Patents
Literature
102results about How to "Satisfactory image" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
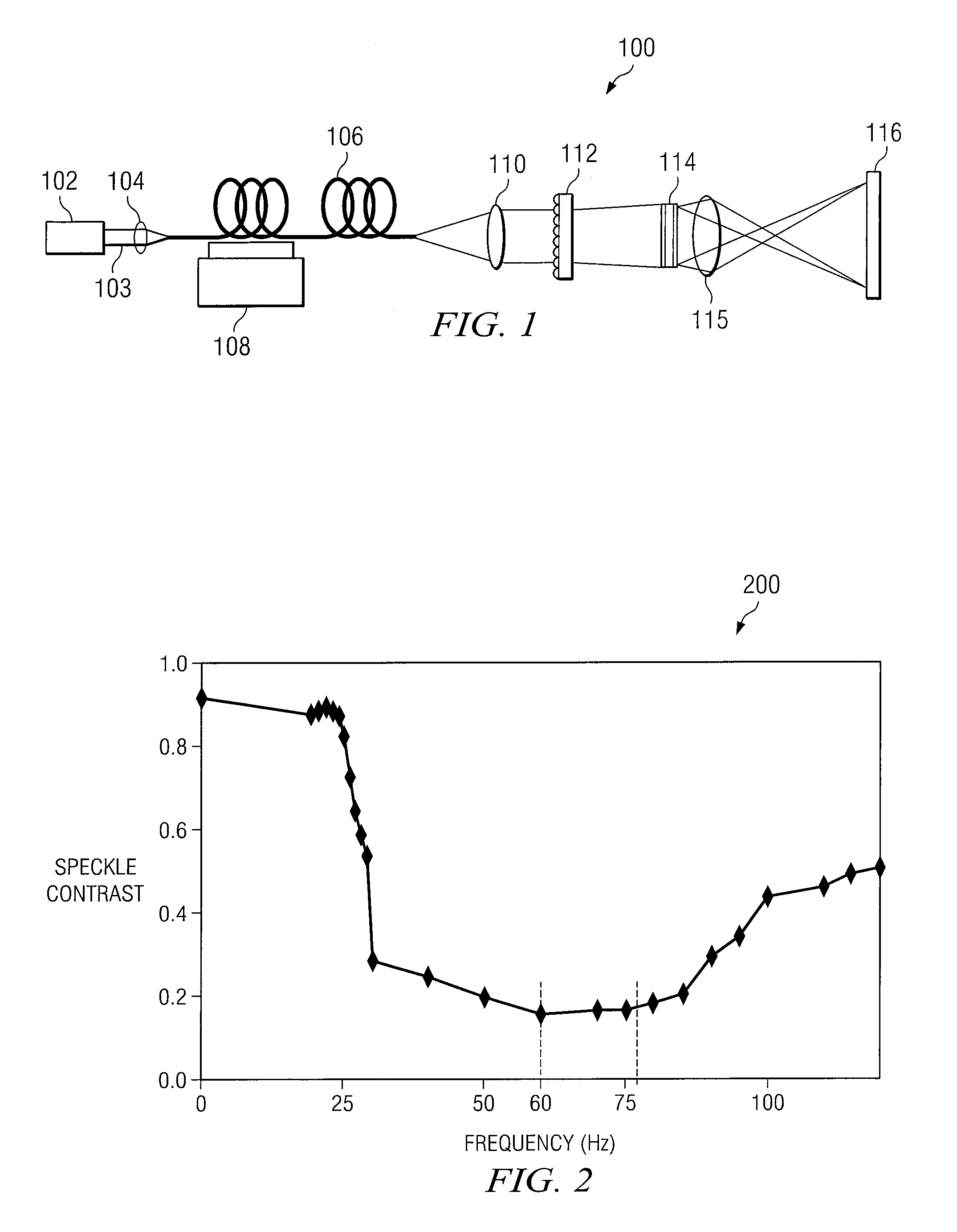
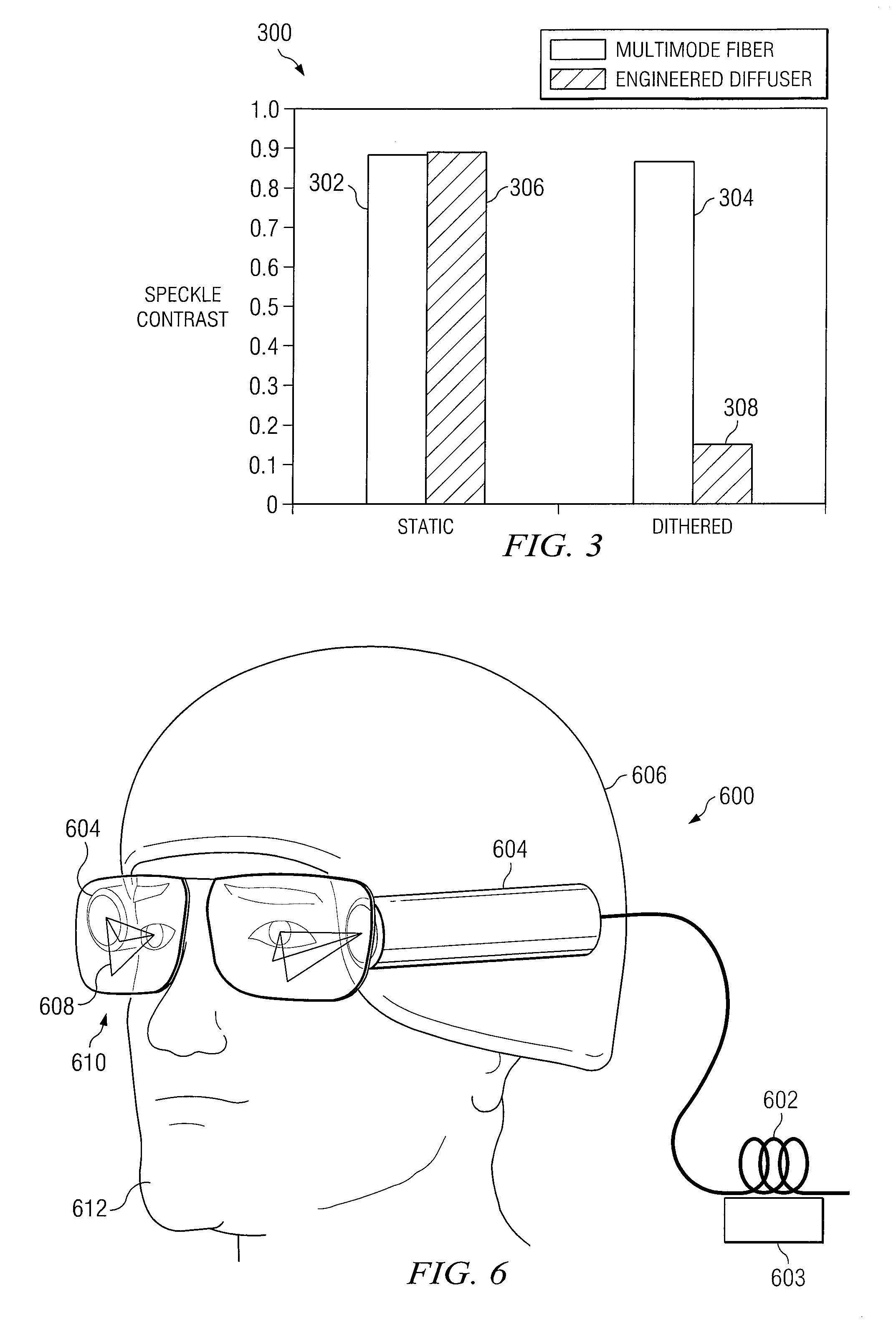
System and method for despeckling an image illuminated by a coherent light source
ActiveUS7969644B2Speckle reductionIncrease contrastCladded optical fibreColor television detailsFiberLight beam
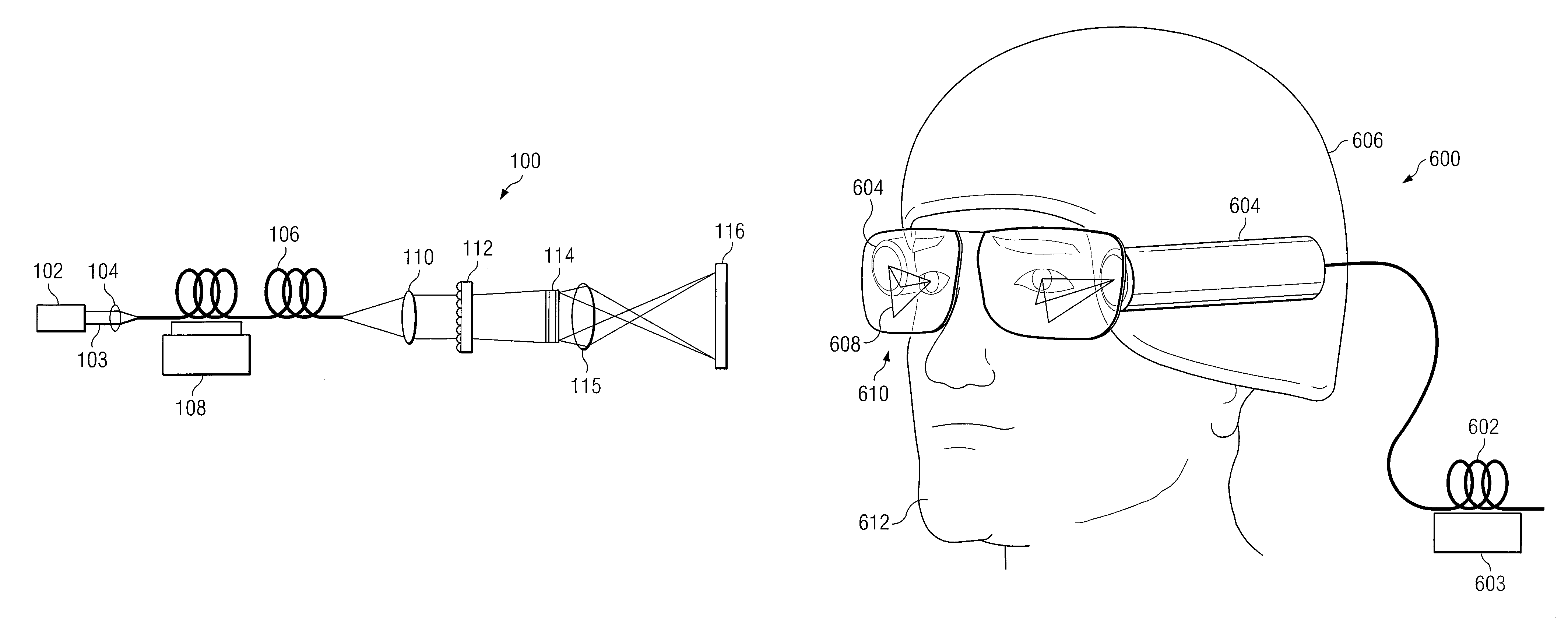
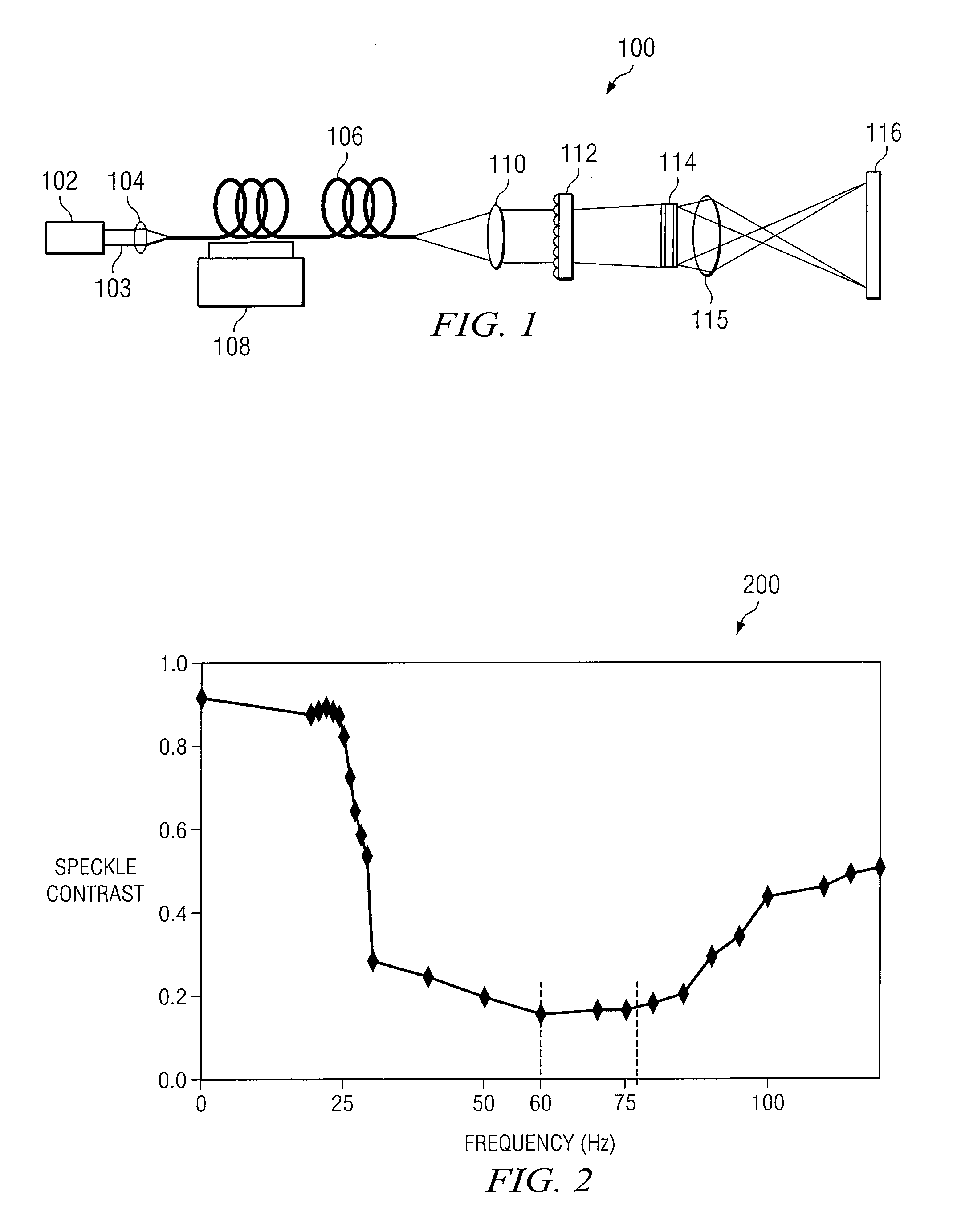
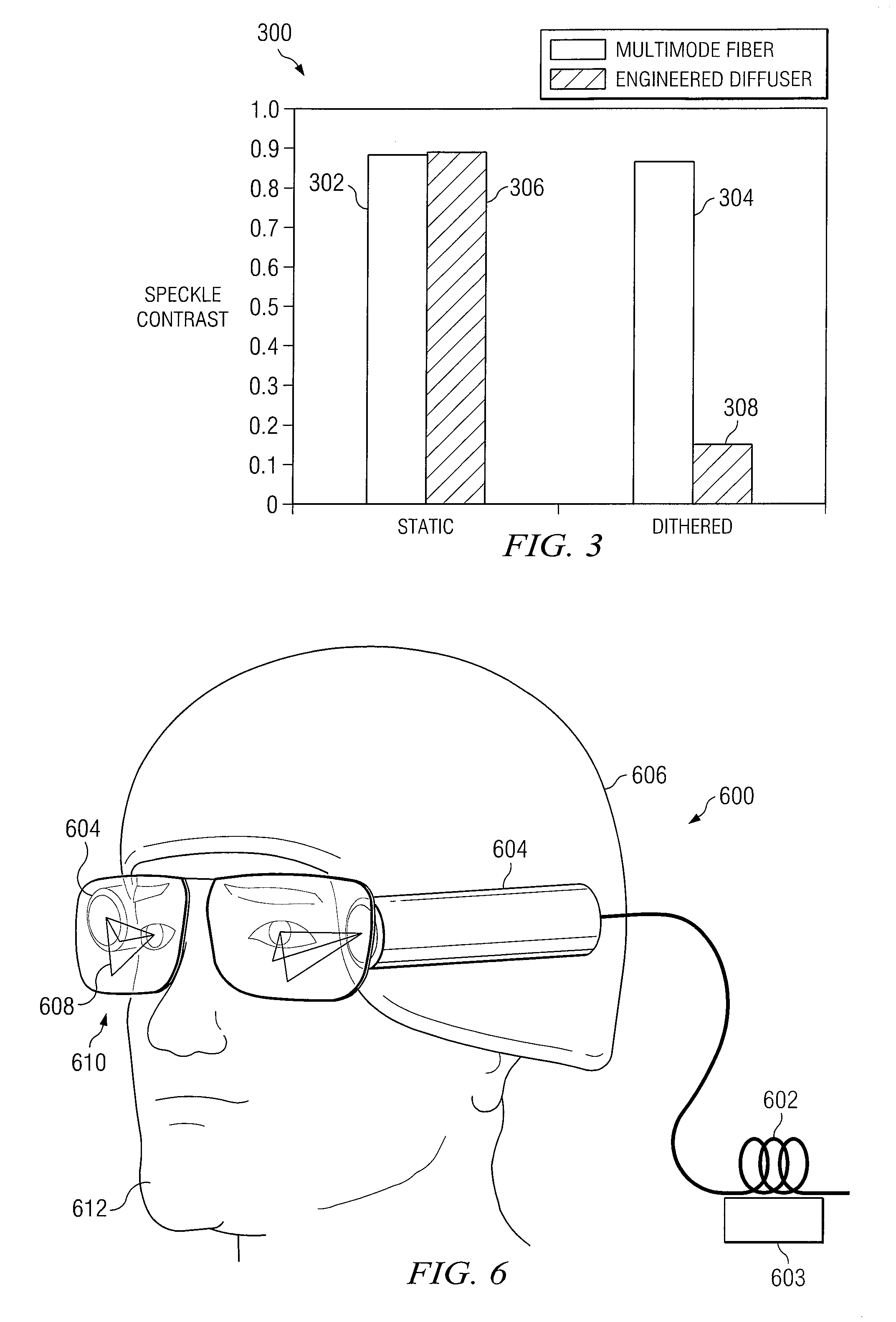
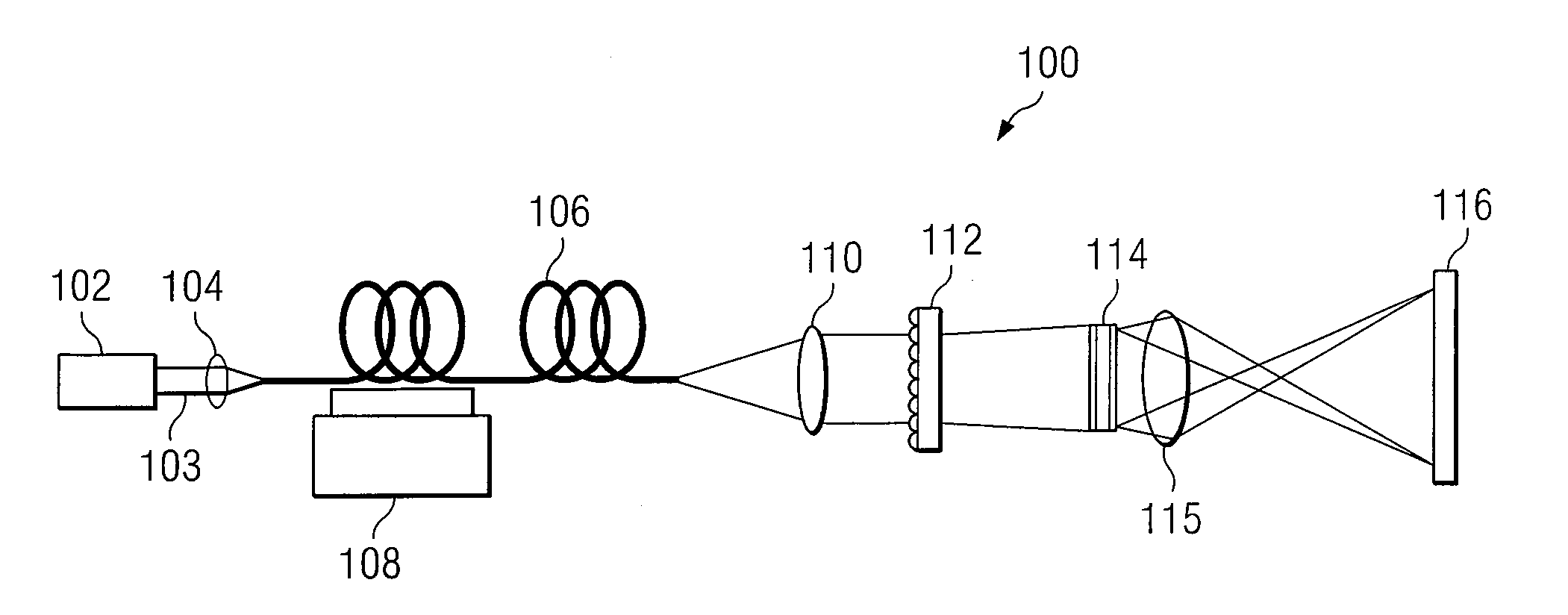
A method and system for reducing speckle in an image produced from a coherent source of radiation is provided. The method includes coupling a source beam received from a coherent optical source into an optical fiber. A position of at least a portion of the fiber may be modulated using a ditherer. The source beam may be refracted by a lens after it is decoupled from the optical fiber, such that the source beam is aimed at a microlens diffuser. In accordance with a particular embodiment, the source beam may be projected from the microlens diffuser onto a spatial modulator. The spatial modulator may be positioned to project the source beam via an imaging lens, to a target.
Owner:ELBIT SYSTEMS OF AMERICA LLC
System and Method for Despeckling an Image Illuminated by a Coherent Light Source
ActiveUS20100053729A1Speckle reductionIncrease contrastCladded optical fibreColor television detailsFiberLight beam
A method and system for reducing speckle in an image produced from a coherent source of radiation is provided. The method includes coupling a source beam received from a coherent optical source into an optical fiber. A position of at least a portion of the fiber may be modulated using a ditherer. The source beam may be refracted by a lens after it is decoupled from the optical fiber, such that the source beam is aimed at a microlens diffuser. In accordance with a particular embodiment, the source beam may be projected from the microlens diffuser onto a spatial modulator. The spatial modulator may be positioned to project the source beam via an imaging lens, to a target.
Owner:ELBIT SYSTEMS OF AMERICA LLC
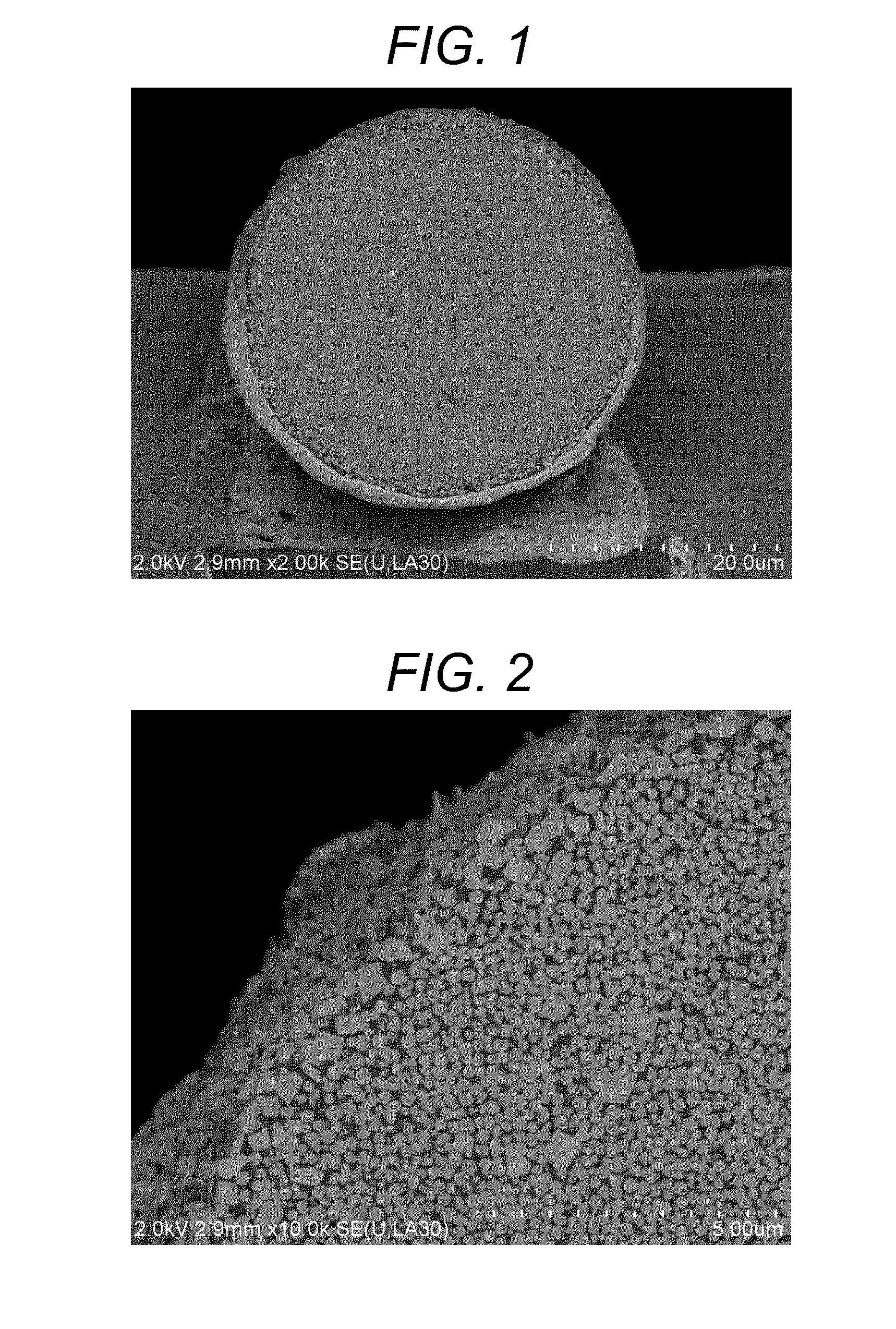
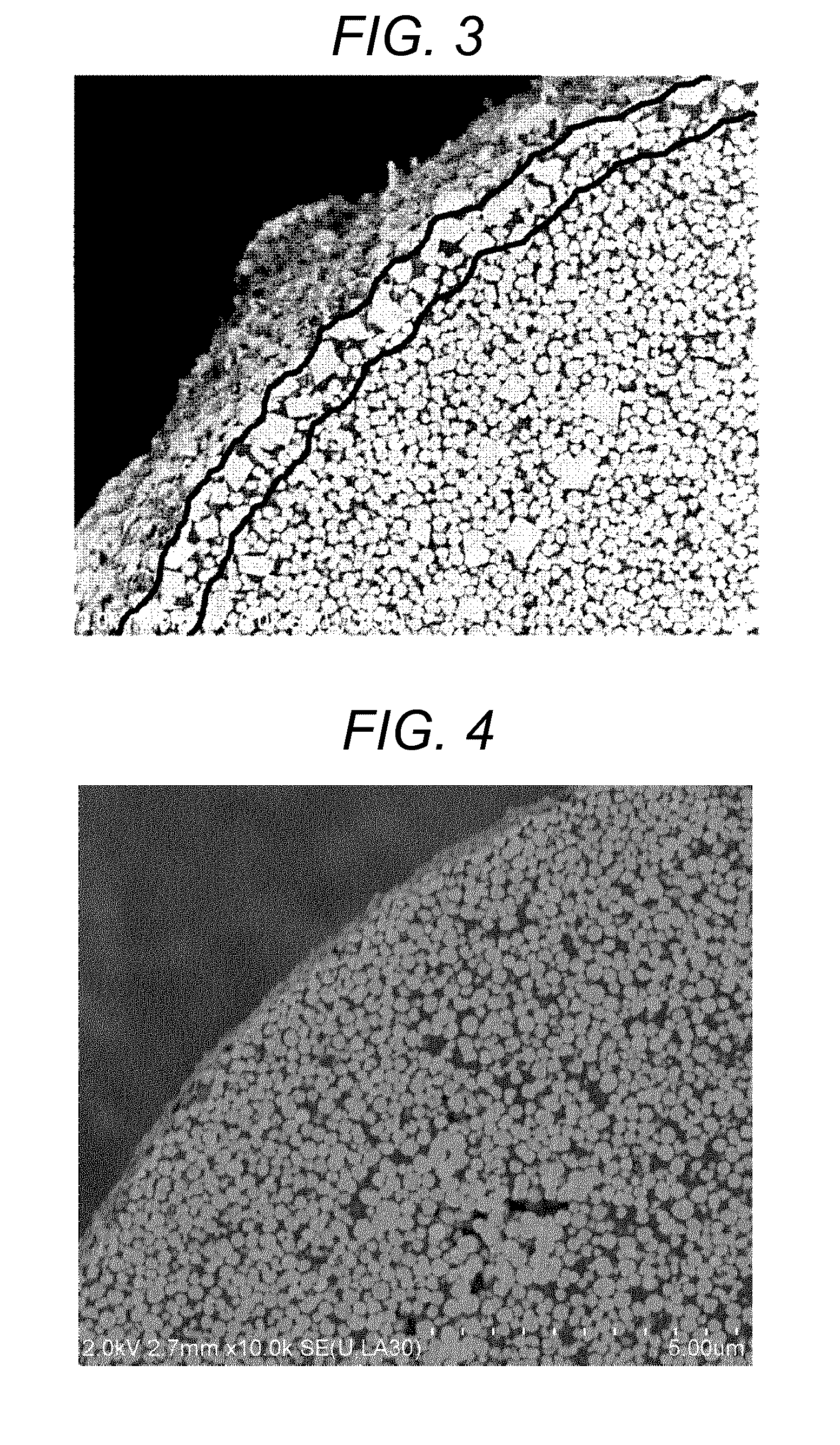
Magnetic carrier and two-component developer
InactiveUS20140134535A1Suppressing white spotsSatisfactory imageDevelopersScanning electron microscopeEngineering
Provided is a magnetic carrier satisfying leakage, white spots, charging property and high developing performance in a low electric field and having excellent durability. The magnetic carrier is a magnetic carrier comprising a magnetic substance-dispersed resin carrier core containing a magnetic substance and a binder resin, and a coating resin on a surface thereof, wherein the magnetic substance comprises a magnetic substance A having a shape without vertexes and a magnetic substance B having a shape with vertexes, the magnetic substance B has a number average particle diameter of 0.40-2.00 μm, and in a reflection electron image of a section of the magnetic substance-dispersed resin carrier core taken by a scanning electron microscope, an area proportion of the magnetic substance B is larger than an area proportion of the magnetic substance A within a region from the surface of the magnetic substance-dispersed resin carrier core to a depth of 1.0 μm.
Owner:CANON KK
Histone deacelylase inhibitors in diagnosis and treatment of thyroid neoplasms
InactiveUS20040132643A1Increase count rateAdequate imagingBiocideRadioactive preparation carriersLymphatic SpreadRadioactive iodine therapy
Disclosed herein are novel approaches to thyroid cancer therapy. These approaches include methods to enhance thyroid specific gene expression, for example methods to enhance expression of thyroglobulin and / or the Na<+> / I<-> symporter in thyroid cancer cells. Enhanced expression of thyroid-specific genes promotes cellular differentiation and reduces biologically aggressive behavior such as invasion and metastasis. In addition, enhanced expression of thyroglobulin and / or the Na<+> / I<31 > symporter increases the ability of thyroid cancer cells to concentrate iodine or iodide, thereby making the cells more susceptible to radioactive iodine therapy. Also disclosed herein are methods for detecting thyroid neoplasms in a subject, by administering a therapeutically effective amount of a histone deacetylase inhibitor, administering a detectable agent whose uptake or concentration in thyroid cells is increased by administration of the histone deacetylase inhibitor, and detecting the detectable agent.
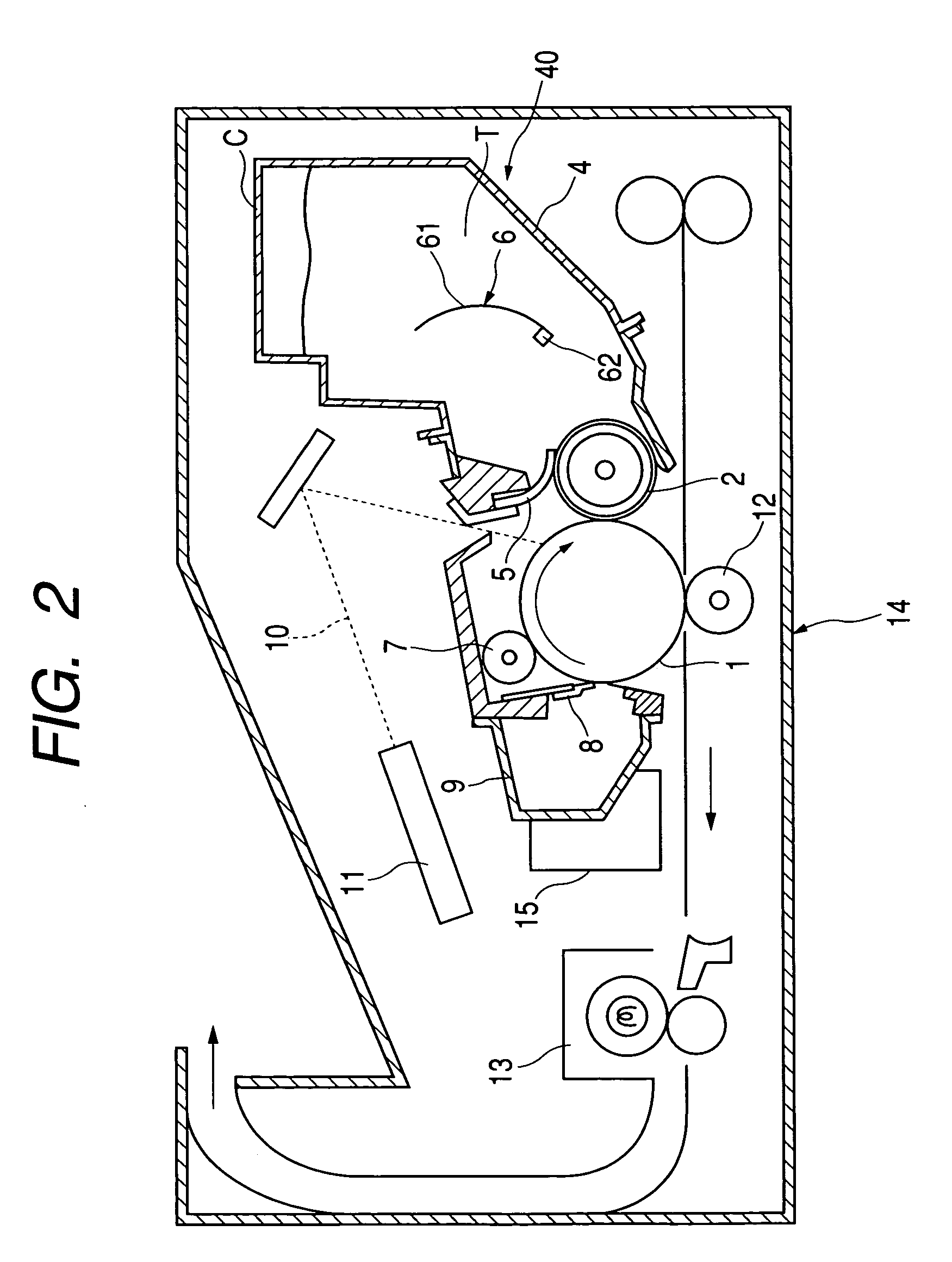
Image-sensing apparatus
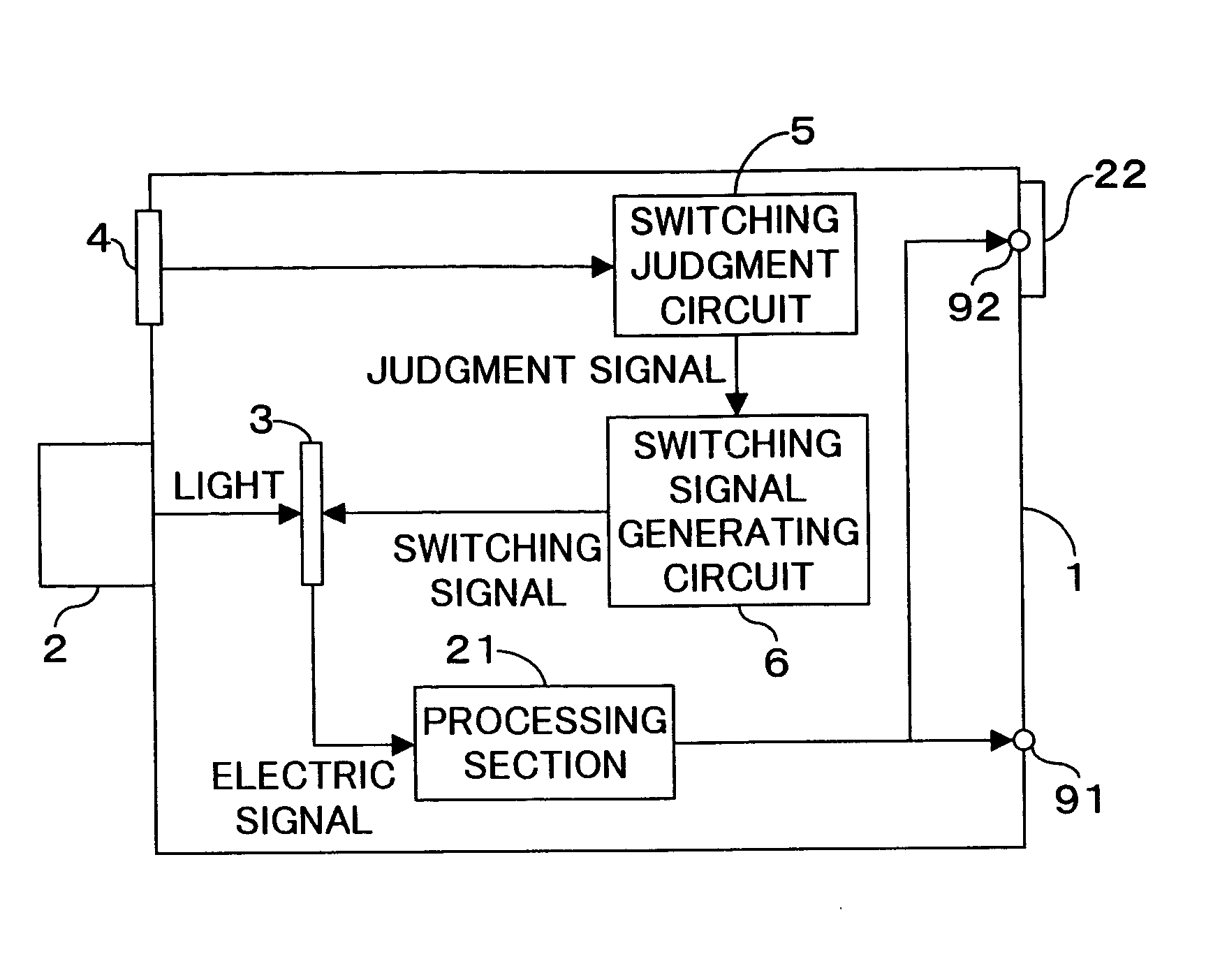
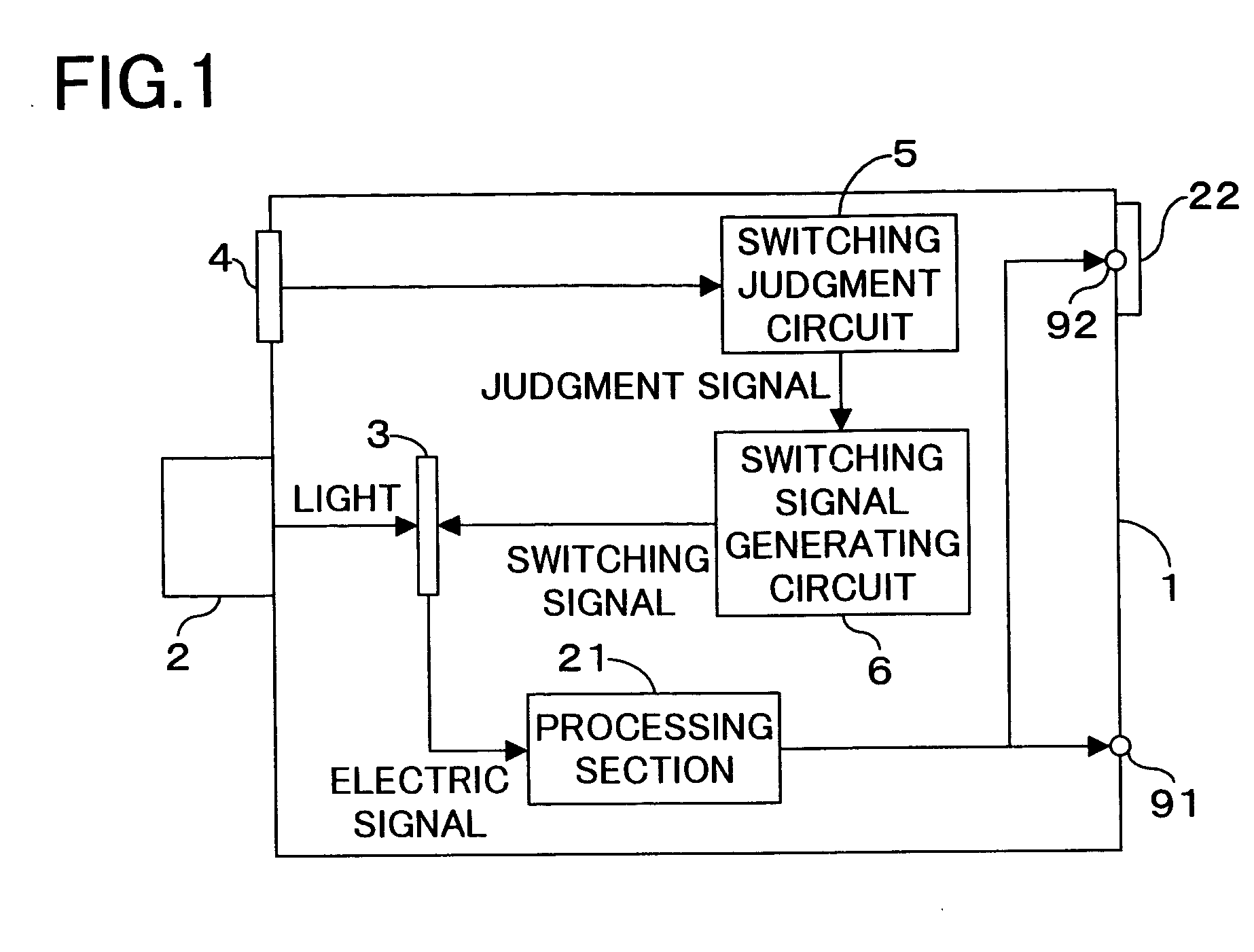
ActiveUS20050052557A1High quality imagingSatisfactory imageTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsSwitching signalEngineering
When the brightness of a subject detected by a detecting device 4 is higher than a predetermined value, for example 700 [cd / m2], a switching judgment circuit 5 judges that an area sensor (solid-state image-sensing device) 3 should perform logarithmic conversion. In response to this judgment by the switching judgment circuit 5, a switching signal generating circuit 6 outputs a switching signal to instruct the area sensor 3 to perform logarithmic conversion. When the brightness of the subject detected by the detecting device 4 is lower than the predetermined value, for example 700 [cd / m2], a switching judgment circuit 5 judges that the area sensor 3 should perform linear conversion. In response to this judgment by the switching judgment circuit 5, the switching signal generating circuit 6 outputs a switching signal to instruct the area sensor 3 to perform linear conversion.
Owner:SONY SEMICON SOLUTIONS CORP
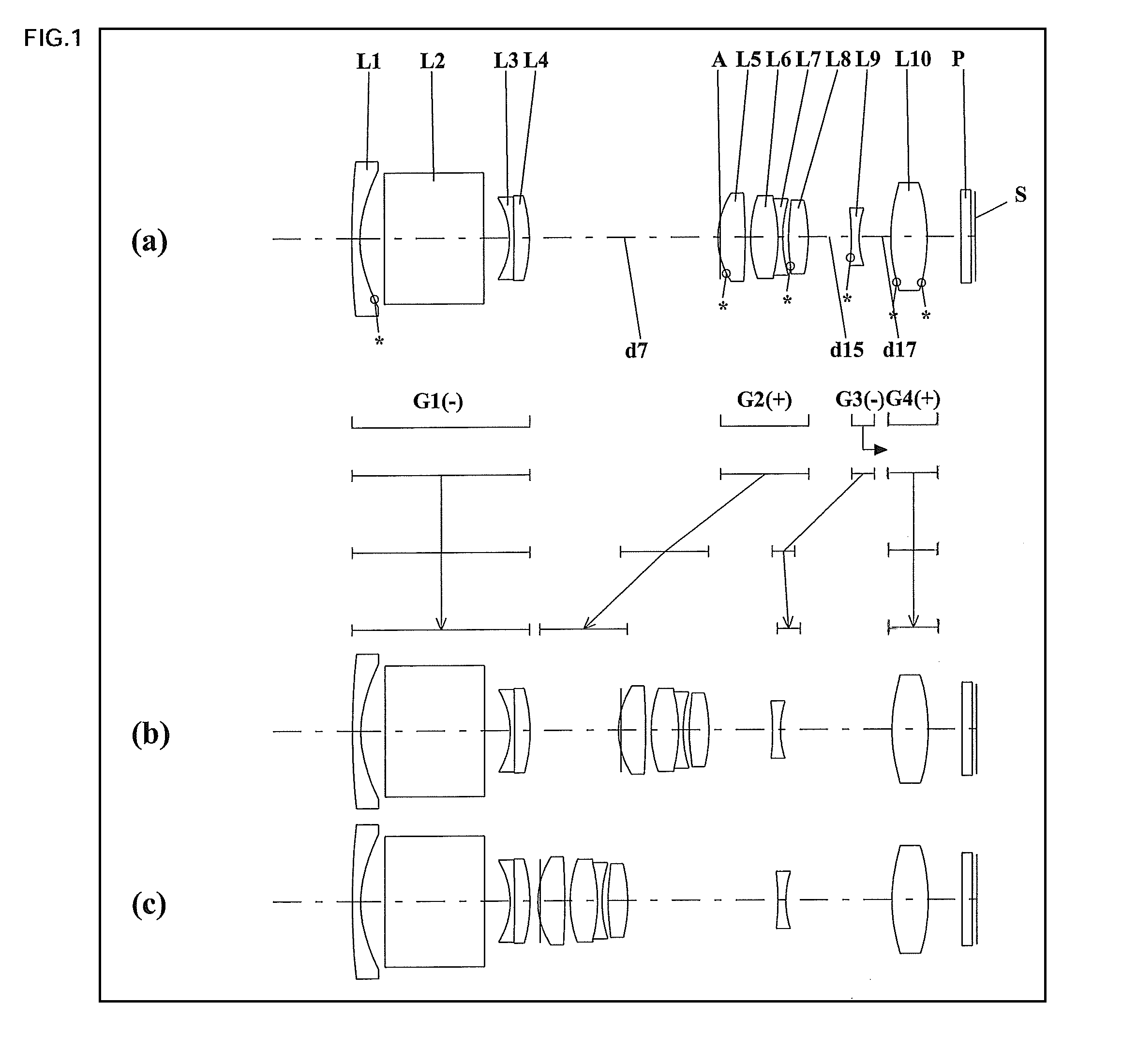
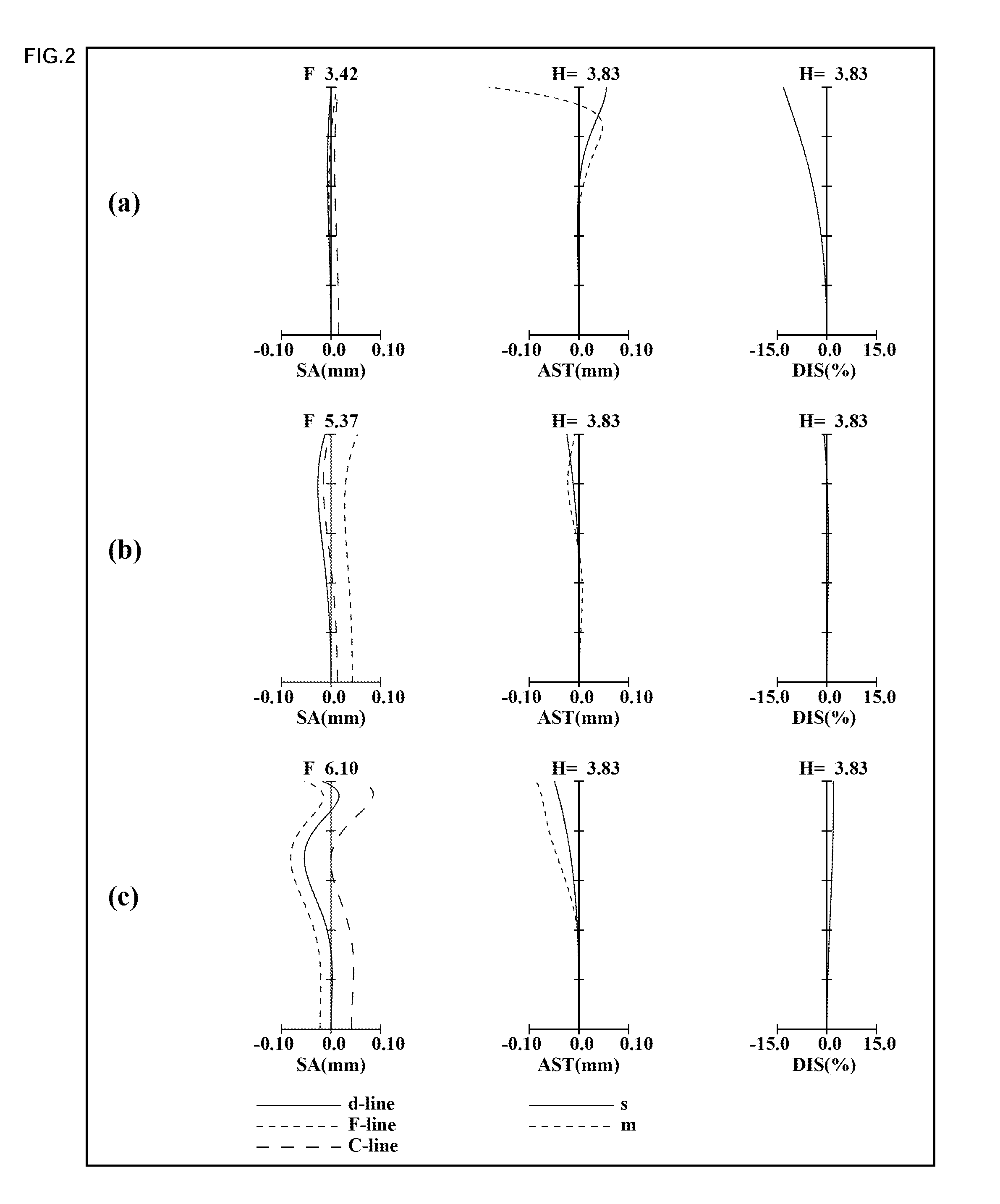
Zoom lens system, imaging device and camera
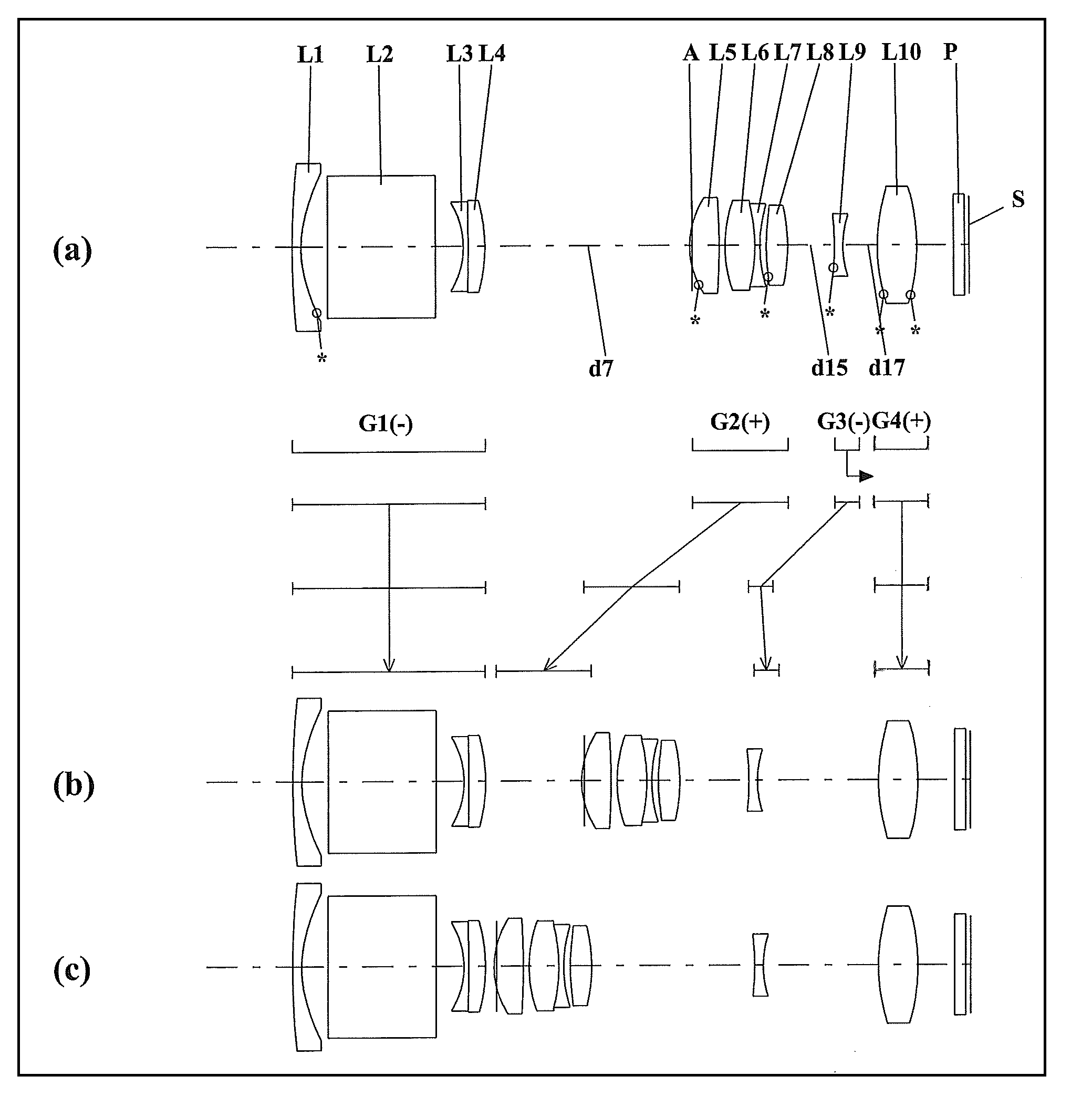
A zoom lens system, in order from an object side to an image side, comprising a first lens unit having negative optical power, a second lens unit having positive optical power, and at least one subsequent lens unit having optical power, wherein in zooming from a wide-angle limit to a telephoto limit, the lens units are moved along an optical axis such that an air space between at least any two lens units among the lens units should vary, so that variable magnification is achieved, wherein the first lens unit includes a lens element having a reflecting surface for bending a light beam incident from the object, and wherein the condition is satisfied: 0.20<|fG1| / fT<0.52 (fT / fW≧4.0, fG1 is a composite focal length of the first lens unit, and each of fT and fW is a focal length of the entire system at a telephoto limit or a wide-angle limit), an imaging device and a camera are provided.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Image forming apparatus provided with a plurality of image holding components
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
Method of manufacturing an electronic device containing a carbon nanotube
InactiveUS6979244B2Improve directivityImprove performanceMaterial nanotechnologyNanoinformaticsCarbon nanotubeElectron
A method of manufacturing an electronic device in which a substrate with a pair of electrodes is provided and a carbon nanotube is formed or arranged to electrically connect the electrodes.
Owner:CANON KK
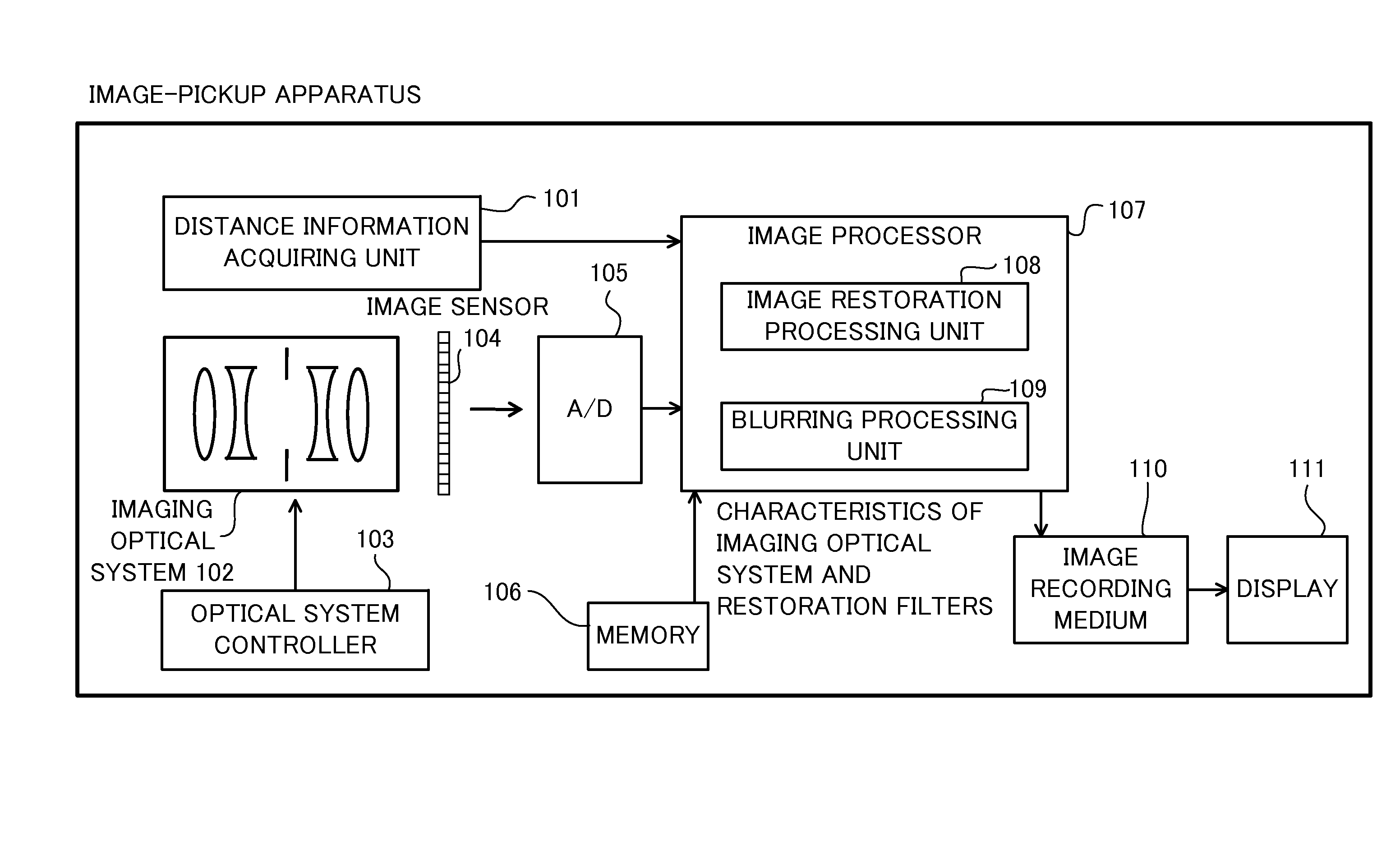
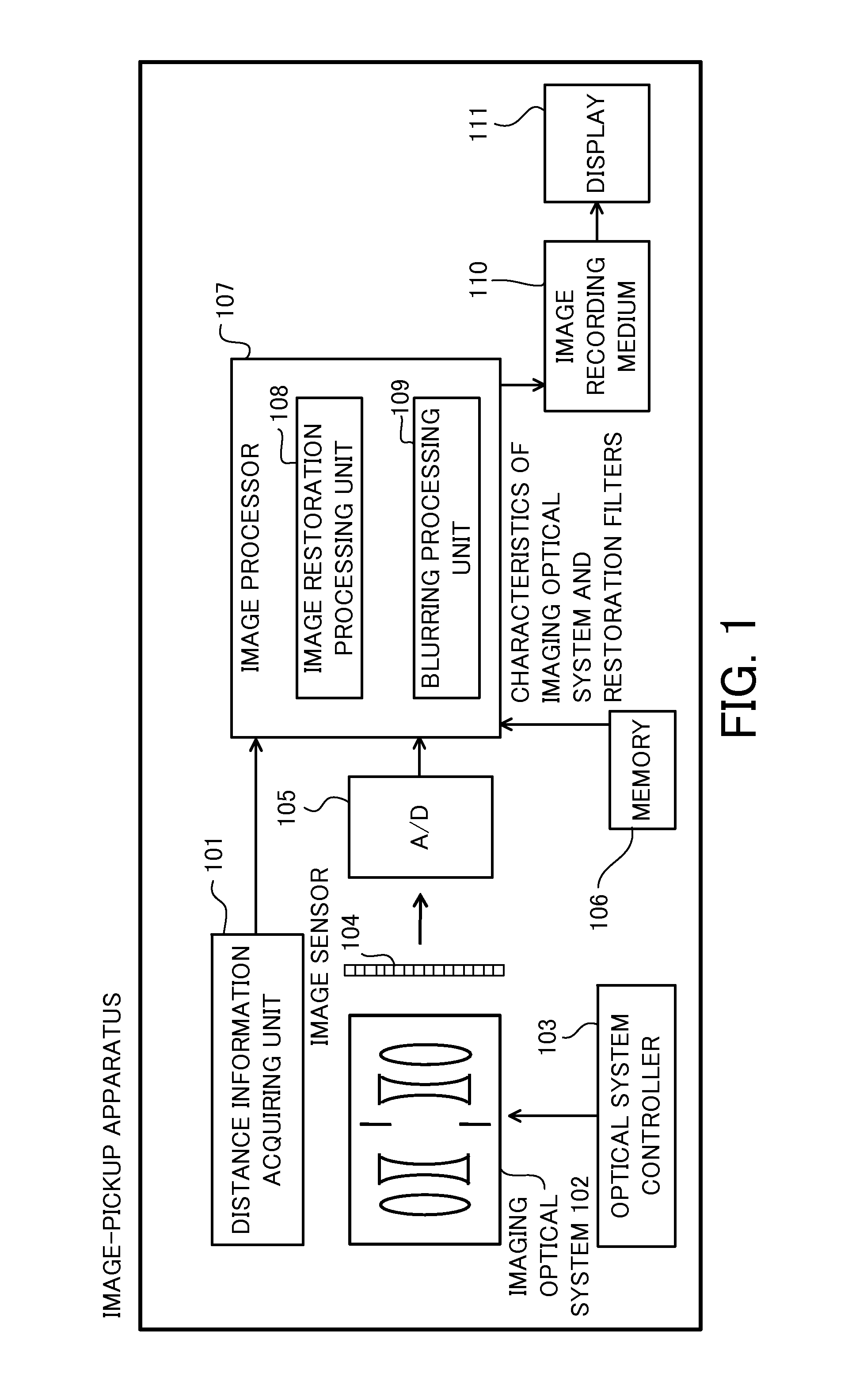
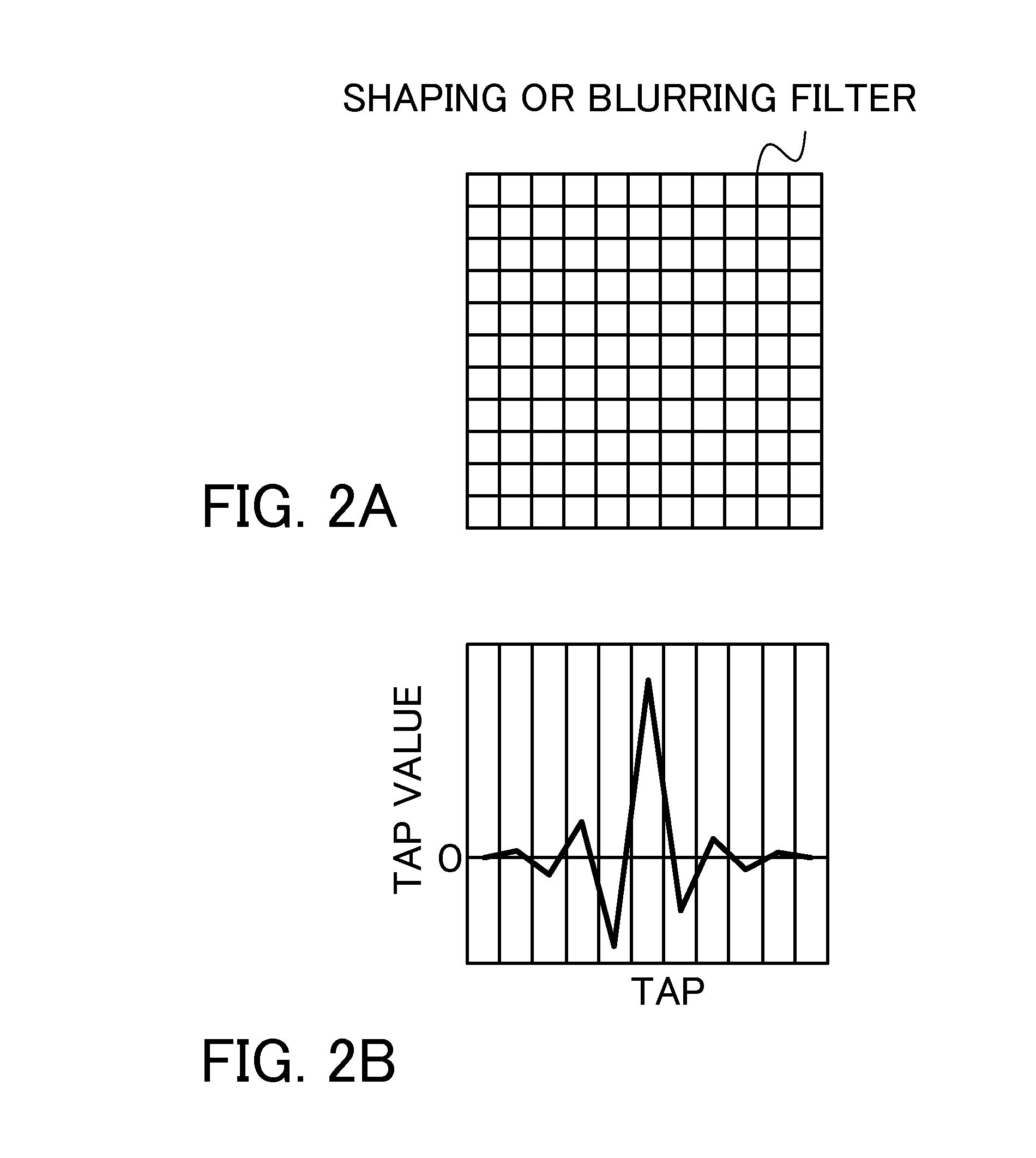
Image processing method, image processing apparatus, non-transitory computer-readable medium, and image-pickup apparatus
ActiveUS20140218557A1Generate imageSatisfactory imageTelevision system detailsColor television detailsImaging processingImage segmentation
A non-transitory computer-readable medium for storing an image processing program configured to enable a computer to execute a shaping step of shaping an input image generated through capturing via an optical system by using a characteristic of the optical system and an image-pickup condition, a blurring step of blurring an image shaped in the shaping step, and a dividing step of dividing the input image into a plurality or layered images according to an object distance. The computer executes the shaping step based upon distance information of an object contained in each layered image.
Owner:CANON KK
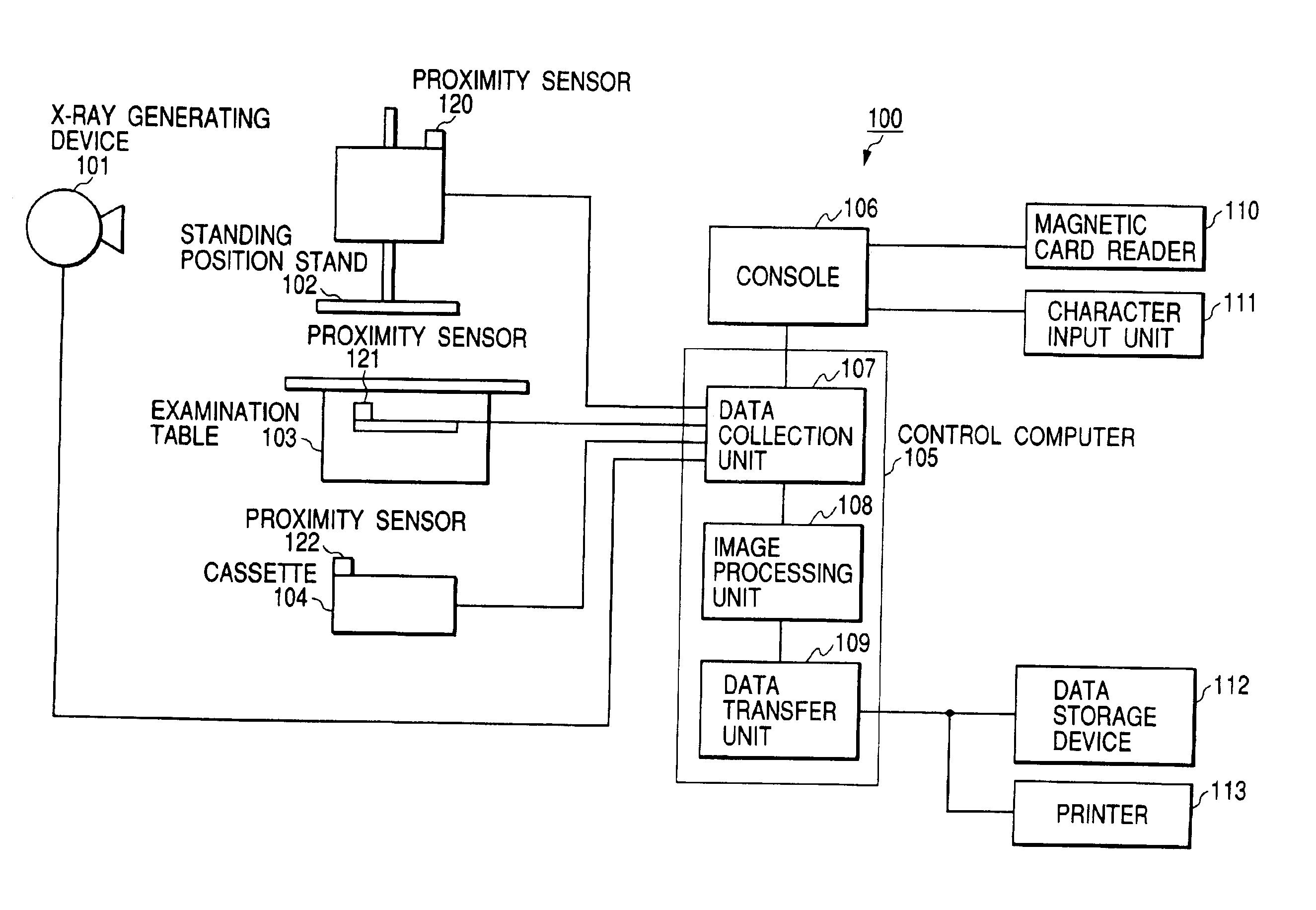
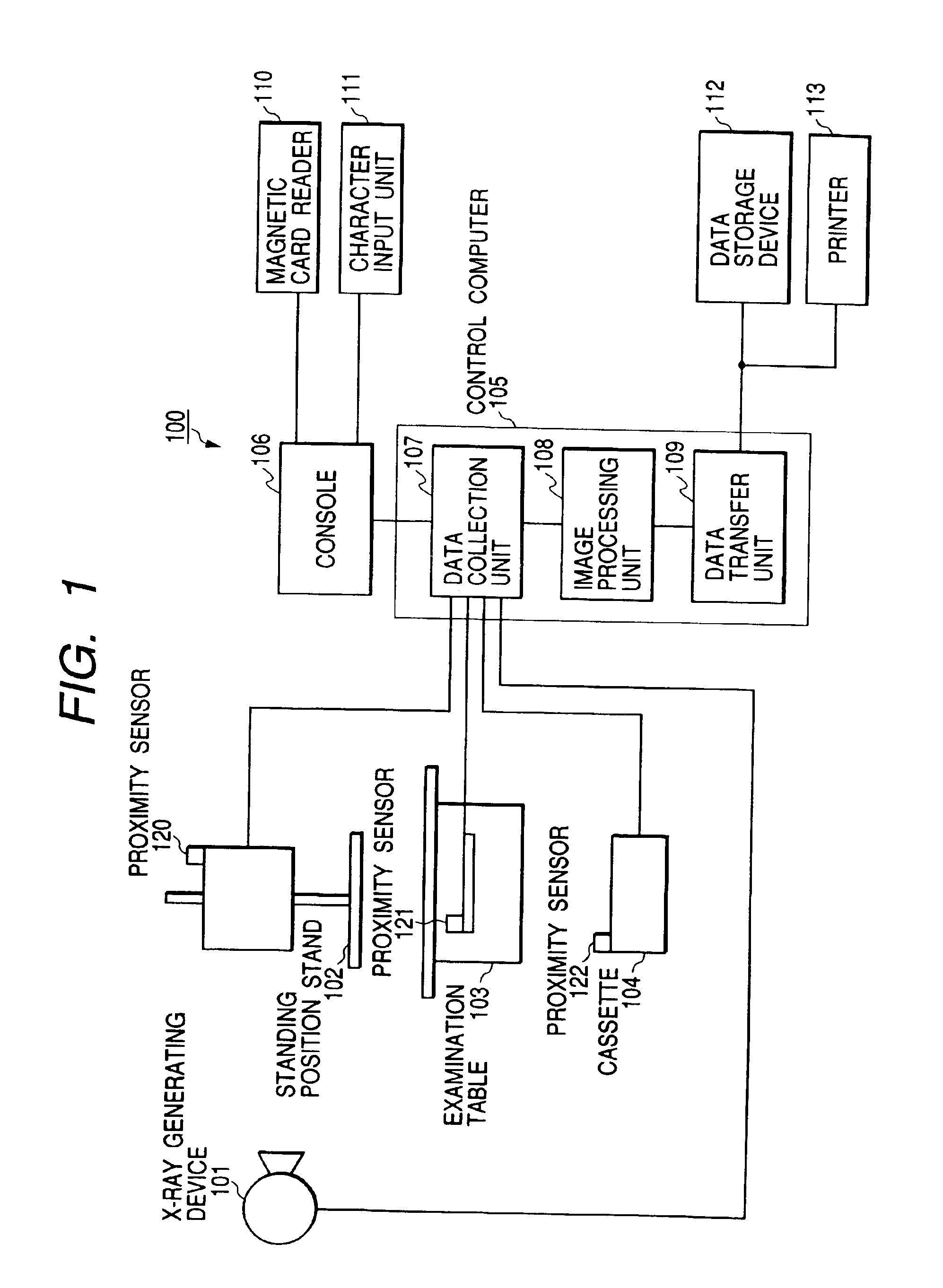
X-ray flat panel detector
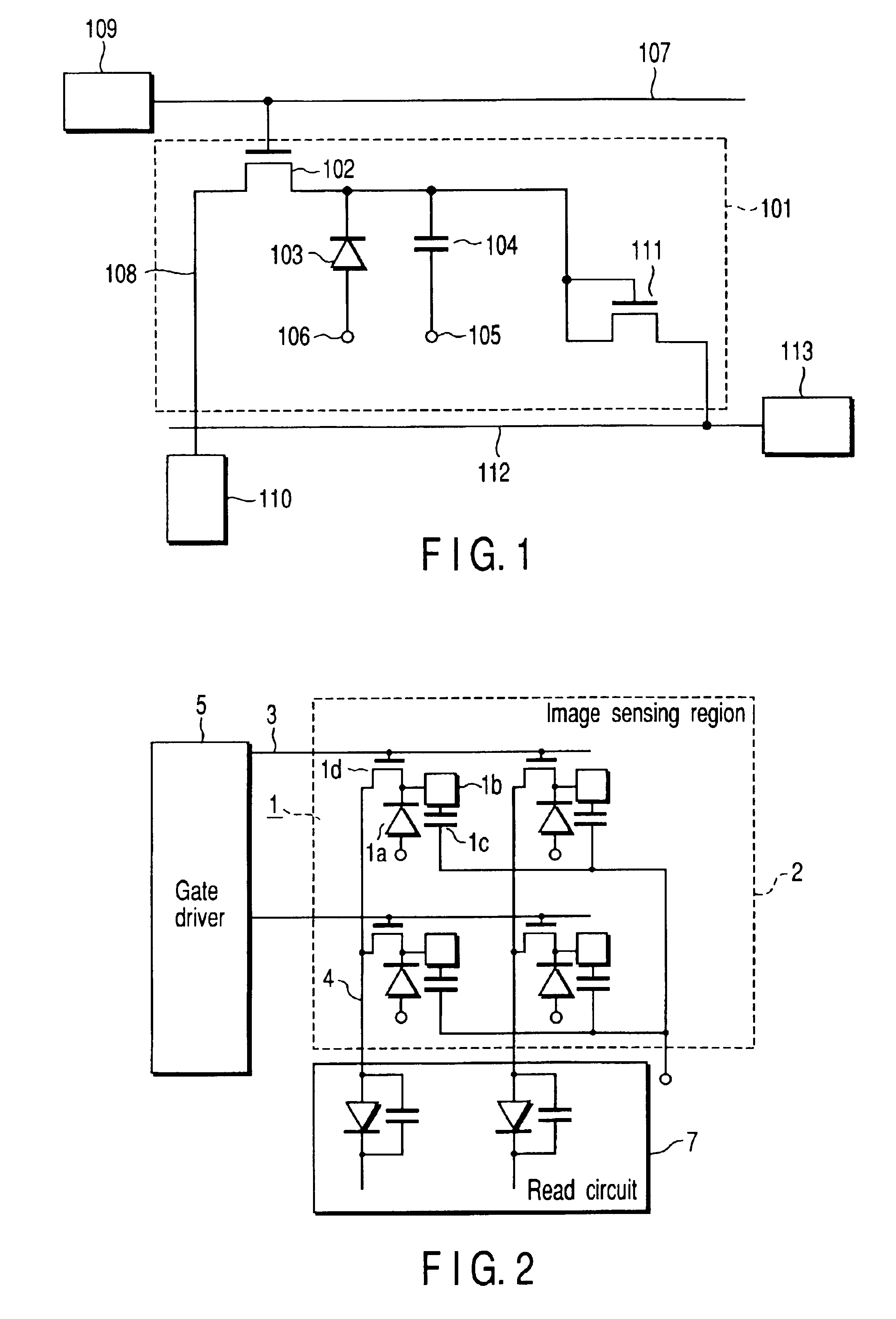
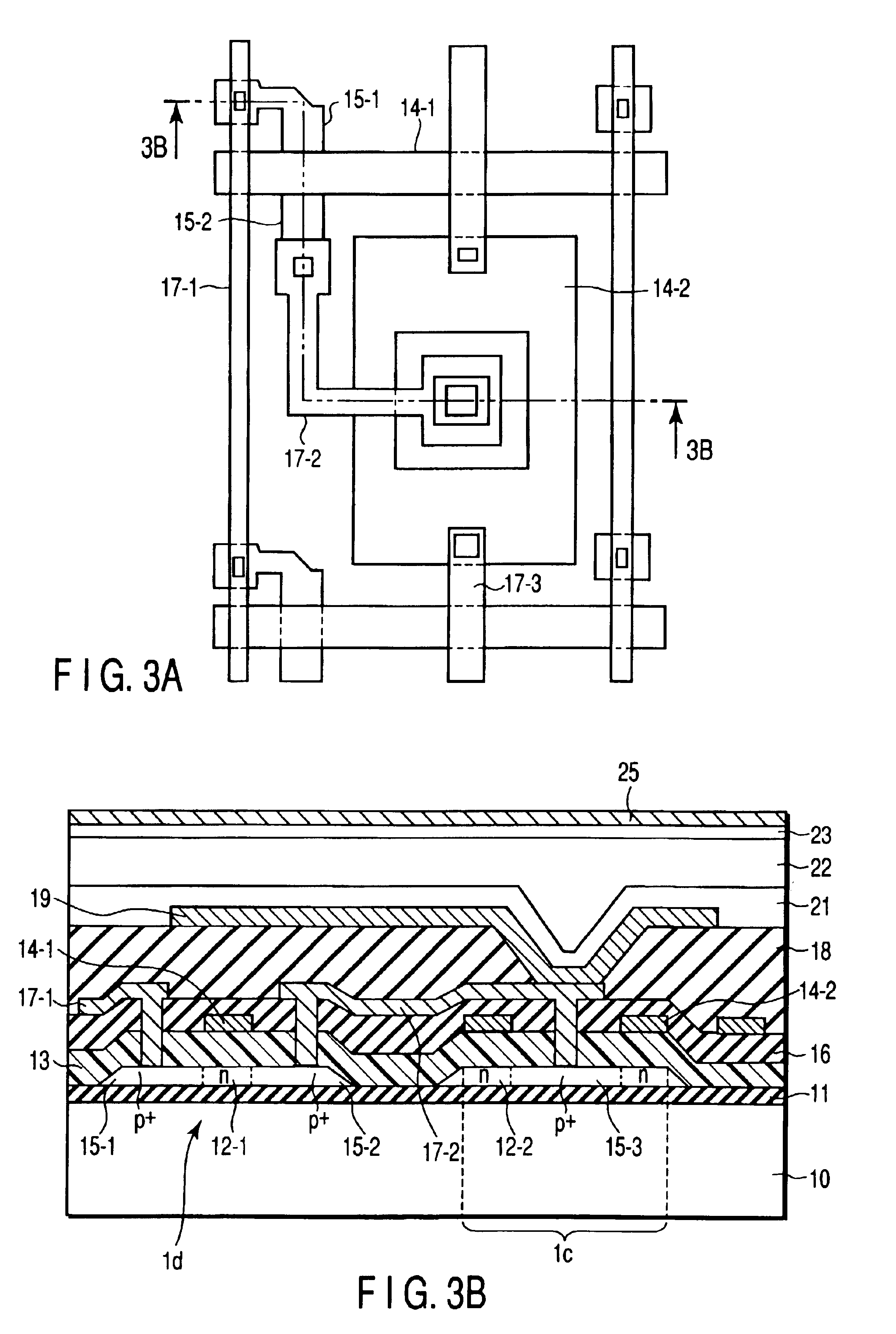
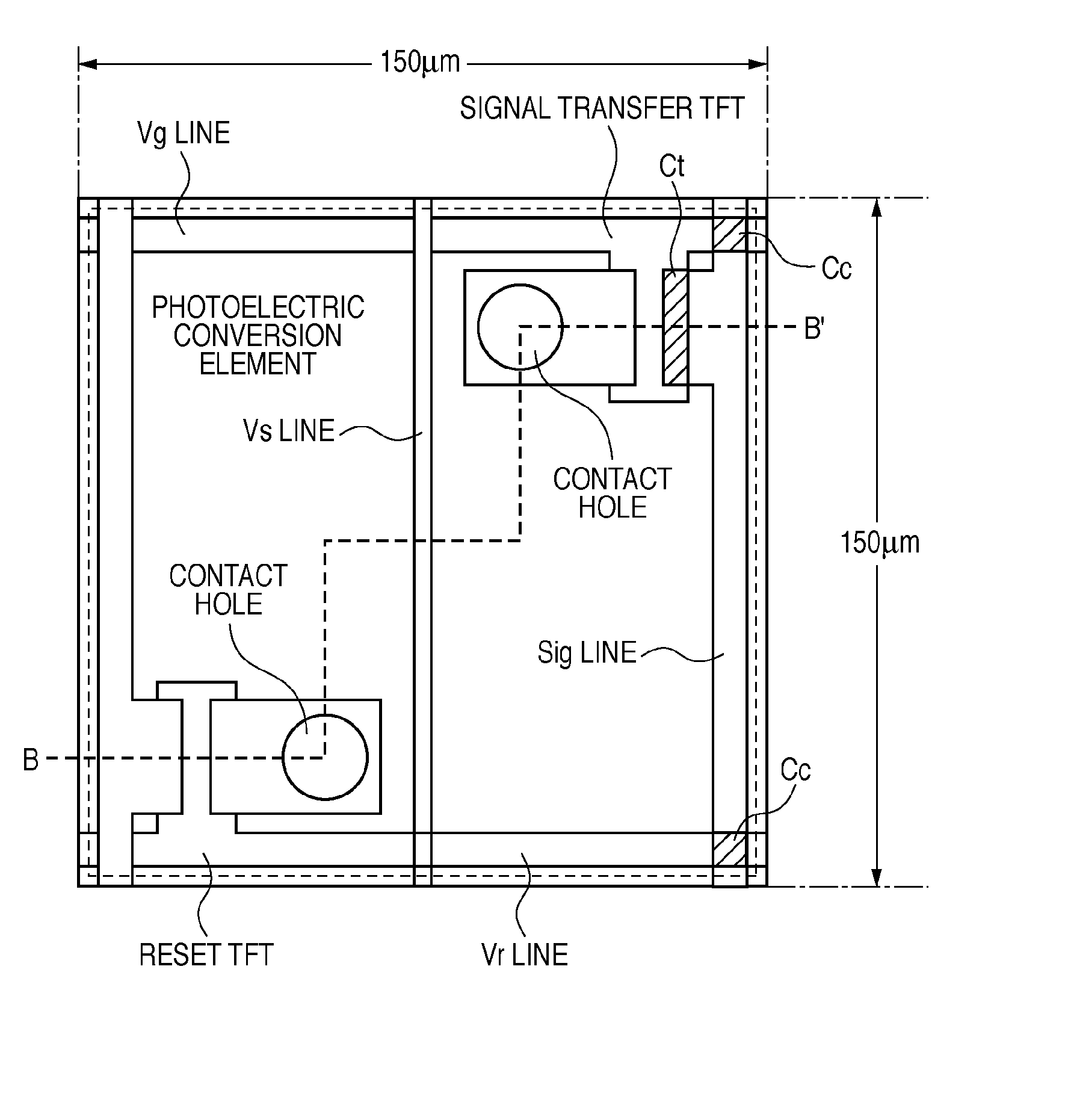
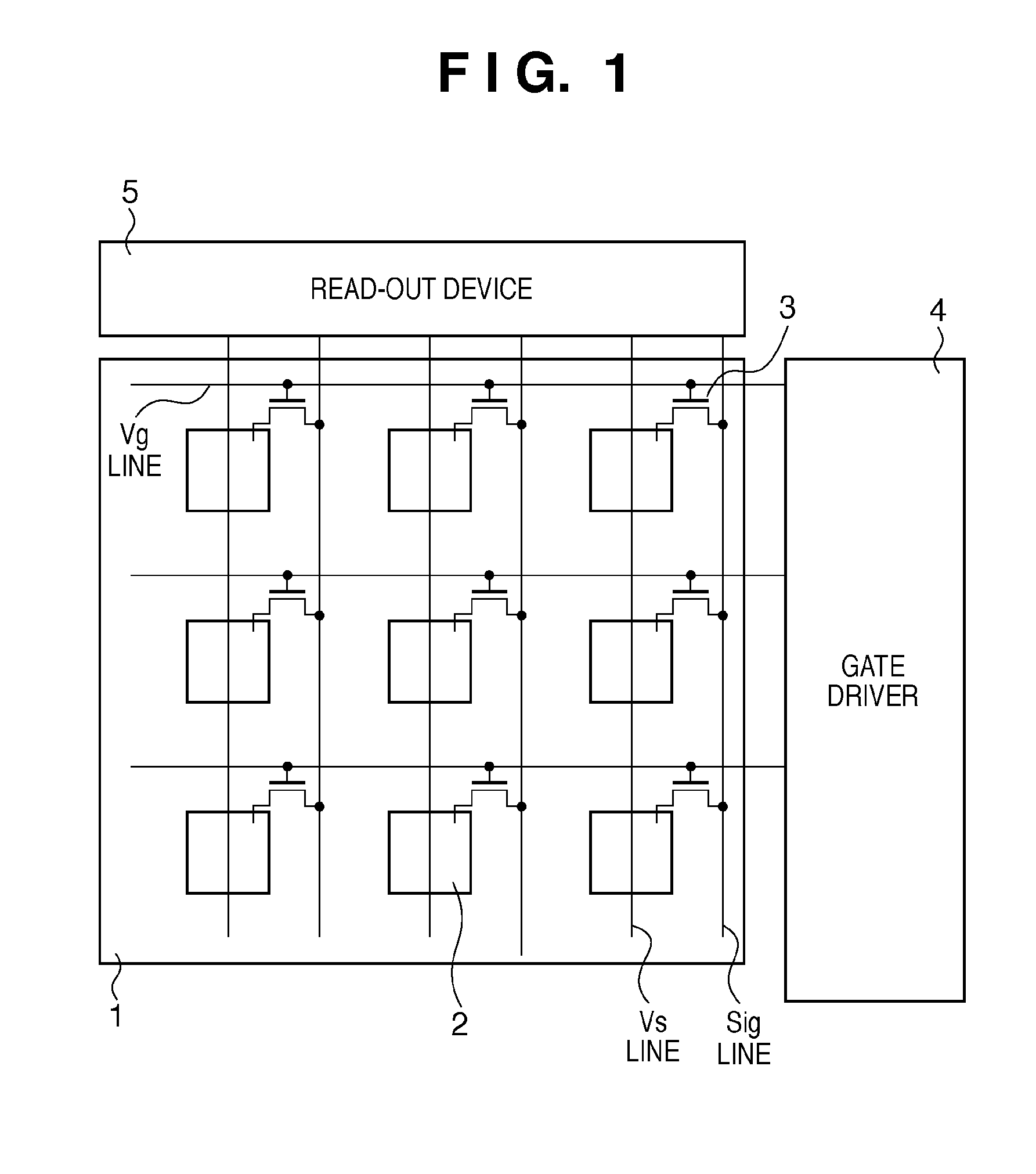
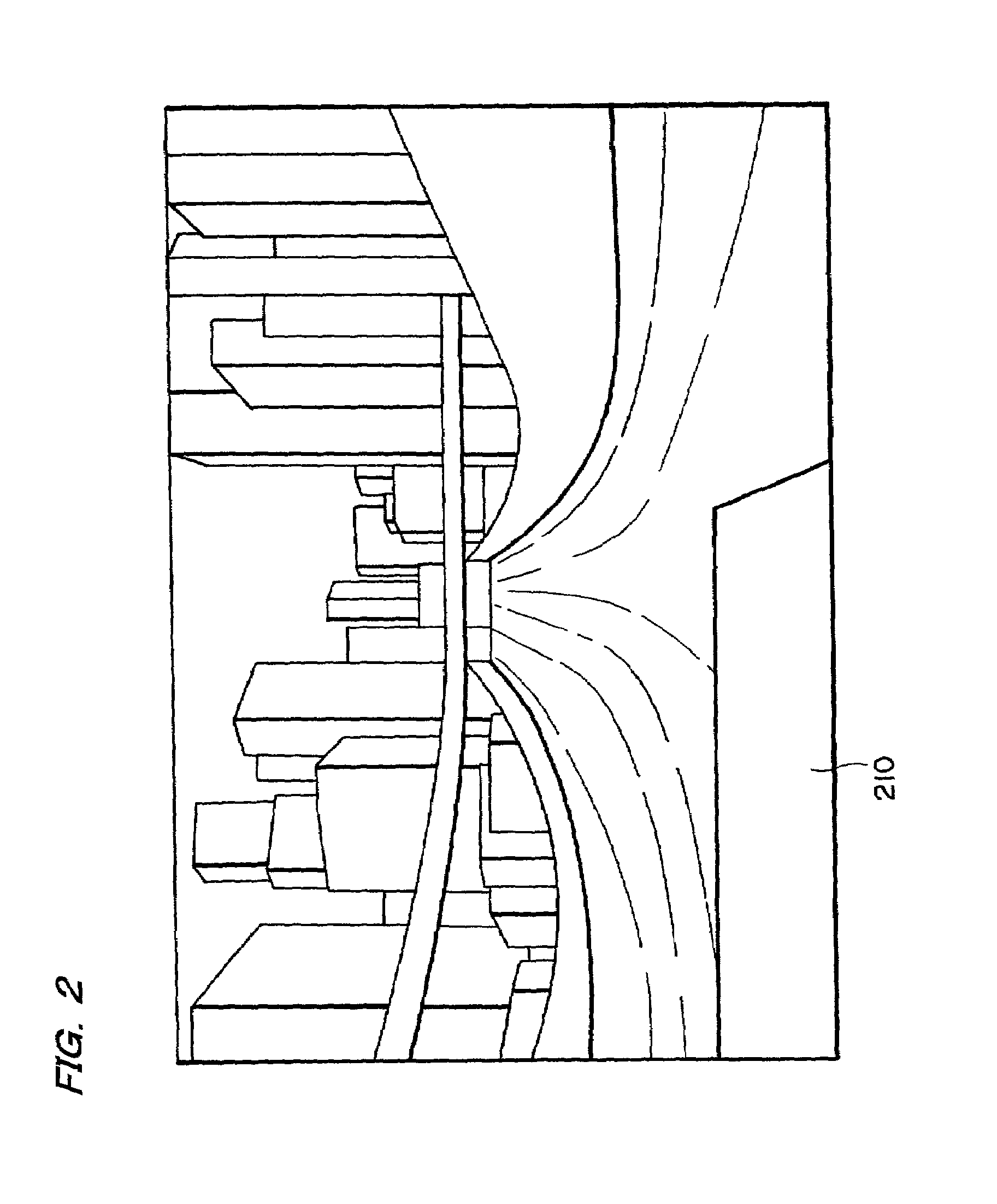
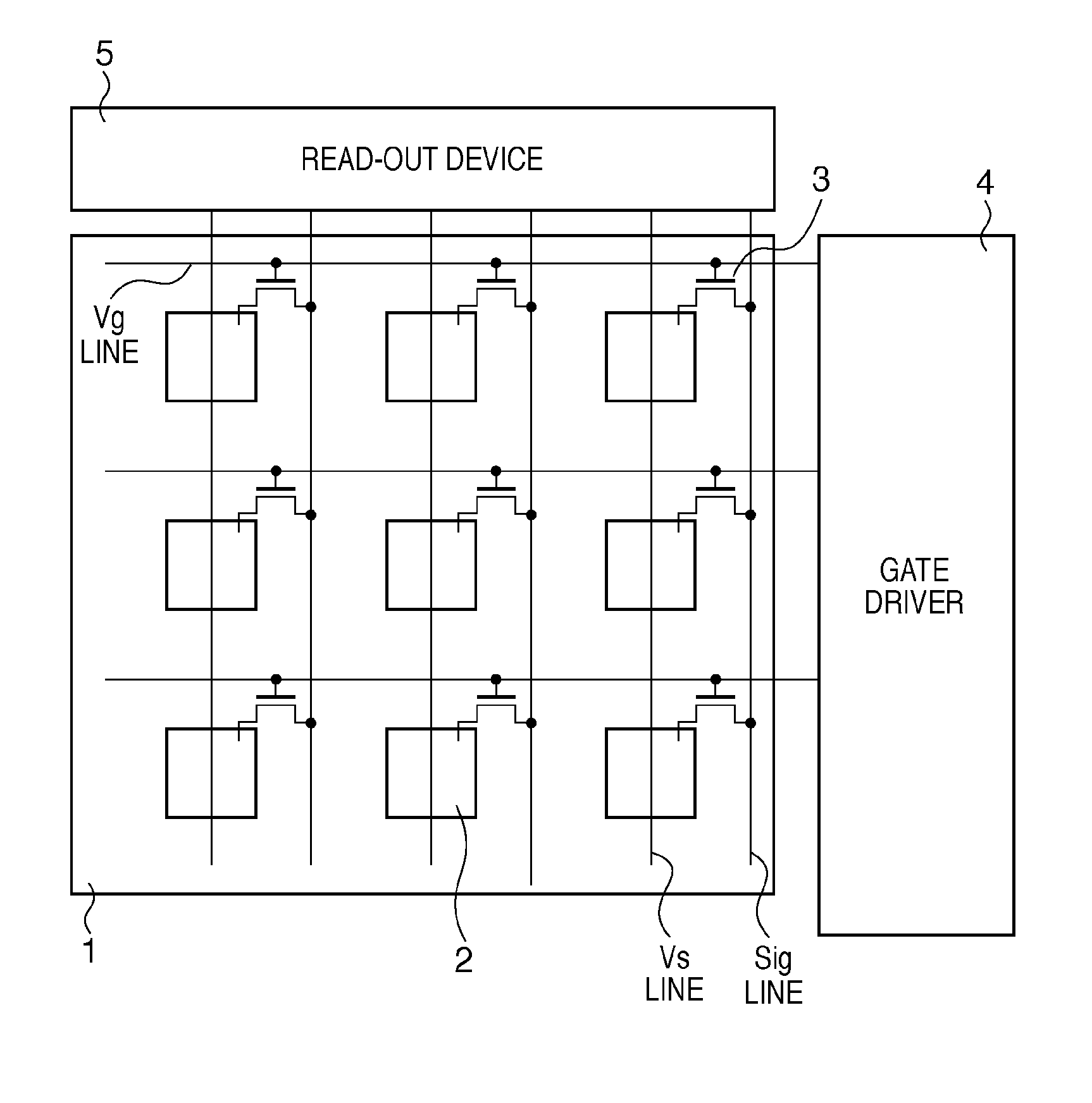
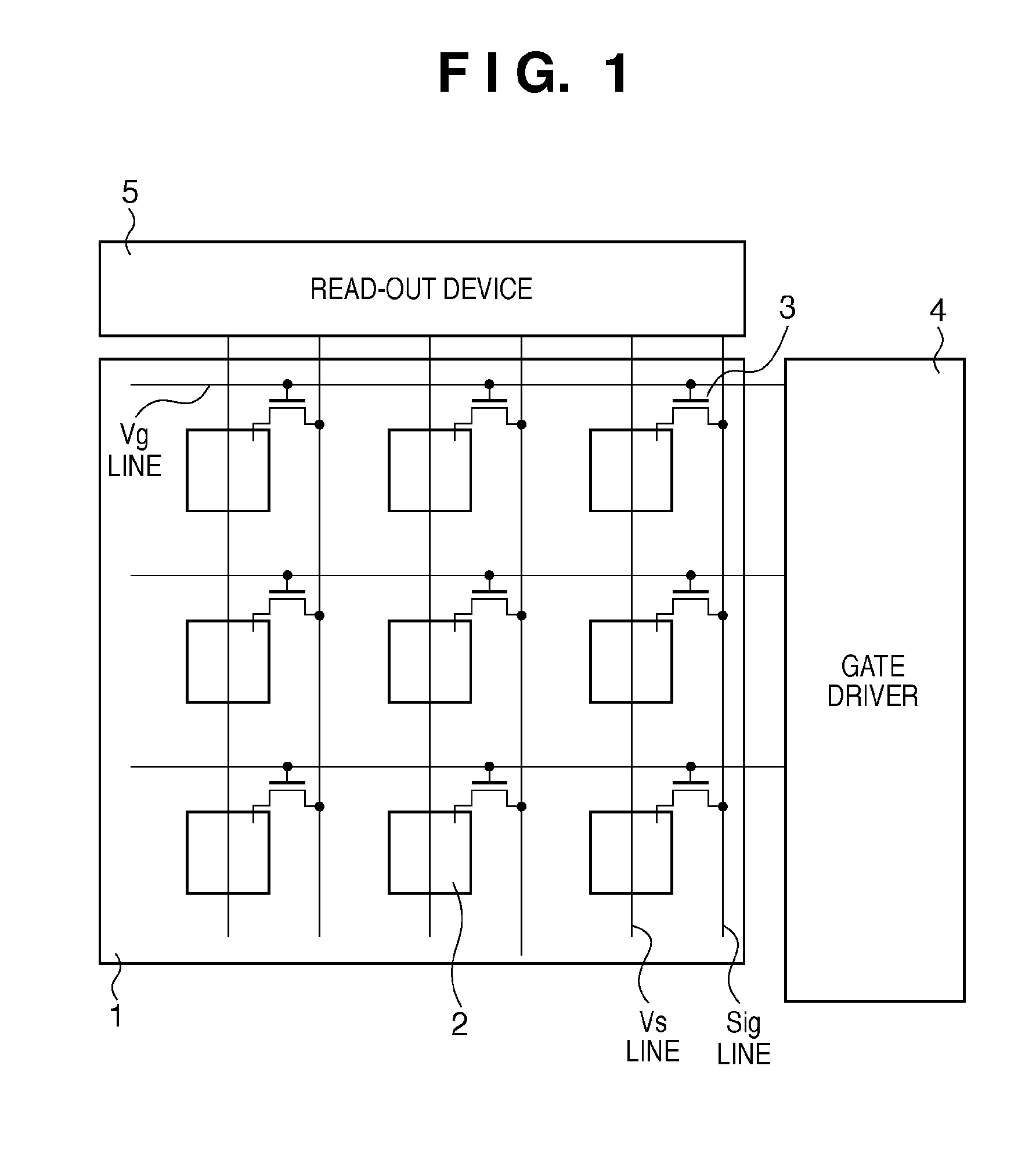
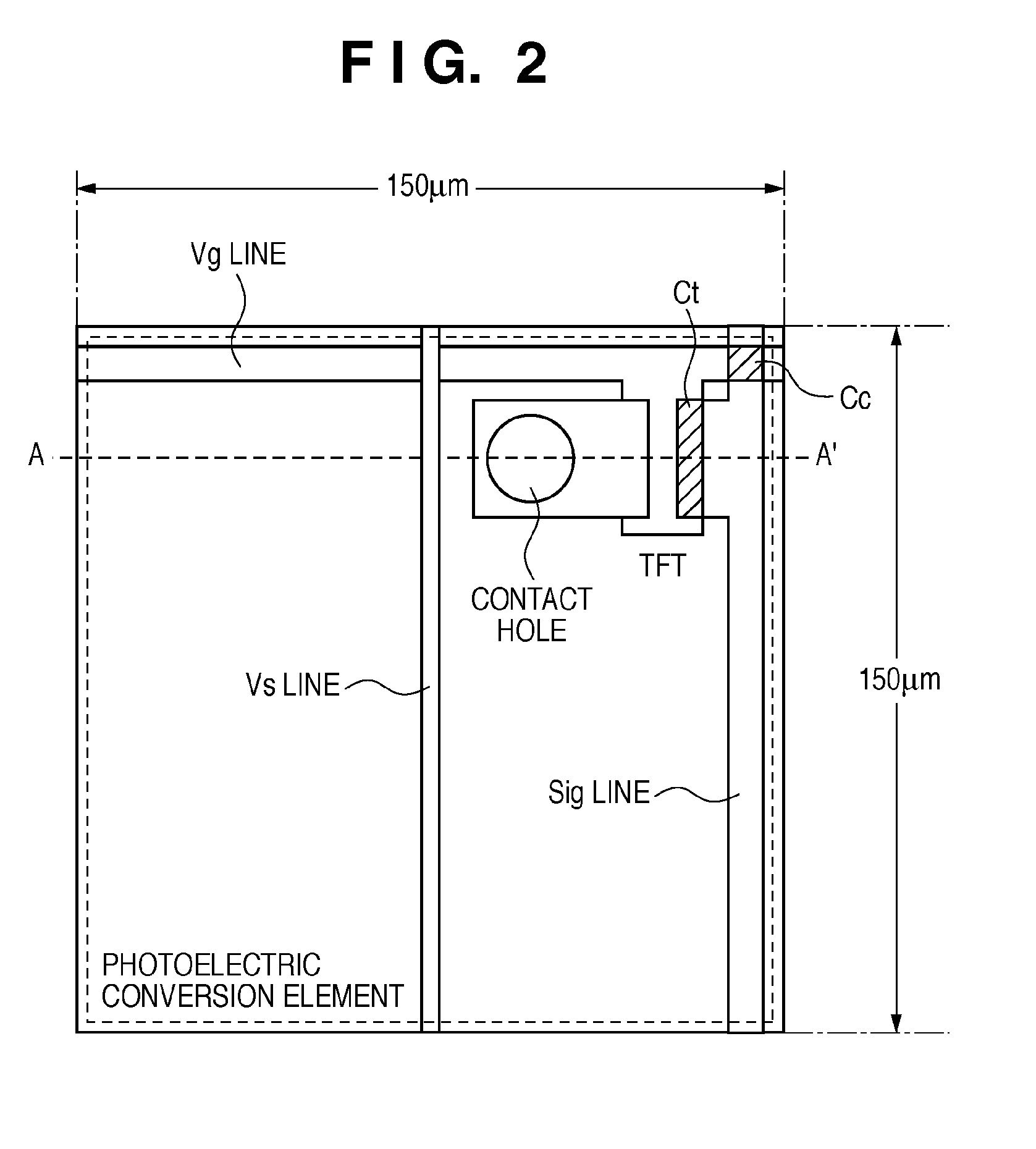
InactiveUS6849853B2Increase in numberSatisfactory imagePhotometry using reference valueSolid-state devicesPhysicsSoft x ray
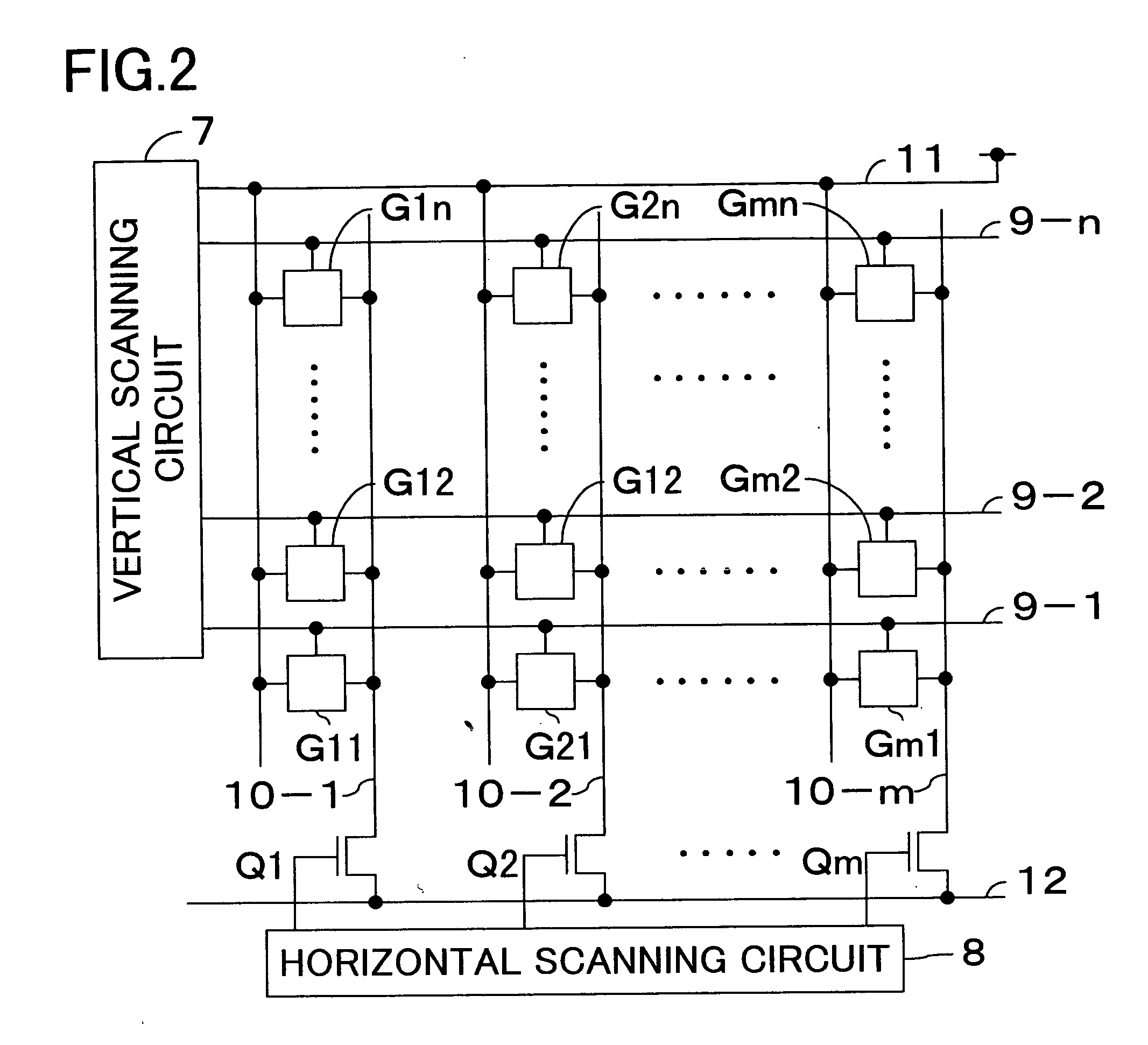
An X-ray flat panel detector includes an X-ray photosensitive film which generates signal charges upon being exposed to incident X-rays, pixel electrodes which are arrayed in contact with the X-ray photosensitive film, a bias voltage application unit which applies a bias voltage to the X-ray photosensitive film so as to make the pixel electrodes collect holes or electrons, which serve as the signal charges generated by the X-ray photosensitive film and have a higher mobility, capacitors which are arranged in correspondence with the pixel electrodes and store the charges generated by the X-ray photosensitive film, switching thin-film transistors which are arranged in correspondence with the pixel electrodes and read the charges in the capacitors, scanning lines which supply a control signal to OPEN / CLOSE-control the switching thin-film transistors, and signal lines which are connected to the switching thin-film transistors to read the charges when the switching thin-film transistors are opened.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Radiation detection apparatus and radiographic imaging system
ActiveUS8368027B2Reduce unevennessSatisfactory imageSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansDielectricCapacitance
Owner:CANON KK
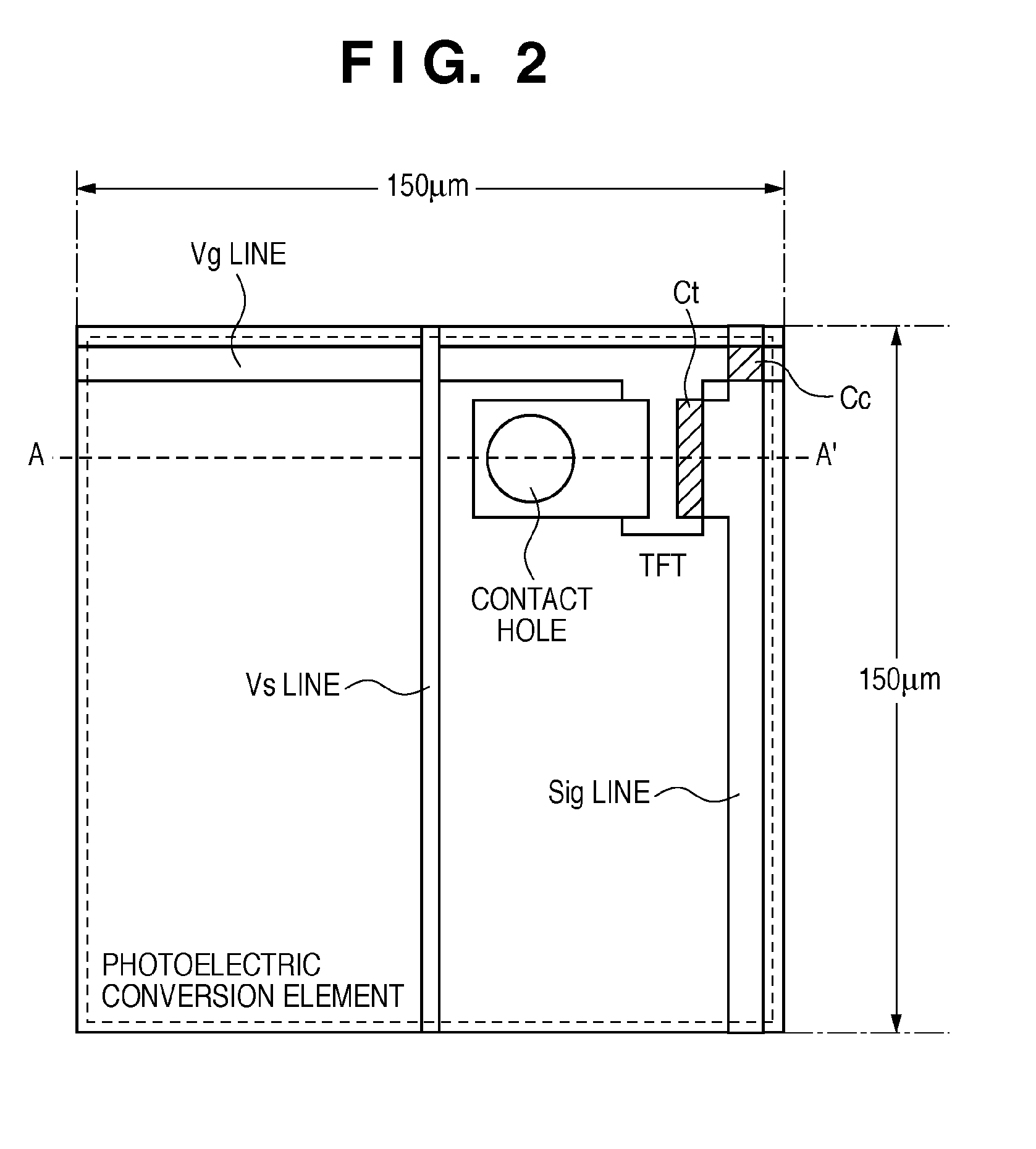
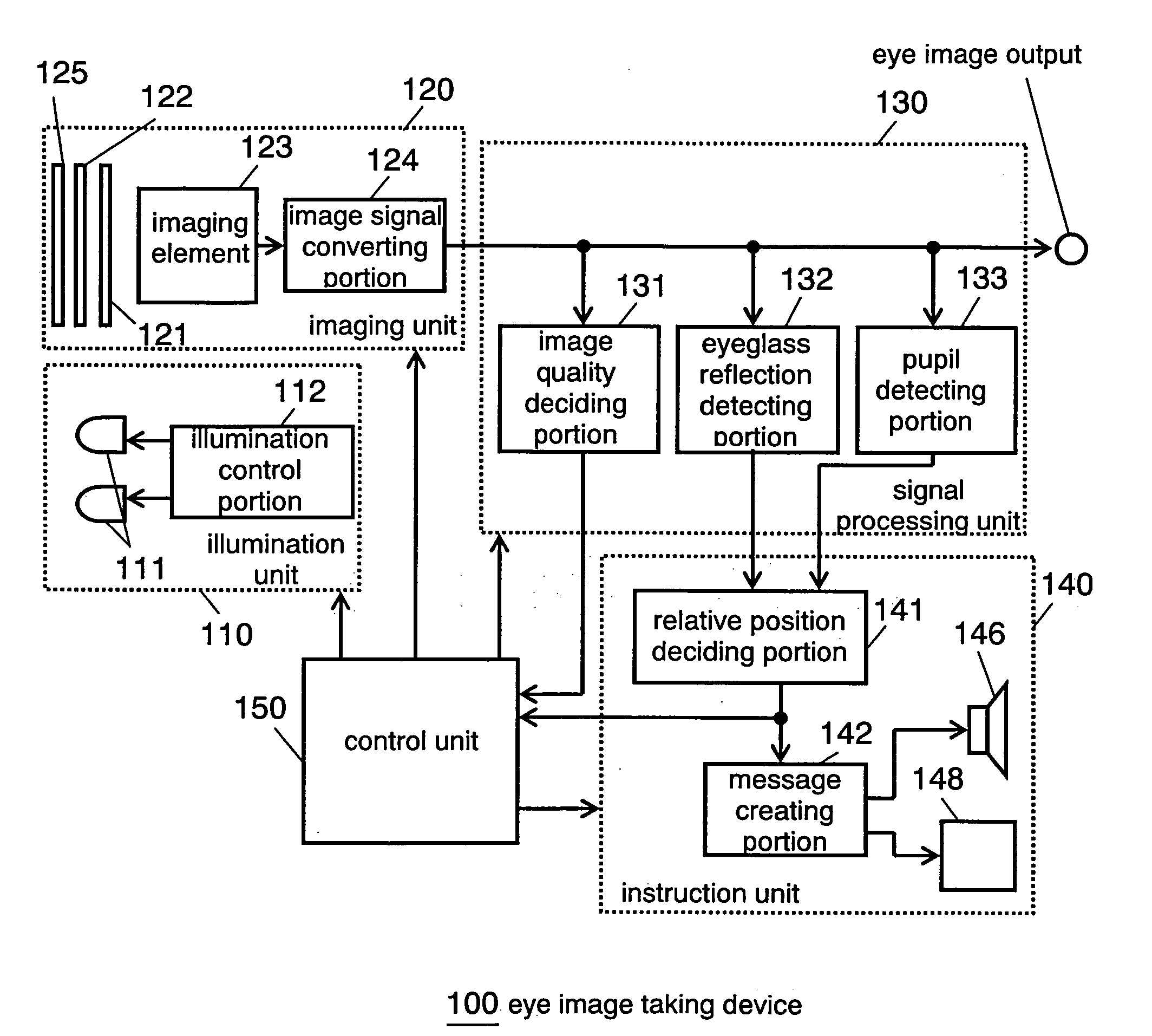
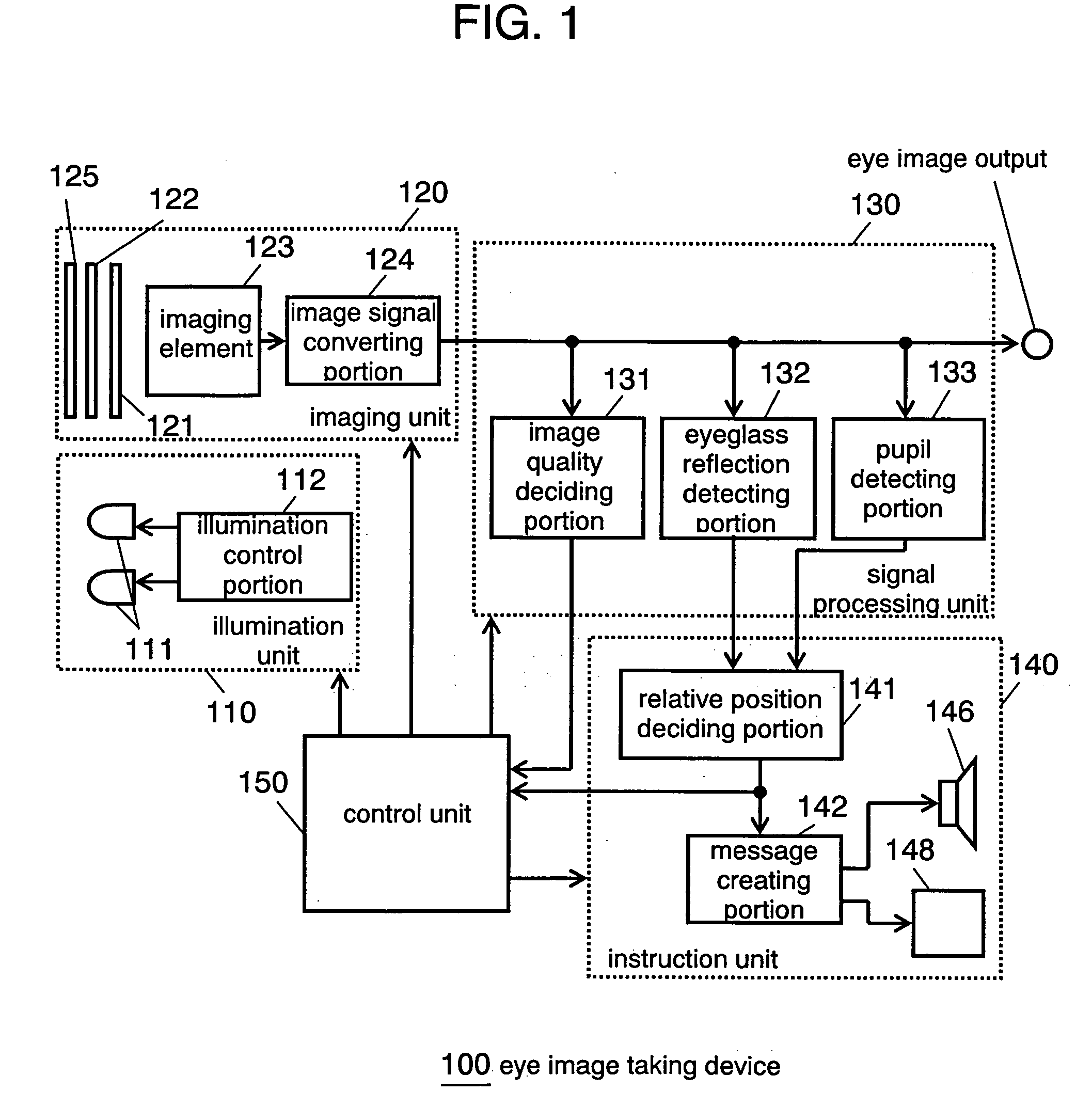
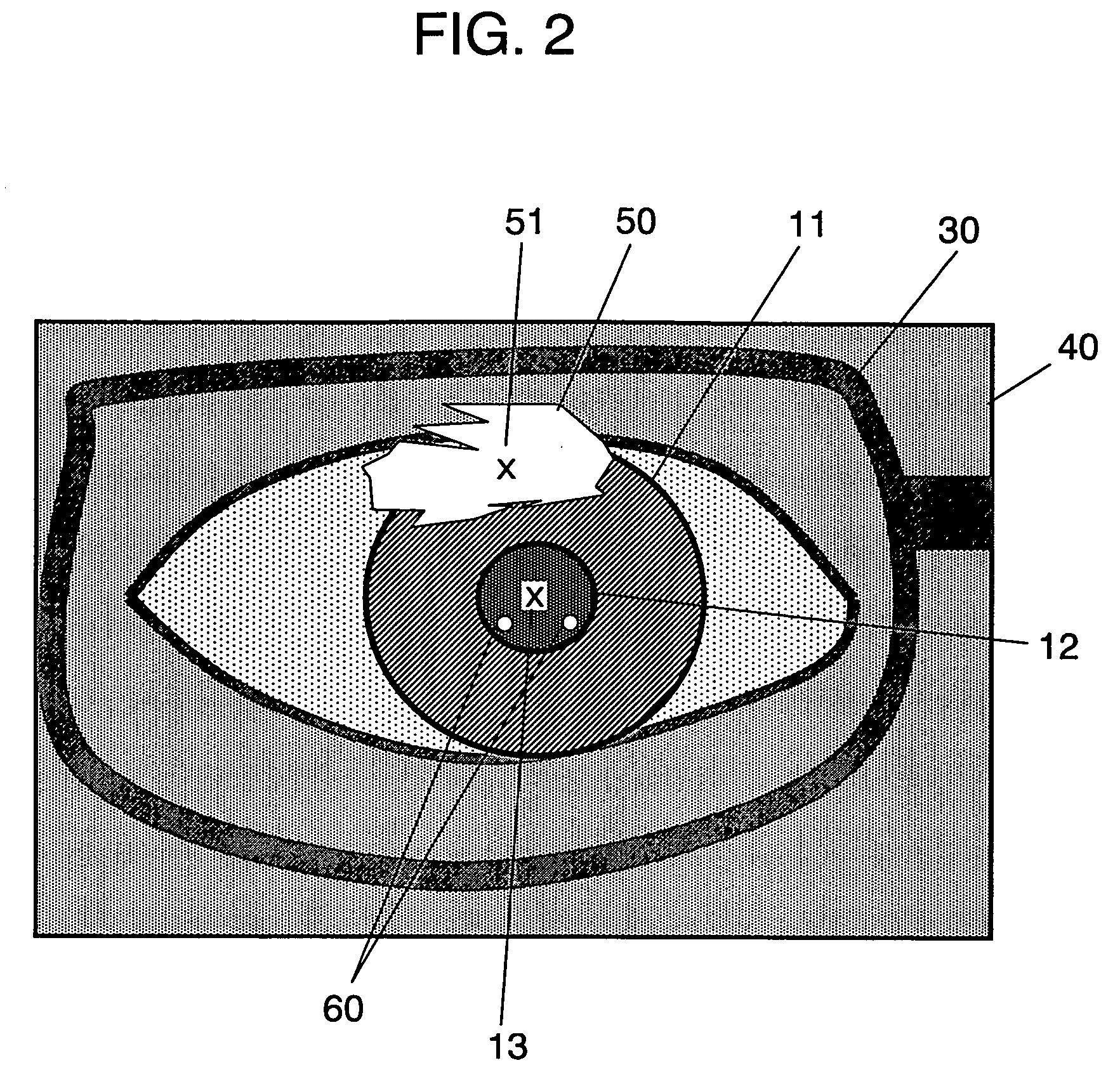
Eye imaging device
InactiveUS20050270483A1Satisfactory imageReduce in quantityPerson identificationAcquiring/recognising eyesInstruction unitEyewear
An eye image taking device comprises: an imaging unit for taking the eye of a person to be authenticated, as an eye image; an illumination unit for illuminating the eye of the person to be authenticated; an eyeglass reflection detecting unit for detecting an eyeglass reflection from the eye image; and an instruction unit for instructing the person to be authenticated the movement of the imaging unit or the direction of the face of the person to be authenticated, in case an eyeglass reflection detecting portion detects the eyeglass reflection.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Wide-angle lenses
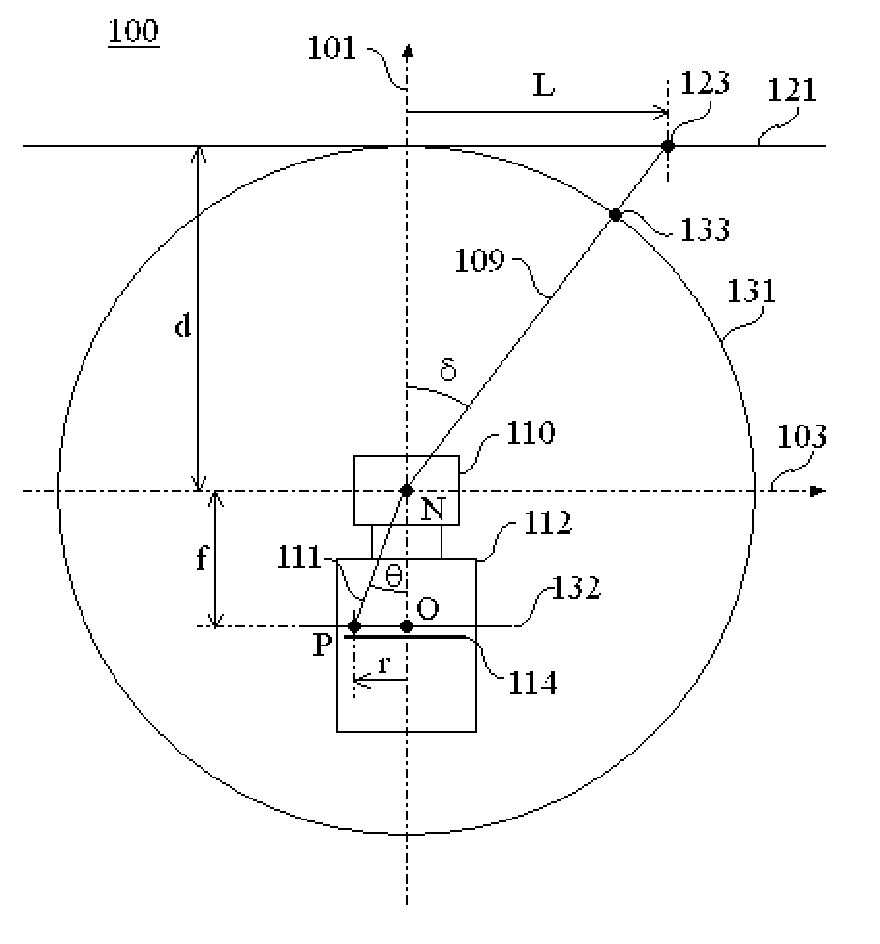
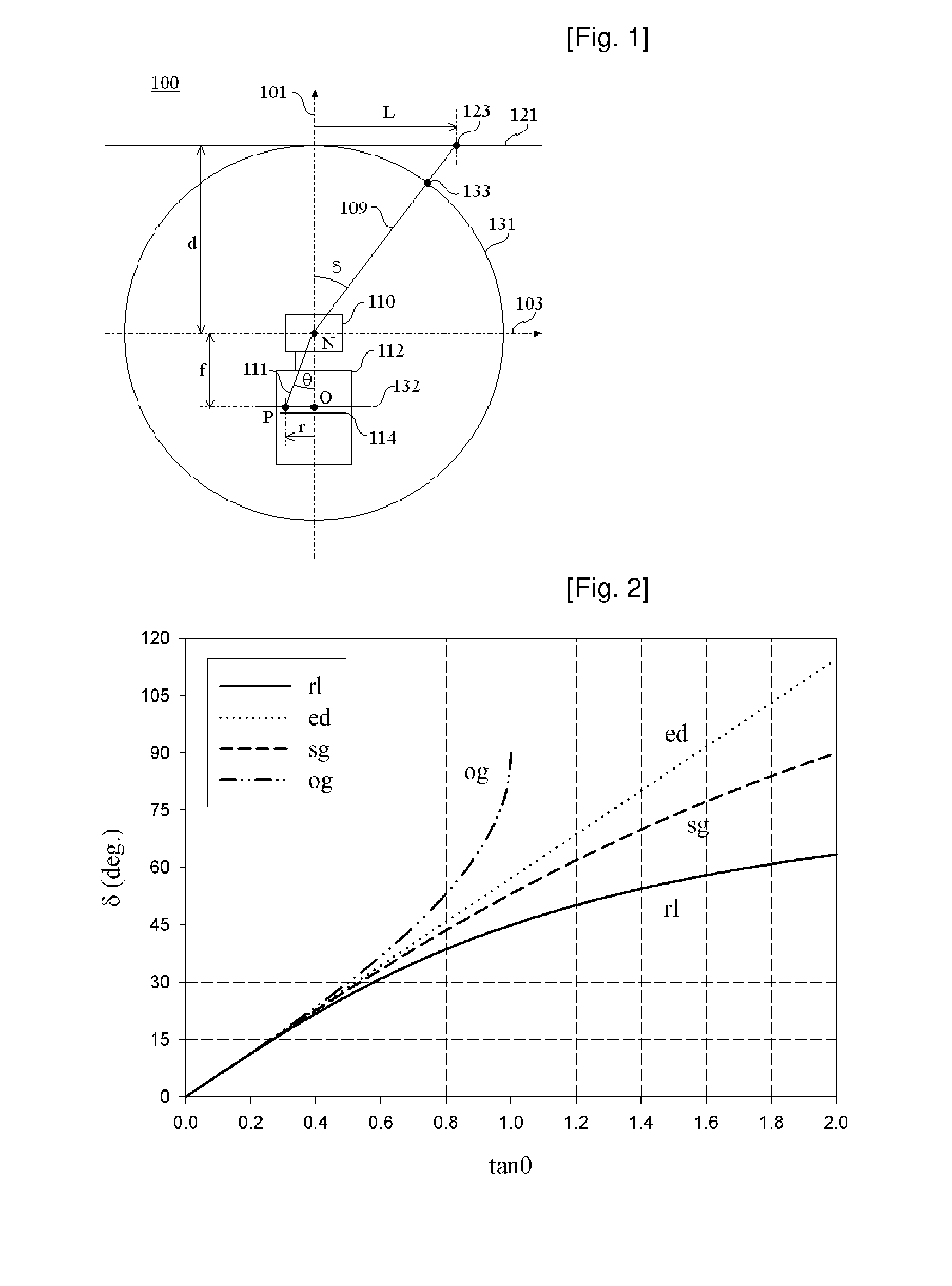
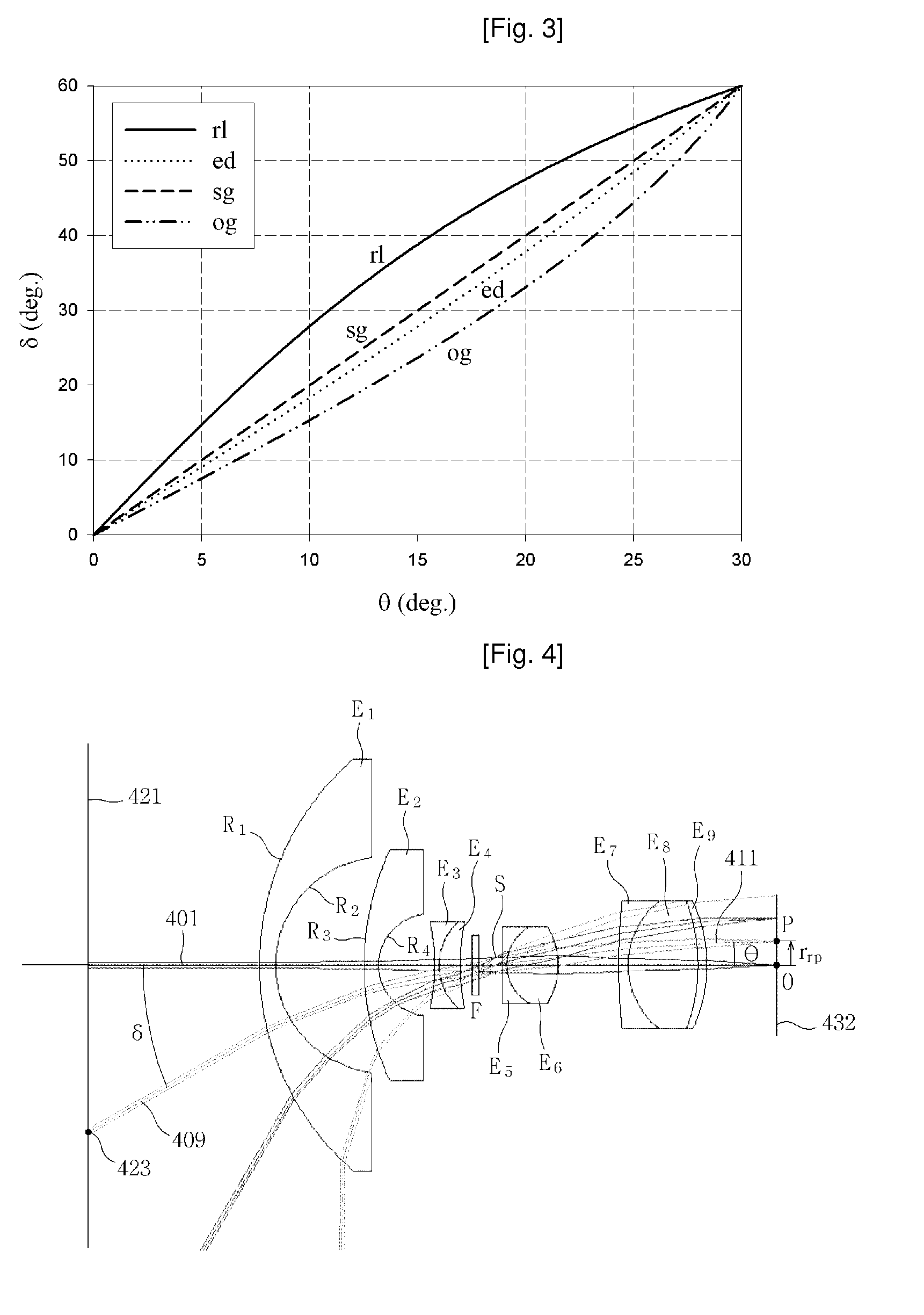
The present invention provides new projection schemes for wide angle imaging lenses rotationally symmetric about optical axis wherein the field of view of lenses and the size of image sensors are directly reflected without any reference to the effective focal length of the lenses. This invention also provides explicit examples of wide-angle lenses implementing the newly developed projection schemes. According to the present invention, by providing new projection schemes explicitly reflecting the physical quantities of direct interest to the user for industrial applicability, namely, the field of view and the image sensor size, it is possible to realize wide-angle lenses providing the most satisfactory images.
Owner:NANOPHOTONICS CO LTD
Image processor for overlaying a graphics object
InactiveUS20100271466A1Satisfactory stereoscopic image renderingLow costSteroscopic systems3D-image renderingGraphicsStereoscopic rendering
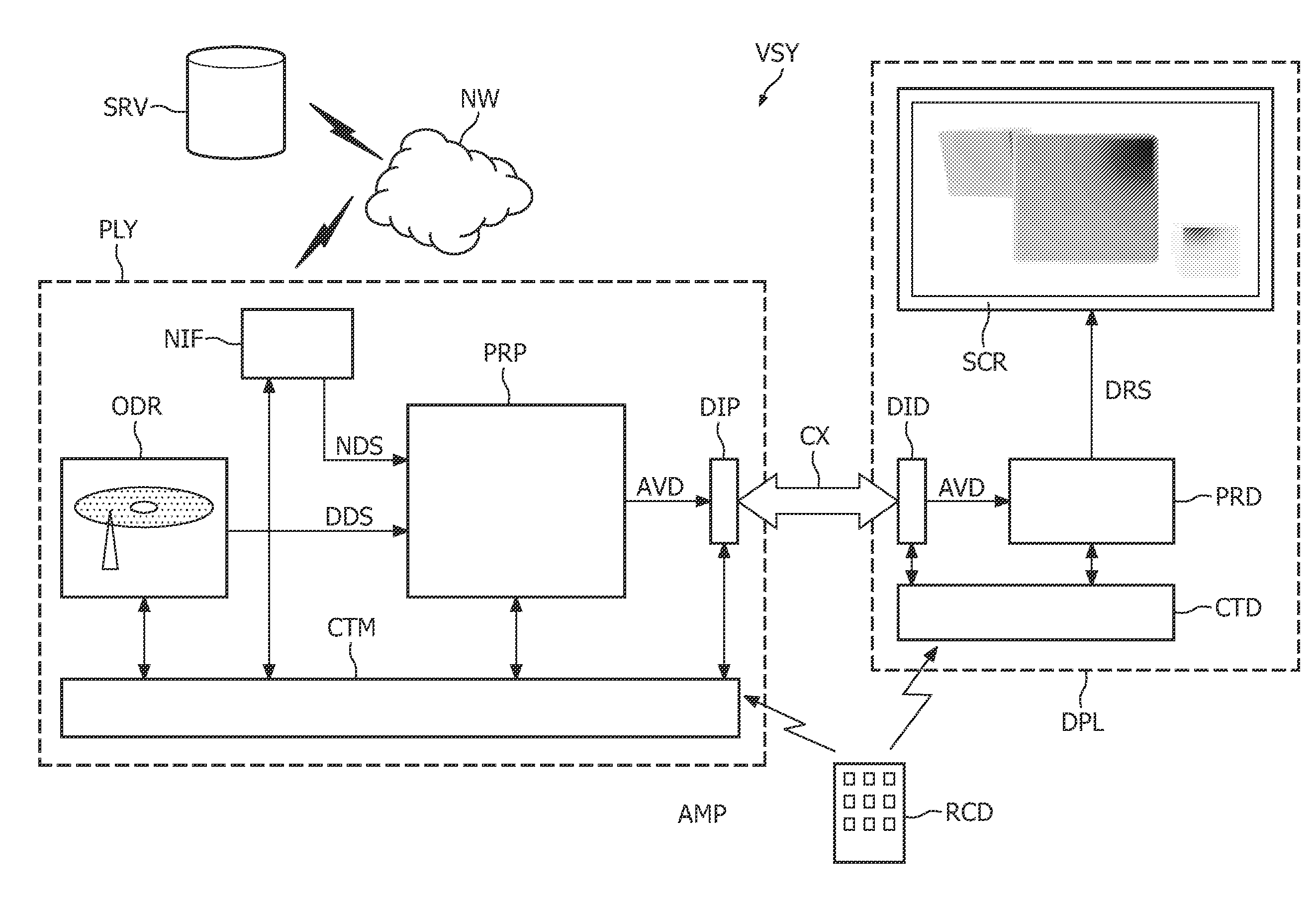
An image processor processes an assembly of data (DDS) that defines an elementary image and a graphics object. The assembly of data (DDS) comprises composition data (CS) that defines a given appearance of the graphics object in an output image, wherein the graphics object overlays a portion of the elementary image. The image processor comprises an occlusion analyzer (OCA) for establishing an occlusion indication (OCS) on the basis of the composition data (CS). The occlusion indication (OCS) specifies an area in the elementary image that the graphics object will occlude in the output image, but which may be de-occluded in a stereoscopic rendering of the output image. An occlusion data generator (ODG) composes an occlusion image on the basis of the occlusion indication (OCS) and the elementary image. The occlusion image represents a portion of the elementary image that corresponds with the area specified by the occlusion indication (OCS).
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Image generating system and program
InactiveUS7106324B1Small sizeDisplay failureGeometric image transformation2D-image generationViewpointsShortest distance
An image generating system and a program enabling scissoring of a polygon in a three-dimensional stage to prevent display failure of a polygon on a screen end or at a short distance from the viewpoint with a reduced computation load. The system performs scissoring processing for a polygon in a three-dimensional stage and generates an image of an object including a new vertex generated by the scissoring. A polygon which is at a short distance from a view point, displaying of which is likely to be missed, is scissored on side surfaces of a quadrangular pyramid forming a view volume, to prevent the display failure of the polygon existing at a short distance from the end of a screen. A polygon arranged in the three-dimensional space is subjected to coordinate transformation into a screen coordinate system, to detect an undrawable vertex, and a polygon containing the detected vertex is scissored at a portion containing the detected vertex, in a predetermined plane.
Owner:BANDAI NAMCO ENTERTAINMENT INC
Radiation detection apparatus and radiographic imaging system
ActiveUS20100001194A1Image unevenness can be reducedSatisfactory imageSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansDielectricCapacitance
A radiation detection apparatus comprises a plurality of pixels each including a conversion element which converts incident radiation into a charge, a switching element which transfers the charge, and an interlayer insulation film disposed between the conversion element and the switching element, a gate line to drive the switching element, and a signal line located to intersect with the gate line and configured to read out the charge transferred from the switching element, wherein Ca≧ε0×ε×S / d and 7d≦P / 2 is satisfied, where P is a pixel pitch, Ca is a sum total of coupling capacitances between the signal line and the gate line, S is an overlapping area of the signal line and the conversion element, d is a thickness of the interlayer insulation film, ε is a relative dielectric constant of the interlayer insulation film, and ε0 is a vacuum dielectric constant.
Owner:CANON KK
Image processing apparatus
InactiveUS7003147B2Eliminate variationSatisfactory imageImage enhancementSolid-state devicesImage synthesisImage processing
An image processing apparatus includes an image processing circuit having a first mode that corrects an offset between a first image and a second image that are adjacent to each other to synthesize the first image and the second image into a new third image, and a second mode that corrects an offset between the third image and a fourth image that are adjacent to each other to synthesize the third image and the fourth image into a new fifth image.
Owner:CANON KK
Method for detecting linear image in planar picture
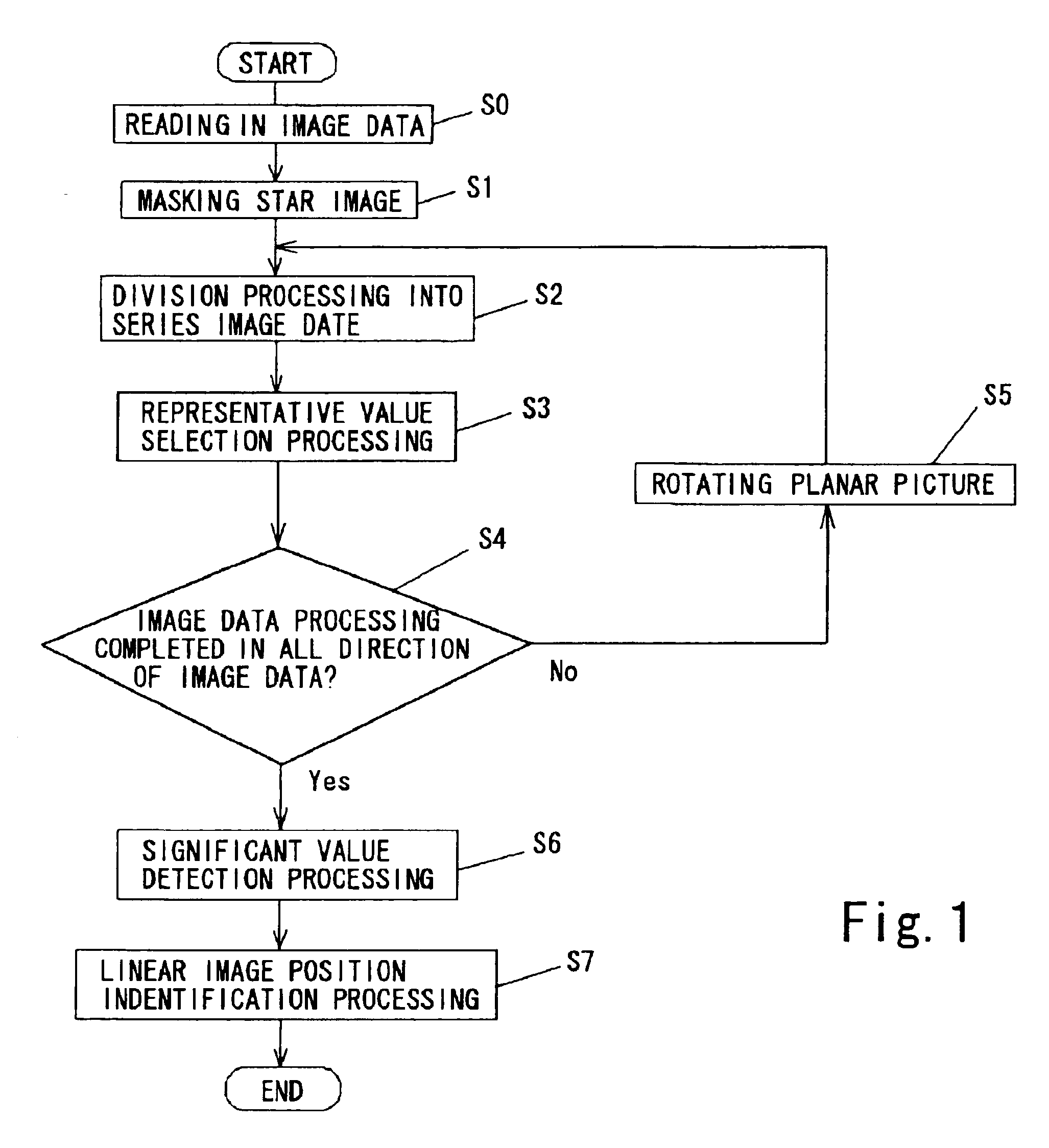
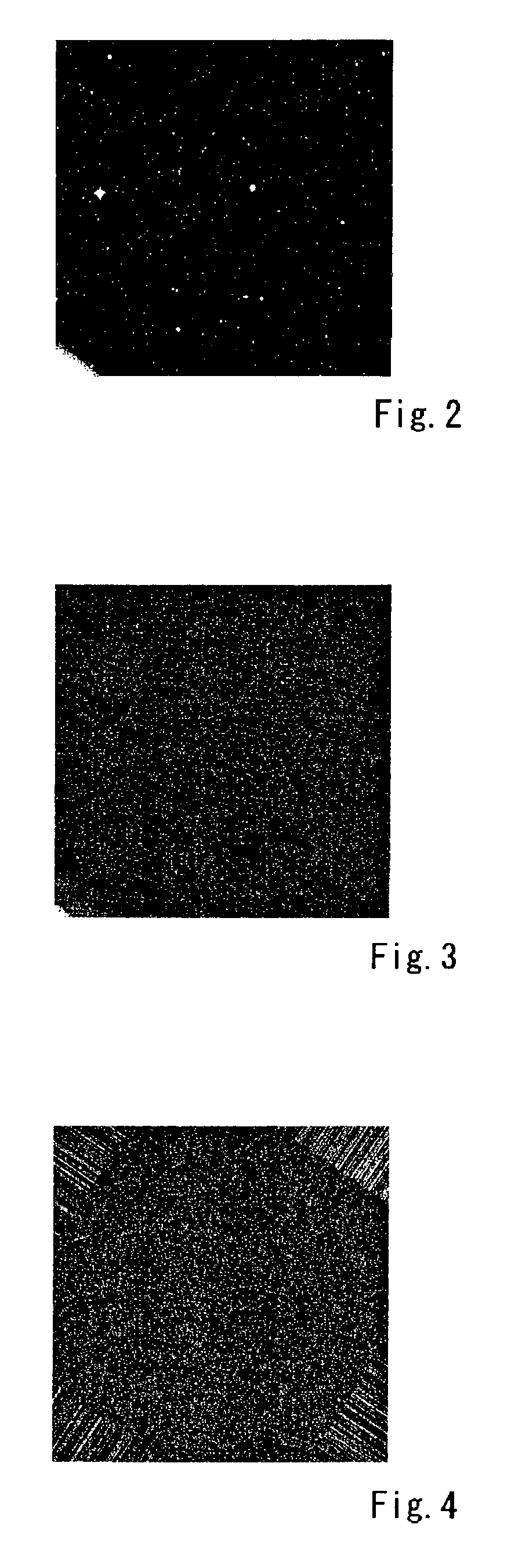
InactiveUS20060110007A1Short exposure timeSatisfactory imageImage analysisCosmonautic vehiclesPattern recognitionLinearity
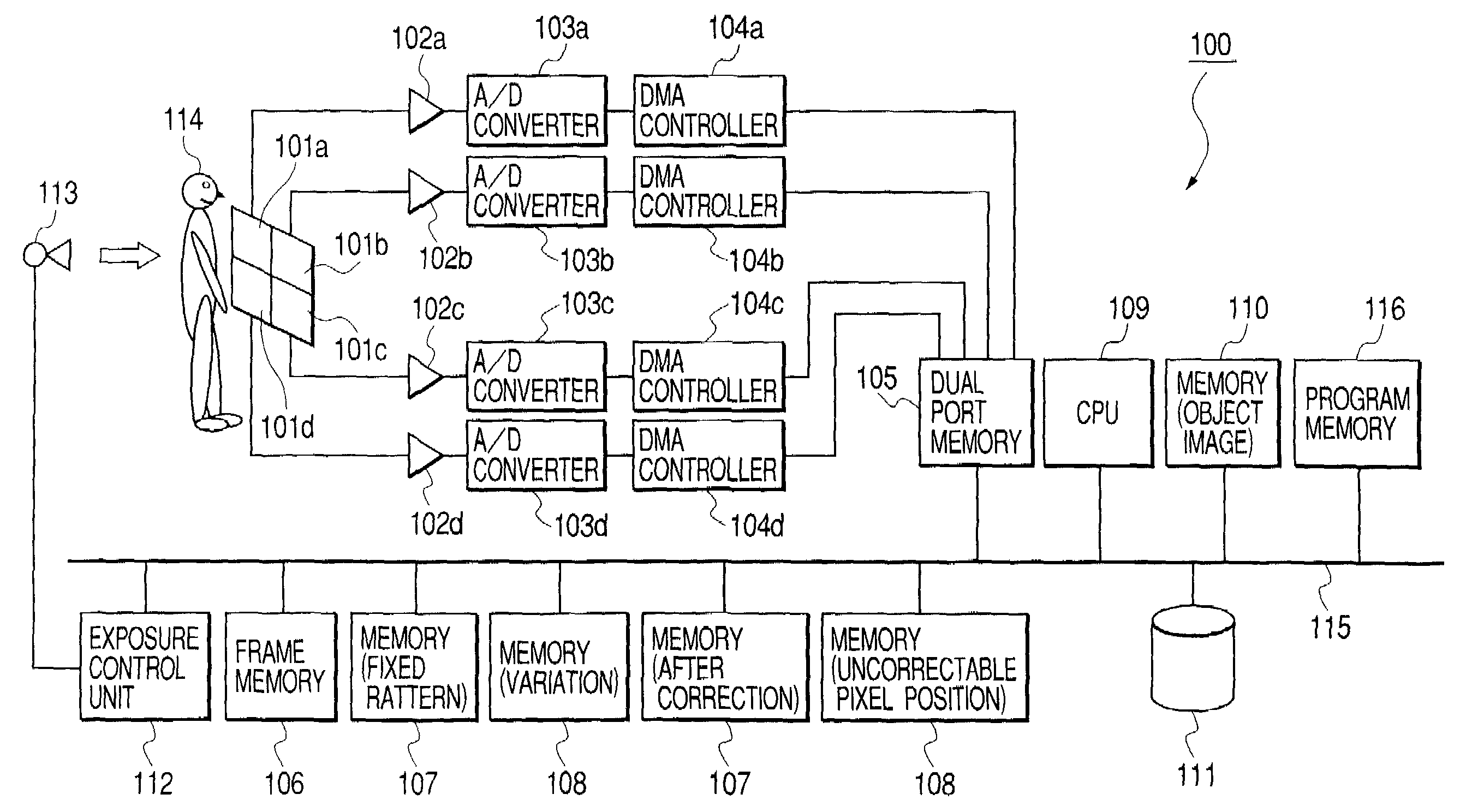
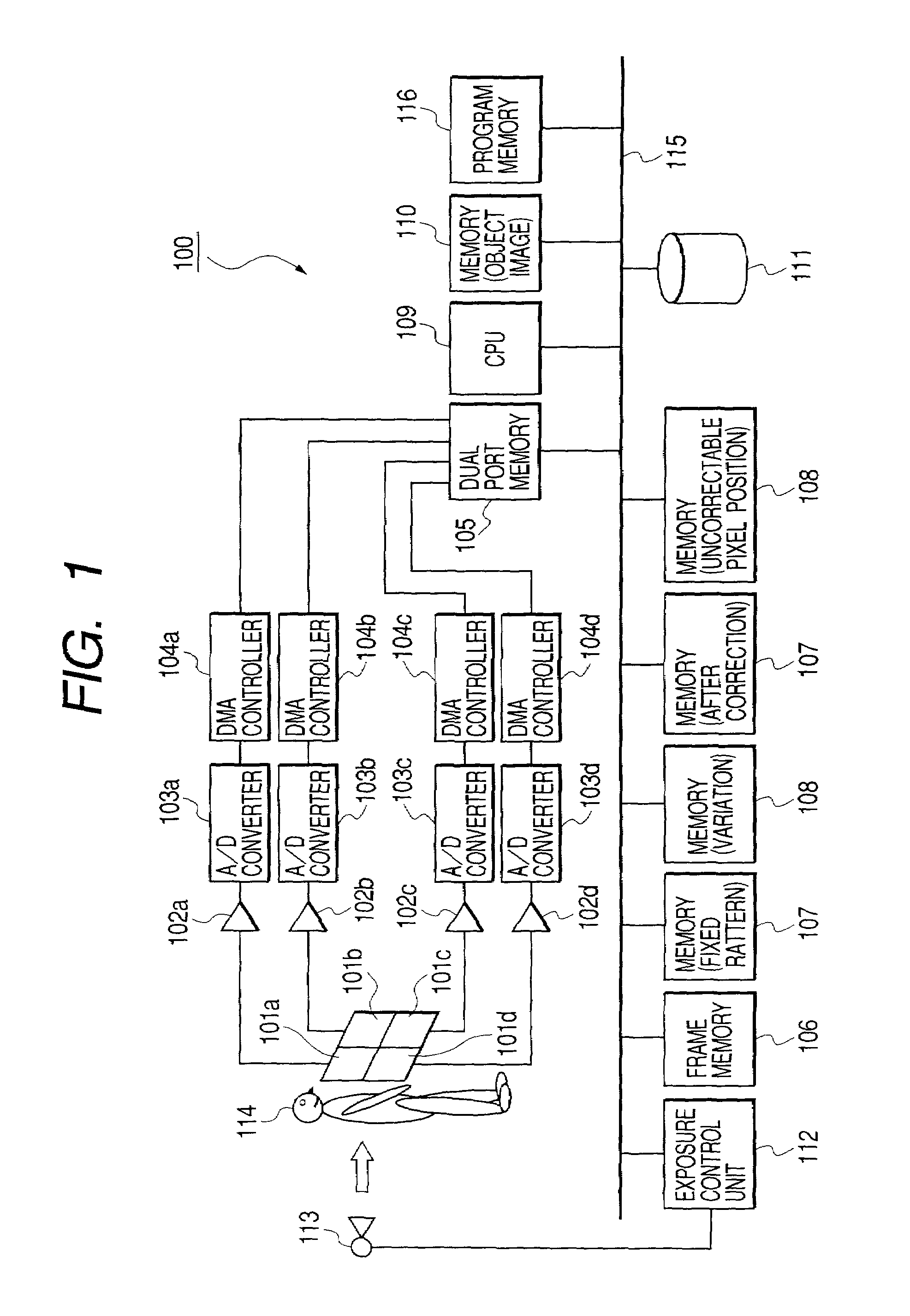
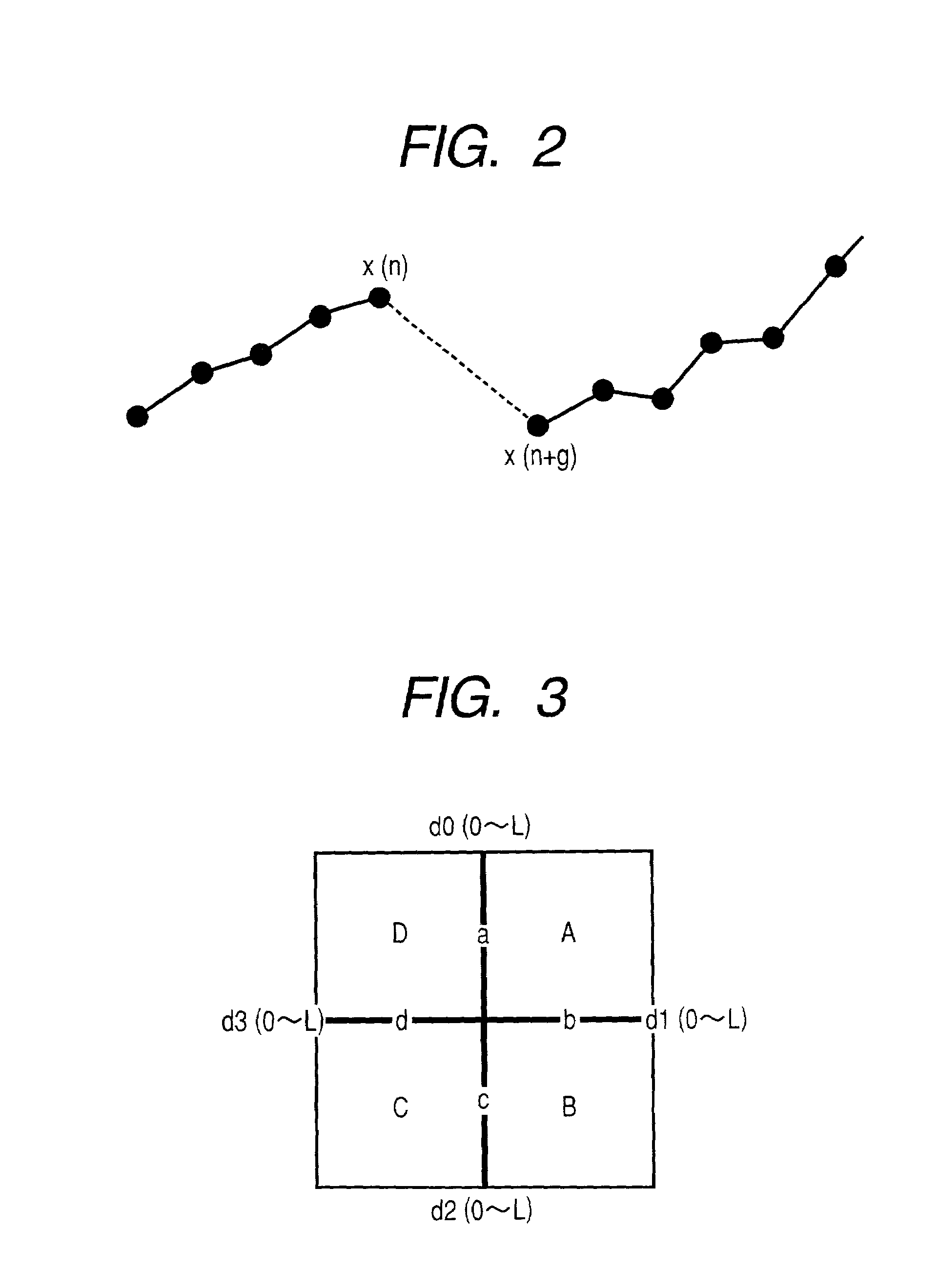
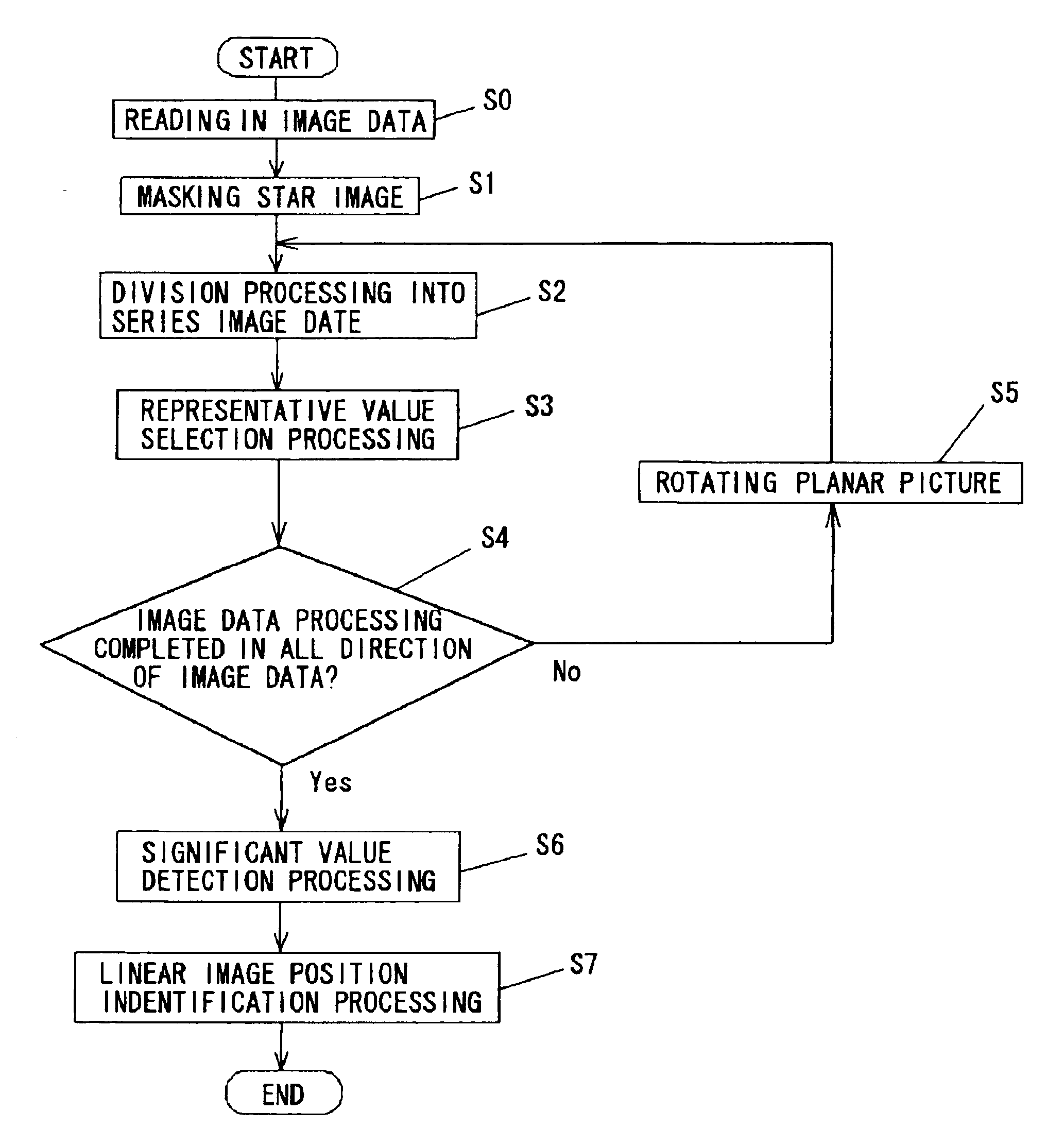
A method for detecting a linear image in a planar picture is provided whereby the positions of a linear image can be determined by devising suitable processing of image data, even if a linear image traced by a moving object, such as space debris, a meteor, or the like, does not appear clearly on a picture. Image data processing, consisting of division processing (S2) for dividing image data of a planar picture captured by an imaging element into a plurality of mutually parallel columnar image data and representative value selection processing (S3) for taking the median value determined for each of the columnar image data as a representative value for the corresponding columnar image data, is performed in every direction of said planar picture, whereupon analysis processing consisting of significant value detection processing (S6) for detecting whether or not said representative value of each of said columnar image data is a significant value, and linear image position identification processing (S7) for identifying the linear position of columnar image data having a representative value indicating a significant value as the position of a linear image resulting from the passage of the moving object or the like, is performed.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP +1
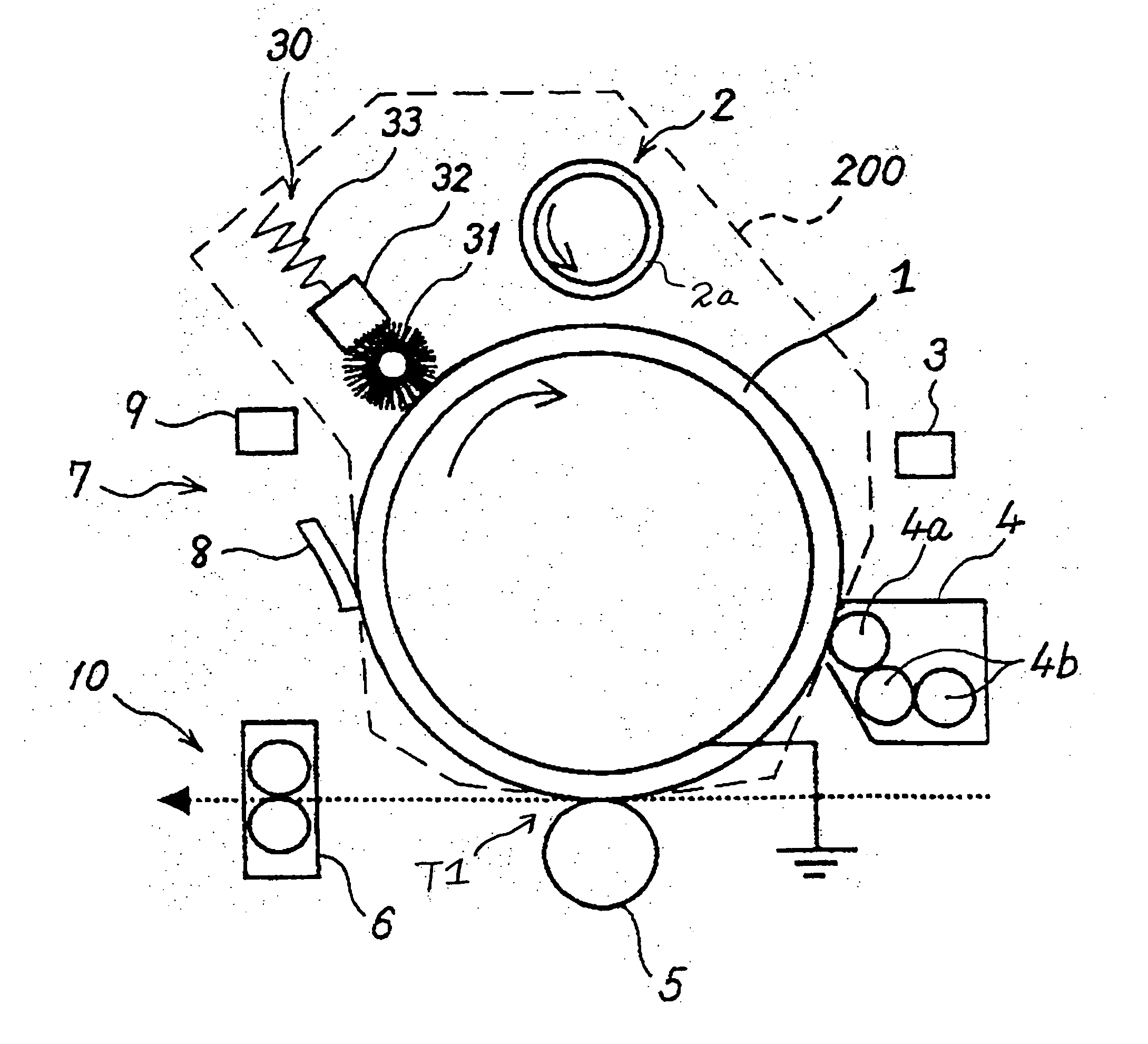
Ink-jet recording apparatus and ink-jet recording process
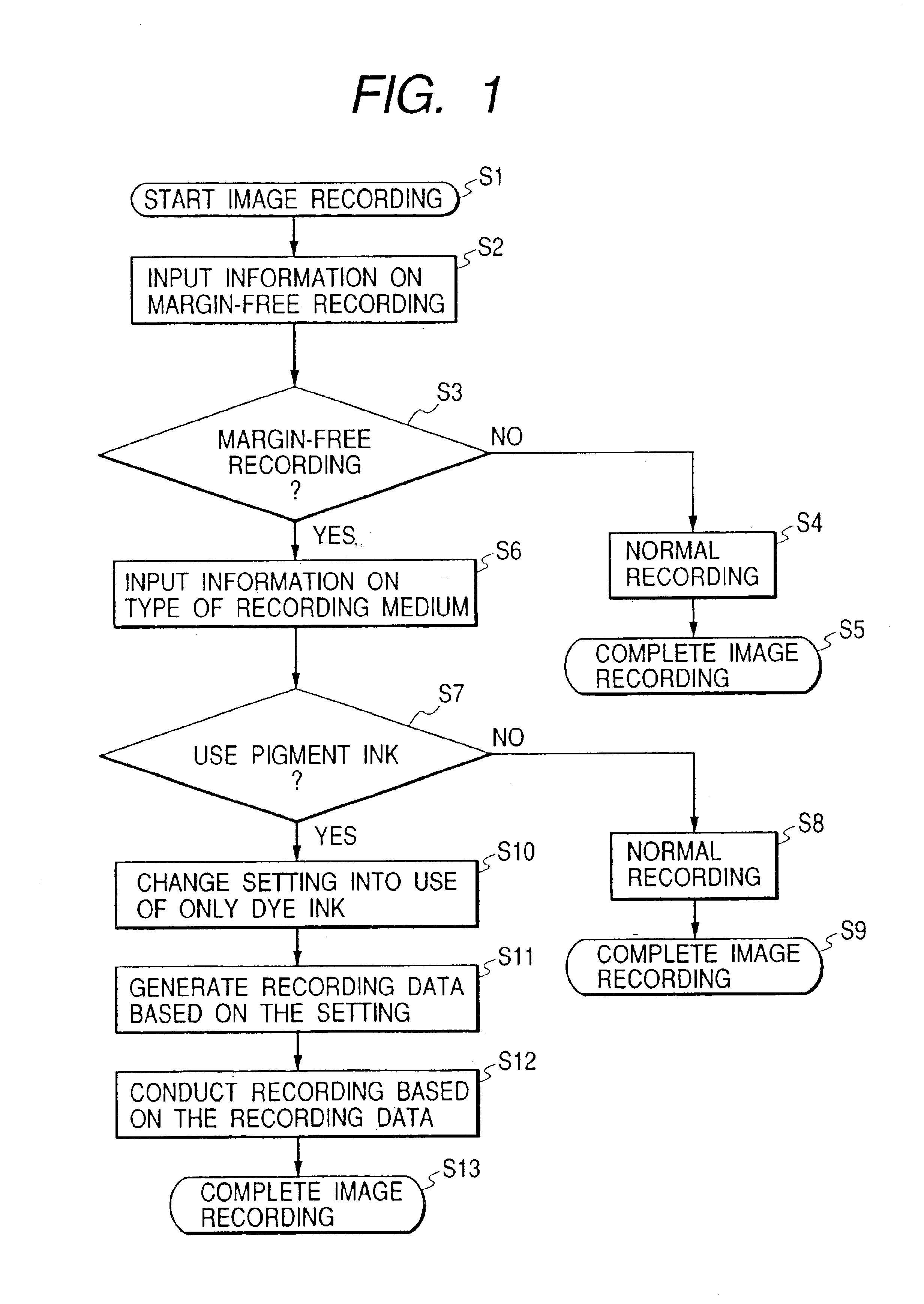
InactiveUS6890069B2Improve water resistanceImprove light resistanceMeasurement apparatus componentsOther printing apparatusImaging qualityComputer science
A novel ink-jet recording apparatus is provided for conducting margin-free recording on the peripheral area of the recording medium including the edge thereof with excellent image quality even in the peripheral area in comparison with quality of the usual printing having a margin. A process therefor is also provided.
Owner:CANON KK
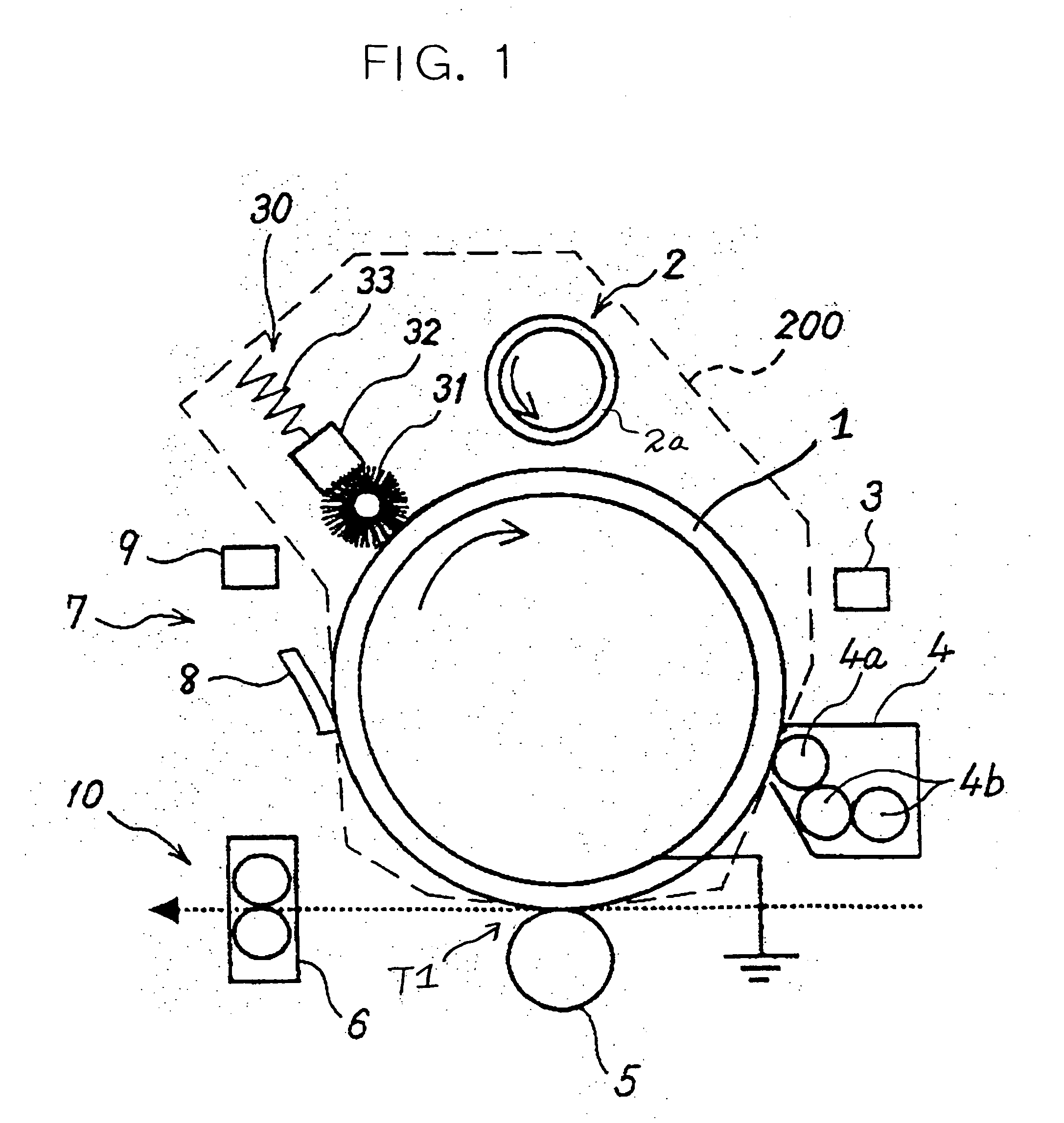
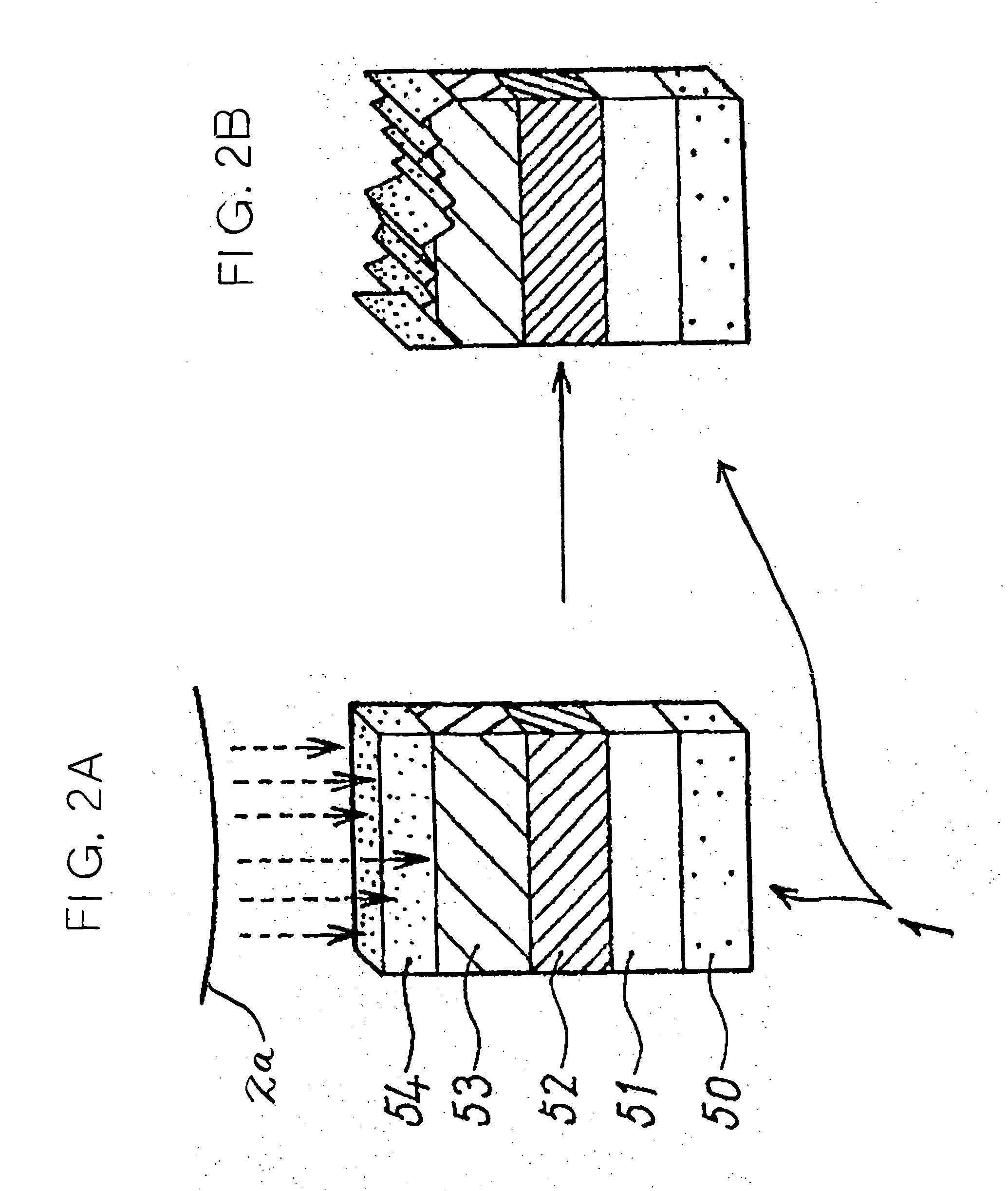
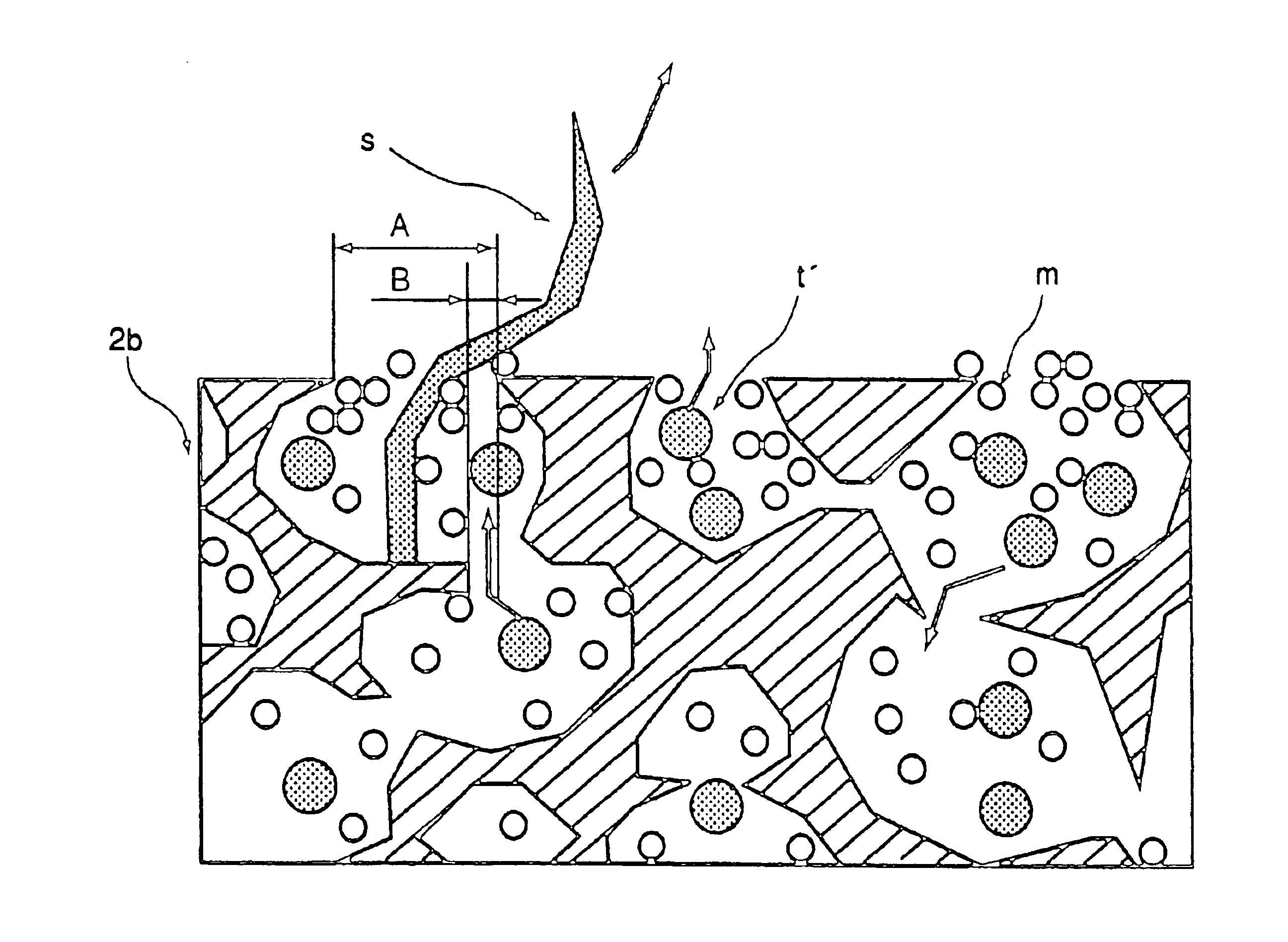
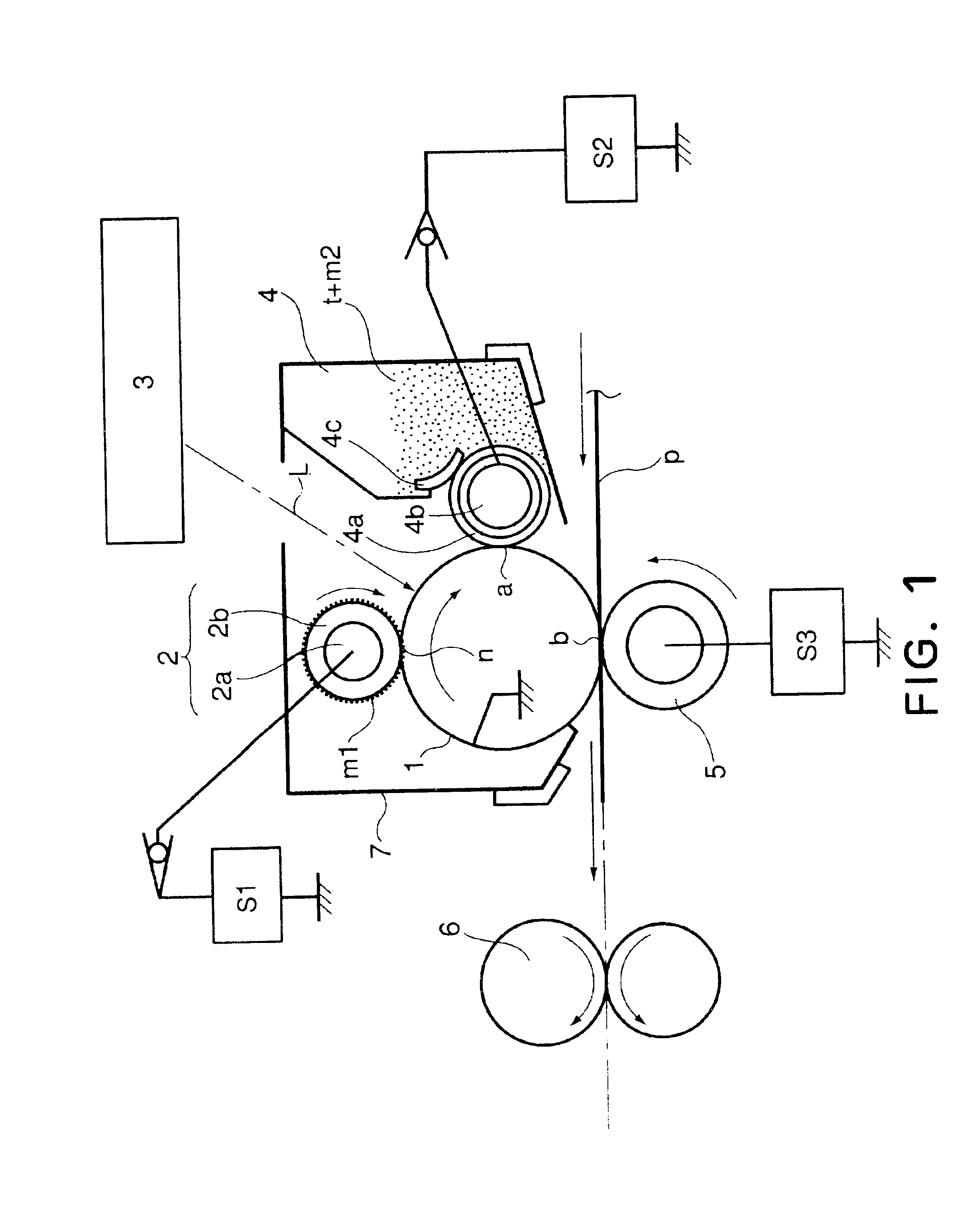
Image forming apparatus and image forming method
ActiveUS20050111883A1Satisfactory imageElectrographic process apparatusDevelopersImage formationMechanical engineering
Owner:KK TOSHIBA +1
Image forming apparatus and image forming method
ActiveUS7079793B2Satisfactory imageDevelopersElectrographic process apparatusImage formationEngineering
Owner:KK TOSHIBA +1
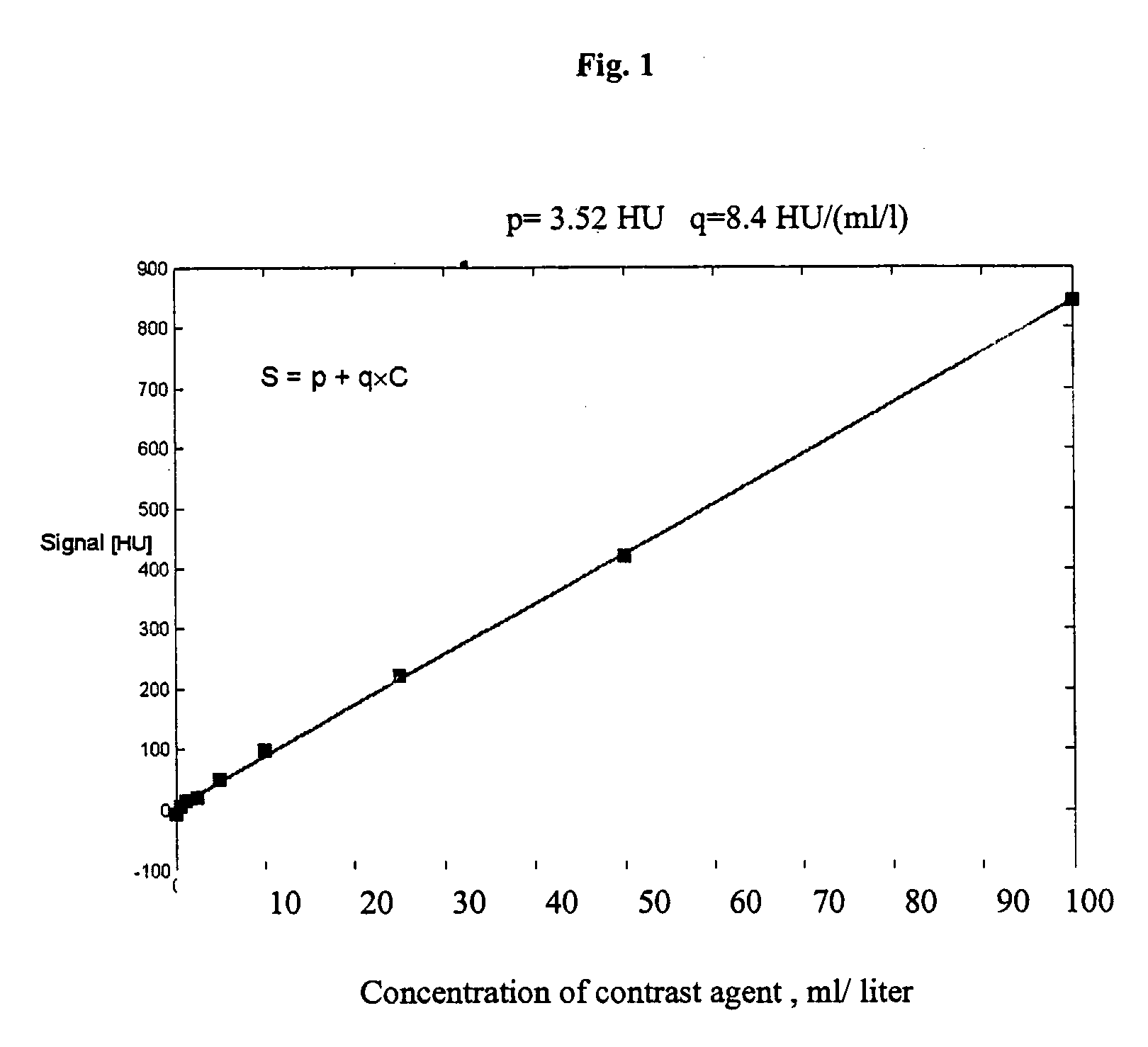
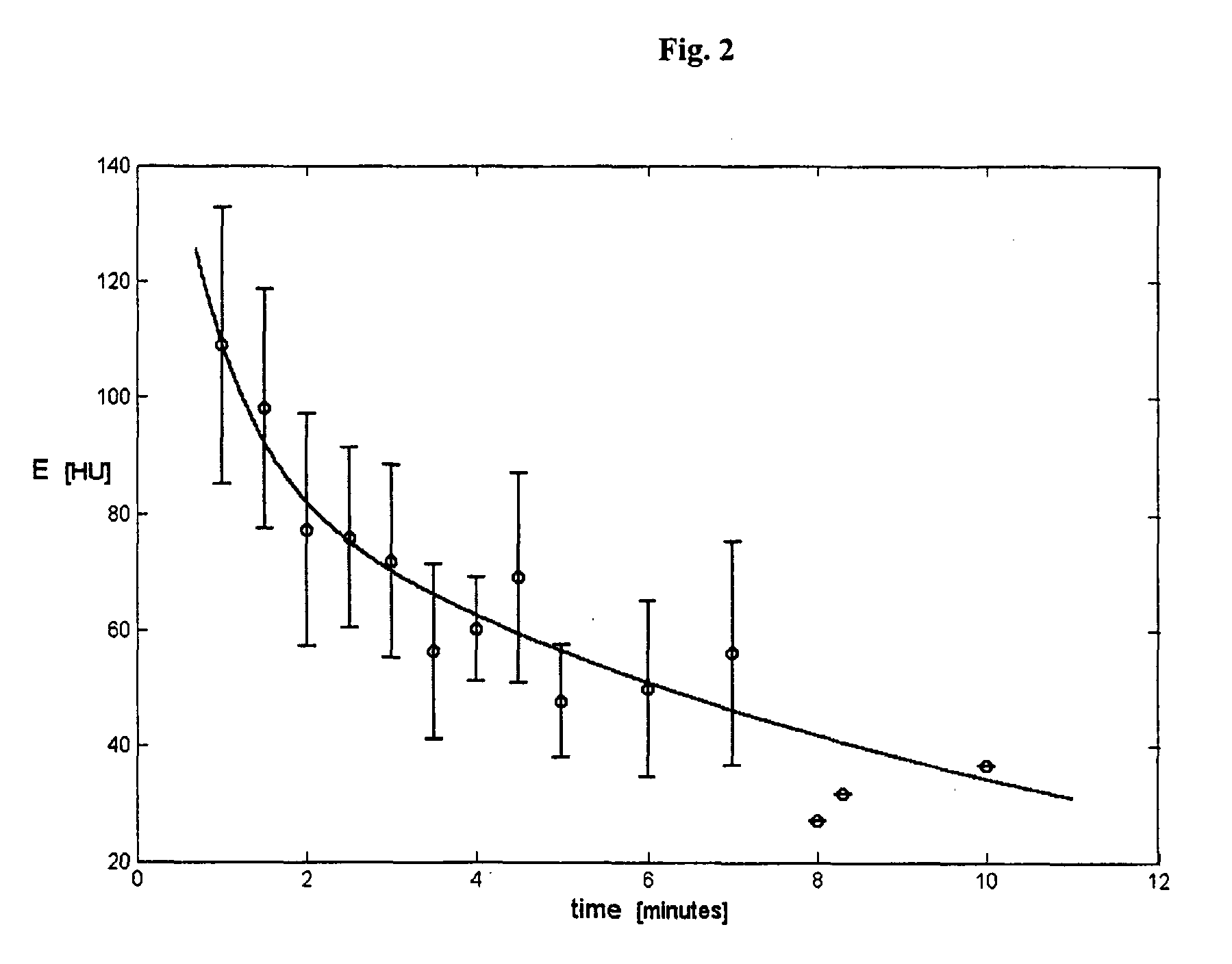
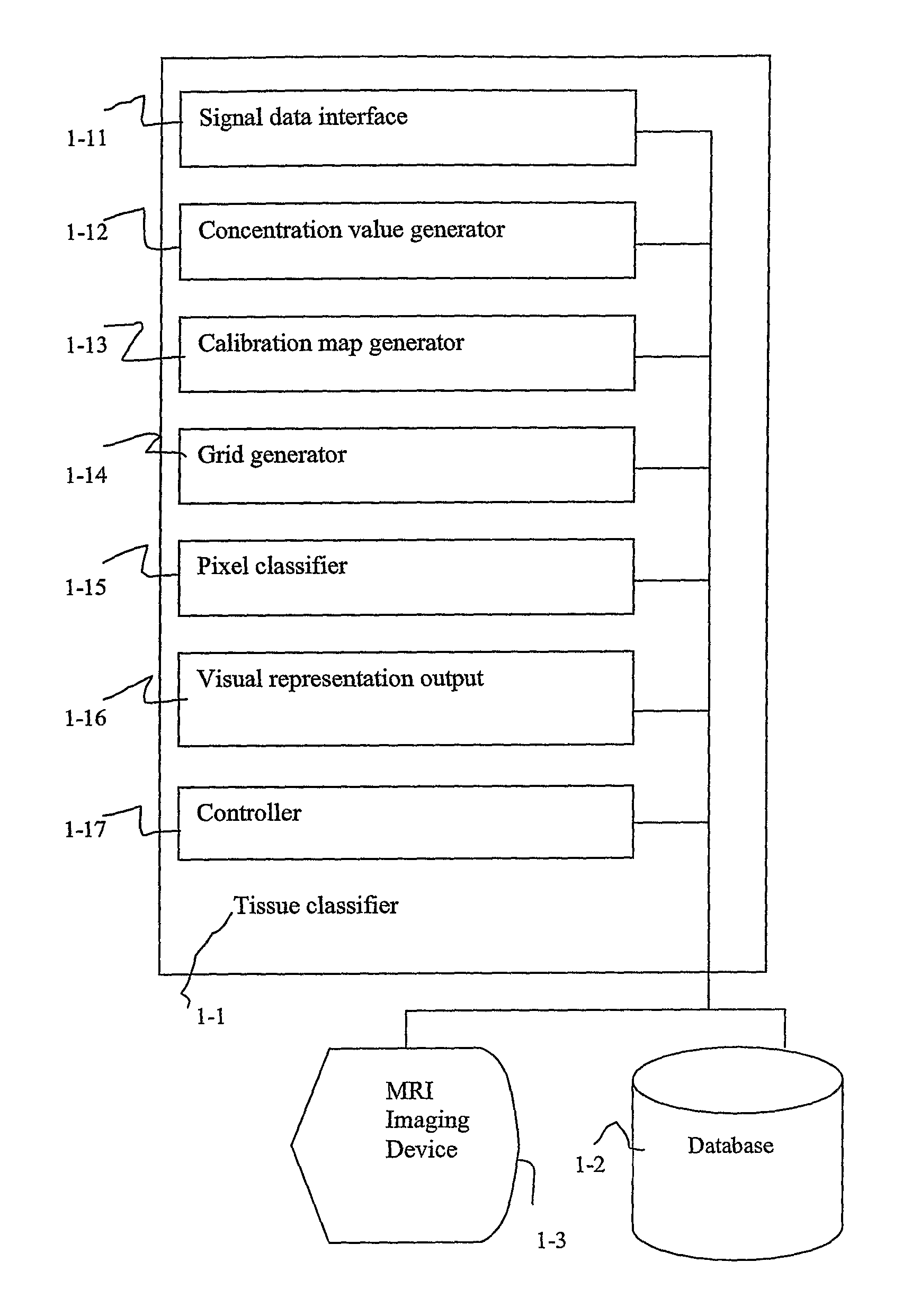
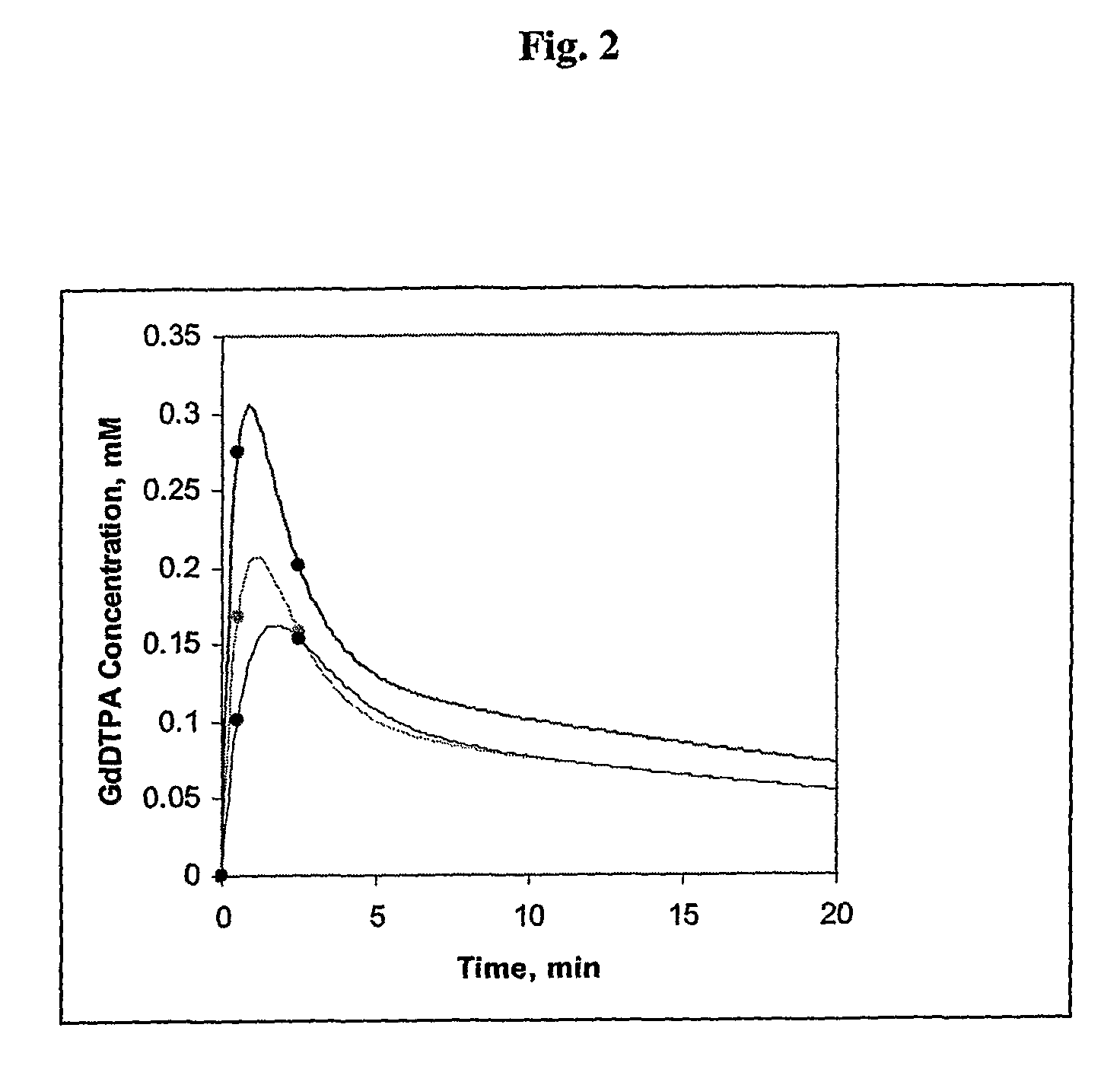
Three Time Point Lung Cancer Detection, Diagnosis and Assessment of Prognosis
InactiveUS20090028405A1Satisfactory imagePrecise shiftImage enhancementImage analysisPeak valueLung cancer
malignancy classification method and medium for classifying a region of lung tissue are disclosed. The classifying includes: setting time points T1 and T2 measured from injection of a contrast agent. TI represents a wash-in time point for malignant lung tissue at which a first concentration value of the injected contrast agent is substantially equal to or near a peak for injected contrast agent concentration in the region of lung tissue. Patient concentration values of the contrast agent for the area of lung tissue at time points T1 and T2 are obtained, and a malignancy classification for the region of lung tissue is provided by comparing the obtained sample concentration values with a predetermined malignancy profile. A visual representation of the malignancy classification of the region of lung tissue is outputted.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
Developing apparatus including agitating member
ActiveUS7003249B2Excellent low temperature fixabilityPrevent deterioration of flowabilityElectrographic process apparatusDevelopersTransmittanceEngineering
A developing apparatus includes a rotatable, developer carrying body for carrying a one-component developer and a rotatable, agitating member for agitating the one-component developer. The one-component developer is magnetic toner at least containing a bonding resin and magnetic iron oxide. When wettability of the magnetic toner relative to a mixture solution of methanol and water is measured at the transmittance of light having a wavelength of 780 nm, a methanol concentration at the transmittance of 80% is within the range of 45 to 65 volume %, and wherein 0.1≦b / a≦0.2 is established where a (rps) denotes the rotation speed of the developer carrying body, and b (rps) denotes the rotation speed of the agitating member.
Owner:CANON KK
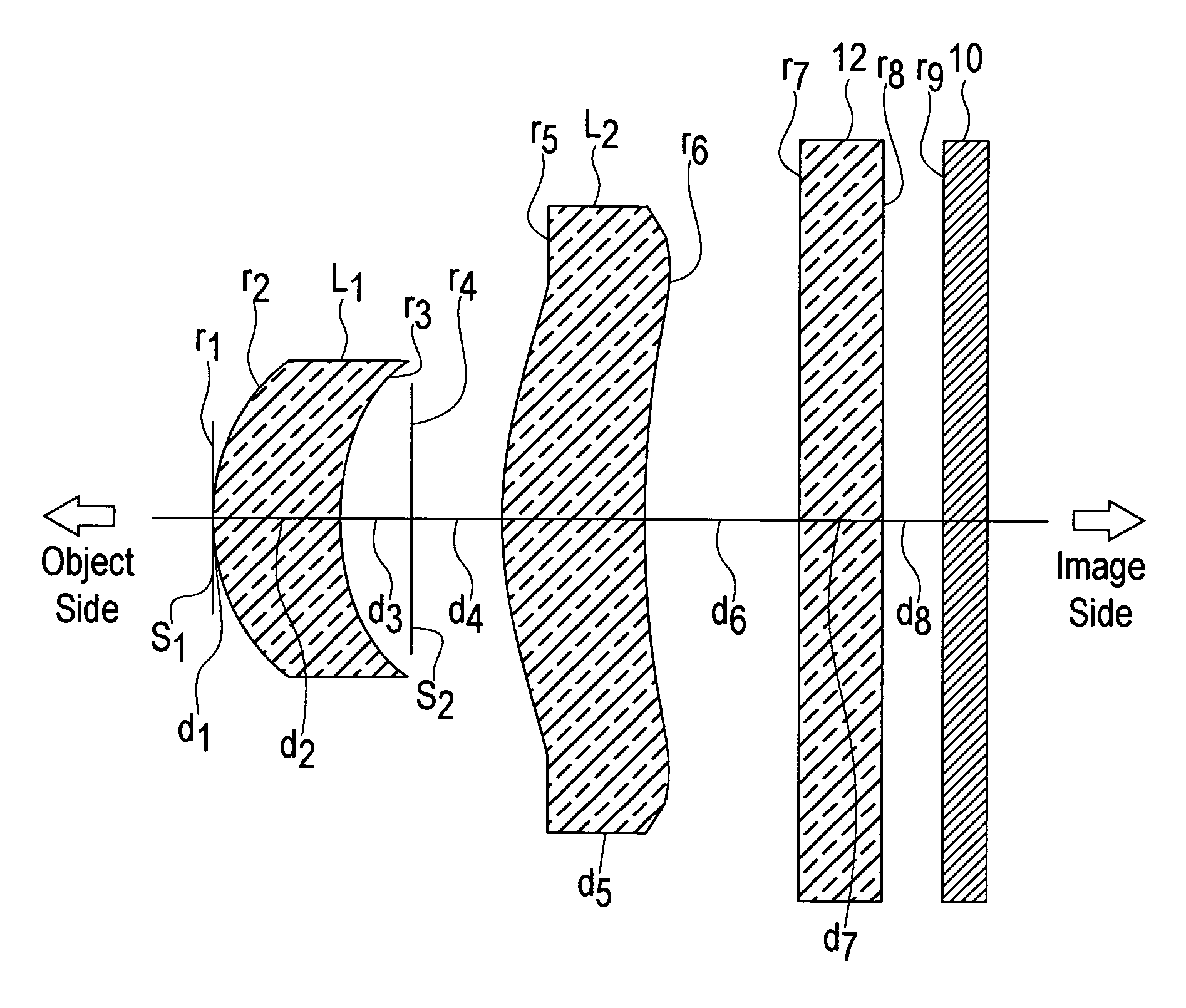
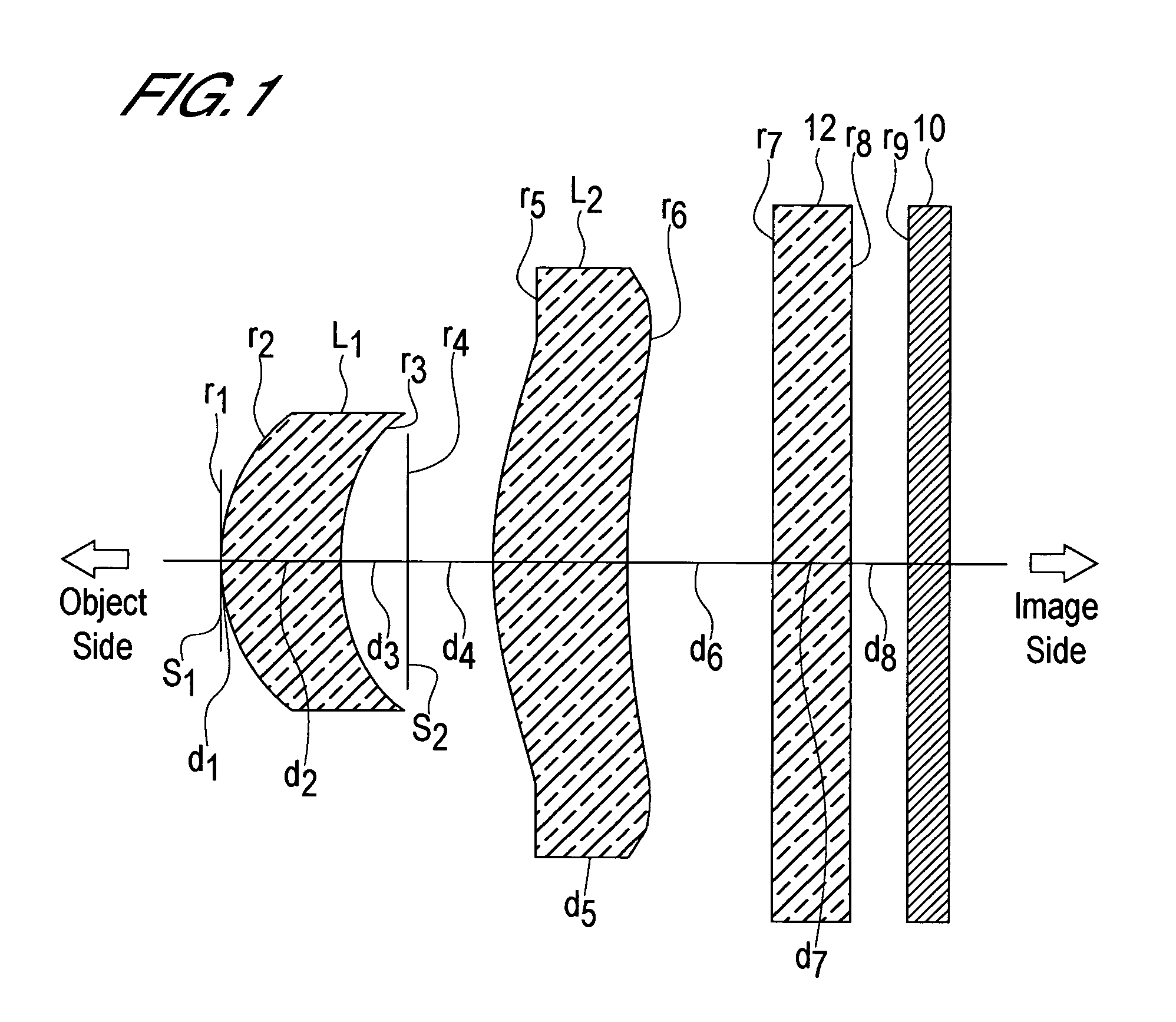
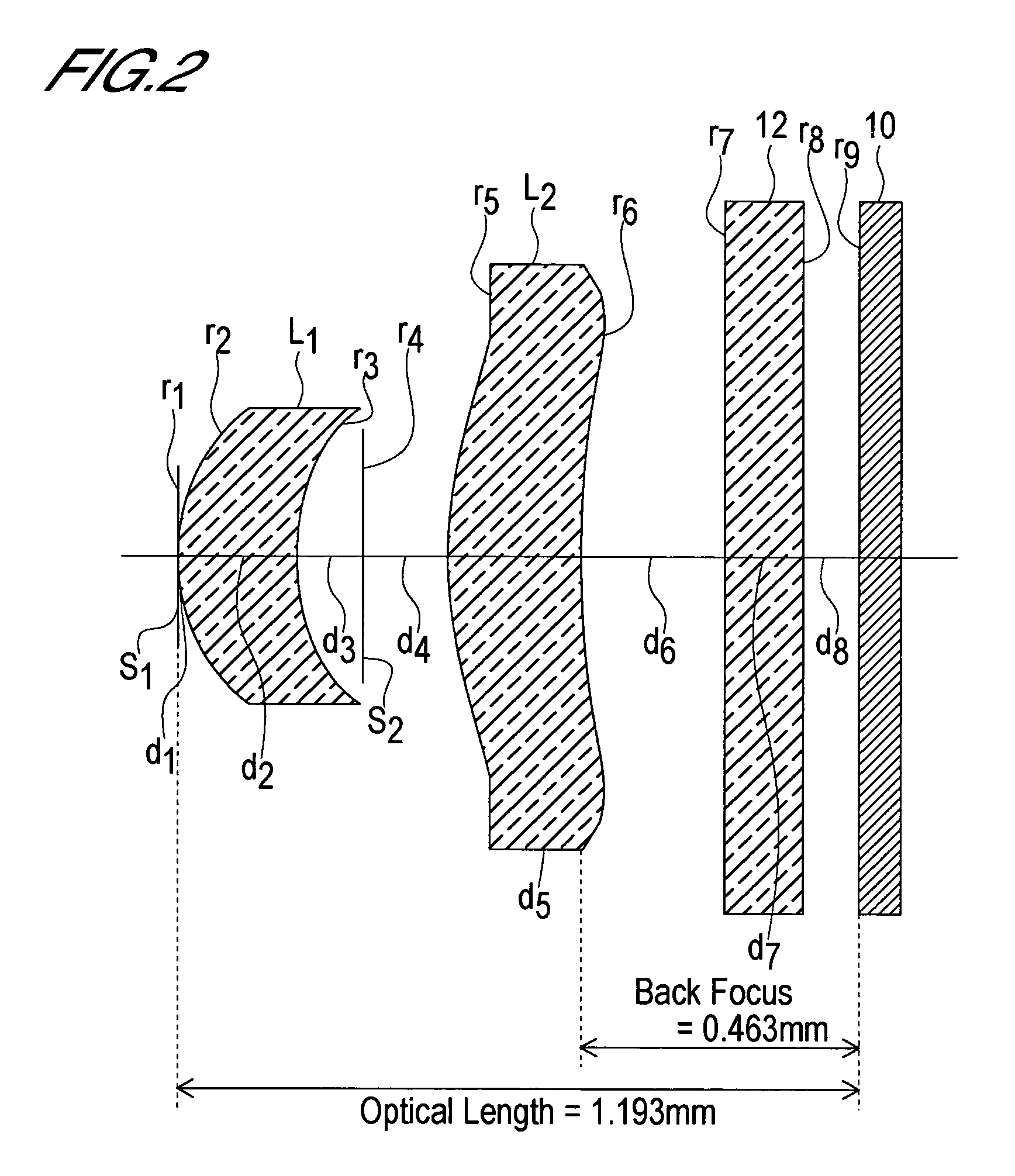
Imaging lens
ActiveUS20050157408A1Satisfactory brightnessSatisfactory imageCamera diaphragmsLensImage contrastConvex side
The present invention relates to an imaging lens with an F-number in the range 2.0 to 4.0, configured from only two lenses, with a short lens optical length, and with sufficiently high image contrast so that sharp images are obtained. The imaging lens is configured by positioning, in order from an object side to an image side, an aperture diaphragm, a first lens, a second diaphragm, and a second lens, satisfying the following conditions. The first lens and second lens are both meniscus-shaped with convex surface facing the object side, and have positive refractive power. 0.3<f1 / f2<1.0 (1) 0.4<bf / f<0.5 (2) 1.0<d / f<1.3 (3) 0.12<D2 / f<0.30 (4) 2.0<Fno<4.0 (5) Here f is the combined focal length of the imaging lens, f1 is the focal length of the first lens, f2 is the focal length of the second lens, bf is the distance (in air) from the image-side surface of the second lens to the image plane, d is the distance (in air) from the object-side surface of the first lens to the image plane, D2 is the interval between the first lens and the second lens, and Fno is the F-number.
Owner:SEIKOH GIKEN
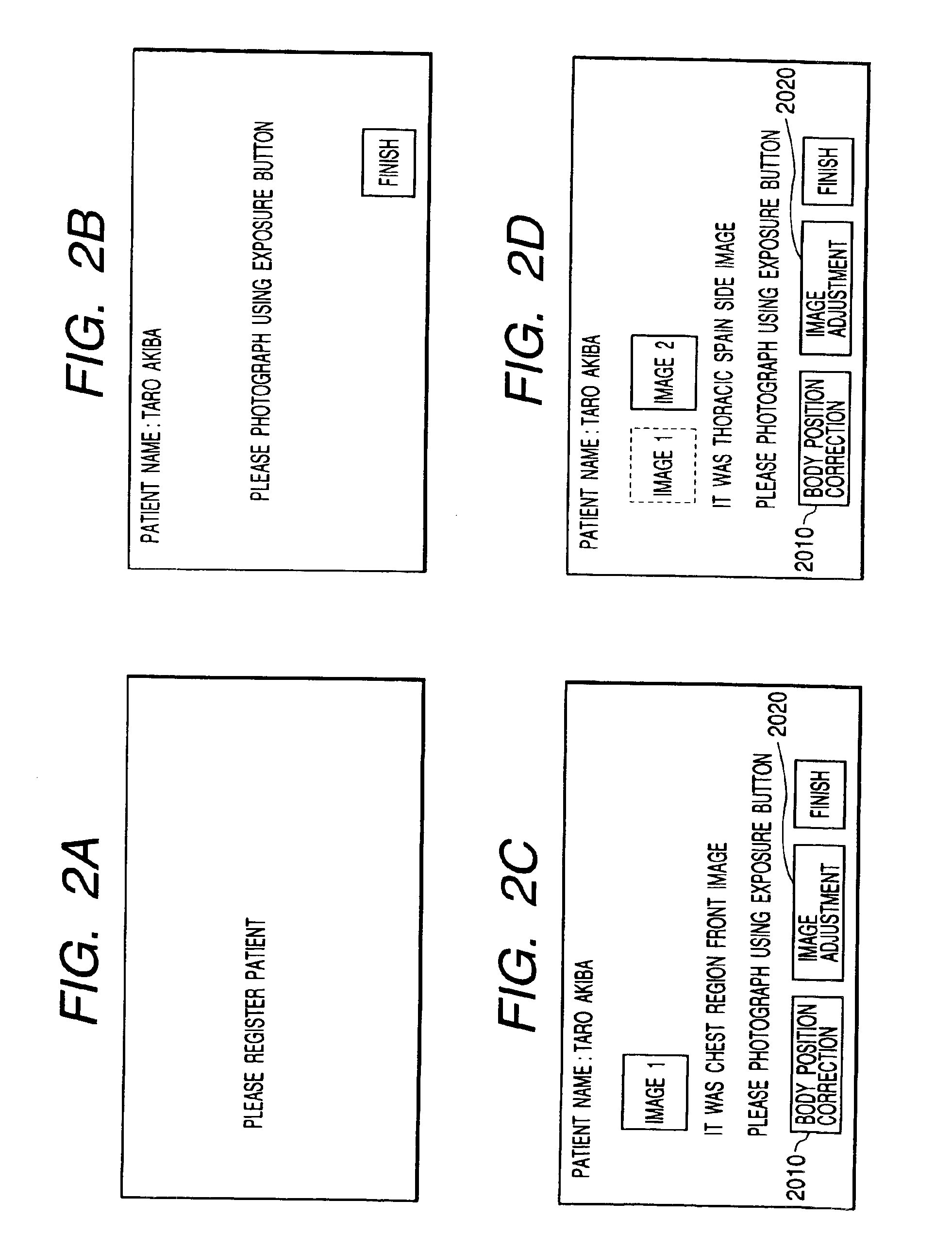
Apparatus, method and memory medium for processing a radiation image
InactiveUS6911988B1Satisfactory imageEasy to correctImage enhancementImage analysisImaging processingRadiation
From a taken image such as a radiation image, plural characteristic amounts (two-dimensional characteristic amounts etc.) are extracted to judge the portion (position) of the object on the taken image, and the result of judgment is displayed. On the image displaying the result of judgment of the object position, the operator confirms whether the object position is correctly judged, and, if the result is erroneous, changes the result of judgment by changing means. Based on the result of judgment changed by the operator or without such change, corresponding image processing parameters are acquired from the parameter table prepared in advance. Such image processing parameters are used for executing the image processing on the taken image.
Owner:CANON KK
Image forming apparatus and process cartridge
ActiveUS20050244176A1Prevent degradationSmall sizeDevelopersElectrographic process apparatusLatent imageMagnetization
In an image forming apparatus that employs a system of charging by adjacent discharge, not only can degradation of the photoreceptor surface caused by adjacent discharge be prevented, but also there is no side effect on the developer, and at the same time size reduction is achieved. The image forming apparatus comprises an object to be charged whose surface moves; a charging device for charging the object to be charged using an electrical discharge generated by applying a voltage comprising an alternating current component to a charging member provided in contact with or in proximity to the object to be charged; a latent image forming device for forming an electrostatic latent image on the surface of the object charged by the charging device; and a developing device for causing a two-component developer to come into contact with the image portion of the electrostatic latent image formed by the latent image forming device and affixing toner thereto. A protective substance is present on the surface of the object to be charged in the discharge region for charging the object to be charged, and the saturation magnetization of the carrier of the two-component developer with respect to an applied magnetic field of 1000 oersted is 40 to 80 emu / g.
Owner:RICOH KK
Charging member having an elastic foam member including cell portions whose gap ratio is 5% to 50%, charging apparatus, process cartridge, and image forming apparatus having such charging member
InactiveUS6904253B2Satisfactory performanceSatisfactory imageAgricultural rollersElectrographic process apparatusElectrical batteryImage formation
A charging member for charging a member to be charged, includes an elastic foam member provided at a surface of the charging member. The elastic foam member includes a plurality of cell portions with wall portion defining the cell portions. The gaps connecting the cell portions have areas which are not less than 5% and not more than 50%, for respective cells.
Owner:CANON KK
Image recording apparatus
ActiveUS20050168521A1Easy to useEasy to cleanTypewritersOther printing apparatusLiquid wasteImage recording
An image recording apparatus for recording an image on a recording medium includes a conveying belt for supporting and conveying the recording medium, and a recording head for recording the image by jetting ink onto the recording medium. The apparatus further includes a plurality of cleaning rollers for cleaning the conveying belt, the cleaning rollers being in pressure-contact with the conveying belt, and a plurality of cleaning liquid baths for respectively storing cleaning liquid to be used to remove dirt deposited on the respective cleaning rollers and for dipping the respective cleaning rollers into the cleaning liquid. The apparatus uses liquid waste as cleaning liquid in a cleaning liquid bath on an upstream side of the conveying belt, the liquid waste having become unable to be used in a cleaning liquid bath on a downstream side of the conveying belt any longer as cleaning liquid.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
Lung cancer diagnosis using magnetic resonance imaging data obtained at three time points
InactiveUS7949164B2Satisfactory imagePrecise shiftImage enhancementImage analysisClassification methodsMalignancy
A malignancy classification method and medium for diagnosing a region of lung tissue based on MRI data are disclosed. The classifying includes: setting time points T1 and T2 measured from injection of a contrast agent. T1 represents a wash-in time point for malignant lung tissue at which a first concentration value of the injected contrast agent is substantially equal to or near a peak for injected contrast agent concentration in the region of lung tissue. Patient concentration values of the contrast agent for the area of lung tissue at time points T1 and T2 are obtained, and a malignancy classification for the region of lung tissue is provided by comparing the obtained sample concentration values with a predetermined malignancy profile. A visual representation of the malignancy classification of the region of lung tissue is outputted.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
Toner, image forming method, image forming apparatus, and process cartridge
InactiveUS20120264048A1Improve chargeabilityImprove stabilityDevelopersElectrographic processes using charge patternEngineeringMonomer
Provided is a toner including: toner particles, each toner particle containing a toner base particle, wherein the toner contains a binder resin; and a colorant, wherein the toner base particle has protrusions at a surface thereof, wherein an average of lengths of long sides of the protrusions is 0.1 μm or more but less than 0.5 μm, a standard deviation of the lengths of the long sides of the protrusions is 0.20 or less, and a coverage rate of the protrusions is 30% to 90%, wherein a resin forming the protrusions is prepared through polymerization of a monomer mixture containing at least a monomer having a sulfonic acid group, and wherein the monomer mixture contains styrene in an amount of 90% by mass or more and the monomer having a sulfonic acid group in an amount of 0.1% by mass to 5% by mass.
Owner:RICOH KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com