Patents
Literature
205 results about "Colour centre" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The colour centre is a region in the brain primarily responsible for visual perception and cortical processing of colour signals received by the eye, which ultimately results in colour vision. The colour centre in humans is thought to be located in the ventral occipital lobe as part of the visual system, in addition to other areas responsible for recognizing and processing specific visual stimuli, such as faces, words, and objects. Many functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) studies in both humans and macaque monkeys have shown colour stimuli to activate multiple areas in the brain, including the fusiform gyrus and the lingual gyrus. These areas, as well as others identified as having a role in colour vision processing, are collectively labelled visual area 4 (V4). The exact mechanisms, location, and function of V4 are still being investigated.
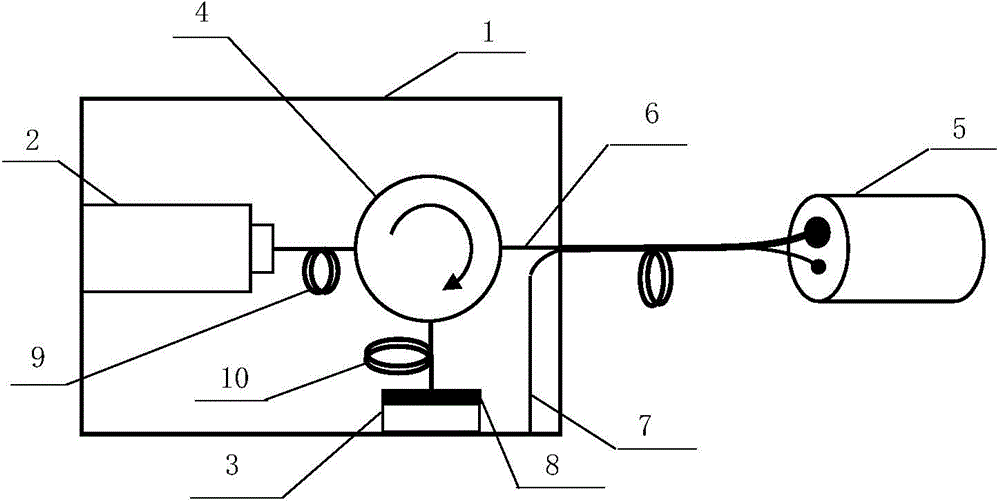
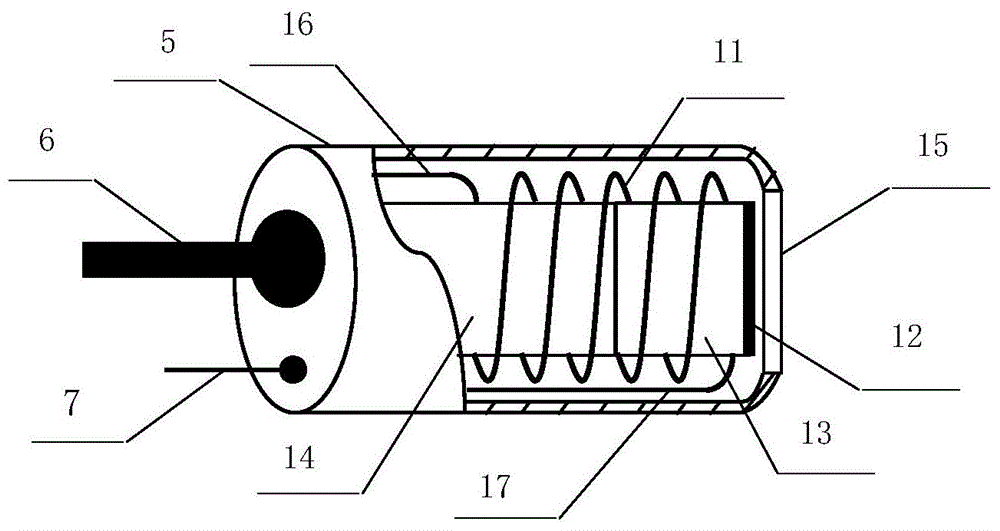
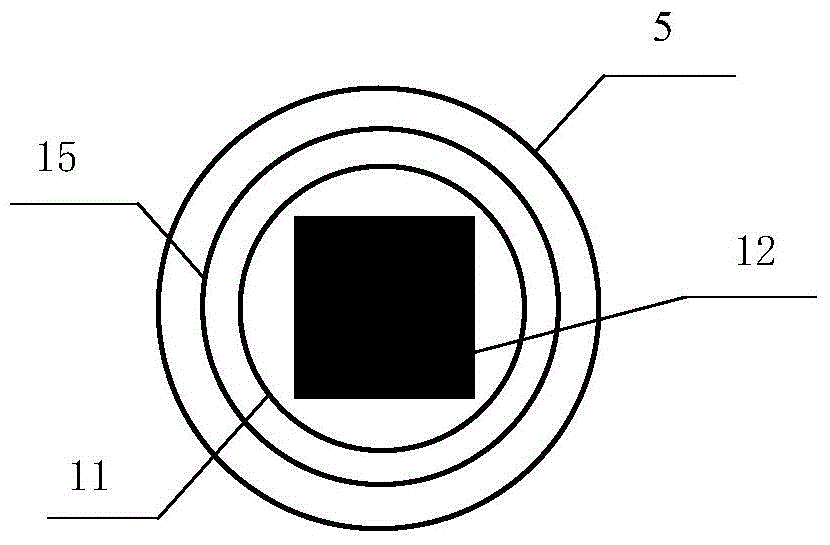
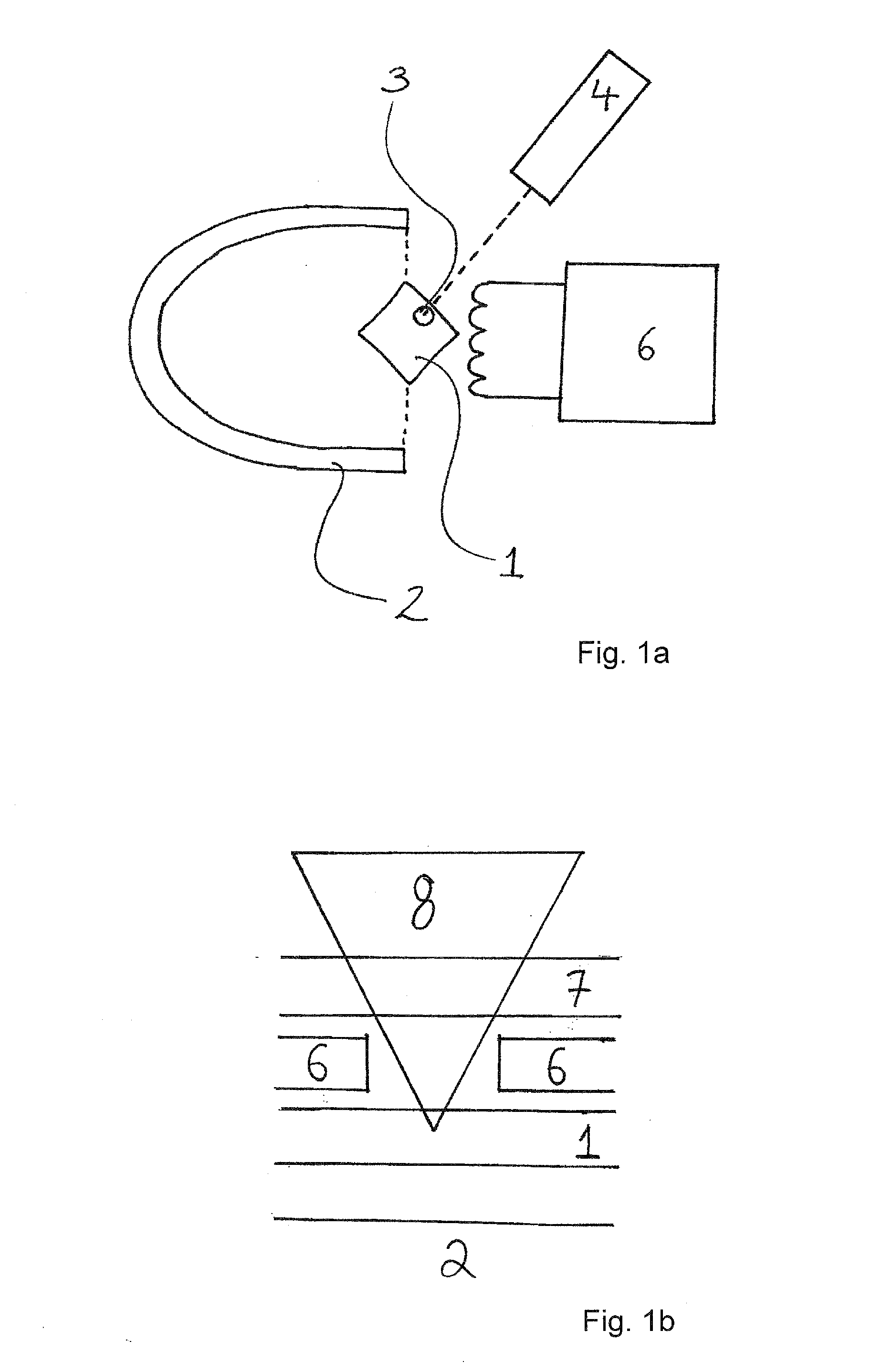
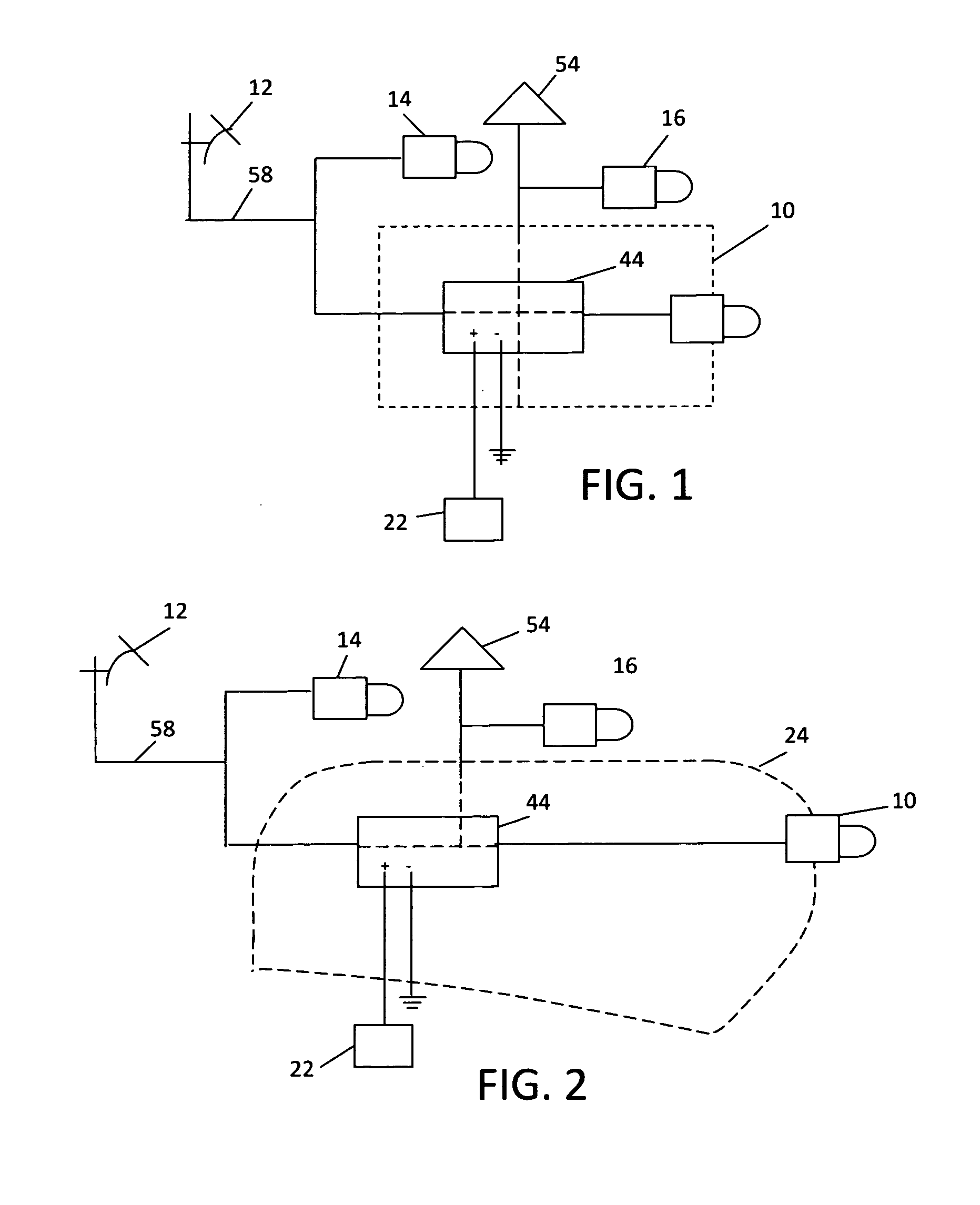
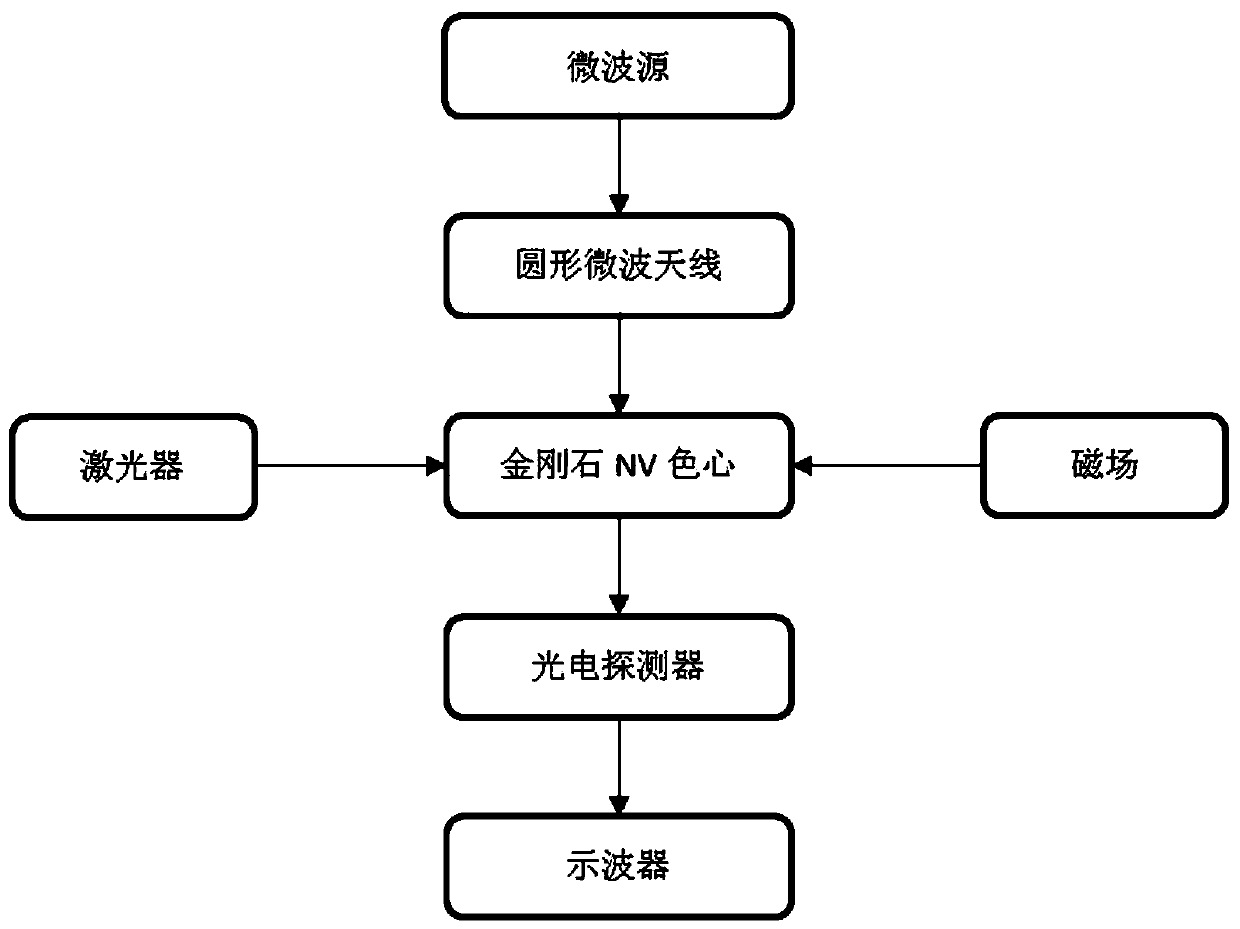
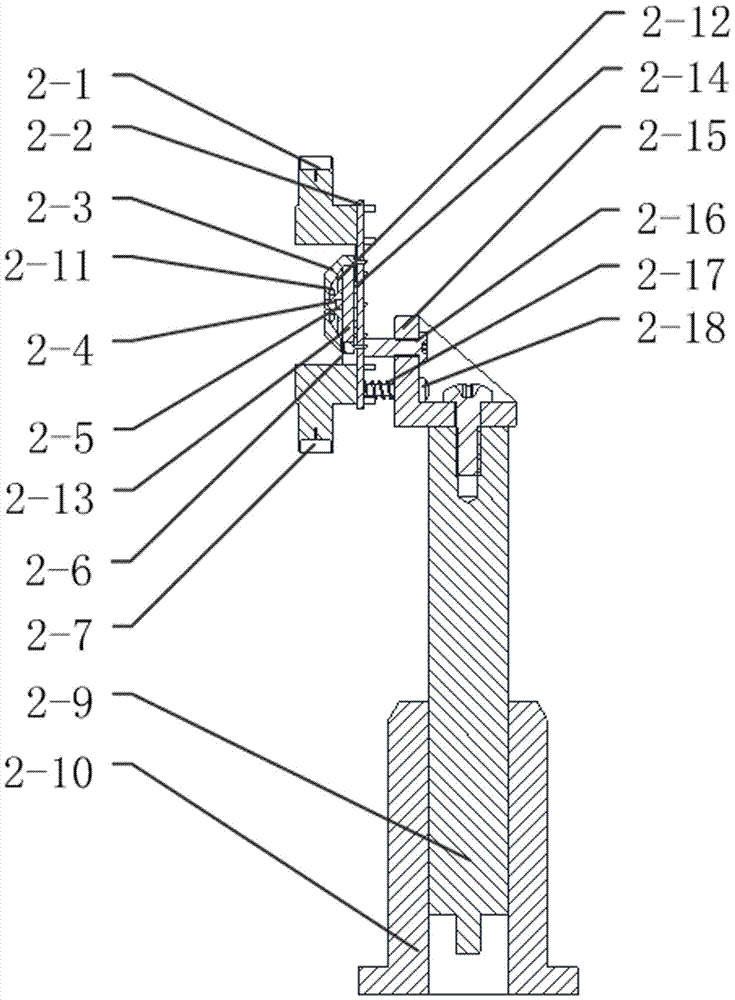
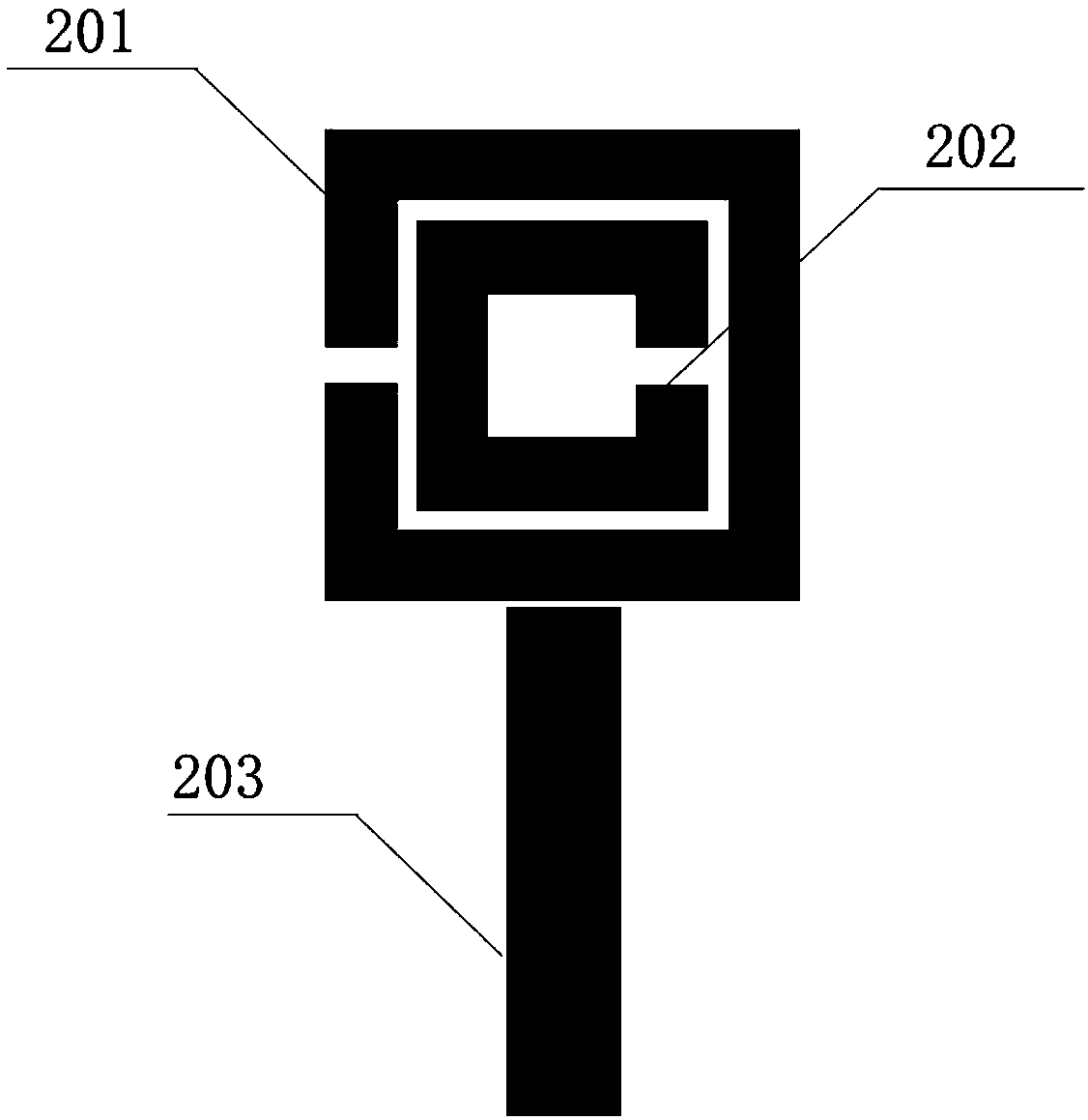
Electromagnetic field near-field imaging system and method based on pulsed light detection magnetic resonance
InactiveCN107356820ASimple structureLow costAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceElectromagentic field characteristicsHigh resolution imagingSingle crystal
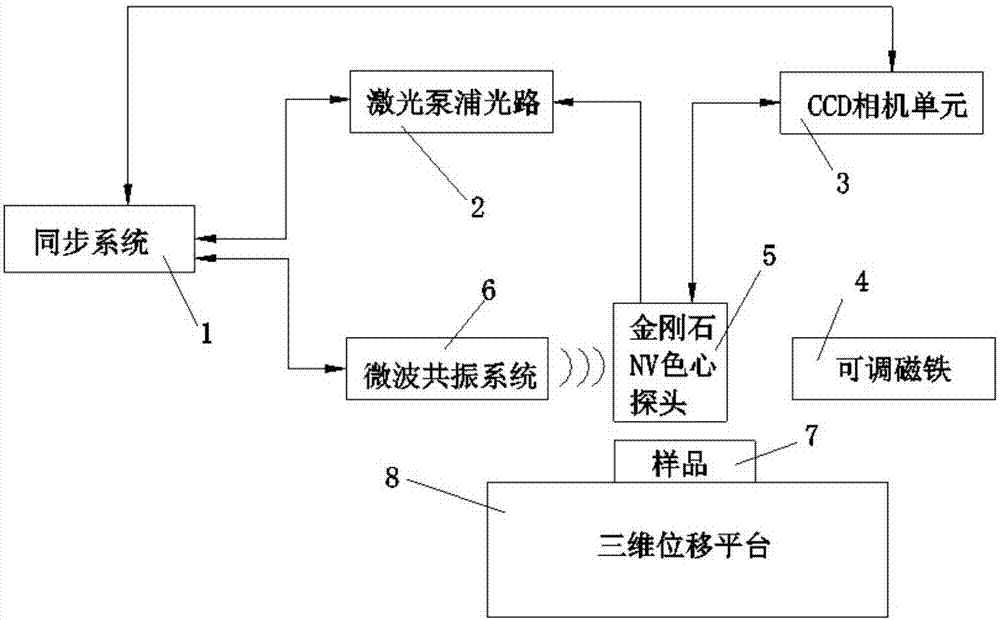
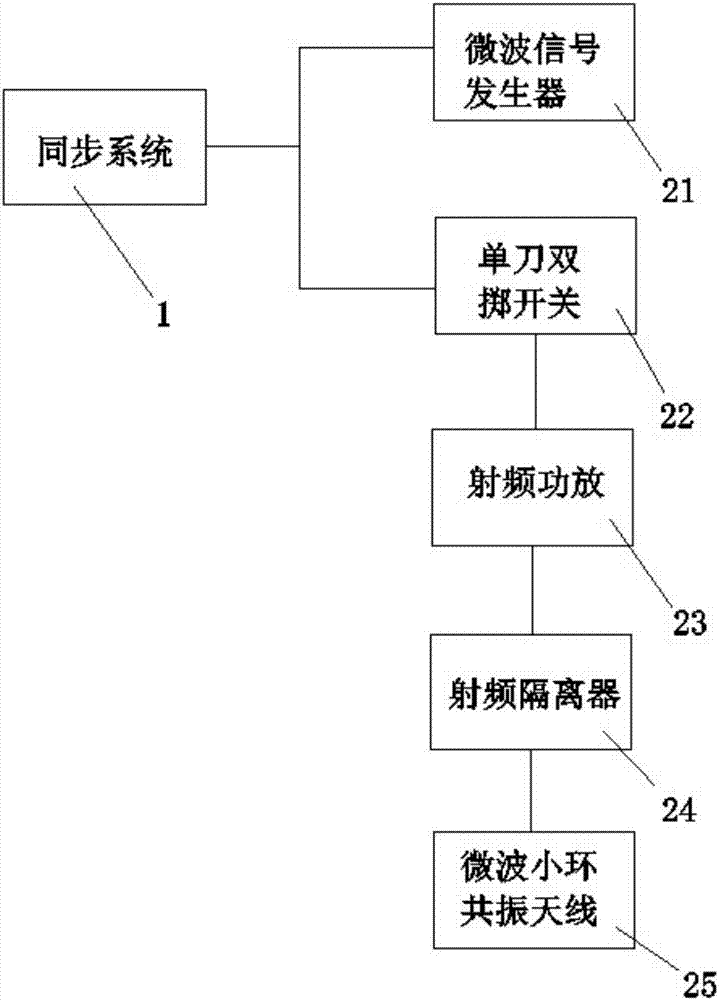
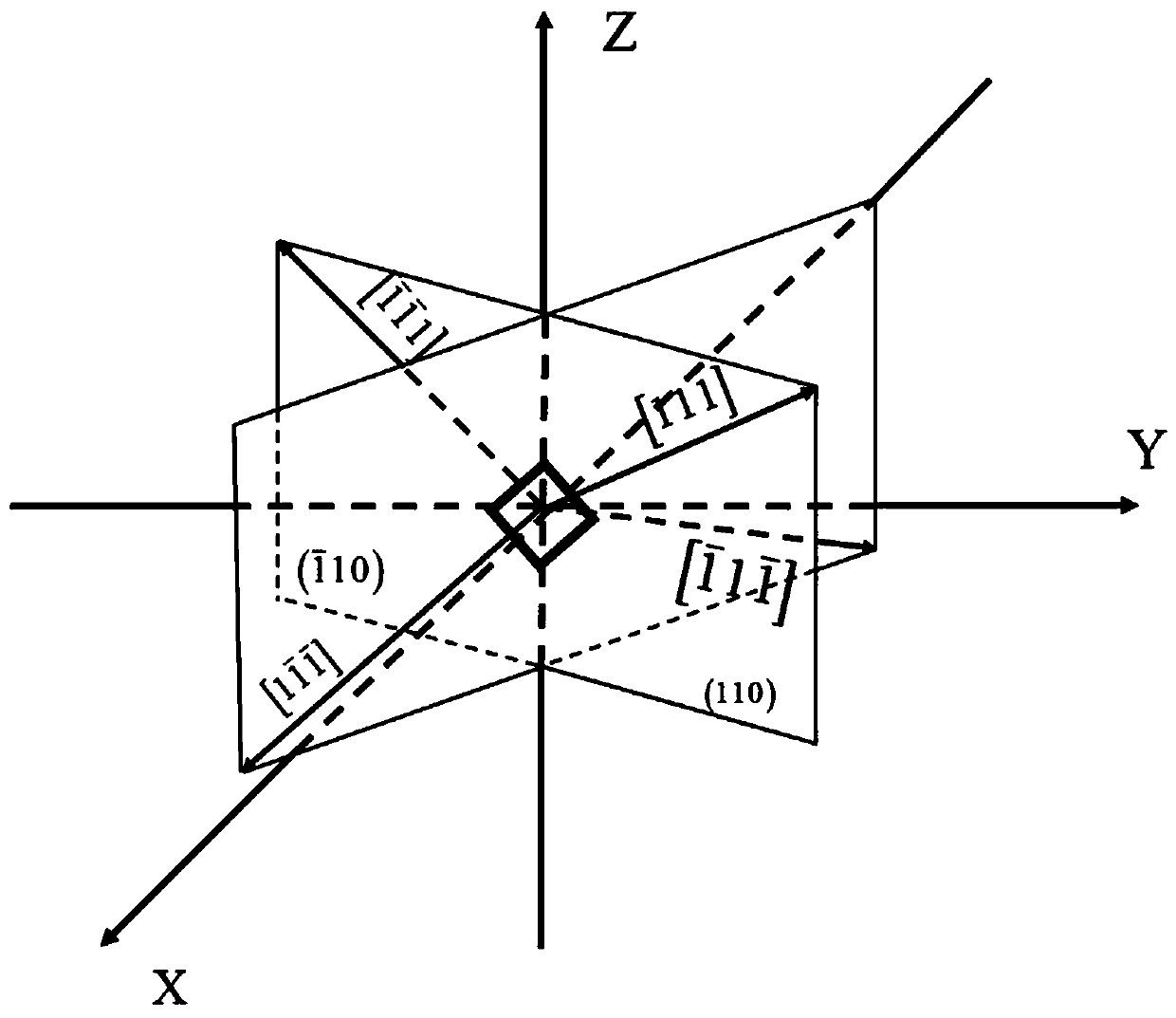
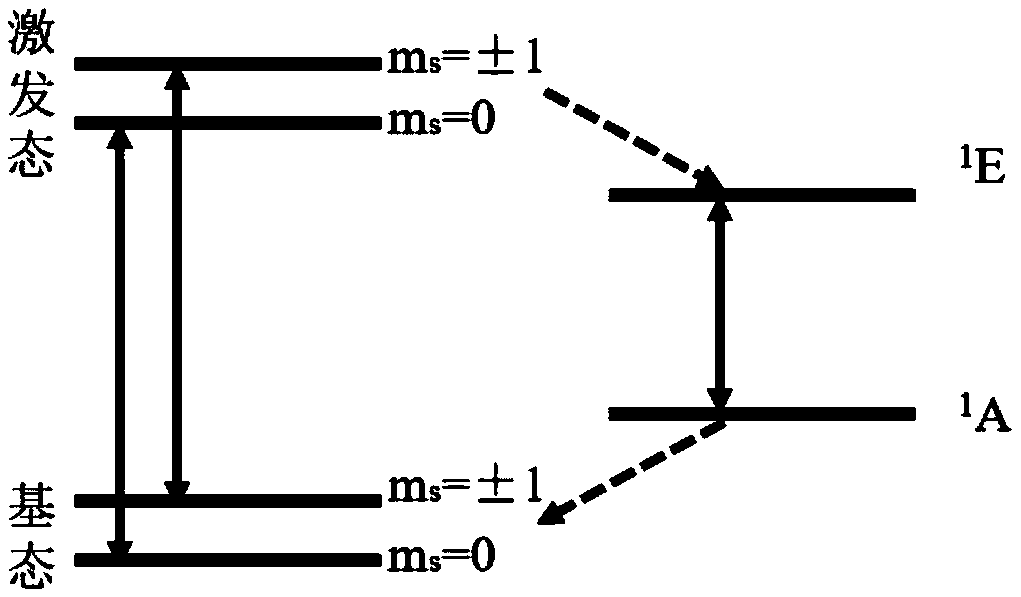
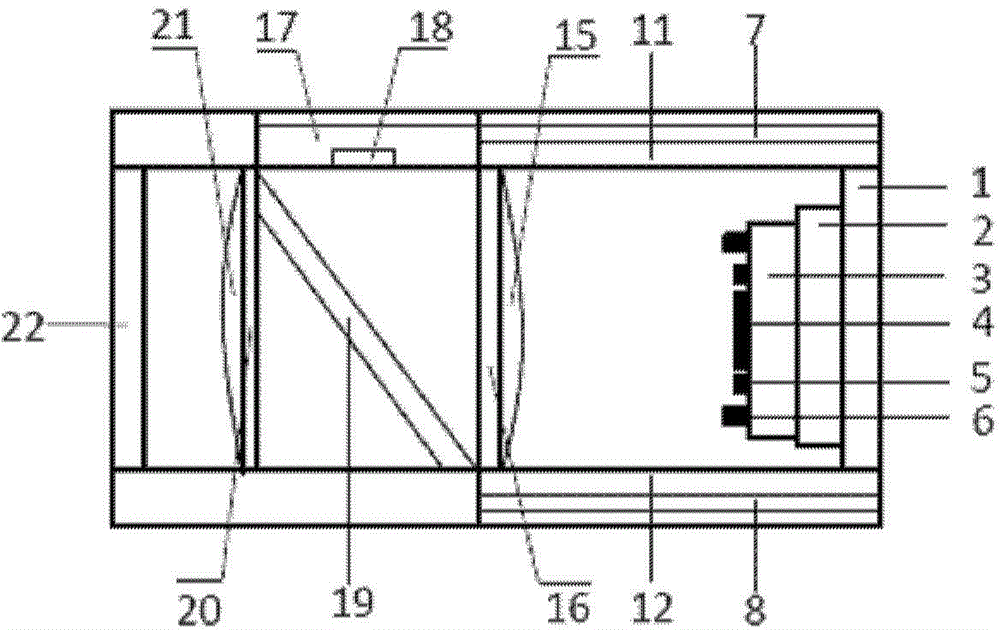
The invention discloses an electromagnetic field near-field imaging system and method based on pulsed light detection magnetic resonance. The system consists of a laser pump optical path, a microwave source, a diamond NV color-center probe, a CCD camera unit, a synchronization system, a displacement scanning platform, control software and a data analysis imaging system. In the system, a large diamond single crystal containing the NV color-center is used as a detection unit, a static magnetic field is used to split a magnetic resonance peak of the diamond NV color-center into eight peaks, the eight resonance peaks correspond to four crystal axis directions <111>, <1-11>, <-111>, <11-1> of a diamond lattice structure, by measuring the Rabi frequency of each resonance peak, the strength of a circularly polarized microwave field perpendicular to the corresponding crystal axis direction is obtained, and through comprehensive calculation of the microwave field strengths in the four directions, the strength and direction of a microwave vector are then reconstructed. Through the microwave near-field high-resolution imaging of a local region of a microwave chip under measurement, the quantitative data can be provided for the failure analysis of the chip.
Owner:南京昆腾科技有限公司
Nanometer level three-dimension magnetic resonance molecule imaging device based on diamond NV-color center
InactiveCN105738845ADecreased fluorescence intensityMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsMicrowaveColour centre
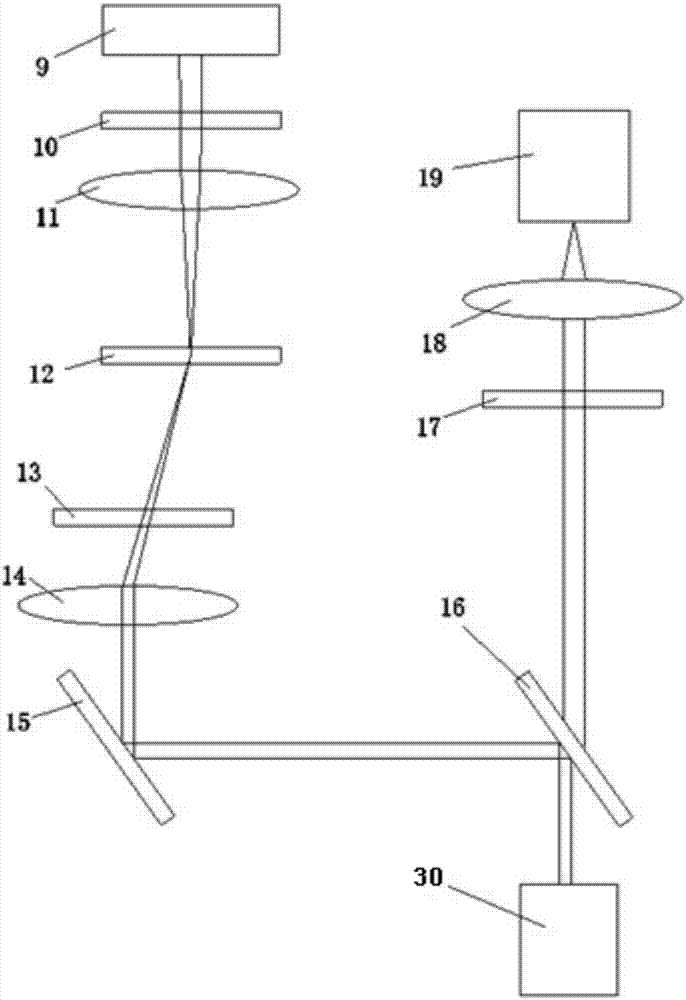
The invention discloses a diamond-based NV ‑ A nanoscale three-dimensional magnetic resonance molecular imaging device for color centers, comprising: a glass base; a laser, arranged inside the glass base, for emitting laser light to the outside; containing NV ‑ The diamond with the color center is arranged on the upper surface of the glass base, and the laser emitted by the laser is directly irradiated to the diamond; the microwave pulser is used to input microwave pulses to the diamond; the microscope objective lens is used to make the NV of the diamond ‑ Fluorescence from the color center is emitted outward through the microscope objective; a monochromatic filter for filtering the NV of the diamond ‑ Fluorescence from color centers; nanoconvex lenses that filter the NV of the diamond ‑ The fluorescence emitted by the color center is further concentrated; the distributed optical imaging lens is used to realize the imaging function; the packaging device is used to realize the functions of stable temperature, electromagnetic shielding and isolation protection.
Owner:HARBIN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Microwave sensor based on NV color center diamond
ActiveCN104360152ASolve the accuracy problemSolution volumeFrequency measurement arrangementMagnetic field measurement using magneto-optic devicesColour centreNitrogen
The invention discloses a microwave sensor based on an NV color center diamond. A diamond internally containing a Nitrogen-Vacancy color center is adopted as a sensitive element, electronic energy level stimulation is achieved through lasers, an additionally-arranged static magnetic field is scanned, and the microwave frequency and the microwave intensity are measured through fluorescence intensity detection. Dependency of electronic rabi-flopping of the NV color center in the diamond on the external microwave magnetic field is brought into play, high theoretical accuracy and good stability are achieved, the microwave sensor has the advantages of being small in size, low in cost, high in accuracy, large in temperature range, simple in operation condition and the like and rotates on the basis of solid atoms, and the microwave sensor can serve in all the fields with the requirements for the low-cost high-accuracy microwave frequency and intensity detection in the future.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Method for the hyperpolarisation of nuclear spin in a diamond via a long-range interaction
ActiveUS20160061914A1Narrow line widthEfficient transferQuantum computersNanoinformaticsColour centreOptical pumping
The invention concerns a method for the hyperpolarisation of 13C nuclear spin in a diamond, comprising an optical pumping step, in which colour centre electron spins in the diamond are optically pumped. The method further comprises a transfer step in which the polarisation of a long-lived state of the colour centre electron spins is transferred to 13C nuclear spins in the diamond via a long-range interaction.
Owner:UNIV ULM
Diamond gyroscope with color core
ActiveCN103557855AReduce volumeIncrease the number ofTurn-sensitive devicesHigh concentrationGyroscope
The invention relates to a diamond gyroscope with a color center, adopts a diamond material internally containing the high-concentration nitrogen-vacancy (NV-) color center as a sensitive element, realizes the control and the detection in the electronic energy level by using optical and microwave means and realizes the carrier angular velocity measurement. The diamond gyroscope with the color center has the advantages of room temperature operation, small volume, low cost and the like; compared with an existing gyroscope such as an MEMS (Micro Electro Mechanical System) and the like under same positioning, the diamond gyroscope with the color center is higher in theoretical sensitivity, and better in stability, has an important value on developing atomic spinning effect-based high-stability and small-volume solid-state atomic gyroscope, and is used for an inertial navigation and gesture measurement system in all fields in future, specially in the civil low-precision field.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
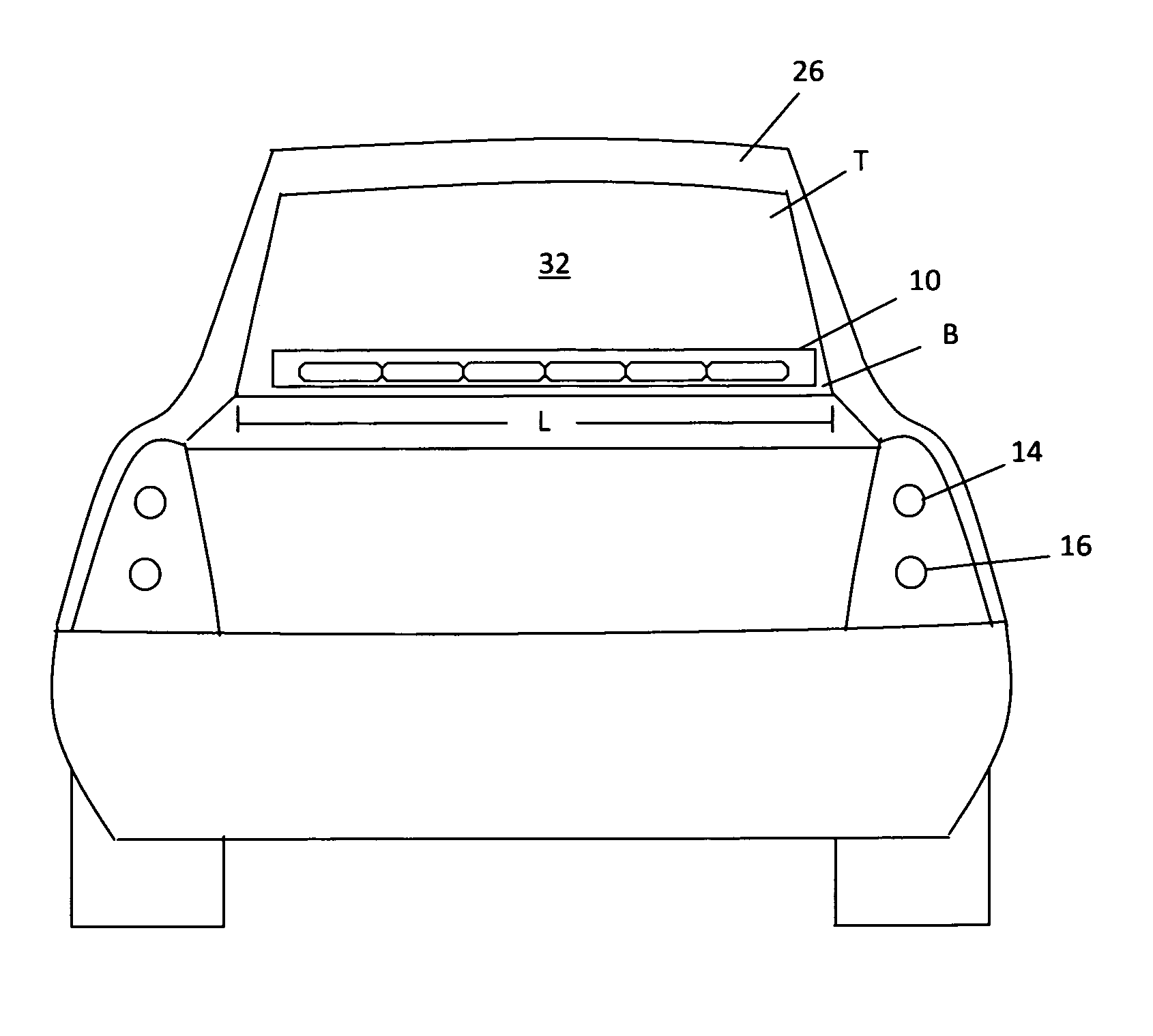
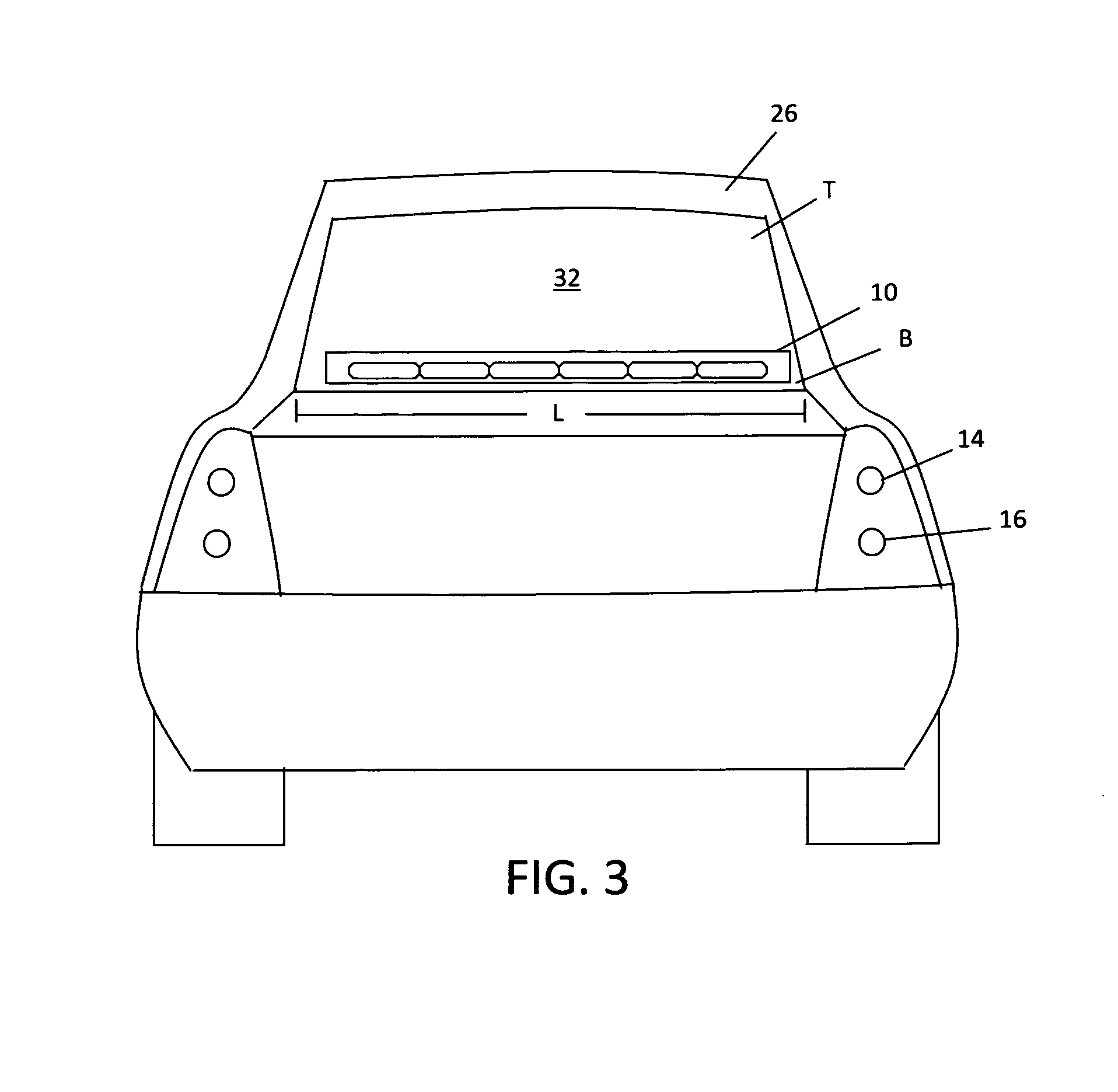
Multifunctional Multiple Color Center High Mounted Stop Lamp
InactiveUS20140301101A1Easily employedEnhance a hazard flashing systemOptical signallingRefractorsMobile vehicleColour centre
The present invention relates generally to a center high mounted stop lamp for a vehicle, such as a four- or two or three-wheeled motor vehicle, which makes a vehicle behind aware of its approach to a vehicle ahead in accordance with an actuation of the latter's brake system. In particular, it relates to a multifunctional multiple color center high mounted stop lamp for mounting in the interior or exterior of the vehicle, which includes multiple light emitting diodes (LEDs) configured to emit different colors through a single optical lens. This present invention enhances the safety of the vehicle by combining the advantages of a center high mounted stop lamp with the advantages of a hazard warning / signaling device. Combining these advantages into the multifunctional multiple color center high mounted stop lamp cooperate to increase overall vehicle safety and creates a synergistic effect.
Owner:MR DEREK TERRELL RUSS
Three-axis solid-state atomic magnetic sensor based on diamond NV color center and magnetic field detecting method
ActiveCN108519564AMagnetic field measurement using magneto-optic devicesElectric/magnetic detectionFluorescencePermalloy
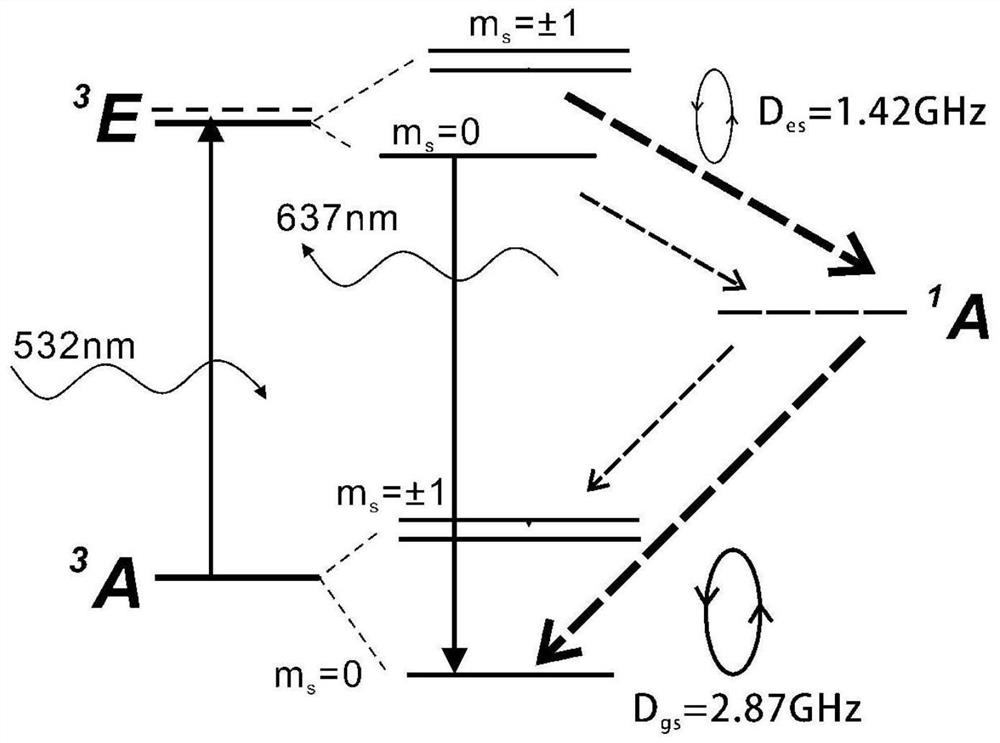
The method of the invention includes that a spin triplet state electronic ground state based on a diamond NV color center uses the diamond NV color center as a sensitive component under different magnetic field conditions, and the NV color center is excited by the laser 532 nm; the NV color center emits fluorescence through external microwave, and further, an ODMR spectrum is obtained. Three pairsof distinct Zeeman split peaks can be extracted from the spectrum, and the resonance frequency difference between each pair of peaks is measured. The three different frequency differences come from three different NV directions, and the magnitudes of the three frequency differences are proportional to the magnetic field strength along projections of three symmetry axes in the NV color center, andthe three orientations is sufficient to extract three components of the magnetic field, which is the total field strength in this state. The measured weak magnetic field of the magnetized permalloy is obtained by subtracting the known magnetic field from the total field strength. Furthermore, the detection of the weak magnetic field of the local spin triplet state electronic ground state based onthe diamond NV color center is realized.
Owner:ZHONGBEI UNIV
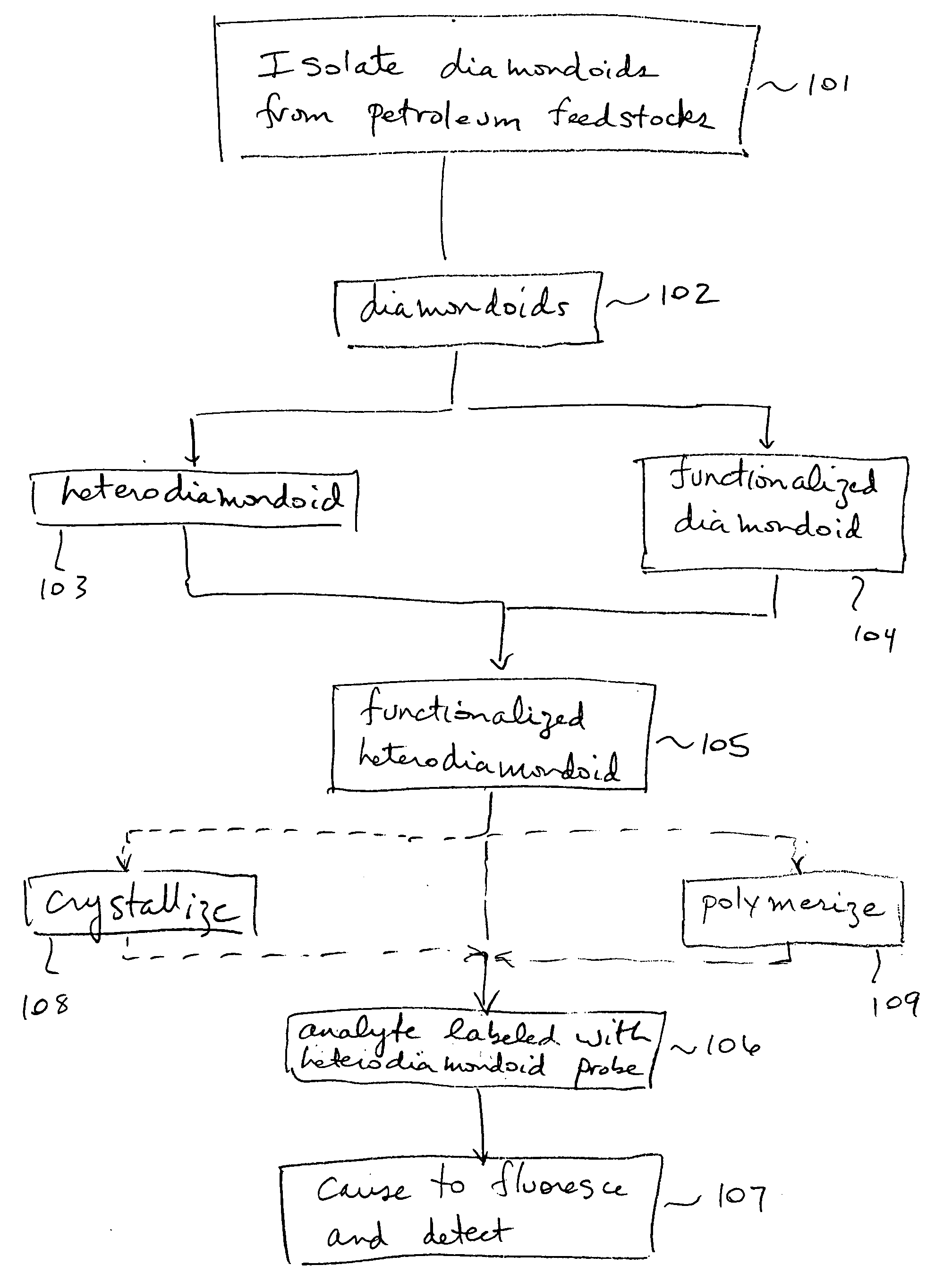
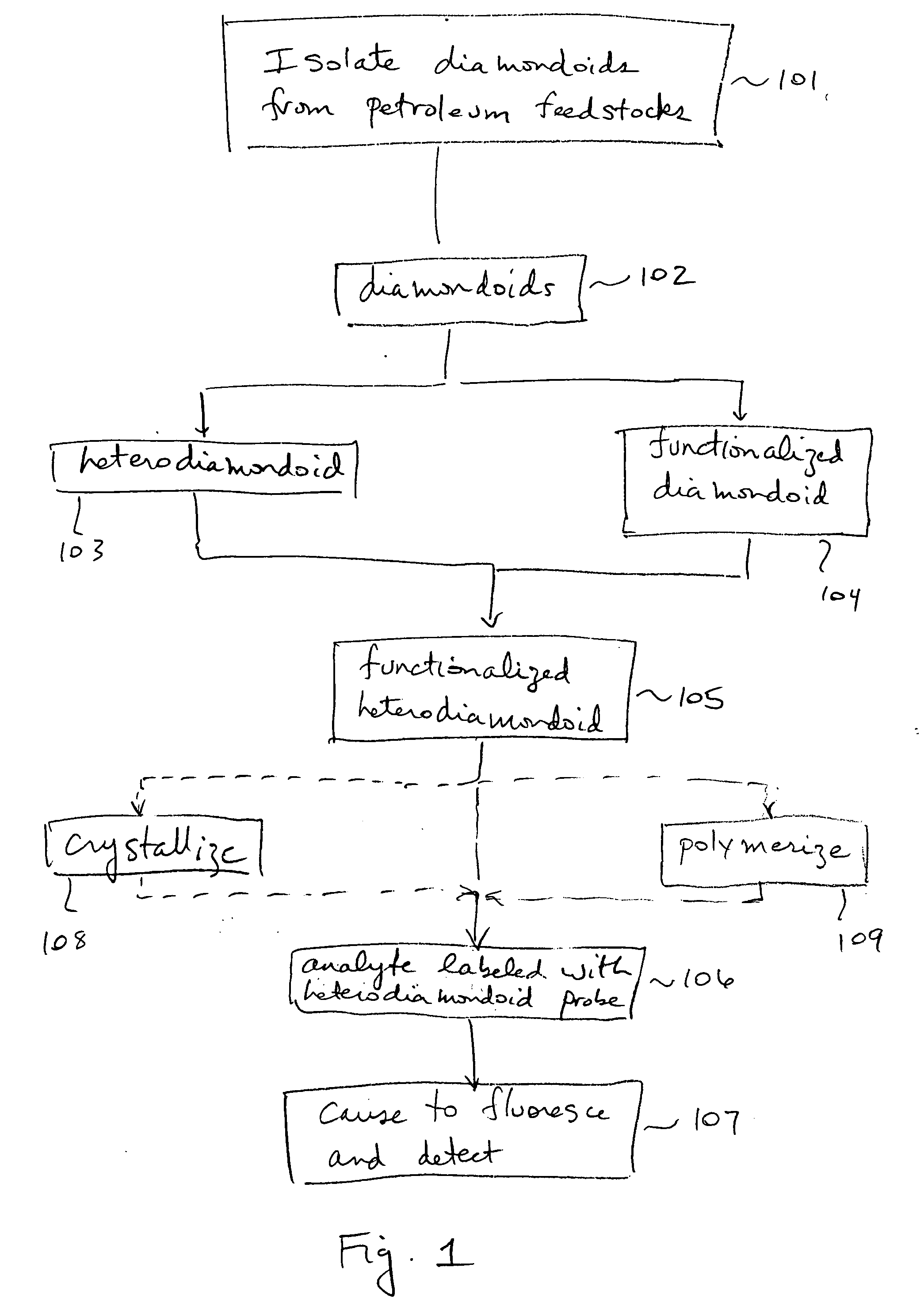
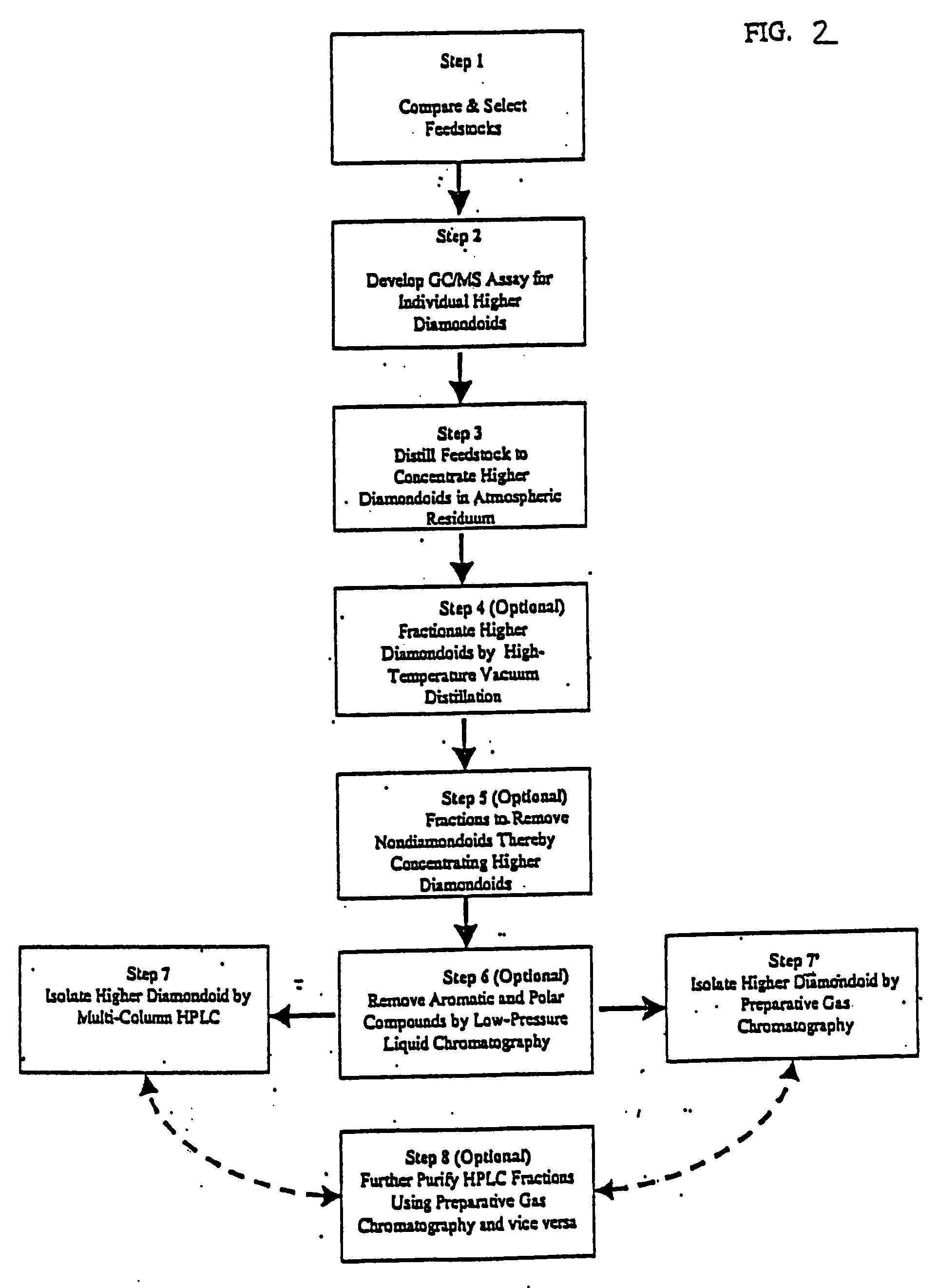
Luminescent heterodiamondoids as biological labels
InactiveUS20050019955A1Biological testingChemical vapor deposition coatingTarget analysisColour centre
Novel biological labels are disclosed herein. The label comprises a functionalized heterodiamondoid functioning as a biological probe, the probe having an affinity for a target analyte molecule. Upon absorption of incident excitation radiation, color center(s) located within the heterodiamondoid are caused to luminesce. The photoemitted light may be detected and analyzed to yield information about the analyte. The color centers in the heterodiamondoid will typically comprise nitrogen-vacancy and / or nitrogen-pore complexes, but may also comprise a dopant impurity atom such as a rare earth or transition metal element.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
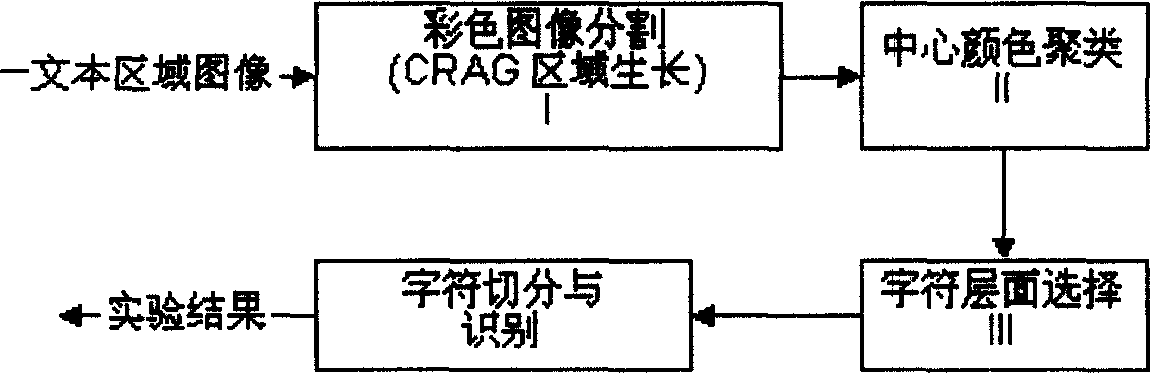
Character extracting method from complecate background color image based on run-length adjacent map
InactiveCN1588431AHigh correct extraction rateCharacter and pattern recognitionImage extractionCharacter analysis
The invention is a character extracting method in complex background color image based on runlength adjacency graph, which belongs to character extracting field in preprocess of color image character identification. All color connection sections are acquired with CRAG (color run-length adjacency graph) region growing algorithm after the digital color image is acquired, then the color average is carried on with color classification, acquires several color centers, forms different color layers with the color centers, then the color connection regions accordant to connection region differentiation rule are distributed onto several color layers. Finally the character is selected out through character analysis and size consistency differentiation, and acquires the character image. The method has a high speed and accuracy.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method for non-destructive measuring of radiation dose
InactiveUS7098470B2Accurate acquisitionMaterial analysis by optical meansBy pulling from meltDosimetry radiationFluorescence
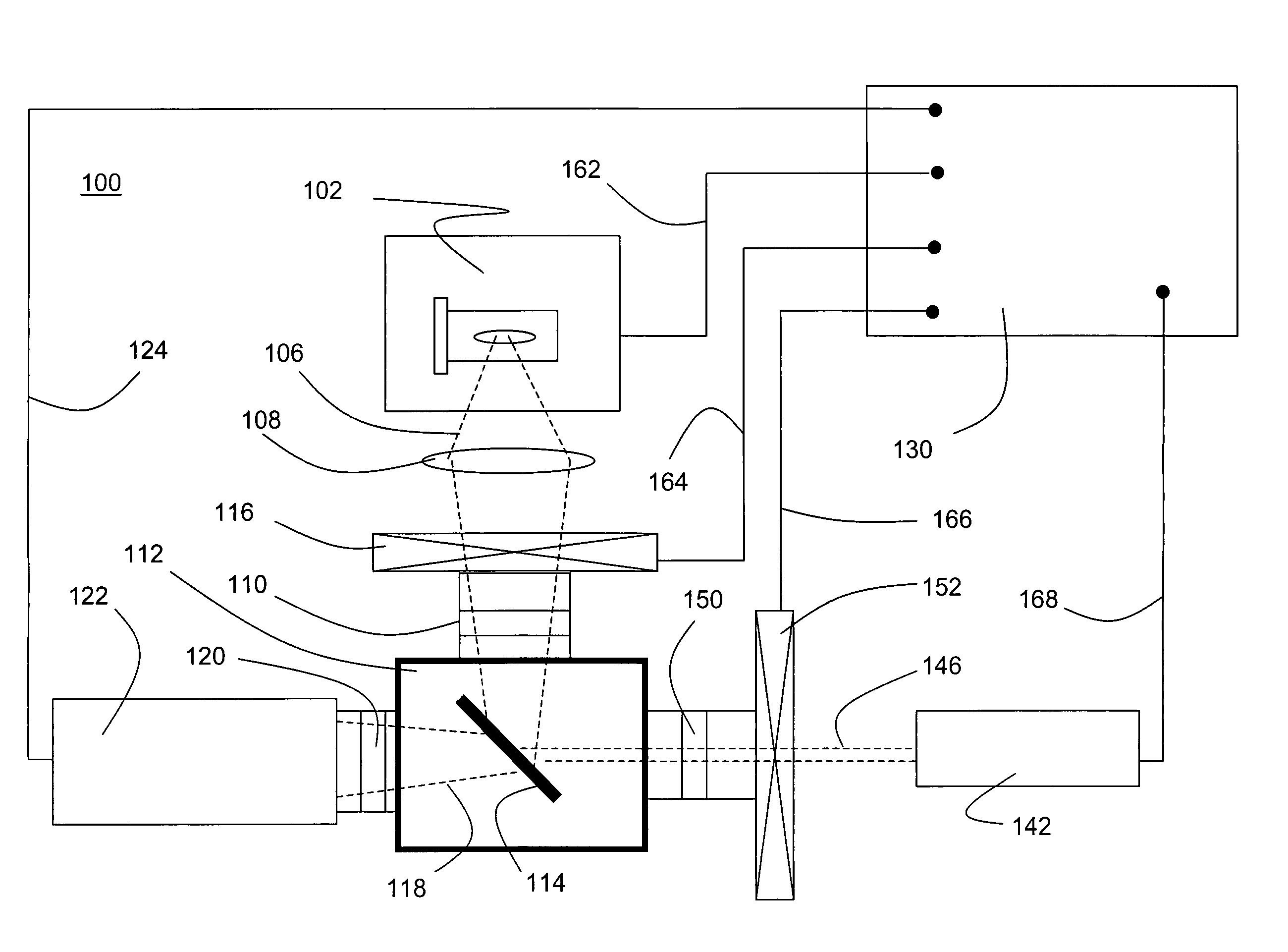
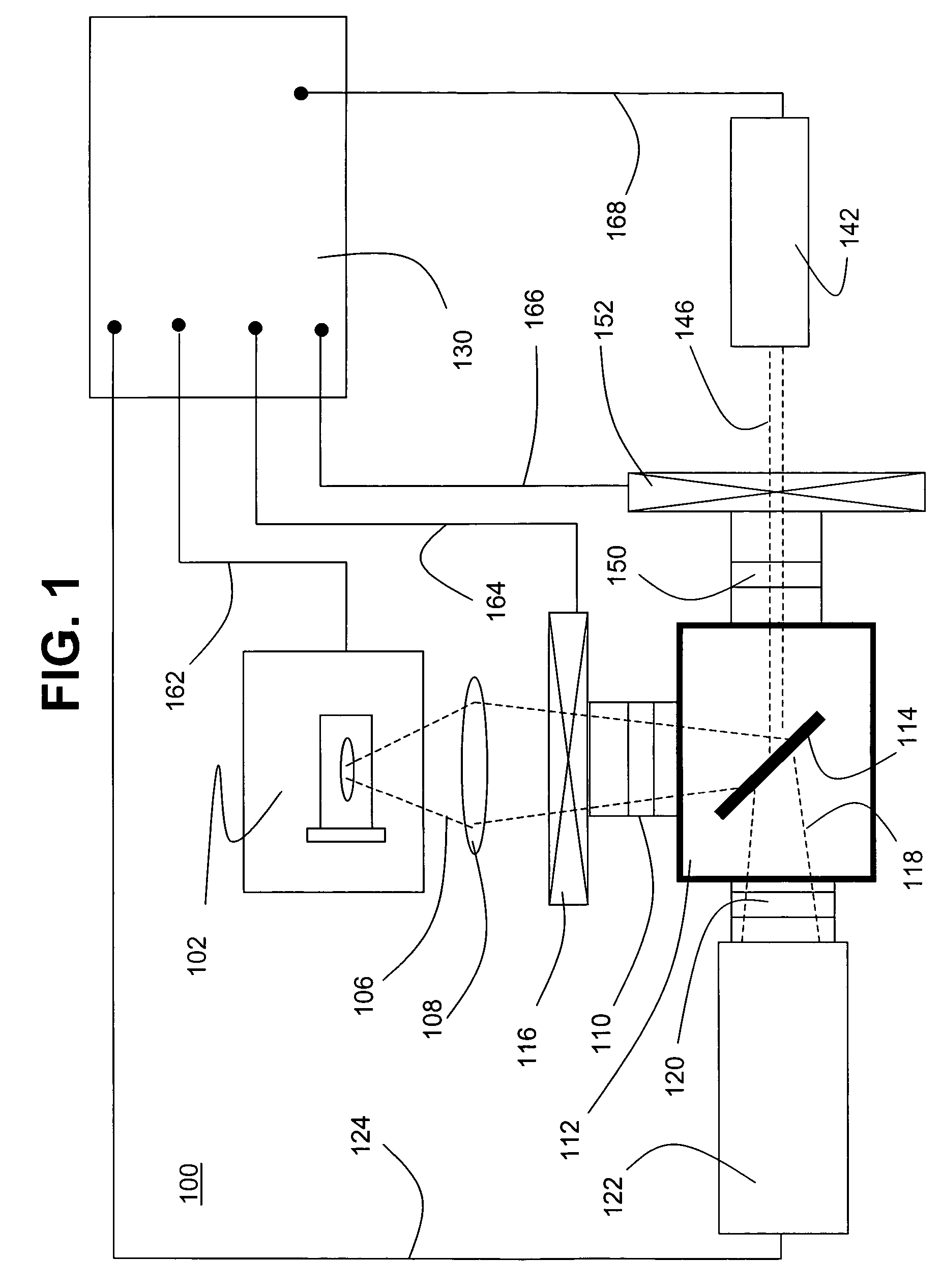
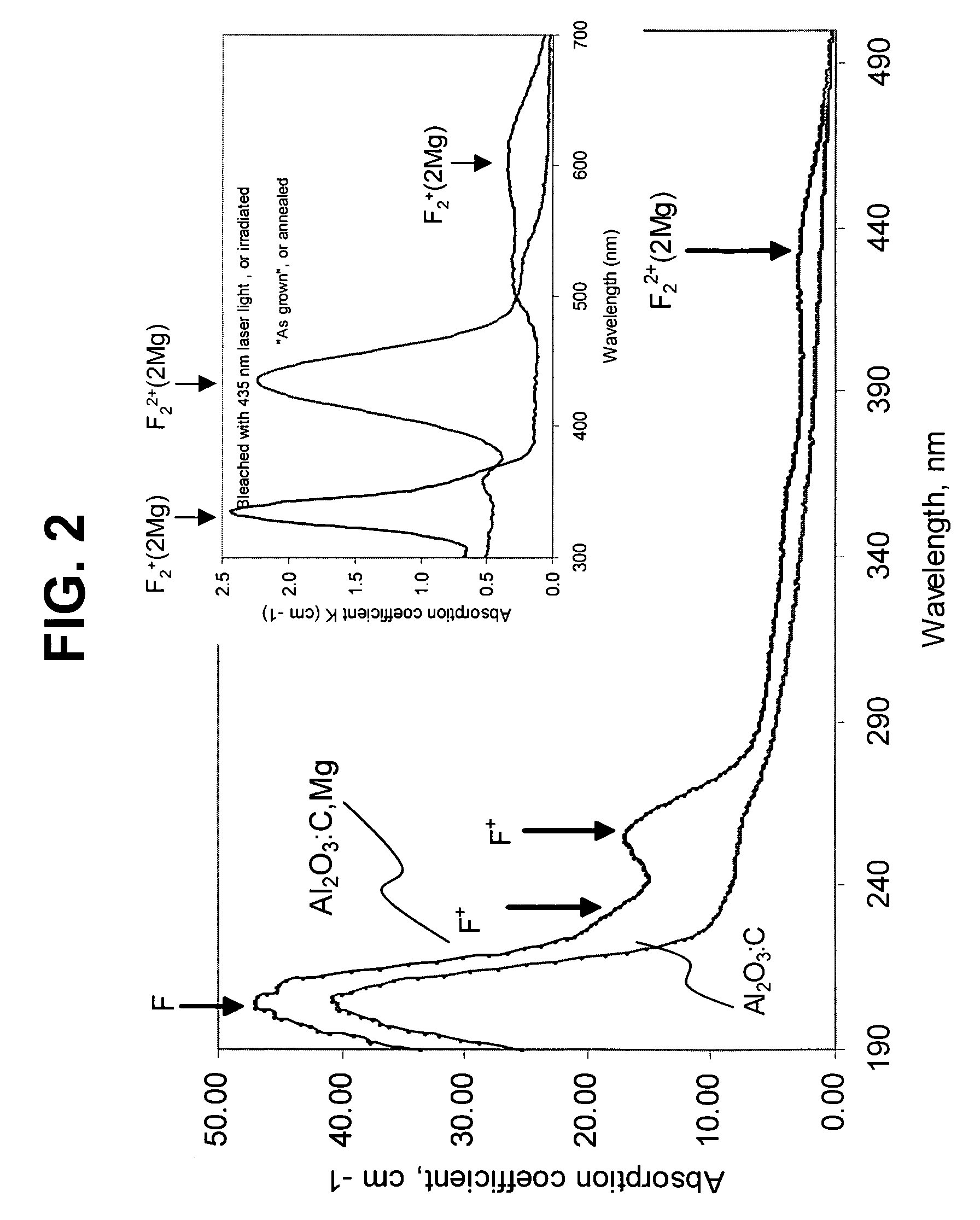
The invention presents a method of radiation dosimetry and radiation field imaging. It utilizes luminescent material based on aluminum oxide doped with carbon and magnesium (Al2O3:C,Mg) and containing aggregate oxygen vacancy defects. Storage of dosimetric information is based on ionization of the crystal matrix, generation of free electrons and capture of electrons and holes by traps and color centers. An absorbed dose is determined by non-destructive readout of fluorescence from color centers induced by radiation. The preferred mode of measurements is to illuminate the Al2O3:C,Mg phosphor with a red laser (at 635 or 650 nm) and to measure the intensity of 750 nm fluorescence. Method allows for high temperature and environmental stability of dose information. The detector material is insensitive to room light before and after the irradiation and provides a fast data rate during scanning for imaging of radiation fields.
Owner:LANDAUER INC
Chip-level diamond NV-color center magnetic imaging device and method
ActiveCN105137371AReduce volumeQuick responseMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringMedical diagnosisElectromagnetic shielding
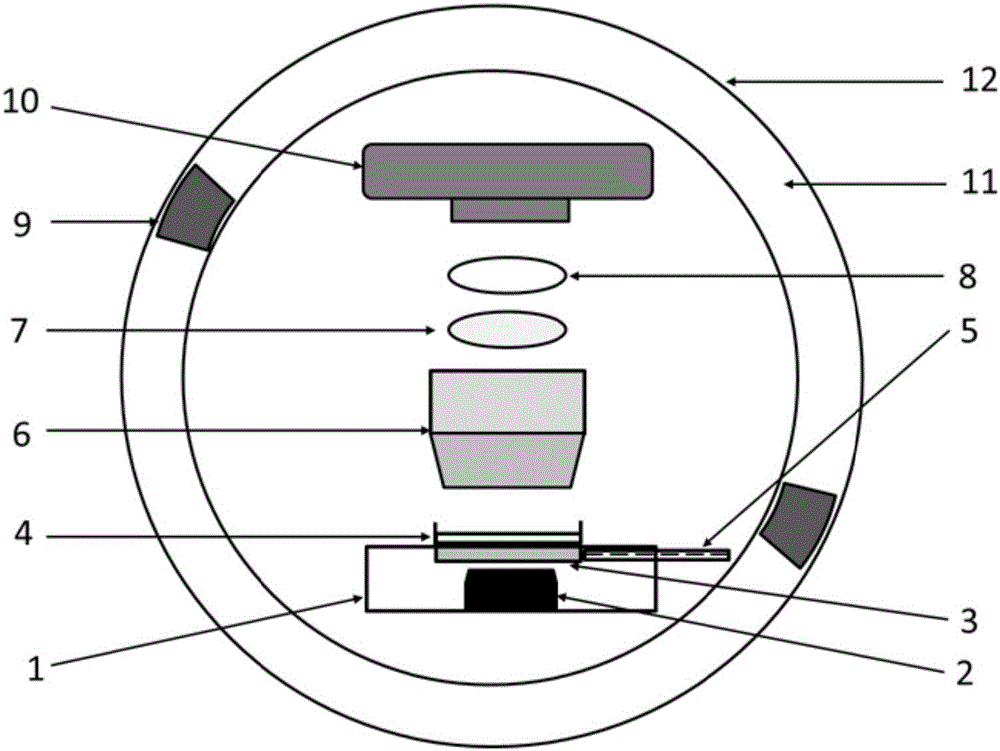
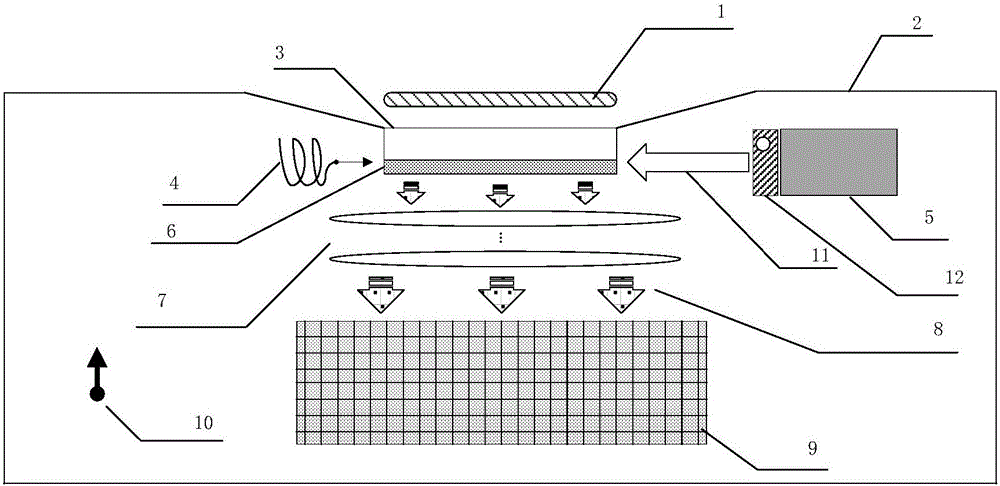
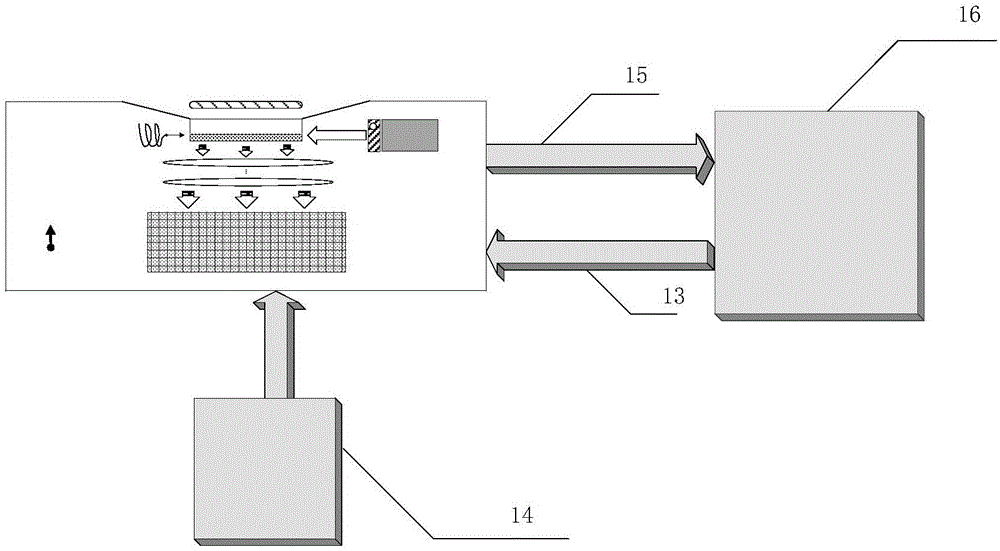
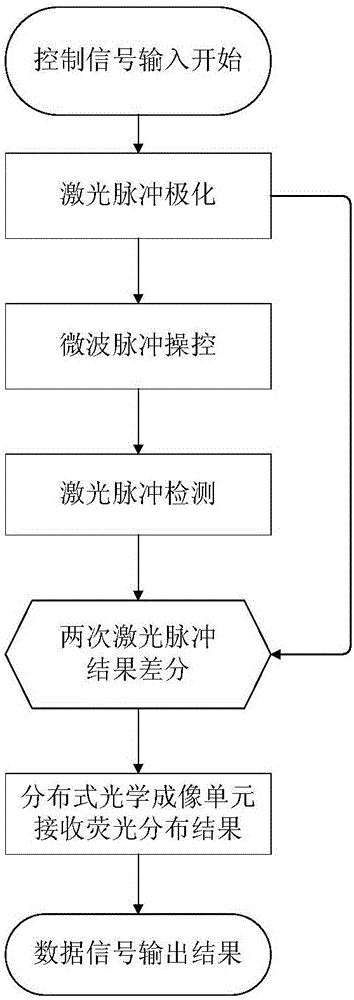
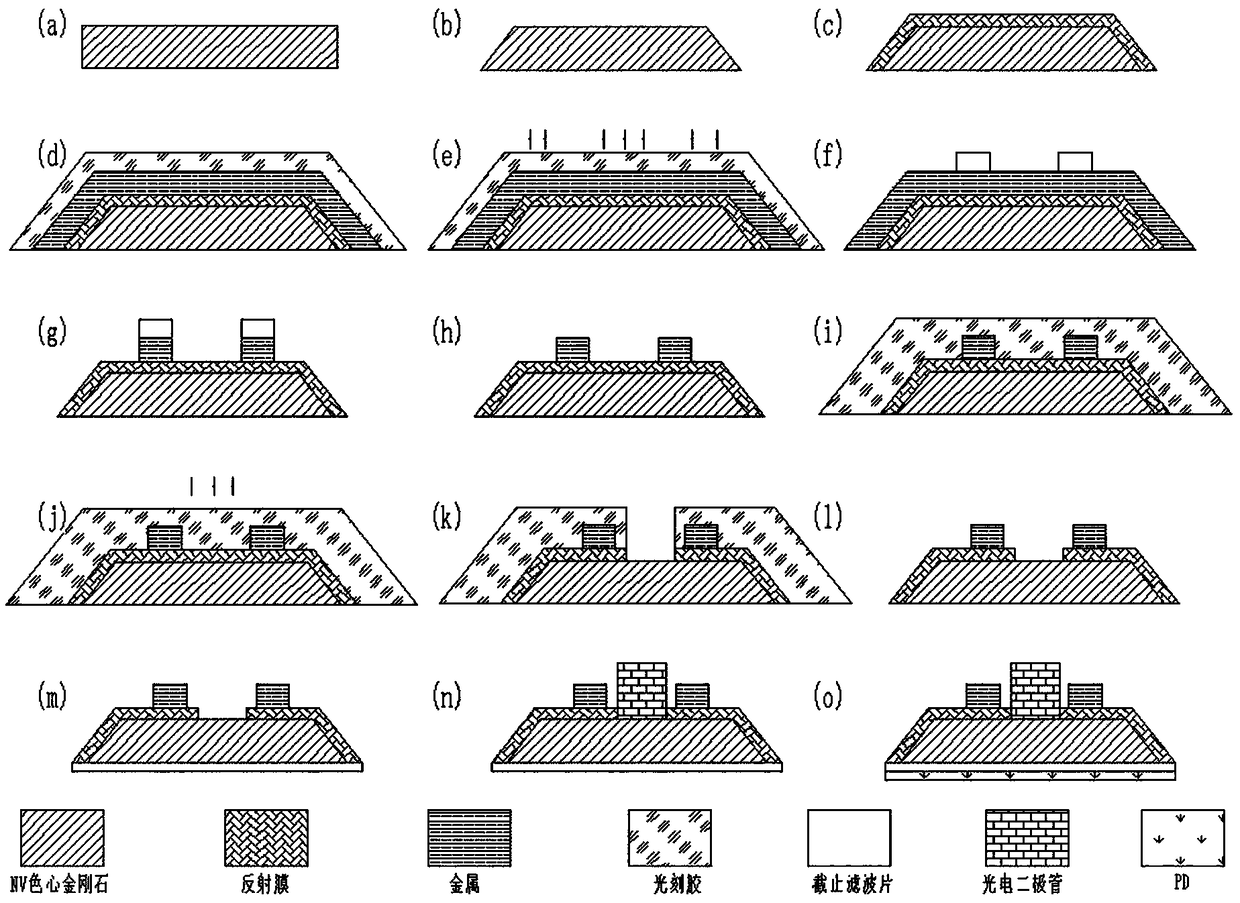
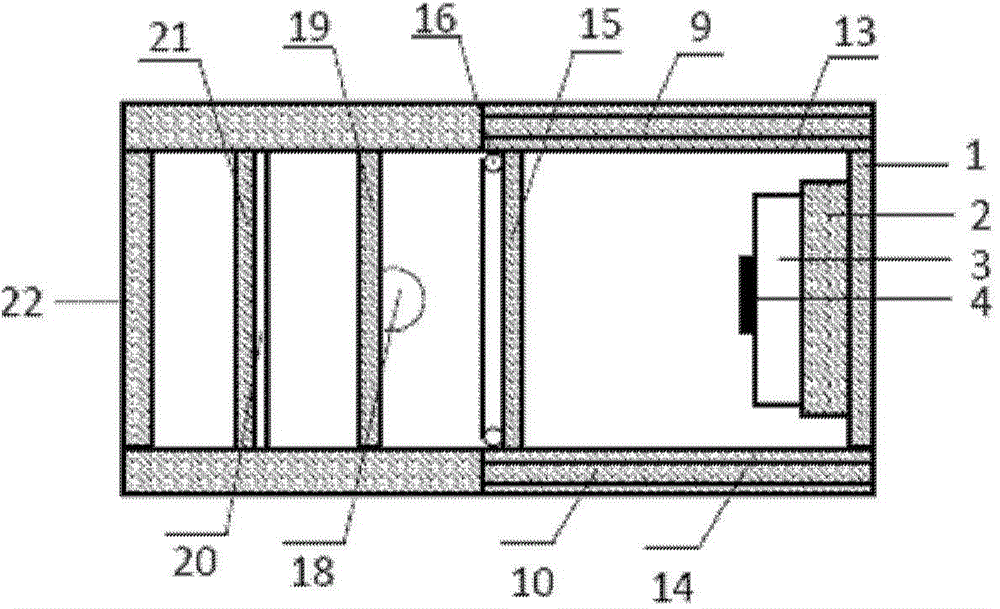
The invention discloses a chip-level diamond NV-color center magnetic imaging device and method, and the method achieves the hyperfine magnetic field imaging of the two-dimensional surface of an object, such as a magnetic image of a biological cell. The method comprises the steps: carrying out the polarization of a laser pulse and a microwave pulse; generating fluorescent light generated at the NV-color center of a diamond in an external magnetic field; employing the laser pulse to generate fluorescent light again, wherein the difference result of fluorescent light of two times can reflect the magnetic field intensity of the NV-color center, thereby achieving the conversion of magnetic field information to optical information; and employing a nano-level convex lens group and a distributed optical imaging unit to convert an optical signal into an electric signal. The invention also relates to a packaging method for enabling a whole system to be packaged in a manner of chip level, and the method comprises temperature control and electromagnetic shielding. The method is great in value in the fields of biomedical research and medical diagnosis.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV +1
ODMR functional part integrated diamond NV magnetometer and manufacturing technology thereof
ActiveCN108983121AFor maximum integrationEfficient collectionMagnitude/direction of magnetic fieldsMicro nanoManufacturing technology
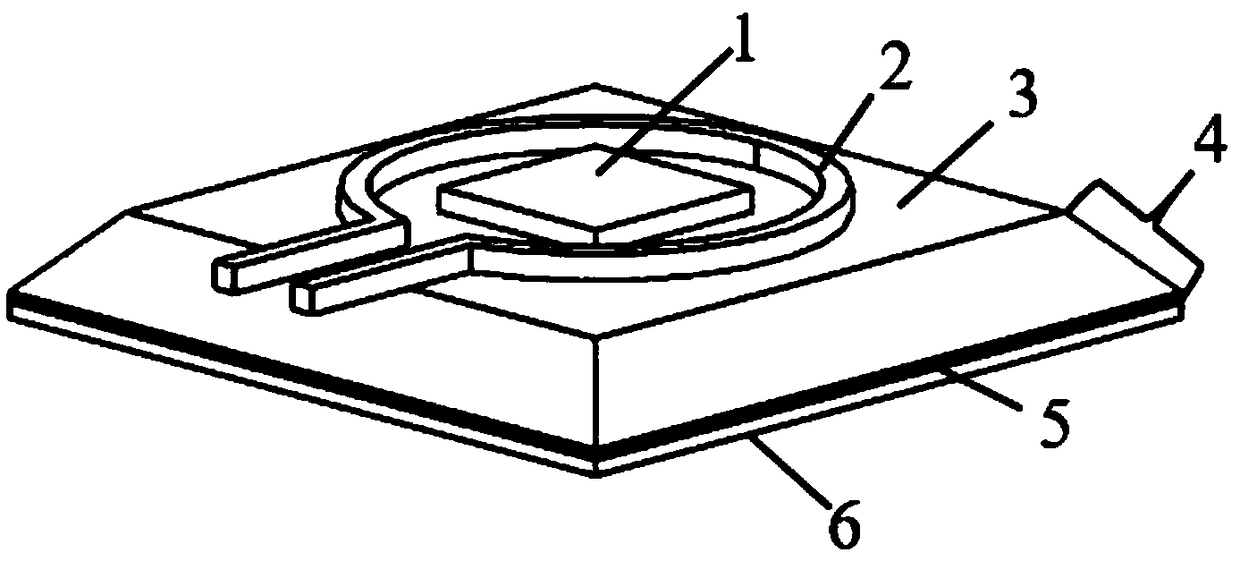
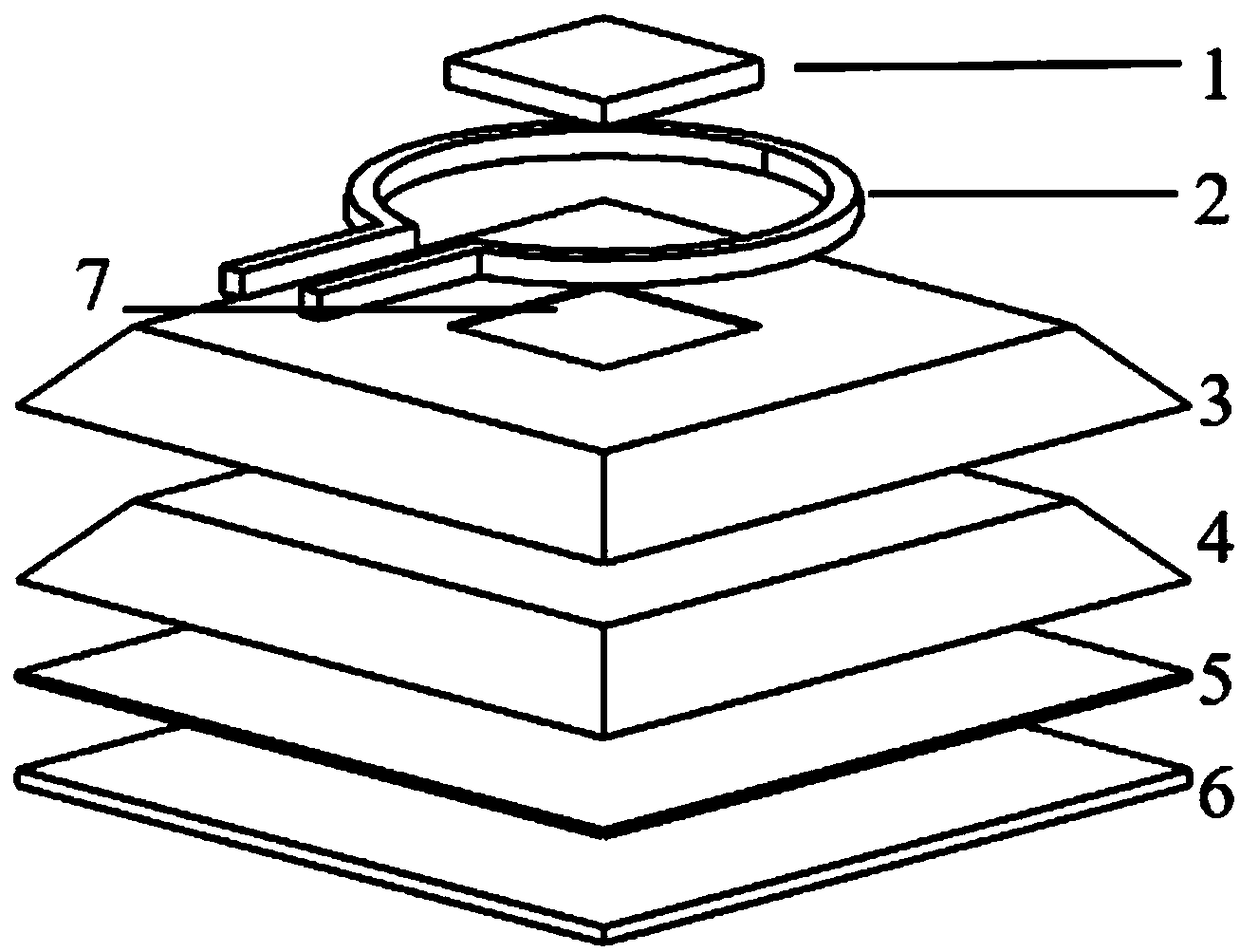
The invention discloses an ODMR functional part integrated diamond NV magnetometer and a manufacturing technology thereof, and belongs to the fields of solid state atom magnetometers and micro nano processing. A block-shaped diamond prepared with an NV color center ensemble is edged and shaped into a step-shaped diamond, a multi-layer medium combined reflective film is prepared in the upper surface of the diamond in a film growth technology, a multi-layer medium combined cutoff filtering film is prepared in the bottom, the two types of optical functional films wrap a diamond medium to form a light tripping structure, an annular microwave antenna is prepared on the light tripping structure with the diamond as the main body, a light through hole is cut, a laser diode and a photodiode are microfabricated, and the integrated NV magnetometer is realized. The total light tripping cavity structure and system modulation photon collecting functional parts are designed by taking the diamond as the core, the sensitivity of the solid atom magnetometer can be maximized, and the size of the device is reduced.
Owner:ZHONGBEI UNIV
Diamond nanocrystal single-photon source with wavelength converter
InactiveUS20090034737A1Key distribution for secure communicationElectromagnetic transmission optical aspectsColour centreLength wave
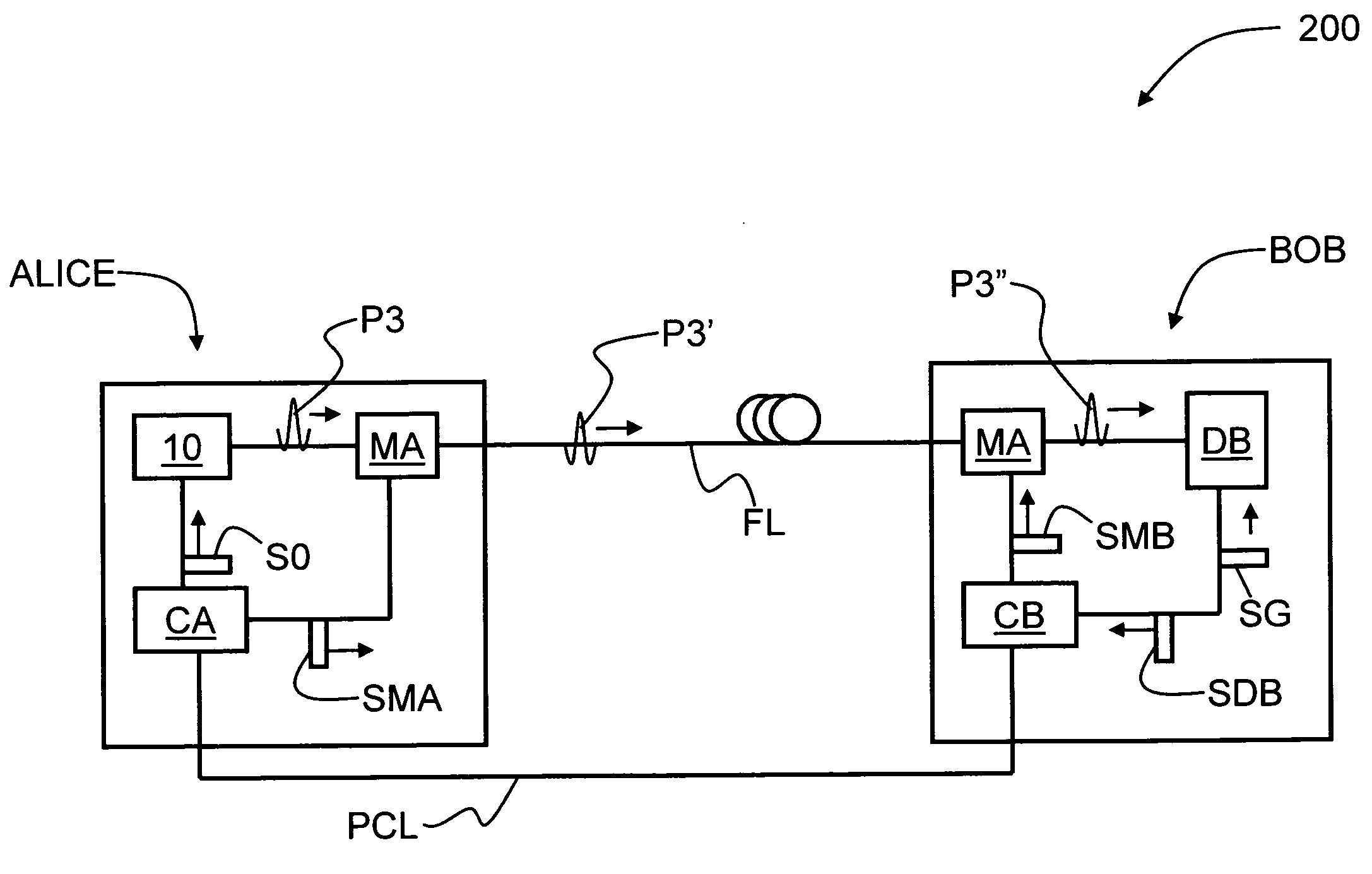
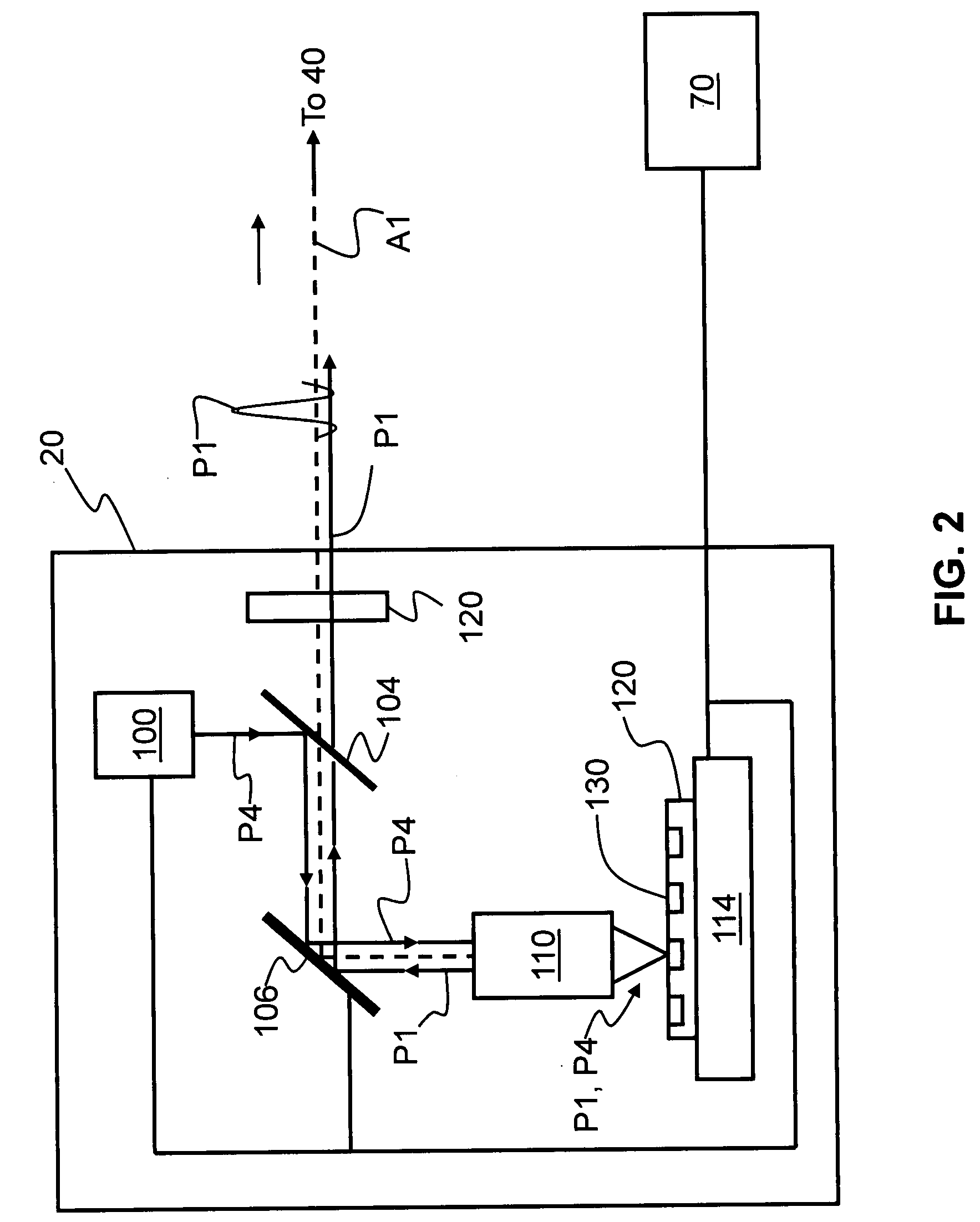
A single-photon source (SPS) (10) adapted to output single-photons (P3) at telecommunication wavelengths is disclosed. The SPS includes a color-centered diamond-nanocrystal (CCDN) single-photon source (SPS) (20) adapted to emit input photons (P1) having a wavelength A1 that lies outside of the main telecommunication wavelength bands. A non-linear optical medium (50) pumped using pump photons (P2) of wavelength A2 receives the input photons and optically downconverts them to output photons (P3) having a wavelength λ3>λ1 wherein λ3 is within a telecommunication wavelength band. An optical filter (60) arranged downstream of the non-linear optical medium substantially blocks the pump photons (P2) while allowing for the transmission of the output photons. A QKD system that uses the SPS source of the present invention is also disclosed.
Owner:MAGIQ TECH INC
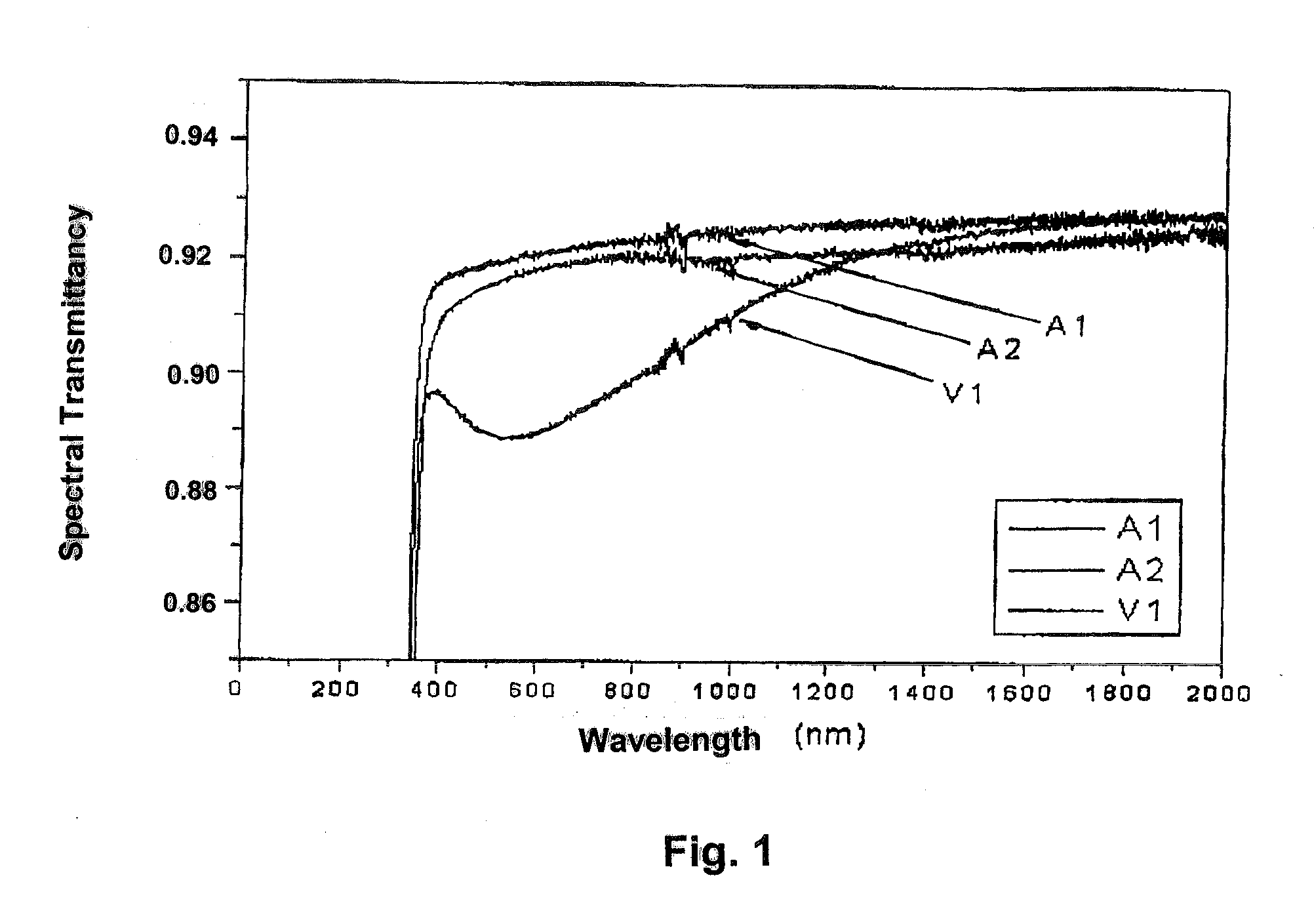
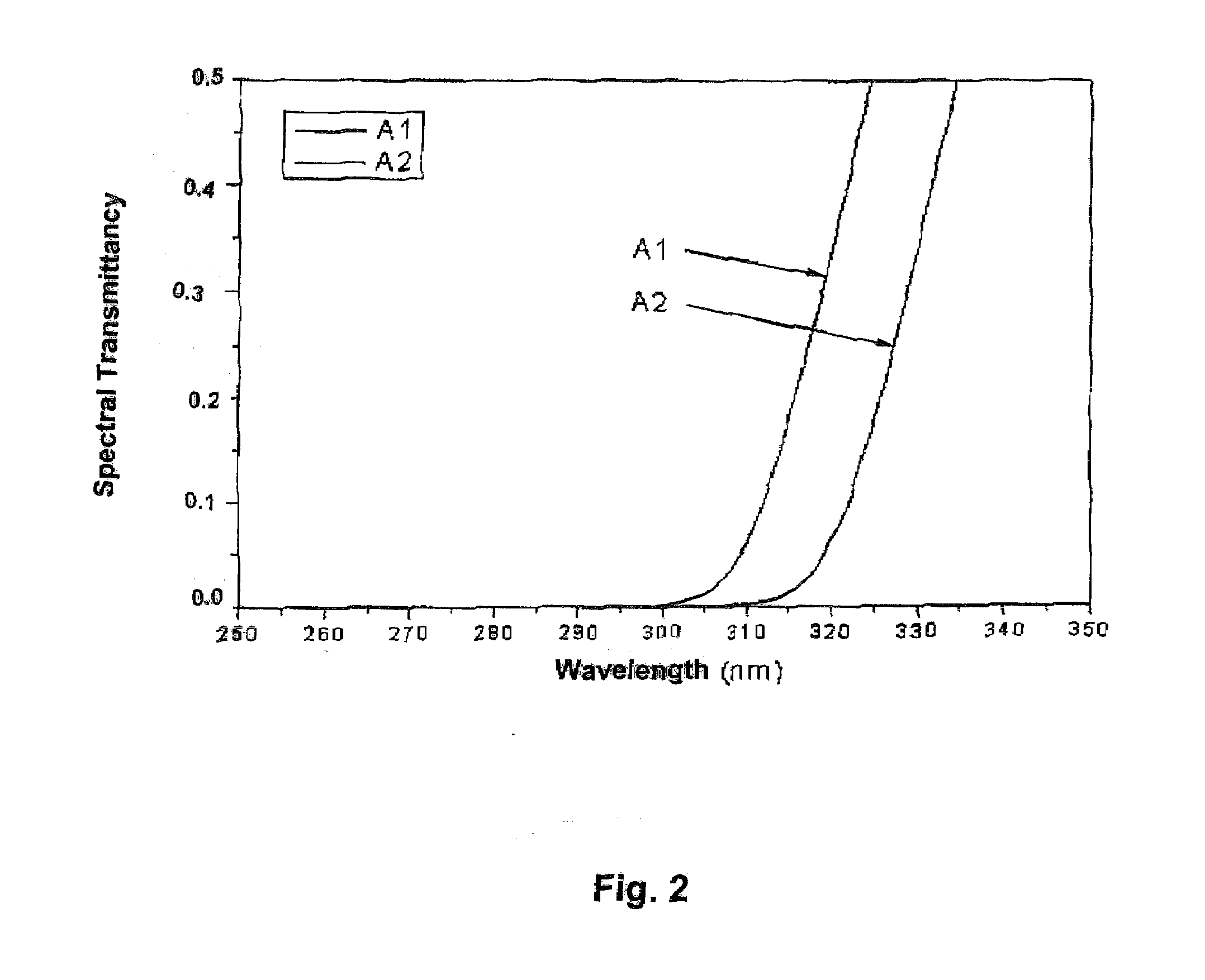
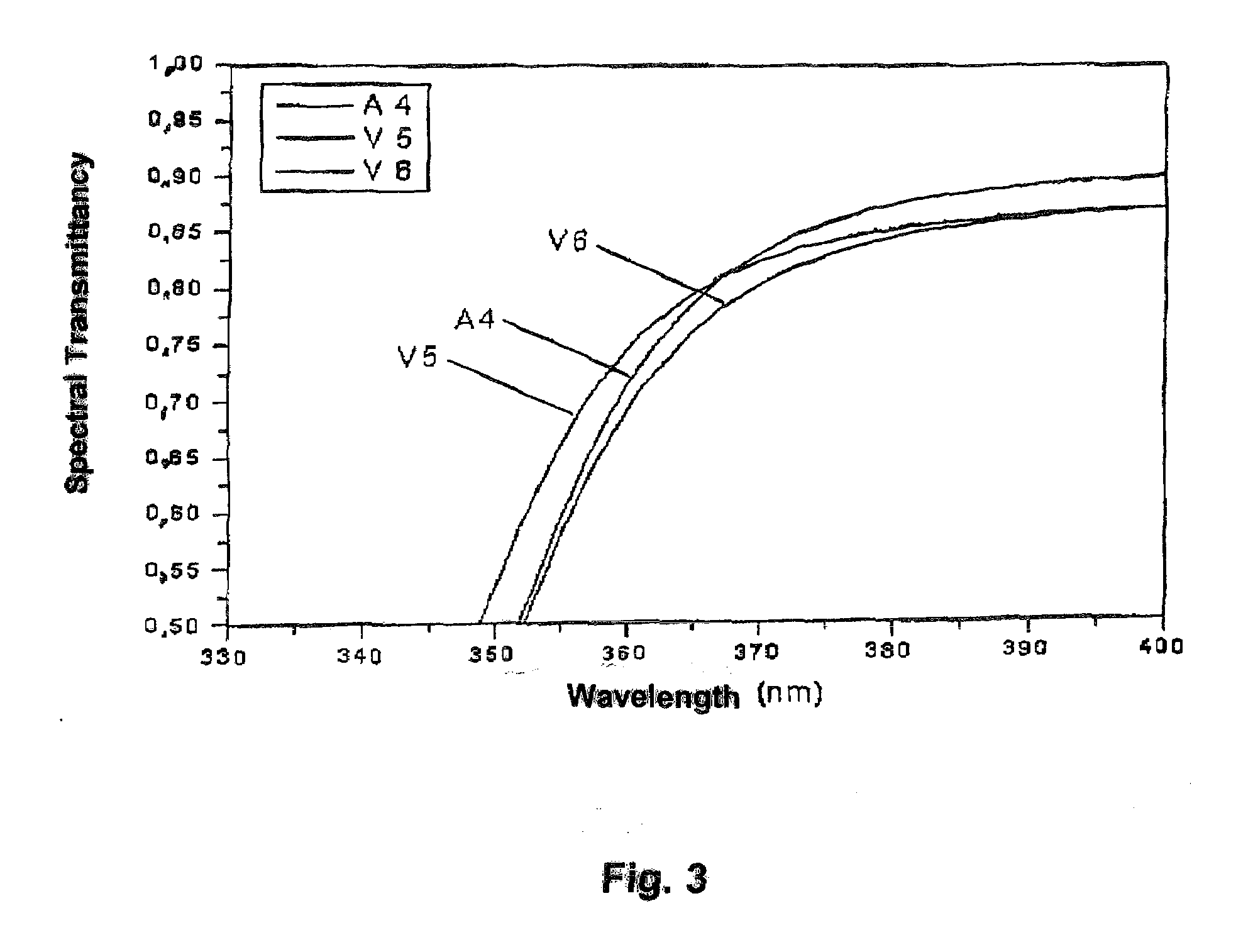
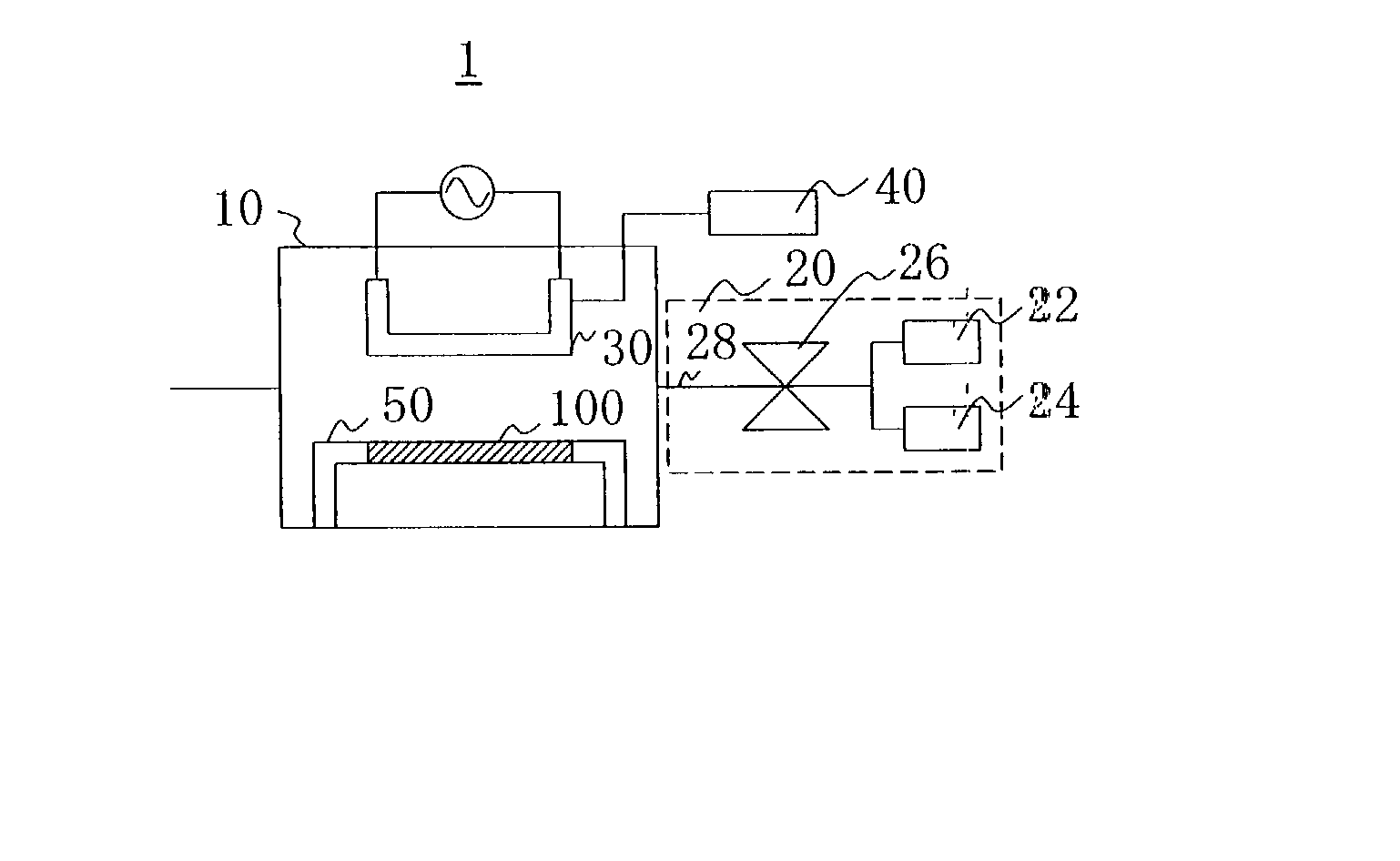
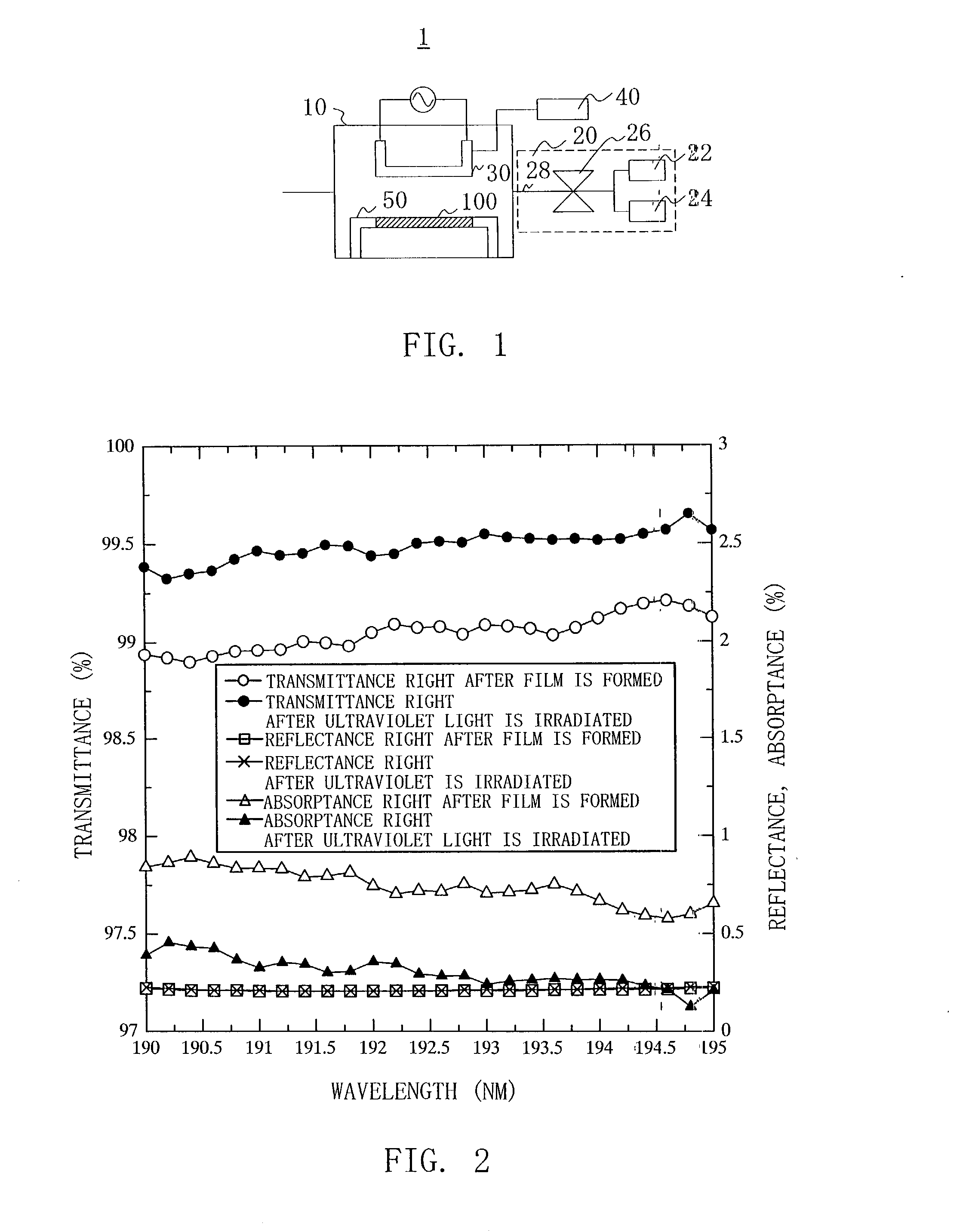
Uv-radiation absorbing glass with reduced absorption of visible light and method of making and using same
InactiveUS20080254301A1Effectively block UV radiationImprove transmittanceGlass furnace apparatusGlass/slag layered productsColour centreDisplay device
The PbO-free UV-absorbing glass is made under oxidative conditions and has a composition, in % by weight, of: SiO2, 55-79; B2O3, 3-25; Al2O3, 0-10; Li2O, 0-10; Na2O, 0-10; K2O, 0-10; MgO, 0-2; CaO, 0-3; SrO, 0-3; BaO, 0-3; ZnO, 0-3; ZrO2, 0-3; CeO2, 0-1; Fe2O3, 0-1; WO3, 0-3; Bi2O3, 0-3; MoO3, 0-3; ΣLiO+Na2O+K2O=0.5 to 16 and ΣMgO+CaO+SrO+BaO+ZnO=0-10. It also contains from 0.1 to 10% TiO2 with at least 95% of the titanium as Ti+4 so that it has a high visible transmission, reduced color centers, and a sharp UV absorption edge. It is especially useful in lamps display devices and glass-to-metal seals.
Owner:SCHOTT AG
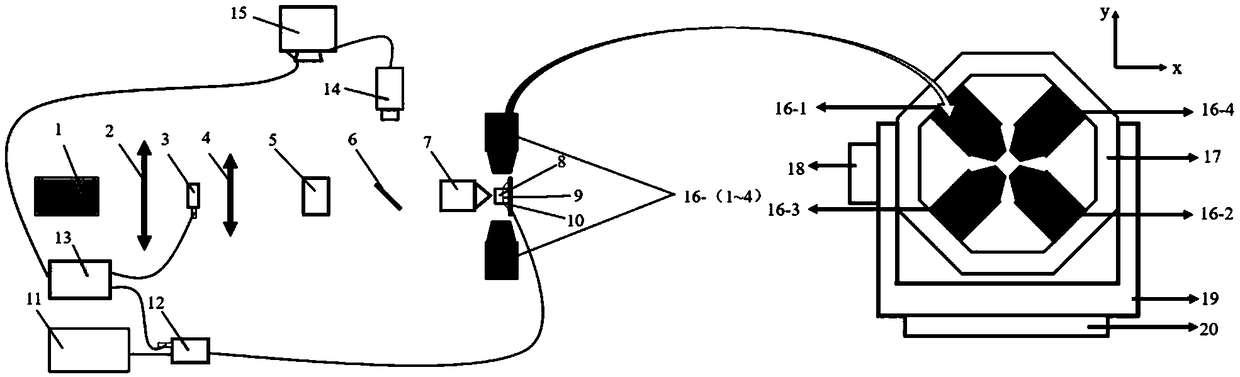
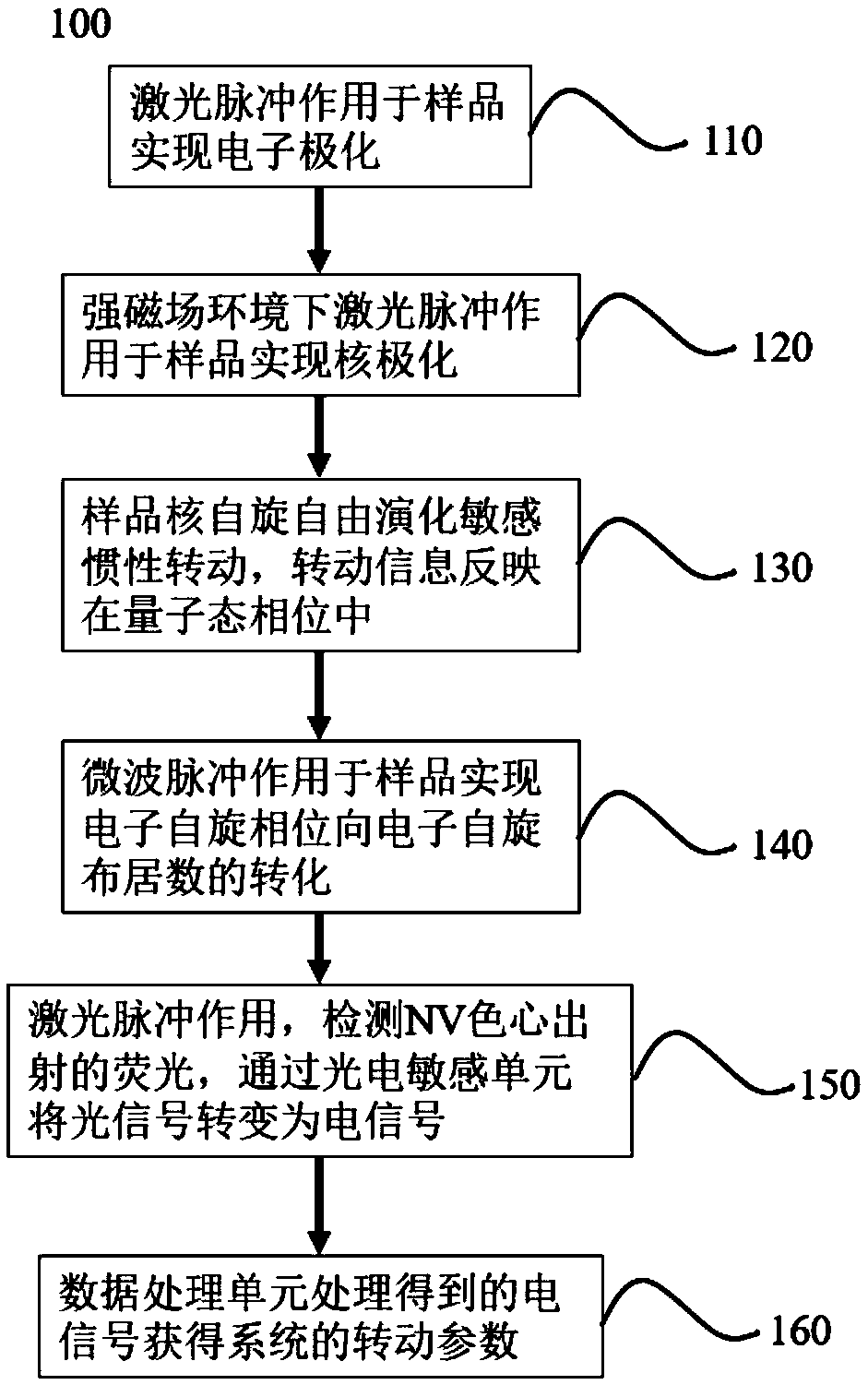
Inertia measurement device and method based on diamond NV color center under high magnetic field
ActiveCN108759810AAchieve nuclear polarizationSimple structureTurn-sensitive devicesHigh concentrationMeasurement device
The invention discloses an inertia measurement device and method based on a diamond NV color center under a high magnetic field. The method adopts a diamond material containing a high-concentration nitrogen-vacancy (NV) color center as a sensitive element, laser and the about 500 gauss of high magnetic field are used for achieving the polarization of nuclear angular momentum, and pulse laser and pulse microwave are used for achieving the operation, control and detection of the diamond NV color center, thereby achieving the measurement of inertial rotation. Compared with the inertial rotation measurement by using electron spin, the measurement sensitivity is significantly improved through nuclear polarization, it is of great value for the development of an inertial measurement system basedon a quantum theory, and the device serves for various fields in the future, especially for civil miniaturized inertial navigation and attitude determination systems.
Optical fiber current transformer based on diamond NV color center and measuring method
ActiveCN113804941ASimple structureLow costCurrent measurements onlyVoltage/current isolationColour centreCurrent sensor
The invention relates to the technical field of current sensors, and provides an optical fiber current transformer based on a diamond NV color center and a measuring method. The optical fiber current transformer comprises laser excitation and reflected light receiving analysis equipment, a diamond NV color center probe, a magnetic concentrator and microwave excitation equipment, wherein the transformer adopts three measurement methods, namely an all-optical measurement method, a non-all-optical measurement method and a combined measurement method. The optical fiber current transformer is simple in structure, high in practicability, capable of resisting external interference and high in robustness, the optical fiber is only used for transmission of exciting light and collection of fluorescent light, thus bending and twisting of the optical fiber do not affect a detection result to a certain extent, and the use is more convenient; in addition, by optimizing the NV color center concentration and the spinning property in the diamond, the sensitivity of magnetic field measurement can be remarkably improved, and the possibility is provided for current measurement with higher precision.
Owner:ANHUI GUOSHENG QUANTUM TECH CO LTD
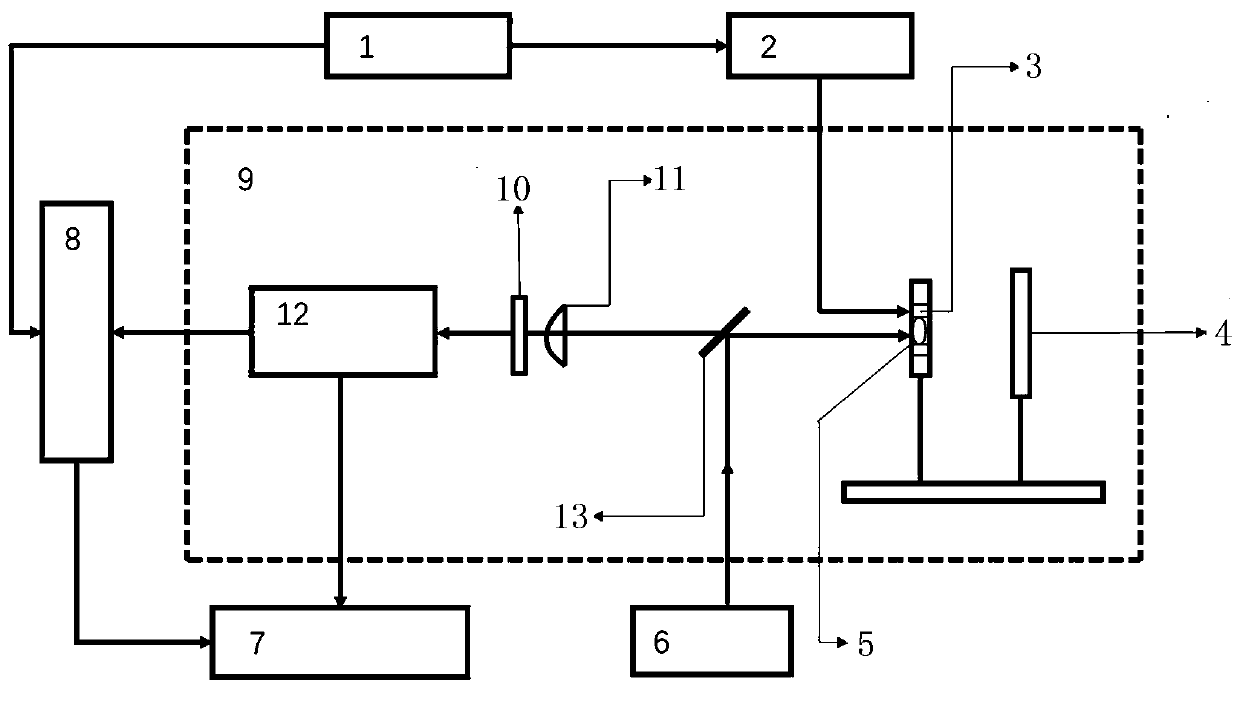
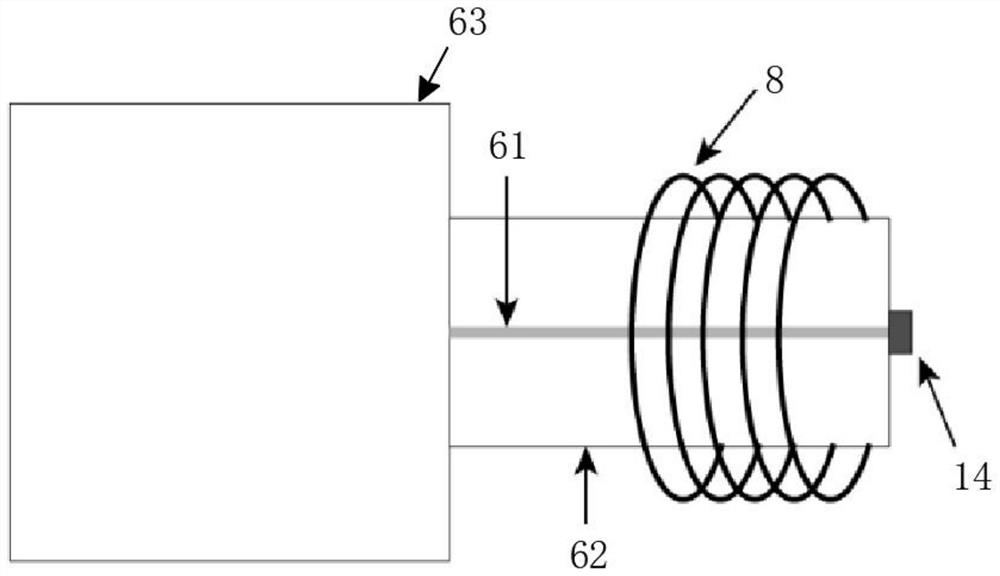
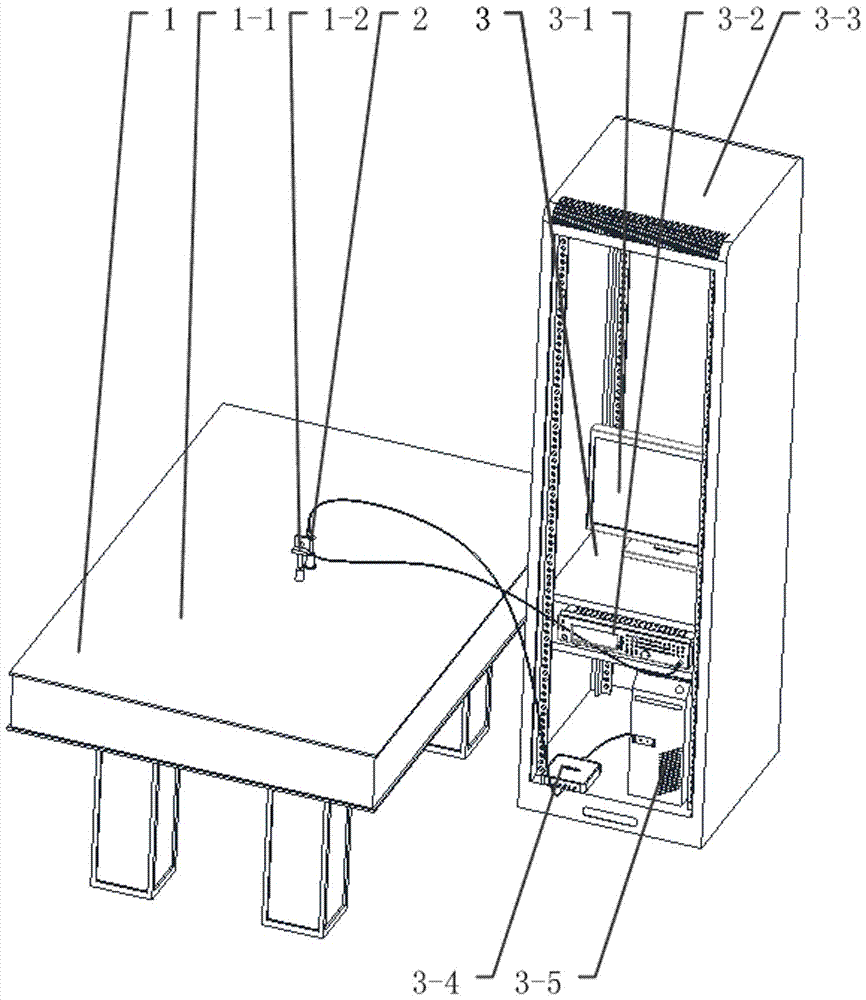
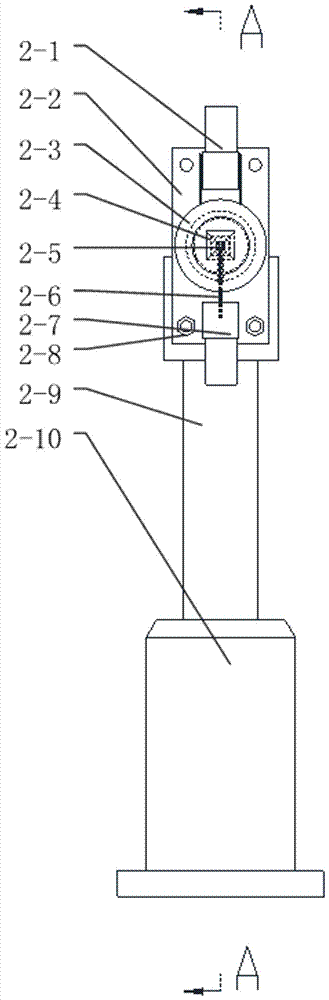
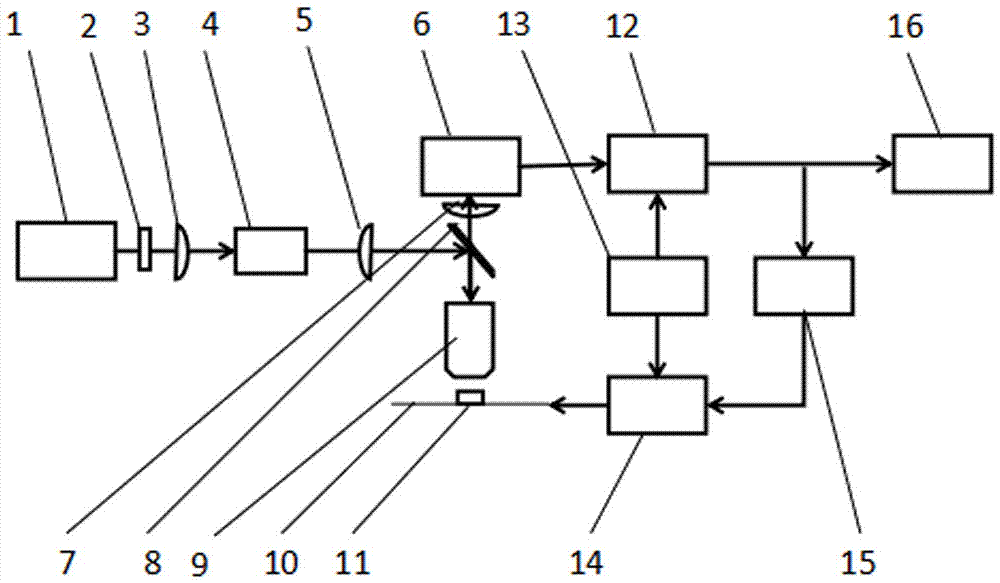
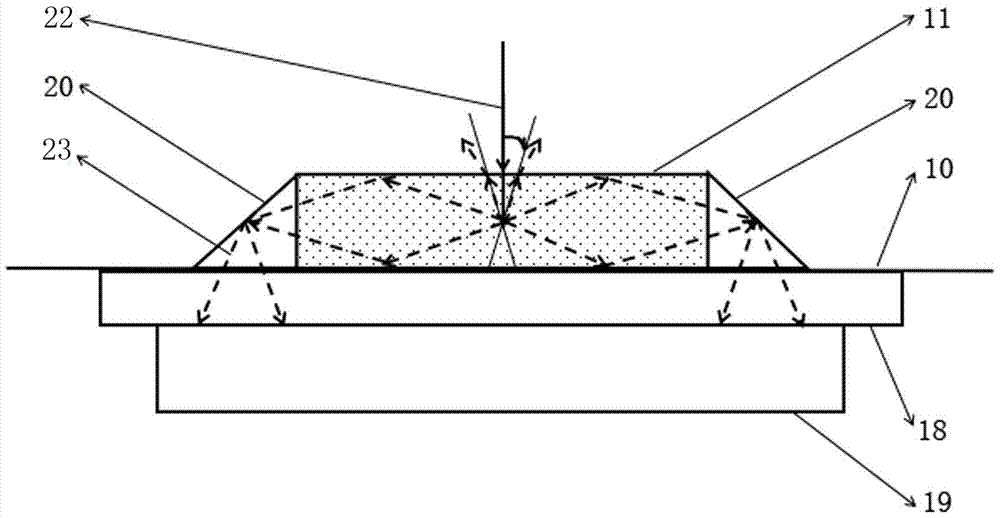
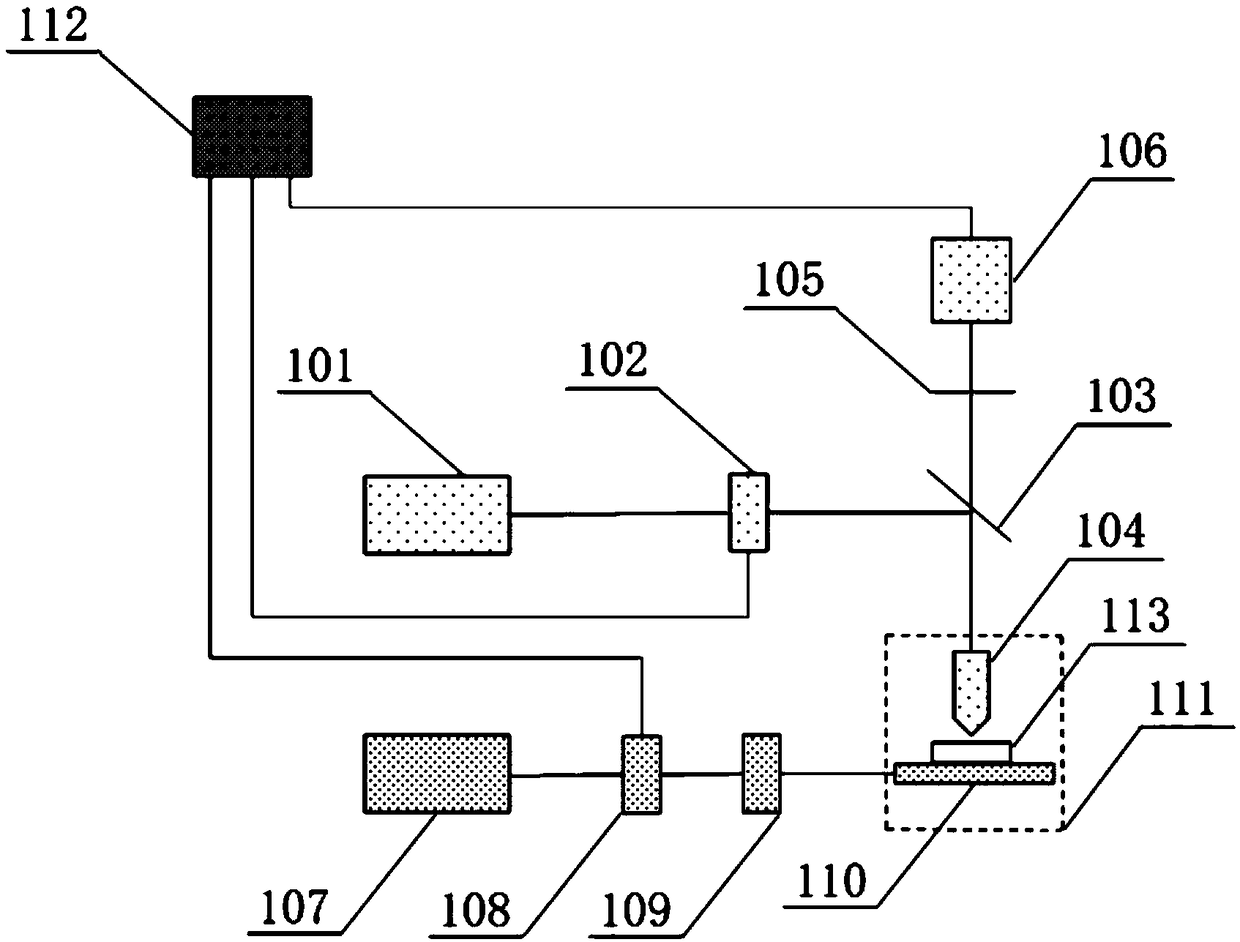
Efficient diamond NV (nitrogen-vacancy) color center fluorescence collection device
ActiveCN107449758AHave a heart-adjusting effectFluorescence acquisition does not affectPhotometry using electric radiation detectorsFluorescence/phosphorescenceMicrowaveColour centre
The invention belongs to the field of optical experiment platform instruments and particularly relates to an efficient diamond NV (nitrogen-vacancy) color center fluorescence collection device. The efficient diamond NV color center fluorescence collection device mainly comprises an experiment platform, a high integration density exciting and acquiring module and a controller, wherein the high integration density exciting and acquiring module is installed on the experiment platform, laser radiates on a diamond after going into a laser incidence port of a reflection prism through an objective lens, a microwave antenna emits microwave for excitation, the reflection prism constantly reflects, and the fluorescence is finally reflected and radiates on a fluorescence acquiring photodiode through an optical filter, and is finally transmitted to a mainframe to be processed. The transparent antenna is used to integrate a PCB and a flexible aligning clamping method is matched, the diamond is accurately installed and located, the transparent packaging antenna is used to efficiently excite, the internal reflection of the internal pyramid-shape reflection prism is used to basically irradiate the fluorescence on the fluorescence acquiring photodiode to efficiently acquire the fluorescence, and the efficient diamond NV color center fluorescence collection device has the advantages of scientific design, reasonable structure, high locating accuracy and modularization.
Owner:ZHONGBEI UNIV
High-efficiency fluorescence detection device based on solid-state spin system
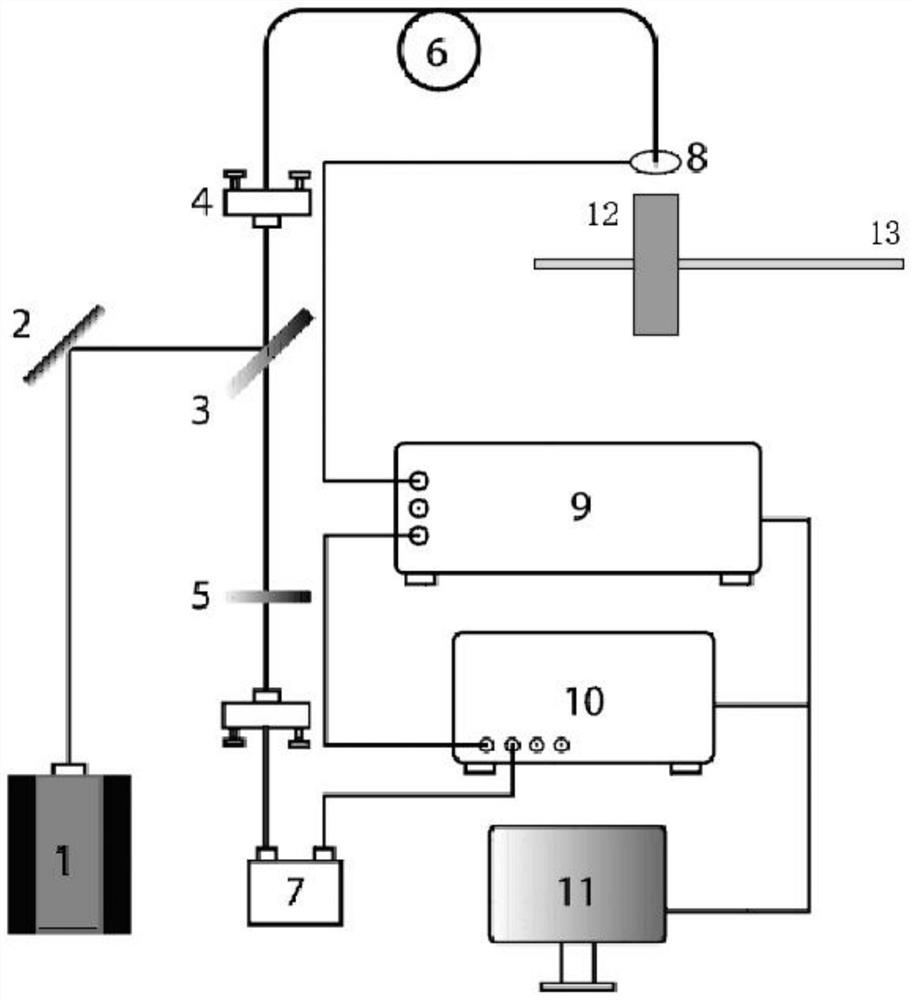
InactiveCN107131875AEasy to collectImprove collection efficiencyTurn-sensitive devicesFluorescenceCollection system
The invention relates to an NV color center gyro fluorescence collection system and in particular relates to a high-efficiency fluorescence detection device based on a solid-state spin system. The device comprises a 532 laser machine, wherein a polarizing film, a first convex lens, an acoustic optical modulator, a second convex lens and a fourth convex lens are sequentially arranged on a light path of the 532 laser machine; the fourth convex lens is directly opposite to a diamond; the diamond is arranged on a filter; the lower side of the filter is in contact with a photodiode; a prism reflector is arranged on the filter; the photodiode is connected with a lock-in amplifier; the lock-in amplifier is respectively connected with a PID (Proportion Integration Differentiation) controller and an acquisition card; the output end of the PID controller is connected with a microwave source; a signal source output end is respectively connected with the lock-in amplifier and the microwave source; and a radio frequency antenna is connected to the microwave source. According to the device disclosed by the invention, fluorescence side band collection is realized, the traditional confocal measurement method is replaced, the improved system structure is greatly simplified, the collection efficiency is greatly improved, and the device is very suitable for miniaturized installation and lays a foundation for later system integration.
Owner:ZHONGBEI UNIV
Optical element fabrication method, optical element, exposure apparatus, device fabrication method
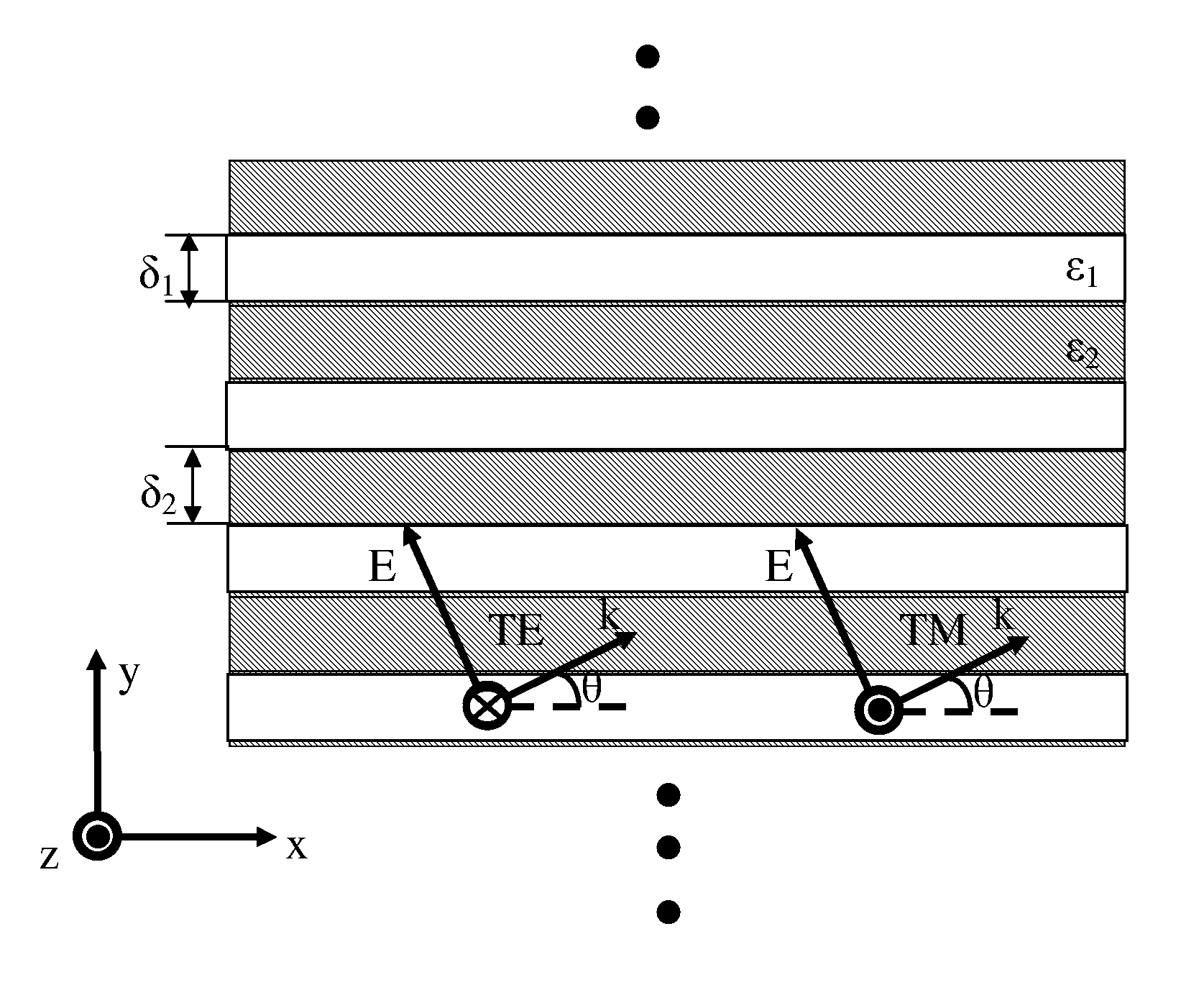
InactiveUS20030108665A1Reduce absorptionExcellent optical propertiesRadiation applicationsVacuum evaporation coatingColour centreOptoelectronics
Owner:CANON KK
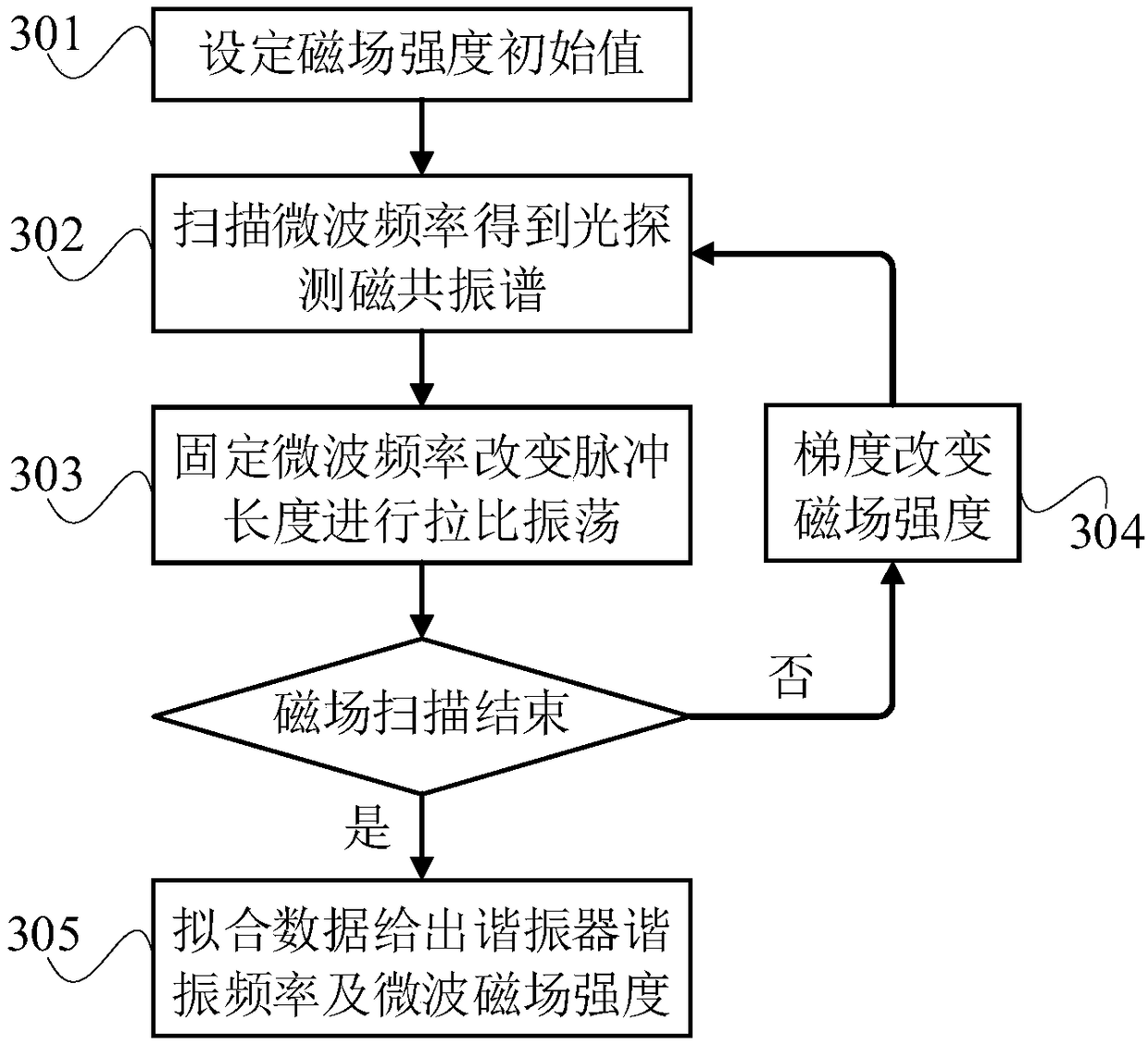
System and method for measuring resonant frequency of near-field microwave resonator
ActiveCN109061295APractical measurementAccurate measurementFrequency measurement arrangementFrequency measurementsFluorescence
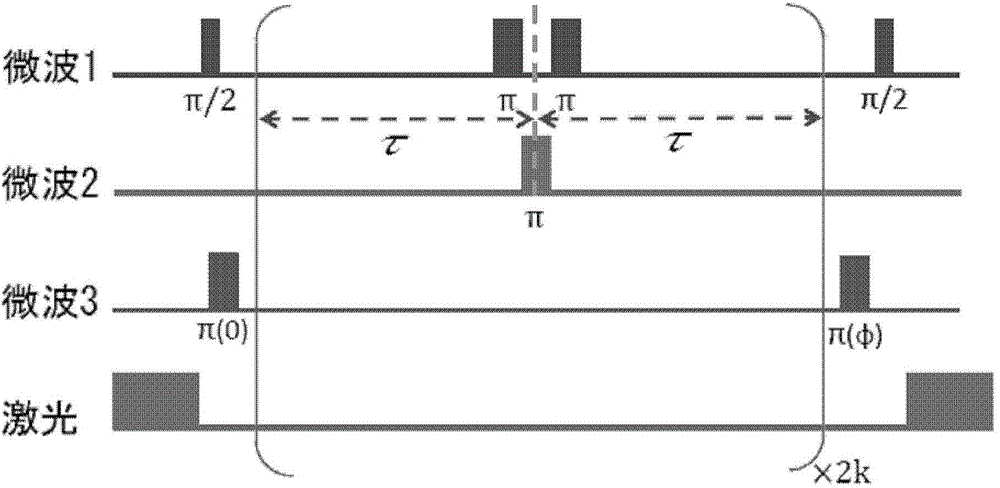
The invention relates to a system and method for measuring resonant frequency of near-field microwave resonator, which utilizes electron spin resonance and diamond nitrogen vacancy defect (NV color center) to pull the oscillation frequency and the intensity of the microwave to place the diamond in a static magnetic field. In the process, the microwave pulse frequency and the magnetic field intensity are changed to perform photodetection magnetic resonance and rabbi oscillation measurement, and a series of rabbi oscillation frequencies are obtained, from which the resonator resonance frequencyis extracted. The measuring system comprises an optical module, a microwave module, a magnetic field device, a diamond and a control device, wherein the diamond is embedded with a NV color core; theoptical module can generate and guide light to the diamond, and simultaneously detect the fluorescent signal emitted by the diamond. The microwave module can generate a microwave control field and load it onto the diamond. The magnetic field device can generate a static magnetic field. The invention can measure the resonant frequency and the effective magnetic field strength of the microwave resonator practically and accurately, has high precision, and can be used under near-field conditions.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
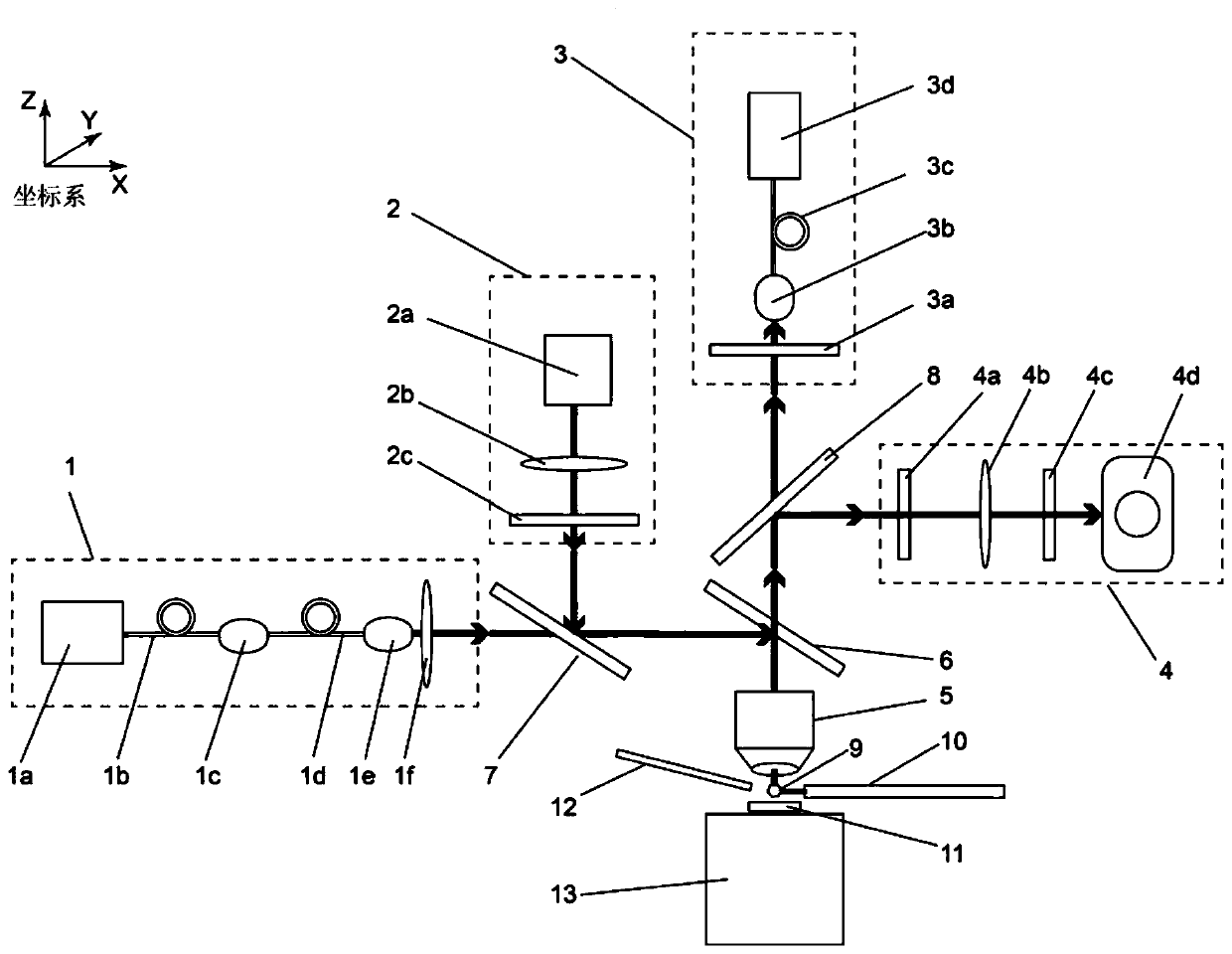
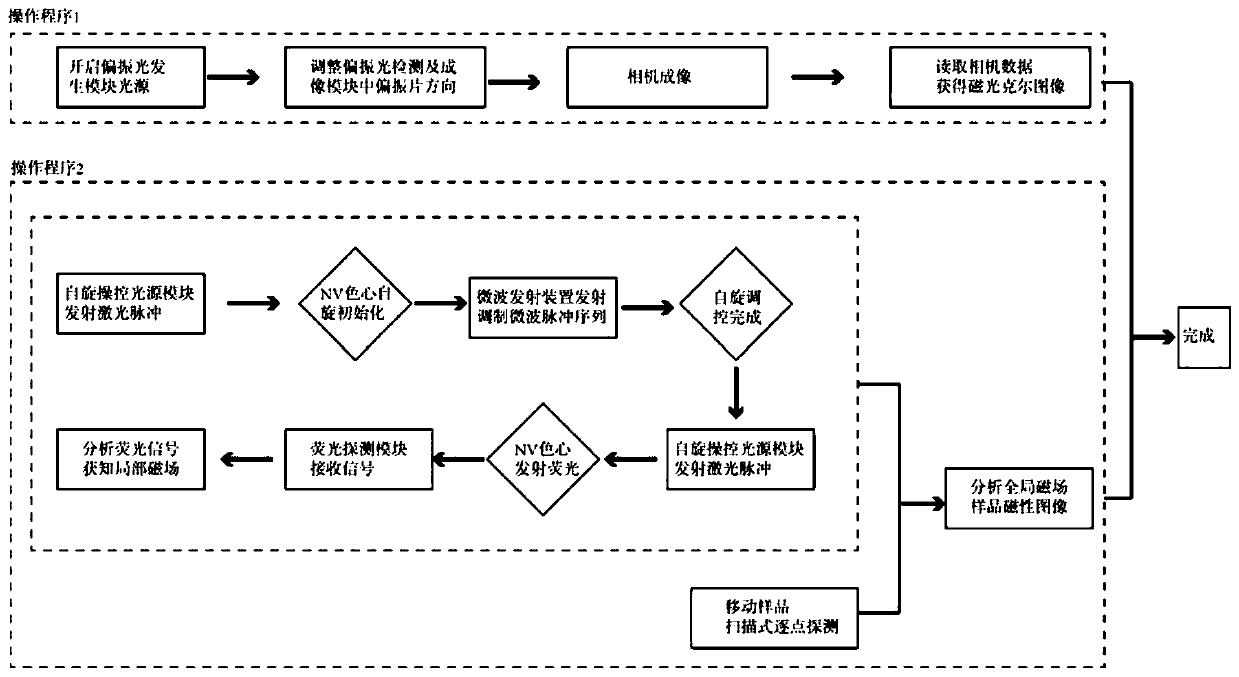
Magnetic imaging device and imaging method based on diamond NV color center and Kerr effect
PendingCN111239653AMeet the resolutionMeet needsMagnetic property measurementsMagnetic field measurement using magneto-optic devicesColour centreFluorescence
The invention discloses a magnetic imaging device and imaging method based on a diamond NV color center and a Kerr effect. A spinning control light source module provides a beam of incident laser, theincident laser passes through a dichroscope system and irradiates the NV color center of the diamond probe after being focused by the microscope objective lens, and fluorescence generated by the NV color center returns to the dichroscope system through the microscope objective lens and enters the fluorescence detection module. The polarized light generation module generates polarized light, the polarized light enters the microscope objective lens through transmission and / or reflection of the dichroscope system and then irradiates a sample placed on the displacement table, and after the polarized light is reflected by the sample, part of the polarized light enters the microscope objective lens again and then enters the polarized light detection and imaging module through the dichroscope system. Through the compatible design, high-resolution, global and large-view imaging of the sample is realized.
Owner:致真精密仪器(青岛)有限公司
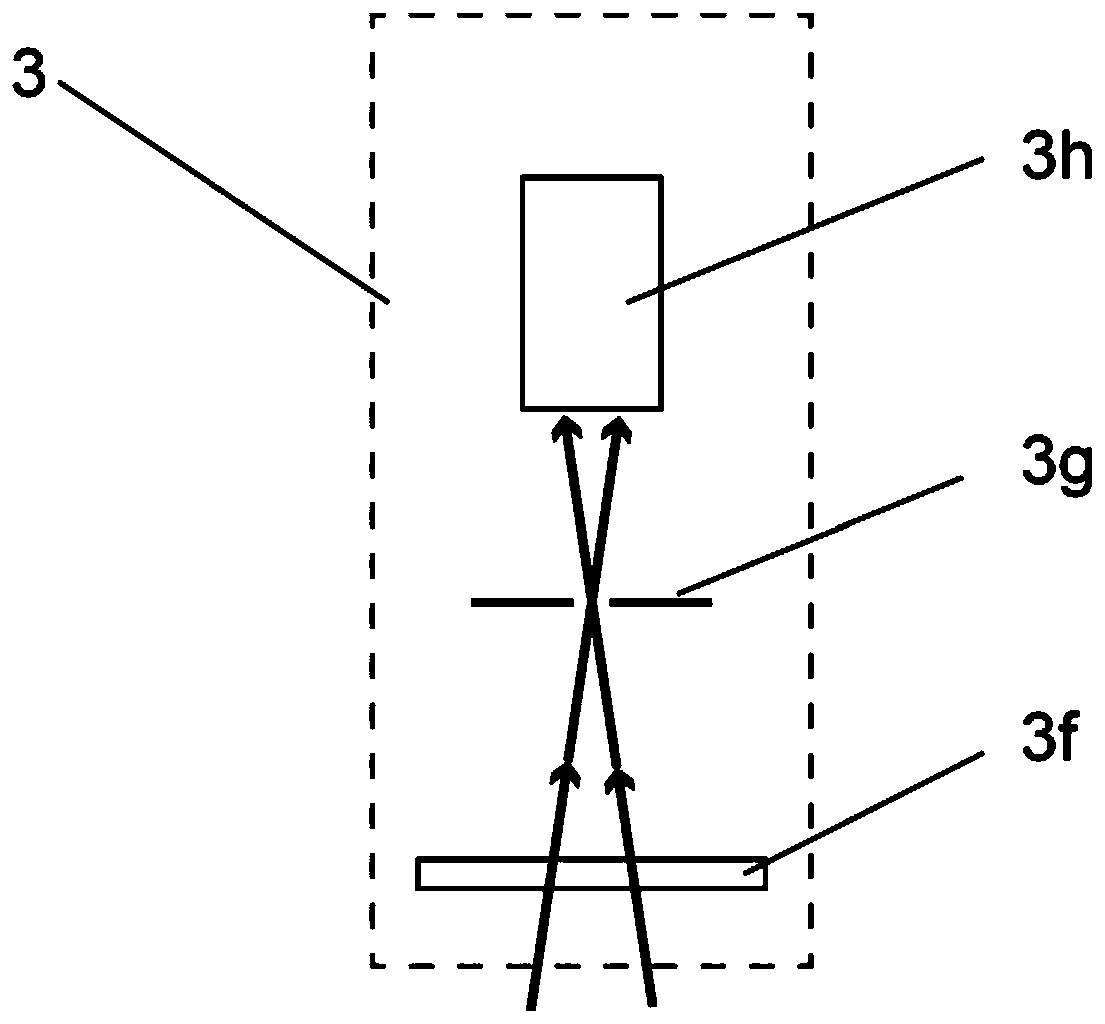
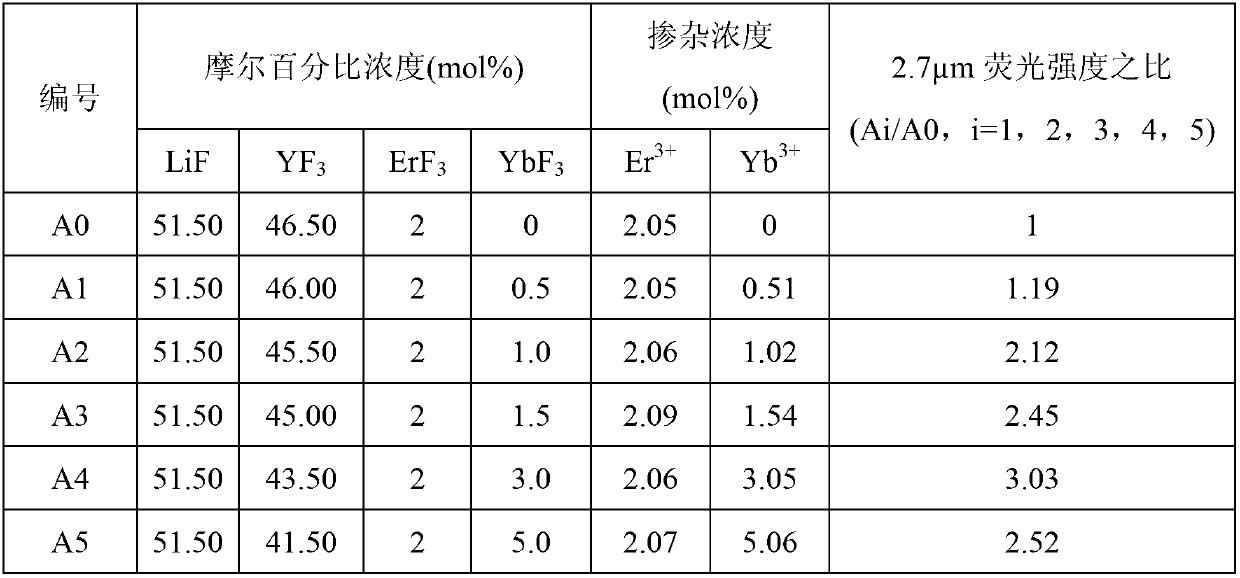
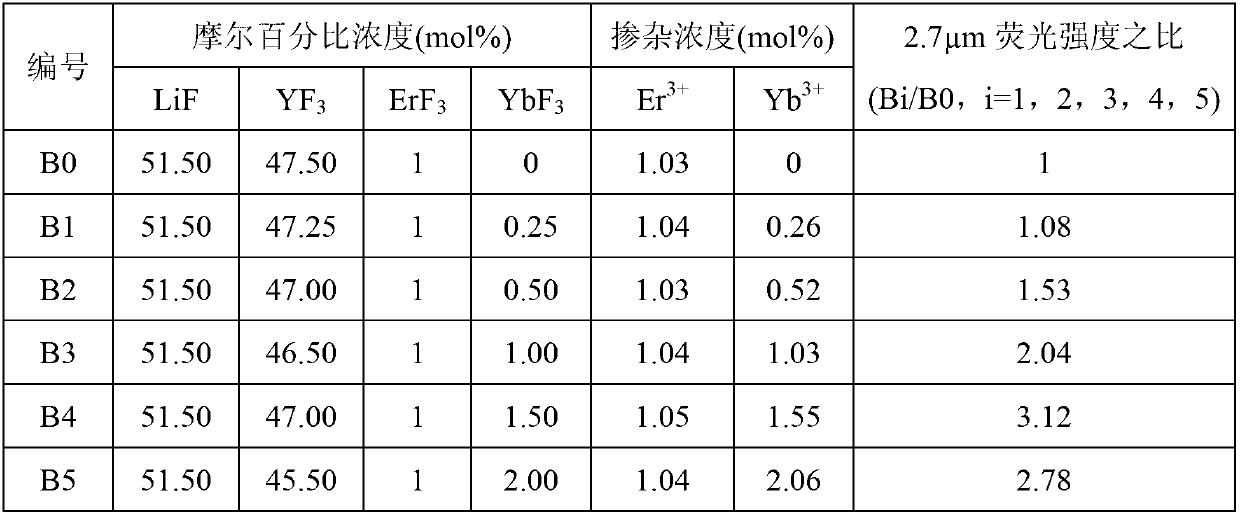
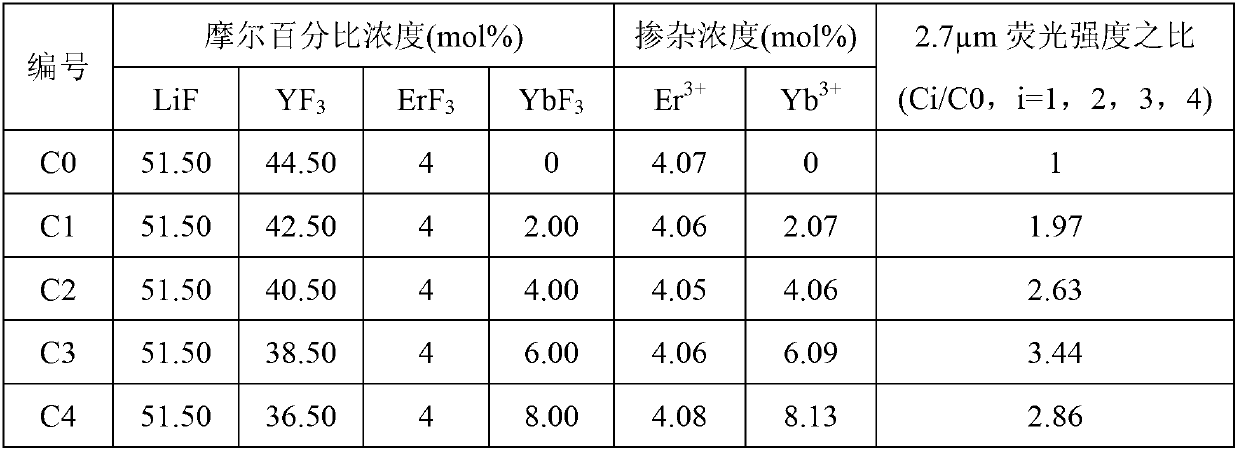
Er<3+>/Yb<3+> co-doped yttrium lithium fluoride monocrystal and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102978701AHigh phonon energyPhonon energy low highPolycrystalline material growthFrom frozen solutionsWater vaporOxygen
The invention discloses an Er<3+> / Yb<3+> co-doped yttrium lithium fluoride monocrystal and a preparation method thereof. The yttrium lithium fluoride monocrystal is a rare earth ion Er<3+> / Yb<3+> co-doped monocrystal; the molecular formula is LiY(1-x-y)ErxYbyF4, wherein x is greater than or equal to 0.008 and less than or equal to 0.085, and y is greater than or equal to 0.002 and less than or equal to 0.170; the segregation coefficients of Yb<3+> and Er<3+> in the yttrium lithium fluoride are about 1, and efficient intermediate infrared laser of 2.7 microns can be output; and the yttrium lithium fluoride monocrystal has high transmittance of intermediate infrared laser, has better thermal, mechanical and chemical stabilities than those of glass state materials and has the characteristics of low phonon energy, high optical transmittance of wavebands with width of 300-5500nm, less color center forming amount, low thermal lens effect and the like, thereby being more easily processed and more suitably used in laser devices. In the preparation method disclosed by the invention, a sealing crucible falling technology is used, so that the operation is simple; the raw material is fluorated at high temperature in a sealed water-free and oxygen-free environment, so that the crystal is isolated from air and water vapor during the growth; and therefore, the high-quality Er<3+> / Yb<3+> co-doped LiYF4 monocrystal containing little OH<-> ion and oxide is obtained.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
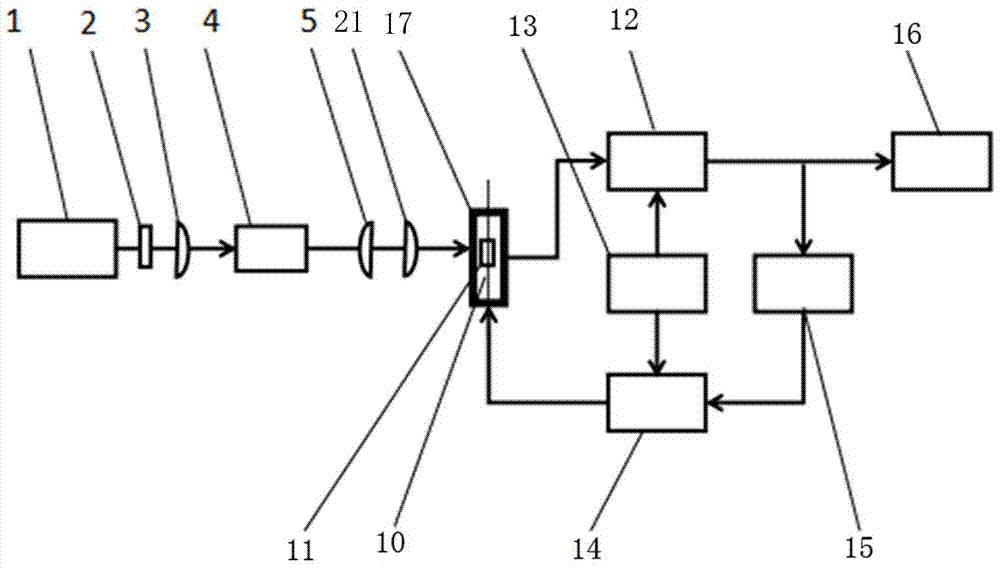
Scanning detection system based on diamond NV color center
ActiveCN111398231ASimple structureEasy to measureRaman/scattering spectroscopyRadiation pyrometryFluorescenceOptical fiber probe
The invention discloses a scanning detection system based on a diamond NV color center. A diamond NV color center is fixed at the end part of one end of the multimode optical fiber to form a probe structure capable of realizing laser pumping and fluorescence collection. A dichroscope is arranged at the other end of the multimode optical fiber. A laser beam of the light source can enter the multimode optical fiber after being reflected by the dichroscope. Then, the multimode optical fiber is fixed on a probe displacement table for moving the multimode optical fiber. A laser beam of the light source is reflected by the dichroscope and then enters the multimode optical fiber. Laser is pumped at one end of the multimode optical fiber to excite the NV color center of the nano-diamond. Fluorescence is collected by means of the multimode fiber taper. Feedback fluorescence of the multimode optical fiber is received through the single-photon detector. Physical field ultrahigh spatial resolutiondetection based on the diamond NV color center is achieved, the nano-diamond NV color center serves as a sensitive element and is bonded to the head of the optical fiber probe, laser excitation and fluorescence signal collection are achieved by means of the optical fiber probe, the structure is simple, and measurement is convenient.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Method for making grayscale photo masks and optical grayscale elements
InactiveUS20060210886A1High resolutionLow costPhotomechanical apparatusOriginals for photomechanical treatmentResistColour centre
A positive photo resist is provided on a surface of a photo mask blank. Light is then exposed onto the photo resist to form a predetermined pattern of unexposed and exposed portions in the photo-resist. After development, the exposed portions are removed and ions are implanted to obtain a modulated ion density in the photo mask blank. The implanted ions become color centers which absorb a specific wavelength of light and the modulated distribution of the color substrates create the grayscale photo mask. The photo resist structure is finally removed to produce a grayscale photo mask.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Diamond color center gyroscope based on Aharonov-Anandan geometric phase and angular velocity measuring method
The invention discloses a diamond color center gyroscope based on Aharonov-Anandan geometric phase and an angular velocity measuring method. The gyroscope comprises a reflector, a permanent magnet, a substrate, a diamond sample, first microwave coils, second microwave coils, multiple area array CCDs, multiple filters, a third microwave coil, a first convex lens, a laser device, a polarizing sheet, a dichroscope and a second convex lens. The method for measuring angular velocity by means of the diamond color center gyroscope is further provided. The gyroscope has the advantages of being small in size, large in measuring range and the like, and therefore the gyroscope has potential application in producing ammunition.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Single-photon generator and method of enhancement of broadband single-photon emission
A single-photon generator contains nitrogen-vacancies or other color centers in diamond as emitters of single photons which are excited by the laser beam or another optical source and can work stably under normal conditions, the metamaterial with hyperbolic dispersion as enhancing environment, and photonic guiding structure to collect and transmit single photons further. Single photons generators are fundamental elements for quantum information technologies such as quantum cryptography, quantum information storage and optical quantum computing
Owner:NANO META TECKNOLOGIES INC
Optical fiber fluorescent all-optical magnetic field sensor and system
PendingCN108254708AHigh measurement response frequencySimple core structureMagnetic field measurement using magneto-optic devicesColour centreFluorescence
The invention discloses an optical fiber fluorescent all-optical magnetic field sensor and a sensing system. The sensor comprises an optical fiber and a nano-diamond NV color-centered fluorescent layer which is arranged at one end of the optical fiber. The nano-diamond NV color-centered fluorescent layer is attached to one end of the optical fiber through the optical glue. The optical fiber comprises an inner optical fiber core and the nano-diamond NV color center is arranged at one end of the optical fiber through being embedded at one end of the optical fiber core. According to the invention, only optical signals in the optical fiber are measured based on the sensor technology. Therefore, the measurement response frequency is high, and the core structure is simple.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Enhanced photoelectron sources using electron bombardment
ActiveUS20140265828A1Improve quantum efficiencyExtended photocathode lifetimeElectrode and associated part arrangementsPhotoelectric discharge tubesQuantum efficiencyElectron source
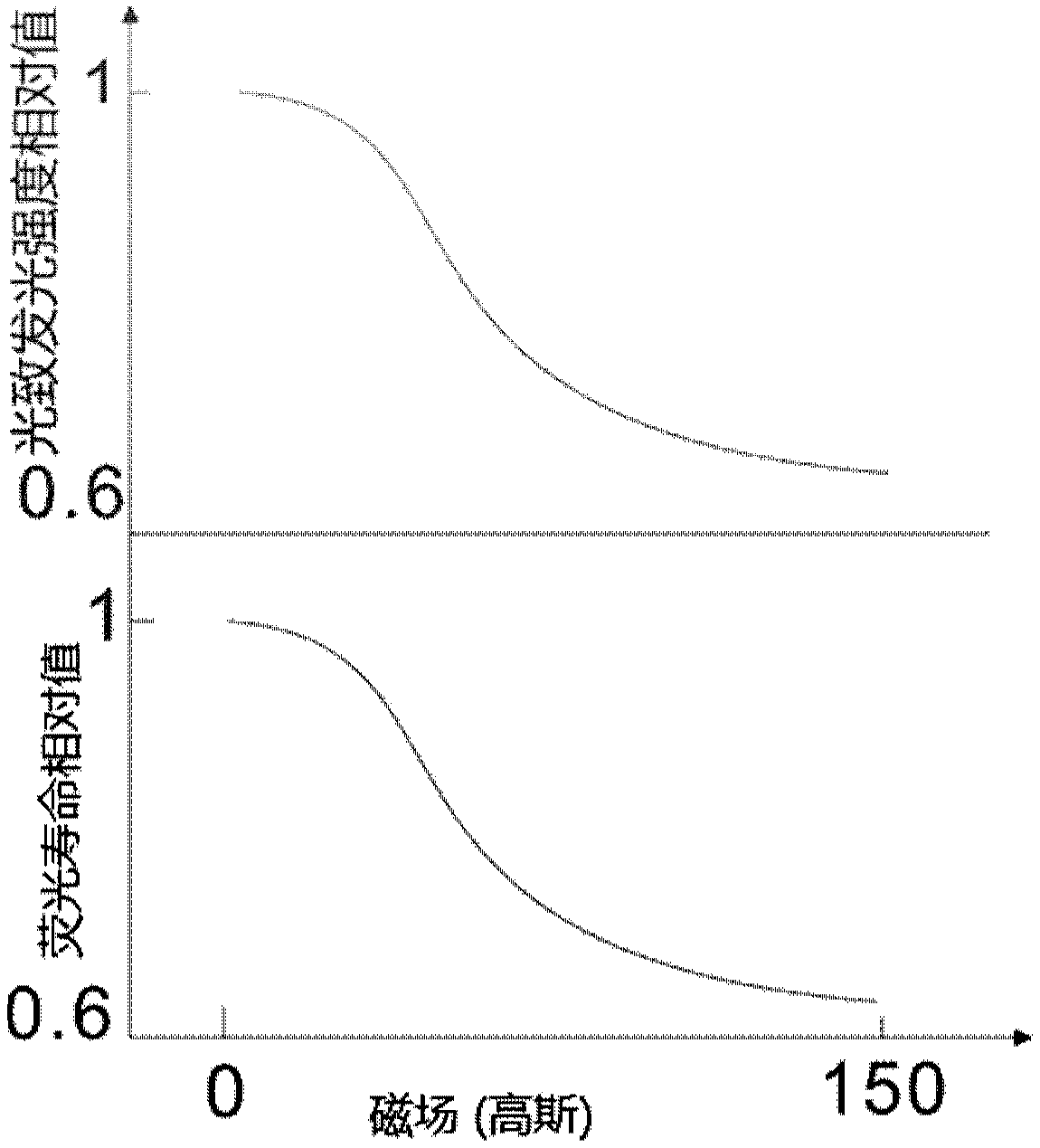
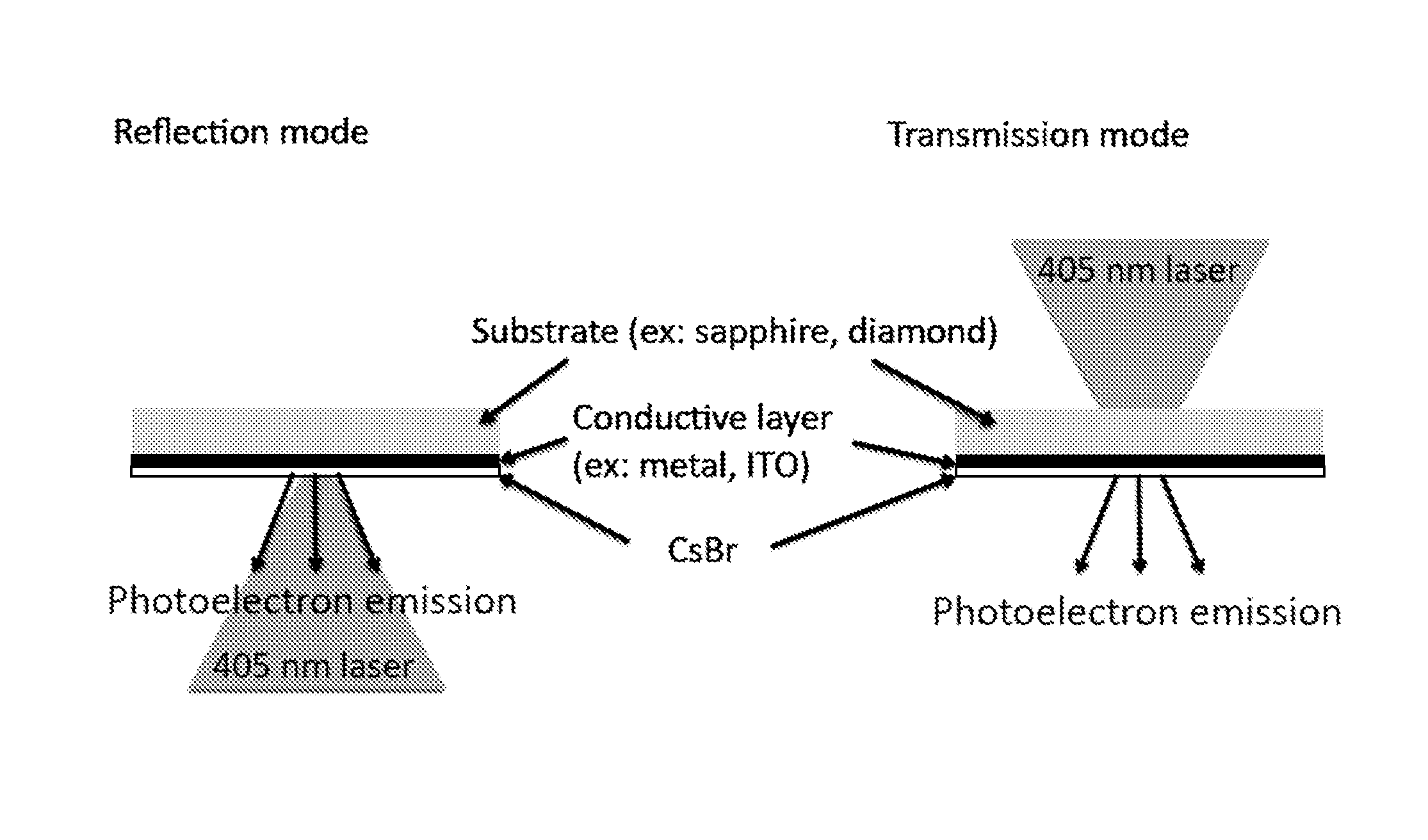
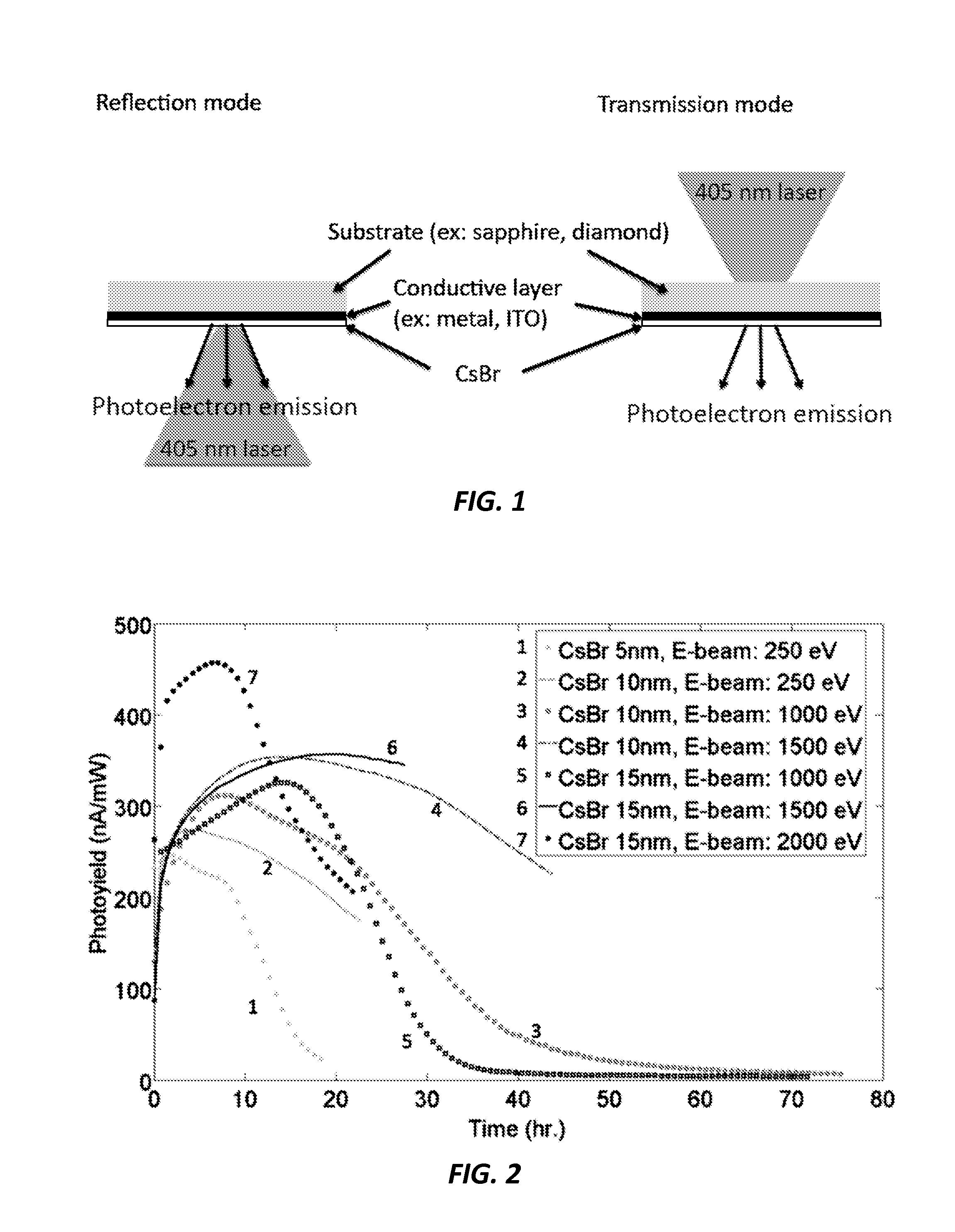
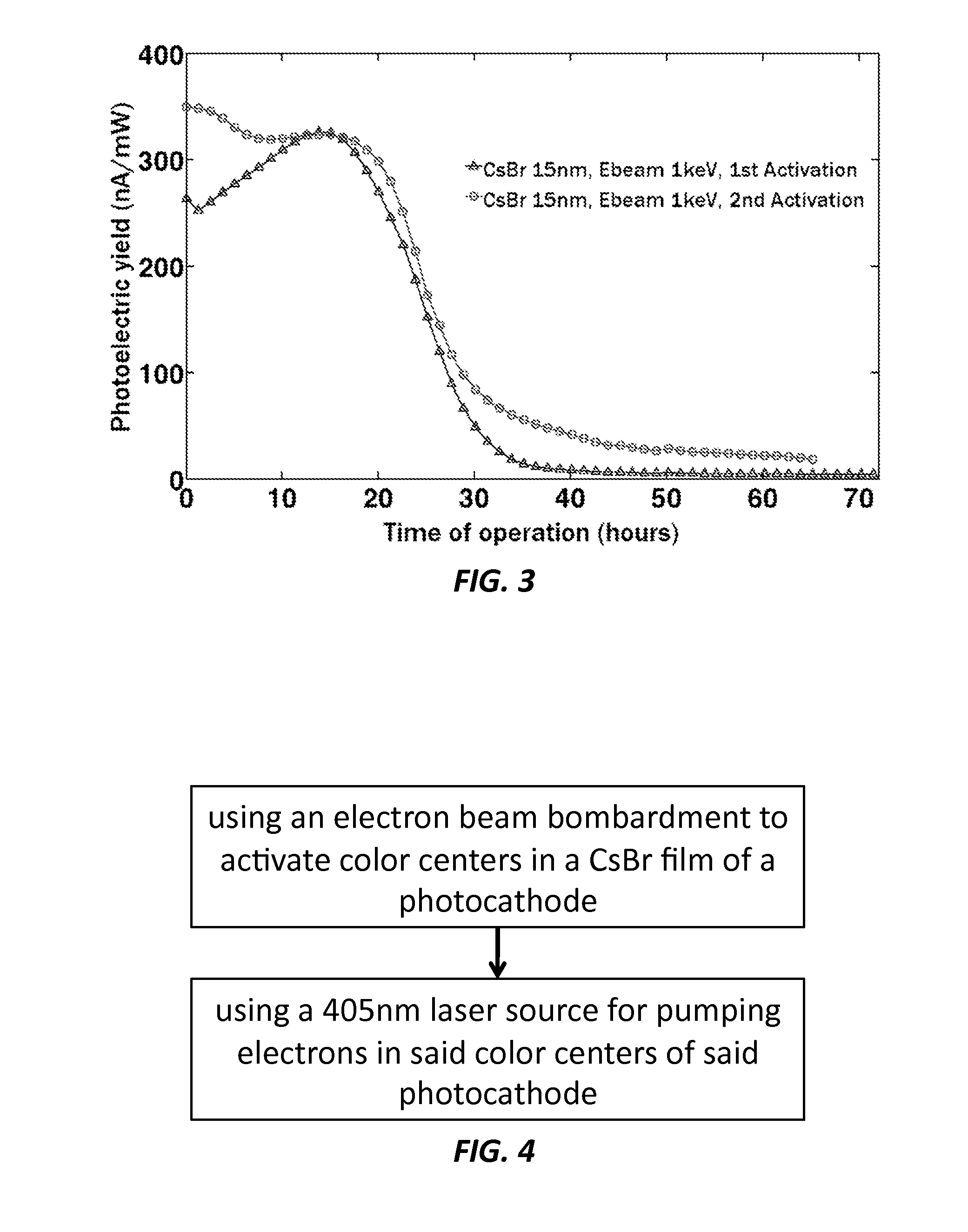
A method of achieving heightened quantum efficiencies and extended photocathode lifetimes is provided that includes using an electron beam bombardment to activate color centers in a CsBr film of a photocathode, and using a laser source for pumping electrons in the color centers of the photocathode.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
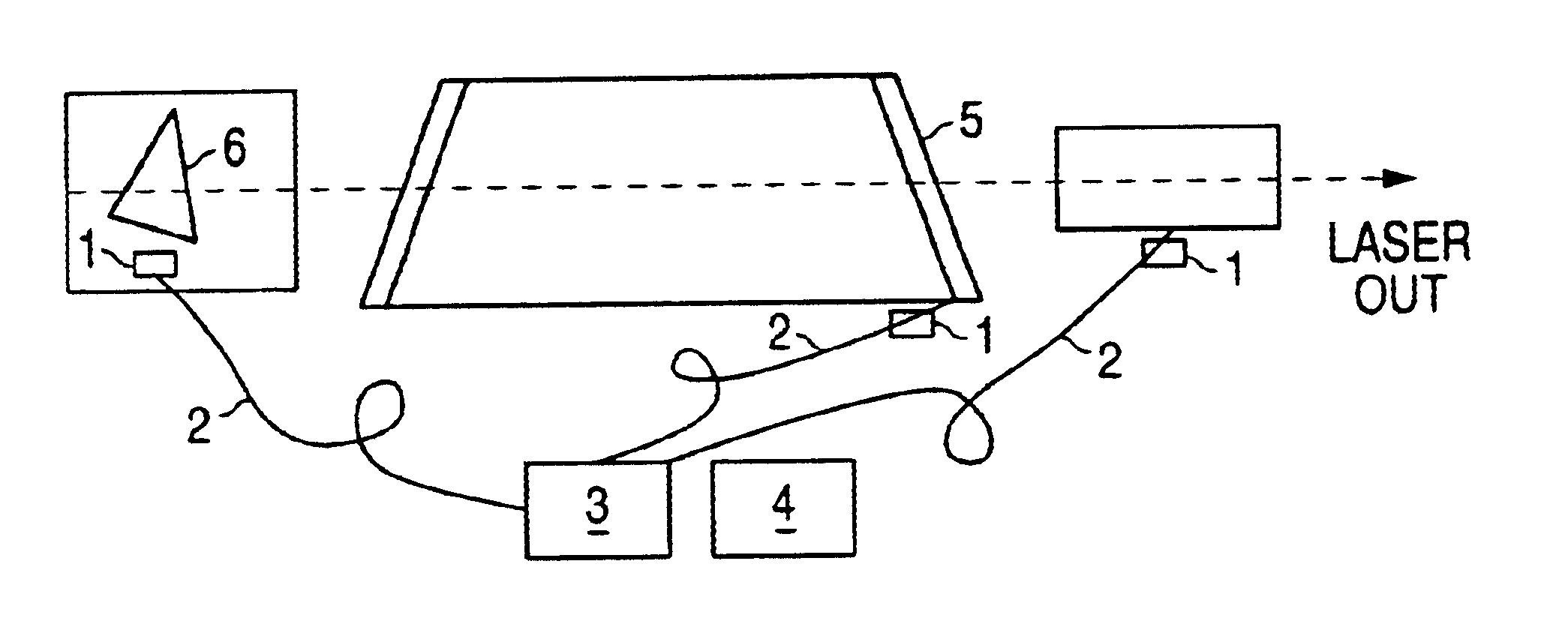
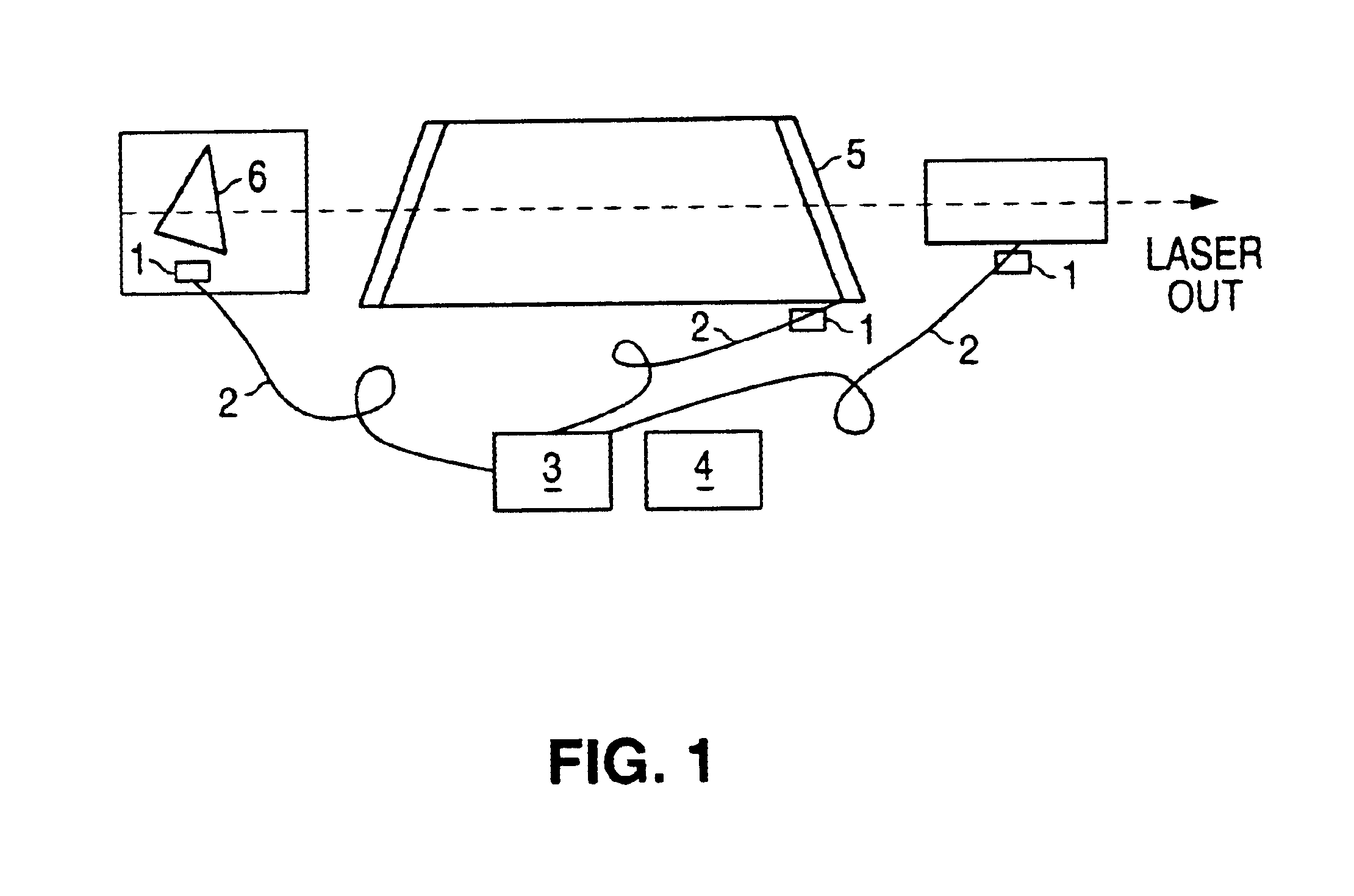
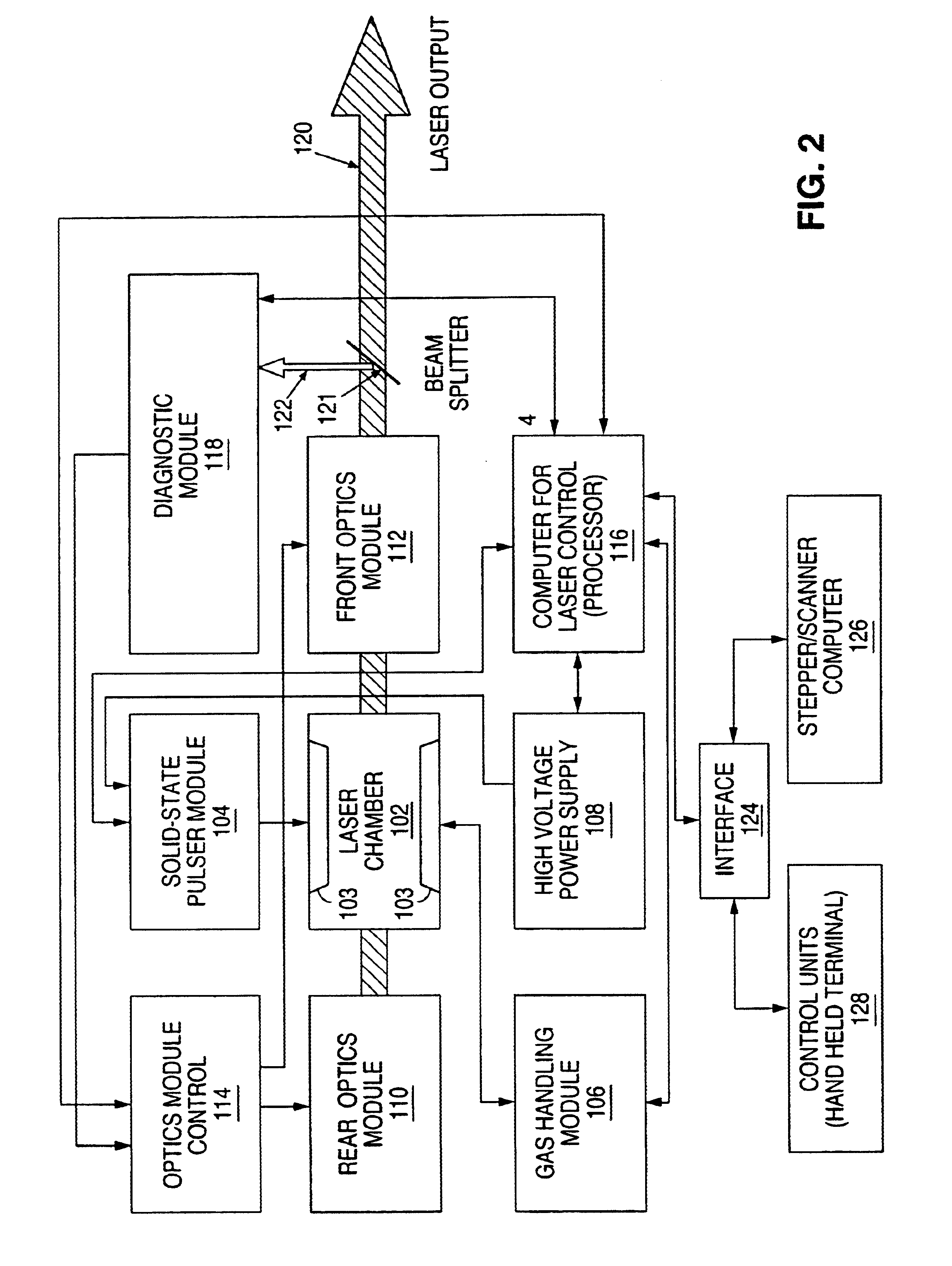
On-line quality control of the key optical components in lithography lasers using laser induced fluorescence
InactiveUS6839375B1PhotometryOptical resonator shape and constructionColour centreLithographic artist
Some of the key optical components of lithography lasers are very sensitive to intensive UV radiation. Intensive UV radiation can cause color center formation in these components. The color centers are reason for laser energy dropping, worse laser-bandwidth and limited life-time. The on-line monitoring of the color-center formation during operation of the lithography lasers detecting laser induced fluorescence and investigation of the fluorescence spectrum can be helpful for maintenance of lithography lasers. The fluorescence signal is analyzed and delivers information about optics quality.
Owner:COHERENT GMBH
Method for assessment of color processing mechanism in the human brain for diagnosis and treatment
ActiveUS20080139941A1Accurate checkBlood flow measurement devicesInfrasonic diagnosticsVisual perceptionCBF - Cerebral blood flow
The present invention is a method for assessment of color processing mechanism in the human brain using cerebral blood flow velocity monitoring, specifically transcranial Doppler ultrasound. The method including steps of transluminating color discs from a light source of a specific color temperature, which act on the visual pathways and color centers to alter mean blood flow velocity in the cerebral arteries. The mean flow velocity is analyzed and using Fourier computation to calculate spectral density estimates. Opponent mechanism in the cortical and subcortical regions determined as opposing tendency for short wavelength versus medium wavelength or for medium wavelength versus long wavelength colors. The method is applied for diagnosis, and treatment of variety of conditions.
Owner:CHIDICON MEDICAL CENT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com