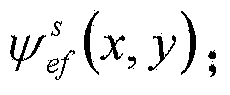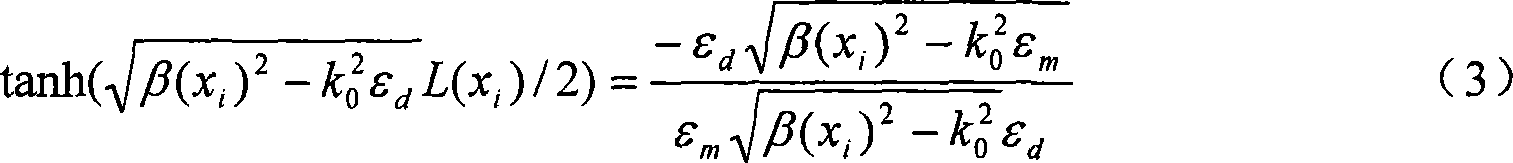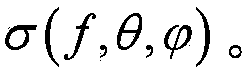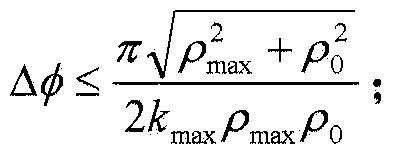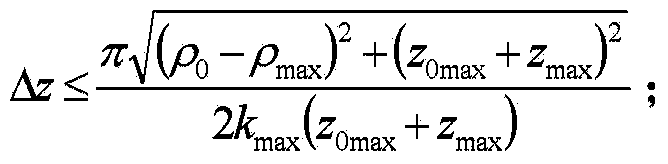Patents
Literature
85 results about "Near field imaging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
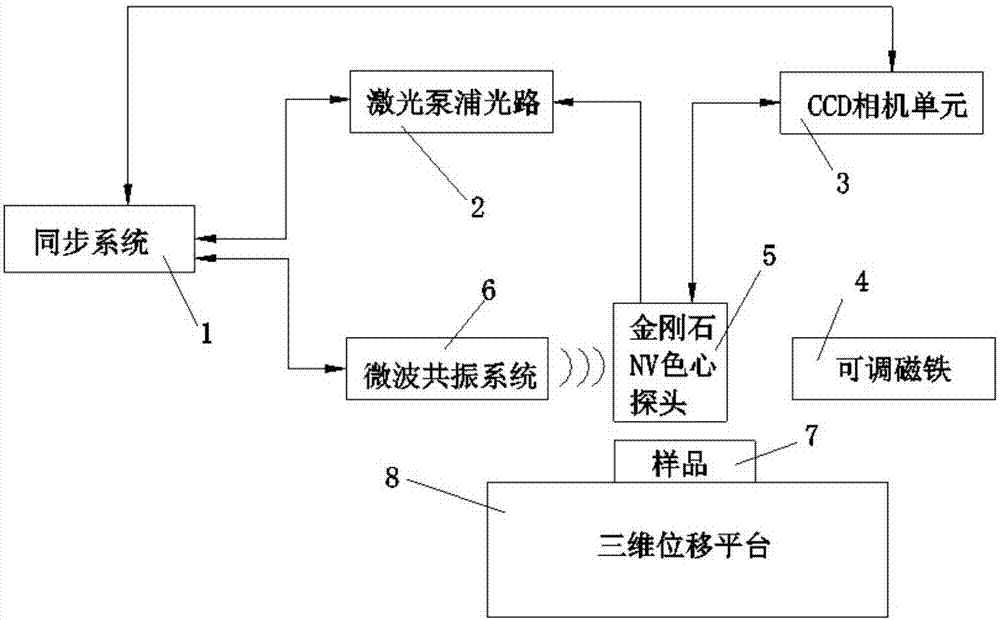
Electromagnetic field near-field imaging system and method based on pulsed light detection magnetic resonance
InactiveCN107356820ASimple structureLow costAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceElectromagentic field characteristicsHigh resolution imagingSingle crystal
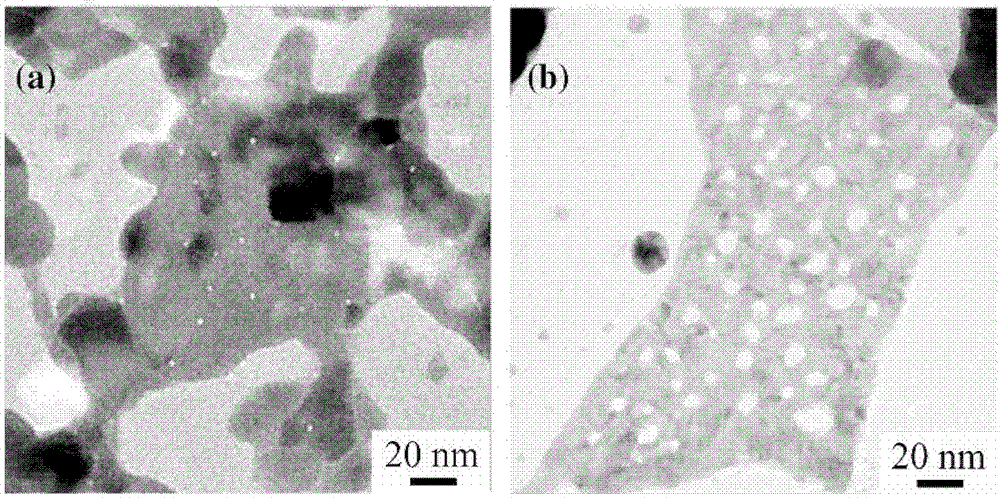
The invention discloses an electromagnetic field near-field imaging system and method based on pulsed light detection magnetic resonance. The system consists of a laser pump optical path, a microwave source, a diamond NV color-center probe, a CCD camera unit, a synchronization system, a displacement scanning platform, control software and a data analysis imaging system. In the system, a large diamond single crystal containing the NV color-center is used as a detection unit, a static magnetic field is used to split a magnetic resonance peak of the diamond NV color-center into eight peaks, the eight resonance peaks correspond to four crystal axis directions <111>, <1-11>, <-111>, <11-1> of a diamond lattice structure, by measuring the Rabi frequency of each resonance peak, the strength of a circularly polarized microwave field perpendicular to the corresponding crystal axis direction is obtained, and through comprehensive calculation of the microwave field strengths in the four directions, the strength and direction of a microwave vector are then reconstructed. Through the microwave near-field high-resolution imaging of a local region of a microwave chip under measurement, the quantitative data can be provided for the failure analysis of the chip.
Owner:南京昆腾科技有限公司
Method and device for near-field dual-wave modality imaging
InactiveUS20110040176A1Organ movement/changes detectionMaterial analysis by optical meansDiagnostic Radiology ModalityAcoustics
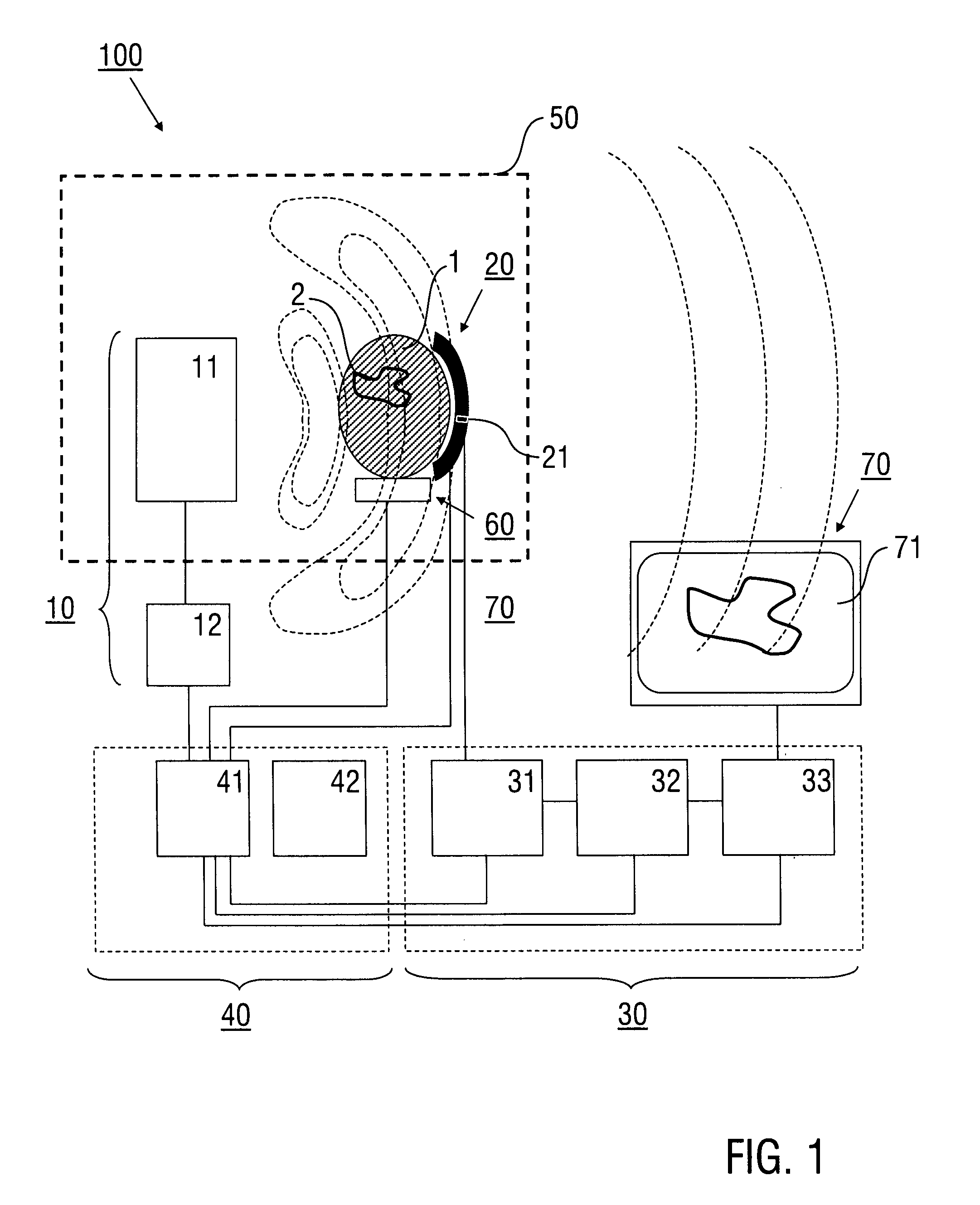
A method of near-field imaging of a region of interest includes emitting an input of near-field electromagnetic radiofrequency energy from a near-field source device into the region of interest, detecting a mechanical wave response generated in the region of interest in response to the near-field electromagnetic energy input using a detector device, and providing image data representing an image of the region of interest based on the mechanical wave response.
Owner:HELMHOLTZ ZENT MUNCHEN DEUTES FORSCHUNGSZENT FUR GESUNDHEIT & UMWELT
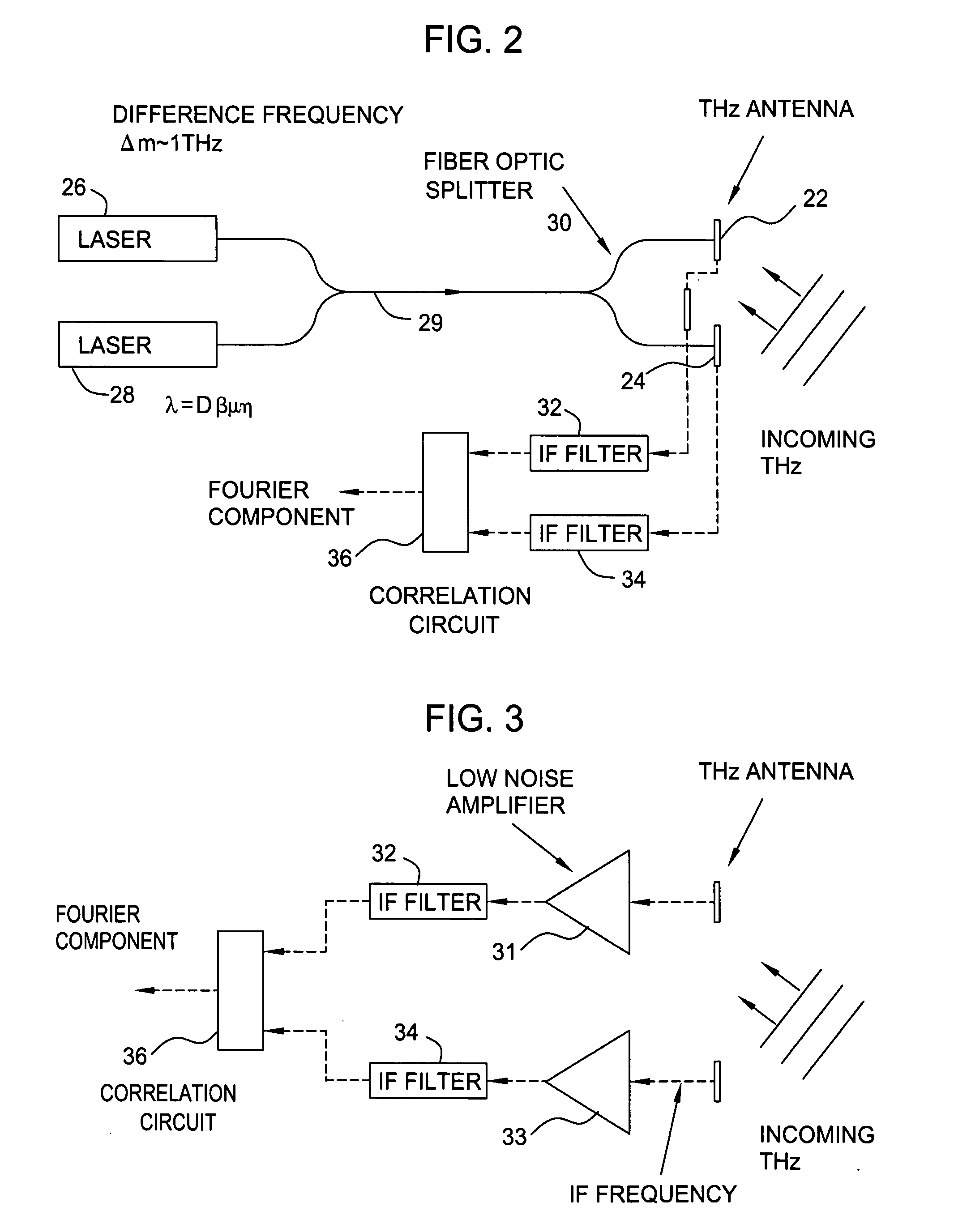
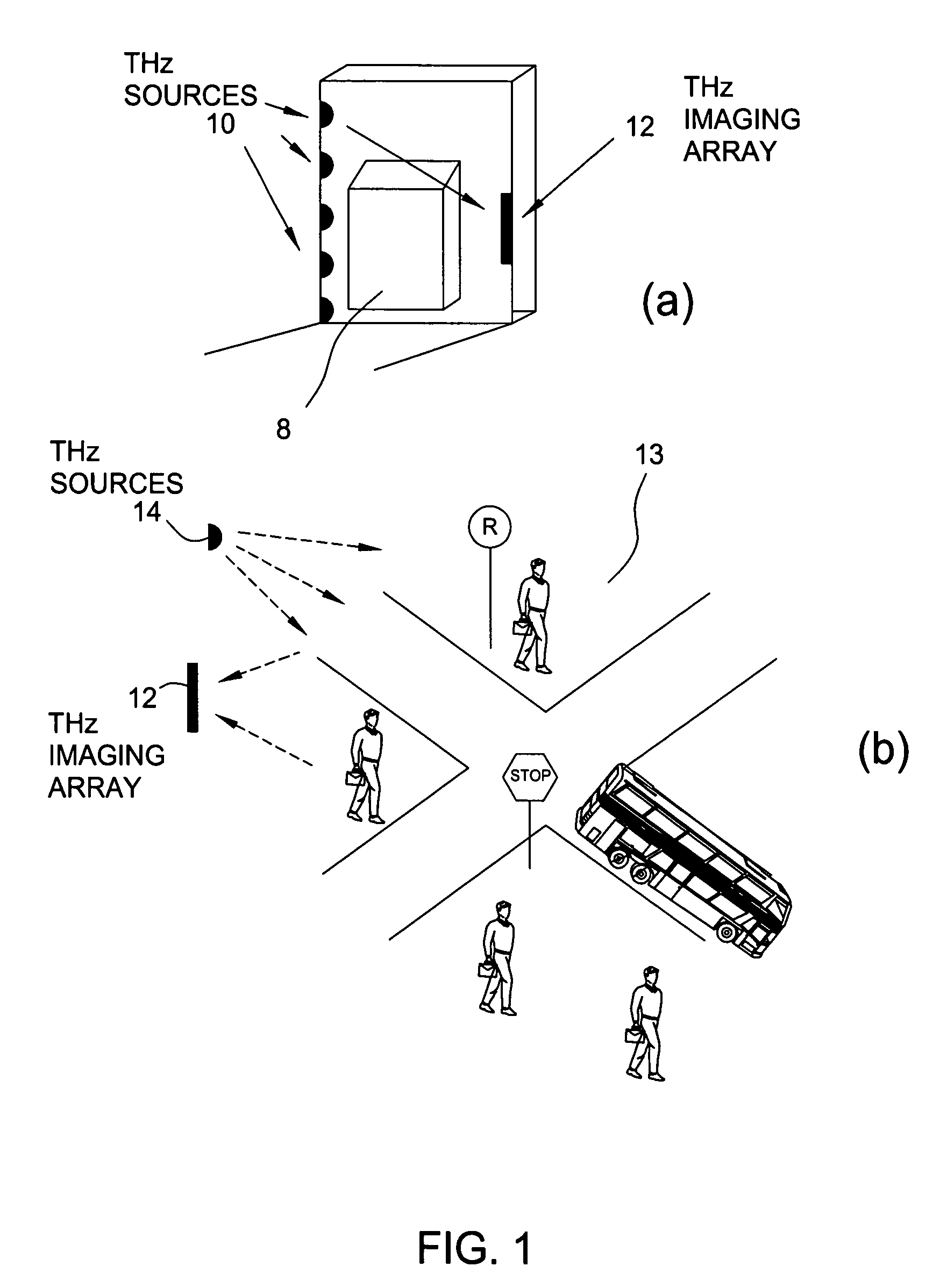
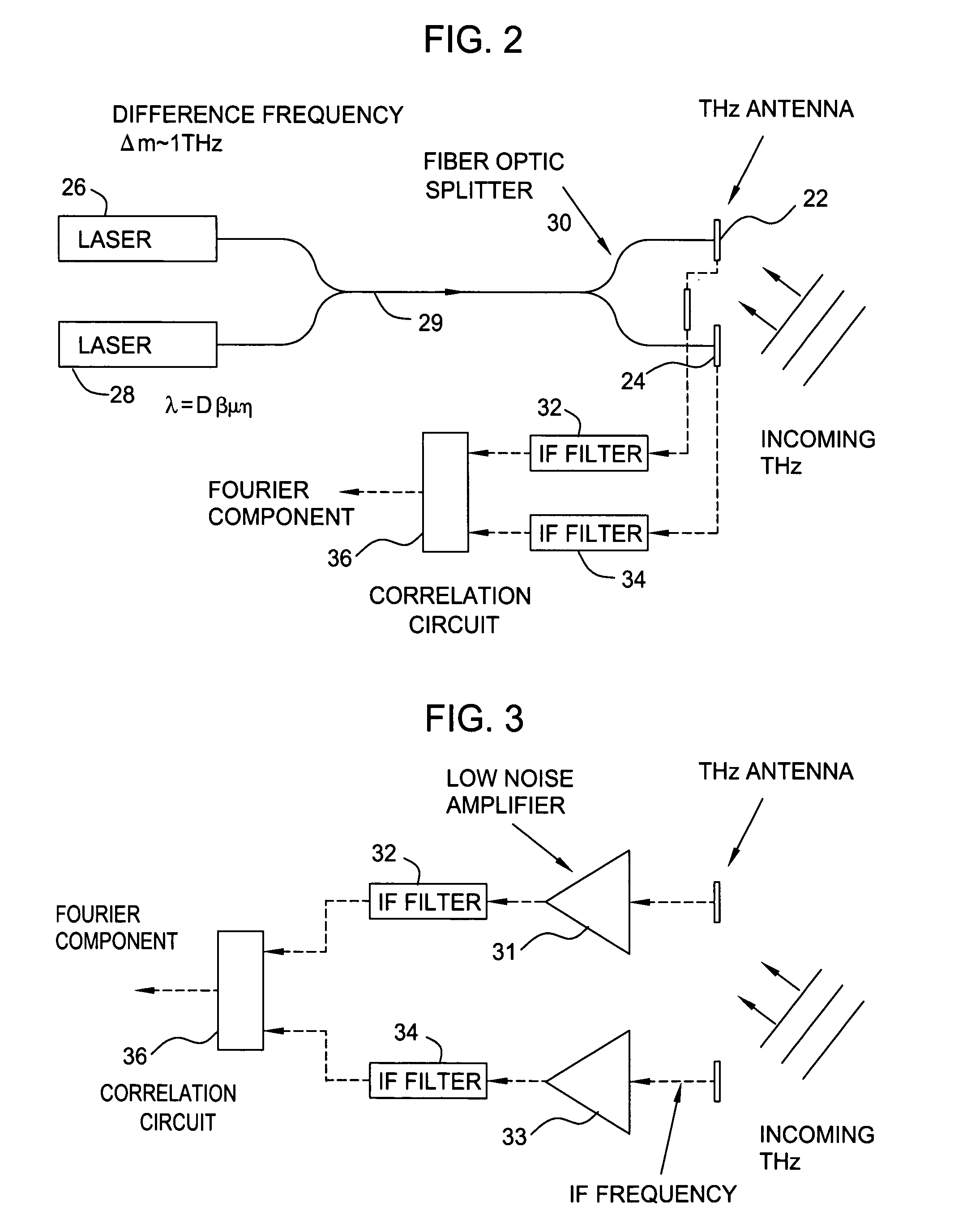
Terahertz imaging for near field objects
ActiveUS20060054824A1Distortion problemEffective regulationRadiation pyrometryAbsorption/flicker/reflection spectroscopyInterferometric imagingDetector array
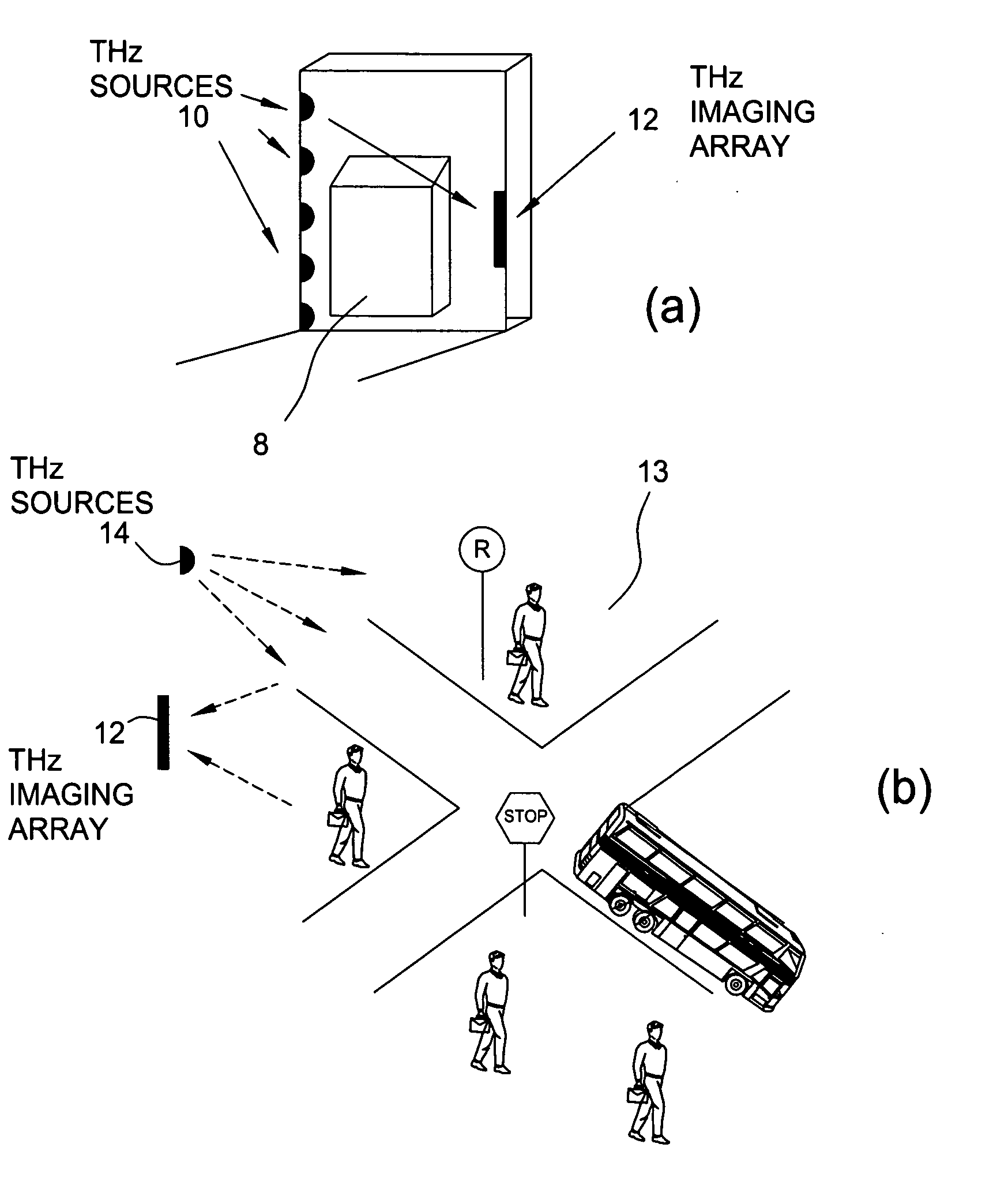
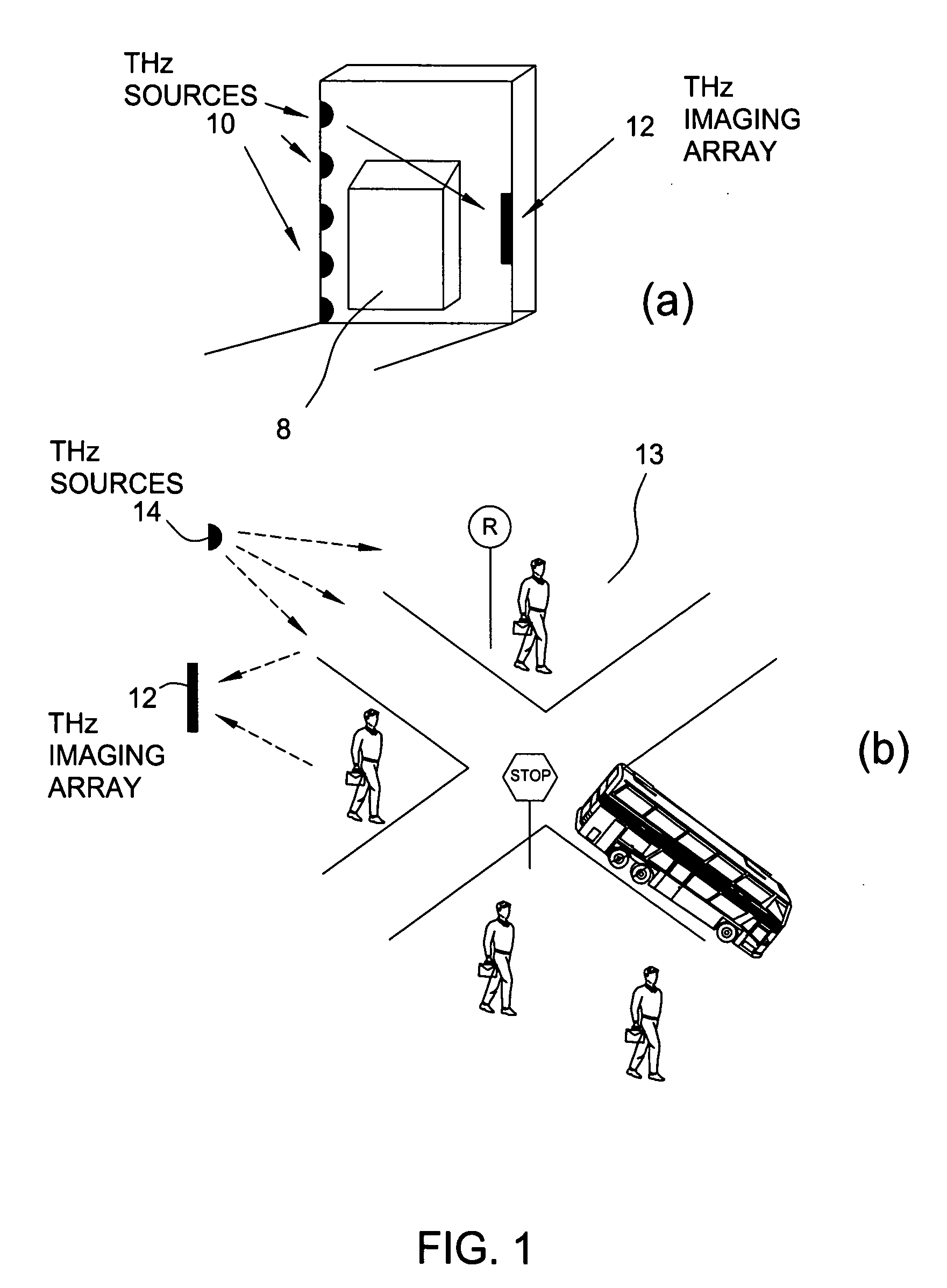
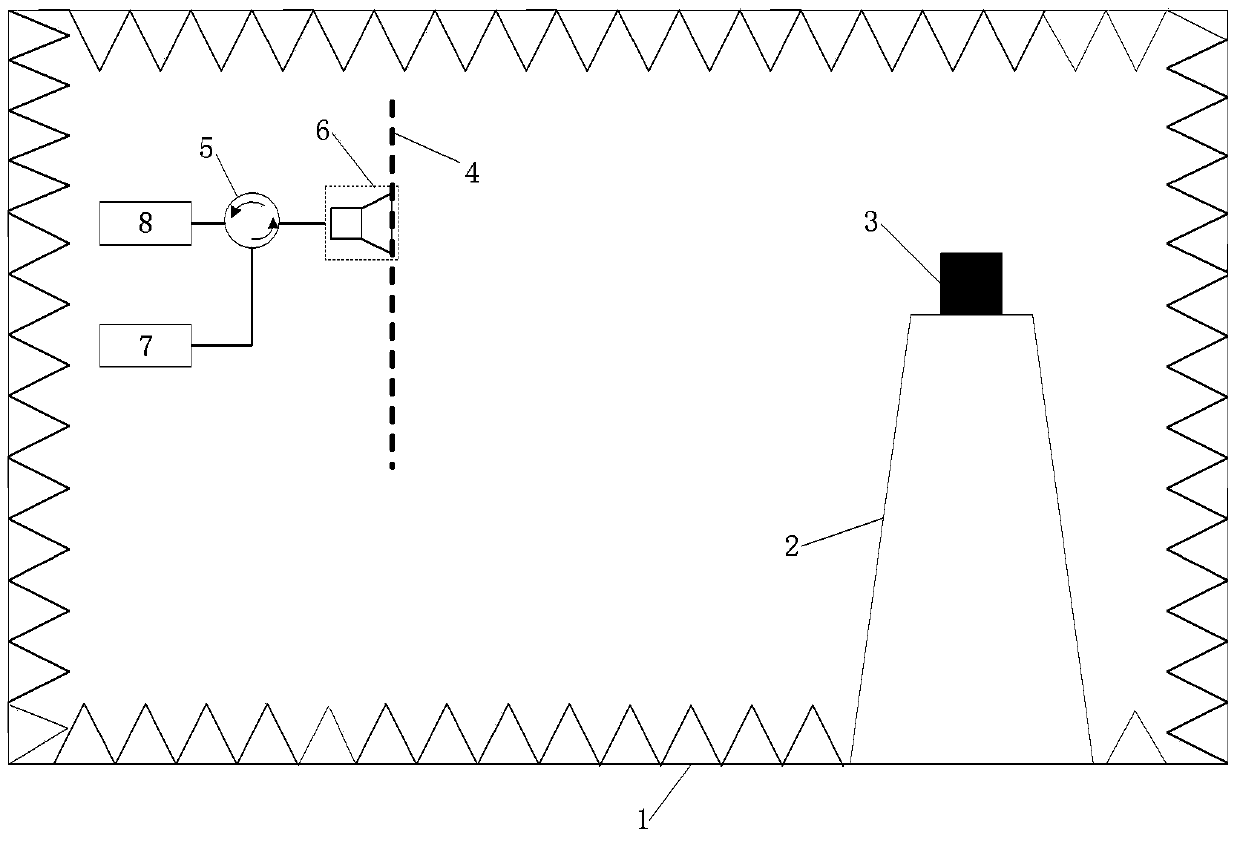
Near field imaging using a THz imaging system is realized by utilizing an interferometric imaging detector array that includes detector elements disposed on a surface curved, physically or artificially, to match substantially the curvature of the wave front for received THz signals. Generally, the near field is an environment wherein the distance to an object of interest is on the order of 10-100 times larger than the physical size of the THz imaging array. Typical distances from the object or target to the imaging array is anticipated to be in the 0.5 m-50 m range. Curvature of the detector array corrects a distortion problem in prior THz imaging systems that utilized planar interferometric imaging arrays based on a planar wave front assumption for received THz signals.
Owner:NEW JERSEY INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
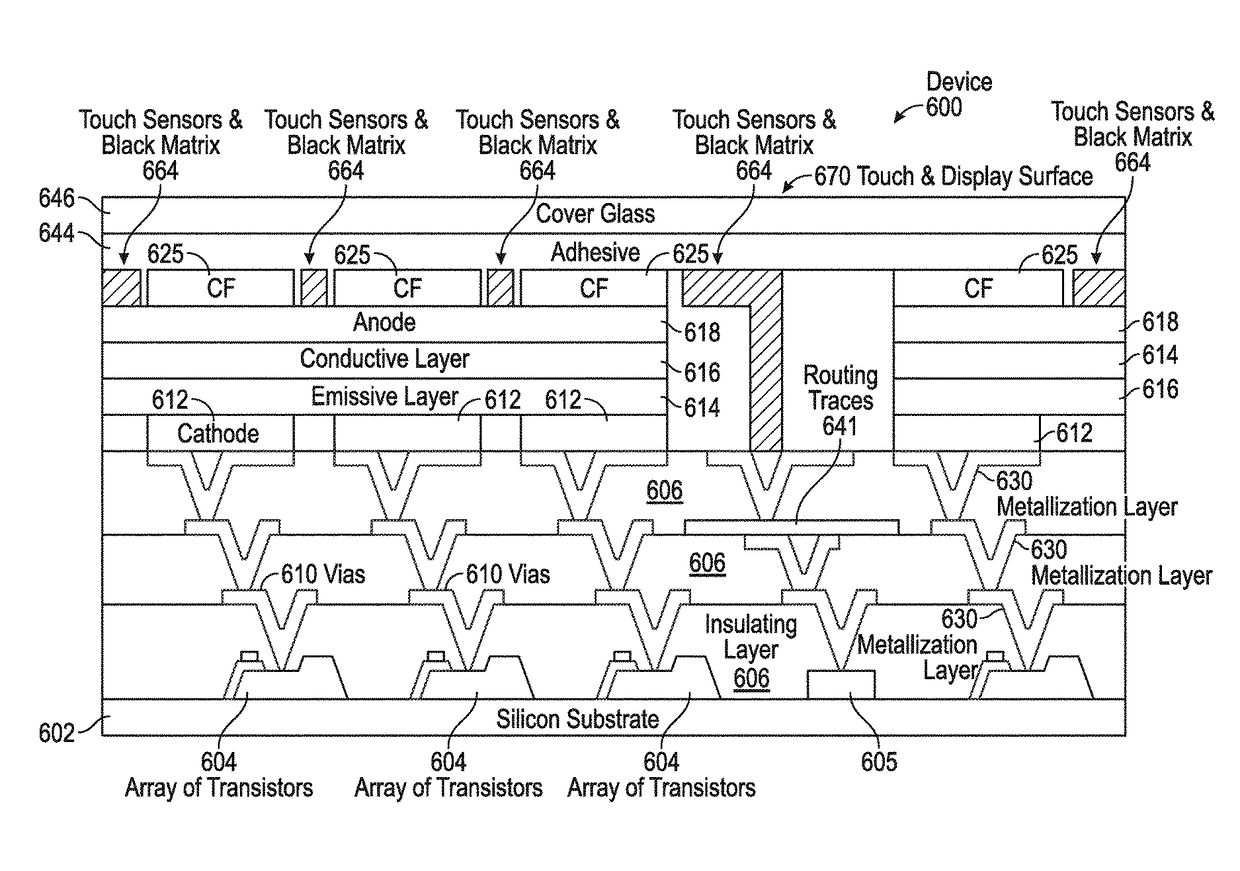
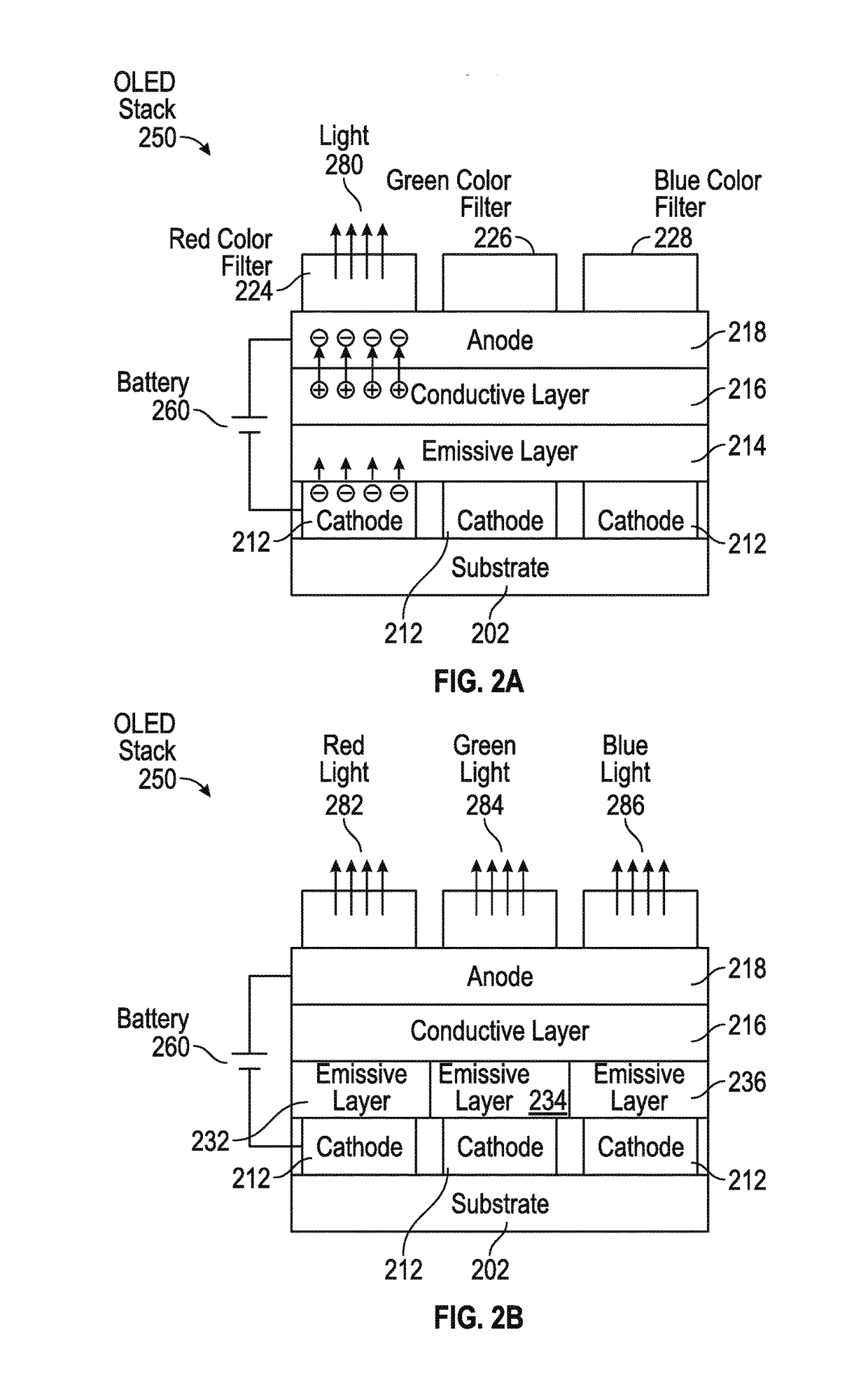
Integrated silicon-OLED display and touch sensor panel
ActiveUS9836165B2Wide viewing angleIncrease contrastSolid-state devicesPrint image acquisitionTransistor arrayGranularity
An integrated Silicon-OLED display and touch sensor panel is disclosed. The integrated Silicon-OLED display and touch sensor panel can include a Silicon substrate, an array of transistors, one or more metallization layers, one or more vias, an OLED stack, color filters, touch sensors, and additional components and circuitry. Additional components and circuitry can include an electrostatic discharge device, a light shielding, a switching matrix, one or more photodiodes, a near-infrared detector and near-infrared color filters. The integrated Silicon-OLED display and touch sensor panel can be further configured for near-field imaging, optically-assisted touch, and fingerprint detection. In some examples, a plurality of touch sensors and / or display pixels can be grouped into clusters, and the clusters can be coupled to a switching matrix for dynamic change of touch and / or display granularity.
Owner:APPLE INC
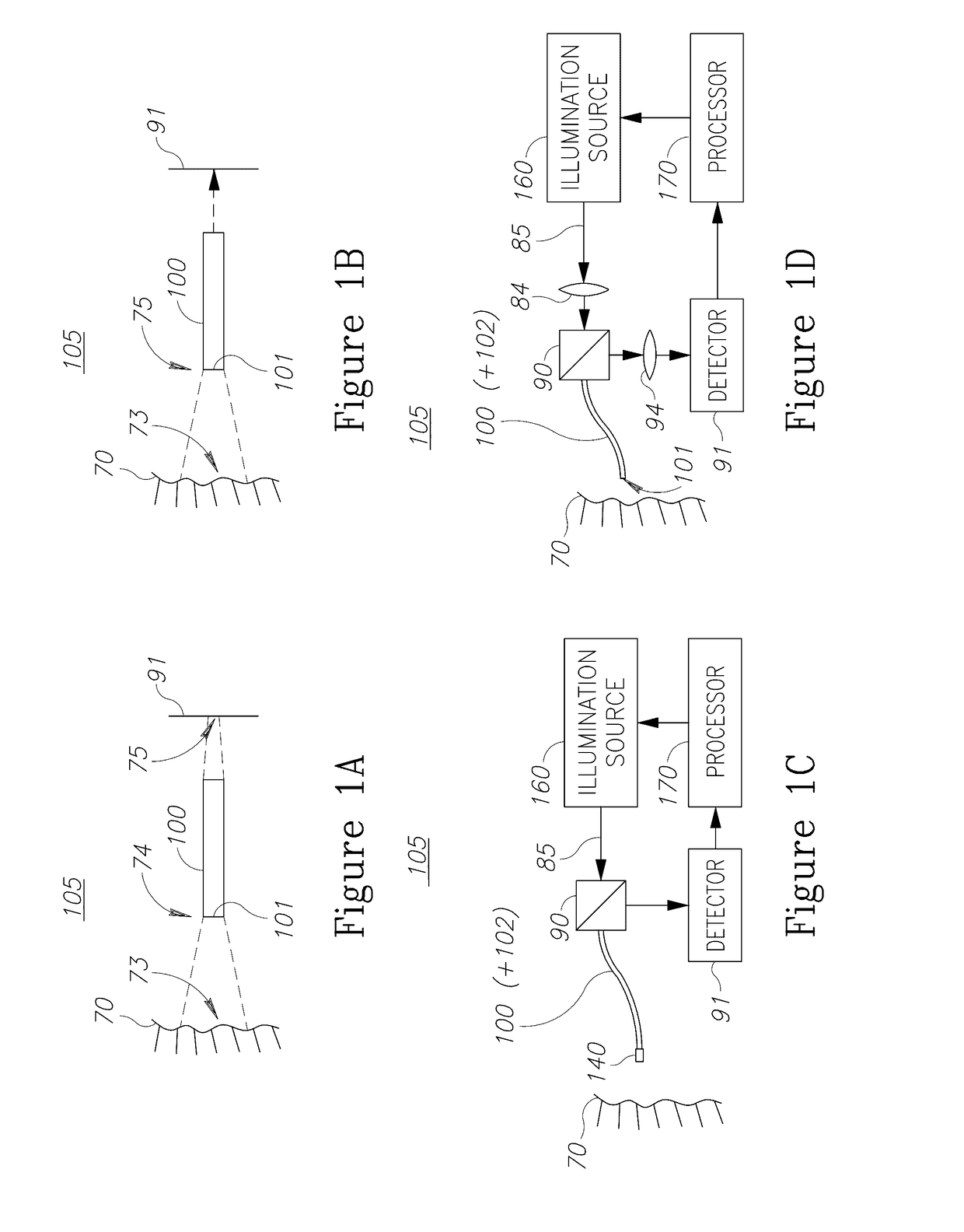
Multicore fiber endoscopes
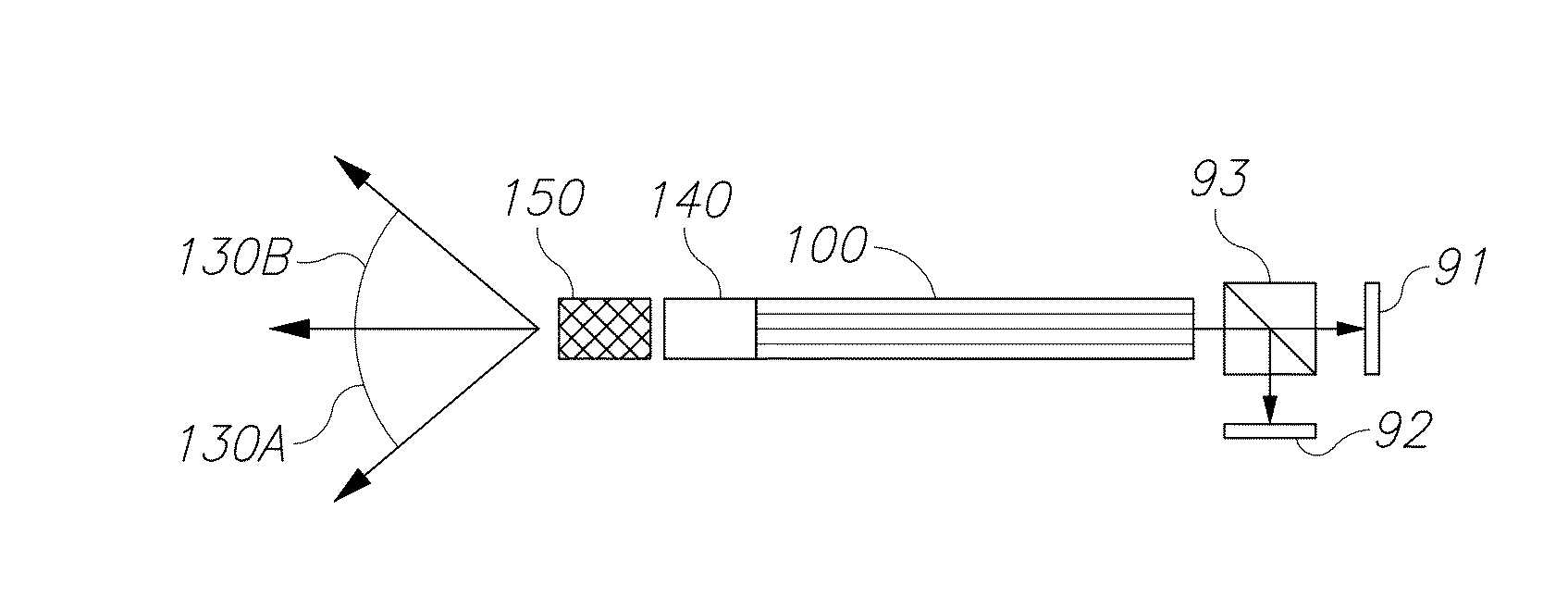
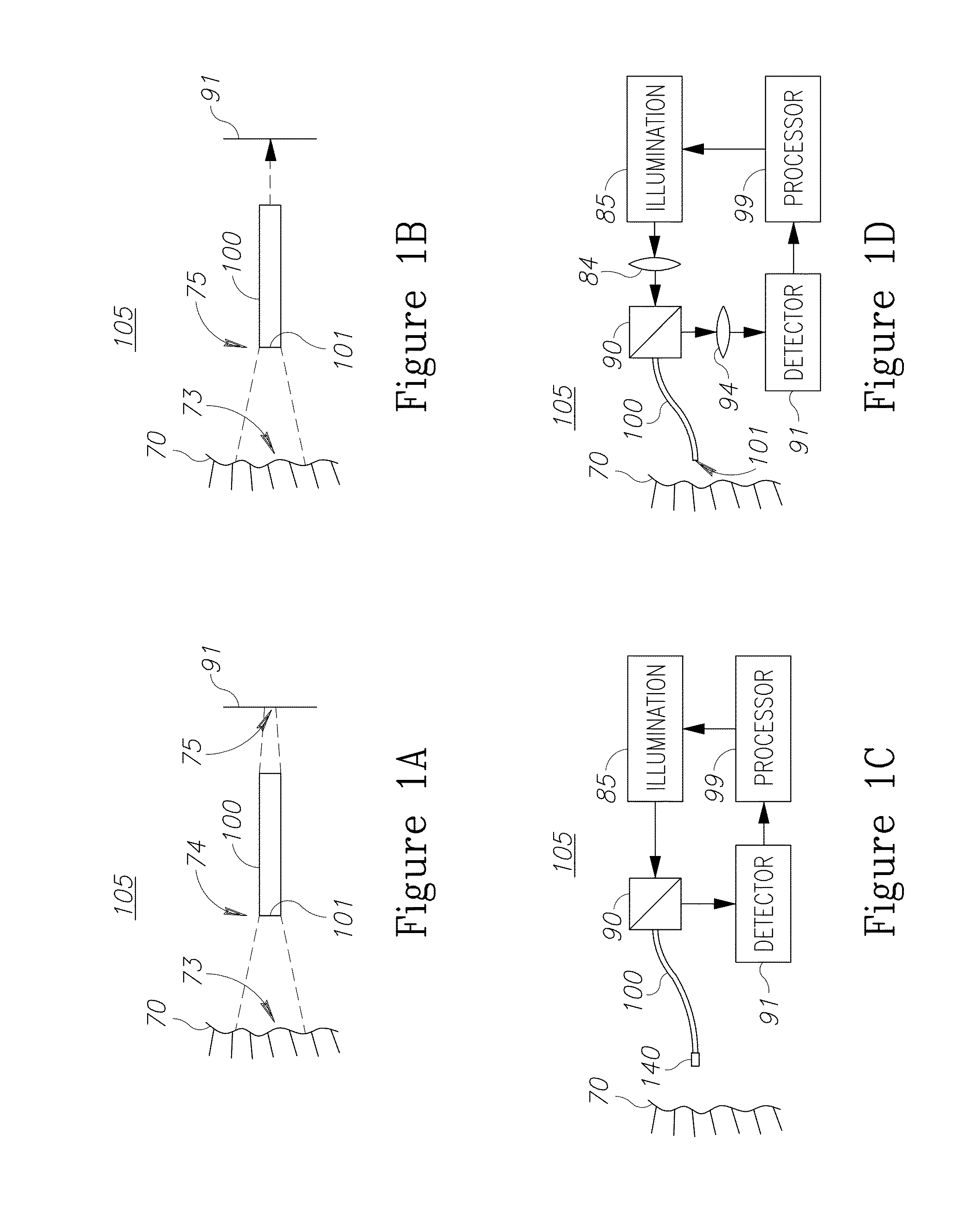
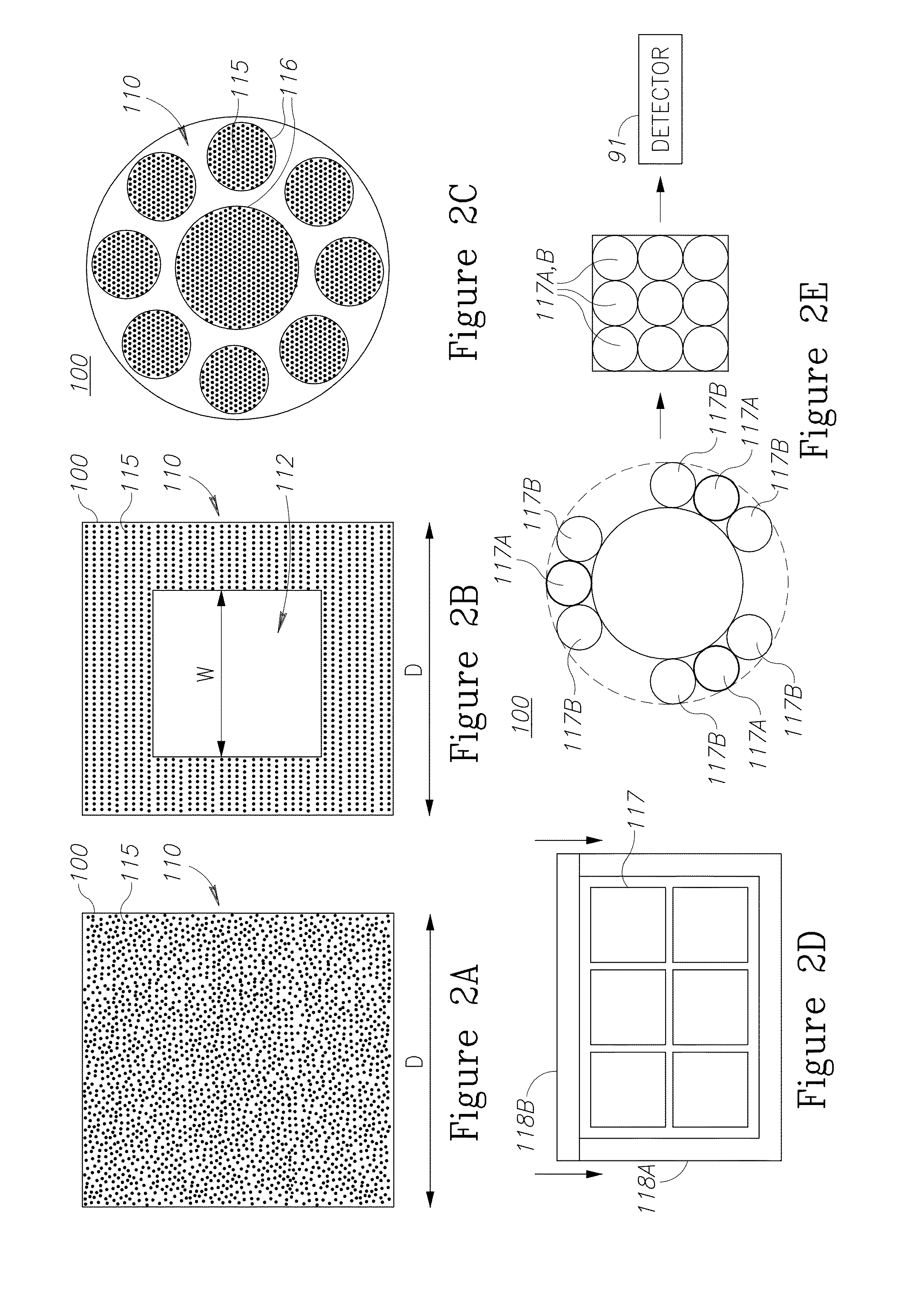
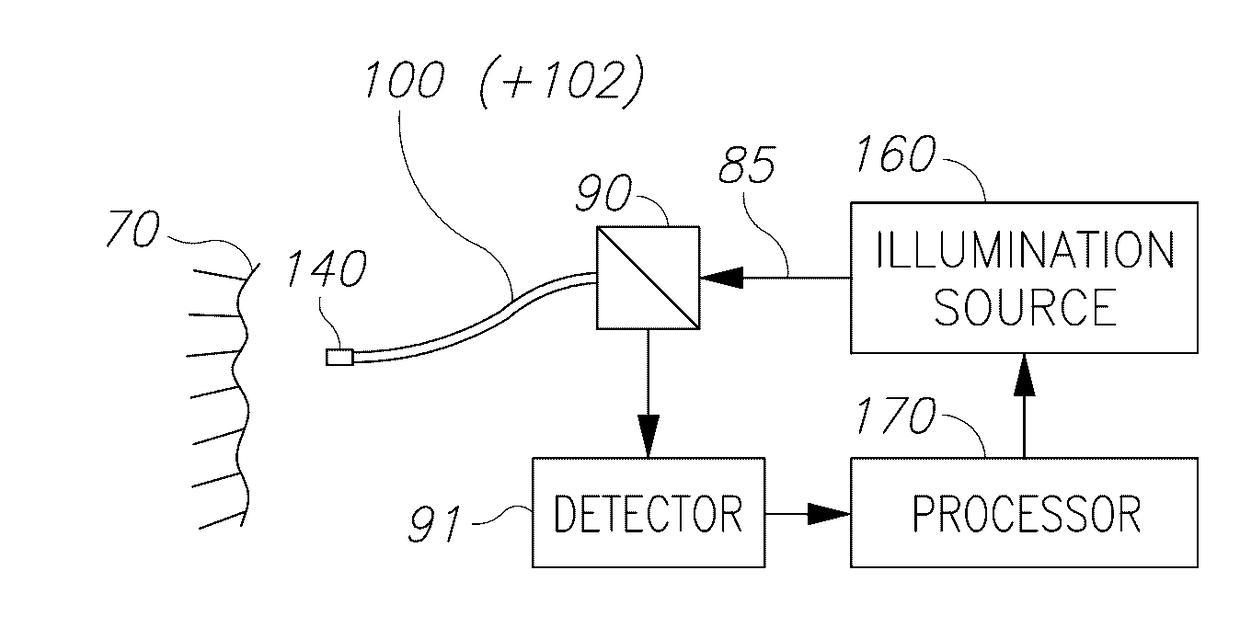
Endoscopes, multicore endoscope fibers and configuration and operation methods are provided. The fibers may have hundreds or thousands of cores and possibly incorporate working channel(s) and additional fibers. The fiber may be used at different optical configurations to capture images of tissue and objects at the distal tip and to enhance a wide range of optical characteristics of the images such as resolution, field of view, depth of field, wavelength ranges etc. Near-field imaging as well as far-field imaging may be implemented in the endoscopes and the respective optical features may be utilized to optimize imaging. Optical elements may be used at the distal fiber tip, or the distal fiber tip may be lens-less. Diagnostics and optical treatment feedback loops may be implemented and illumination may be adapted to yield full color images, depth estimation, enhanced field of views and / or depths of field, and additional diagnostic data.
Owner:Z SQUARE LTD
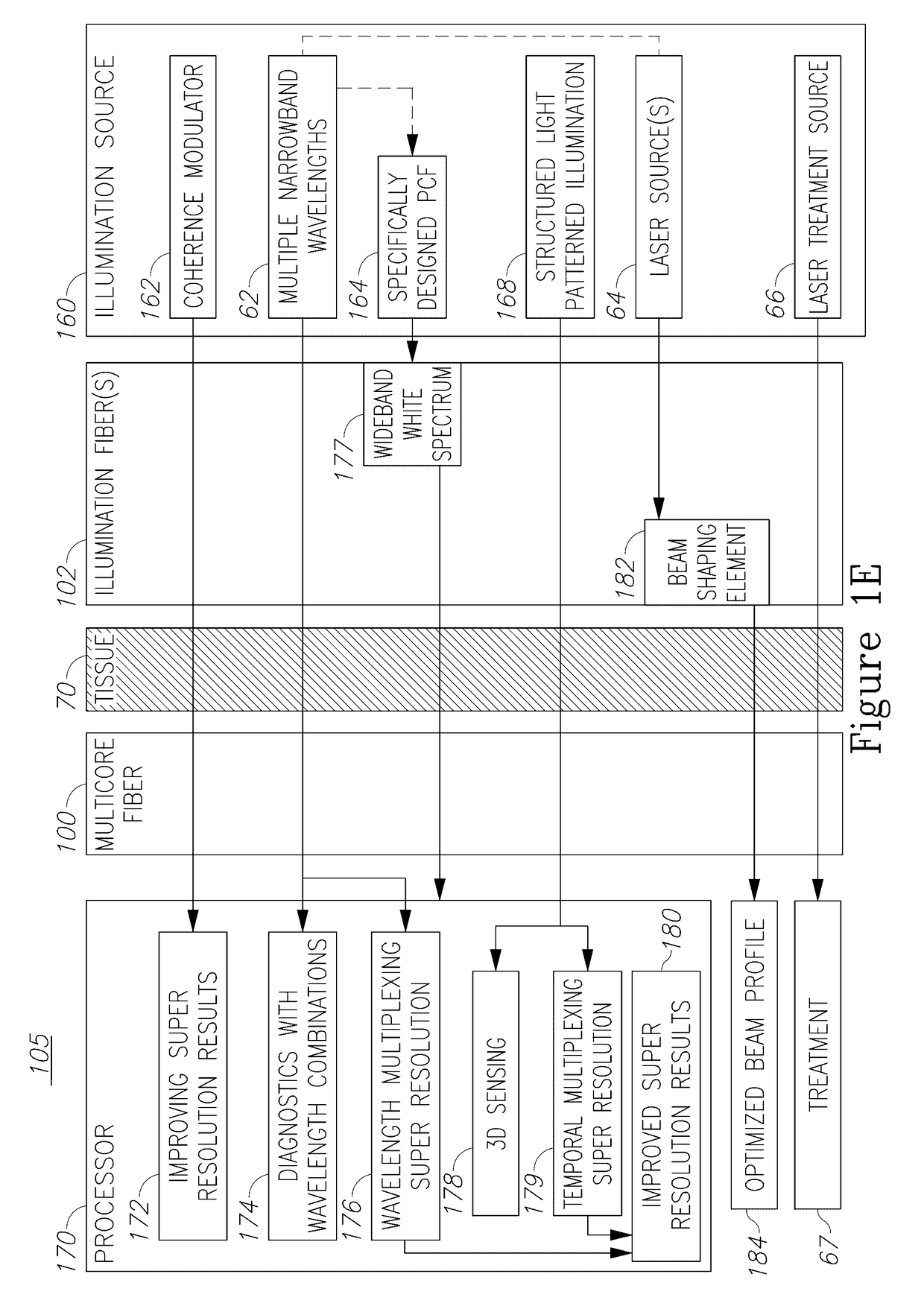
Illumination sources for multicore fiber endoscopes
Endoscopes, multicore endoscope fibers and configuration and operation methods are provided. The fibers may have hundreds or thousands of cores and possibly incorporate working channel(s) and additional fibers. The fiber may be used at different optical configurations to capture images of tissue and objects at the distal tip and to enhance a wide range of optical characteristics of the images such as resolution, field of view, depth of field, wavelength ranges etc. Near-field imaging as well as far-field imaging may be implemented in the endoscopes and the respective optical features may be utilized to optimize imaging. Optical elements may be used at the distal fiber tip, or the distal fiber tip may be lens-less. Diagnostics and optical treatment feedback loops may be implemented and illumination may be adapted to yield full color images, depth estimation, enhanced field of views and / or depths of field, and additional diagnostic data.
Owner:Z SQUARE LTD
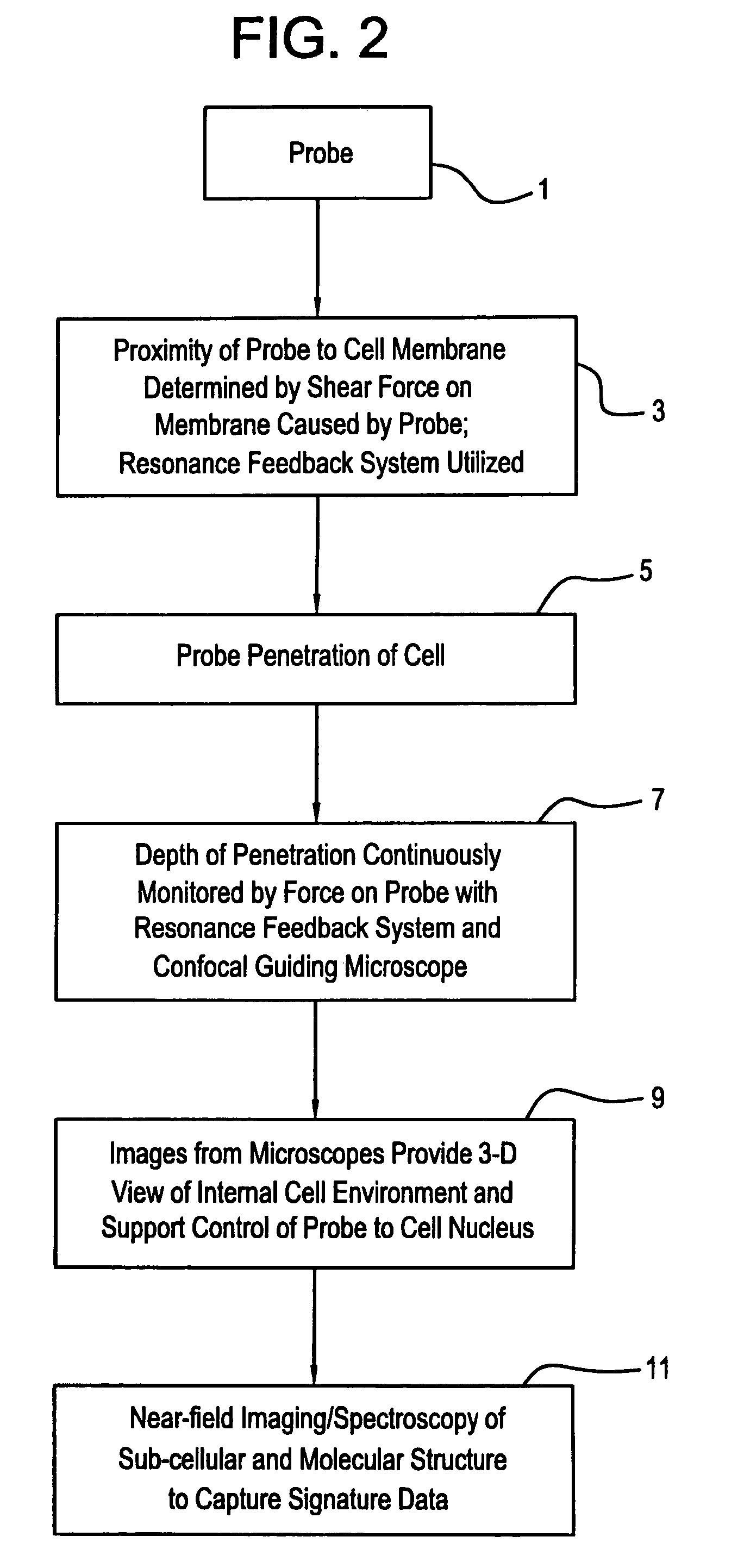
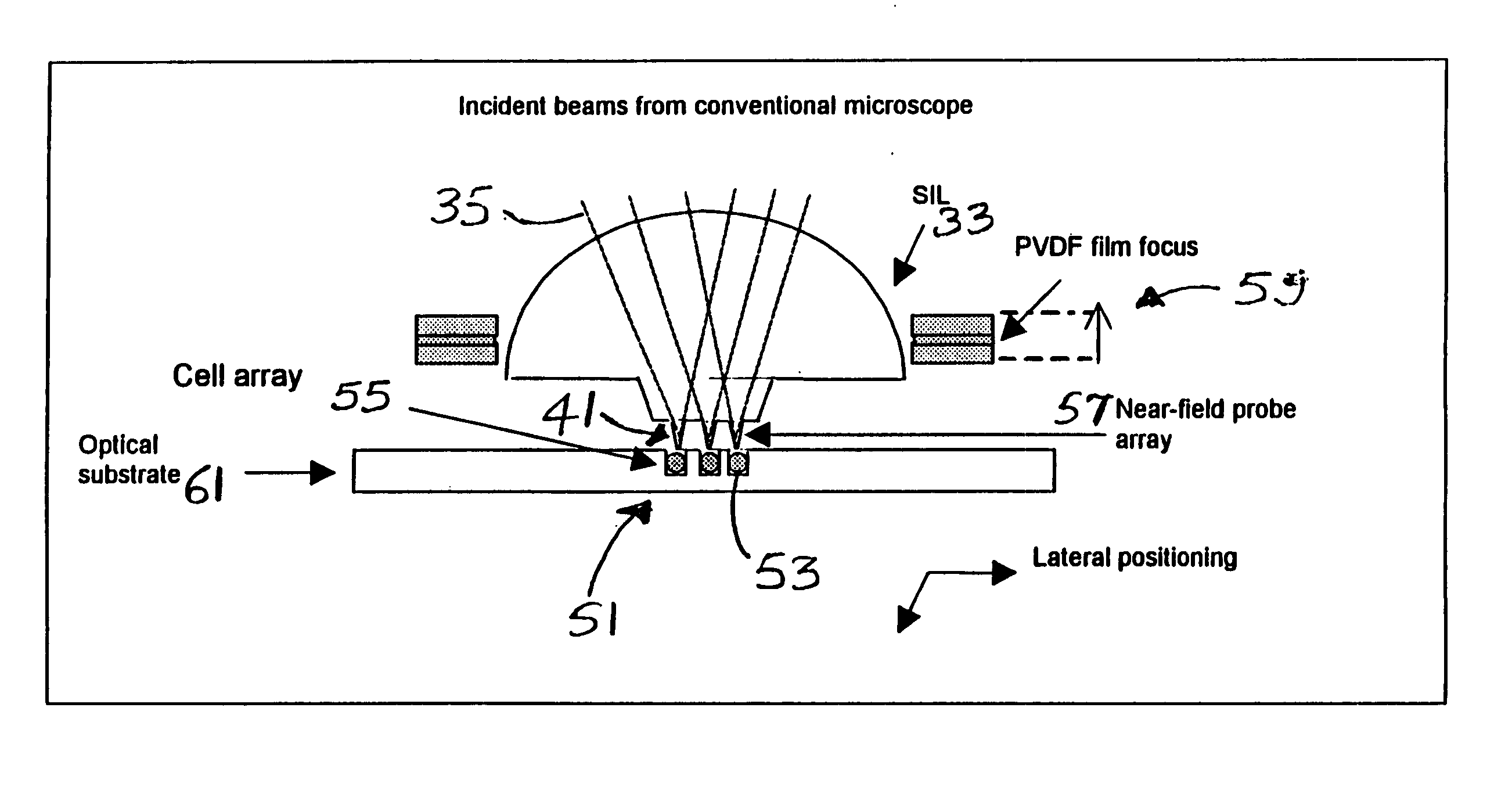
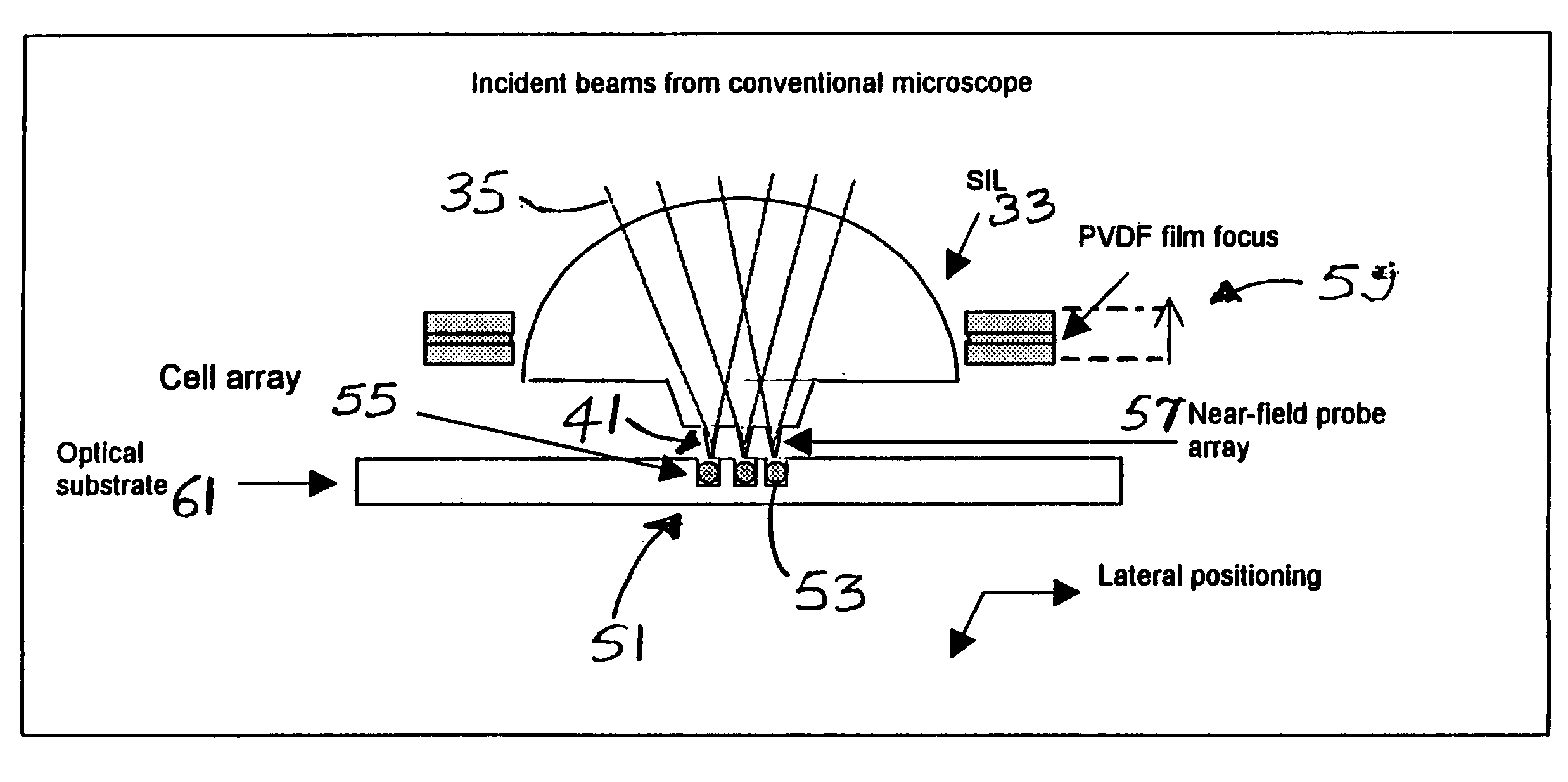
Precision optical intracellular near field imaging/spectroscopy technology
InactiveUS7129454B2Facilitates molecular analysisMore powerSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansDiseaseMolecular analysis
A Precision Optical Intracellular Near Field Imaging / Spectroscopy Technology (POINT / NANOPOINT) is a high-resolution instrument for analyzing and comparing molecular characteristics of cells. A nanosensor array is provided which is capable of imaging inner regions of living cells without destroying its natural environment and providing new information about molecular makeup of cells. The POINT probe collects data from high-resolution imagery, providing an imaging tool for investigating cells at sub-cellular and molecular levels. Data are then incorporated into a signature facilitating molecular analysis of diseases. The POINT probe non-invasively penetrates cell membranes to image insides of intact cells allowing the POINT probe to collect data without destroying cell structures. The probe provides cellular imaging to enable the viewing of both imaging and spectroscopy of internal regions of cells. The POINT system may be attached to existing microscopes to achieve a very high resolution.
Owner:NANOPOINTS
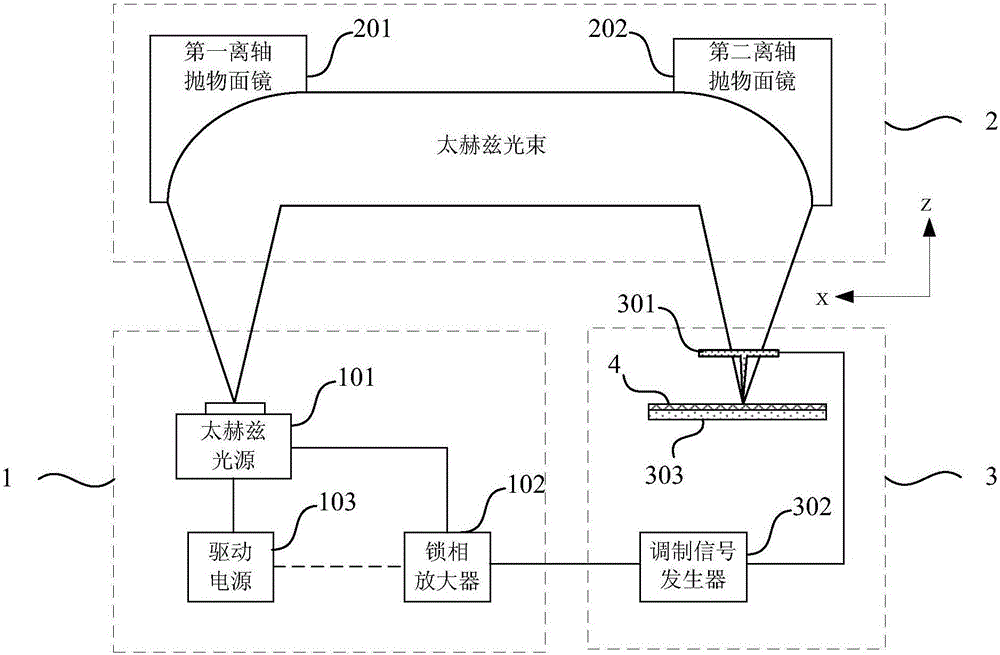
Terahertz near-field imaging system and terahertz near-field imaging method
ActiveCN106442394AImprove defectsHigh precisionSpectrum investigationMaterial analysis by optical meansMixing effectTerahertz quantum cascade laser
The invention provides a terahertz near-field imaging system and a terahertz near-field imaging method. The terahertz near-field imaging system comprises terahertz coherent light source module, an external light path module and a near-field probe module. A high-power terahertz quantum-cascade laser is adopted to generate high-power THz (terahertz) radiation, a near-field terahertz signal of a target is detected through a probe technique and a self-mixing effect of the laser, and accordingly a high-resolution-rate imaging function is realized. The terahertz near-field imaging system and the terahertz near-field imaging method have the advantages that the self-mixing effect is adopted to substitute for a near-field detector, so that a light path system is simple and compact; the near-field terahertz signal reflected by the near-field probe shares a light path with an incident signal, so that the terahertz near-field imaging system is high in precision and simple in structure, defects of a traditional near-field imaging technique are overcome remarkably, and development and application of a high-precision terahertz near-field imaging technique is promoted positively.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
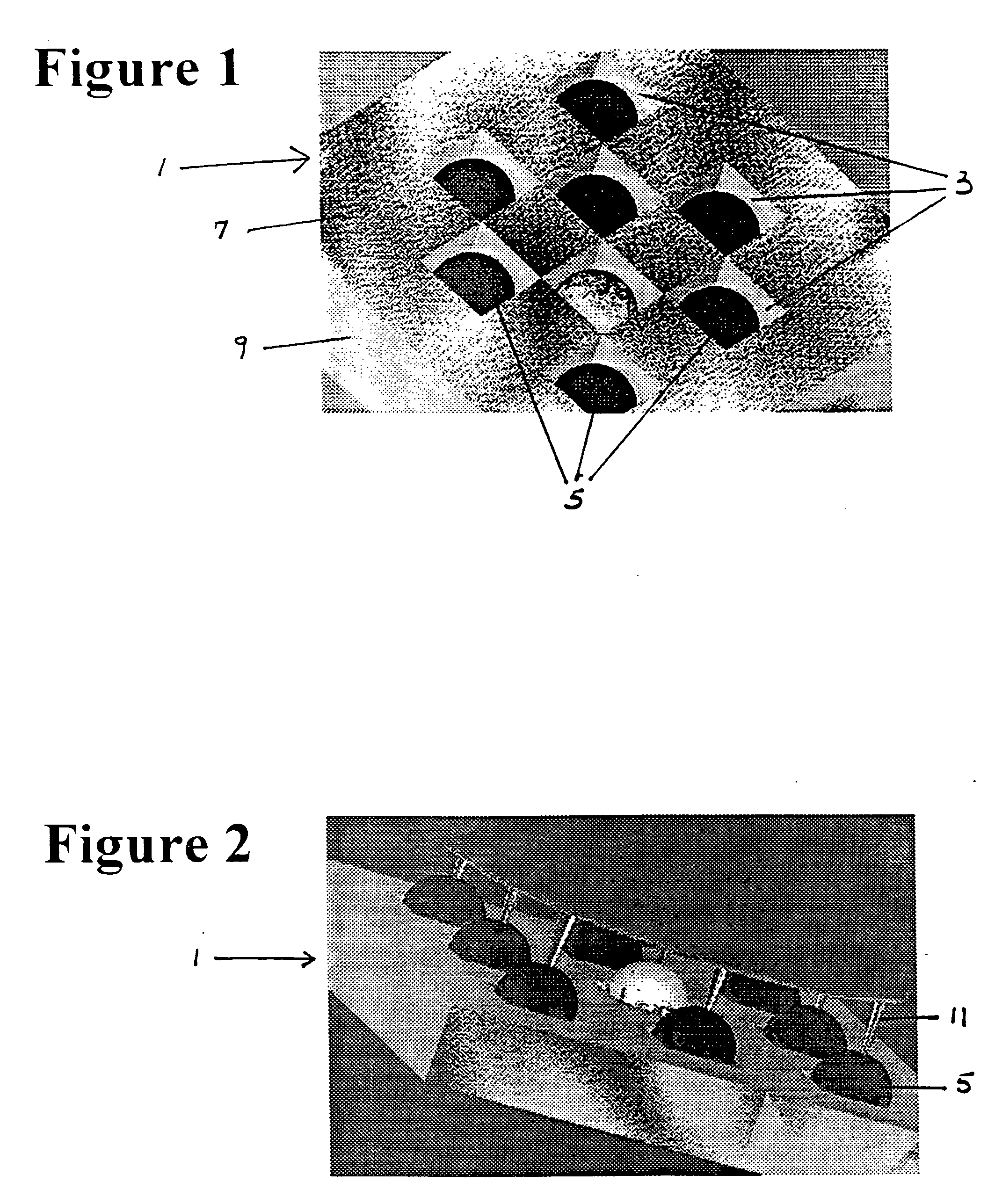
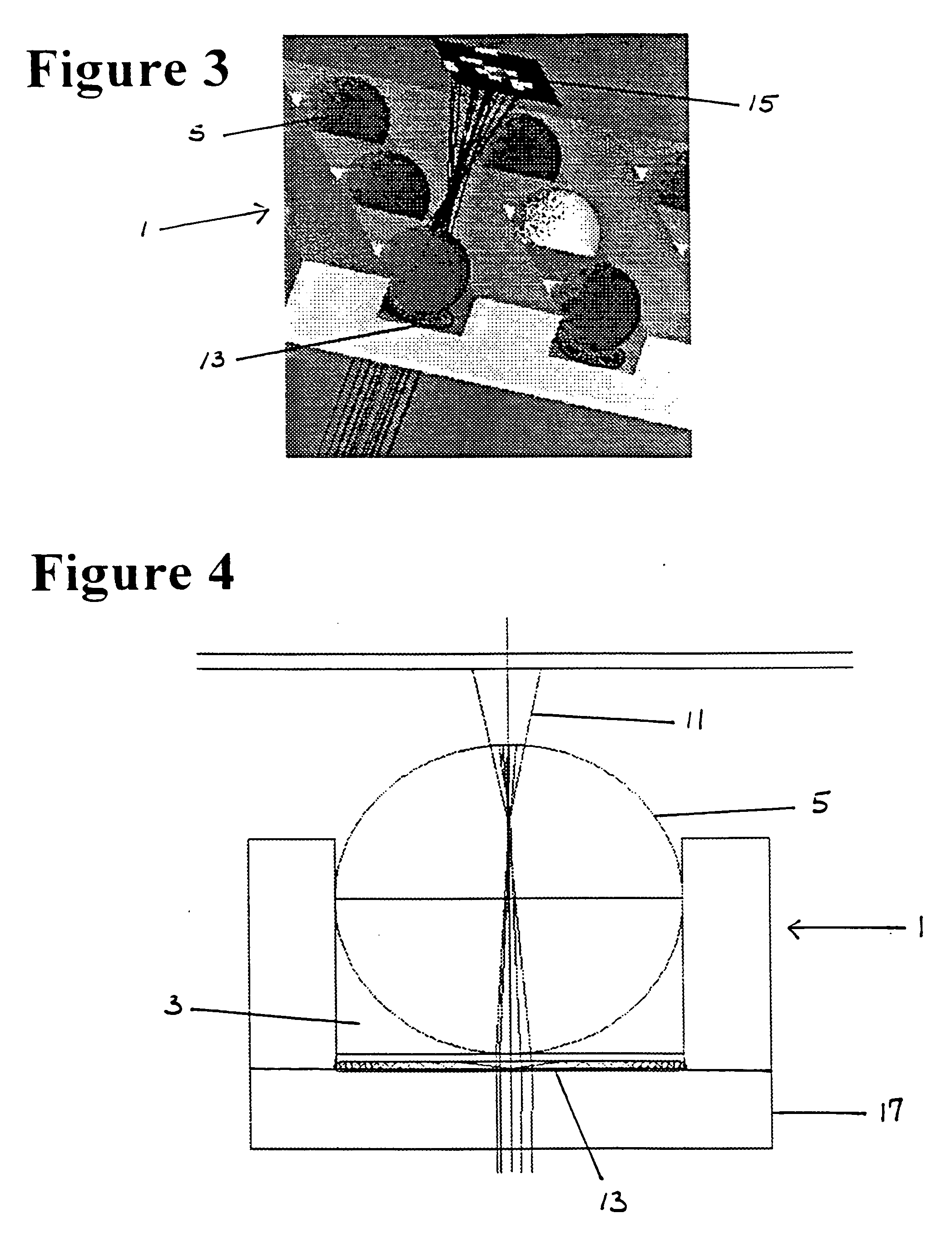
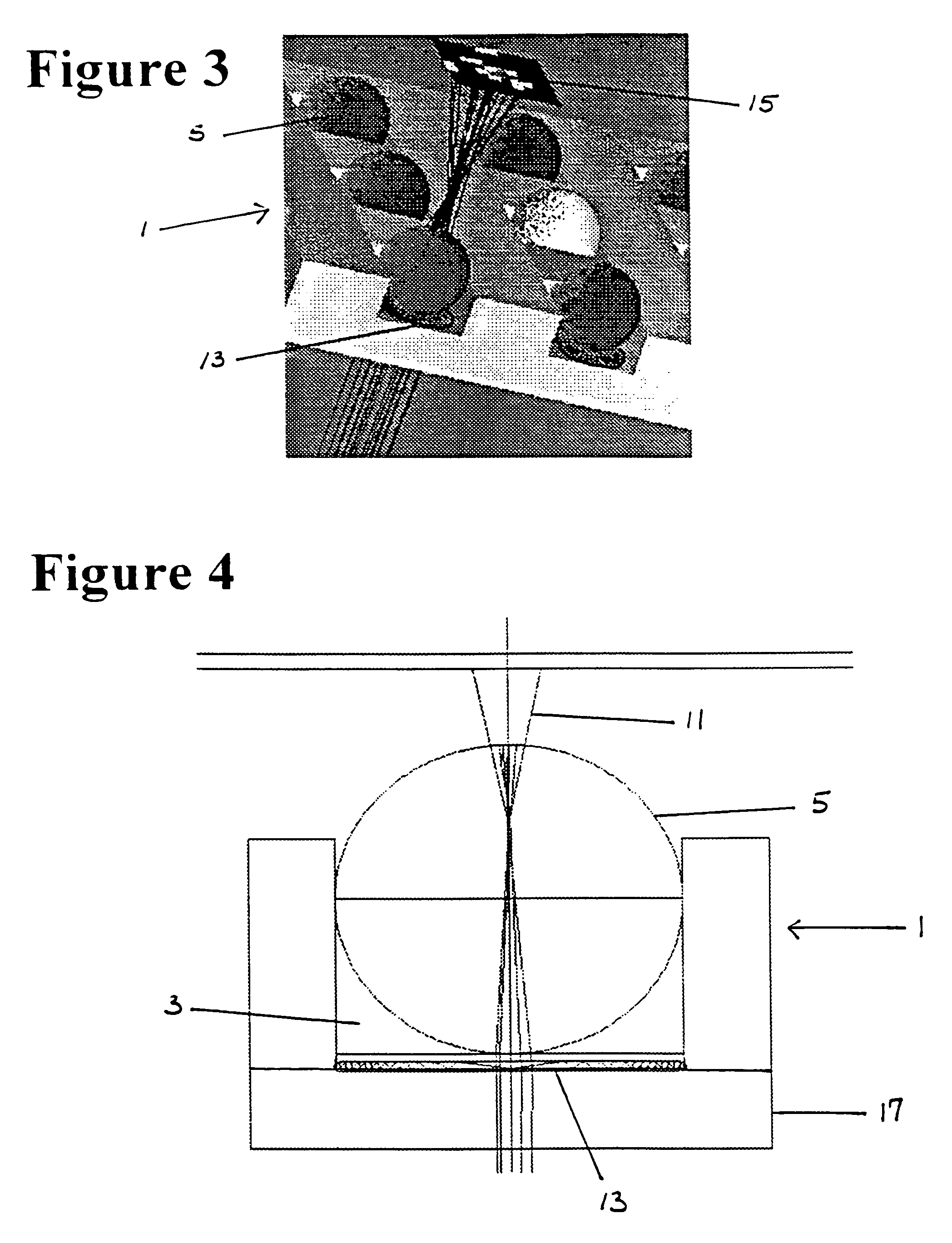
Cell tray
ActiveUS20060119843A1Mass productionIncrease pointsRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationMicroscope slideMulti dimensional
A cell tray has a multi-dimensional array of cells in precise, equally spaced wells (cubicles or silos) containing medium of interest. The ordered cell array enables automated processing as well as simultaneous monitoring and analyzing of a large matrix of cells, biological fluids, chemicals and / or solid samples. The invention is an integrated device and is fabricated into substrates similar to microscope slides. The ordered array of cells in precise locations helps in parallel analysis and processing of cells simultaneously. Each cell cubicle or silo in the array is located equidistant from its nearest neighbors in an orthogonal direction. The location of each well can be precisely measured and recorded in an automated processing system. Included in the bottom of each cell well is an optional micro-lens. An array of probes provides parallel cell processing and monitoring capabilities, including microinjection and microscope analysis. The cell tray when integrated with the Precision Optical Intracellular Near Field Imaging / Spectroscopy Technology (POINT or NANOPOINT) device results in sub-wavelength high-resolution imaging with a nanosensor array capable of imaging inner regions of living cells without destroying its natural environment.
Owner:NANOPOINT
High resolution near-field imaging method and apparatus
InactiveUS20080230707A1High resolution imageMaterial analysis by optical meansX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentData setHigh resolution image
A device and method are disclosed for imaging. Coded aperture arrays are used in conjunction with macro-collimators, on either side or both sides of the coded aperture arrays, to produce coded images, which are then used to produce a decoded image. Various parameters, including the distances between the radiation source and the code and between the code and the detector, the relative lengths of macro-collimator tubes, sizes of pin-holes in the coded aperture arrays, and number and sizes of the macro-collimator tubes, can be selected to achieve high resolution images of the radiation source. The macro-collimator eliminates wide angles rays and reduces ghost images in the reconstruction. Combining data sets from two gamma camera heads reduces the noise in OSEM reconstruction by improving the definition of object borders. Rotation of the coded apertures eliminates near field artifacts from the Fourier reconstruction of the image.
Owner:TRIUMPH STATE BANK
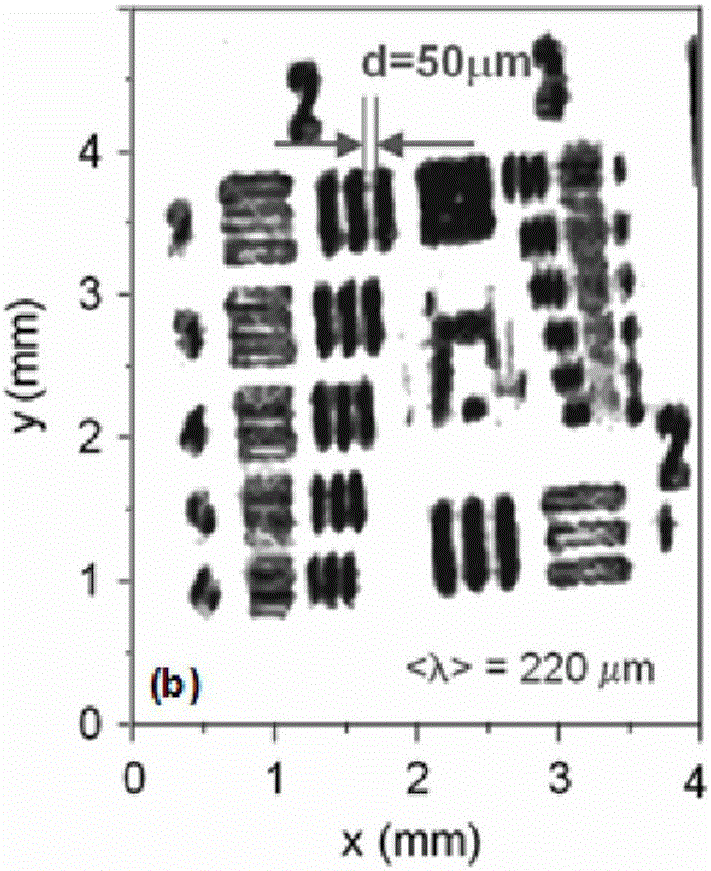
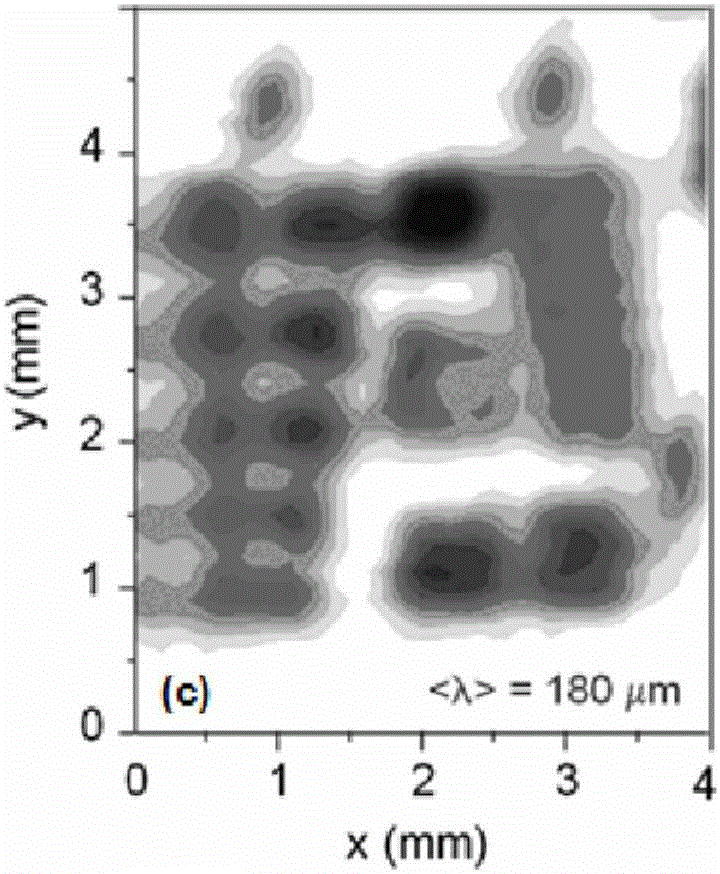
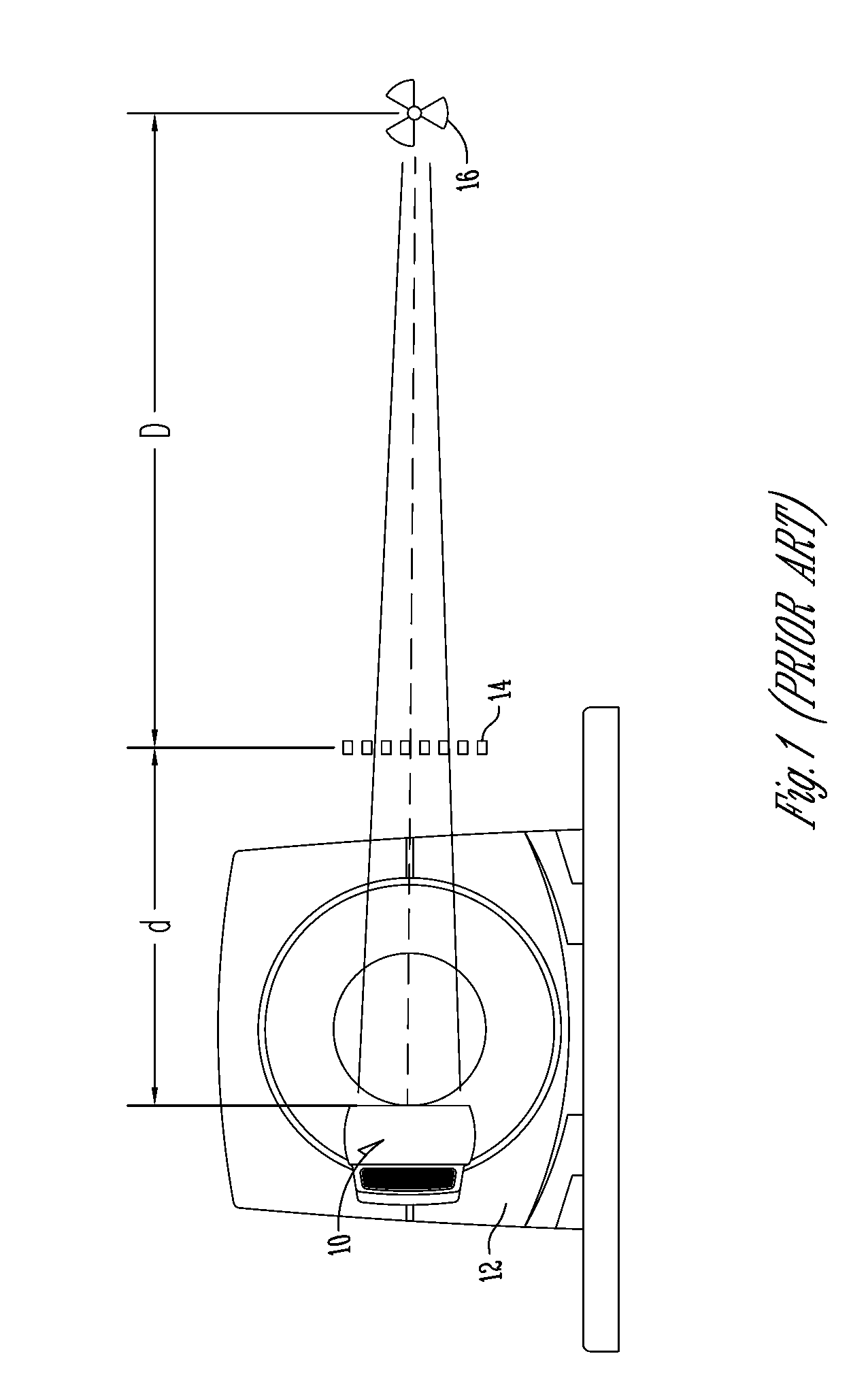
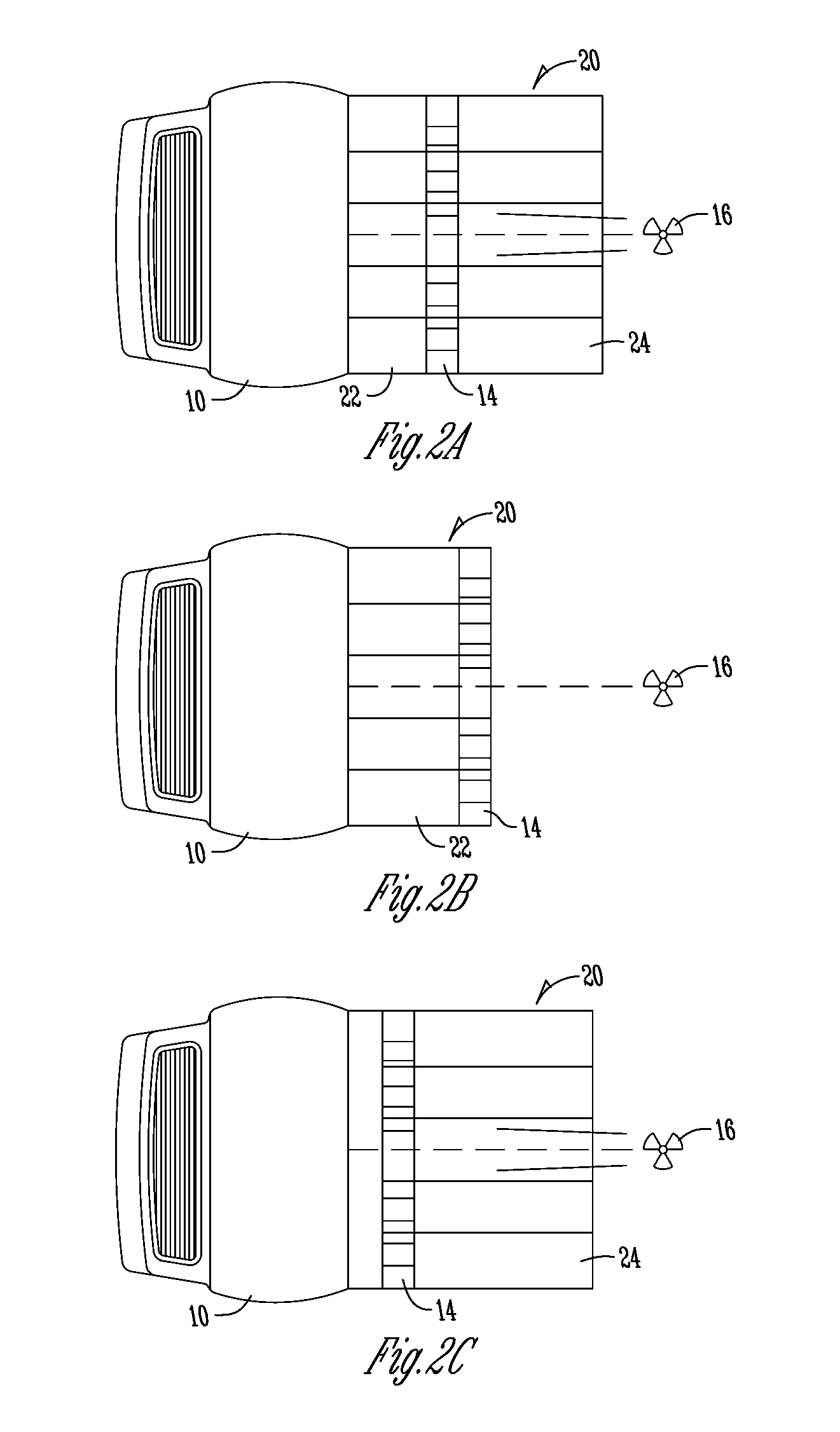
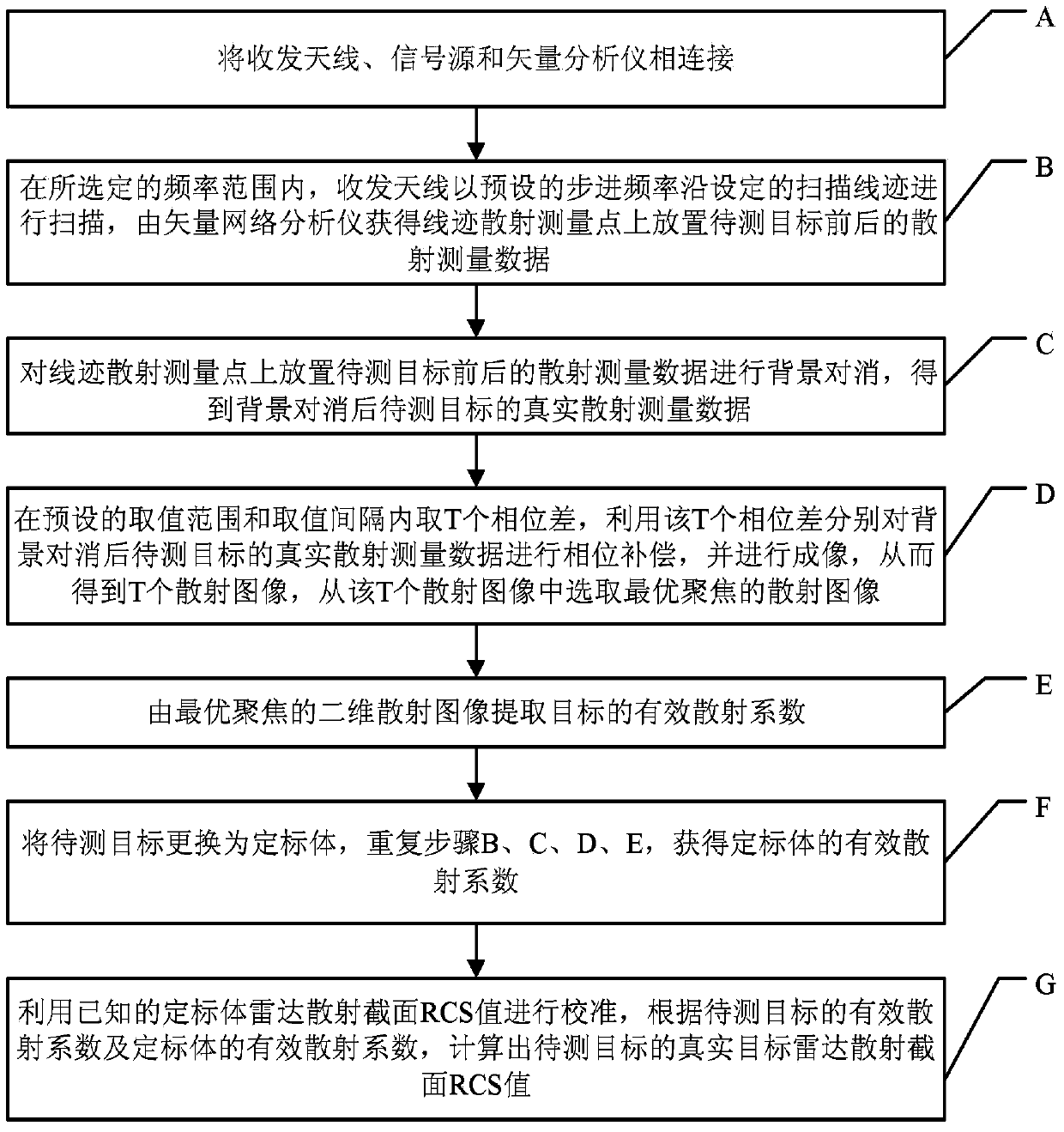
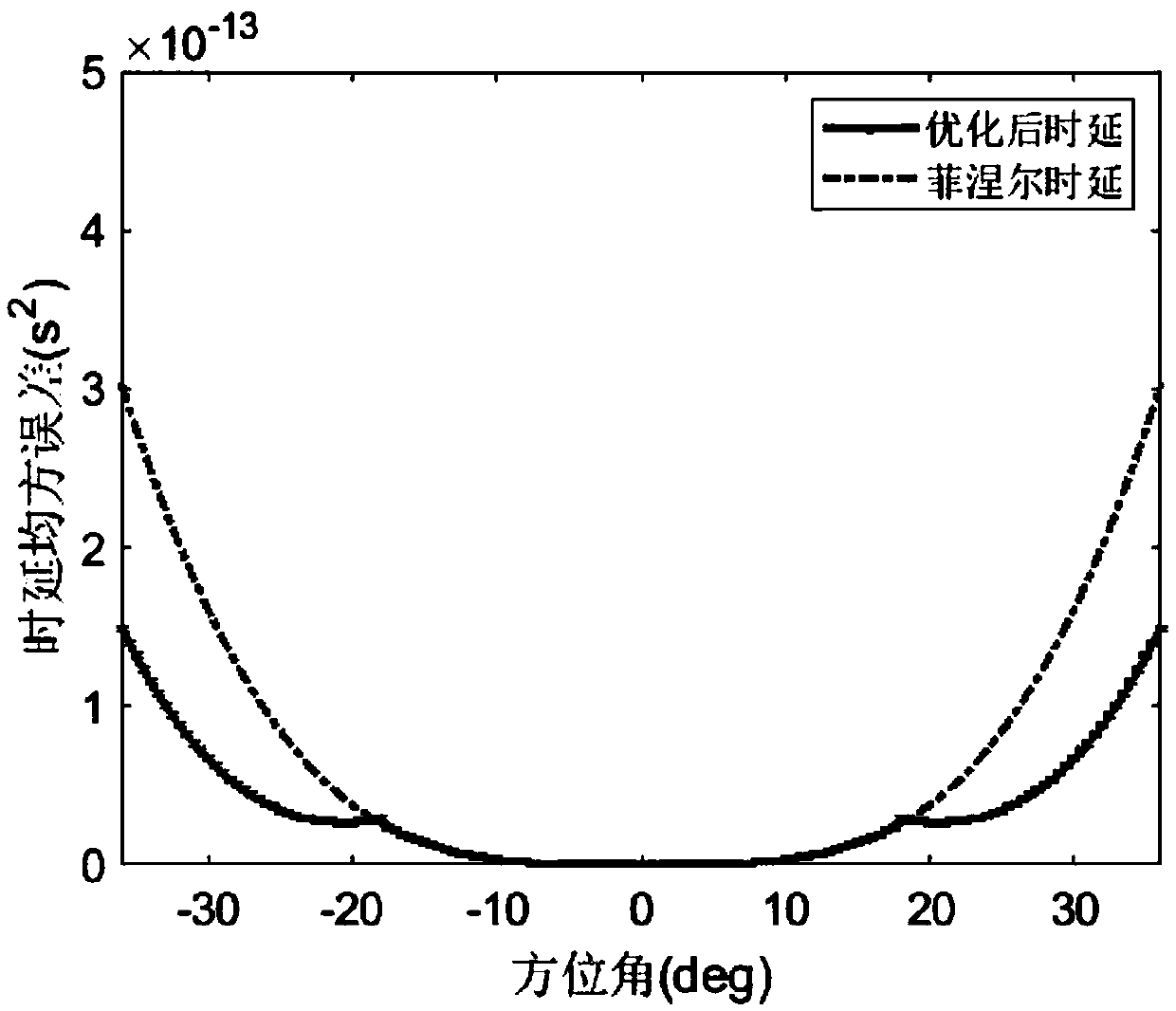
Backscattering cross section measuring method based on trace scanning two-dimensional near field imaging
ActiveCN104199026AImprove space utilizationImprove confidentialitySpecial data processing applicationsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionScattering cross-sectionTransceiver
The invention provides a backscattering cross section measuring method based on trace scanning two-dimensional near field imaging. The backscattering cross section measuring method comprises the following steps: a transceiver antenna scans along a set scanning trace at a predetermined step frequency within a selected frequency range and a vector network analyzer obtains scattering measurement data before and after a target to be measured is placed in a trace scattering measurement point; background cancellation is performed on the scattering measurement data before and after a target to be measured is placed in a trace scattering measurement point; the optimally focused scattering image P is selected; the effective scattering coefficient as shown in the description of the target is extracted from the optimally focused two-dimensional scattering image P; the target to be measured is replaced by a calibration object and the effective scattering coefficient as shown in the description of the calibration object is obtained, and then the real target radar scattering cross-section (RCS) value of the target to be measured is calculated. The backscattering cross section measuring method based on trace scanning two-dimensional near field imaging is capable of obtaining either the scattering image of the target or the RCS value of the target, and further is capable of obtaining the electromagnetic scattering characteristics of the target more clearly, more specifically and more comprehensively.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Ultrafast laser pulse method for forming nanopores with diameters of 2 nanometers
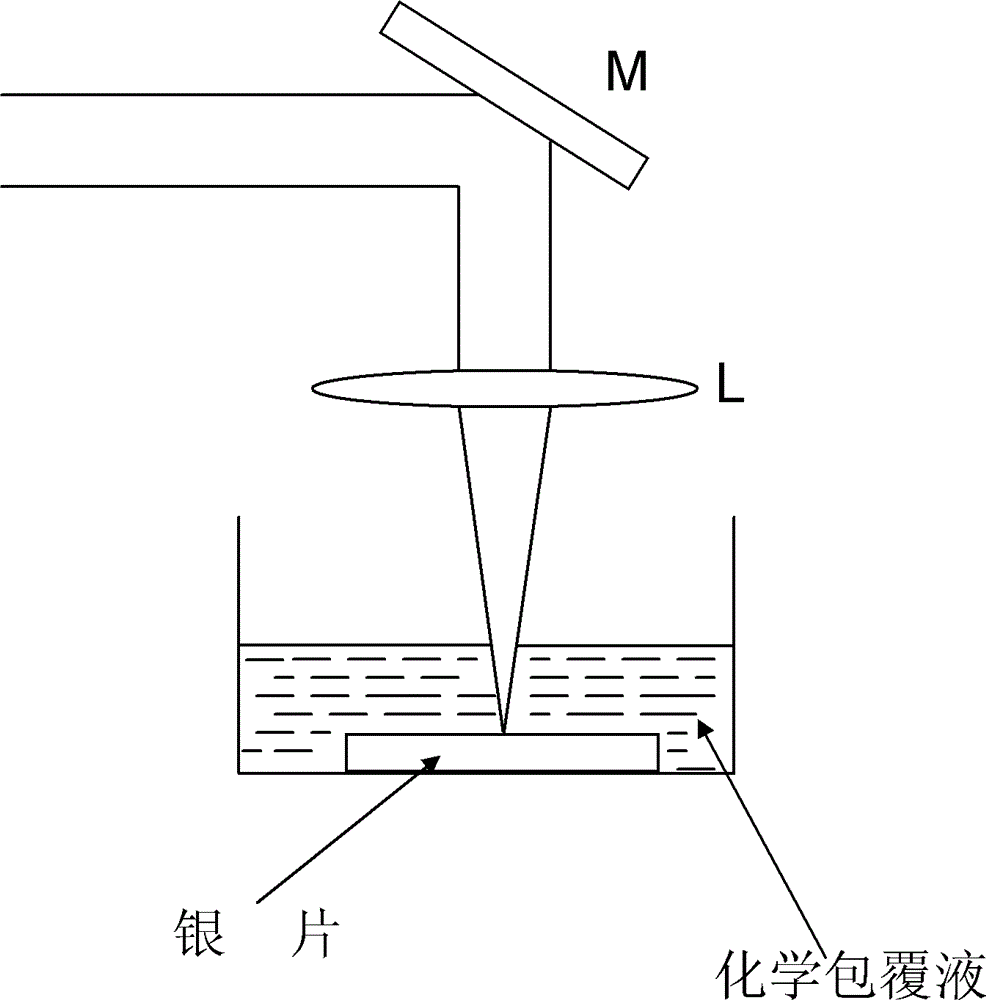
ActiveCN102795596AExpand application spaceEnhanced Raman ScatteringNanostructure manufactureBiological testingCarbon filmMaterials science
The invention provides an ultrafast laser pulse method for forming nanopores with the diameters of 2 nanometers. The thickness of a metal film layer where the ultra small nanopores with the diameters of 2 nanometers is formed is about 3nm, the nanopores are discretely formed in the metal film layer, and the diameter of each nanopore is about 2nm. The ultrafast laser pulse method comprises the following steps of: dissolving a sodium citrate crystal and poly-vinyl pyrrolidone (PVP) powder in deionized water to form a chemical coating solution; putting a metal sheet into watch glass, and injecting the chemical coating solution into the upper surface of the metal sheet; putting the watch glass near a focal distance of a condenser in a light path, ablating by using an ultrafast laser pulser to obtain suspension containing metal nano products, dripping the suspension containing the metal nano products to a copper screen covered by a carbon film, and drying to obtain the ultra small nanopore; and a metal film in which the ultra small nanopore are formed is applied to porous metal mask plates during near-field imaging with aperture probes, surface-enhanced Raman scattering, detection of single-pore biomolecules and the like.
Owner:INST OF PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Terahertz imaging for near field objects
ActiveUS7105820B2Distortion problemEffective regulationRadiation pyrometryAbsorption/flicker/reflection spectroscopyWavefrontInterferometric imaging
Near field imaging using a THz imaging system is realized by utilizing an interferometric imaging detector array that includes detector elements disposed on a surface curved, physically or artificially, to match substantially the curvature of the wave front for received THz signals. Generally, the near field is an environment wherein the distance to an object of interest is on the order of 10–100 times larger than the physical size of the THz imaging array. Typical distances from the object or target to the imaging array is anticipated to be in the 0.5 m–50 m range. Curvature of the detector array corrects a distortion problem in prior THz imaging systems that utilized planar interferometric imaging arrays based on a planar wave front assumption for received THz signals.
Owner:NEW JERSEY INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
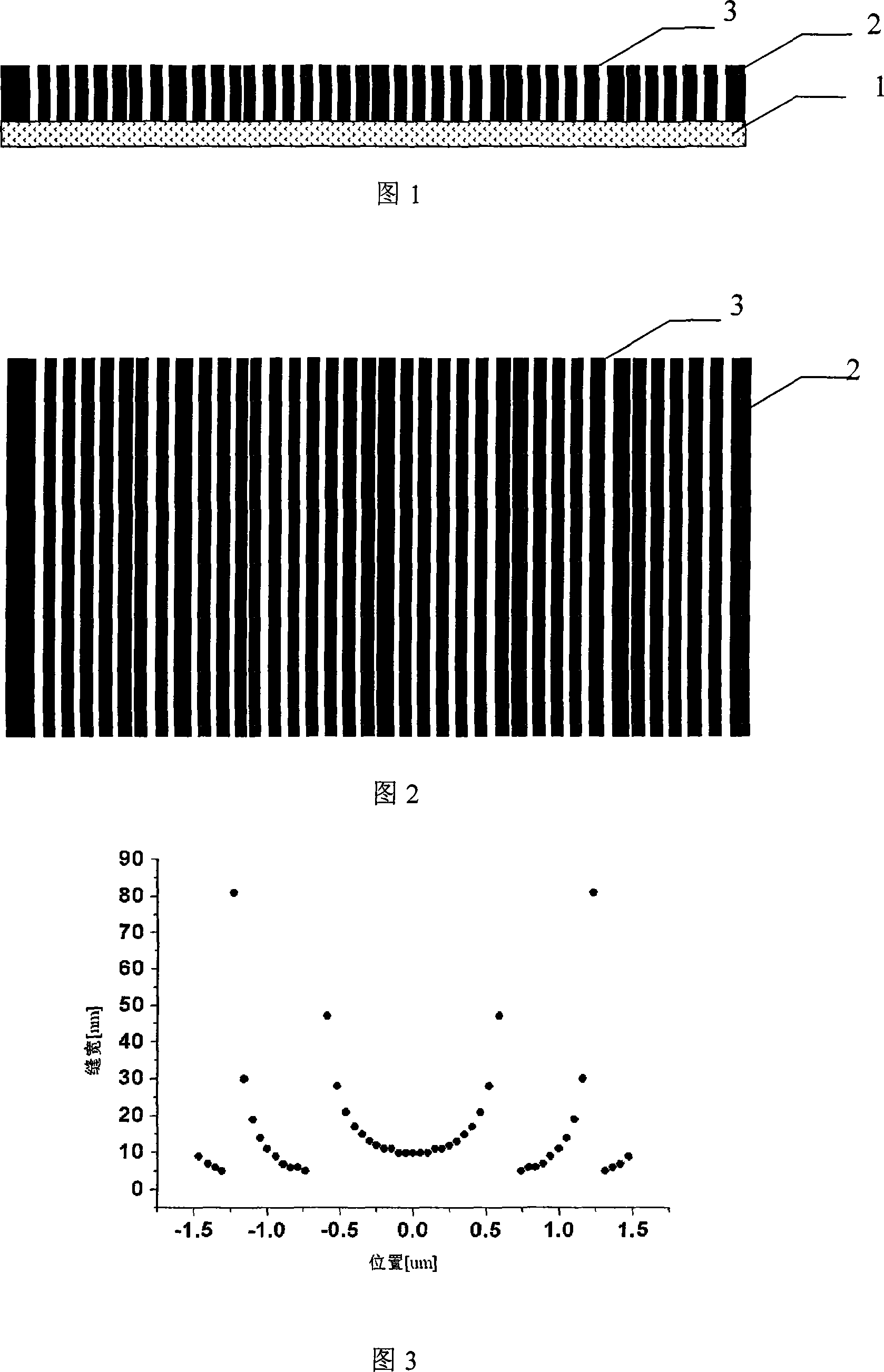
Metal membrane lens including nano seam
ActiveCN101158727ASimple structureAchieve imagingMaterial analysis by optical meansLensSystem integrationIncident wave
The invention relates to a metal film lens with nano-suture, and is characterized in that: an incident wave is firstly determined, and then proper substrate material is chosen, a layer of metal film is vapor deposited on a substrate, the incidence of the incident wave is vertical to the surface of a metal film, and then the skin depth of the incident wave in the chosen metal film is computed; the direction of X axis is chosen along the metal film, and sampling is implemented along the forward direction of X axis; then the width of the metal suture of each sample point is computed by computing the phase offset and the propagation constant of each sample point; a suture distribution along the negative direction of the X axis which is symmetrical to the suture distribution along the forward direction is chosen; finally the suture width of each sample point is obtained according to the design; then a metal film lens with nano-suture is produced by using the existing processing technology. The invention can change the suture distribution of the metal film lens according to the position of any given objective image to achieve the near field imaging or the distant field imaging, simultaneously the designed lens of the invention has simple structure, and can be used for the optical system integration extremely conveniently, the lens has extensive application prospect.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Coded aperture imager
InactiveUS20070040124A1Minimize artifactMaterial analysis by optical meansX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentCoded apertureOptics
The invention is based on the discovery that using at least two detectors in near-field imaging, wherein each detector is located on opposing sides of an object at about a 180 degree angle relative to the other detector, and equipping the detectors with two different copies of the same coded aperture, rotated at about a 90 degree angle relative to each other, minimizes near-field artifacts in images of non-static objects. The near-field coded aperture device and a method for minimizing artifacts by utilizing the device are provided. A method for detecting contraband in cargo is also provided.
Owner:THE CHILDRENS HOSPITAL OF PHILADELPHIA
Backscatter cross section measurement method based on cylinder scanning three-dimensional near-field imaging
ActiveCN104215953AAccurate measurementEasy to measureRadio wave reradiation/reflectionScattering cross-sectionRadar
The invention provides a backscatter cross section measurement method based on the cylinder scanning three-dimensional near-field imaging. The method includes in a determined frequency range, allowing a transceiving antenna to perform scanning test along the set cylinder surface in the certain step frequency, and acquiring the scattered echo data before and after the placement of a target to be measured; calculating the actual scattered echo data of the target to be measured after background cancellation according to the scattered echo data before and after the placement of the target to be measured; performing three-dimensional imaging by means of the actual scattered echo data of the target to be measured after background cancellation, and acquiring a target three-dimensional radar scattering image psi e (x, y, z); acquiring a calibration body three-dimensional radar scattering image psi ecal (x, y, z); calculating a target radar scattering cross section RCS value (img file = 'DDA0000561332250000011.TIF' wi = '240' he = '77' / ) of the target to be measured. By the aid of the method, the target three-dimensional radar scattering image can be acquired, the target RCS value in a certain solid angle domain can be also acquired, and the target electromagnetic scattering characteristics can be acquired more clearly, more specifically and completely.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
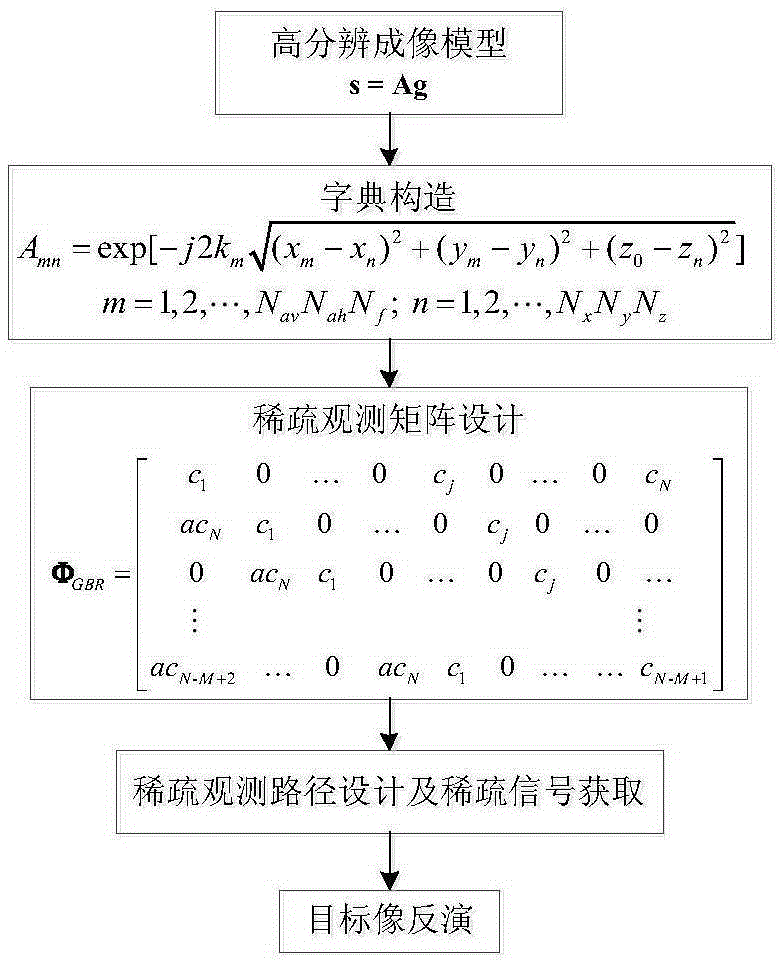
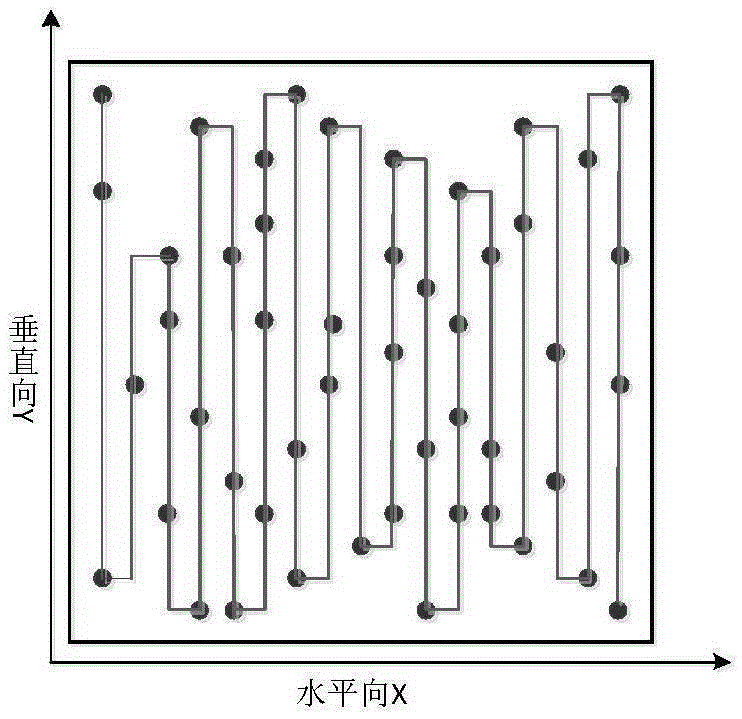
Near-field RCS quick measuring method based on high-resolution imaging
InactiveCN105388473AFocusImprove measurement efficiencyRadio wave reradiation/reflectionHigh resolution imagingHigh resolution image
The invention provides a near-field RCS quick measuring method based on high-resolution imaging, comprising the steps of building a high-resolution near-field imaging model and a dictionary, designing a sparse observation moment, designing a RCS quick measuring path, and finally, carrying out image solving to obtain a target high-resolution image. According to the invention, the measurement efficiency is improved through sparse sampling, and high-resolution imaging is realized based on the theory of compressed perception optimization reconstruction. Because of the adoption of sparse observation and a sparse signal recovery concept, the measurement efficiency is significantly improved, and the problem that near-field RCS measurement is time-consuming and large-scale data obtained through test is difficult to store is solved. Based on an obtained sparse observation signal and a compression perception theory, the traditional imaging mechanism is broken, target high-resolution imaging is realized, and a strong guarantee is provided for nondestructive detection, hidden object detection, and stealth and anti stealth design.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Probe antenna for terahertz waveband near-field imaging
InactiveCN105846070AInput electric field enhancementEasy to manufactureRadiating elements structural formsAntennas earthing switches associationMaterial defectResonant cavity
Owner:JILIN UNIV
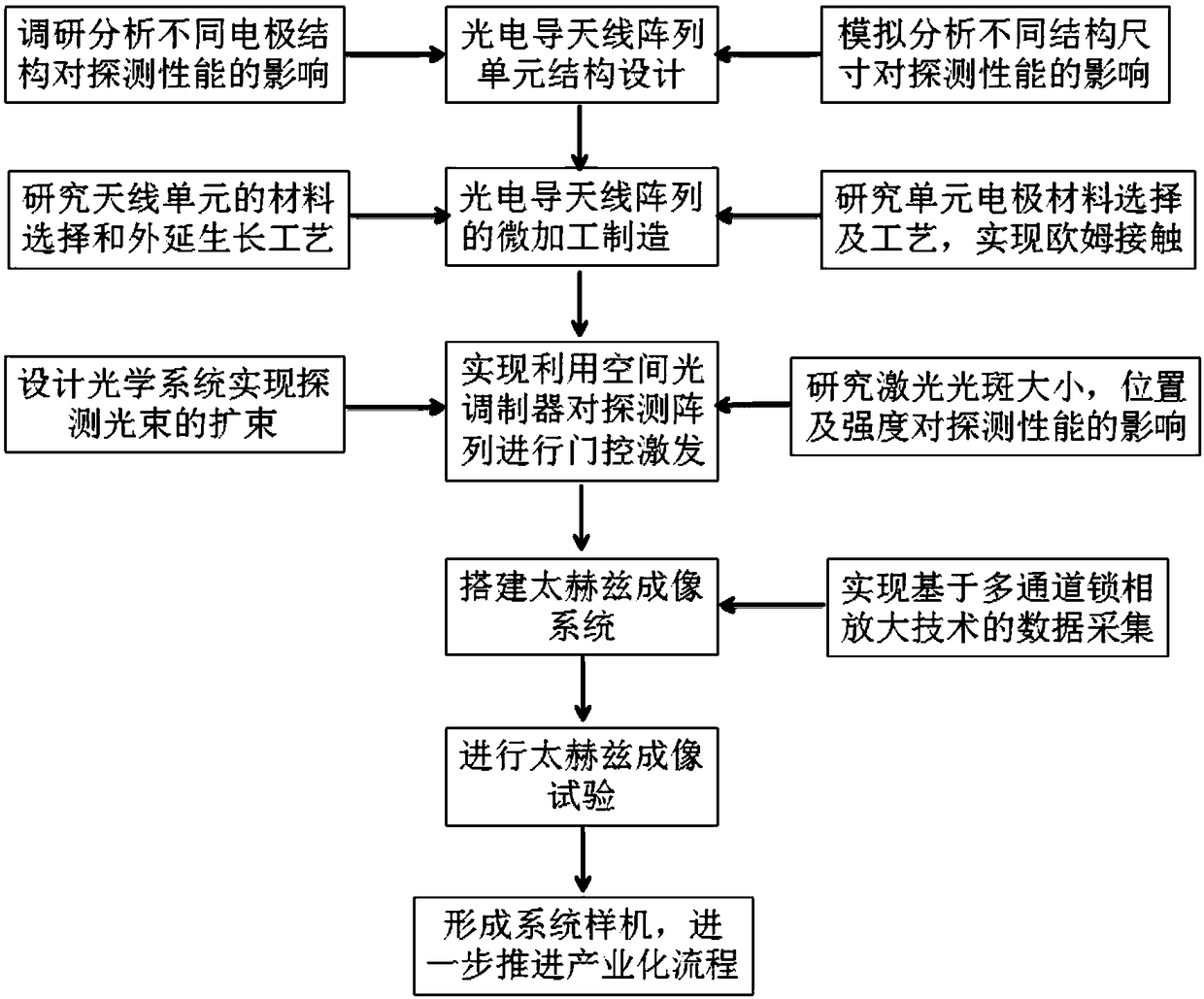
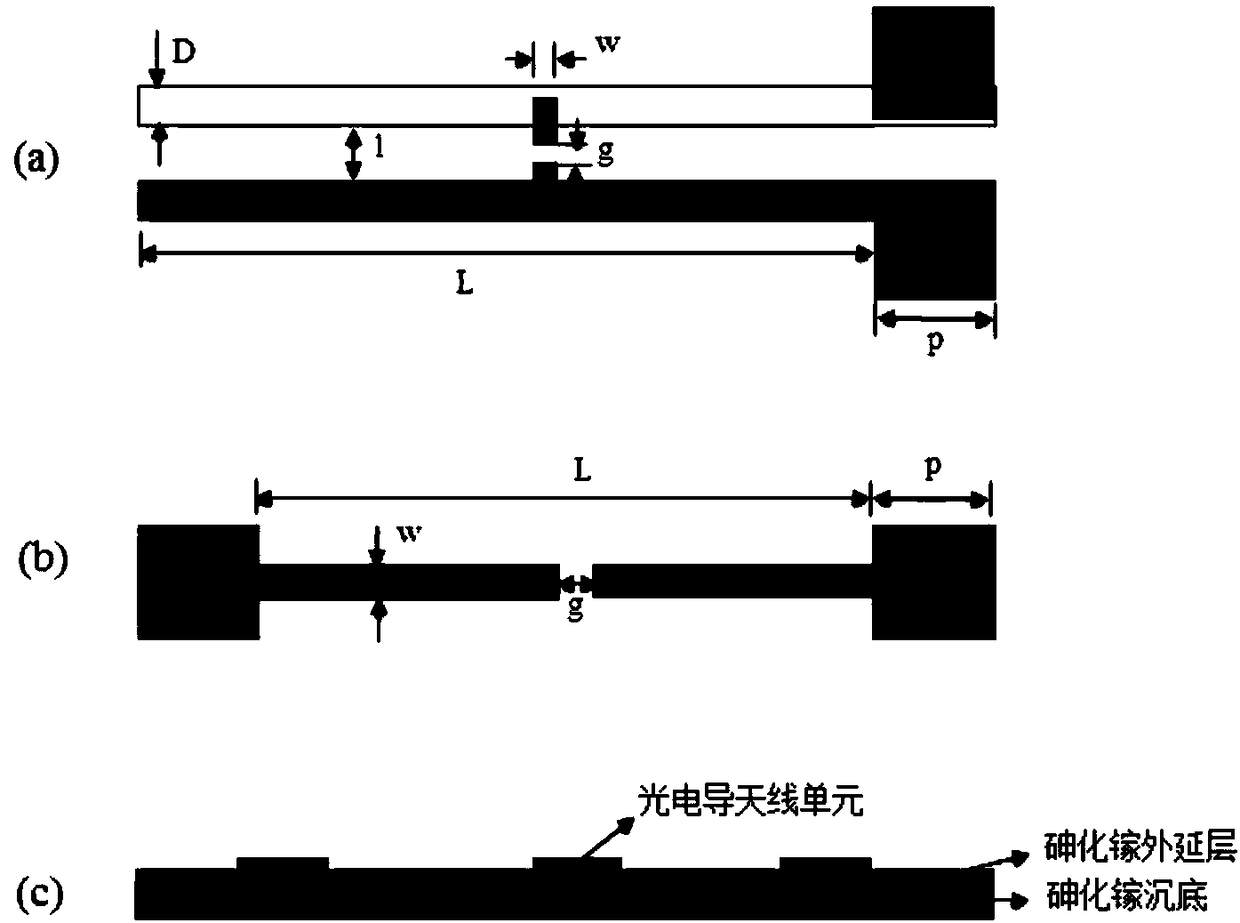
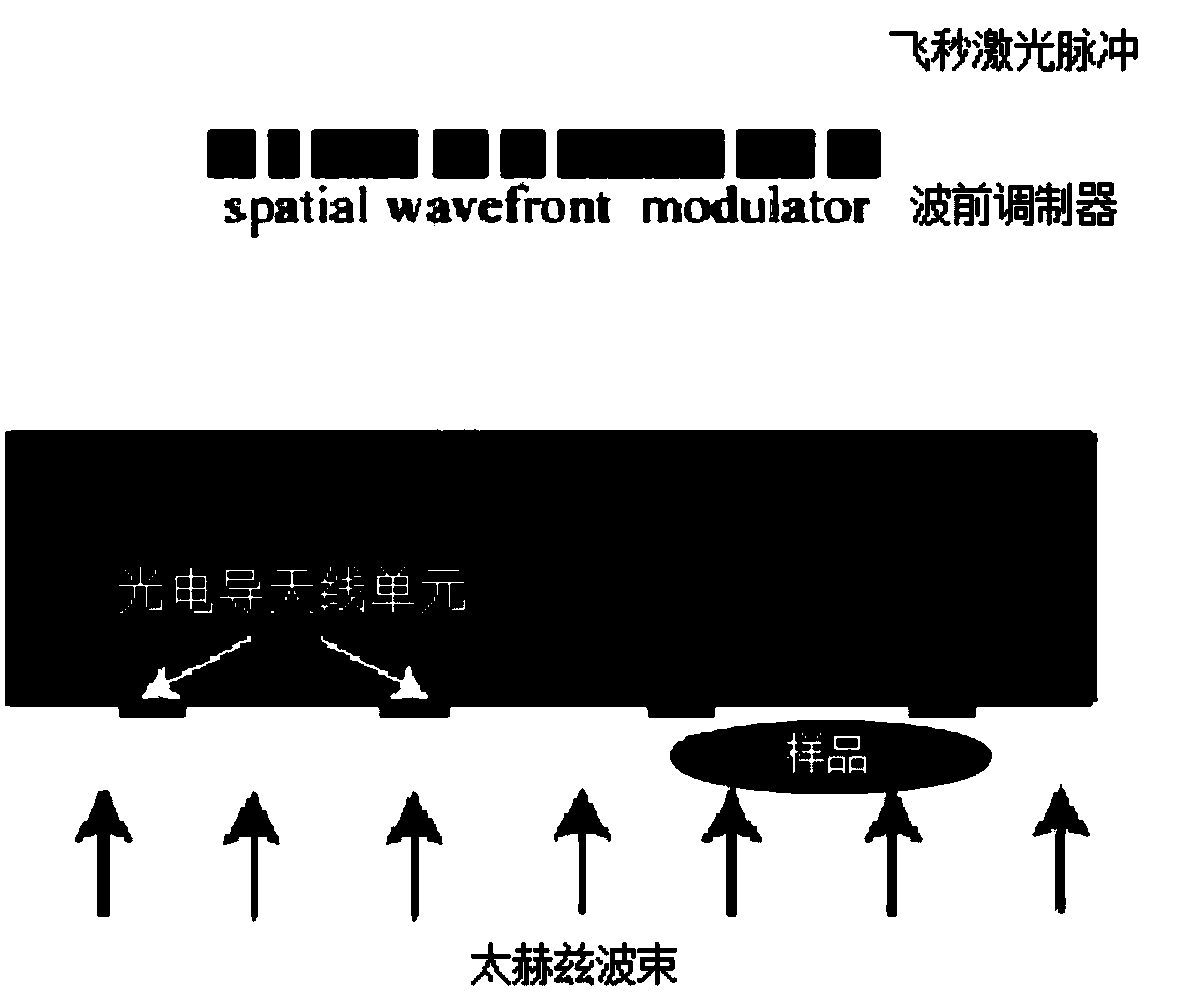
Quick dynamic terahertz near field imaging system based on photoconductive antenna array and construction method thereof
ActiveCN109490241AHigh resolutionExcellent unit signal to noise ratioMaterial analysis by optical meansSpatial light modulatorSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
The invention discloses a quick dynamic terahertz near field imaging system based on a photoconductive antenna array and a construction method thereof. The method comprises the following steps: preparing an optimized probe unit structural design; micro-processing and manufacturing the photoconductive antenna array; and carrying out gating activation on a probe array by using a spatial optical modulator and constructing a pulse terahertz imaging system. Compared with the prior art, the system and the method have the following advantages: (1) the quick dynamic terahertz near field imaging systembased on the photoconductive antenna array achieves the photoconductive antenna array which detects terahertz waves efficiently, and the resolution of the system is superior to lambda / 10 and the unitsignal-noise ratio is superior to 70 dB; and (2) the system carries out gating activation on the photoconductive antenna array by using the spatial optical modulator and combines a multichannel lockphase amplification technique, so that a dynamic, flexible, efficient and rapid data acquisition method is achieved.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for reducing MIMO imaging radar near-field grating lobes
ActiveCN105738895AImprove image qualityHigh grating lobe problem overcomeRadio wave reradiation/reflectionImaging qualityRadar imaging
The invention discloses a method for reducing MIMO imaging radar near-field grating lobes. Grating lobe performance of an MIMO array when near-field imaging is performed can achieve an index requirement through usage of the method. Aiming at the fact that a near-field directional diagram has a characteristic of spatial variability, optimization is performed on the MIMO array obtained through design based on a virtual array theory, an emitting array is prolonged in an equal interval manner, windowing processing is performed on the emitting array, envelope sidelobes of the near-field directional diagram of the emitting array are overall lowered firstly, and then grating lobes of a receiving array all fall into an envelope sidelobe region of the emitting array, so the grating lobe performance of the MIMO array when the near-field imaging is performed can achieve the index requirement, low grating lobe near-field imaging is achieved through adoption of the optimized MIMO array, and a certain degree of universality is possessed. Compared with an existing technology, the method can overcome a high grating lobe problem, resulted from near-field directional diagram distortions of the emitting and receiving arrays, of a synthetic directional diagram of the MIMO array, and the method improves the imaging quality of an MIMO radar for a near-field target.
Owner:苏州理工雷科传感技术有限公司
Method for realizing dual-channel nano printing and dual-channel holography based on laminated super surface
The invention relates to a method for realizing dual-channel nano printing and dual-channel holography based on a laminated super surface. The method comprises steps that a super surface unit structure is constructed, wherein the super surface unit structure comprises a substrate, a first nano brick arranged on the substrate and a second nano brick embedded in the substrate; structural parametersof a first nano brick and a second nano brick are obtained through optimization; a super surface structure array is constructed, and the super surface structure array comprises a plurality of super surface unit structures; according to the imaging requirements that incident light passes through the first nano brick and the second nano brick in sequence and enters the second nano brick and then enters a near-field pattern and a far-field pattern in two modes of the first nano brick, arrangement of a first nano brick turning angle theta 1 and a second nano brick turning angle theta 2 which can simultaneously meet intensity distribution of near-field imaging and can form a phase-type Fourier hologram in a far field id found out, and thereby the super surface material capable of realizing dual-channel nano printing and dual-channel holography is obtained. The method is advantaged in that four completely independent images can be coded on one super surface material.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Stepping frequency synthetic aperture radar-based near-distance RCS measurement electronic system
ActiveCN110133650AReduce design requirementsReduce design costRadio wave reradiation/reflectionDigital signal processingRadar systems
The invention discloses a stepping frequency synthetic aperture radar-based near-distance RCS measurement electronic system, and relates to a frequency stepping technology, an SAR image processing andan FPGA digital signal processing. Compared with a traditional method such as far-field measurement and compact-field measurement, the radar RCS near-field imaging method has the advantages that theacquired information quantity is greatly increased, and richer target scattering characteristic distribution can be obtained with regard to near-distance measurement of a target relative to a radar system. Aiming at defect of a background technology, the radar system employs a stepping frequency narrow pulse signal to transmit and receive a shared antenna, the distance blind region is small, the measurable range is large, and the problem of isolation of a continuous wave mechanism is prevented; the stepping frequency signal belongs to one of pulse signals; in the radar employing the frequencystepping signal, large bandwidth at an arbitrary frequency can be flexibly acquired by carrier frequency jump of each pulse in a coherent pulse string, and an effect of high distance resolution is obtained by IDFT processing on pulse echo; and meanwhile, the index requirements of instantaneous bandwidth processing of a digital signal and digital processing hardware of an echo signal of a receivingare reduced.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
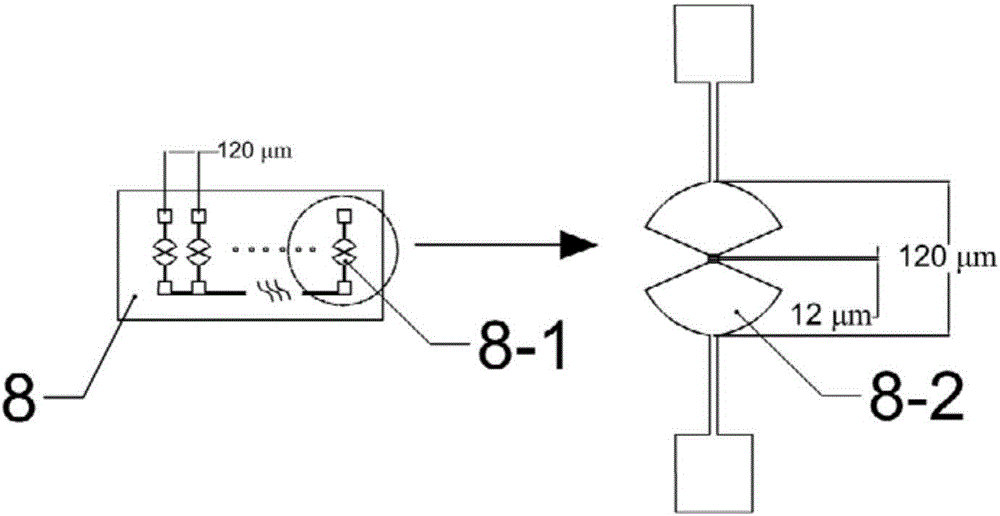
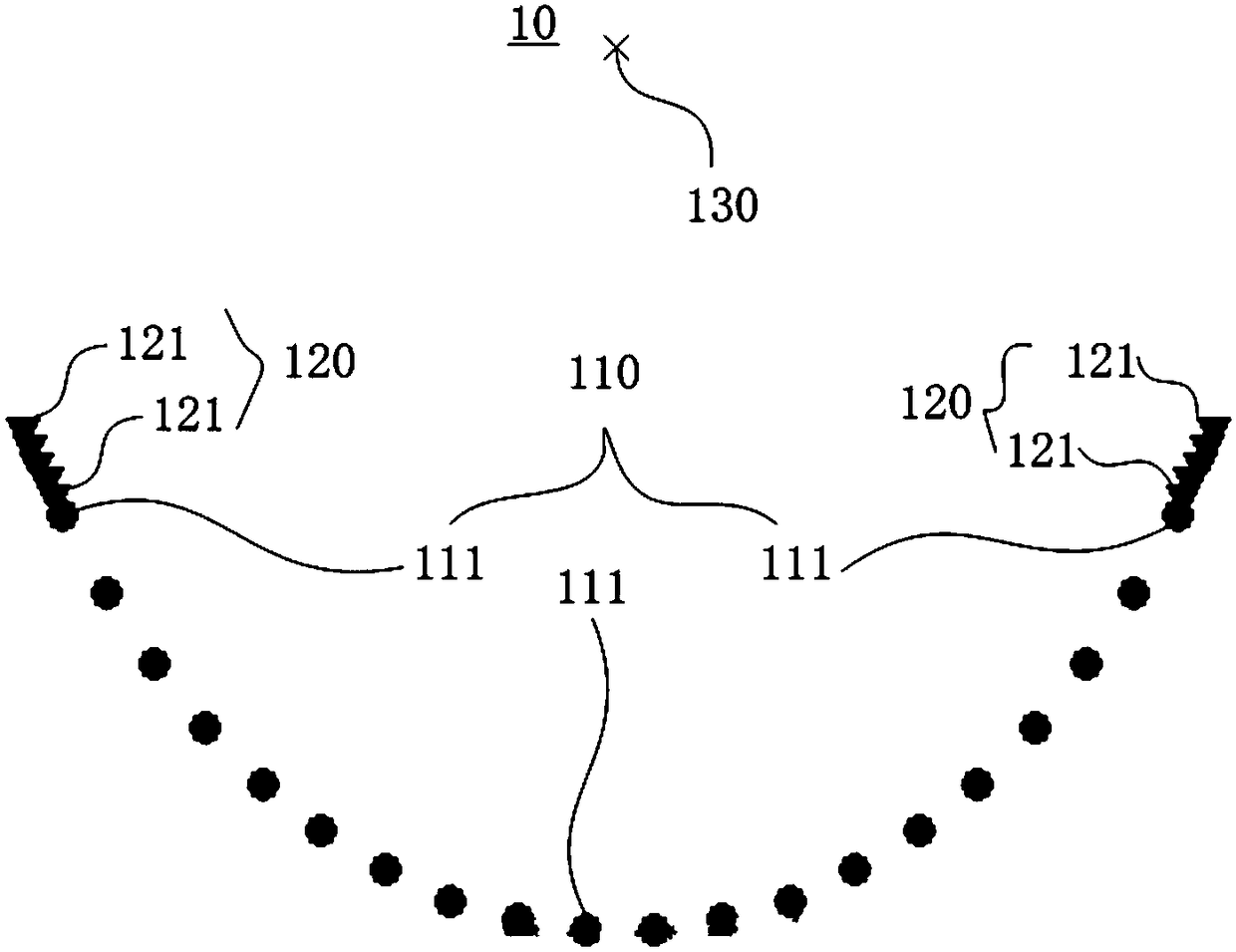
Antipodal vivaldi antenna array for biomedical imaging
ActiveUS9504404B1Reduce reflectionIncreases dimension of antennaDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsMicrowave applicationsImpedance matching
A high-performance, broad-band antenna that is small enough to be used in an array for biomedical imaging, yet has an aperture large enough to allow operations in the 1 GHz to 2.7 GHz frequency range. The present antenna advantageously uses a Vivaldi antenna with unique lobe designs to provide a small antenna that provides excellent near field imaging. The ends of each lobe have a tilted half-disc shape that increases the aperture of the antenna without increasing overall size. Other unique features of the lobes include exponential structures and an impedance matching design. Multiple units of the present antipodal Vivaldi antenna can be used in an array of antennas. Such an array, or stack or multiple arrays, can be used in many microwave applications for biomedical imaging.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
Terahertz subwavelength resolution imaging device
ActiveCN106769994AFast imagingImproving Imaging EfficiencyMaterial analysis by optical meansImaging qualityFrequency multiplier
The invention discloses a terahertz subwavelength resolution imaging device. In order to solve the problems in the prior art, the invention provides a terahertz wave near-field detection subwavelength resolution imaging device; the imaging device can improve the space resolution of terahertz wave near-field imaging to the order of magnitude higher than 0.02 lambda, thus improving the near-field imaging quality, and expanding the application field of a terahertz near-field imaging technology. The imaging device comprises a control computer, a frequency-adjustable terahertz solid-state frequency multiplier source with frequency of 0.15-0.5THz, an off-axis paraboloid mirror, a polyethylene (PE) focusing lens, a polytetrafluoroethylene sample pool, a polyethylene terephthalate (PET) protection sheet, a linear column terahertz detector, a polyurethane absorbing layer, a pre-amplifier, a reading circuit, an analog-digital (AD) converter, and the like. The terahertz subwavelength resolution imaging device is applied to the technical field of terahertz imaging.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Near-field wide-view-angle beam forming method of real-time three-dimensional imaging sonar
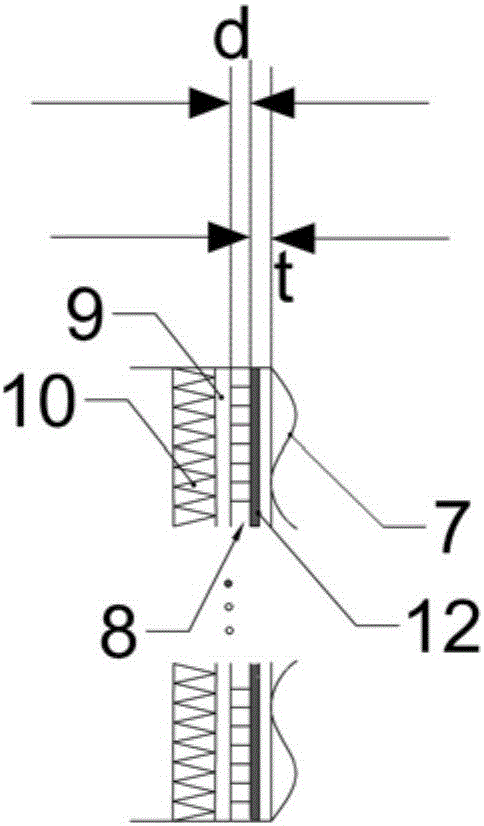
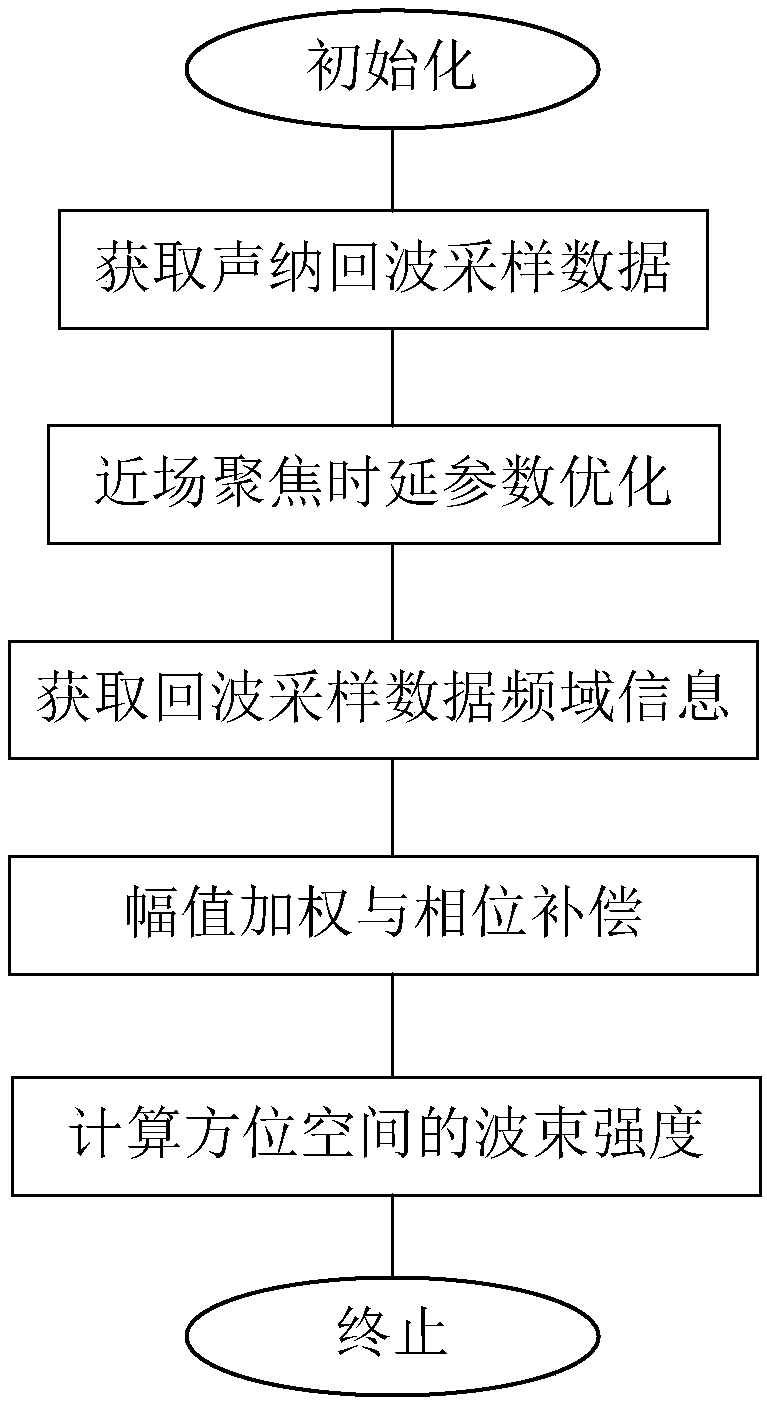
ActiveCN109581388AWiden perspectiveHigh near-field focusing accuracyAcoustic wave reradiationTime delaysWeight coefficient
The invention belongs to the technical field of three-dimensional sonar, and discloses a near-field wide-view-angle beam forming method of real-time three-dimensional imaging sonar. The near-field wide-view-angle beam forming method comprises the following steps that an echo sampling data matrix S of a sonar system is obtained; a time delay weighting coefficient k1 of a focusing target point inside a Fresnel time delay area and a time delay weighting coefficient k2 of the focusing target point outside the Fresnel time delay area are calculated; echo sampling data are subjected to L-point discrete Fourier transformation, and thus an echo signal S(l) is obtained; the echo signal S(l) is subjected to amplitude weighting and phase compensation, and thus a compensated echo signal tilde{S(l)} isobtained; .and the compensated echo signal tilde{S(l)} is subjected to fast Fourier transformation, an expression of the spatial beam intensity is obtained, and the spatial beam intensity is calculated. As for the situations that the focusing target point is located outside the Fresnel time delay area and located in a set imaging view angle range, the time delay weighting coefficients are optimized through a least squares method, under the premise of ensuring near-field beam forming calculation efficiency, near-field focusing accuracy can be effectively improved, and the view angle of near-field imaging is expanded.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Cell tray
ActiveUS7190449B2Increase pointsRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationMicroscope slideHigh resolution imaging
A cell tray has a multi-dimensional array of cells in precise, equally spaced wells (cubicles or silos) containing medium of interest. The ordered cell array enables automated processing as well as simultaneous monitoring and analyzing of a large matrix of cells, biological fluids, chemicals and / or solid samples. The invention is an integrated device and is fabricated into substrates similar to microscope slides. The ordered array of cells in precise locations helps in parallel analysis and processing of cells simultaneously. Each cell cubicle or silo in the array is located equidistant from its nearest neighbors in an orthogonal direction. The location of each well can be precisely measured and recorded in an automated processing system. Included in the bottom of each cell well is an optional micro-lens. An array of probes provides parallel cell processing and monitoring capabilities, including microinjection and microscope analysis. The cell tray when integrated with the Precision Optical Intracellular Near Field Imaging / Spectroscopy Technology (POINT or NANOPOINT) device results in sub-wavelength high-resolution imaging with a nanosensor array capable of imaging inner regions of living cells without destroying its natural environment.
Owner:NANOPOINT
Large-aperture light beam collimating and measuring device
ActiveCN105675265AReduce volumeAvoid damagePhotometryTesting optical propertiesLight beamImaging lens
The invention relates to a large-aperture light beam collimating and measuring device based on far-field sampling. The collimating and measuring device comprises a small hole of a space filter, a first space filter lens, a second space filter lens, a first light leakage reflector, a beam compressing lens, a near-field imaging system composed of a near-field imaging lens and a near-field detector, and a far-field imaging system composed of a far-field imaging lens and a far-field detector; the output end of the near-field detector and the output end of the far-field detector are connected with a computer; the computer is connected with a collimation adjusting motor reflector group; and the collimation adjusting motor reflector group is composed of a first motor reflector and a second motor reflector. The collimating and measuring device is characterized by also comprising a wedge plate, a rectangular prism, a total reflective mirror and an energy meter assembled on a guide rail. The large-aperture light beam collimating and measuring device is characterized by simple devices, easy adjustment, small size, low cost, and capabilities of collimation and energy measurement.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
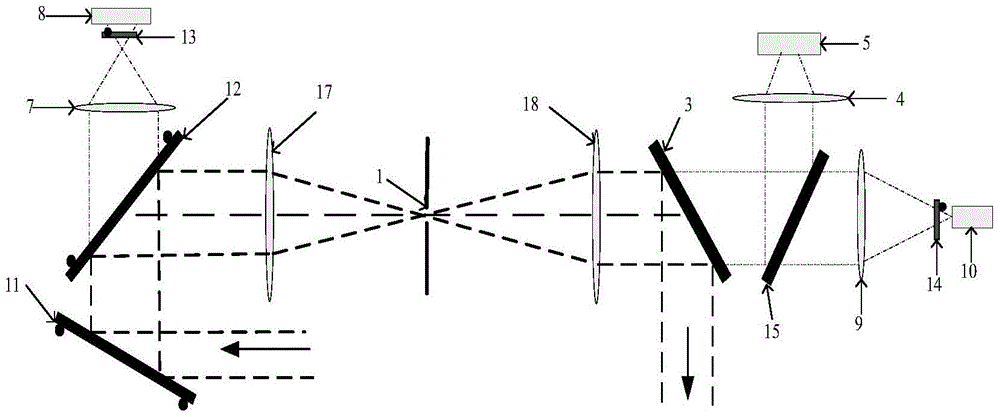
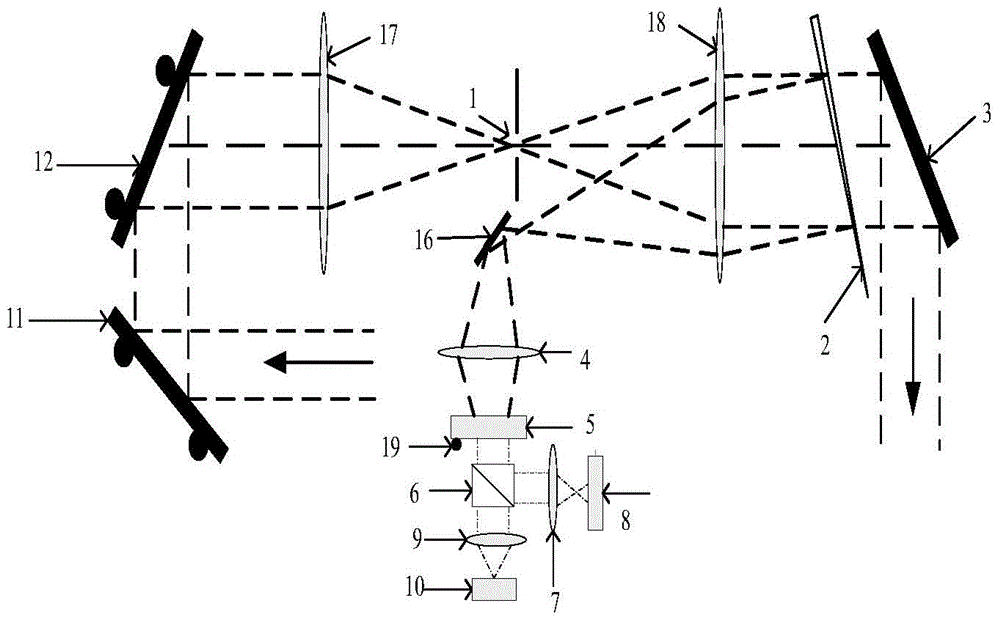
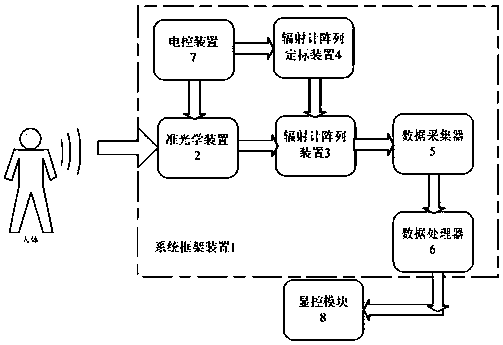
Internal and external calibration method used for radiometer imaging
ActiveCN107991675AImprove spatial resolutionGood effectRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadiometer calibrationData acquisition
Disclosed is an internal and external calibration method used for radiometer imaging. An internal and external calibration system comprises a system frame device (1), a quasi optical device (2), a radiometer array device (3), a radiometer array calibration device (4), a data collector (5), a data processor (6), an electric control device (7) and a display control module (8). Among the devices, a millimeter wave focal plane array imaging technology is employed, radiometers and feed source antenna arrays are utilized to cover a horizontal field of view and reflector mechanic scanning is utilizedto cover a vertical field of view, and the resolution of a near field imaging space is increased through ellipsoidal focusing antennas. Through the radiometer array calibration device (4) among the devices, the effect and the precision of radiometer imaging can be improved firstly in an internal calibration way and then in an external calibration way. Compared with conventional radiometer calibration methods, the method of the invention has the advantages that the testing efficiency is high, great image effects are provided, the precision is high, etc.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF REMOTE SENSING EQUIP
MIMO antenna array, MIMO array antenna and security inspection system
ActiveCN109167168AEvenly distributedSolve the problem of severe side gate artifactsAntenna arraysAntennas earthing switches associationField conditionsImaging quality
The present application provides a MIMO antenna array, MIMO array antenna and security inspection system for terahertz near-field imaging. The receiving antenna and the plurality of transmitting antennas are arranged on the same circular arc and uniformly distributed respectively. The receiving antenna and the plurality of transmitting antennas are arranged on the same arc, so that the distance between the receiving antenna and the plurality of transmitting antennas and the center of the circle is equal. Based on the principle of equivalent phase center, the combination of any pair of transmitting and receiving antennas can be replaced by an antenna which is located in the center of the two antennas. Only in the far-field condition, the equivalent phase center principle can hold true, andthe approximate error in the near-field condition can not be ignored. MIMO antenna array utilizes the characteristic that the distance from any point on the circle to the center of the circle is equal, The method of designing linear MIMO antenna array based on the principle of equivalent phase center is modified, which solves the problem of serious side-gate artifacts in near-field imaging of linear MIMO array based on the principle of equivalent phase center, and improves the imaging quality.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Terahertz aperture coding three-dimensional target scanning imaging method
ActiveCN107942328AReduce memory configuration requirementsImprove operational efficiencyRadio wave reradiation/reflectionHigh resolution imagingHigh resolution image
Currently, the two-dimensional imaging technology under the aperture coding imaging system is no longer suitable for a three-dimensional target. To solve the above defect in the prior art, the invention provides a terahertz aperture coding three-dimensional target scanning imaging method. In the invention, an entire three-dimensional imaging area where a three-dimensional target is located is evenly divided into three-dimensional imaging units with the same size and, for each three-dimensional imaging unit, an updated lens phase modulation factor is calculated according to the position of thesingle three-dimensional imaging unit, such that complete coverage of the three-dimensional imaging units can be realized and complete scanning of the three-dimensional imaging area is achieved. The method of the invention can achieve forward-looking high-resolution imaging for a close-distance three-dimensional target, effectively increases the imaging range and speed of terahertz aperture codingimaging, improves the imaging efficiency, reduces the requirements for computer memory configuration, and is applicable to the security inspection and counter-terrorism, target detection and identification and other near-field imaging fields.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com