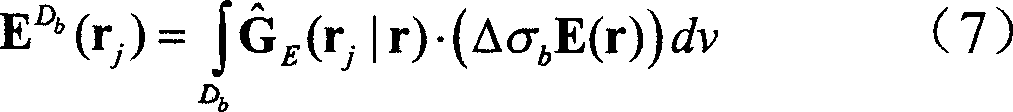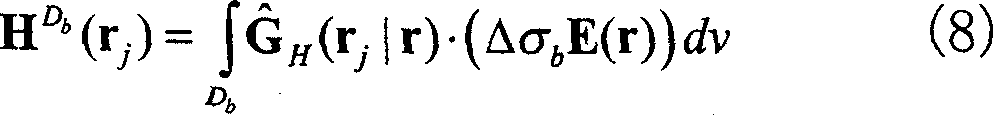Patents
Literature
356 results about "Phase response" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In signal processing, phase response is the relationship between the phase of a sinusoidal input and the output signal passing through any device that accepts input and produces an output signal, such as an amplifier or a filter.
Electroacoustic devices with noise-reducing capability
InactiveUS7466838B1Adverse noise reduction effectMinimize sound reflectionEar treatmentSupra/circum aural earpiecesPhase responseTime delays
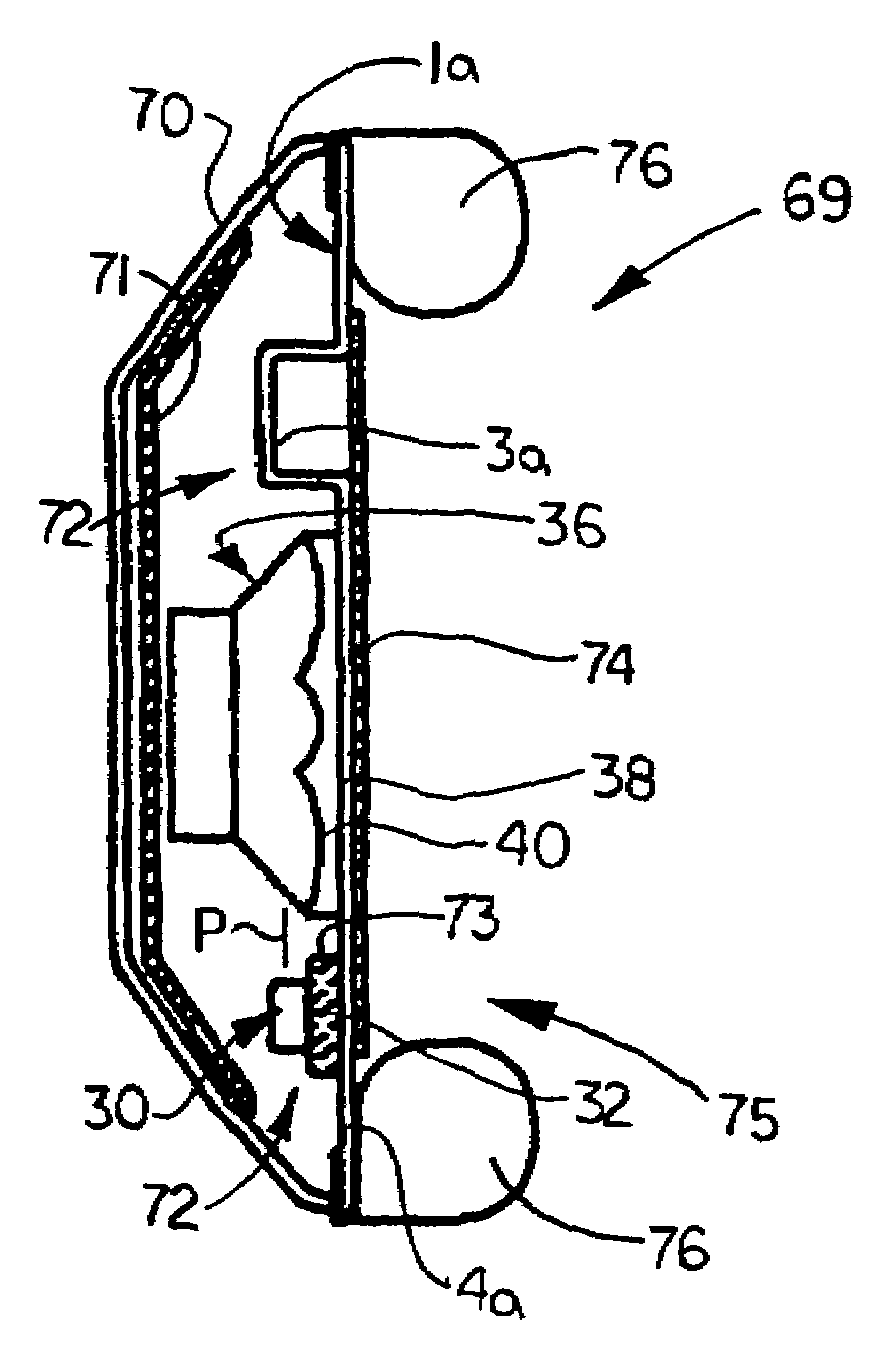
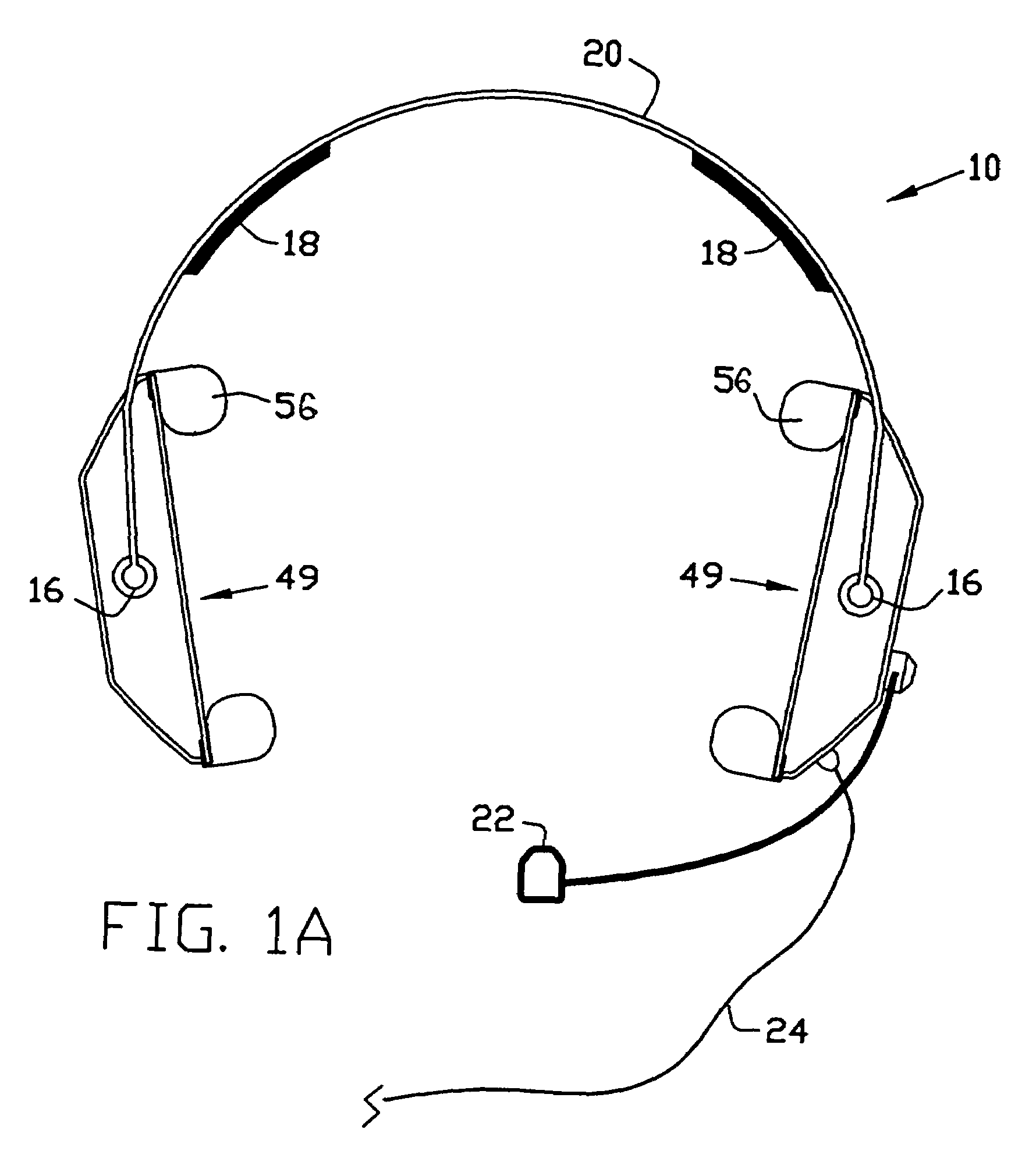
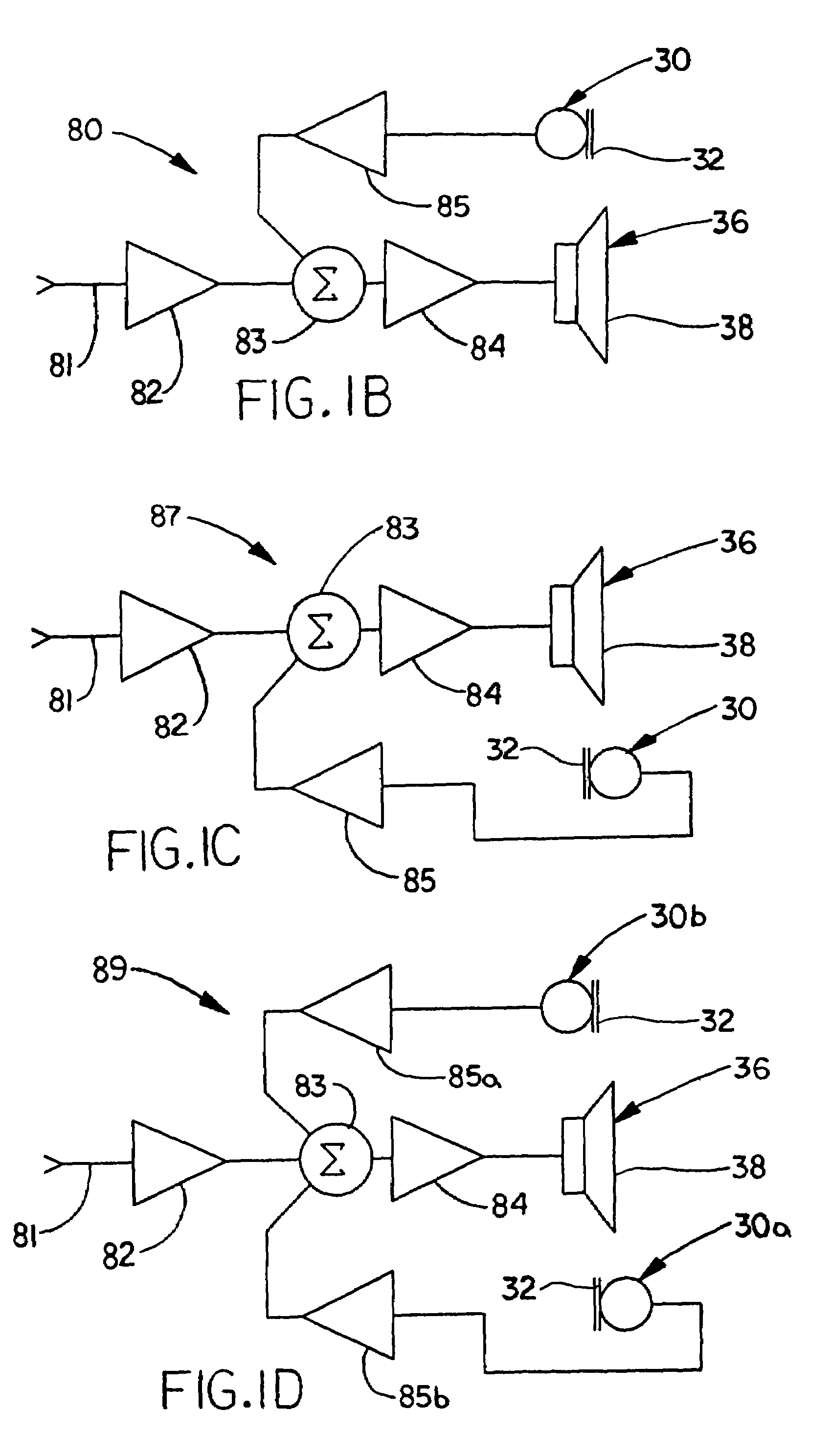
New and improved electroacoustic devices each including at least one transducer assembly having one or more microphones typically mounted on a baffle plate and disposed in substantially the same acoustic plane as a speaker or speakers. In the various embodiments, at least one microphone and at least one speaker face the same or opposite directions. Each microphone may be parallel to or oriented at an angle with respect to the speaker. In other embodiments, the speaker includes a central opening or cavity in which a microphone having one of various orientations is provided. The orientations of the microphone or microphones with respect to the speaker or speakers minimize adverse noise reduction effects associated with the differences in sensitivities, frequency responses and phase responses and acoustic time delays between the microphones and the speaker or speakers, as well as minimize sound reflections that are picked up by the microphone or microphones.
Owner:MOSELEY WILLIAM T
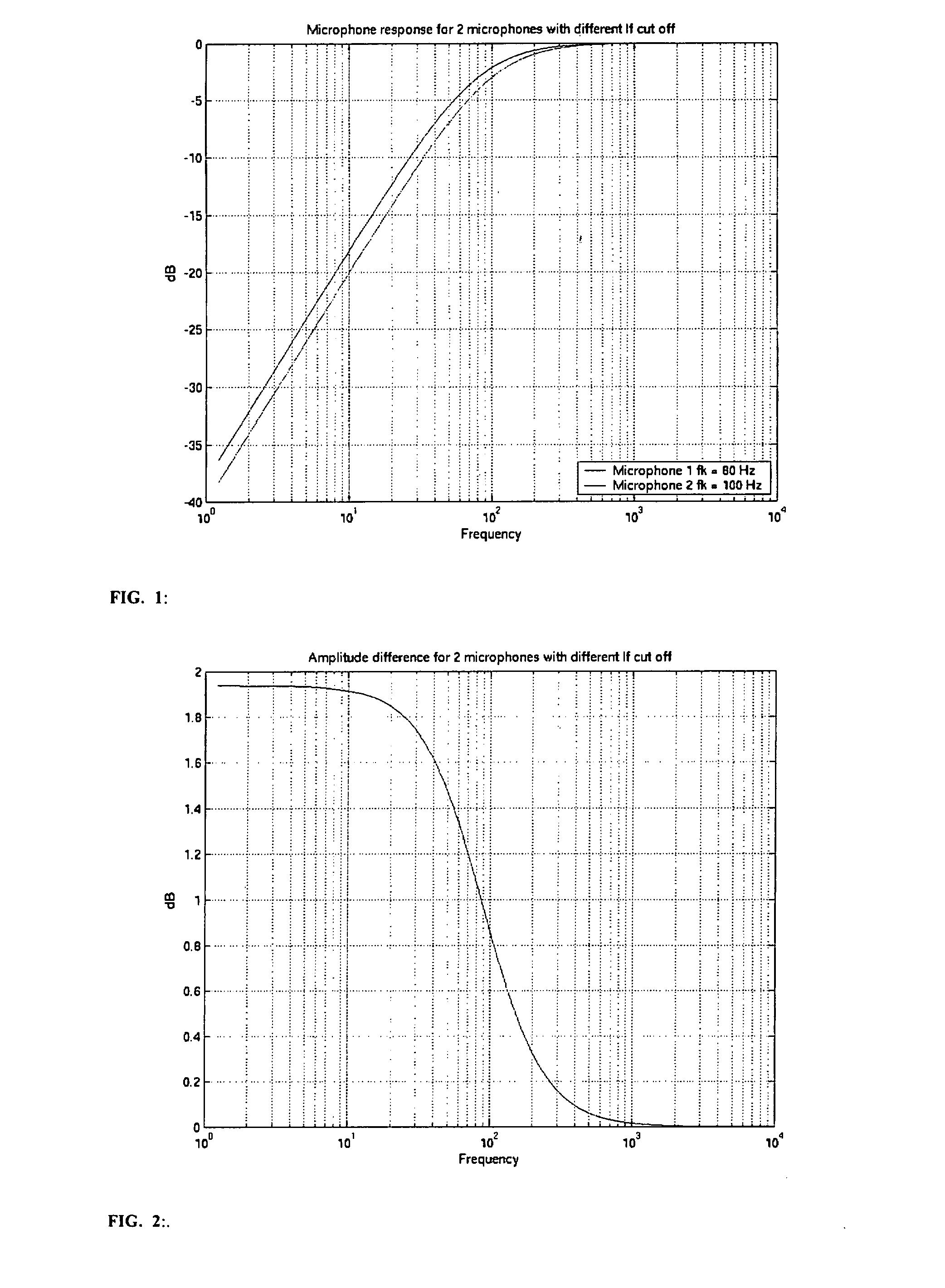
Low Frequency Phase Matching for Microphones
InactiveUS20070258597A1Reliable and adequate correctionStereophonic arrangmentsIir filteringPhase response
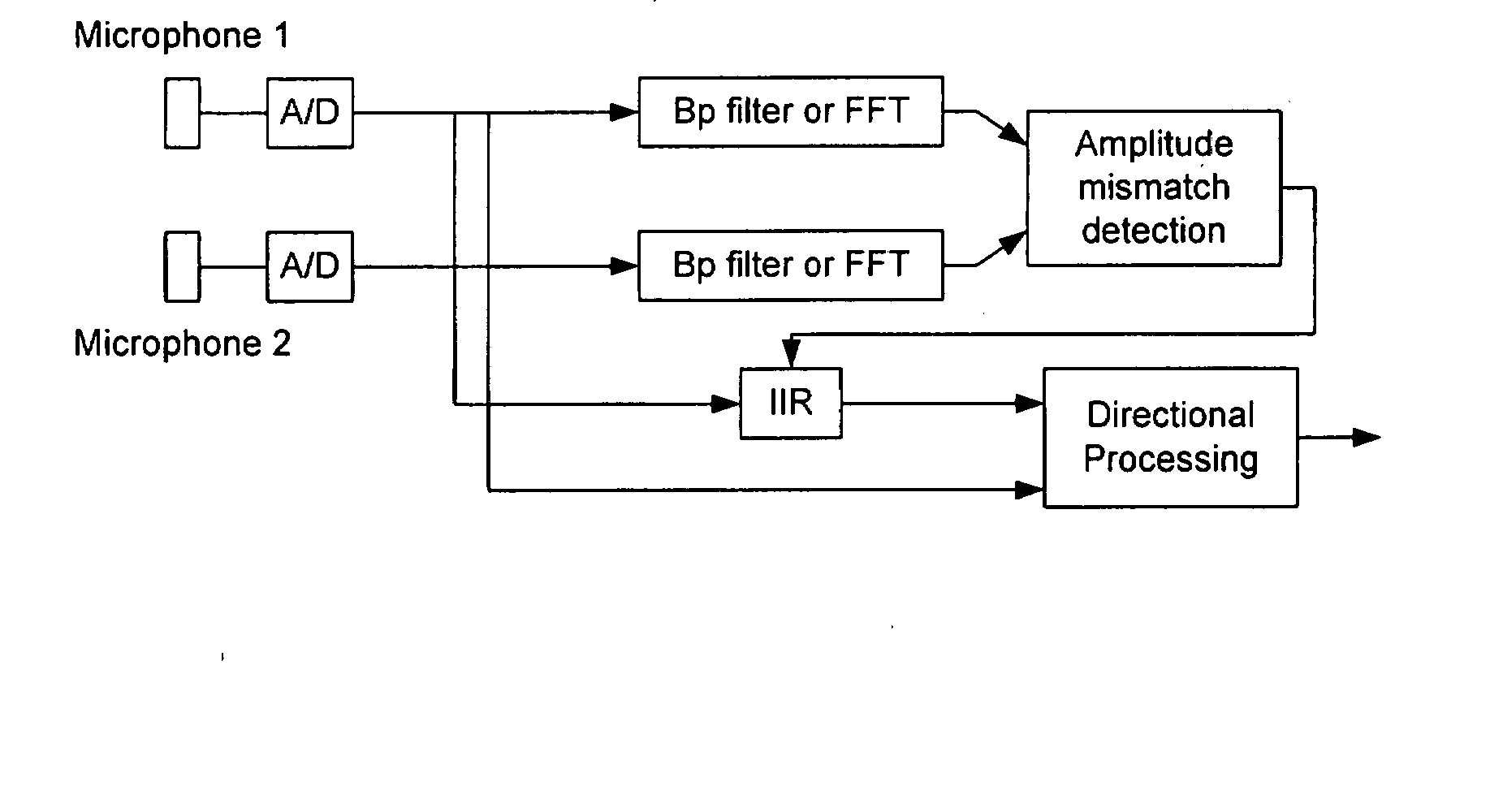
The invention relates to a communication device having at least two microphones, where in order to match the microphone performance in respect of the phase response a correction filter in the form of a IIR filter is implemented and where the amplitude of the transfer function for the correction filter is the inverse of the difference between the two microphone amplitudes.
Owner:OTICON
Pilot adaptive vector correlator
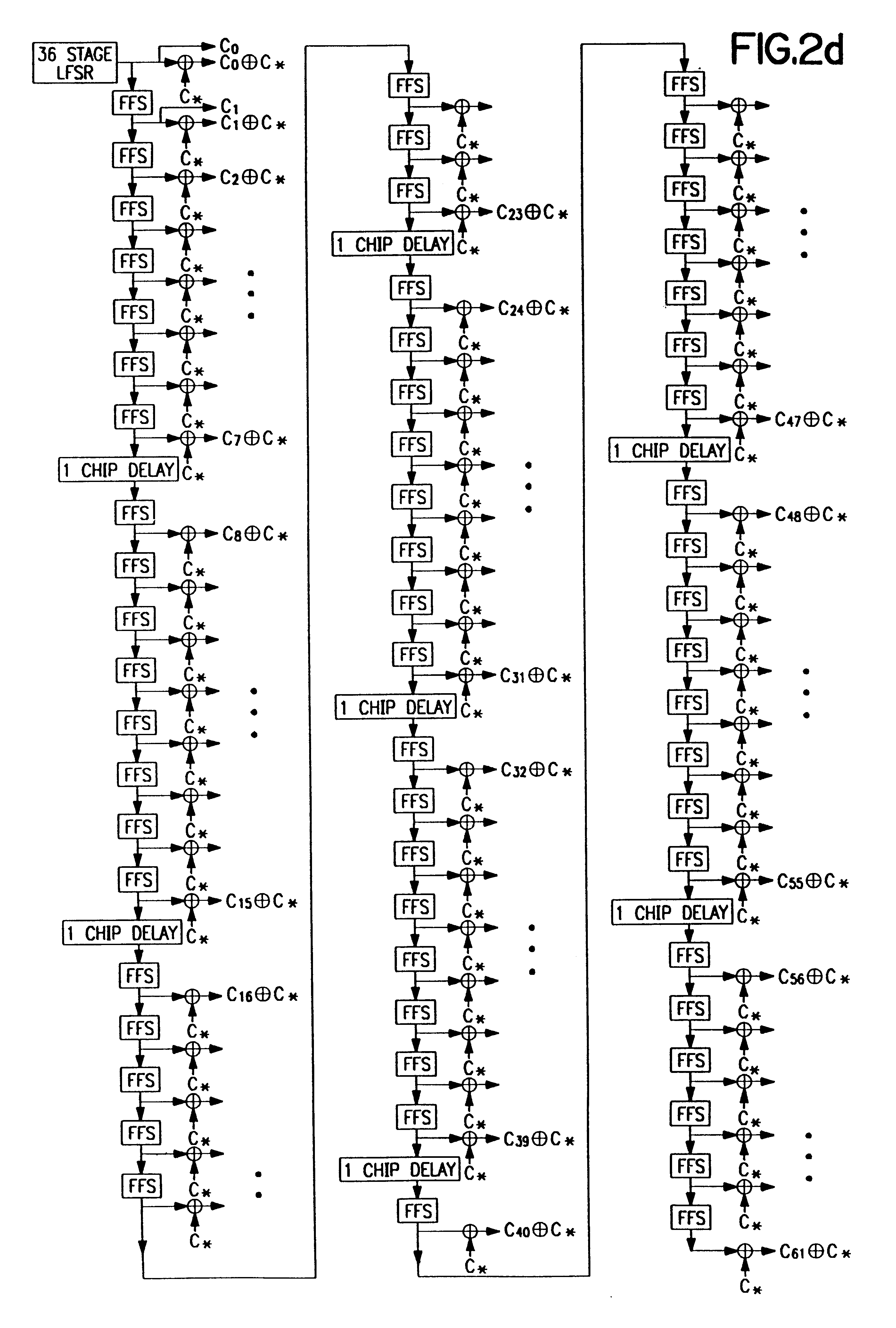
A CDMA modem includes a modem transmitter having: a code generator which provides an associated pilot code signal and which generates a plurality of message code signals; a spreading circuit which produces a spread-spectrum message signal by combining each of the information signals with a respective one of the message code signals; and a global pilot code generator that provides a global pilot code signal to which the message code signals are synchronized. The CDMA modem also includes a modem receiver having an associated pilot code generator and a group of associated pilot code correlators for correlating code-phase delayed versions of the associated pilot signal with a receive CDM signal to produce a despread associated pilot signal. The code phase of the associated pilot signal is changed responsive to an acquisition signal value until a pilot signal is received. The associated pilot code tracking logic adjusts the associated pilot code signal in phase responsive to the acquisition signal so that the signal power level of the despread associated pilot code signal is maximized. Finally, the CDMA modem receiver includes a group of message signal acquisition circuits, each including a plurality of receive message signal correlators which correlate respective local received message code signal to the CDM signal to produce a respective despread received message signal.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL TECH CORP
Nonlinear digital signal processor
InactiveUS20080080644A1Multiple-port networksAdaptive networkDigital signal processingPhase response
A digital signal processor (DSP) comprises an input terminal configured to receive an input, an adaptive nonlinear phase filter coupled to the input terminal, the adaptive nonlinear phase filter having a time-varying phase response, and an adaptive nonlinear amplitude filter coupled to the input terminal, the adaptive nonlinear amplitude filter having a time-varying amplitude response.A method of processing a signal comprises receiving the signal, sending the signal to an adaptive nonlinear phase filter, the adaptive nonlinear phase filter having a time-varying phase response, and sending the signal to an adaptive nonlinear amplitude filter, the adaptive nonlinear amplitude filter having a time-varying amplitude response.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
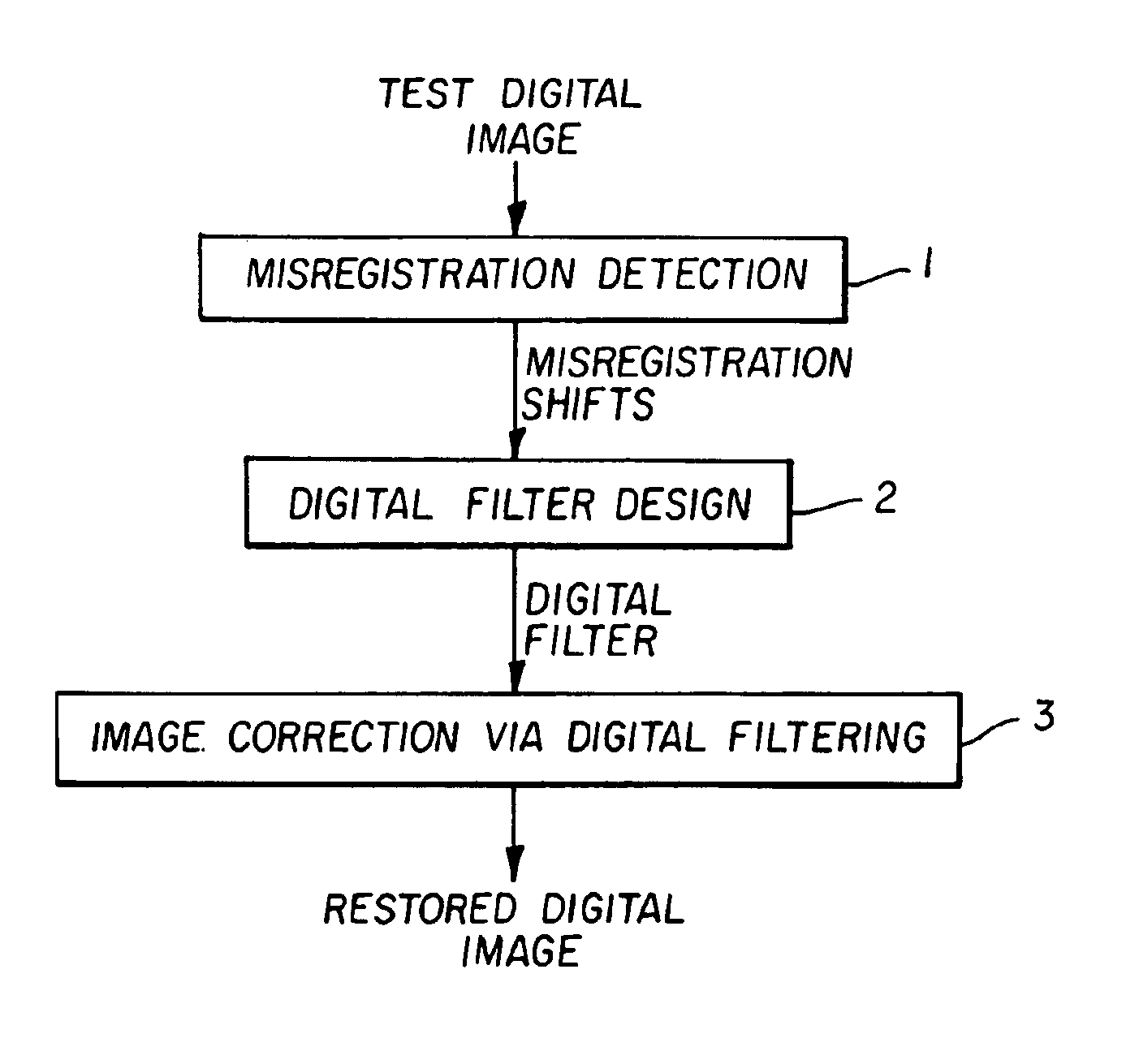
Image processing for improvement of color registration in digital images
InactiveUS6870564B1Improve clarityIncreasing certain spatial frequencies in the imageTelevision system detailsImage analysisImaging processingPhase response
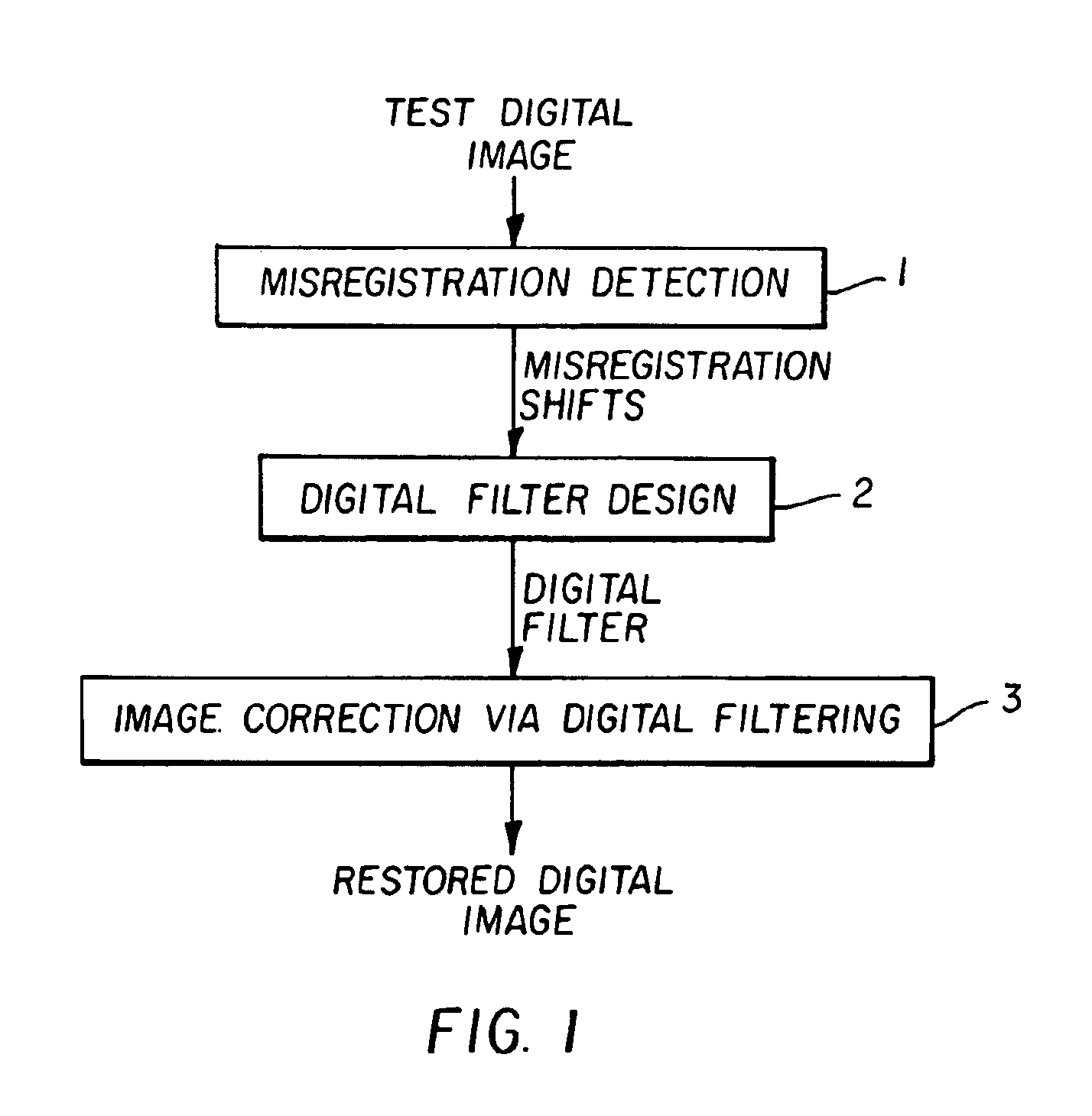
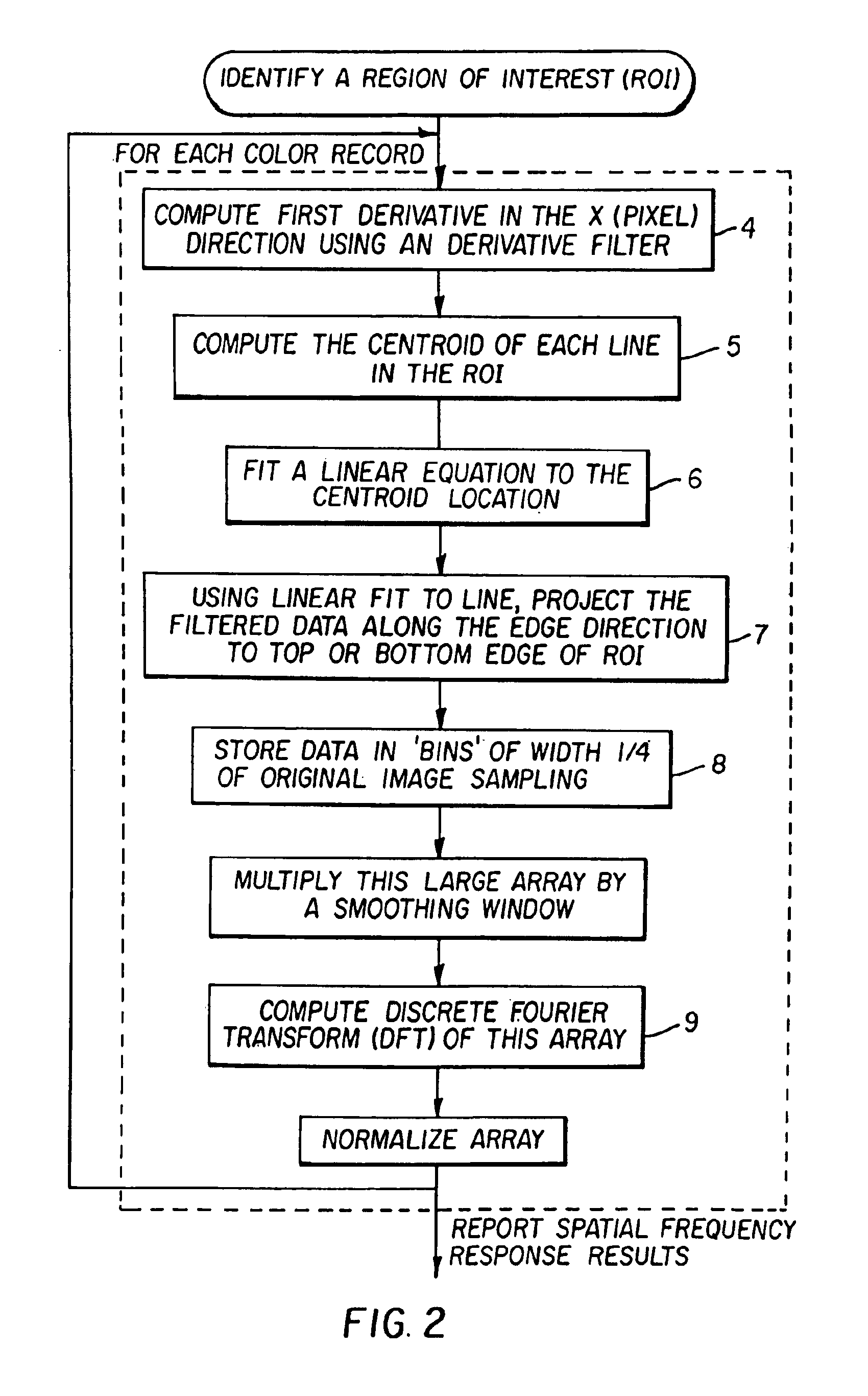
A method for improving the wavelength dependent registration of digital images includes the steps of (a) detecting a similar feature in two or more digital records of the same scene, (b) determining from the feature a shift due to misregistration of at least one of the digital records relative to another of the digital records, and (c) processing the shifted digital record(s) with a digital filter having a phase response that compensates for the shift, thereby providing a correction for the wavelength dependent misregistration between the digital records.
Owner:MONUMENT PEAK VENTURES LLC
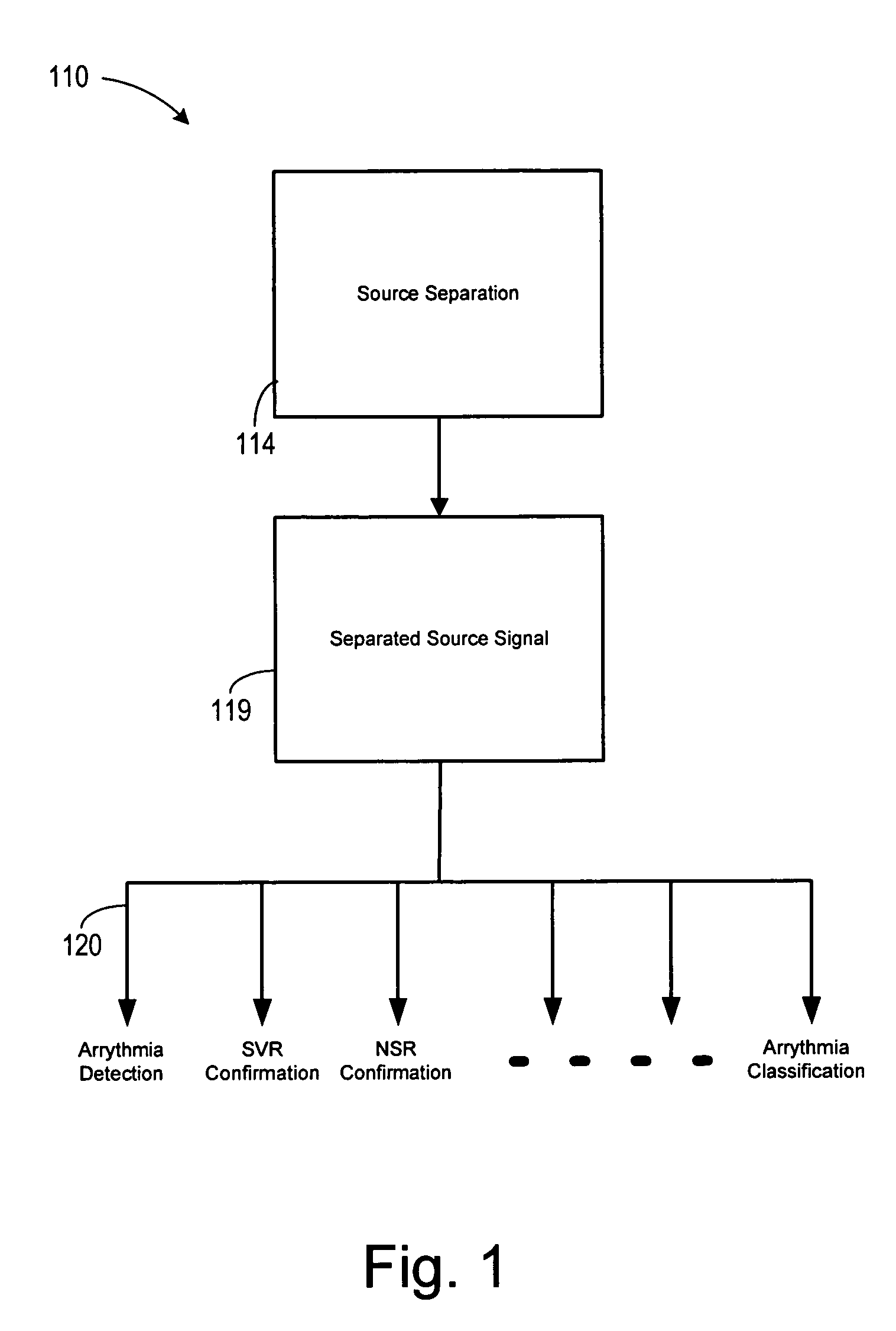
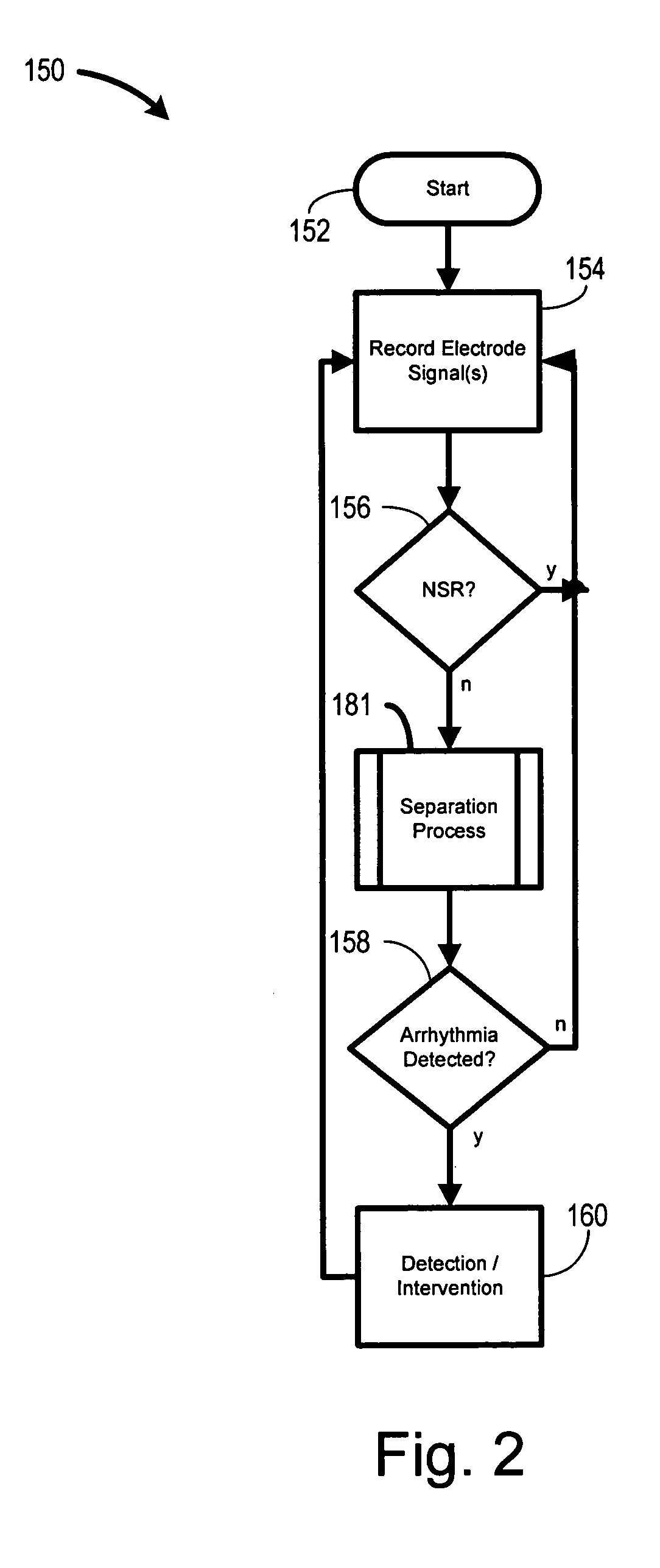
Biopotential signal source separation using source impedances
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Spatially Multiplexed Dielectric Metasurface Optical Elements
ActiveUS20170219739A1Improve performanceEasy to createNon-linear opticsOptical elementsDielectricPhase response
A multifunctional dielectric gradient metasurface optical device has a layer of nanoscale dielectric gradient metasurface optical antenna elements deposited on a substrate layer, arranged with spatially varying orientations, shapes, or sizes in the plane of the device such that the optical device has a spatially varying optical phase response capable of optical wavefront shaping. The spatially varying optical phase response is a spatial interleaving of multiple distinct phase profiles corresponding to multiple optical sub-elements, thereby providing multifunctional wavefront shaping in the single optical element.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +2
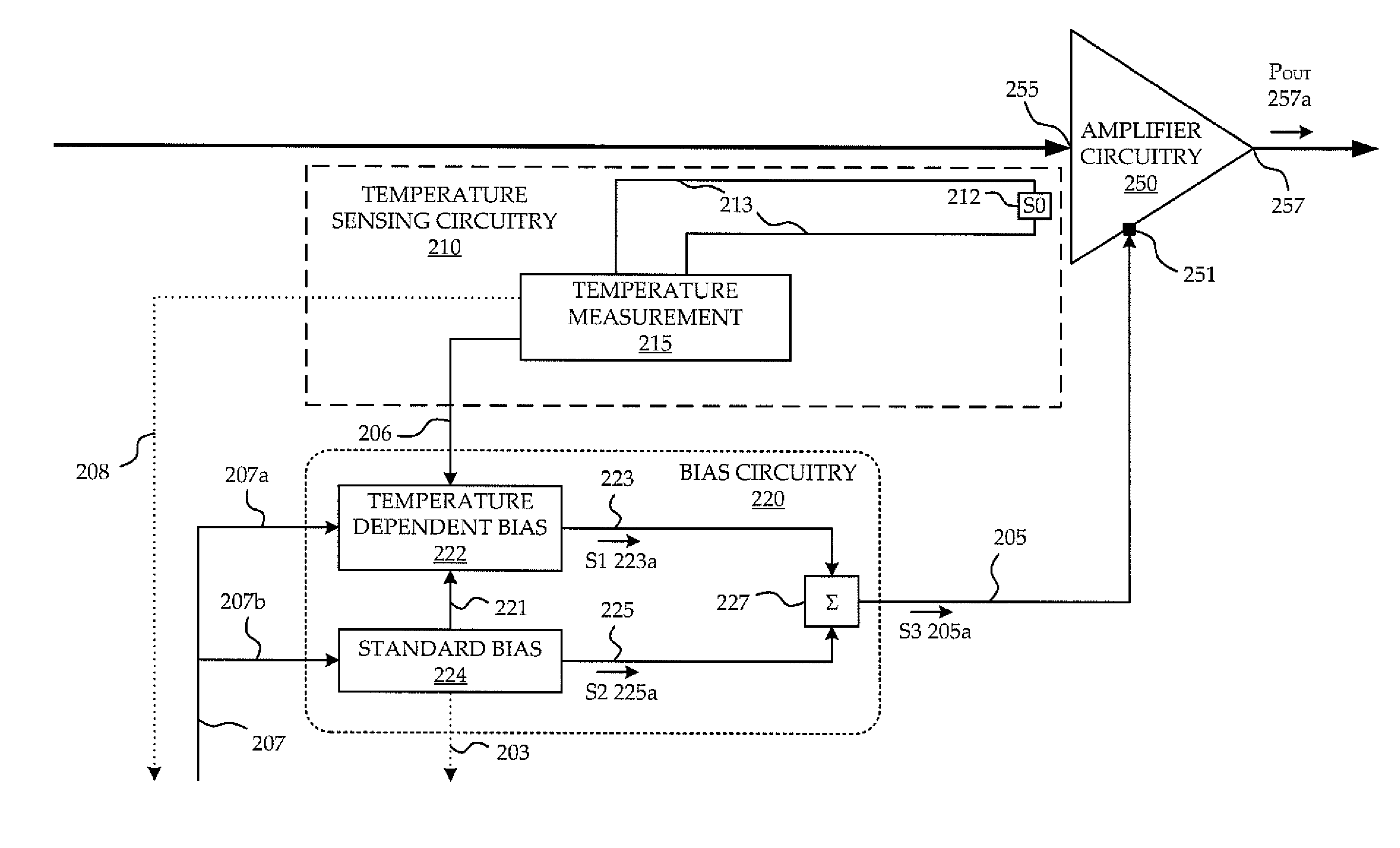
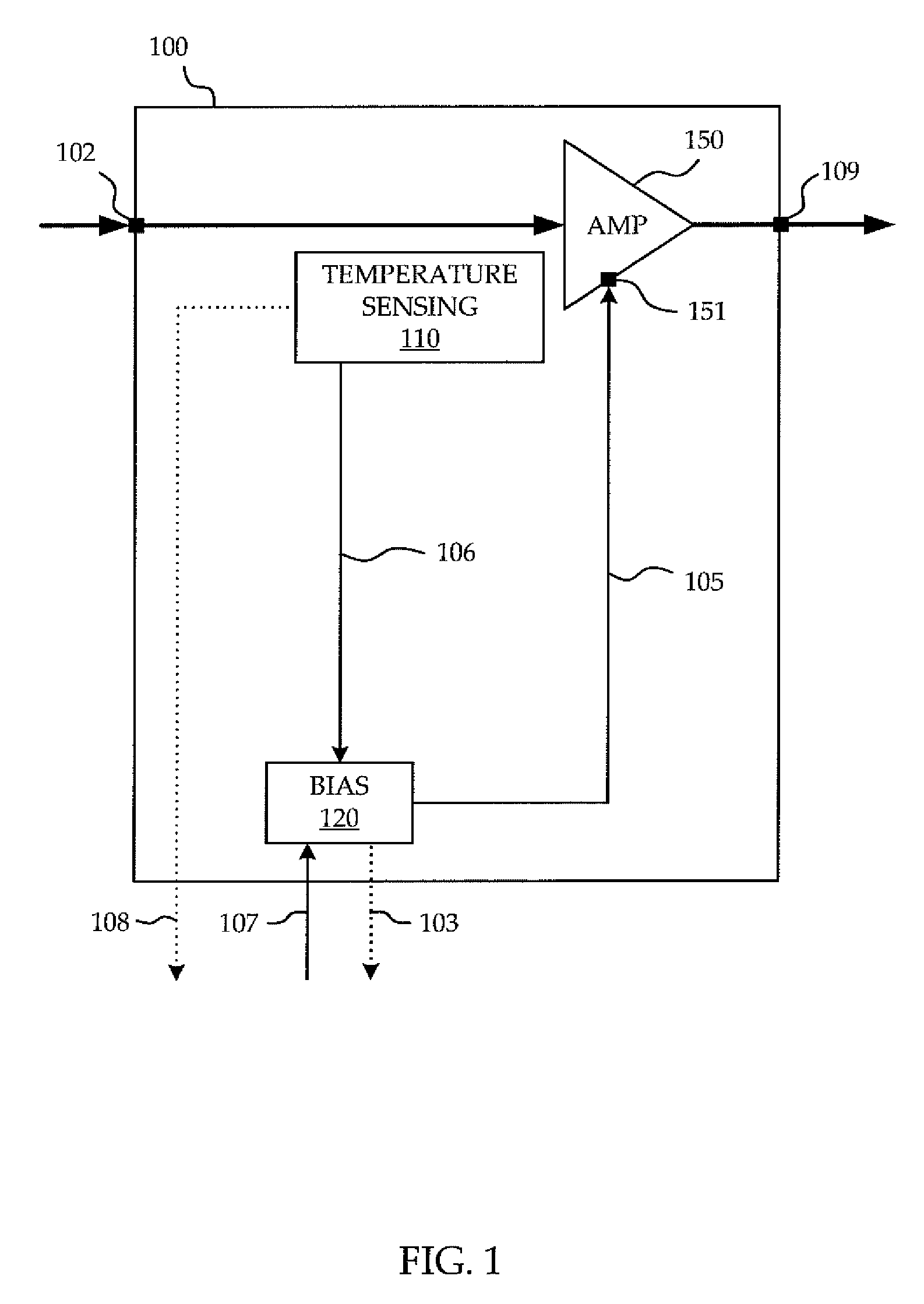
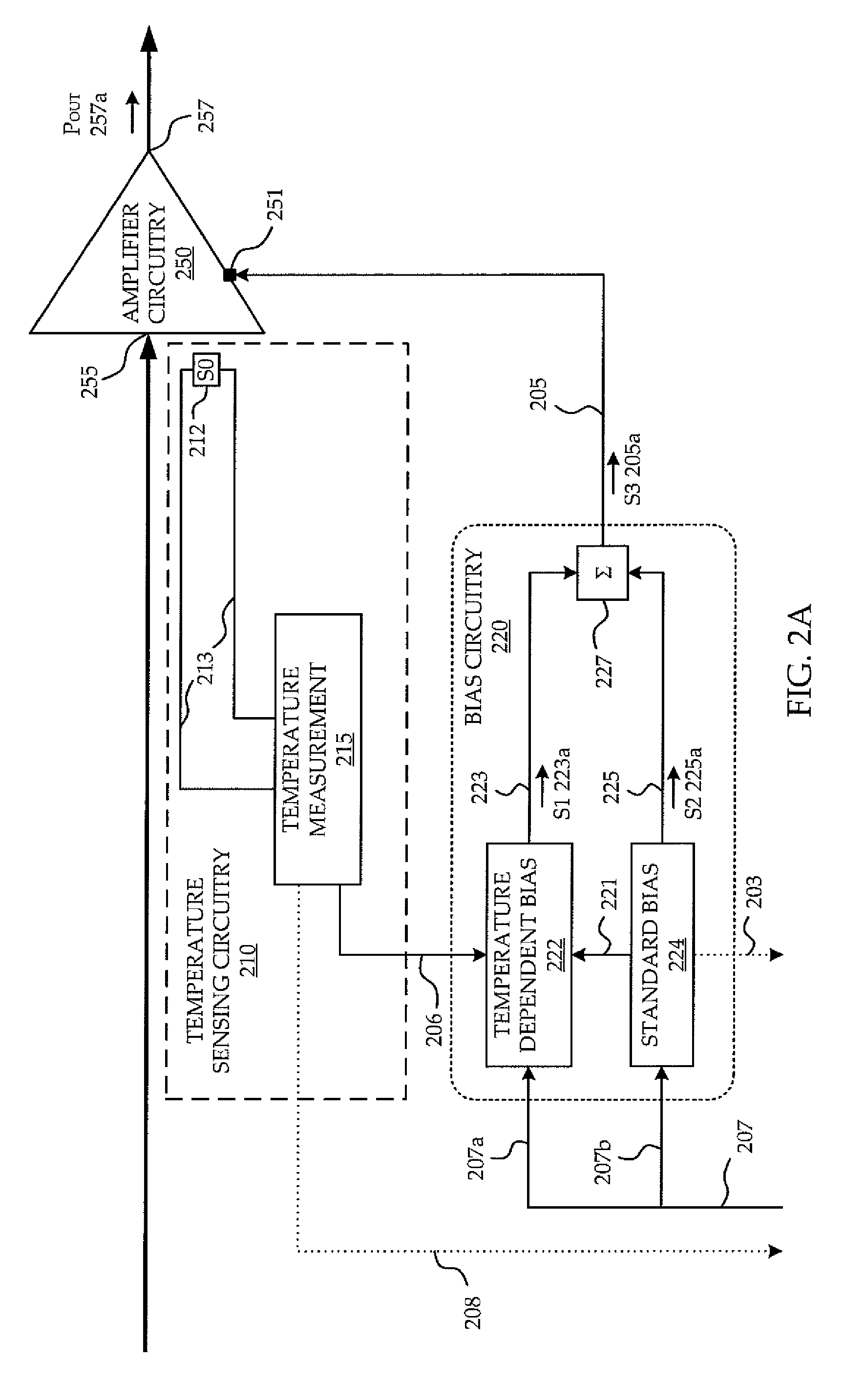
Circuit and method of temperature dependent power amplifier biasing
ActiveUS7994862B1High frequency amplifiersAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationAudio power amplifierPhase response
A circuit and method are provided for reducing dynamic EVM of a power amplifier (PA) used for RF communication. A temperature dependent boost bias signal is applied to the bias input port of amplifier circuitry of the PA in dependence upon a temperature of the amplifier circuitry to compensate for transience in the gain or phase response of the PA while components of the PA is differentially warming-up, advantageously taking into account an actual temperature of the amplifier circuitry.
Owner:SIGE SEMICON
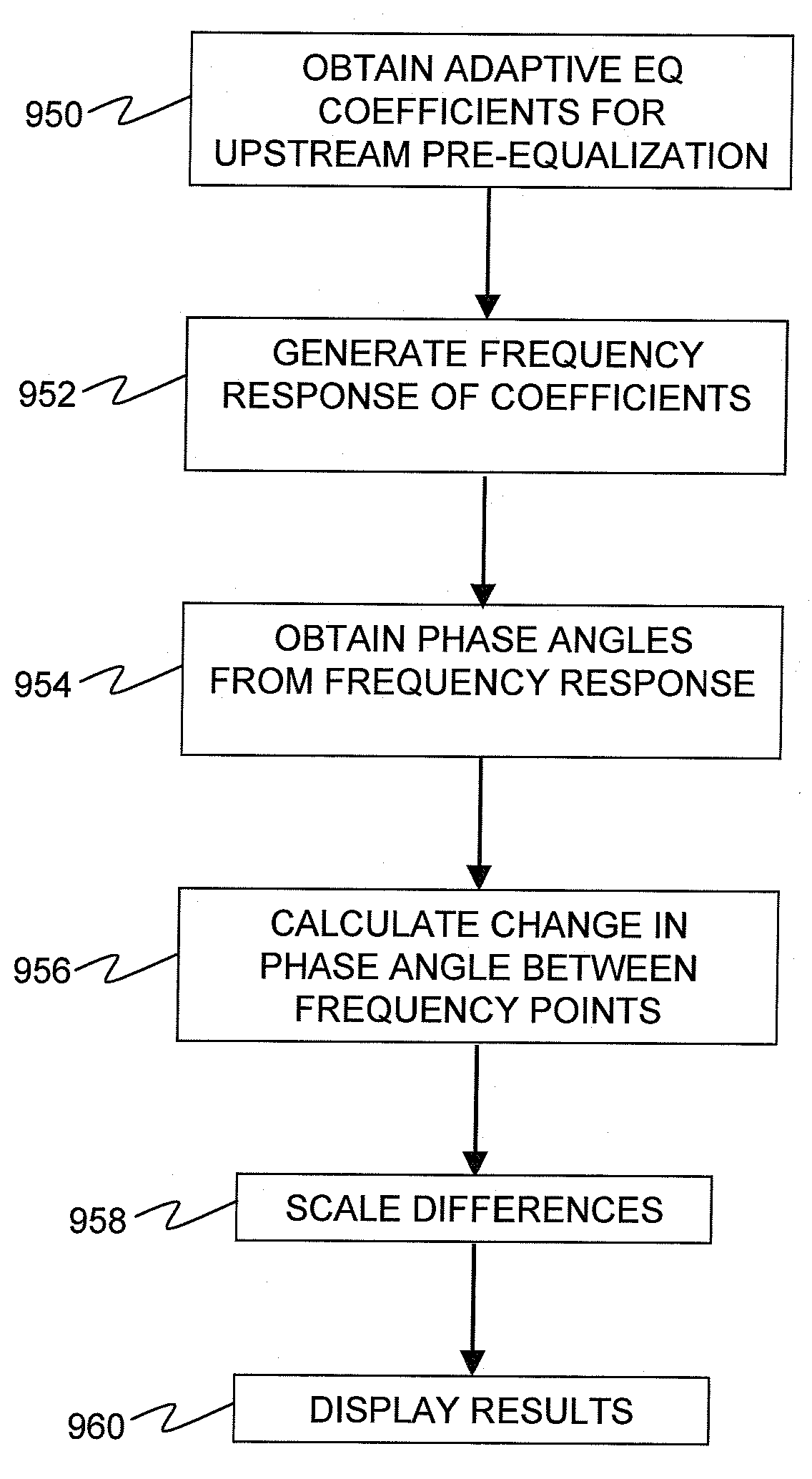
Characterizing Broadband Communication Networks
ActiveUS20070121712A1Correct operation testingFrequency-division multiplex detailsPhase responseModem device
A remote testing device, including a cable modem circuit, requests an IP address from a remote cable modem termination system (CMTS) and receives back IP connection information including adaptive equalizer coefficients, which represent compensation and / or correction for transmission path noise. Using the equalizer coefficients, the remote testing device can determine a phase response, phase angles for each frequency increment over a channel bandwidth, and group delay.
Owner:VIAVI SOLUTIONS INC
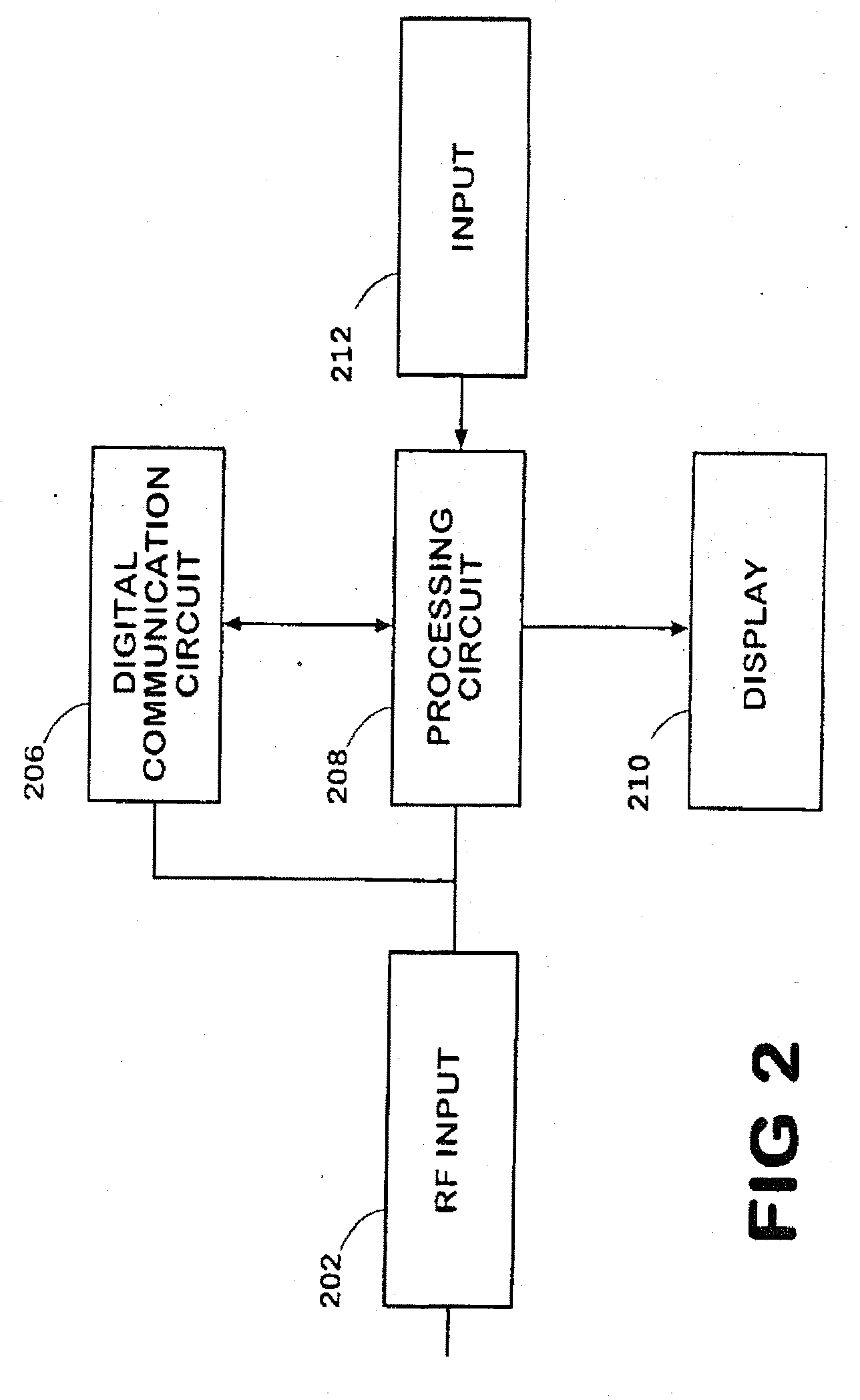
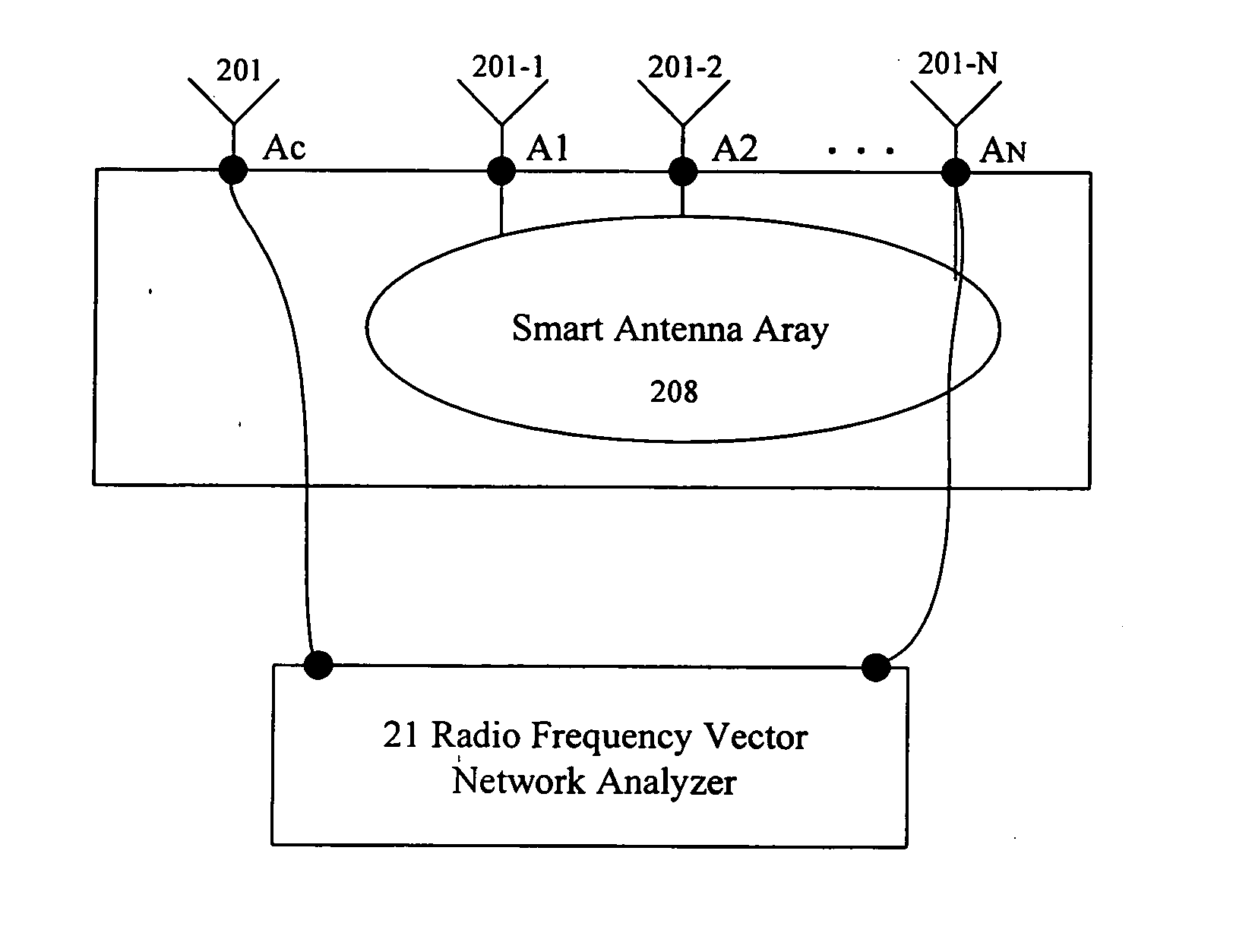
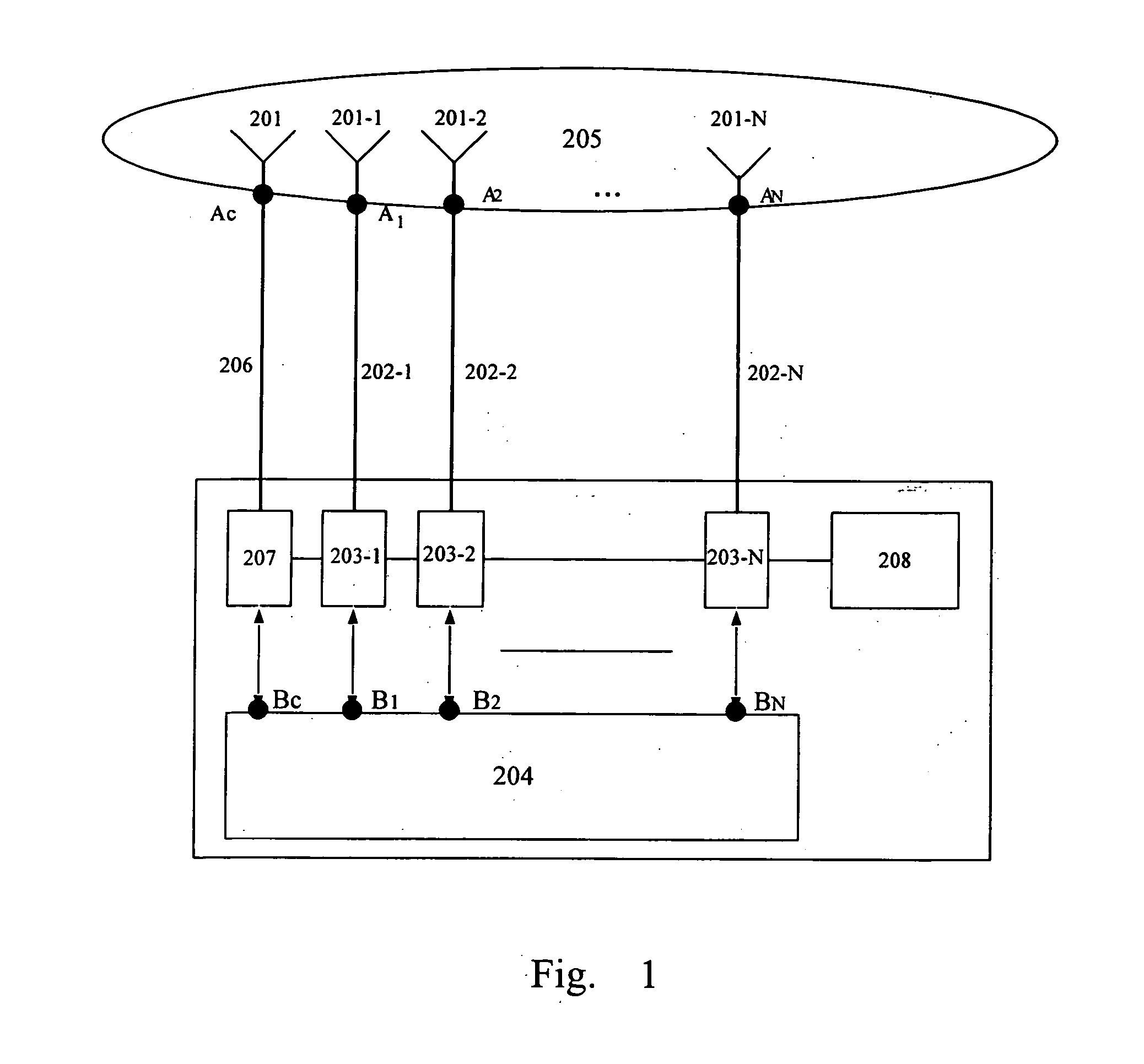
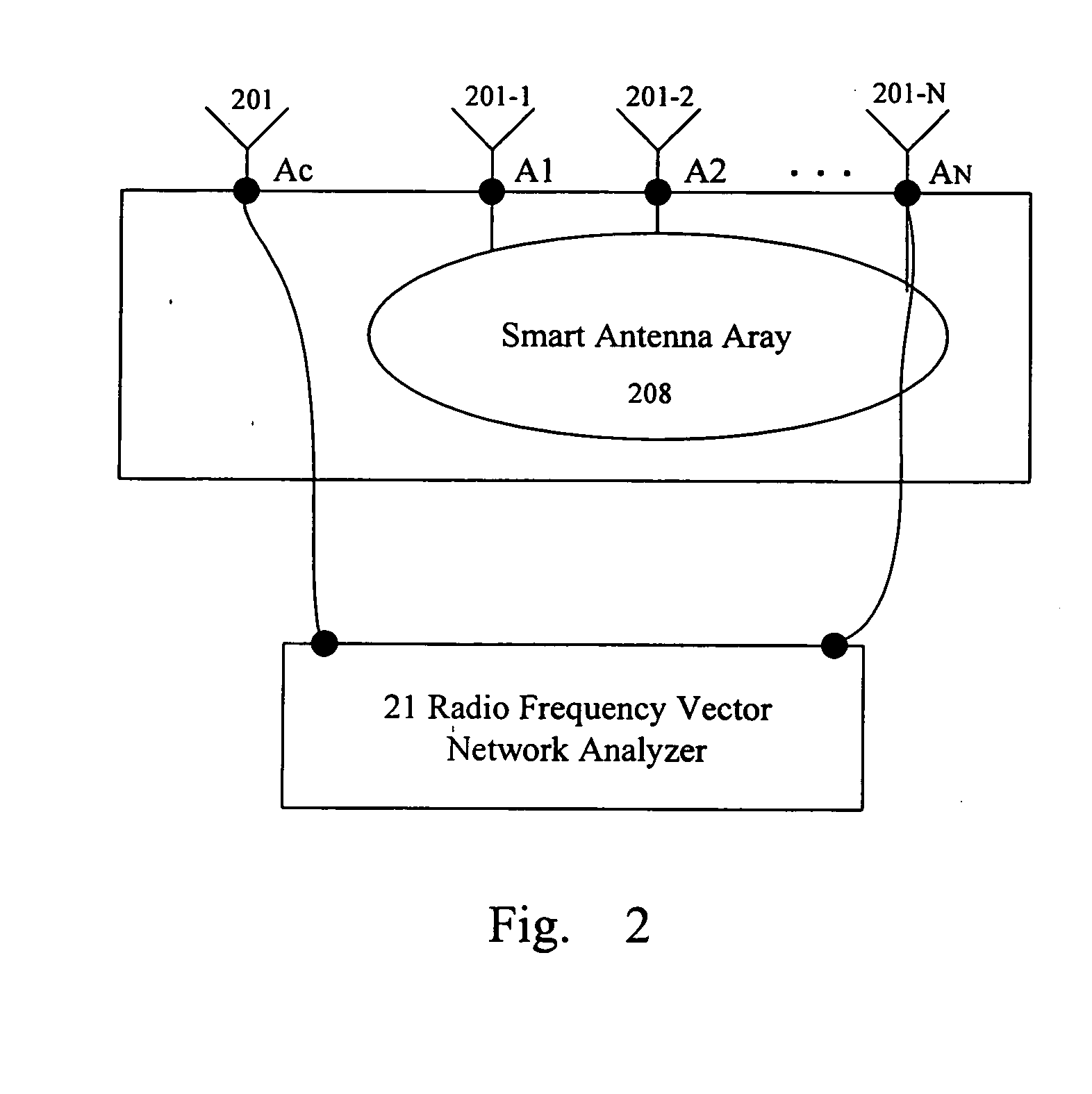
Method for calibrating smart antenna array systems in real time
ActiveUS20060009162A1Easy to implementReduce transmit powerDiversity/multi-antenna systemsTransmission monitoringPhase responseSmart antenna
Transmitting and receiving compensation coefficients of each antenna element relative to a calibration antenna element are obtained in the pre-calibration of a smart antenna. After the antenna array is installed, in transmitting calibration, amplitude and phase response of each transmitting link is computed according to the calibration signals received by the calibration link and, together with the transmitting compensation coefficient obtained in the pre-calibration, the compensation coefficient of each transmitting link is computed to compensate the downlink data of a base station. In receiving calibration, the amplitude and phase response of each receiving link is computed based on the signals received by the receiving links and, together with the receiving compensation coefficient obtained in pre-calibration, the compensation coefficient of each receiving link is computed to compensate the uplink data of the base station. The calibration signal of each antenna element is generated by a periodic cycling shift of a basic calibration sequence.
Owner:DATANG MOBILE COMM EQUIP CO LTD
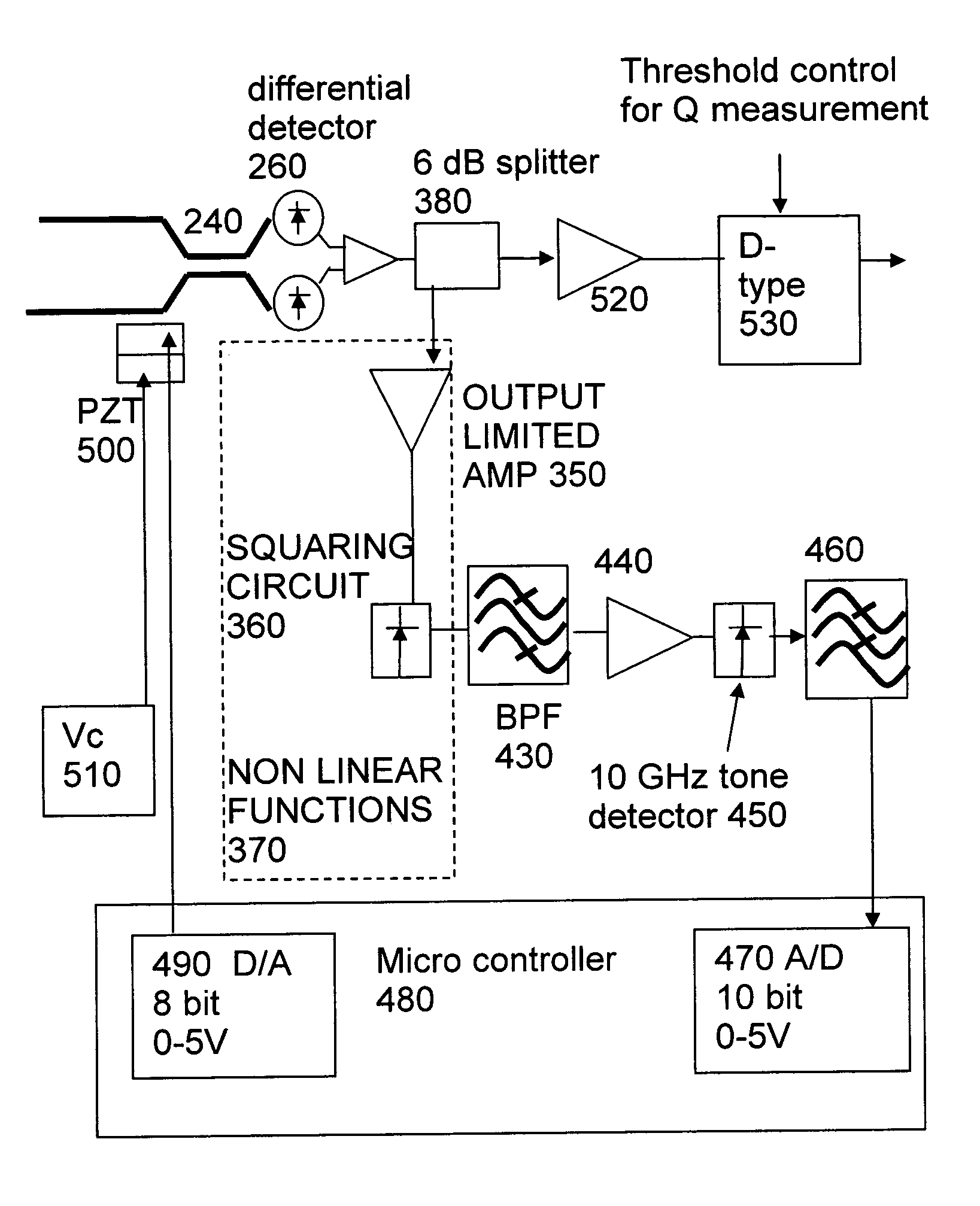
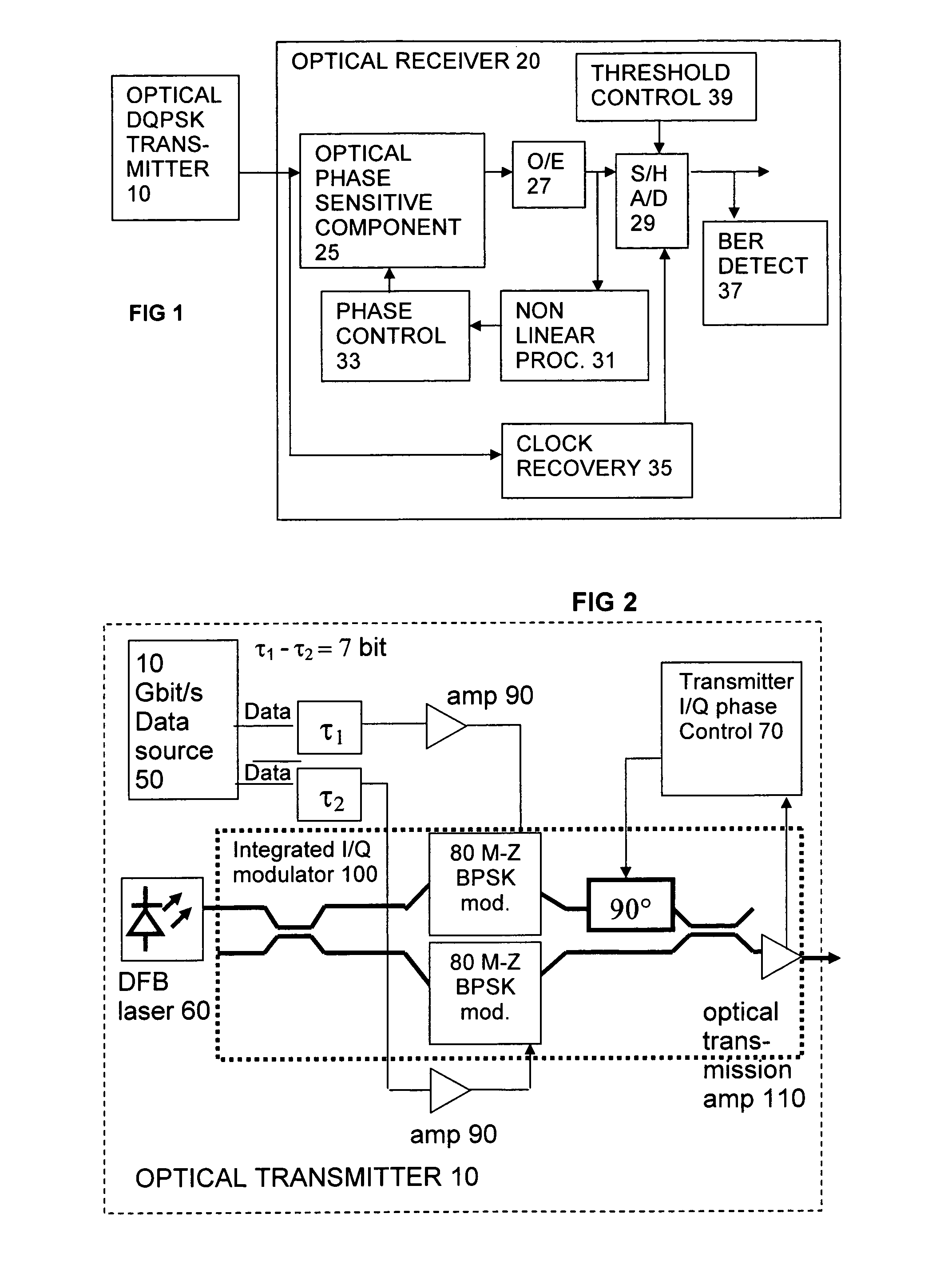
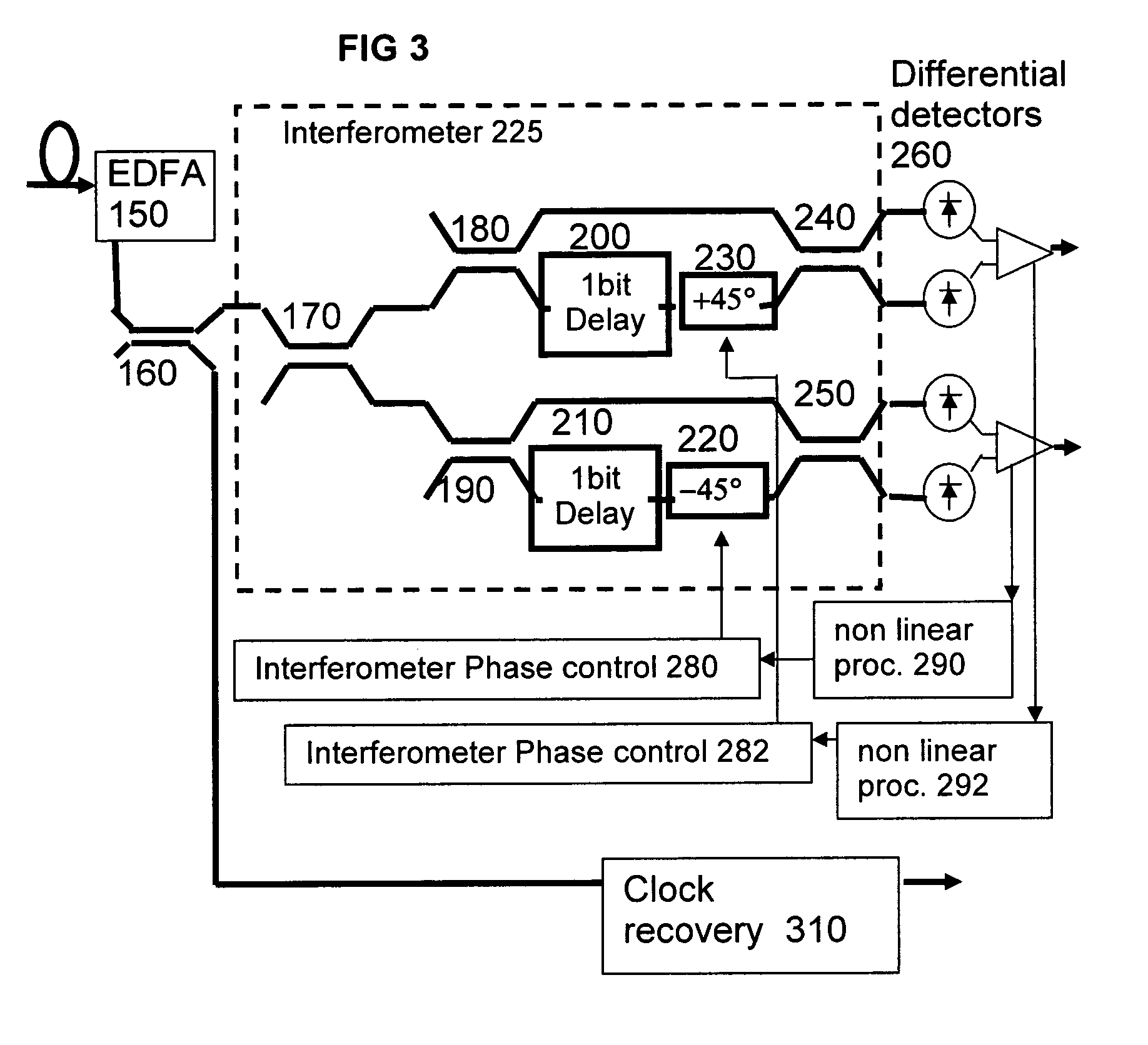
DQPSK receiver phase control
ActiveUS7389055B1Effective and reliable controlOptimal Rate of ChangeOptical multiplexElectromagnetic receiversPhase responseDifferential phase
An optical receiver for receiving an optical differential phase shift keyed signal has an optical component sensitive to the optical phase of the signal, such as an interferometer, a device arranged to generate a control signal by non linear limiting of an output of the optical component, such as an RF amplifier arranged to operate in a region near saturation point, and a phase controller for tuning a phase response of the optical component to the received signal according to the control signal.
Owner:CIENA
Method and system of beamforming a broadband signal through a multiport network
ActiveUS20110201283A1Polarisation/directional diversityLine-faulsts/interference reductionPhase responseBroadband
Aspects of a method and system for beamforming a broadband signal through a multiport network are provided. In this regard, a plurality of signals received via a plurality of antennas may be detected and a plurality of transmit signals may be generated, wherein a phase of at least one of the plurality of transmit signals is responsive to at least one of the detected phases of the received signals. Each of the generated plurality of transmit signals may be separately amplified to generate a plurality of amplified signals. A plurality of the amplified signals may be input to a plurality of first ports of a multi-port network, wherein at least one second port of the multi-port network may be responsive to signals input to at least two of the plurality of first ports.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Method and apparatus for reducing crosstalk interference in an inline Fabry-Perot sensor array
Owner:WEATHERFORDLAMB +1
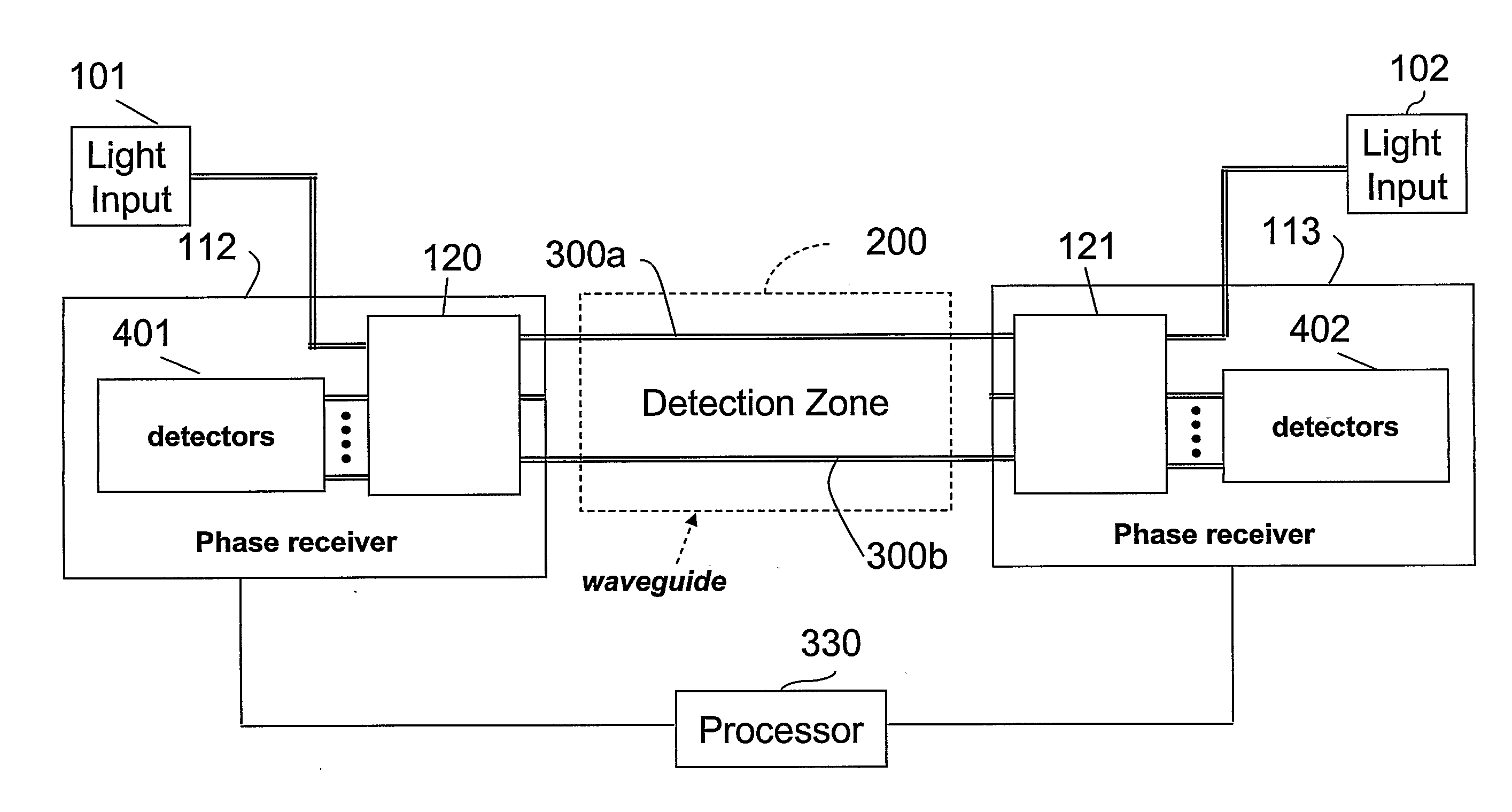
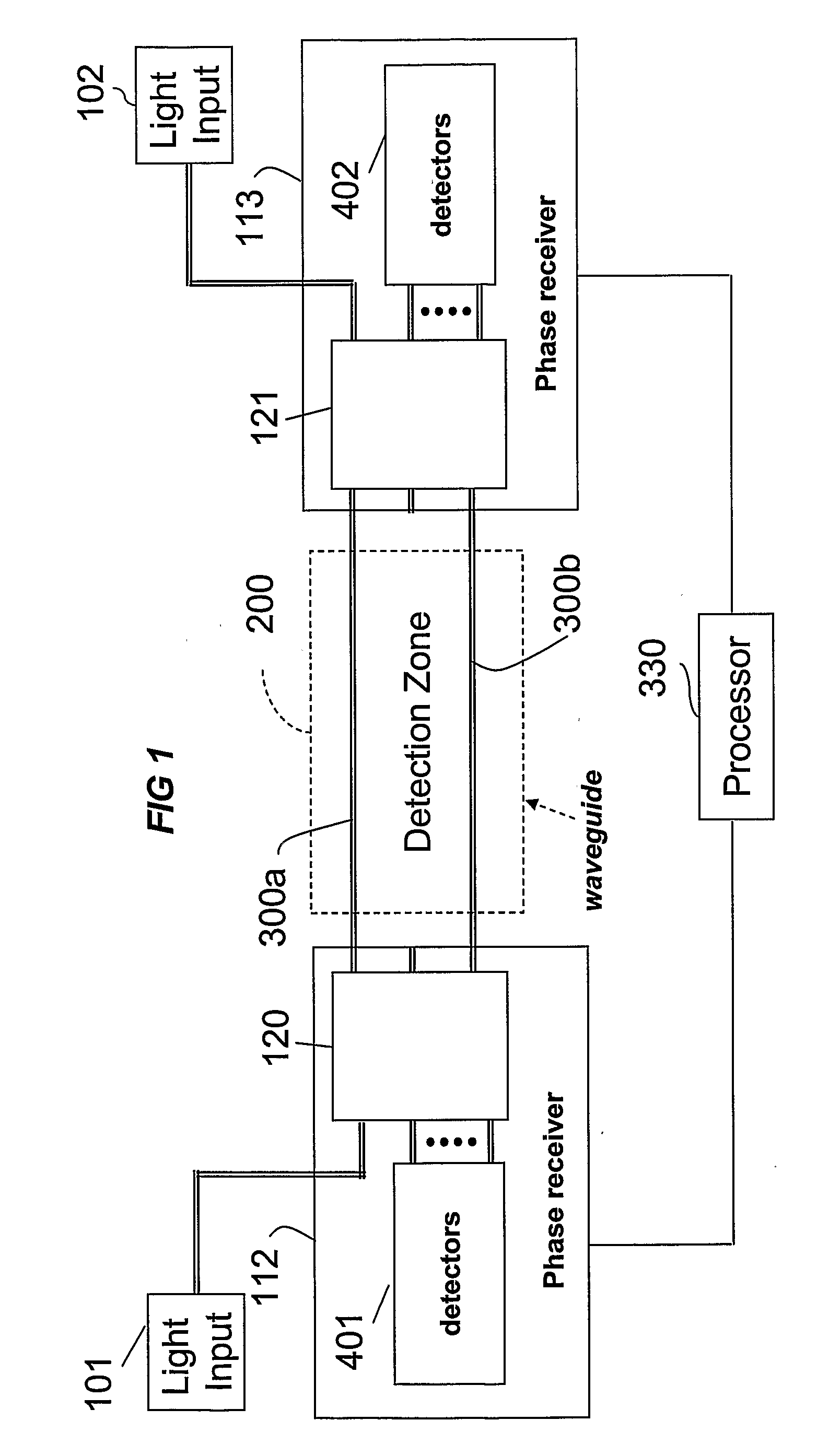
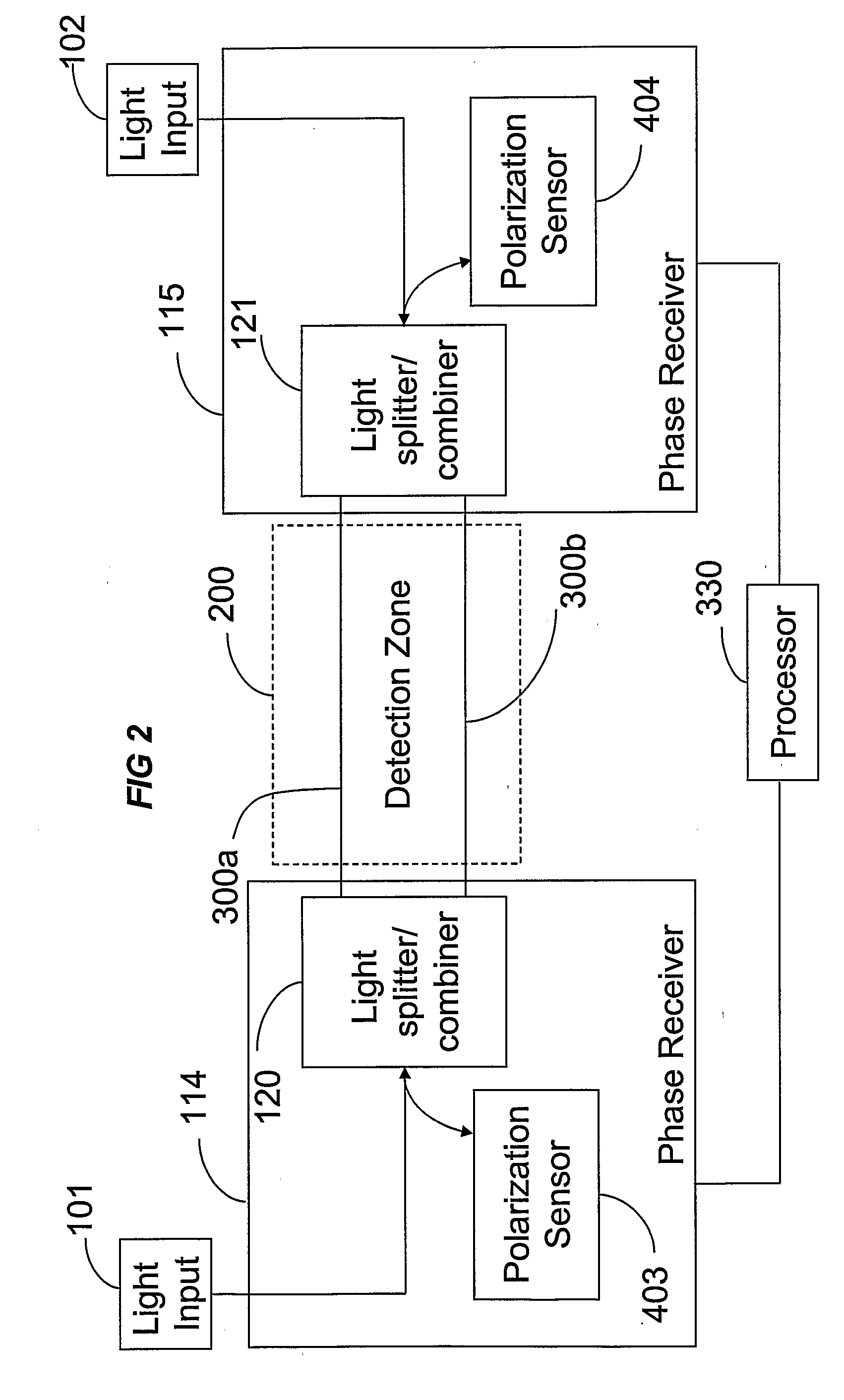
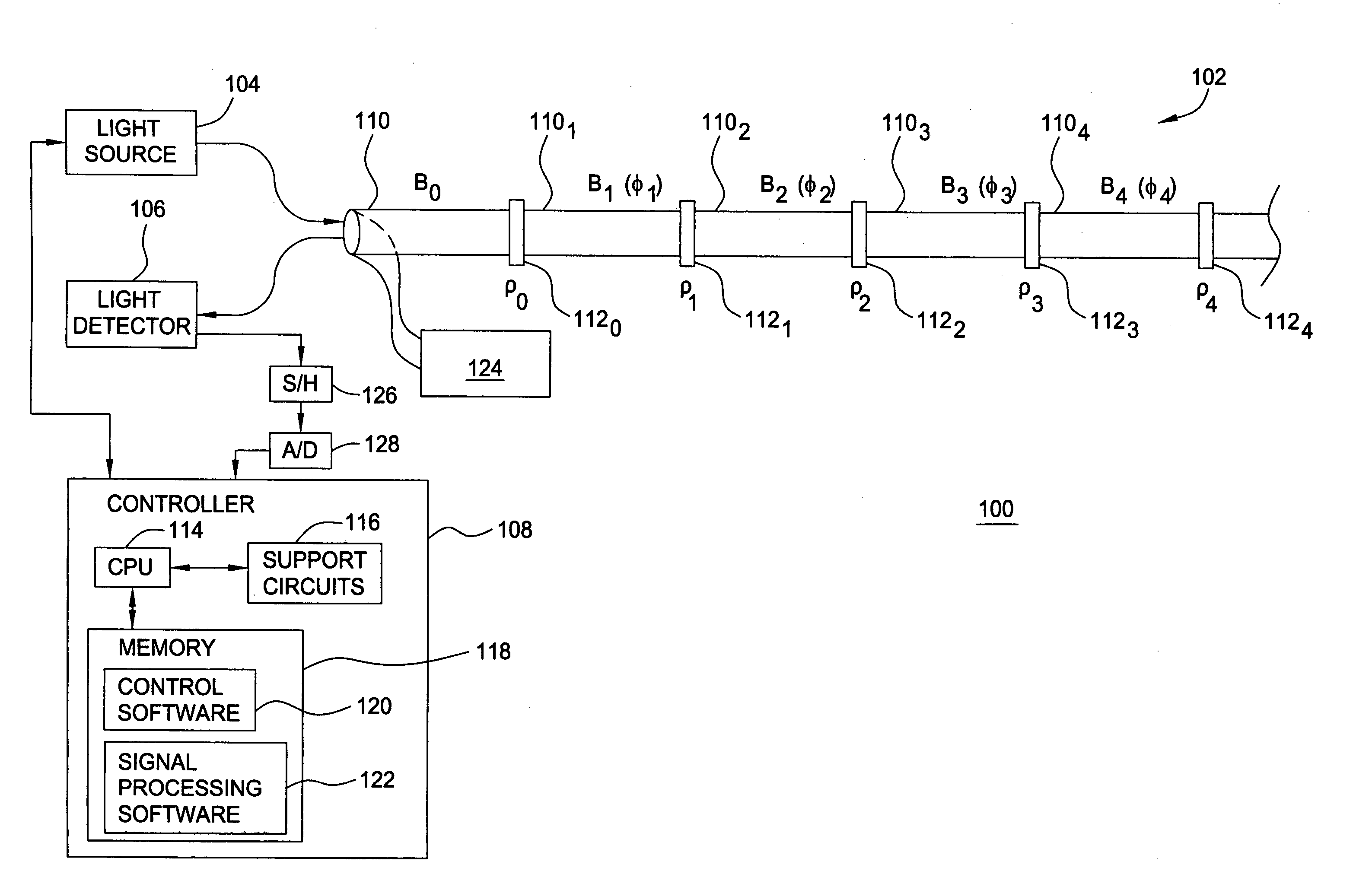
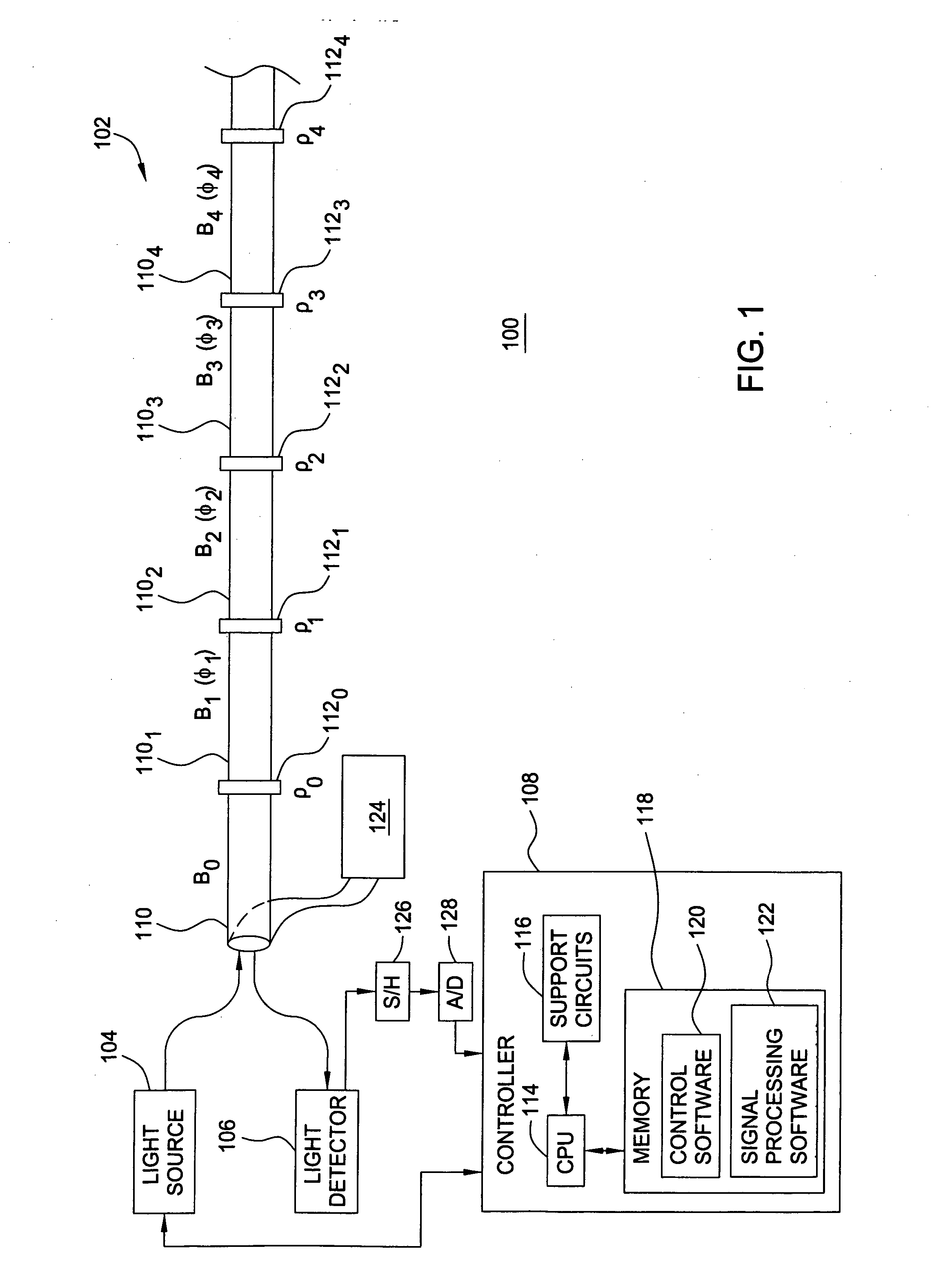
Phase Responsive Optical Fiber Sensor
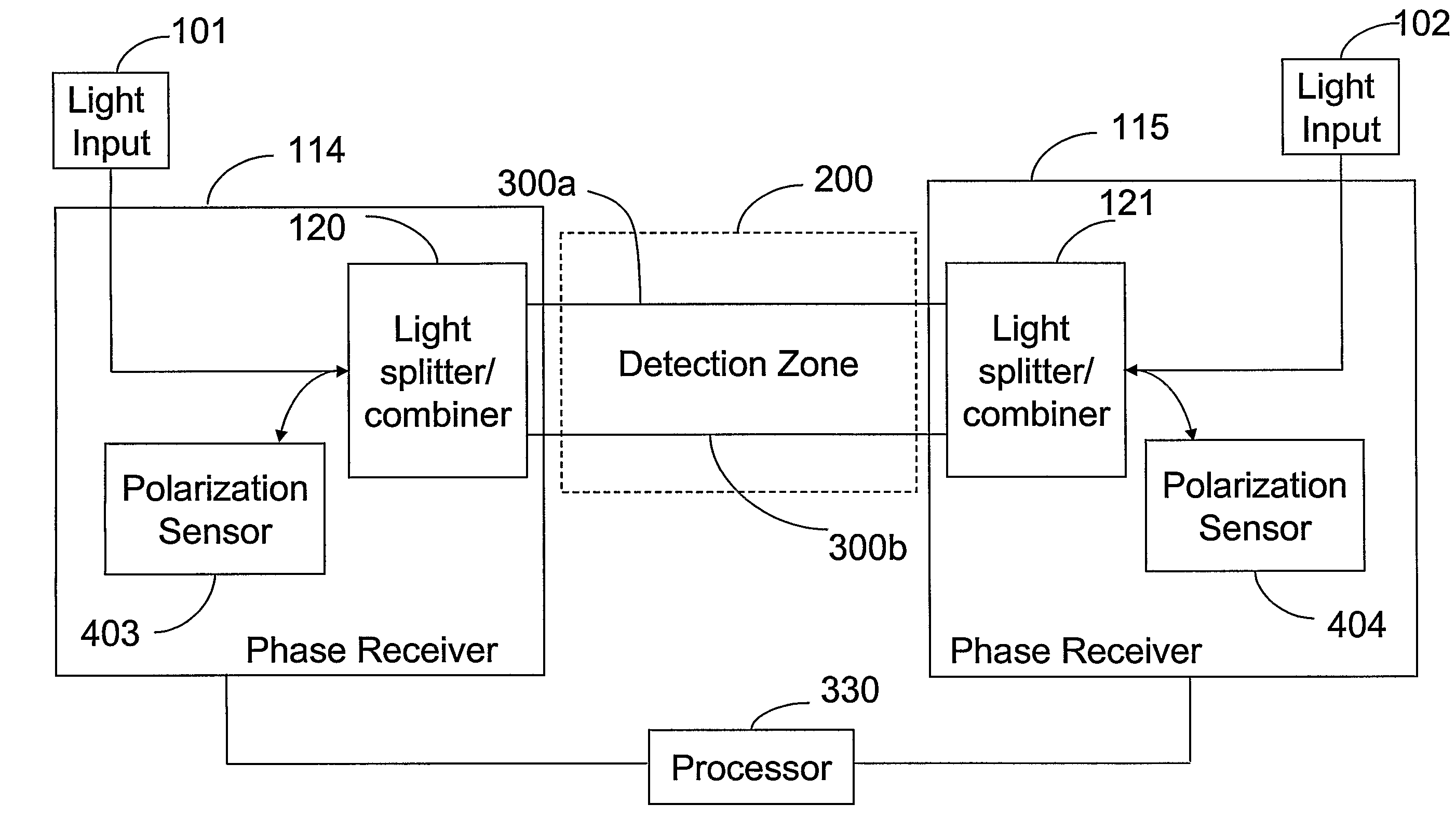
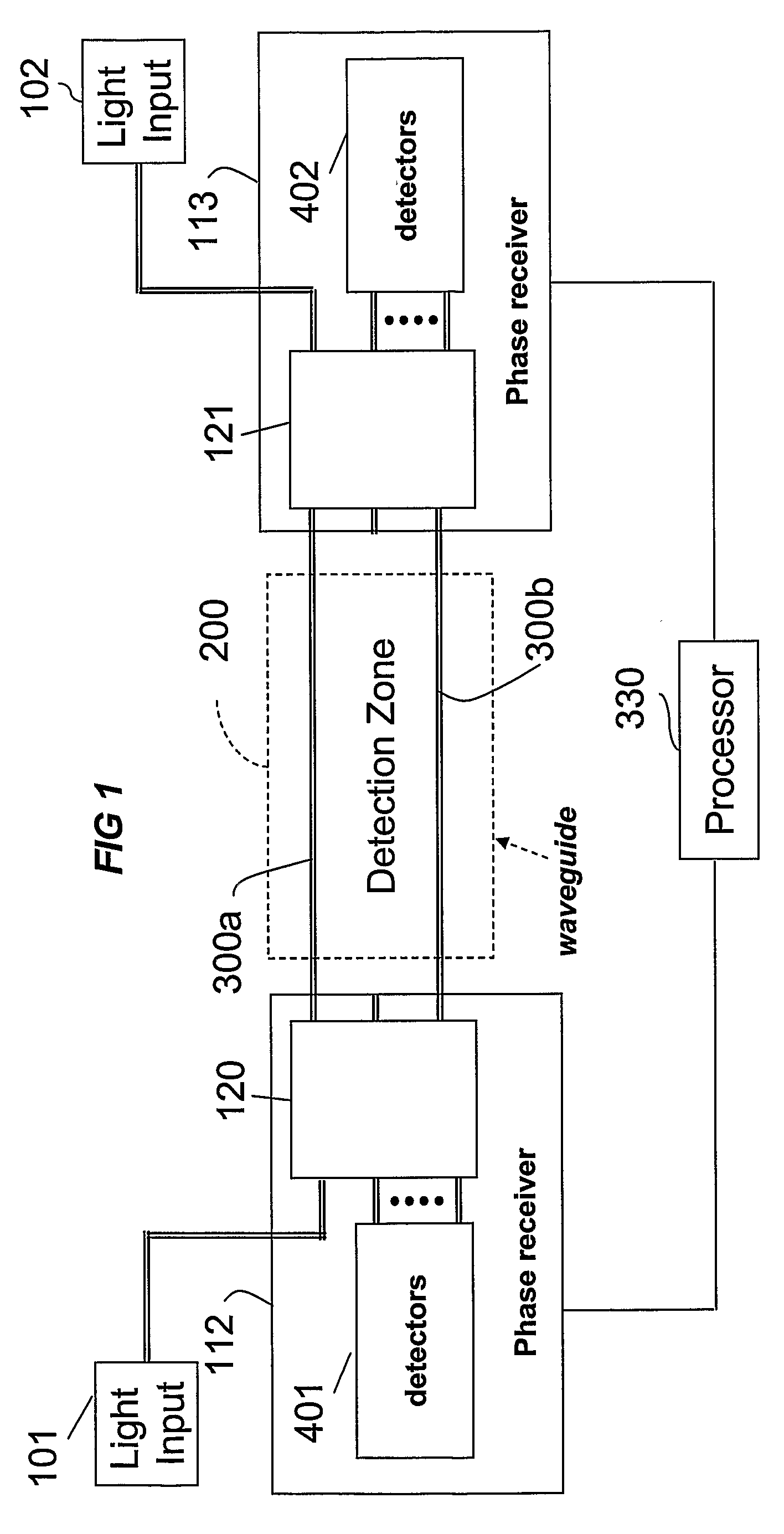
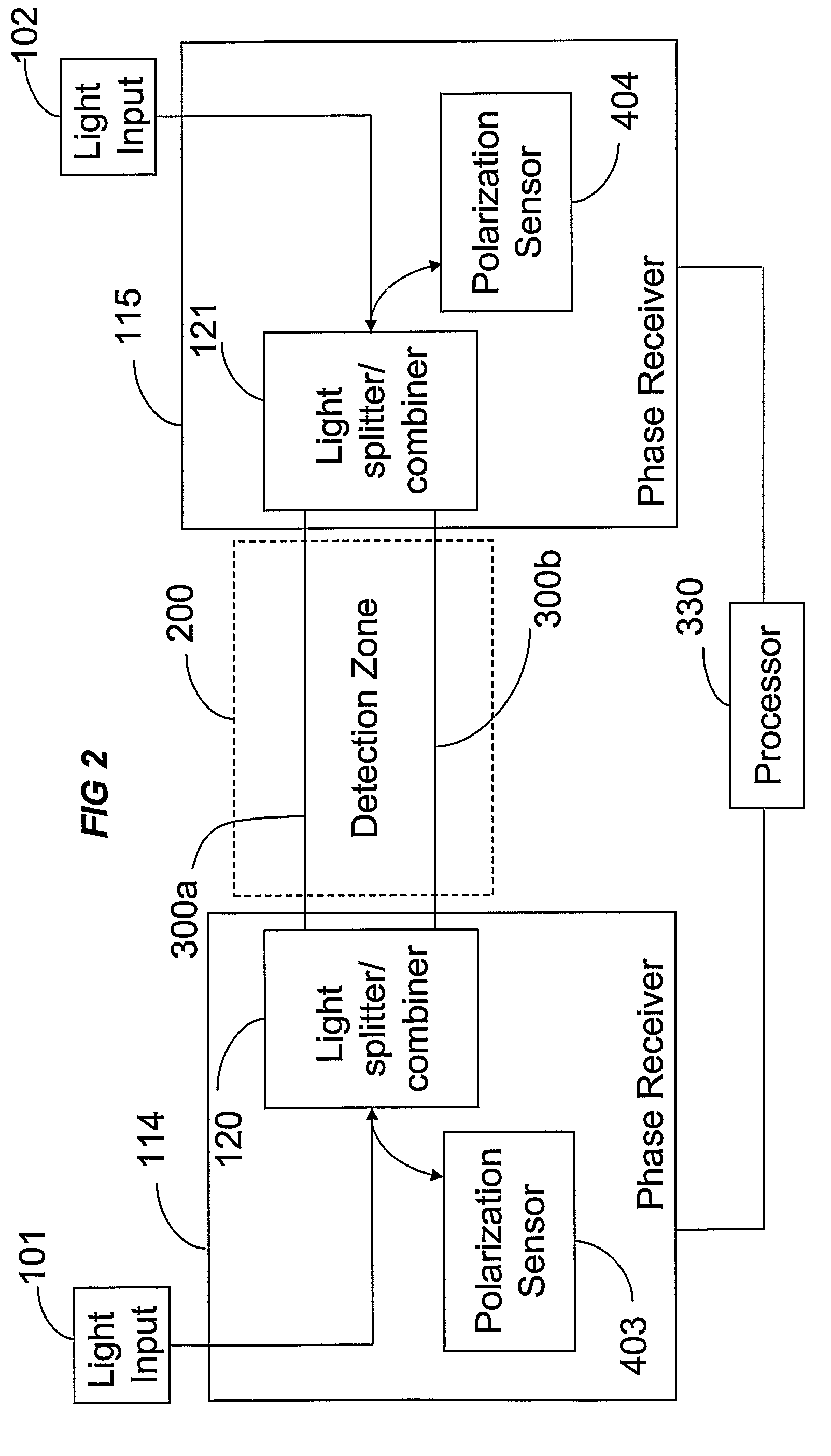
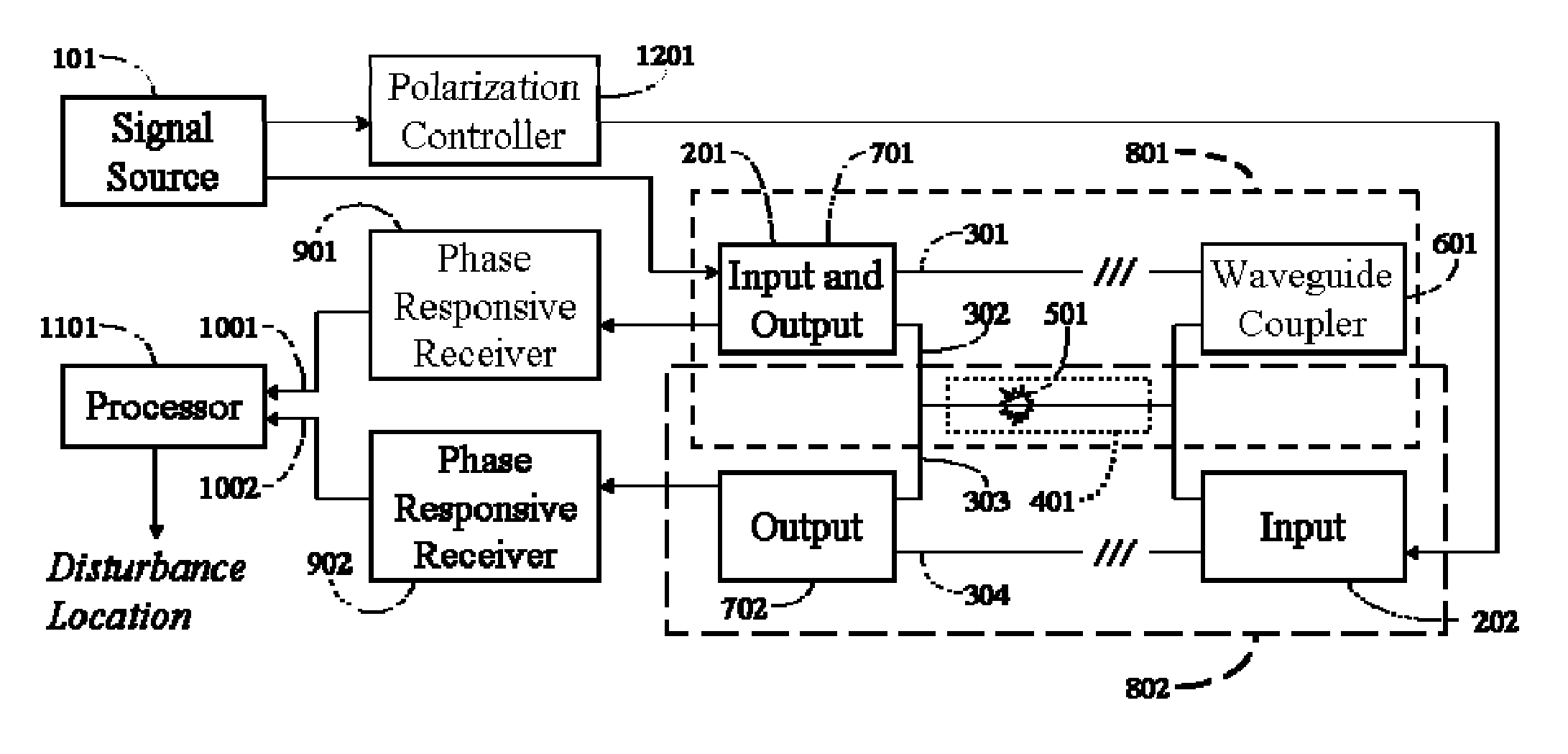
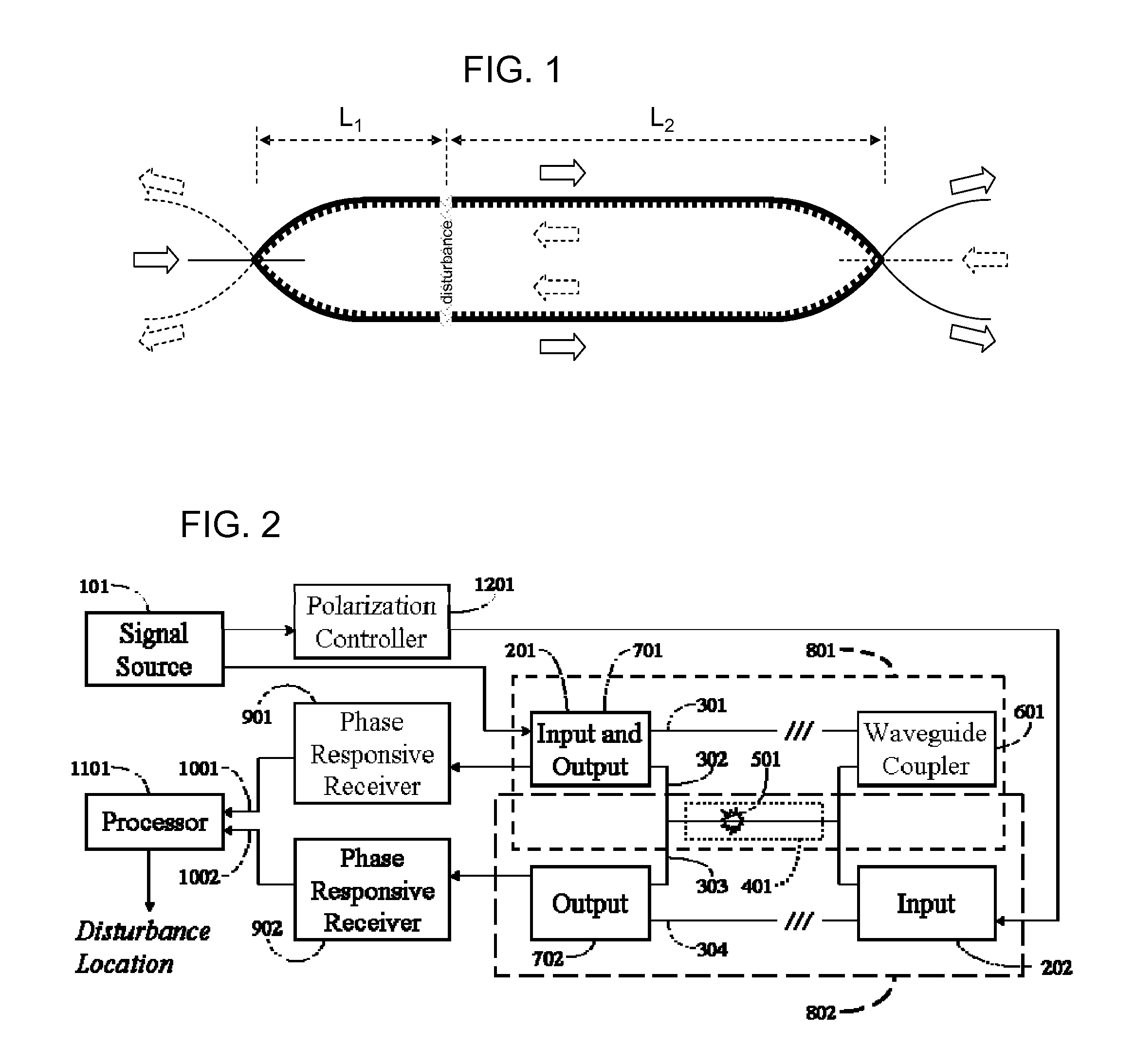
The location of a physical disturbance along an optical waveguide is determined by measuring different propagation times for the resulting phase variation to propagate to phase responsive receivers at ends of bidirectional signal paths. Each receiver can have a coupler that functions as a beam combiner and as a beam splitter inserting the opposite signal. On each receiving end, the coupler provides one or more detectors with signals from which phase related independent variable values are taken, processed and mapped to phase angles. Relative phase angle versus time is derived for each opposite signal pair and correlated at a time difference, i.e., a difference in propagation time from which the location of the disturbance is resolved. Polarization sensitive and polarization insensitive examples are discussed with various optical fiber arrangements.
Owner:OPTELLIOS
Phase responsive optical fiber sensor
The location of a physical disturbance along an optical waveguide is determined by measuring different propagation times for the resulting phase variation to propagate to phase responsive receivers at ends of bidirectional signal paths. Each receiver can have a coupler that functions as a beam combiner and as a beam splitter inserting the opposite signal. On each receiving end, the coupler provides one or more detectors with signals from which phase related independent variable values are taken, processed and mapped to phase angles. Relative phase angle versus time is derived for each opposite signal pair and correlated at a time difference, i.e., a difference in propagation time from which the location of the disturbance is resolved. Polarization sensitive and polarization insensitive examples are discussed with various optical fiber arrangements.
Owner:OPTELLIOS
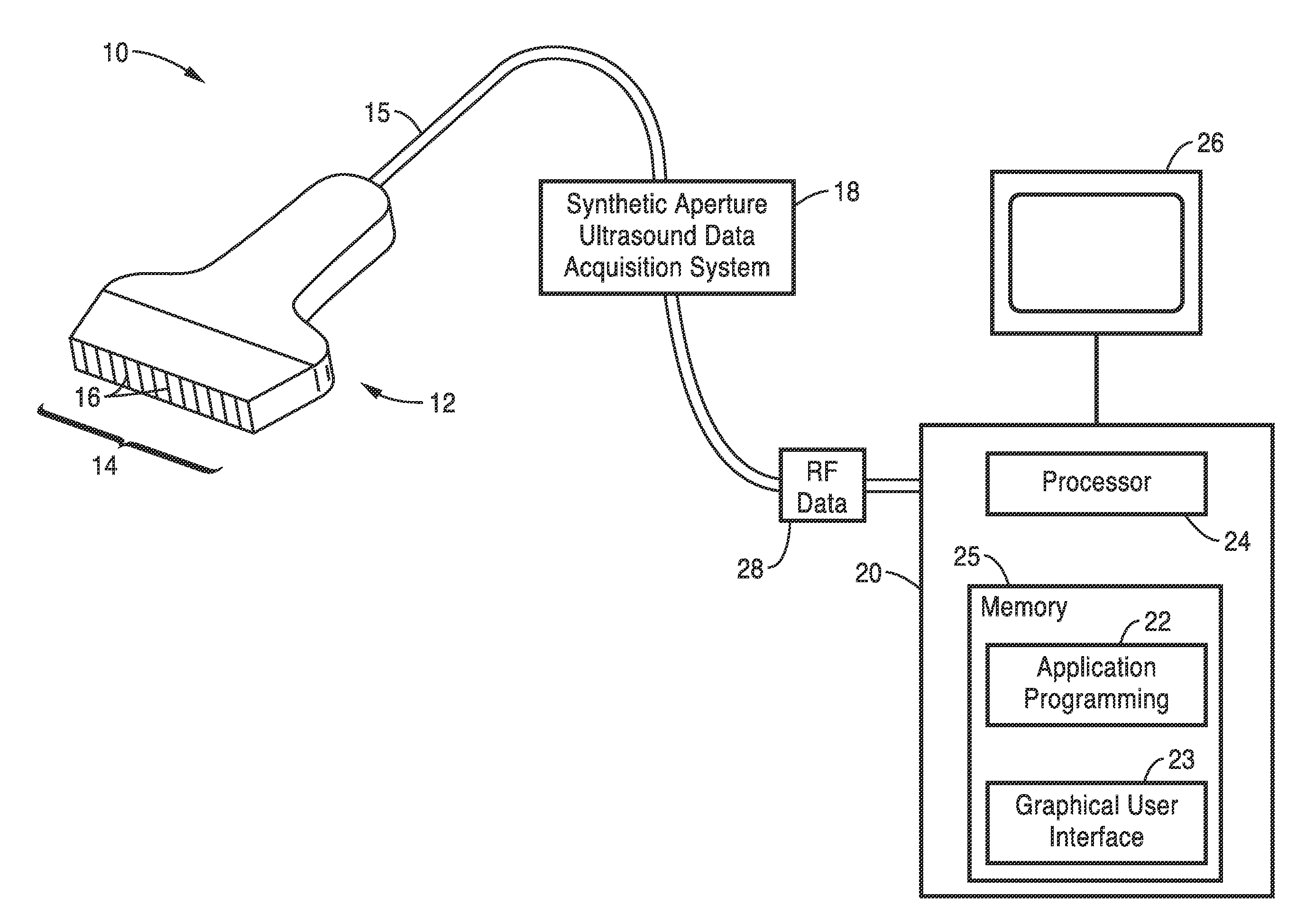
Time reversal and phase coherent music techniques for super-resolution ultrasound imaging
ActiveUS20140364733A1Accurate scatterer localizationHigher-resolution ultrasound imageOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsPhase responseSonification
Systems and methods for super-resolution ultrasound imaging using a windowed and generalized TR-MUSIC algorithm that divides the imaging region into overlapping sub-regions and applies the TR-MUSIC algorithm to the windowed backscattered ultrasound signals corresponding to each sub-region. The algorithm is also structured to account for the ultrasound attenuation in the medium and the finite-size effects of ultrasound transducer elements. A modified TR-MUSIC imaging algorithm is used to account for ultrasound scattering from both density and compressibility contrasts. The phase response of ultrasound transducer elements is accounted for in a PC-MUSIC system.
Owner:TRIAD NAT SECURITY LLC
Array microphone apparatus for generating a beam forming signal and beam forming method thereof
Embodiments described in the present disclosure relate to an array microphone apparatus for generating a beam forming signal. The apparatus includes first, second, and third omni-directional microphones, each converting an audible signal into a corresponding electrical signal. The three microphones are arranged in a horizontal coplanar alignment, and the second microphone is disposed between the other two microphones. The apparatus includes a first directional microphone forming device to jointly output a first directional microphone signal with a first bi-directional pattern, and a magnitude and phase response handler device to output a second directional microphone signal with an omni-directional pattern shifted by a prefixed value with respect to first directional microphone signal. The apparatus further includes a combining device receiving the first and second directional microphone signals and outputting a combined directional microphone signal with a combined beam pattern correlated to the first bi-directional and second omni-directional patterns, the combined directional microphone signal being perpendicular to the horizontal coplanar alignment of the first, second, and third omn-directional microphones.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
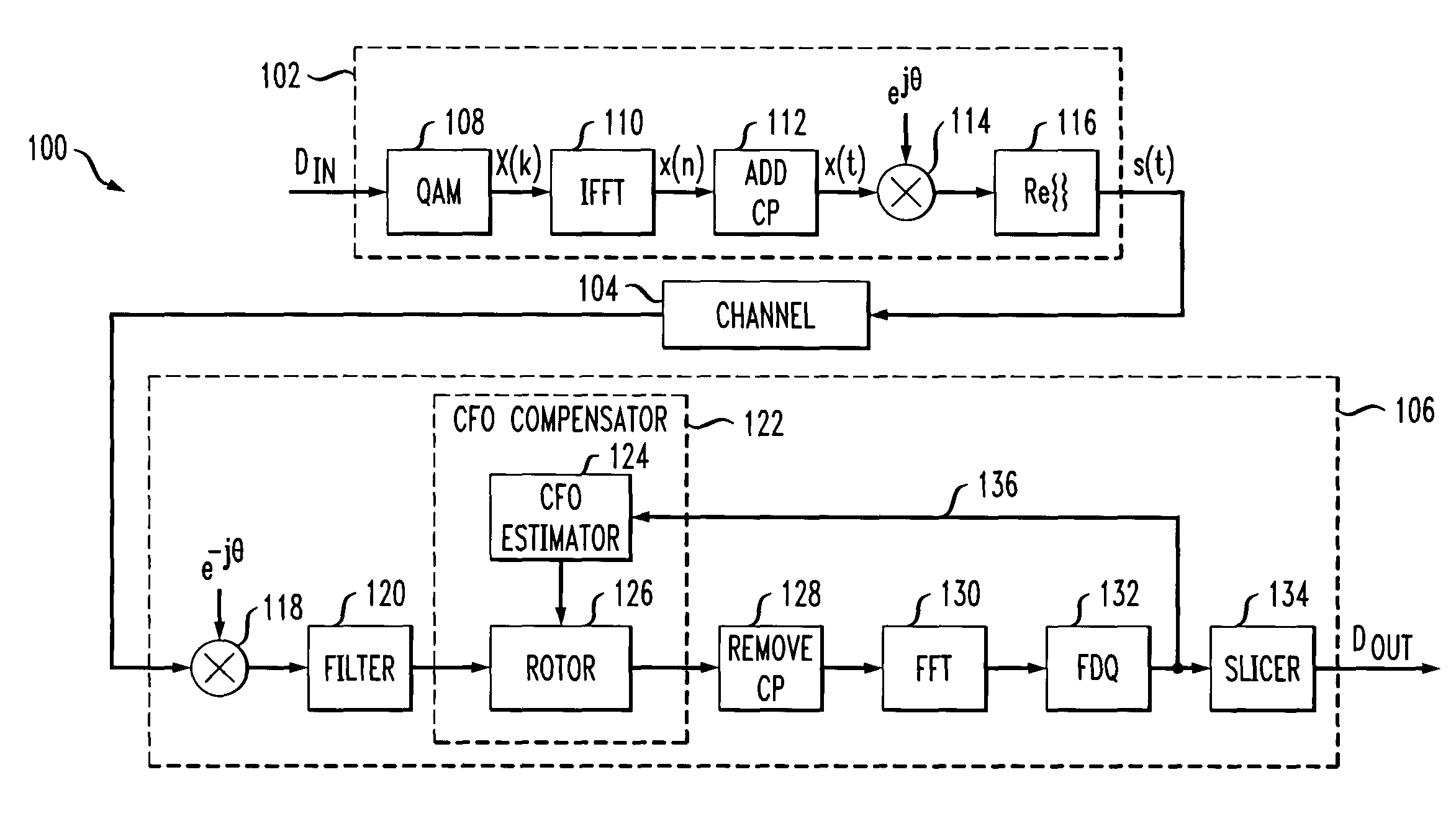
Carrier frequency offset estimation in a wireless communication system
InactiveUS7039131B2Easy to optimizeImprove performanceAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsSecret communicationCommunications systemPhase response
An OFDM receiver includes a demodulator for receiving a passband signal having multiple symbols, one or more of the symbols being a reference symbol, and for converting the passband signal to a baseband signal, a CFO compensation circuit for receiving the baseband signal and modifying a phase of the baseband signal in response to a first control signal, a transformation circuit for translating the baseband signal from the CFO compensation circuit into a frequency domain constellation, an equalizer for receiving the frequency domain constellation and modifying the frequency domain constellation based at least in part on the reference symbol, and a CFO estimation circuit coupled between an output of the equalizer and the CFO compensation circuit in a feedback configuration. The CFO estimation circuit is capable of measuring a difference in phase error between multiple symbols received from the equalizer and generating the first control signal, which is representative of the measured phase error difference.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Detection and location of boundary intrusion, using composite variables derived from phase measurements
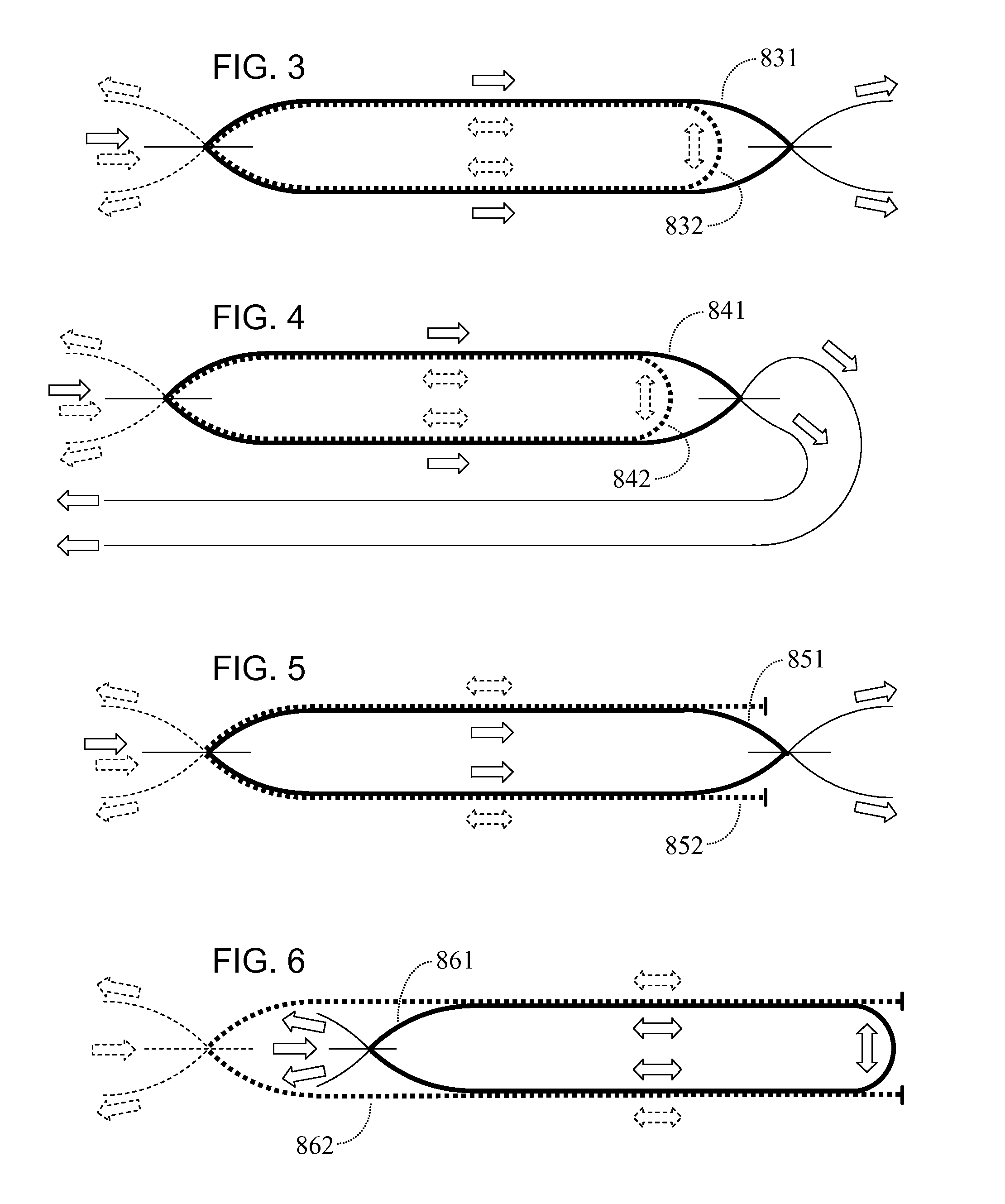
A disturbance, such as vibration from human activity, is located along a fiberoptic waveguide configuration (301-304) with two interferometers (801, 802) of the same or different types, such as Mach-Zehnder, Sagnac, and Michelson interferometers. Carrier signals from a source (101) are split at the interferometer inputs (201, 202) and re-combined at the outputs (701, 702) after propagating through the detection zone (401), where phase variations are induced by the disturbance (501). Phase responsive receivers (901, 902) detect phase relationships (1001, 1002) between the carrier signals over time. A processor (1101) combines the phase relationships into composite signals according to equations that differ for different interferometer configurations, with a time lag between or a ratio of the composite signals representing the location of the disturbance. The detected and composite values are unbounded, permitting phase displacement to exceed the carrier period and allowing disturbances of variable magnitudes to be located.
Owner:OPTELLIOS
High-speed bandpass serial data link
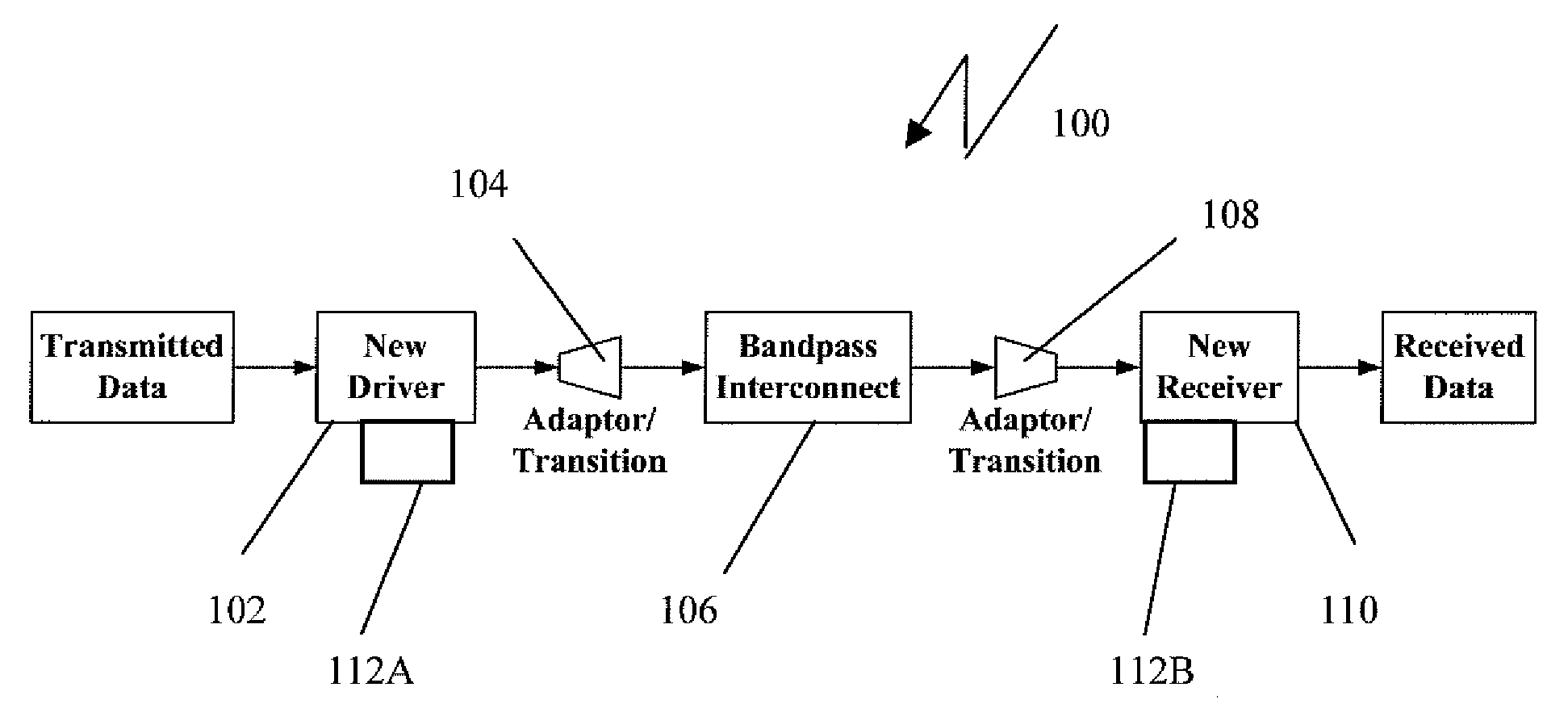
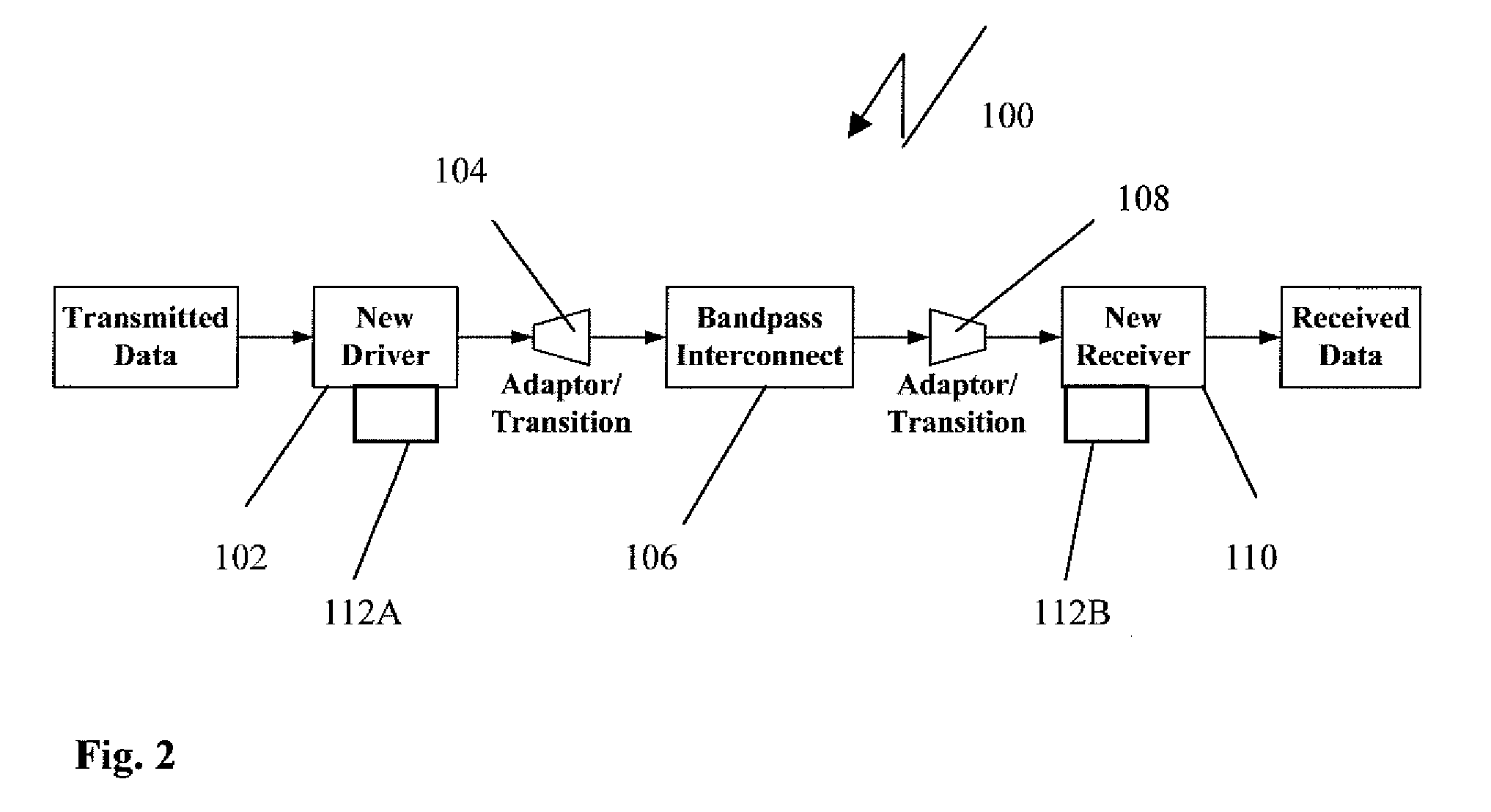
ActiveUS20090220240A1High-speed data communicationMultiple-port networksWavelength-division multiplex systemsPhase responseData signal
The present invention relates to a method and system for high-speed bandpass serial data communication. A driver receives at least one data signal and generates a bandpass data signal for transmission through a bandpass waveguide interconnect. The bandpass data signal is launched into the bandpass waveguide interconnect using a first adaptor and extracted therefrom after transmission using a second adaptor. A receiver connected to the second adaptor recovers the at least one data signal from the extracted bandpass data signal. A dispersion compensation circuit receives one of the at least one data signal and the bandpass data signal and information indicative of a phase response of the bandpass waveguide interconnect and dispersion compensates the one of the at least one data signal and the bandpass data signal by compensating the phase response of the bandpass waveguide interconnect.
Owner:MCGILL UNIV
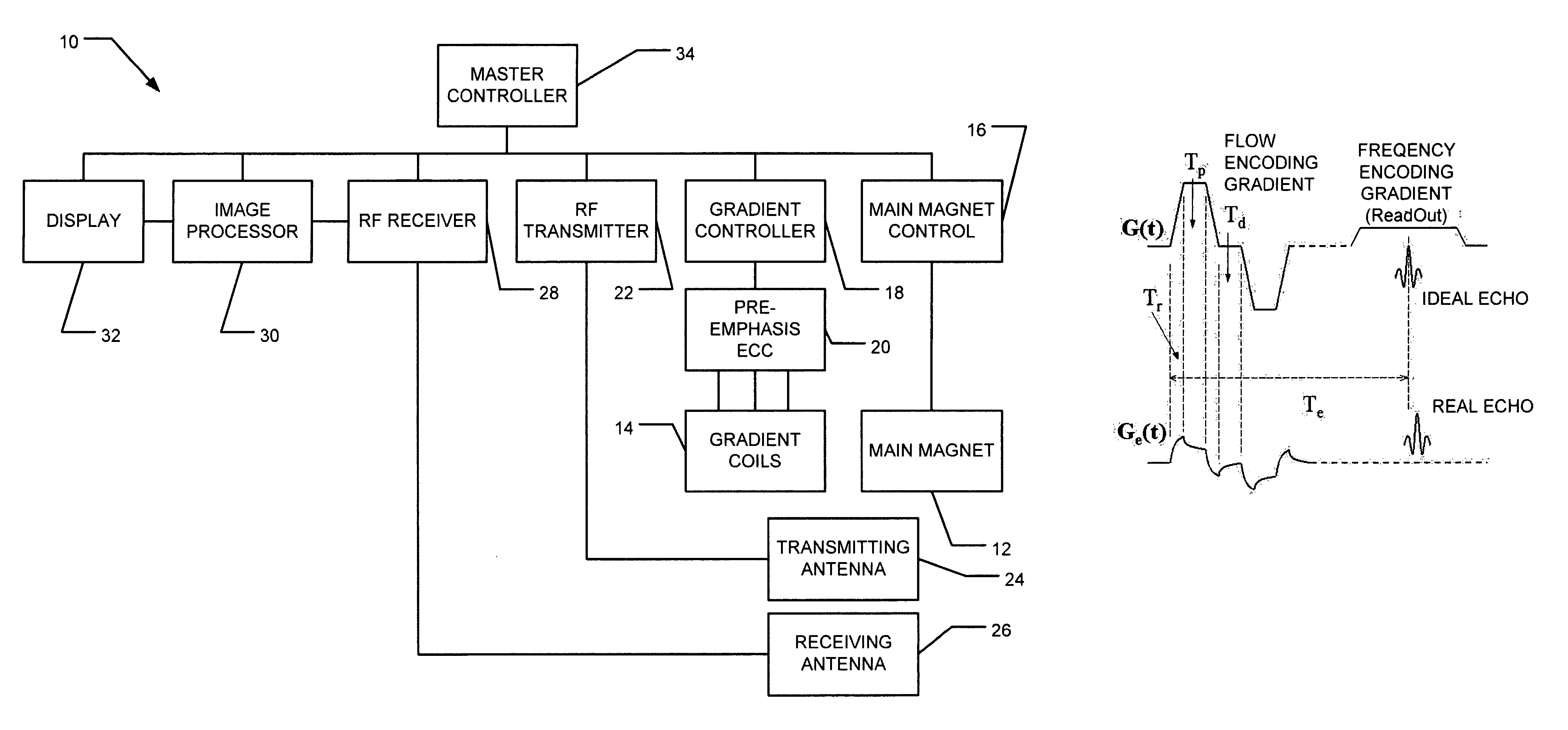
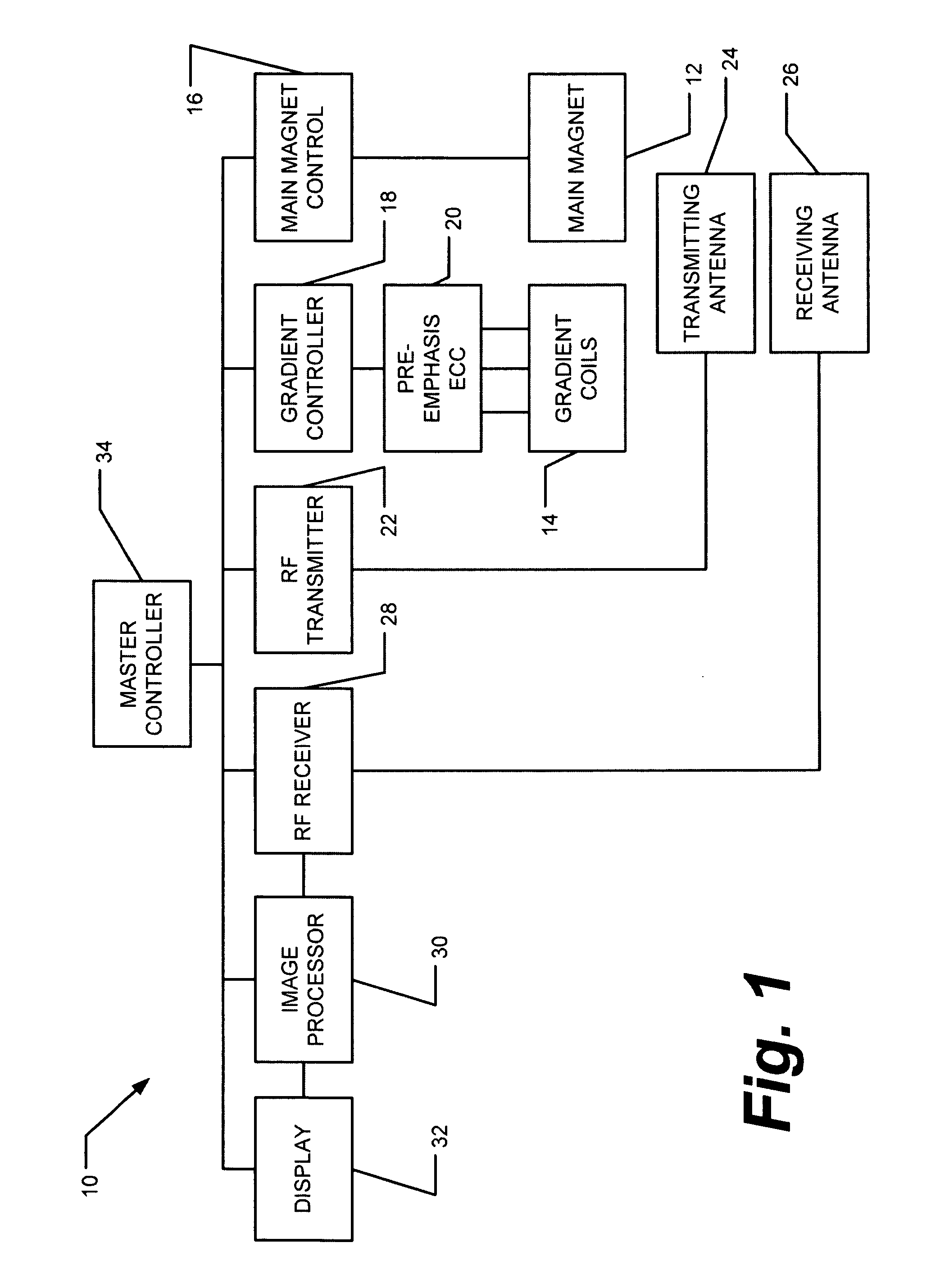
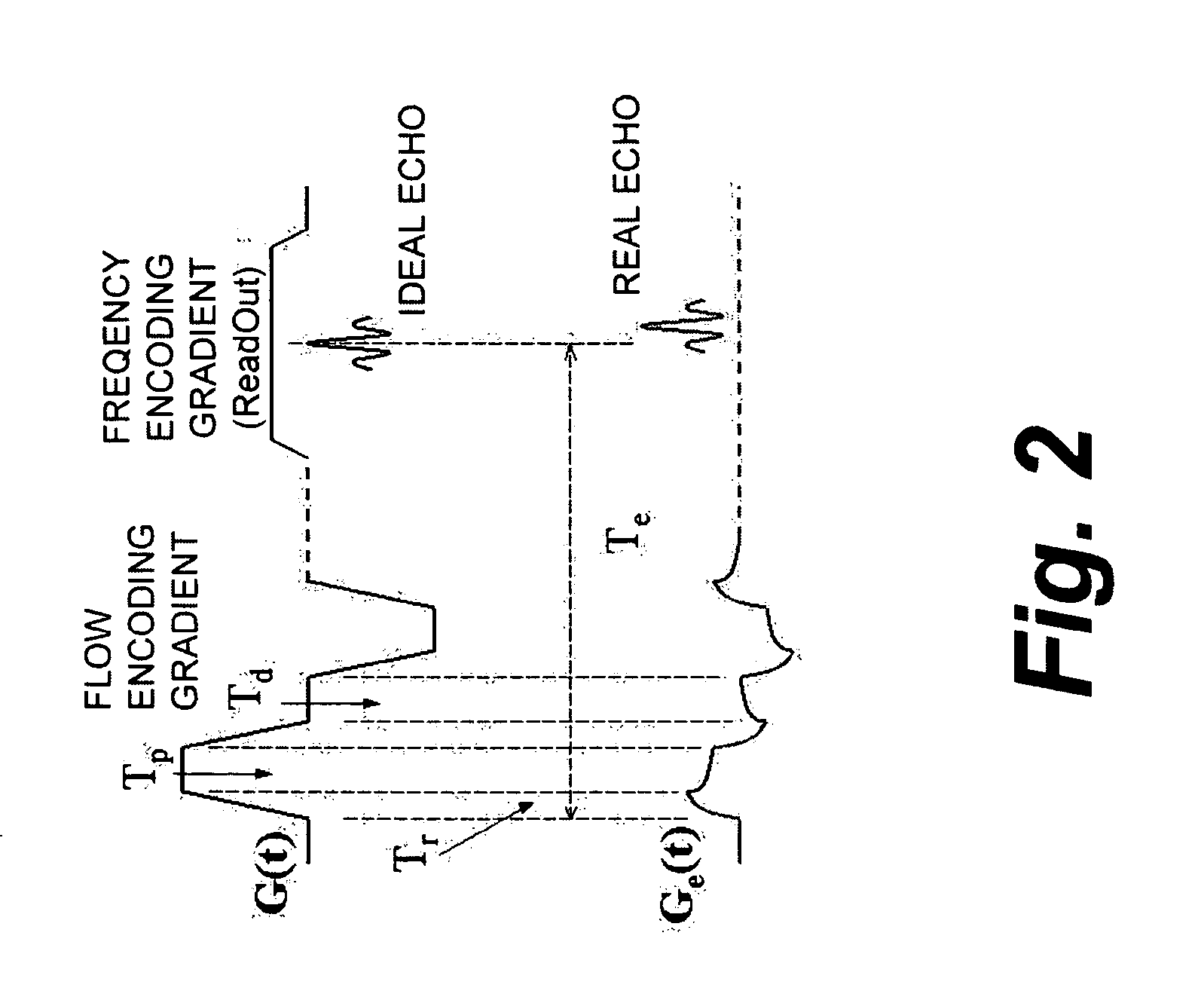
Eddy current measurement and correction in magnetic resonance imaging systems
ActiveUS20060022674A1Easy CalibrationMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionPhase responsePhase difference
Measuring and correcting for eddy currents in a magnetic imaging system includes running a pulse sequence using bipolar gradients to acquire a phase-difference image and a phase response of a static phantom that fills a majority of a field of view (FOV) of the magnetic imaging system, fitting the phase difference image to a two-dimensional second order polynomial, and changing the pulse sequence to provide a different delay. The method further includes iterating the running a pulse sequence and fitting the phase difference image and phase response with different delays to determine coefficients of the second order polynomial and a time constant of the phase response. The method also includes correcting a pre-emphasis system of the magnetic imaging system in accordance with the time constant of the phase response, determining an amplitude of correction to reduce the determined coefficients, and storing the determined corrections in the pre-emphasis system.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Optical channel selector
InactiveUS6580534B2Multiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsCommunications systemPhase response
A channel selector which selects one or more channels from input multi-channel optical signals for routing to predetermined destinations within an optical communication system is disclosed. The channel selector selects one or more channels by first splitting portions of the input multi-channel optical signals across two or more optical paths. Thereafter, a desired phase response is applied to the split portions of the multi-channel optical signals. The desired phase response is applied to the split portions of the multi-channel optical signals so the channels therein interfere with each other either constructively or destructively when the split portions of the multi-channel optical signals are combined. The channel selector has a structure which includes a plurality of input ports, a plurality of output ports, a splitter, a combiner, one or more all-pass optical filters, and a plurality of optical paths.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC +1
3D electromagnetic fast inversion method of minimized target
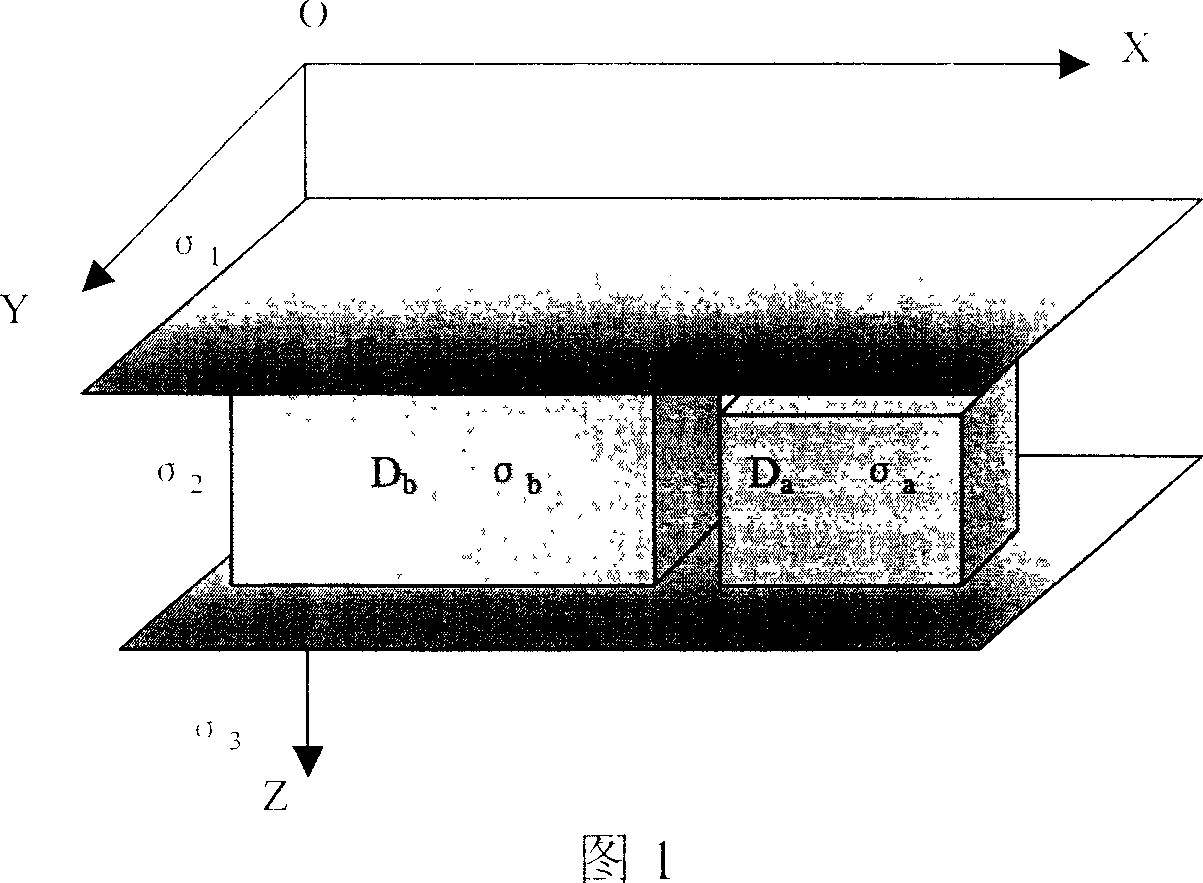
ActiveCN101004454AInversion target is smallFast 3D InversionElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingAcoustic wave reradiationPhase responseData treatment
A 3-D electromagnetic fast inversing method of object minimization includes confirming known object region according to known geologic data, setting up background conductivity combination according to known conductivity parameter and 3-D interpolation, calculating background field of said combination, inversing unknown region as per requirement of production, obtaining general field, carrying out 3-D interpolation on phase curve and actually measured conductivity curve, inversing frequency and fitting inversed frequency to obtain underground conductivity set of object.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
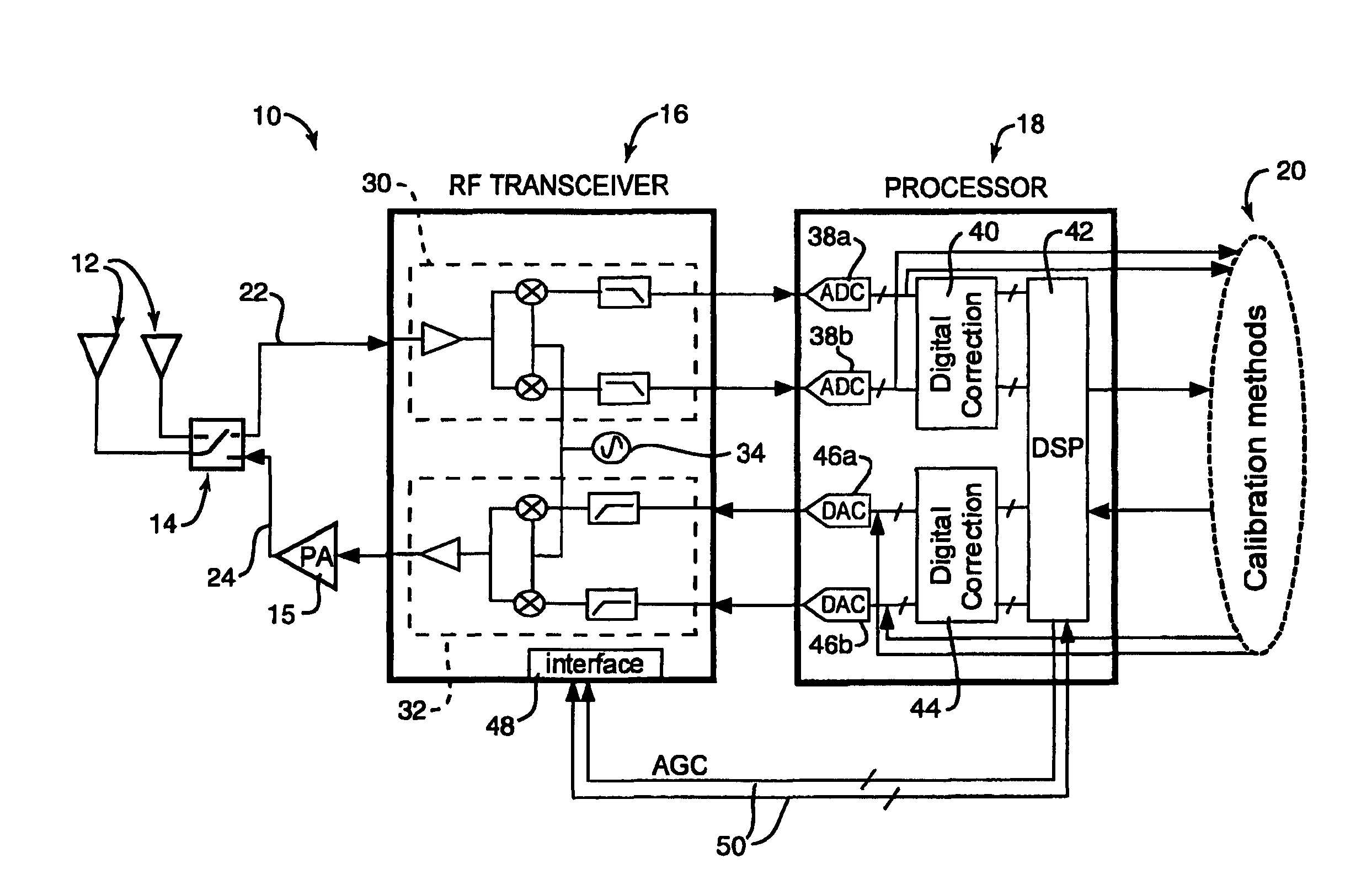
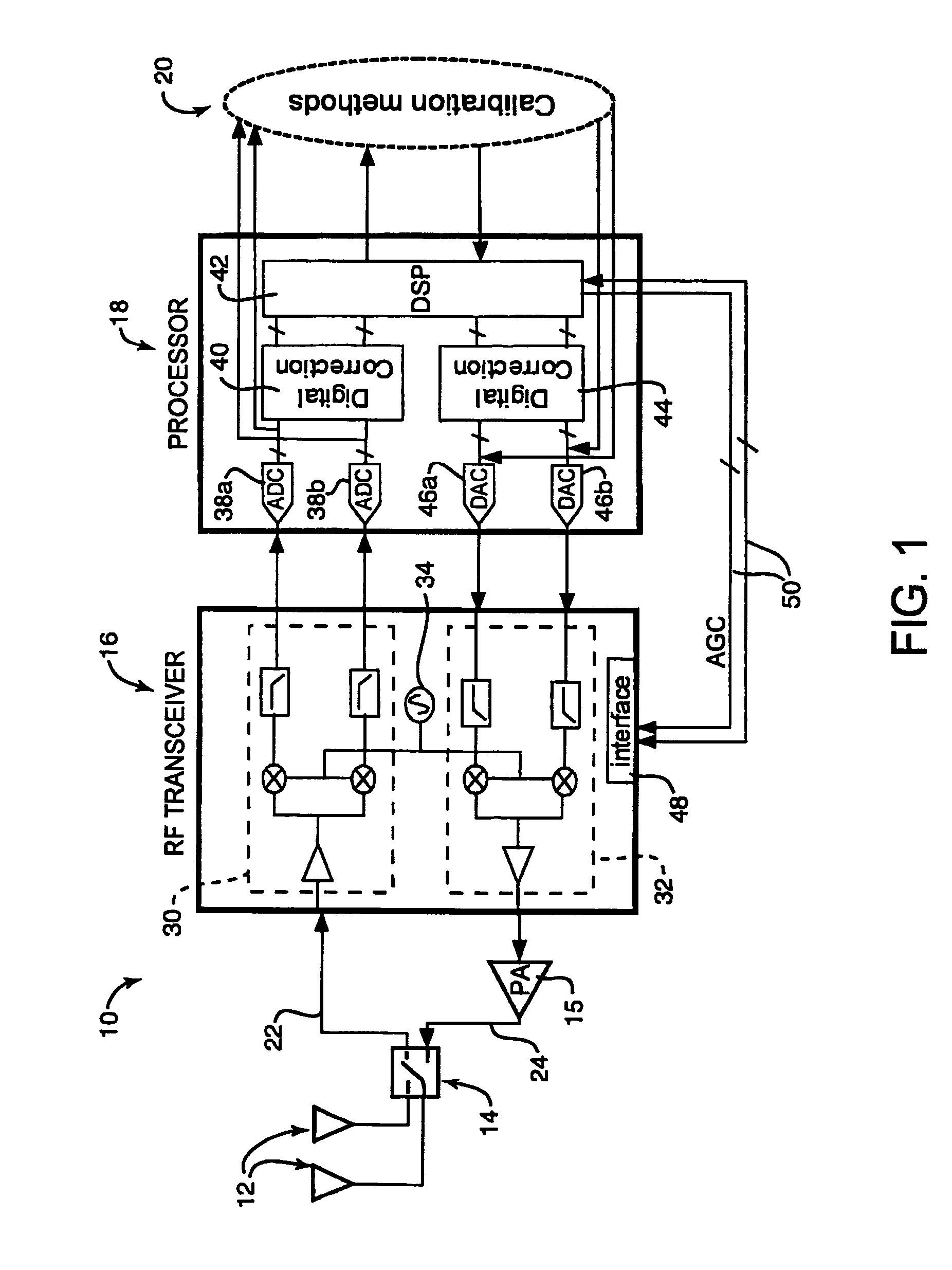
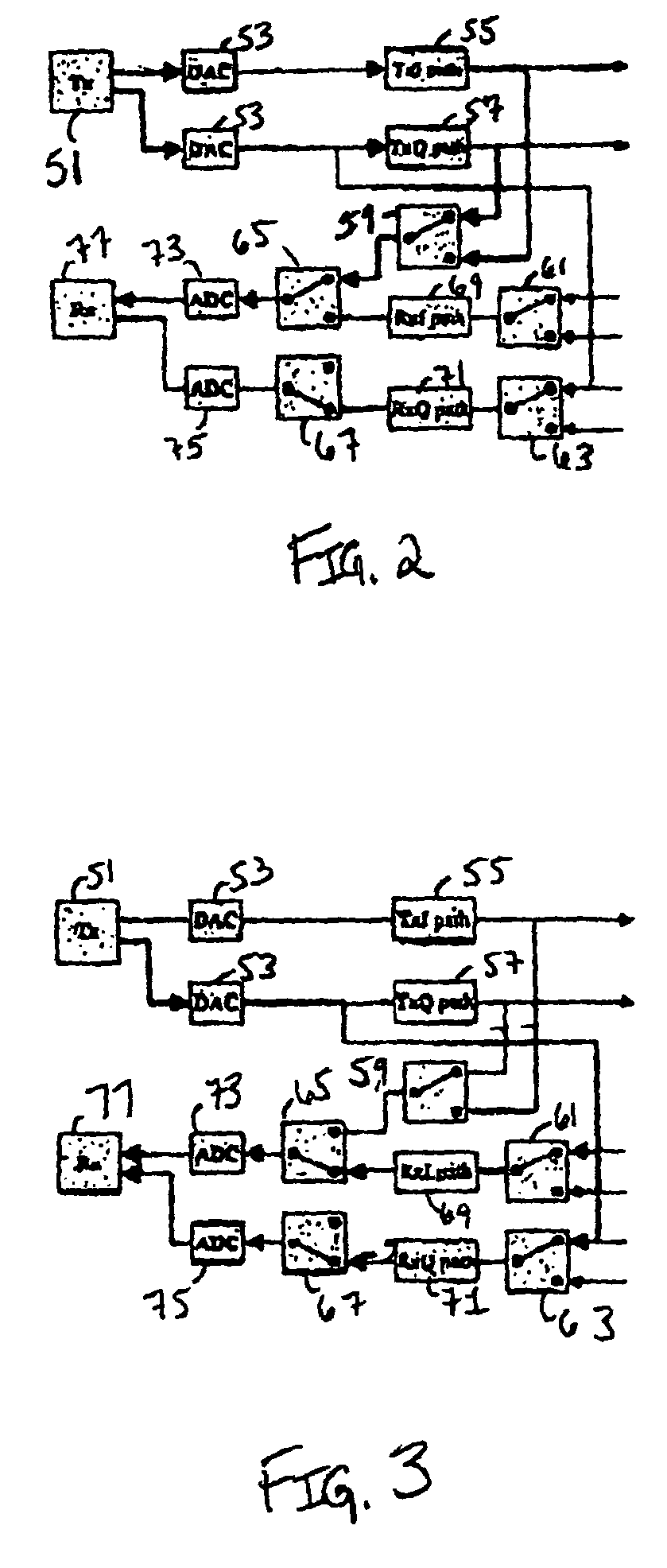
Method and system for measuring IQ path mismatch
Aspects for measuring IQ path mismatch in signal modulation are described. The aspects include estimating a transmitter IQ mismatch in a form of gain and phase response for transmitter I and Q paths sharing a receiver path, and estimating a receiver IQ mismatch in a form of gain and phase response for receiver I and Q paths sharing a signal source. Further included is compensating for the difference of the transmitter and receiver I and Q paths using a digital FIR filter. Iterative estimation is utilized for filter tap parameters during the compensating.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Method and apparatus for reducing crosstalk interference in an inline Fabry-Perot sensor array
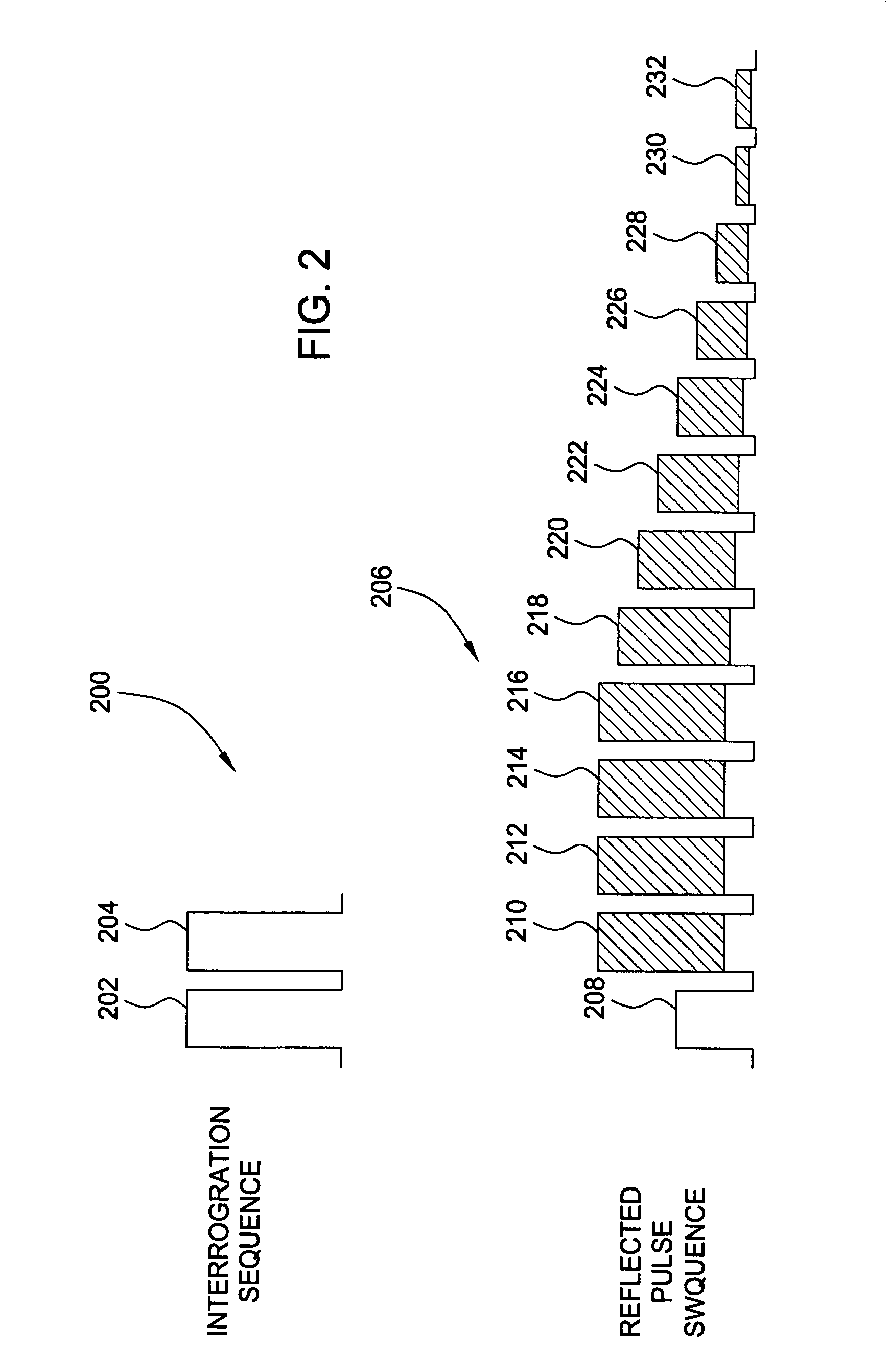
A method and apparatus for reducing crosstalk between sensors in an inline Fabry-Perot (FP) sensor array. The inline FP sensor array comprises a plurality of fiber Bragg gratings arranged periodically along an optical fiber. The sensors are formed between each of the Bragg gratings. A light source provides multiplexed pulses as interrogation pulses for the array. The light pulses are applied to one end of the sensor array and a light detector detects reflected pulses. The detected pulses comprise a composite of reflections from all the Bragg gratings along the fiber. The apparatus processes the detected signals using an inverse scattering algorithm to detect an accurate phase response from each of the Bragg sensors while reducing crosstalk from other Bragg sensors within the array. One form of inverse scattering algorithm is a layer-peeling algorithm.
Owner:WEATHERFORDLAMB +1
Apparatus and Method for Characterization of Acute Otitis Media
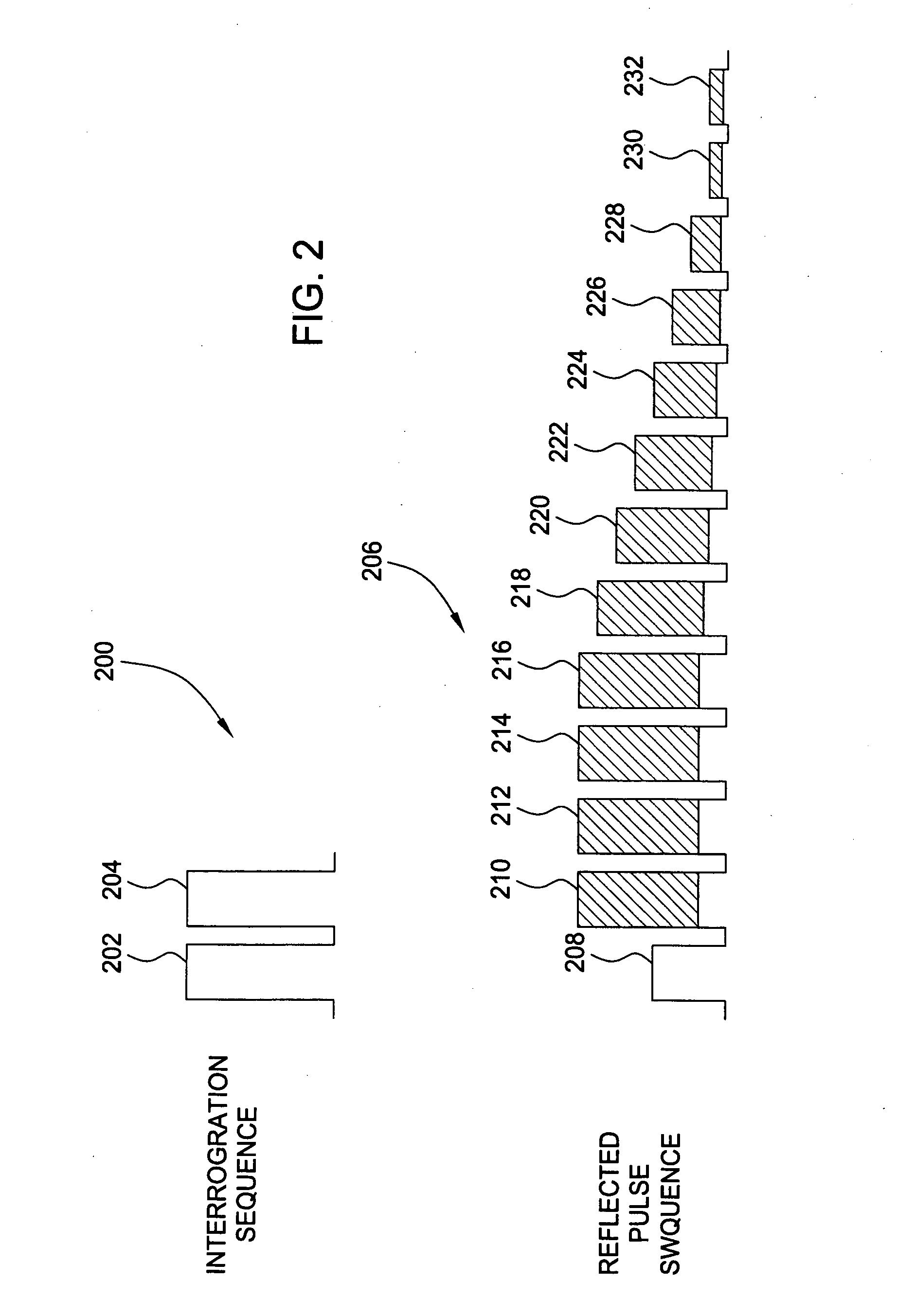
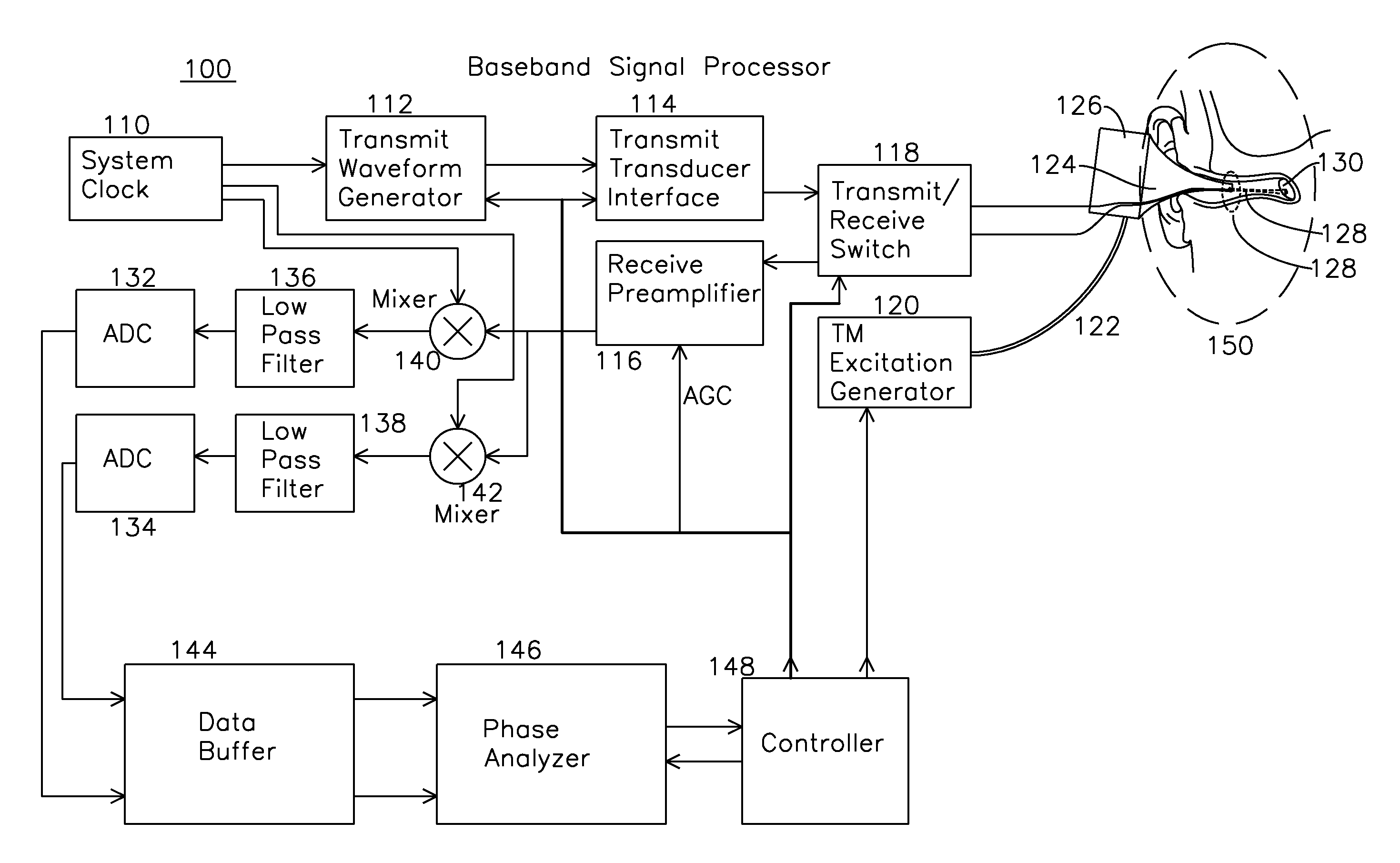
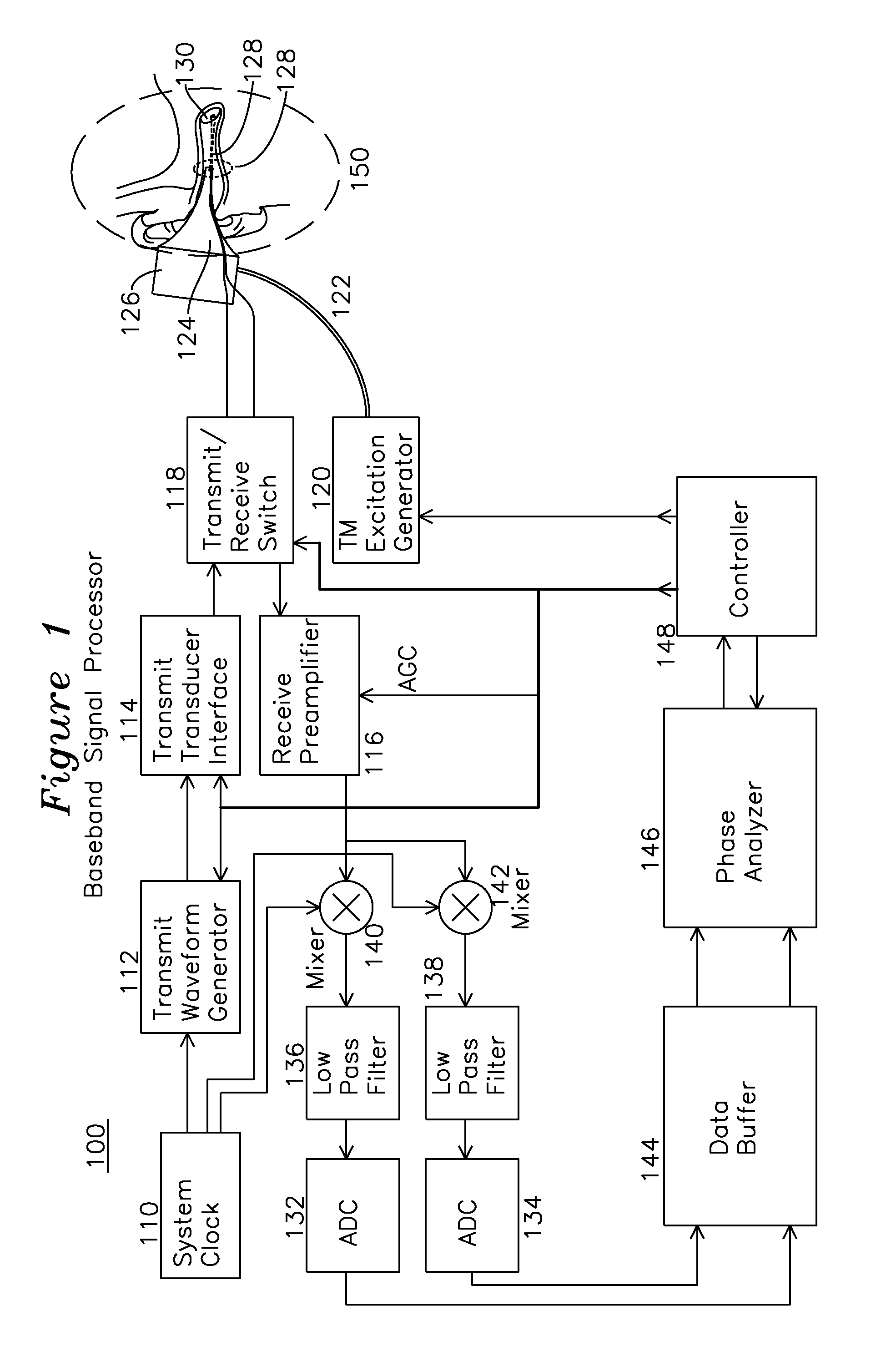
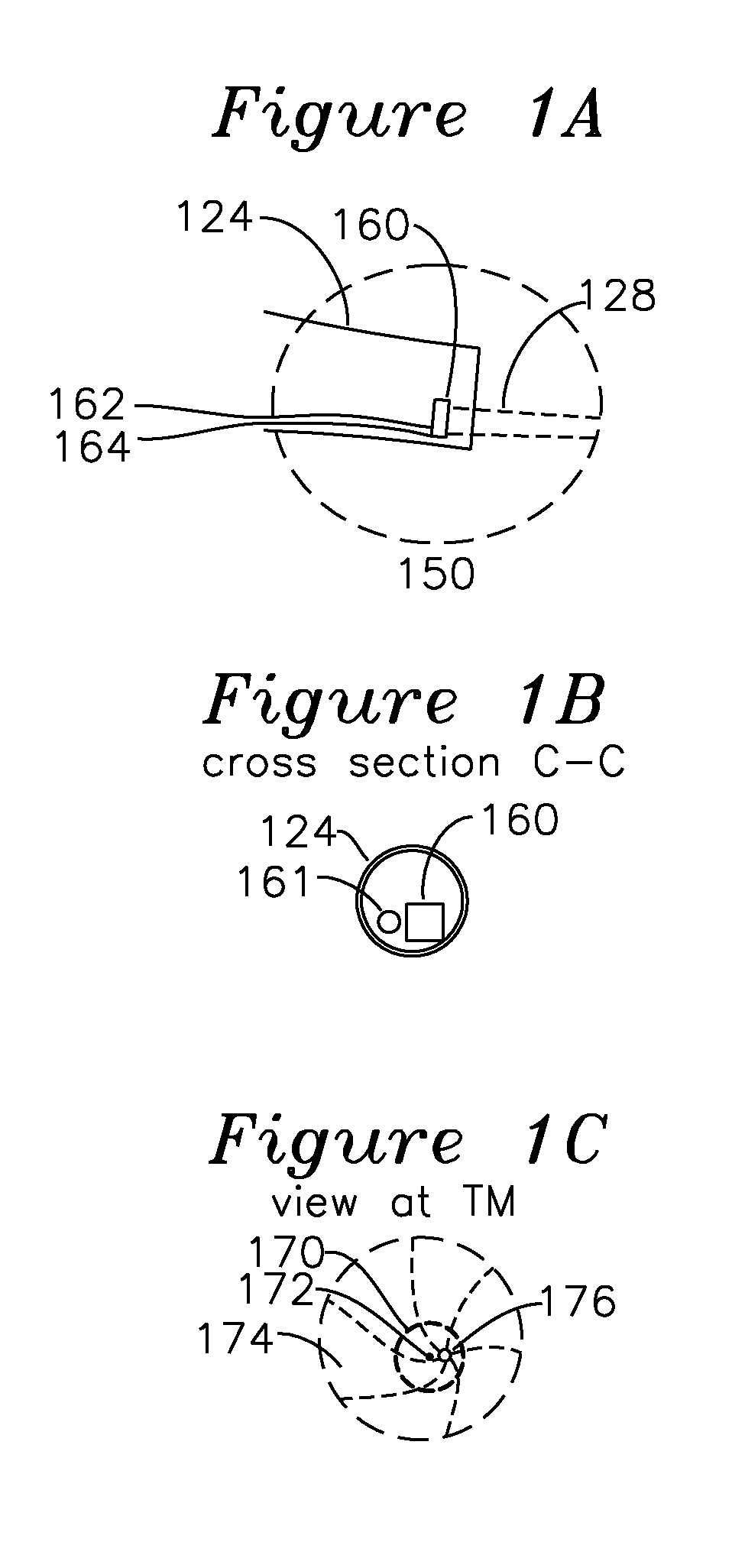
ActiveUS20170014053A1Determine viscosityOrgan movement/changes detectionOtoscopesSonificationPhase response
An ultrasound signal processor uses an excitation generator to cause displacement of a tympanic membrane while a series of ultrasound pulses are applied to the tympanic membrane. Phase differences between a transmitted signal and received signal are examined to determine the movement of the tympanic membrane in response to the applied excitation. An examination of the phase response of the tympanic membrane provides a determination as to whether the fluid type behind the tympanic membrane is one of: no fluid, serum fluid, or purulent fluid.
Owner:OTONEXUS MEDICAL TECHNOLIGIES INC
Continuous-time integrating filter with minimum phase variation, and bandpass sigma delta modulator using such a filter
The disclosure pertains to continuous-time filtering. More particularly, it relates to filtering in a feedback control loop, for example in a sigma-delta (SigmaDelta) modulator. The making of a filter for this type of application comes up against a major problem linked to the relativity between the amplitude and phase responses. This limits the possibilities of choice in order to take steps against the instability of the loop. A continuous-time filter with minimum phase variation carries out the bandpass integration of the signal presented at its input. The making of the continuous-time filter as a bandpass integrator raises the problem of achieving a compromise between gain variations and phase variations close to the -1 critical point, This compromise must lead to the stability of the loop. This problem is resolved by using a continuous-time bandpass integrating filter comprising at least one resonance device with minimum phase variation.
Owner:THALES SA
Array microphone apparatus for generating a beam forming signal and beam forming method thereof
ActiveUS20130051577A1Reduce usageReduce comingMicrophonesSignal processingPhase responseBeam pattern
Embodiments described in the present disclosure relate to an array microphone apparatus for generating a beam forming signal. The apparatus includes first, second, and third omni-directional microphones, each converting an audible signal into a corresponding electrical signal. The second omni-directional microphone is disposed between the other two omni-directional microphones. The apparatus includes a first directional microphone forming device to jointly output a first directional microphone signal with a first bi-directional pattern, and a magnitude and phase response handler device to output a second directional microphone signal with an omni-directional pattern shifted by a prefixed value with respect to first directional microphone signal. The apparatus further includes a combining device receiving the first and second directional microphone signals and outputting a combined directional microphone signal with a combined beam pattern correlated to the first bi-directional and second omni-directional patterns, the combined directional microphone signal being in a broadside configuration.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
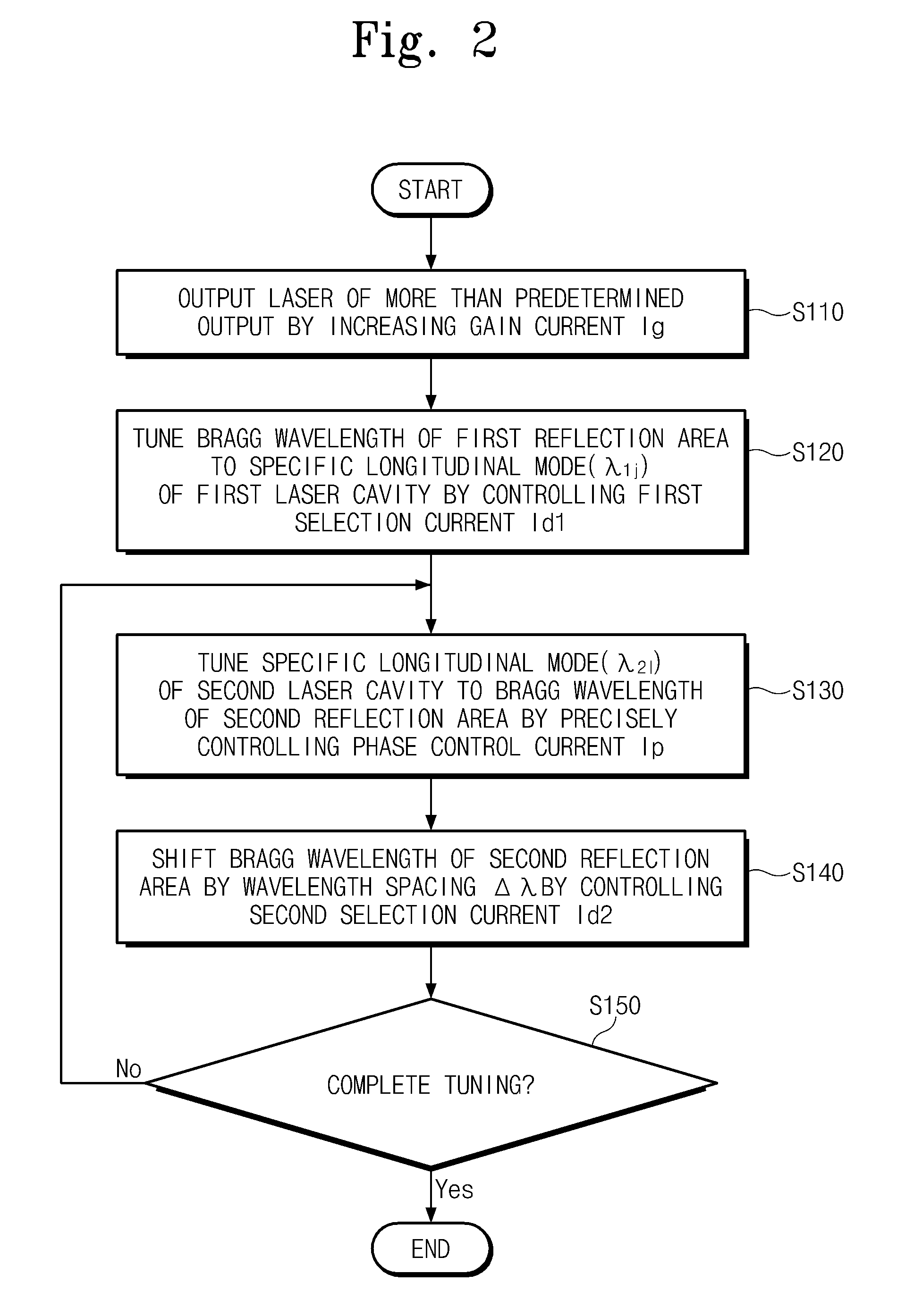
Semiconductor laser device
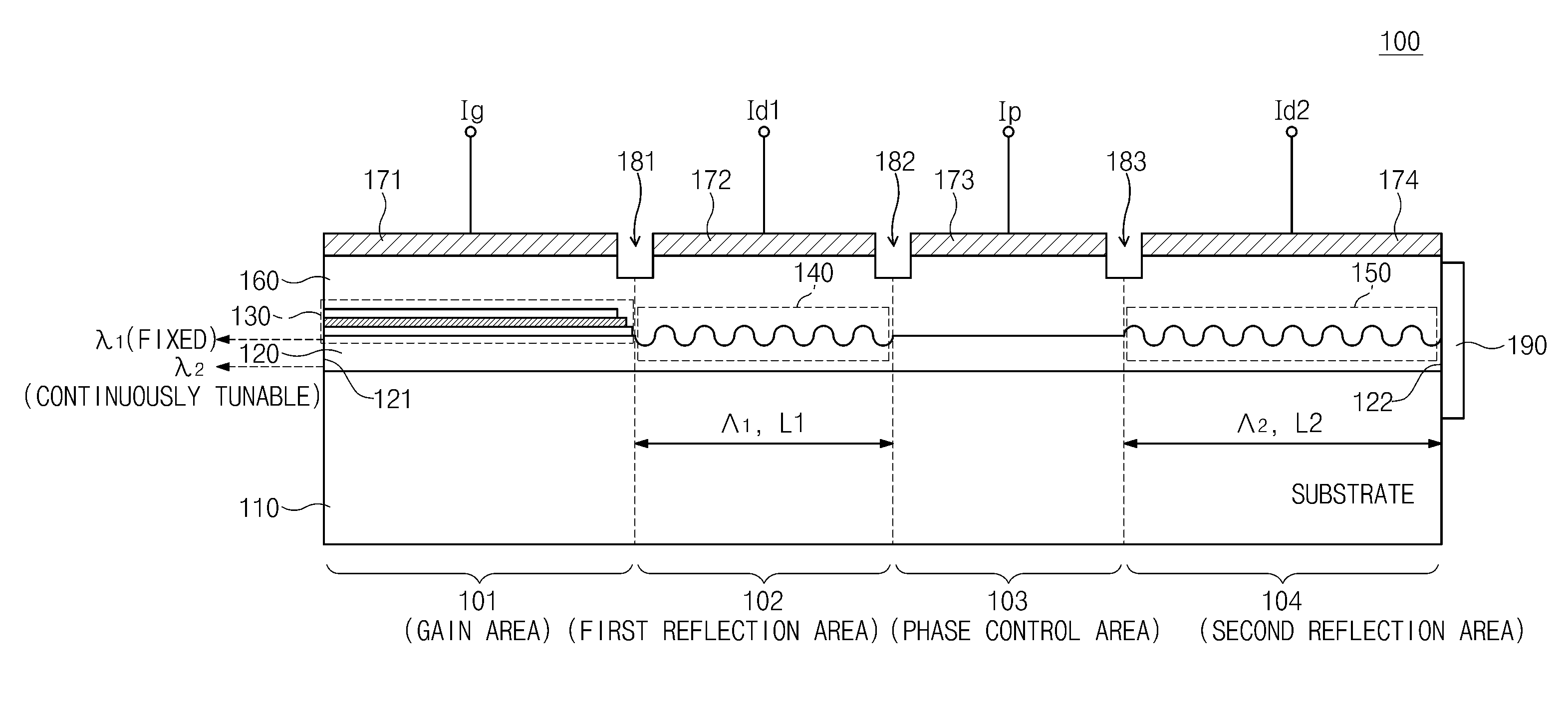
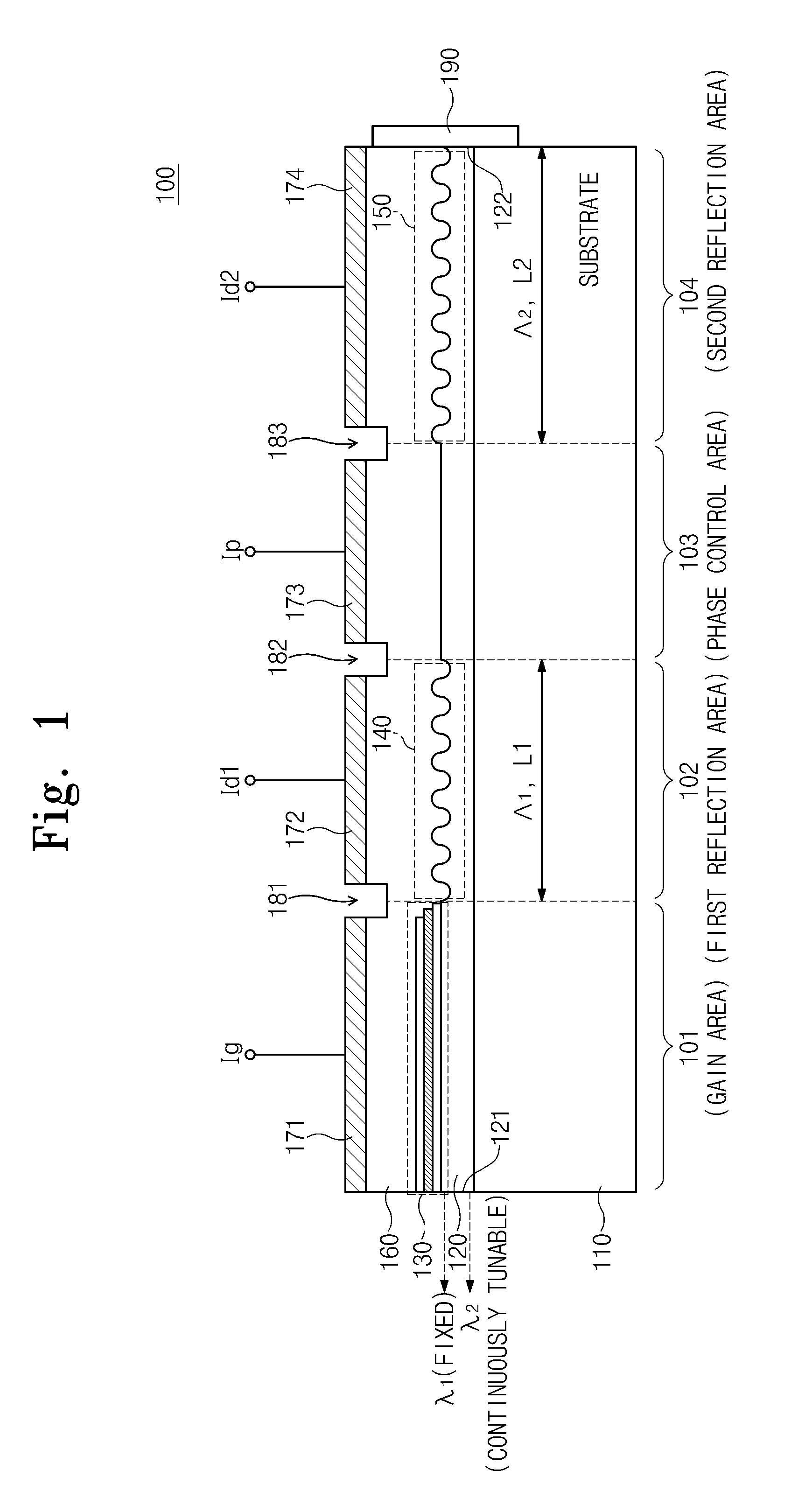
Provided is a semiconductor laser device including: a gain area where multi-wavelength lights are generated and gain are provided; a first reflection area where among the multi-wavelength lights, a first-wavelength light is reflected to the gain area in response to a first selection signal; a second reflection area where among the multi-wavelength lights, a second-wavelength light is reflected to the gain area; and a phase control area where a phase of the second-wavelength light is shifted in response to a phase control signal, the phase control area being disposed between the first reflection layer and the second reflection layer.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
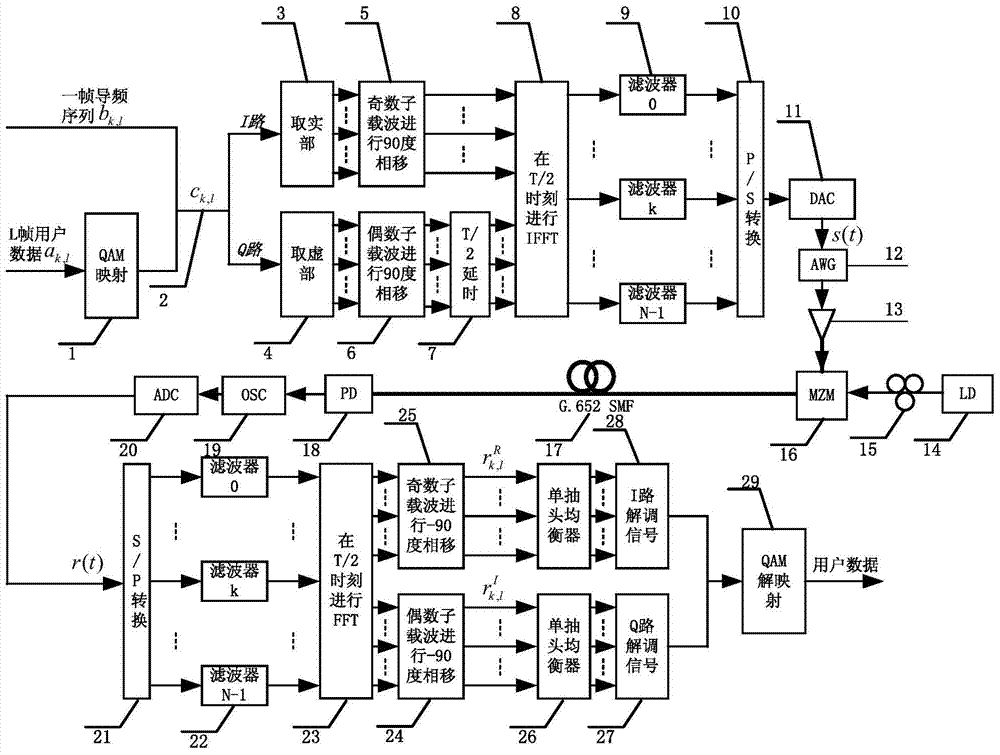
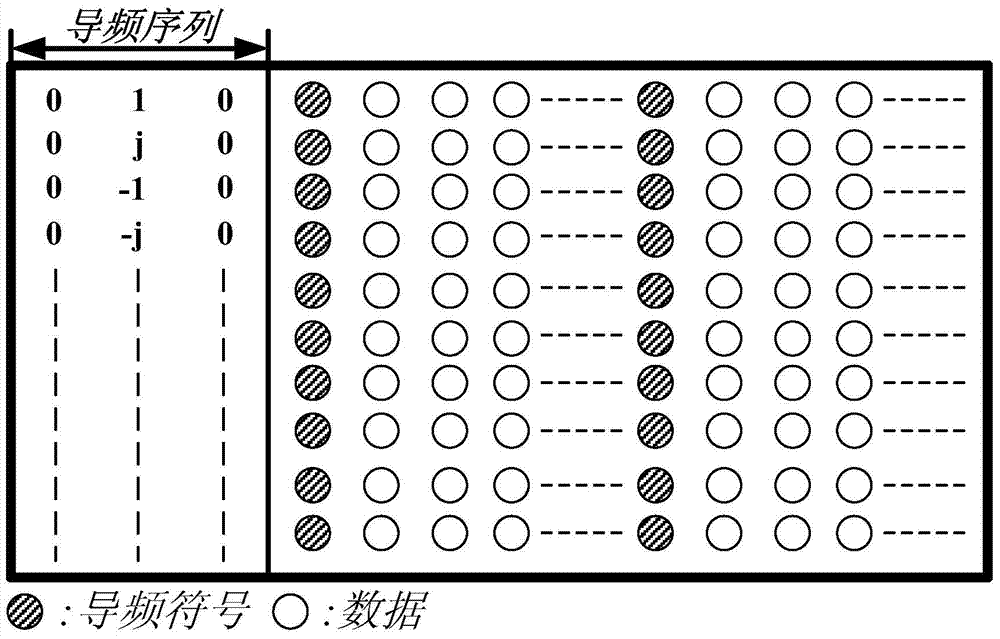
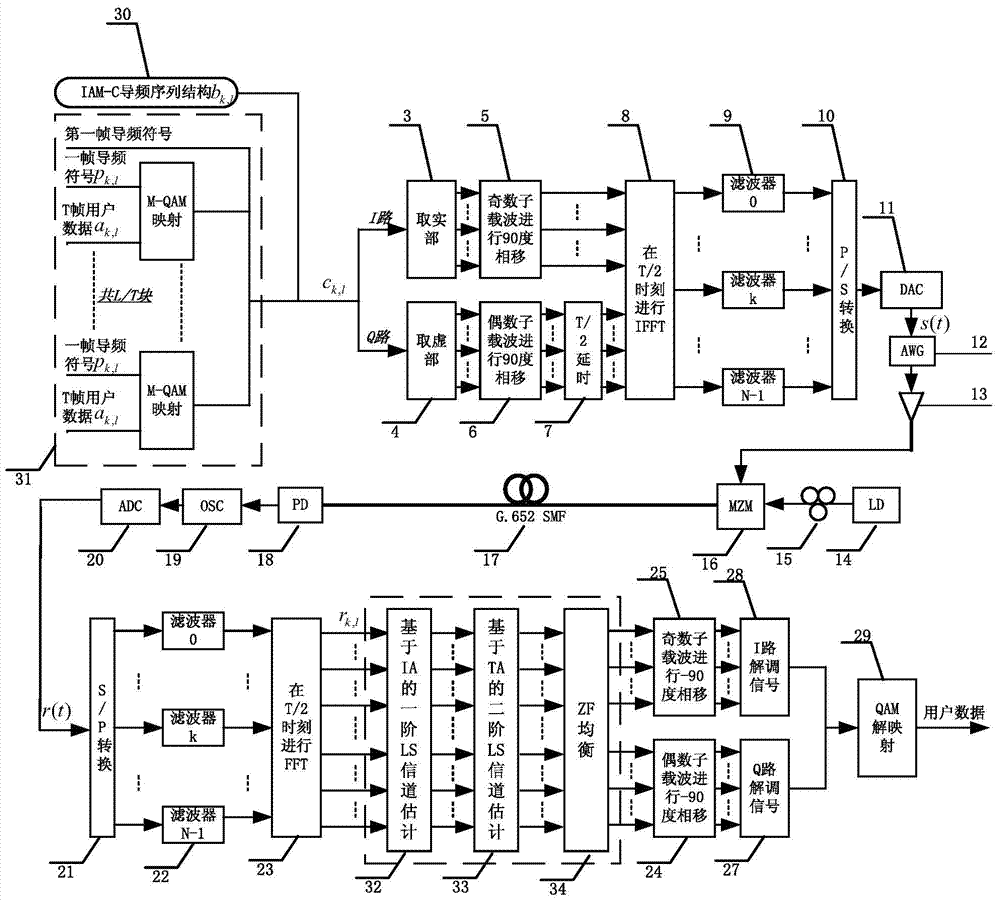
Channel estimation method for improving receiving sensitivity of OQAM (Offset Quadrate Amplitude Modulation)-OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing) light transmission system
InactiveCN104506467AAccurate estimateEliminate distractionsBaseband system detailsMulti-frequency code systemsTime domainPhase response
The invention provides a channel estimation method for improving receiving sensitivity of an OQAM (Offset Quadrate Amplitude Modulation)-OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing) light transmission system, and aims at solving the problems that the traditional channel estimation algorithm for the light OQAM-OFDM cannot treat intersymbol interference and inter-subcarrier interference caused by the orthogonal damage of a subcarriers, and the decrease of the receiving sensitivity of the system caused by the accompanying gaussian noise and the like produced by devices in the system is ignored. The channel estimation method has the advantages that the interference approximating utilization based time-domain averaging channel estimation method (IATA-CE) comprising the steps of first-order LS channel estimation, second-order LS channel estimation and ZF balancing is performed during receiving to accurately estimate complex gain and phase response of a fiber channel; in addition, the interference from gaussian noise produced by the devices in the system can be resisted well; therefore, accurate channel estimation coefficients can be obtained, and as a result, the BER performance and receiving sensitivity of the system can be improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com