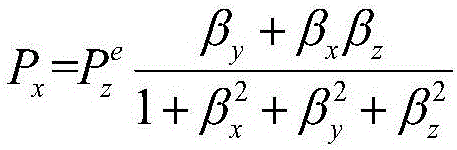Patents
Literature
1050results about "Magnetic field measurement using magneto-optic devices" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Atomic magnetometer and operating method of the same
ActiveUS20160116553A1Extend detection bandwidthHigh bandwidthMagnetic field measurement using magneto-optic devicesElectric/magnetic detectionNegative feedbackAudio power amplifier
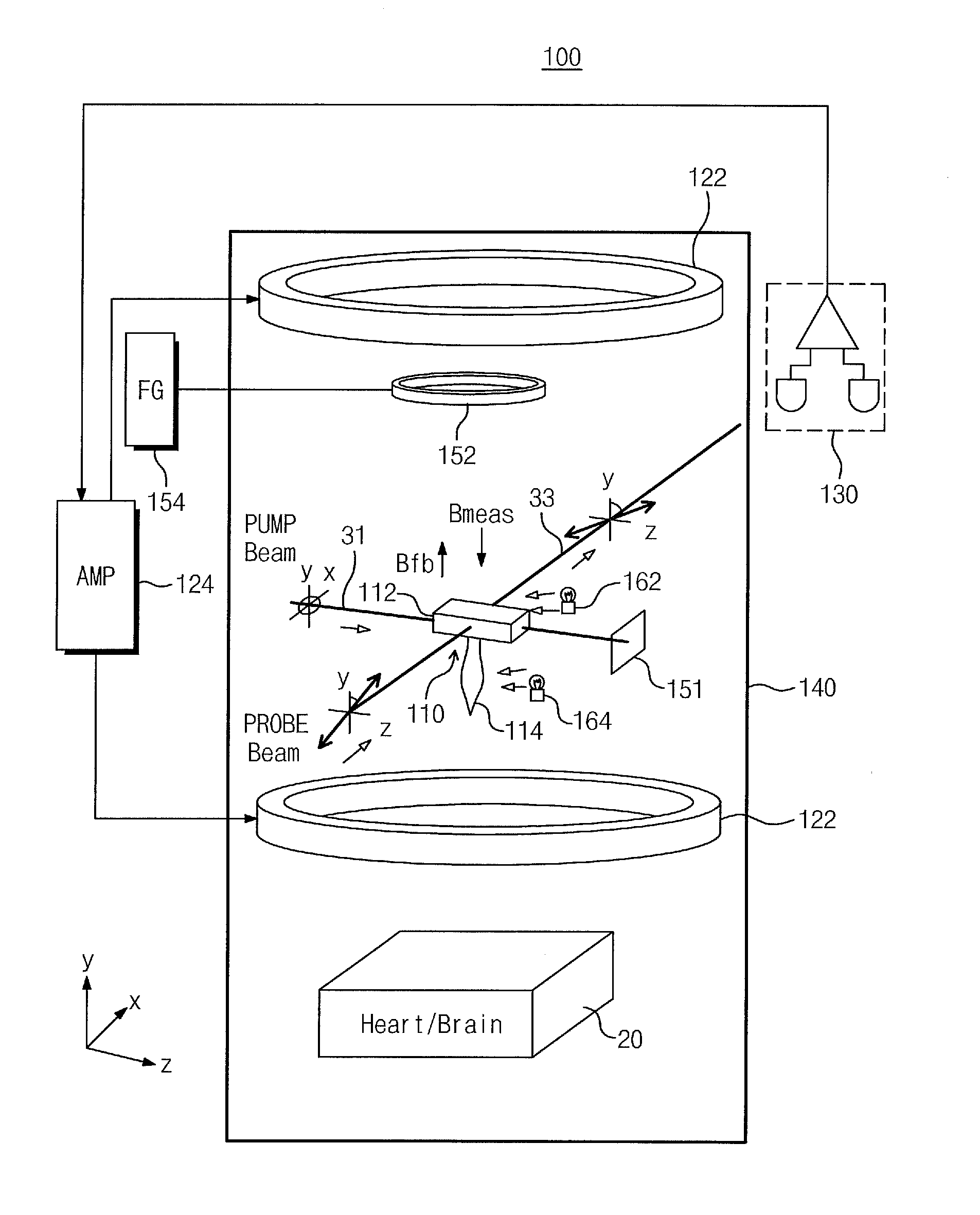
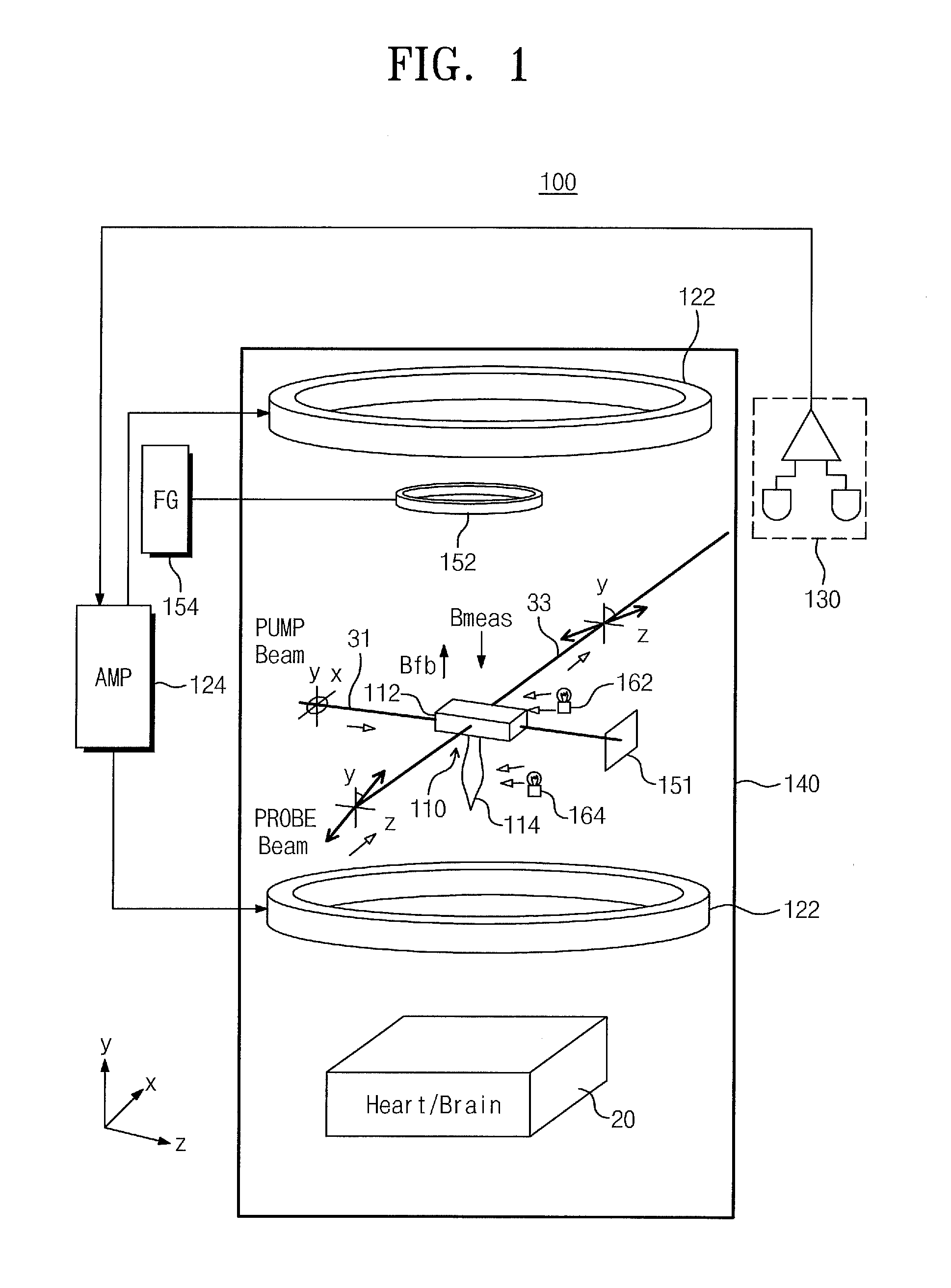
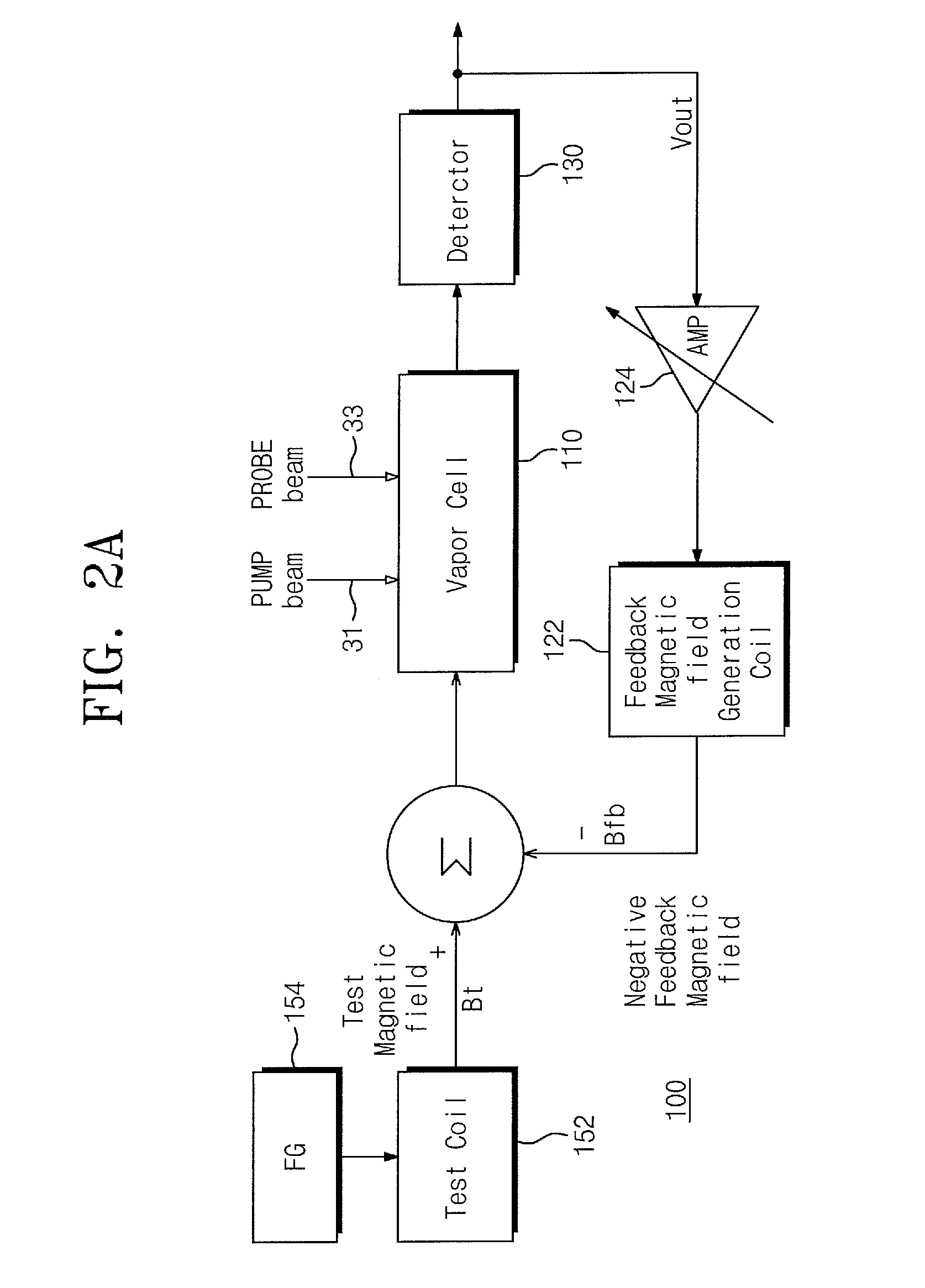
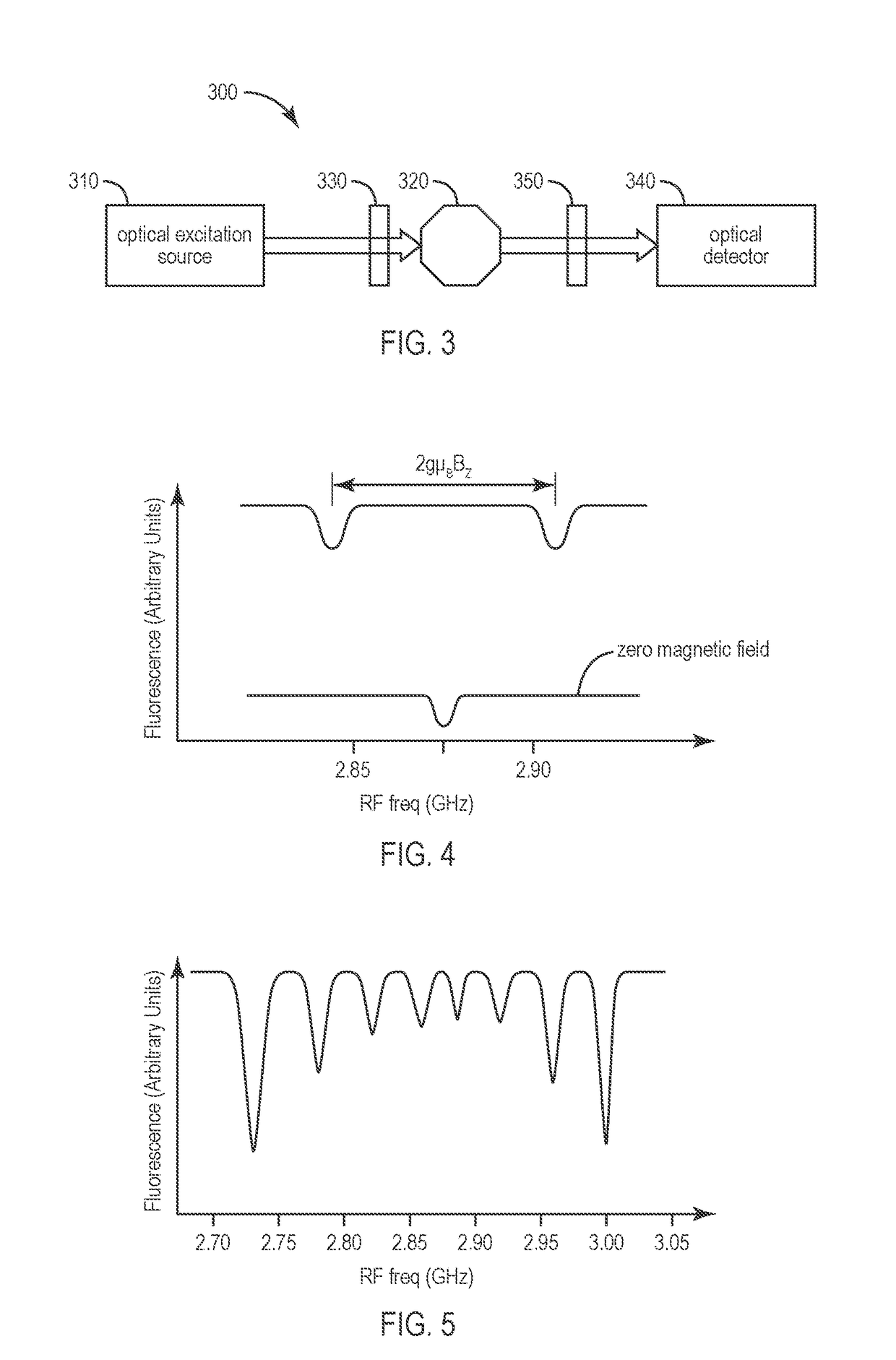
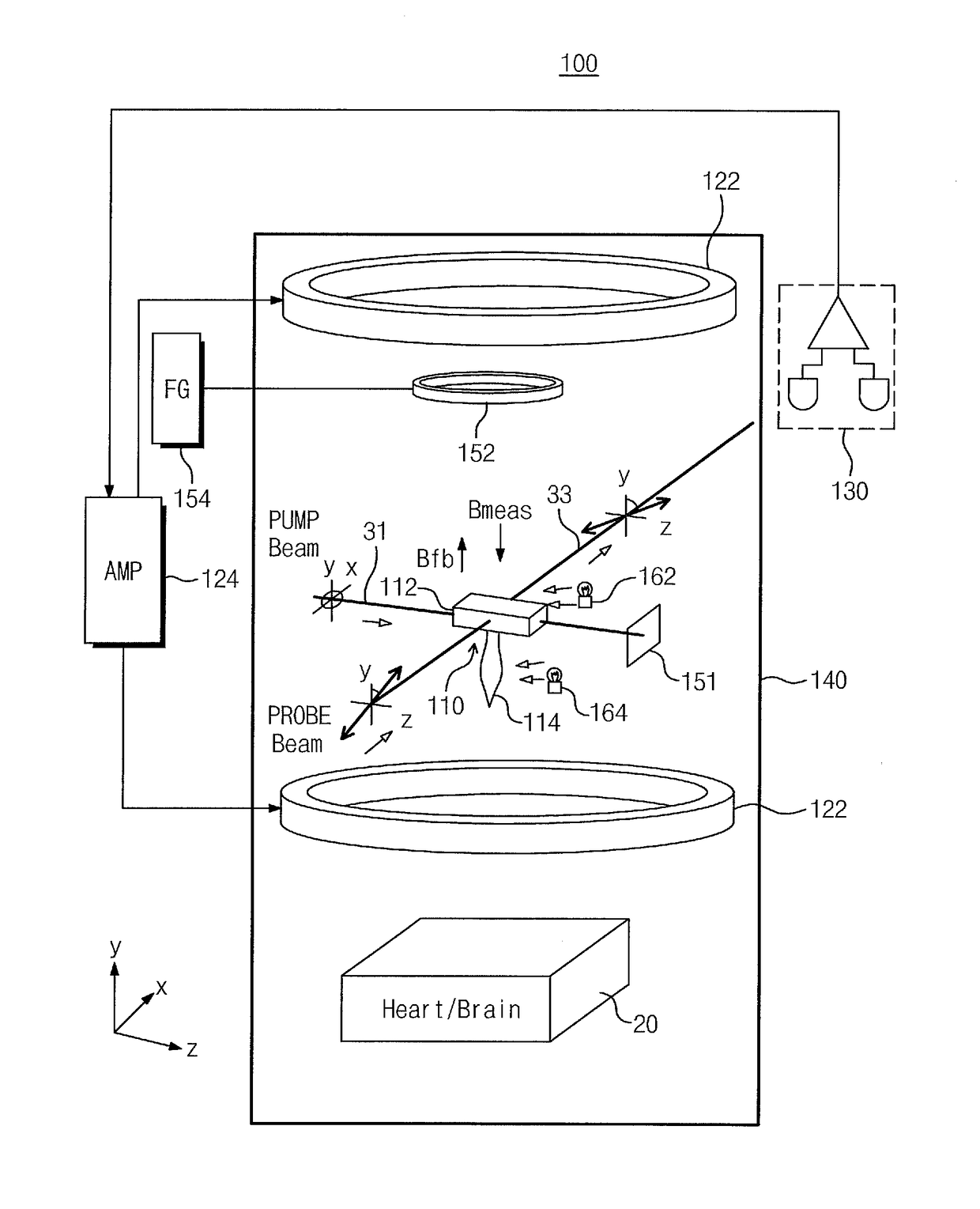
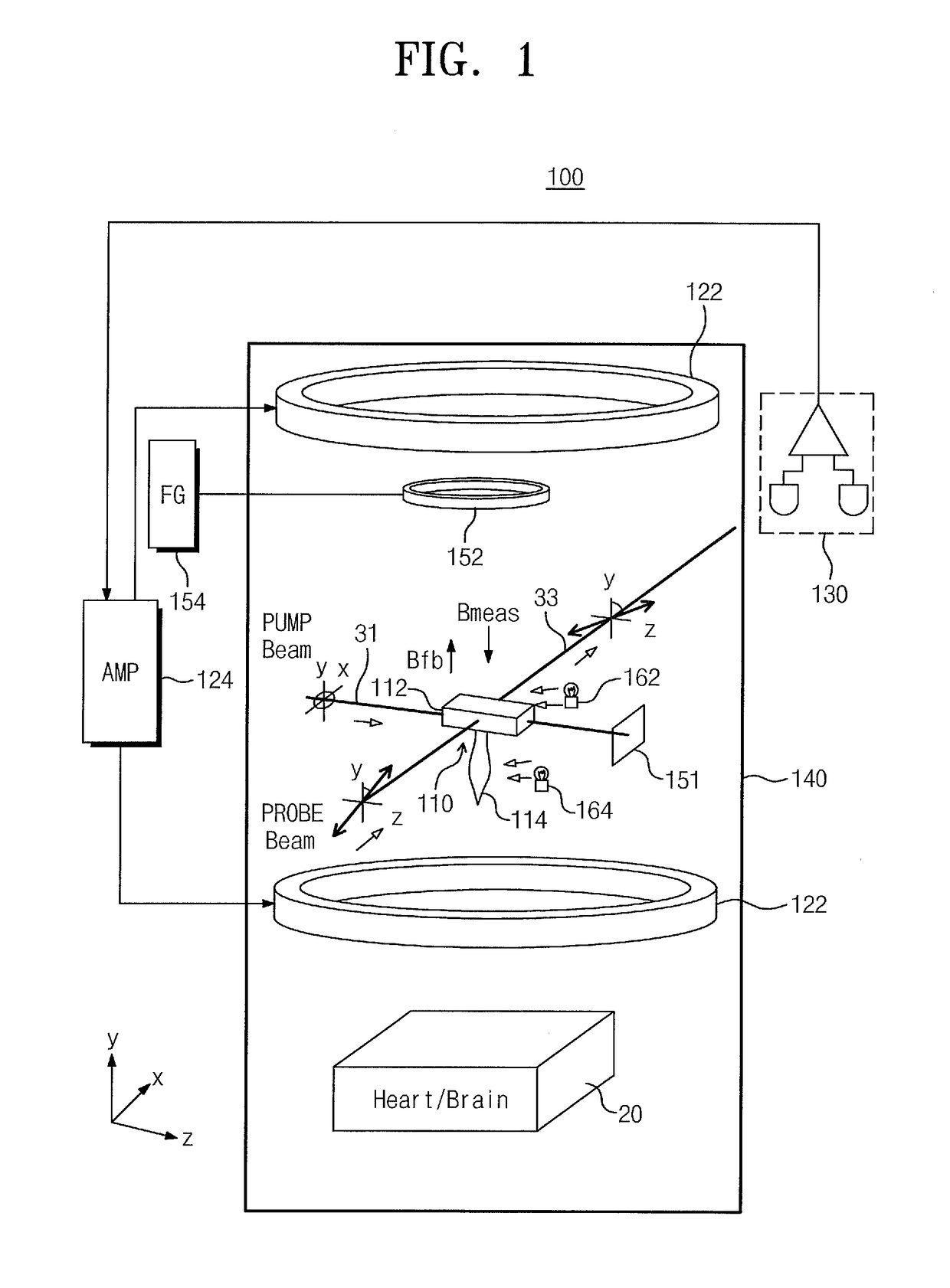
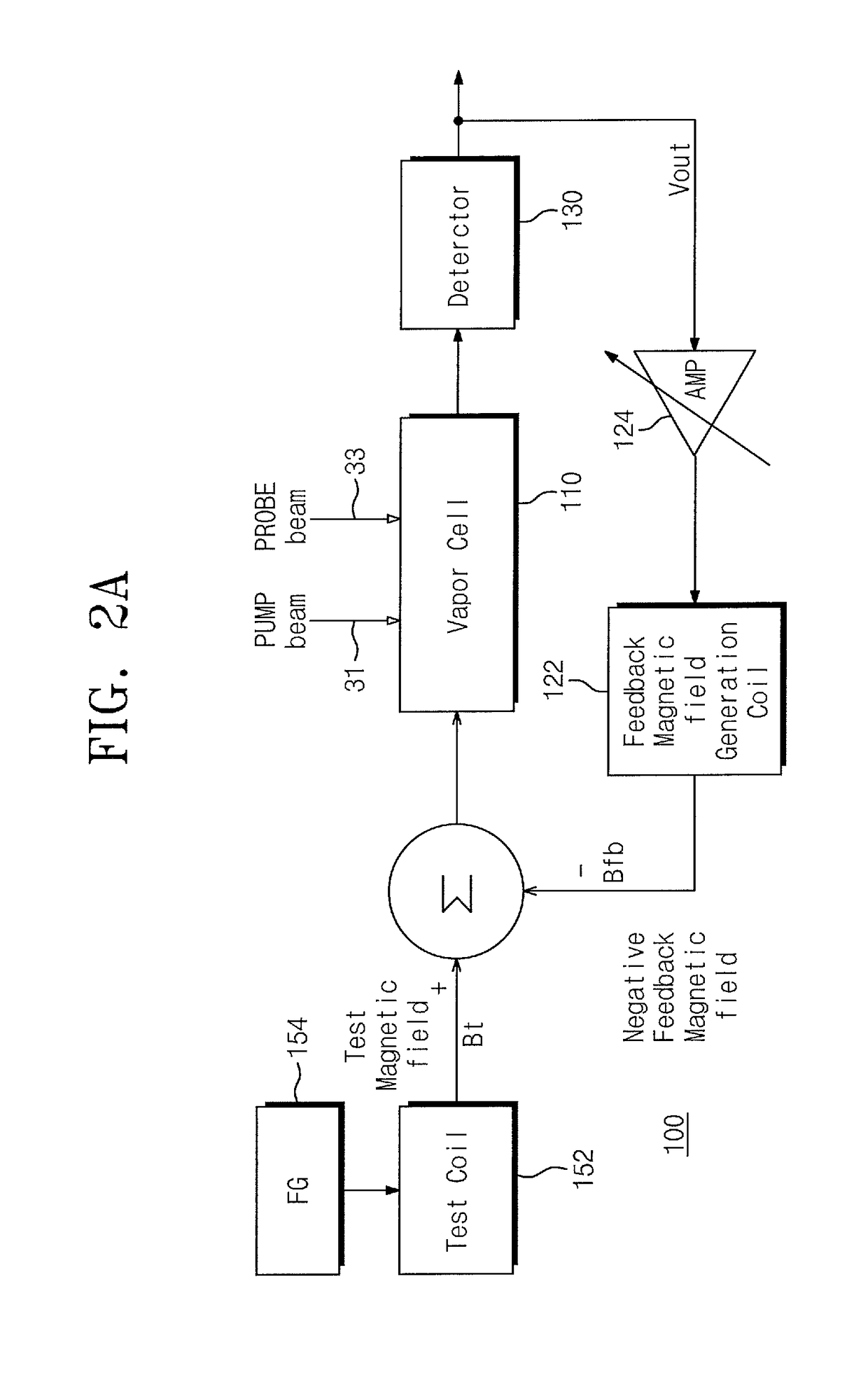
Provided are an atomic magnetometer and an operating method of the same. The atomic magnetometer includes a vapor cell receiving a circularly polarized pump beam and a linearly polarized probe beam and containing an alkali metal vapor, a detector adapted to receive the probe beam passing through the vapor cell to measure magneto-optical rotation of the probe beam, a feedback coil to establish a negative feedback magnetic field signal orthogonal to a first plane defined by traveling directions of the probe beam and the pump beam and provide the negative feedback magnetic field signal to the vapor cell, and a feedback amplifier adapted to provide feedback current to the feedback coil such that the negative feedback magnetic field proportional to a measurement magnetic field is established. The measurement magnetic field of a measurement target provides magneto-optical rotation of the probe beam in the vapor cell.
Owner:KOREA RES INST OF STANDARDS & SCI
Tuned optical cavity magnetometer
An atomic magnetometer is disclosed which utilizes an optical cavity formed from a grating and a mirror, with a vapor cell containing an alkali metal vapor located inside the optical cavity. Lasers are used to magnetically polarize the alkali metal vapor and to probe the vapor and generate a diffracted laser beam which can be used to sense a magnetic field. Electrostatic actuators can be used in the magnetometer for positioning of the mirror, or for modulation thereof. Another optical cavity can also be formed from the mirror and a second grating for sensing, adjusting, or stabilizing the position of the mirror.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
Magnetic measurement apparatus
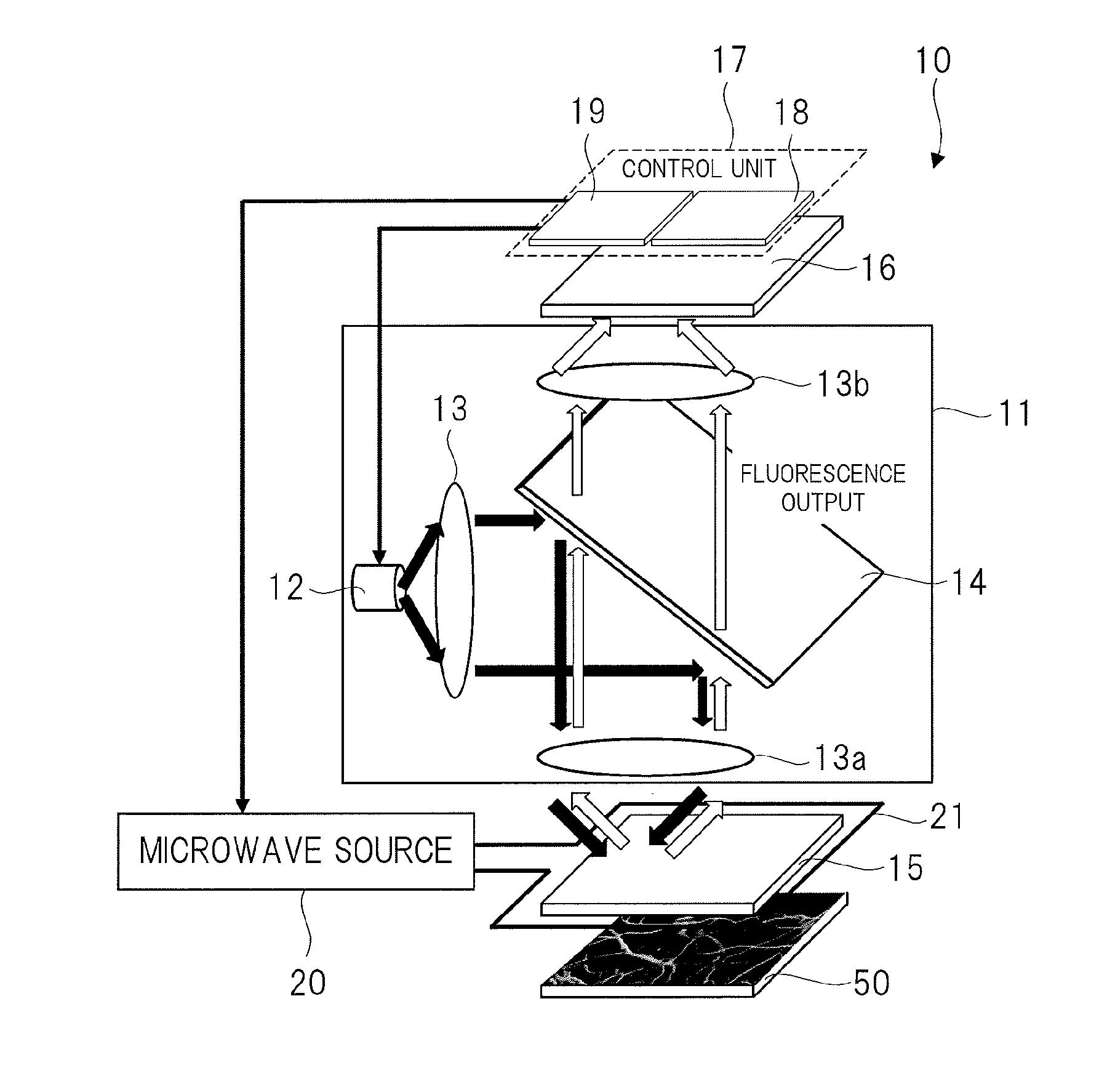
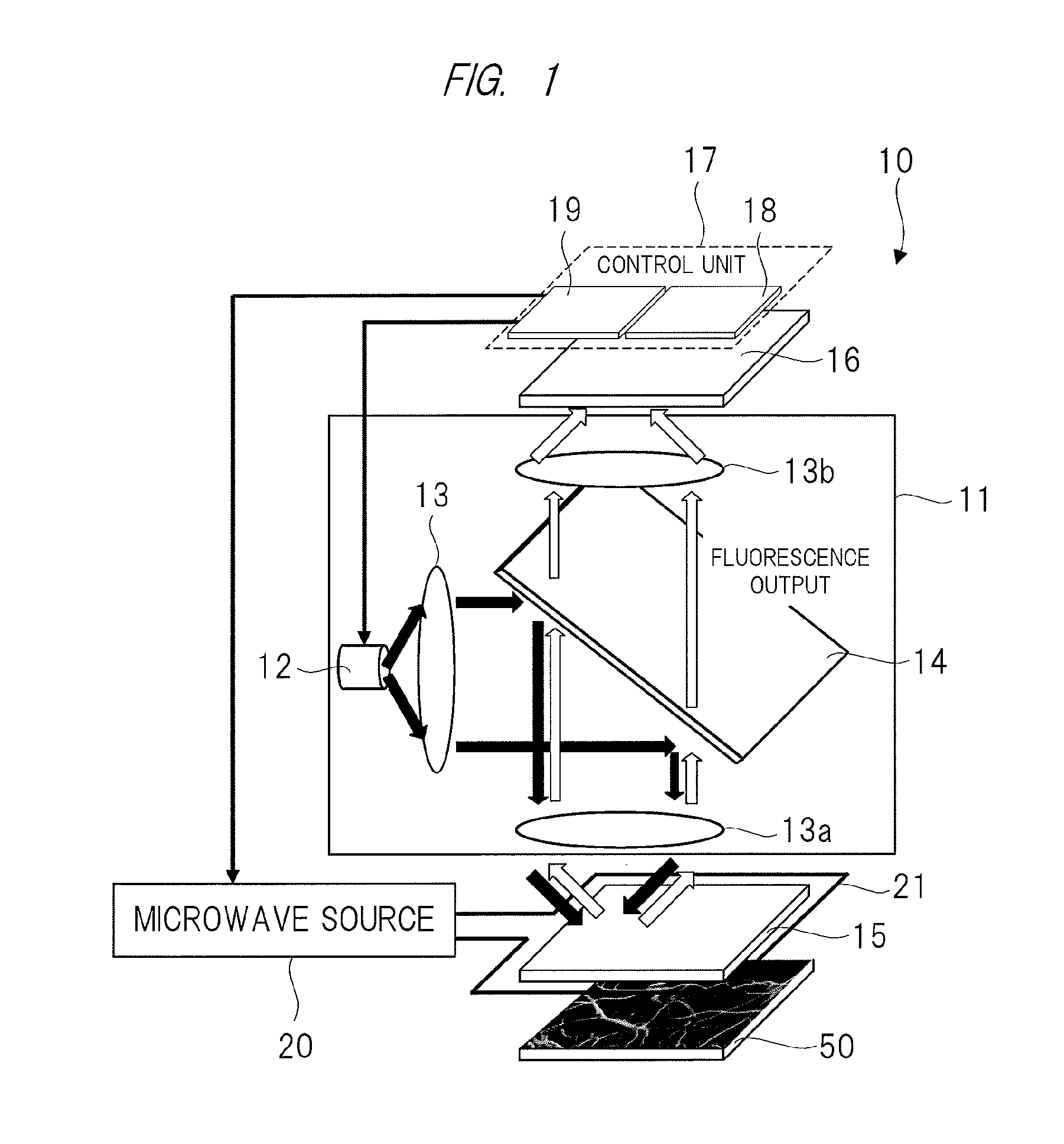
ActiveUS20150374250A1High measurement accuracyImprove detection accuracyPolycrystalline material growthDianostics using fluorescence emissionMagnetic measurementsDiamond crystal
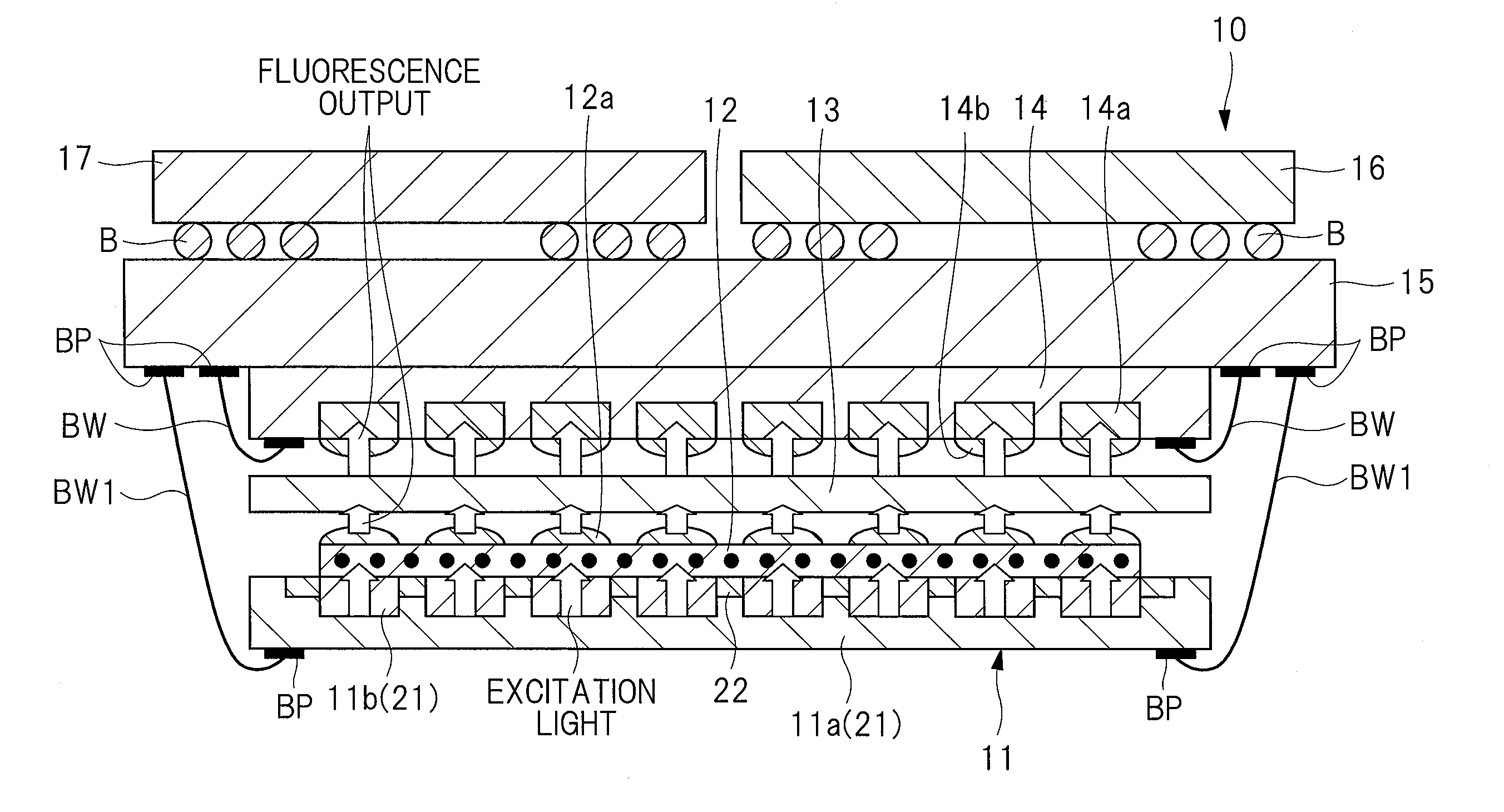
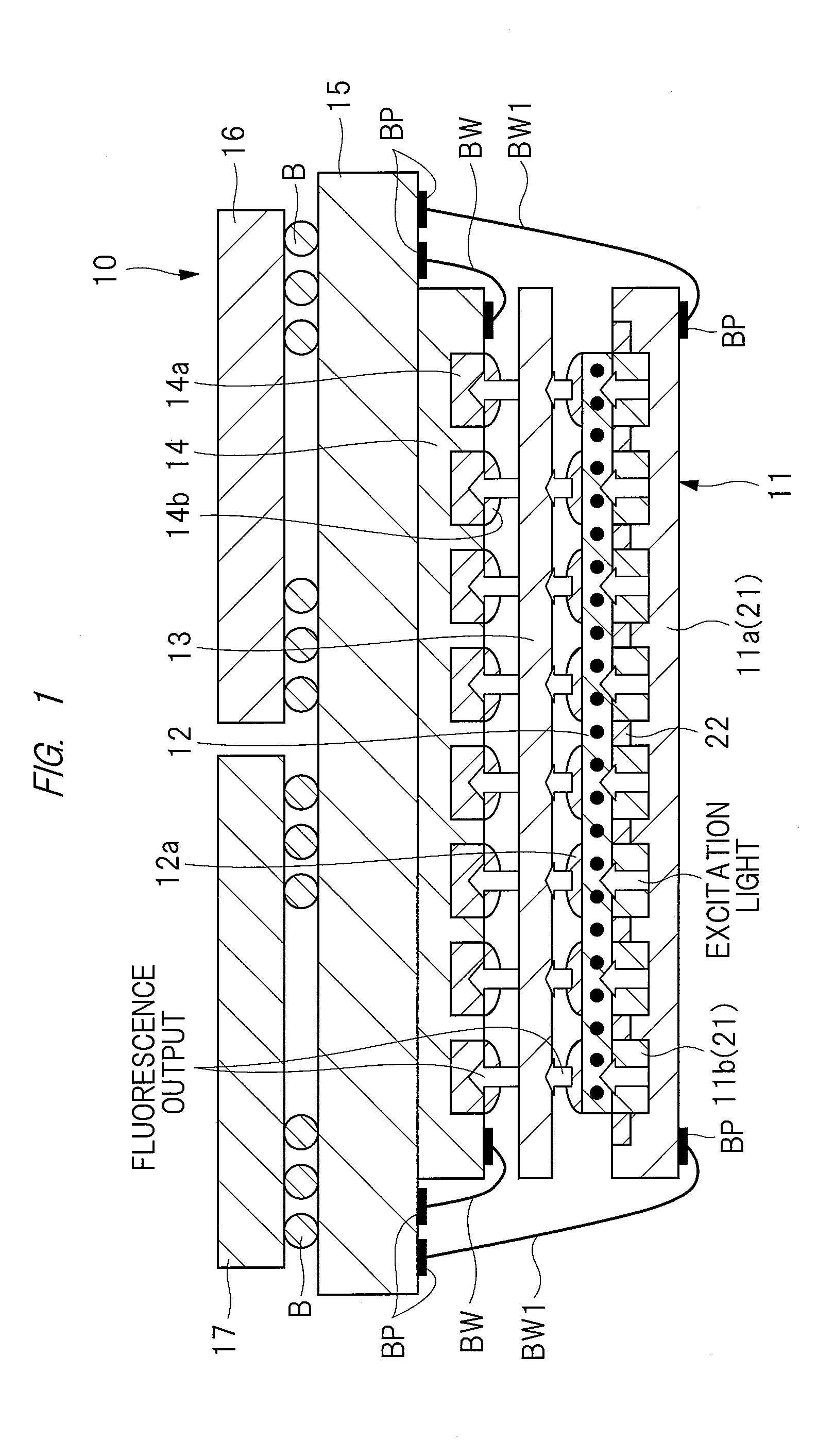
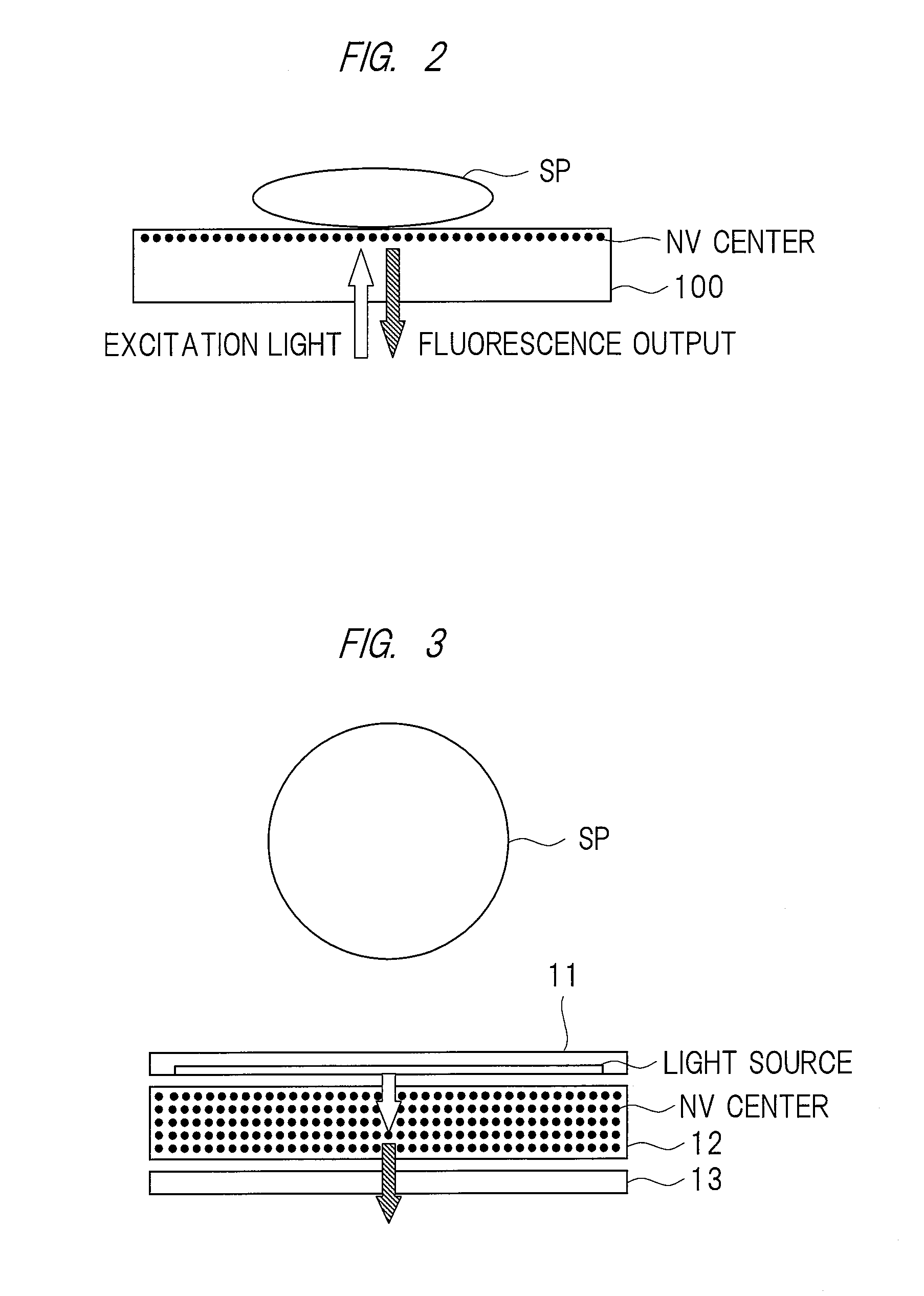
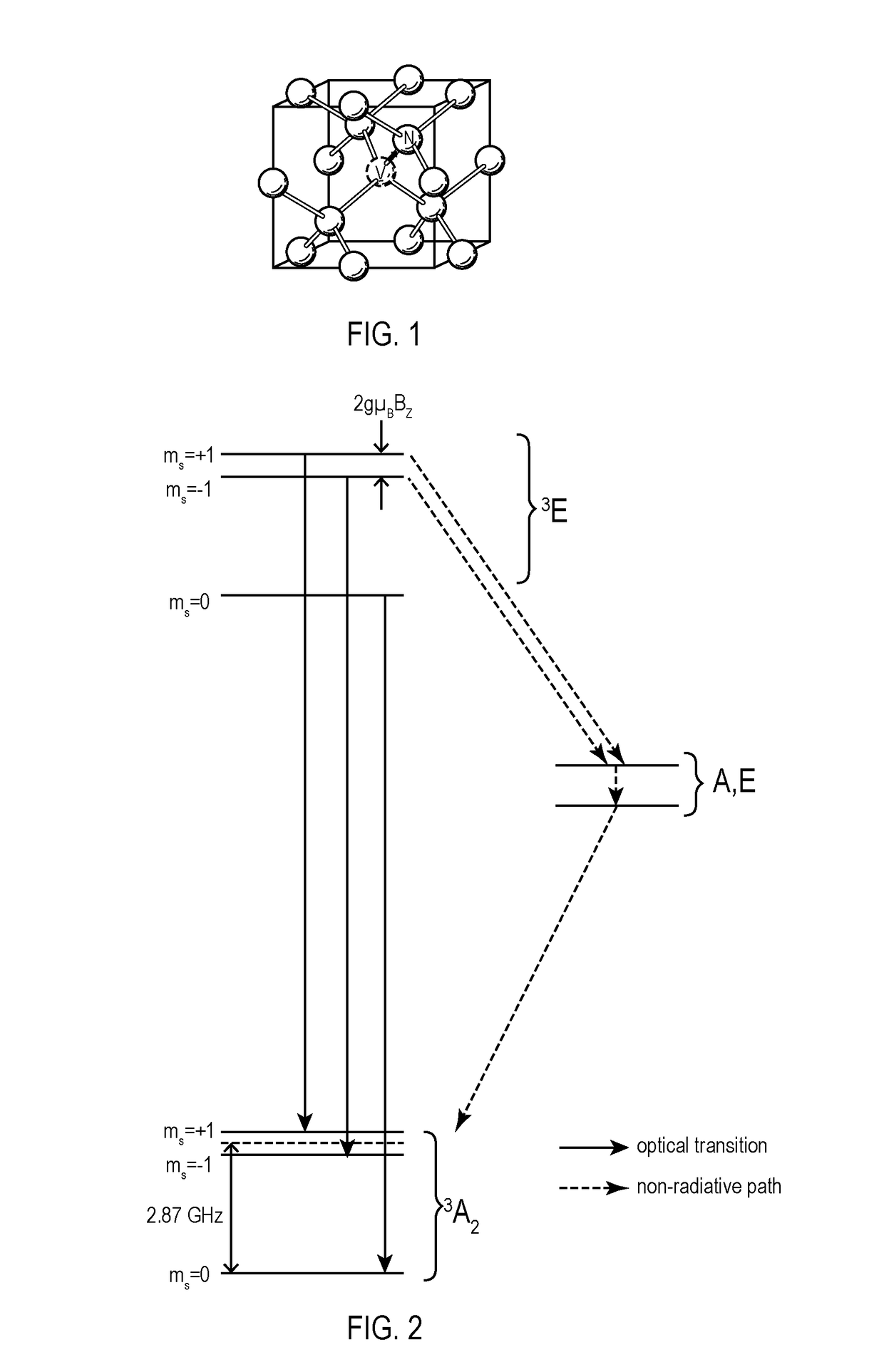
High-accuracy magnetic measurement is performed by efficiently using nitrogen-vacancy pairs in all orientations. A magnetic measurement apparatus includes a diamond crystal and an image sensor. The diamond crystal has nitrogen-vacancy pairs. The image sensor detects the intensities of fluorescence generated by an exciting light applied to the diamond crystal by using a plurality of pixels. The nitrogen-vacancy pairs of the diamond crystal are made to one-to-one correspond to the pixels. The fluorescence generated by one nitrogen-vacancy pair is received by one pixel made to correspond to the nitrogen-vacancy pair.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Nanoscale scanning sensors
ActiveUS20150253355A1High sensitivityReduce data collection timeMeasurements using electron paramagnetic resonanceMagnetic field measurement using magneto-optic devicesRelative motionFluorescent light
A sensing probe may be formed of a diamond material comprising one or more spin defects that are configured to emit fluorescent light and are located no more than 50 nm from a sensing surface of the sensing probe. The sensing probe may include an optical outcoupling structure formed by the diamond material and configured to optically guide the fluorescent light toward an output end of the optical outcoupling structure. An optical detector may detect the fluorescent light that is emitted from the spin defects and that exits through the output end of the optical outcoupling structure after being optically guided therethrough. A mounting system may hold the sensing probe and control a distance between the sensing surface of the sensing probe and a surface of a sample while permitting relative motion between the sensing surface and the sample surface.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Magnetic measuring device
InactiveUS20160313408A1Magnetic field measurement using magneto-optic devicesFluorescence/phosphorescenceMeasurement deviceOptoelectronics
A magnetic measuring device can be downsized. The magnetic measuring device includes a diamond crystal, a microwave source, a light source array / microwave circuit chip, an image sensor, and a signal controller. The diamond crystal contains a plurality of nitrogen-vacancy pairs. The microwave source generates the microwave that is irradiated to the diamond crystal. The microwave circuit unit in the light source array / microwave circuit chip irradiates the diamond crystal with the microwave. The light source array in the light source array / microwave circuit chip irradiates the diamond crystal with excitation light. The image sensor detects an intensity of fluorescent light generated from the diamond crystal. The signal controller performs image processing of a fluorescent image taken-in by the image sensor, and controls operations of the light source array / microwave circuit chip and the microwave source. The light source array / microwave circuit chip is provided on a first surface side of the diamond crystal, and the image sensor is provided on a second surface side opposed to the first surface of the diamond crystal.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
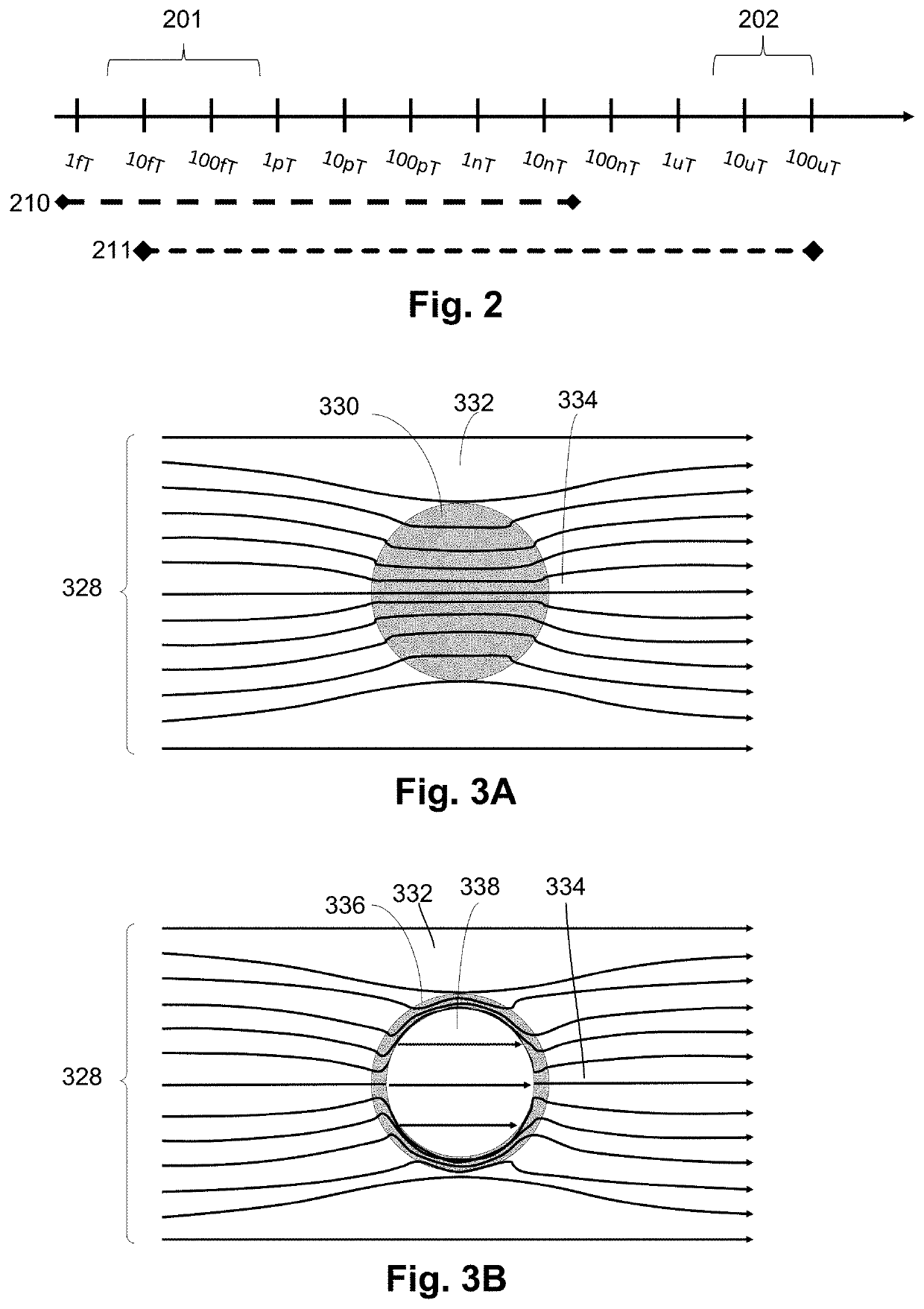
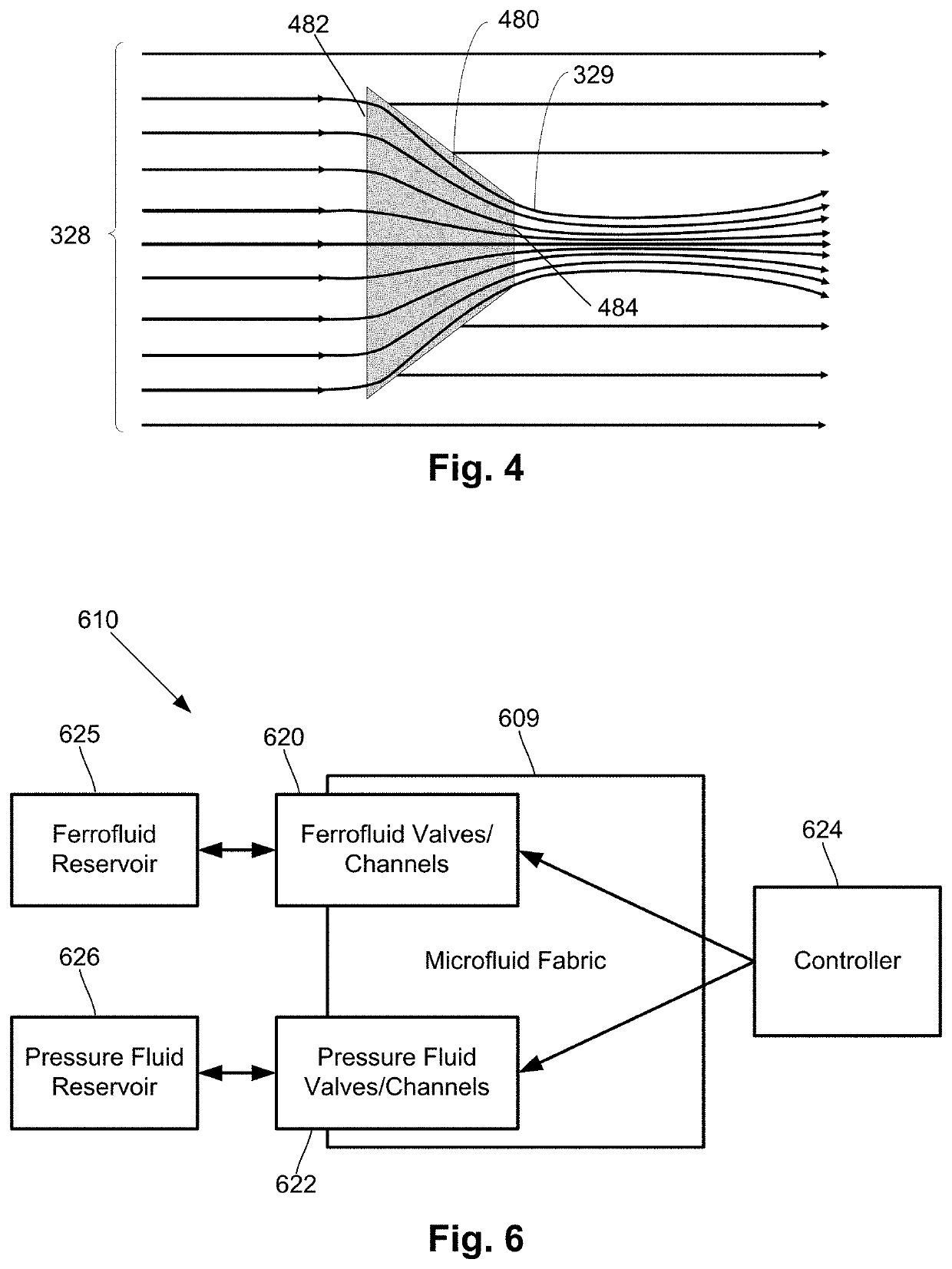
Dynamic magnetic shielding and beamforming using ferrofluid for compact magnetoencephalography (MEG)
ActiveUS20200088811A1Magnetic field measurement using superconductive devicesMagnetic field measurement using magneto-optic devicesMagnetoencephalographyMagnetic shield
A magnetic field measurement system can include at least one magnetometer; and a ferrofluid shield disposed at least partially around the at least one magnetometer. For example, the ferrofluid shield can include a microfluid fabric and a ferrofluid disposed in or flowable into the microfluid fabric. As another example, the ferrofluid shield can include a ferrofluid and a controller configured to alter an arrangement of the ferrofluid within the ferrofluid shield.
Owner:HI LLC
Magnetic field shaping components for magnetic field measurement systems and methods for making and using
ActiveUS20200057115A1High materialIncrease surface areaMagnetic field offset compensationMagnetic sensor packagingMagnetic fluxCondensed matter physics
A magnetic field measurement system includes at least one magnetometer; and at least one flux concentrator made of a high magnetic permeability material and configured to receive magnetic field signals from a source, to concentrate the magnetic field signals or reorient the magnetic field signals in a preselected direction, and to direct the concentrated or reoriented magnetic field signals toward at least one of the at least one magnetometer. In addition to, or as an alternative to, the flux concentrator, the system can include a passive shield made of the high magnetic permeability material. The system may also include active shielding.
Owner:HI LLC
Magnetic field measuring apparatus
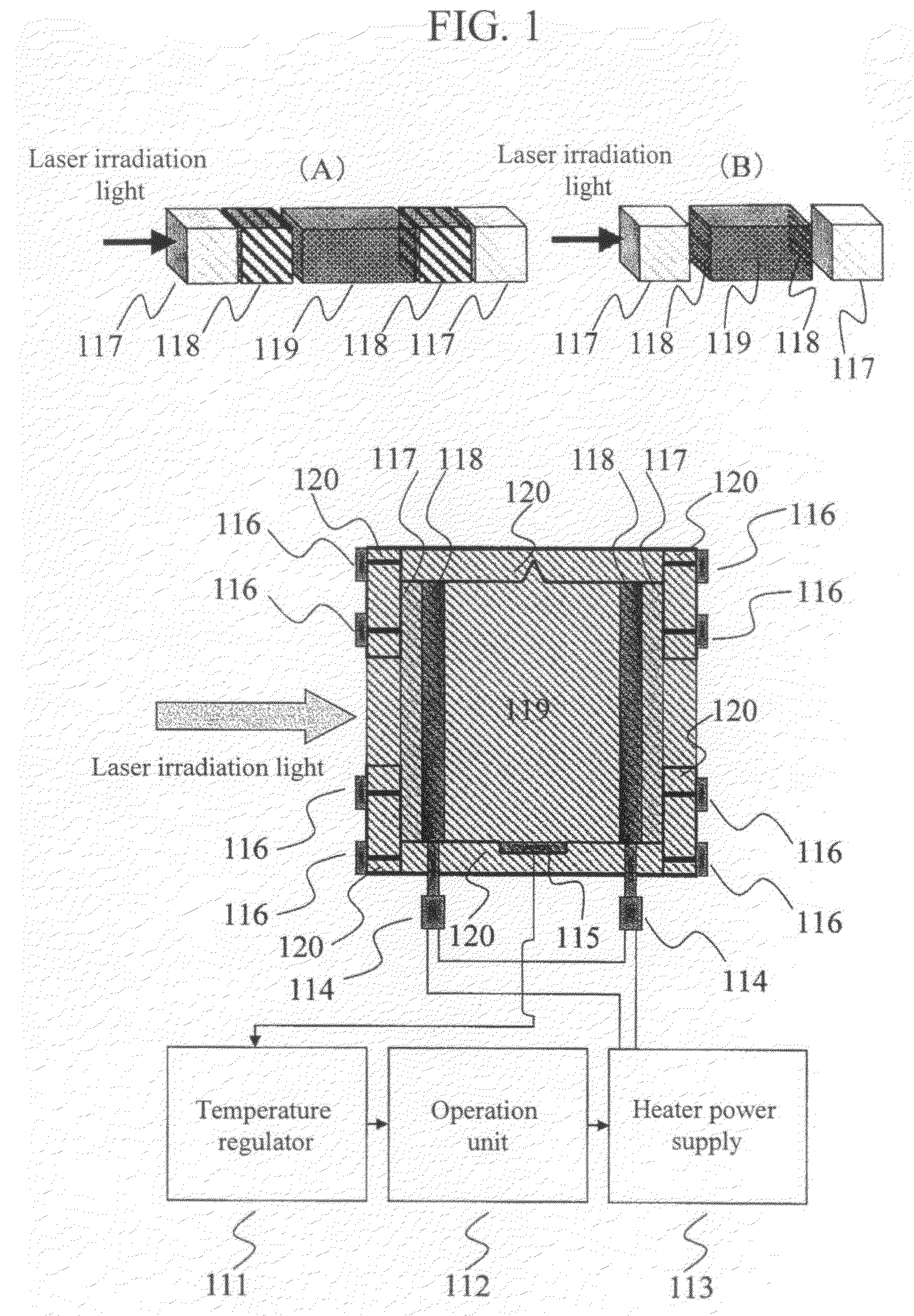
InactiveUS20090001979A1Guaranteed monitoring effectQuickly bringGaseous masersMagnetic field measurement using magneto-optic devicesMagnetic tension forceTemperature control
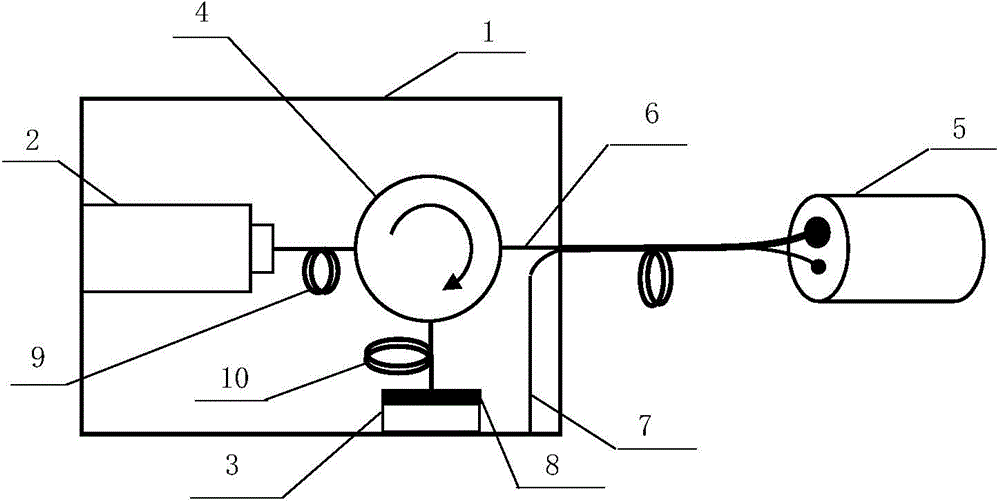
Providing: quickly brining a vapor cell 119 to a desired temperature when retaining the heat of the vapor cell 119 to enhance the magnetic field detection performance of an optically pumped magnetometer; preventing adherence of atoms in the vapor cell 119 to a laser irradiation light passing-through part of the vapor cell 119; downsizing the periphery of the vapor cell 119; and suppressing the effect of a magnetic field from a heater used to retain the heat of the vapor cell 119. The present invention includes: a transparent film heater 118 provided to a laser irradiation light passing-through part of a vapor cell 119, the vapor cell 119 being a magnetic detection part of the optically pumped magnetometer; a temperature detector 115 provided at a center part of a side of the vapor cell 119; a temperature regulator 111 that sets a desired temperature for heat retention of the vapor cell 119 and compares the desired temperature and the actual temperature of the vapor cell measured by the temperature detector 115; an operation unit 112 that upon receipt of a PID control signal for temperature control from the temperature regulator 111, performs a temperature adjustment and switches on / off, in a pulsed manner, current applied to the transparent film heater 118 after the desired temperature is reached; and a heater power supply 113 that upon receipt of an operation signal from the operation unit 112, applies current to the transparent film heater 118.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
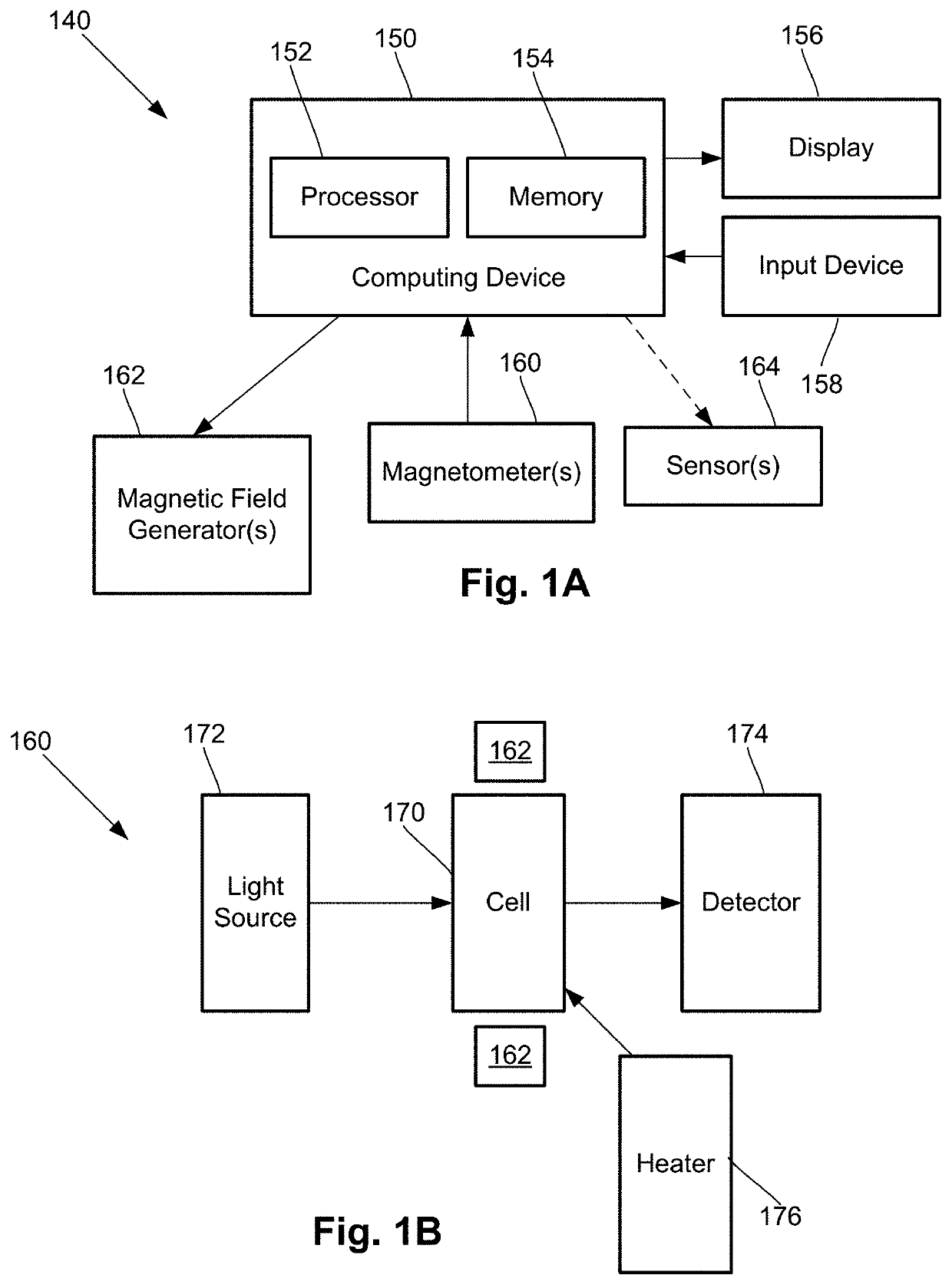
Magnetic field measurement systems and methods of making and using
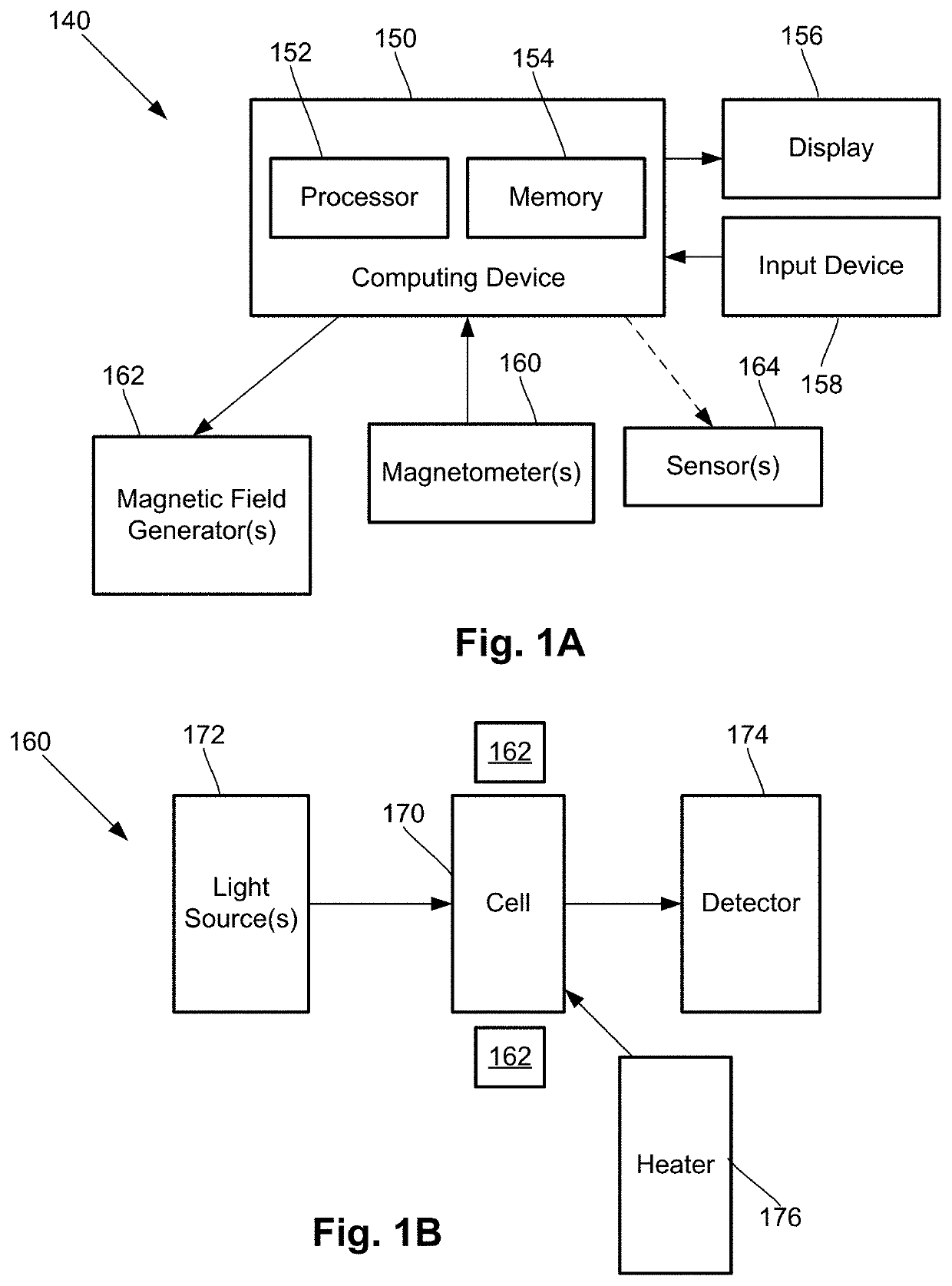
InactiveUS20190391213A1Magnetic field offset compensationMagnetic field measurement using flux-gate principleMagnetic tension forceCondensed matter physics
A magnetic field measurement system includes an array of magnetometers; at least one magnetic field generator with each of the at least one magnetic field generator configured to generate a first magnetic field at one or more of the magnetometers, wherein the generated first magnetic field combines with the ambient magnetic field to produce a directional magnetic field at the one or more of the magnetometers, where a magnitude and direction of the directional magnetic field is selectable using the at least one magnetic field generator; and a controller coupled to the magnetometers and the at least one magnetic field generator, the controller including a processor configured for receiving signals from the magnetometers, observing or measuring a magnetic field from the received signals, and controlling the at least one magnetic field generator to generate the first magnetic field and select the direction of the directional magnetic field.
Owner:HI LLC
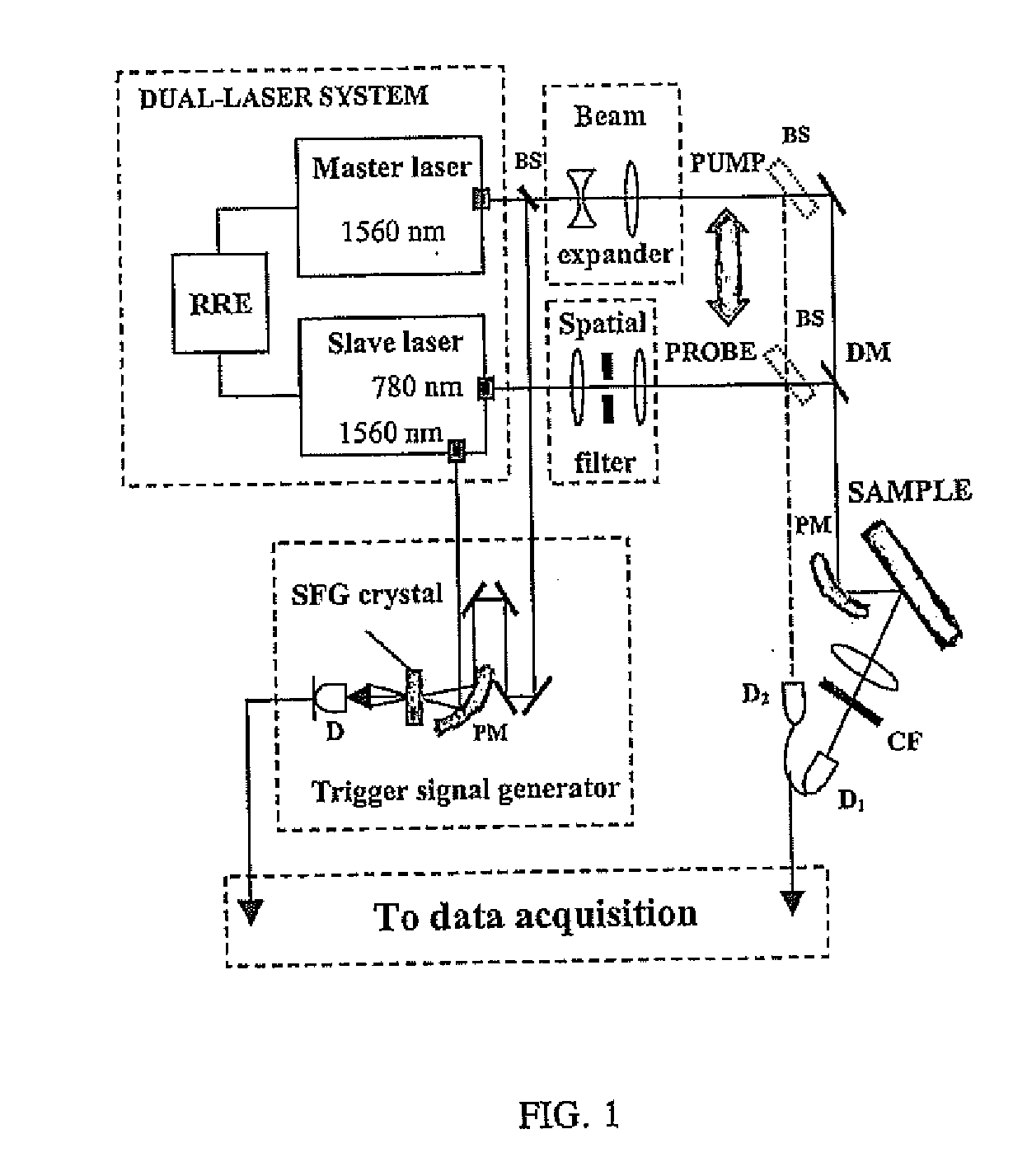
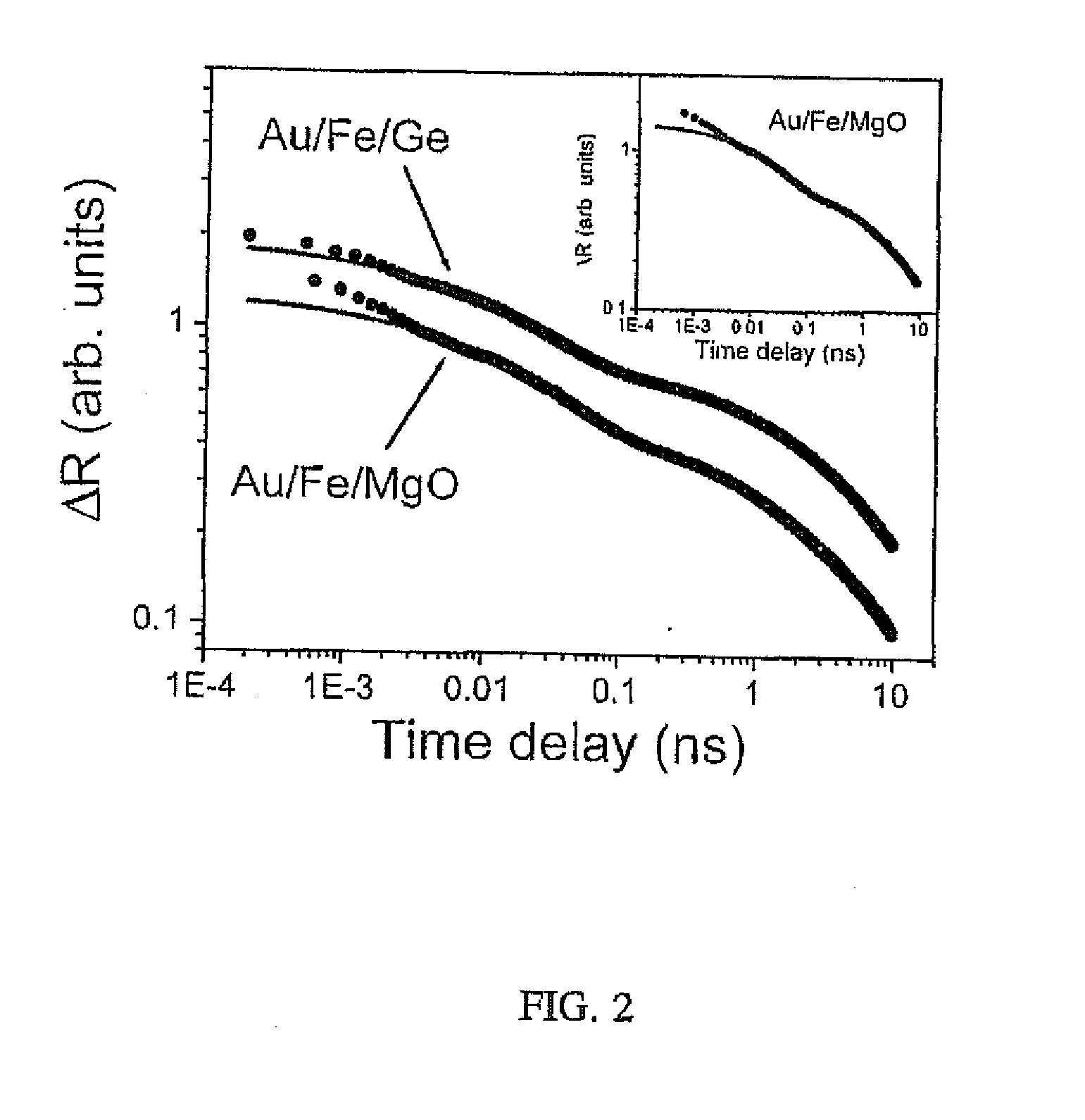
Method and system for measuring at least one property including a magnetic property of a material using pulsed laser sources
ActiveUS20090212769A1Efficient and sensitiveUsing optical meansMagnetic field measurement using magneto-optic devicesLength wavePulse sequence
A method of measuring at least one property including a magnetic property of target material is provided. The method includes the step of generating a pump pulse train having one or more pump pulses at a repetition rate along a first propagation path, each pump pulse having a pulse energy density, a laser wavelength within a range of laser wavelengths, and a pulse duration The method further includes the step of irradiating the target material with at least a portion of the one or more pump pulses focused into at least one spot having a spot shape and size so as to cause transient perturbation in the target material. The method still further includes the step of generating at least one probe pulse train having one or more probe pulses at a repetition rate along a second propagation path, each probe pulse having a pulse energy density, a laser wavelength within a range of laser wavelengths, and a pulse duration. The method further includes the step of irradiating the target material with at least a portion of the one or more probe pulses focused into at least one spot having a spot shape and size to obtain one or more reflected probe pulses which are modulated based on the transient perturbation. The method still further includes the step of electronically controlling a time interval between a time at which the target material is irradiated by each of the focused pump pulses and a time at which the target material is irradiated by each of its corresponding focused probe pulses. The method further includes the step of detecting each modulated probe pulse to obtain one or more corresponding signals. The method still further includes the step of processing the one or more signals to obtain one or more measurement signals which represents the at least one property including the magnetic property of the target material.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
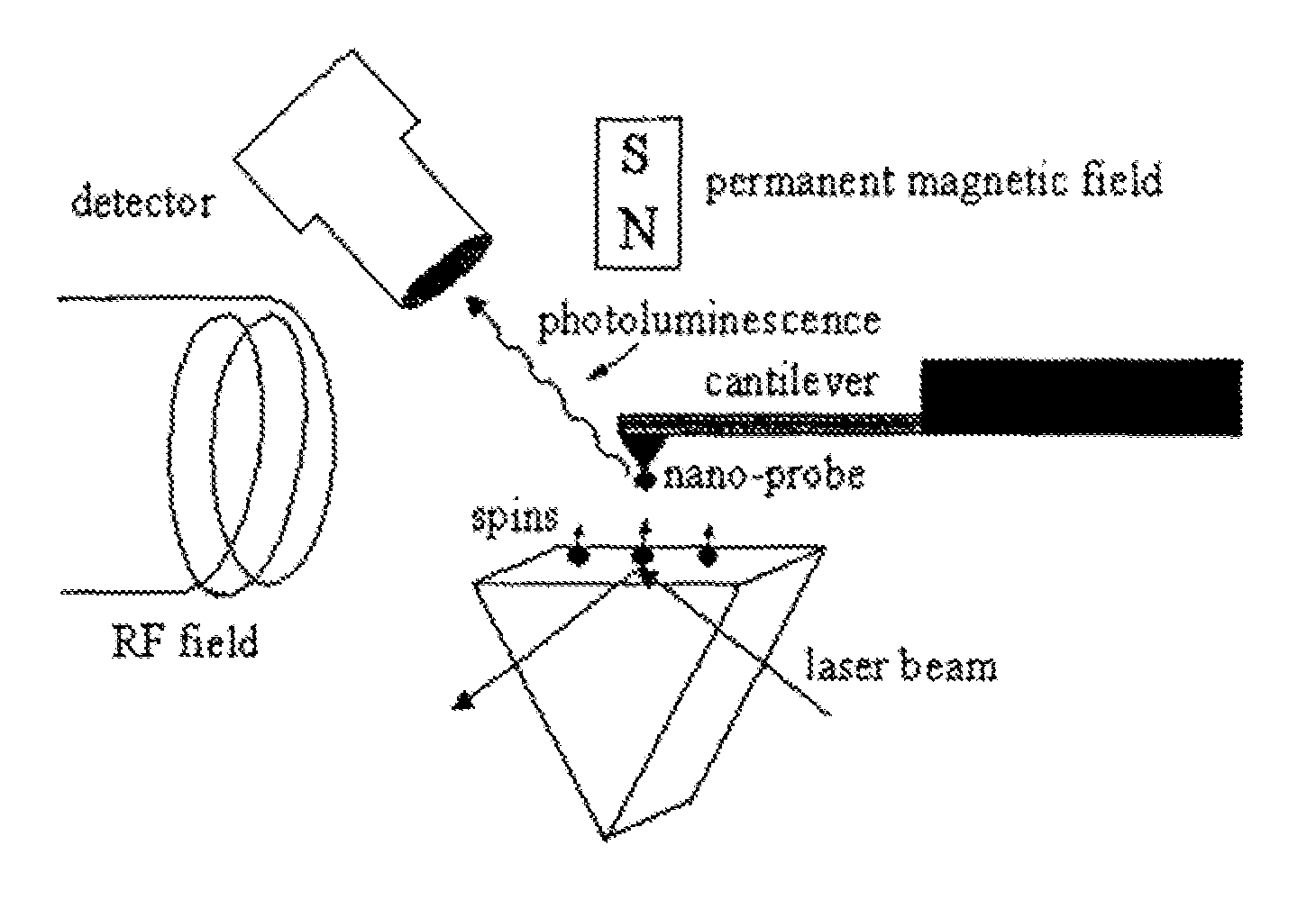
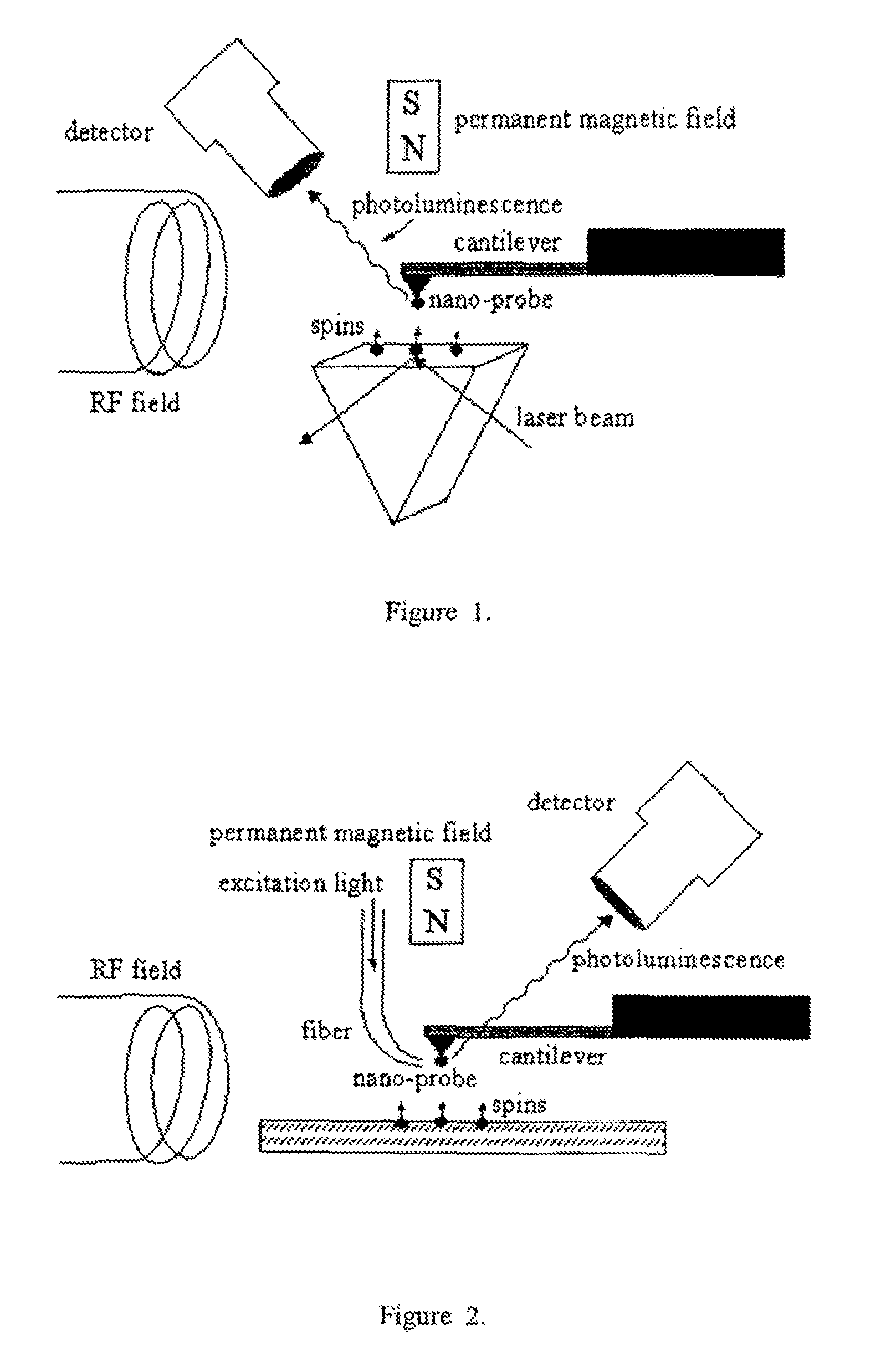
Spin microscope based on optically detected magnetic resonance
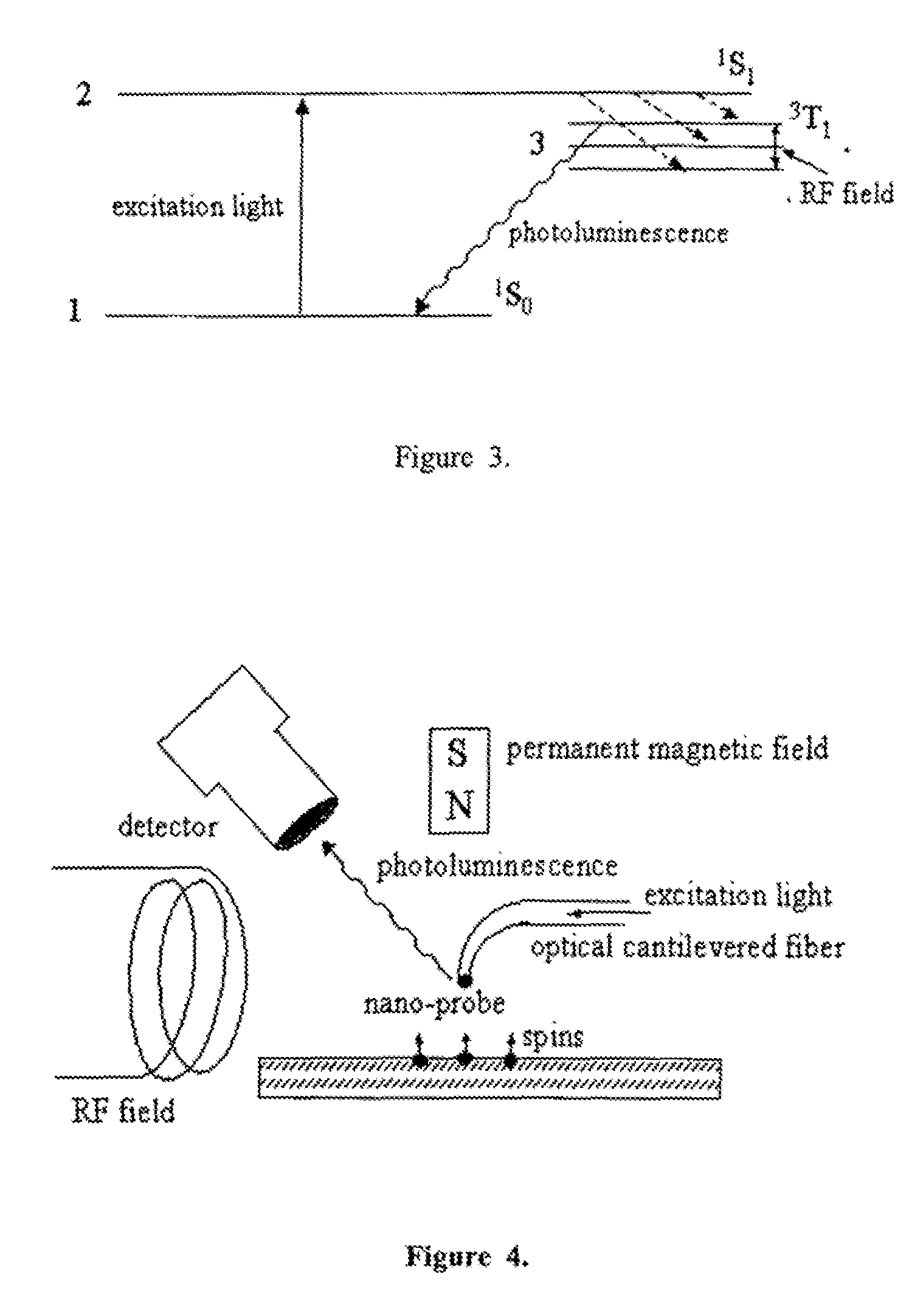
InactiveUS7608820B1NanomagnetismMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMagnetic force microscopePhotoluminescence
The invention relates to scanning magnetic microscope which has a photoluminescent nanoprobe implanted in the tip apex of an atomic force microscope (AFM), a scanning tunneling microscope (STM) or a near-field scanning optical microscope (NSOM) and exhibits optically detected magnetic resonance (ODMR) in the vicinity of unpaired electron spins or nuclear magnetic moments in the sample material. The described spin microscope has demonstrated nanoscale lateral resolution and single spin sensitivity for the AFM and STM embodiments.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY
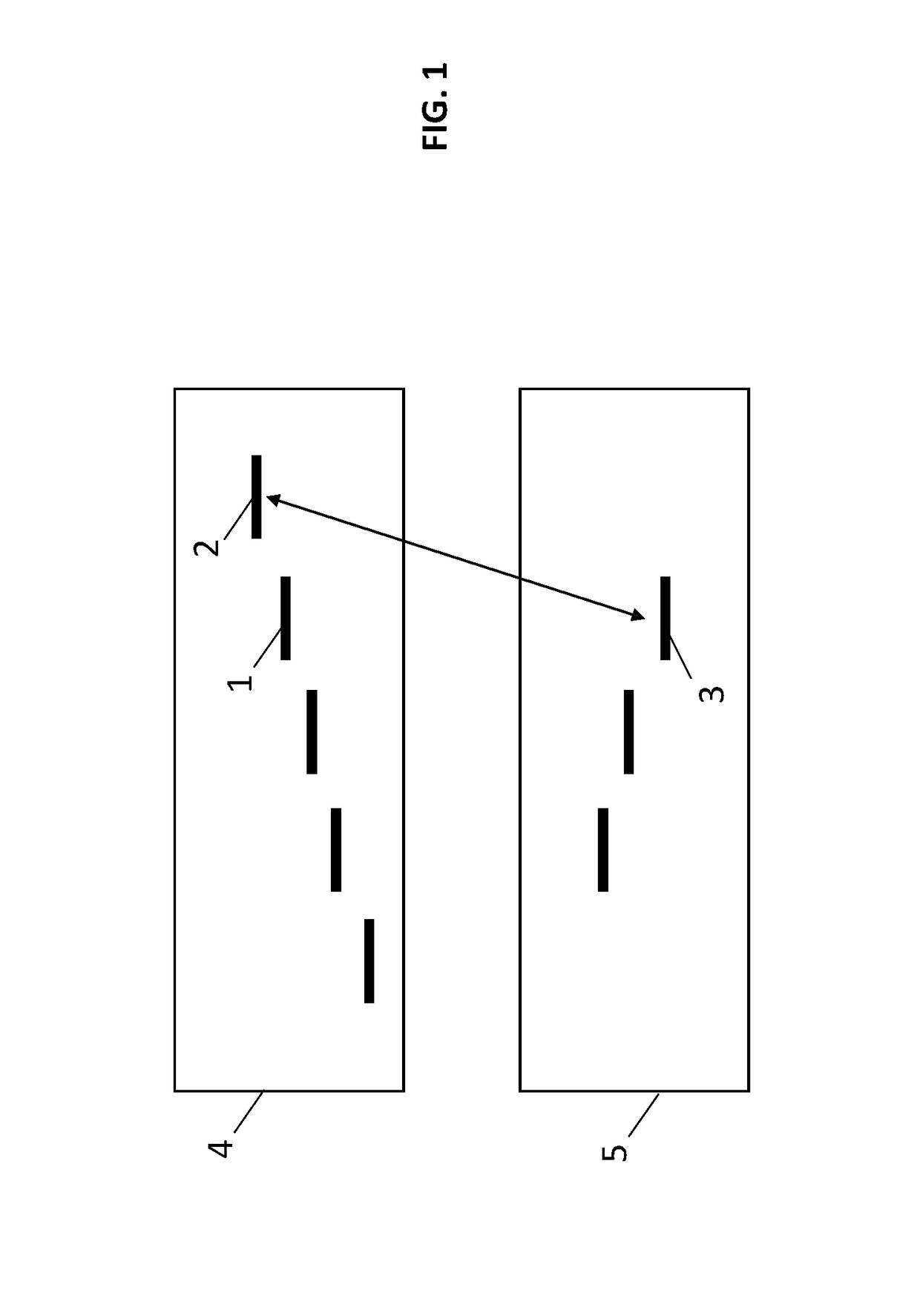
Rotation and/or tilt angle detection means for a ball and socket joint
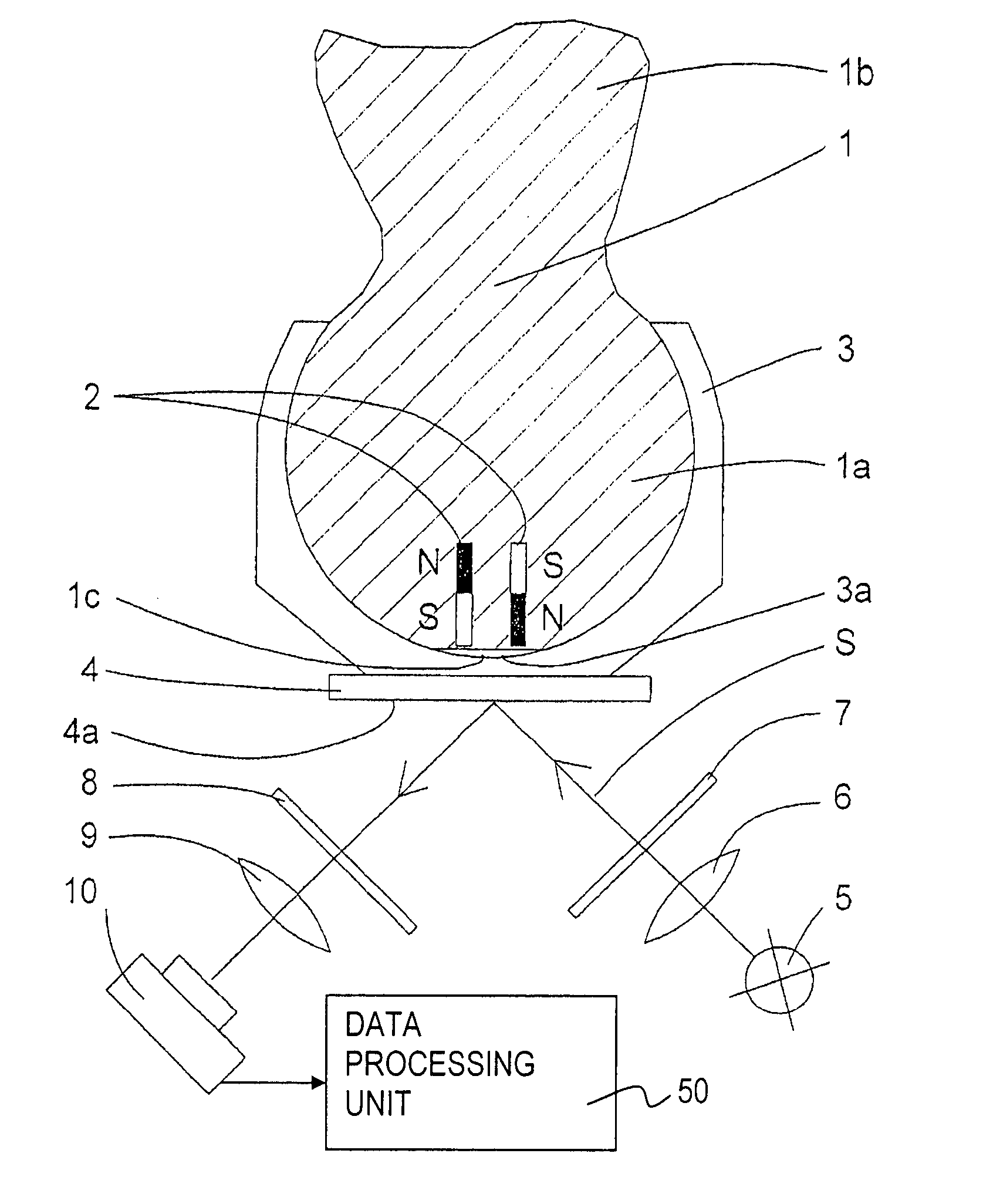
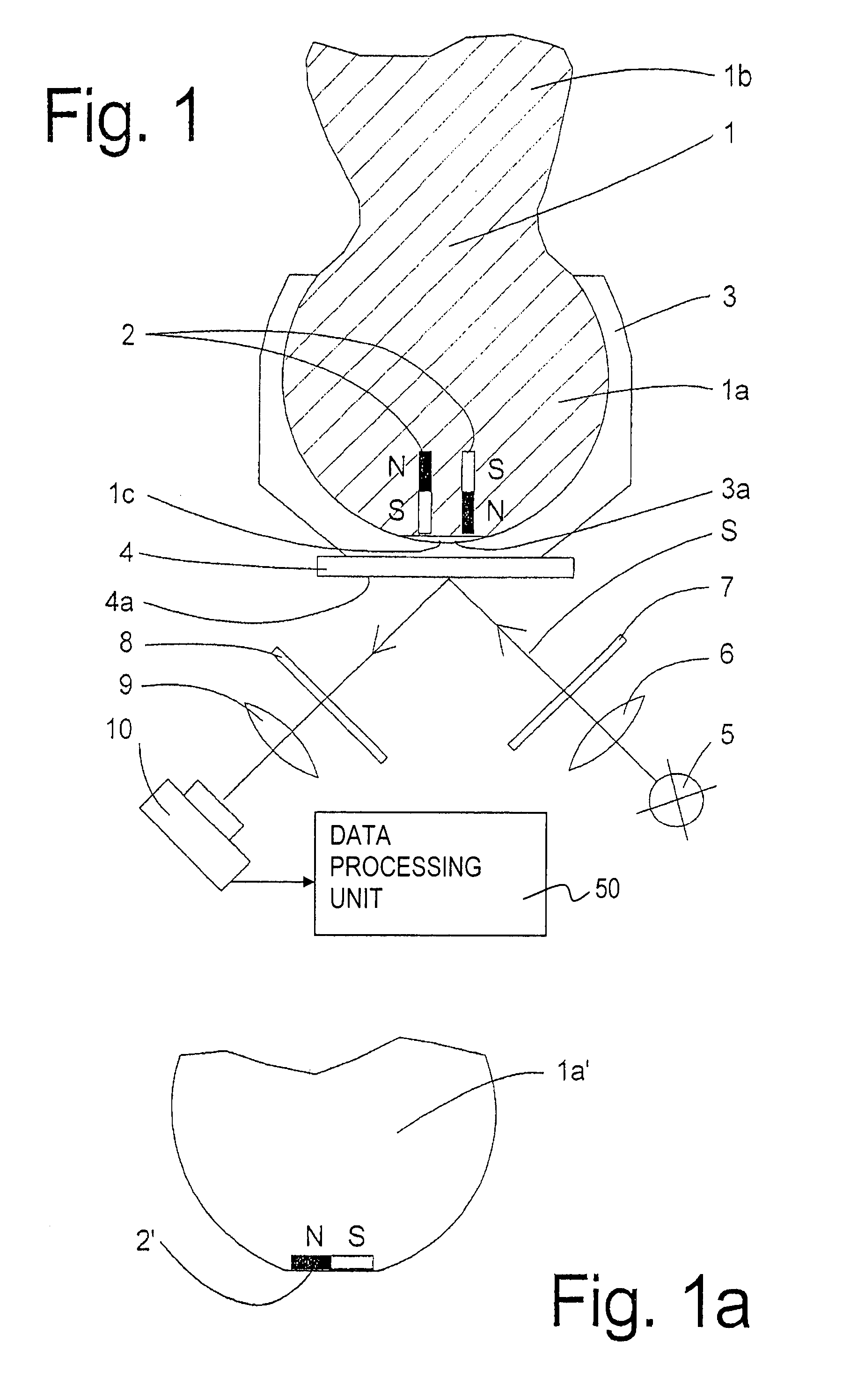
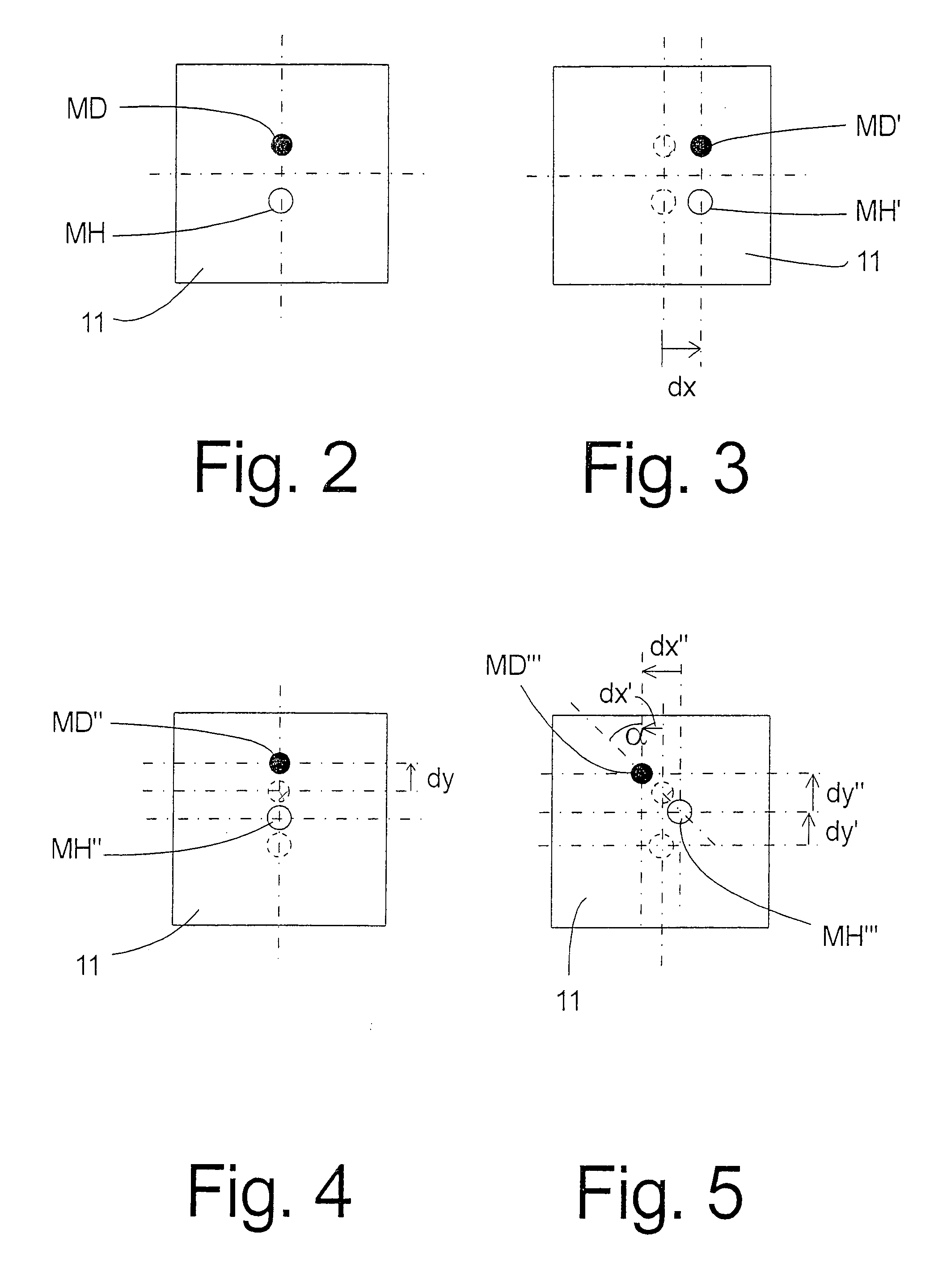
InactiveUS7171330B2Simple designSimple sensor arrayPivotal connectionsIncline measurementImage detectionDisplay device
A rotation and / or tilt angle detection device for a ball and socket joint is provided wherein at least one magnet (2), especially a permanent magnet, is arranged in the joint ball (1a), wherein a display device (4) displays the magnetic field of the at least one magnet (2) by means of the magnetooptic effect. An image detection deice (10) detects the information displayed by the display device (4). A data processing unit (50) calculates the relative position of the joint ball (1a) and the ball socket (3) of the ball and socket joint on the basis of the information detected.
Owner:ZF LEMFOERDER METALLWAREN AG
Magnetofluid filling photonic crystal optical fiber F-P magnetic field sensor
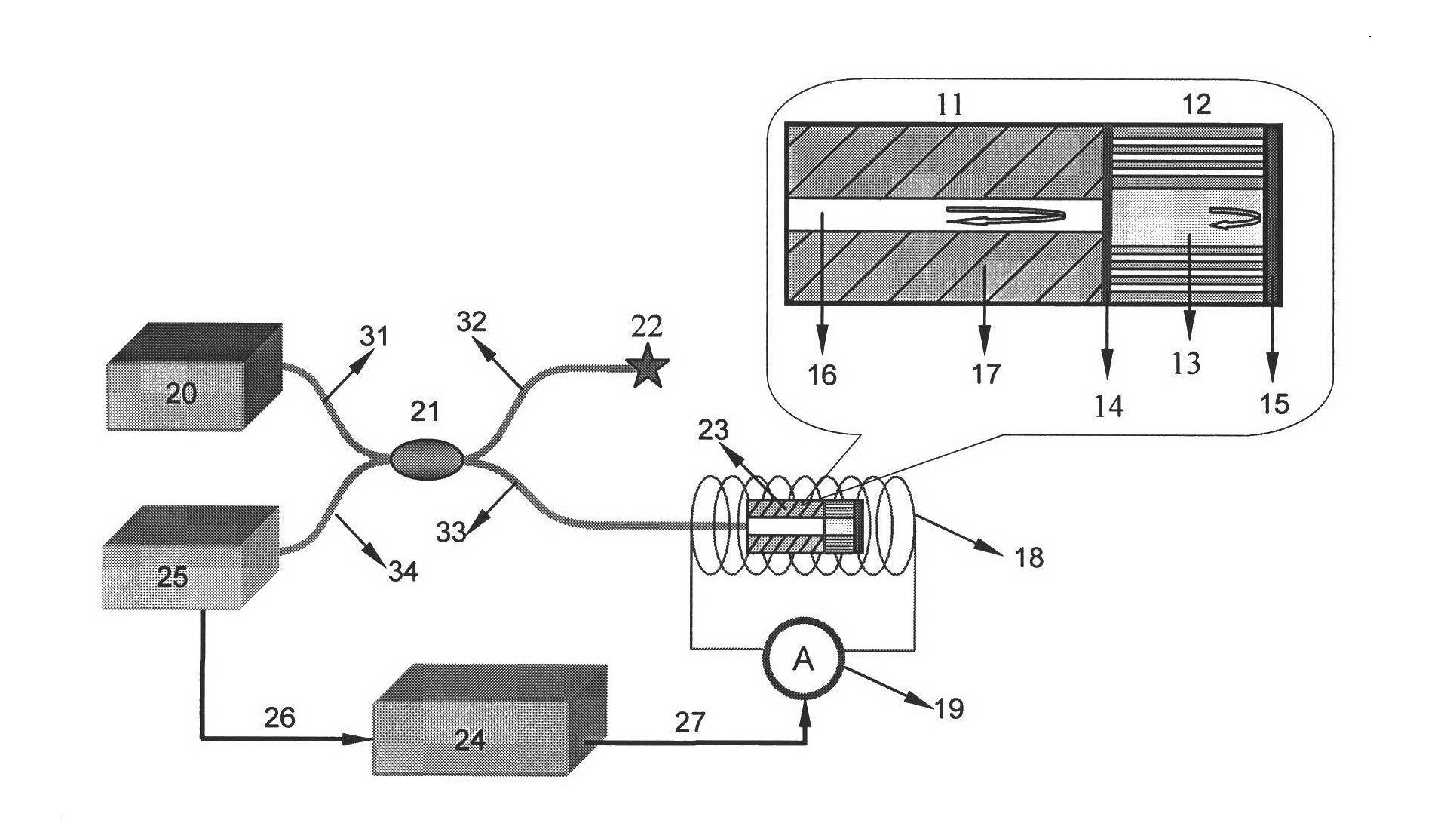
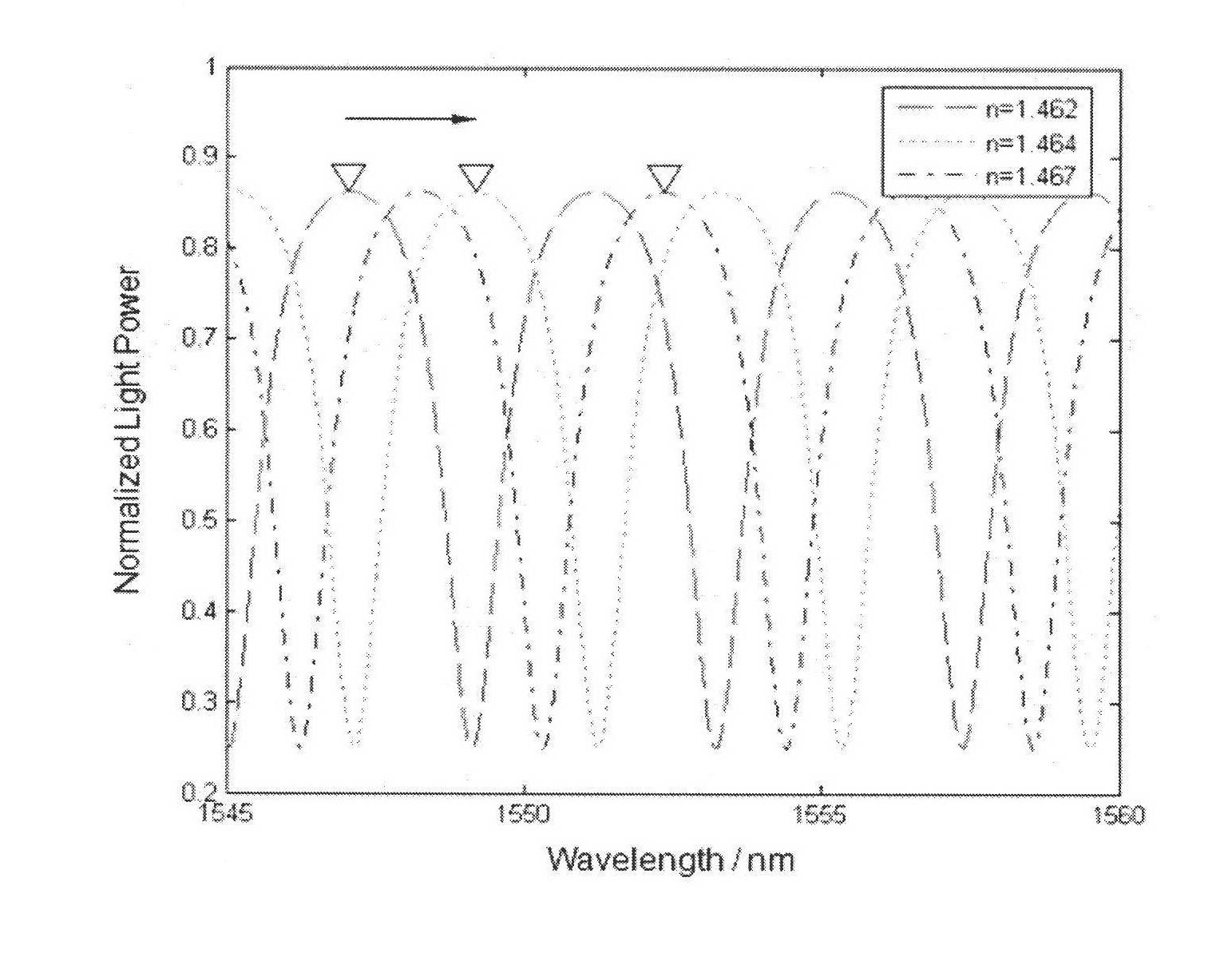
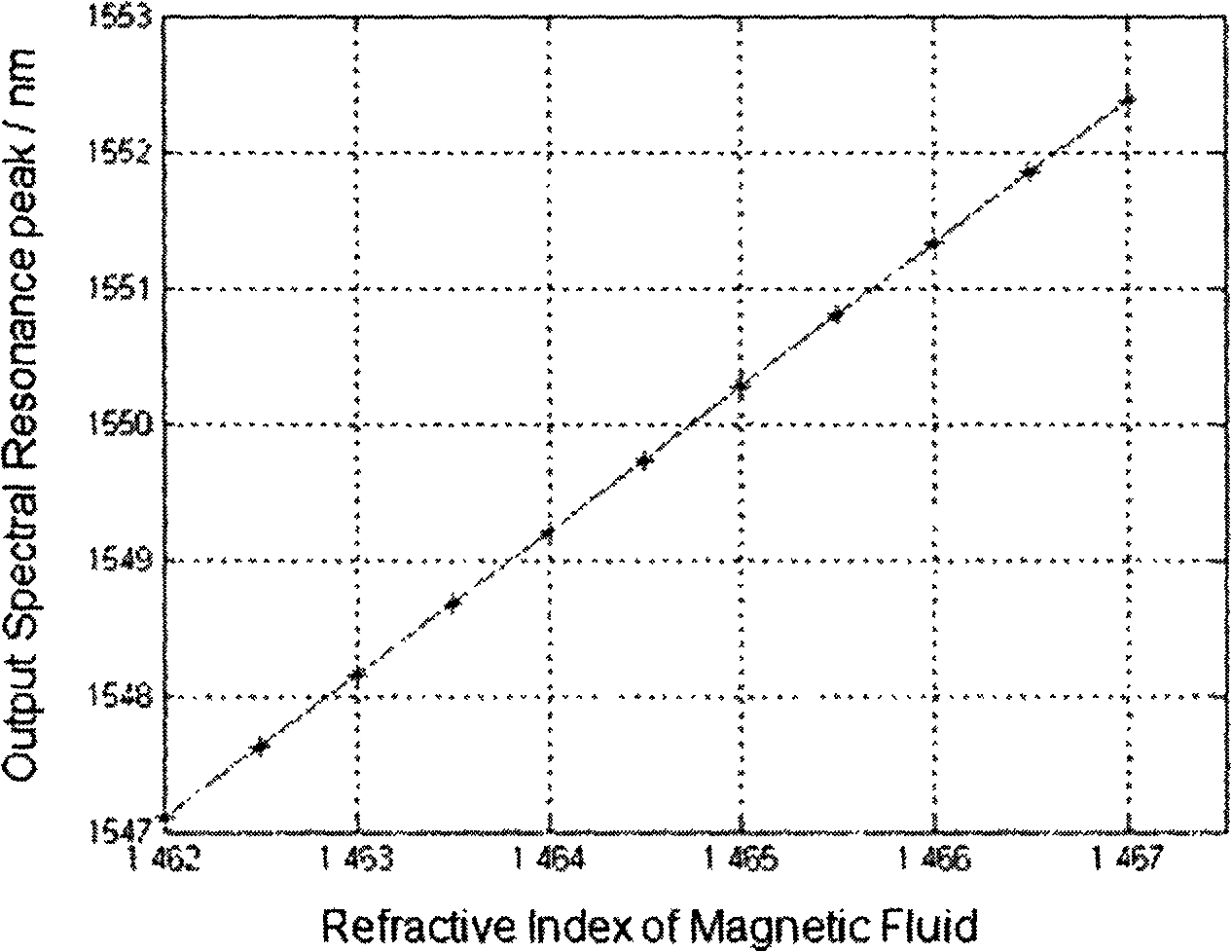
InactiveCN102221679ASimple structureInnovative designCladded optical fibreMagnetic field measurement using magneto-optic devicesSpectrum analyzerOptical fiber coupler
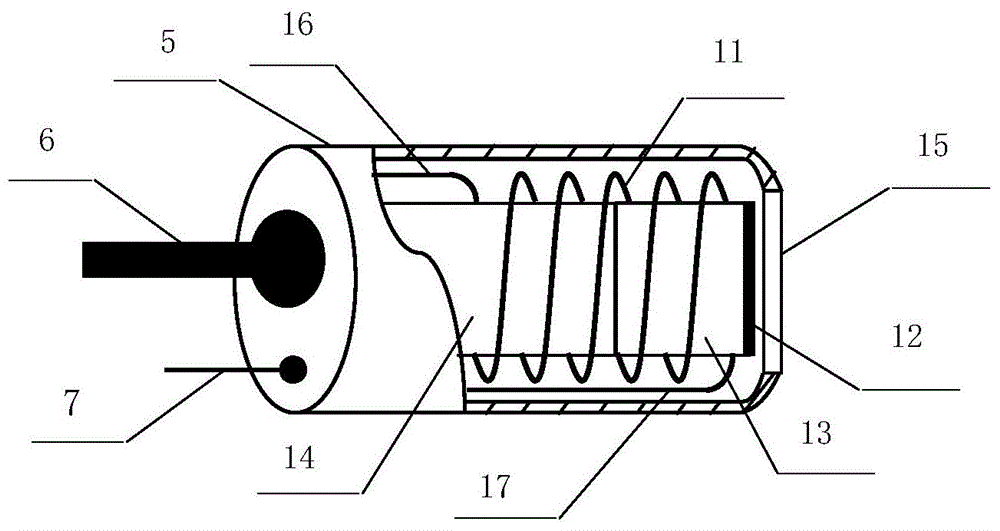
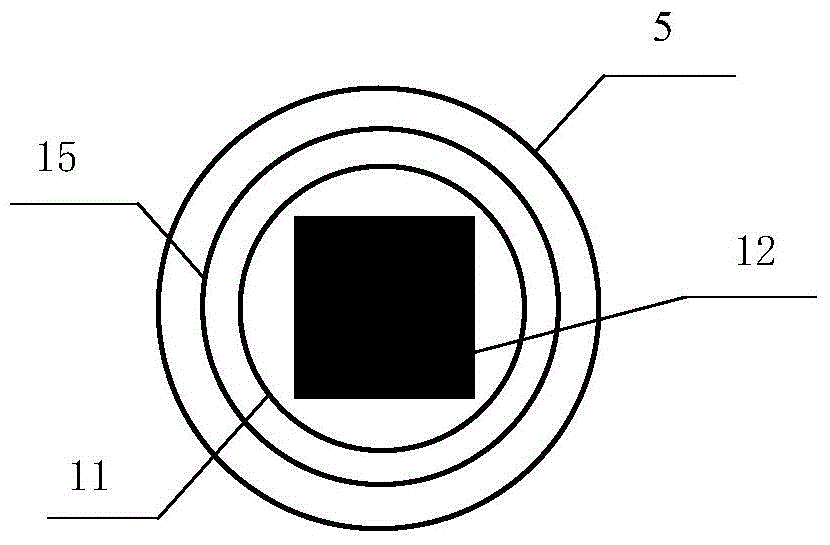
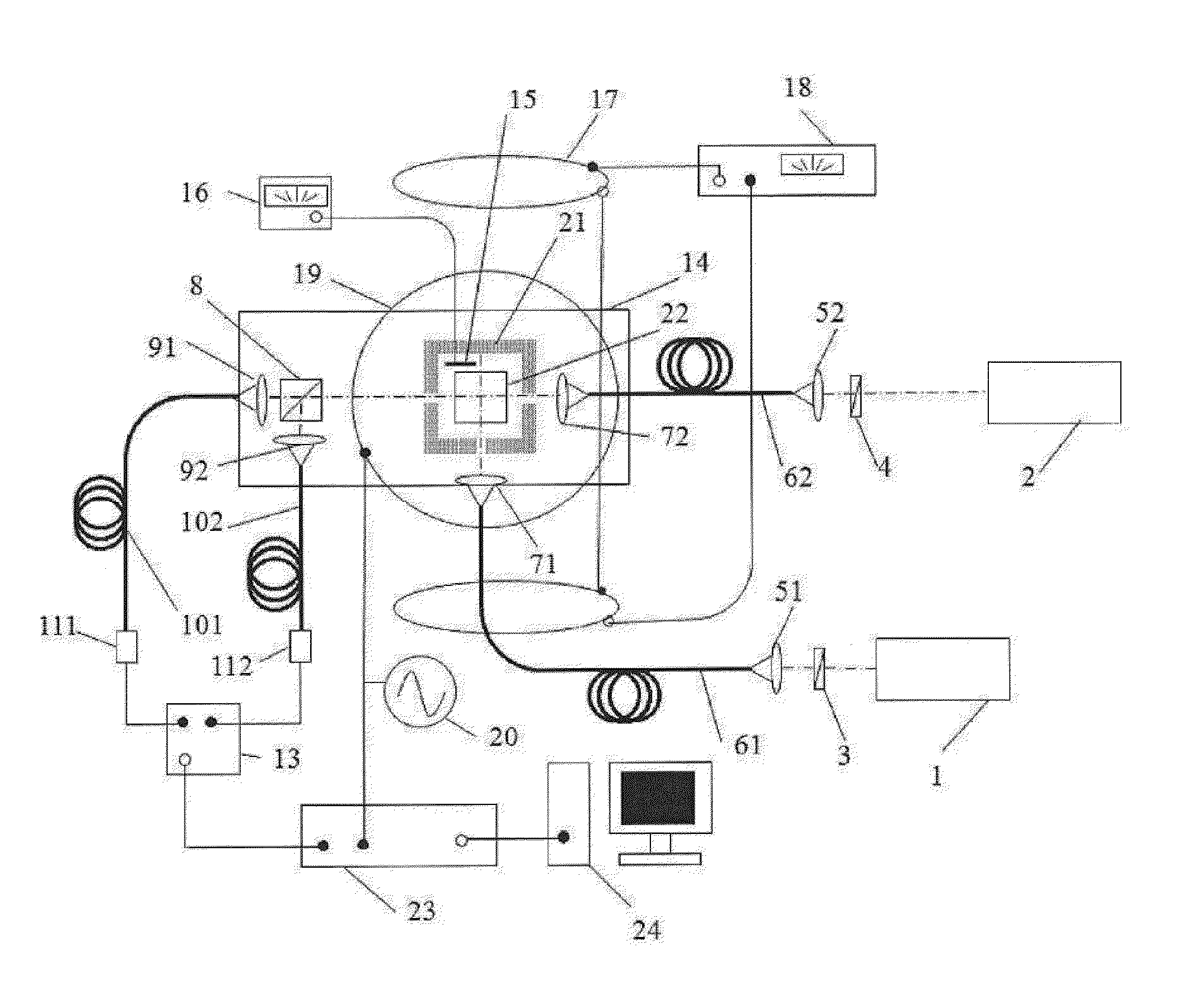
The invention discloses a magnetofluid filling photonic crystal optical fiber F-P magnetic field sensor, which belongs to the technical field of optical fiber sensing, and consists of a broadband light source 20, an optical fiber coupler 21 and optical fiber links (31, 32, 33 and 34) of the optical fiber coupler 21, a refractive index matching fluid 22, a sensor probe 23, an electromagnetic coil 18 and a current driving system 19 of the electromagnetic coil, a spectrum analyzer, a computer 24 as well as a connecting cable 26 and a connecting cable 27. The magnetofluid filling photonic crystal optical fiber F-P magnetic field sensor is characterized in that the sensor probe is formed by fusing a section of hollow photonic crystal optical fiber 12 filled with a magnetofluid 13 and a simple module optical fiber 11; the two ends of the hollow photonic crystal optical fiber are respectively stuck by a partial reflection film 14 and a total reflection mirror 15 to form an optical fiber F-P interferometric cavity structure; and the reflection rate of the magnetofluid serving as a medium in the F-P interferometric cavity is changed due to a magnetic field generated by the electromagnetic coil after conducted with a current, thereby causing the change of output spectrums so as to realize magnetic field measurement. The magnetofluid filling photonic crystal optical fiber F-P magnetic field sensor has the advantages of being low in temperature influences, simple in structure, small in size and easy to realize multi-point distribution type sense.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Micro-fabricated atomic magnetometer and method of forming the magnetometer
ActiveUS8836327B2Low costSmall sizeSolid-state devicesMagnetic field measurement using magneto-optic devicesLaser lightPhotodiode
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
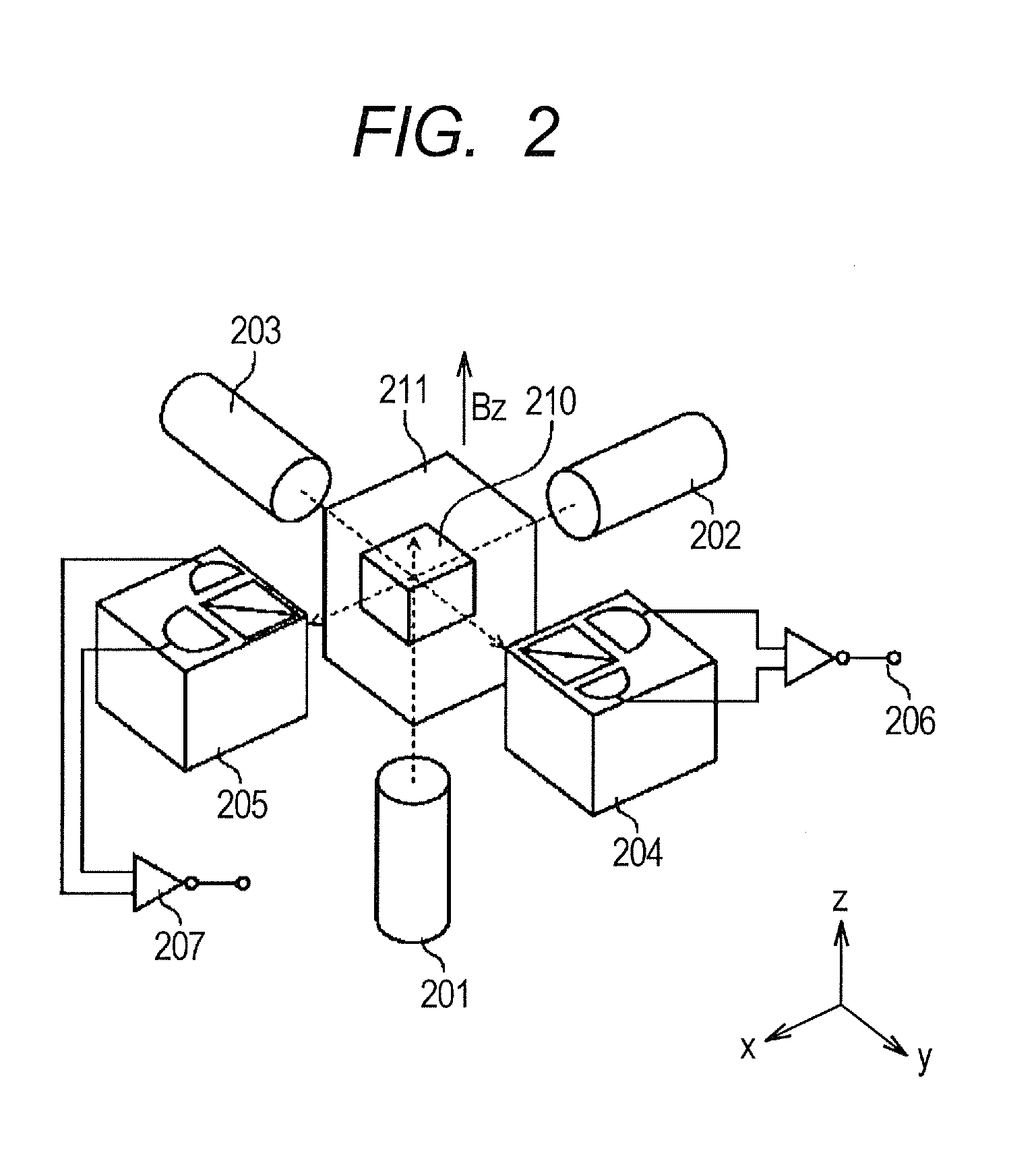
Atomic magnetometer and magnetic sensing method
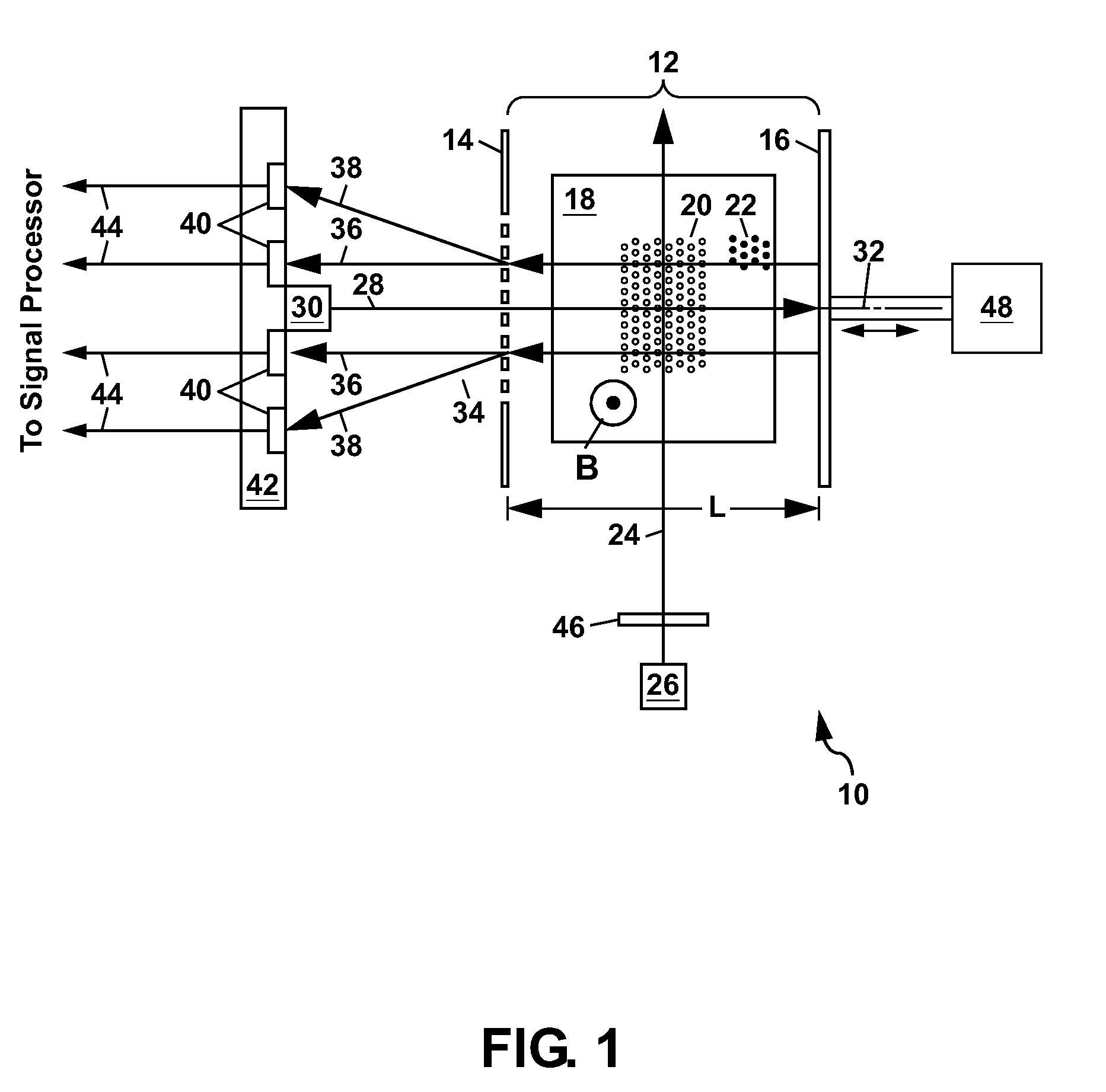
ActiveUS8405389B2High-sensitivity sensorMagnetic field measurement using magneto-optic devicesMagnetic gradient measurementsLight beamAtomic magnetometer
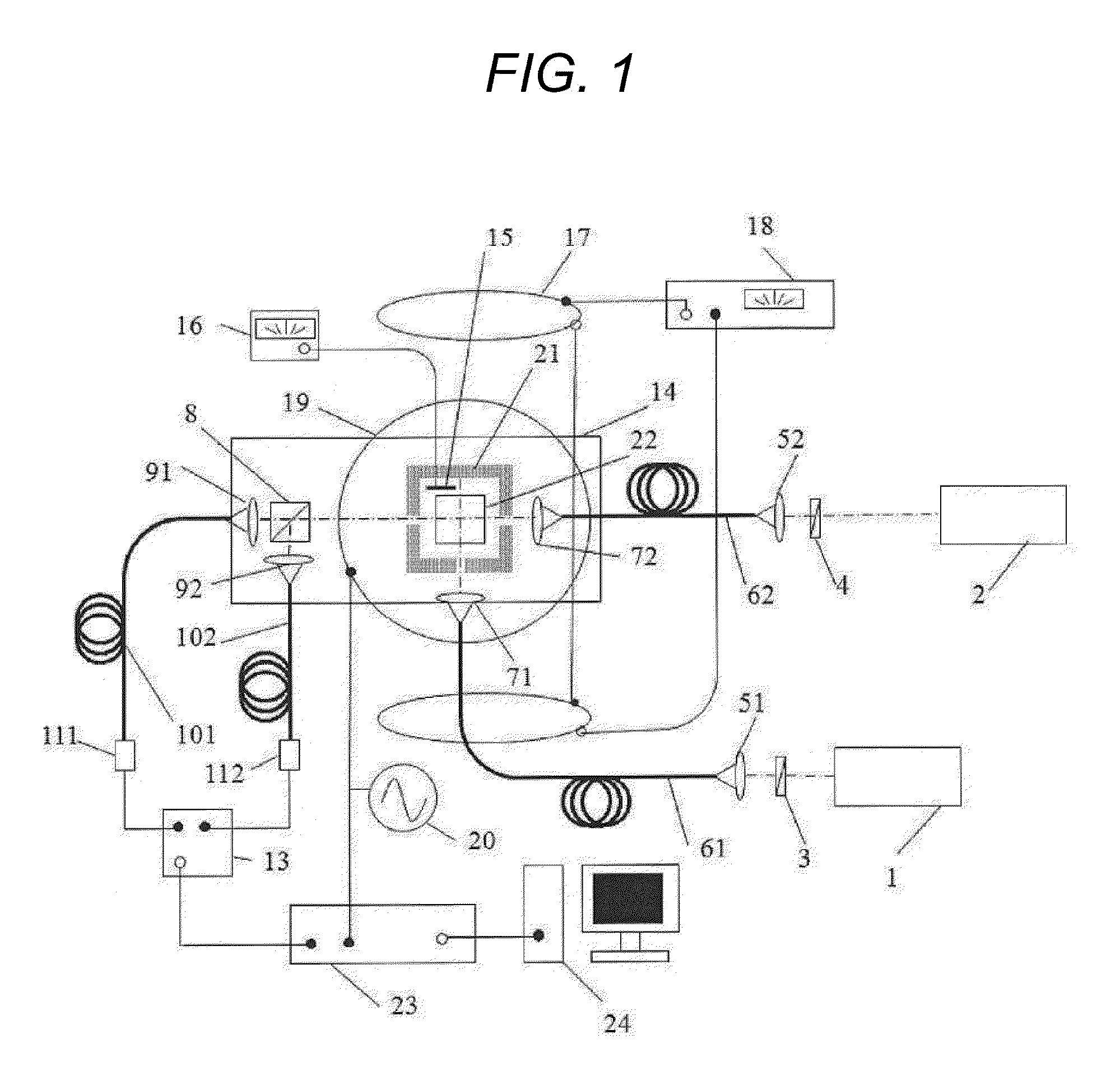
An atomic magnetometer includes a light source for a probe beam and a medium in which the probe beam is to be propagated. The medium is a substance which changes a polarization rotation angle of the probe beam depending on a magnetic field intensity at a first measurement position and a magnetic field intensity at a second measurement position different from the first measurement position. The atomic magnetometer directly measures a difference between the magnetic field intensity at the first measurement position and the magnetic field intensity at the second measurement position as a difference in polarization rotation angle, along a propagation path of the probe beam.
Owner:CANON KK
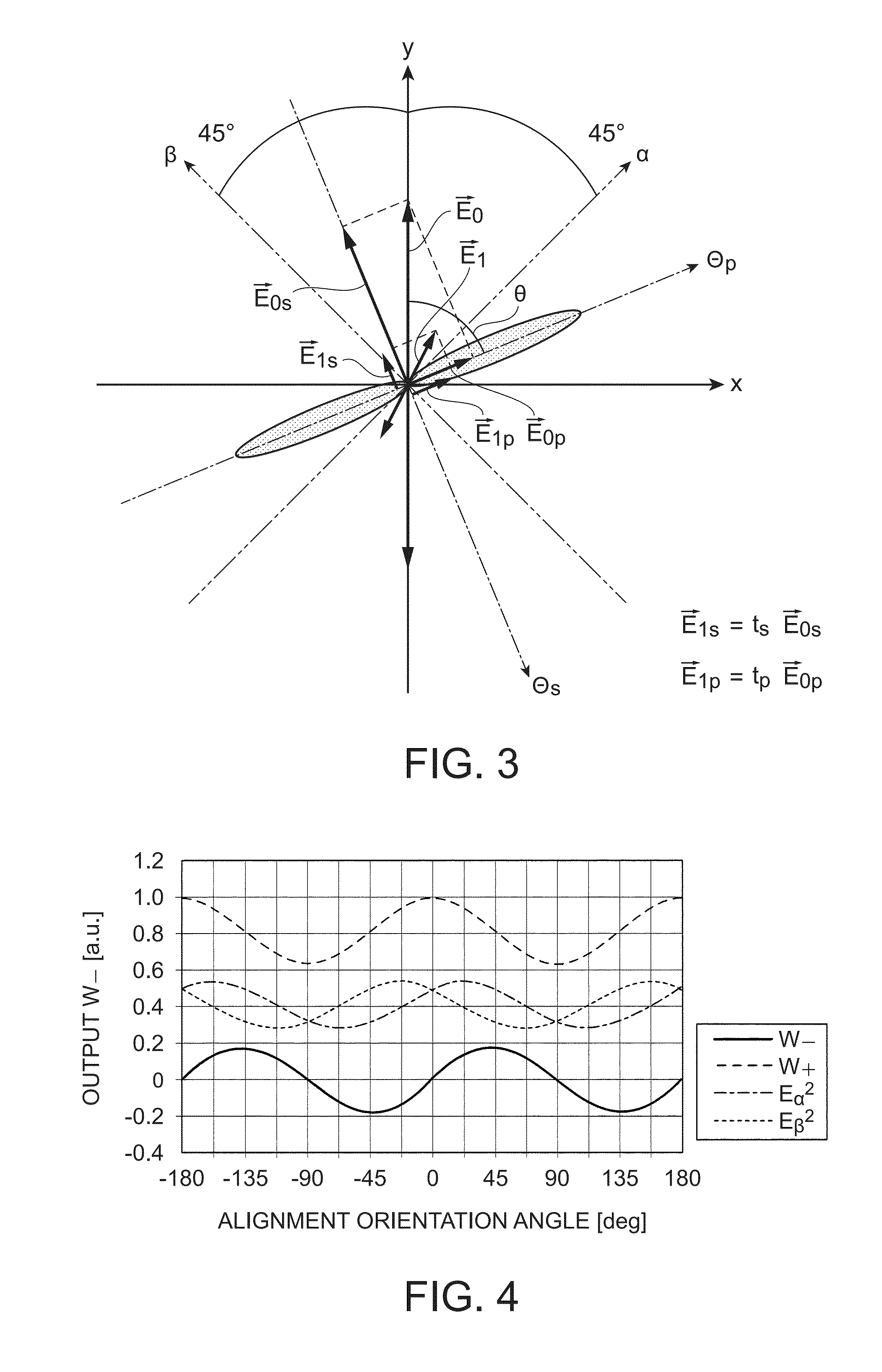
Inspection Device and Inspection Method
ActiveUS20140225606A1High magnetic field sensitivityHigh sensitivityPolarisation-affecting propertiesMagnetic field measurement using magneto-optic devicesLight irradiationLength wave
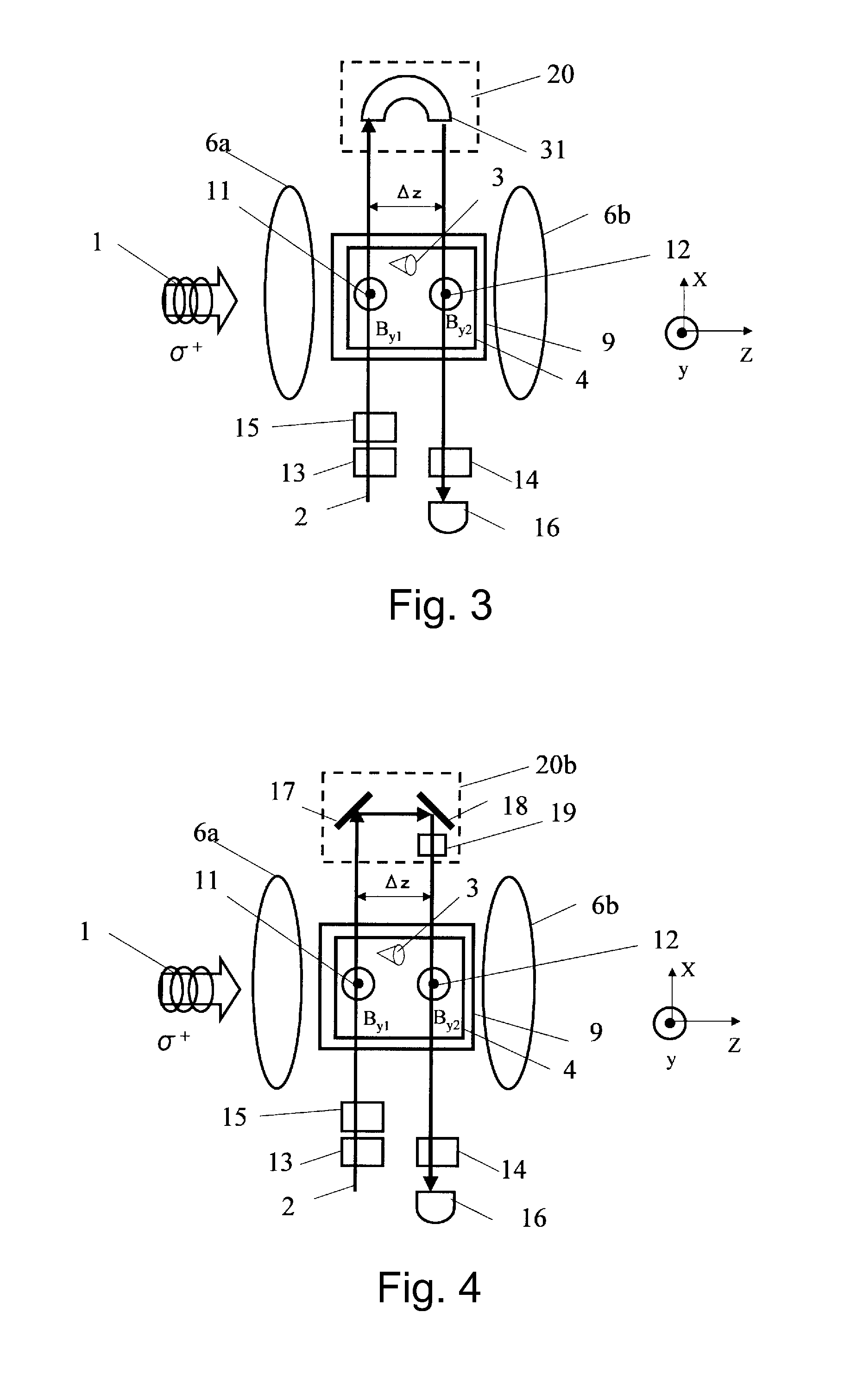
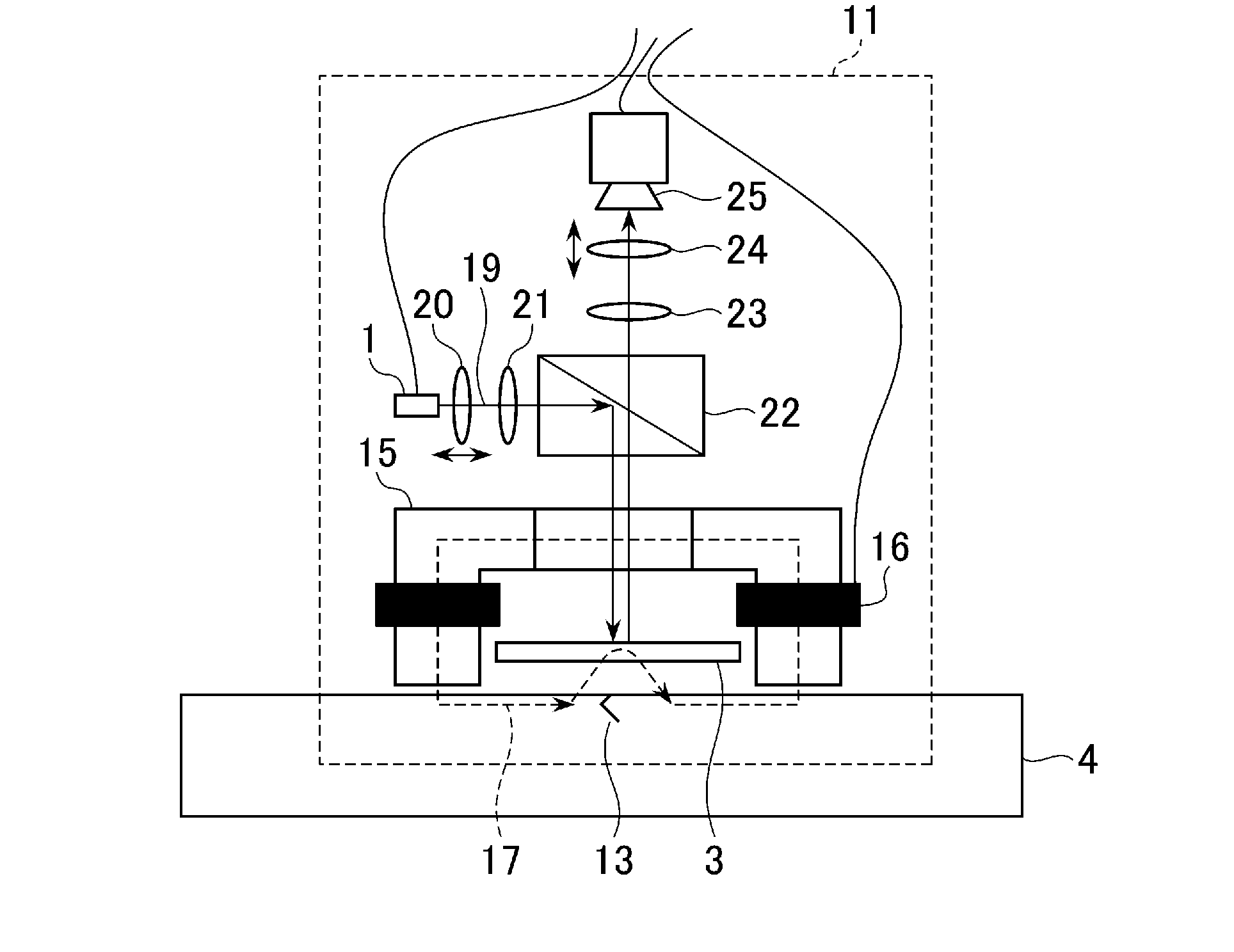
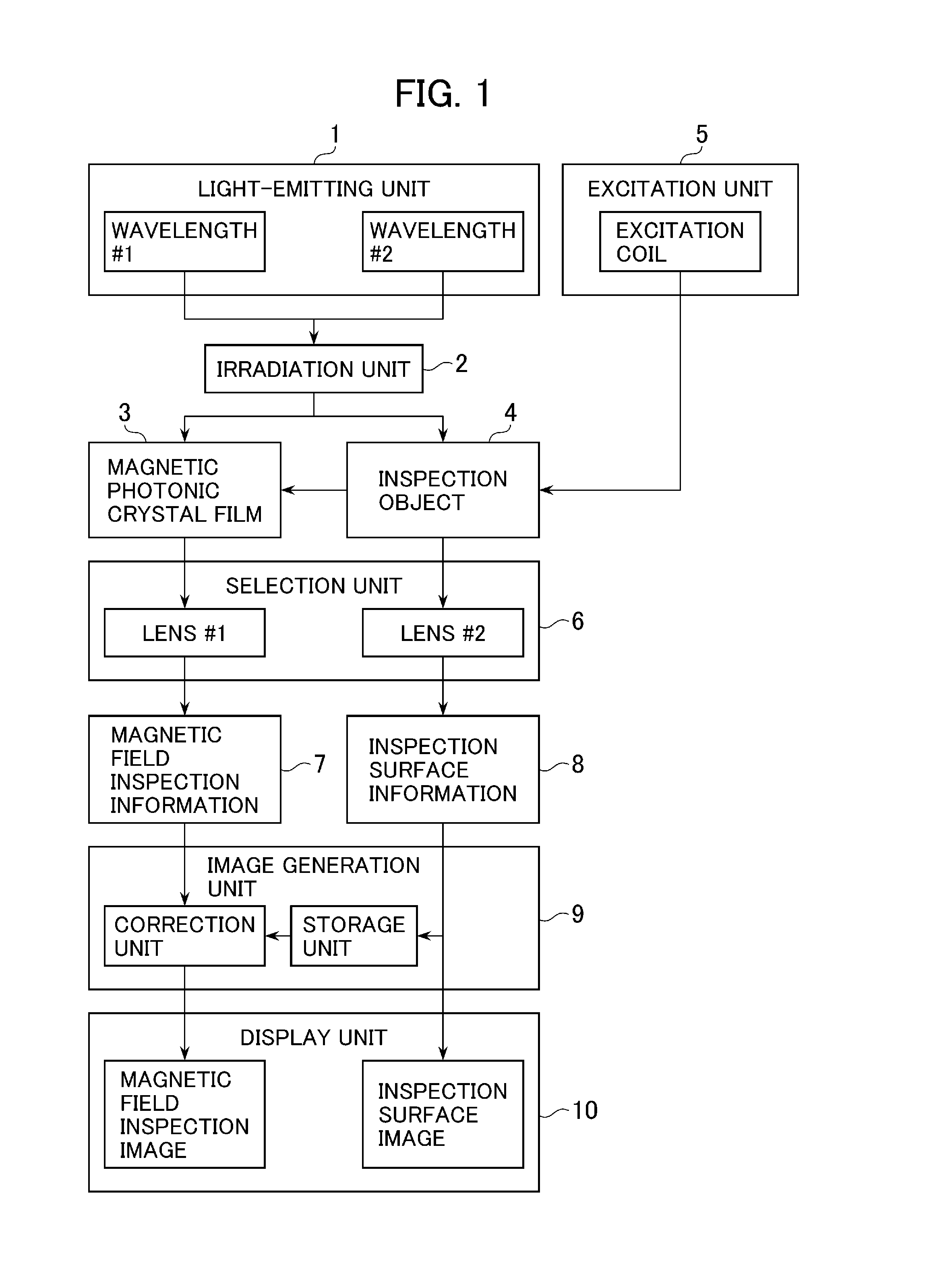
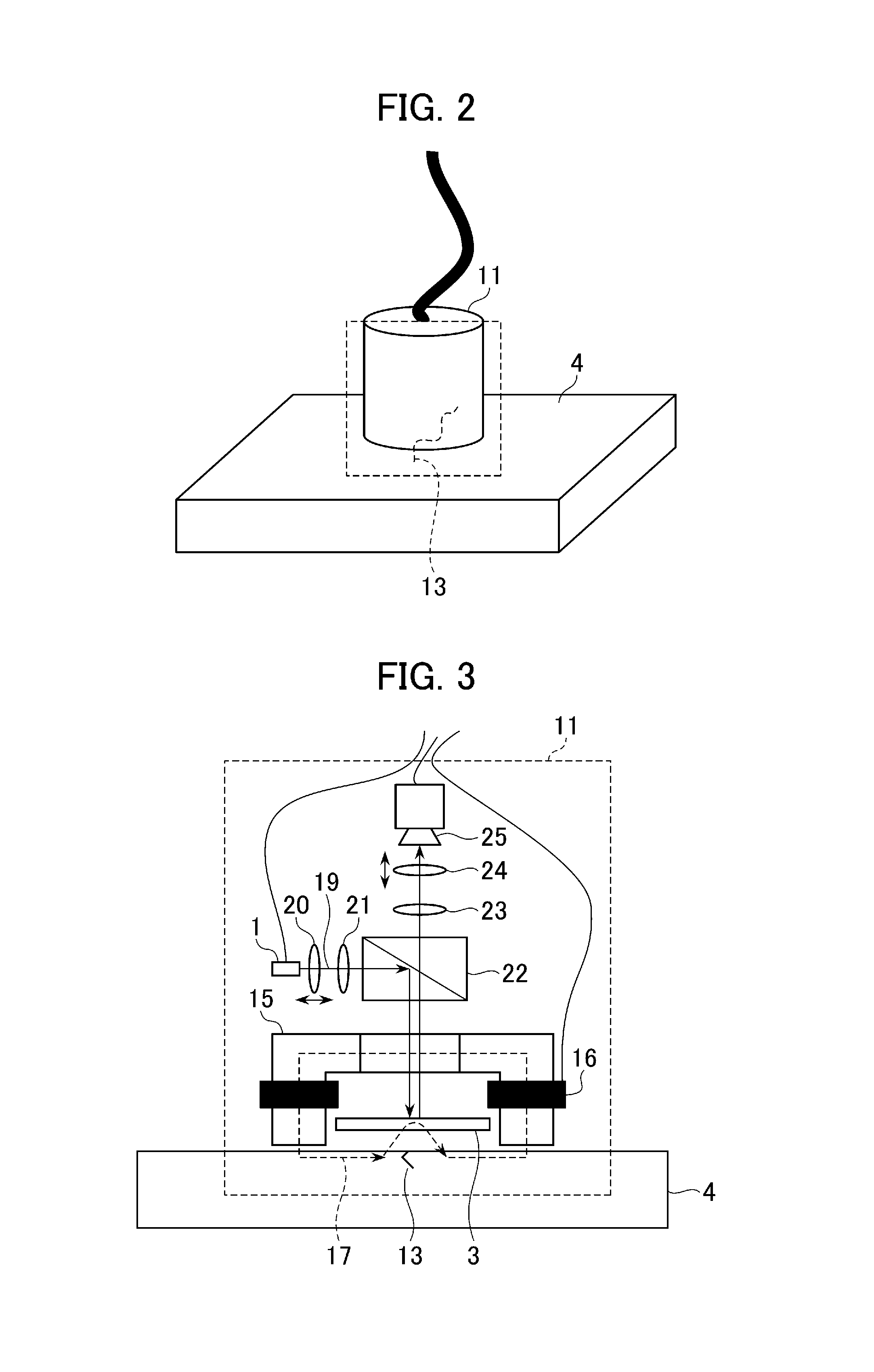
Provided are an inspection device and an inspection method capable of achieving improved magnetic field sensitivity by using a magnetic thin film of a small film thickness. A light-emitting unit 1 emits light of a first wavelength for acquiring magnetic field inspection information and a second wavelength for acquiring inspection object surface information. A selection unit 6 selects information from an inspection object 4 and information from a magnetophotonic crystal film 3 acquired by light irradiation performed by an irradiation unit 2. An image generation unit 9 generates image data based on the magnetic field inspection information acquired with the first wavelength and the inspection object surface information acquired with the second wavelength selected by the selection unit. Each of the generated image data is displayed on a display unit 10.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
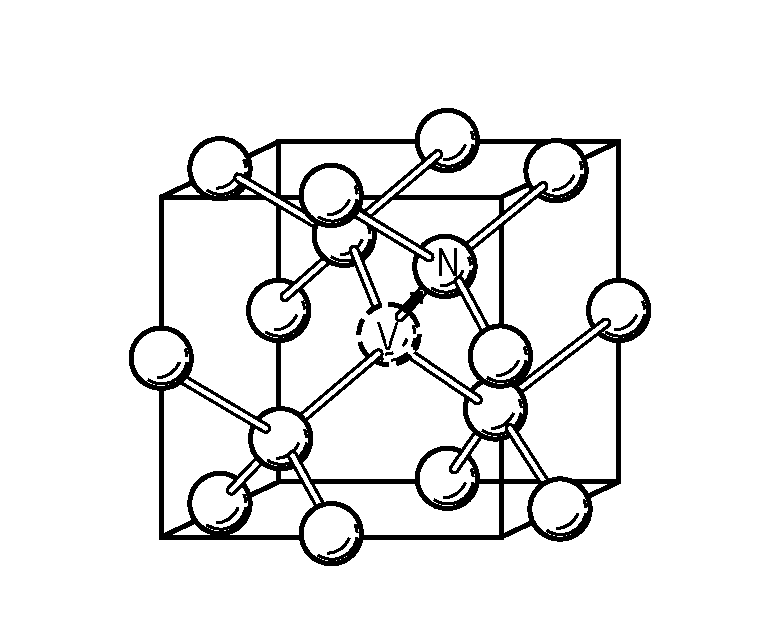
Microwave sensor based on NV color center diamond
ActiveCN104360152ASolve the accuracy problemSolution volumeFrequency measurement arrangementMagnetic field measurement using magneto-optic devicesColour centreNitrogen
The invention discloses a microwave sensor based on an NV color center diamond. A diamond internally containing a Nitrogen-Vacancy color center is adopted as a sensitive element, electronic energy level stimulation is achieved through lasers, an additionally-arranged static magnetic field is scanned, and the microwave frequency and the microwave intensity are measured through fluorescence intensity detection. Dependency of electronic rabi-flopping of the NV color center in the diamond on the external microwave magnetic field is brought into play, high theoretical accuracy and good stability are achieved, the microwave sensor has the advantages of being small in size, low in cost, high in accuracy, large in temperature range, simple in operation condition and the like and rotates on the basis of solid atoms, and the microwave sensor can serve in all the fields with the requirements for the low-cost high-accuracy microwave frequency and intensity detection in the future.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
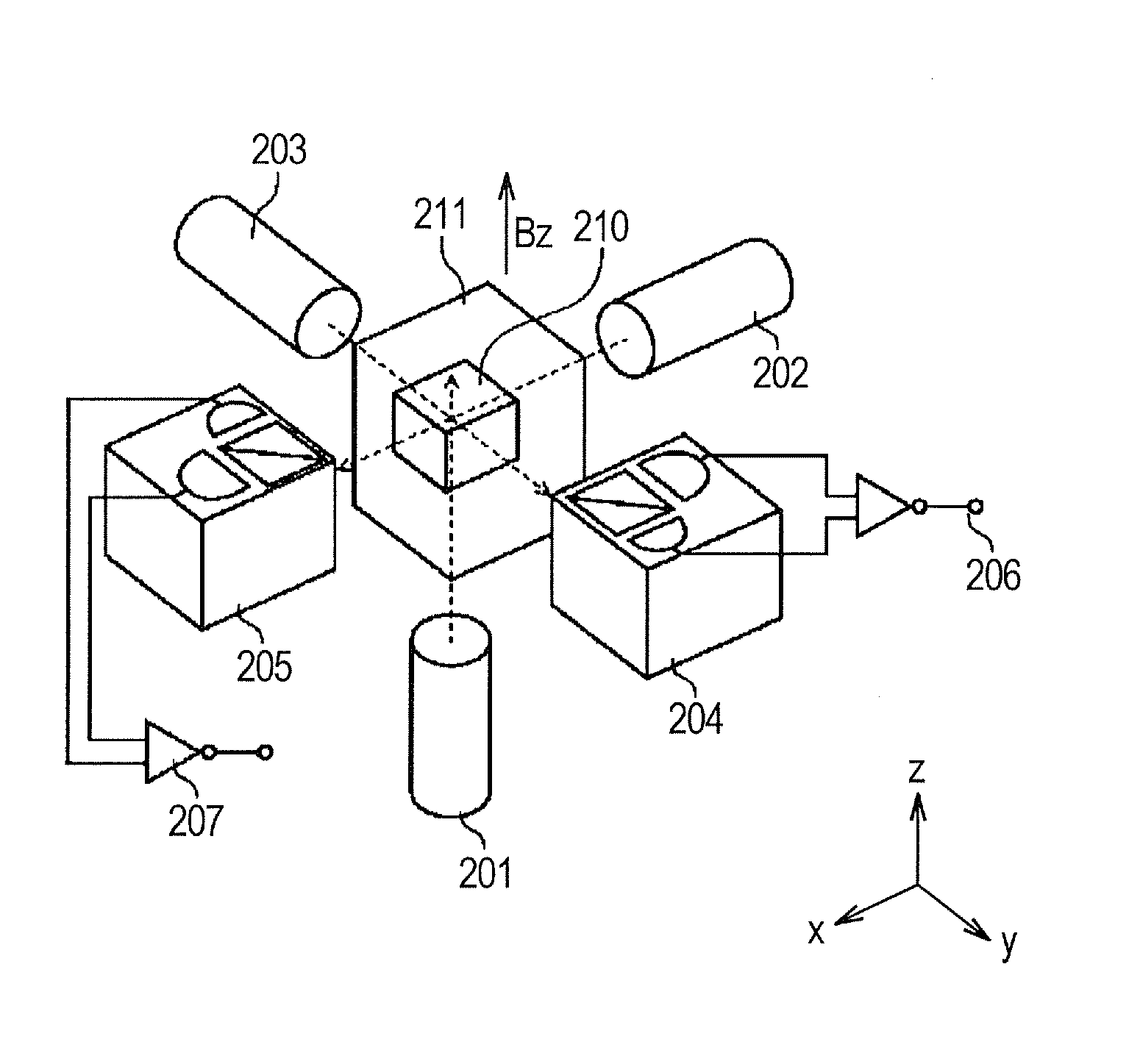
Biaxial atomic spinning magnetometer
InactiveCN106443520APromote formationSimple structureMagnetic field measurement using magneto-optic devicesNon magneticQuenching
The invention discloses a biaxial atomic spinning magnetometer. The biaxial atomic spinning magnetometer comprises an alkali metal gas chamber, non-magnetic electric heating equipment, a three-dimensional magnetic coil, a magnetic shielding layer, a pumping laser module and a detecting laser module. The alkali metal gas chamber is filled with alkali metal atoms, a quenching gas and a buffering gas; the non-magnetic electric heating equipment and the magnetic shielding layer enable the alkali metal atoms to work in a high-temperature and low-magnetic field environment, and ensure the alkali metal atoms in a non-spinning exchange relaxation state; the pumping laser module is used for polarizing the alkali metal atoms; the detecting laser module comprises two beams of independent detecting laser which are perpendicular to each other, and are used for sensing the magnetic field intensity in two directions which are perpendicular to each other simultaneously; measurement results are demodulated through a phase-locked amplifier. The biaxial atomic spinning magnetometer can acquire biaxial magnetic field information simultaneously through one alkali metal gas chamber, has the characteristics of high sensitivity, high integration degree and low cost, and has a wide application prospect in the fields of brain magnetic measurement, magnetocardiographic measurement and the like.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Integrated magnetometer arrays for magnetoencephalography (MEG) detection systems and methods
ActiveUS20200309873A1Analysis using optical pumpingDiagnostic recording/measuringWaferingEngineering
An array of optically pumped magnetometers includes a vapor cell arrangement having a wafer defining one or more cavities and alkali metal atoms disposed in the cavities to provide an alkali metal vapor; an array of light sources, each of the light sources arranged to illuminate a different portion of the one or more cavities of the vapor cell arrangement with light; at least one mirror arranged to reflect the light from the array of light sources after the light passes through the one or more cavities of the vapor cell arrangement; and an array of detectors to receive light reflected by the at least one mirror, wherein each of the detectors is arranged to receive light originating from one of the light sources.
Owner:HI LLC
Magnetic field measuring apparatus and method for manufacturing same
InactiveUS20140306700A1Easy pressure controlHigh sensitivityWave amplification devicesManufacture of electrical instrumentsInternal pressureMeasurement device
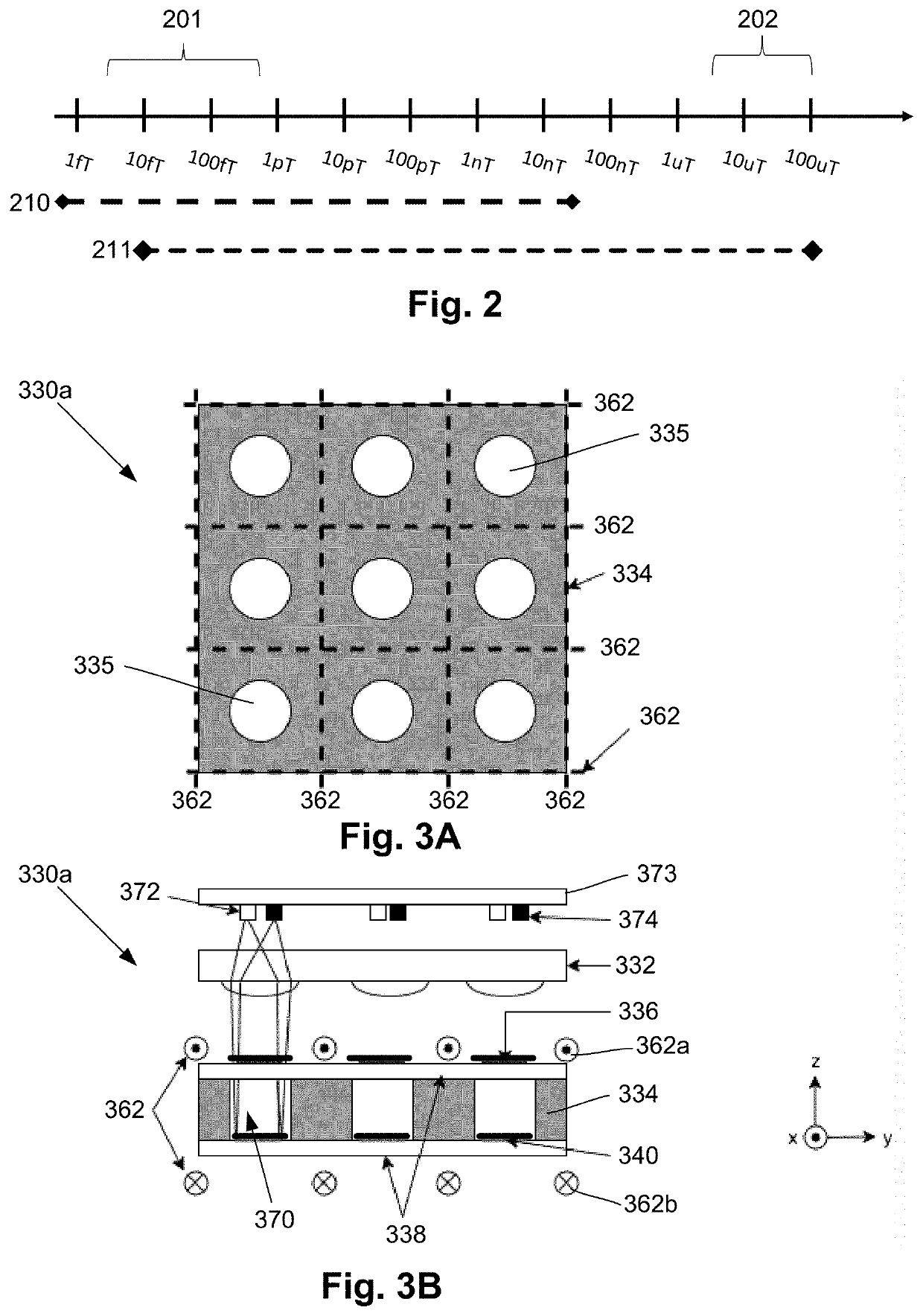
In order to provide a magnetic field measuring apparatus facilitating the pressure control in a gas cell, or capable of inspecting the internal pressure of the gas cell without using any special process, the magnetic field measuring apparatus is configured such that a process layer of the magnetic field measuring apparatus has such a structure that includes a first hollow portion and a second hollow portion provided opposed to first hollow portion with a first isolation wall interposed therebetween. Alternatively, a method for manufacturing the magnetic field measuring apparatus includes breaking the first isolation wall after generating alkali metal (FIG. 17 and FIG. 20).
Owner:HITACHI LTD
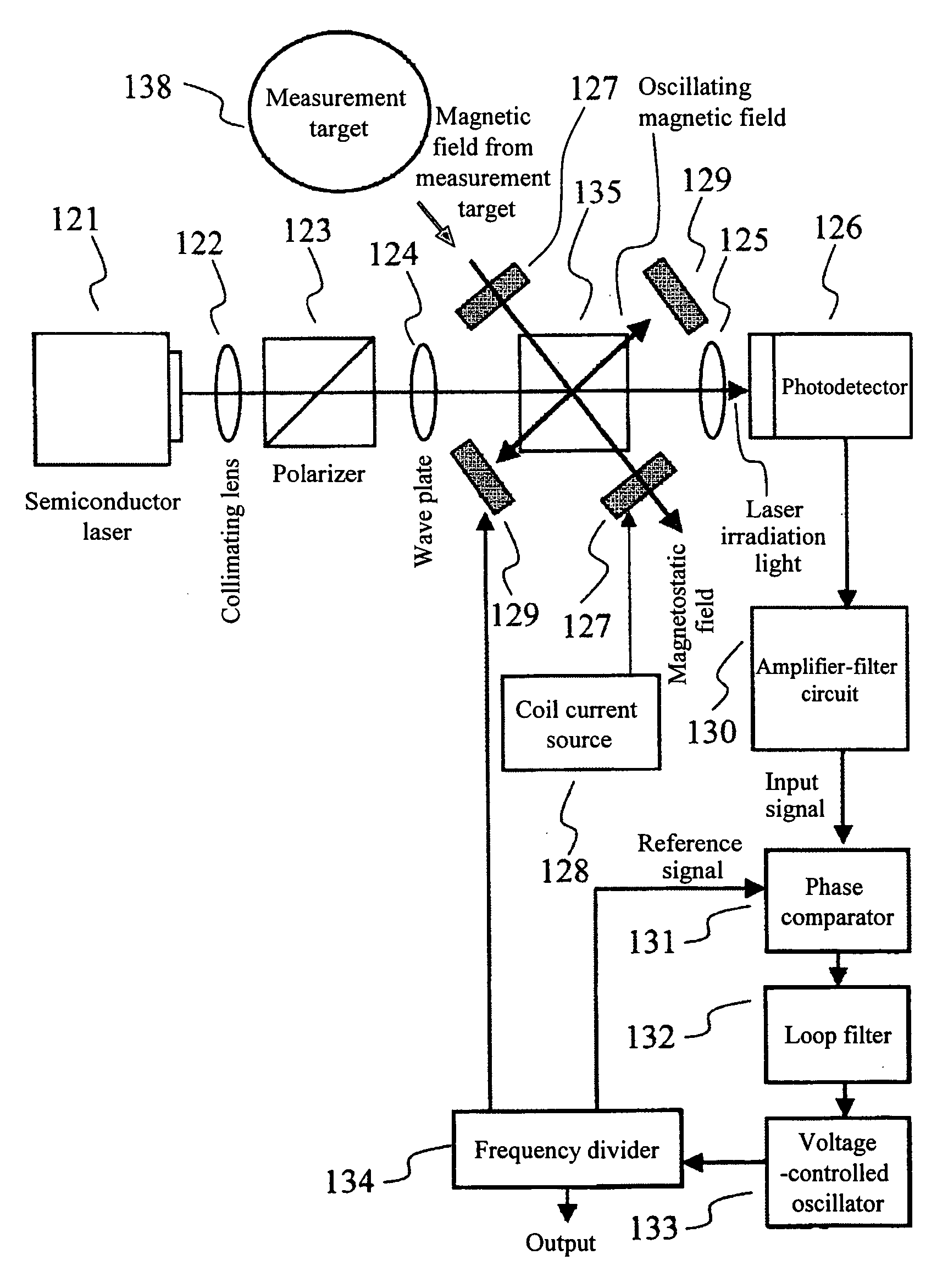
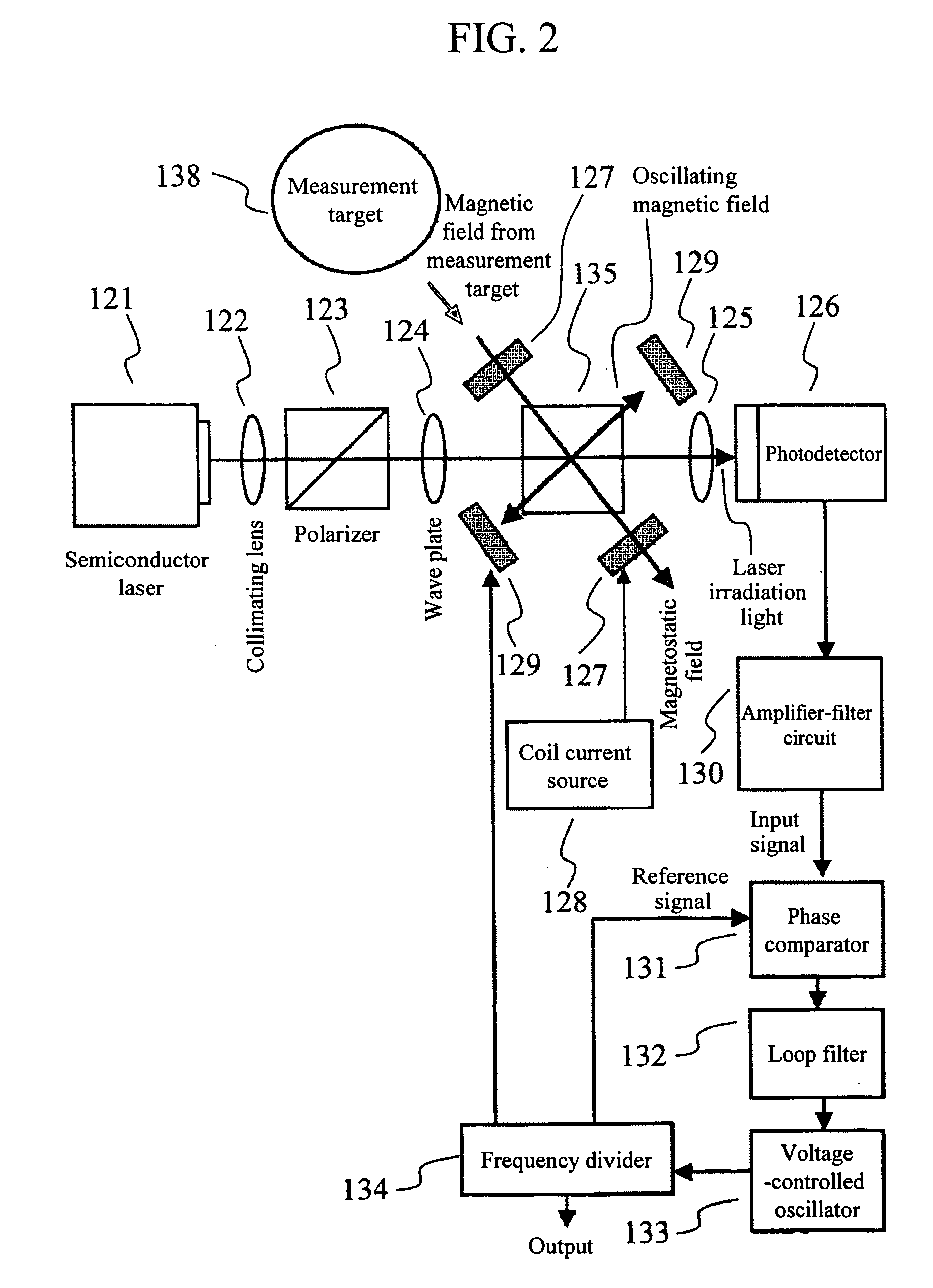
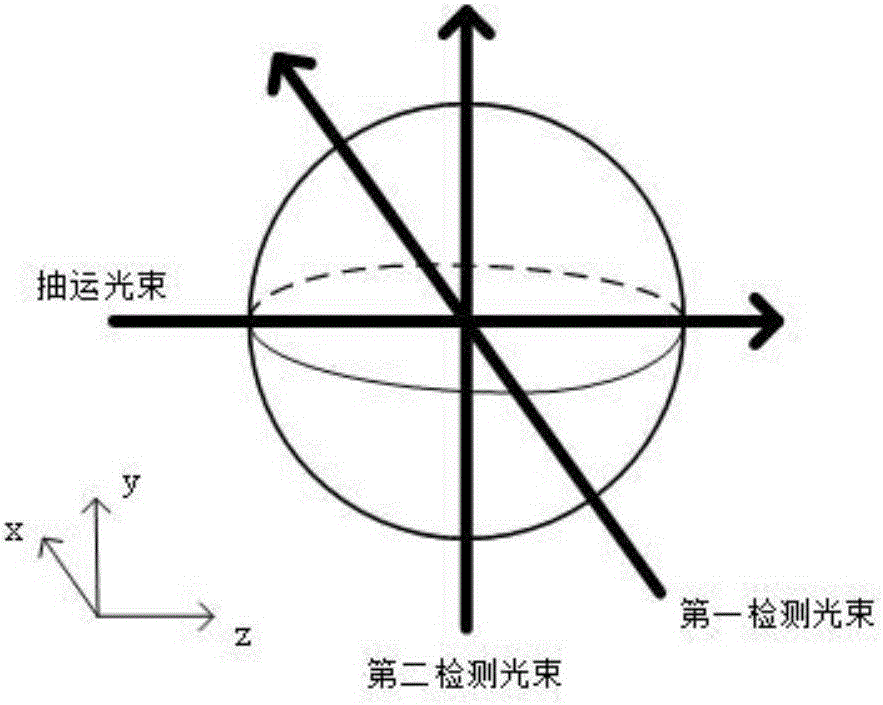
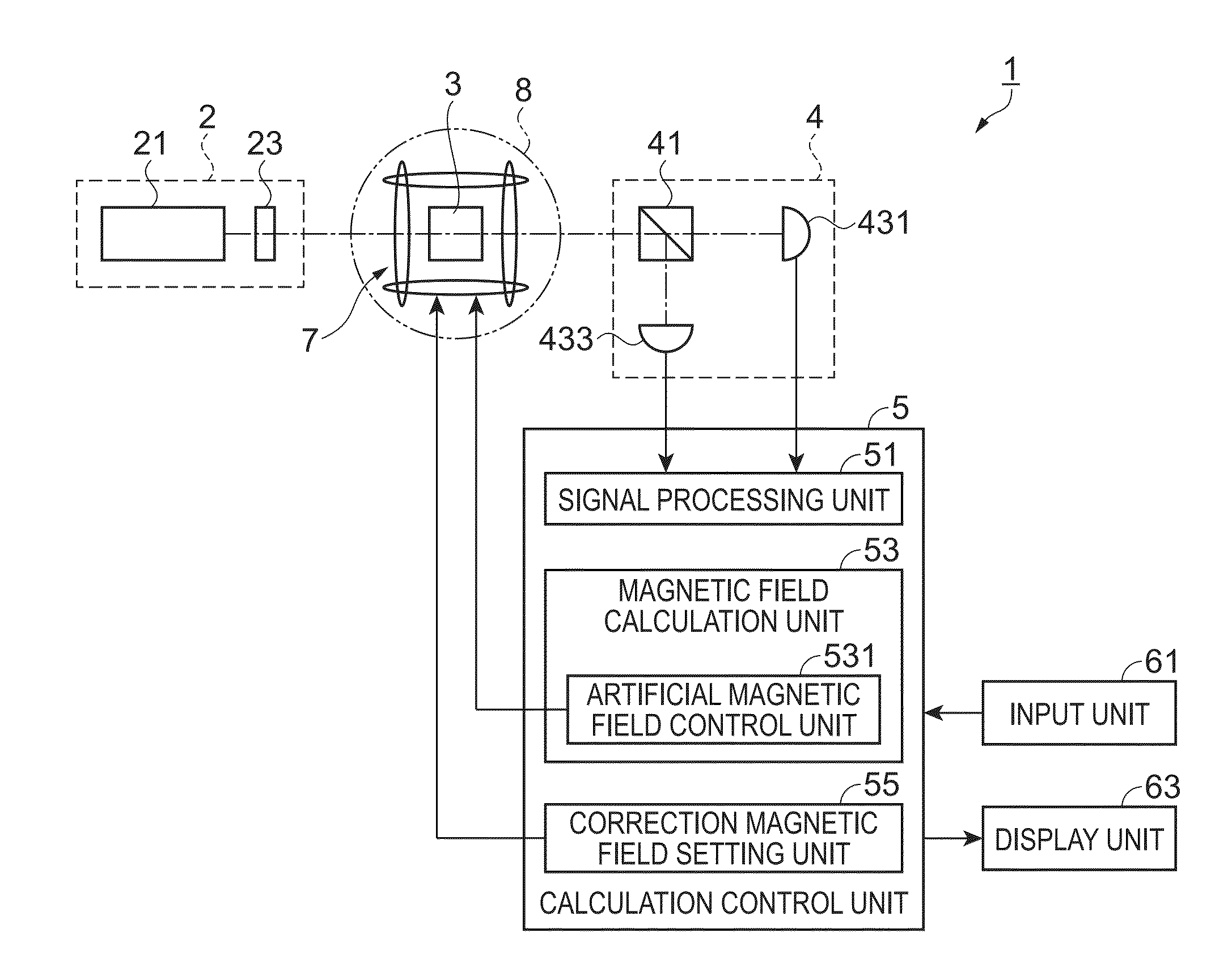
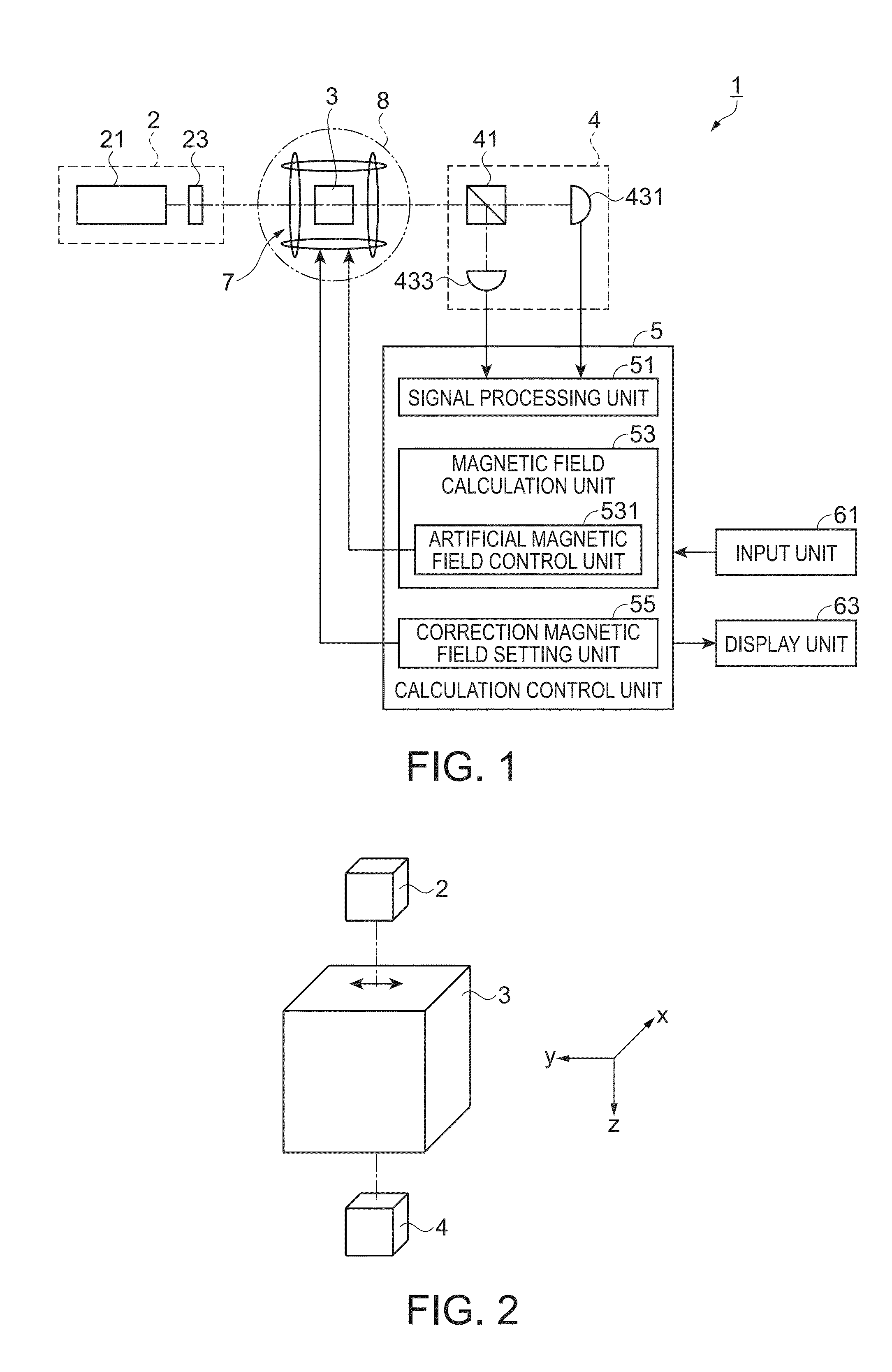
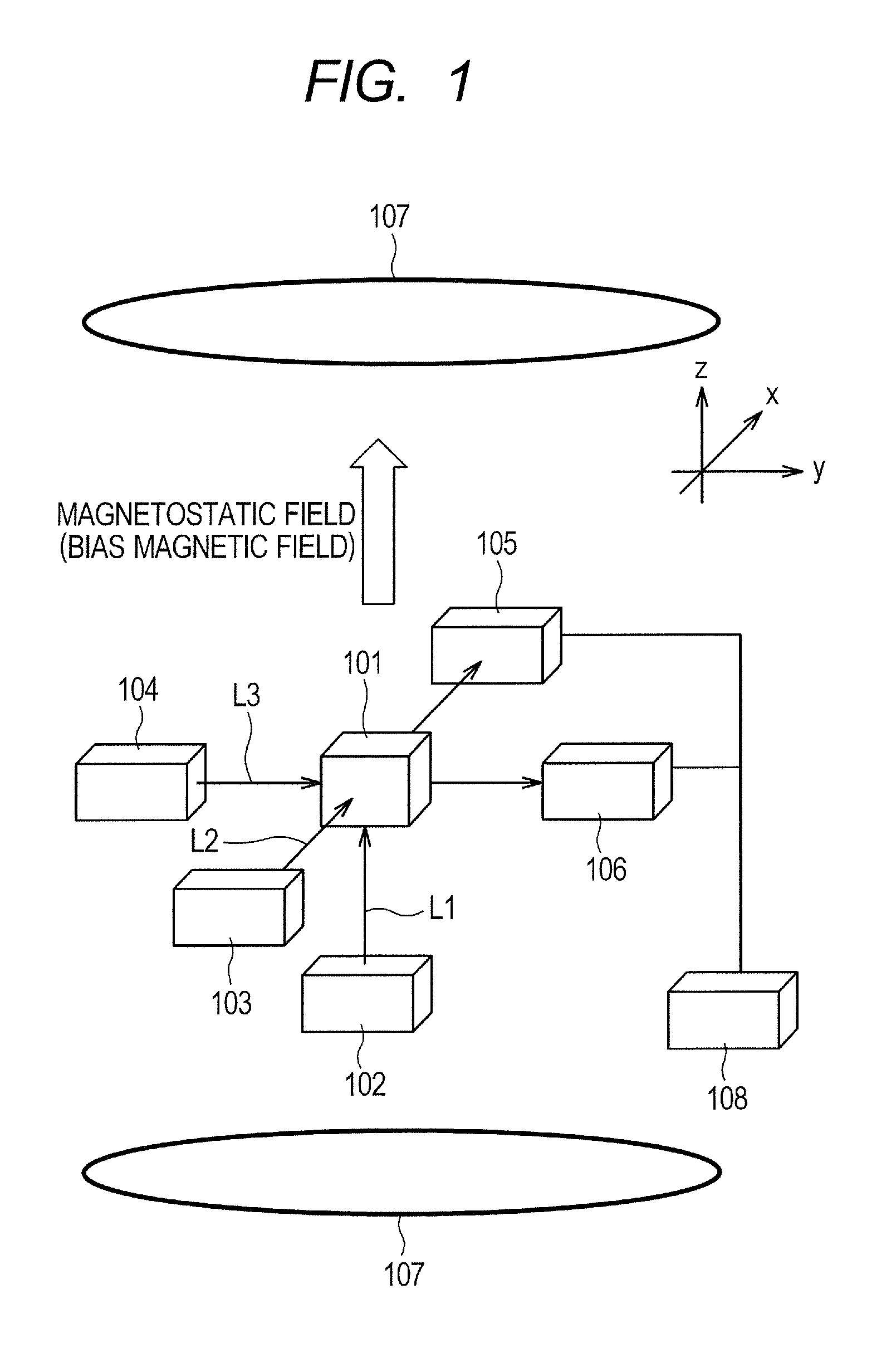
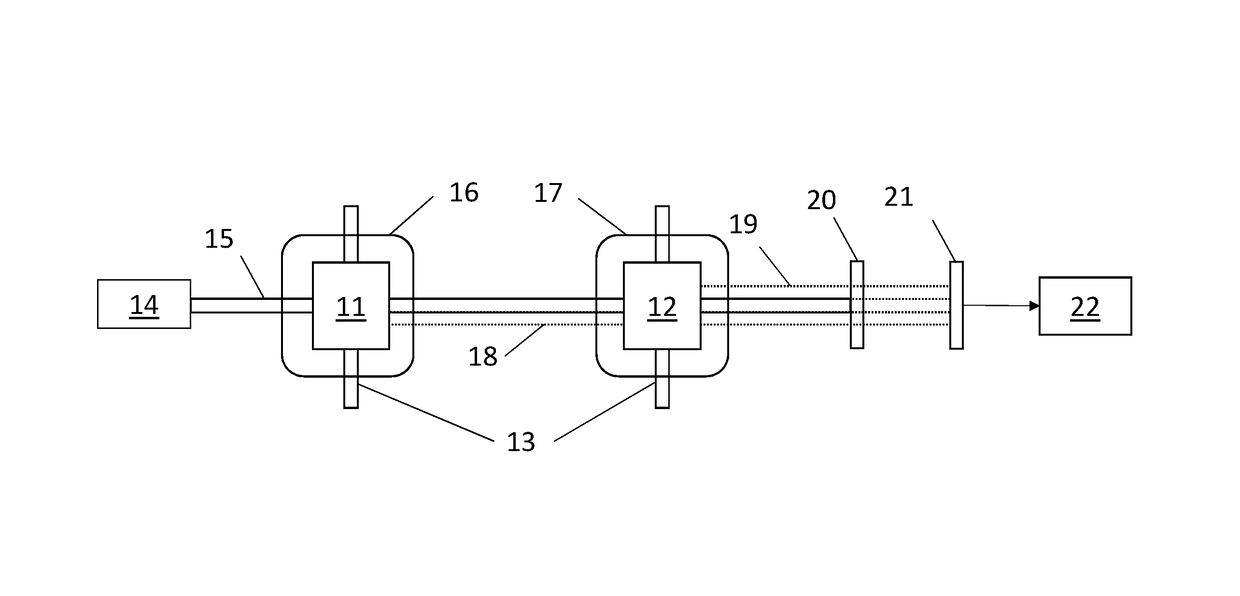
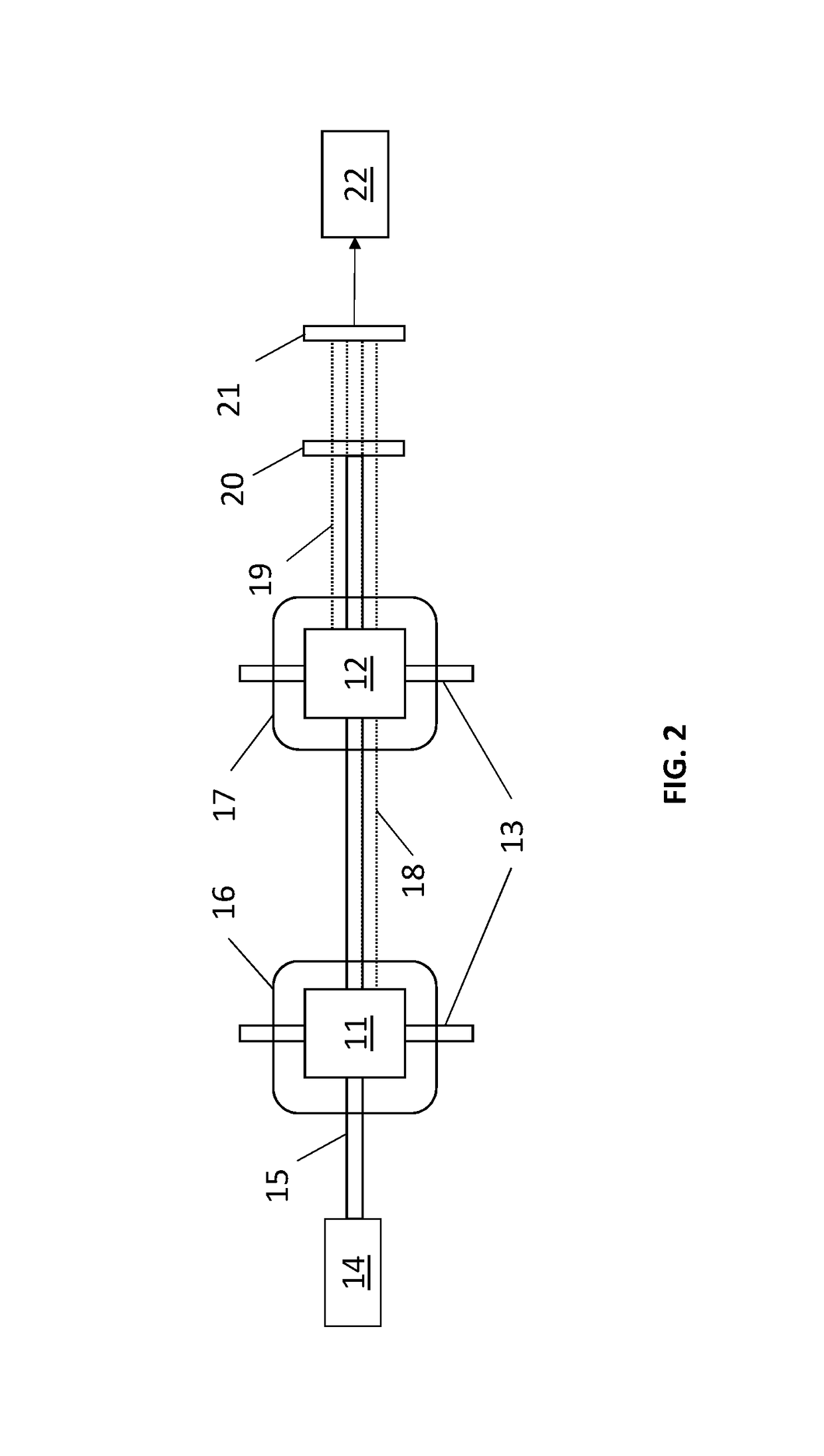
Magnetic field measurement method and magnetic field measurement device
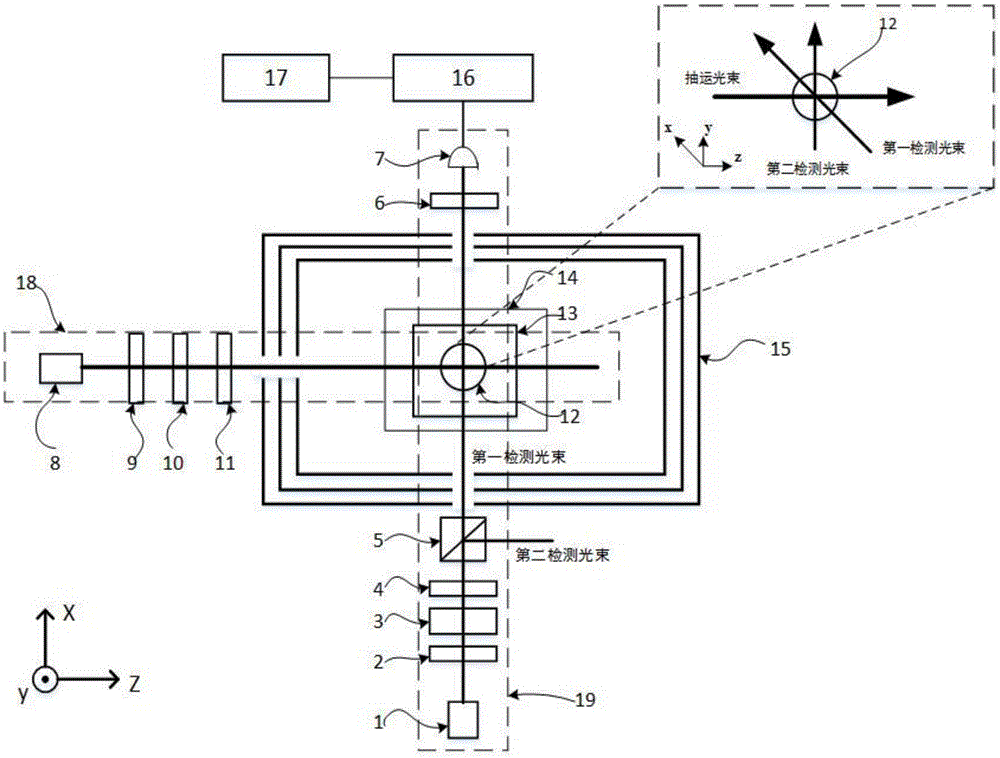
A light source unit irradiates a gas cell disposed in a measurement region with linearly polarized light in which the direction of travel is a z-axis direction and the vibration direction of an electric field is a y-axis direction. A polarimeter detects optical characteristics of light passing through the gas cell. A magnetic field generator applies an artificial magnetic field, capable of varying an x-axis component, a y-axis component, and a z-axis component, to the measurement region. A calculation control unit generates a plurality of artificial magnetic fields, calculates a magnetization value or a value corresponding to the magnetization value on the basis of the detection results of the polarimeter, and calculates an original magnetic field present in the measurement region, using an artificial magnetic field when the magnetization value or the value corresponding to the magnetization value satisfies a condition for external value.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Diamond nitrogen vacancy sensed ferro-fluid hydrophone
ActiveUS20170211947A1Material analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesSeismologyHydrophoneNitrogen
Systems and apparatuses are disclosed for a hydrophone using a nitrogen vacancy center diamond magnetic sensor.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Neural feedback loop filters for enhanced dynamic range magnetoencephalography (MEG) systems and methods
ActiveUS20200256929A1Analysis using optical pumpingDiagnostic recording/measuringLow-pass filterSoftware engineering
One embodiment is a magnetic field measurement system that includes at least one magnetometer having a vapor cell, a light source to direct light through the vapor cell, and a detector to receive light directed through the vapor cell; at least one magnetic field generator disposed adjacent the vapor cell; and a feedback circuit coupled to the at least one magnetic field generator and the detector of the at least one magnetometer. The feedback circuit includes at least one feedback loop that includes a first low pass filter with a first cutoff frequency. The feedback circuit is configured to compensate for magnetic field variations having a frequency lower than the first cutoff frequency. The first low pass filter rejects magnetic field variations having a frequency higher than the first cutoff frequency and provides the rejected magnetic field variations for measurement as an output of the feedback circuit.
Owner:HI LLC
Diamond magnetometer
ActiveUS9851418B2Magnetic field measurement using magneto-optic devicesFluorescence/phosphorescenceMicrowaveFluorescence
A magnetometer comprising:a sensor formed of diamond material and comprising a plurality of spin centers;a microwave source configured to subject the plurality of spin centers to microwave pulses;a light source configured to subject the plurality of spin centers to light pulses; anda detector configured to detect a fluorescent output signal emitted from the plurality of spin centers,wherein the magnetometer is configured to integrate the fluorescent output signal over a signal averaging time and process the fluorescent output signal such that a standard deviation of the fluorescent output signal decreases with the square root of the signal averaging time over a time period which spans at least two orders of magnitude in the signal averaging time to achieve a standard deviation of less than 100 picotesla.
Owner:ELEMENT SIX TECH LTD
Atomic magnetometer and operating method of the same
ActiveUS9927501B2High bandwidthMagnetic field measurement using magneto-optic devicesMeasurements using magnetic resonanceNegative feedbackAudio power amplifier
Owner:KOREA RES INST OF STANDARDS & SCI
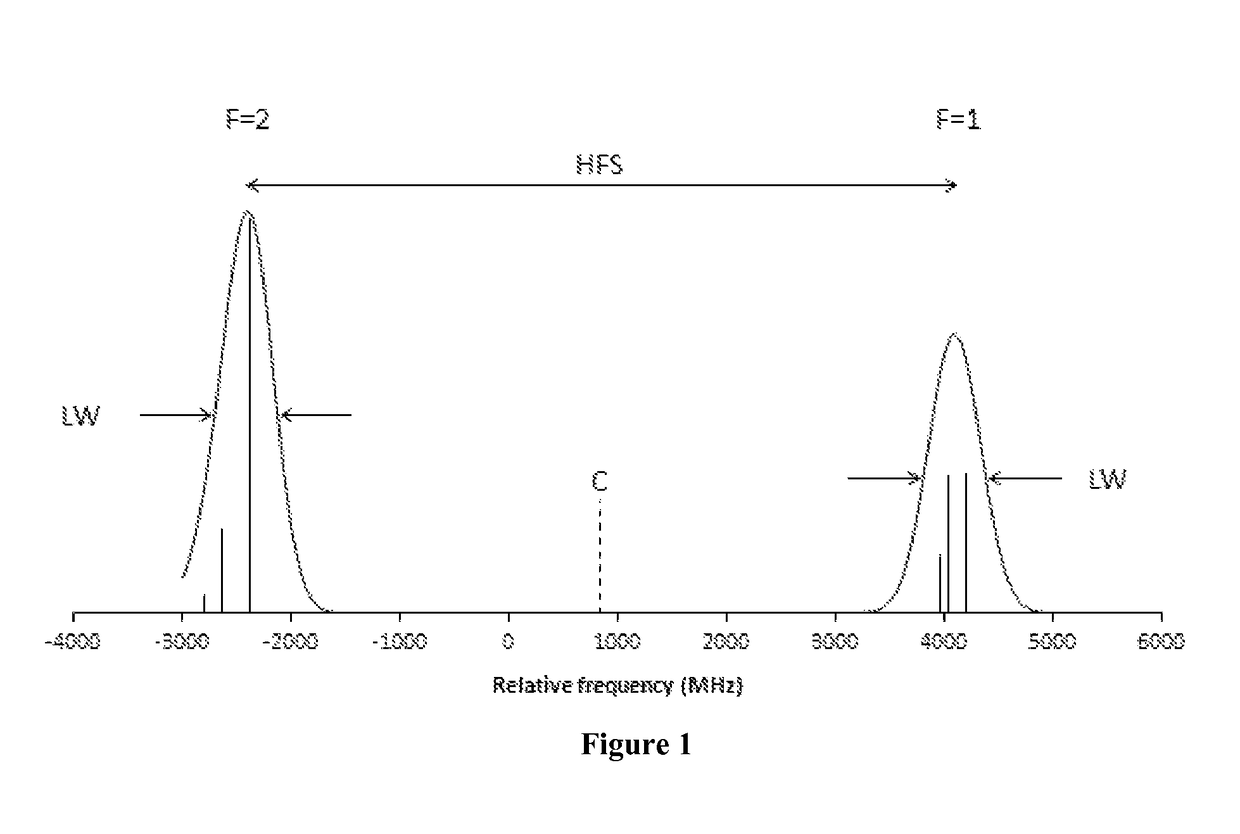
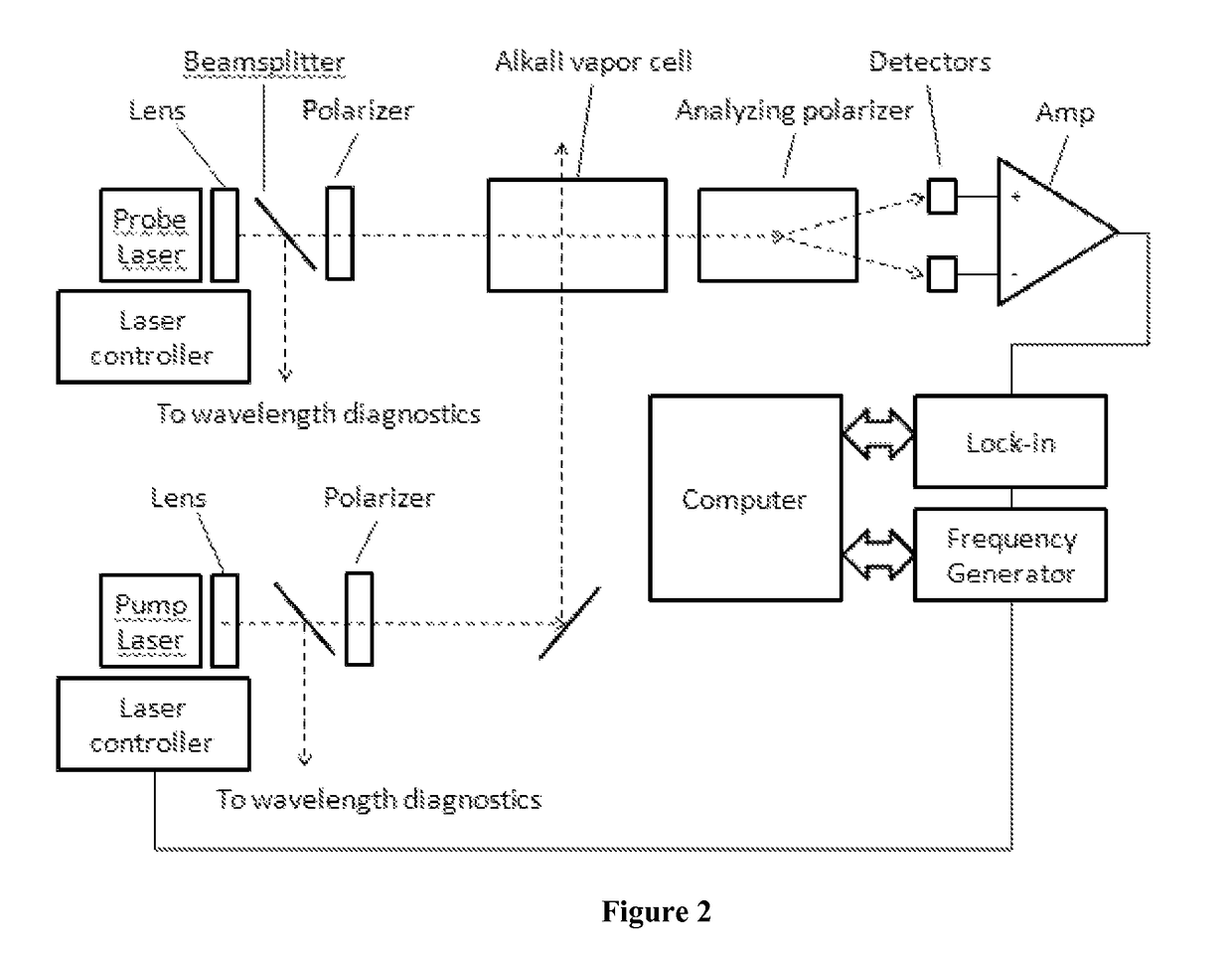
Wavelength-modulated coherence pumping and hyperfine repumping for an atomic magnetometer
ActiveUS9869731B1Magnetic field measurement using magneto-optic devicesMeasurements using magnetic resonanceLight beamWavelength modulation
An FM-NMOR magnetometer and concomitant magnetometry method comprising providing a linearly-polarized pump beam generator, employing a center wavelength approximately equal to a center wavelength of hyperfine peaks, and employing a modulation amplitude in the range HFS-3×LW to HFS.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Optically pumped magnetometer and magnetic sensing method
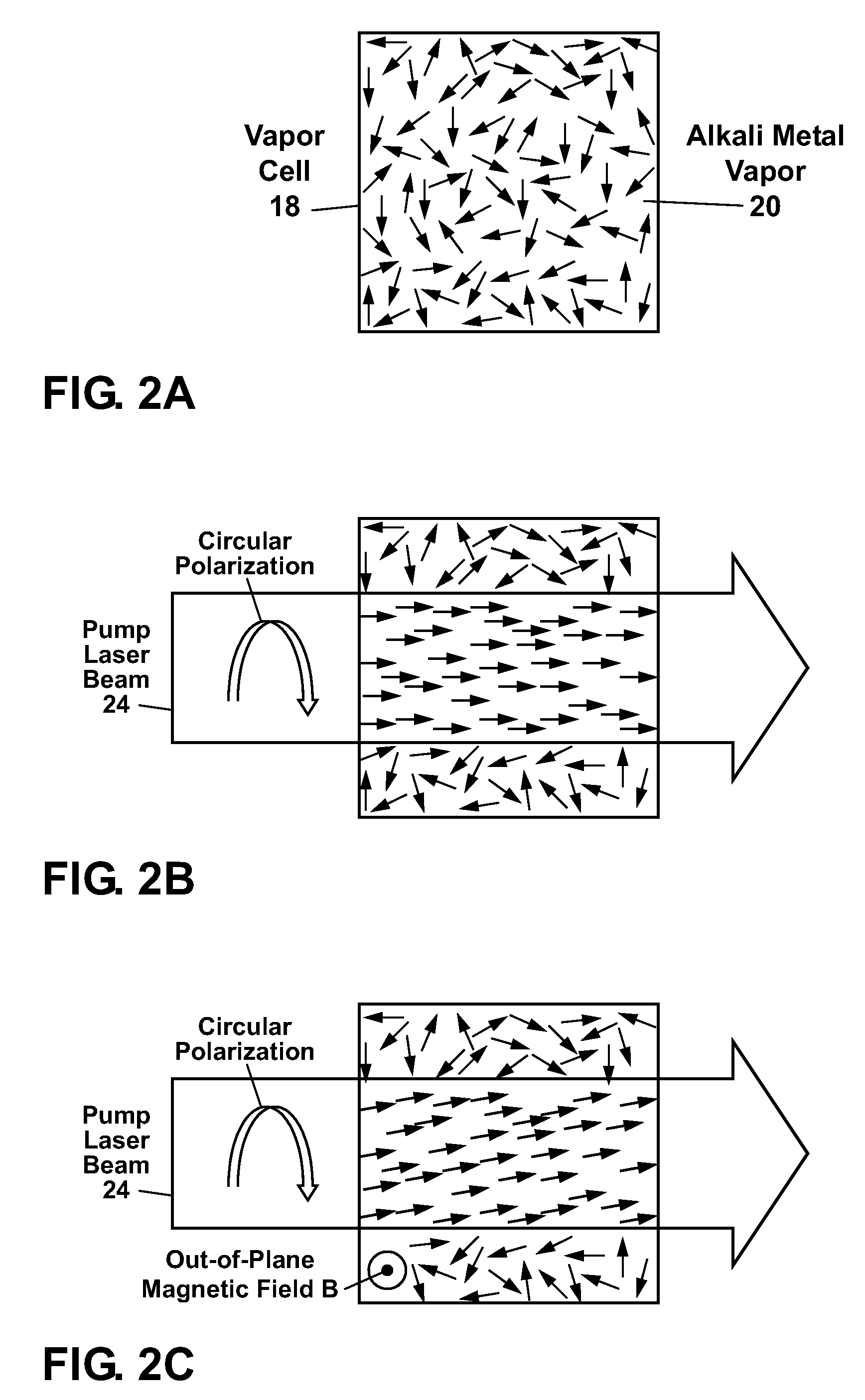
ActiveUS8941377B2Magnetic field measurement using magneto-optic devicesOptical polarizationAlkali metal
An optically pumped magnetometer and a magnetic sensing method acquire information as to strengths of magnetic fields in two different directions. A pump light having a circularly polarized component, first probe light having a liner polarized component and second probe light having a linearly polarized component are emitted to a cell containing a group of alkali metal atoms so as to form a crossing region A magnetic field applying unit applies a static magnetic field in a direction of the pump light incident on the crossing region during the emission of the pump light, the first probe light and the second probe light. And, information as to strengths of magnetic fields in two different directions perpendicular to the direction of the static magnetic field in the cell from the rotation angles of a polarization planes of the first and second probe lights during passage through the cell is calculated.
Owner:CANON KK
System and method for measuring a magnetic gradient field
ActiveUS10088535B1Improve signal-to-noise ratioEfficient detectionMagnetic property measurementsMagnetic field measurement using magneto-optic devicesMagnetic field gradientPhotodetector
A system and method is described to measure the magnetic field gradient using an optically pumped magnetometer configured as an intrinsic gradiometer. Atoms are prepared in a freely precessing coherent superposition of the magnetically sensitive hyperfine ground states in two or more physically separated locations. A probe laser beam is used to interrogate atoms in both locations. As the probe light beam passes through the coherent atoms, optical sidebands are self-generated at the ground state hyperfine frequency of the magnetically sensitive states. Each of the two sets of atoms produces distinct sidebands at a frequency separation proportional to the magnetic field experienced by each set of atoms. The probe light is captured using a photodetector. The self-generated probe optical sidebands interfere to produce a beat note whose frequency is proportional to the magnetic field gradient between the two sets of atoms. Measuring the frequency of the beat note therefore provides an accurate reading of the magnetic field gradient. An optical filter or a polarizer can be additionally used to remove the central frequency of the probe light, thus removing the noise produced by the residual probe beam.
Owner:QUSPIN
Mutually calibrated magnetic imaging array
ActiveUS9791536B1More transportableLess cumbersomeDiagnostic recording/measuringElectrical measurementsMagnetic tension forceMagnetic source
A mutually calibrated magnetic imaging array system is described. The system includes a non-target magnetic source rigidly attached to a magnetometer, and an attached control unit to measure and adjust several parameters of a magnetic imaging array. A non-target magnetic field source is used to generate a well-defined and distinguishable spatial magnetic field distribution. The source is rigidly attached directly to a magnetometer, while the relative positions of the magnetometers are unknown. The magnetic imaging array is used to measure the strength of the non-target source magnetic fields and the information is used to calibrate several parameters of the array, such as, but not limited to, effective magnetometer positions and orientations with respect to each other and cross-talk between the magnetometers. The system, and method described herein eliminates the need for a separate calibration phantom.
Owner:QUSPIN
Optical pumping magnetometer and magnetic sensing method
ActiveUS9244137B2Improve responseHigh sensitivity measurementMagnetic field measurement using magneto-optic devicesMeasurements using magnetic resonanceMagnetic tension forceOptical pumping
An optical pumping magnetometer is provided that is capable of improving the response of the magnetometer with respect to a magnetic field that varies with a period shorter than the transverse relaxation time of electron spin of an alkali metal atom.
Owner:CANON KK
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com