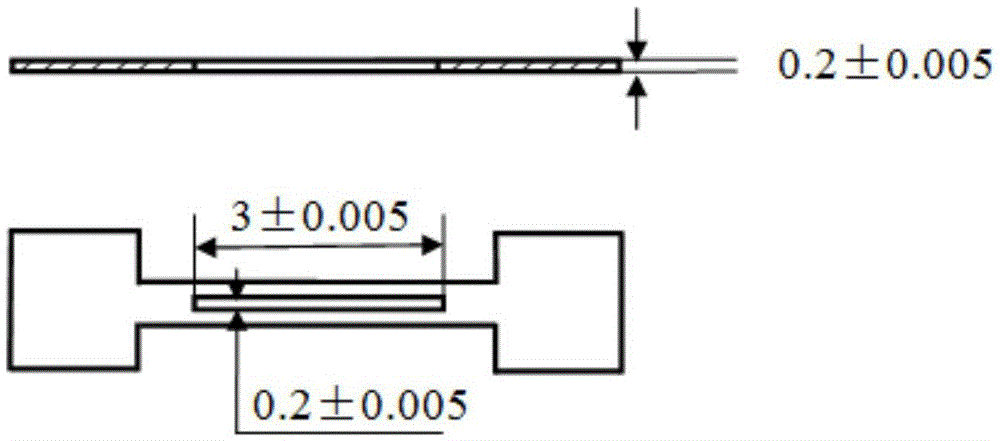
Patents
Literature
30results about How to "Breaking through the diffraction limit" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
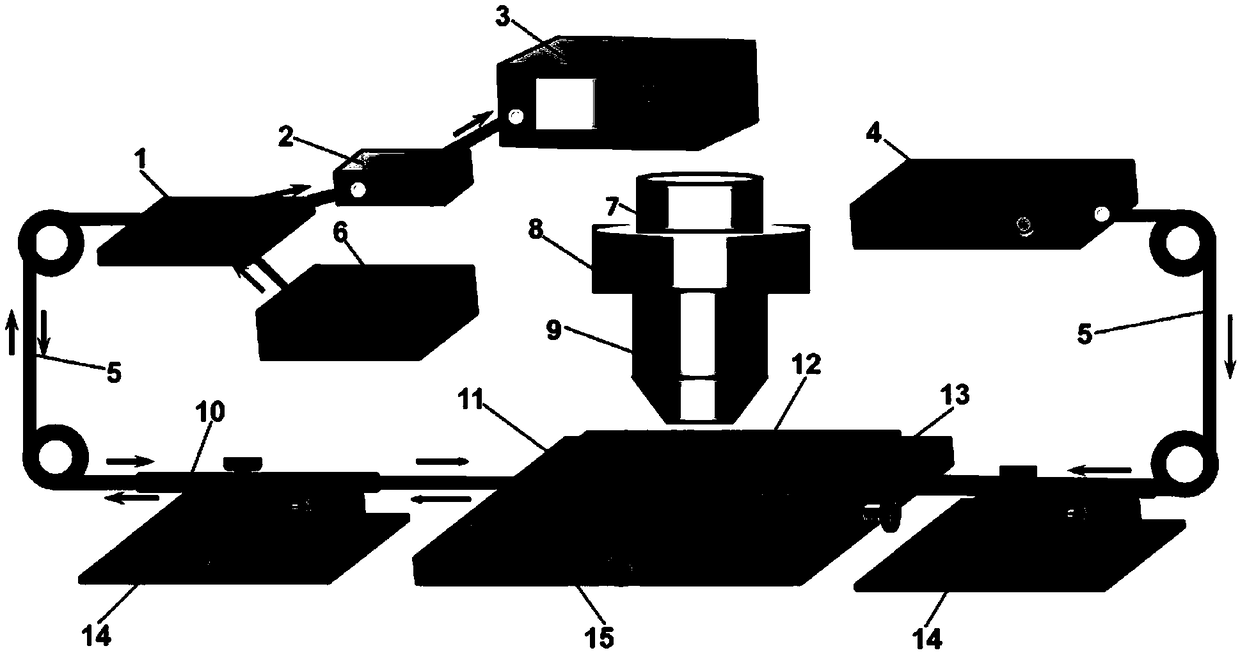
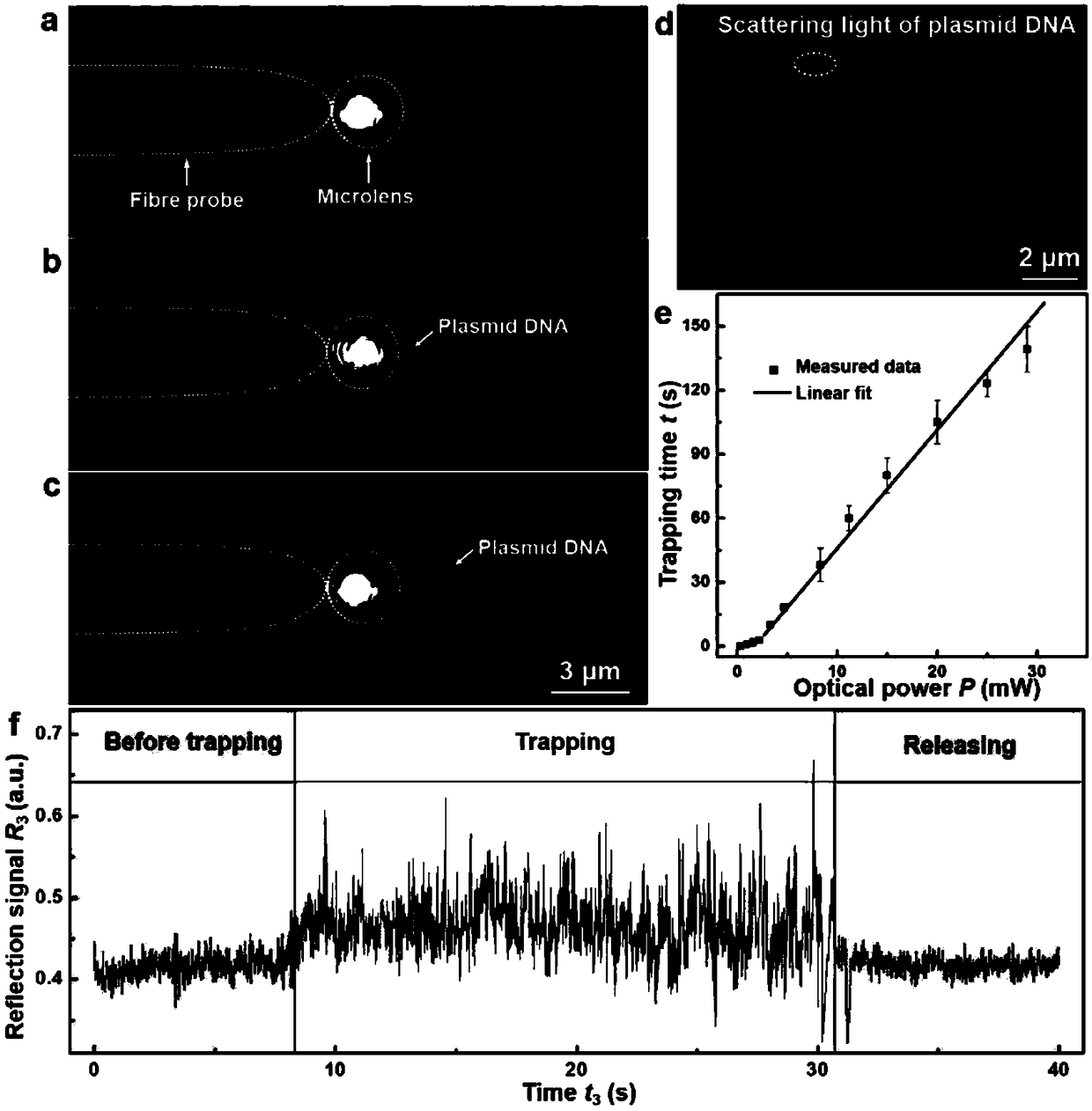
Nanometer optical tweezers device and method for accurately controlling nanoparticles and biomolecules
InactiveCN106898407ABreaking through the diffraction limitEasy to controlMicroscopesCoupling light guidesBand-pass filterOptical fiber coupler
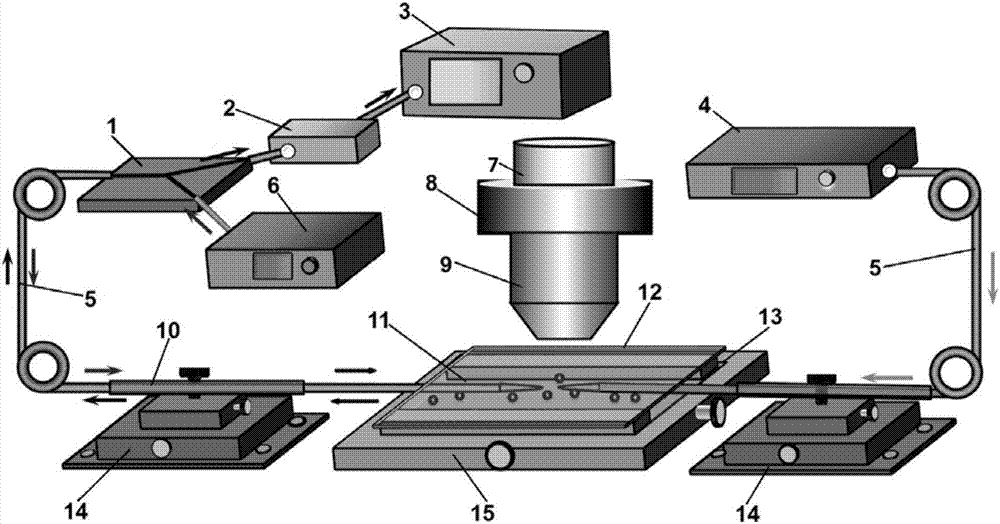
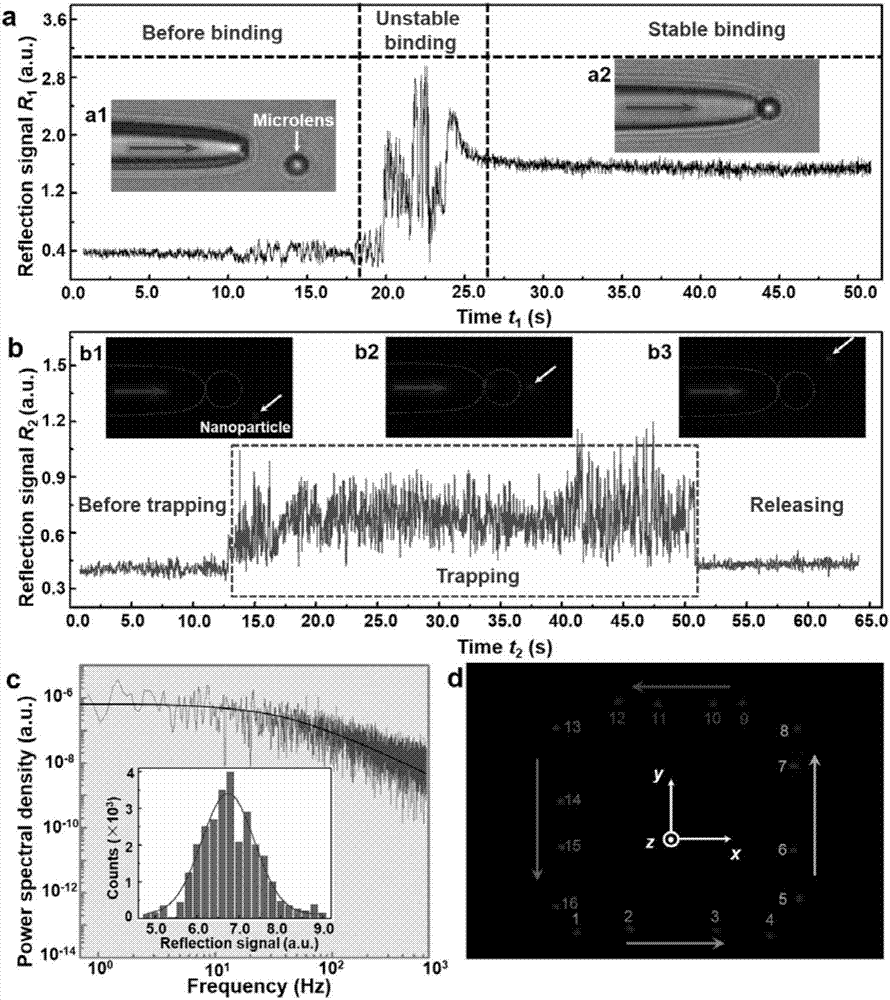
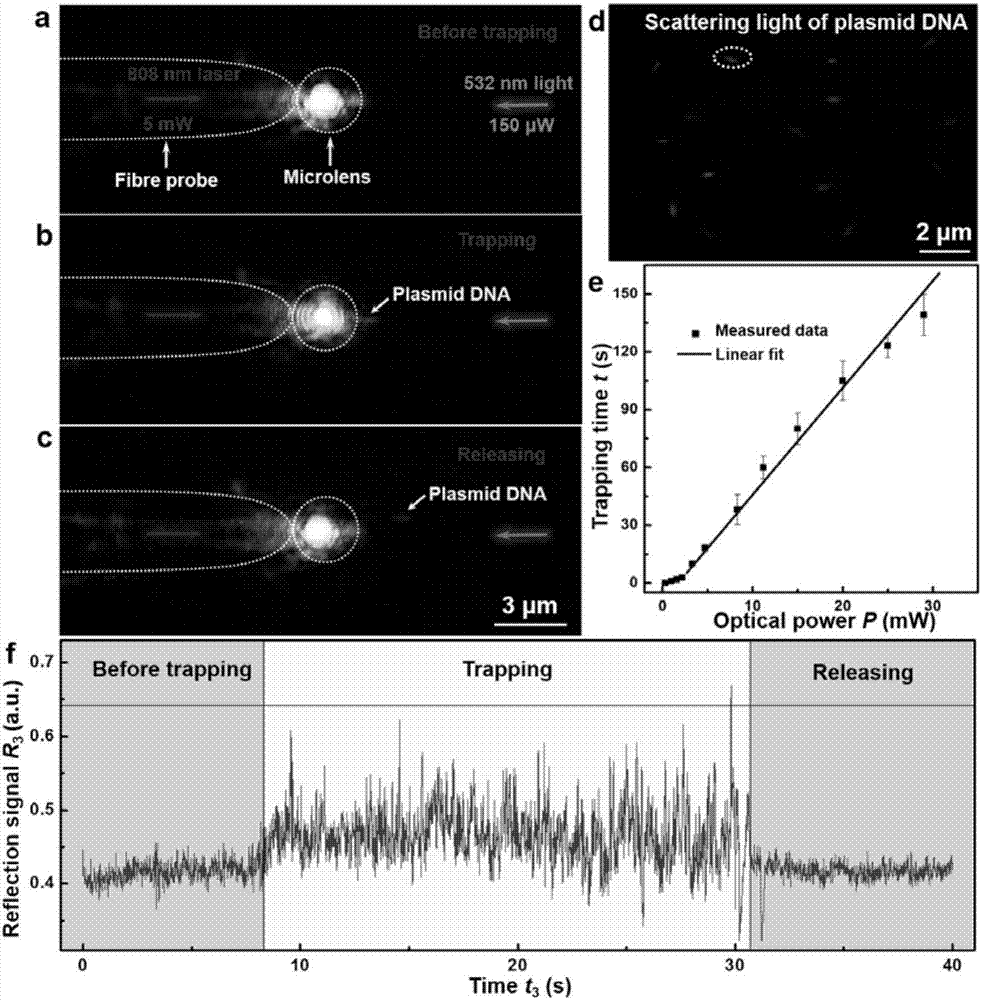
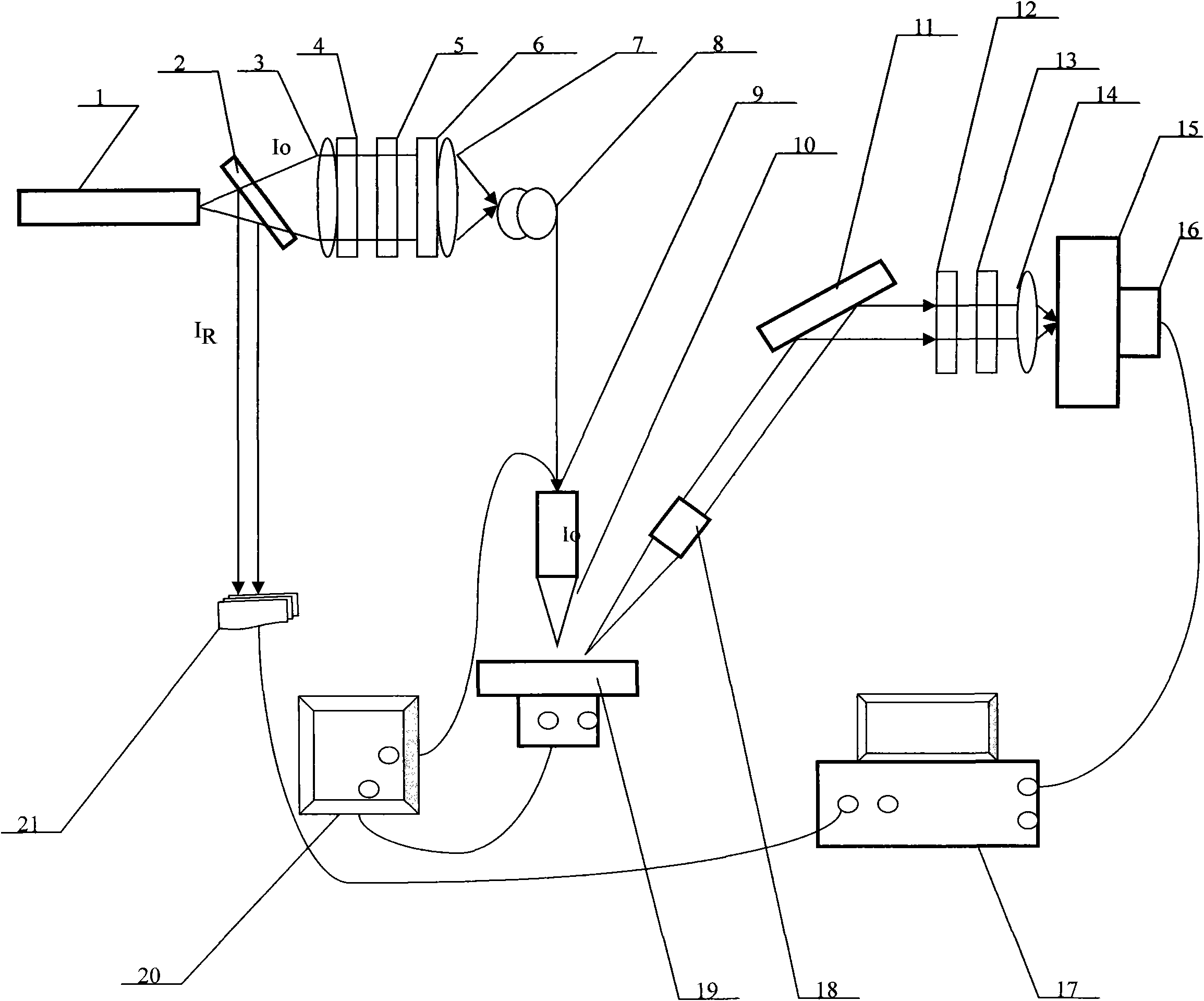
The invention discloses a nanometer optical tweezers device and method for accurately controlling nanoparticles and biomolecules. The device includes a microscope, a microflow channel is arranged on an objective table of the microscope, the microflow channel comprises cover glass and a glass slide, two optical fibers are arranged in the microflow channel and are sleeved by glass capillaries, the glass capillaries are fixed on adjustable optical fiber adjusting frames, the other end of one of the optical fibers is connected with a Y type optical fiber coupler, two other arms of the Y type optical fiber coupler are connected with a band-pass filter and a fiber laser, the other end of the band-pass filter is connected with a photoelectric detector, and the other end of the other optical fiber is connected with a laser. The method includes the following specific steps: 1. preparing a parabola-shaped optical fiber tip used for accurate control; 2. fixing a micro lens on the optical fiber tip; 3. using the micro lens assembled in the Step 2 to capture and control fluorescent nanoparticles; and 4. capturing and controlling DNA molecules.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
High resolution micro-vision system based on calculating ghost imaging and method of obtaining images
ActiveCN106097269ABreaking through the diffraction limitImprove imaging resolutionImage enhancementImage analysisSpatial light modulatorSystems design
The invention discloses a high resolution micro-vision system based on calculating ghost imaging and a method of obtaining images. The system successively comprises, on a light path, a laser source, a first diaphragm, a laser beam expanding lens, a collimating lens, a second diaphragm, a polarizer, a spatial light modulator, a polarization analyzer, a third diaphragm, a reflector, a beam splitter mirror, a convergent lens and a CCD camera, and also comprises a precision positioning objective table located on another light path of the beam splitter mirror and connected with a computer; the computer is also separately in connection with the spatial light modulator and the CCD camera, and obtains high resolution images through the calculating ghost imaging technology. The high resolution micro-vision system has a simple and compact structure, and employs light field intensity correlation measurement to recover object information, thereby eliminating the problem of classic optical system imaging distortion, and can obtain high accuracy and contrast images. The high resolution micro-vision system is very helpful for micro-vision system design and ghost imaging technology research.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Plasma slab lens and near-field focusing method thereof
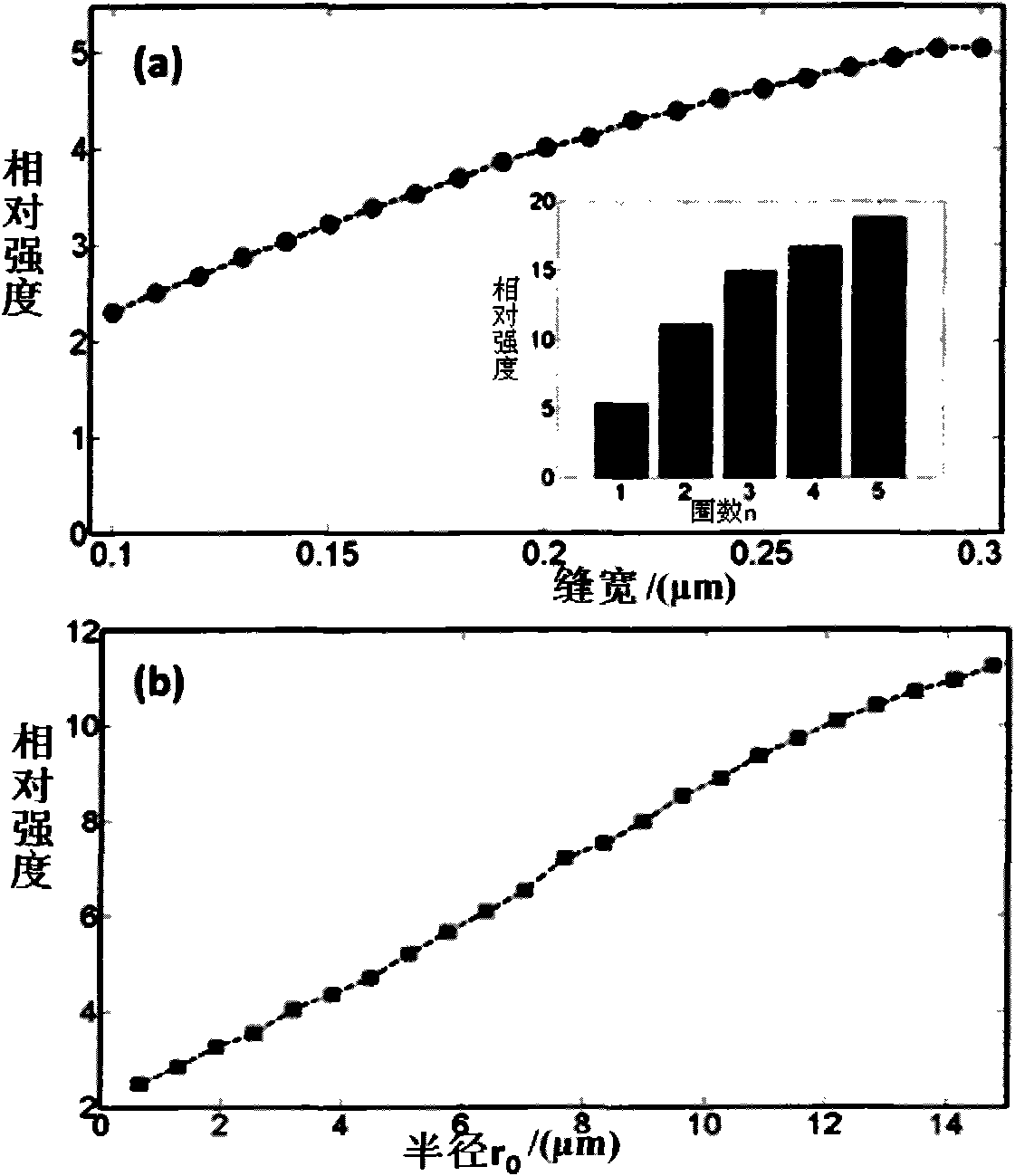
The invention provides a plasma slab lens which comprises a light-permeable substrate and a metal film made on the light-permeable substrate, wherein the metal film is provided with a levorotatory or dextrorotatory helical structure; the helical structure meets the condition that Phi is greater than or equal to 0 but is less than or equal to 2pi, wherein n is equal to 1, 2, 3...; k is equal to 1,2, 3...; rn (Phi) is a distance from a phase Phi of the No. n circle of the helical structure to the center in a polar coordinate; rn0 is the shortest distance from each circle of the helical structure to the center; and lambda sp is a wavelength of the surface plasma of the metal film. A preparing process of the plasma slab lens is compatible with an existing process, is easy to integrate and islow in cost. The center of a light source needs not be aligned with the center of the lens structure and the plasma slab lens can be more conveniently and simply used and can be easily made into a lens array; the plasma slab lens can break through a diffraction limit and has a huge focus depth; and the field intensity at a focal point can be controlled by adjusting the shape and size of the helical structure.
Owner:THE NAT CENT FOR NANOSCI & TECH NCNST OF CHINA
Large view field super resolution imaging device
ActiveCN106199997AEasy to manufactureEasy to implementOptical elementsElectromagnetic wave equationWavelength
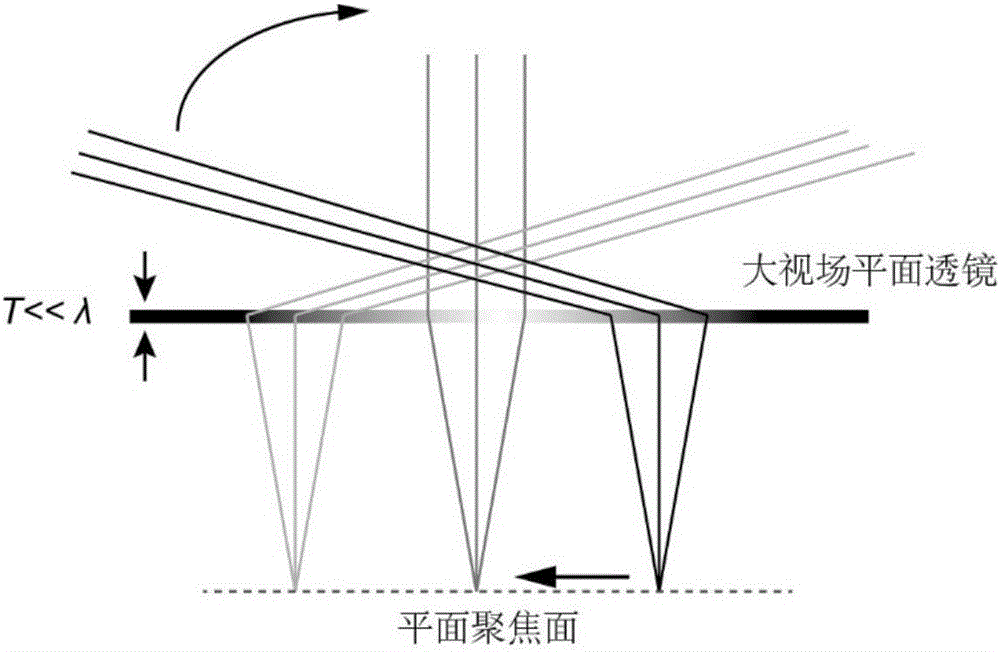
The invention discloses a large view field super resolution imaging device which comprises a base and a super-surface, wherein the base and the super-surface are successively arranged in the bottom-up sequence. The super-surface is composed of nano-unit structure arrays which are arranged in succession on an ultra-thin metal or a dielectric film. A nano-unit structure is a deep sub-wavelength structure. According to the invention, geometric phase on the nanostructure is used to control the electromagnetic wave symmetry; electromagnetic waves are converted from rotation symmetry to translational symmetry to acquire large view field perfect focusing near 180 degrees; if curved face or multi-plane combination is used, large view field imaging can be realized; the work bandwidth can cover the entire electromagnetic spectrum; the resolution is close to or even beyond the diffraction limit; and the device has a wide application prospect in the field of large view field super resolution imaging.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Near field spectrum correlation imaging apparatus
InactiveCN102735620AGood imaging authenticityBreaking through the diffraction limitColor/spectral properties measurementsOptical pathCollections data
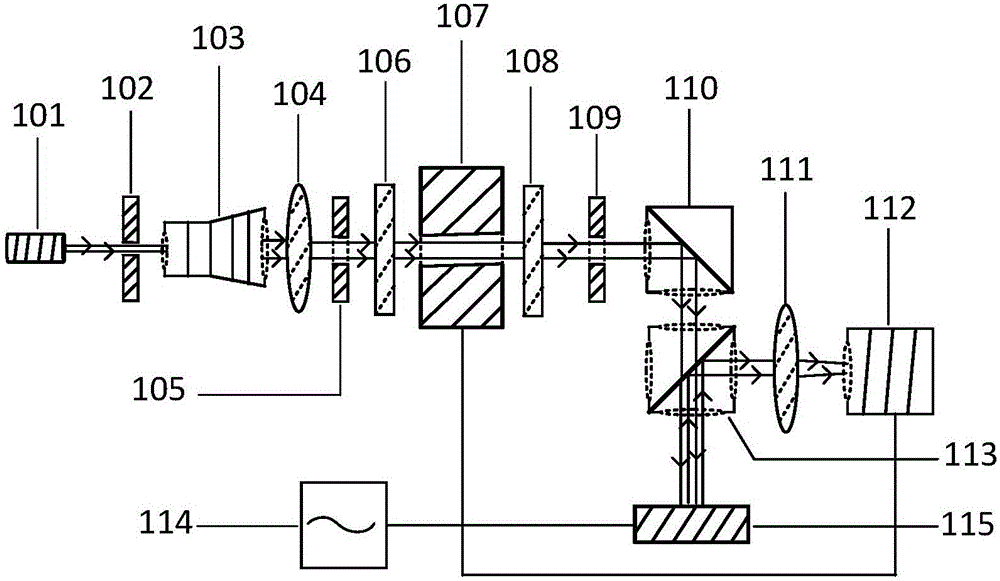
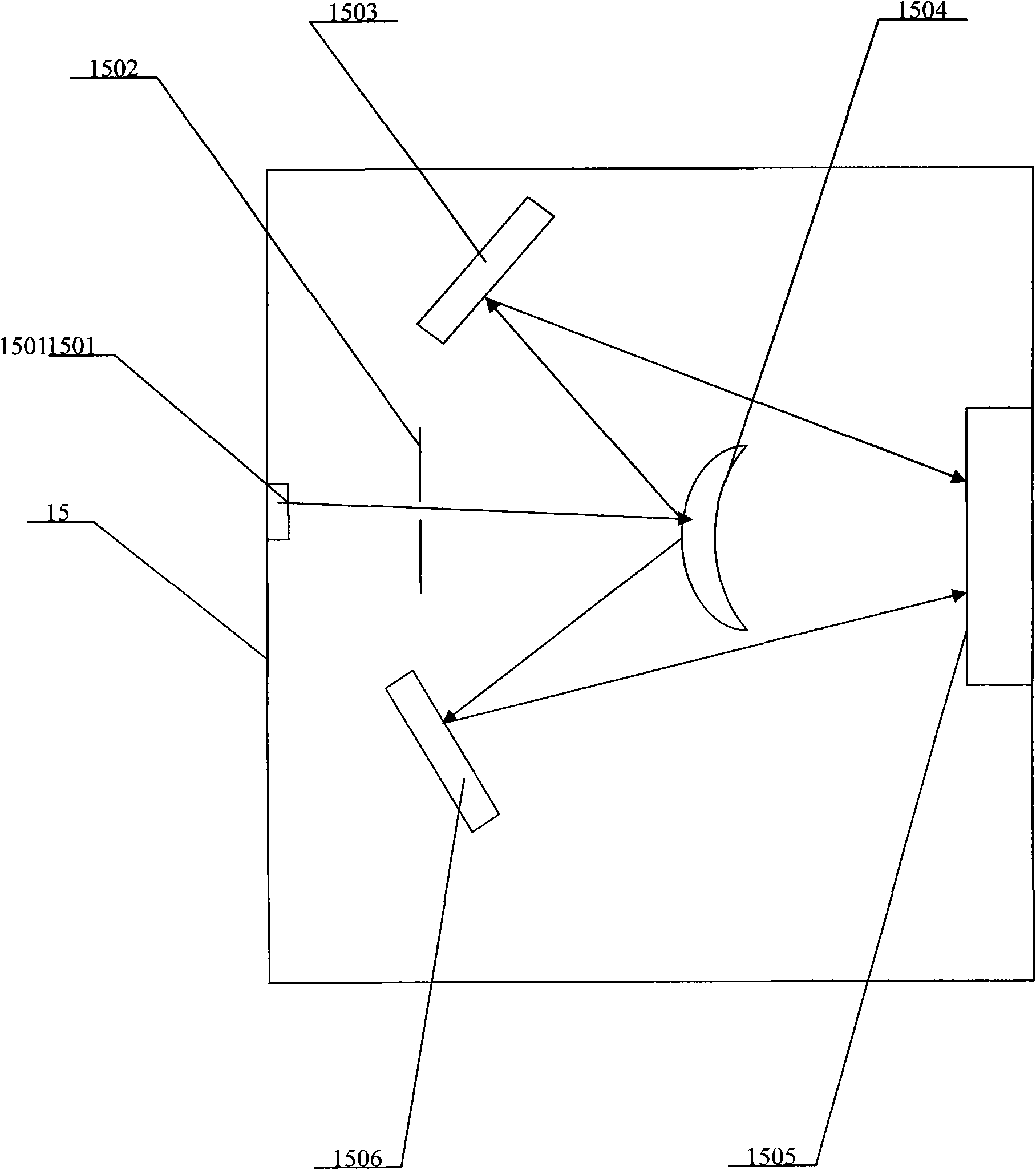
A spectrum correlation imaging apparatus comprises a light source, a splitter, a light source filter, a polarization revolver, a quarter wave plate, a splitter, a light source condenser, an optical fiber, a probe coupling seat, a probe, a reflector, a polarization analyzer, a spectral filter, a spectral collection mirror, an inner optical path spectrograph, a photoelectric receiver, a data collection processor, a signal collector, a sample workbench, and a scan controller. The apparatus of the invention has the advantages of improvement of the high resolution of near field detection, whole solidification of the whole device, simple structure, and easy operation.
Owner:金石琦
Laser ablation processing method for quartz crystal
ActiveCN105522281AAddress mechanical strength requirementsAddressing Accuracy RequirementsLaser beam welding apparatusMicrometerBase frequency
The invention discloses a laser ablation processing method for quartz crystal. The laser ablation processing method specifically comprises the steps of selecting lasers, preparing control software, designing processing drawings, carrying out laser ablation, carrying out post-processing treatment and carrying out detection. The method for processing the quartz crystal is designed on the basis of limitation to the condition of each step, the quartz crystal can be effectively processed for forming various shapes and can be thinned through the processing method, the thickness of the thinned quartz crystal is small, the corresponding base frequency is high, and the strength of the processed quartz crystal is high. In addition, the processing method is simple, the processing accuracy is high, and the processing dimensional accuracy of the quartz crystal can be controlled to be within the range of + / - 5 micrometers.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF RADIO METROLOGY & MEASUREMENT
Diffraction super-resolution Microscopic imaging method and system
ActiveCN110836892AAchieve lightingBreaking through the diffraction limitMaterial analysis by optical meansLight spotRadiology
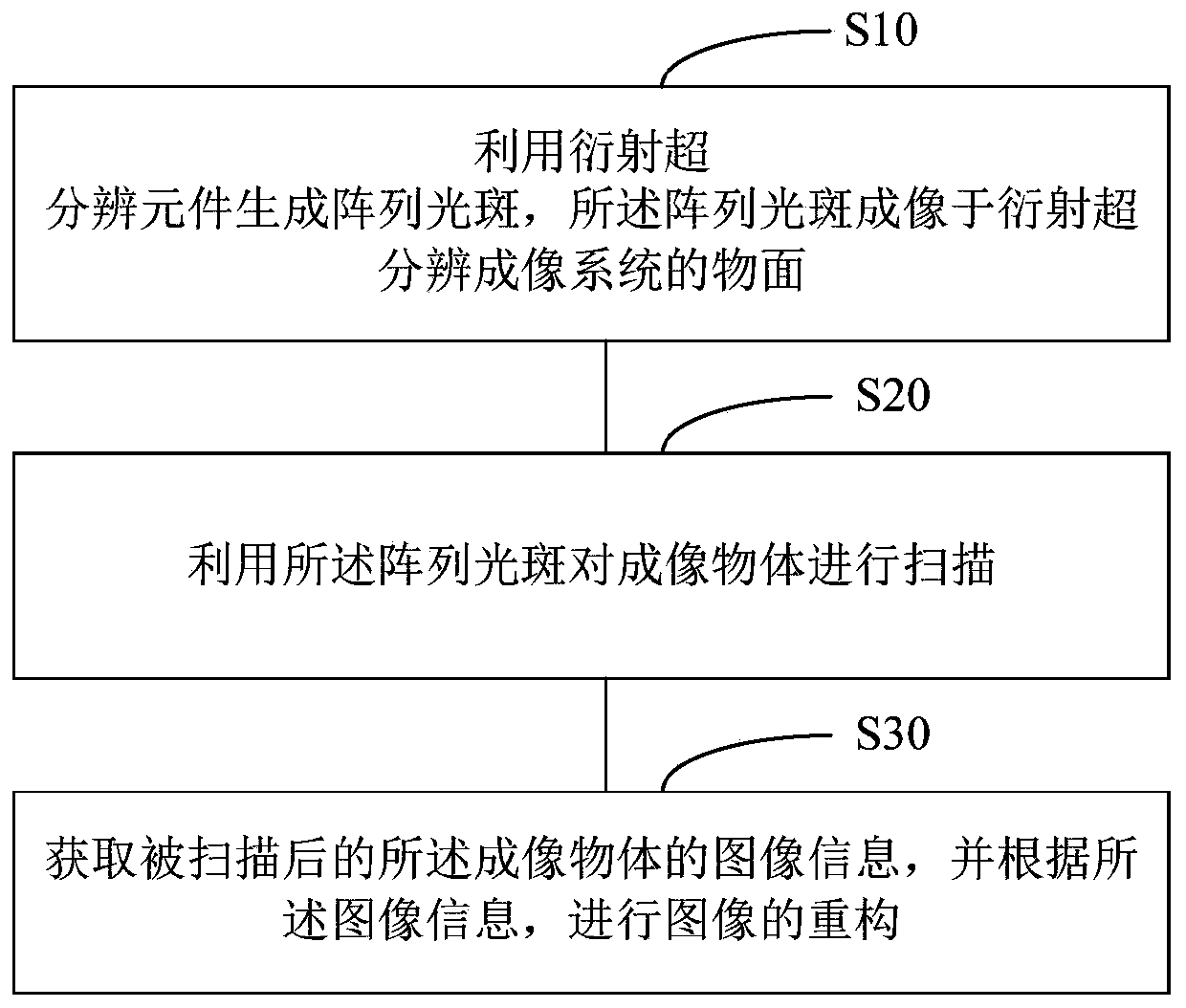
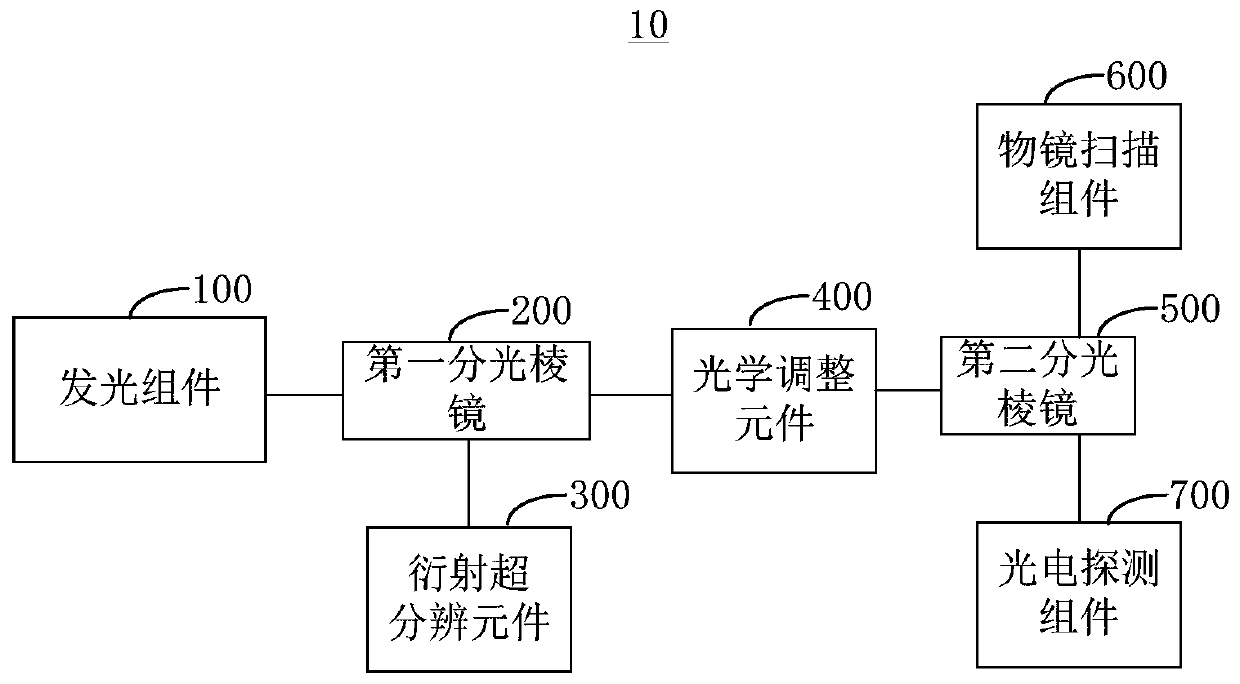
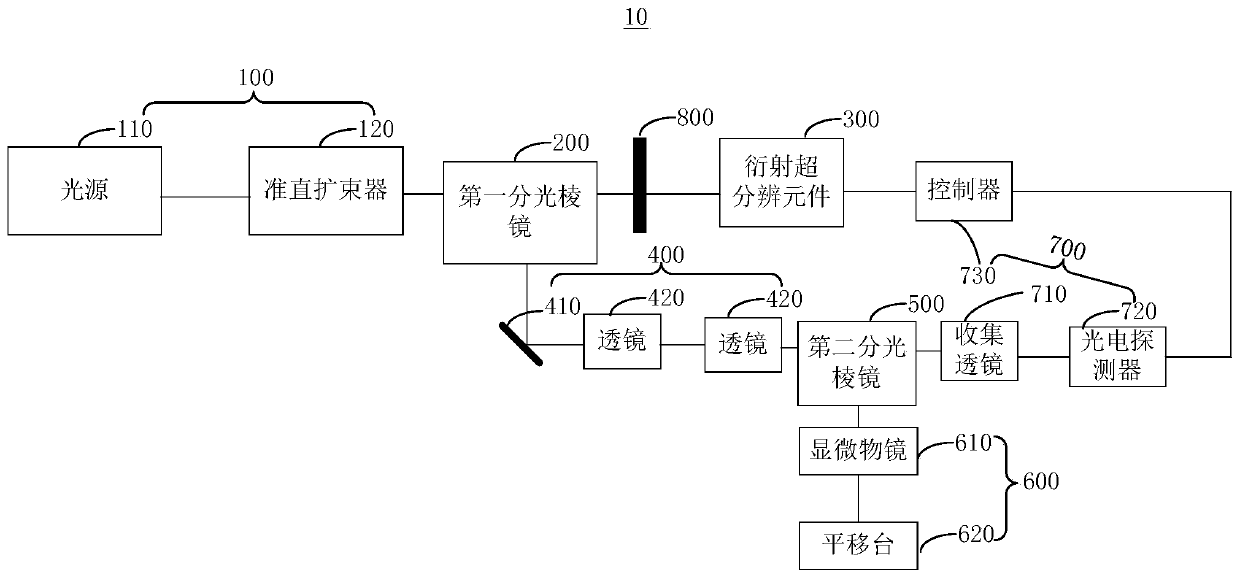
The invention relates to a microscopic imaging method and system. According to the microscopic imaging method, array light spots (larger than or equal to two) are generated by utilizing a diffractionsuper-resolution element, wherein the array light spots are imaged on an object plane of the microscopic imaging system so as to realize illumination of an imaged object, and then the imaging efficiency is improved. The imaged object is scanned by utilizing the array light spots, image information of the scanned imaged object is obtained, and image reconstruction is carried out according to the image information. According to the microscopic imaging method, the diffraction super-resolution element is utilized to modulate an illumination light beam to generate the super-resolution array light spots, the diffraction limit of an optical system can be broken through, optical super-resolution imaging is realized, and the super-resolution capability is adjustable. t
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
GaN-based metal-ultrathin oxide-semiconductor composite structure nanolaser and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106785913AUniform diameter and lengthSmall optical mode volumeLaser detailsLaser active region structureBiological imagingLaser light
The invention discloses a GaN-based metal-ultrathin oxide-semiconductor composite structure nanolaser, which comprises a substrate and an InGaN / Ga quantum well nano-column, wherein the structure of the substrate sequentially comprises a SiO2-Si substrate, a metal layer and an ultrathin oxide layer; the InGaN / Ga quantum well nano-column is put on the surface of the ultrathin oxide layer and structure of the InGaN / Ga quantum well nano-column sequentially comprises a sapphire substrate layer, an n-type GaN layer, an In<x>Ga<x-1>N / GaN quantum well active layer and a p-type GaN layer. The invention further discloses a preparation method of the GaN-based metal-ultrathin oxide-semiconductor composite structure nanolaser. The nanolaser has the advantages that (1) the nanolaser has very small optical mode volume and can break through a diffraction limit of light, and the submicron-sized laser can be achieved; (2) the laser has an extremely low lasing threshold and an MUTOS laser light structure can lase under an optical pump of 0.15kW / cm<2>; and (3) the mode of laser light can be regulated and controlled and single-mode and multi-mode laser light transmission is achieved. The laser structure has potential application value in the aspects of ultra-high resolution intelligent displaying, complicated biological imaging, and photoelectric interconnection of a silicon-based integration circuit and a photoelectronic device.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
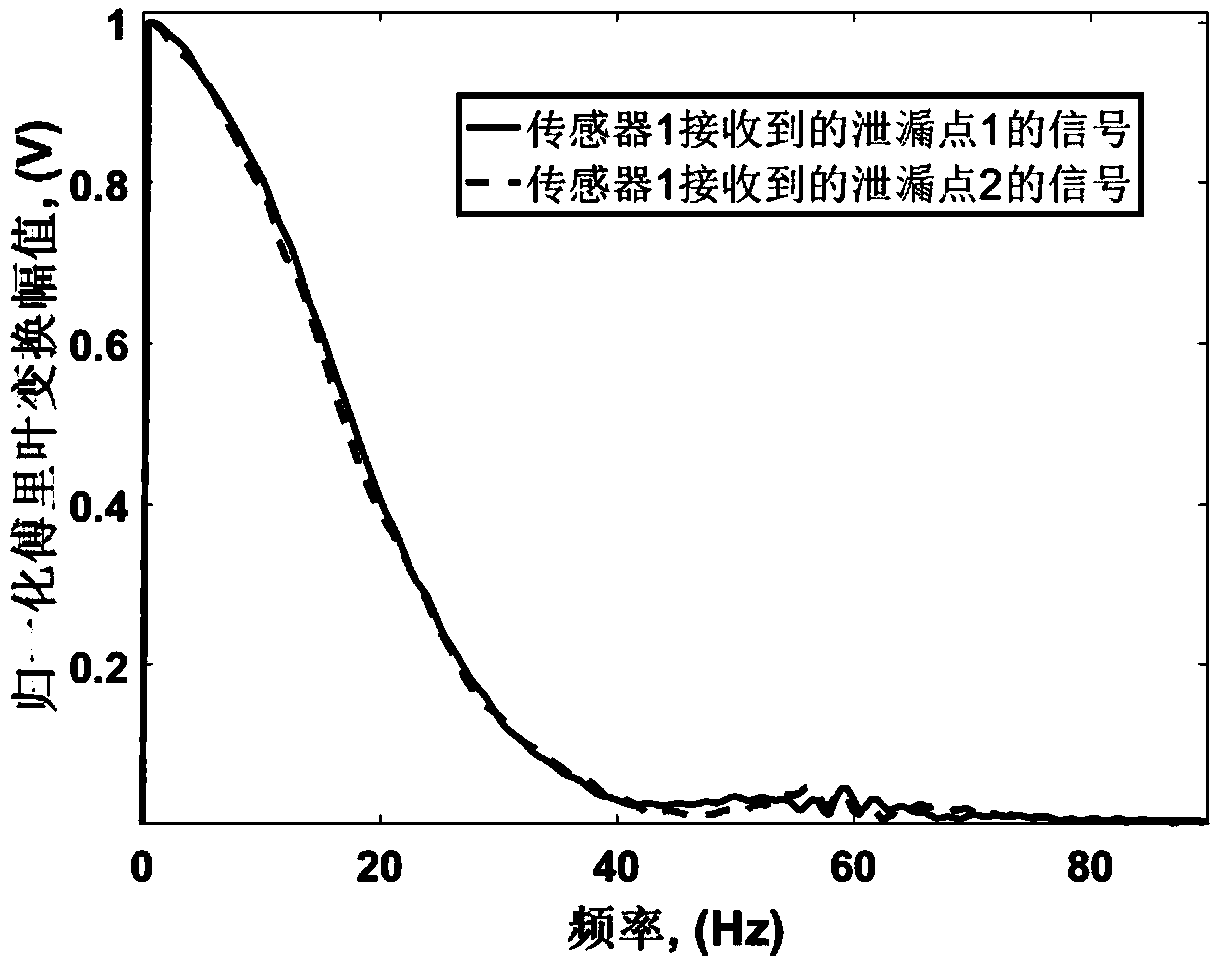
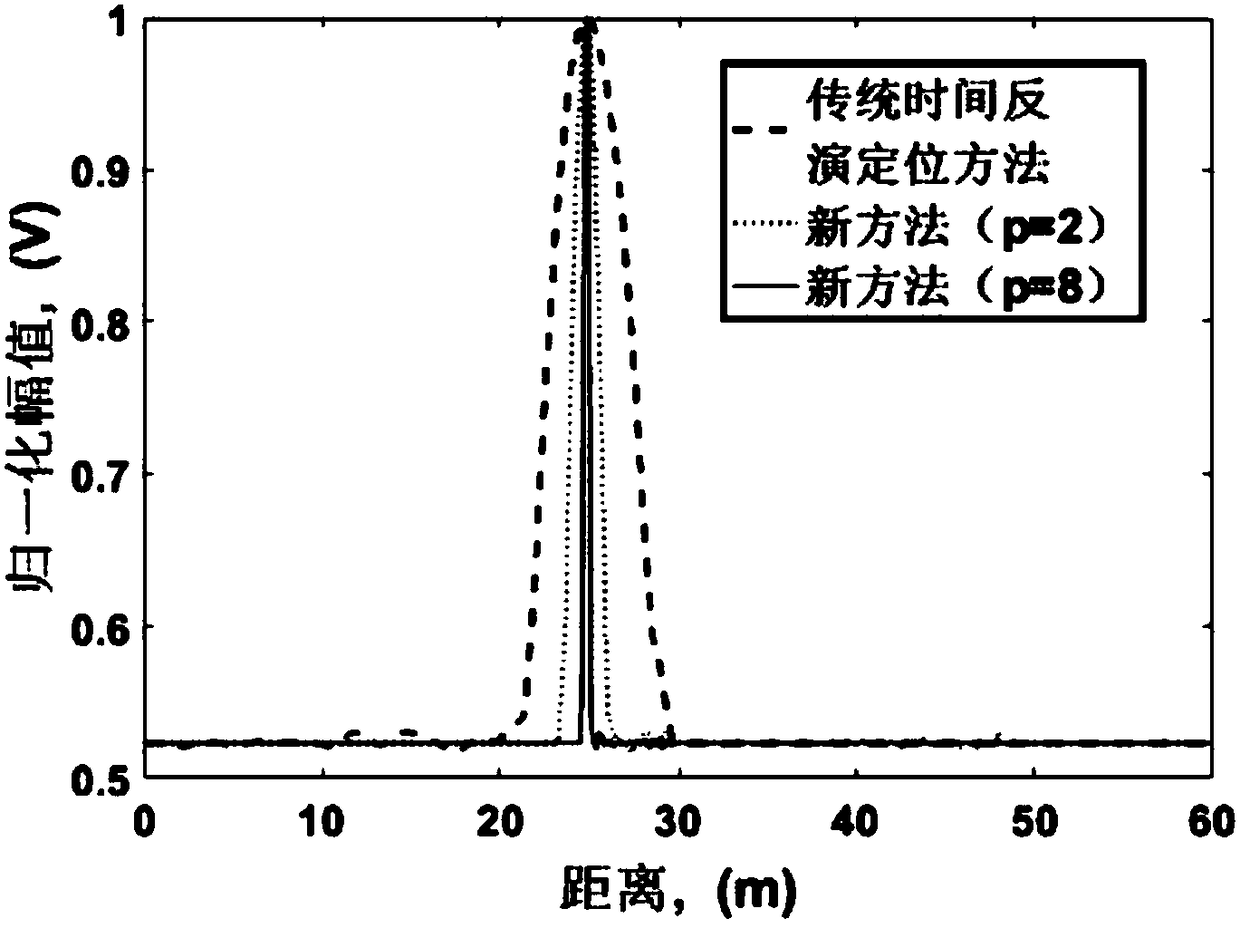
Time-inversion super-resolution pipeline leakage monitoring method
ActiveCN108120573ALow costHigh-resolutionFluid-tightness measurement using electric meansTime domainImage resolution
The invention discloses a time-inversion super-resolution pipeline leakage monitoring method. Compared with the prior art, the invention has the advantages as follows: in allusion to the defect that ametamaterial component is required to be used near a signal source for achieving super-resolution imaging positioning in a conventional scheme, a time-inversion super-resolution time domain adjustment function is provided and designed, and through adjustment of the function, the resolution can be increased and a resolution diffraction limit can be broken through. By the time-inversion super-resolution pipeline leakage monitoring method, super-resolution is achieved by an algorithm and the metamaterial component is not required to be used, so that the time-inversion super-resolution pipeline leakage monitoring method has higher practicality and lower cost than the conventional time-reversion super-resolution imaging positioning scheme. Therefore, by using the novel technology, low-cost andsuperhigh-resolution leakage monitoring of a long-distance gas pipeline can be achieved.
Owner:DONGGUAN UNIV OF TECH
A nano-optical tweezers device and method for precise manipulation of nanoparticles and biomolecules
InactiveCN106898407BBreaking through the diffraction limitEasy to controlMicroscopesCoupling light guidesBio moleculesBand-pass filter
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Method for carrying out super-resolution imaging by utilizing micron-scale liquid drops generated in real time
PendingCN111982812AModerate growth rateThe size is easy to controlPhase-affecting property measurementsLight beamErbium lasers
The invention relates to a method for carrying out super-resolution imaging by utilizing micron-scale liquid drops generated in real time. An adopted device comprises an optical tweezer system, an imaging system and a sample pool. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: initializing an optical tweezer system, adjusting the power of a laser to enable the power of a laser beamreaching a sample pool solution to be 1w, and forming and operating liquid drops; preparing a mixed solution, uniformly mixing a phosphate buffer solution and ethanol according to a volume ratio of 1: (3-8), and injecting the mixed solution into a sample pool; generating droplets available for imaging: the sample pool is placed on a three-dimensional displacement table, the displacement table isadjusted to enable laser beams to converge at the axial middle position of the sample pool, and the particle size of the liquid drops is controlled by controlling the laser intensity and the irradiation time; observing and imaging: after the droplet growth is completed, reducing the laser of the laser so that the droplet does not grow any more, and meanwhile, the optical trap can still capture thedroplet and adjust the displacement table to move upwards, and thus the droplet is just in contact with a specified area of the sample for observing and imaging.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
A kind of laser etching processing method of quartz crystal
ActiveCN105522281BRealize fine processingMinimize and eliminate negative effectsLaser beam welding apparatusMicrometerBase frequency
The invention discloses a laser ablation processing method for quartz crystal. The laser ablation processing method specifically comprises the steps of selecting lasers, preparing control software, designing processing drawings, carrying out laser ablation, carrying out post-processing treatment and carrying out detection. The method for processing the quartz crystal is designed on the basis of limitation to the condition of each step, the quartz crystal can be effectively processed for forming various shapes and can be thinned through the processing method, the thickness of the thinned quartz crystal is small, the corresponding base frequency is high, and the strength of the processed quartz crystal is high. In addition, the processing method is simple, the processing accuracy is high, and the processing dimensional accuracy of the quartz crystal can be controlled to be within the range of + / - 5 micrometers.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF RADIO METROLOGY & MEASUREMENT
A large field of view super-resolution imaging device
The invention discloses a large view field super resolution imaging device which comprises a base and a super-surface, wherein the base and the super-surface are successively arranged in the bottom-up sequence. The super-surface is composed of nano-unit structure arrays which are arranged in succession on an ultra-thin metal or a dielectric film. A nano-unit structure is a deep sub-wavelength structure. According to the invention, geometric phase on the nanostructure is used to control the electromagnetic wave symmetry; electromagnetic waves are converted from rotation symmetry to translational symmetry to acquire large view field perfect focusing near 180 degrees; if curved face or multi-plane combination is used, large view field imaging can be realized; the work bandwidth can cover the entire electromagnetic spectrum; the resolution is close to or even beyond the diffraction limit; and the device has a wide application prospect in the field of large view field super resolution imaging.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
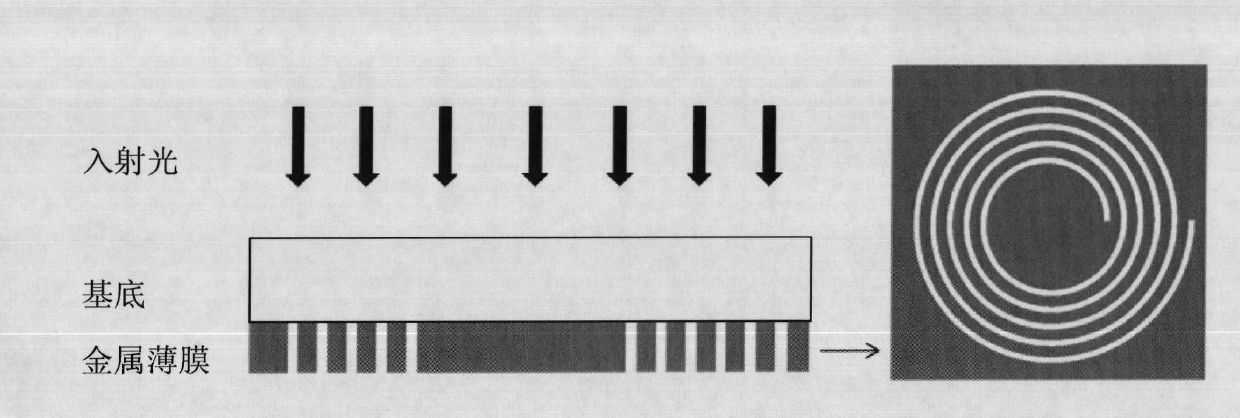
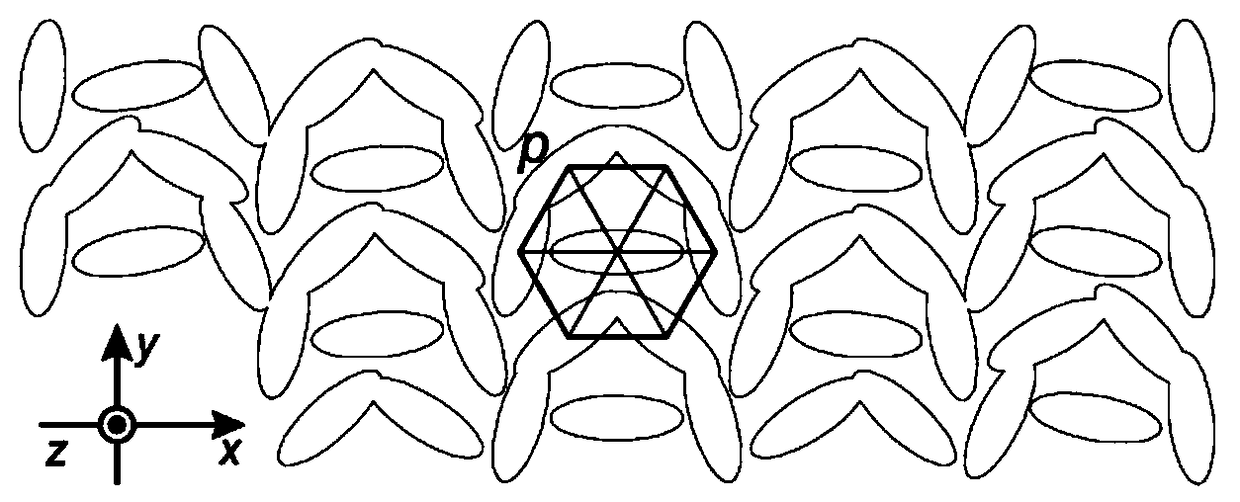
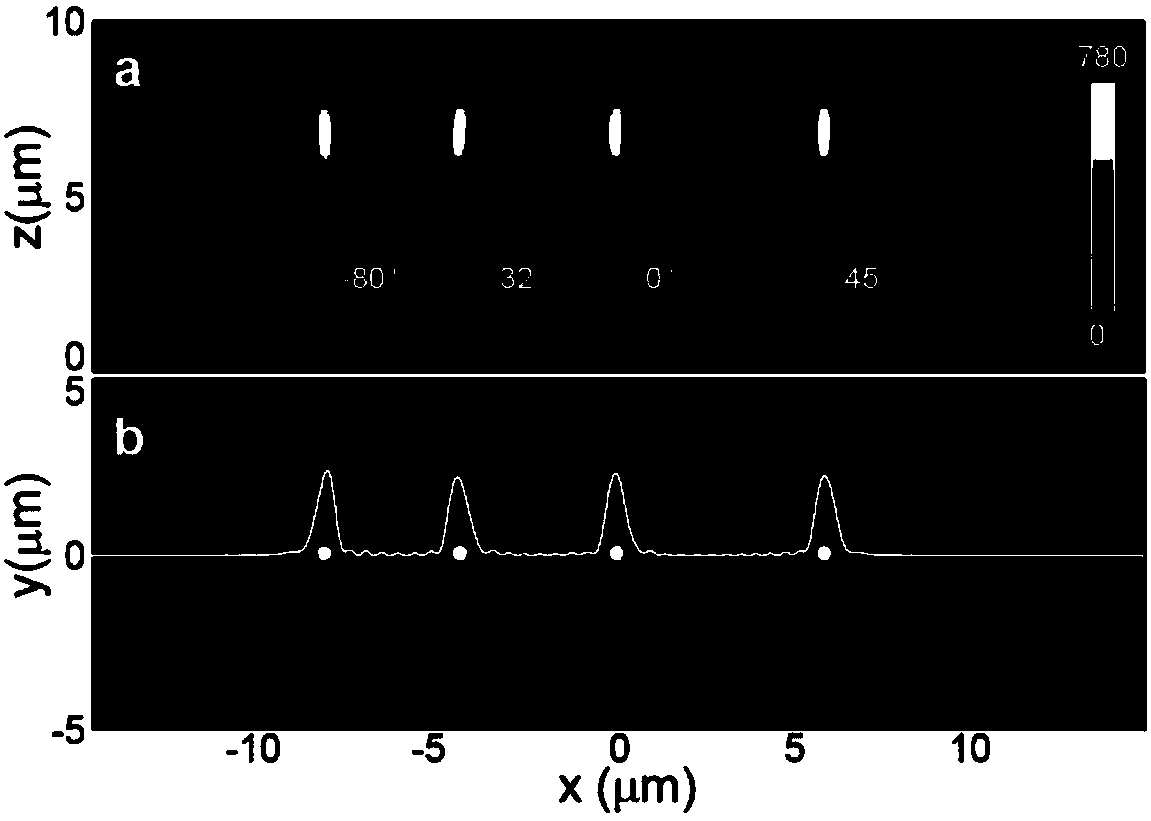
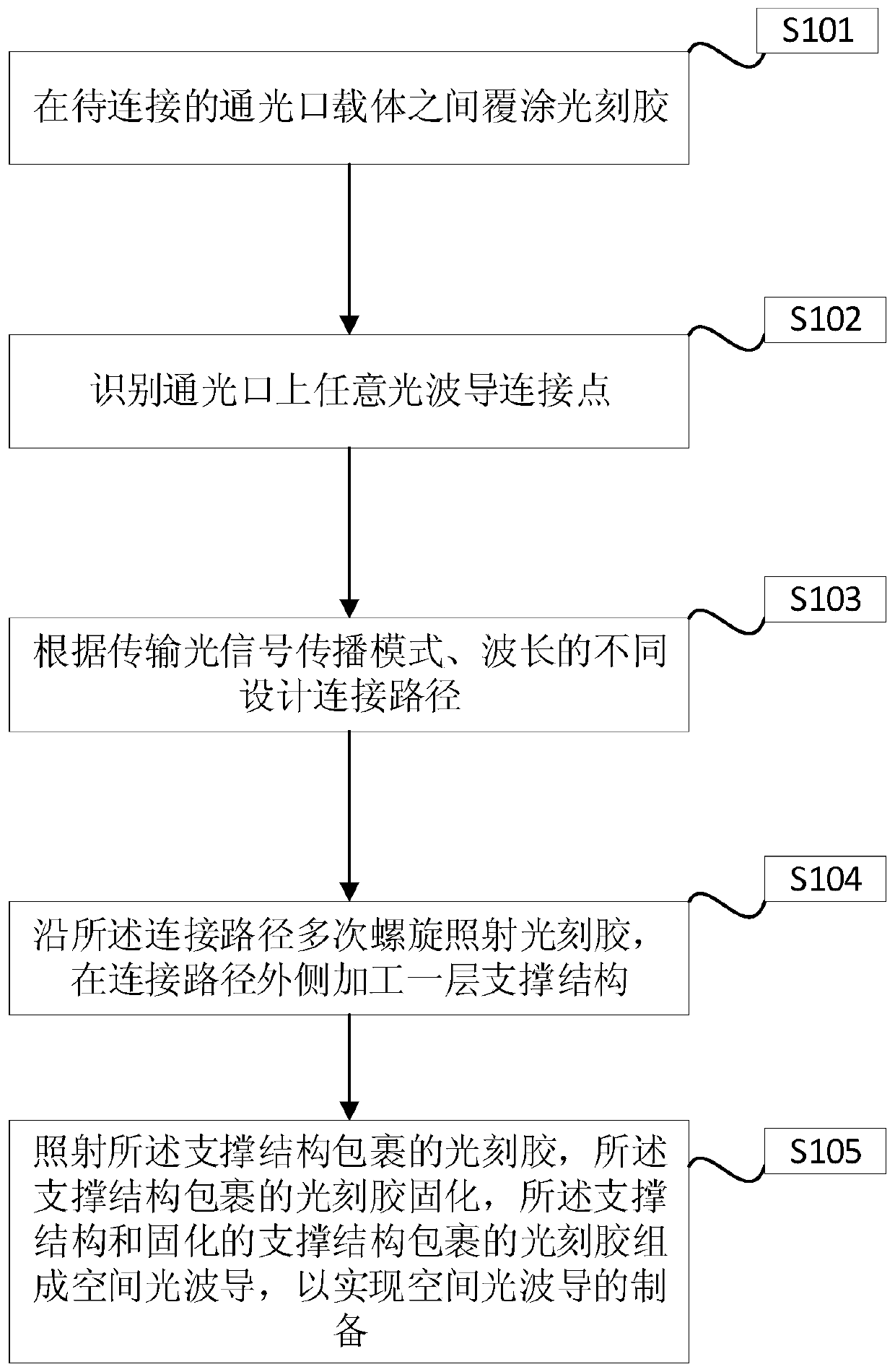
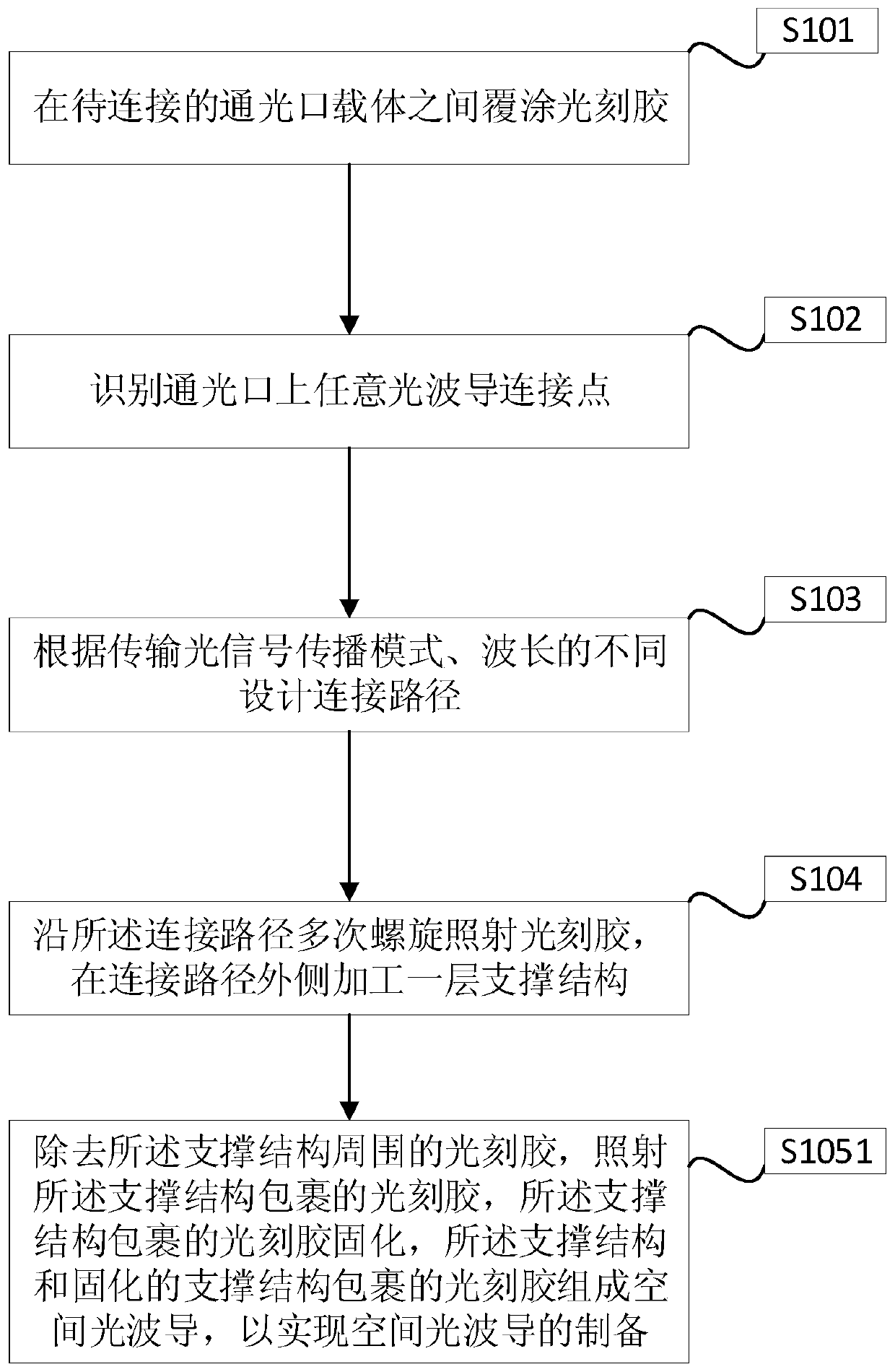
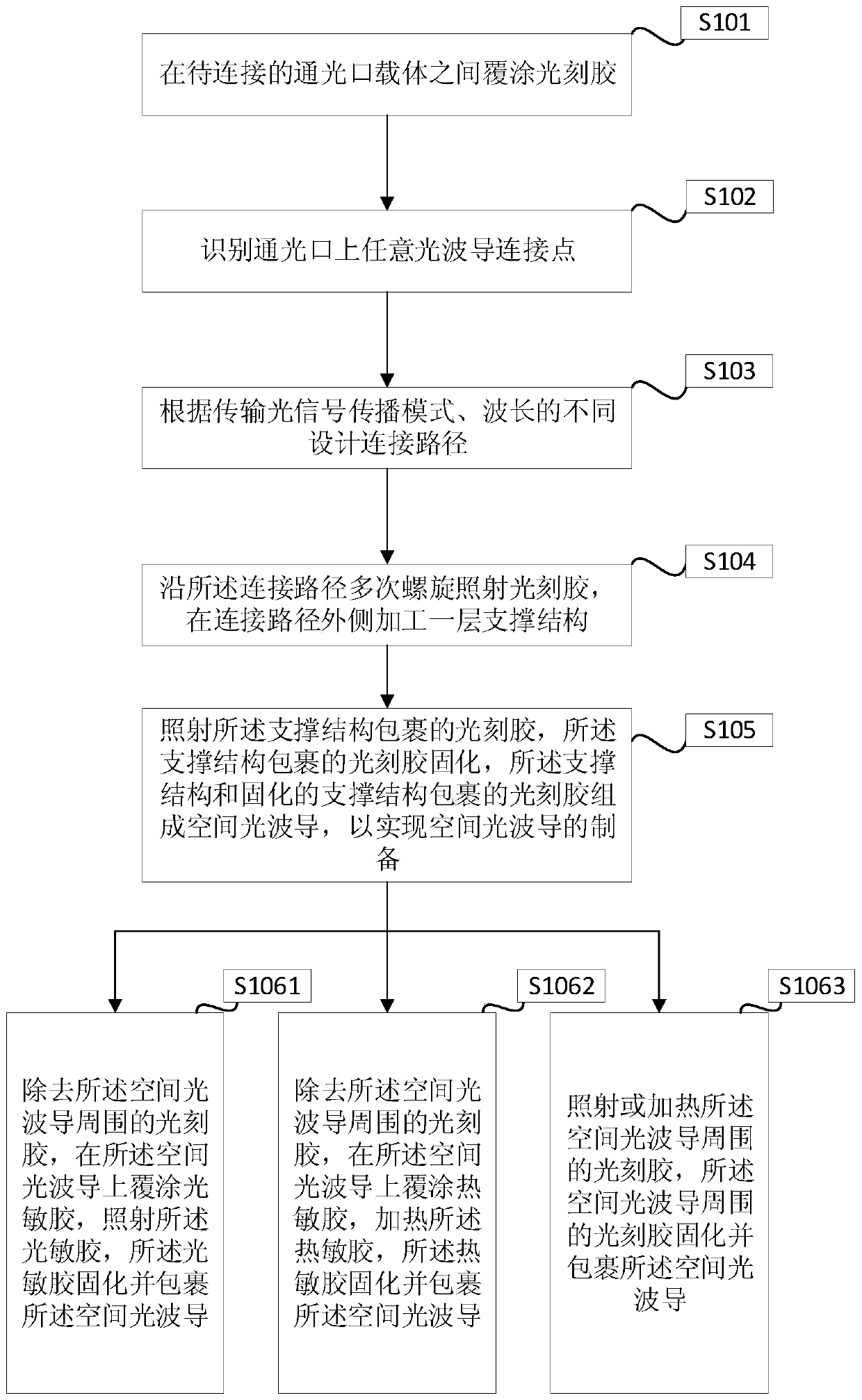
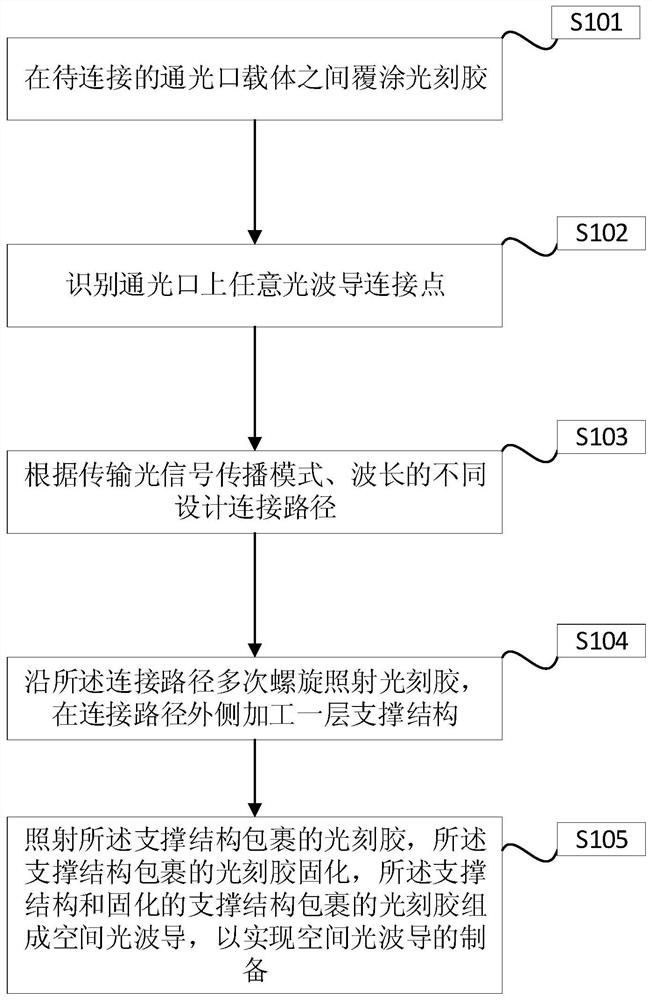
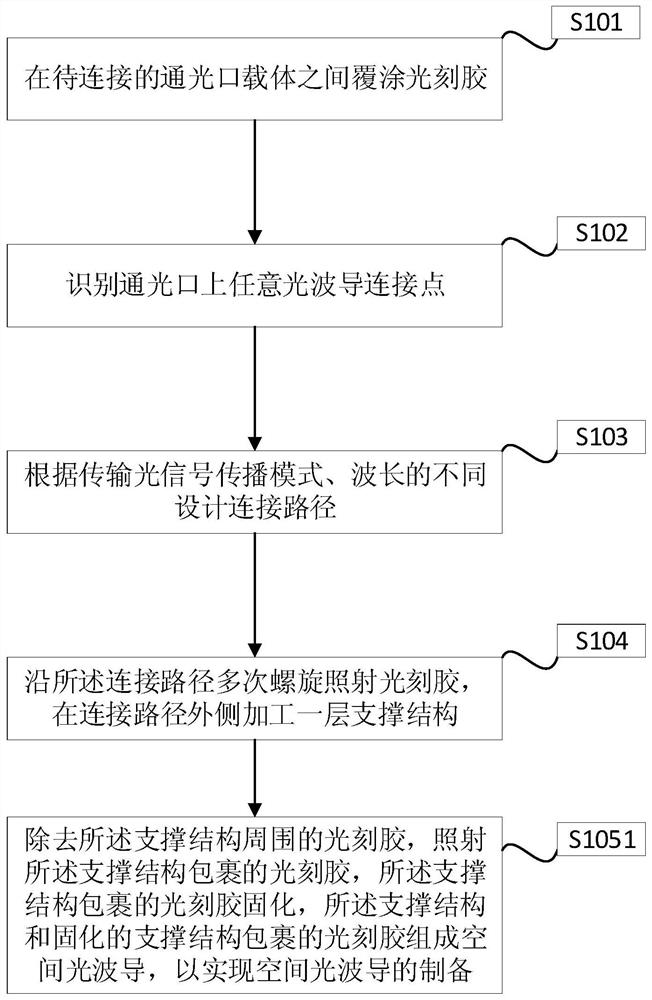
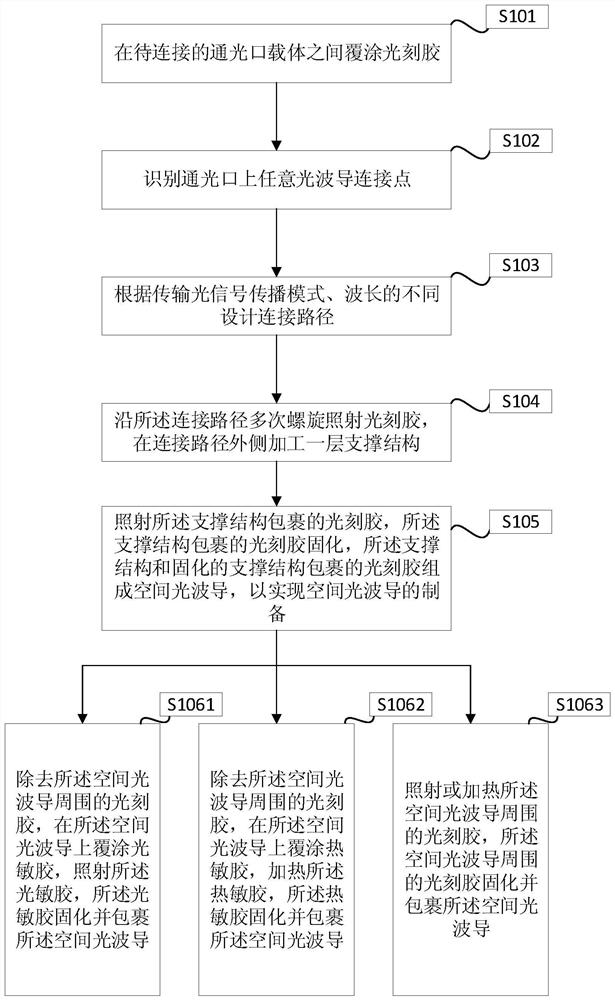
Space optical waveguide fabrication method
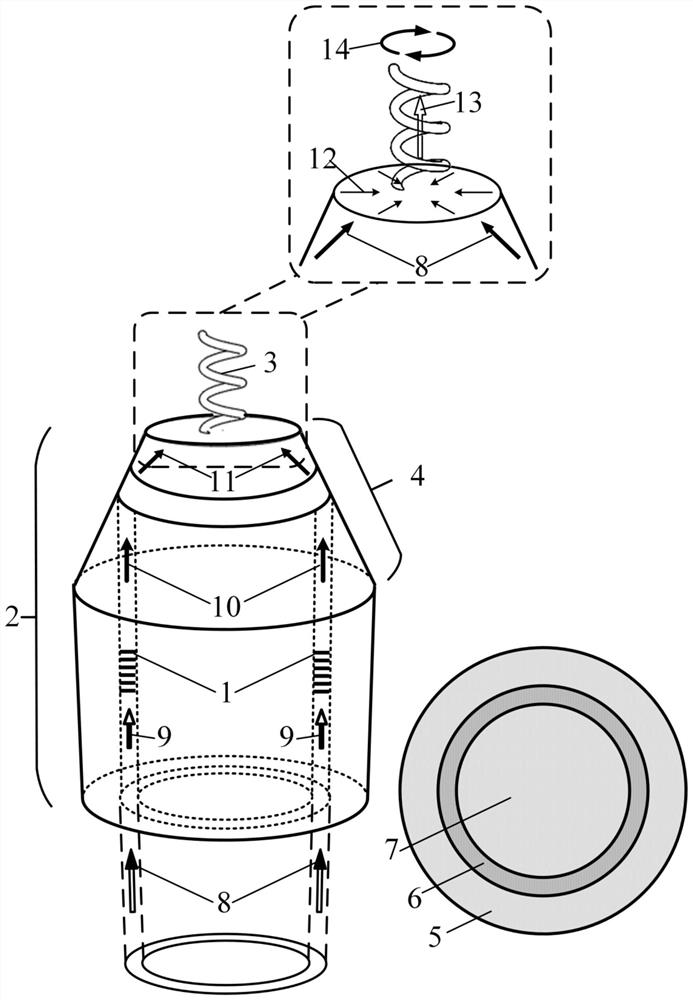
The invention discloses a space optical waveguide fabrication method. The method comprises the steps of coating photoresist among to-be-connected optical opening carriers, identifying and designing aconnection path, and achieving fabrication of a space optical waveguide by the space optical waveguide comprising a support structure, fabricated by spiral irradiation of the photoresist for many times, and the photoresist wrapped with the cured support structure. According to the space optical waveguide fabrication method, the polymerization and crosslinking reaction of the photoresist is facilitated and the photoresist is cured by a non-linear absorption effect of the photoresist on irradiation light energy, the diffraction limit can be broken through, the processing of the space optical waveguide with an arbitrary three-dimensional form and processing resolution smaller than 100 nanometers achieved, thus, matching of the three-dimensional form of the space optical waveguide and the sizes of the to-be-connected optical openings can be achieved, the loss during the optical waveguide coupling process is reduced, the intensity of the space optical waveguide is improved by the spirally-processed support structure, and interconnection of high-quality large-distance devices is achieved.
Owner:YANTAI MAGIC NANOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
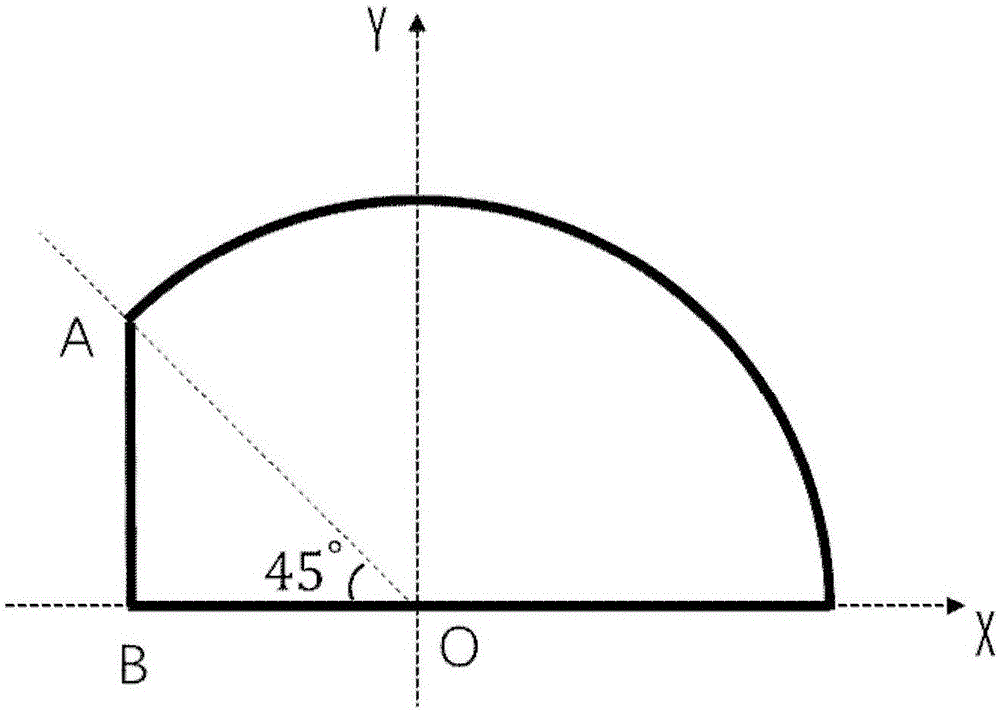
Light focusing structure
The invention discloses a light focusing structure. The light focusing structure is a three-dimensional taper asymmetric structure made of photoresist; two faces of the sides of the tapered asymmetric structure are tapered planes, and the other face is a tapered arc surfacer; the bottom surface of the tapered asymmetric structure is a plane; and the surface of the tapered non-asymmetric structure is plated with a metal layer. Incident light is coupled as plasma wave on the metal surface to focus on a structure tip, which can break through a diffraction limit and makes the diameter of a focusing facula smaller than 100 nanometers. Besides, the light focusing structure has no a symmetric axis in any direction, so that the light focusing structure can effectively utilize polarized light energy of any polarization direction under radiation of a wide light spectrum light source without polarization processing and can maximally utilize the incident light energy. The light focusing structure is high in feasibility, can be used for manufacturing the optical fiber probe to be used for near field optical detection, can be applied in the optical cutting edge field like the single molecule fluorescence imaging and has a high scientific research value and a wide market application prospect.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Photonic crystal super-resolution imaging device with variable period grating
InactiveCN109839749BImprove imaging resolutionBreaking through the diffraction limitOptical elementsRefractive indexWavelength
The invention relates to a variable-period grating photonic crystal super-resolution imager. There is a gap of the same width between the incident surface of the crystal and the exit surface of the photonic crystal. The equivalent refractive index of the photonic crystal is -1. The number of columns, the point light source enters the photonic crystal after passing through the sub-wavelength grating, and realizes super-resolution imaging that breaks through the diffraction limit. By adding a sub-wavelength grating on the surface of the photonic crystal, the coupling effect of the light field is enhanced, the half-width of the image point is compressed, the imaging resolution is improved and the diffraction limit is broken.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Multi-mode excitation structure based on compact resonator
ActiveCN113036386BStrong field binding abilityBreaking through the diffraction limitPhase-affecting property measurementsResonatorsResonant cavityRefractive index
Owner:CHINA ACADEMY OF SPACE TECHNOLOGY
Super-resolution telescope imaging method and system
ActiveCN108398805BBreaking through the diffraction limitImprove spatial resolutionOptical elementsImage resolutionTelescope
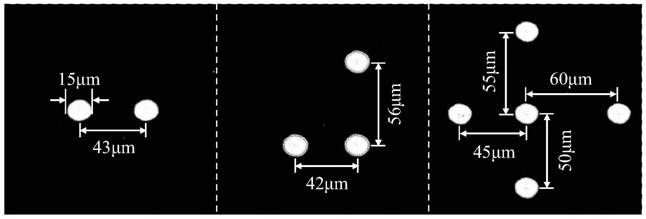
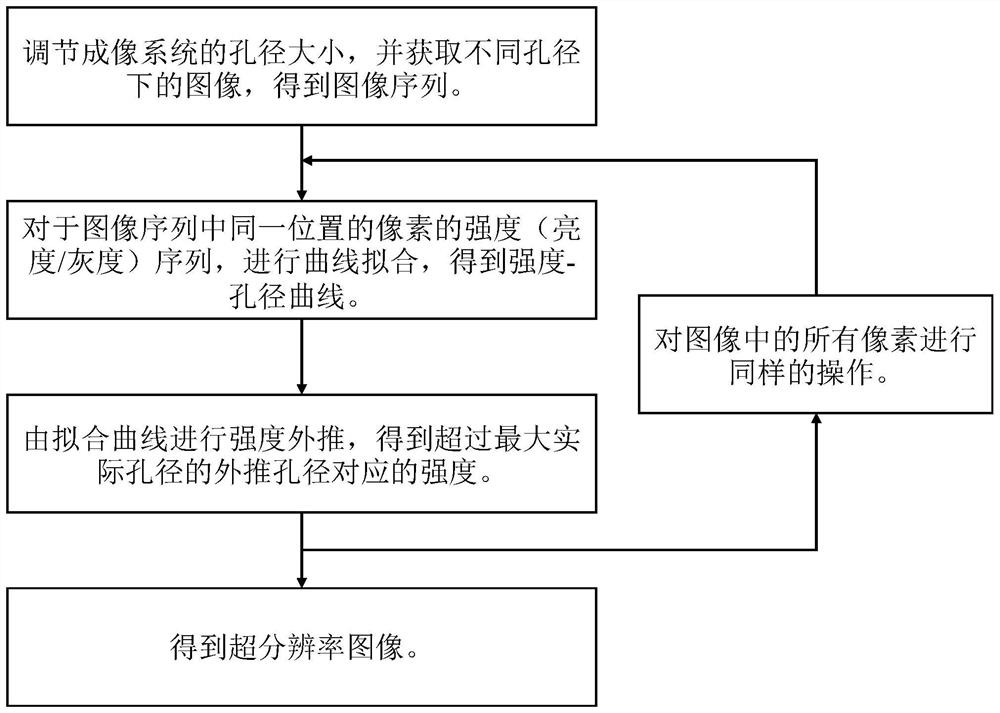
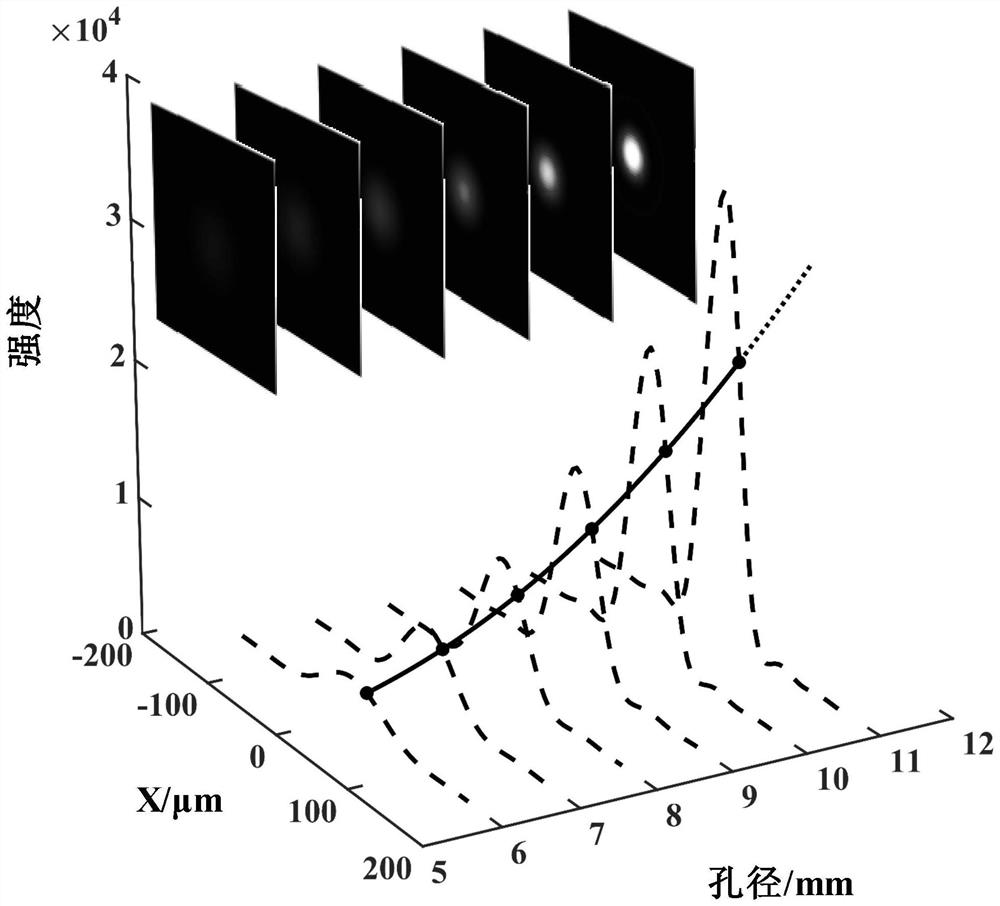
A super-resolution imaging method and a system thereof are disclosed. The method comprises the following steps S1 an aperture size of an imaging system is adjusted; S2 corresponding images under different apertures are collected, and an image sequence is obtained; S3 a series of intensity-aperture data for pixels at a location in the image sequence is subjected to curve fitting operation, and a fitted intensity-aperture curve is obtained; S4 according to the obtained fitted curve, an intensity corresponding to an extrapolated aperture exceeding an actual maximum aperture of the imaging systemis extrapolated; S5 all pixels in the image sequence are extrapolated to an intensity of the same extrapolated aperture in accordance with steps S3 and S4; S6 all obtained extrapolated intensities form an image according to original pixel positions. Via the method and the system disclosed in the invention, details that cannot be distinguished originally can now be distinguished, a diffraction limit is broken, and a spatial resolution can be improved. Artificial radiation illumination on an object being observed is not needed, and prior information of the object being observed is also not needed.
Owner:NANJING INST OF ASTRONOMICAL OPTICS & TECH NAT ASTRONOMICAL OBSE
Optical fiber helical antenna wave field converter
PendingCN113687464AWith polarization state modulation functionBreaking through the diffraction limitCoupling light guidesFiberLong-period fiber grating
The invention provides an optical fiber helical antenna wave field converter. The optical fiber helical antenna wave field converter is characterized by consisting of a section of annular core optical fiber 2 with a long-period fiber grating 1 and a helical antenna 3 in the center of a fiber end, wherein the fiber end of the annular core optical fiber 2 is ground to form a fiber end cone frustum 4, and the annular core optical fiber 2 comprises an outer cladding 5, an annular fiber core 6 and an inner cladding 7; input light 8 is injected into the annular core fiber 2 to form a low-order conduction mode 9, modulated by the long-period fiber grating 1 and converted into a radial polarization mode 10, total internal reflection occurs at an interface of the outer cladding 5 and an external medium when the input light is transmitted through the fiber end cone frustum 4, and reflected light waves 11 are diffracted in the fiber end cladding and transmitted to the end face of the fiber end and then focused at the fiber end; constructive interference 12 is generated at the focusing position, so that a longitudinal polarized light field 13 with enhanced interference is generated at the center of the fiber end, and the longitudinal polarized light field 13 outputs a circular polarized light field 14 after being modulated by the spiral antenna 4. The optical fiber helical antenna wave field converter can be applied to the fields of wave field conversion, signal detection, light control and the like.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
A Light Focusing Structure
ActiveCN106324753BFocus spot is smallBreaking through the diffraction limitCoupling light guidesFluorescenceLight energy
The invention discloses a light focusing structure. The light focusing structure is a three-dimensional taper asymmetric structure made of photoresist; two faces of the sides of the tapered asymmetric structure are tapered planes, and the other face is a tapered arc surfacer; the bottom surface of the tapered asymmetric structure is a plane; and the surface of the tapered non-asymmetric structure is plated with a metal layer. Incident light is coupled as plasma wave on the metal surface to focus on a structure tip, which can break through a diffraction limit and makes the diameter of a focusing facula smaller than 100 nanometers. Besides, the light focusing structure has no a symmetric axis in any direction, so that the light focusing structure can effectively utilize polarized light energy of any polarization direction under radiation of a wide light spectrum light source without polarization processing and can maximally utilize the incident light energy. The light focusing structure is high in feasibility, can be used for manufacturing the optical fiber probe to be used for near field optical detection, can be applied in the optical cutting edge field like the single molecule fluorescence imaging and has a high scientific research value and a wide market application prospect.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Integrated terahertz wave far-field super-diffraction focusing imaging system
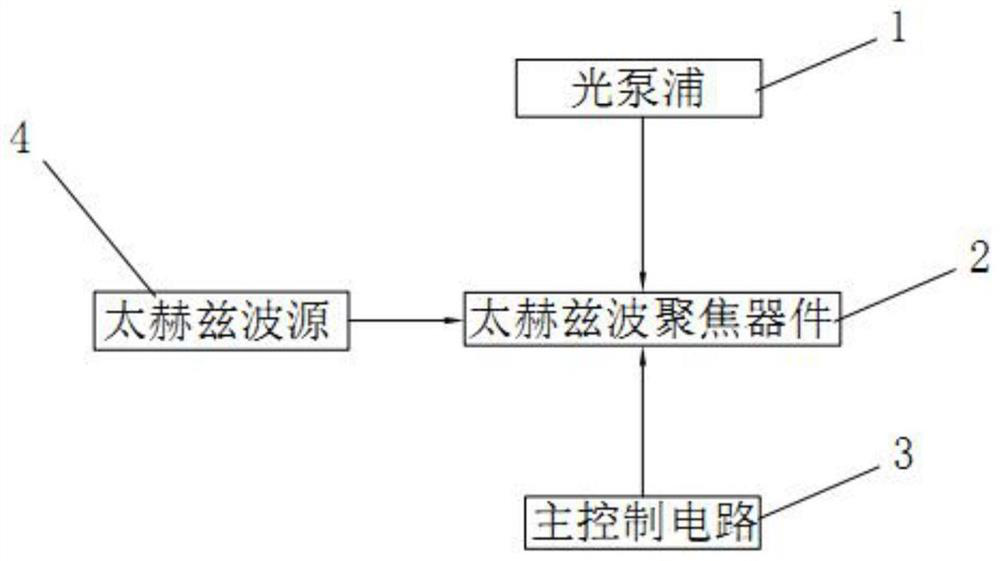
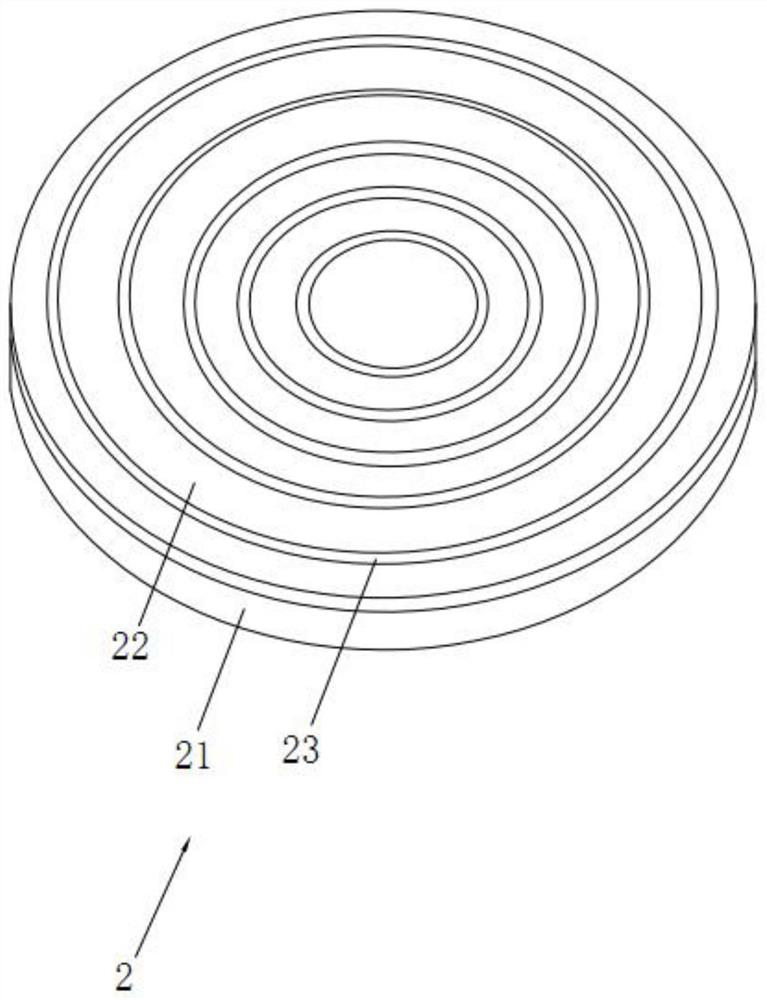
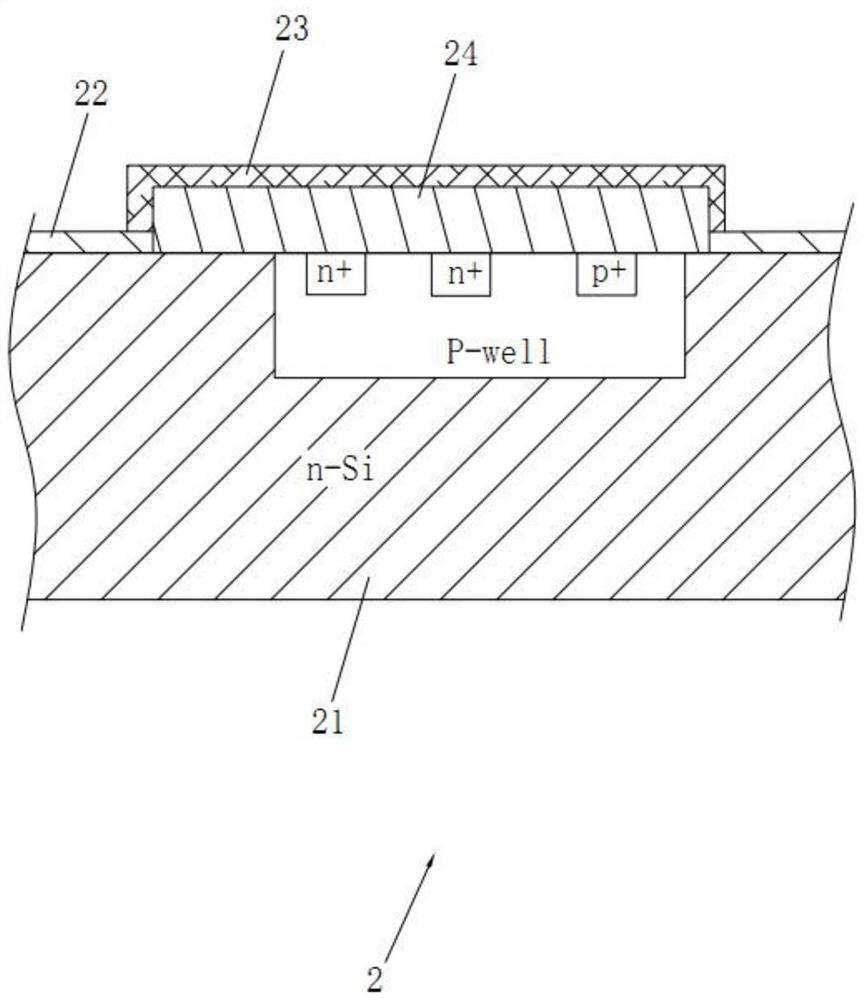
ActiveCN109119870BIncrease flexibilitySuper-resolution focusing imaging is easy to operateSolid masersOptical pumpingImage resolution
The invention discloses an integrated terahertz wave far-field ultra-diffraction focusing imaging system, relates to the technical field of terahertz wave imaging, and solves the problems that the conventional terahertz wave imaging technology is based on the near-field optical principles although the conventional terahertz wave imaging technology achieves the super-resolution imaging. The conventional imaging technology has the problems that the focal length is very small, the dynamic focusing cannot be achieved, the width is narrower and the diffraction efficiency is smaller. The main pointsof the technical scheme are that the system comprises a terahertz wave source, an optical pump, a terahertz wave focusing device and a main control circuit. The terahertz wave source is used for emitting the terahertz waves, and the optical pump is used for generating continuous visible light to irradiate the terahertz wave focusing device. The terahertz wave focusing device is used for changingthe transmissivity of terahertz waves, and the main control circuit is used for applying a bias voltage to the terahertz wave focusing device. The system is large in focal length, achieves the ultra-diffraction limiting resolution, achieves the dynamic focusing, increases the bandwidth, and improves the diffraction efficiency.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
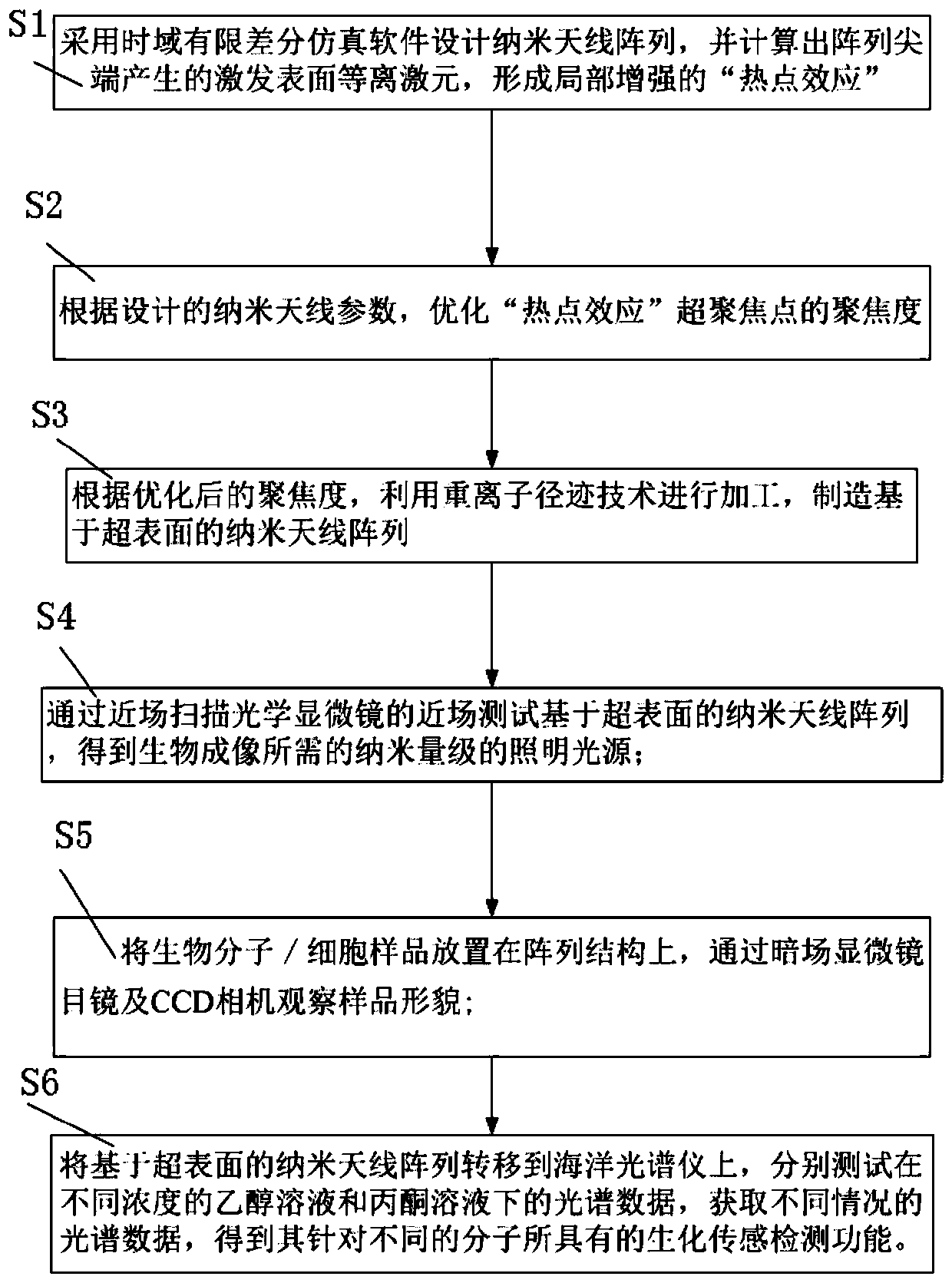
Manufacturing method and application of metasurface nanoantenna array based on heavy ion track technology
InactiveCN108647467BEasy to detectHigh-resolutionDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsEyepieceBiological imaging
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Rapid super-resolution detection device and detection method for optical element defect based on random phase shift
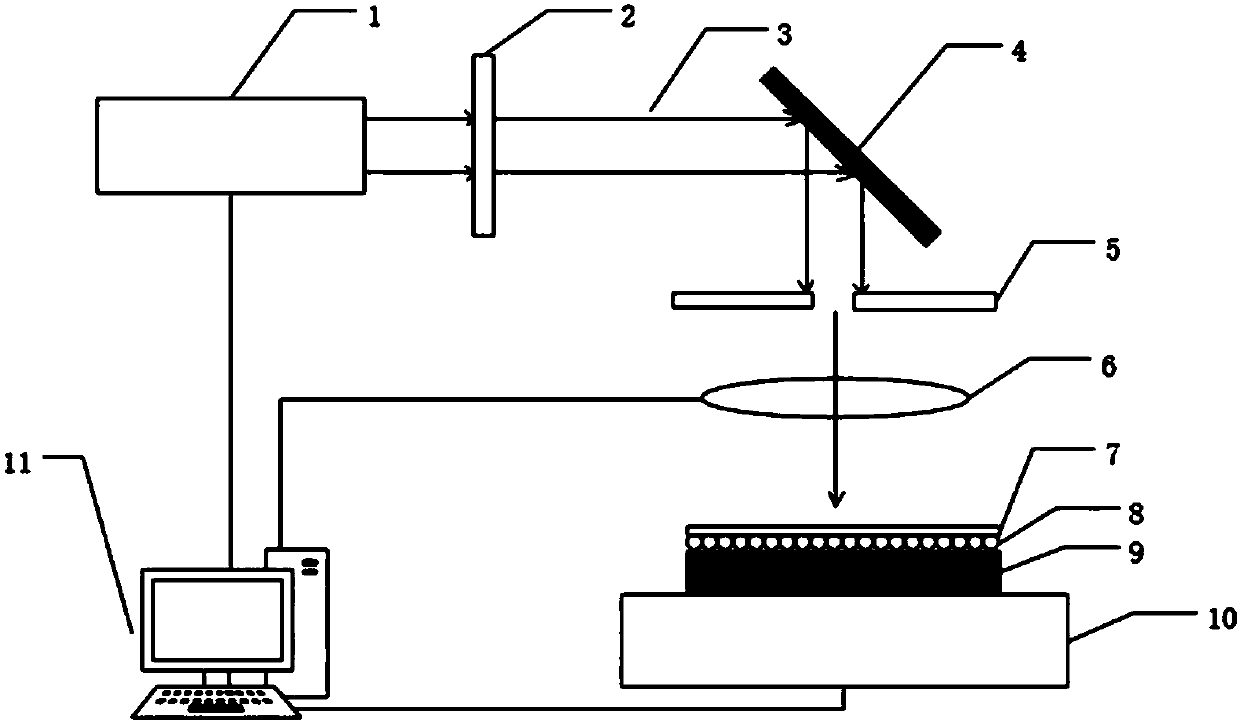
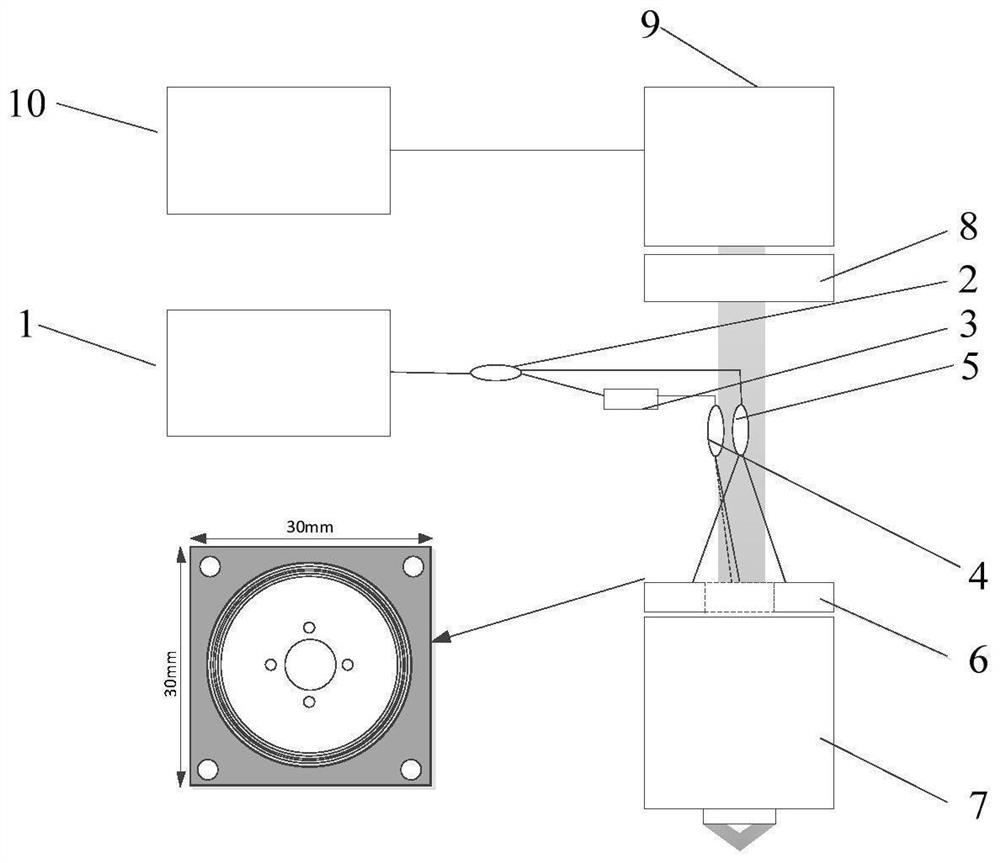
ActiveCN112858345ASimplify the acquisition processImprove collection efficiencyMaterial analysis by optical meansImaging lensLaser light
The invention discloses a random phase shift-based optical element defect rapid super-resolution detection device and method. The device is characterized in that a laser light source is equally divided into two beams through a 1*2 optical fiber coupler I, one beam is subjected to laser polarization state adjustment through an extrusion type polarization controller, and is equally divided into two beams through a 1*2 optical fiber coupler II, the other beam of laser output by the 1*2 optical fiber coupler I is equally divided into two beams by a 1*2 optical fiber coupler III, the four beams of illumination laser are symmetrically irradiated on the surface of a sample through an entrance pupil of a microscope objective for interference to form illumination light with a two-dimensional cosine structure, the microscope objective is used for receiving reflected and scattered light of the structured illumination light modulated by the surface of the sample, and final returned imaging signal collection is completed in a high-speed camera through an imaging lens. According to the invention, the purposes of miniaturization, portability, high efficiency, random phase shift and low cost are achieved.
Owner:LASER FUSION RES CENT CHINA ACAD OF ENG PHYSICS
Preparation method of self-organized periodic micro-nano structure with glass and crystal alternately arranged
ActiveCN110171801B11 Ability EnhancementsImprove thermal stabilityDecorative surface effectsChemical vapor deposition coatingNano structuringPrism
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
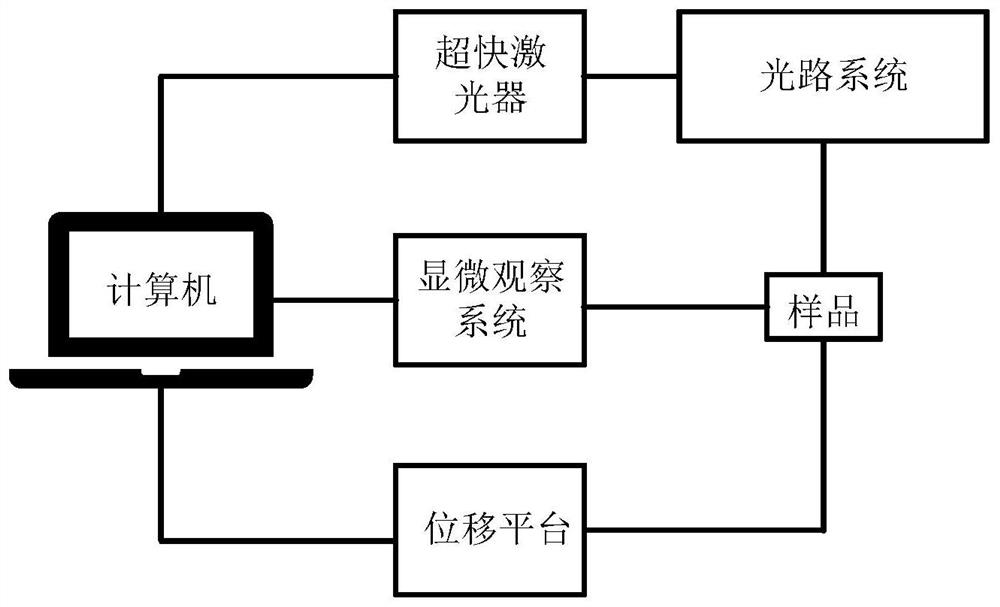
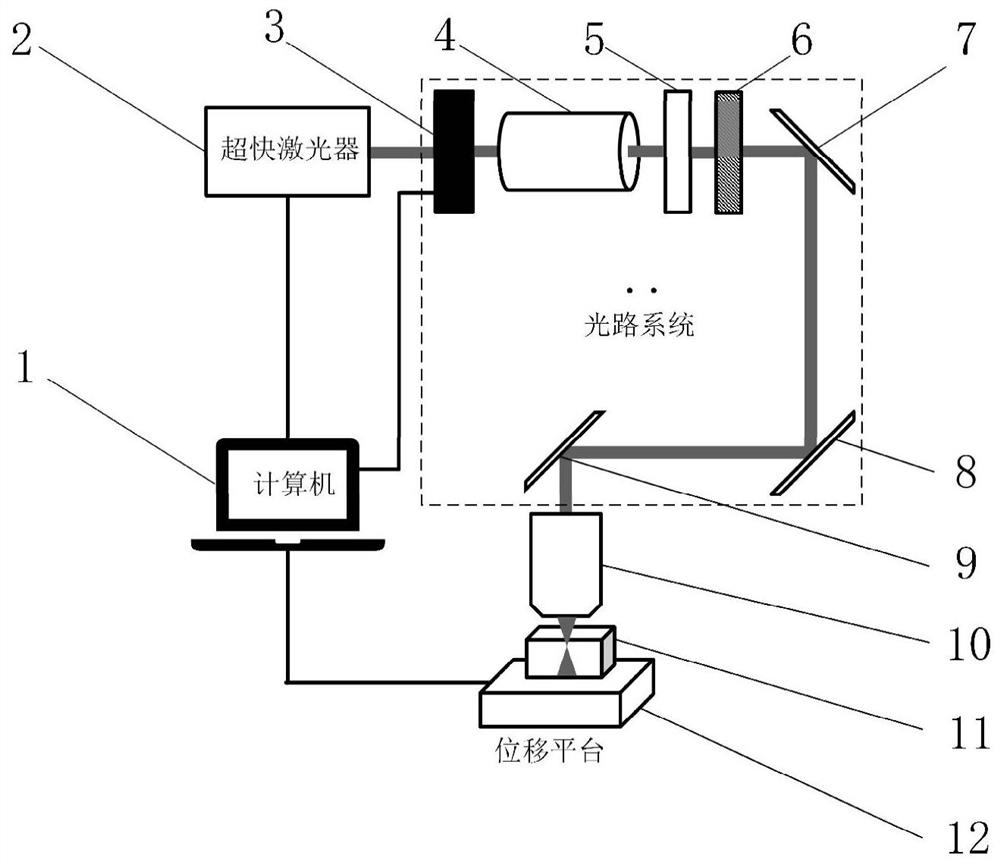
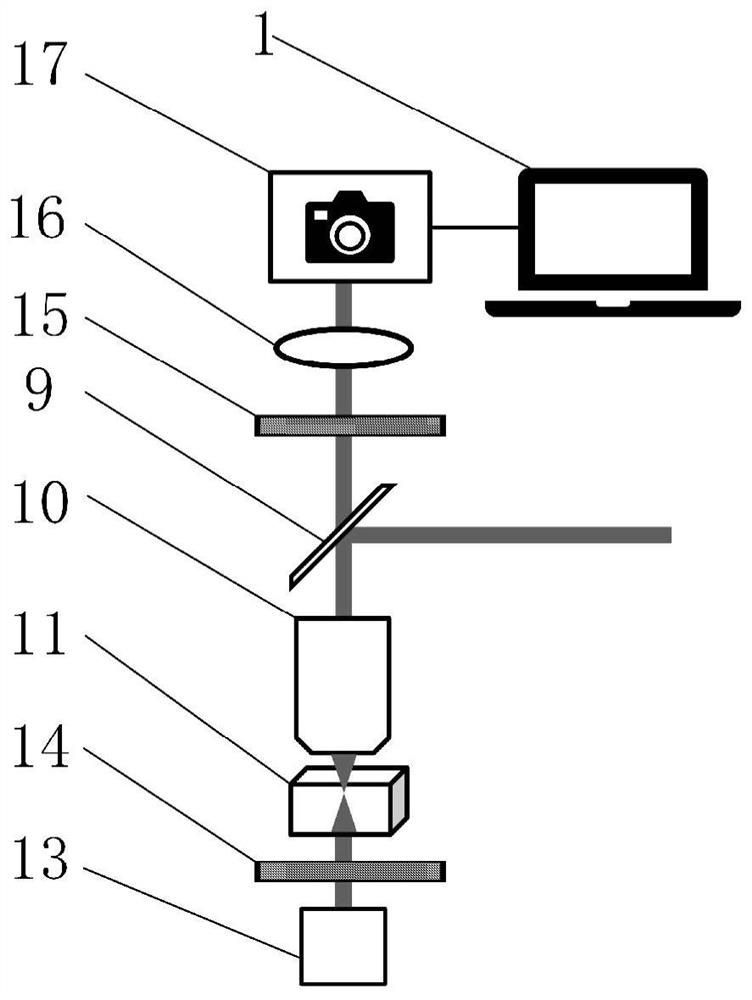
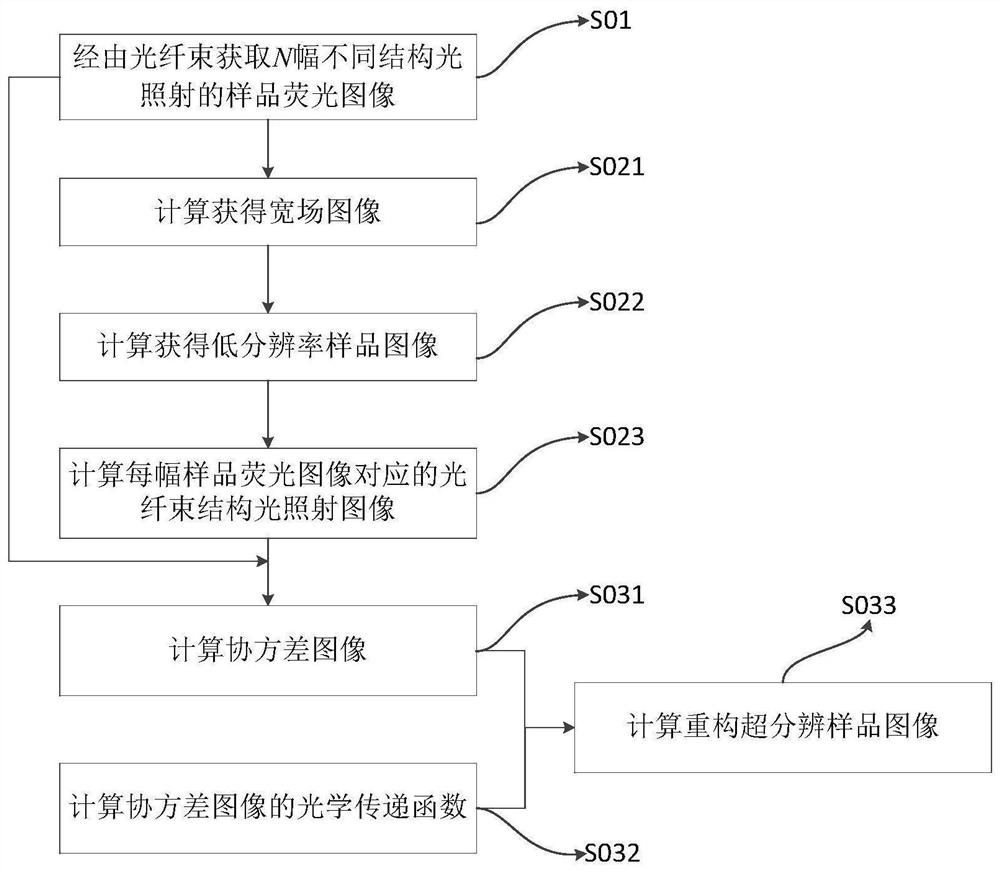
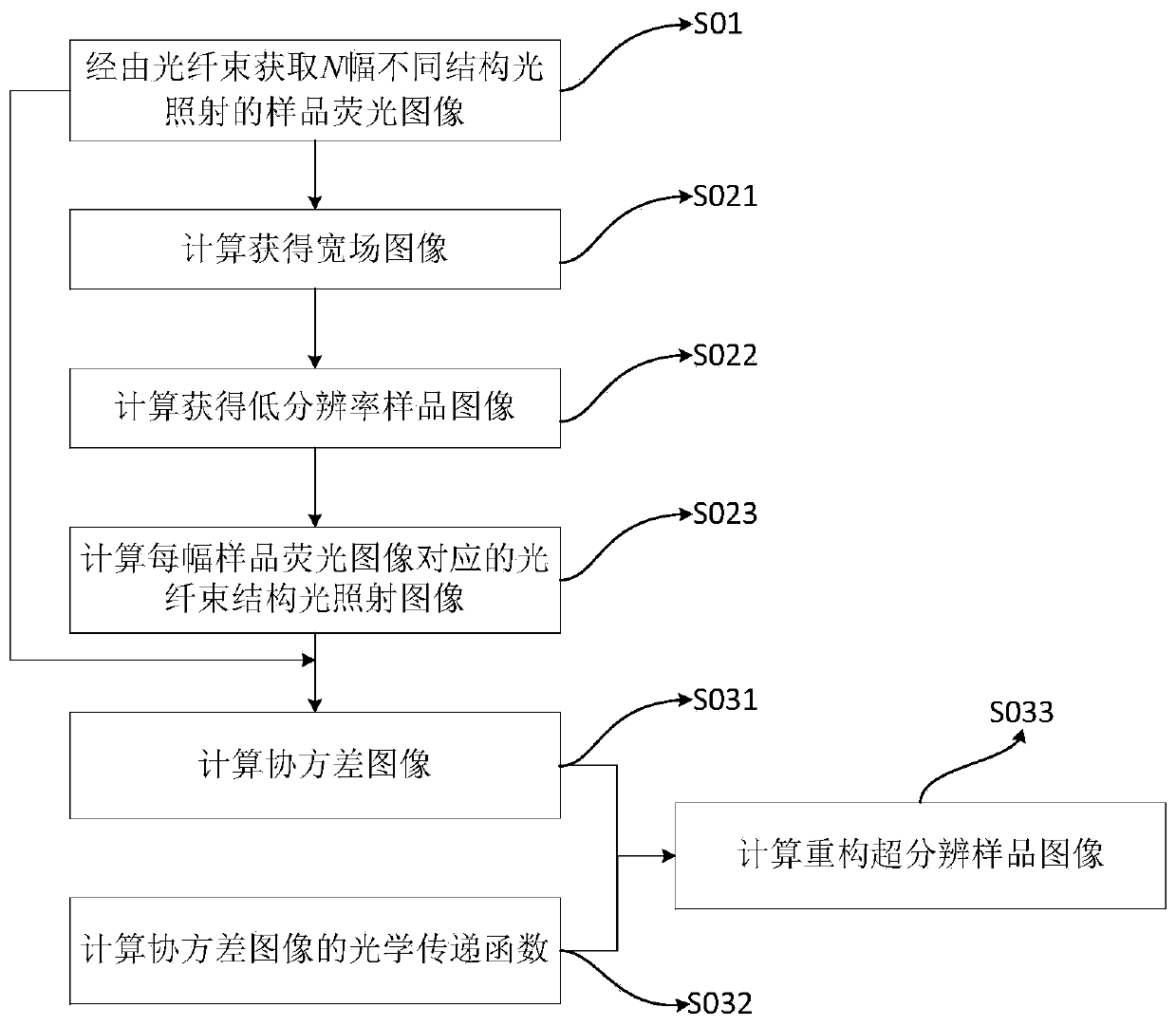
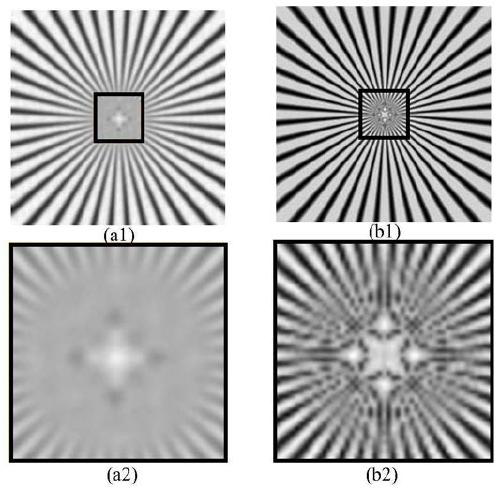
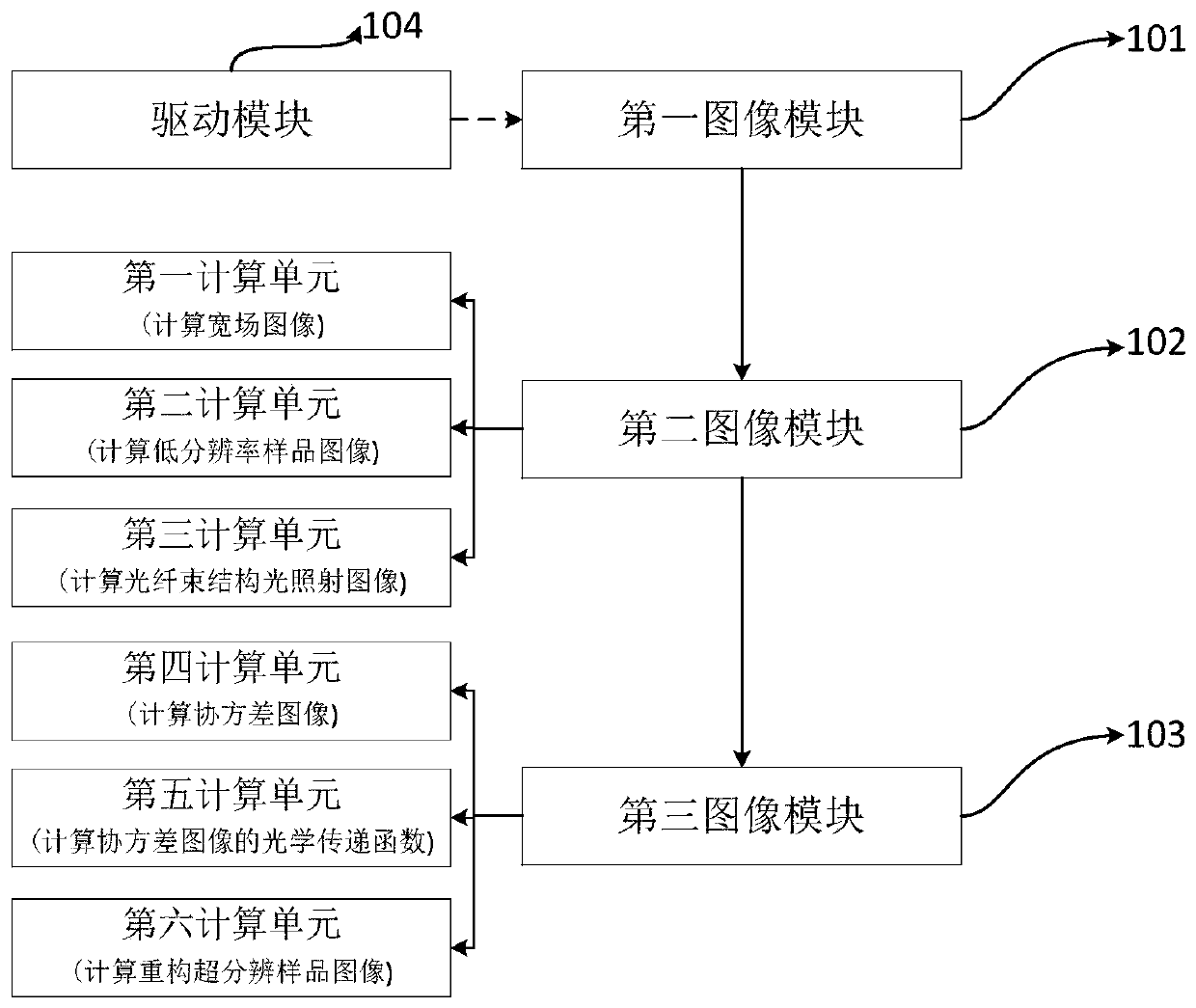
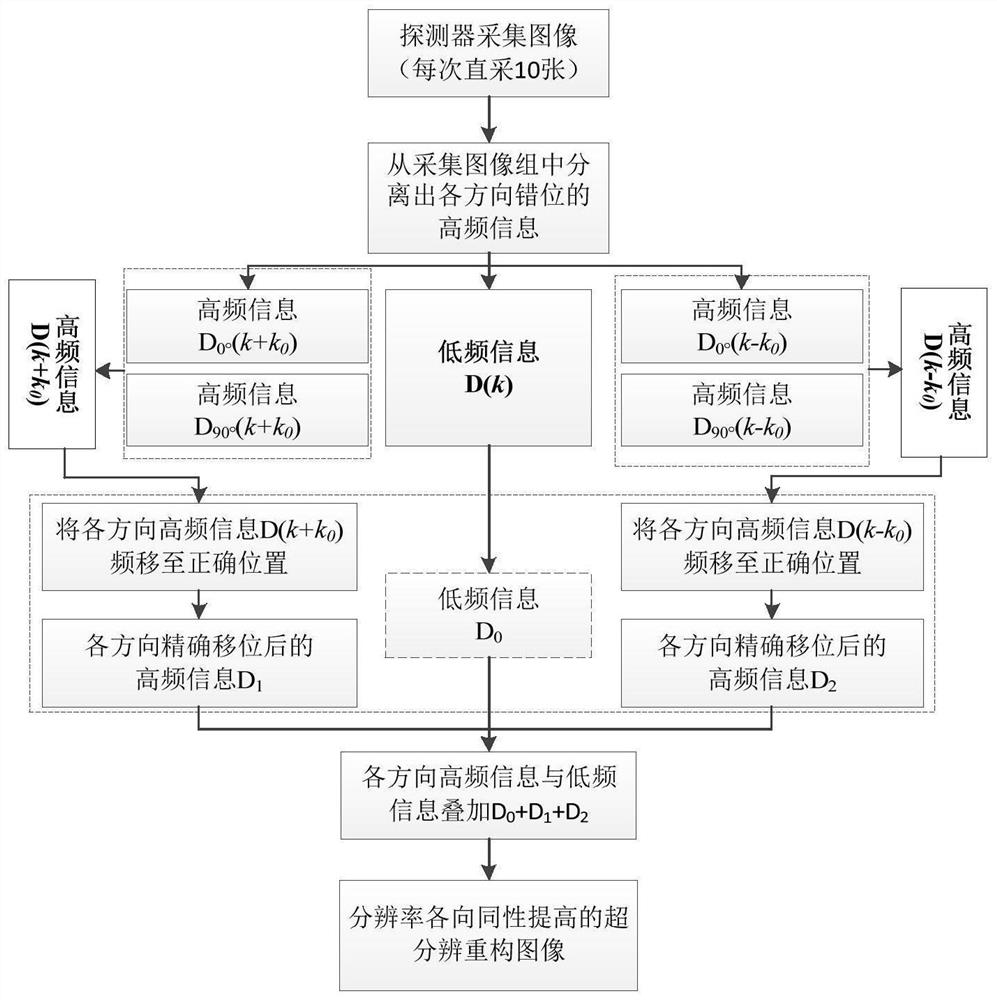
Optical fiber bundle super-resolution imaging method, system, computer equipment and storage medium
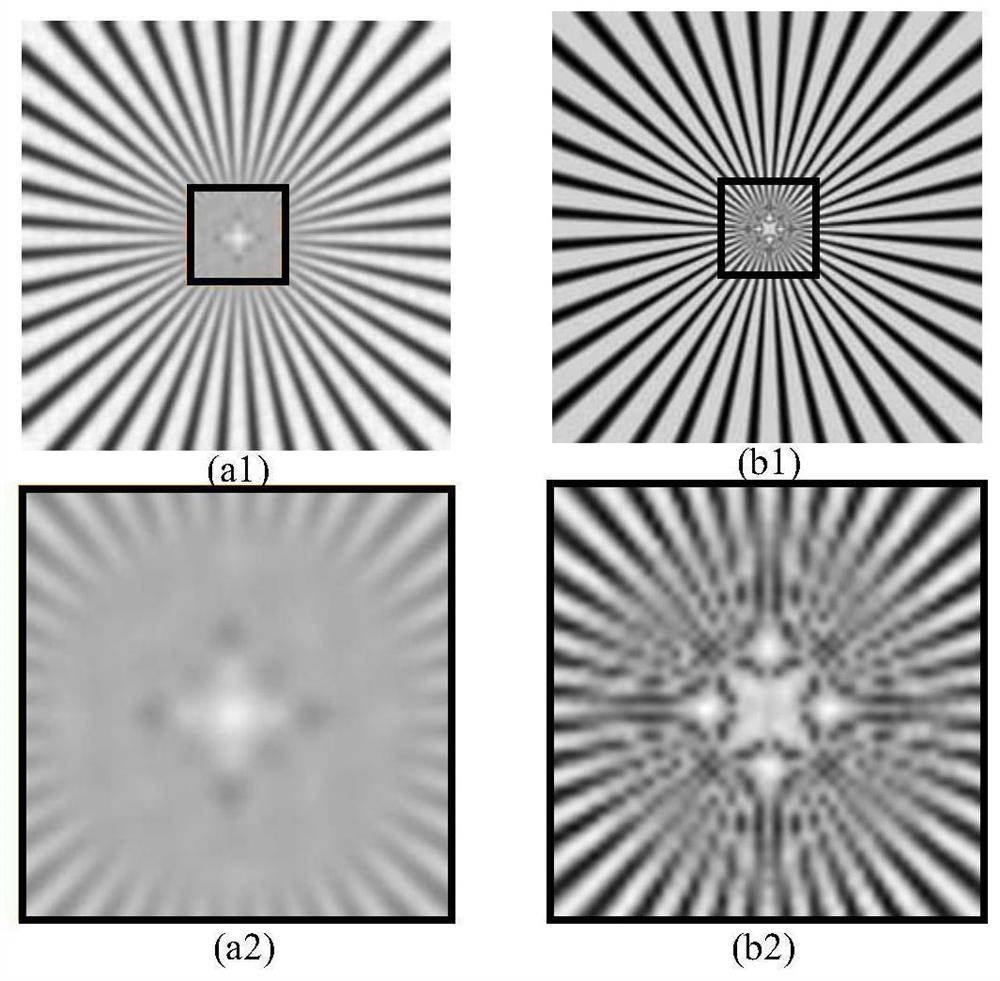
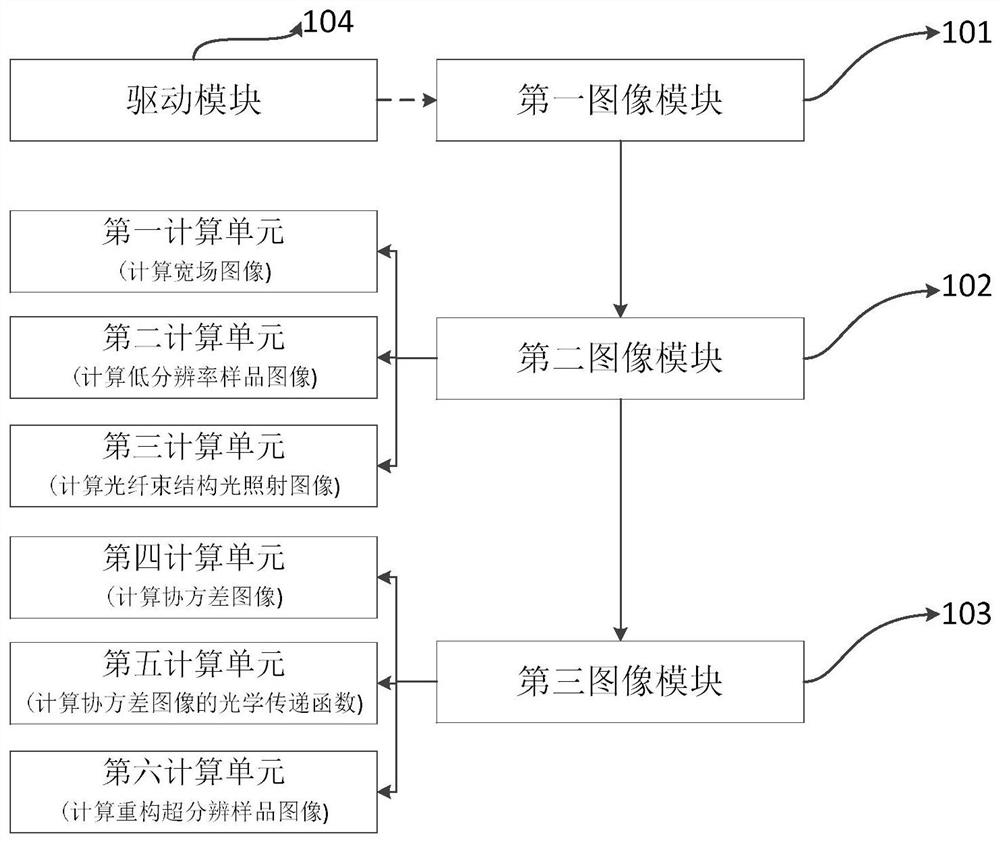
ActiveCN111461975BBreaking through the diffraction limitHigh resolution imagingImage enhancementImage analysisHigh resolution imagingFluorescence
The invention discloses an optical fiber bundle super-resolution imaging, a system, computer equipment and a storage medium, and belongs to the field of optical fiber bundle imaging. The method includes: acquiring a plurality of sample fluorescence images irradiated by different structured light through the optical fiber bundle; calculating and obtaining a wide-field image; The low-resolution sample image is obtained by calculation; the optical fiber bundle structured light illumination image corresponding to each sample fluorescence image is calculated; the covariance image and its optical transfer function are calculated; the super-resolution sample image is calculated and reconstructed. The invention can not only remove the honeycomb structure existing in the optical fiber bundle image, but also apply the super-resolution concept to the optical fiber bundle imaging to realize high-resolution imaging.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICAL ENG & TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
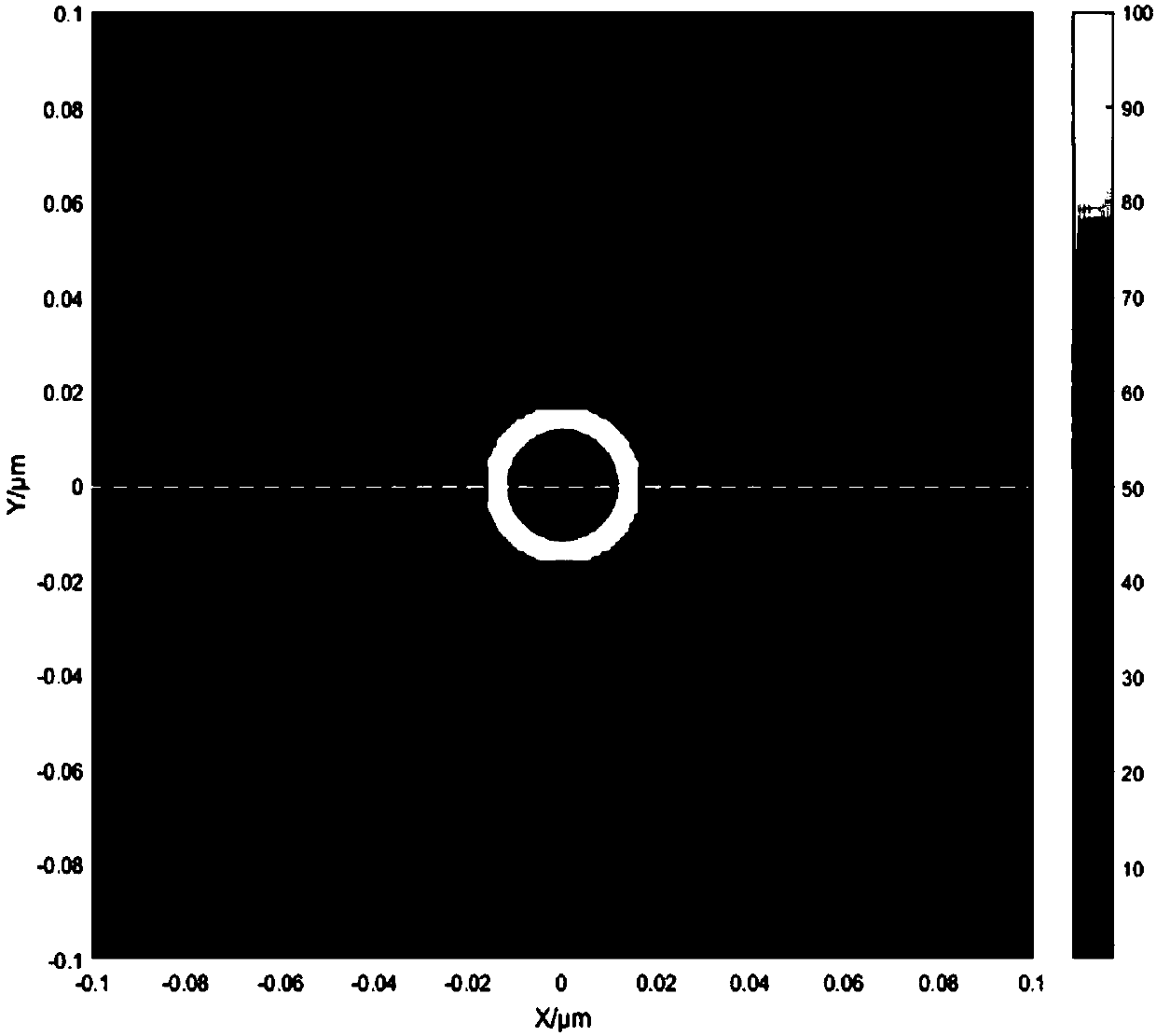
A laser processing device and method for annular microholes
ActiveCN105945435BEnhanced Laser Radiation EnergyBreaking through the diffraction limitDecorative surface effectsChemical vapor deposition coatingComputer control systemLaser processing
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
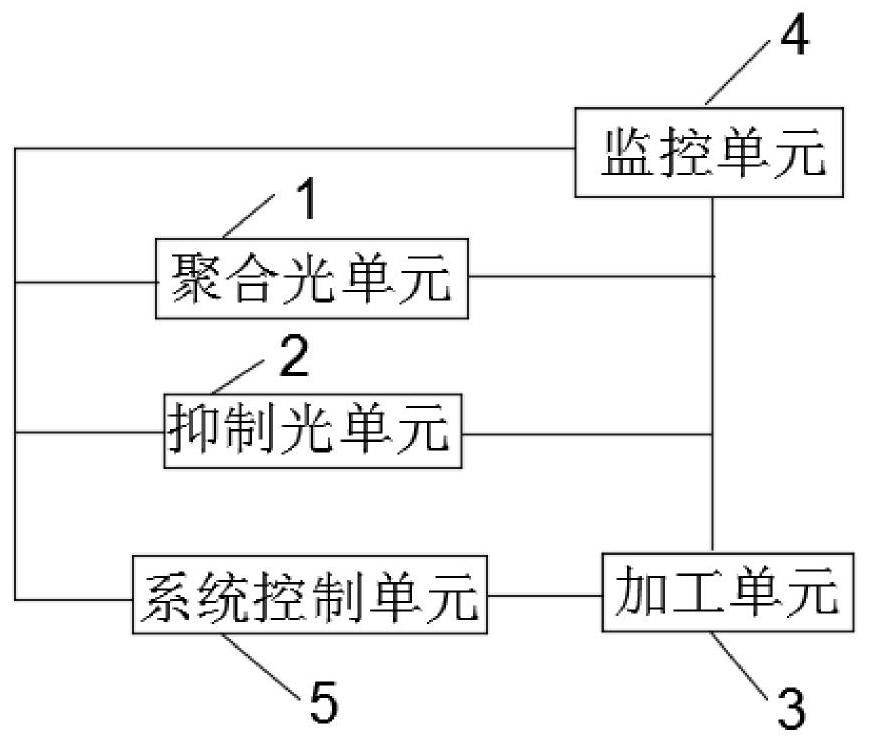
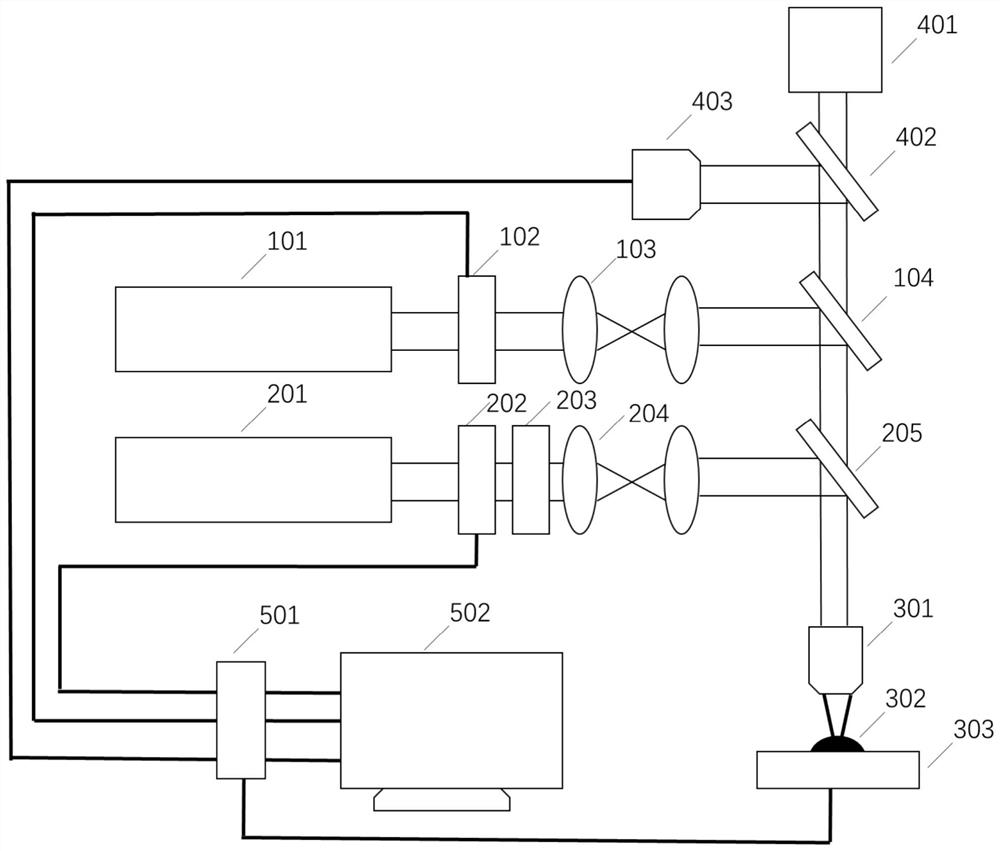
A cross-scale three-dimensional laser direct writing processing device
ActiveCN110653485BAchieve machining accuracyBreaking through the diffraction limitAdditive manufacturing apparatusLaser beam welding apparatusEngineeringMicroscope objective
The invention discloses a cross-scale three-dimensional laser direct writing processing device, which includes a converging light unit, a suppressing light unit, a processing unit, a monitoring unit and a system control unit, and the converging light of the converging light unit and the inhibiting light of the suppressing light unit enter the processing unit , the monitoring unit includes an illumination source, a half-mirror 1 and a camera, the illumination source is located in the transmission direction of the half-mirror 1, the camera is located in the reflection direction of the half-mirror 1, the converging light unit, the suppressing light unit, the processing The unit and the monitoring unit are connected with the system control unit. The invention realizes cross-scale three-dimensional laser direct writing processing based on two-photon polymerization laser direct writing, and realizes processing accuracy covering micron to nanometer scales; by introducing photoinhibition reactions to adjust the size of effective polymeric elements, it breaks through the diffraction limit of the focusing lens , it is possible to use a focusing objective lens with a small numerical aperture to achieve high-precision processing.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
A kind of spatial optical waveguide preparation method
Owner:YANTAI MAGIC NANOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Optical fiber bundle super-resolution imaging method and system, computer equipment and storage medium
ActiveCN111461975ABreaking through the diffraction limitHigh resolution imagingImage enhancementImage analysisSample imageHoneycomb like
The invention discloses an optical fiber bundle super-resolution imaging method and system, computer equipment and a storage medium, and belongs to the field of optical fiber bundle imaging, and the method comprises the steps: obtaining a plurality of sample fluorescence images irradiated by different structured light through an optical fiber bundle; calculating and obtaining a wide-field image; calculating and obtaining a low-resolution sample image; calculating an optical fiber bundle structured light irradiation image corresponding to each sample fluorescence image; calculating a covarianceimage and an optical transfer function thereof; and calculating a reconstructed super-resolution sample image. According to the invention, the honeycomb structure of the optical fiber bundle image can be removed, and the super-resolution concept is applied to the optical fiber bundle imaging, so that the high-resolution imaging is realized.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICAL ENG & TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
A fast super-resolution detection device and detection method for optical element defects with random phase shift
ActiveCN112858345BSimplify the acquisition processImprove collection efficiencyMaterial analysis by optical meansLaser lightImaging lens
The invention discloses a fast super-resolution detection device and detection method for random phase-shifting optical element defects. The controller adjusts the polarization state of the laser, which is divided into two beams in equal proportions through the 1×2 fiber coupler II, and the other laser output through the 1×2 fiber coupler I passes through the 1×2 fiber coupler III Equally divided into two beams; the four beams of illumination laser light are symmetrically hit on the sample surface through the entrance pupil of the microscope objective lens for interference to form a two-dimensional cosine structured illumination light; the microscope objective lens is used to receive the structured illumination light and modulate it on the sample surface After the reflected and scattered light, the final return imaging signal collection is completed in the high-speed camera through the imaging lens. To achieve the goals of miniaturization, portability, high efficiency, random phase shift and low cost.
Owner:LASER FUSION RES CENT CHINA ACAD OF ENG PHYSICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com