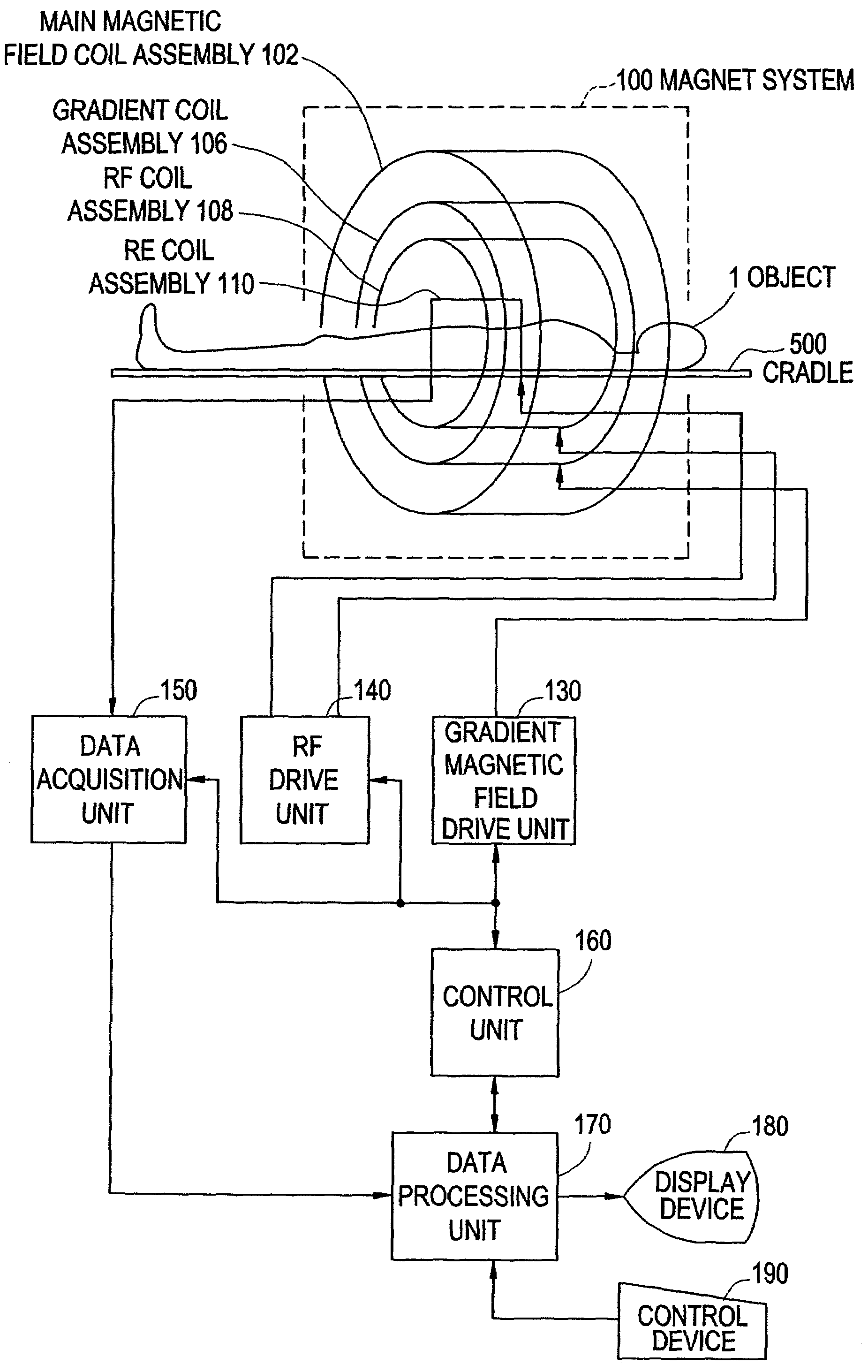
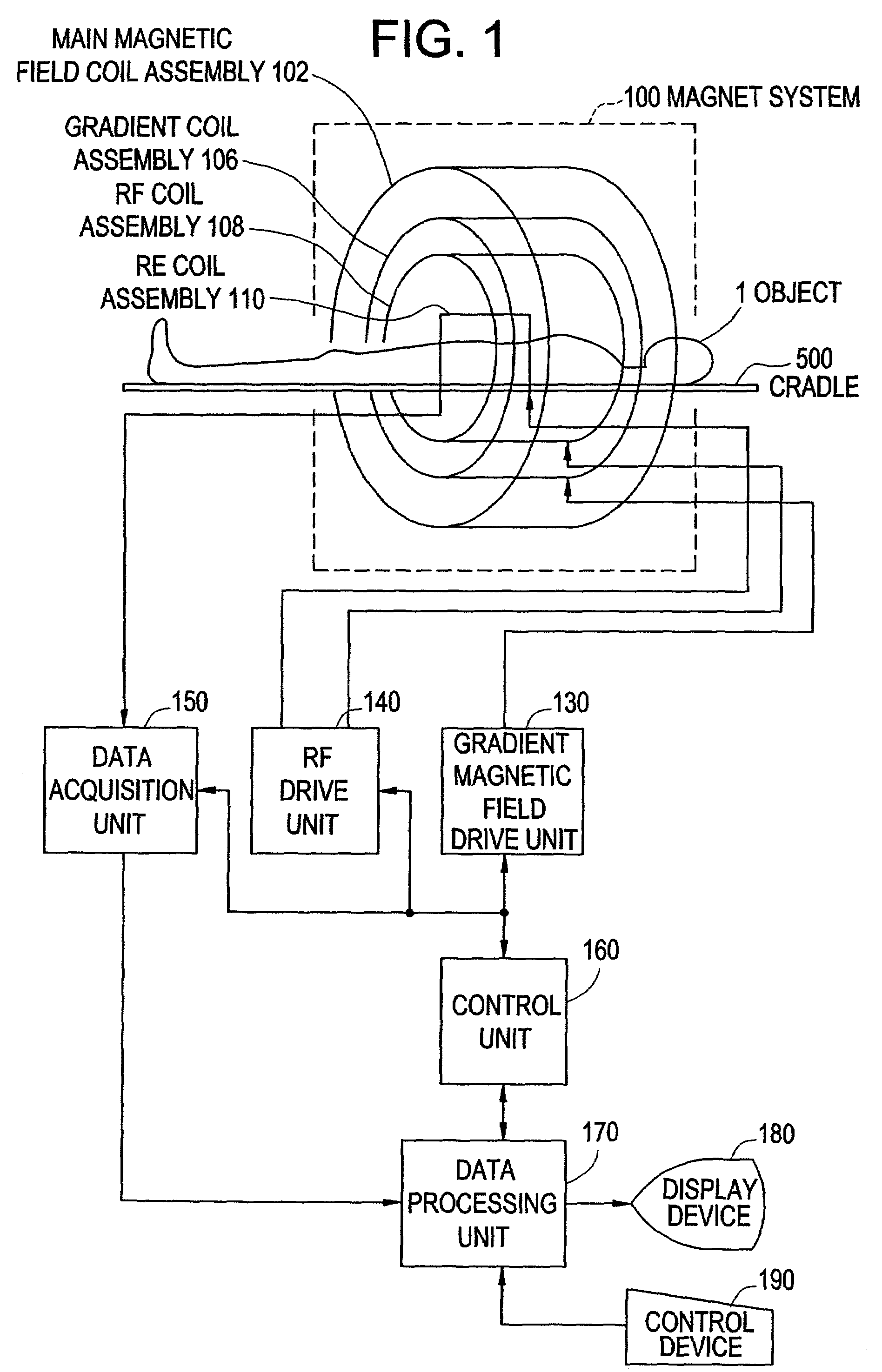
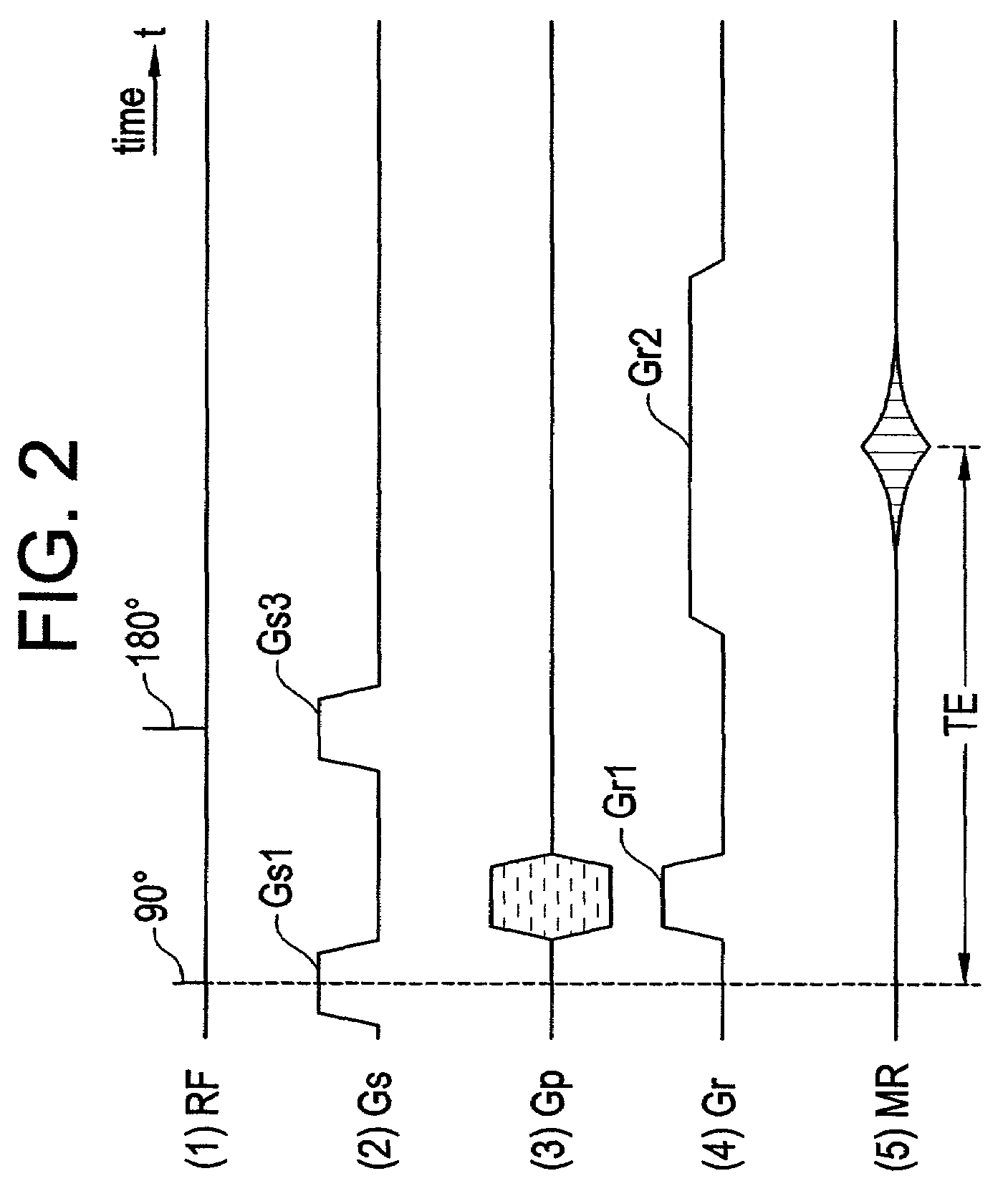
Patents
Literature
57 results about "Saddle coil" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
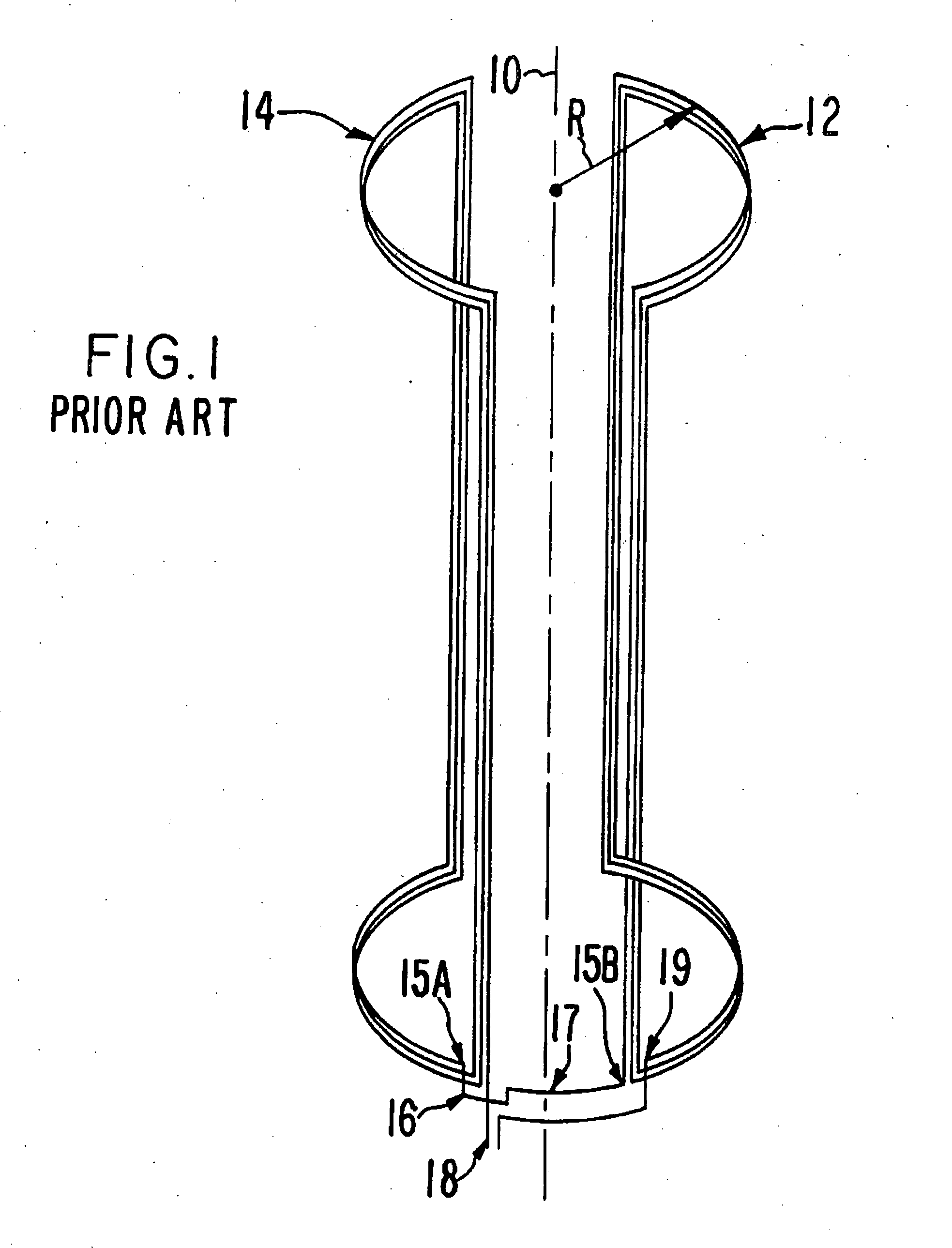
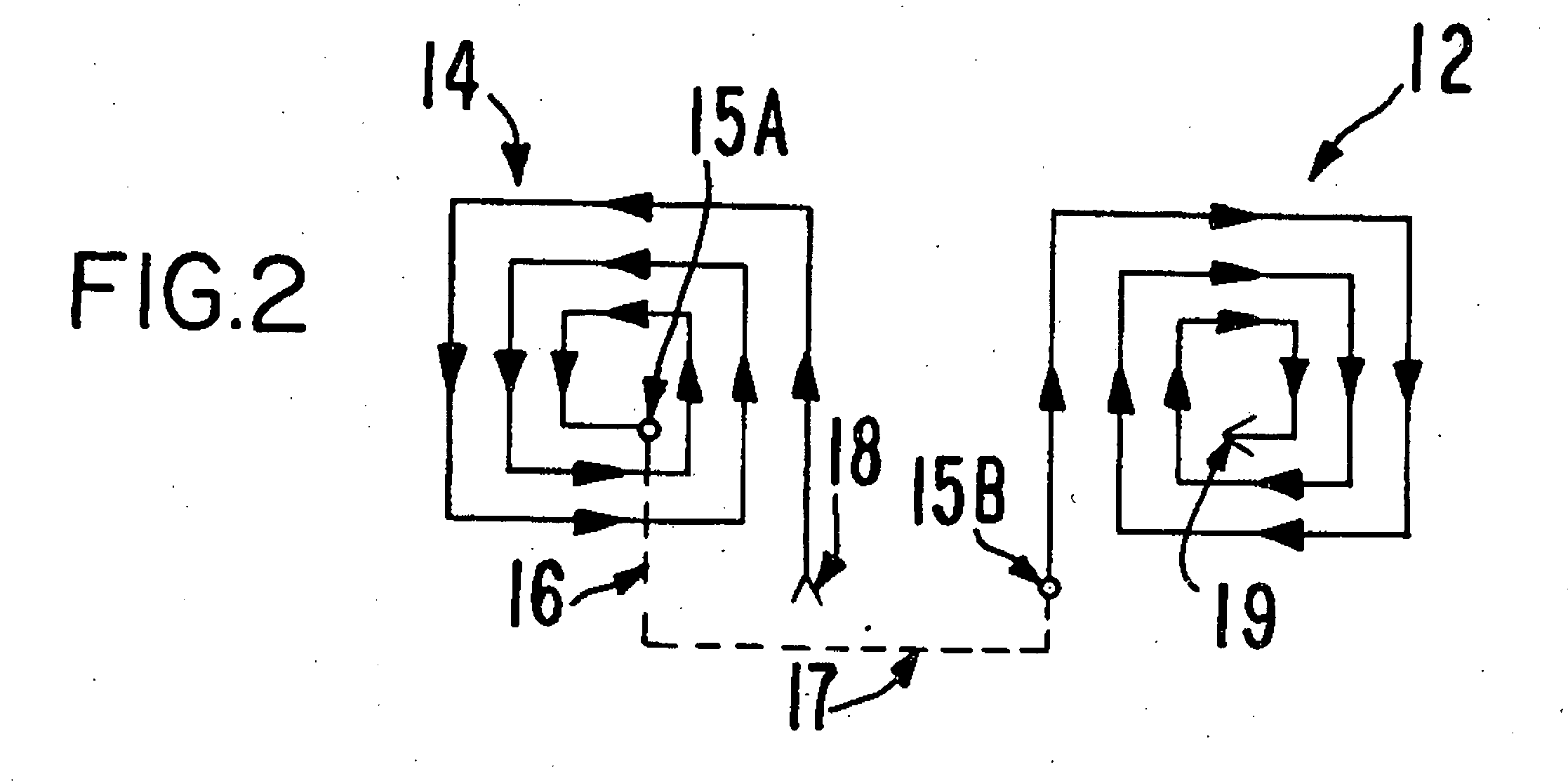
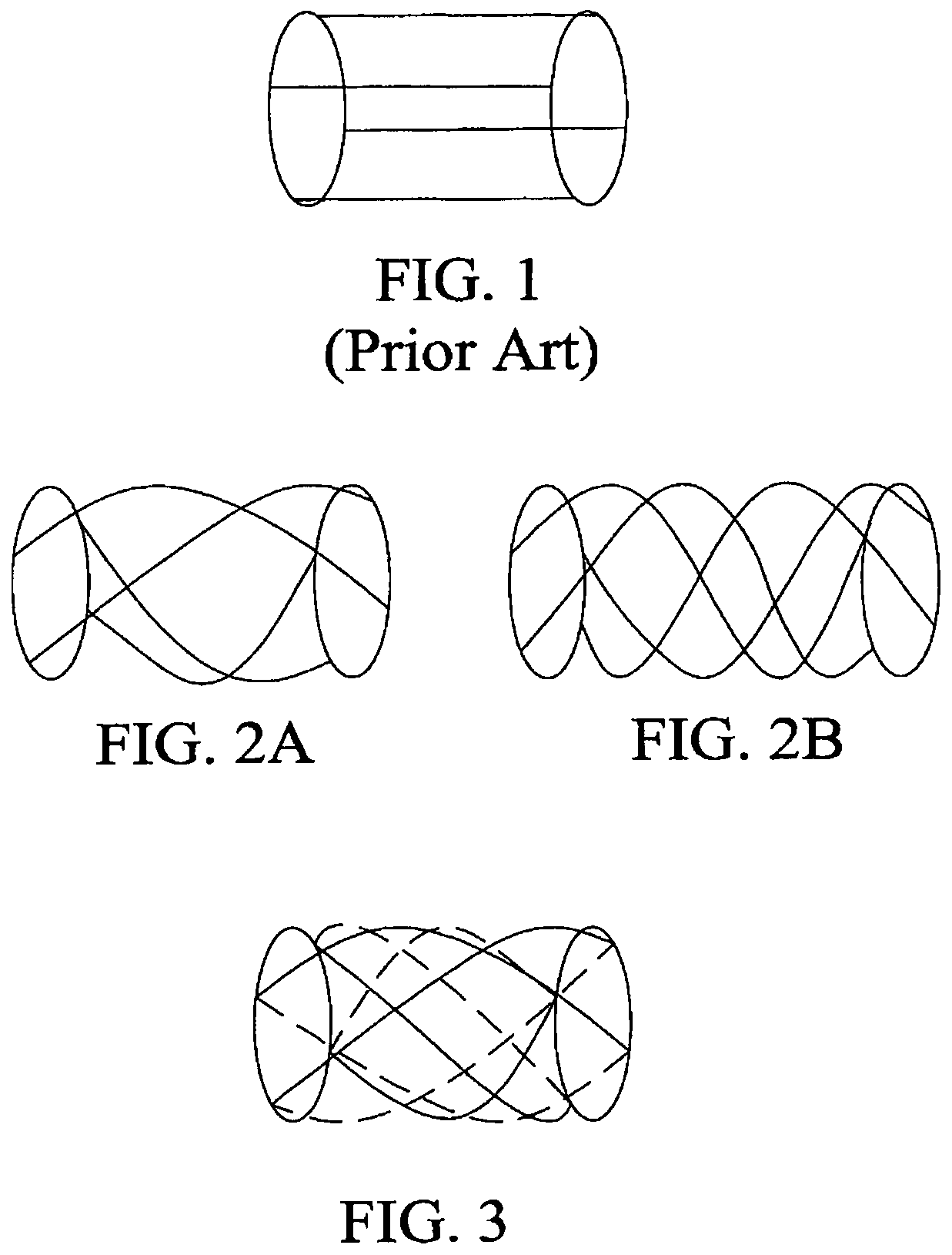
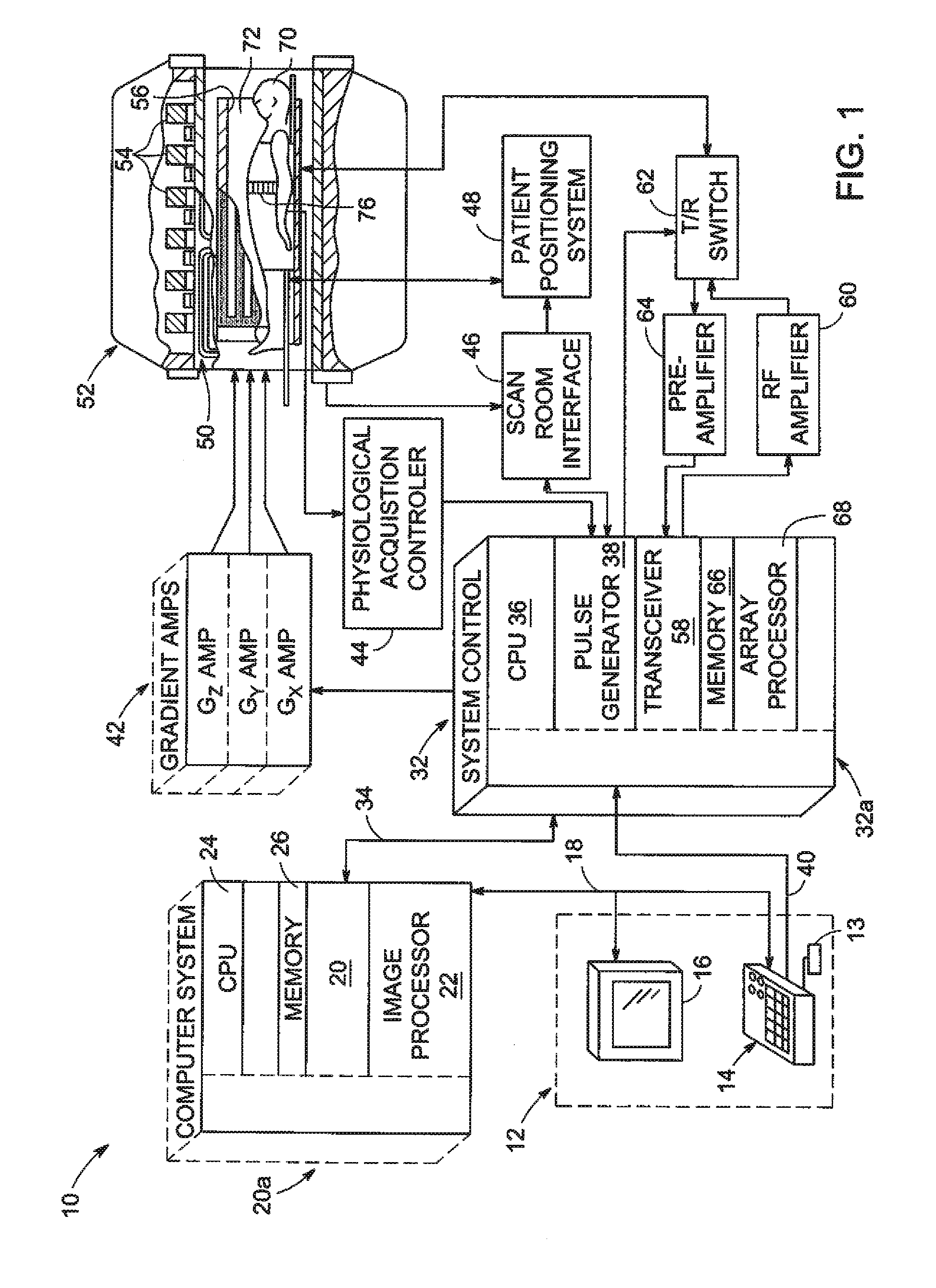
Shielding method and apparatus using transverse slots
InactiveUS6566881B2Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingLoop antennasUltrasound attenuationEngineering
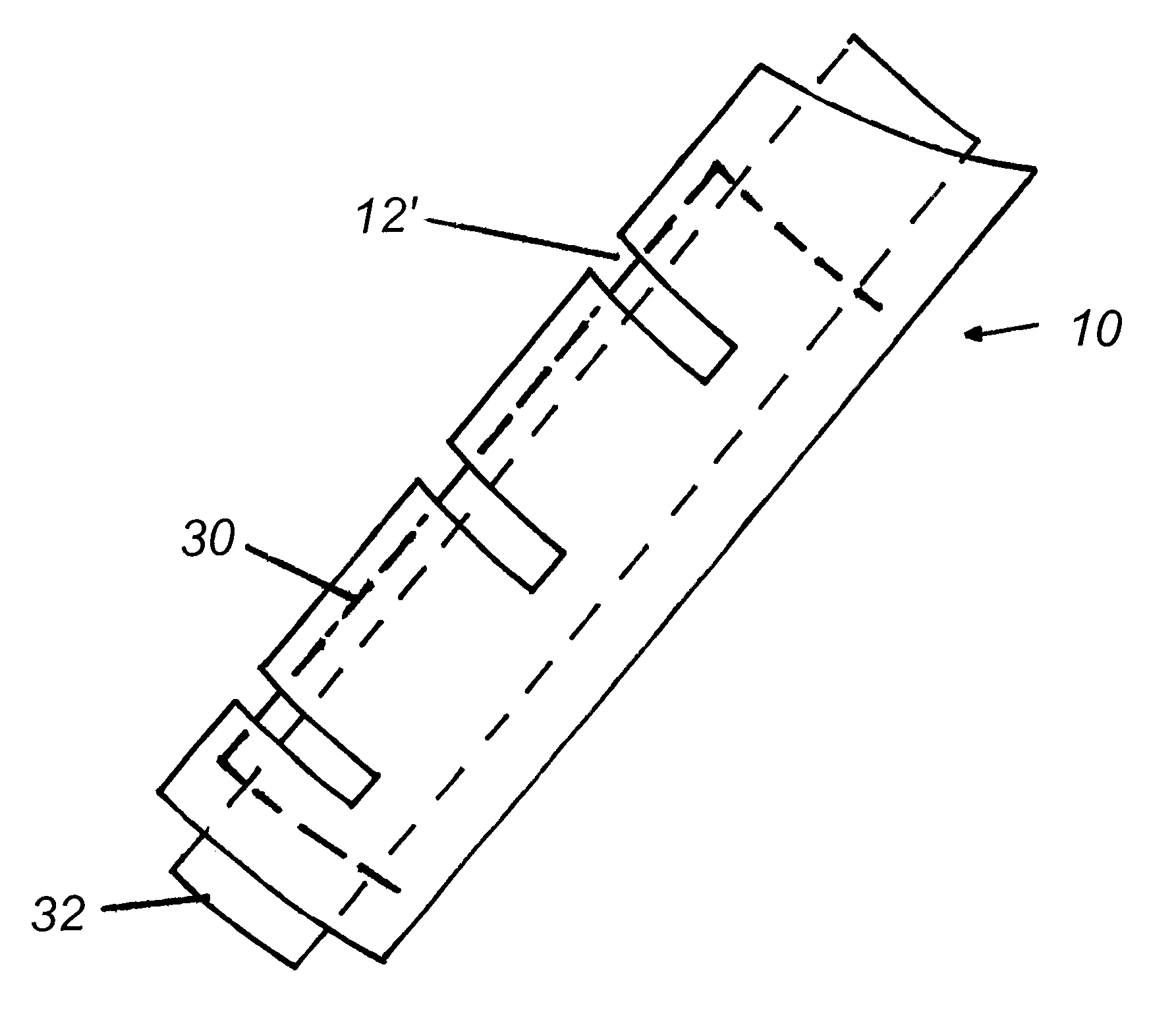
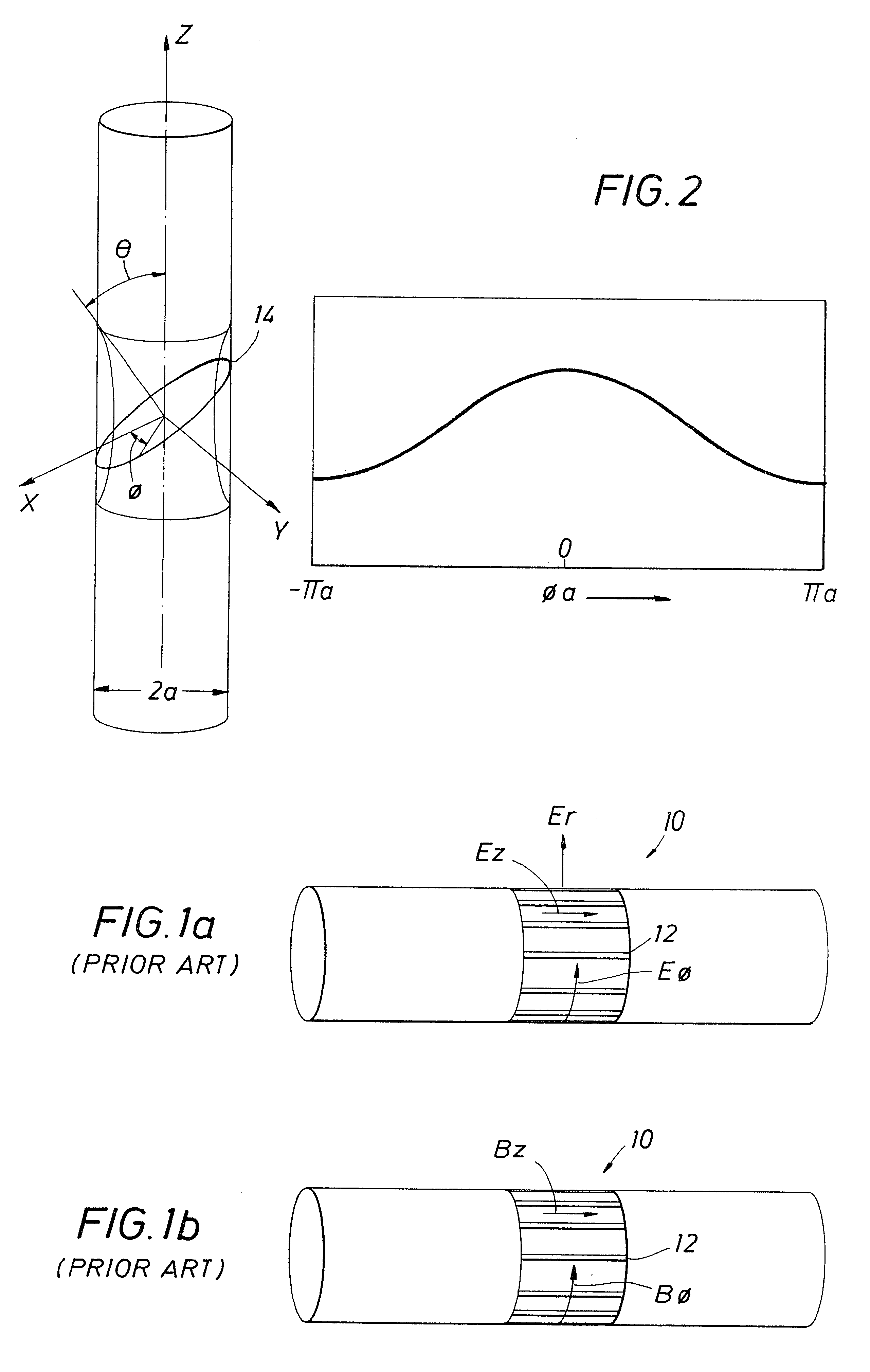
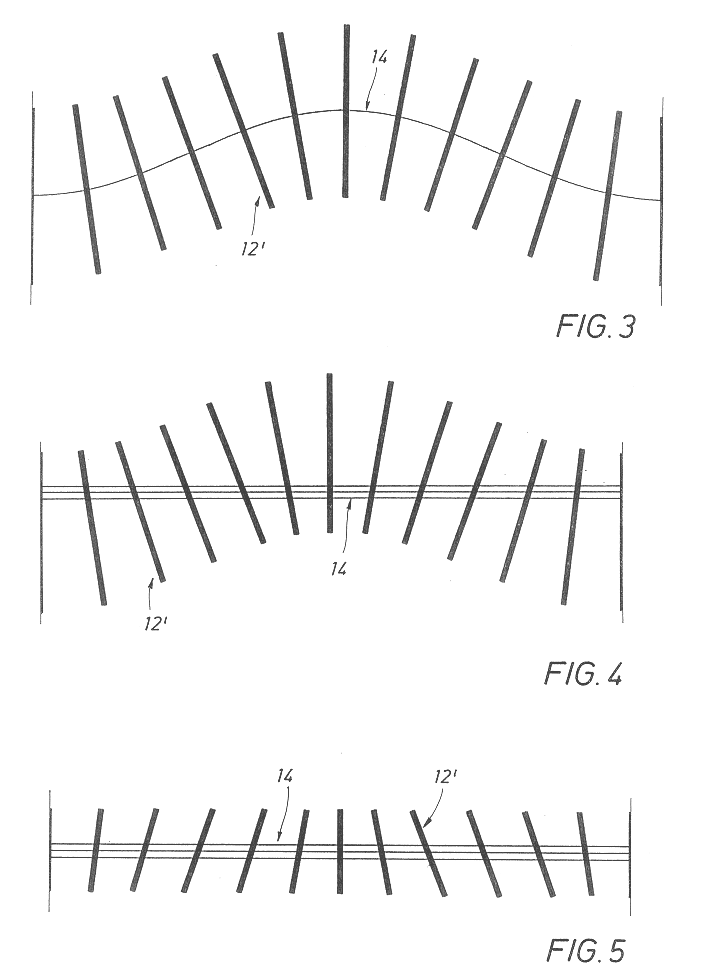
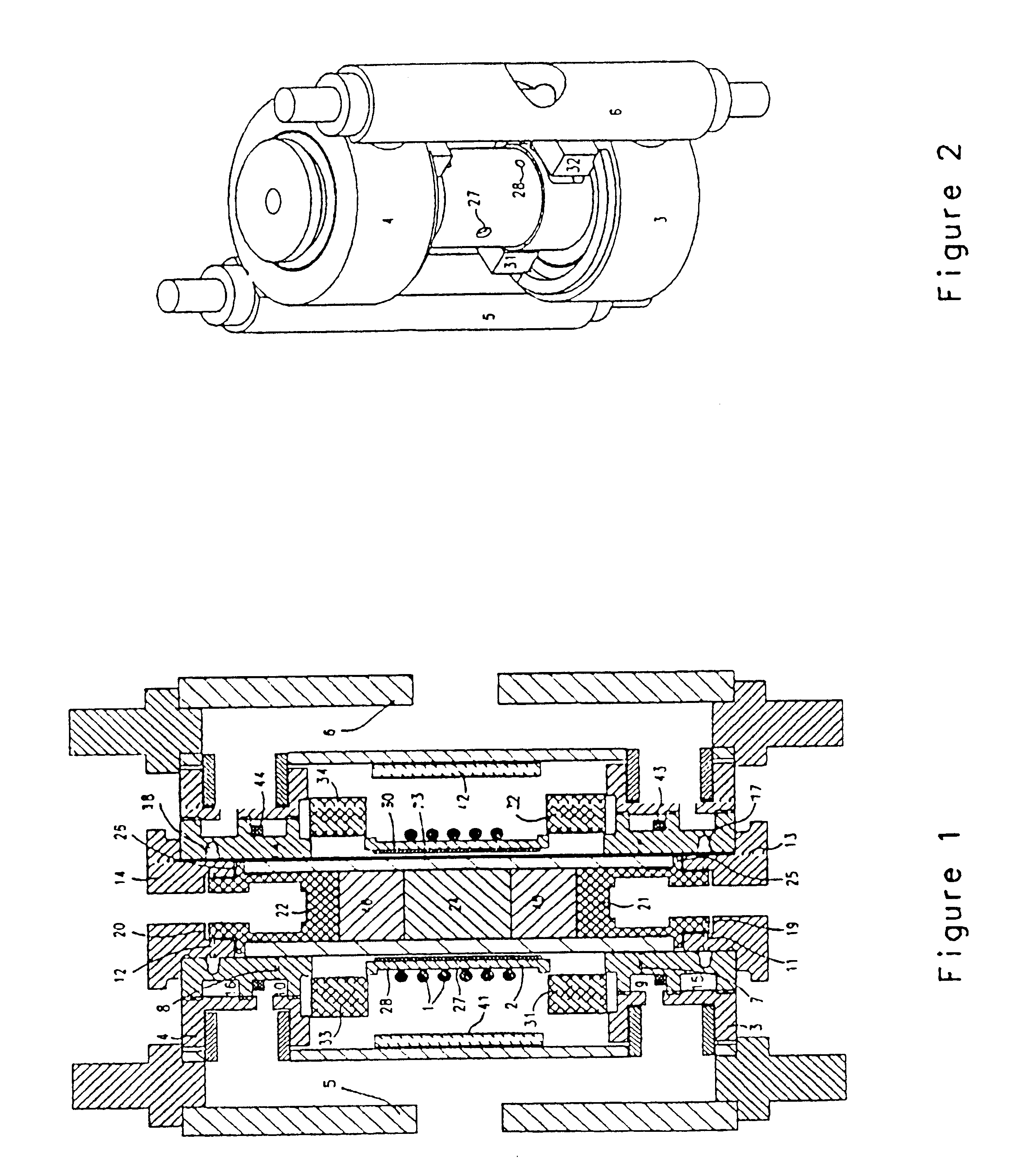
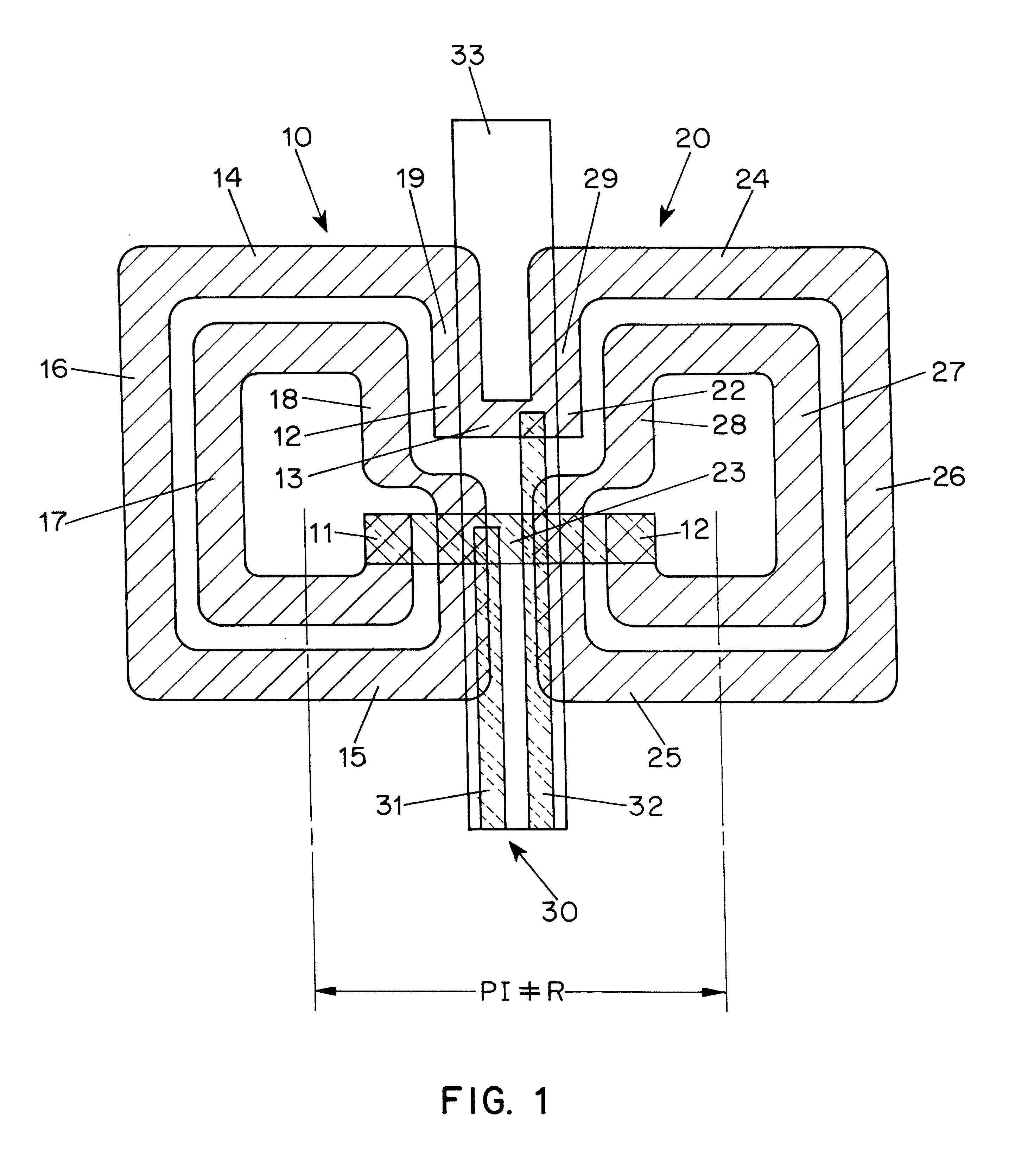
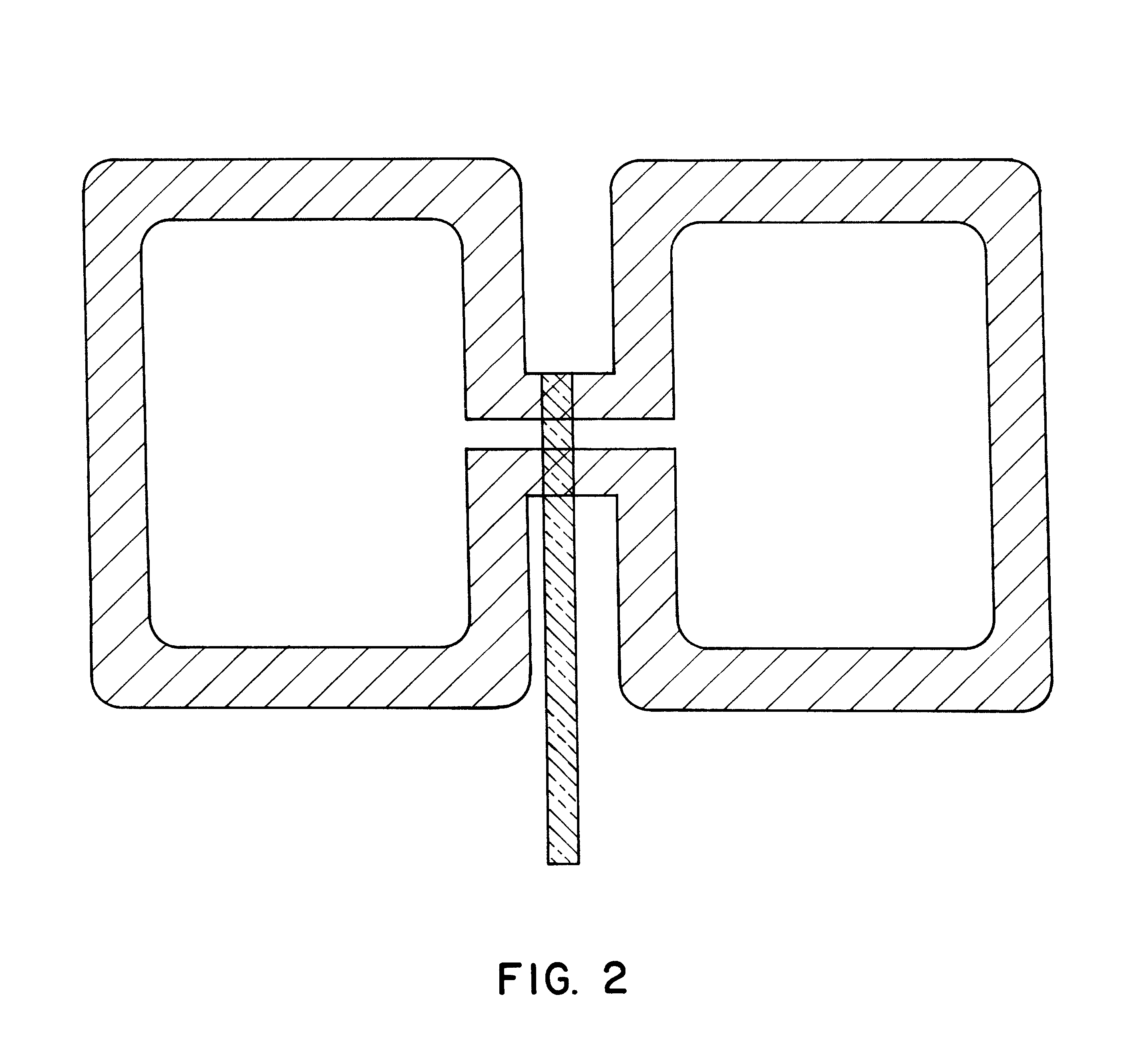
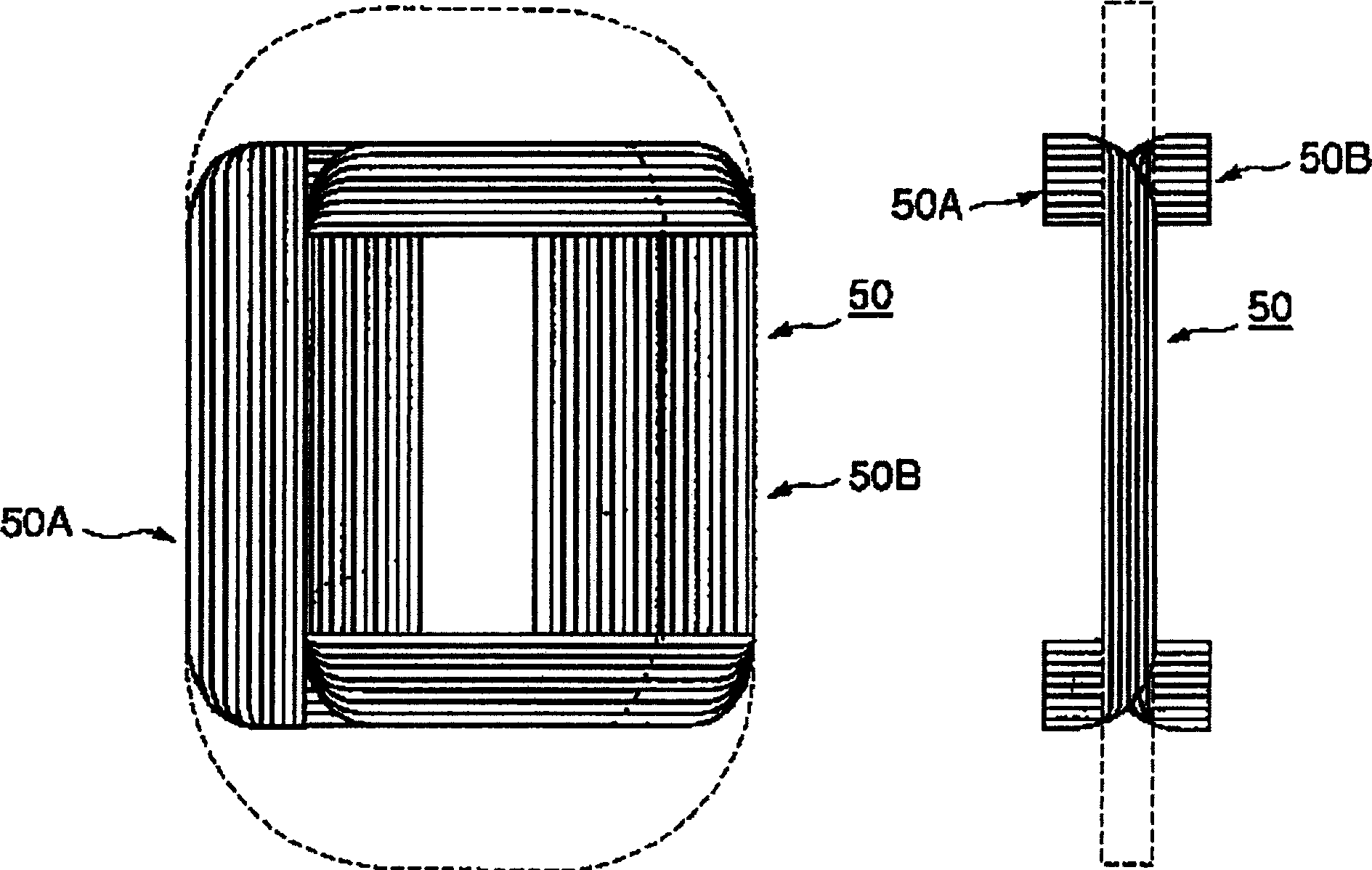
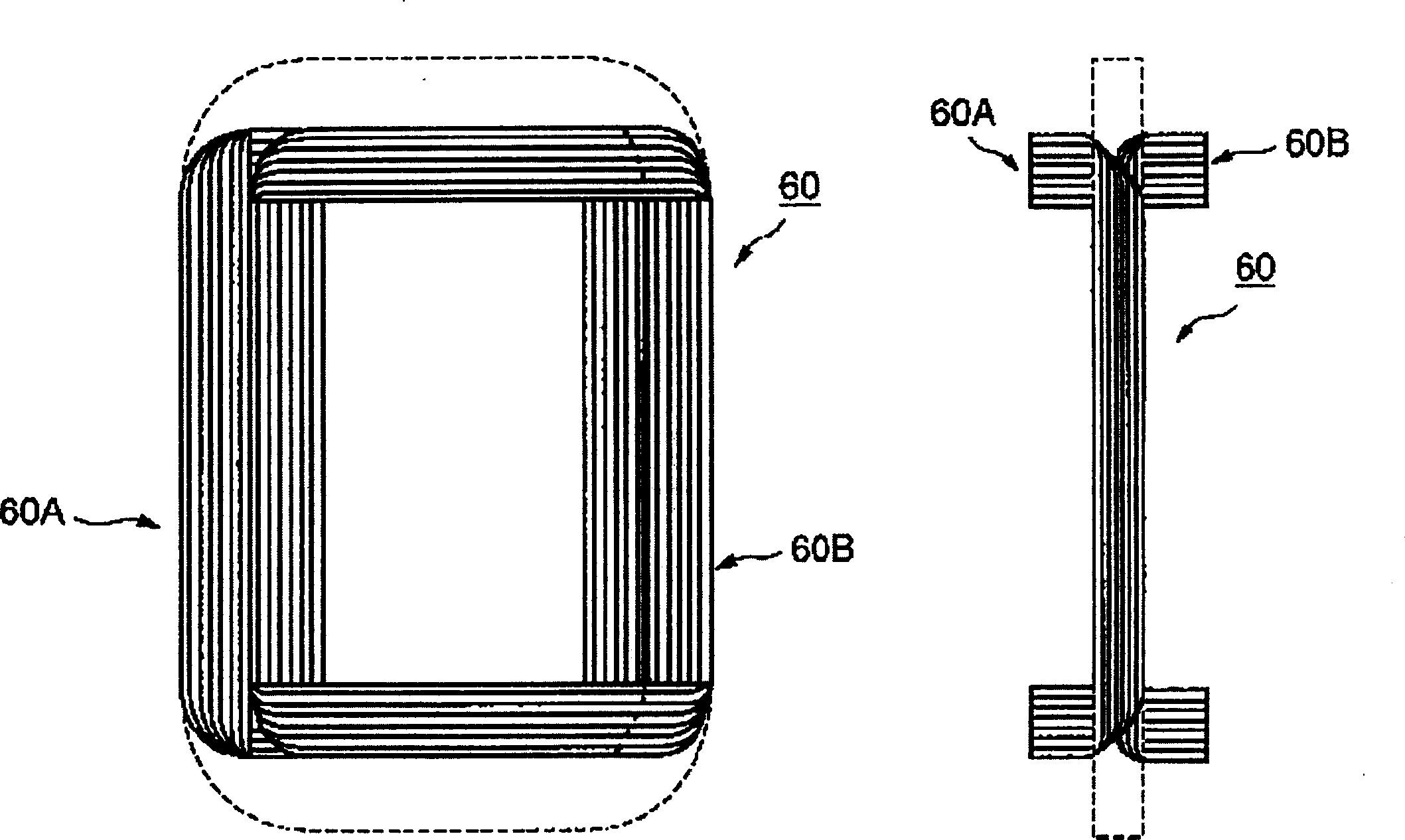
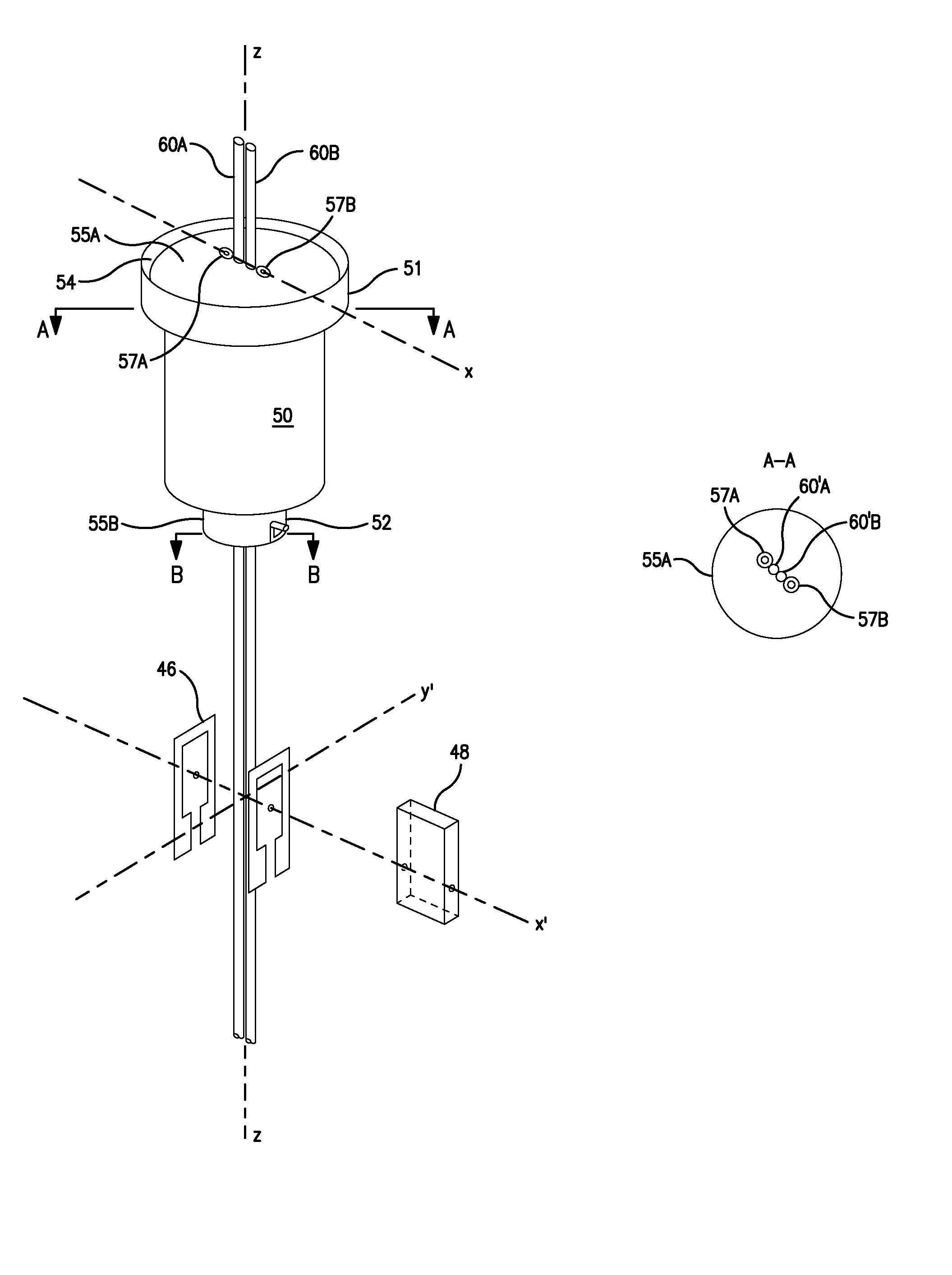
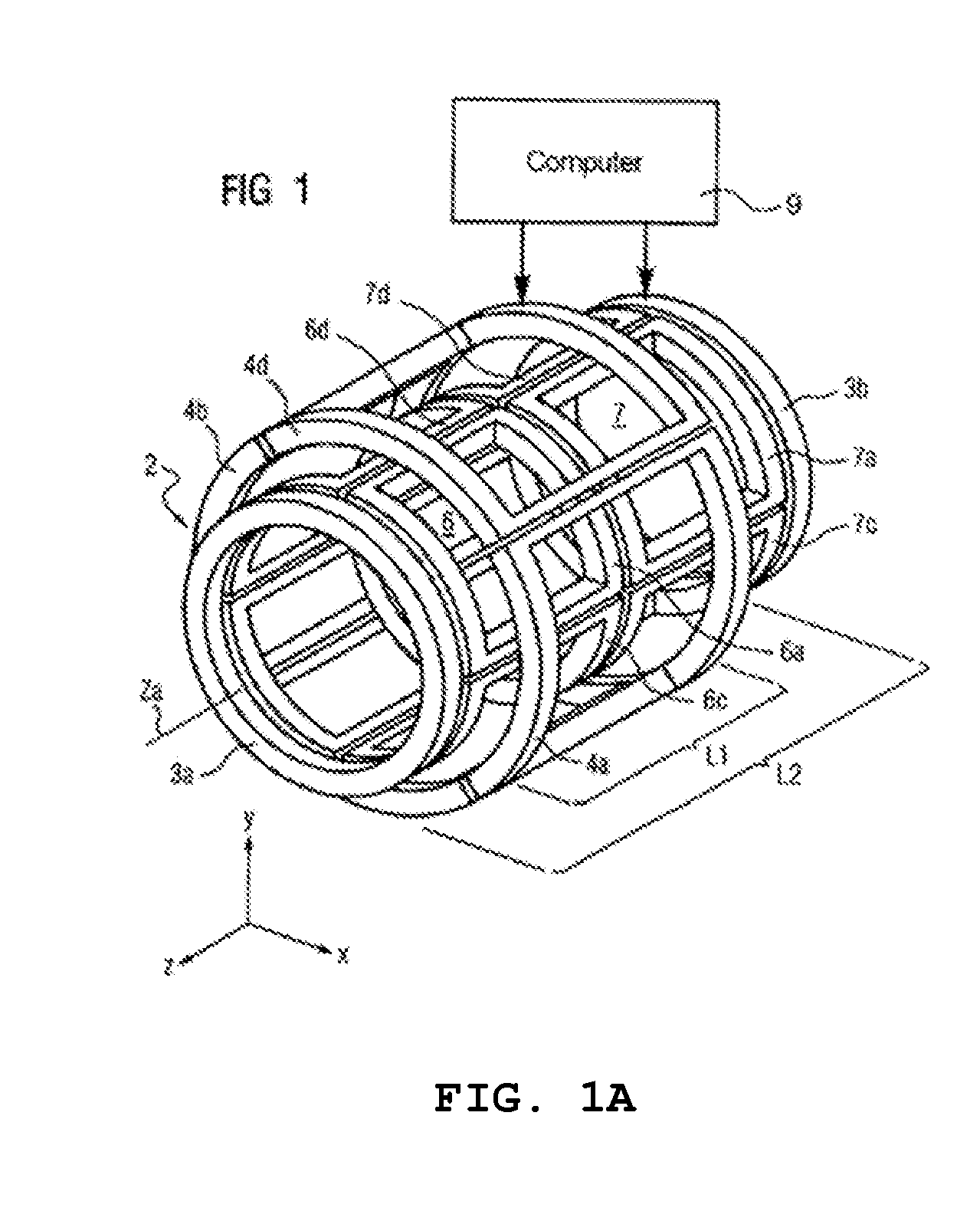
A shielding method and apparatus for an antenna disposed on an elongated support adapted for disposal within a borehole. The shield providing predetermined attenuation of one or more electromagnetic energy field components as the field components interact with the shield. The shield composed of a flexible strip or cylindrical body and respectively comprising a transverse conductive element or a transverse slot therein. The shields being adapted to cover an antenna mounted on the support. The shields being compatible for use in conjunction with saddle, tilted coils or multi-layered tri-axial coils to produce a pure transverse magnetic dipole electromagnetic field. The shields are also used in methods for shielding an antenna disposed on a support to provide predetermined attenuation of an electromagnetic field component as the field components interact with the shield.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Thermal buffering of cross-coils in high-power NMR decoupling
InactiveUS6320384B1Improve thermal conductivityElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceDielectricMagnetic susceptibility
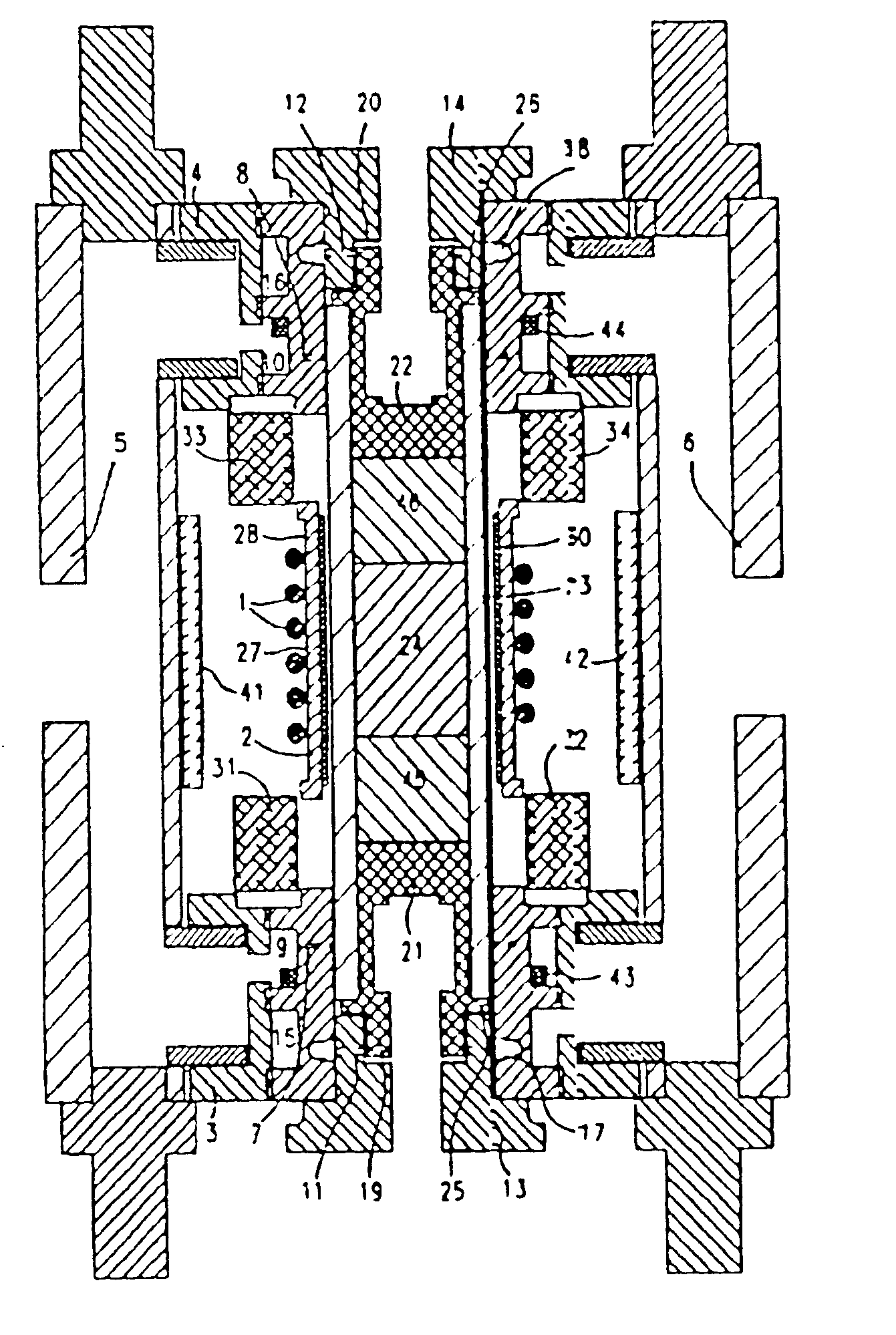
A transverse rf saddle coil (30) for use in NMR is affixed in intimate thermal conract on one surface of a ceramic coilform (23) of high thermal conductivity. The probe is mostly for use with solid samples at high fields where the axis of the coilform is not alignedwith the main field. An orthogonal rf coil (1) is mounted in intimate thermal contact to the first saddle coil (30) via a ceramic spacer or coilform (2). The coilform is cooled by high-velocity gas flow and is also often associated with bearing exhaust gas from a high speed sample spinner. The two coils are tuned to different rf frequencies with circuits capable of supporting high rf currents. The rf coils (30, 1) may be magnetically compensated and expansion controlled, and passive geometric compensation of magnetic susceptibility effects from a sample spinner stator may also be incorporated. Novel coil mounting techniques, including metallurgical bonds to ceramics and capturing by dielectric clam-shells, are also disclosed.
Owner:DOTY SCI
Head coil arrays for parallel imaging in magnetic resonance imaging
InactiveUS6930480B1Measurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionSaddle coilCoil array
A partially parallel acquisition RF coil array for imaging a human head includes at least a first, a second and a third loop coil adapted to be arranged circumambiently about the lower portion of the head; and at least a forth, a fifth and a sixth coil adapted to be conformably arranged about the summit of the head. A partially parallel acquisition RF coil array for imaging a human head includes at least a first, a second, a third and a fourth loop coil adapted to be arranged circumambiently about the lower portion of the head; and at least a first and a second Figure-8 or saddle coil adapted to be conformably arranged about the summit of the head.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
MRI coil system for breast imaging
InactiveUS6850065B1Electric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceSaddle coilHelmholtz coil
A RF receive coil system for imaging a breast on a human chest with a horizontal field MRI system includes a volume saddle coil adapted to be contoured about the chest; and a Helmholtz coil having a lower portion adapted to be contoured about the chest and an upper portion adapted to be above the chest The coils are operable in quadrature mode.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
NMR probe having an inner quadrature detection coil combined with a spiral wound outer coil for irradiation
InactiveUS6876200B2Minimal mutual inductanceImprove reliability and power efficiency and sensitivityElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceClose couplingSaddle coil
A high resolution NMR probe having two or more resonators, an inner resonator which is closely coupled to a sample and is used to stimulate and receive a response from one nuclear species, and an outer resonator to induce transitions in another nuclear species, wherein the resonators may be provided with cooling capability and may be made of superconducting material, and wherein the inner resonator may be a saddle coil or a birdcage coil with capability of being tuned, and wherein the outer resonator may be one or more spiral wound saddle coil.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
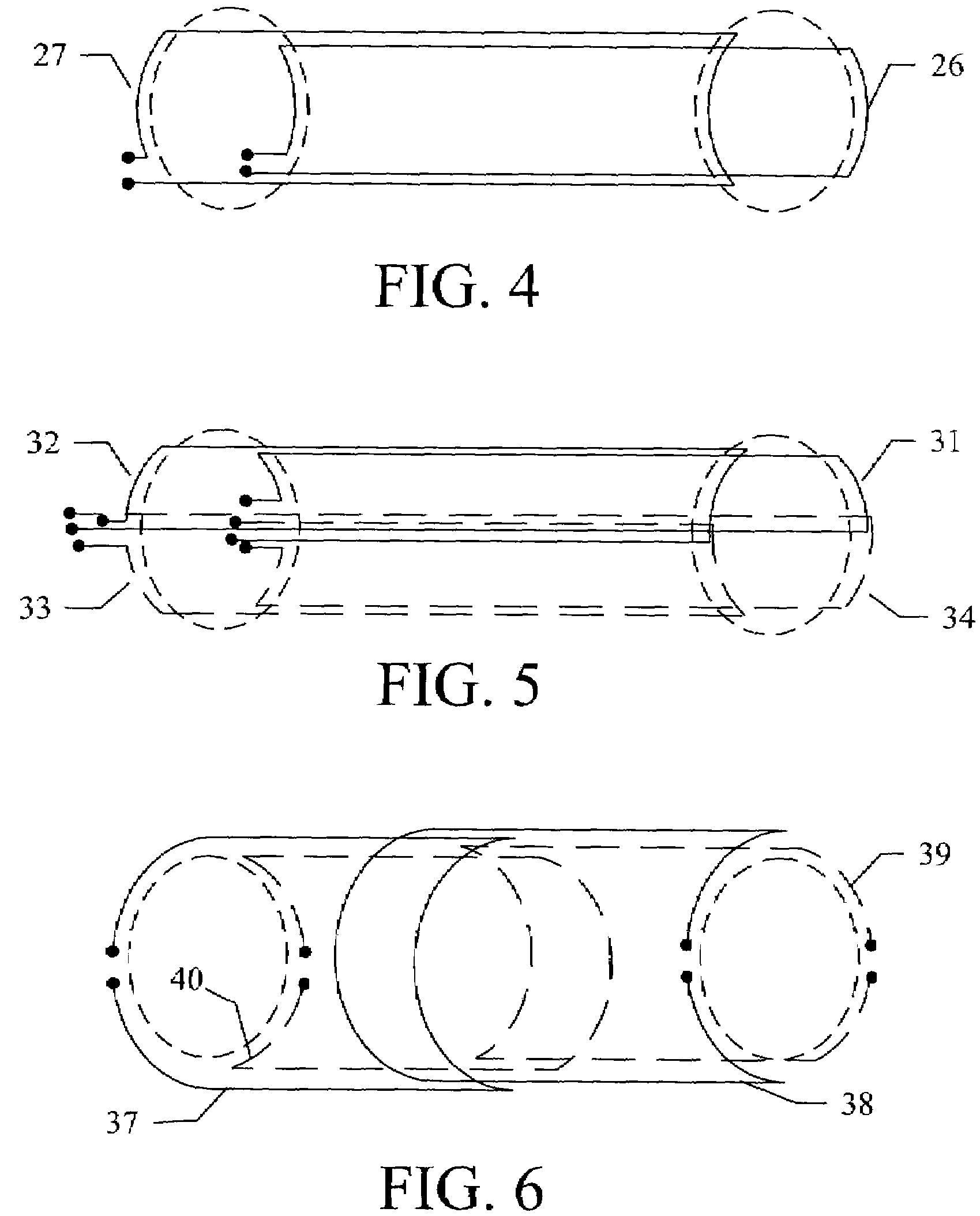
Center-fed paralleled coils for MRI
InactiveUS6175237B1Increasing differential twin-line modeElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceSaddle coilEngineering
The two halves of a conventional RF saddle coil, such as spirals or other related structures for use in high resolution NMR or MRI, are disposed on opposite sides of a cylindrical coilform, and rotated from the conventional orientation 90 degrees about the B1 axis, so that the leads are paralleled near the axial center of the RF coil.
Owner:DOTY SCI
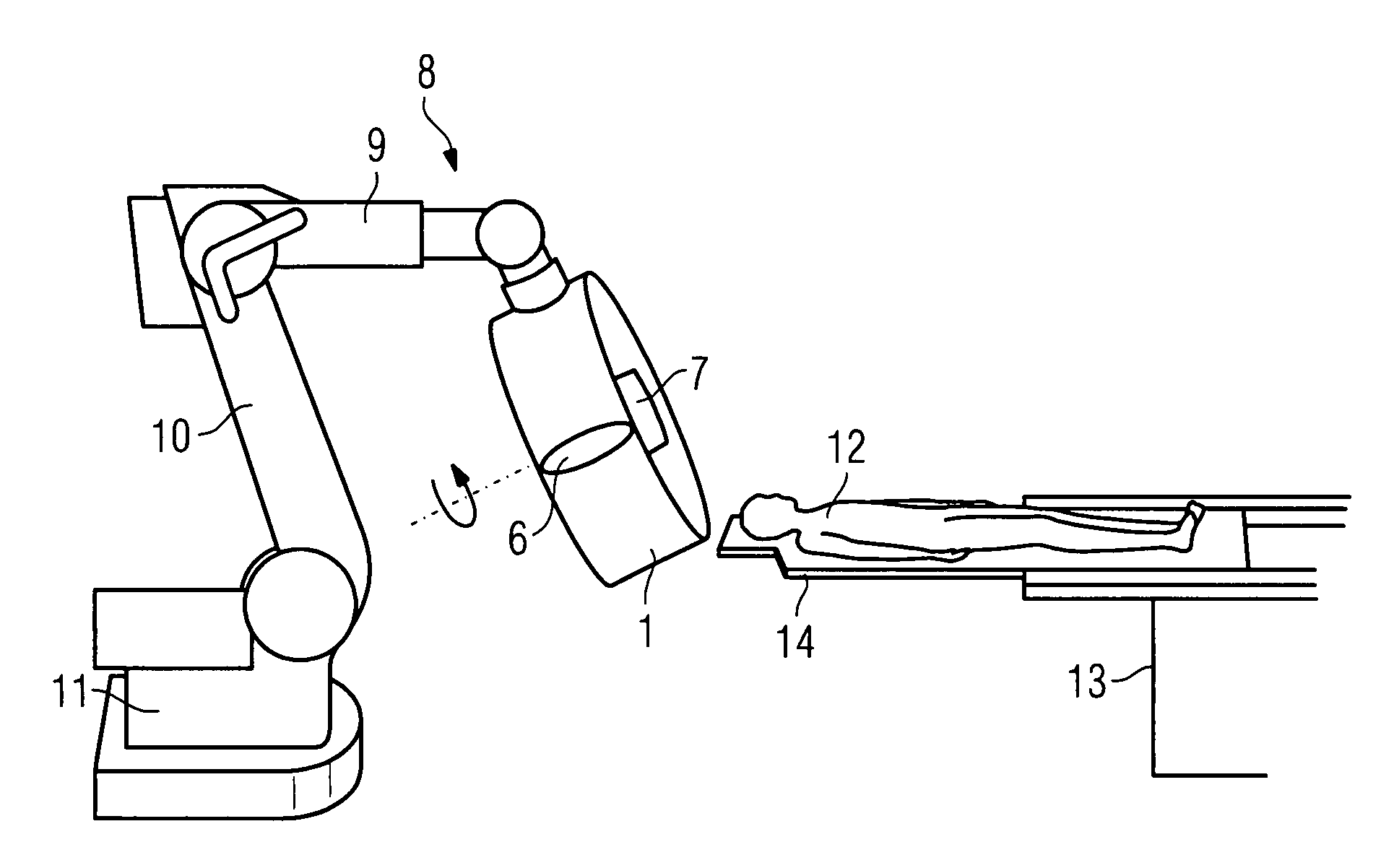
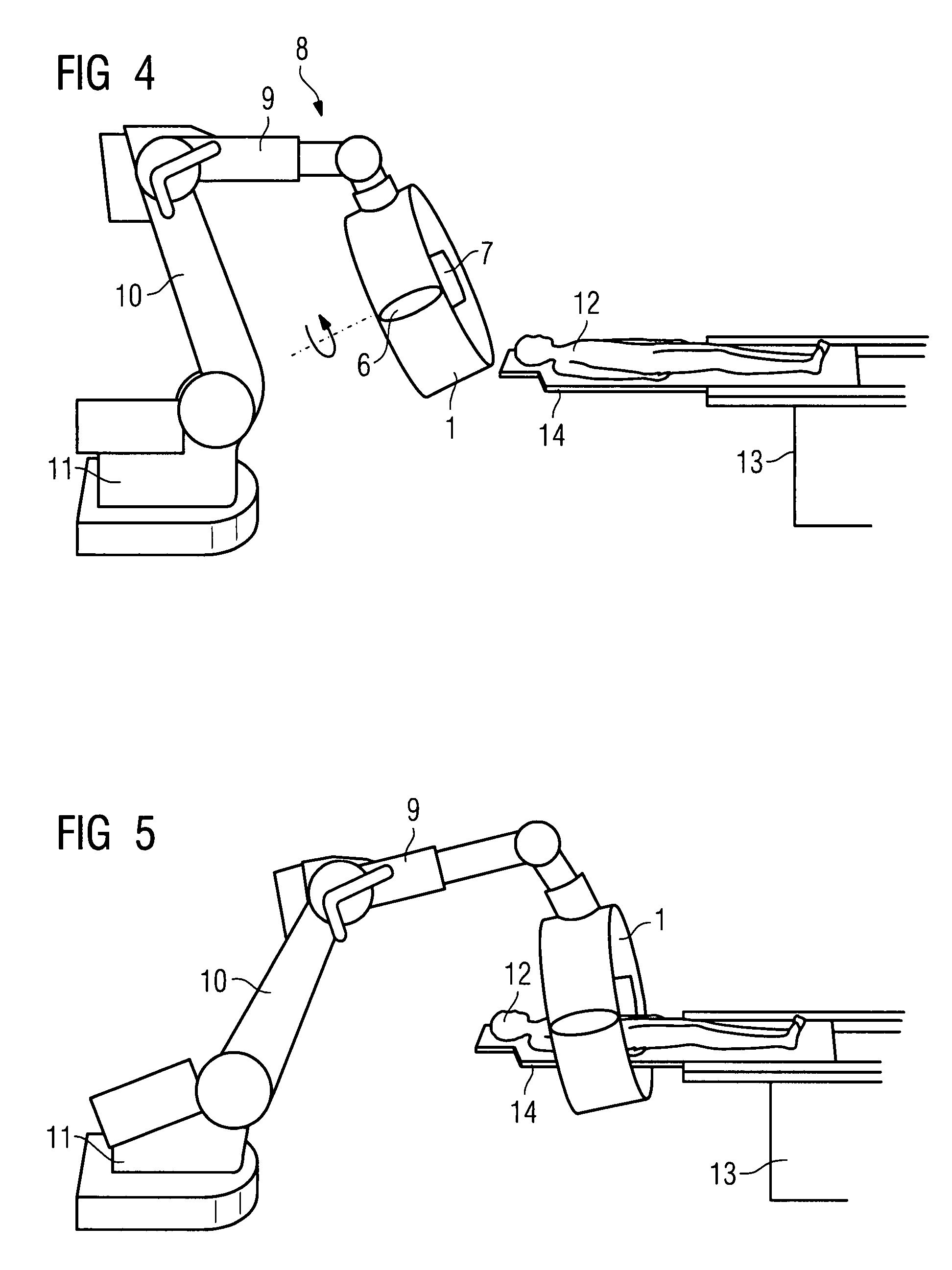
Medical examination and/or treatment apparatus
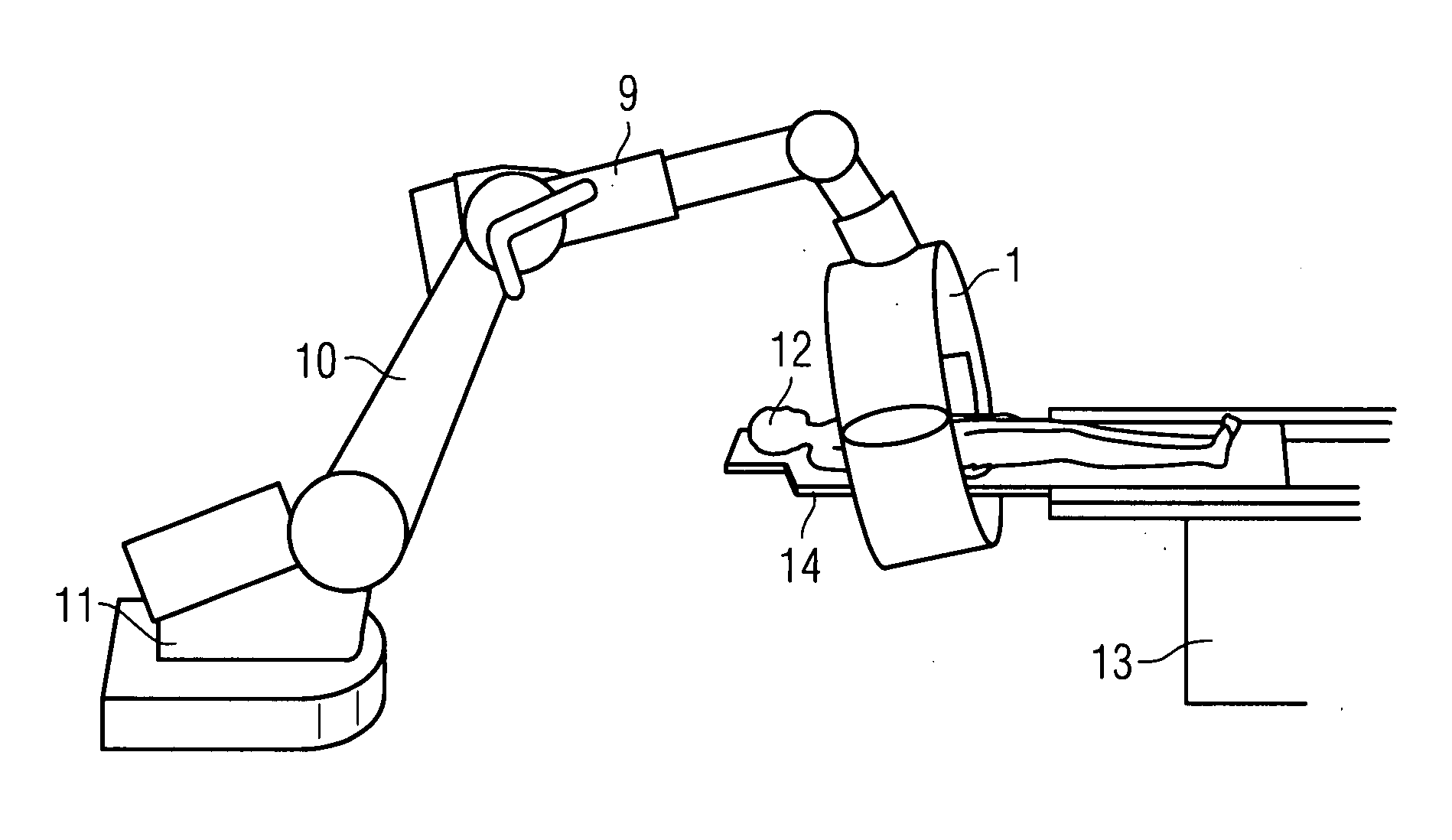
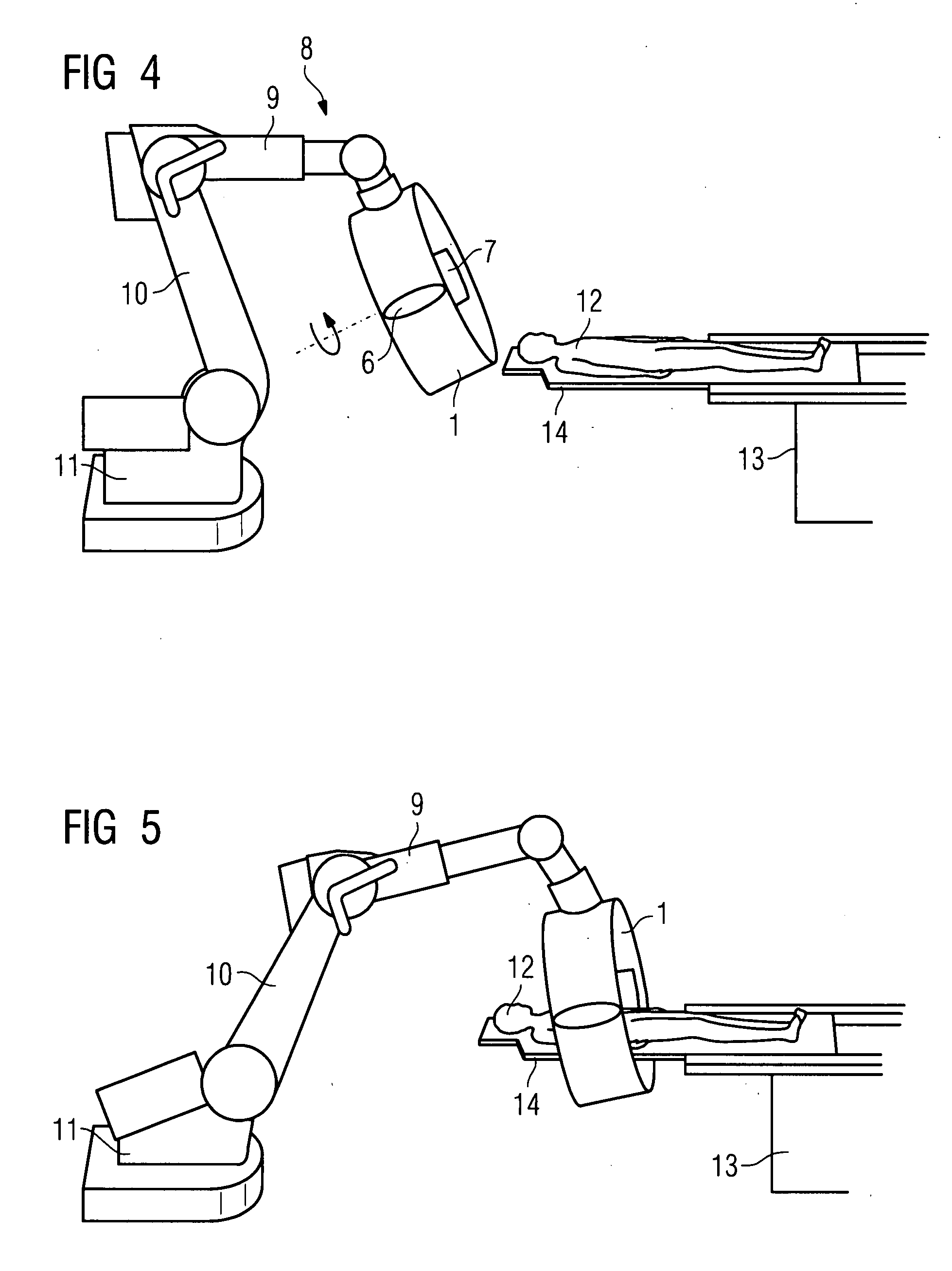
InactiveUS20080103388A1Prevent Image ArtifactsHigh strengthElectromagnets without armaturesSurgical navigation systemsSaddle coilTherapeutic Devices
There is described a medical examination and / or treatment apparatus with an electromagnet for generating a magnetic field for navigating a medical instrument and an x-ray device having an x-ray source and an x-ray detector attached to a bracket for visual control during the navigation, with the x-ray source and the x-ray detector being arranged on the electromagnet embodied as a hollow cylinder, on the front ends of which are located two ring coils which are arranged in parallel, between which a number of saddle coils arranged in the peripheral direction are arranged, with the hollow cylinder being arranged on a bracket which can be moved about a number of axes.
Owner:SIEMENS HEATHCARE GMBH
Nmr resonators optimized for high q factor
InactiveUS20030193380A1Lower resistancePromotes RF lossResonatorsElectric/magnetic detectionSaddle coilElectrical conductor
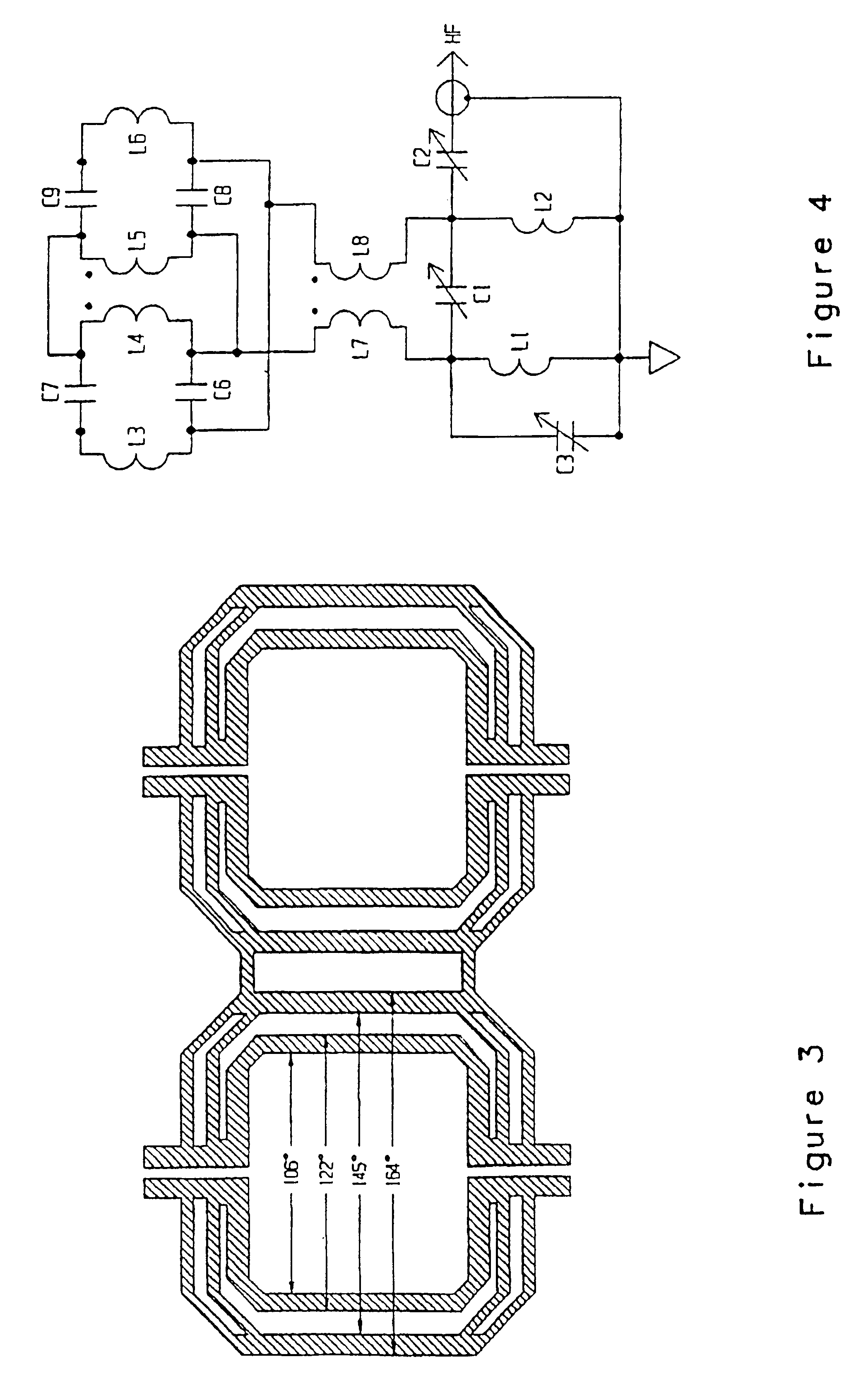
A birdcage resonator has a pair of conductor rings separated from each other along a central axis and a plural number of axially disposed conductor rungs, which extend between the rings and are evenly spaced around the central axis. Each of the rungs has a sectional shape with thickness or a radial extension comparable to or greater than its width or its azimuthal extension. Measures of the width and thickness of the rungs may be determined by using them as parameters to calculate the values of Q factor from an analytical procedure to locate parameter value ranges corresponding to maximal Q. Geometric calculations for filling factor yield ranges of parameters providing for compromise parameter values. Saddle coils have been found to exhibit similar enhancement of Q with radially oriented conductor cross section.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
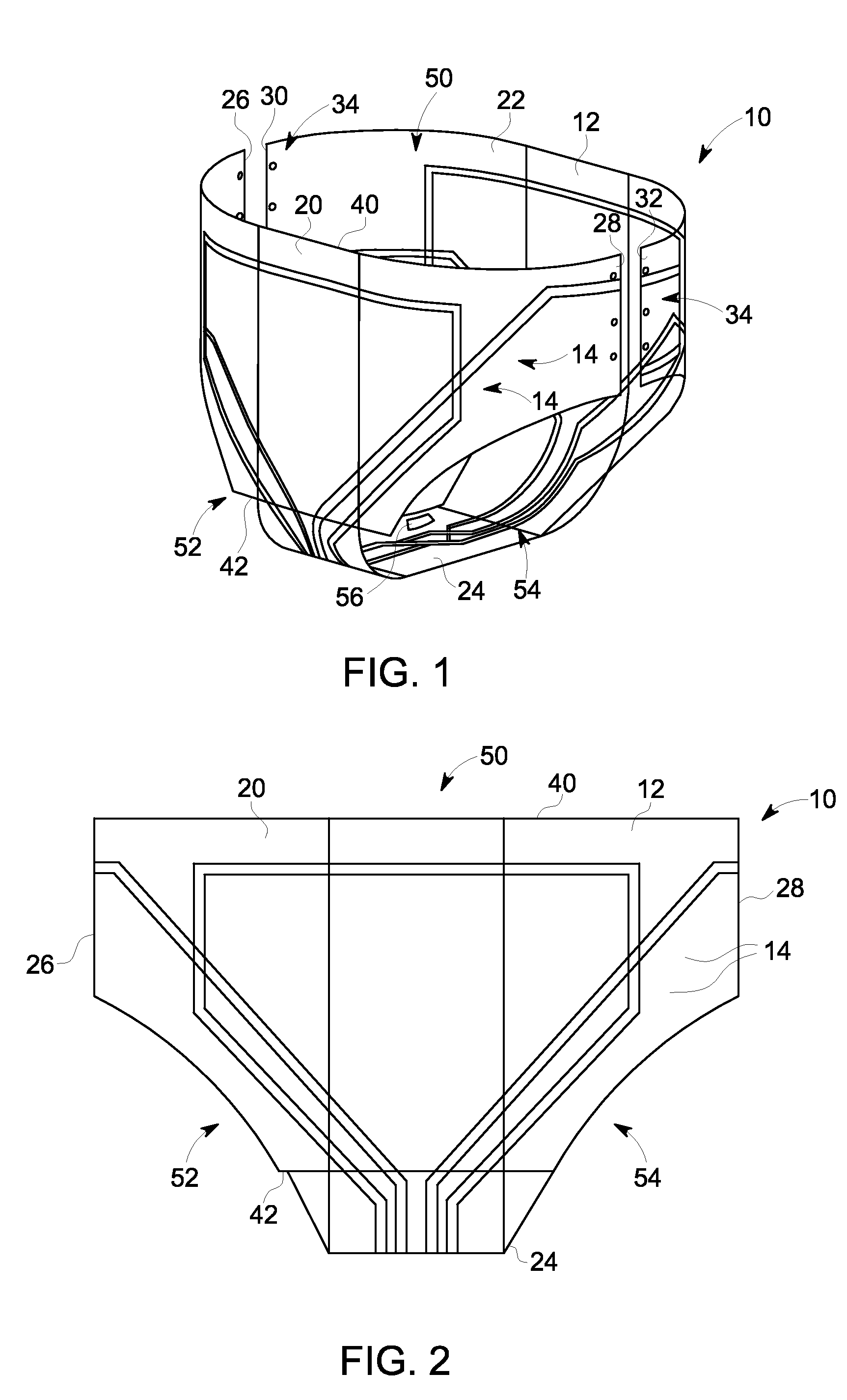
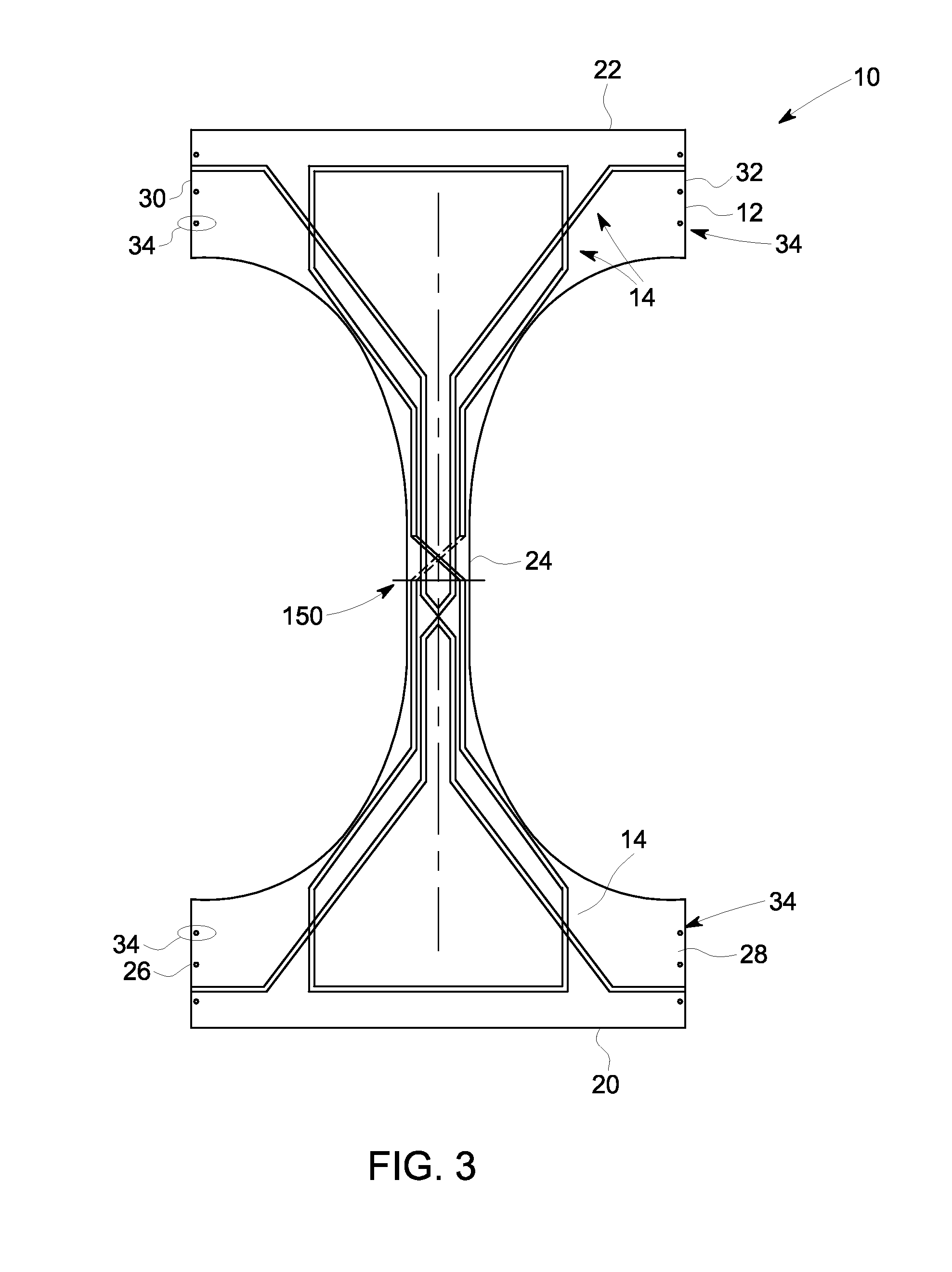
Method and apparatus for imaging a subject using local surface coils
A Radio Frequency (RF) coil apparatus for generating a Magnetic Resonance (MR) image includes a body adapted to be worn by a subject being scanned, the body comprising an anterior portion, a posterior portion, and a transition portion coupled between the anterior and posterior portions, a first RF receive-only saddle coil including a first coil positioned in the anterior portion and a second coil positioned in the anterior portion, the first RF saddle coil configured to be positioned on the anterior and posterior sides of the subject. An MRI imaging system and method are also described herein.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method and apparatus for imaging a subject using local surface coils
A Radio Frequency (RF) coil apparatus for generating a Magnetic Resonance (MR) image includes a body adapted to be worn by a subject being scanned, the body comprising an anterior portion, a posterior portion, and a transition portion coupled between the anterior and posterior portions, a first RF receive-only saddle coil including a first coil positioned in the anterior portion and a second coil positioned in the anterior portion, the first RF saddle coil configured to be positioned on the anterior and posterior sides of the subject. An MRI imaging system and method are also described herein.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
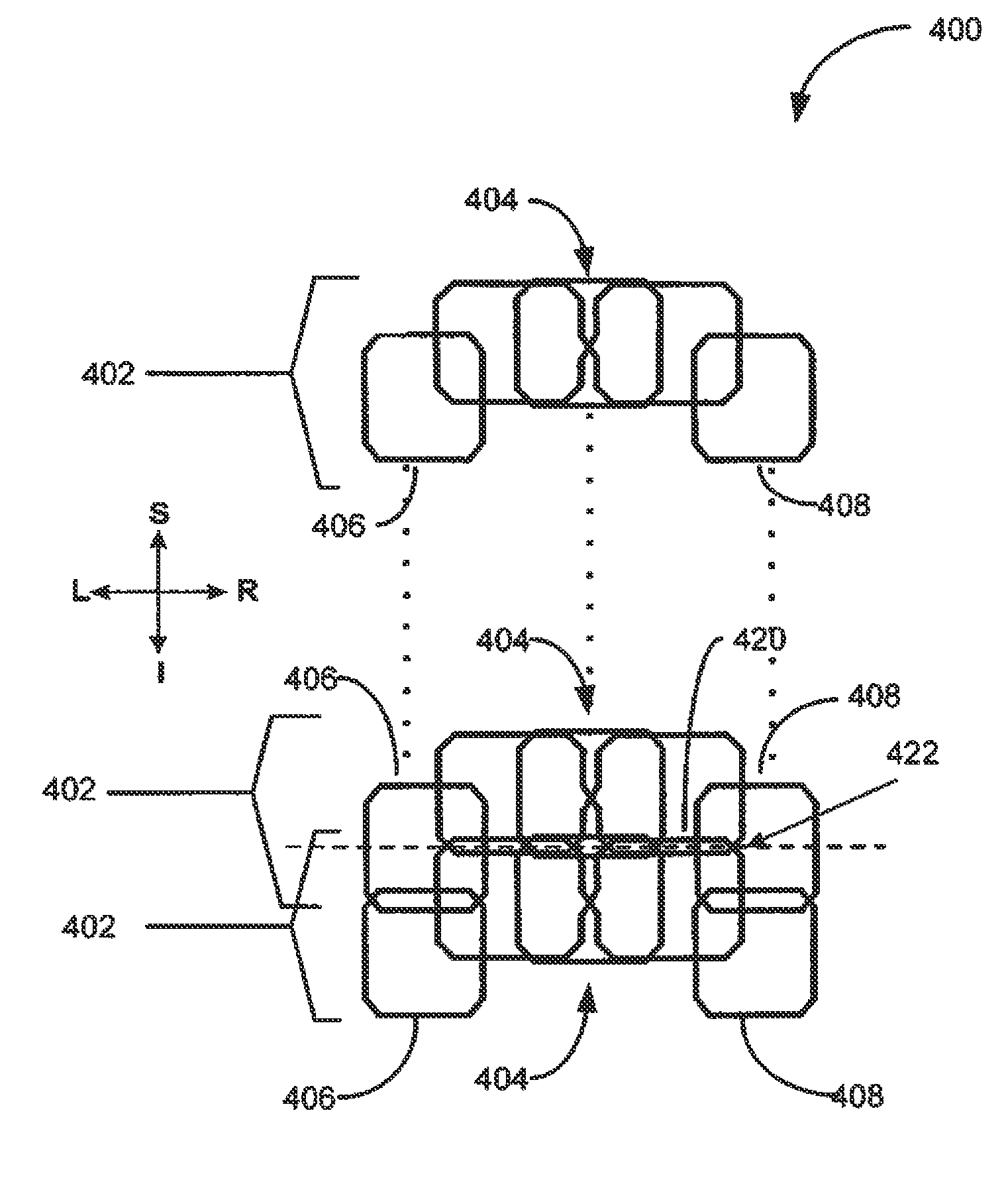
Quadrature and linear RF coil array for MRI of human spine and torso
InactiveUS8441258B2Transformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsDiagnostic recording/measuringSaddle coilCoil array
A radio frequency (RF) coil array includes a plurality of RF coil sections arranged in a superior-inferior direction. Each RF coil section includes a first linear coil element, a loop-saddle coil quadrature pair and a second linear coil element configured in an overlapping arrangement in a left-right direction. The position of the first linear coil element and the second linear coil element on the left and right may be shifted in the superior-inferior direction with respect to the center loop-saddle coil quadrature pair.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
RF coil, RF signal transmitter receiver, RF signal receiver, and magnetic resonance imaging system for the inferior abdomen
InactiveUS7177671B2Easy to wearSatisfactory imageDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsHuman bodySaddle coil
For the purpose of providing an RF coil that enables satisfactory imaging of the prostate, the RF coil is composed of a first saddle coil and a second saddle coil. The first saddle coil has two loop portions opposed to each other so that they can sandwich the inferior abdomen of a human body antero-posteriorly. The second saddle coil has two loop portions opposed to each other so that they will permit insertion of the inferior limbs of a human body thereinto and can sandwich the inferior abdomen thereof laterally.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
RF coil array for cardiac and thoracic magnetic resonance imaging
A radio frequency (RF) coil array includes a first coil section and a second coil section mechanically coupled to the first coil section. The first coil section includes a first row of a plurality of double asymmetric saddle coil pairs arranged in a left-right direction and a second row of a plurality of double asymmetric saddle coil pairs arranged in a left-right direction. The first row and the second row are arranged along a superior-inferior direction. The second coil section includes a plurality of loop coils arranged around at least a portion of a perimeter of the first coil section.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Voice coil motor and three-phase linear motor
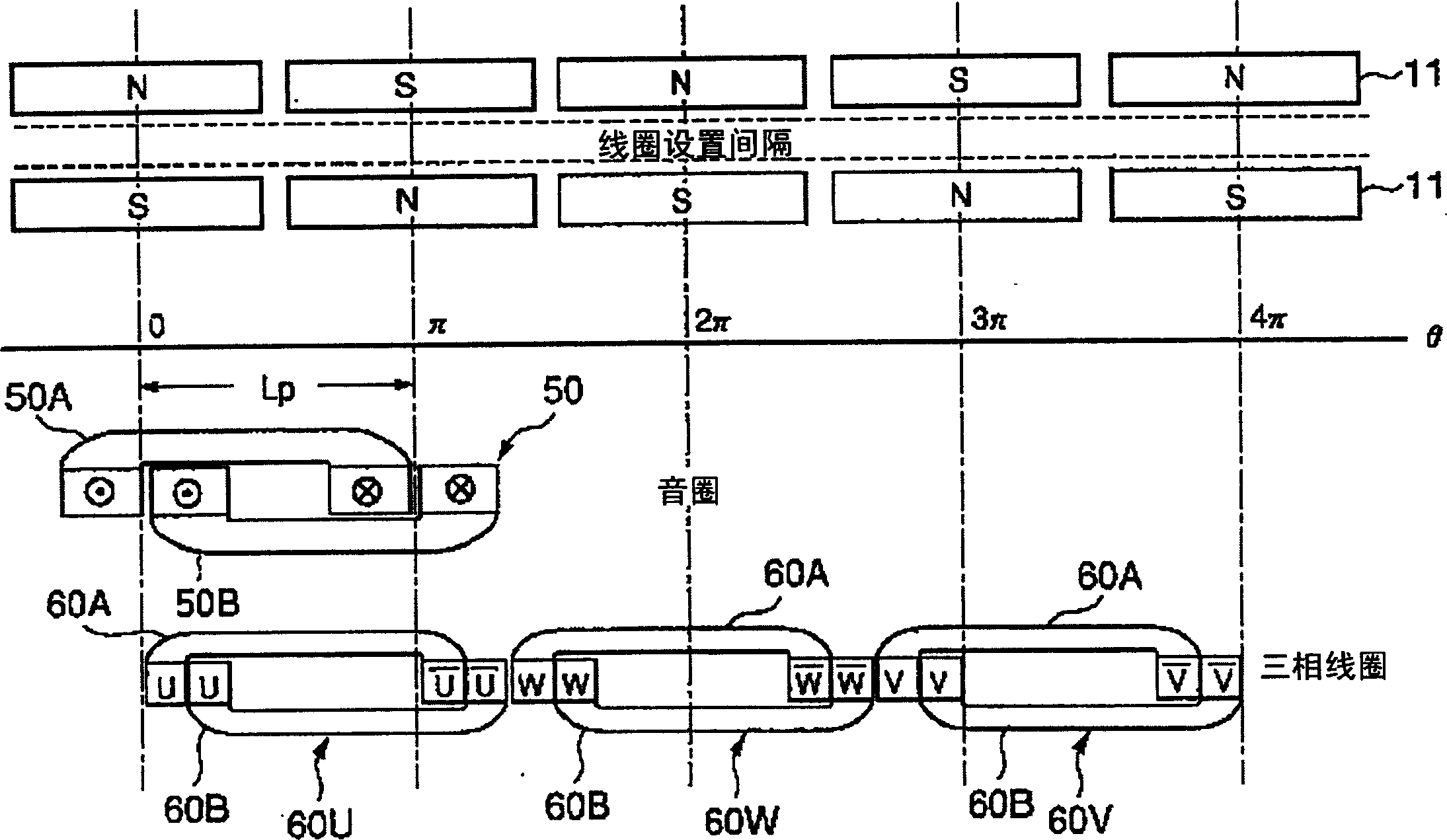
InactiveCN1592050AReduce feverReduce the number of wiringManufacturing dynamo-electric machinesPropulsion systemsSaddle coilMagnetic poles
To provide a three-phase linear motor effective in the reduction of heating from coils. The three-phase linear motor is so constituted that a plurality of pairs of permanent magnets in which different magnetic poles are opposed to each other are arranged with a coil installation space in which three-phase coils are placed, positioned in-between; and the permanent magnets adjoining in the direction of movement are different from each other in magnetic pole. Coils 60U, 60W, and 60V in respective phases comprise two saddle coils 60A and 60B in which the short sides of a substantially rectangular coil are constituted as folded portions that form an angle of approximately 90[deg.] to the straight portions of the long sides. The saddle coils are so combined that the two folded portions in each saddle coil face in opposite directions. At the same time, they are so combined that the two straight portions between the two folded portions of either saddle coil are brought as tight-contact straight portions into tight contact with the two straight portions between the two folded portions of the other saddle coil. The coils in the individual phases are so arranged that they are lined in series in the direction of movement, and the tight-contact straight portions of the coils in adjacent phases are brought into tight contact with each other.
Owner:SUMITOMO HEAVY IND LTD
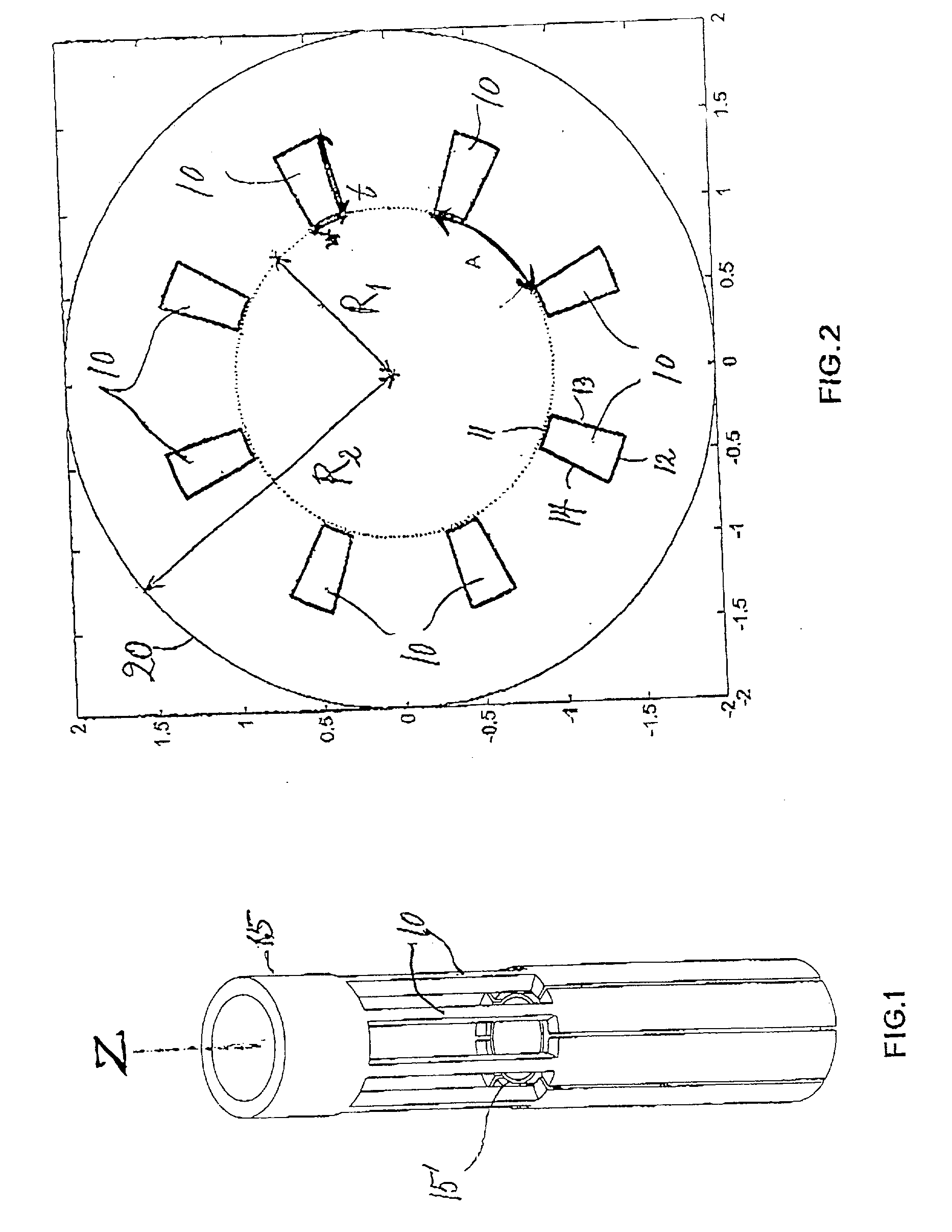
Low loss NMR sample holder
InactiveUS7557578B1Electric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceSaddle coilCylindrical lens
An elongate sample volume matching an elongate region of uniform RF magnetic field established by a saddle coil, is approximated by at least one pair of cylindrical sample tubes in parallel orientation with the geometric axis of the saddle coil. The displacement of the two cylindrical tubes defines a direction transverse to the tube axes and this transverse direction is aligned parallel with the RF magnetic field of the saddle coil.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
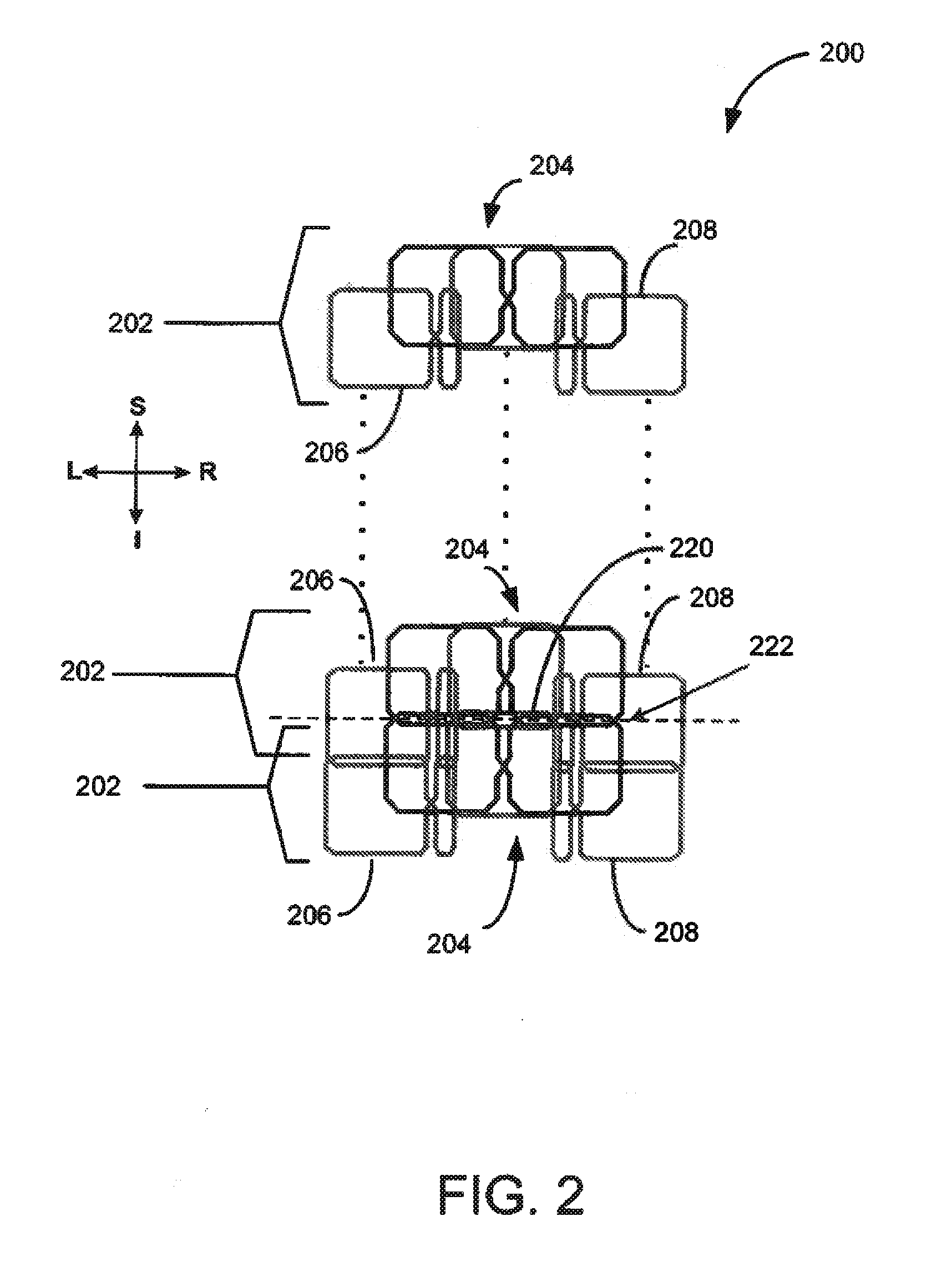
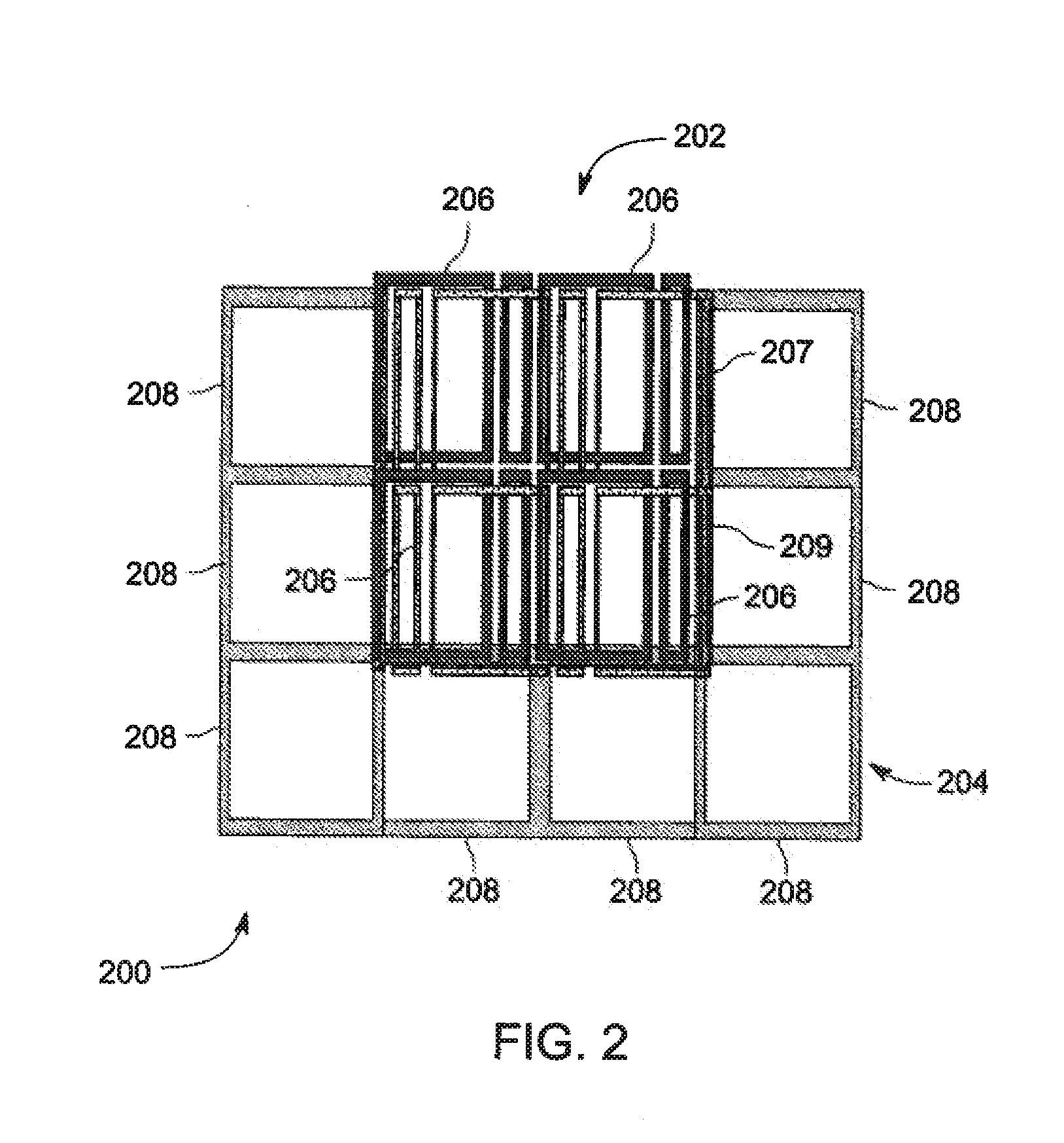
Magnetic resonance imaging system with satellite gradient coils
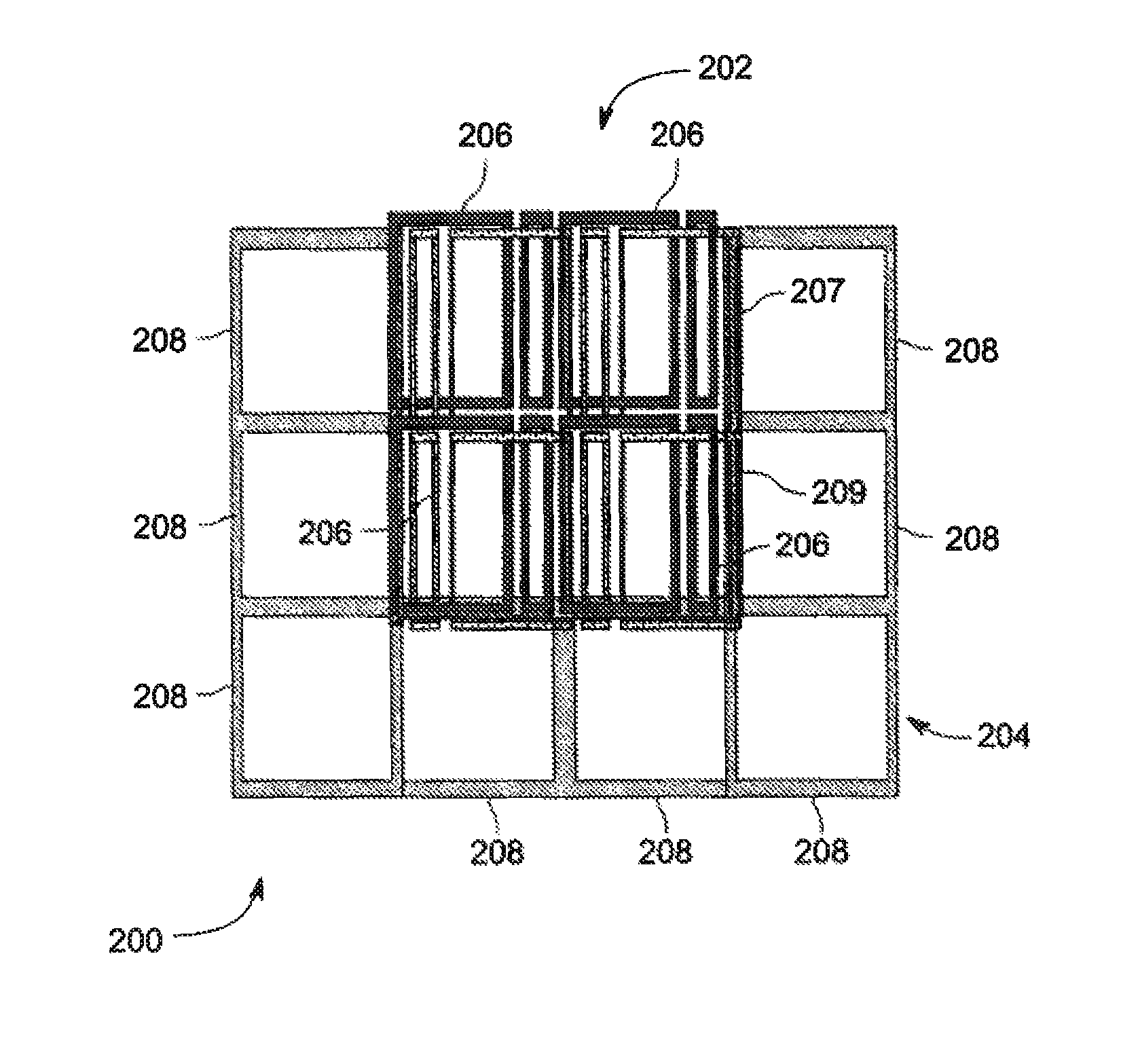
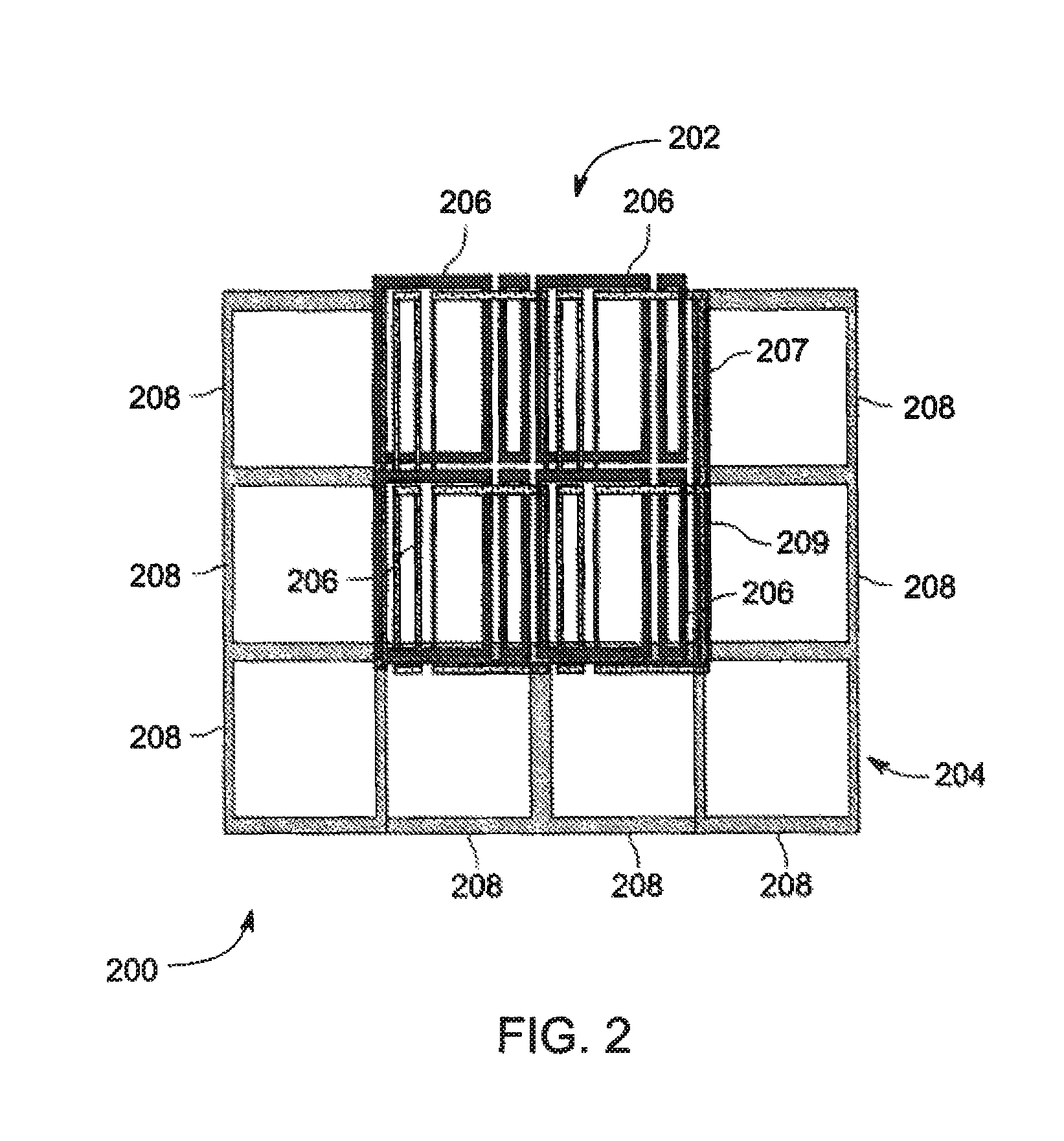
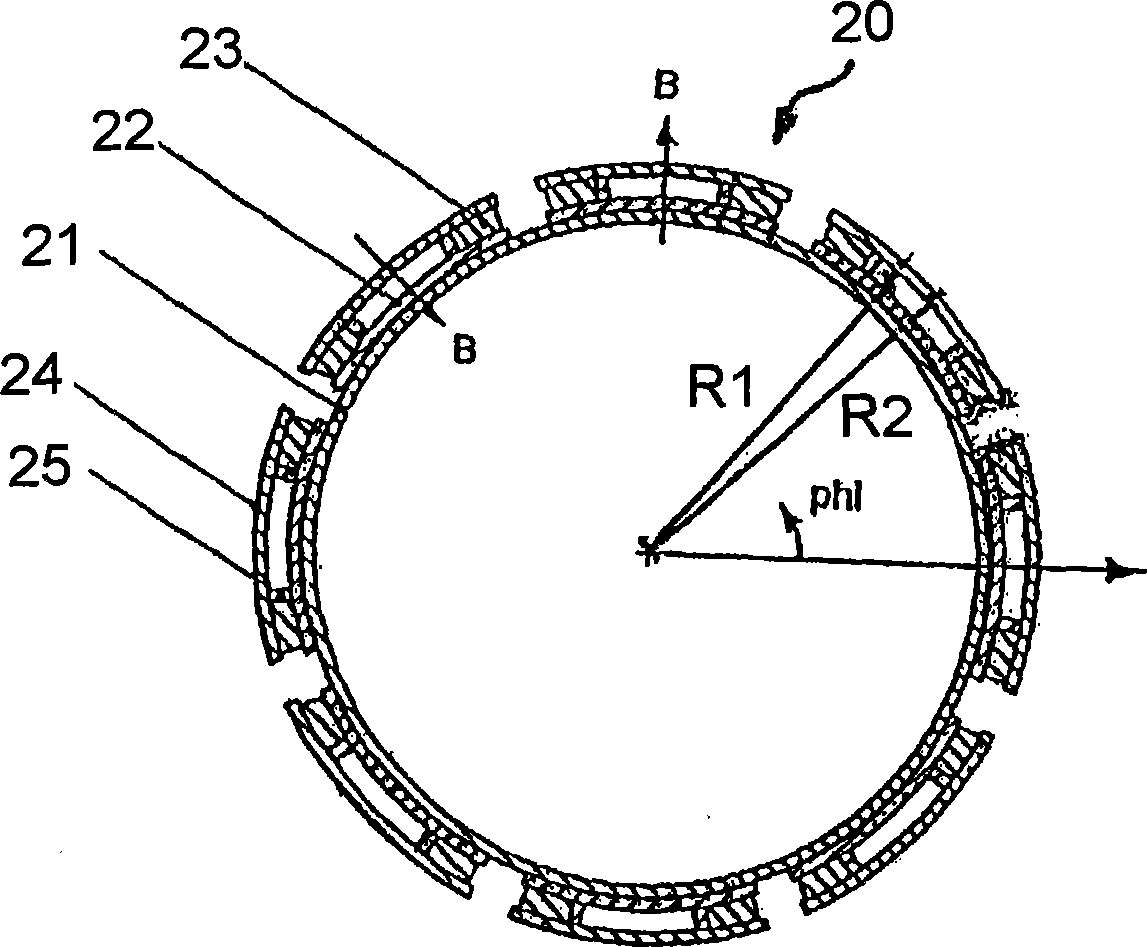
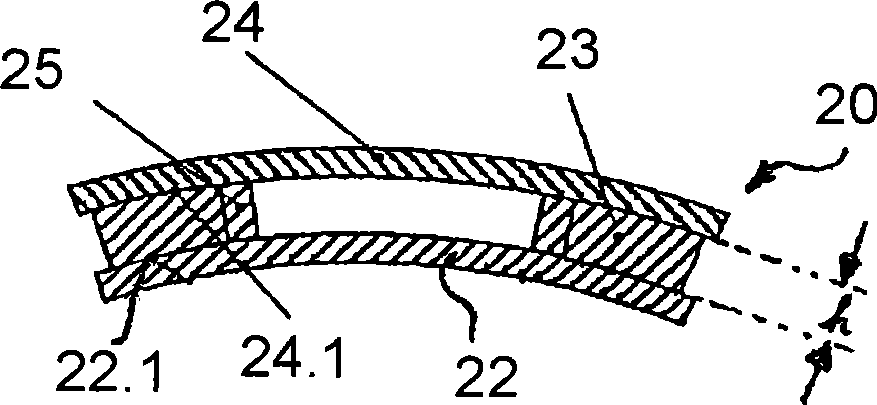
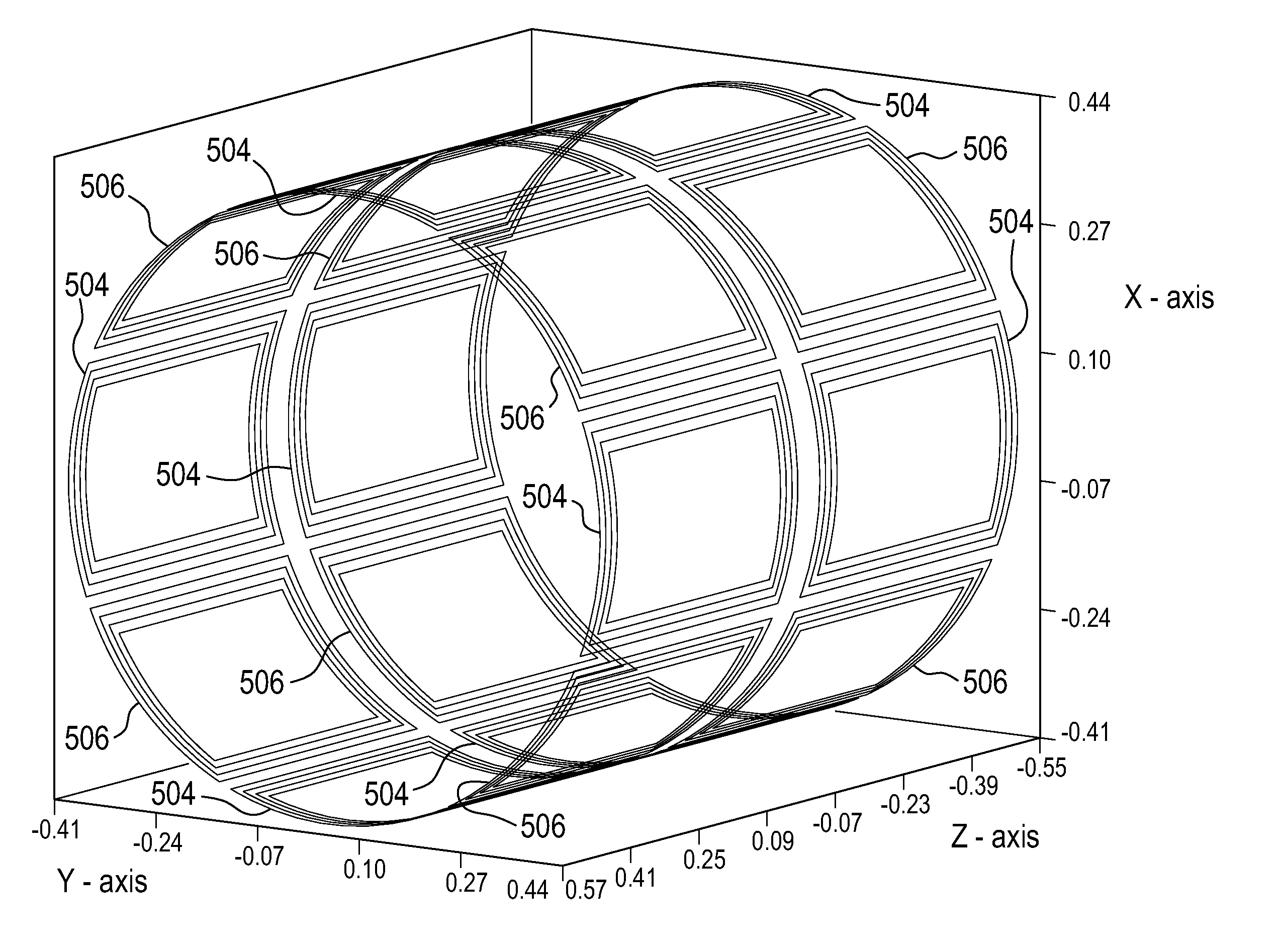
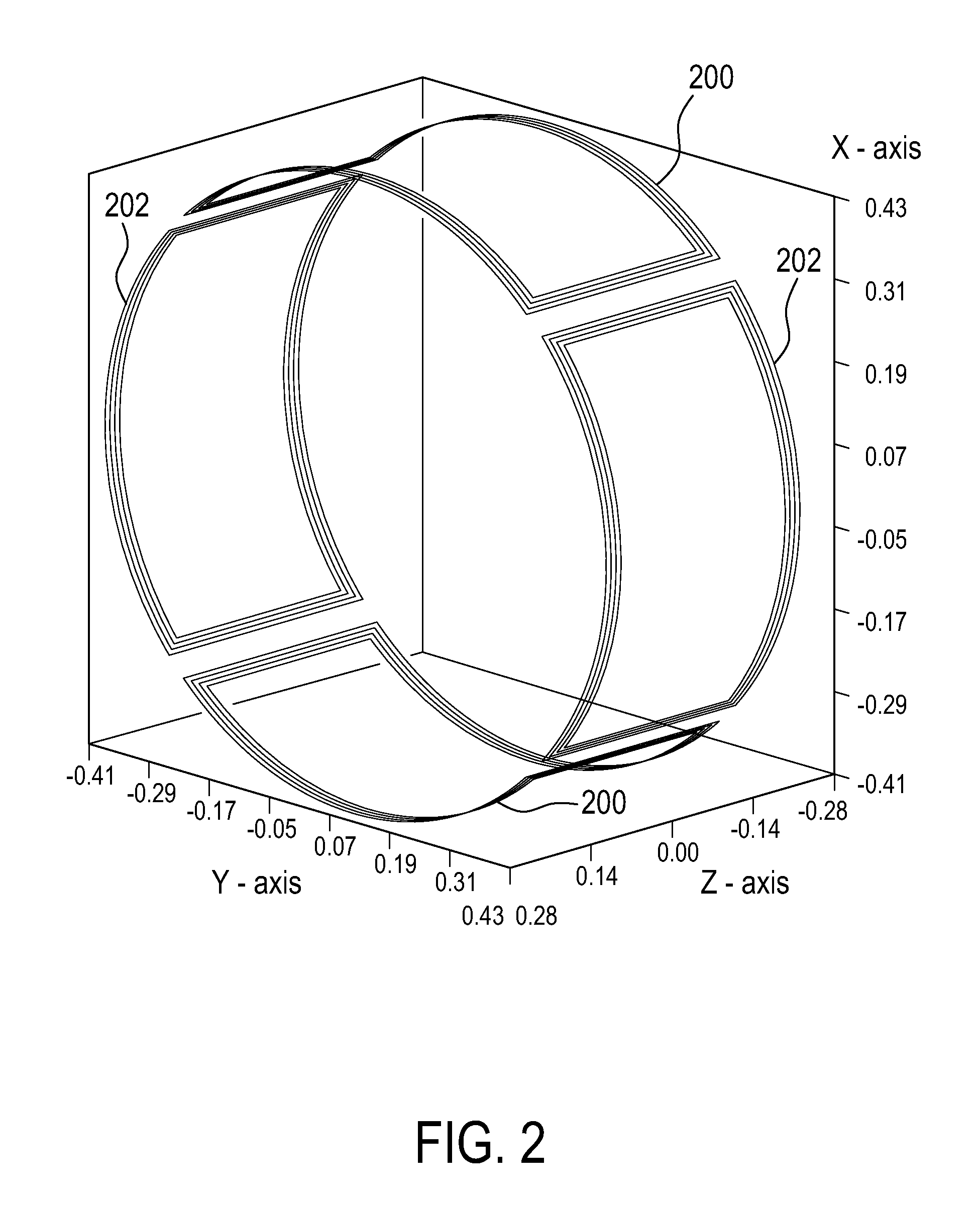
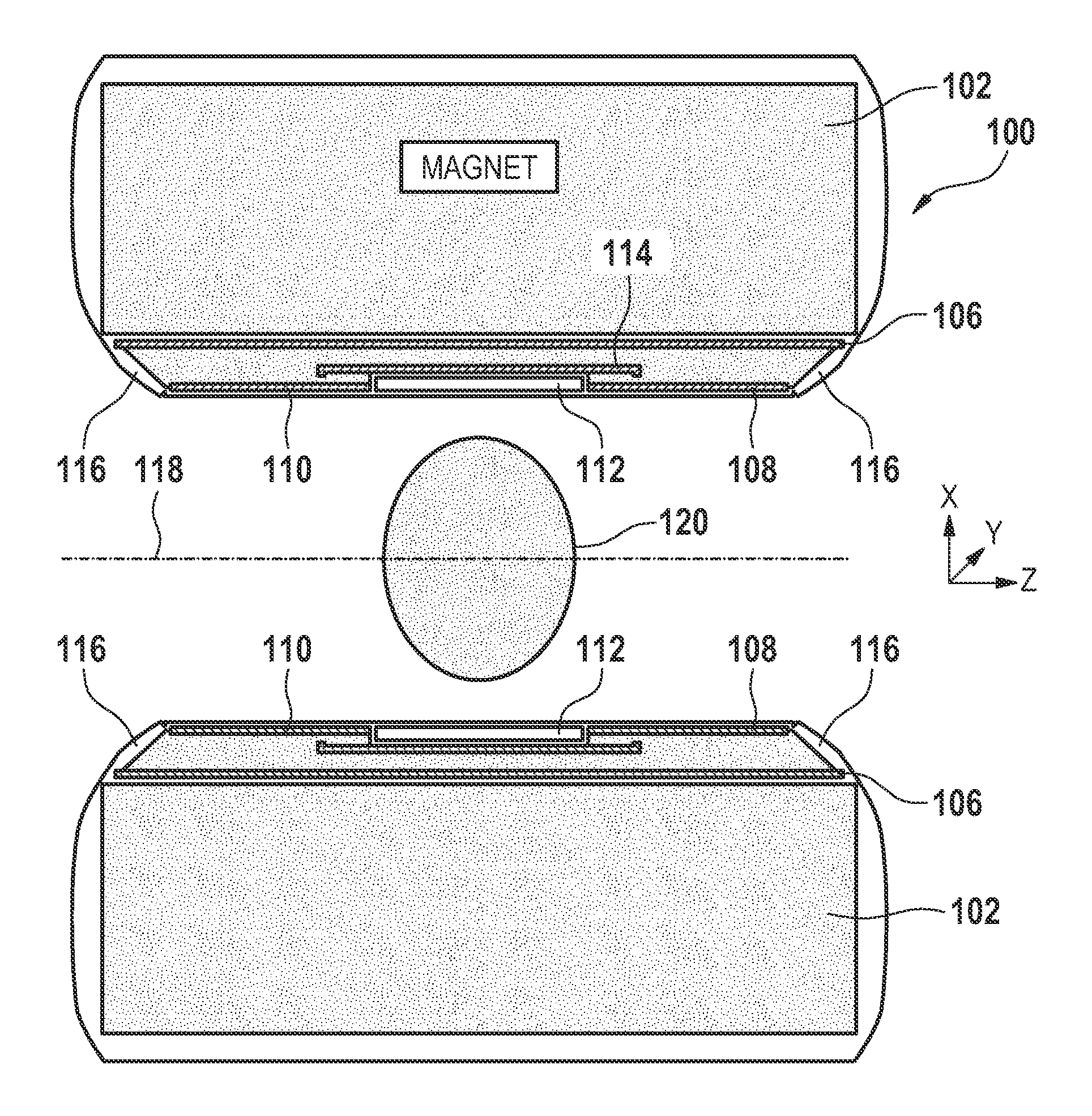
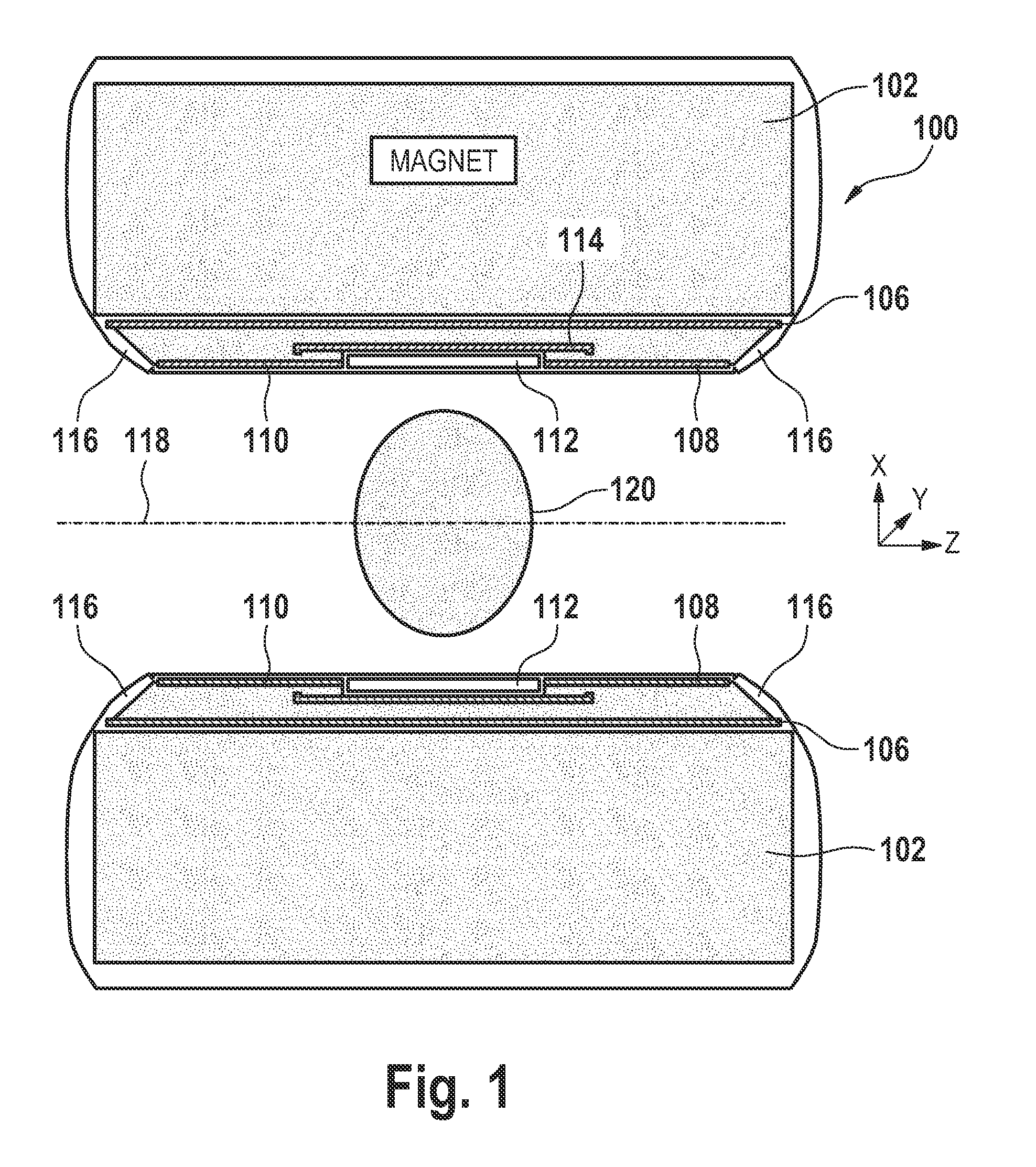
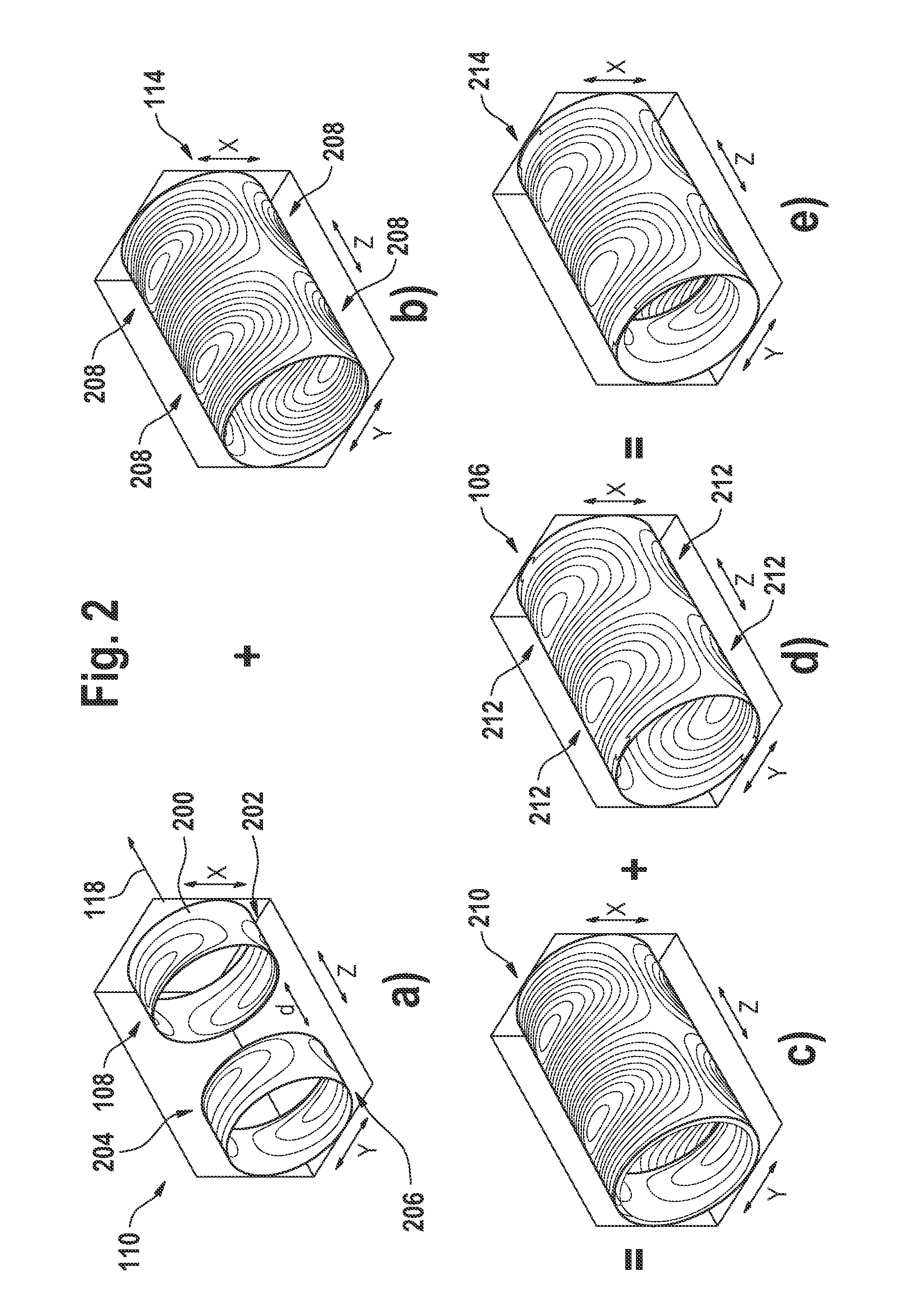
ActiveUS20110227573A1Low costEasy to insertElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using NMRSaddle coilCoil structure
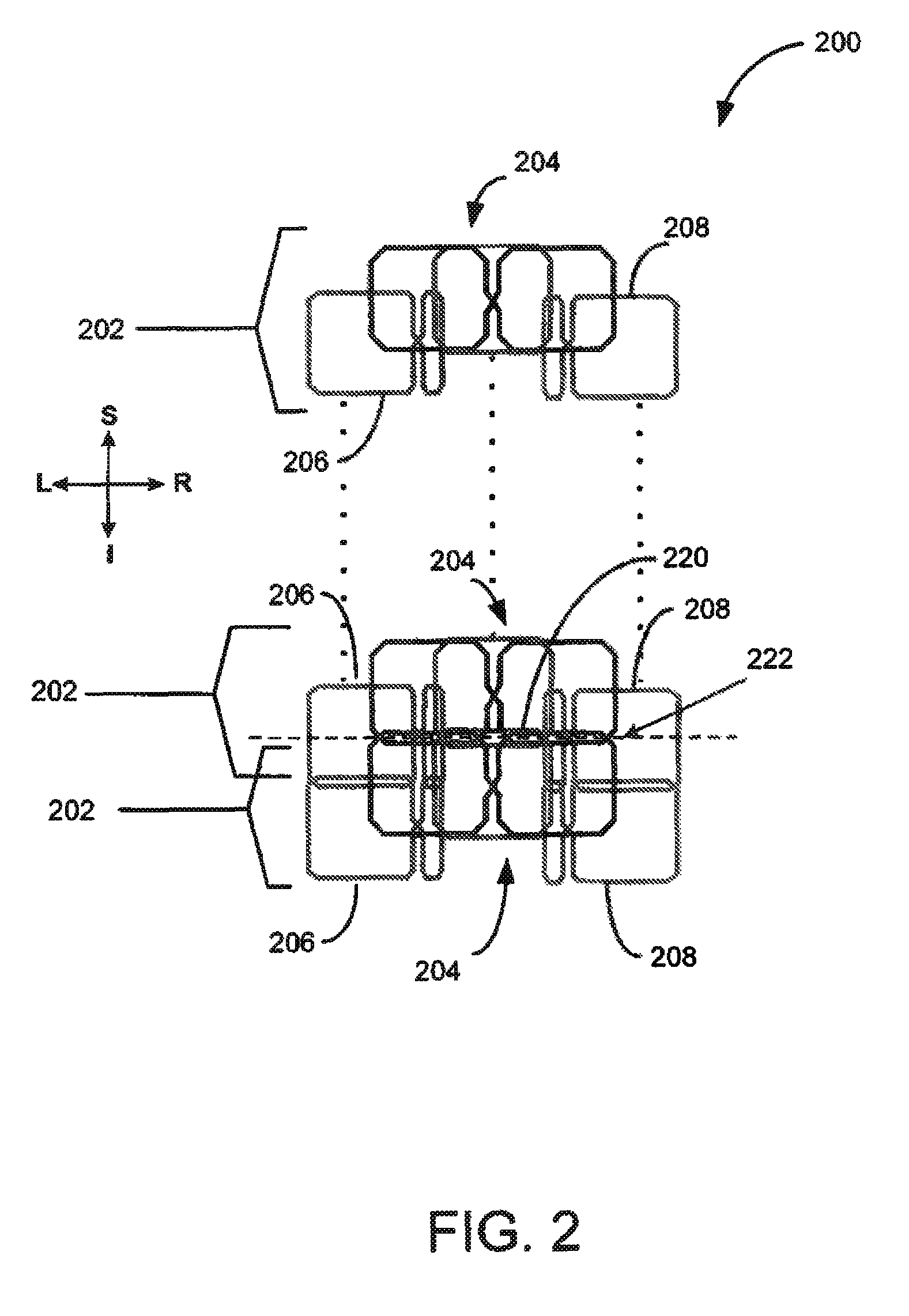
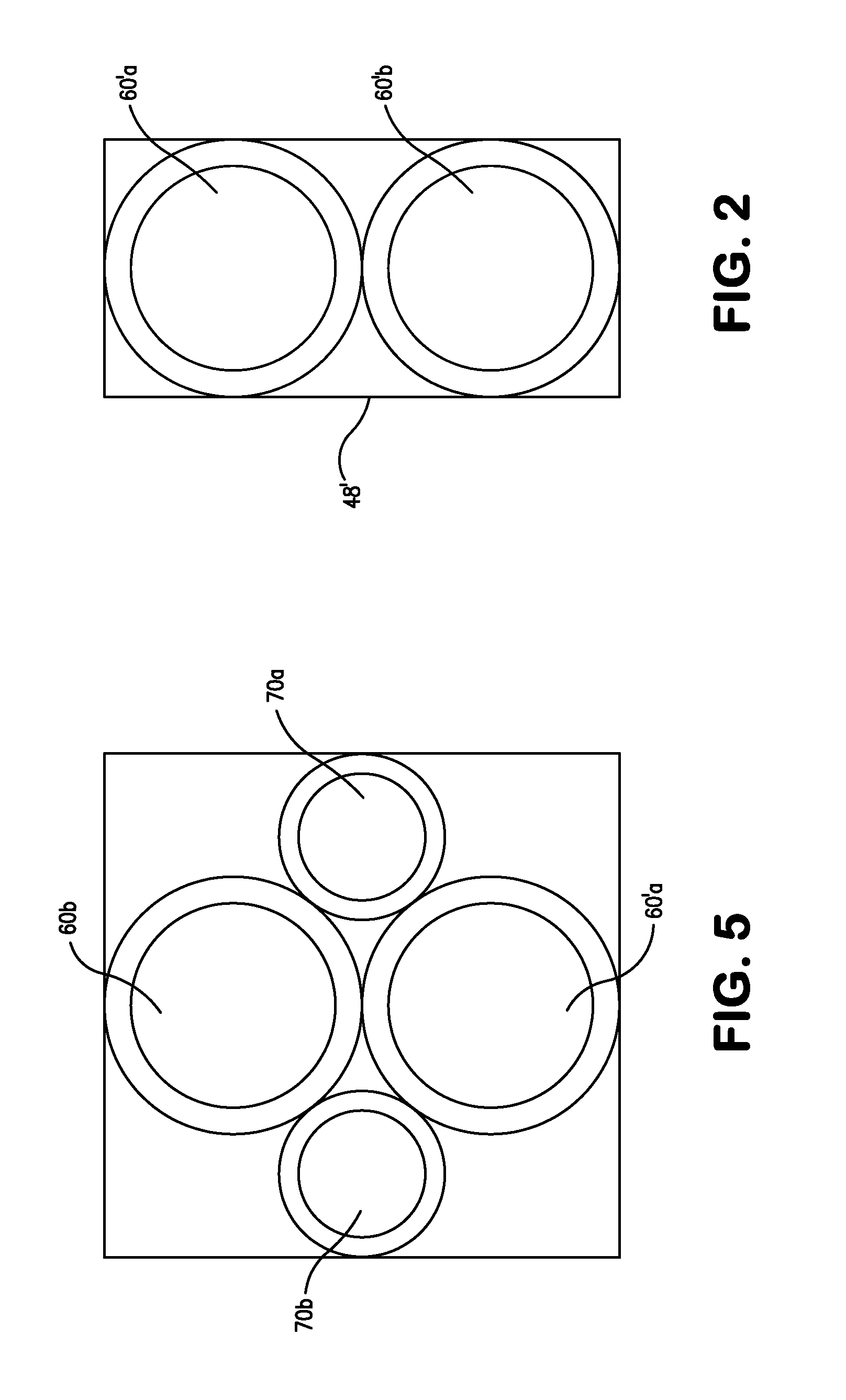
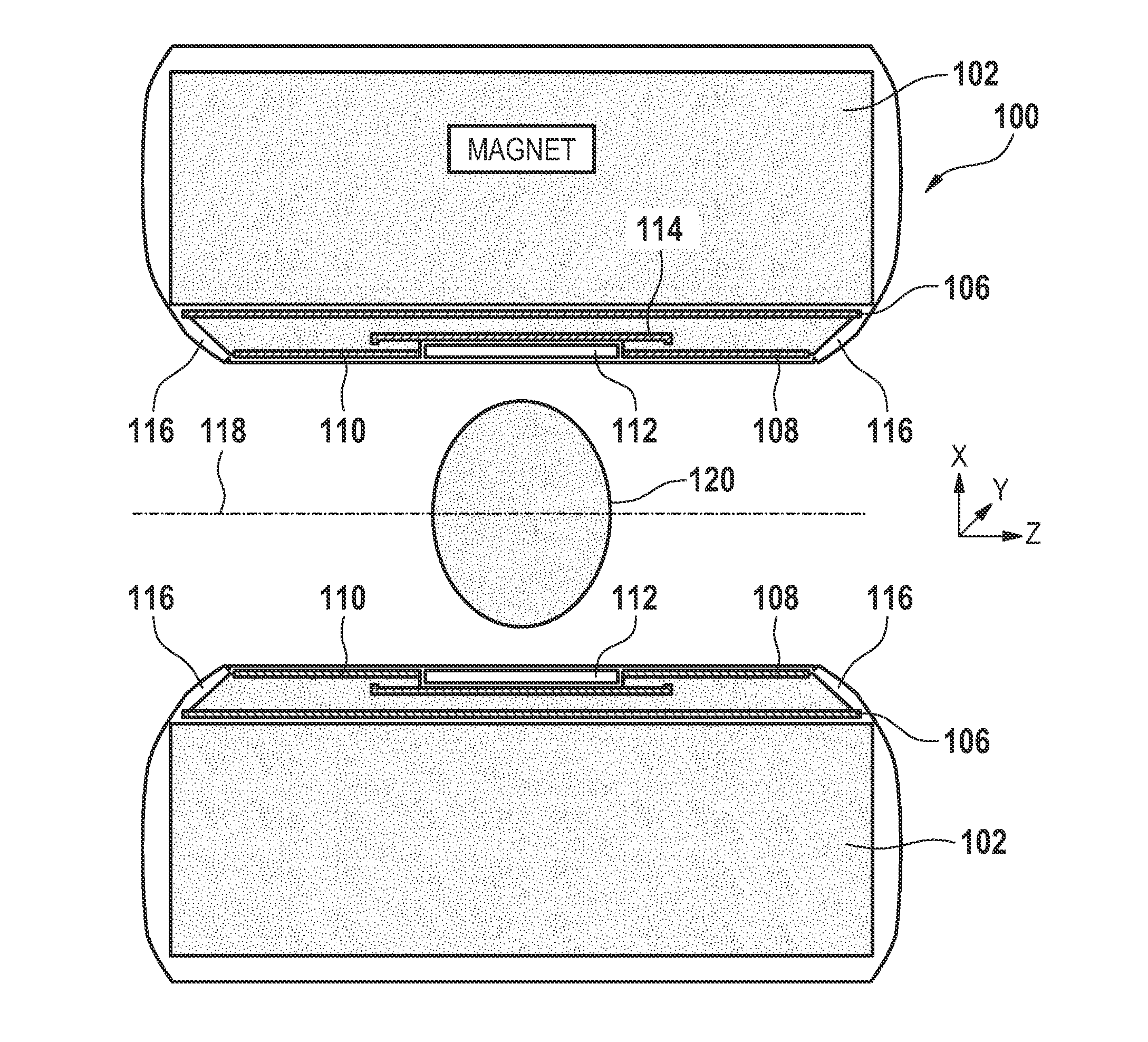
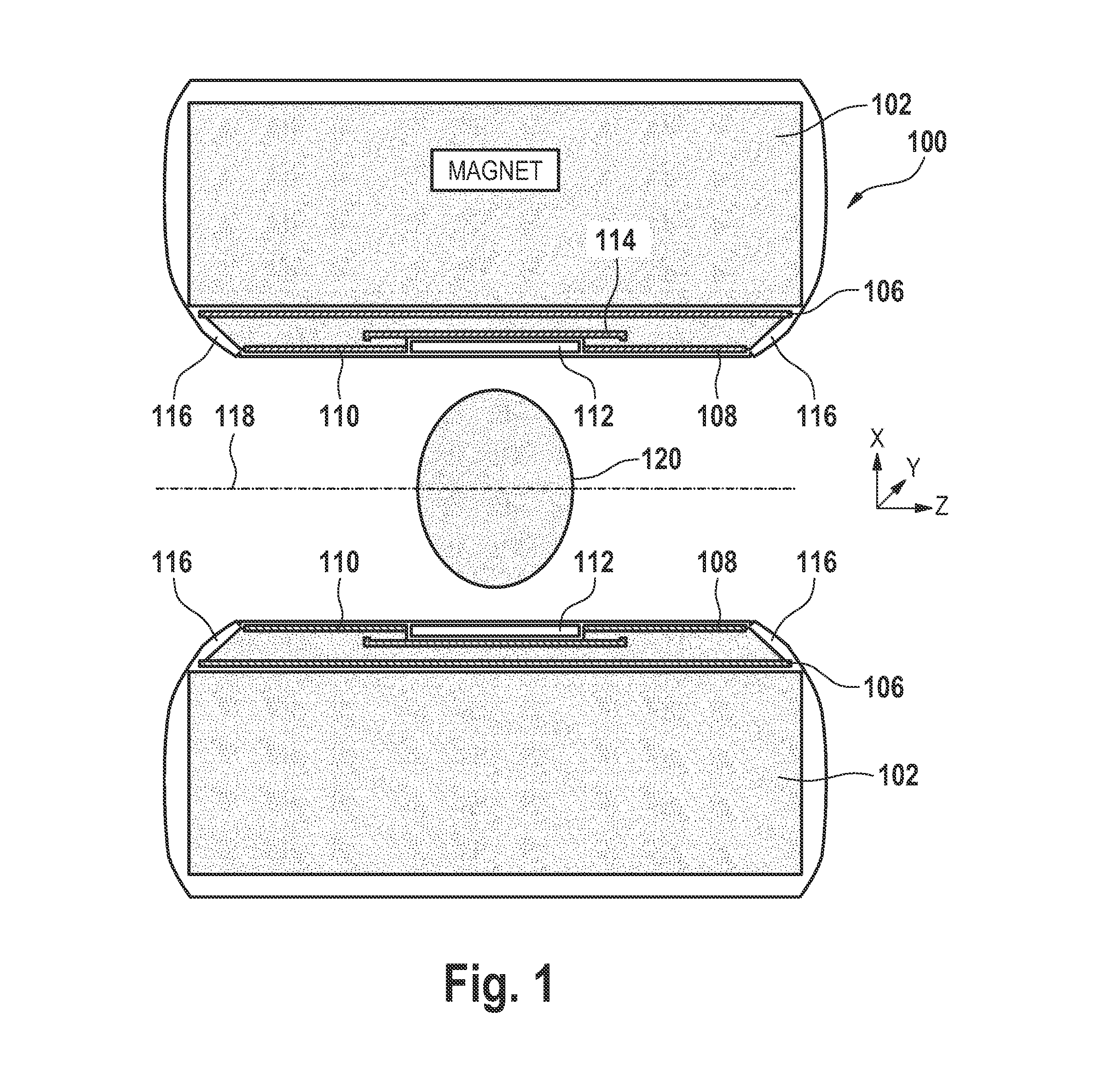
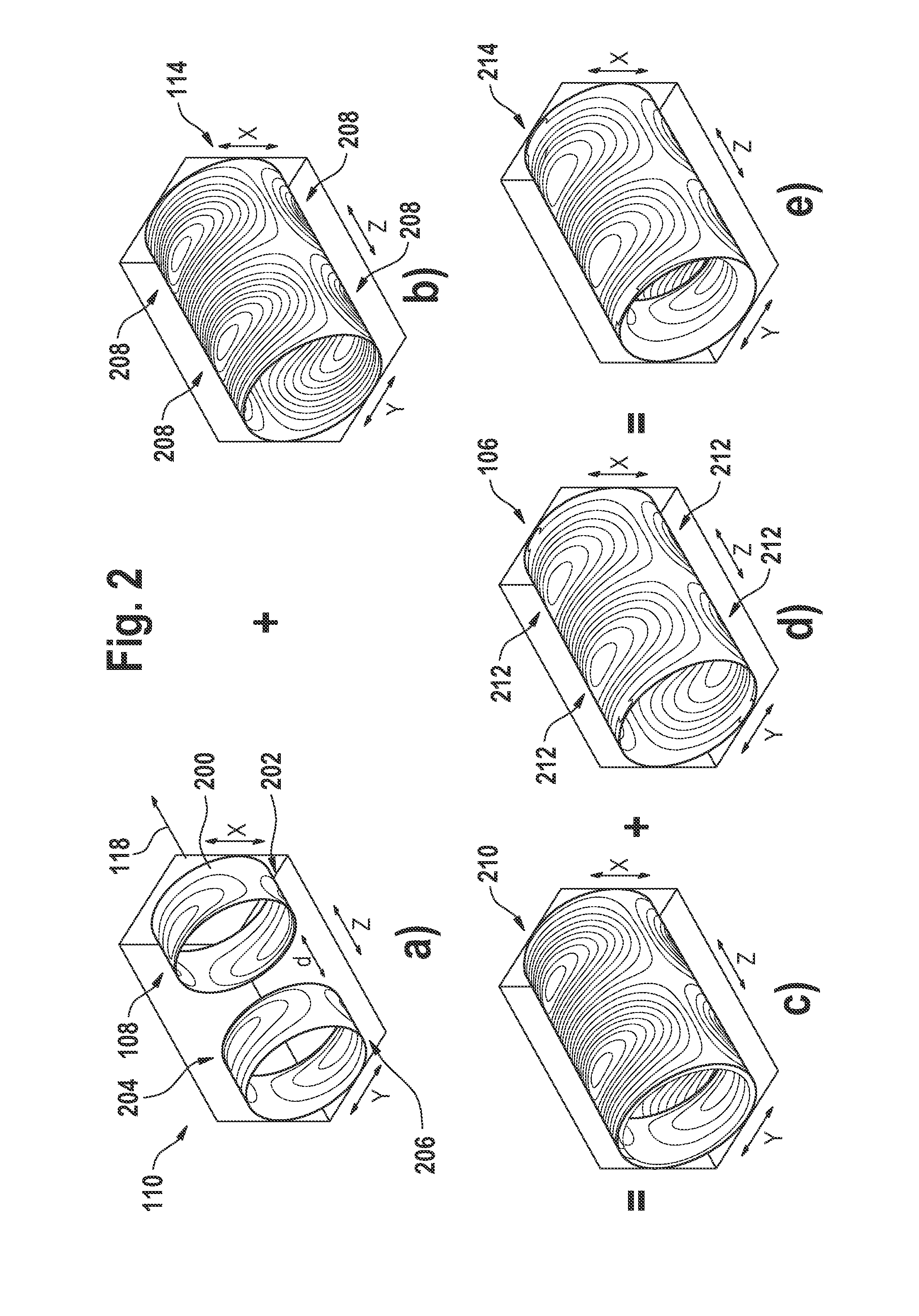
The present invention relates to a magnetic resonance imaging system comprising a main magnet (102), the main magnet (102) comprising a magnet bore, the bore having a longitudinal axis (118) parallel to the main magnetic field of the main magnet (102), the magnet bore comprising a gradient coil system, wherein the gradient coil system comprises a first (108) satellite coil and an inner coil (114), wherein the first satellite coil comprises at least one pair of saddle coils (200; 202; 204; 206) arranged oppositely over the magnet bore and wherein the inner coil (114) comprises at least two pairs of saddle coils (208) arranged oppositely over the magnet bore, wherein the inner coil (114) is located at a larger diameter from the central axis (118) than the first (108) satellite coil, wherein the first satellite coil and the inner coil form a stepped coil structure.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Transmission line probe for nmr
InactiveUS20120081119A1Measurements using magnetic resonanceElectric/magnetic detection for transportSaddle coilCapacitance
A probe for an NMR device is disclosed in which a saddle coil is disposed on one side of a flexible insulating material, and an additional conductor is disposed on the opposite side. The additional conductor and the conductors of the saddle coil create a capacitance across the insulating material. This capacitance acts with the inductance of the saddle coil such that the probe itself forms a transmission line. The probe is thus inherently broadband and requires no tuning. It also presents a constant impedance, thus facilitating impedance matching to an NMR spectrometer. In a preferred embodiment, a chip resistor is disposed on the flexible insulating material, terminating the transmission line.
Owner:MURPHREE JR DENNIS HAAGA +2
Method and apparatus for magnetic resonance imaging incorporating a spiral coil
InactiveUS7233147B2Improve signal-to-noise ratioHighly desirable resultElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceSaddle coilHelmholtz coil
The subject invention pertains to a method and apparatus utilizing one or more spiral coils, such as spiral birdcage coils, spiral saddle coils, Helmholtz coil pairs, and other spiral volume and spiral surface coils. The spiral coils of the subject array can be substantially isolated from each other while covering nearly the same volume or surface. For cylindrical geometrics, isolation can be enhanced by having the rotation, or change in direction from one end of the coil to the other, be 2nπ, where n is an integer.
Owner:INVIVO CORP
Quadrature and linear RF coil array for MRI of human spine and torso
InactiveUS20110156705A1Transformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsDiagnostic recording/measuringSaddle coilCoil array
A radio frequency (RF) coil array includes a plurality of RF coil sections arranged in a superior-inferior direction. Each RF coil section includes a first linear coil element, a loop-saddle coil quadrature pair and a second linear coil element configured in an overlapping arrangement in a left-right direction. The position of the first linear coil element and the second linear coil element on the left and right may be shifted in the superior-inferior direction with respect to the center loop-saddle coil quadrature pair.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Medical examination and/or treatment apparatus with an electromagnet for navigating a medical instrument and an x-ray device for visual inspection during the navigation
InactiveUS7933641B2High strengthImprove accessibilityElectromagnets without armaturesSurgical navigation systemsSaddle coilTherapeutic Devices
There is described a medical examination and / or treatment apparatus with an electromagnet for generating a magnetic field for navigating a medical instrument and an x-ray device having an x-ray source and an x-ray detector attached to a bracket for visual control during the navigation, with the x-ray source and the x-ray detector being arranged on the electromagnet embodied as a hollow cylinder, on the front ends of which are located two ring coils which are arranged in parallel, between which a number of saddle coils arranged in the peripheral direction are arranged, with the hollow cylinder being arranged on a bracket which can be moved about a number of axes.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
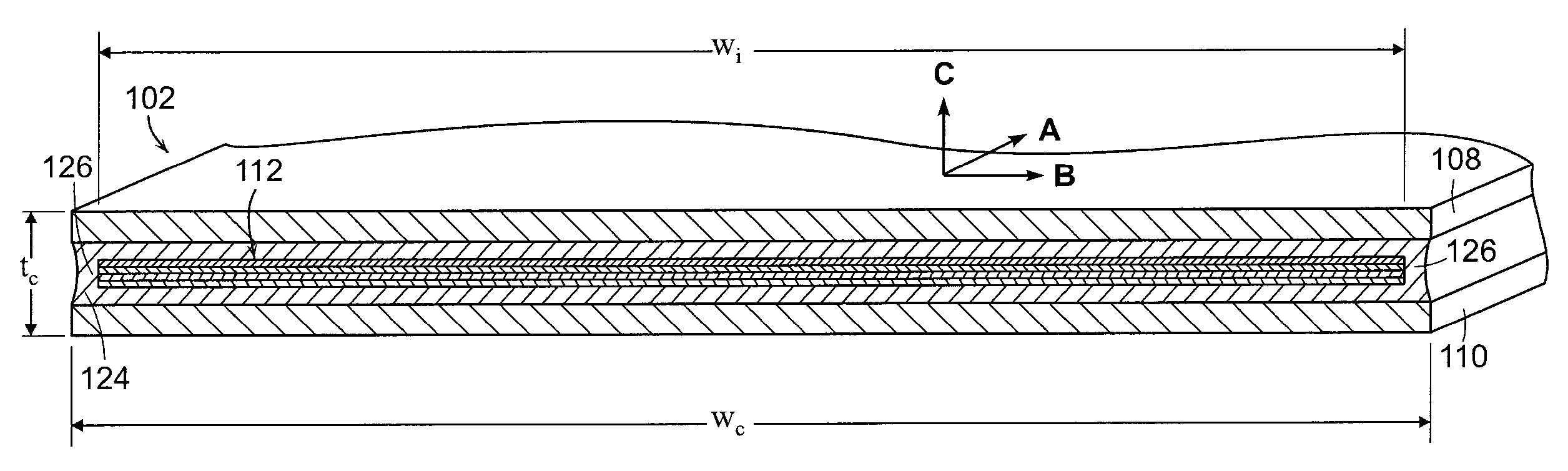
Wide electrical conductor having high C-axis strength
ActiveUS8791052B2Avoid layeringPermit superconductivitySuperconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconductor device manufacture/treatmentSaddle coilElectrical conductor
A rotating machine includes a stator and a rotor configured to rotate within the stator. Rotor windings are supported in the rotor and are formed of a laminated electrical conductor in a single-layer saddle coil configuration. The conductor includes a first support lamina, a second support lamina, an insert including a high temperature superconductor disposed between the first and second support lamina, and a filler material surrounding the insert that bonds the insert to each of the first and second support lamina. At the location between the first support lamina and second support lamina corresponding to the location of the insert, the width dimension of the filler material on each side of the insert is at least 10 percent of a width of the conductor. The conductor is configured to carry at least 600 Amperes per turn and have a C-axis tensile strength of at least 21 MPa.
Owner:AMERICAN SUPERCONDUCTOR
RF coil array for cardiac and thoracic magnetic resonance imaging
A radio frequency (RF) coil array includes a first coil section and a second coil section mechanically coupled to the first coil section. The first coil section includes a first row of a plurality of double asymmetric saddle coil pairs arranged in a left-right direction and a second row of a plurality of double asymmetric saddle coil pairs arranged in a left-right direction. The first row and the second row are arranged along a superior-inferior direction. The second coil section includes a plurality of loop coils arranged around at least a portion of a perimeter of the first coil section.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
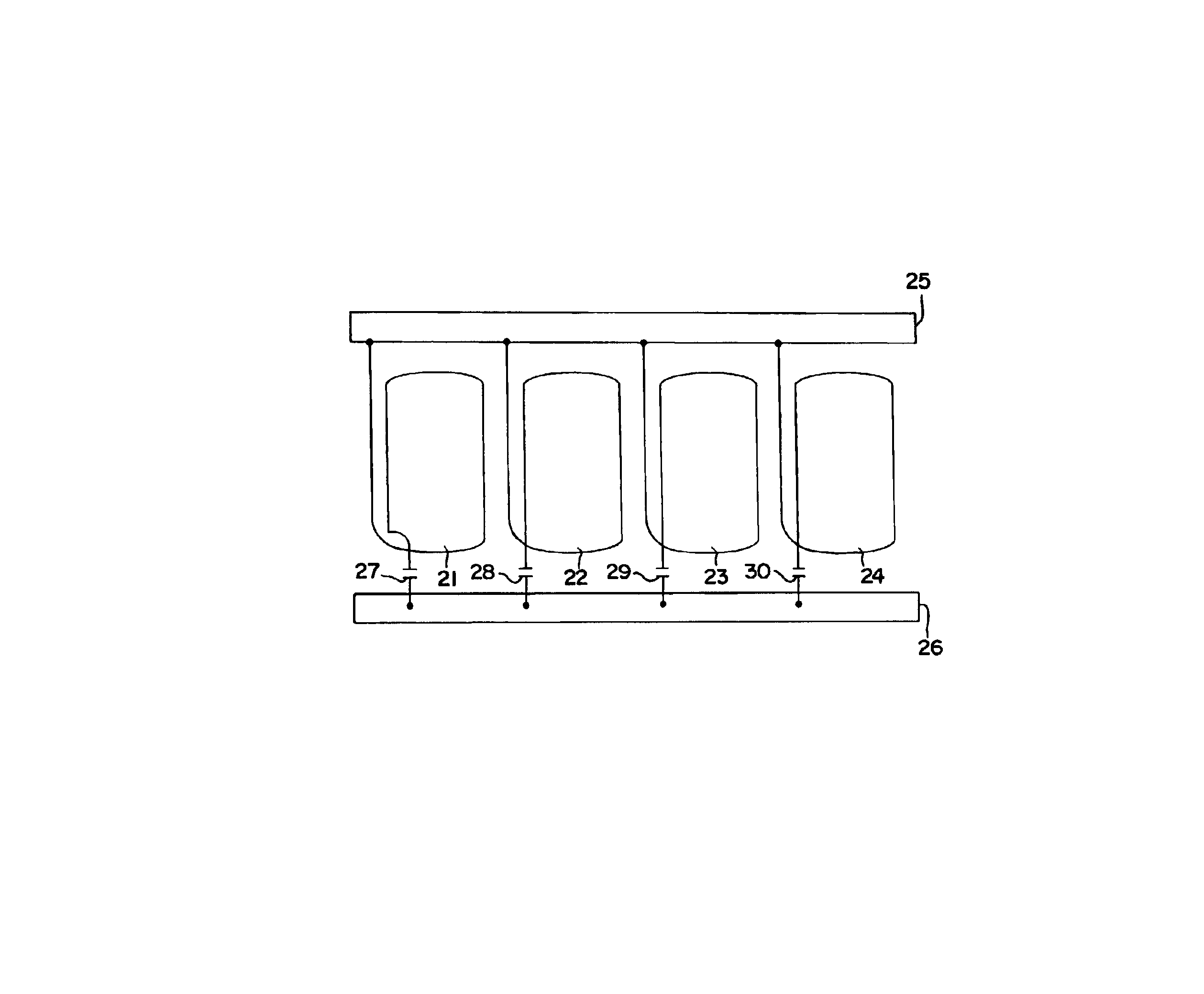
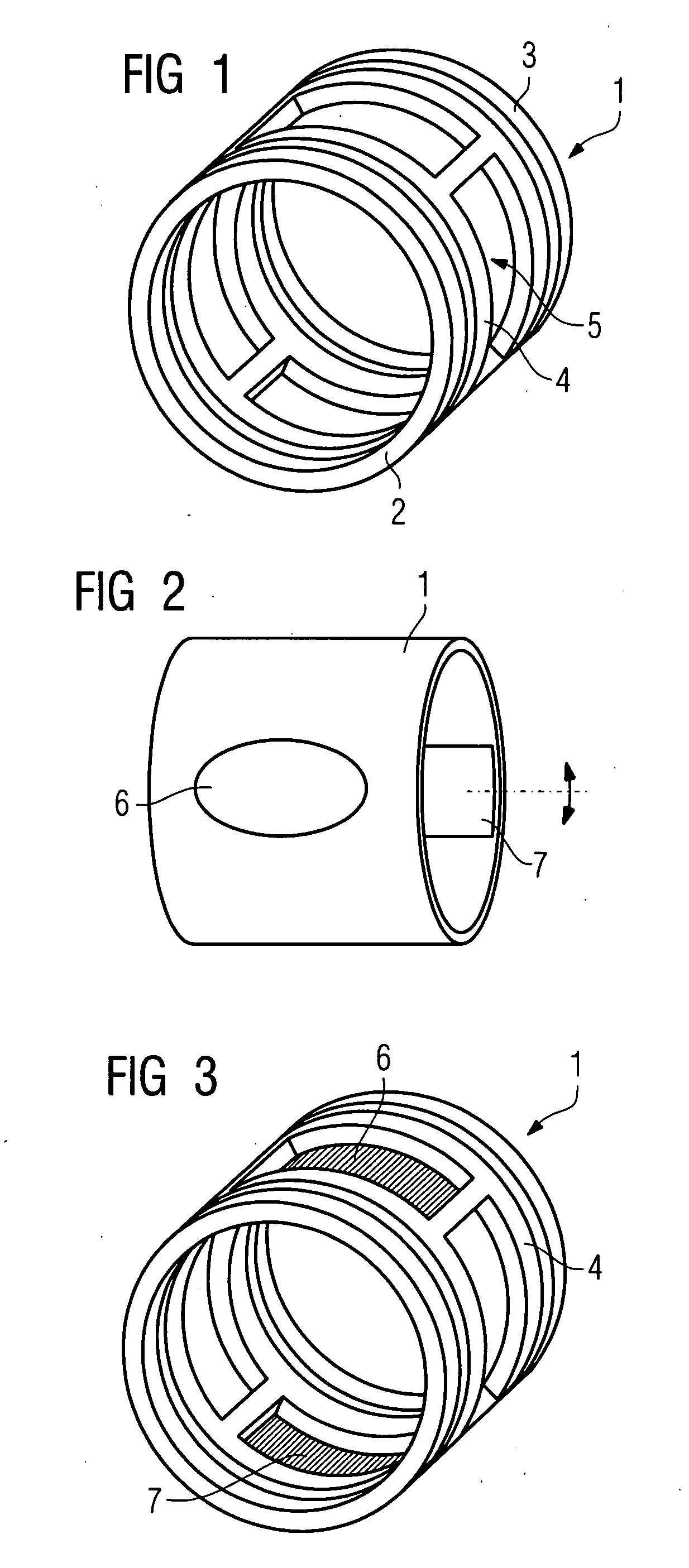
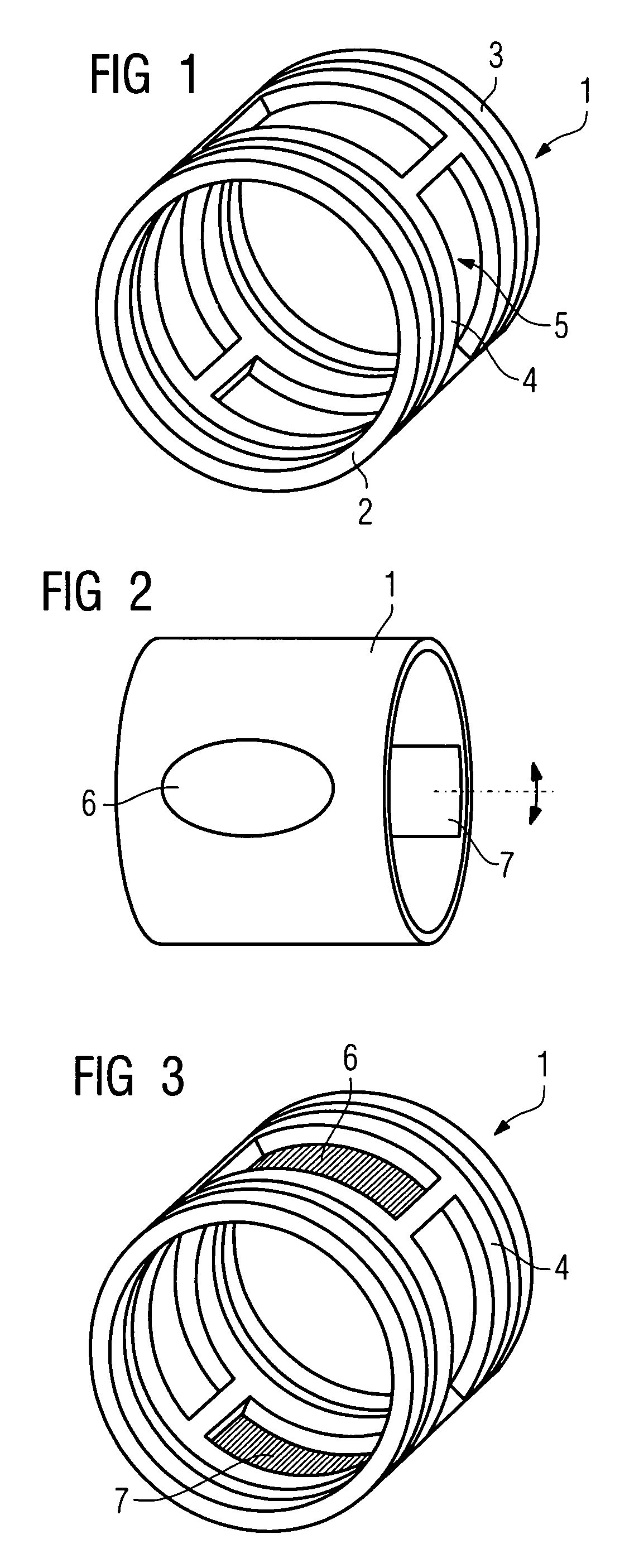
Manufacturing process of radial superconducting shimming coils
Provided is a manufacturing process of radial superconducting shimming coils. Firstly, the coil contours of the radial superconducting shimming coils (1) unfolded into planes are drawn on a film substrate (3); then, the film substrate (3) is fixed to a winding cylinder (4) in a covering mode; superconducting wires (7) are wound on the basis of the coil contours; the superconducting wires (7) are fixedly supported through epoxy sheets (6) and glass fiber fabric pre-impregnated materials (9) and meanwhile are further reinforced through UV glue (10) in a winding procedure; a plurality of saddle coils of the radial superconducting shimming coils (1) are manufactured in sequence; at last, the saddle coils are heated in a drying oven to be completely solidified, and the winding cylinder (4) is removed so as to obtain a set of radial superconducting shimming coils.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Winding form for winding a saddle coil
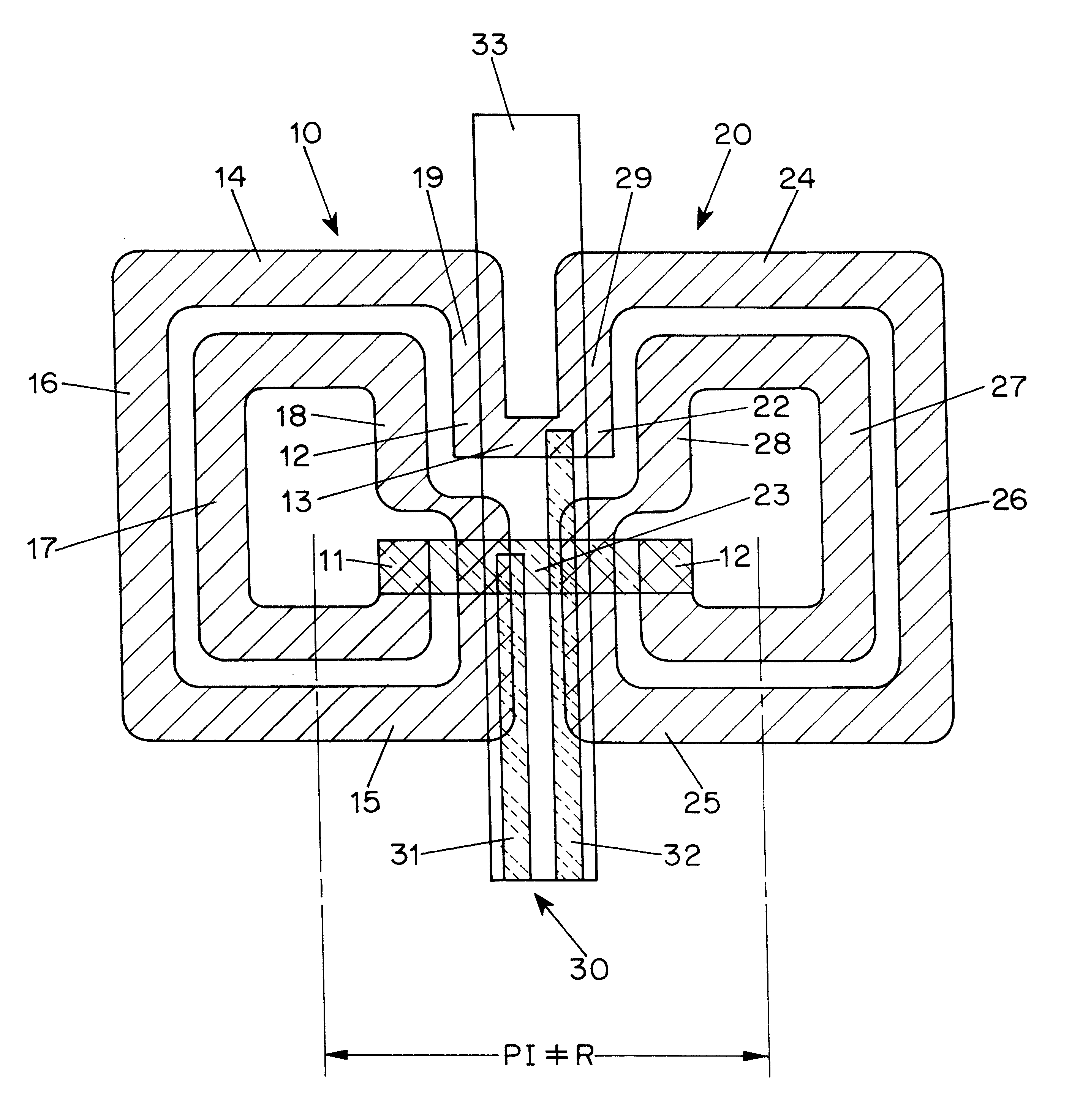
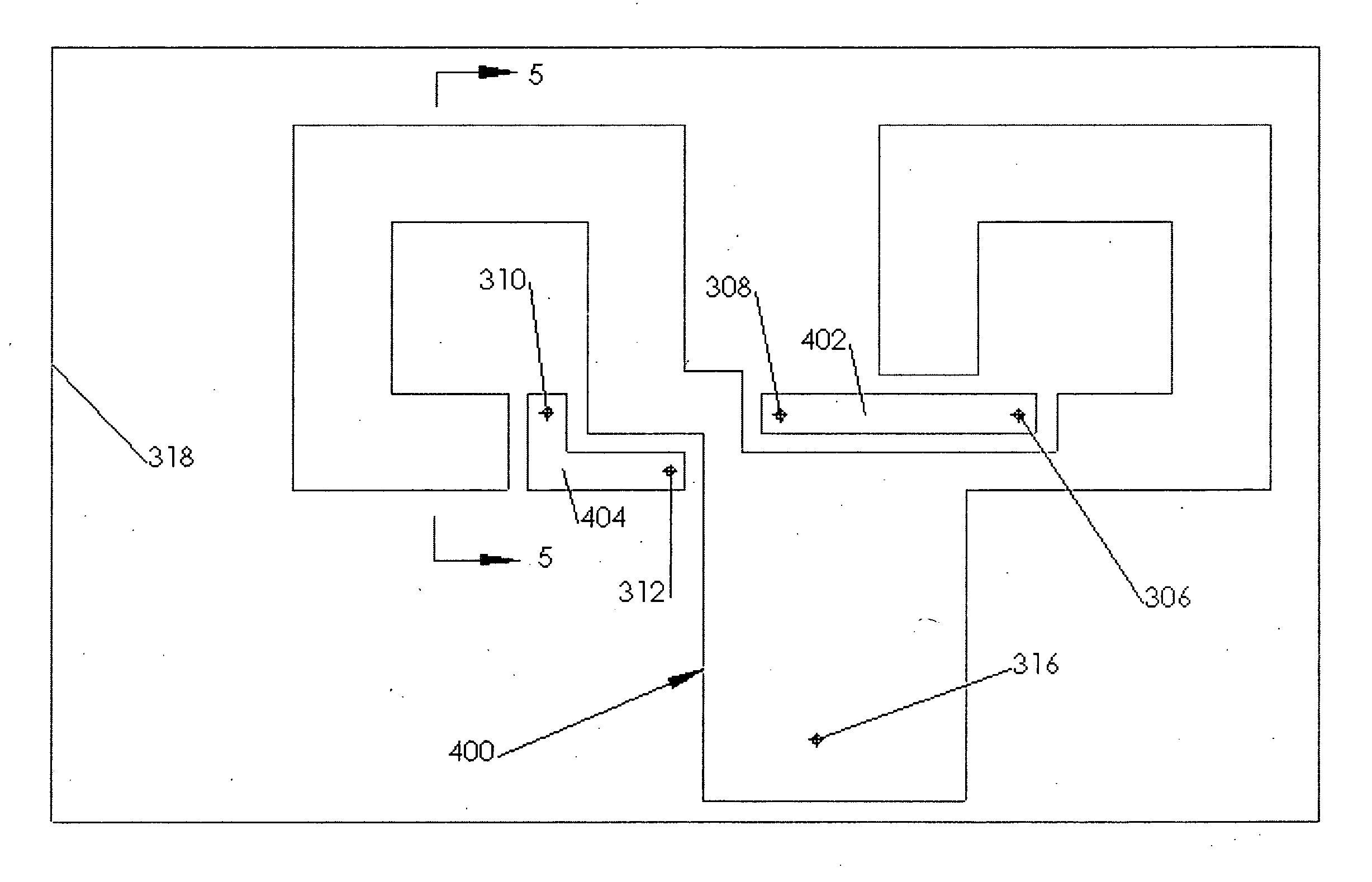
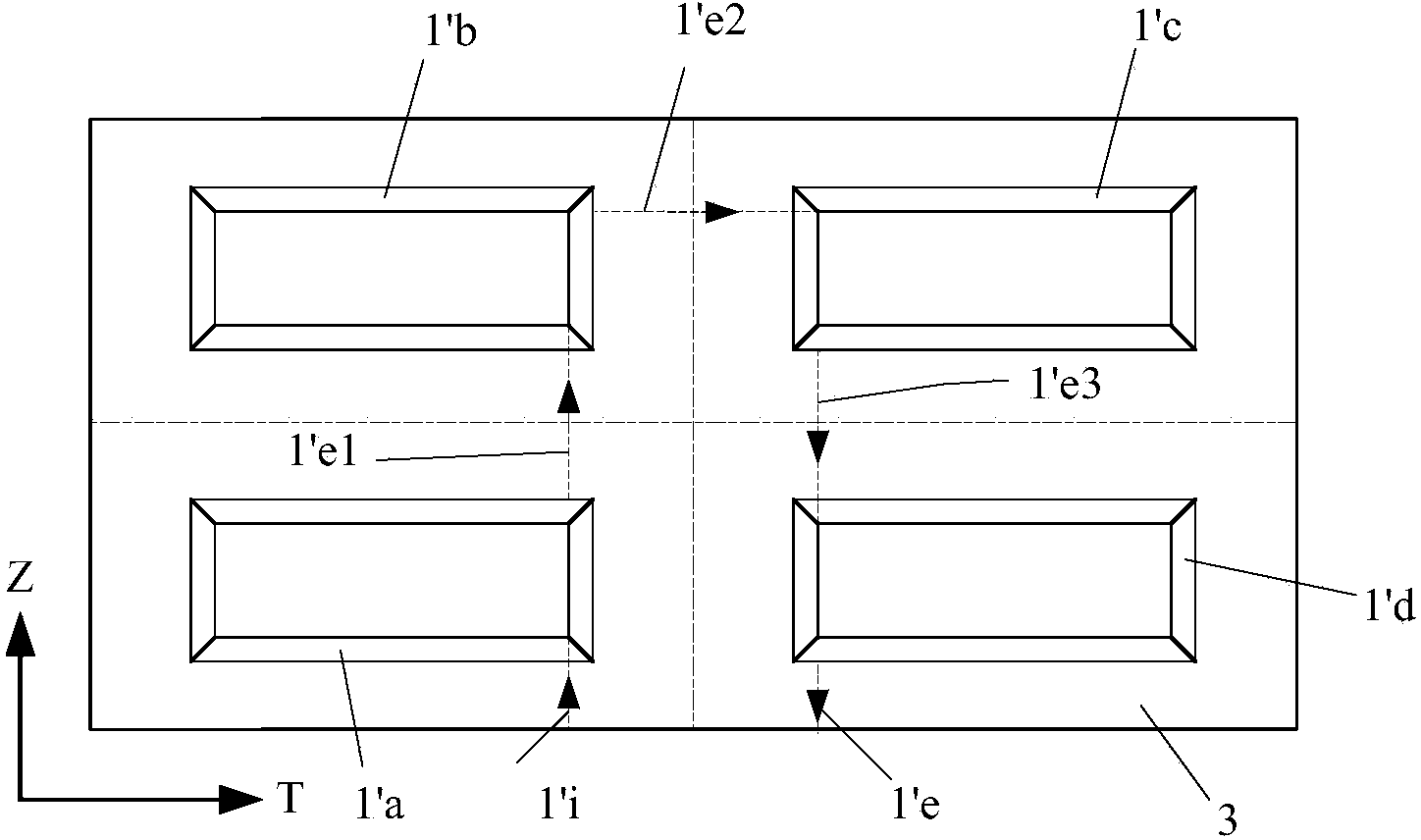
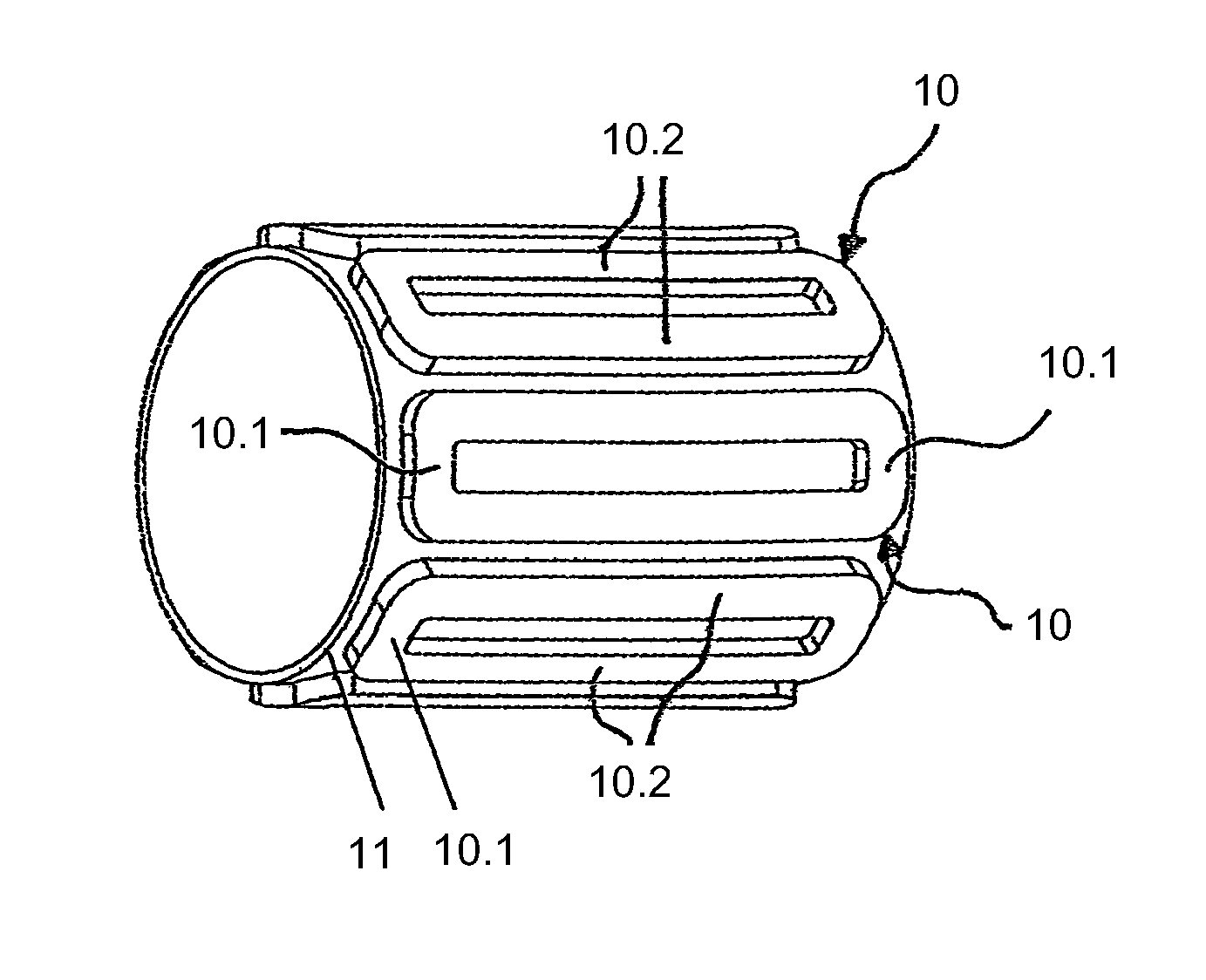
InactiveCN101425728AAvoid damageEasy to installWindingsMagnetic circuit rotating partsSaddle coilThin layer
The invention relates to a winding body (80) including a winding support (85) between a first plate (82) and a second plate for a saddle coil winding made from a thin layer HTSC, which is destined for a cylindrical armature of an electrical machine, and which has two longitudinal legs parallel to the armature axis between two winding ends, wherein the winding support for each winding end has a bearing surface (85.1); if the area in the longitudinal direction between the first plate (82) and the second plate is a hollow barrel section matching with the surroundings of the armature and each bearing surface (85.1) of the winding end is such twisted that the length difference between the upper edge (85.13) of the bearing surface (85.1) and the lower edge (85.12) of the bearing surface divided by the quotient of the width of the bearing surface (85.1) and average edge length of both edges (85.13, 85.12) is at most corresponding to curvature about 3 degrees per meter, the thin HTSL can be wound into the saddle coil without damaging the HTSL thin layer.
Owner:泽奈基电力公司
Tesseral shim coil for a magnetic resonance system
ActiveUS9081070B2Lower the volumeSignificant radial savingsMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionSaddle coilResonance
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
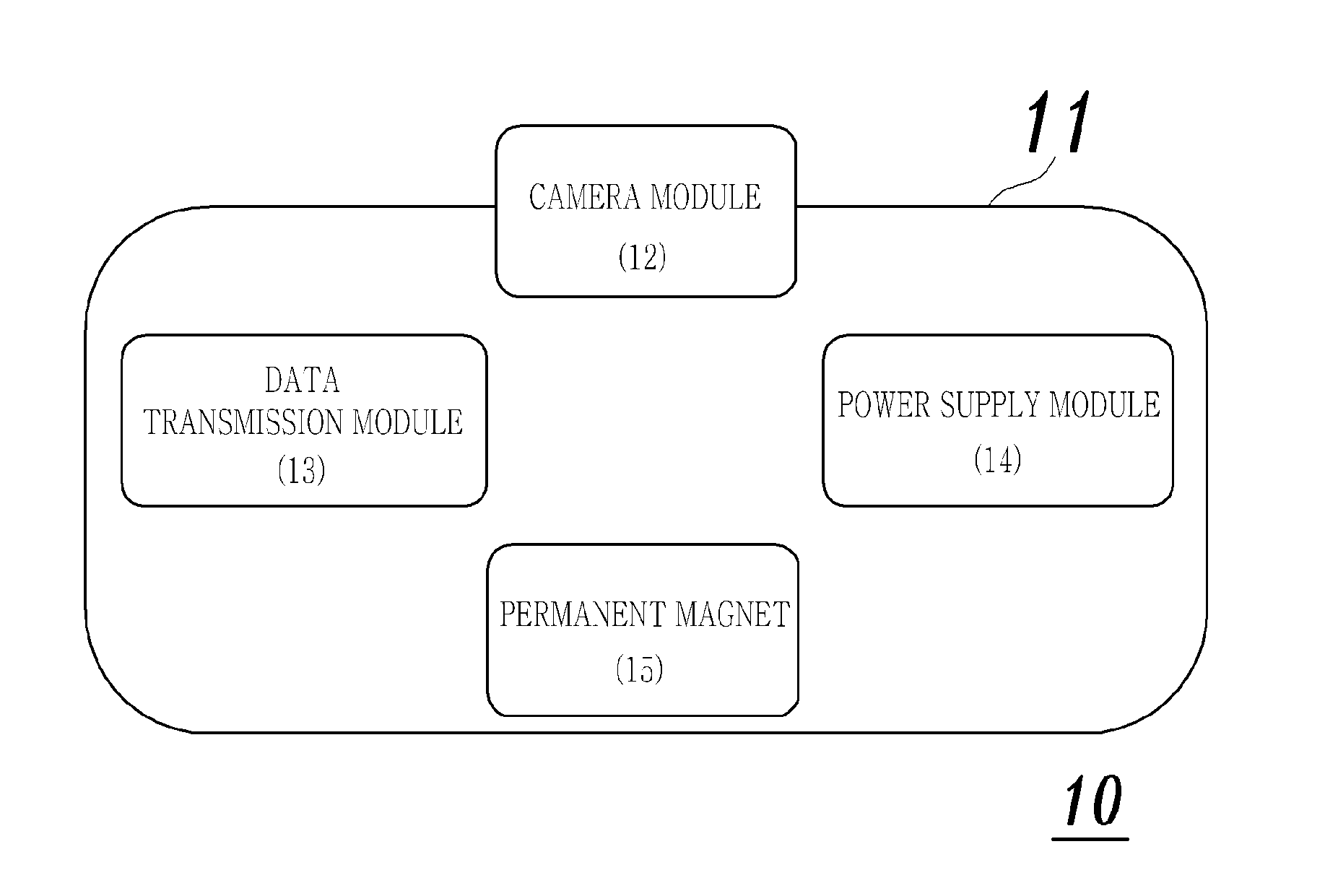
Actuation control system of a capsule endoscope
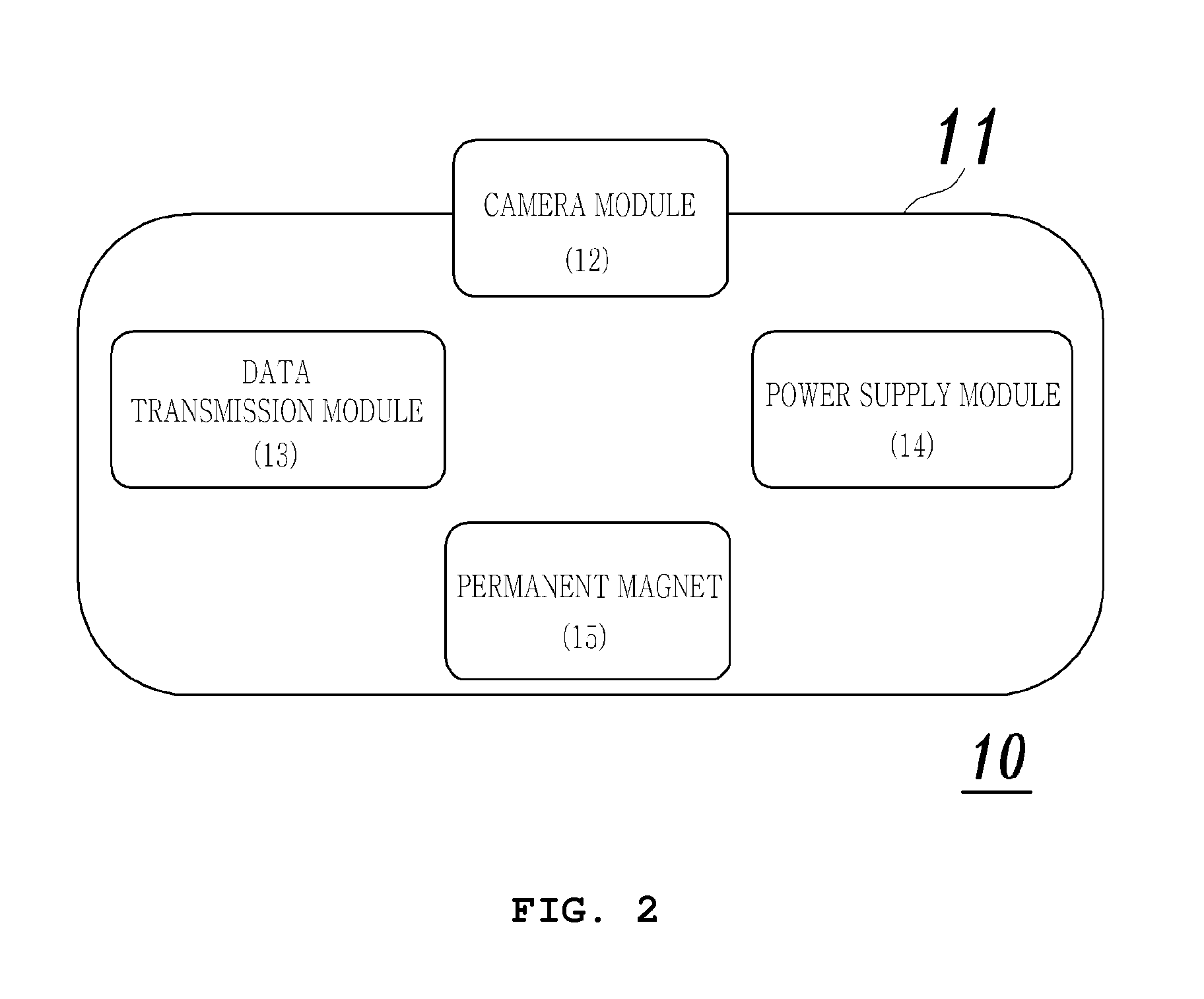
A system for controlling actuation of a capsule endoscope includes a receiving unit receiving an image transmitted from the capsule endoscope; a coil unit generating a magnetic field for actuating the capsule endoscope by using current applied thereto; a power supply unit supplying power to the coil unit; and an actuation controller control the current applied to the coil unit and a coil rotational motor for adjusting of a posture and the location of the capsule endoscope based on the identified lesion or location of the capsule endoscope, wherein the coil unit includes a pair of Helmholtz coils and a pair of Maxwell coils that are fixedly disposed on a main axis; and a pair of uniform saddle coils and a pair of gradient saddle coils that are located inside the pair of the Helmholtz coils and the pair of the Maxwell coils to rotate around the main axis.
Owner:IND FOUND OF CHONNAM NAT UNIV
Method and apparatus for imaghing a subject using local surface coils
InactiveCN102830378ADiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsSaddle coilResonance
The invention is named method and apparatus for imaghing a subject using local surface coils. A Radio Frequency (RF) coil apparatus (10) for generating a magnetic resonance (MR) image includes a main body (12) adapted to be worn by a subject being scanned, wherein the main body comprises an anterior portion (20), a posterior portion (22), and a transition portion (24) coupled between the anterior and posterior portions; a first RF receive-only saddle coil (100) includes a first coil (110) positioned in the anterior portion and a second coil (112) positioned in the anterior portion, the first RF saddle coil configured to be positioned on the anterior and posterior sides of the subject. An MRI imaging system (200) and method are also described herein.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Magnetic control pulling single crystal superconducting magnet coil and superconducting magnet device
PendingCN113889314AReduce winding difficultyWinding Difficulty EaseSuperconducting magnets/coilsSaddle coilSuperconducting Coils
The invention discloses a magnetic control pulling single crystal superconducting magnet coil and a superconducting magnet device, the magnetic control pulling single crystal superconducting magnet coil comprises two coil groups, the two coil groups are oppositely arranged, each coil group is of an arc-shaped ring structure, each coil group is composed of at least two annular sub-coils, and the at least two sub-coils are sequentially arranged side by side. According to the embodiment of the invention, on the basis that the advantages of high magnetic field utilization rate of a saddle-shaped coil, small superconducting wire usage amount under the same magnetic field intensity requirement and the like are reserved, the winding difficulty of a single coil is reduced by adopting a multi-coil structure, and the production efficiency is improved. And meanwhile, the stress of the multi-coil structure is more reasonable under the action of strong electromagnetic force, and the risk of quenching of the coils in the operation process is relieved.
Owner:XIAN JUNENG SUPERCONDUCTING MAGNET TECH
Magnetic resonance imaging system with satellite gradient coils
ActiveUS9435869B2Low costEasy to insertElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using NMRSaddle coilCoil structure
The present invention relates to a magnetic resonance imaging system comprising a main magnet (102), the main magnet (102) comprising a magnet bore, the bore having a longitudinal axis (118) parallel to the main magnetic field of the main magnet (102), the magnet bore comprising a gradient coil system, wherein the gradient coil system comprises a first (108) satellite coil and an inner coil (114), wherein the first satellite coil comprises at least one pair of saddle coils (200; 202; 204; 206) arranged oppositely over the magnet bore and wherein the inner coil (114) comprises at least two pairs of saddle coils (208) arranged oppositely over the magnet bore, wherein the inner coil (114) is located at a larger diameter from the central axis (118) than the first (108) satellite coil, wherein the first satellite coil and the inner coil form a stepped coil structure.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Winding former for a saddle coil winding
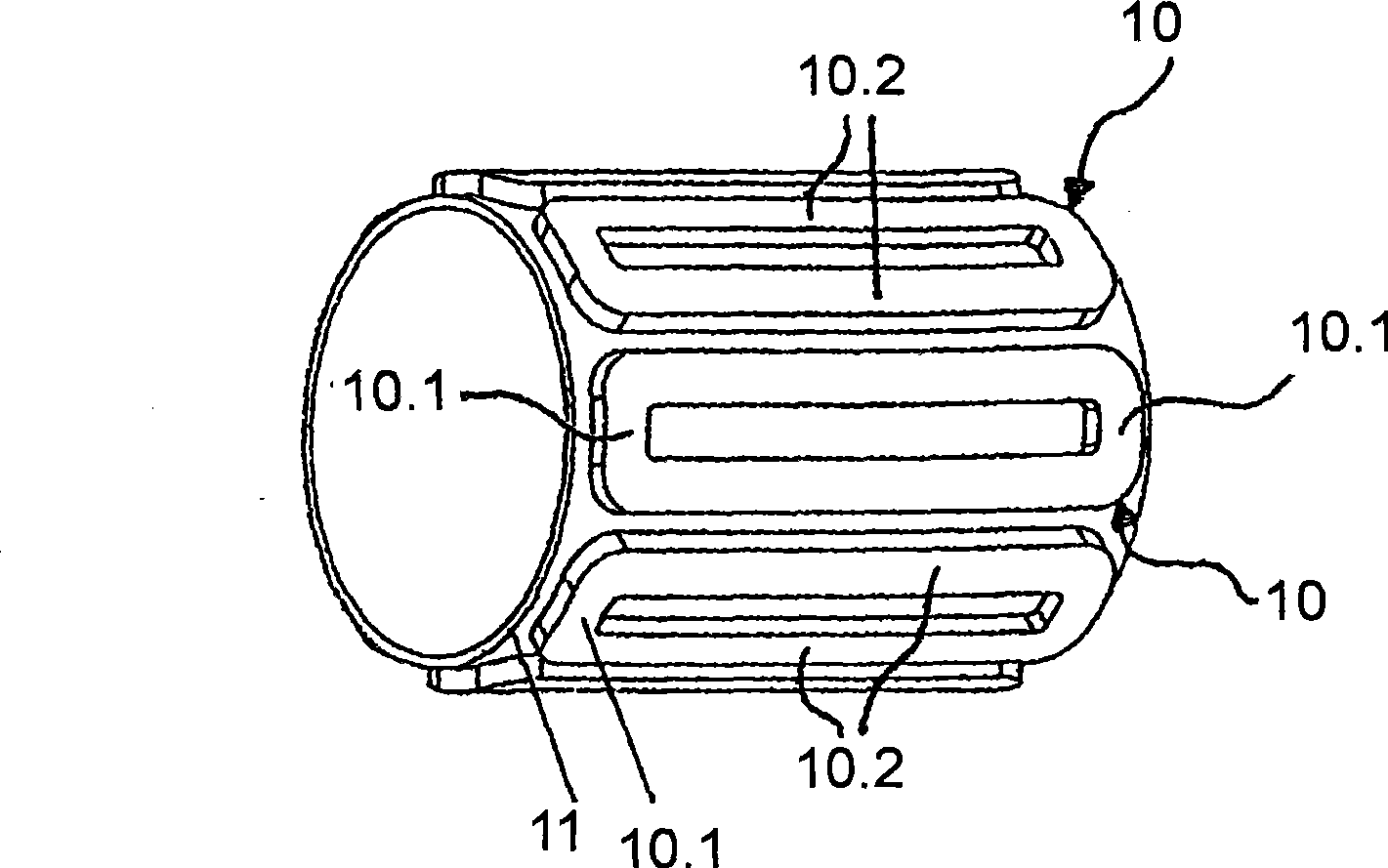
InactiveUS8058764B2Avoid damageAvoid deformationWindingsMagnetic circuit rotating partsSaddle coilThin layer
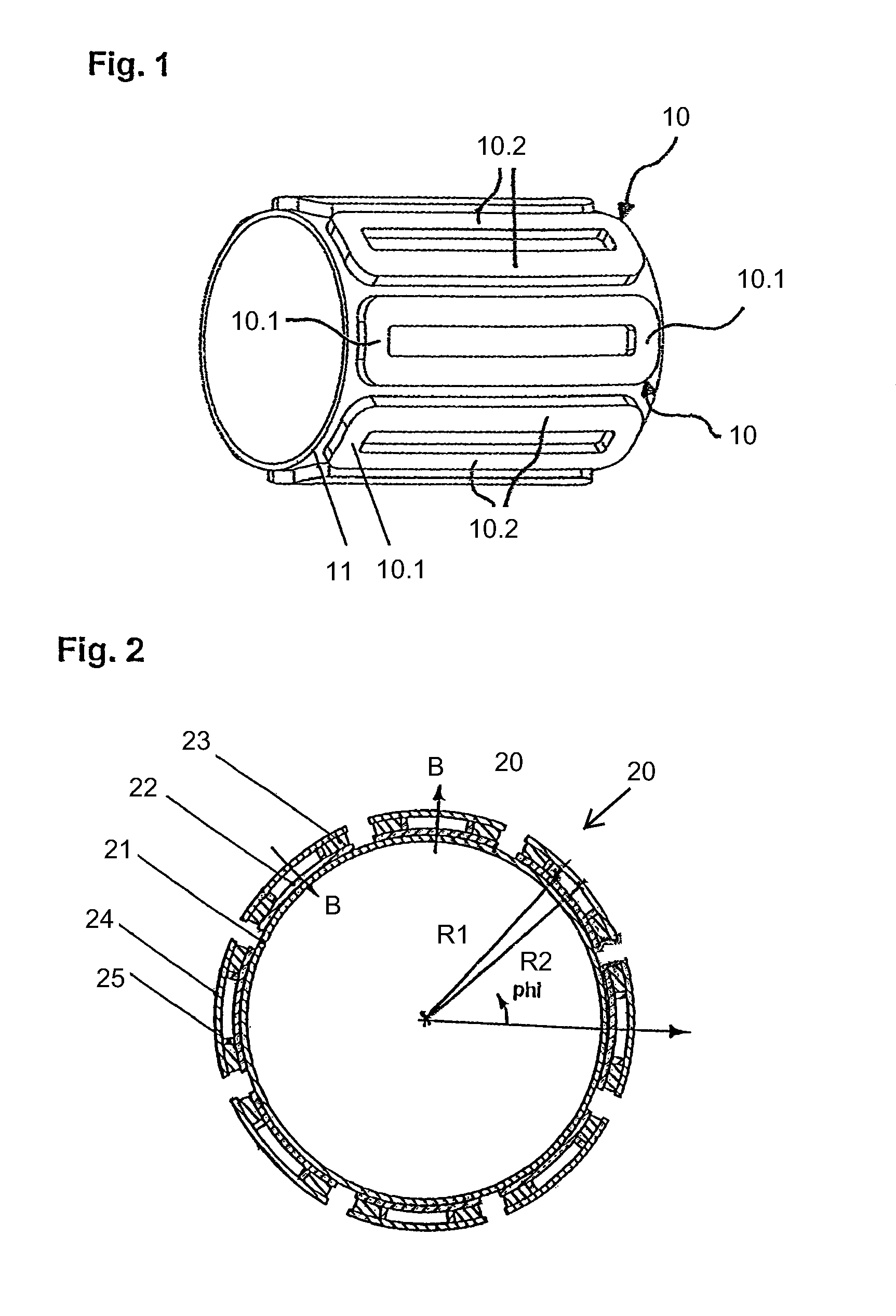
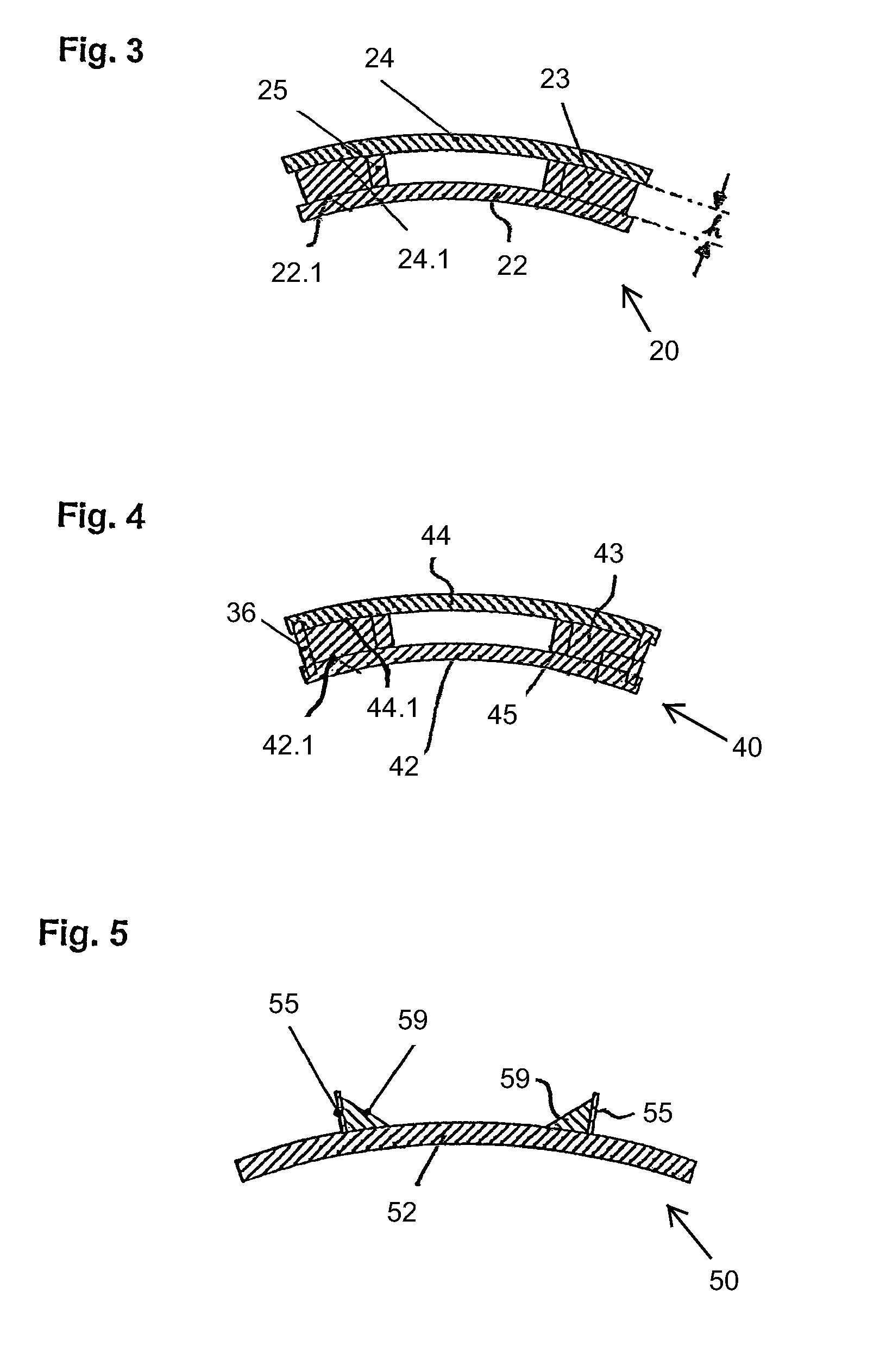
A winding former with a winding support between a first plate and a second plate for a saddle coil winding made up from a thin layer HTSC, which is destined for a cylindrical armature of an electrical machine, and which has two longitudinal legs parallel to the armature axis between two winding ends, wherein the winding support for each winding end has a bearing surface, which enables the thin layer HTSC to be wound to form a saddle coil without damaging the HTSC thin layer.
Owner:ZENERGY POWER
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com