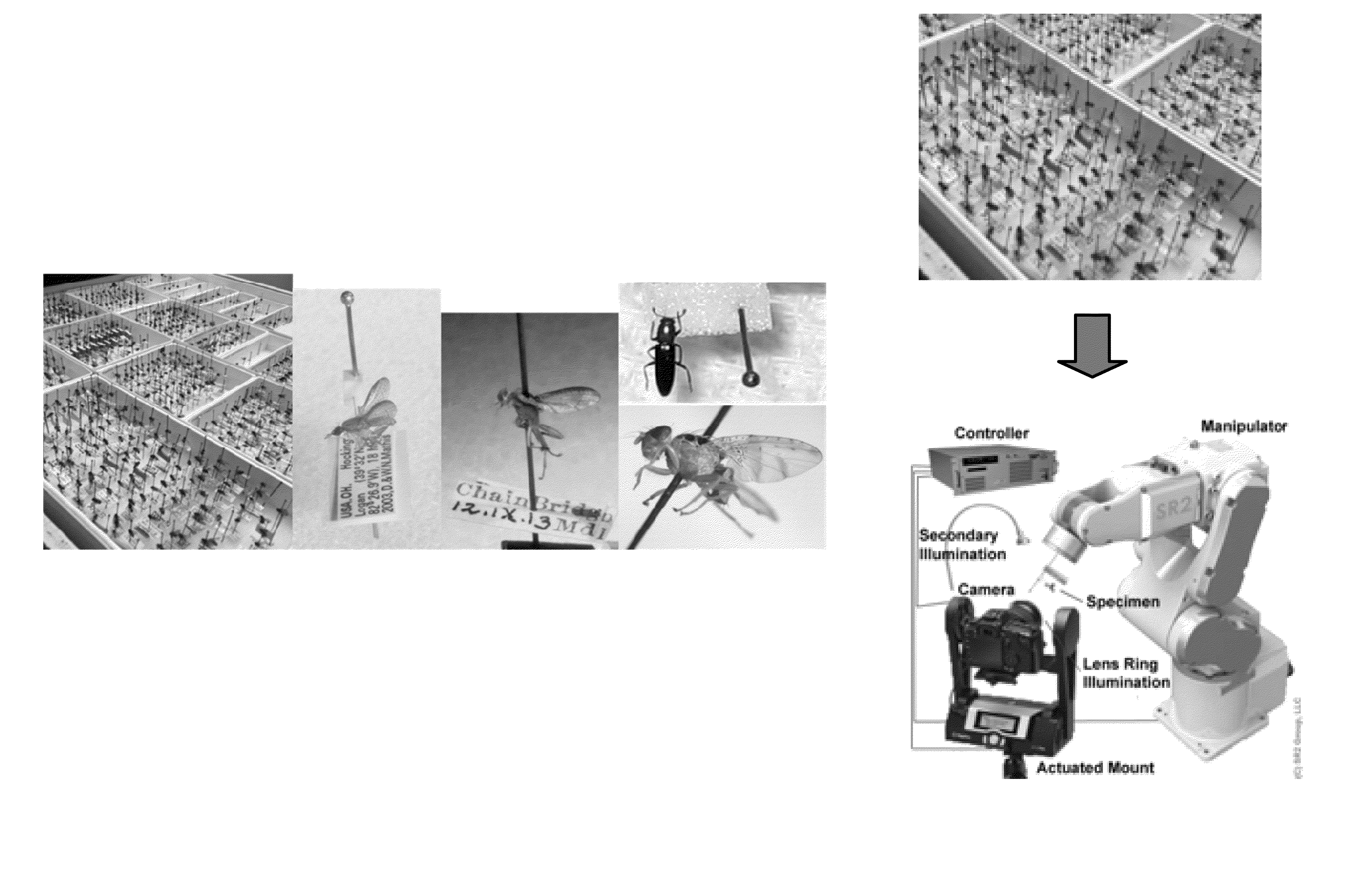Patents
Literature
74 results about "Adaptive imaging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
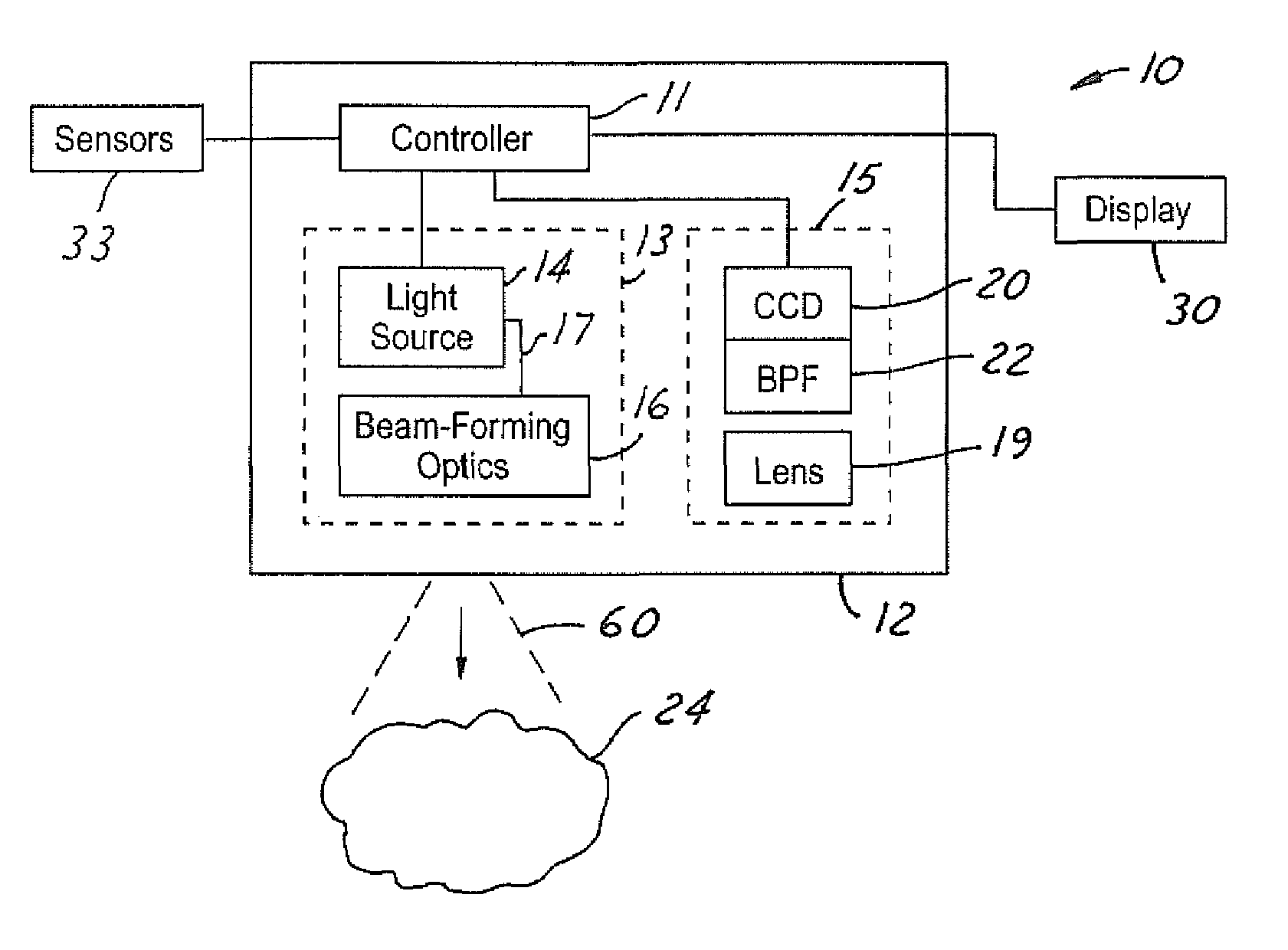
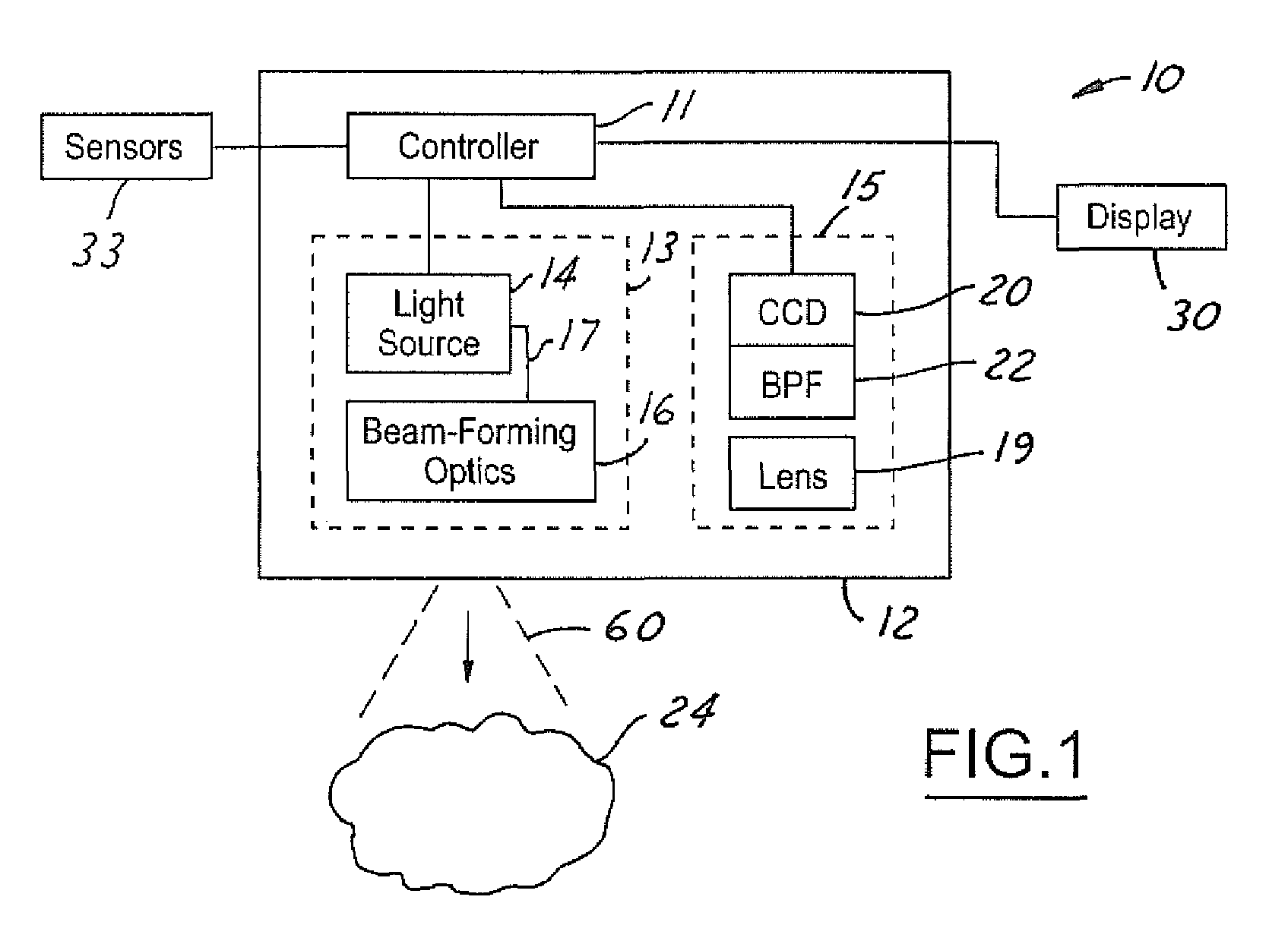
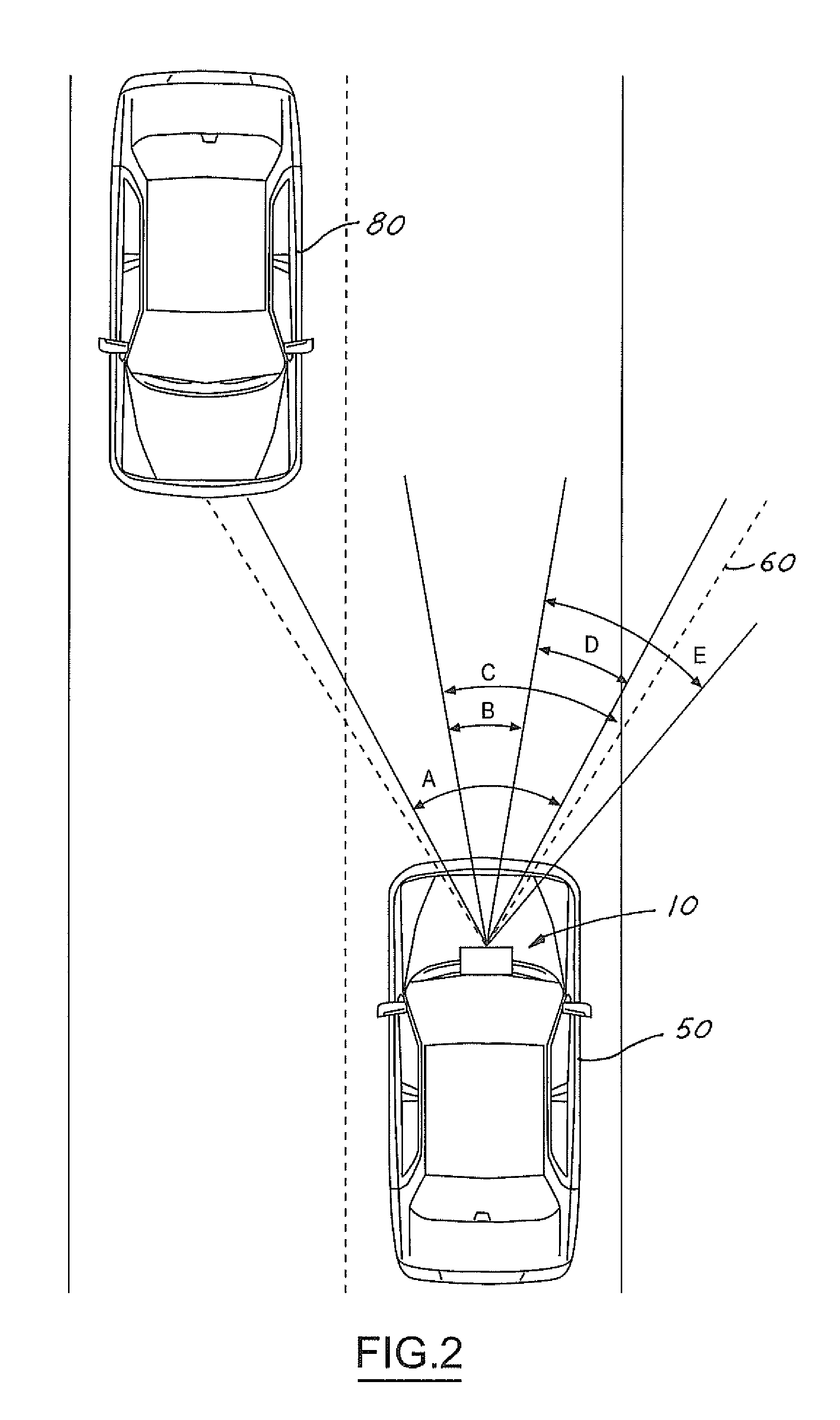
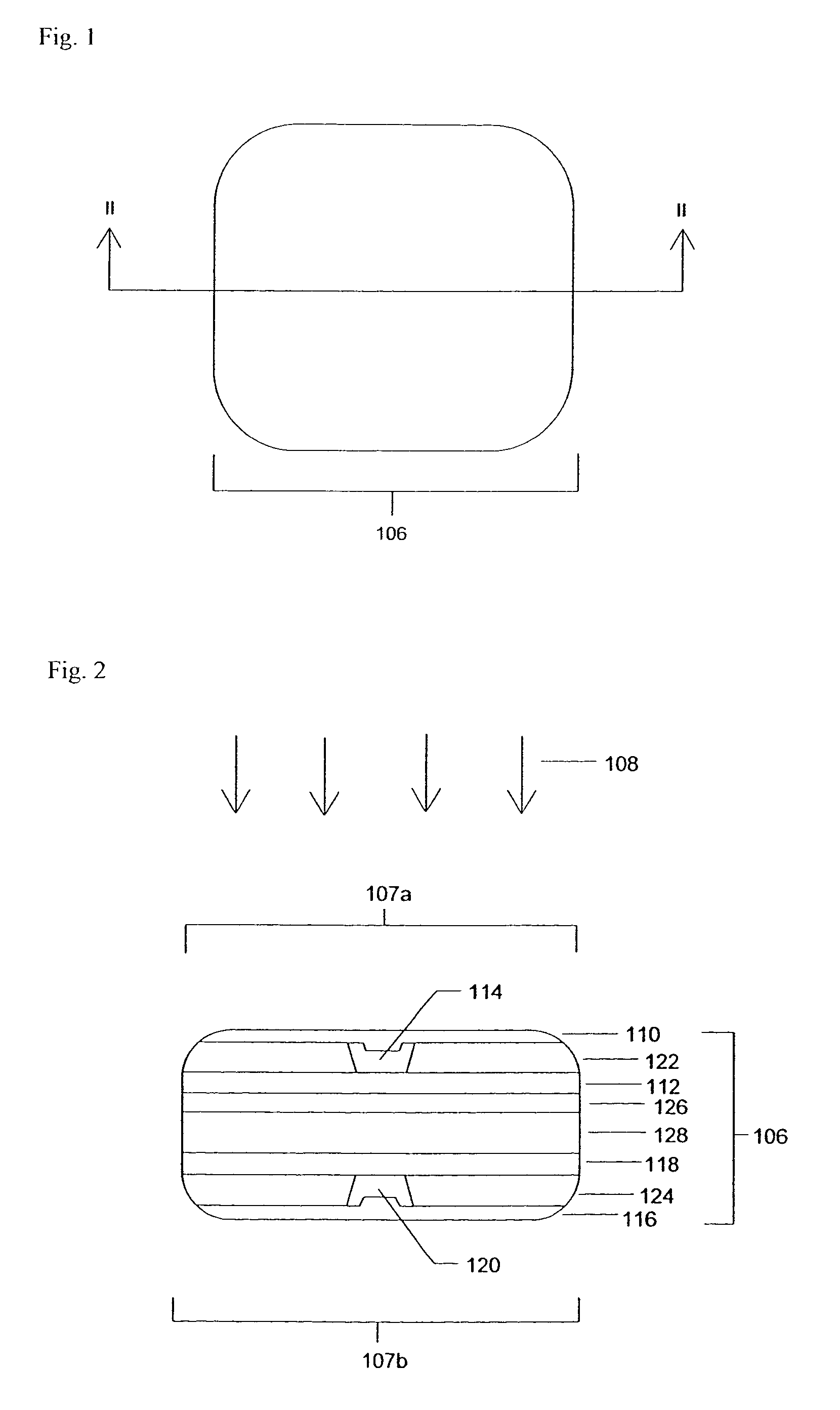
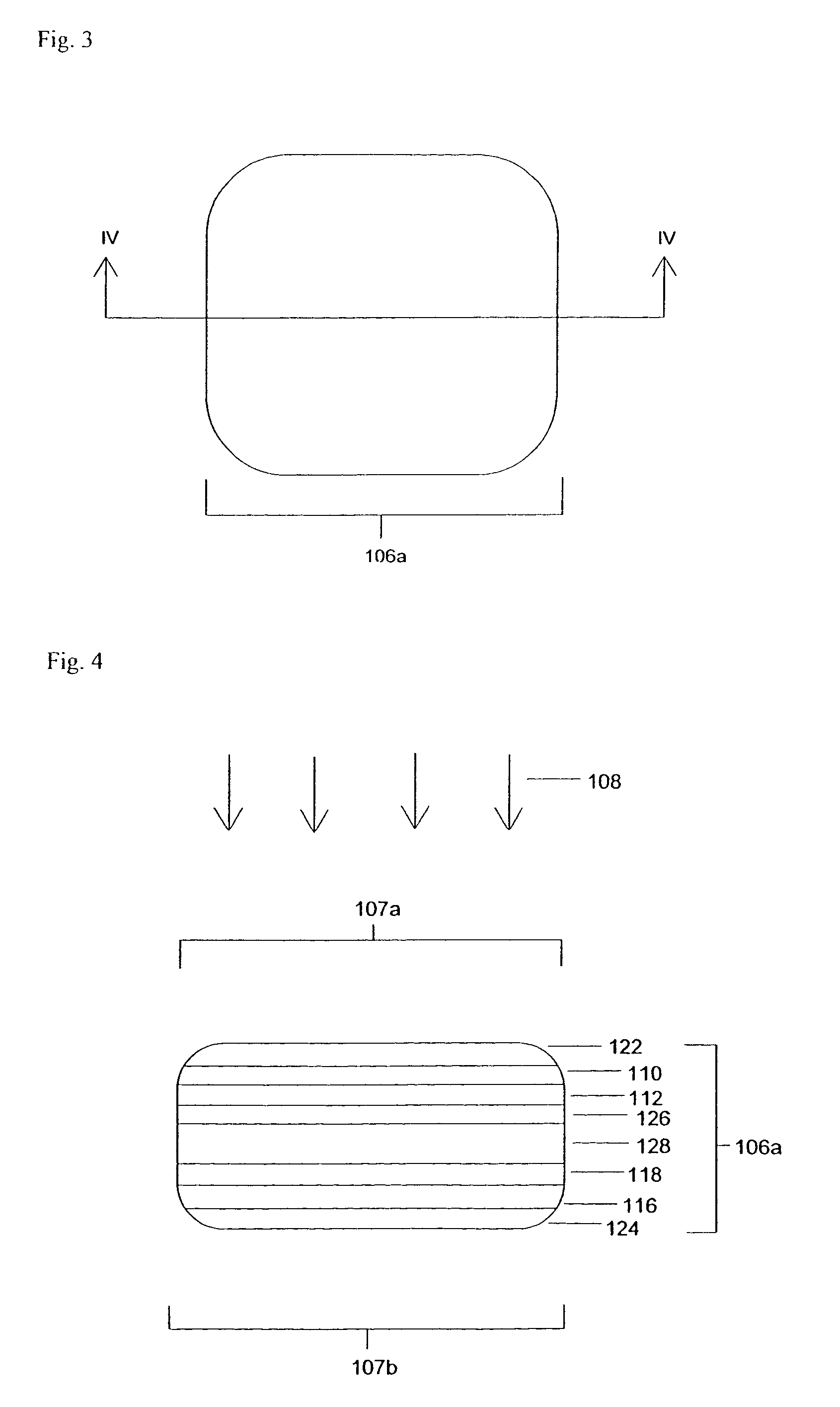
Active night vision with adaptive imaging
InactiveUS6967569B2Minimize complexityLow costAnti-collision systemsColor television detailsNight visionAdaptive imaging
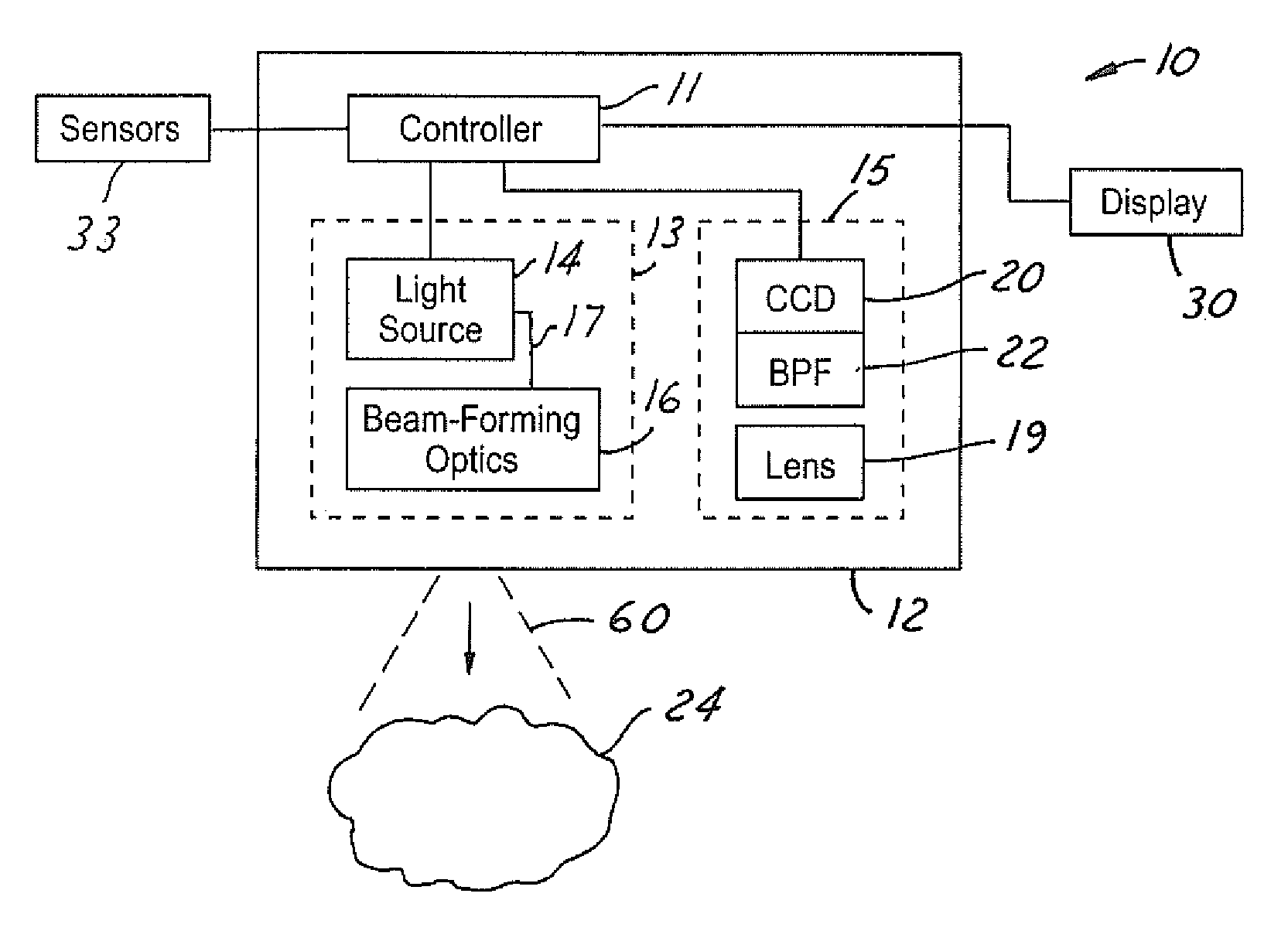
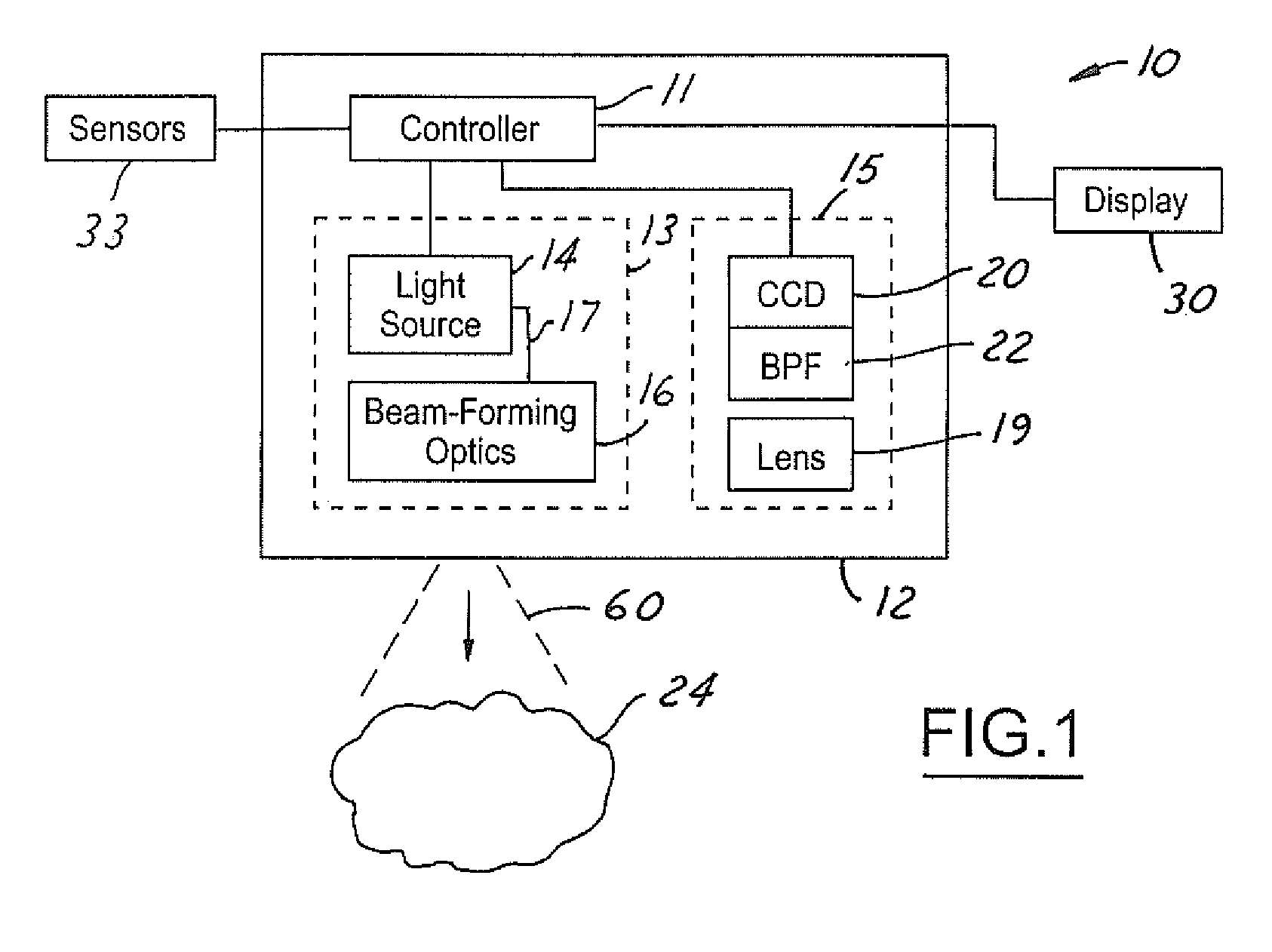
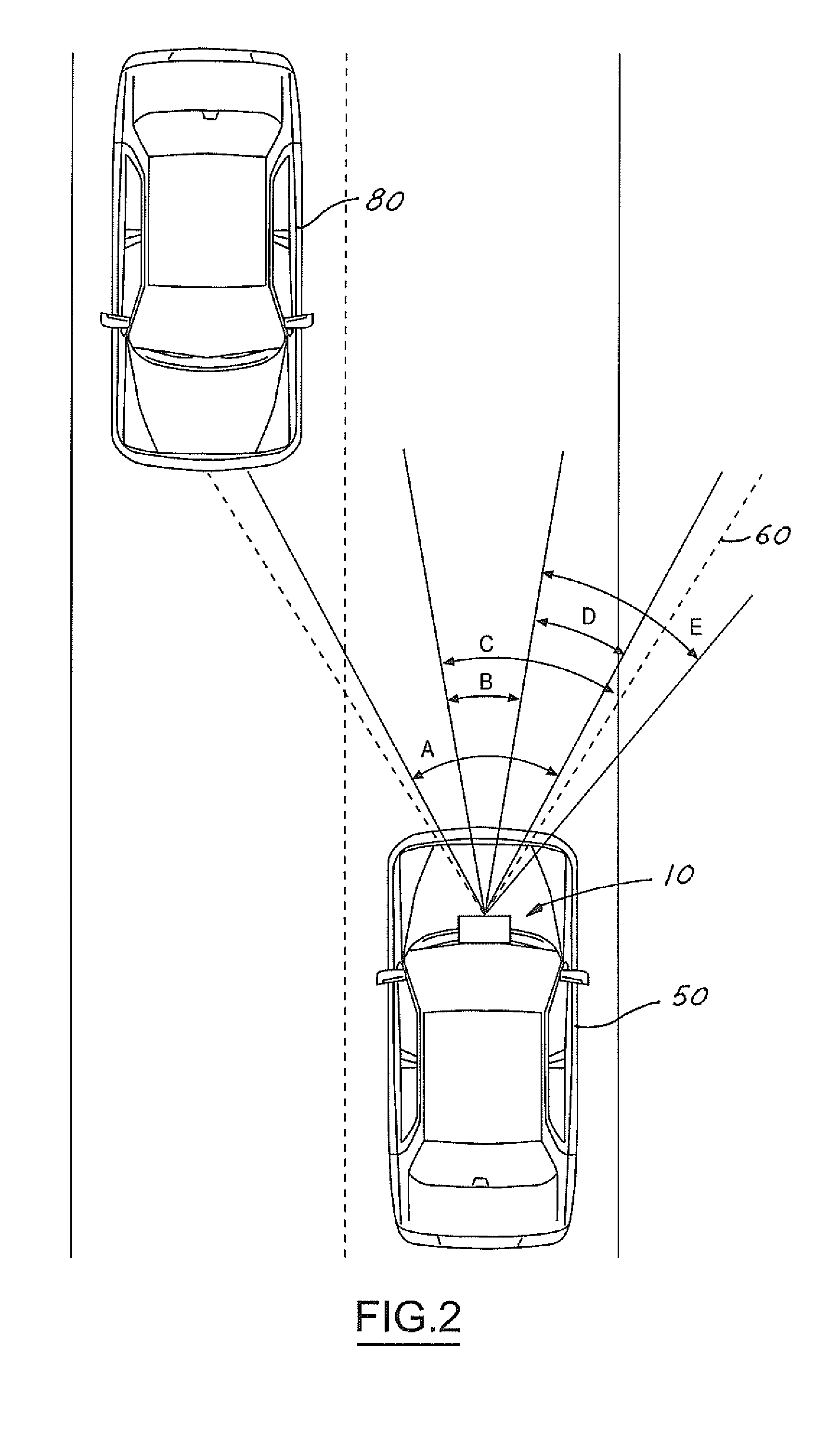
A vision system for a vehicle includes a light source generating an illumination beam, a receiver having a pixel array for capturing an image in response to at least a reflected portion of the illumination beam, the image corresponding to a first horizontal field of view (FOV) angle, and a controller coupled to the light source and the receiver. The controller receives a vehicle speed input and, in response, selects a portion of the image as a non-linear function of the vehicle speed to generate a second horizontal FOV angle for displaying to the vehicle operator. The displayed angular FOV decreases, non-linearly, as the vehicle speed increases.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
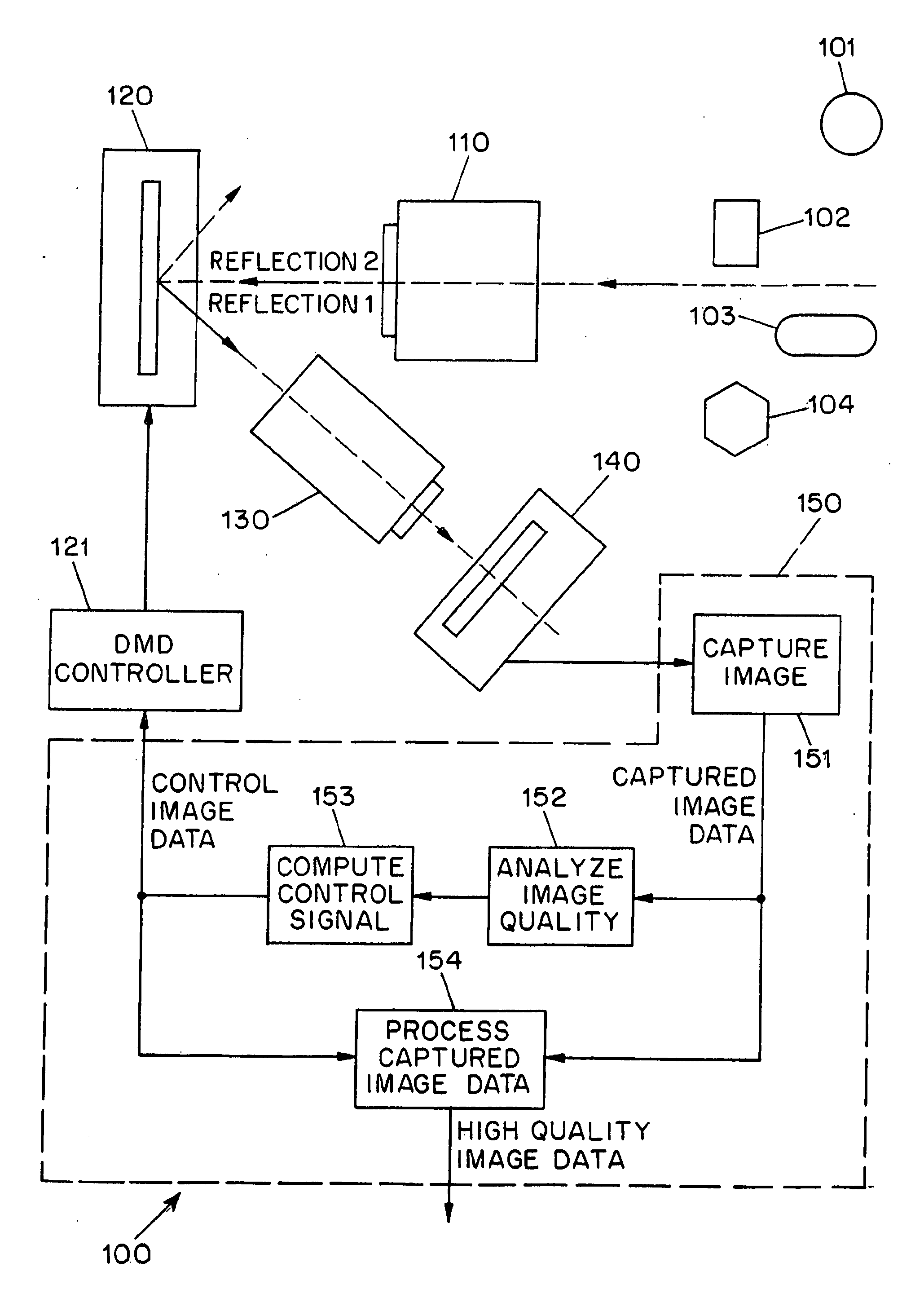
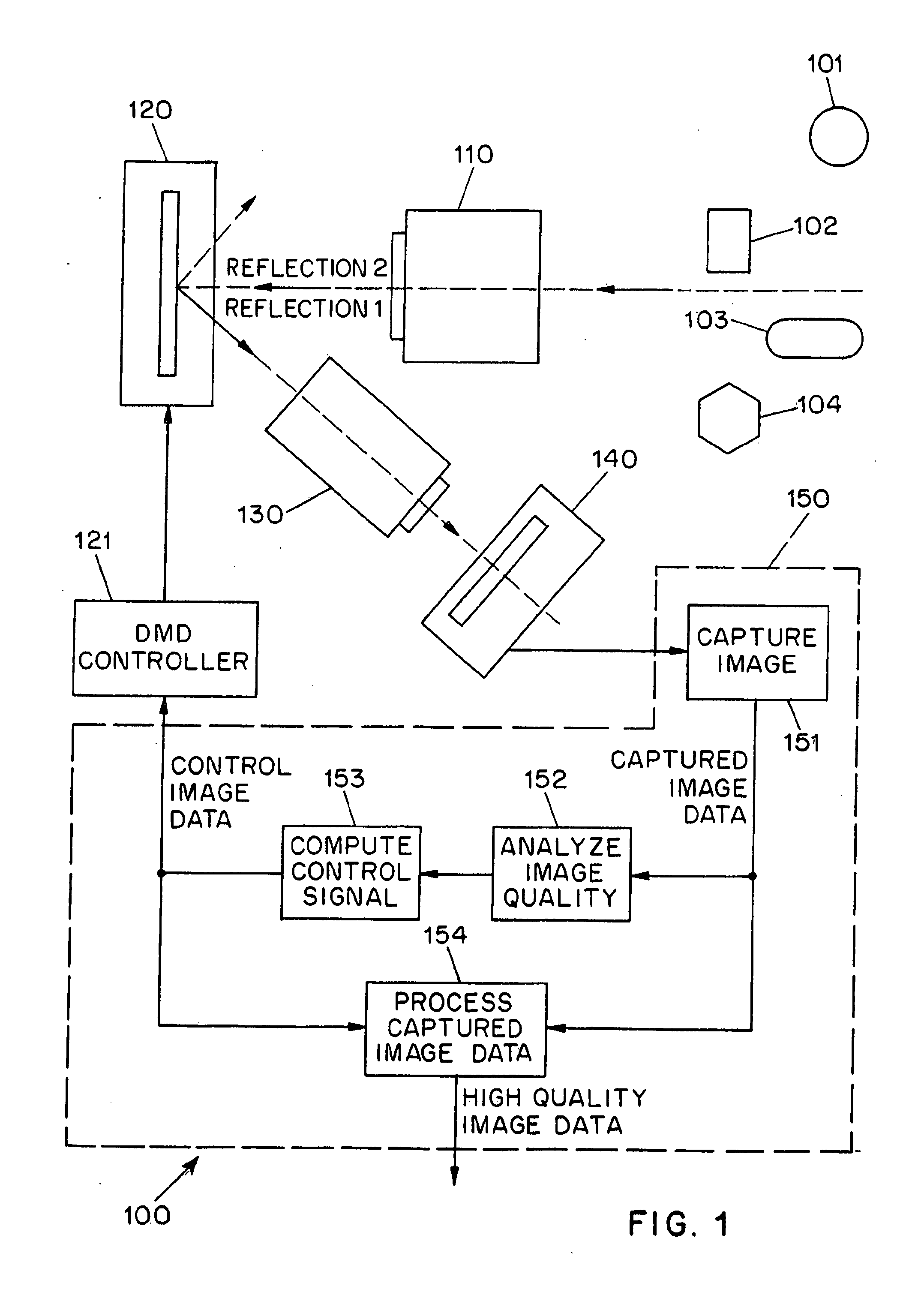
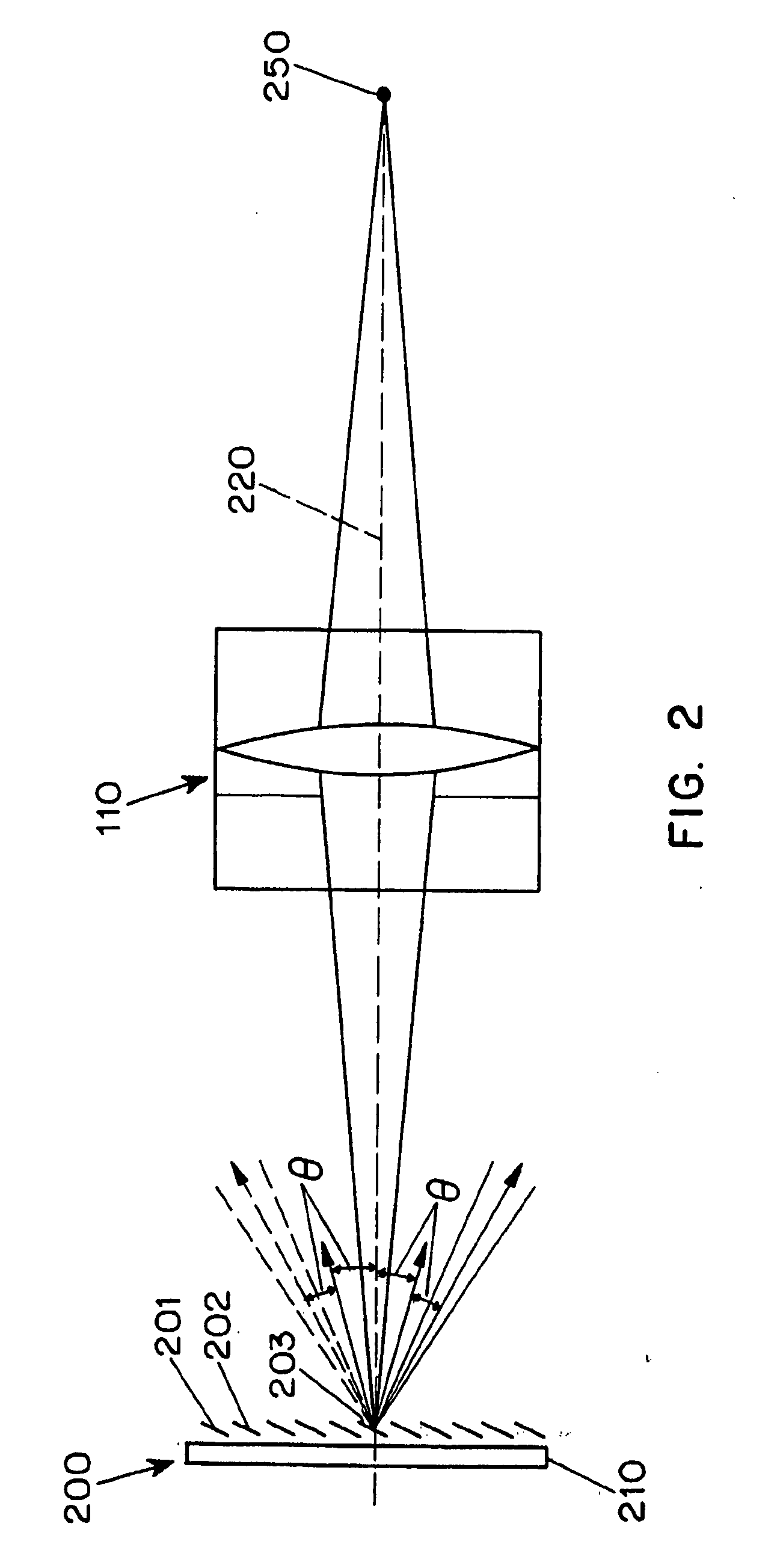
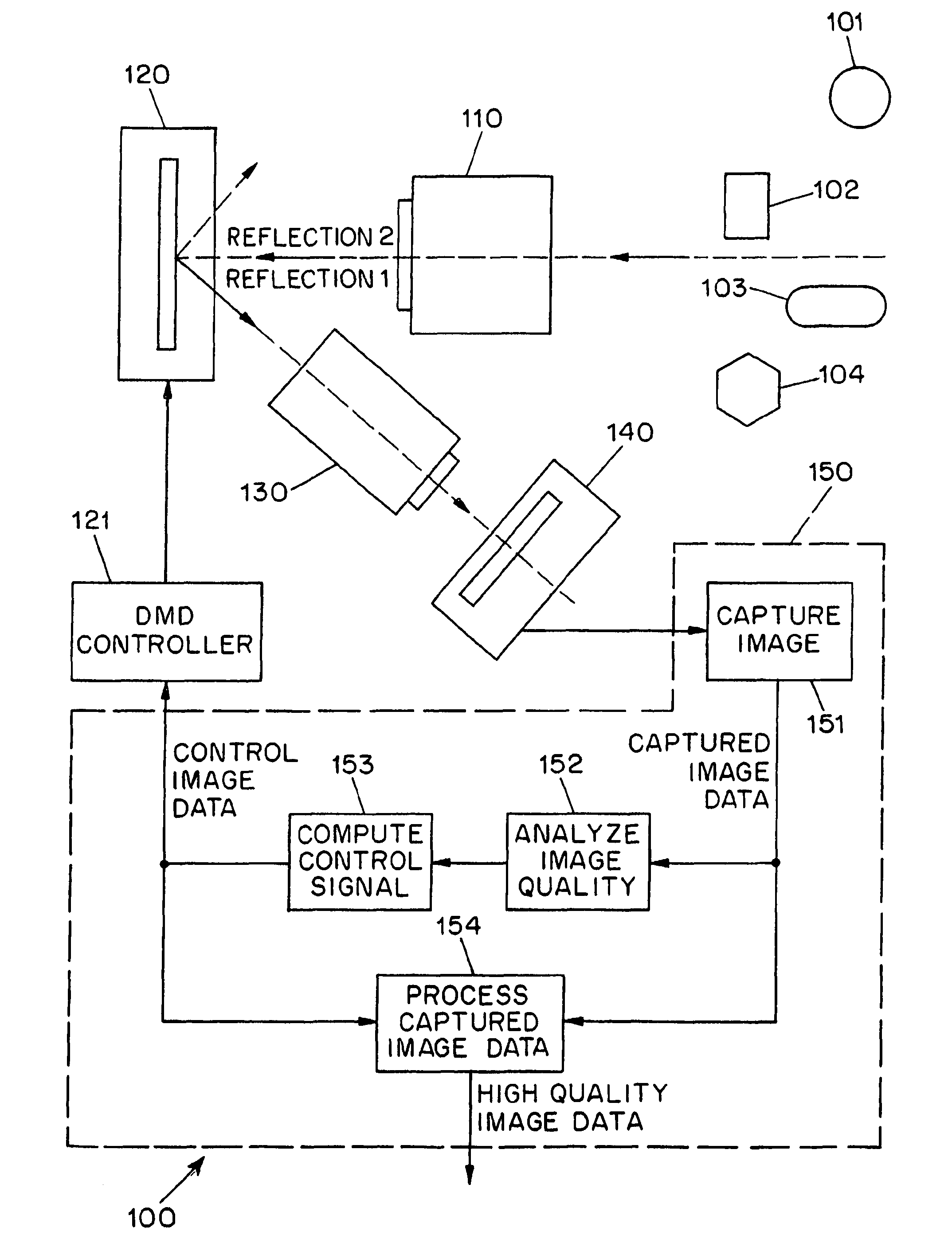
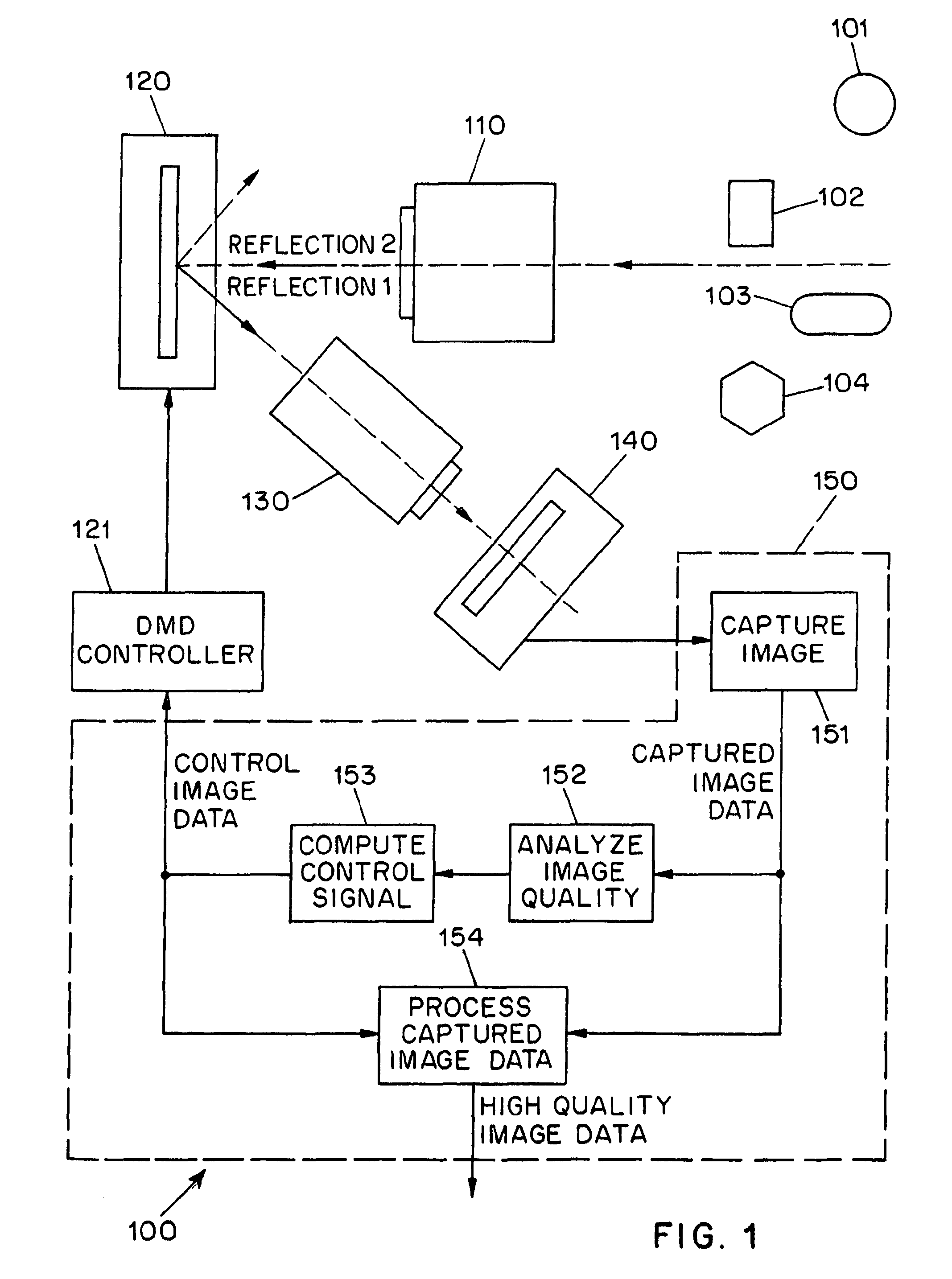
Adaptive imaging using digital light processing
ActiveUS20110211077A1High imageIncrease rangeTelevision system detailsColor television detailsDigital signal processingAdaptive imaging
A system (100) for the adaptive imaging of a scene includes a digital light processing apparatus (150) adapted for controllably reflecting an image of the scene in at least a first direction to thereby reflect an intensity modulated image of the scene along at least the first direction, an image detector (140) for detecting the intensity modulated image of the scene and generating corresponding image data, and an image data processor (154) for processing the image data into control data and providing the control data to the digital light processing (150) apparatus for control thereof.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
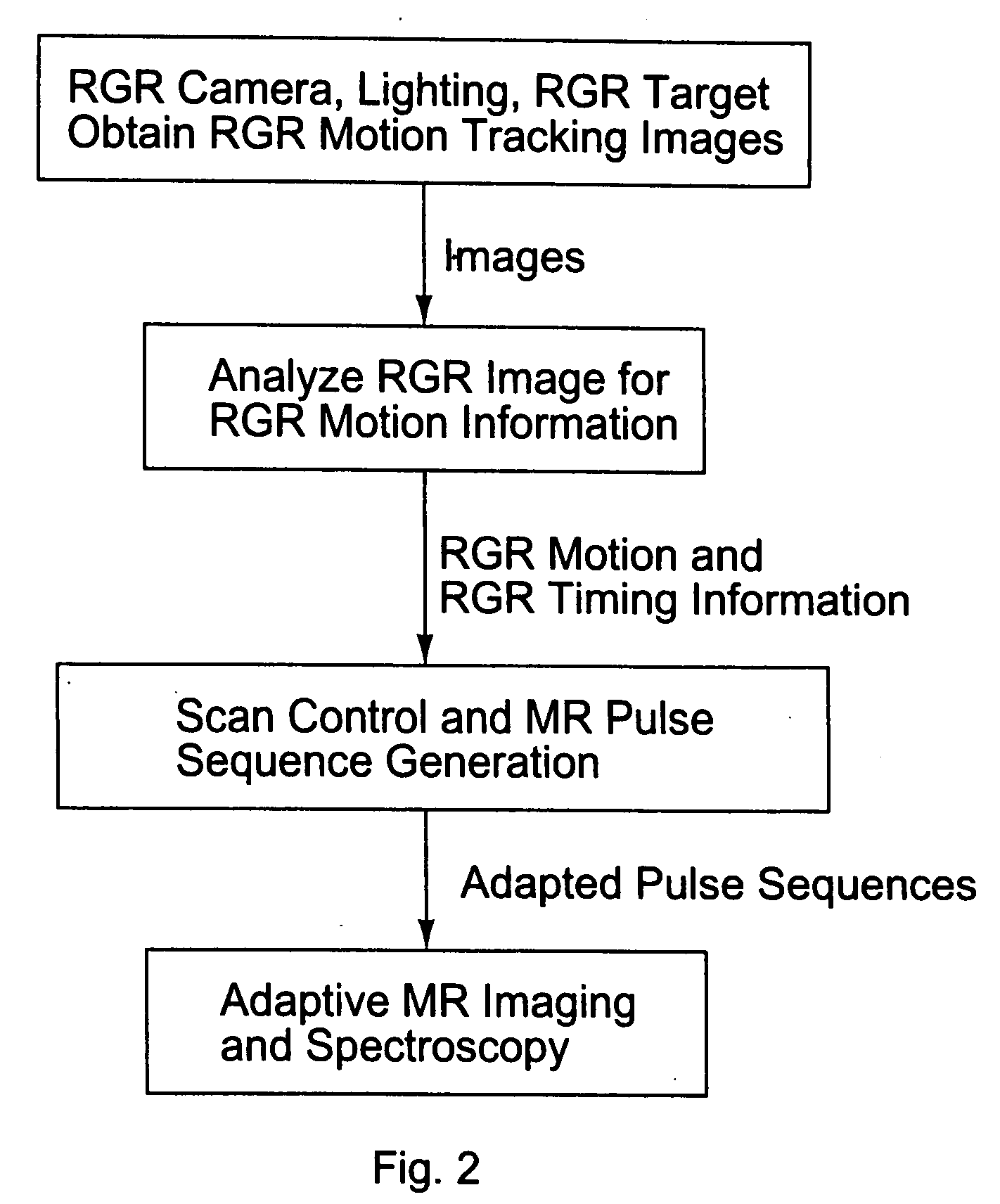
Motion tracking system for real time adaptive imaging and spectroscopy
ActiveUS20070280508A1Improve performanceImprove accuracyImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionAdaptive imagingUsability
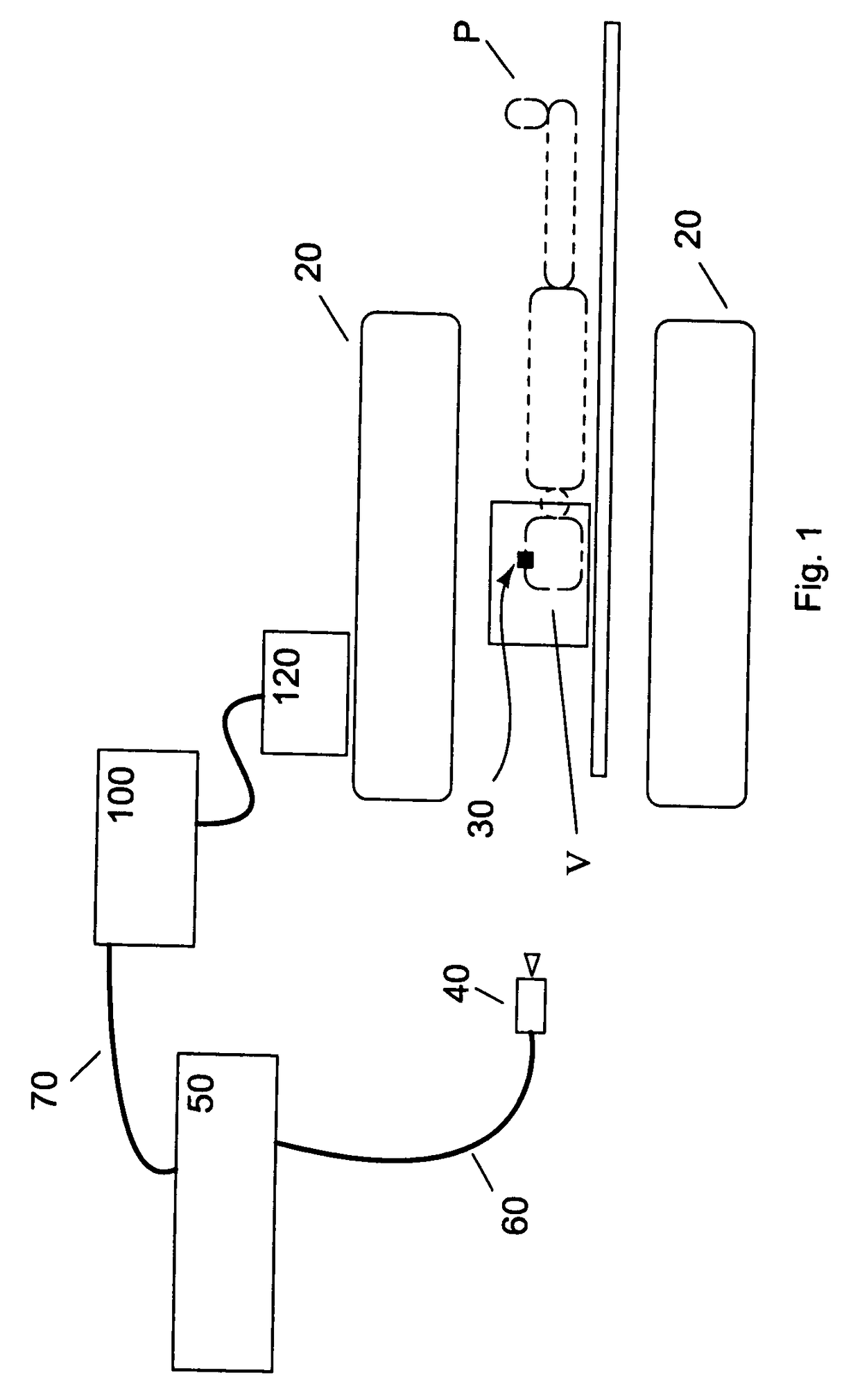
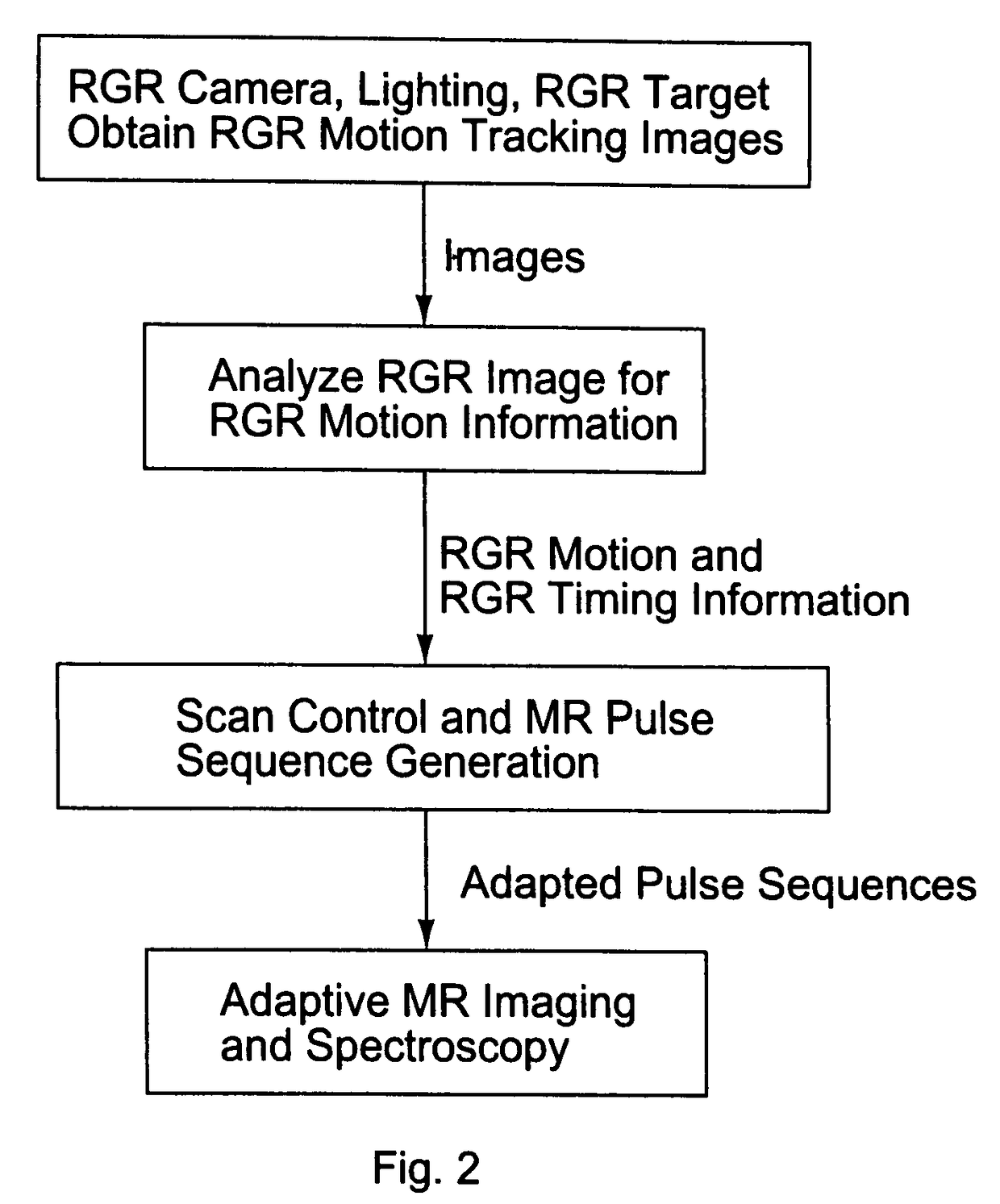
Current MRI technologies require subjects to remain largely motionless for achieving high quality magnetic resonance (MR) scans, typically for 5-10 minutes at a time. However, lying absolutely still inside the tight MR imager (MRI) tunnel is a difficult task, especially for children, very sick patients, or the mentally ill. Even motion ranging less than 1 mm or 1 degree can corrupt a scan. This invention involves a system that adaptively compensates for subject motion in real-time. An object orientation marker, preferably a retro-grate reflector (RGR), is placed on a patients' head or other body organ of interest during MRI. The RGR makes it possible to measure the six degrees of freedom (x, y, and z-translations, and pitch, yaw, and roll), or “pose”, required to track the organ of interest. A camera-based tracking system observes the marker and continuously extracts its pose. The pose from the tracking system is sent to the MR scanner via an interface, allowing for continuous correction of scan planes and position in real-time. The RGR-based motion correction system has significant advantages over other approaches, including faster tracking speed, better stability, automatic calibration, lack of interference with the MR measurement process, improved ease of use, and long-term stability. RGR-based motion tracking can also be used to correct for motion from awake animals, or in conjunction with other in vivo imaging techniques, such as computer tomography, positron emission tomography (PET), etc.
Owner:UNIV OF HAWAII +3
Device and system for improved imaging in nuclear medicine and mammography
InactiveUS7147372B2Easy to optimizeEnhance analysis capabilityMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingAdaptive imagingDetector array
A method and apparatus for detecting radiation including x-ray, gamma ray, and particle radiation for radiographic imaging, and nuclear medicine and x-ray mammography in particular, and material composition analysis are described. A detection system employs fixed or configurable arrays of one or more detector modules comprising detector arrays which may be electronically manipulated through a computer system. The detection system, by providing the ability for electronic manipulation, permits adaptive imaging. Detector array configurations include familiar geometries, including slit, slot, plane, open box, and ring configurations, and customized configurations, including wearable detector arrays, that are customized to the shape of the patient. Conventional, such as attenuating, rigid geometry, and unconventional collimators, such as x-ray optic, configurable, Compton scatter modules, can be selectively employed with detector modules and radiation sources. The components of the imaging chain can be calibrated or corrected using processes of the invention. X-ray mammography and scintimammography are enhanced by utilizing sectional compression and related imaging techniques.
Owner:MINNESOTA IMAGING & ENG
Motion tracking system for real time adaptive imaging and spectroscopy
ActiveUS8121361B2Accurately determinedAccurately determineImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionAdaptive imagingSpectroscopy
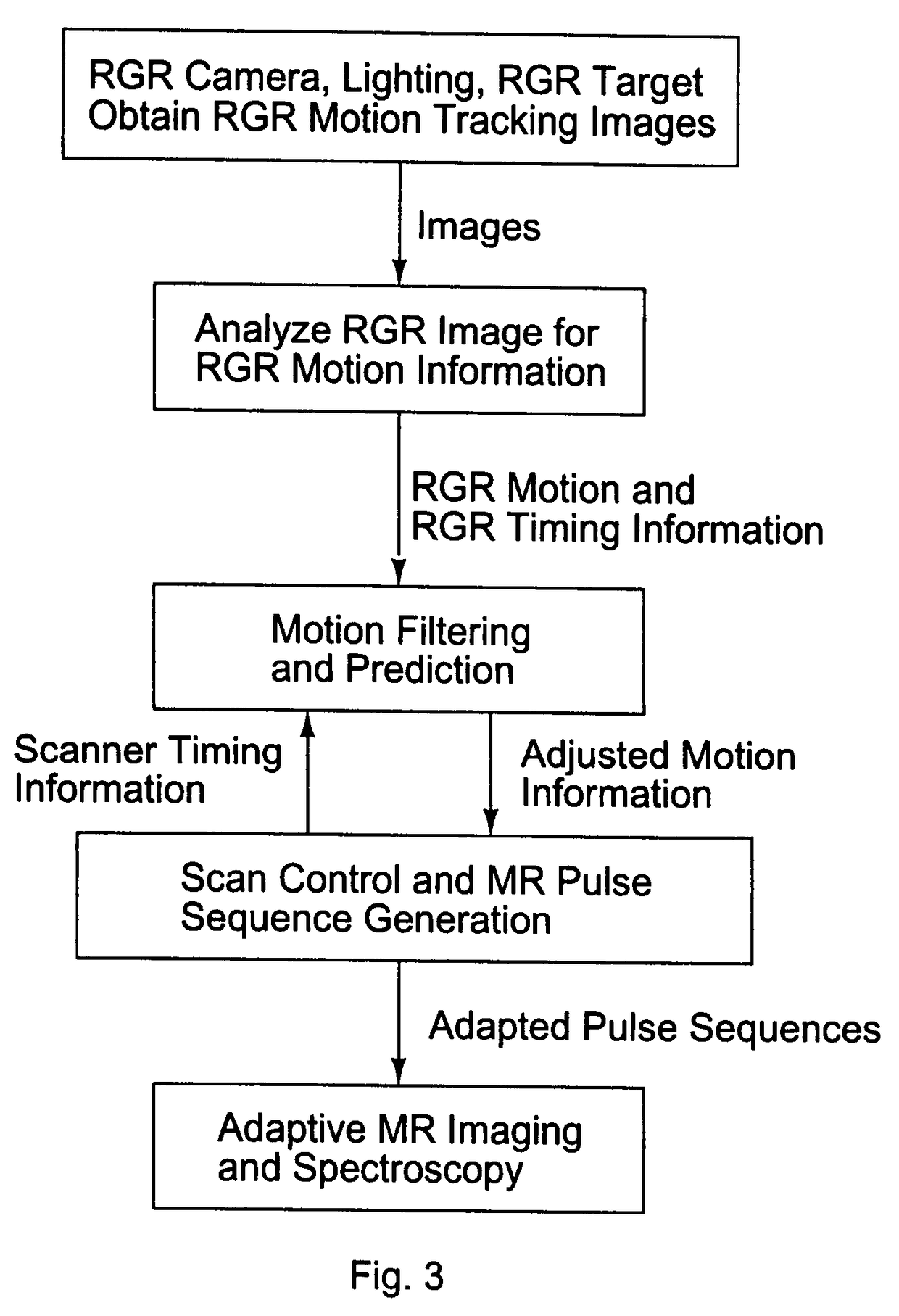
Current MRI technologies require subjects to remain largely motionless for achieving high quality magnetic resonance (MR) scans, typically for 5-10 minutes at a time. However, lying absolutely still inside the tight MR imager (MRI) tunnel is a difficult task, especially for children, very sick patients, or the mentally ill. Even motion ranging less than 1 mm or 1 degree can corrupt a scan. This invention involves a system that adaptively compensates for subject motion in real-time. An object orientation marker, preferably a retro-grate reflector (RGR), is placed on a patients' head or other body organ of interest during MRI. The RGR makes it possible to measure the six degrees of freedom (x, y, and z-translations, and pitch, yaw, and roll), or “pose”, required to track the organ of interest. A camera-based tracking system observes the marker and continuously extracts its pose. The pose from the tracking system is sent to the MR scanner via an interface, allowing for continuous correction of scan planes and position in real-time. The RGR-based motion correction system has significant advantages over other approaches, including faster tracking speed, better stability, automatic calibration, lack of interference with the MR measurement process, improved ease of use, and long-term stability. RGR-based motion tracking can also be used to correct for motion from awake animals, or in conjunction with other in vivo imaging techniques, such as computer tomography, positron emission tomography (PET), etc.
Owner:UNIV OF HAWAII +3
System and method for adaptively conformed imaging of work pieces having disparate configuration
ActiveUS9258550B1Using optical meansBiometric pattern recognitionRelative displacementScene segmentation
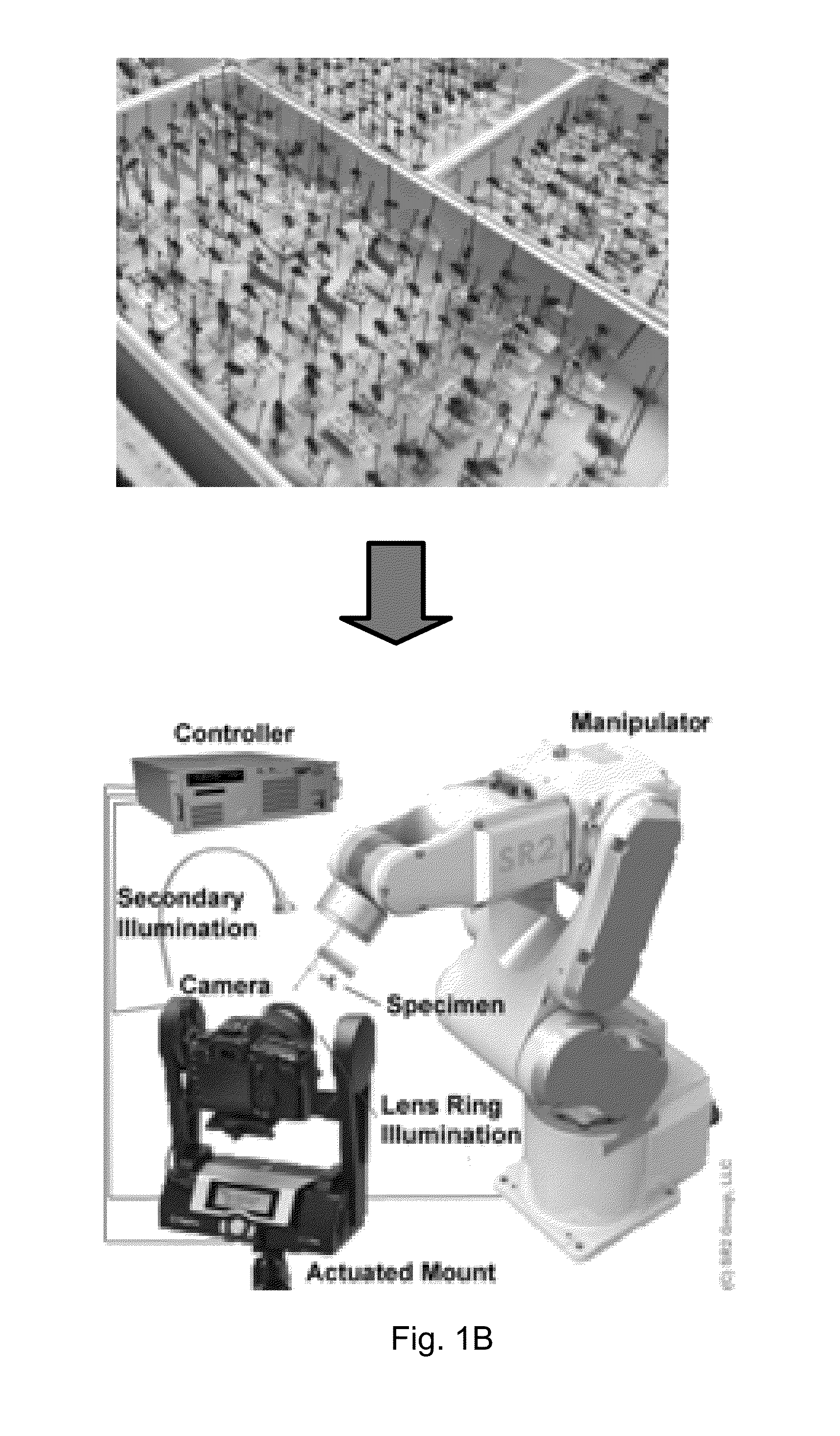
A system is provided for adaptively conformed imaging of work pieces having disparate configurations, which comprises a mount unit for holding at least one work piece, and an imaging unit for capturing images of the work piece held by the mount unit. At least one manipulator unit is coupled to selectively manipulate at least one of the mount and imaging units for relative displacement therebetween. A controller coupled to automatically actuate the manipulator and imaging units executes scene segmentation about the held work piece, which spatially defines at least one zone of operation in peripherally conformed manner about the work piece. The controller also executes an acquisition path mapping for the work piece, wherein a sequence of spatially offset acquisition points are mapped within the zone of operation, with each acquisition point defining a vantage point for the imaging unit to capture an image of the work piece from.
Owner:REALITY ANALYTICS INC
Adaptive imaging quality optimization method for unmanned aerial vehicle autonomous inspection of power transmission line
ActiveCN111272148AGuarantee the final image qualityGuaranteed image qualityTelevision system detailsColor television detailsAdaptive imagingImaging quality
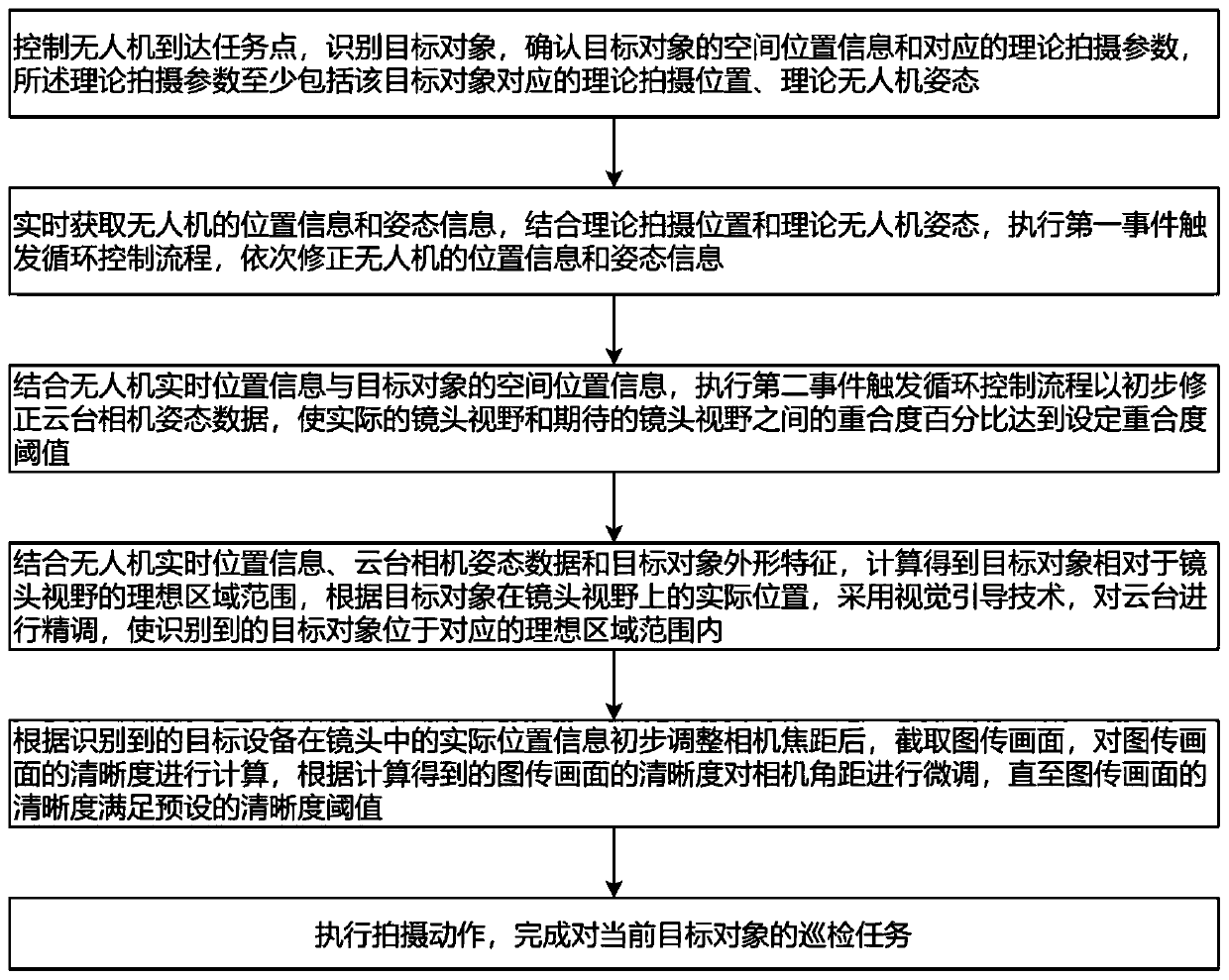
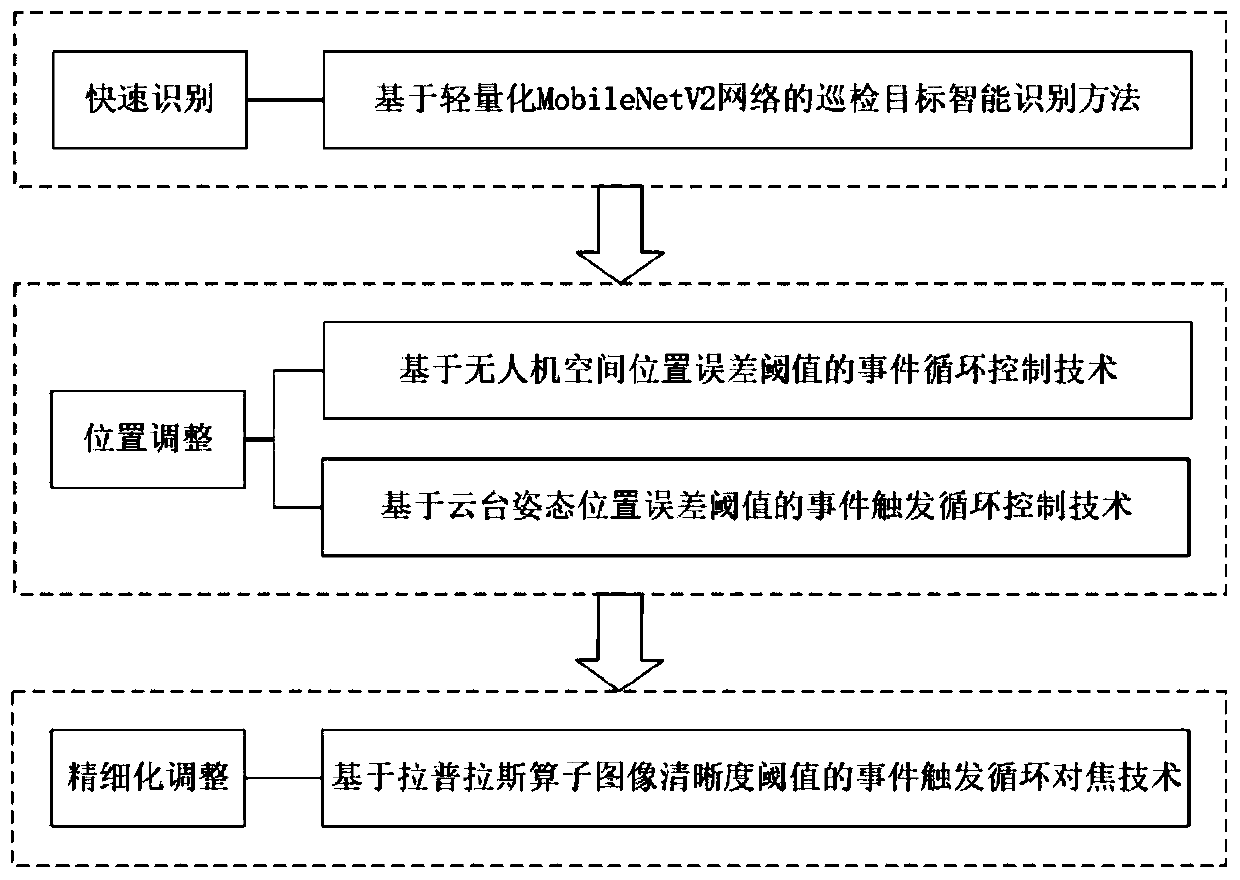
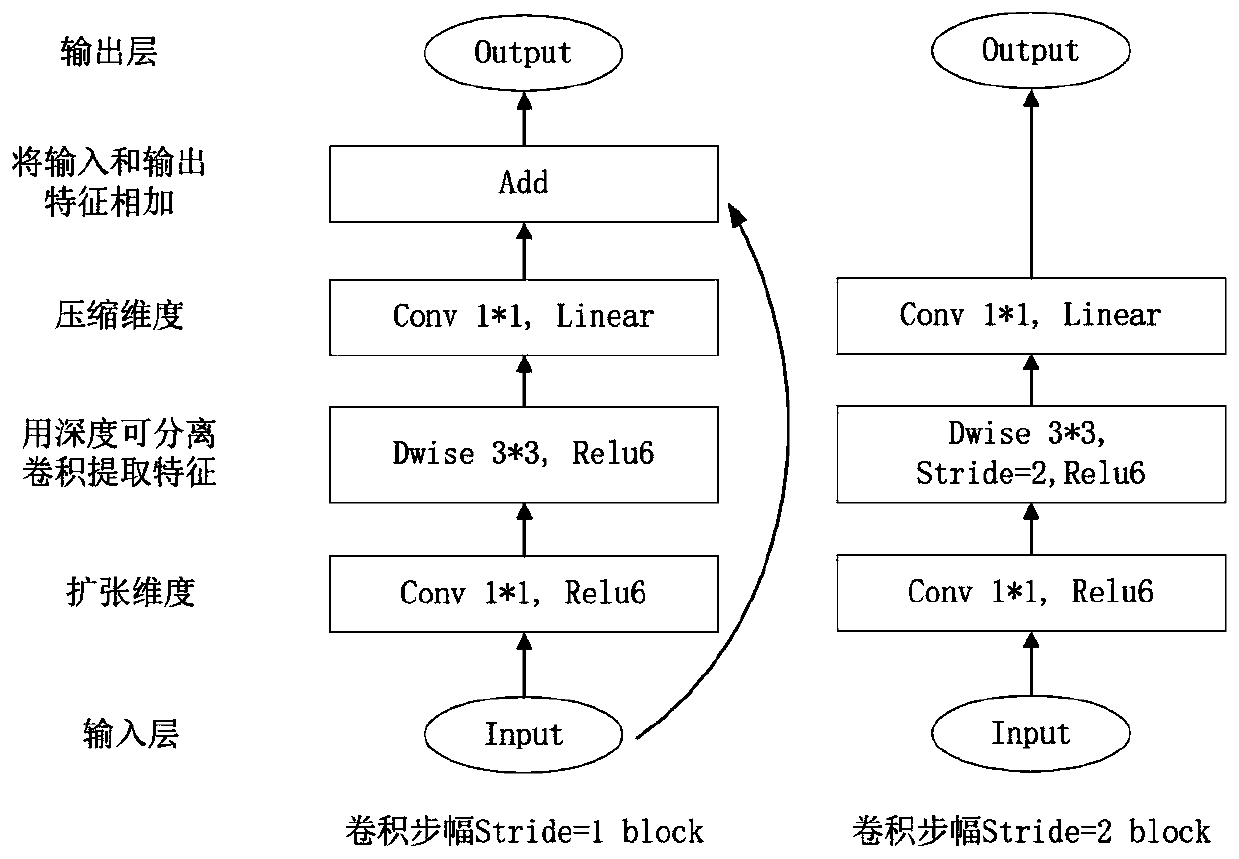
The invention discloses an adaptive imaging quality optimization method for the unmanned aerial vehicle autonomous inspection of a power transmission line. According to the present invention, an eventtrigger loop control technology based on an unmanned aerial vehicle spatial position error threshold, an event trigger loop control technology based on a pan-tilt attitude position error threshold and an event trigger loop focusing technology based on a Laplace operator image definition threshold are used in sequence, the imaging quality of the inspection photos is detected at the aspects of photo shooting angle, lens focusing condition, photo clarity and the like, and a corresponding method is adopted for optimization, so that the final imaging quality of the photos is ensured. An iterativethought is adopted, the photo shooting angle is gradually optimized from the shooting position, the head direction and the pan-tilt camera attitude information, and the photo shooting angle precisionis improved, so that a target device is located at the image center position as much as possible, the subsequent focusing, definition adjustment and the like are facilitated, and the imaging quality is ensured. Meanwhile, the adjustment amplitude of the pan-tilt camera attitudes is reduced, and the mechanical loss is reduced.
Owner:JIANGSU FRONTIER ELECTRIC TECH +1
Methods and systems for adaptive tomographic imaging
ActiveUS20130105699A1Improves image quality metricMaterial analysis by optical meansCharacter and pattern recognitionPresent methodAdaptive imaging
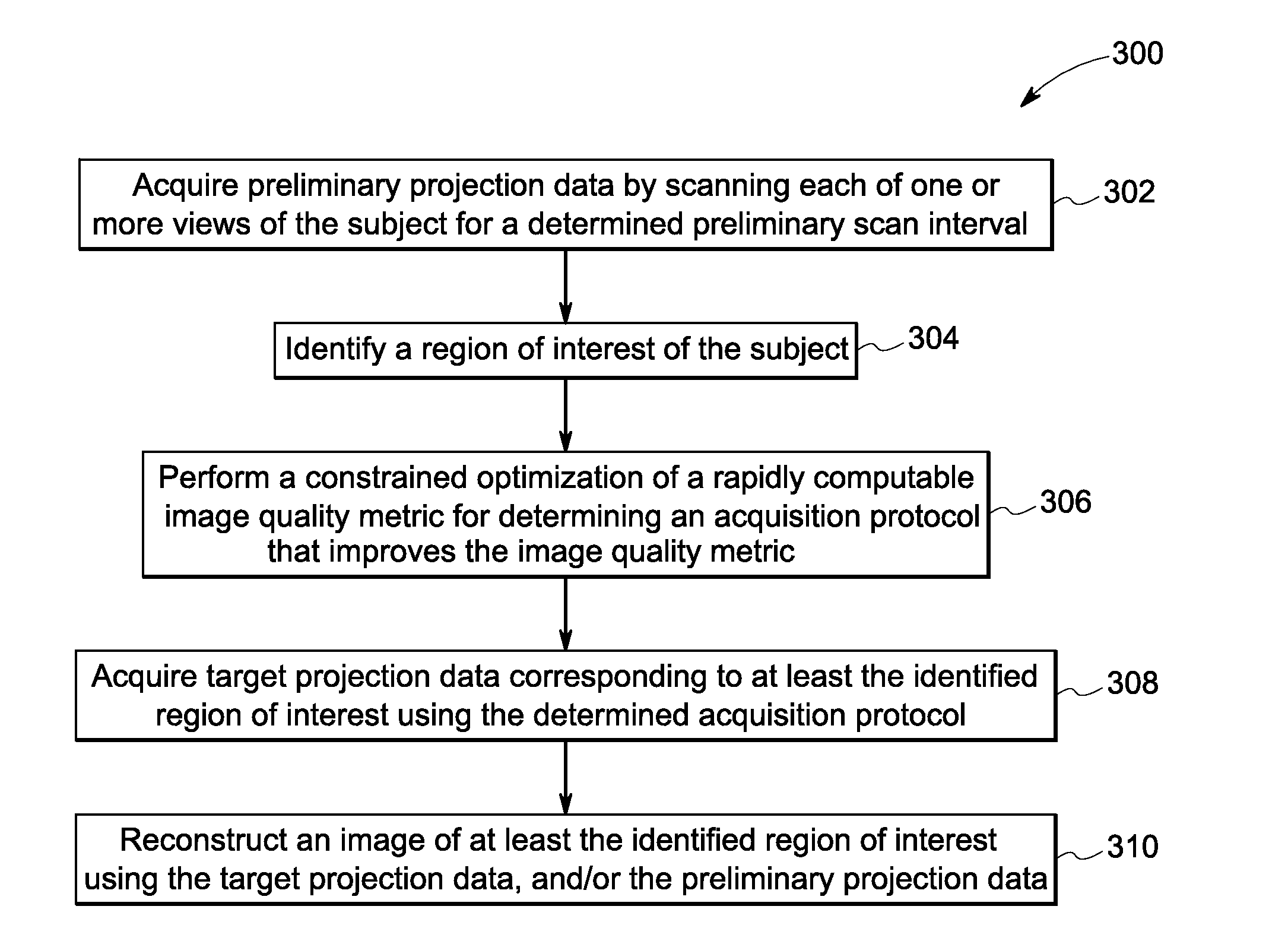
Nuclear imaging systems, non-transitory computer readable media and methods for adaptive imaging are presented. Particularly, the present method includes acquiring preliminary projection data by scanning each of one or more views of a subject for a determined preliminary scan interval. Further, a region of interest of the subject is identified. The preliminary projection data is then used to perform a constrained optimization of a rapidly computable image quality metric for determining an acquisition protocol that improves the image quality metric at the identified region of interest. Particularly, the determined acquisition protocol is used to acquire target projection data corresponding to at least the identified region of interest. Further, an image of at least the identified region of interest is reconstructed using the target projection data, the preliminary projection data, or a combination thereof.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Multi-phasic microphotodiode retinal implant and adaptive imaging retinal stimulation system
InactiveUS7139612B2Facilitate cognitionImprove abilitiesEye implantsHead electrodesColor imageAdaptive imaging
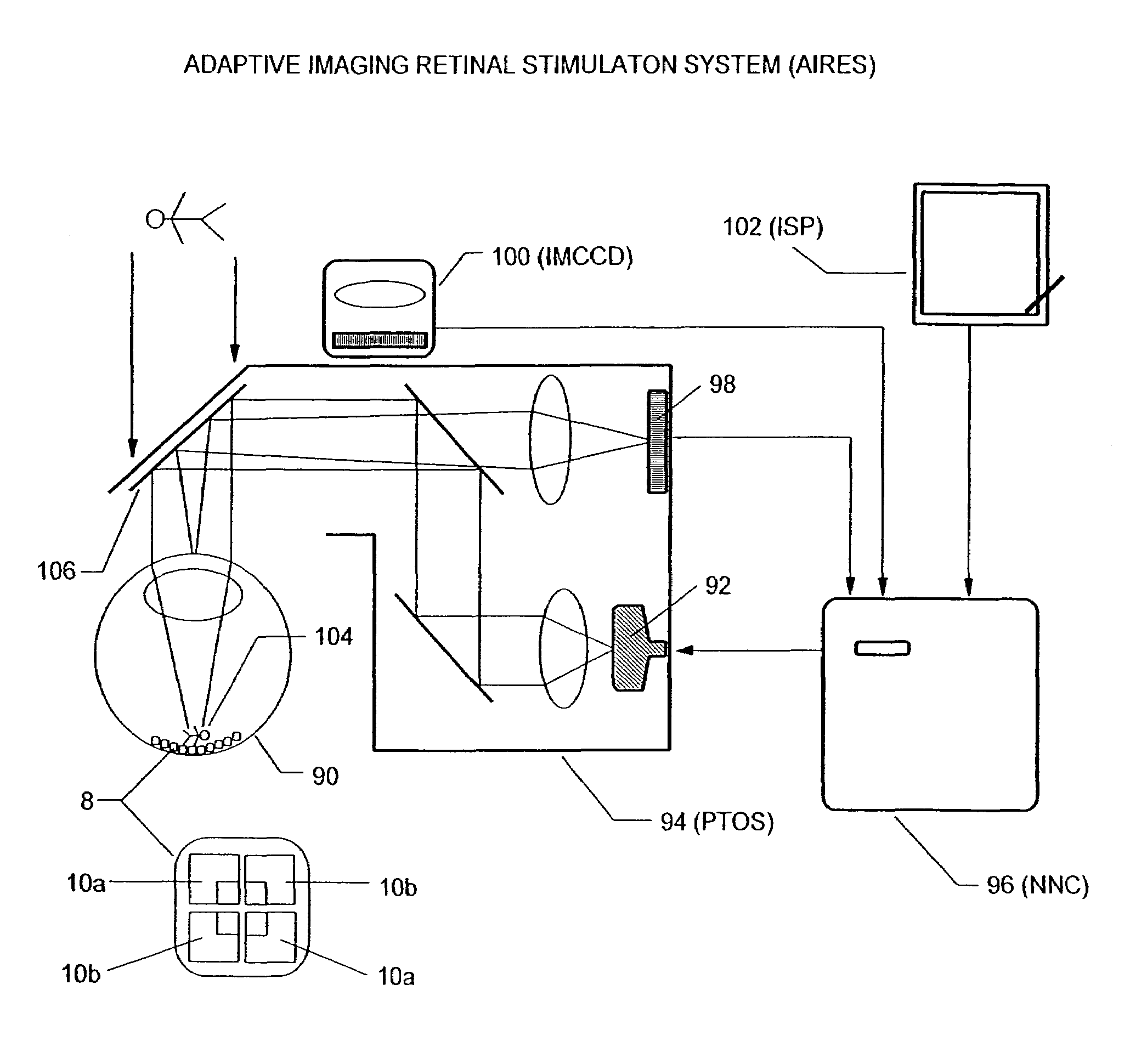
An artificial retina device and a retinal stimulation system and method for stimulating and modulating its function is disclosed. The artificial retina device includes multi-phasic microphotodiode subunits. In persons suffering from blindness due to outer retinal layer damage, a plurality of such devices, when surgically implanted into the subretinal space, may allow useful formed artificial vision to develop. By projecting real or computer controlled visible light images, and computer controlled infrared light images or illumination, simultaneously or in rapid alternation onto the artificial retina device, the nature of induced retinal images may be modulated and improved. The retinal stimulation system may be worn as a headset. Color images may be induced by programming the stimulating pulse durations and frequencies of the stimulation.
Owner:PIXIUM VISION SA
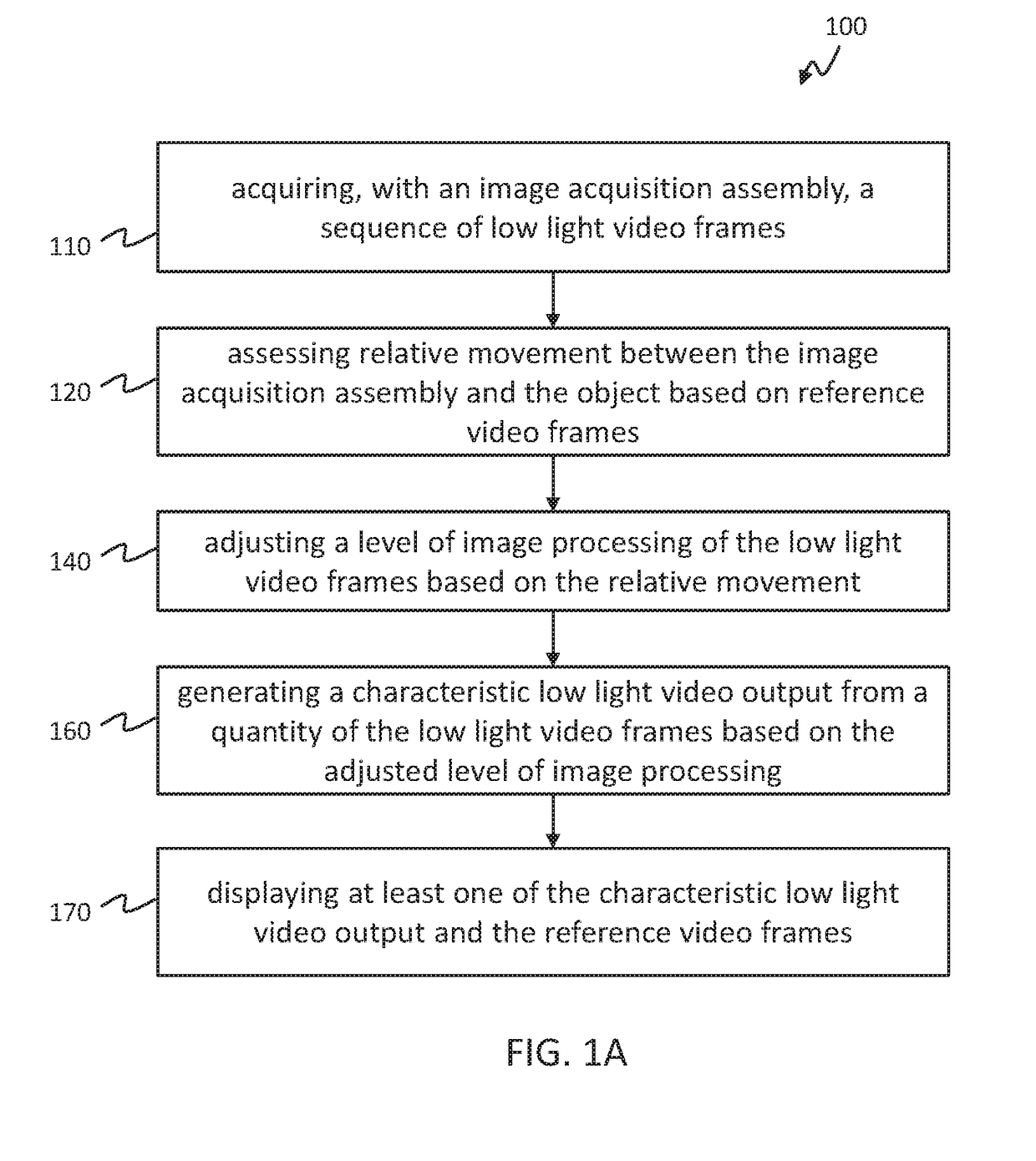
Methods and systems for adaptive imaging for low light signal enhancement in medical visualization
ActiveUS20170354392A1Improve visualizationLimiting introductionTelevision system detailsImage enhancementObject basedImaging processing
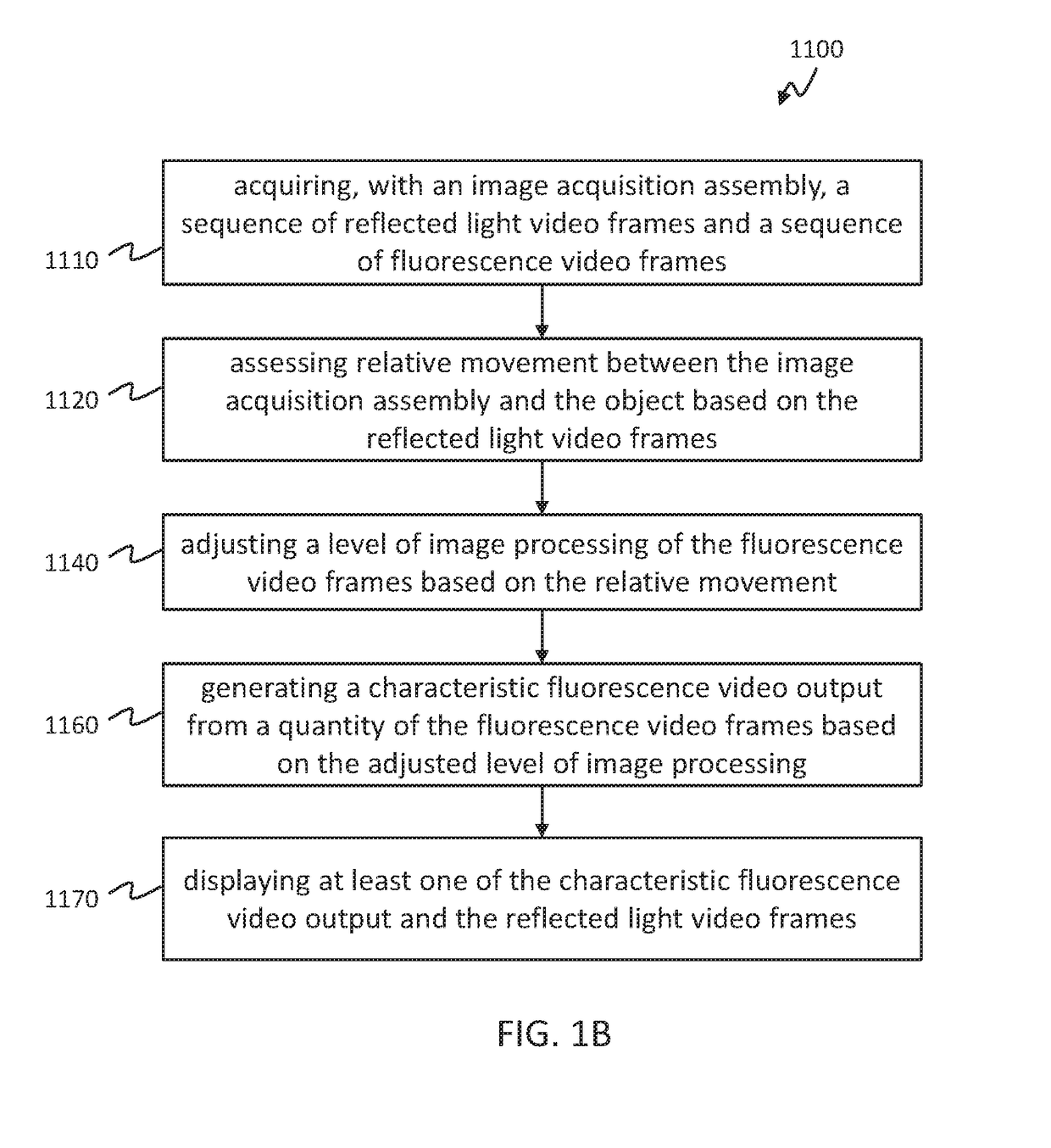
Adaptive imaging methods and systems for generating enhanced low light video of an object for medical visualization are disclosed and include acquiring, with an image acquisition assembly, a sequence of reference frames and / or a sequence of low light video frames depicting the object, assessing relative movement between the image acquisition assembly and the object based on at least a portion of the acquired sequence of reference video frames or the acquired sequence of low light video frames, adjusting a level of image processing of the low light video frames based at least in part on the relative movement between the image acquisition assembly and the object, and generating a characteristic low light video output from a quantity of the low light video frames, wherein the quantity of the low light video frames is based on the adjusted level of image processing of the low light video frames.
Owner:STRYKER EUROPEAN OPERATIONS LIMITED
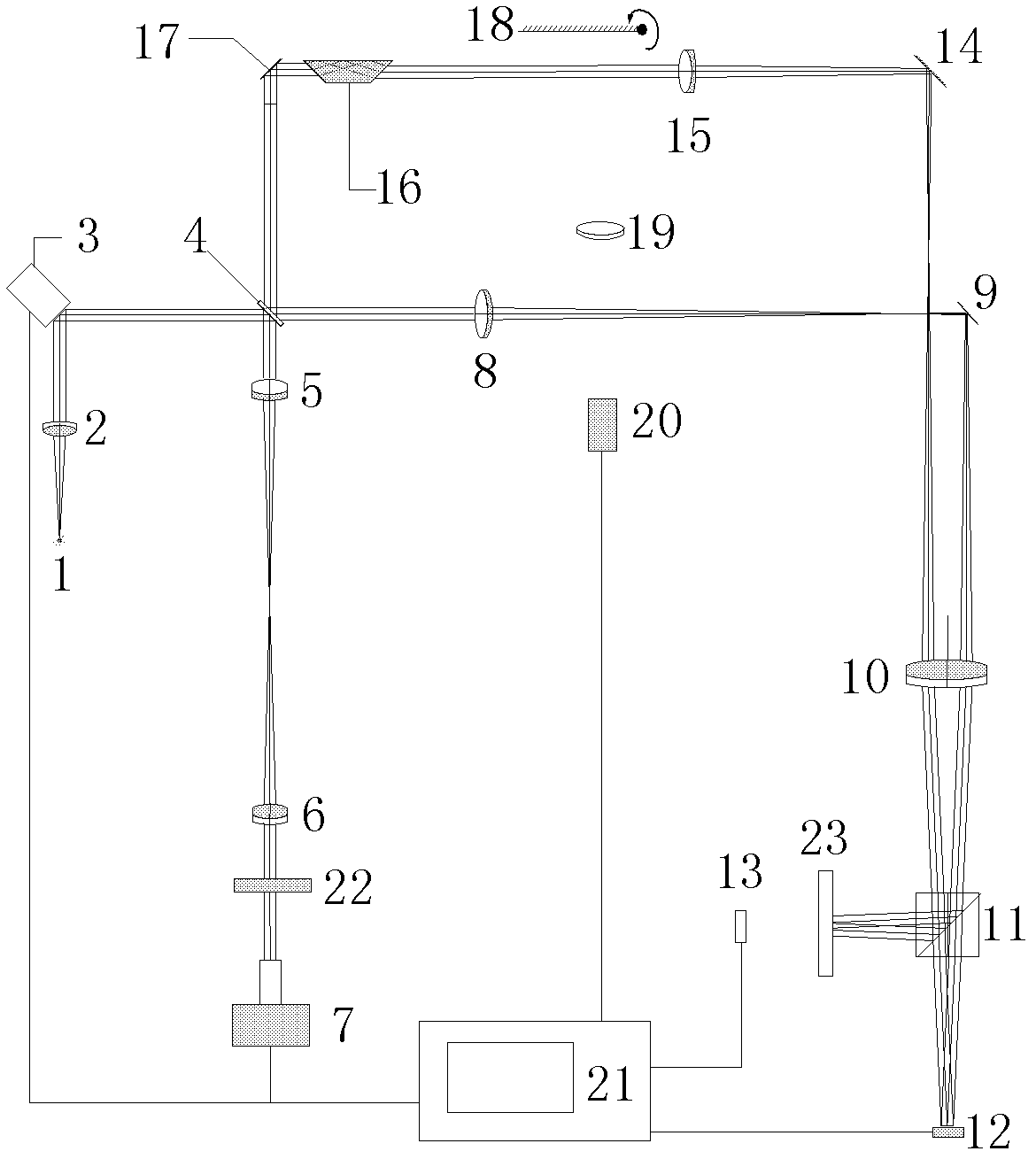
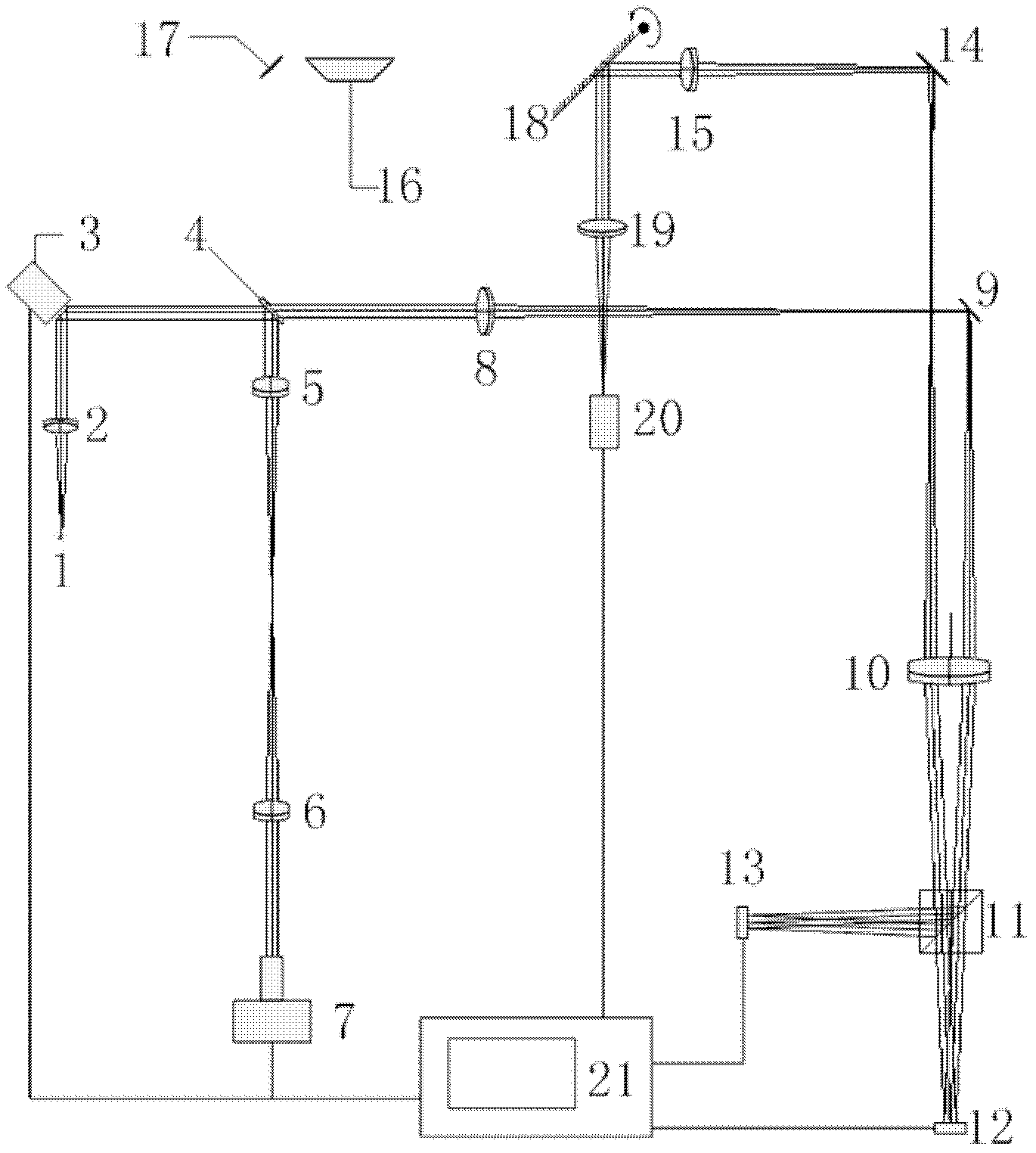
Full-eyeball optical coherent tomography adaptive system and full-eyeball optical coherent tomography adaptive method
InactiveCN103565401AQuality improvementSolve the problem of not being able to be in the front section at the same timeEye diagnosticsAdaptive imagingTomography
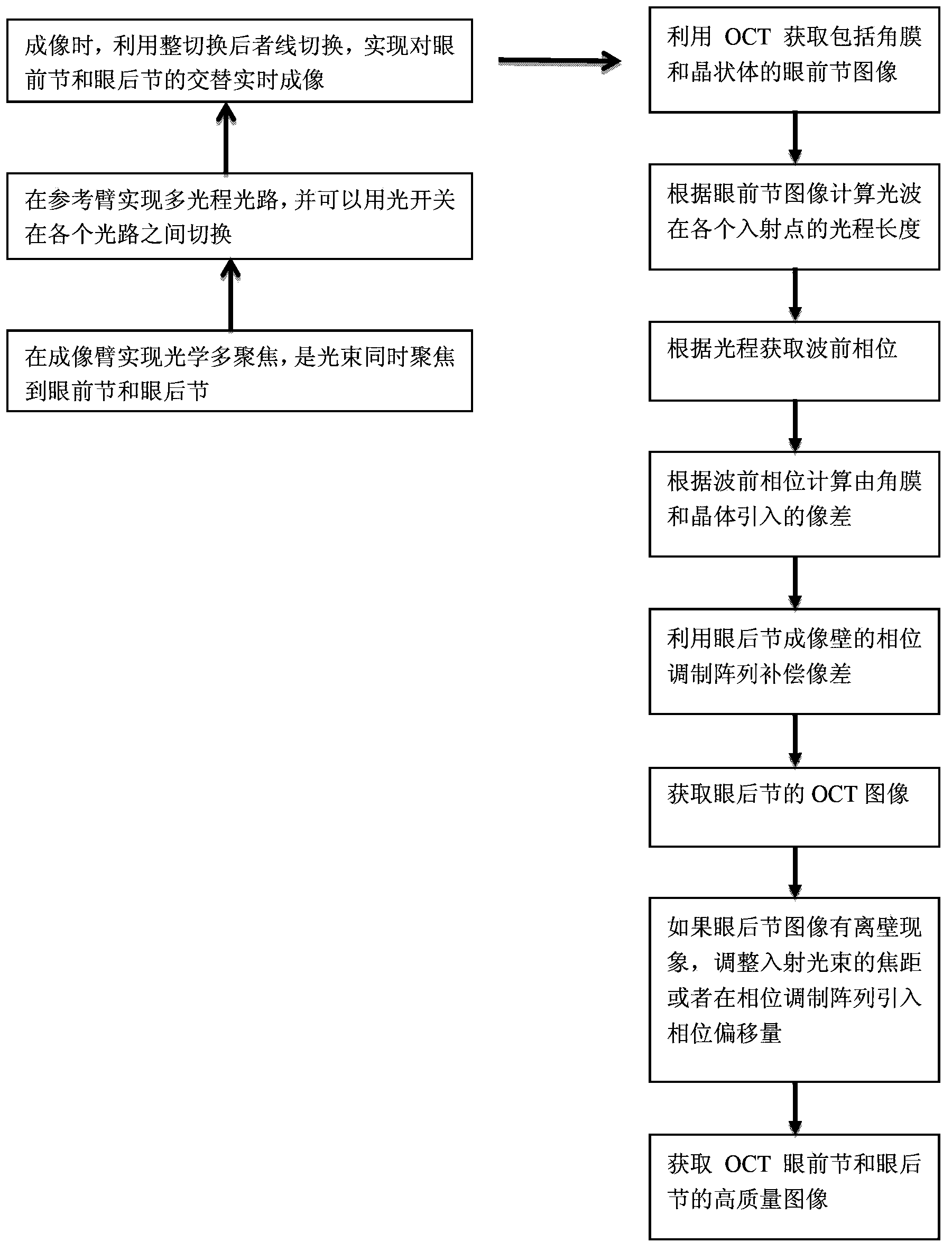
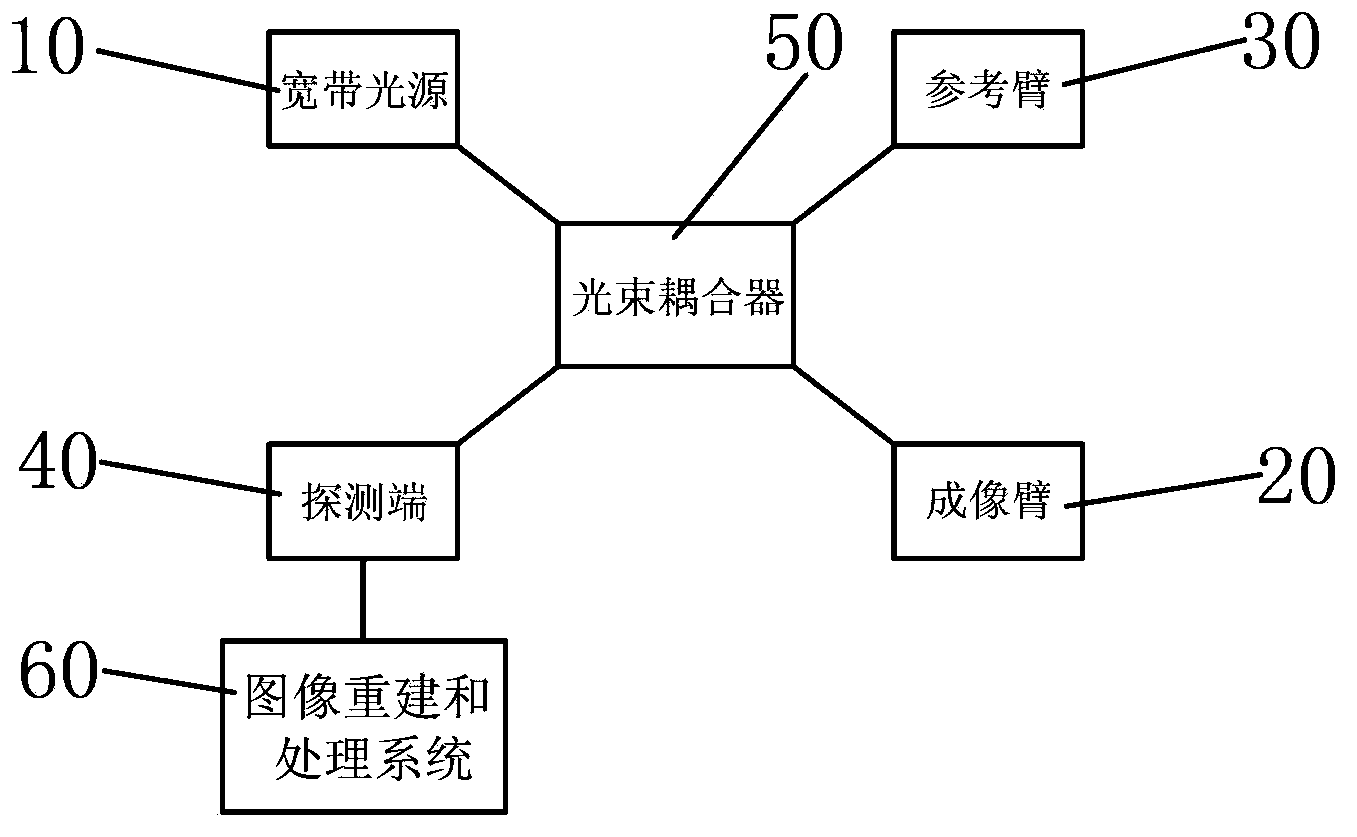
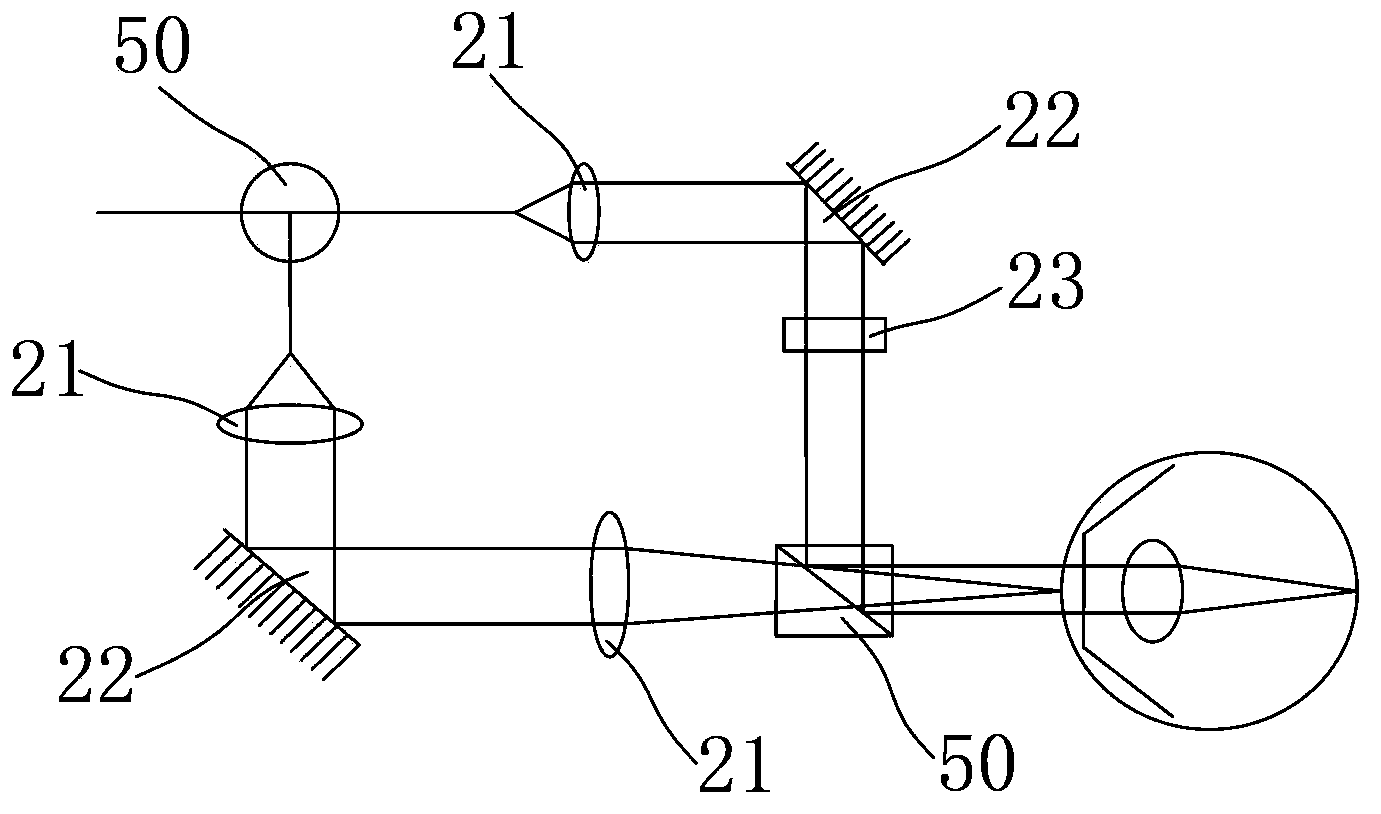
The invention aims to provide a full-eyeball optical coherent tomography adaptive system and a full-eyeball optical coherent tomography adaptive method. Compared with the prior art, the full-eyeball optical coherent tomography adaptive system and the full-eyeball optical coherent tomography adaptive method have the advantages that the problem that high-quality OCT (optical coherent tomography) images cannot be simultaneously acquired at ocular anterior segments and ocular posterior segments by means of optical coherent tomography in the prior art can be effectively solved, focusing can be simultaneously carried out on ocular anterior segments and ocular posterior segments by a multi-focus imaging arm, and reference arms with different optical path differences are switched and are combined with the imaging arm, so that the ocular anterior segments and the ocular posterior segments can be imaged simultaneously; aberration introduced at the ocular anterior segments can be computed in real time by the aid of images of the ocular anterior segments, and aberration compensation can be carried out by the aid of a phase modulation array in the imaging arm, so that the high-quality OCT images can be simultaneously acquired at the ocular anterior segments and the ocular posterior segments by the aid of the full-eyeball optical coherent tomography adaptive system and the full-eyeball optical coherent tomography adaptive method.
Owner:SHANGHAI WEIJING BIOTECH CO LTD
Active night vision with adaptive imaging
InactiveUS20050206510A1Reduce system costMinimize complexityAnti-collision systemsColor television detailsNight visionAdaptive imaging
A vision system for a vehicle includes a light source generating an illumination beam, a receiver having a pixel array for capturing an image in response to at least a reflected portion of the illumination beam, the image corresponding to a first horizontal field of view (FOV) angle, and a controller coupled to the light source and the receiver. The controller receives a vehicle speed input and, in response, selects a portion of the image as a non-linear function of the vehicle speed to generate a second horizontal FOV angle for displaying to the vehicle operator. The displayed angular FOV decreases, non-linearly, as the vehicle speed increases.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
High resolution imaging self-adaptive optical telescope suitable for working at daytime
InactiveCN1908722AImprove the correction effectImprove quantum efficiencyTelescopesRadiation controlled devicesHigh resolution imagingAdaptive imaging
The high-resolution adaptive imaging optical telescope comprises: a telescope system, a precise track system with EMCCD (reading noise < 1e-) as the core detective member, an adaptive optical system, and an imaging system, wherein the precise track and detection system is arranged in Kuder room to keep all of the track system and track loop and high-order error correction loop on one OA; the Hartmann sensor works on near-IR range to reduce background effect, and the near-IR detector in imaging system can overcome effect from strong back light and air turbulence to improve imaging resolution.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Universal liquid crystal adaptive aberration correcting retina imaging system
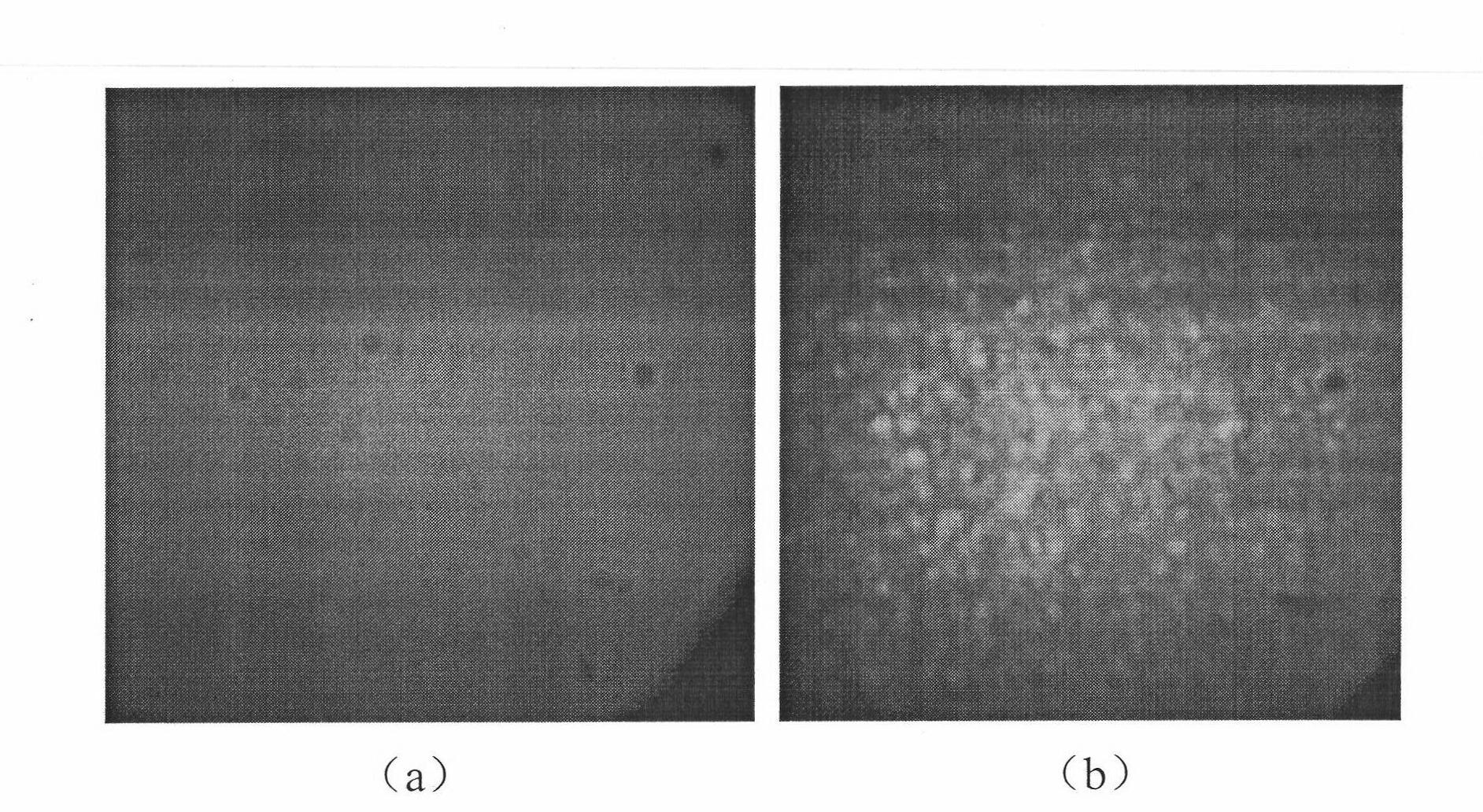
The invention belongs to the technical field of microscope imaging, relates to a high-order aberration correcting optical design for high-ametropia human eyes, and discloses a universal liquid crystal adaptive aberration correcting retina imaging system. An LCD screen is adopted for displaying a sighting target point light source, and the sighting target is designed into an E shape so that the self-adjusting effect of visibility is enhanced; and meanwhile, E-shaped micro displacement is easily controlled on the LCD screen so that the position of an imaging area can be quantitatively changed. Through the sign of a plurality of key devices, the universality of the liquid crystal adaptive system in fundus imaging is improved, the problem of difficult clear imaging of the fundus adaptive imaging technology under the condition of over 800-degree myopia or 200-degree astigmatism can be solved, and the system can acquire a high-resolution retina image on the human eye of 200-degree astigmatism.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Optical wave-front recovery for active and adaptive imaging control
InactiveUS20110157600A1Minimize wave-front sensingMinimize control timeOptical measurementsInterferometersWavefrontAdaptive imaging
An optical telescope system, method of actively, adaptively providing optical control to an array of articulated mirrors in a sparse aperture in the optical telescope system and a computer program product therefor. Array apertures are selected sequentially for imaging. Each aperture is temporally modulating at a unique / different frequency and, simultaneously, focal plane images are detected for each array aperture with known and separable temporal dependencies. The images are processed for the current set of said focal plane images to detect an image wavefront. The feeding back wavefront errors are fed back to aperture actuators for controlling the array.
Owner:NASA
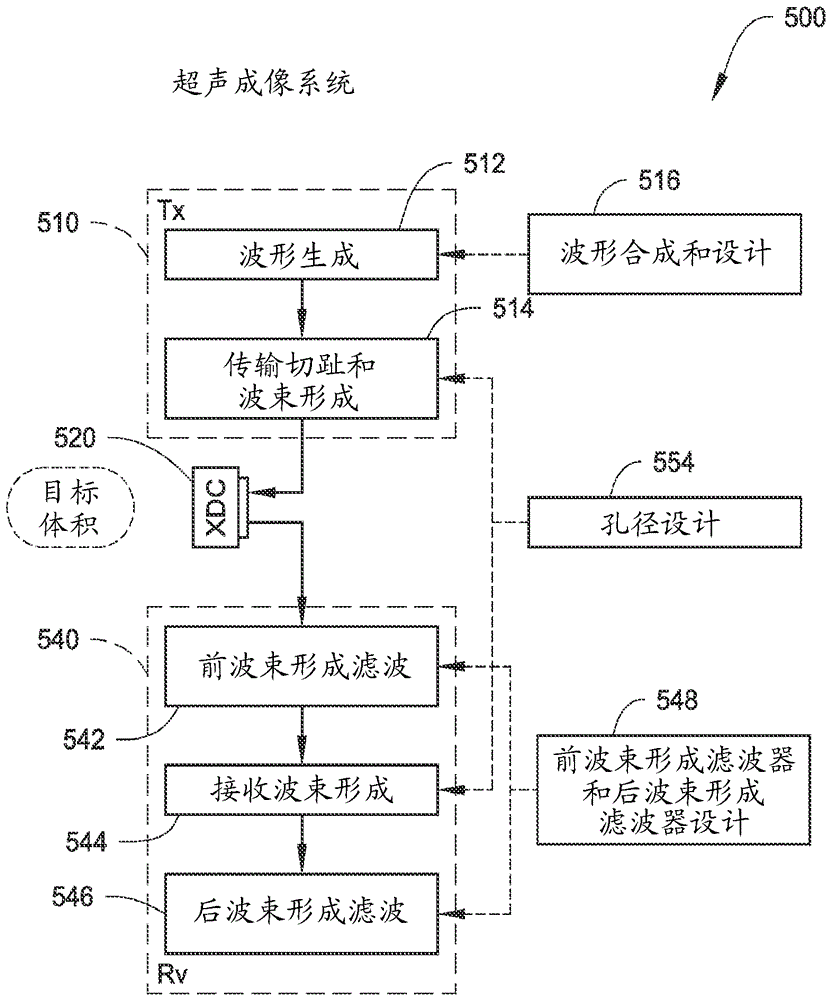
Ultrasound image formation and/or reconstruction using multiple frequency waveforms
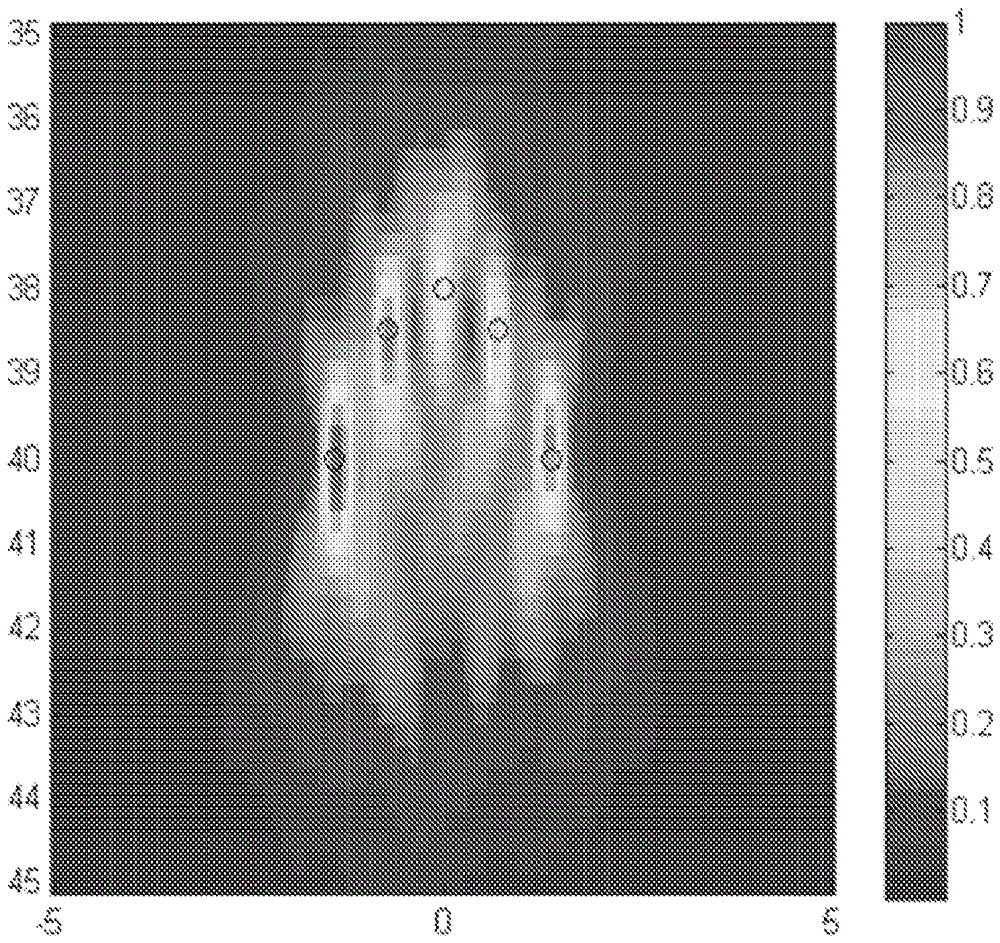
ActiveCN105793729AUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyAdaptive imagingSonification
Ultrasound adaptive imaging methods and / or systems provide for modification of waveform generation to drive a plurality of transducer elements. The modification may be based on at least one of contrast ratio or signal to noise ratio as determined with respect to control points in a region of interest. Further, image reconstruction may be performed upon separating, from pulse echo data received, at least a portion thereof received at each ultrasound transducer element from the region of interest in response to the delivered ultrasound energy corresponding to a single frequency of one or more image frequencies within a transducer apparatus bandwidth. The image reconstructed from the separated pulse-echo data corresponding to the single frequency of the one or more image frequencies may be used alone or combined with like image data (e.g., to provide an image representative of one or more properties in the region of interest).
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA
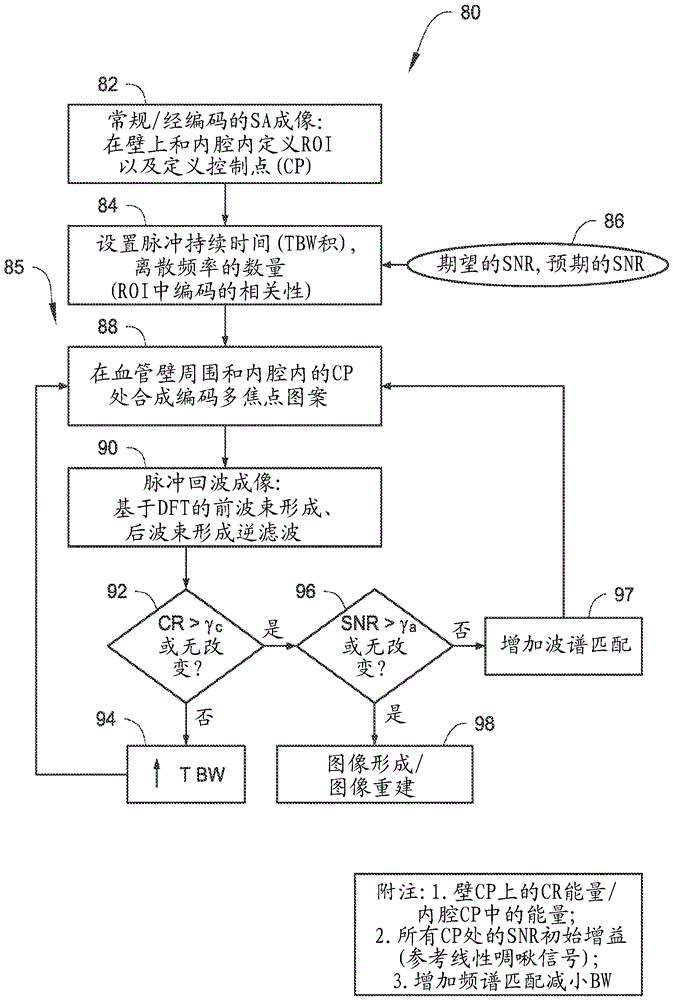
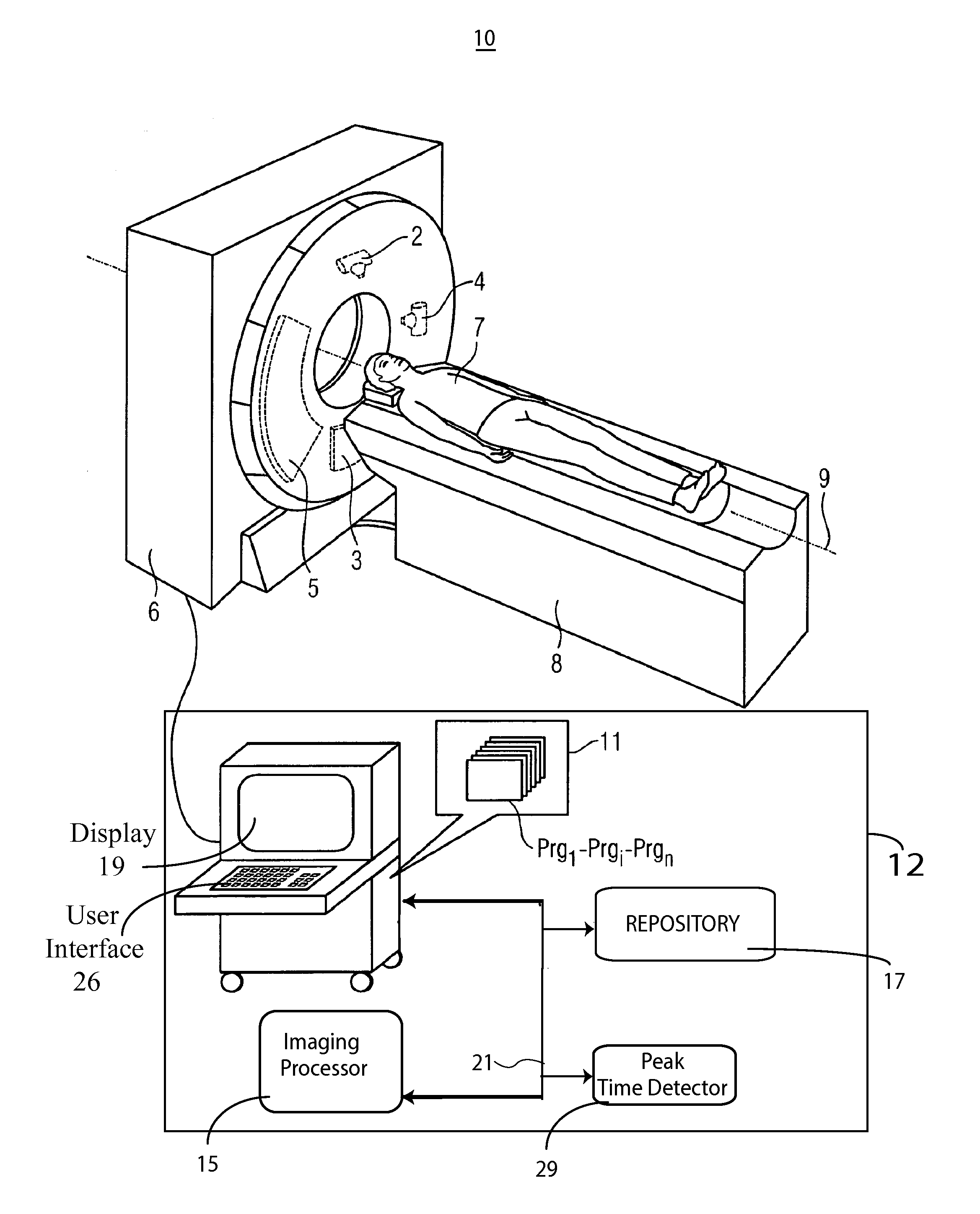
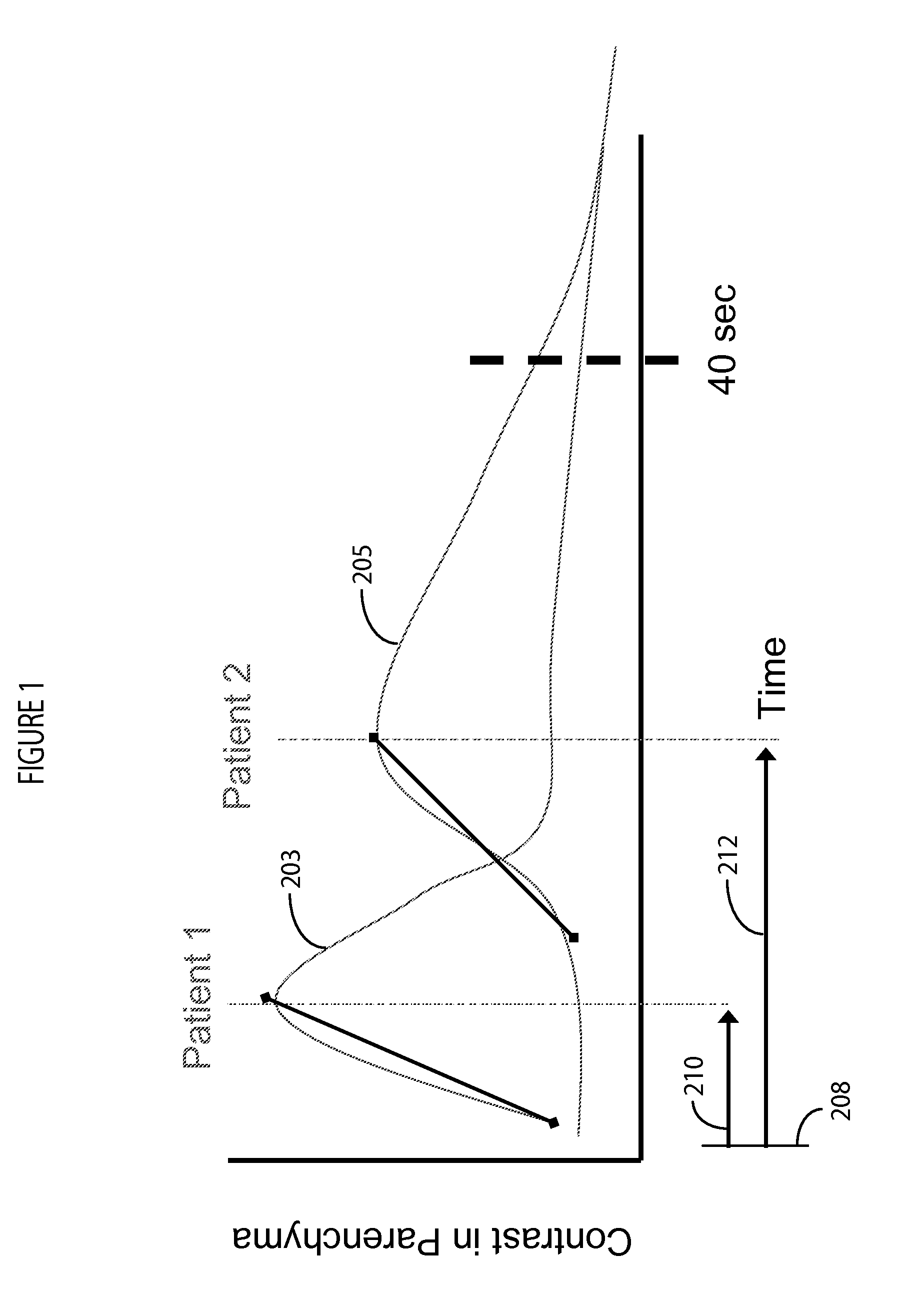
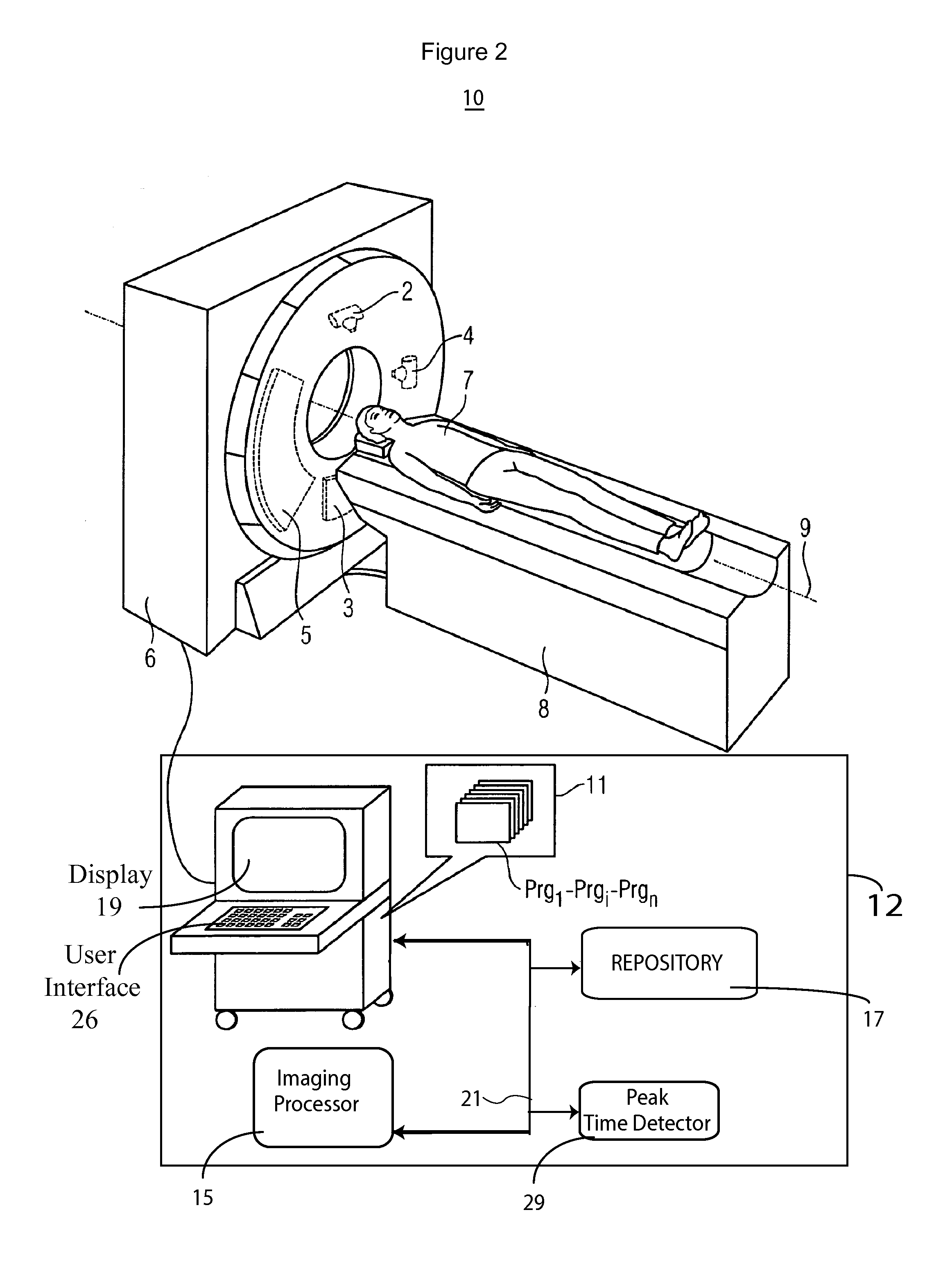
Contrast Agent Perfusion Adaptive Imaging System
ActiveUS20130066198A1Health-index calculationComputerised tomographsInformation repositoryStart time
An imaging system selects a medical imaging protocol using a repository of information associating multiple ranges of contrast agent peak time with corresponding different imaging protocols. An imaging protocol comprises a method for acquiring images using an imaging system and using data identifying at least one of (a) an imaging rate within an imaging scan cycle and (b) an interval between imaging scans. A contrast agent peak time comprises a time a contrast agent concentration substantially reaches a peak value in an anatomical region of interest of a patient relative to a time of start of contrast agent injection. A contrast agent peak time detector detects a contrast agent peak time. An imaging processor adaptively selects an imaging protocol from the imaging protocols in response to a comparison of a detected contrast agent peak time with at least one of the plurality of ranges.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
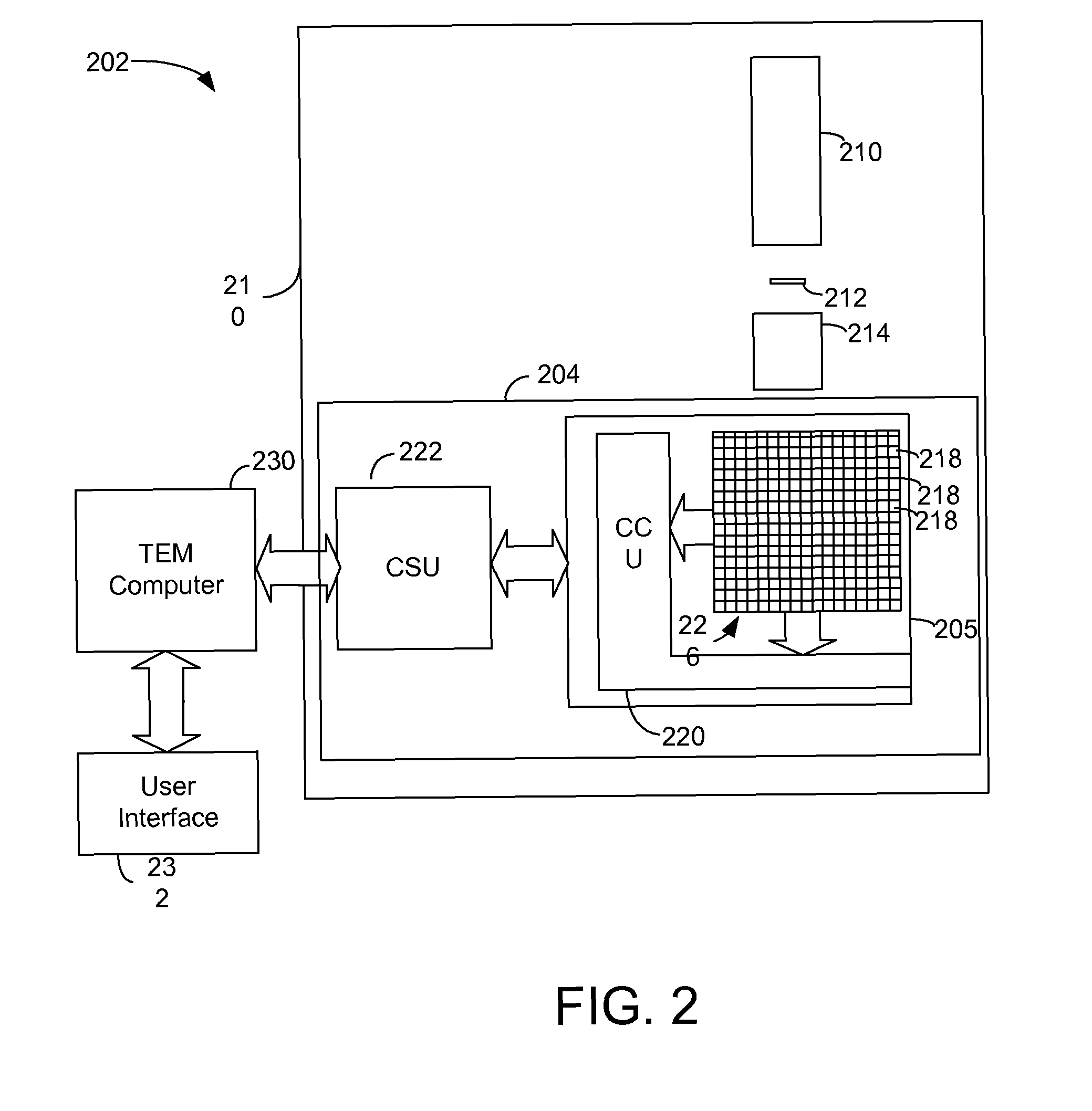
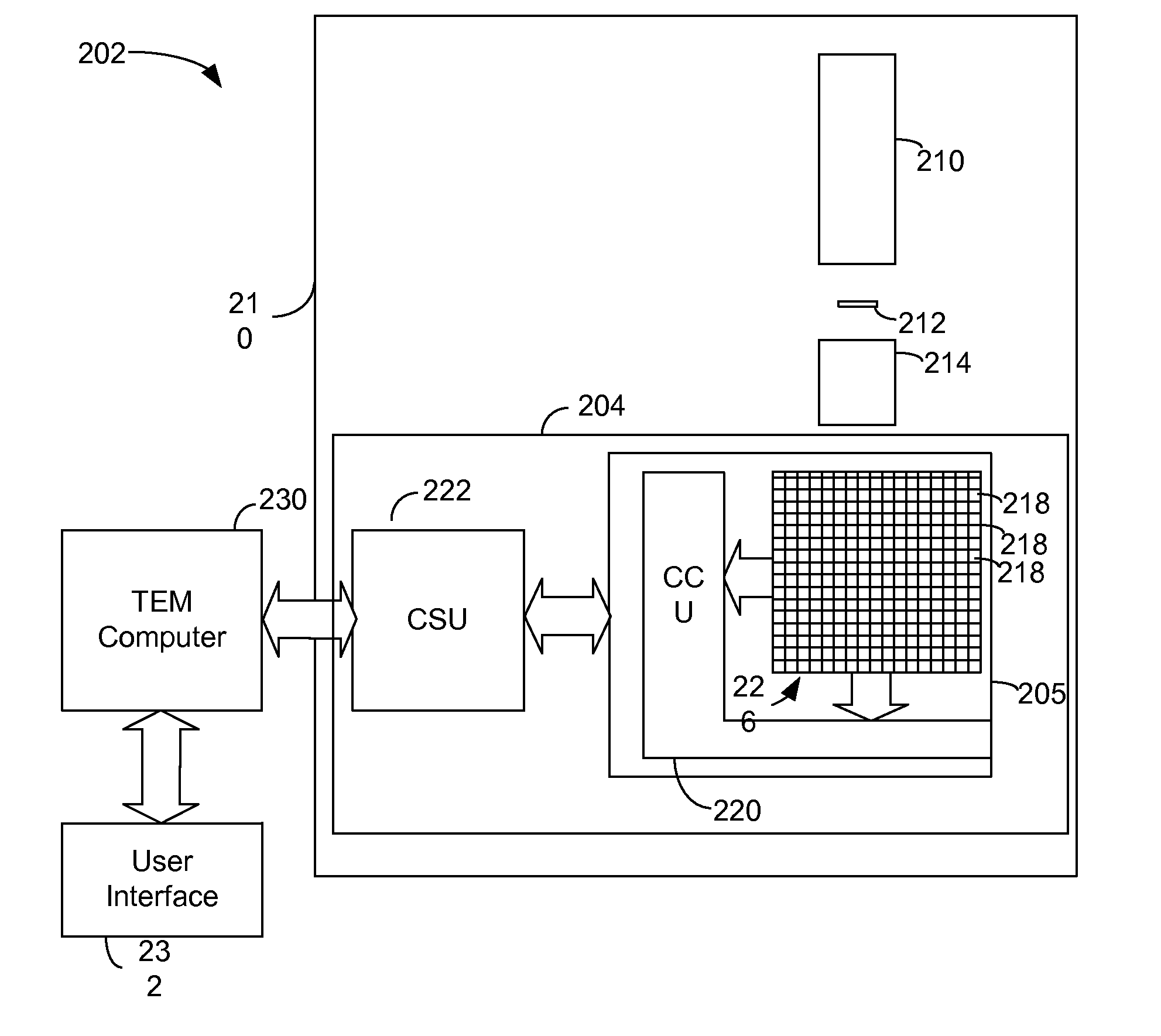
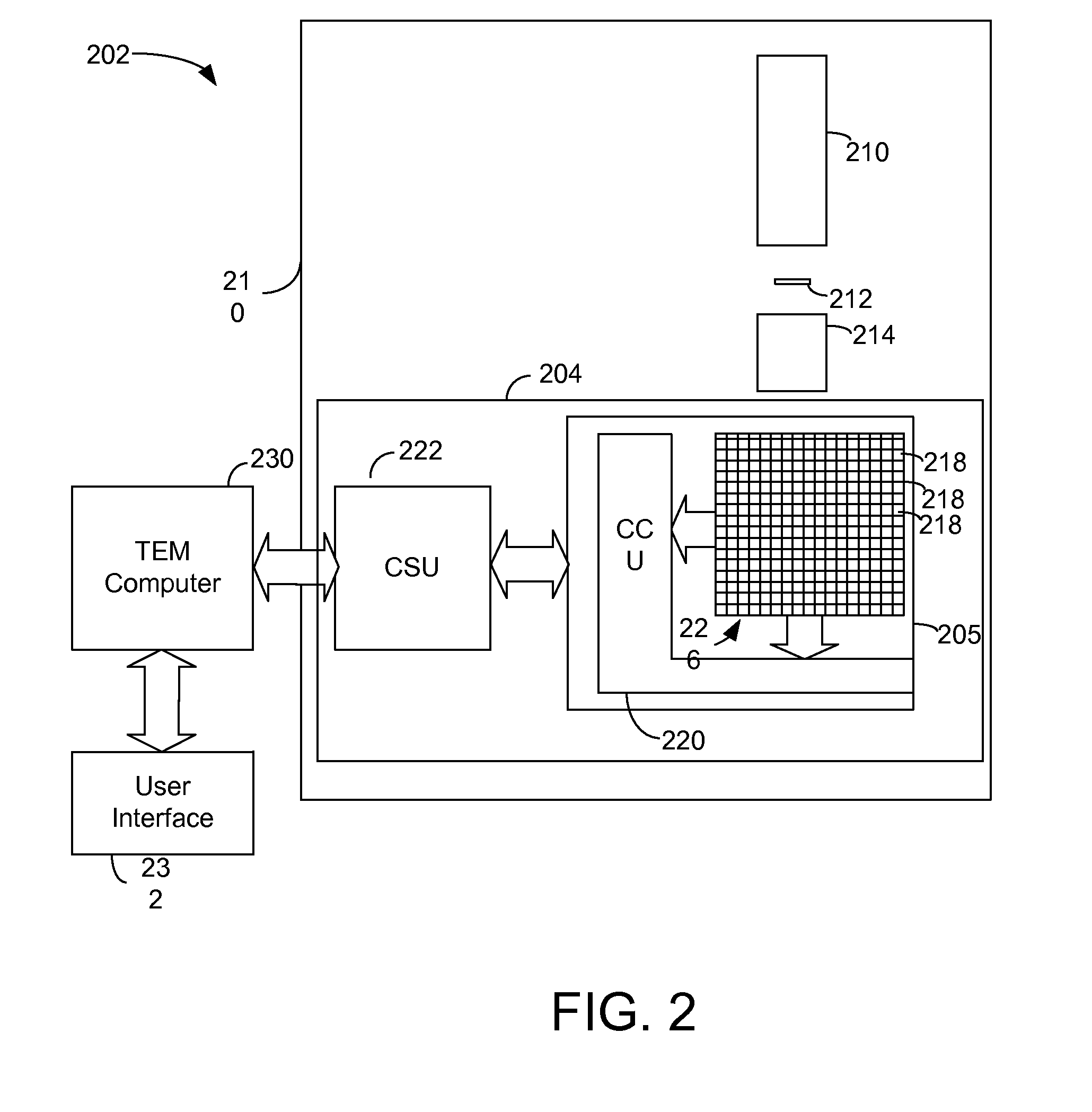
Detector system for transmission electron microscope
ActiveUS8338782B2Quality improvementMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesAdaptive imagingSelf adaptive
Owner:FBI
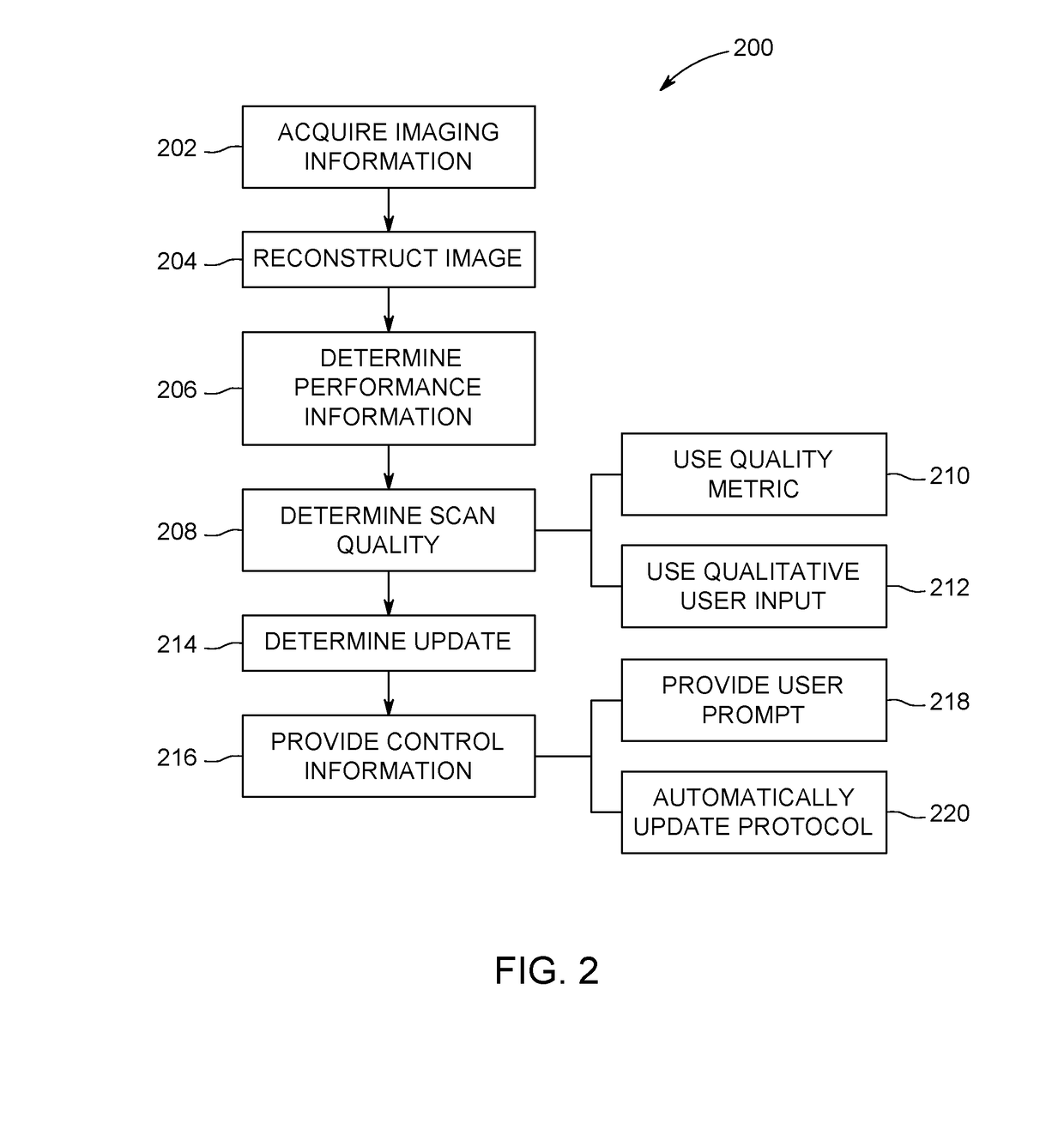
Systems and methods for adaptive imaging systems
ActiveUS20180061045A1Image enhancementReconstruction from projectionAdaptive imagingComputer science
A system includes an imaging acquisition unit, a reconstruction unit, and a determination system. The imaging acquisition unit is configured to perform a scan to acquire imaging information of a patient. The reconstruction unit is configured to reconstruct an image using the imaging information. The determination system is communicatively coupled to the imaging acquisition unit and the reconstruction unit. The determination system includes at least one processor configured to: acquire performance information corresponding to the scan; determine a scan quality for the scan based on the performance information; determine an update to a protocol used to at least one of acquire the imaging information or reconstruct the image; and provide control information to at least one of the imaging acquisition unit or the reconstruction unit to implement the determined update for at least one of performing a subsequent scan or reconstructing a subsequent image.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
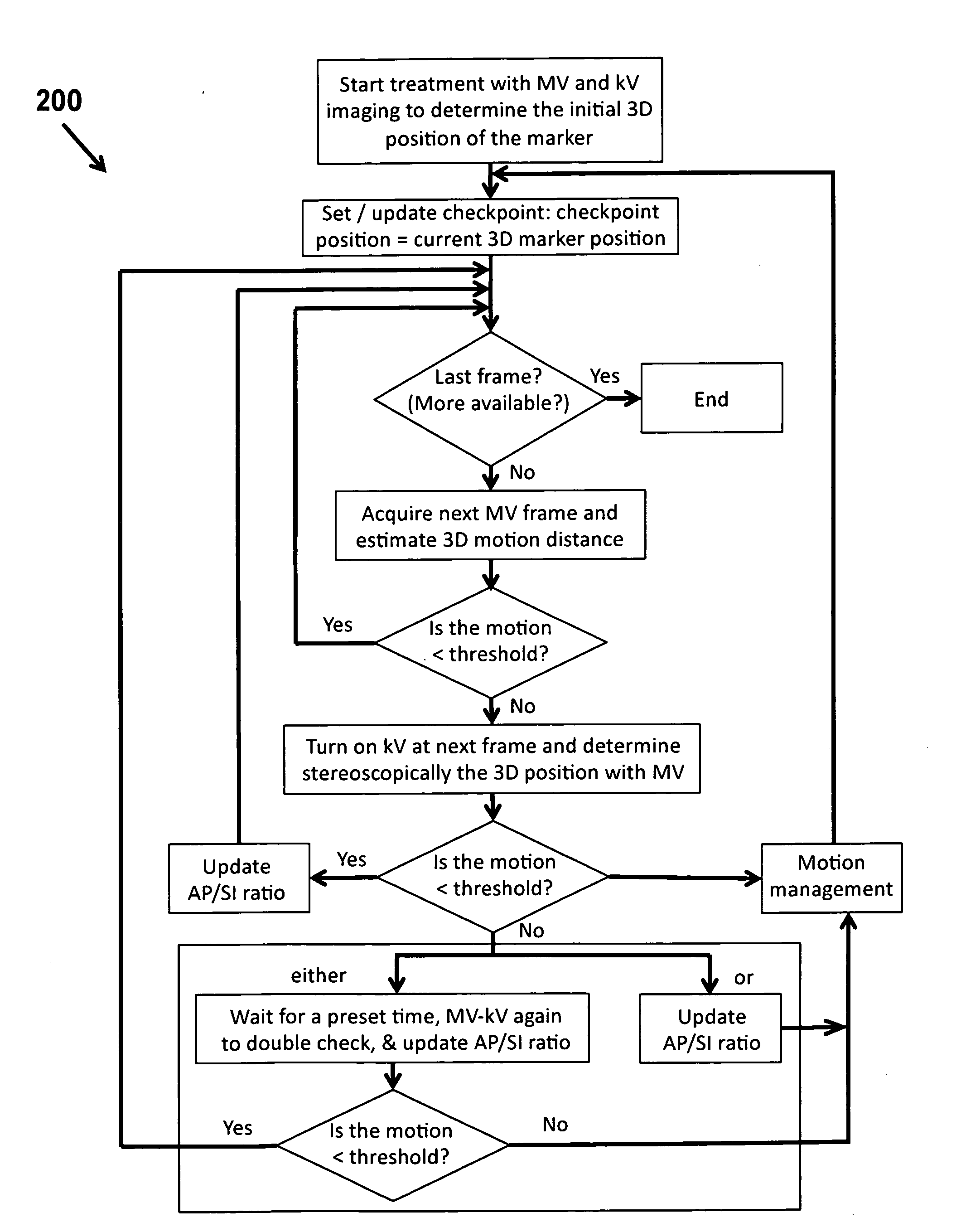
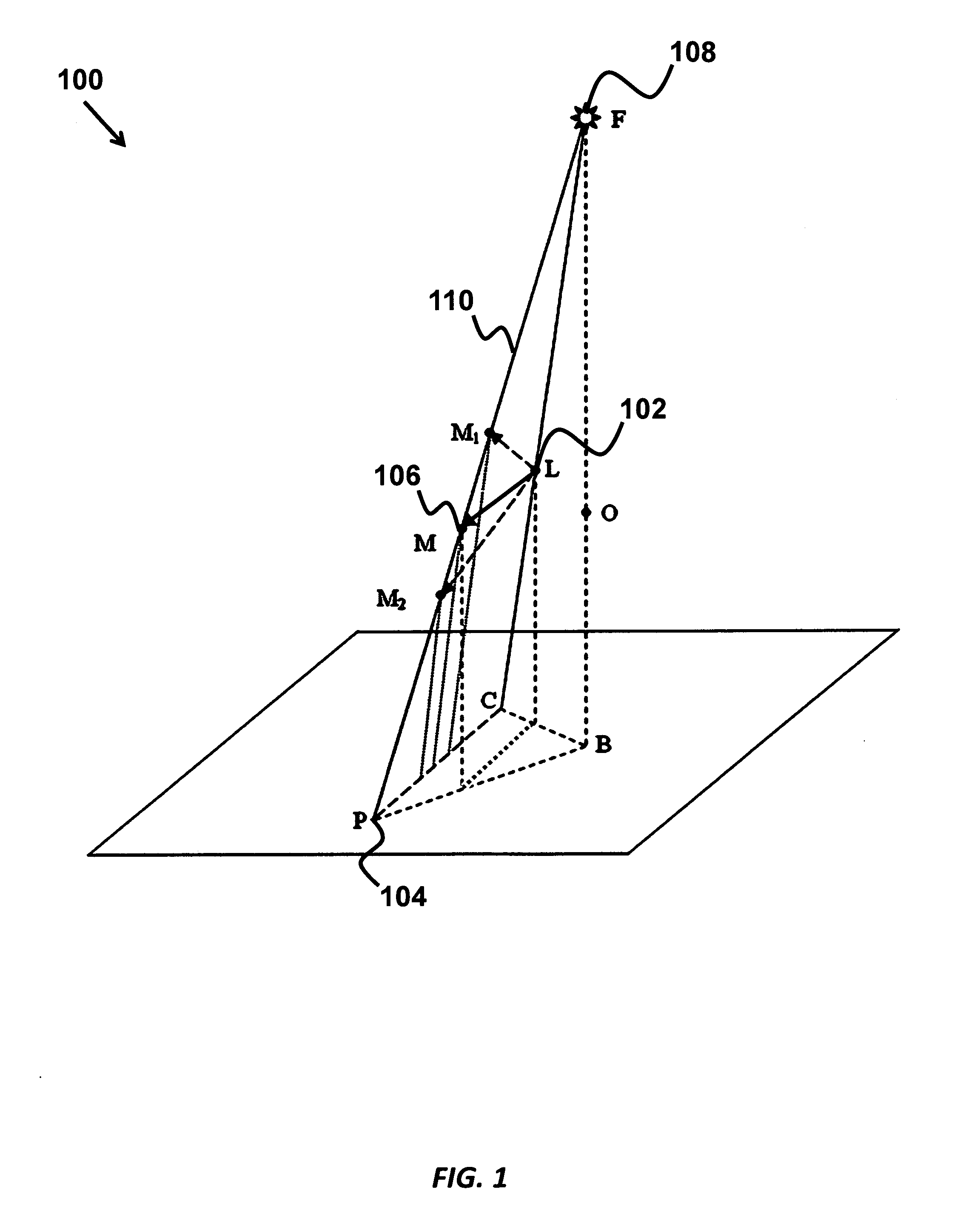
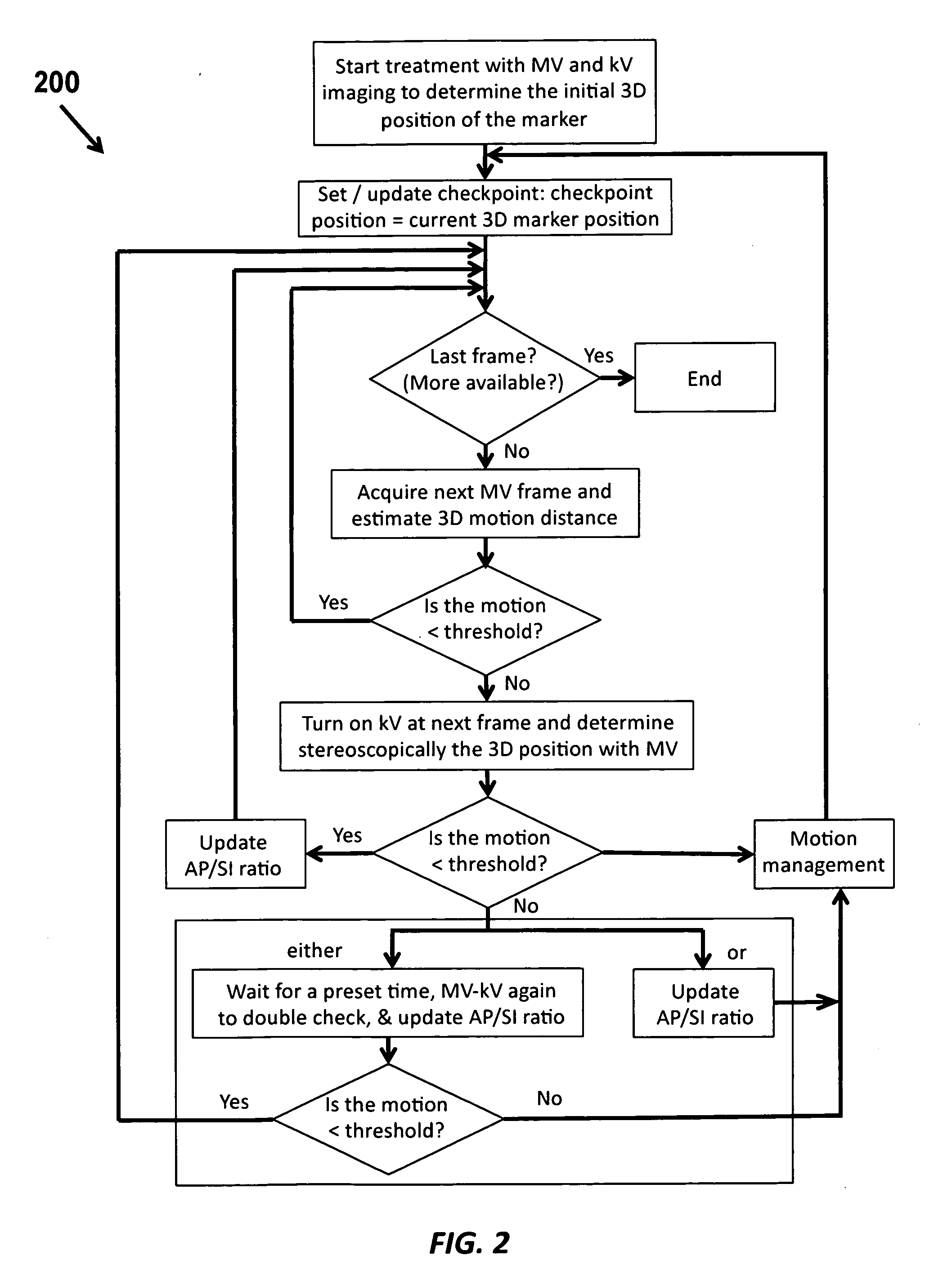
Intrafraction motion management using a rough to accurate monitoring strategy
InactiveUS20110075807A1Accurately determineMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyAdaptive imagingTreatment delivery
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
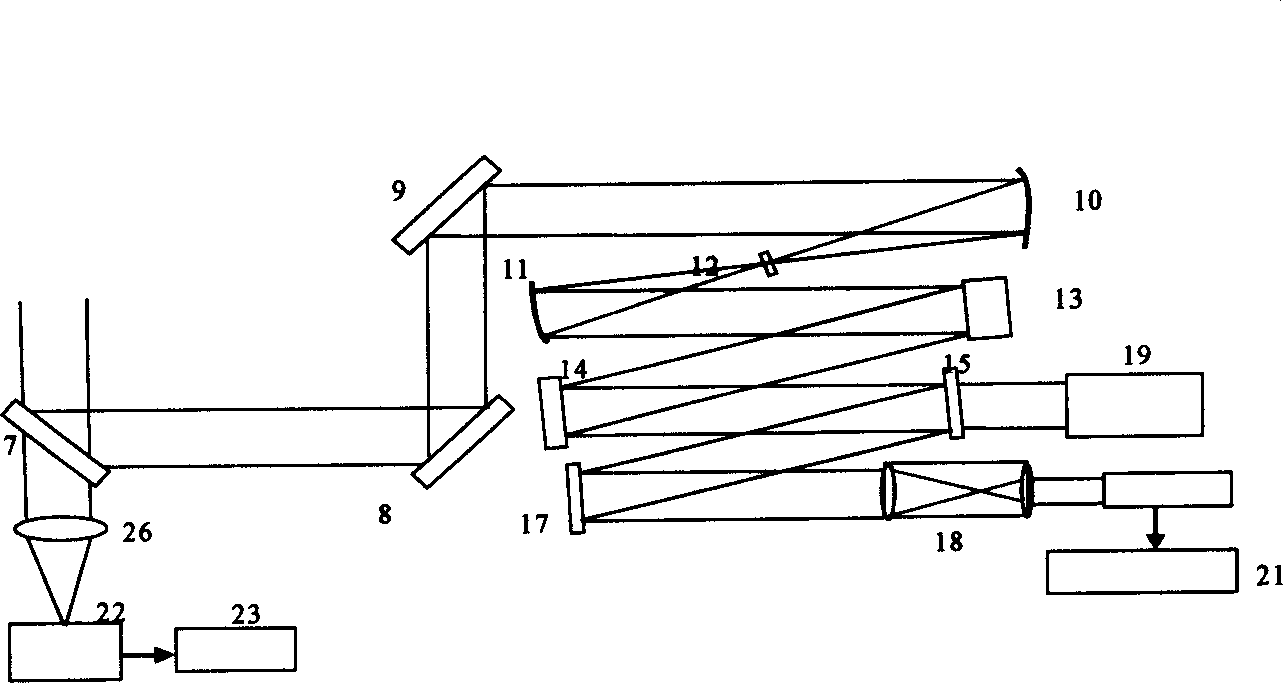
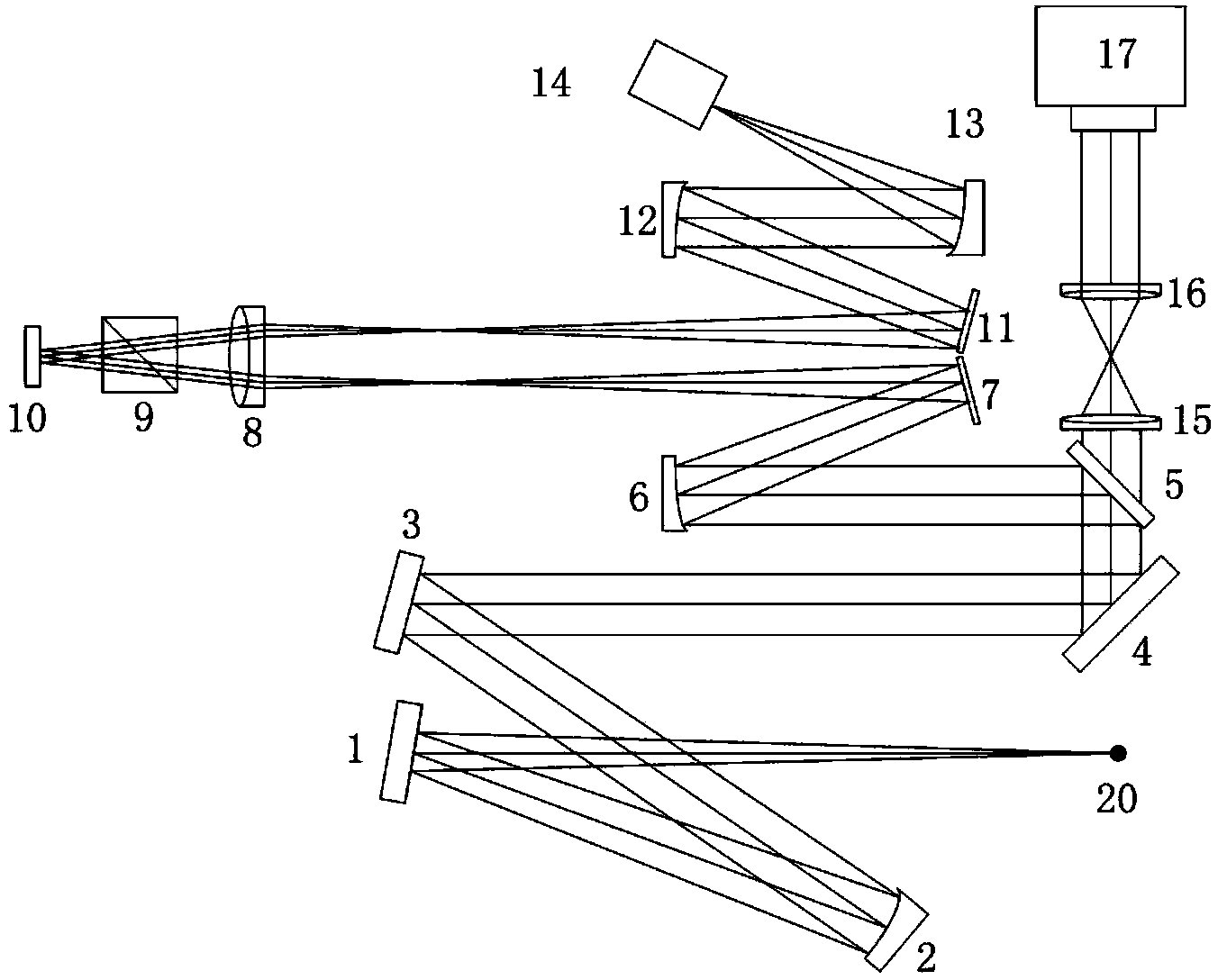
Method for designing light beam folding type liquid crystal adaptive optical system
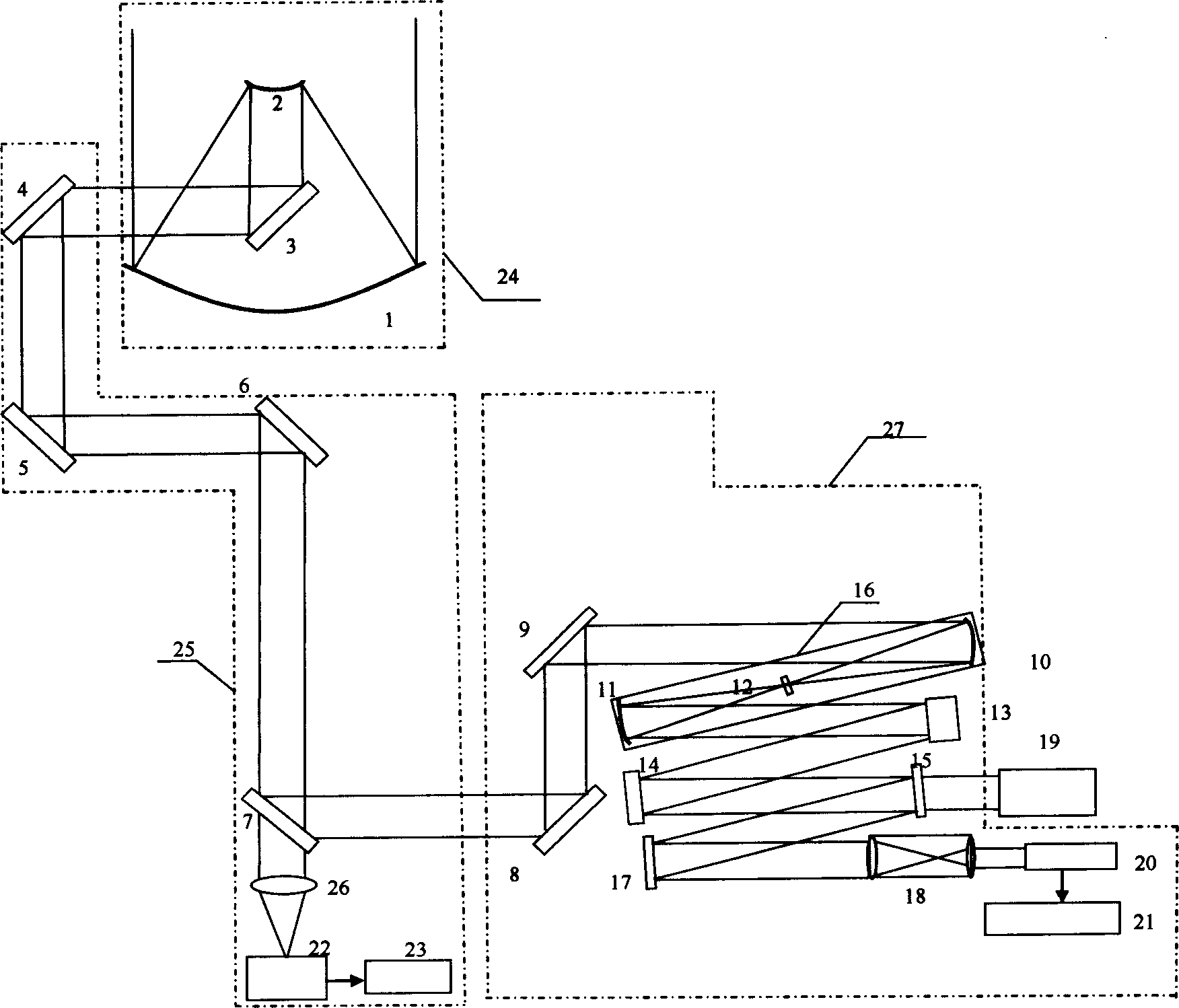
The invention belongs to the field of adaptive optics, and discloses a method for designing a light beam folding type liquid crystal adaptive optical system. As is shown in figure 1, a plurality of off-axis parabolic mirrors and reflectors are introduced and combined to fold light beams many times, and the size of the system is reduced. Due to the fact that a Hartmann detector and a liquid crystal corrector are under feedforward control, the feedforward control should be switched into feedback control when signal measurement is responded, the fourth off-axis parabolic mirror 13 is removed out of a light path, emergent parallel light beams aligned to the third off-axis parabolic mirror 12 are inserted into the fifth reflector 18 which is arranged by 45 degrees in a detection branch, light beams passing through the liquid crystal corrector 10 enter the Hartmann wavefront detector 17 after axis folding, light beams emitted out of a third lens 16 are cut off, and meanwhile a fast galvanometer 4 is only adopted as a common reflector. An adaptive imaging light path and a liquid crystal corrector response signal measurement light path can be switched, and the alignment misplacing problem of a middle light path of the adaptive system after and before switching is avoided well.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
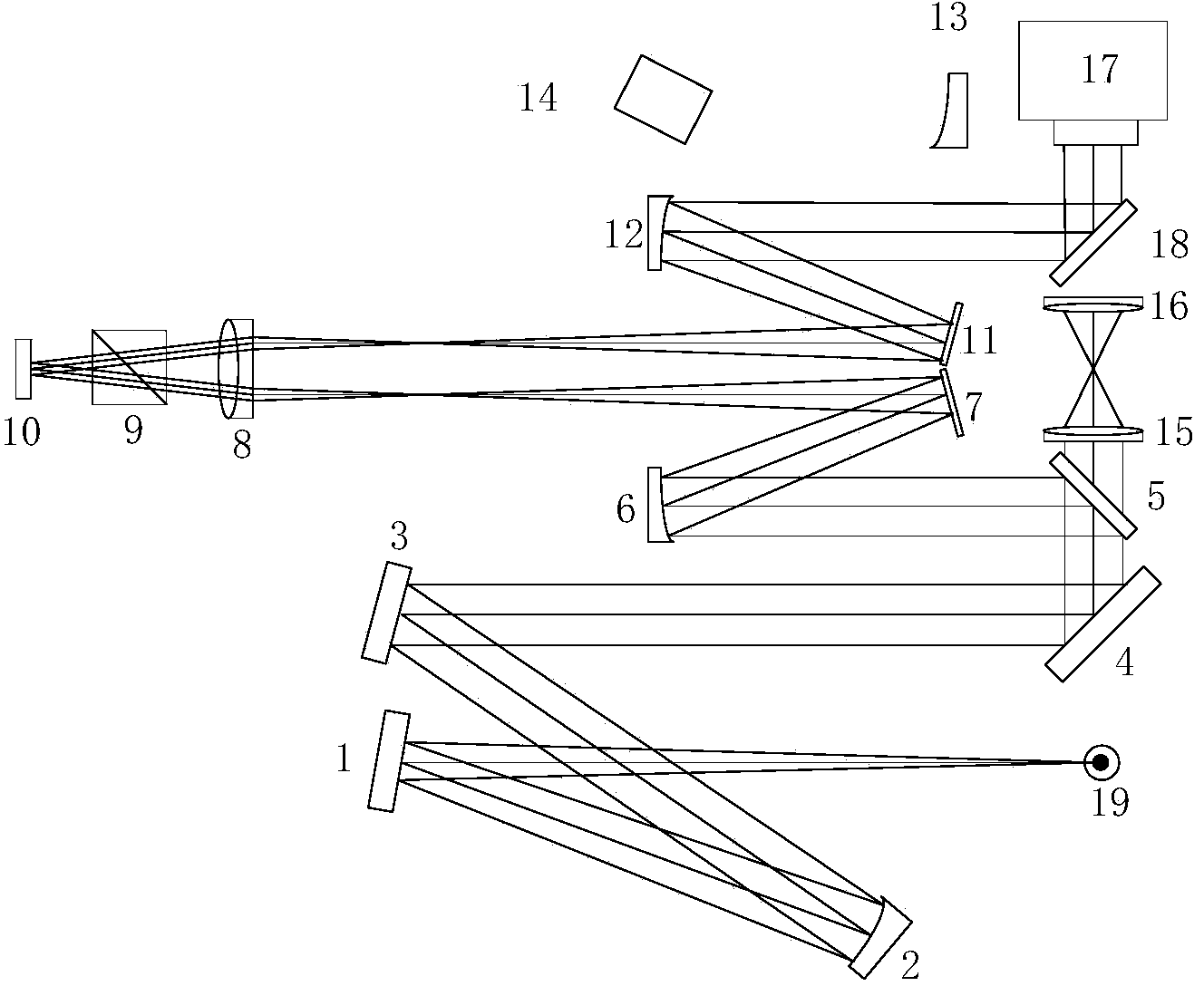
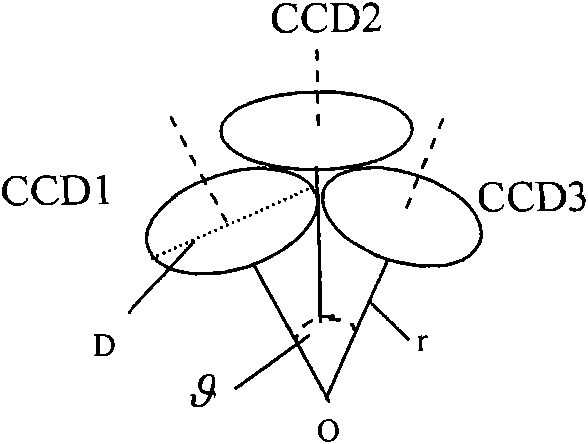
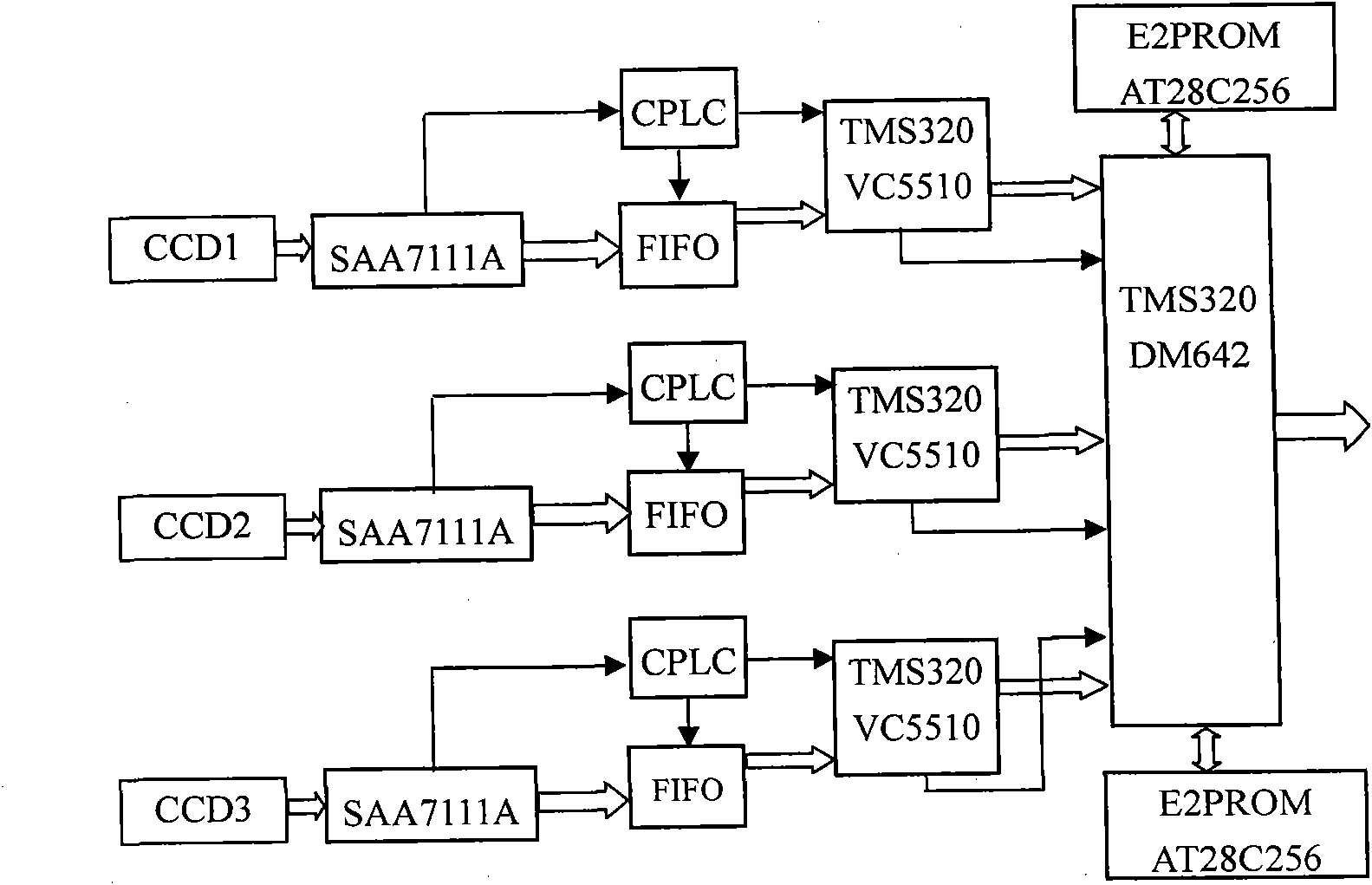
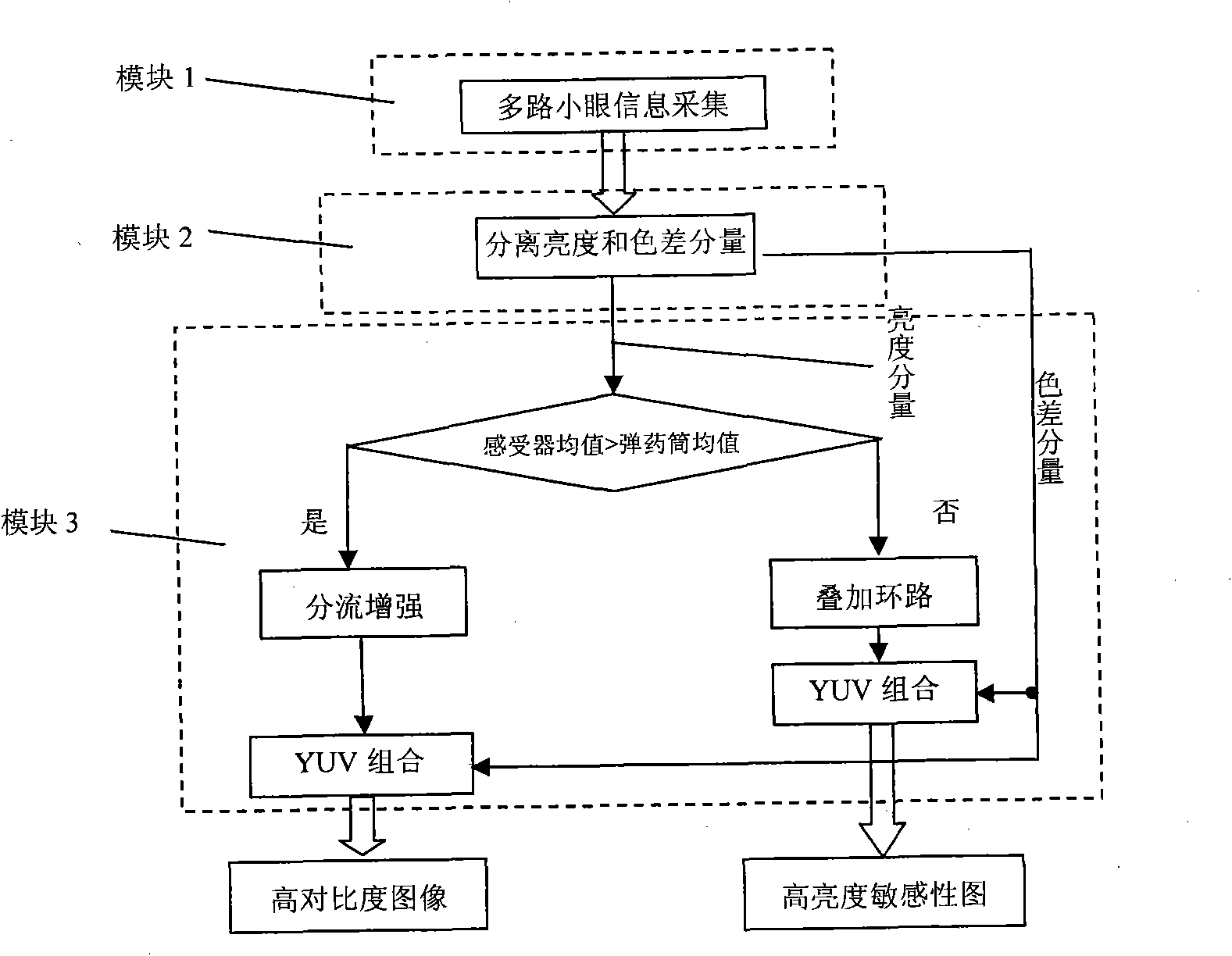
Multi-charge coupled device group self-adaptive imaging instrument of cambered optical structure and method thereof
InactiveCN101867828AHigh brightness sensitivityBreak through the limitations of poor daytime imagingTelevision system detailsClosed circuit television systemsAdaptive imagingNeural processing
The invention relates to a multi-charge coupled device group self-adaptive imaging instrument of a cambered optical structure and a method thereof, belonging to a field of the image information acquisition and processing. By imitating an ommateum to adjust the nerve conduction mode with the change of the illumination under the condition of day alternates with night to obtain a self-adaptive imaging effect principle, the instrument uses a plurality of common charge coupled devices (CCD), corresponding auxiliary circuits and a neural processing algorithm to construct a biomimic self-adaptive adjustment imaging instrument. The imaging instrument has an imaging function of self adjusting fusion modes with the change of illumination conditions, can acquire a high-contrast image under a normal illumination condition, and also can acquire a high-brightness sensitive image under a weak illumination condition. The invention realizes high-definition surveillance and monitoring under the condition of day alternates with night, belonging to the image information acquisition and processing field.
Owner:NANJING INST OF TECH
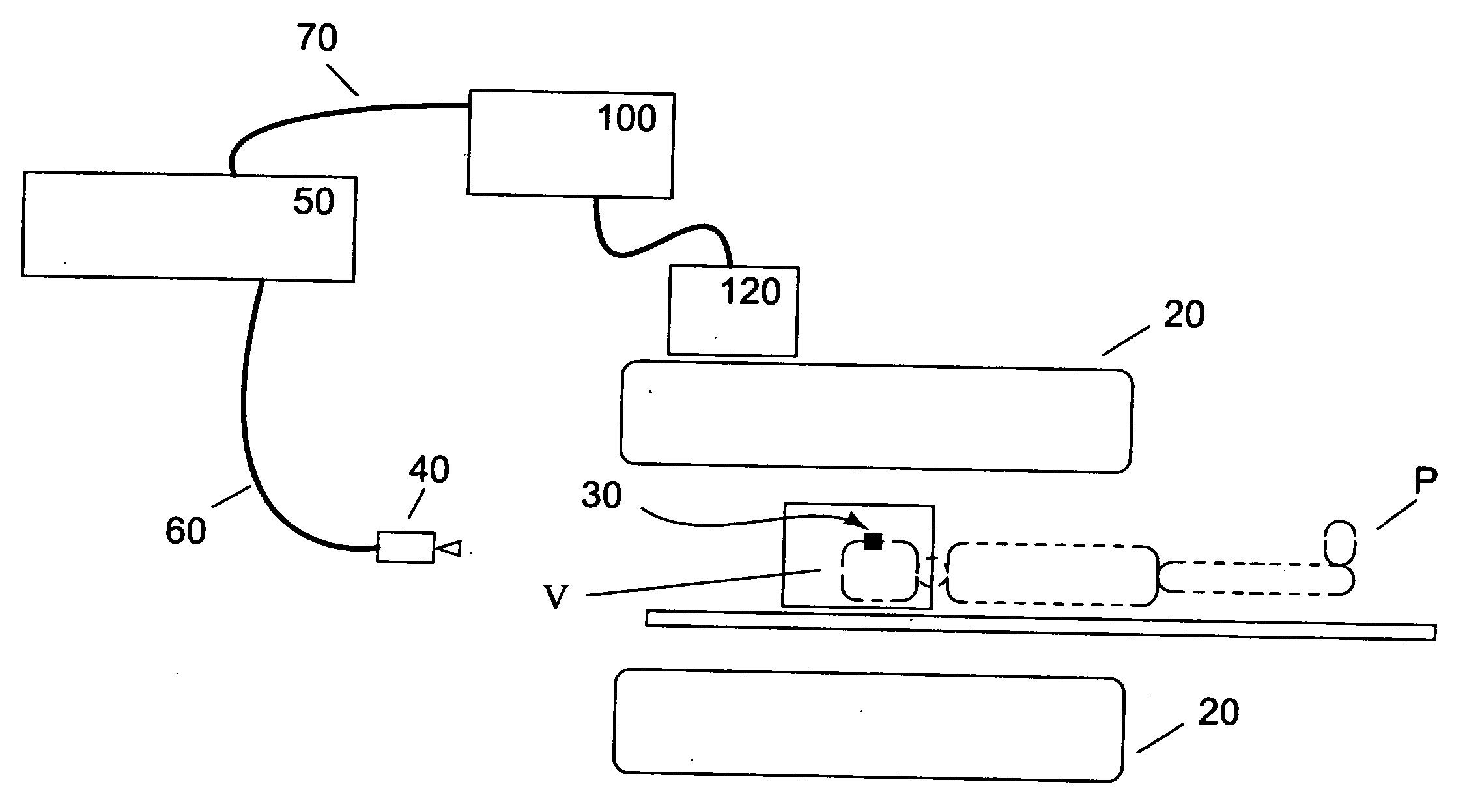
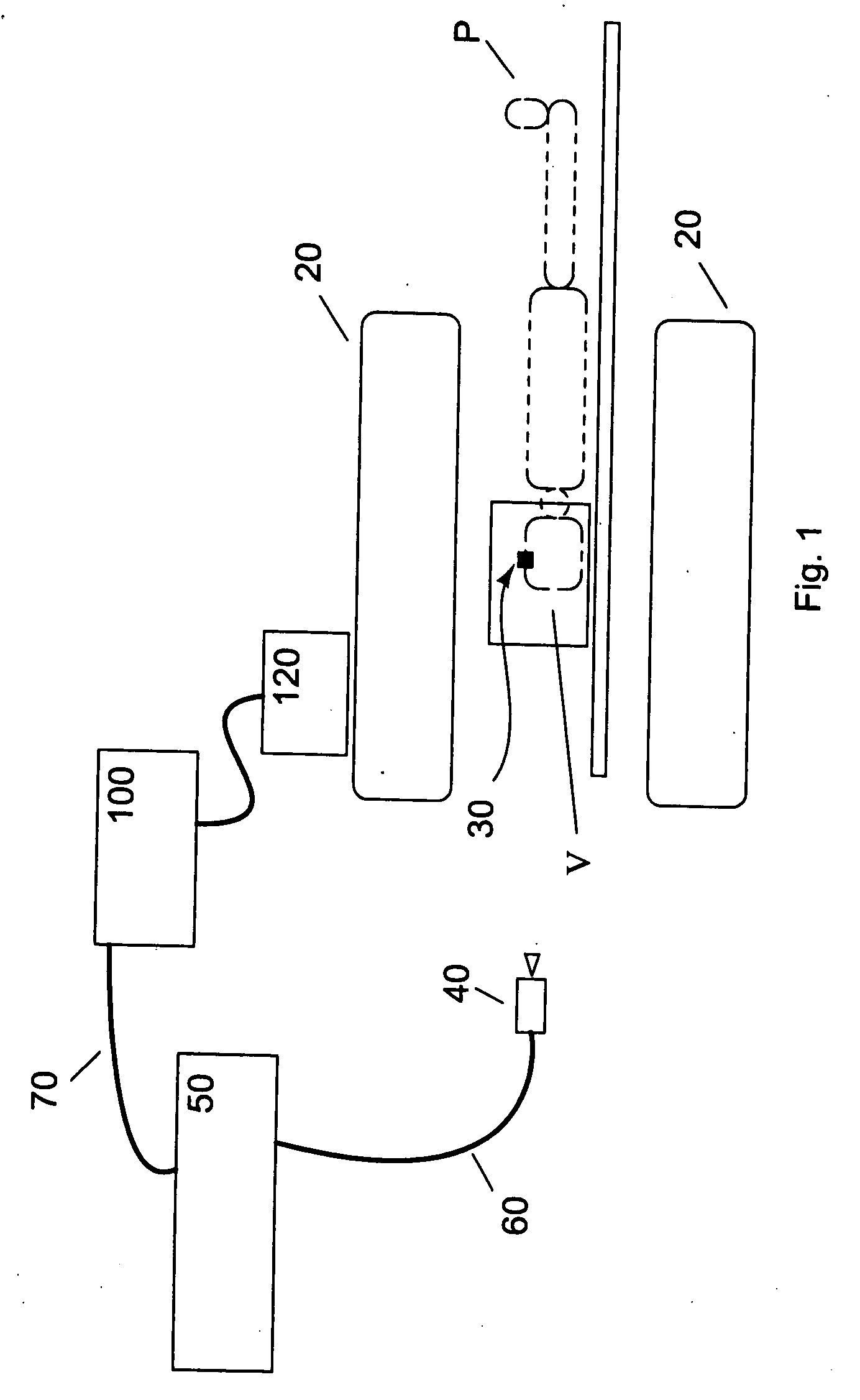
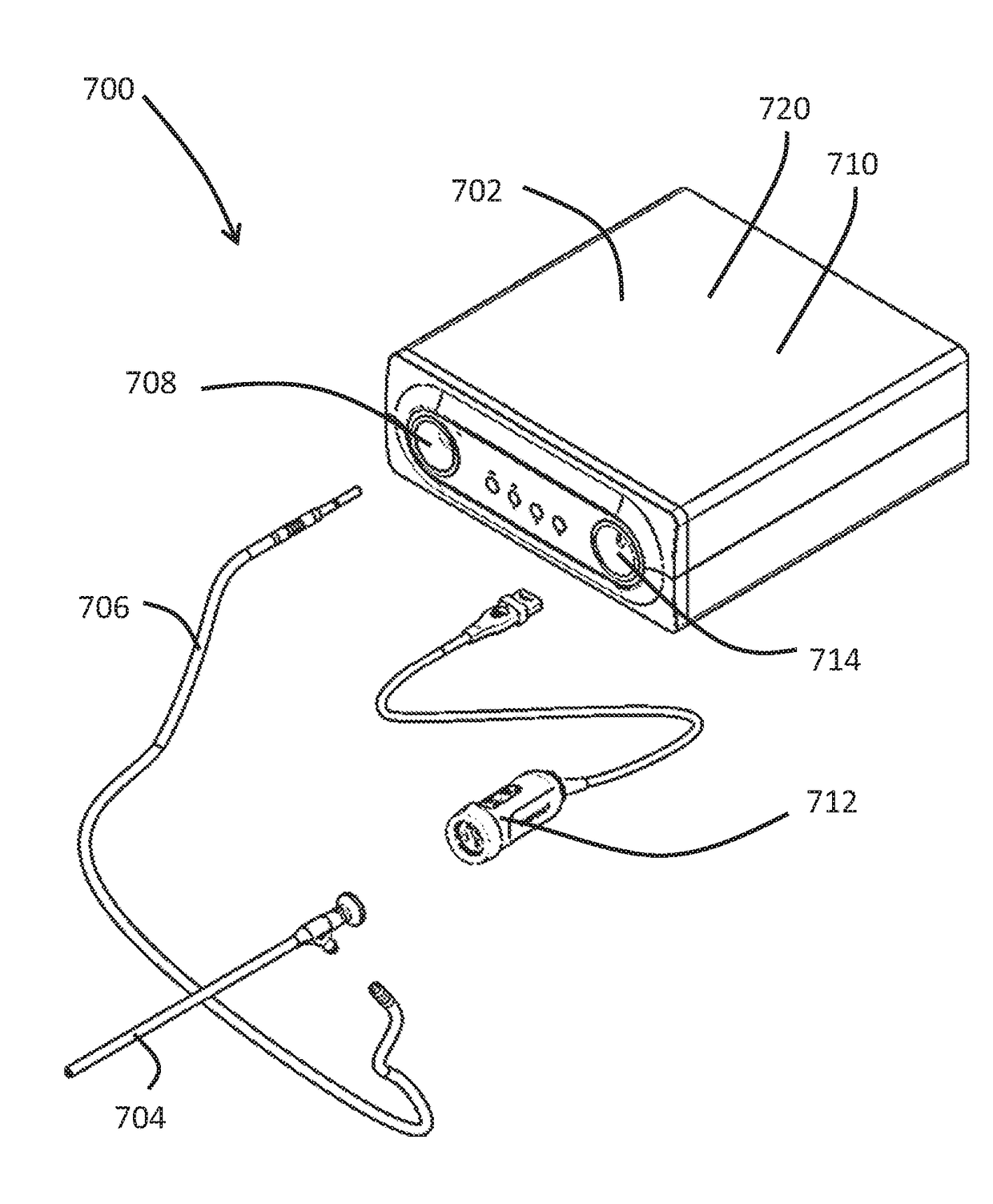
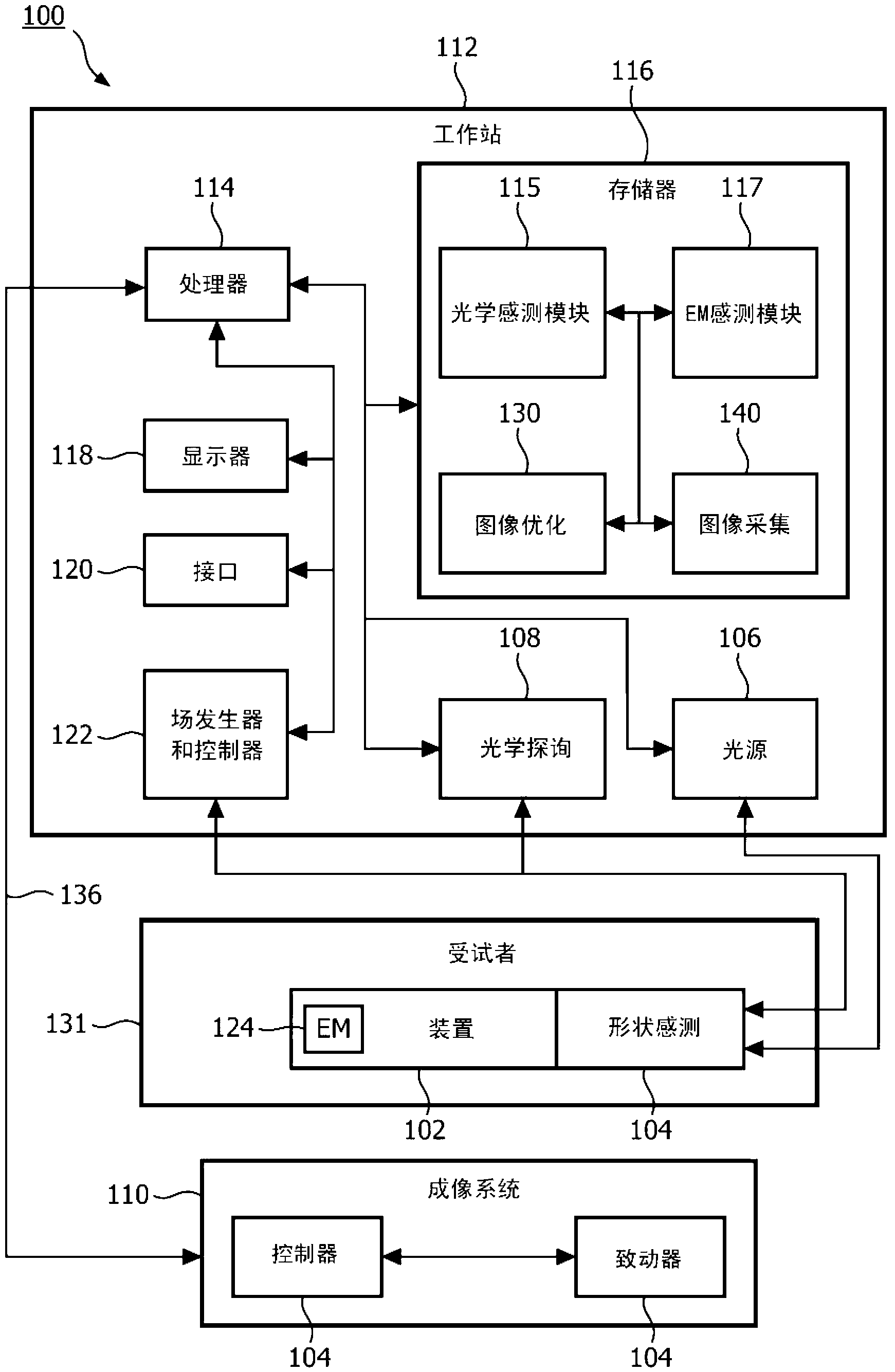
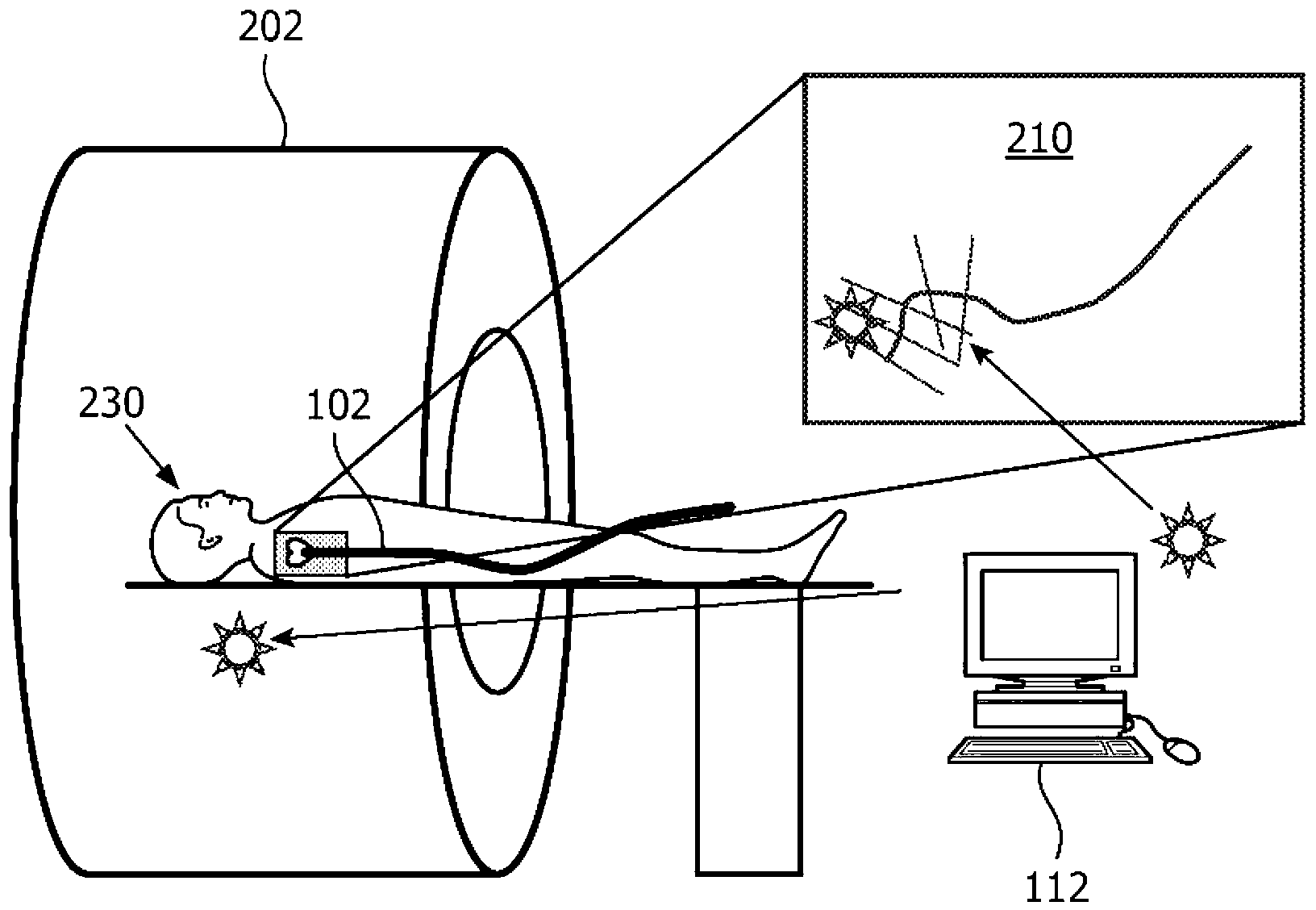
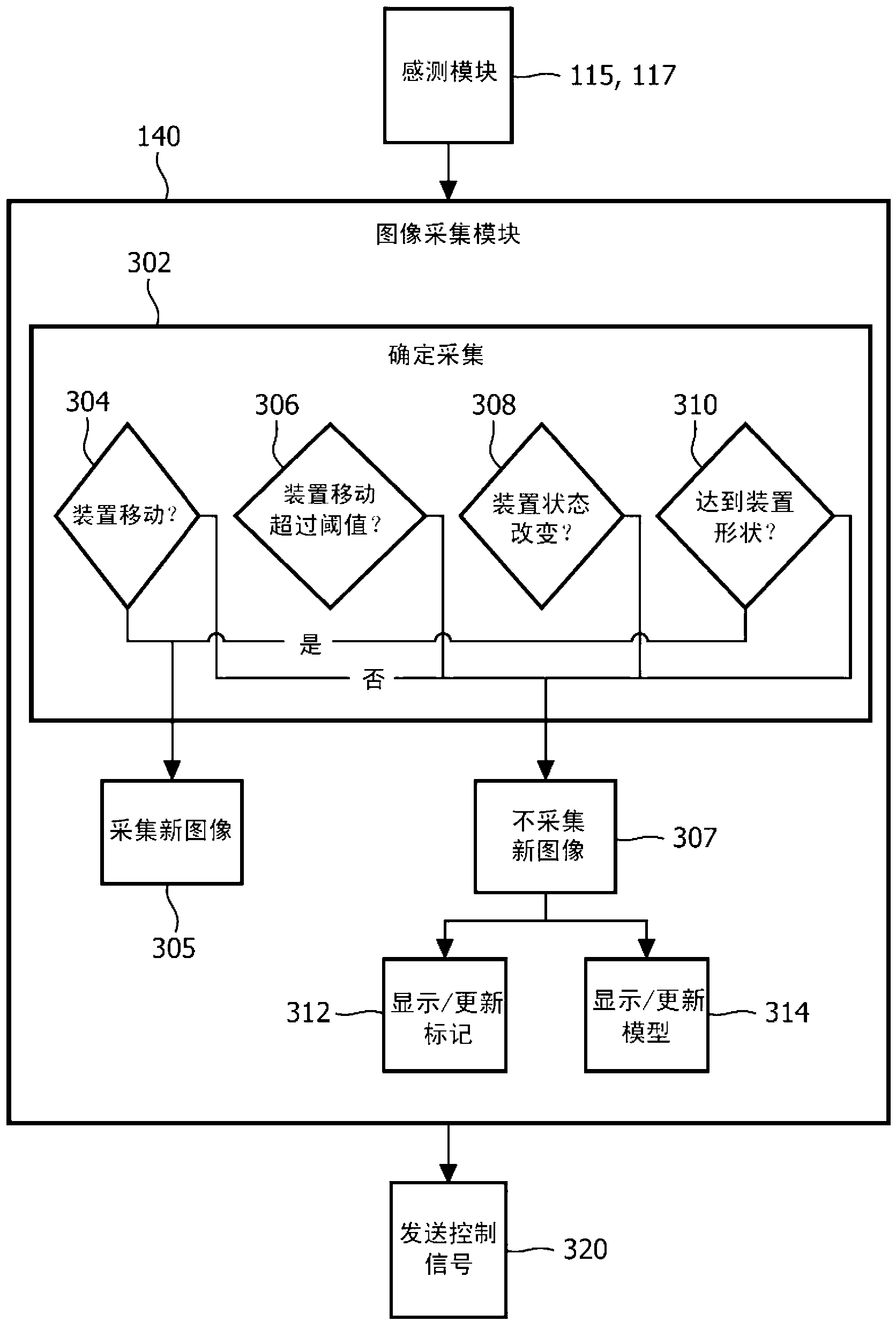
Adaptive imaging and frame rate optimizing based on real-time shape sensing of medical instruments
ActiveCN103179916ARadiation diagnostic device controlSurgical navigation systemsAdaptive imagingControl signal
A system and method for adaptive imaging include a shape sensing system (115, 117) coupled to an interventional device (102) to measure spatial characteristics of the interventional device in a subject. An image module (130) is configured to receive the spatial characteristics and generate one or more control signals in accordance with the spatial characteristics. An imaging device (110) is configured to image the subject in accordance with the control signals.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
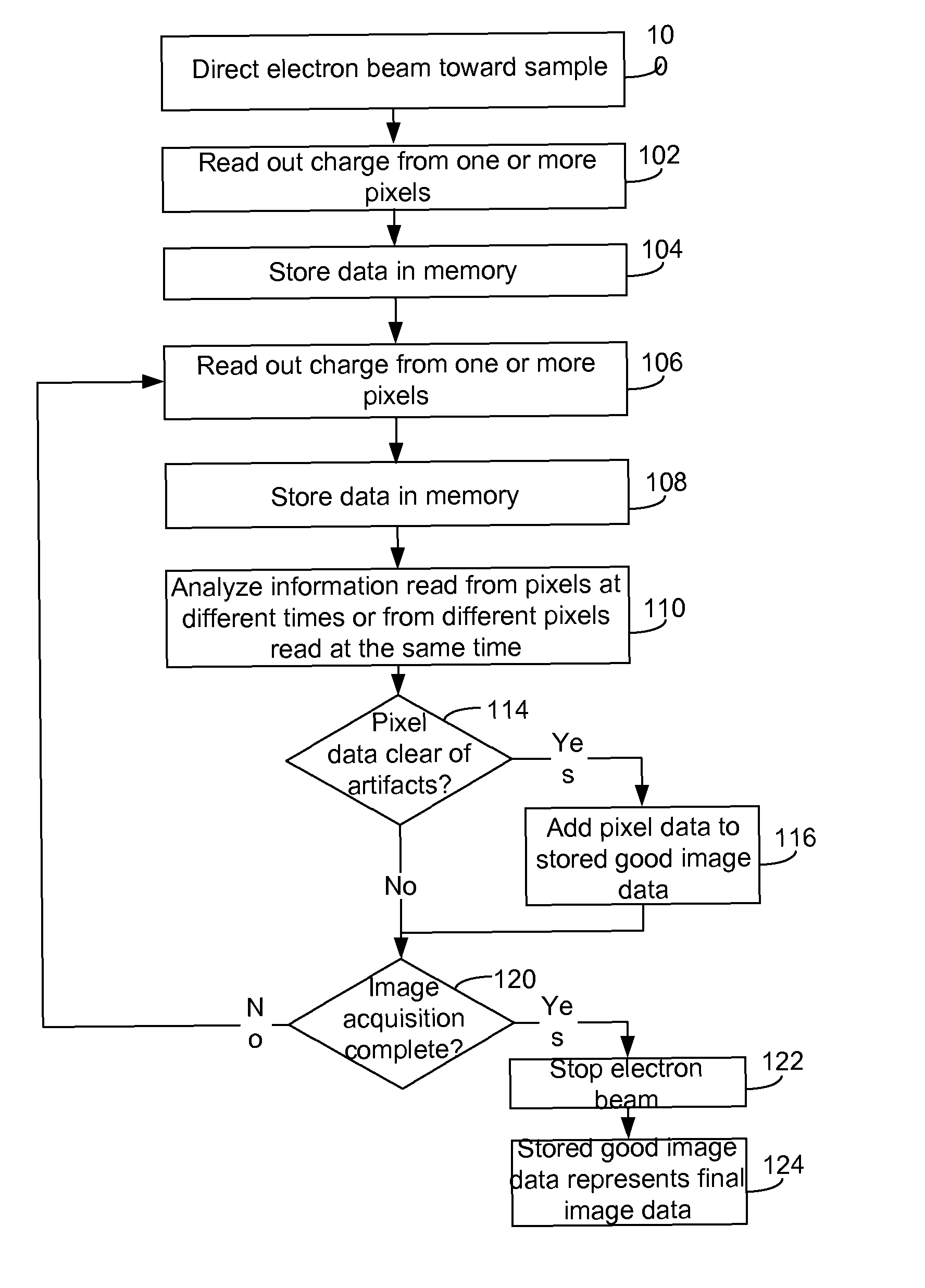
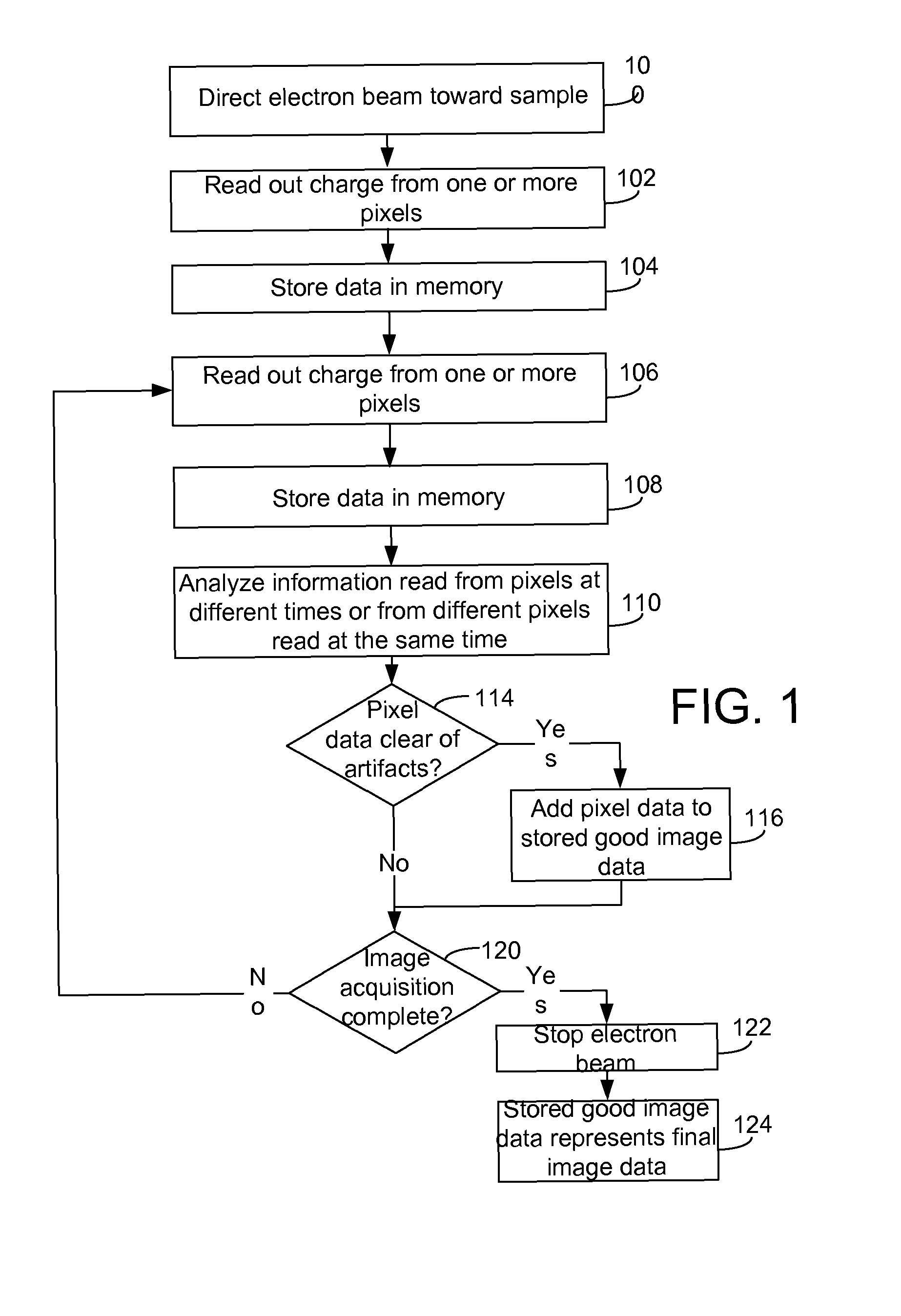
Detector System for Transmission Electron Microscope
ActiveUS20120049061A1Quality improvementMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesAdaptive imagingElectron microscope
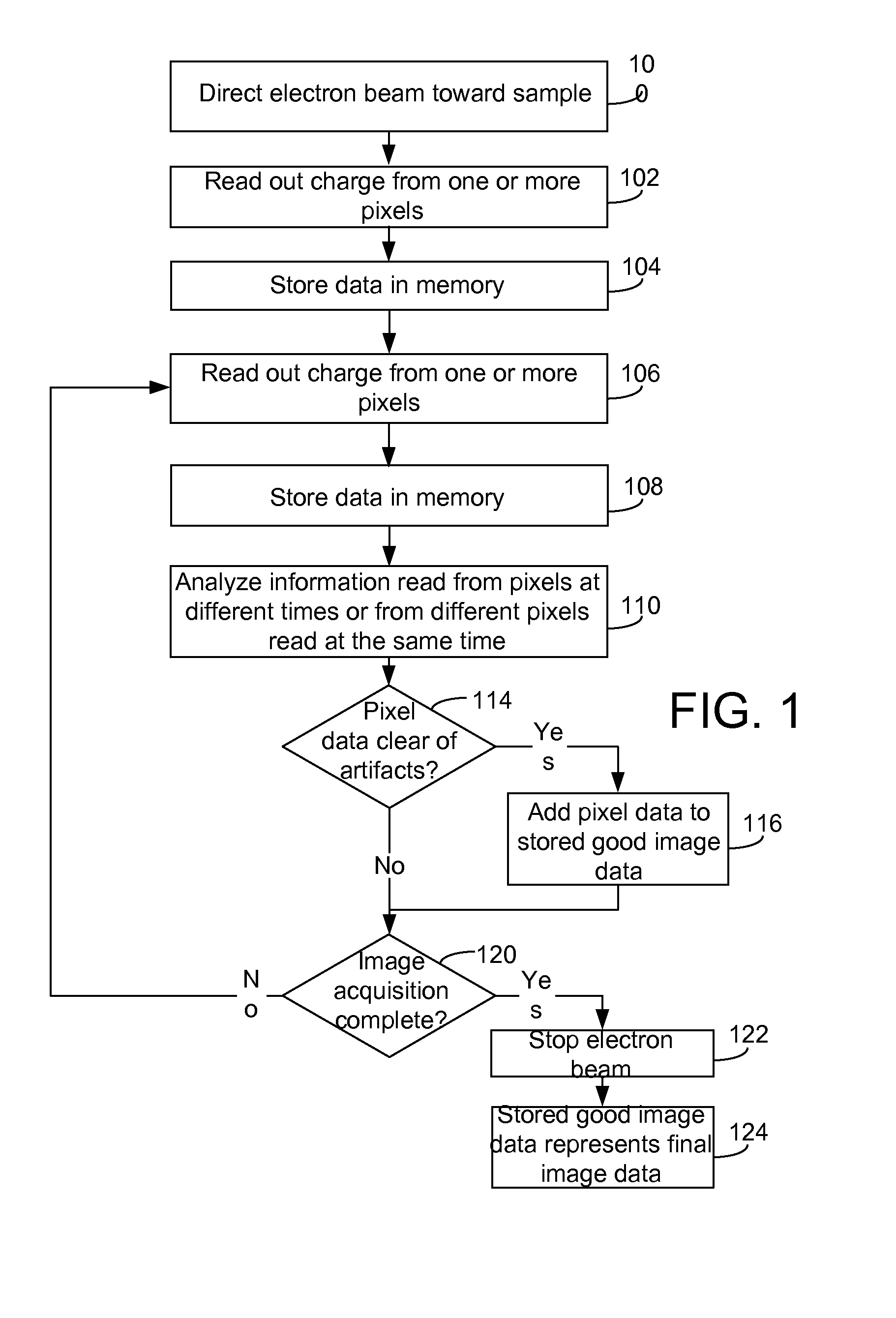
In a transmission electron microscope detector system, image data is read out from the pixels and analyzed during an image acquisition period. The image acquisition process is modified depending on the results of the analysis. For example, the analyses may indicate the inclusion in the data of an image artifact, such as charging or bubbling, and data including the artifact may be eliminated form the final image. CMOS detectors provide for selective read out of pixels at high data rates, allowing for real-time adaptive imaging.
Owner:FBI
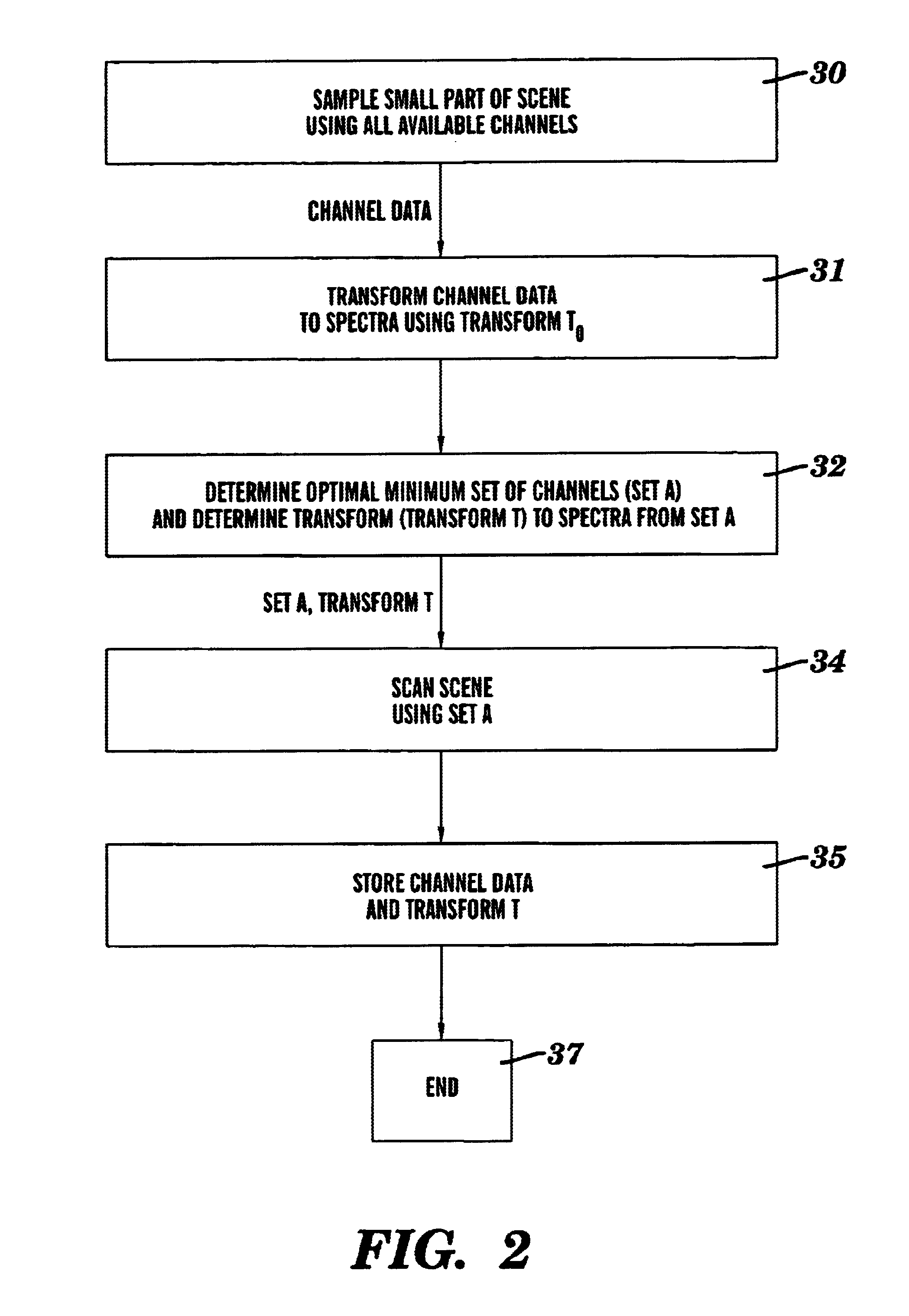
Data-efficient and self adapting imaging spectrometry method and an apparatus thereof
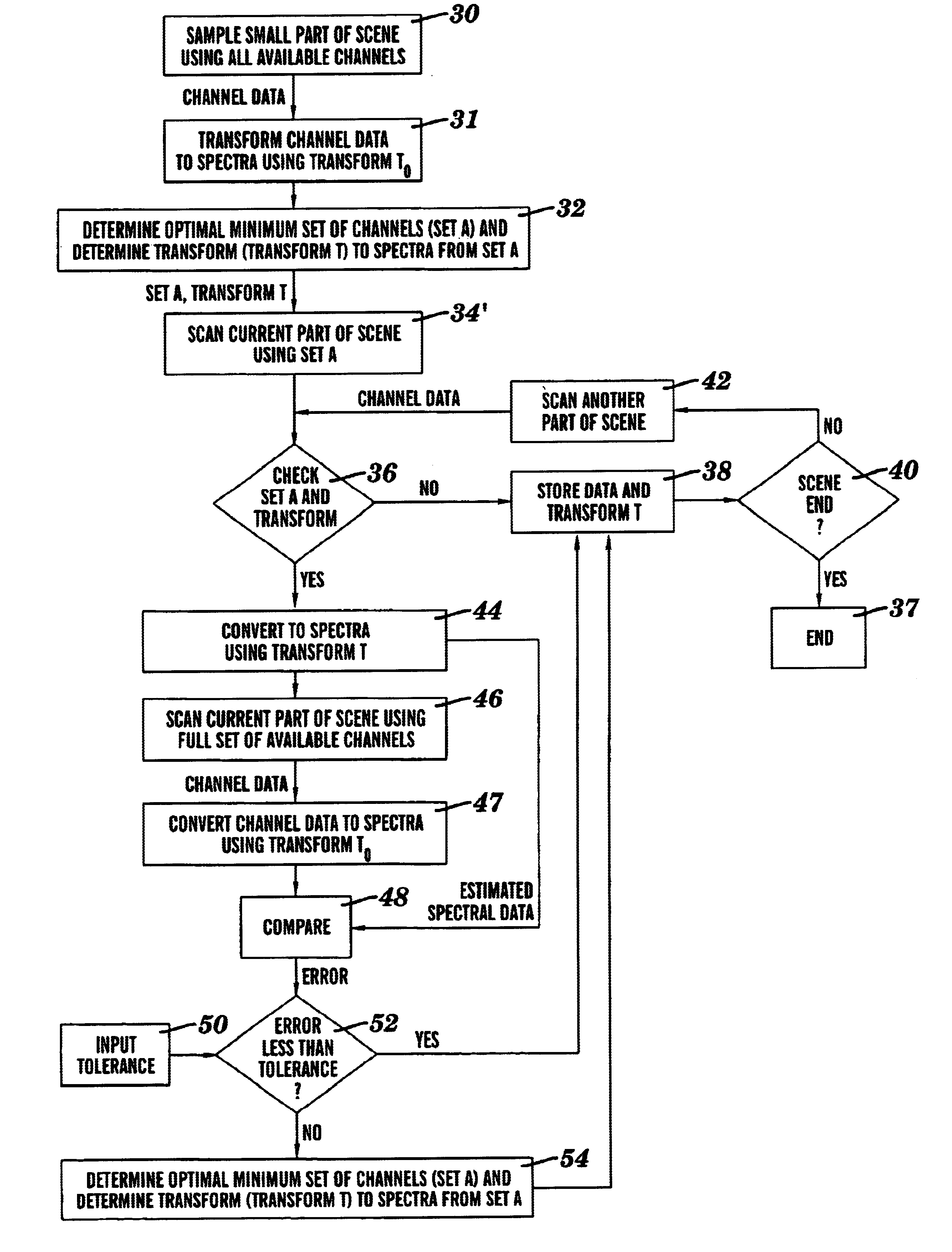
InactiveUS6920244B2Improve accuracyLow bandwidthSpectrum investigationPower distribution line transmissionAdaptive imagingImage resolution
A method for spectral imaging includes capturing high spectral resolution data of at least a portion of an image using a plurality of channels, determining a first set of channels from the plurality of channels which can reconstruct spectra of the portion of the image to within a first error tolerance from the captured high spectral resolution data, and capturing estimated spectral resolution data of the image using the first set of channels.
Owner:ROCHESTER INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Iterative self-adaptive high-resolution imaging method of distributed array radar
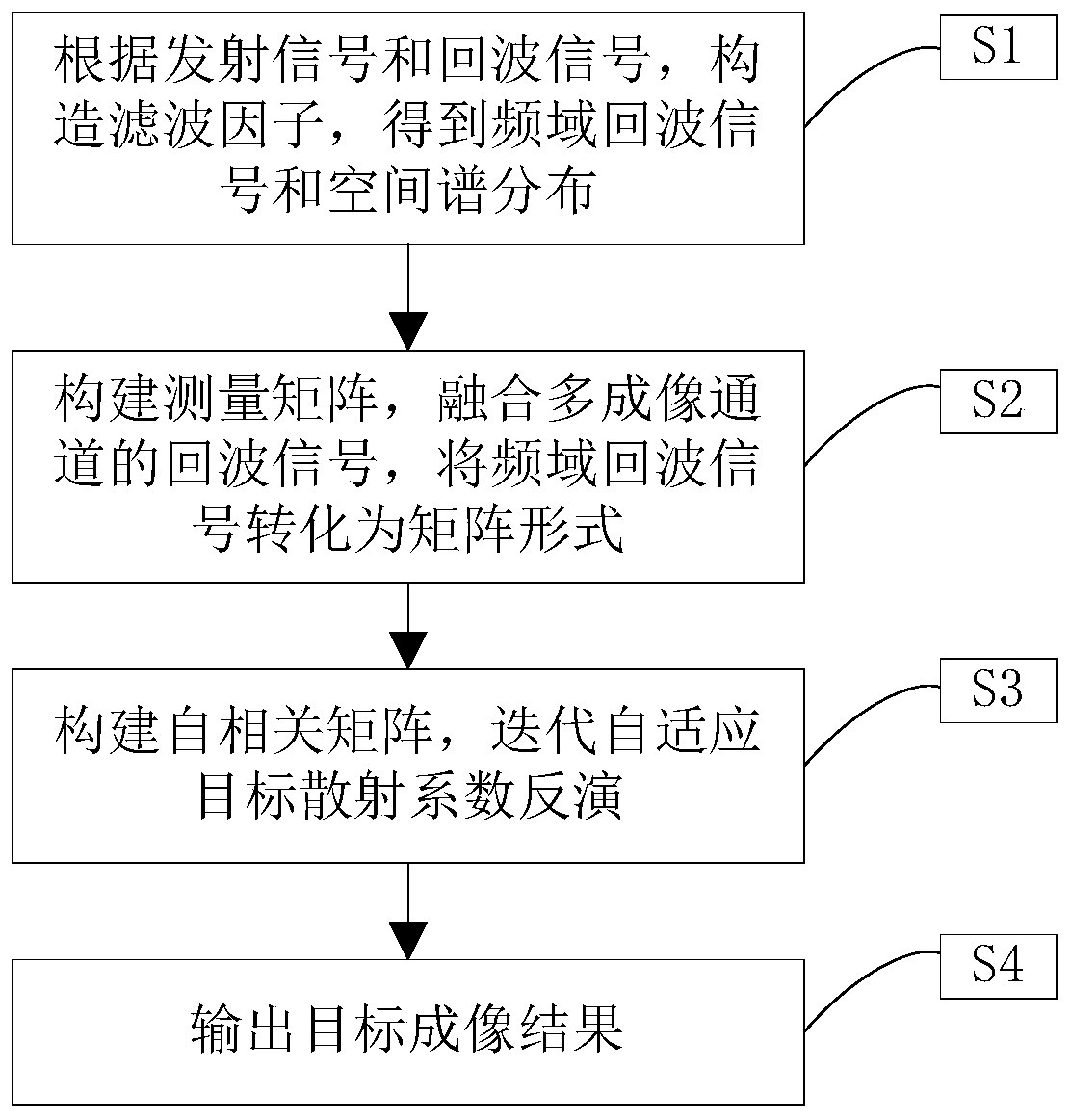
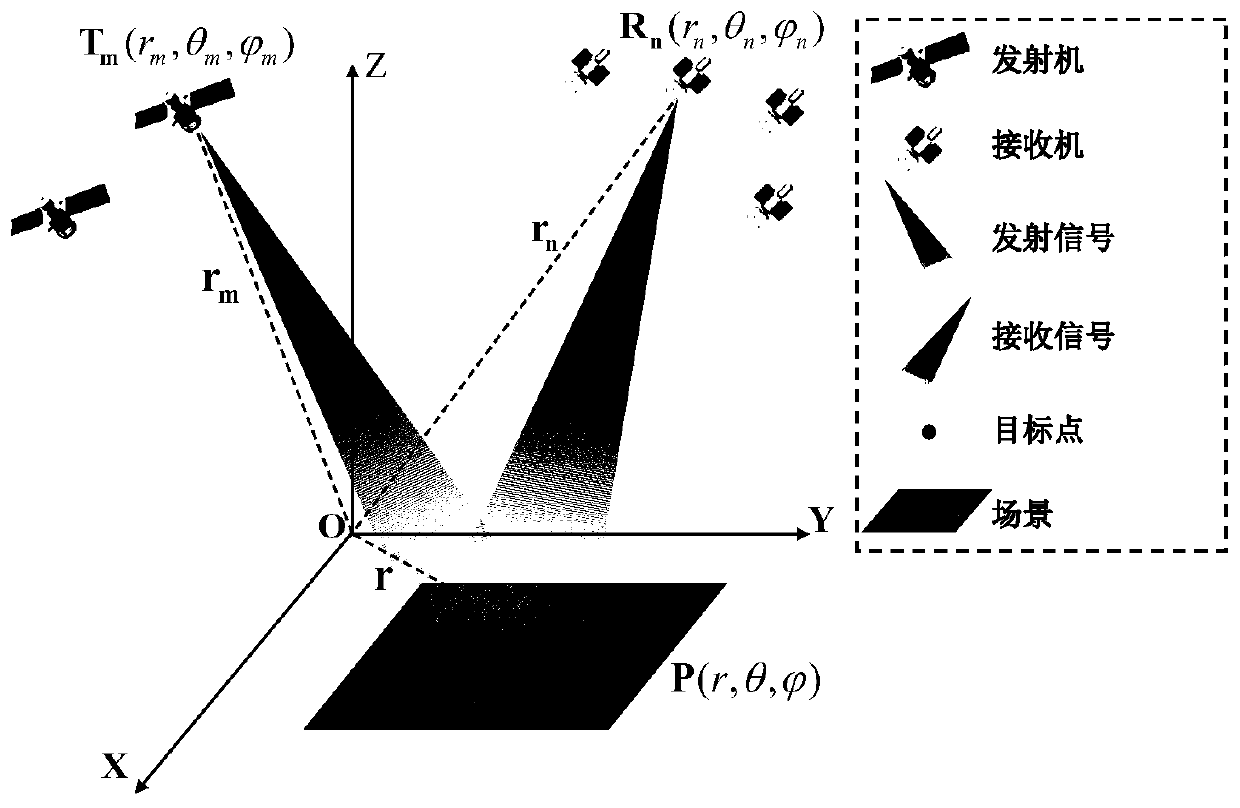
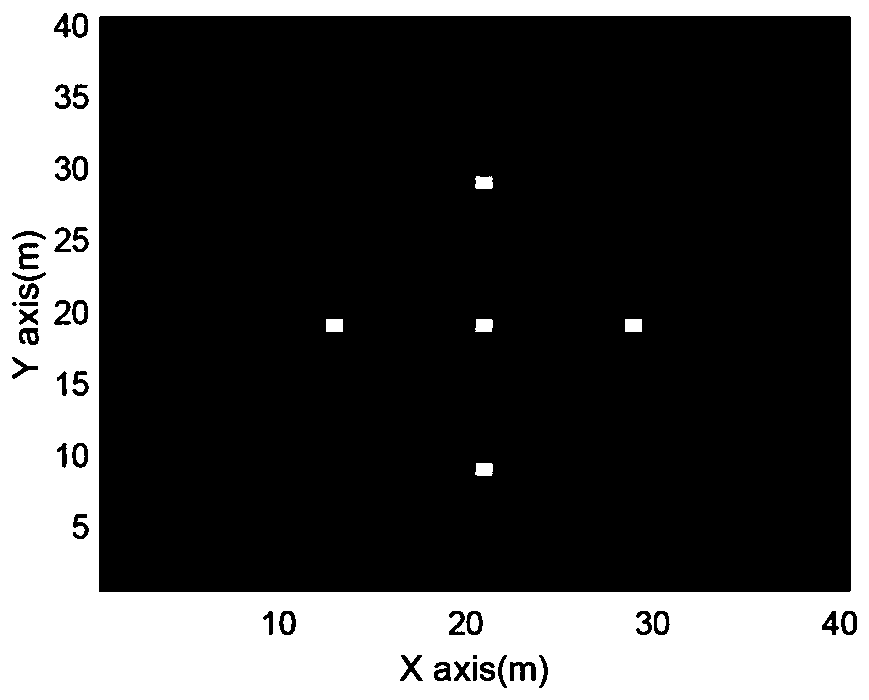
InactiveCN110346793AReduce dependenceRadio wave reradiation/reflectionHigh resolution imagingRadar systems
The invention provides an iterative self-adaptive high-resolution imaging method of a distributed array radar, and belongs to the technical field of radar imaging. Aiming at the problem of configuration dependence of a traditional distributed array radar, the iterative self-adaptive high-resolution imaging method comprises the steps of firstly, deriving spatial spectrum distribution of a distributed radar array according to a space region of sparse array of the distributed array radar; secondly, constructing a distributed array radar system observation matrix according to the distributed radarspatial spectrum distribution and a system parameter; and finally, employing the iterative self-adaptive imaging processing method to achieve high-resolution imaging of the distributed array radar inorder to reduce the configuration dependence during the imaging processing process. The dependence of the distributed array radar on configuration is reduced by iterative self-adaptive convergence during the target solving process.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
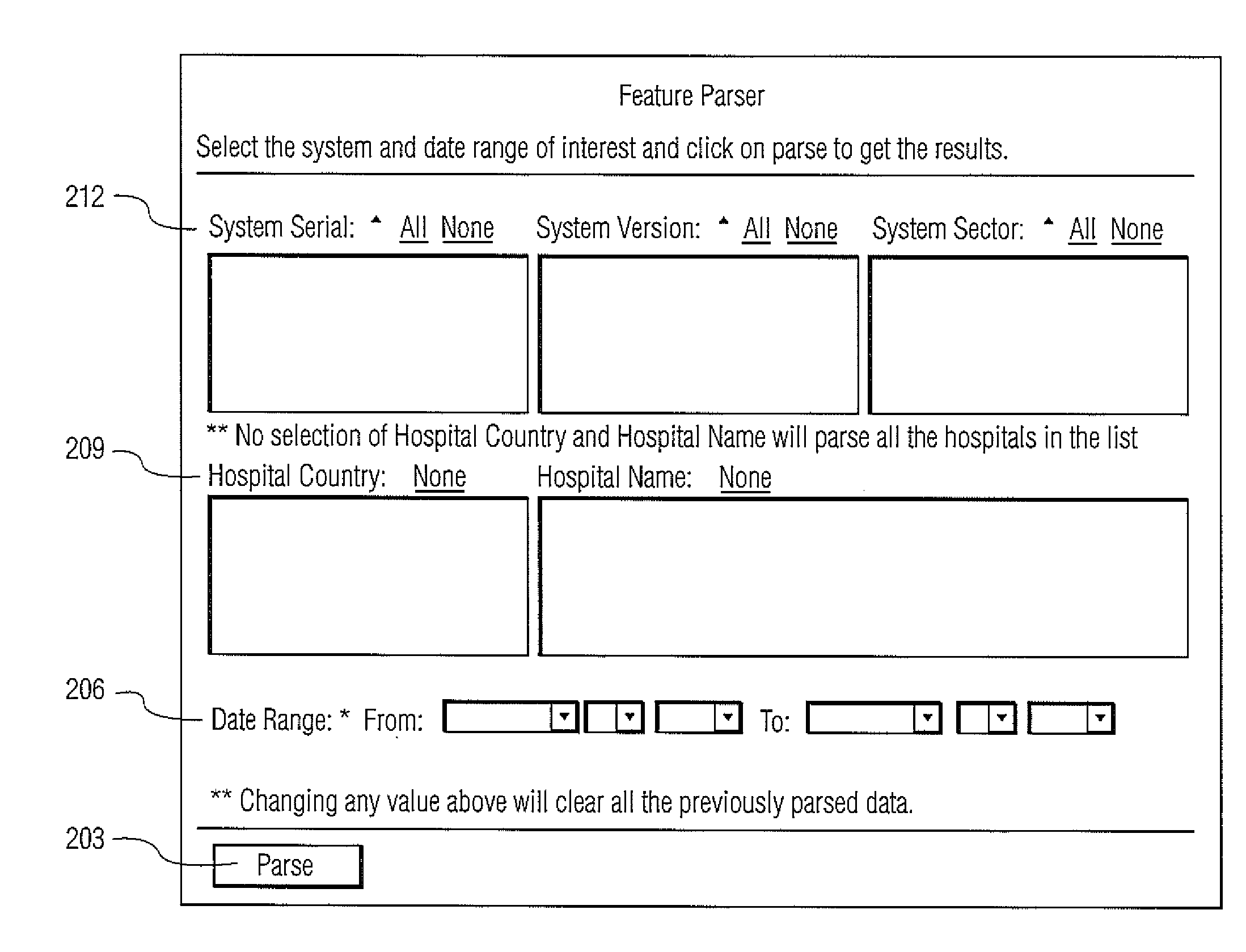
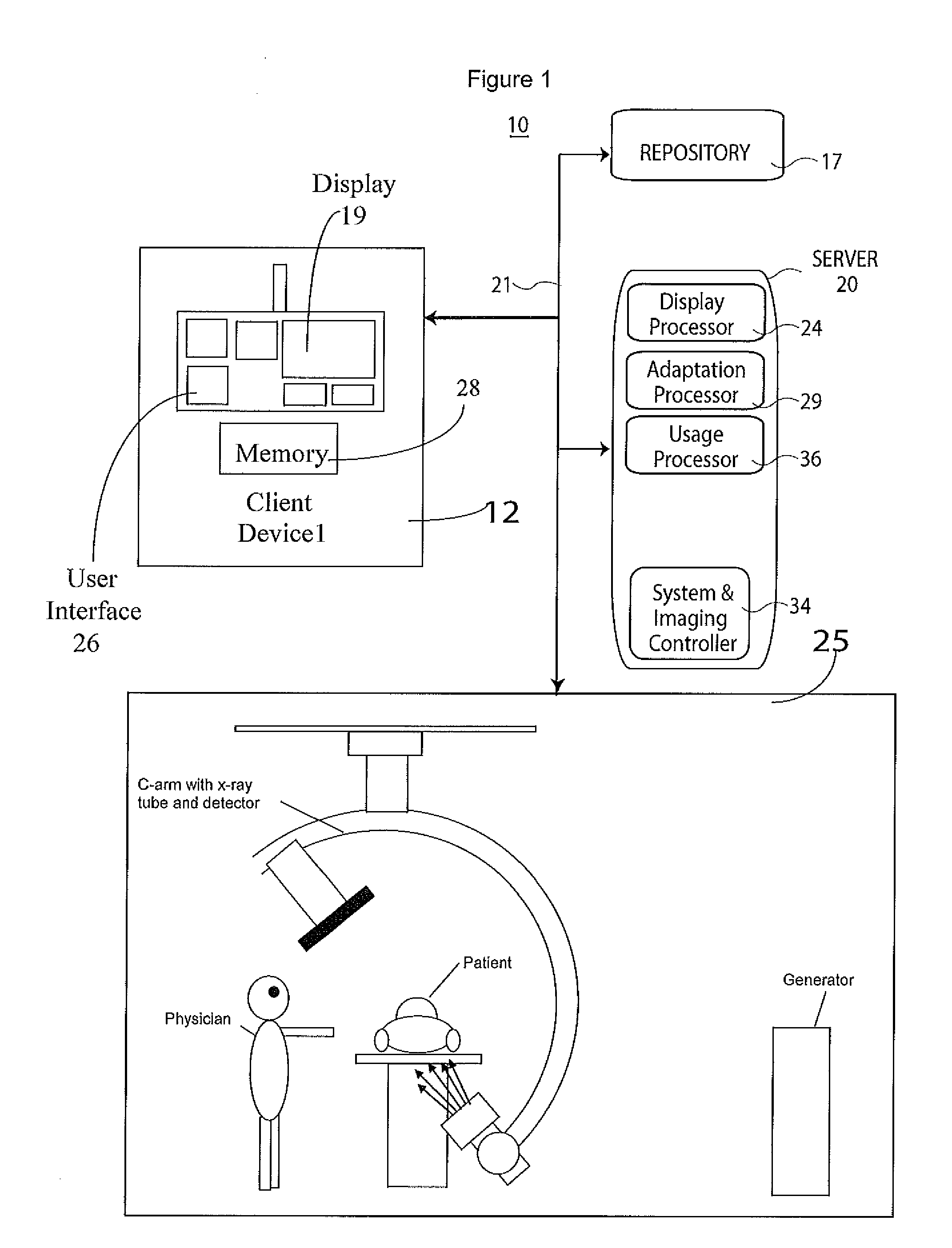
Adaptive Imaging System Workflow & User Interface System
A system configures a medical imaging system using utilization information. The system includes at least one repository storing records indicating usage and an associated time of usage, of particular features of a medical imaging system. A processor coupled to the at least one repository analyzes the records to determine, (a) frequency of usage of particular features of the medical imaging system and (b) a sequence of usage of the particular features of the medical imaging system and provide utilization data, by identifying in the records particular text strings using predetermined information associating predetermined text strings with corresponding features. An adaptation processor uses the utilization data to modify, delete or add a task to a task sequence employing the particular features. A display processor generates data representing at least one display image enabling a user to perform an adapted task sequence.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
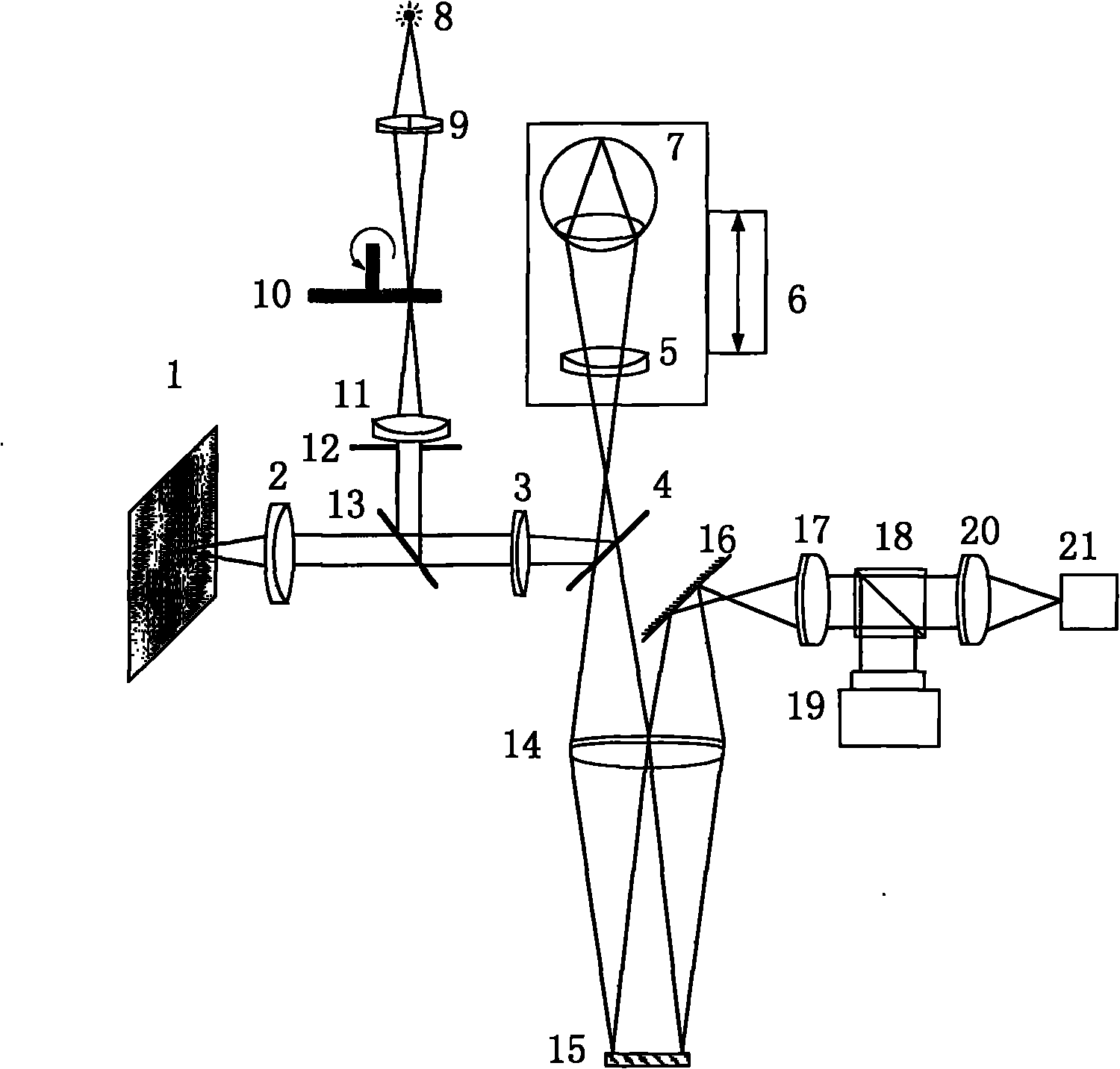
Liquid-crystal adaptive optical system with compact structure and high sensitivity
ActiveCN102540453AAlignment accuracy is not affectedNo beam flip issuesOptical elementsAdaptive imagingWavefront
The invention belongs to the field of adaptive optics, relates to a liquid-crystal adaptive optical imaging system for an atmospheric channel, and discloses a liquid-crystal adaptive optical system with compact structure and high sensitivity for realizing energy optimization and distribution of a detection branch and a correction imaging branch. The liquid-crystal adaptive optical system consistsof a wavefront detection branch, a correction imaging branch, a third reflecting lens and a Dove prism. Through introducing and optically combing the Dove prism with a fixed reflecting lens, a rotatable reflecting lens and a dichroic mirror, the switching between an adaptive imaging optical path and a liquid-crystal corrector response measuring optical path is realized, so that the aligning precision of the optical paths is not affected, the problem that in two processes of wavefront detection and corrector response matrix measurement, the section of an optical beam entering a Hartmann wavefront detector turns over is solved, and the reading sequences of detection data and corrector response measuring data are consistent; and the butt joint of the response matrix measuring optical path and the wavefront detection is finished by the dichroic mirror, so that the optical design of the detection branch is simplified.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Adaptive imaging using digital light processing
ActiveUS8675119B2High imageIncrease rangeTelevision system detailsColor television detailsDigital signal processingAdaptive imaging
A system (100) for the adaptive imaging of a scene includes a digital light processing apparatus (150) adapted for controllably reflecting an image of the scene in at least a first direction to thereby reflect an intensity modulated image of the scene along at least the first direction, an image detector (140) for detecting the intensity modulated image of the scene and generating corresponding image data, and an image data processor (154) for processing the image data into control data and providing the control data to the digital light processing (150) apparatus for control thereof.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
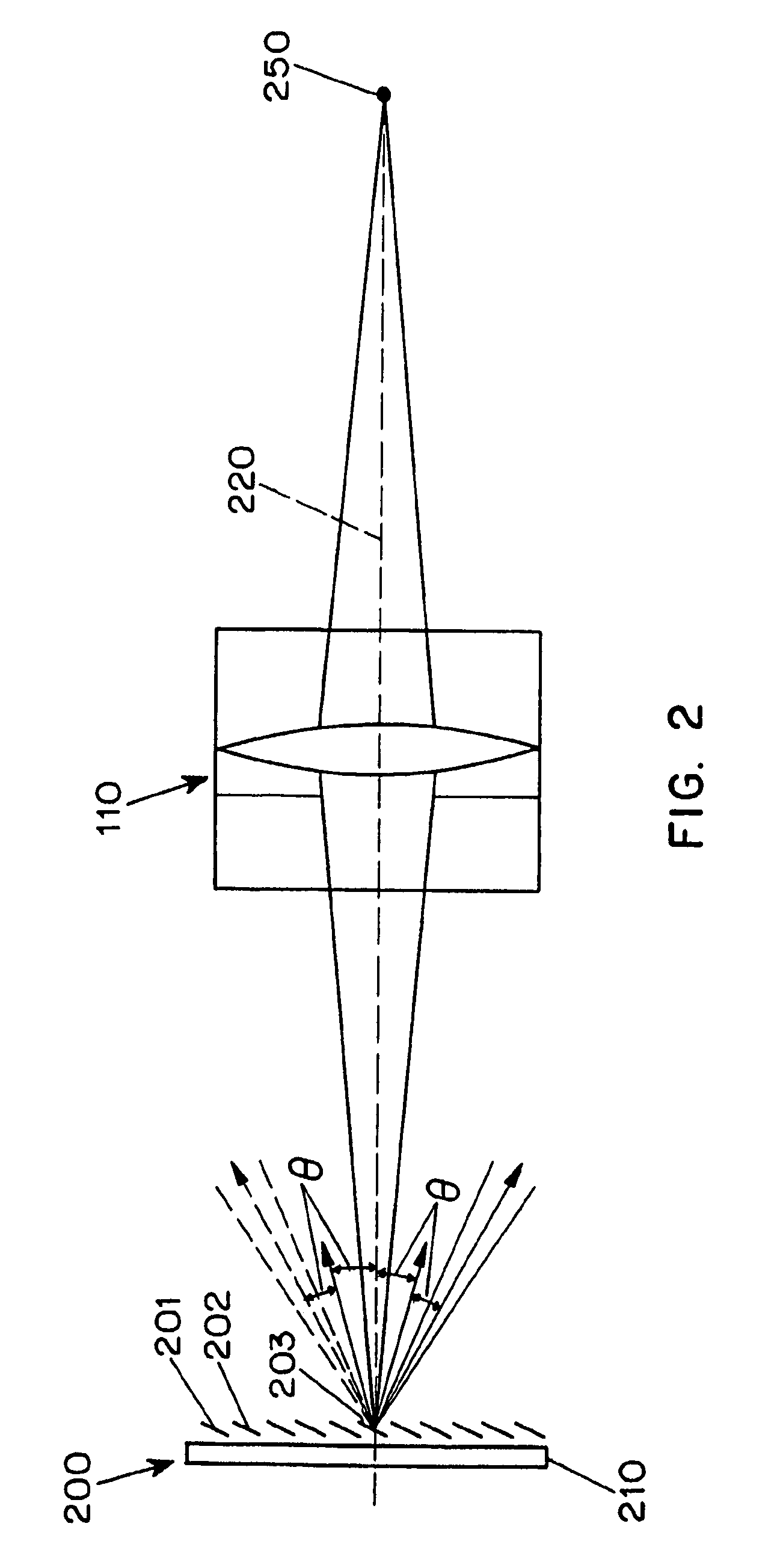
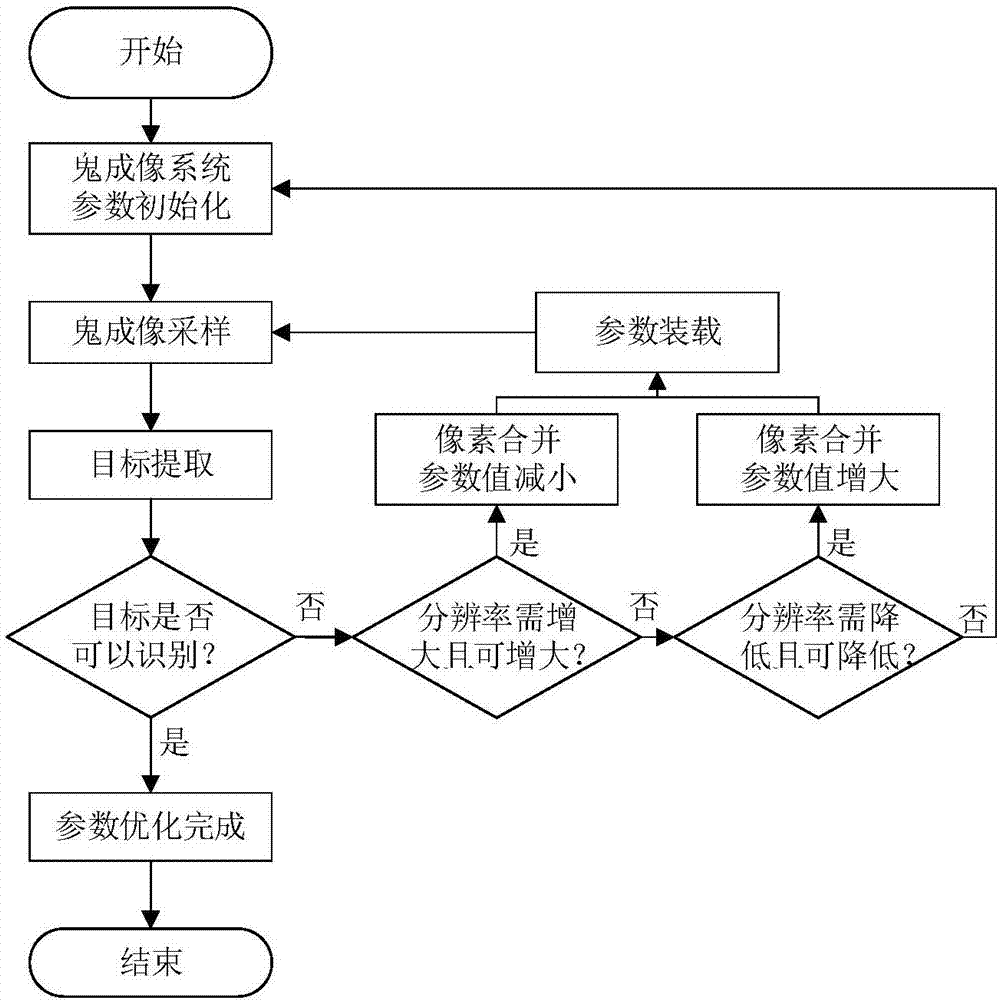
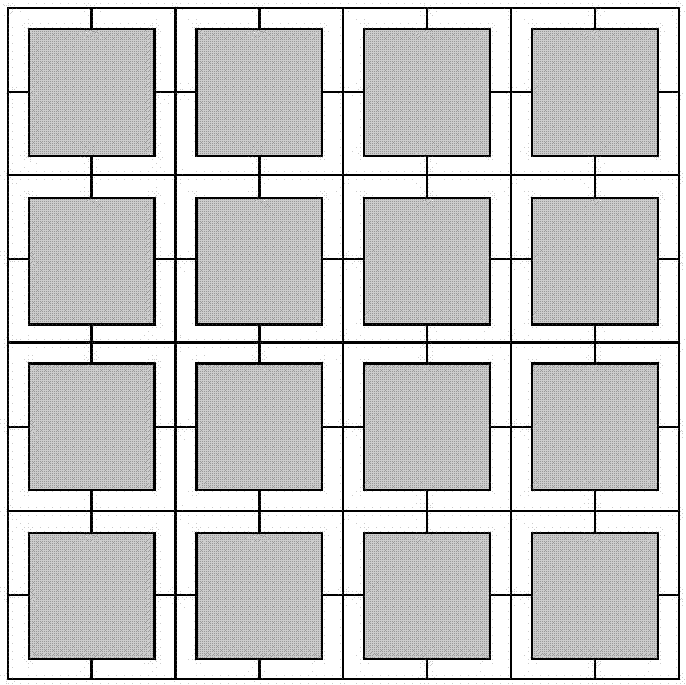
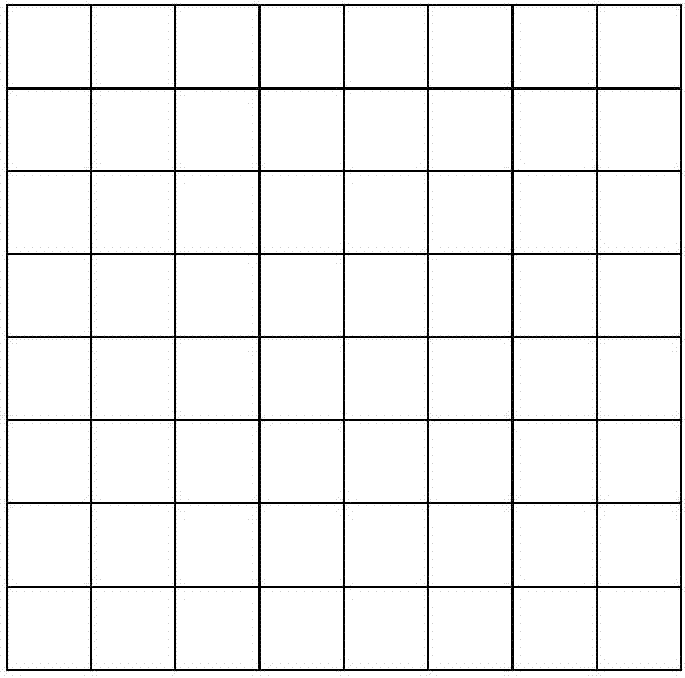
Adaptive imaging method used for improving ghost imaging efficiency
ActiveCN107016637AImproving Imaging EfficiencyImprove general performanceGeometric image transformationImage data processing detailsAdaptive imagingImage resolution
The invention relates to an adaptive imaging method used for improving the ghost imaging efficiency, and belongs to the technical field of optical imaging. The object of the invention is to provide an adaptive imaging method used for improving the ghost imaging efficiency in order to solve the problem that in the practical application of the ghost imaging technology, the imaging efficiency is low since the resolution is a fixed value and cannot be adaptively adjusted according to different conditions. According to the method, during the application of the ghost imaging technology, the resolution can be adaptively adjusted by employing a pixel combination mode according to the practical application condition requirement, and the ghost imaging efficiency is improved; besides, the method can be applicable to a calculation ghost imaging system and a classic ghost imaging system, an extra mechanism is not needed, and the universality is high.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com