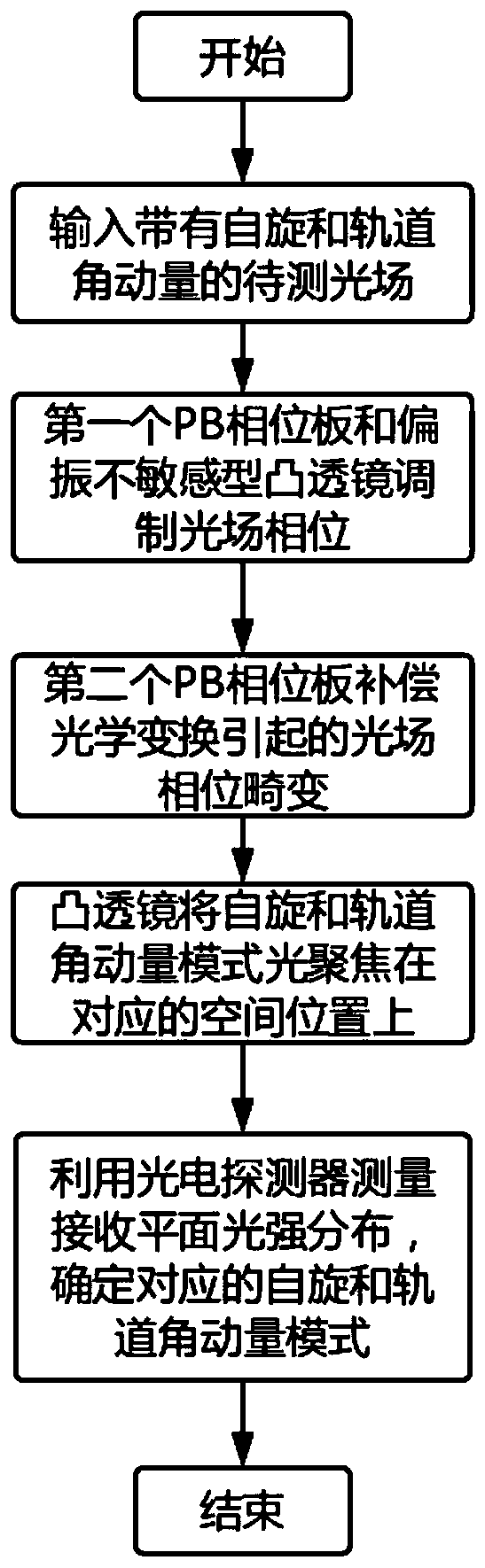
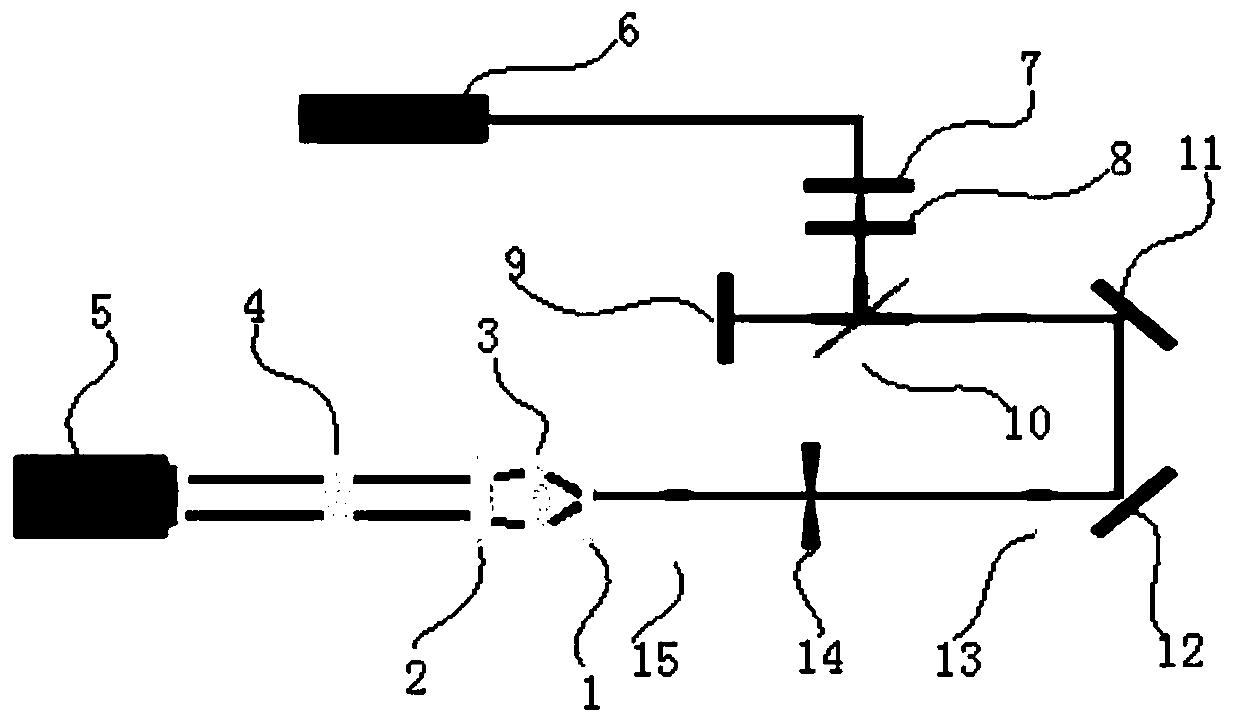
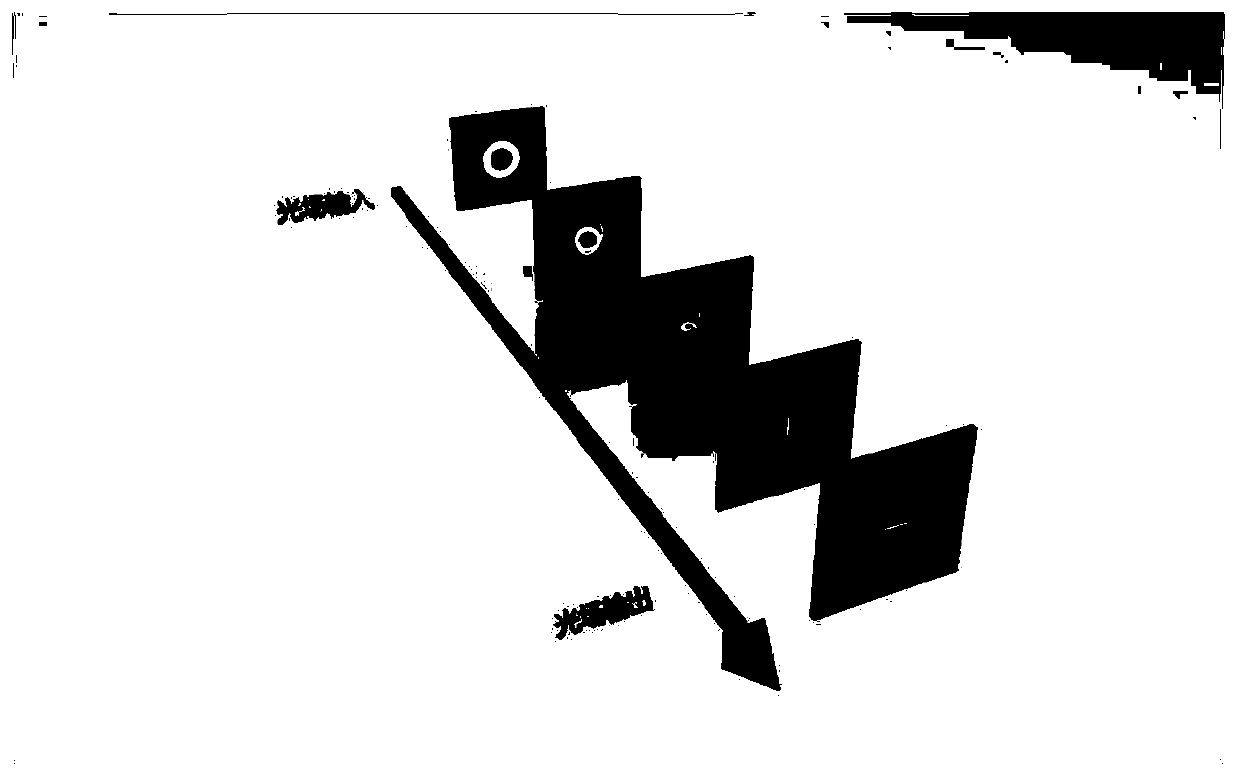
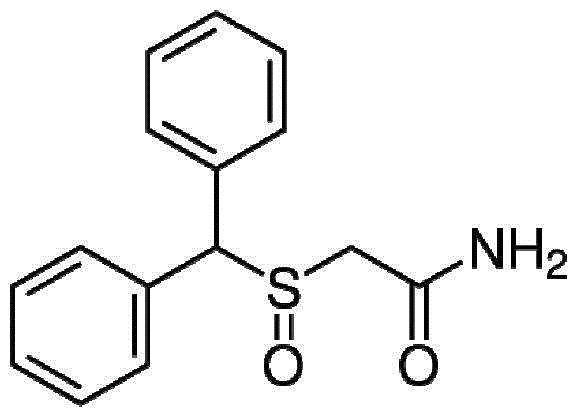
Patents
Literature
155 results about "Dextrorotatory" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The ability of an optically active substance to rotate the plane of polarized light clockwise (to the right).
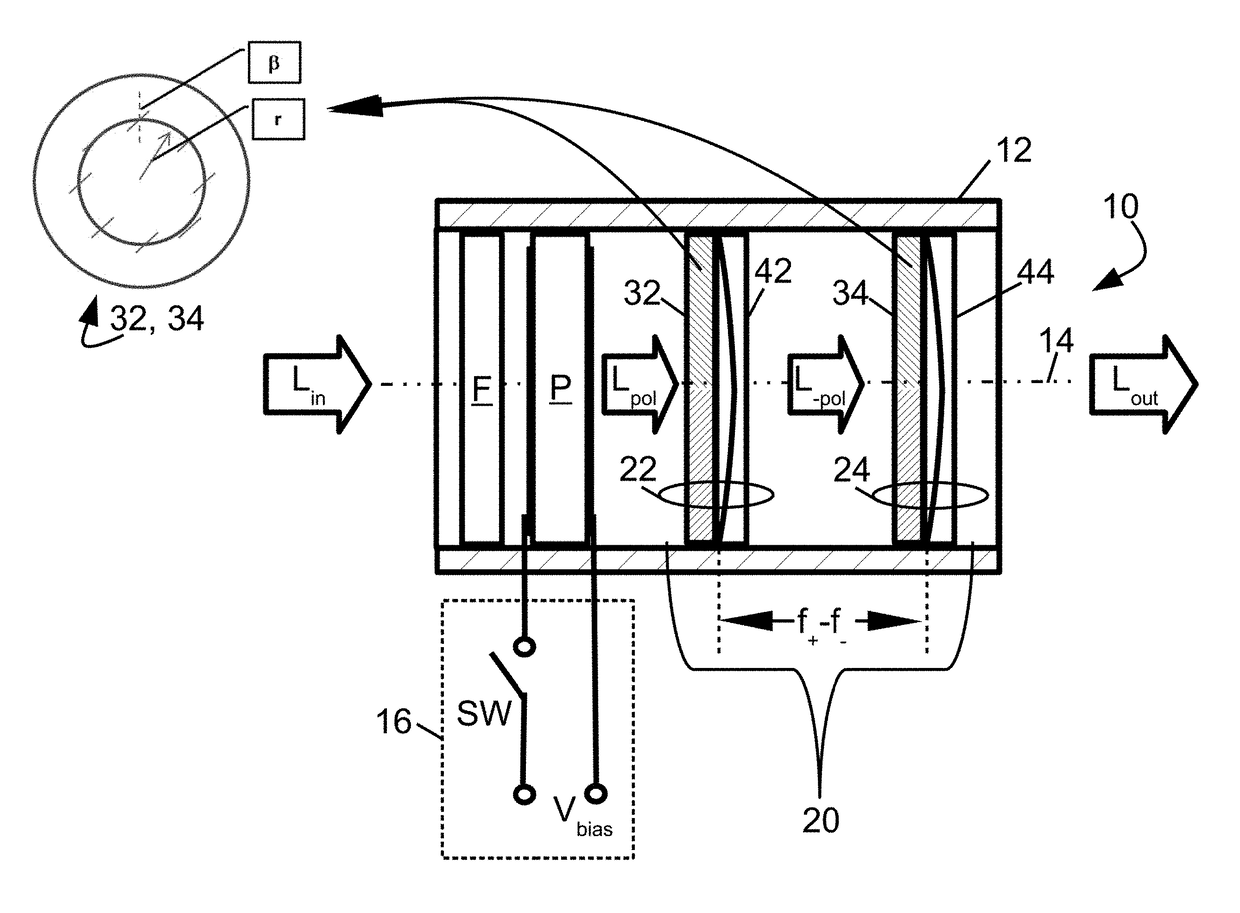
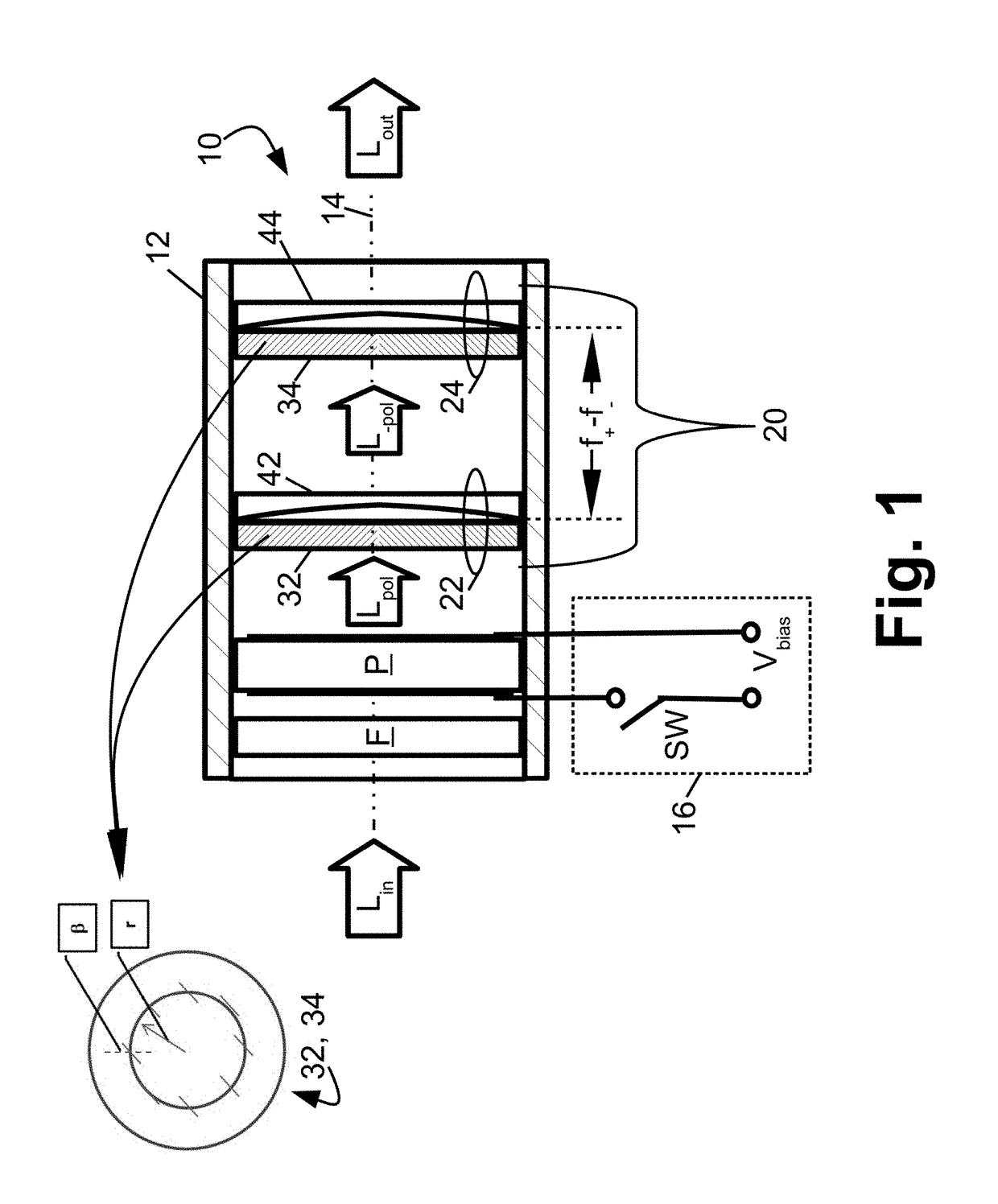
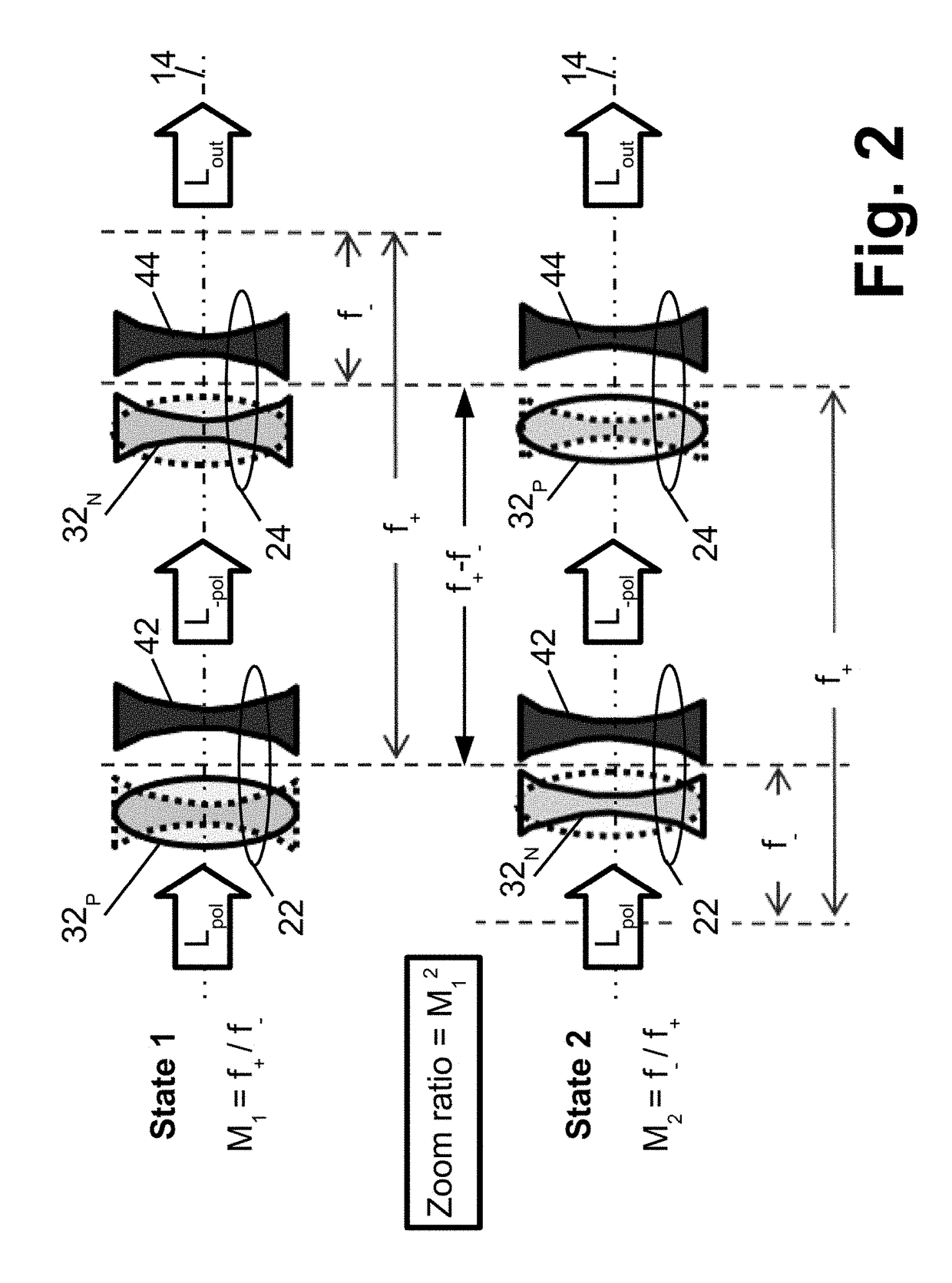
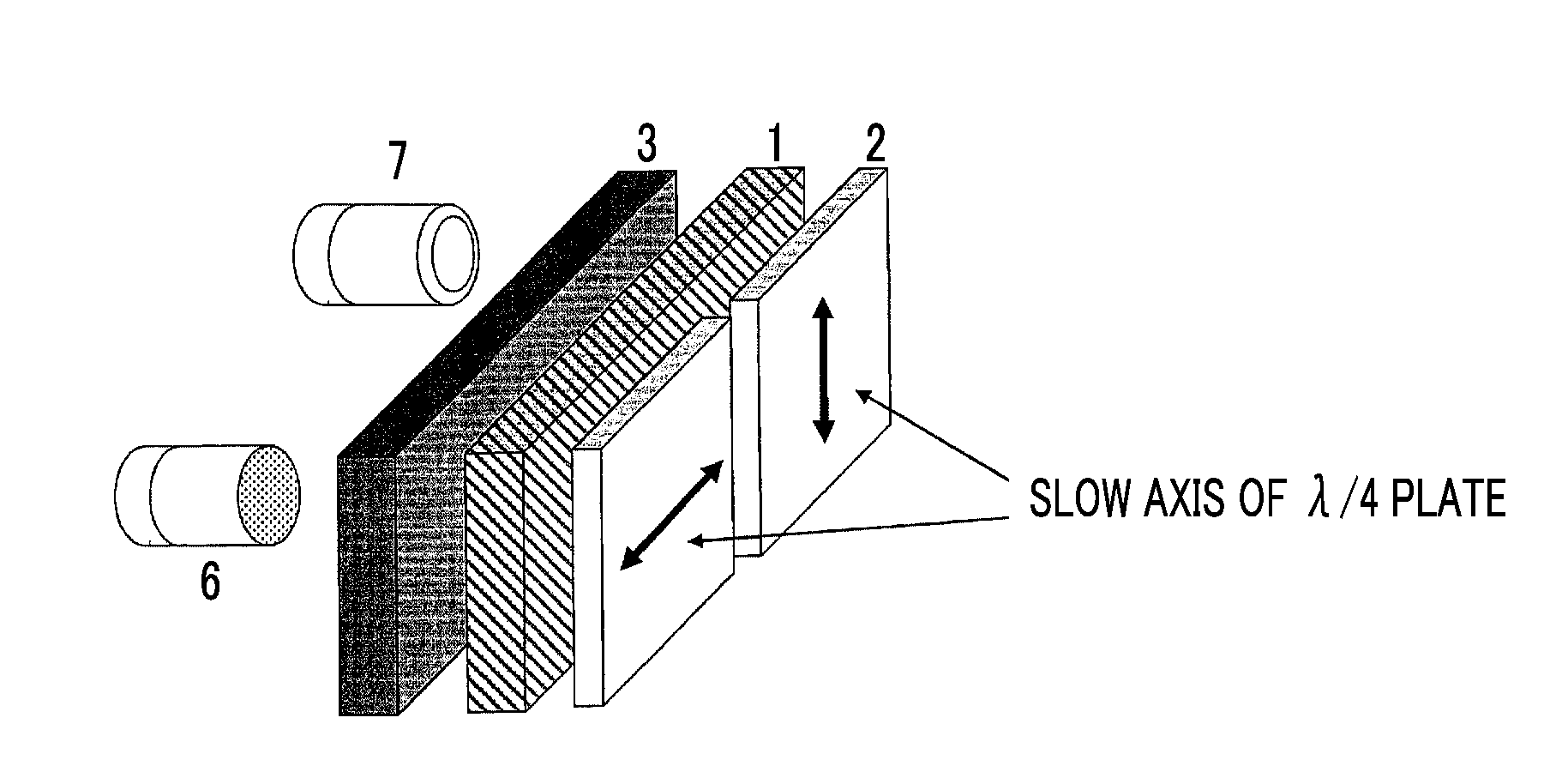
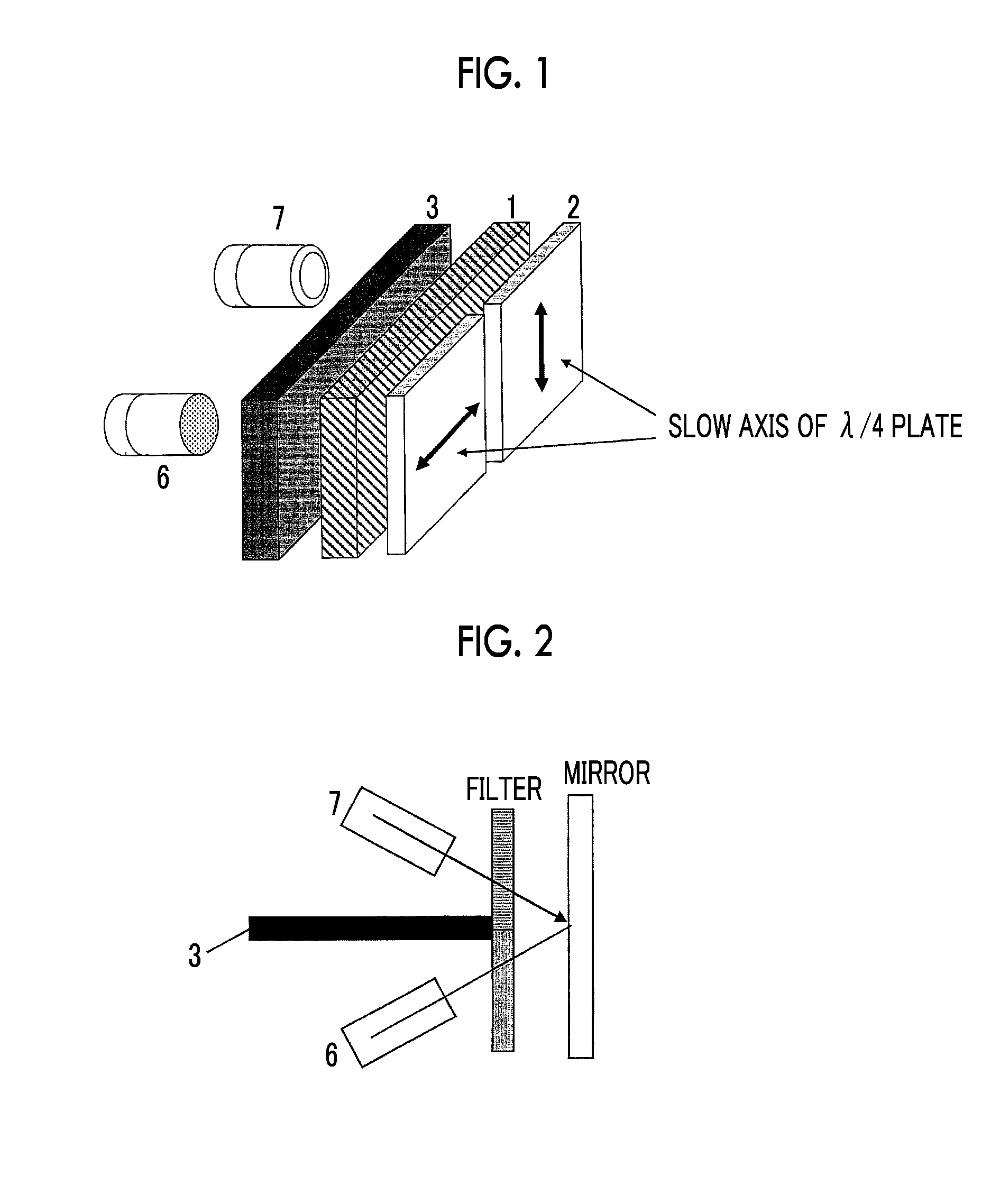
Compact non-mechanical zoom lens
An optical magnification system comprises two Pancharatnam lenses, and provides a first magnification for left-hand circularly polarized light and a second magnification different from the first magnification for right-hand circularly polarized light. An optical magnification system comprises two lenses, each having different focal lengths for left-handed and right-handed circularly polarized light, respectively, and configured to provide a first magnification for left-handed circularly polarized light and a second magnification different from the first magnification for right-handed circularly polarized light.
Owner:KENT STATE UNIV
High-precision coherent population trapping (CPT) rubidium atom magnetometer
ActiveCN109799468AReduce volumeReduce power consumptionMagnetic field measurement using magneto-optic devicesPopulationPower consumption
The invention discloses a high-precision coherent population trapping (CPT) rubidium atom magnetometer, comprising a VCSEL (vertical-cavity surface emitting laser), a calibrating lens, an electrooptical modulator, a lambda / 2 wave plate, a polarization splitting prism, a reflector, a lambda / 4 wave plate, an ITO heater, an atomic vapor cell, a photoelectric detector, a feedback module, a temperaturecontrol module, a data acquisition module, an upper computer, a circuit control module and a 3.417GHz microwave source. Laser is modulated into left-hand circular polarized light and right-handed circular polarized light which have the same light intensity, the left-hand circular polarized light and the right-handed circular polarized light pass through the atomic vapor cell to generate two CPT signals, the CPT signals are subjected to differential treatment to obtain the Larmor prescession frequency, and finally, accurate measurement to a magnetic field is realized according to the relationbetween the Larmor prescession frequency and the magnetic field intensity. Since a feedback system and the novel atomic vapor cell are added, the magnetometer has the advantages of high precision, high flexibility, low power consumption, small size and the like, and has great significance in terms of biomedicine, physical geography, military detection and the like.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Polarization filter and sensor system
ActiveUS20160109630A1High sensitivityAvoid desensitizationLiquid crystal compositionsRadiation pyrometryLiquid crystallinePhase difference
According to the present invention, there are provided a polarization filter and a sensor system. The polarization filter includes a circularly polarized light-separating layer having a cholesteric liquid crystalline phase fixed therein, in which the circularly polarized light-separating layer is a layer which selectively transmits one of the left-hand circularly polarized light and the right-hand circularly polarized light in the specific wavelength band, a λ / 4 phase difference layer for light in the specific wavelength band is disposed on one of the surfaces of the circularly polarized light-separating layer, and the λ / 4 phase difference layer includes a first phase difference region and a second phase difference region of which slow axis directions are orthogonal to each other. The sensor system includes the polarization filter, a light source which emits light having a wavelength in the specific wavelength band, and a light-receiving element which can detect light having a wavelength in the specific wavelength band. The polarization filter of the present invention can improve the sensitivity of a sensor system using polarized light, and the sensor system of the present invention has high sensitivity and is extremely cost effective.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Spiro bisimine and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN101519356ASilicon organic compoundsOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCarbeneInsertion reaction
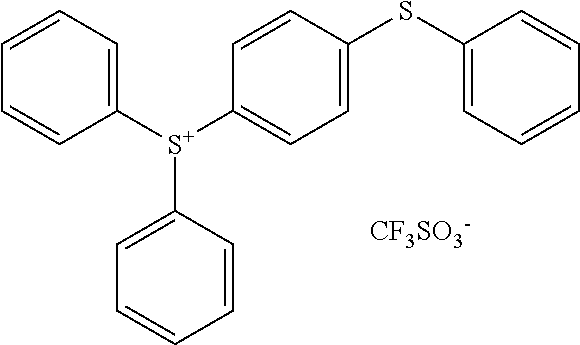
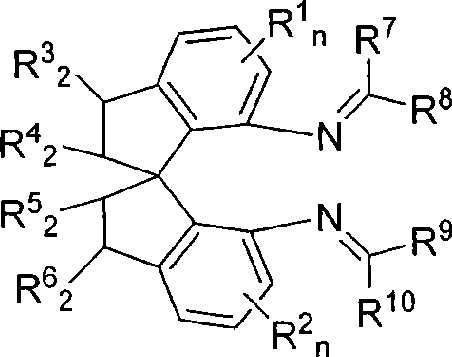
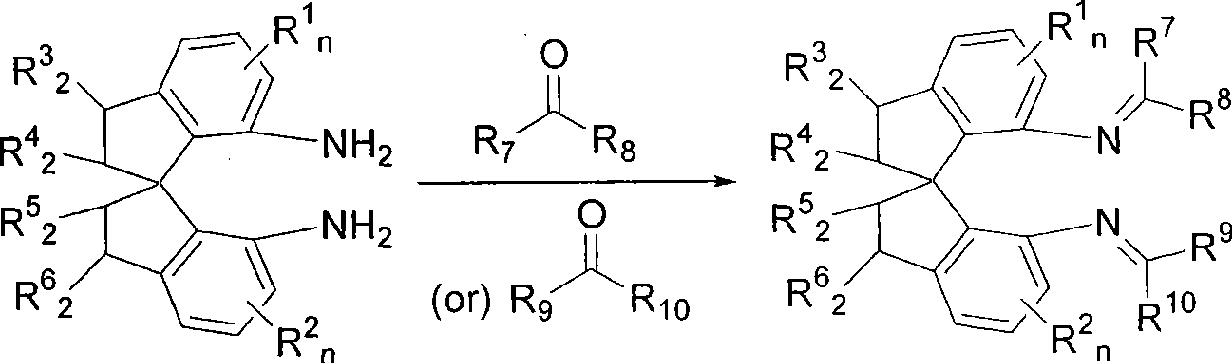
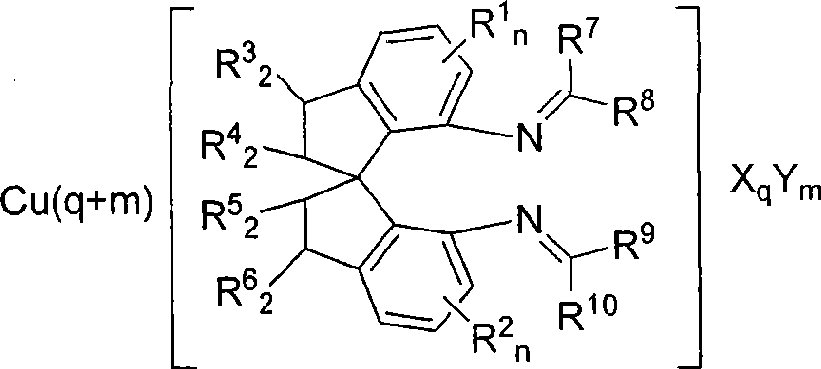
The invention relates to a spiro bisimine and a preparation method and application thereof. Spiro diamine is adopted as raw material to generate spiro bisimine. The spiro skeleton structure in the spiro bisimine has axial chirality, therefore, the class of compound has two optical isomers, namely, right spiro bisimine and left spiro bisimine; and the commensurable mixture of the two optical isomers become racemization spiro bisimine. The complex compound of the spiro bisimine and copper can be taken as a chiral catalyst which is used in asymmetric insertion reaction of carbene to silicon-hydrogen bond, and has very high activity and enantio selectivity (as high as 99.2 percent ee). The chemical formula of the spiro bisimine is as follows: n=0-3; and the values of R<1>, R<2>, R<3>, R<4>, R<5>, R<6>, R<7>, R<8>, R<9> and R<10> are defined as claim of right 1.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
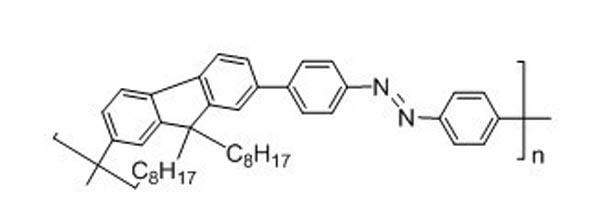
Preparation method of photo-response type chirality intelligent nanometer particles
The invention discloses a preparation method of photo-response type chirality intelligent nanometer particles. The preparation method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: preparing a trichloromethane solution with a repetitive unit concentration of 3*10<-2> mg / mL from a 9,9-dioctylfluorene-azobenzene alternating copolymer, wherein Mn in the 9,9-dioctylfluorene-azobenzene alternating copolymer is equal to 7770 g / mol and the ratio of Mw to Mn is equal to 2.62; uniformly mixing the solution with alcohol the volume of which is the same as that of the solution; and irradiating the mixture for 1-30 minutes by using levorotatory or dextrotatory polarized light so as to obtain left-handed helix or right-handed helix chirality nanometer particles. By using the preparation method provided by the invention, the problems that when the traditional method is adopted to synthesize the polymer chirality intelligent nanometer particles, a chiral reagent is expensive, synthetic steps are complex and the like are solved; the obtained product is alternatively irradiated by the levorotatory or dextrorotatory polarized light, thus the chiral spiral direction of the nanometer particles can be changed, so as to present the good properties of a photo switch.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
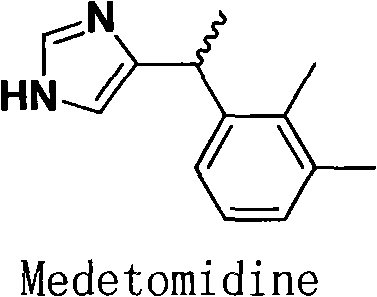
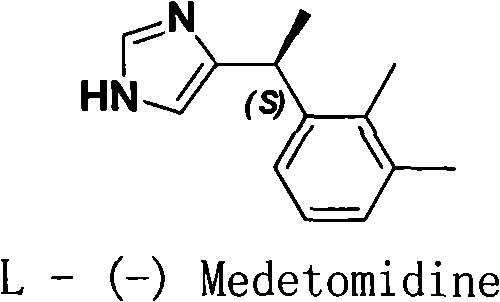
Method for resolution of levorotatory enantiomer and dexiotropic enantiomer of medetomidine
The invention discloses a method for obtaining levorotatory enantiomer and dexiotropic enantiomer by separation from medetomidine (chemical name: 4-(1-(2,3-dimethylphenyl)-ethyl)-1H-imidazole) of racemate, which comprises the steps of reacting medetomidine racemate with optically active acid so that medetomidine racemate can be converted into salts of diastereoisomer, and then separating the saltsof the diastereoisomer by using a half-dose resolution method so as to obtain single enantiomer with particular optical purity.
Owner:北京华禧联合科技发展有限公司
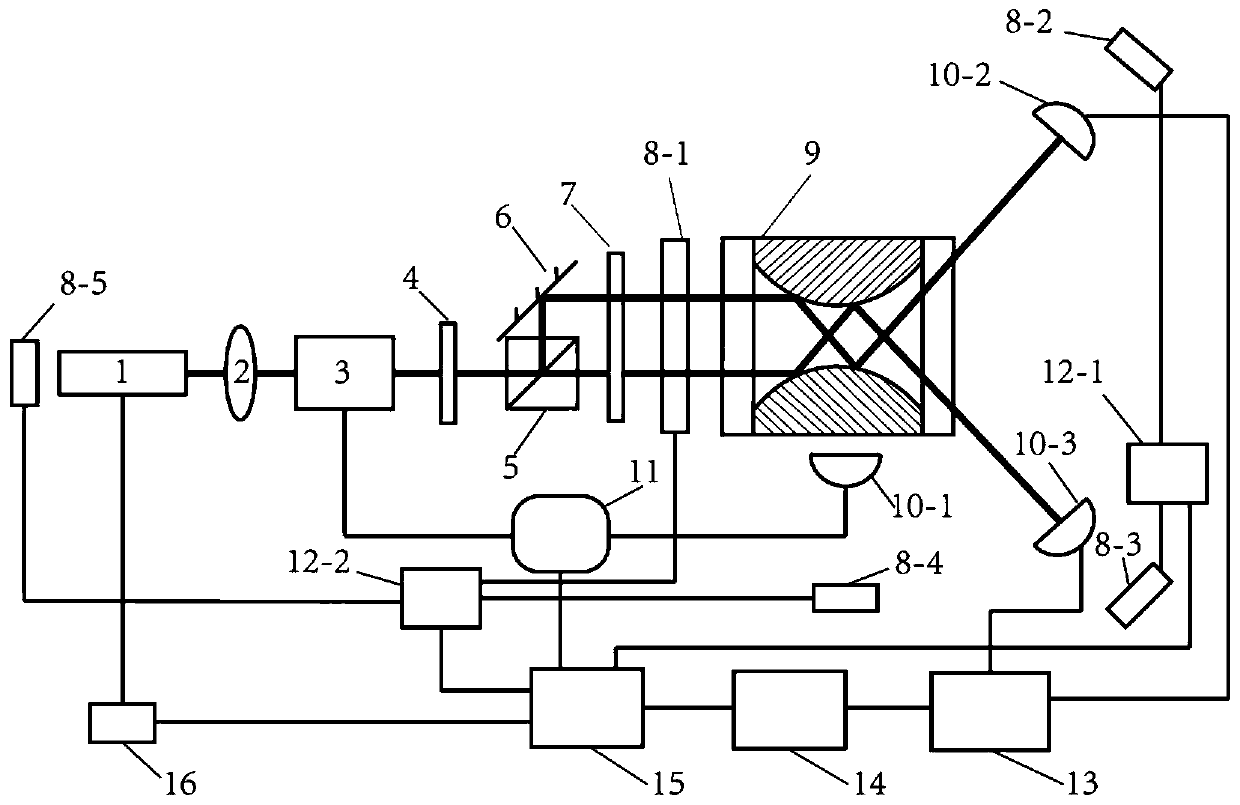
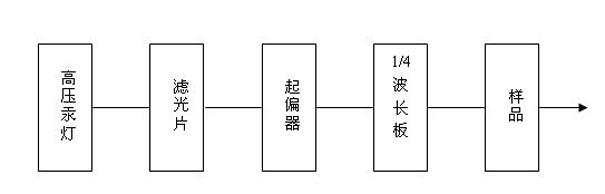
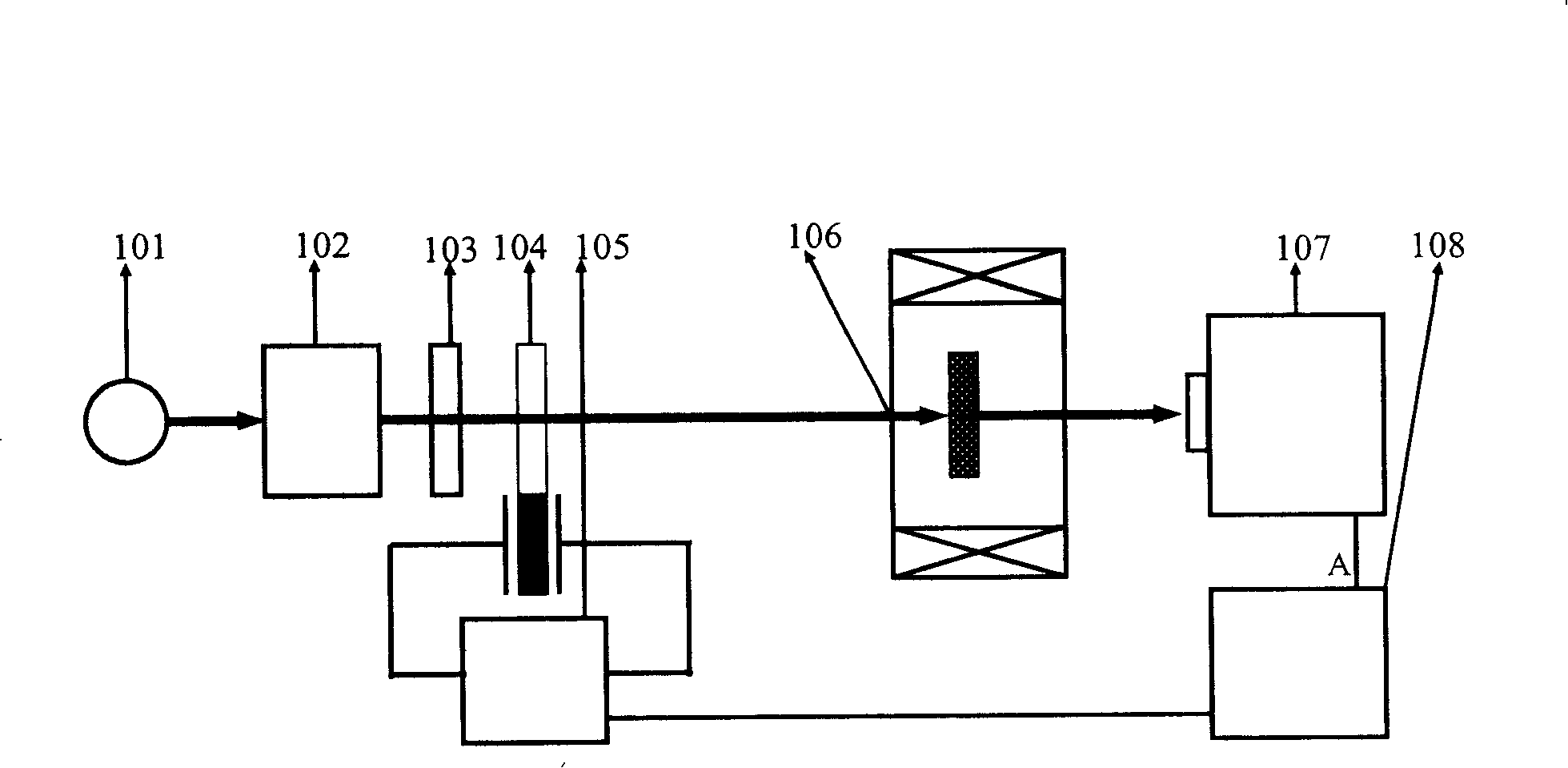
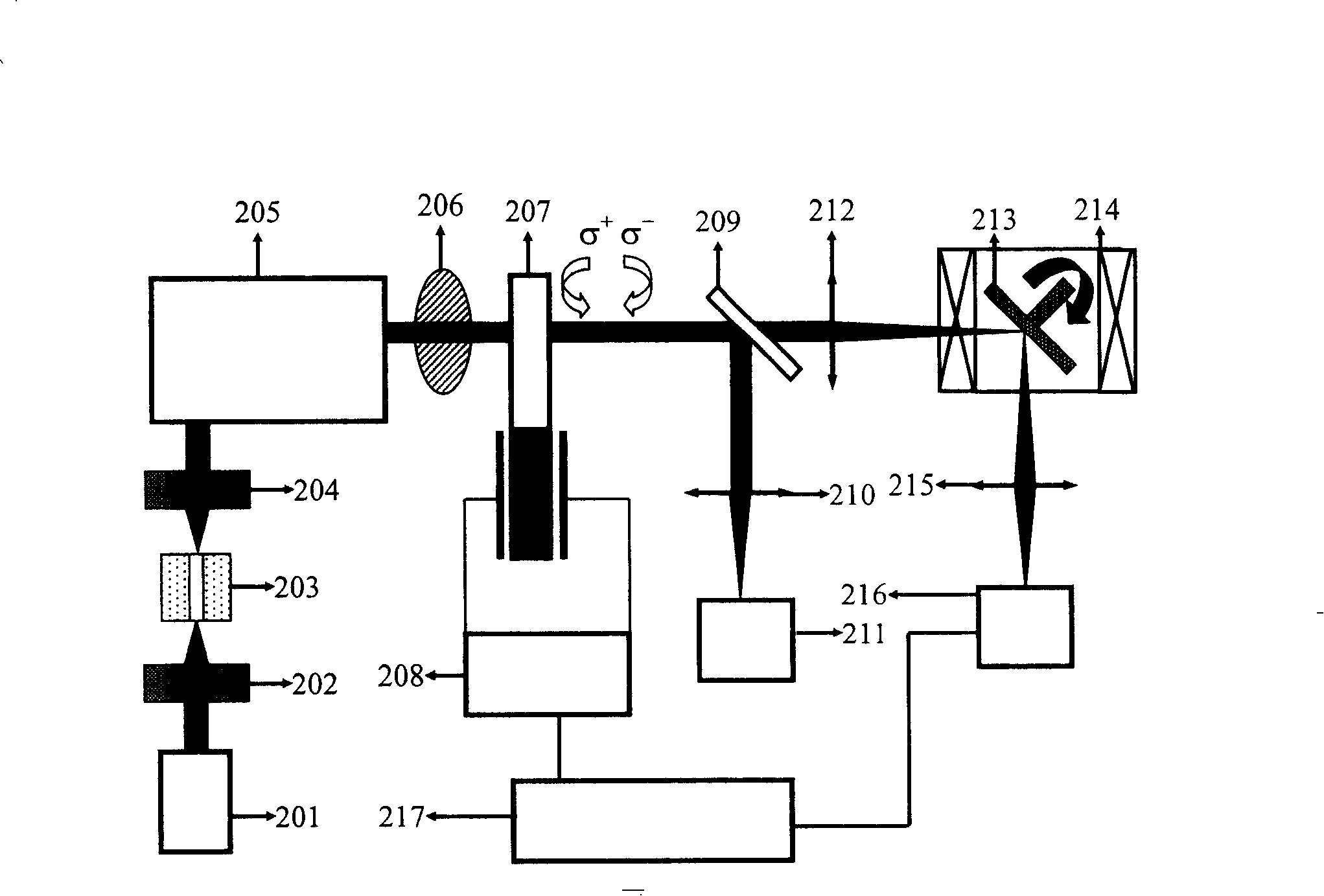
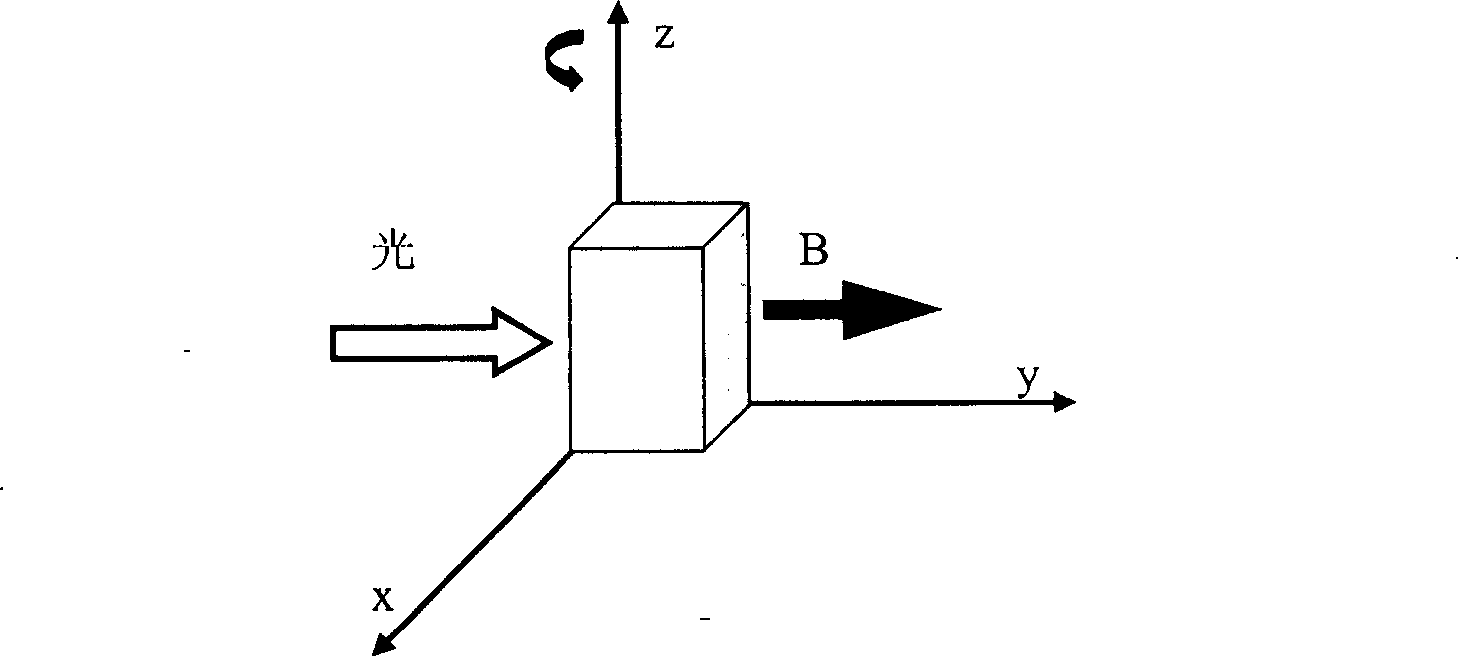
Magneto-optic circular polarization dichroism measuring system capable of adjusting measuring geometry
InactiveCN101196559AGood collimationNo lossMagnetic property measurementsTesting optical propertiesFrequency spectrumLantern
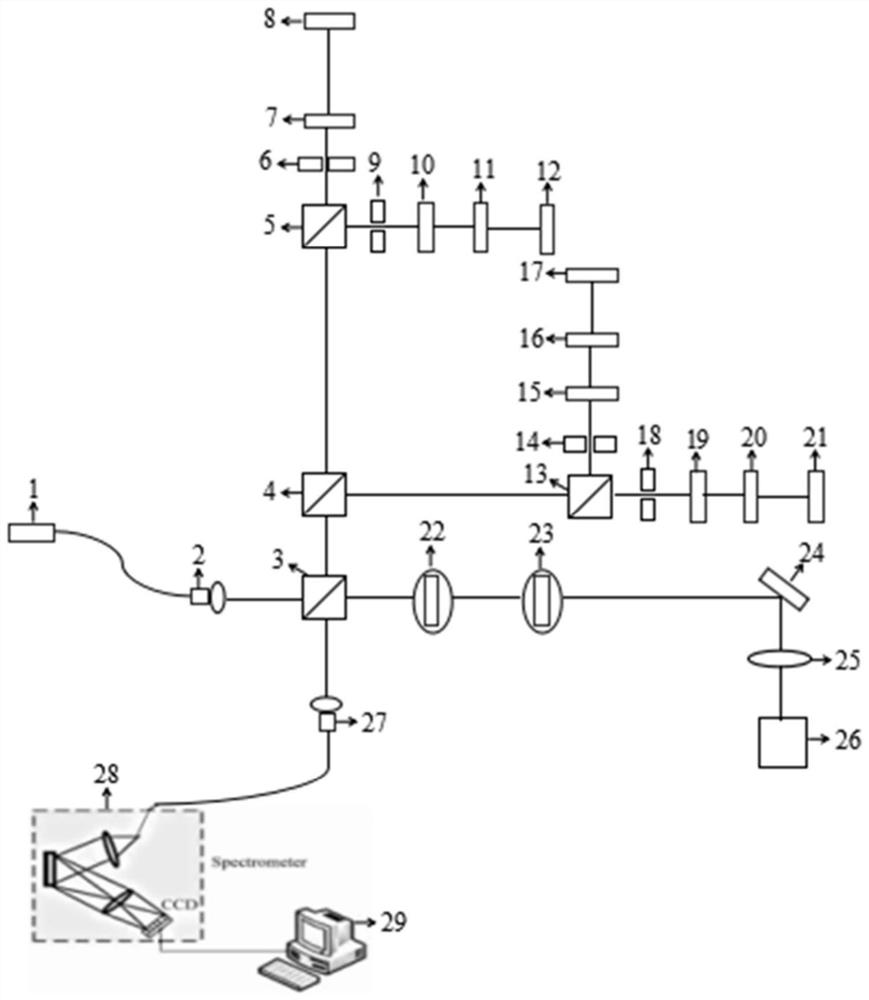
A measuring system for measuring the dichroism of the magneto-optical circular polarization with adjustable measuring geometry is provided, whose structure is that: a femtosecond laser excites the white light of the ultra-continuous spectrum, and divides the light by a monochrometer, which forms a monochromatic light whose wavelength can be adjustable. The monochromatic light can polarize through a purified Glan-Taylor prism with the extinction coefficient of 10 <5>; a lantern fly modulator, whose optical axis is 45degree angled with the optical axis of the Glan-Taylor prism to make the light become the circularly polarized light with the alternative variation of the sinistrality and the dextrorotation; a sample, which is put on the center of the cryogenic magnet; The circularly polarized light focuses on the sample, and the reflex reflected from the sample is focuses on the first LED detector; a phase-locking amplifier, whose reference signal is provided by the lantern fly modulator used for testing the difference of light intensity between the sinistrality and the dextrorotation of the circularly polarized light. The invention can not only test the frequency spectrum of the dichroism of the magneto-optical circular polarization of the materials, magnetic density and temperature dependence, but also can test the magnetocrystalline anisotropy of the magnetic semiconductor.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
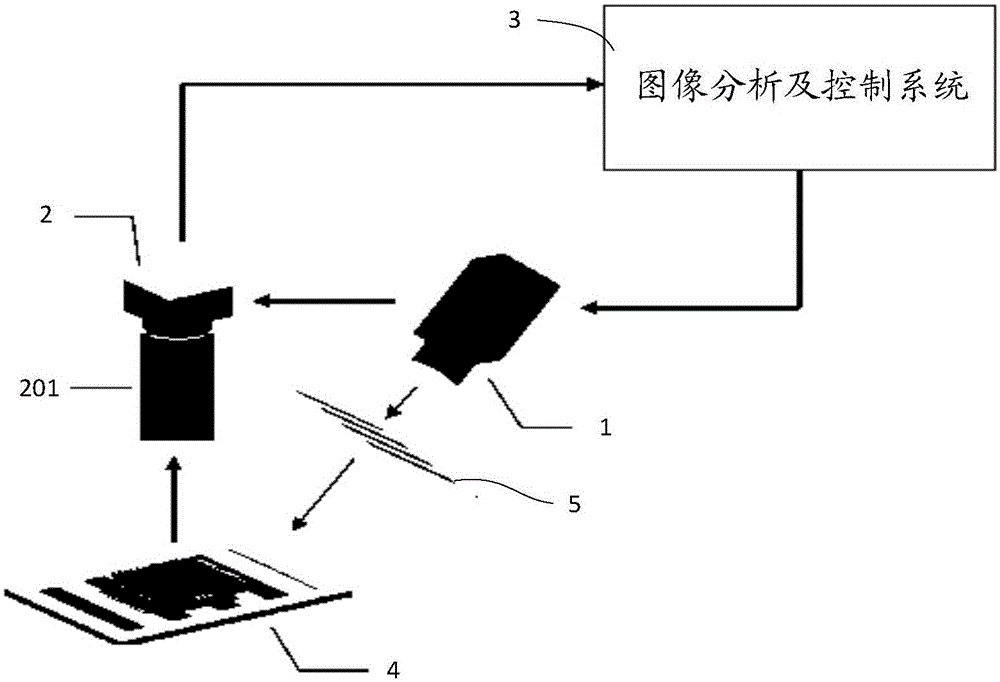
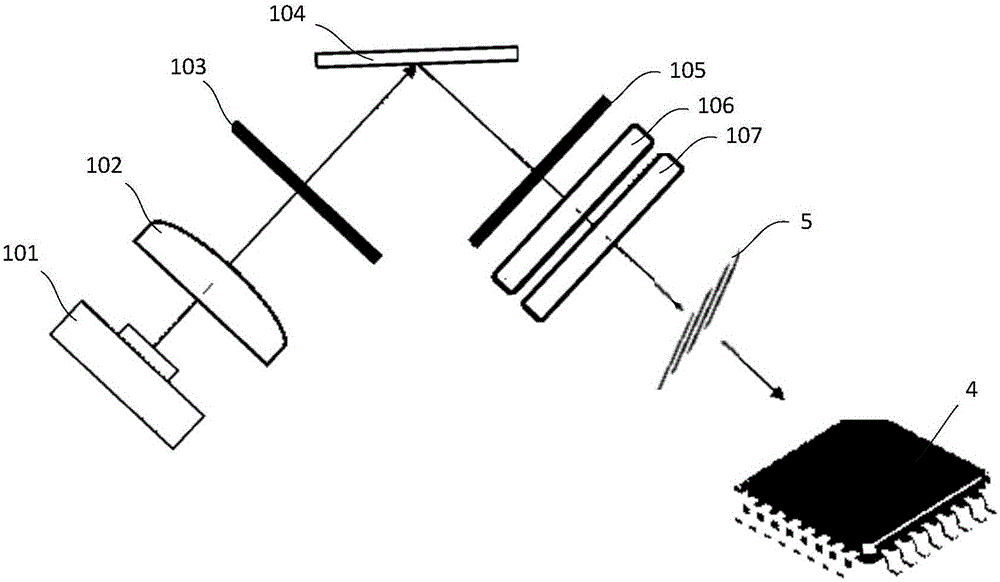
Three-dimensional measuring system capable of reducing light reflection on surface of measured object
InactiveCN105136059AReduce excessive reflectionAccurate height valueUsing optical meansImaging analysisControl system
The invention relates to a tree-dimensional measuring system capable of reducing light reflection on the surface of a measured object. The system comprises an image analysis and control system, a projector, and a camera. The image analysis and control system is used to make the projector produce structured light. The projector is used to project the structured light from a first direction to the surface of a measured object so as to form a deformed structured light pattern on the surface of the measured object. The image analysis and control system is further used to acquire the deformed structured light pattern from a second direction through the camera and analyze the deformed structured light pattern in order to acquire depth information of the surface of the measured object. The system is characterized in that the projector includes a first circular polarizer; structured light passes through the first circular polarizer to form circularly-polarized structured light which is projected to the surface of a measured object; a second circular polarizer is mounted at the front end of the lens of the camera; the second circular polarizer is used to eliminate the non-circularly-polarized light portion in the light entering the camera; and the first circular polarizer and the second circular polarizer are left-handed circular polarizers or right-handed circular polarizers.
Owner:东莞市盟拓智能科技有限公司
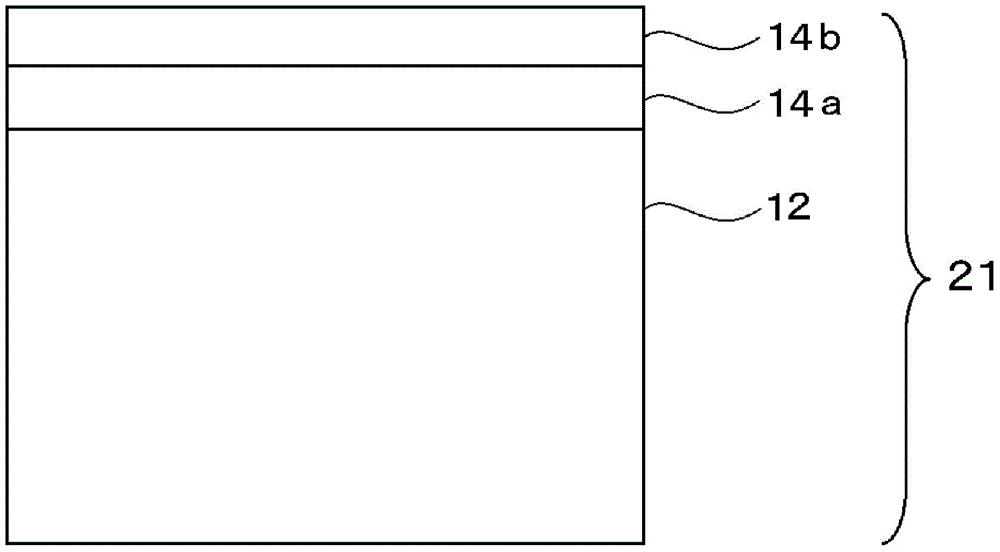
Multilayered cholesteric liquid crystal, process for producing same, and laminate of multilayered cholesteric liquid crystal
InactiveCN104871046AHas reflective propertiesIncrease reflectionSynthetic resin layered productsPolarising elementsSelective reflectionLight reflection
A multilayered cholesteric liquid crystal which comprises at least one light reflection layer (Xa) that is a light reflection layer obtained by fixing a cholesteric liquid-crystal phase and that contains a dextrorotatory chiral agent having an HTP of 30 μm-1 or more and at least one light reflection layer (Xb) that is a light reflection layer obtained by fixing a cholesteric liquid-crystal phase and that contains a levorotatory chiral agent having an HTP of 30 μm-1 or more, all of the light reflection layers (Xa) and all of the light reflection layers (Xb) having a selective-reflection wavelength in the range of 400-750 nm and the selective-reflection wavelength of at least one of the light reflection layers (Xa) being equal to the selective-reflection wavelength of at least one of the light reflection layers (Xb), and in which all the adjoining light reflection layers obtained by fixing a cholesteric liquid-crystal phase have been superposed so as to be in contact with each other. In the multilayered cholesteric liquid crystal, dextrorotatory and levorotatory, inversely twisted, cholesteric liquid-crystal layers have been superposed so as to be in contact with each other without using a pressure-sensitive adhesive therebetween. This multilayered cholesteric liquid crystal has good surface properties and high transparency, selectively reflects light in the visible-light region, and has high reflection performance.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
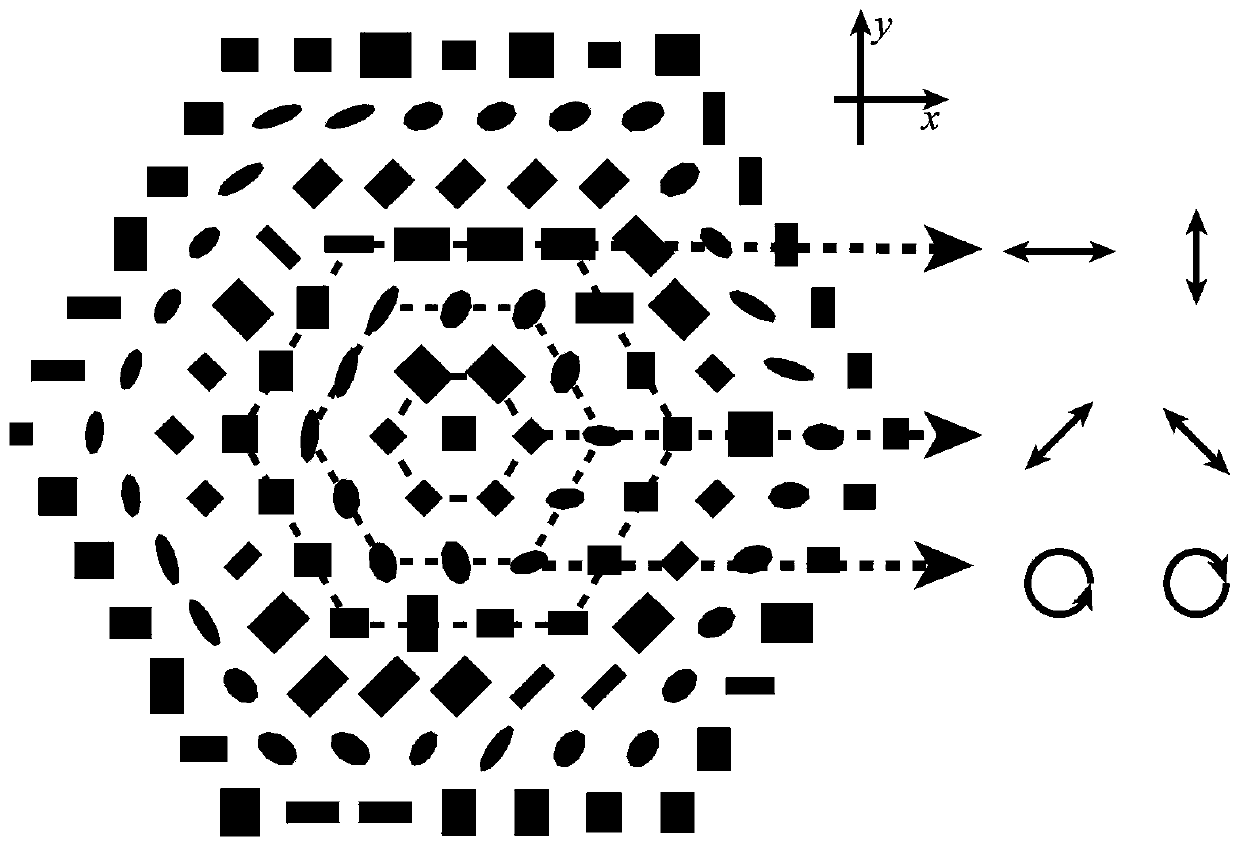
Circular polarization dichroic super lens and light path system comprising same
The invention discloses a circular polarization dichroic super lens and a light path system comprising the same. The super lens comprises a substrate and a surface structure; the surface structure comprises a metal layer and a plurality of spiral surface structures arranged in an array, the metal layer is formed on the spiral surface structures, and the plurality of spiral surface structures are arranged on the substrate. The range of the rotation angle of the plurality of spiral surface structures along the radial direction is 0-360 degrees, and the phase of the left-handed circularly polarized light and the right-handed circularly polarized light passing through the super lens can realize full-phase delay. The super lens of the embodiment of the invention can provide a new idea for realizing the combined function of focusing imaging and circular dichroism for a single device, and has great application prospect in the aspects of chiral sensing measurement, imaging, display, biologicaldetection and the like.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Circular polarizing filter and application thereof
ActiveUS20160154156A1High sensitivityImprove the circular polarizancePhotometryPolarising elementsLiquid crystallineTransmittance
According to the invention, there is provided a circular polarizing filter for selectively transmitting circularly polarized light of any one sense of either right-handed circularly polarized light or left-handed circularly polarized light at a specific wavelength in which scattering transmittance / vertical transmittance when circularly polarized light of the sense of the specific wavelength enters from any one surface is less than scattering reflectance / regular reflectance when circularly polarized light of the other sense enters from the surface. The circular polarizing filter includes a circularly-polarized light separating layer, the circularly-polarized light separating layer includes a reflected light-scattering circularly-polarized light separating layer, and may further include a reflected light-non-scattering circularly-polarized light separating layer, the reflected light-scattering circularly-polarized light separating layer is composed of a layer having a cholesteric liquid crystalline phase fixed therein, and the reflected light-non-scattering circularly-polarized light separating layer is composed of a layer having a cholesteric liquid crystalline phase fixed therein, or a laminate including a linearly-polarized light separating layer and a λ / 4 phase difference layer. The circular polarizing filter of the invention has a high circular polarizance, and a high-sensitivity sensor system can be provided using the circular polarizing filter of the invention.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
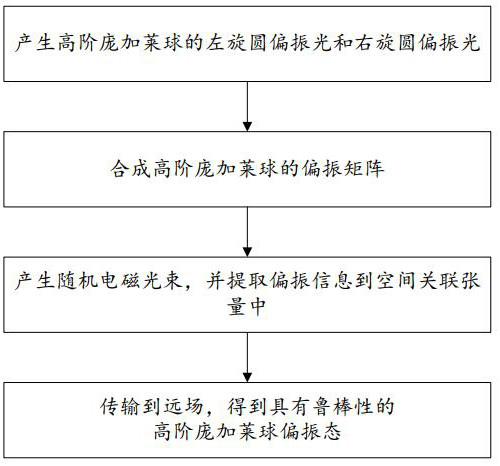
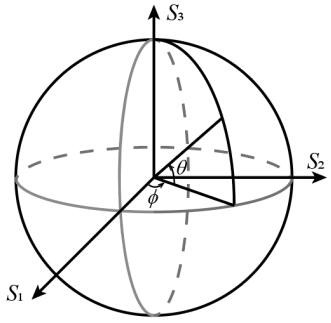
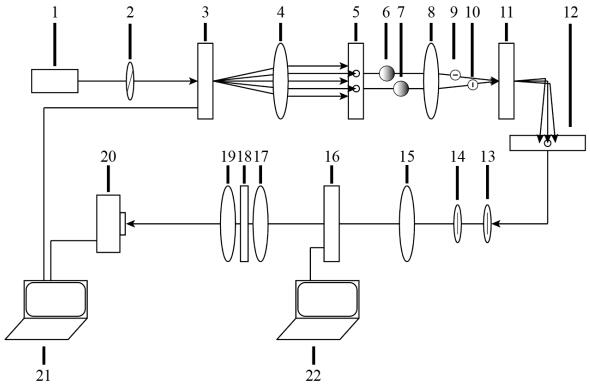
Method and system for generating polarization state of high-order Poincare sphere with robustness
The invention discloses a method and system for generating a polarization state of a high-order Poincare sphere with robustness. The method comprises the following steps of: loading a vortex phase on a completely coherent vector light beam, and then regulating and controlling the completely coherent vector light beam into left-handed circularly polarized light and right-handed circularly polarized light of the high-order Poincare sphere; synthesizing the left-handed circularly polarized light and the right-handed circularly polarized light into vector polarized light on the high-order Poincare sphere, and generating a polarization matrix of the high-order Poincare sphere through adjustment; reducing the spatial coherence of the polarized light, obtaining a random electromagnetic beam through shaping, and extracting polarization information in a polarization matrix to a spatial correlation tensor of the random electromagnetic beam; transmitting a random electromagnetic beam to a far field, in the far field, transferring polarization information from a space correlation tensor to a polarization matrix of the random electromagnetic beam, and obtaining a high-order Poincare sphere polarization state with robust characteristics. The problems that an existing high-order Poincare spherical polarized beam is difficult to generate, does not have the robust characteristic and is easily damaged by the external environment are solved.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
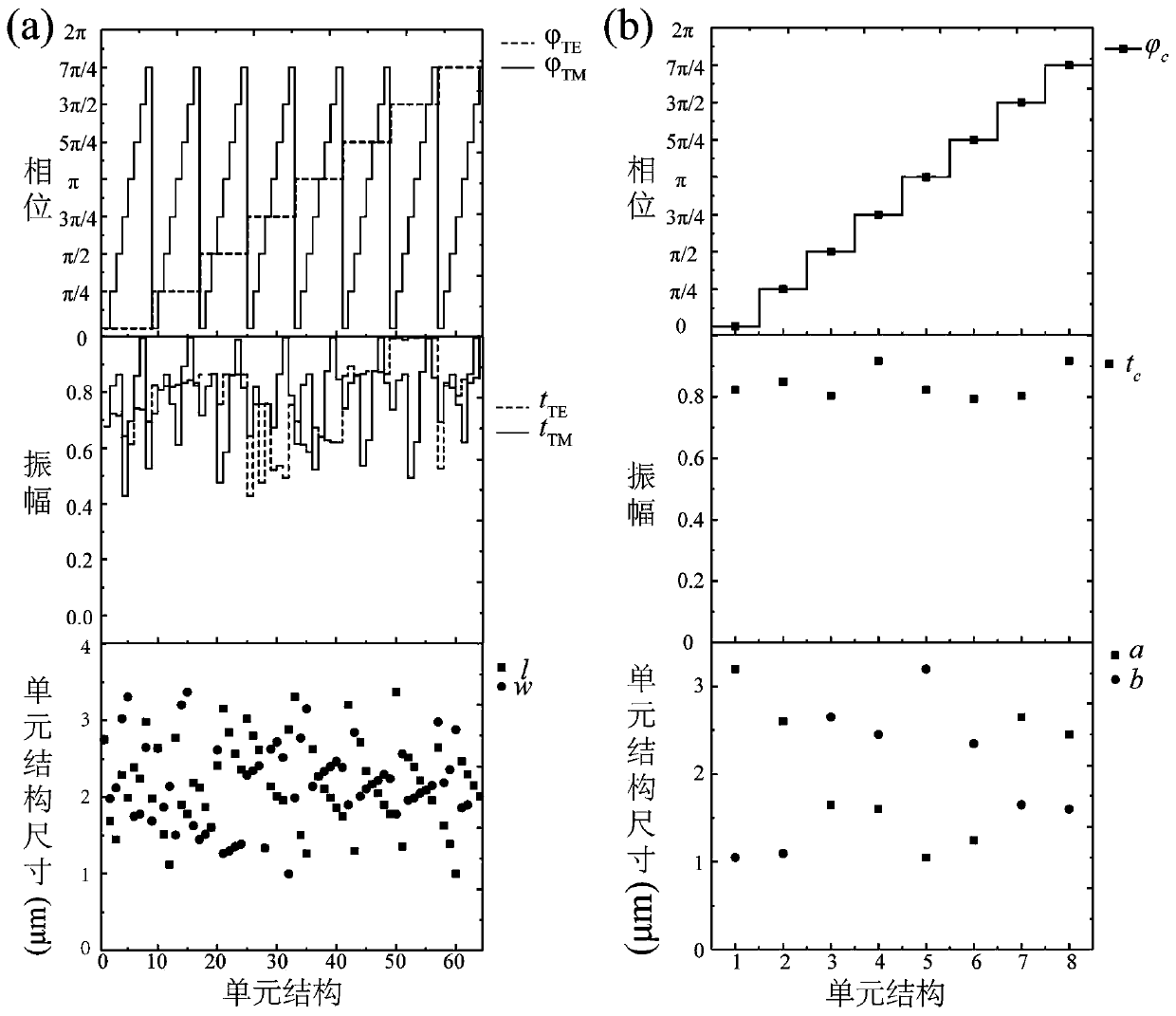
Full Stokes infrared polarization imager based on metasurface
ActiveCN110954974ASmall sizeReduce distractionsPolarising elementsElectromagnetic responseDextrorotatory
The invention provides a full Stokes infrared polarization imager based on a metasurface. The full Stokes infrared polarization imager based on the metasurface can achieve real-time detection and imaging of all polarized light of an infrared band by regulating and controlling the geometrical characteristics and the arrangement mode of a sub-wavelength unit structure. The polarization imager is mainly composed of an ultra-thin single-layer sub-wavelength unit structure array arranged on a substrate layer, sub-wavelength unit structures with different geometric dimensions have different electromagnetic response characteristics on x, y, 45 degrees, 135 degrees, levorotatory circularly polarized light and dextrorotatory circularly polarized light, and independent regulation and control on thesix kinds of polarized light can be achieved. The polarization imager mainly depends on a focal plane polarization imaging mode, six kinds of polarized light can be focused at different positions of the same focal plane at the same time, and when any polarized light irradiates a device, the polarization state of incident light can be calculated through a Stokes vector function. The polarization imager has important application in the field of infrared polarization imaging detection.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
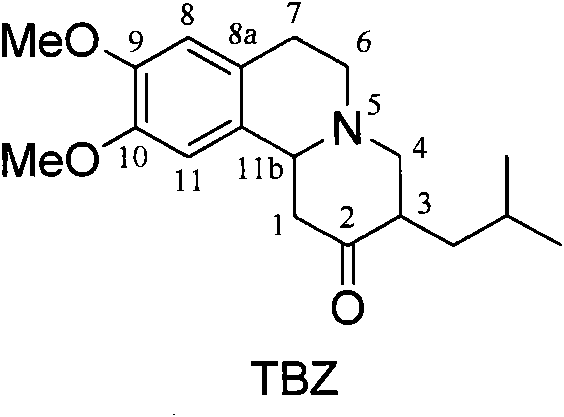
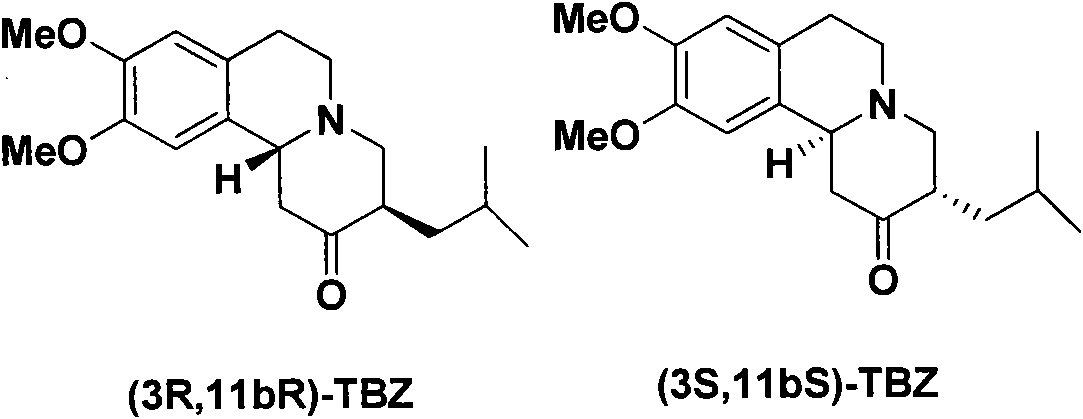
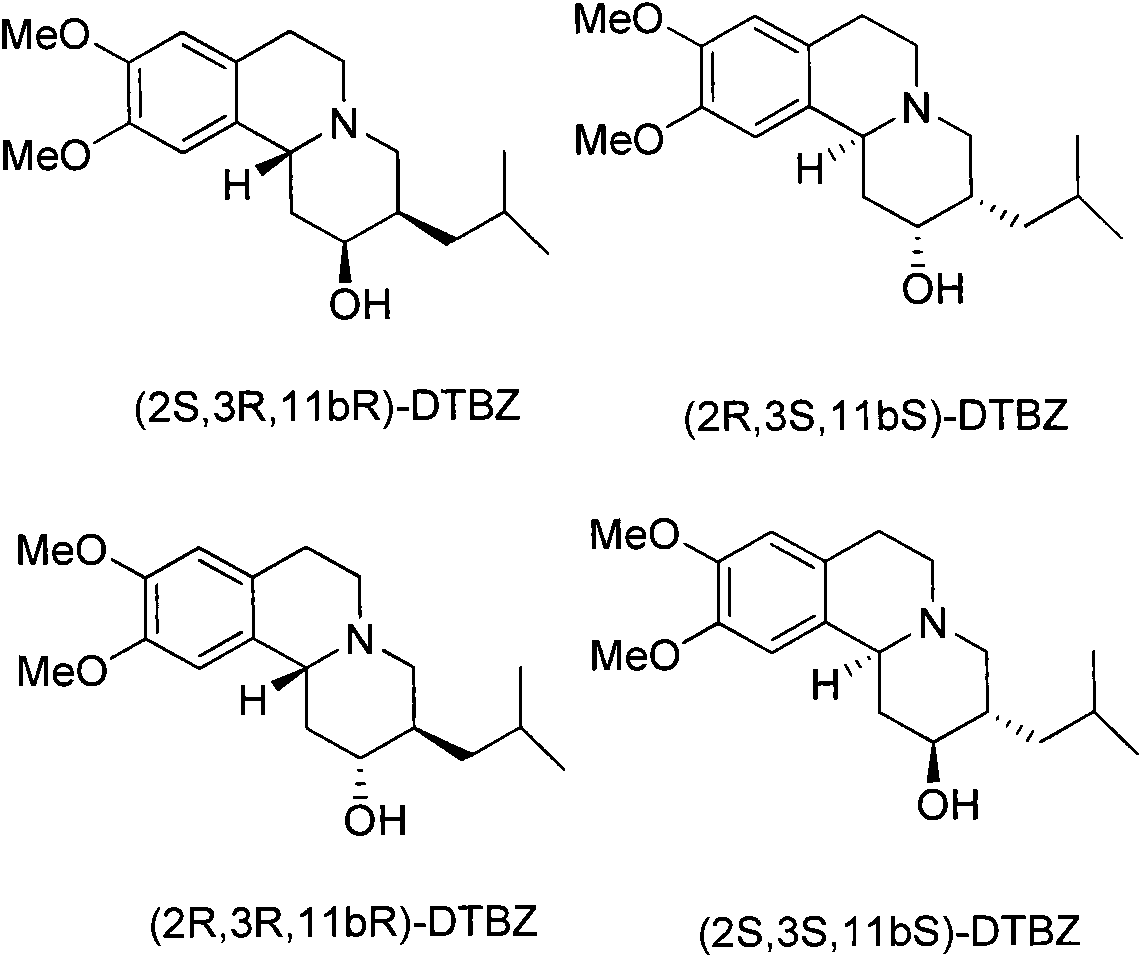
Resolution method of tetrabenazine
InactiveCN101985447AOptically-active compound separationOrganic racemisationDextrorotatoryMedicinal chemistry
The invention relates to a chiral resolution method of tetrabenazine and provides a salt formed by tetrabenazine and dextrorotatory or levorotatory chiral acid and a preparation method thereof. Tetrabenazine racemate is served as a raw material, and the dextrorotatory or levorotatory camphorsulfonic acid and the other chiral acids are served as a resolving agent to simply and efficiently prepare high-purity (+)-(3R, 11bR)-tetrabenazine and (-)-(3R, 11bS)-tetrabenazine.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
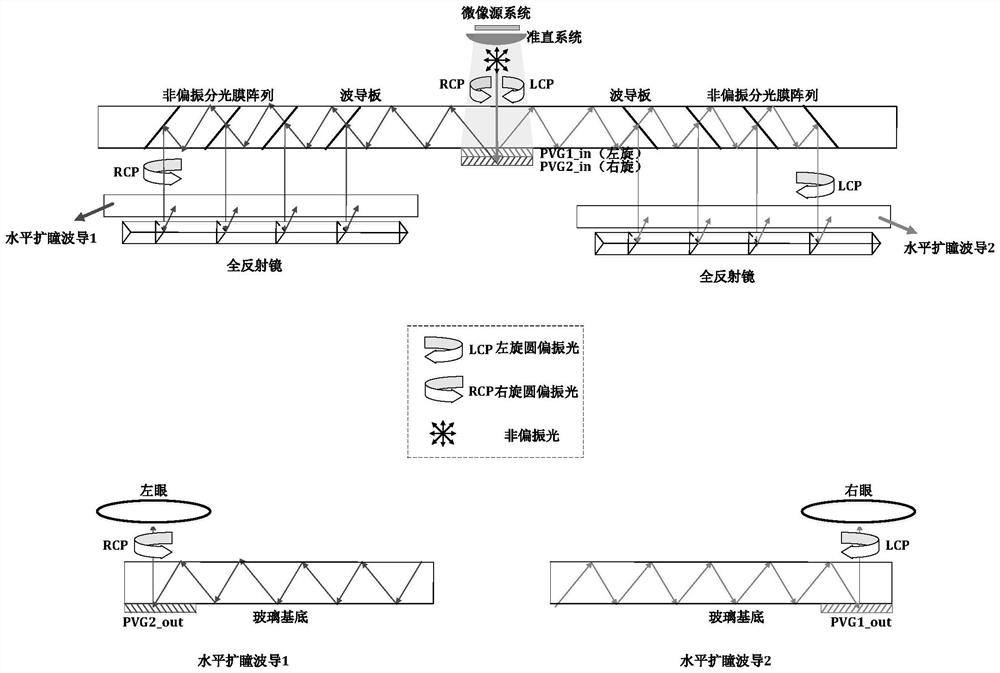
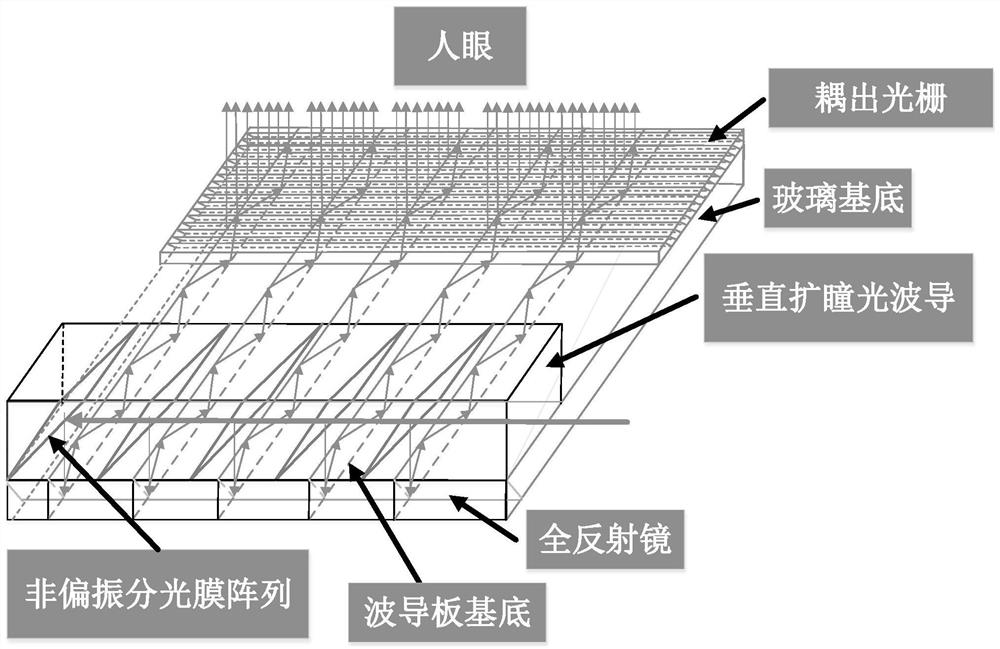
Two-dimensional pupil-expanding binocular waveguide near-to-eye display device and augmented reality display equipment
PendingCN114647080ASimple structureReduce volumeDiffraction gratingsOptical waveguide light guideGratingDisplay device
The invention relates to a two-dimensional pupil-expanding binocular waveguide near-eye display device and augmented reality display equipment, the two-dimensional pupil-expanding binocular waveguide near-eye display device comprises an optical-mechanical system for loading and outputting an image and emitting the collimated and corrected image to a coupling-in diffraction optical element group; the coupling-in diffraction optical element is formed by stacking and compounding a first polarization body holographic grating and a second polarization body holographic grating so as to be coupled into the left-hand circularly polarized light beam and the right-hand circularly polarized light beam respectively; the vertical pupil expanding optical waveguide is used for carrying out light ray expansion on the left-handed circularly polarized light beam and the right-handed circularly polarized light beam in the vertical direction so as to couple out multiple light rays to the glass substrate; the total reflection mirror deflects the light emitted by the vertical pupil-expanding optical waveguide at a preset angle and then emits the light into the glass substrate at a target angle capable of meeting a total reflection condition; the glass substrate is used for transmitting the light emitted by the vertical pupil-expanding optical waveguide to the coupling-out grating in a total reflection manner; and the coupling-out grating is used for coupling out the light rays to the left eye and the right eye of a person respectively.
Owner:北京谷东网科技有限公司
Ultrathin transmission type terahertz circular polarization asymmetric focusing lens
InactiveCN111830620ABreak symmetryAchieve asymmetric focusPolarising elementsDextrorotatoryWave band
The invention discloses an ultrathin transmission type terahertz circular polarization asymmetric focusing lens. According to the terahertz focusing lens with the double-layer rectangular metal arraystructure and the thin film substrate, asymmetric focusing of ultrathin transmission type terahertz circular polarization light is realized in a terahertz waveband for the first time; a focus can be generated when right-handed rotation circular polarization is incident from the front face, focusing cannot be achieved when right-handed rotation circular polarization is incident from the back face,the symmetry of the structure is broken through superposition of the two layers of rectangular metal structures, and the function which cannot be achieved by a common lens is achieved. The two layersof metal rectangular array structures are attached to the thin film substrate layer, the thickness is only 25.3 mum, and conversion frequency point adjustment and focal length adjustment can be achieved by adjusting structural parameters and structural rotation angles according to actual application occasions and requirements. The lens has the advantages of low loss, ultra-thinness, small size, easiness in integration and the like; and the focusing lens is simple in structure, wide in material source and convenient to process and prepare.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Method for chiral synthesis of levorotatory menthol
ActiveCN102010297AHigh activityThe synthesis process is simpleOrganic compound preparationHydroxy compound preparationMentholEnantioselective synthesis
The invention discloses a method for chiral synthesis of levorotatory menthol. In the process, dextrorotatory pulegone is used as a starting material; catalytic hydrogenation is carried out on the dextrorotatory pulegone by a chiral rhodium catalyst to generate levorotatory menthone; and the catalytic hydrogenation is carried out on the levorotatory menthone by a chiral ruthenium catalyst to synthesize the levorotatory menthol. In the process for synthesizing the levorotatory menthol through an asymmetric synthesis technology, the yield of the levorotatory menthone is more than 90%, the ee value of the levorotatory menthone is more than 99%, the total yield of the levorotatory menthol is greater than 83%, the ee value of the levorotatory menthol is greater than 98%, and the specific rotation is from-49 degrees to -50 degrees. The synthetic process is simple and is suitable for industrial production of the levorotatory menthol in a large scale, and the prepared levorotatory menthol hasthe advantages of high yield, good selectivity, high catalyst activity and other characteristics, is simple to recover.
Owner:GUANGDONG FOOD IND INST +1
Composition kit, laminate and method for producing same, and bandpass filter
InactiveUS20180030161A1Easy to produceReduced angle dependenceLiquid crystal compositionsOptical elementsCrystallographyBandpass filtering
The present invention provides a composition kit which is suitably used for more convenient production of a bandpass filter with reduced angle dependence, a laminate and a method for producing the same, and a bandpass filter. The composition kit of the present invention includes a first composition containing a liquid crystal compound having a polymerizable group and a dextrorotatory chiral agent, a second composition containing a liquid crystal compound having a polymerizable group and a levorotatory chiral agent, and a third composition containing a color material.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Measurement method for photon spin-orbital angular momentum joint mode and measurement system
ActiveCN111130637AReduce crosstalkEasy to implementMultimode transmissionSpin angular momentum of lightParticle physics
The invention discloses a measurement method for a photon spin-orbital angular momentum joint mode and a measurement system. The measurement method comprises the steps of vertically inputting a to-be-measured optical field with spin-orbital angular momentum into a plane (x, y), and enabling the center of the optical field to be aligned with the center of the plane; introducing phase modulation QL(x, y) into left-handed circular polarization state incident light with a spiral wavefront, and introducing phase modulation QR(x, y) into right-handed circular polarization state incident light with aspiral wavefront; enabling light fields with different spin angular momentum to be expanded along a spiral line and be separated to different positions on a plane (u, v); introducing a compensation phase PL(x, y) into the left-handed circular polarization incident light with the spiral wavefront, introducing a compensation phase PR(x, y) into the right-handed circular polarization incident lightwith the spiral wavefront, and converging the light fields passing through the plane (u, v) at different positions of the plane (m, n); and detecting light intensity distribution of the plane (m, n) to measure a spin-orbital angular momentum joint mode input into the light field or to demodulate the spin-orbital angular momentum joint mode input into the light field.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Optically pure Sibutramine and process for preparing salt derivative thereof
InactiveCN101514163AAdvantages of preparation processHigh optical purityAmino compound purification/separationAmino preparation from aminesDextrorotatoryDiastereomer
The invention discloses a preparation process of optically pure Sibutramine. In the process, chiral O,O'-diaryl formacyl tartaric acid is taken as a resolving agent to resolve Sibutramine raceme to obtain diastereomer salt thereof; and the diastereomer salt is separated, alkalized and extracted to obtain optically pure levorotatory Sibutramine or optically pure dextrorotatory Sibutramine. The invention further discloses a preparation process of a salt derivative of the optically pure Sibutramine, and the optically pure Sibutramine obtained by the process is combined with an acid compound to form the salt derivative of the optically pure Sibutramine. The preparation process of the optically pure Sibutramine is characterized by high resolving efficiency, simple and practical process, short resolving cycle and the like; and the used resolving agent can be recovered and recycled. Furthermore, the salt derivative of the optically pure Sibutramine prepared by the invention can expand Sibutramine application scope.
Owner:广州市金匮贸易有限公司
Use of modafinil in the treatment of cocaine addicts
InactiveCN104159575AEasy to recycleOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderOral medicationMedicine
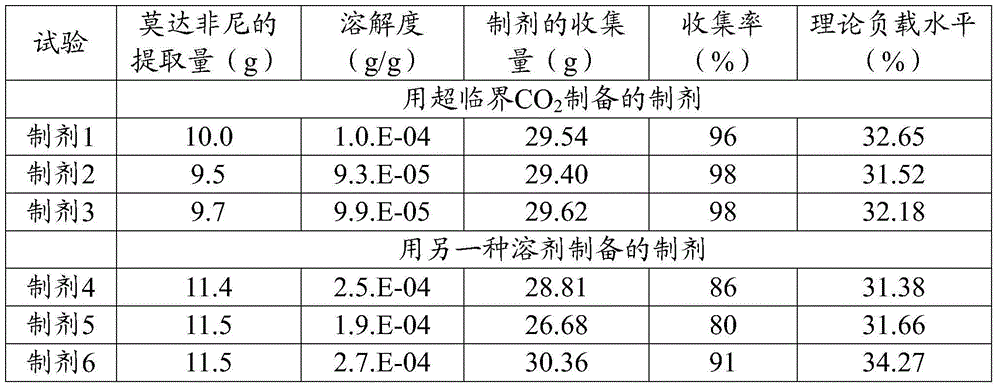
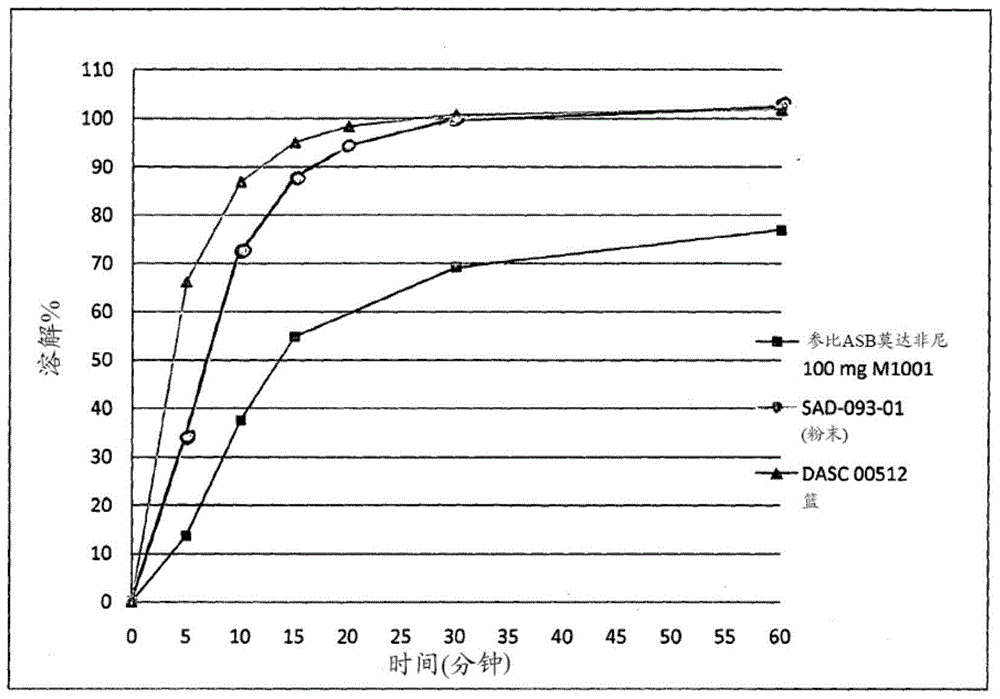
The present invention relates to the use of modafinil in cocaine addiction. The modafinil used is the dextrorotatory enantiomer thereof (modafinil S), having a very rapid release time of less than 1 hour, preferably 15-30 minutes, and very reduced wakefulness-promoting effects of less than 4 hours, preferably less than 2 hours. Said modafinil is to be taken in the form of a pharmaceutical composition via oral administration, each unit dose comprising 25-200 mg, preferably 50-100 mg, of modafinil S. The invention further relates to the use of said pharmaceutical composition as a substitution treatment for cocaine addicts.
Owner:DEBREGEAS & ASSOCIES PHARMA
Free space type Mueller OCT imaging system for full-automatic time division detection and imaging method
PendingCN112147080AHigh acquisition rateQuick collectionPolarisation-affecting propertiesAutomatic controlOptical polarization
The invention discloses a free space type Mueller OCT imaging system for full-automatic time division detection and an imaging method. Four optical channels with different polarization types, namely horizontal type, vertical type, 45-degree linear polarization type and right-handed circular polarization type, are arranged in a reference wall, and meanwhile, a sample wall realizes polarized light of the four states by using a software program to control a rotating wave plate of a precision rotating worktable; a software program is also used in the reference wall to control an optical switch toselect different channels in the reference wall, and polarized light of the channels returns to interfere with the polarized light scattered by the sample wall correspondingly, so that time division detection of polarization information is realized; and meanwhile, 16 element images of a Mueller matrix of a sample are reconstructed, so that the collection of complete polarization information is realized. According to the free space type Mueller OCT imaging system for full-automatic time division detection and the imaging method, full-automatic control is realized, image acquisition can be rapidly carried out, and the sampling rate is improved.
Owner:FUJIAN NORMAL UNIV
Circular polarization-type polarization diversity element, scanning element using same, and lidar
ActiveUS20200300992A1Reduce the effect of temperaturePromote sportsPolarising elementsElectromagnetic wave reradiationPolarization diversityGrating
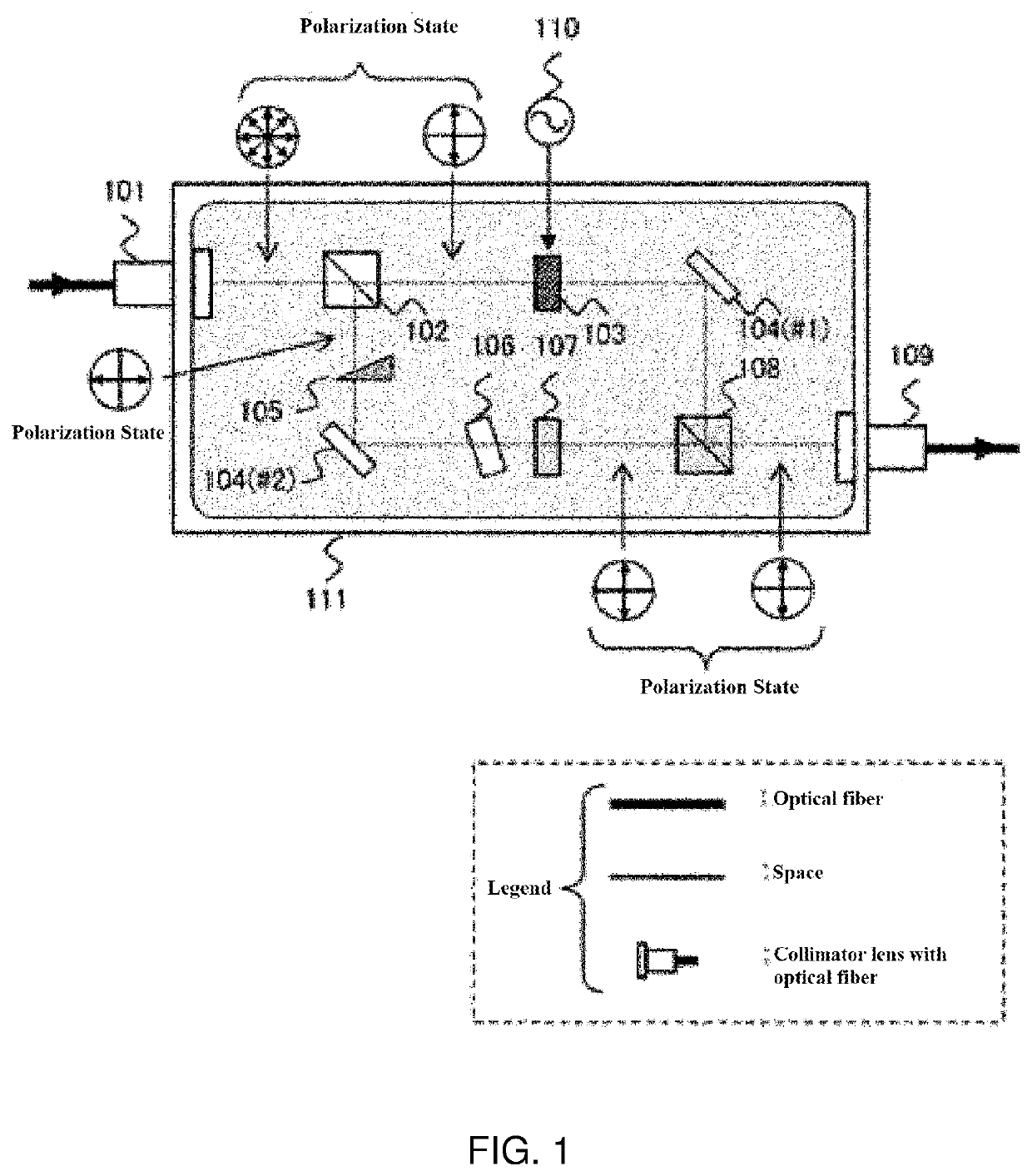
In the prior art, a scanning element used for Lidar in the self-driving car technology employed a mirror or the like continuously rotated by MEMS, and due to the inertia of the mirror or the like, the scanning element was suited for a raster scan that scans a scene in one stroke, but was incapable of discontinuous movement from one arbitrary point to another, and programmable scanning with an arbitrary frequency in an arbitrary pattern, as fast as the raster scan. In the present invention, there was fabricated Lidar, which is composed of a polarization diversity scheme and a scanning element, wherein the polarization diversity scheme uses two polarization gratings, each polarization grating having a thickness such that it becomes a half-wave plate, wherein birefringent directors of each polarization grating rotate with a period Λ, wherein these polarization gratings are disposed with a desired interval from each other, wherein a half-wave plate is inserted in either one of two paths of separated, exiting right-handed or left-handed circularly polarized light beam, depending on a rotation direction of the circularly polarized light, to thereby enable conversion of light beams into parallel proximate circularly polarized light beams with the same rotational direction, and wherein the scanning element has a multistage structure of polarization switch-polarization grating sets connected in combination, with a polarization switch and a polarization grating being defined as one set.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
Binocular waveguide display method based on reflective polarization multiplexing liquid crystal lens
The invention discloses a binocular waveguide display method based on a reflective polarization multiplexing liquid crystal lens. The method is based on a waveguide display device, the waveguide display device comprises an optical waveguide plate, an in-coupling liquid crystal lens, a right-handed out-coupling grating and a left-handed out-coupling grating are arranged at the same side of the optical waveguide plate, and the in-coupling liquid crystal lens is positioned between the right-handed out-coupling grating and the left-handed out-coupling grating. The method comprises the steps that an image source is placed on a focal plane of an in-coupling liquid crystal lens, and the in-coupling liquid crystal lens collimates and couples two kinds of circularly polarized light from the image source into an optical waveguide plate; the left-handed circularly polarized light and the right-handed circularly polarized light are propagated in the waveguide plate in the opposite directions by means of total reflection; and after touching the left-handed-out coupling grating and the right-handed-out coupling grating, the light is diffracted and coupled out of the waveguide. The method solves the problems that in a traditional near-eye waveguide display system, a collimating lens needs to be used, and a gap exists between the collimating lens and the waveguide plate.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
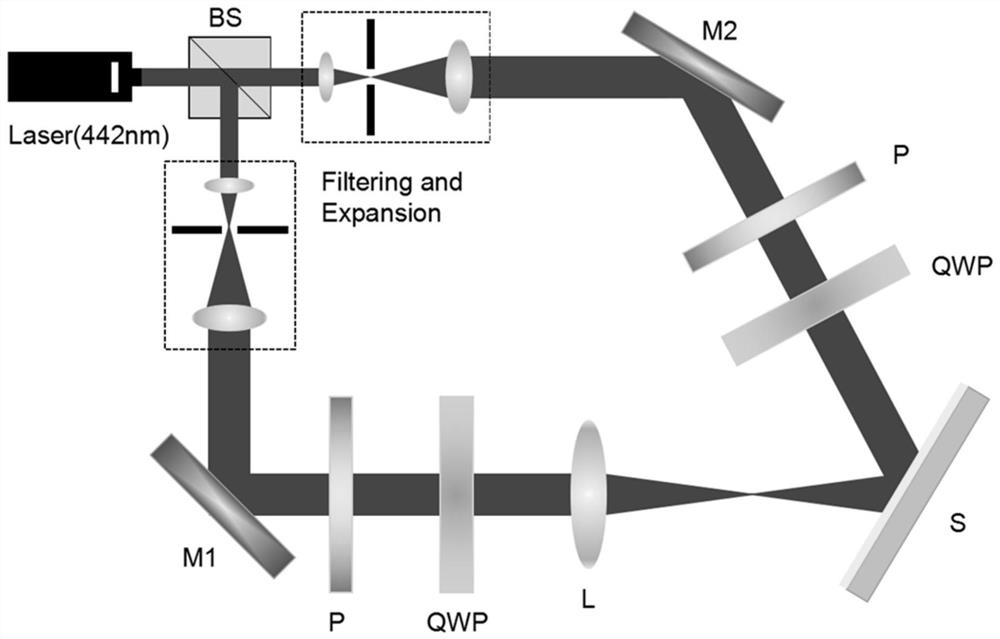
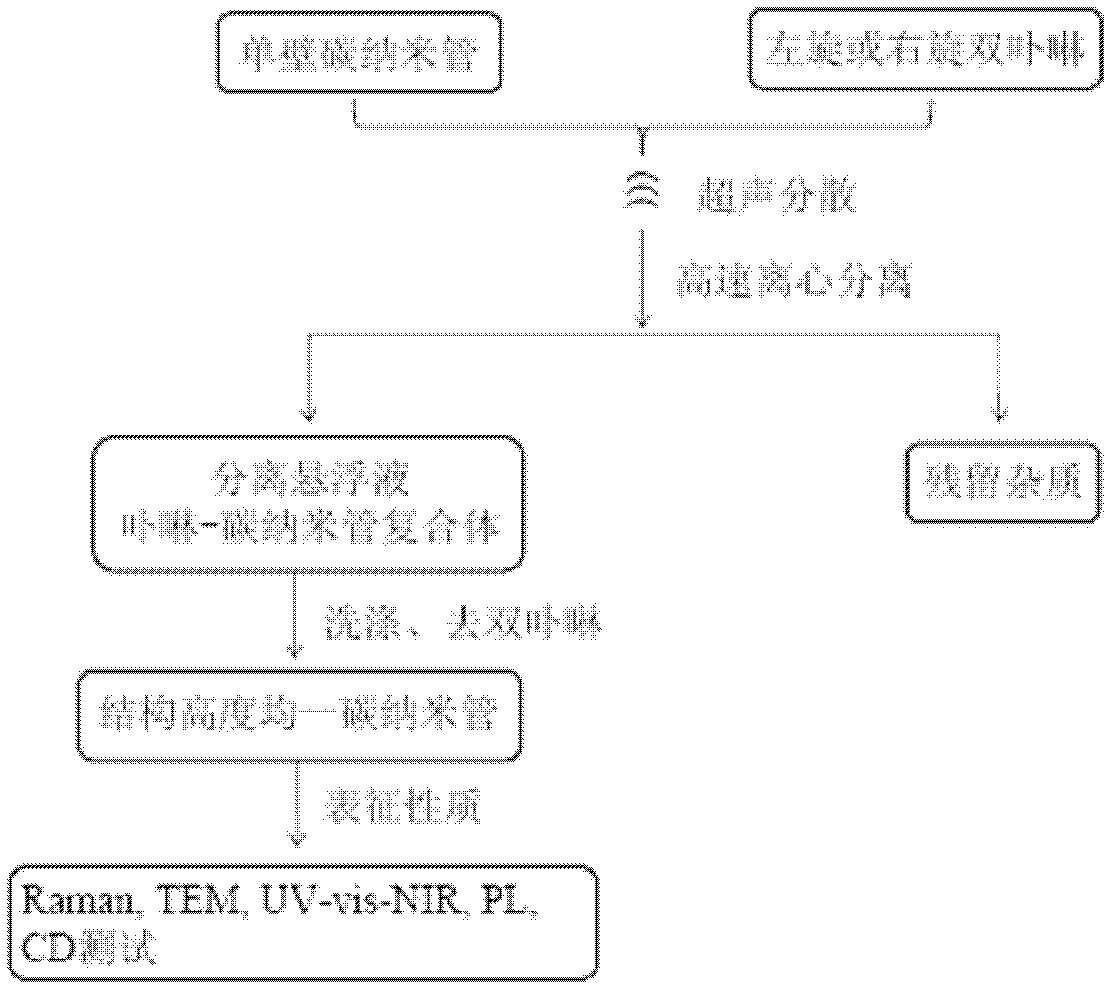
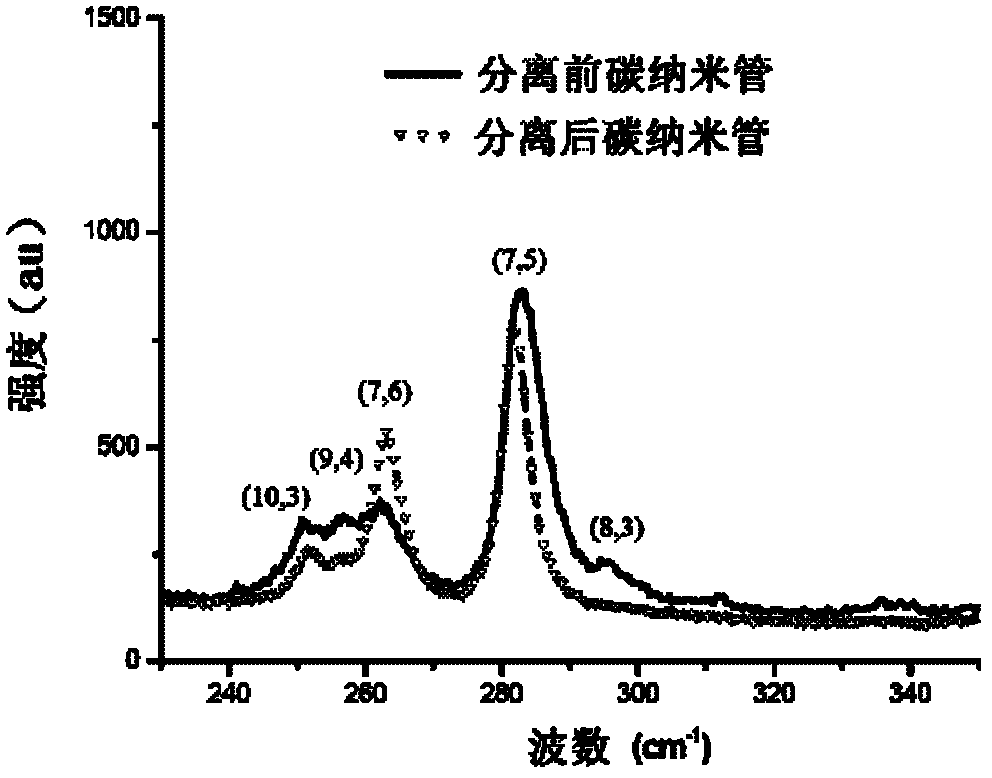
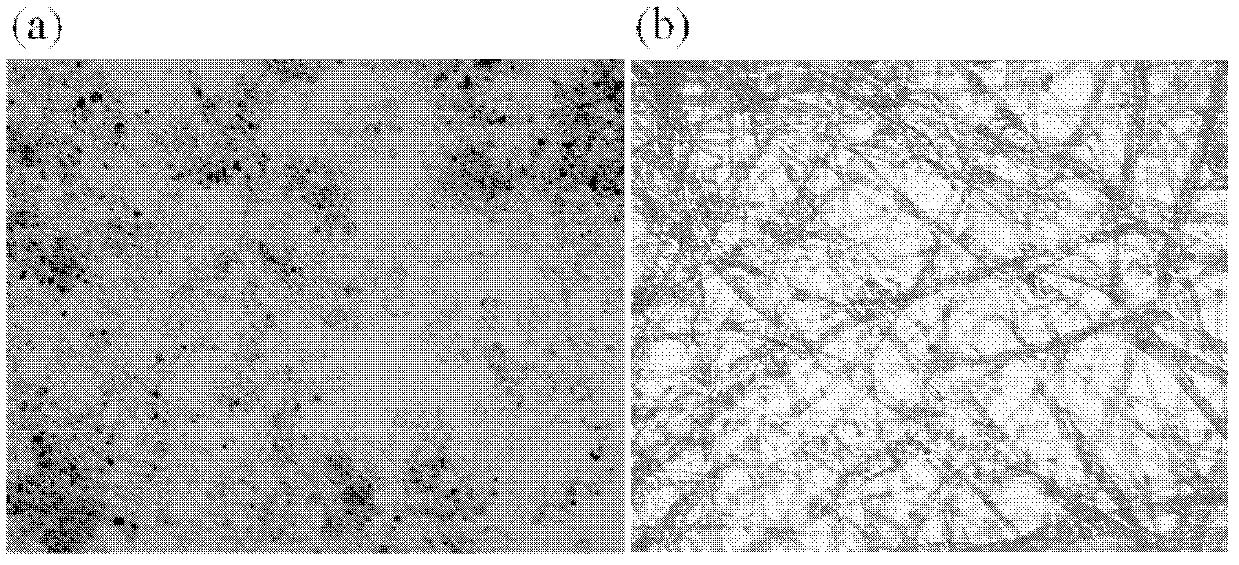
Chiral porphyrin complex nanotweezers and its preparation method and application in the separation of single-walled carbon nanotubes
InactiveCN102268002AOptically activeThe method of separation is simple and practicalOrganic chemistryChemical structureAryl
The present invention relates to chiral porphyrin complex nanotweezers and a preparation method thereof and a method for separating narrow (n, m) value distribution and optically active carbon tubes from single-walled carbon nanotubes by the chiral porphyrin complex nanotweezers. It has a chemical structural formula represented by the following general formula R or general formula S: wherein, Ar is a soluble aryl group; M is a transition metal element; the general formula R is a right-handed nanotweezer molecule, and the general formula S is a left-handed nanotweezer molecule. The beneficial effects of the present invention are: the chiral porphyrin complex of the present invention can effectively separate narrow (n, m) value distribution and optically active carbon tubes from single-walled carbon nanotubes, and the separation method is relatively simple and practical, The separated carbon nanotubes have dual properties: one is optically active and can be used for chiral sensor research; the other has narrow (n, m) value distribution, which can be used to construct various organic photoelectric devices.
Owner:WUHAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Cholesterol liquid crystal display device
The invention relates to a cholesterol liquid crystal display device, comprising a substrate, a light absorption layer and a cholesterol liquid crystal layer. The light absorption layer is arranged on the substrate. The cholesterol liquid crystal layer is arranged above the light absorption layer and comprises a plurality of lines of levorotatory cholesterol liquid crystals and a plurality of lines of dextrorotatory cholesterol liquid crystals which are alternately arranged. The cholesterol liquid crystal display device in the invention respectively reflects a levorotatory light and a dextrorotatory light by virtue of the levorotatory cholesterol liquid crystals and the dextrorotatory cholesterol liquid crystals, thus an observer can see different images with the eyes so as to form 3D development effect.
Owner:华映视讯(吴江)有限公司 +1
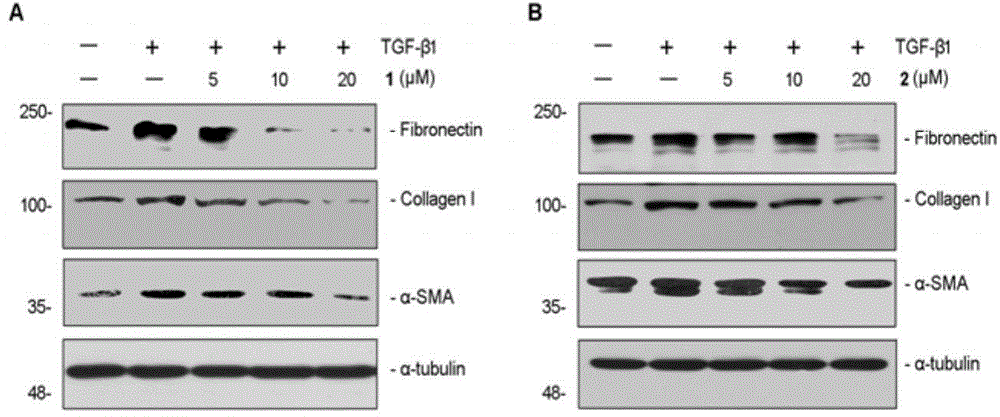
Ganoderma cochlear phenols A and B, pharmaceutical compositions of ganoderma cochlear phenols A and B and applications of ganoderma cochlear phenols A and B and pharmaceutical compositions in preparation of medicines and food
InactiveCN104447783AOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryPhosphorylationRenal Tubular Epithelial Cells
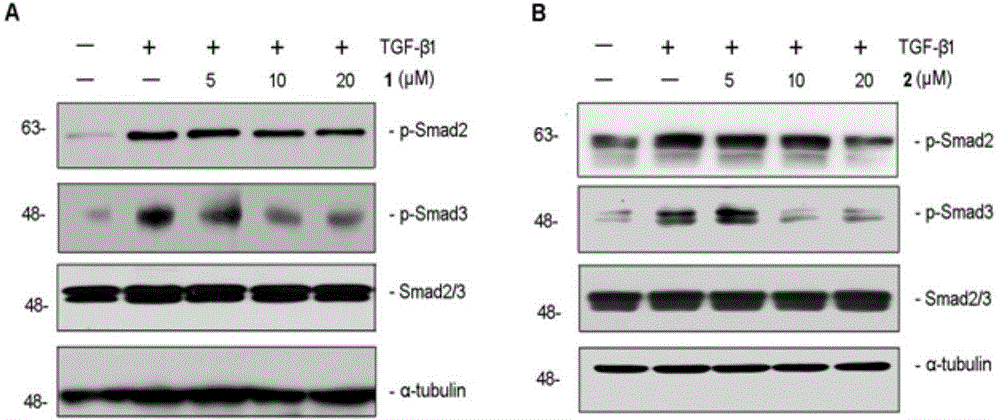
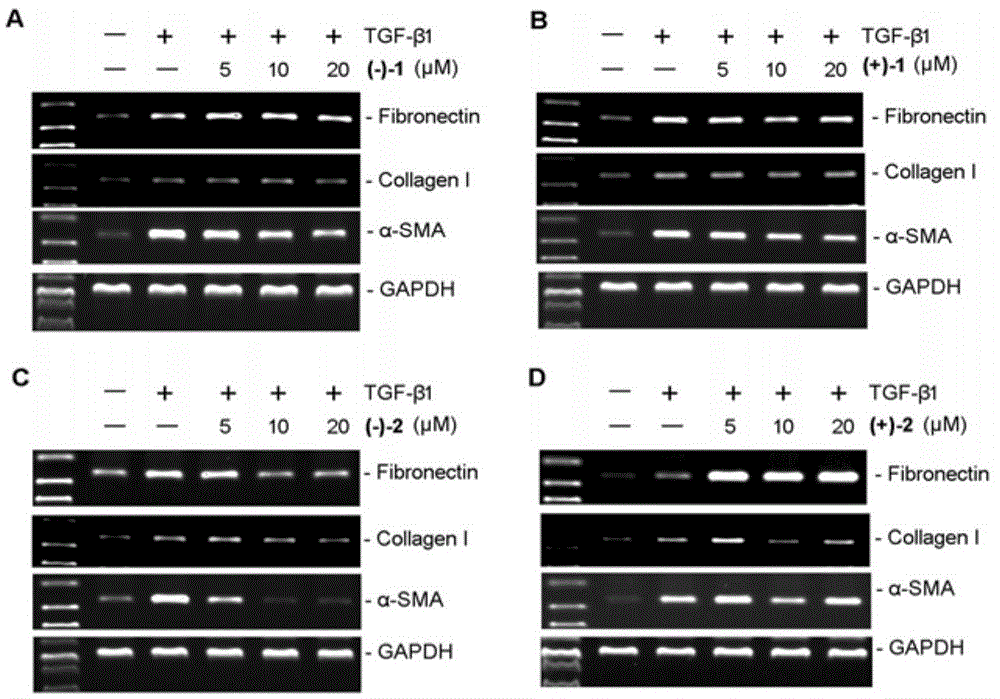
The invention relates to ganoderma cochlear phenols A and B, pharmaceutical compositions of ganoderma cochlear phenols A and B and applications of ganoderma cochlear phenols A and B and the pharmaceutical compositions thereof in preparation of medicines and food. Two racemates are separated from ganoderma cochlear and identified, and then the two racemates are split into two pairs of optical enantiomers which are named as levorotatory or dextrorotatory ganoderma cochlear phenols A and B respectively. Researches show that both the racemates and the enantiomers are capable of significantly inhibiting TGF-beta1-induced renal tubular epithelial cell from generating fibronectin, I type collagen and alpha-smooth muscle actin (alpha-SMA), and researches further find that both the racemates and the enantiomers are capable of significantly inhibiting the TGF-beta1-induced renal tubular epithelial cell Smad3 from phosphorylation, which means that the compounds have application prospects in the field of preparation of medicines for resisting renal fibrosis and chronic nephrosis.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF BOTANY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
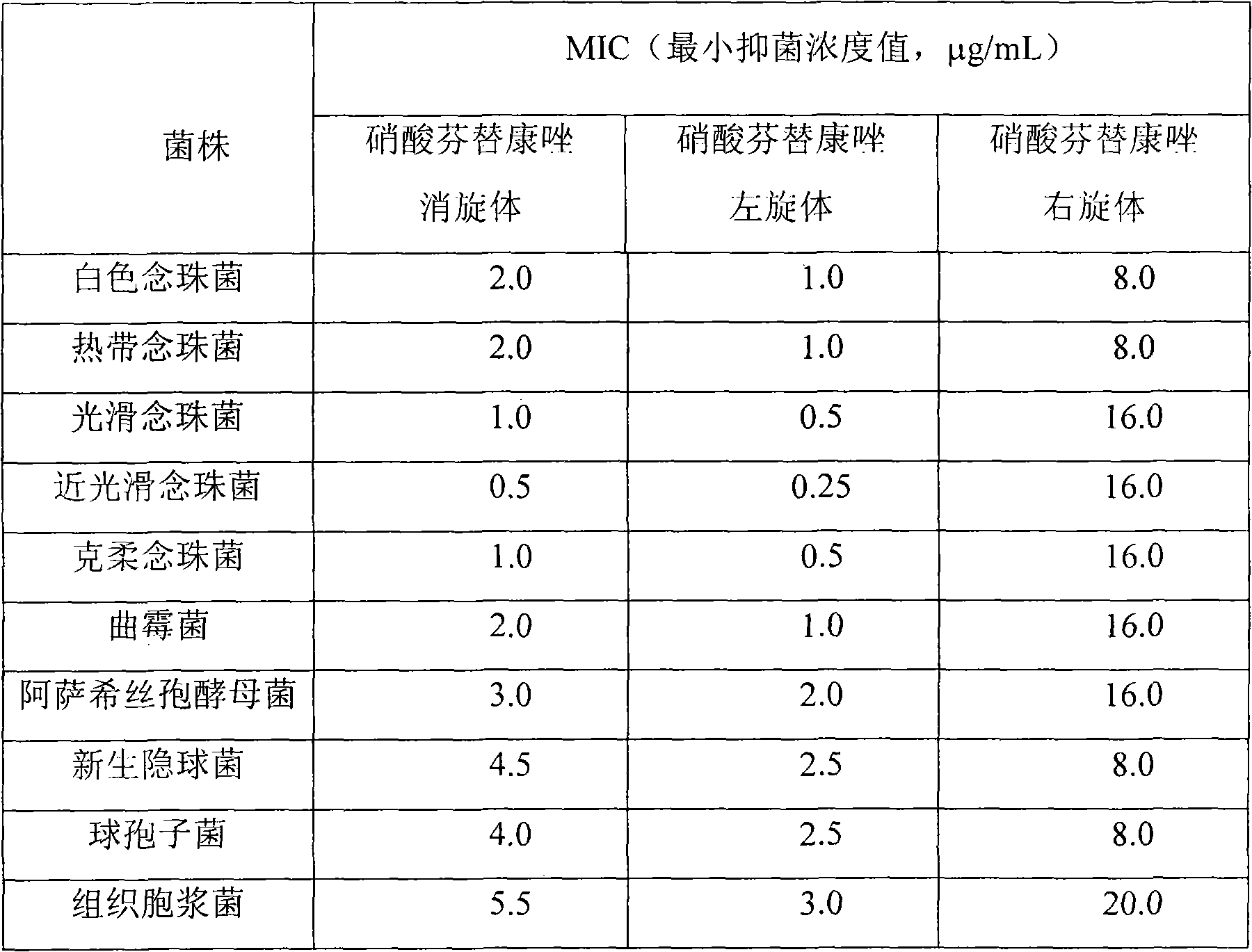
Fenticonazole nitrate, preparation of levorotatory form and dextrorotatory form and application of levorotatory form in preparing antifungal medicaments
ActiveCN101955462ASynthetic process yield is highIncrease contentOrganic active ingredientsAntimycoticsAntifungalDextrorotatory
The invention relates to a synthesis process for fenticonazole nitrate. In the synthesis process, thiophenol and para aminobenzoic acid are taken as raw materials, and are subjected to seven-step reaction to form the fenticonazole nitrate, and the yield is higher. The invention relates to a preparation method for a levorotatory form and a dextrorotatory form of the fenticonazole nitrate, which solves the problem that the levorotatory form and the dextrorotatory form cannot be well obtained due to complicated and fussy operation according to documents. The levorotatory form and the dextrorotatory form have high purity and high industrial application value. Experiments prove that the antibacterial activity of the levorotatory form of the fenticonazole nitrate is greater than that of racemate and the dextrorotatory form. The invention relates to application of the levorotatory form of the fenticonazole nitrate in preparing antifungal medicaments.
Owner:NANJING HEALTHNICE MEDICAL TECH +1
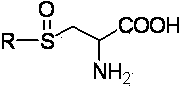
Method for preparing thioalkyl/alkenyl cysteine sulfoxide by fractional crystallization
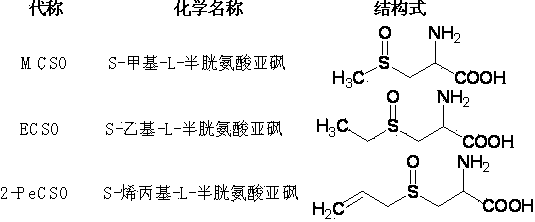
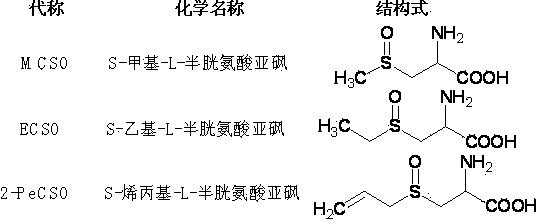
ActiveCN104140384AHigh purityOptically activeOrganic chemistryOrganic compound preparationThiosulfinateBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
The invention discloses a method for preparing thioalkyl / alkenyl cysteine sulfoxide by fractional crystallization, belonging to the technical field of compound preparation. The method comprises the following steps: adding cysteine or cysteine salts, a sodium hydroxide solution and an R group (alkyl or alkenyl)-derived material into absolute ethanol in sequence for reaction to synthesize coarse ACSs, re-crystallizing ACSs, purifying, oxidizing to form ACSOs, and fractionally crystallizing to obtain natural dextrorotatory ACSOs, wherein the R group-derived material is replaced to synthesize different types of ACSOs in allium; enantiomers in racemes are separated by adopting the fractional crystallization method to obtain natural dextrorotatory ACSOs with optical activity. Compared with a conventional extraction method, the method has the characteristics that the yield and the purity are high, a conventional complicated extraction process is avoided, the product has the optical activity, and the physical property is close to that of natural extract; the product is used in the fields of health products, pharmaceuticals and the like, the effects of resisting bacteria and cancers, reducing blood fat and the like of ACSOs are brought into play, or the product serves as an intermediate such as an active ingredient-diallyl thiosulfinate for synthesizing allium.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for splitting ketoprofen enantiomer by temperature gradient simulated moving bed chromatogram
InactiveCN102516068AAchieve separationHigh purityOptically-active compound separationCarboxylic compound separation/purificationDistillationSimulated moving bed
The invention discloses a method for splitting ketoprofen enantiomer by temperature gradient simulated moving bed chromatogram. The method comprises the following steps of: preparing a mobile phase as an eluate; using the eluate as a solvent to prepare a ketoprofen racemate solution as a charging liquid; introducing the charging liquid and the eluate with a temperature difference or with a same temperature into an open-loop simulated moving bed chromatogram to split the ketoprofen racemate and obtain levorotatory ketoprofen solution with a purity higher than 98% and a dextrorotatory ketoprofen solution; collecting the obtained levorotatory ketoprofen solution and the dextrorotatory ketoprofen solution; and carrying out distillation, recrystallization and drying respectively to obtain levorotatory ketoprofen enantiomer crystal and dextrorotatory ketoprofen enantiomer crystal with purity higher than 98%. The method has advantages of high separation efficiency, small solvent amount, continuous production and large operation elasticity, and has good commercialized application prospect.
Owner:WENZHOU UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com