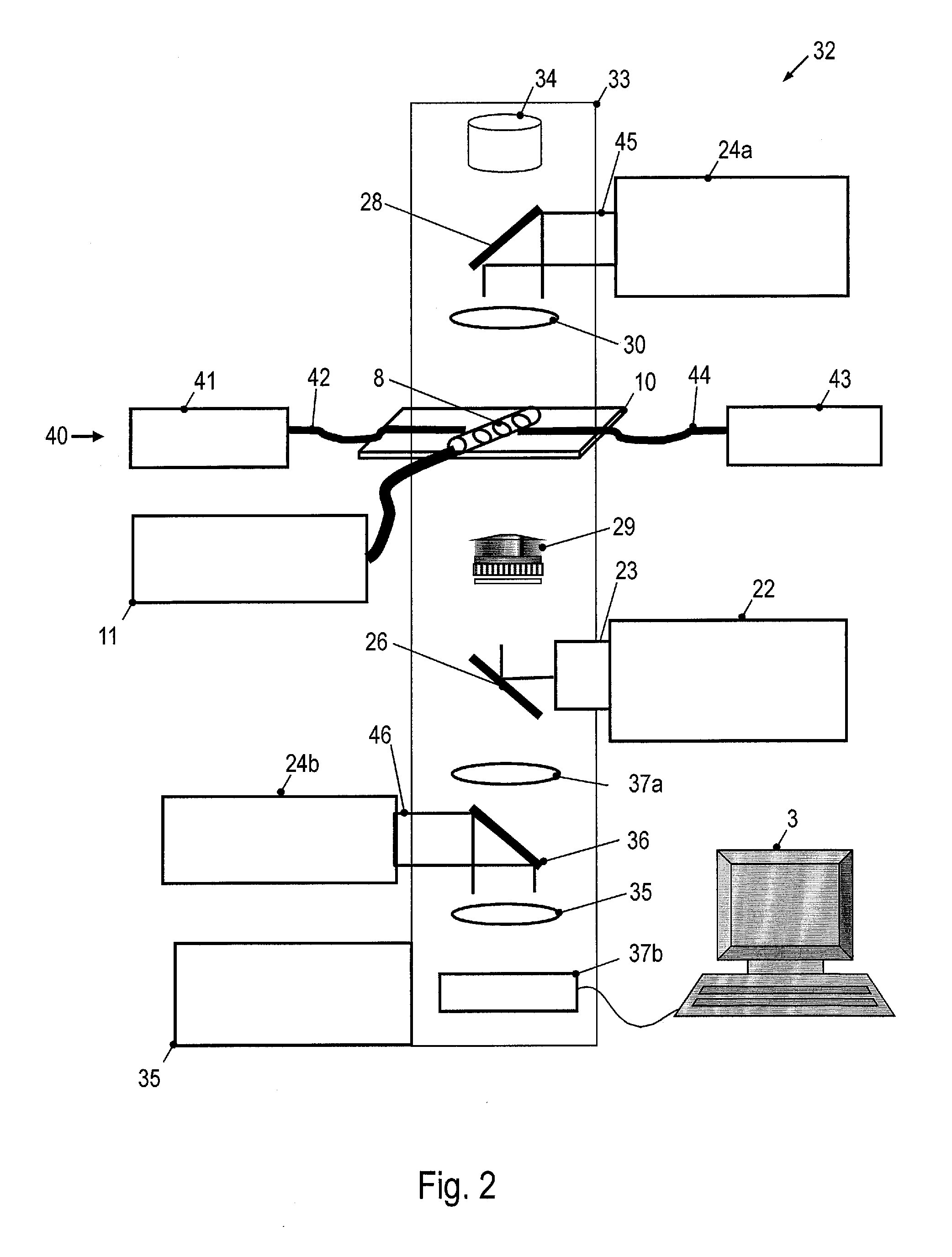
Optoelectronic tweezers for microparticle and cell manipulation
ActiveUS7612355B2Easy to operateEasy to createElectrostatic separatorsSludge treatmentMicroparticleOpto electronic
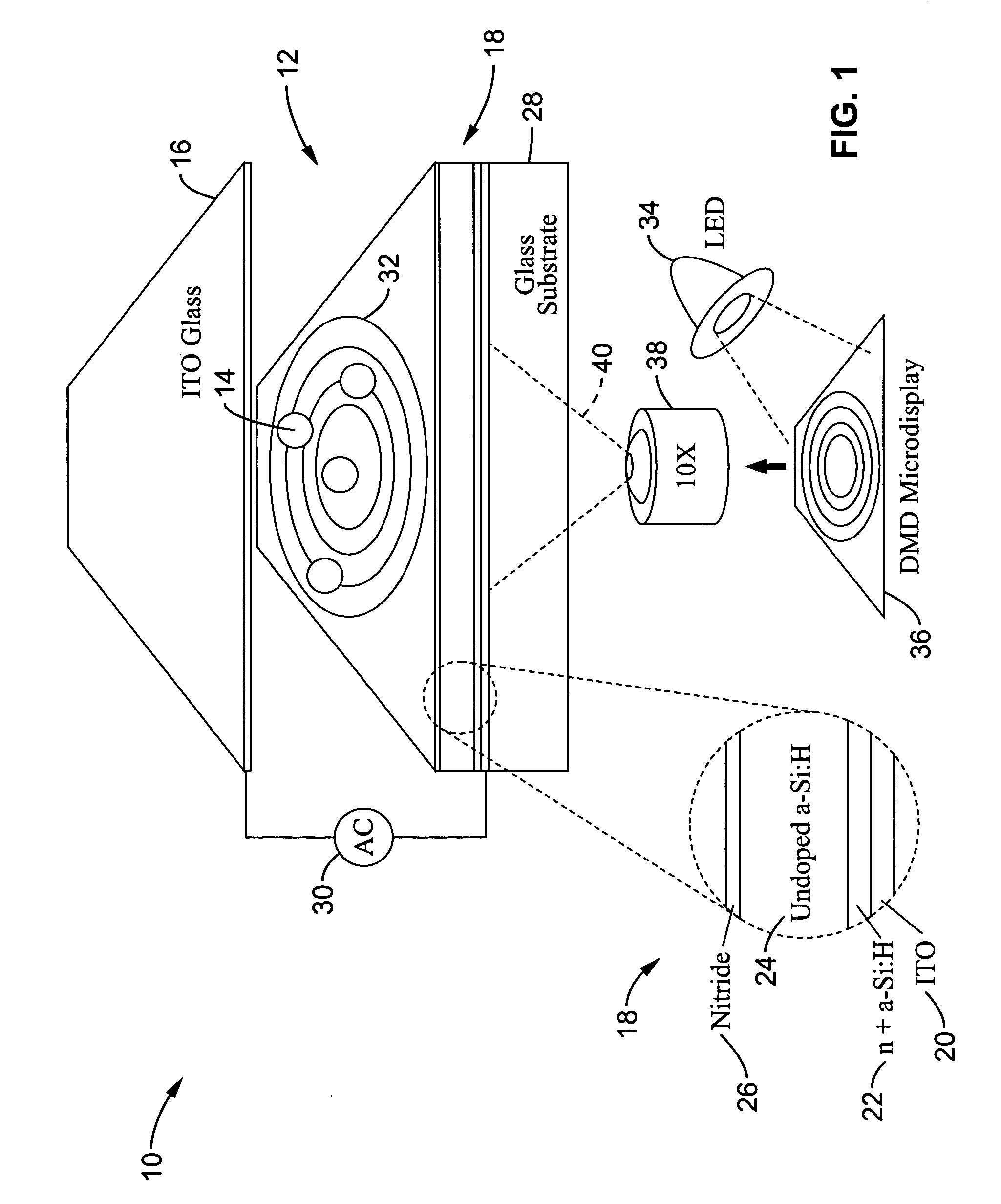
An optical image-driven light induced dielectrophoresis (DEP) apparatus and method are described which provide for the manipulation of particles or cells with a diameter on the order of 100 μm or less. The apparatus is referred to as optoelectric tweezers (OET) and provides a number of advantages over conventional optical tweezers, in particular the ability to perform operations in parallel and over a large area without damage to living cells. The OET device generally comprises a planar liquid-filled structure having one or more portions which are photoconductive to convert incoming light to a change in the electric field pattern. The light patterns are dynamically generated to provide a number of manipulation structures that can manipulate single particles and cells or groups of particles / cells. The OET preferably includes a microscopic imaging means to provide feedback for the optical manipulation, such as detecting position and characteristics wherein the light patterns are modulated accordingly.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Optoelectronic tweezers for microparticle and cell manipulation
ActiveUS20090170186A1Easy to operateEasy to createElectrostatic separatorsSludge treatmentMicroparticleDielectrophoresis
An optical image-driven light induced dielectrophoresis (DEP) apparatus and method are described which provide for the manipulation of particles or cells with a diameter on the order of 100 μm or less. The apparatus is referred to as optoelectric tweezers (OET) and provides a number of advantages over conventional optical tweezers, in particular the ability to perform operations in parallel and over a large area without damage to living cells. The OET device generally comprises a planar liquid-filled structure having one or more portions which are photoconductive to convert incoming light to a change in the electric field pattern. The light patterns are dynamically generated to provide a number of manipulation structures that can manipulate single particles and cells or groups of particles / cells. The OET preferably includes a microscopic imaging means to provide feedback for the optical manipulation, such as detecting position and characteristics wherein the light patterns are modulated accordingly.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Multiple laminar flow-based particle and cellular separation with laser steering
InactiveUS20050121604A1Save a lot of timeImprove throughputDielectrophoresisLaser detailsCellular componentBlood component
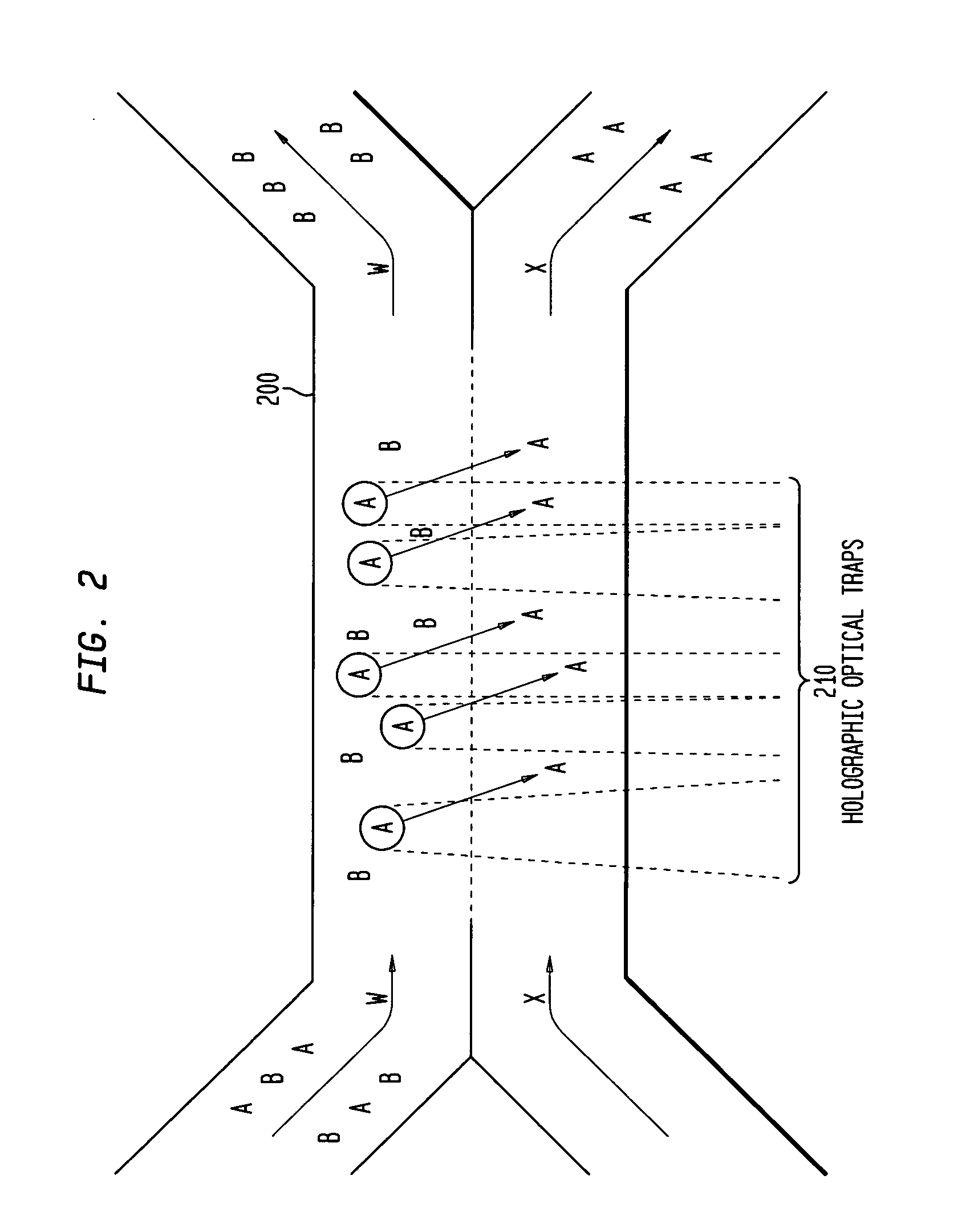
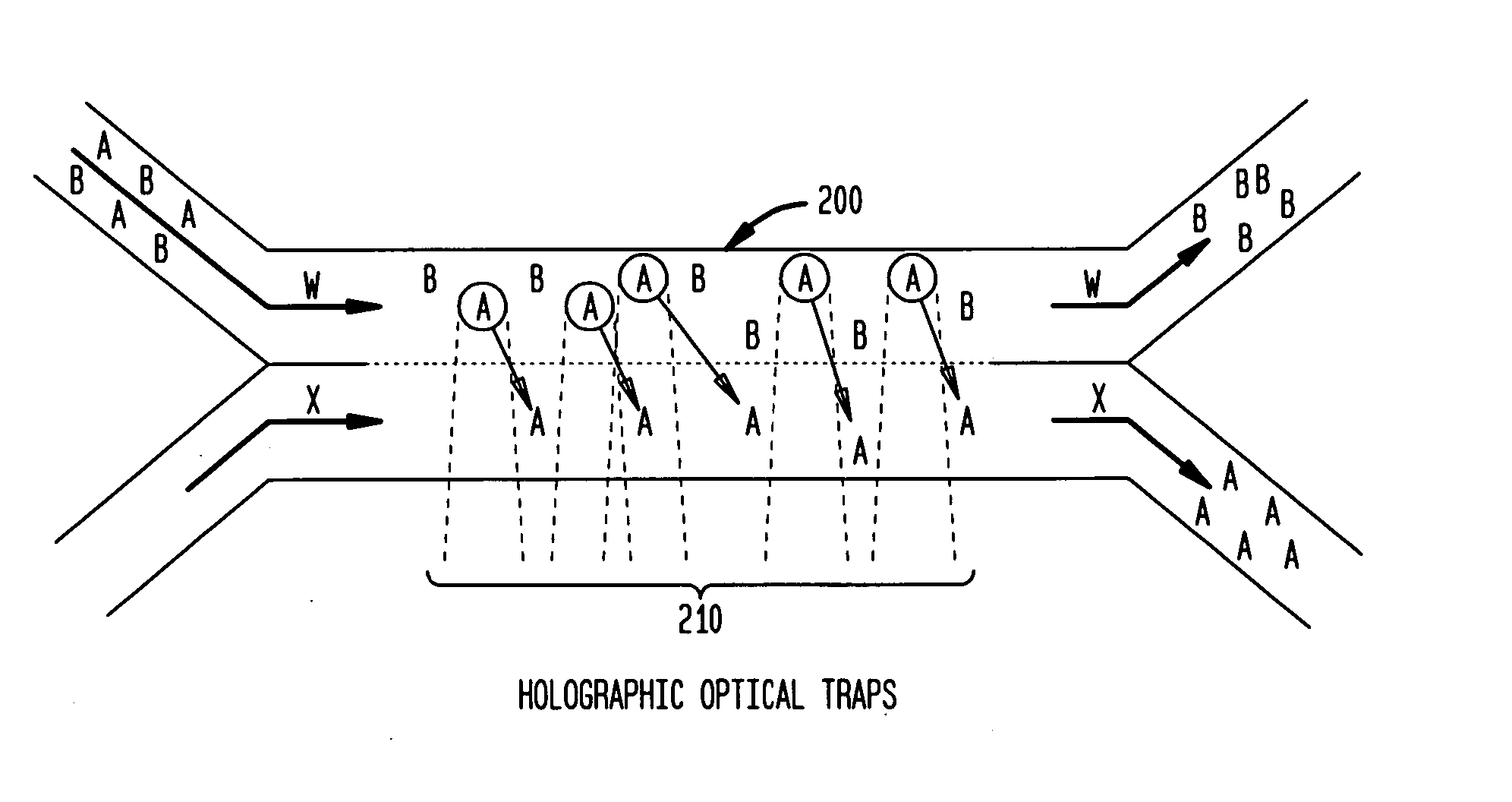
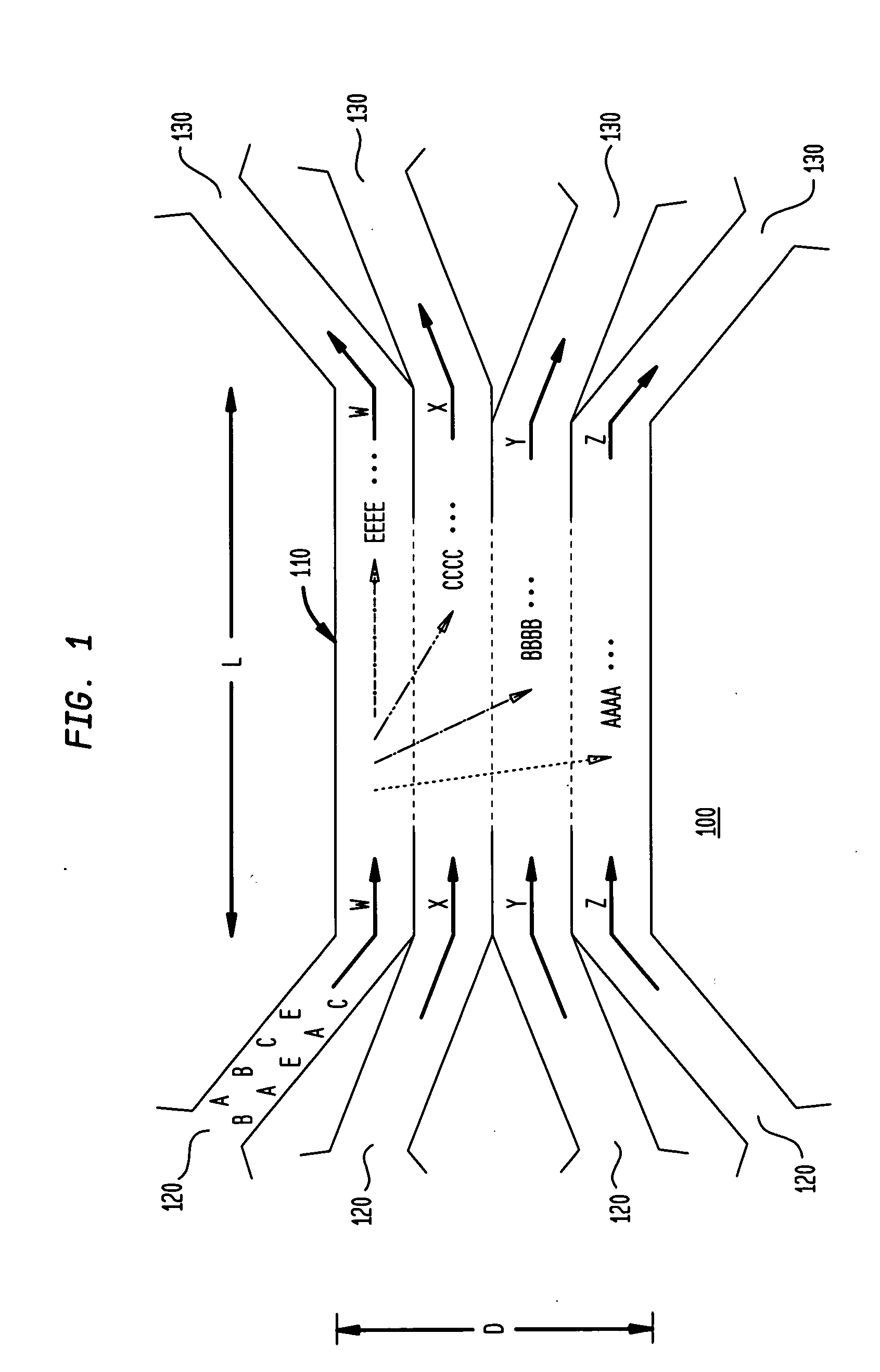
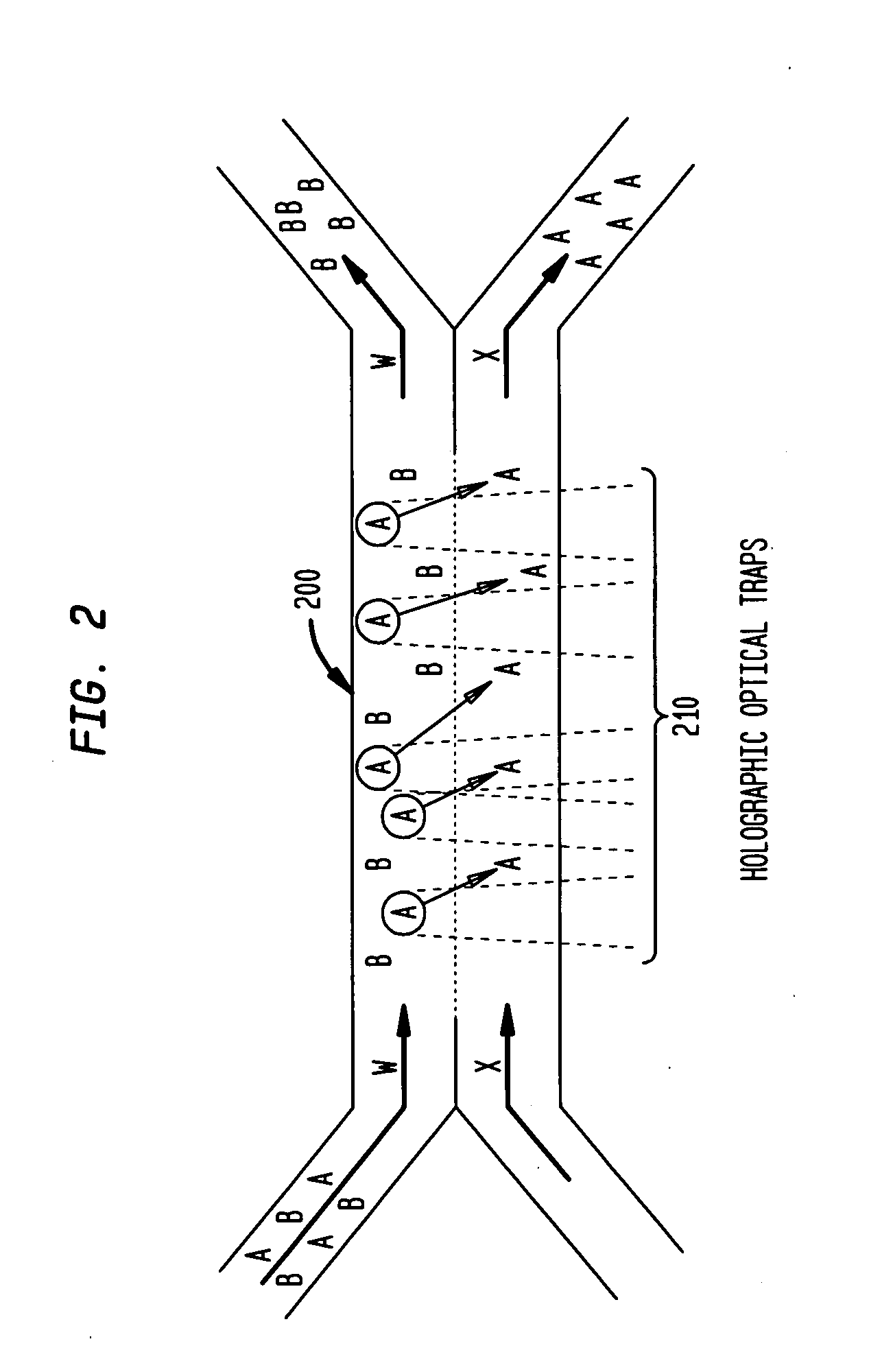
The invention provides a method, apparatus and system for separating blood and other types of cellular components, and can be combined with holographic optical trapping manipulation or other forms of optical tweezing. One of the exemplary methods includes providing a first flow having a plurality of blood components; providing a second flow; contacting the first flow with the second flow to provide a first separation region; and differentially sedimenting a first blood cellular component of the plurality of blood components into the second flow while concurrently maintaining a second blood cellular component of the plurality of blood components in the first flow. The second flow having the first blood cellular component is then differentially removed from the first flow having the second blood cellular component. Holographic optical traps may also be utilized in conjunction with the various flows to move selected components from one flow to another, as part of or in addition to a separation stage.
Owner:PREMIUM GENETICS UK
Multiple laminar flow-based rate zonal or isopycnic separation with holographic optical trapping of blood cells and other static components
ActiveUS20050061962A1Improve throughputSave a lot of timeDielectrophoresisOther blood circulation devicesCellular componentBlood component
The invention provides a method and apparatus for separating blood into components, may be expanded to include other types of cellular components, and can be combined with holographic optical manipulation or other forms of optical tweezing. One of the exemplary methods includes providing a first flow having a plurality of blood components; providing a second flow; contacting the first flow with the second flow to provide a first separation region; and differentially sedimenting a first blood cellular component of the plurality of blood components into the second flow while concurrently maintaining a second blood cellular component of the plurality of blood components in the first flow. The second flow having the first blood cellular component is then differentially removed from the first flow having the second blood cellular component. Holographic optical traps may also be utilized in conjunction with the various flows to move selected components from one flow to another, as part of or in addition to a separation stage.
Owner:ABS GLOBAL
Optofluidic microscope device with photosensor array
ActiveUS20110181884A1Improve abilitiesPrevent rotationScattering properties measurementsTransmissivity measurementsElectric fieldMicroscope
Embodiments of the present invention relate to techniques for improving optofluidic microscope (OFM) devices. One technique which may be used eliminates the aperture layer covering the light detector layer. Other techniques retain the aperture layer, reversing the relative position of the light source and light detector such that light passes through the aperture layer before passing through the fluid channel to the light detector. Another technique adds an optical tweezer for controlling the movement of objects moving through the fluid channel. Another technique adds an optical fiber bundle to relay light from light transmissive regions to a remote light detector. Another technique adds two electrodes at ends of the fluid channel to generate an electrical field capable of moving objects through the fluid channel while suppressing rotation. These techniques can be employed separately or in combination to improve the capabilities of OFM devices.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
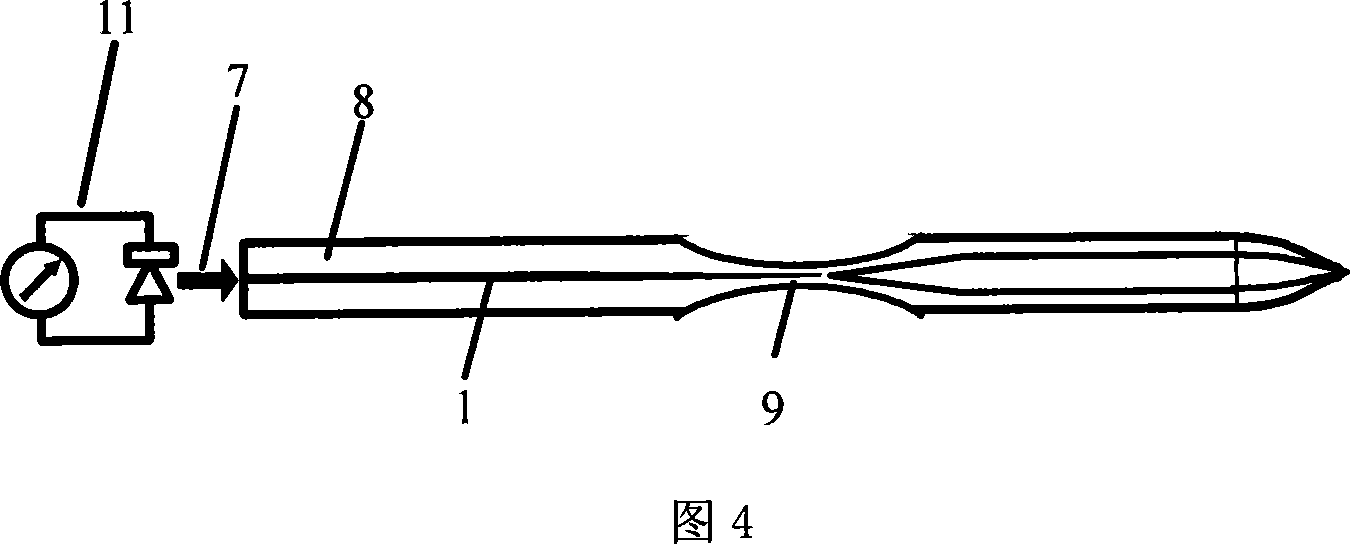
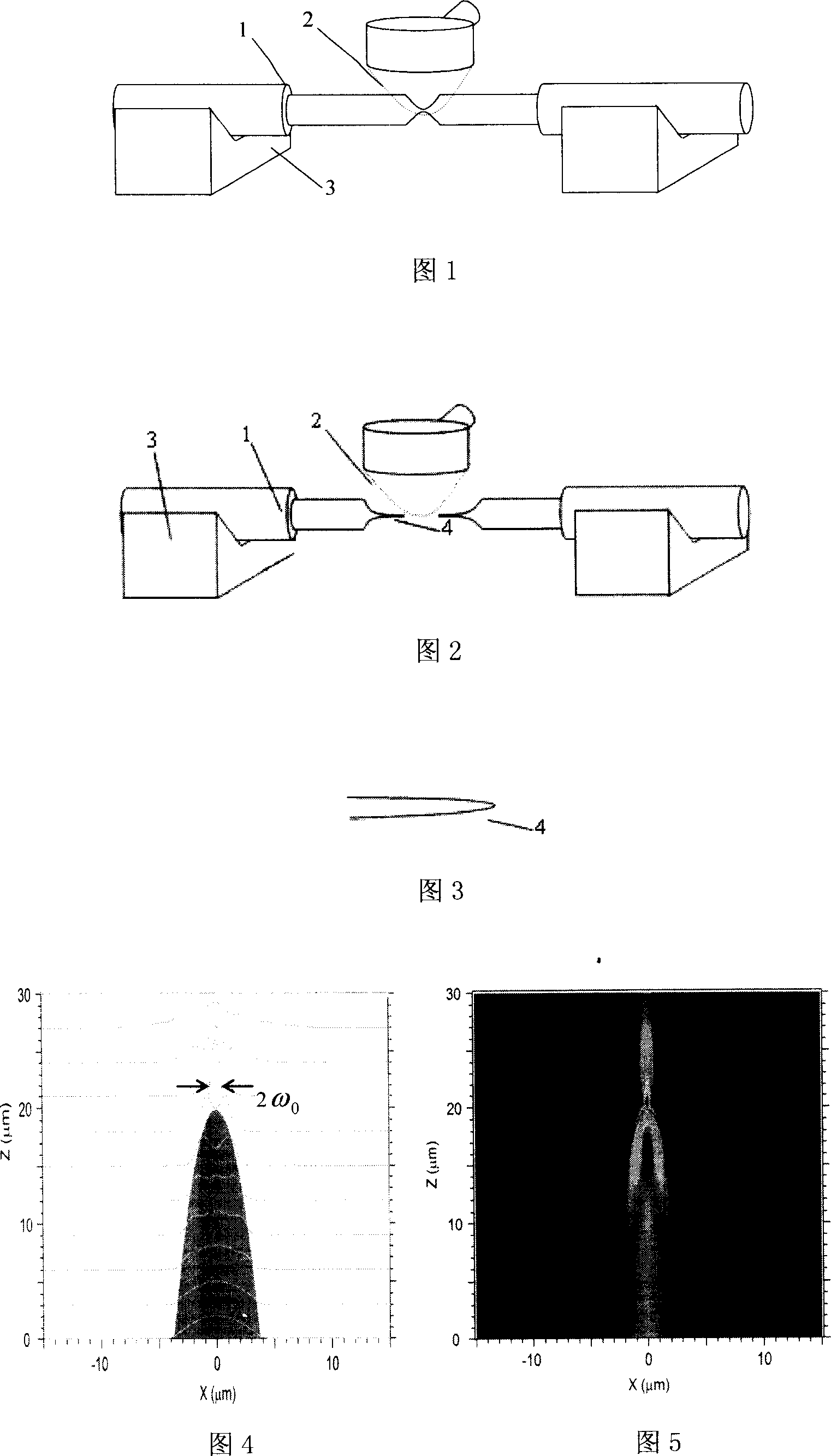
Double core single optical fiber optical tweezers for capturing minute particle and its manufacture method
InactiveCN101149449AOptimizing Mechanical Trapping PropertiesImproved capture characteristicsRadiation/particle handlingOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingLight beamSingle fiber
This invention provides a kind of twin-core single fiber light probe which is used to seize minute particle and its preparation method. It includes the fiber, the said fiber is win-core fiber which includes two individual fiber cores in fiber public cladding, one end of the fiber is fused probe and the sintered cone fiber tip, and one end of the cone fiber tip has lenticule. The twin-core fiber light probe in this invention has two optical conversion section, one is twin-beam across lange-angle derivation collection section, changes the transmit direction of light wave in each fiber core of the twin-core fiber by the cone fiber whose cone angle change quickly, to lead the two beam to the tip end of the cone fiber; the other is light field compression section which forms large grads light field, realizes the light field compression of two beam by the lenticule in fiber tip end. The twin-core fiber light probe provided in this invention can be used for seizing the live biologic cell or the fixation, transpor and assembly of minute particles.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
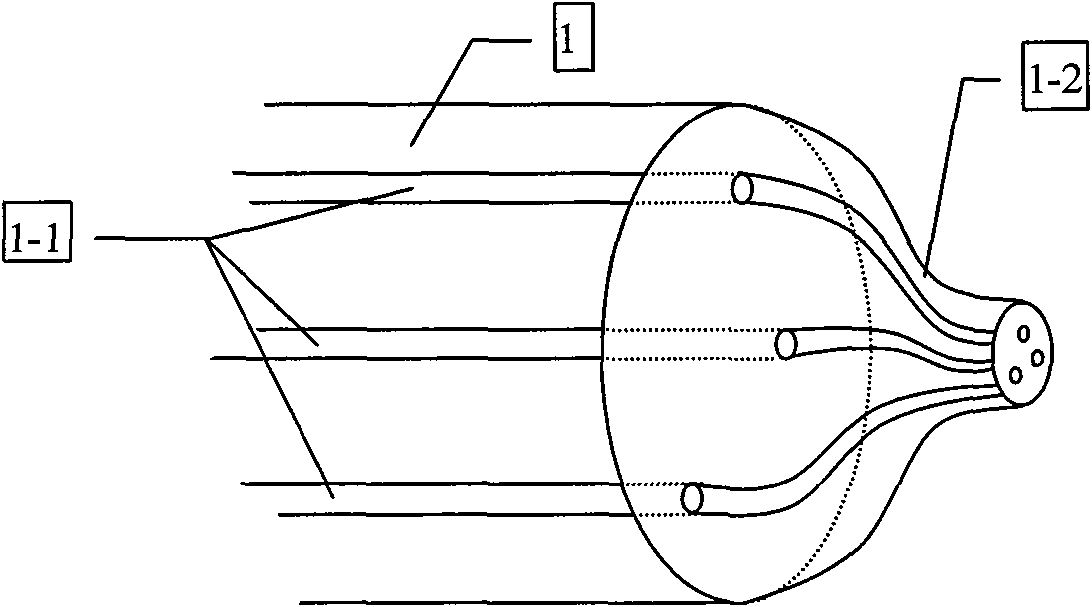
Array optical tweezers based on multicore polarization-preserving fiber and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN101907742AReduce harmSave physical spaceRadiation/particle handlingOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingPhysical spacePolarization-maintaining optical fiber
The invention provides array optical tweezers based on multicore polarization-preserving fiber and a manufacturing method thereof. The array optical tweezers comprise the multicore polarization-preserving fiber, standard single-mode fiber and a laser light source, wherein the laser light source is connected with one end of the standard single-mode fiber, the other end of the standard single-mode fiber is connected with the multicore polarization-preserving fiber in a fusion conical pull coupling mode, and the other end of the multicore polarization-preserving fiber is manufactured into a centrum shape through fusion conical pull processing equipment. In the invention, a plurality of optical waveguide fiber cores are integrated in one fiber, thus not only saving physical space but also significantly reducing system input light power and reducing harm on particles to be captured. Meanwhile, the multicore fiber composite optical tweezers can capture particles more flexibly and accurately, and has adjustability, thus greatly improving the practicability of fiber and optical tweezers technologies. More importantly, the array optical tweezers can form a compact interference grid optical field array, so as to form optical potential wells at coherence enforcement points to realize functions such as filtering particles.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Multifunctional optical micro-control device
InactiveCN101216414AOvercome singleOvercome deficienciesSurface/boundary effectMaterial analysis by optical meansFemto second laserCcd camera
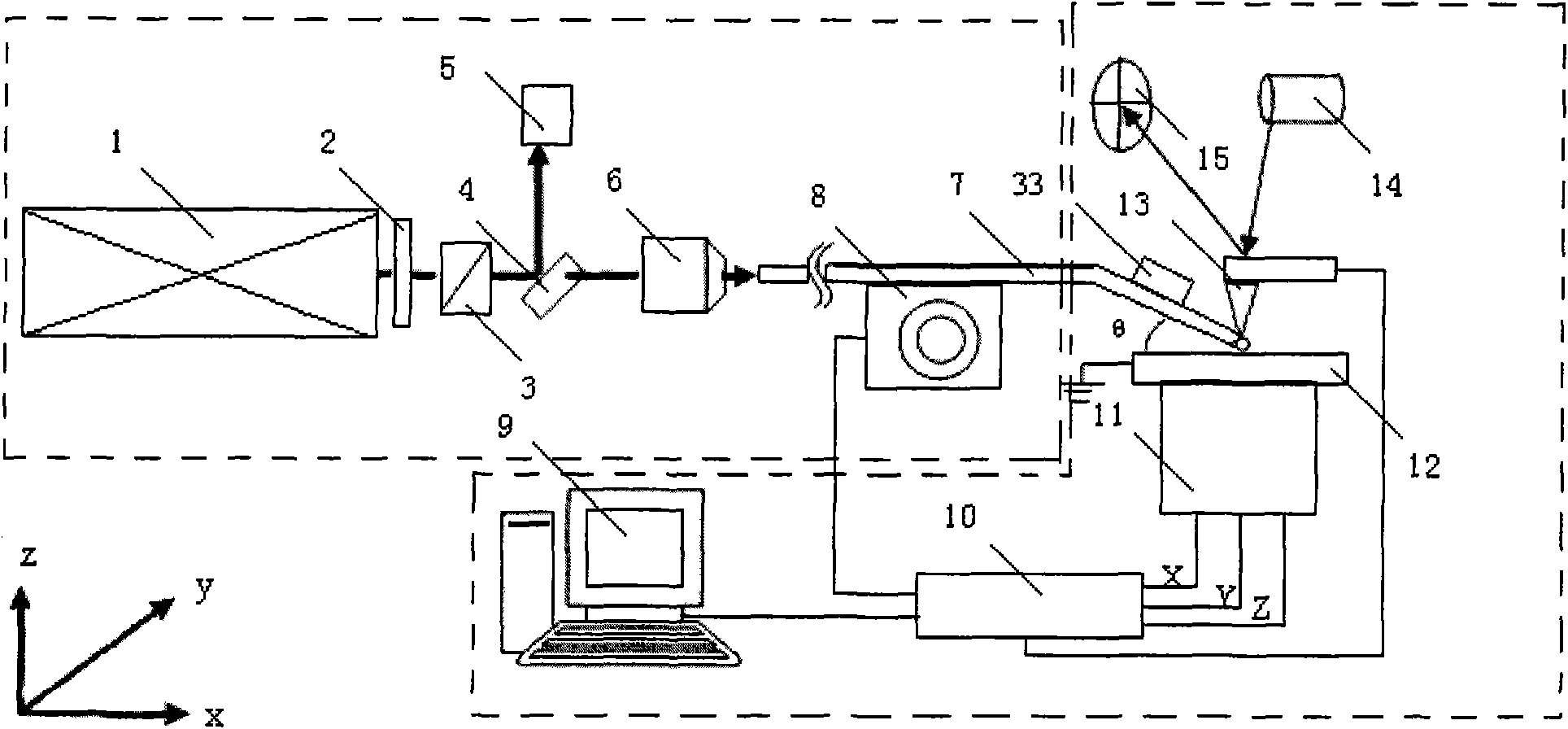
A multifunctional optical micro-manipulation device comprises a femtosecond laser, an optical tweezers laser, an optical system, a stage, a light source system, an imaging system, a spectral measurement system and a computer, wherein the optical system comprises a shutter, an attenuator, a focusing lens, a near IR reflector and a microscopic objective lens; the light source system comprises an illumination light source and a condenser lens; the microscopic objective lens is arranged on the stage for condensing a laser beam emitted by a laser generator onto a sample; the condenser lens is arranged below the stage for condensing a visible light emitted by the illumination light source onto the sample; and the imaging system includes an IR filter and CCD camera sequentially disposed on the projection light path of the near IR reflector. By integrating three functions of laser tweezers, femtosecond laser scissors and microspectrometer in one system, the invention can overcome the singleness and the disadvantages of the prior laser micro-beam technology and can be widely used for studying in biological, medical, biophysical, material chemistry and nano-technology fields.
Owner:XI'AN INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Achromatic Converter Of A Spatial Distribution Of Polarization Of Light
InactiveUS20090122402A1Reduce displayAberration correctionPolarising elementsNon-linear opticsHalf wavePhotolithography
An achromatic converter of spatial distribution of polarization from a first to a second pre-defined distribution of polarization is described. The converter comprises a plurality of photo-aligned quarter-wave or half-wave liquid crystal polymer layers, wherein the patterns of alignment of the layers are correlated with each other so as to make polarization conversion achromatic. Achromatic polarization vortices can be formed. The polarization conversion efficiencies over 97% have been demonstrated over most of the visible spectrum of light. The polarization converters can be used in imaging, photolithography, optical tweezers, micromachining, and other applications.
Owner:JDS UNIPHASE CORP
Near-field Raman spectroscopy
Near-field Raman imaging is performed by holding a dielectric microsphere (e.g. of polystyrene) on or just above the surface of a sample in a Raman microscope. An illuminating laser beam is focused by the microsphere so as to produce a near-field interaction with the sample. Raman scattered light at shifted wavelengths is collected and analysed. The microsphere may be mounted on a cantilever of an atomic force microscope or other scanning probe microscope, which provides feedback to hold it in position relative to the sample surface. Alternatively, the microsphere may be held on the sample surface by an optical tweezer effect of the illuminating laser beam.
Owner:RENISHAW PLC
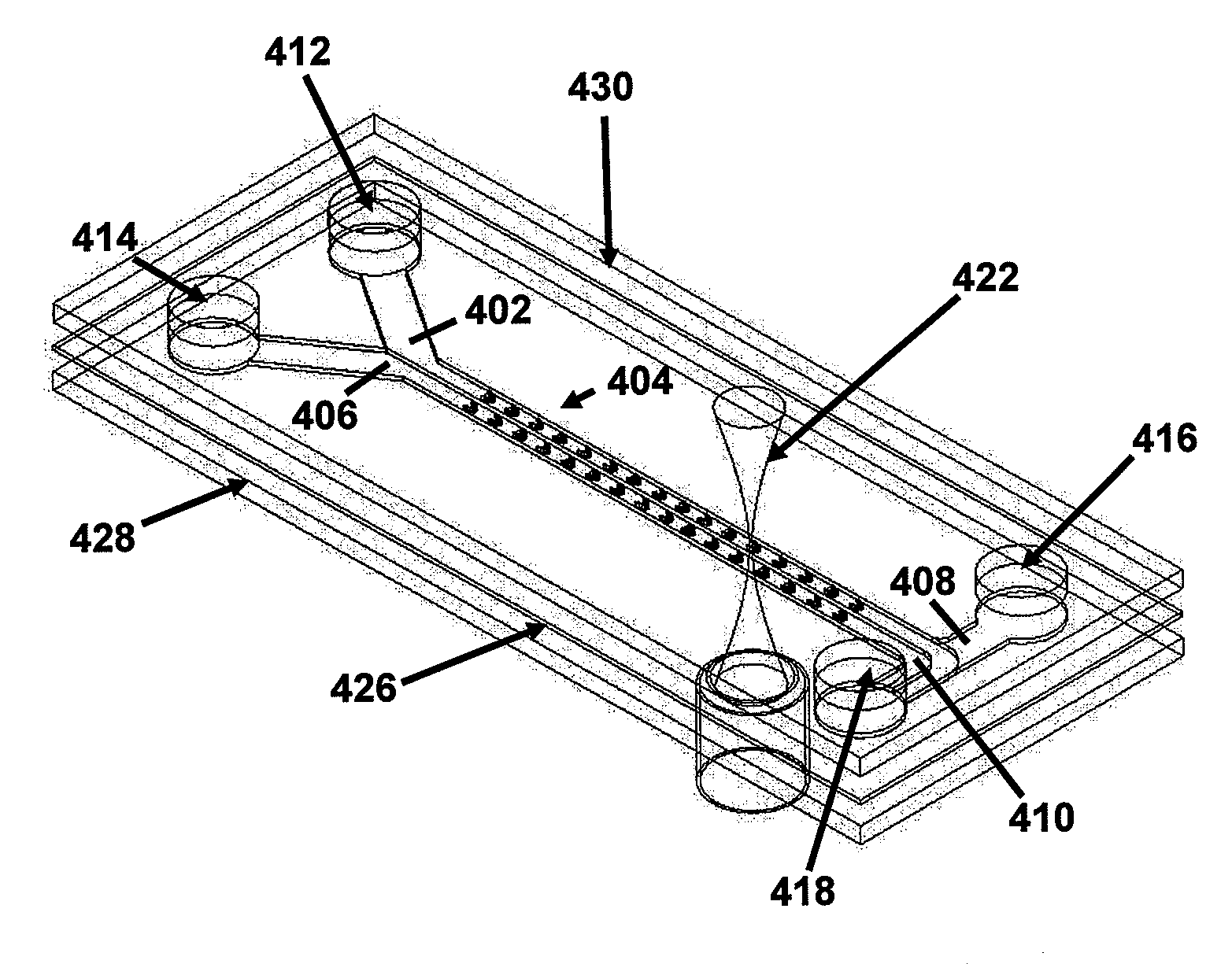
Combinatorial chemistry reaction cell with optical tweezers
InactiveUS20100273681A1Sequential/parallel process reactionsLaboratory glasswaresChemical reactionMulti stream
Methods for synthesizing chain molecules on particles in a multi-stream laminar flow, microfluidic reaction cells in which the methods can be carried out, and microfluidic systems incorporating the microfluidic reaction cells are provided. The methods, cells and systems are well suited for the rapid, large-scale production of chain biomolecules, such as oligonucleotides, in parallel.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Device for measuring fractional-order optical vortex topology charge values and measuring method thereof
Provided are a device for measuring fractional-order optical vortex topology charge values and a measuring method thereof. The measuring method comprises the steps of writing generated calculating holographic images into a spatial light modulator through a computer holographic technique, acquiring wrapped phase images of vortex light beams through Michelson interference light paths and a four-step phase shifting technique, analyzing distribution of real phases theta of the vortex light beams through a phase image unwrapping algorithm, and calculating according to the topology charge definition of m=theta / 2pi to obtain topology charge values m of any fractional-order accuracy. The device and method achieve the measurement of any step (0.1 step) of topology charge values of the fractional-order vortex light beams, can correct measurement of topology charge values of vortex light beams from existing half-integer step (0.5 step) to any step and can be widely applied to measurement of topology charge values in the fields of bose-einstein condensation, quantum communication, information coding and transmission, particle confinement, optical tweezers, optical wrenches and the like.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Sensor for nano gold particles and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103630515ASimple structureReduce volumeMaterial analysis by optical meansFiberGold particles
The invention provides a sensor for nano gold particles and a preparation method thereof. The end surface of a multi-core optical fiber is of a conical-platform structure; a total-reflection film is plated on the surface of the conical platform; the nano gold particles which are distributed regularly are fixed on the end surface of the optical fiber plated with the total-reflection film; exciting light is injected into one fiber core of the multi-core optical fiber, is reflected to the end surface of the optical fiber at the film-plated position of the conical platform and generates total internal reflection on the end surface of the optical fiber, and a generated evanescent field excites a localized surface plasmon resonance effect of the nano gold particles; the reflected light is collected by the fiber core symmetrical to the fiber core injected with the exciting light, and the change of the physical quantity of external substances is sensed by the spectrum of the reflecting light. The sensor and the preparation method have the advantages that the multi-core optical fiber, a self-assembly technology of a near-field optical tweezer and the localized surface plasmon resonance effect of the nano gold particles are combined, and the near-field optical tweezer of the multi-core optical fiber can be utilized for capturing the nano gold particles, so that the optical self-assembly and regular distribution is carried out on the nano gold particles according to the distribution rule of the capturing areas; the structure is simple, the volume is smaller and the repeatability is high.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Melting and pulling method for manufacturing optical tweezers of parabolic microstructure single fiber
InactiveCN1963583ARealization of single-fiber optical tweezersProcessing conditions no special requirementsGlass making apparatusMaterial analysis by optical meansSingle fiberOptoelectronics
This invention provides one single fiber light nipper melt process method to catch and operate arc micro structure for micro object, wherein, it processes one end of light fiber with arc micro structure light fiber; other end of fiber is coupled to micro light; the laser is reflected from fiber needle to form focus field to form stable three dimensional position well to realize single fiber light nipper.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
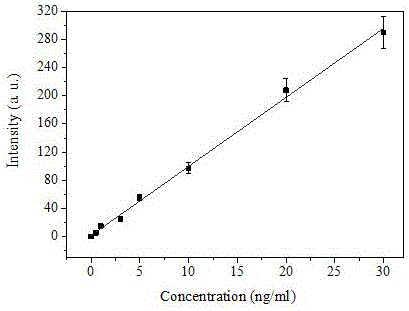
Liquid-phase suspension biochip based on multi-optical trap encoding bead array and two-photon fluorescence detection
InactiveCN105784662AReal-time analysisSimplify the enrichment processFluorescence/phosphorescenceMicrosphereBand-pass filter
The invention provides a liquid-phase suspension biochip based on multi-optical trap encoding bead array and two-photon fluorescence detection. The liquid-phase suspension biochip has a configuration as follows: a near-infrared laser beam emitted by a near-infrared laser is expanded by a beam expanding system, is sequentially reflected by a telescope system and a dichroscope by using a holographic technology or a time-share scanning technology, and is focused into a sample pool through a high numerical aperture objective lens, to form multi-optical-trap optical tweezers; the multi-optical-trap optical tweezers capture a plurality of encoding beads enriched with objects to be detected, to form a bead array in the solution; after an infrared laser signal is filtered by a band-pass filter, a two-photon fluorescence signal from each bead is focused to an image detector by a lens and is subjected to imaging detection. The liquid-phase suspension biochip can perform real-time quantitative analysis on nucleic acids, proteins, virus particles and a plurality of objects to be detected, and has the advantages of high sensitivity, strong anti-interference ability, simultaneous determination of a plurality of components and the like.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
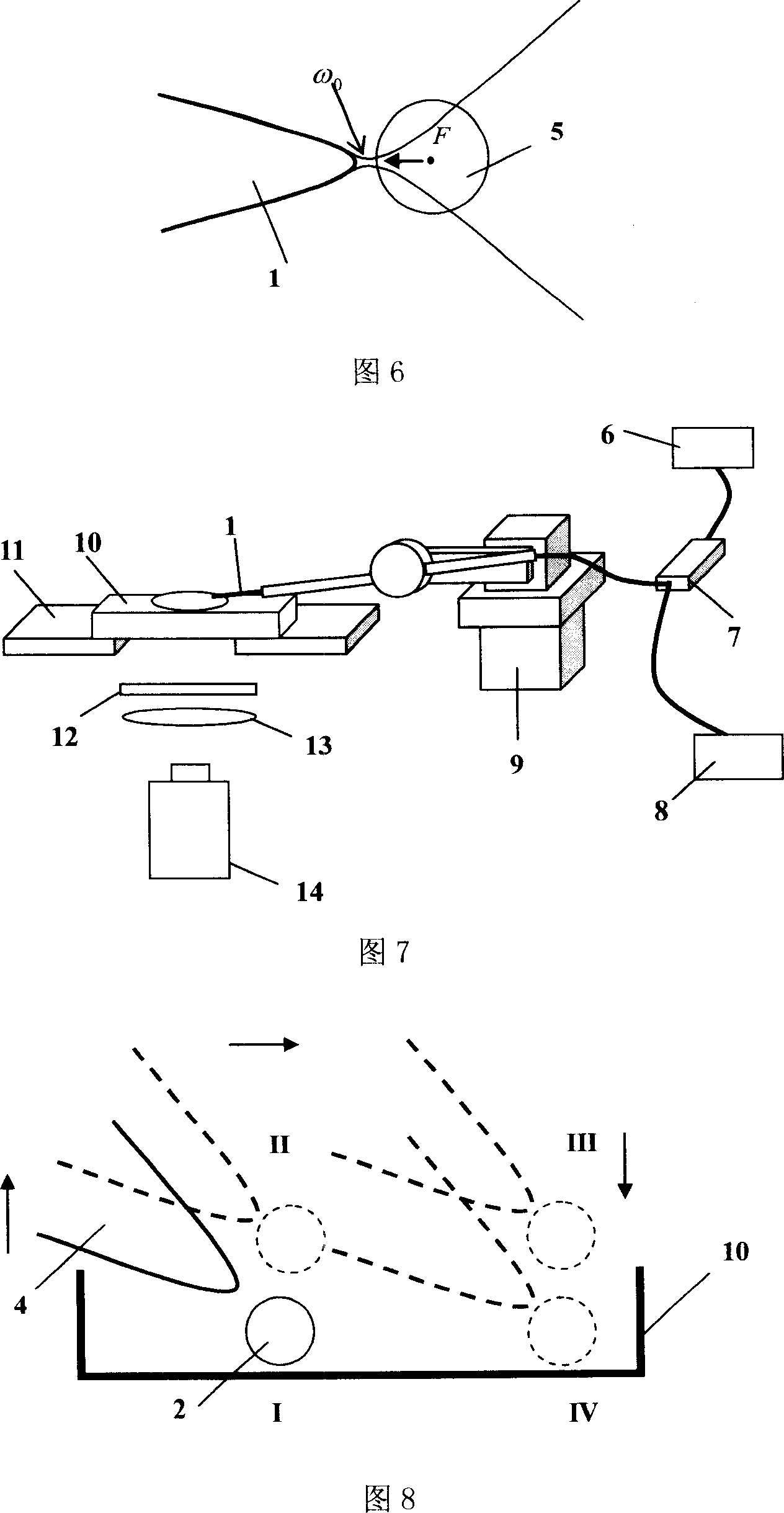
Capillary pipe optical fibre light forceps and its manufacture method
The invention provides a capillary fiber optical tweezers and a manufacturing method thereof. One end of the hollow capillary fiber with an annular core layer is processed with a cone which causes the emergent light to form an annular pyramidal decussation light field; a small hole is opened on one side of the middle of the hollow capillary optical fiber with the annular core layer; the small hole is connected with a barometric pressure adjusting device and the other end of the hollow capillary optical fiber with the annular core layer is welded with a standard solid optical fiber; the standard solid optical fiber and the hollow capillary optical fiber with the annular core layer are integrated into a whole by drawing the welding position into a conical transition region. In the capillary fiber optical tweezers of the invention, the capillary provides a storage location for micro particles; on one hand, the captured micro particles can be stored in the capillary through the micro negative pressure absorption function in the capillary; on the other hand, the micro particles can be supplied to a fiber-end tweezers through micro positive pressure, thus realizing the operation of continuous assembly of a large amount of micro particles.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Optical tweezers type optical fiber Raman microprobe and manufacturing method
The invention provides an optical tweezers type optical fiber Raman microprobe and a manufacturing method. The probe has two optical channels which are coaxial, wherein an annular optical fiber core provides a Raman exciting light channel and a channel in the coaxial center is used for receiving Raman probe light; and by performing fine taper angle grinding on the fiber ends of coaxial dual waveguide channel optical fibers, a rotary symmetrical plane (or chambered surface) structure is formed. The structure can converge Raman exciting light transmitted by the annular core in a micron order, and on the one hand, the converged exciting light has an ability of capturing micron-order and nanoscale particles and on the other hand, the converged exciting light interacts with the particles, so that a back scattering Raman optical signal generated by the exciting light converged by the Raman scattering light can be collected and transmitted to a Raman spectrometer through an intermediate large-core fire cores. The microprobe provided by the invention can capture micro living matters of cell living bodies to effectively excite the Raman spectrum of the matters in cells and to obtain the Raman spectrum so as to achieve Raman measurement of micro liquids, single cells in living bodies and inner substances thereof.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
Optofluidic microscope device with photosensor array
ActiveUS8314933B2Improve abilitiesPrevent rotationScattering properties measurementsMicroscopePhotoelectric sensor
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
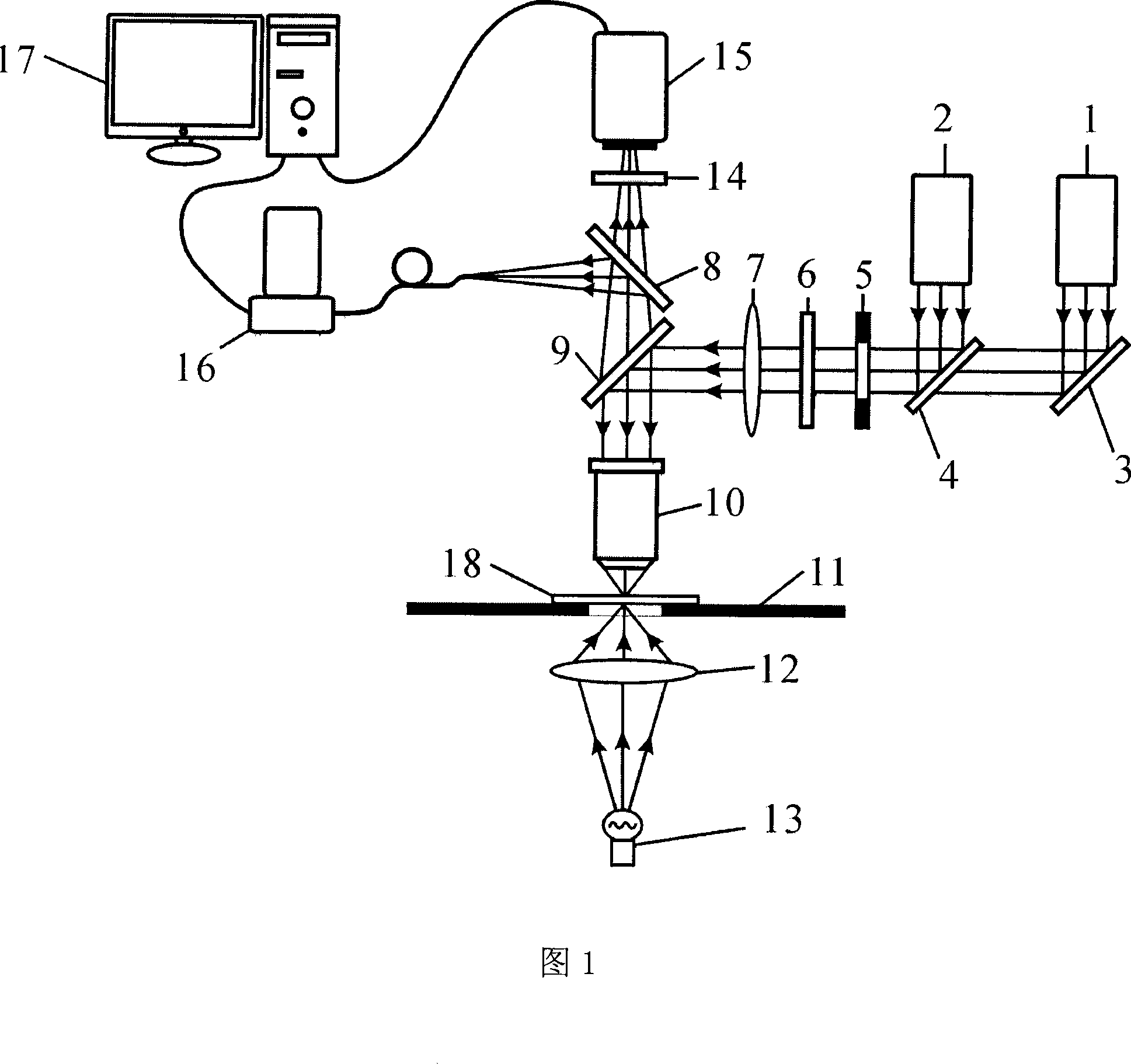
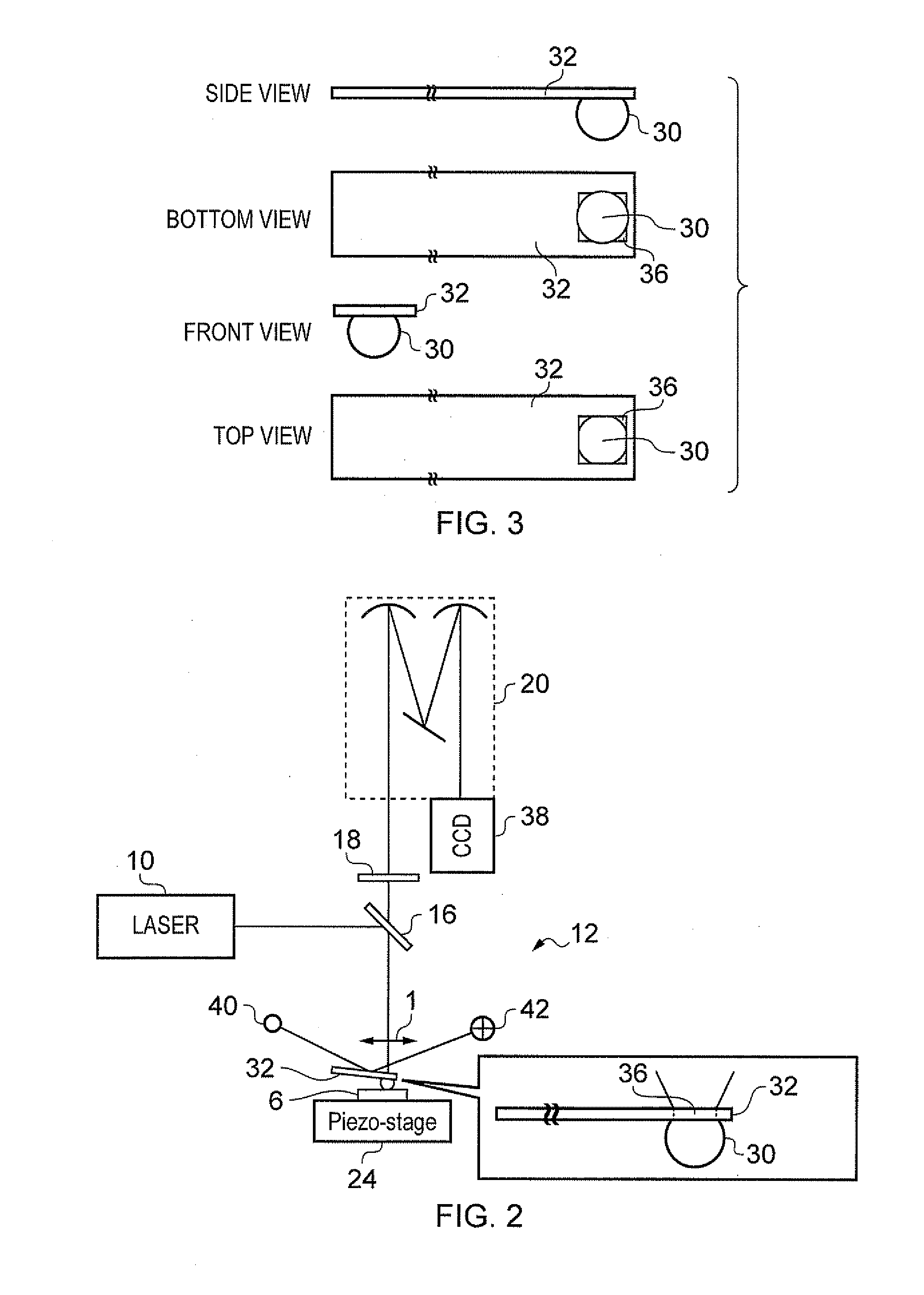
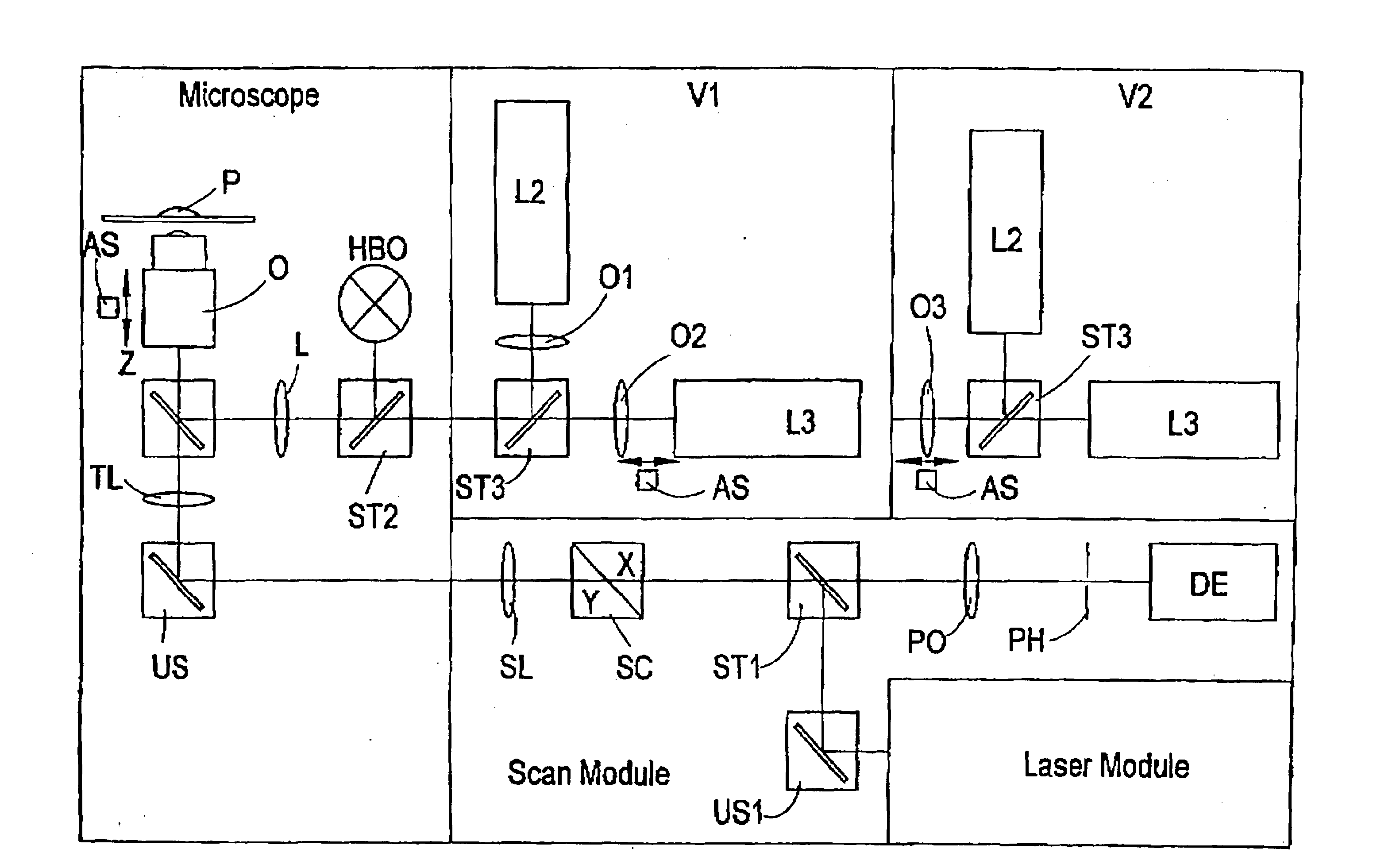
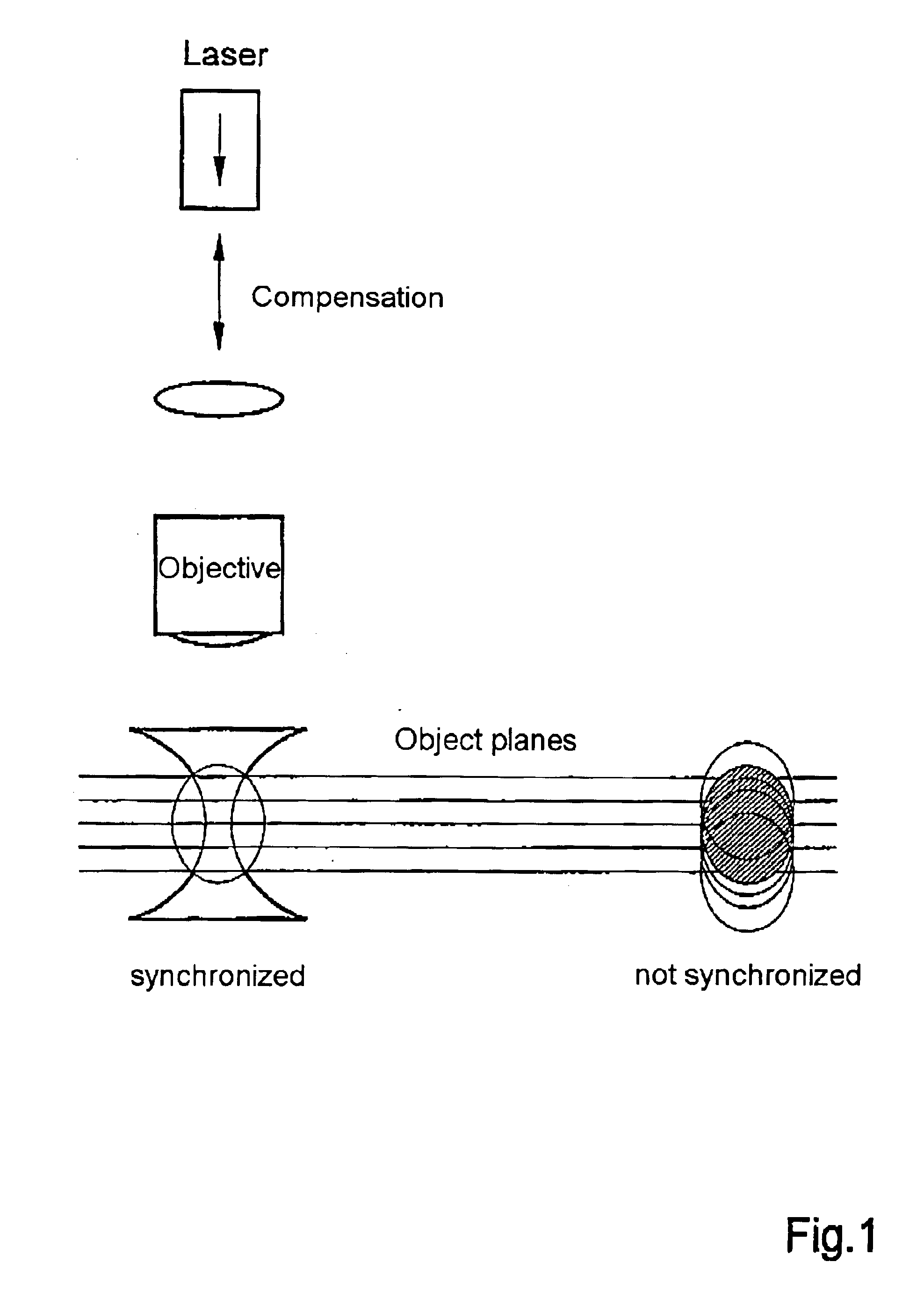
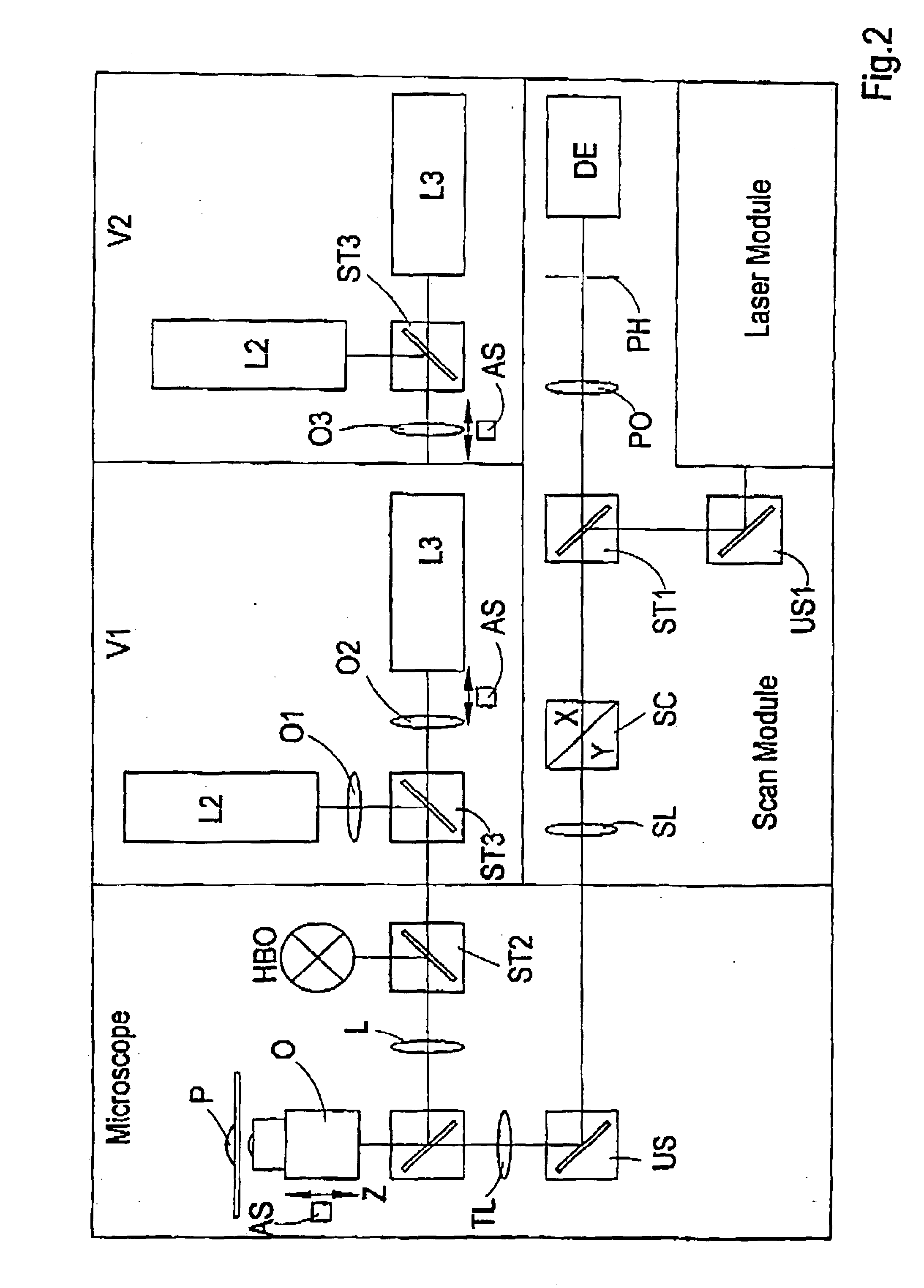
System for introducing optical tweezers and/or a treatment beam into a laser scanning microscope
An arrangement for coupling at least one beam of optical tweezers for trapping particles and / or a treatment beam into a microscope beam path, preferably in a laser scanning microscope, wherein means are provided for changing the position of the beam focus of the optical tweezers and / or of the treatment beam in a freely adjustable manner for purposes of changing the focal position of the microscope.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MICROSCOPY GMBH
Liquid drop whispering gallery mode laser and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN104852259AFine surfaceHigh Q valueActive medium materialActive medium shape and constructionWhispering gallerySpectrograph
The invention provides a liquid drop whispering gallery mode laser and a manufacturing method thereof. According to the liquid drop whispering gallery mode laser, a first single-mode optical fiber with the middle being provided with a cone area is connected with a pump light source and a spectrograph, a second single-mode optical fiber is connected to a trapping light source and an annular core optical fiber, the front end of the annular core optical fiber is processed into a cone frustum shaped optical fiber tip, a laser beam emitted by the trapping light source is injected into a fiber core of the annular core optical fiber through the second single-mode optical fiber, total reflection and refraction occur in light at an inclined plane of the cone frustum shaped optical fiber tip of the annular core optical fiber, an annular convergence optical field is formed near the cone frustum shaped optical fiber tip so as to realize an optical tweezers function, the optical tweezers stably capture a micro liquid drop, the captured liquid crystal micro liquid drop is enabled to be close to the cone area of the first single-mode optical fiber, the pump light source injects from the front end of the first single-mode optical fiber, and the spectrograph detects excited laser light at the rear end of the first single-mode optical fiber. According to the invention, a high Q-value liquid drop micro spherical cavity with a perfect surface is formed by surface tension, and the optical tweezers stably control the liquid drop micro-sphere. The liquid drop whispering gallery mode laser provided by the invention has an extremely low threshold.
Owner:黑龙江省敏动传感科技有限公司
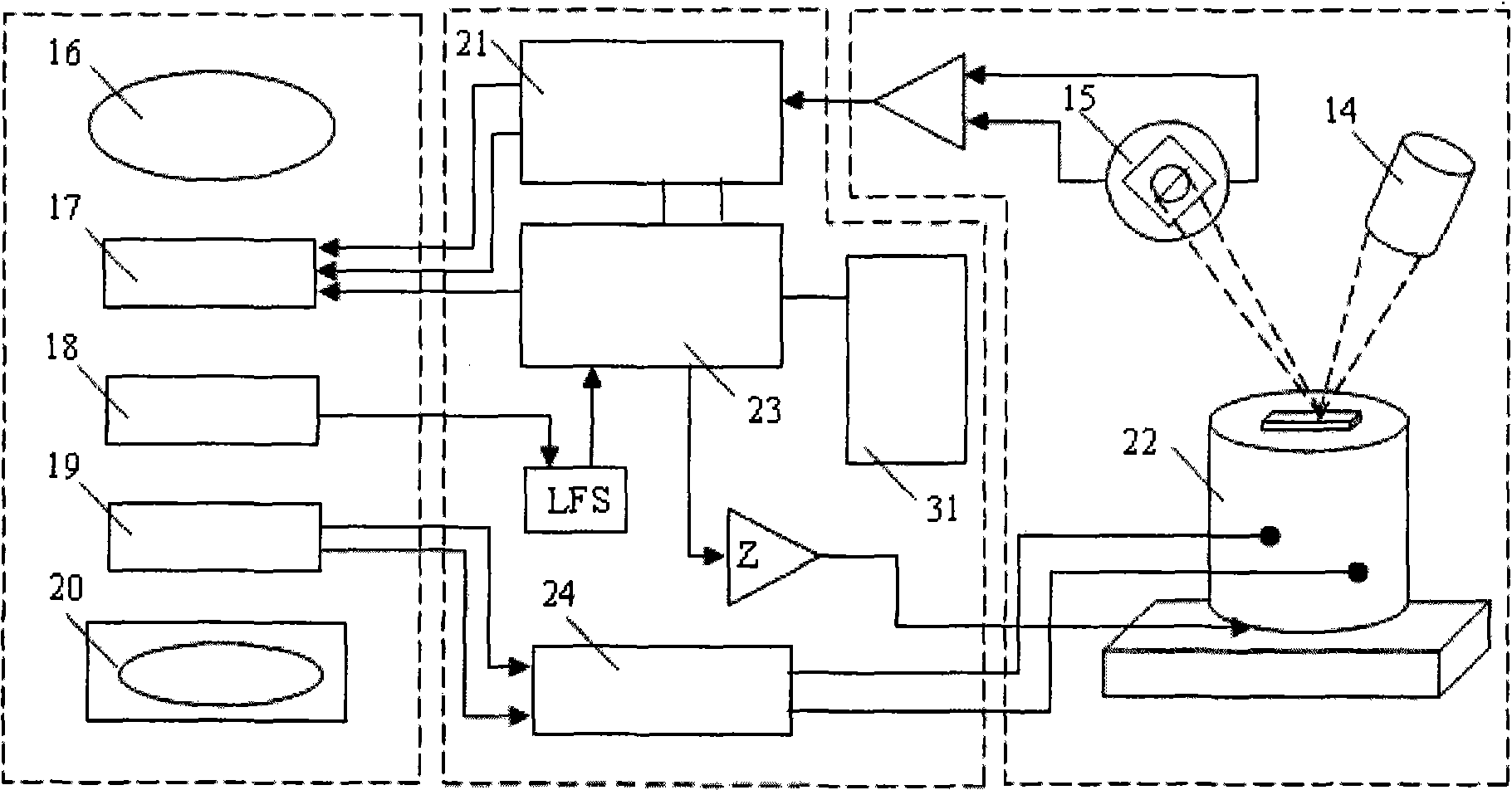
Method and apparatus for characterizing biological objects
InactiveUS20130171685A1Simple and fast and accurate characterizationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsElectricityRadio frequency
In order to quantitatively characterize biological objects, for example individual cells, a stimulus is applied to a biological object in a contactless fashion. A measurement and a further measurement are performed on the biological object in order to ascertain a response of the biological object to the stimulus, wherein the measurement and the further measurement comprise detecting Raman scattering on and / or in the biological object and / or capturing data using digital holographic microinterferometry (DHMI). The biological object is characterized according to a result of the measurement and is sorted if needed. The stimulus can be applied by means of a laser beam that creates optical tweezers or an optical trap, by means of ultrasonic waves or an electric or magnetic radio frequency field.
Owner:CELLTOOL GMBH
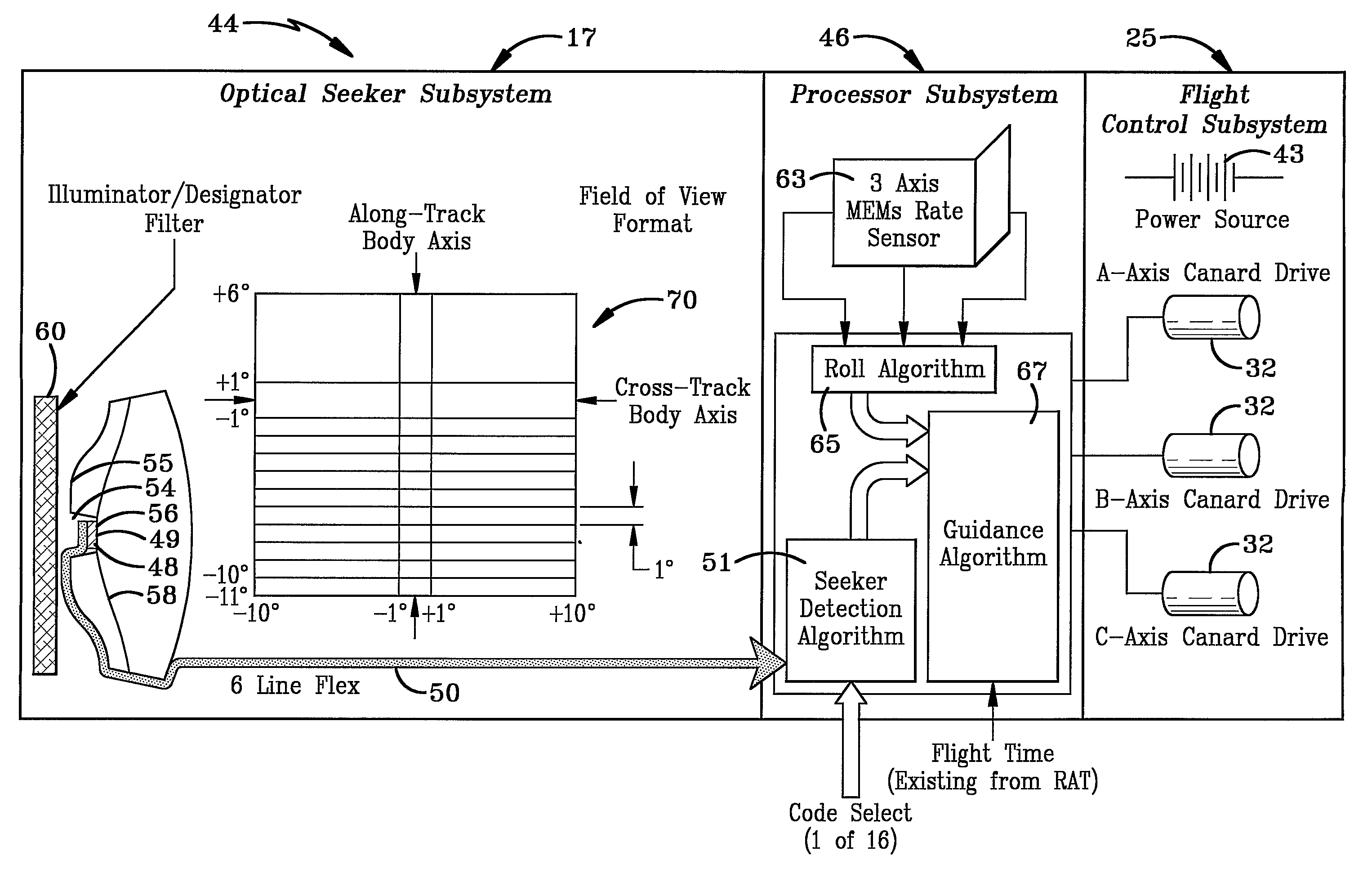
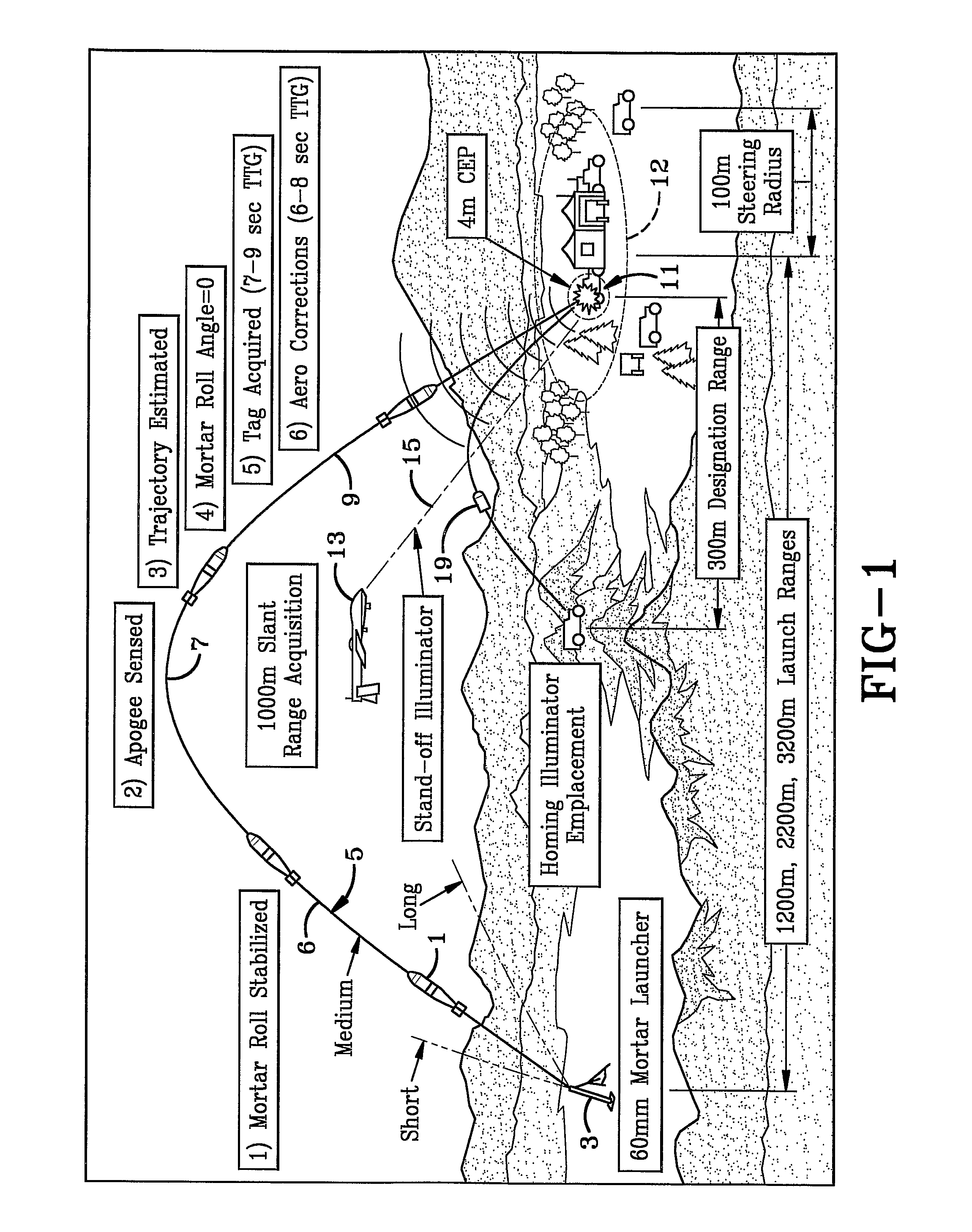
Optically guided munition
ActiveUS7533849B2Low costAvoid explosionAmmunition projectilesDirection controllersSurvivabilityDrive motor
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTEGRATION INC
Method for real-time detection of diffraction phase of structure light field
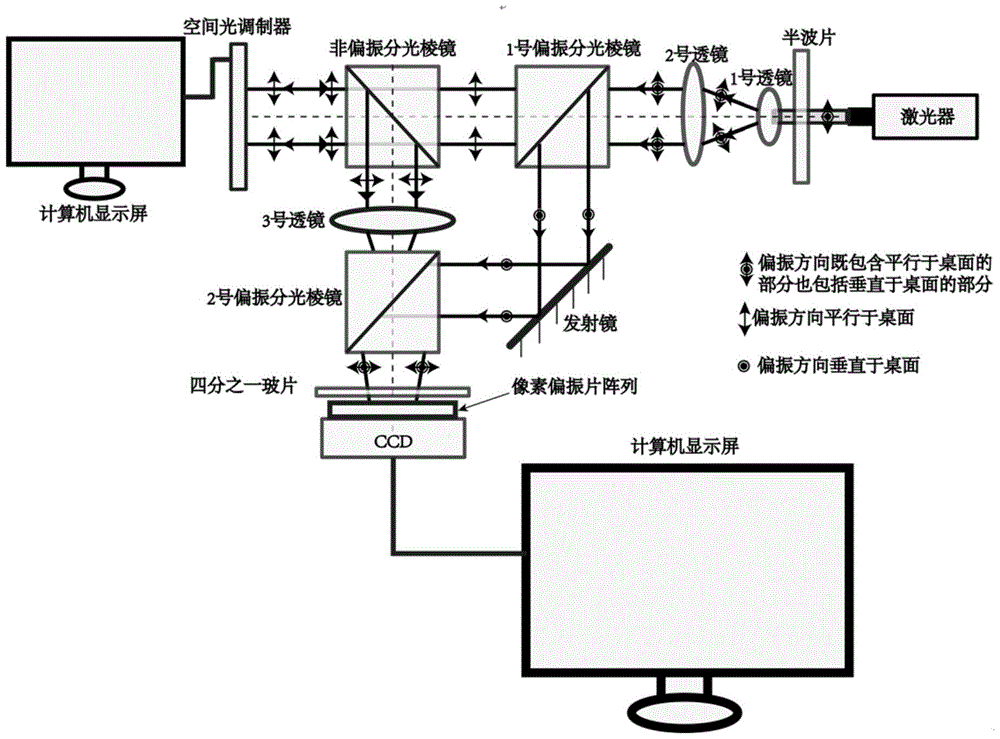
InactiveCN105675150AOvercome the disadvantage of not being able to measure dynamic light fieldsReduce the cumbersomeness of useOptical measurementsPhotometry using electric radiation detectorsSpatial light modulatorPolarizer
The invention discloses a method for real-time detection of the diffraction phase of a structure light field. The method includes the steps of: utilizing a camera integrated with a pixel polarizing film array to collect fringe patterns generated by interference of reference light beam output through a preset optical path and structured light beam generated by adjustment of a spatial light modulator, the dimensions of each polarizing film unit in the pixel polarizing film array and pixel dimensions of a photosensitive element in the camera being consistent and in one-to-one alignment; and extracting four fringe patterns of different polarization directions from the fringe patterns generated by interference of the structured light and the reference light according to the polarization directions of the polarizing film units so as to calculate the diffraction phase of the structure light field. The method disclosed by the invention realizes real-time measurement of light intensity and phase information of the structure light field, enables a user to deeply know physical characteristics of the structure light field, and has a very large driving function for the structure light field in the fields of optical tweezers, laser micromachining and optical signal propagation.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Modulated optical tweezers
InactiveUS20060163463A1Reduce stiffnessFacilitate object ' escapeLaser detailsComponent separationMicrometerEngineering
A method and apparatus for selecting a specific fraction from a heterogeneous fluid-borne sample using optical gradient forces in a microfluidic or fluidic system are presented. Samples may range in size from a few nanometers to at least tens of micrometers, may be dispersed in any fluid medium, and may be sorted on the basis of size, shape, optical characteristics, charge, and other physical properties. The selection process involves passive transport through optical intensity field driven by flowing fluid, and so offers several advantages over competing techniques. These include continuous rather than batch-mode operation, continuous and dynamic tunability, operation over a wide range of samples, compactness, and low cost.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
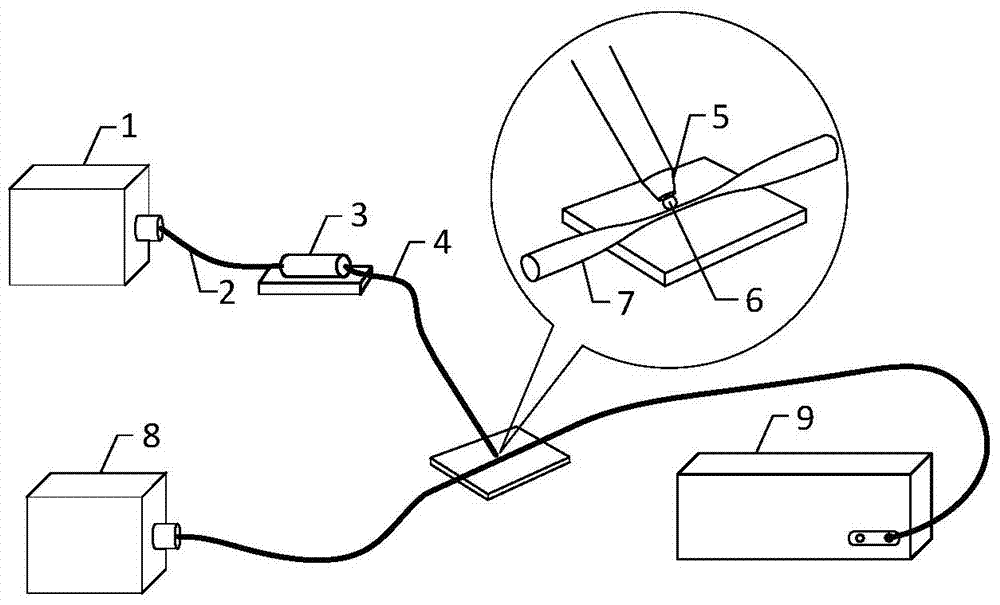
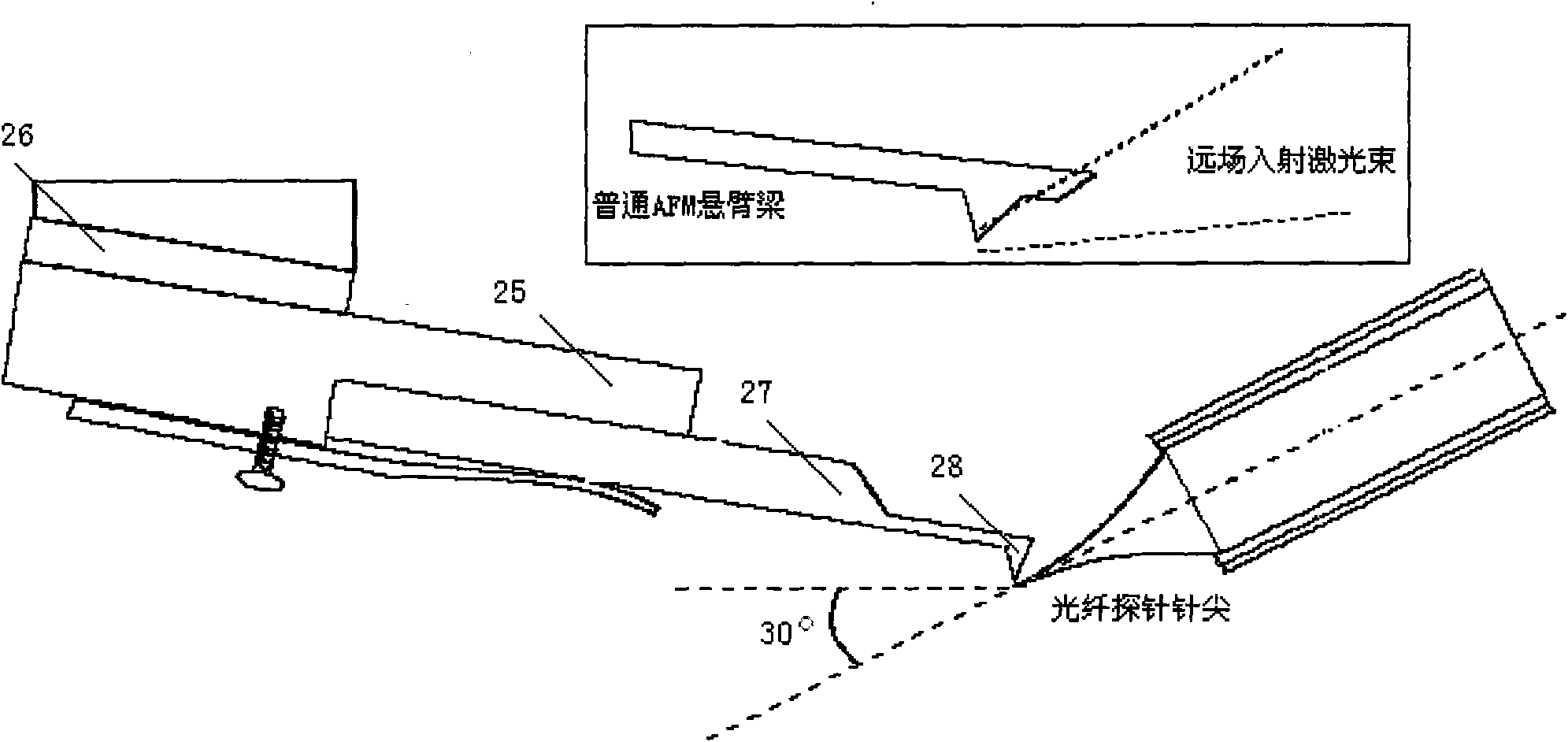
Nanomanipulation method for compounding laser near-field optical tweezers and AFM probe
InactiveCN101788571AEasy to operateImprove flexible working abilityScanning probe microscopyNanoparticleTrapping
The invention relates to a nanomanipulation method for compounding laser near-field optical tweezers and an AFM probe. In the method of the invention, optical fiber probe type near-field optical tweezers are introduced into a sample chamber from an interface of an AFM system sample chamber with the outside, and a coupling force effect generated after compounding is used for carrying out sample particle nanomanipulation. After the AFM probe is positioned in the near-field region of the optical fiber probe, a three-dimensional stable light trap formed by coupling locally enhanced light field of the AFM probe and the optical fiber probe emergent light field can balance external interference, and realize stable and efficient trapping of nanoparticles.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
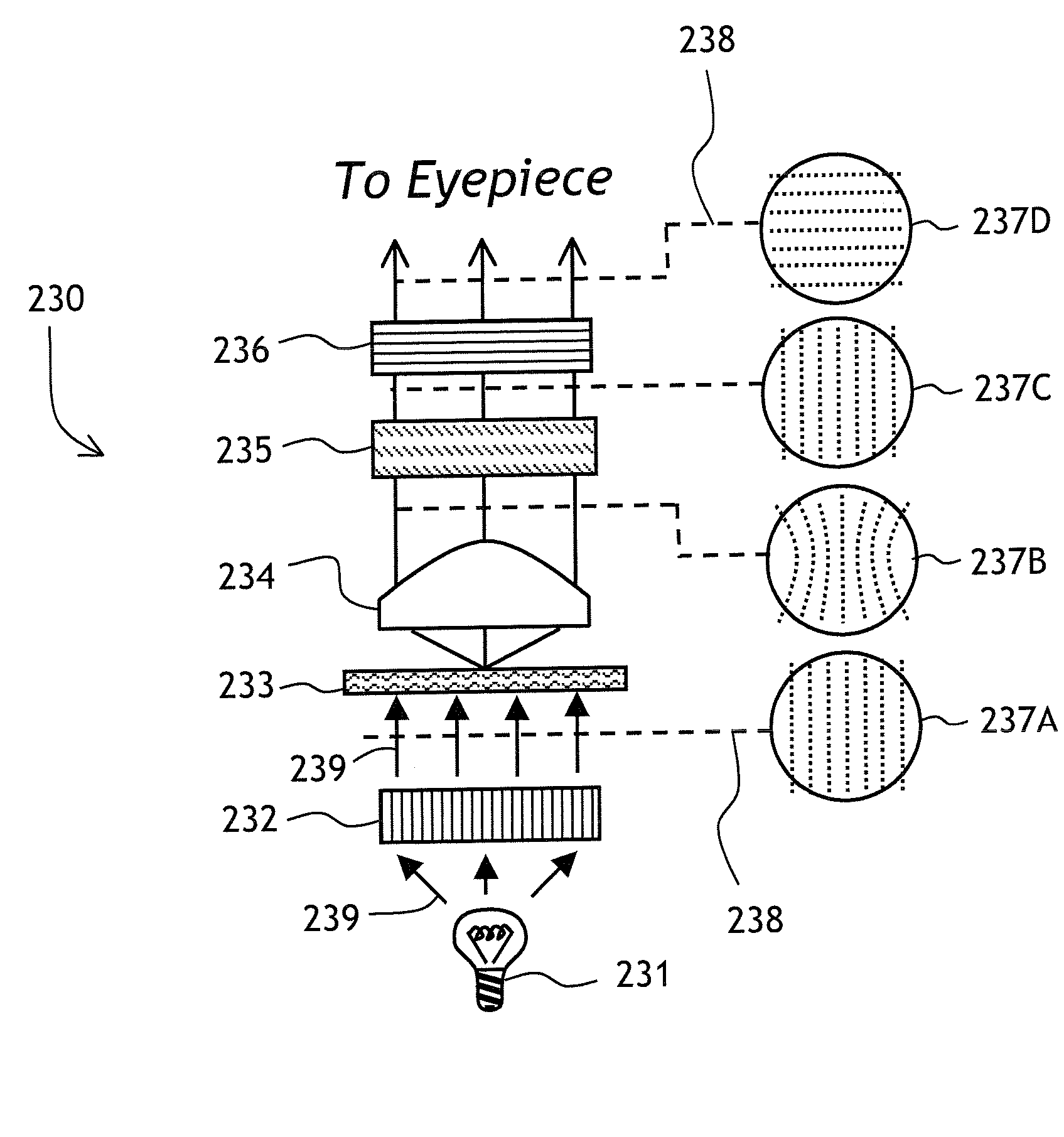
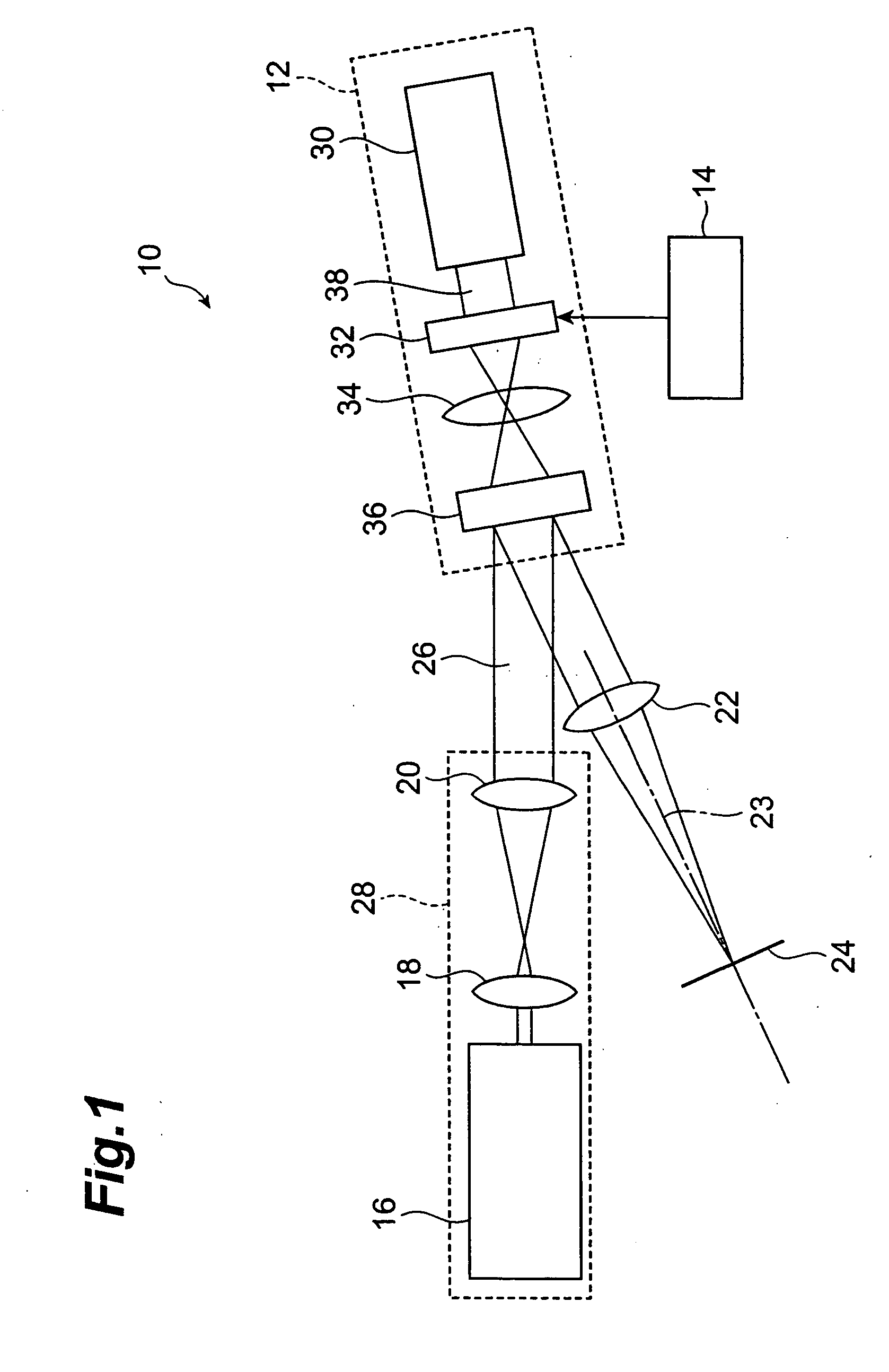
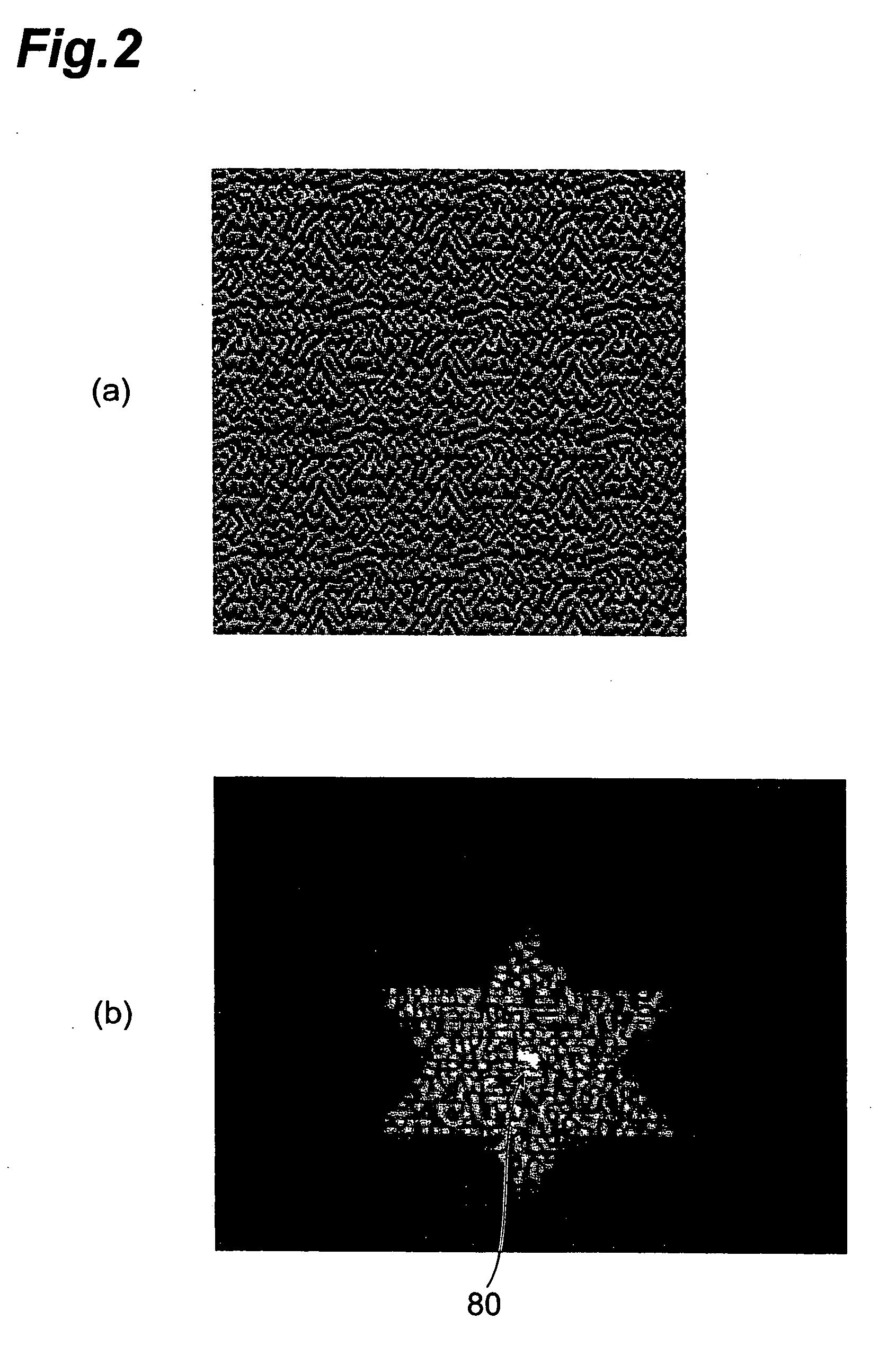
Method of forming an optical pattern, optical pattern formation system, and optical tweezer
ActiveUS20060043184A1Reduce orderActive addressable light modulatorSensing by electromagnetic radiationSpatial light modulatorLightness
Reading light (26) is phase-modulated by a phase-modulating spatial light modulator (12), the phase-modulated reading light (26) is Fourier-transformed, and an image of the Fourier-transformed reading light is focused on an output plane (24) to form an optical pattern. In this method, 0-order light in the phase-modulated reading light (26) is blurred on the output plane (24). As the 0-order light is blurred, the luminance of the 0-order light is reduced on the output plane (24). Since the 0-order light is not blocked, the shape of the optical pattern is not limited.
Owner:HAMAMATSU PHOTONICS KK
Nano operating device with near-field optical tweezers and AFM probe
InactiveCN101799482AImprove flexible working abilityPrecise XYZ direction controlIndividual molecule manipulationScanning probe microscopyImage resolutionOptical fiber probe
The invention discloses a nano operating device with a pair of near-field optical tweezers and an AFM probe. The nano operating device comprises a microoperation microscope and a pair of optical-fiber probe type near-field optical tweezers. After the pair of optical-fiber probe type near-field optical tweezers is led into a sample chamber through a microoperation microscope sample chamber and an outside interface, the particles of the sample is subjected to the nano operation by using the coupling force effect generated by compounding. Integrating the advantages of both the laser near-field optical tweezers and the AFM system, the nano operating device can ensure that devices can be coupled and connected more easily, the system can be operated efficiently and flexibly and compounded easily to have higher resolution ratio and higher reliability, and the nano particles can be effectively caught for characteristic study. The nano operating device is a higher-precision operating tool used in the field of the nanotechnology.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Nanometer optical tweezers device and method for accurately controlling nanoparticles and biomolecules
InactiveCN106898407ABreaking through the diffraction limitEasy to controlMicroscopesCoupling light guidesBand-pass filterOptical fiber coupler
The invention discloses a nanometer optical tweezers device and method for accurately controlling nanoparticles and biomolecules. The device includes a microscope, a microflow channel is arranged on an objective table of the microscope, the microflow channel comprises cover glass and a glass slide, two optical fibers are arranged in the microflow channel and are sleeved by glass capillaries, the glass capillaries are fixed on adjustable optical fiber adjusting frames, the other end of one of the optical fibers is connected with a Y type optical fiber coupler, two other arms of the Y type optical fiber coupler are connected with a band-pass filter and a fiber laser, the other end of the band-pass filter is connected with a photoelectric detector, and the other end of the other optical fiber is connected with a laser. The method includes the following specific steps: 1. preparing a parabola-shaped optical fiber tip used for accurate control; 2. fixing a micro lens on the optical fiber tip; 3. using the micro lens assembled in the Step 2 to capture and control fluorescent nanoparticles; and 4. capturing and controlling DNA molecules.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
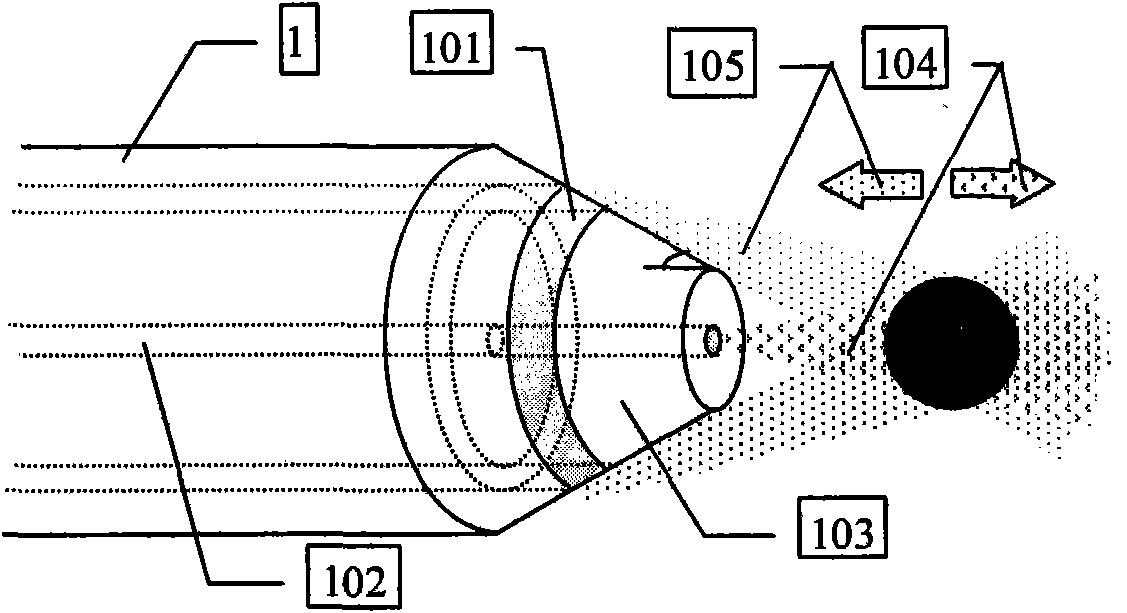
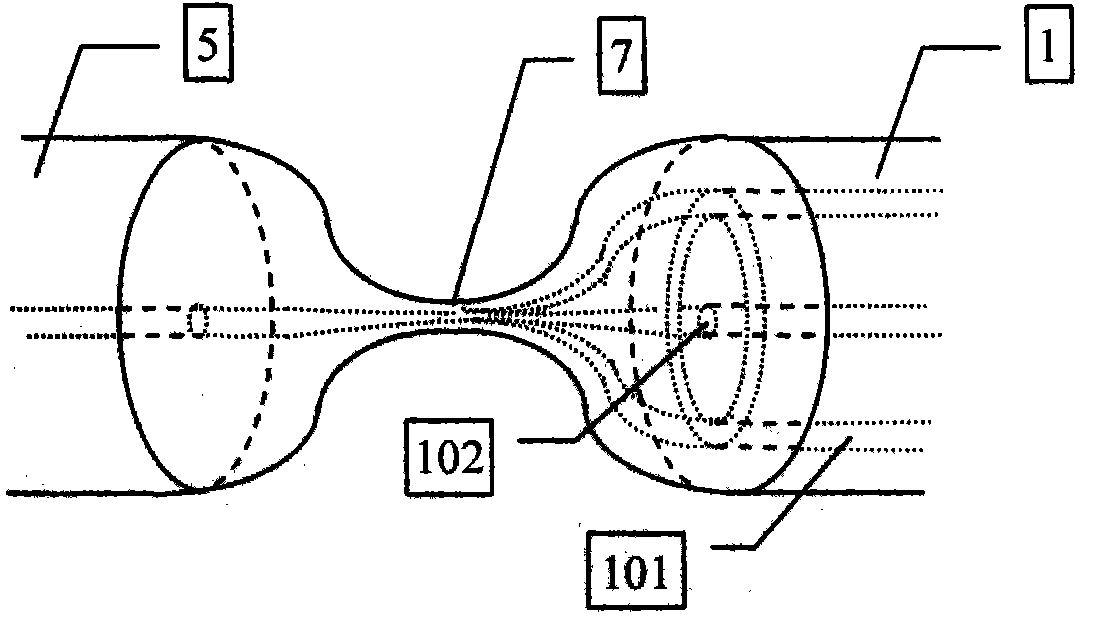
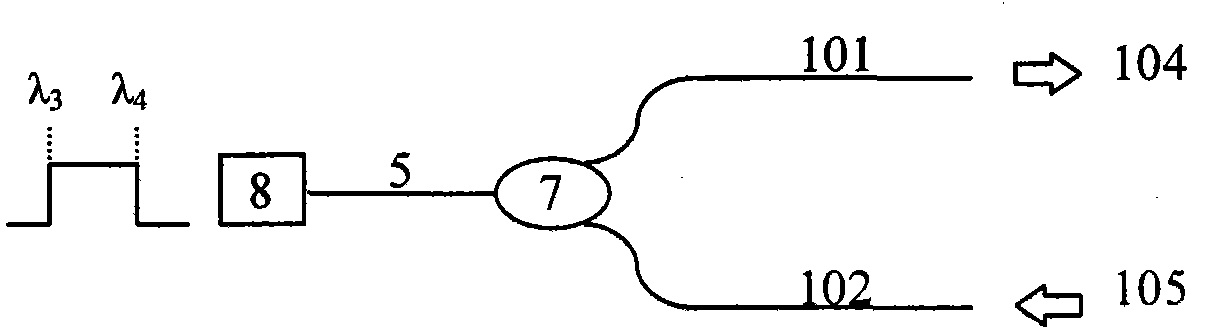
Throughput type fiber optical tweezers based on coaxial dual-waveguide structure and preparation method
InactiveCN101907743AStable captureCapture flexibleRadiation/particle handlingOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingCoaxial cableMicrostructure fiber
The invention provides throughput type fiber optical tweezers based on a coaxial dual-waveguide structure and a preparation method. The throughput type fiber optical tweezers mainly comprise a coaxial double-waveguide microstructure fiber [1], an LD light source with the output wavelength of lambda 1, an LD light source [3] with the output wavelength of lambda 2, a wavelength division multiplexing device [4] and a standard single-mode fiber [5]),wherein the output ends of the light source [2] and the light source [3] are connected with the two input ends of the wavelength division multiplexing device [4]; the output end of the wavelength division multiplexing device [4] is coupled with the coaxial double-waveguide fiber [1]; and the other end of the coaxial double-waveguide fiber [1] is finely ground to obtain the cone structure. The invention controls the particles by utilizing the coaxial double-waveguide fiber, changes the luminous power of the light source by adjustment, and can realize throughput, transmission and resorption of stable trapped particles; and meanwhile, the invention can trap the particles in a more flexible and accurate way, has adjustability, and greatly enhances the practicality of the fiber optical tweezers.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Composite grating used for detecting multiplexing vortex light beams and measuring method
ActiveCN105136289AQuick and accurate determinationDiffraction gratingsPhotometry using electric radiation detectorsMultiplexingMomentum
The invention discloses a novel composite grating and a method and device using the grating to detect orbital angular momentum state of multiplexing vortex light beams. When the vortex light beams are irradiated to the composite grating, the orbital angular momentum state of the vortex light beams can be obtained by observation of the position where gauss beams occur in a far-field diffraction pattern. The measuring range of the orbital angular momentum state of the composite grating is -24 to +24, and the range can satisfy detection of multiplexing vortex light beams under most circumstances. Using the composite grating can rapidly detect all orbital angular momentum components of the multiplexing vortex light beams, and when different multiplexing vortex light beams are incident, a light path does not need to be readjusted, so the operation is extremely simple and convenient. The novel composite grating and the method and device using the grating to detect the orbital angular momentum state of the multiplexing vortex light beams are of great significance to research of future photo-communication, optical tweezers technology, quantum communication and the like.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com