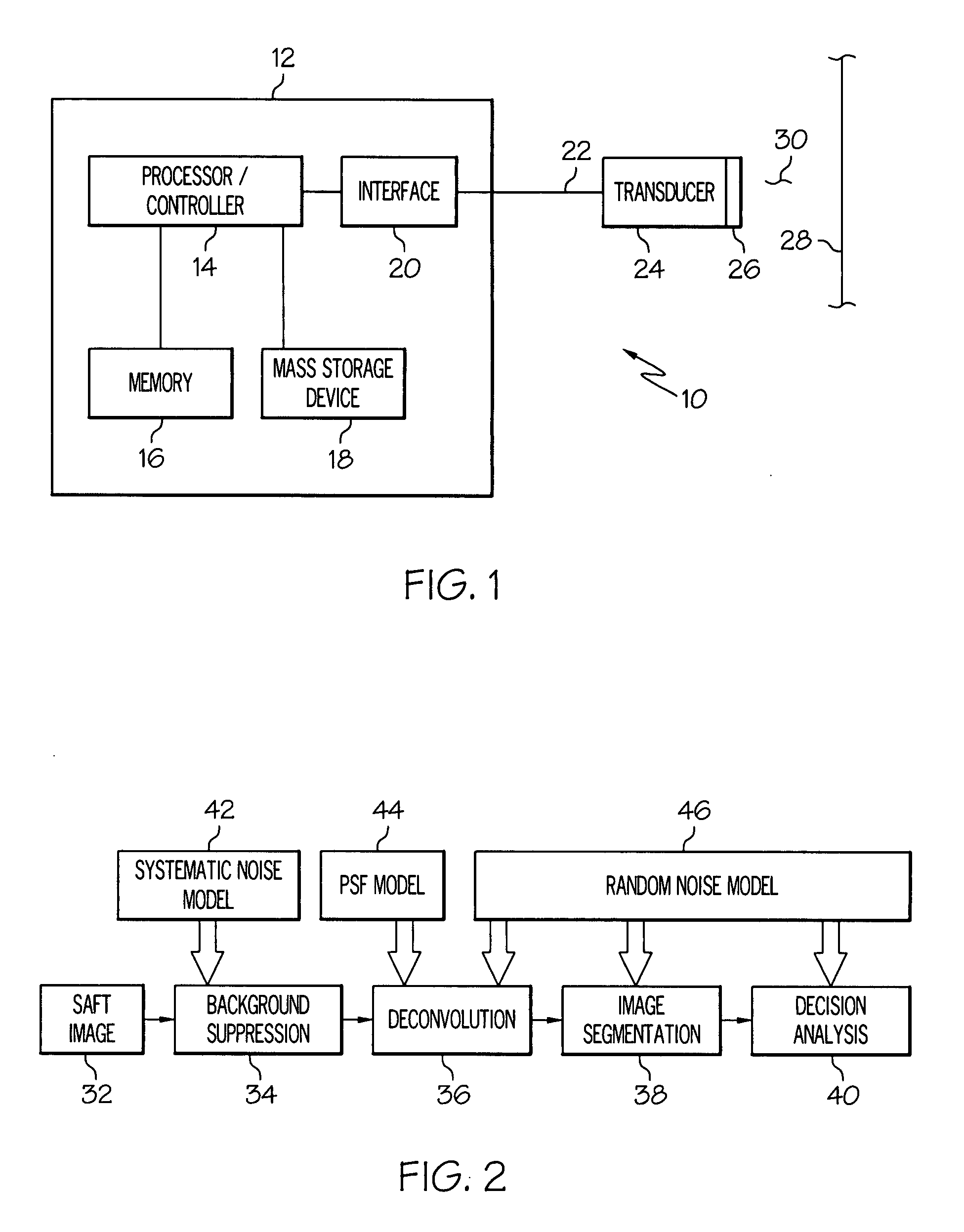
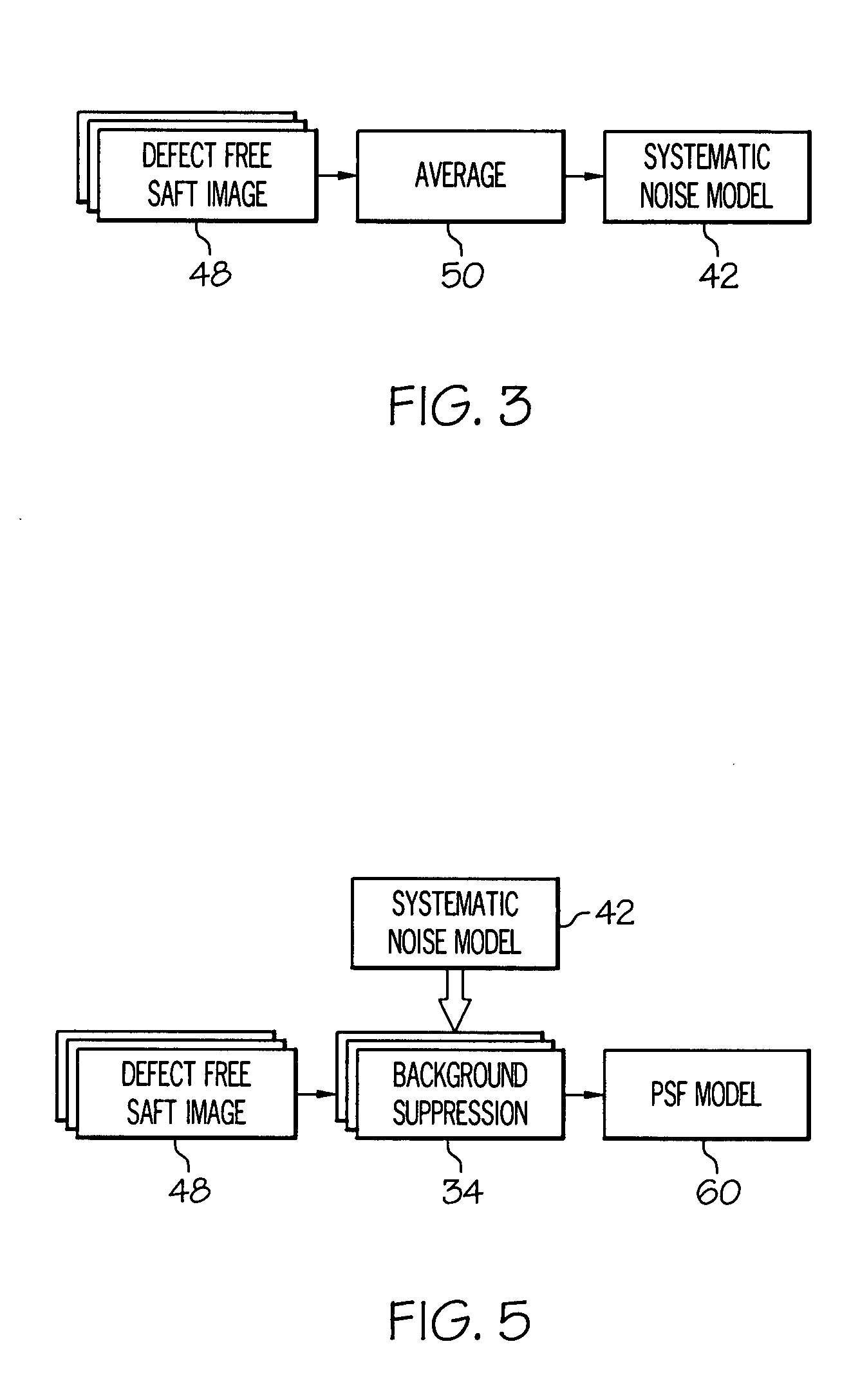
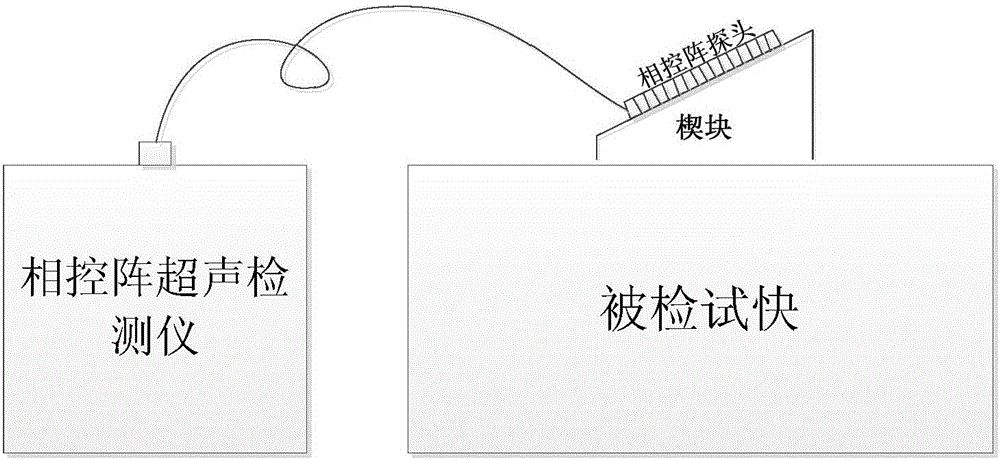
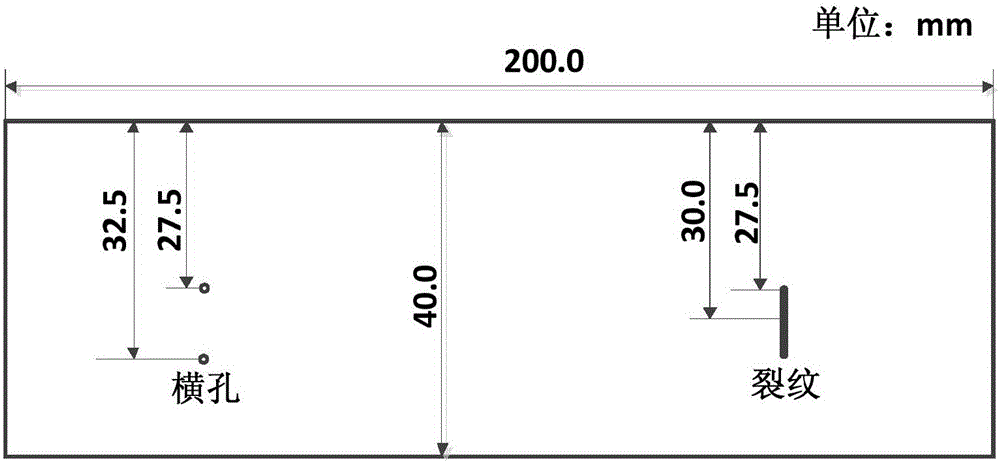
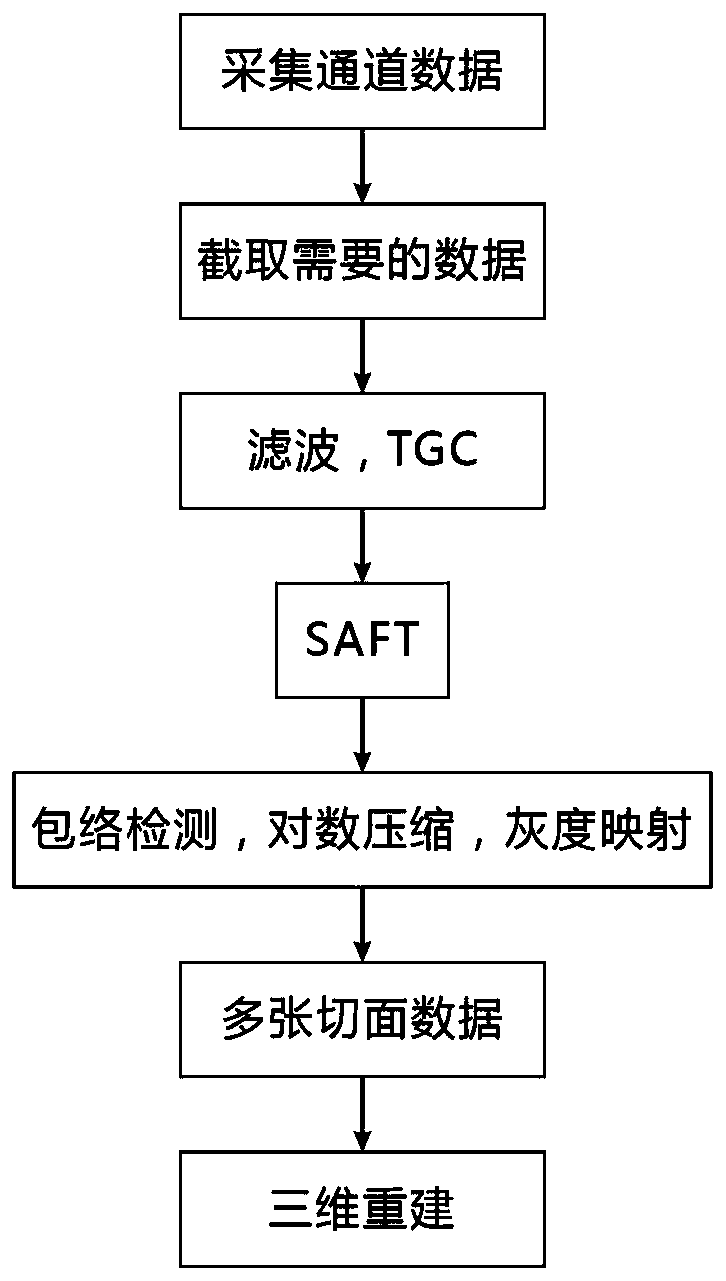
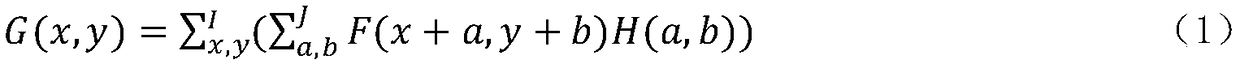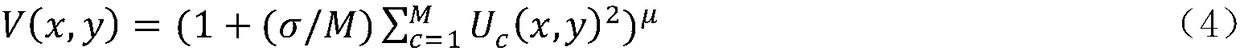Patents
Literature
78 results about "Synthetic aperture focusing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
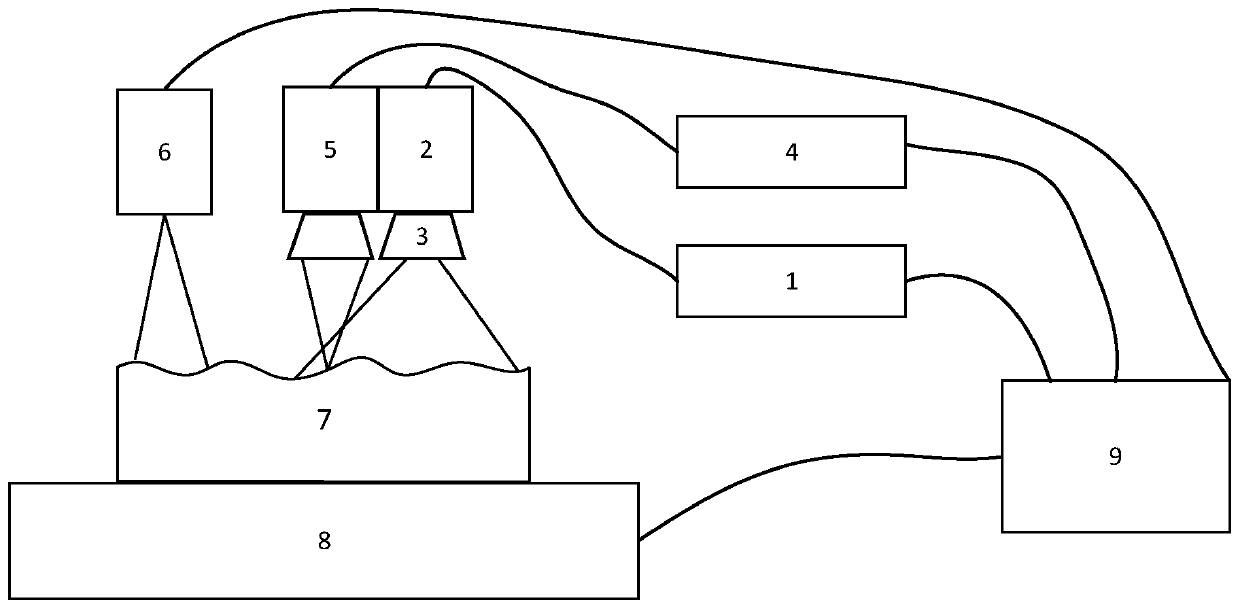
Method and system for high resolution ultrasonic imaging of small defects or anomalies.
InactiveUS6128092ARadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometrySonificationSynthetic aperture focusing
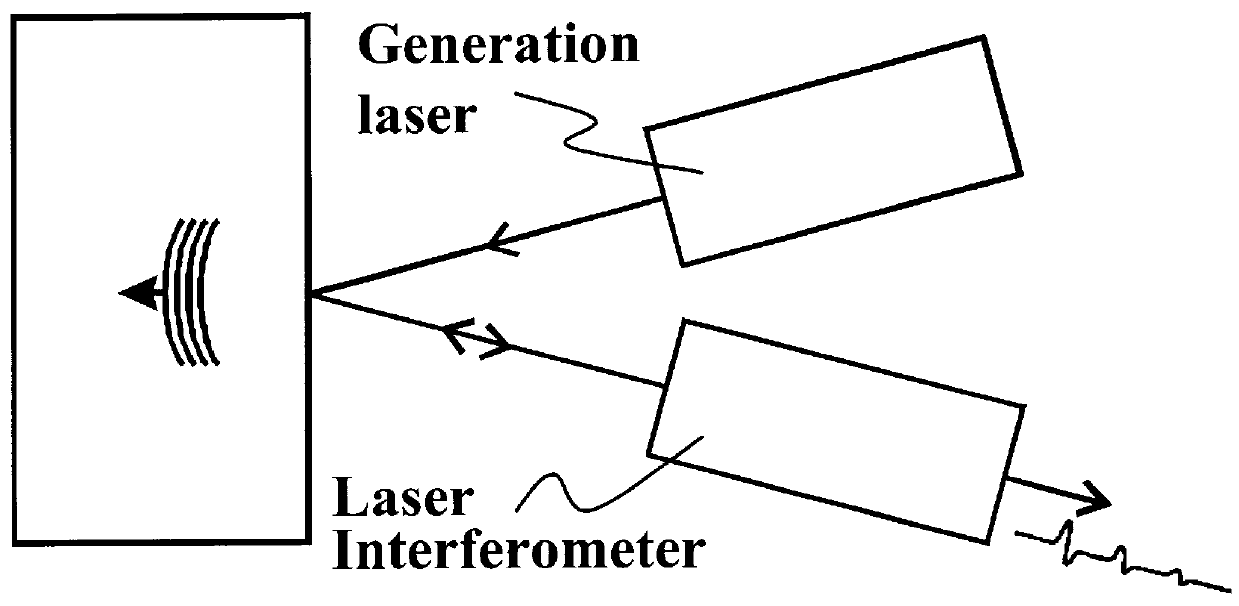
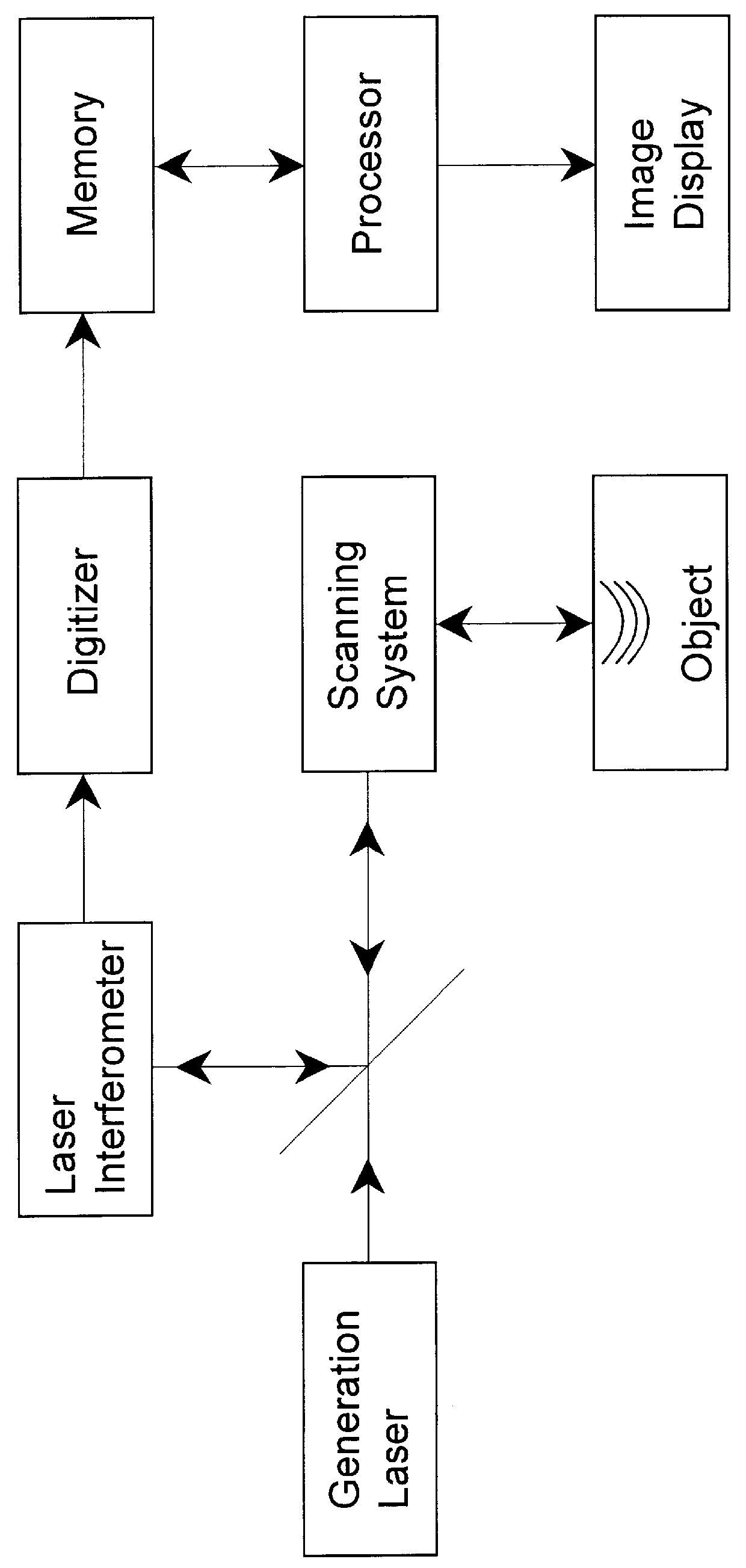
A method and system is provided for enhanced ultrasonic detection and imaging of small defects inside or at the surface of an object. The Synthetic Aperture Focusing Technique (SAFT) has been used to improve the detectability and to enhance images in conventional ultrasonics and this method has recently been adapted to laser-ultrasonics. In the present invention, an improved version of the frequency-domain SAFT (F-SAFT) based on the angular spectrum approach is described. The method proposed includes temporal deconvolution of the waveform data to enhance both axial and lateral resolutions, control of the aperture and of the frequency bandwidth to improve signal-to-noise ratio, as well as spatial interpolation of the subsurface images. All the above operations are well adapted to the frequency domain calculations and embedded in the F-SAFT data processing. The aperture control and the spatial interpolation allow also a reduction of sampling requirements to further decrease both inspection and processing times. This method is of particular interest when ultrasound is generated by a laser and detected by either a contact ultrasonic transducer or a laser interferometer.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
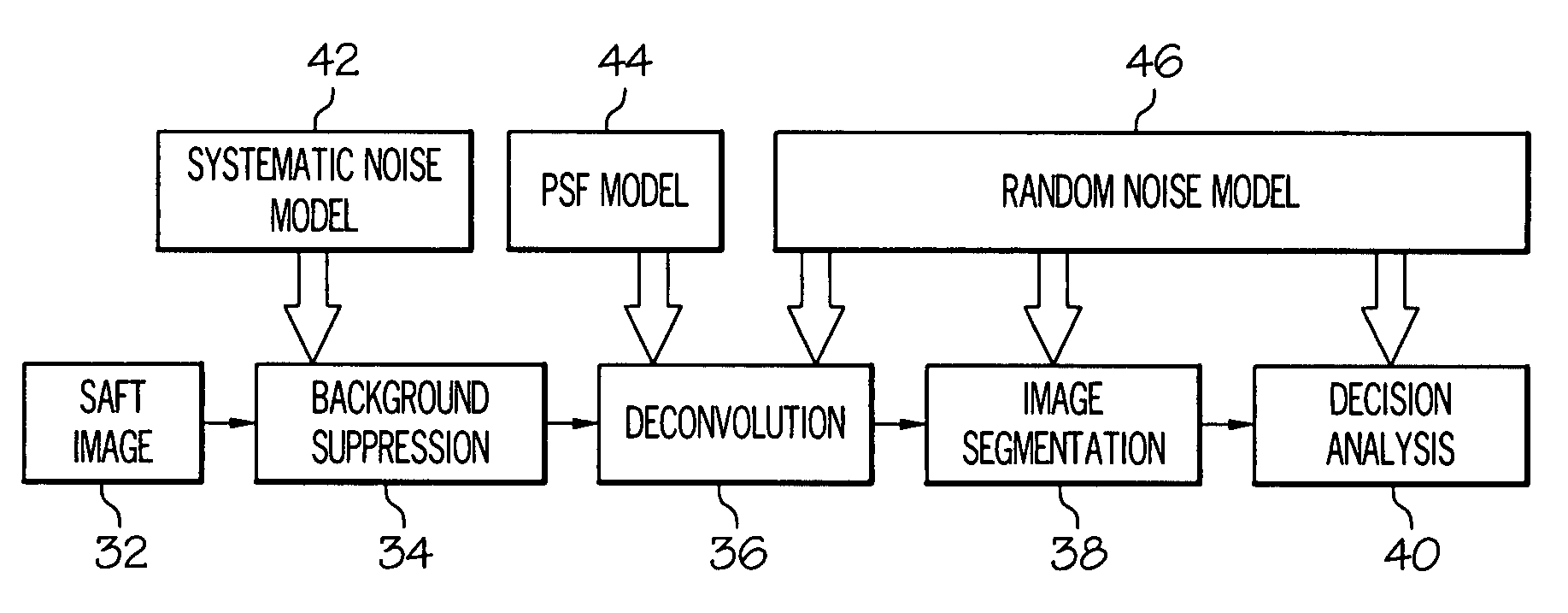
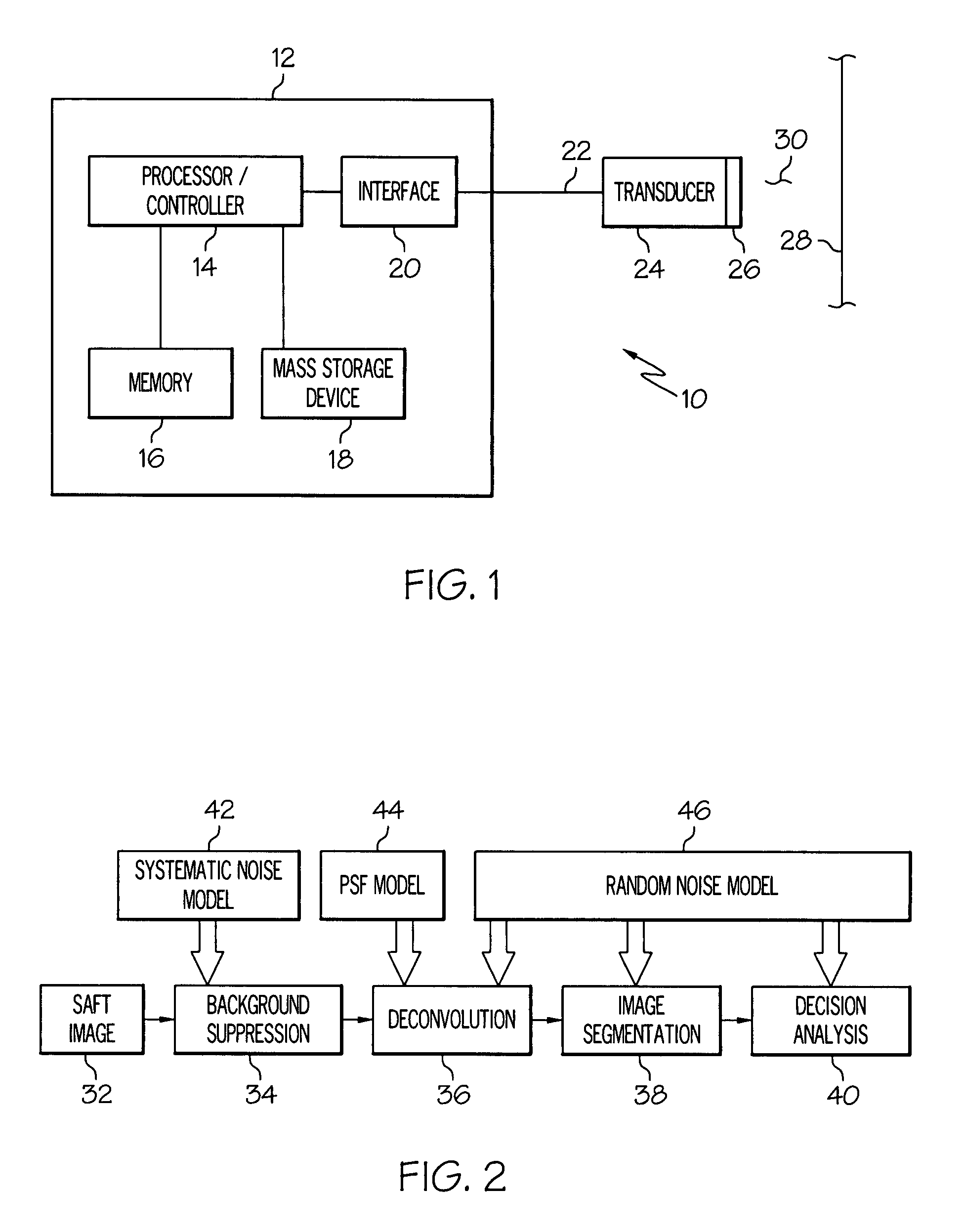
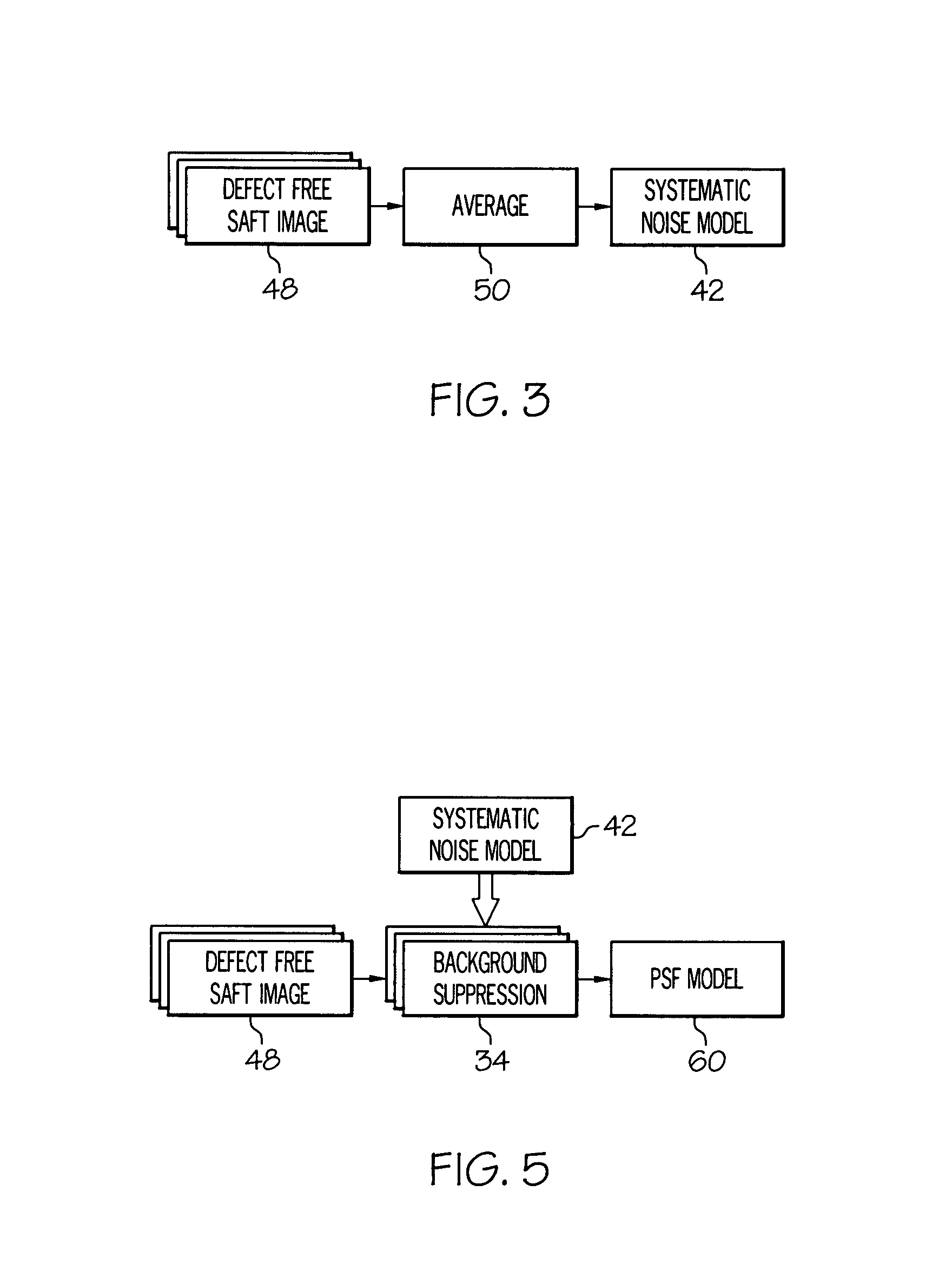
Automated defect detection of corrosion or cracks using saft processed lamb wave images
A system, method and computer program product is provided for automated defect detection of corrosion or cracks using synthetic aperture focusing technique (SAFT) processed Lamb wave images. The method comprises processing the first image using a synthetic aperture focusing technique (SAFT) to enhance a resolution and a signal to noise ratio of a first extracted ultrasonic image, applying a systemic background noise suppression algorithm to the first extracted ultrasonic image to render a second extracted ultrasonic image having reduced noise, and applying a deconvolution linear filtering process to the second extracted ultrasonic image to render a third extracted ultrasonic image.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Defect two-dimensional morphology imaging detection method based on multi-mode acoustic beam synthetic aperture focusing
ActiveCN106770669ARealize automatic real-time imagingHigh engineering applicationAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesSonificationElectron
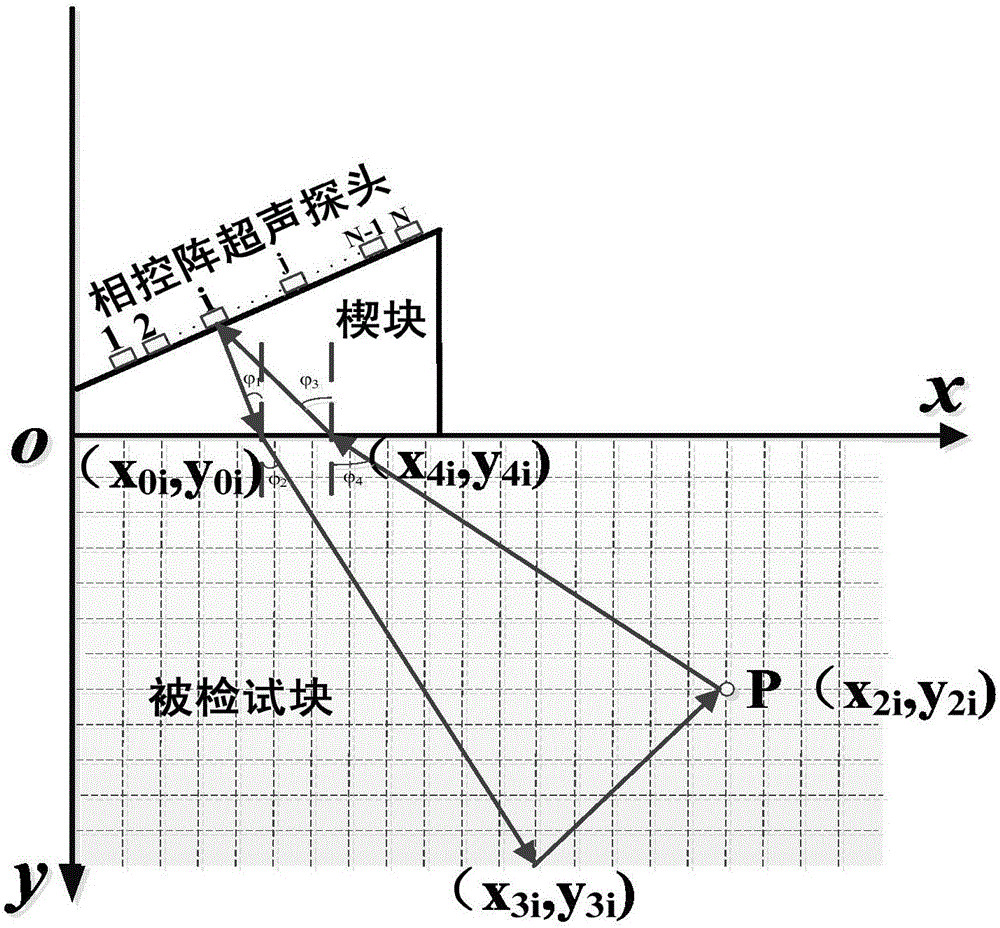
The invention discloses a defect two-dimensional morphology imaging detection method based on multi-mode acoustic beam synthetic aperture focusing, belonging to the technical field of nondestructive testing. According to the method, a phased array ultrasonic detector, a phased array ultrasonic probe and a phased array ultrasonic detection system of an oblique wedge block are adopted; and signal acquisition of a detected test block is performed by the electronic scanning function of the phased array ultrasonic detector to obtain A-scanning signal of each aperture of the phased array ultrasonic probe. According to different mode conversion types of excitation acoustic beam of each aperture on the interface between the wedge block and test block, at the bottom of the test block and on the defect surface, proper multi-mode acoustic beam is selected from 8 acoustic beam transmission modes. Based on SAFT imaging principle and Fermat's theorem, the transmission delay of the multi-mode acoustic beam of each aperture is calculated, and amplitudes are overlapped to obtain a reconstructed SAFT image, thus realizing complete representation of defect two-dimensional morphology features. The invention can realize correct recognition of volume type and area type defects so as to realize accurate quantification of defect length, depth and orientation, and has relatively high engineering application value.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Mm-wave sfcw radar and saf based imaging inspection system
ActiveUS20180196134A1Geological detection using milimetre wavesRadio wave reradiation/reflectionDigital signal processingImage Inspection
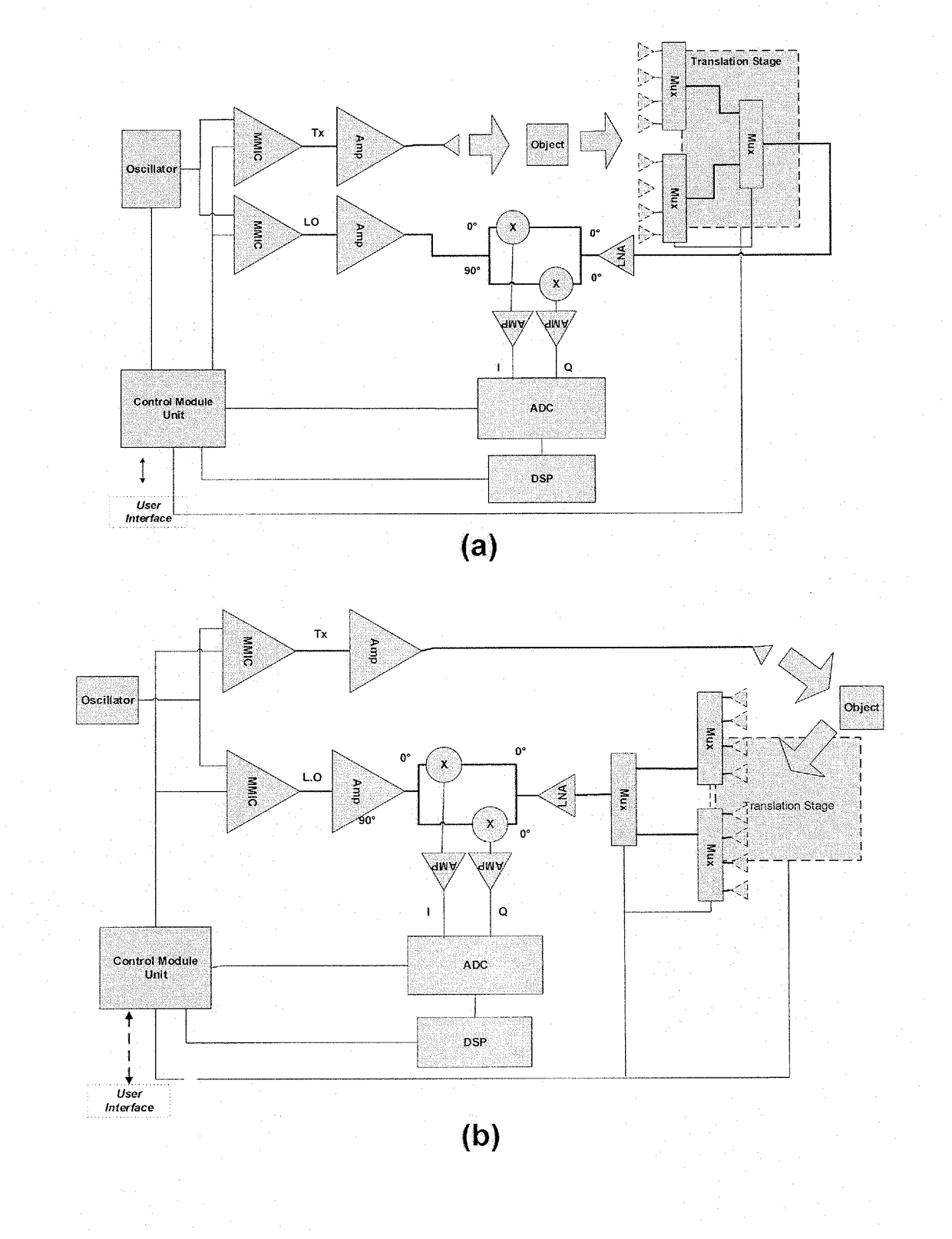
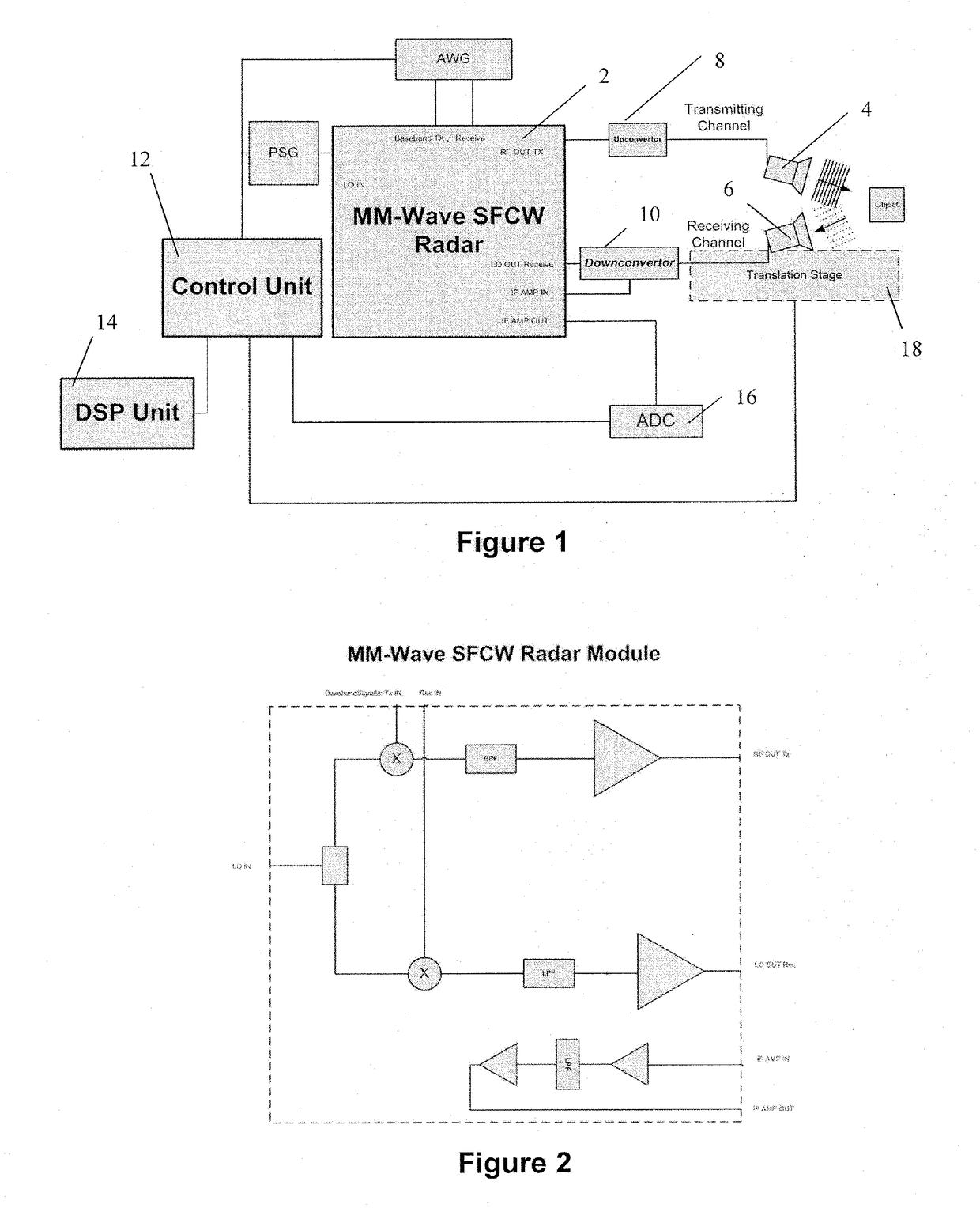
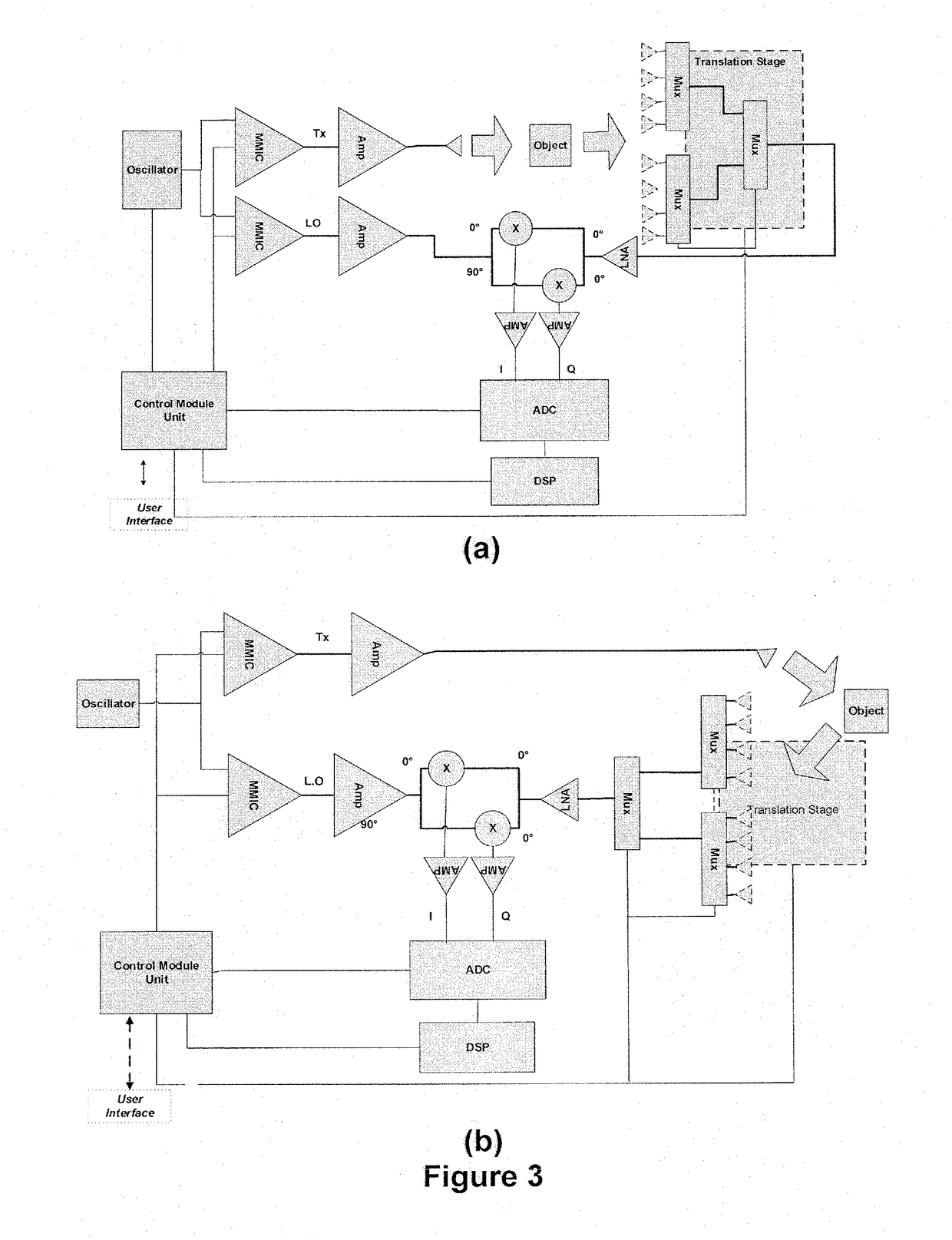
The present invention presents a flexible, stepped frequency, radar based, imaging inspection system. The imaging inspection system can be used in airports, seaport sites, borders, postal processing centres, and sensitive sites. It comprises a millimetre-wave Stepped Frequency Continuous Wave (SFCW) radar module (2) connected to a transmitting channel and a receiving channel. The transmitting channel may comprise a frequency upconvertor (8) and the receiving channel may comprise a frequency downconvertor (10). A digital signal processing unit (14) reconstructs a conductivity profile and a permittivity profile of an object under test (OUT) from measurement data collected via a phase-array antenna or a translational stage (18) based on synthetic aperture focusing (SAF).
Owner:OZ OPTICS
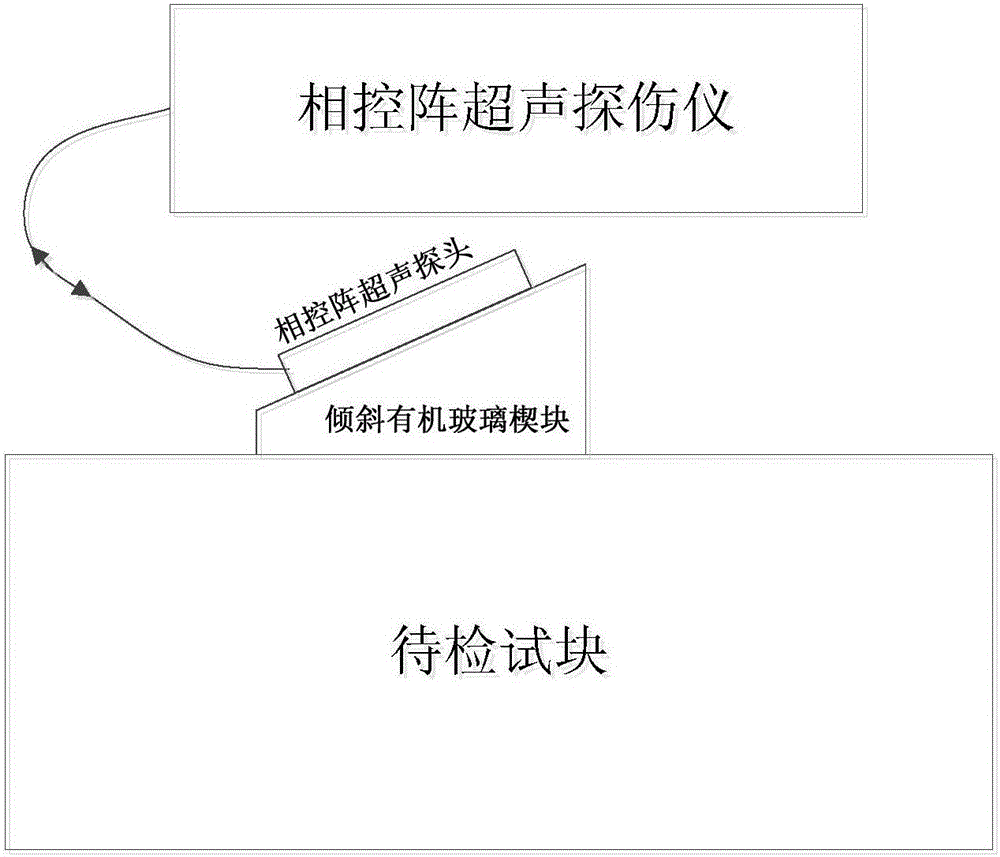
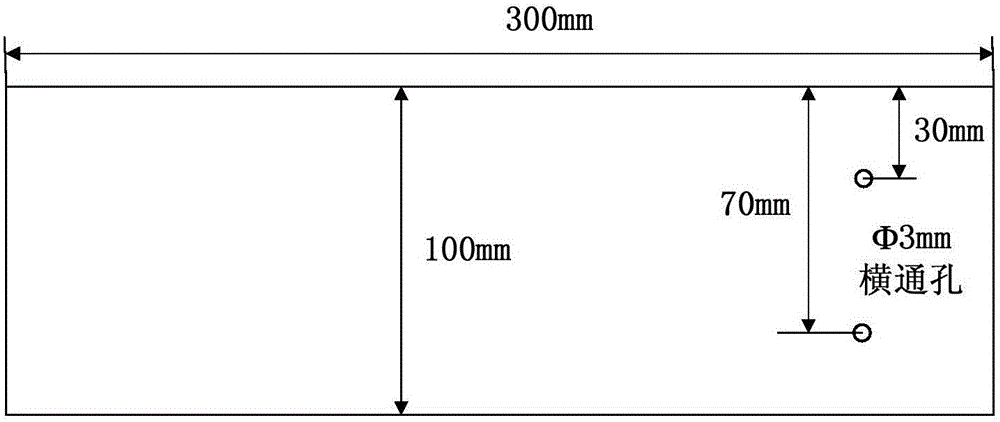
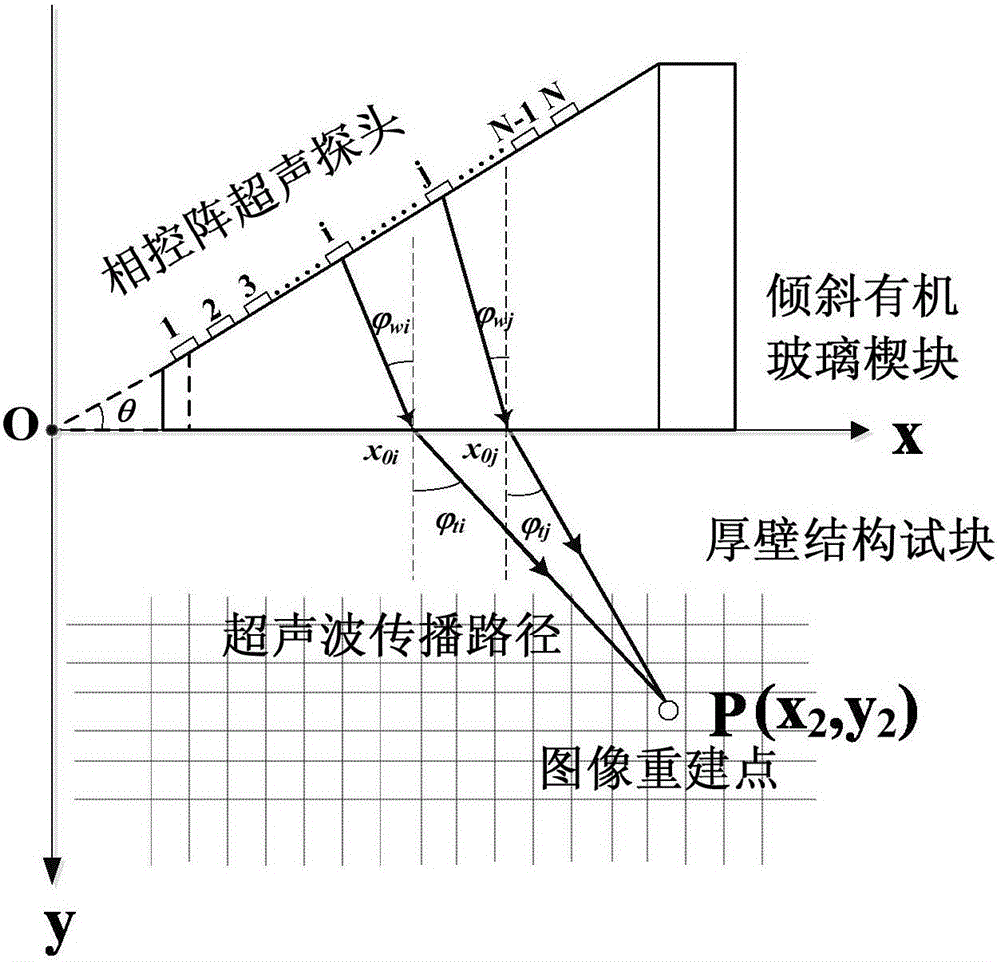
Oblique incident ultrasonic synthetic aperture focusing-based thick wall structure defect detection method
ActiveCN106093205ALarge energy coverageImprove defect detection efficiencyAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesUltrasonic attenuationThick wall
The invention discloses an oblique incident ultrasonic synthetic aperture focusing-based thick wall structure defect detection method, and belongs to the technical field of nondestructive detection. The method comprises the following steps: a thick wall structure test block is detected through using a phased array electron scanning function by using an ultrasonic detection system comprising a phased array ultrasonic flaw detector, a phased array ultrasonic probe and an oblique organic glass wedge in order to obtain the A scanning signal set of all phased array elements; the Fermat's theorem is used to solve the emission point positions of all the phased array elements and image reconstruction points in the wedge / test block interface, and all A scanning signals undergo time delaying and amplitude superposing processing; and the processed A scanning signals undergo Hilbert transformation, and a difference function is used to obtain a reconstructed ultrasonic detection B scanning image. The method has the advantages of high defect detection resolution, large detection range, detection efficiency increase, and provision of an effective solving technology for the nondestructive detection problem of the defect of a thick wall structure. The method also can be embedded to the flaw detector to realize automatic real-time imaging, and has high engineering application values.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
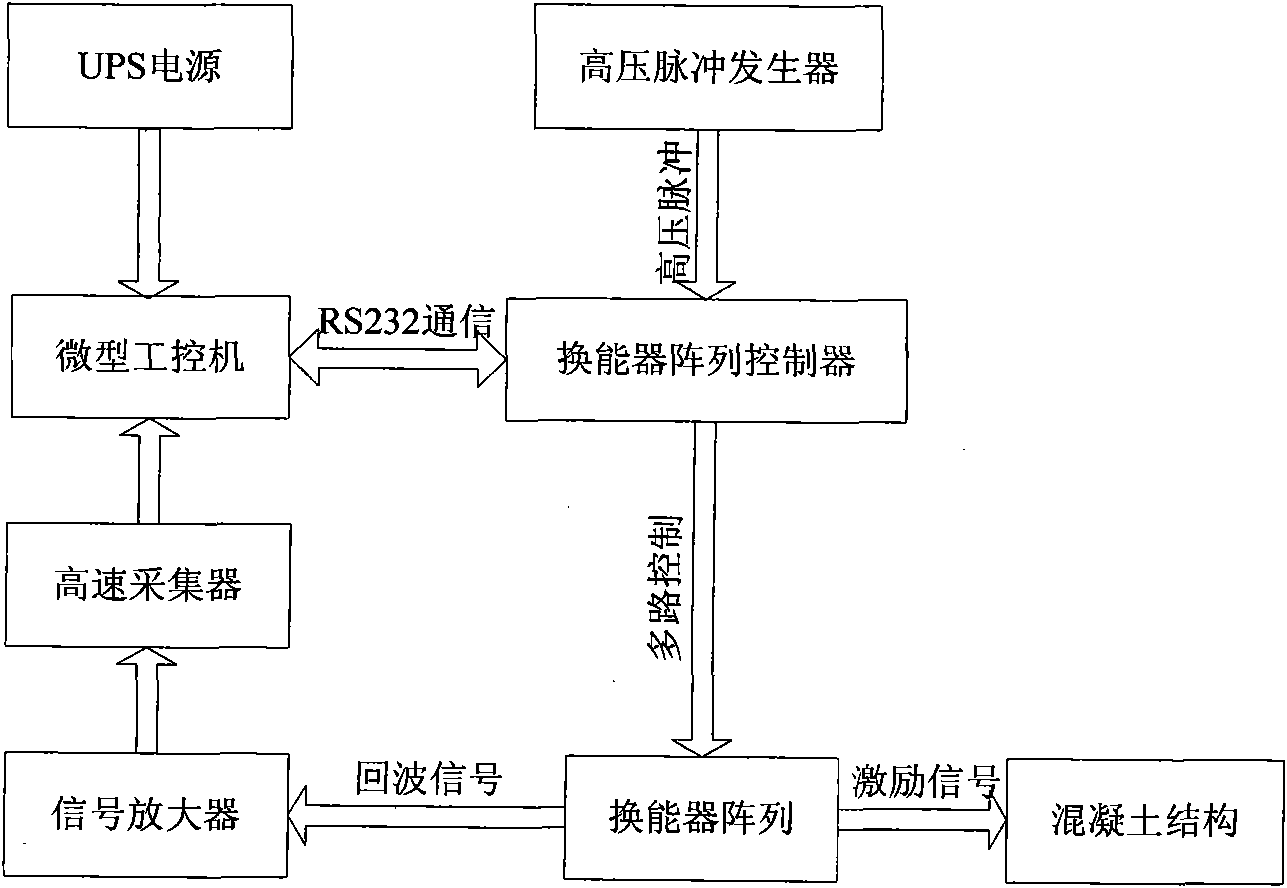
Virtual instrument based system and method for detecting ultrasonic imaging by synthetic aperture focusing
InactiveCN101930069AReduce volumeCompact structureAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesAcoustic wave reradiationSonificationSynthetic aperture sonar
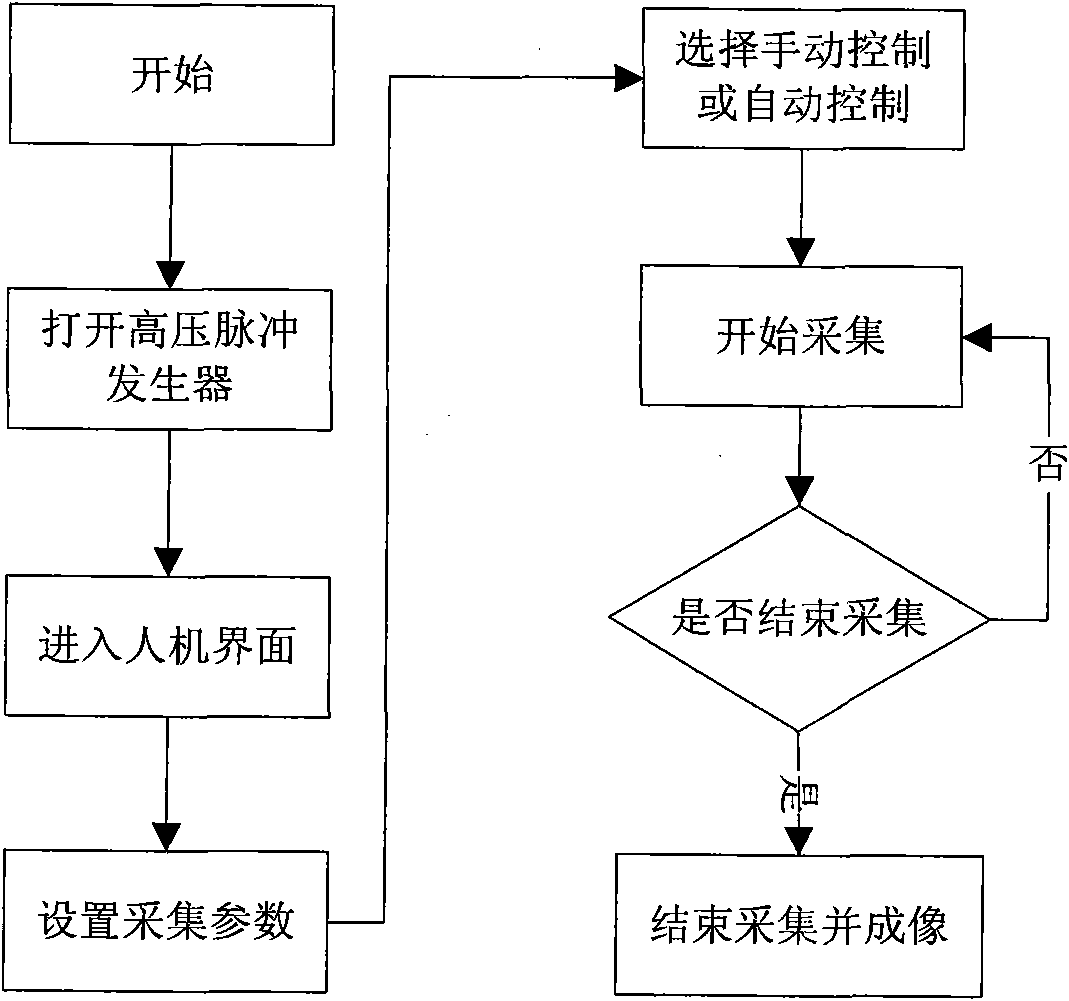
The invention relates to virtual instrument based system and method for detecting ultrasonic imaging by synthetic aperture focusing. The virtual instrument based system comprises a virtual instrument system, a 12-way energy converter array, an energy converter array controller and a UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply), wherein the energy converter array controller can control a 24-way energy converter array, the virtual instrument system comprises a high-voltage pulse generator, a signal amplifier, a high-speed signal collector and a mini-size industrial personal computer which are all provided with PXI interfaces, wherein the mini-size industrial personal computer is equipped with a Labview software program. The invention adopts the integrated design, thereby having compact structure and being convenient for carrying, remote transportation and outdoor work; the invention adopts human-machine interface, thereby having high intellectualization and integration degree and simple operation procedure; the invention adopts a rough detection process and a detailed detection process, can reach an area of 60cm through primary rough detection, can detect structures with high requirements for resolution ratio through detailed detection and achieve the resolution ratio of 1cm; and the system can remotely control the signal amplifier and the energy converter array, and the detection function of the system can be fulfilled by only operating the industrial personal computer.
Owner:PLA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
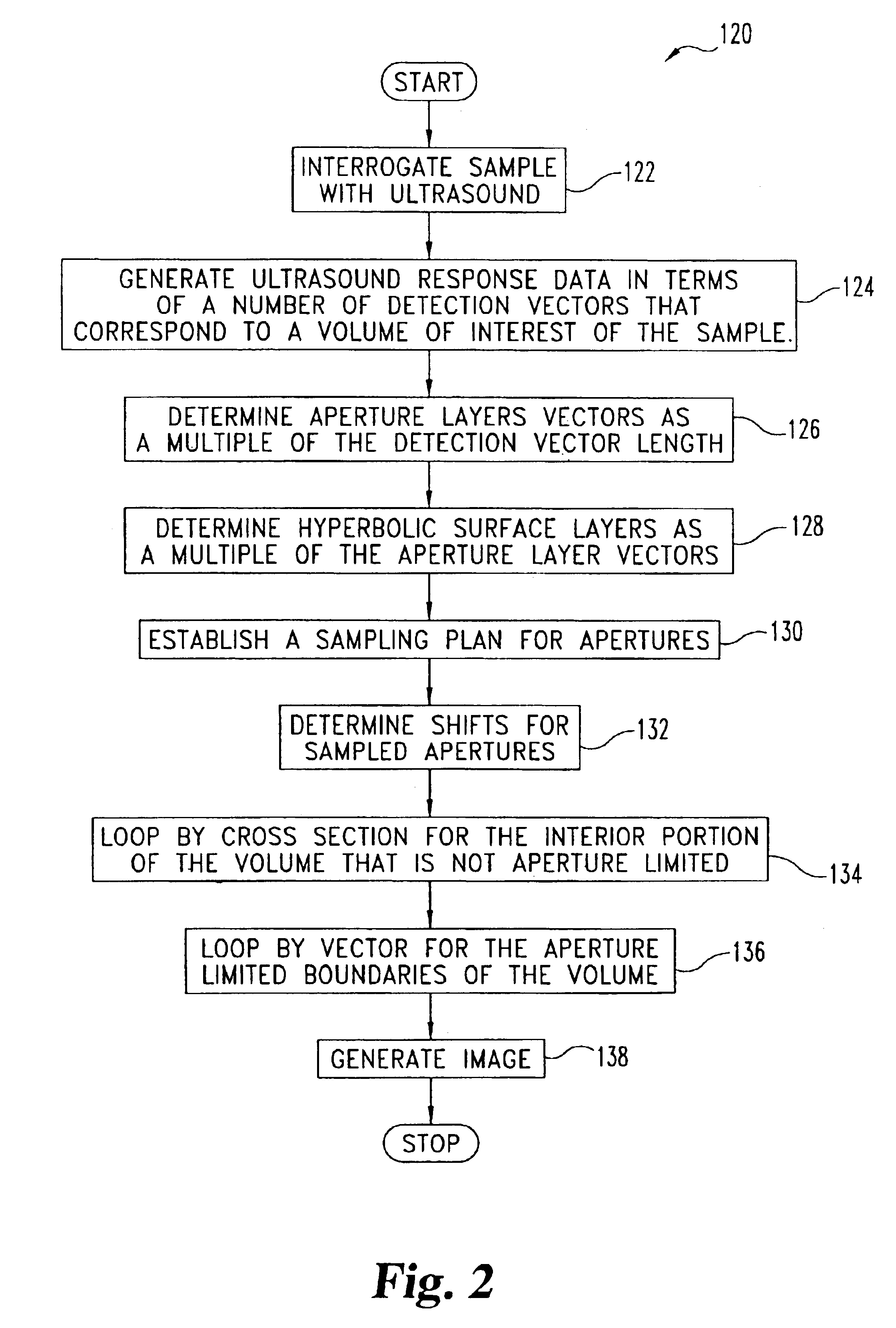
Apparatus, systems, and methods for ultrasound synthetic aperature focusing
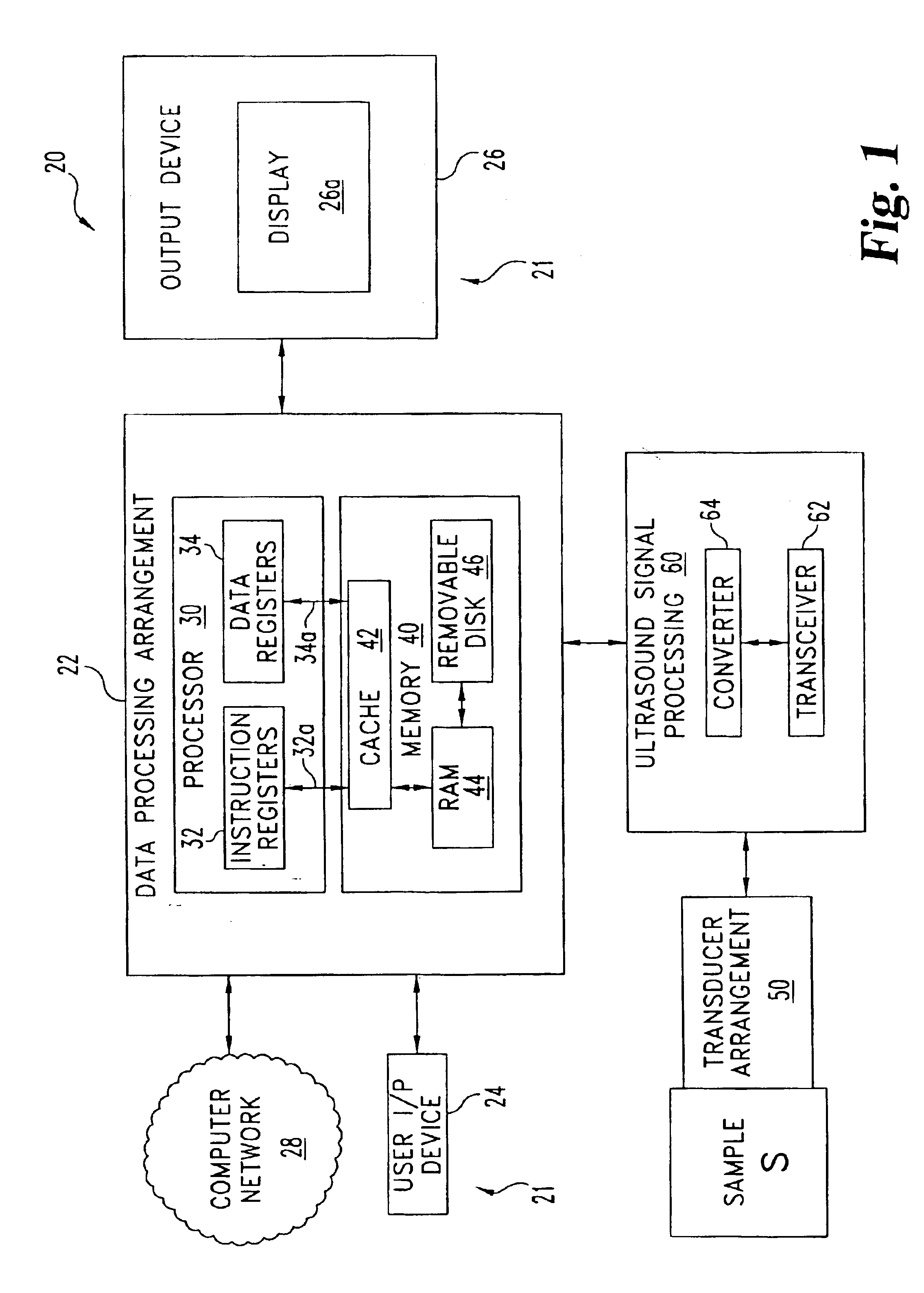
InactiveUS6877376B1Analysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMaterial analysis by optical meansSonificationUltrasound energy
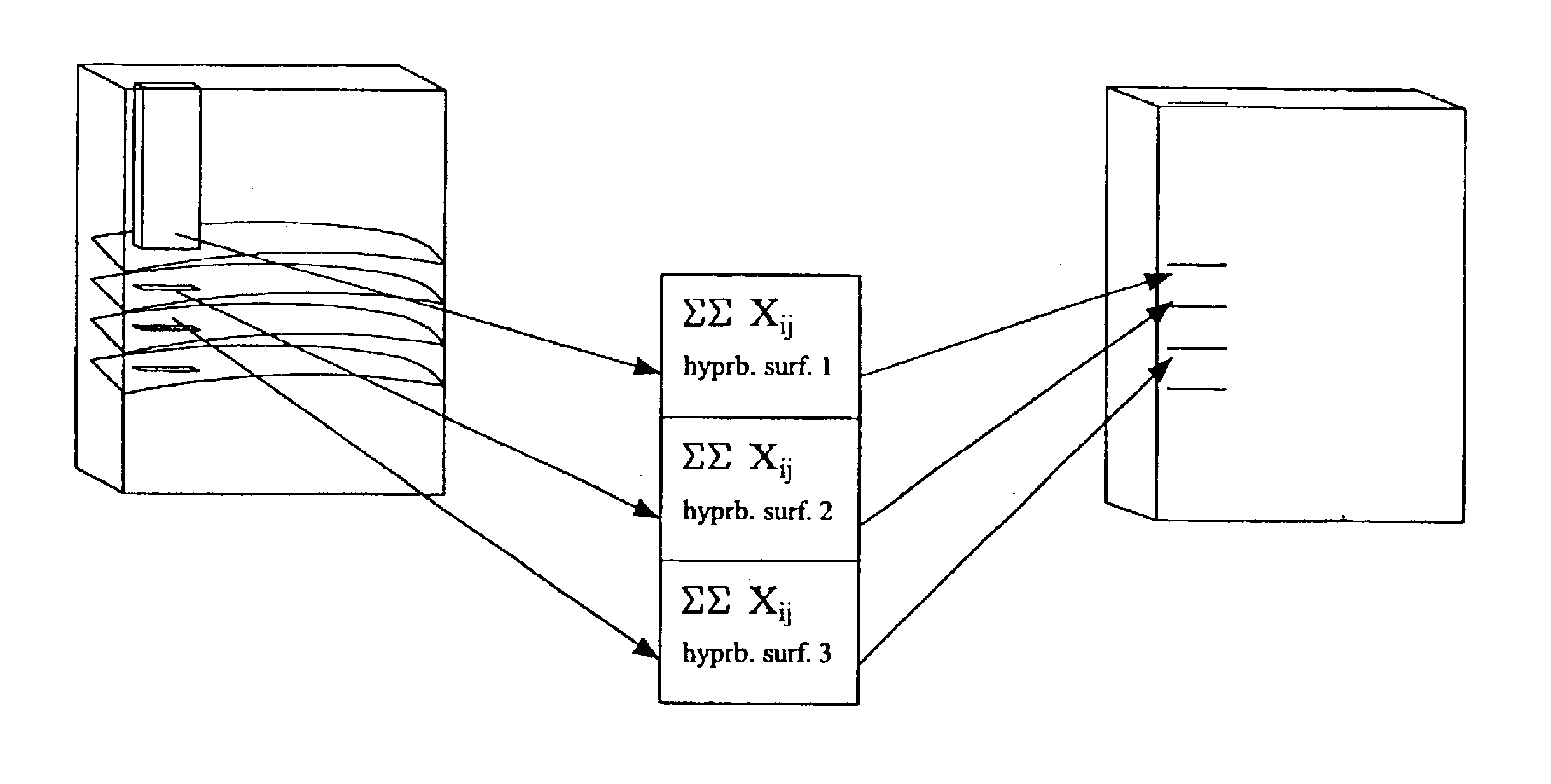
One form of the present invention is a technique for interrogating a sample with ultrasound which includes: generating ultrasonic energy data corresponding to a volume of a sample and performing a synthetic aperture focusing technique on the ultrasonic energy data. The synthetic aperture focusing technique includes: defining a number of hyperbolic surfaces which extend through the volume at different depths and a corresponding number of multiple element accumulation vectors, performing a focused element calculation procedure for a group of vectors which are representative of the interior of a designated aperture, performing another focused element calculation procedure for vectors corresponding to the boundary of the aperture, and providing an image corresponding to features of the sample in accordance with the synthetic aperture focusing technique.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
Ultrasonic C scanning imaging method based on two-dimensional neighborhood synthetic aperture focusing
ActiveCN102539532AFocusHigh precisionAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesProcessing detected response signalSynthetic aperture sonarMathematical model
The invention discloses an ultrasonic C scanning imaging method based on two-dimensional neighborhood synthetic aperture focusing, which includes five steps including performing visualization for an acoustic beam spread angle of a probe, building a mathematical model for a neighborhood of a focusing treatment point, collecting ultrasonic A wave signals, synthesizing focusing treatment ultrasonic A wave signals and performing ultrasonic C scanning imaging for a defect. The technical effect of the invention lies in that through focusing the two-dimensional neighborhood taking an objective pointas a center and simultaneously taking the wafer diameter, the near field length and the acoustic beam spread angle of the probe into consideration, the neighborhood of the synthetic aperture focusingtreatment point is confirmed, so that the scanning result is more accurate as compared with that of the conventional SAFT (synthetic aperture focusing technique) method, the adverse effects of the acoustic beam spread angle on the ultrasonic nondestructive detection can be effectively restrained, and the accuracy of the ultrasonic C scanning imaging is improved.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
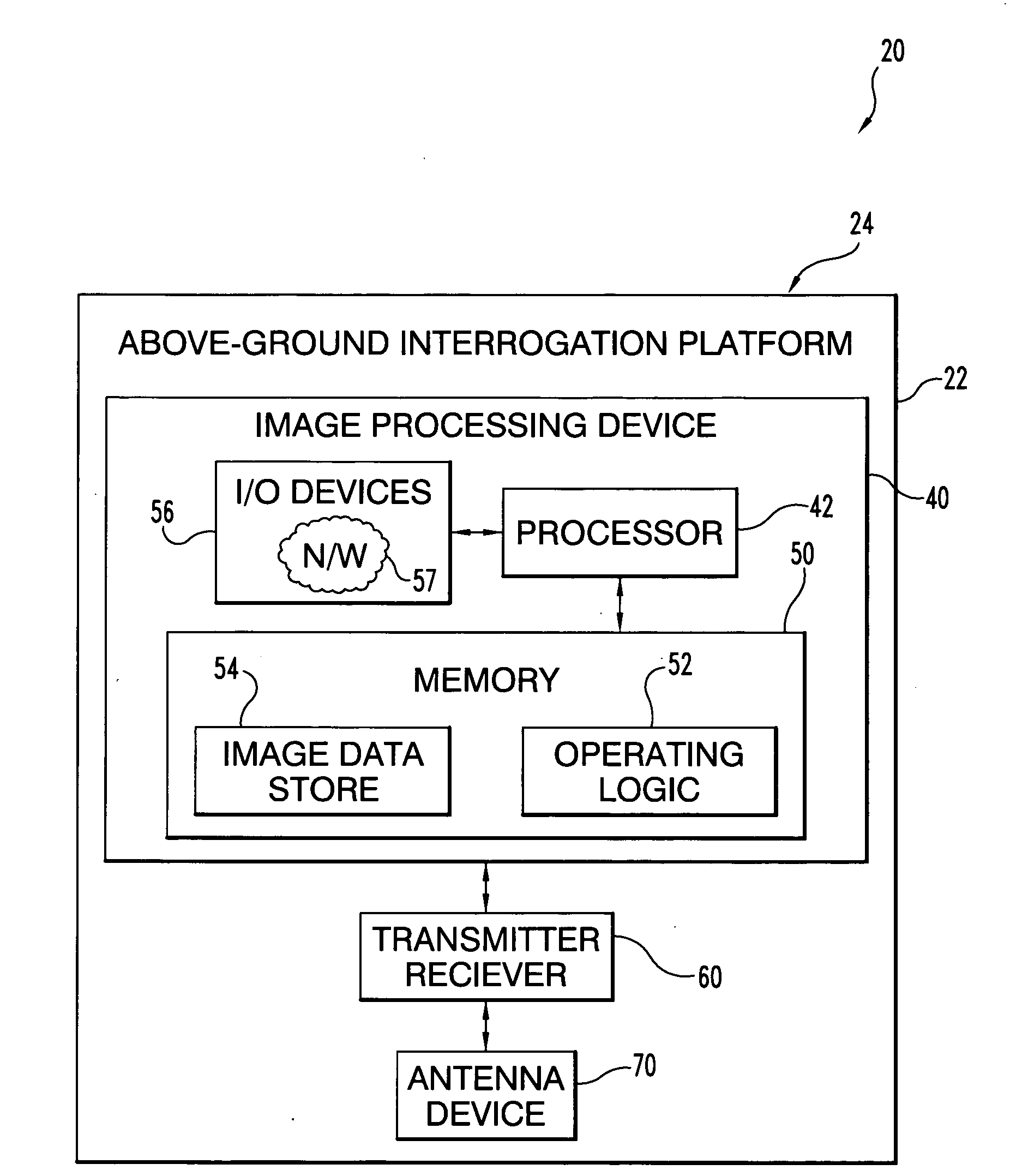
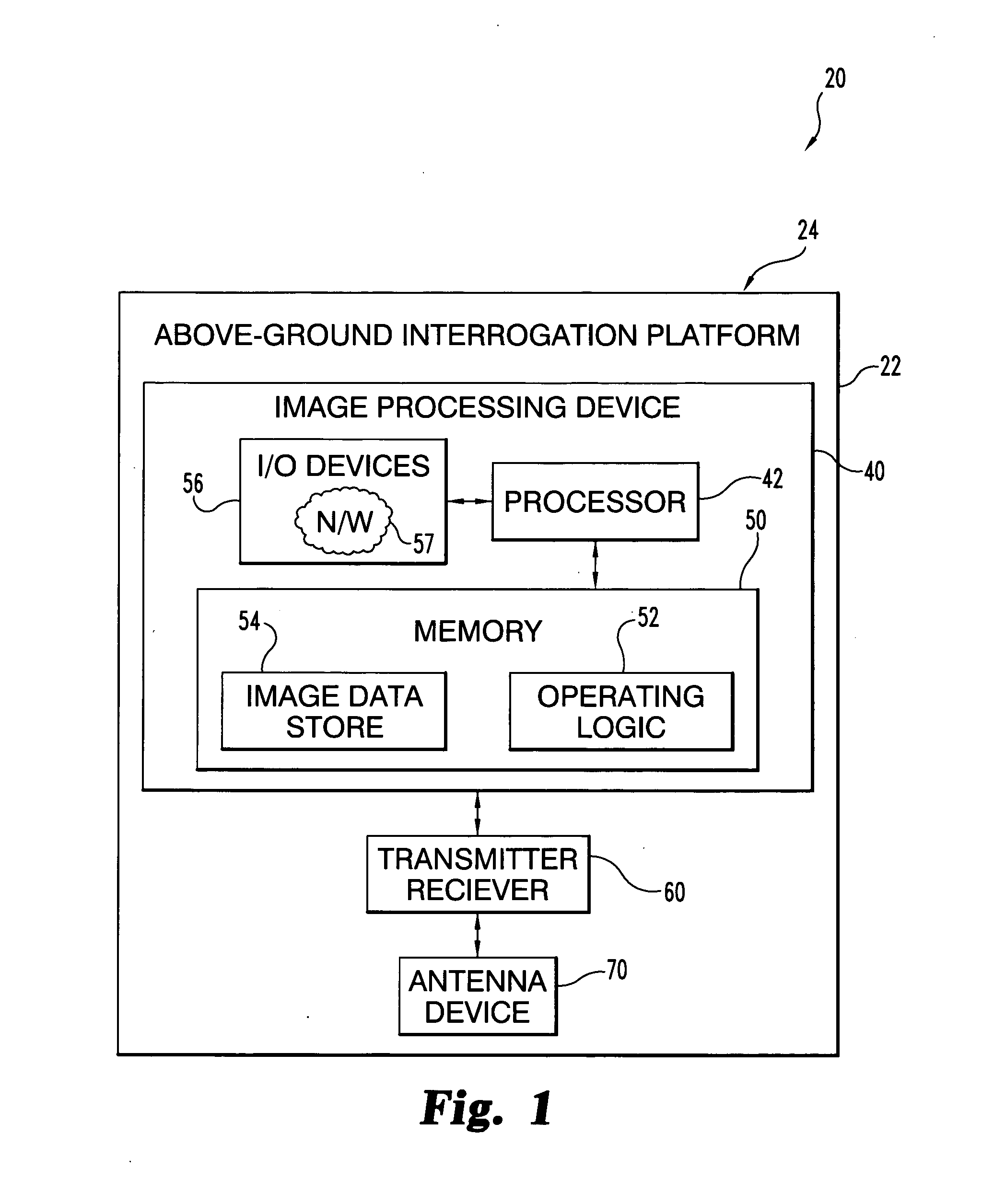
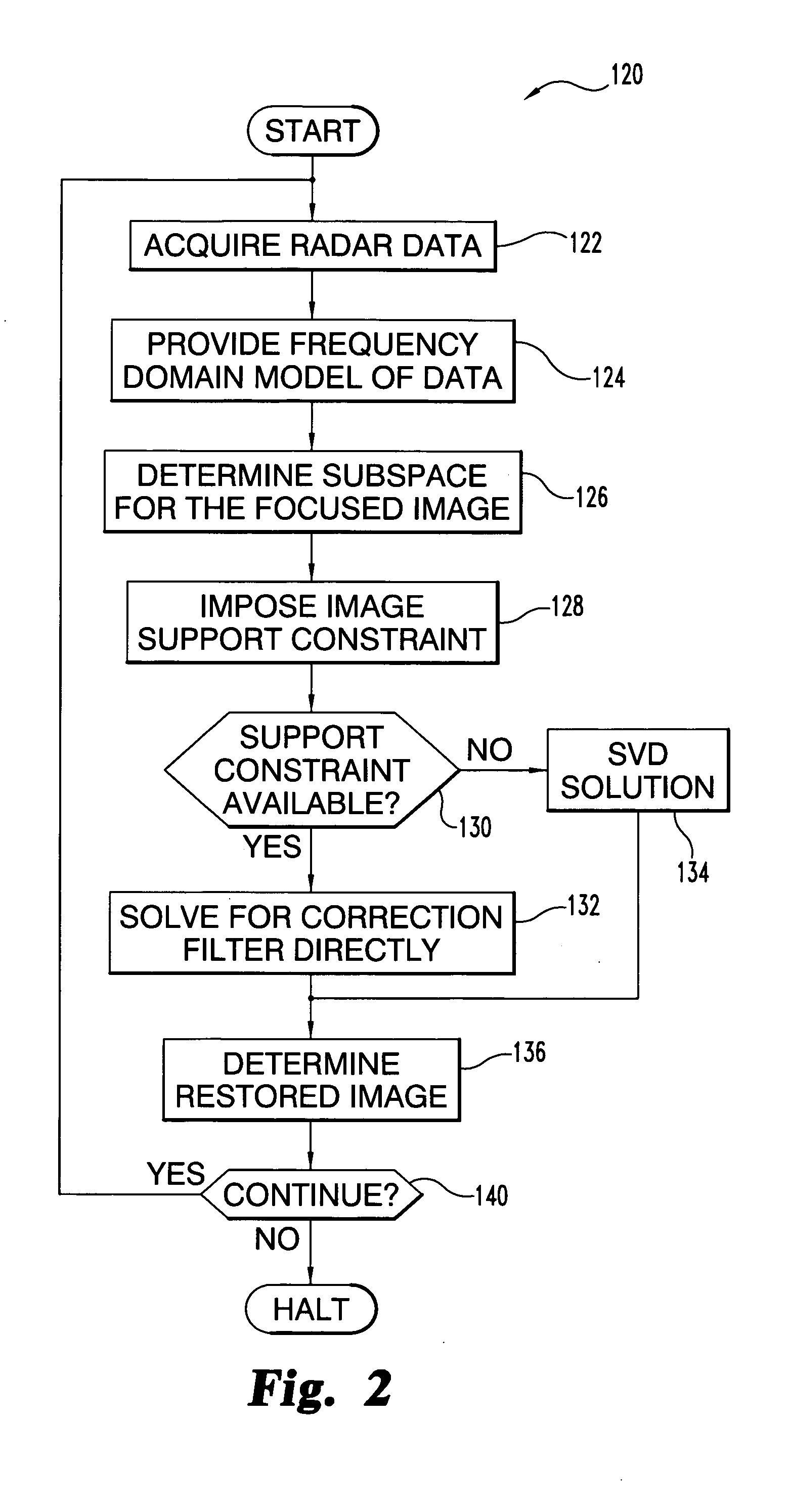
Synthetic Aperture focusing techniques
The present application describes an apparatus that includes a radar antenna device to acquire synthetic aperture radar data, radar receiver and transmitter equipment coupled to the radar antenna device, and a synthetic aperture radar processing device in communication with the radar receiver and transmitter equipment. This processing device includes a processor structured to process the synthetic aperture radar data, which is representative of a defocused image. The processor is further structured to define an image processing constraint corresponding to an image region expected to have a low radar return and generate one or more output signals as a function of the image processing constraint and the data. The one or more output signals are representative of a more focused form of the defocused image.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
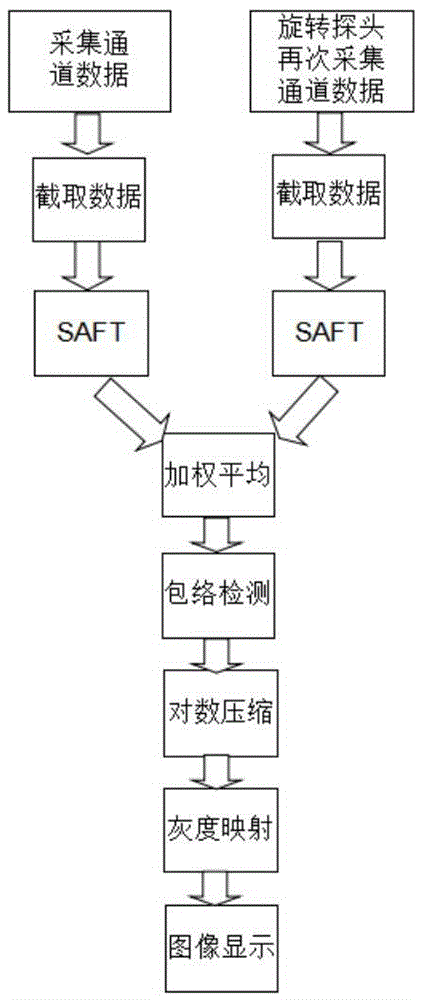
Ultrasonic CT-based synthetic aperture imaging method and system
ActiveCN105411626AHigh-resolutionIncrease contrastUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsComputerised tomographsImage resolutionArray element
The invention discloses an ultrasonic CT-based synthetic aperture imaging method and system. The method comprises the following steps: S1, acquiring data received through ultrasonic reflection by utilizing an ultrasonic CT annular array probe, so as to obtain raw echo data; S2, conducting synthetic aperture focusing on the echo data, so as to obtain values of all imaging points; S3, rotating the ultrasonic CT annular array probe and repeating the steps S1-S2, so as to obtain a plurality of groups of imaging point values, wherein each rotating angle is smaller than an included angle between two adjacent array elements and the circle center of the annular array probe; S4, conducting weighted averaging on the imaging point values, and then carrying out envelope detection, logarithmic compression and grey mapping treatment in sequence, so as to obtain a final high-resolution image. The invention further provides the system for implementing the method. According to the method and the system, the raw data are acquired based on ultrasonic CT (UCT) in a multi-rotating manner, and such treatment measures as weighted stacking are adopted, so as to effectively reduce the influence of noise and improve the image resolution.
Owner:WUHAN WESEE MEDICAL IMAGING CO LTD
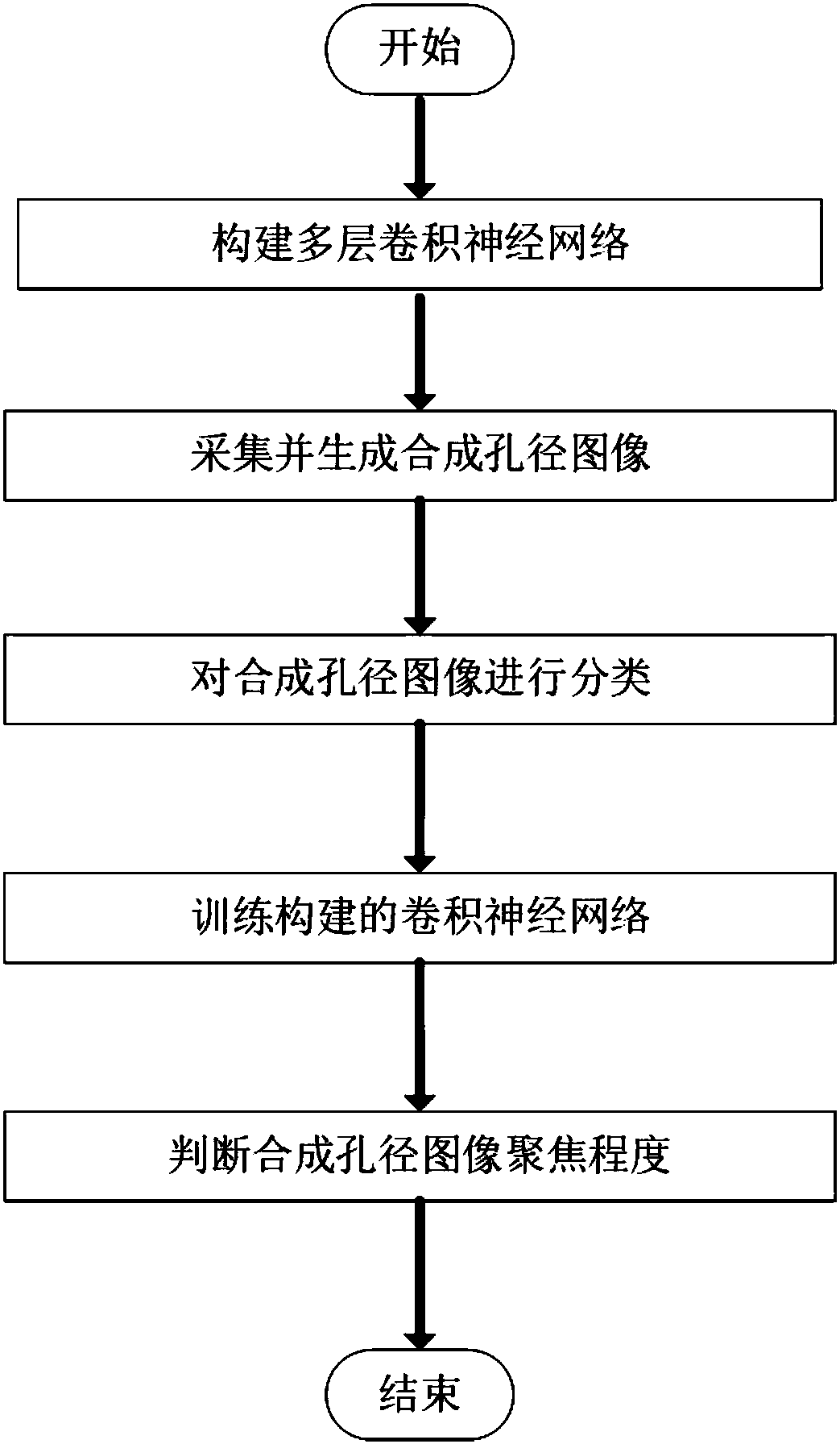
Convolutional neural network-based synthetic aperture focused imaging depth assessment method
ActiveCN108427961AImprove the accuracy of judgmentReduce complexityCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesSynthetic aperture radarSynthetic aperture focusing
The invention discloses a convolutional neural network-based synthetic aperture focused imaging depth assessment method. The method comprises the following steps of: constructing a multilayer convolutional neural network; acquiring and generating synthetic aperture images; classifying the synthetic aperture images; training the constructed convolutional neural network; and judging focusing degreesof the synthetic aperture images. According to the method, single synthetic aperture images are taken as inputs, and a convolutional neural network deep learning tool is adopted to extract focusing features in the synthetic aperture images, so that relatively high judging correctness is provided for the synthetic aperture images with relatively small focusing part areas; and compared with existing method, the method is capable of effectively reducing the calculation complexity, shortening the calculation time, improving the judging correctness and enhancing the expandability, and can be usedfor automatic focusing of synthetic aperture images.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
Synthetic aperture ultrasonic imaging system for calculating delay time based on non-linear correlation
InactiveCN103257349AImprove image qualityHigh resolutionAcoustic wave reradiationLinear correlationSonification
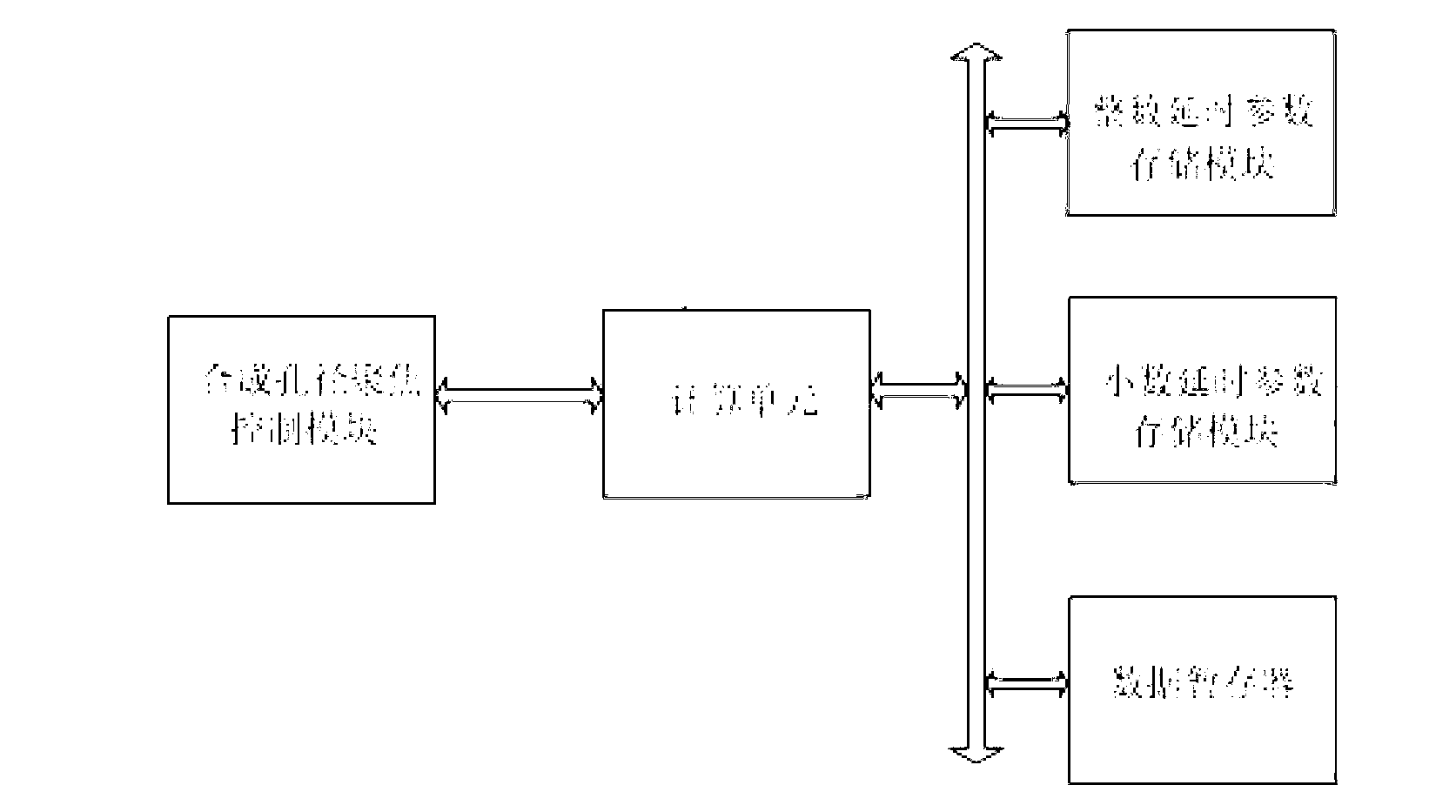
The invention belongs to the field of ultrasonic imaging, and discloses a synthetic aperture ultrasonic imaging system for calculating delay time based on non-linear correlation. The synthetic aperture ultrasonic imaging system for calculating the delay time based on the non-linear correlation comprises a channel receiving and amplifying module, a channel amplifying and driving module, an analog / digital (A / D) conversion module, a digital / analog (D / A) conversion module, a sampling control module, a wave beam synthesizing module, a wave beam forming module, an emission control module, a universal serial bus (USB) subsidiary communication module and a USB communication module. The wave beam synthesizing module calculates the delay time of reconstruction of a synthetic aperture based on the non-linear correlation, and can solve the problem that large deviation exists between a synthetic aperture focusing algorithm based on the delay superposition and reality when the delay time of a transducer and theoretical calculation time differ so much.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
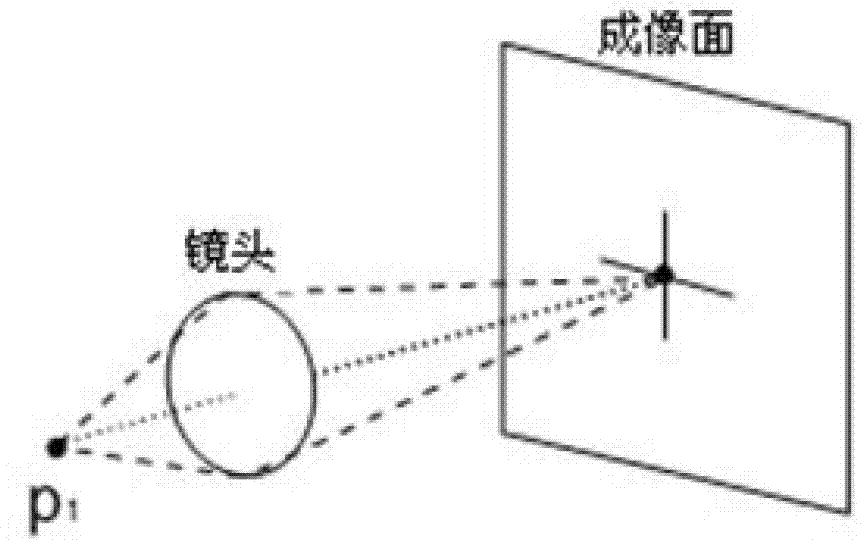
Target ranging method based on synthetic aperture focused images
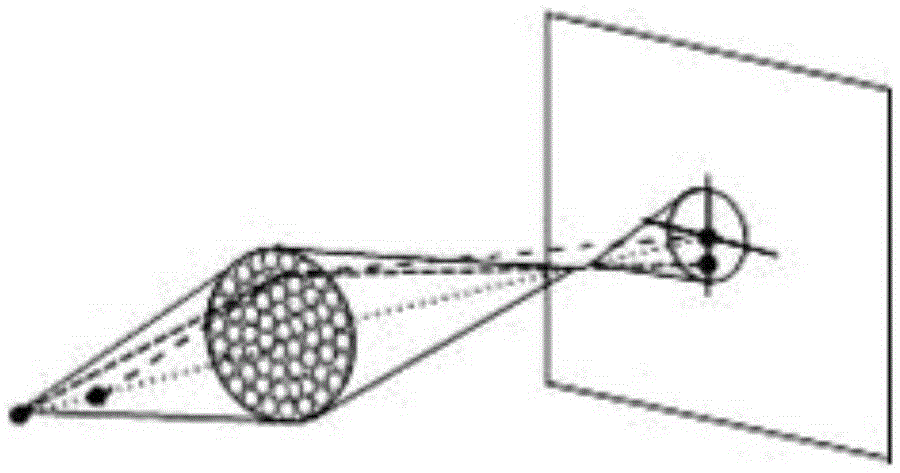
ActiveCN103033166AAvoid mechanical action for focusing imagingFlexible moving processOptical rangefindersSynthetic aperture sonarIntersection of a polyhedron with a line
The invention discloses a target ranging method based on synthetic aperture focused images. The target ranging method disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps of: step 1, obtaining an equally-spaced line array camera position image sequence vertical to a target sight line by virtue of a small-hole imaging model camera, and taking a image of the camera position at the intersection point of a line array and a target sight line as a reference image; step 2, dividing a measurable distance range into a plurality of distance sections, and obtaining an aberration corrected and superposed image corresponding to each distance section, wherein each distance section is corresponding to one aberration corrected and superposed image; step 3, calculating the similarity between a neighbourhood area of each pixel in the reference image and a corresponding area in each aberration corrected and superposed image, and selecting the pixels as ranging pixels, wherein the changing ranges of the distances of the similarity of the pixels along with the aberration corrected and superposed images are greater than a preset threshold; and step 4, finding the distance section corresponding to the aberration corrected and superposed image with the maximum similarity, namely, the distance section in which target points corresponding to the ranging pixels are located. The target ranging method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of being low in realization cost, high in anti-interference capacity, simple in algorithm, and the like.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Anti-perspective plane transformation-based ultrasonic plane wave imaging method
ActiveCN106780329AHigh resolutionImprove efficiencyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsGeometric image transformationSonificationImage resolution
The invention discloses an anti-perspective plane transformation-based ultrasonic plane wave imaging method. The method comprises the following steps of (1) collecting data; (2) preprocessing the data: converting imaging points on an original imaging plane into imaging points on a new plane by utilizing plane conversion, calculating delay time according to the imaging points on the new plane to obtain corrected delay time, then receiving and focusing the imaging points on the original imaging plane by utilizing a synthetic aperture focusing technology according to the corrected delay time, and obtaining a value of each imaging point on the original imaging plane; and (3) post-processing the data: performing envelope detection, logarithmic compression and grayscale mapping in sequence, and finally obtaining an ultrasonic plane wave imaging image. According to the method, a key delay time calculation mode is improved and matched with the synthetic aperture focusing technology, so that compared with the prior art, the problem of low plane wave imaging quality can be effectively solved and the ultrasonic plane wave imaging resolution is effectively increased.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
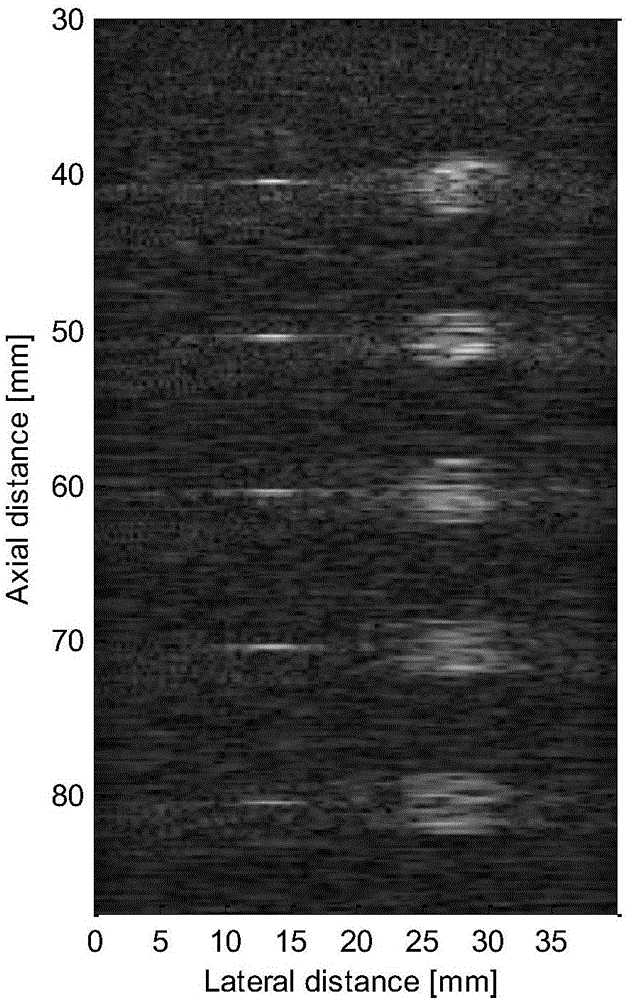
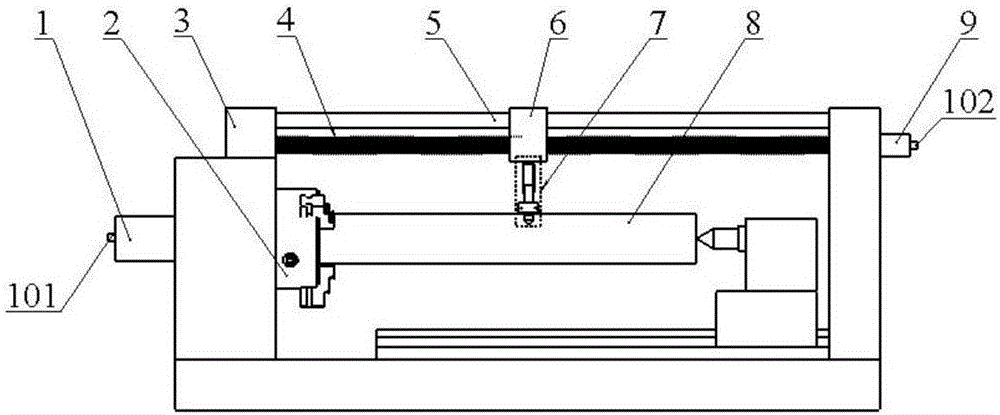
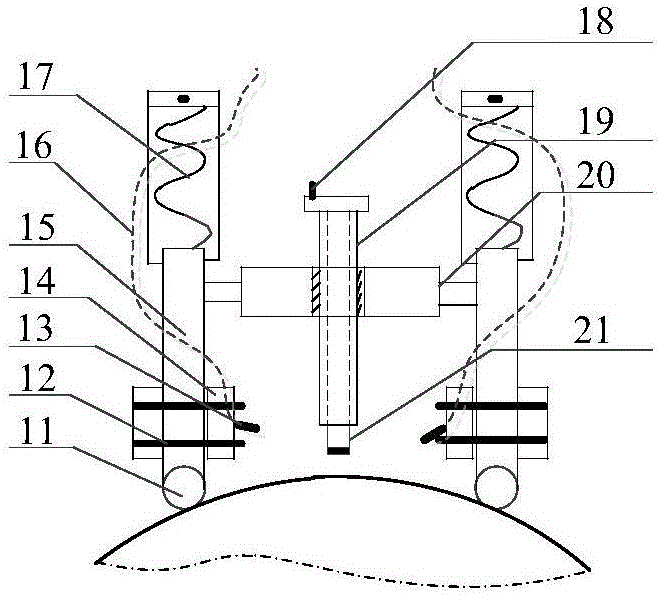
Solid shaft ultrasonic synthetic aperture focusing detection device and imaging method
ActiveCN106556645AAvoid damageSolve the problem of low imaging resolutionAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesImage resolutionSingle probe
The invention discloses a solid shaft ultrasonic synthetic aperture focusing detection device and an imaging method for high resolution automatic ultrasonic detection imaging of a solid shaft. The detection device includes a probe frame component and a controller assembly, and is used for controlling the automatic positioning and axial movement of a probe. The imaging method is used for synthetic aperture focusing imaging under a polar coordinate system in the shaft. The technical effects of the invention lie in that the detection device can adapt to automatic ultrasonic detection of solid shafts with different diameters, realizes axial and radial positioning of defects, and improves the detection efficiency and scope; and the synthetic aperture focusing imaging method of the polar coordinate system in the shaft provided by the invention can solve the problem of low imaging resolution in traditional single probe ultrasonic detection of the solid shaft, and improves detection precision.
Owner:CHANGSHA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Single-channel bidirectional receiving and transmitting ultrasonic guided wave pipeline monitoring system and imaging method
InactiveCN110646512AIncrease the monitoring distanceImproving Imaging AccuracyAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesSensor arrayMonitoring system
The invention discloses an ultrasonic guided wave array pipeline defect imaging detection system and an imaging method. The system has the advantages of being long in monitoring distance, simple in structure, low in power consumption and high in imaging precision. The method comprises the steps that firstly, one annular excitation sensor array and two annular receiving sensor arrays are arranged on a pipeline, the annular receiving sensor arrays are located at the two sides of the annular excitation sensor array and receive ultrasonic guided wave signals bidirectionally and simultaneously, bidirectional simultaneous monitoring of the annular excitation sensor array is realized, the monitoring distance is greatly prolonged, and system cost is lowered; secondly, array elements of the annularexcitation sensor array sequentially perform excitation, the annular receiving sensor arrays at the two sides receive the ultrasonic guided wave signals sequentially and cyclically, it is only neededto maintain operation of one excitation array element and two receiving array elements in the monitoring process, hardware configuration of the system is simplified, operation is performed in a low-power-consumption state, and long-time online monitoring is realized; and thirdly, a pipeline monitoring region is imaged through collected full-matrix data in combination with full-waveform inversion,synthetic aperture focusing, full focusing and other algorithms, and positioning and quantitative monitoring of pipeline corrosion and other defects are realized.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Improved time domain ultrasonic signal synthetic aperture algorithm
InactiveCN108415020AReduce overlayReduce artifactsAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesAcoustic wave reradiationTime domainSynthetic aperture sonar
The invention discloses an improved time domain ultrasonic signal synthetic aperture algorithm. The algorithm comprises the steps that (1) firstly, a head wave acoustic time method is used to determine the approximate distribution of test piece defects, and the head wave acoustic time method can adopt a reflection method or a transmission method to detect a test piece; (2) secondly, the distribution position of the defects is imaged by means of synthetic aperture focusing; a probe is used to move along a detection line; each time the probe steps a fixed displacement, after each time the probesteps a fixed displacement, an echo signal is collected, numbered and stored; and (3) finally, a focusing algorithm is implemented; the echo signal of each step position is processed; according to a vector addition and synthesis method, delayed superposition of the focusing radius with a smaller number of apertures on the left and right is carried out to acquire a beam with good directivity. According to the invention, possible errors during signal transmission and receiving are reduced, and the accuracy of an imaging result is improved.
Owner:ZHONGBEI UNIV
Ultrasound tomography calculation optimization method and system based on distributed system
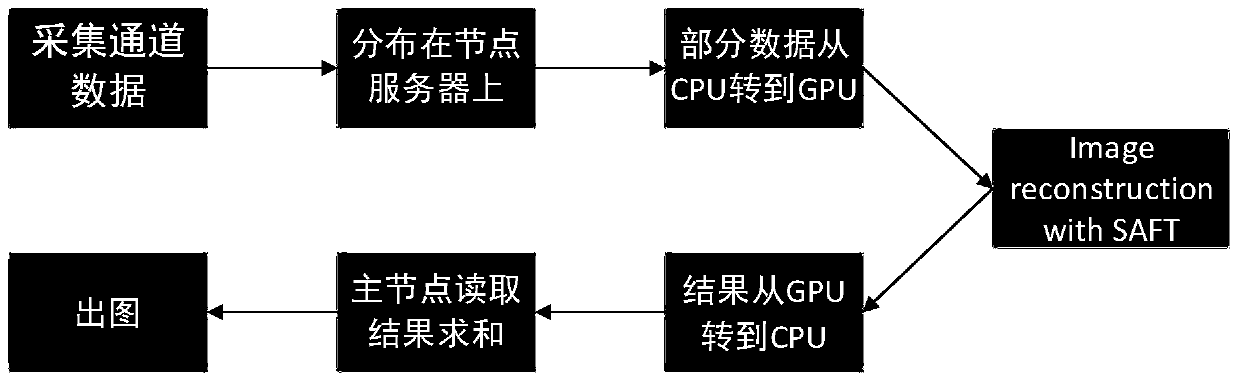
ActiveCN110179495ASolve the large amount of dataResolution timeUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsSynthetic aperture focusingUltrasound image
The invention belongs to the field of ultrasound imaging large data volume processing and discloses an ultrasound tomography calculation optimization method and system based on a distributed system. The method comprises the steps of: preparation: arranging the distributed system comprising X distributed node servers and allowing array elements of a probe to correspond to the appropriate node servers, wherein the quantities of the array elements corresponding to the node servers are equal; and data acquisition and storage: conducting filtration preprocessing on received signals after acquiringall the signals, and conducting image reconstruction, wherein the image reconstruction comprises the steps of independent reconstruction of each node and major node server integration. The method andthe system process the ultrasound signals (acquired by the array elements) received by an ultrasound tomography system by using a distributed cluster system schema and the multinode servers based on aprinciple of a synthetic aperture focusing technique (SAFT), and can solve the problems of large data volume, long image reconstruction time and the like of the ultrasound tomography system.
Owner:维视医学影像有限公司
Surface leakage wave ultrasonic synthetic aperture focusing imaging method
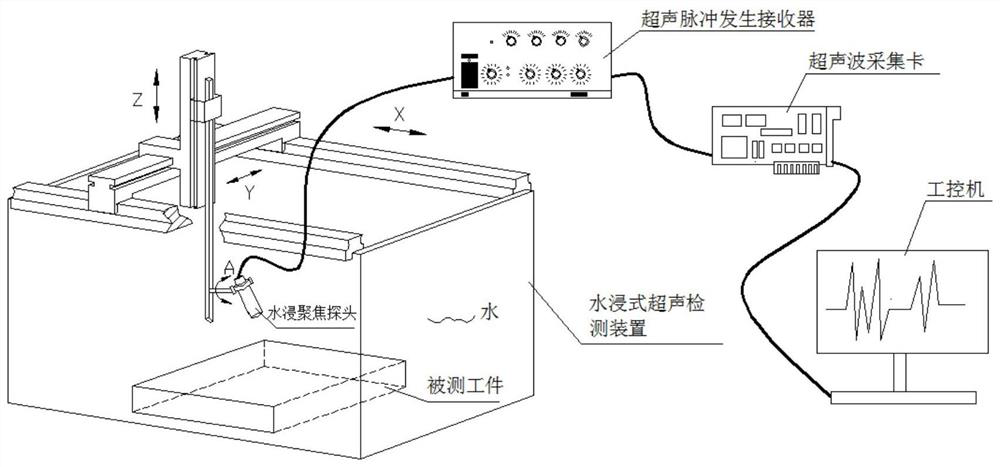
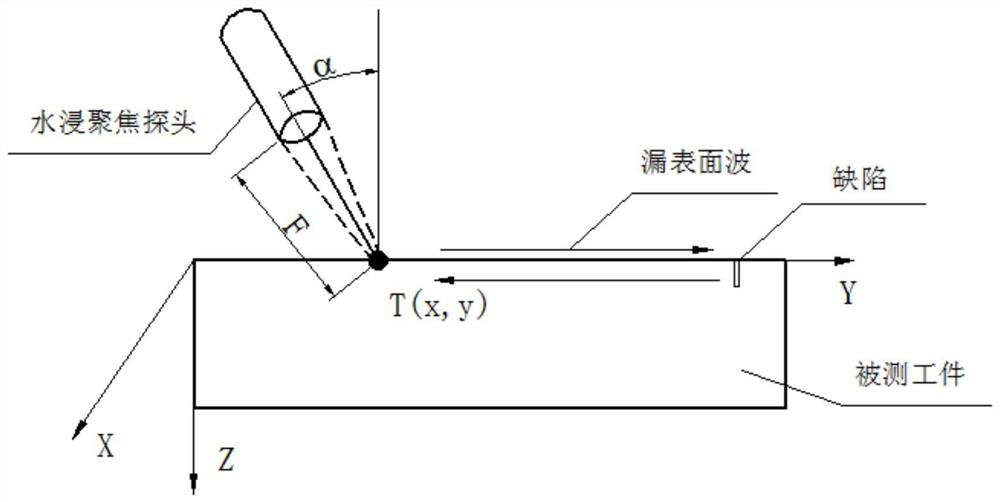
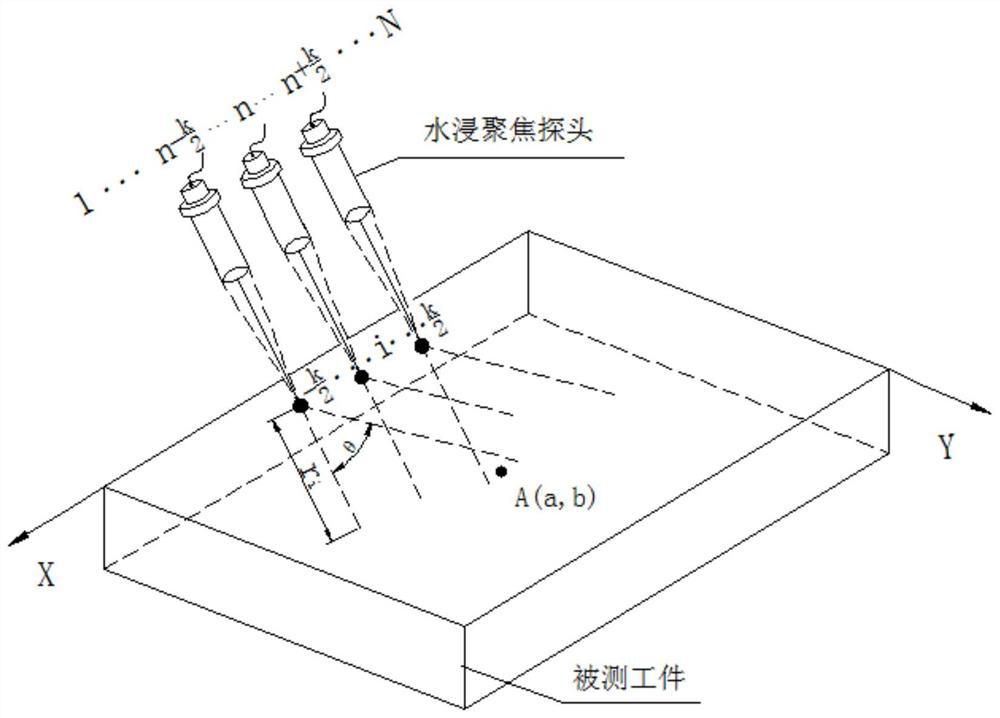
ActiveCN111751448AImaging RealizationImprove detection efficiencyAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesProcessing detected response signalHigh resolution imagingImage detection
The invention discloses a surface leakage wave ultrasonic synthetic aperture focusing imaging method. Efficient high-resolution imaging detection of defects on the surface or near surface of a part isachieved. A four-axis motion detection device controls a water immersion focusing probe to obliquely enter the surface of a workpiece to generate surface leakage waves, then surface leakage wave pulse echo signals are collected, and finally the surface leakage wave pulse echo signals are subjected to synthetic aperture focusing imaging to achieve defect recognition. The method has the technical effects that imaging of defects on the surface or the near surface of the part can be efficiently achieved in a non-contact mode, the detection efficiency and the imaging resolution are improved, and an effective nondestructive detection method is provided for evaluating the surface quality of a metal component.
Owner:CHANGSHA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
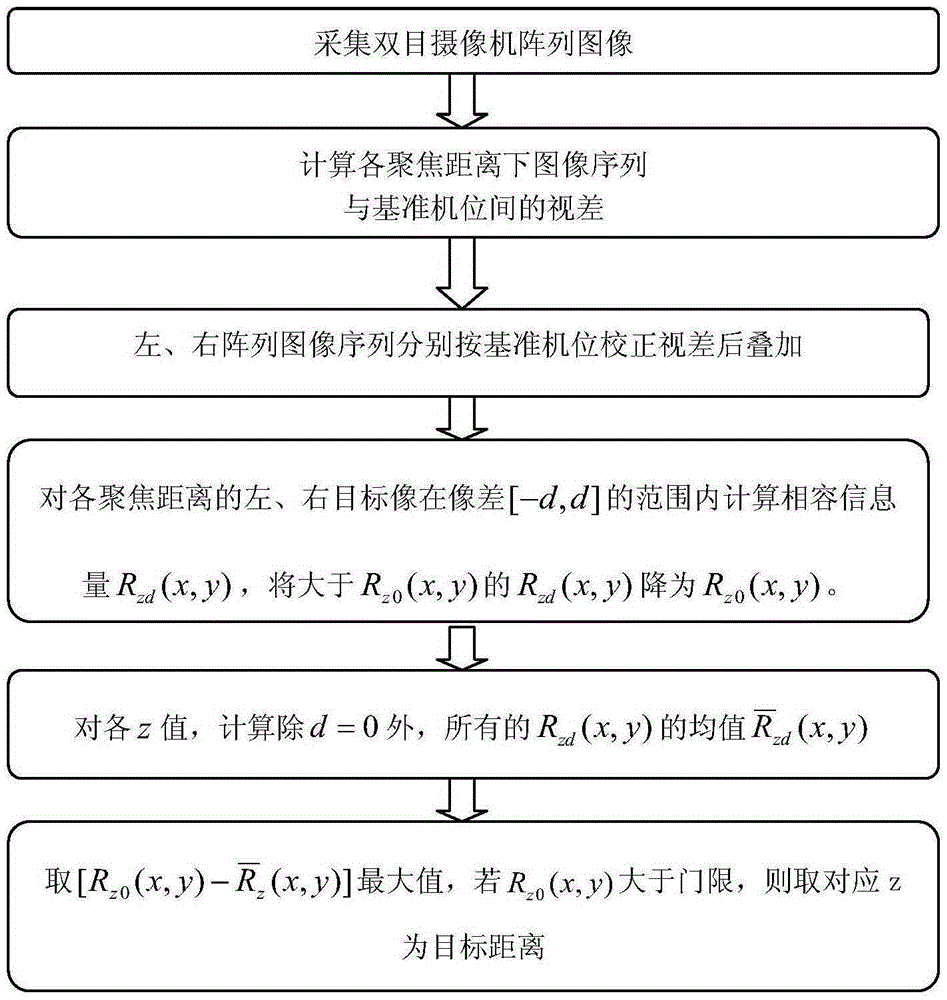
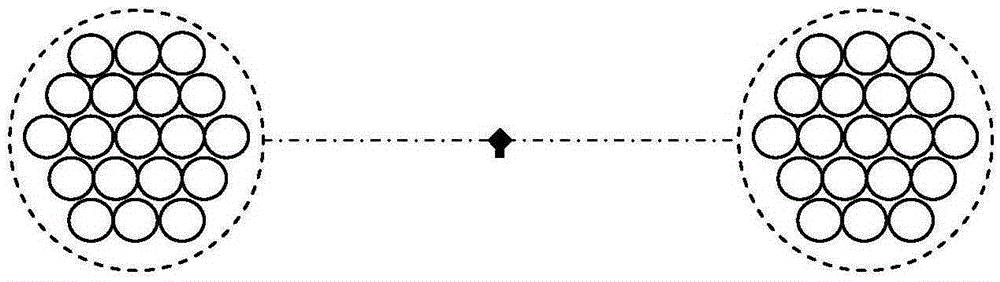
Target range finding method and apparatus based on binocular synthetic aperture focus image
ActiveCN105258673ARealize convergent/scattering measurementFlexible moving processOptical rangefindersFindings methodsSynthetic aperture focusing
The invention discloses a target range finding method based on a binocular synthetic aperture focus image. The method comprises the following steps: first taking a symmetric center of two area arrays identical in structures as a benchmark position, respectively carrying out the optical synthetic aperture imaging for a scene in which a target stays, and respectively obtaining a group of synthetic aperture images corresponding to different focusing distances; then taking the difference between binocular matching position compatibility information amount and binocular mismatch position compatibility information amount as a detection amount, finding out a maximum focusing distance of the detection amount, if the binocular matching position compatibility information amount of the focusing distance is greater than a preset compatibility information amount threshold value, the focusing distance is a target distance. The invention also discloses a target range finding apparatus based on the binocular synthetic aperture focus image. Compared with the prior art, the common-mode error and misfocus imaging interference can be effectively inhibited, and the synthetic aperture focus image range finding performance is improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Ultrasonic TOFD dead zone inhibition method based on synthetic aperture focusing and mode converted wave
ActiveCN110243945AImprove image qualityImproving Defect Quantification AccuracyAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesProcessing detected response signalSynthetic aperture sonarTime delays
The invention discloses an ultrasonic TOFD dead zone inhibition method based on synthetic aperture focusing and mode converted wave, and belongs to the technical field of the nondestructive detection. The method adopts a TOFD detection system composed of an ultrasonic flaw detector, a TOFD probe, an inclined organic glass wedge and a scanning device; the method comprises the following steps: implementing scanning and image collection along a surface of a to-be-tested workpiece, acquiring an A scanning signal set at different scanning locations; performing time delay and amplitude overlapping processing on all A scanning signals when solving the shortest propagation sound of the mode converted waves at various locations according to Fermat theorem, and realizing TOFD scanning image reconstruction through point-by-point focusing, weakening a lateral redundancy signal, and improving imaging quality. The end point depth of the defect in the dead zone range can be computed by utilizing the relevancy between the mode converted display depth and the defect end point depth in the reconstructed image. Compared with the existing mode converted wave method, the method can improve the defect quantitative precision when inhibiting the TOFD dead zone, and the method has high engineering application and popularization value.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Imaging method and device for track board internal defect detection
PendingCN111323485AEasy to operateImprove signal-to-noise ratioAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesProcessing detected response signal3d imageMATLAB
The invention discloses an imaging method and device for track board internal defect detection. The imaging method is characterized in that the imaging method comprises the following steps: exciting by using an ultrasonic transmitting and receiving device, transmitting an ultrasonic signal with the frequency between 20 and 100kHz into a track plate by using an ultrasonic array sensor, acquiring areflection echo signal of an internal defect of the track plate by using the ultrasonic array sensor in a one-transmitting and multi-receiving mode, and transmitting the reflection echo signal to a computer; and then adopting MATLAB software by the computer to carry out data storage and signal processing on the received reflection echo signal, and then obtaining a three-dimensional image of the internal defect of the track plate according to a time domain synthetic aperture focusing imaging algorithm and a three-dimensional imaging technology. According to the method, the internal defects of the track plate can be efficiently detected in a nondestructive and real-time manner, the detection result is basically not influenced by the external environment, and the detection precision is high.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV OF ENG SCI
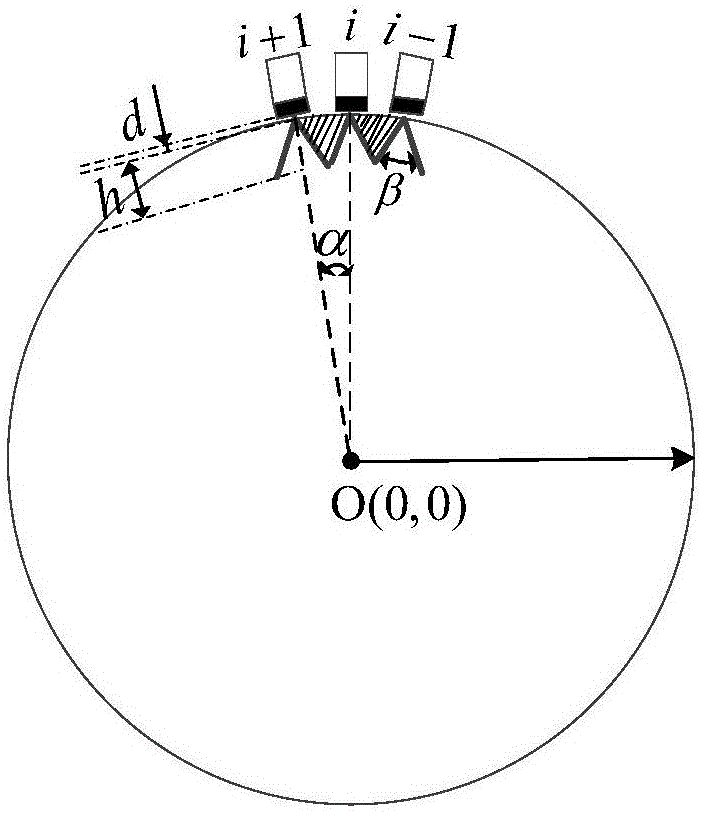
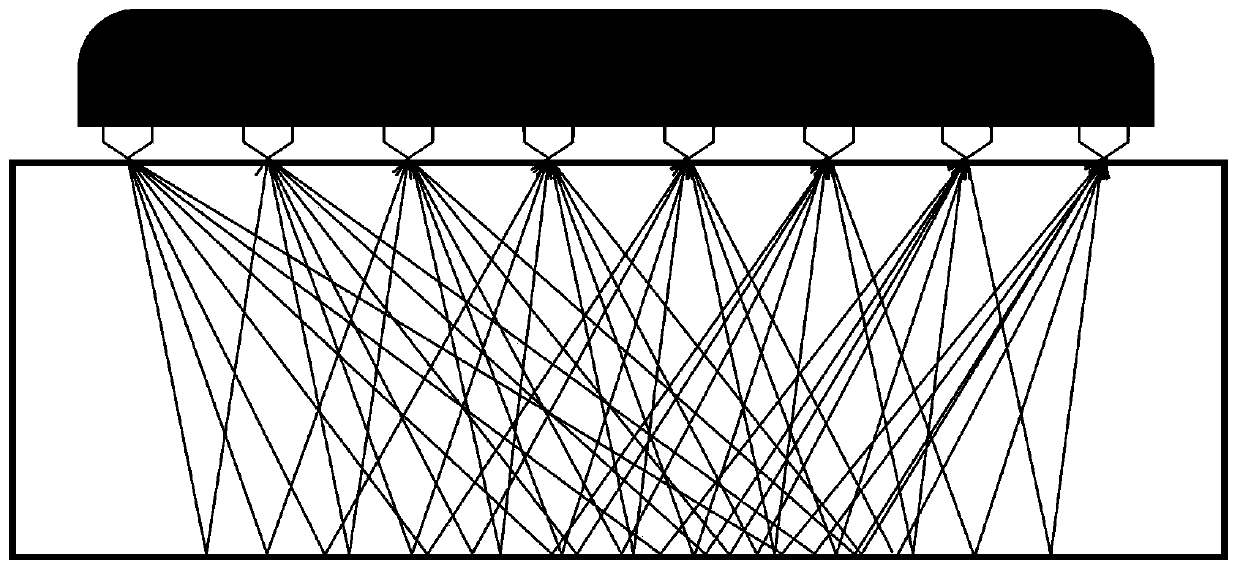
Ultrasonic borehole wall imaging method applied to cylindrical ultrasonic array
ActiveCN109281651AHigh-resolutionReduce the number of independent channelsSurveyConstructionsAcousticsSynthetic aperture focusing
The invention relates to an ultrasonic borehole wall imaging method applied to a cylindrical ultrasonic array. The method comprises: step 1) driving each transducer array element in the cylindrical ultrasonic array, sequentially transmitting ultrasonic signals separately, all transducer array elements receiving echo signals corresponding to each transmitted signal at the same time; step 2) using the echo signals obtained in step 1), performing point-by-point focusing imaging processing on each imaging point according to a synthetic aperture focusing algorithm, to obtain echo amplitude data corresponding to each imaging point; and step 3) splicing the echo amplitude data corresponding to each imaging point, to obtain an amplitude imaging image in an entire imaging plane. The ultrasonic wellbore wall imaging method is applied in ultrasonic borehole wall detection, and would greatly reduce the number of independent channels of the cylindrical array ultrasonic borehole wall imaging system,reduce hardware cost of a system, and the method can improve resolution ratio of borehole wall imaging detection under the condition that the frequency of a downhole transducer is low.
Owner:INST OF ACOUSTICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
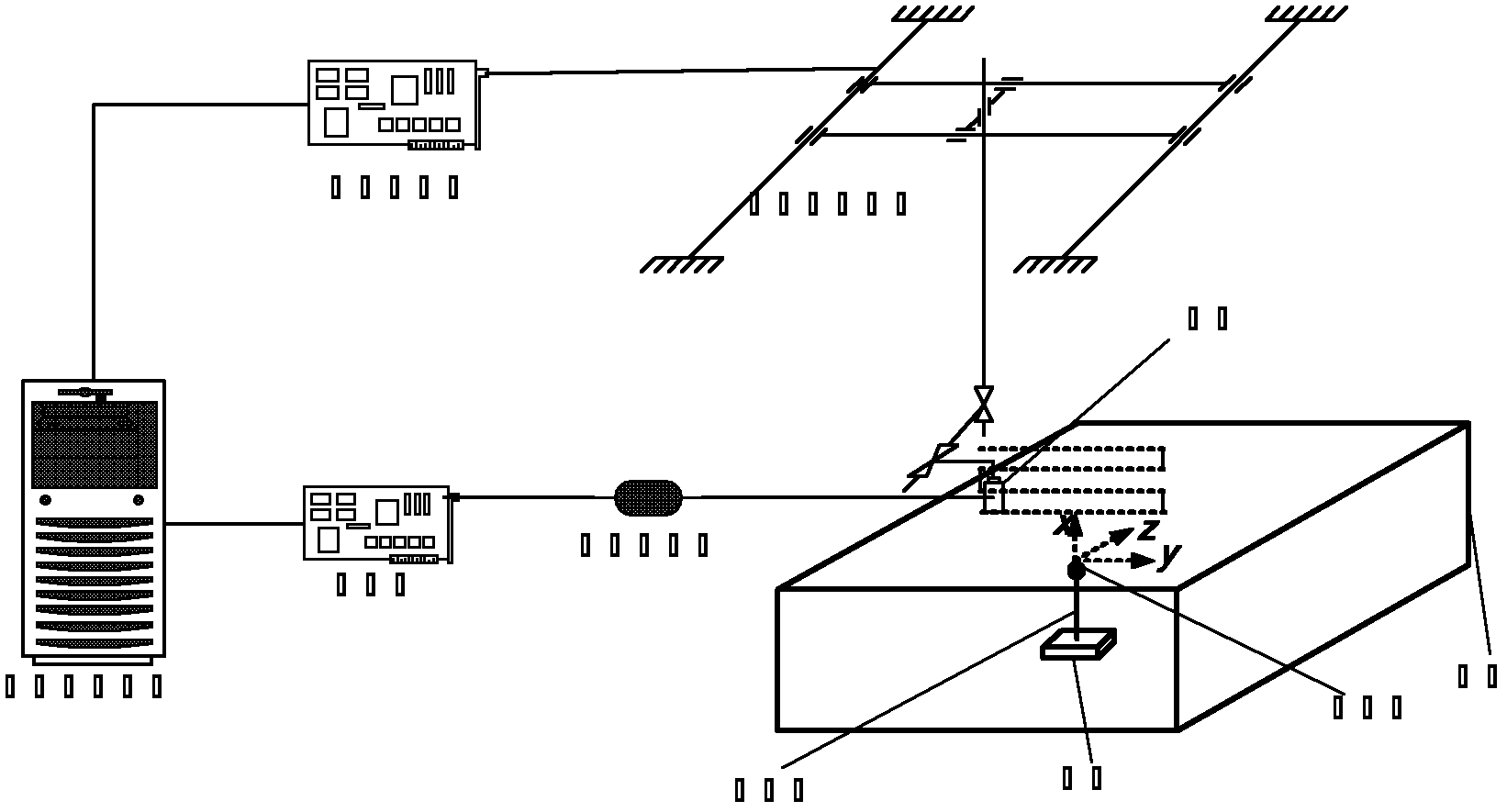
Laser ultrasonic detection device and method based on synthetic aperture focusing imaging
The embodiment of the invention discloses a laser ultrasonic detection device and method based on synthetic aperture focusing imaging. The device comprises a pulse laser, a three-dimensional galvanometer, a scanning lens, an interferometer, a laser displacement sensor, a three-dimensional translation platform and an industrial personal computer; the three-dimensional translation table is used forplacing a sample; the three-dimensional galvanometer, the interferometer and the laser displacement sensor are arranged right above the three-dimensional translation platform; the scanning lens is arranged at one end, right opposite to the three-dimensional translation stage, of the three-dimensional galvanometer; the industrial personal computer is connected with the pulse laser and the three-dimensional translation stage, and the pulse laser is connected with the three-dimensional galvanometer. According to the device and the method provided by the embodiment of the invention, SAFT imaging of internal defects can be carried out on samples with any surface shapes.
Owner:GUANGDONG POWER GRID CO LTD +1
Automated defect detection of corrosion or cracks using SAFT processed Lamb wave images
ActiveUS7783433B2Image enhancementAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesSonificationLinear filter
A system, method and computer program product is provided for automated defect detection of corrosion or cracks using synthetic aperture focusing technique (SAFT) processed Lamb wave images. The method comprises processing the first image using a synthetic aperture focusing technique (SAFT) to enhance a resolution and a signal to noise ratio of a first extracted ultrasonic image, applying a systemic background noise suppression algorithm to the first extracted ultrasonic image to render a second extracted ultrasonic image having reduced noise, and applying a deconvolution linear filtering process to the second extracted ultrasonic image to render a third extracted ultrasonic image.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
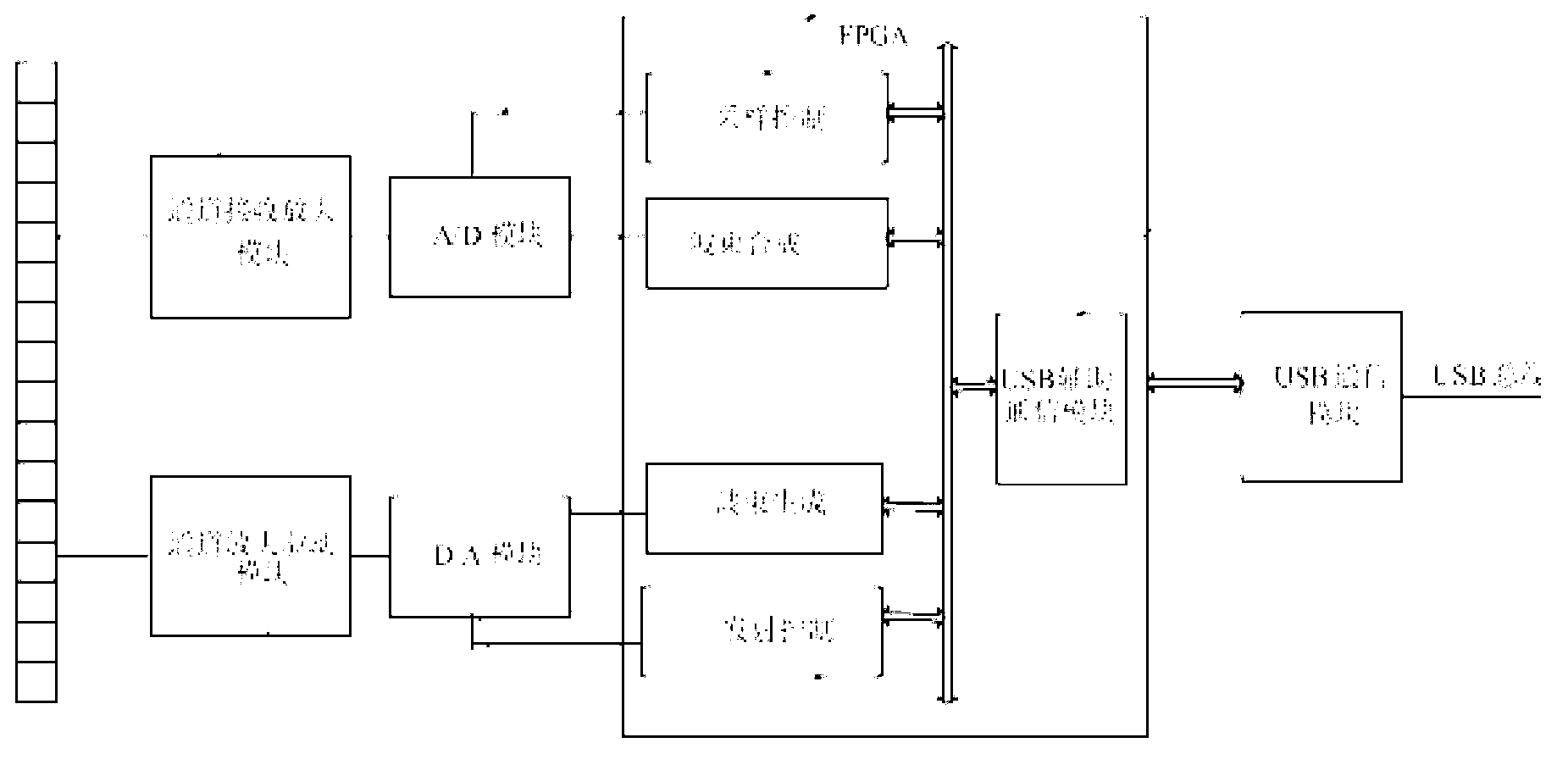
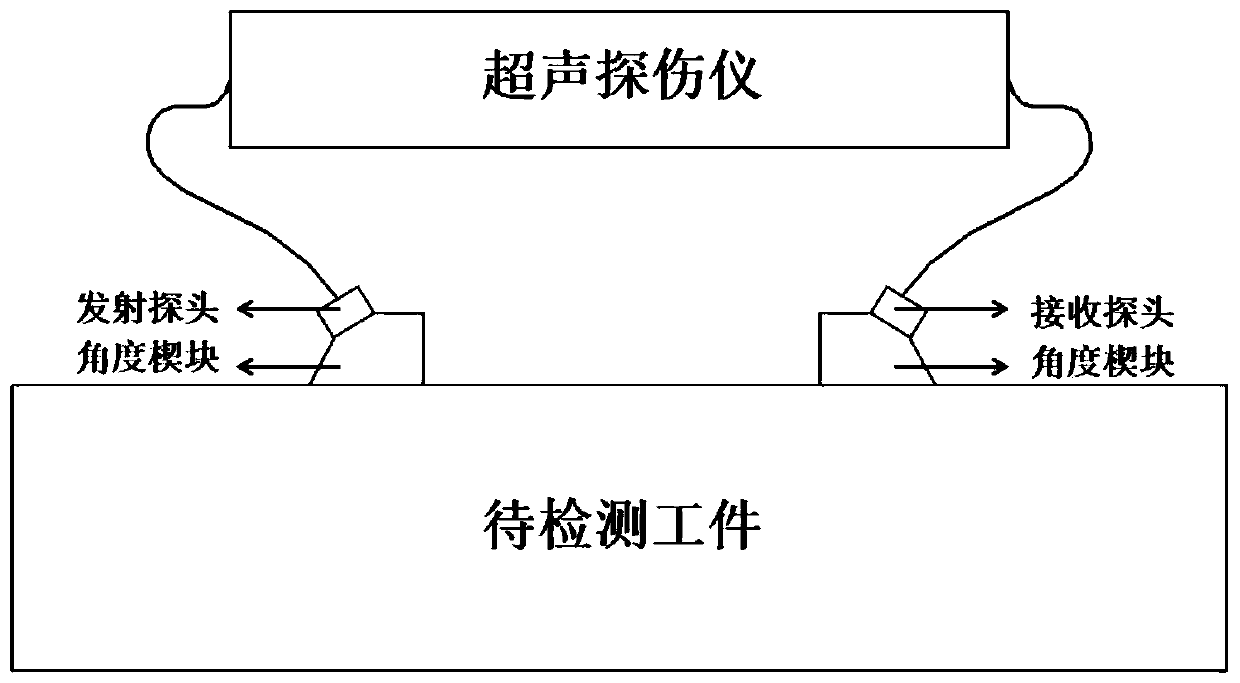
Ultrasonic nondestructive testing system for large blacksmith welding pieces
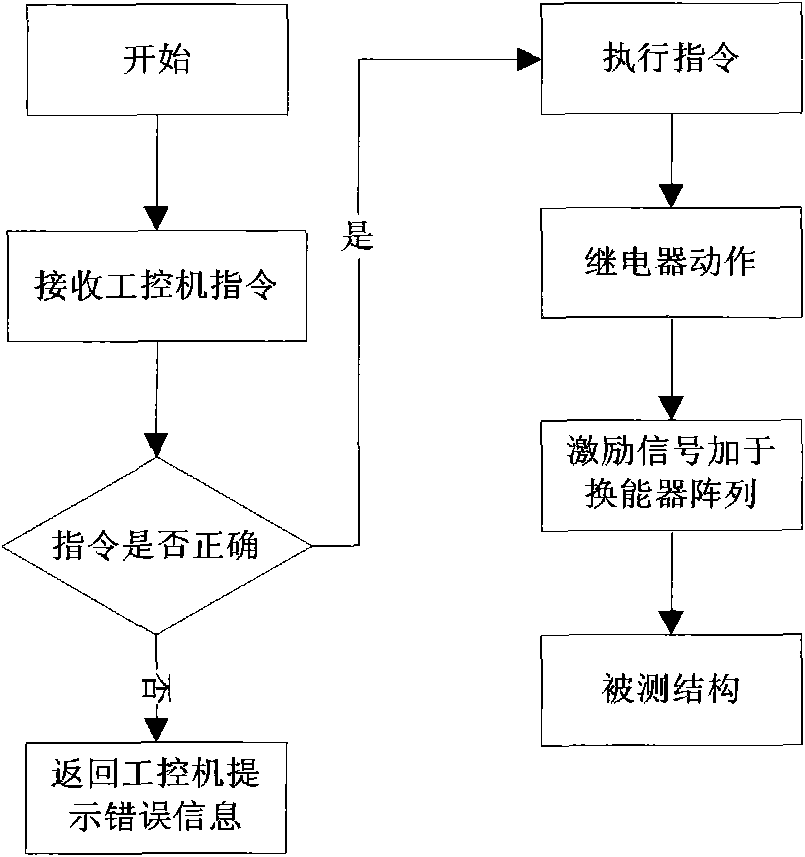
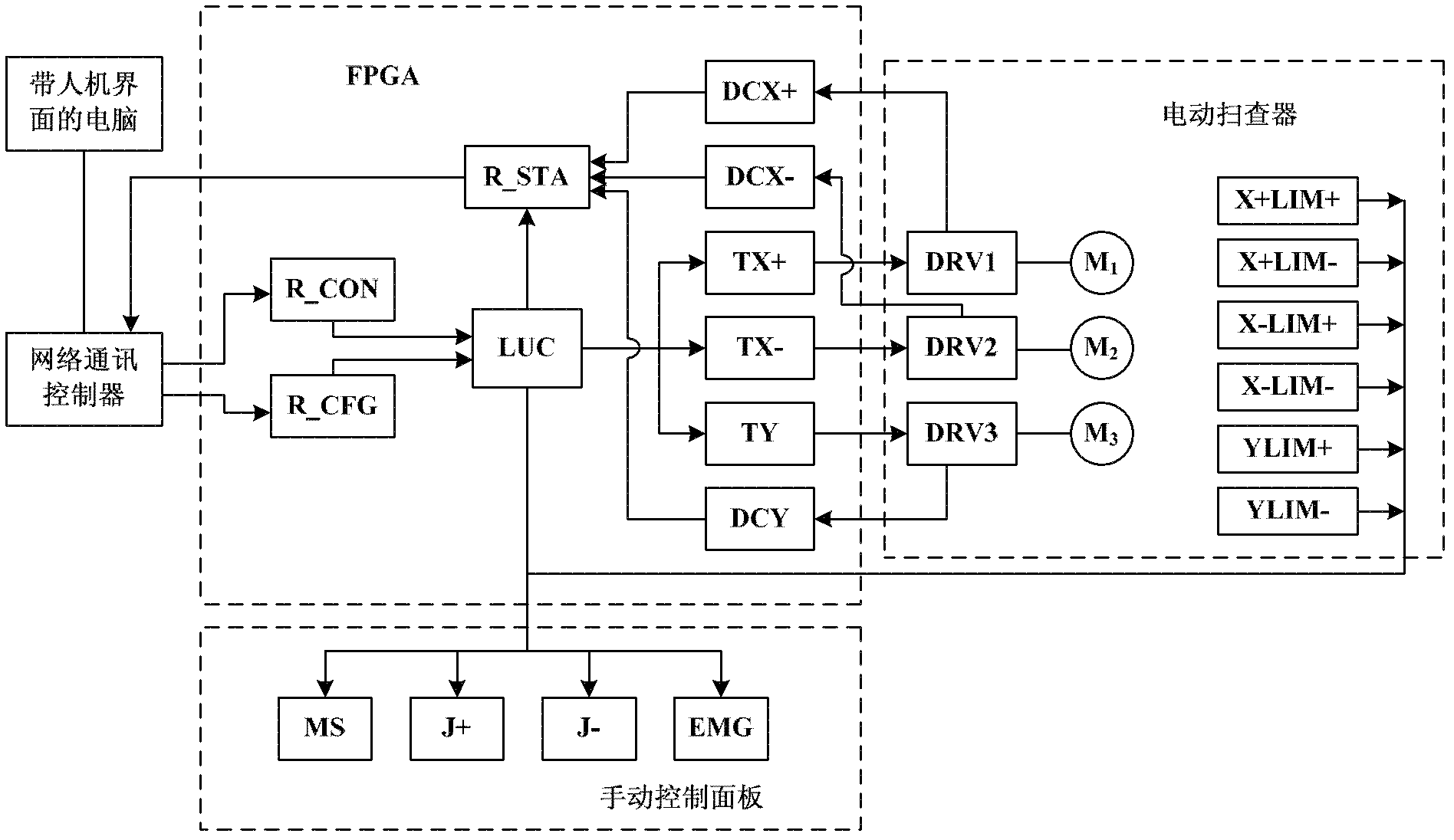
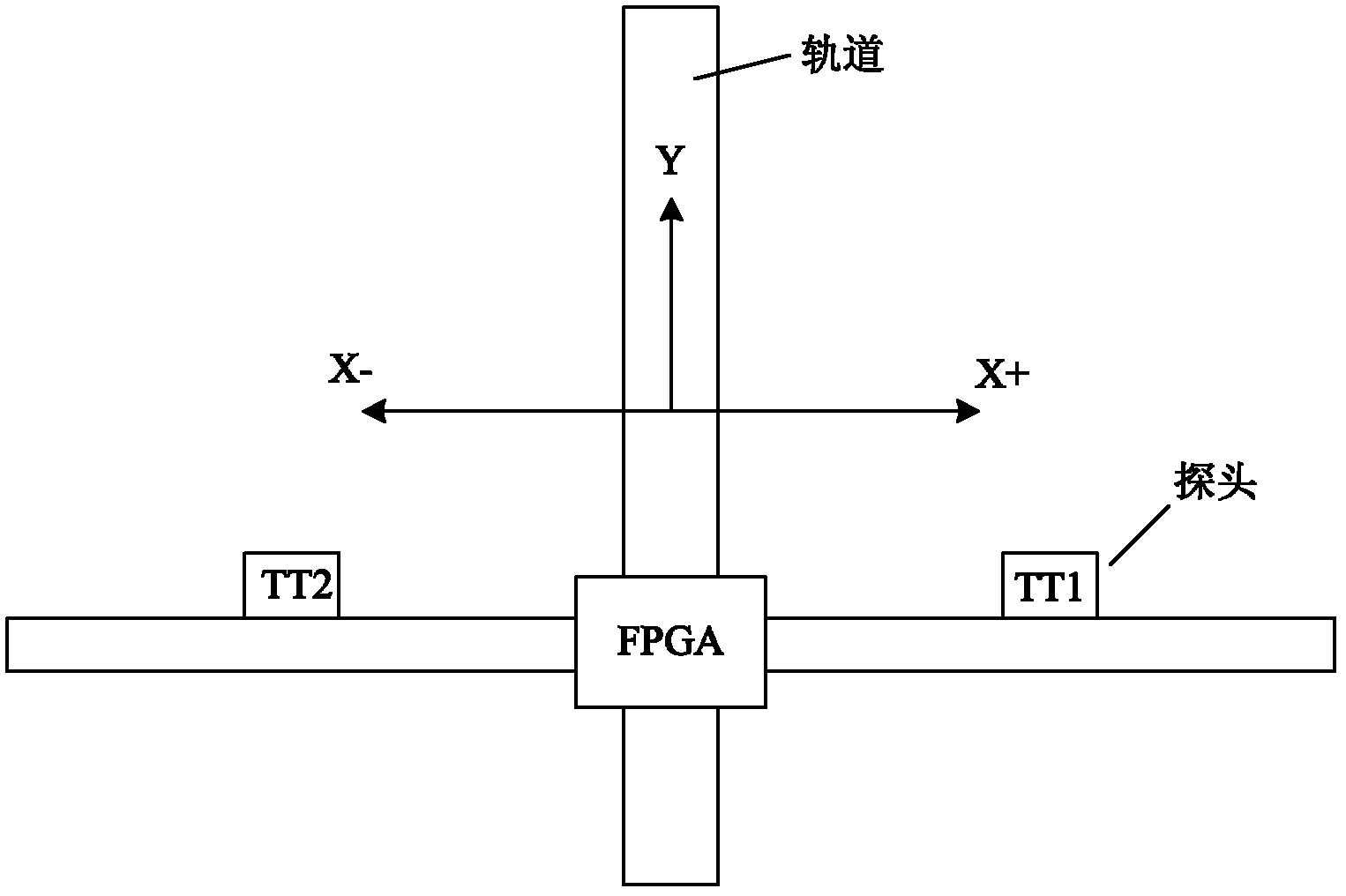
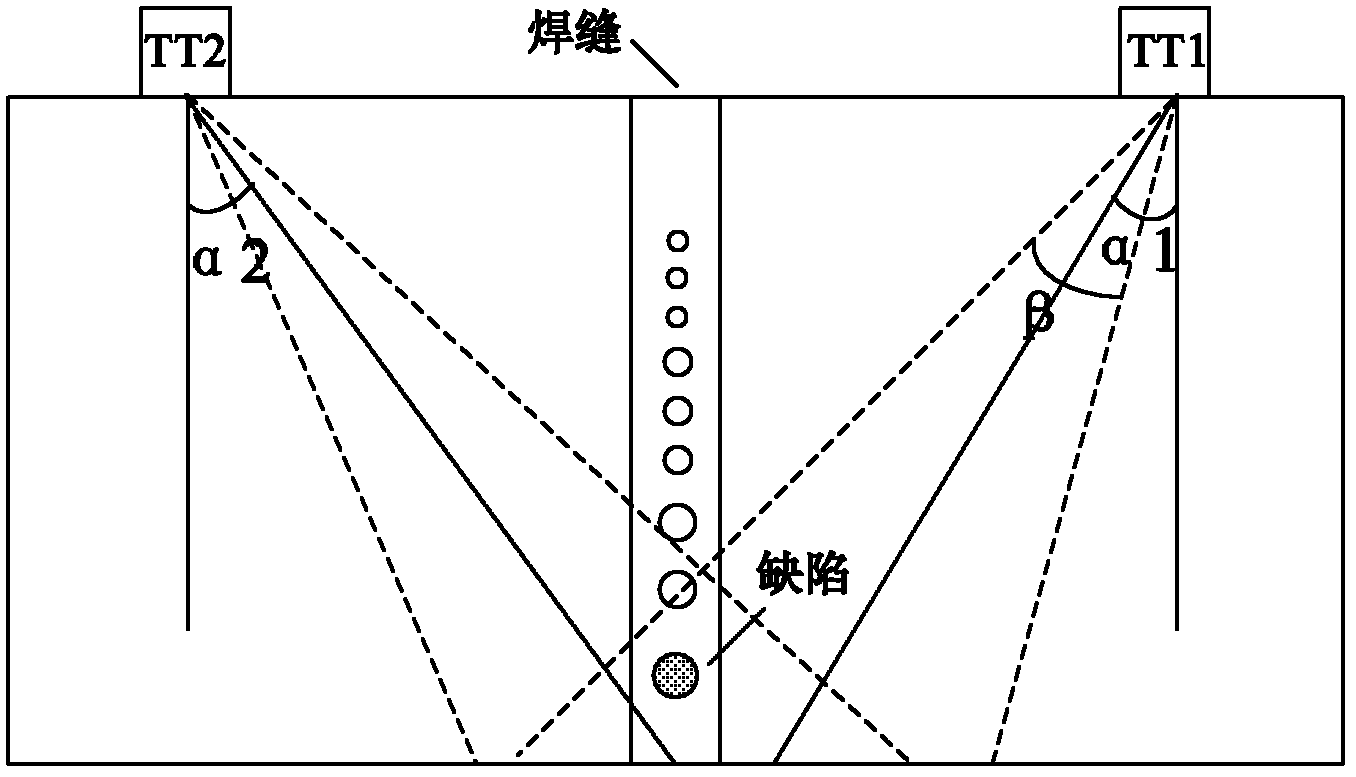
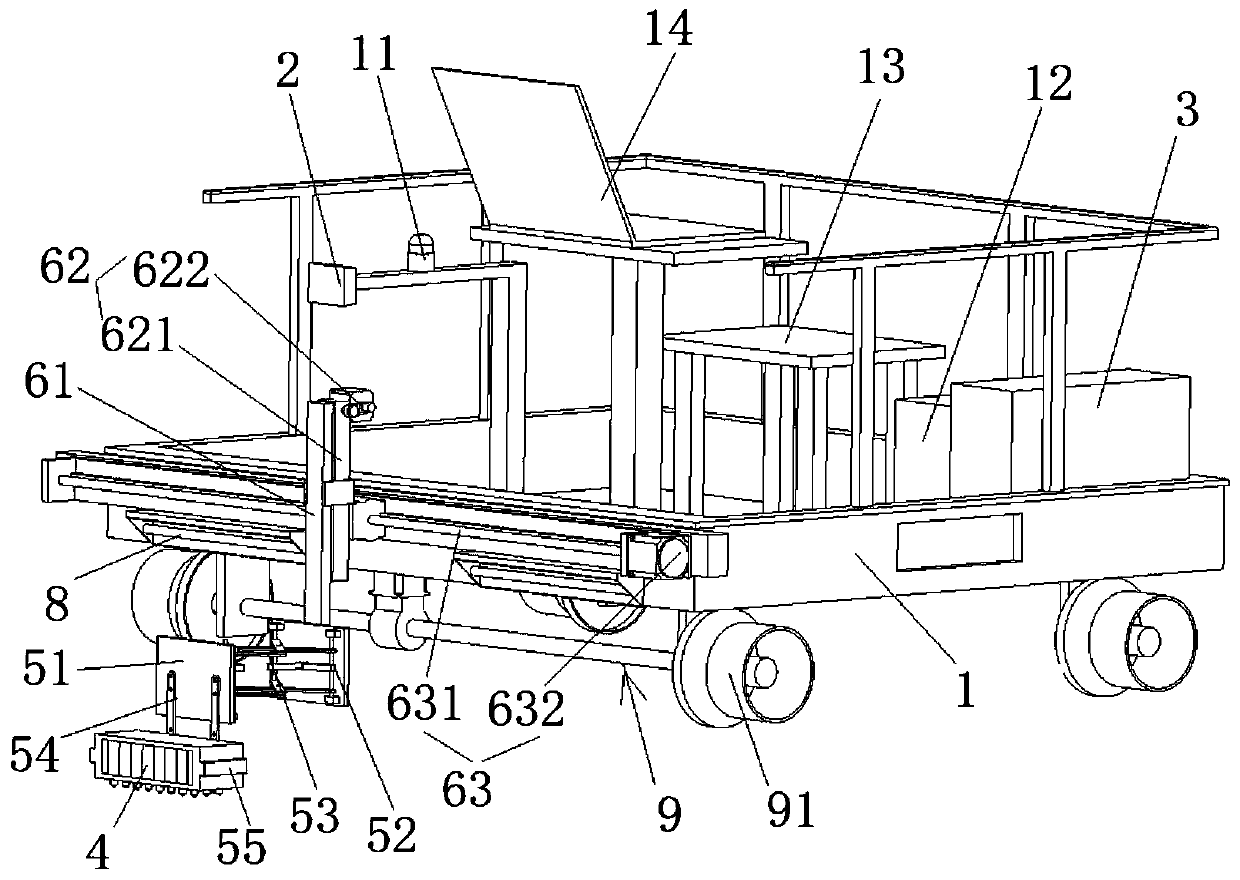
InactiveCN102590342AMeet the requirements of ultrasonic non-destructive testingImprove detection accuracyAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesHuman–machine interfaceSignal on
The invention relates to an ultrasonic nondestructive testing system for large blacksmith welding pieces, which comprises a computer with a human-computer interface, an FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array), a network communication controller, an electric scanning device and a manual control panel, wherein the FPGA comprises a logic control unit (LCU), a pulse generator of a moving shaft, a control register, a status register, a parameter register and a decoding circuit, the electric scanning device comprises two ultrasonic angle probes transmitting and receiving ultrasonic signals on the same plane, an alternating servo motor driver and a driving motor, and the manual control panel comprises a manual selective switch, an inching button, a scram button and a limit switch. The position and the size of a defect in a weld joint is determined after SAFT (Synthetic Aperture Focusing Technique) treatment is carried out on ultrasonic signals of the two ultrasonic angle probes of the system, the testing precision and the reliability are obviously improved, the maximum thickness of the tested weld joint is 600mm, and the testing system can meet the ultrasonic nondestructive testing requirement of a super-large blacksmith welding piece with the thickness of 400 mm-600 mm.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Imaging method and device for realizing automatic track board crack detection
ActiveCN111452830AImplement automatic detectionHigh energyImage analysisRailway auxillary equipmentImaging algorithmEngineering
The invention discloses an imaging method and device for realizing automatic track board crack detection. The imaging method comprises the steps: using a camera for detecting track board crack surfacedefects; carrying out exciting by using an ultrasonic transmitting and receiving device, and transmitting an ultrasonic signal in the frequency of 1-5MHz to the interior of a track board through an ultrasonic linear array probe; acquiring a diffusion field signal in the track board in a self-transmitting and self-receiving mode by the ultrasonic linear array probe and transmitting the diffusion field signal to a computer; passively extracting a Green function from the received signal by the computer through MATLAB software; performing cross-correlation on the diffusion field signal, reconstructing a Green function between array elements, obtaining non-delayed response between the array elements, recovering early defect information submerged by noise, and then performing track plate crackimaging according to a frequency domain synthetic aperture focusing imaging algorithm. According to the invention, the defects on the crack surface and inside the crack of the ballastless track boardcan be efficiently detected in real time in a nondestructive manner.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV OF ENG SCI
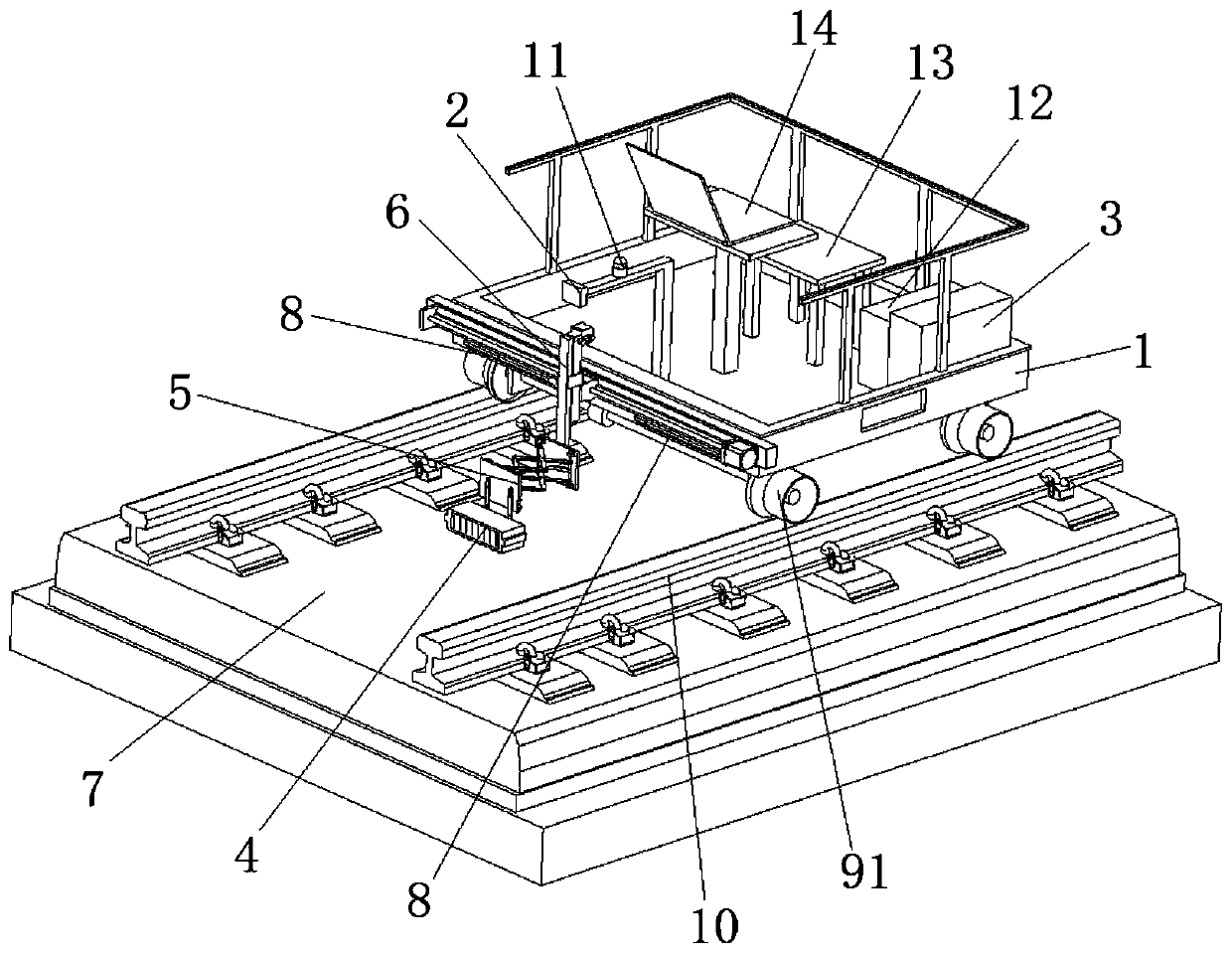
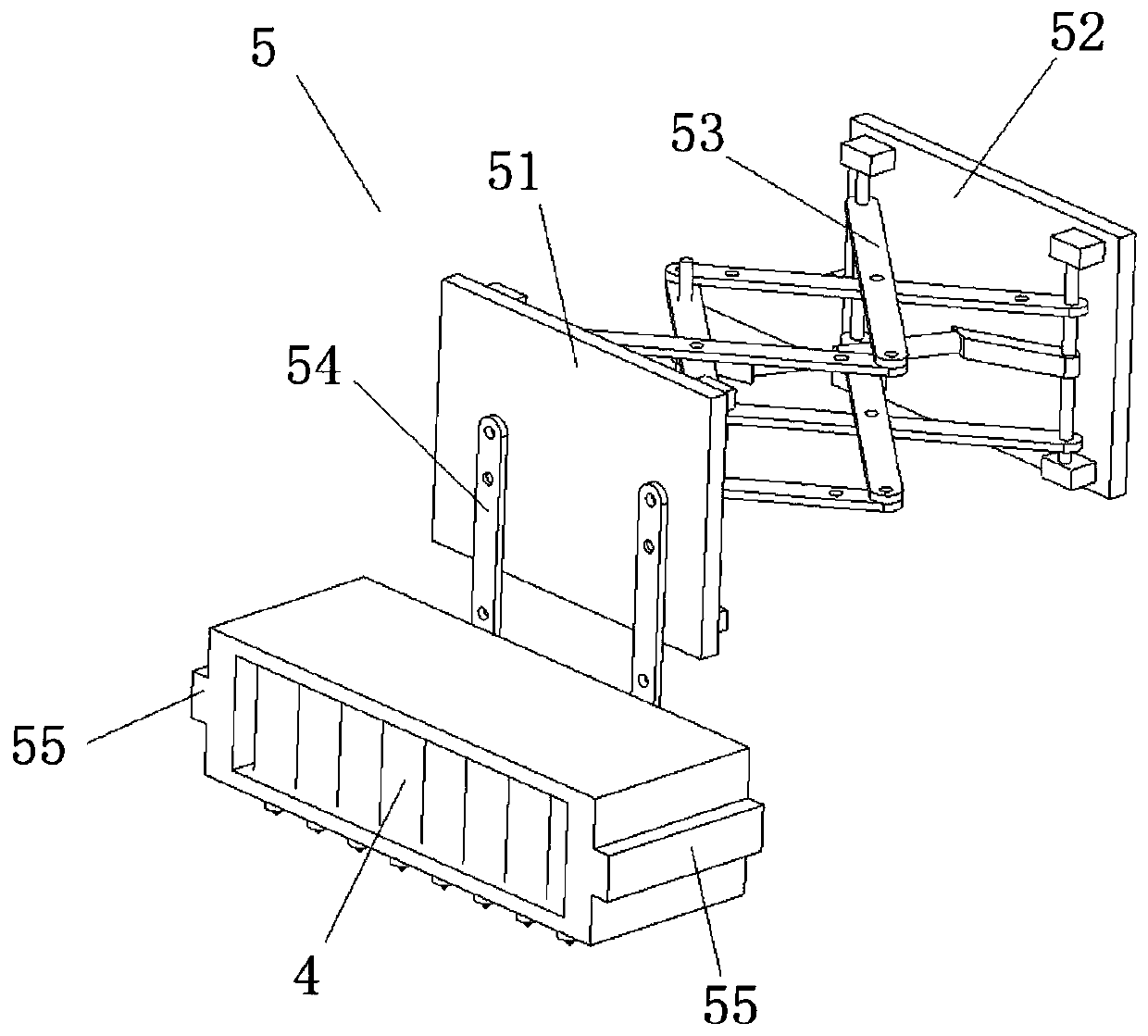
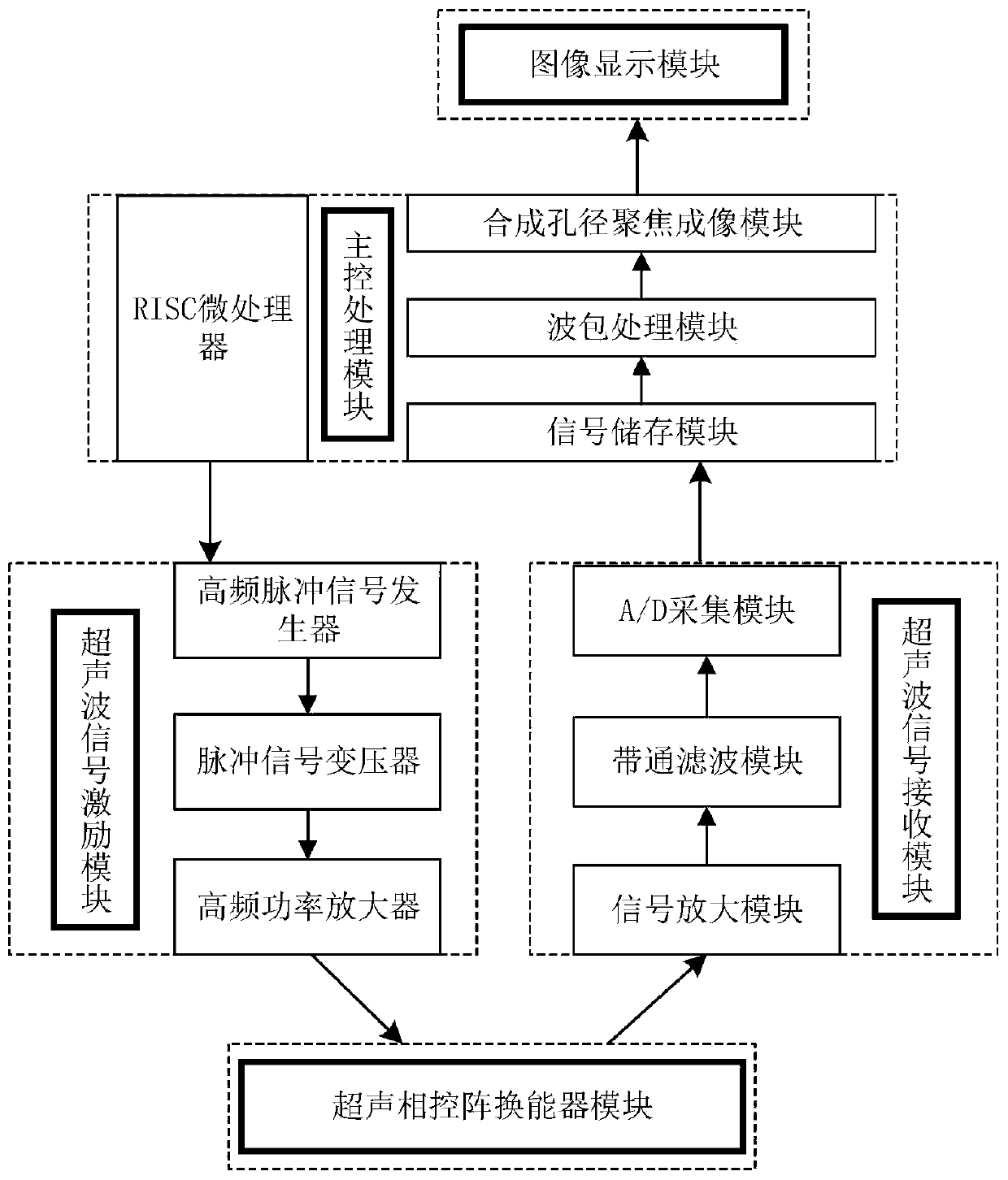
Ultrasonic array concrete detection system based on synthetic aperture focusing imaging
InactiveCN110412133AHigh-resolutionReduced sampling timeAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesAcoustic arrayImaging algorithm
The invention relates to an ultrasonic array concrete detection system based on synthetic aperture focusing imaging. The system is mainly used for detecting defects in damaged concrete. The ultrasonicarray concrete detection system based on synthetic aperture focusing imaging comprises a main control processing module, an ultrasonic signal stimulation module, an ultrasonic signal receiving module, an ultrasonic array energy converter module and an image displaying module. Due to the fact that the detection system adopts an ultrasonic array energy converter with receiving and transmitting integration and is combined with a synthetic aperture focusing imaging algorithm, during actual use, the problems are solved that a common concrete ultrasonic detection system is small in detection area and low in detection efficiency, a receiving energy converter is difficultly aligned with a transmitting energy converter, and a detection result is difficult to judge, and the ultrasonic array concrete detection system has high accuracy and applicability in application in a detection site for the defects in the damaged concrete.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Synthetic aperture imaging method based on C-shaped probe
ActiveCN110974293AHigh resolutionFast operationInfrasonic diagnosticsUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic dianostic techniques3d imageArray element
The invention belongs to the technical field of high-resolution ultrasonic imaging, and discloses a synthetic aperture imaging method based on a C-shaped probe. The method comprises the following steps: (1) acquiring original data; (2) preprocessing data: for the original echo data, reserving ultrasonic signals received and acquired by L receiving array elements on the left side of a transmittingarray element and L receiving array elements on the right side of the transmitting array element at most; (3) performing filtering; and (4) reconstructing an image: performing gridding processing on an imaging area, performing one-by-one imaging point focusing on the filtered signals by imaging points based on the principle of a synthetic aperture focusing technology, performing calculating to obtain data values of all imaging points, and finally performing reconstructing to obtain a section image. The method preferably comprises a step (5) of reconstructing a three-dimensional image. The method can effectively solve the problem of ultrasonic image reconstruction of a C-type probe by improving the integral flow design of the ultrasonic imaging method of the C-type probe and particularly improving a key echo preprocessing step, compositions of functional modules of the corresponding imaging system, cooperative working mode of the functional modules and the like.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Target ranging method based on synthetic aperture focused images
ActiveCN103033166BAvoid mechanical action for focusing imagingFlexible moving processOptical rangefindersSmall holeImage sequence
The invention discloses a target ranging method based on synthetic aperture focused images. The target ranging method disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps of: step 1, obtaining an equally-spaced line array camera position image sequence vertical to a target sight line by virtue of a small-hole imaging model camera, and taking a image of the camera position at the intersection point of a line array and a target sight line as a reference image; step 2, dividing a measurable distance range into a plurality of distance sections, and obtaining an aberration corrected and superposed image corresponding to each distance section, wherein each distance section is corresponding to one aberration corrected and superposed image; step 3, calculating the similarity between a neighbourhood area of each pixel in the reference image and a corresponding area in each aberration corrected and superposed image, and selecting the pixels as ranging pixels, wherein the changing ranges of the distances of the similarity of the pixels along with the aberration corrected and superposed images are greater than a preset threshold; and step 4, finding the distance section corresponding to the aberration corrected and superposed image with the maximum similarity, namely, the distance section in which target points corresponding to the ranging pixels are located. The target ranging method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of being low in realization cost, high in anti-interference capacity, simple in algorithm, and the like.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com