Patents
Literature
141 results about "Horizontal field" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
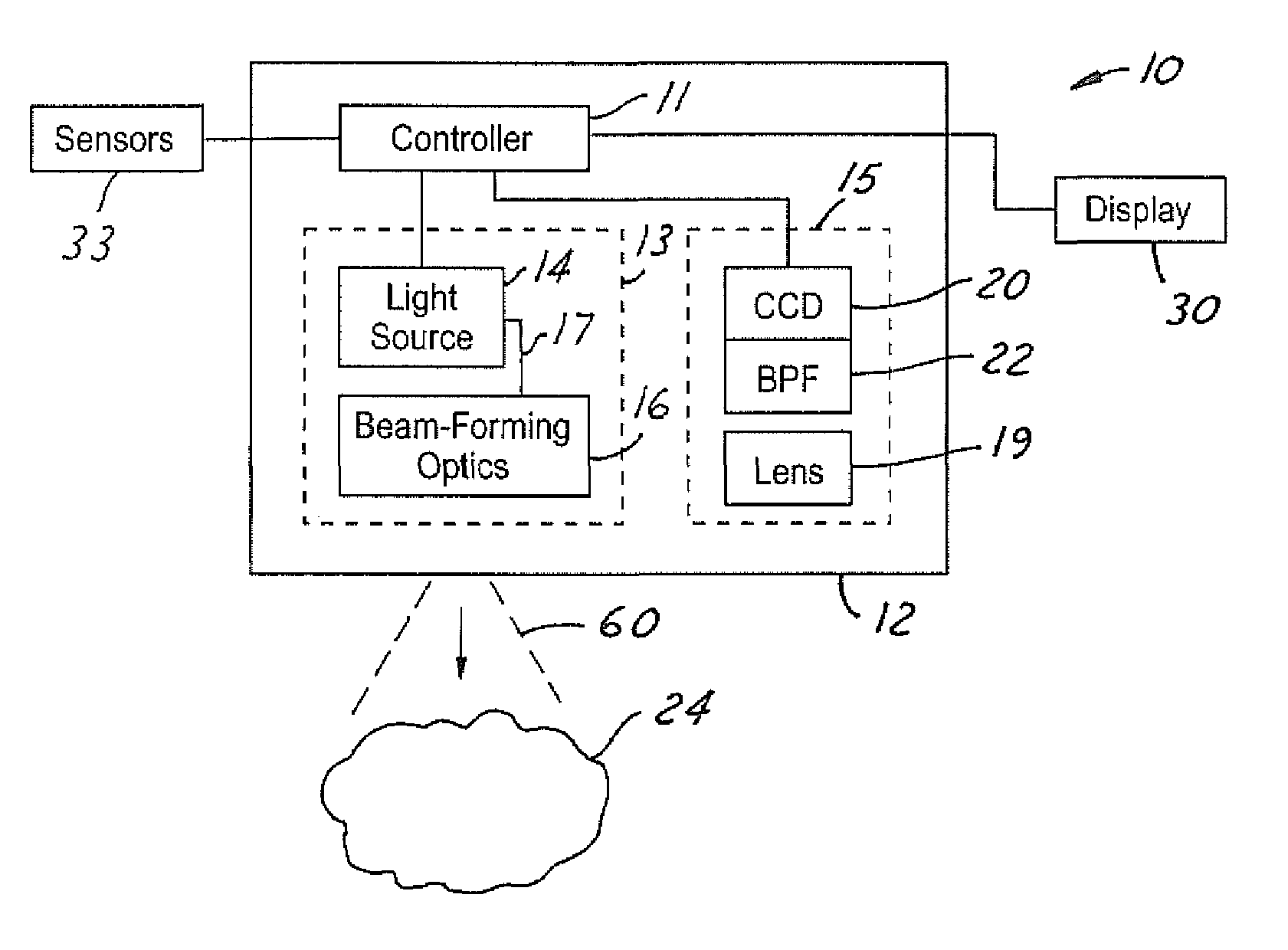
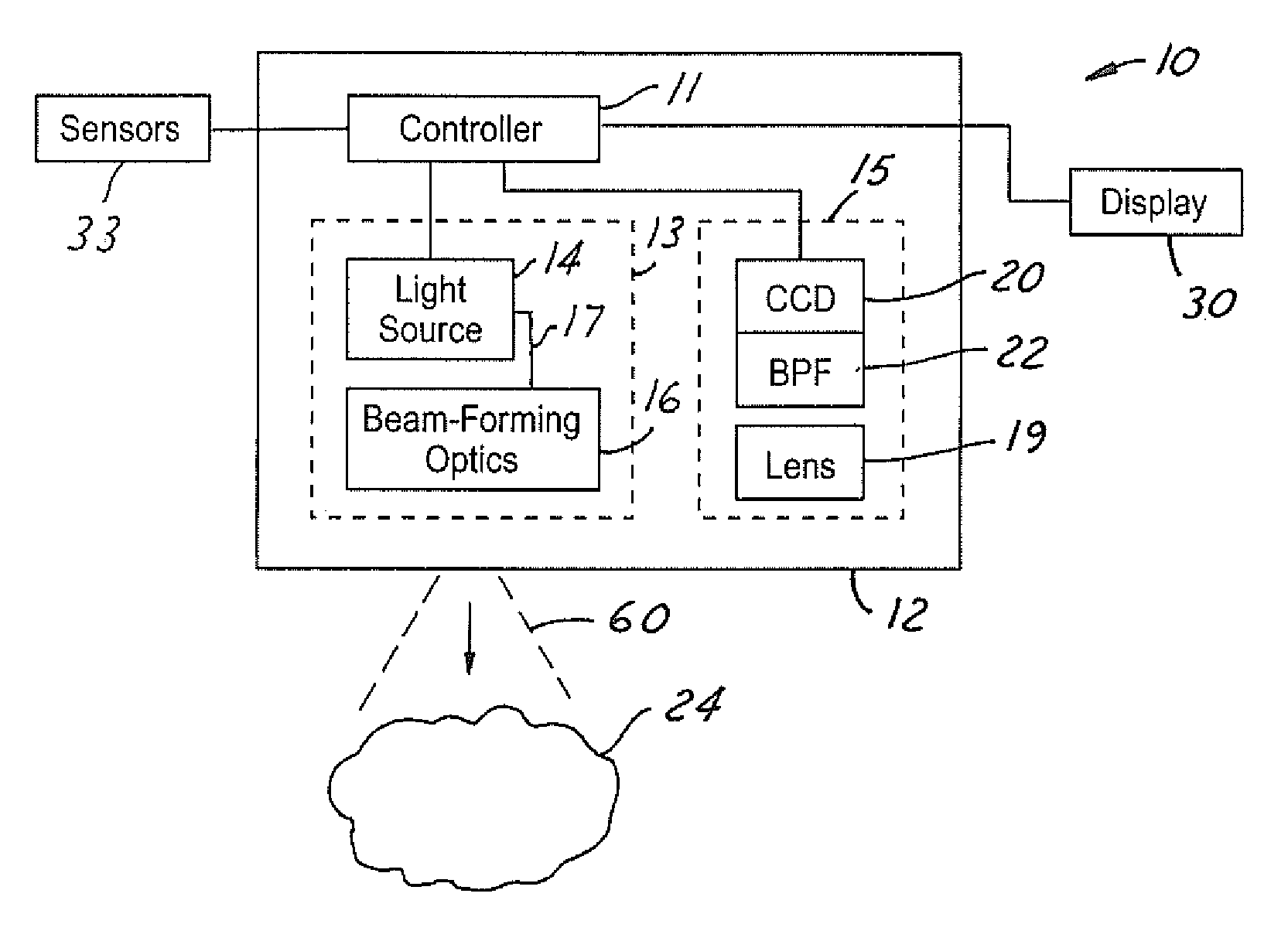
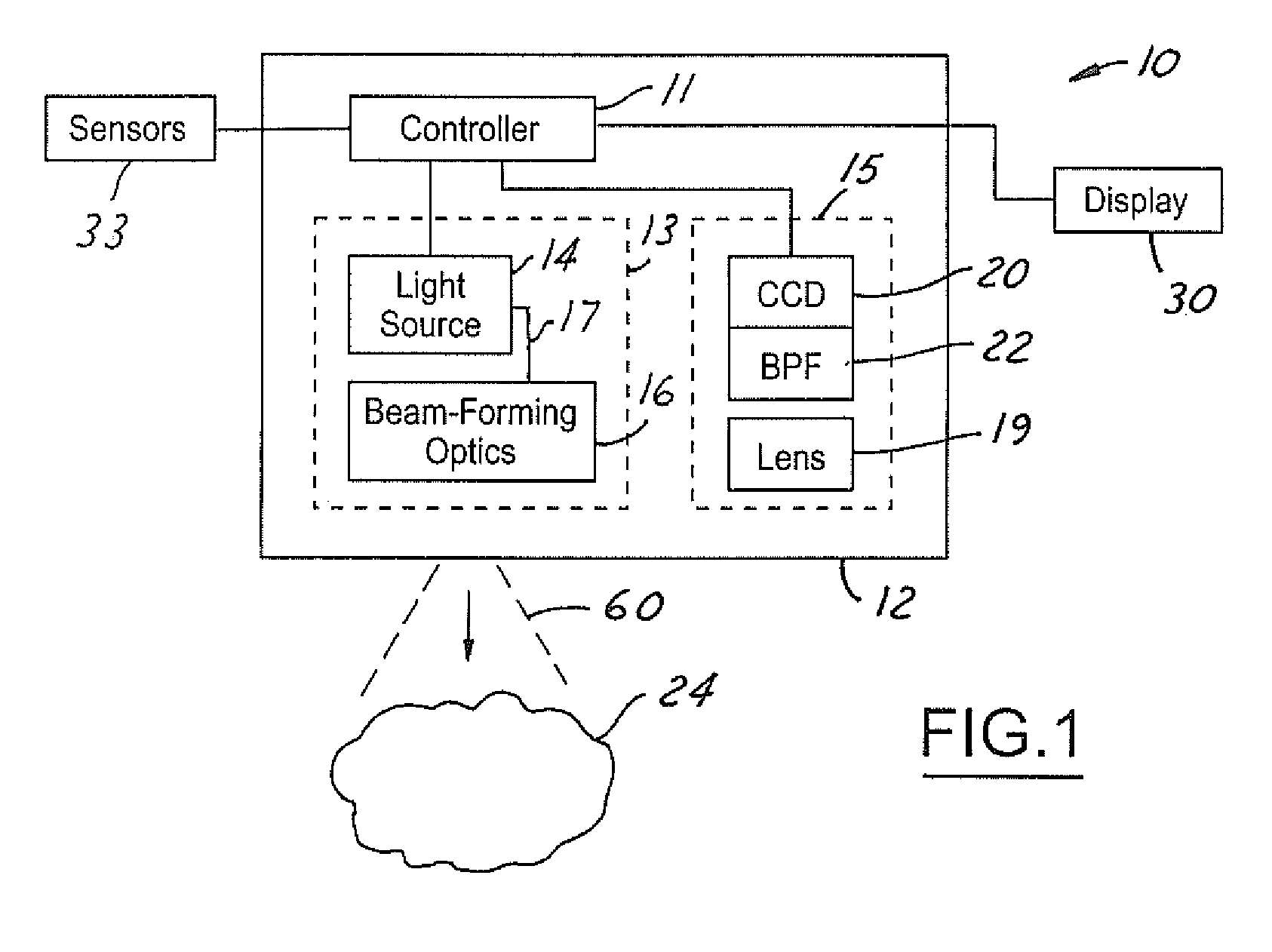
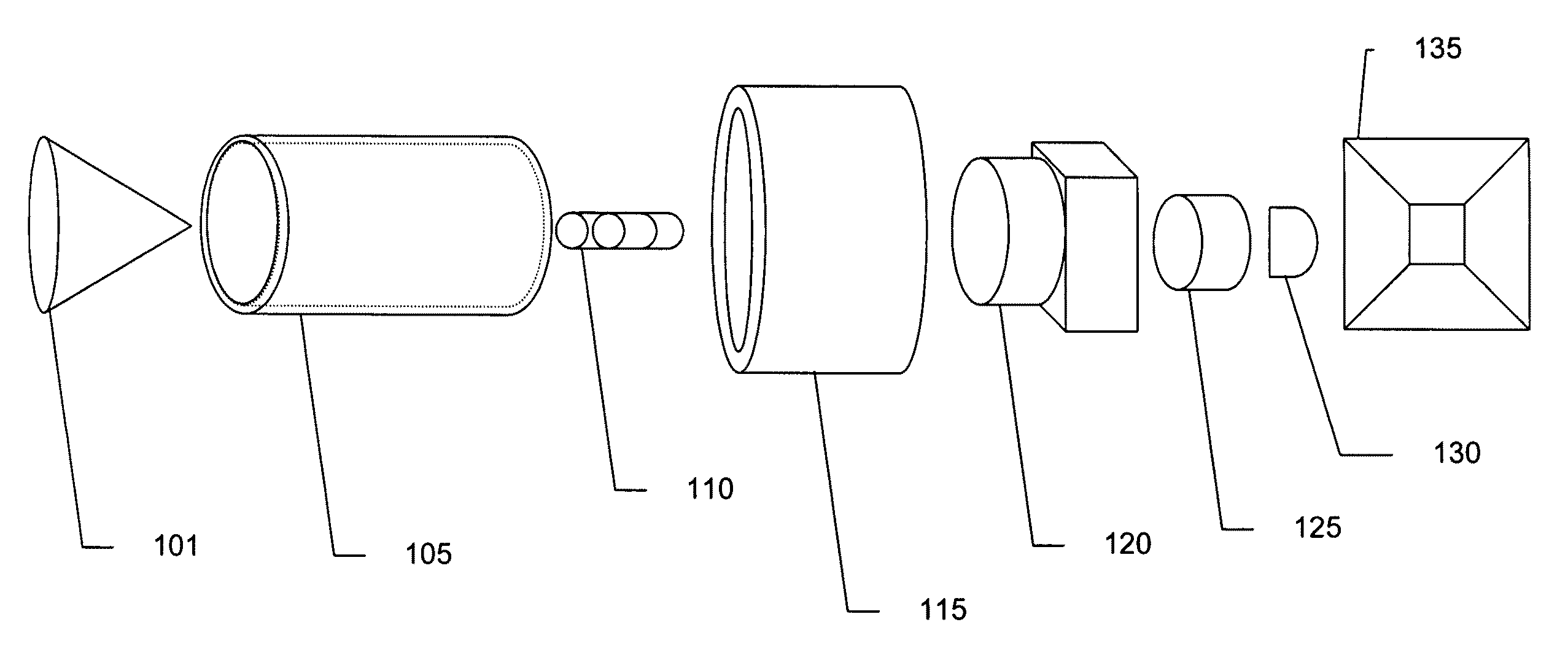
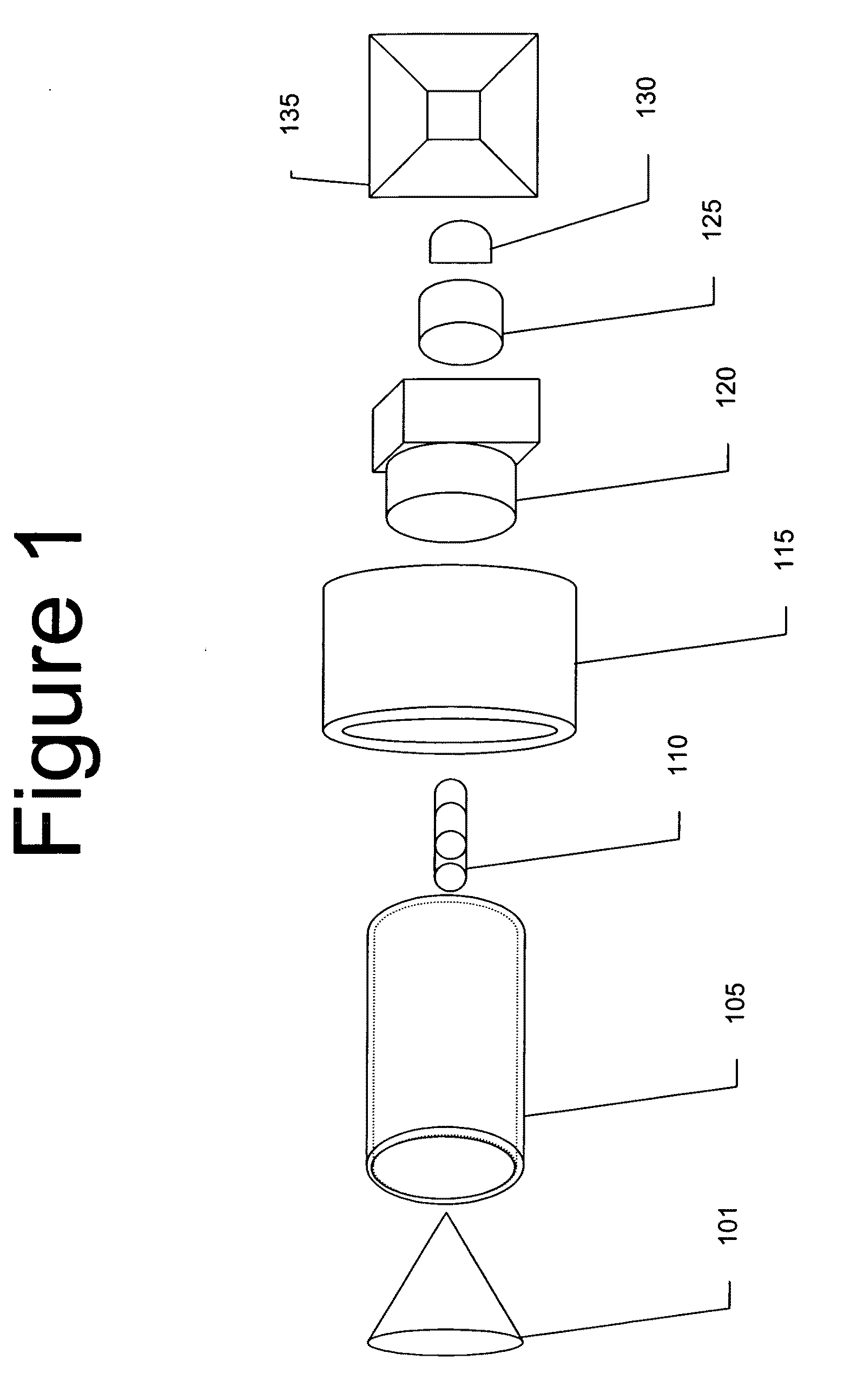
Panoramic video system with real-time distortion-free imaging
ActiveUS20060023105A1Minimizing software overheadHighly efficient regional transformationImage enhancementTelevision system detailsTime distortionGraphic card
A panoramic annular lens system (PAL), a unitary video camera and a PC-based software system that unwraps a 360° video image into a seamless, distortion free horizontal image image in real time. The PAL system of the preferred embodiment has a 360° horizontal field of view and a 90° vertical field of view in a 40 mm diameter compact package. The invention is not limited to any particular type of lens system. In fact, there are numerous lens systems for providing a 360° panoramic view. The video camera may be a CCD or CMOS based device having a pixel resolution of either 1280×1024 (high resolution) or 720×480 (NTSC). The unwrapping system is a radiometric ray tracing program carried out using a computer's graphics card capabilities to produce highly efficient regional transformation while minimizing software overhead. The result is real time, high resolution 30 fps conversion from a spherical distorted image to a flat panoramic image in Cartesian coordinates.
Owner:PHYSICAL OPTICS CORP
Panoramic video system with real-time distortion-free imaging
ActiveUS7336299B2Highly efficient regional transformationMinimize overheadImage enhancementTelevision system detailsTime distortionGraphic card
A panoramic annular lens system (PAL), a unitary video camera and a PC-based software system that unwraps a 360° video image into a seamless, distortion free horizontal image image in real time. The PAL system of the preferred embodiment has a 360° horizontal field of view and a 90° vertical field of view in a 40 mm diameter compact package. The invention is not limited to any particular type of lens system. In fact, there are numerous lens systems for providing a 360° panoramic view. The video camera may be a CCD or CMOS based device having a pixel resolution of either 1280×1024 (high resolution) or 720×480 (NTSC). The unwrapping system is a radiometric ray tracing program carried out using a computer's graphics card capabilities to produce highly efficient regional transformation while minimizing software overhead. The result is real time, high resolution 30 fps conversion from a spherical distorted image to a flat panoramic image in Cartesian coordinates.
Owner:PHYSICAL OPTICS CORP
Active night vision with adaptive imaging
InactiveUS6967569B2Minimize complexityLow costAnti-collision systemsColor television detailsNight visionAdaptive imaging
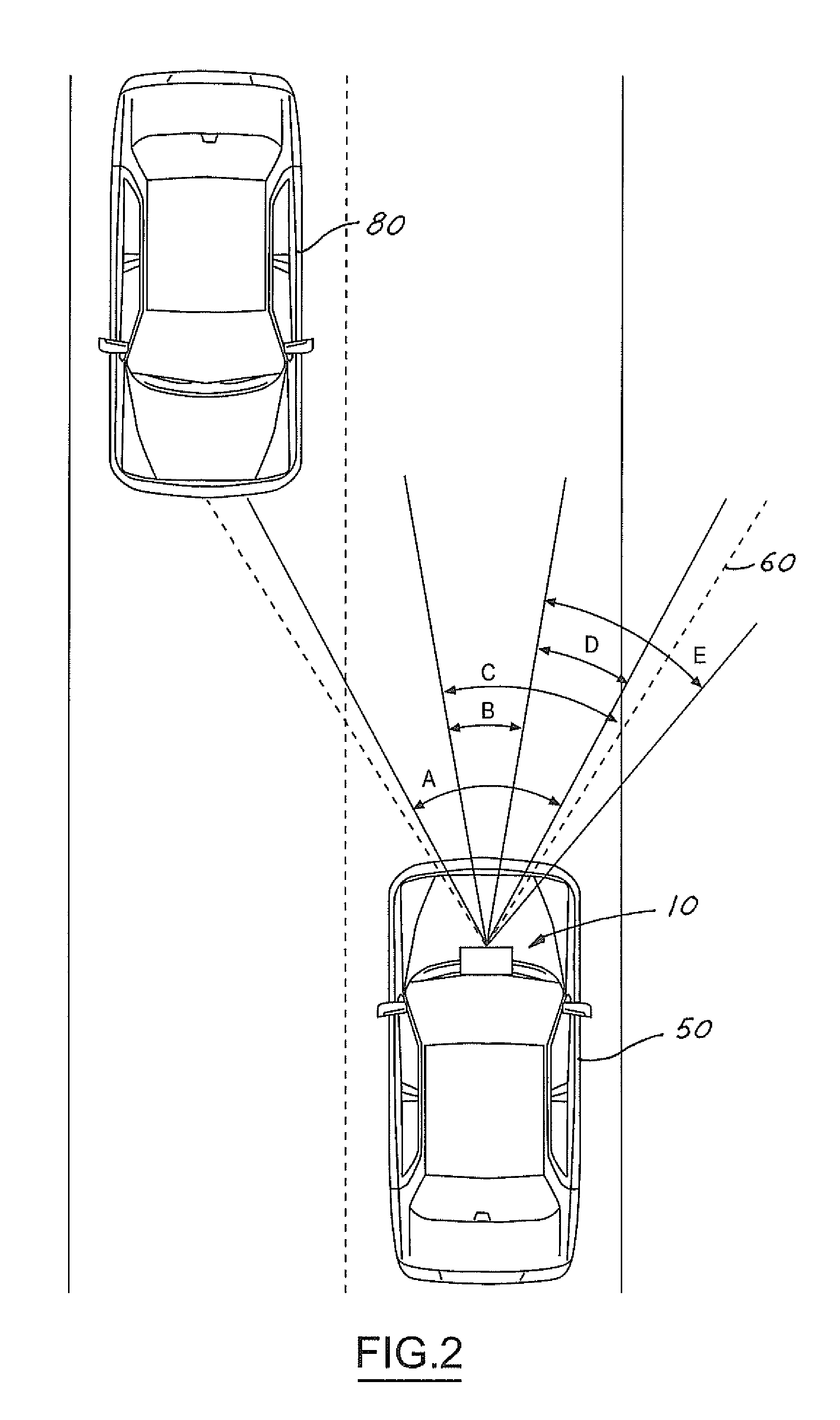
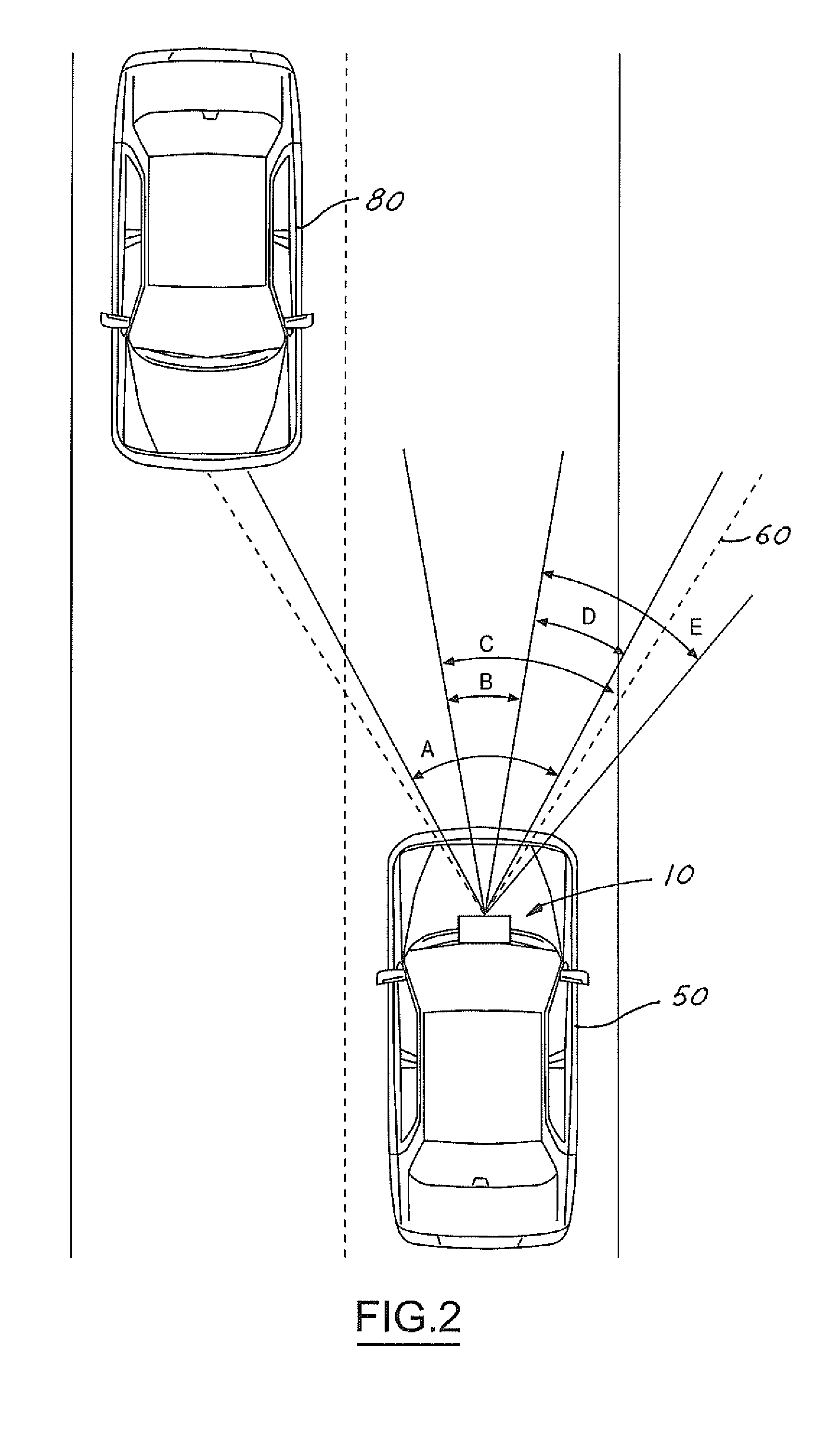
A vision system for a vehicle includes a light source generating an illumination beam, a receiver having a pixel array for capturing an image in response to at least a reflected portion of the illumination beam, the image corresponding to a first horizontal field of view (FOV) angle, and a controller coupled to the light source and the receiver. The controller receives a vehicle speed input and, in response, selects a portion of the image as a non-linear function of the vehicle speed to generate a second horizontal FOV angle for displaying to the vehicle operator. The displayed angular FOV decreases, non-linearly, as the vehicle speed increases.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Integrated hemt and a combination, method as well as a system of a horizontal field effect rectifier
ActiveCN101562182AIncrease powerHigh noise environmentTransistorSolid-state devicesSemiconductor materialsOhmic contact
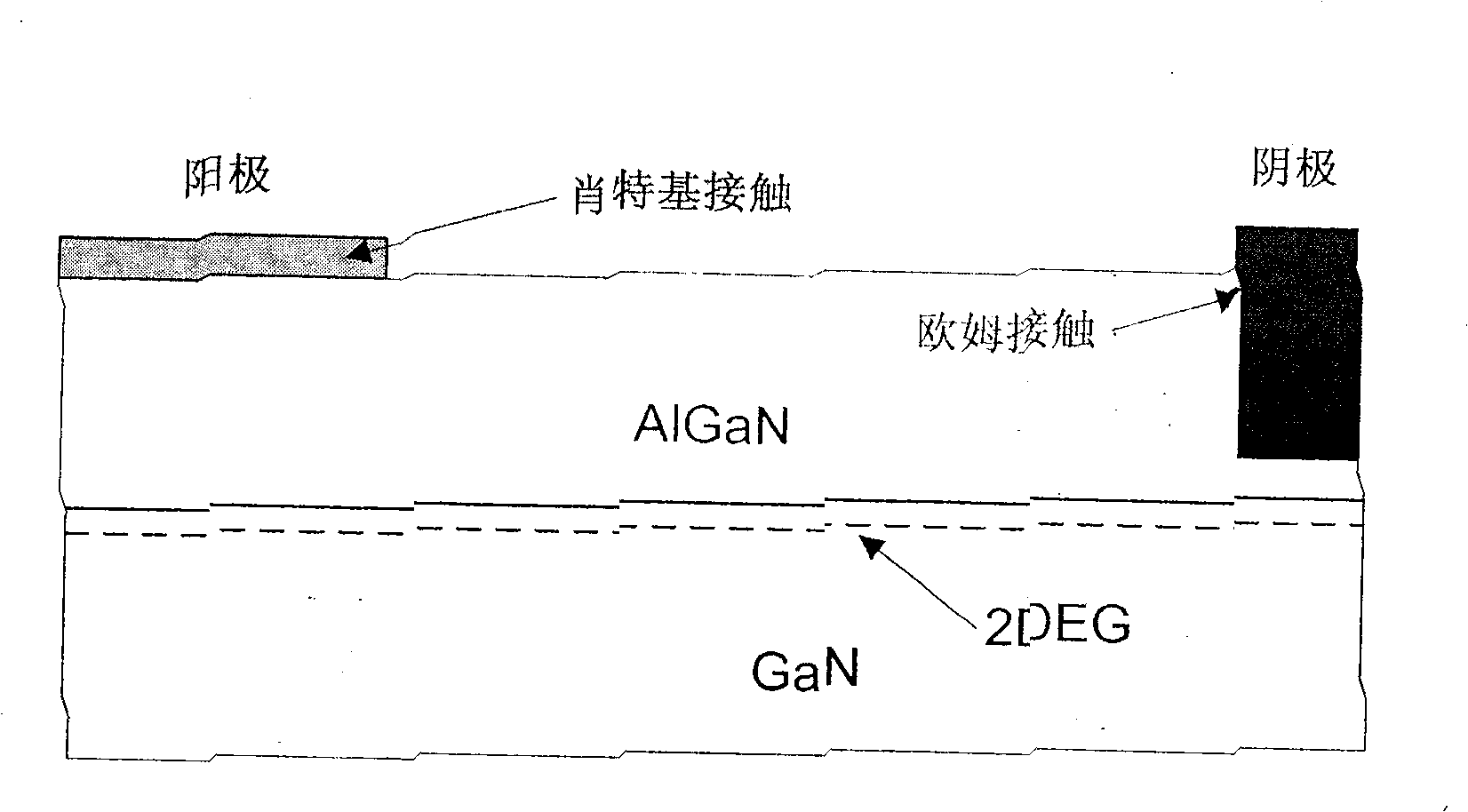
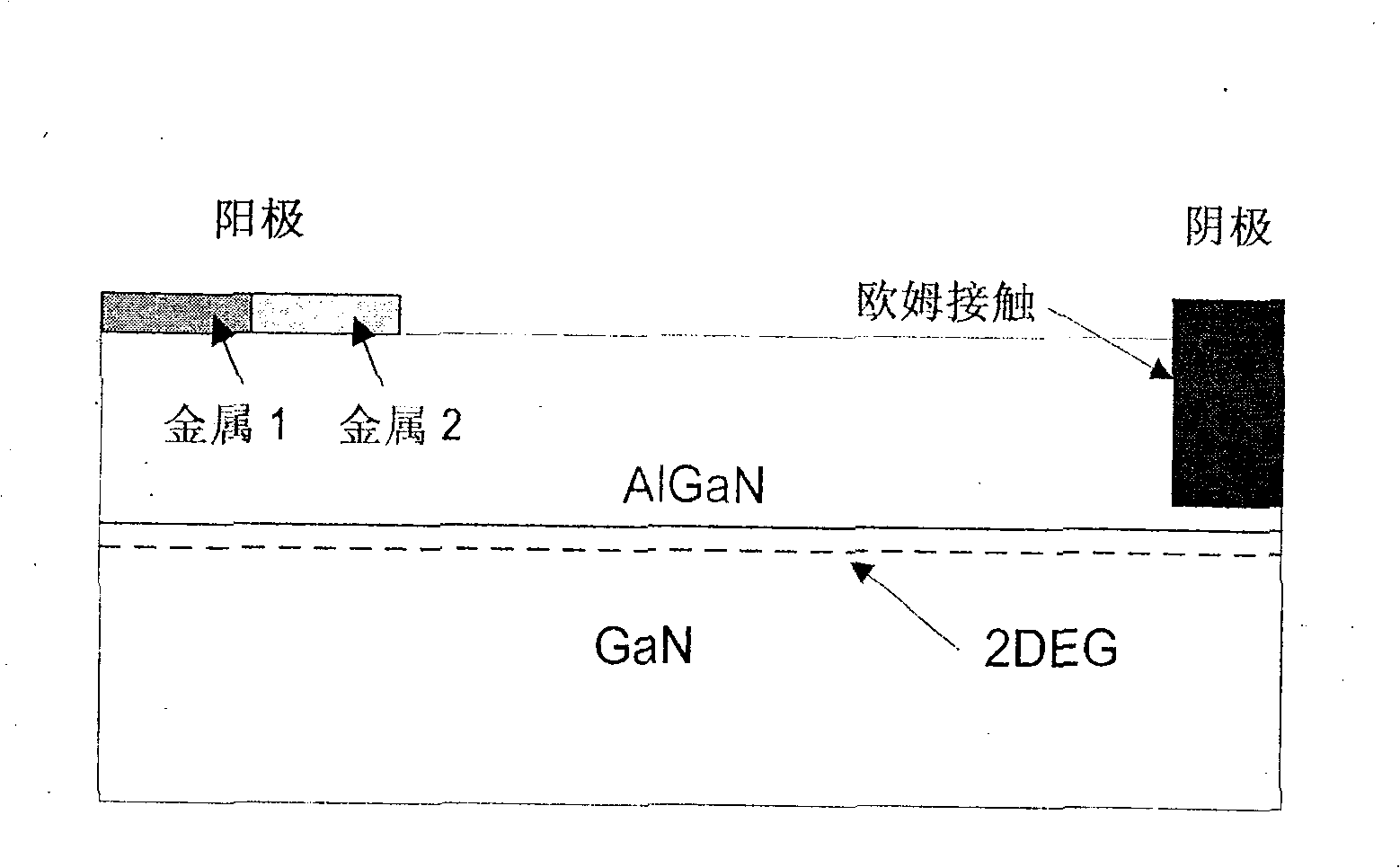
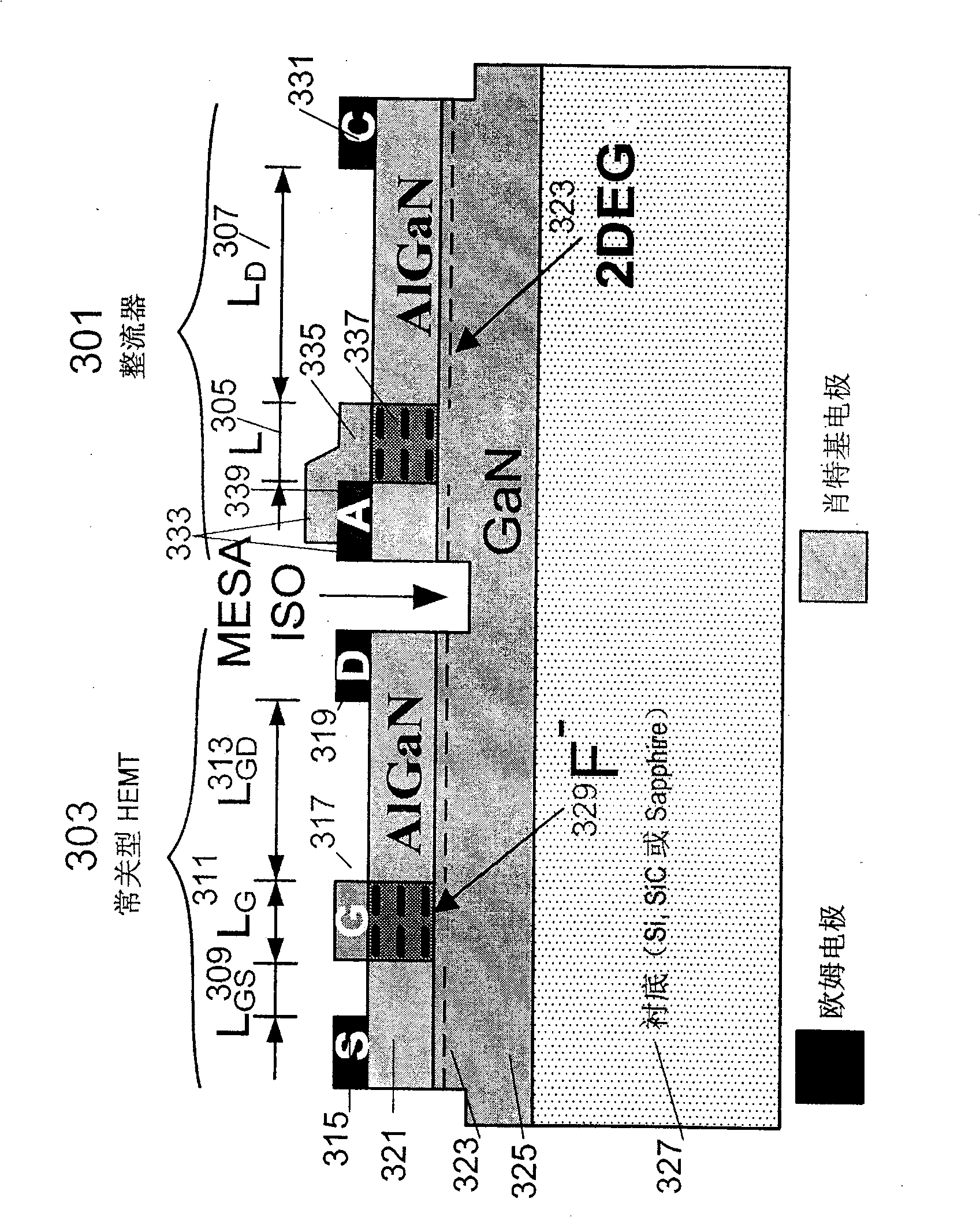
The invention provides integrated HEMT and a combination, a method as well as a system of a horizontal field effect rectifier. The invention discloses an integrated highly efficient field effect rectifier and a device of HEMT based on GaN or other similar semi-conductor material, a method for manufacturing the integrated device and a system comprising the integrated device. The horizontal field effect rectifier is provided with an anode which comprises short-circuit ohmic contact and Schottky contact, a cathode which comprises an ohmic contact; while HEMT preference is provided with a grid comprising Schottky contact. Two zones provided with fluorine ion are respectively formed right beneath the Schottky contact of the rectifier and HEMT, in order to pinch off a (electron gas) groove of hetero-junction interface between epilayers of two structures.
Owner:THE HONG KONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
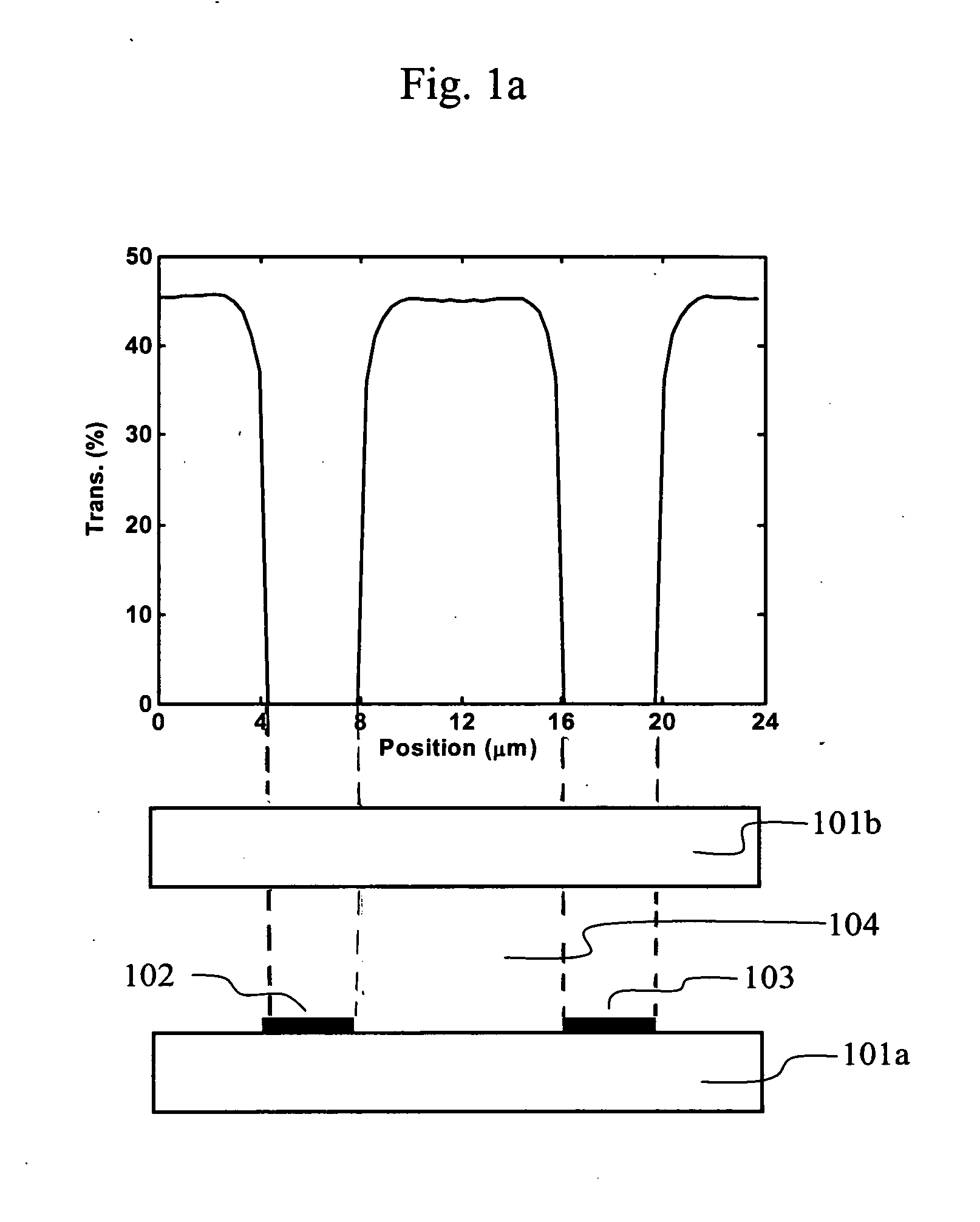
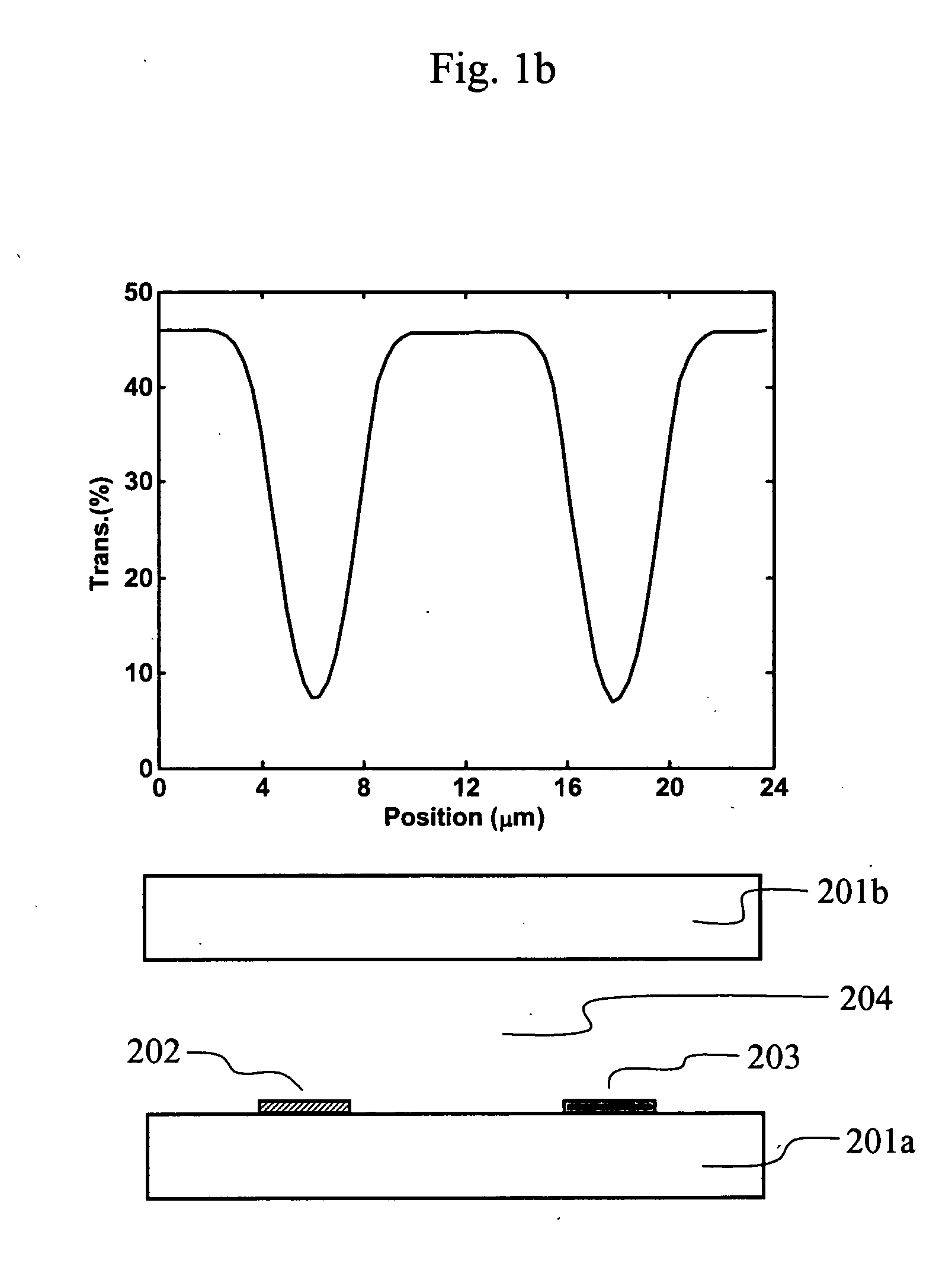
Liquid crystal display devices with high transmittance and wide viewing angle
InactiveUS20070115417A1Increase opening ratioWide viewing angleStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayPolarizer
Apparatus, methods, systems and devices for high aperture ratio, high transmittance, and wide viewing angle liquid crystal display having first and second substrates each with an alignment layer and polarizer on the interior and exterior surface thereof and a liquid crystal material therebetween forming plural pixels each having a common electrode group and a pixel electrode group each having at least one common and pixel electrode. A fringe field drives the molecules in the regions above and below the electrodes and a horizontal field drives the molecules between the electrode groups to achieve high transmittance. In an embodiment an insulating layer separates the substrate and alignment layer and the pixel electrodes are on the substrate and the common electrodes are on the insulating layer. In another embodiment a compensation film is layered between one of the substrates and corresponding polarizer.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC +1
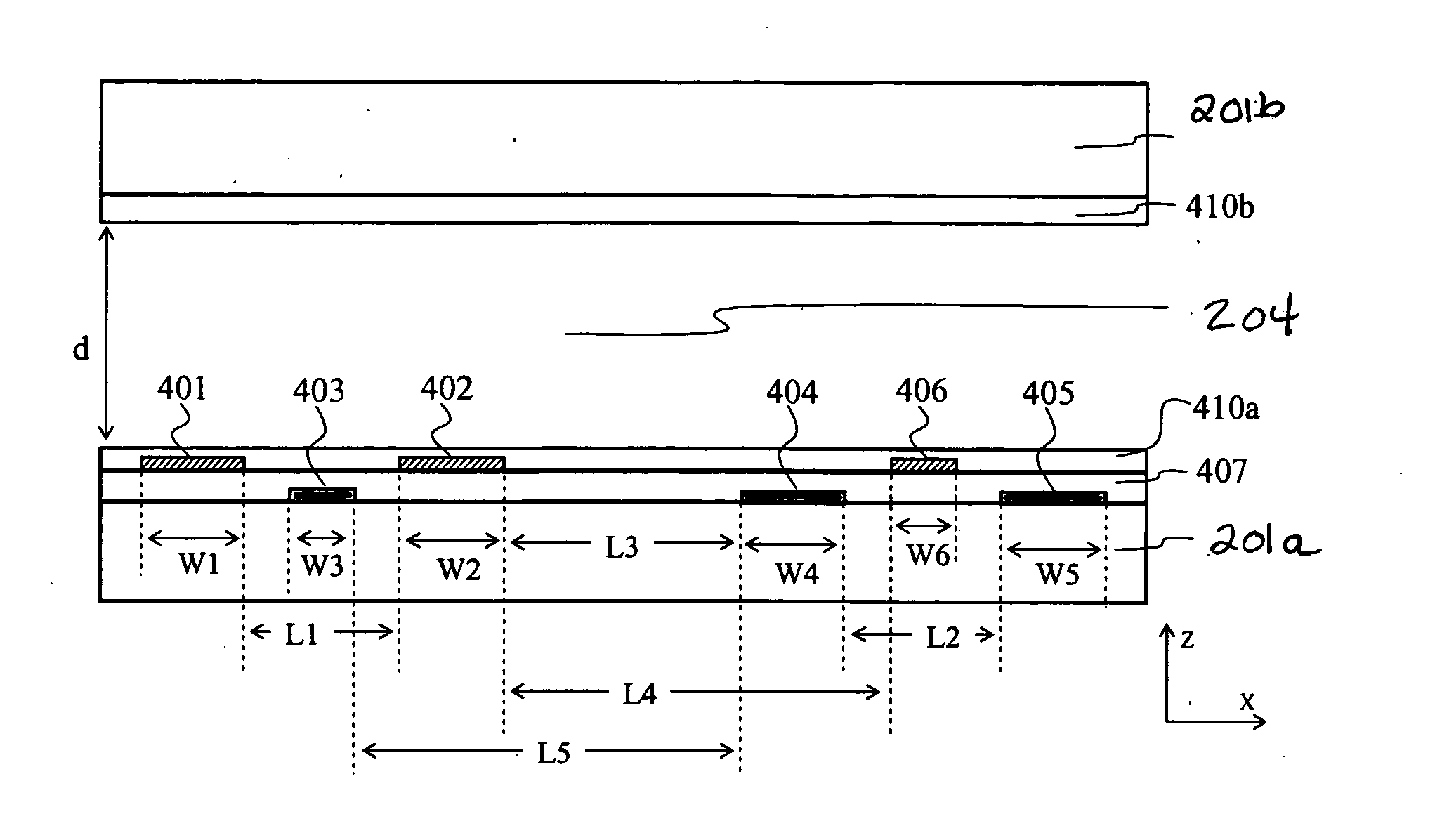
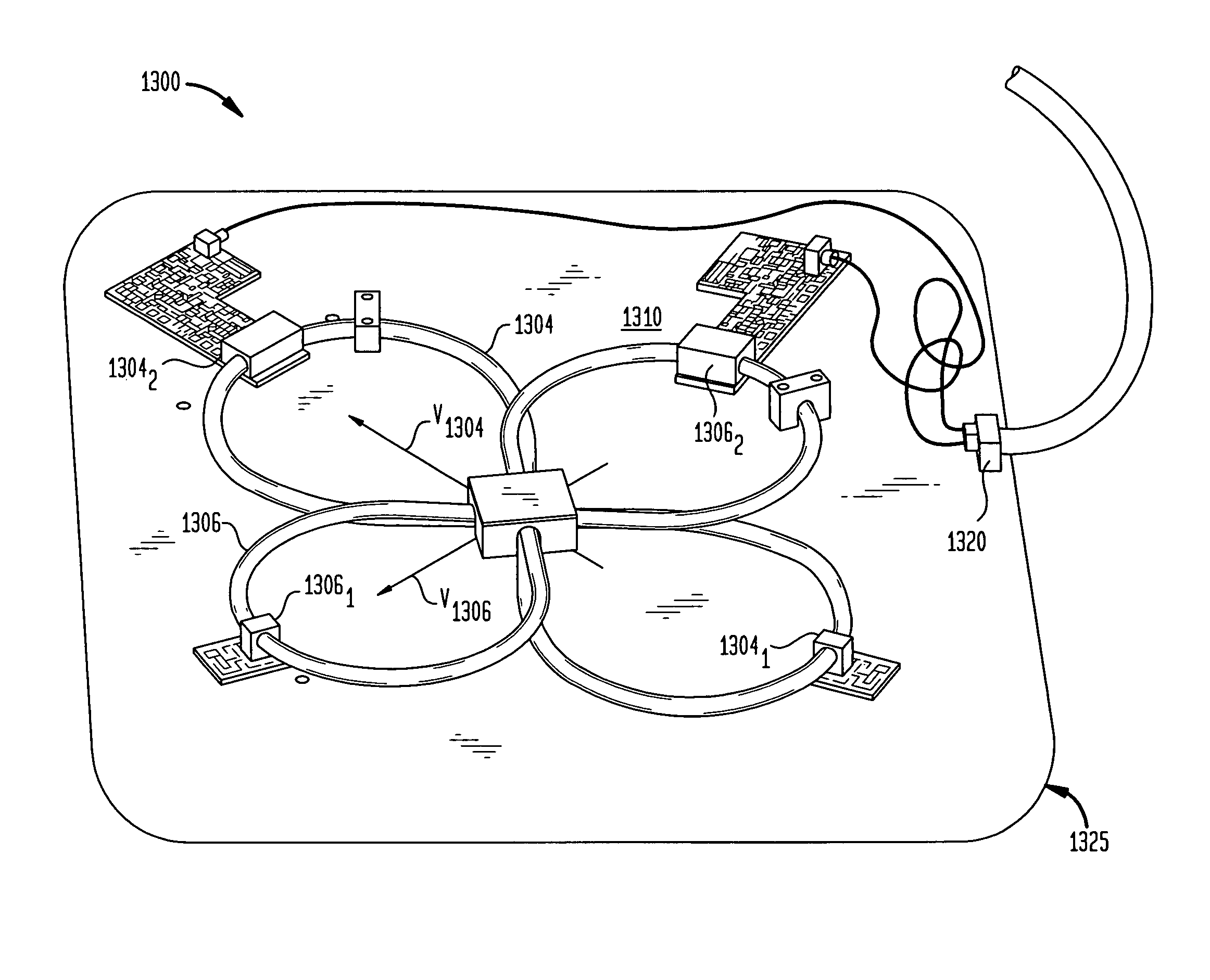
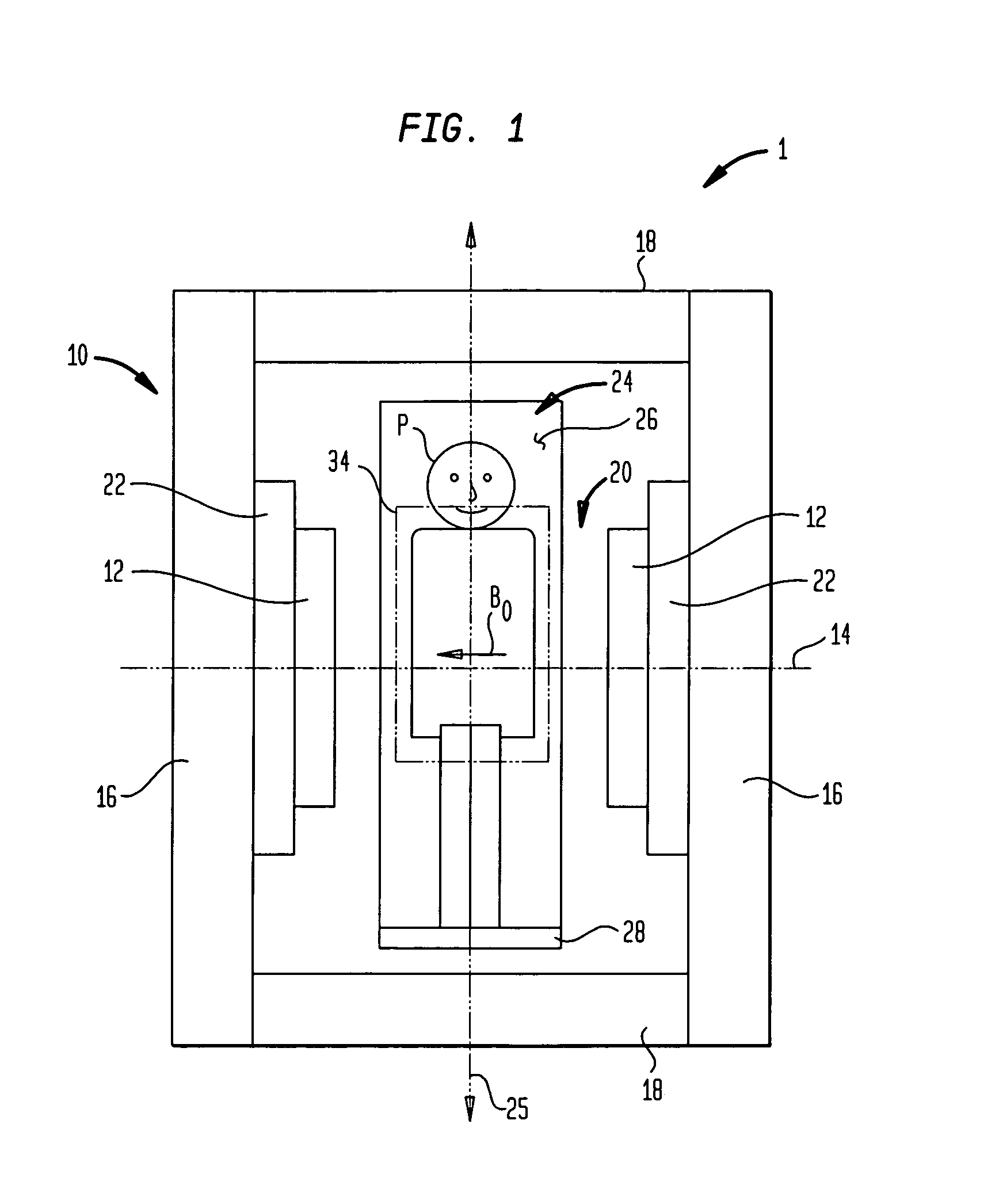
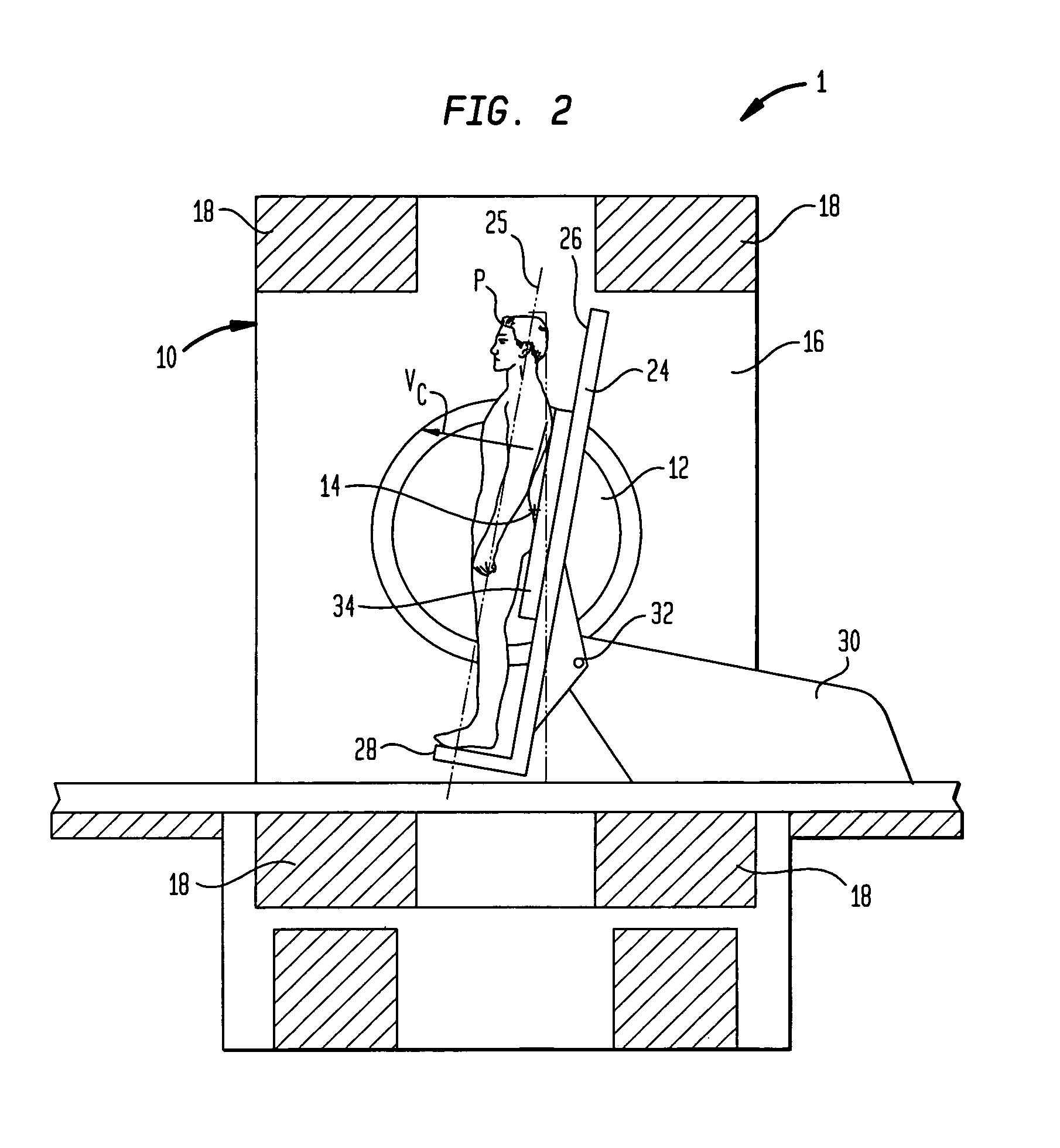
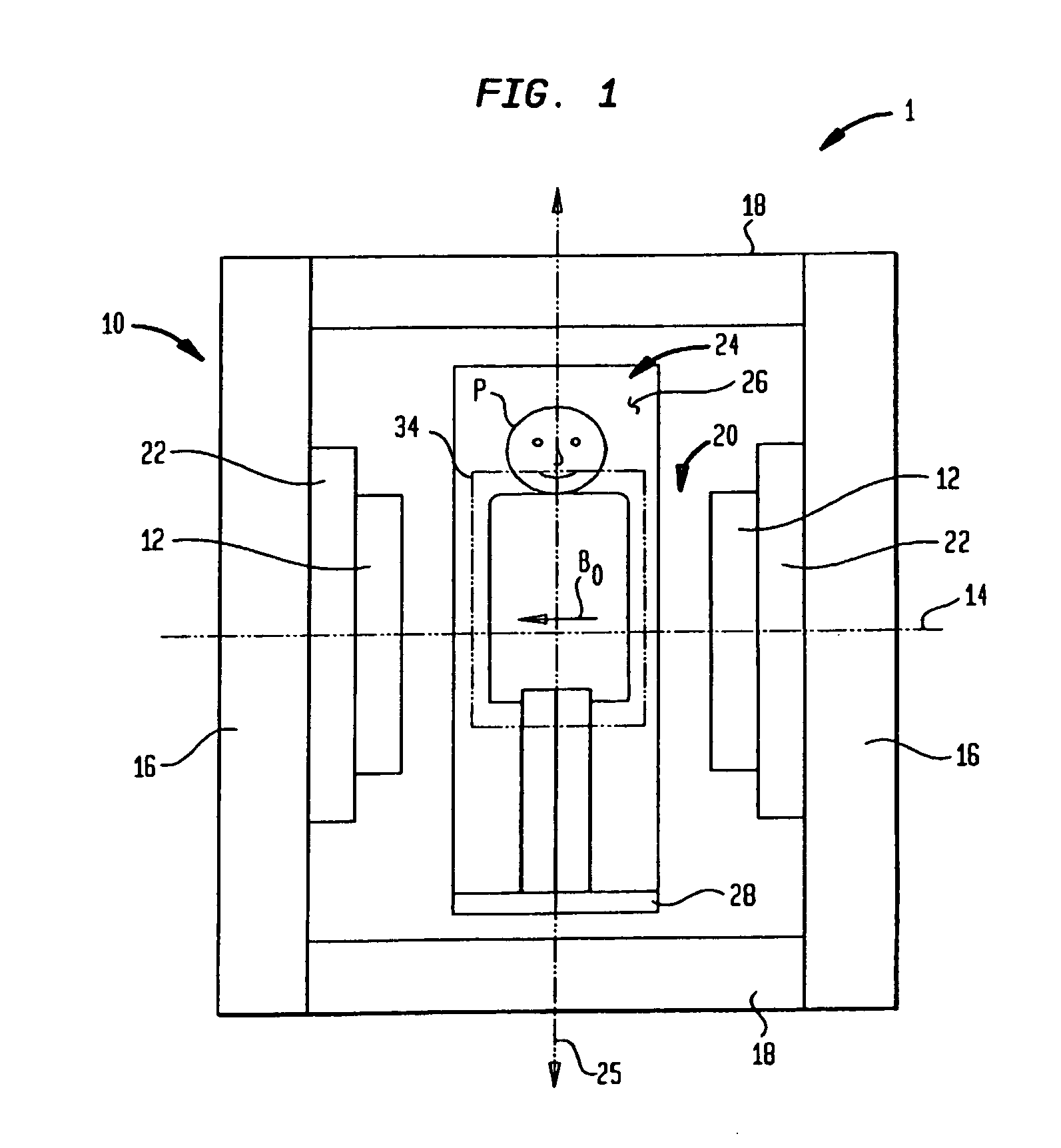
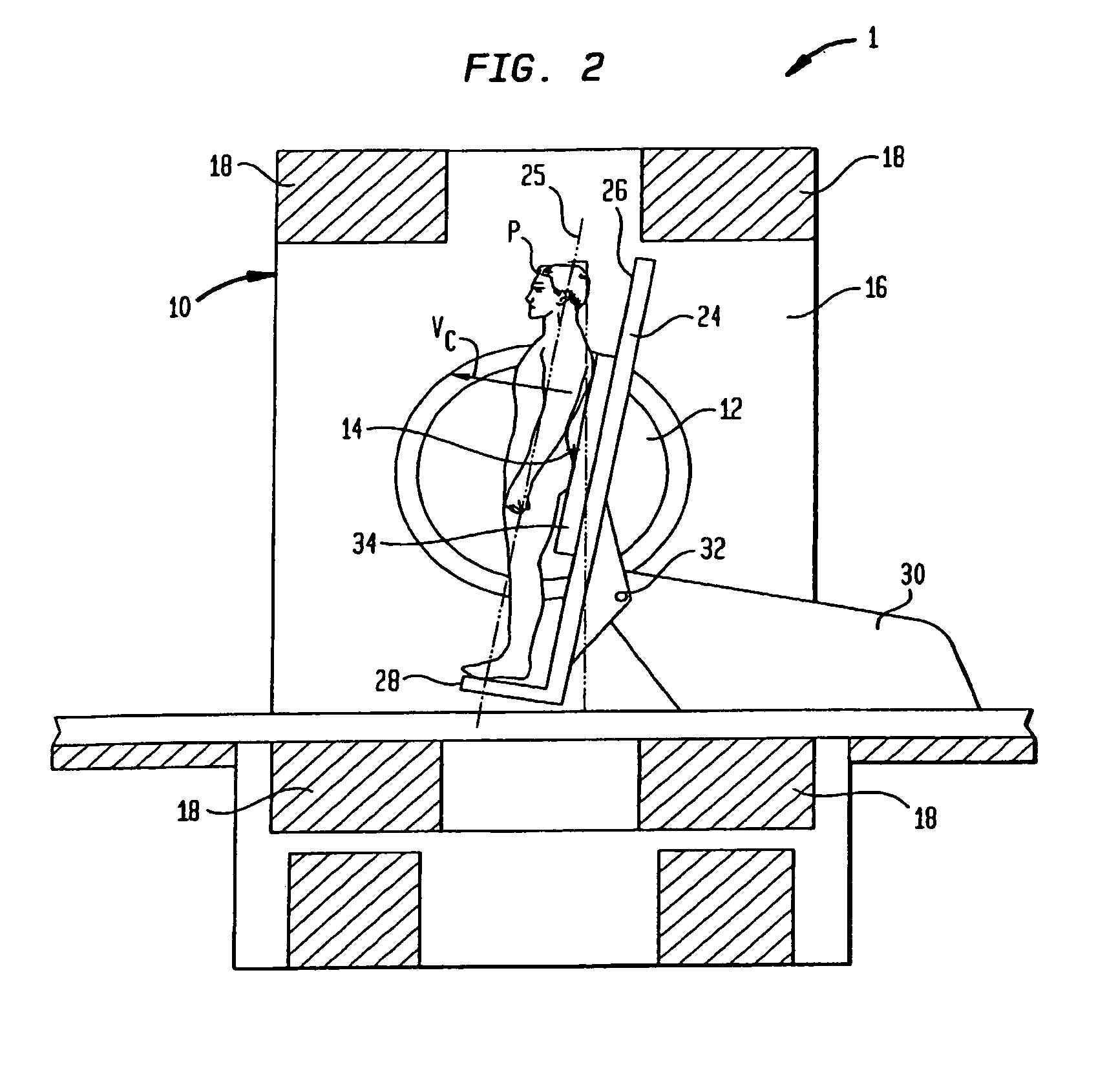
Coils for horizontal field magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveUS7701209B1PerformanceMore detailMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringResonanceMri image
Apparatus for performing magnetic resonance imaging are disclosed. In one aspect coil antennas for use with a horizontal field magnetic resonance imaging apparatus are placed in proximity to the scanning region to obtain magnetic resonance images. The coils are arranged in quadrature geometry and housed in a planar structure.
Owner:FONAR
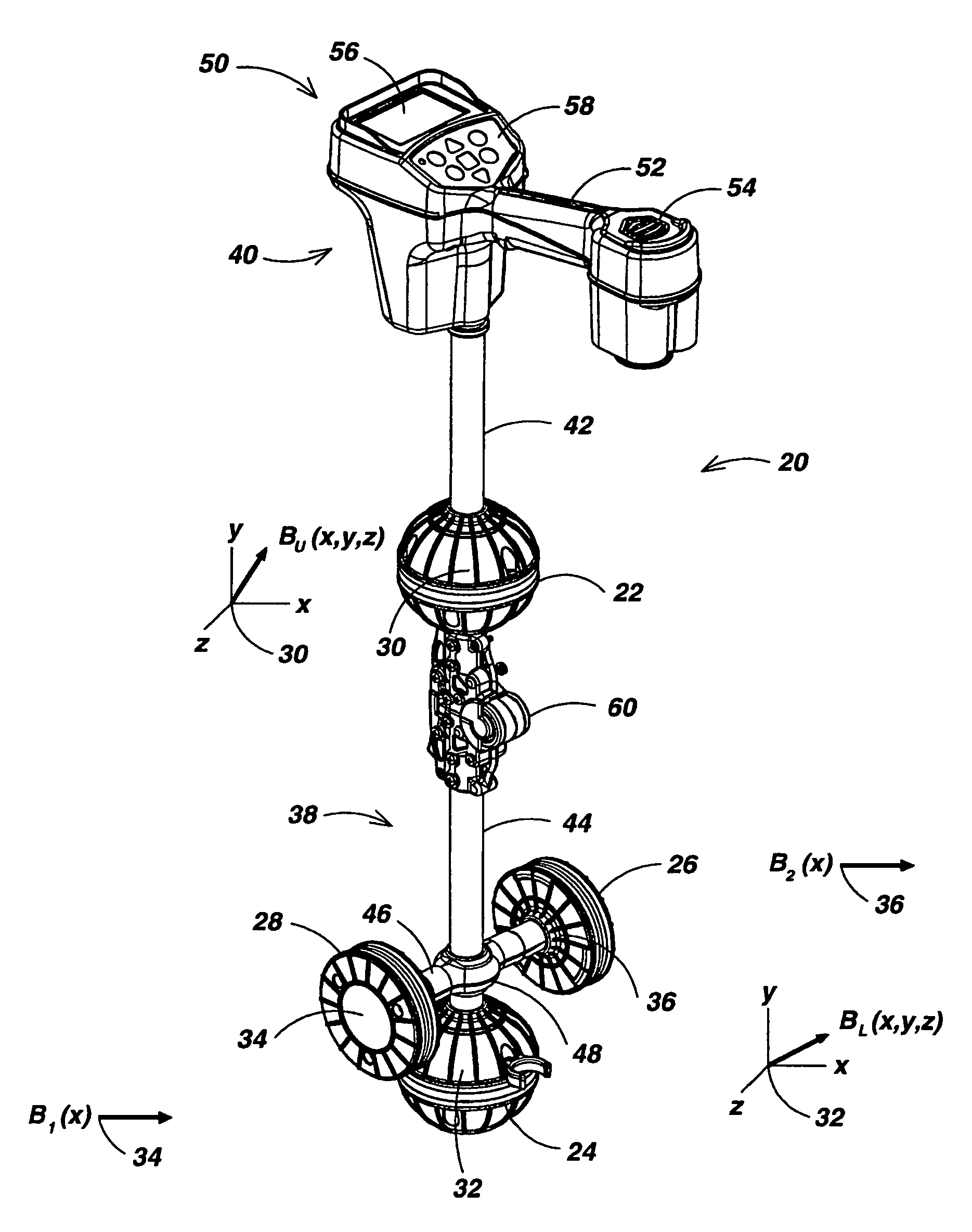
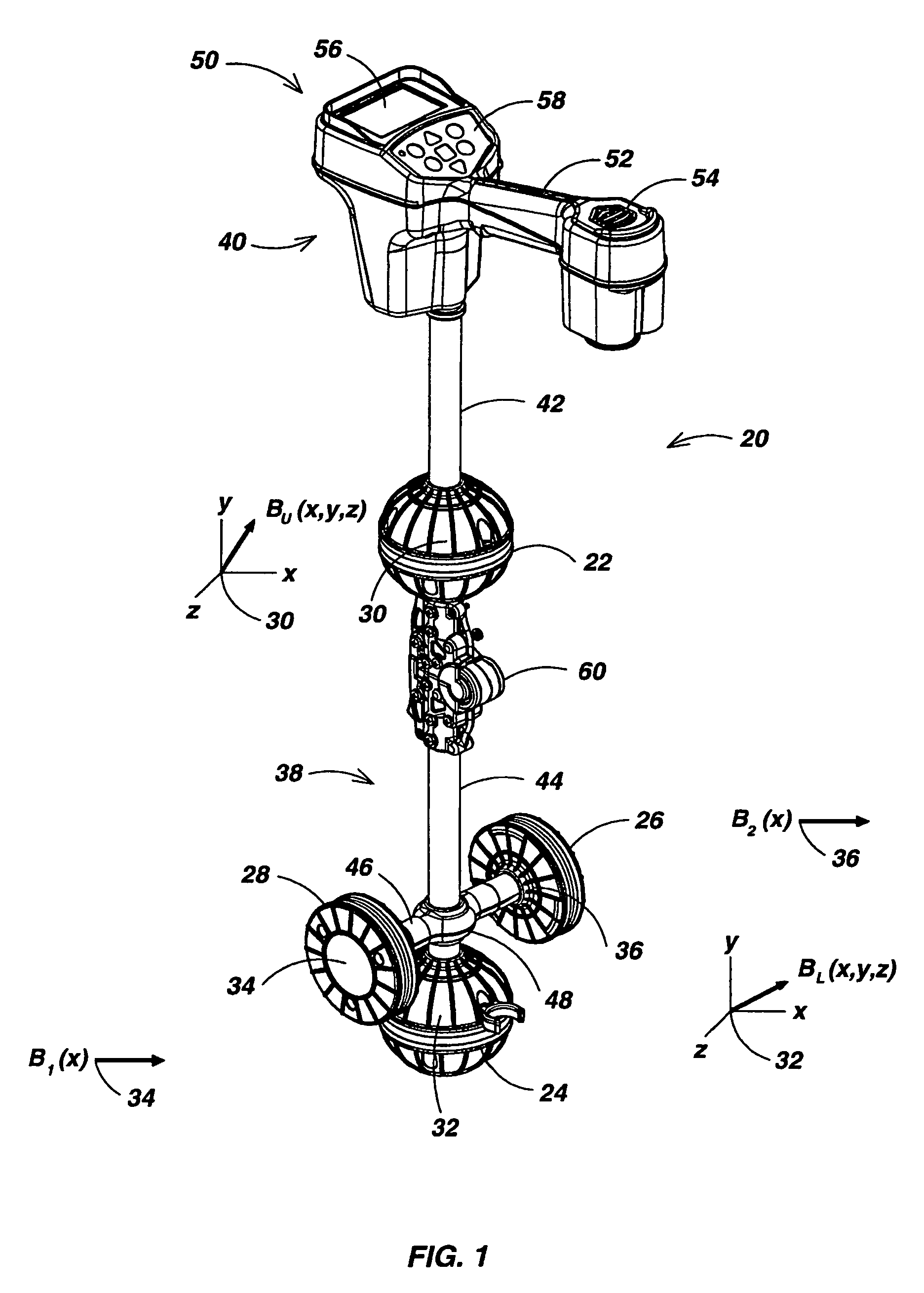
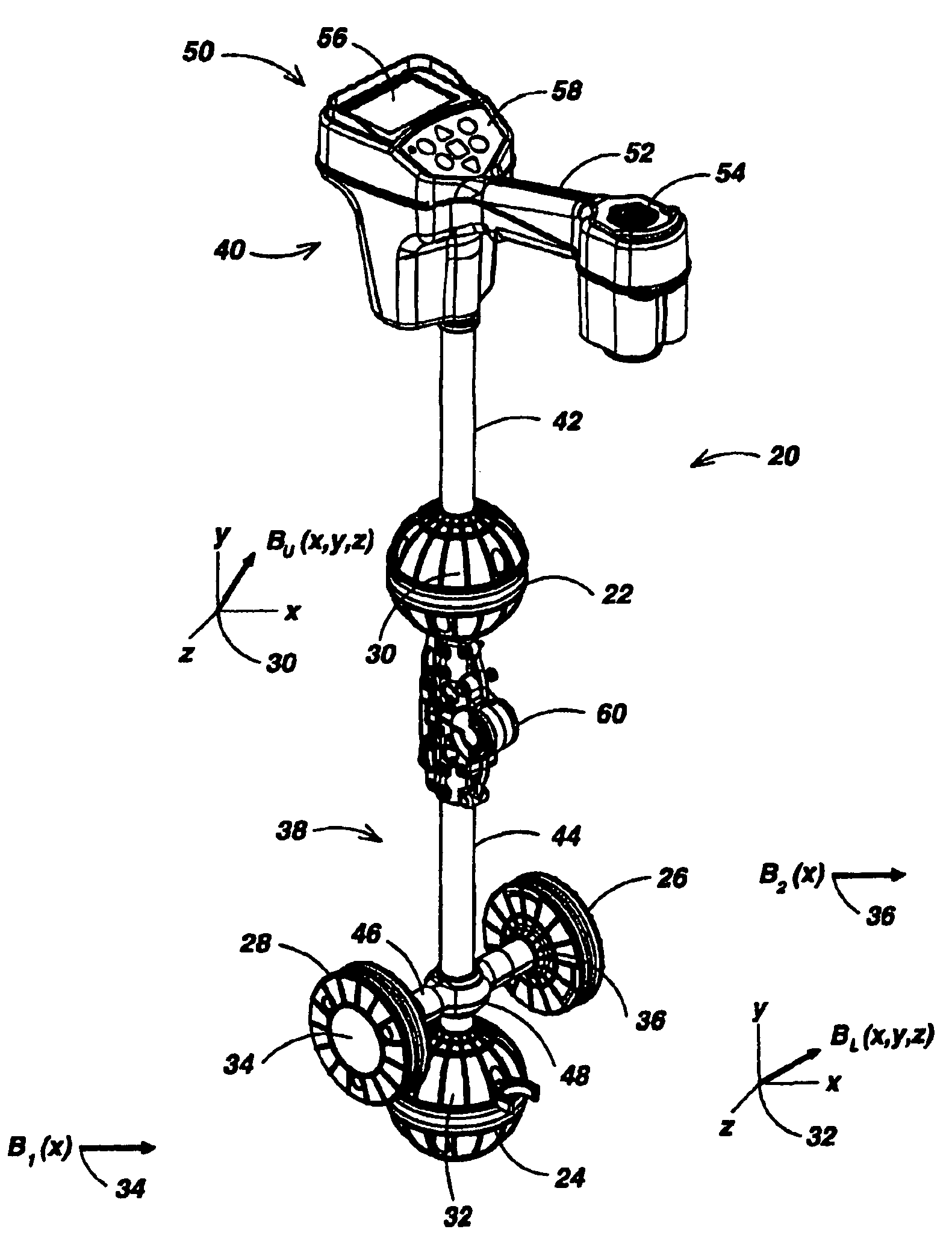
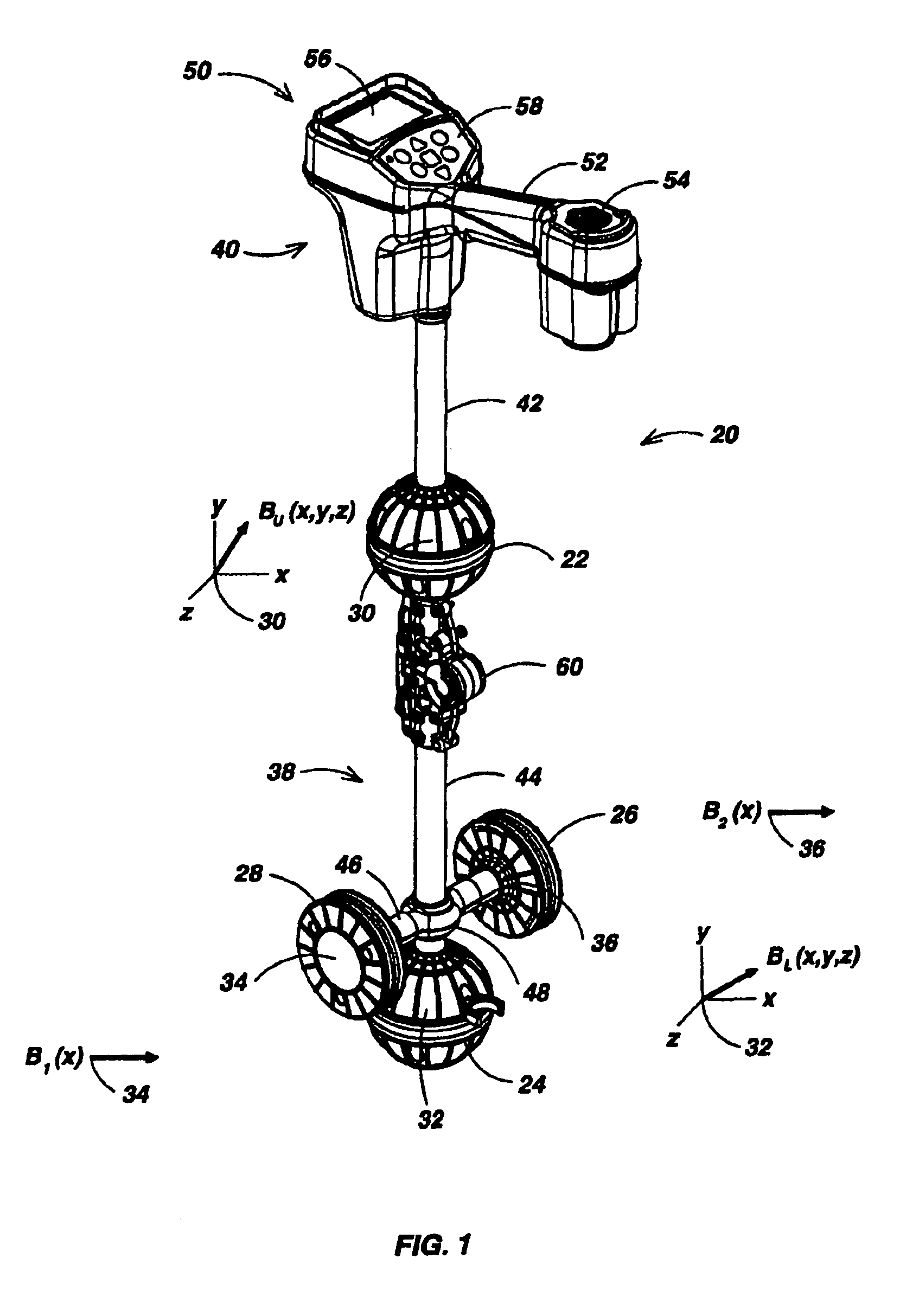
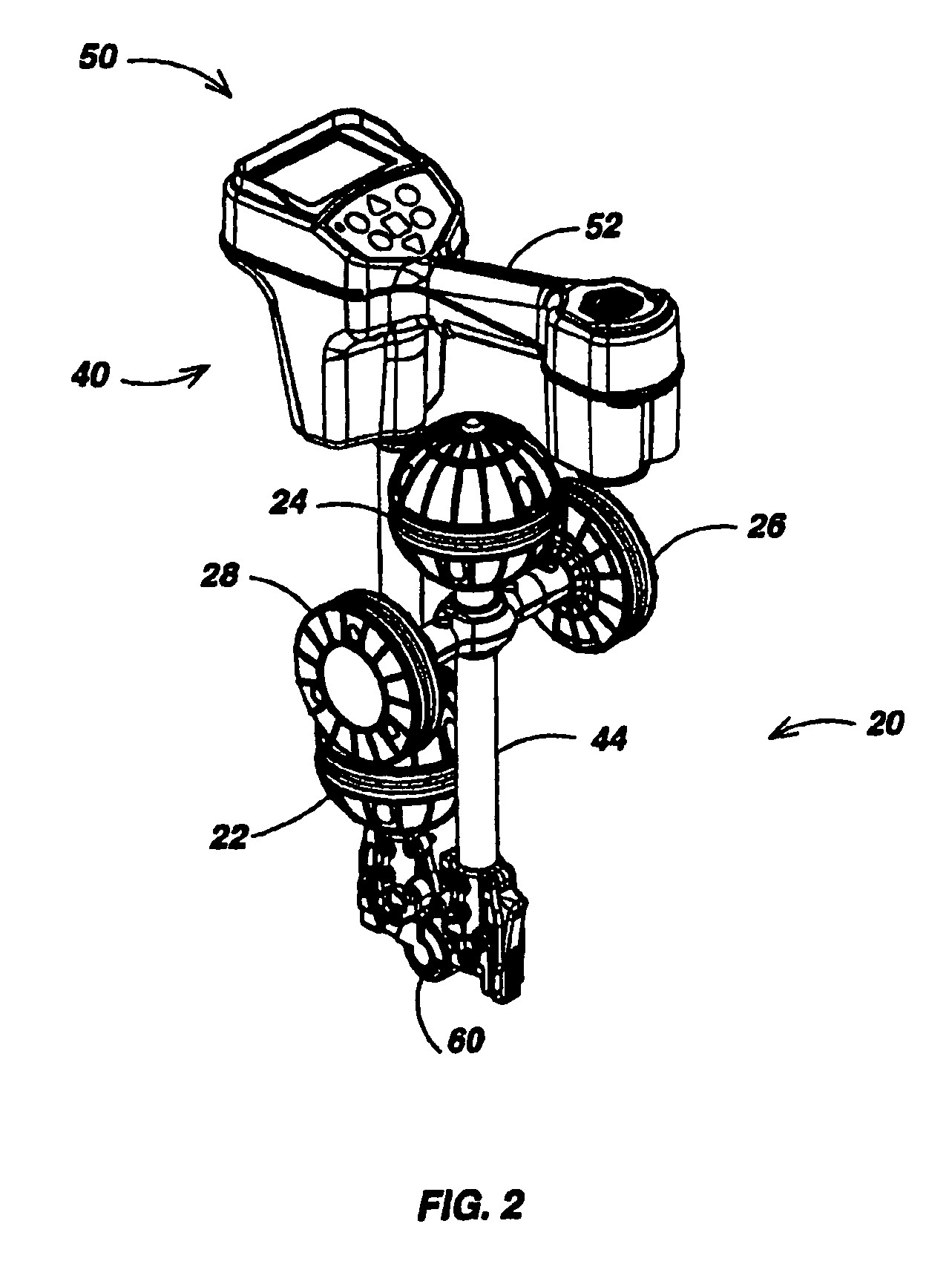
Locator with apparent depth indication
ActiveUS7332901B2Easy to measureGood user interfaceMagnetic measurementsCurrent/voltage measurementSensor arrayElectromagnetic field
A human-portable utility locator system for locating and tracing a buried utility line characterized by an electromagnetic field emission. The locator may include a horizontal spaced sensor pair for detecting the horizontal field asymmetry of the emitted field in one or more independent frequency bands, which is employed to assist in determining an accurate “virtual depth” measurement for producing detection events. An event detector may be disposed to detect events corresponding to extremum in the B-field gradient with respect to time and a user interface (UI) coupled to the event detector signals the detected event to a user. In a preferred embodiment, one pair of spaced-apart 3D magnetic sensor arrays is disposed substantially orthogonal to another intermediate spaced-apart pair of sensors.
Owner:SEEK TECH
Locator with apparent depth indication
ActiveUS20060232259A1Easy to measureReliable horizontal field asymmetry measurementMagnetic measurementsCurrent/voltage measurementSensor arrayElectromagnetic field
A human-portable utility locator system for locating and tracing a buried utility line characterized by an electromagnetic field emission. The locator may include a horizontal spaced sensor pair for detecting the horizontal field asymmetry of the emitted field in one or more independent frequency bands, which is employed to assist in determining an accurate “virtual depth” measurement for producing detection events. An event detector may be disposed to detect events corresponding to extremum in the B-field gradient with respect to time and a user interface (UI) coupled to the event detector signals the detected event to a user. In a preferred embodiment, one pair of spaced-apart 3D magnetic sensor arrays is disposed substantially orthogonal to another intermediate spaced-apart pair of sensors.
Owner:SEEK TECH
Locator with current-measuring capability
ActiveUS7498797B1Easy to measureGood user interfaceCurrent/voltage measurementMagnetic property measurementsSensor arrayElectromagnetic field
A human-portable utility locator system for locating and tracing a buried utility line characterized by an electromagnetic field emission. The locator may include a horizontal spaced sensor pair for detecting the horizontal field asymmetry of the emitted field in one or more independent frequency bands, which is employed to assist in determining an accurate “virtual depth” measurement for producing detection events. An event detector may be disposed to detect events corresponding to extremum in the B-field gradient with respect to time and a user interface (UI) coupled to the event detector signals the detected event to a user. In a preferred embodiment, one pair of spaced-apart 3D magnetic sensor arrays is disposed substantially orthogonal to another intermediate spaced-apart pair of sensors.
Owner:SEEKTECH
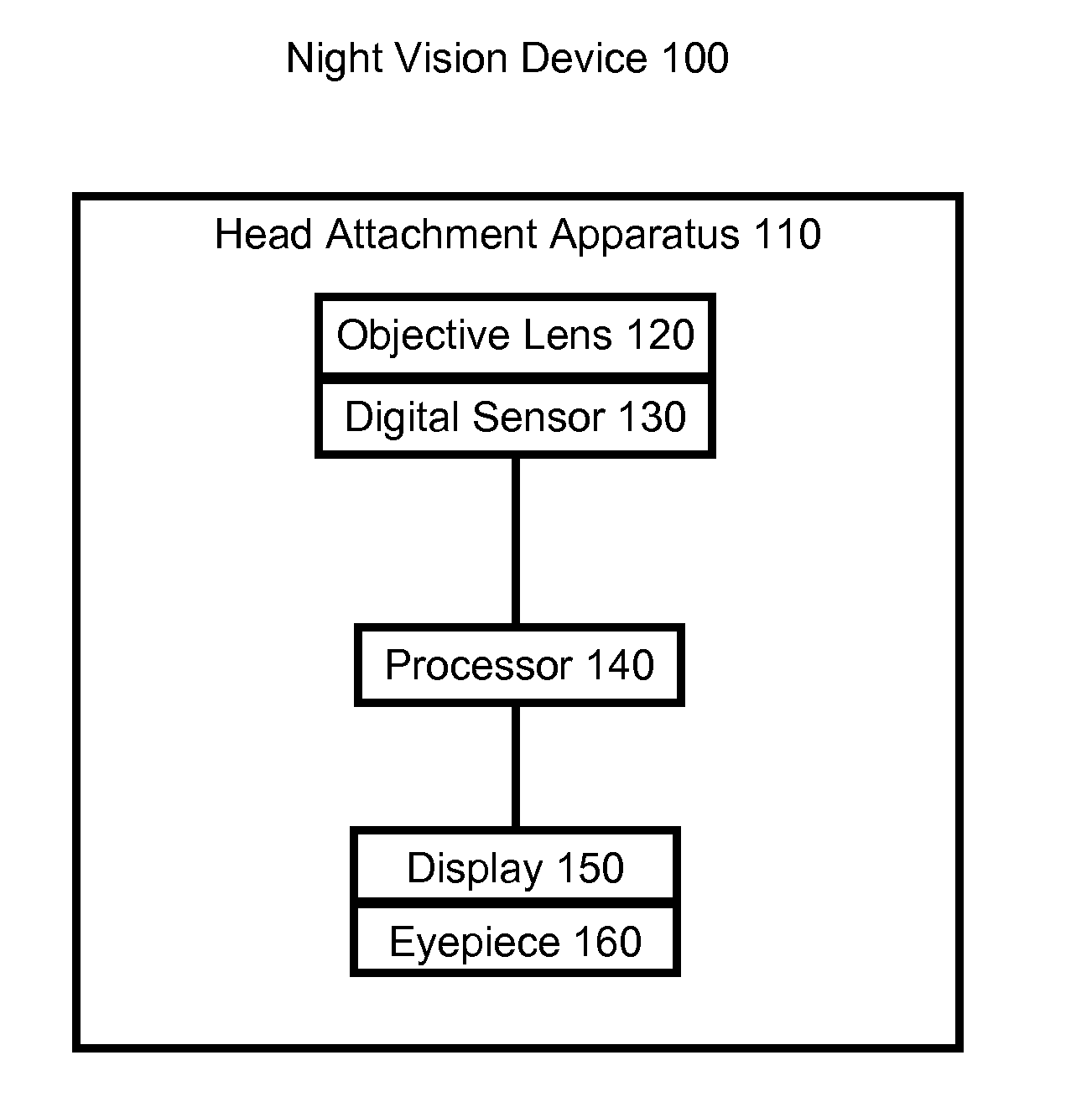
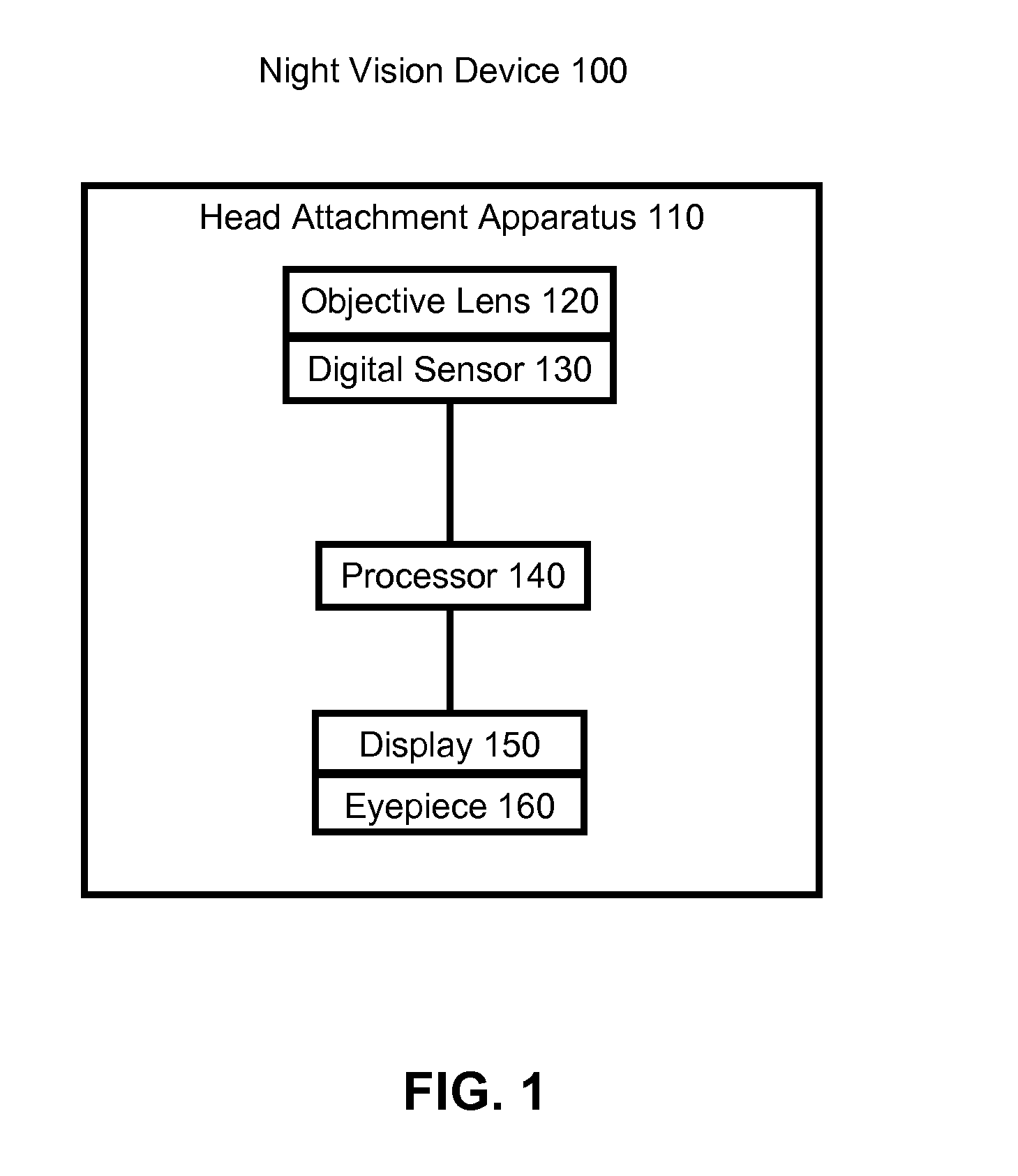
High Resolution Wide Field of View Digital Night Vision System
ActiveUS20120257005A1Reducing engineering constraintOvercome limitationsTelevision system detailsOptical elementsNight visionVisual field loss
A wide field of view night vision system is described. The system comprises a head attachment apparatus configured to attach to a user's head and a night vision subsystem. The night vision subsystem comprises one or more night vision image sensors attached to the head attachment apparatus. Each sensor receives input light and produces a digital image of the input light. A processor processes the digital image(s) to produce a wide-field image. The wide-field image spans at least 60 degrees of a user's horizontal field of view. A display and eyepiece attached to the head attachment apparatus receives and displays the wide-field image. The eyepiece is positionable between the display and the user's eye to image the wide-field image into the user's eye.
Owner:VISION PROD LLC
MRI coil system for breast imaging
InactiveUS6850065B1Electric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceSaddle coilHelmholtz coil
A RF receive coil system for imaging a breast on a human chest with a horizontal field MRI system includes a volume saddle coil adapted to be contoured about the chest; and a Helmholtz coil having a lower portion adapted to be contoured about the chest and an upper portion adapted to be above the chest The coils are operable in quadrature mode.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
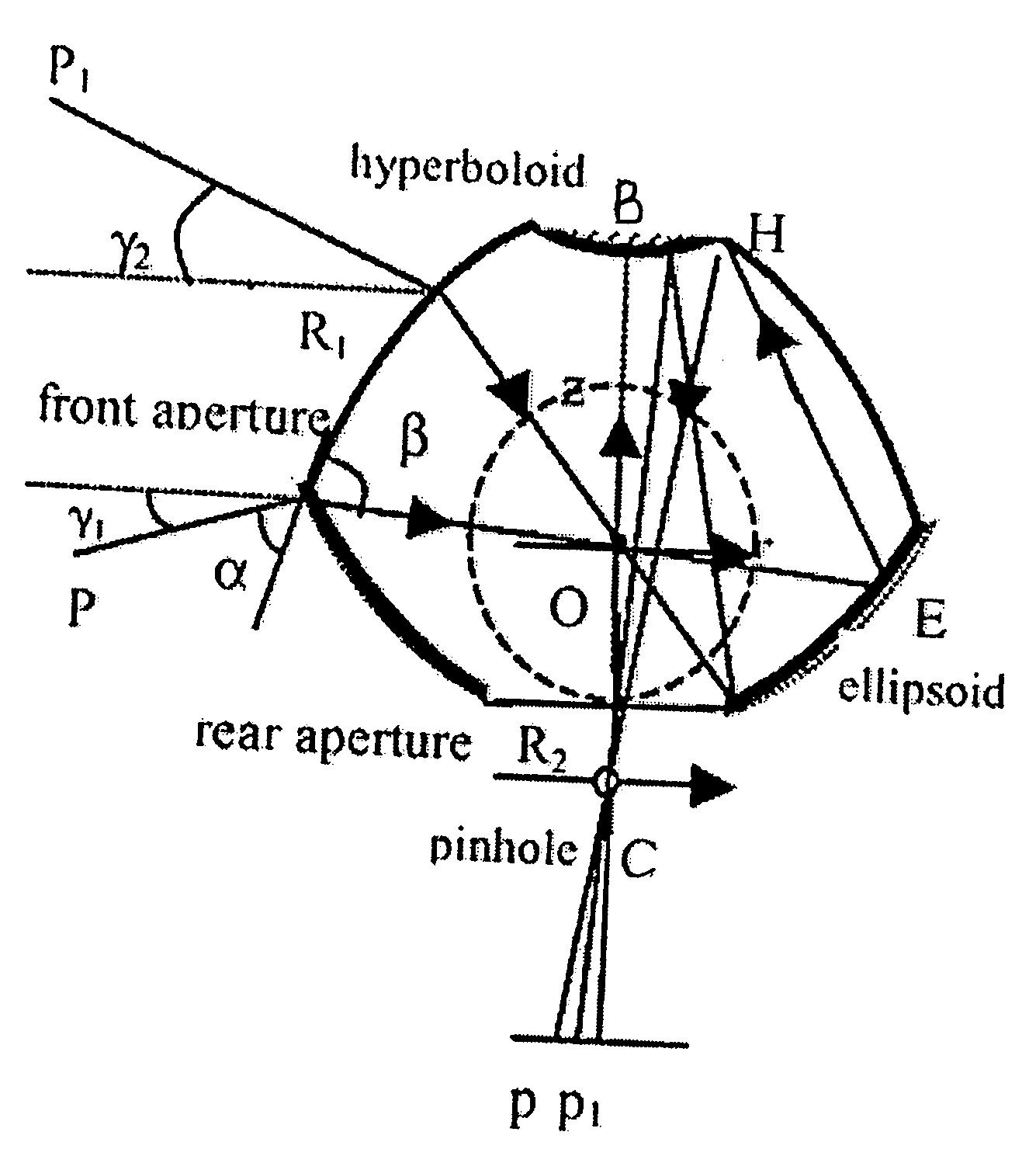
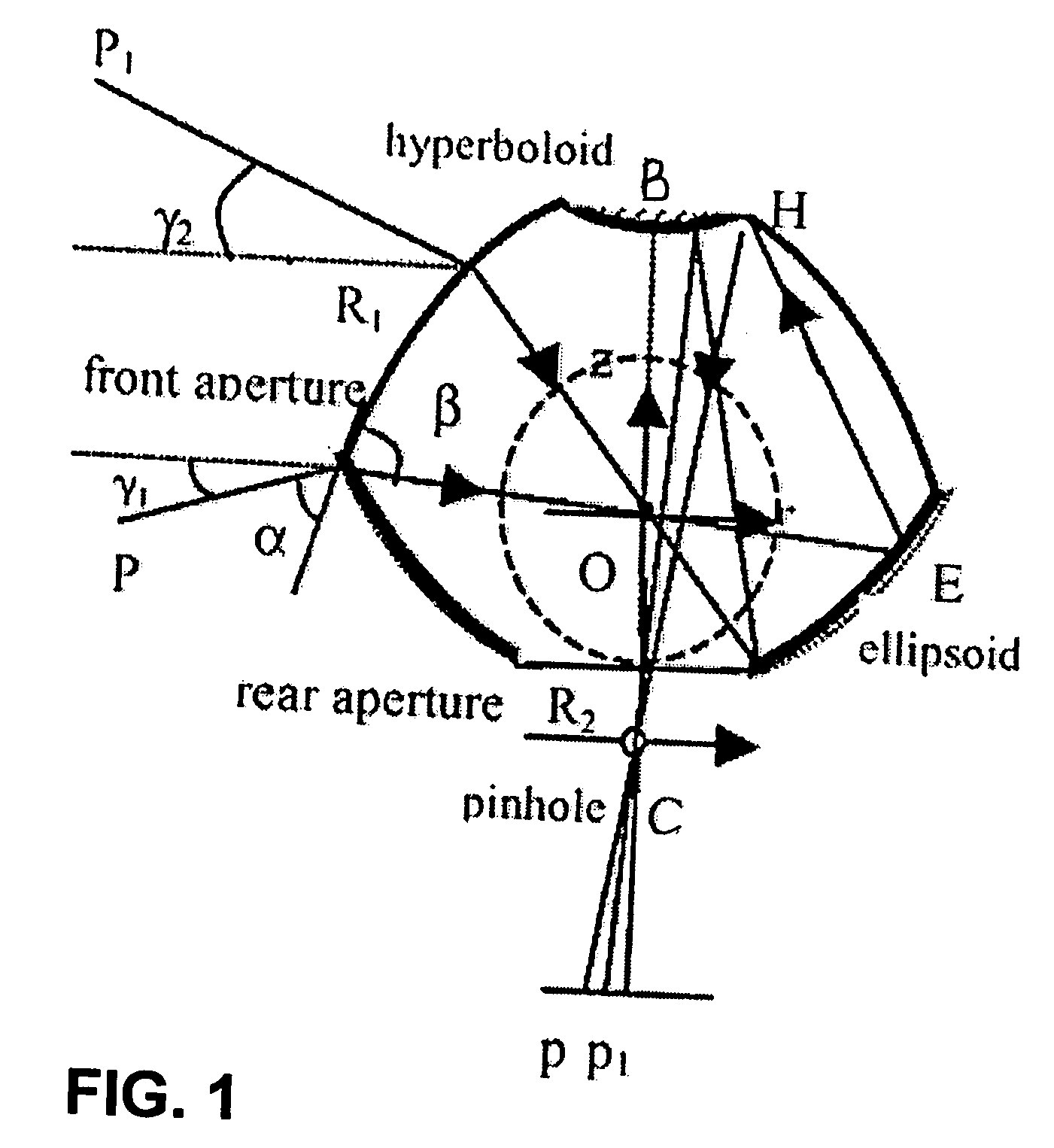
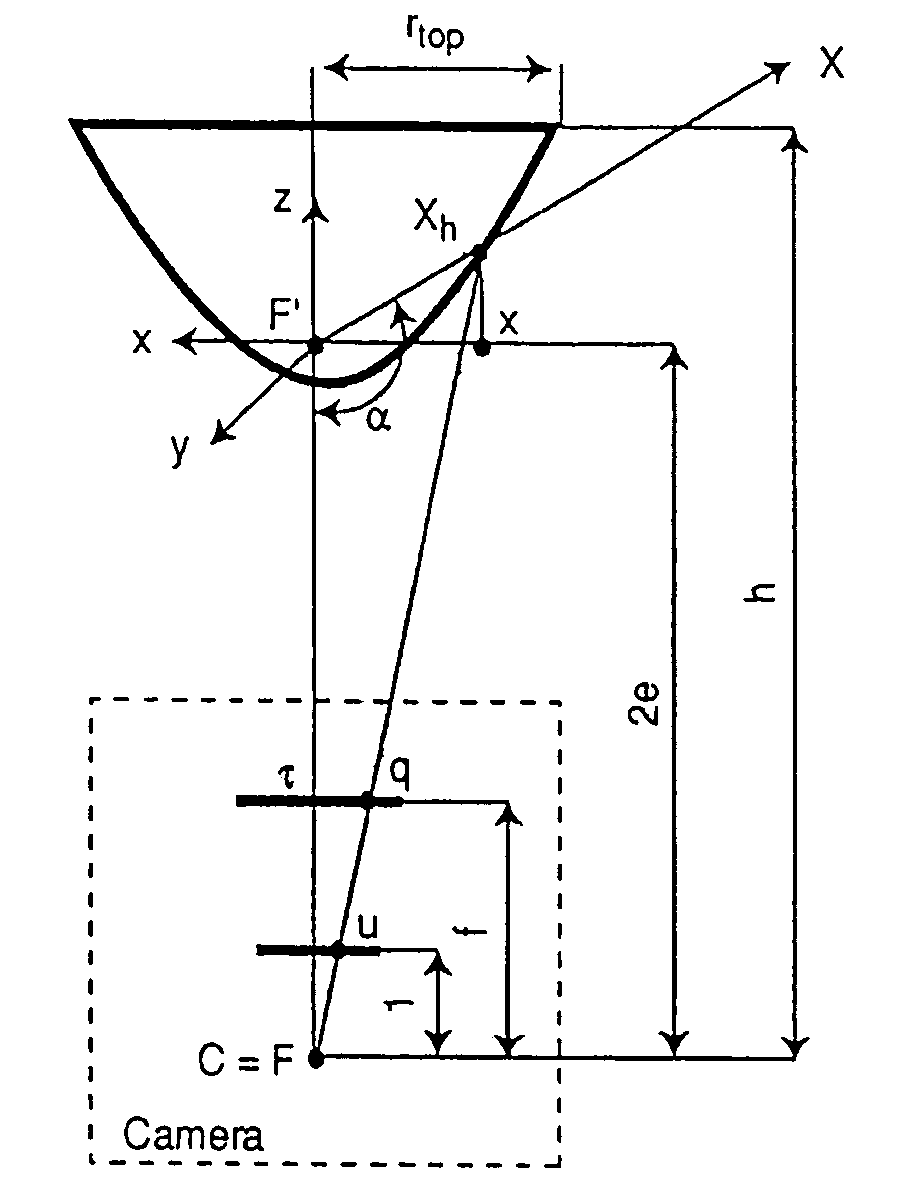
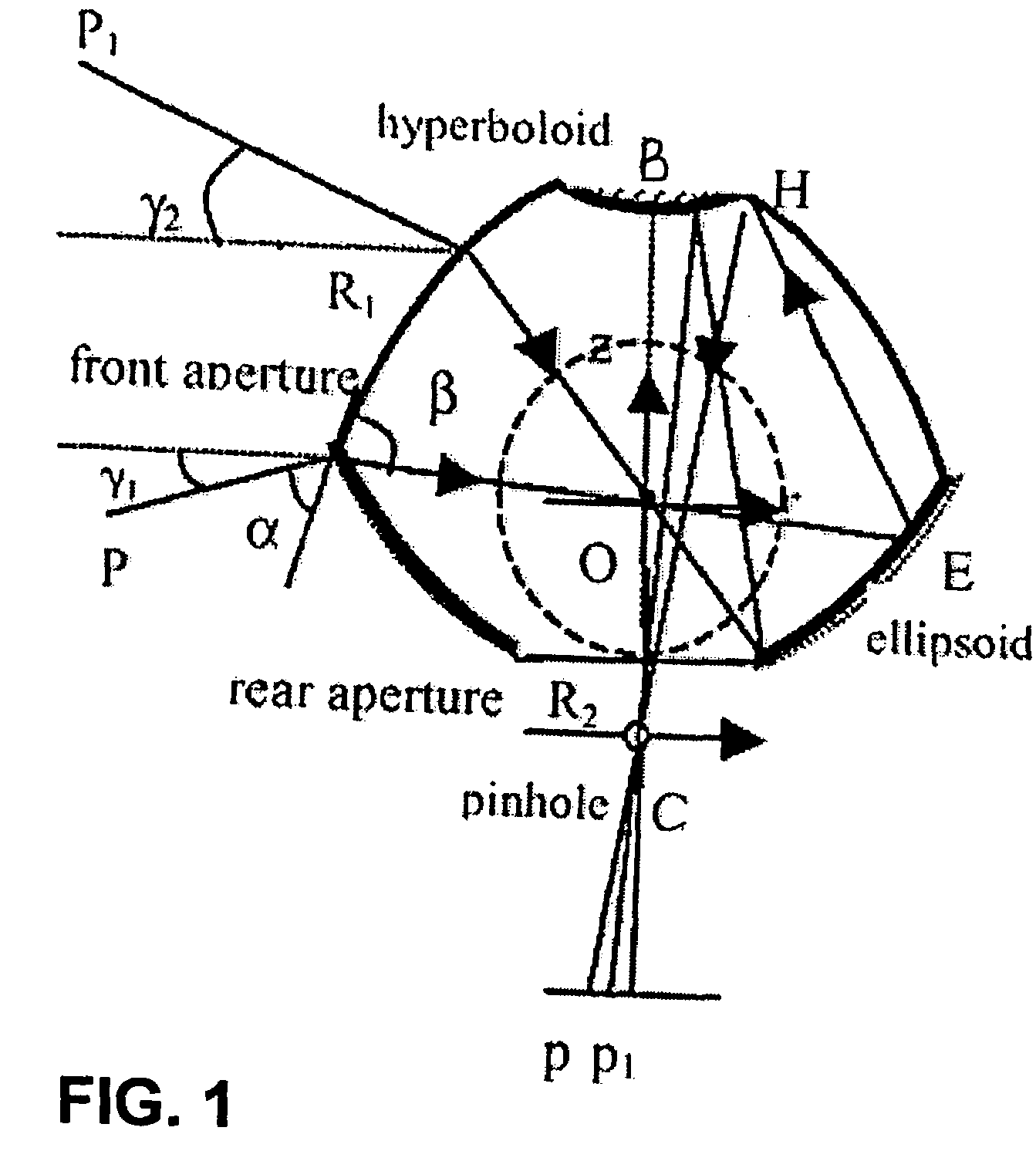
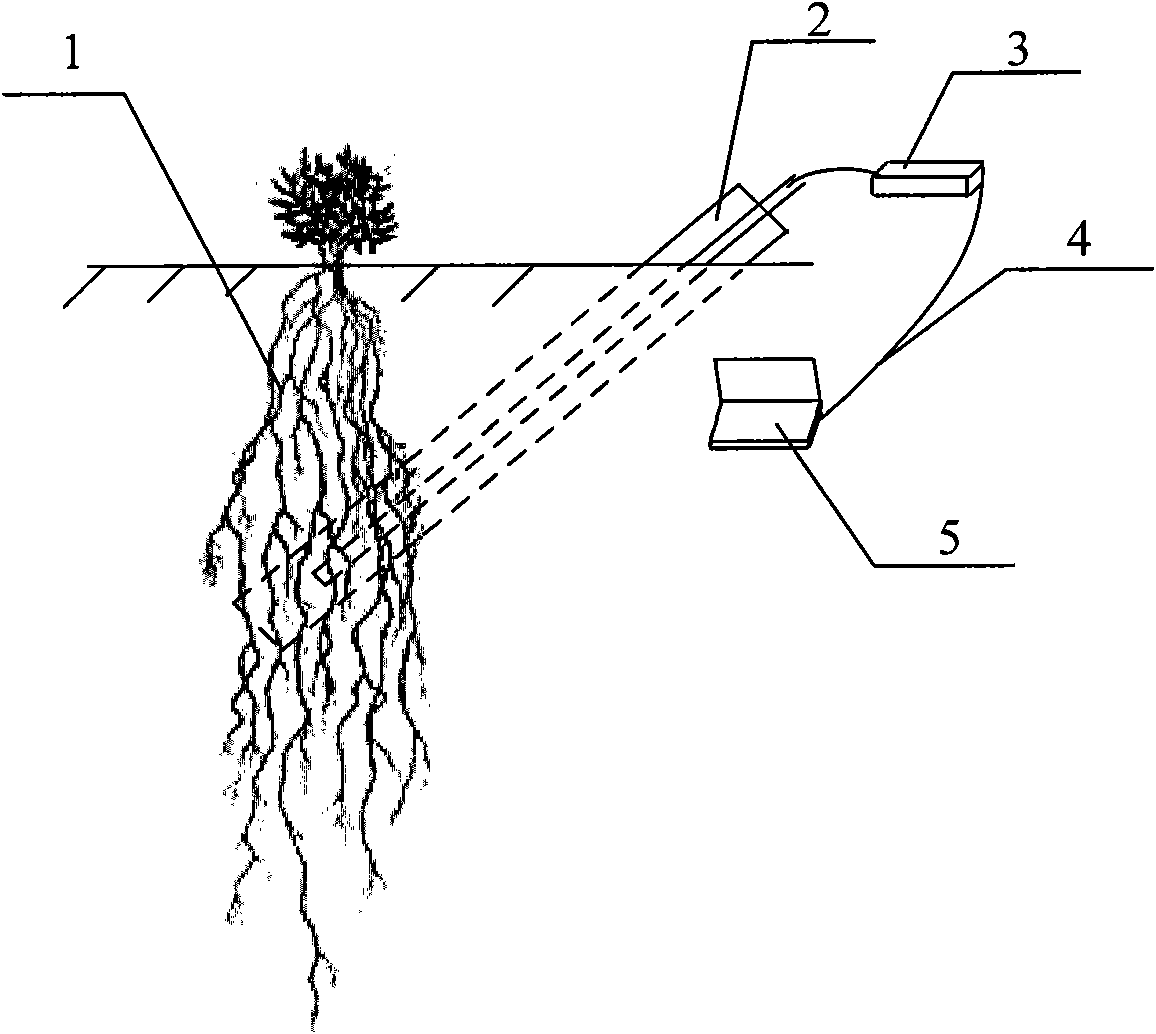
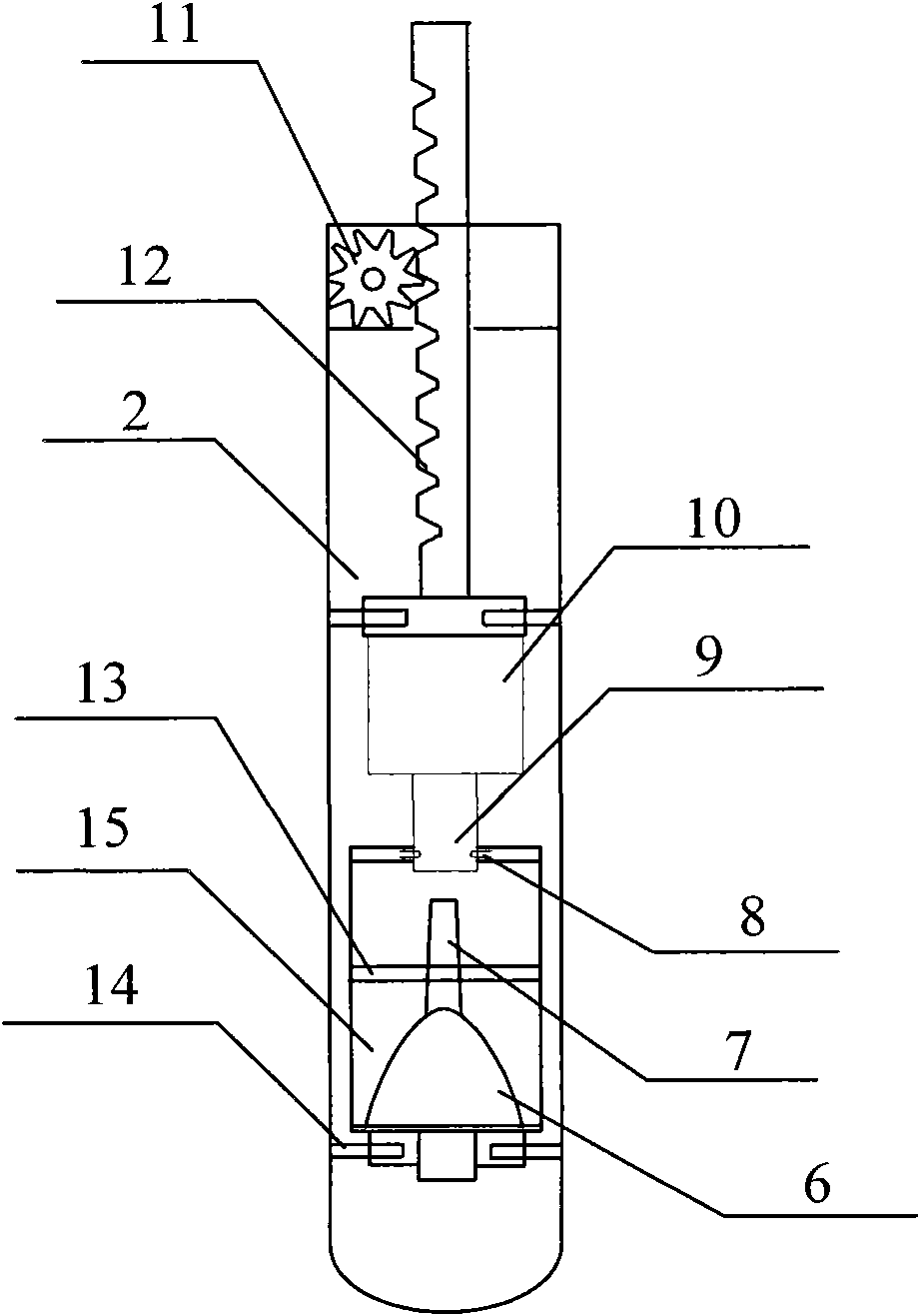
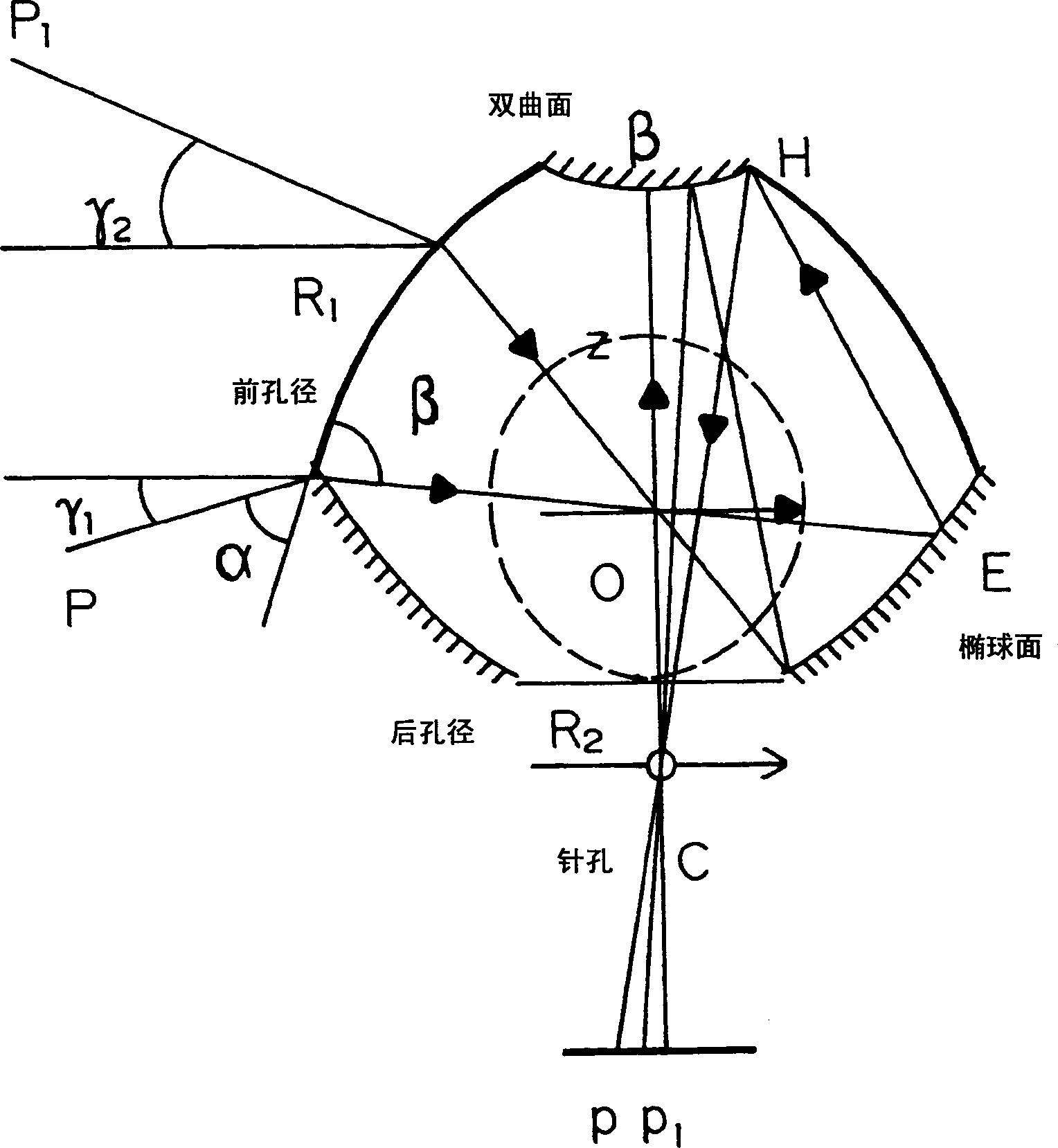
Plant root system monitoring system based on hyperboloidal mirror
InactiveCN101963584AMonitoring dynamic growth cyclesImprove collection efficiencyMaterial analysis by optical meansCanal wallMechanical design
The invention discloses a plant root system monitoring system based on a hyperboloidal mirror, which comprises a micro root canal, a hyperboloidal mirror and a digital camera unit, wherein the micro root canal is arranged in a field where a monitored plant grows, the hyperboloidal mirror is arranged inside the micro root canal, and the digital camera unit is arranged inside the micro root canal and positioned above the hyperboloidal mirror and connected with an image acquisition card. In the invention, a CCD (Charge Coupled Device) camera can obtain a 360-degree horizontal field integral image around the reflector through each acquisition, the camera is only controlled to move up and down along the canal wall of the micro root canal without rotating; and in the post-stage image processing, the image can be vertically spliced only. Therefore, according to the technical scheme, the root system image is acquired by adopting the plant root system monitoring system, the complexity of mechanical design and post-stage image processing is reduced, and the image acquiring efficiency is improved.
Owner:BEIJING RES CENT OF INTELLIGENT EQUIP FOR AGRI
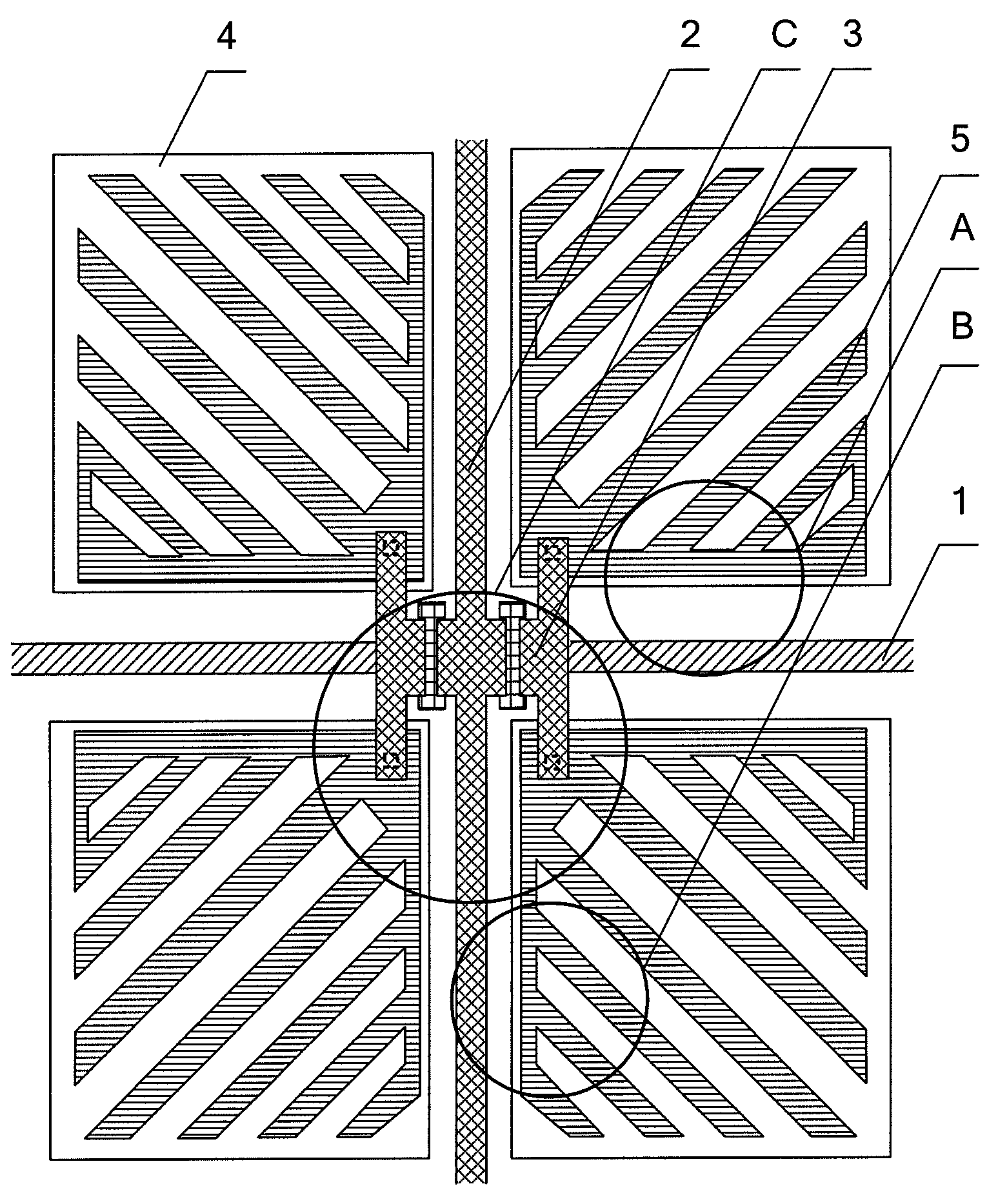
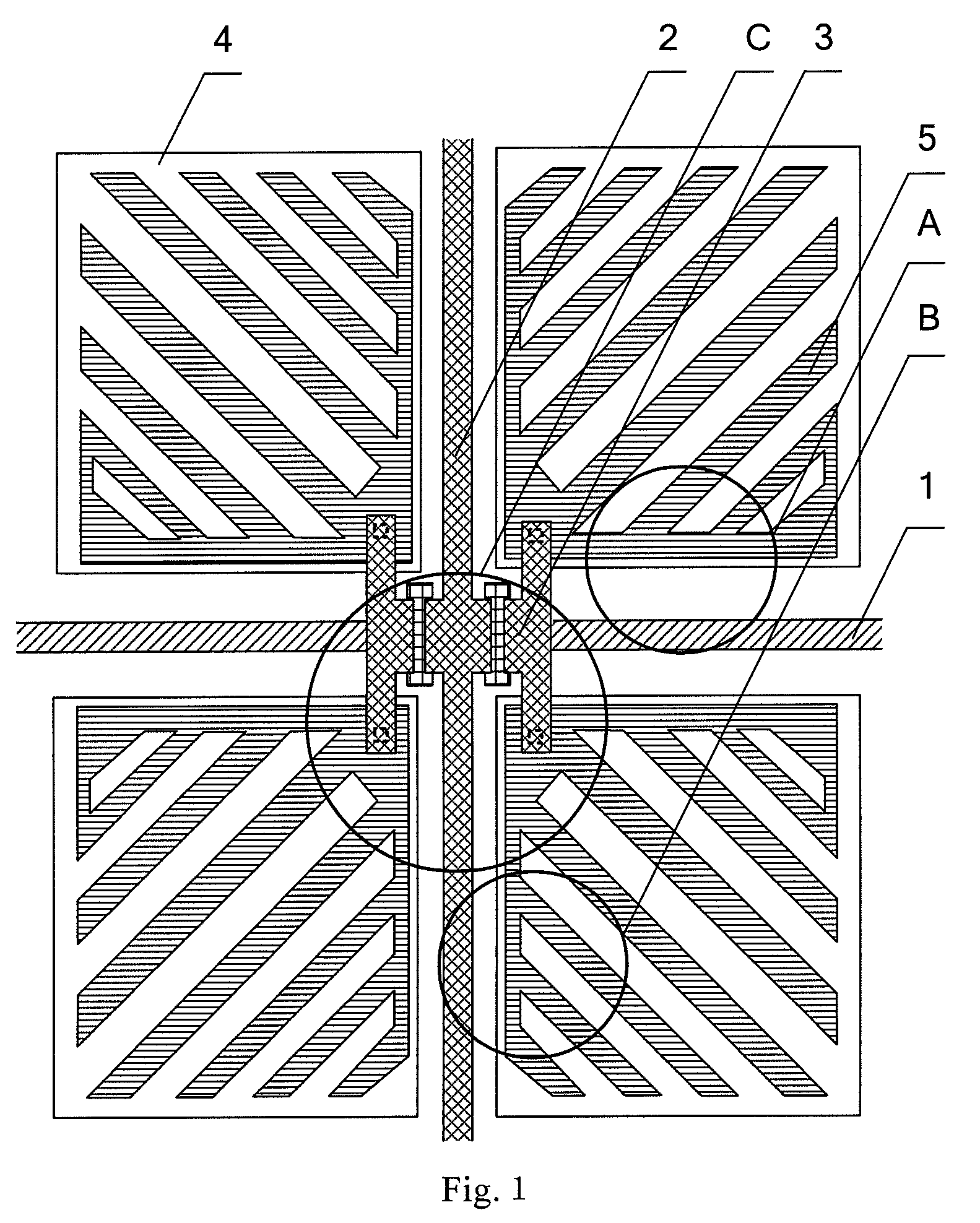
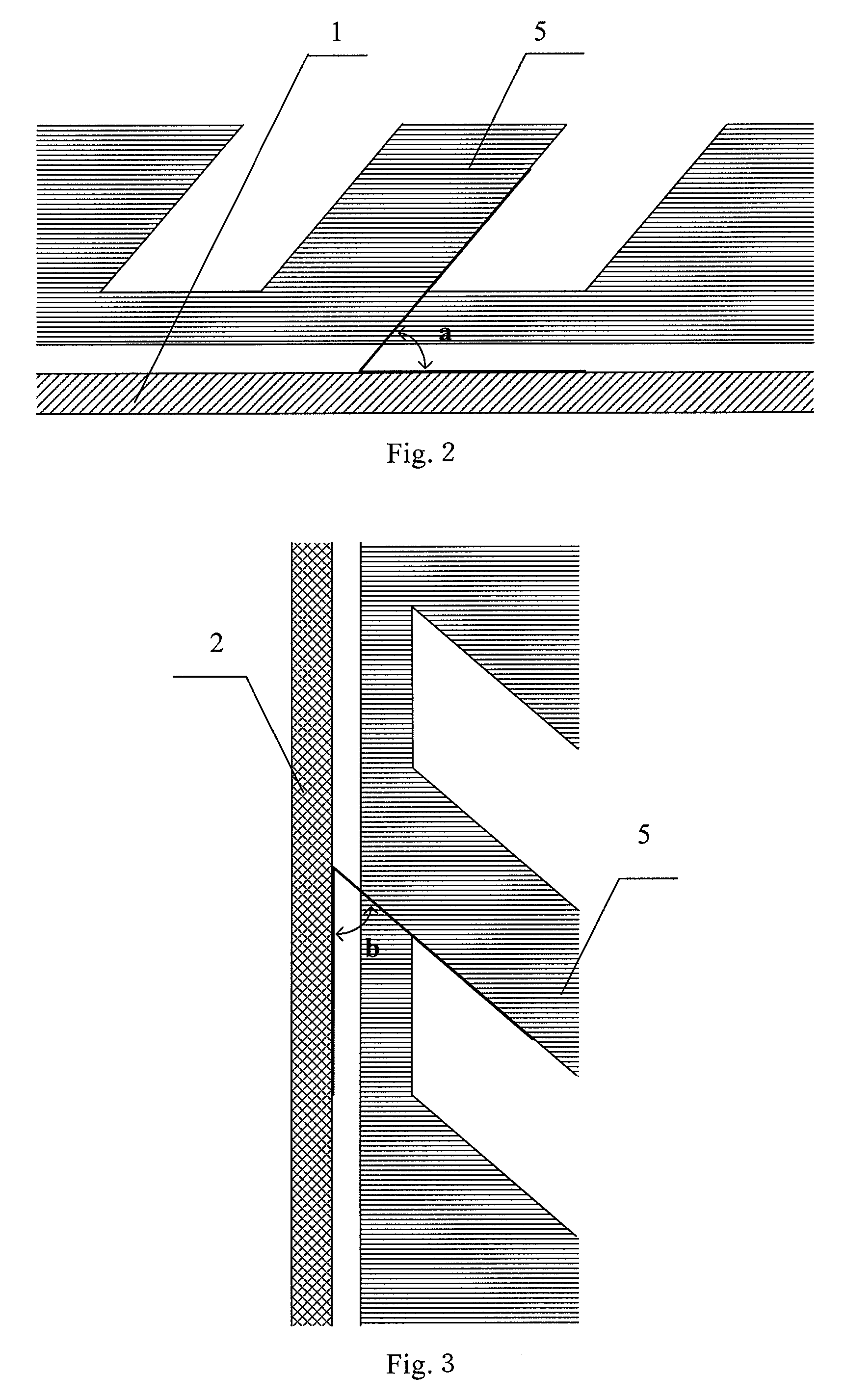
Pixel structure of horizontal field liquid crystal display
ActiveUS20090086149A1Improve viewing angleVisual effect is not affectedNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayComputer science
A pixel structure for a horizontal field LCD comprises a plurality of pixel units. Each of the pixel units comprises a gate line corresponding to the pixel unit, a data line corresponding to the pixel unit, and at least one TFT, wherein the TFT is electrically connected with the gate line and the data line, the gate line and the data line divide the pixel unit into four sub-pixels, the sub-pixel is provided with a pixel electrode which is electrically connected with the TFT, and the pixel electrode is provided with a plurality of slits in a predetermined direction.
Owner:BEIJING BOE OPTOELECTRONCIS TECH CO LTD +1
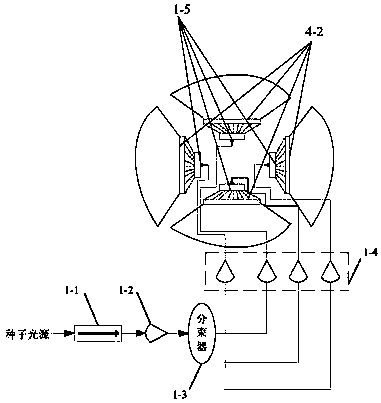
Onboard 3D imaging solid state laser radar system
PendingCN107678040AHigh precisionIncrease flexibilityElectromagnetic wave reradiationRadar systemsBeam splitter
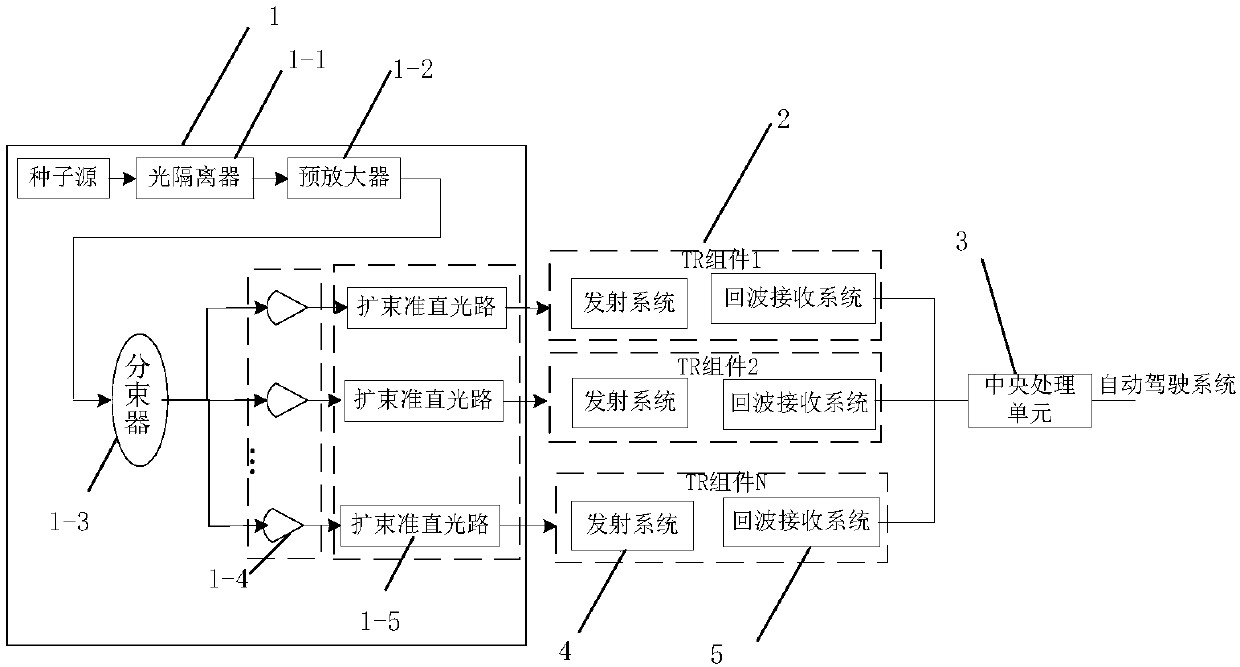
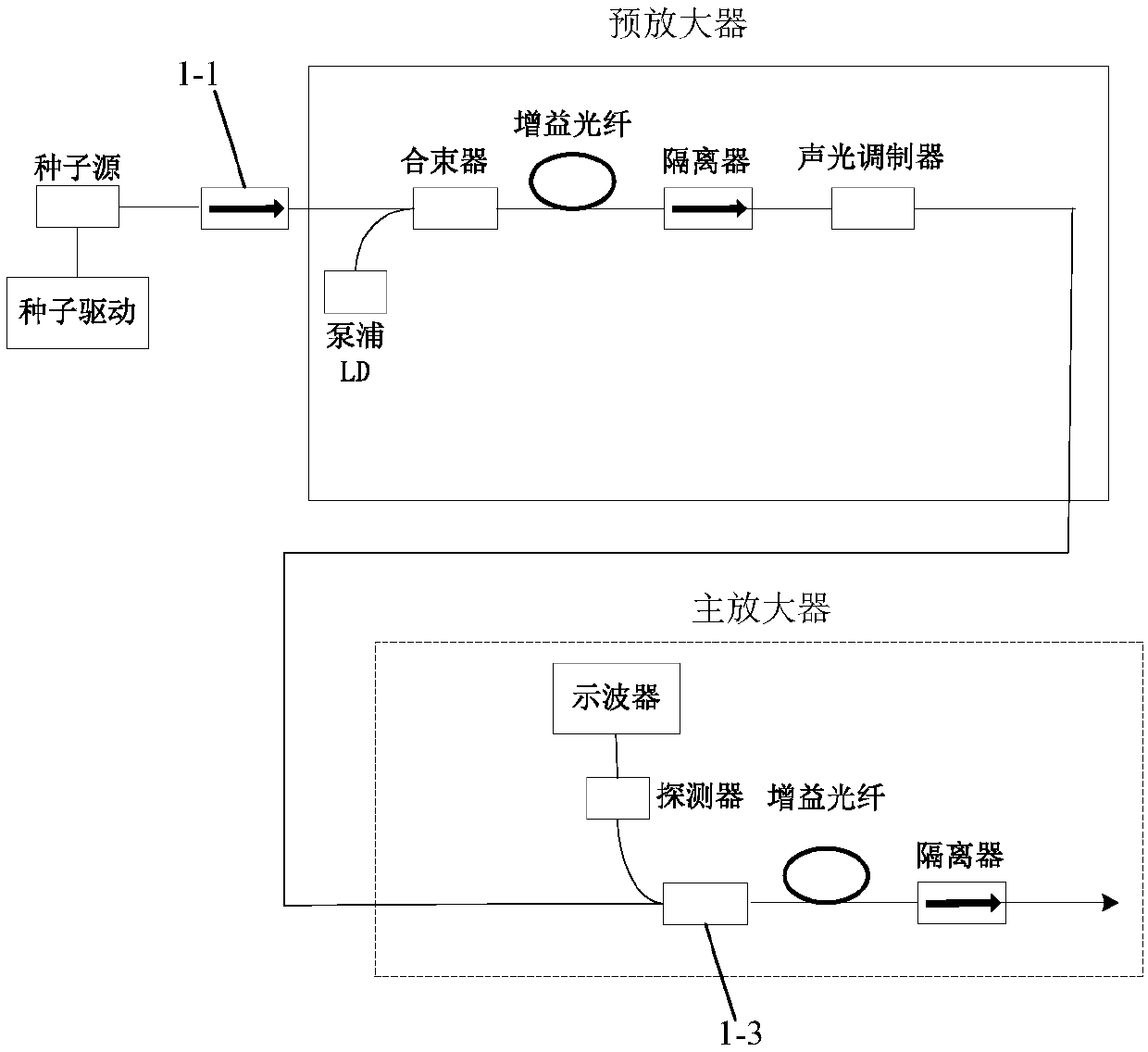
The invention discloses an onboard 3D imaging solid state laser radar system, and relates to the field of onboard laser radars. The system herein can address the technical problems of slow scanning, large size, low receiving signal to noise ratio and low safety factor of conventional mechanical scanning laser radars. The system herein includes a laser device, a plurality of TR assembles and a central processing unit. The laser device includes an optoisolator, a pre-amplifier, a beam splitter, a main amplifier array, and a beam expanding collimated light path. Each TR assembly includes a transmitting system and an echo receiving system. The transmitting system includes a unidirectional glass array and a liquid crystal polarized grating array. The echo receiving system includes an optical filter array, a gathering lens array photoelectric detector array and a plurality of playback circuits. According to the invention, a radar has no mechanical rotary parts, which can greatly reduce the size of a laser radar system; a single TR assembly has no processor, and all the TR assemblies are under uniform control of a central processing unit of the laser radar system, which facilitates integration; and the arrangement of the plurality of TR assemblies can cover a 360 degree horizontal field of view and a 20 degree vertical field of view.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Liquid crystal panel and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN101995700AIncrease opening ratioIncrease vertical distanceNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayParasitic capacitance
The invention relates to a liquid crystal panel and a manufacturing method thereof. The liquid crystal panel comprises two display substrates capable of being perfectly bonded together, wherein raster scanning lines and data lines are formed on the first display substrate, and enclose to form a pixel unit; a thin film transistor (TFT) is arranged in the pixel unit; a pixel electrode and a common electrode are respectively formed in each pixel area of the second lining substrate; a first pad object containing a conducting material is formed between the first display substrate and the second display substrate, and connects the pixel electrode on the second display substrate and a drain electrode exposed through a first hole; and a common electrode line is formed on the first lining substrate or the second lining substrate, and is electrically connected with the common electrodes. A technical means of separately arranging the pixel electrodes and the common electrodes forming a horizontal field and the data lines on the two display substrates is adopted, and the parasitic capacitance between the pixel electrodes and the data lines cannot be improved when adjacent pixel electrodes are close to each other.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD +1
Panoramic and horizontally immersive image display system and method
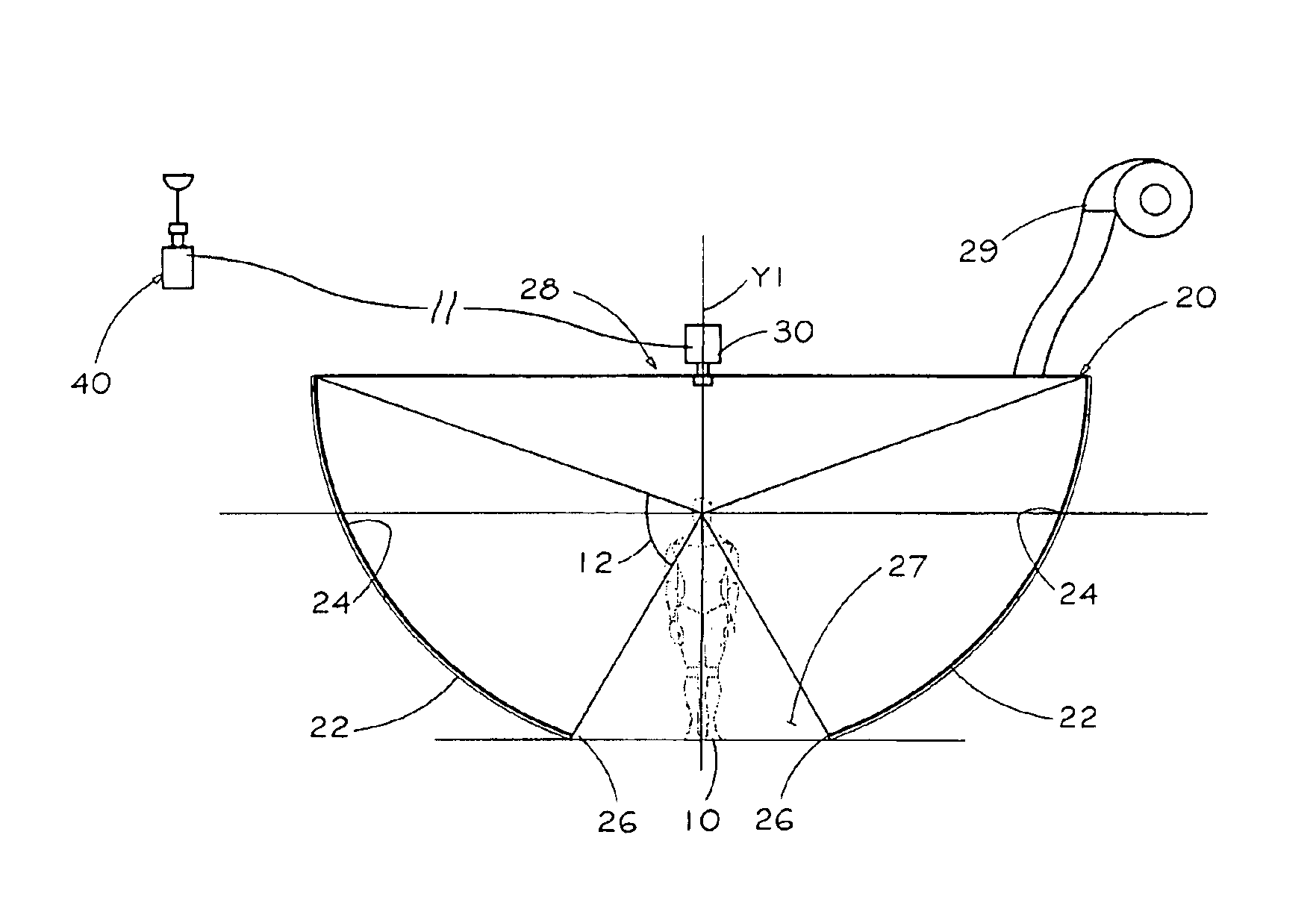
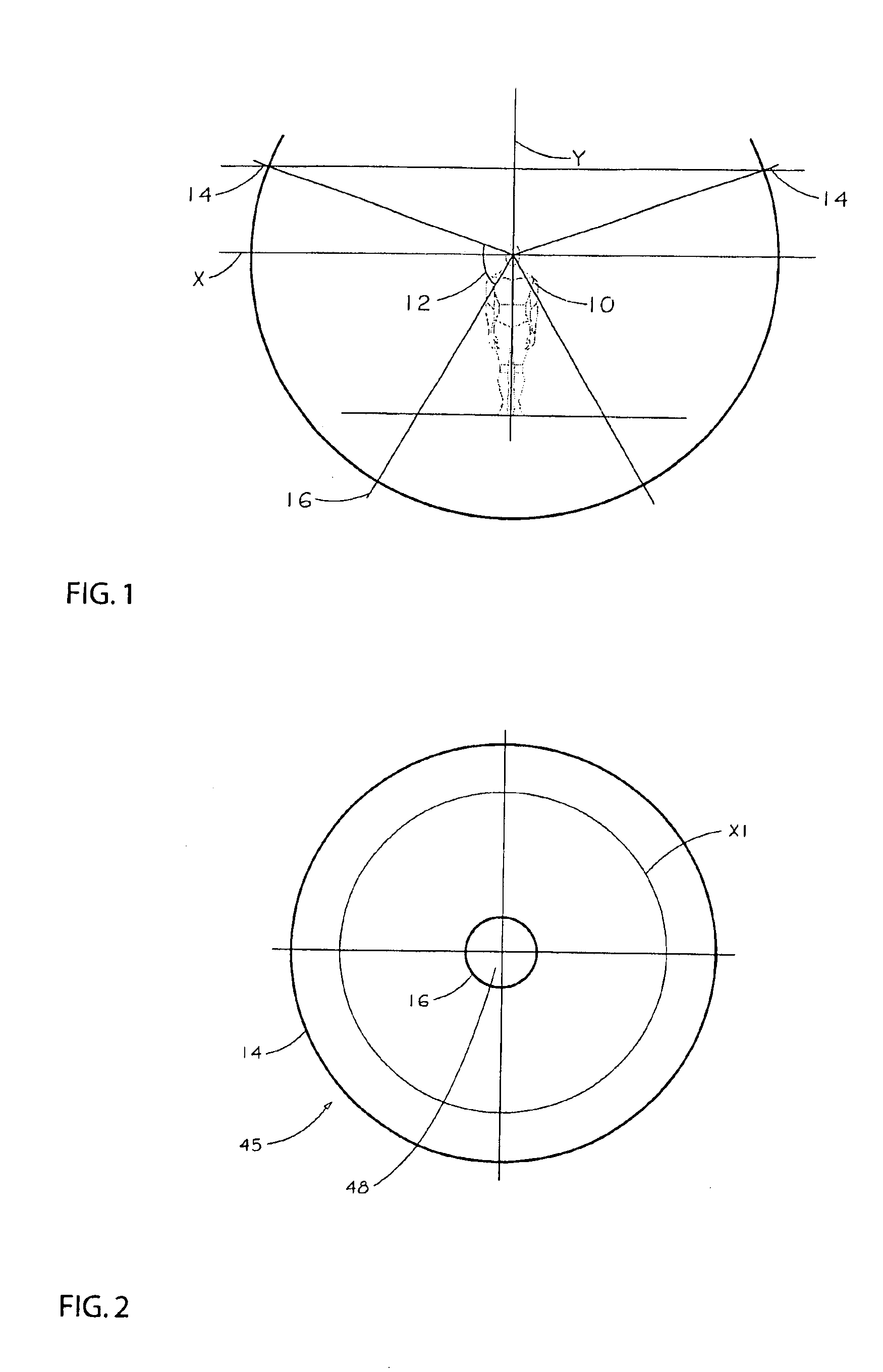
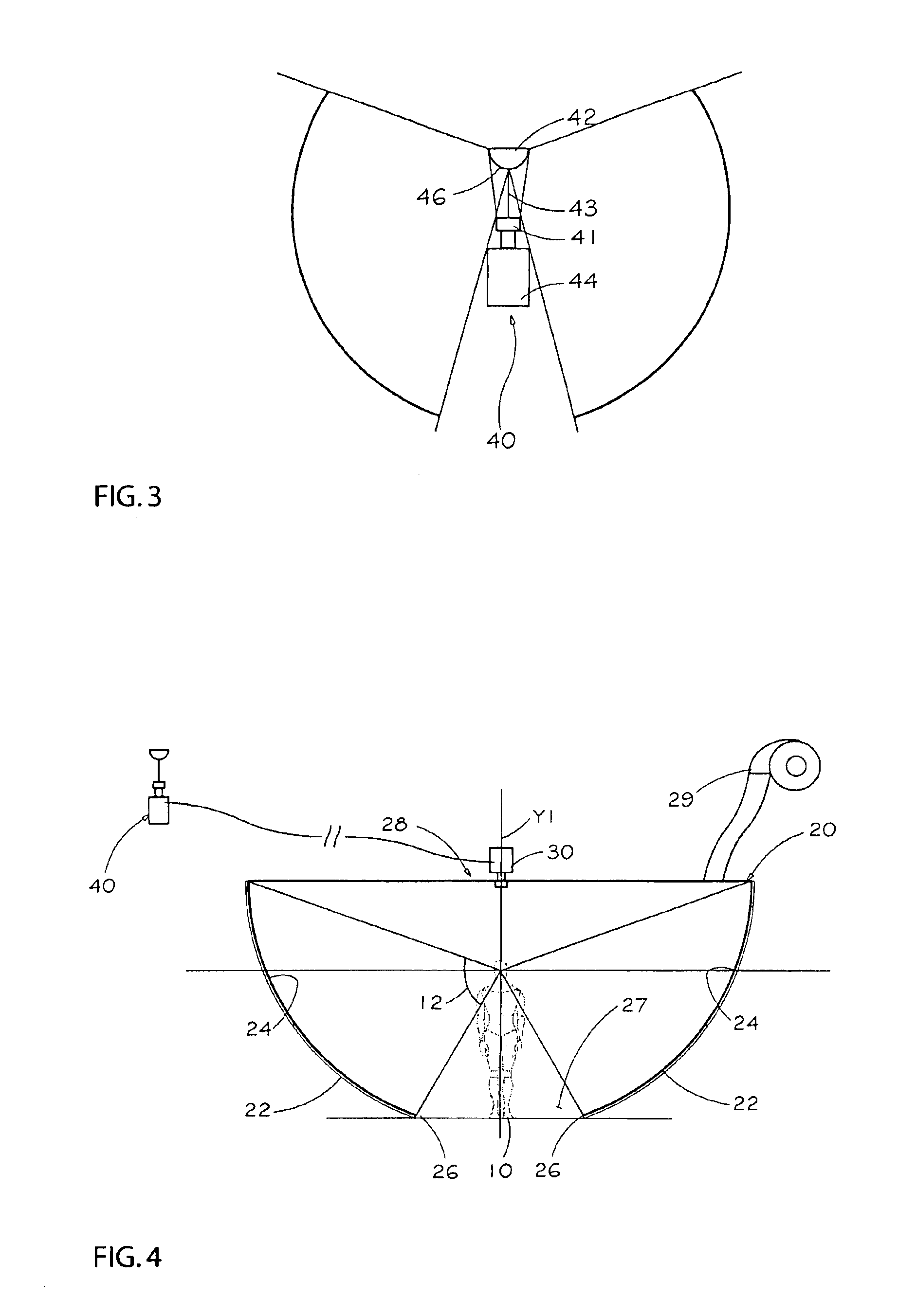
An image display system for surrounding a horizontal field of view of a viewer with images. The image display system comprises a portion of a sphere having a concavity defining an inner surface. A projection device is adapted to project images from a center of a radius of curvature of the portion of a sphere so as to project images on the inner surface of the portion of a sphere. The image display system is adapted to partially receive viewers in the concavity such that at least a horizontal field of view of the viewers is surrounded by an image projected from the center on the inner surface of the portion of a sphere.
Owner:COURCHESNE LUC
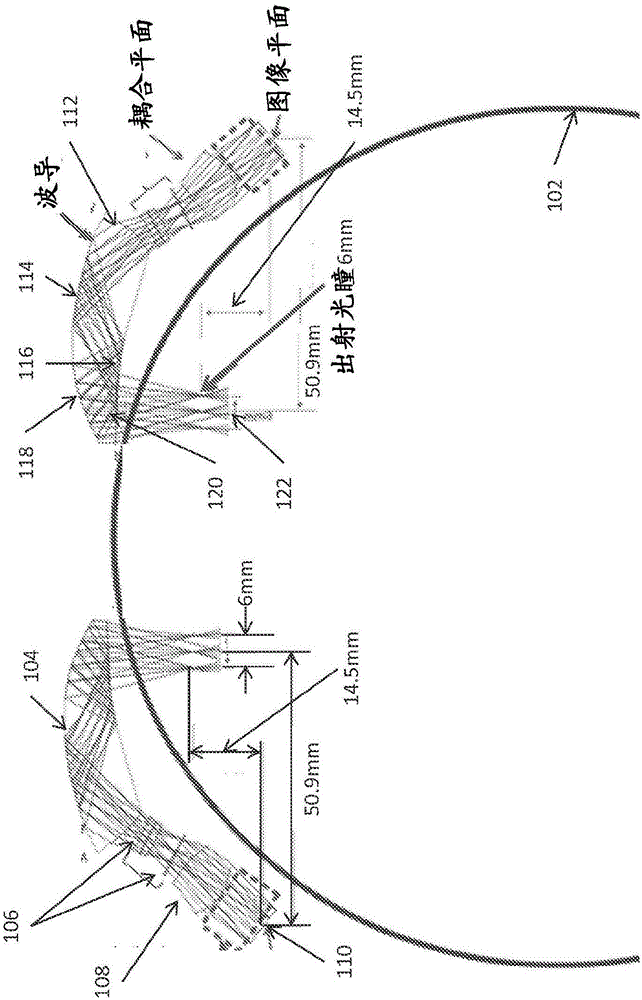
Waveguide Image Combiner for Augmented Reality Displays
ActiveUS20190056593A1High light efficiencyImprove transmittanceImage data processingOptical elementsDisplay devicePupil
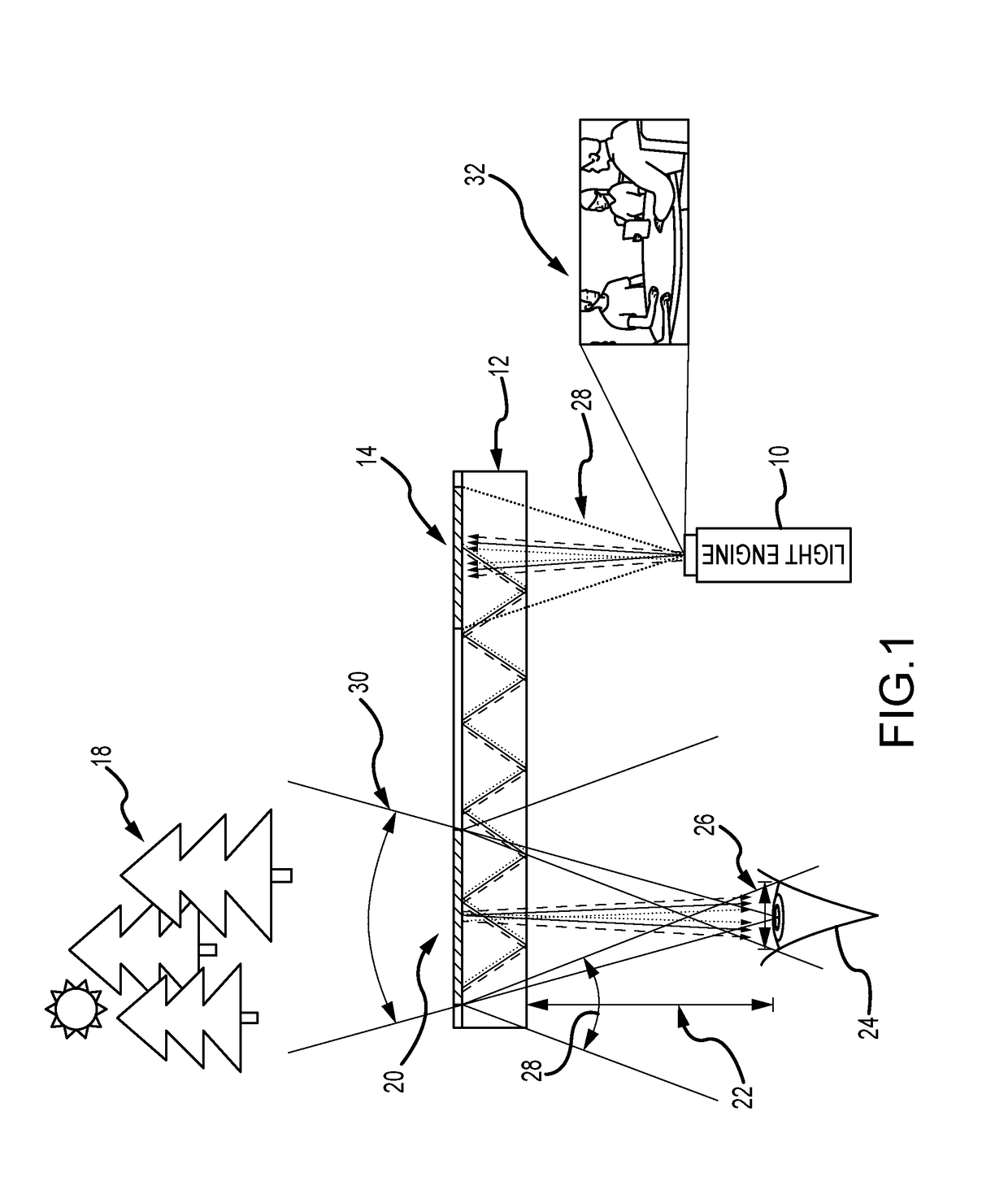
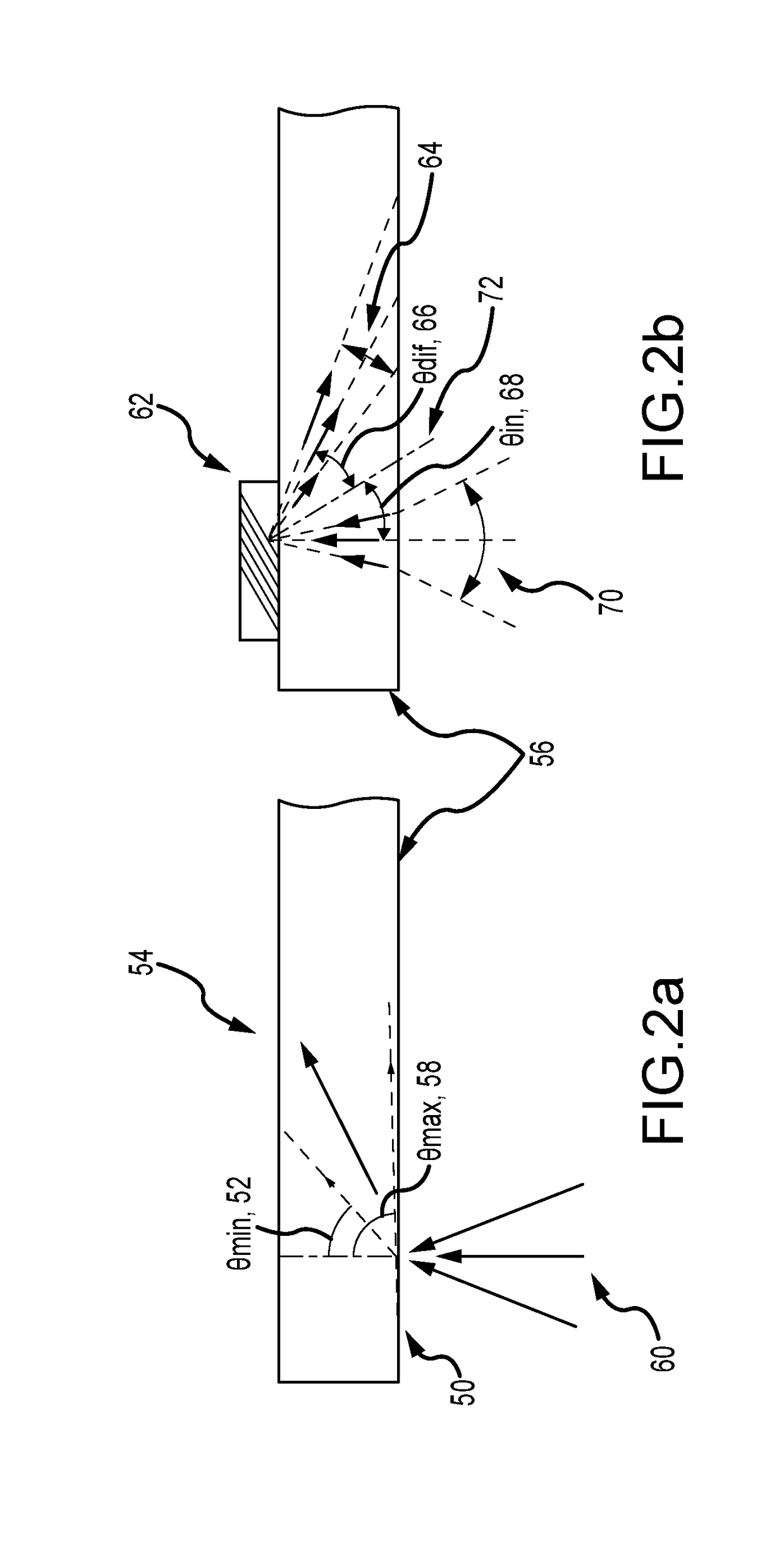
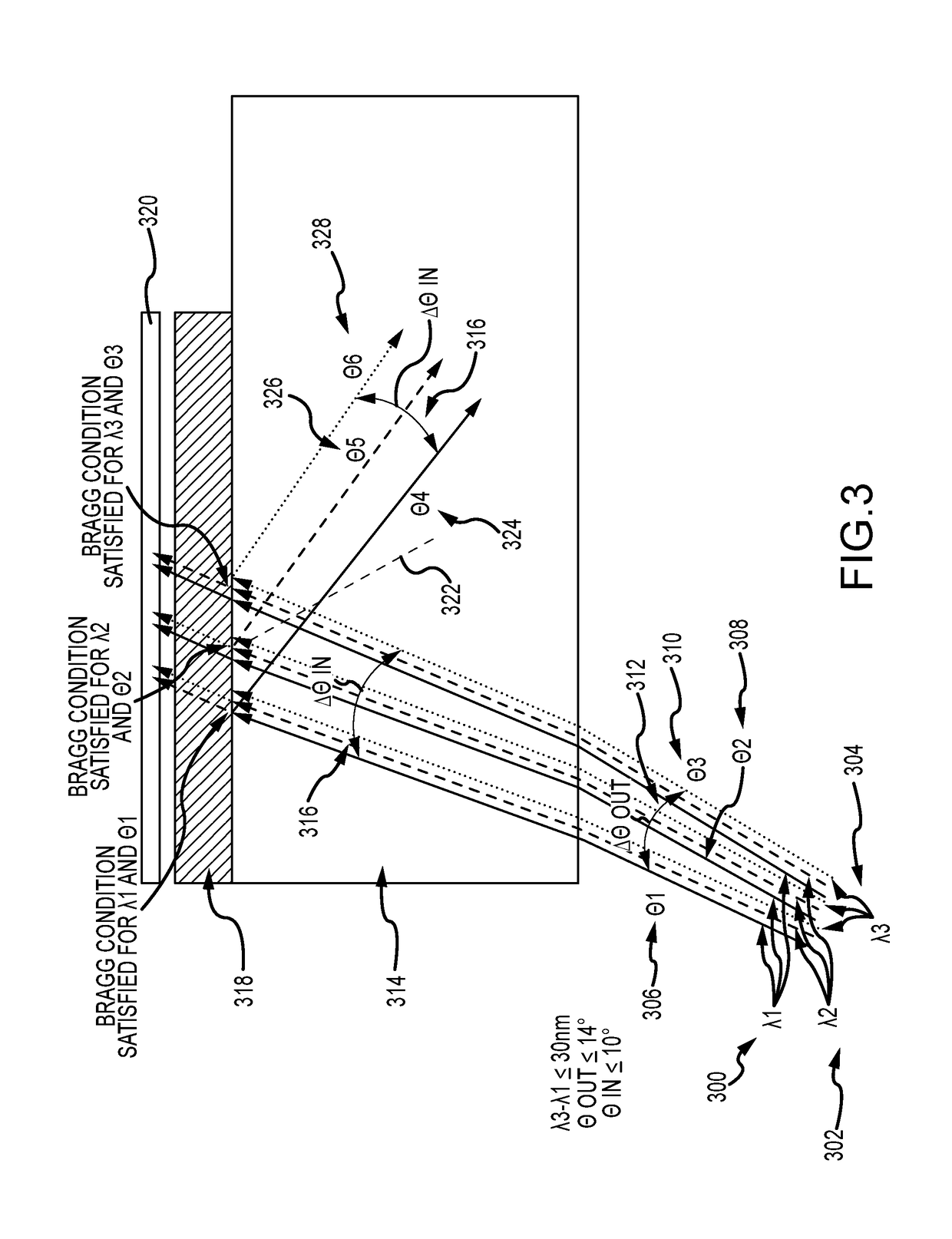
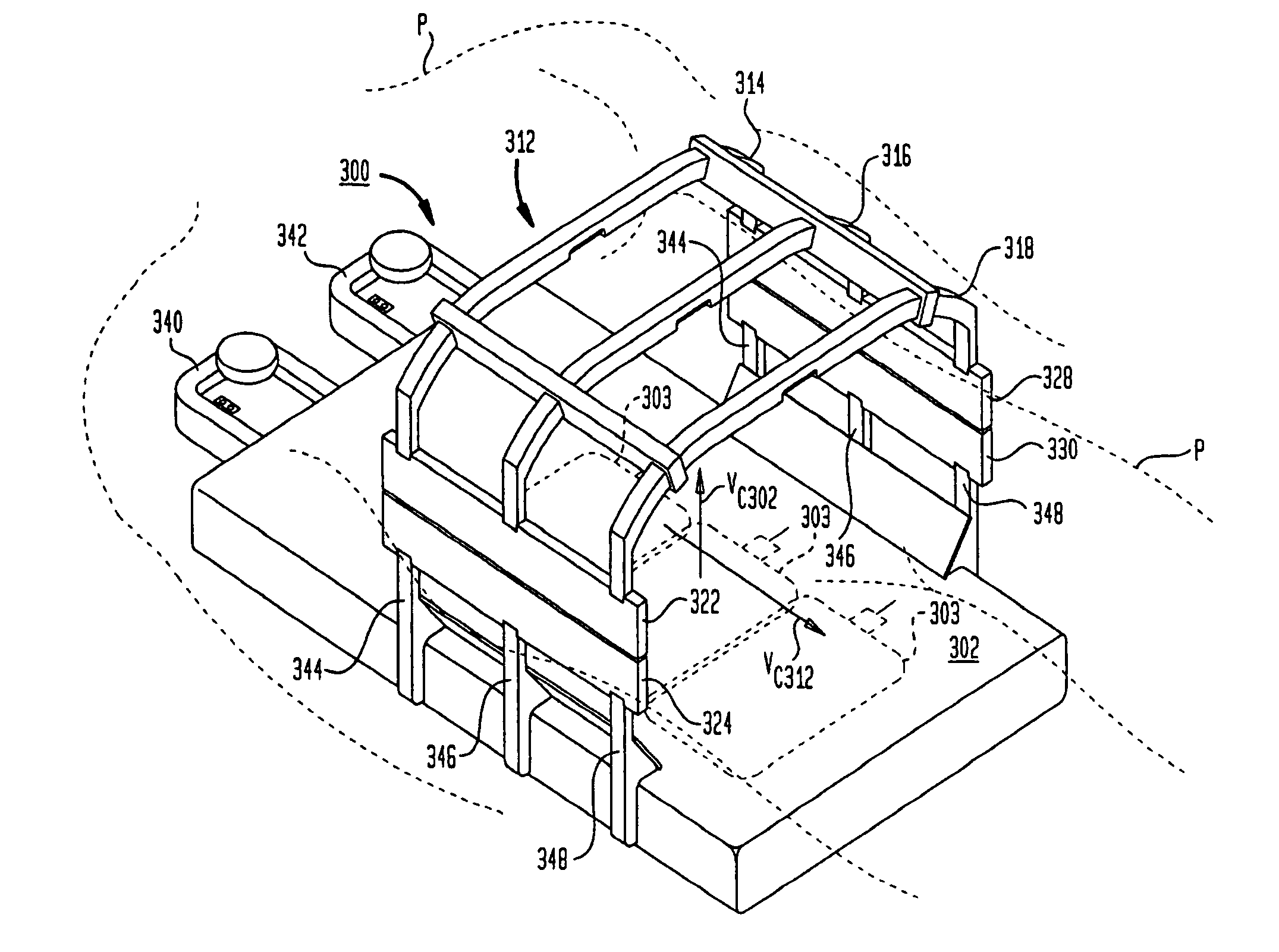
A waveguide image combiner is used to transmit a monochrome or full-color image in an augmented reality display. The combiner uses multiple pairs of overlapping incoupling and outcoupling VHOEs to expand the horizontal FOV and a Y expander to expand the vertical FOV. This suitably provides an expanded horizontal and vertical FOV that offers a diagonal FOV≥50°, a horizontal FOV≥40 and a vertical FOV≥25°. The combiner also delivers a large horizontal eye box up to 20 mm and a vertical eye box of 10 mm while maintaining high light efficiency of the real scene (e.g. >80%). The system is able to use a light engine based on broadband (10 nm≤Δλ≤30 nm) LEDs and maintain a large horizontal field of view and high transmission of the real imagery. The approach resolves issues with current embodiments including astigmatism, image overlap, color balance, and small light engine pupils leading to reduced eye boxes.
Owner:A9 COM INC
Coils for horizontal field magnetic resonance imaging
Methods and apparatus for performing magnetic resonance imaging are disclosed. In one embodiment coil antennas for use with a horizontal field magnetic resonance imaging apparatus are placed in proximity to the scanning region to obtain magnetic resonance images. In accordance with another aspect of the invention the coil antennas are arranged so as to provide zero mutual inductance between the coils so as to increase the sensitivity of the measurement. Additional embodiments include quadrature coil antennas including two antennas, each having their vector fields substantially perpendicular to each other and to a static magnetic field. Methods for using the disclosed antennas in acquiring magnet resonance scans is also disclosed.
Owner:FONAR
Active night vision with adaptive imaging
InactiveUS20050206510A1Reduce system costMinimize complexityAnti-collision systemsColor television detailsNight visionAdaptive imaging
A vision system for a vehicle includes a light source generating an illumination beam, a receiver having a pixel array for capturing an image in response to at least a reflected portion of the illumination beam, the image corresponding to a first horizontal field of view (FOV) angle, and a controller coupled to the light source and the receiver. The controller receives a vehicle speed input and, in response, selects a portion of the image as a non-linear function of the vehicle speed to generate a second horizontal FOV angle for displaying to the vehicle operator. The displayed angular FOV decreases, non-linearly, as the vehicle speed increases.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Method for providing output image in either cylindrical mode or perspective mode
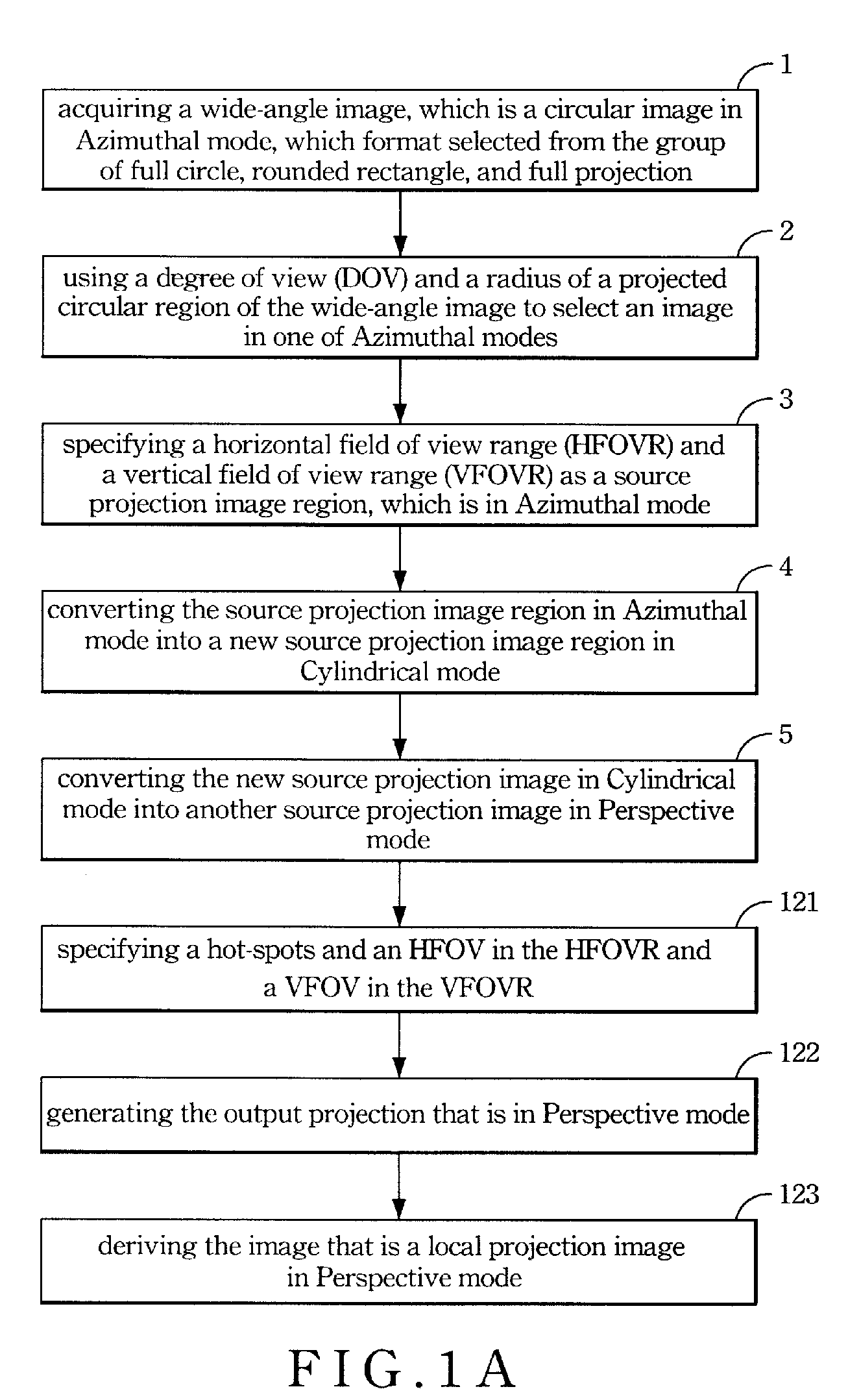
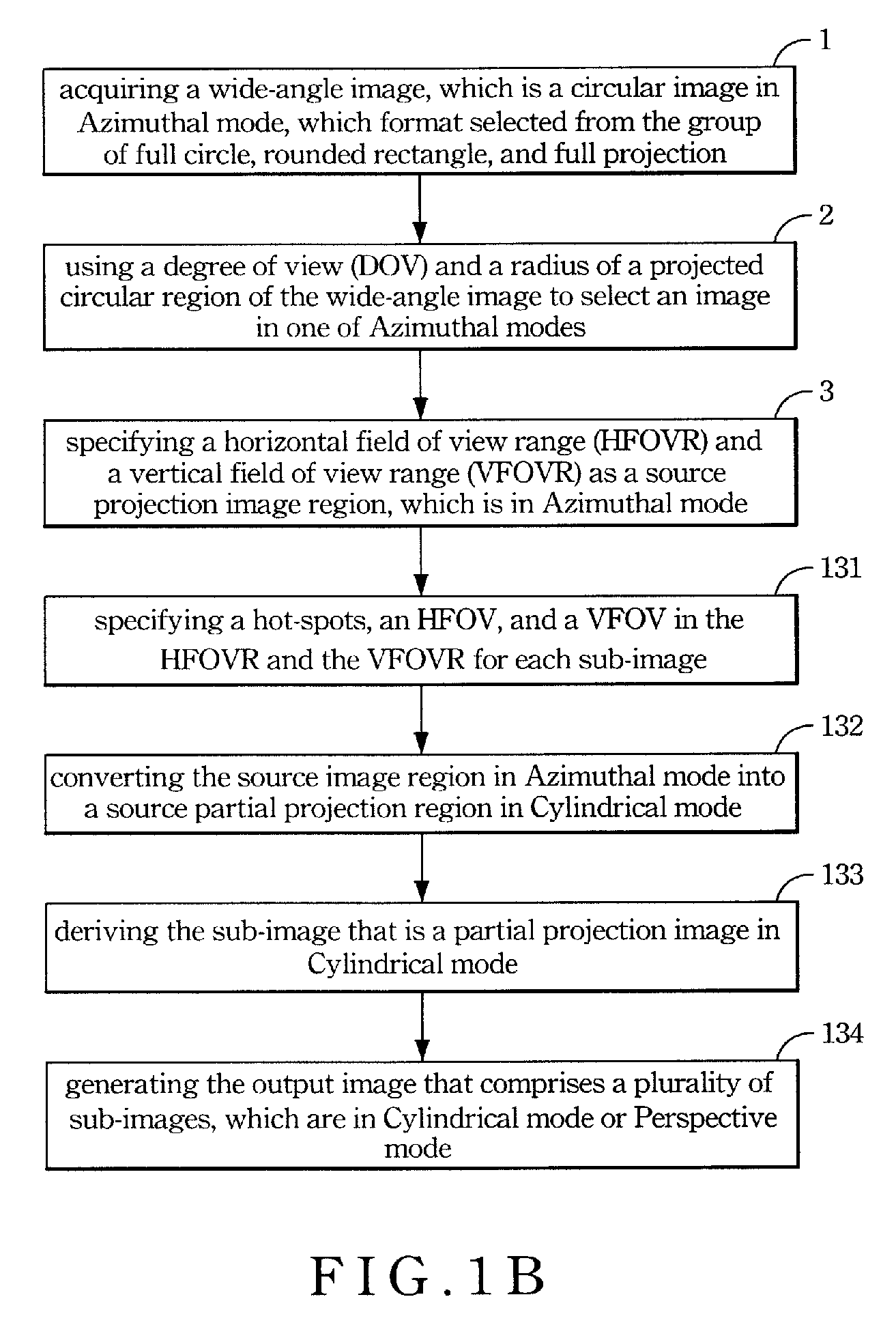
InactiveUS7961980B2Reduce distortion problemsGeometric image transformationCharacter and pattern recognitionRounded RectangleProjection image
A method is disclosed for transforming a wide-angle video image in to a Perspective view or a Cylindrical video image with reduced distortion. The method for providing an output image in either a Cylindrical mode or a Perspective mode, and comprising steps of: (1) acquiring a wide-angle image, which is a circular projection image, which format selected from the group of full circle, rounded rectangle, and full projection; (2) using a degree of view (DOV) and a radius of a projected circular region of the wide-angle image to select an image in one of Azimuthal modes; (3) specifying a horizontal field of view range (HFOVR) and a vertical field of view range (VFOVR) as a source projection image region, which is in Azimuthal mode; (4) converting the source projection image region in Azimuthal mode into a new source projection image region in Cylindrical mode; (5) converting the new source projection image in Cylindrical mode into another source projection image in Perspective mode; and (6) generating the output image.
Owner:IMAY SOFTWARE
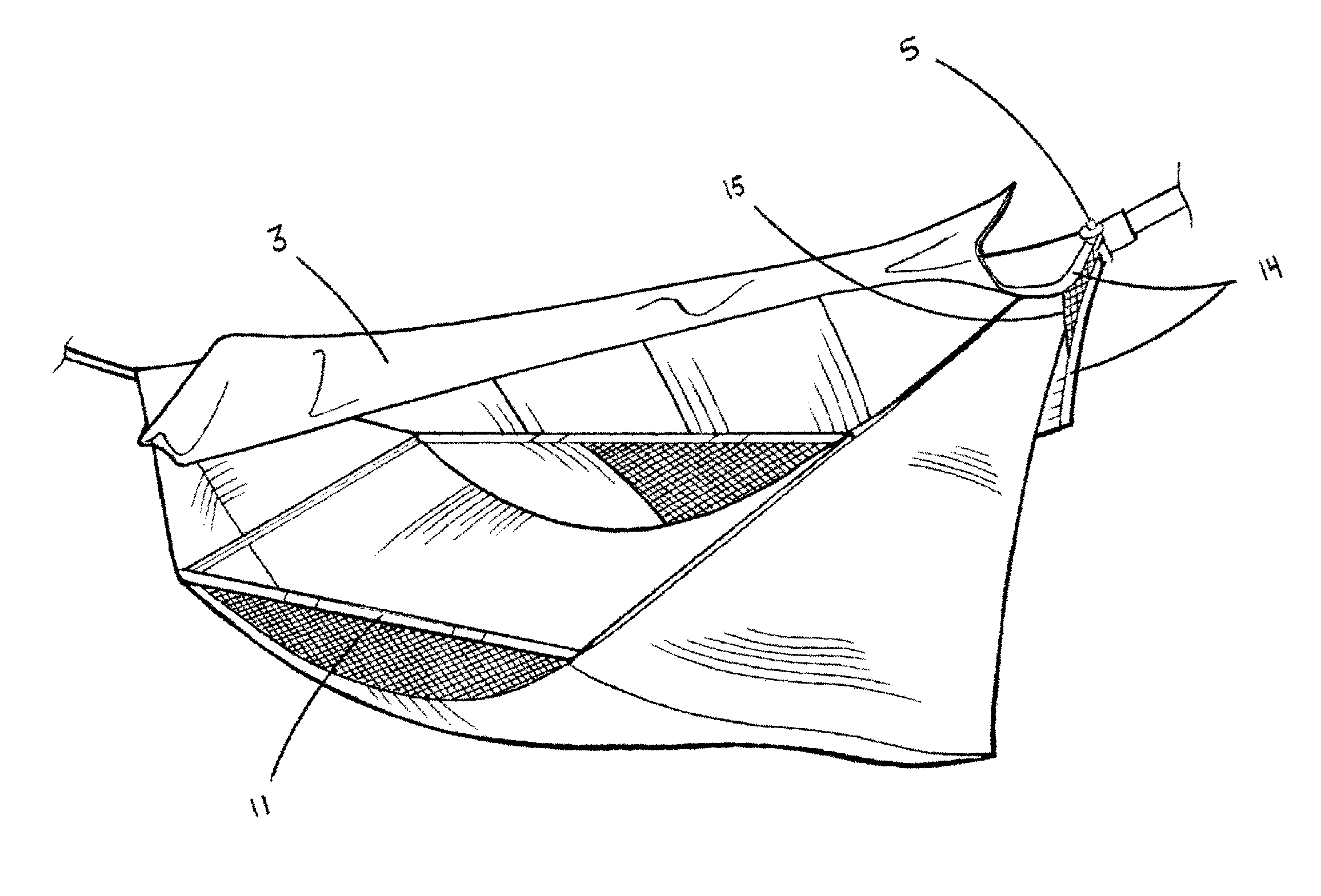
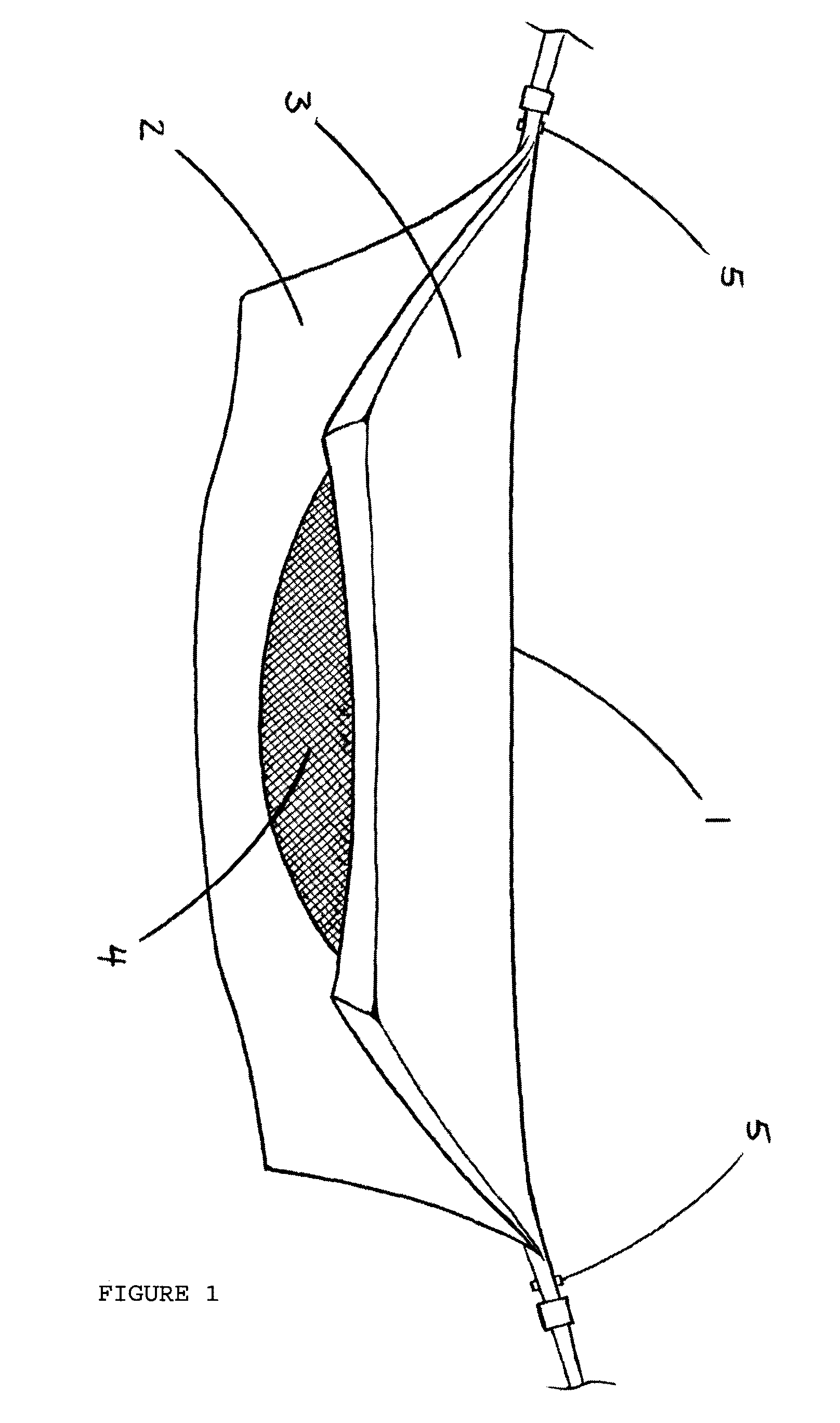
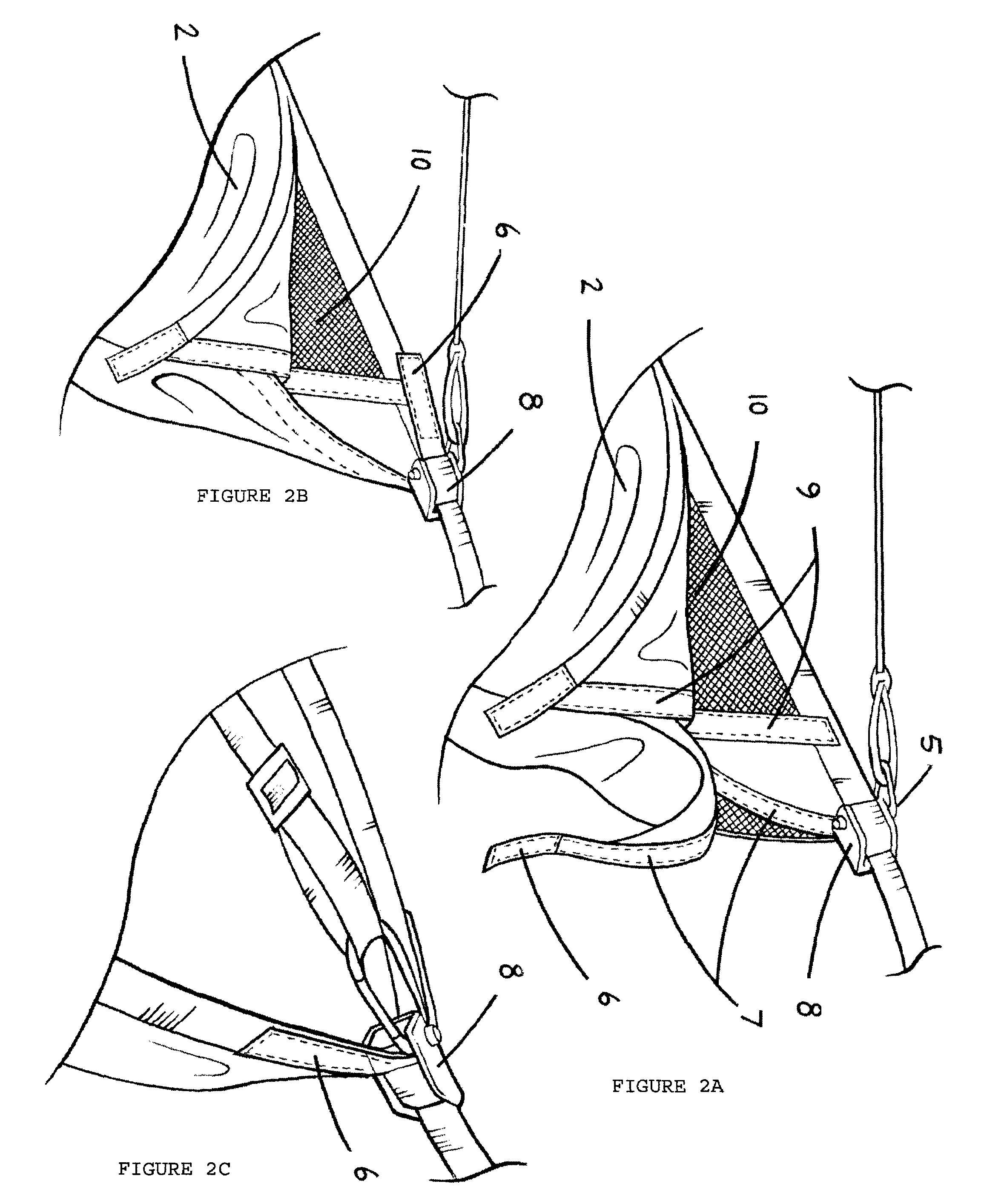
Hammock tent
InactiveUS7699068B2Increase awarenessQuick installationTravelling sacksTents/canopiesVisibilityEngineering
Owner:HELSDON DAVID
Method to reduce sensitivity of a perpendicular recording head to external fields
InactiveUS20060245113A1Record information storageManufacture of flux-sensitive headsElectrical conductorEngineering
In a read-write head, the shields can serve as magnetic flux conductors for external fields, so that they direct a certain amount of flux into the recording medium. This problem has been overcome by the addition to the shields of a pair of tabs located at the edges closest to the ABS. These tabs serve to prevent flux concentrating at the edges so that horizontal fields at these edges are significantly reduced. Said tabs need to have aspect ratios of at least 2 and may be either triangular or rectangular in shape. Alternatively, the tabs may be omitted and, instead, outer portions of the shield's lower edge may be shaped so as to slope upwards away from the ABS.
Owner:HEADWAY TECH INC
Multiple program and 3D display screen and variable resolution apparatus and process
InactiveUS20060012542A1Save electricityTime can be spentStatic indicating devicesSteroscopic systemsComputer graphics (images)Image resolution
In a first preferred embodiment, this invention provides a low cost means for reliably producing an auto-stereoscopic 3D front project display screen. The screen is engineered to distribute discrete portions of light across a range of discrete horizontal on and off axis viewing angles corresponding with perspective correct 3D images. The screen also distributes each of these pixels concurrently through a wide vertical range to enable users in vertical on axis and off axis viewing positions to see the pixels within their narrow horizontal field of vie yet through a wide vertical field of view. In a second embodiment, a 3D filter is provided that enables a display to automatically switch between displaying 3D media of a first 3D resolution and to display 3D media of a second 3D resolution. Both embodiments also enable multiple users to concurrently watch different programs on the same display at the same time.
Owner:ALDEN RAY M
Low-frequency-stage magnetic sensor background noise measuring method
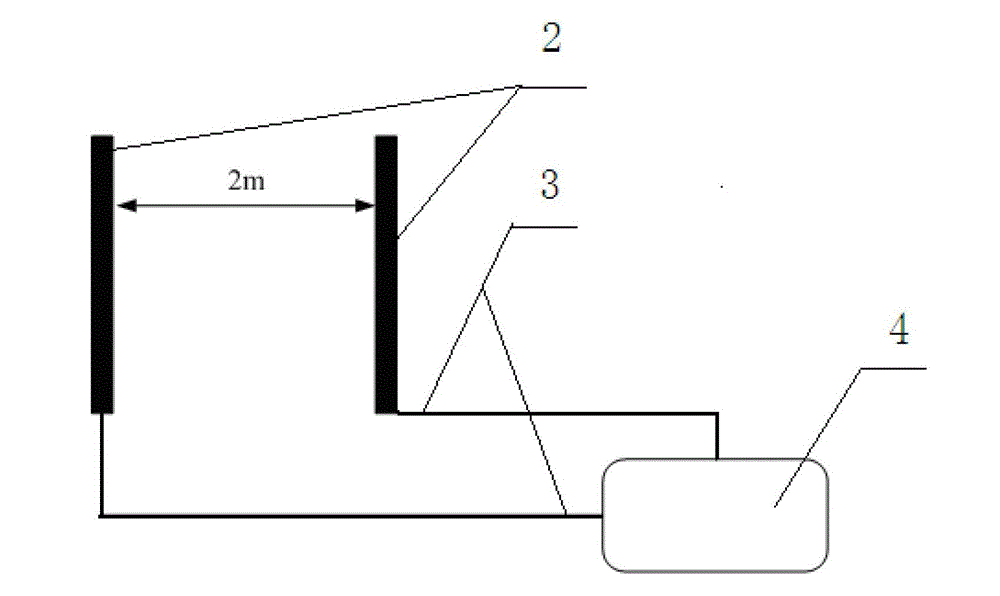
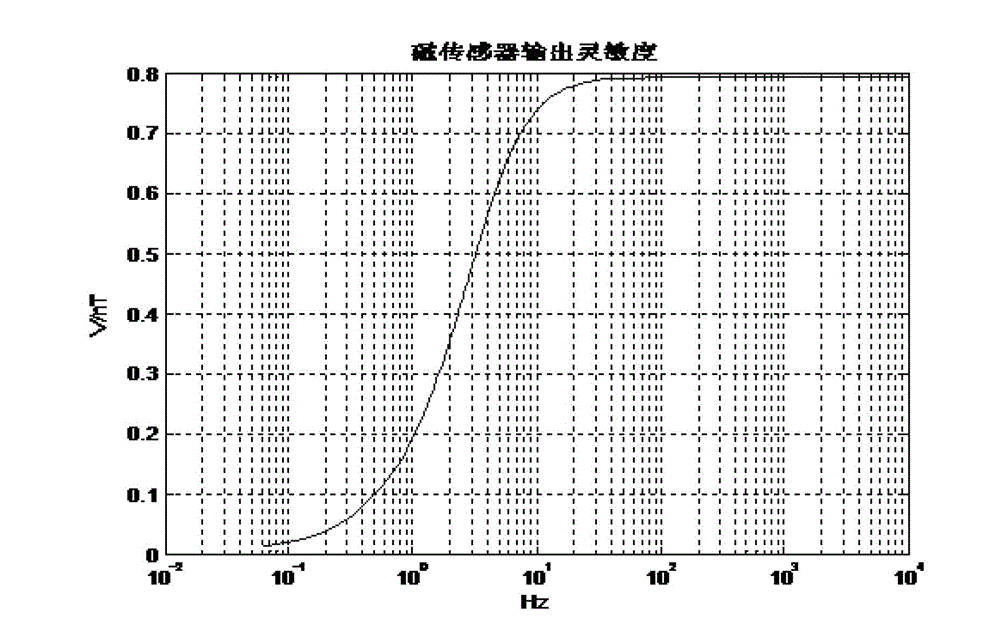
ActiveCN102944765AAccurately measure the noise floorReflect the actual noise levelNoise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementNoise levelLow frequency band
The invention relates to a low-frequency-stage magnetic sensor background noise measuring method which is applicable to measuring the background noise of a low-frequency-stage magnetic sensor in a wild environment or a big shielding room. The method comprises the following steps that: response characteristics of amplitude frequencies and phase frequencies of two magnetic sensors are respectively adjusted to be accordant; the two sensors are horizontally arranged in parallel with a distance of 2-2.5m; two ends of the sensors are in parallel and level; the sensors sense identical natural horizontal field signals which belong to relevant signals; natural field signals can be eliminated by using a differentiation method; however, the background noise of the two sensors refers to an irrelevant random signal; and signal energy after the differentiation is the sum of noise energy of the two sensors. An average power spectrum of the signals after the differentiation is calculated, the average power spectrum is divided by 2 and is subjected to extraction of a root, and the background noise of a single sensor is calculated according to the output sensitivity of the magnetic sensors. The background noise of the low frequency stage magnetic sensor in a response bandwidth is accurately measured, and compared with a theoretical analysis method, the actual noise level of the magnetic sensor is relatively accurately reflected.
Owner:NO 722 RES INST OF CHINA SHIPBUILDING IND
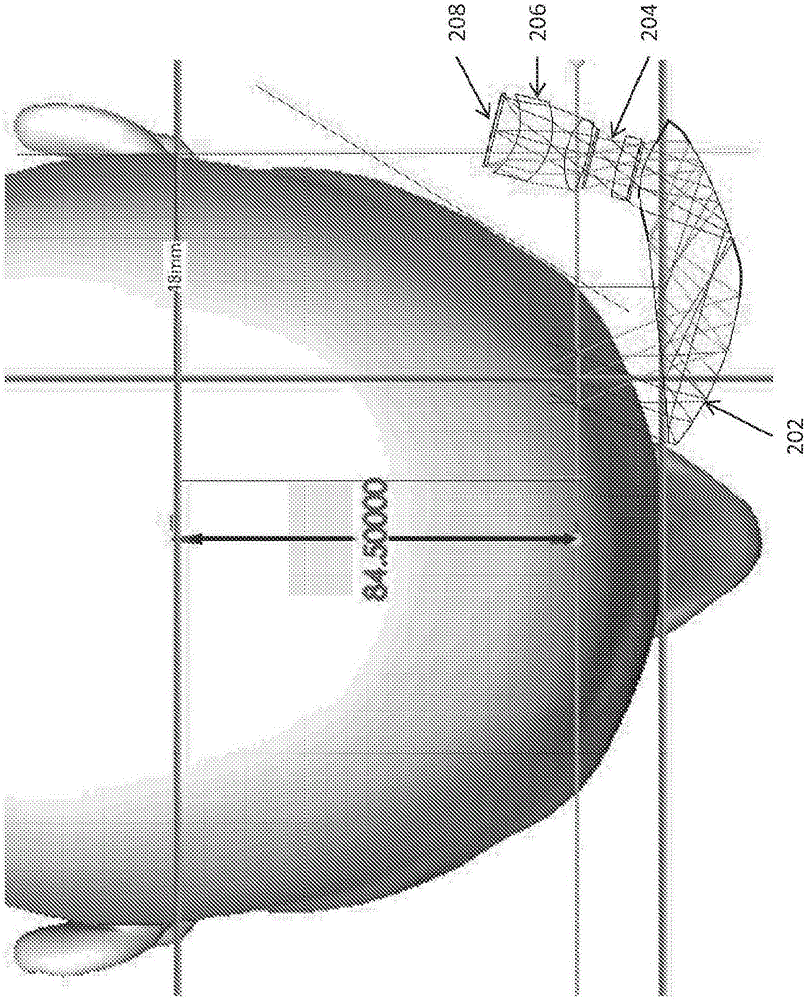
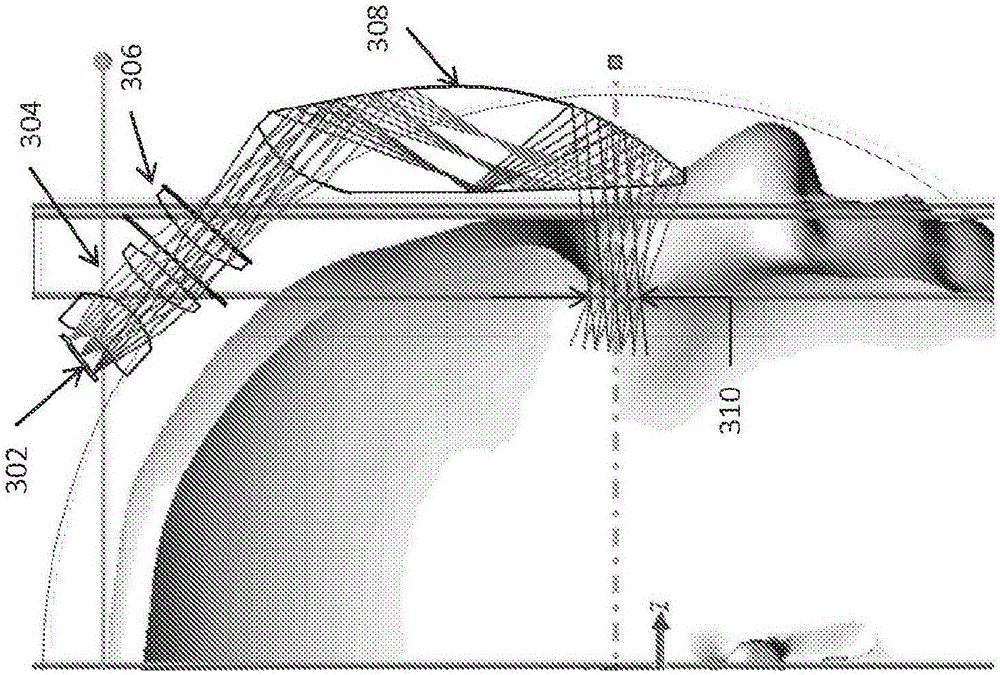
Methods and systems for displaying stereoscopy with a freeform optical system with addressable focus for virtual and augmented reality
Several unique hardware configurations and methods for freeform optical display systems are disclosed. A freeform display system includes primary freeform optical element(s) and secondary freeform optical element(s) in tiled arrangements to expand the horizontal field of view (FOV) or the vertical field of view. The system may include a variable focusing system that produces intermediate pupil and changes the focal distance of a single focal plane or switches among multiple focal planes for rendering objects in focus while resolving accommodation-convergence conflict. The system may map light samples to appropriate light rays in physical space and use a cluster of projectors to project the mapped light rays to produce the light field of the virtual display content. Methods for making tiled freeform optical display systems and methods for producing virtual content with variable focus freeform optics and rendering light fields are also disclosed.
Owner:MAGIC LEAP
Low cost threat detection sensor
ActiveUS20090226109A1Without effectivenessWithout sensitivityRadiation pyrometryOptical rangefindersAutomotive batteryEngineering
The present invention addresses issues of cost and weight that prevent other threat detection systems intended to detect and identify locations of incoming munitions fire such as RPGs, anti-tank missiles, and other such weapons, from being used more broadly.The invention consists of a portable, optical sensor that has a 360-degree horizontal field of view and a selectable vertical field of view that can cover up to 90 degrees. An embodiment of the invention is meant for use and transport by an individual or group of individuals, and does not require significant support electronics or power supplies in excess of a typical car-battery in size and weight. Other embodiments may be vehicle mounted, or may be further enhanced to work with other detection or response systems.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
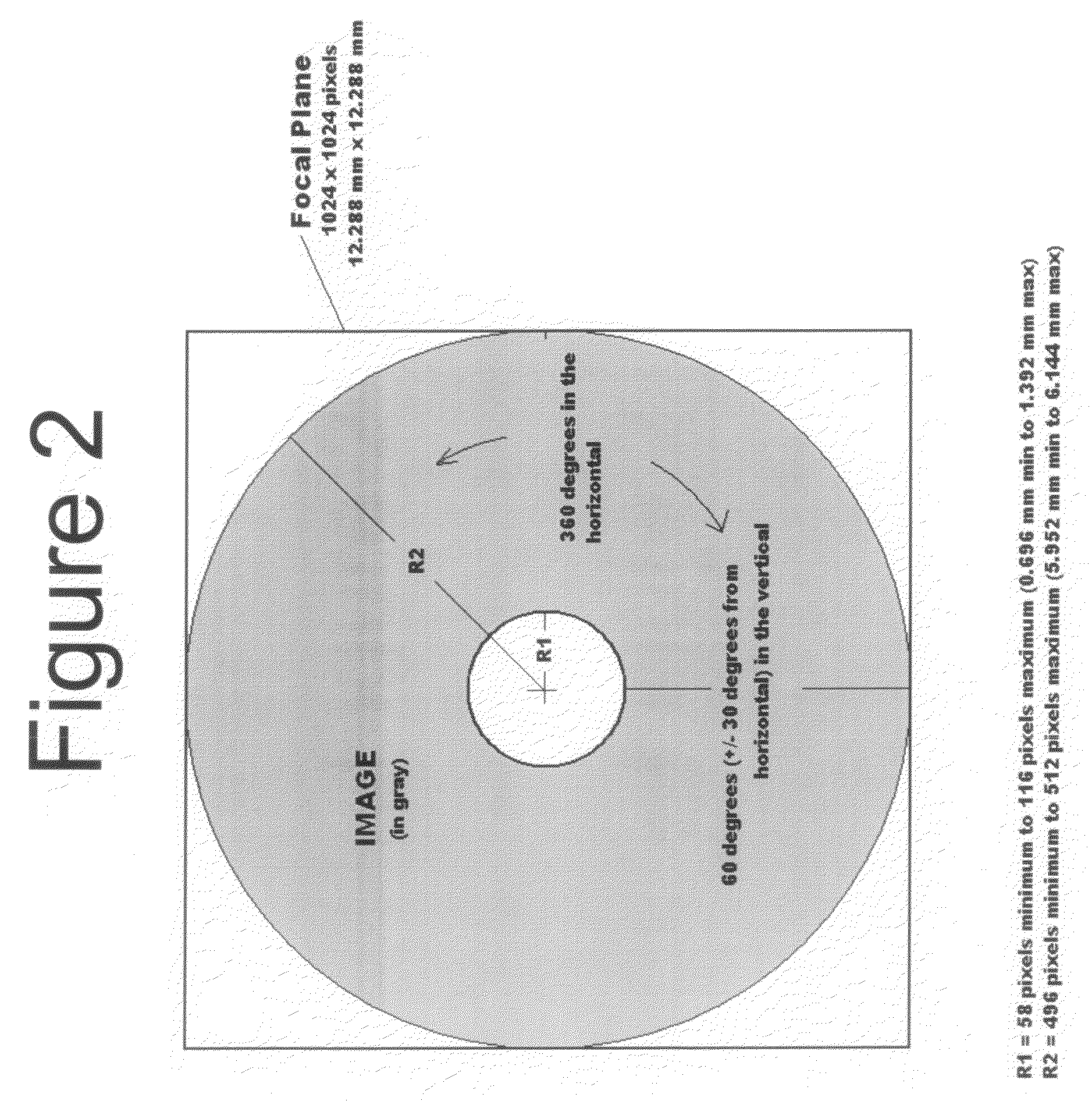
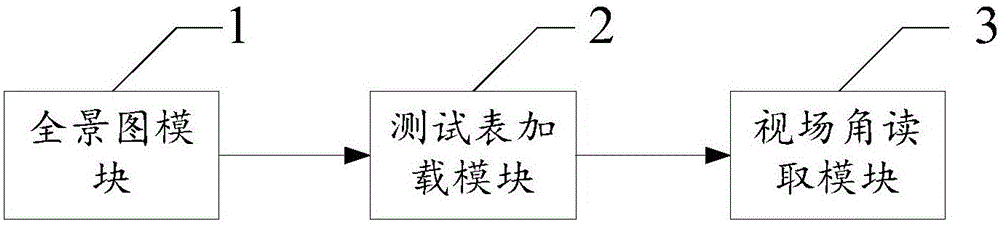
Method and system for detecting field angle of virtual reality display device
ActiveCN105787980AAccurate readingEasy field of view detectionImage analysis2D-image generationDisplay deviceComputer vision
The invention relates to a method and system for detecting field angle of a virtual reality display device. The method comprises the following steps: 1) selecting a panoramic image, format and optical parameters of which are matched with those of a detected virtual reality display device according to the detected virtual reality display device; 2) loading a test pattern to the panoramic image to generate a panoramic image having scale marks, and importing the panoramic image having the scale marks to the detected virtual reality display device; and 3) obtaining a horizontal field angle by observing the scale marks at the left and right boundaries of the panoramic image of the detected virtual reality display device, and / or obtaining a vertical field angle by observing the scale marks at the upper and lower boundaries of the panoramic image of the detected virtual reality display device. The method is suitable for all virtual reality display devices, is accurate in reading, and has the advantages convenient, direct, fast and efficient detection of the field angle of the detected virtual reality display device.
Owner:MUDAN SHIYUAN ELECTRONICS BEIJING
Panoramic video system with real-time distortion-free imaging
A panoramic annular lens system (PAL), a unitary video camera and a PCbased software system that unwraps a 360 DEG video image into a seamless, distortion free horizontal image in real time. The PAL system of the preferred embodiment has a 360 DEG horizontal field of view and a 90 DEG vertical field of view in a 40mm diameter compact package. The invention is not limited to any particular type of lens system. In fact, there are numerous lens systems for providing a 360 DEG panoramic view. The video camera may be a CCD or CMOS based device having a pixel resolution of either 1280 x 1024 (high resolution) or 720 x 480 (NTSC). The unwrapping system is a radiometric ray tracing program carried out using a computer's graphics card capabilities to produce highly efficient regional transformation while minimizing software overhead. The result is real time, high resolution 30 fps conversion from a spherical distorted image to a flat panoramic image in Cartesian coordinates.
Owner:PHYSICAL OPTICS CORP
Cervical-thoracic-lumbar spine phased array coil for horizontal field MRI systems
A phased array coil for a Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) system is provided that includes a first coil and a second coil adjacent the first coil. The first and second coils are configured in a shifted arrangement from a center of examination of the MRI system.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
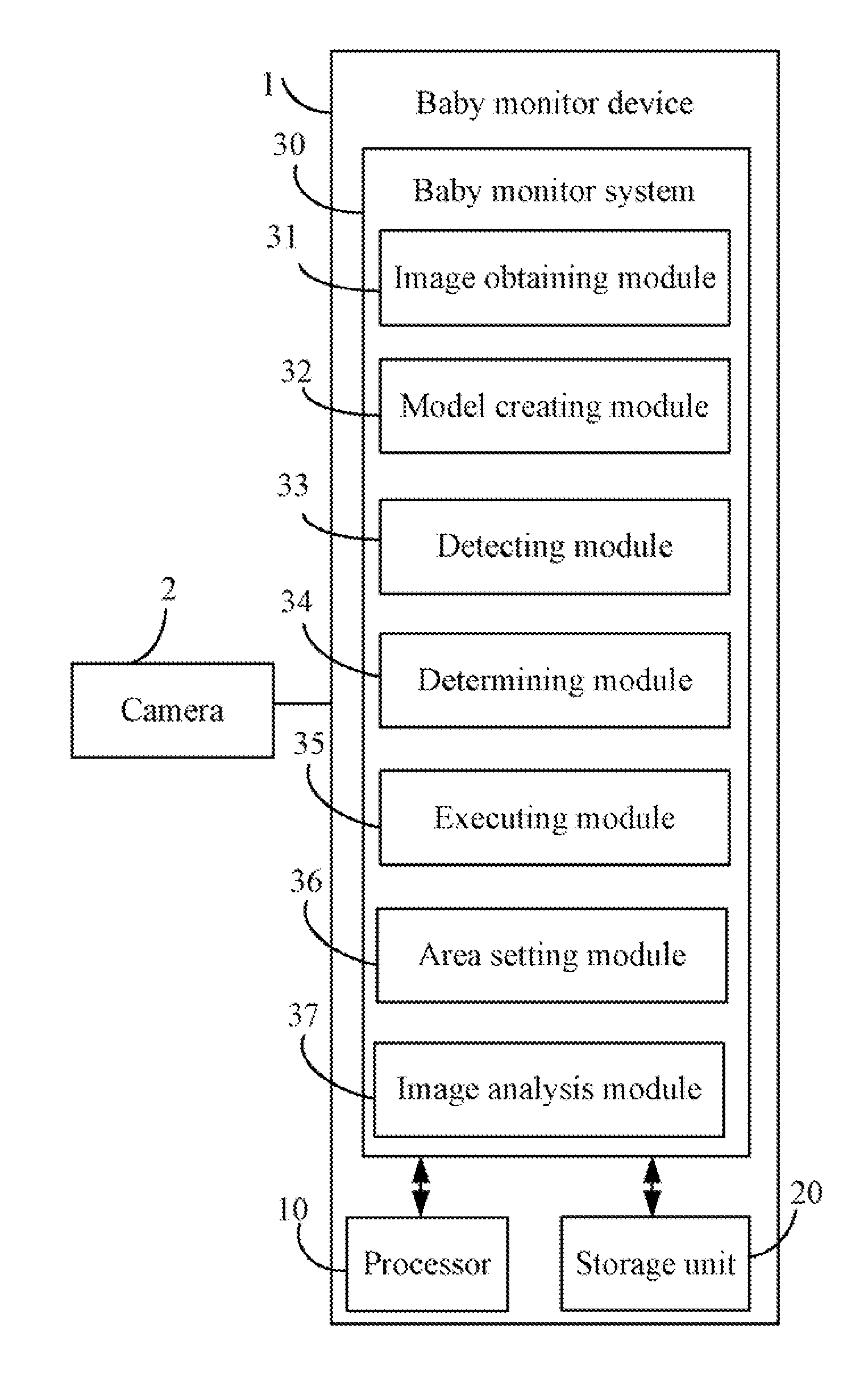
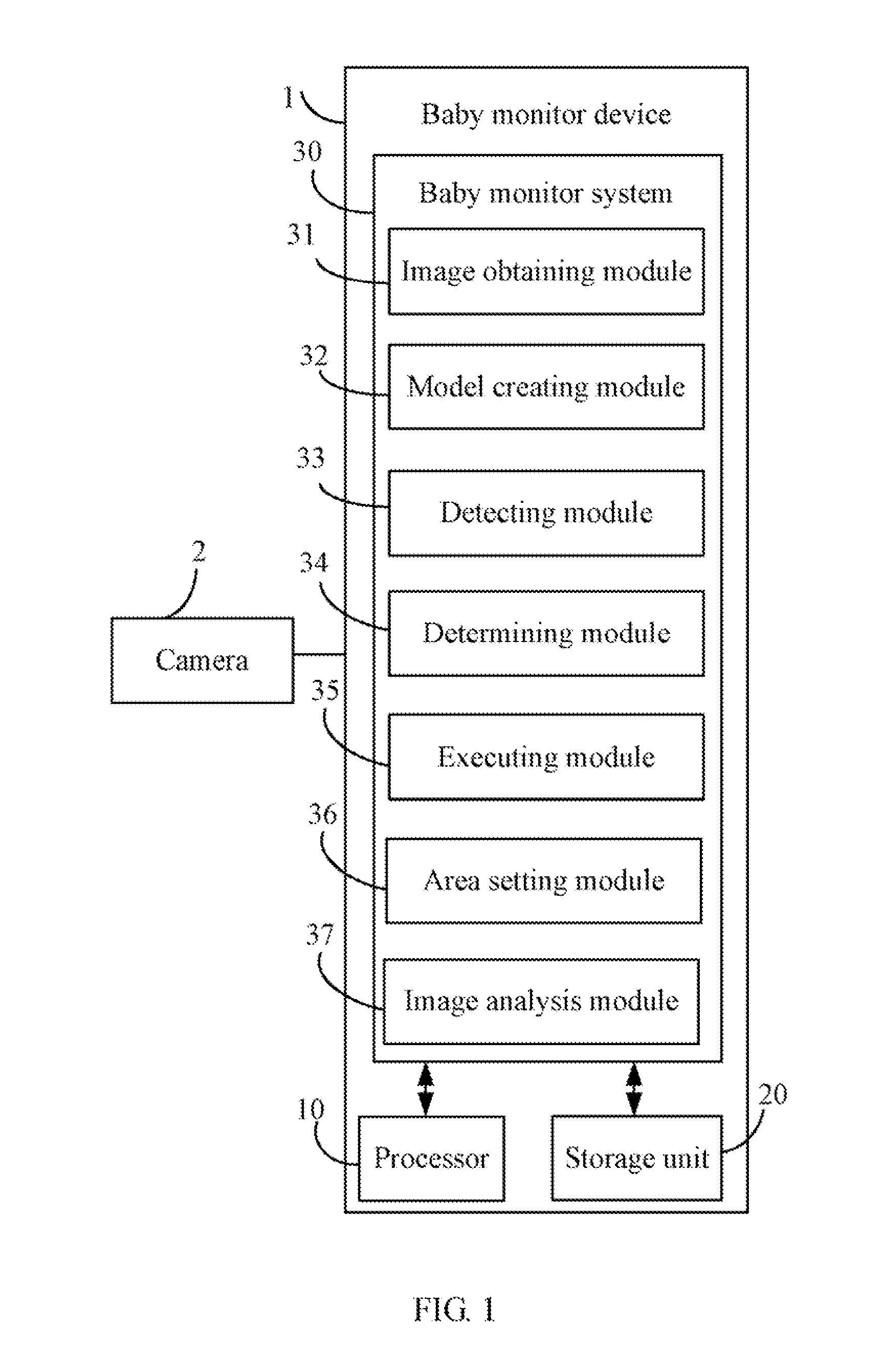
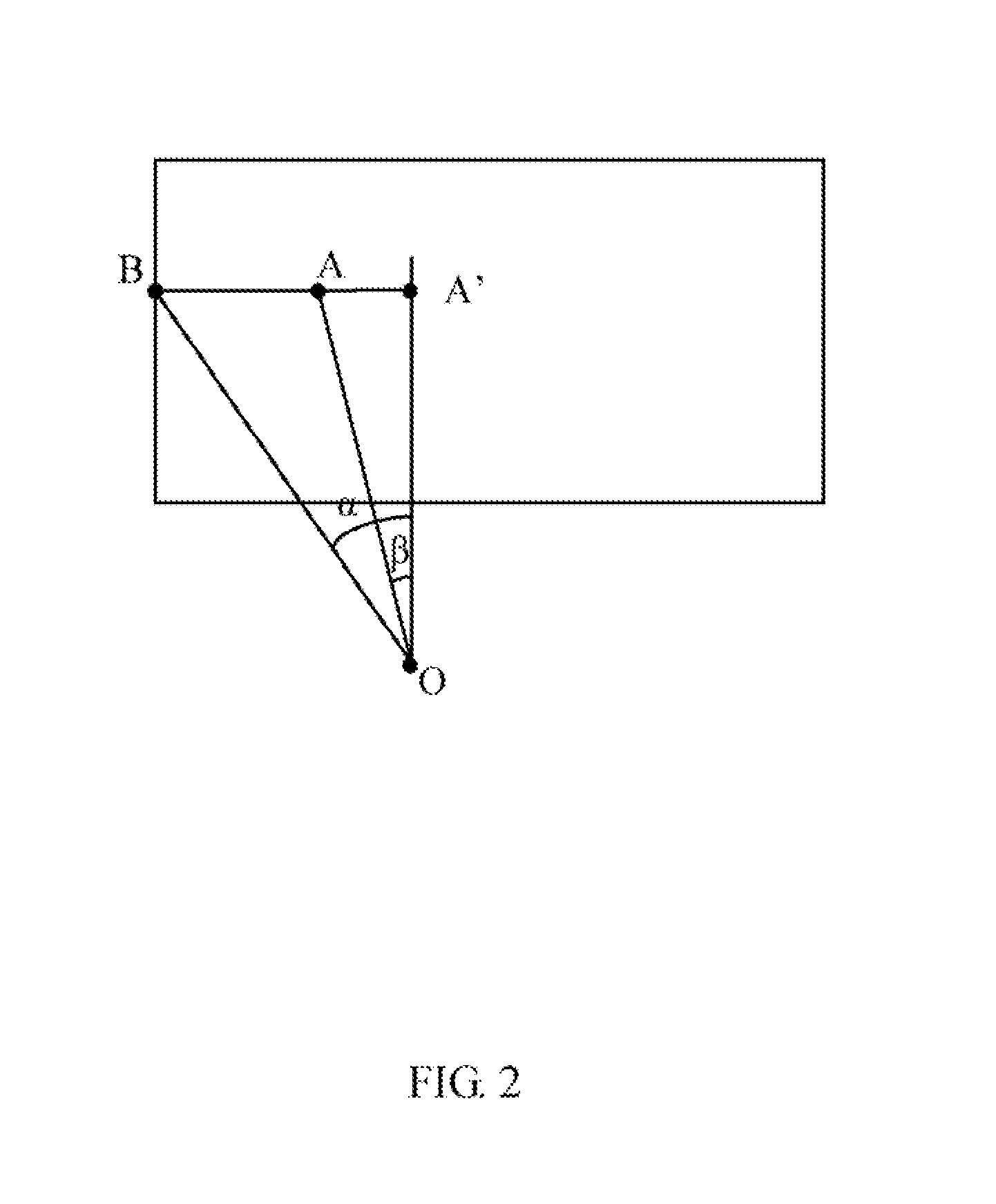
Baby monitoring system and method
An exemplary baby monitoring method includes obtaining an image captured by a camera. The image includes a distance information indicating distances between the camera and objects captured by the camera. The method then creates a 3D scene model according to the captured image and the distances between the camera and objects captured by the camera. Next, the method determines whether any baby appears in the created 3D scene model, and further determines whether the distances between the babies and electronic appliances are less than a preset value according to the distances between the camera and the babies, the distances between the camera and the electronic appliances, and a stored horizontal field of view of the camera. The method then outputs a warning and cuts off power supply to the electronic appliances whose distance to the one or more babies are less than the preset value.
Owner:HON HAI PRECISION IND CO LTD
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com