Patents
Literature
267 results about "Magnetic imaging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Head Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the head uses a powerful magnetic field, radio waves and a computer to produce detailed pictures of the brain and other cranial structures that are clearer and more detailed than other imaging methods.
Methods of, and materials for, treating vascular defects with magnetically controllable hydrogels
Embolic devices and materials include an expansible polymer, and magnetically responsive material that allow the embolic devices and materials to be guided into, and held within, vascular defects, while the expansible polymer expands. In some embodiments, the expansion of the expansible polymer reduces the density of the magnetic material, so that subsequent magnetic surgery and magnetic imaging procedures can still employed.
Owner:STEREOTAXIS
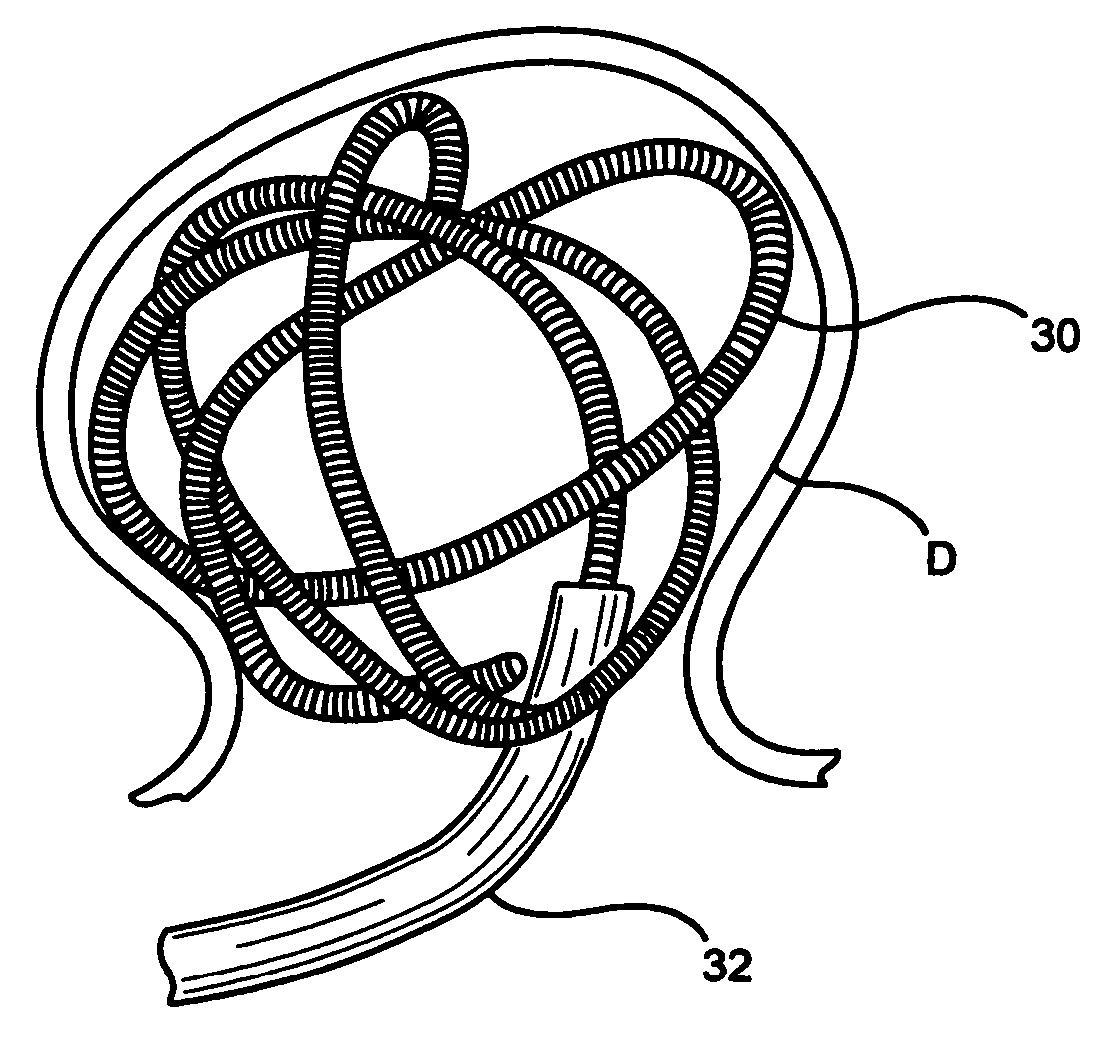
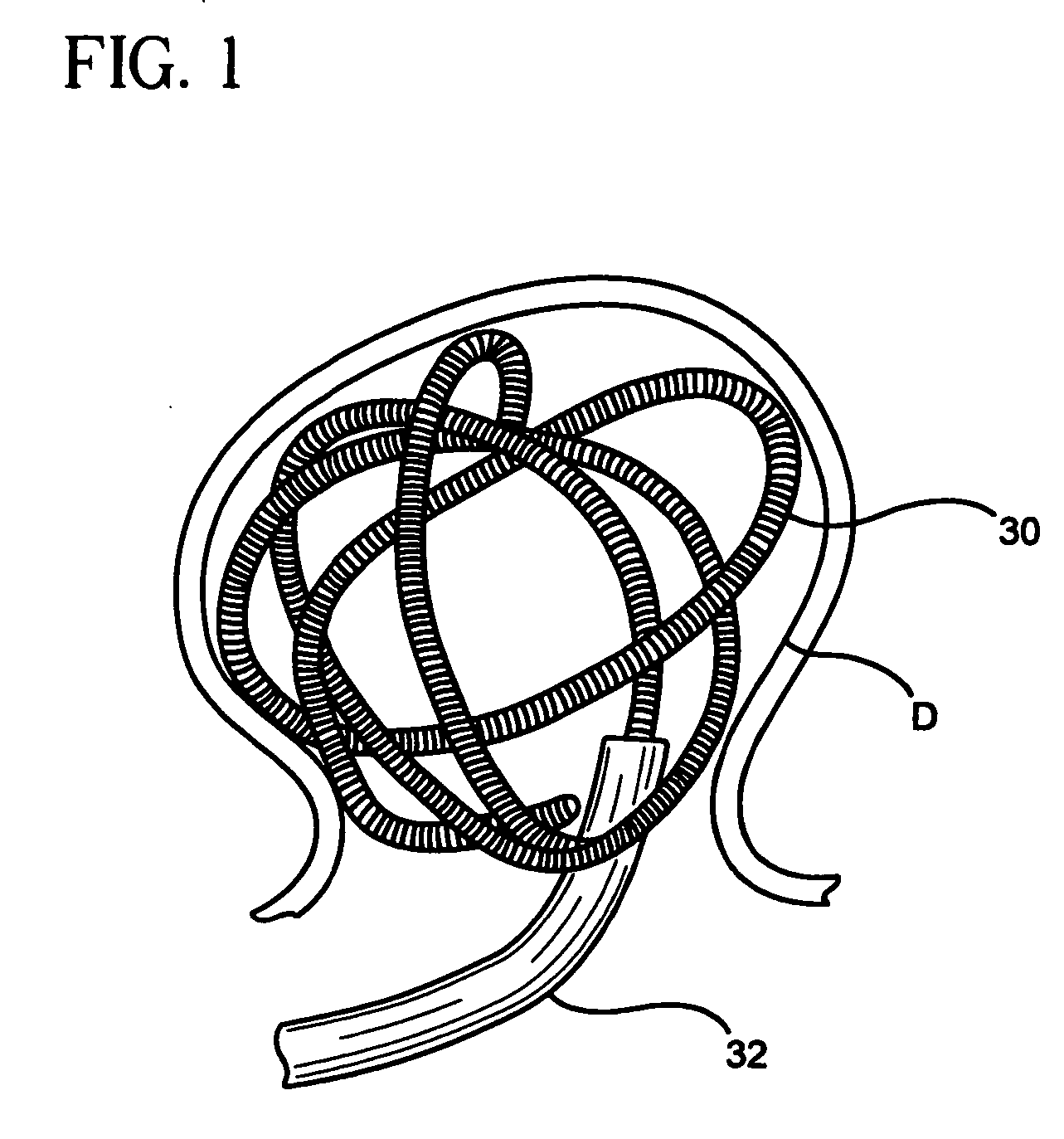
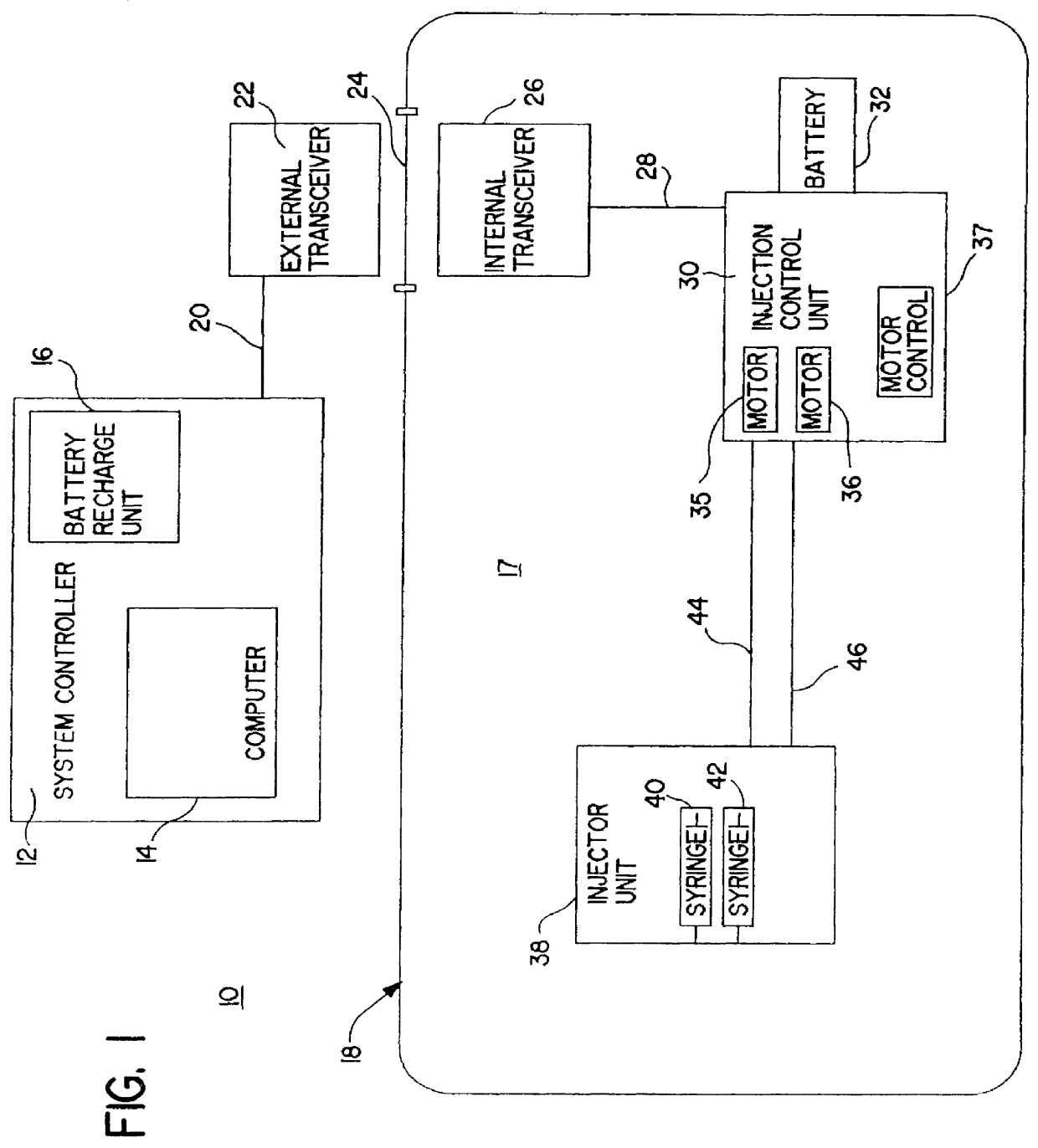
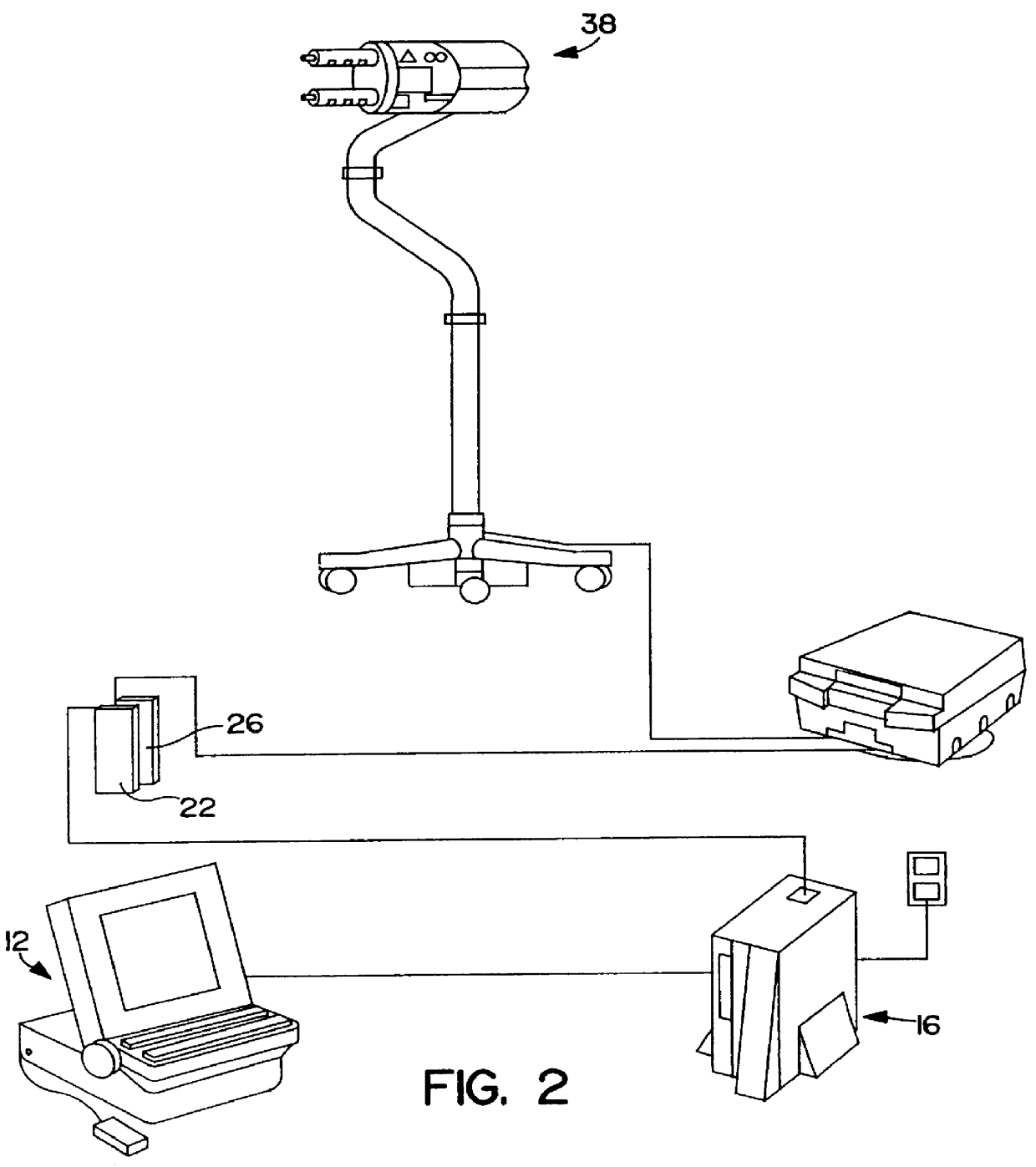
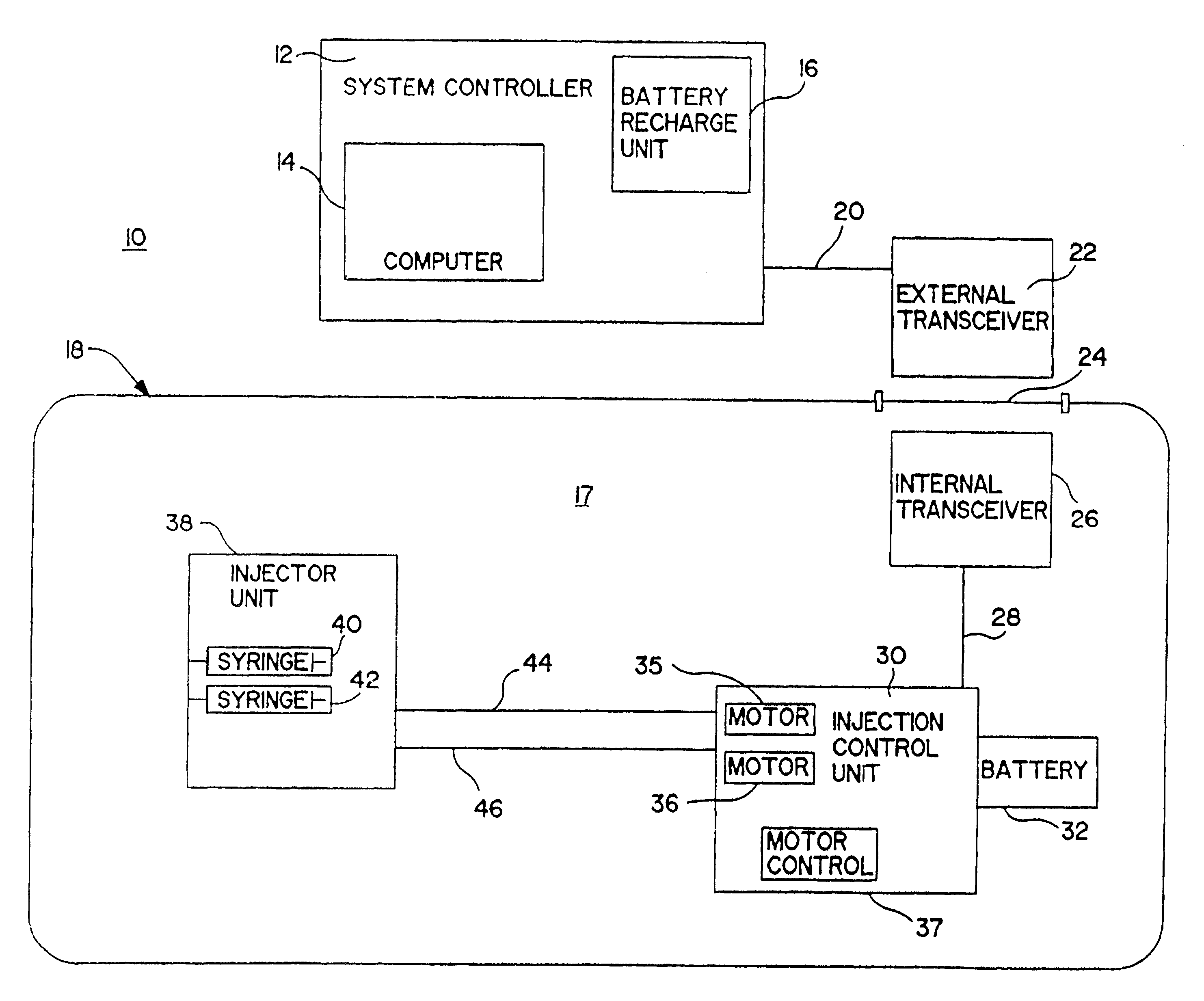
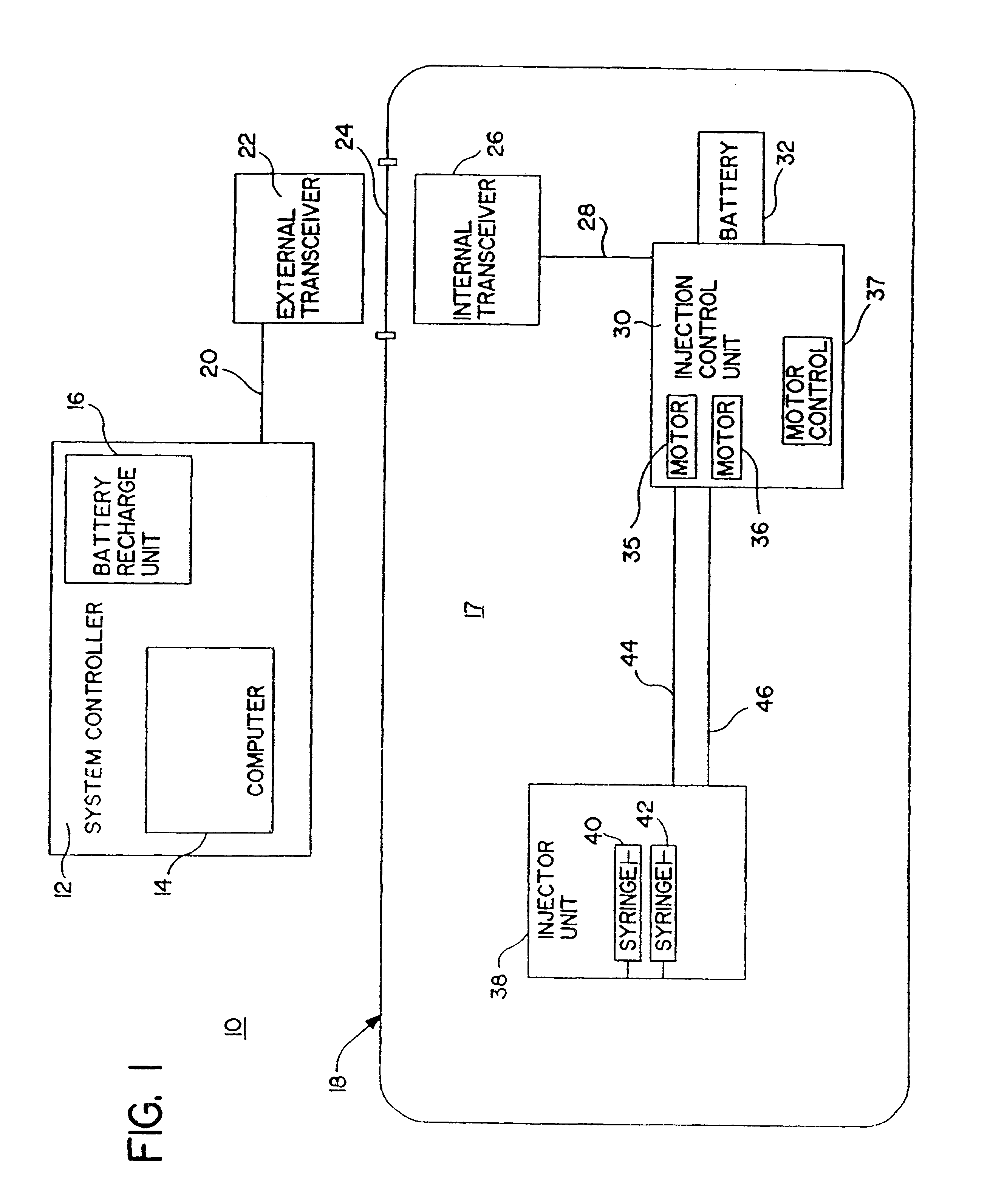
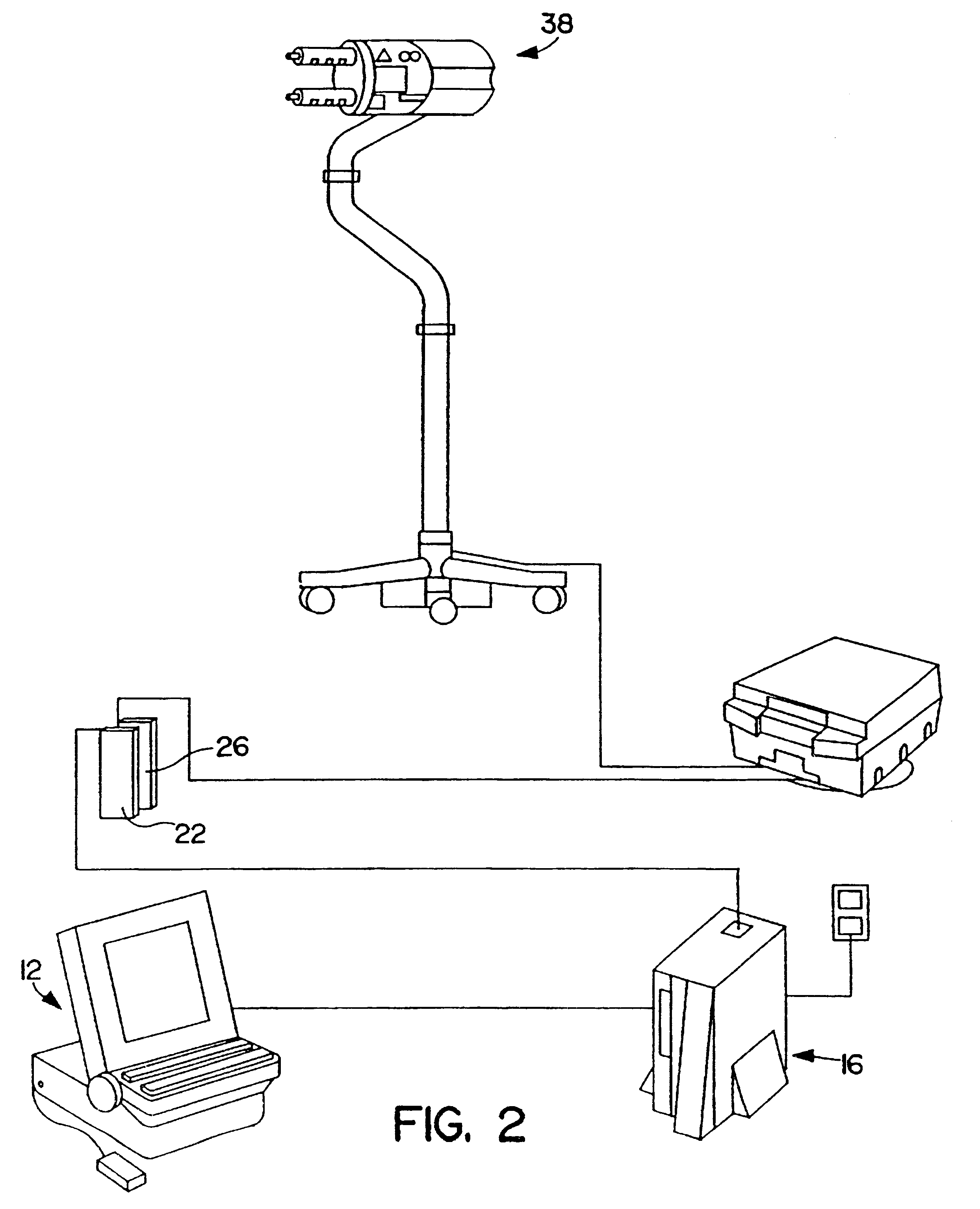
Patient infusion system for use with MRI
InactiveUSRE36648E1Maintenance characteristicMaintain integritySurgeryMedical devicesTelecommunications linkEngineering
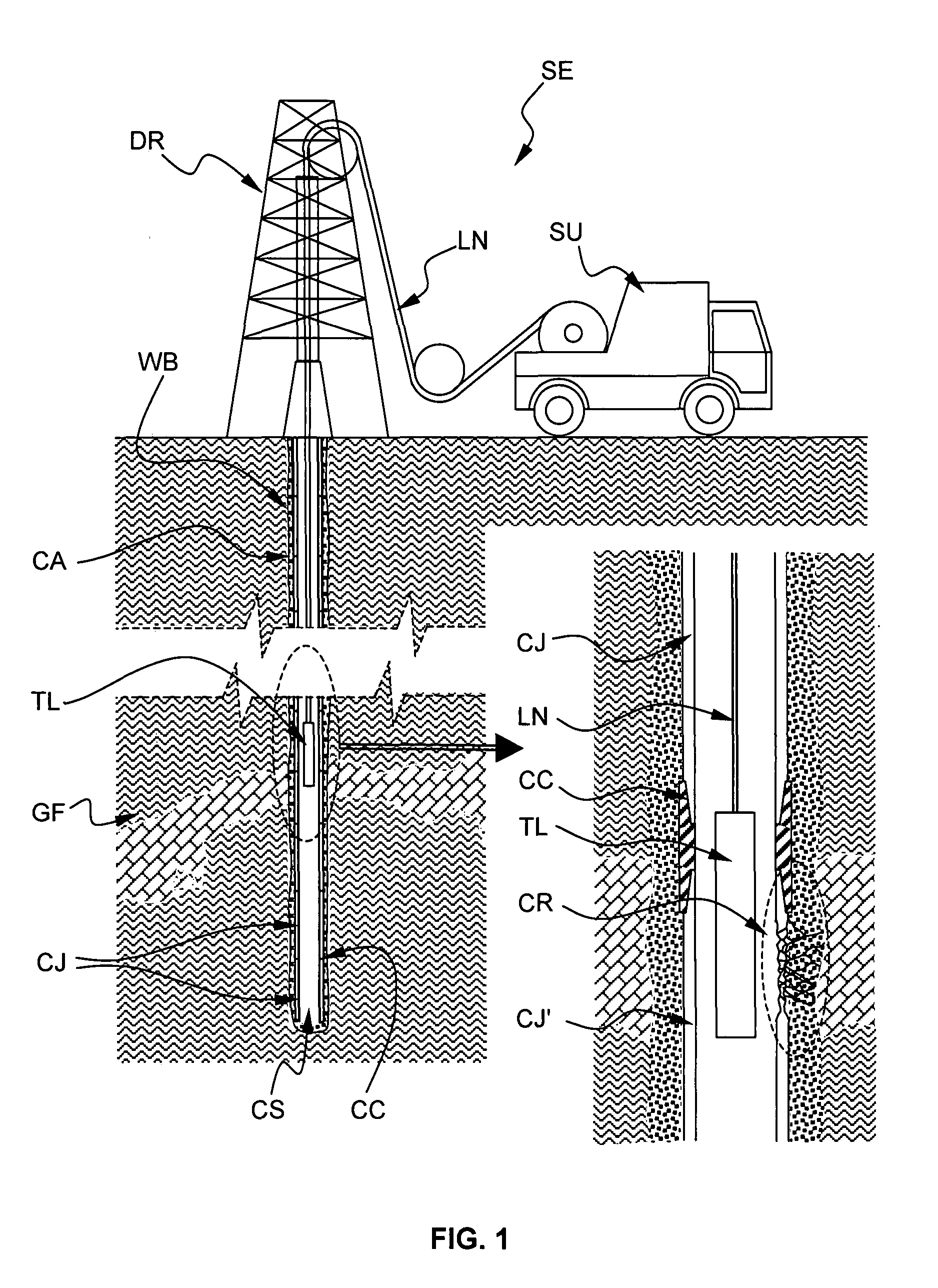
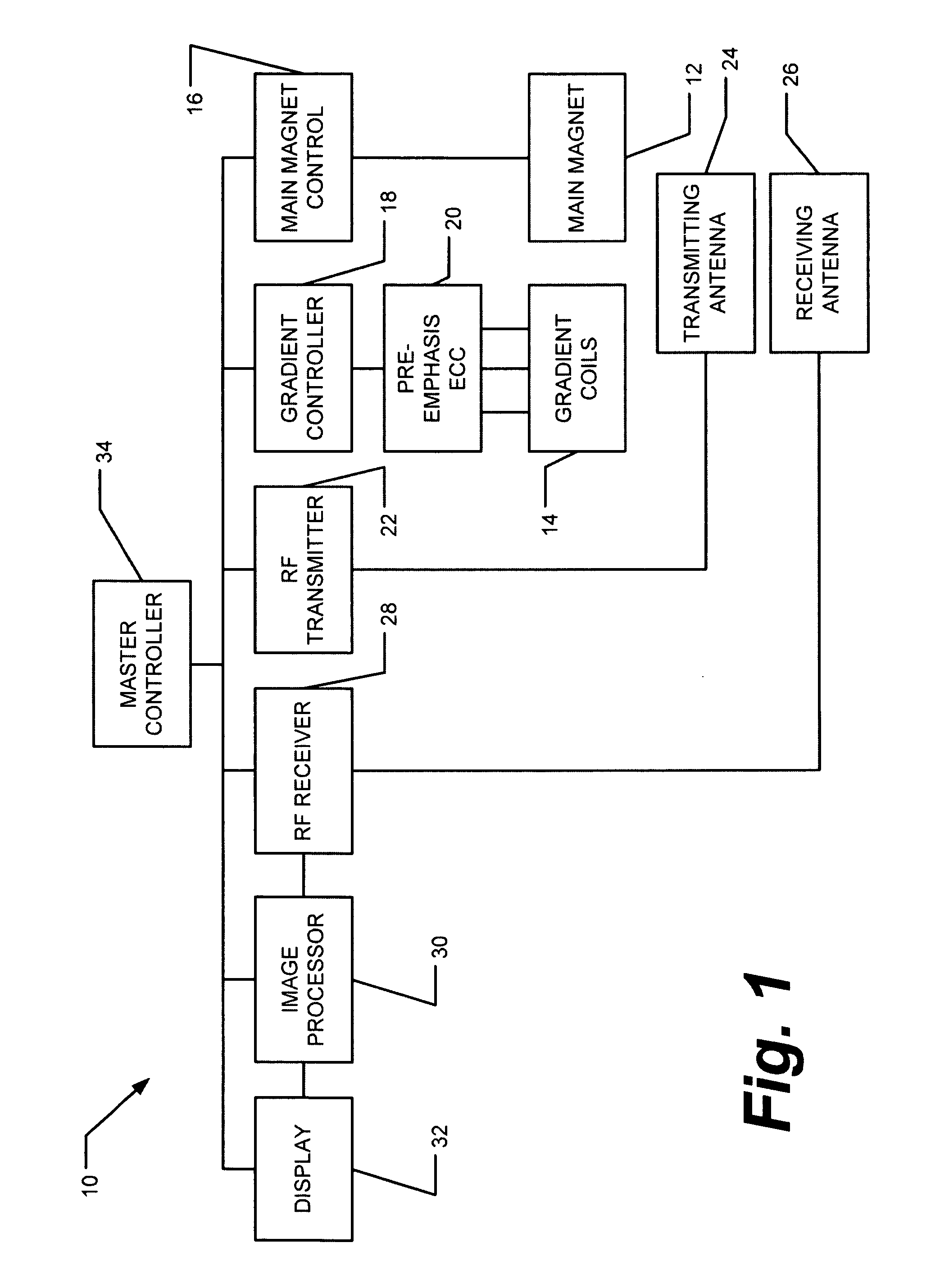
This invention relates generally to the field of Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) systems for generating diagnostic images of a patient's internal organs and more particularly, this invention relates to improved MRI systems with decreased interference between the magnetic field used for producing diagnostic images and the magnetic fields generated by the electric motors used for driving the pistons of the contrast media injectors. Additionally, the system employs an improved communication link between an externally located system controller and the injection head control unit located within the electromagnetic isolation barrier which defines the magnetic imaging room.
Owner:MEDRAD INC.
Patient infusion system for use with MRI
InactiveUSRE37602E1Reduce amountIncreasing portability and easeSurgeryMedical devicesMedicineControl cell
This invention relates generally to the field of Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) systems for generating diagnostic images of a patient's internal organs and more particularly, this invention relates to improved MRI systems with decreased interference between the magnetic field used for producing diagnostic images and the magnetic fields generated by the electric motors used for driving the pistons of the contrast media injectors. Additionally, the system employs an improved communication link between an externally located system controller and the injection head control unit located within the electromagnetic isolation barrier which defines the magnetic imaging room.
Owner:BAJER MEDIKAL KEHA INK
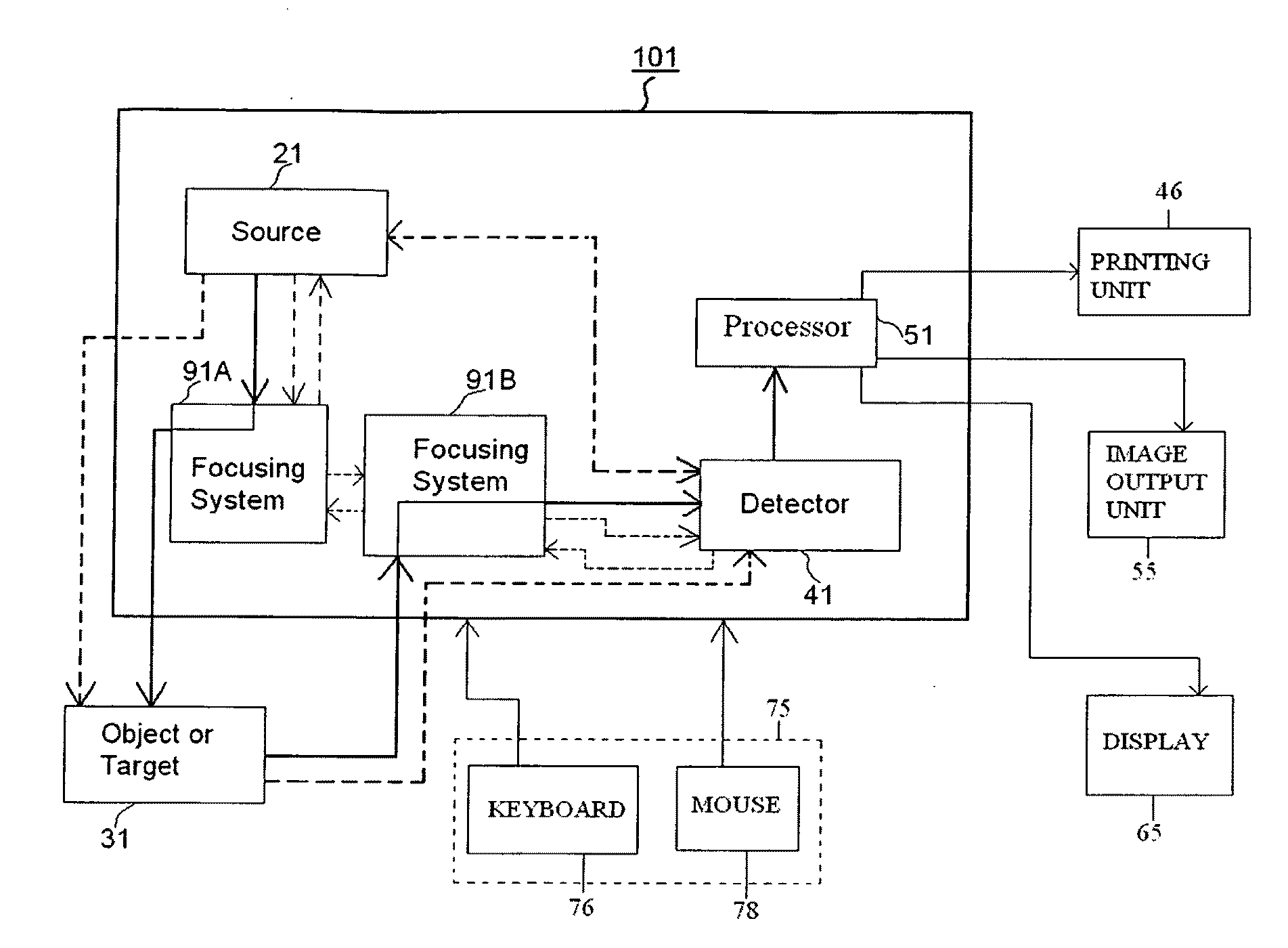
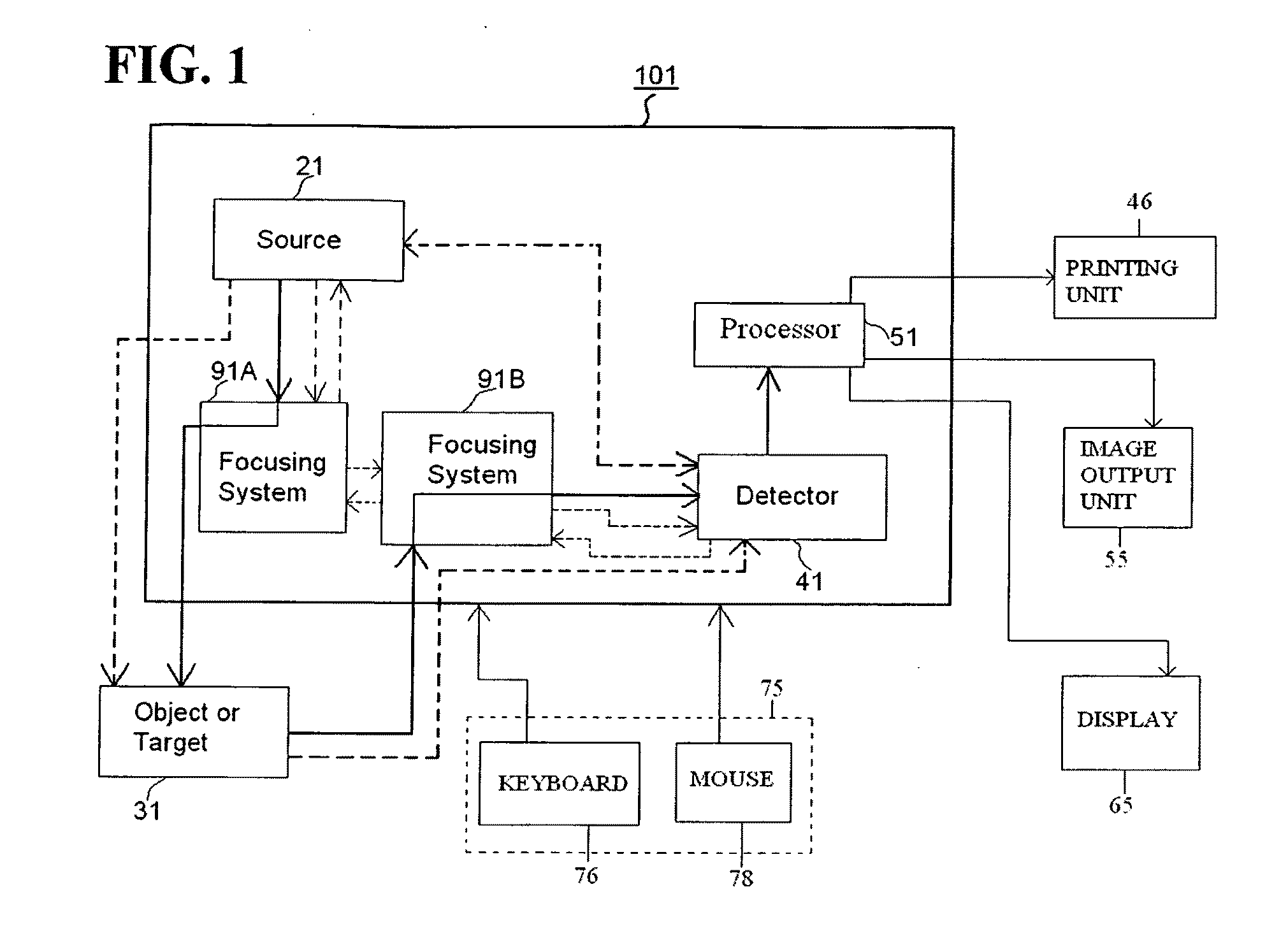
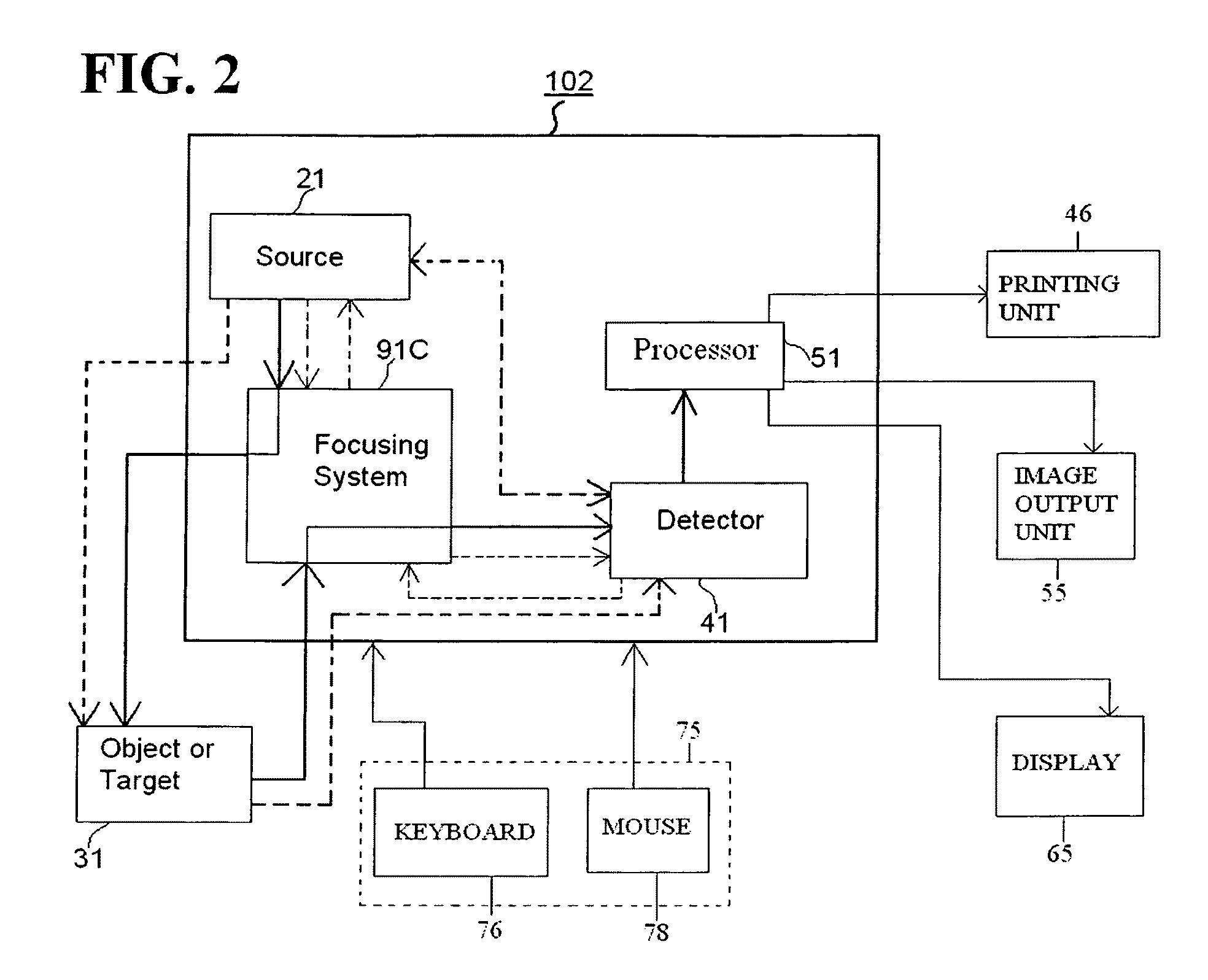
Direct magnetic imaging apparatus and method
InactiveUS20110204891A1Measurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionElectromagnetic fieldPerformed Imaging
Methods and apparatuses of the present invention perform imaging using a metamaterial lens structure. The apparatus according to one embodiment comprises: a field source capable of generating an electromagnetic field directed to an area in an object or target; a field detector arranged downstream from the field source, the field detector being capable of detecting a field signature associated with the area in the object or target; and a metamaterial lens structure arranged downstream from the field source, the metamaterial lens structure concentrating the electromagnetic field produced by the field source to the area in the object or target, or concentrating the field signature from the area in the object or target to the field detector.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Synthesis and conjugation of iron oxide nanoparticles to antibodies for targeting specific cells using fluorescence and MR imaging techniques
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
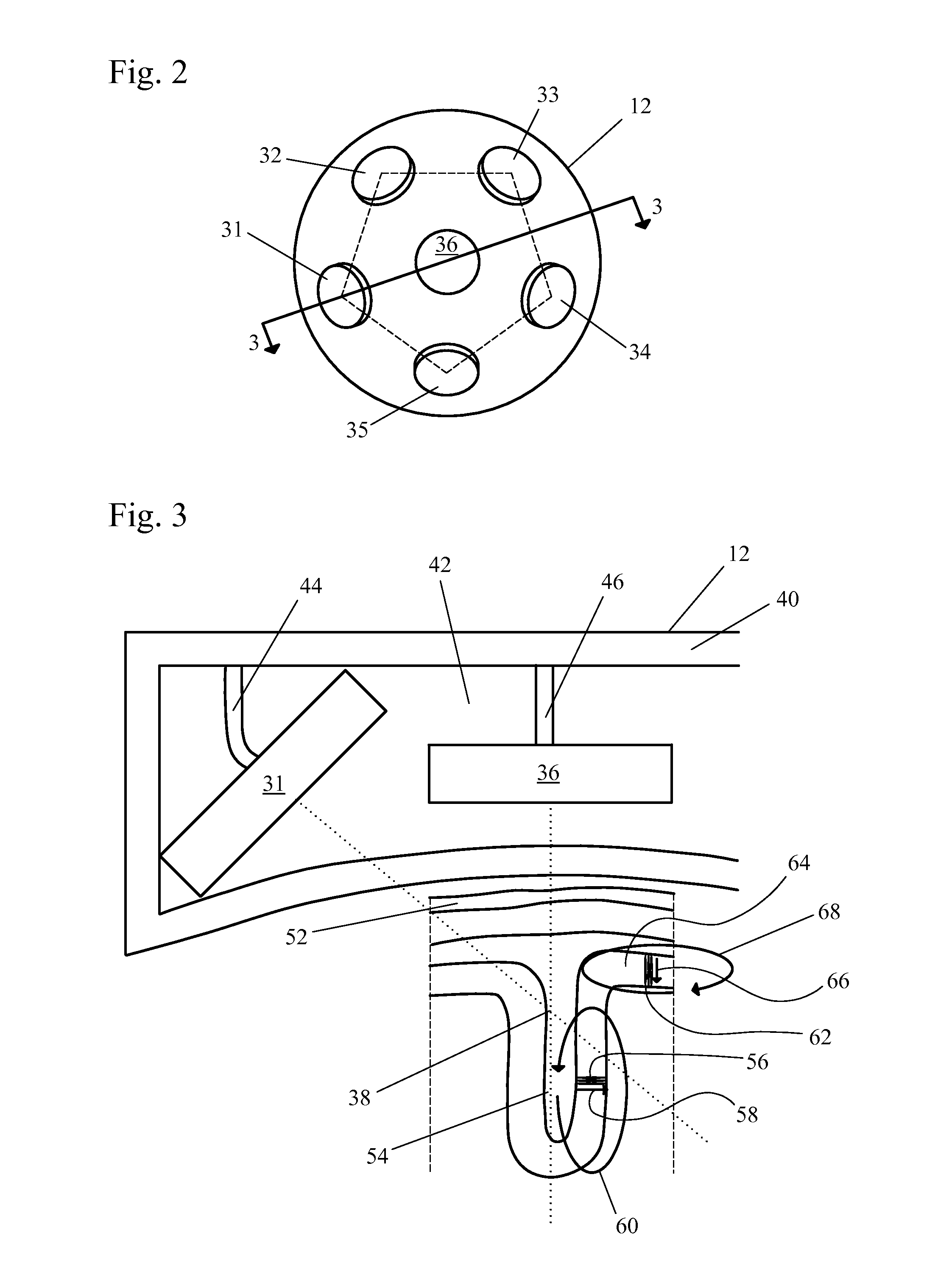
Mutually calibrated magnetic imaging array
ActiveUS9791536B1More transportableLess cumbersomeDiagnostic recording/measuringElectrical measurementsMagnetic tension forceMagnetic source
A mutually calibrated magnetic imaging array system is described. The system includes a non-target magnetic source rigidly attached to a magnetometer, and an attached control unit to measure and adjust several parameters of a magnetic imaging array. A non-target magnetic field source is used to generate a well-defined and distinguishable spatial magnetic field distribution. The source is rigidly attached directly to a magnetometer, while the relative positions of the magnetometers are unknown. The magnetic imaging array is used to measure the strength of the non-target source magnetic fields and the information is used to calibrate several parameters of the array, such as, but not limited to, effective magnetometer positions and orientations with respect to each other and cross-talk between the magnetometers. The system, and method described herein eliminates the need for a separate calibration phantom.
Owner:QUSPIN
Synthesis and conjugation of iron oxide nanoparticles to antibodies for targeting specific cells using fluorescence and mr imaging techniques
InactiveUS20100209352A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsDispersion deliveryFluorescenceAntibody conjugate
The invention provides for methods for producing water-soluble iron oxide nanoparticles comprising encapsulating the nanoparticles in phospholipids micelles. Also provided are methods for conjugating the inventive nanoparticles via functionalized phospholipids to a target molecule, such as an antibody. The invention further provides methods for using the nanoparticle-antibody conjugate of the invention as a contrast agent to image specific cells or proteins in a subject using fluorescent and magnetic imaging techniques.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
System and method for measuring object characteristics using phase differences in polarized light reflections
InactiveUS6956658B2Easy to measurePolarisation-affecting propertiesScattering properties measurementsPhase differenceLight reflection
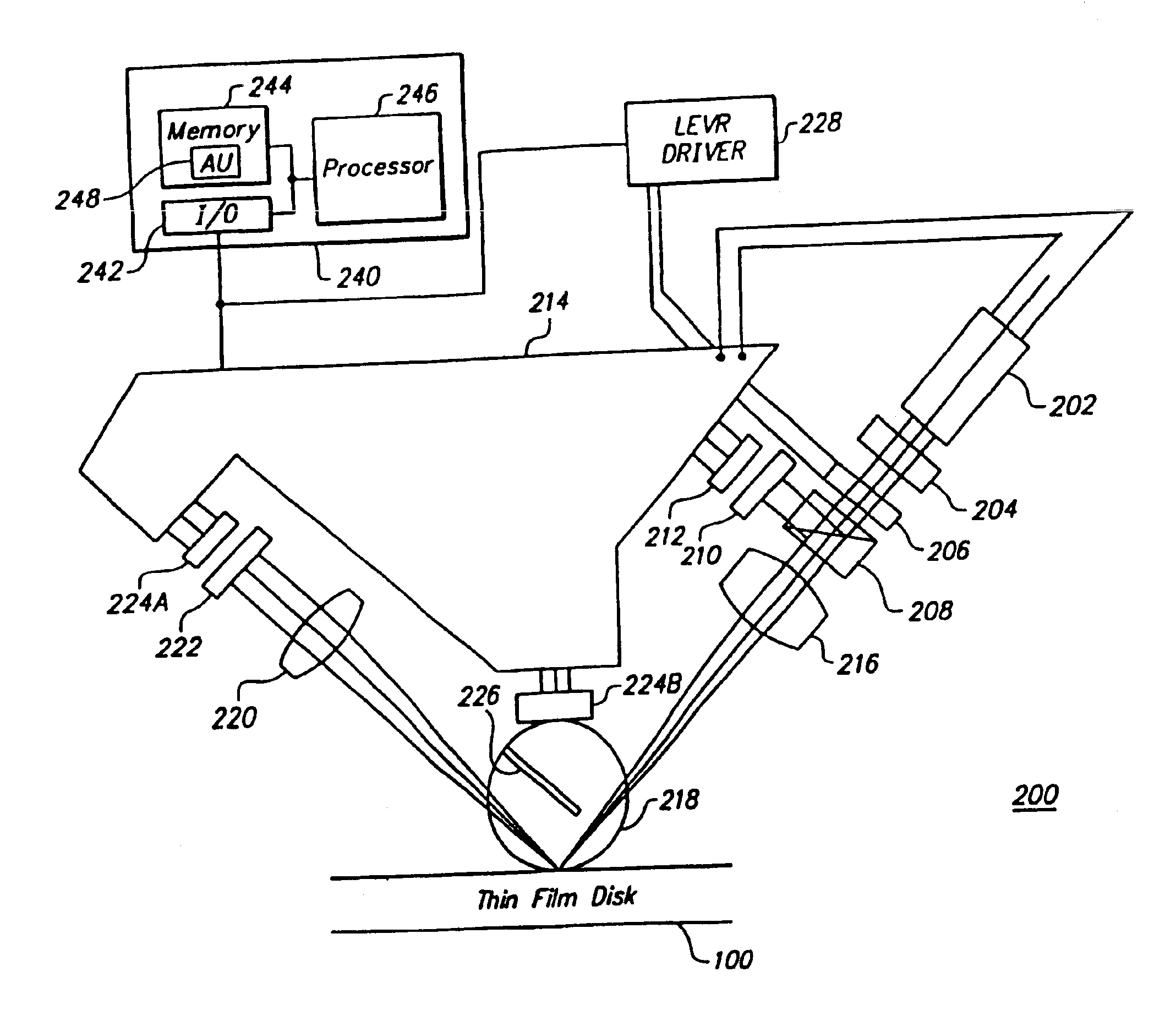
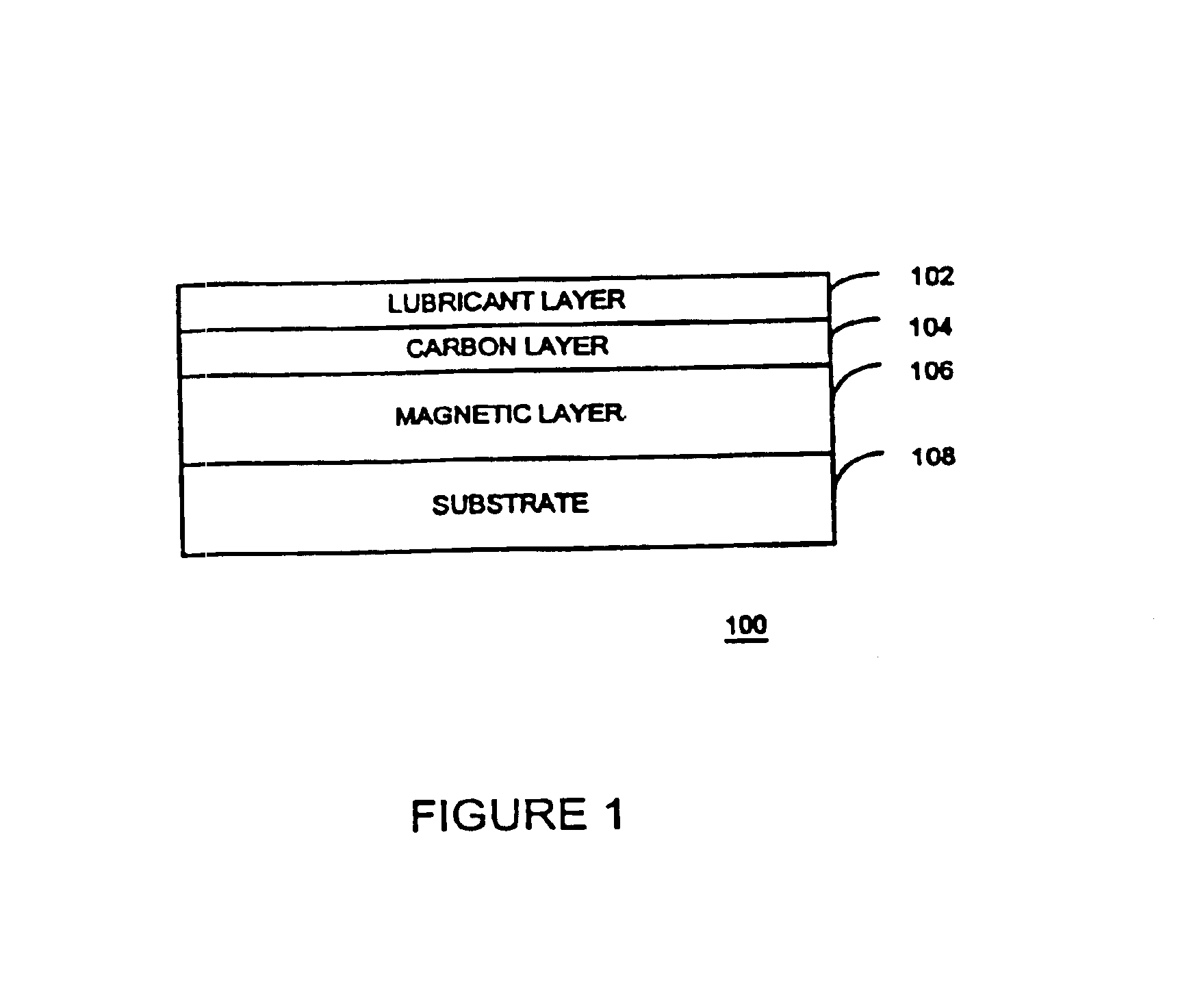
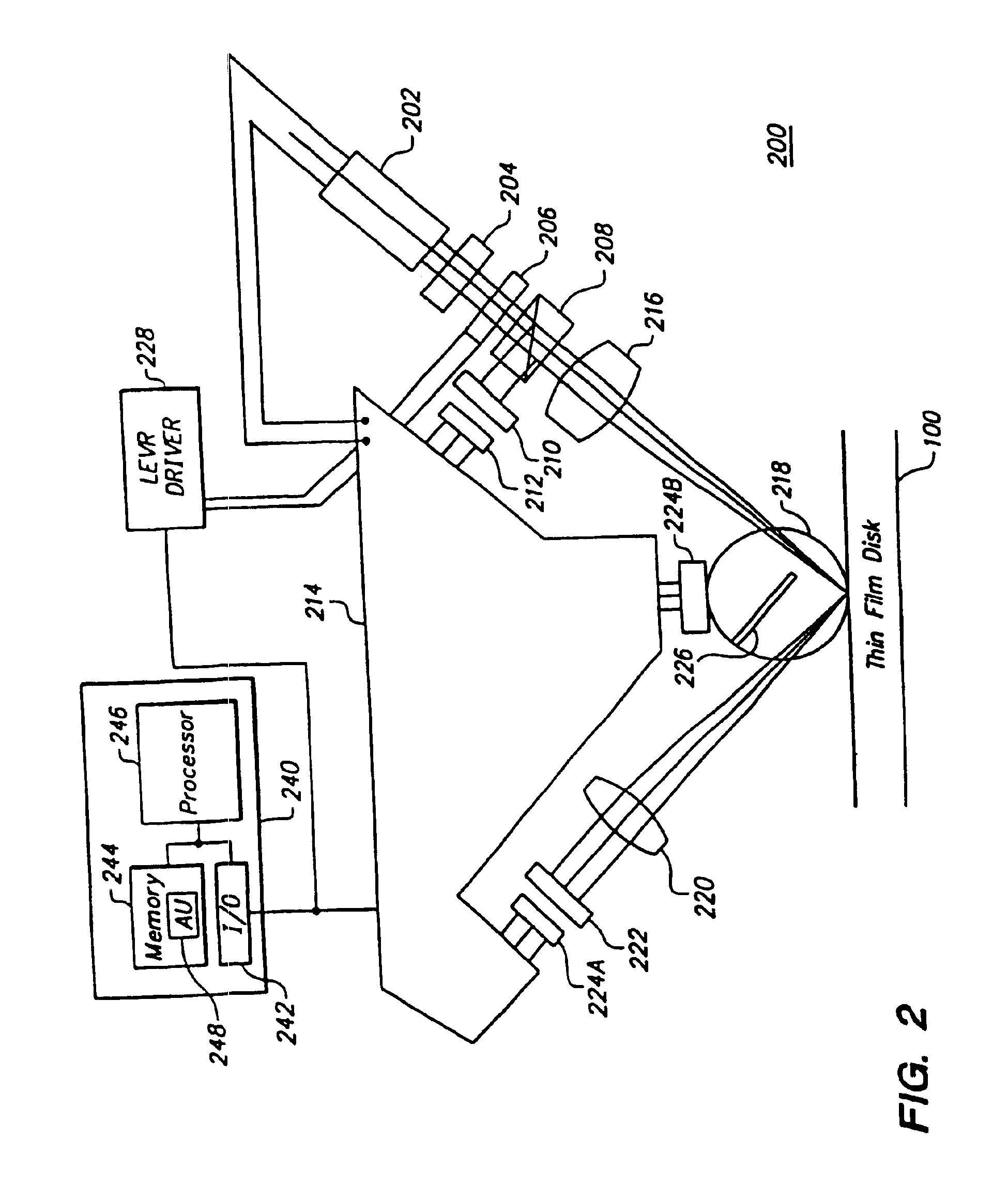
A system and method for performing a magnetic imaging, optical profiling, and measuring lubricant thickness and degradation, carbon wear, carbon thickness, and surface roughness of thin film magnetic disks and silicon wafers at angles that are not substantially Brewster's angle of the thin film (carbon) protective overcoat is provided. The system and method involve a focused optical light whose polarization can be switched between P or S polarization is incident at an angle to the surface of the thin film magnetic disk. This generates both reflected and scattered light that may be measured to determine various values and properties related to the surface of the disk, including identifying the Kerr-effect in reflected light for determination of point magnetic properties. In addition, the present invention can mark the position of an identified defect.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Electromagnetic imaging method and device
InactiveUS7960969B2Accurate electromagnetic imageImprove accuracyElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMagnetic property measurementsTransmitter coilEngineering
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
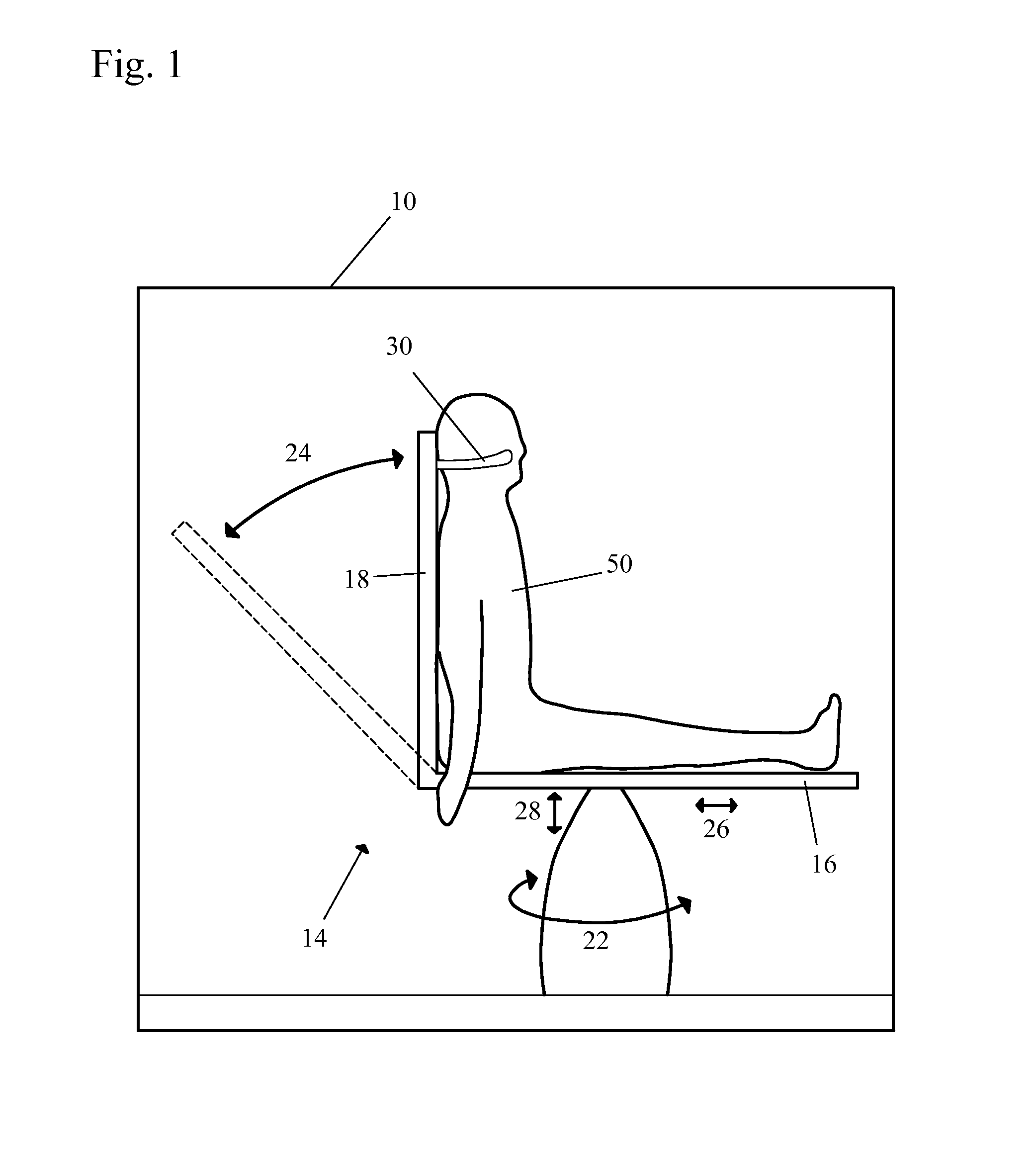
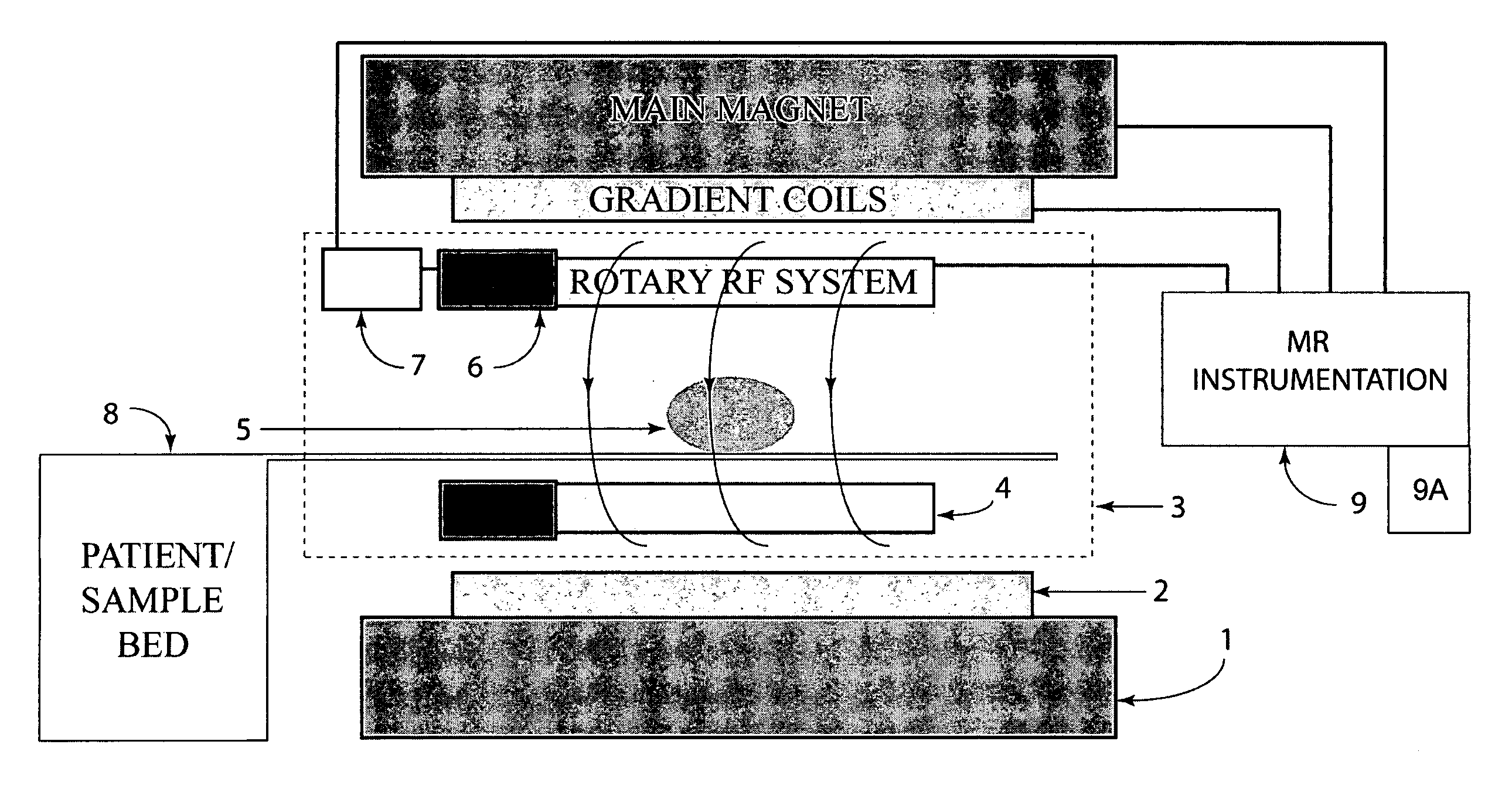
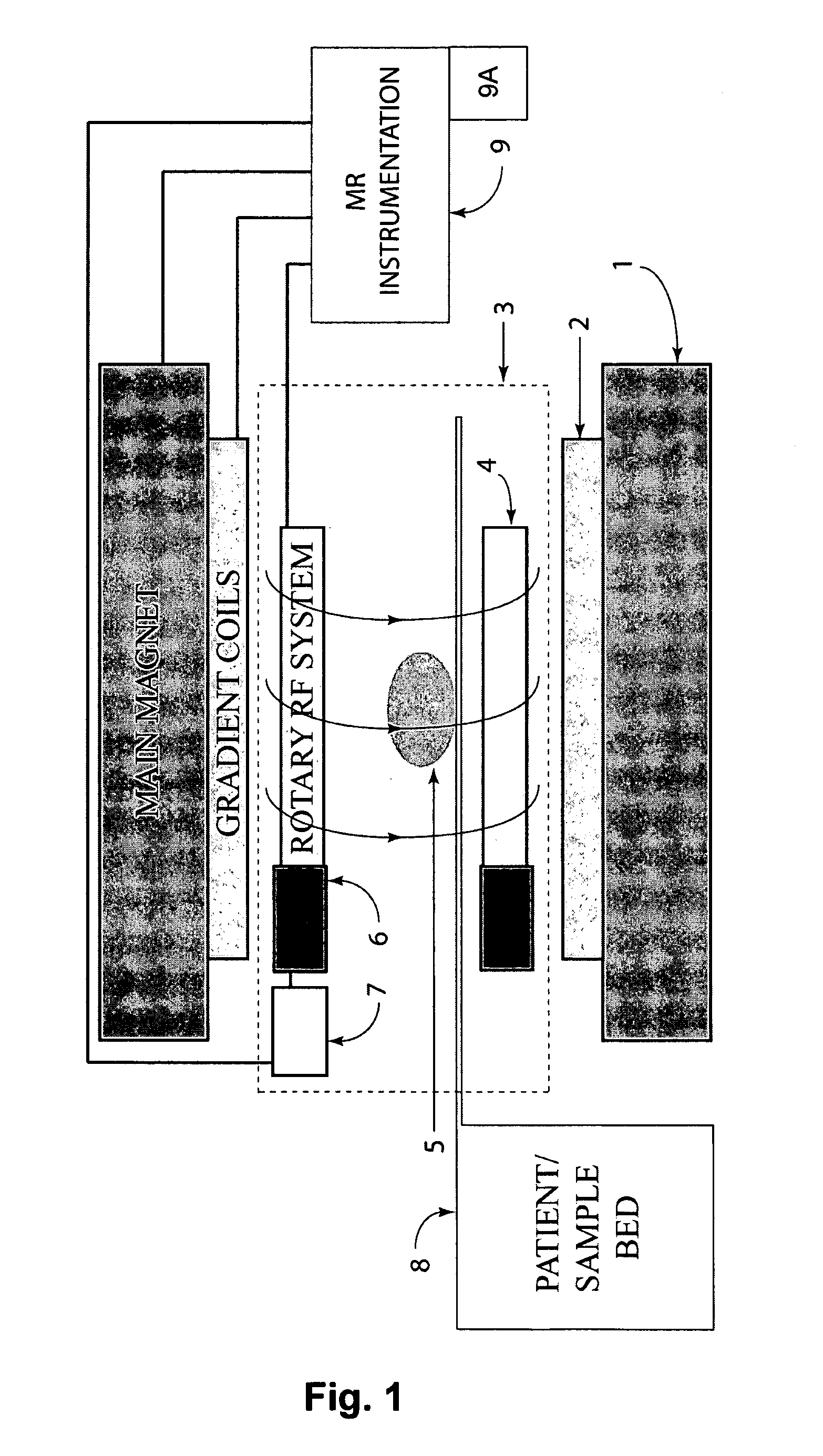
MRI apparatus and method with moving field component
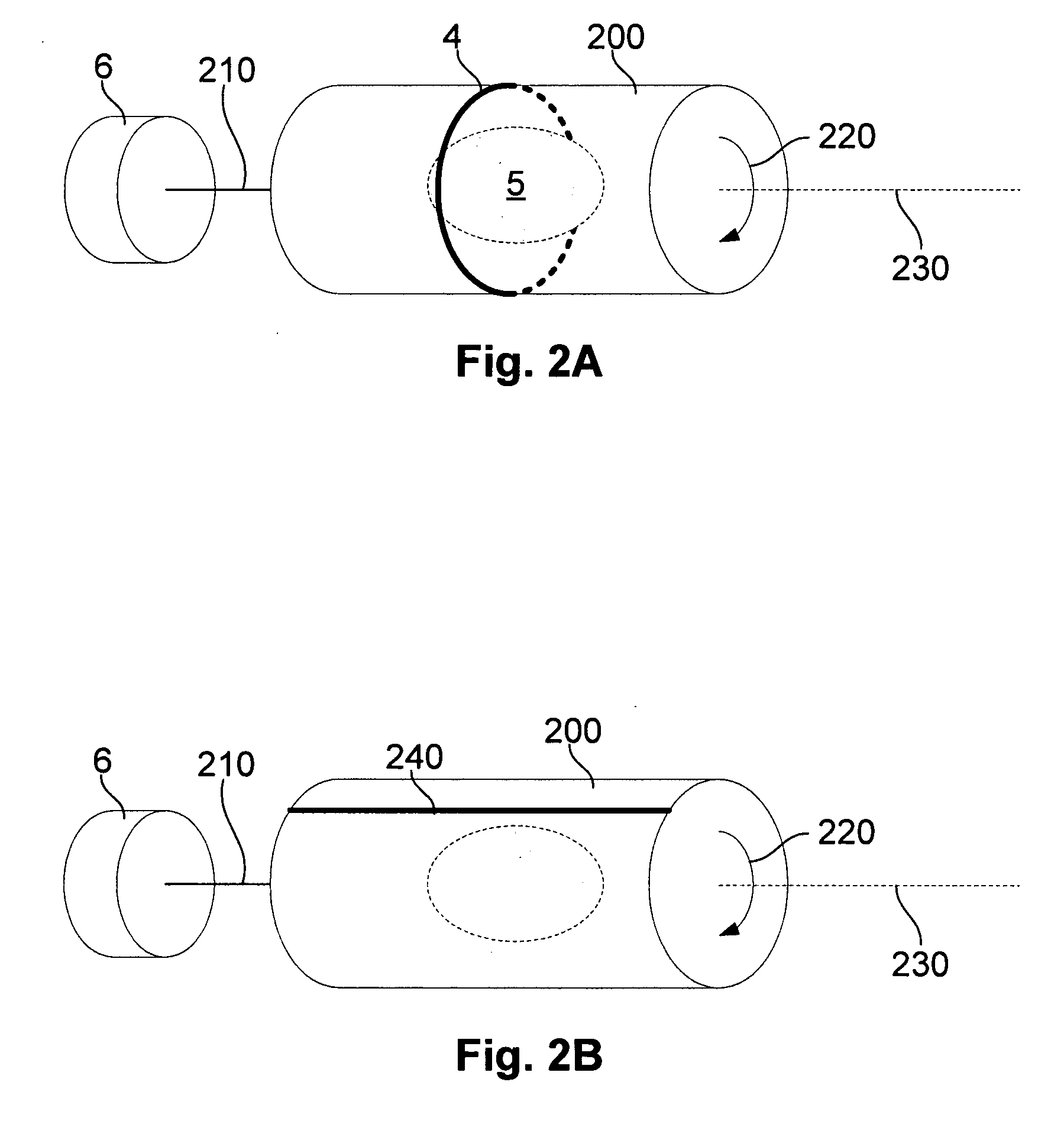
ActiveUS20110210735A1Measurements using NMR spectroscopyAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceElectromagnetic fieldMR - Magnetic resonance
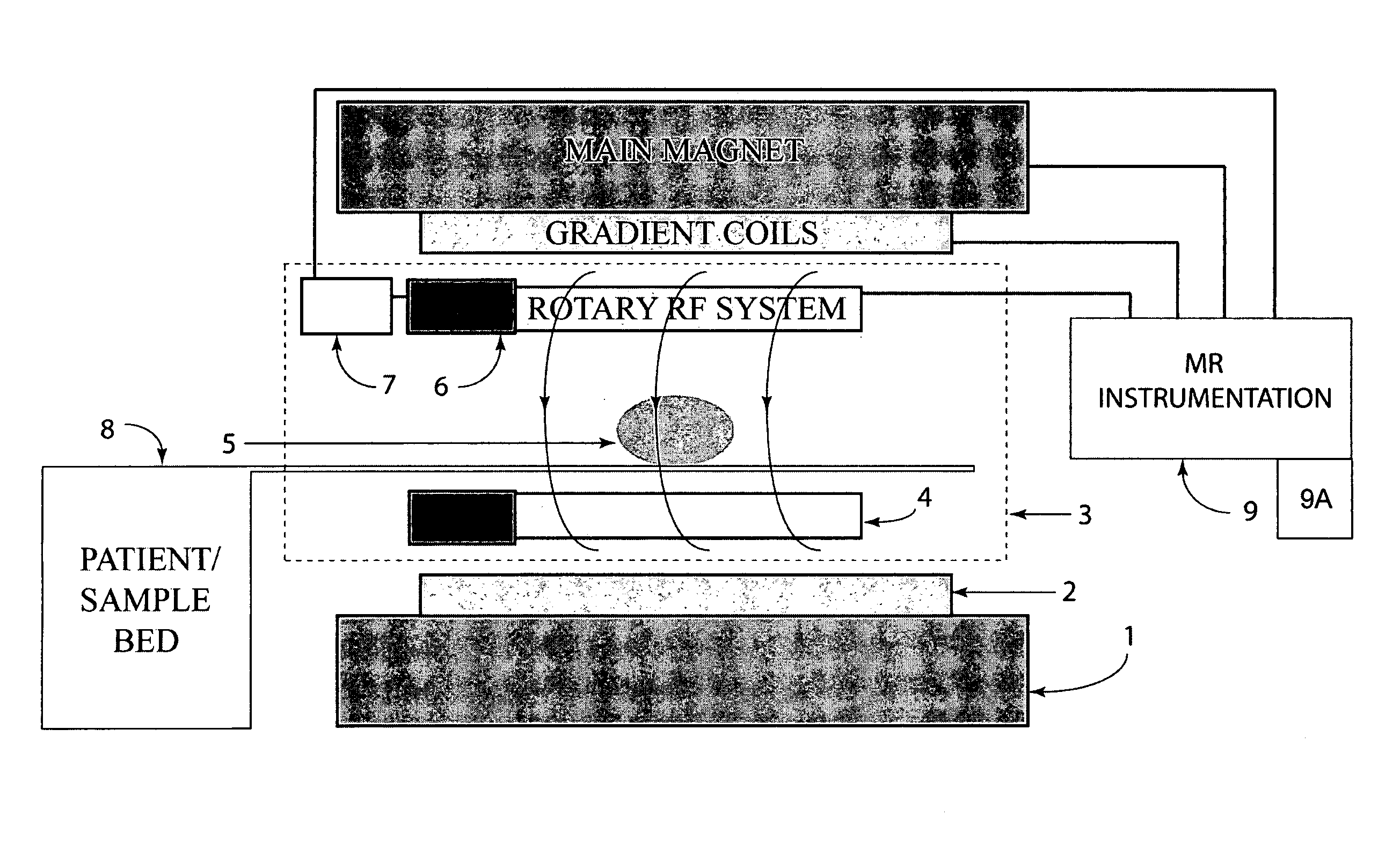
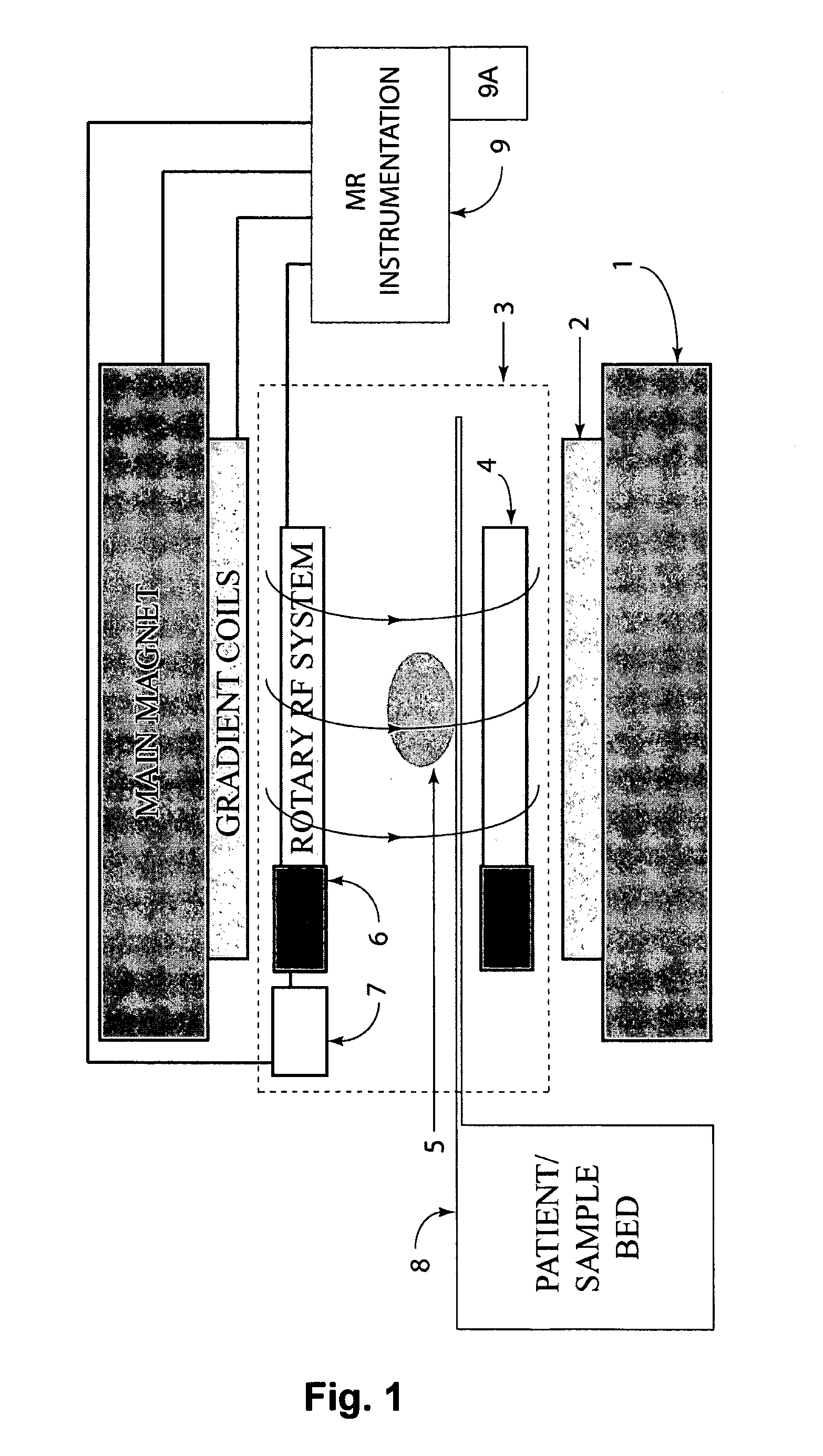
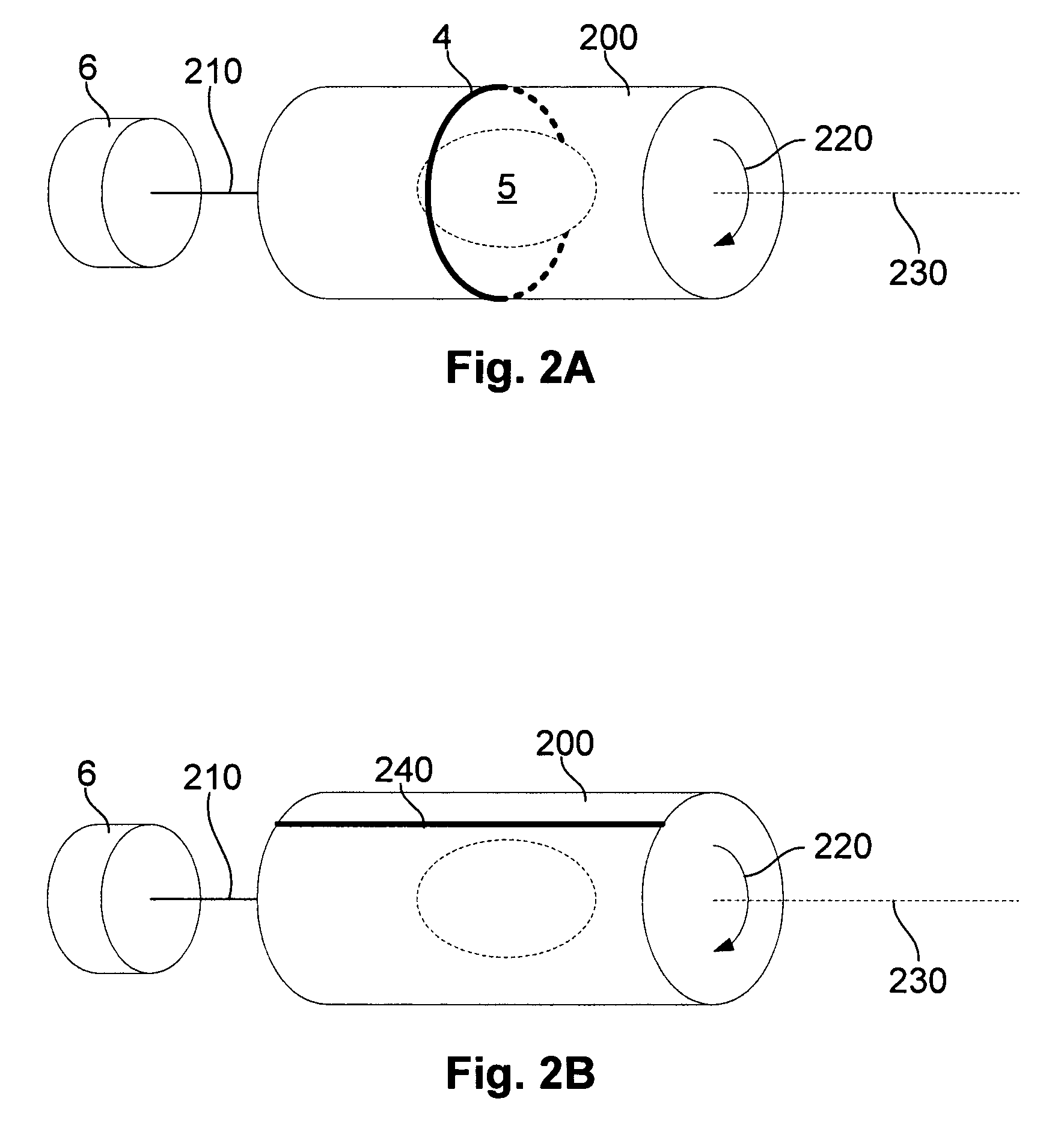
Apparatus for use in a magnetic resonance imaging system, the imaging system generating a magnetic imaging field in an imaging region (5), the apparatus including at least one coil for at least one of transmitting, receiving or transceiving an electromagnetic field, a field component (4) (such as a coil or a shield) and a drive (6) coupled to the field component for moving the field component (4) relative to the imaging region (5) to thereby modify the electromagnetic field during imaging process. The same concept can also be applied to nuclear imaging or nuclear spectroscopy apparatus.
Owner:THE UNIV OF QUEENSLAND
System for continuously calibrating a magnetic imaging array
A calibration system and method is described to continuously measure and adjust several parameters of a magnetic imaging array. One or more non-target magnetic field source(s) are used to generate a well-defined and distinguishable spatial magnetic field distribution. The magnetic imaging array is used to measure the strength of the non-target magnetic fields and the information is used to calibrate several parameters of the array, such as, but not limited to, effective magnetometer positions and orientations, gains and their frequency dependence, bandwidth, and linearity. The calibration can happen continuously or periodically, while the imaging array is operating to create magnetic field images, if the modulation frequencies for calibration are outside the frequency window of interest.
Owner:QUSPIN
Imaging method for obtaining spatial distribution of nanoparticles in the body
InactiveUS20100066363A1Accurate and high-spatially resolved imageAccurate focusDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsVoxelHigh spatial resolution
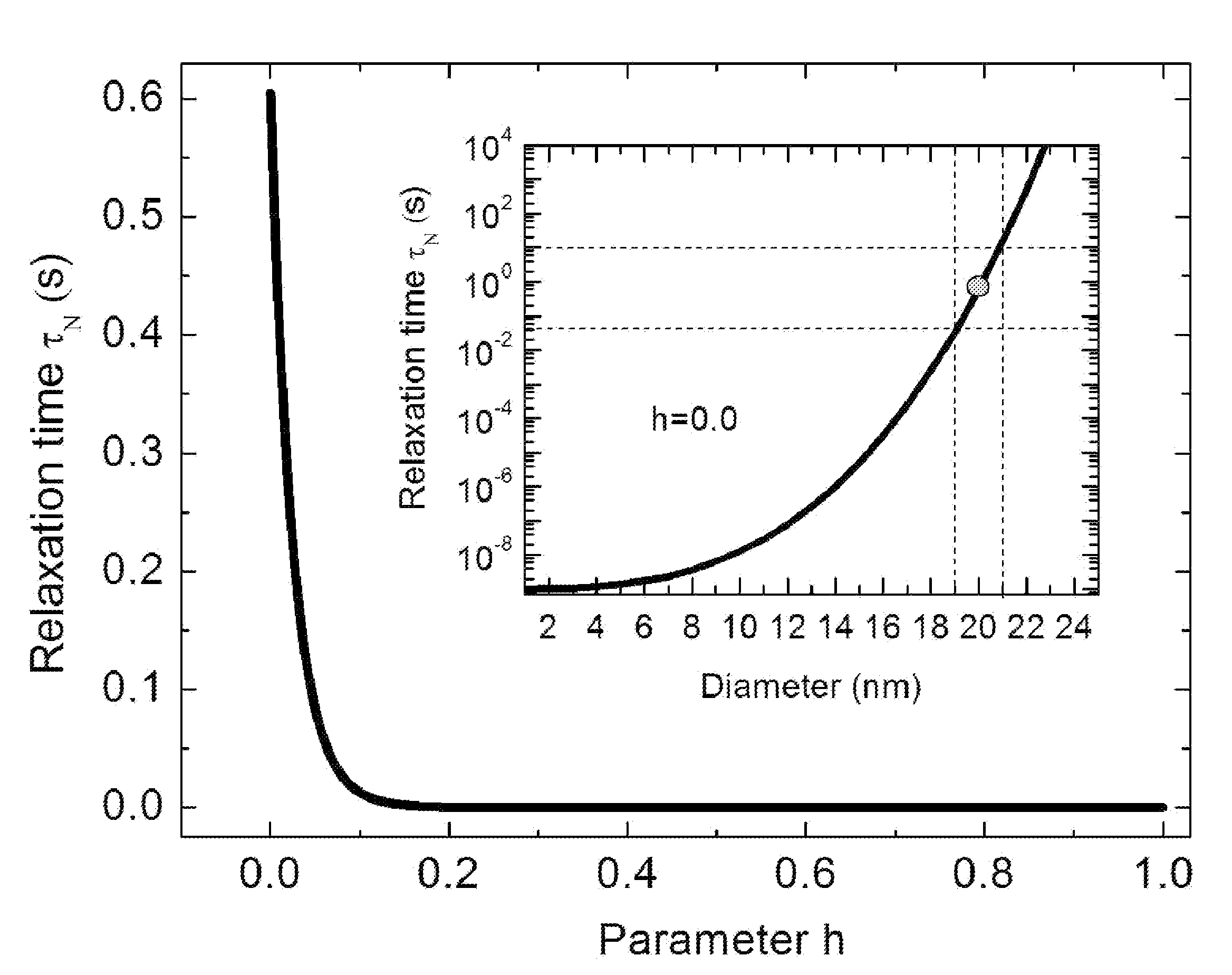
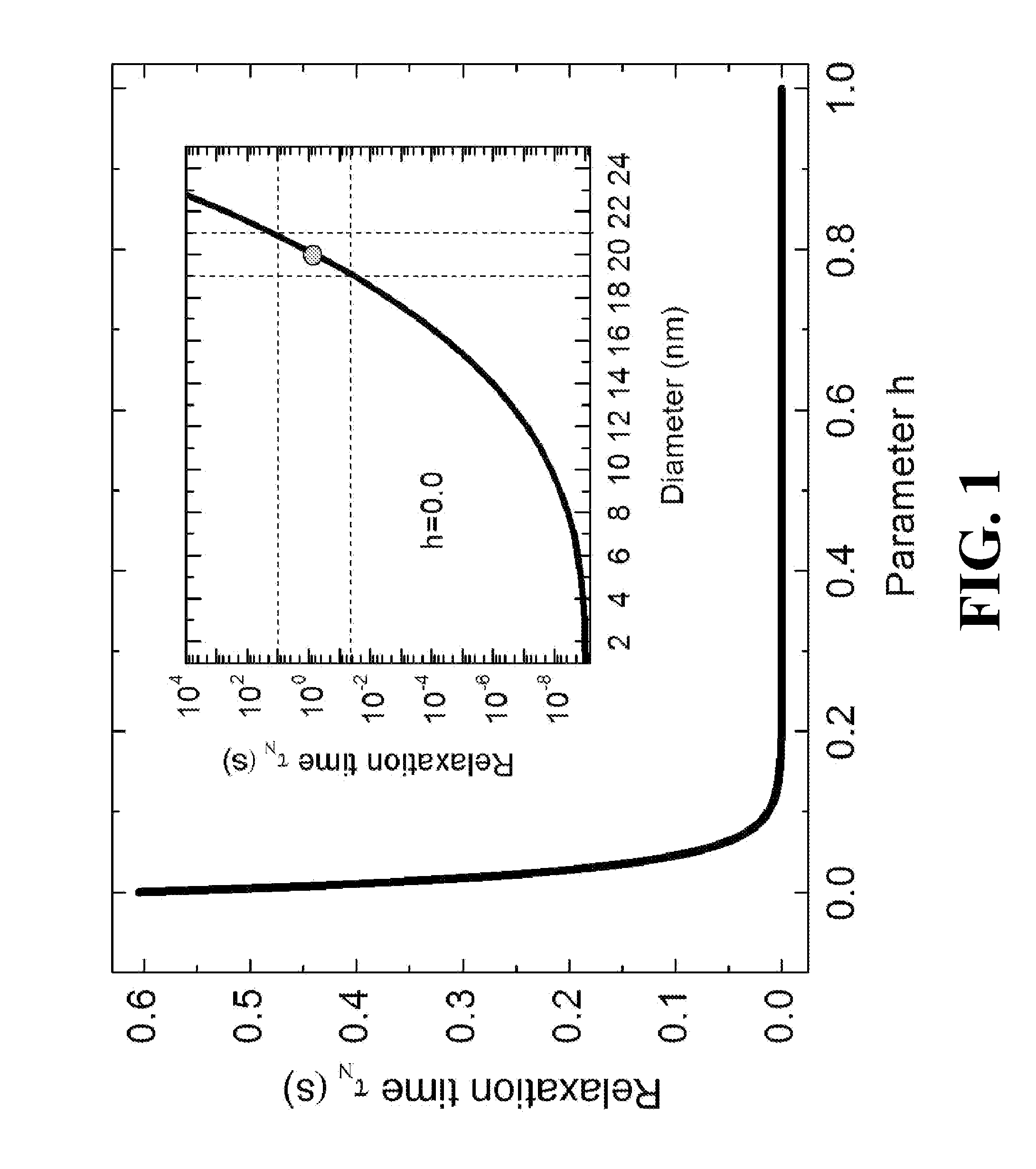
A well-posed magnetic imaging method is disclosed that exploits the non-linear behavior of the characteristic time scale of the Neel relaxation for obtaining accurate high-spatial resolution images of magnetic tracers. The method includes placing an object in a selection field (static field) generated by three pairs of orthogonally arranged coil (drive coils), supplying prudently choice currents to the drive coils, a zero field voxel (ZFV) is formed that can be positioned anywhere in the local region of interest (ROI), switching the magnetizing field off, and collecting an image.
Owner:UNIV HOUSTON SYST
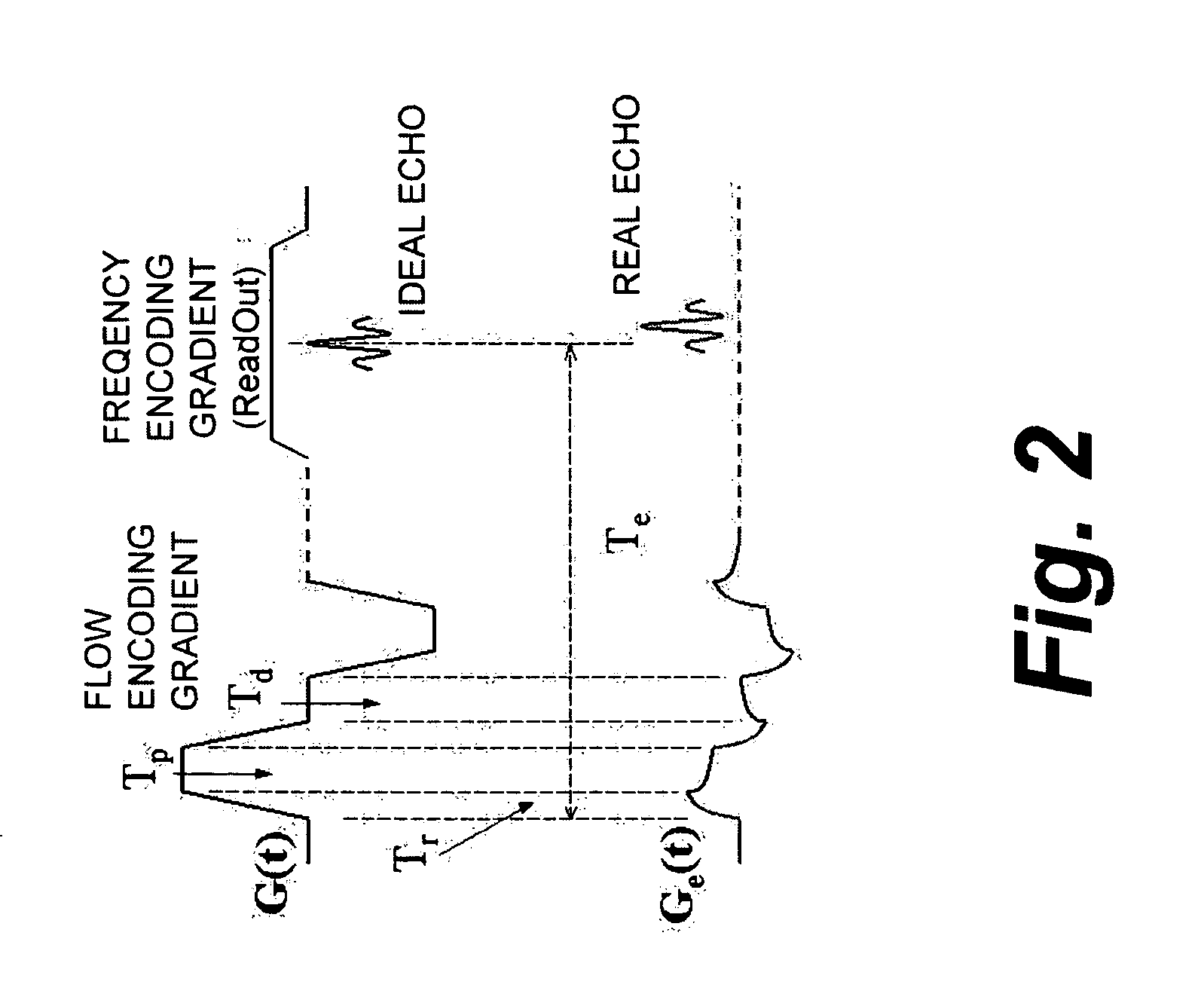
Eddy current measurement and correction in magnetic resonance imaging systems
ActiveUS20060022674A1Easy CalibrationMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionPhase responsePhase difference
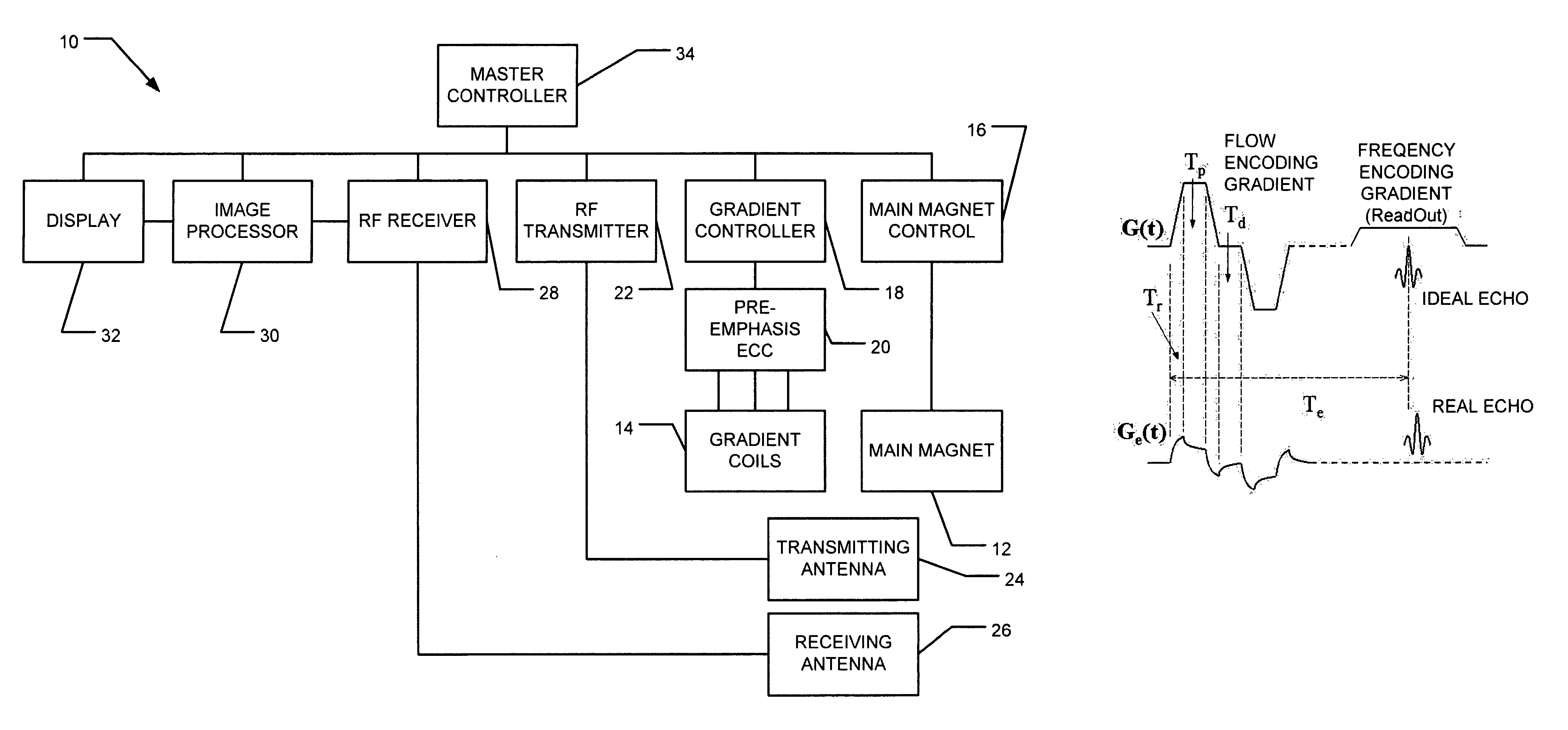
Measuring and correcting for eddy currents in a magnetic imaging system includes running a pulse sequence using bipolar gradients to acquire a phase-difference image and a phase response of a static phantom that fills a majority of a field of view (FOV) of the magnetic imaging system, fitting the phase difference image to a two-dimensional second order polynomial, and changing the pulse sequence to provide a different delay. The method further includes iterating the running a pulse sequence and fitting the phase difference image and phase response with different delays to determine coefficients of the second order polynomial and a time constant of the phase response. The method also includes correcting a pre-emphasis system of the magnetic imaging system in accordance with the time constant of the phase response, determining an amplitude of correction to reduce the determined coefficients, and storing the determined corrections in the pre-emphasis system.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
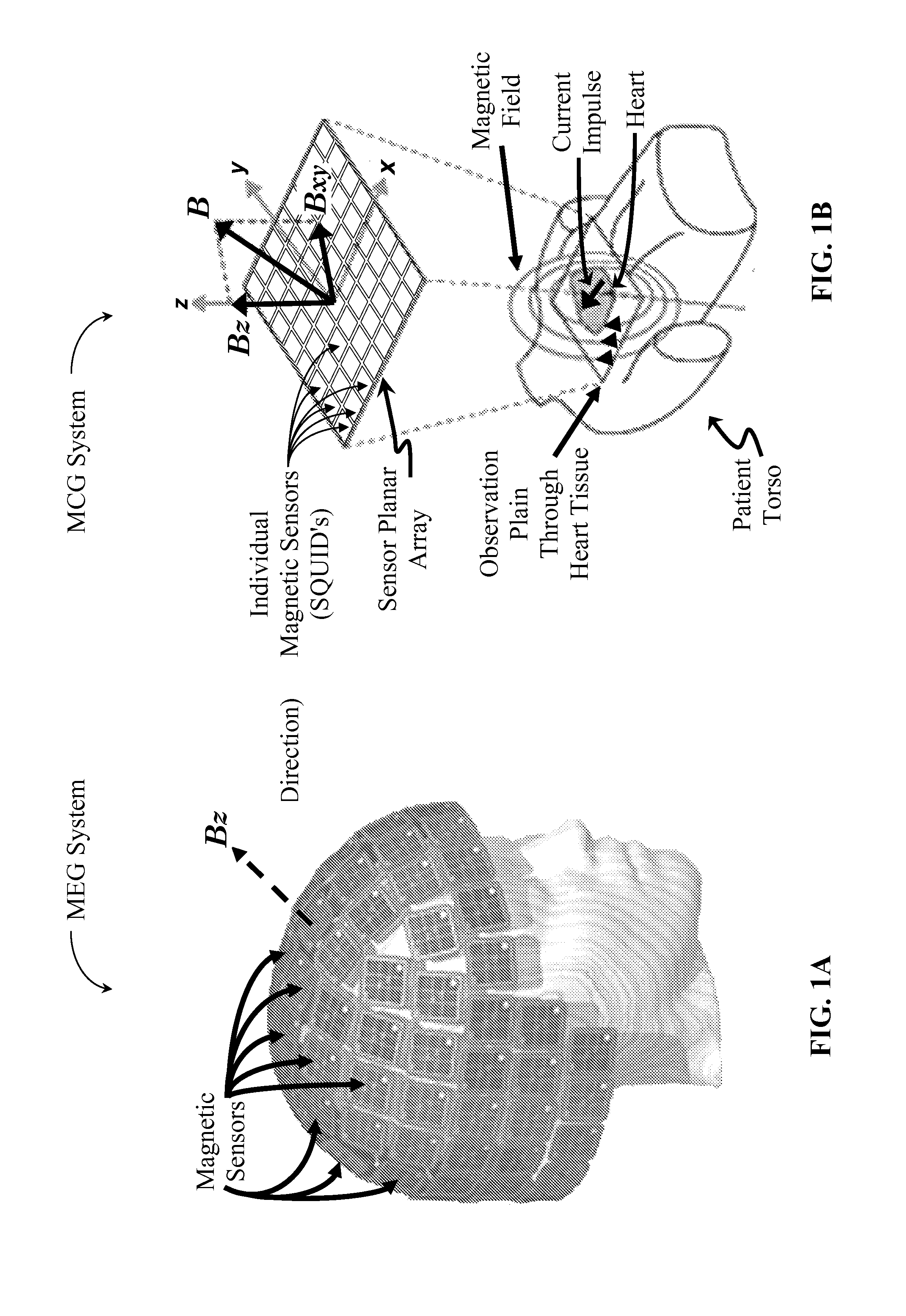
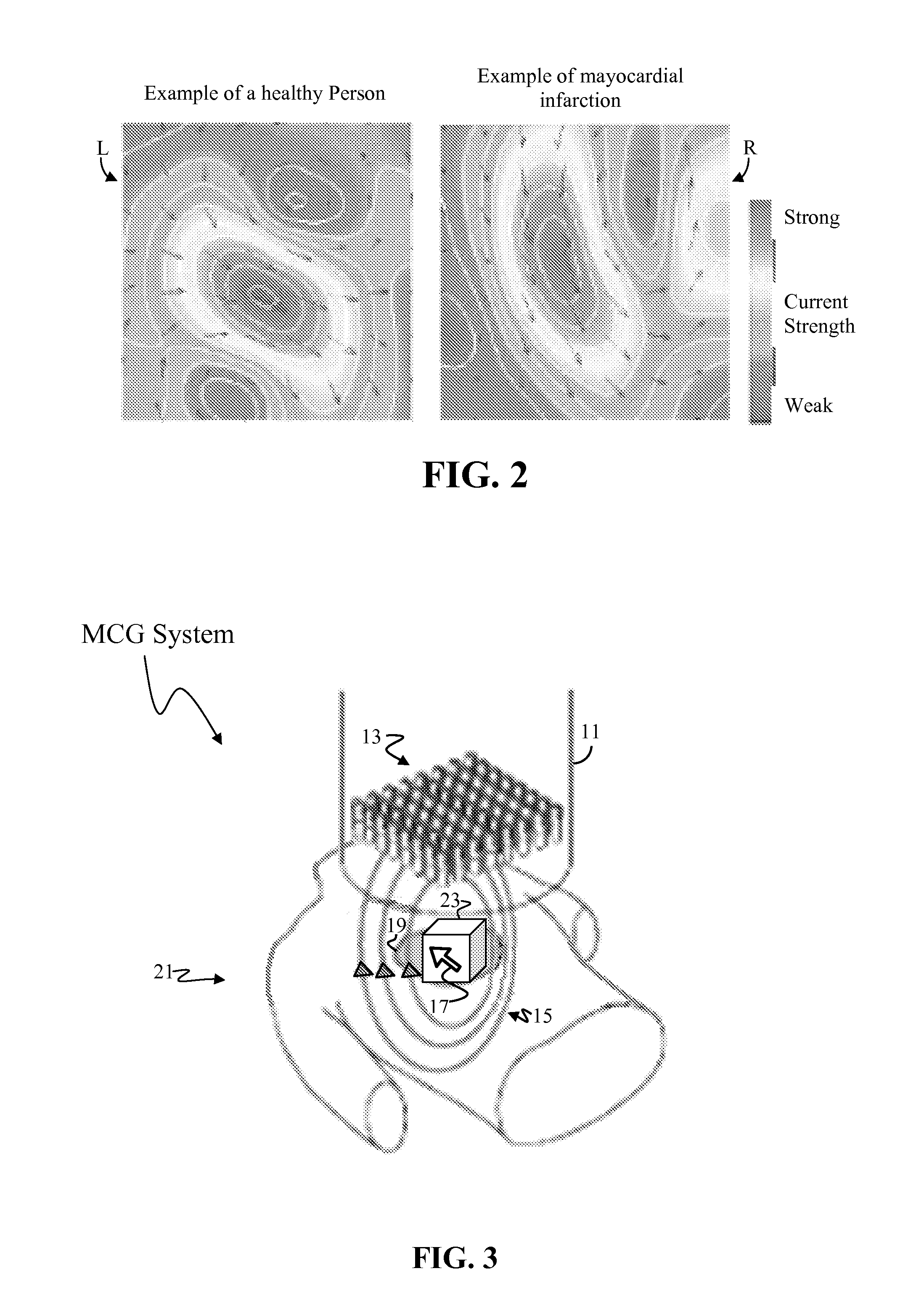
2D Dipole Localization Using Absolute Value of MCG Measurements
A magnetic imaging systems produces magnetic magnitude images using magnetic sensors capable of determining only the absolute value of a detected magnetic field and provide no information regarding the positive or negative sign of the detected magnetic image. A 2D dipole location is determines the 2D location of a dipole within a magnetic magnitude image by finding the minimum of the derivative of the absolute value of the magnetic field. This 2D dipole location is then used to determine the 3D position and momentum of a current dipole responsible for the observed magnetic magnitude image. The current dipole is used to generate a magnetic image that incorporate positive and negative sign information.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Rock heterogeneous quantitative evaluation method based on magnetic resonance imaging
InactiveCN103353462AOvercoming the Difficulties of Unrepresentative SamplingSimple processing capacityAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonancePorosityPhase Code
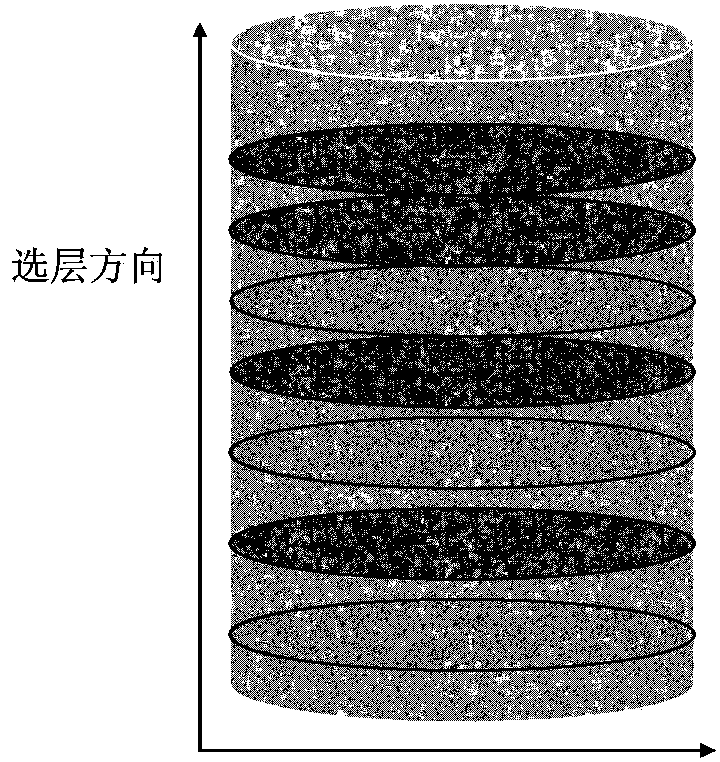
The invention discloses a rock heterogeneous quantitative evaluation method based on magnetic resonance imaging. Three-dimensional space orientation of rock can be realized by layer selection pulse, phase coded pulse and frequency coded pulse. An imaging signal can be obtained by applying a spin-echo sequence, and optimization selection of imaging experimental parameters can be carried out through experimental scale. On the basis, a nuclear magnetic imaging signal obtained by experimental measurement is subjected to digital image processing so as to generate a pseudo color graph. By means of the relationship between the porosity and nuclear magnetic imaging signal intensity of a stand sample, the total porosity and porosity and distribution spectrum of a single layer can be obtained. Multi-layer imaging results are compared and a porosity heterogeneous coefficient is defined, so that the longitudinal porosity distribution characteristic and heterogeneity of rock can be obtained. In addition, by applying a first-order spherical variation function model and a grid search method, characteristic parameters of a variation function can be obtained. Heterogeneous coefficients and relative heterogeneous coefficients can be defined to realize longitudinal and horizontal heterogeneous quantitative characterization of rock.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
System for facilitating security check of shipment of cargo
InactiveUS20130015083A1Convenient security checkKeep goingSynthetic resin layered productsLarge containersCold chainFresh fish
The present invention provides a system for facilitating security check of cold-chain air freight cargo using a magnetic imaging scanner for shipping at the airport. Cold-chain material includes most perishables such as produce, fresh fish, biological parts, pharmaceuticals and similar that need to be kept at a lower temperature for preservation and freshness.
Owner:AIRDEX INT
Chip-level diamond NV-color center magnetic imaging device and method
ActiveCN105137371AReduce volumeQuick responseMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringMedical diagnosisElectromagnetic shielding
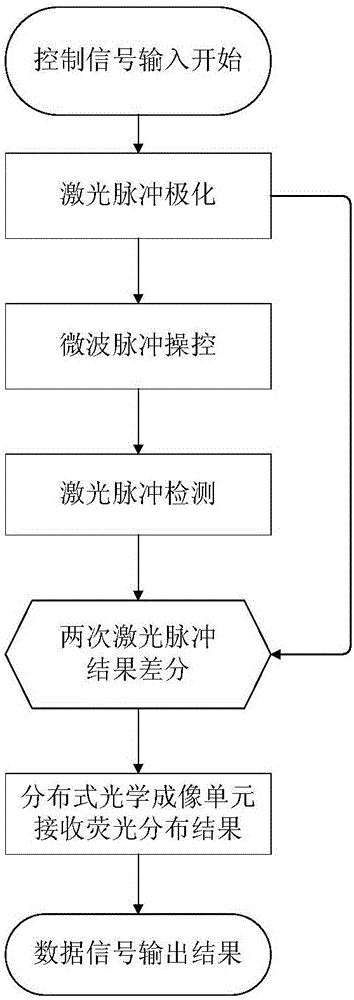
The invention discloses a chip-level diamond NV-color center magnetic imaging device and method, and the method achieves the hyperfine magnetic field imaging of the two-dimensional surface of an object, such as a magnetic image of a biological cell. The method comprises the steps: carrying out the polarization of a laser pulse and a microwave pulse; generating fluorescent light generated at the NV-color center of a diamond in an external magnetic field; employing the laser pulse to generate fluorescent light again, wherein the difference result of fluorescent light of two times can reflect the magnetic field intensity of the NV-color center, thereby achieving the conversion of magnetic field information to optical information; and employing a nano-level convex lens group and a distributed optical imaging unit to convert an optical signal into an electric signal. The invention also relates to a packaging method for enabling a whole system to be packaged in a manner of chip level, and the method comprises temperature control and electromagnetic shielding. The method is great in value in the fields of biomedical research and medical diagnosis.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV +1
Magnetic resistance Z-axis gradient sensor chip
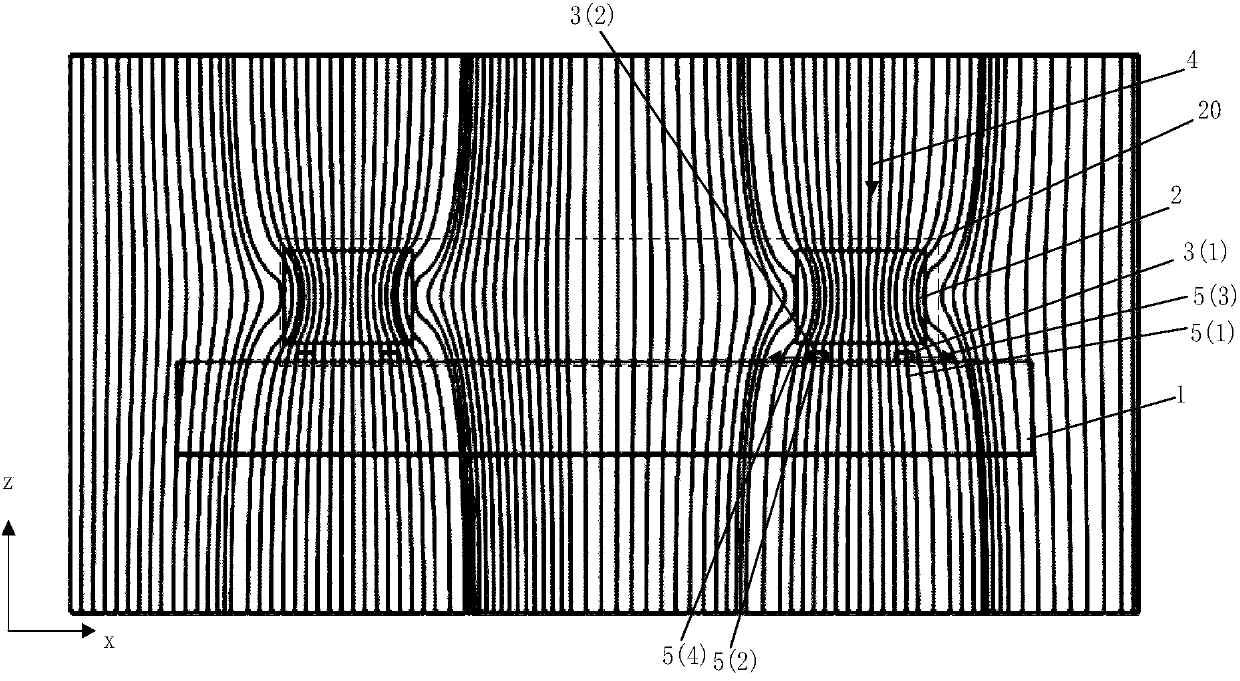
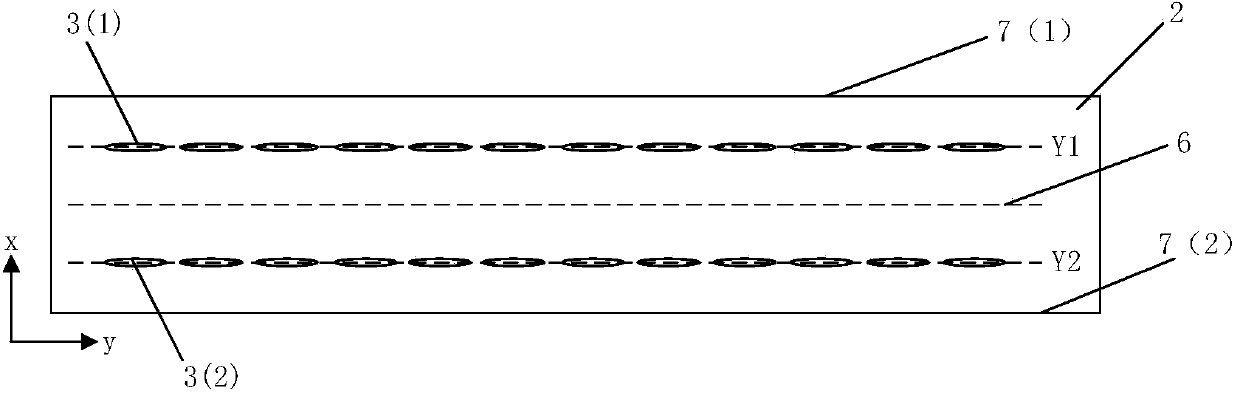
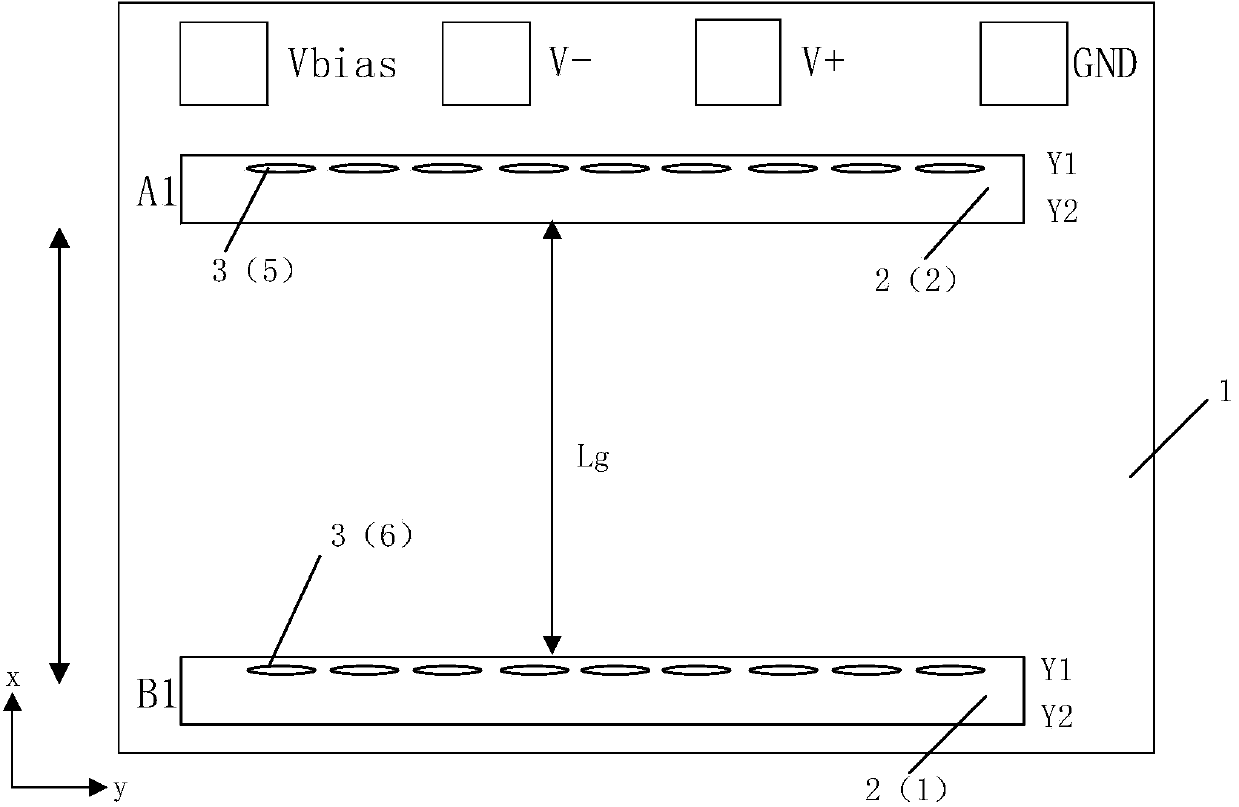
ActiveCN103995240ASmall sizeReduce power consumptionMagnetic field measurement using flux-gate principleMagnetic field measurement using galvano-magnetic devicesMagnetic field gradientElectrical resistance and conductance
The invention discloses a magnetic resistance Z-axis gradient sensor chip which is used for detecting the gradients of components of a Z-axis magnetic field generated by magnetic media in the X-Y plane so as to conduct magnetic imaging on the magnetic media. The magnetic resistance Z-axis gradient sensor chip comprises a Si substrate, two or two groups of sets containing a plurality of flux leaders and magnetic resistance sensing units which are electrically connected, wherein the distance between the sets is Lg. The magnetic resistance sensing units are located on the Si substrate and located above or below the edges of the flux leaders, the components of the Z-axis magnetic field are converted into the mode that the components of the Z-axis magnetic field are parallel to the surface of the Si substrate and in the direction of the sensitive axes of the magnetic resistance sensing units, and the magnetic resistance sensing units are electrically connected into a half-bridge or whole-bridge gradient meter, wherein the distance between opposite bridge arms is Lg. The sensor chip can be used together with a PCB, a PCB and back magnetor a PBC and back magnet and packaging shell. According to the magnetic resistance Z-axis gradient sensor chip, measurement of the Z-axis magnetic field gradient is achieved by using plane sensitive magnetic resistance sensors, and the magnetic resistance Z-axis gradient sensor chip has the advantages of being small in size and low in power consumption, having higher magnetic field sensitivity than a Hall sensor and the like.
Owner:MULTIDIMENSION TECH CO LTD
Apparatus and method for image alignment for combined positron emission tomography (PET) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scanner
ActiveUS20080269594A1Large capacityMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringResonanceMagnetic Resonance Imaging Scan
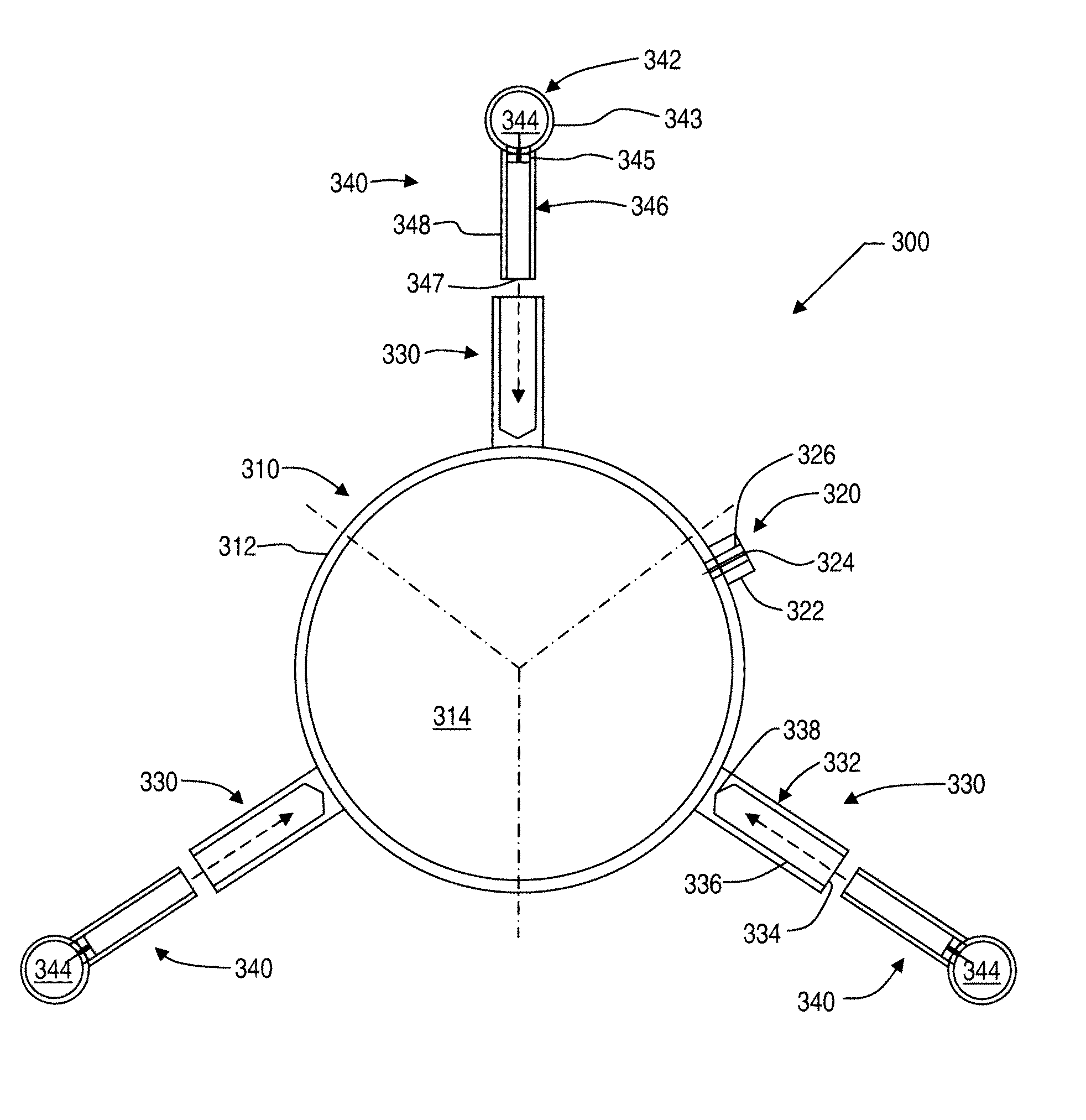
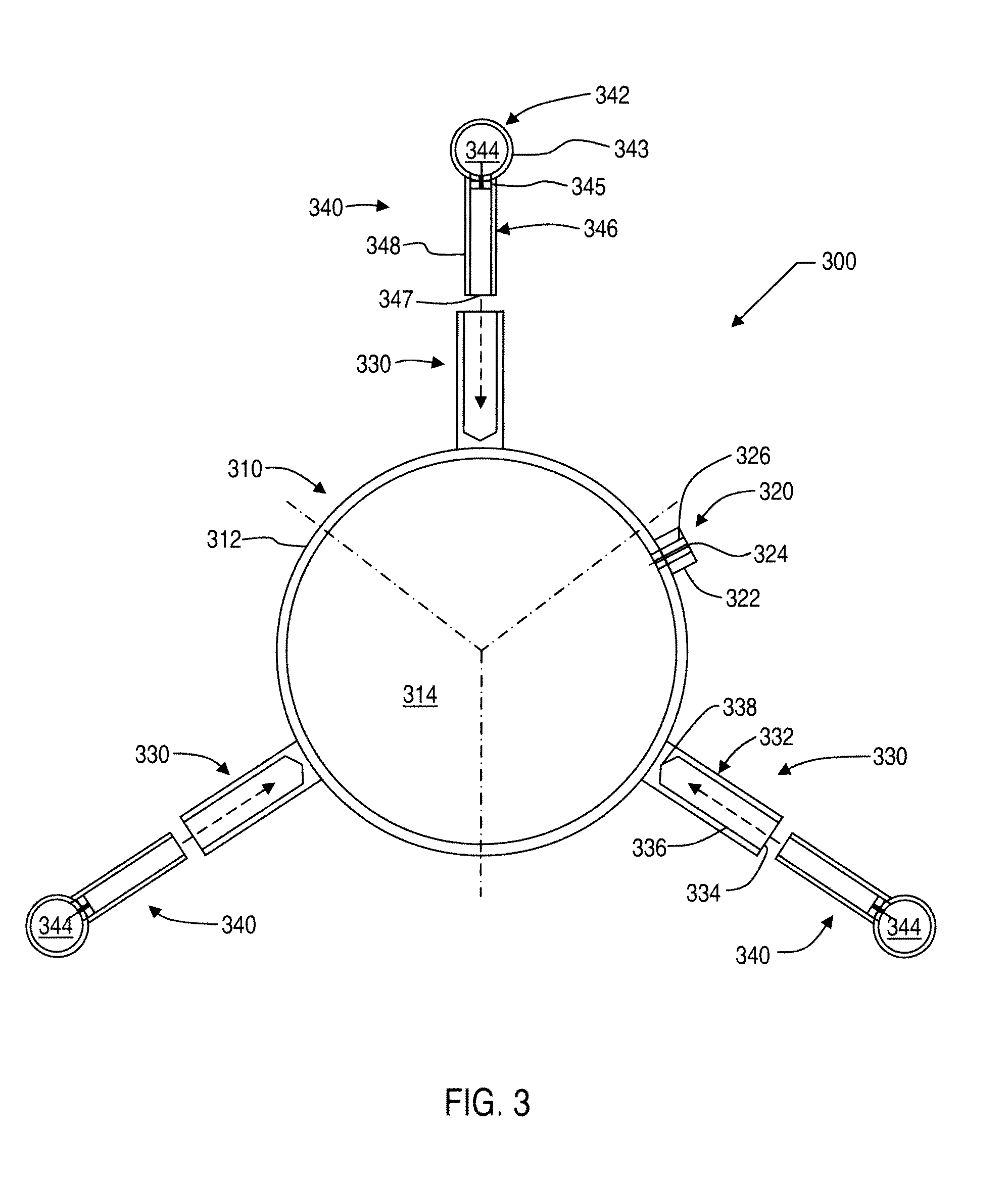
A phantom and method are provided for co-registering a magnetic resonance image and a nuclear medical image. The phantom includes a first housing defining a first chamber configured to receive a magnetic resonance material upon which magnetic resonance imaging can be performed in order to produce the magnetic resonance image. The phantom also includes three or more second housings configured to be attached to the first housing, where the second housings each define a second chamber configured to receive a radioactive material upon which nuclear imaging can be performed in order to produce the nuclear medical image and upon which the magnetic imaging can be performed in order to produce the magnetic resonance image. The first chamber has a volumetric capacity that is larger than a volumetric capacity of each second chamber.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
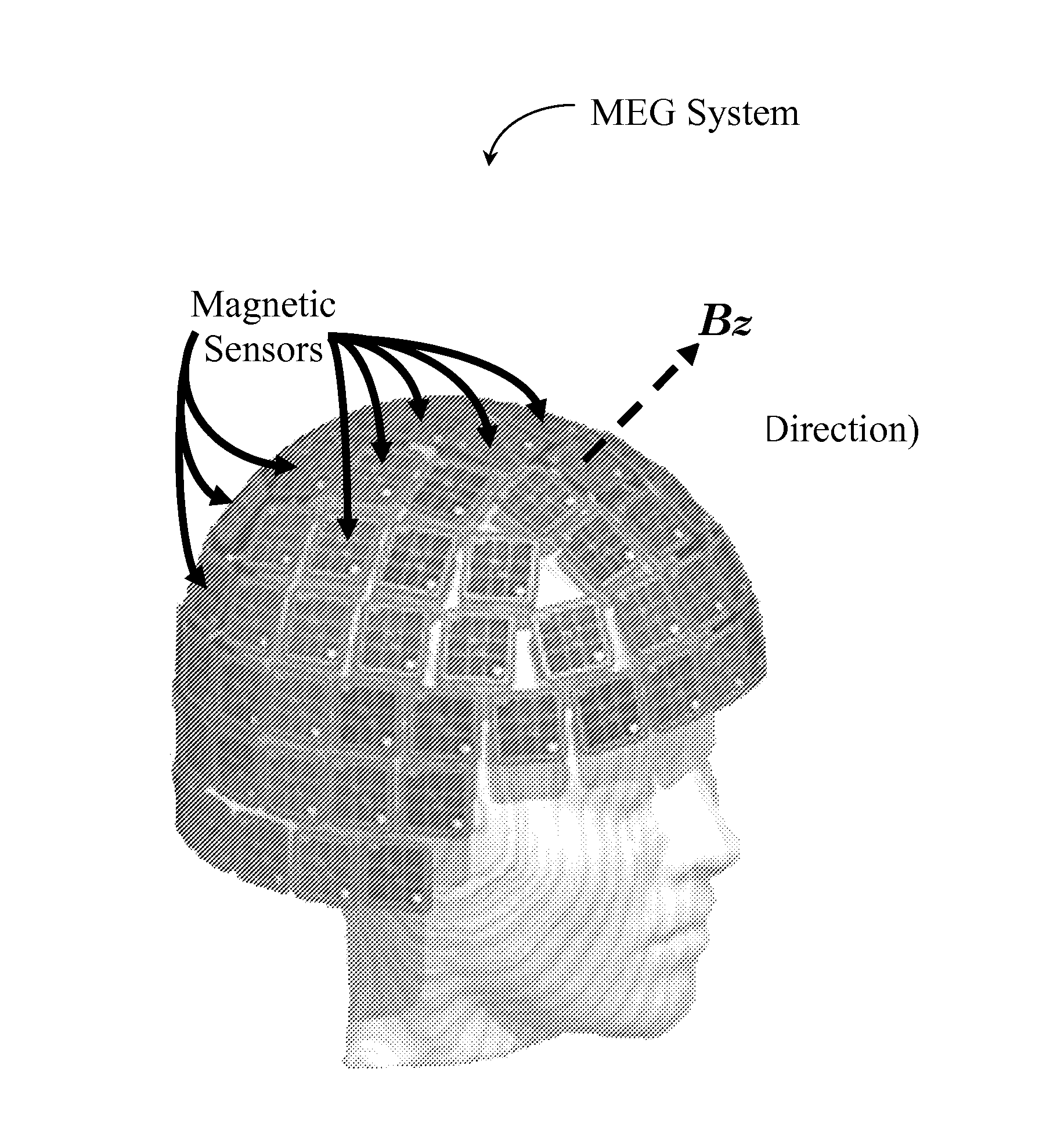
Magnetic Imaging Device To Inventory Human Brain Cortical Function
Systems and methods detect electrical activity in the human brain in the form of the generated magnetic fields and map the magnetic field strength to the surface of the cerebral cortex. By mapping the measured magnetic fields to the sulcal-defined gyrus of the cerebral cortex rather than to its three-dimensional volume, the data complexity and the resulting image are dramatically reduced. The device allows an inventory of brain function, including, but not limited to, vision, sound, sensory, and cognition, with the sensors placed over the corresponding region or regions of interest of the brain.
Owner:FORD JOHN P
MRI apparatus and method with moving field component
Apparatus for use in a magnetic resonance imaging system, the imaging system generating a magnetic imaging field in an imaging region (5), the apparatus including at least one coil for at least one of transmitting, receiving or transceiving an electromagnetic field, a field component (4) (such as a coil or a shield) and a drive (6) coupled to the field component for moving the field component (4) relative to the imaging region (5) to thereby modify the electromagnetic field during imaging process. The same concept can also be applied to nuclear imaging or nuclear spectroscopy apparatus.
Owner:THE UNIV OF QUEENSLAND
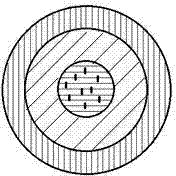
Multifunctional multilayered micro/nano core-shell structure
InactiveCN104490846AIndependent effective packagingSimple processEnergy modified materialsIn-vivo testing preparationsMicro nanoDisease
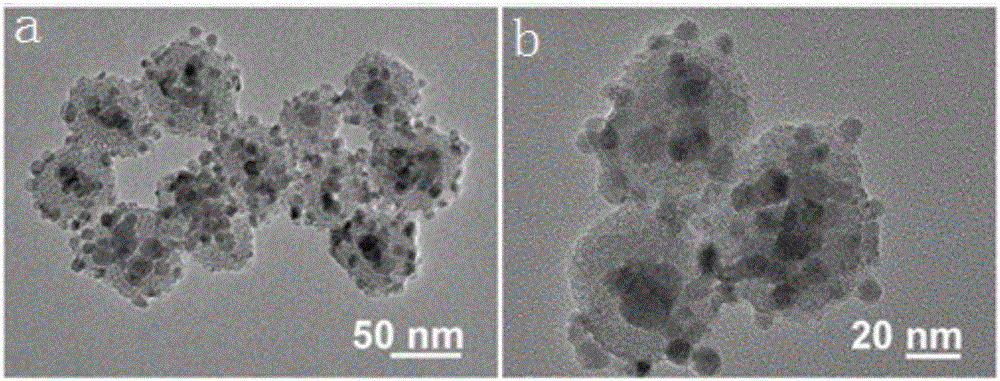
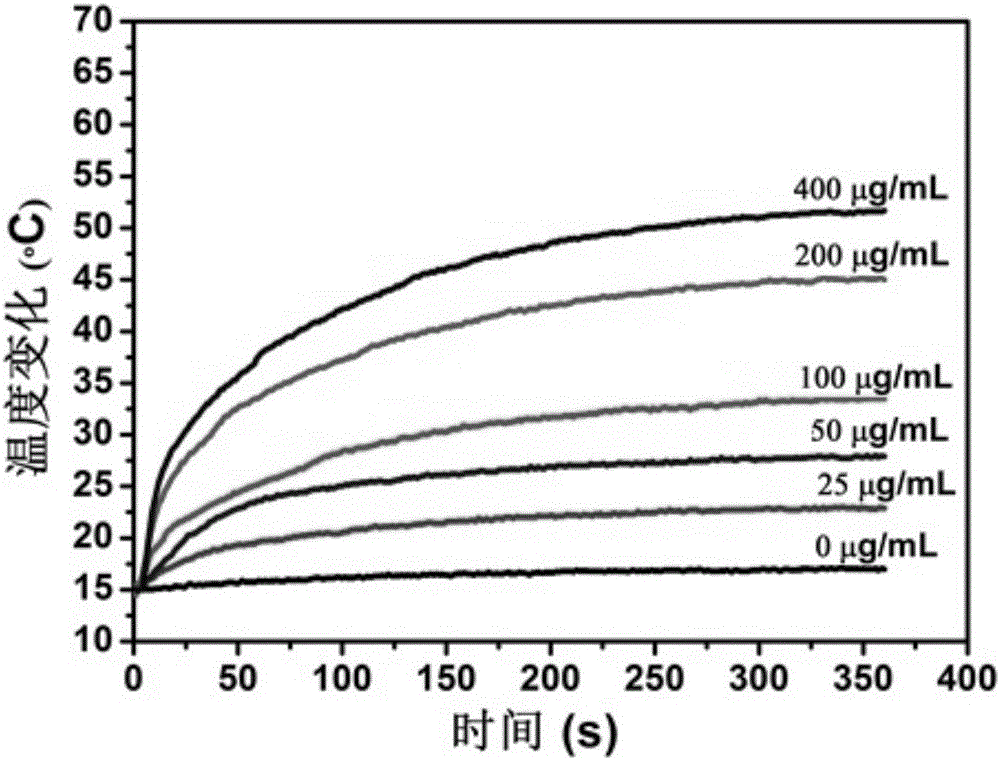
The invention discloses a multifunctional multilayered micro / nano core-shell structure. The core-shell structure is a micro / nanoscale spherical structure, and the ''multilayer'' includes three or more layers. At least one layer of material is a liquid phase. The liquid phase can selectively be removed. Thickness of each shell is controllable, and each shell can effectively and independently coat multiple materials or anti-cancer drugs with different properties at the same time. By adding functional auxiliary materials into each phase, combination of multifunctional characteristics can be realized. By integrating advantages of the multilayered core-shell structure and excellent optical, electrical, magnetic, sound and biological characteristics, drug controlled release and medical imaging application can be realized. The multifunctional multilayered micro / nano core-shell structure has an application prospect especially in aspects of disease treatment and medical imaging and is used as a bimodal ultrasonic / magnetic imaging diagnosis contrast agent and drug release control carrier.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Water-soluble magnetic titanium dioxide and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN104353075ASignificant photodynamic propertiesOvercoming non-targeting challengesEnergy modified materialsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsChemical ligationWater soluble
The invention relates to water-soluble magnetic titanium dioxide and a preparation method and an application thereof. The problem of medication for treating tumors can be effectively solved. The water-soluble magnetic titanium dioxide is formed by doping ferroferric oxide into titanium dioxide molecules and chemically bonding with a hydrophilic group, wherein the mass content ratio of titanium dioxide to ferroferric oxide is (1-10) to (10-1); titanium dioxide is rutile or anatase titanium dioxide; and the particle size of the water-soluble magnetic titanium dioxide is 1-1000nm. The water-soluble magnetic titanium dioxide is simple in synthetic process; significant light dynamic characteristics of titanium dioxide, and unique tumor cell magnetic targeting, auxiliary anti-tumor activity and nuclear magnetic imaging function of Fe3O4 are organically integrated into a whole; the water-soluble magnetic titanium dioxide is capable of physically loading the medicine with the antitumor activity, thereby overcoming the non-targeted problem of traditional tumor treatment, and reducing injuries to normal tissue in the treatment process; and the water-soluble magnetic titanium dioxide has efficient and controllable advantages in comparison with traditional tumor treatment, and is an innovation in medicines for treating tumors.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
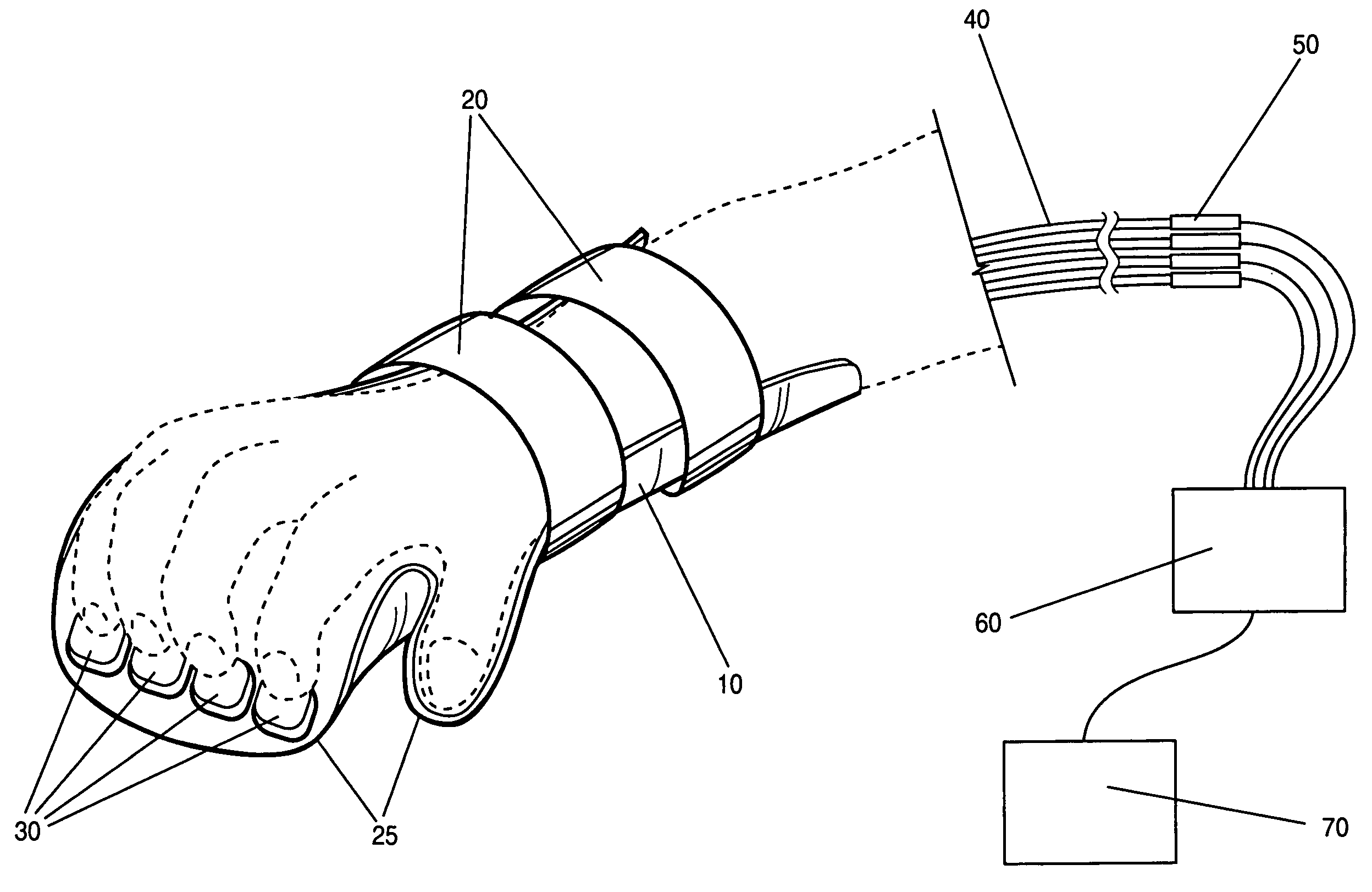
Optical switches and switching methods
InactiveUS7340125B1Eliminate needReduce signal noiseMagnetic measurementsCoupling light guidesFiberEngineering
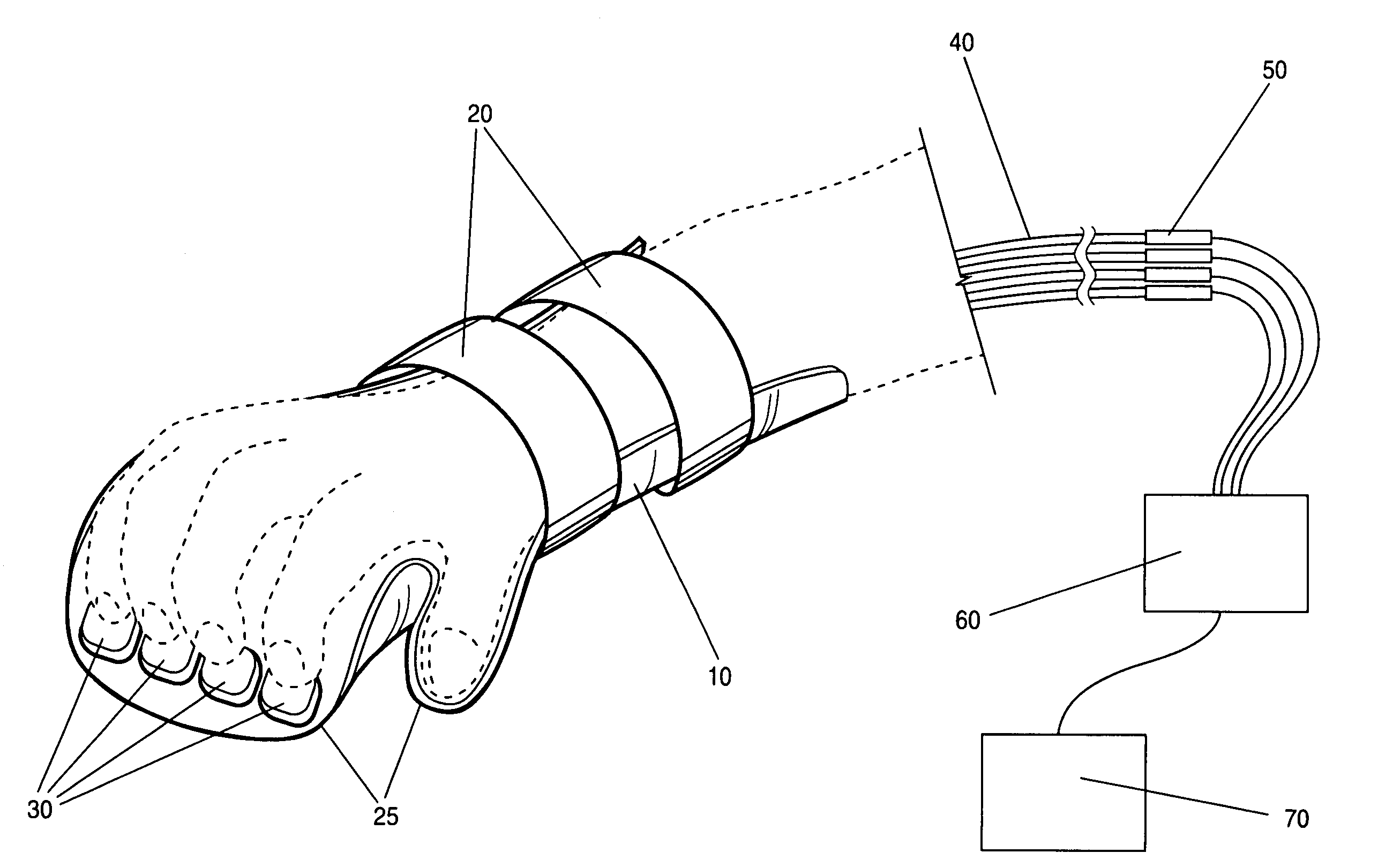
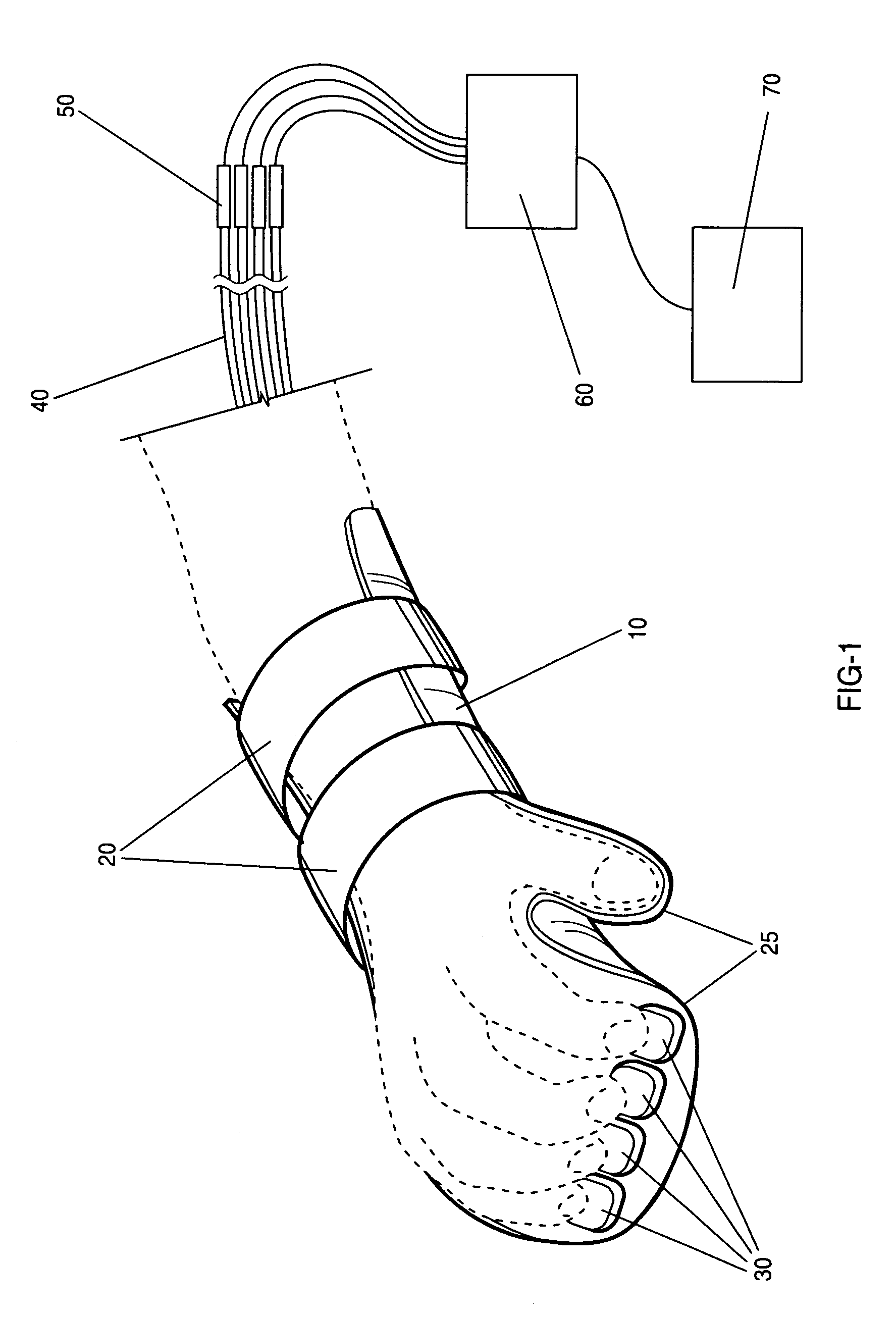
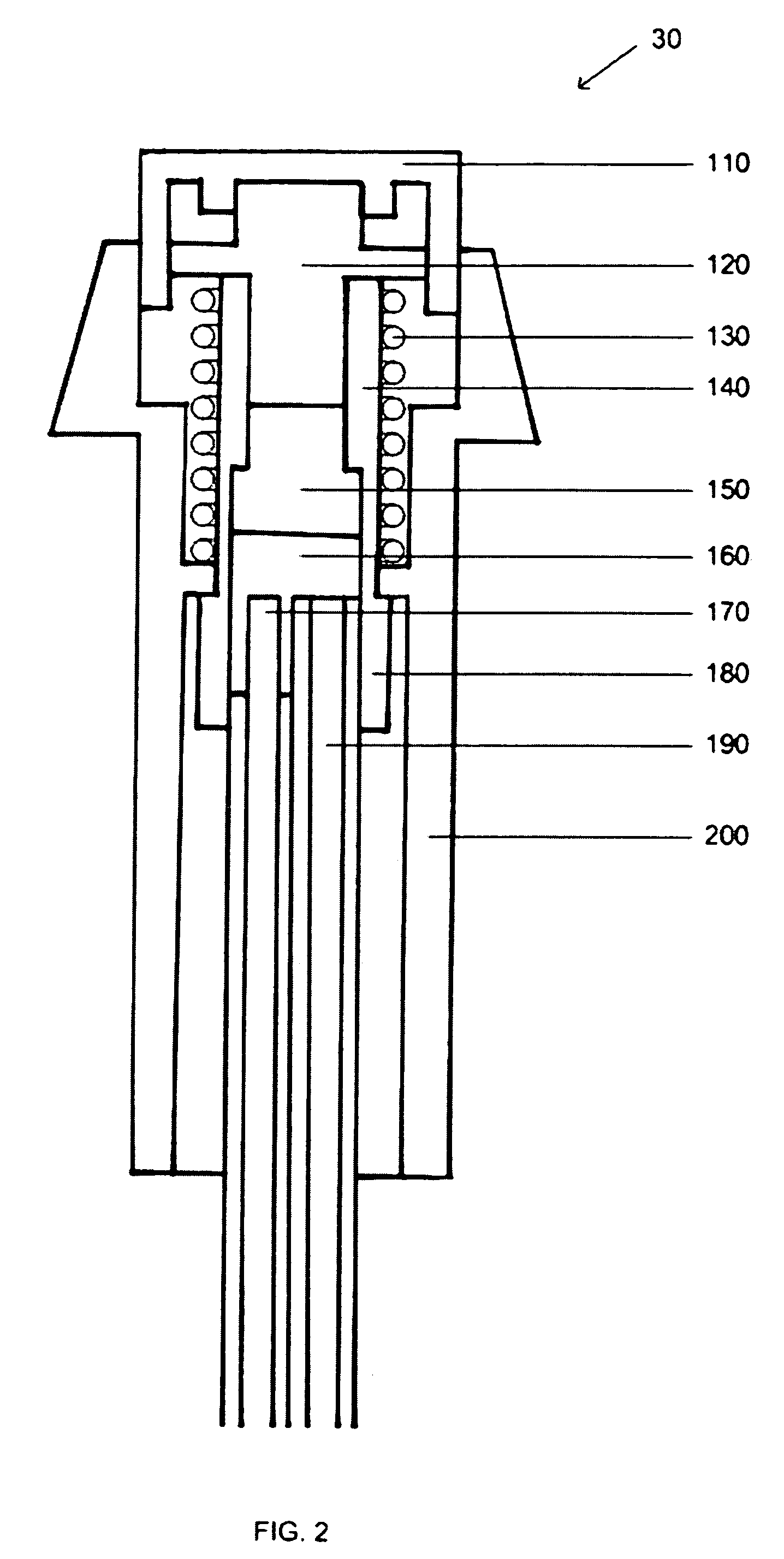
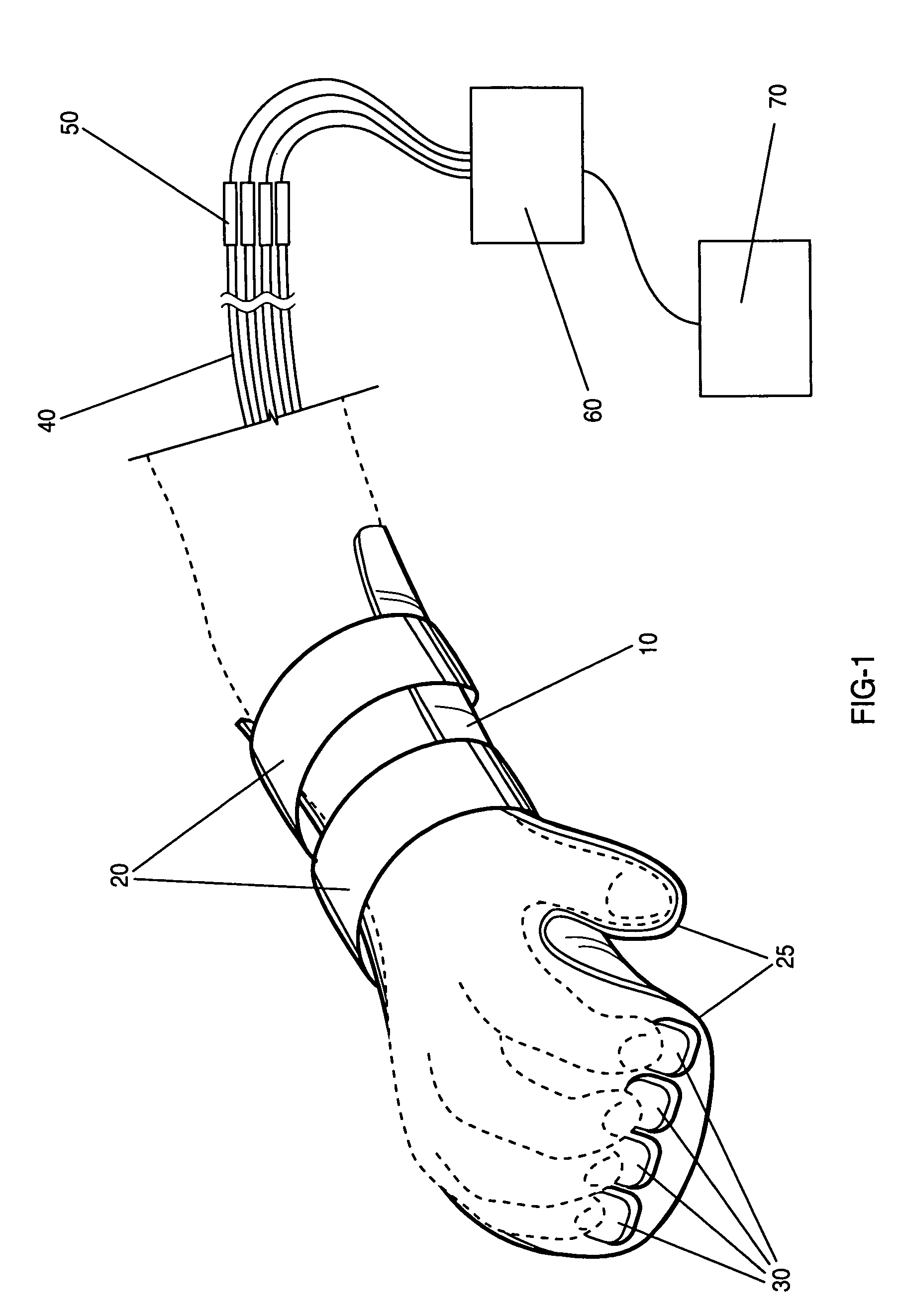
A device and method for collecting subject responses, particularly during magnetic imaging experiments and testing using a method such as functional MRI. The device comprises a non-metallic input device which is coupled via fiber optic cables to a computer or other data collection device. One or more optical switches transmit the subject's responses. The input device keeps the subject's fingers comfortably aligned with the switches by partially immobilizing the forearm, wrist, and / or hand of the subject. Also a robust nonmetallic switch, particularly for use with the input device and methods for optical switching.
Owner:MIND INST THE
Folic acid coupled targeted ferriferrous oxide/mesoporous silica/copper sulfide nano-composite particle as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN105920601AAchieve synergyExcellent photothermal performanceOrganic active ingredientsEnergy modified materialsSide effectCancer cell
The invention relates to a folic acid coupled targeted ferriferrous oxide / mesoporous silica / copper sulfide nano-composite particle as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. The nano-composite particle consists of Fe3O4@mSiO2 core-shell structural nanoparticles, wherein the core-shell structural nanoparticles take Fe3O4 nanoparticles as cores and mSiO2 as shells, and copper sulfide nanoparticles and folic acid cover the surfaces of the shells; the folic acid is grated on one part of the mesoporous silica (mSiO2) and the copper sulfide particles are loaded on the other part of the mesoporous silica; and polyethylene glycol is grated on the surface of the copper sulfide nanoparticles. Compared with the prior art, the nano-composite particles disclosed by the invention has a broad application prospect in the aspects of nuclear magnetic resonance imaging, drug loading and photothermal therapy; anti-cancer drugs and photothermal reagents can be transmitted to tumor parts in a targeted mode; the nano-composite particle can reduce toxic and side effects on normal tissues and cells, and meanwhile, the nano-composite particle can effectively kill cells, so that a treatment effect is further improved; and moreover, the nano-composite particle is relatively low in preparation condition demand and cost.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV OF ENG SCI
Isotropic metamaterial lens for magnetic imaging applications
InactiveUS20130002253A1High resolutionIncrease field strengthMaterial analysis by using resonanceElectric/magnetic detectionElectricityImage resolution
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Magnetic imaging device and imaging method based on diamond NV color center and Kerr effect
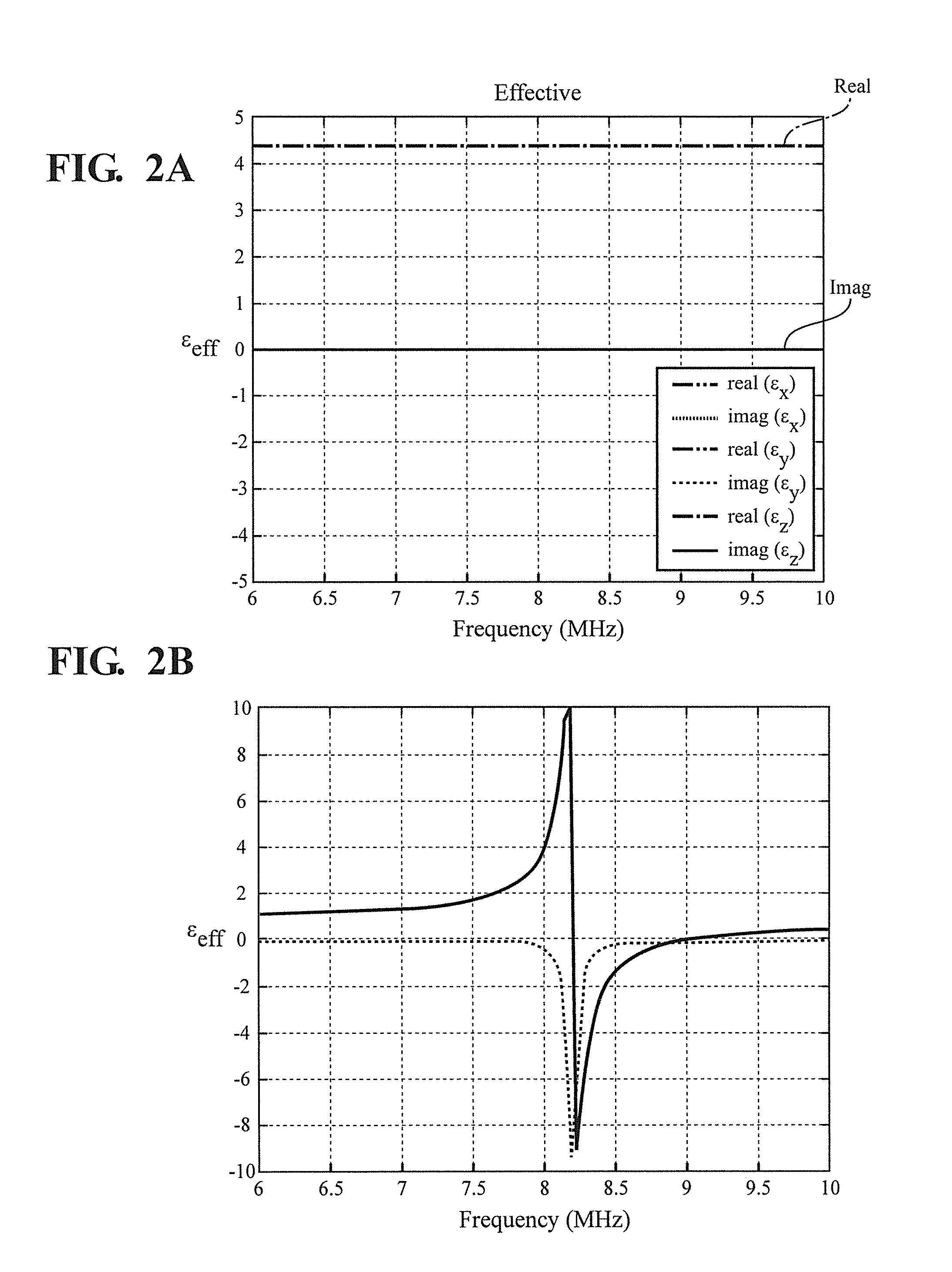
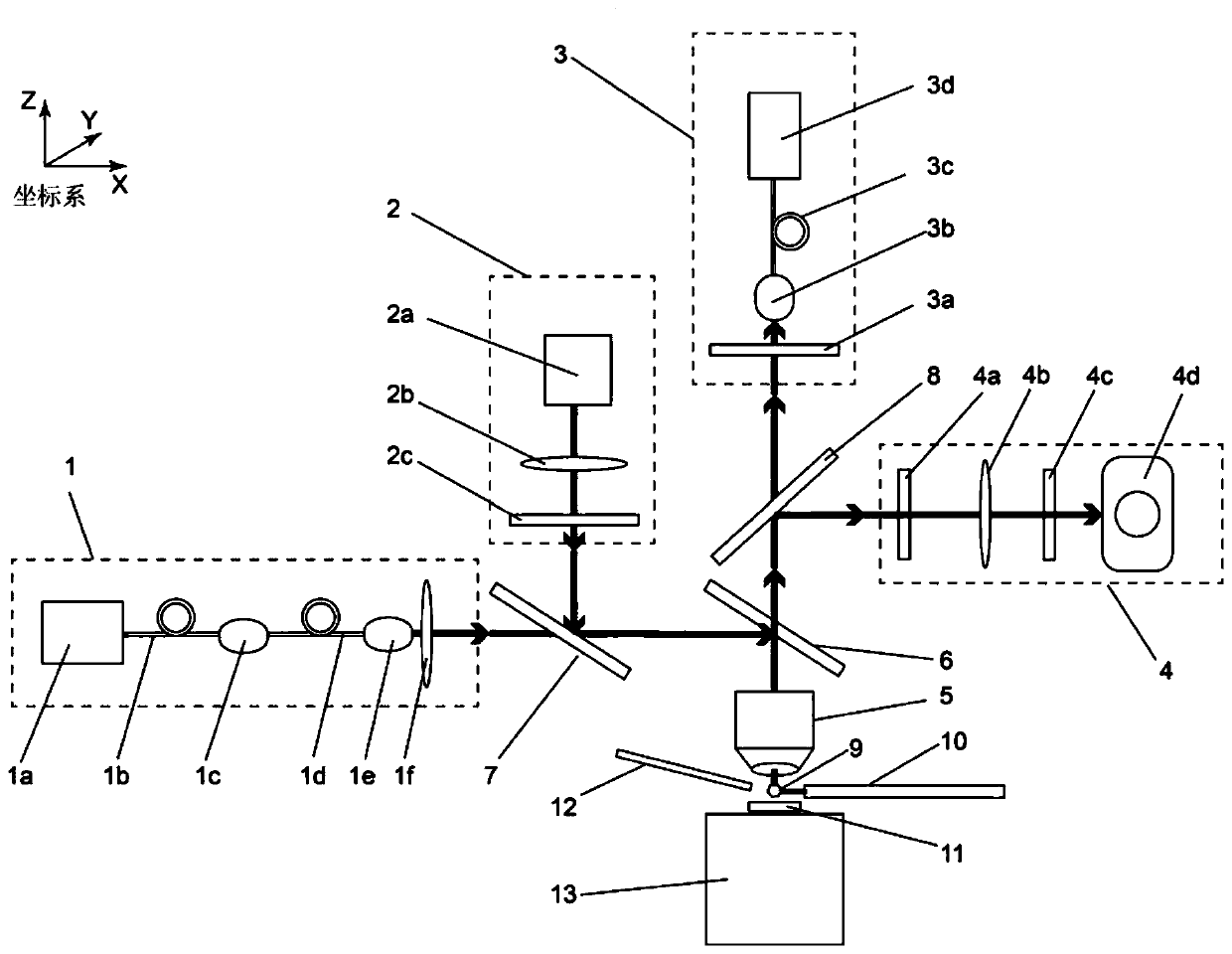
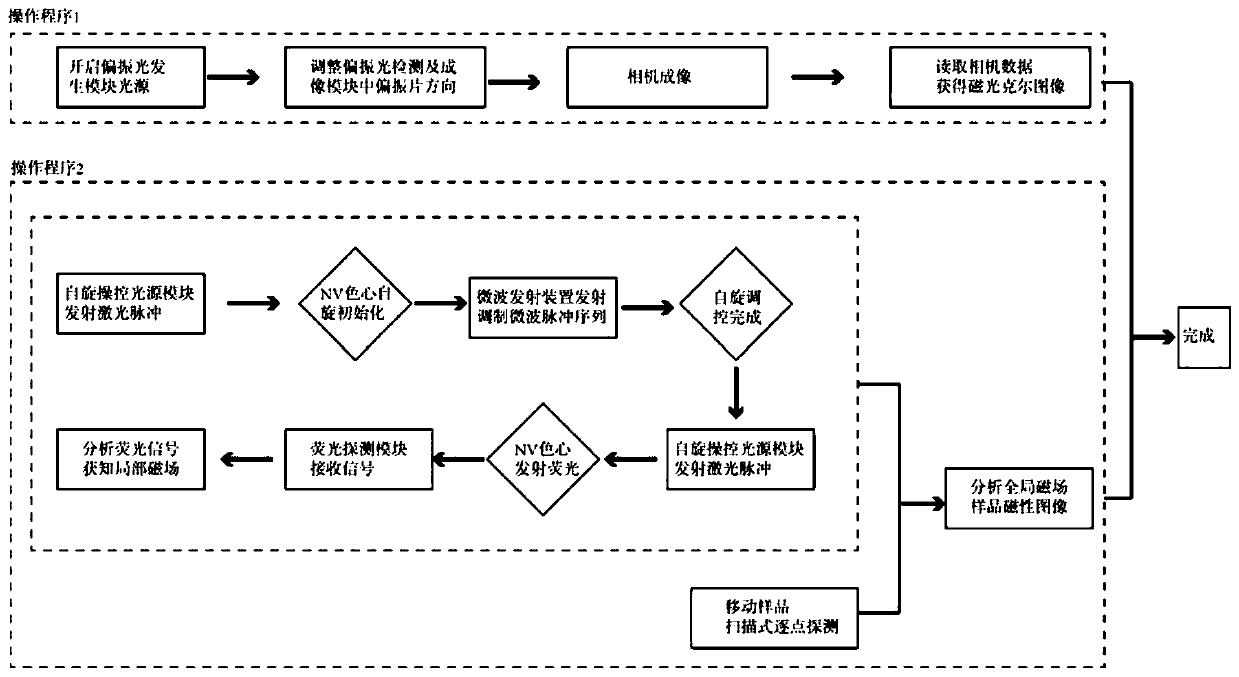
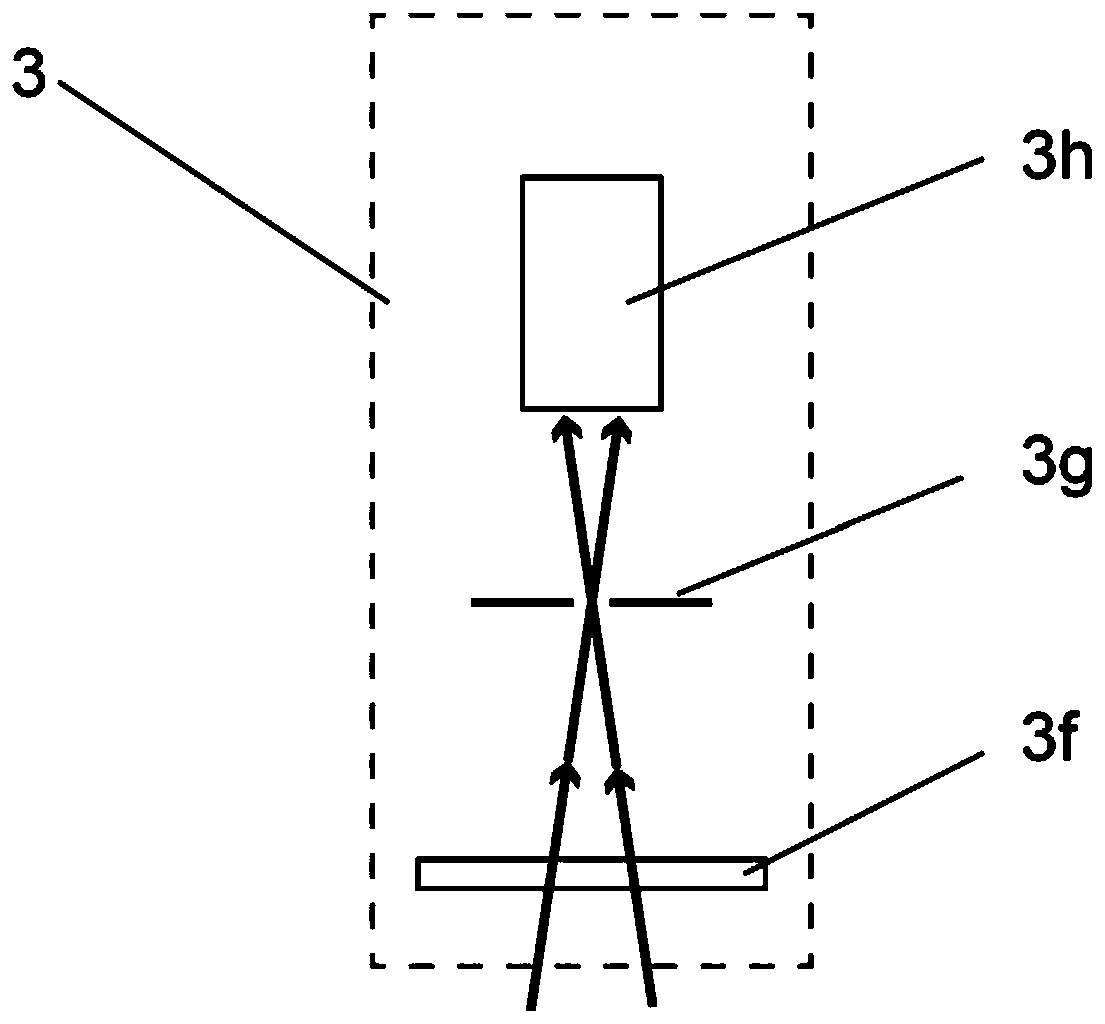
PendingCN111239653AMeet the resolutionMeet needsMagnetic property measurementsMagnetic field measurement using magneto-optic devicesColour centreFluorescence
The invention discloses a magnetic imaging device and imaging method based on a diamond NV color center and a Kerr effect. A spinning control light source module provides a beam of incident laser, theincident laser passes through a dichroscope system and irradiates the NV color center of the diamond probe after being focused by the microscope objective lens, and fluorescence generated by the NV color center returns to the dichroscope system through the microscope objective lens and enters the fluorescence detection module. The polarized light generation module generates polarized light, the polarized light enters the microscope objective lens through transmission and / or reflection of the dichroscope system and then irradiates a sample placed on the displacement table, and after the polarized light is reflected by the sample, part of the polarized light enters the microscope objective lens again and then enters the polarized light detection and imaging module through the dichroscope system. Through the compatible design, high-resolution, global and large-view imaging of the sample is realized.
Owner:致真精密仪器(青岛)有限公司
Zirconium oxide tooth implantation system
InactiveCN101810517AGood biocompatibilityNo side effectsDental implantsBite force quotientSide effect
The invention discloses a zirconium oxide tooth implantation system, and is characterized in that all devices are made of zirconium oxide. The system is divided into a one-stage type and a two-stage type. A one-stage type implantation body is provided with screw threads, the surface of a dentogingival part is smooth, and the body is combined with the base station integrally. The surface of the two-stage type implantation body has a smooth type and a screw-thread type, and the implantation body and the base station is embedded with each other by polyhedral angle and Moll's taper and is connected and fixed by the central screw nail. The invention has the following advantages that: the zirconium oxide implantation body without toxic side effect is capable of being integrated with alveolar bone; the total porcelain crown supported by the zirconium oxide base is attractive in appearance; and the zirconium oxide implantation teeth can resist the functionating of good occlusal force without influencing CT and nuclear magnetic imaging inspection.
Owner:杨建军 +2
Nonmetallic input device for magnetic imaging and other magnetic field applications
InactiveUS7039266B1Eliminate needReduce signal noiseMagnetic measurementsCoupling light guidesFiberEngineering
A device and method for collecting subject responses, particularly during magnetic imaging experiments and testing using a method such as functional MRI. The device comprises a non-metallic input device which is coupled via fiber optic cables to a computer or other data collection device. One or more optical switches transmit the subject's responses. The input device keeps the subject's fingers comfortably aligned with the switches by partially immobilizing the forearm, wrist, and / or hand of the subject. Also a robust nonmetallic switch, particularly for use with the input device.
Owner:MIND INST THE
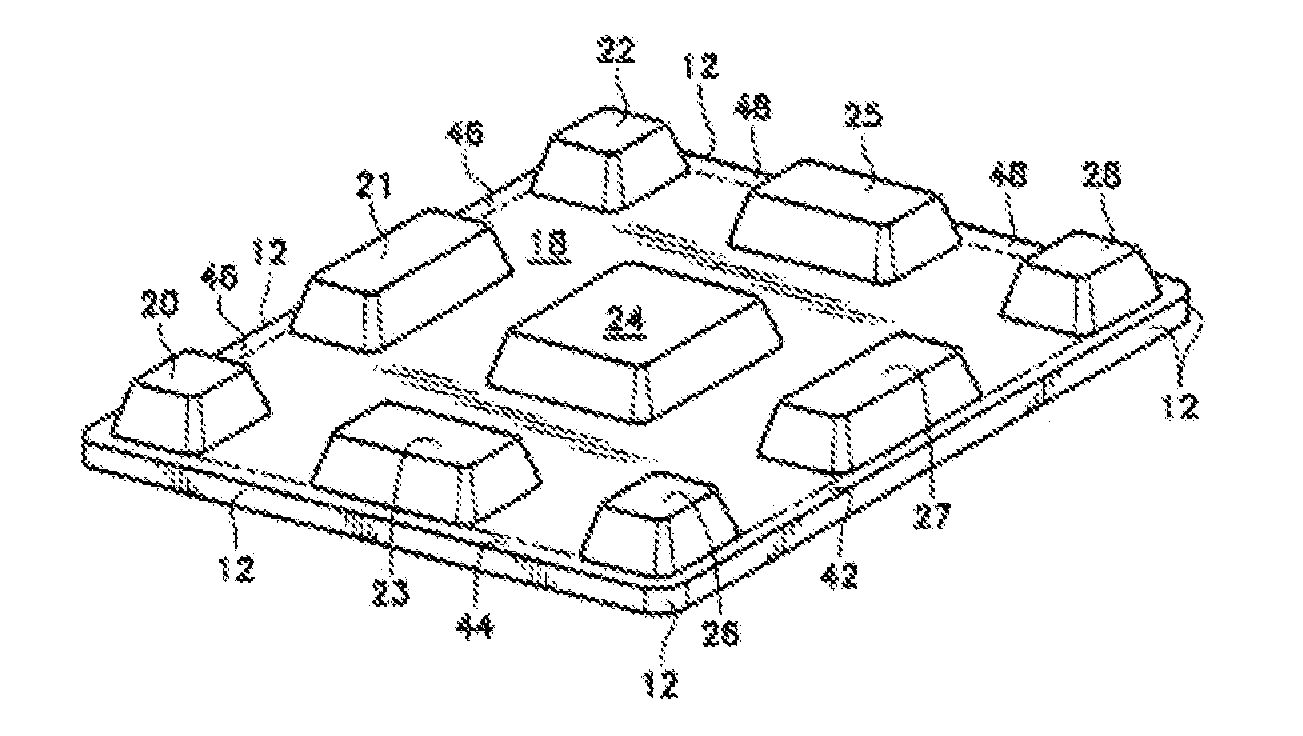
Flexible multi-lead cap-type brain magnetic instrument and high-precision imaging method thereof
ActiveCN109620201AImproving Imaging AccuracyComfortable to wearAntifouling/underwater paintsNatural rubber coatingsSensor arrayDiagnostic Radiology Modality
The invention discloses a flexible multi-lead cap-type brain magnetic instrument and a high-precision imaging method thereof. The brain magnetic instrument comprises a flexible multi-lead cap, a magnetic sensor array, a magnetic shielding and compensation module, a magnetic sensor position and posture calibration module, a signal detection and storage module and a brain magnetic imaging module. According to the flexible multi-lead cap-type brain magnetic instrument, by introducing the magnetic sensor position and posture calibration module, the center positions of a magnetic sensor and a standard point can be determined, the posture of the magnetic sensor relative to the tested head can be determined, and the imaging precision can be improved. According to the MEG imaging method based on CT and multi-mode MRI, multi-mode MRI at least comprises T1, T2 and DT1, and the problem of low precision of brain magnetic imaging of infants can be solved. The flexible multi-lead cap-type brain magnetic instrument is flexible to use, comfortable to wear and low in production cost; the imaging method of the instrument is easy to operate and high in imaging precision.
Owner:南京国科精准医学科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com