Patents
Literature
1309 results about "Plane wave" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In physics, a plane wave is a special case of wave or field: a physical quantity whose value, at any moment, is constant over any plane that is perpendicular to a fixed direction in space.
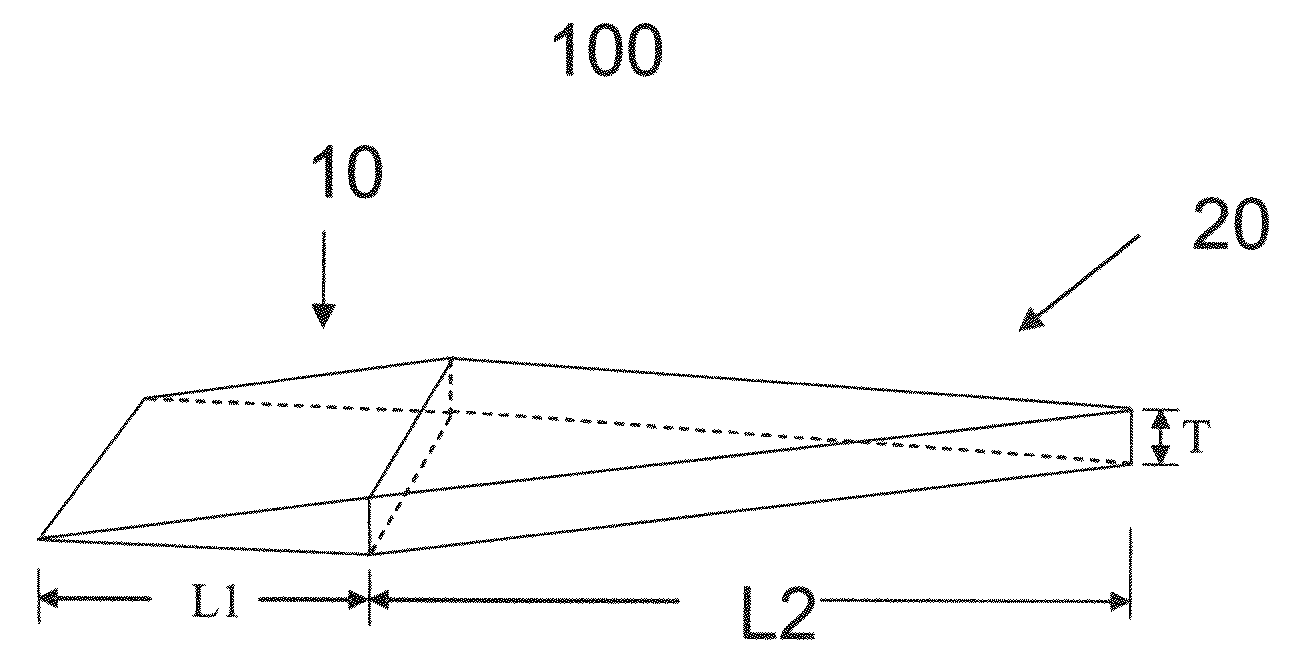
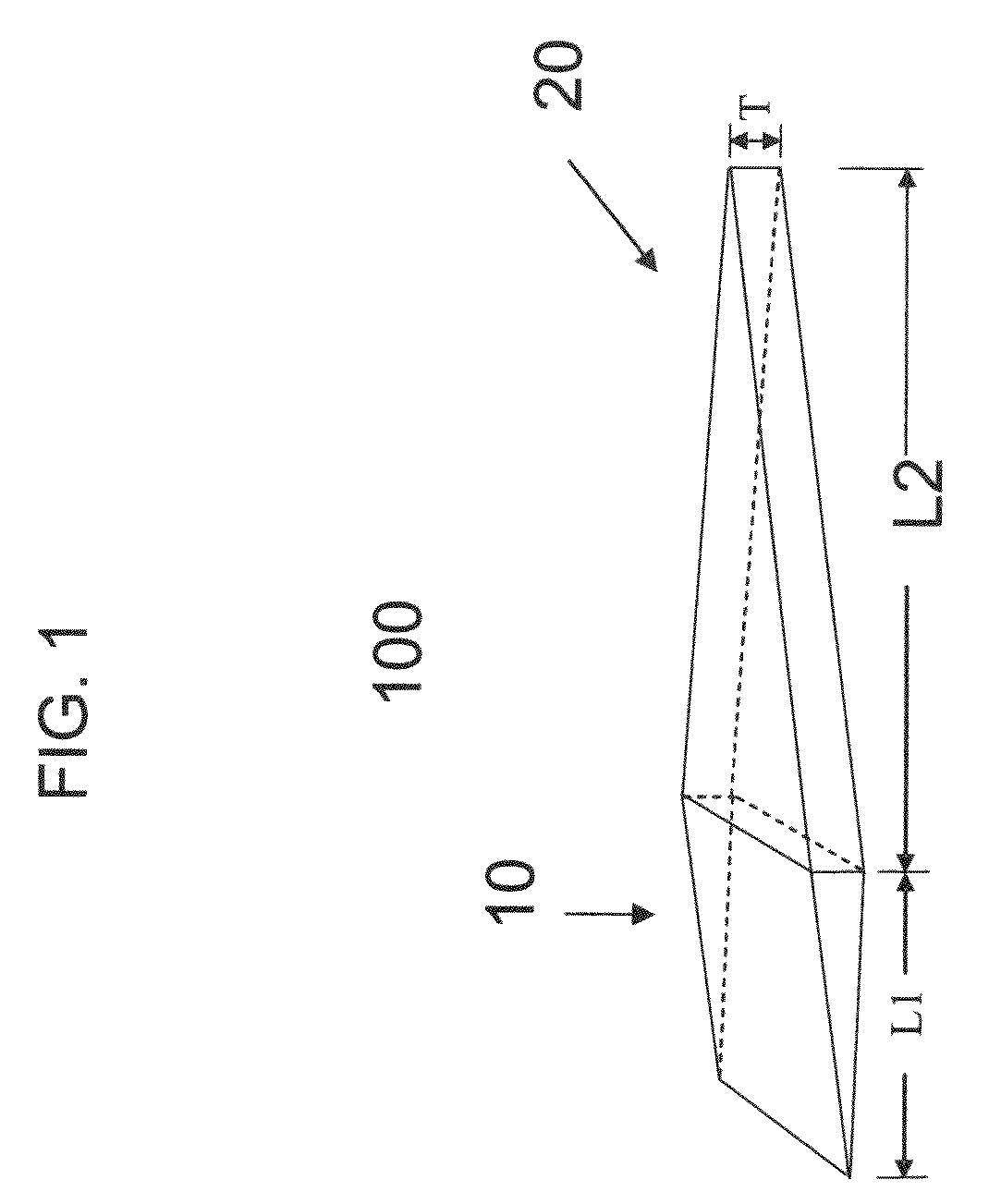
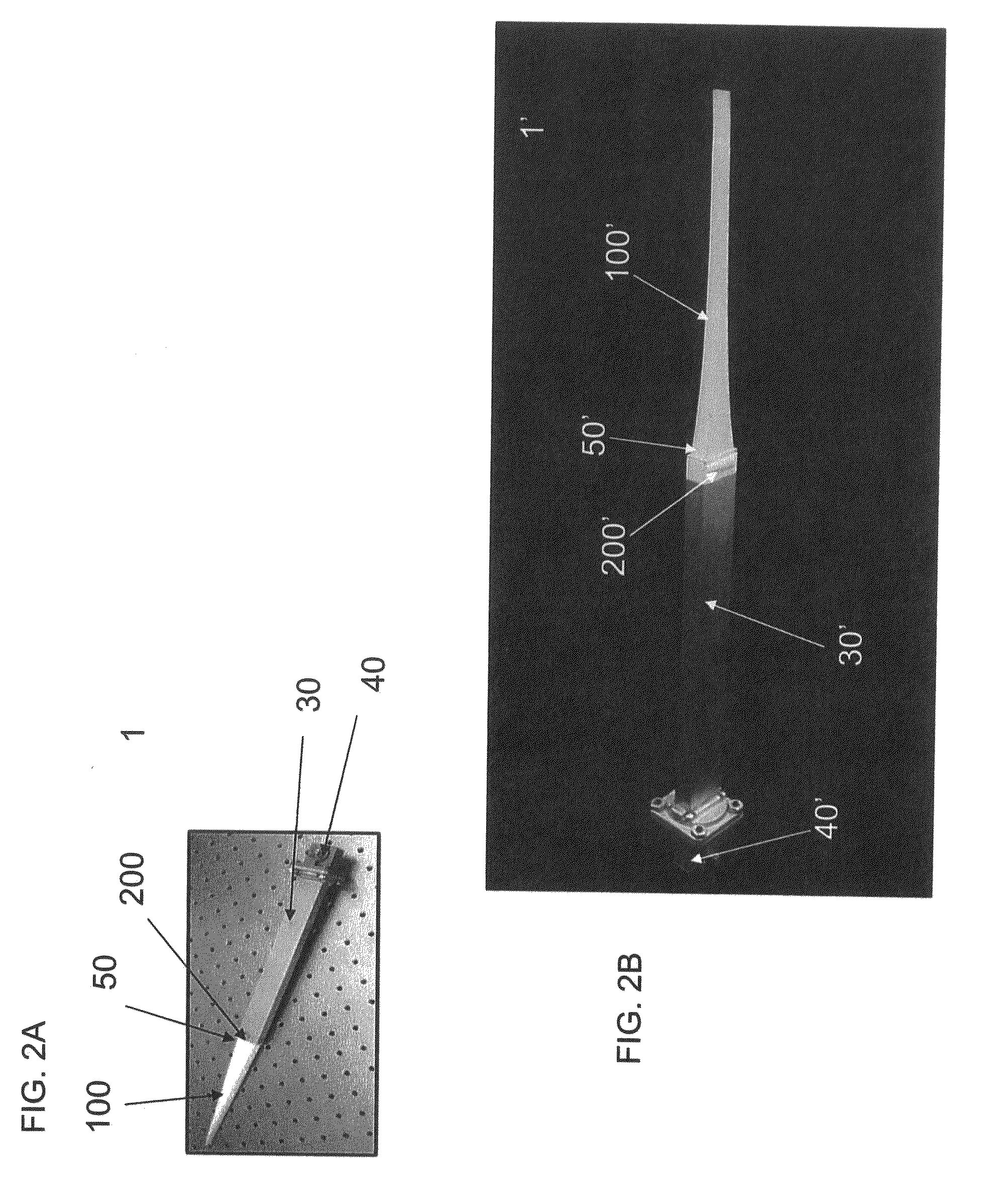
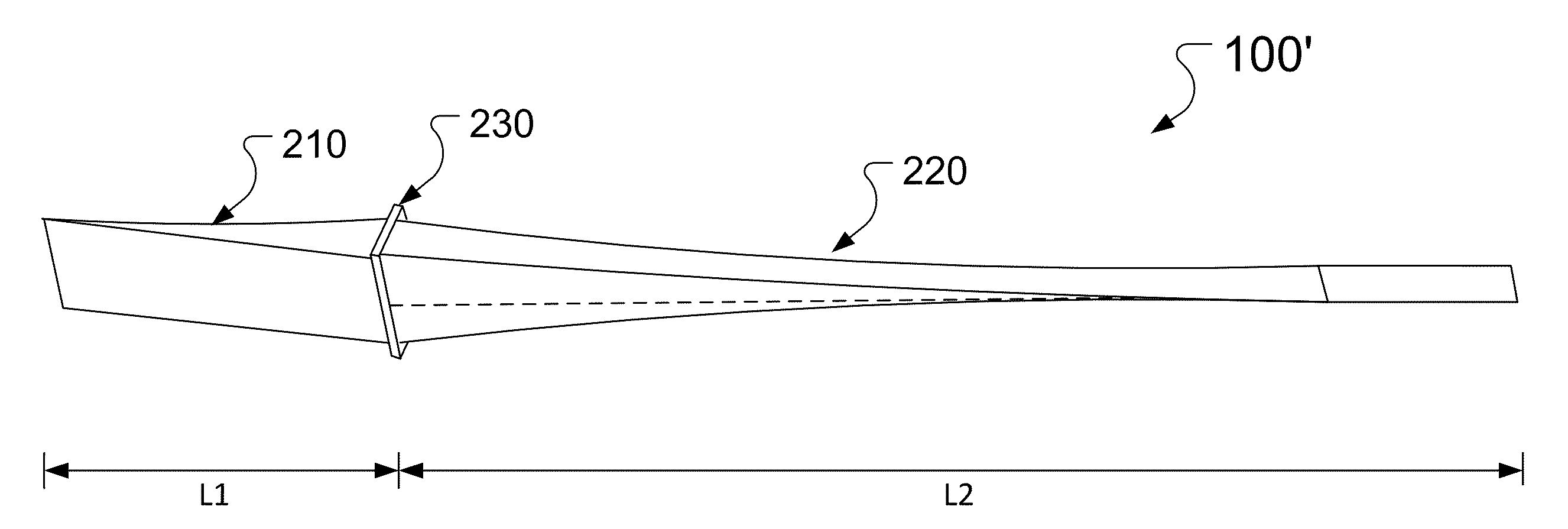
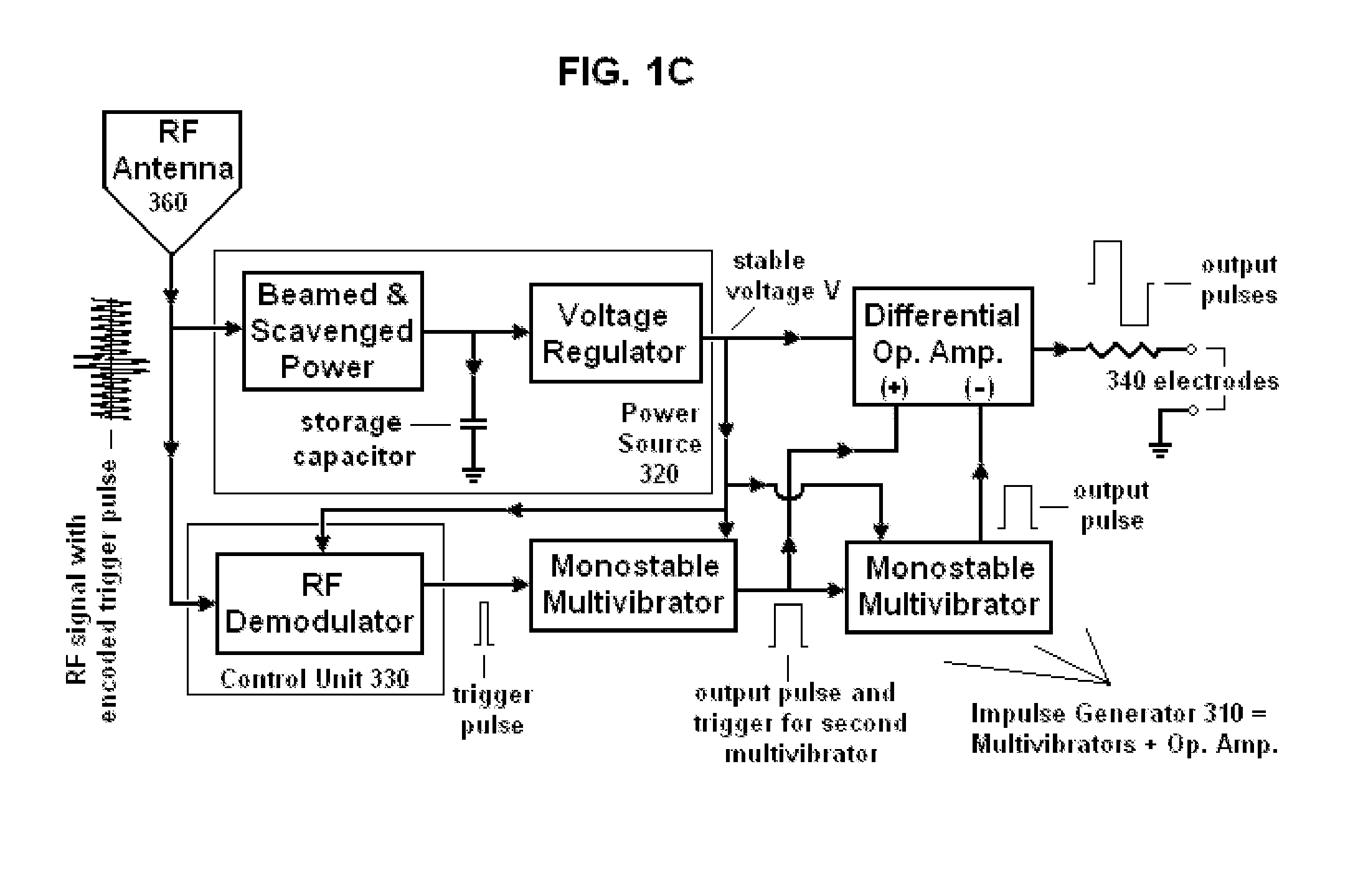
Aperture matched polyrod antenna
InactiveUS20080252541A1Minimizes and reduces end reflection and phase variationMinimizing and reducing diameterAdditive manufacturing apparatusWaveguide type devicesGaussian beamLight beam
A dielectric polyrod having at least one tapered section, where a section exposed outside of the waveguide is tapered a long a curve that depends on the dielectric constant of the material used. The invention also relates to an aperture matched polyrod antenna which includes the same and an inductive tuning element used to achieve wideband impedance match and to create a Gaussian beam in the radiating near field of the antenna, suitable to mimic a small region plane wave.
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
Aperture matched polyrod antenna
InactiveUS7889149B2Minimizes and reduces end reflection and phase variationMinimizing and reducing diameterAdditive manufacturing apparatusCoupling devicesGaussian beamLight beam
A dielectric polyrod having at least one tapered section, where a section exposed outside of the waveguide is tapered a long a curve that depends on the dielectric constant of the material used. The invention also relates to an aperture matched polyrod antenna which includes the same and an inductive tuning element used to achieve wideband impedance match and to create a Gaussian beam in the radiating near field of the antenna, suitable to mimic a small region plane wave.
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
Compact broad-band admittance tunnel incorporating gaussian beam antennas
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
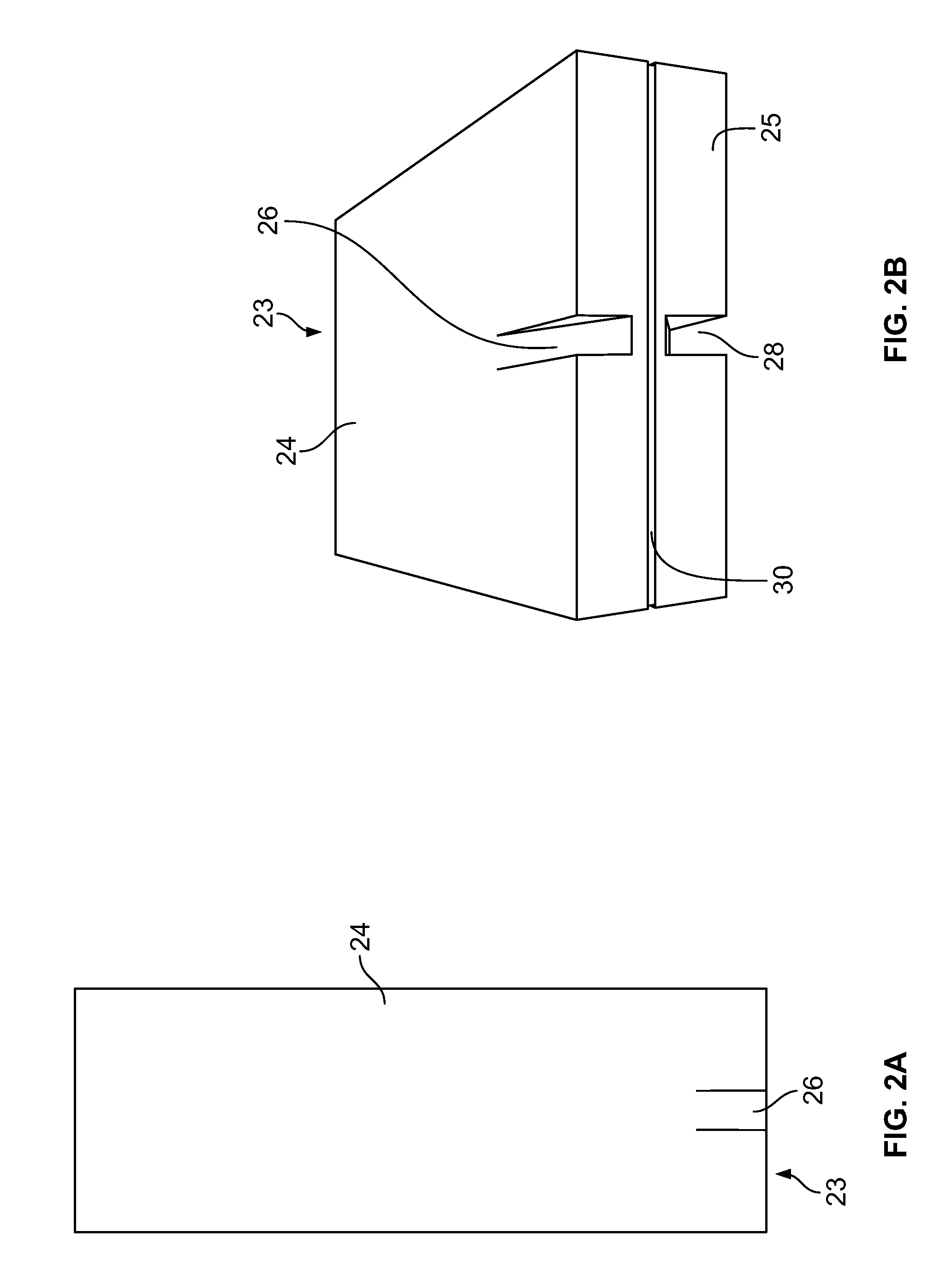
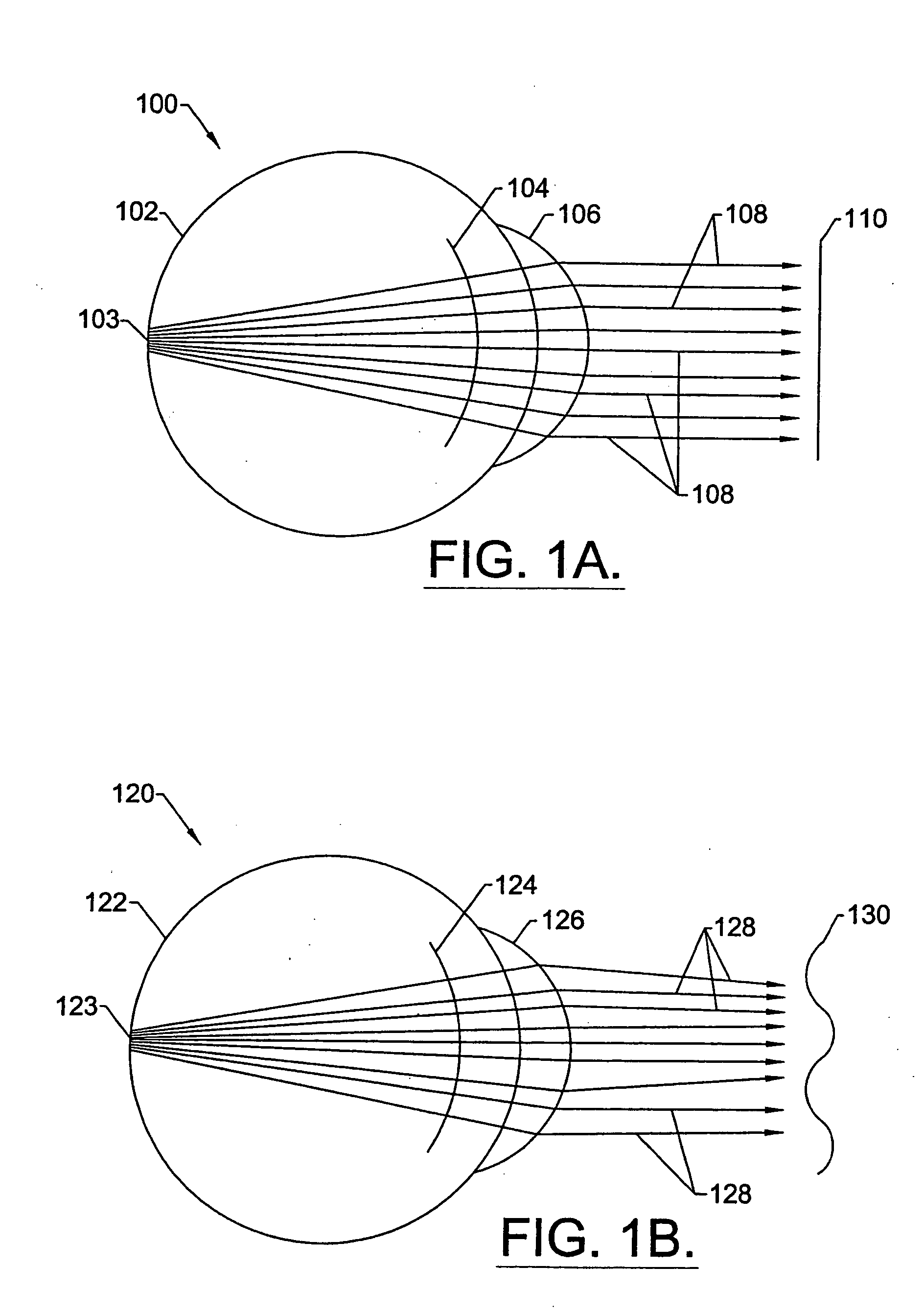
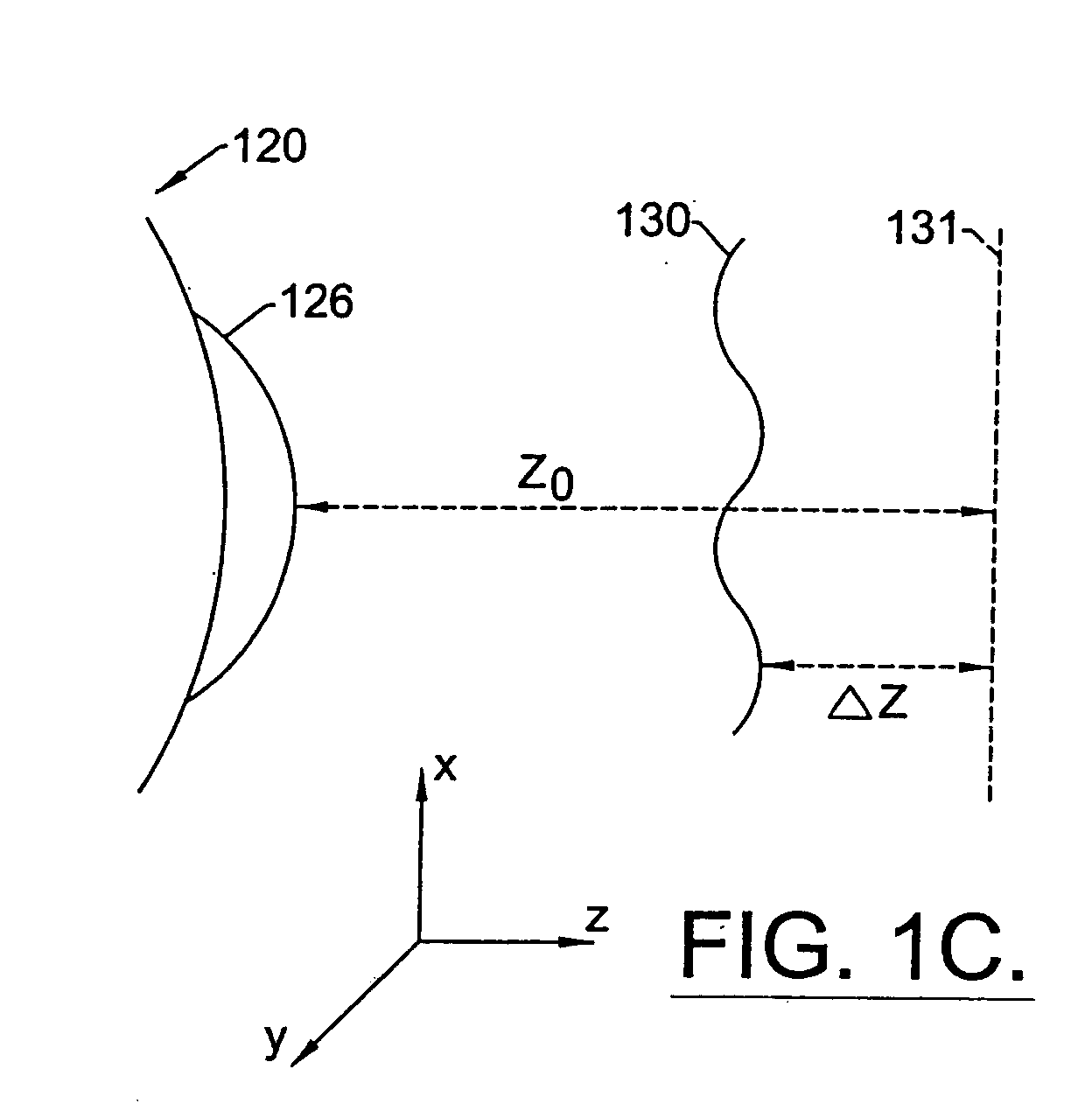
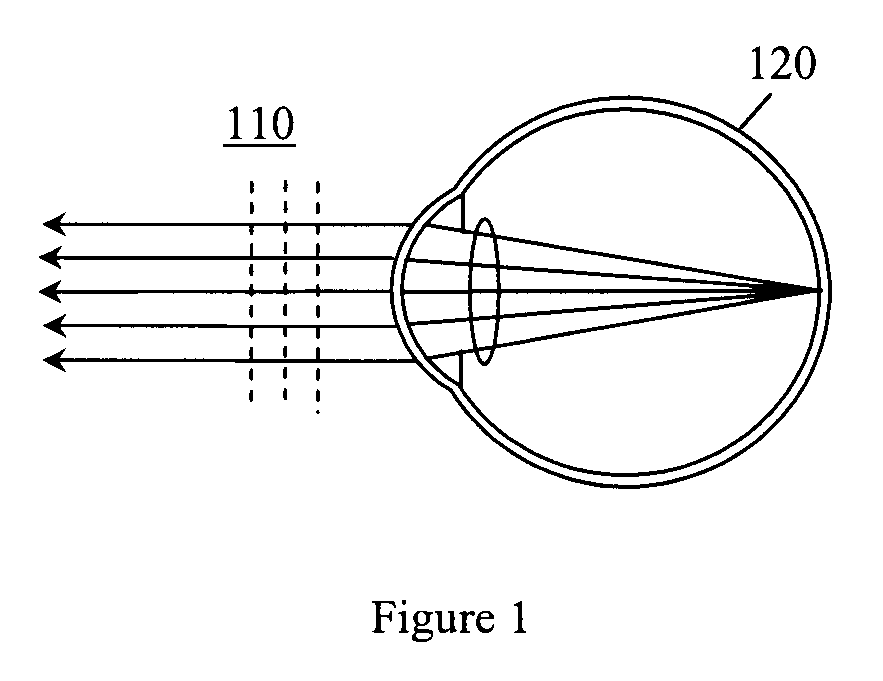
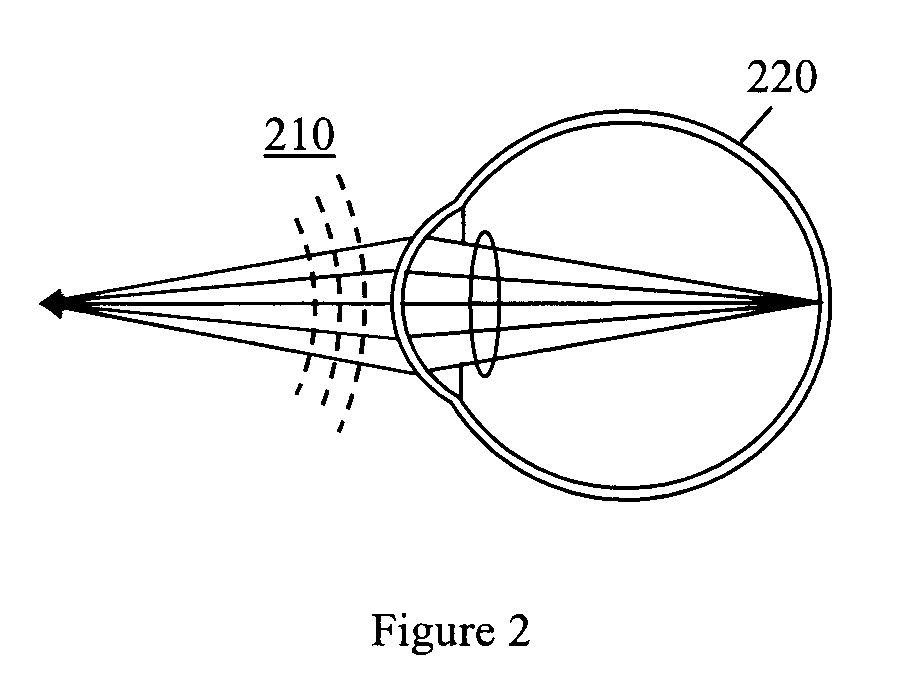
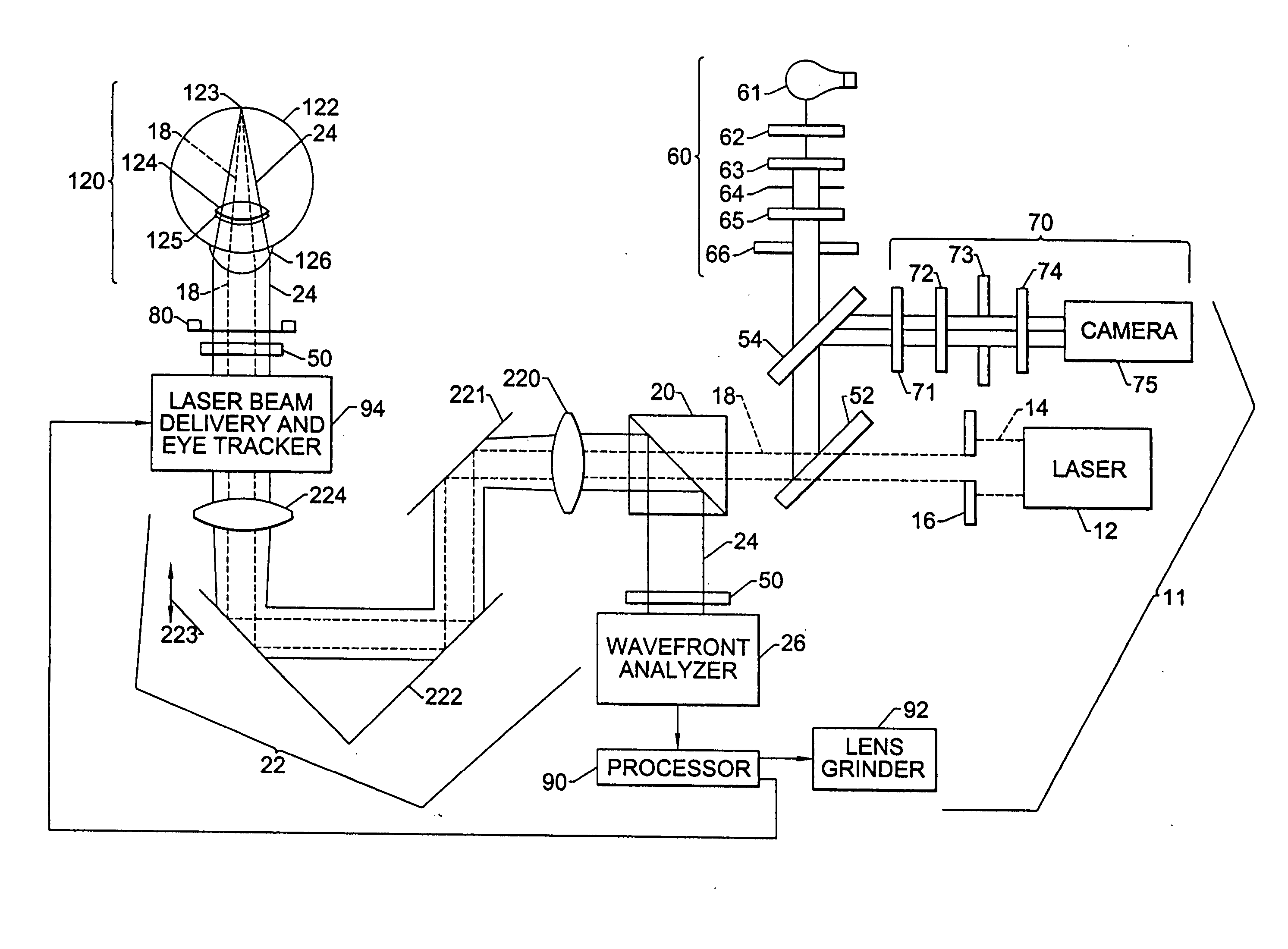
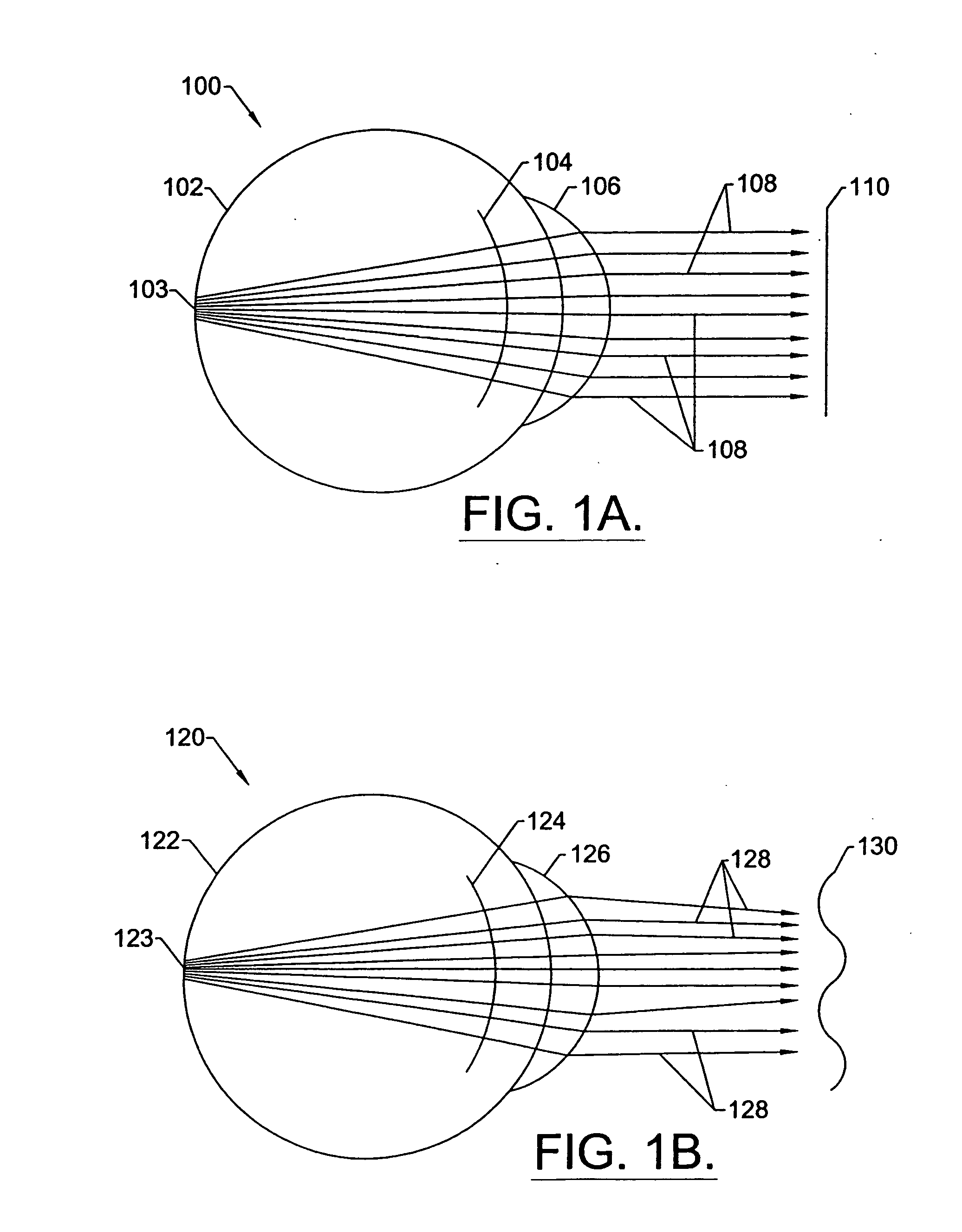
Method for determining and correcting vision
InactiveUS20050124983A1Simple and inexpensive designImprove visual effectsLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsRefractive indexOptical path length
A method for enhancing vision of an eye includes a laser delivery system having a laser beam for ablating corneal material from the cornea of the eye. Measurements are made to determine an optical path difference between a plane wave and a wavefront emanating from the retina of the eye for a location at a surface of the cornea. An optical correction is provided to the laser delivery system for the location based on the optical path difference and refractive indices of media through which the wavefront passes. The optical correction includes dividing the optical path difference by a difference between an index of refraction of corneal material and an index of refraction of air. The laser beam is directed to the location on the surface of the cornea and corneal material ablated at the location in response to the optical correction to cause the wavefront to approximate the shape of the plane wave at that location.
Owner:FREY RUDOLPH W +4
Planar waveguide lens design
InactiveUS8064744B2Easy to mergeLess susceptible to stray lightCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideForeign matterWaveguide
Owner:ZETTA RES & DEV LLC RPO SERIES
Method for coupling light into a thin planar waveguide
ActiveUS8155489B2Efficient couplingEnhanced couplingPlanar/plate-like light guidesCoupling light guidesOptical powerDisplay device
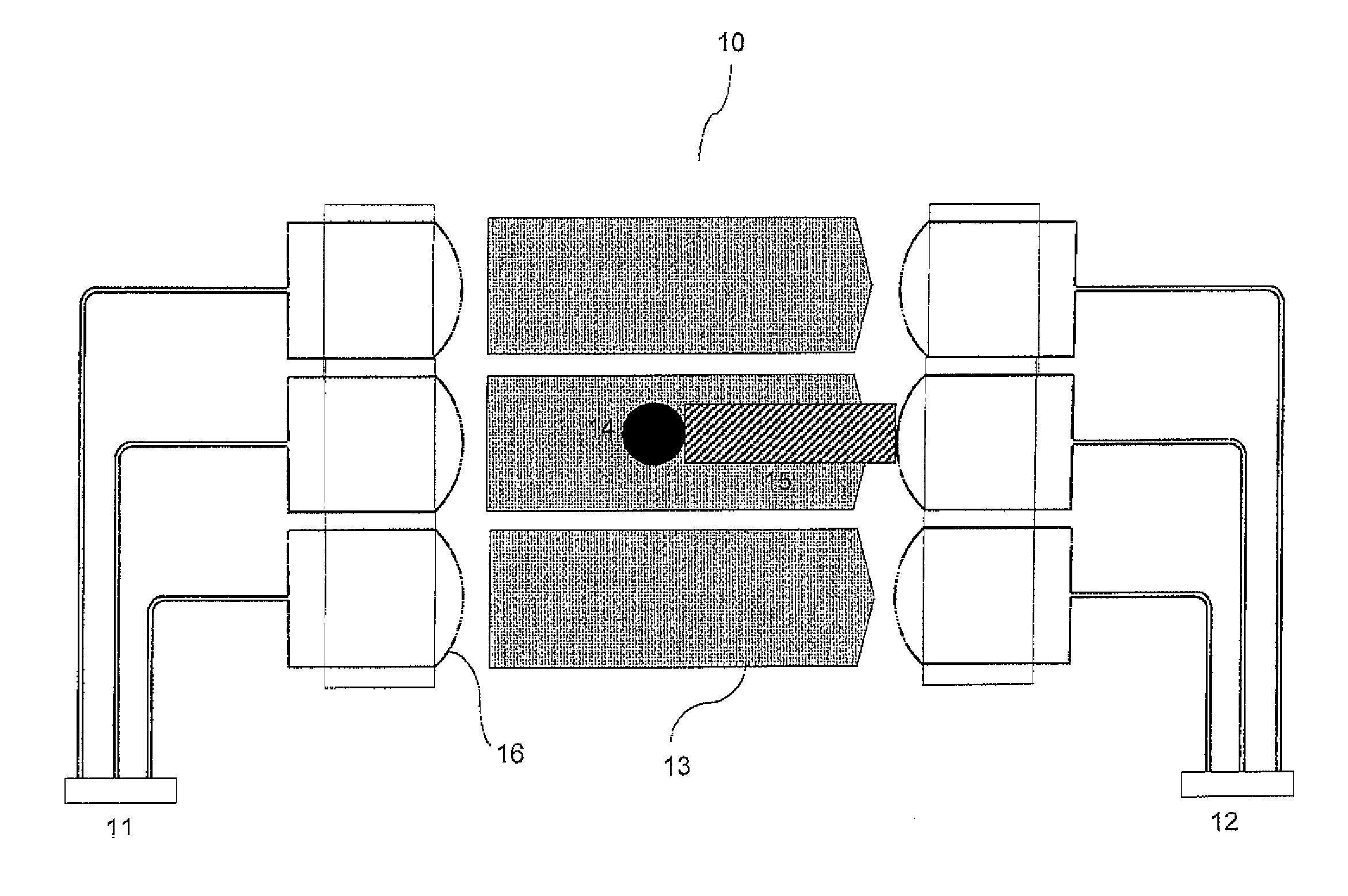
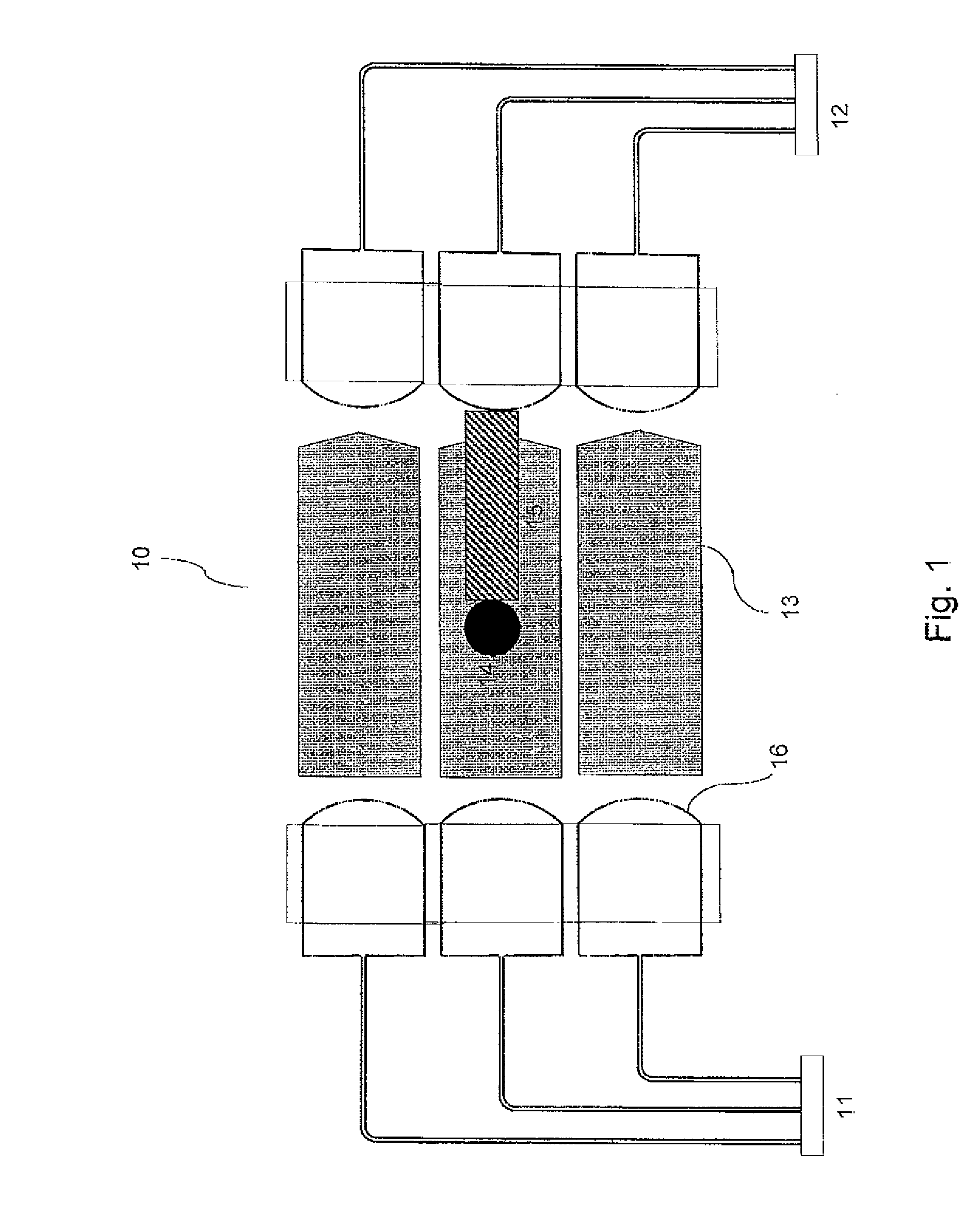
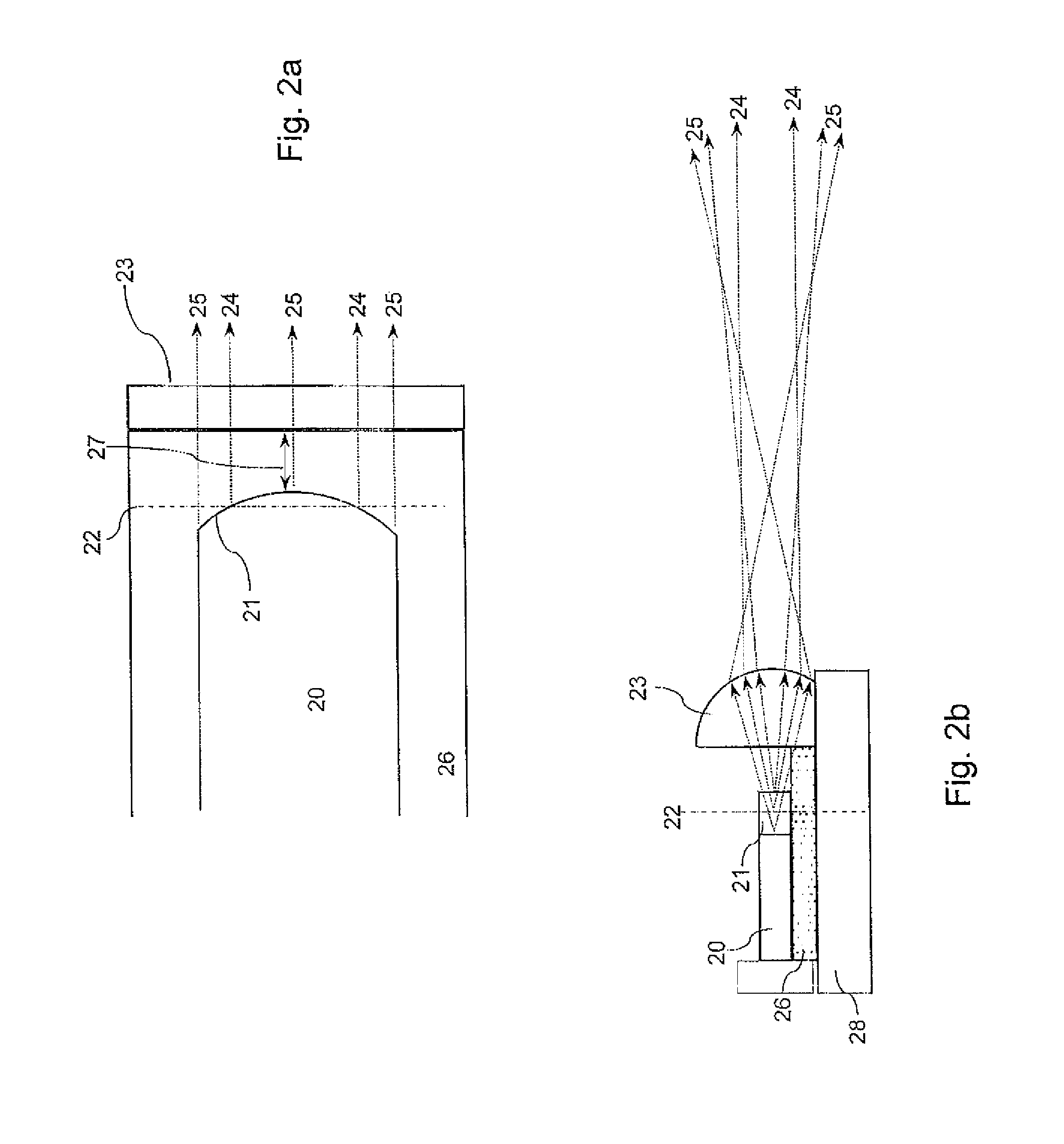
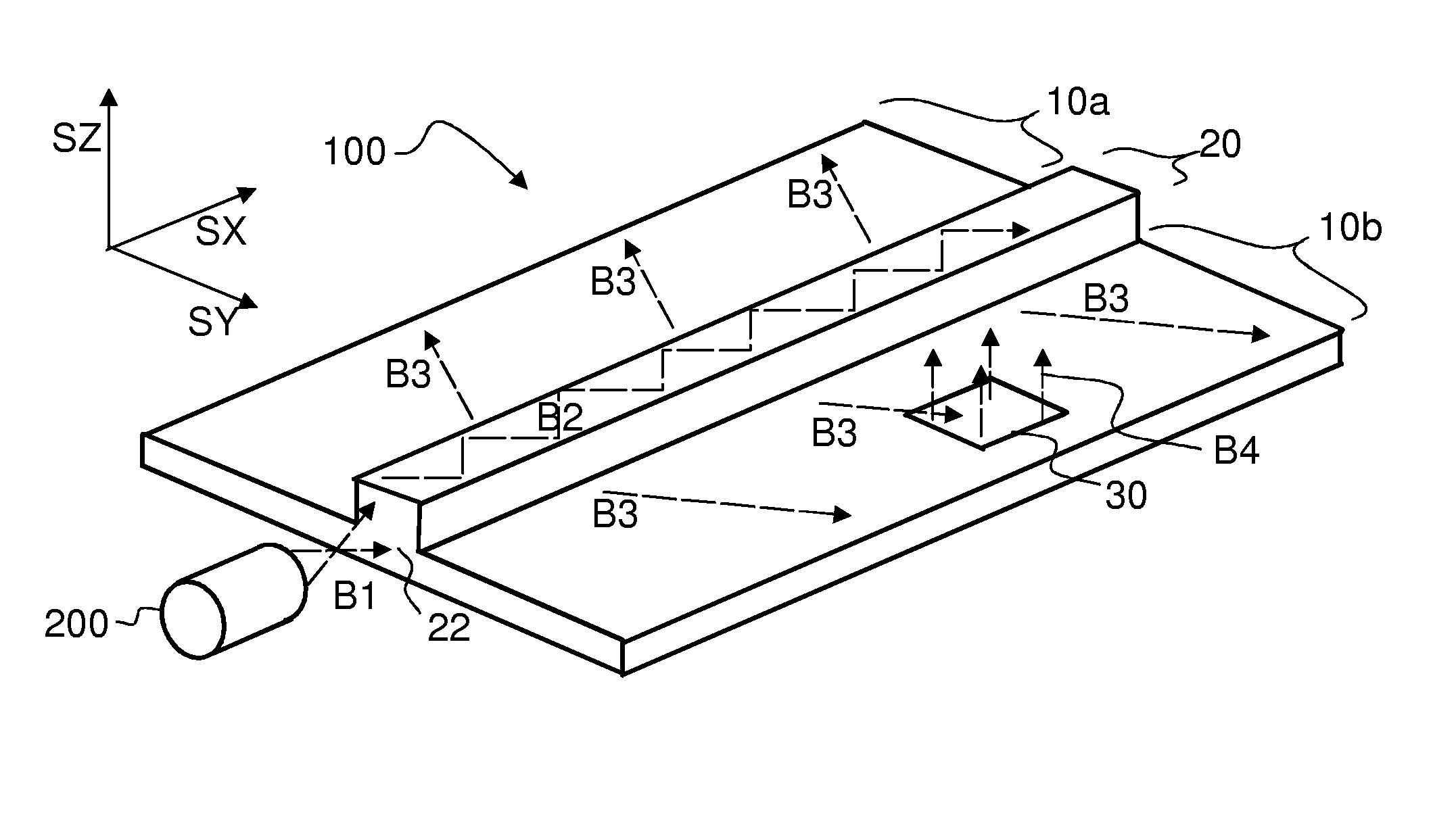
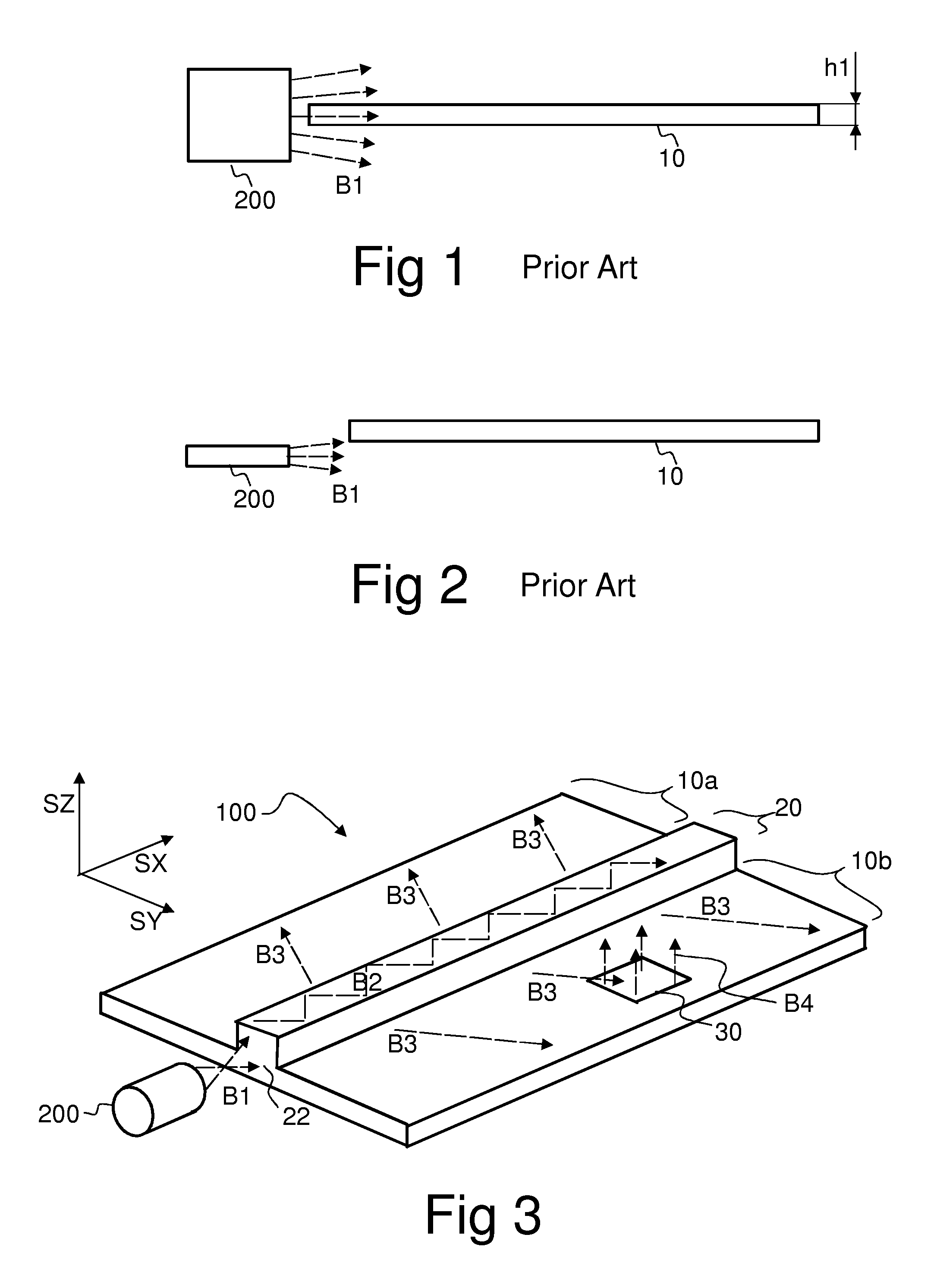
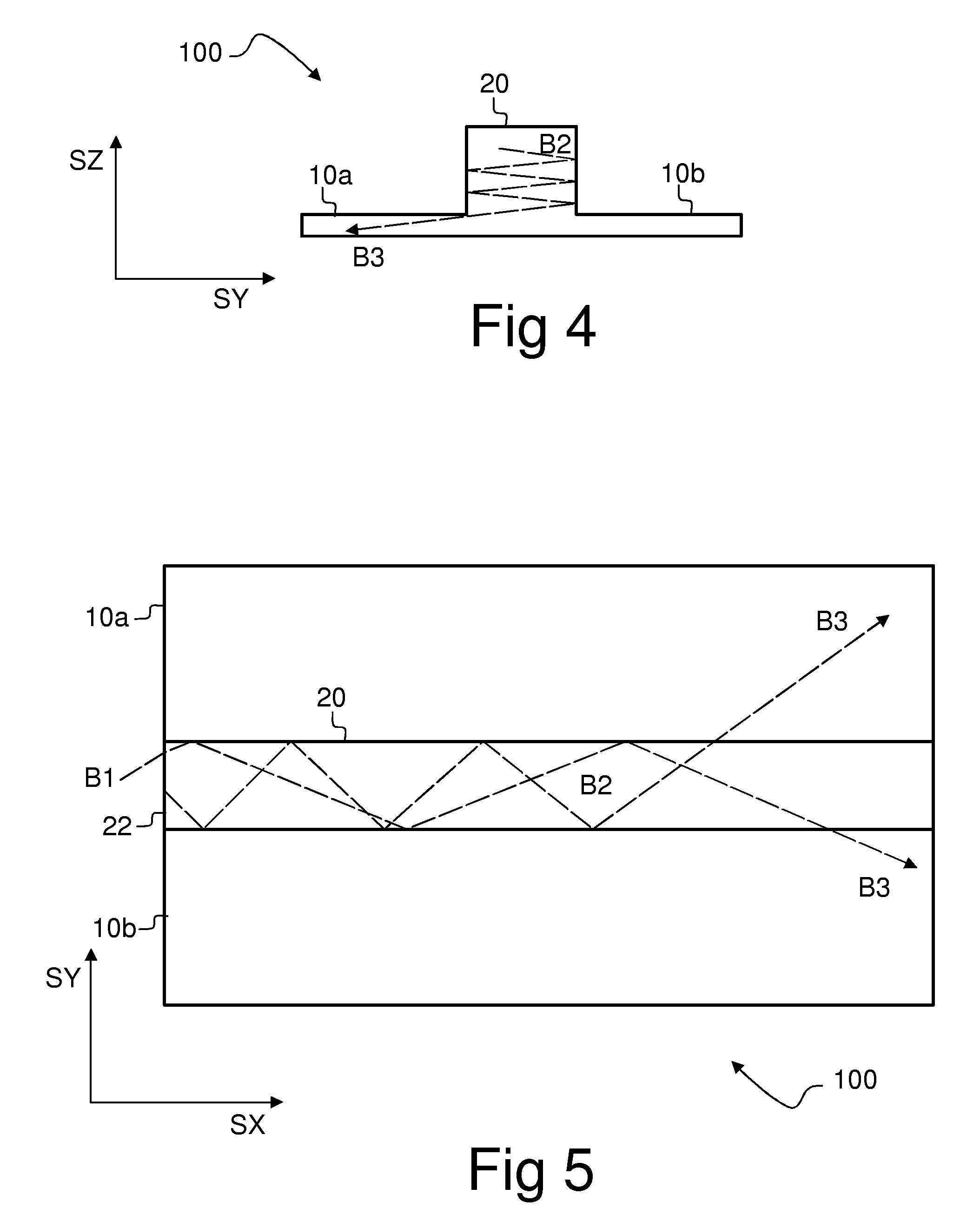
A light distributing device (100) comprises a thin planar waveguide (10) and a waveguiding ridge (20). An incoming light beam (B1) coupled into the ridge (20) forms a second light beam (B2) waveguided in the ridge (20). The ridge (20) and the planar waveguide (10) have a common portion (23) such that light is further coupled from the side of the ridge (20) into the planar waveguide (10) through said common portion (23). Thus, optical power of a broad incoming beam (B1) may be effectively coupled to a relatively thin planar waveguide (10). The planar waveguide (10) may further comprise diffractive out-coupling elements (30) to direct light towards a display (400).
Owner:NOKIA TECH OY
Controlled lens antenna apparatus and system
Present configuration concerns microelectronics; for instance, compact antenna devices applied in mobile communications and other equipment operating in millimeter range. The controlled lens antenna apparatus may include antenna elements in an integrated circuit configured to transmit beams. The apparatus may also include a dielectric lens antenna configured to generate a plane wave based in the beams transmitted. The apparatus may include a plate configured to deflect the generated plane wave at a random angle.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
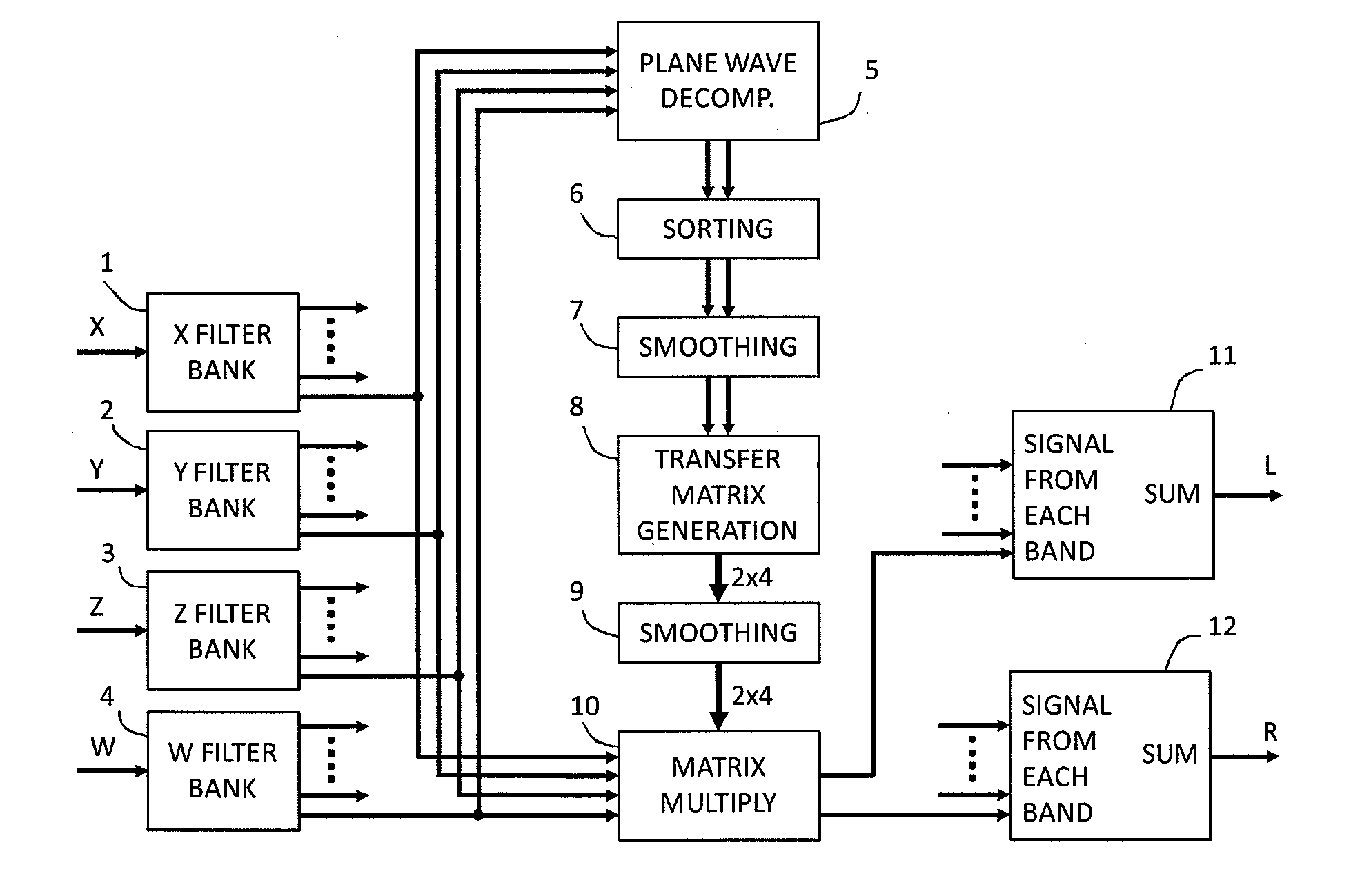
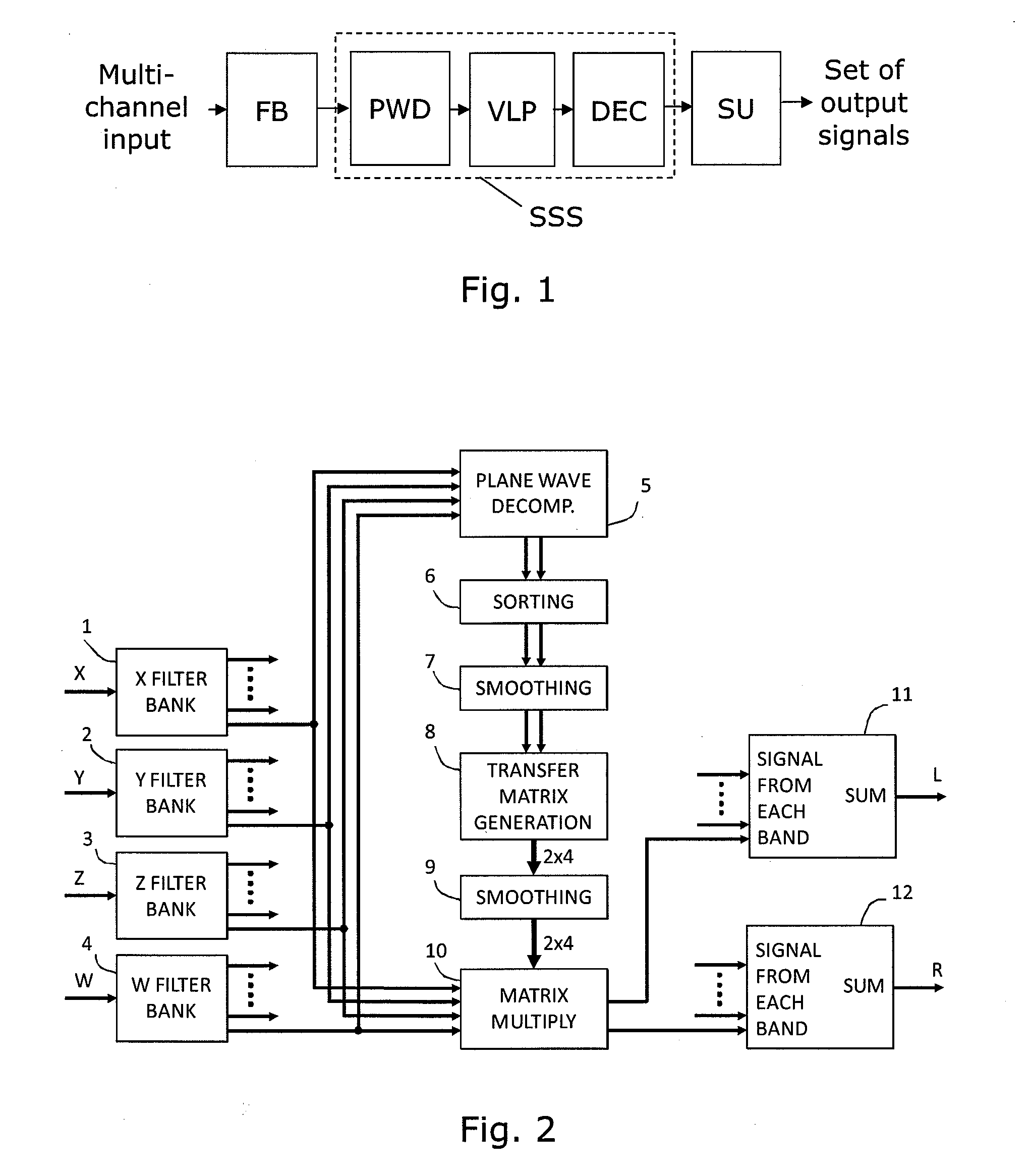
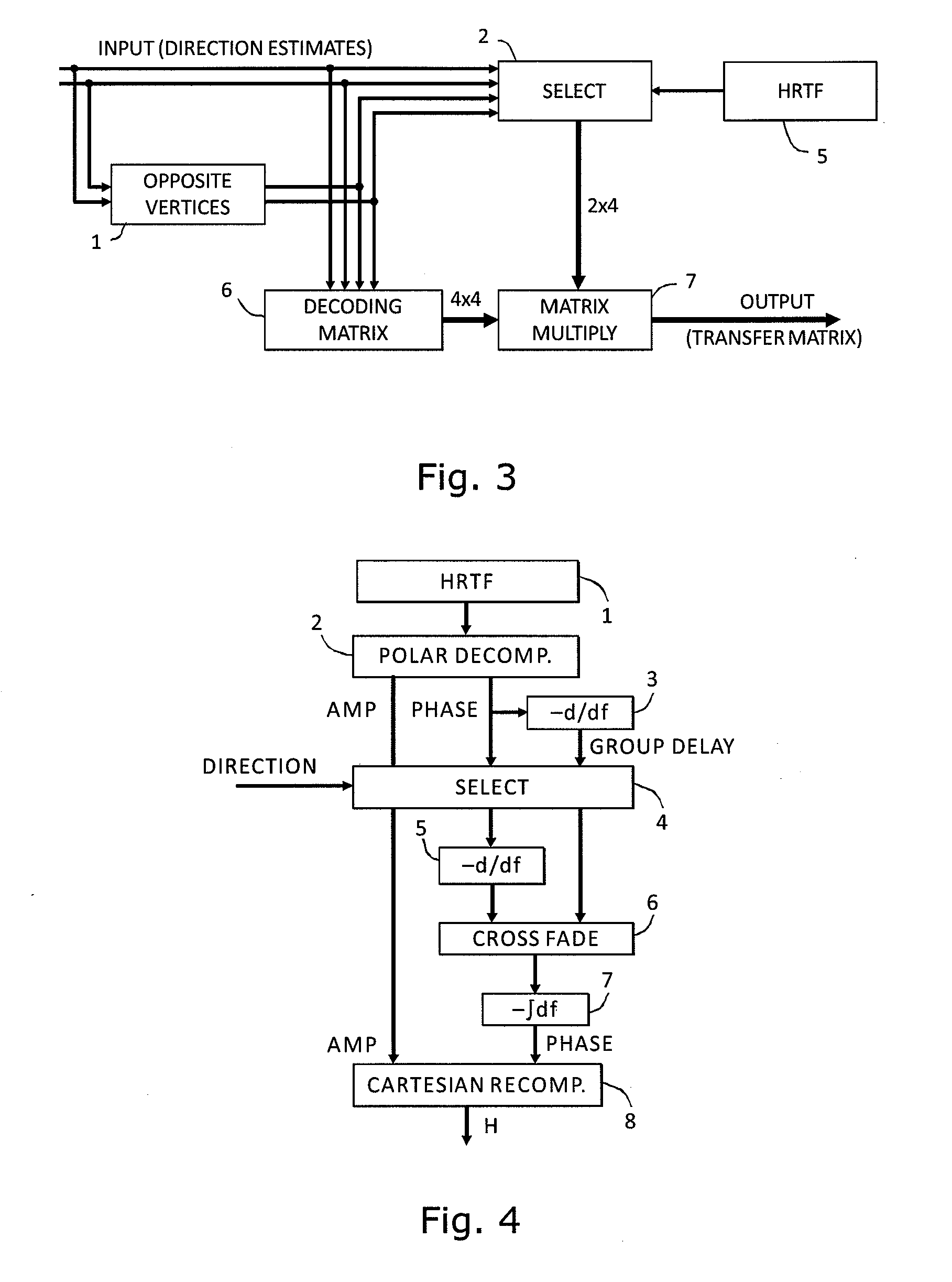
Device and method for converting spatial audio signal
ActiveUS20100329466A1Promote reproductionPromote conversionSignal processingLoudspeaker signals distributionSound sourcesHeadphones
An audio processor for converting a multi-channel audio input signal, such as a B-format sound field signal, into a set of audio output signals, such as a set of two or more audio output signals arranged for headphone reproduction or for playback over an array of loudspeakers. A filter bank splits each of the input channels into frequency bands. The input signal is decomposed into plane waves to determine one or two dominant sound source directions. The(se) are used to determine a set of virtual loudspeaker positions selected such that the dominant direction(s) coincide(s) with virtual loudspeaker positions. The input signal is decoded into virtual loudspeaker signals corresponding to each of the virtual loudspeaker positions, and the virtual loudspeaker signals are processed with transfer functions suitable to create the illusion of sound emanating from the directions of the virtual loudspeakers. A high spatial fidelity is obtained due to the coincidence of virtual loudspeaker positions and the determined dominant sound source direction(s). Improved performance can be obtained in the case where Head-Related Transfer Functions are used by differentiating the phase of a high frequency part of the HRTFs with respect to frequency, followed by a corresponding integration of this part with respect to frequency after combining the components of HRTFs from different directions.
Owner:HARPEX LTD
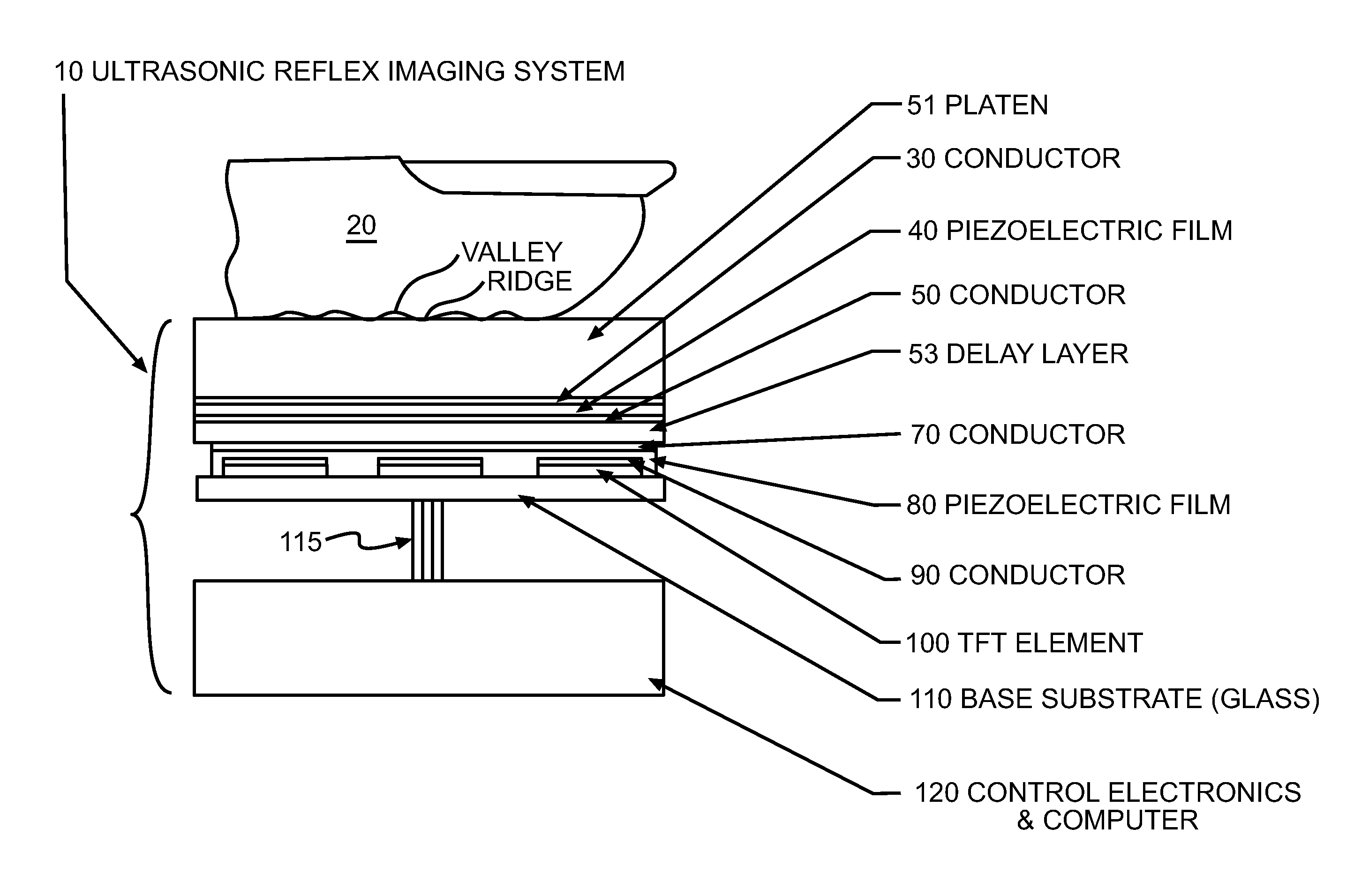
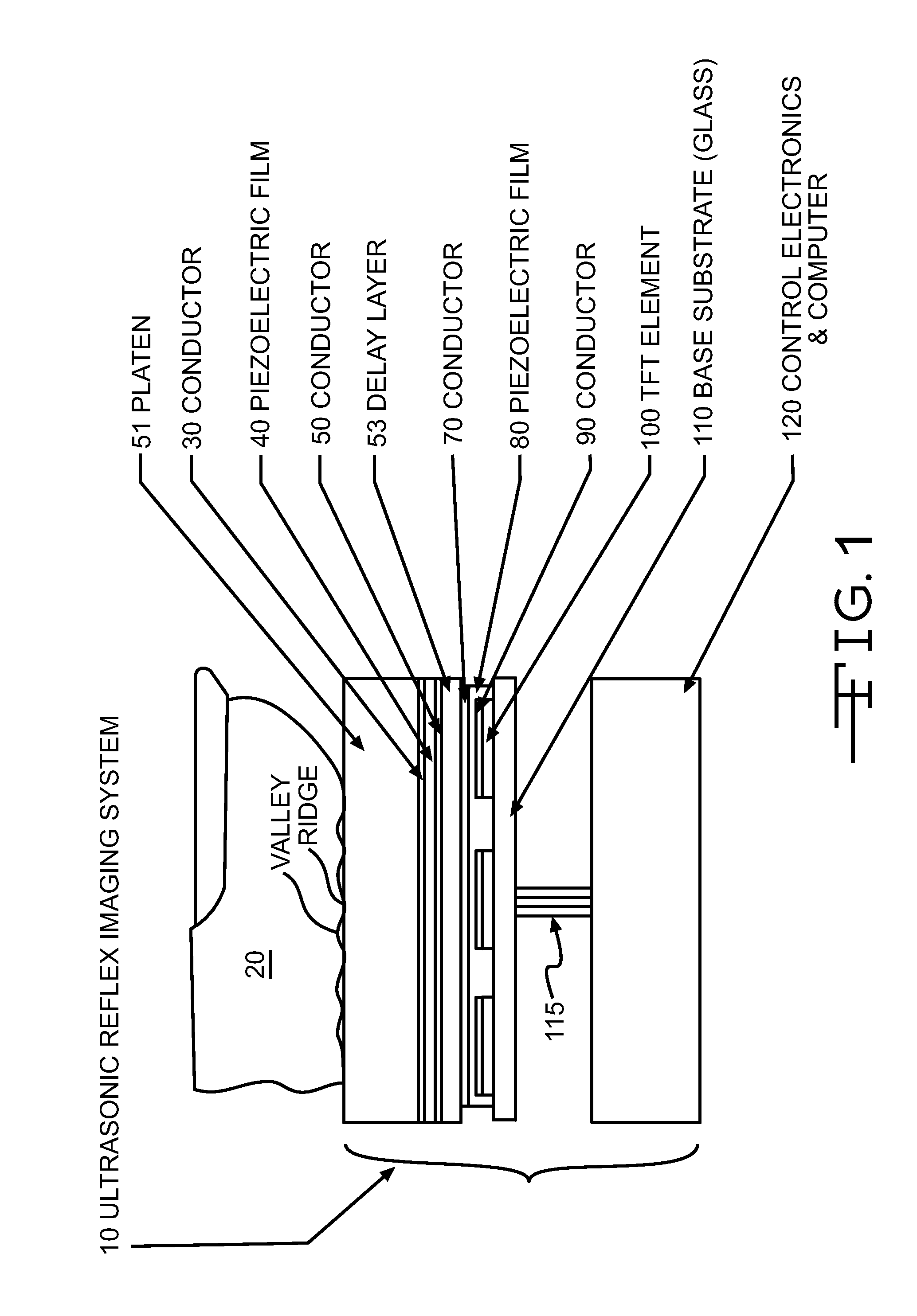
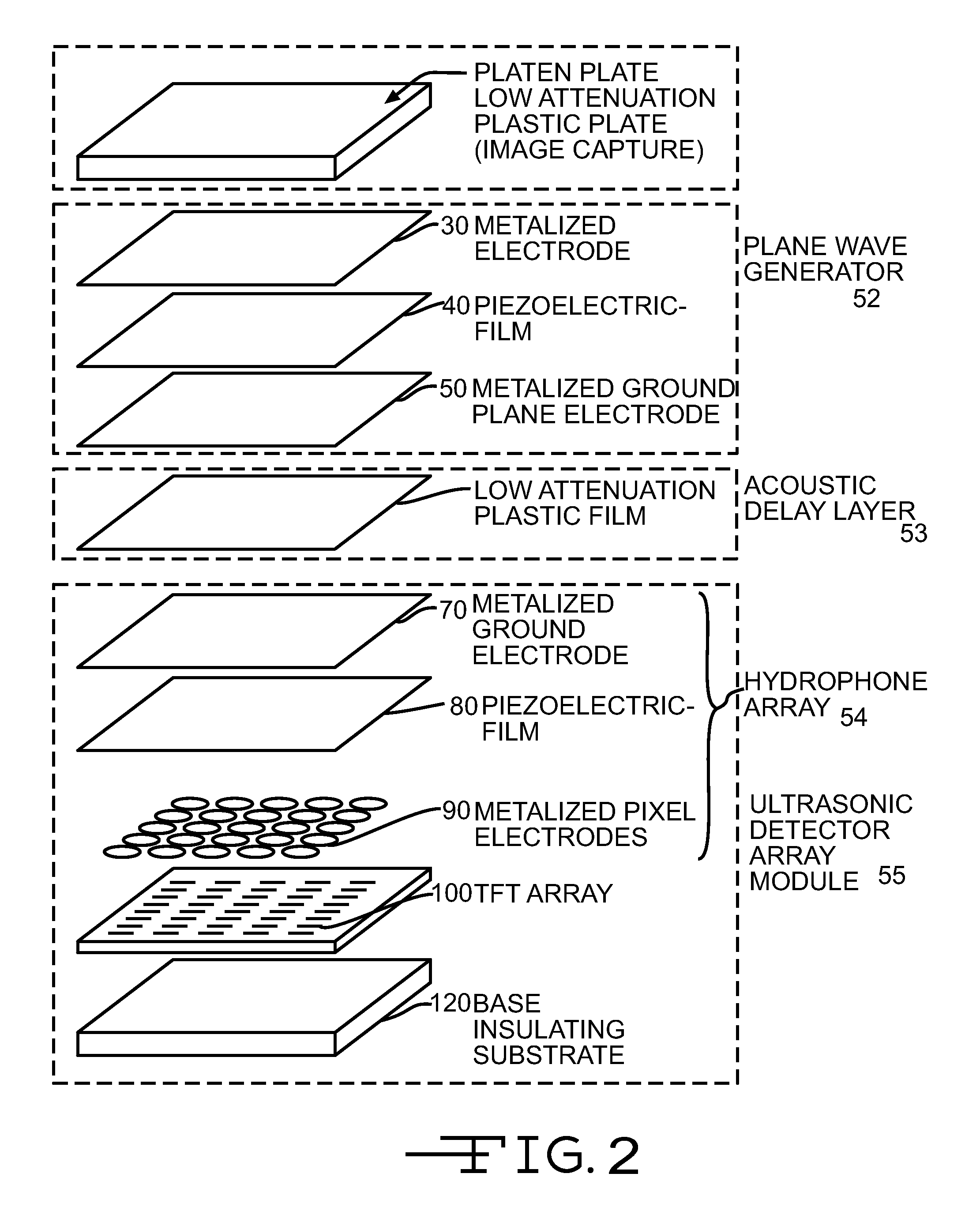
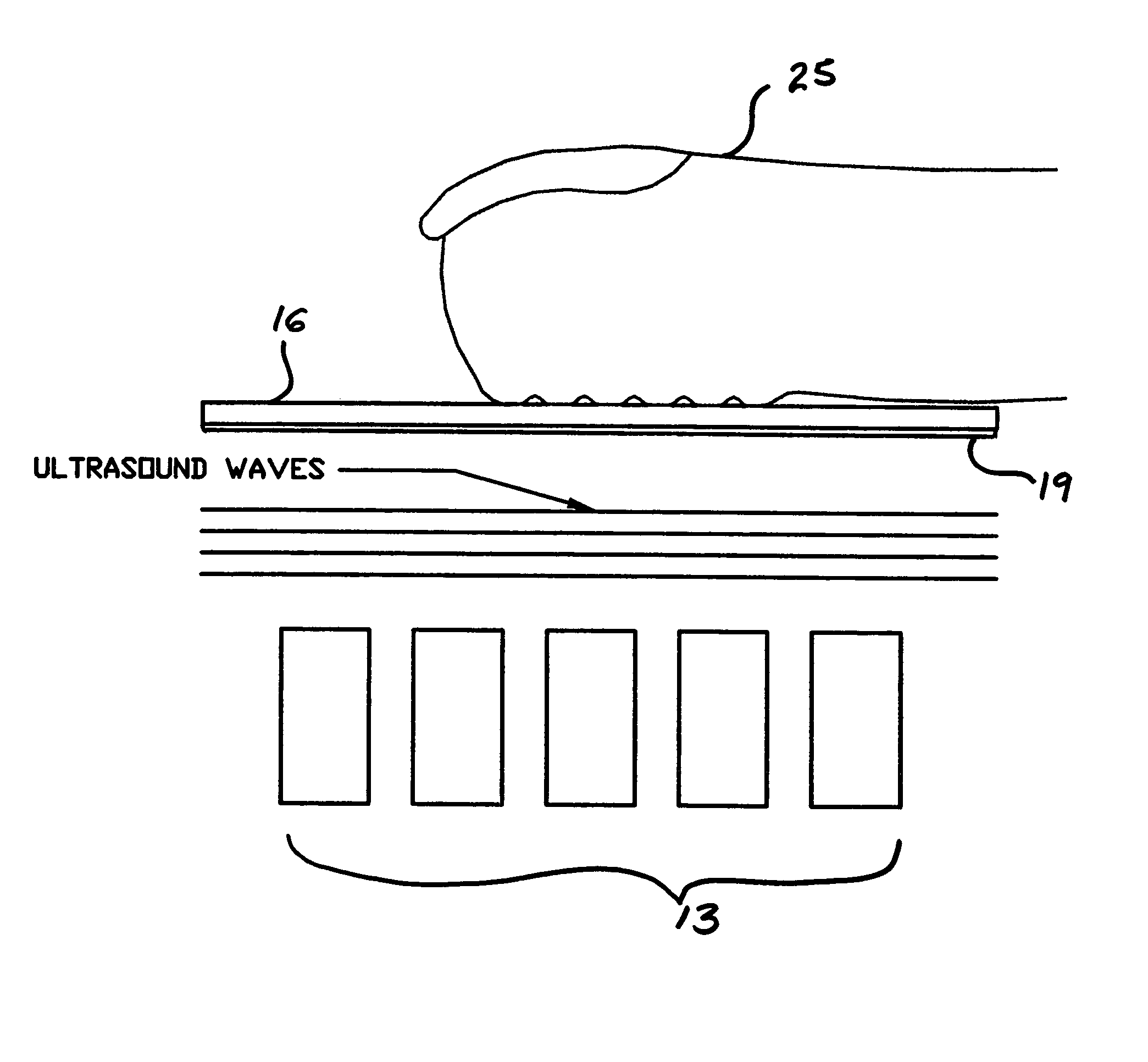
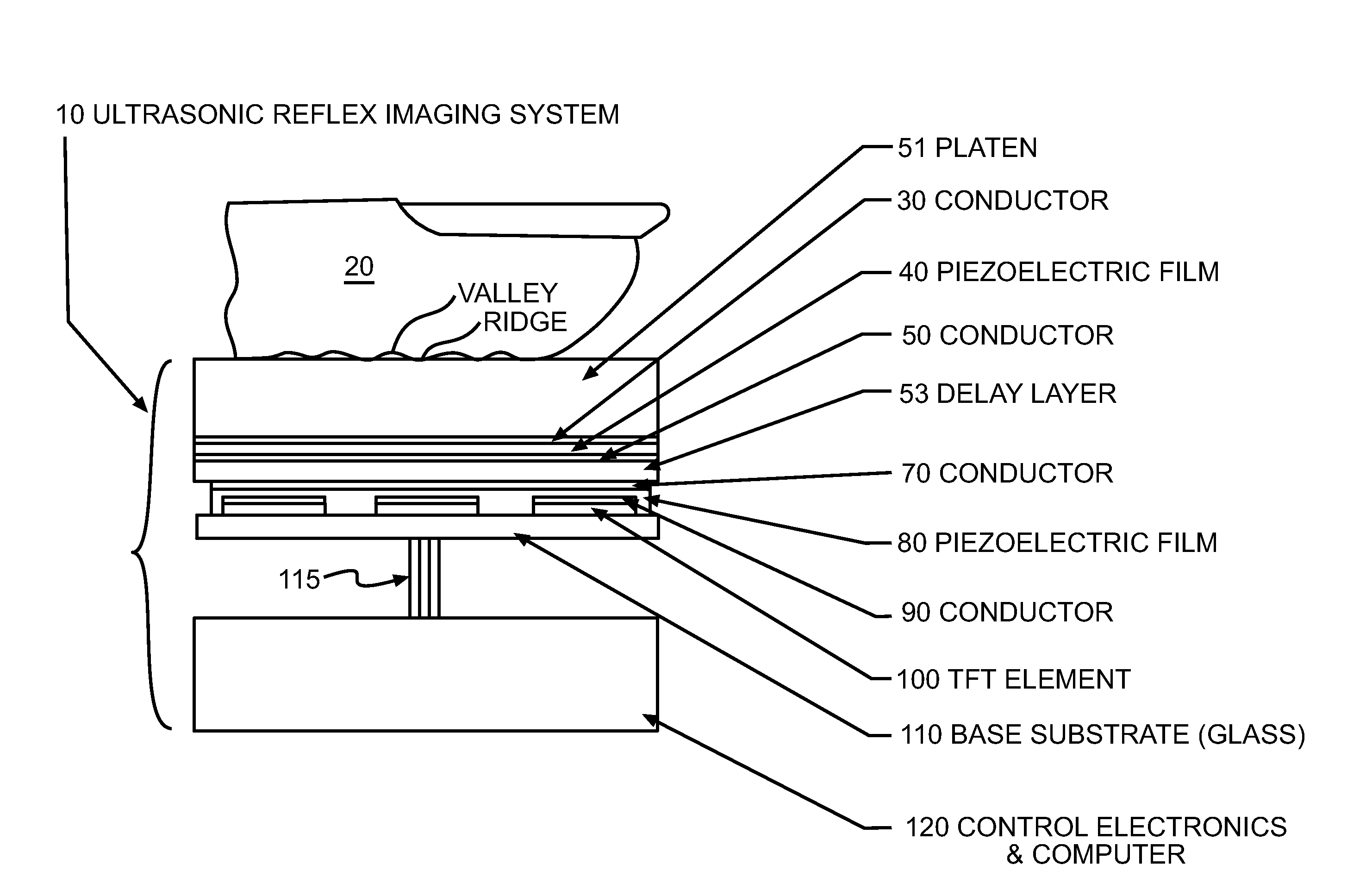
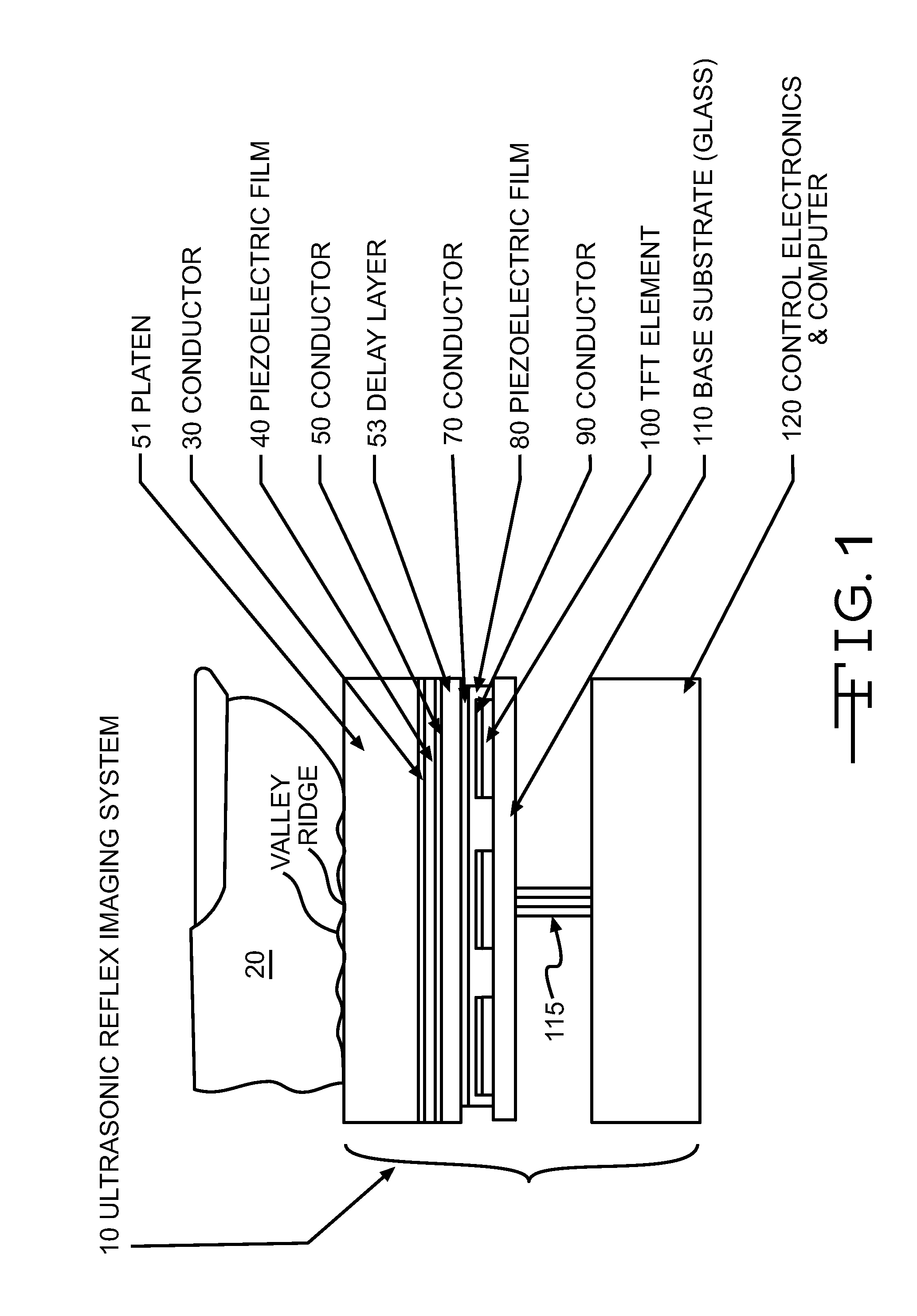
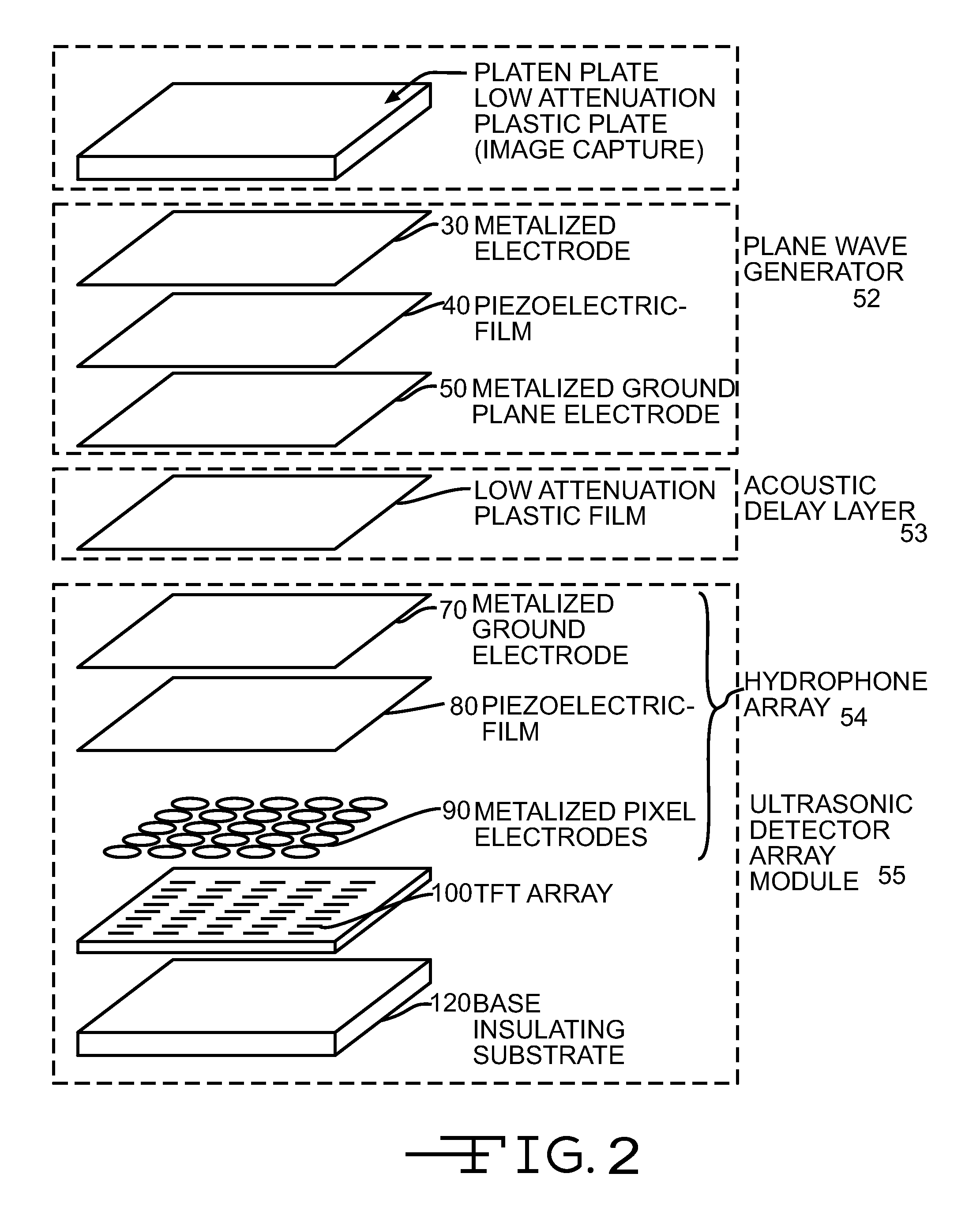
Ultrasonic fingerprint scanning utilizing a plane wave
ActiveUS7739912B2Easy accessEnhance the imageUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesPlane waveUltrasonic generator
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Nerve stimulator system
ActiveUS9205258B2Without sacrificing performanceSame effectImplantable neurostimulatorsArtificial respirationElectrical impulseElectromagnetic radiation
Owner:ELECTROCORE
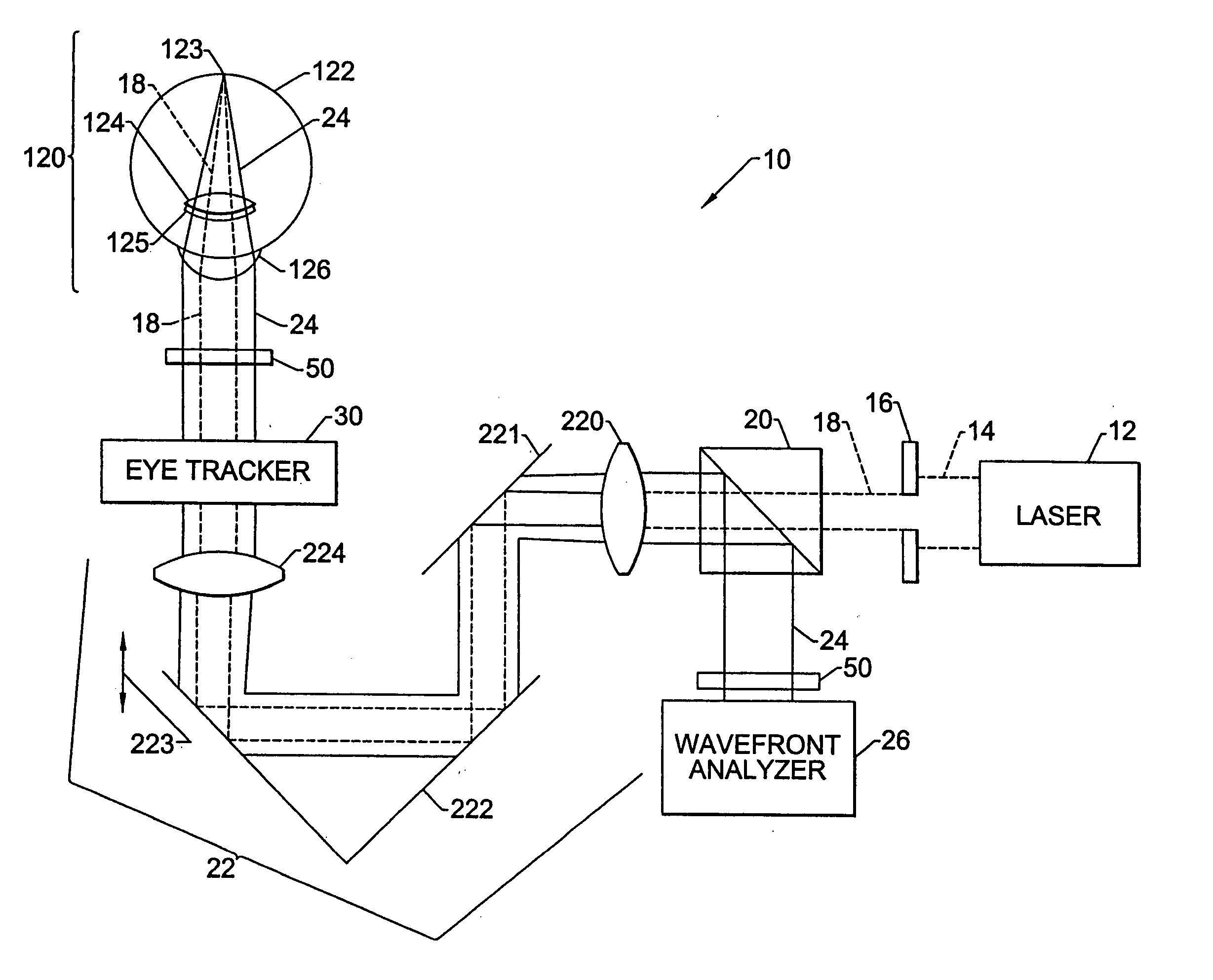
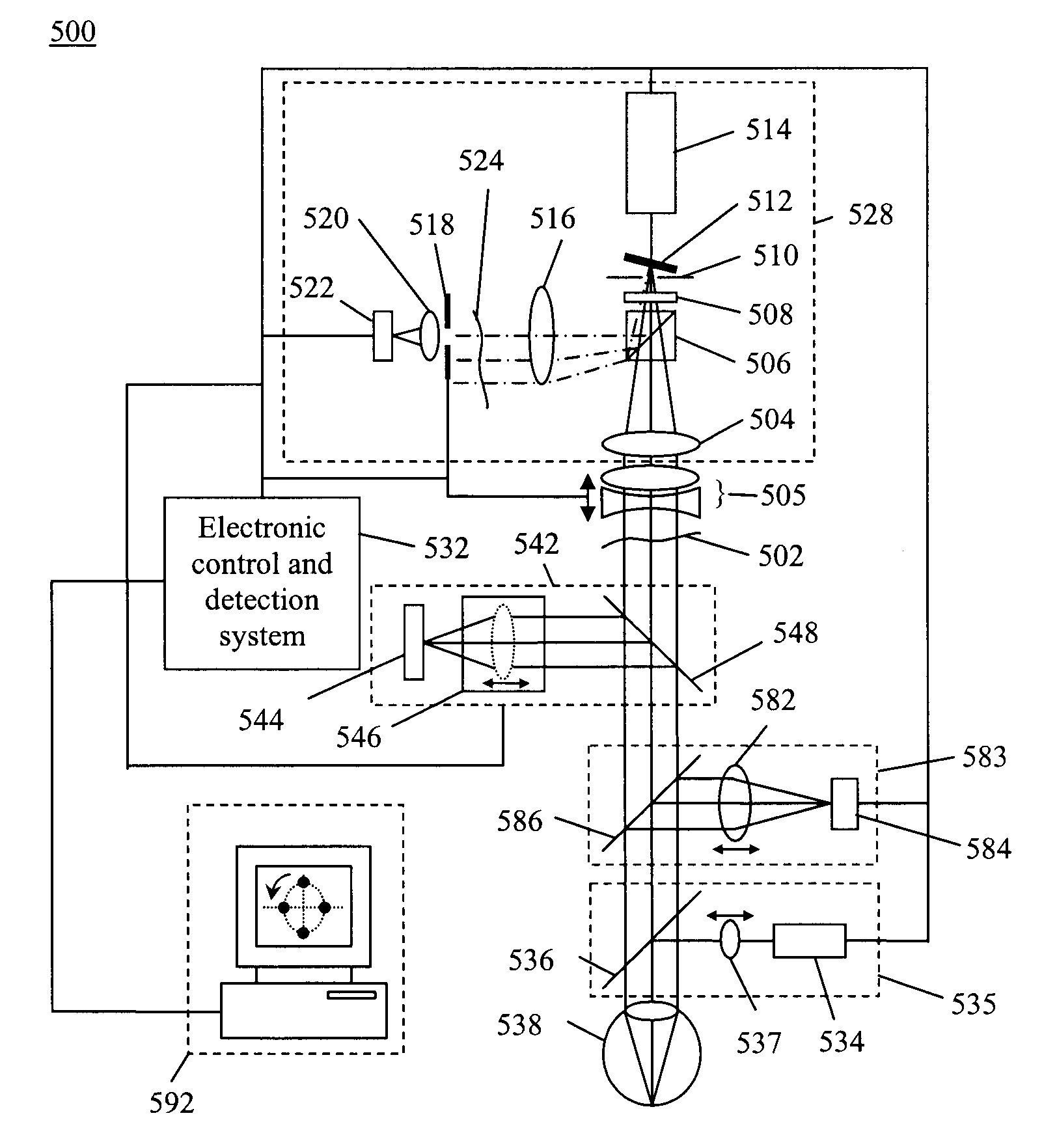
Optimizing vision correction procedures
InactiveUS8100530B2Easy to understandOptical measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringWavefront sensorVisual acuity
Example embodiments include a dynamic wavefront sensor, a controllable wavefront offsetting element and a controller that controls the controllable wavefront offsetting element to offset selected non-plane wave aberration components in order to allow remaining non-plane wave aberration components to be more efficiently detected and measured.
Owner:CLARITY MEDICAL SYST
Apparatus and method for objective measurement and correction of optical systems using wavefront analysis
InactiveUS20050099600A1Simple and inexpensive designPractical applicationLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsRefractive indexOptical path length
A method for enhancing vision of an eye includes a laser delivery system having a laser beam for ablating corneal material from the cornea of the eye. Measurements are made to determine an optical path difference between a plane wave and a wavefront emanating from the retina of the eye for a location at a surface of the cornea. An optical correction is provided to the laser delivery system for the location based on the optical path difference and refractive indices of media through which the wavefront passes. The optical correction includes dividing the optical path difference by a difference between an index of refraction of corneal material and an index of refraction of air. The laser beam is directed to the location on the surface of the cornea and corneal material ablated at the location in response to the optical correction to cause the wavefront to approximate the shape of the plane wave at that location.
Owner:FREY RUDOLPH W +4
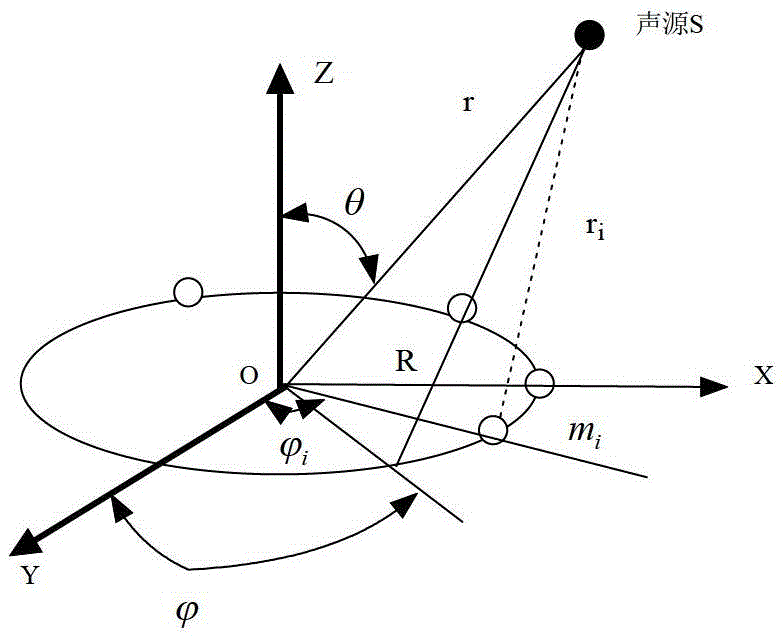
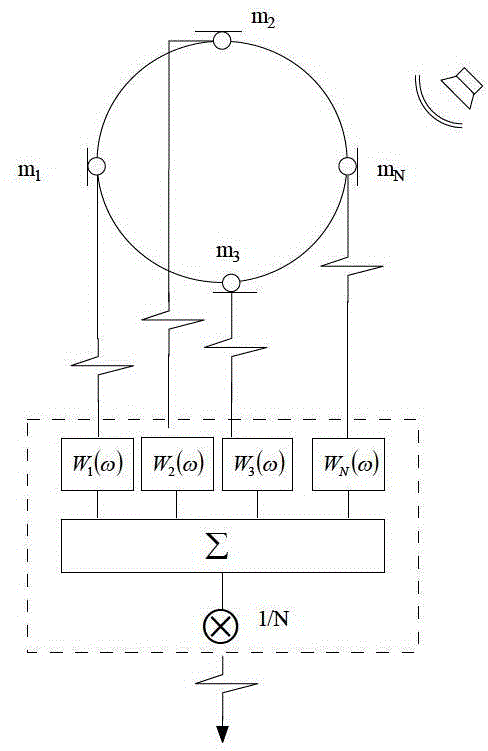
SRP-PHAT multi-source spatial positioning method
InactiveCN104142492AEasy to separateHighlight true peaksPosition fixationSpatial positioningSound sources
The invention provides a SRP-PHAT multi-source spatial positioning method. The method comprises the steps that the number and spatial positions of all microphones in a uniform circular microphone array are assumed to be unchanged in the data obtaining process at first, the isotropous microphones are evenly distributed on a circumference which has the radius r and is located on an x-y plane, the direction of arrival of a plane wave s is expressed by polar coordinates, the original point of the coordinate system is located on a circle center position of the circular array, multiple sound source signals are divided into non-overlapped time frequency point sets, each time frequency window contains only one movable source signal, and weak W orthogonal separation conditions are met; a Hamming window is selected, a controllable response power function is calculated and a target function is obtained through a SRP-PHAT algorithm, wave beams are controlled to carry out scanning in all the possible receiving directions, and the wave beams output the direction value with the maximum power to obtain the direction of a sound source, so that the DOA estimation of the multiple sound sources has the better separating performance in the strong noise and moderate reverberation acoustic environment, the real peak value is obviously outstanding, and high positioning precision is achieved.
Owner:FOSHAN UNIVERSITY
System and method for estimating seismic material properties
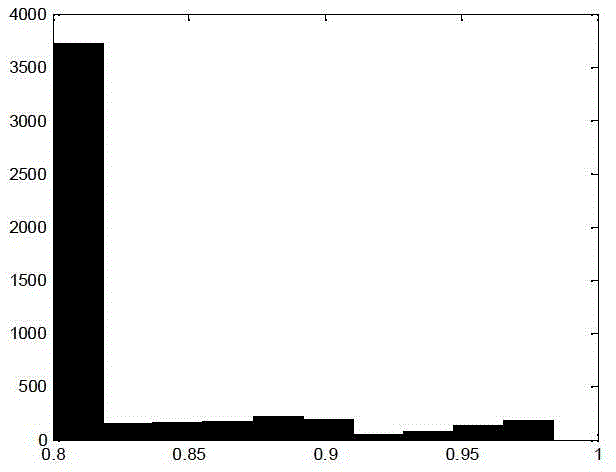
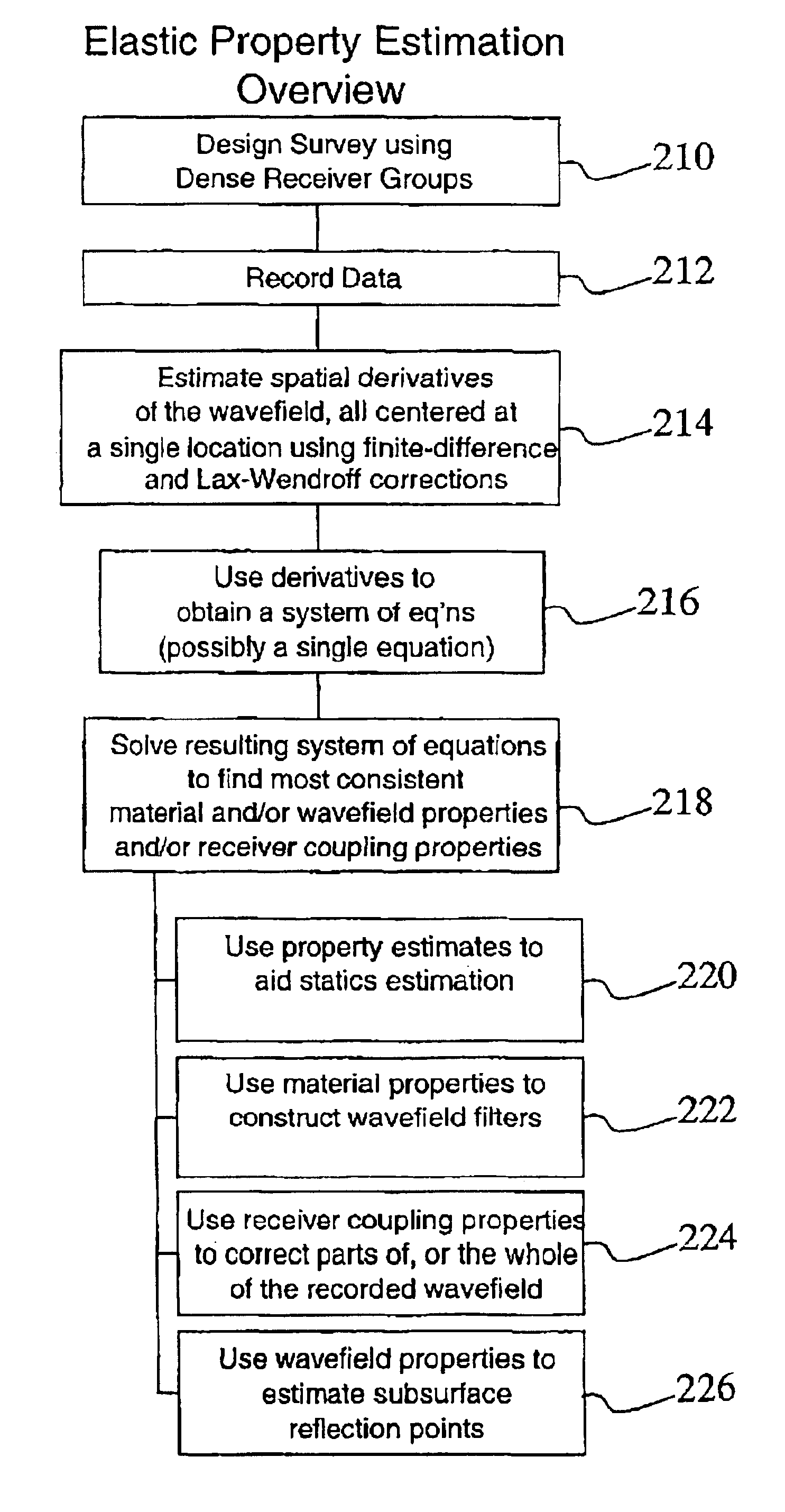
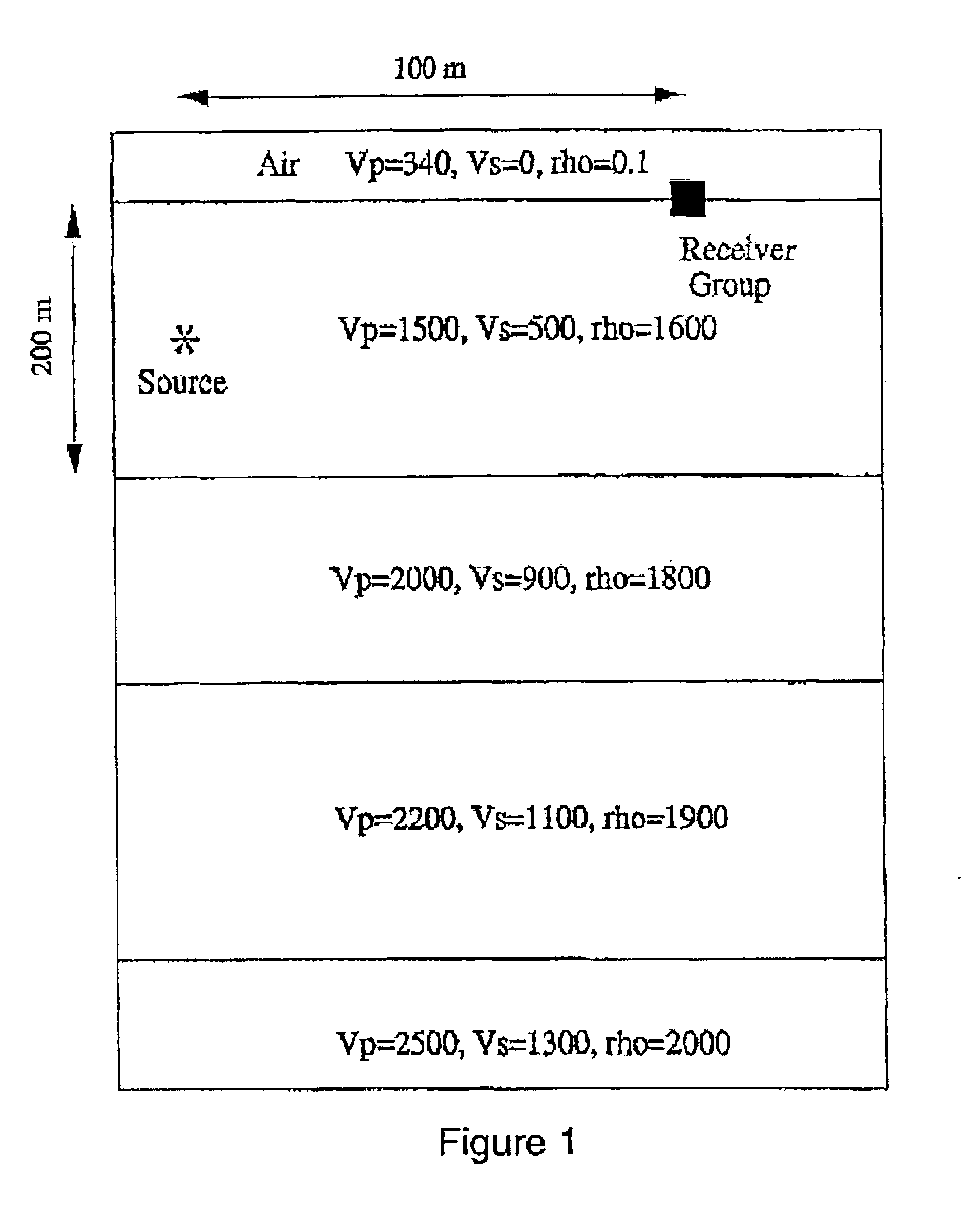
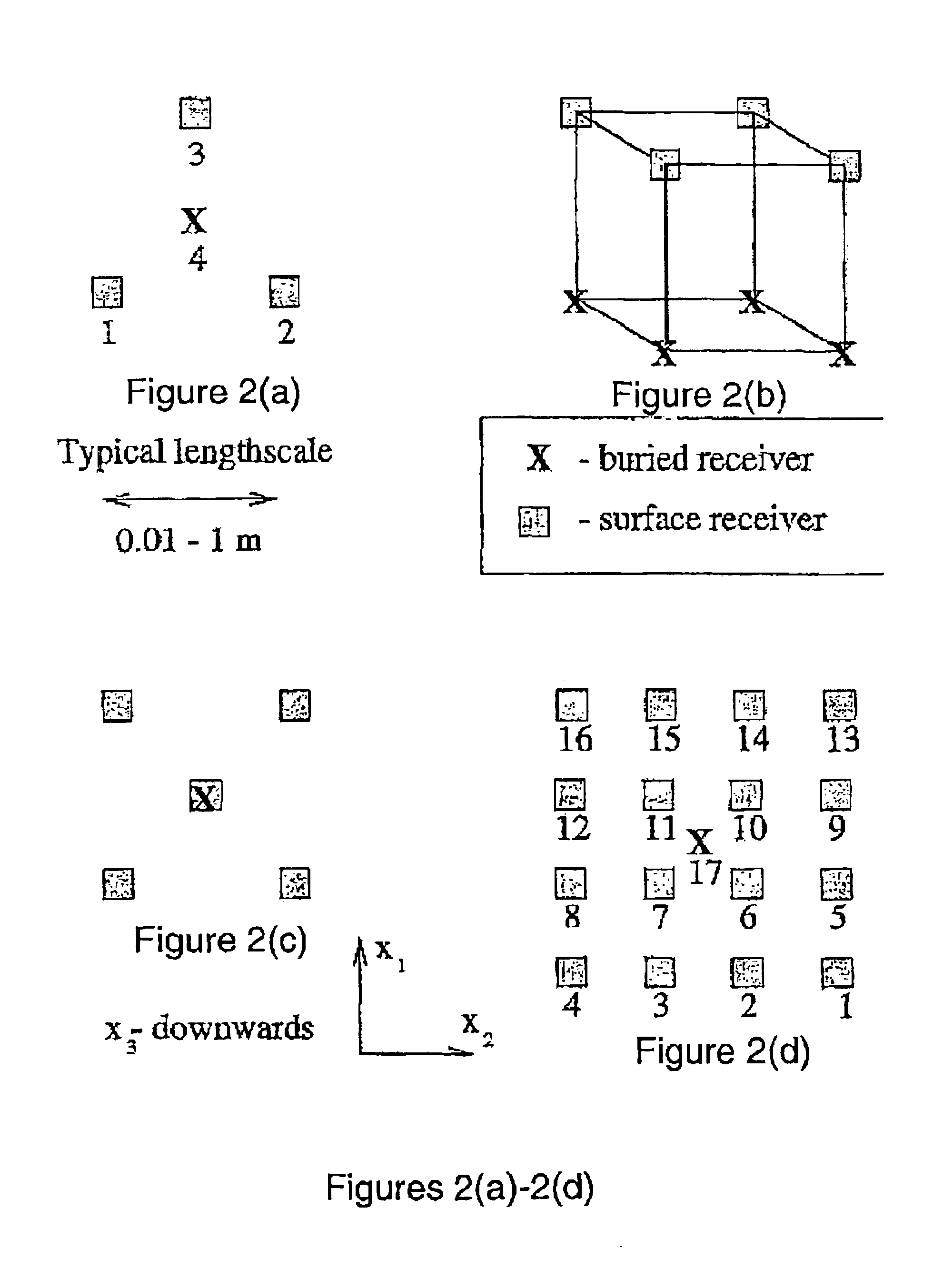
InactiveUS6903999B2Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSeismic signal receiversWave equationWave field
A method for estimating near-surface material properties in the vicinity of a locally dense group of seismic receivers is disclosed. The method includes receiving seismic data that has been measured by a locally dense group of seismic receivers. Local derivatives of the wavefield are estimated such that the derivatives are centered at a single location preferably using the Lax-Wendroff correction. Physical relationships between the estimated derivatives including the free surface condition and wave equations are used to estimate near-surface material properties in the vicinity of the receiver group. Another embodiment of the invention is disclosed wherein the physical relationships used to estimate material properties are derived from the physics of plane waves arriving at the receiver group, and the group of receivers does not include any buried receivers.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Microscope
InactiveUS20100265575A1Increase depth of focusShadowing is preferably also reduced or preventedMicroscopesAcute angleLight beam
A microscope including an imaging objective for imaging a sample on a detector and means for illuminating the sample with a light sheet in the focus plane of the imaging objective. The illumination means includes an illumination source which emits coherent light, and Bessel optics which generate at least two plane waves from the light beam and give propagation directions for the plane waves. The propagation direction of each of the plane waves encloses an acute angle with the focus plane in each instance, the magnitude of the acute angle being identical for each of the plane waves, so that the plane waves undergo constructive interference in the focus plane so that a light sheet is generated. Similarly, the illumination means can also include an optical element by which a rotationally symmetric Bessel beam is generated from the light beam for dynamic generation of a light sheet.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MICROSCOPY GMBH
Light field image sensor, method and applications
ActiveUS20110174998A1Accurate predictionThe implementation process is simpleBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsInstruments for comonautical navigationTalbot effectAngle–sensitive pixel
An angle-sensitive pixel (ASP) device that uses the Talbot effect to detect the local intensity and incident angle of light includes two local diffraction gratings stacked above a photodiode. When illuminated by a plane wave, the upper grating generates a self-image at a selected Talbot depth. The second grating, placed at this depth, blocks or passes light depending upon incident angle. Several such structures, tuned to different incident angles, are sufficient to extract local incident angle and intensity. Arrays of such structures are sufficient to localize light sources in three dimensions without any additional optics.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
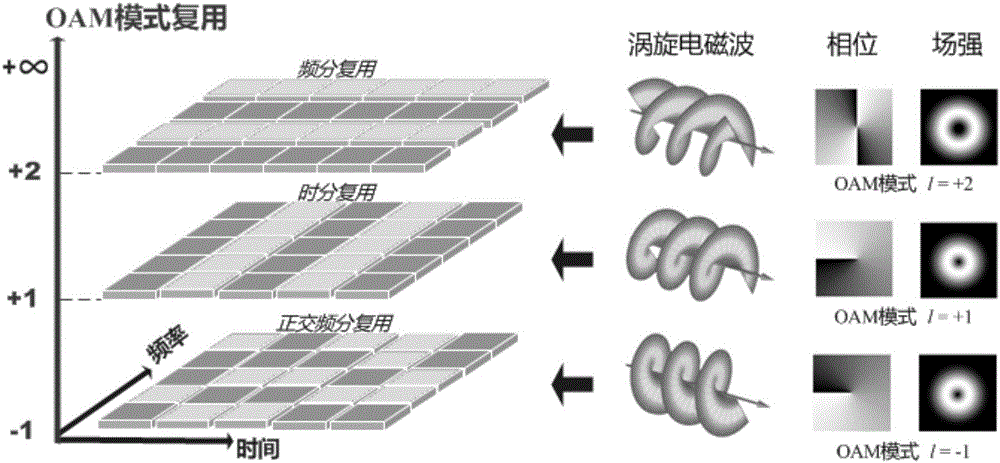
Multimodal orbital angular momentum multiplexing system and method
ActiveCN106130655AImprove spectral efficiencyIncrease transfer rateMulti-frequency code systemsElectromagnetic transmissionFrequency spectrumAnnular array
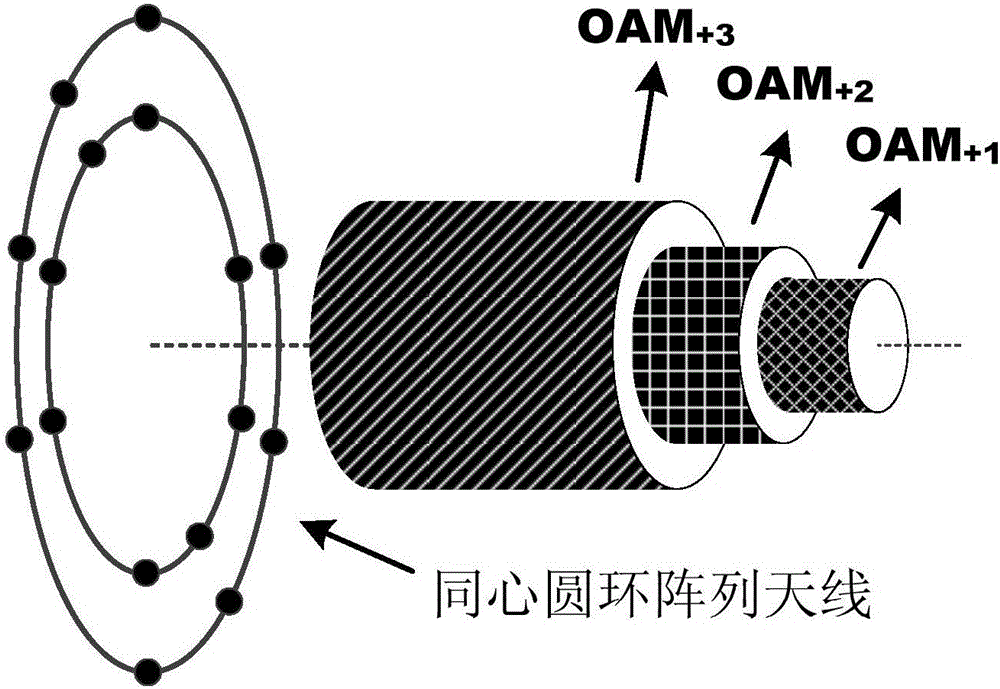
The invention relates to a multimodal orbital angular momentum multiplexing system and method. The system comprises a transmitting device and a receiving device which are in mutual communication connection. The transmitting device comprises a bit level processing module, a constellation mapping module, an orbital angular momentum modulation module, a digital domain orbital angular momentum multimodal multiplexing module, a DAC module, an upper conversion module and a ring array transmitting antenna. The receiving device comprises a ring array receiving antenna, a down conversion module, an ADC module, a digital domain orbital angular momentum demodulation and demultiplexing module and a detection decoding module. According to the system and the method, a vortex electromagnetic wave multimodal OAM (Orbital Angular Momentum) multiplexing communication technology of which physical feature is clearly different from that of a traditional plane wave is realized; the spectral efficiency and the transmission rate are multiplied; and the improvement space and potential of the modal multiplexing quantity is further expanded. The system and the method can be applied to the multimodal OAM multiplexing communication system in a microwave or millimeter wave band.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Over-the-Air Test
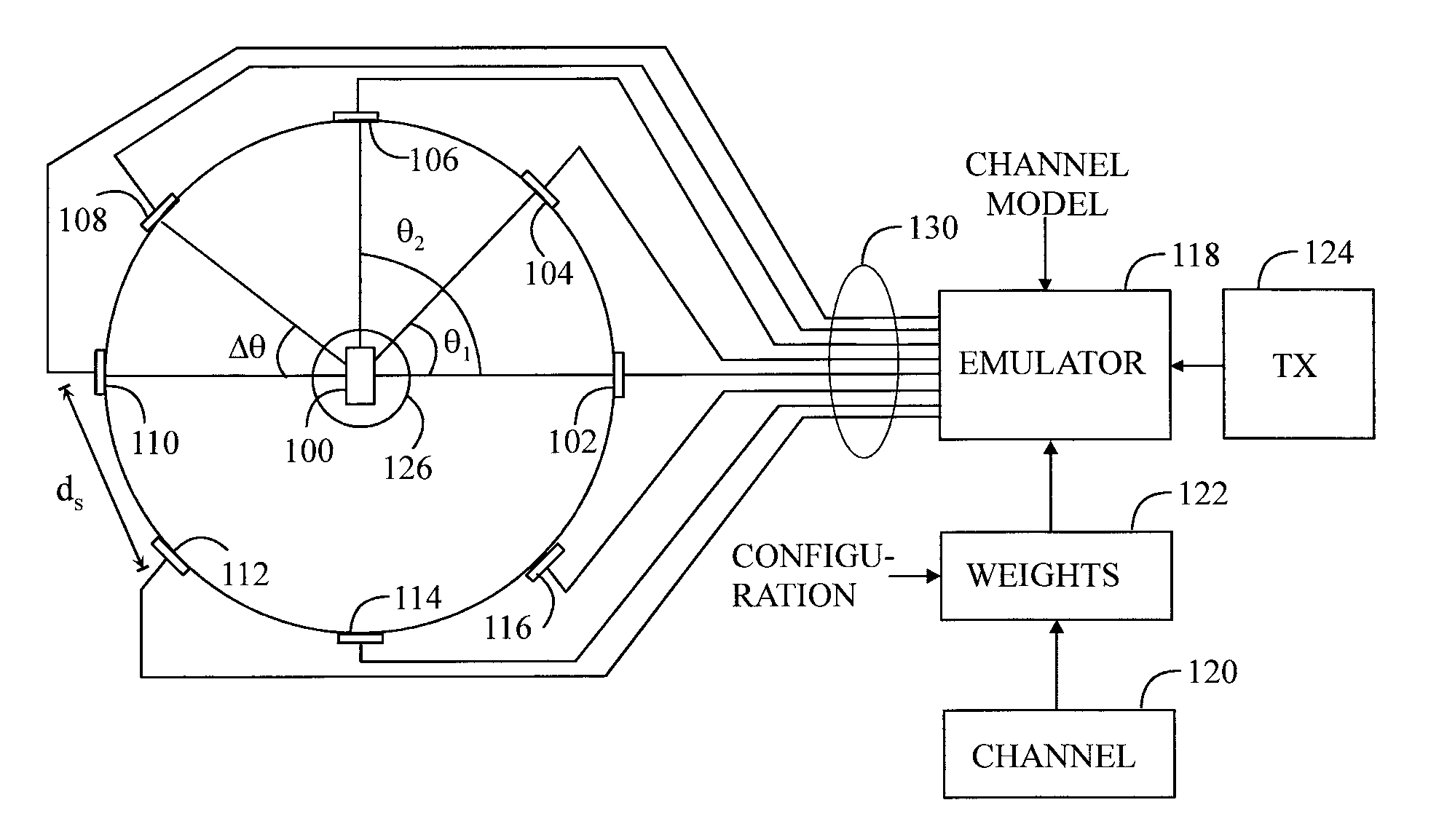
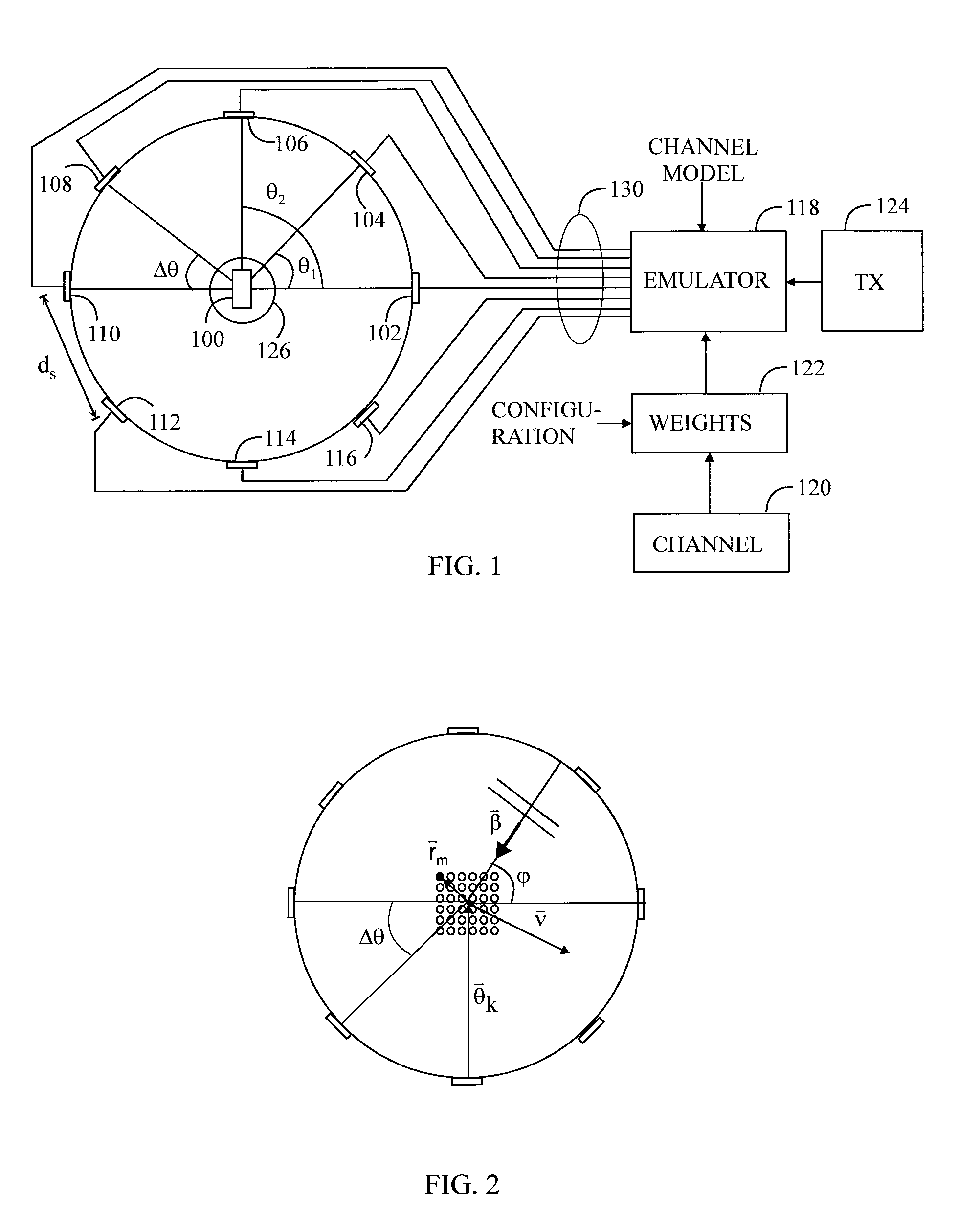
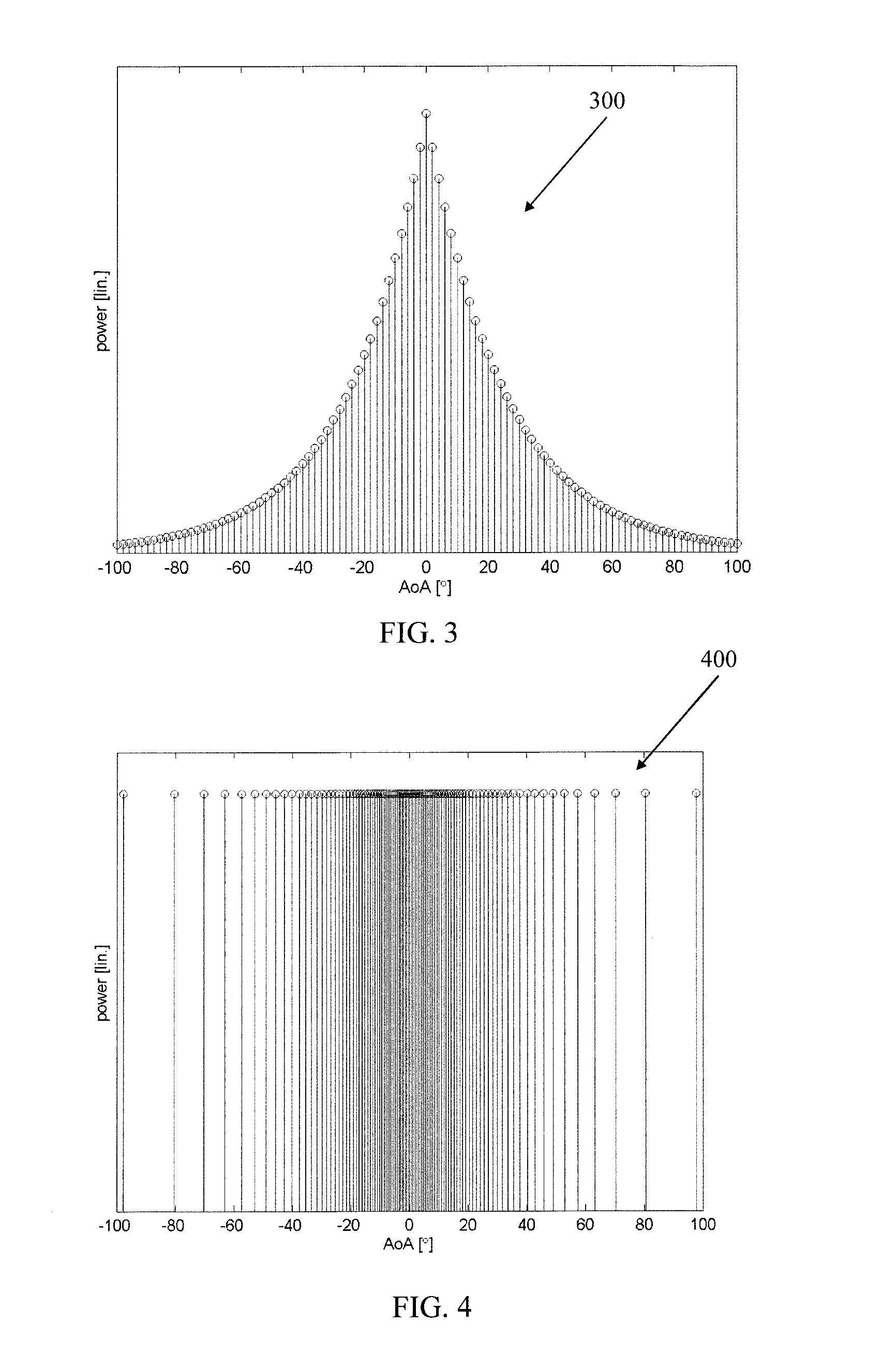
An apparatus forms a weight for each signal path associated with an antenna of a plurality of antennas around a test zone in an over-the-air chamber by a comparison of a desired target electric field based on a radio channel model and an electric field obtainable by the plane waves associated with the test zone, the plane waves being transmittable by the antennas and being based on at least one basis waveform in each signal path.
Owner:KEYSIGHT TECH SINGAPORE (SALES) PTE LTD
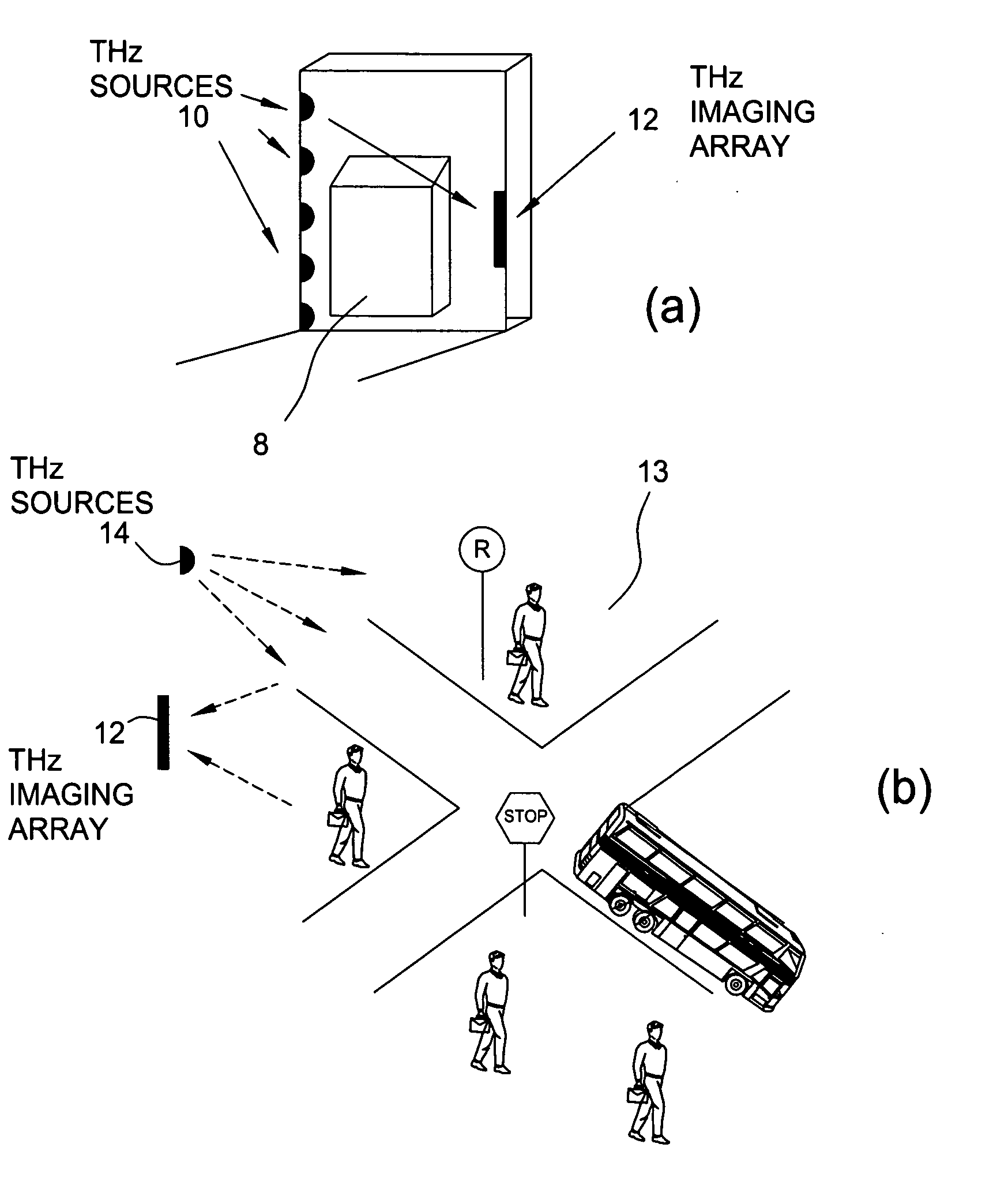
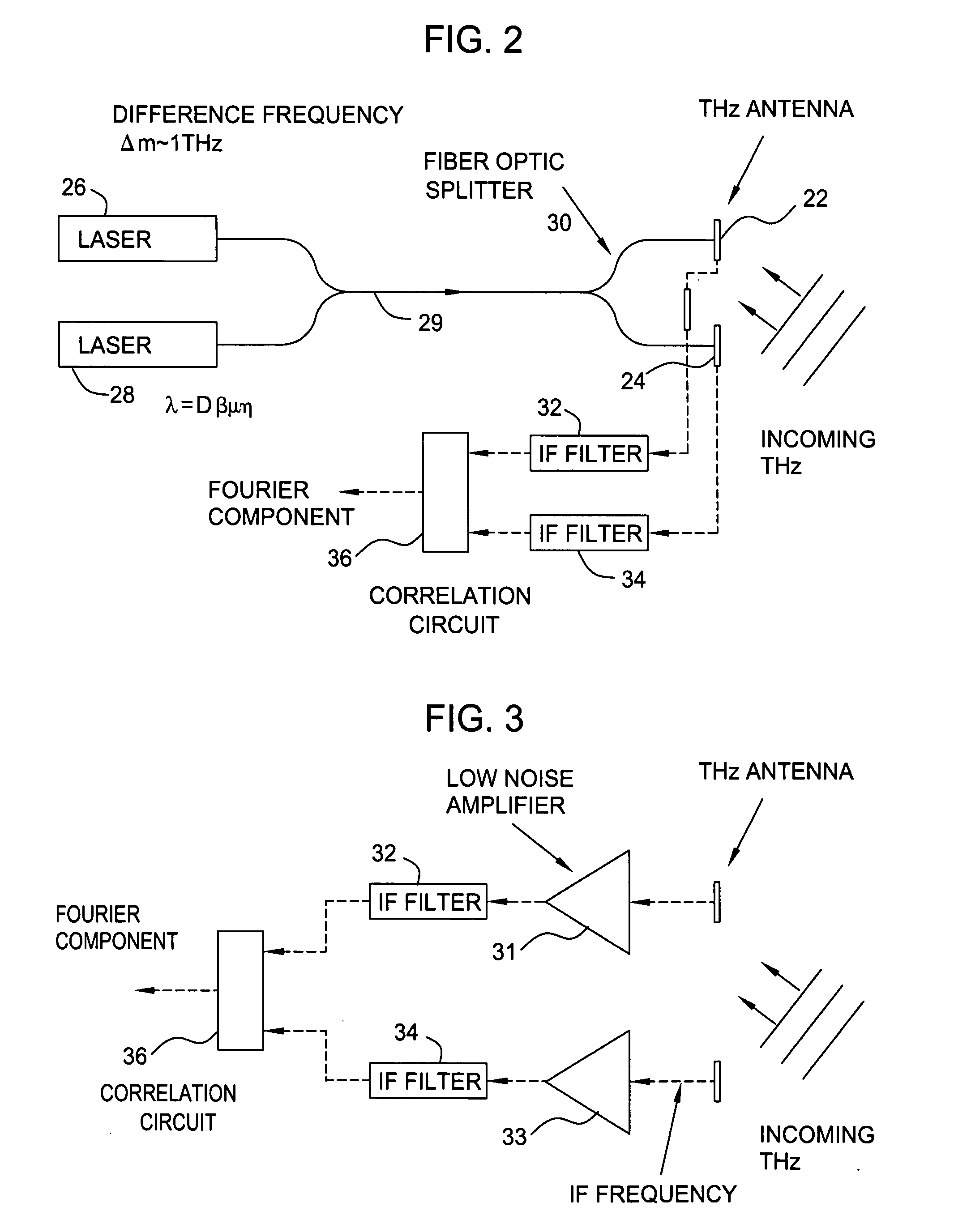
Terahertz imaging for near field objects
ActiveUS20060054824A1Distortion problemEffective regulationRadiation pyrometryAbsorption/flicker/reflection spectroscopyInterferometric imagingDetector array
Near field imaging using a THz imaging system is realized by utilizing an interferometric imaging detector array that includes detector elements disposed on a surface curved, physically or artificially, to match substantially the curvature of the wave front for received THz signals. Generally, the near field is an environment wherein the distance to an object of interest is on the order of 10-100 times larger than the physical size of the THz imaging array. Typical distances from the object or target to the imaging array is anticipated to be in the 0.5 m-50 m range. Curvature of the detector array corrects a distortion problem in prior THz imaging systems that utilized planar interferometric imaging arrays based on a planar wave front assumption for received THz signals.
Owner:NEW JERSEY INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
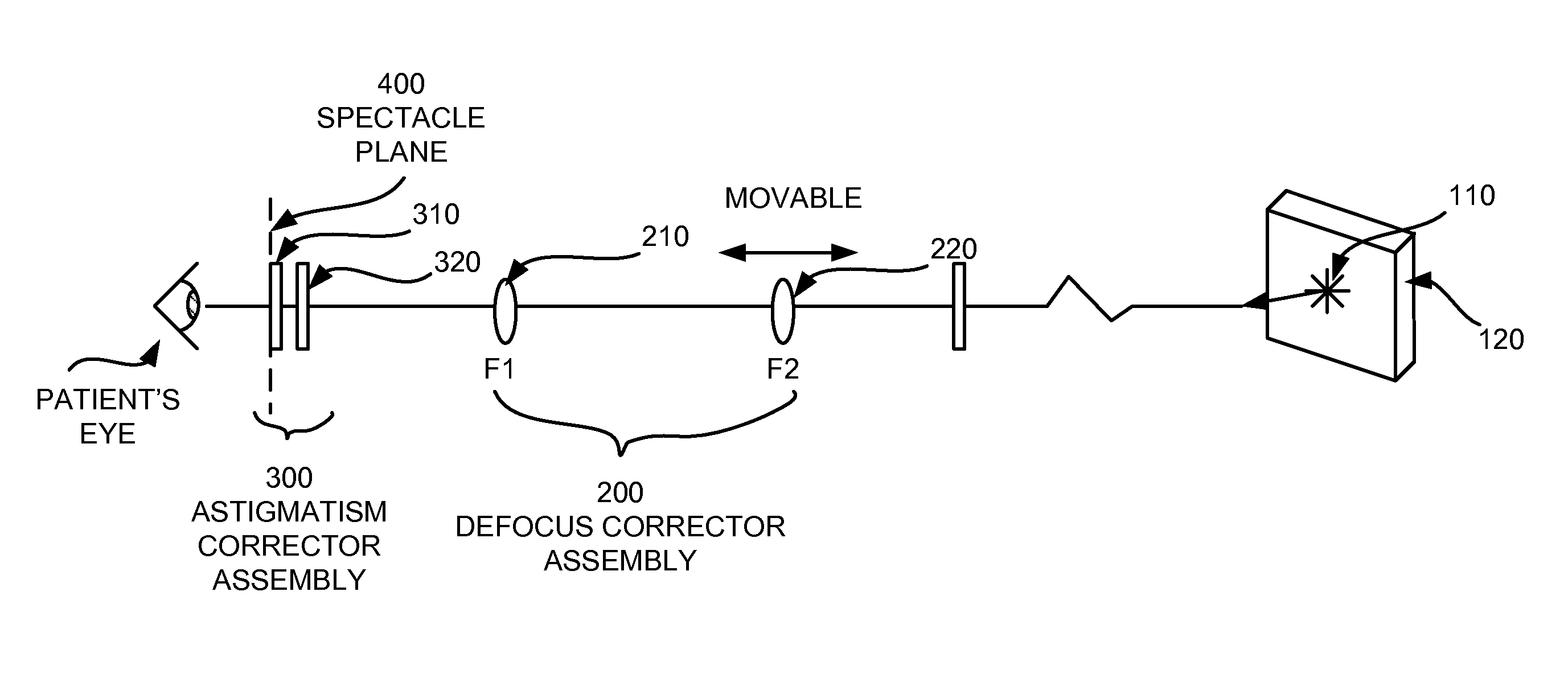
Subjective Refraction Method and Device for Correcting Low and Higher Order Aberrations
ActiveUS20070195264A1Drawback can be obviatedLong dimensionPhoroptersOptical partsAxis–angle representationOptical axis
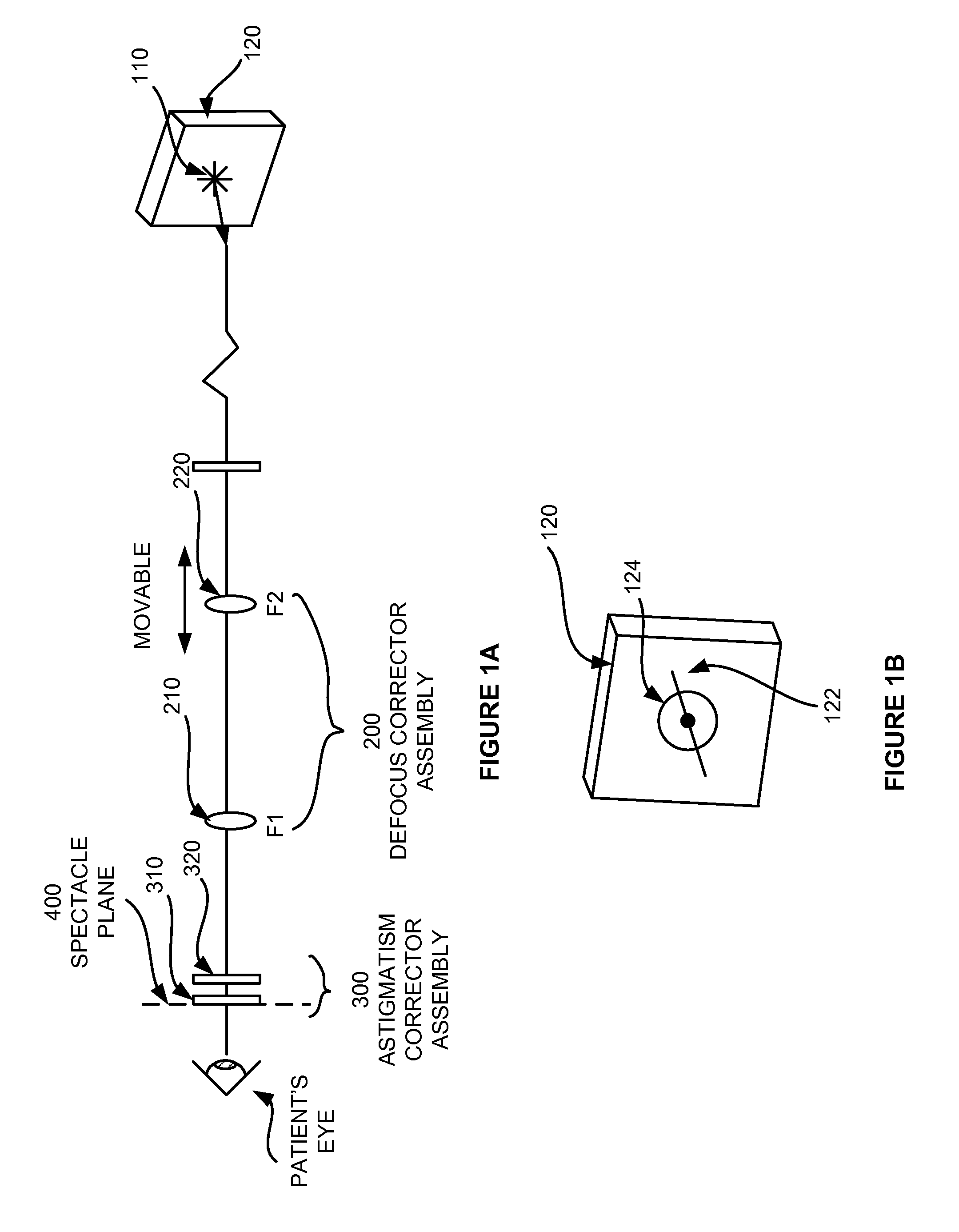
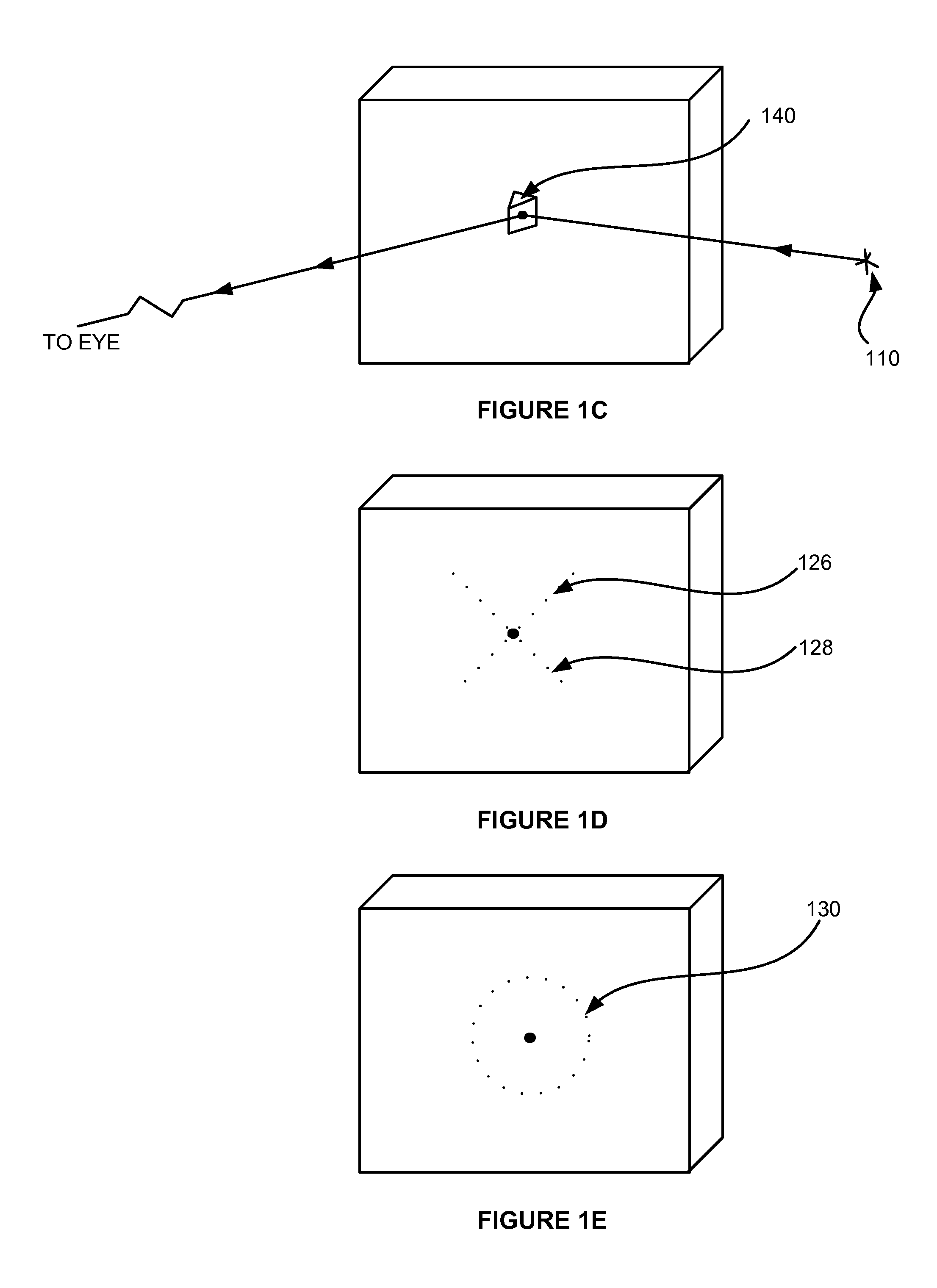
A subjective refraction technique uses a plane wave light source including substantially a point as a viewing target. The refraction method provide for a number of distinct identifiable end points. By finding such end points the process leads to an aberration-corrected vision. A defocus corrector assembly (DCA) includes a lens that is moveable along an optical axis between a patient's eye and the point light source for adjusting defocus power until the patient indicates that the blurry image has become a relatively focused line image. An astigmatism corrector assembly (ACA) which is capable of continuously variable in its amplitude is provided including a pair of astigmatism plates for adjusting astigmatism power and axis angle. The ACA is adjusted until the patient indicates that the line image has become a substantially round image. A reference marker provides displayed items including a sweep line overlapping at the point source and having an orientation which is adjustable. The patient may subjectively control the sweep angle of the sweep line and indicate that the sweep line is aligned with the sharp line image of the point source, thereby providing axis angle data of astigmatism errors of the patient's eye.
Owner:LAI SHUI T
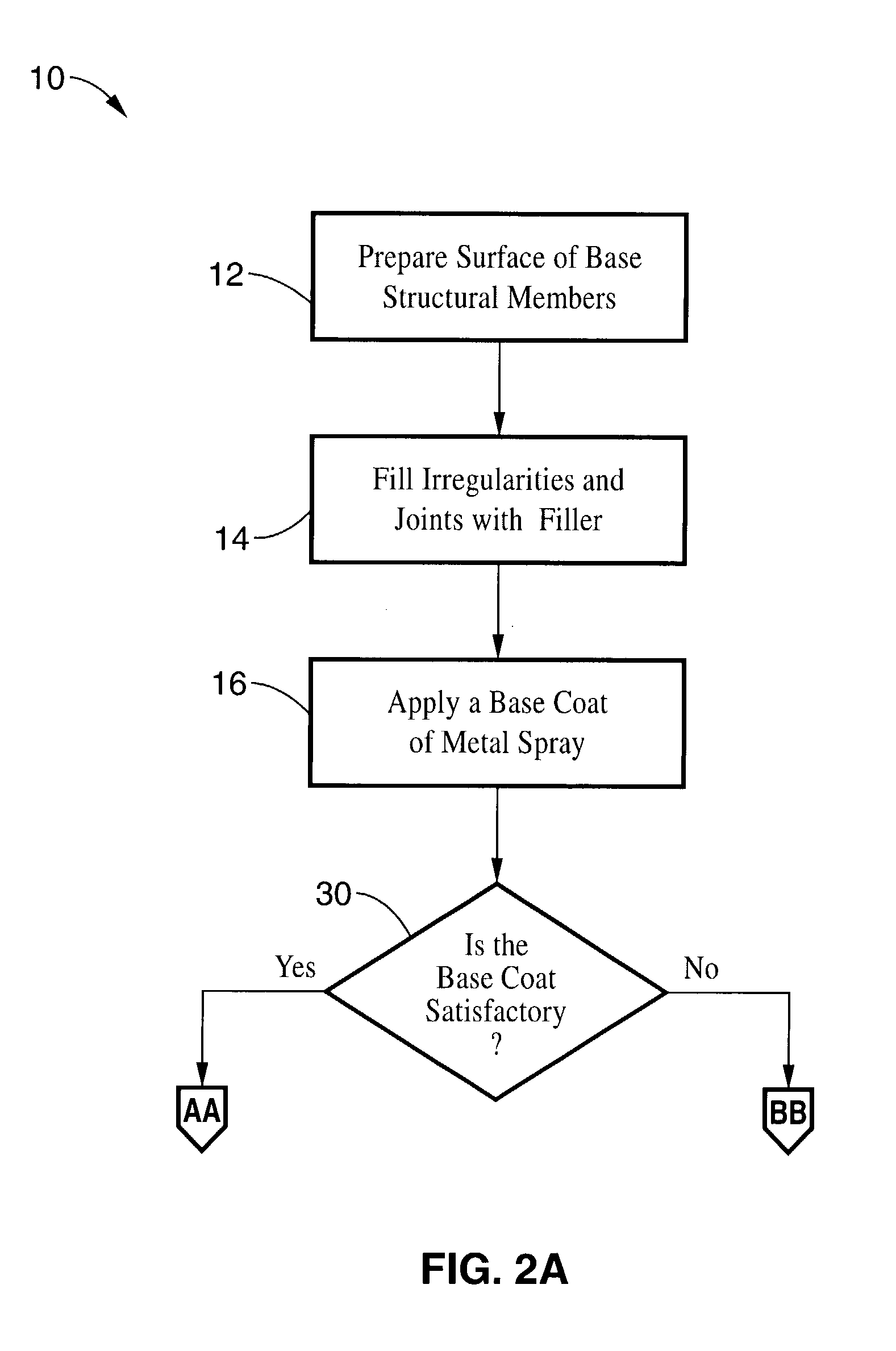
Process for creating a durable EMI/RFI shield between two or more structural surfaces and shield formed therefrom
InactiveUS7063767B1Easy to transportMaintain performanceMagnetic/electric field screeningUltrasound attenuationEngineering
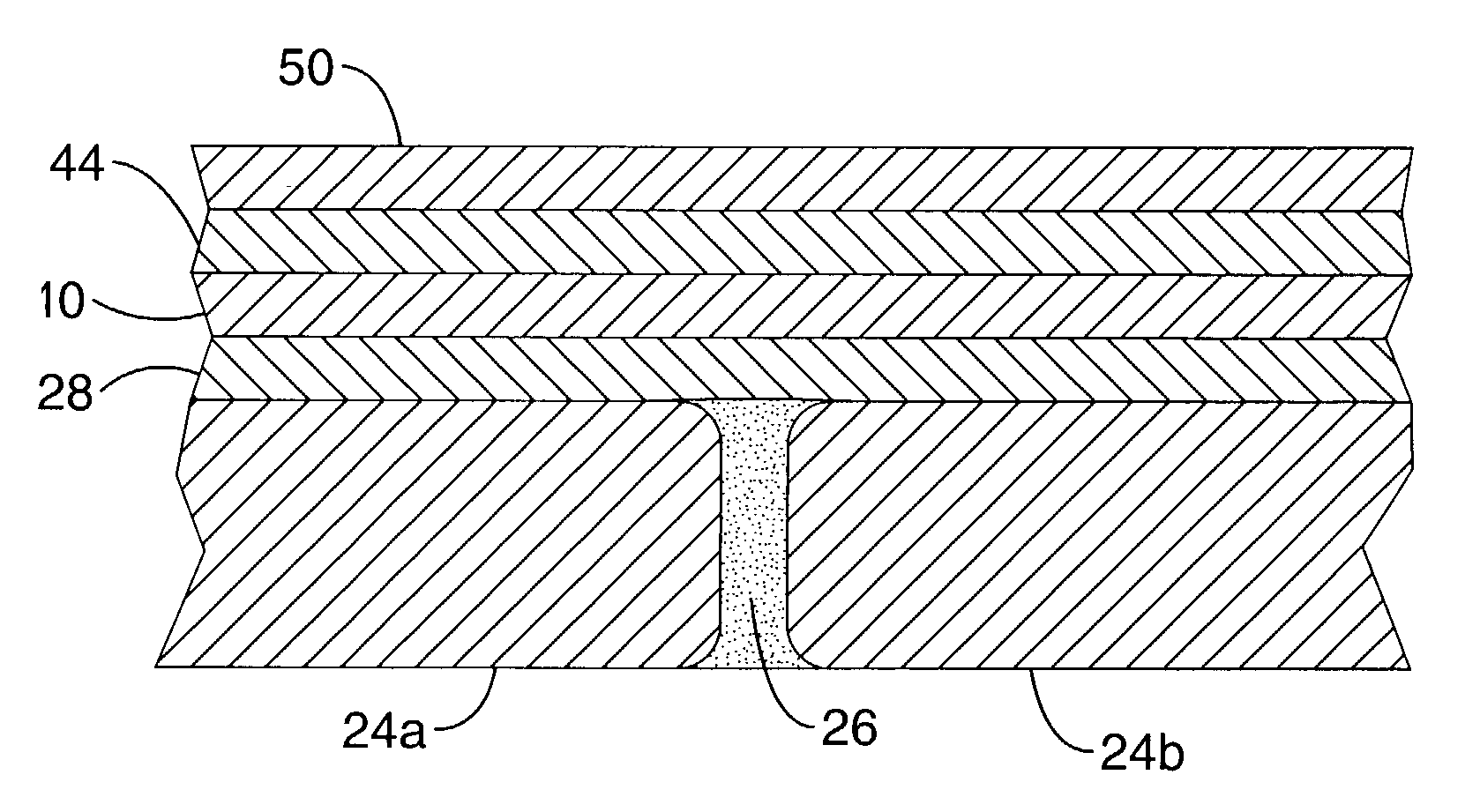
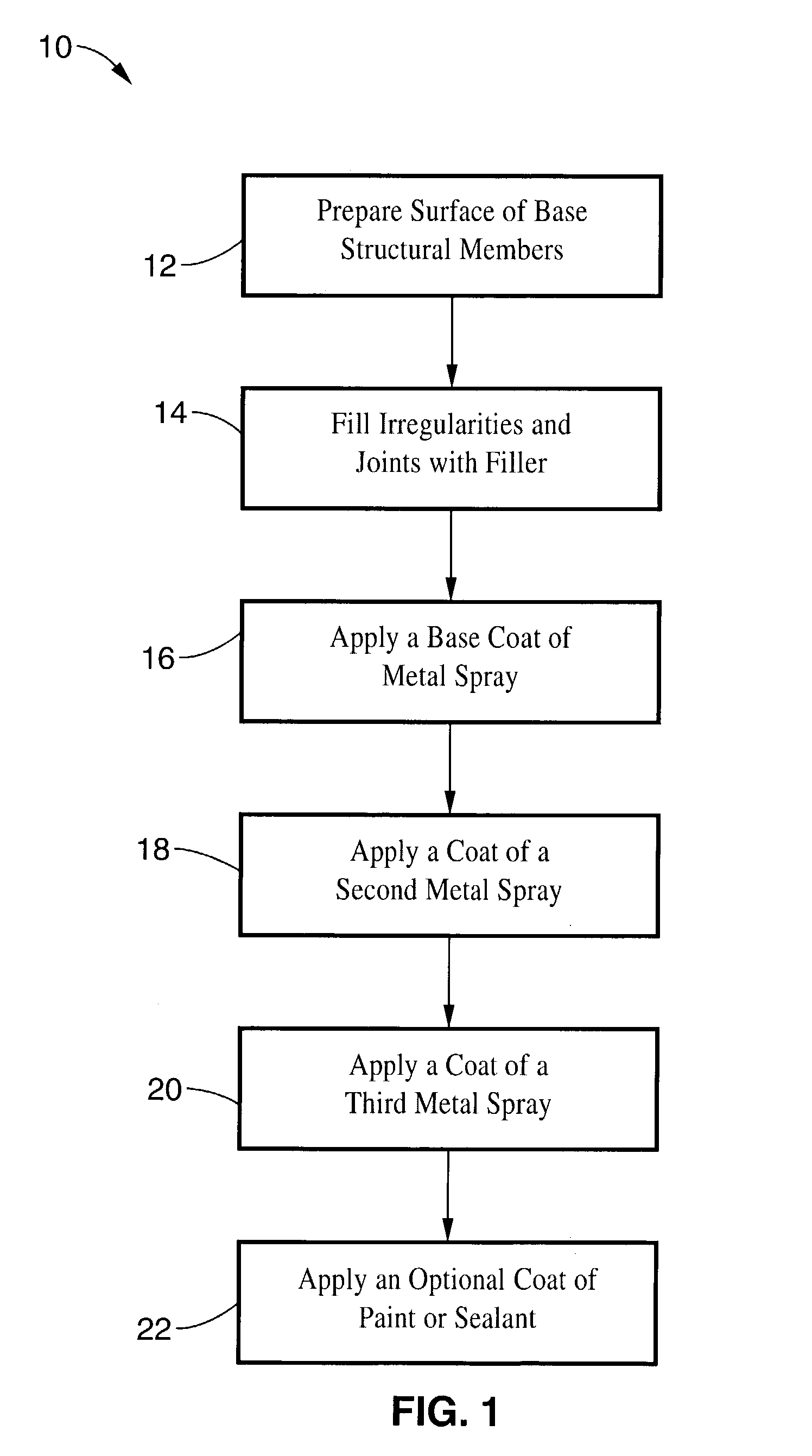
A method for producing a durable electromagnetic and radio frequency interference shield between two or more structural members of a wall or enclosure and a shielded shelter produced using the method. In one embodiment, joints between structural members are preferably filled with an electrically conductive filler. A base coat of a metal spray that adheres well to the filler and structural member is then applied. At least one layer of a metal spray with magnetic field attenuation properties such as steel, and at least one layer of a metal spray that has plane wave attenuation properties such as tin are applied to the base coat. Optionally, a coat of protective or conductive paint is then applied to the top surface of the metal spray layers. An enclosure with shielded joints according to the present invention has superior shielding capability and durability over the art.
Owner:TYSON KENNETH E +1
Method using three-dimensional mechanics and tissue specific imaging of blood vessels and plaques for detection
InactiveCN104398271ARealize three-dimensional mechanical property detectionRealize simultaneous measurementOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsVulnerable plaqueShear rate
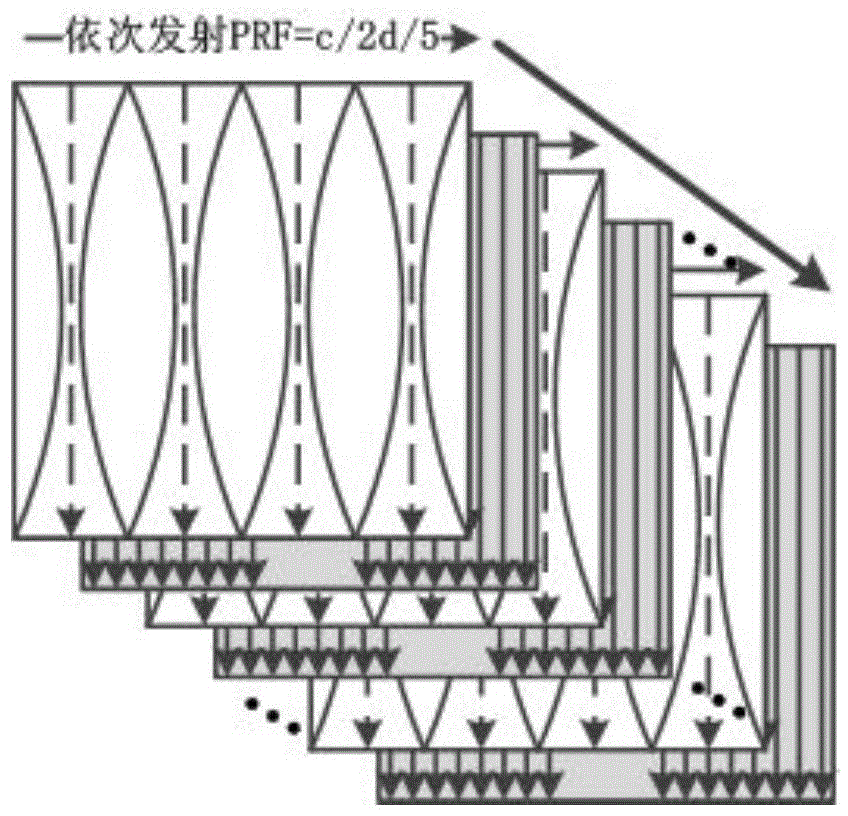
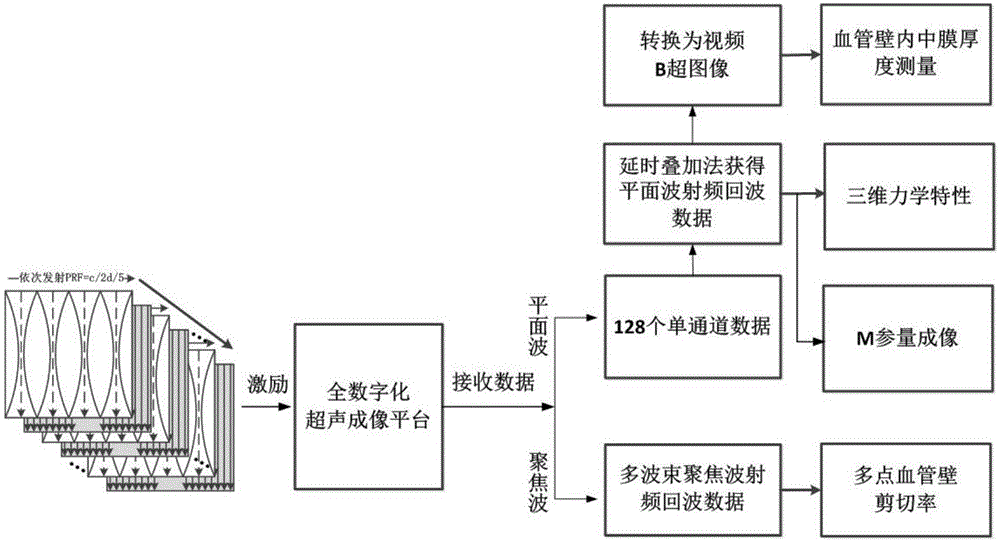
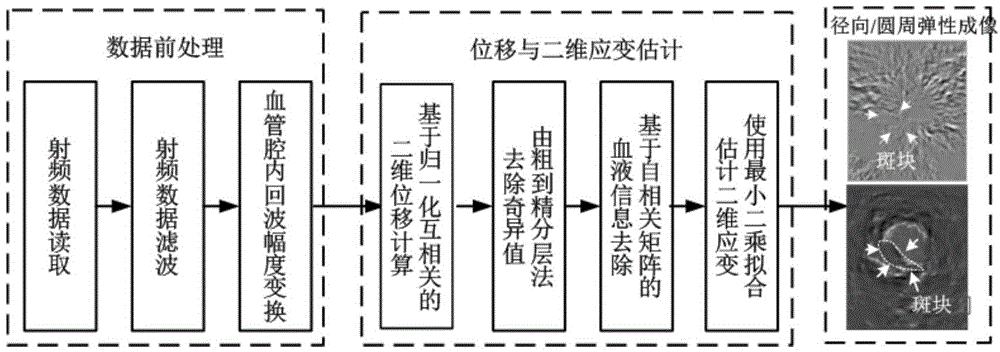
The invention relates to a method using three-dimensional mechanics characteristics and tissue specific imaging of blood vessels and plaques for detection. The method is on the basis of a multi-beam focus wave and superfast plane wave alternative transmitting sequence and can also be extended to a line-by-line scan imaging manner; the forms and the functions of the blood vessels and the plaques are evaluated and imaged respectively from the aspects of the radial-direction, circumferential and axial-direction three-dimensional mechanics characteristics, blood vessel wall shear rate, plaque form and tissue characterization, and the like; the new method which is provided for detection of the vulnerable plaques of a carotid artery is regarded as the improvement of the existing method.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
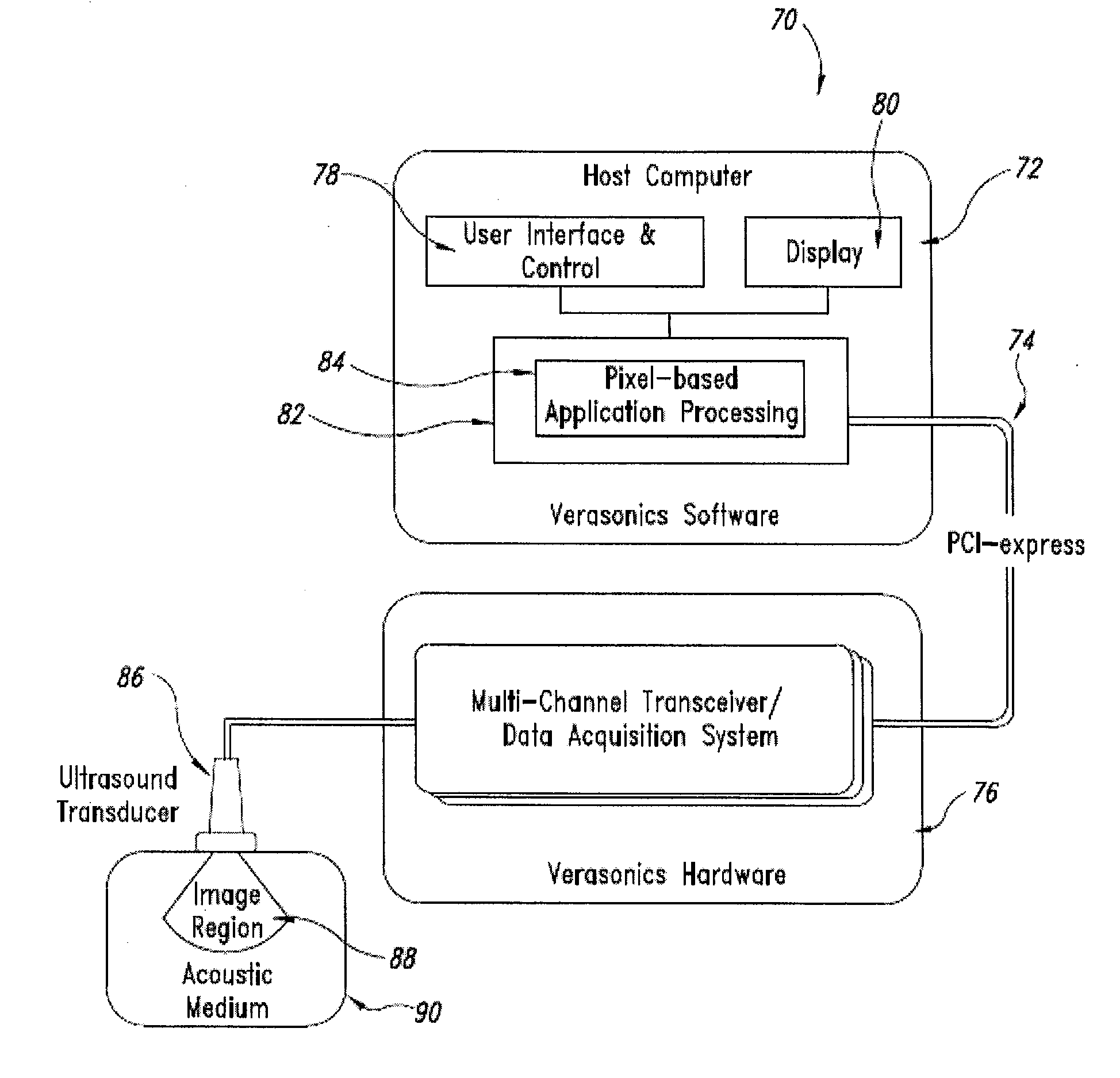
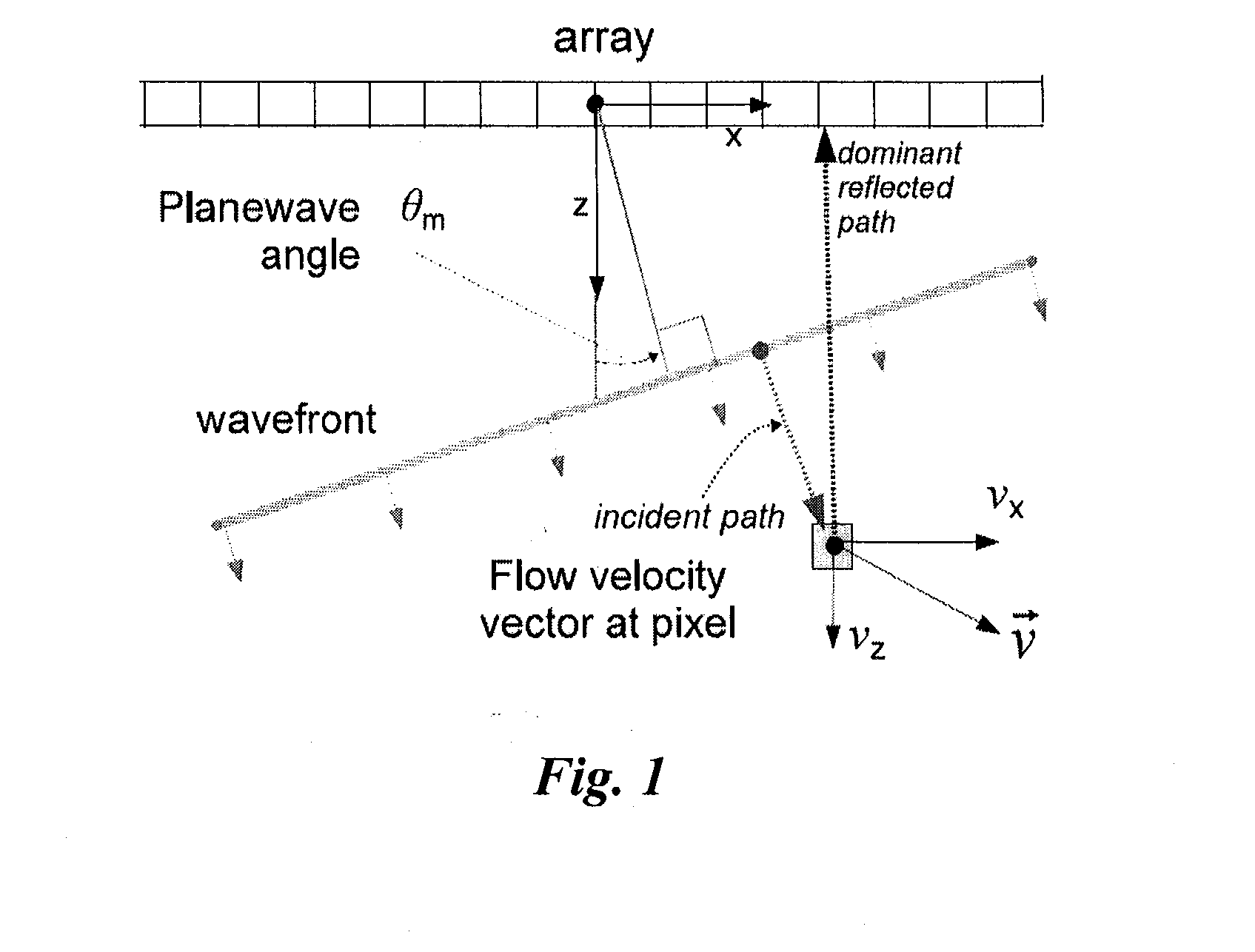
Estimation and display for vector doppler imaging using plane wave transmissions
ActiveUS20140371594A1High precisionGood for observationBlood flow measurement devicesOrgan movement/changes detectionColor dopplerUltrasonic sensor
Vector Doppler Imaging (VDI) improves on conventional Color Doppler Imaging (CDI) by giving speed and direction of blood flow at each pixel of a display generated by a computing system. Multiple angles of Plane wave transmissions (PWT) via an ultrasound transducer conveniently give projected Doppler measurements over a wide field of view, providing enough angular diversity to identify velocity vectors in a short time window while capturing transitory flow dynamics. A fast, aliasing-resistant velocity vector estimator for PWT is presented, and VDI imaging of a carotid artery with a 5 MHz linear array is shown using a novel synthetic particle flow visualization method.
Owner:VERASONICS
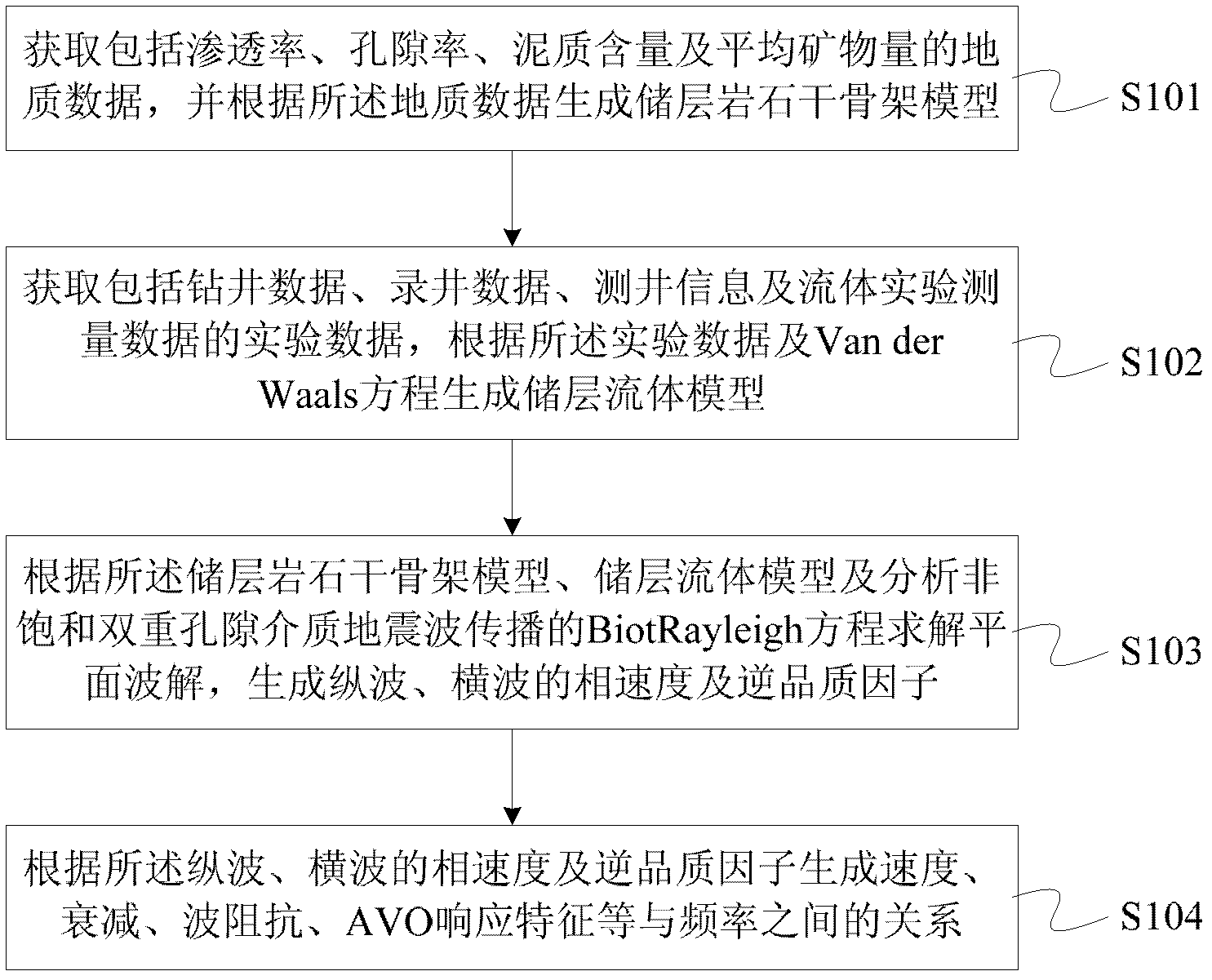
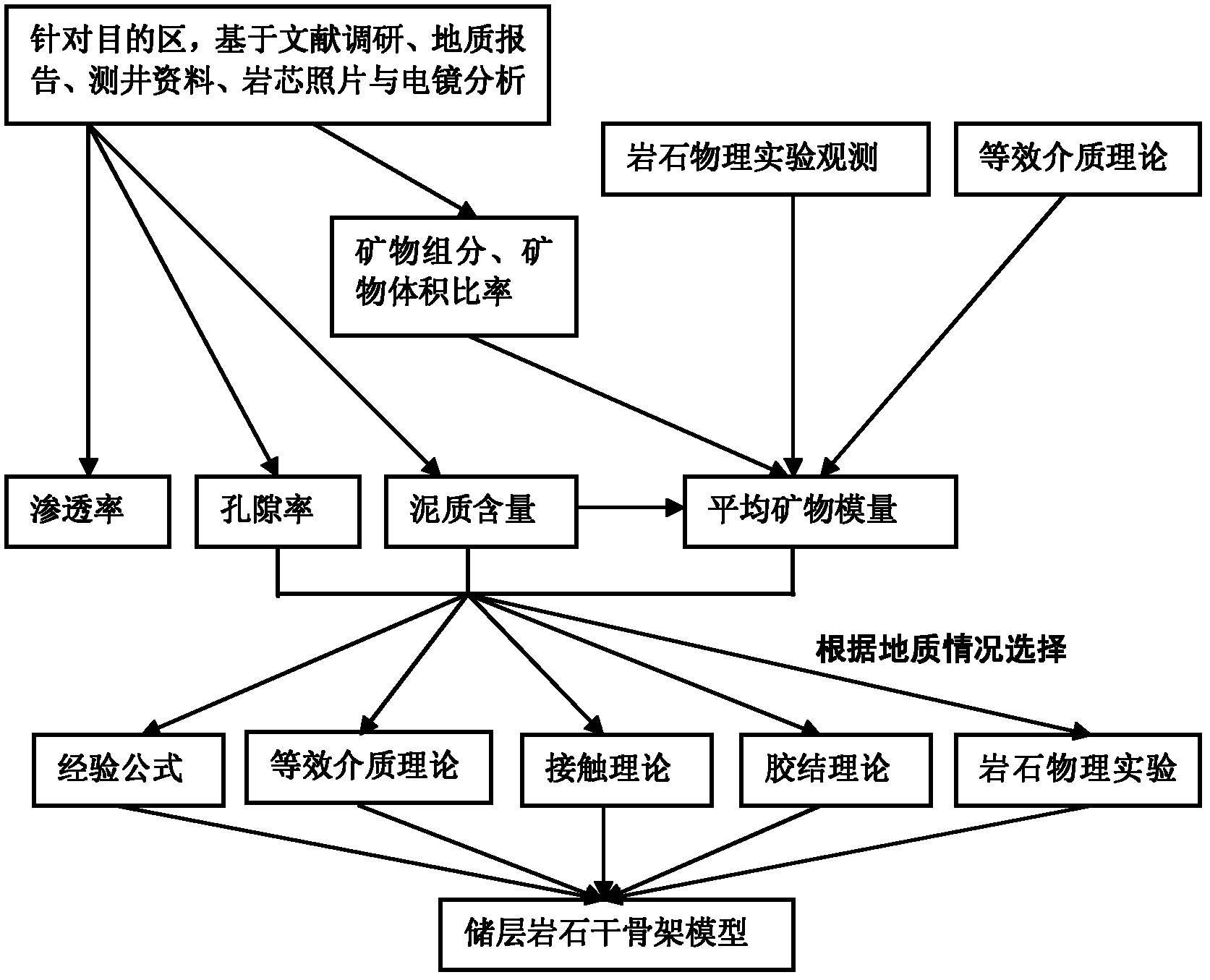
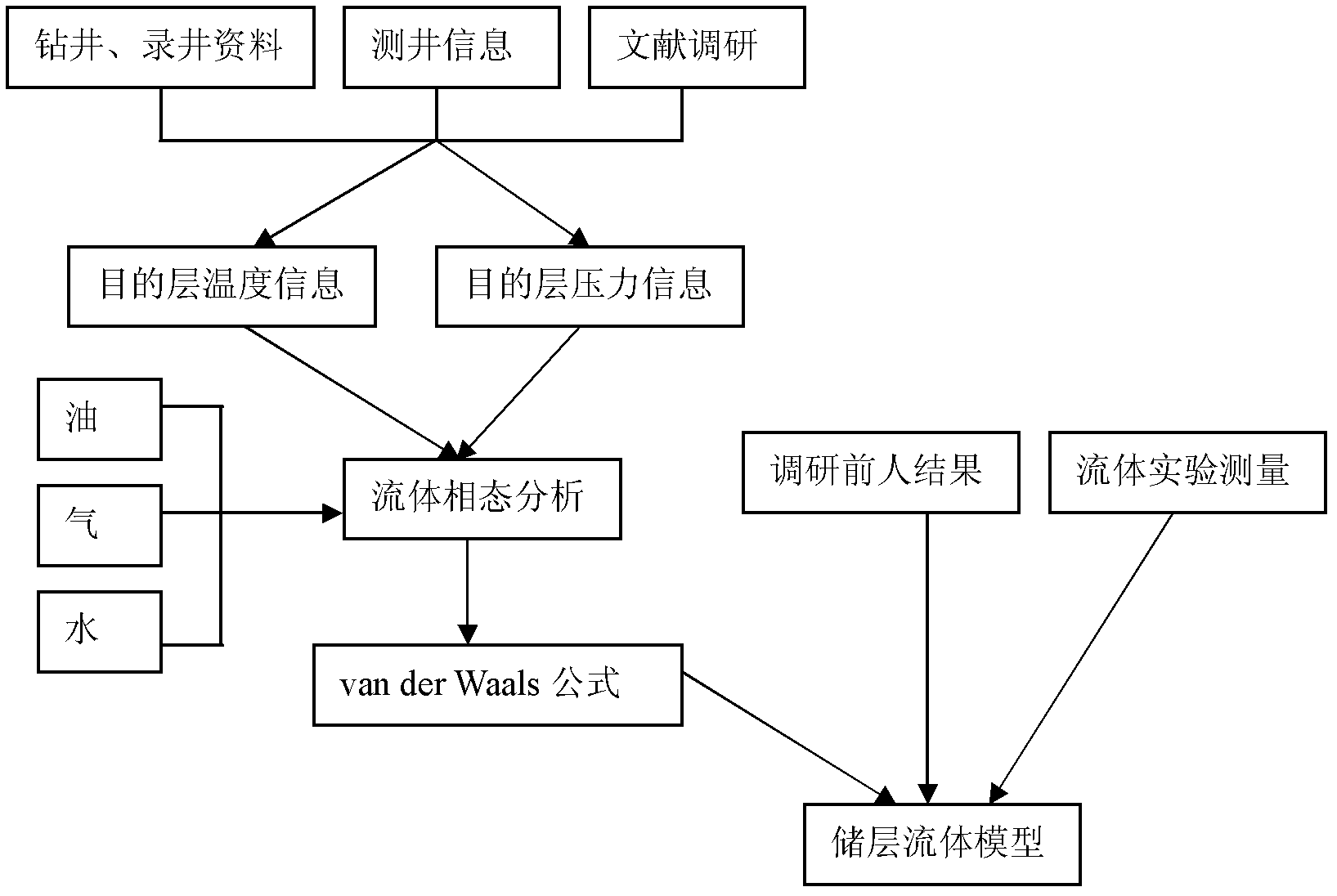
Method and device for analyzing dispersion and attenuation of unsaturated double-porosity medium earthquake waves
ActiveCN102508296AGood physical achievabilitySeismic signal processingSeismology for water-loggingPorositySeismic wave propagation
The invention discloses a method and a device for analyzing the dispersion and attenuation of unsaturated double-porosity medium earthquake waves. The method comprises the following steps of: 1, acquiring geological data including penetration rate, porosity, shale content and mineral components and generating a reservoir rock dry framework model according to the geological data; 2, acquiring measured data including drilling data, logging data, logging information and fluid experiment measured data and generating a reservoir fluid model according to the measured data and a Van derWaals equation; 3, solving plane waves according to the reservoir rock dry framework model, the reservoir fluid model and a Biot-Rayleigh equation for describing the spread of the unsaturated double-porosity medium earthquake waves, and generating phase speed and inverse quality factors of longitudinal waves and horizontal waves; and 4, generating relationships between frequency and each of speed, attenuation,wave impedance, AVO (Amplitude Versus Offset) response characteristic and the like according to the phase speed and inverse quality factors of the longitudinal waves and the horizontal waves.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Optical fiber communication equipment and its applied optical systems
InactiveUS7164865B2Optical efficiencyHigh densityWavelength-division multiplex systemsSemiconductor laser optical deviceLaser lightLasing wavelength
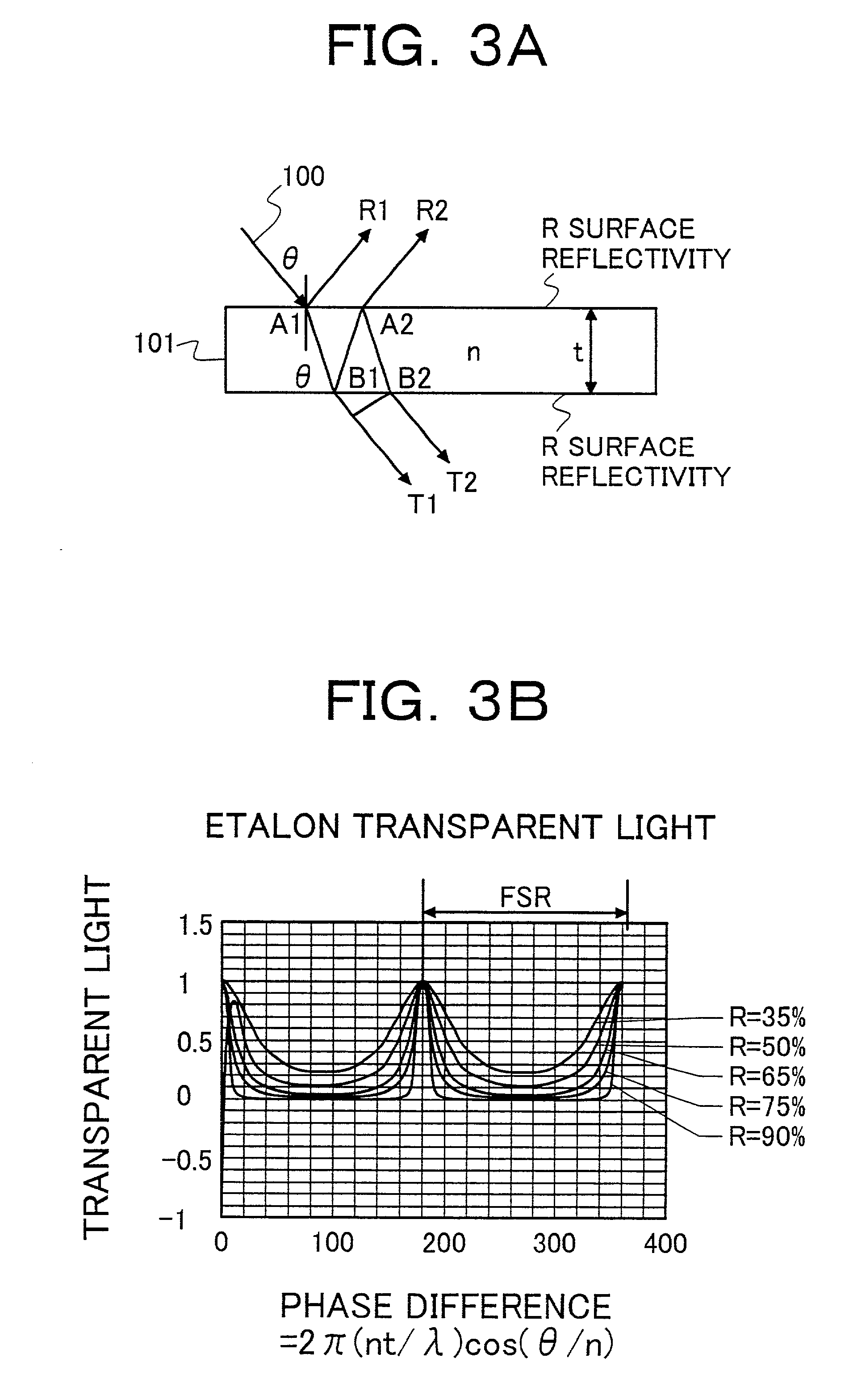
An object of disclosed technology is to control lasing wavelengths so that a wavelength shift does not occurs. Another object is to permit wavelengths of a light source for wavelength division multiplexing optical-fiber communication system to be variable in response to an ITU-TS grid. A means for achieving the objects is as follows: locating an etalon in a light path of diode laser light, which is a parallel plane wave changed by a collimator lens; generating a wavelength error signal from a difference between both of divided pieces of light from transmitted light or reflected light; and locking a wavelength of a diode laser device according to the wavelength error signal.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP +1
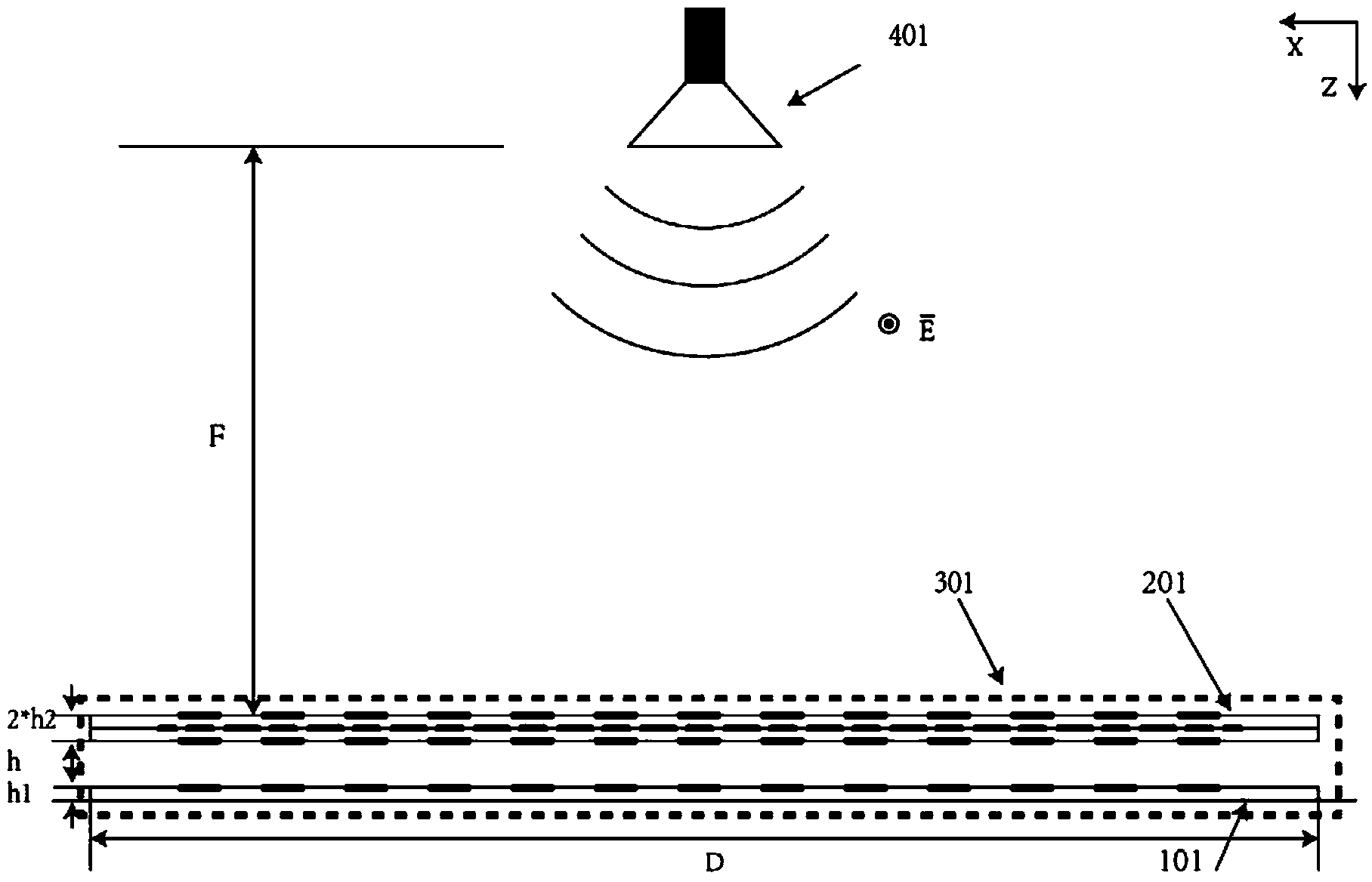
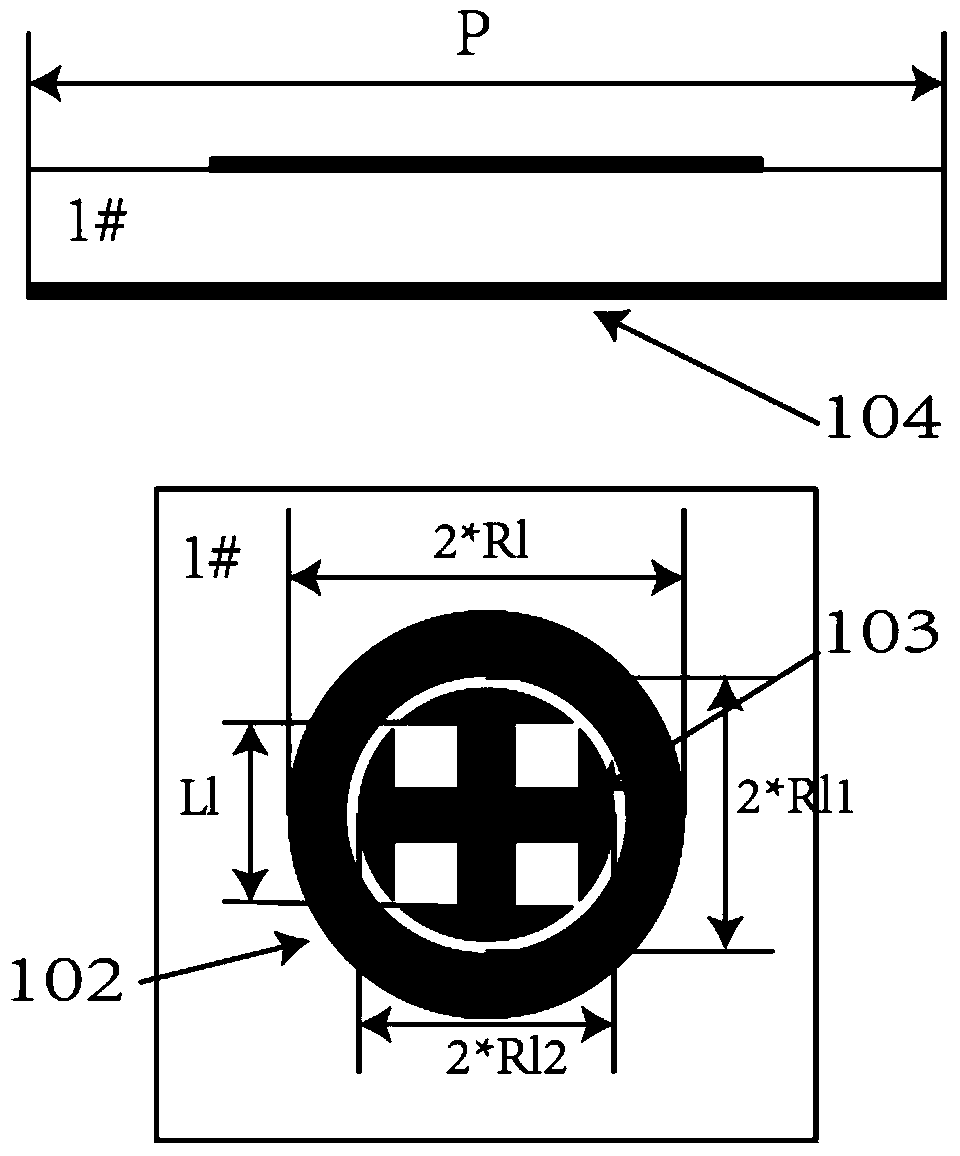
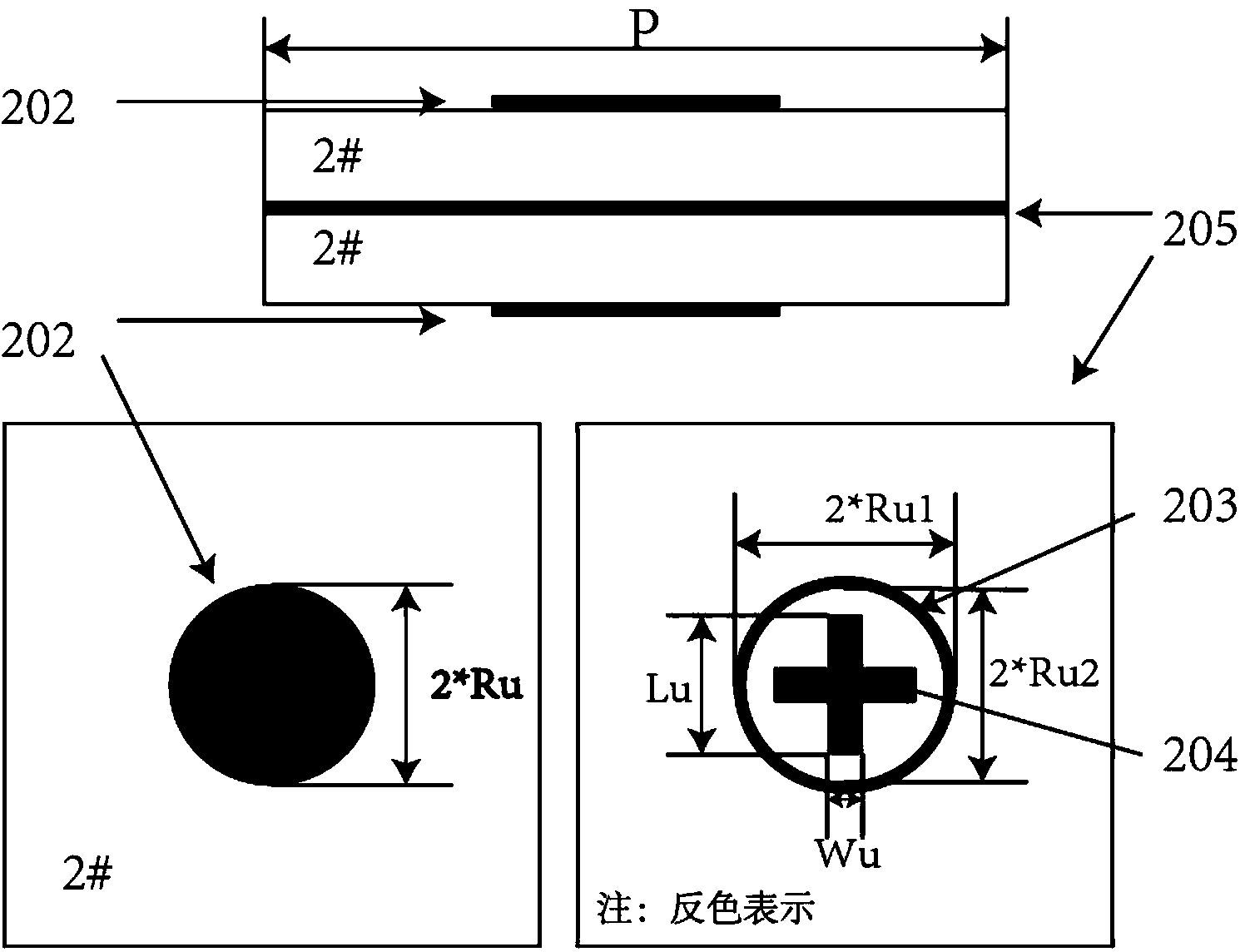
Reflection array antenna beam scanning antenna based on rotation phase shift surface technology
The invention provides a reflection array antenna beam scanning antenna based on a rotation phase shift surface technology. The reflection array antenna beam scanning antenna comprises a feed source antenna (401) and a reflection array panel (301); the reflection array panel (301) comprises a partial wave beam micro-strip reflection array layer (101) and a high transmittance phase shift surface layer (201); the partial wave beam micro-strip reflection array layer (101) is a micro-strip reflection array panel capable of achieving feed source wave beam deflection and the high transmittance phase shift surface layer (201) is a phase shift surface panel capable of achieving plane wave beam deflection. The partial wave beam micro-strip reflection array layer (101) and the high transmittance phase shift surface layer (201) are stacked through certain air space so that the reflection array panel (301) can be assembled. The positive feeding type is adopted by a feed source antenna (401). The central axis of the reflection array panel (301) serves as an axis and two layers are rotated respectively so that scanning of antenna beams can be achieved. The reflection array antenna beam scanning antenna based on the rotation phase shift surface technology is simple in structure, easy to manufacture, capable of responding to any polarized electromagnetic wave, suitable for sending and receiving the polarized electromagnetic waves and capable of bearing high power.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
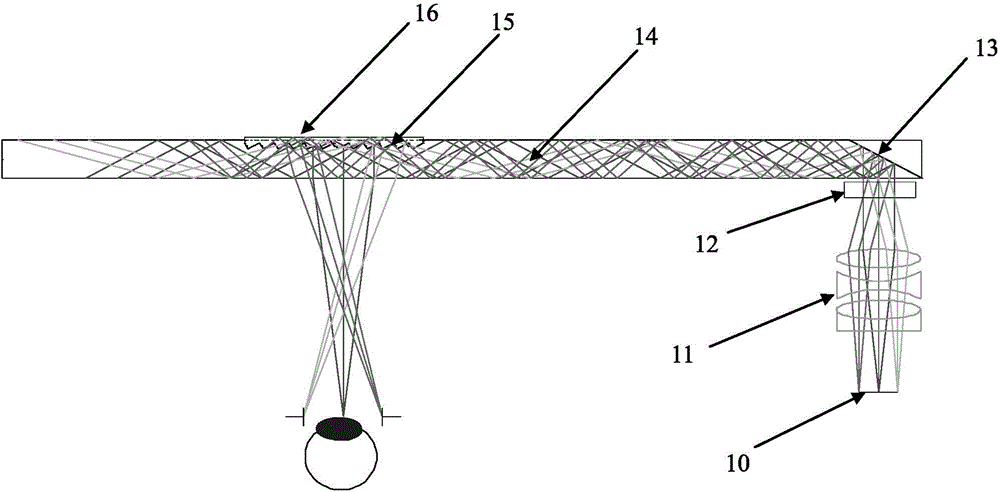
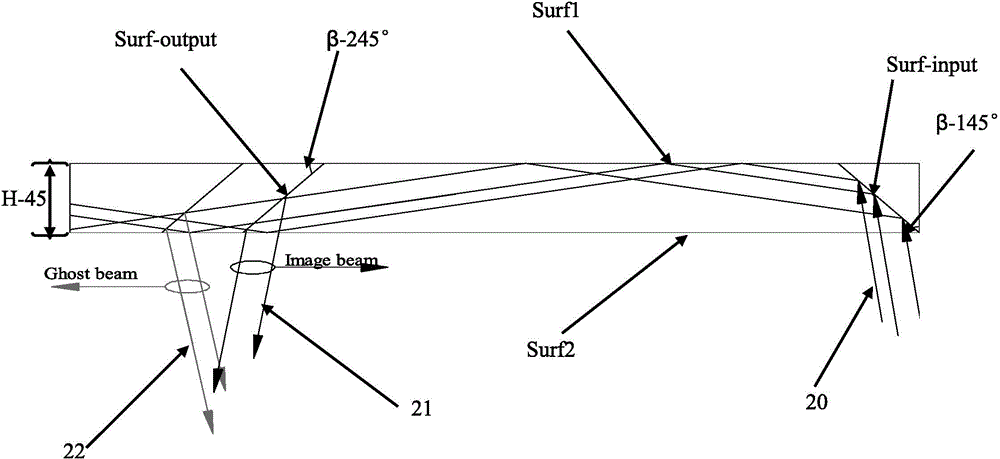
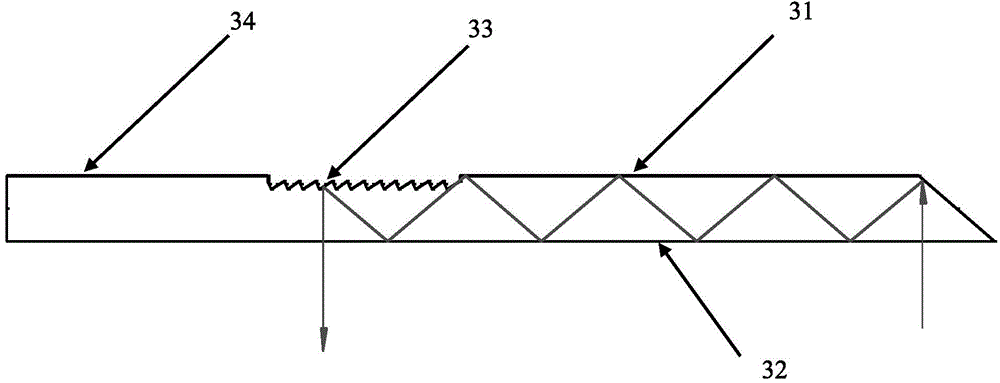
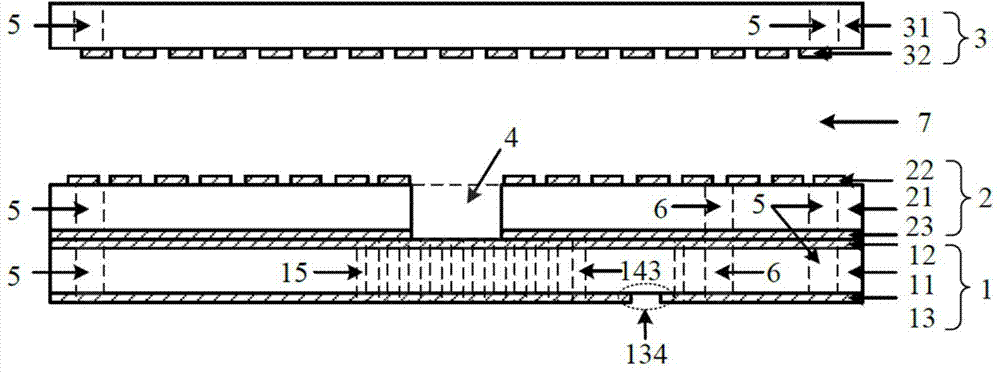
Saw tooth structure plane waveguide visual optical display device for enhancing reality
The invention provides a saw tooth structure plane waveguide visual optical display device for enhancing reality. The saw tooth structure plane waveguide visual optical display device for enhancing the reality comprises an image display light source, a collimating lens group, a lengthways expansion structure, a coupling reflection plane, a plane waveguide substrate, a saw tooth grove structure and a prism effect elimination cover piece, wherein the image display light source sends out needed display light waves, the collimating lens group collimates light source light waves, the lengthways expansion structure expands a view field in the vertical direction, the coupling reflection plane couples the light waves after being expanded into the plane waveguide substrate, the plane waveguide substrate transmits the light waves which are coupled into the plane waveguide substrate in total reflection mode, a saw tooth structure is used for view field expansion in the horizontal direction and coupling output of the light waves, and the cover piece is used to eliminate ghost shadows and improve definition of an image. The saw tooth structure plane waveguide visual optical display device for enhancing the reality has the advantages of easily expanding a horizontal view field and the vertical view field, and being light and thin in waveguide, compact in structure, simple in processing technology and low in cost, and not only can be worn for display, but also can be used in fields of scene training simulation, medical ear mirrors, naked eye 3D (three dimensional) display, mobile display and the like.
Owner:上海理湃光晶技术有限公司
Millimeter wave folding-type reflective array antenna integrated with plane feed source
ActiveCN103490156AAvoid lossReduce thicknessRadiating elements structural formsPolarised antenna unit combinationsCommunications systemMiniaturization
The invention discloses a millimeter wave folding-type reflective array antenna integrated with a plane feed source. The millimeter wave folding-type reflective array antenna is of a layered structure and is sequentially provided with a polarization grid, a reflective array and the plane feed source from top to bottom. On the basis of a plane substrate integration waveguide structure, a substrate integration waveguide gap array antenna is used as the feed source for conducting feed on folding-type reflection, phase compensation is obtained on a reflection face, spherical waves are converted to plane waves, and therefore the antenna which is high in gain and efficiency and stable in beam pointing is realized. Under the Q-LINKPAN application background and directing at the development demands of a plane-integration and miniaturized long-distance wireless communication system, the low-section antenna which is high in gain and efficiency and capable of being integrated with a plane millimeter wave circuit is realized, the millimeter wave folding-type reflective array antenna has the advantages of being simple in structure, compact in size and low in cost, and the requirements for plane circuit integration are met.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com