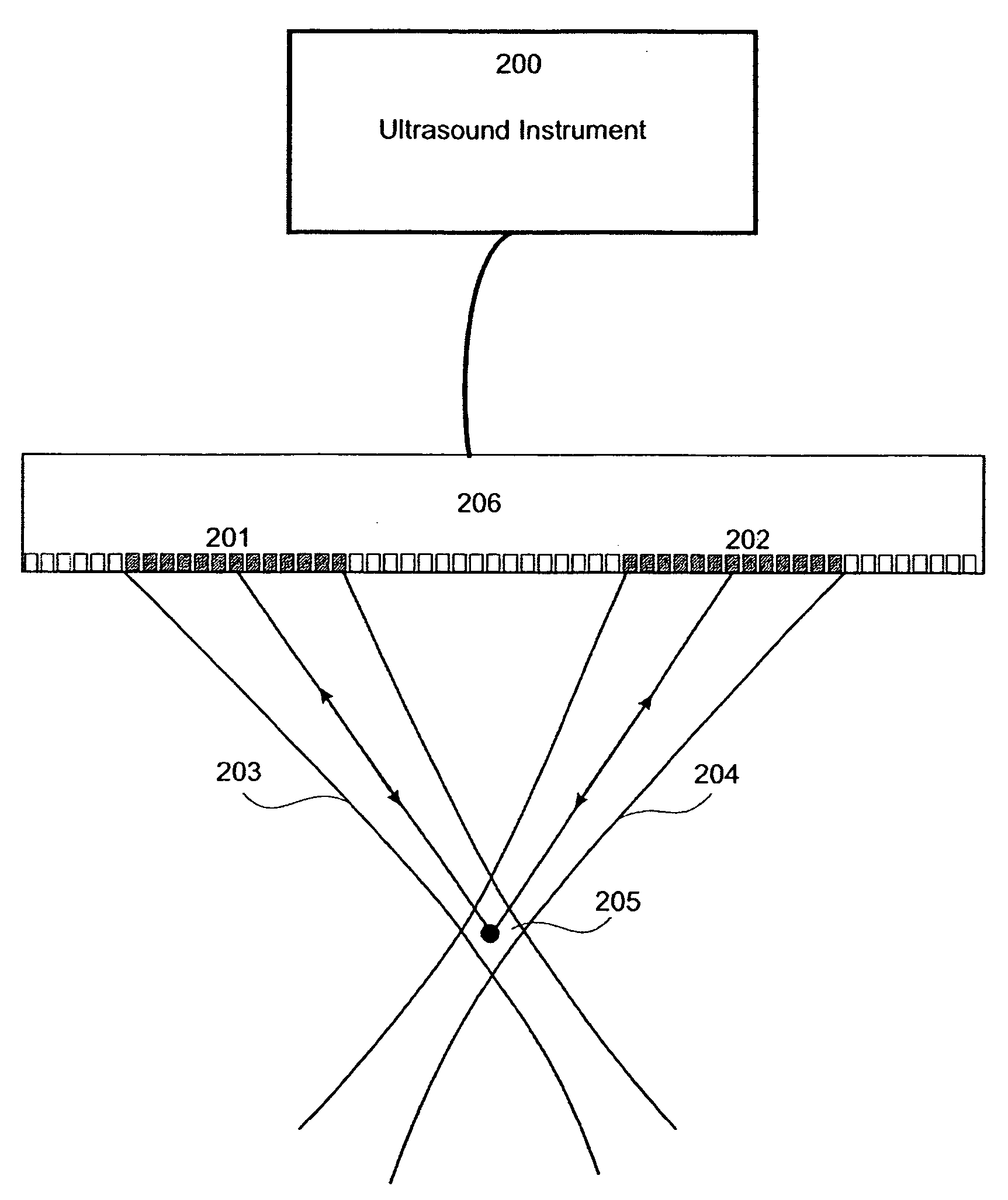
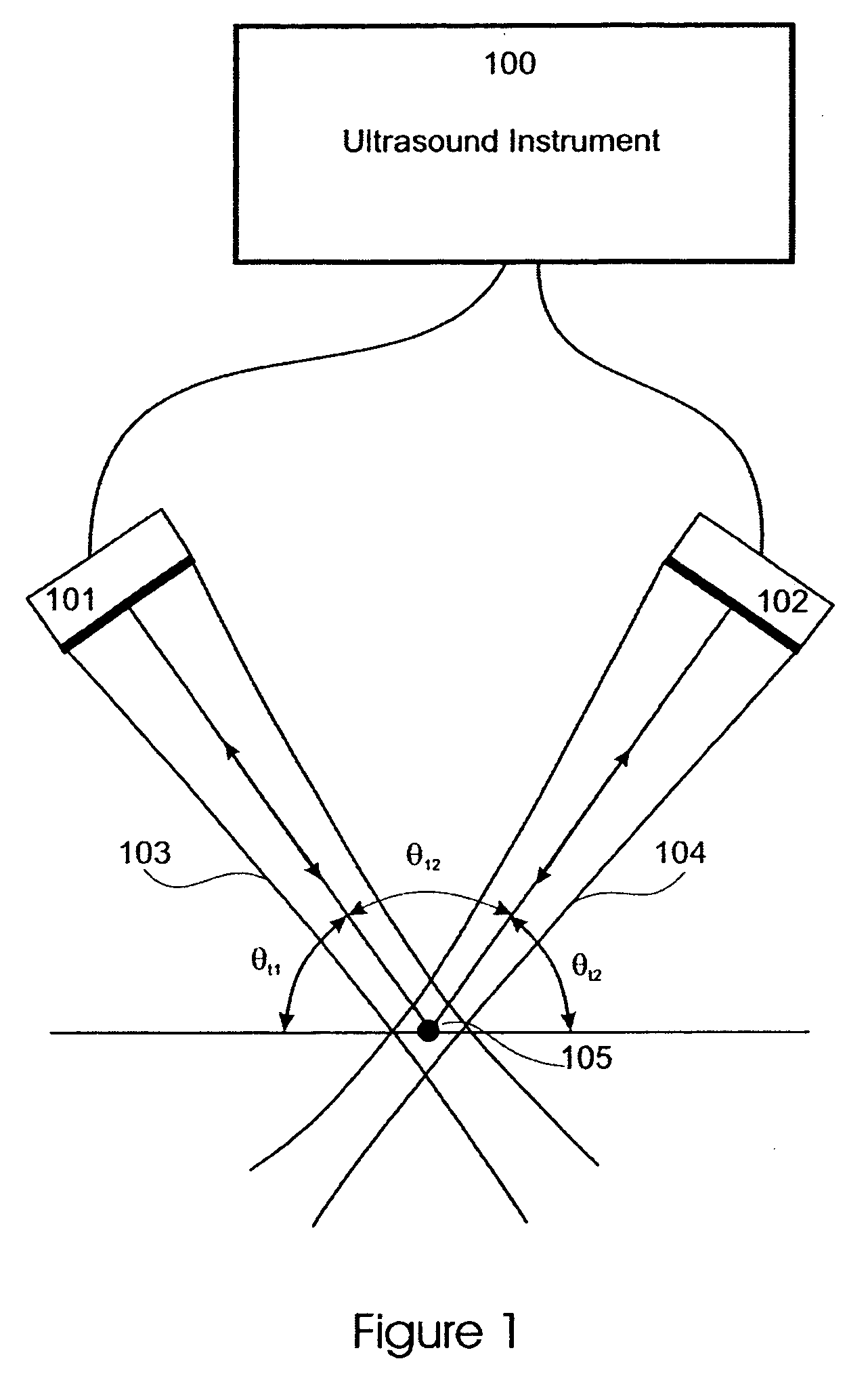
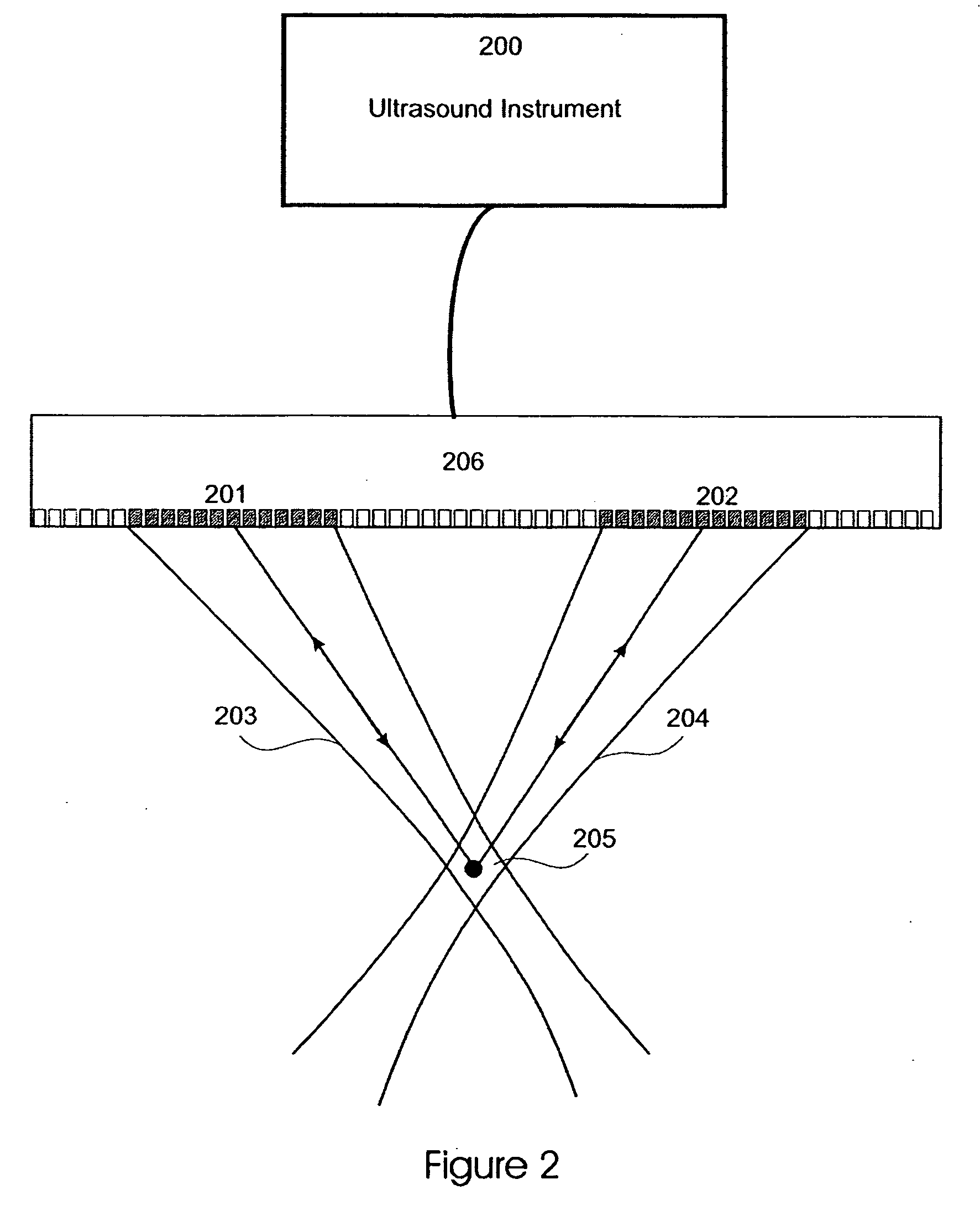
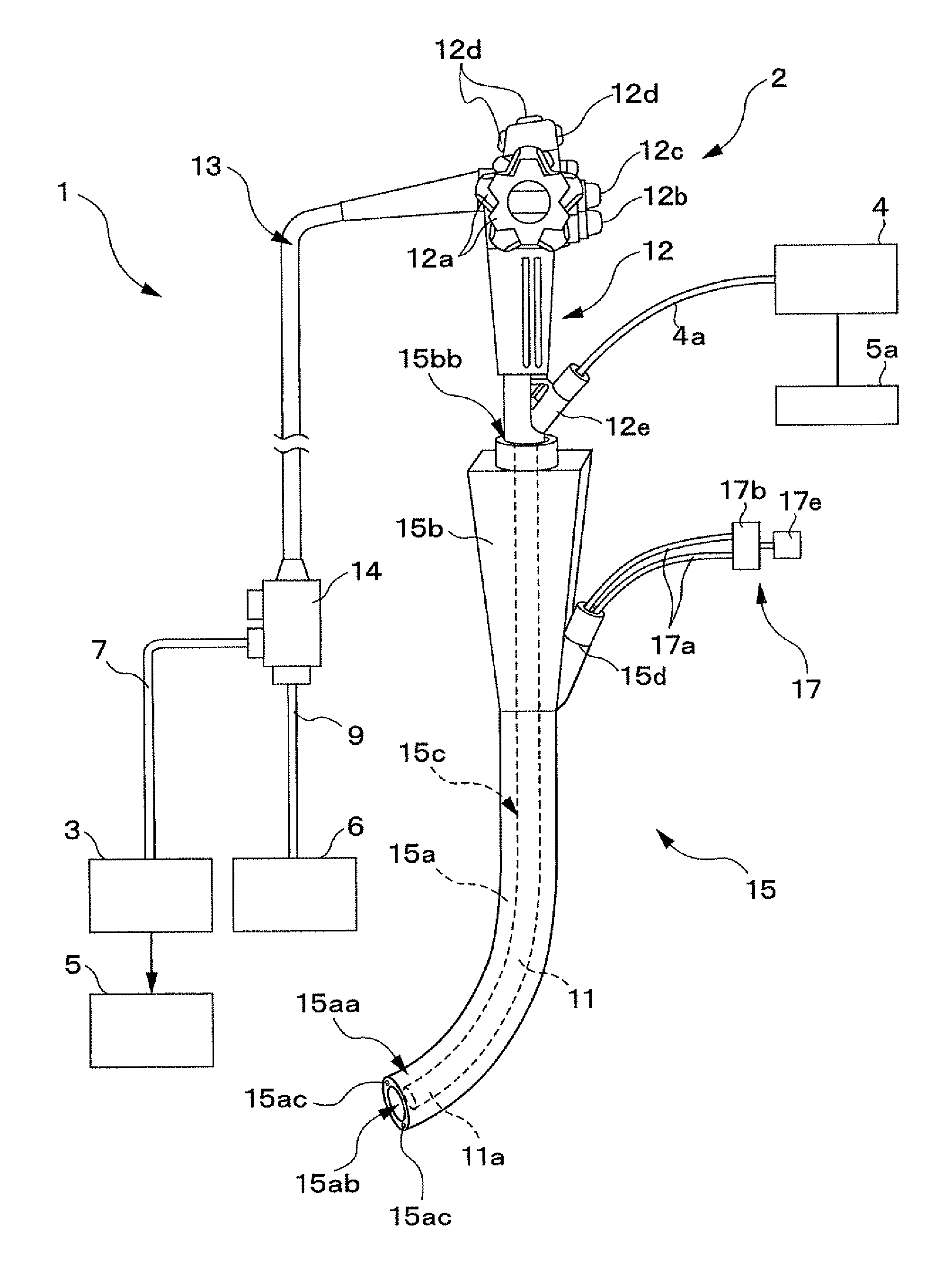
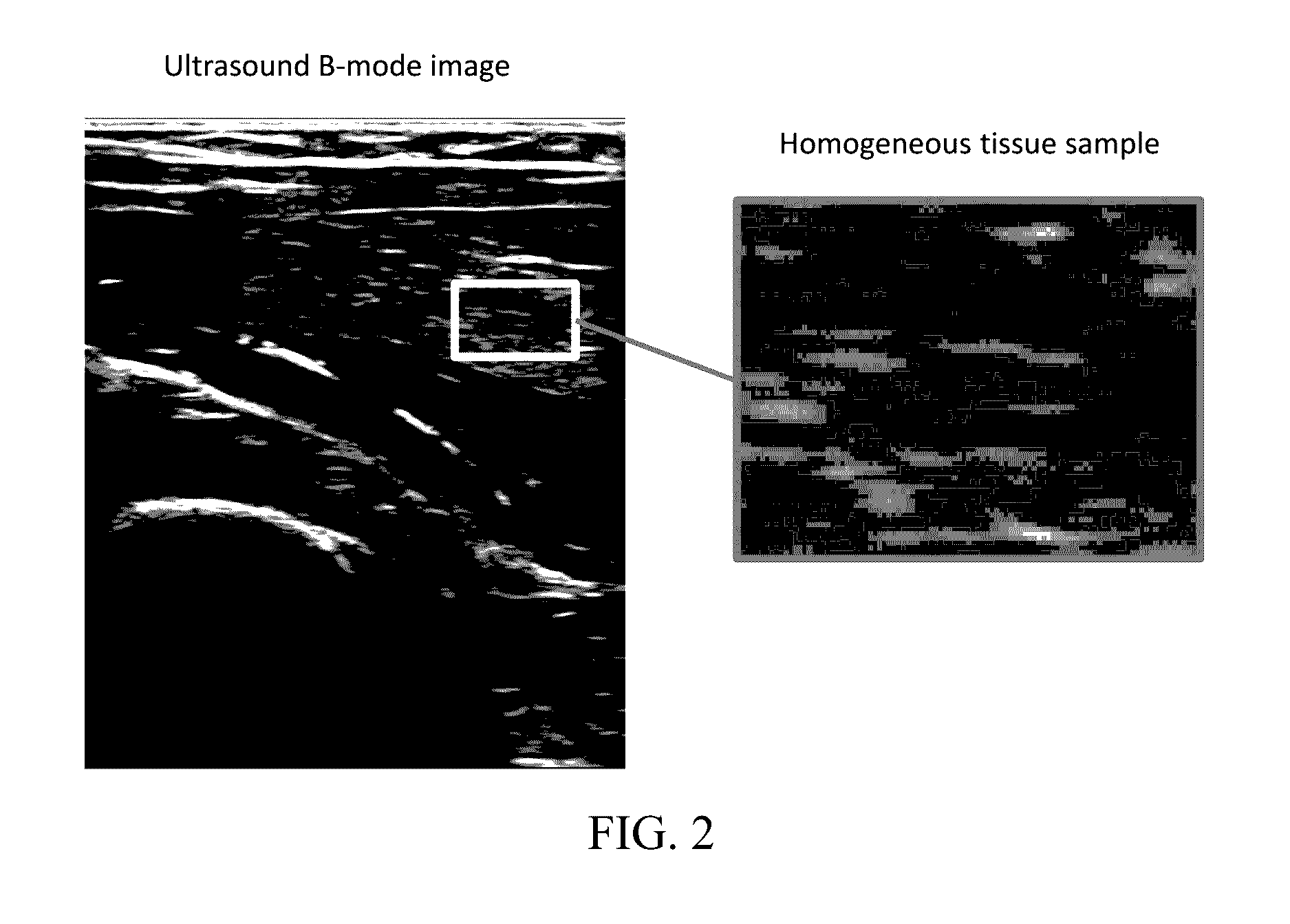
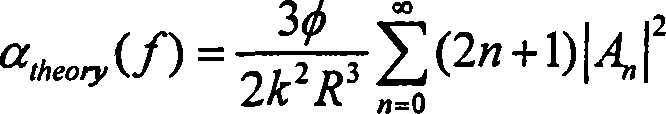Patents
Literature
39 results about "Ultrasound scattering" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Grain graininess and concentration measuring method and device thereof
InactiveCN101135626ADecay GranularityReduce concentrationMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesParticle size analysisObservational errorMeasurement device
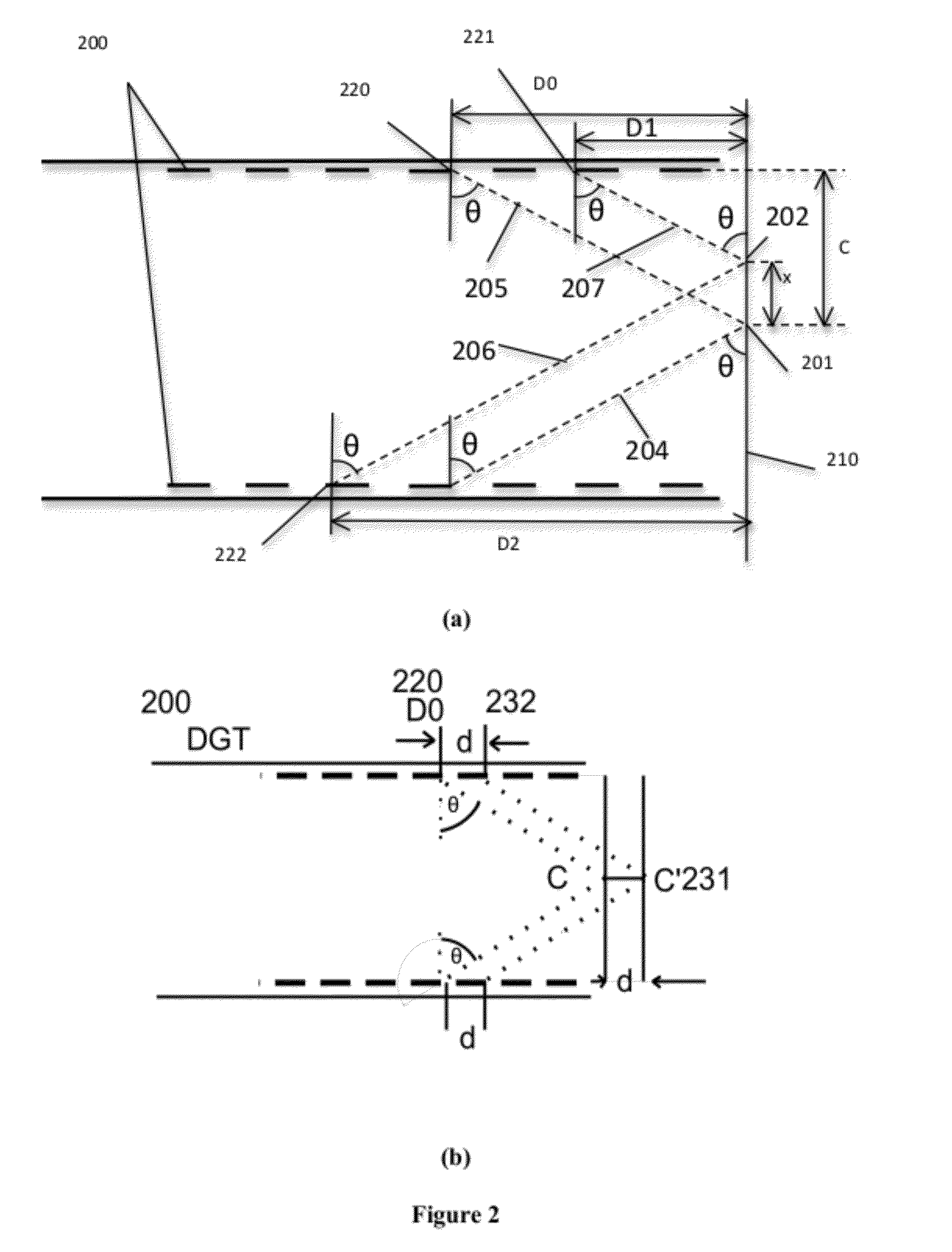
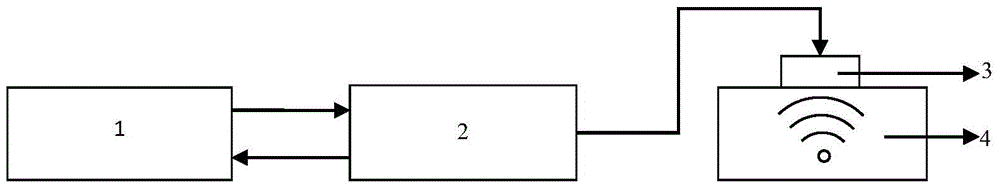
The measuring device comprises a computer used for data process, a signal process circuit connected to the computer, a pulse wave transmitting / receiving circuit connected to the signal processing circuit; a bandwidth transmitting / receiving transducer assembly connected to the pulse transmitting / receiving circuit. The data process program compares the measuring signal with the preset standard substance; the actually measured acoustic attenuation spectrum is combined with the acoustic attenuation spectrum obtained based on the scattering formula computational theory to construct the matrix and linear equation; using dual frequency attenuation ratioing to realize the calculation of average particle size; according to the particle size, inversely computes the particle concentration.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Time reversal and phase coherent music techniques for super-resolution ultrasound imaging
ActiveUS20140364733A1Accurate scatterer localizationHigher-resolution ultrasound imageOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsPhase responseSonification
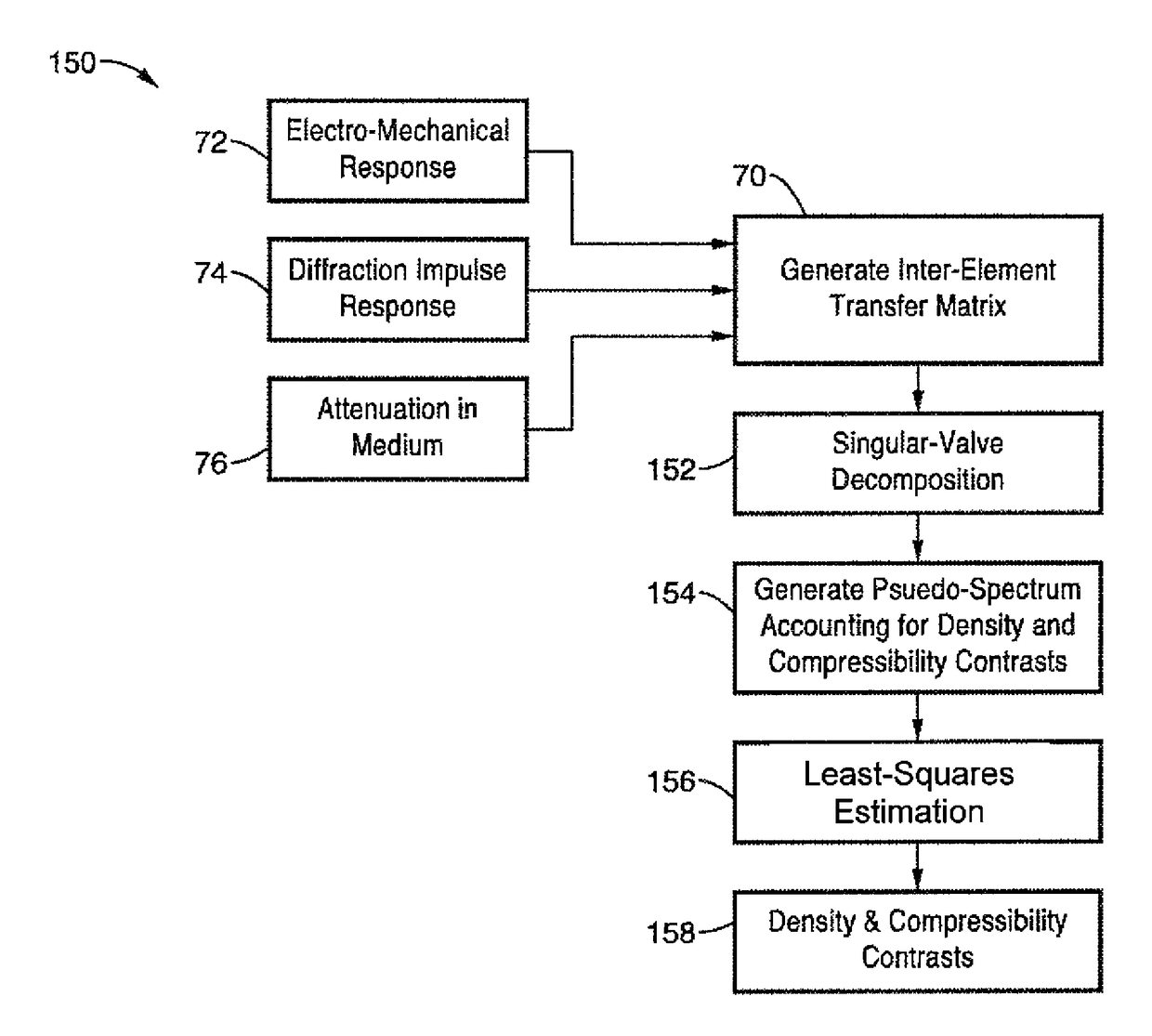
Systems and methods for super-resolution ultrasound imaging using a windowed and generalized TR-MUSIC algorithm that divides the imaging region into overlapping sub-regions and applies the TR-MUSIC algorithm to the windowed backscattered ultrasound signals corresponding to each sub-region. The algorithm is also structured to account for the ultrasound attenuation in the medium and the finite-size effects of ultrasound transducer elements. A modified TR-MUSIC imaging algorithm is used to account for ultrasound scattering from both density and compressibility contrasts. The phase response of ultrasound transducer elements is accounted for in a PC-MUSIC system.
Owner:TRIAD NAT SECURITY LLC
Ultrasound system and ultrasound diagnostic apparatus for imaging scatterers in a medium
InactiveUS20020049381A1Processing detected response signalHeart/pulse rate measurement devicesUltrasound imagingSonification
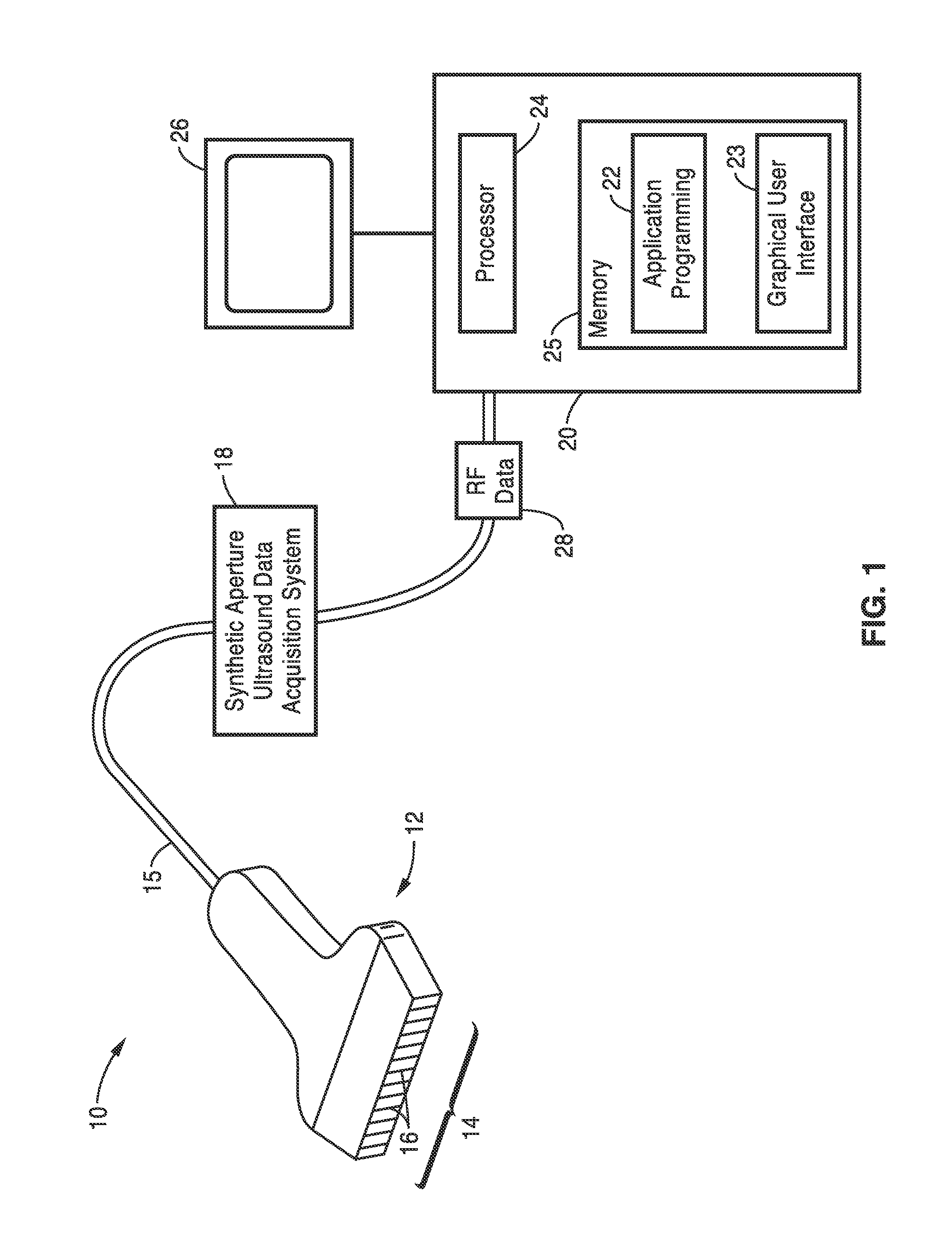
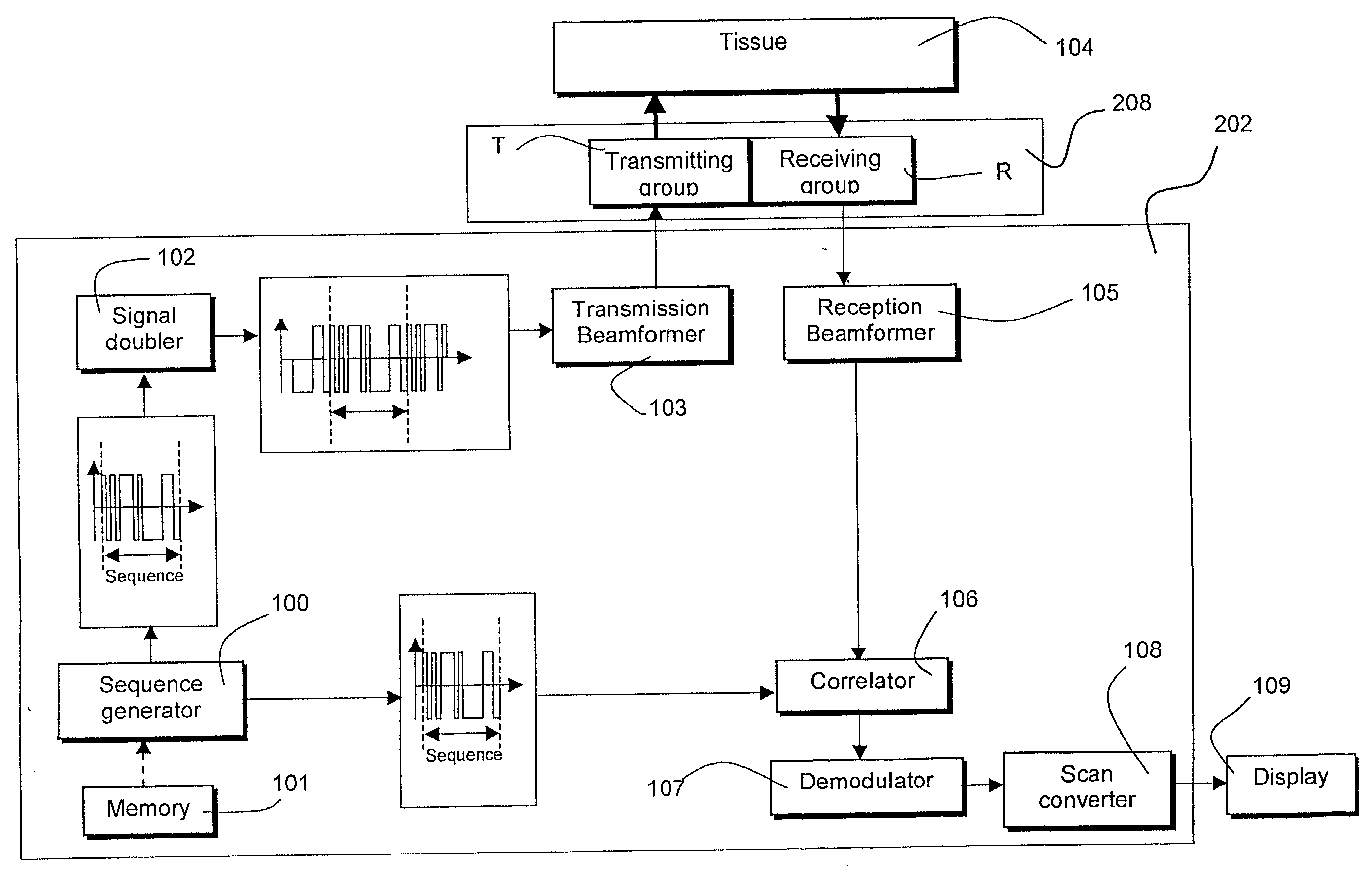
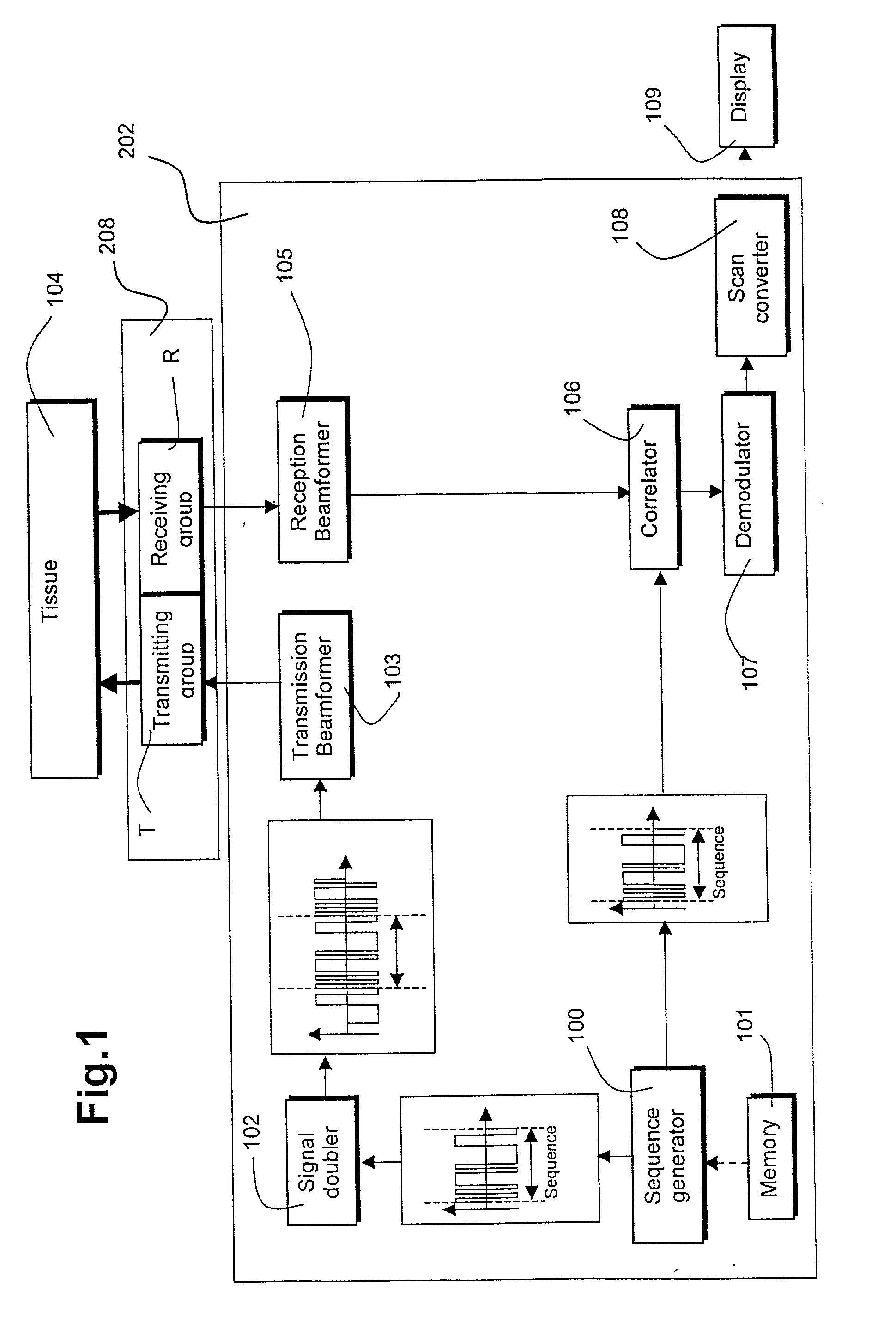
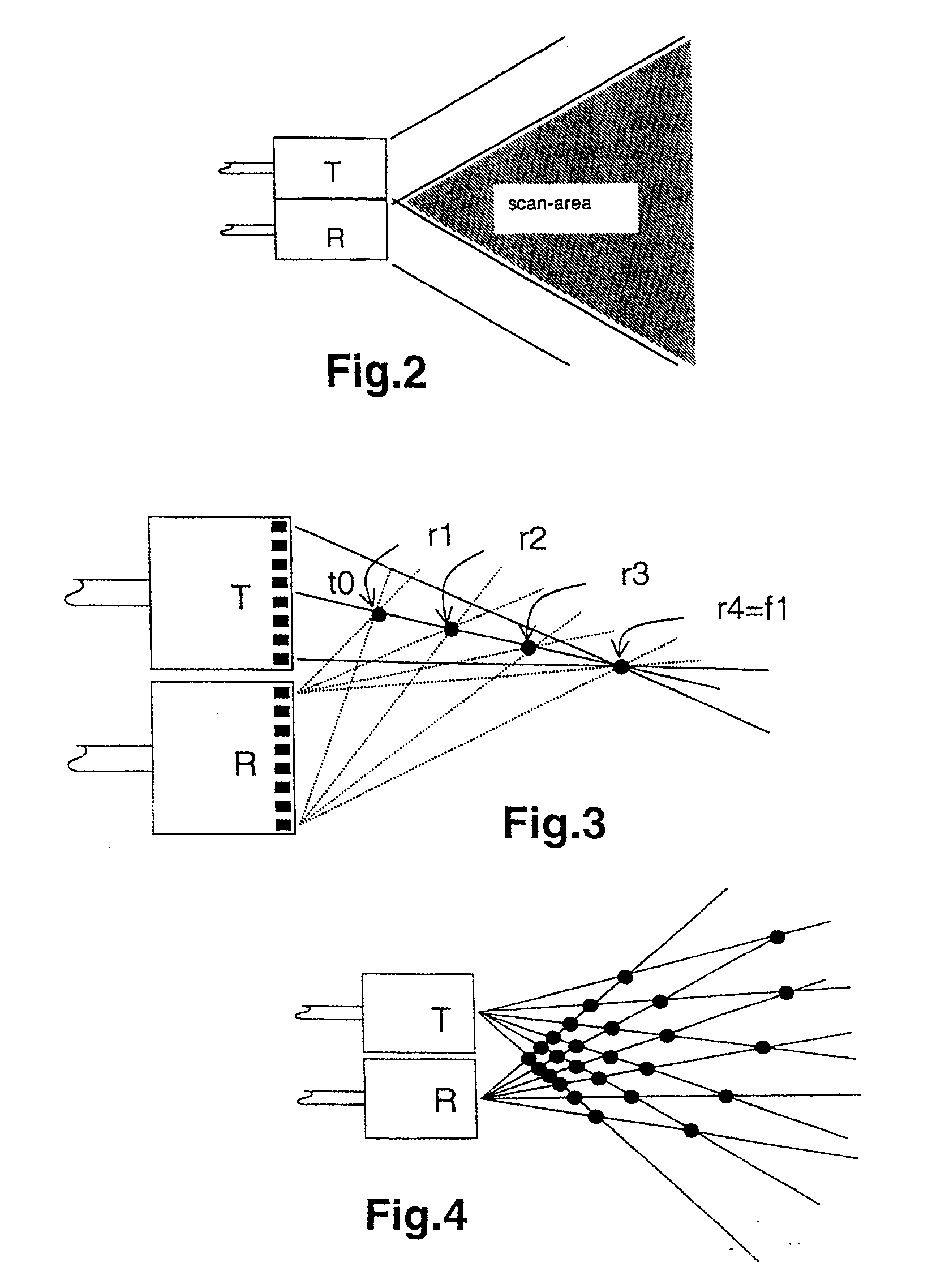
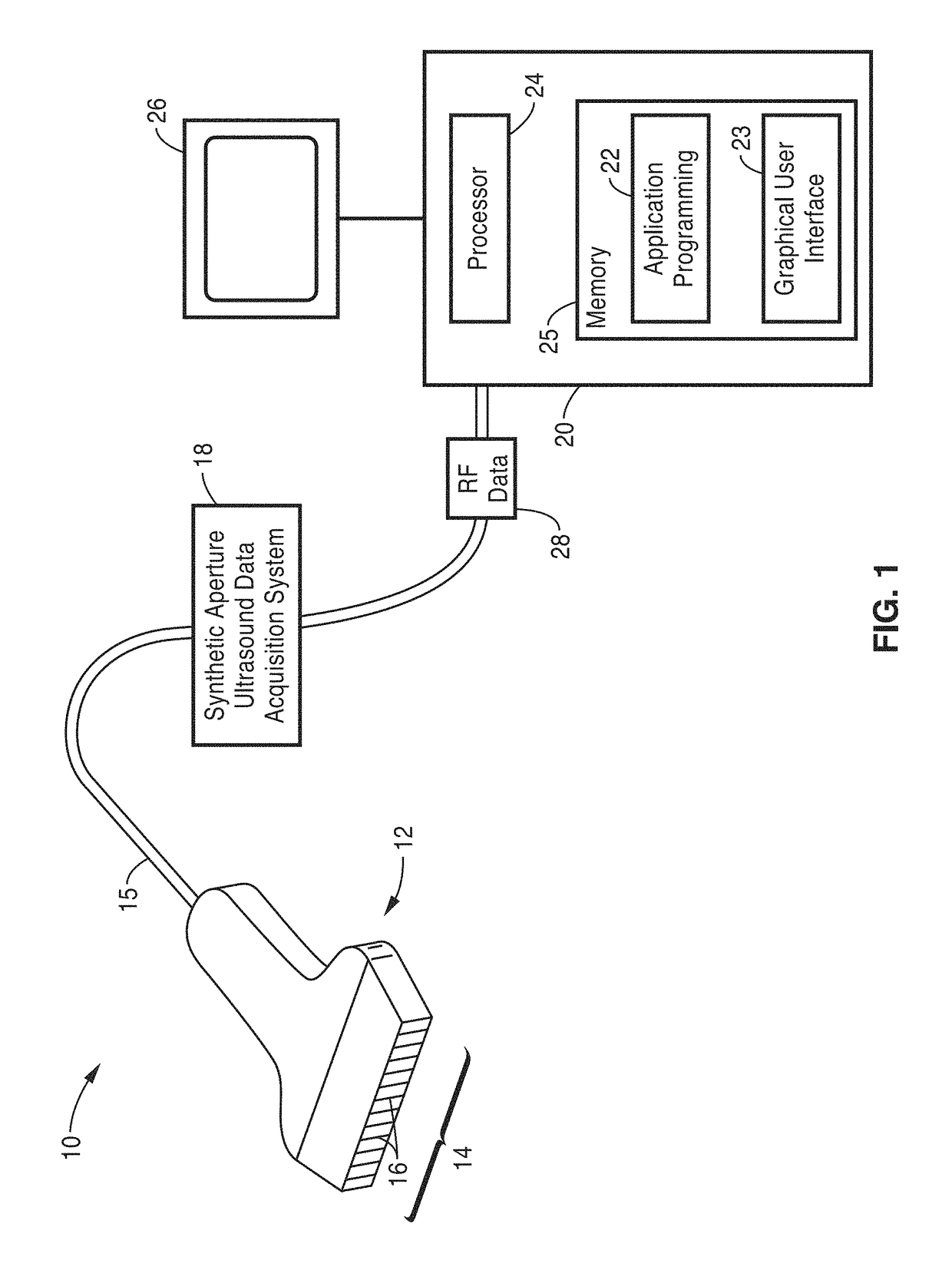
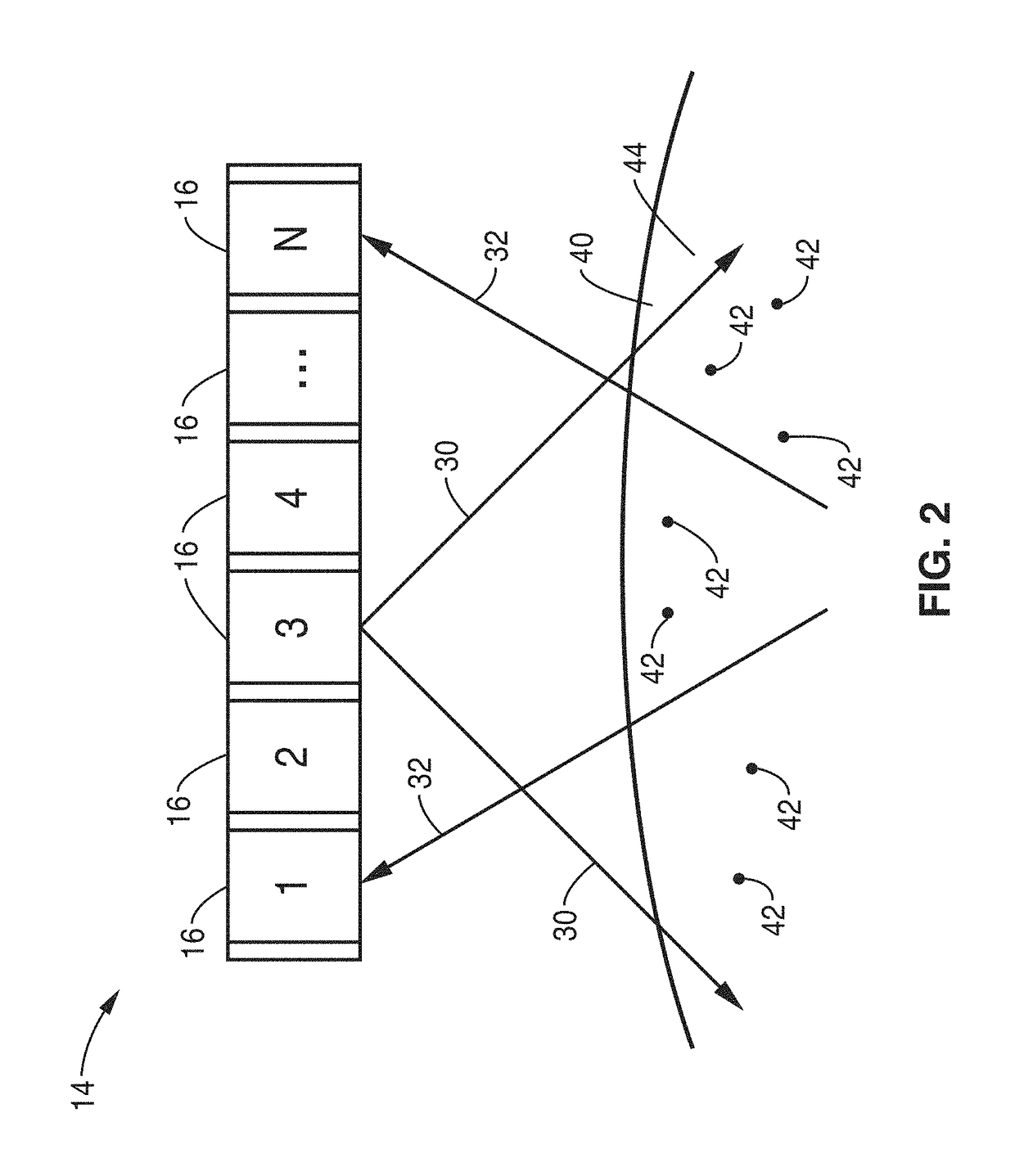
An ultrasound imaging system for imaging ultrasound scatterers, comprising a probe (208) for transmitting ultrasound waves and detecting ultrasound echoes reflected by said ultrasound scatterers, wherein said probe comprises a first group of transducer elements, labeled transmitting group (T), to transmit ultrasound waves, and a distinct second group of transducer elements, labeled receiving group (R), to detect ultrasound echoes reflected by said ultrasound scatterers. The system also comprises a processing system (202) comprising transmission and reception means, coupled to said probe (208), for providing coded signal to said transmitting group (T) and receiving signals from said receiving group (R) respectively; transmission beam-forming means (103) for focussing the ultrasound waves on a focus line, reception beam-forming means (105) for forming beam-summed received signals from signals received from the focus line and processing means for processing said beam-summed received signals to form decoded signals so as; and means for displaying an image (109) that is a function of said decoded signals.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
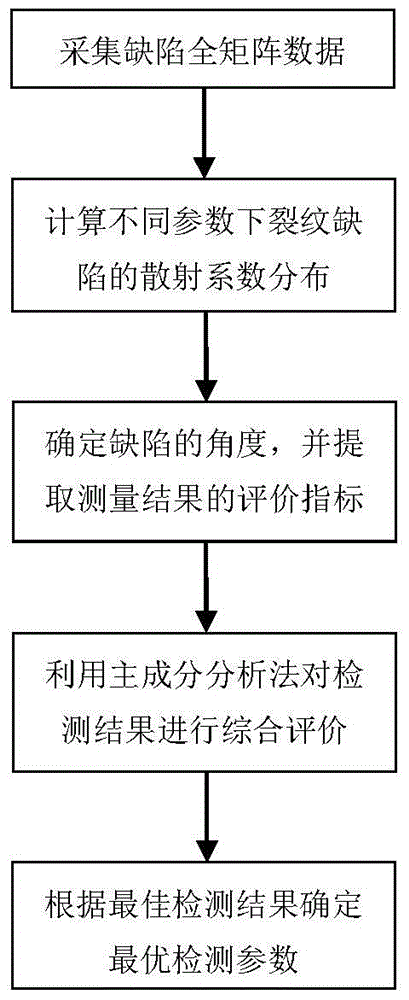
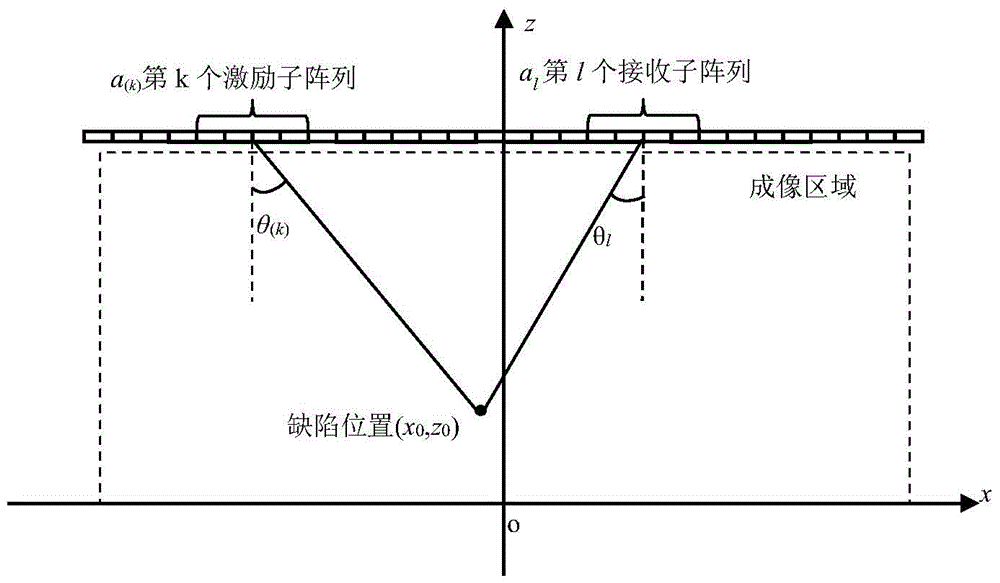
Ultrasonic scattering coefficient optimal computation method for crack direction recognition
ActiveCN104280455AAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesProcessing detected response signalFull matrixMeasurement precision
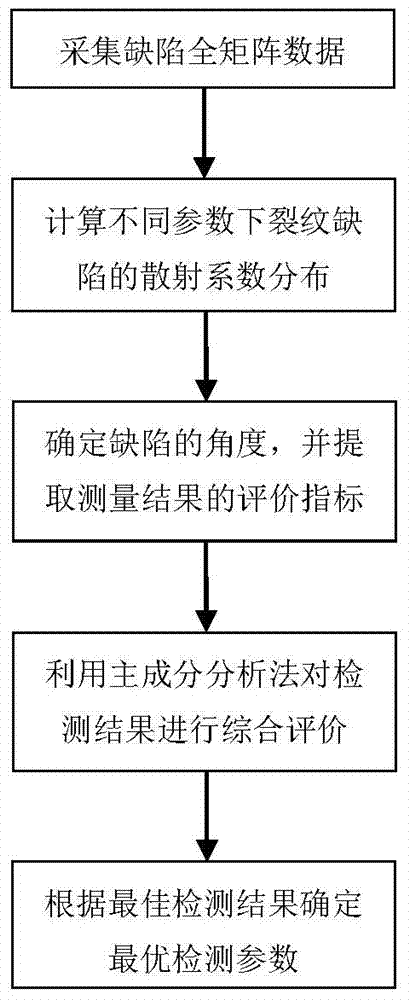
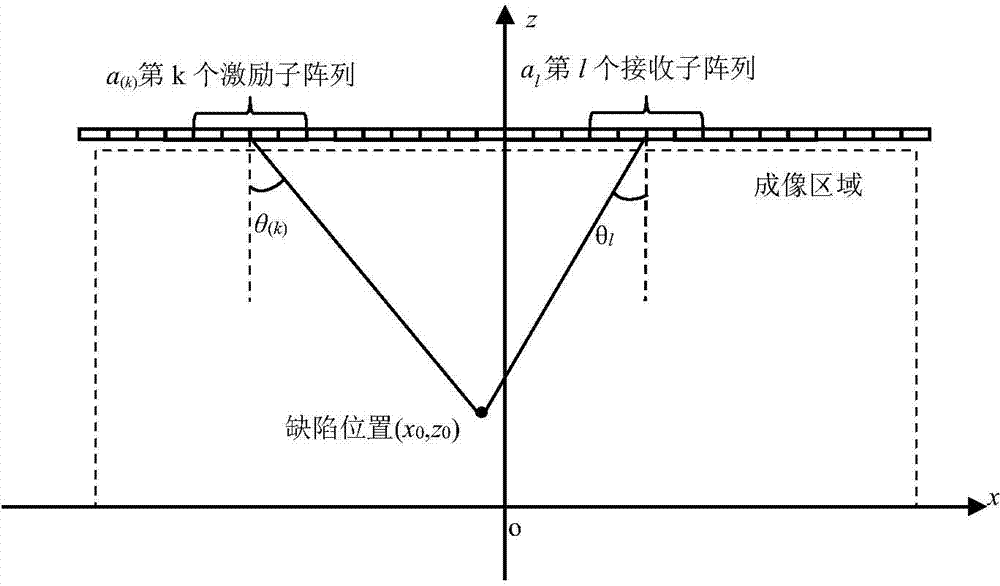
The invention relates to an ultrasonic scattering coefficient optimal computation method for crack direction recognition, belonging to the field of nondestructive examination. According to the method, an ultrasonic phased array detection system is used for acquiring full-matrix data of a crack defect; firstly, the acquired data are used for performing full-focusing imaging on the defect to determine the position of the defect and then a scattering coefficient space distribution of the crack defect is computed to determine an angle of the crack; the quantity of wafers included in a sub array and the quantity of wafers between adjacent sub arrays greatly affect the measurement precision of the crack angle. A plurality of evaluation indexes are used for evaluating the quantity of a crack angle measurement result according to the quantities of the wafers included in different sub arrays and the wafers between the adjacent sub arrays, and the measurement result is comprehensively evaluated by a main component analysis method to obtain an optimal measurement result; corresponding parameters, namely the quantities of the wafers included in the sub arrays and the quantity of the wafers between the adjacent sub arrays, are optimal detection parameters.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Property determining apparatus for determining a property of an object
ActiveUS20130041259A1Improve accuracyFacilitate ablationBlood flow measurement devicesSurgical needlesSonificationPerfusion
A monitoring apparatus for monitoring an ablation procedure applied to an object comprises an ultrasound signal providing unit for providing an ultrasound signal. The ultrasound signal is produced by sending ultrasound pulses out to the object, by subsequently receiving dynamic echo series after the ultrasound pulses have been reflected by the object, and finally by generating the ultrasound signal depending on the received dynamic echo series, whereby ultrasound scattering properties of the object are determined that represent blood perfusion. The monitoring apparatus further comprises an ablation depth determination unit for determining an ablation depth from the provided ultrasound signal.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
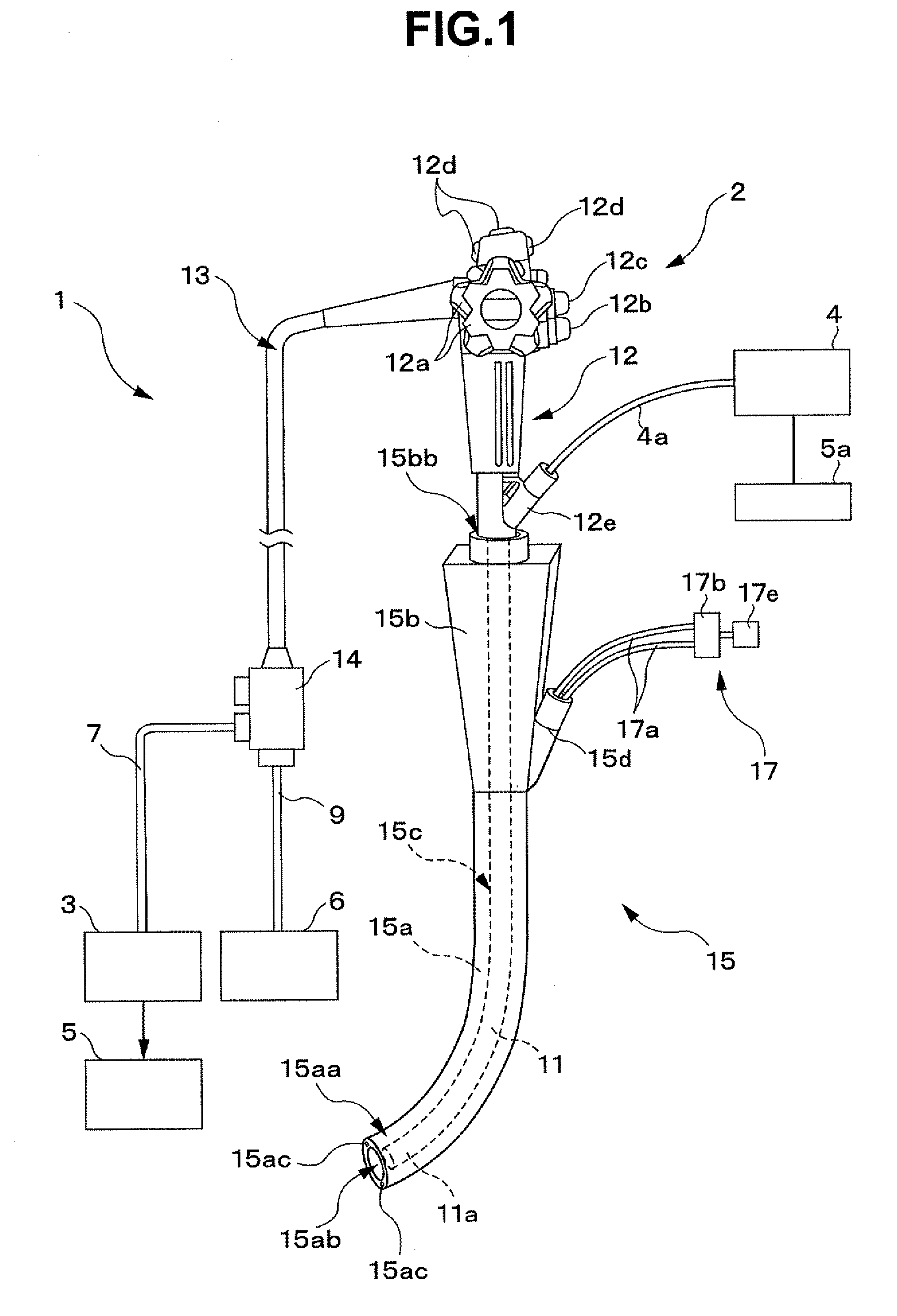
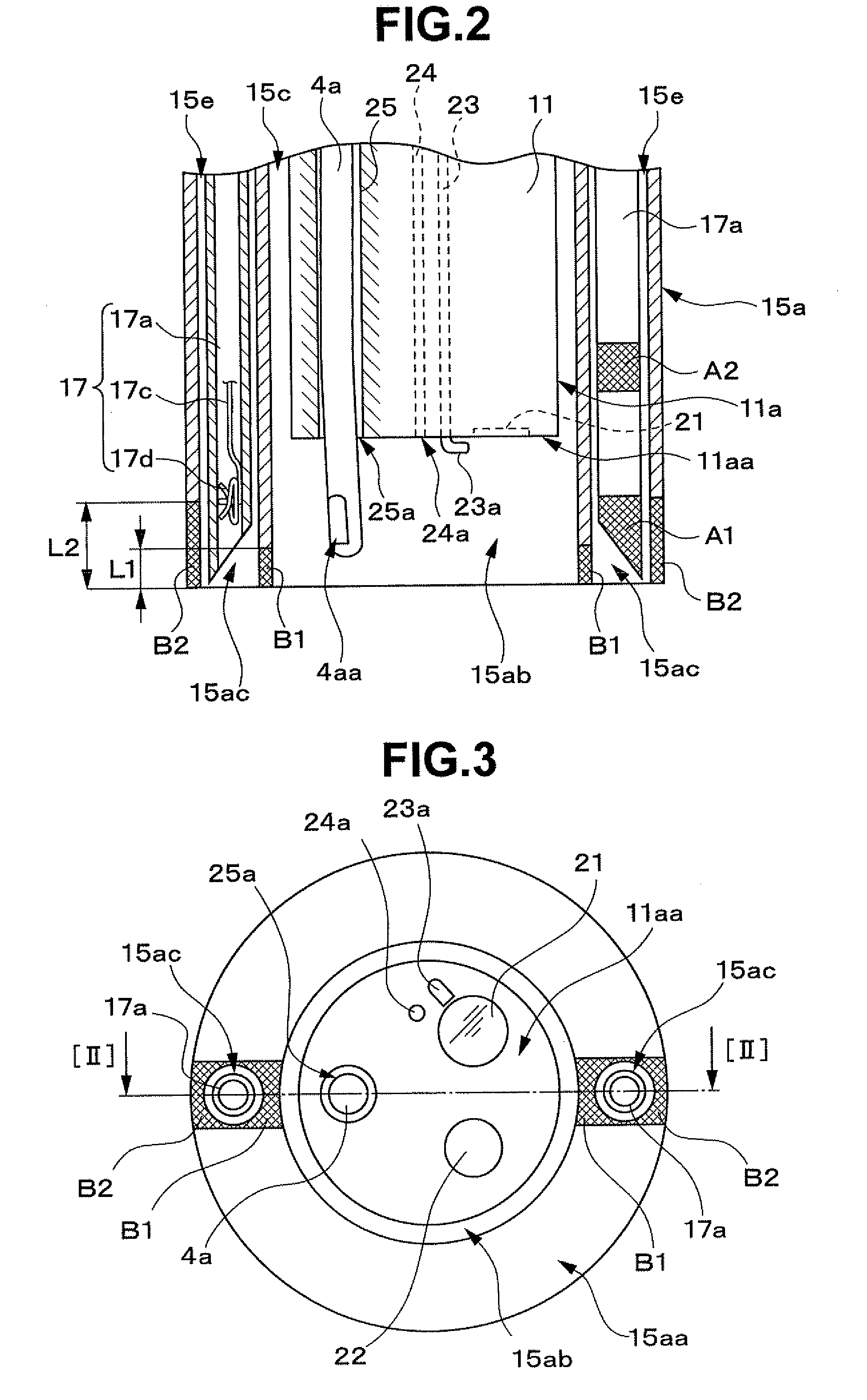
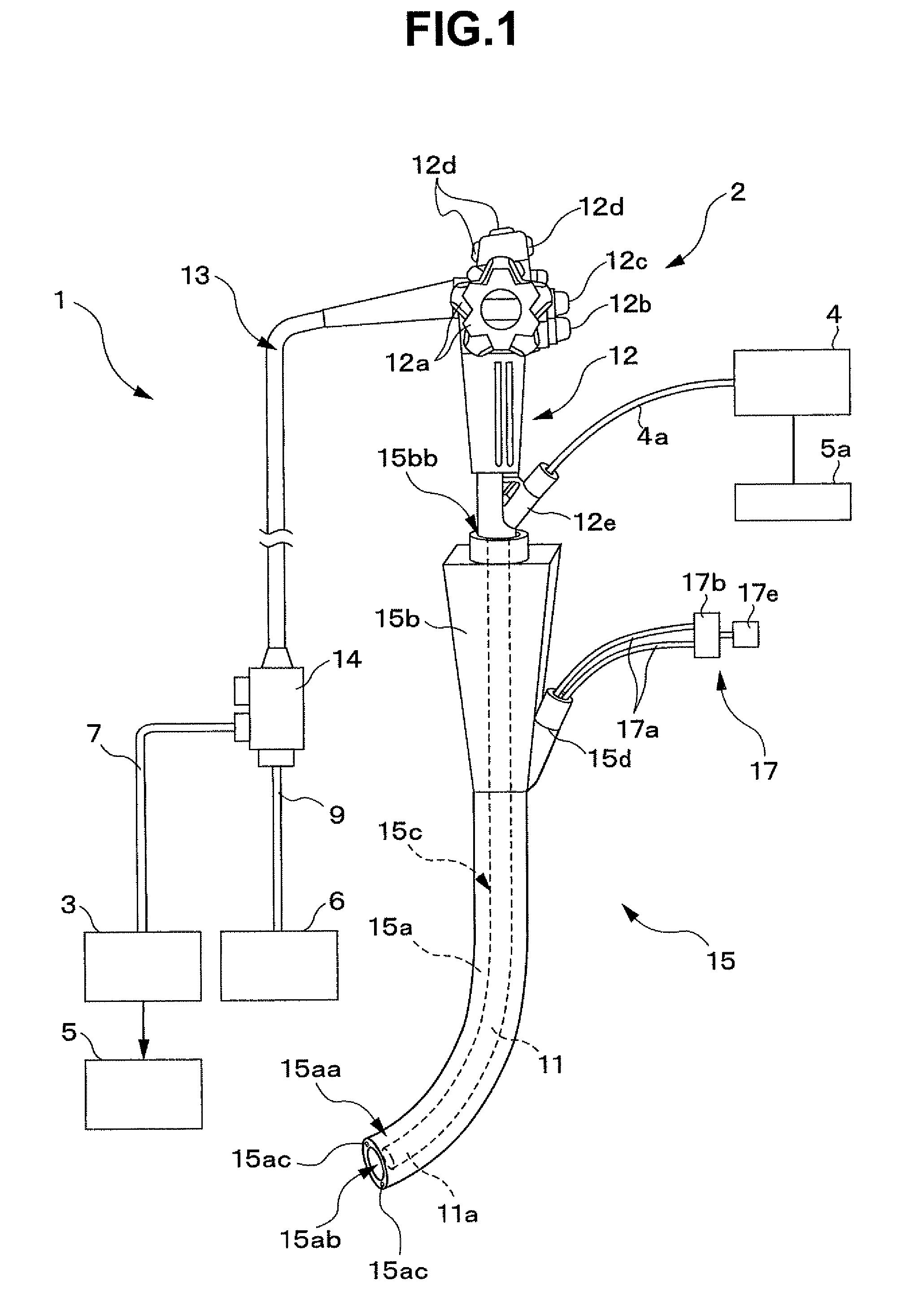
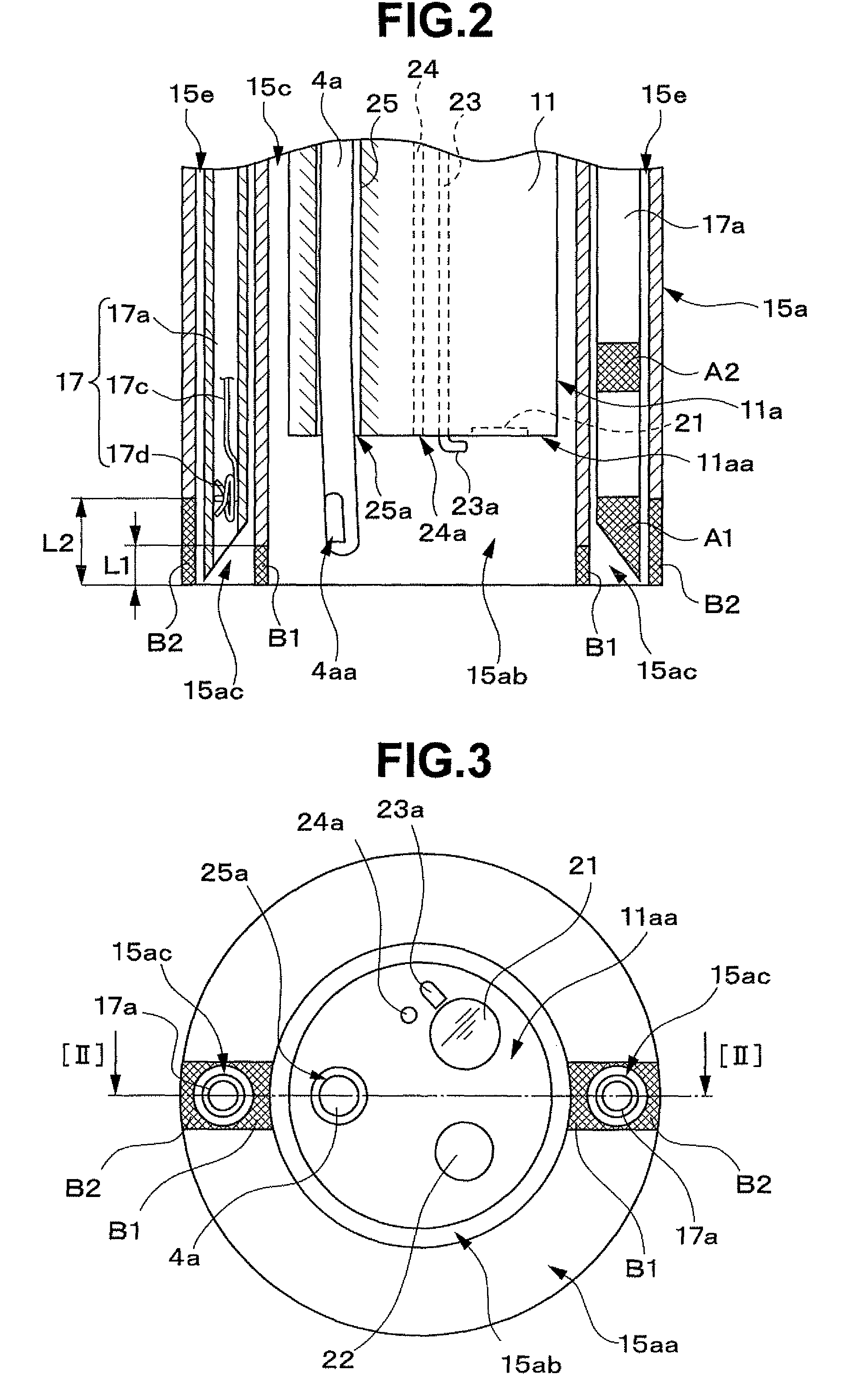
Treatment instrument system
A treatment instrument system according to the present invention includes: an endoscope having a treatment instrument channel; an ultrasound probe inserted through the treatment instrument channel of the endoscope; an ultrasound observing apparatus having a blood flow display function and a distance measuring function; a treatment instrument having, at a distal end portion, an ultrasound scattering portion for scattering ultrasound; and an over tube having an endoscope insertion path through which the endoscope can be inserted and a treatment instrument insertion path through which the treatment instrument can be inserted, and having, at a distal end portion, an ultrasound scattering portion for scattering ultrasound.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Ultrasonic scatterer, ultrasonic imaging method and ultrasonic imaging apparatus
InactiveUS20050004469A1Improve spatial resolutionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsWave based measurement systemsUltrasonic scatteringUltrasound probe
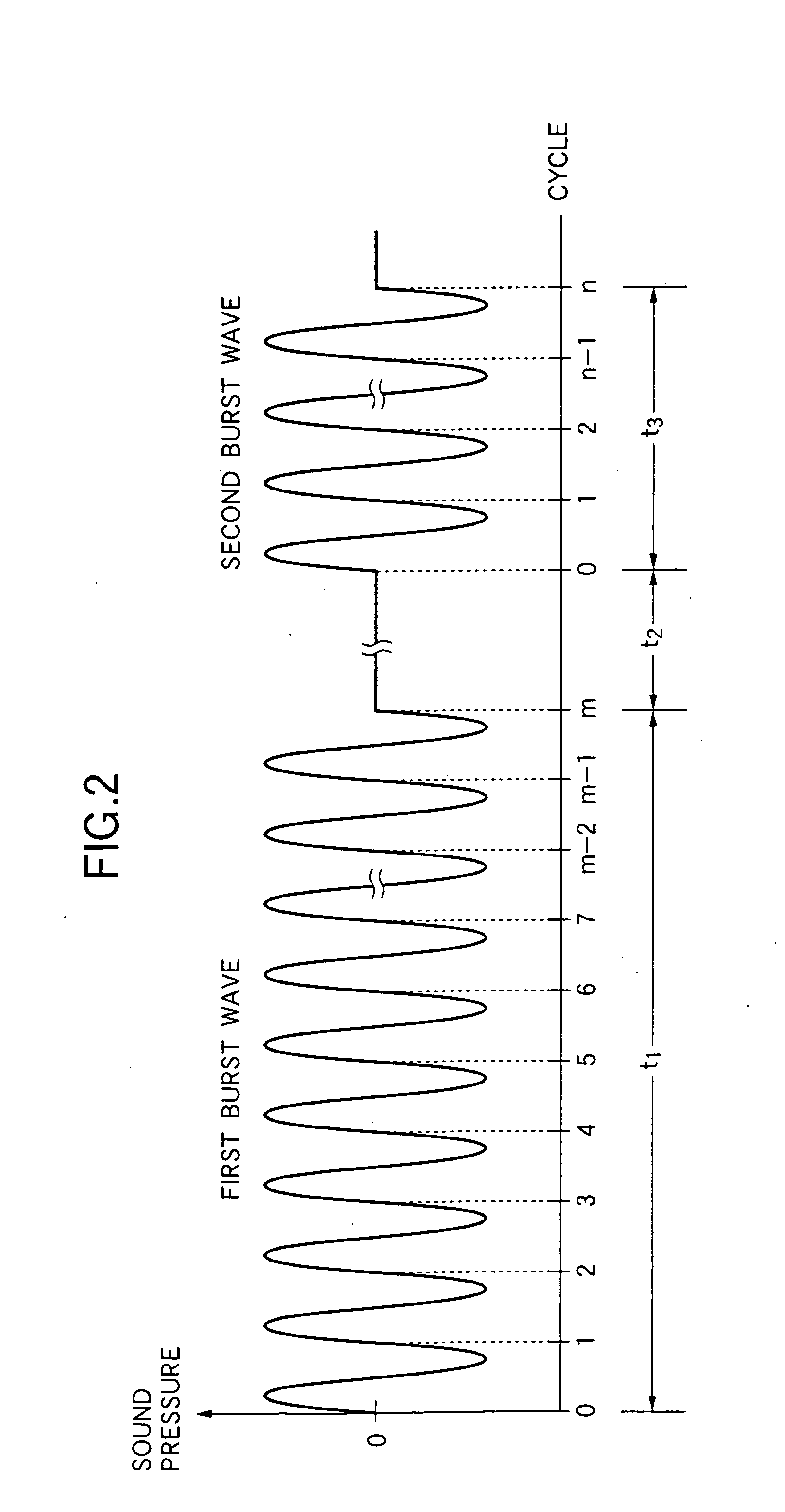
The ultrasonic scatterer of the invention comprises gas-containing particles having an average particle size of 0.01 μm to 10 μm, the ultrasonic imaging method of the invention comprises transmitting an ultrasonic wave continuing for ten cycles or more; transmitting an ultrasonic wave continuing for four cycles or more and less than ten cycles after a predetermined period passes, and the ultrasonic imaging apparatus of the invention comprises transmitting means for sending a driving signal to the ultrasonic probe so as to transmit, to a subject, an ultrasonic wave continuing for four cycles or more and less than ten cycles after a predetermined period passes subsequently to transmitting, to the subject, of an ultrasonic wave continuing for ten cycles or more.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
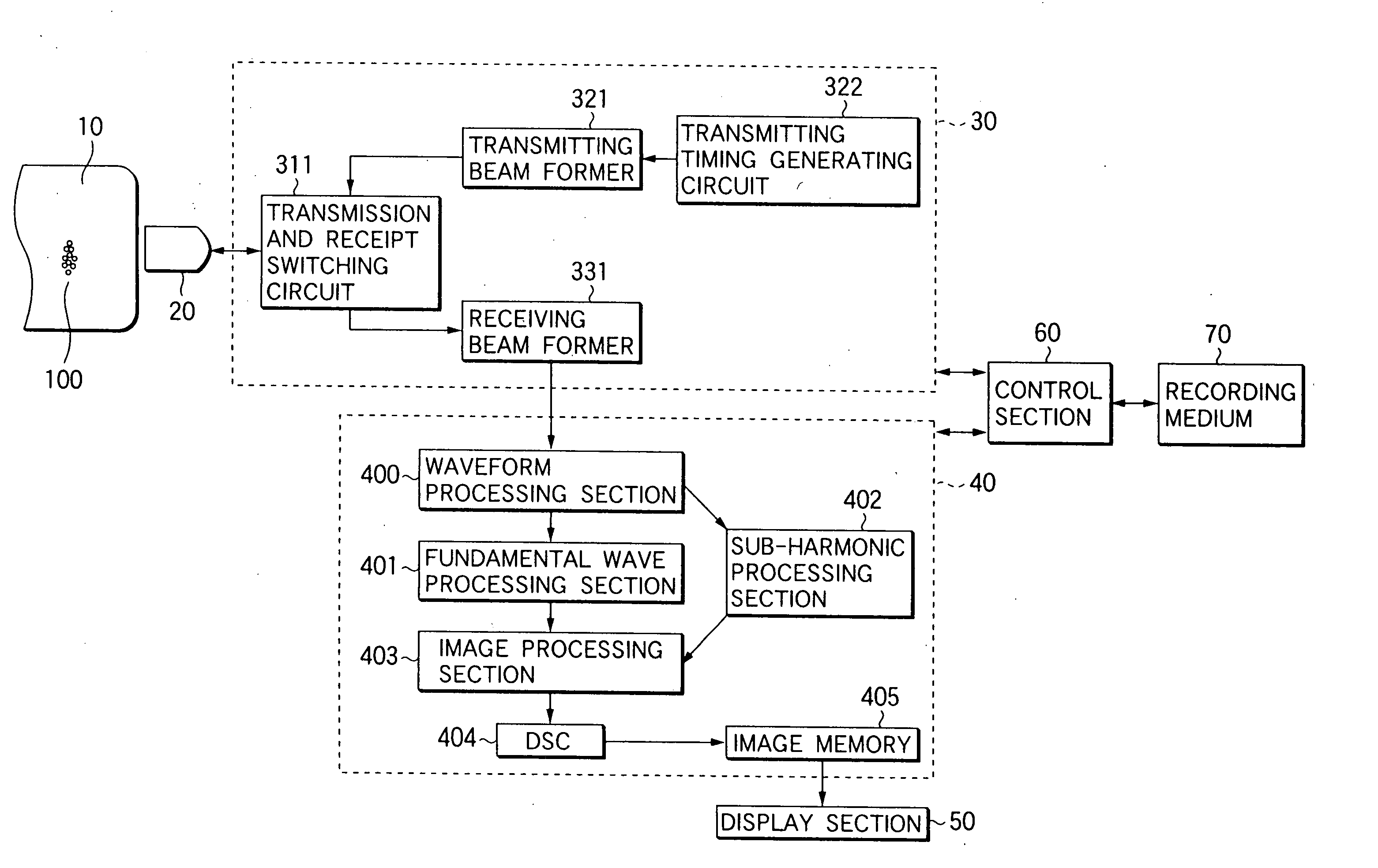
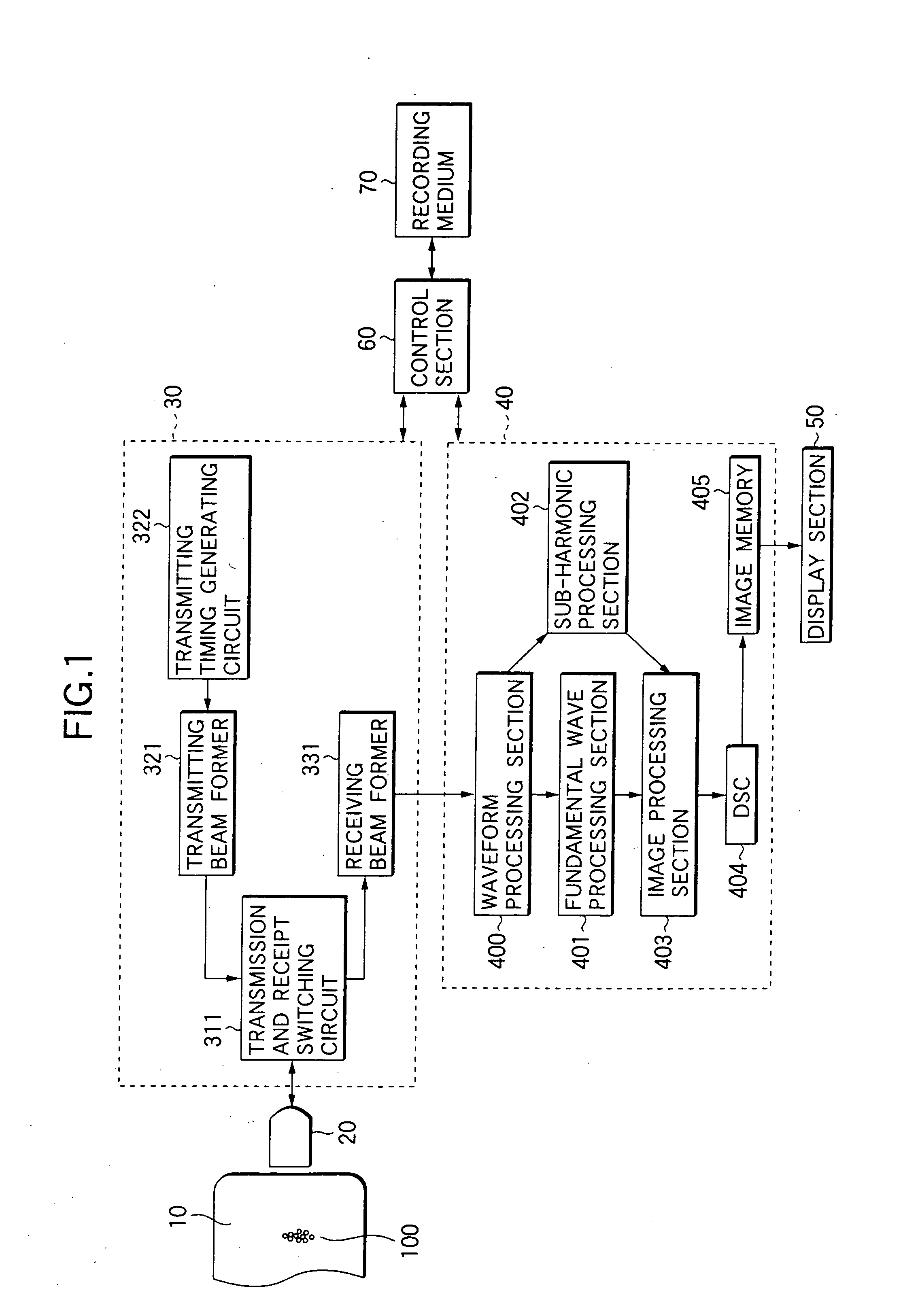
Method and system of ultrasound scatterer characterization
ActiveUS9389204B2Analysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesWave based measurement systemsSonificationSpatial organization
A method for characterizing ultrasound scatterers in a medium comprising providing ultrasound data representing a region of interest comprising a plurality of scatterers in a medium, the plurality of scatterers including clusters of scatterer sub-units, the scatterers having a physical property value to be estimated and the scatterer sub-units having at least one known physical parameter value; modelling the ultrasound data using an at least second order function of a spatial organization parameter defining the spatial organization of the scatterers; and estimating the physical property value of the scatterers from the modelled ultrasound data and the at least one known physical parameter of the sub-units by a regression of the spatial organization parameter as a function of frequency. A system for characterizing ultrasound scatterers is also included.
Owner:VAL CHUM PARTNERSHIP
Methods of estimating ultrasound scatterer parameters in soft tissues
InactiveUS20050182324A1Reduces effect of absorption attenuationEliminate the effects ofUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsAtheromaLinear arrays
A method for characterizing ultrasound scatterers in soft tissue, wherein scattered signals are used to eliminate the absorption attenuation of an ultrasound wave from estimated parameters and to obtain directional scattering information. The scattered signals are obtained from either multiple regions where one region is used as a reference or multiple scattering directions, creating known reference signals from the same scattering region. The method provides new ultrasound parameters for the characterization and contrast enhancement of tissue structures in ultrasound imaging, such as tumor structures, ischemia of a myocardial wall and / or plaque compositions in vascular atheroma. The method of the invention can be used with various arrangements of ultrasound transducers, particularly switched linear arrays.
Owner:ANGELSEN BJORN A J +1
Treatment instrument system
ActiveUS8167808B2Suture equipmentsUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsEndoscopeUltrasound scattering
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
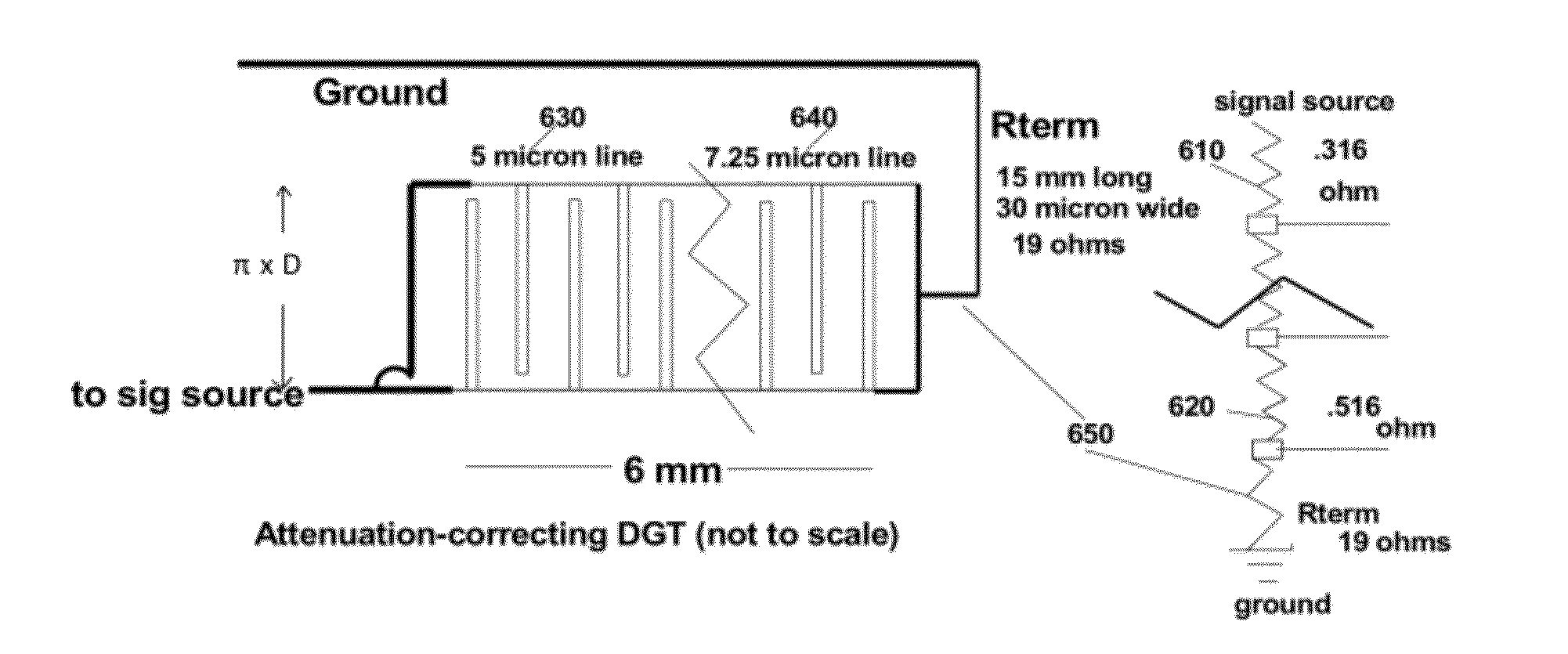
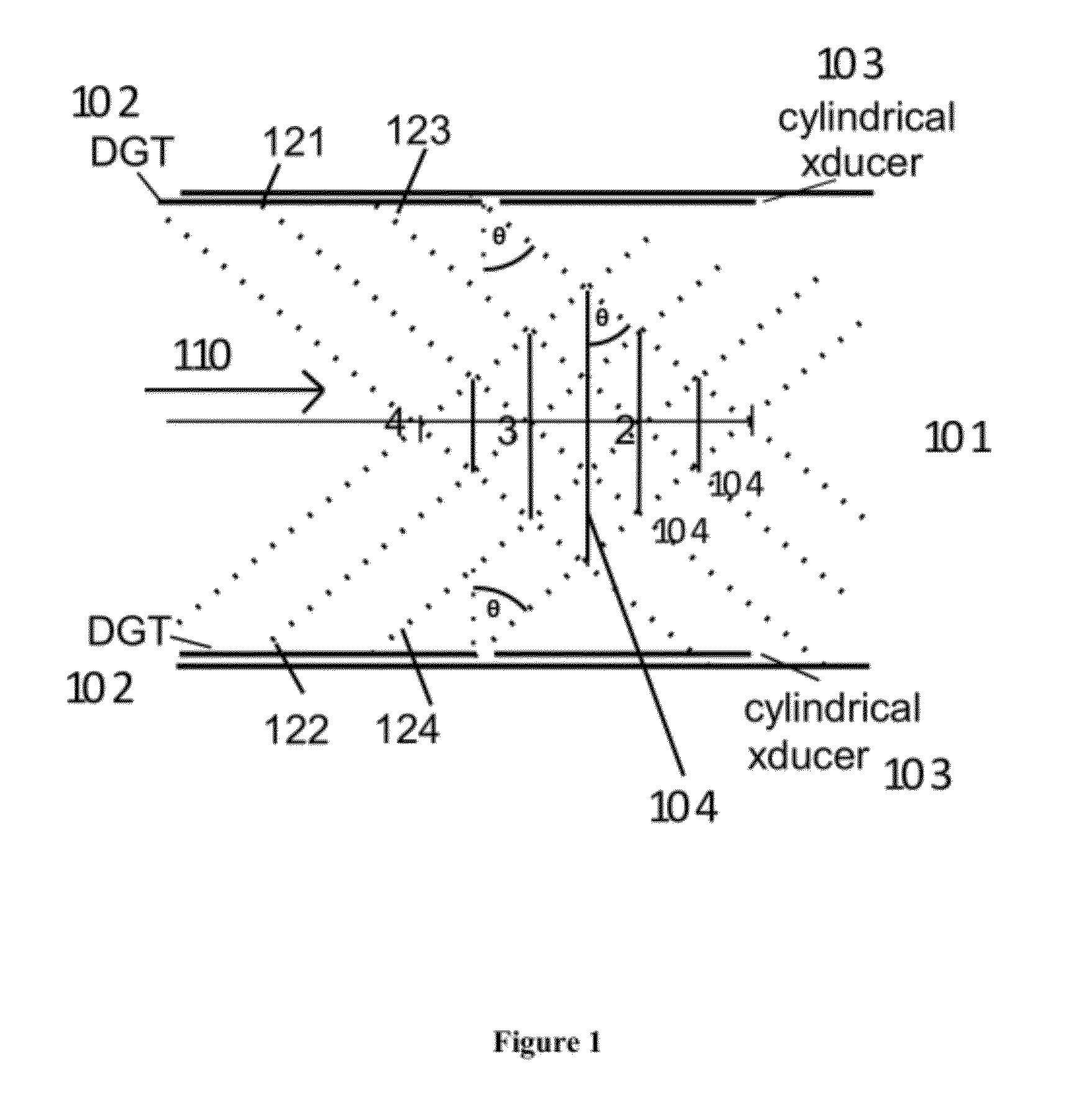
Flow Measurement Apparatus and Method
ActiveUS20120197129A1Accurate flow measurementAccurate measurementMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesBlood flow measurement devicesTransducerThree vessels
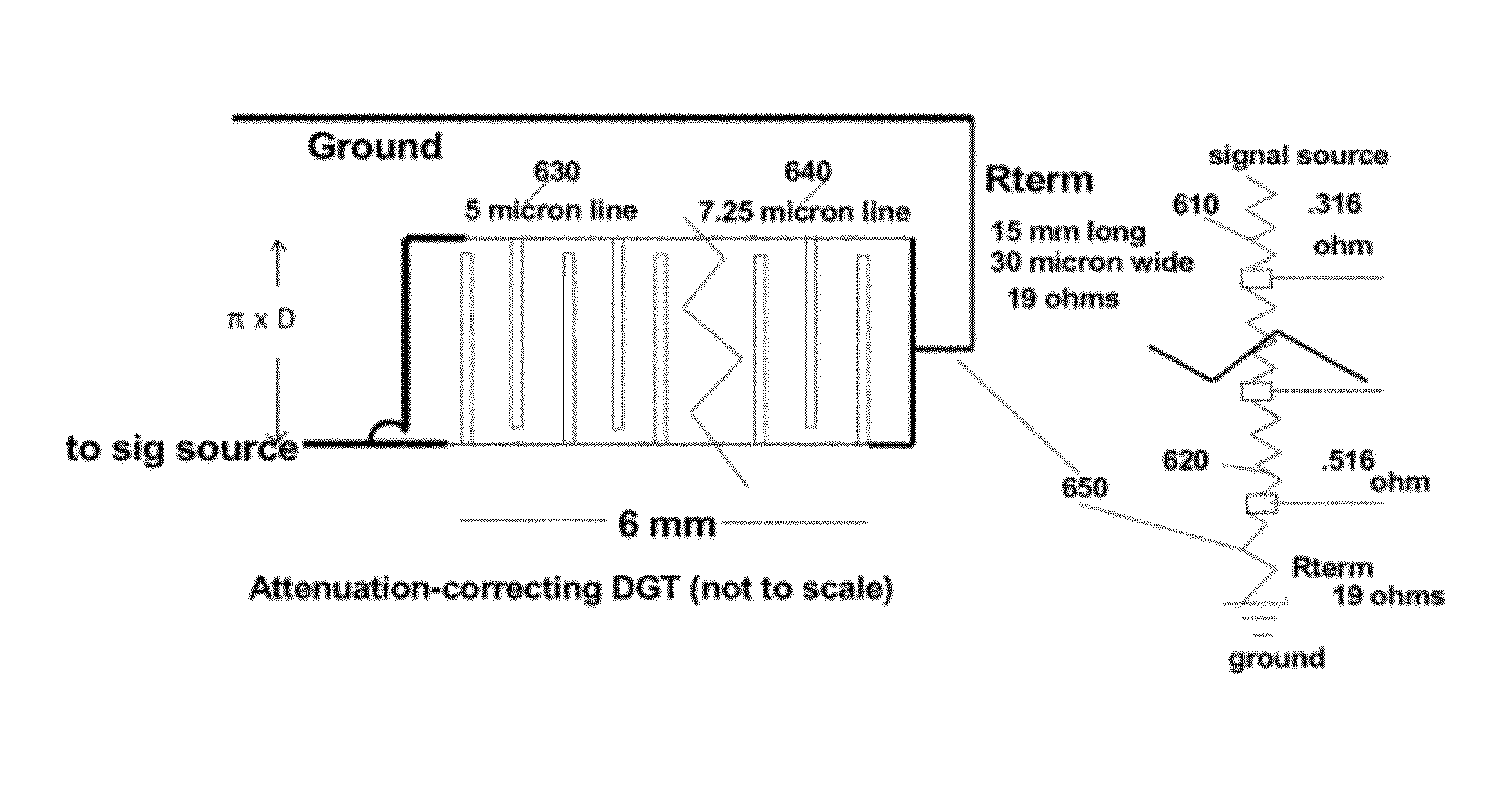
The velocity of fluids containing particles that scatter ultrasound can be measured by determining the Doppler shift of the ultrasound scattered by the particles in the fluid. Measuring fluid flow in cylindrical vessels such as blood vessels is an important use of Doppler ultrasound. This invention teaches using various configurations of cylindrical diffraction-grating transducers and cylindrical non-diffraction-grating transducers that suppress the Doppler shift from non-axial components of fluid velocity while being sensitive to the Doppler shift produced by axial velocity components. These configurations thus provide accurate measurement of the net flow down the vessel, even when the fluid flow is curved or not parallel to the vessel wall.
Owner:DVX LLC
System and method for ultrasound scatterer characterization
ActiveUS8915852B2Health-index calculationOrgan movement/changes detectionSonificationSpatial organization
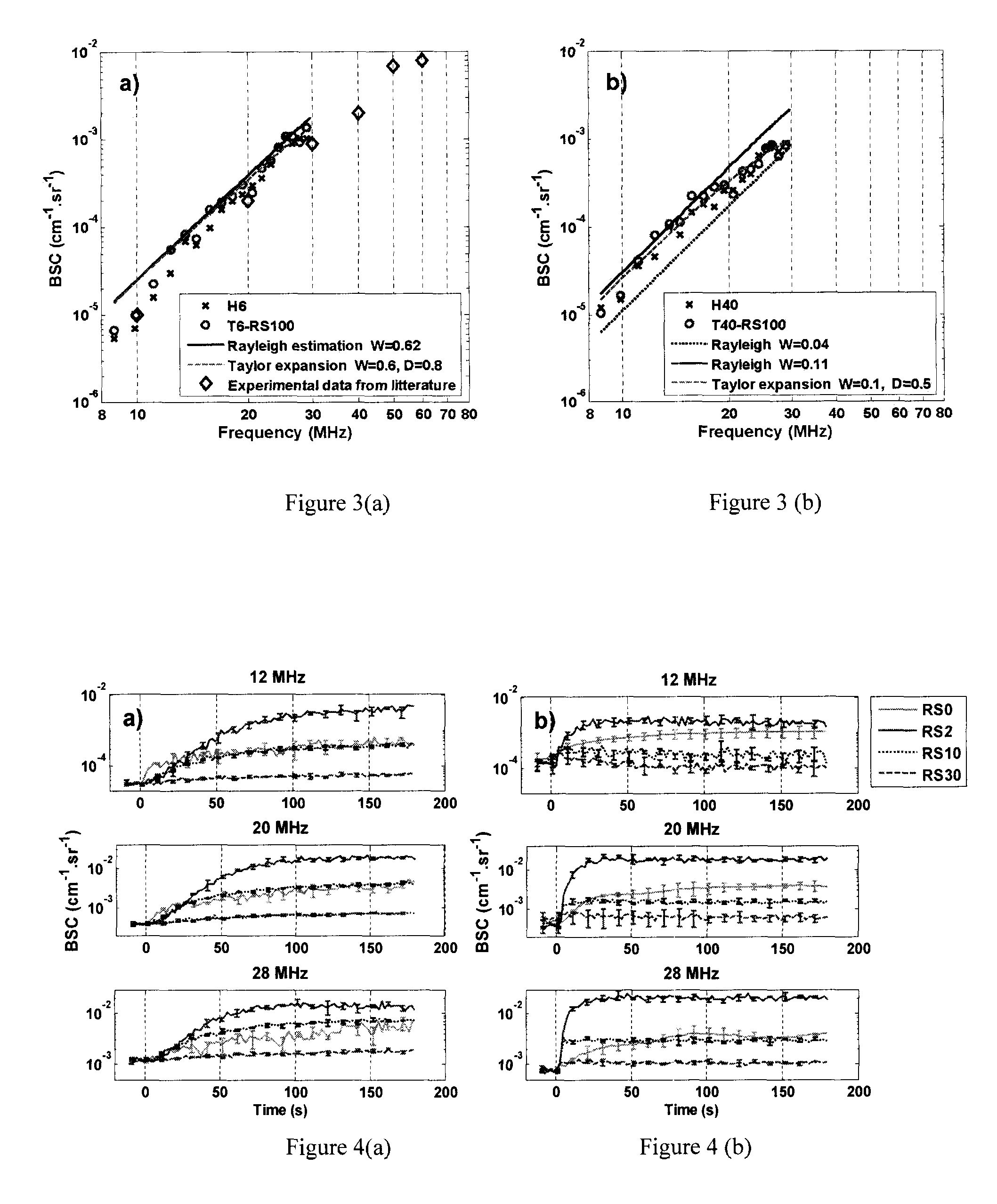
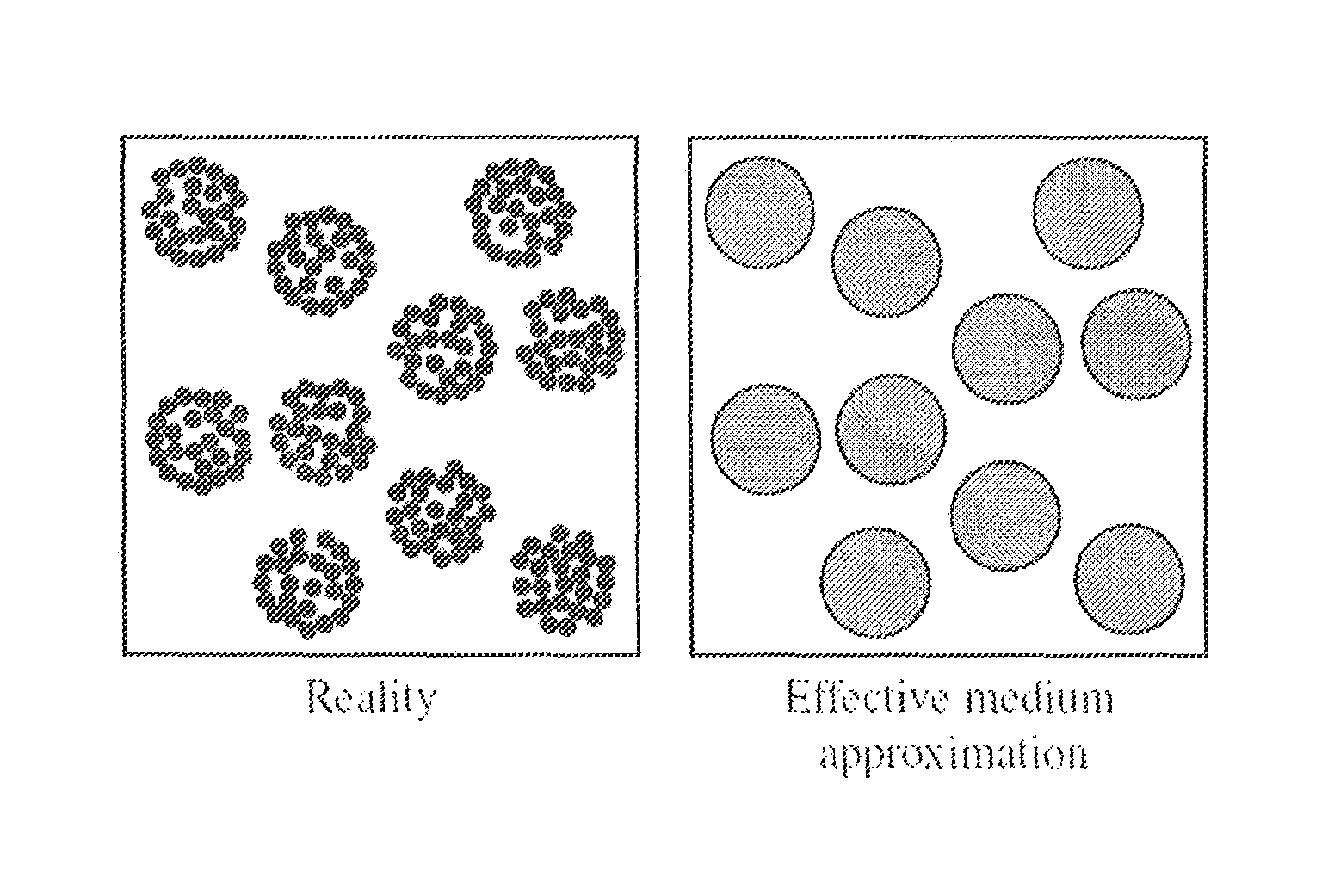
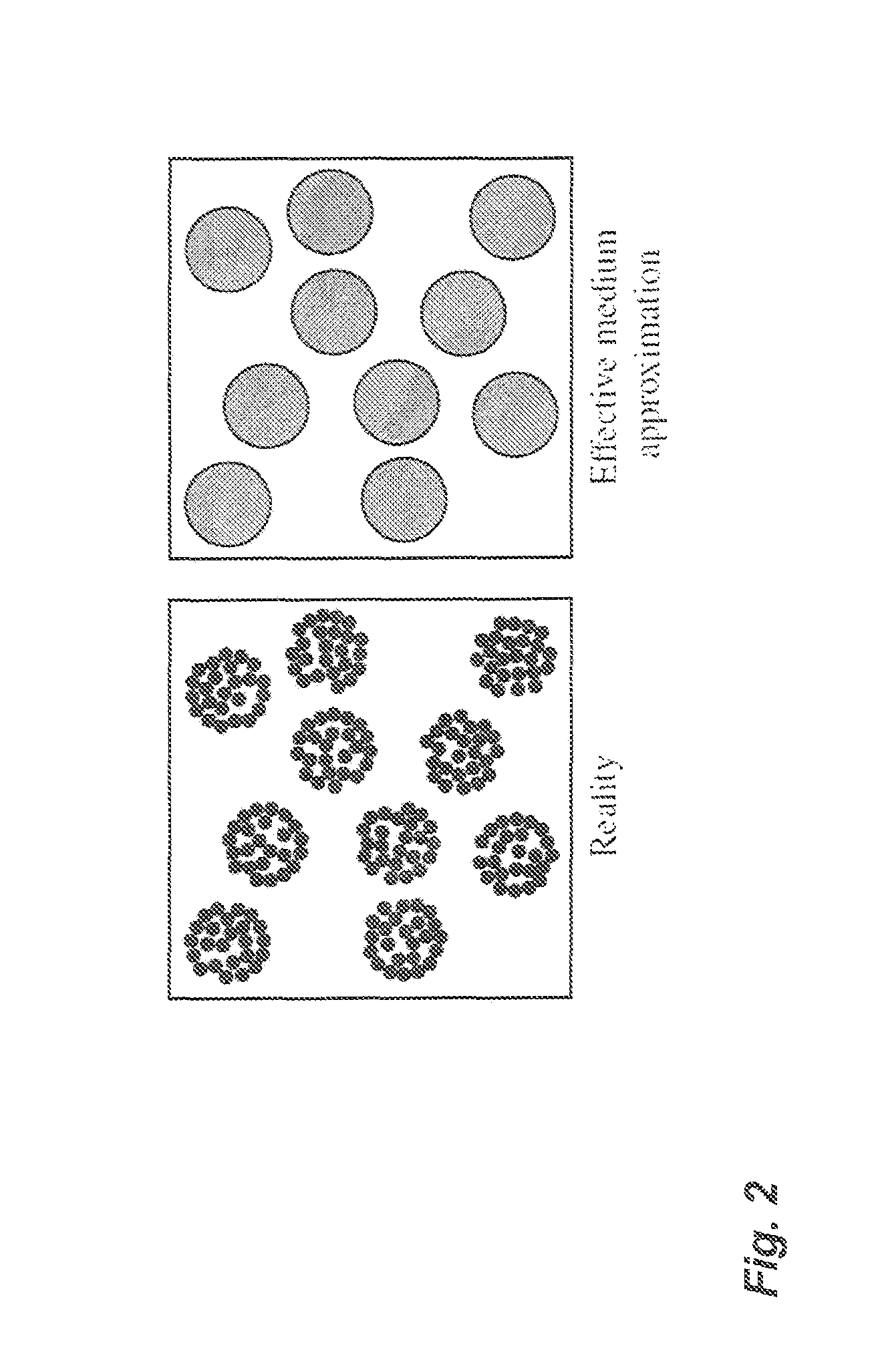
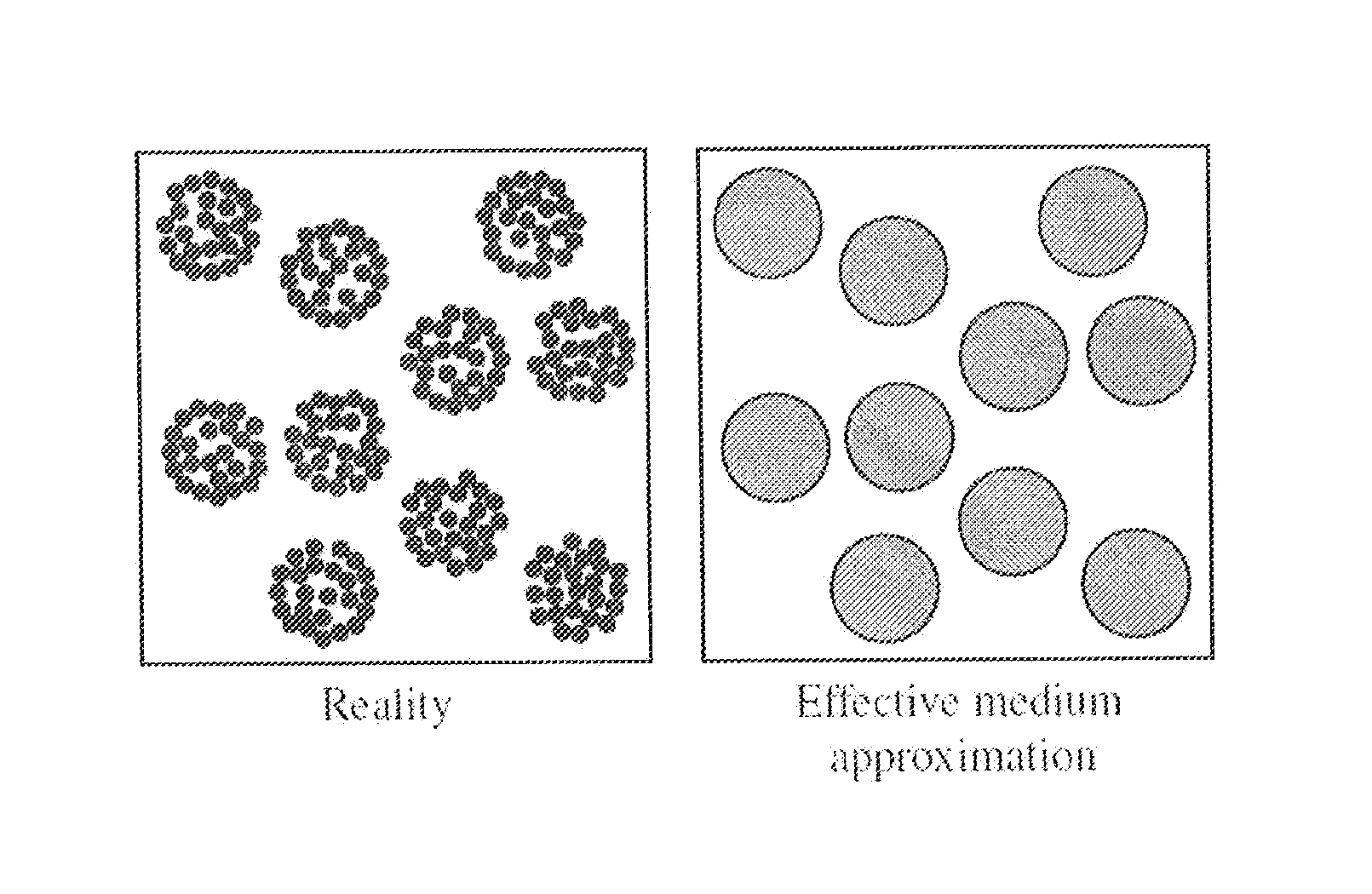
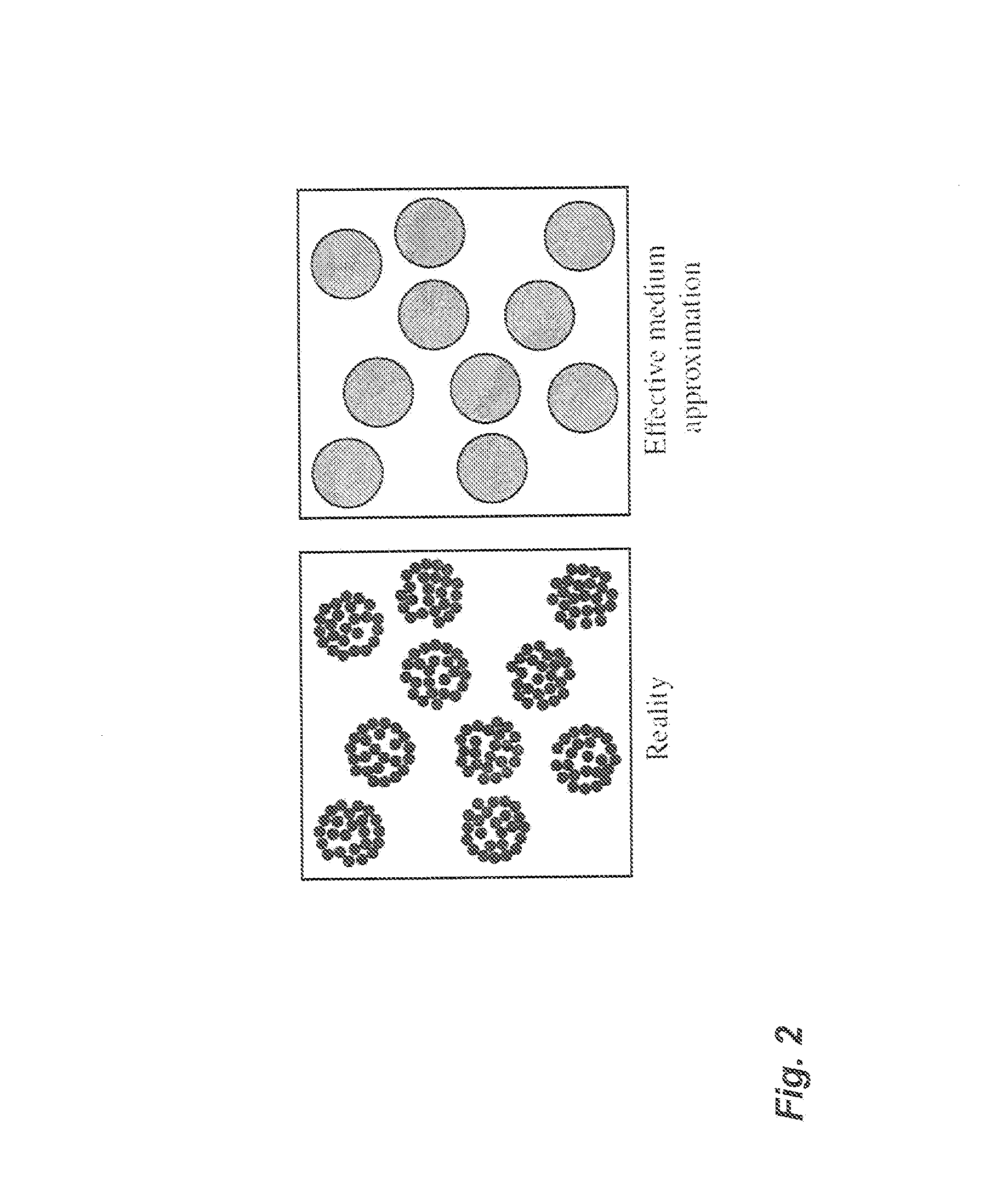
A method for characterizing ultrasound scatterers in a medium comprises receiving ultrasound data representing a region of interest comprising a plurality of scatterers in a medium, the plurality of scatterers including aggregates of the scatterers. The ultrasound data is modeled data using an effective medium theory combined with the structure factor model, the structure factor model defining the spatial organization and concentration of the aggregates. The modeled ultrasound data is compared to theoretical data obtained with the effective medium theory combined with the structure factor model. From the comparison, dimensional data of the aggregates of the scatterers and the volume concentration of scatterers in the medium is determined.
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI +1
Grain characteristic-based improved split spectrum method in cast iron ultrasonic flaw detection
InactiveCN104251887AImprove signal-to-noise ratioHigh detection sensitivityProcessing detected response signalNoiseUltrasound scattering
The invention aims to provide a new method for ultrasonic flaw detection of a pressure-bearing cast iron device, namely a grain characteristic-based improved split spectrum method in ultrasonic flaw detection of the pressure-bearing cast iron device, wherein compared with a conventional cast iron flaw detection, the method enables a system to obtain higher signal-to-noise ratio, faster response time and higher flexibility. Because an internal organizational structure of cast iron is not uniform and the grain size is larger, when ultrasonic waves are used for flaw detection, attenuation of the ultrasonic waves is larger when in propagation, sporadic reflection is prone to generate, and forest-like or grass-like echoes are produced, resulting in poor flaw detection sensitivity. The method utilizes effects of an average grain size and an crystal orientation angle (an included angle of the acoustic wave incident direction and the grain axis) of the cast iron internal grain characteristics on ultrasonic scattering and attenuation, a noise time-frequency characteristic and a flaw echo frequency dispersion characteristic with obvious grain characteristics are caused, optimized split spectrum parameters are obtained through analysis of noise and echo signals, and thus with utilization of the split spectrum technology, the scattering noise can be well reduced and the ultrasonic echo signal sensitivity can be well improved.
Owner:CHINA SPECIAL EQUIP INSPECTION & RES INST +1
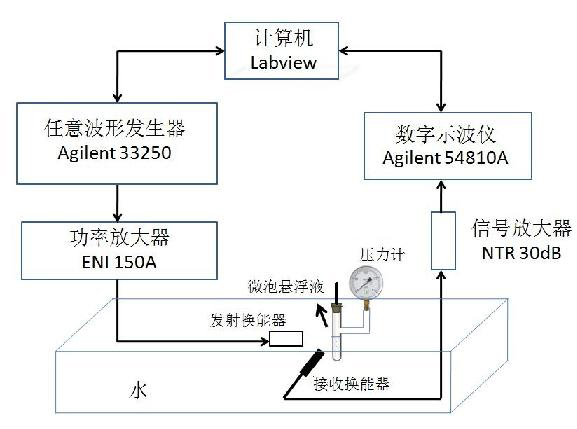
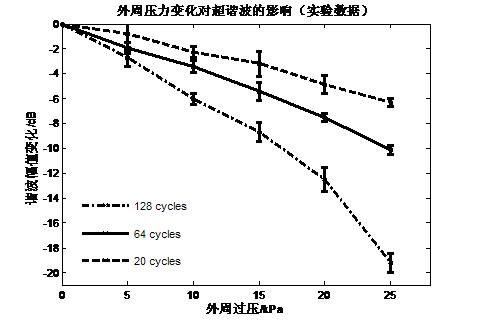
Peripheral static pressure measurement method based on micro-vesicle super-harmonic response
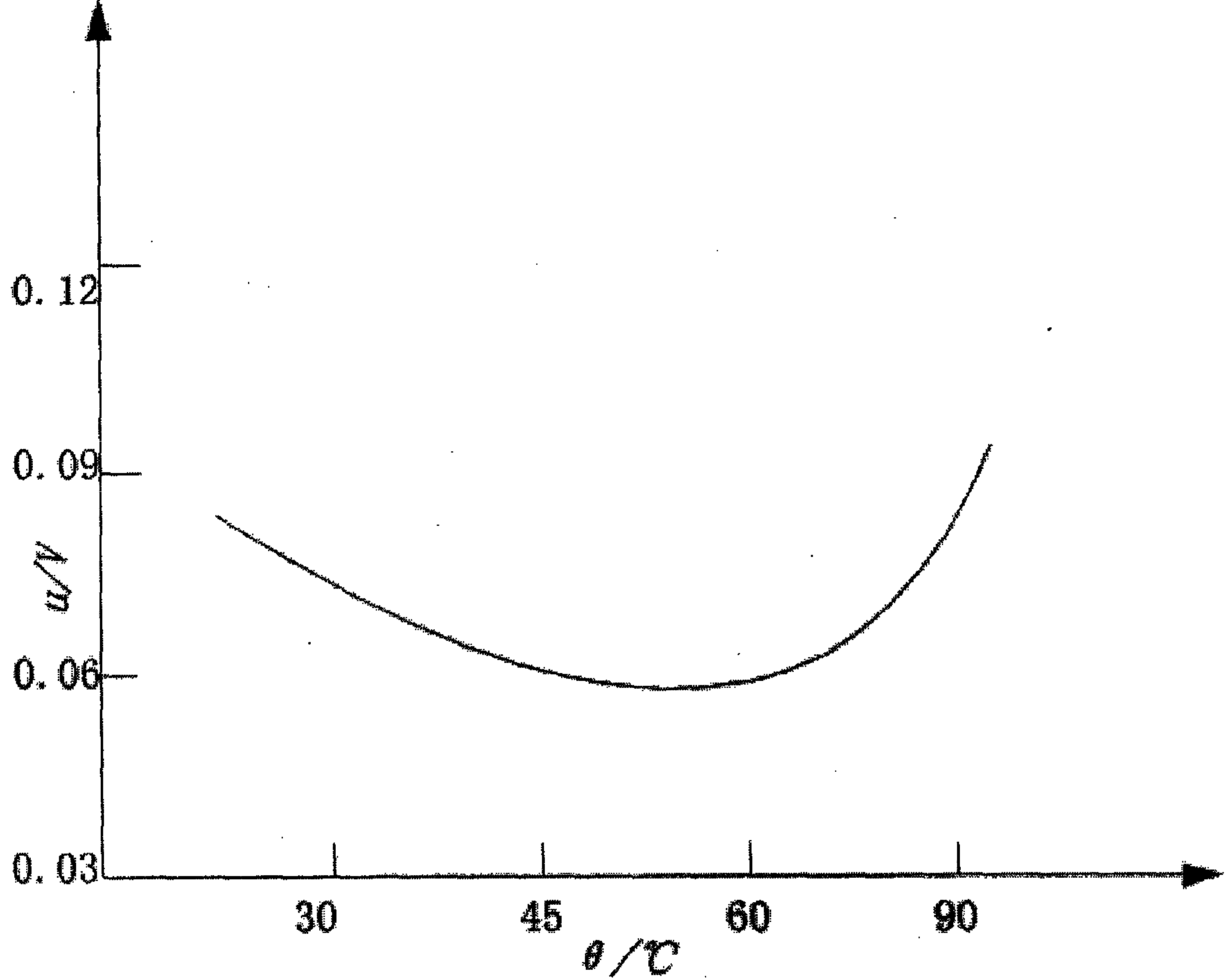
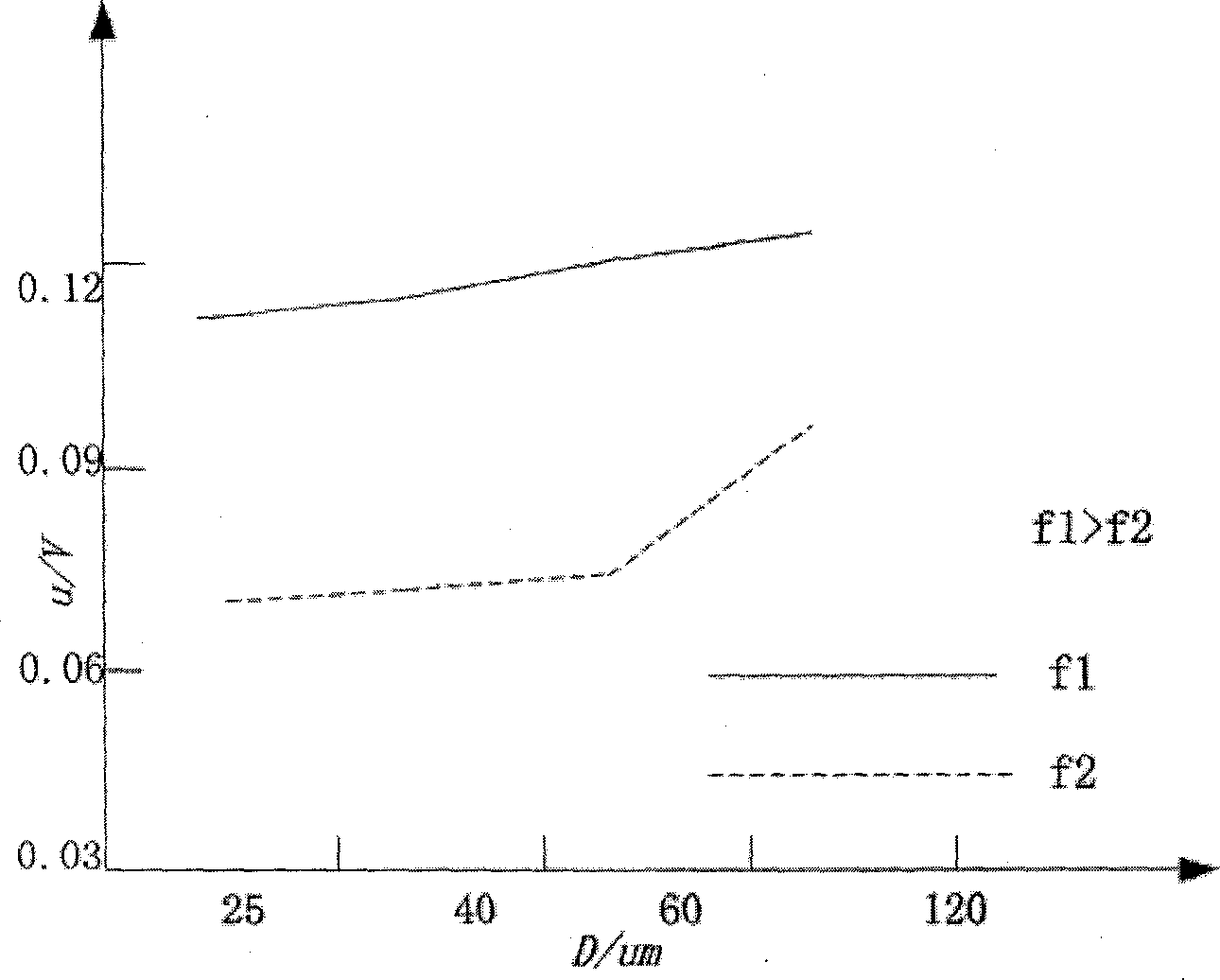
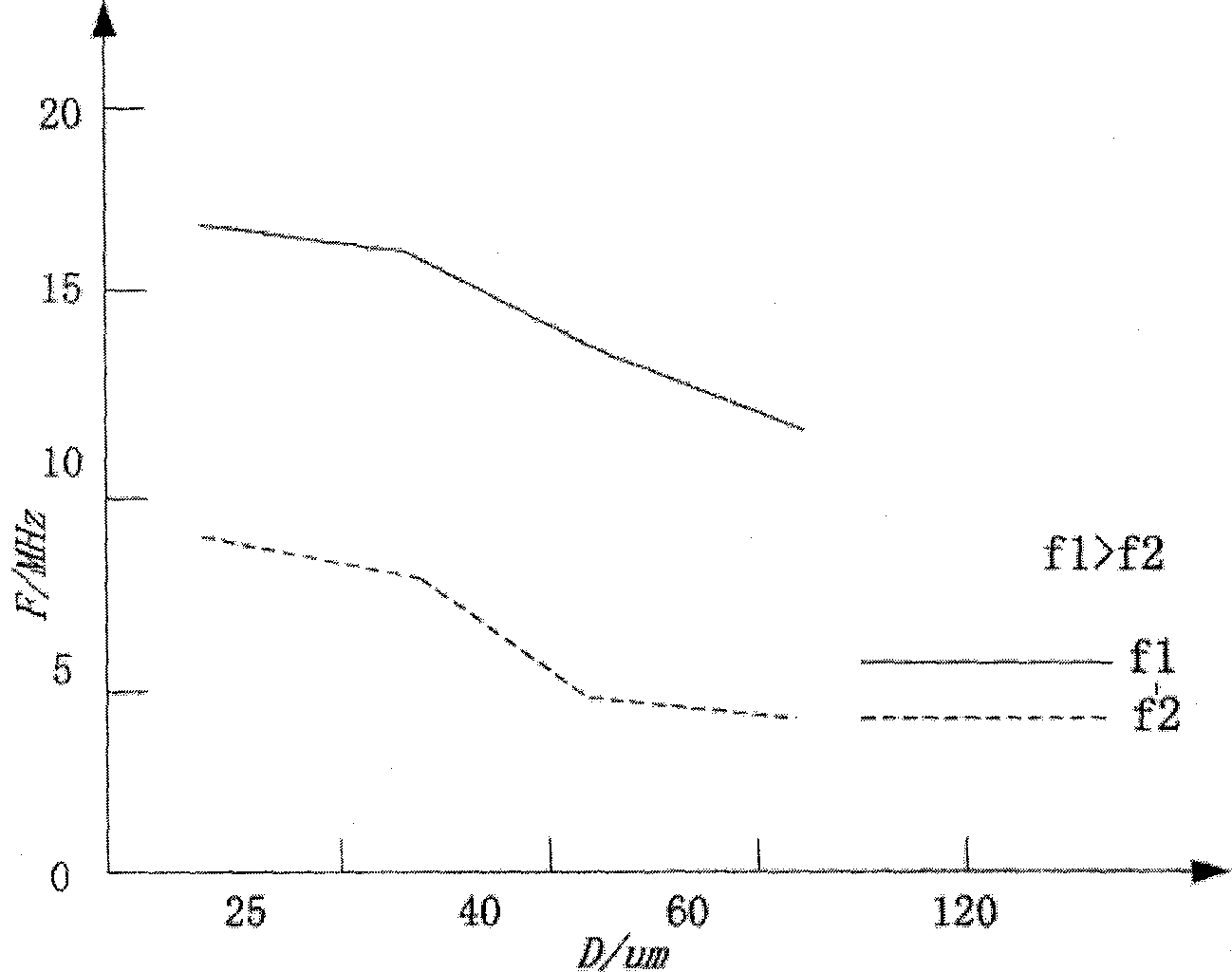
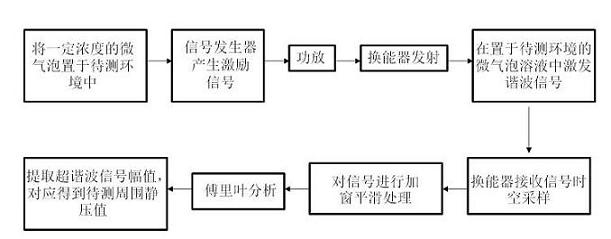
InactiveCN102488532AGood correlationImprove accuracyBlood pressure measurement devicesFrequency spectrumMeasurement precision
The invention provides a peripheral static pressure measurement method based on micro-vesicle super-harmonic response, which belongs to the expansion application field of ultrasound harmonic imaging technology and comprises the steps of arranging micro-vesicle solvents of contrast agents in peripheral static pressure environment to be tested, using a signal generator to generate an excitation signal, and magnifying the excitation signal through a power amplifier; using a transducer as a transmitting transducer, stimulating ultrasound harmonic signals in the micro-vesicle solvents under the action of the peripheral static pressure, and using another transducer as a receiving transducer to receive ultrasound scattered signals; then using fast fourier transform to treat the signals to obtain scattering atlas of the scattered signals and extract super-harmonic components in the frequency spectrograms; and calculating pulmonary artery blood pressure by comparing the change relation between super-harmonic component amplitude and peripheral pressure. The peripheral static pressure measurement method firstly uses the super-harmonic effect for measuring the pulmonary artery blood pressure and can effectively enhance measurement accuracy in the situation of certain excitation frequency and pulse signal periodicity compared with an existing sub-harmonic detection method.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
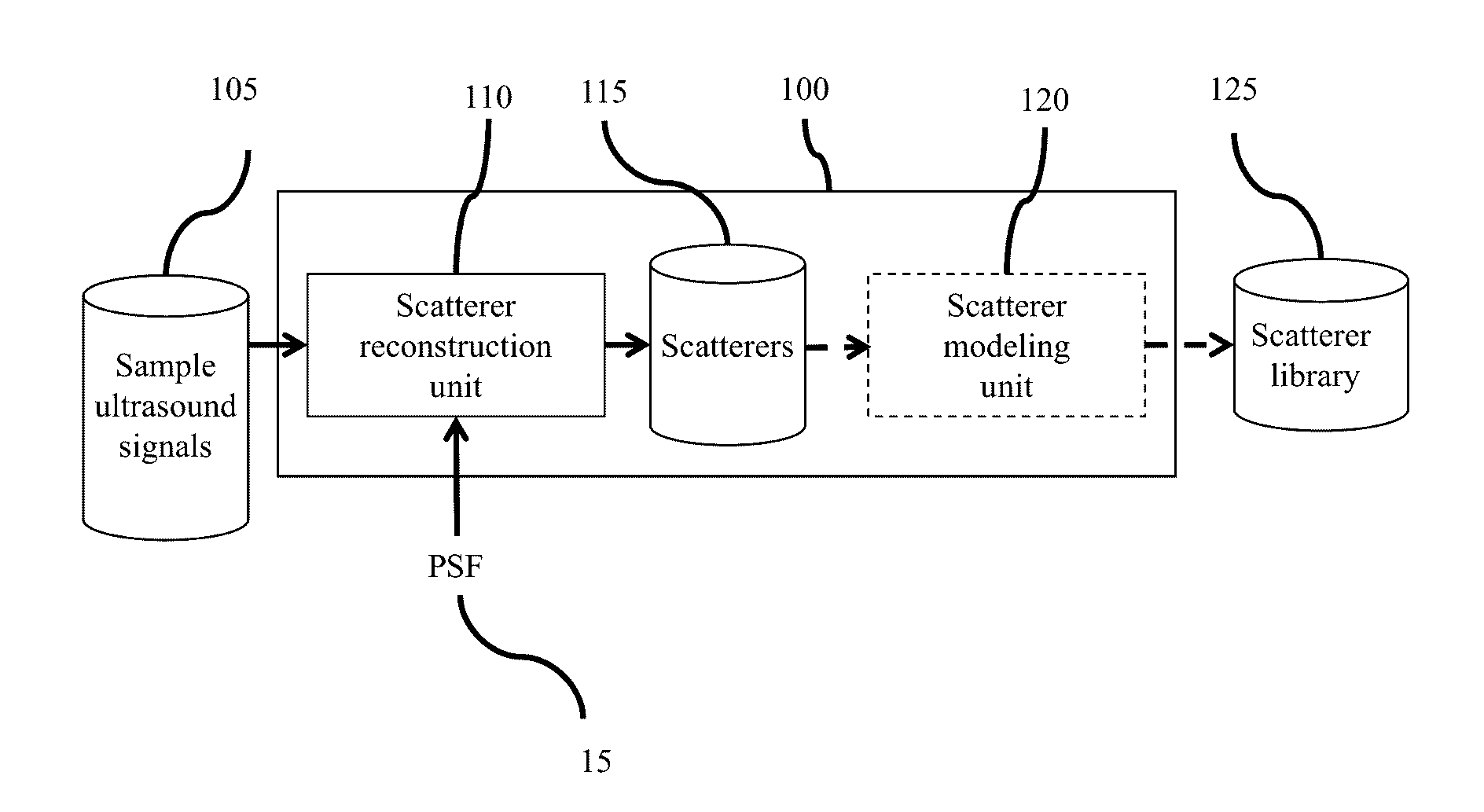
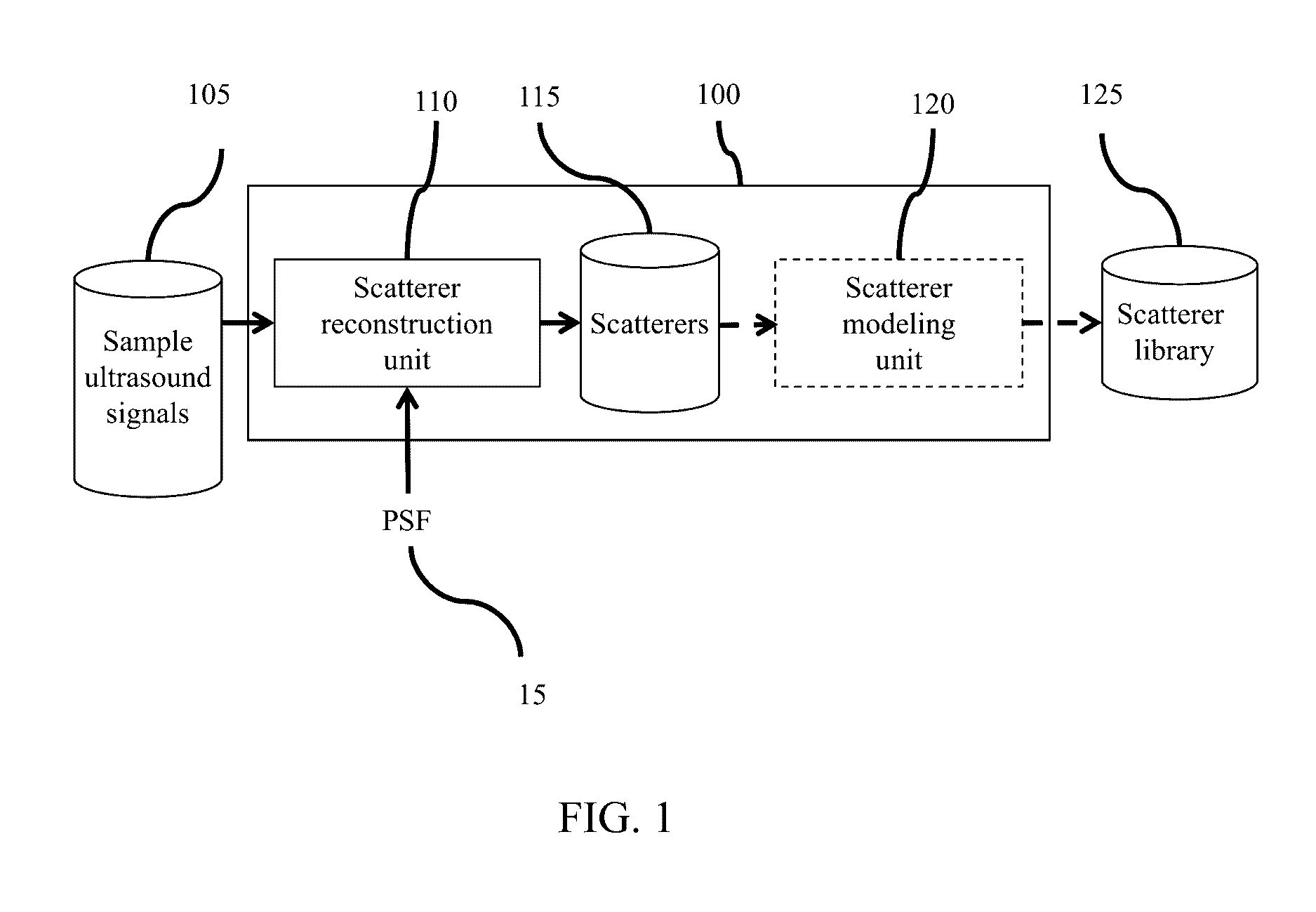
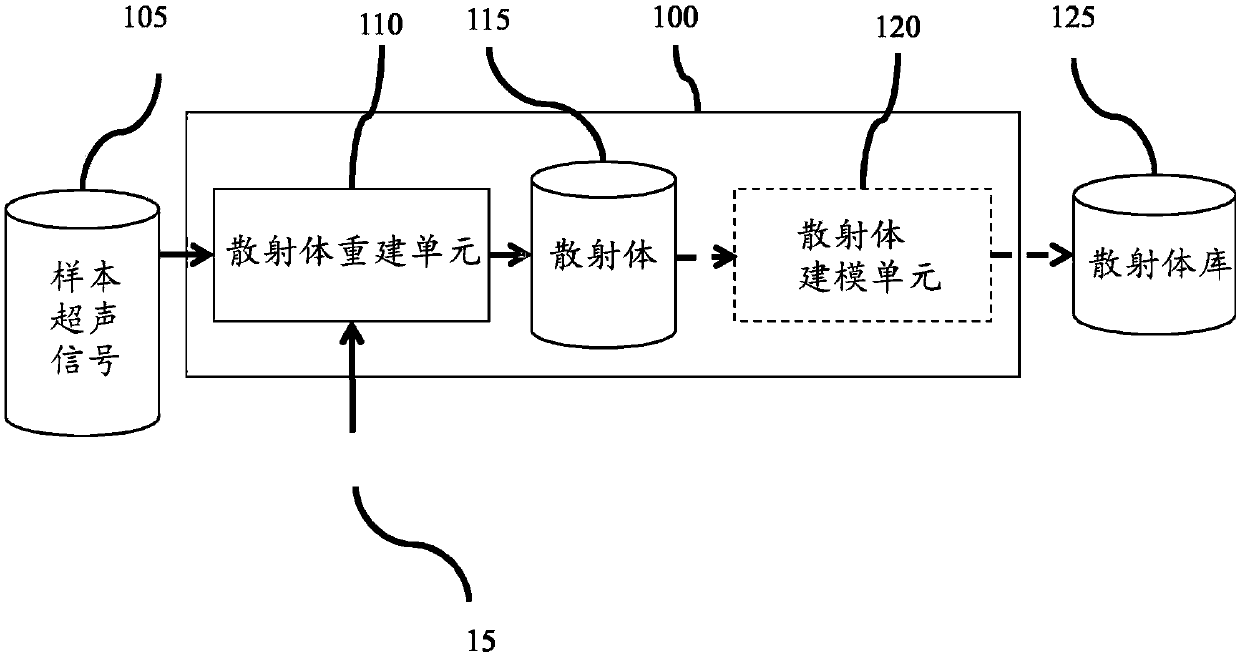
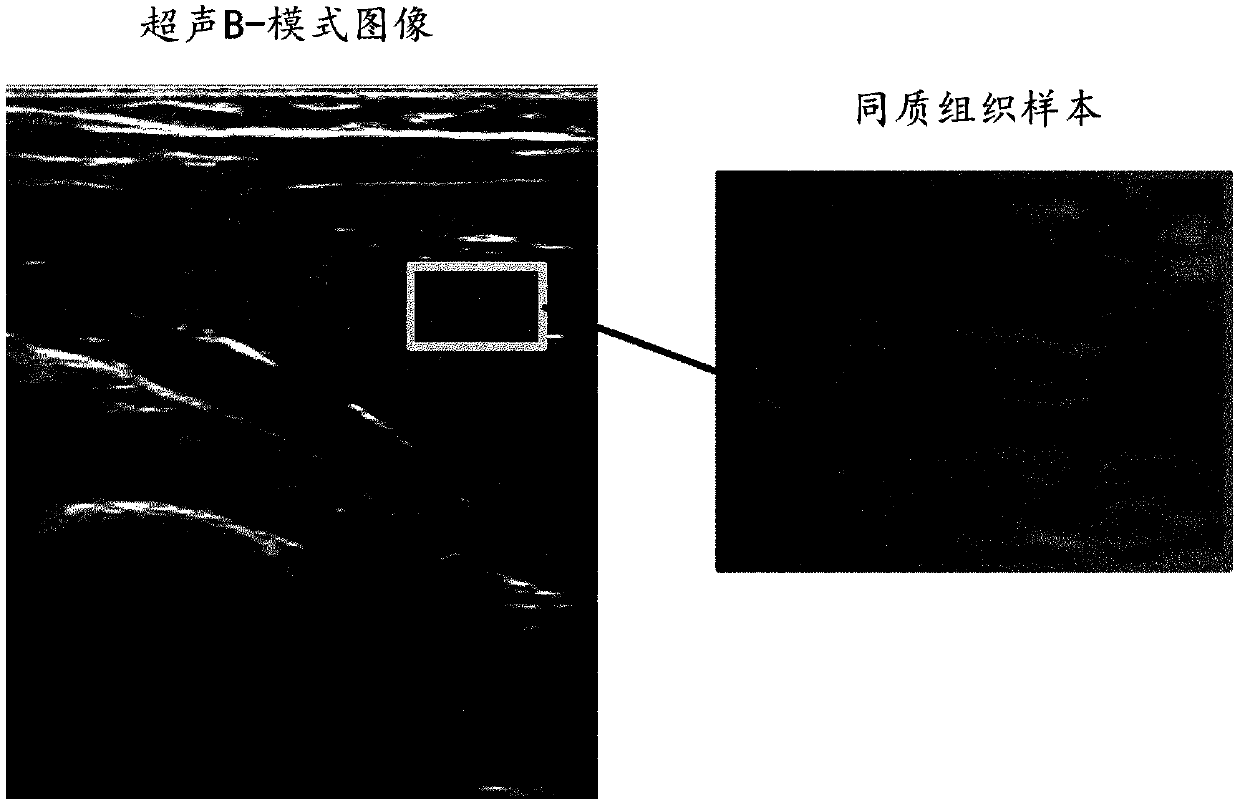
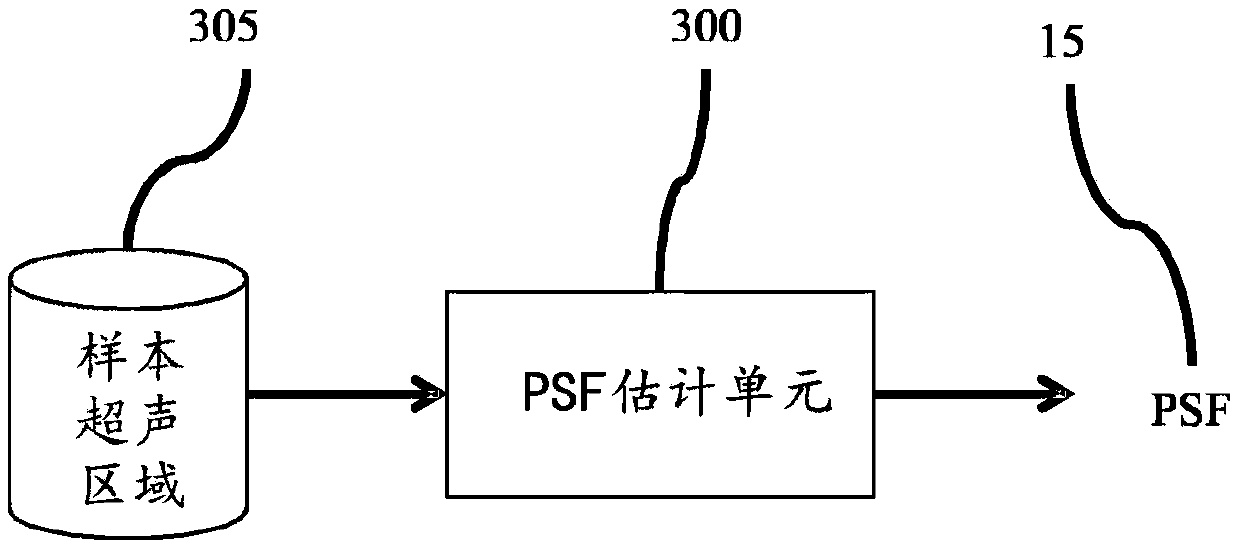
Method and Apparatus For Generating an Ultrasound Scatterer Representation
InactiveUS20170032702A1Image enhancementReconstruction from projectionPoint spreadUltrasound imaging
Realistic ultrasound imaging simulation requires modeling of scatterers corresponding to different imaging speckle appearances. A scatterer generator acquires a plurality of ultrasound signal samples, each corresponding to a different ultrasound capture and reconstructs a scatterer representation from the ultrasound signal samples and associated Point Spread Functions. Point Spread Functions (PSFs) may be estimated from multiple image acquisitions at the same reference position resulting from beam-steering. Reconstructed scatterers may then directly be used in ultrasound simulation or an additional step of modeling the scatterers may be applied. Statistical distribution parametrization or texture synthesis may be used to model the scatterers. Different scatterer models may be used for different homogeneous regions. The reconstructed scatterers and / or the scatterer models may be registered into a library of scatterers by the scatterer generator.
Owner:VIRTAMED
Acceleration and enhancement methods and system for ultrasound scatterer structure visualization
ActiveUS20160133020A1Quality improvementImprove resolutionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementSonificationComputer science
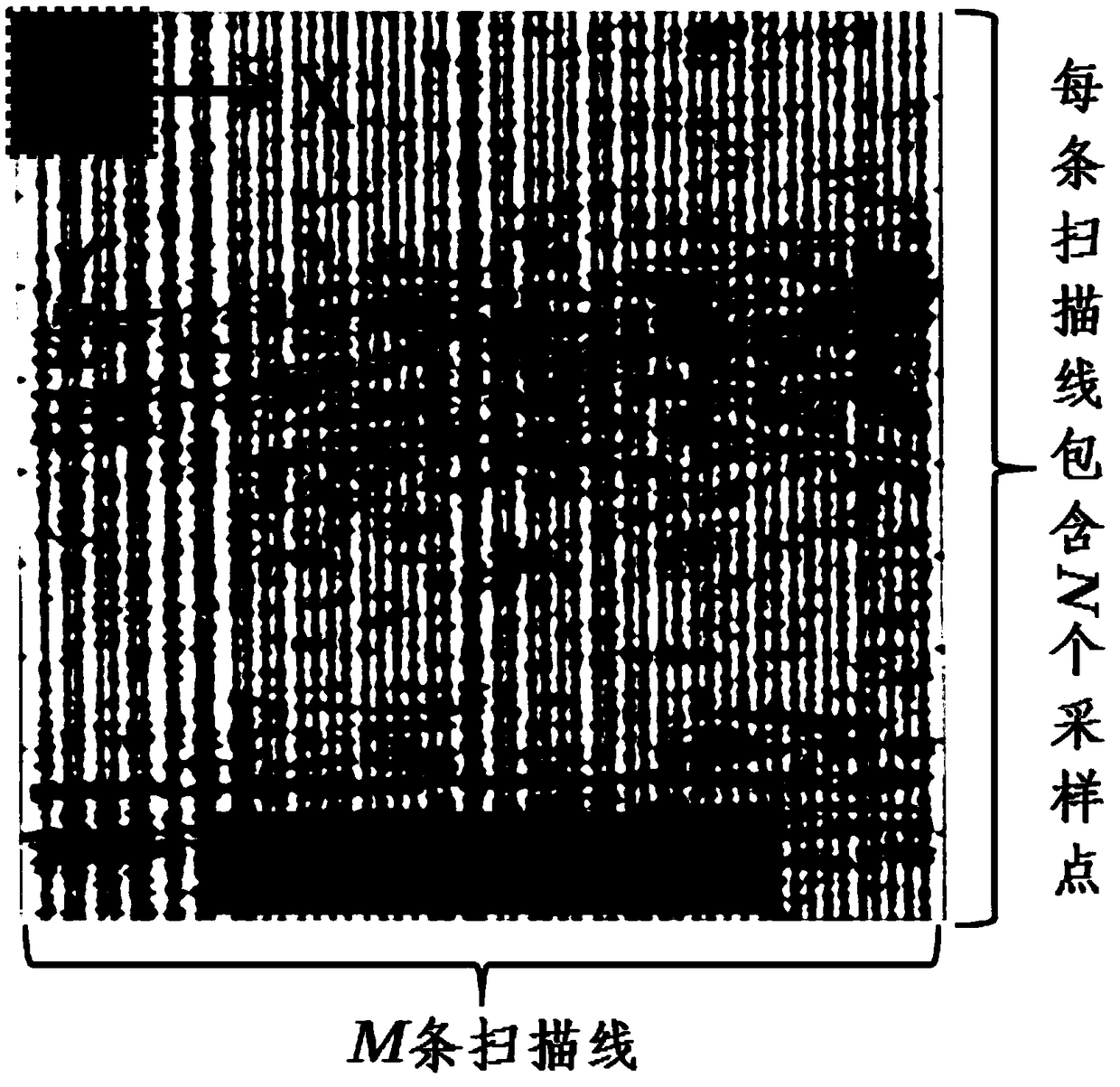
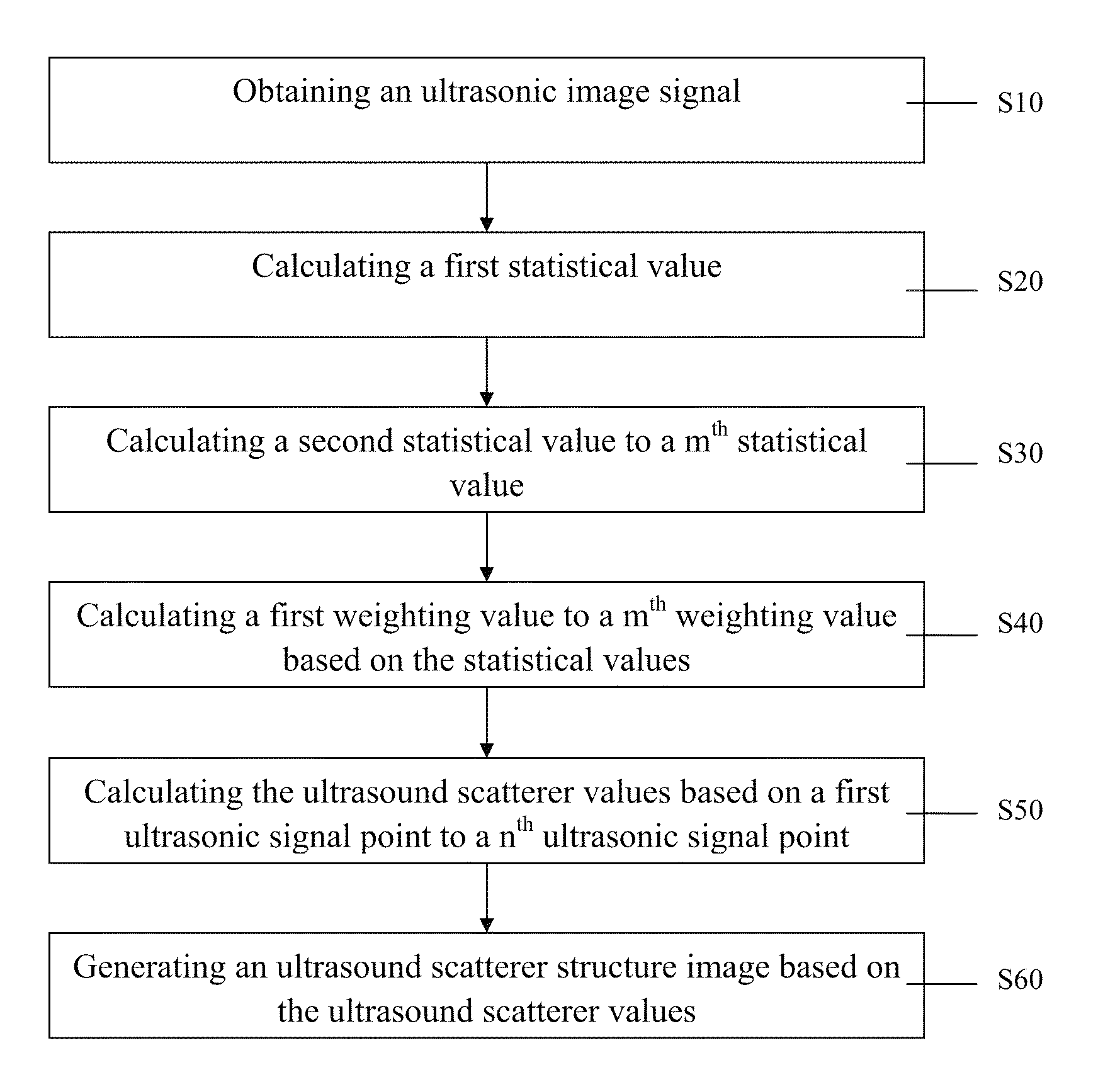
The present invention provides an acceleration and enhancement methods for ultrasound scatterer structure visualization. The method includes: obtaining an ultrasonic image, calculating all values of the ultrasonic signal points in each mth window centered at a nth signal point to obtain a plurality of original statistical values anxm, obtaining a plurality of mth statistical values by averaging value of original statistical values in the same window, calculating a plurality of mth weighting values based on the statistical values by different weighting formulas, multiplying each weighting value with the original statistical values corresponding to the various size of windows, summing up to obtain an ultrasound structure scatterer value of the nth ultrasonic signal point, and generating an ultrasound scatterer structure image based on a matrix of the ultrasound scatterer values. The present invention further combined interpolation method can reduce the computation time and retain the 80% accuracy.
Owner:AMCAD BIOMED CORP
Defect classification method and system based on ultrasonic phased array imaging
ActiveCN114359193AAccurate scatteringAccurately reflectImage analysisAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesPhased arrayUltrasound scattering
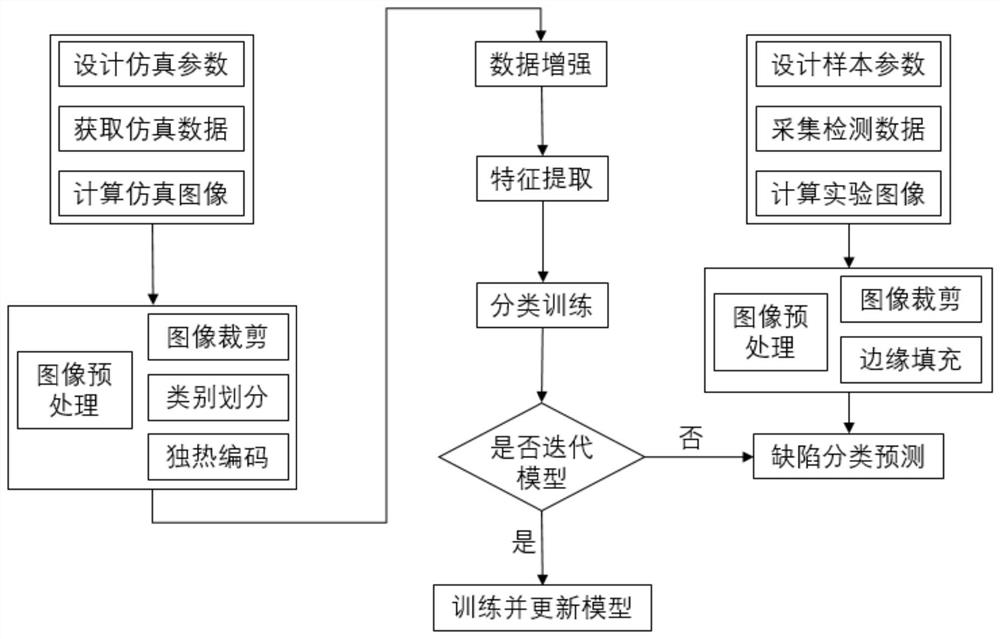
The invention provides a defect classification method and system based on ultrasonic phased array imaging, and belongs to the field of nondestructive detection.The method comprises the steps that ultrasonic phased array imaging is adopted for a to-be-detected sample piece to obtain ultrasonic full-matrix data; performing full-focusing processing on the ultrasonic full-matrix data, performing color coding according to the signal amplitude, and obtaining an image of the sample piece to be detected; preprocessing an image of a to-be-detected sample, inputting the preprocessed image into the classification prediction model, and obtaining defect classification of the to-be-detected sample; a method for training the classification prediction model comprises the following steps of: acquiring simulation data by simulating ultrasonic phased array imaging by utilizing a defect ultrasonic scattering data finite element simulation method; after full-focusing processing is carried out on the simulation data, a simulation image is obtained; preprocessing the simulation image and then performing data enhancement; carrying out image feature extraction on the simulation image by adopting a convolutional neural network; and inputting the image features into a full connection layer, and training a classification prediction model by taking defect classification as output. According to the invention, the accuracy of defect classification is improved.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
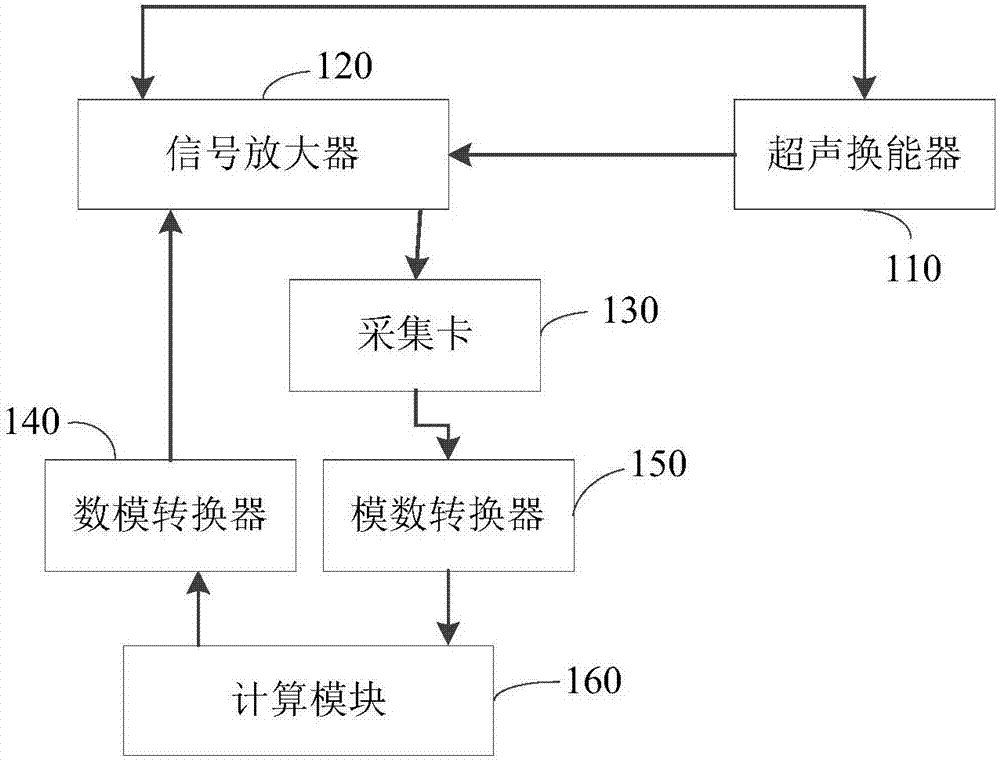
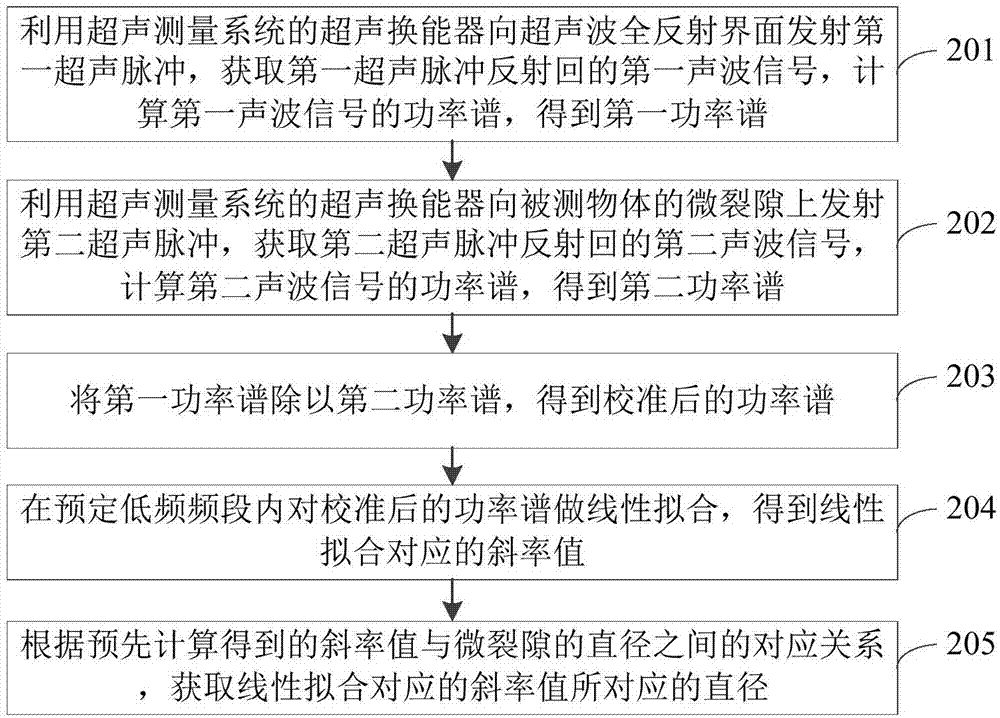
Ultrasonic measurement system and detection method for detecting deep structural fissures
PendingCN107290429AIrrelevantQuantitative Feature ScaleAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesConvertersFrequency spectrum
The present application discloses an ultrasonic measurement system and a detection method for detecting deep structural fissures. By utilizing the detection method, the size of a deep sub-wavelength-scale linear micro-fissure of a material can be quantitatively detected. After being excited by ultrasonic pulses, the micro-fissure deep in the material can generate ultrasonic scattering and reflection; after being received by an ultrasonic transducer, ultrasonic signals pass through a signal amplifier and an analog-to-digital converter and are stored in a computer; and a power spectrum of the ultrasonic signals is obtained by computing. A spectrum parameter, namely a power spectrum slope, can be obtained by carrying out linear fitting on low-frequency bands of the power spectrum, the spectrum slope and the diameter of the micro-fissure are in one-to-one correspondence, and the diameter of the sub-wavelength micro-fissure can be quantitatively evaluated by computing the slope. Because the quantitative detection method needs a low working frequency, the method provides a non-invasive, non-ionizing, cheap and safe method for evaluating the scale of the deep micro-fissure.
Owner:WUXI HAIYING ELECTRONICS MEDICAL SYST
System and method for ultrasound scatterer characterization
A method for characterizing ultrasound scatterers in a medium comprises receiving ultrasound data representing a region of interest comprising a plurality of scatterers in a medium, the plurality of scatterers including aggregates of the scatterers. The ultrasound data is modeled data using an effective medium theory combined with the structure factor model, the structure factor model defining the spatial organization and concentration of the aggregates. The modeled ultrasound data is compared to theoretical data obtained with the effective medium theory combined with the structure factor model. From the comparison, dimensional data of the aggregates of the scatterers and the volume concentration of scatterers in the medium is determined.
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI +1
Time reversal and phase coherent music techniques for super-resolution ultrasound imaging
ActiveUS9955944B2Precise positioningHigh resolutionOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsPhase responseSonification
Systems and methods for super-resolution ultrasound imaging using a windowed and generalized TR-MUSIC algorithm that divides the imaging region into overlapping sub-regions and applies the TR-MUSIC algorithm to the windowed backscattered ultrasound signals corresponding to each sub-region. The algorithm is also structured to account for the ultrasound attenuation in the medium and the finite-size effects of ultrasound transducer elements. A modified TR-MUSIC imaging algorithm is used to account for ultrasound scattering from both density and compressibility contrasts. The phase response of ultrasound transducer elements is accounted for in a PC-MUSIC system.
Owner:TRIAD NAT SECURITY LLC
Phased array ultrasonic evaluation method for grain size
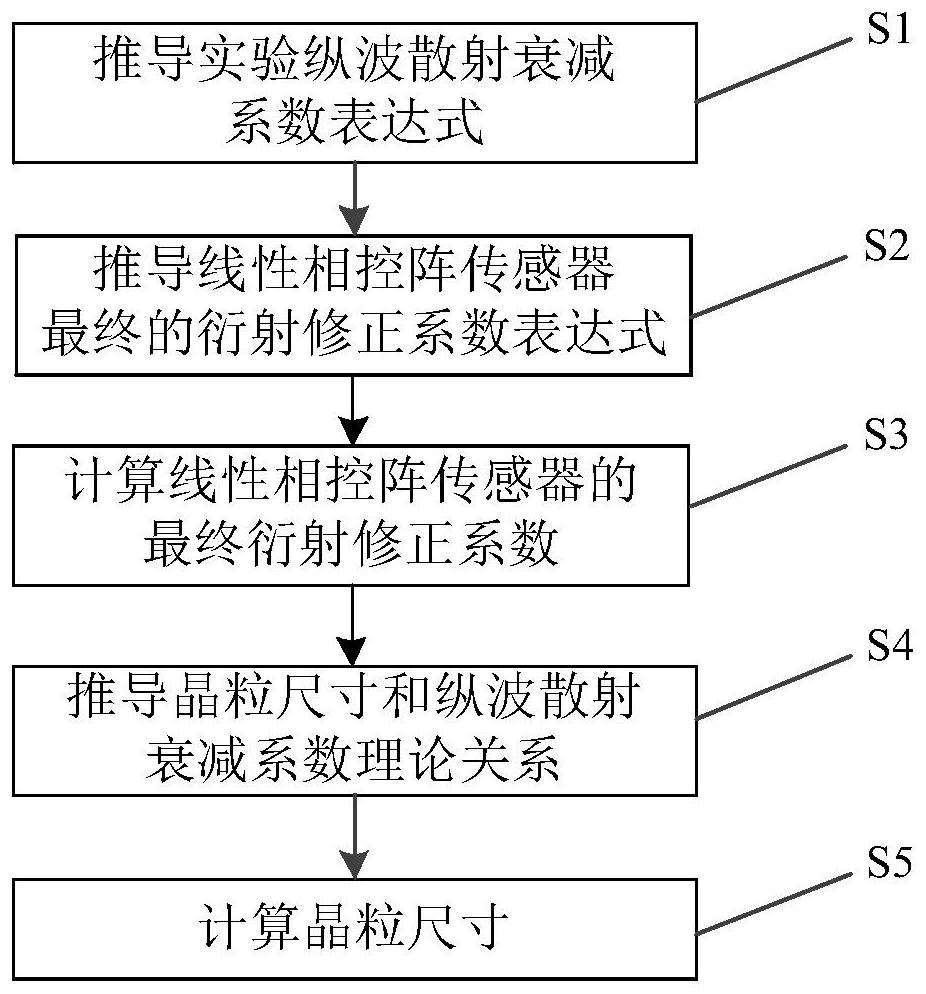
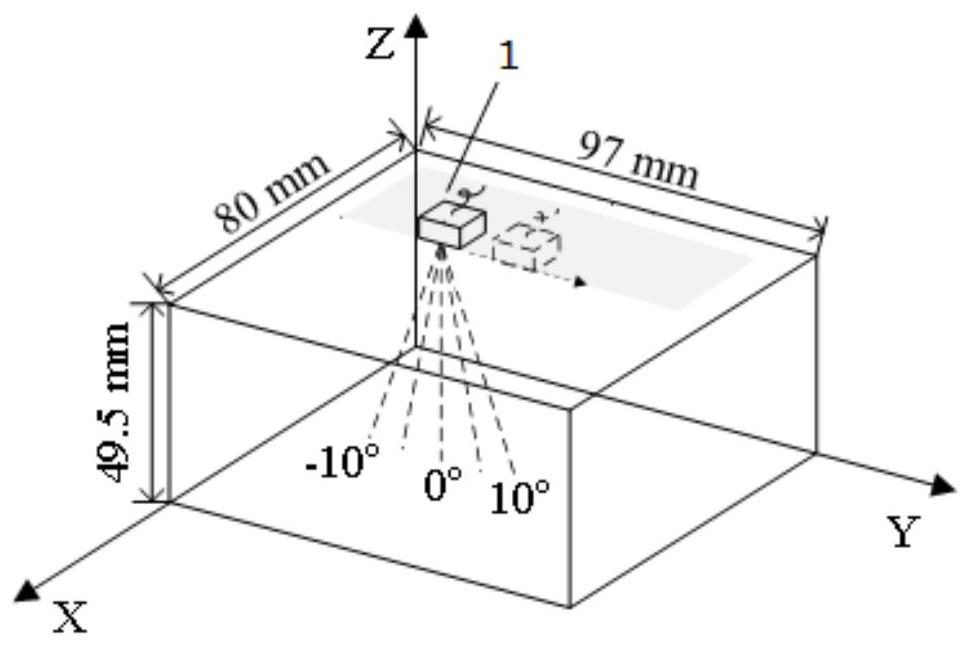
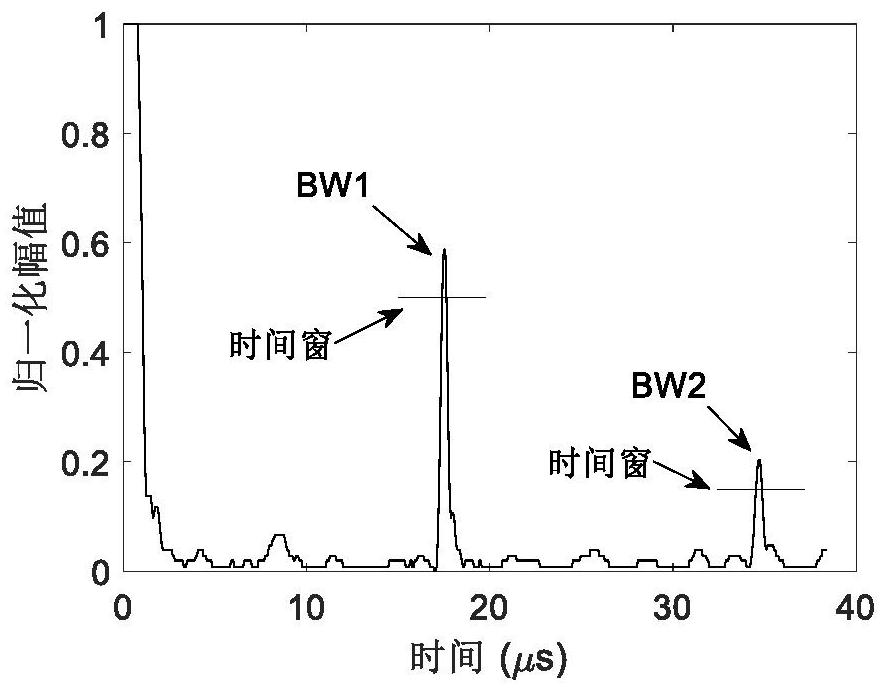
ActiveCN113029880ARelatively small errorFeasible meansAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesProcessing detected response signalAttenuation coefficientUltrasound scattering
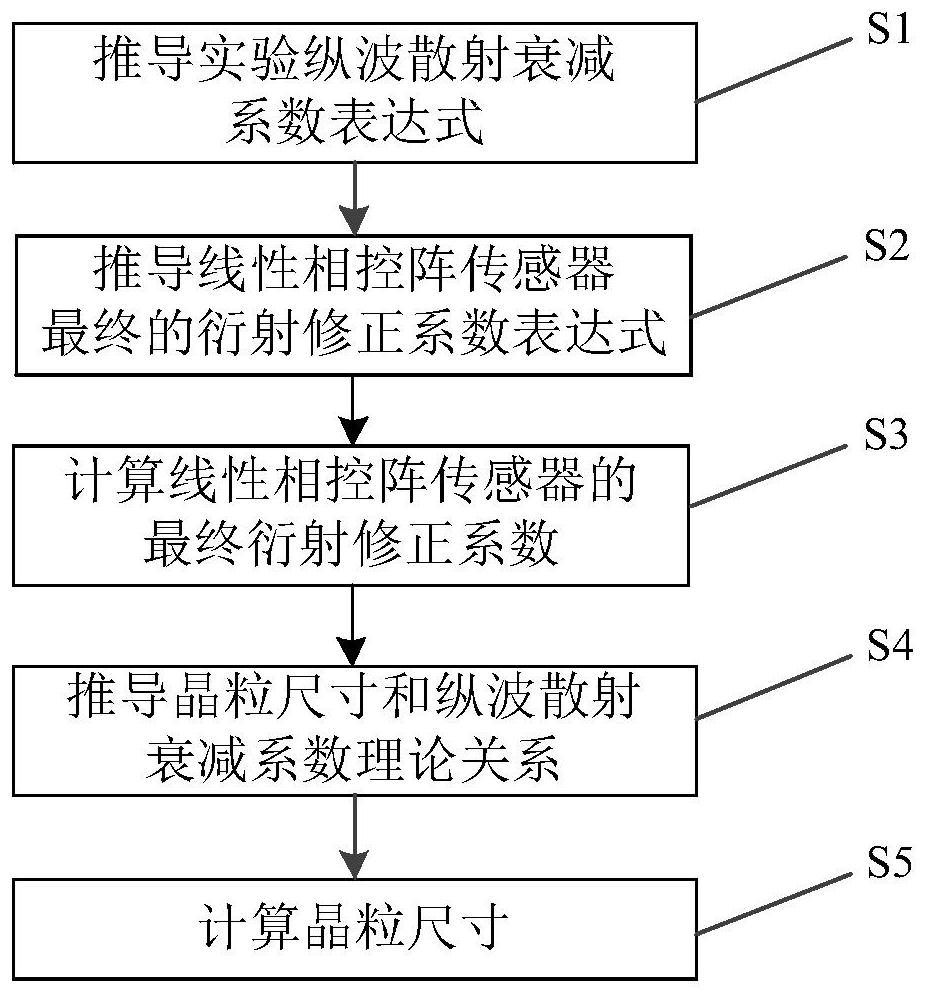
The invention provides a phased array ultrasonic evaluation method for grain size. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining an experimental longitudinal wave scattering attenuation coefficient by using primary bottom surface echo and secondary bottom surface echo; deriving a radiation sound field of the linear phased array probe according to the Huygens principle, receiving average sound pressure through the probe, defining a diffraction correction coefficient of the linear phased array probe, and calculating a final diffraction correction coefficient; obtaining a theoretical relationship between the grain size and the longitudinal wave scattering attenuation coefficient according to a Weaver ultrasonic scattering model, and obtaining an agent model of the grain size and the theoretical longitudinal wave scattering attenuation coefficient by using polynomial fitting based on a nonlinear least square method; and substituting the experimental longitudinal wave scattering attenuation after the diffraction loss is eliminated into the proxy model, and inverting a grain size value. According to the method, diffraction loss interference is eliminated, multi-angle acoustic beam information is fused, compared with a traditional method, relative errors are greatly reduced, and a feasible and reliable means is provided for grain size estimation of polycrystalline materials.
Owner:中国工程物理研究院研究生院
Novel composite fiber based on sweet sorghum skin fiber and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105239199AHigh mechanical strengthPlay utilizationConjugated cellulose/protein artificial filamentsWet spinning methodsFiberFiltration
The invention provides a novel composite fiber based on sweet sorghum skin fiber and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) removing leaves of sweet sorghum stalks which are about 15-20 cm long, cleaning the sweet sorghum stalks, obtaining sweet sorghum skin and flesh pith containing normal juice through a separator, performing squeezing separation on the flesh pith containing the normal juice to obtain stalk flesh residue, cleaning and drying the stalk flesh residue, and obtaining stalk residue powder after smashing and filtration; (2) refining the sweet sorghum skin into skin fiber strips, placing the skin fiber strips in a solvent to undergo ultrasound scattering, washing and drying to obtain the skin fiber; (3) evenly mixing the stalk residue powder and the skin fiber; after distilled water is added for swelling for a period of time, adding chitosan and sodium alginate, performing high-speed stirring at a high temperature, performing vacuum defoamation, and performing filtration to obtain spinning solution; (4) causing the spinning solution to form nascent fiber through a wet spinning technology, and obtaining the composite fiber based on the sweet sorghum skin fiber through drafting, washing and winding. The fiber is a composite fiber integrating toughness, antibiosis, anti-inflammation and greenness.
Owner:HUZHOU SHENXIANG SILK
Flow measurement apparatus and method
ActiveUS8852110B2Accurate measurementAccurate flow measurementAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesTesting/calibration apparatusTransducerBlood vessel
The velocity of fluids containing particles that scatter ultrasound can be measured by determining the Doppler shift of the ultrasound scattered by the particles in the fluid. Measuring fluid flow in cylindrical vessels such as blood vessels is an important use of Doppler ultrasound. This invention teaches using various configurations of cylindrical diffraction-grating transducers and cylindrical non-diffraction-grating transducers that suppress the Doppler shift from non-axial components of fluid velocity while being sensitive to the Doppler shift produced by axial velocity components. These configurations thus provide accurate measurement of the net flow down the vessel, even when the fluid flow is curved or not parallel to the vessel wall.
Owner:DVX LLC
Power spectrum based ultrasonic scattering particle diameter imaging method
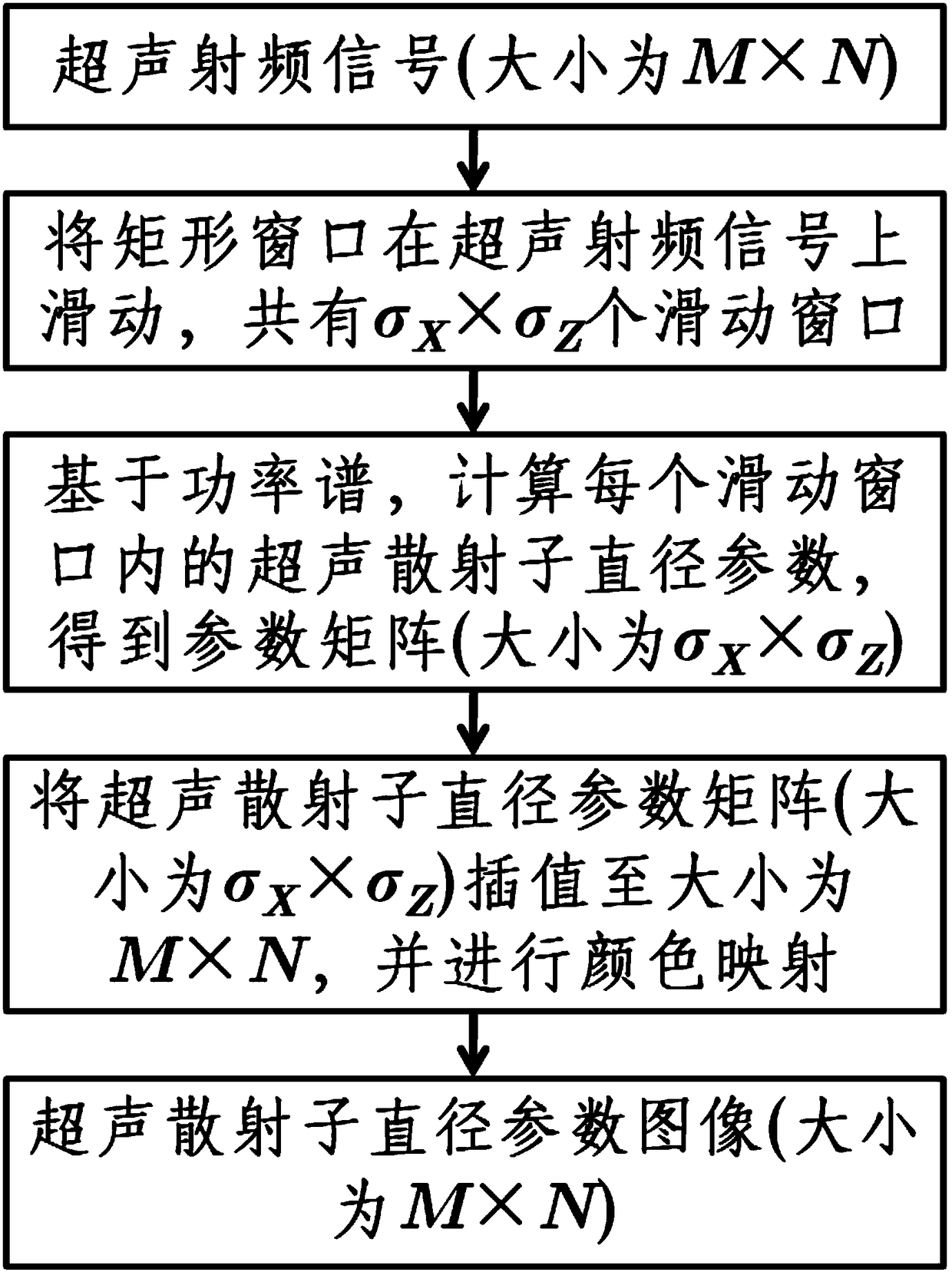
ActiveCN109247951ASatisfy real-timeMeet needsInfrasonic diagnosticsUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic image/data processingColor mappingSlide window
The invention discloses a power spectrum based ultrasonic scattering particle diameter imaging method. Based on ultrasonic radio frequency signals, the method calculates a power spectrum, calculates an ultrasonic scattering particle diameter parameters and calculates an ultrasonic scattering particle diameter parameter image. The method is as below: sliding a sliding window over an ultrasonic RF signal; calculating ultrasonic scattering particle parameters in each sliding window based on the power spectrum to obtain a matrix of ultrasonic scattering particle parameter values; interpolating thematrix of the ultrasonic scattering sub-parameter values into the size of the ultrasonic RF signal; and performing color mapping to obtain an ultrasound scattering particle diameter parameter image.The ultrasonic scattering particle diameter imaging method of the present invention can be used for ultrasonic tissue characterization of biological tissues such as mammary gland, liver and the like.
Owner:SHENZHEN CERTAINN TECH CO LTD
Acceleration and enhancement methods and system for ultrasound scatterer structure visualization
ActiveUS9412167B2Improve quality and resolutionMaintain accuracyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementSonificationComputer science
The present invention provides an acceleration and enhancement methods for ultrasound scatterer structure visualization. The method includes: obtaining an ultrasonic image, calculating all values of the ultrasonic signal points in each mth window centered at a nth signal point to obtain a plurality of original statistical values anxm, obtaining a plurality of mth statistical values by averaging value of original statistical values in the same window, calculating a plurality of mth weighting values based on the statistical values by different weighting formulas, multiplying each weighting value with the original statistical values corresponding to the various size of windows, summing up to obtain an ultrasound structure scatterer value of the nth ultrasonic signal point, and generating an ultrasound scatterer structure image based on a matrix of the ultrasound scatterer values. The present invention further combined interpolation method can reduce the computation time and retain the 80% accuracy.
Owner:AMCAD BIOMED CORP
Ultrasonic phased array detection device and method for automobile third-generation hub bearing outer ring
PendingCN113030266AImprove defect detection performanceSolve the problem of ultrasonic signal recognitionMachine part testingAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMechanical engineeringPhased array
The present invention provides an ultrasonic phased array detection device and method for an automobile third-generation hub bearing outer ring, a phased array probe is arranged on the side wall of the hub bearing outer ring, and a six-degree-of-freedom mechanical arm with the probe is used for conducting ultrasonic phased array detection on the hub bearing outer ring along the section of the hub bearing outer ring, and a phased array probe array element self-transmitting and self-receiving mode is adopted to obtain a reflection echo signal of the hub bearing outer ring defect and transmit the reflection echo signal to a computer. Computer writing software carries out data storage and signal processing on the received reflection echo signals, and finally, a frequency domain synthetic aperture focusing imaging algorithm is used for carrying out defect imaging on the hub bearing outer ring. According to the method, a water immersion ultrasonic phased array detection method is adopted, and the problems are solved that ultrasonic scattering of a small-angle, small-size, thin-wall and complex curved surface of the hub bearing is serious, and the defect detection blind area is large, and the defect detection capability of the hub bearing is improved.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
A loudspeaker box having mosquito repellent function
InactiveCN104661123AWith mosquito repellent functionMosquito repellentTransducer casings/cabinets/supportsAnimal scienceEngineering
The present invention belongs to the technical field of computer hardware, and specifically provides a loudspeaker box having a mosquito repellent function. The loudspeaker includes a housing (1) and a circuit disposed inside the housing (1). A mosquito dispeller is disposed at a lower portion inside the housing (1), and the mosquito dispeller scatters ultrasonic waves via a ultrasonic scattering net (2) disposed below the housing (1). The loudspeaker box having a mosquito repellent function has the advantages of being mosquito repellent ,healthy and environment-friendly, and being capable of serving as a backup USB interface.
Owner:XIAN ZHISHIXIN ELECTRONICS TECH
Phased Array Ultrasonic Evaluation Method of Grain Size
ActiveCN113029880BRelatively small errorFeasible meansAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesProcessing detected response signalScattering attenuationAttenuation coefficient
The invention provides a phased array ultrasonic evaluation method of crystal grain size, the method includes: using the primary bottom echo and the secondary bottom echo to obtain the experimental longitudinal wave scattering attenuation coefficient; deriving the linear phased array from the Huygens principle The probe radiates the sound field, receives the average sound pressure through the probe, defines the diffraction correction coefficient of the linear phased array probe and calculates the final diffraction correction coefficient; according to the Weaver ultrasonic scattering model, the theoretical relationship between the grain size and the longitudinal wave scattering attenuation coefficient is obtained, based on the nonlinear minimum The square method uses polynomial fitting to obtain the proxy model of the grain size and the theoretical longitudinal wave scattering attenuation coefficient; the experimental longitudinal wave scattering attenuation after removing the diffraction loss is substituted into the proxy model to invert the grain size value. The invention eliminates diffraction loss interference, fuses multi-angle sound beam information, and greatly reduces relative error compared with traditional methods, and provides a feasible and reliable means for estimating the grain size of polycrystalline materials.
Owner:中国工程物理研究院研究生院
An Optimal Calculation Method of Ultrasonic Scattering Coefficient for Crack Direction Identification
ActiveCN104280455BAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesProcessing detected response signalFull matrixPhased array
The invention relates to an ultrasonic scattering coefficient optimal computation method for crack direction recognition, belonging to the field of nondestructive examination. According to the method, an ultrasonic phased array detection system is used for acquiring full-matrix data of a crack defect; firstly, the acquired data are used for performing full-focusing imaging on the defect to determine the position of the defect and then a scattering coefficient space distribution of the crack defect is computed to determine an angle of the crack; the quantity of wafers included in a sub array and the quantity of wafers between adjacent sub arrays greatly affect the measurement precision of the crack angle. A plurality of evaluation indexes are used for evaluating the quantity of a crack angle measurement result according to the quantities of the wafers included in different sub arrays and the wafers between the adjacent sub arrays, and the measurement result is comprehensively evaluated by a main component analysis method to obtain an optimal measurement result; corresponding parameters, namely the quantities of the wafers included in the sub arrays and the quantity of the wafers between the adjacent sub arrays, are optimal detection parameters.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Method and apparatus for generating an ultrasound scatterer representation
Realistic ultrasound imaging simulation requires modeling of scatterers corresponding to different imaging speckle appearances. A scatterer generator acquires a plurality of ultrasound signal samples,each corresponding to a different ultrasound capture and reconstructs a scatterer representation from the ultrasound signal samples and associated Point Spread Functions. Point Spread Functions (PSFs) may be estimated from multiple image acquisitions at the same reference position resulting from beam-steering. Reconstructed scatterers may then directly be used in ultrasound simulation or an additional step of modeling the scatterers may be applied. Statistical distribution parametrization or texture synthesis may be used to model the scatterers. Different scatterer models may be used for different homogeneous regions. The reconstructed scatterers and / or the scatterer models may be registered into a library of scatterers by the scatterer generator.
Owner:VIRTAMED
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com