Patents
Literature
126 results about "Artificial vision" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
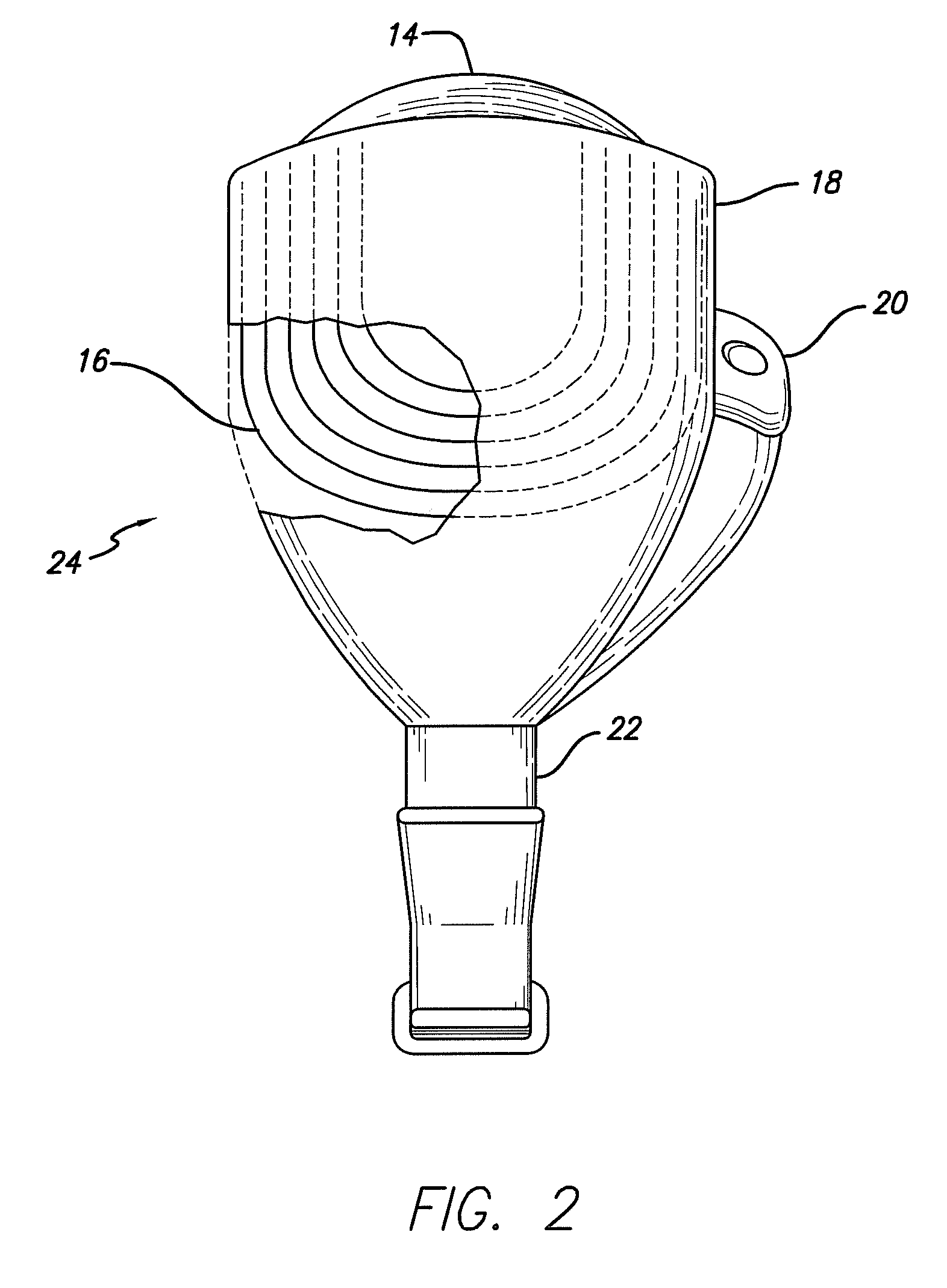
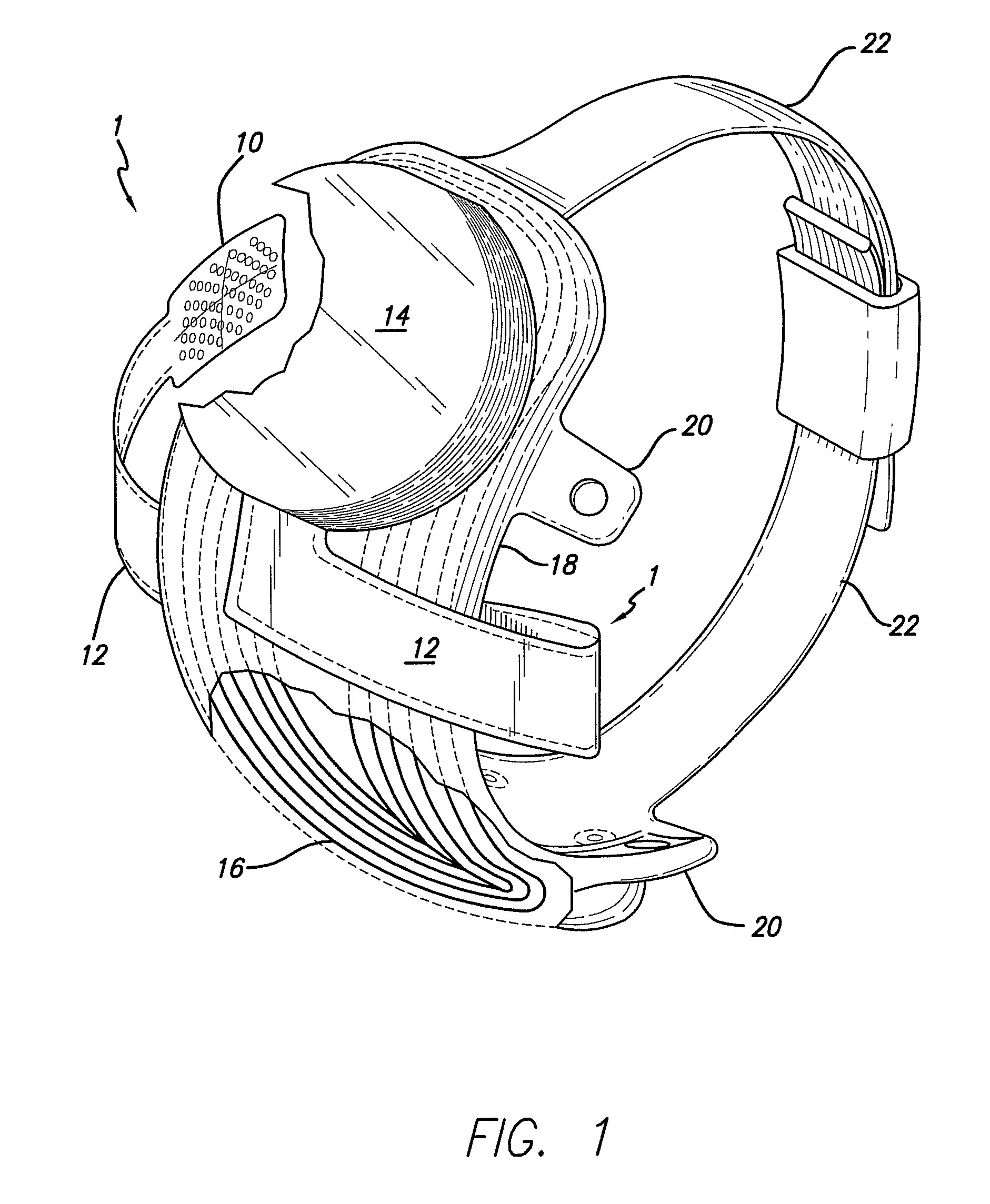
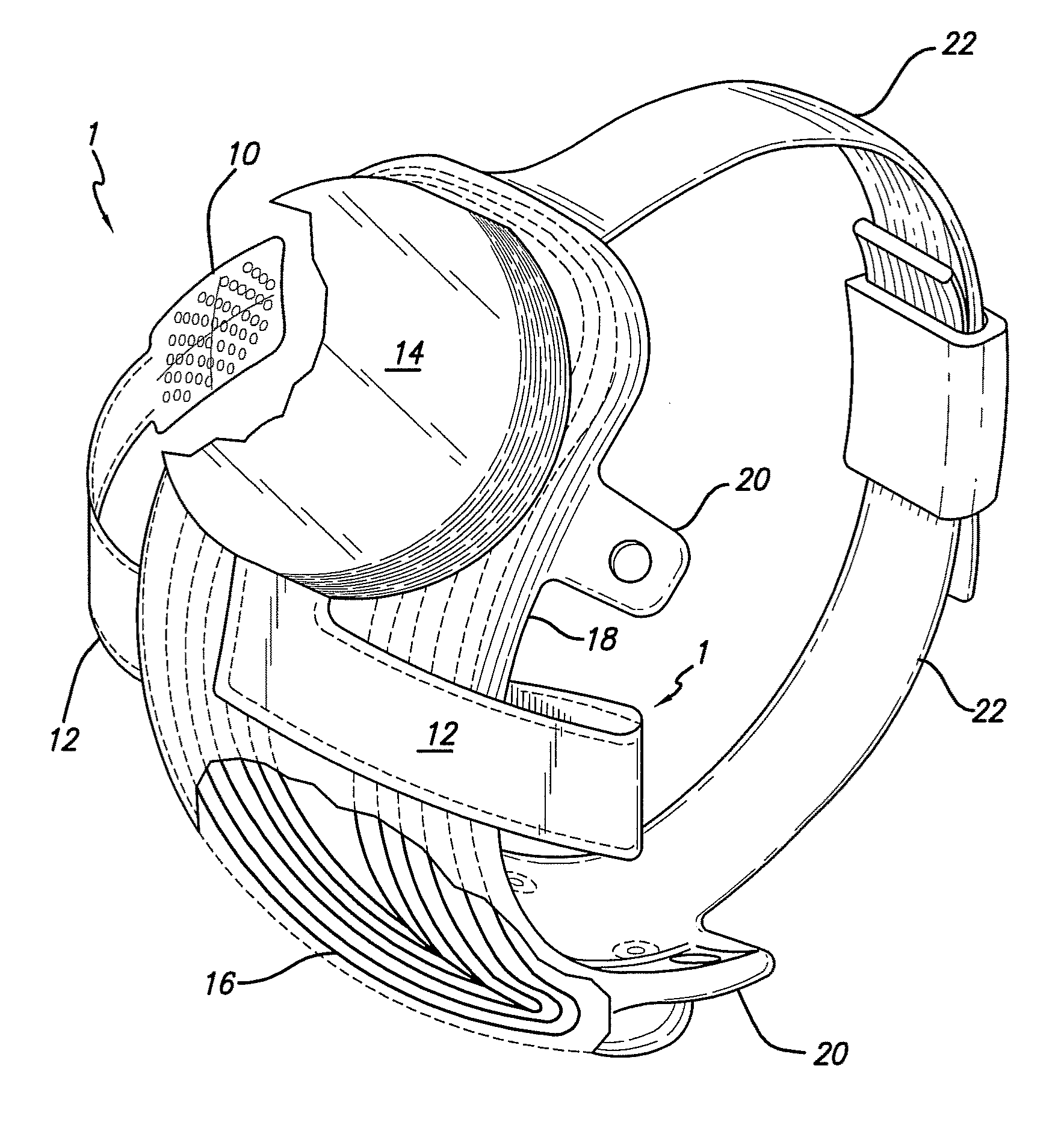
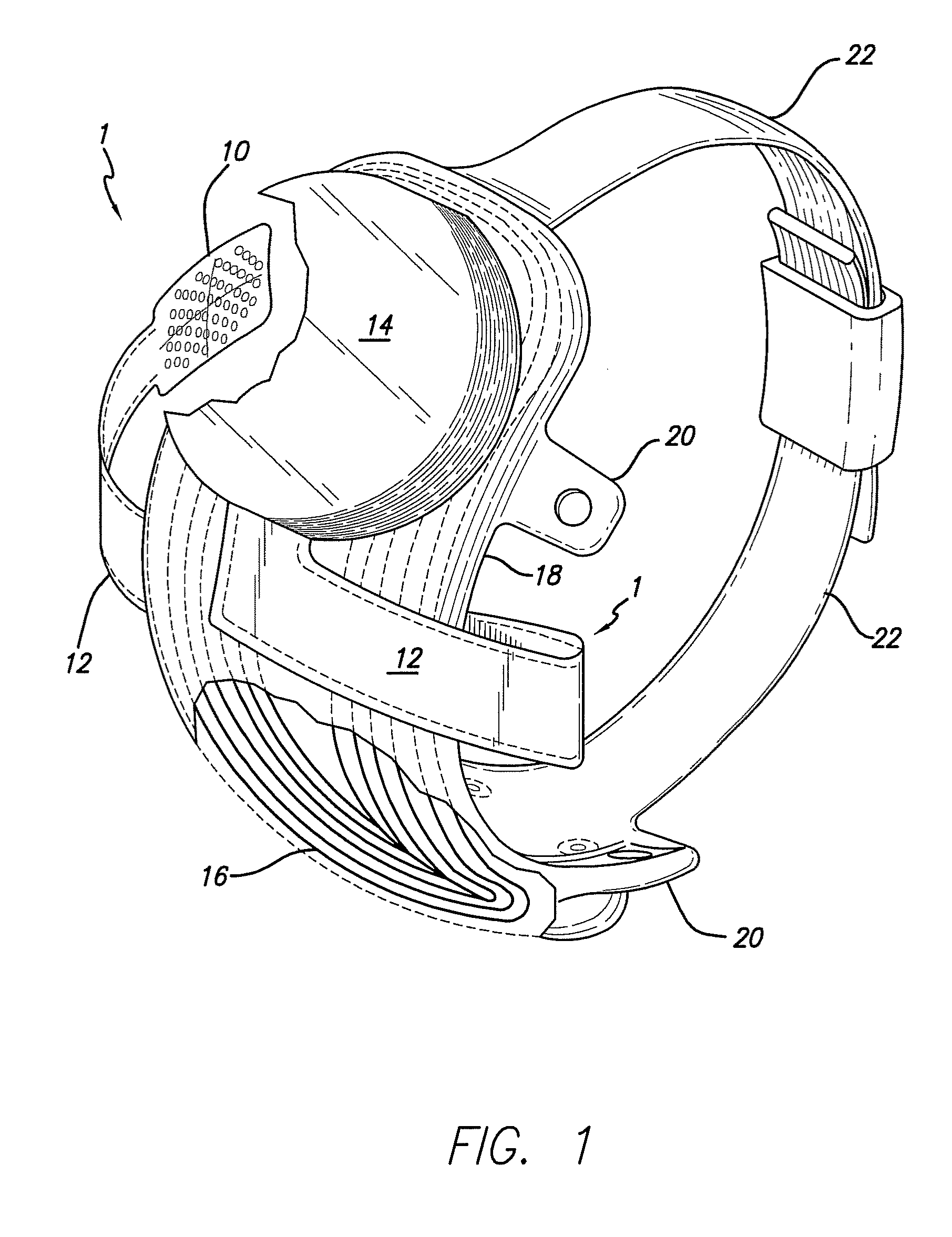
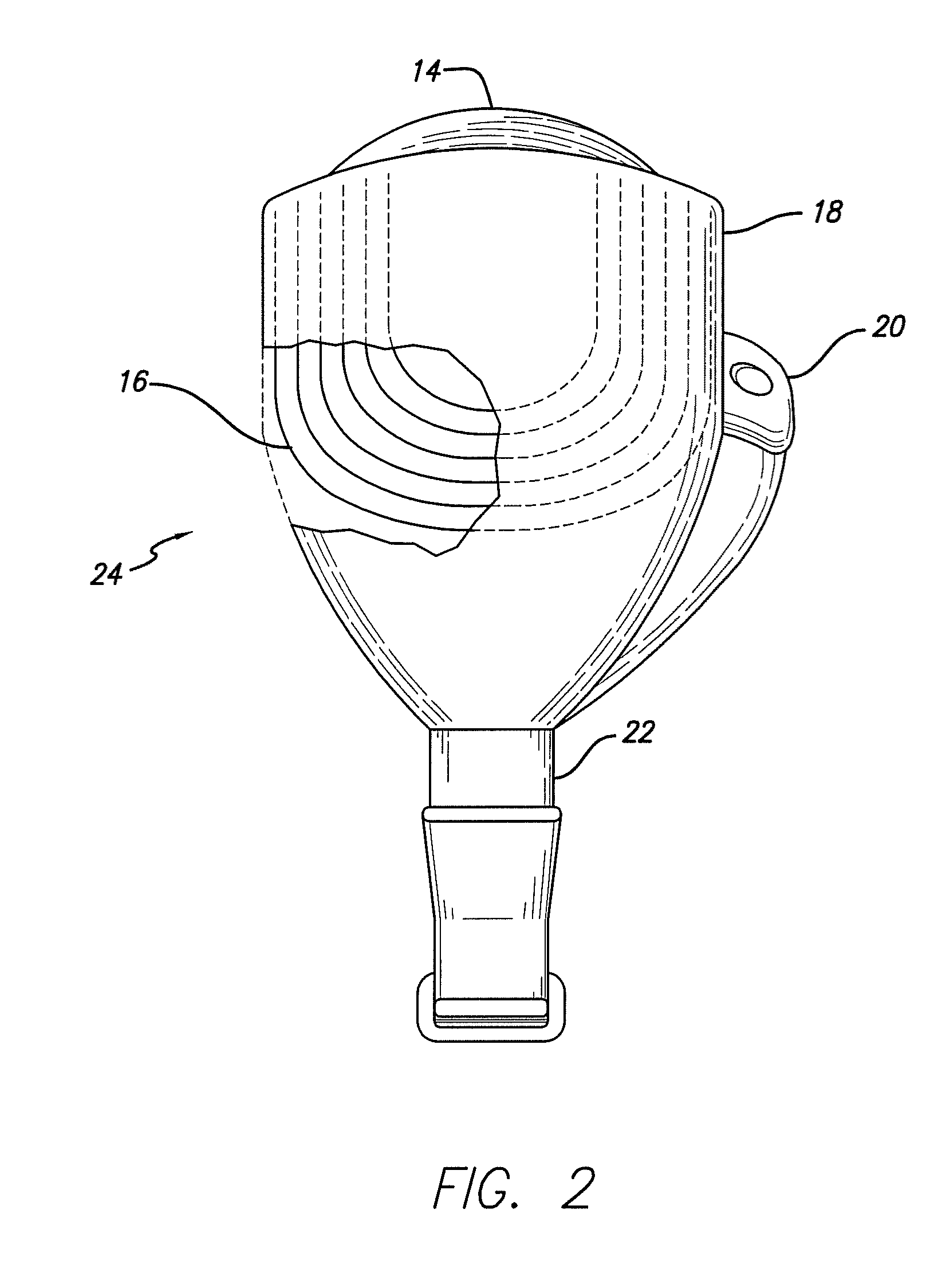
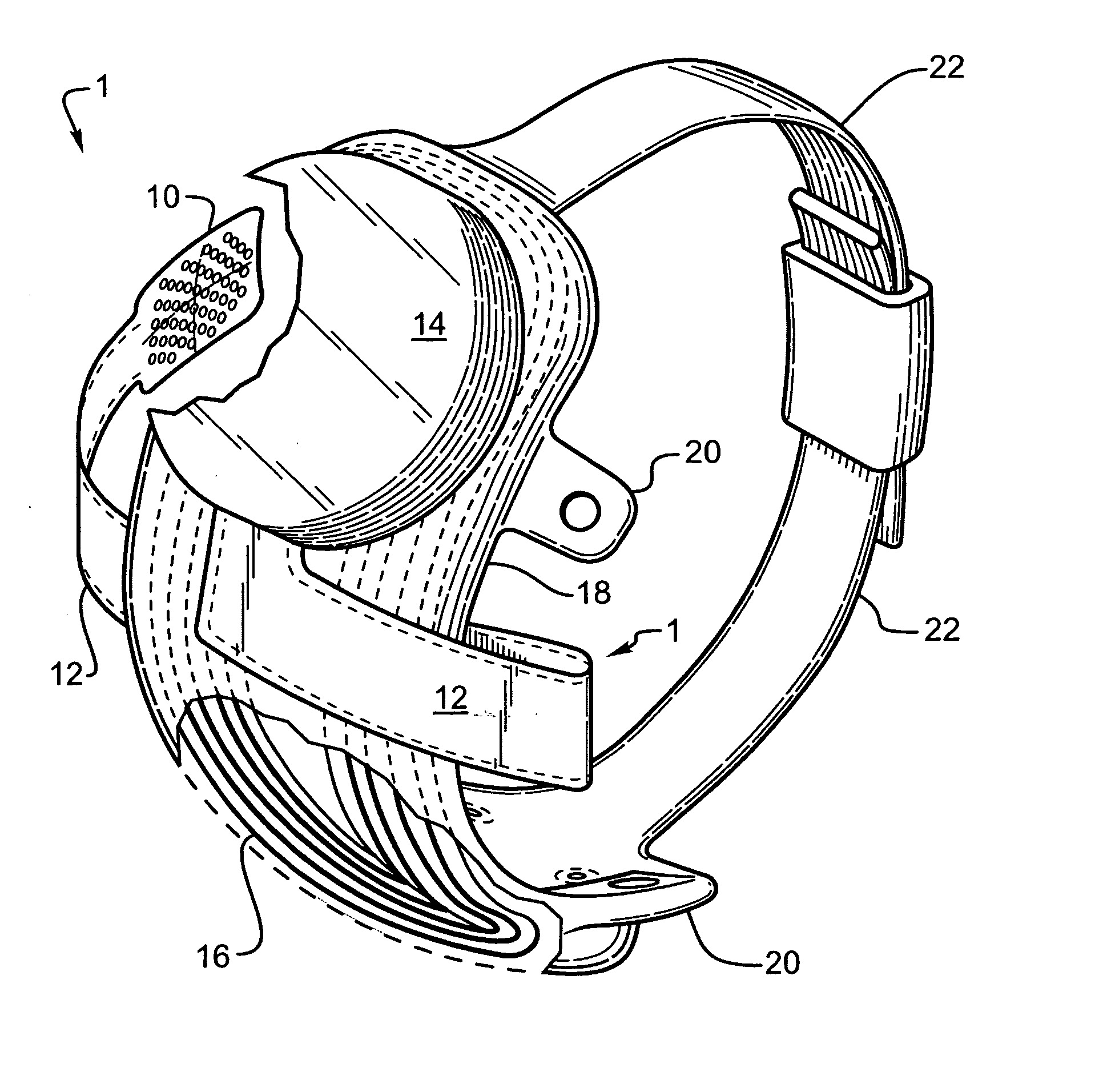
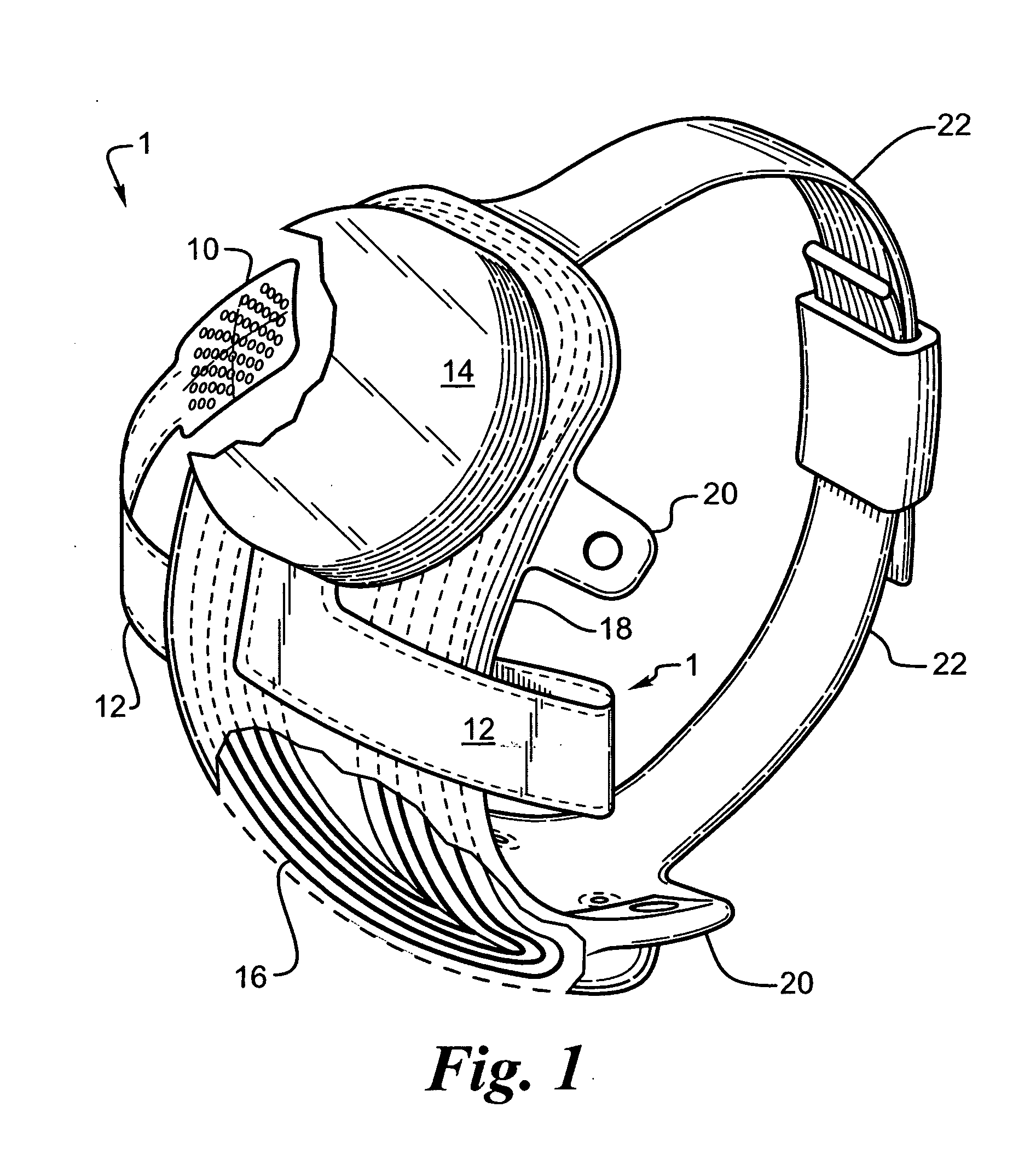
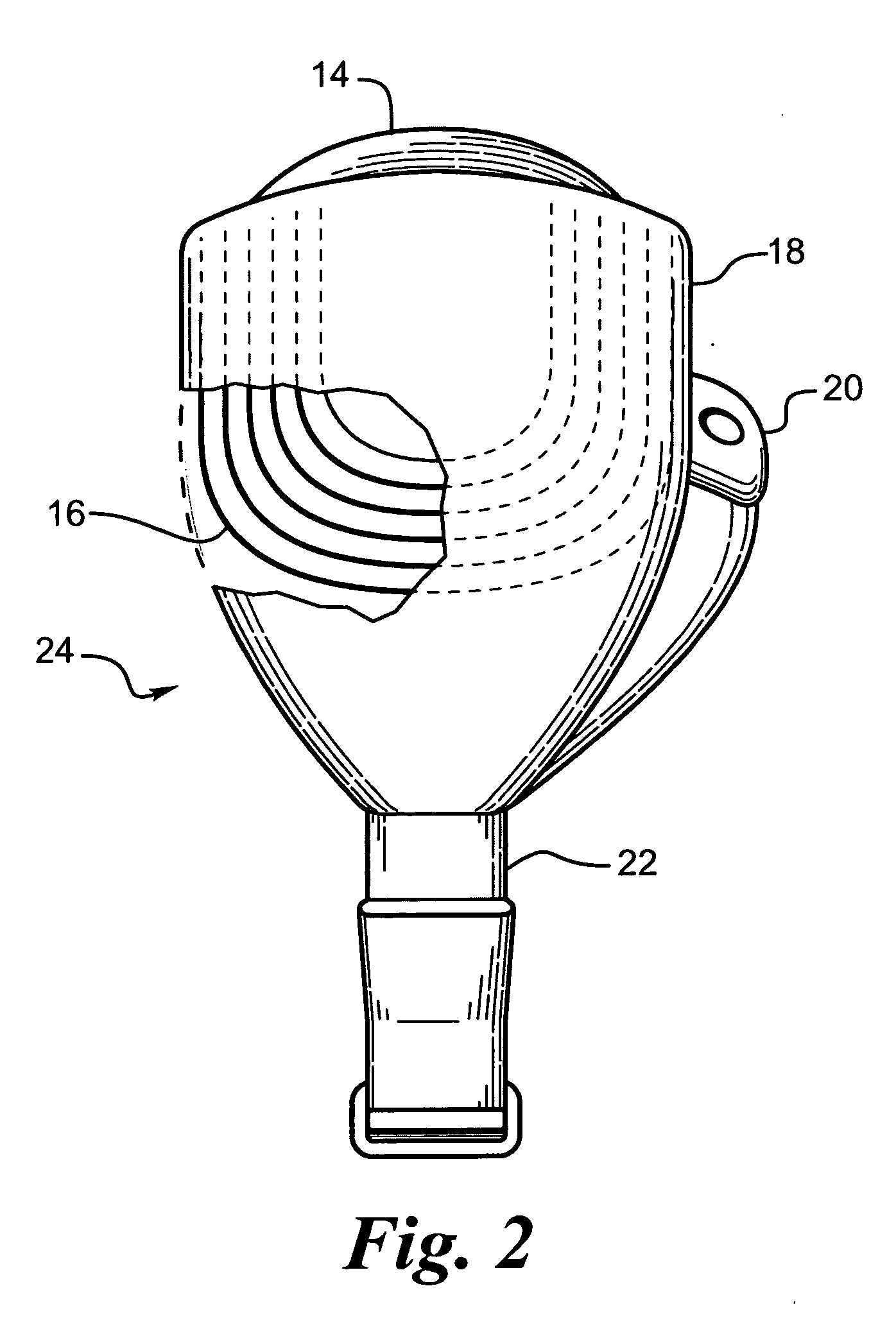
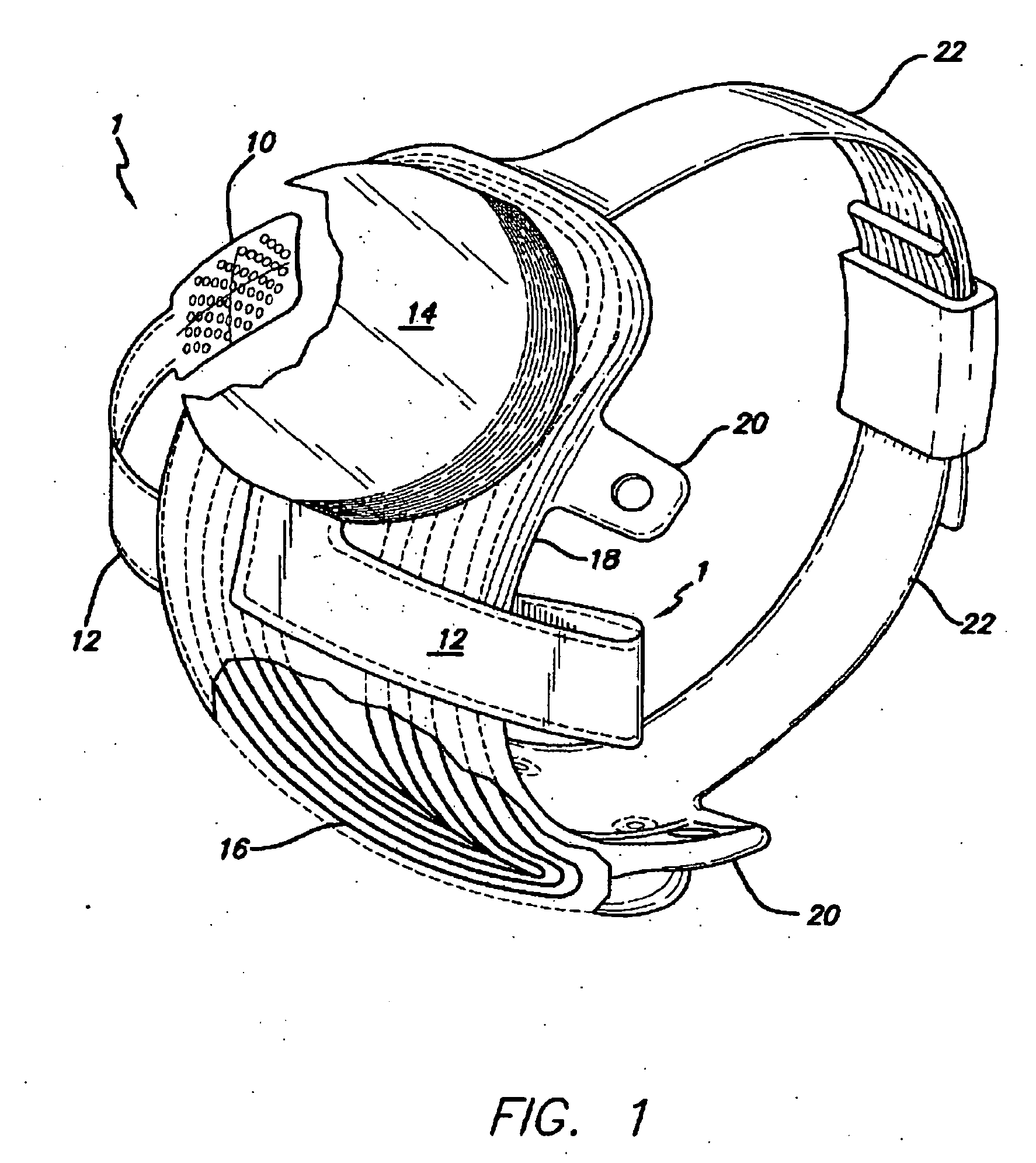
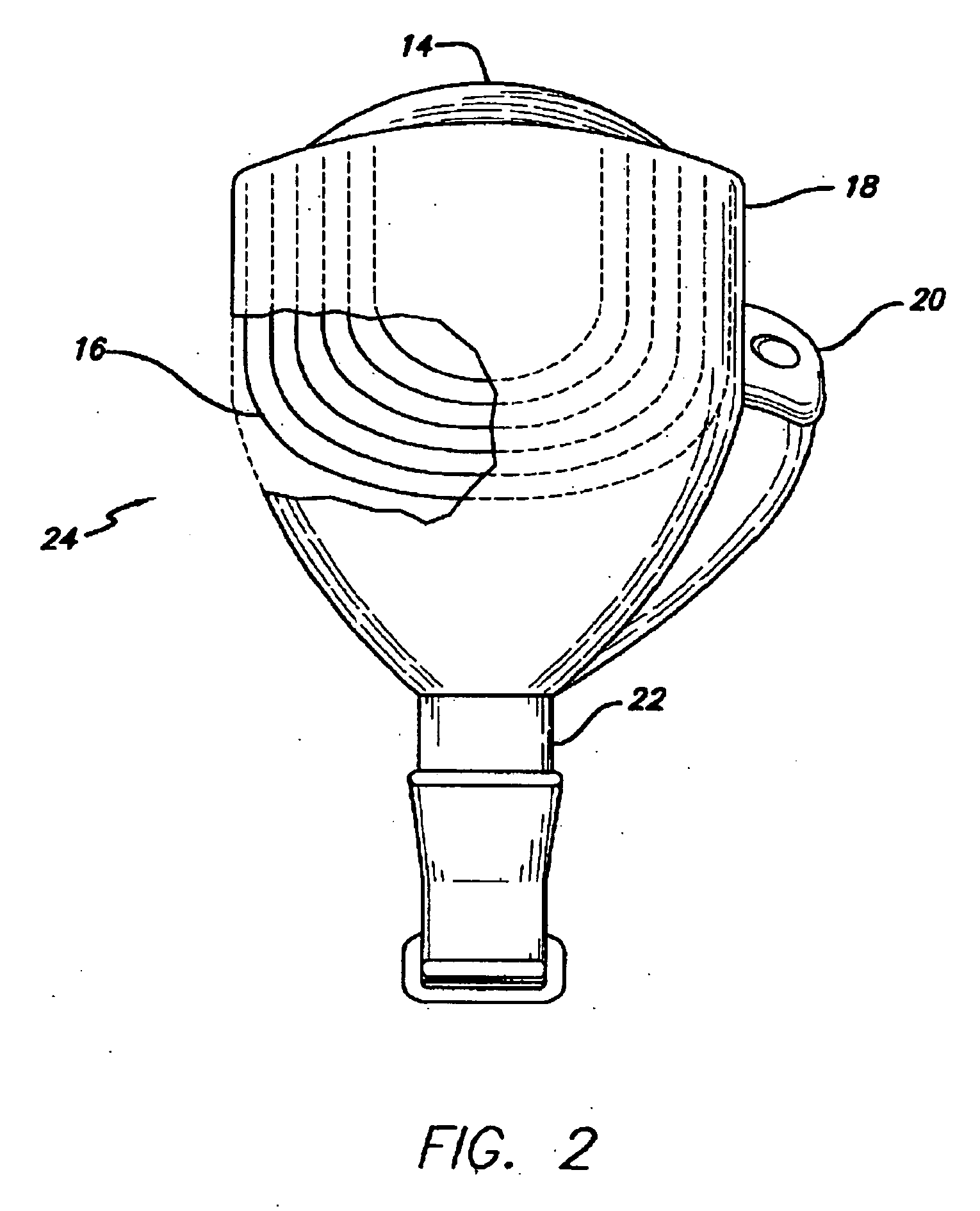
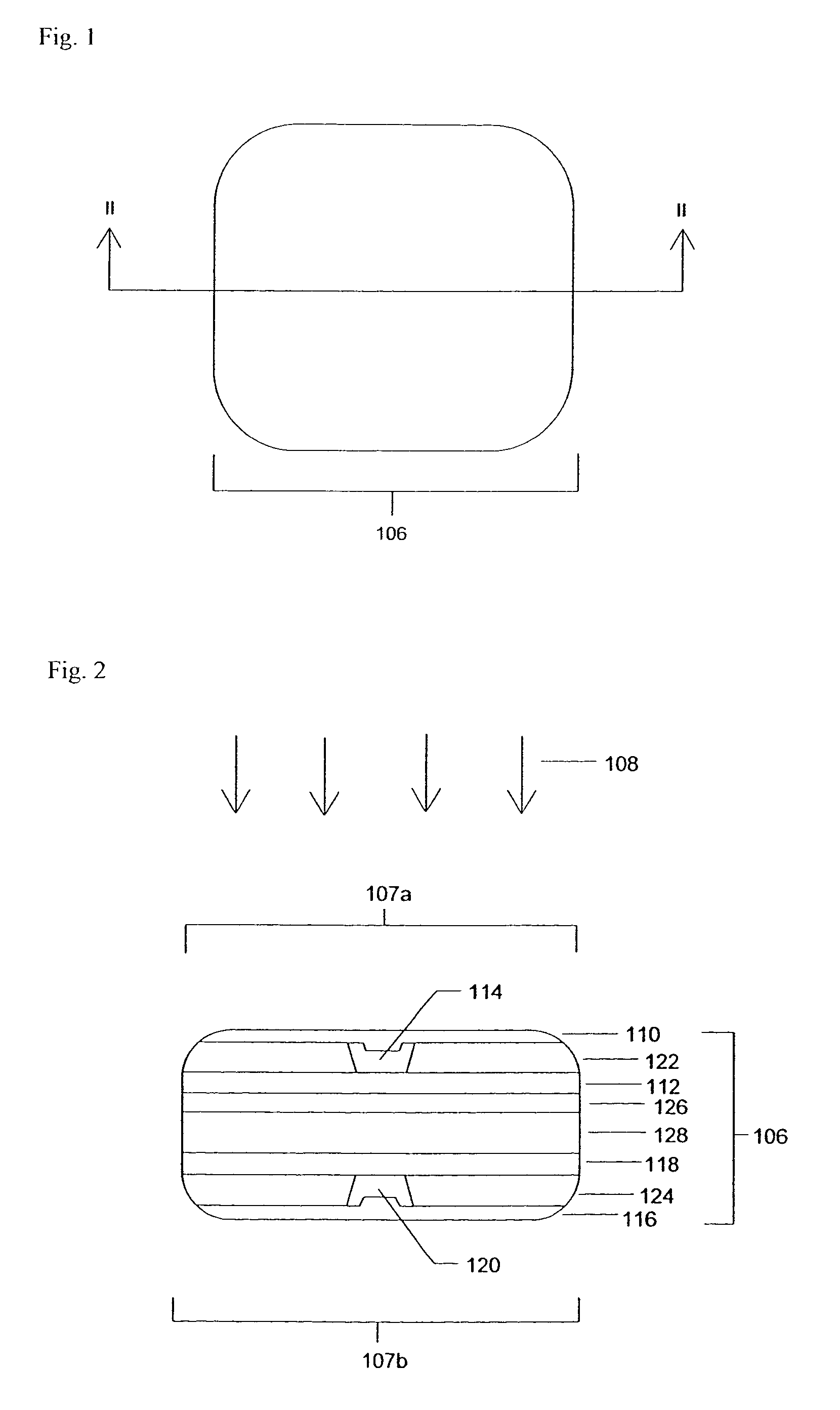
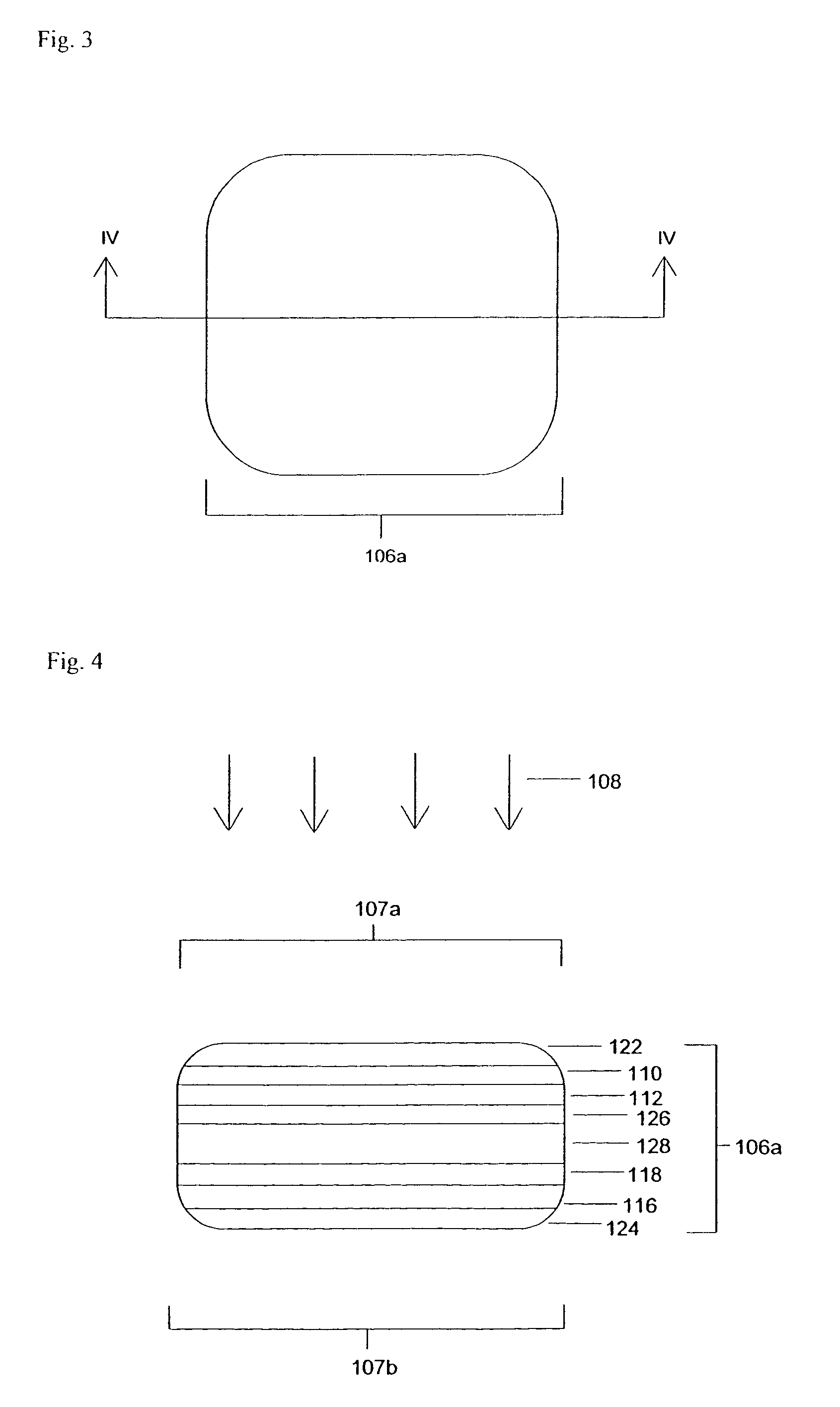
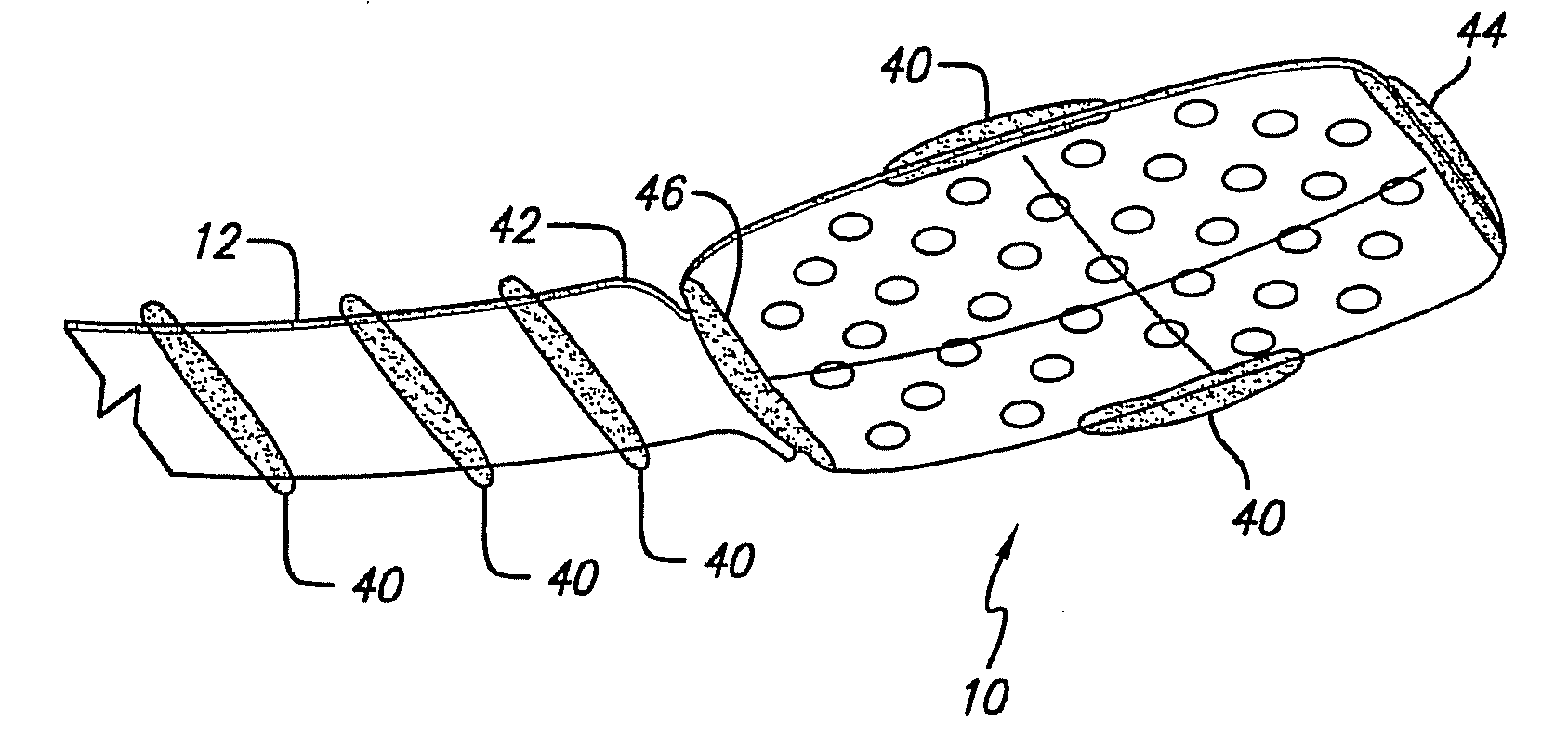
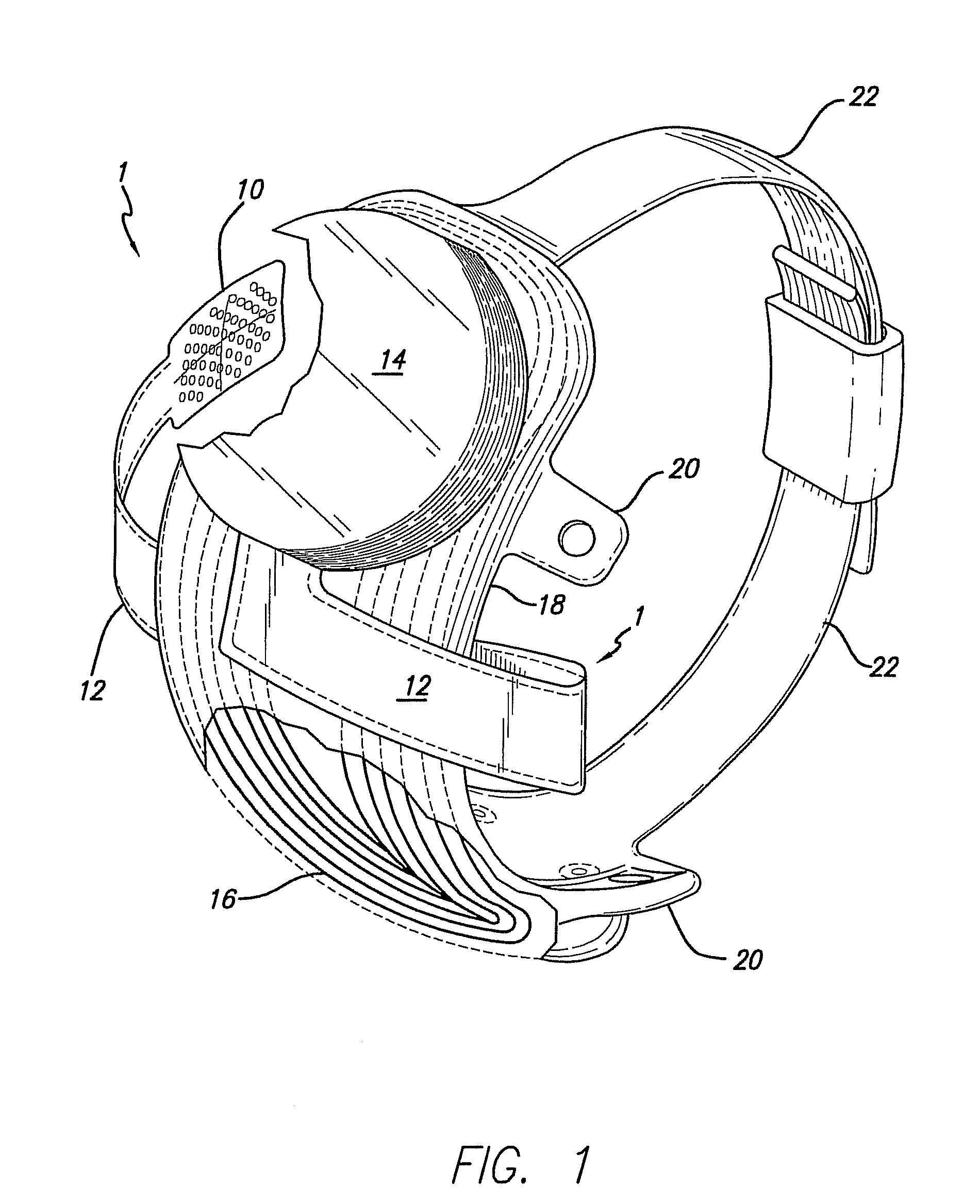
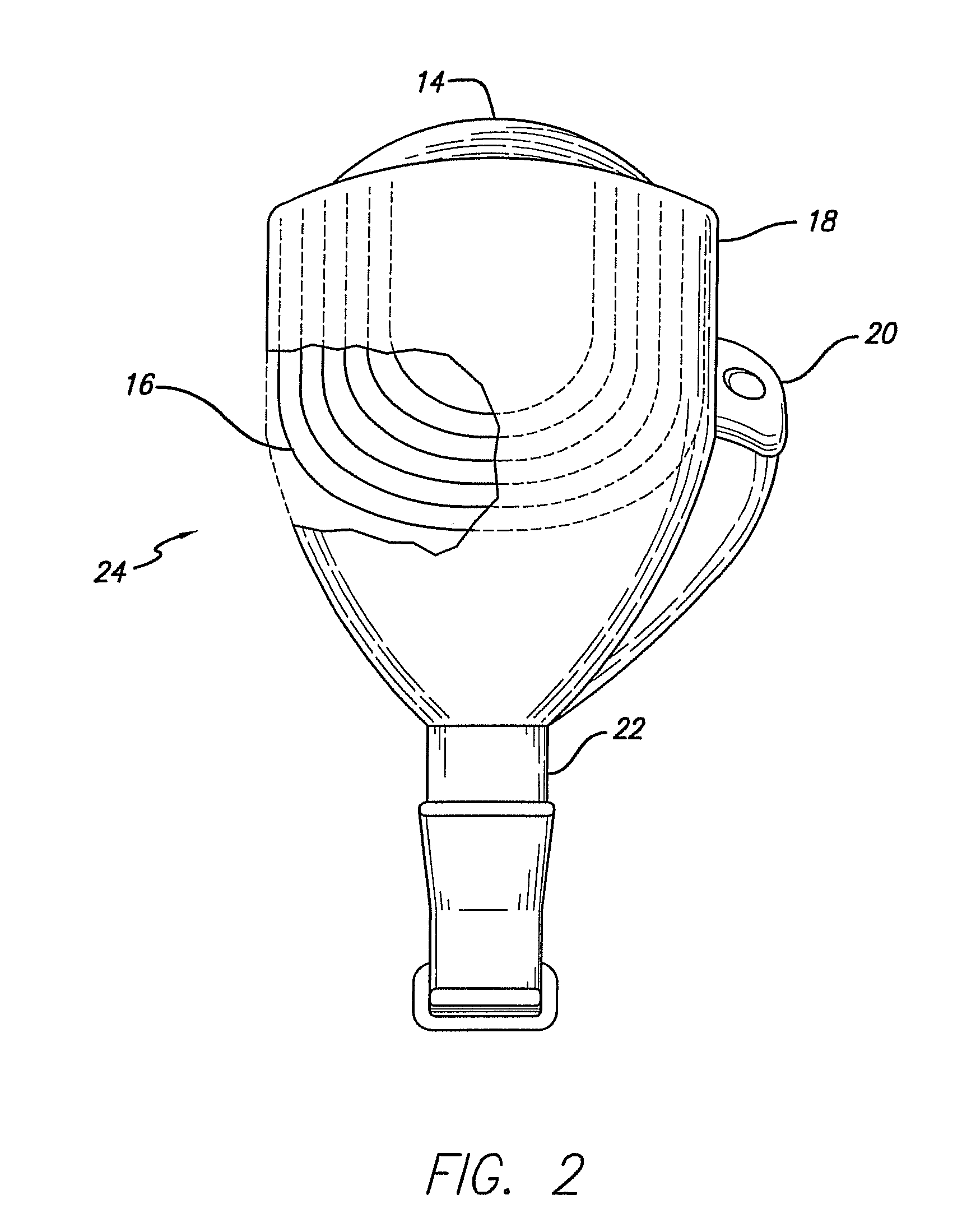
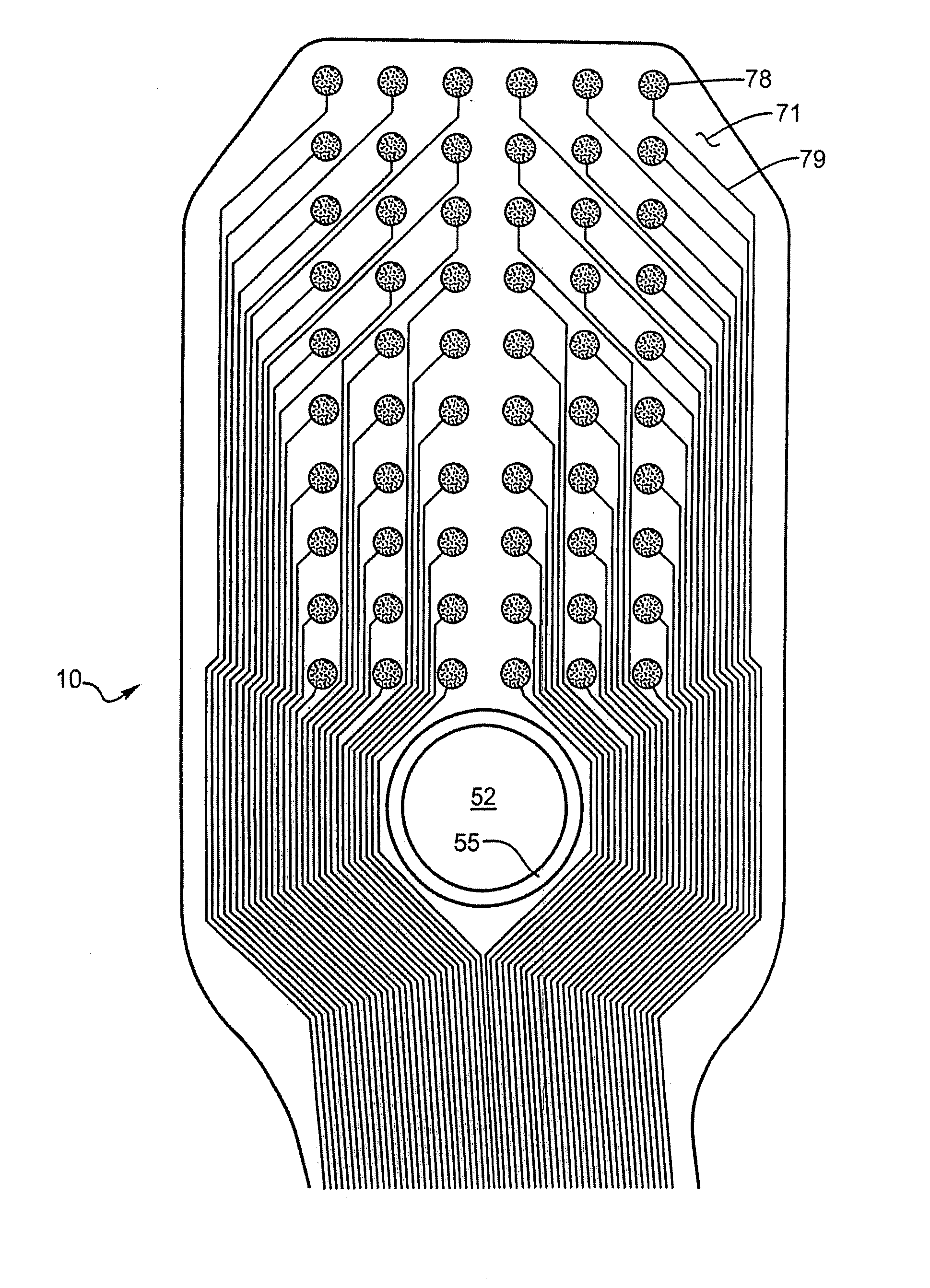
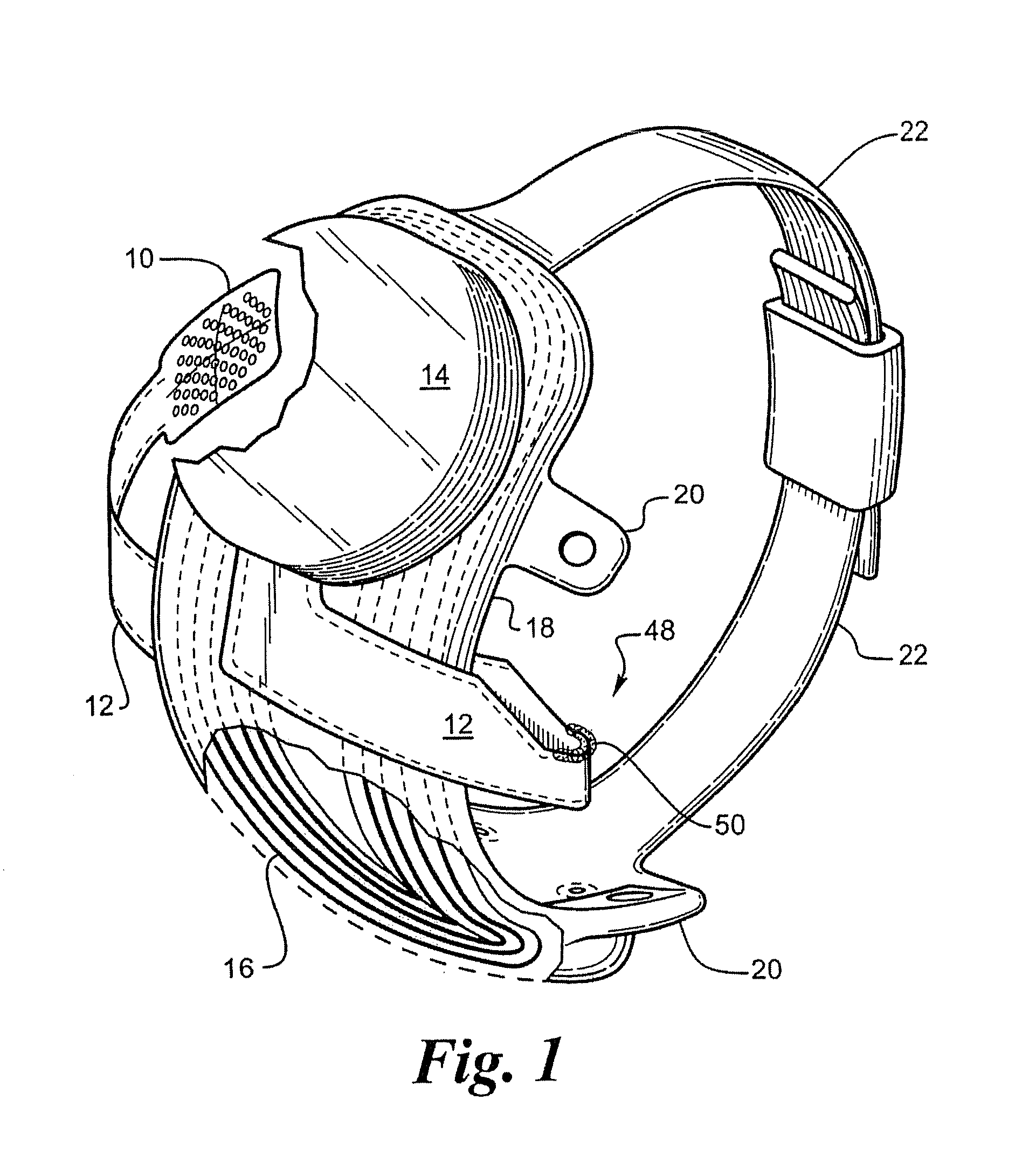
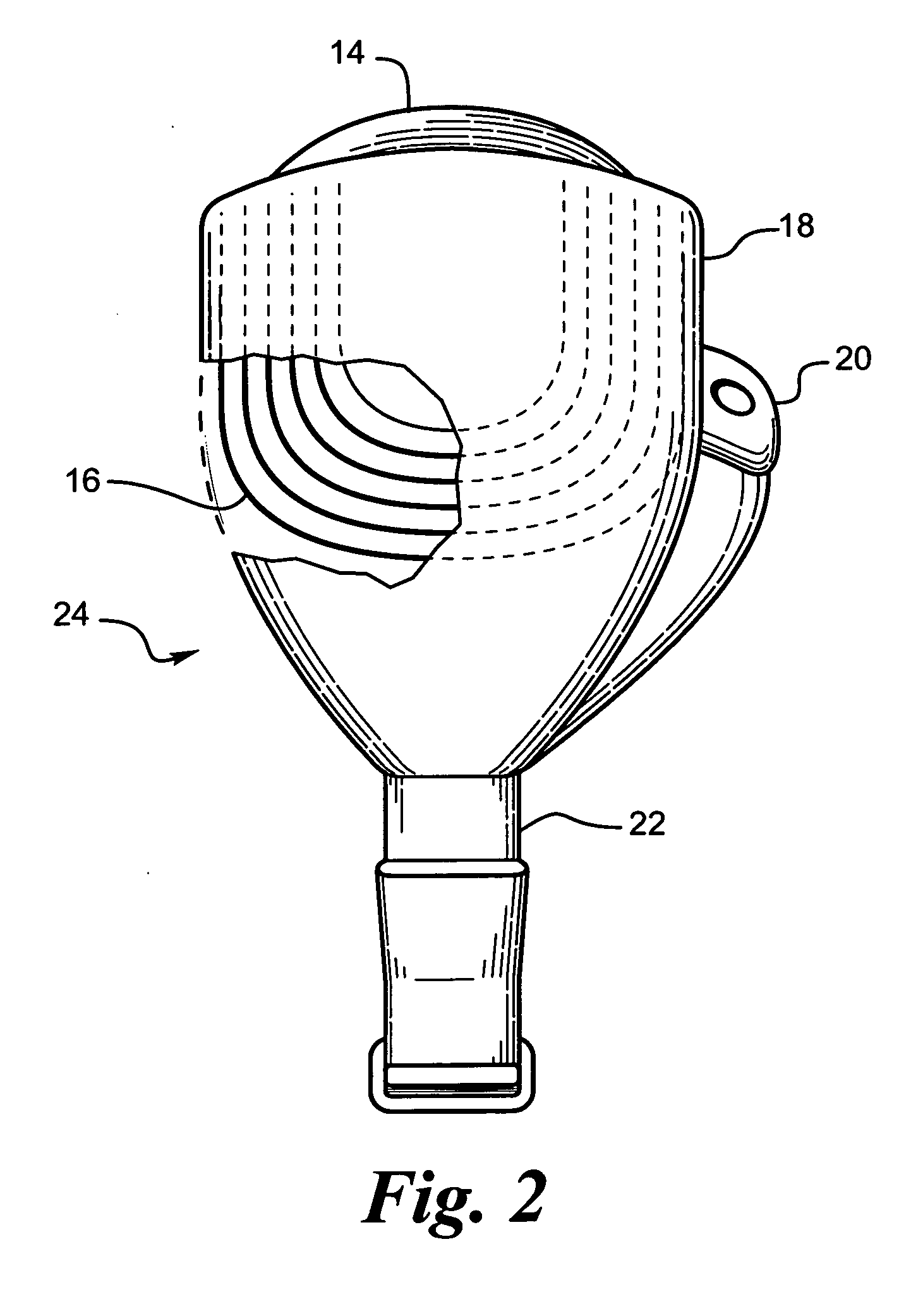
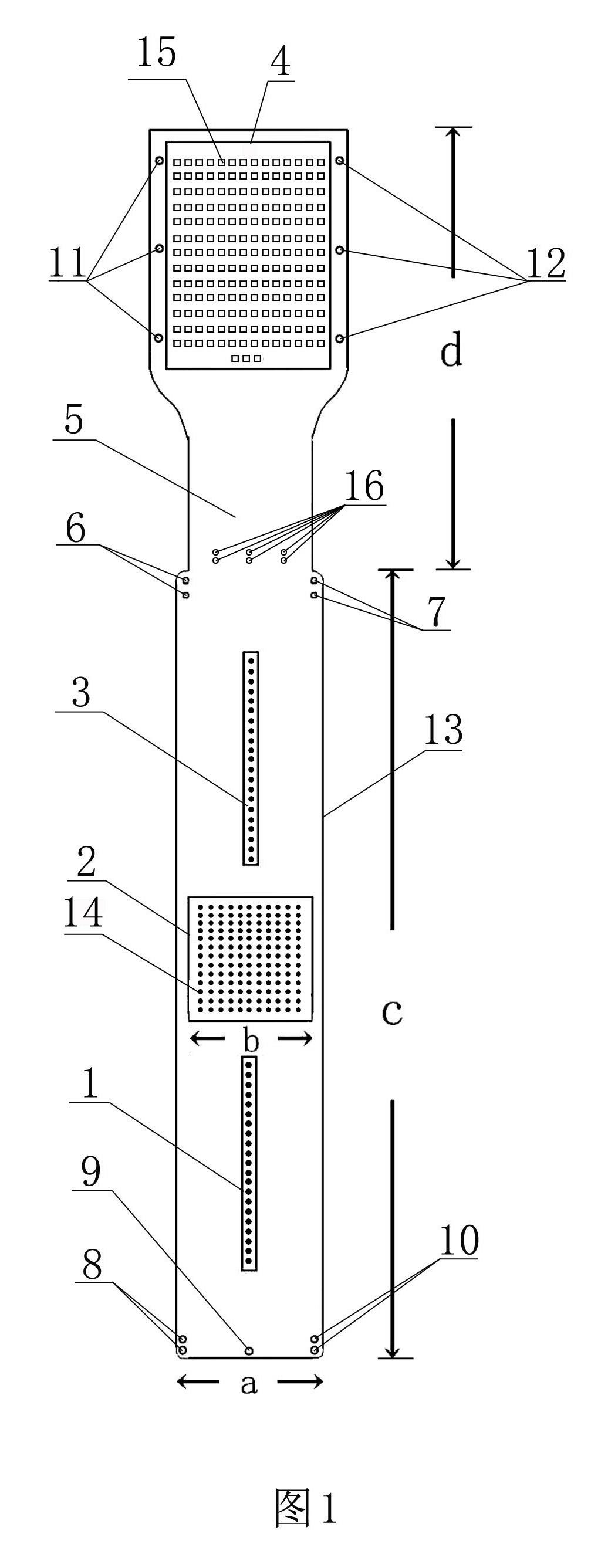
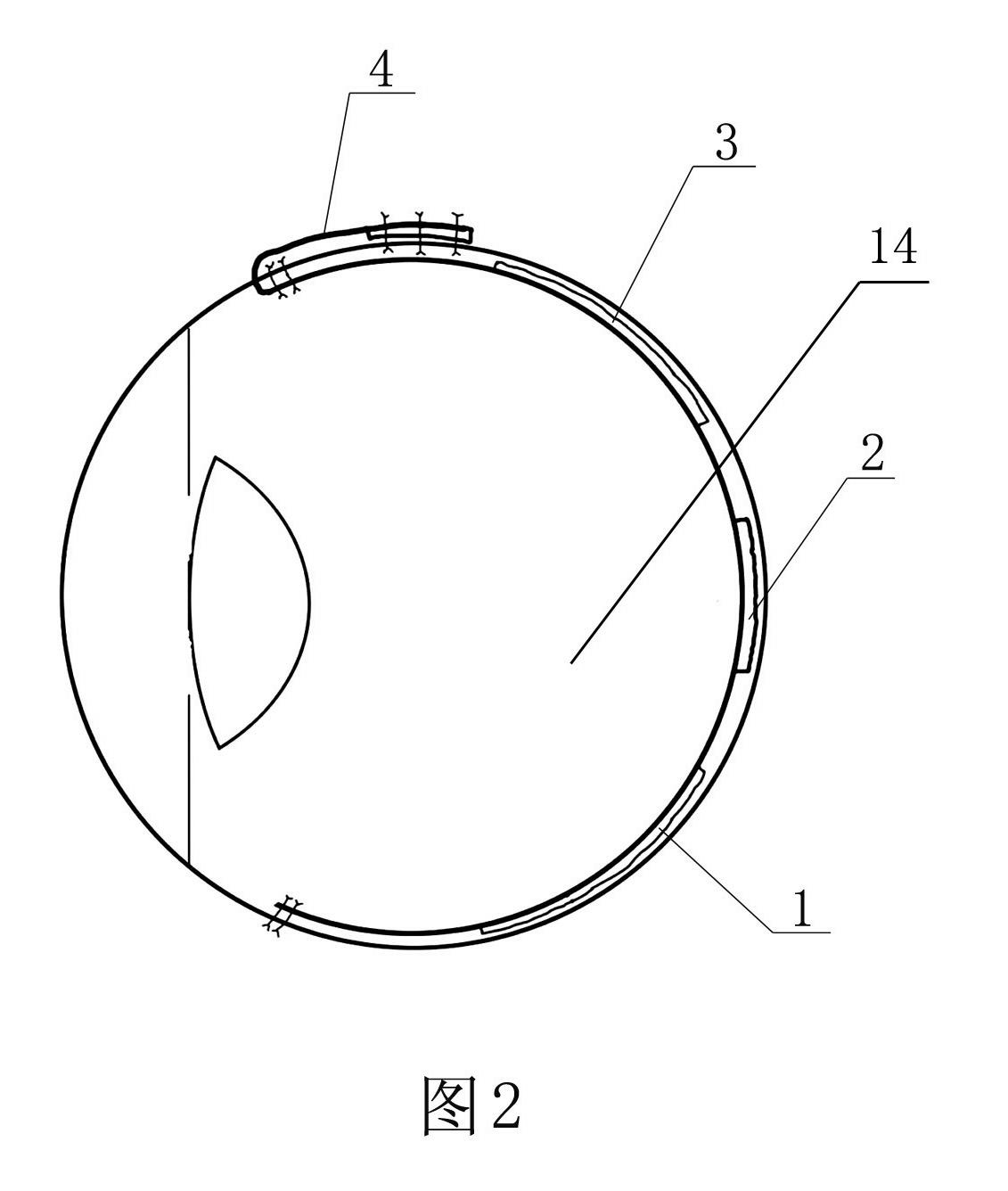
Flexible circuit electrode array
ActiveUS20060247754A1Improve the immunityCut the delicate retinal tissueHead electrodesPrinted circuit manufactureFlexible circuitsHearing perception
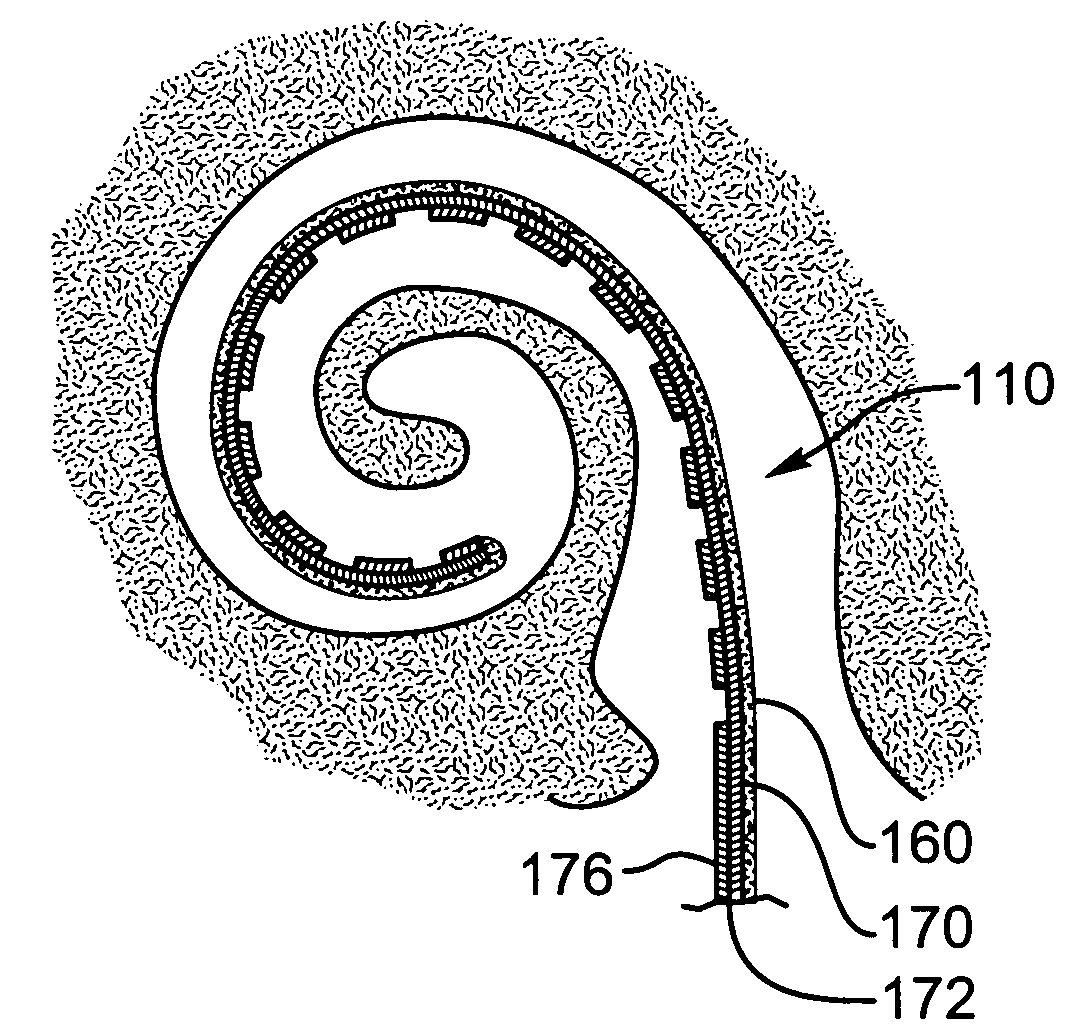
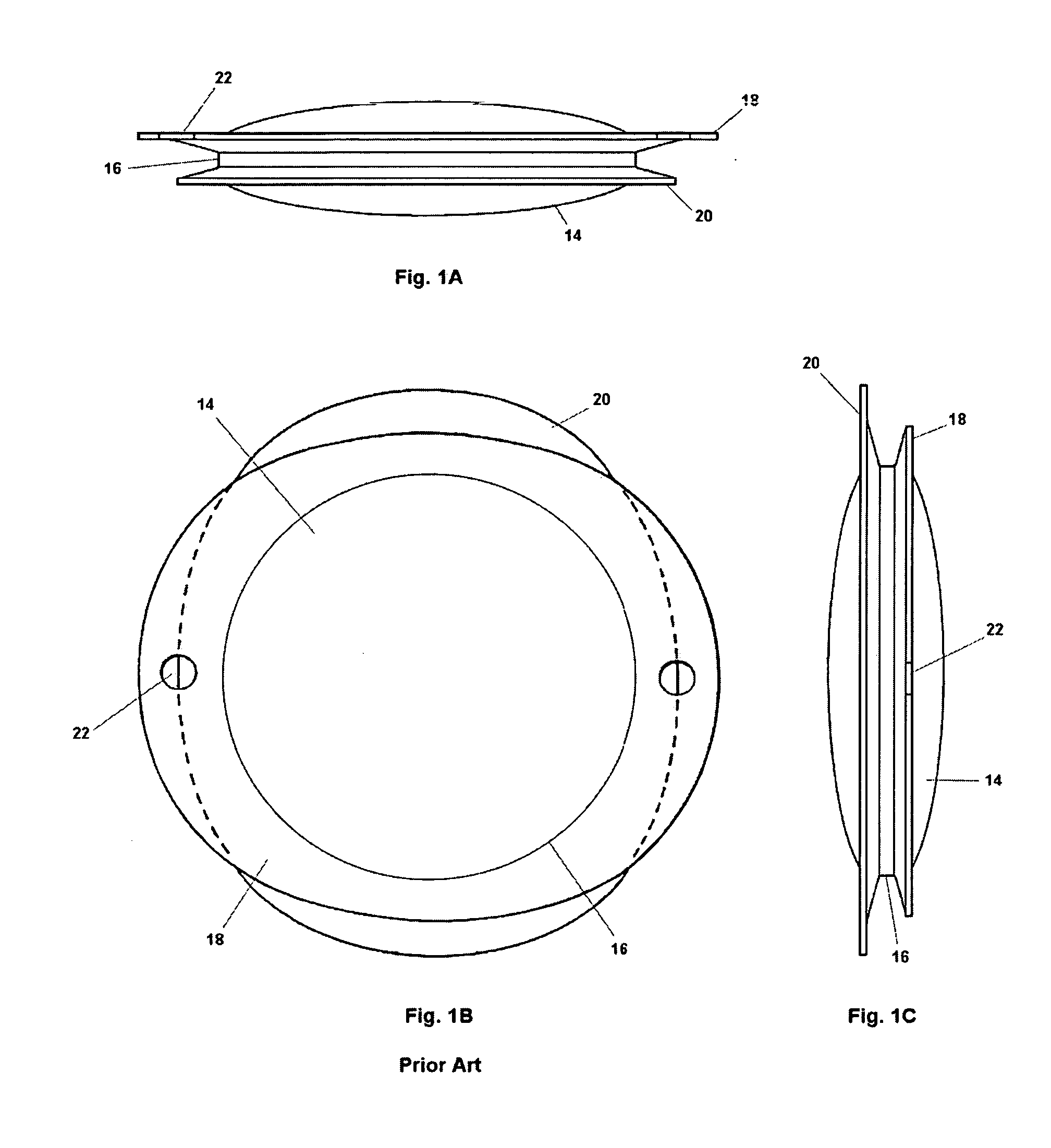
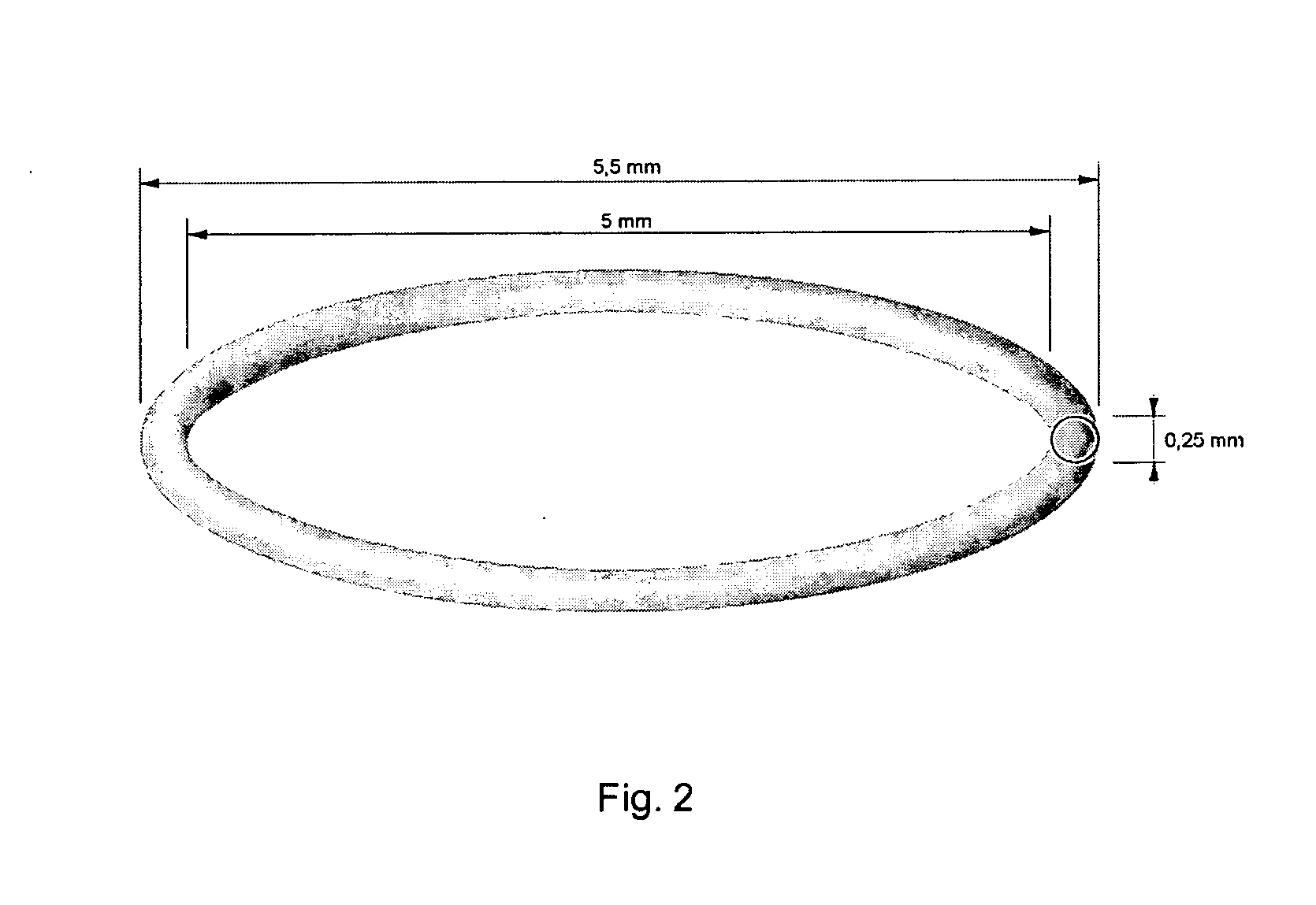
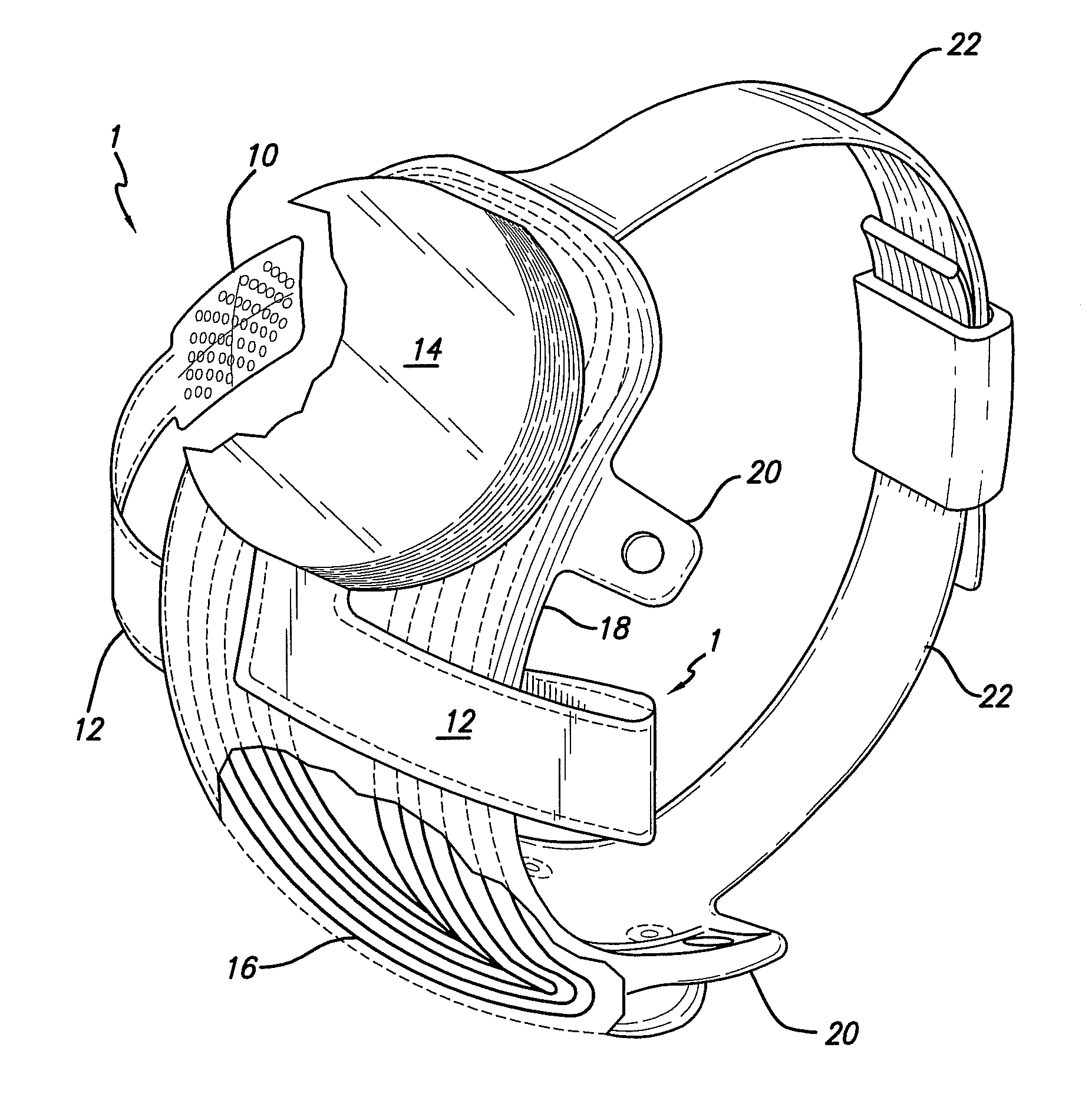
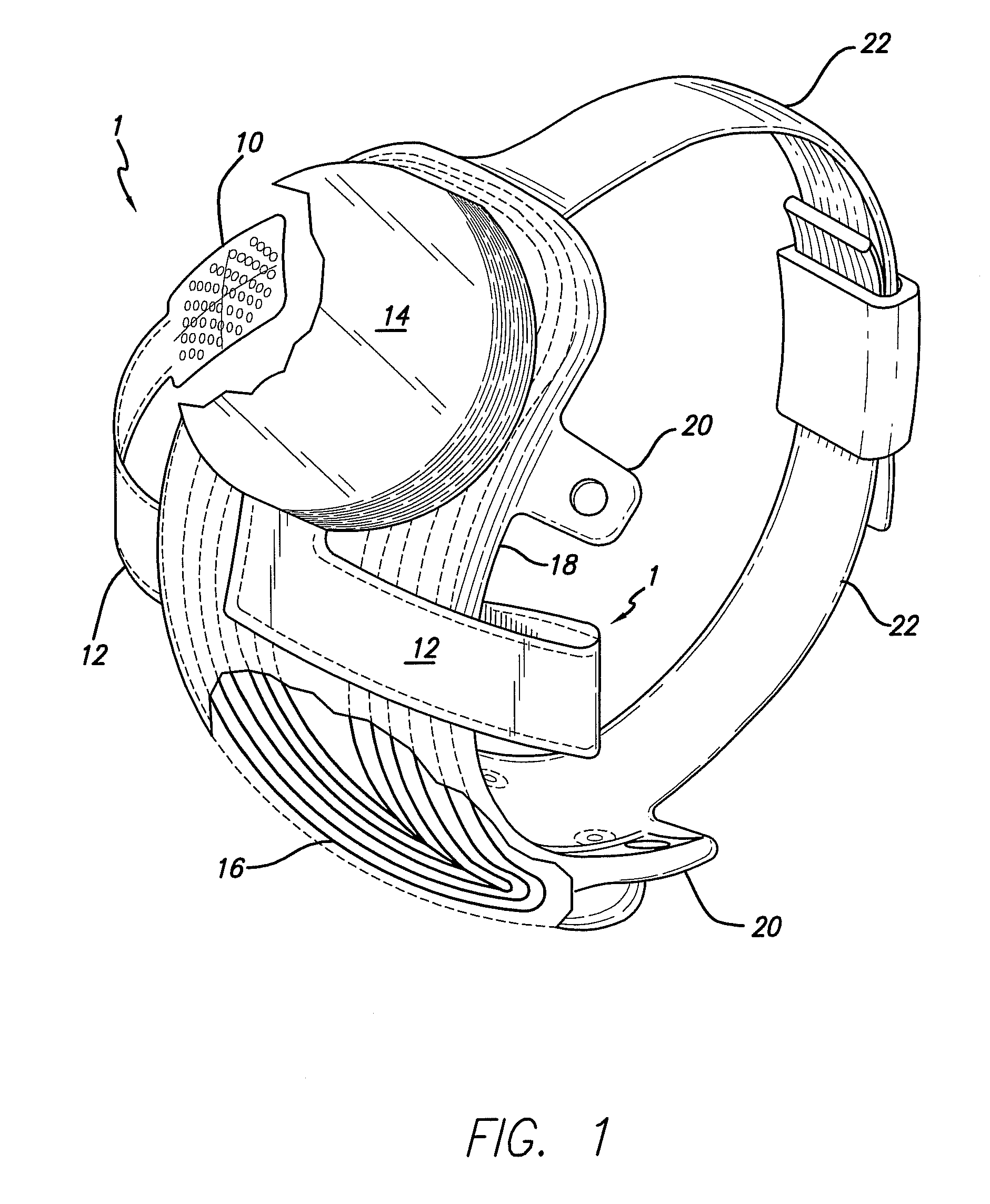
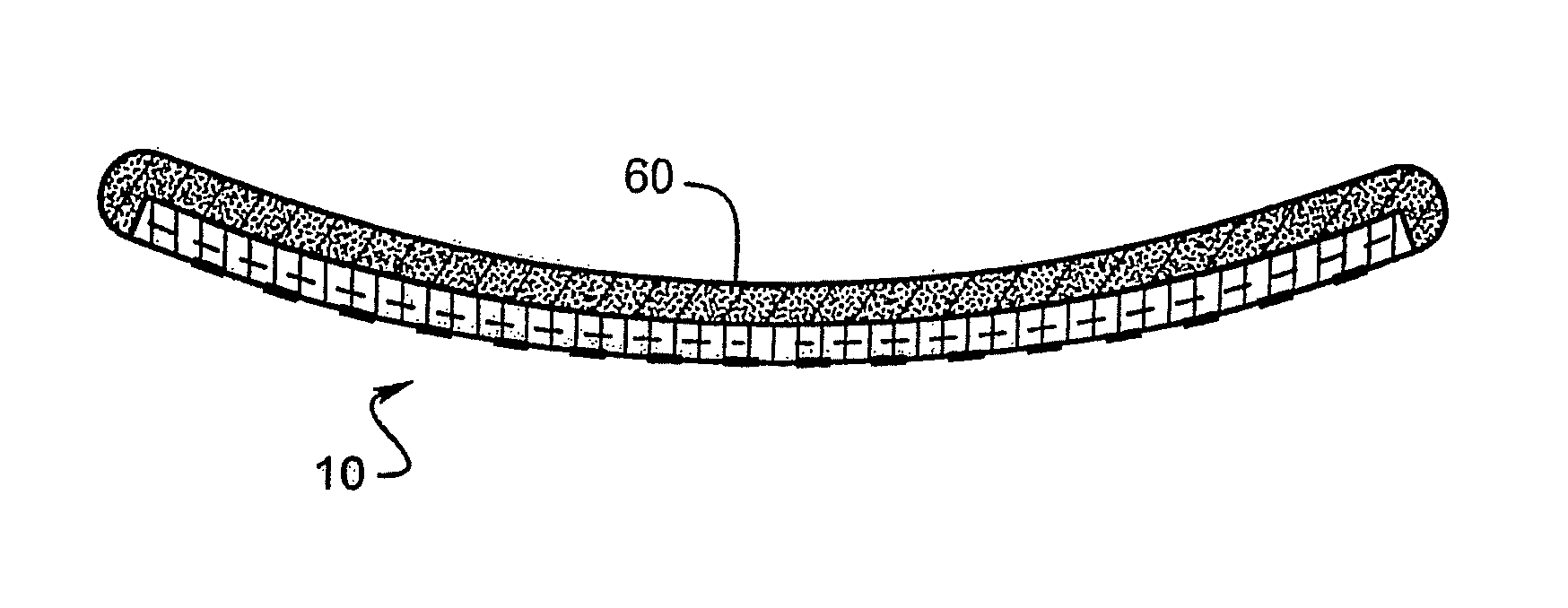
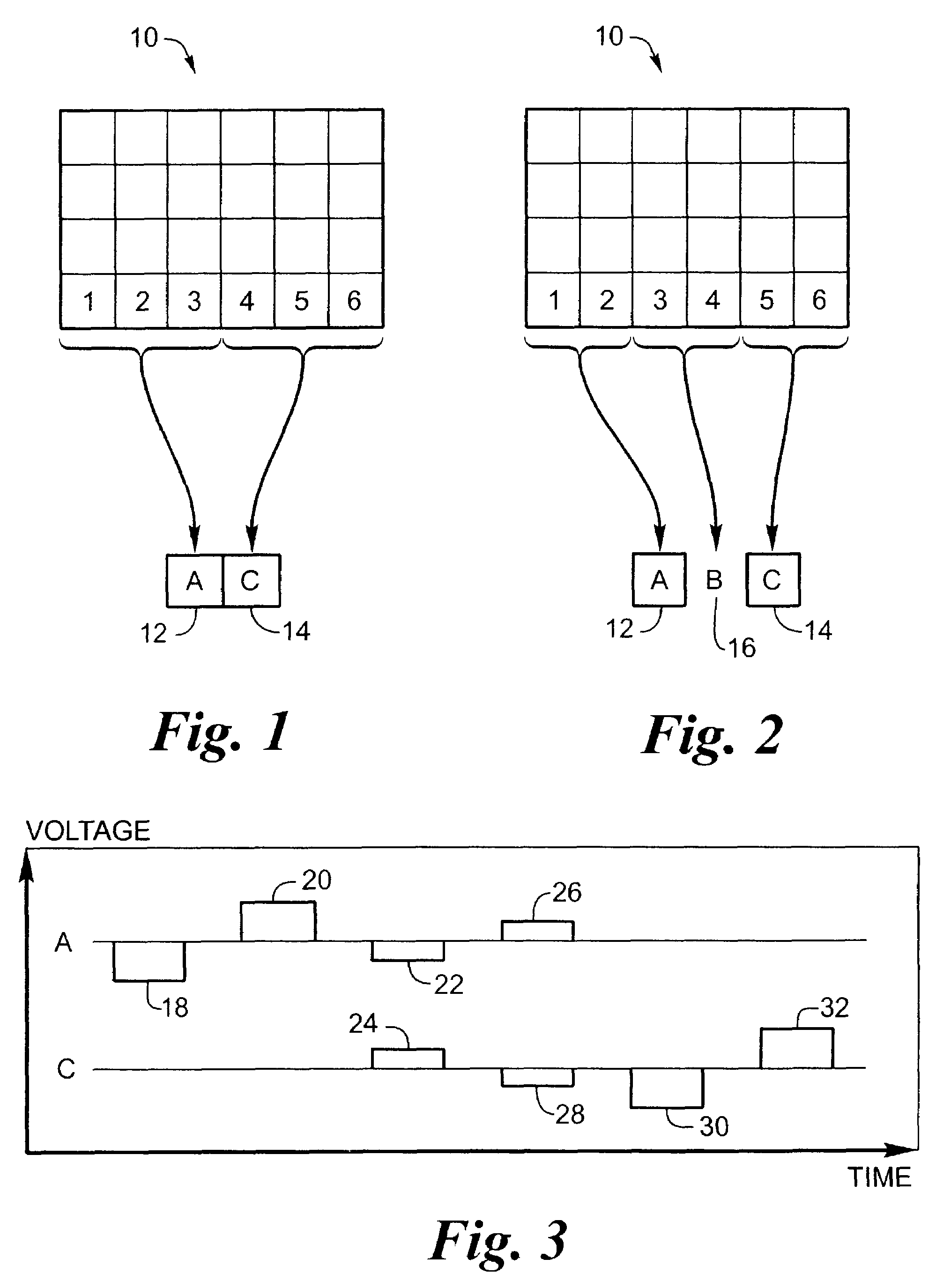
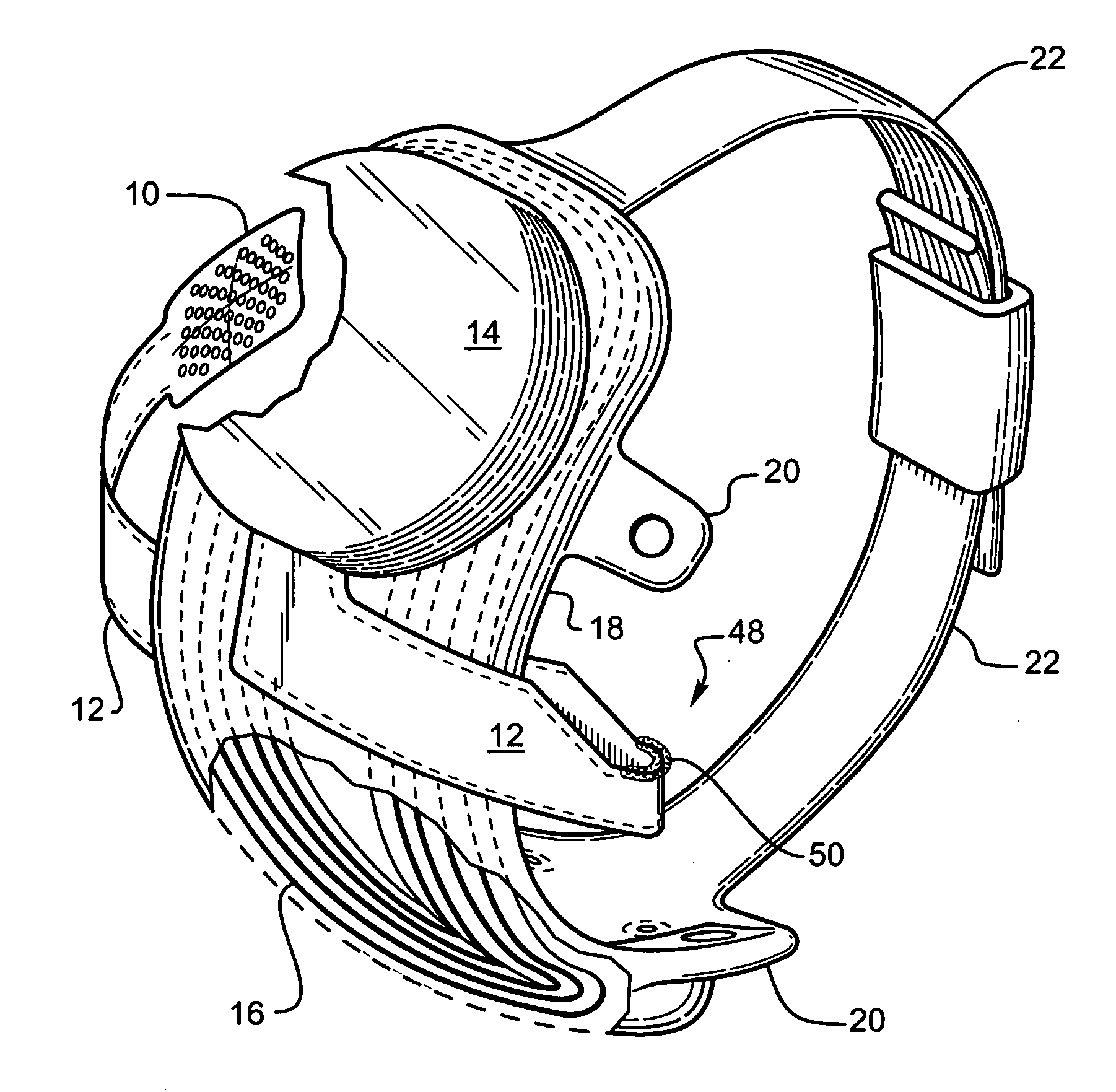
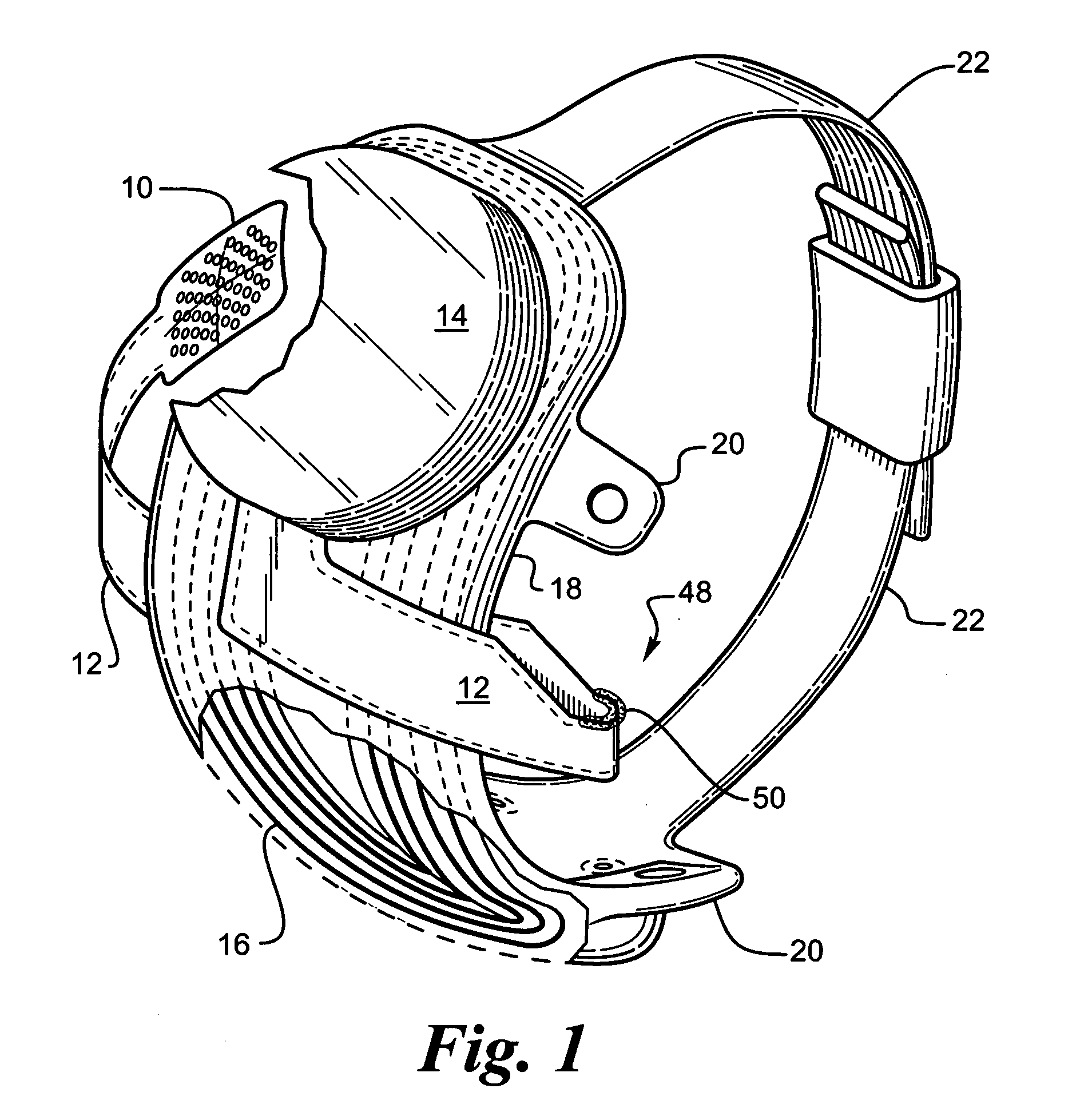
Polymer materials are useful as electrode array bodies for neural stimulation. They are particularly useful for retinal stimulation to create artificial vision, cochlear stimulation to create artificial hearing, or cortical stimulation many purposes. The pressure applied against the retina, or other neural tissue, by an electrode array is critical. Too little pressure causes increased electrical resistance, along with electric field dispersion. Too much pressure may block blood flow. Common flexible circuit fabrication techniques generally require that a flexible circuit electrode array be made flat. Since neural tissue is almost never flat, a flat array will necessarily apply uneven pressure. Further, the edges of a flexible circuit polymer array may be sharp and cut the delicate neural tissue. By applying the right amount of heat to a completed array, a curve can be induced. With a thermoplastic polymer it may be further advantageous to repeatedly heat the flexible circuit in multiple molds, each with a decreasing radius. Further, it is advantageous to add material along the edges. It is further advantageous to provide a fold or twist in the flexible circuit array. Additional material may be added inside and outside the fold to promote a good seal with tissue.
Owner:CORTIGENT INC +1
Bag-in-the-lens intraocular lens with removable optic and capsular accommodation ring
Owner:TASSIGNON MARIE JOSE B
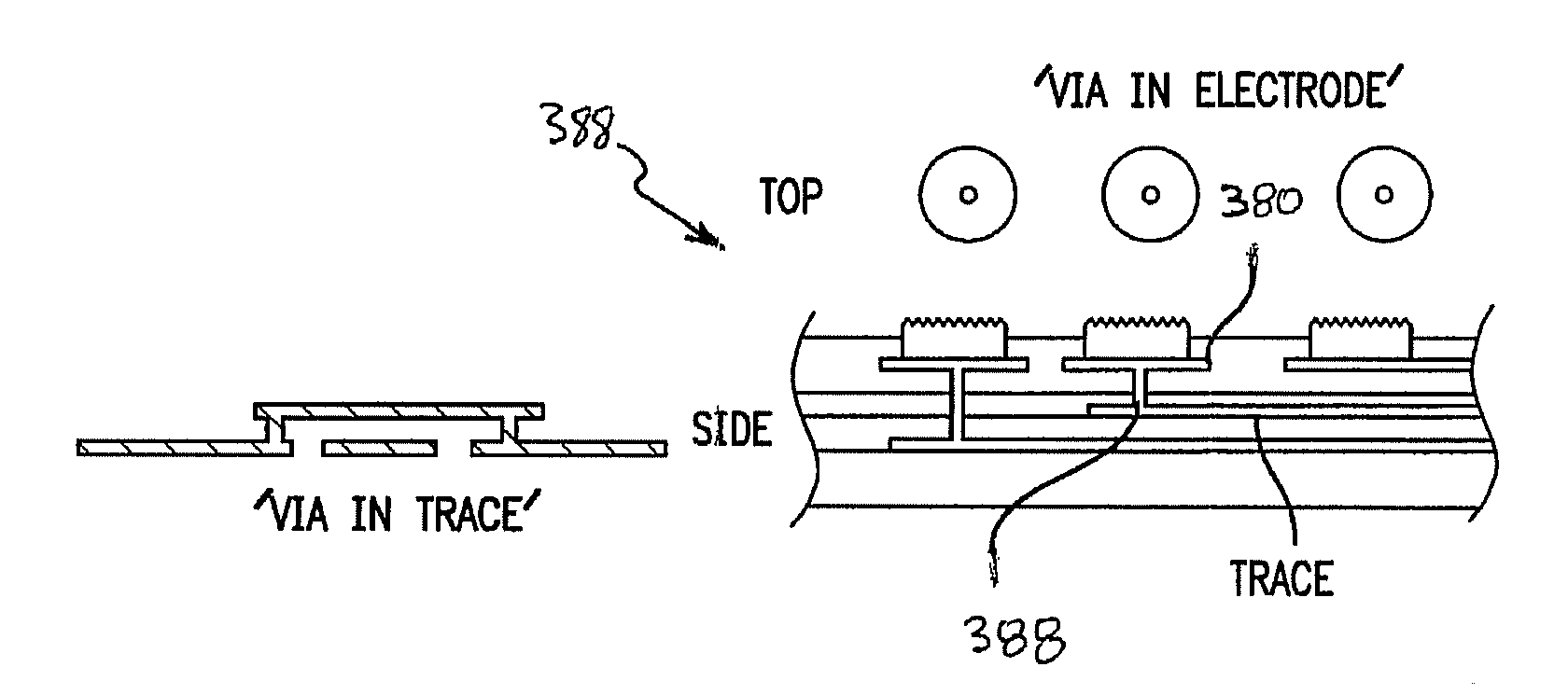
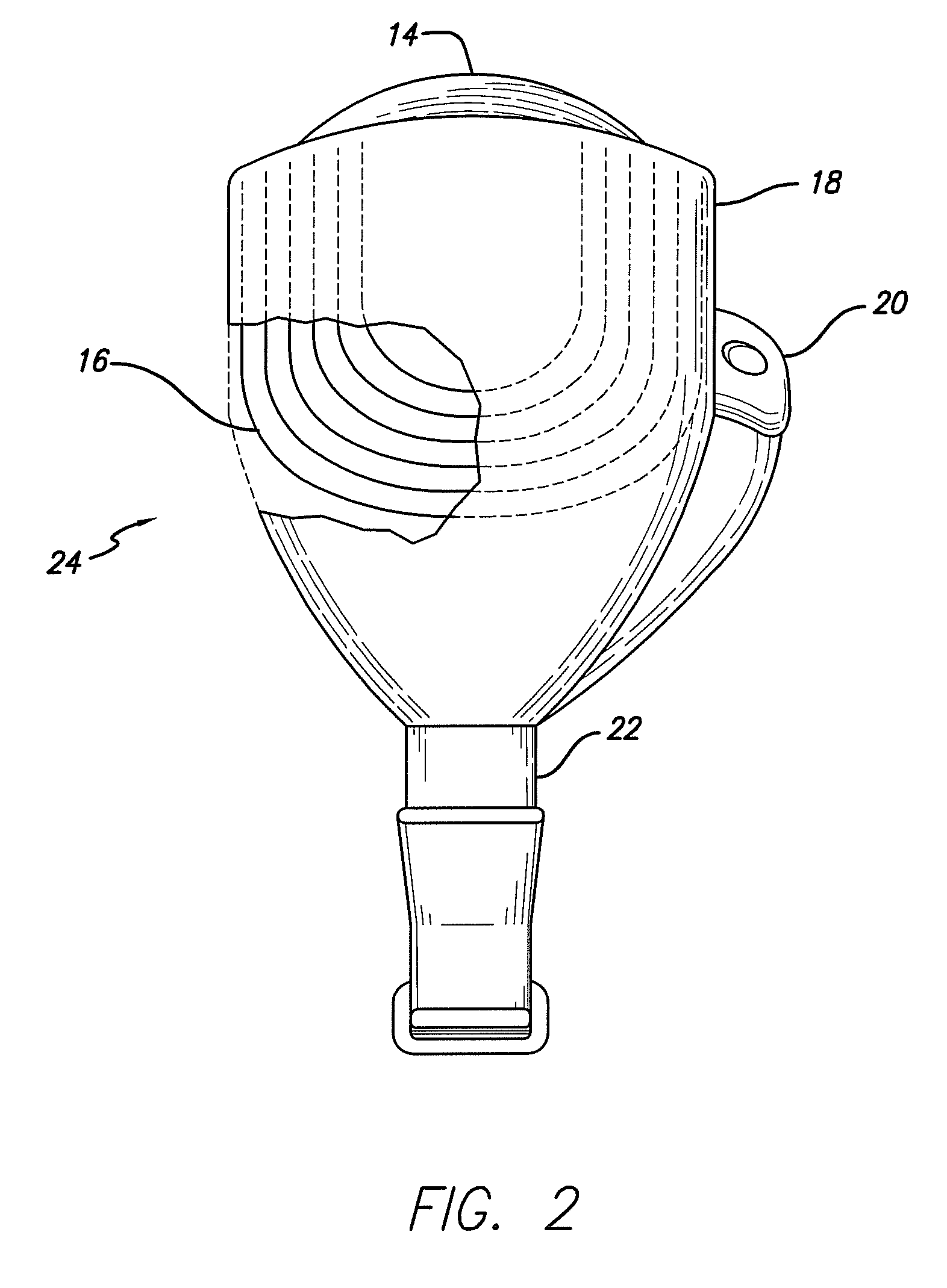
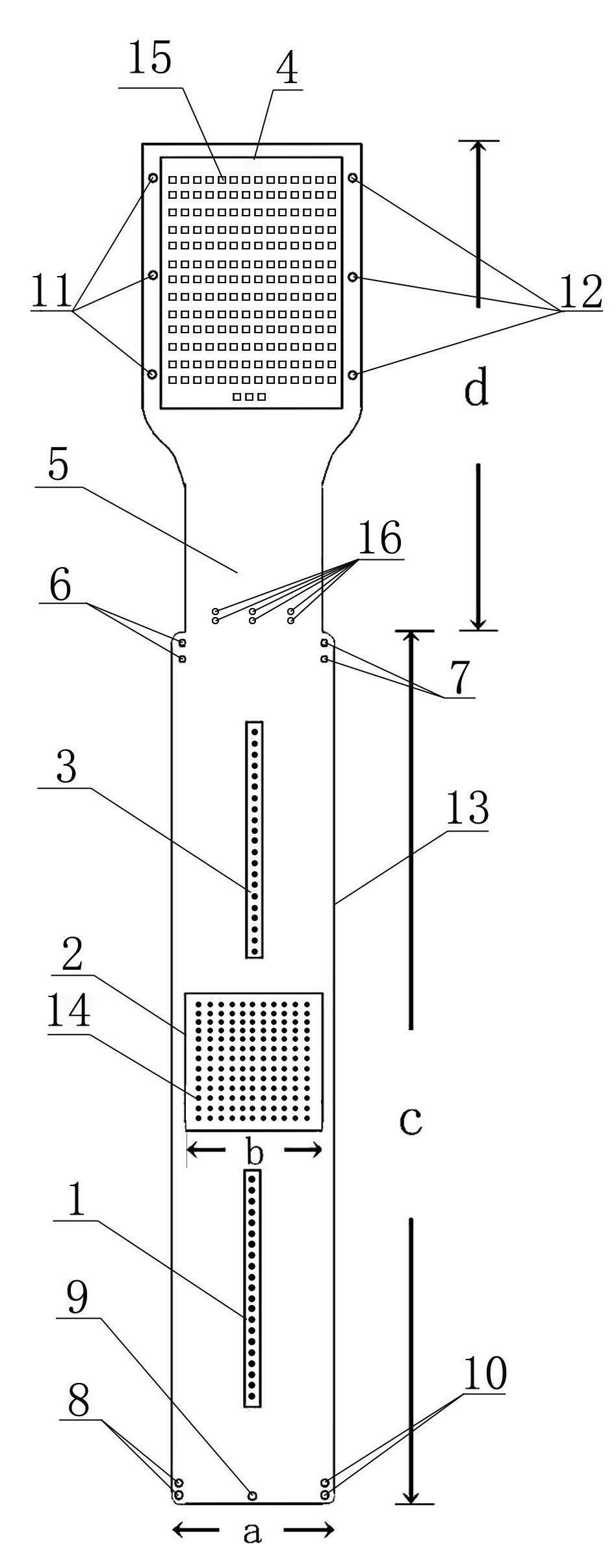
Flexible Circuit Electrode Array
ActiveUS20080288037A1Head electrodesPrinted circuit secondary treatmentFlexible circuitsElectrode array
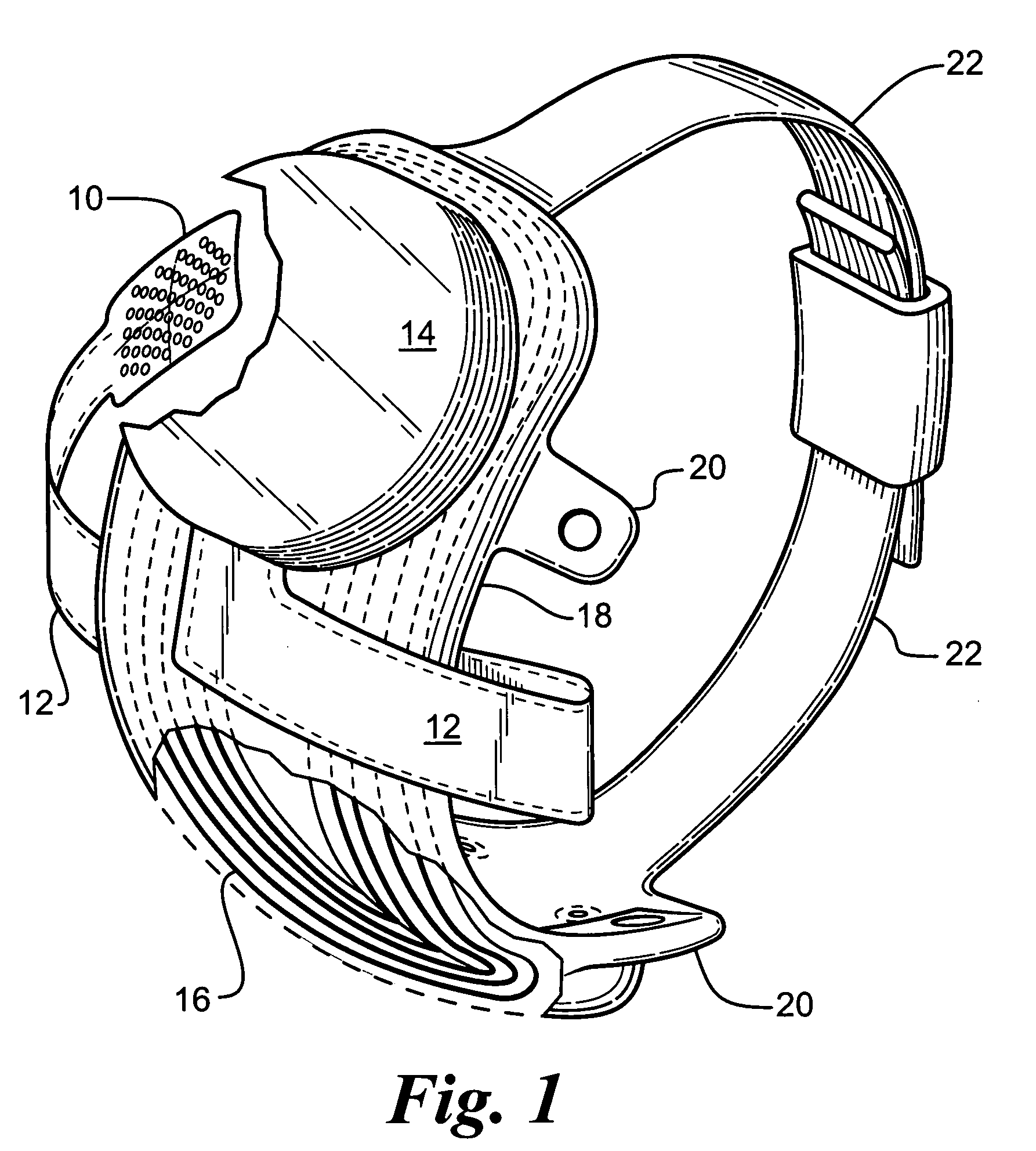
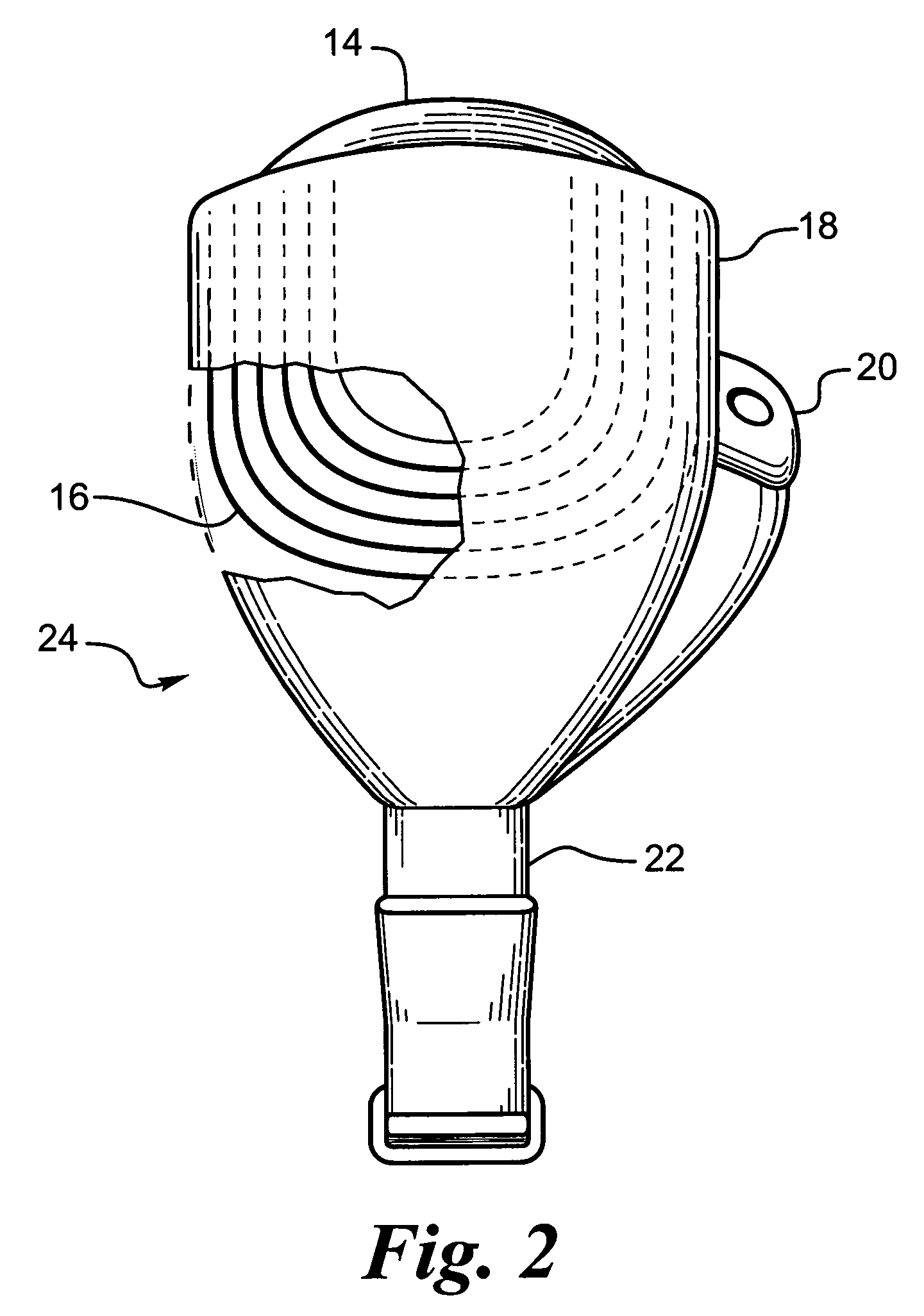
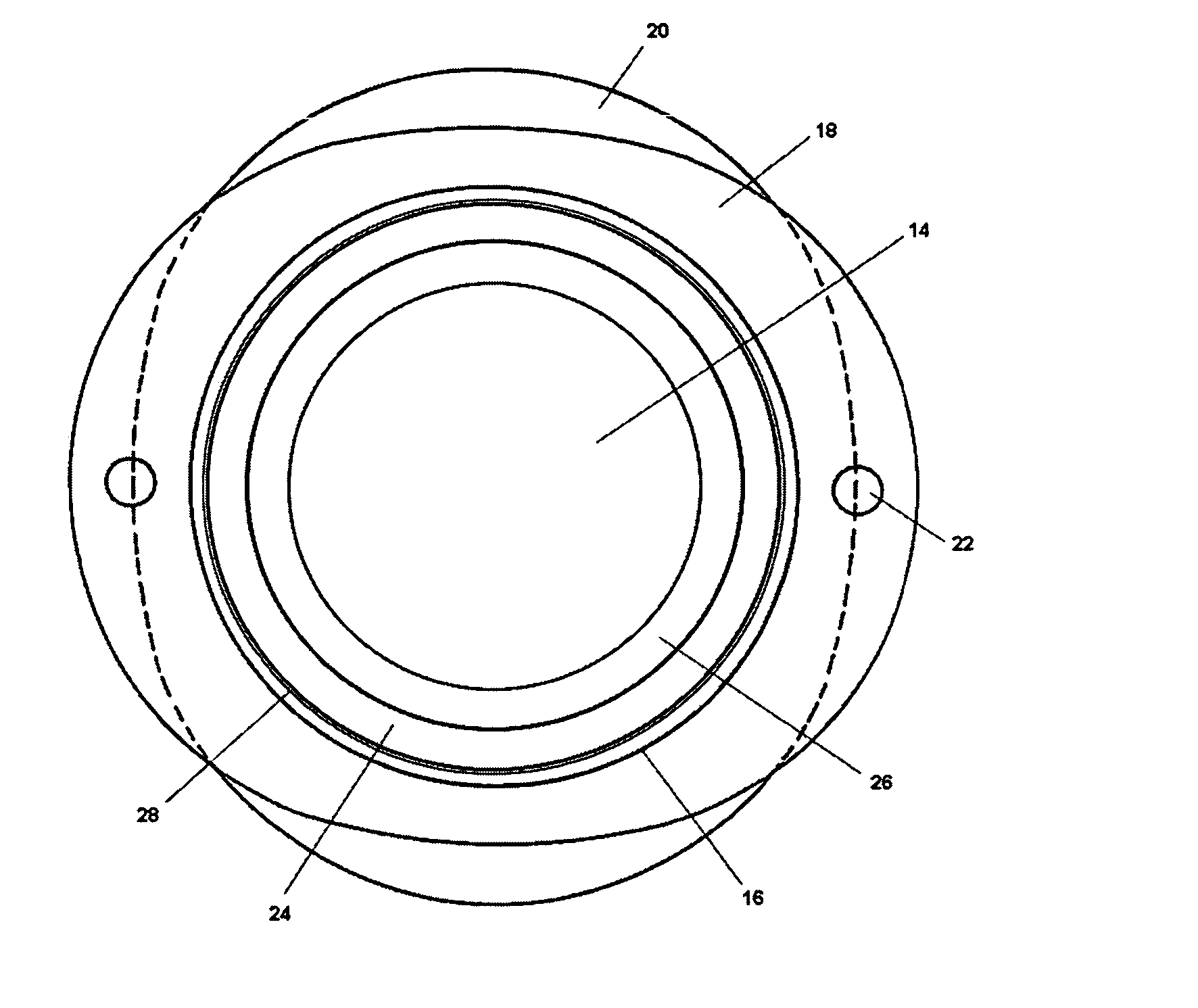
A flexible circuit electrode array with more than one layer of metal traces comprising: a polymer base layer; more than one layer of metal traces, separated by polymer layers, deposited on said polymer base layer, including electrodes suitable to stimulate neural tissue; and a polymer top layer deposited on said polymer base layer and said metal traces. Polymer materials are useful as electrode array bodies for neural stimulation. They are particularly useful for retinal stimulation to create artificial vision, cochlear stimulation to create artificial hearing, or cortical stimulation many purposes. The pressure applied against the retina, or other neural tissue, by an electrode array is critical. Too little pressure causes increased electrical resistance, along with electric field dispersion. Too much pressure may block blood flow.
Owner:CORTIGENT INC
Flexible circuit electrode array
ActiveUS8180460B2Head electrodesPrinted circuit secondary treatmentElectrical resistance and conductanceRetinal stimulation
A flexible circuit electrode array with more than one layer of metal traces comprising: a polymer base layer; more than one layer of metal traces, separated by polymer layers, deposited on said polymer base layer, including electrodes suitable to stimulate neural tissue; and a polymer top layer deposited on said polymer base layer and said metal traces. Polymer materials are useful as electrode array bodies for neural stimulation. They are particularly useful for retinal stimulation to create artificial vision, cochlear stimulation to create artificial hearing, or cortical stimulation many purposes. The pressure applied against the retina, or other neural tissue, by an electrode array is critical. Too little pressure causes increased electrical resistance, along with electric field dispersion. Too much pressure may block blood flow.
Owner:CORTIGENT INC
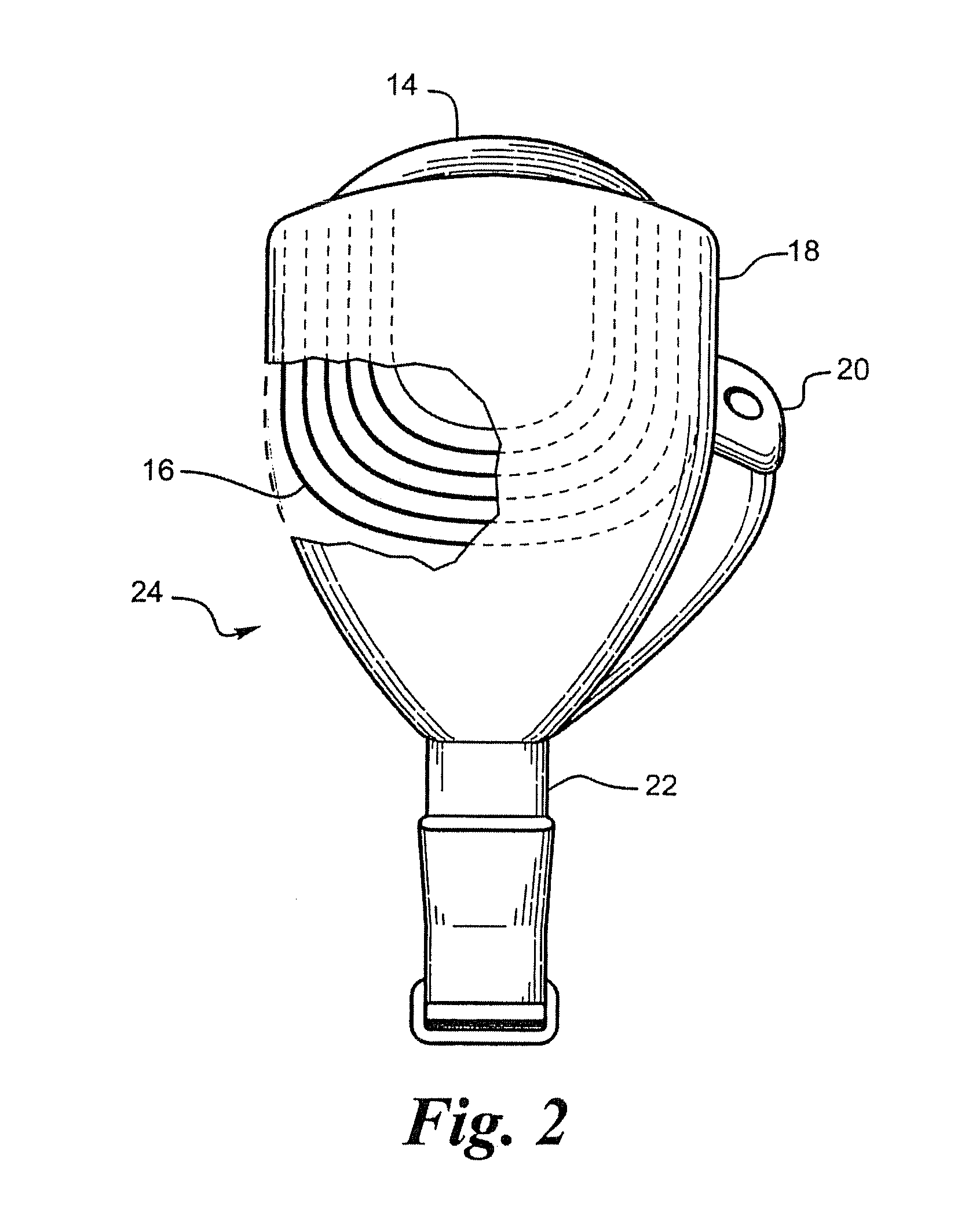
Retinal Prosthesis with a New Configuration
ActiveUS20080275527A1Improve the immunityCut the delicate retinal tissueCircuit bendability/stretchabilityHead electrodesFlexible circuitsRetinal Prosthesis
Polymer materials are useful as electrode array bodies for neural stimulation. They are particularly useful for retinal stimulation to create artificial vision, cochlear stimulation to create artificial hearing, and cortical stimulation, and many related purposes. The pressure applied against the retina, or other neural tissue, by an electrode array is critical. Too little pressure causes increased electrical resistance, along with electric field dispersion. Too much pressure may block blood flow. Common flexible circuit fabrication techniques generally require that a flexible circuit electrode array be made flat. Since neural tissue is almost never flat, a flat array will necessarily apply uneven pressure. Further, the edges of a flexible circuit polymer array may be sharp and cut the delicate neural tissue. By applying the right amount of heat to a completed array, a curve can be induced. With a thermoplastic polymer it may be further advantageous to repeatedly heat the flexible circuit in multiple molds, each with a decreasing radius. Further, it is advantageous to add material along the edges. It is further advantageous to provide a fold or twist in the flexible circuit array. Additional material may be added inside and outside the fold to promote a good seal with tissue.
Owner:SECOND SIGHT MEDICAL PRODS +1
Flexible circuit electrode array
ActiveUS20060259112A1Improve the immunityCut the delicate retinal tissueHead electrodesPrinted circuit manufactureFlexible circuitsHearing perception
Owner:SECOND SIGHT MEDICAL PRODS +2
Retinal prosthesis with a new configuration
ActiveUS20070055336A1CutImprove the immunityCircuit bendability/stretchabilityHead electrodesFlexible circuitsBlood flow
Polymer materials are useful as electrode array bodies for neural stimulation. They are particularly useful for retinal stimulation to create artificial vision, cochlear stimulation to create artificial hearing, and cortical stimulation, and many related purposes. The pressure applied against the retina, or other neural tissue, by an electrode array is critical. Too little pressure causes increased electrical resistance, along with electric field dispersion. Too much pressure may block blood flow. Common flexible circuit fabrication techniques generally require that a flexible circuit electrode array be made flat. Since neural tissue is almost never flat, a flat array will necessarily apply uneven pressure. Further, the edges of a flexible circuit polymer array may be sharp and cut the delicate neural tissue. By applying the right amount of heat to a completed array, a curve can be induced. With a thermoplastic polymer it may be further advantageous to repeatedly heat the flexible circuit in multiple molds, each with a decreasing radius. Further, it is advantageous to add material along the edges. It is further advantageous to provide a fold or twist in the flexible circuit array. Additional material may be added inside and outside the fold to promote a good seal with tissue.
Owner:SECOND SIGHT MEDICAL PRODS +1
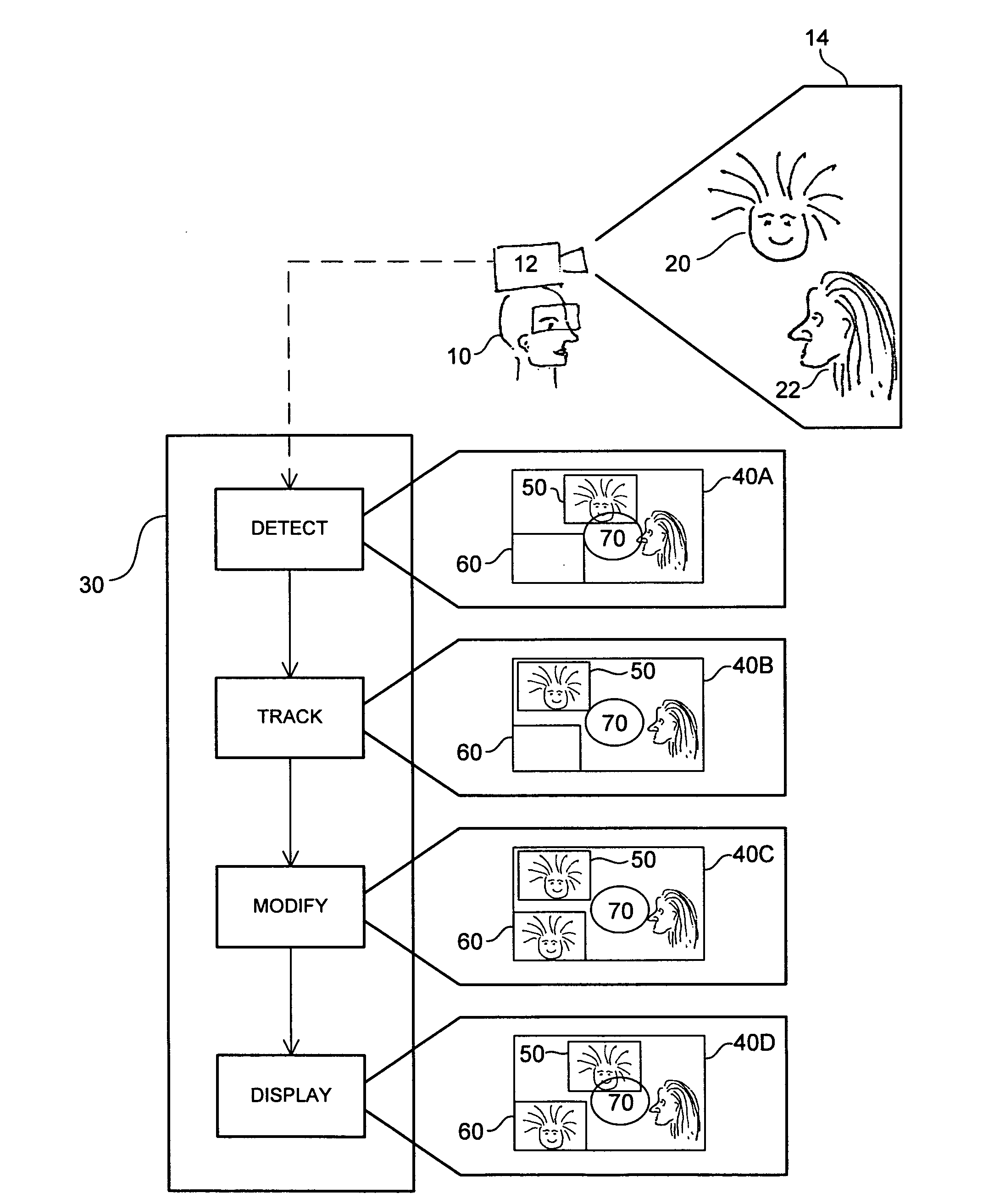
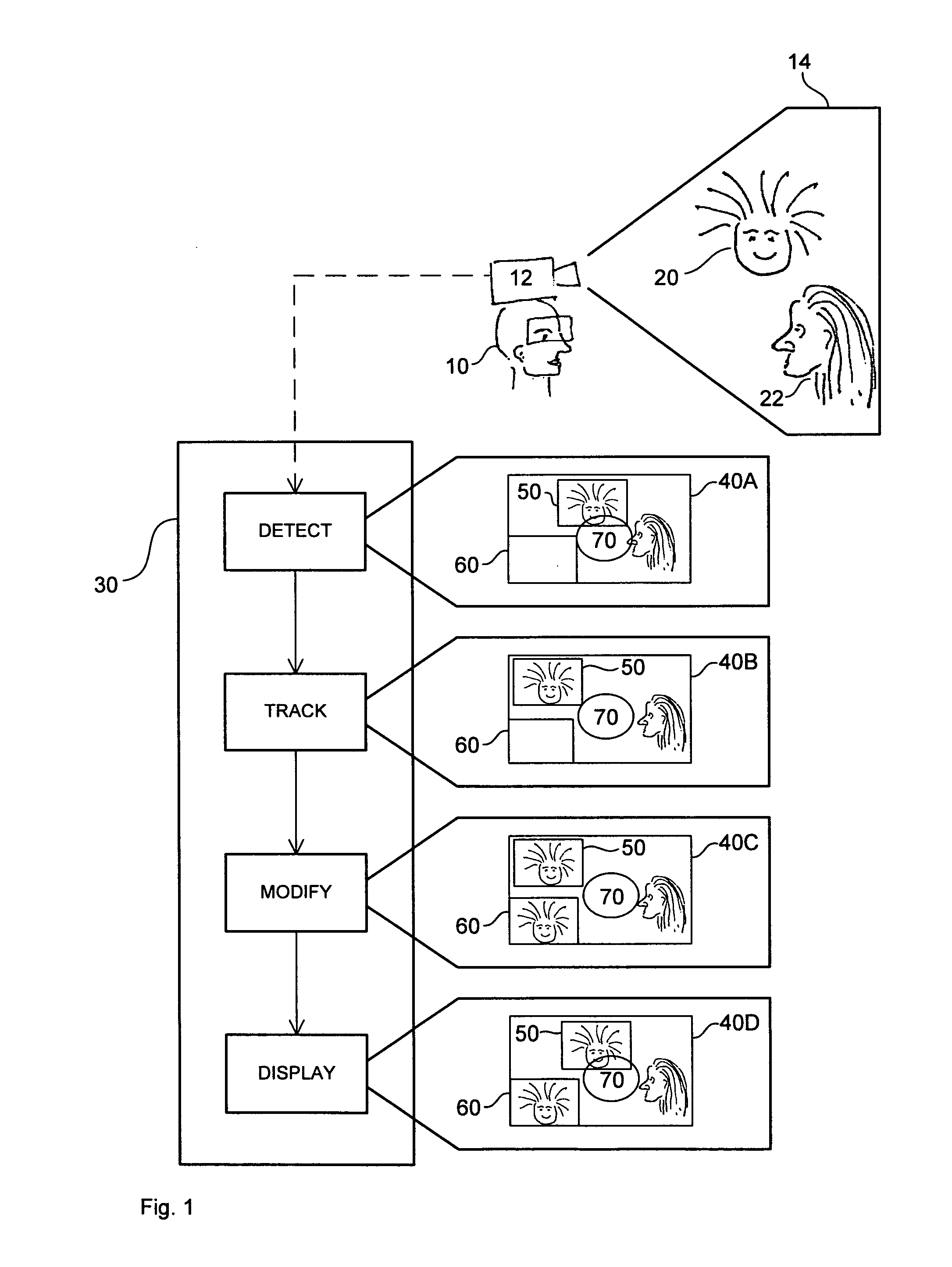
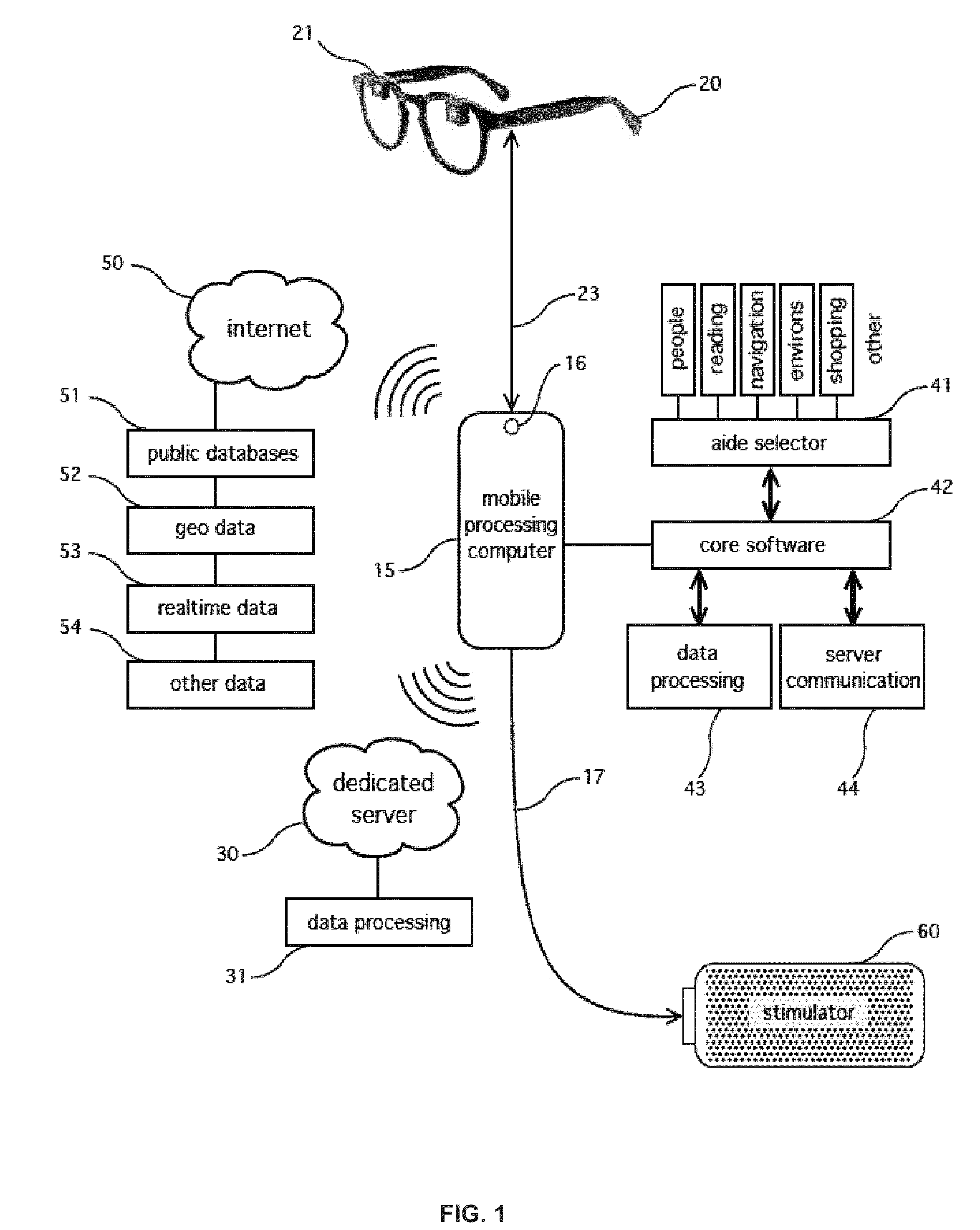
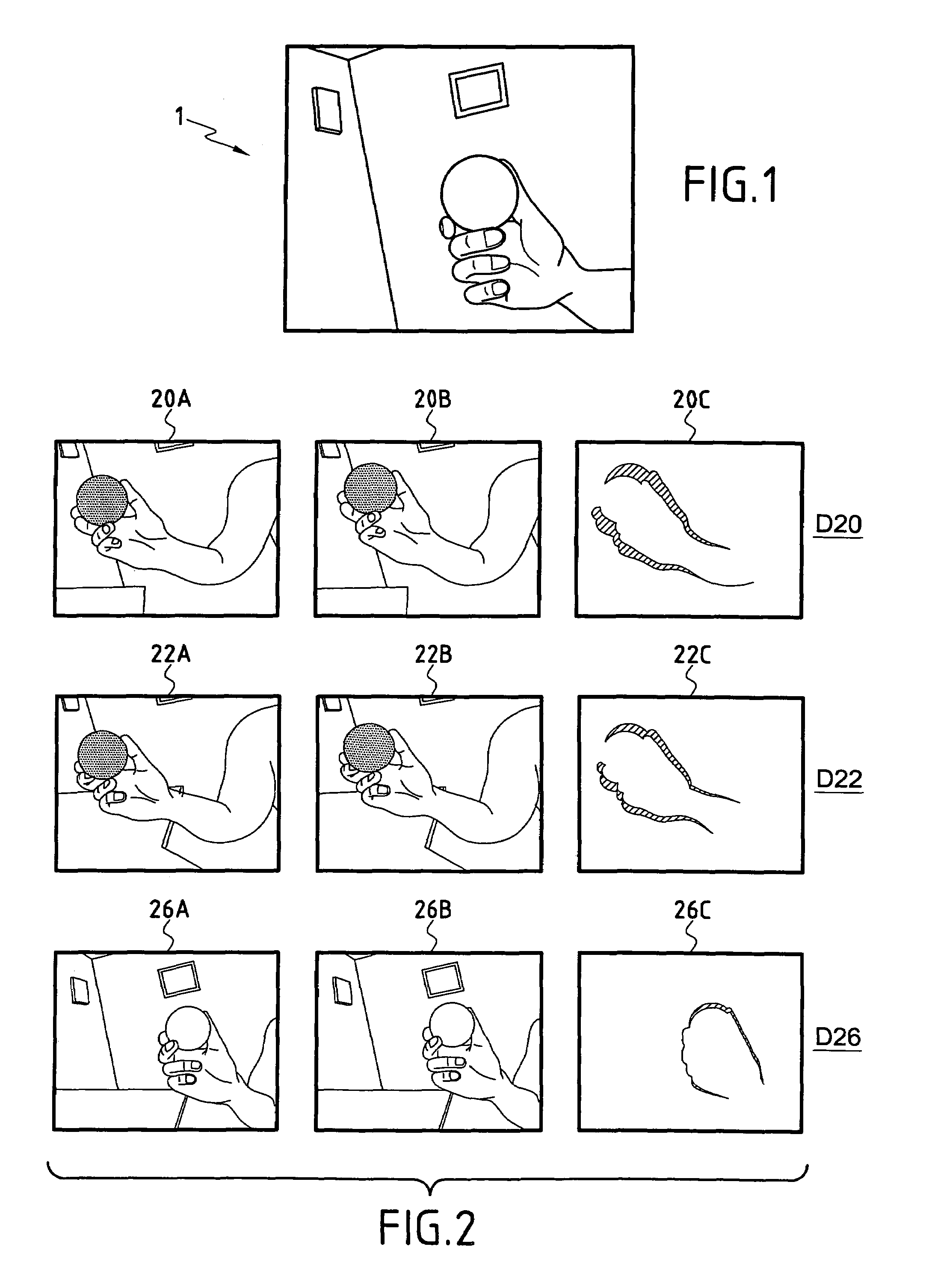
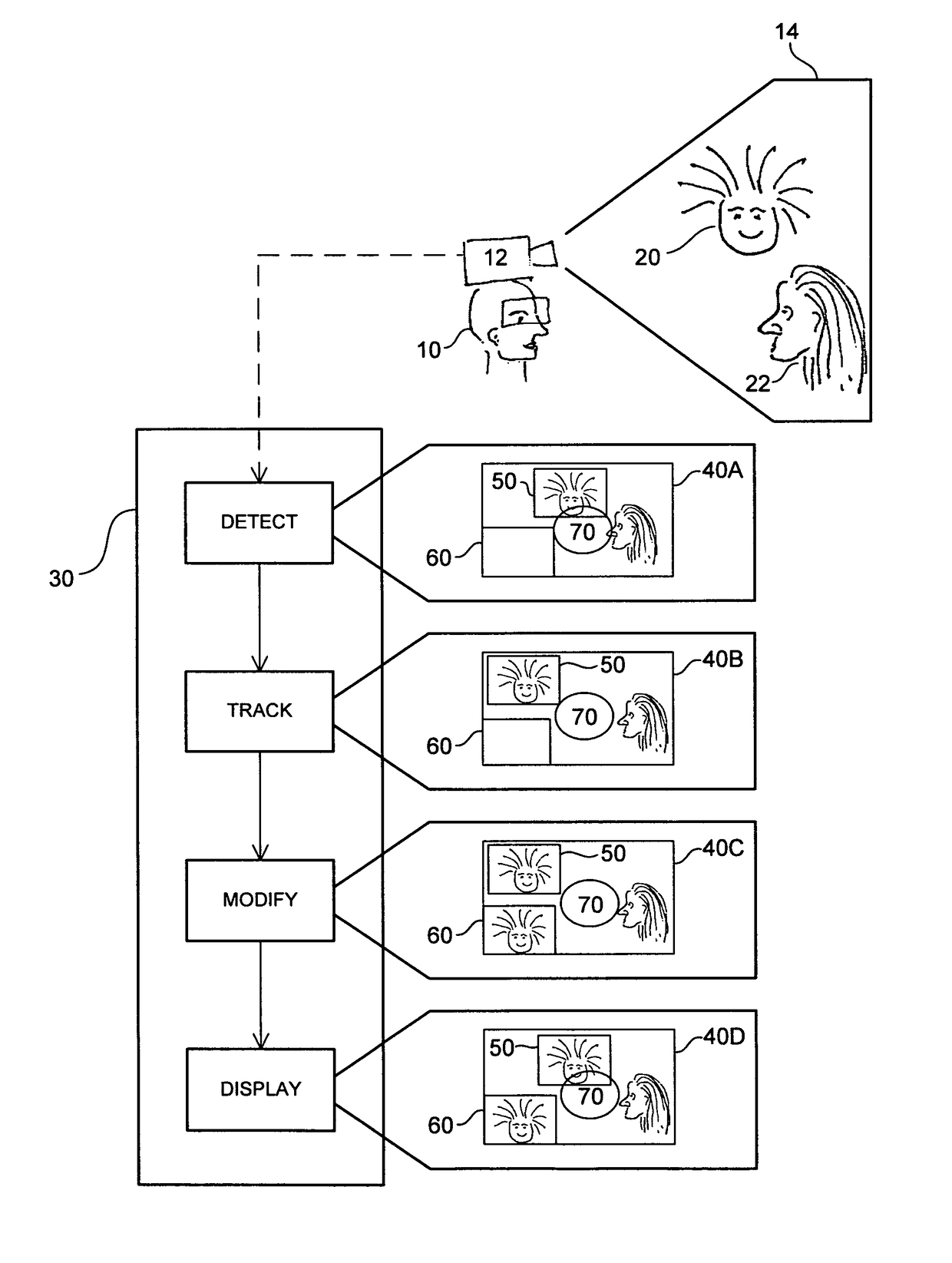
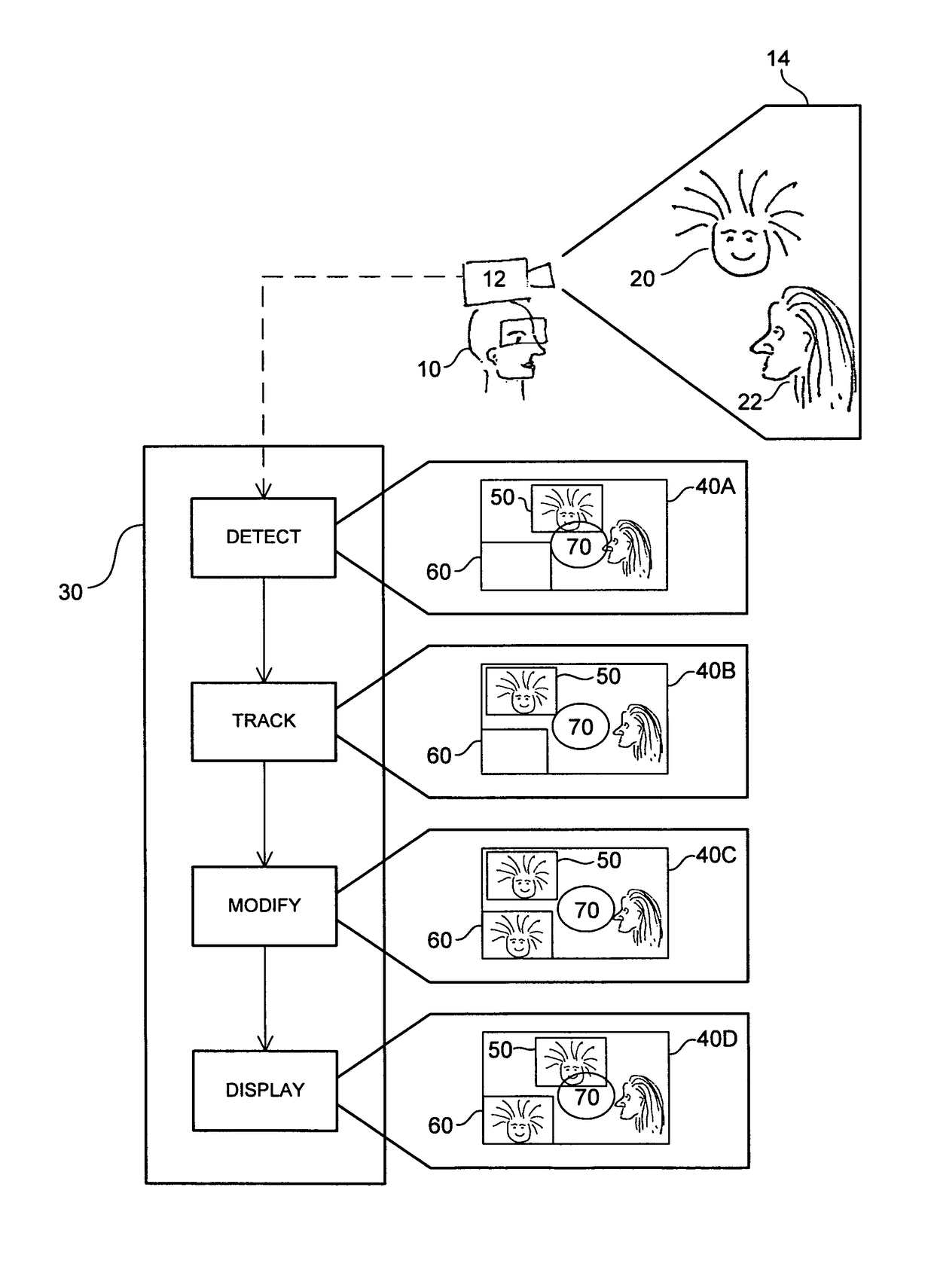
Object Tracking for Artificial Vision
ActiveUS20120212594A1ElectrotherapyCharacter and pattern recognitionVisual impairmentVisual perception
This invention concerns the tracking of objects in video data for artificial vision; for instance for a bionic eye. More particularly, the invention concerns a vision enhancement apparatus for a vision-impaired user. In other aspects, the invention concerns a method for enhancing vision and software to perform the method. The image processor operates to process video data representing images of a scene. Automatically detect and track a user selected object, such as a face, in the images. And, automatically modify the video data, by reserving a user selected area of the displayed images for displaying the tracked object as a separate video tile within the scene. The separate video tile remains in the selected area despite movement of the camera relative to the scene, or movement of the user relative to the object or the scene.
Owner:NAT ICT AUSTRALIA
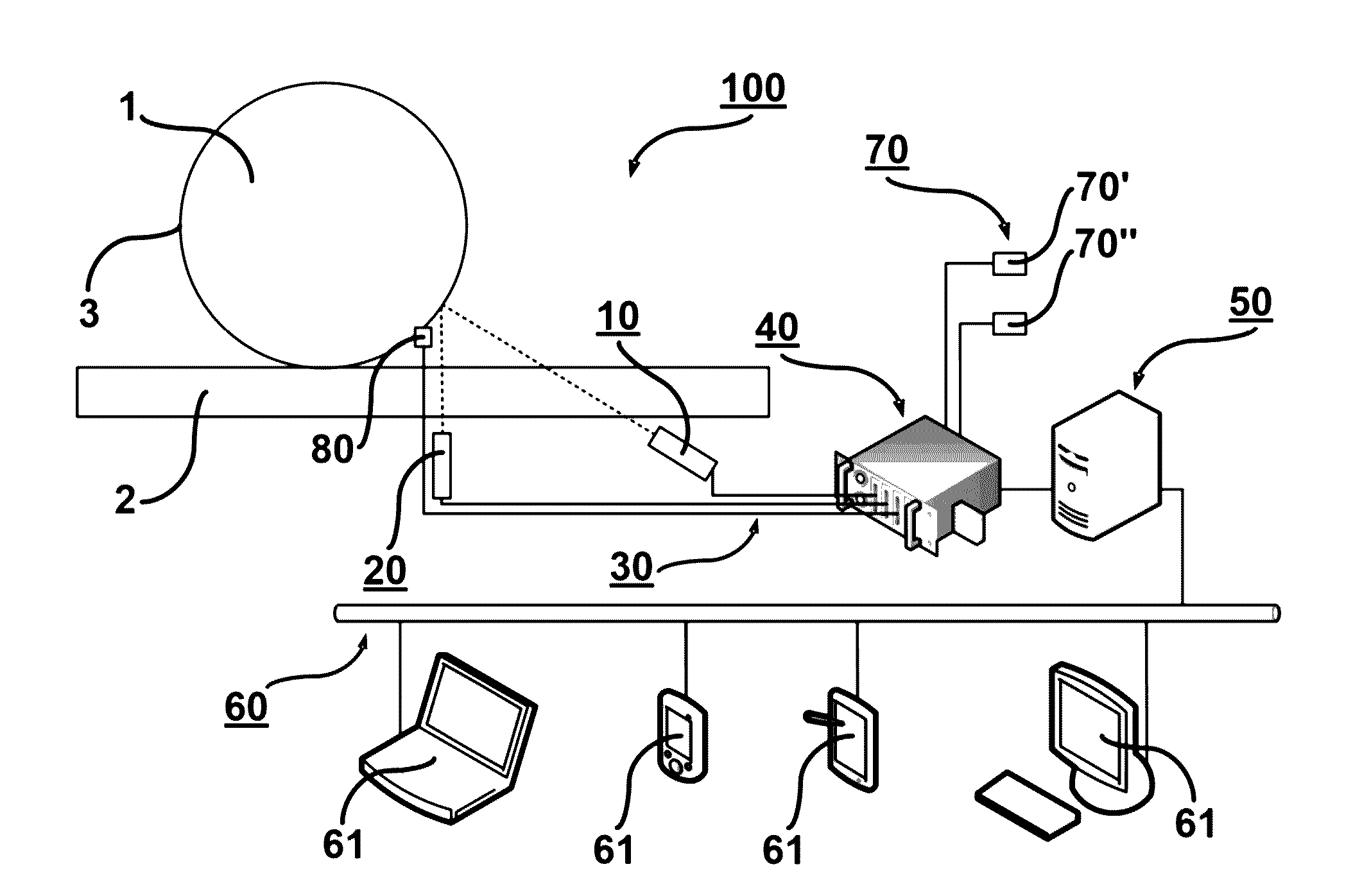
System and method for inspecting the geometric parameters of the wheels of railway vehicles
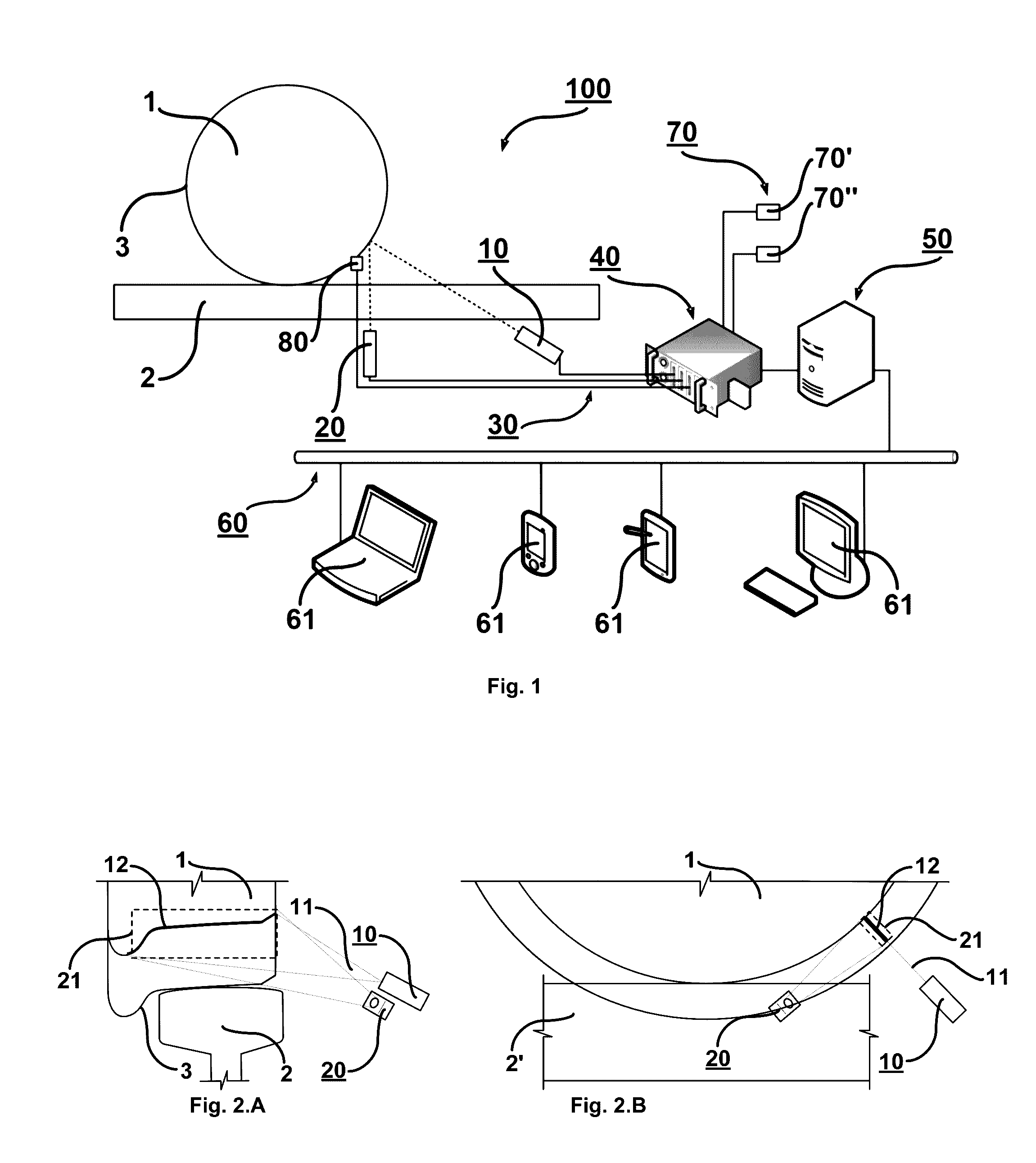
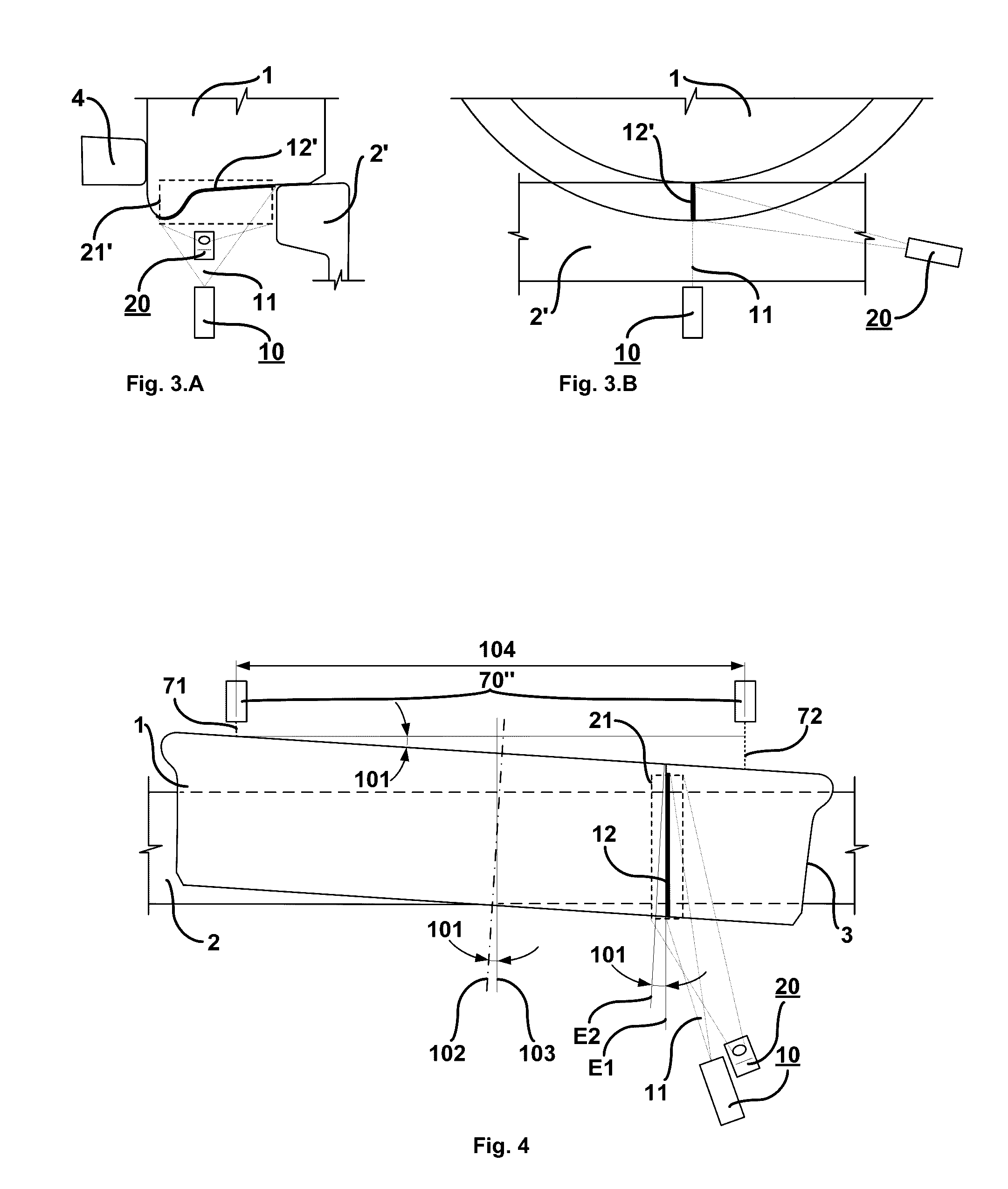
The present invention relates to a system and method for the automated inspection of geometric parameters of railway wheels rolling on a track by artificial vision techniques. The present invention uses a structured light source (10) that illuminates a line of light (12) upon a fraction of the surface of revolution (3) of a wheel (1), a CCD camera (20), which captures an image (21) of the illuminated area, and a data processing system that records, digitalizes, geometrically corrects and reconstructs information of the surface of revolution (3) that is not recorded in the image (21), in order to obtain a numeric description of the complete transverse section of the wheel (1) represented by a reconstructed profilogram (500) for calculating the geometric parameters of the wheel (1).
Owner:EMPRESA DE TRANSPORTE MASIVO DEL VALLE DE ABURRA LTDA METRO DE MEDELLIN LTDA
Method and apparatus to project image on retina at various focal depths utilizing flexible substrate containing optical array
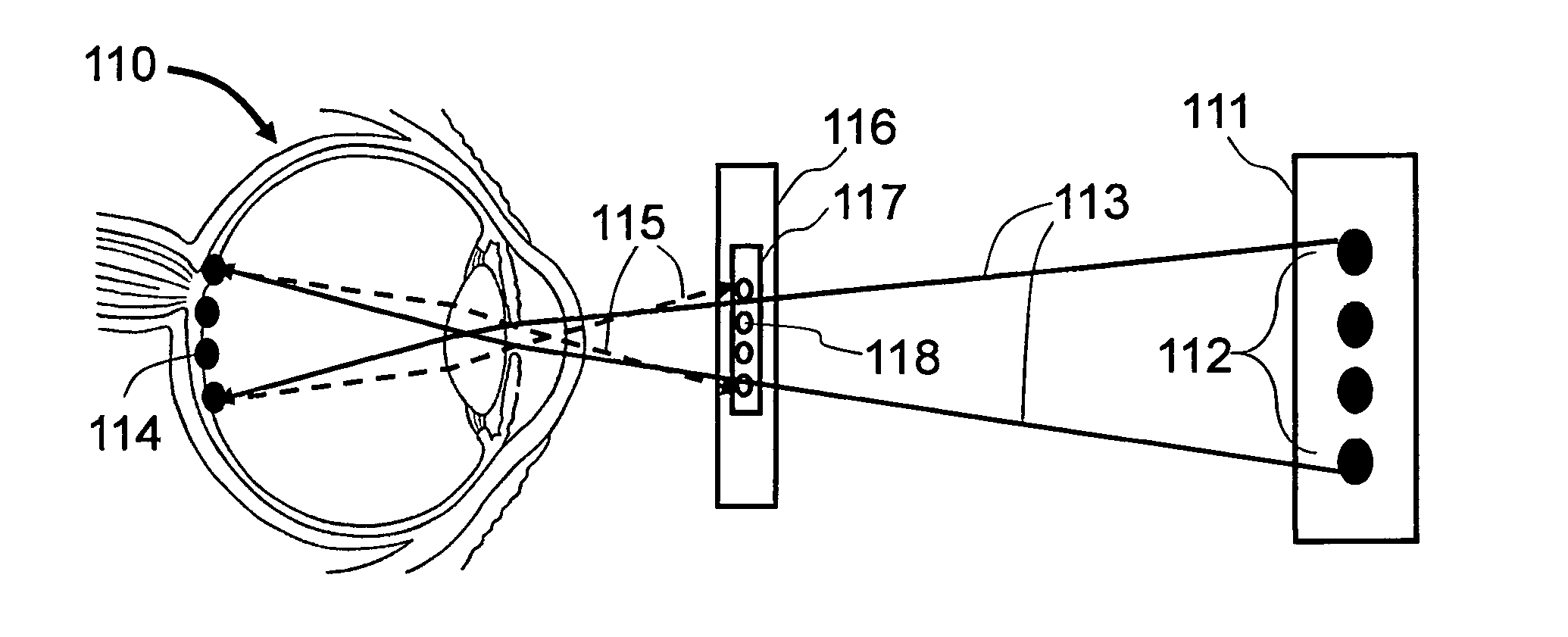
The current invention relates to the method to achieve artificial vision with using flexible substrate based light emitting arrays, or optical passage arrays, to project image upon the retina of a human eye. Further, it relates to the method to detect the real-time focal length change of the eye-lens and modify the flexible substrate curvature and distance from the eye to vary global angle configurations of light beams that go into the eye to produce images on the retina at various focus depth of the eye to achieve re-focusable artificial vision.
Owner:ZHOU YUCHEN
Regular graphic code used for locating indoor mobile robot and locating method
PendingCN107689061ARealize 3D pose measurementAchieve positioningImage enhancementImage analysisGraphicsData information
The invention discloses a regular graphic code used for locating an indoor mobile robot and a locating method which are used for solving the technical problem that an existing indoor mobile robot locating method is low in remote recognition efficiency. According to the technical scheme, the regular graphic code is a two-dimensional graphic code, and the pattern is a regular square module array andis composed of an encoding region and a functional graphic region, wherein the functional graphic region is a detection graph at the outer hollow-square-shaped position and used for locating the regular graphic code position in images collected by a camera; the encoding region is a two-dimensional lattice graph in the hollow-square-shaped region, marking points at the four vertexes of the two-dimensional lattice are used for marking the coordinate direction in the encoding region, and the other marking points serve as data information codes of the encoding region. The regular graphic code isadopted as an artificial vision road sign, three-dimensional pose measurement and location of the indoor mobile robot can be achieved, and remote recognition efficiency and accuracy are improved.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV +1
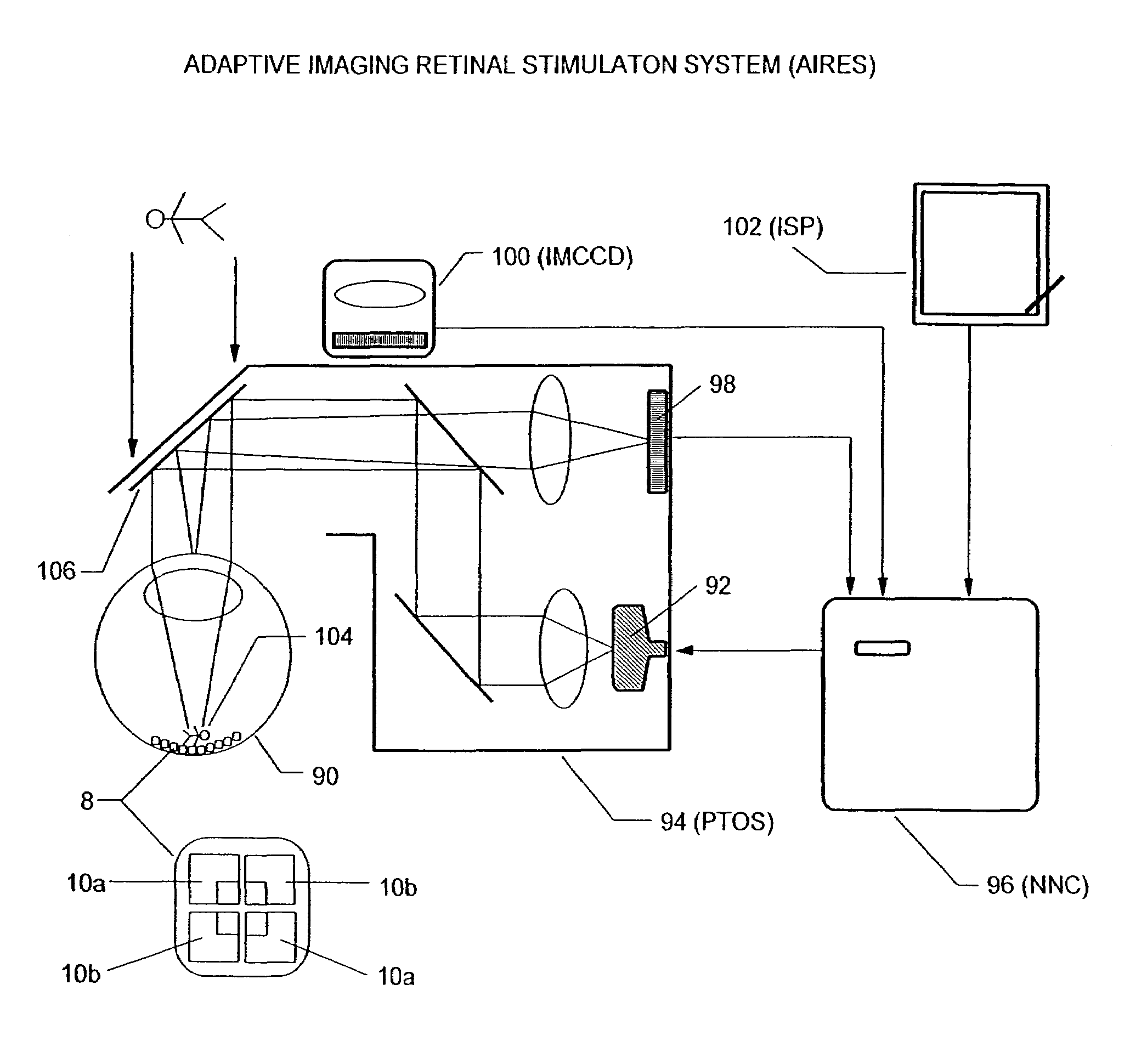
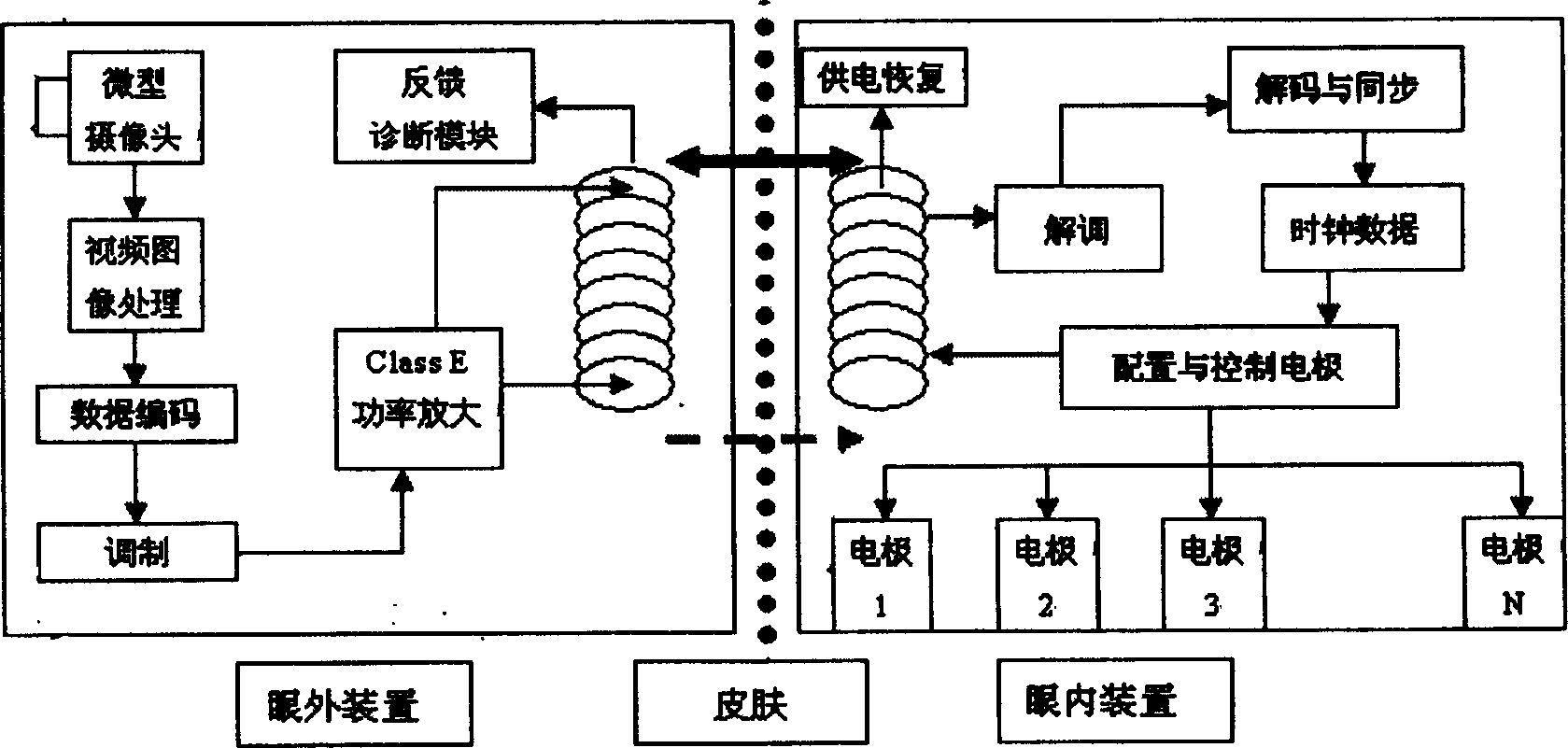
Multi-phasic microphotodiode retinal implant and adaptive imaging retinal stimulation system
InactiveUS7139612B2Facilitate cognitionImprove abilitiesEye implantsHead electrodesColor imageAdaptive imaging
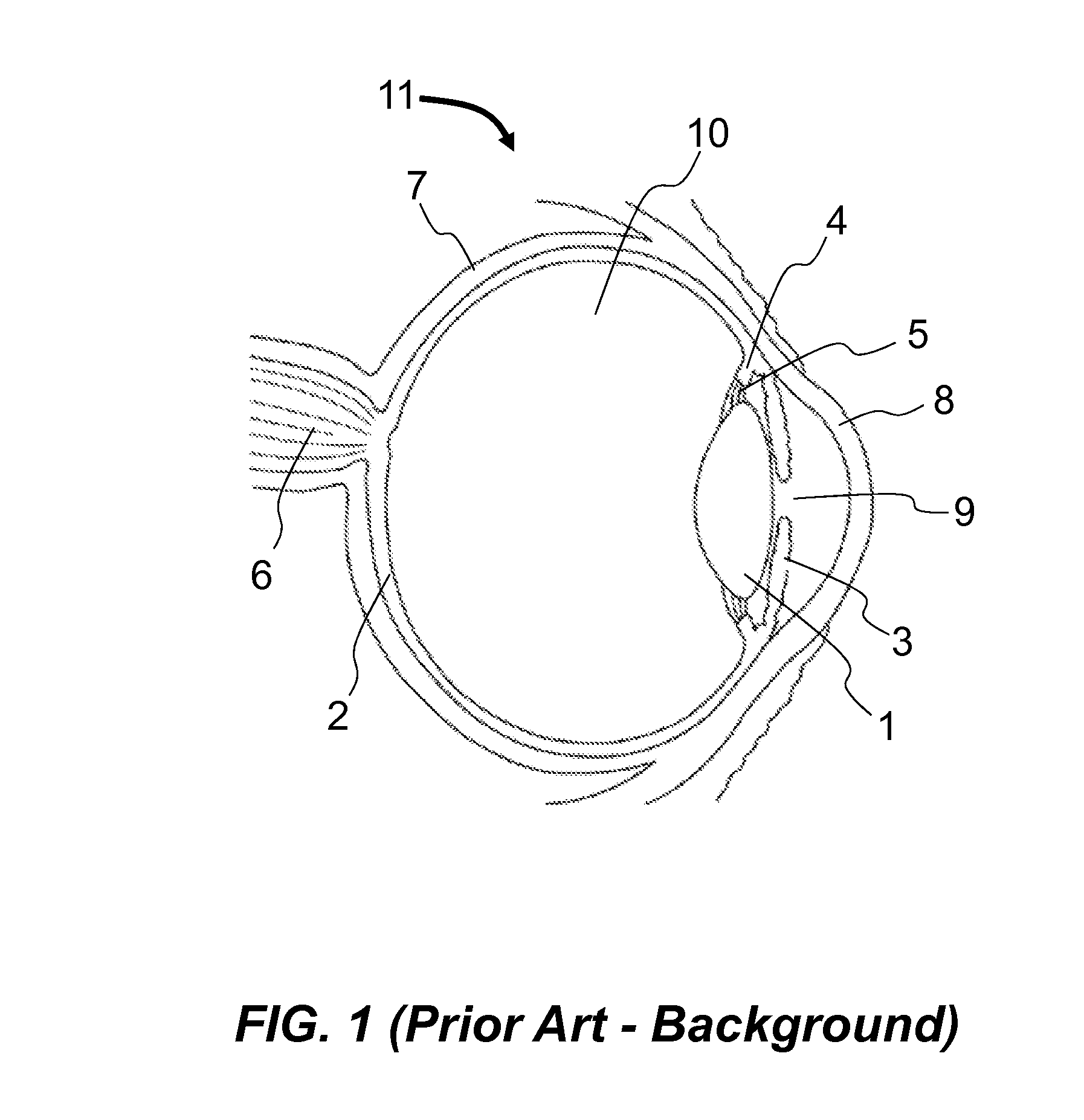
An artificial retina device and a retinal stimulation system and method for stimulating and modulating its function is disclosed. The artificial retina device includes multi-phasic microphotodiode subunits. In persons suffering from blindness due to outer retinal layer damage, a plurality of such devices, when surgically implanted into the subretinal space, may allow useful formed artificial vision to develop. By projecting real or computer controlled visible light images, and computer controlled infrared light images or illumination, simultaneously or in rapid alternation onto the artificial retina device, the nature of induced retinal images may be modulated and improved. The retinal stimulation system may be worn as a headset. Color images may be induced by programming the stimulating pulse durations and frequencies of the stimulation.
Owner:PIXIUM VISION SA
Visual Prosthesis for Phosphene Shape Control
ActiveUS20090287276A1Accurate video preproductionSimple methodHead electrodesEye treatmentVisual prosthesisElectrode array
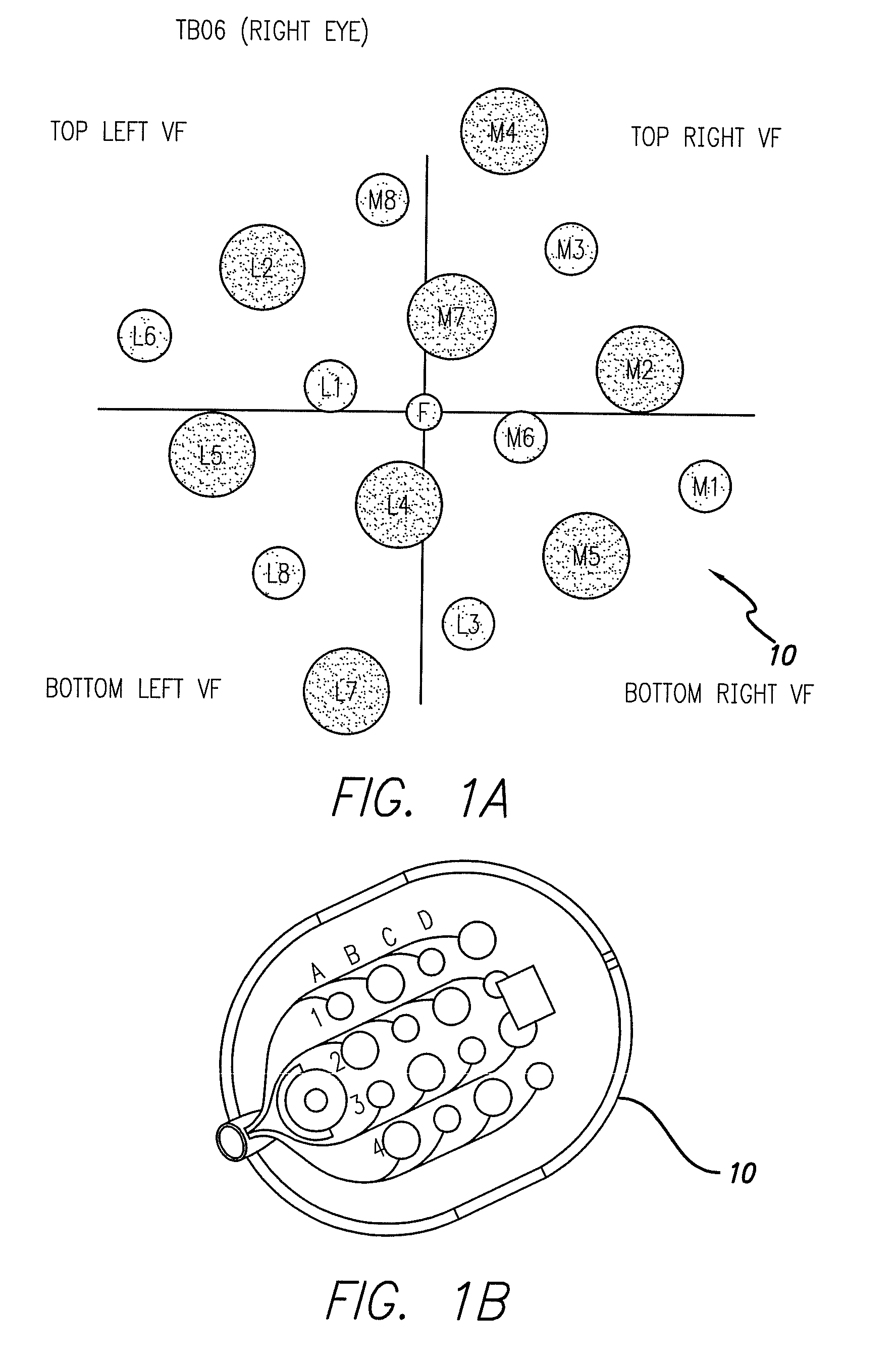
The present invention is an improved method of stimulating visual neurons to create artificial vision. It has been found that varying current of visual stimulation can create varying percept brightness, varying percept size, and varying percept shape. By determining the attributes of predetermined current levels, and using those attributes to program a video processor, more accurate video preproduction can be obtained.The present invention also includes an electrode array having alternating large and small electrodes in rows at a 45 degree angle to horizontal in the visual field.
Owner:CORTIGENT INC
Vision prosthesis device based on optical-disc micro-electrode array
InactiveCN101396583AAvoid damageRepair visual functionEye treatmentArtificial respirationProsthesisMicroelectrode
A visual prosthetic device is based on videodisc microelectrode array, belonging to the technical field of medical appliance. The device comprises a microelectrode array substrate, a microelectrode array and an electrode cable, and is characterized by further comprising a cover board and a retina nail; wherein, the two ends of the microelectrode array substrate are respectively provided with a through hole of the retina nail, the middle of microelectrode array substrate is provided with 18 electrode through holes, and the retina nail passes through the through hole of the retina nail to fix the microelectrode array substrate on a videodisc of the retina; the microelectrode array consists of 18 wire electrodes which are fixed in the electrode through holes that are arranged in the center of the microelectrode array substrate, one ends of the wire electrodes are connected in vitro by the electrode cables, and the cover board covers above the electrode through holes of the microelectrode array substrate to fix the microelectrode array. The visual prosthetic device is applied for generating artificial vision and is the medical device for helping the retina blindness patients to gain brightness and vision again.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
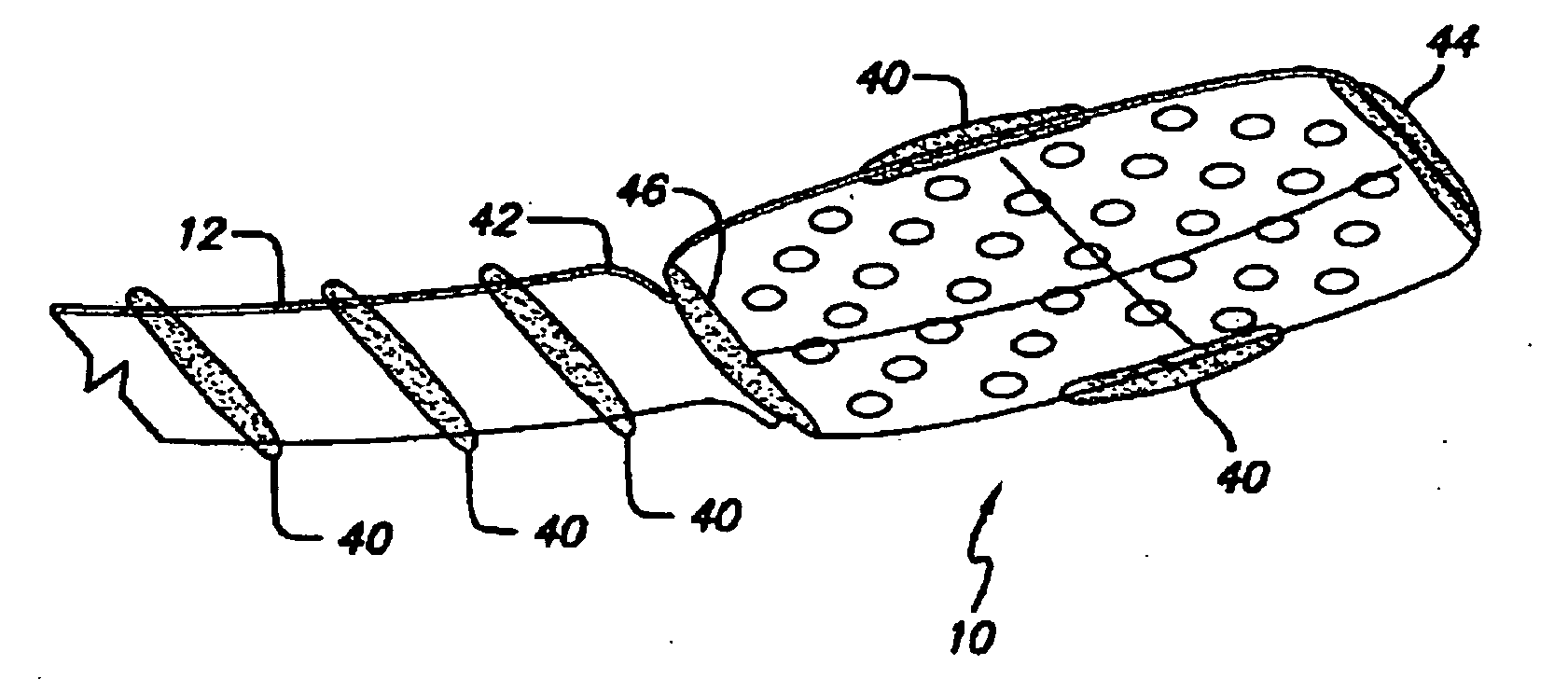
Method of manufacturing a flexible circuit electrode array
ActiveUS8524311B1Electrical resistance increaseAvoid flowHead electrodesPharmaceutical containersRetinal stimulationFlexible circuits
Polymer materials make useful materials as electrode array bodies for neural stimulation. They are particularly useful for retinal stimulation to create artificial vision. Regardless of which polymer is used, the basic construction method is the same. A layer of polymer is laid down. A layer of metal is applied to the polymer and patterned to create electrodes and leads for those electrodes. A second layer of polymer is applied over the metal layer and patterned to leave openings for the electrodes, or openings are created later by means such as laser ablation. Hence the array and its supply cable are formed of a single body. A method for manufacturing a flexible circuit electrode array, comprises:a) depositing a metal trace layer on an insulator polymer base layer;b) applying a layer of photoresist on said metal trace layer and patterning said metal trace layer and forming metal traces on said insulator polymer base layer; andc) activating said insulator polymer base layer and depositing a top insulator polymer layer and forming one single insulating polymer layer with said base insulator polymer layer; wherein the insulator polymer layers were treated at a temperature from 80-150° C. and then at a temperature from 230-350° C.
Owner:CORTIGENT INC
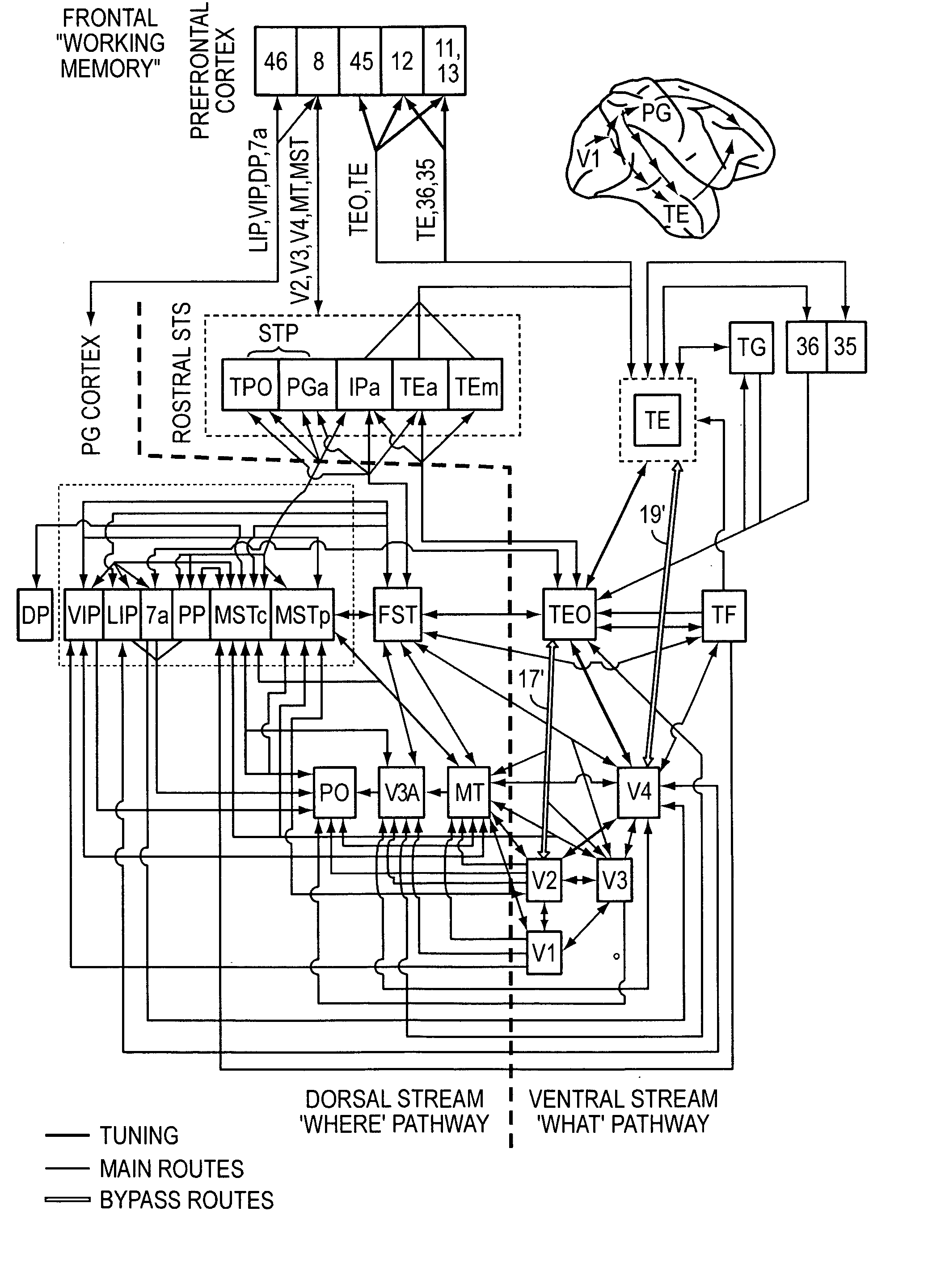
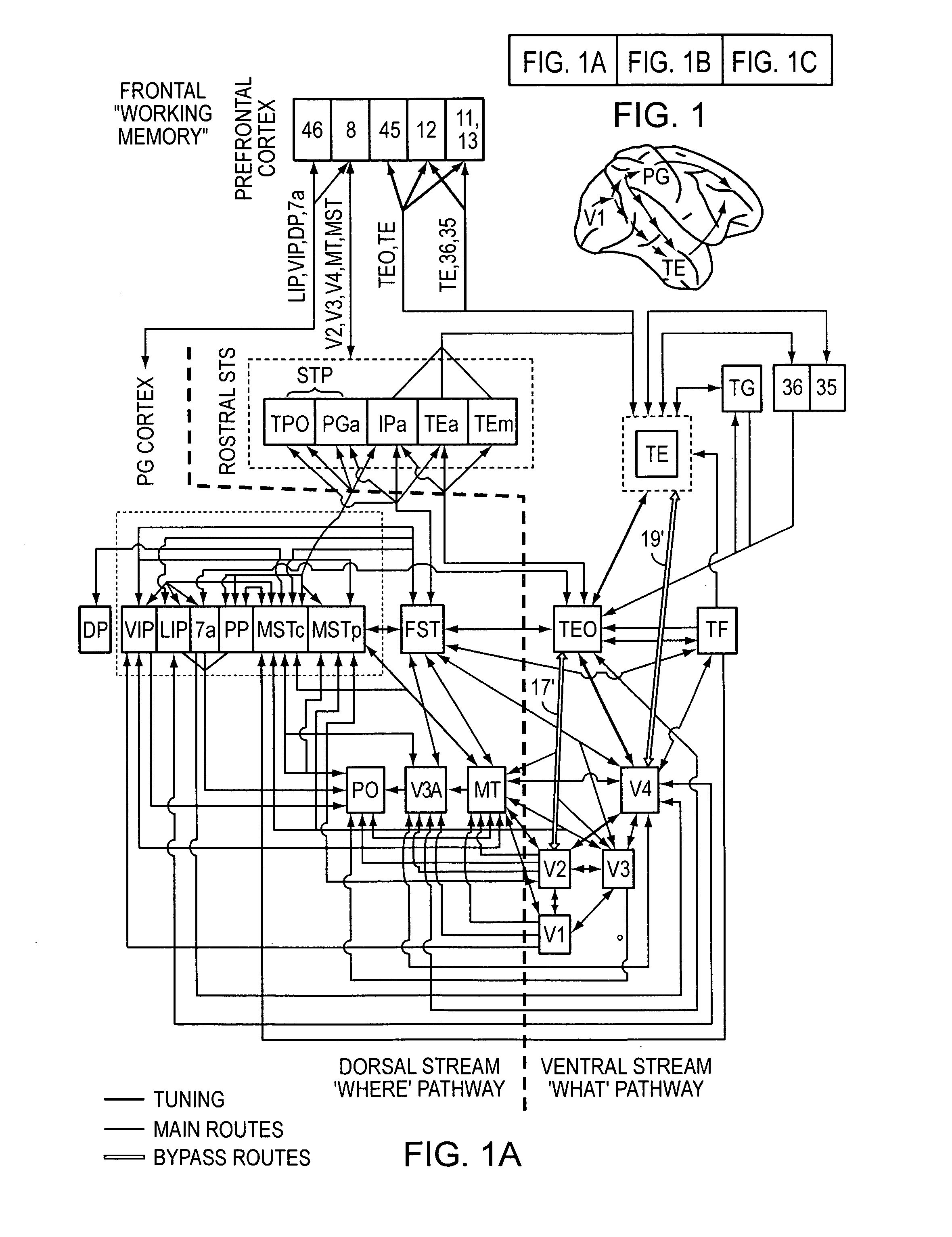
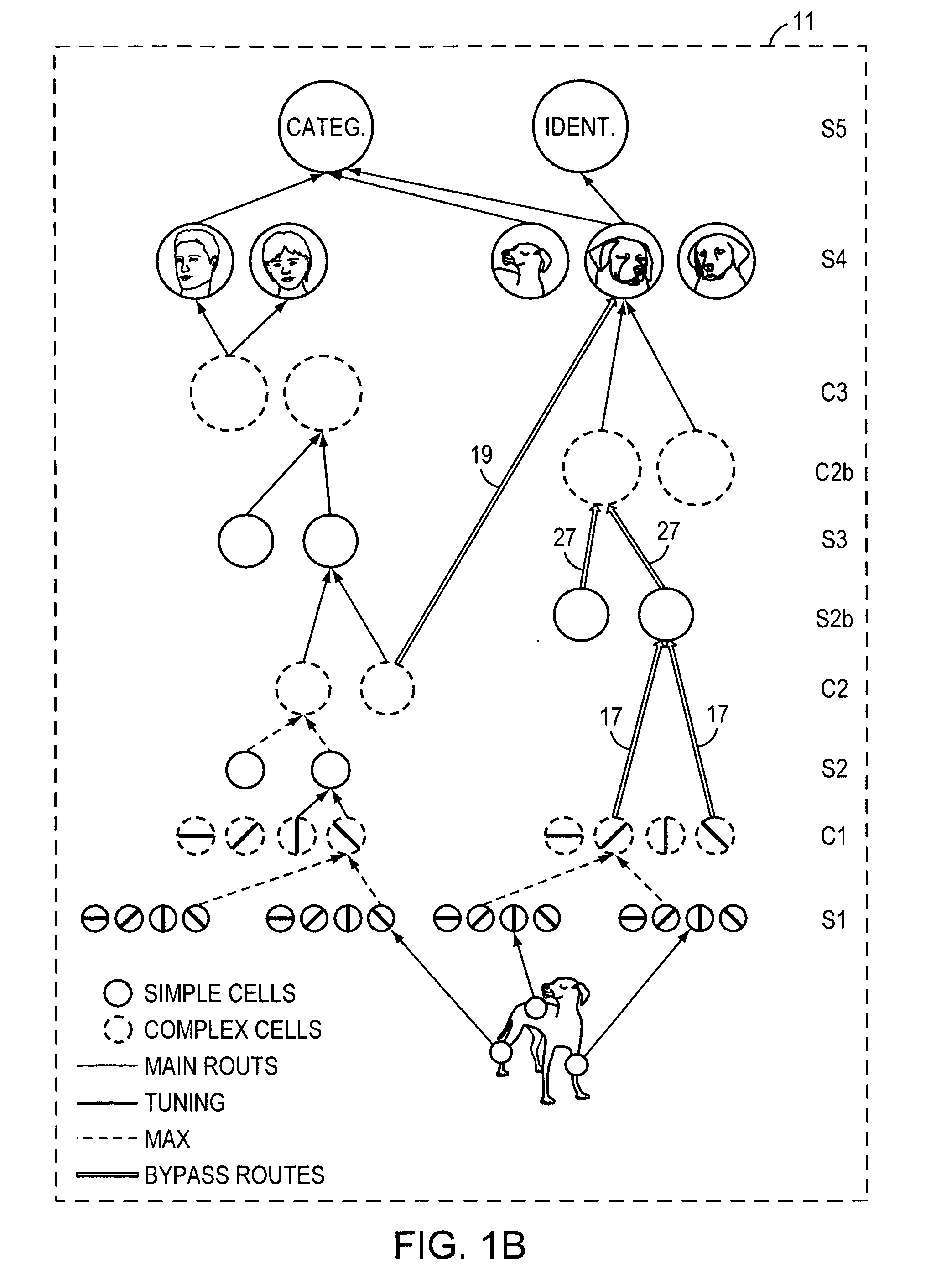
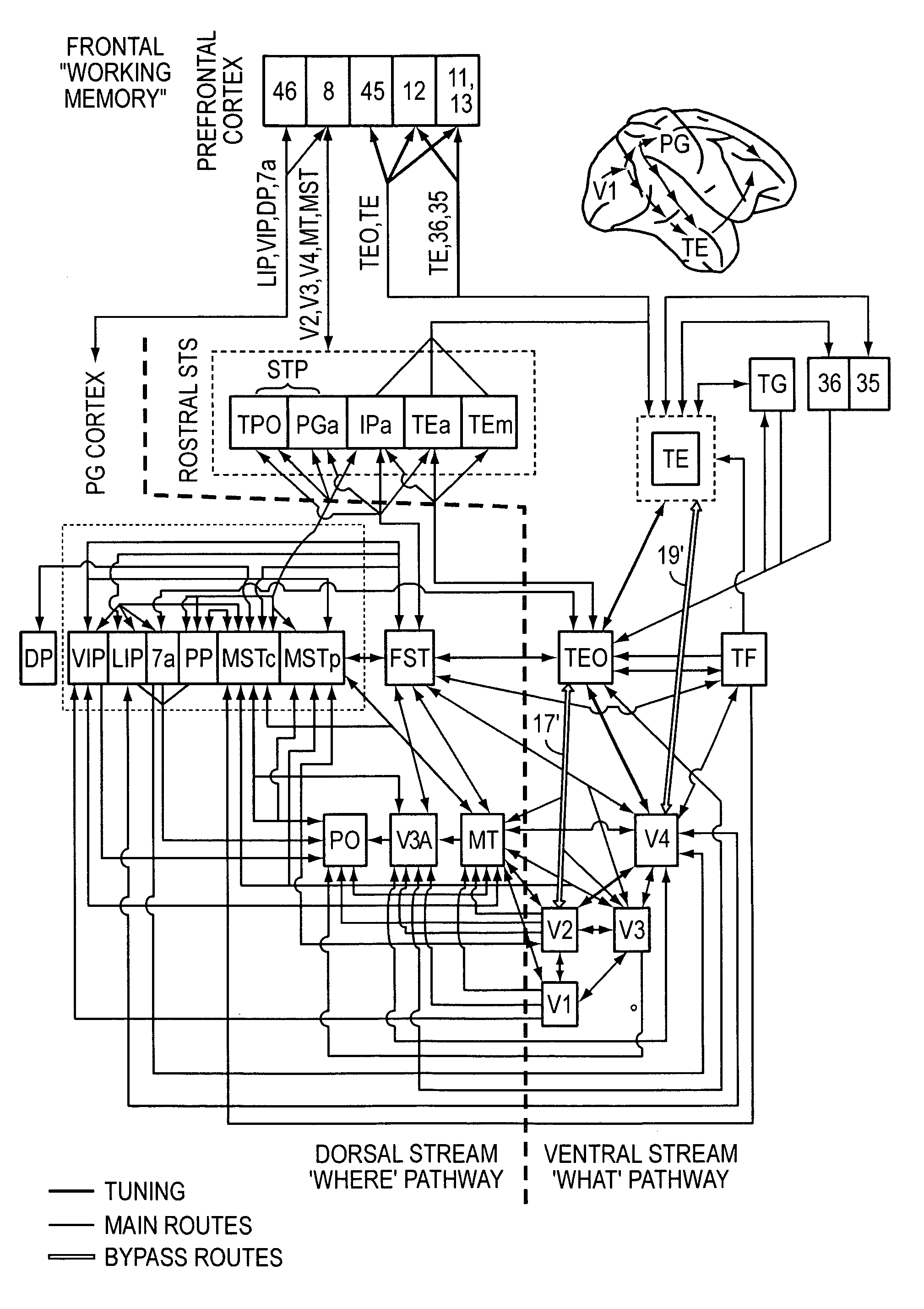
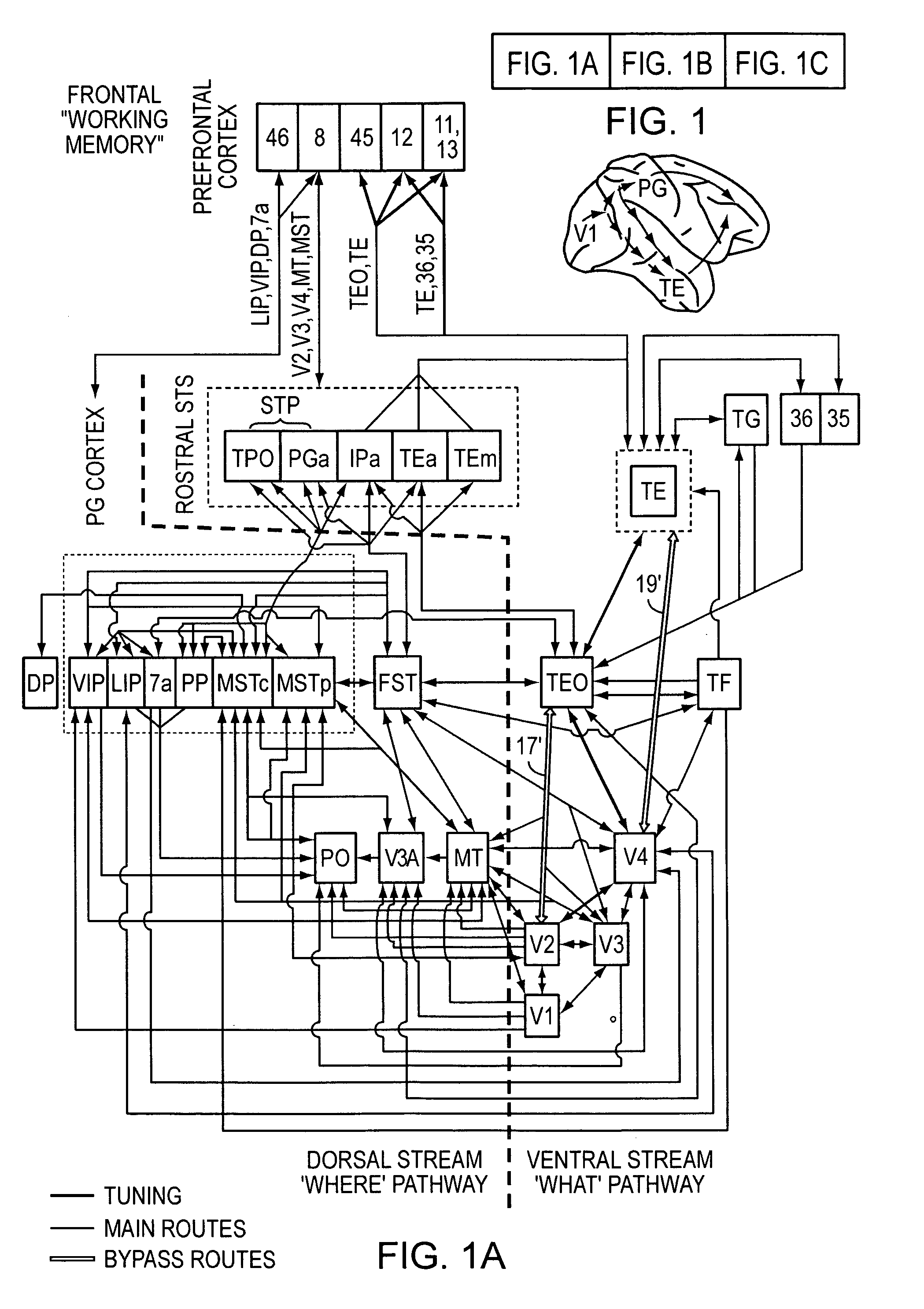
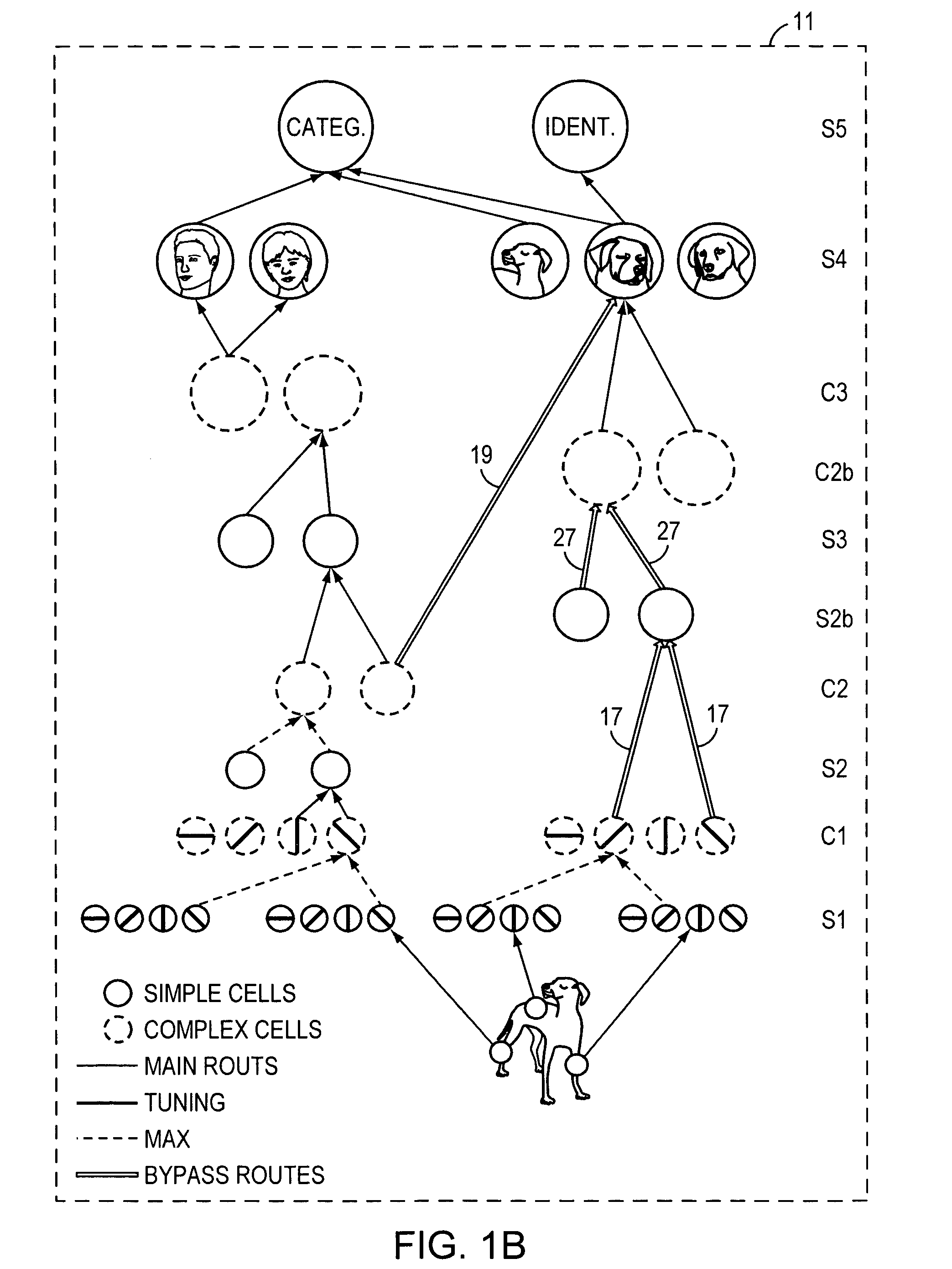
High-performance vision system exploiting key features of visual cortex
InactiveUS20080071710A1Better trade-offLittle inputDigital computer detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionVisual cortexVisual recognition
An artificial visual recognition system and method employ a digital processor and a model executed by the digital processor. The model has a loose hierarchy of layers. Each layer, from a lowest hierarchy level to a top level, provides relatively increasing selectivity and invariance of the input image. The hierarchy allows bypass routes between layers. On output, the model produces feature recognition and classification of an object in the input image. In some embodiments, windowing means provide windows of the input image to the model, and the model responds to shape-based objects in the input image. In another feature, segmenting means segment the input image and enables the model to determine texture-based objects in the input image.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Flexible Circuit Electrode Array
ActiveUS20120192416A1Head electrodesPrinted circuit secondary treatmentElectrical resistance and conductanceRetinal stimulation
Owner:CORTIGENT INC
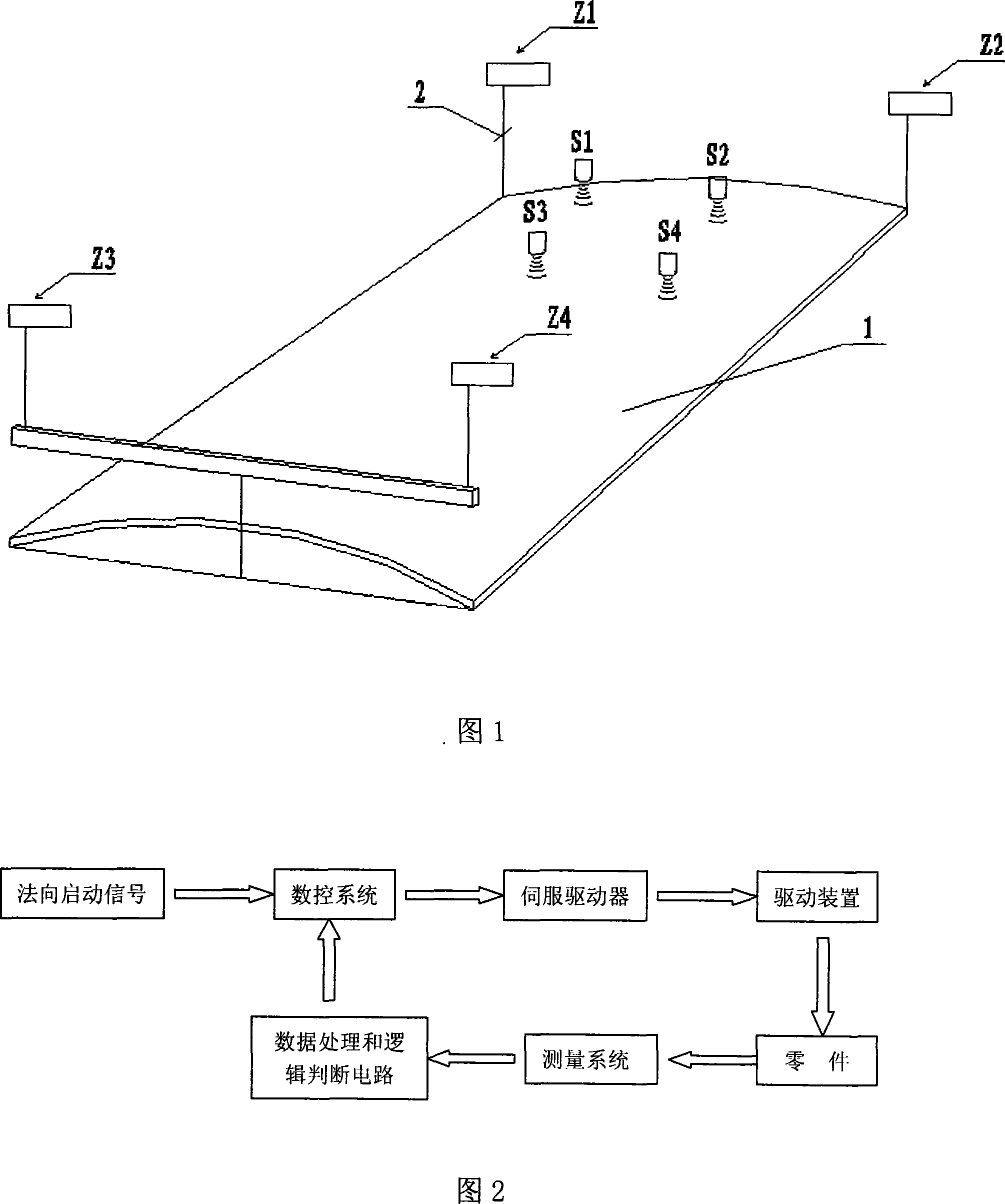
Control method for normally riveted curved member
ActiveCN101109946ALow costImprove efficiencyOther manufacturing equipments/toolsNumerical controlSquare arrayTransducer
The utility model relates to a control mode for the rivet joint quintessence piece with normal direction. A square array is arranged on the same horizontal plane which is situated just above the spare parts. The square array is composed of four measuring transducers which are arranged via the diagonal line center of the automatic riveter axle. Four servo-moving parts hang the spare parts on the three points at both sides hereof via the iron chain, so as to construct a suspended spare parts carriage. Four sensors are respectively used to control the hoisting of four moving parts. According to actual conditions, the data processing software is adopted to ascertain the sensor value at the theoretical position of the normal direction. Also, as per the error, the tolerance zone is worked out to correspond with the observed value of the sensor. The vertical adjustment shall be made for the corresponding points of the spare parts. The riveting signal shall not be sent out until the altitude difference of the four points is limited within the allowable scope. The utility model introduces the three-point suspension spare parts carriage which replaces the normal direction control via the artificial vision, so as to realize the control for the normal direction riveting of the quintessence piece which can not be solved through the four-point side-by-side mounting spare parts. Therefore, the utility model has the advantages of low cost, high efficiency and reliability.
Owner:CHENGDU AIRCRAFT INDUSTRY GROUP
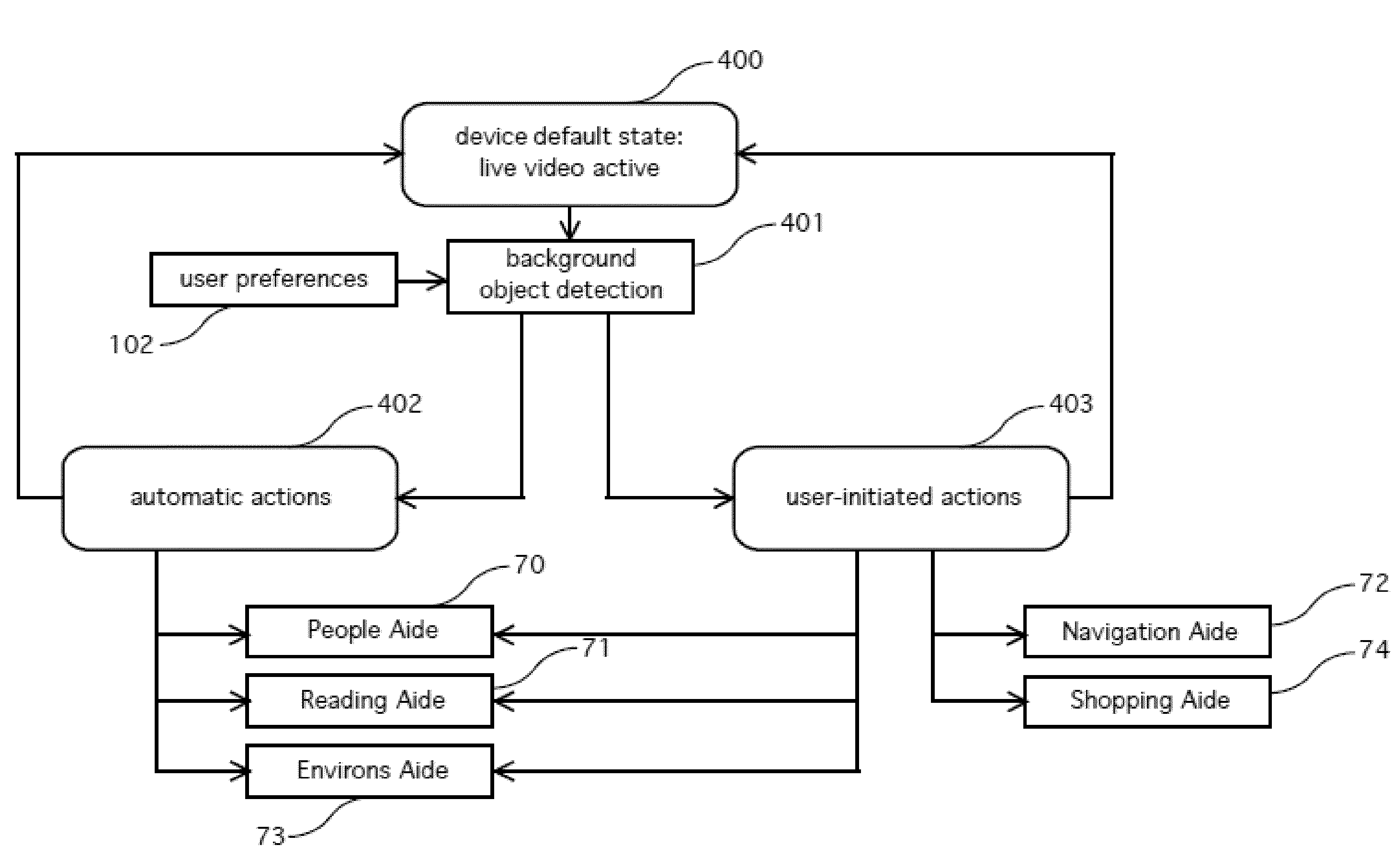
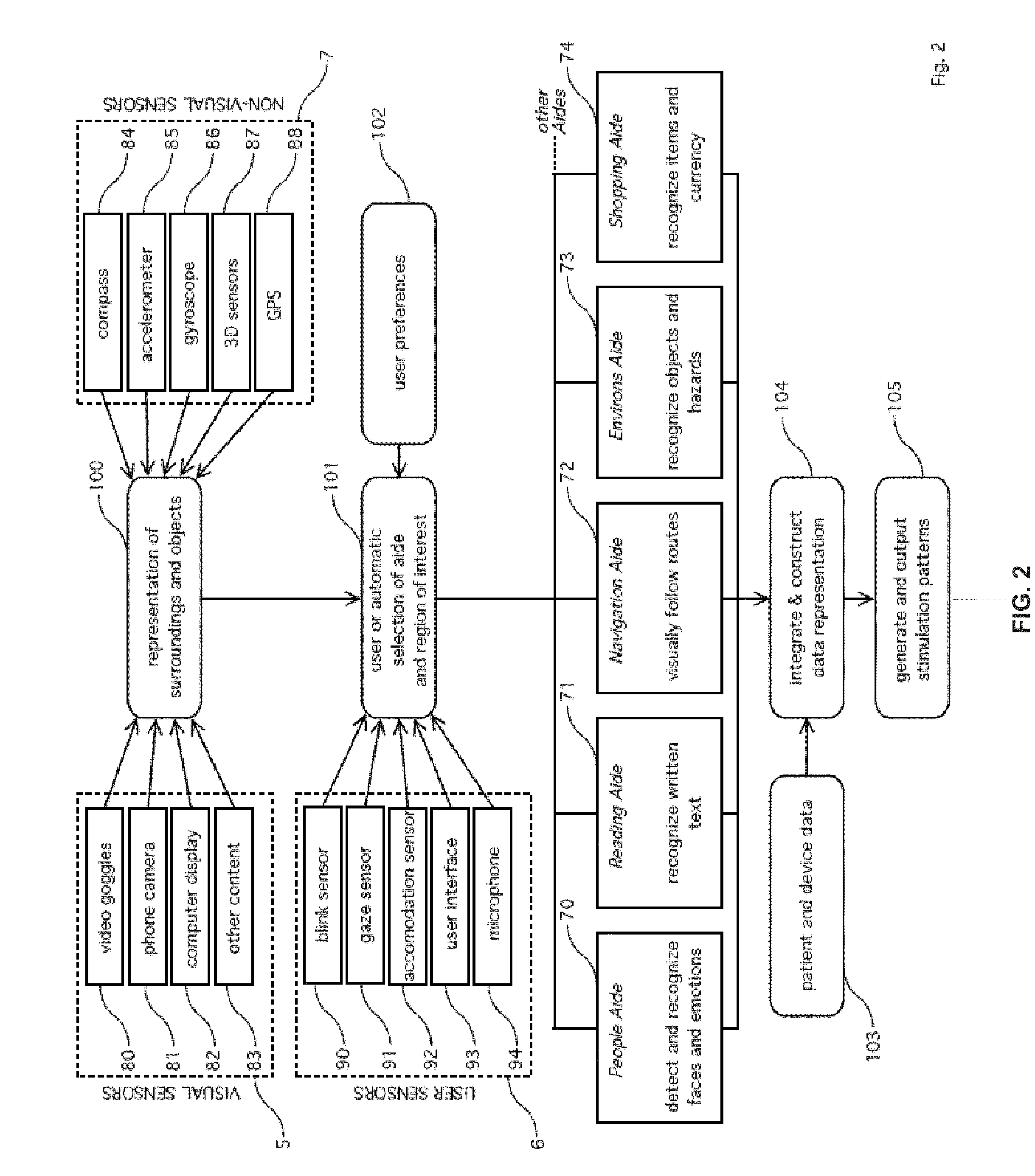
Smart prosthesis for facilitating artificial vision using scene abstraction
A method of providing artificial vision to a visually-impaired user implanted with a visual prosthesis. The method includes configuring, in response to selection information received from the user, a smart prosthesis to perform at least one function of a plurality of functions in order to facilitate performance of a visual task. The method further includes extracting, from an input image signal generated in response to optical input representative of a scene, item information relating to at least one item within the scene relevant to the visual task. The smart prosthesis then generates image data corresponding to an abstract representation of the scene wherein the abstract representation includes a representation of the at least one item. Pixel information based upon the image data is then provided to the visual prosthesis.
Owner:PIXIUM VISION SA
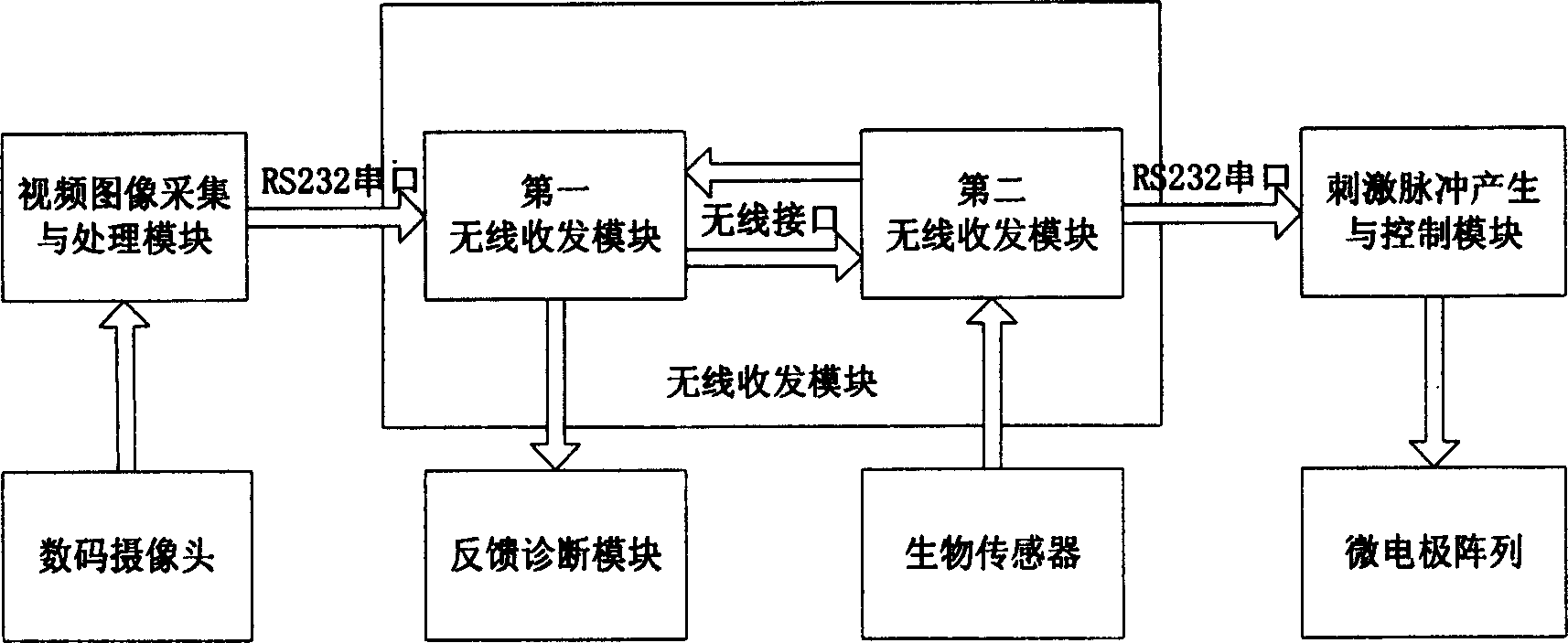
Artificial vision emulation and experiment system
InactiveCN1849993AIncrease data transfer rateHigh channel fault toleranceDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsBiological bodyComputer module
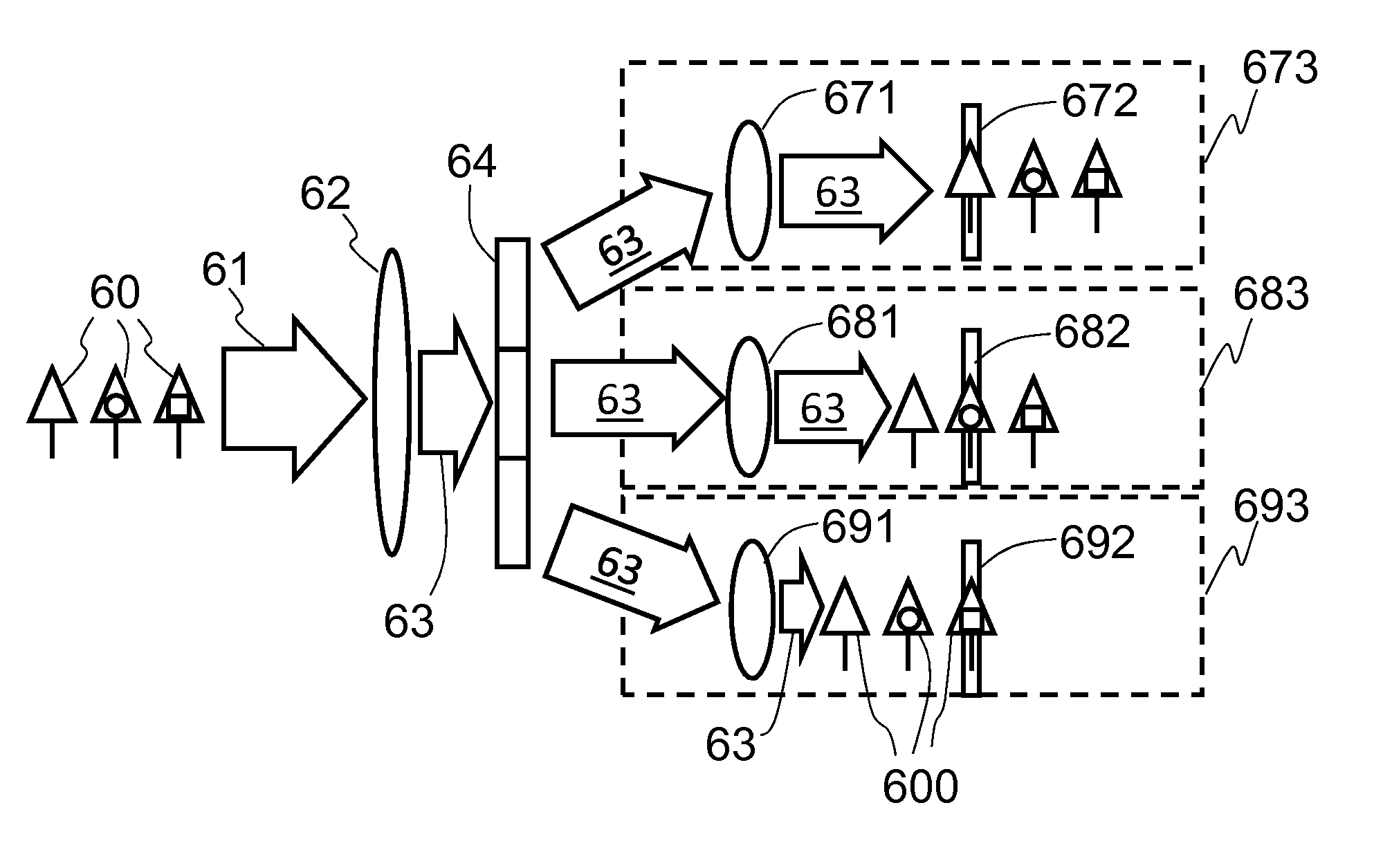
The present invention relates to an artificial vision simulation and experimental system in the field of biomedical engineering technology. Said simulation and experimental system includes the following several modules: video image acquisition and processing module, stimulation pulse generation and control module and feedback diagnosis module. Said invention also provides the concrete action of the above-mentioned every module, and can simulate whole process of artificial vision, and can obtain the key technique and data of artificial vision process.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Method of Manufacturing a Flexible Circuit Electrode Array
ActiveUS20130319972A1Electrical resistance increaseAvoid flowHead electrodesPrinted circuit manufactureRetinal stimulationPolymer science
Polymer materials make useful materials as electrode array bodies for neural stimulation. They are particularly useful for retinal stimulation to create artificial vision. Regardless of which polymer is used, the basic construction method is the same. A layer of polymer is laid down. A layer of metal is applied to the polymer and patterned to create electrodes and leads for those electrodes. A second layer of polymer is applied over the metal layer and patterned to leave openings for the electrodes, or openings are created later by means such as laser ablation. Hence the array and its supply cable are formed of a single body.
Owner:CORTIGENT INC
Field focusing and mapping in an electrode array
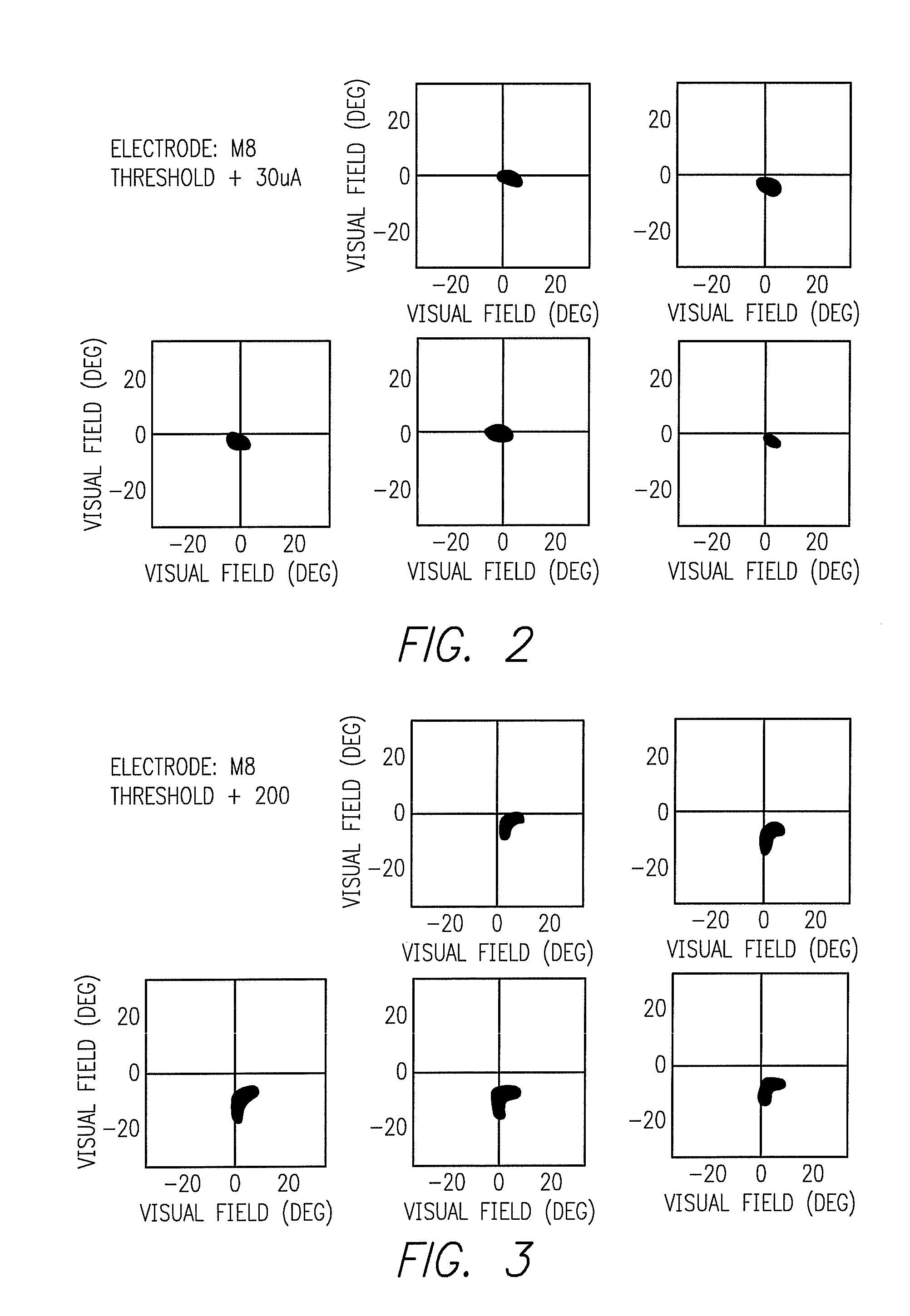
ActiveUS7565202B2High resolutionLower the thresholdHead electrodesHeart defibrillatorsSub thresholdImage resolution
The present invention is a system for mapping a high resolution image to a lower resolution electrode array and, by applying varying stimulus to neighboring electrodes, creating a perceived image greater in resolution than the electrode array. The invention is applicable to a wide range of neural stimulation devices including artificial vision and artificial hearing. By applying a sub-threshold stimulus to two neighboring electrodes where the sum of the stimuli is above the threshold of perception, a perception is created in neural tissue between the two electrodes. By adjusting the stimulus on neighboring electrodes, the location of stimulation can be altered. Further, noise can be applied to the stimulating electrode or its neighboring electrodes to reduce the threshold of stimulation.
Owner:CORTIGENT INC
Colored printed matter defect automatic detection system and detection method based on machine vision
InactiveCN106556611AReduce labor intensityImprove detection accuracyMaterial analysis by optical meansImaging processingMachine vision
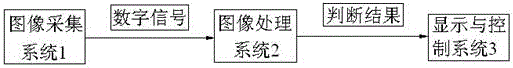
The invention discloses a colored printed matter defect automatic detection system and detection method based on machine vision. The automatic detection system comprises: an image acquisition system, an image processing system connected to the image acquisition system, and a display and control system connected to the image processing system. The image acquisition system converts the acquired printed matter image and color information into digital signals that can be processed by the image processing system, the image processing system computes the digital signals, extracts target characteristics, and then outputs the judgment result according to a preset judge criterion. The display and control system outputs the judgment result of the image processing system. By the way, the system and the method provided by the invention can improve the flexibility and automation degree of production, replace artificial vision, reduce the labor intensity of workers, improve the production efficiency and automation degree, and reduce the defective rate.
Owner:SUZHOU HUACHONG PRECISION MACHINERY
Visual prosthesis for improved circadian rhythms and method of improving the circadian rhythms
ActiveUS20060190058A1Improving circadian rhythmIncrease brightnessHead electrodesNormal circadian rhythmNervous system
Owner:CORTIGENT INC +1
High-performance vision system exploiting key features of visual cortex
InactiveUS7606777B2Better trade-offLittle inputDigital computer detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionVisual cortexVisual recognition
An artificial visual recognition system and method employ a digital processor and a model executed by the digital processor. The model has a loose hierarchy of layers. Each layer, from a lowest hierarchy level to a top level, provides relatively increasing selectivity and invariance of the input image. The hierarchy allows bypass routes between layers. On output, the model produces feature recognition and classification of an object in the input image. In some embodiments, windowing means provide windows of the input image to the model, and the model responds to shape-based objects in the input image. In another feature, segmenting means segment the input image and enables the model to determine texture-based objects in the input image.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Method and apparatus to produce re-focusable vision by direct retinal projection with mirror array
The current invention relates to the method to achieve artificial vision with using MEMS based mirror array to directly project image upon the retina of a human eye. Further, it relates to the method to detect the real-time focal length change of the eye lens and modify the MEMS based mirror array angular position configurations to change image projected upon the retina to achieve re-focusable artificial vision.
Owner:ZHOU YUCHEN
Intelligent safety door and control method thereof
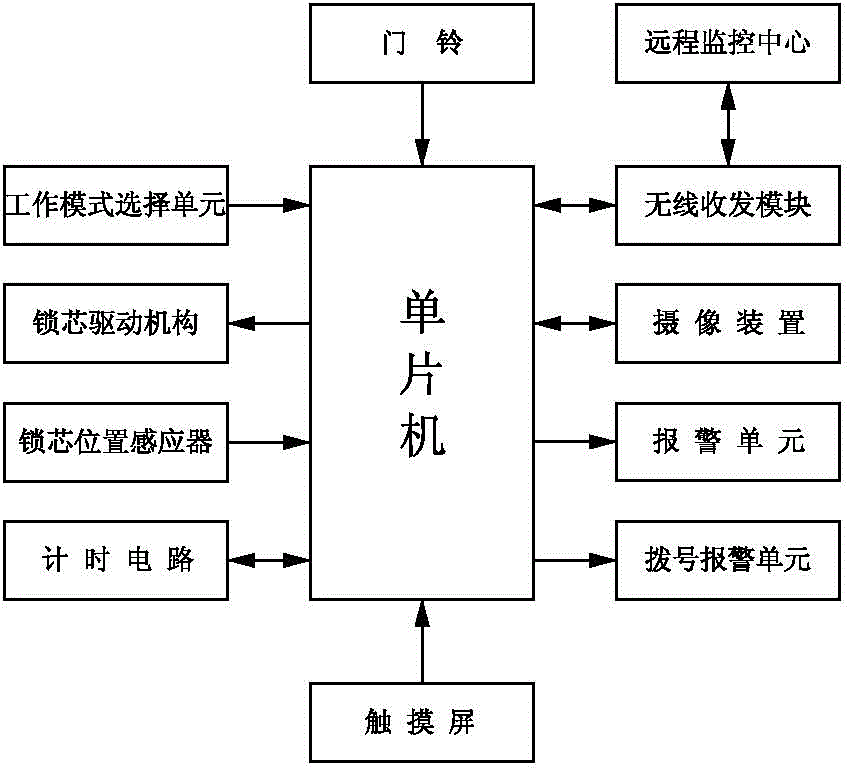
ActiveCN104929498ARealize automatic controlImprove securityBurglary protectionIndividual entry/exit registersComputer hardwareSingle chip
The invention discloses an intelligent safety door. The intelligent safety door comprises a single chip computer, a remote monitoring center, a photographic device used for collecting outdoor images, a lock cylinder driving mechanism used for driving a lock cylinder to unlock and lock, an alarm unit used for outputting an alarm on site and a working mode selecting unit used for selecting normal mode / monitoring mode, and the remote monitoring center is in wireless communication connection with the single chip computer through a wireless receiving and transmitting module; the invention further discloses a control method of the intelligent safety door, the control method comprises the steps that under the monitoring mode, if a door bell is rung, the single chip computer controls the photographic device to collect the outdoor images, the outdoor images are transmitted to the remote monitoring center through the wireless receiving and transmitting module, and the remote monitoring center transmits an alarm signal or an unlocking signal through artificial vision judgment; when the single chip computer receives the alarm signal, the alarm unit outputs the alarm; when the unlock signal is received, the single chip computer controls the lock cylinder driving mechanism to unlock electrically; under the normal mode, the single chip computer is kept to be in a powered off state, and the safety door is unlocked manually or locked.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF INDAL TECH
Micro-electrode array chip before retina in field of artificial vision
The invention discloses a micro-electrode array chip before retina in the field of artificial vision. The micro-electrode array chip comprises a chip substrate, a lead buried in the chip substrate and micro-electrodes protruding the surface of the substrate and forming an array. The edge of the lower end of the chip substrate is provided with at least two lower suture line preformed holes; a micro-electrode arrangement lower area, a micro-electrode arrangement middle area, a micro-electrode arrangement upper area, a substrate reduction area and a substrate expansion area are sequentially arranged on the chip substrate from bottom to top; the substrate expansion area contains contacts corresponding to the electrode arrangement areas, and are connected with the micro-electrodes through the lead buried in the chip substrate; the chip substrate close to the lower end of the substrate reduction area is provided with at least three groups of two sclera cut suture line preformed holes, and two edges are respectively provided with at least two upper suture line preformed holes; and two sides of the substrate expansion area are provided with eye external suture line preformed holes. The micro-electrode array chip can stimulate retinal ganlion cells of the blind to recover partial vision of the blind, and avoids rhegmatogenous retinal detachment, choroidal hemorrhage and sympathetic ophthalmia caused by iatrogenic retinal breaks.
Owner:PEOPLES HOSPITAL PEKING UNIV
Adaptive artificial vision method and system
InactiveUS7477759B2Efficient bootstrappingImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionStatic modeSelf adaptive
The adaptive artificial vision method comprises the following steps: (a) defining successive couples of timesteps (t−1, t; t, t+1; . . . ) synchronized by a clock (101), (b) comparing two successive images (It−, It; It, It+1, . . . ) from an input device (102, 103) at each couple of synchronized timesteps (t−1, t; t, t+1; . . . ) spaced by a predetermined time delay τ0 for obtaining a delta image Δt which is the result of the computation of the distance between each pixel of the two successive images (It−1, It; It, It+1, . . . ) in view of characterizing movements of objects, (c) extracting features from the delta image Δt for obtaining a potential dynamic patch Pt which is compared with dynamic patches previously recorded in a repertory which is progressively constructed in real time from an initial void repertory, (d) selecting the closest dynamic patch Di in the repertory or if no sufficiently close dynamic patch still exists, adding the potential dynamic patch Pt to the repertory and therefore obtaining and storing a dynamic patch Di from the comparison of two successive images (It−1, It; It, It+1, . . . ) at each couple of synchronized timesteps (t−1, t; t, t+1; . . . ), and (e) temporally integrating stored dynamic patches Di of the repertory in order to detect and store stable sets of active dynamic patches representing a characterization of a reoccuring movement or event which is observed. A process of static pattern recognition may then be efficiently used.
Owner:SONY FRANCE
Object tracking for artificial vision
Owner:NAT ICT AUSTRALIA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com