Patents
Literature
127results about How to "Better trade-off" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
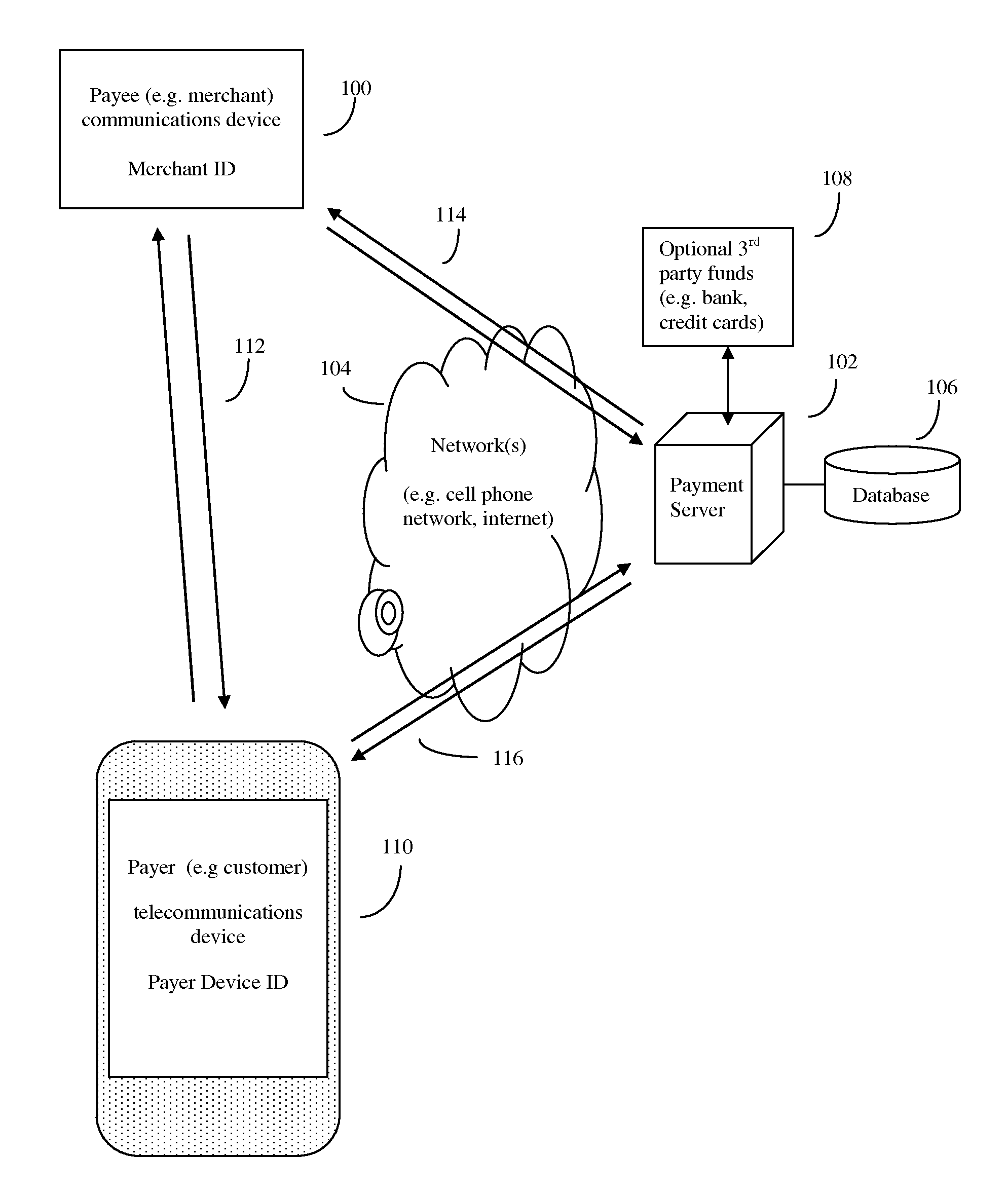
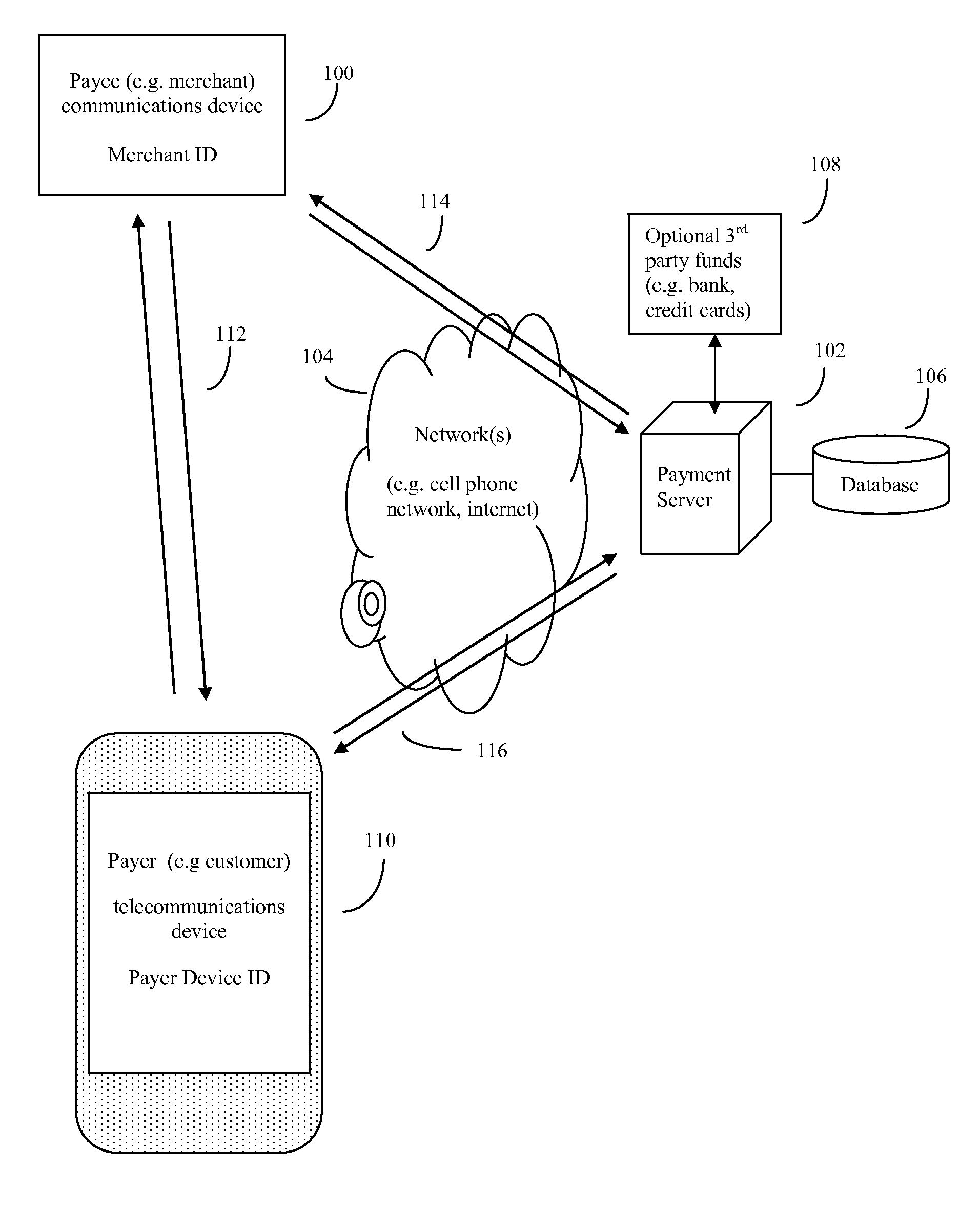
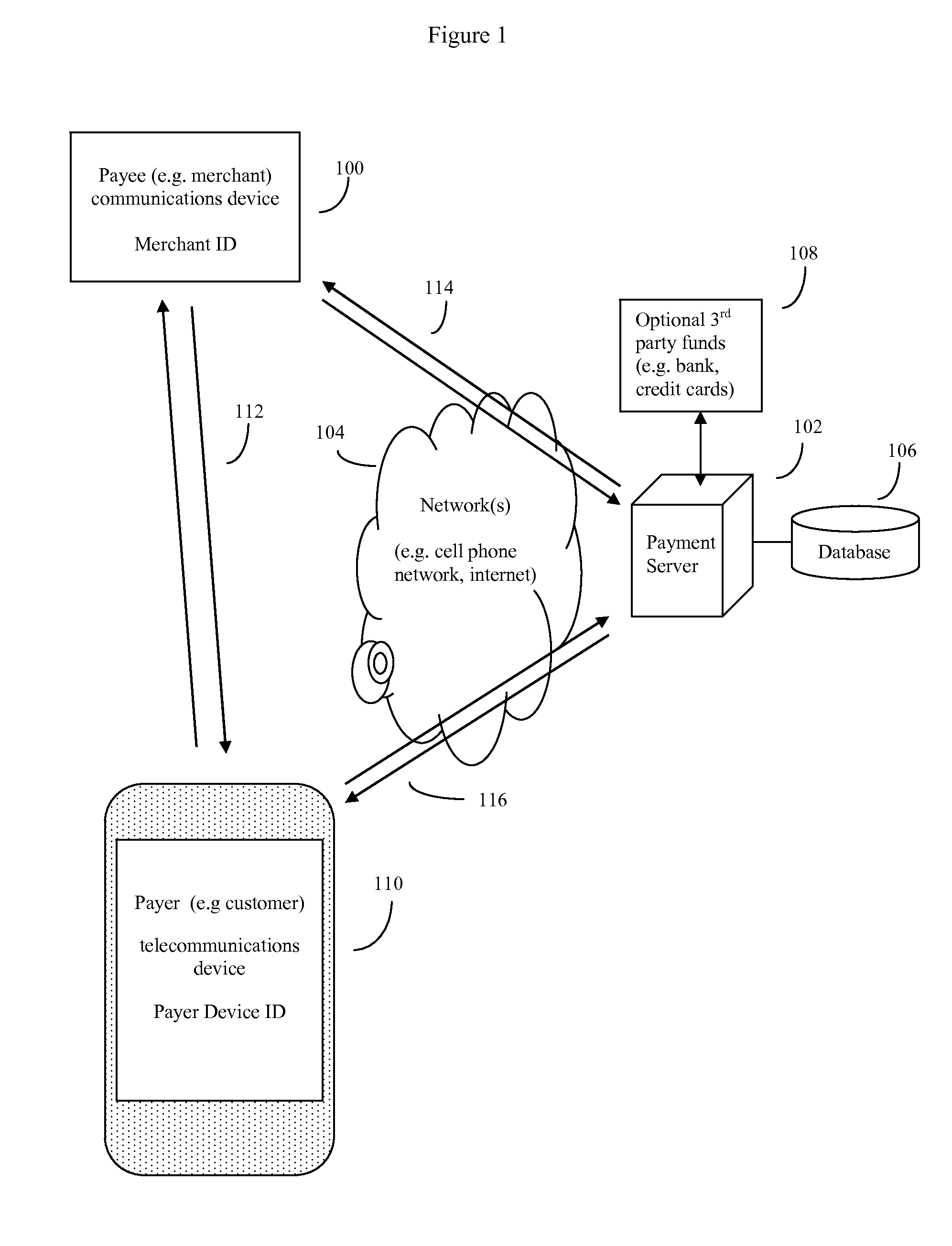
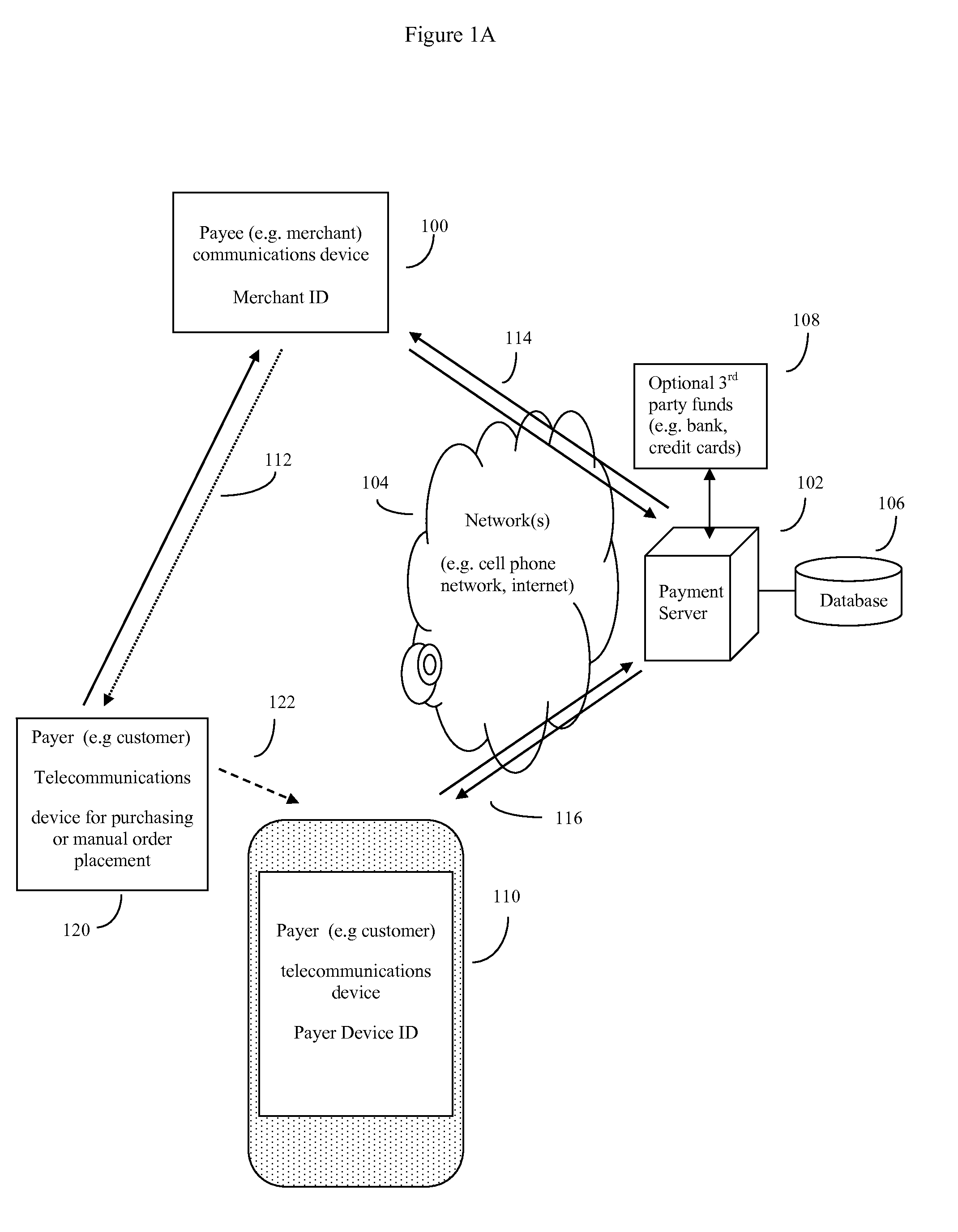
System and method of electronic payment using payee provided transaction identification codes
InactiveUS20130124364A1High degreeImprove conveniencePayment architectureBuying/selling/leasing transactionsPaymentFinancial transaction
A computerized method of payment based on short, temporary, transaction ID numbers which protect the security of the payer's (customer's) financial accounts. The payee will first register a source of funds and a payer device with a unique ID (such as a mobile phone and phone number) with the invention's payment server. Then once a payee (merchant) and the payer have agreed on a financial transaction amount, the payee requests a transaction ID from the payment server for that amount. The payment server sends the payee a transaction ID, which the payee then communicates to the payer. The payer in turn relays this transaction ID to the server, which validates the transaction using the payer device. The server then releases funds to the payee. The server can preserve all records for auditing purposes, but security is enhanced because the merchant never gets direct access to the customer's financial account information.
Owner:MITTAL MILLIND
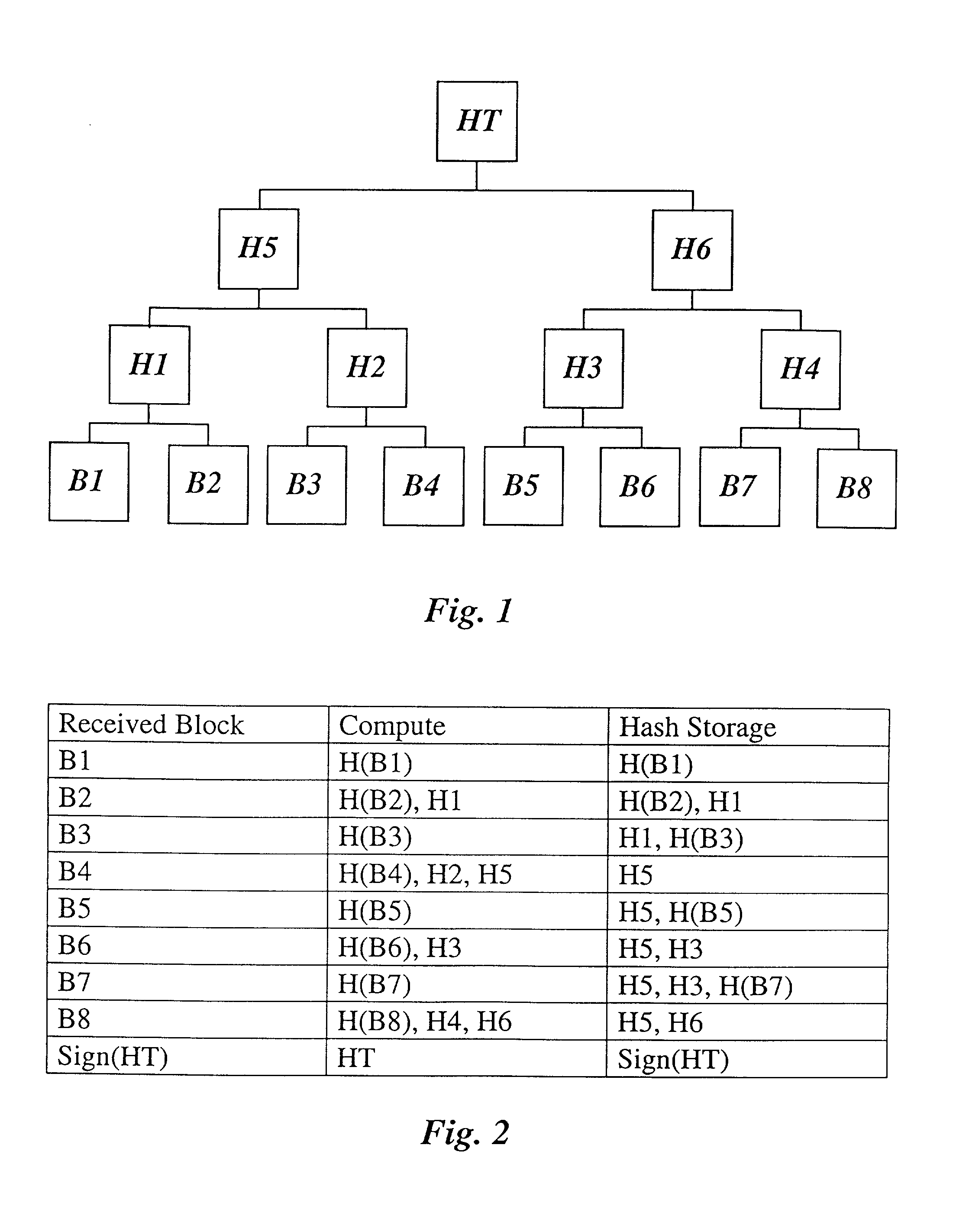
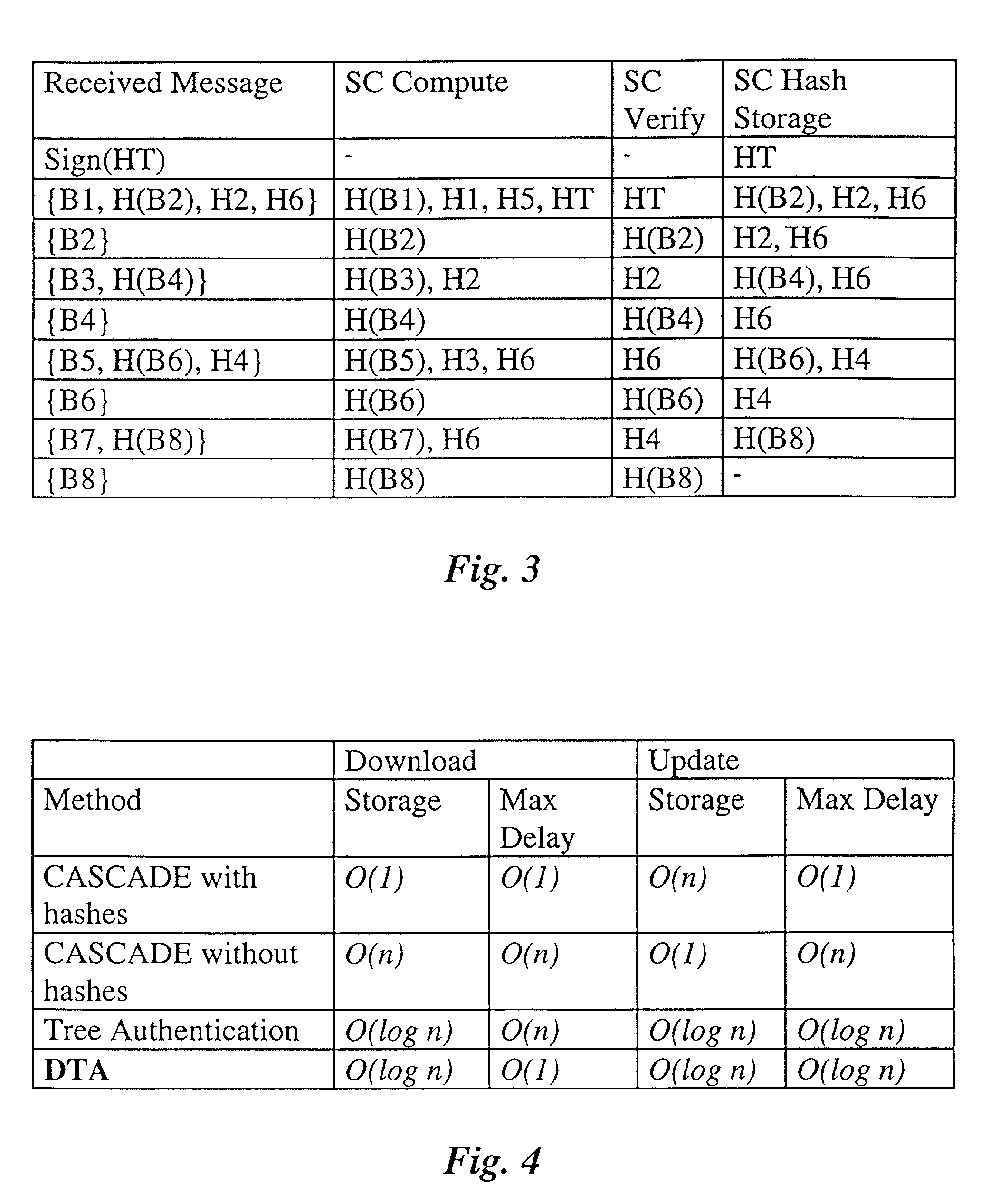
Method and apparatus for secure transmission of data and applications
InactiveUS20010034839A1Reduce delaysEfficient formationUser identity/authority verificationUnauthorized memory use protectionComputer basedCommunication bandwidth
Authenticated transmissions are usually time-consuming and often provide delayed error recognition and correction. This is a problem particularly with hand-held computing devices like personal digital assistants (PDAs), smart phones or smartcards, since these usually possess limited memory, processing power and communications bandwidth. Because of these limitations and generally low transfer rates between the device and a provider or central computer base, such transmissions are time-consuming and delay applications. The late detection of unavoidable transmission errors is especially cumbersome. By applying an optimally taylored authentication scheme to a block-wise transmission and in particular by applying a tree structure for the authentication process during such transfers, the present invention minimes the unavoidable delays and thus provides a solution for these problems.
Owner:IBM CORP
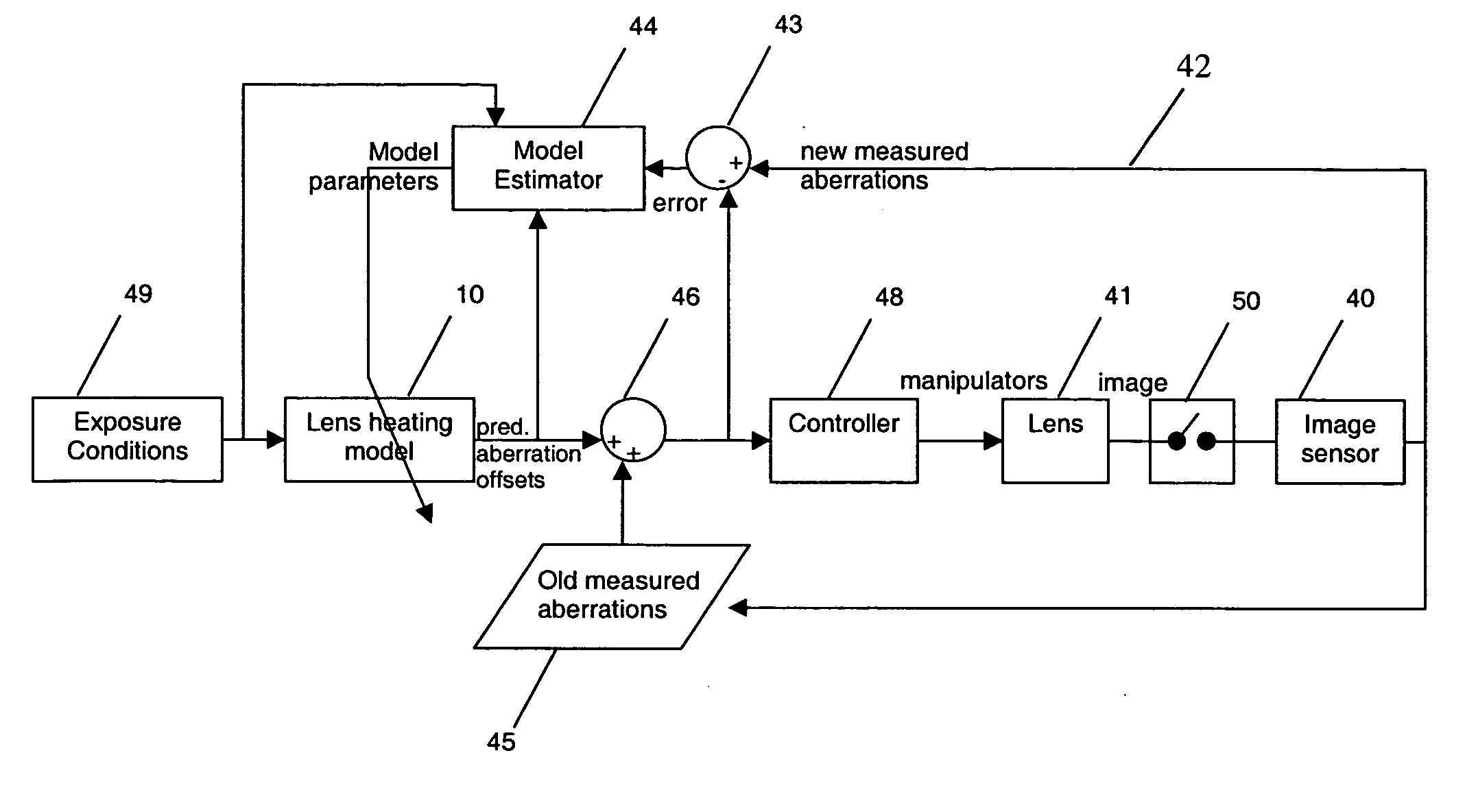
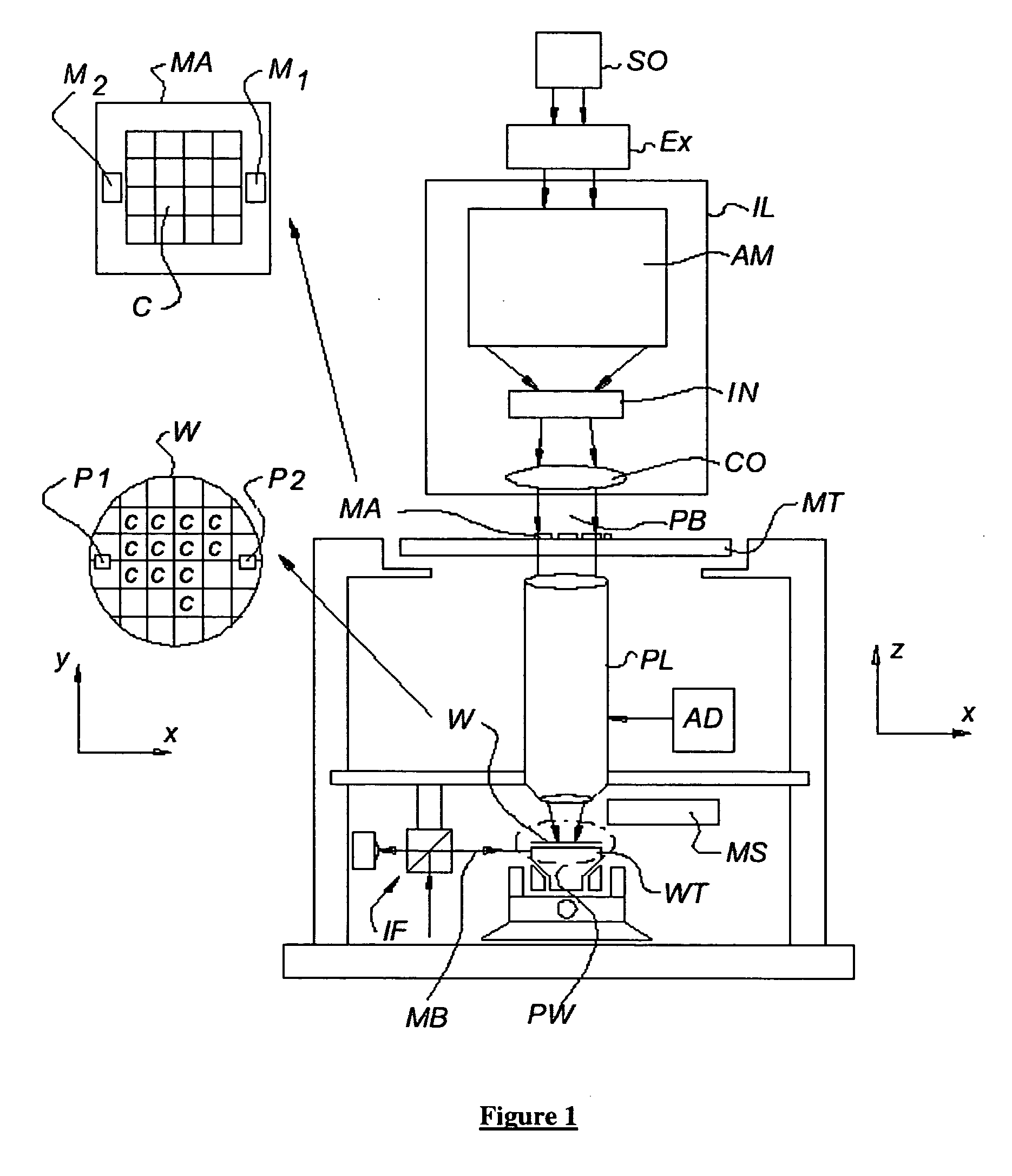
Lithographic projection apparatus and device manufacturing method using such lithographic projection apparatus
ActiveUS20060114437A1Reduce throughputAvailability is not compromisedPhotomechanical apparatusPhotographic printingControl systemControl signal
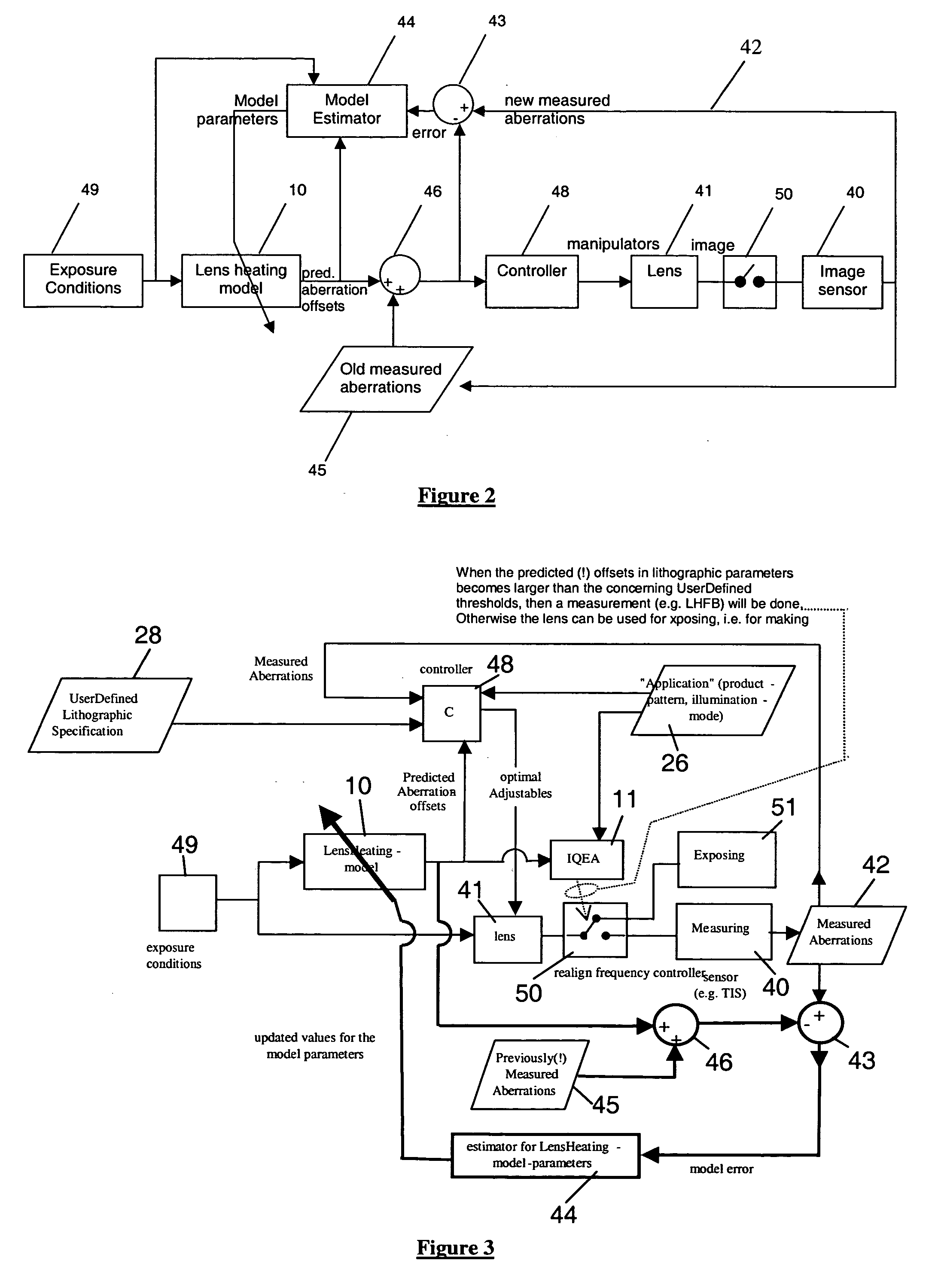
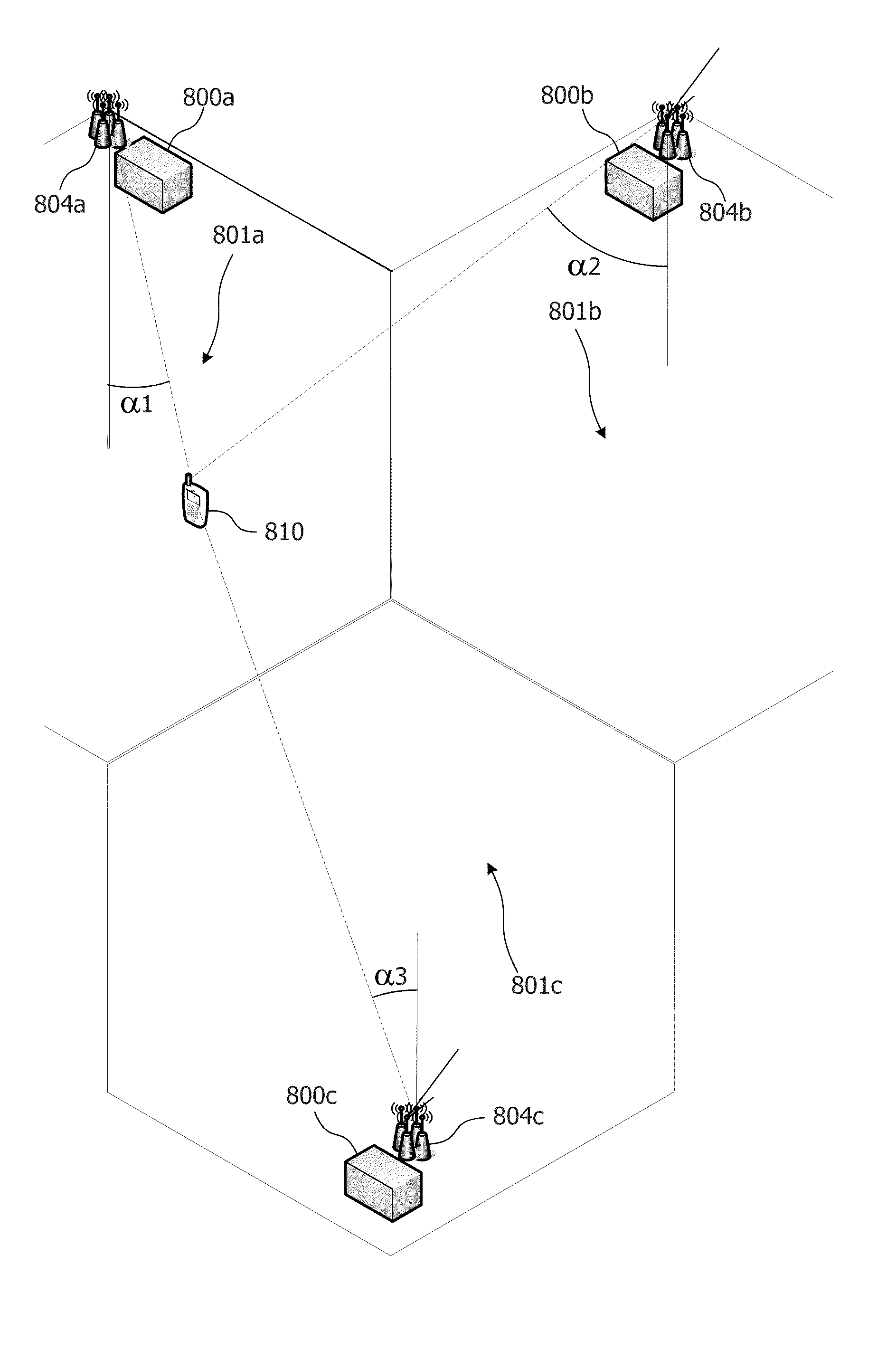
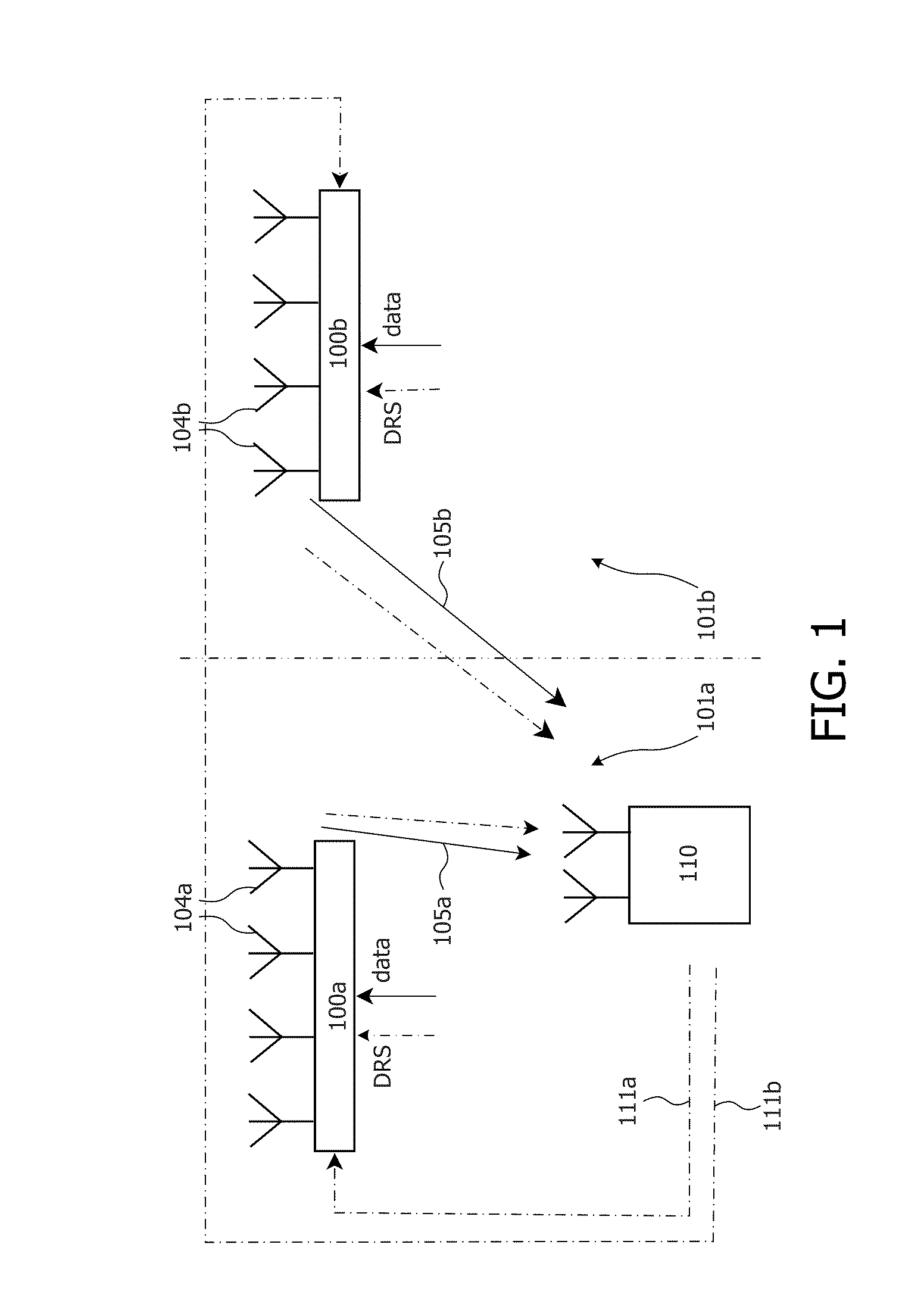
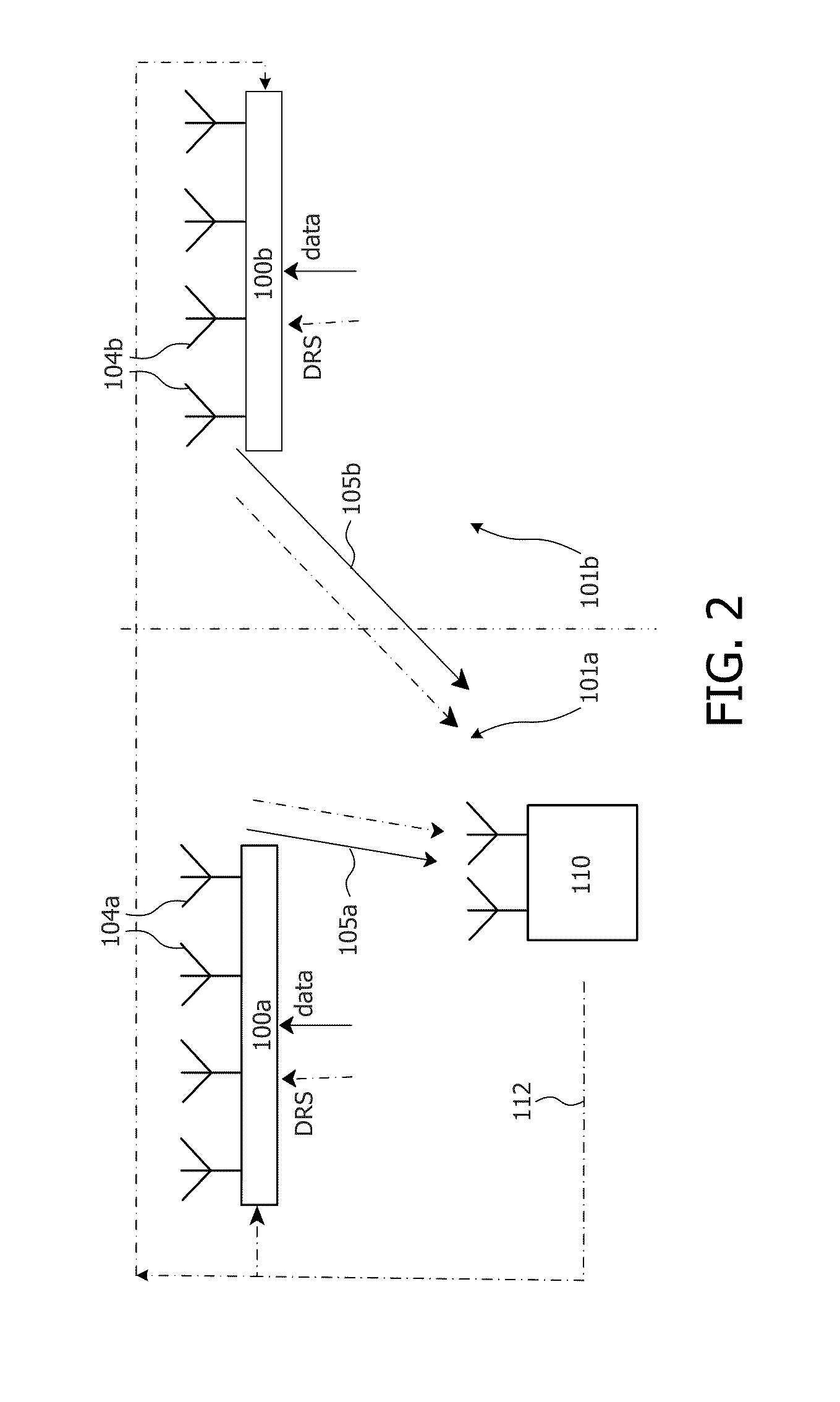
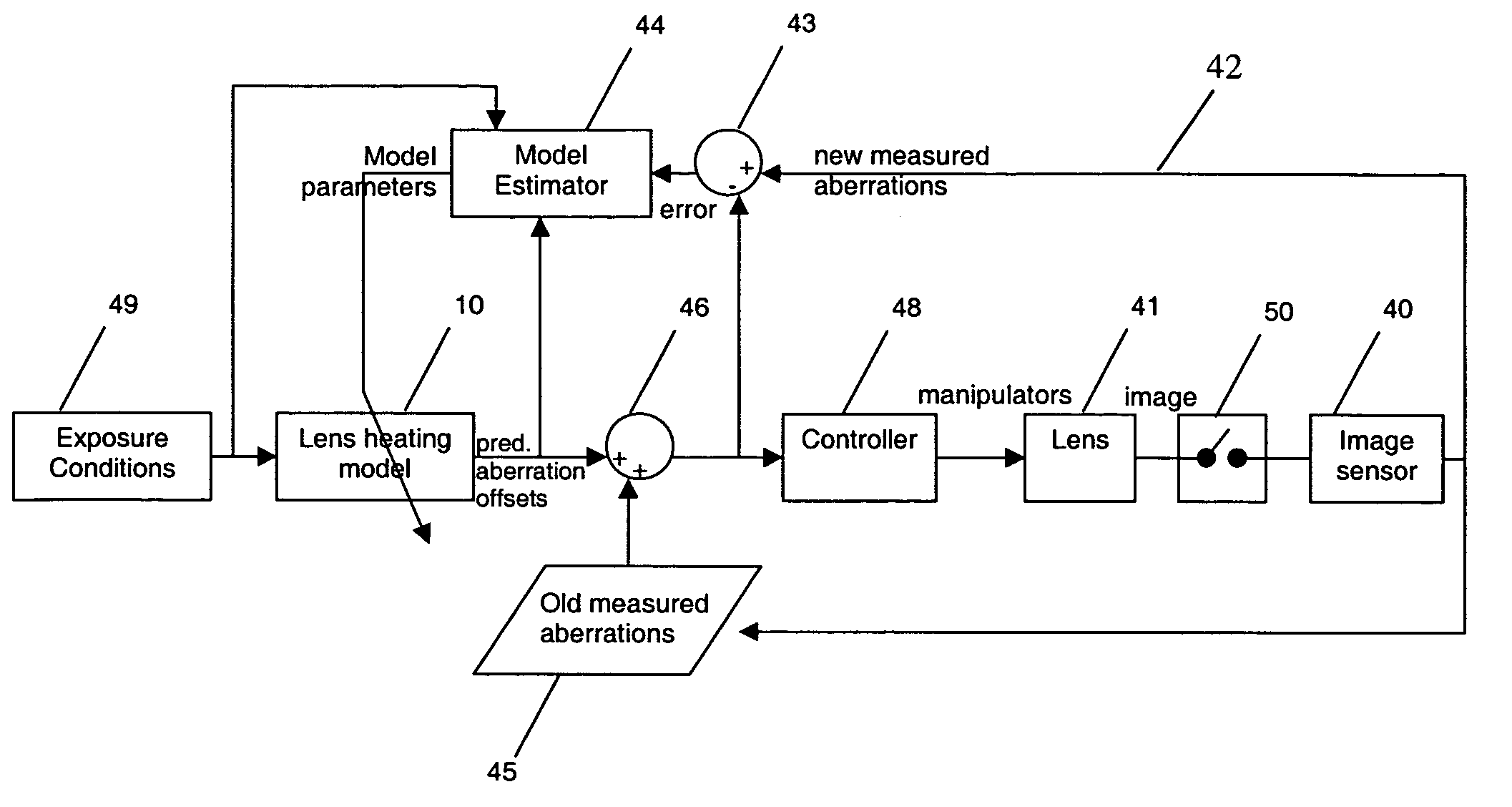
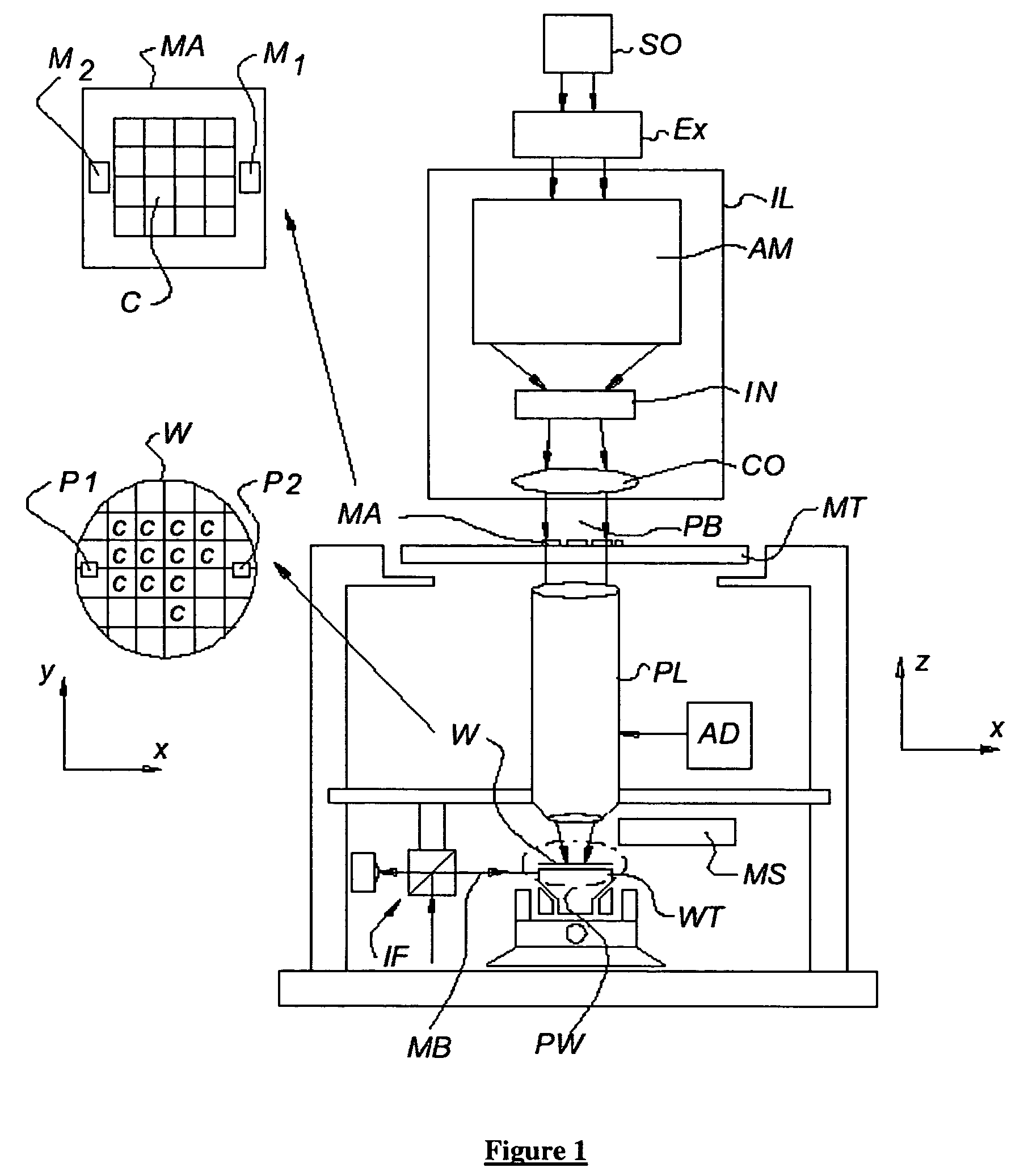
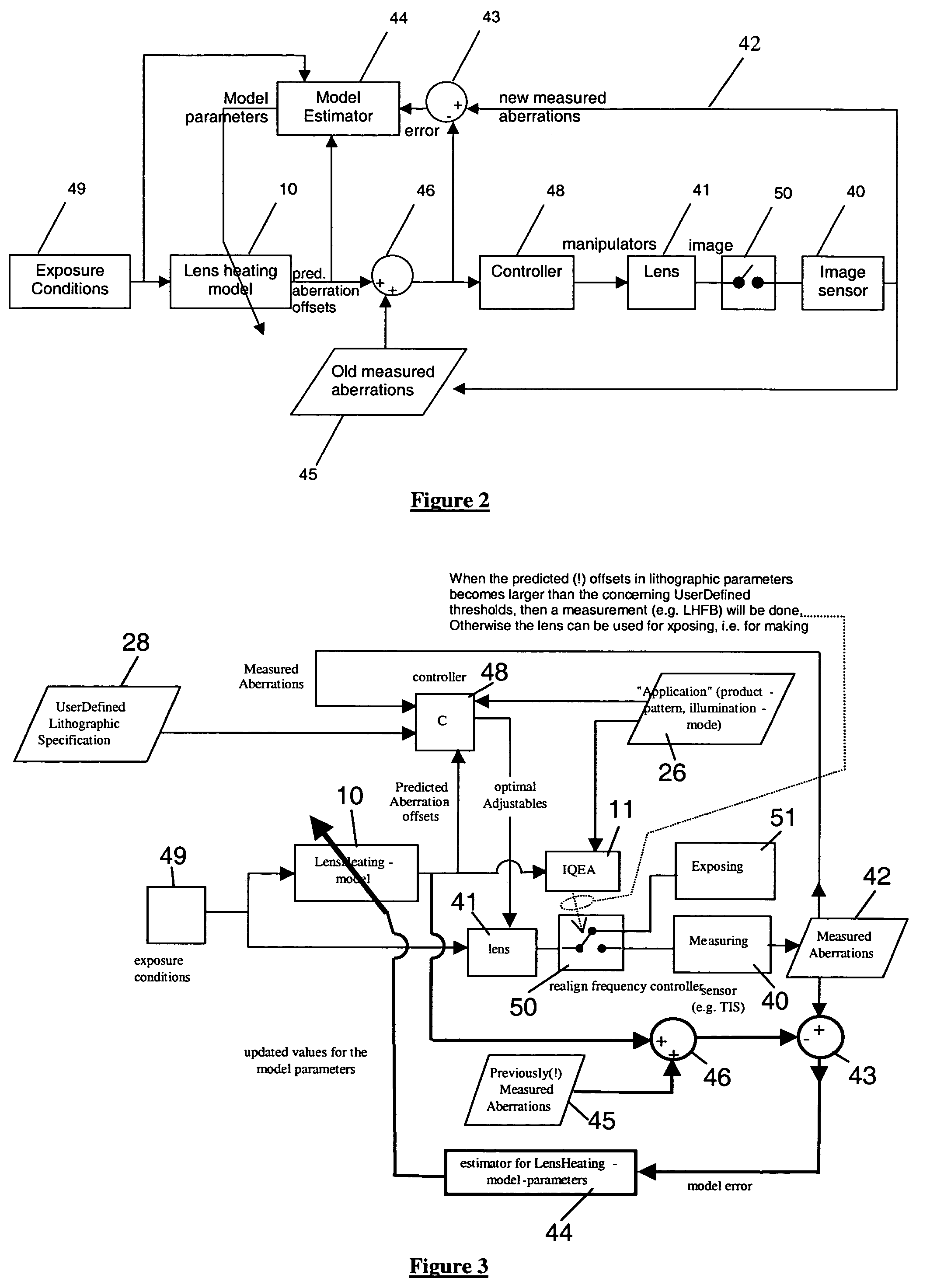
A lithographic projection apparatus includes a measurement system for measuring changes in projection system aberrations with time, and a predictive control system for predicting variation of projection system aberrations with time on the basis of model parameters and for generating a control signal for compensating a time-varying property of the apparatus, such as the OVL values (X-Y adjustment) and the FOC values (Z adjustment) of a lens of the projection system for example. An inline model identification system is provided for estimating model parameter errors on the basis of projection system aberration values provided by the predictive control system and measured projection system aberration values provided by the measurement system, and an updating system utilizes the model parameter errors for updating the model parameters of the predictive control system in order to maintain the time-varying property within acceptable performance criteria.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Privacy Preserving Statistical Analysis on Distributed Databases
ActiveUS20140281572A1Maintain privacyEnhance privacyUnauthorized memory use protectionHardware monitoringThird partyPrivacy preserving
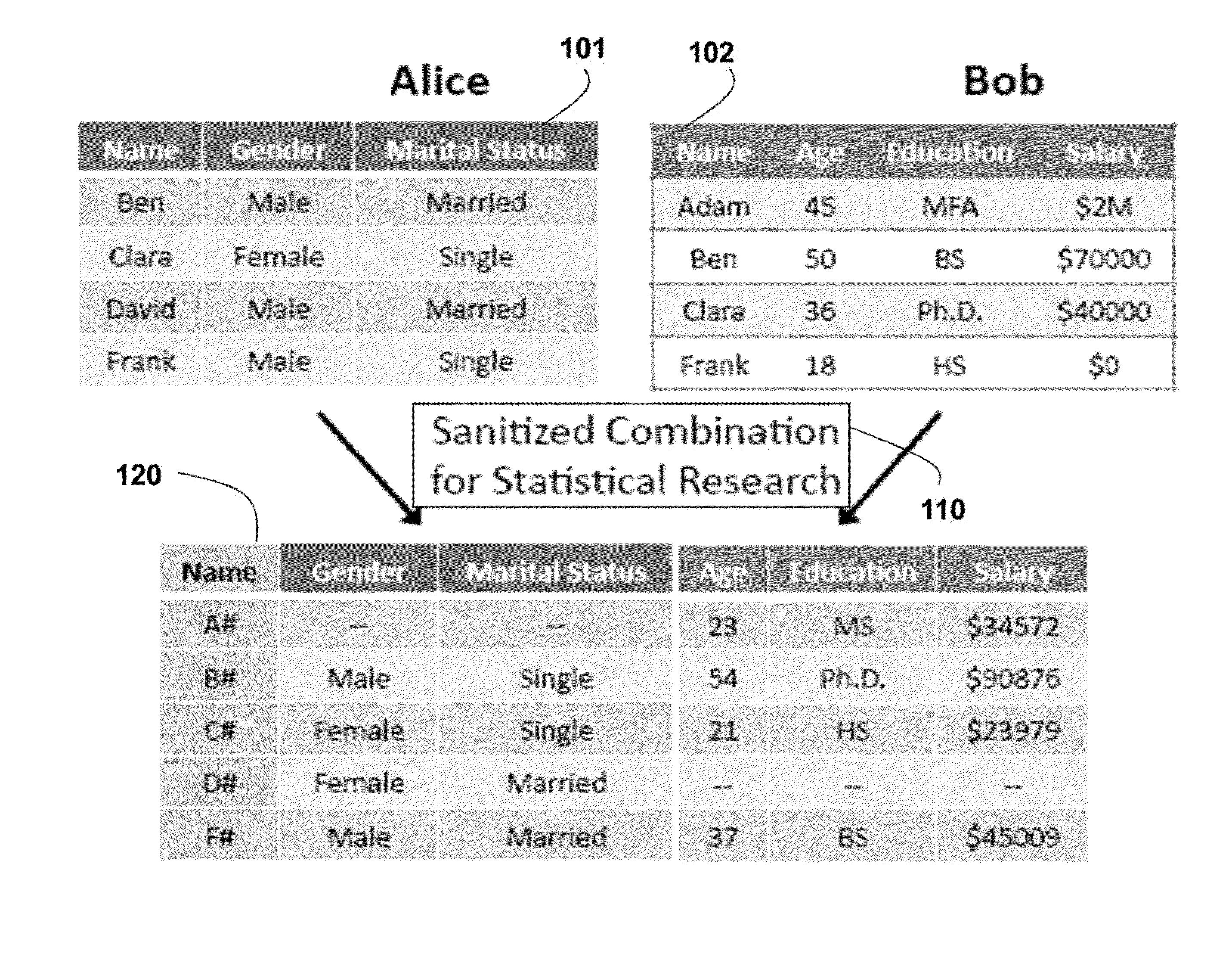
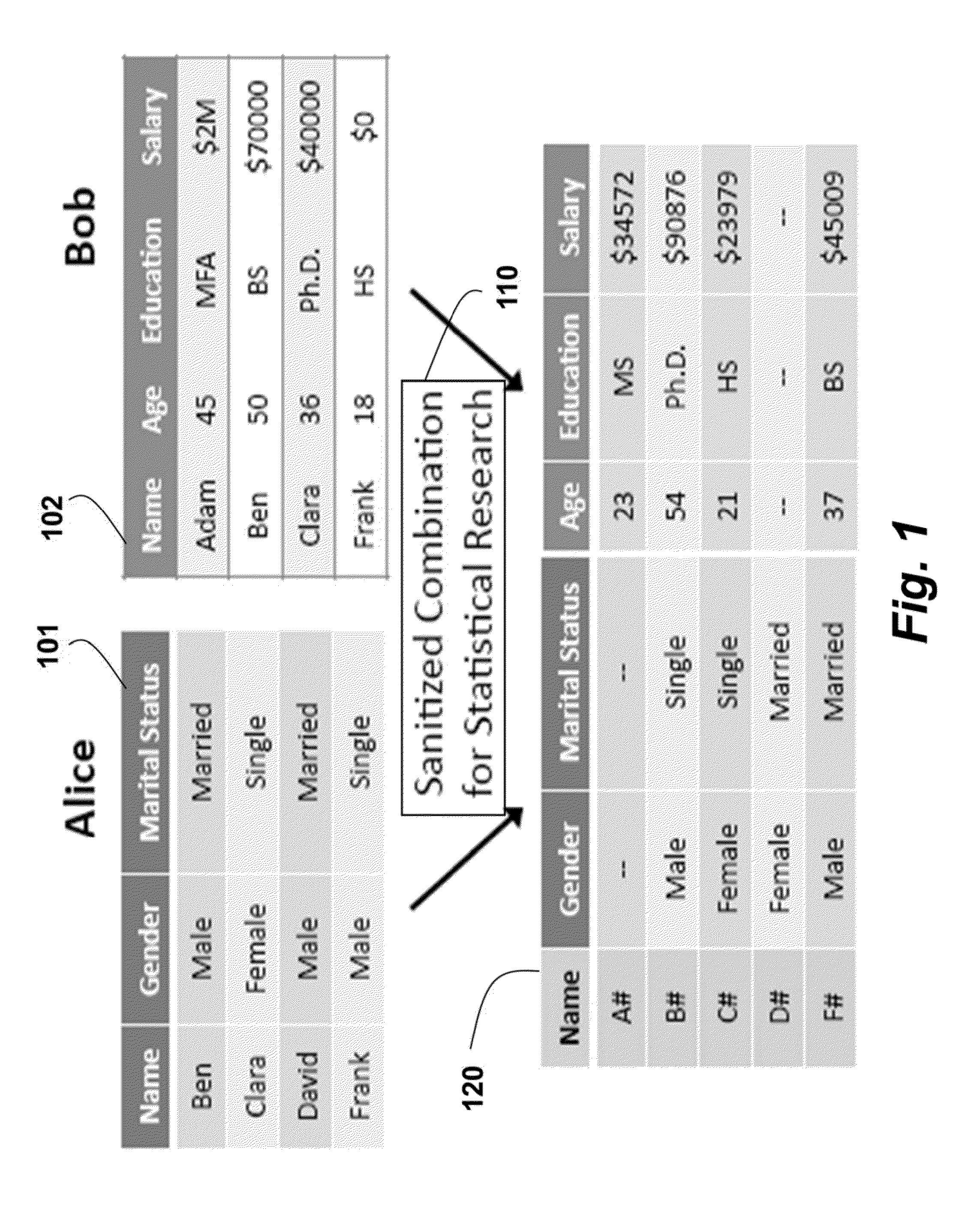
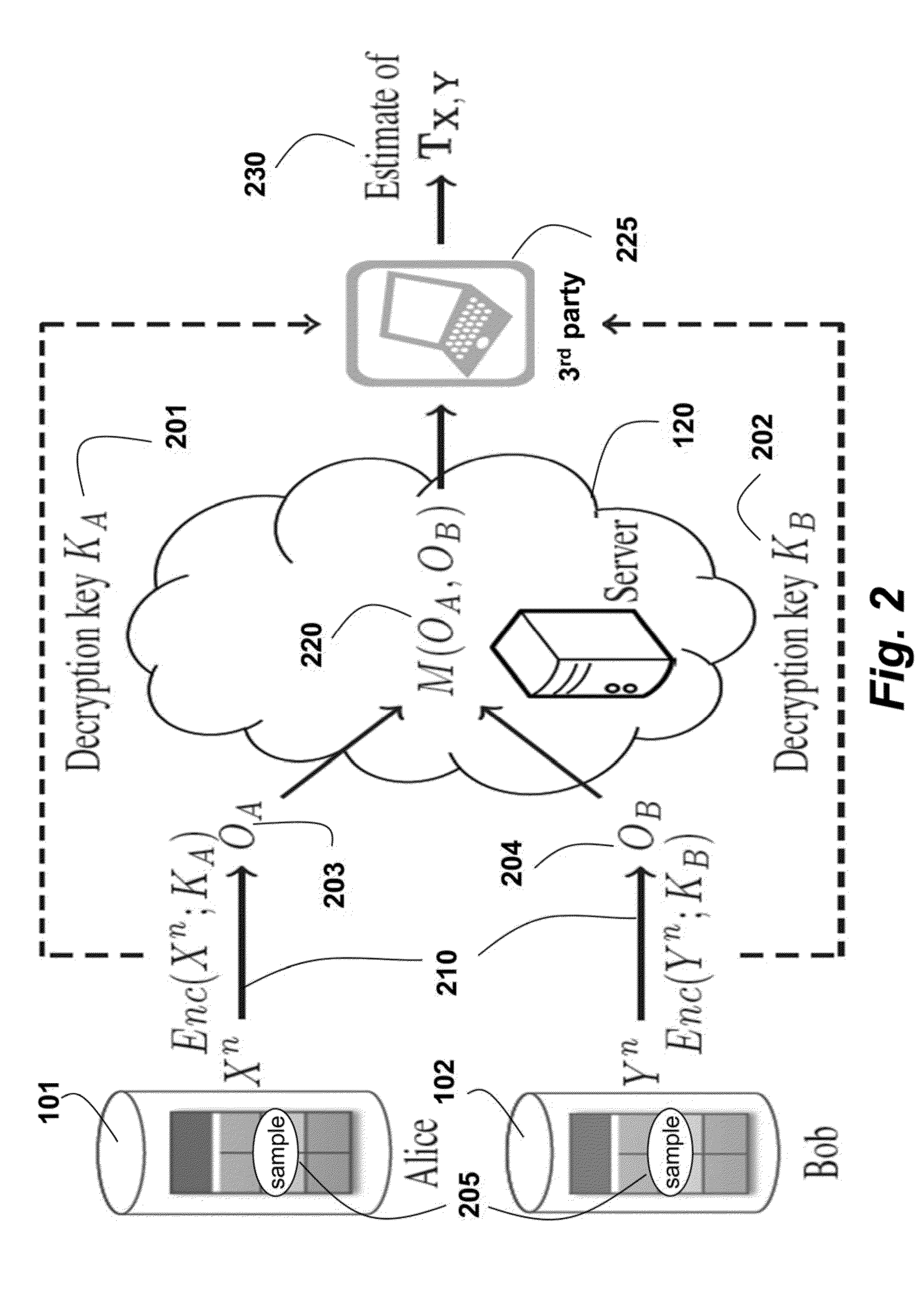
Aggregate statistics are securely determined on private data by first sampling independent first and second data at one or more clients to obtain sampled data, wherein a sampling parameter substantially smaller than a length of the data. The sampled data are encrypted to obtain encrypted data, which are then combined. The combined encrypted data are randomized to obtain randomized data. At an authorized third-party processor, a joint distribution of the first and second data is estimated from the randomized encrypted data, such that a differential privacy requirement of the first and second is satisfied.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
System-level power estimation using heteregeneous power models
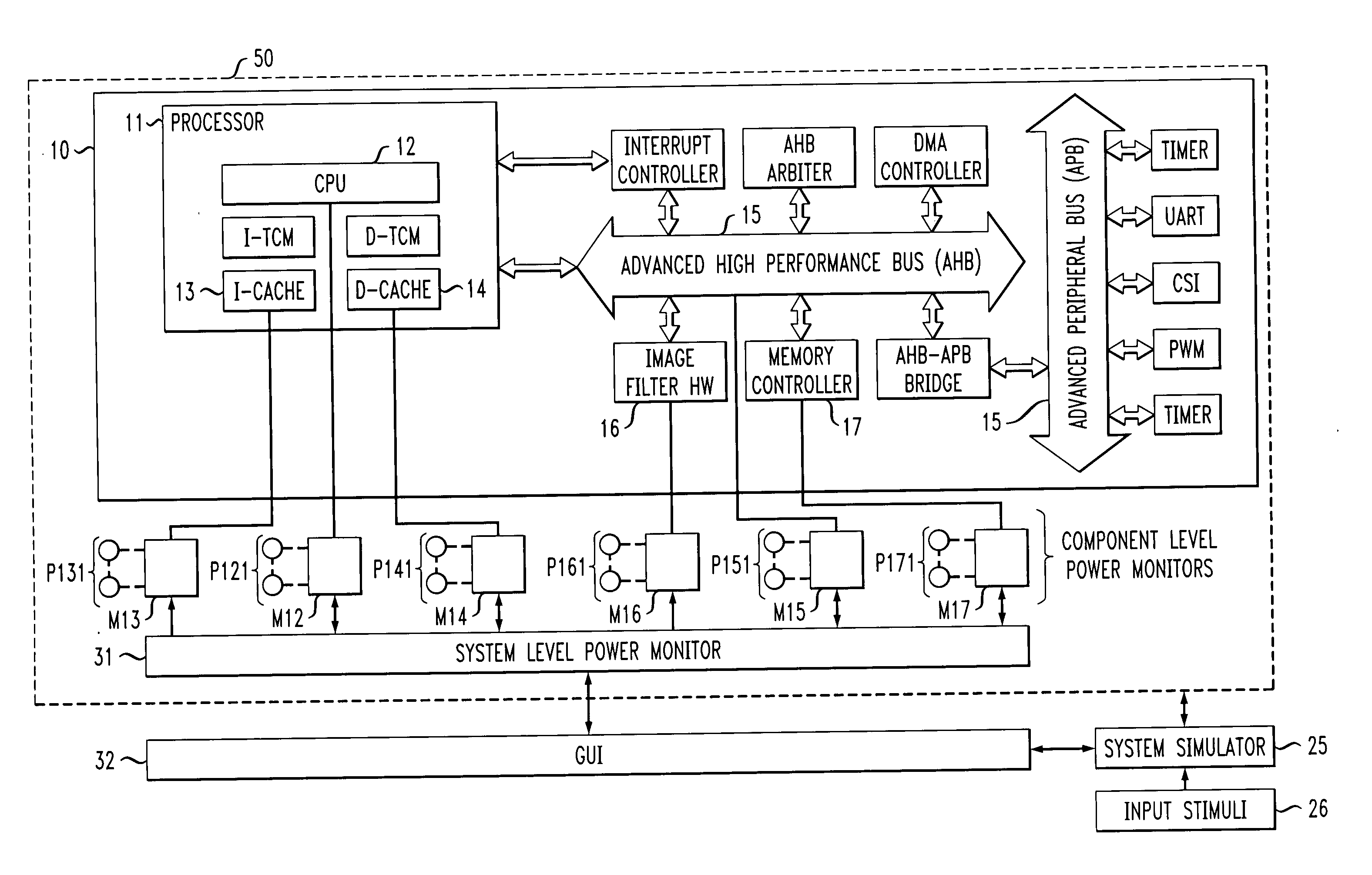
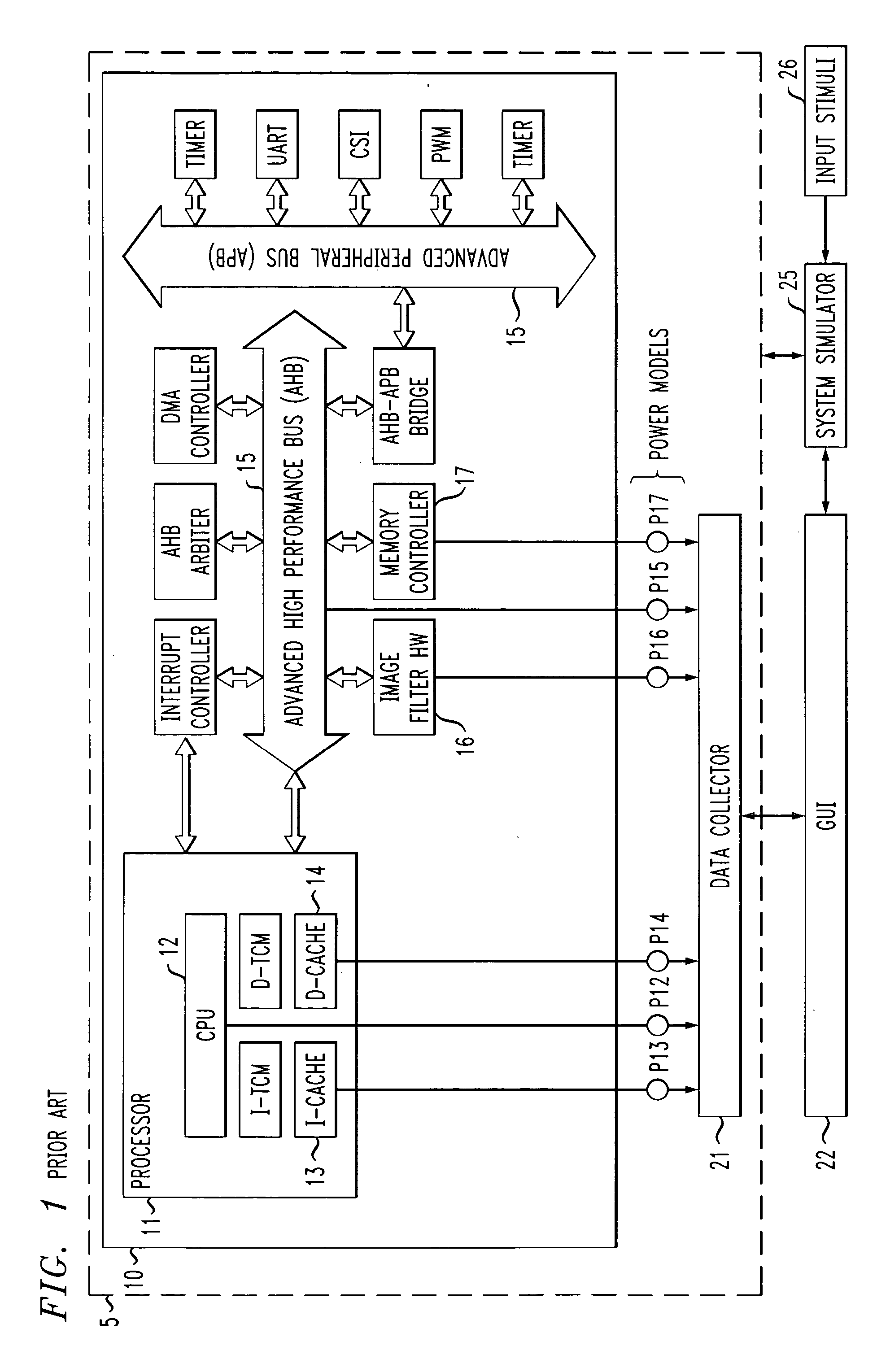
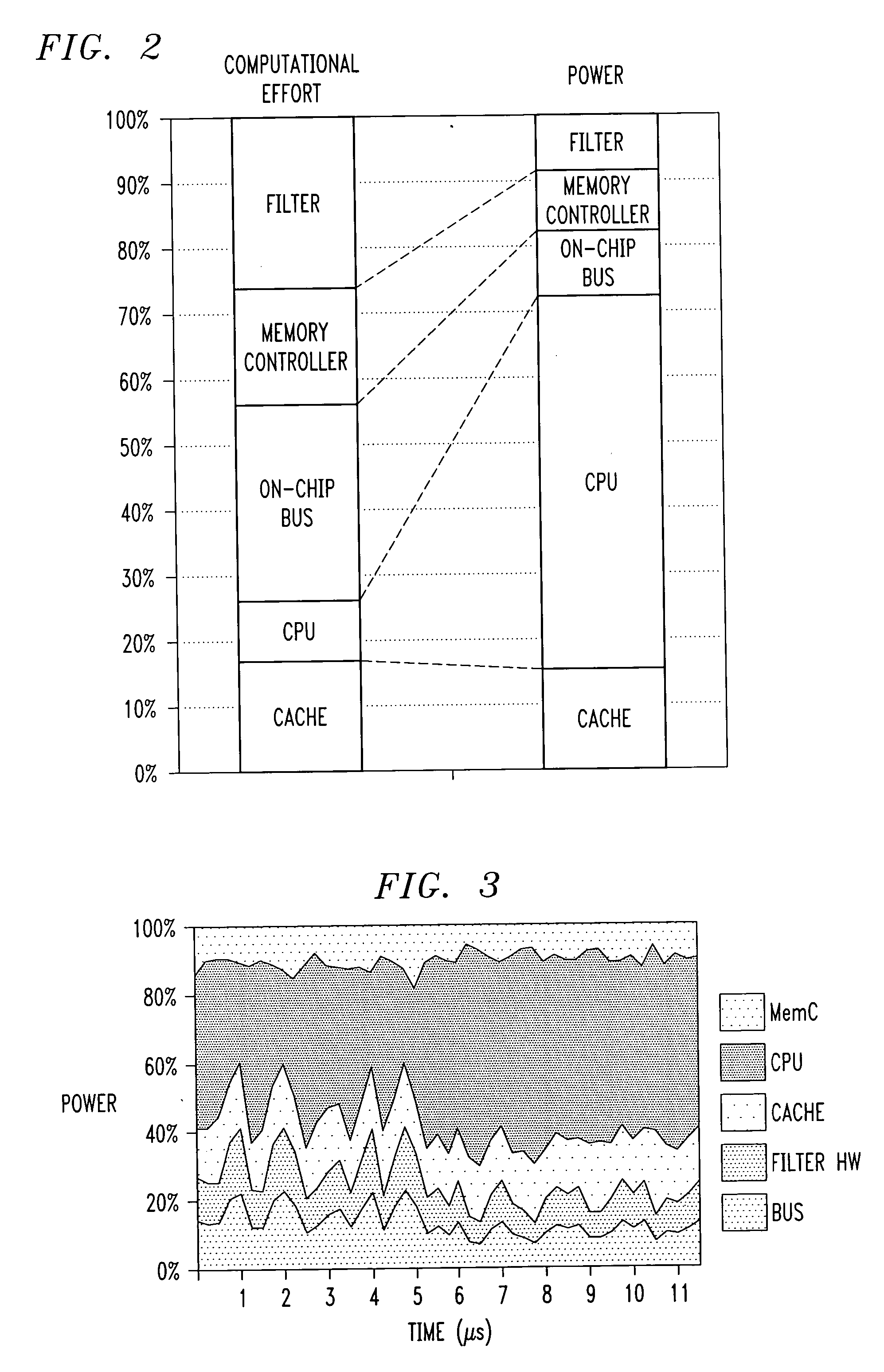
InactiveUS20060080076A1Reduce the amount of calculationReduces overall power estimation computational effortDetecting faulty computer hardwareAnalogue computers for nuclear physicsTrade offsEngineering
A power estimation framework based on a network of power monitors that observe component- and system-level execution and power statistics at run time. Based on those statistics, the power monitors (i) select between multiple alternative power models for each component and / or (ii) configure the component power models to best negotiate the trade-off between efficiency and accuracy. This approach effectuates a co-coordinated, adaptive, spatio-temporal allocation of computational effort for power estimation. This approach yields large reductions in power estimation overhead while minimally impacting power estimation accuracy.
Owner:NEC LAB AMERICA +1
Entropy encoding and decoding scheme
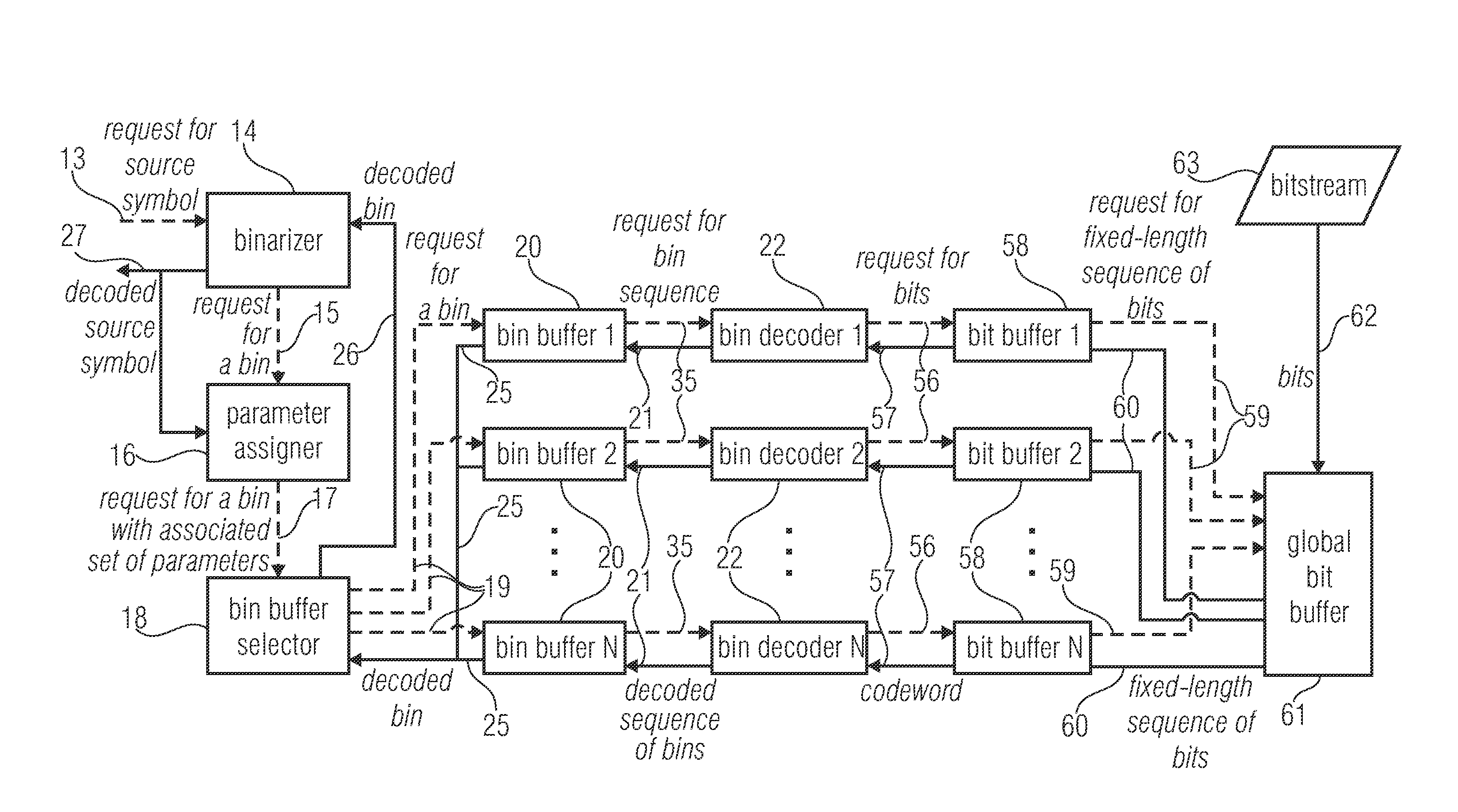
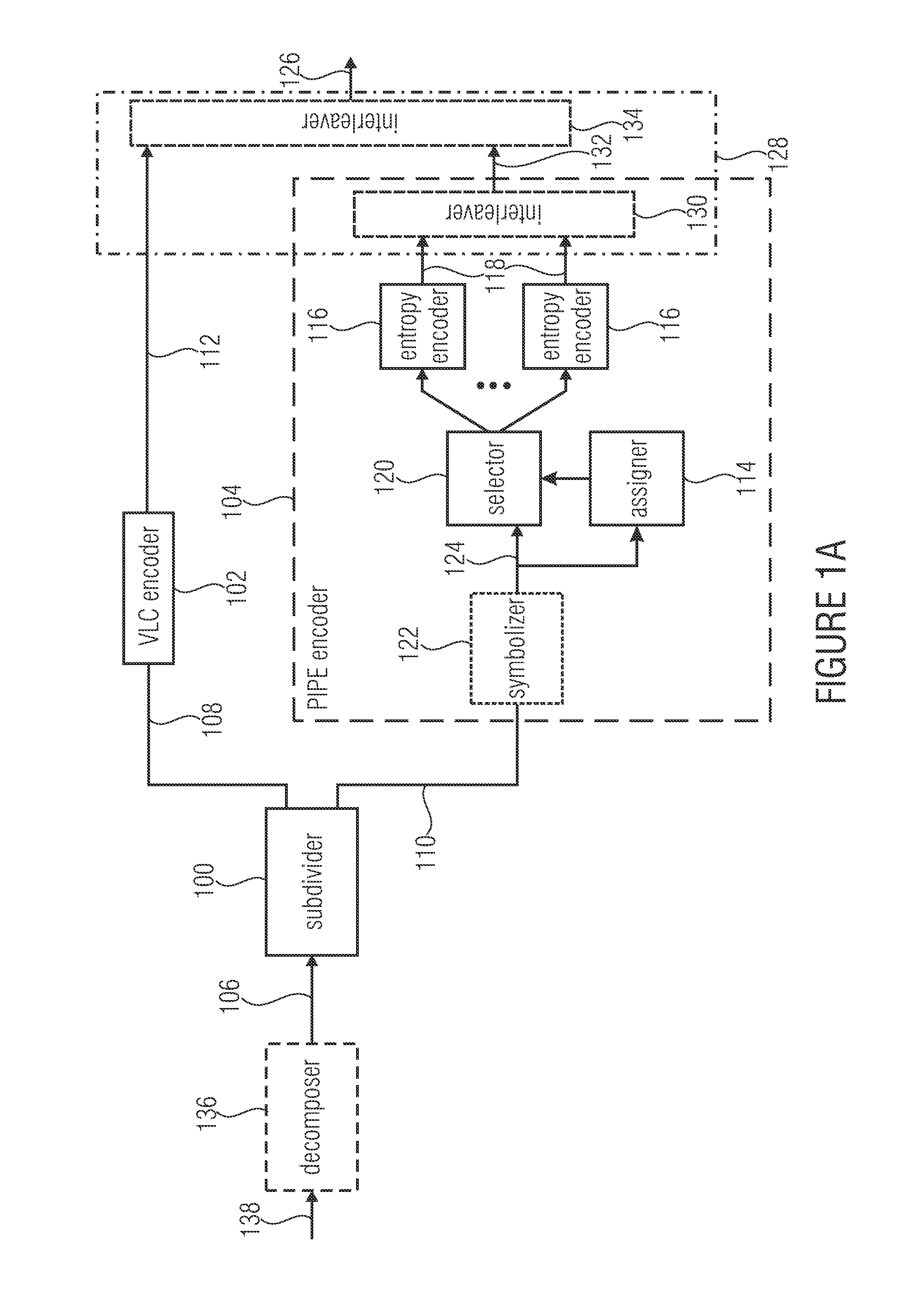
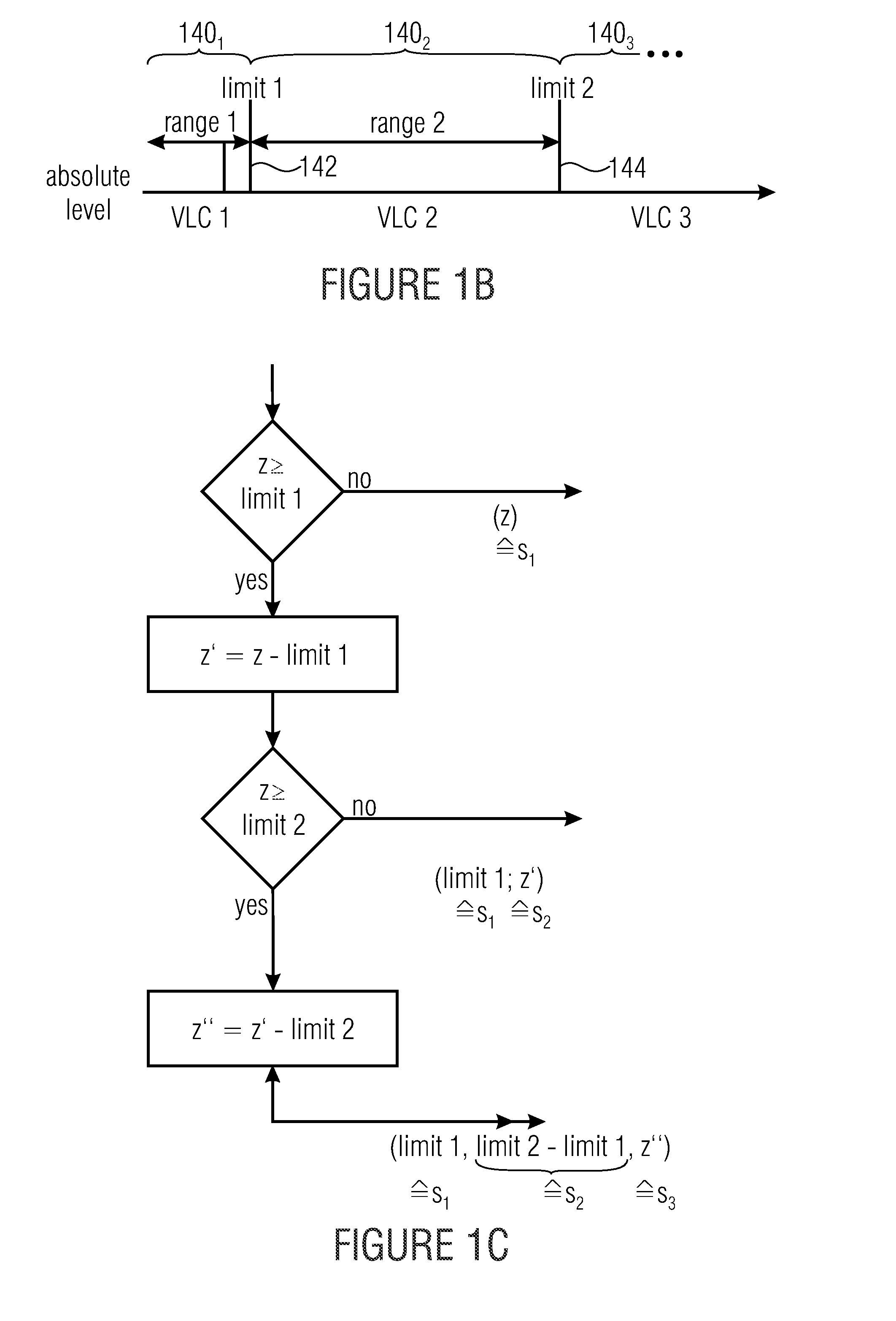
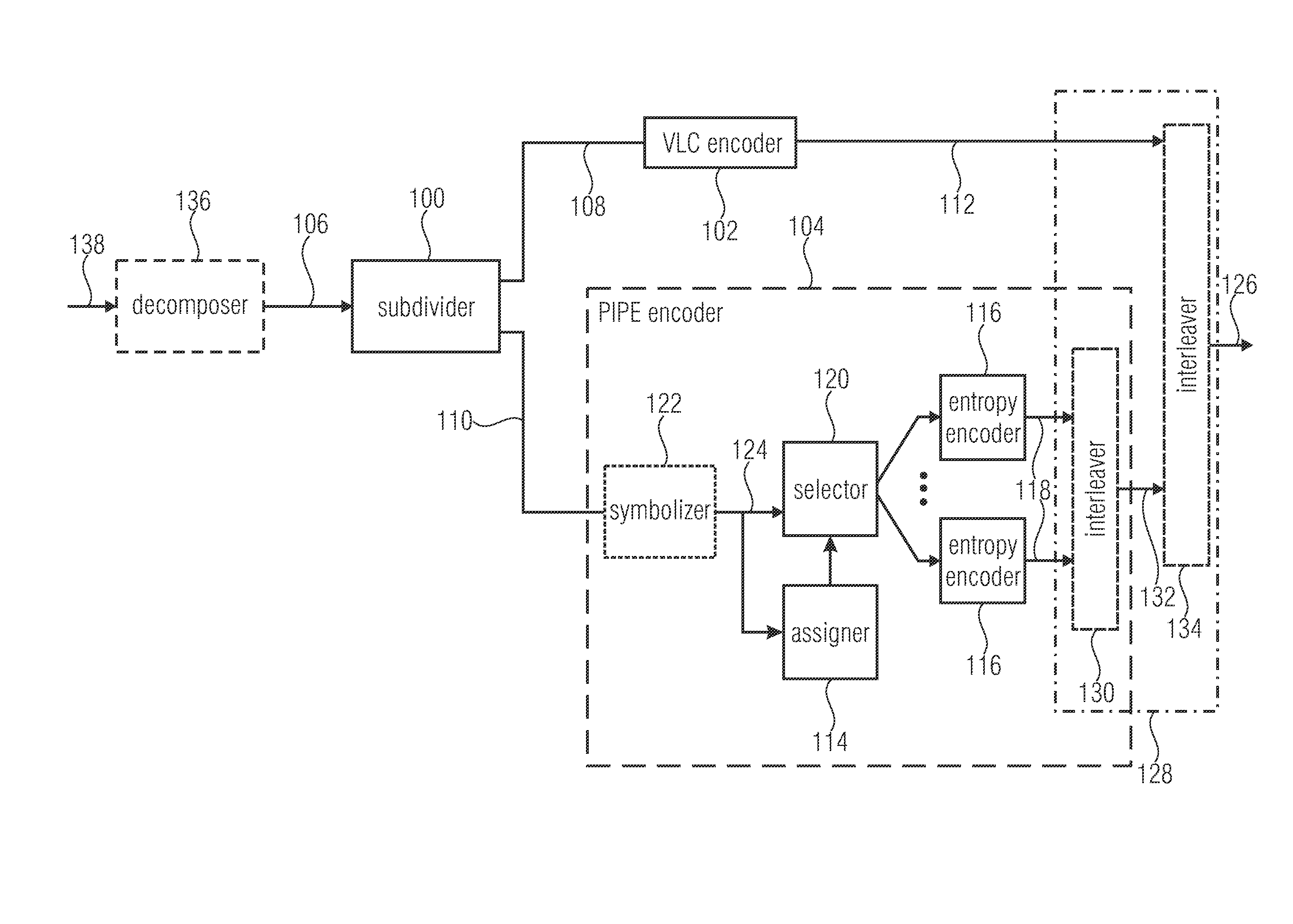
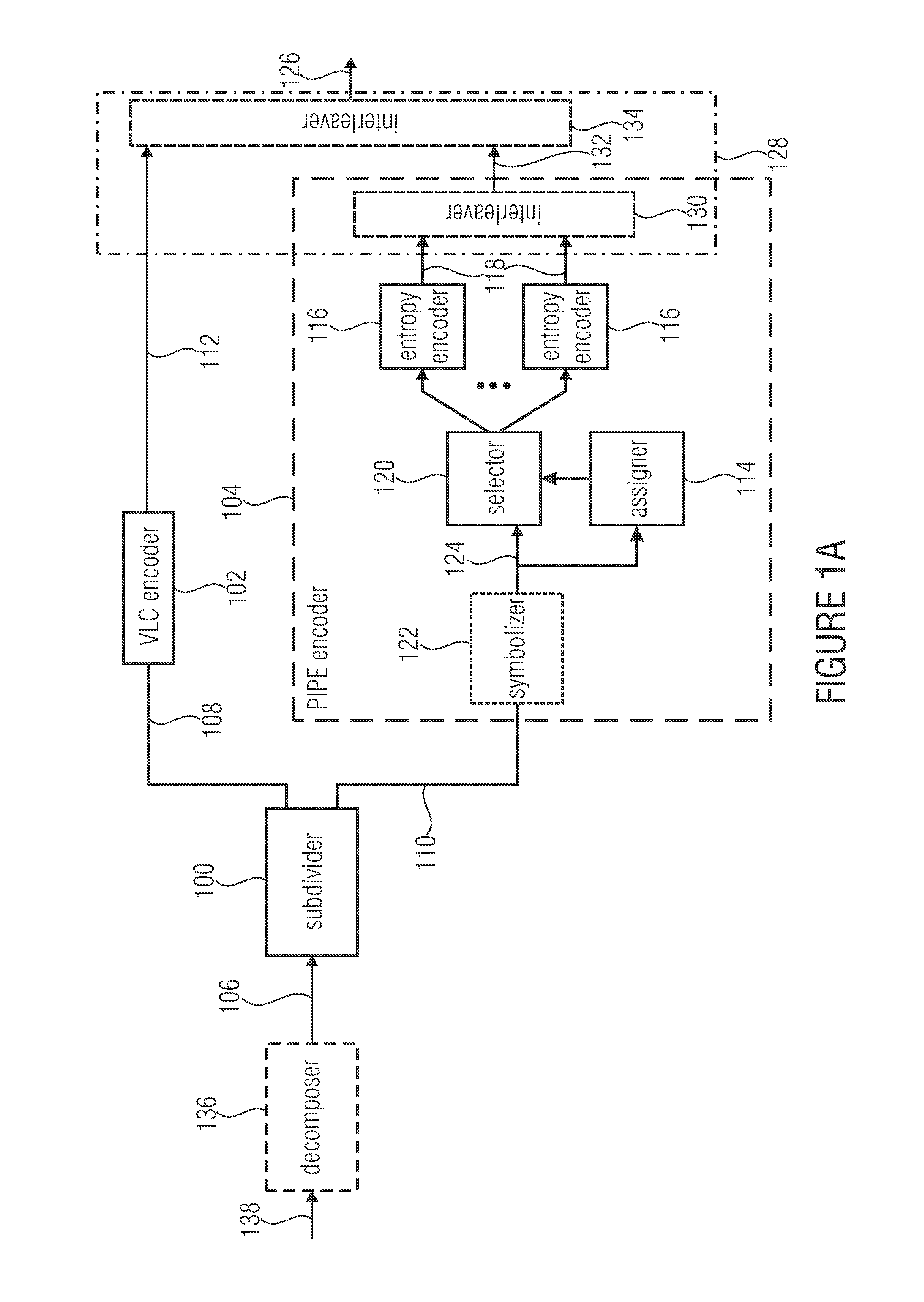
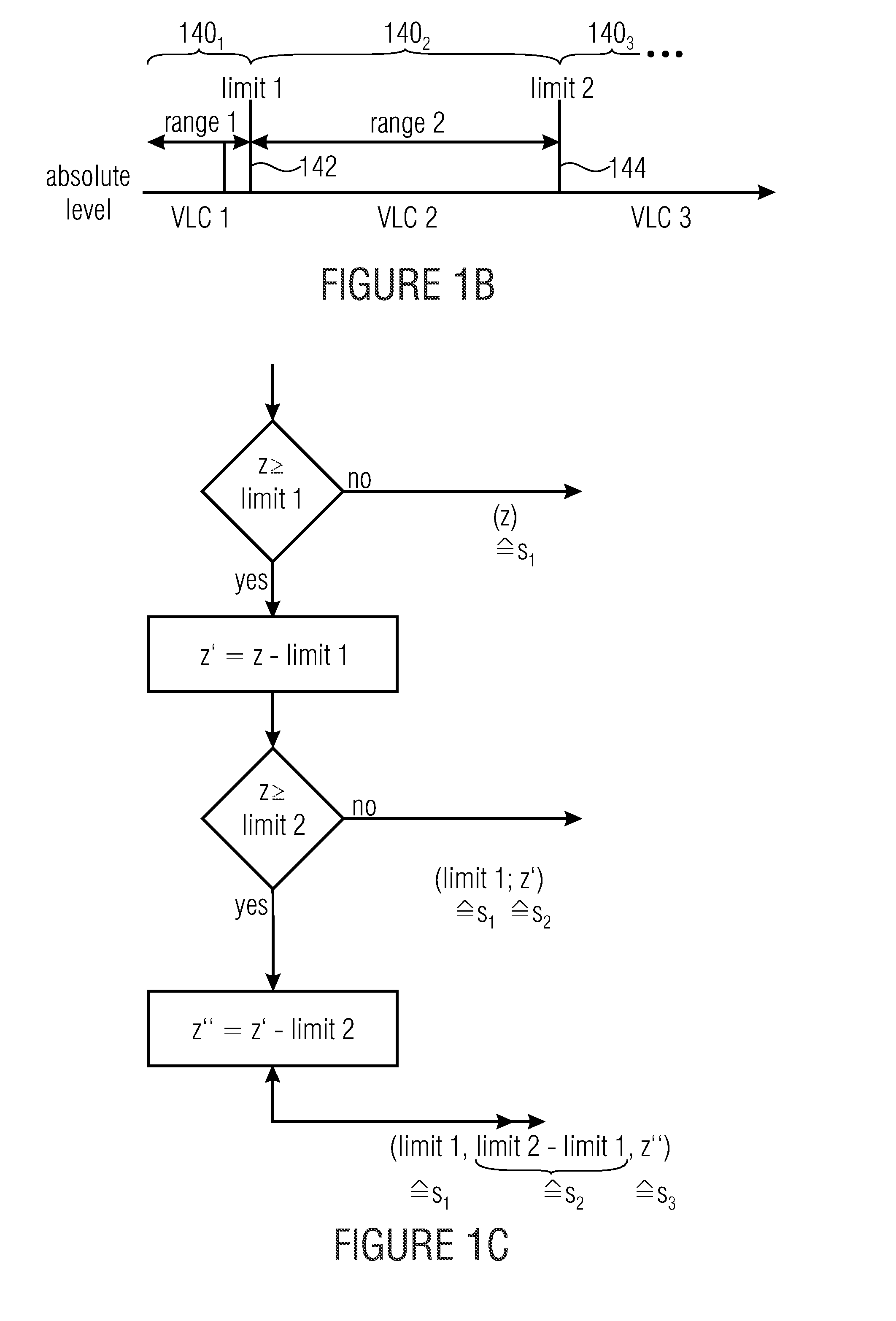
ActiveUS20130300591A1Improve compression efficiencyModerate coding overheadCode conversionDigital video signal modificationSyntaxComputer science
Decomposing a value range of the respective syntax elements into a sequence of n partitions with coding the components of z laying within the respective partitions separately with at least one by VCL coding and with at least one by PIPE or entropy coding is used to greatly increase the compression efficiency at a moderate coding overhead since the coding scheme used may be better adapted to the syntax element statistics. Accordingly, syntax elements are decomposed into a respective number n of source symbols si with i=1 . . . n, the respective number n of source symbols depending on as to which of a sequence of n partitions into which a value range of the respective syntax elements is sub-divided, a value z of the respective syntax elements falls into, so that a sum of values of the respective number of source symbols si yields z, and, if n>1, for all i=1 . . . n−1, the value of si corresponds to a range of the ith partition.
Owner:GE VIDEO COMPRESSION LLC
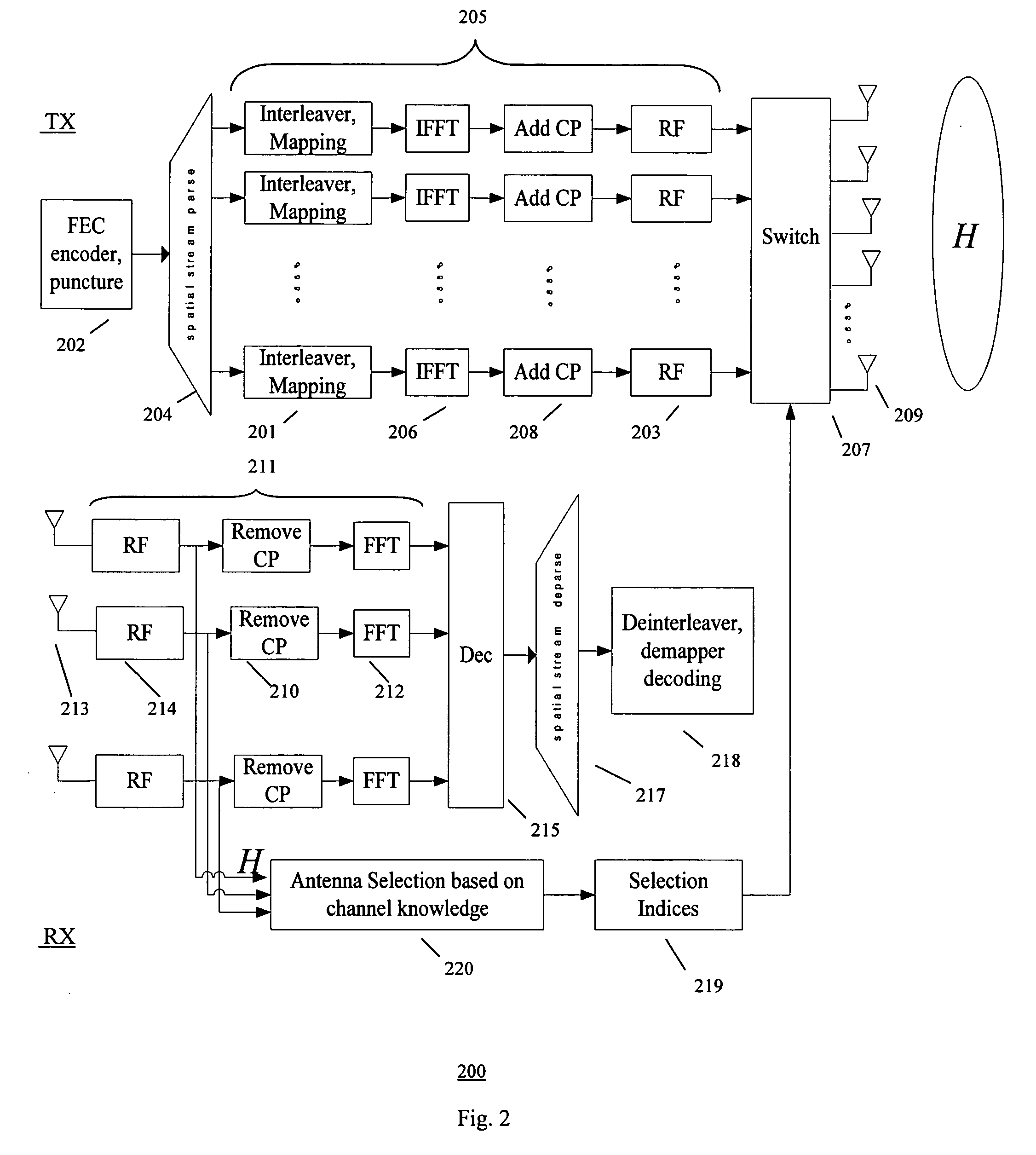
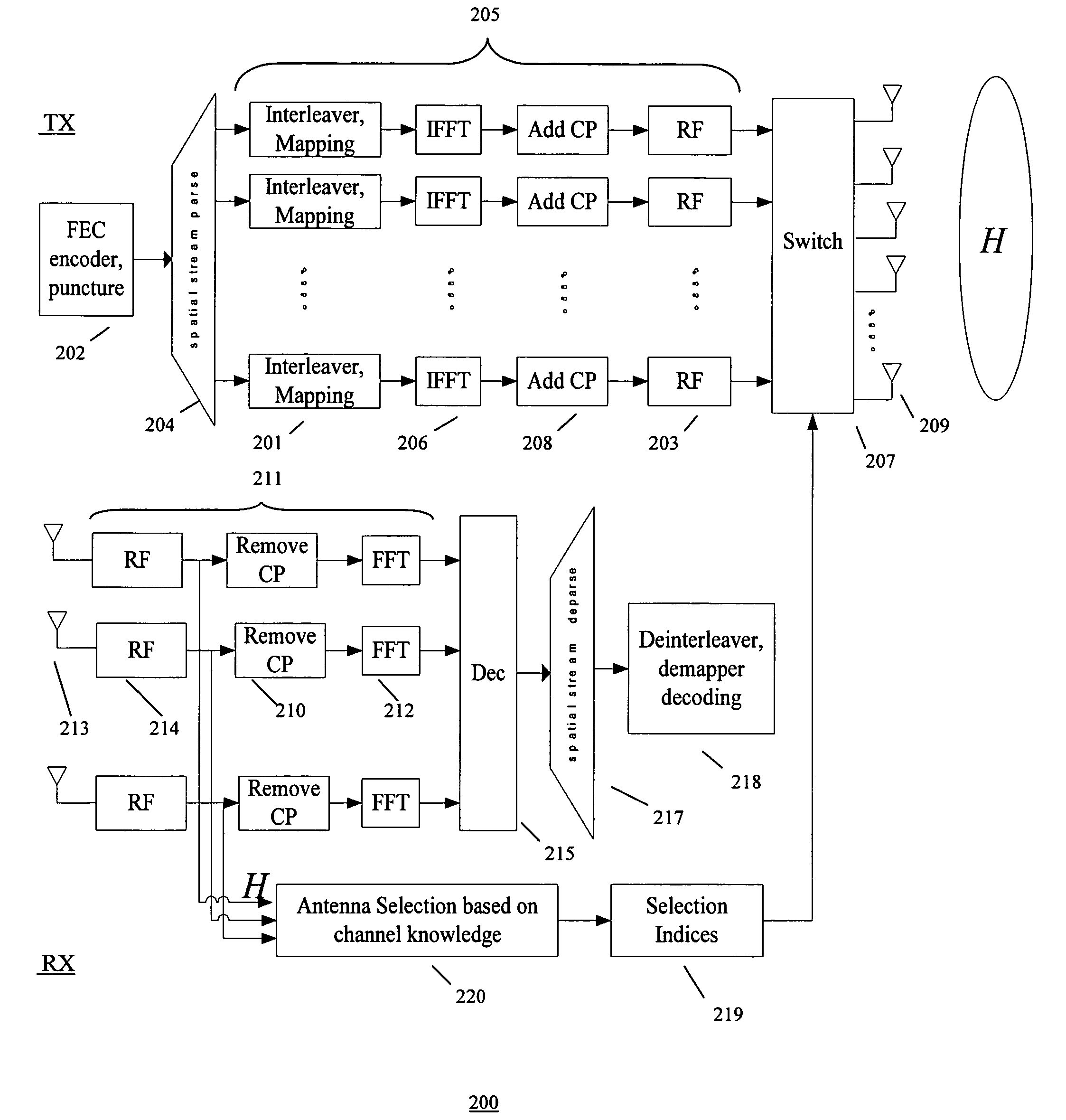
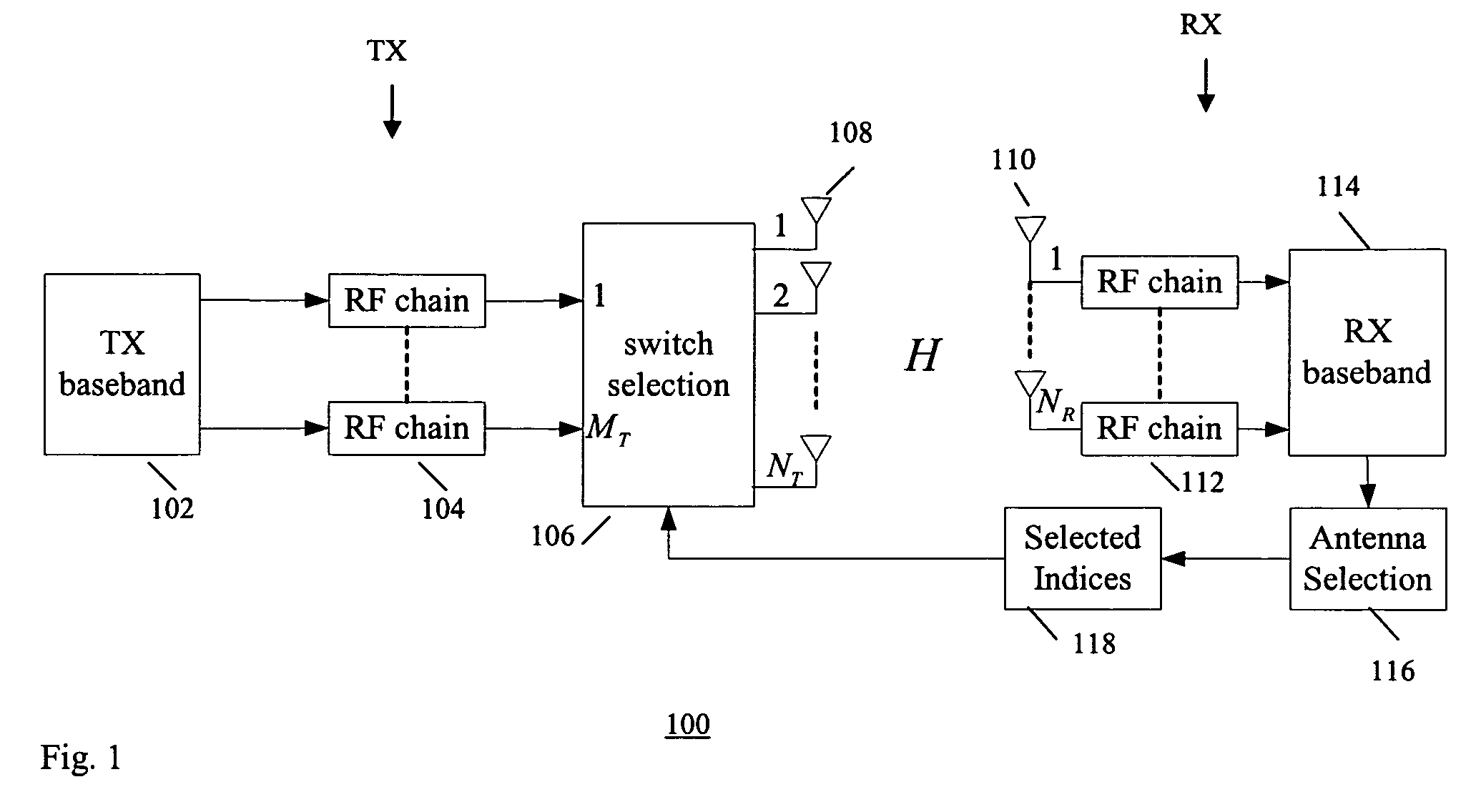
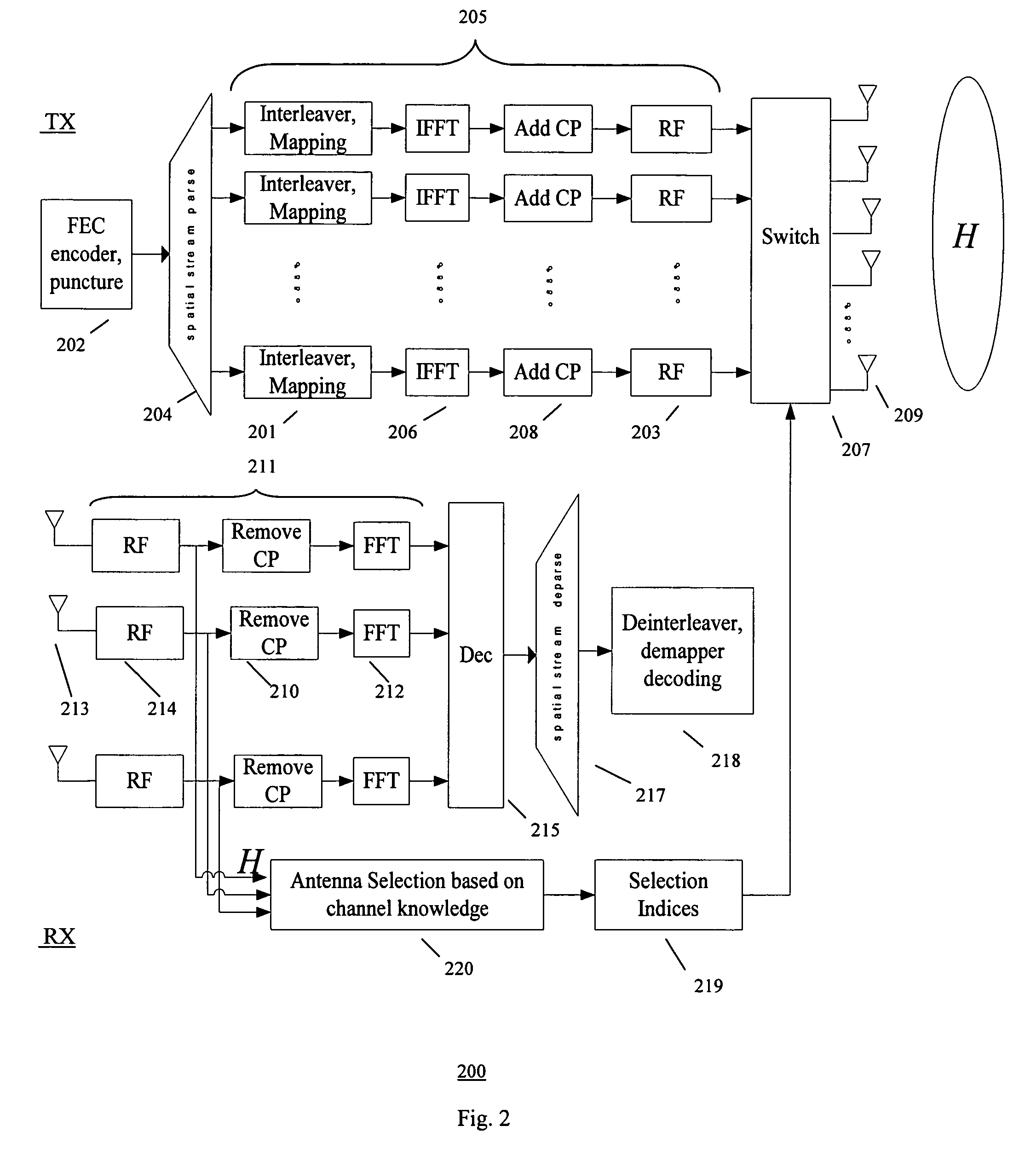
Methods of antenna selection for downlink MIMO-OFDM transmission over spatial correlated channels
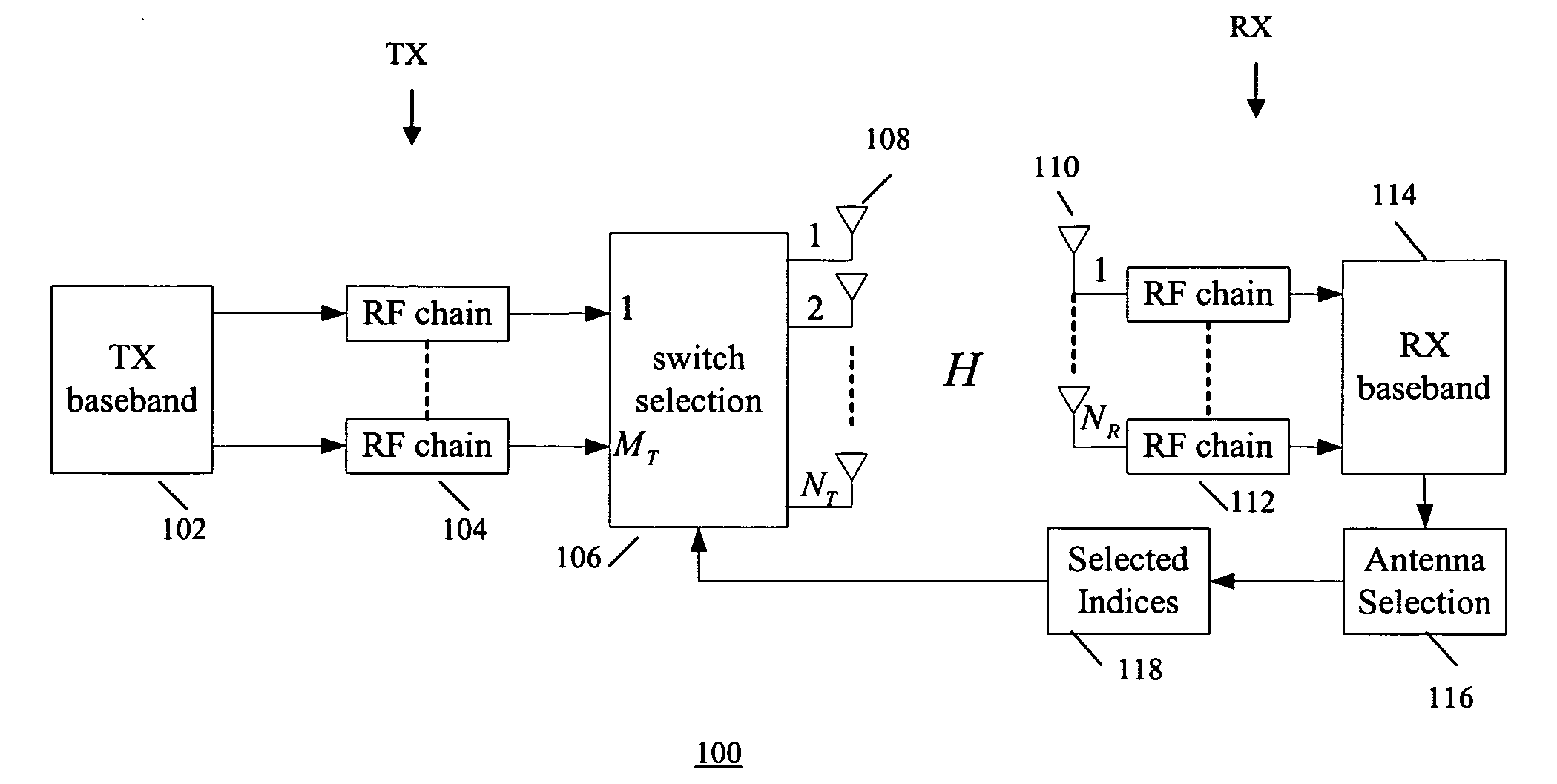
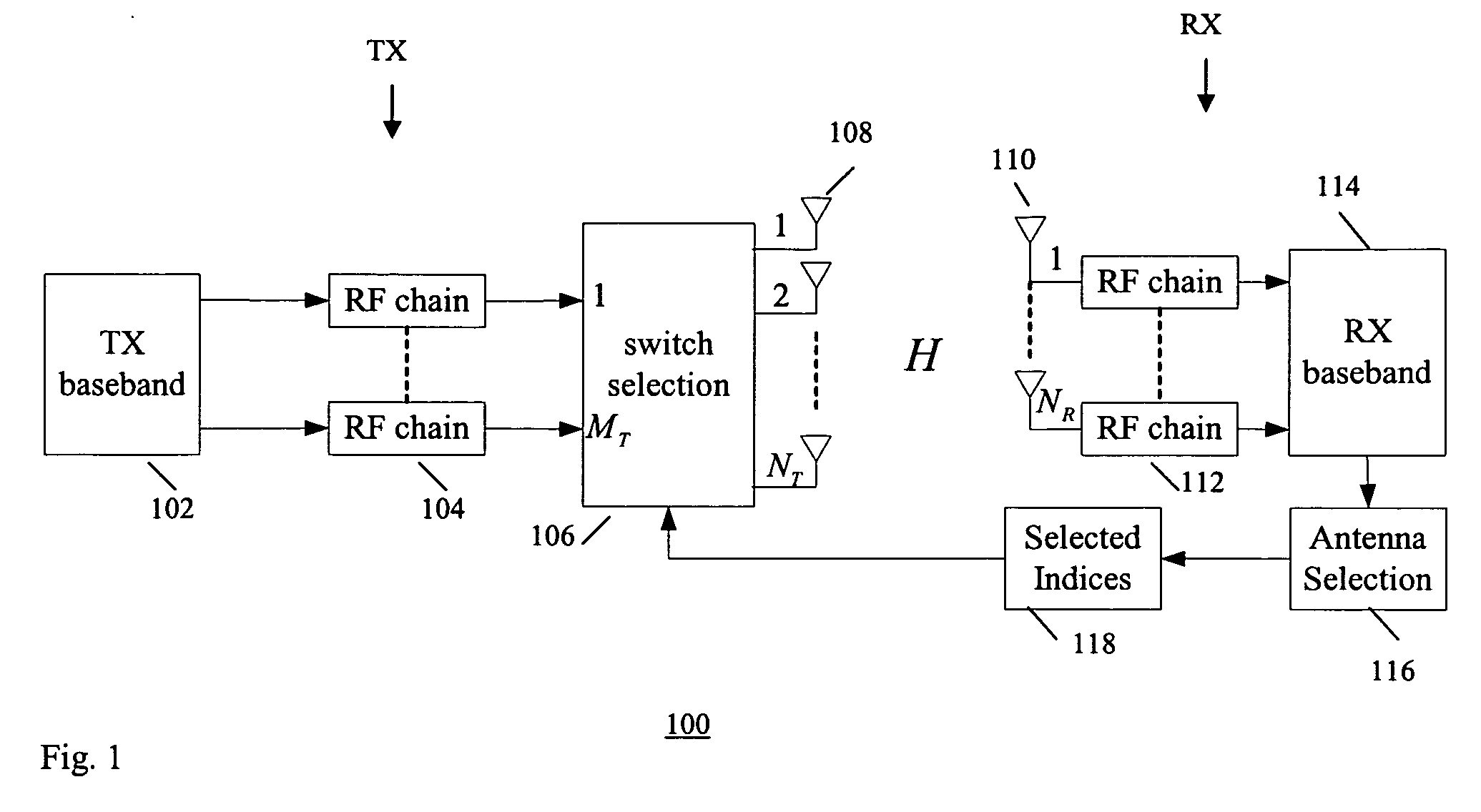
InactiveUS20070099584A1Low costImprove performanceSpatial transmit diversityModulated-carrier systemsSpatial correlationChannel state information
An antenna selection technique (transmitter / receiver antenna selection) that reduces the cost of the MIMO system while maintaining high performance. A combined selection algorithm for MIMO-OFDM is provided which offers the best tradeoff between spatial correlation and instantaneous SNR. In one case, antenna selection is based on instant channel information. In another case antenna is based on statistical channel state information. In another case, antenna selection is based on a hybrid of instant channel state information and statistical channel state information.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
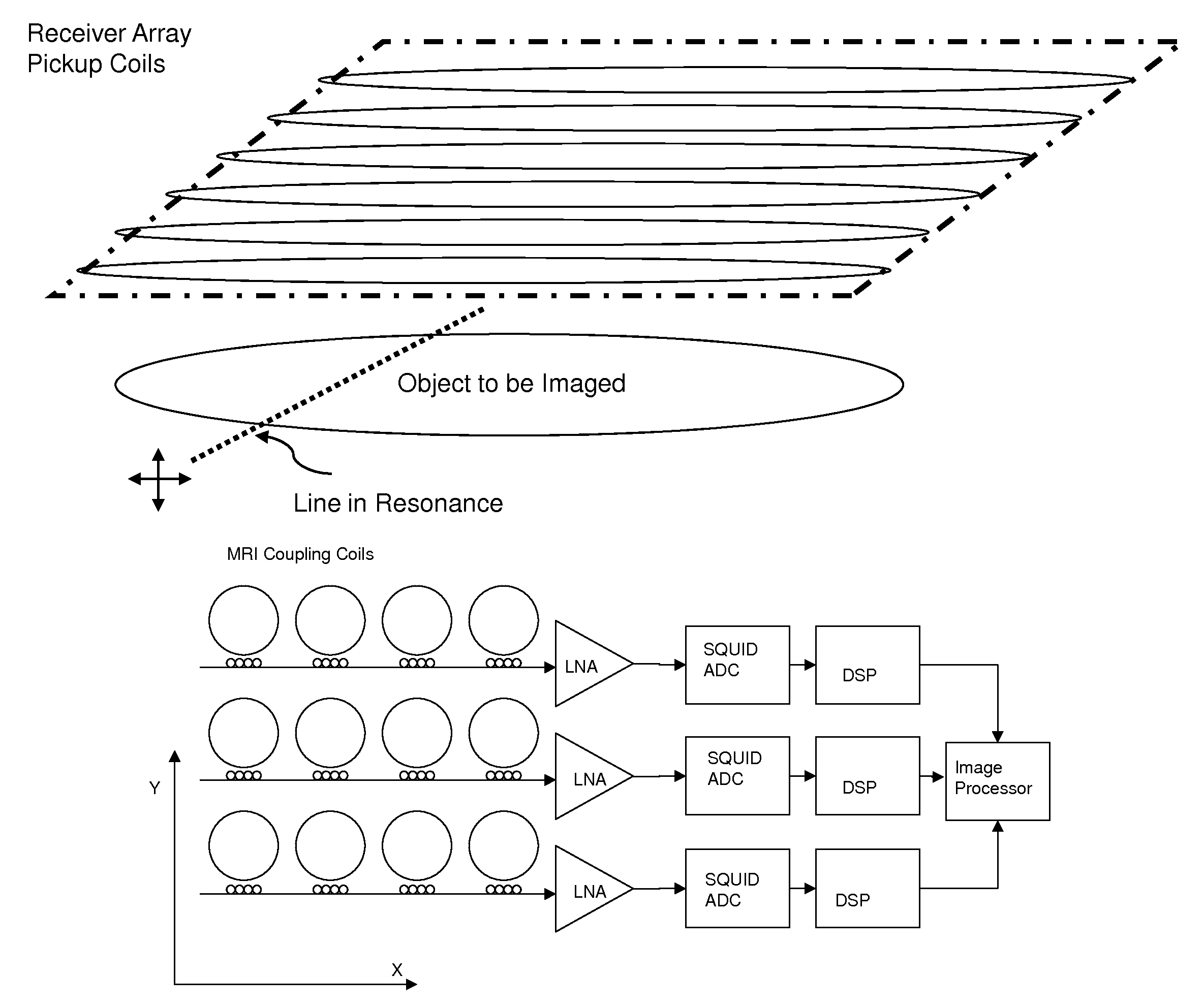
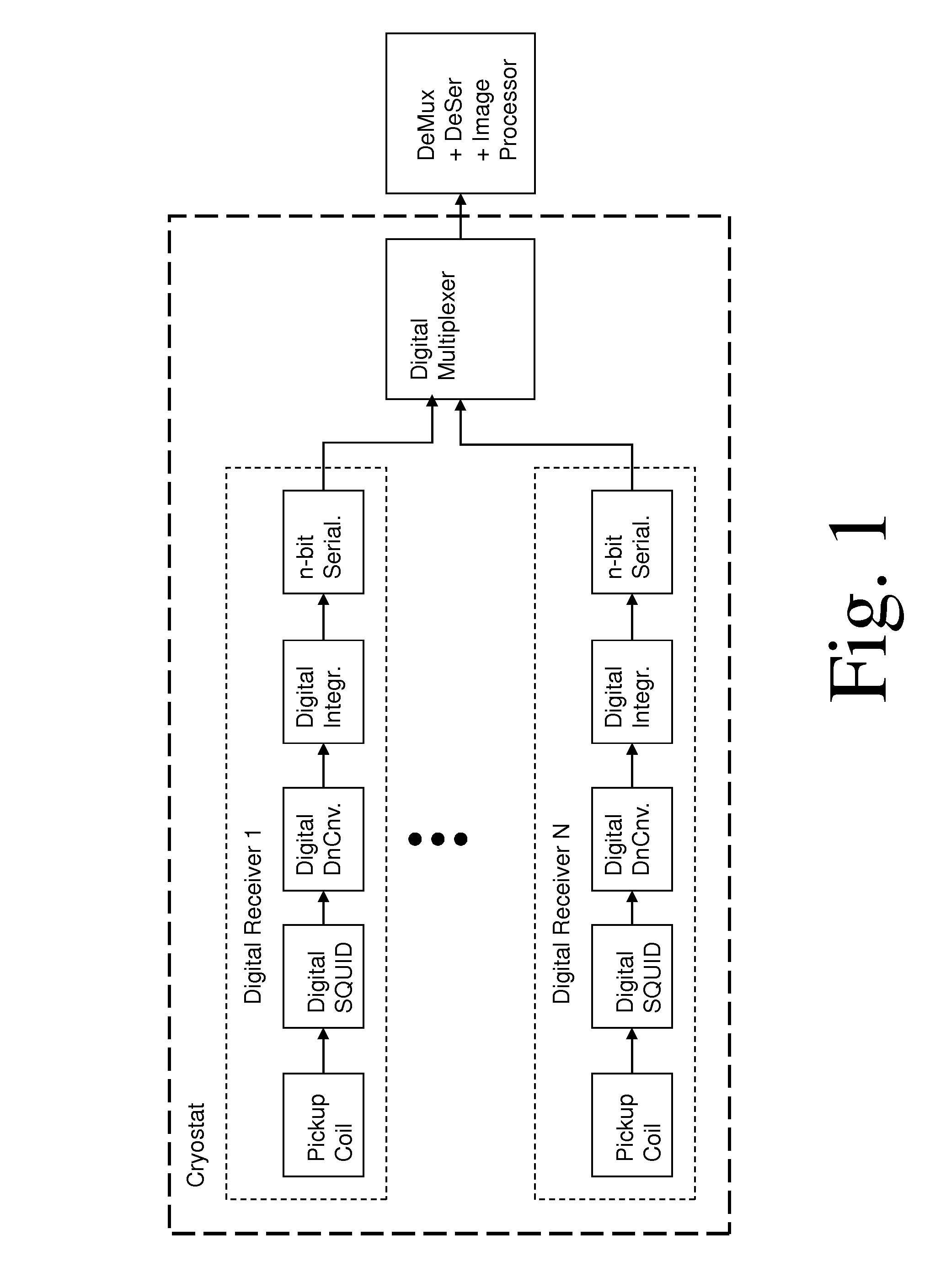
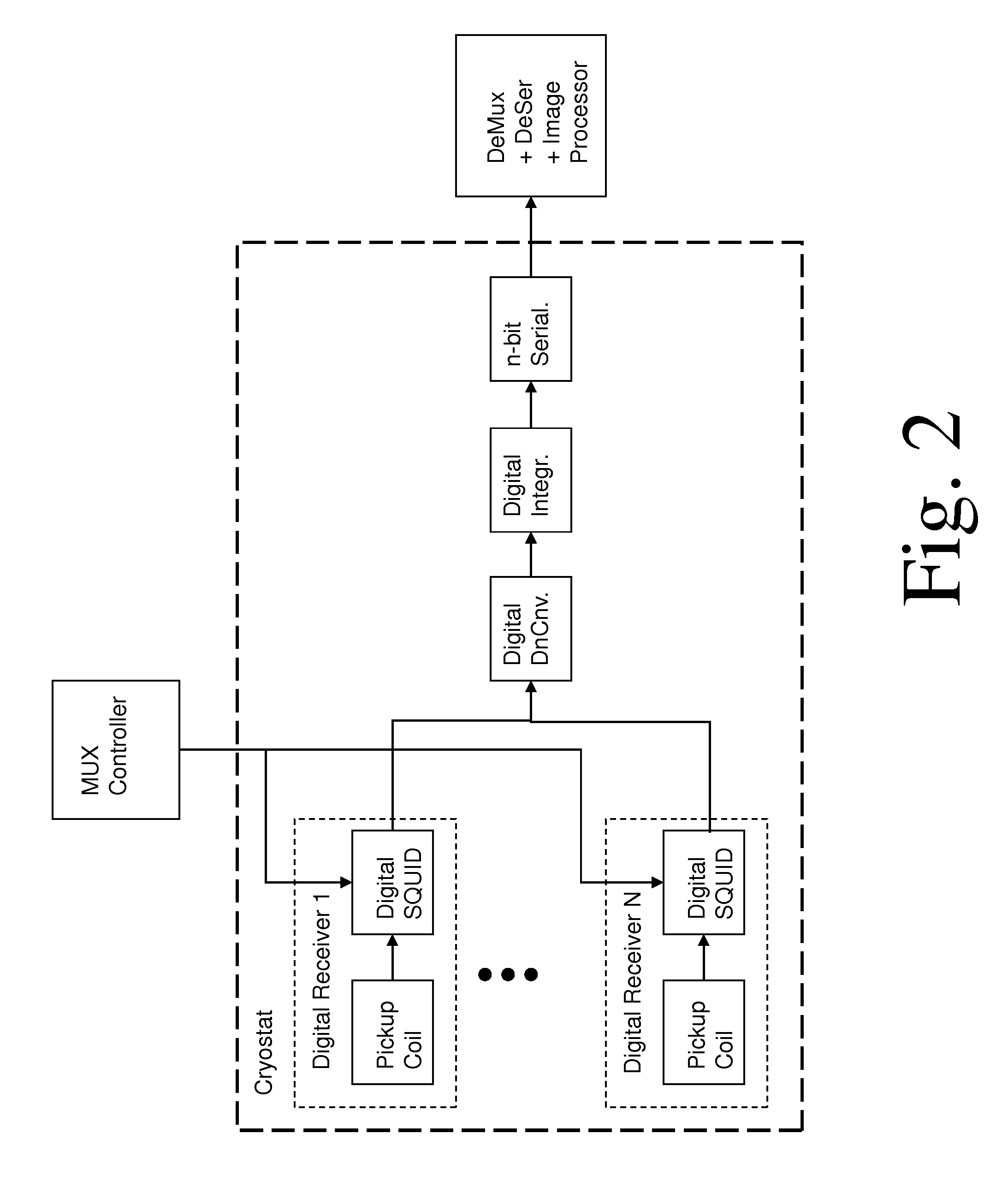
Magnetic resonance system and method employing a digital squid
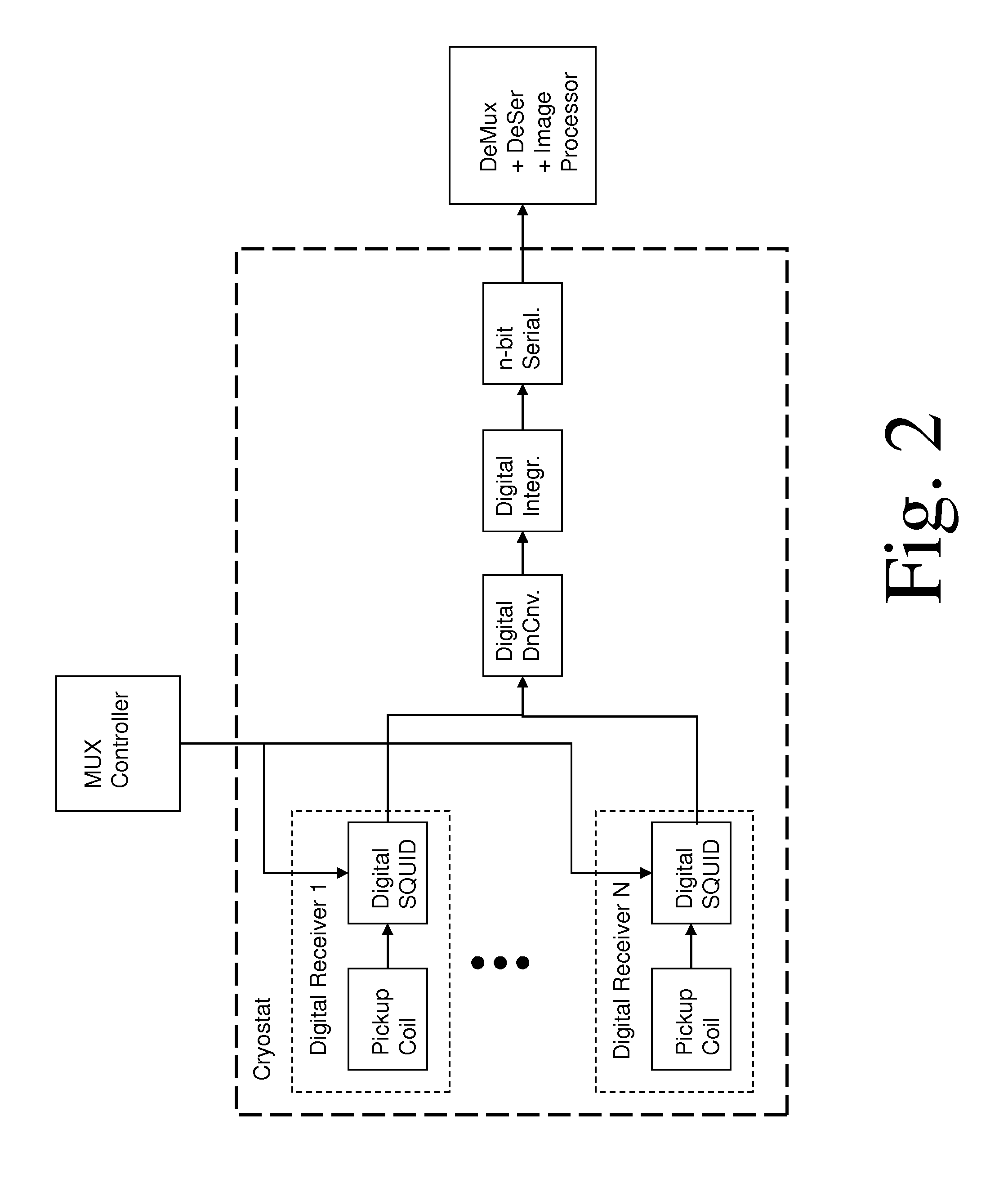
ActiveUS8593141B1Fast imagingImprove spatial resolutionMagnetic property measurementsMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsVoxelData acquisition
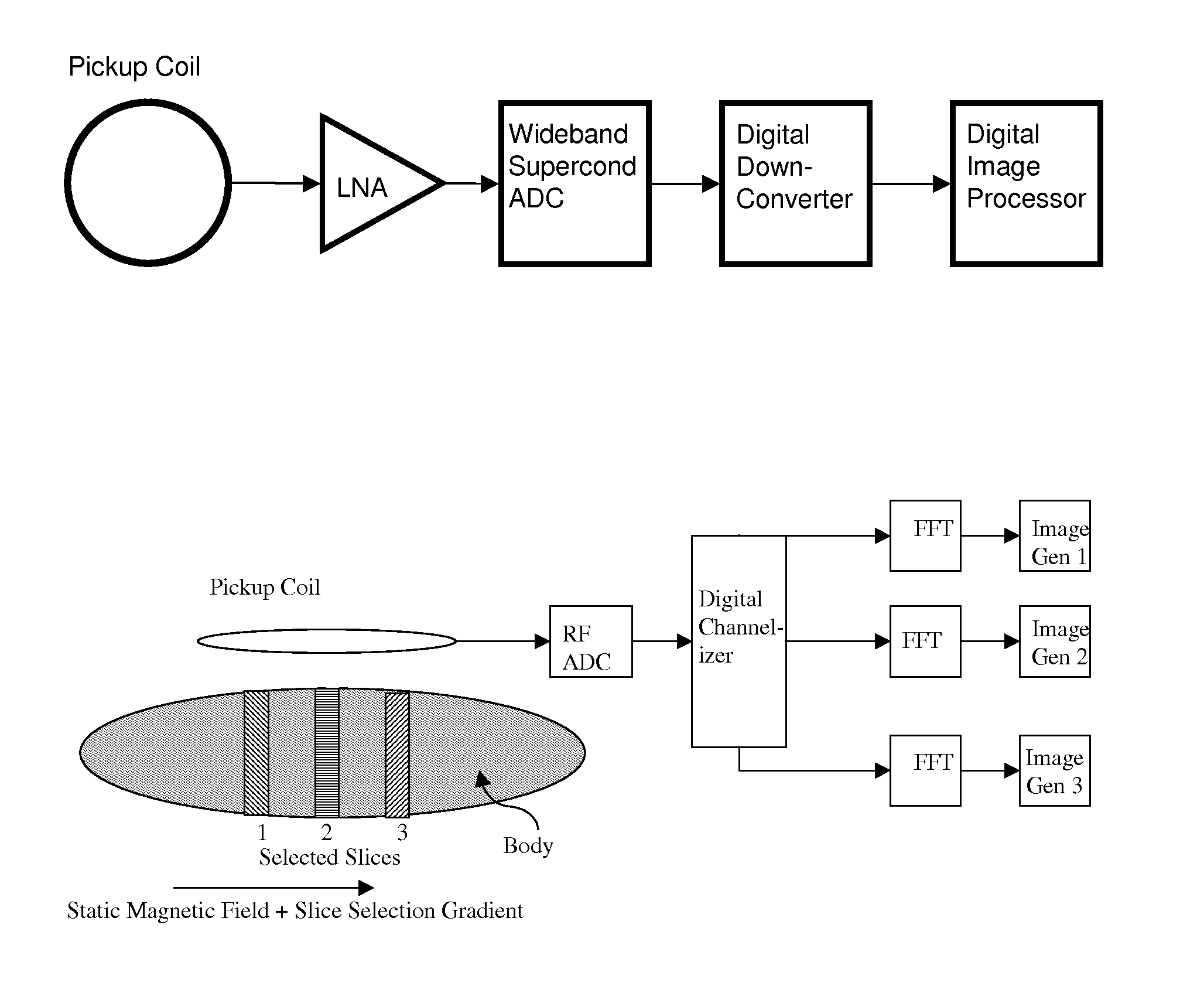
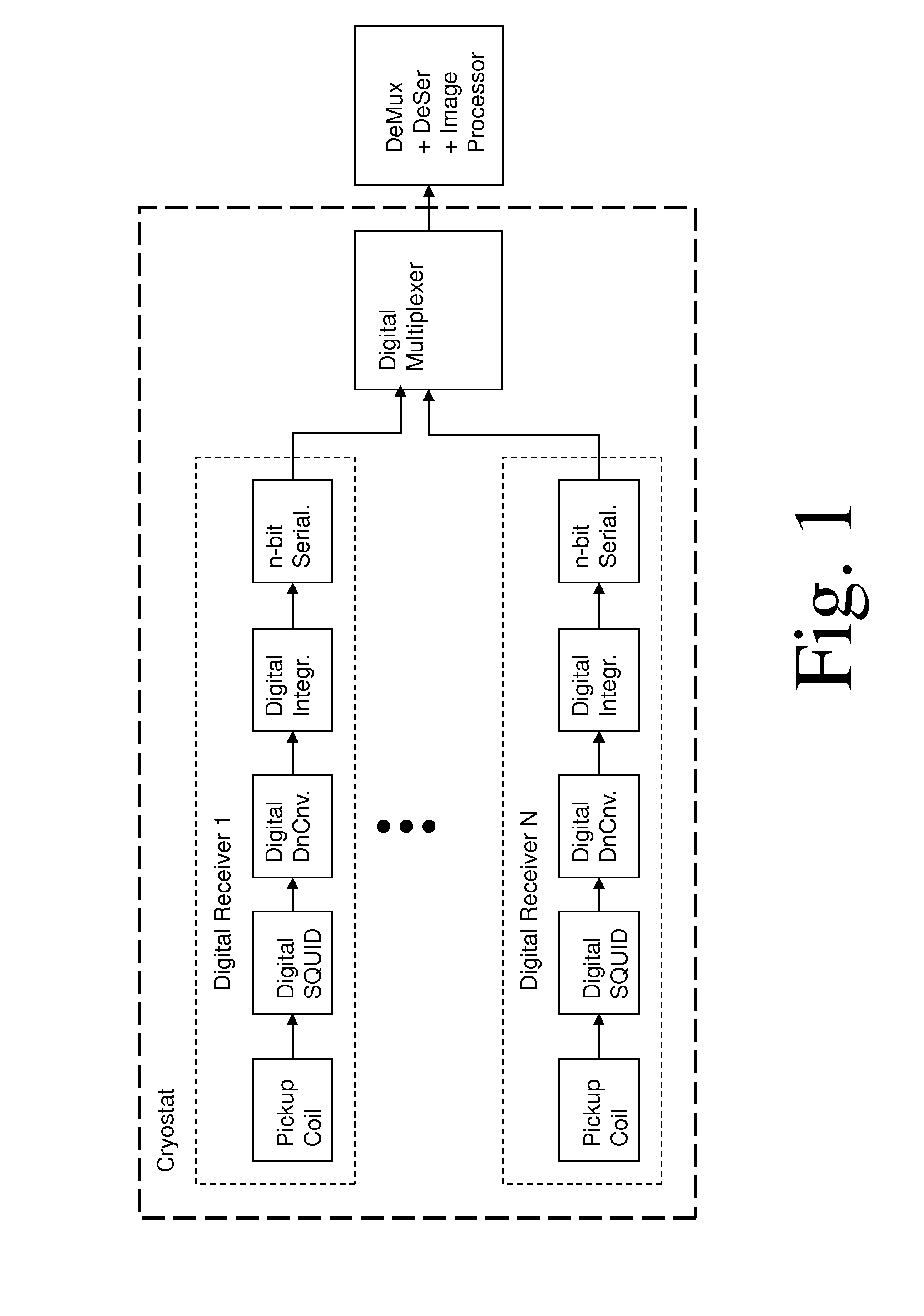
A magnetic resonance system, comprising at least one SQUID, configured to receive a radio frequency electromagnetic signal, in a circuit configured to produce a pulsatile output having a minimum pulse frequency of at least 1 GHz which is analyzed in a processor with respect to a timebase, to generate a digital signal representing magnetic resonance information. The processor may comprise at least one rapid single flux quantum circuit. The magnetic resonance information may be image information. A plurality of SQUIDs may be provided, fed by a plurality of antennas in a spatial array, to provide parallel data acquisition. A broadband excitation may be provided to address a range of voxels per excitation cycle. The processor may digitally compensate for magnetic field inhomogeneities.
Owner:THE JOHNSON REVOCABLE TRUST DATED 6 25 2003
Method for signalling a precoding in a cooperative beamforming transmission mode
ActiveUS20110081901A1Keep certain amountReduce data volumeSite diversitySpatial transmit diversityPrimary stationTransceiver
The present invention relates to a method for operating a secondary station in a network, the secondary station comprising a transceiver adapted for simultaneously receiving transmissions from a primary station controlling a first cell and at least one primary station controlling a second cell, the method comprising the secondary station(a) selecting a first precoding matrix for the first cell out a primary set of precoding matrices for the first cell,(b) selecting a subset of at least one precoding matrix for the at least one second cell in dependence on the first precoding matrix, out of a set of subsets of precoding matrices for the second cell,(c) selecting a second precoding matrix for the at least one second cell out of the selected subset of precoding matrices for the second cell,(d) transmitting a first indicator representative of the first precoding matrix.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Lithographic projection apparatus and device manufacturing method using such lithographic projection apparatus
ActiveUS7262831B2Reduce throughputAvailability is not compromisedPhotomechanical apparatusPhotographic printingOnline modelControl system
A lithographic projection apparatus includes a measurement system for measuring changes in projection system aberrations with time, and a predictive control system for predicting variation of projection system aberrations with time on the basis of model parameters and for generating a control signal for compensating a time-varying property of the apparatus, such as the OVL values (X-Y adjustment) and the FOC values (Z adjustment) of a lens of the projection system for example. An inline model identification system is provided for estimating model parameter errors on the basis of projection system aberration values provided by the predictive control system and measured projection system aberration values provided by the measurement system, and an updating system utilizes the model parameter errors for updating the model parameters of the predictive control system in order to maintain the time-varying property within acceptable performance criteria.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Magnetic resonance system and method employing a digital SQUID
ActiveUS8618799B1Fast imagingImprove spatial resolutionMagnetic property measurementsMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsVoxelData acquisition
A magnetic resonance system, comprising at least one SQUID, configured to receive a radio frequency electromagnetic signal, in a circuit configured to produce a pulsatile output having a minimum pulse frequency of at least 1 GHz which is analyzed in a processor with respect to a timebase, to generate a digital signal representing magnetic resonance information. The processor may comprise at least one rapid single flux quantum circuit. The magnetic resonance information may be image information. A plurality of SQUIDs may be provided, fed by a plurality of antennas in a spatial array, to provide parallel data acquisition. A broadband excitation may be provided to address a range of voxels per excitation cycle. The processor may digitally compensate for magnetic field inhomogeneities.
Owner:THE JOHNSON REVOCABLE TRUST DATED 6 25 2003
Method for Representing Objects with Concentric Ring Signature Descriptors for Detecting 3D Objects in Range Images
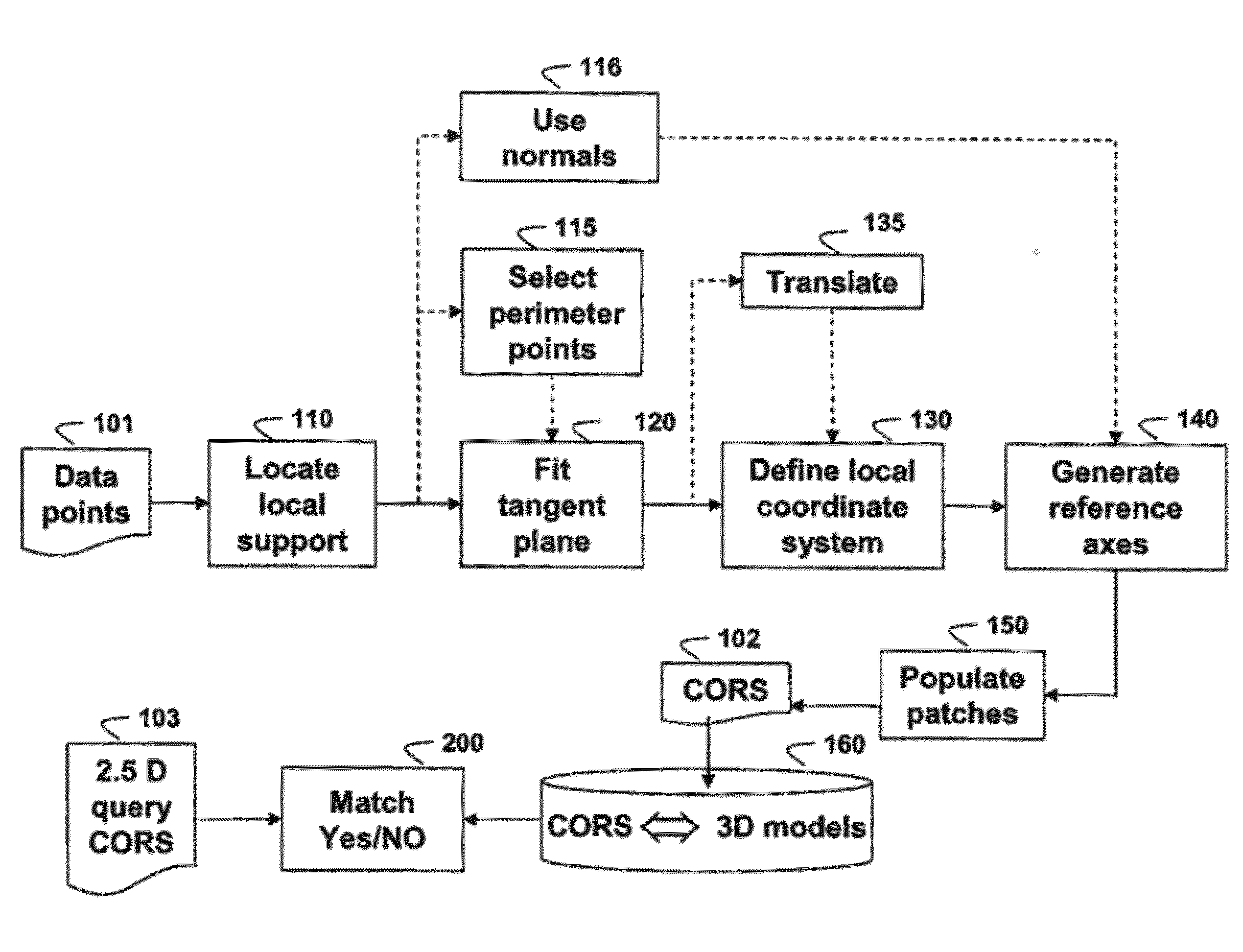
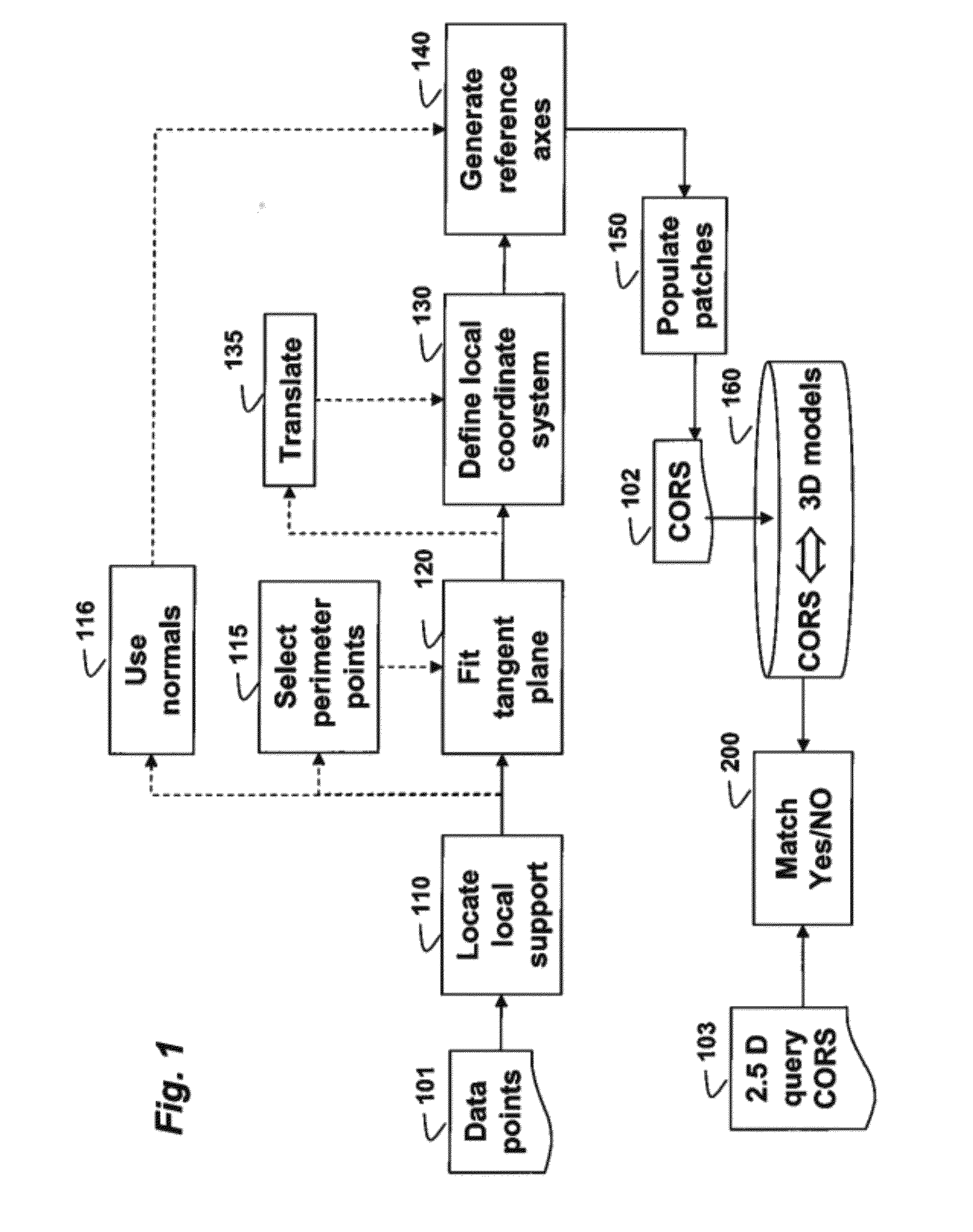
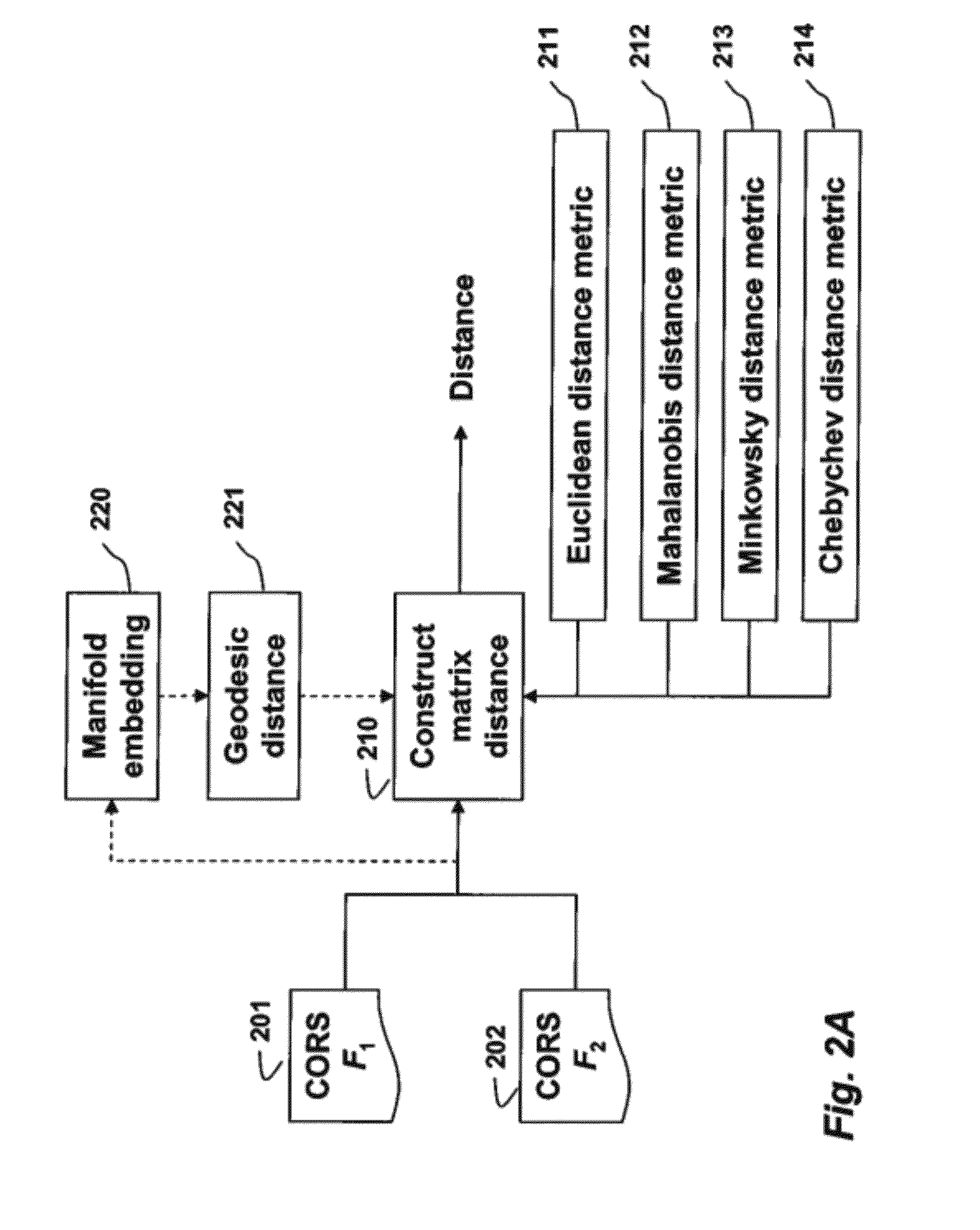
ActiveUS20120206438A1Quick fixImprove match3D-image renderingThree-dimensional object recognitionElevation - valueConcentric ring
A 3D object is represented by a descriptor, wherein a model of the 3D object is a 3D point cloud. A local support for each point p in the 3D point cloud is located, and reference x, y, and z axes are generated for the local support. A polar grid is applied according to the references x, y, and z axes a along an azimuth and a radial directions on an xy plane centered on the point p such that each patch on the grid is a bin for a 2D histogram, wherein the 2D histogram is a 2D matrix F on the grid and each coefficient of the 2D matrix F corresponds to the patch on the grid. For each grid location (k, l), an elevation value F(k, l) is estimated by interpolating the elevation values of the 3D points within the patches to produce the descriptor for the point p.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
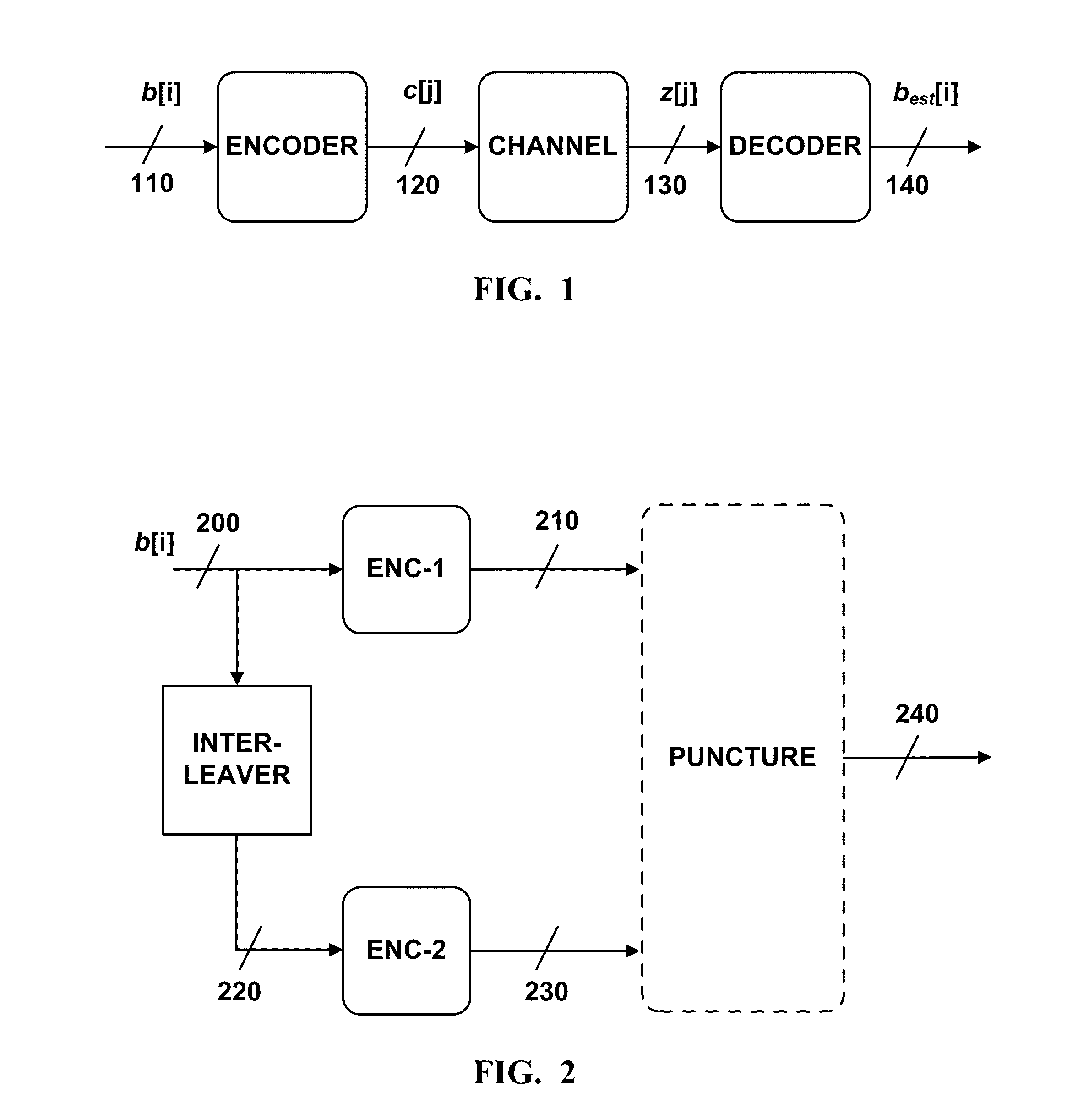
Method for video decoder memory reduction
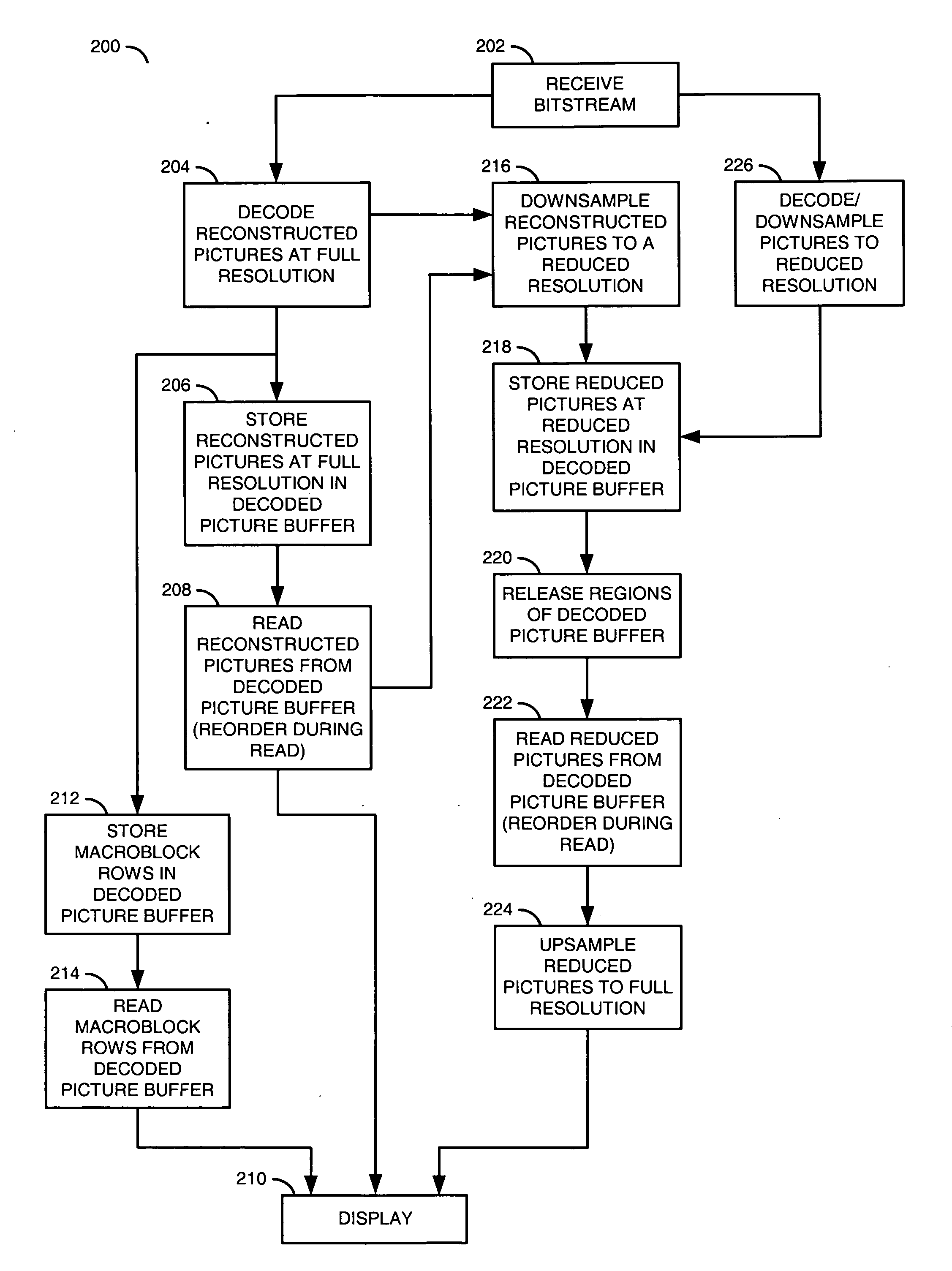
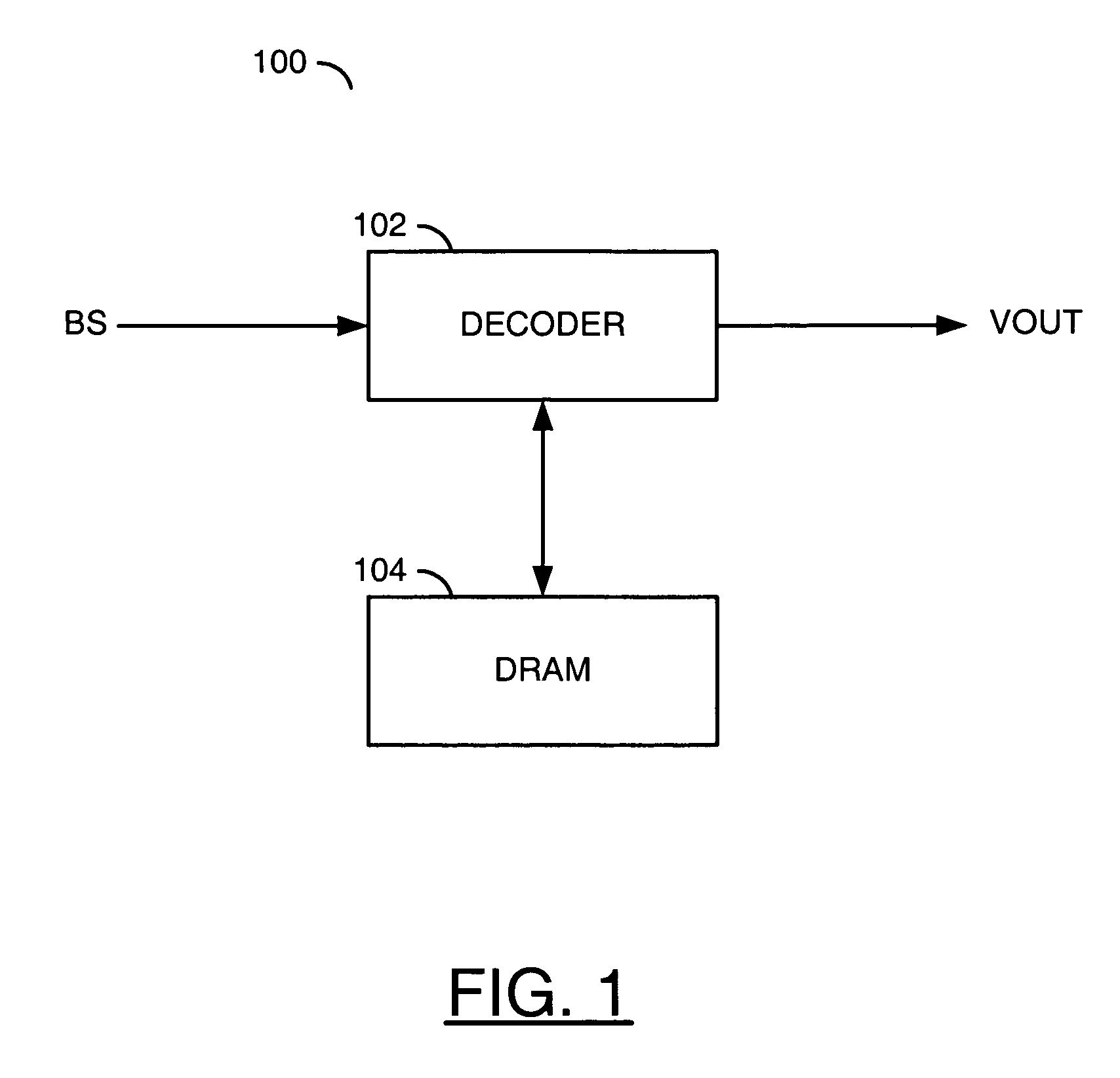
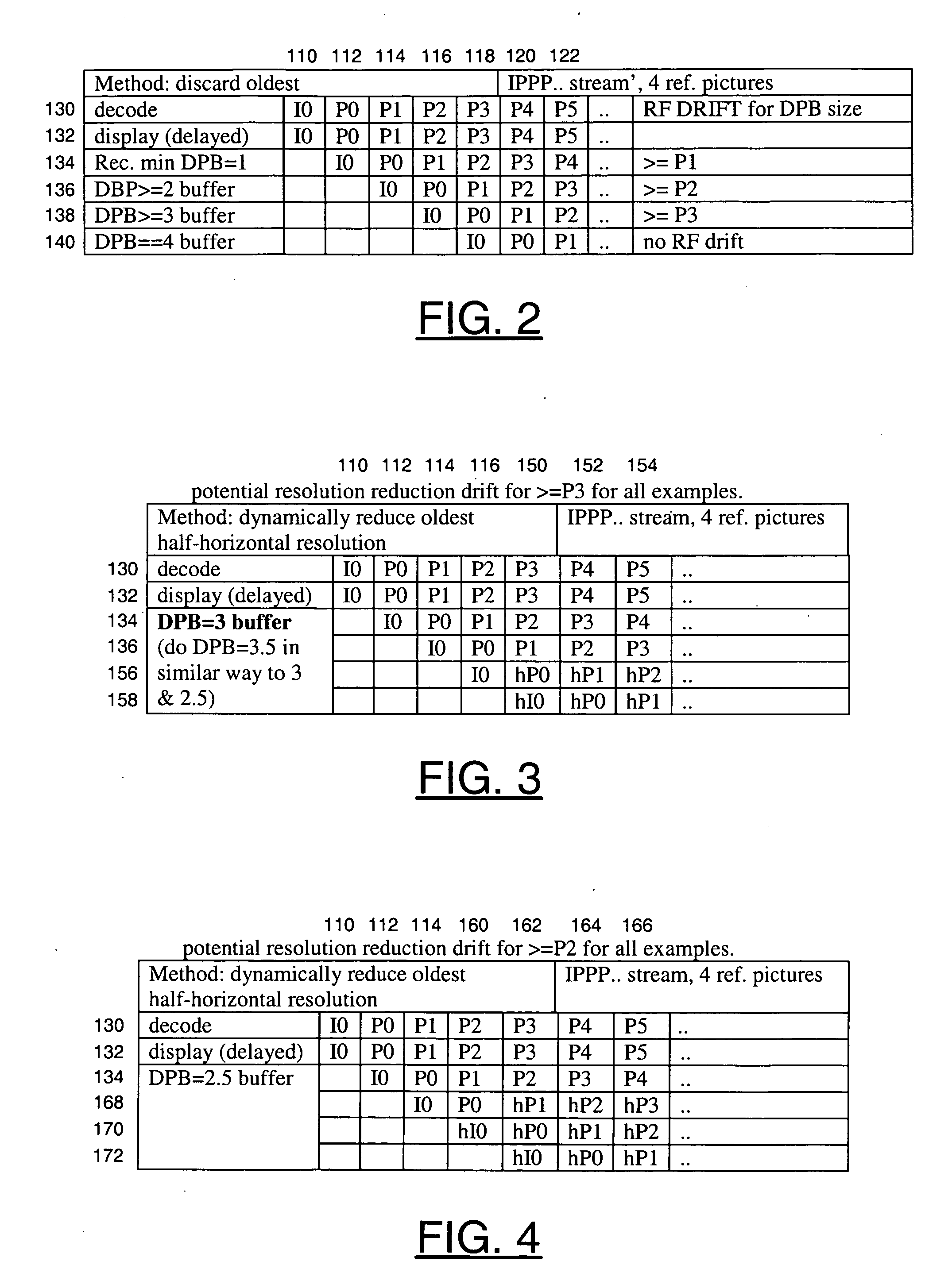
ActiveUS20080025407A1Small sizeBetter trade-offTelevision system detailsColor television with pulse code modulationComputer hardwareImage resolution
A method for video decoding is disclosed. The method generally includes the steps of (A) decoding a first picture from a bitstream, the first picture having a first resolution, (B) storing the first picture at the first resolution in a memory and (C) storing the first picture at a second resolution in the memory, wherein the second resolution is lower than the first resolution.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
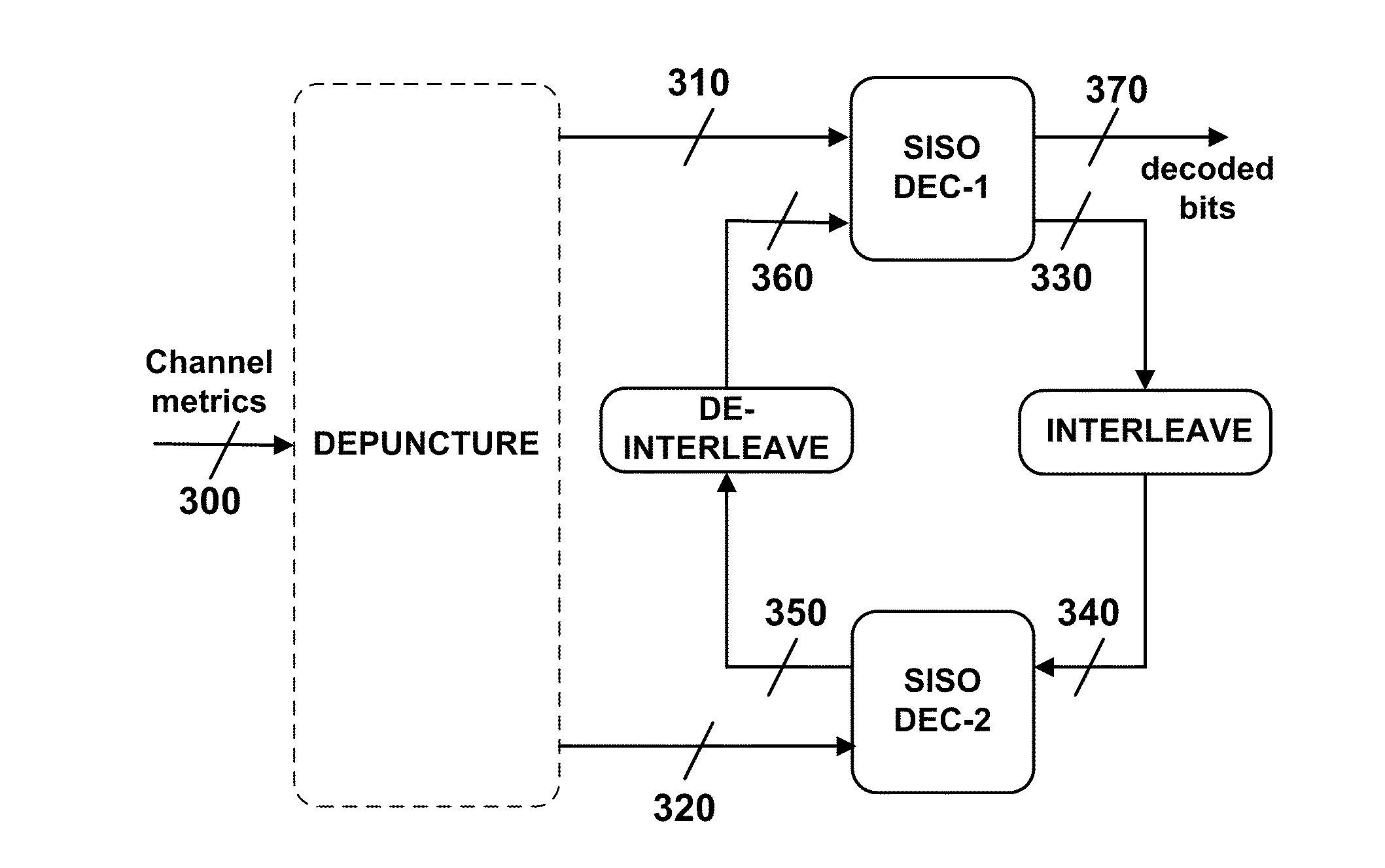
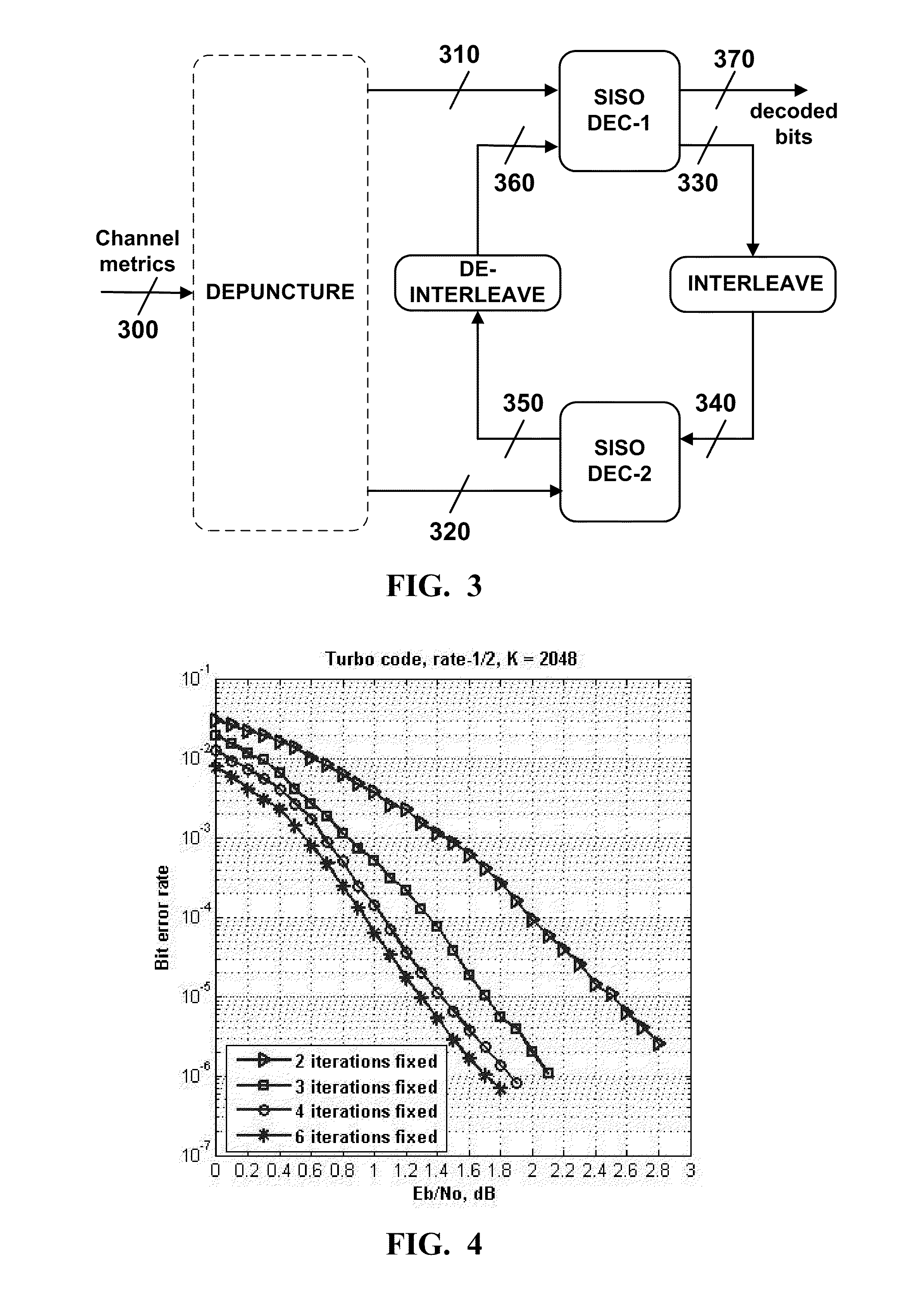
Tunable early-stopping for decoders
ActiveUS20110113294A1Better trade-offOther decoding techniquesCode conversionEarly stoppingComputer science
Owner:TRELLIS WARE TECH
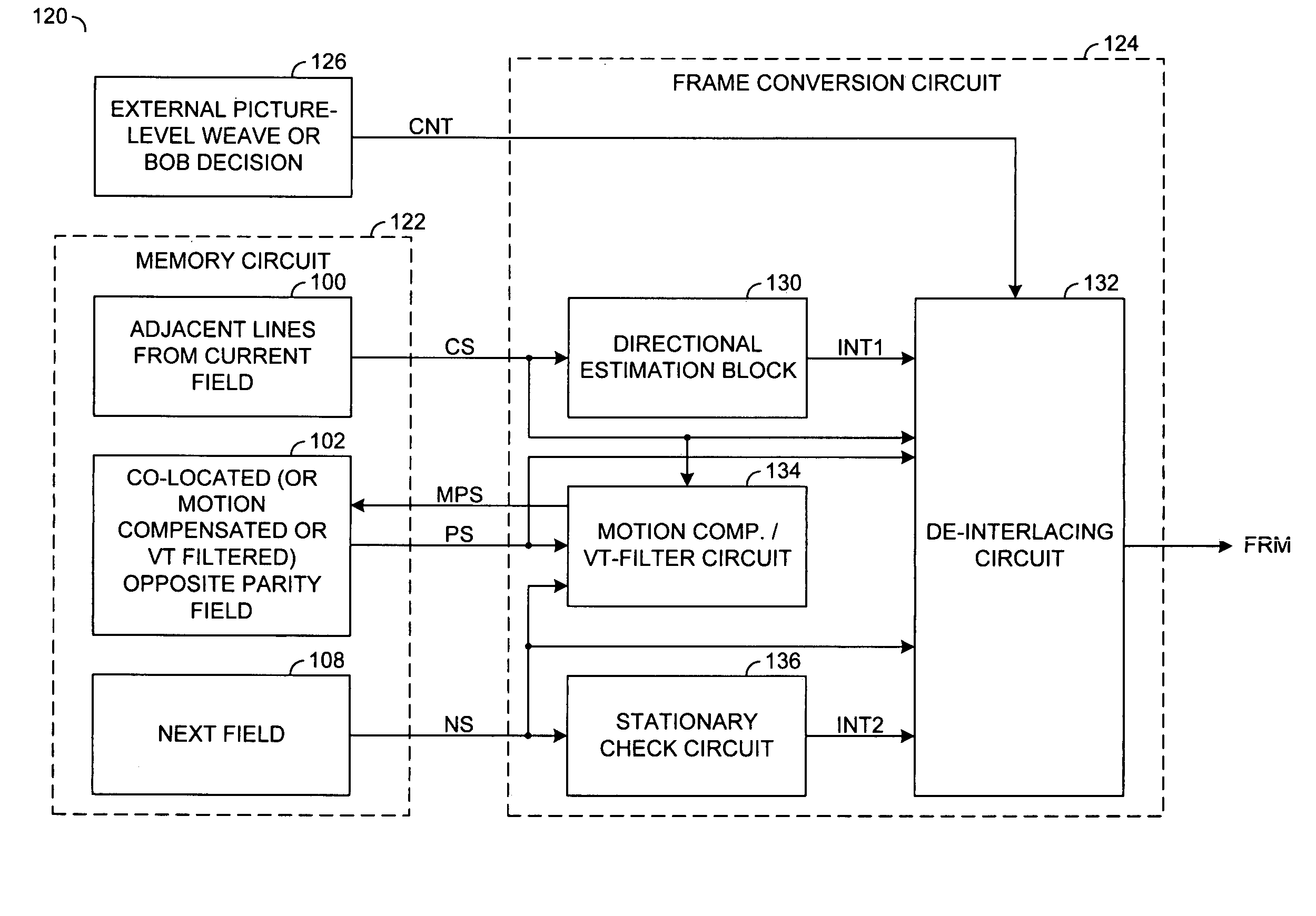
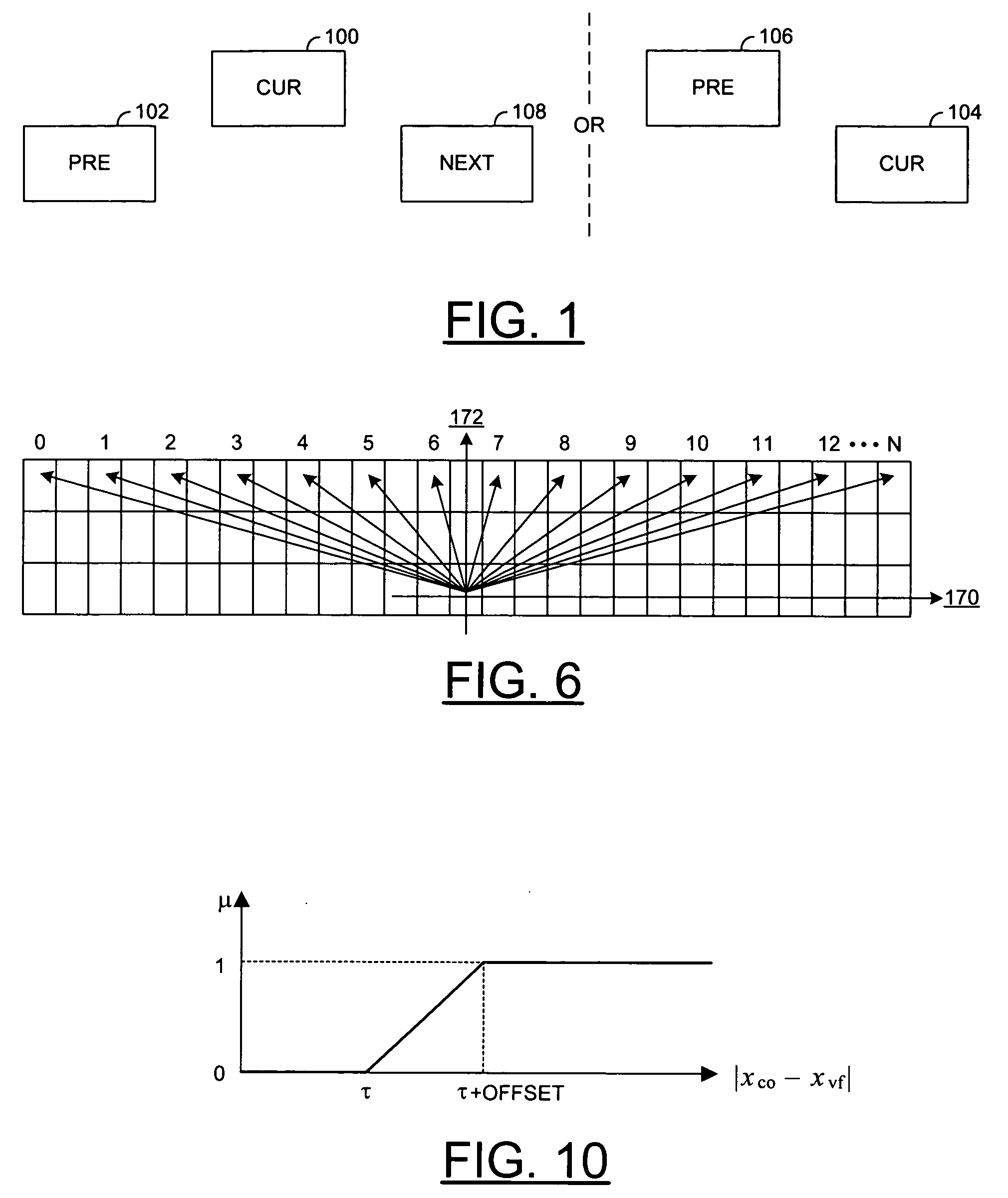
Method and apparatus for video and image deinterlacing and format conversion
ActiveUS7170561B2Minimal memory bandwidthQuality improvementTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesCurrent sampleField line
A method and apparatus for deinterlacing a picture is disclosed. The method generally includes the steps of (A) calculating a plurality of differences among a plurality of current samples from a current field of the picture, the differences being calculated along a plurality of line segments at a plurality of angles proximate a particular position between two field lines from the current filed, (B) generating a first sample at the particular position by vertical filtering the current field in response to the differences indicating that the particular position is a non-edge position in the picture and (C) generating a second sample at the particular position by directional filtering the current field in response to the differences indicating that the particular position is an edge position in the picture.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
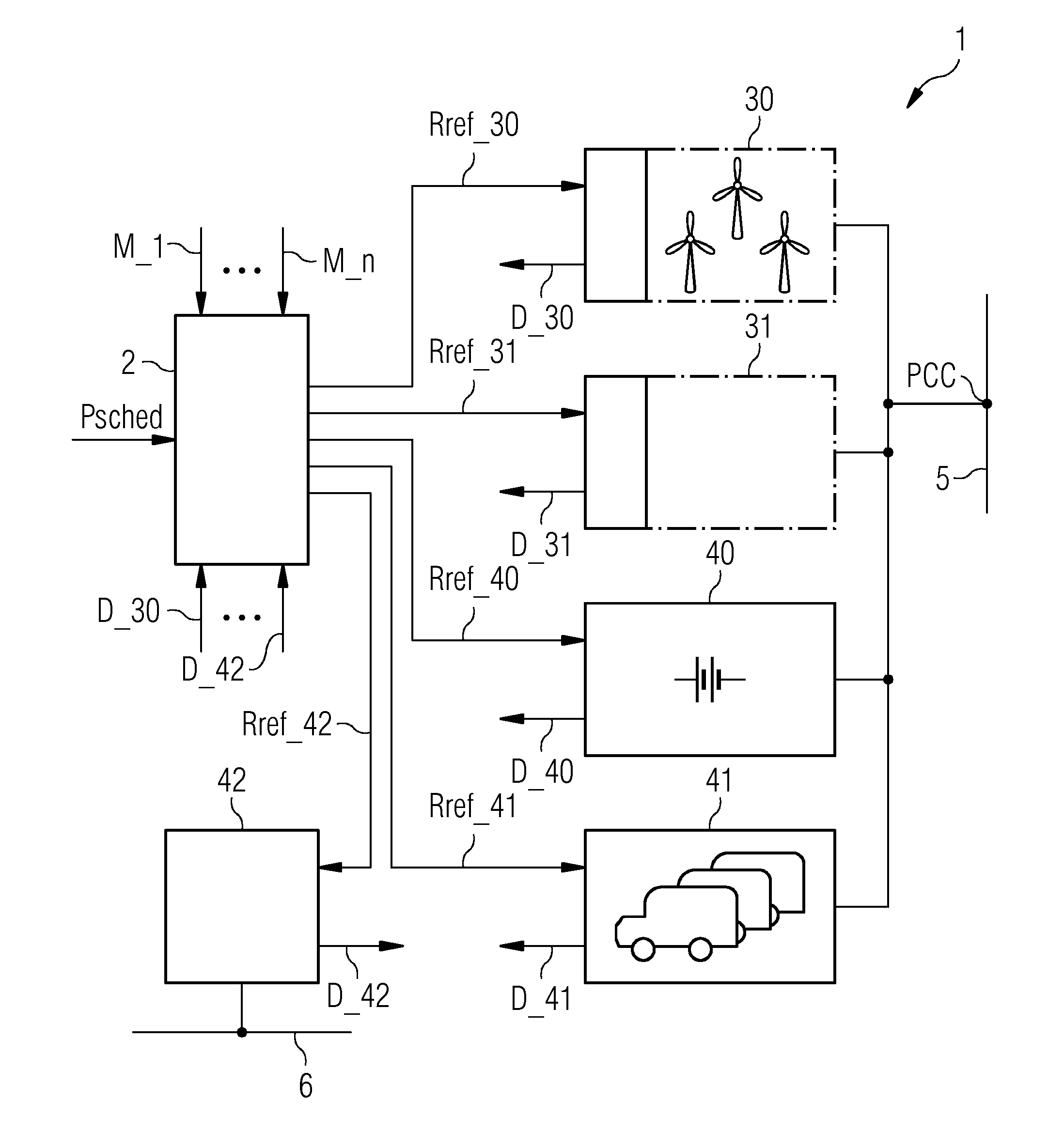
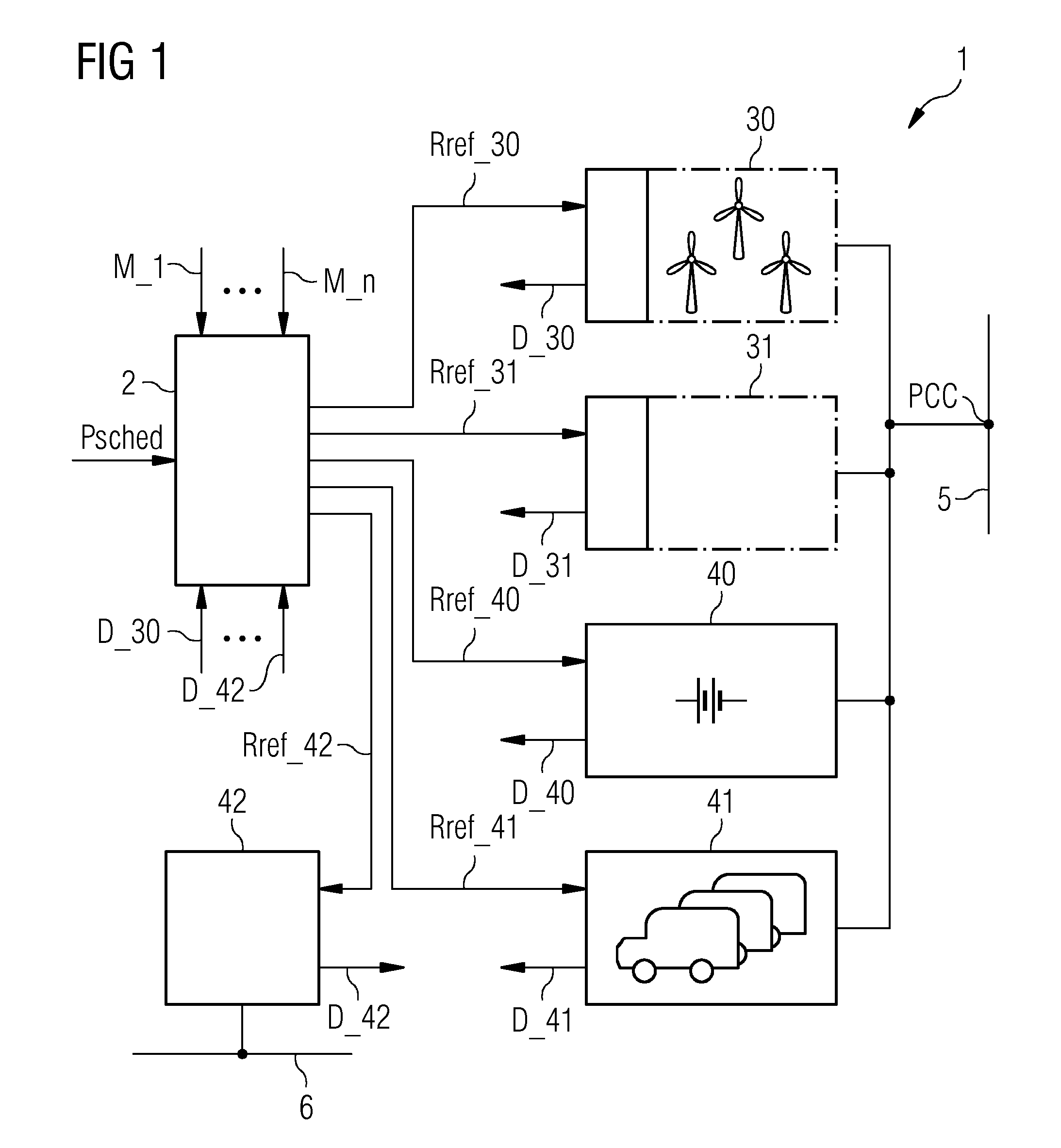
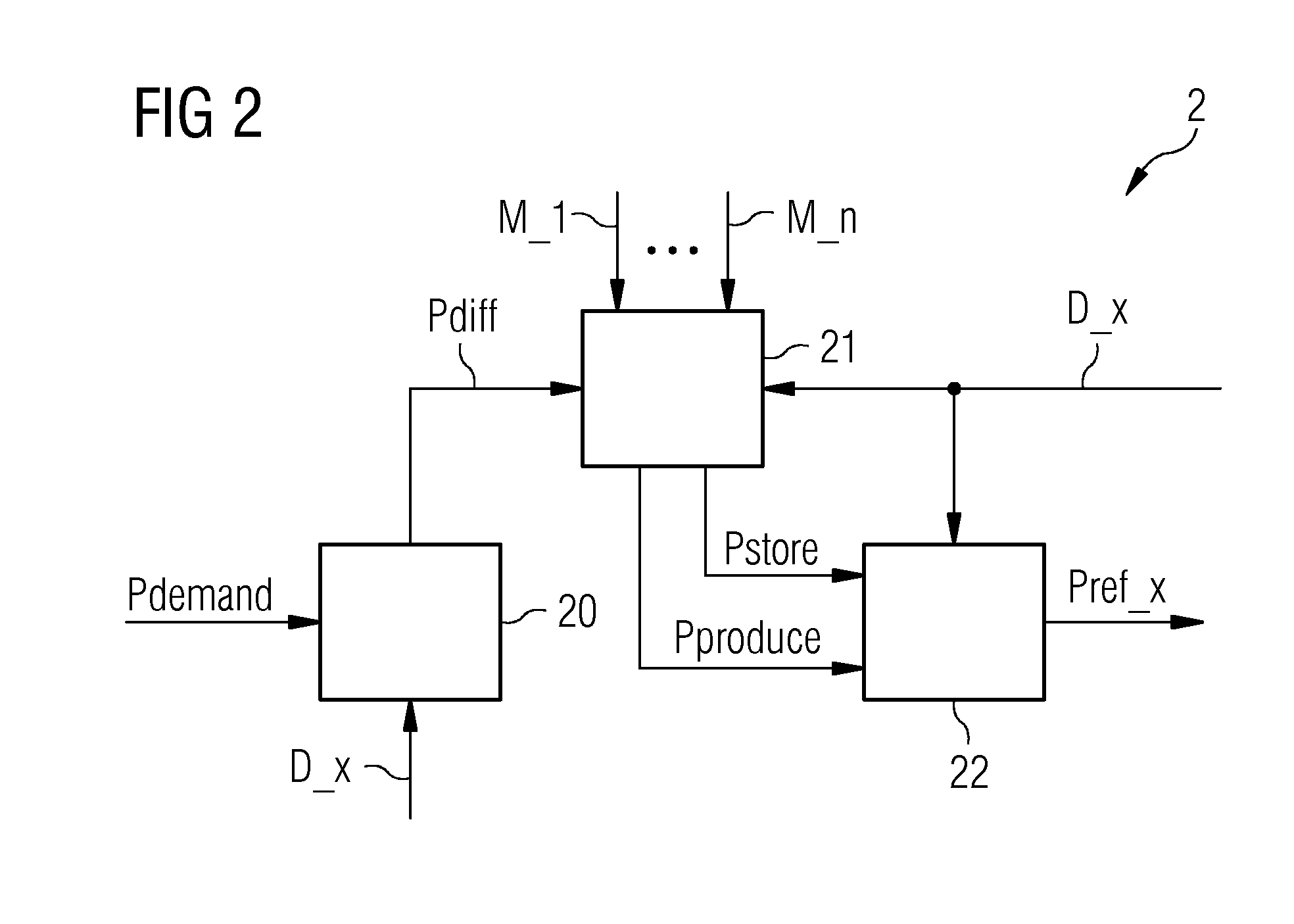
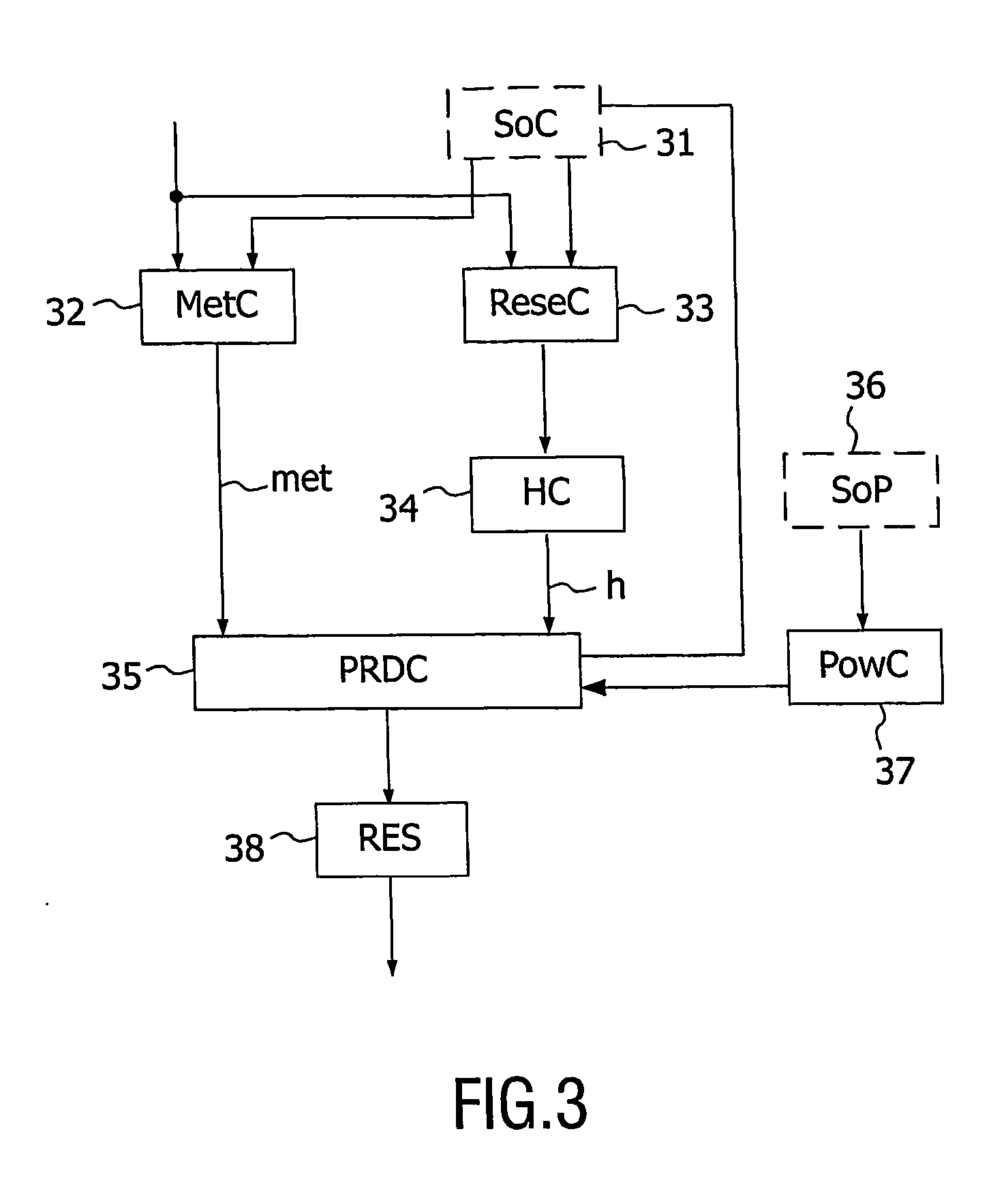
Method of controlling a power network
ActiveUS20140142779A1Way of increaseSmoothen power production of powerLevel controlEmission reduction for energy storagePower gridEngineering
A method is provided for controlling a power network that includes a plurality of power generation facilities connected to an electricity grid and a plurality of power storage facilities connected to the power generation facilities. The method includes monitoring a production capacity of the power generation facilities, monitoring a storage capacity of the power storage facilities and determining an optimal facility control plan on the basis of the storage capacity and the production capacity. The method further includes operating the power network, according to the facility control plan, to feed power from the power generation facilities into the electricity grid and / or to transfer power from the power generation facilities to the power storage facilities and / or to consume power from the power storage facilities.
Owner:SIEMENS GAMESA RENEWABLE ENERGY AS
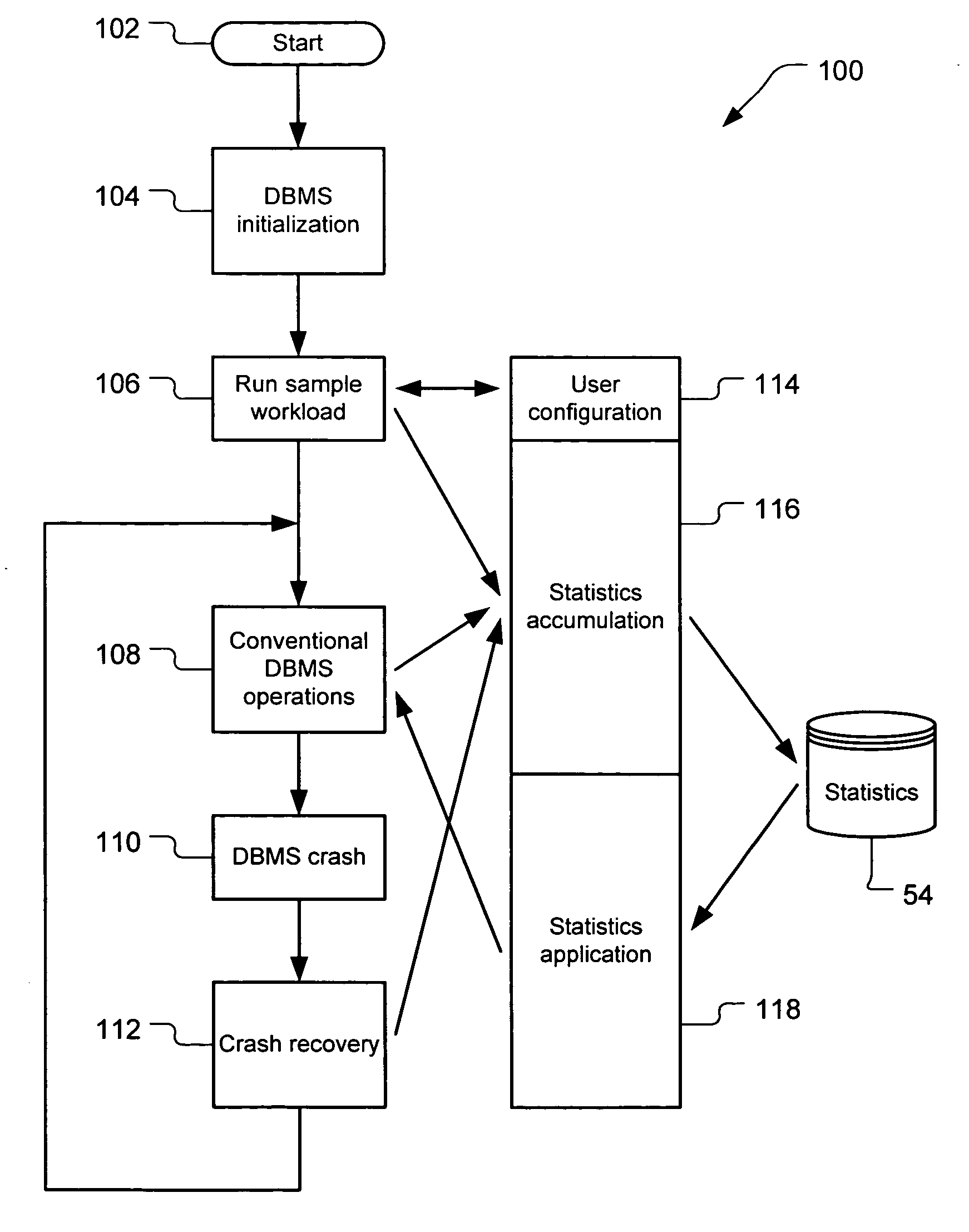
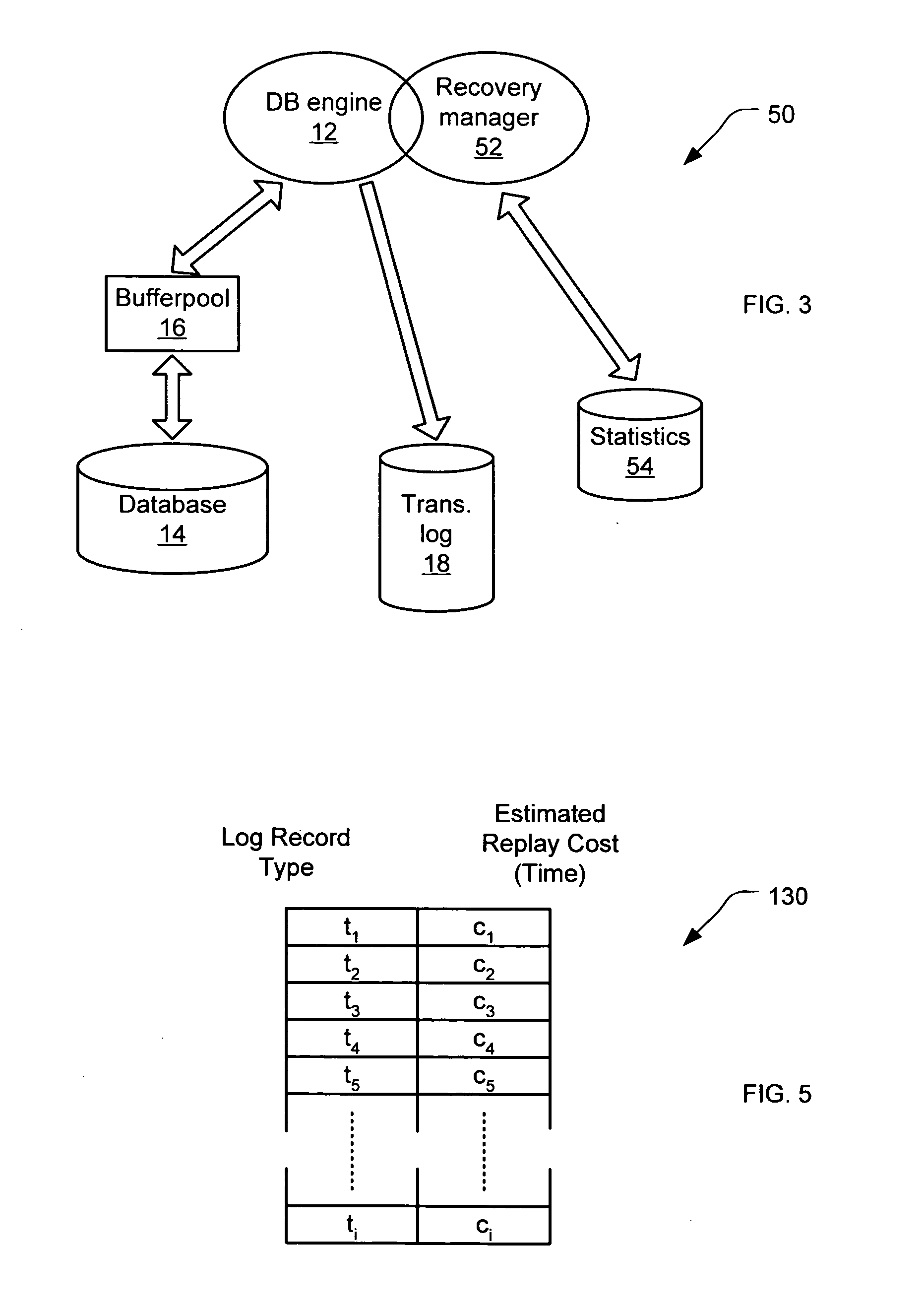
System for deterministic database recovery time
ActiveUS20060101083A1Flexible adaptabilityFlexible and adaptableError detection/correctionDigital data processing detailsDatabase serverDeterministic analysis
A system for limiting the amount of time for a database server to perform a crash recovery process. A maximum recovery time for the database server to perform the crash recovery process is specified. An estimated recovery time for the crash recovery process that is less than the maximum recovery time is calculated, based on at least one of a deterministic analysis of cost accumulation during prior instances of the crash recovery process or an empirical analysis of cost accumulation during regular transaction processing in the database server. The crash recovery process is then conformed to the estimated recovery time.
Owner:TWITTER INC
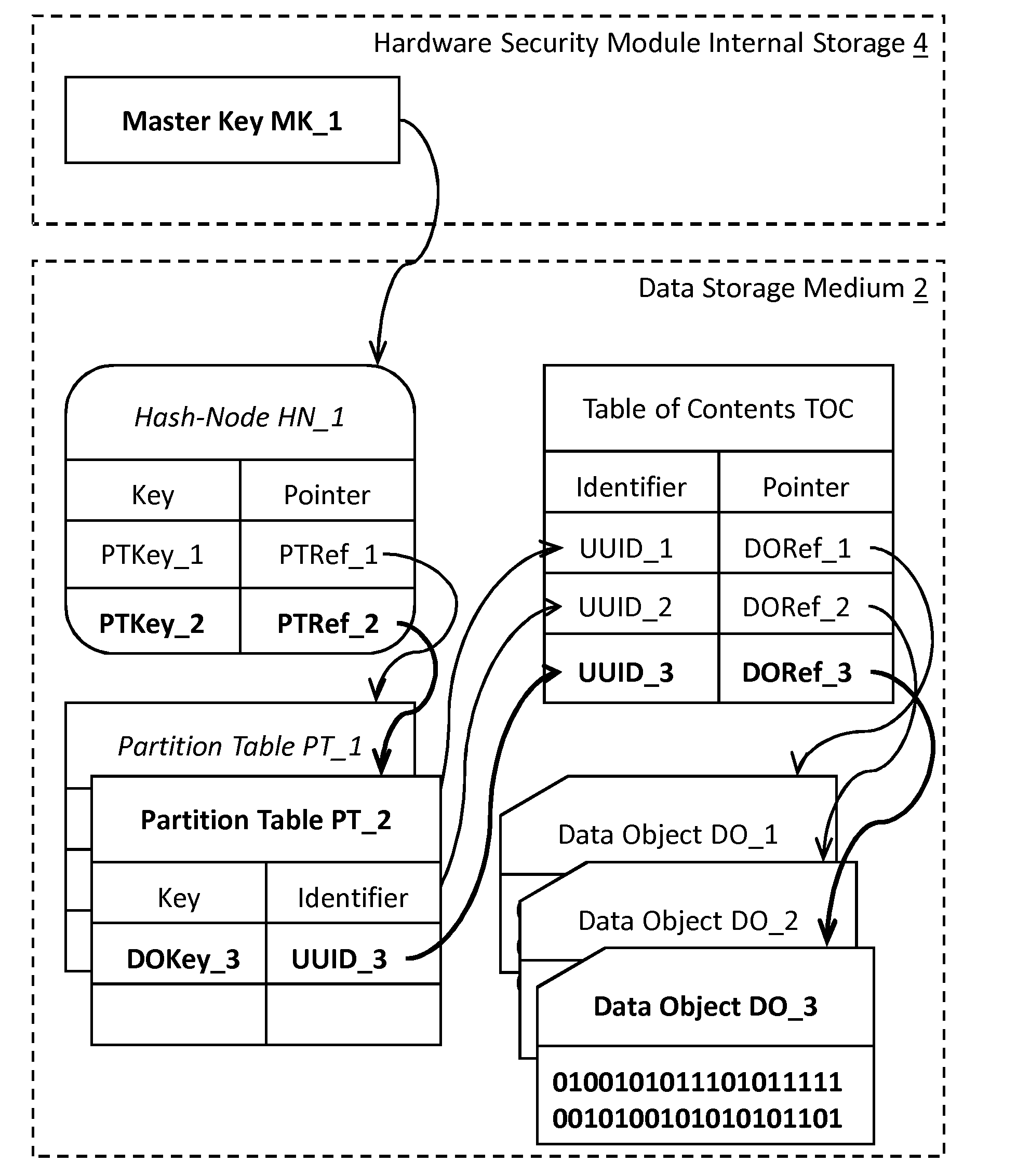
Deletion of content in digital storage systems
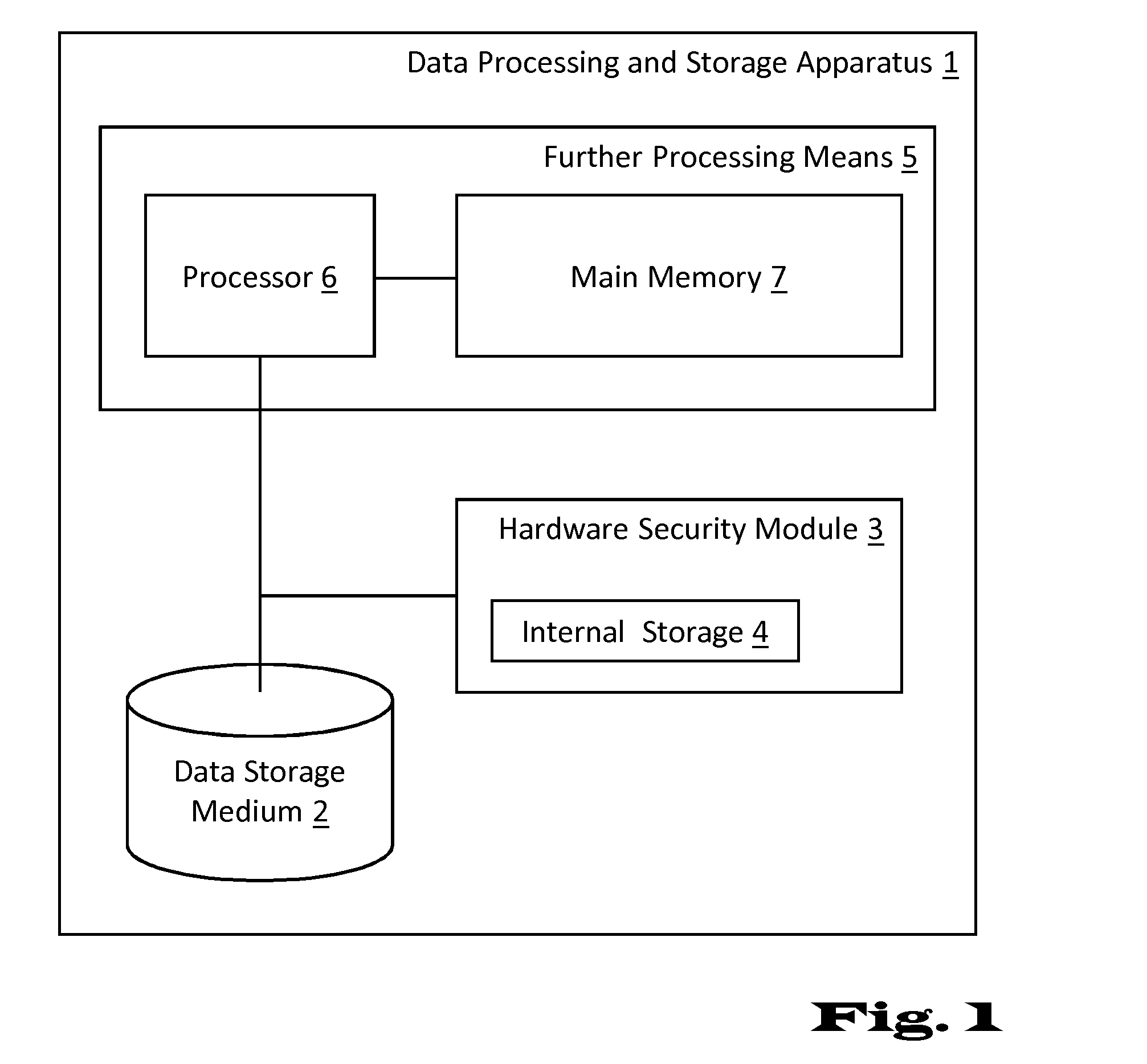
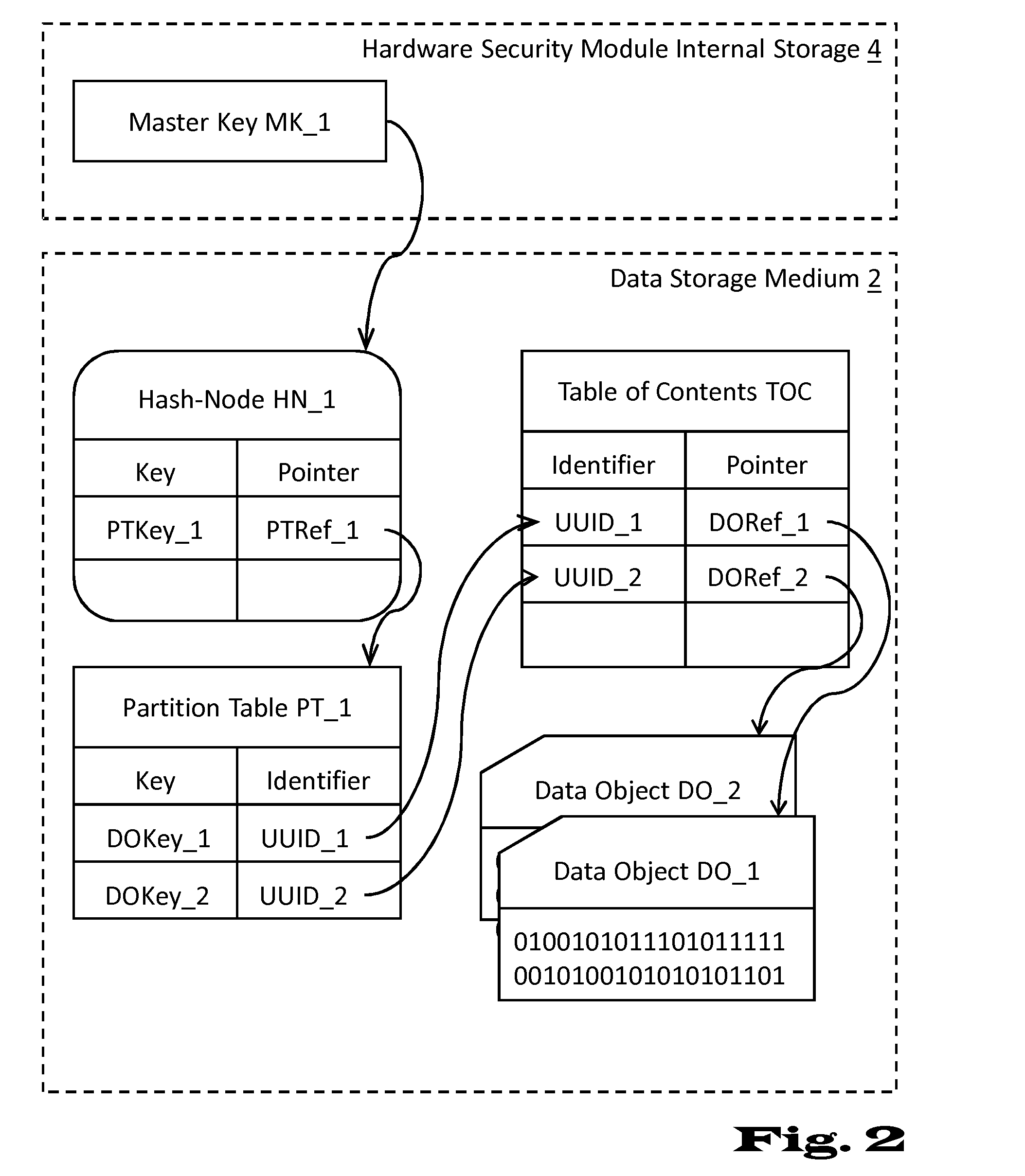
InactiveUS20150143136A1Good storage bandwidth/throughputImprove security levelMemory architecture accessing/allocationMultiple keys/algorithms usageHardware security moduleParallel computing
A data processing and storage apparatus has a hardware security module and a data storage medium storing encrypted data objects and a hierarchical data maintenance structure of encrypted partition tables and hash-nodes forming a rooted tree, where a given partition table comprises a first reference to a given encrypted data object and a first cryptographic key for decryption thereof, where a given hash-node comprises a second reference to a partition tables or hash-node and a second cryptographic key being suitable for decryption thereof, and where the root node is decipherable using a master cryptographic key stored in the hardware security module, the given data object being assigned to the root node via the first and second references of the given partition table and the given hash-nodes forming a set of successive nodes in the rooted tree.
Owner:IBM CORP
Entropy encoding and decoding scheme using VLC coding and pipe or entropy coding for high compression efficiency
ActiveUS9083374B2Improve compression efficiencyModerate codingCode conversionDigital video signal modificationSyntaxComputer science
Decomposing a value range of the respective syntax elements into a sequence of n partitions with coding the components of z laying within the respective partitions separately with at least one by VLC coding and with at least one by PIPE or entropy coding is used to greatly increase the compression efficiency at a moderate coding overhead since the coding scheme used may be better adapted to the syntax element statistics. Accordingly, syntax elements are decomposed into a respective number n of source symbols si with i=1 . . . n, the respective number n of source symbols depending on as to which of a sequence of n partitions into which a value range of the respective syntax elements is sub-divided, a value z of the respective syntax elements falls into, so that a sum of values of the respective number of source symbols si yields z, and, if n>1, for all i=1 . . . n−1, the value of si corresponds to a range of the ith partition.
Owner:GE VIDEO COMPRESSION LLC
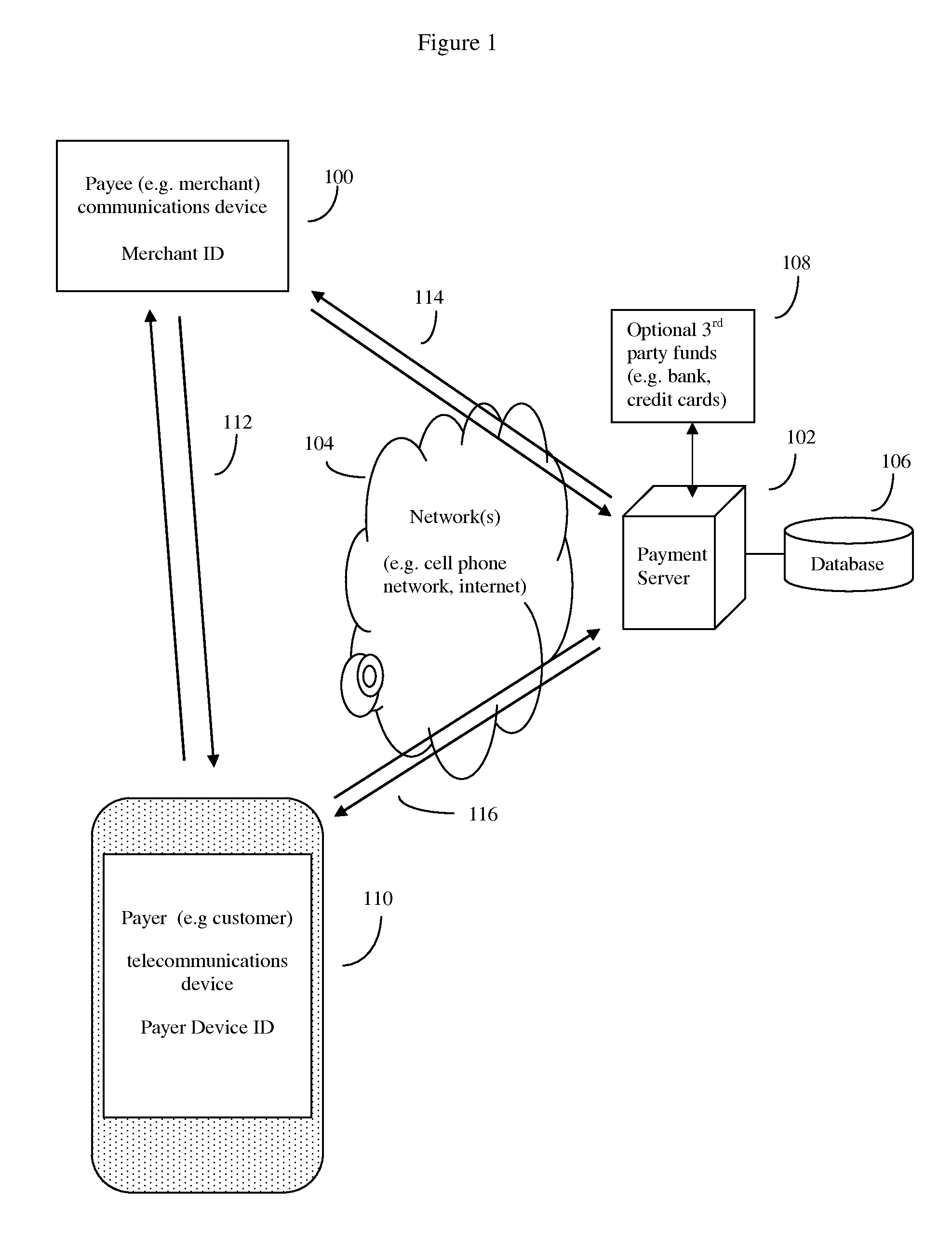
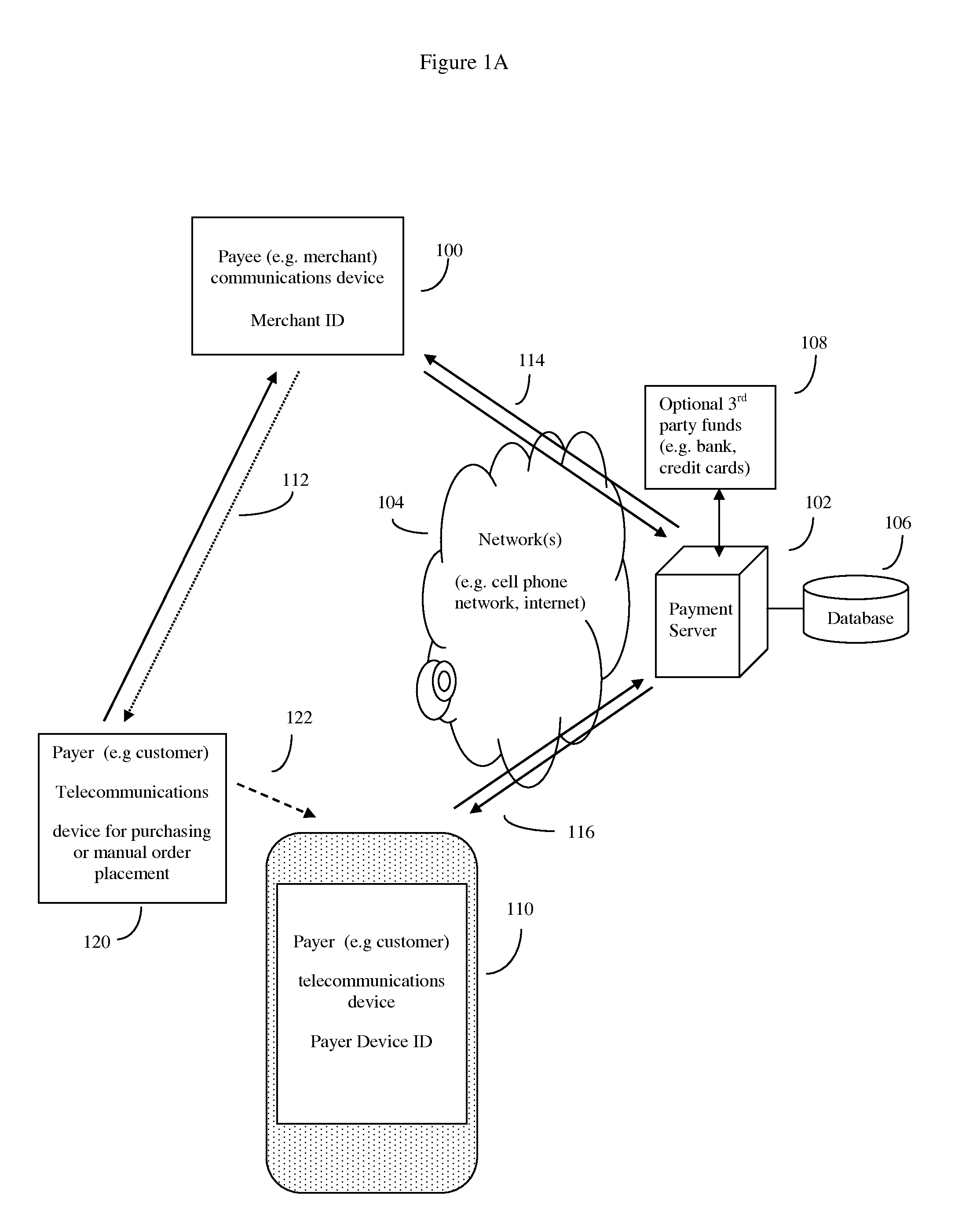
System and method of electronic payment using payee provided transaction identification codes
InactiveUS20140297533A1High degreeImprove convenienceFinancePayment protocolsOperating systemMonetary Amount
Computerized payment method using short, temporary, transaction ID (TID) symbols for secure payer (customer) financial transactions. Payees (e.g. merchants) register their unique ID telecommunications devices (e.g. Smartphone and phone number), and financial institution a payment server. When a payee (merchant) and wish to do a financial transaction, the payee requests a TID from the server for that amount. The server sends a TID to the payee, which the payee then communicates to the payer. The payer in turn relays this TID to the server, which validates the transaction using the payer device. The server then releases funds to the payee. The server preserves records for auditing, but security is enhanced because the merchant never directly accesses the customer's financial account. Use of GPS coordinates and / or payer provided Group IDs may also be used to reduce the number of symbols used in the TID while continuing to ensure uniqueness.
Owner:MITTAL MILLIND
Method and apparatus for measuring viscosity and surface tension
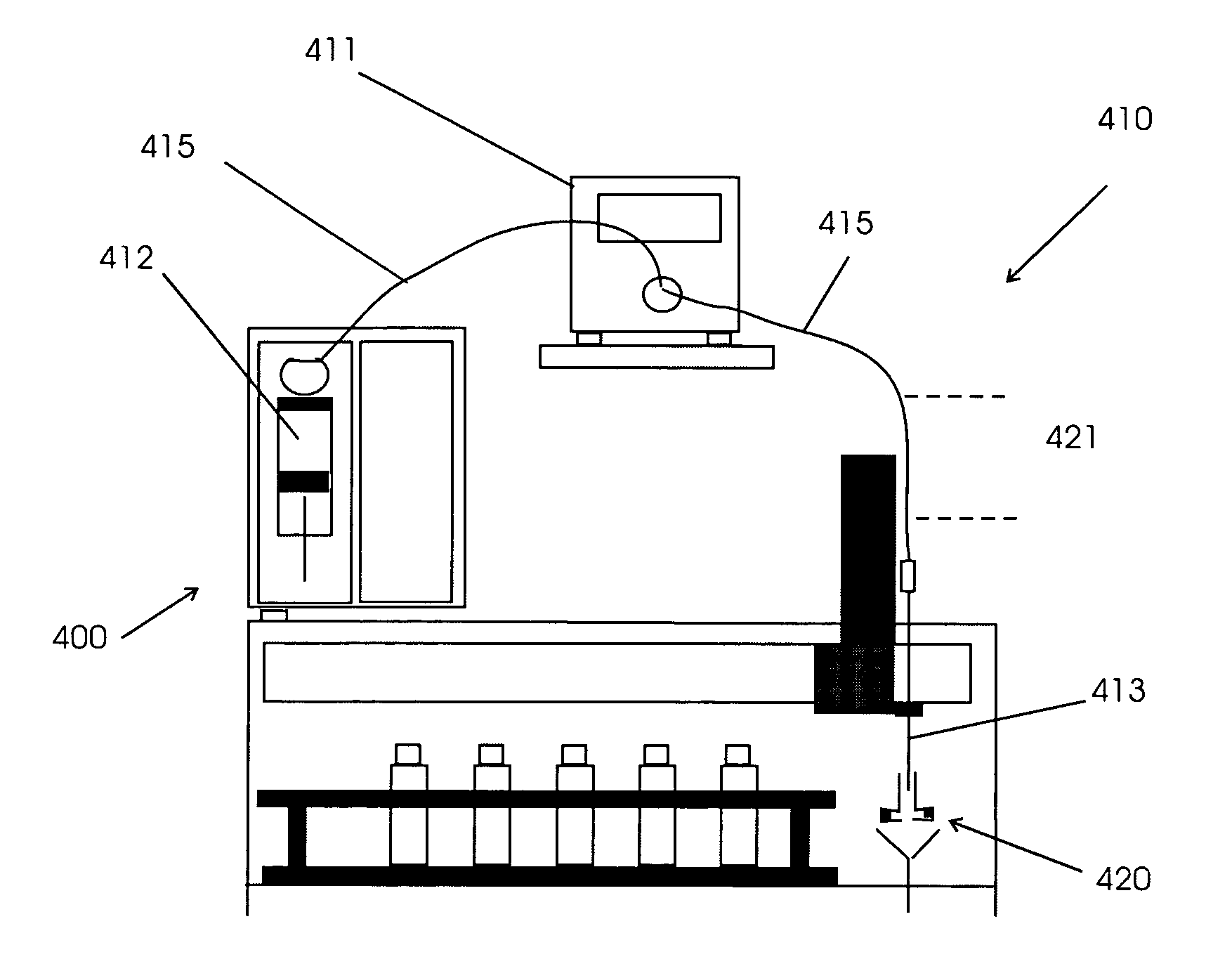
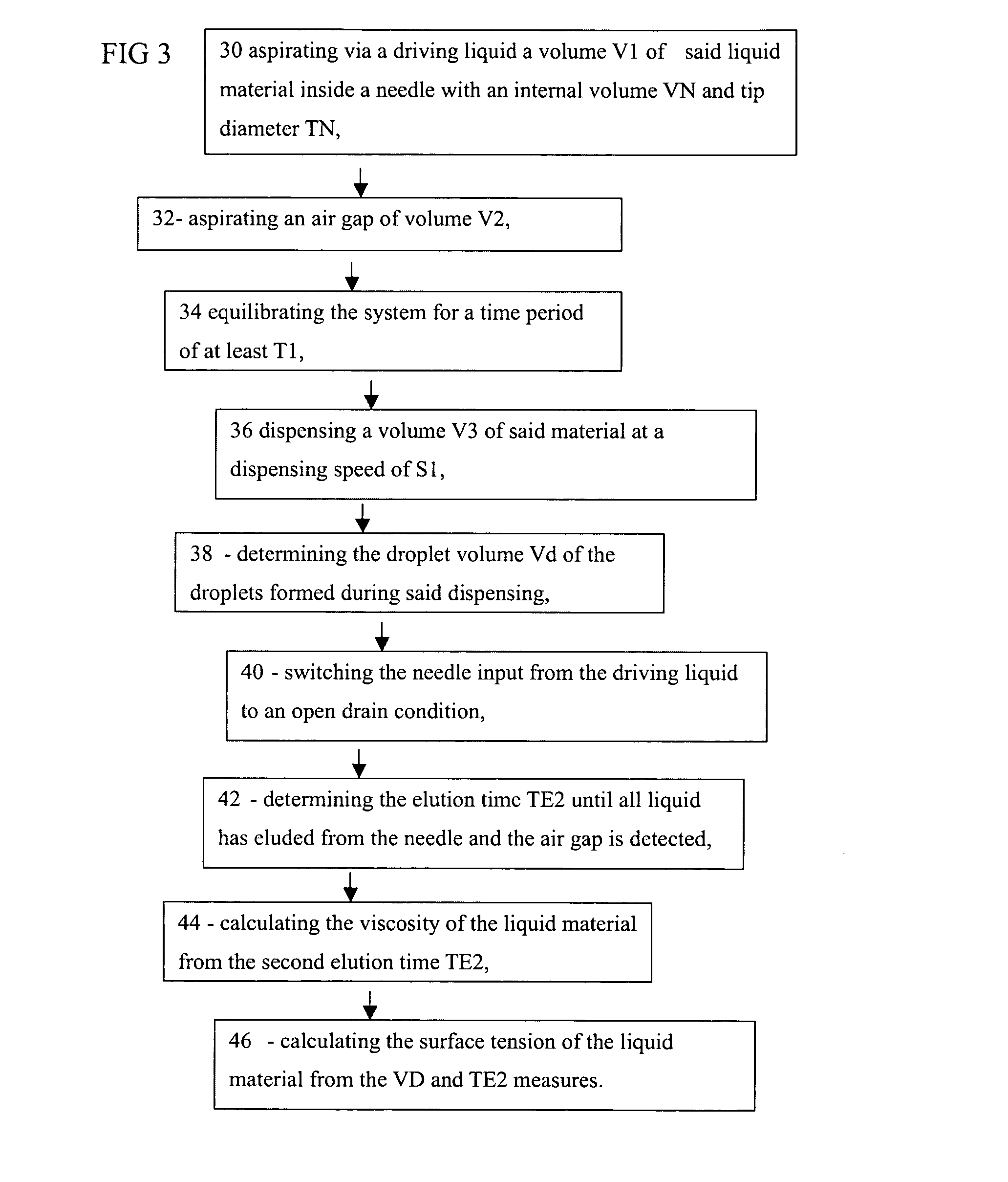
InactiveUS20090320568A1Better trade-offIncrease speedDirect flow property measurementSurface tension analysisPipetteElution
Methods and apparatus for measuring viscosity and / or surface tension of a liquid are described in which droplets are formed at a needle or pipette containing a sample of the test liquid and a size-related characteristic of the droplets such as droplet size, volume, diameter, or weight of the test liquid are measured by means of by capturing an image of the droplets and obtaining the size-related characteristic from the captured image. Subsequently or previously, a volume of the same sample of the test liquid is drained from the needle or pipette under pump pressure or a hydrostatic pressure, and an elution time is measured. The method and apparatus allows or includes determining the viscosity from the elution time, and determining the surface tension from the viscosity and the size-related characteristic of the droplet such as droplet size, volume, diameter, or weight of the test liquid.
Owner:FLAMAC
Finite field serial-serial multiplication/reduction structure and method
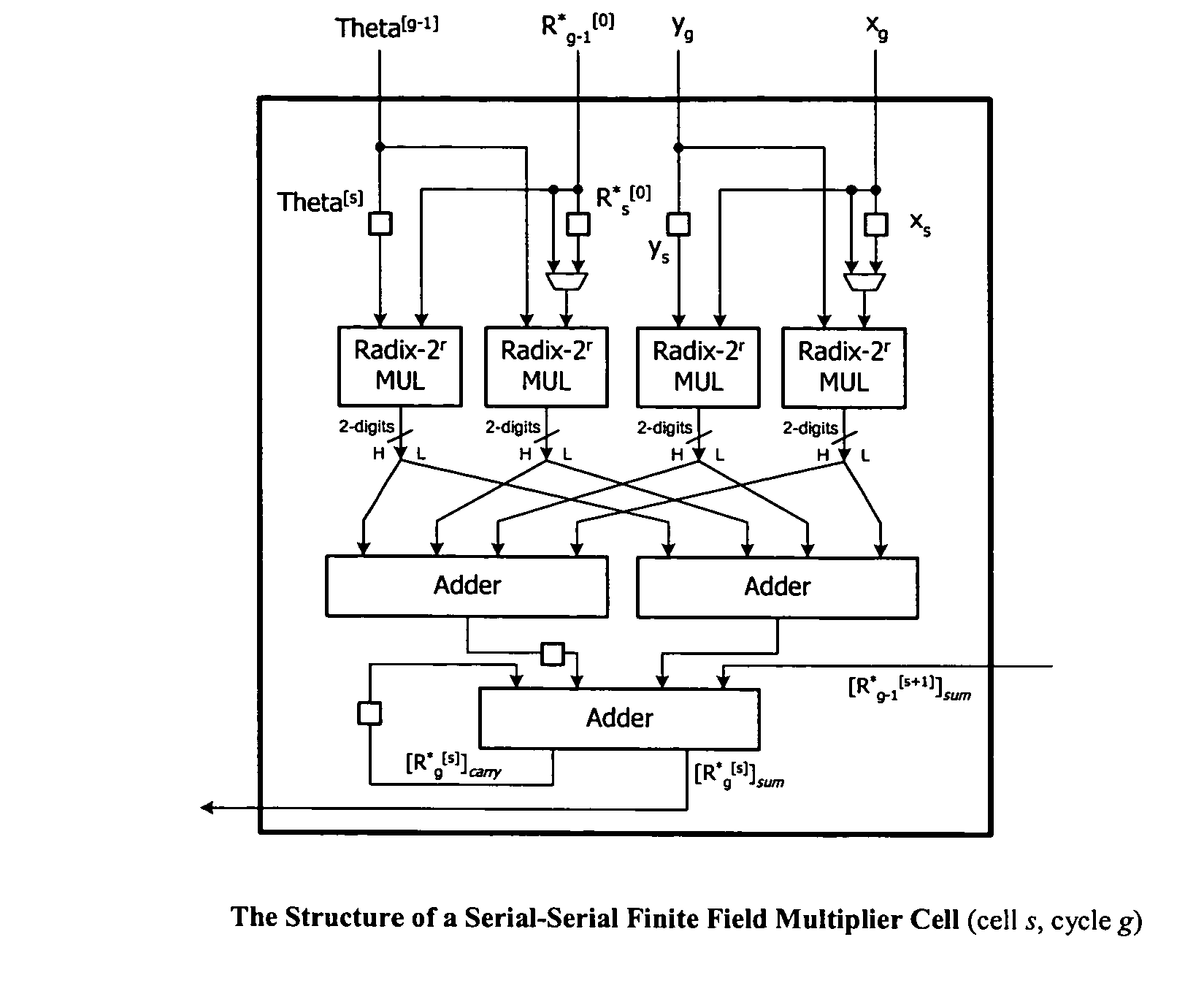
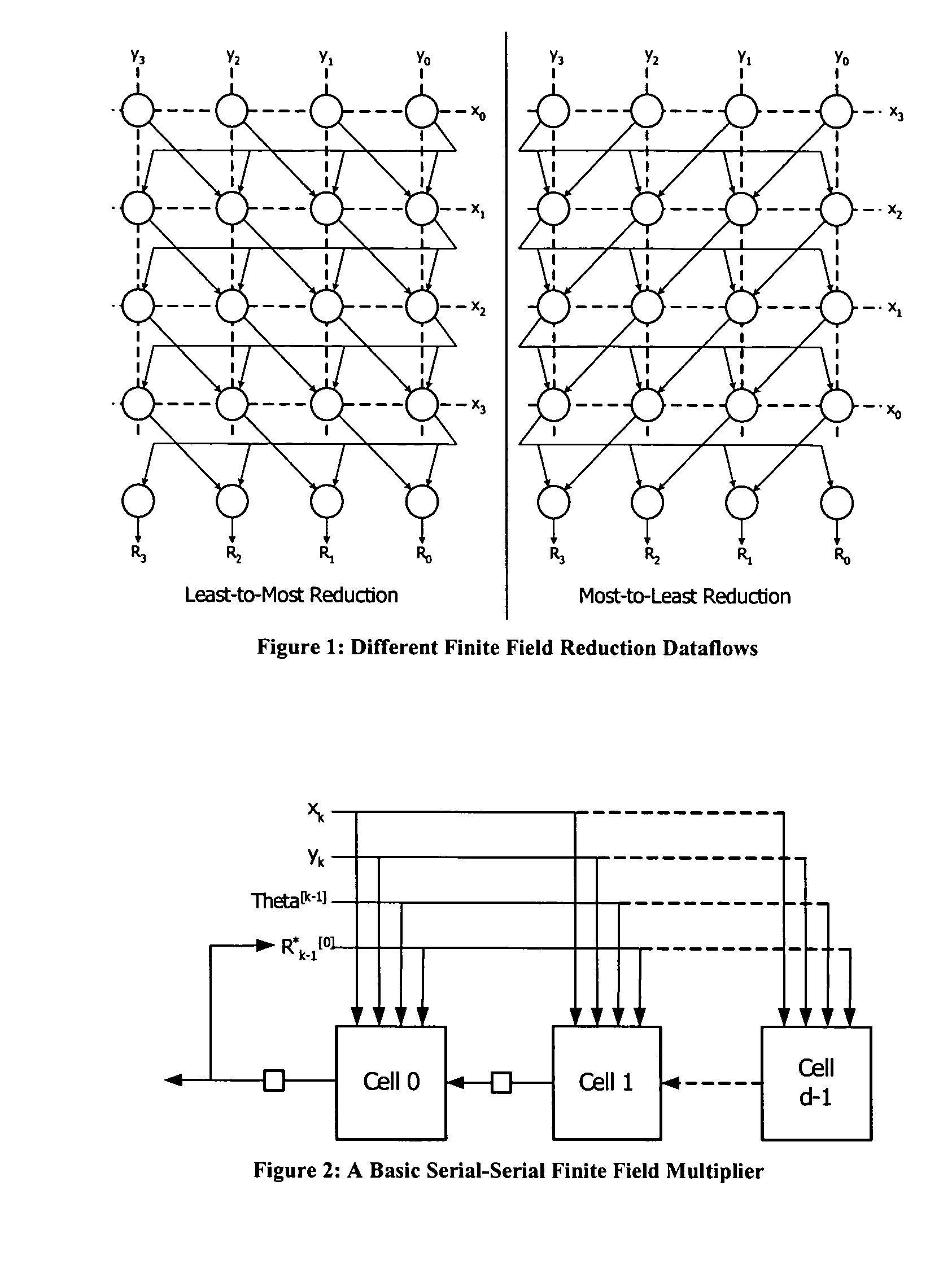
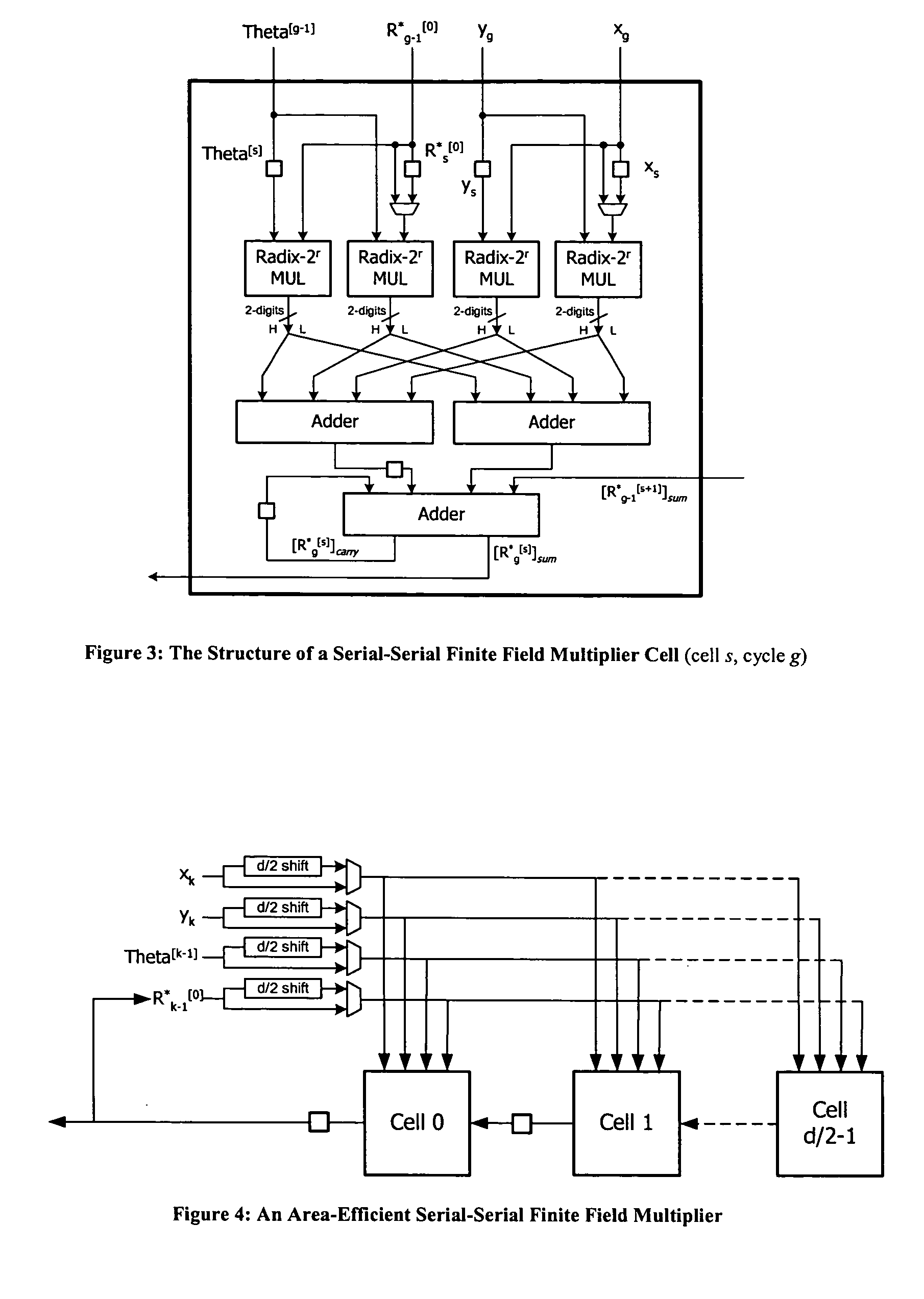
InactiveUS20050267926A1Reduce bus widthCommunication securityDigital computer detailsComputations using residue arithmeticSerial transferBinary multiplier
The present invention contemplates a method or cryptographic system for communicating securely over an insecure communication channel of the type which communicates a message from a transmitter to a receiver. The method includes the step of providing a finite filed serial-serial multiplication / reduction structure wherein an initial delay and clock-cycle are inherently independent of word length and wherein input operands are serially entered one digit at a time and the output result is computed serially one digit at a time, wherein the digit size can be one bit or more. As disclosed, the multiplication structure is scalable and a serial transfer reduces the bus width needed to transfer data back and forth between memory and a multiplication / reduction step. A finite field multiplication structure in which an operand multiplication and a finite field reduction are formulated as a serial-serial computation is also disclosed. Further, a digit serial-serial finite field multiplication / reduction method and structure as an integral operation in a cryptographic system is disclosed. In such methods and structures, the inherent word length independence of the initial delay is achieved by defining both operand multiplication and field reduction as serial-serial computation. In such computations, all of the numbers needed for the computation are fed serially one digit at a time. Therefore, the inter-connection between the memory module and the multiplier module need only to support the transfer of data one digit at a time.
Owner:KING FAHD UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND MINERALS
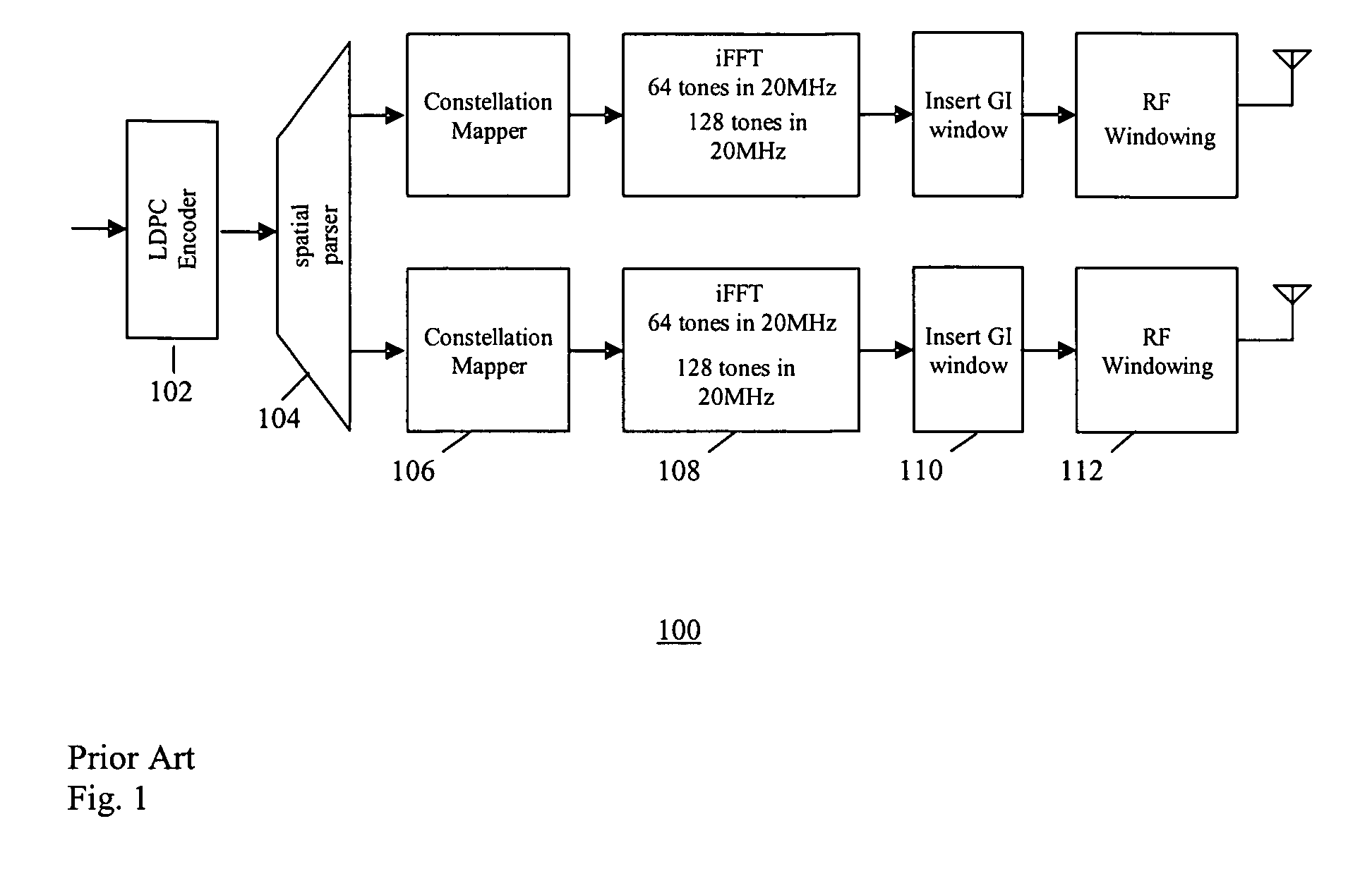
Method of encoding for handheld apparatuses
ActiveUS20060209953A1Video decoder or a video encoder, to be reducedBetter trade-offColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionHand held devicesTheoretical computer science
The present invention relates to a method of encoding a sequence of pictures, a picture being divided into blocks of data, said encoding method comprising the steps of:—computing a residual error block from a difference between a current block contained in a current picture and a candidate area using of a prediction function,—computing an entropy of the residual error block,—computing an overall error between said current block and said candidate area,—estimating a power consumption of a video processing device adapted to implement said prediction function,—computing a rate-distortion value on the basis of the entropy, the overall error and the estimated power consumption of the video processing device, —applying the preceding steps to a set of candidate areas using a set of prediction functions in order to select a prediction function according to the rate-distortion value.
Owner:NXP BV
Method of generating structured irregular low density parity checkcodes for wireless systems
InactiveUS20070136635A1High diversity orderInterleaving capabilityError detection/correctionCode conversionDiversity schemeSystem parameters
A method of generating structured irregular LDPC codes for a wireless network such as a wireless local area network (WLAN) system, allowing systematic generation of improved code ensembles using density evolution, and providing essentially the best tradeoff between decoding threshold and decoding complexity. Such an LDPC code has a higher diversity order for MIMO systems, with better built-in interleaving capability. Further, the code dimension can be tailored to 802.11n system parameters such as the number of sub-carriers and delay. The code also provides an improved girth control scheme, provides flexible length with different expanding factors, and supports simple encoding and shortening for multiple rates.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Methods of antenna selection for downlink MIMO-OFDM transmission over spatial correlated channels
InactiveUS7657244B2Low costImprove performanceSpatial transmit diversityModulated-carrier systemsSpatial correlationChannel state information
An antenna selection technique (transmitter / receiver antenna selection) that reduces the cost of the MIMO system while maintaining high performance. A combined selection algorithm for MIMO-OFDM is provided which offers the best tradeoff between spatial correlation and instantaneous SNR. In one case, antenna selection is based on instant channel information. In another case antenna is based on statistical channel state information. In another case, antenna selection is based on a hybrid of instant channel state information and statistical channel state information.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
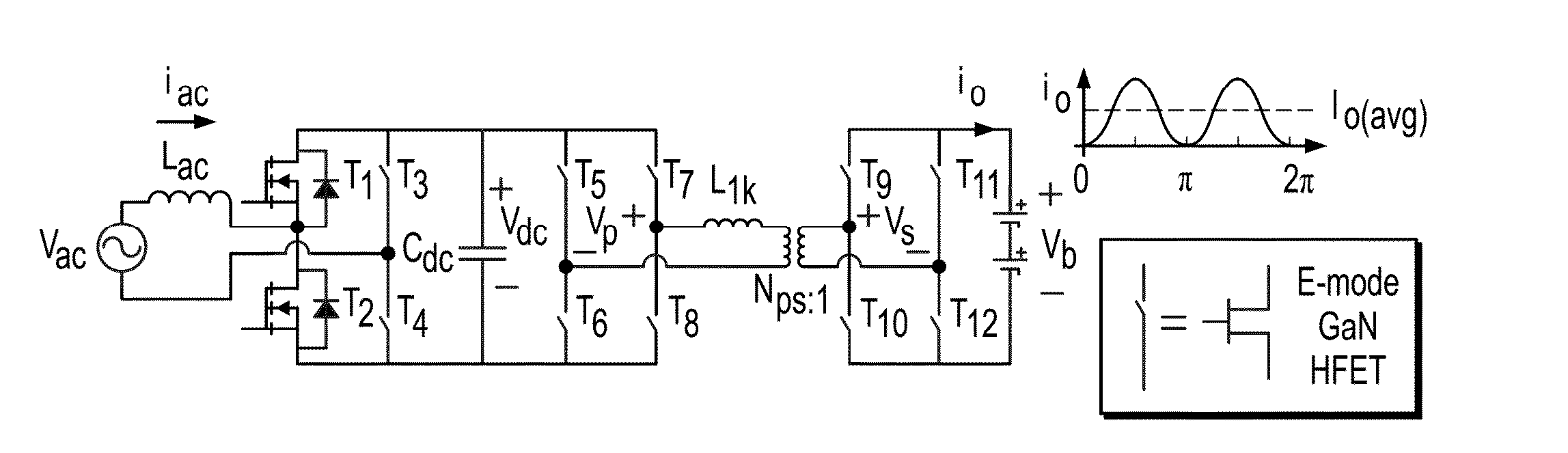
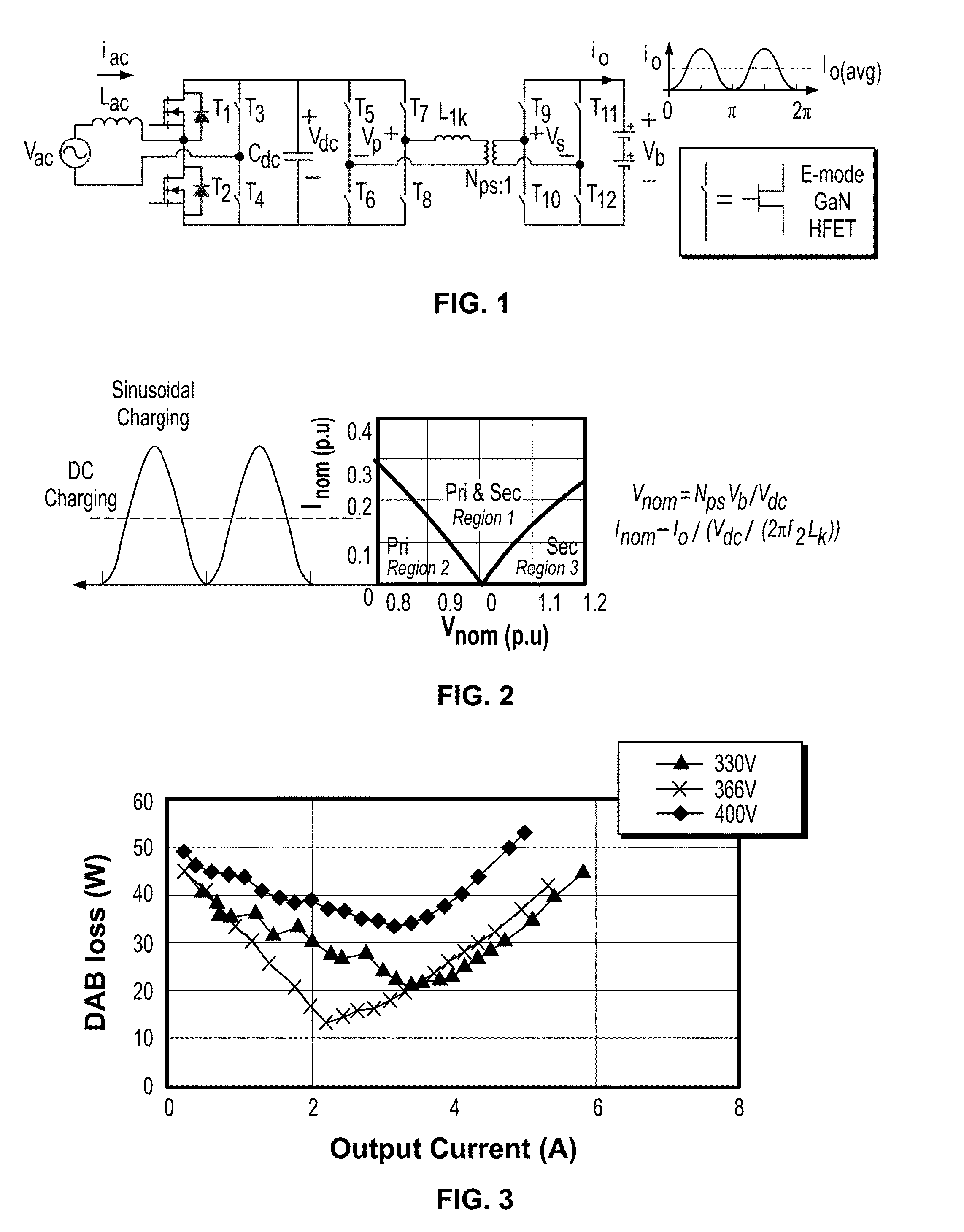
Optimal Battery Current Waveform for Bidirectional PHEV Battery Charger
ActiveUS20160172877A1High densityLong life-timeAc-dc conversionElectric powerDc voltageBattery charger
The present invention provides a battery charger and battery charging method controlled with a charging waveform input of an AC-DC switching circuit to a DC link and a DC-DC stage converter for outputting a regulated DC voltage. The method determining the charging waveform comprising the steps of selecting a Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) zero-off charging waveform signal input to the AC-DC switching circuit and calculating a ripple power at the DC link based on the signal input power and output power of the regulated DC voltage output.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
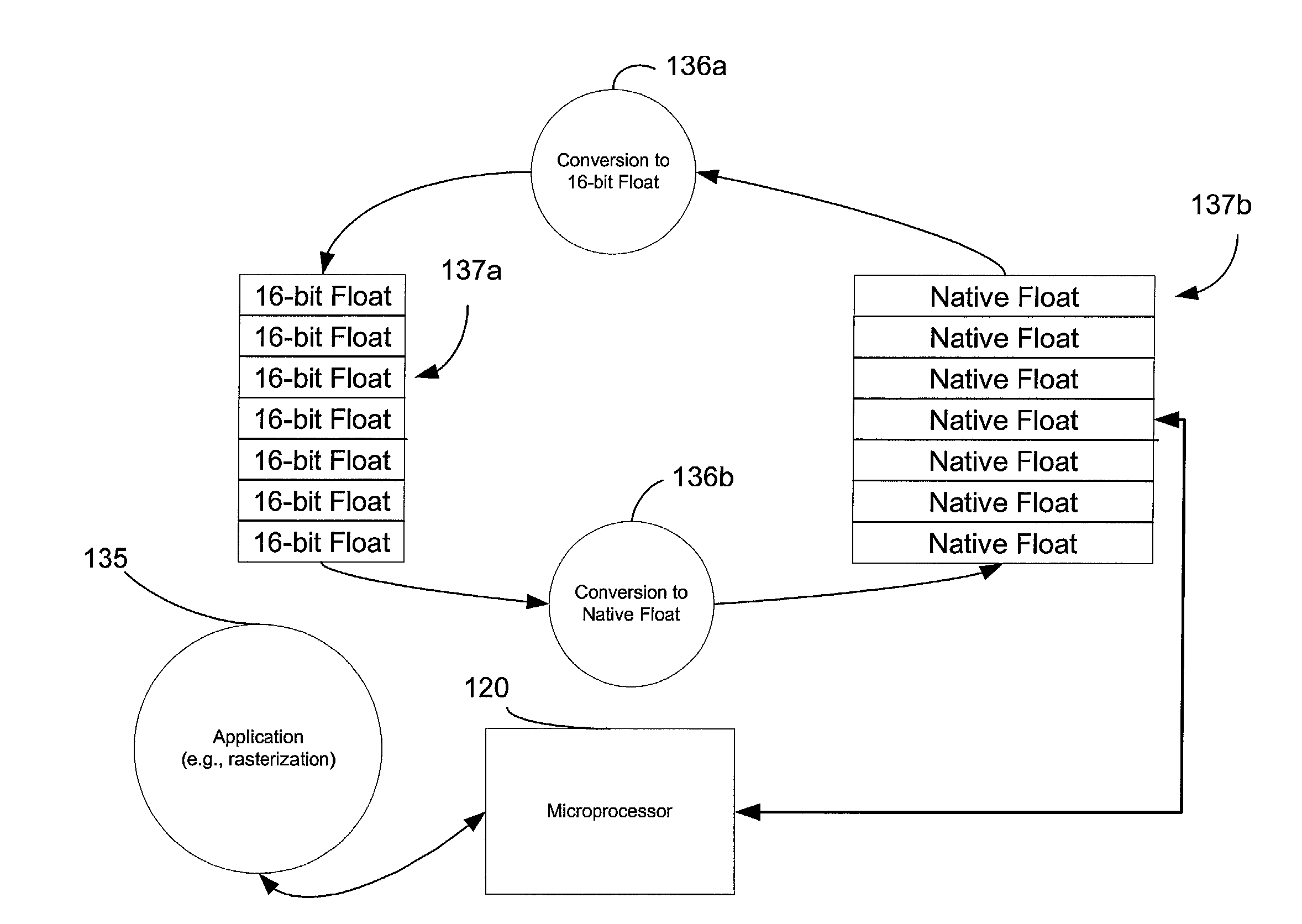
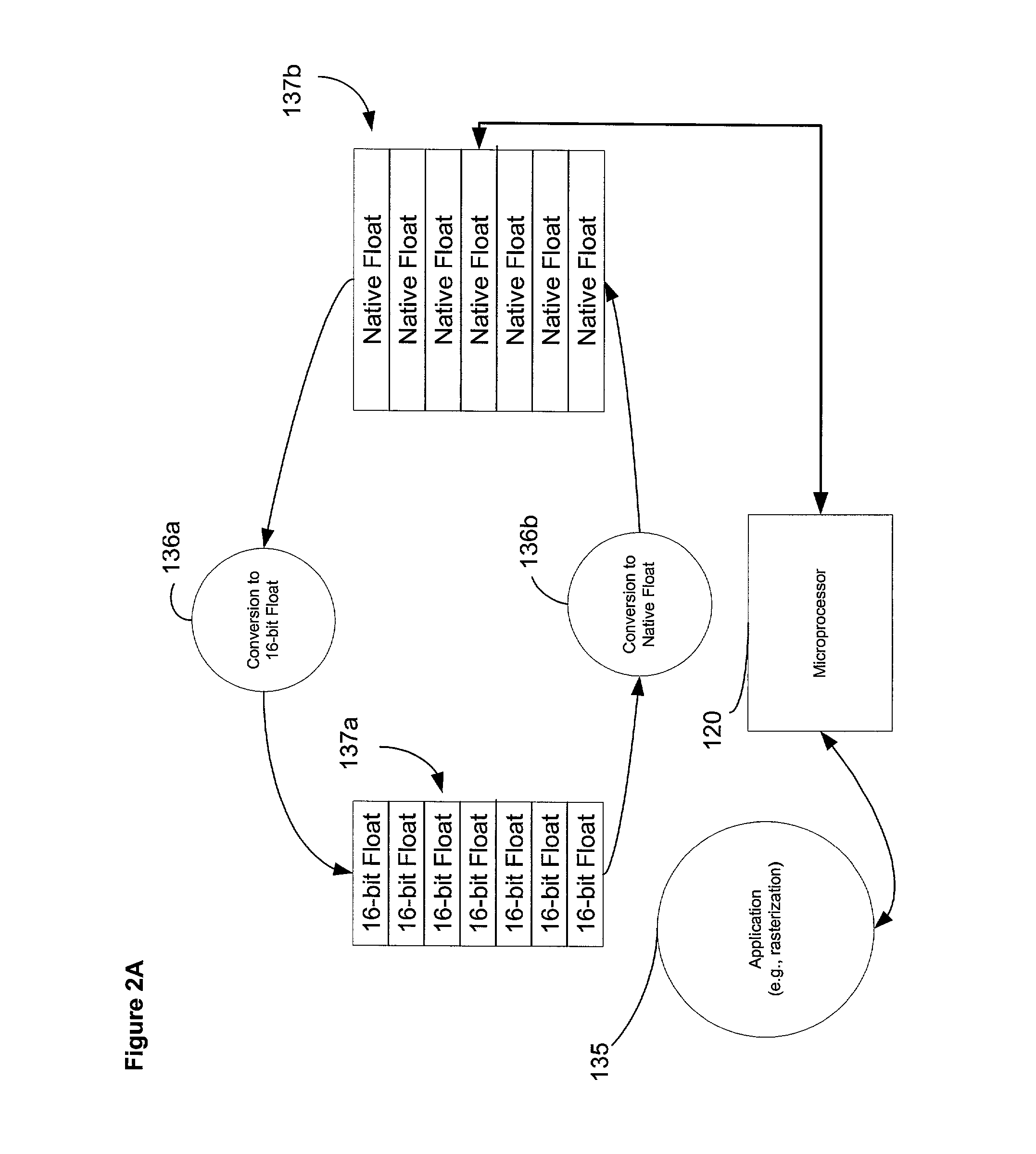
System and method for using native floating point microprocessor instructions to manipulate 16-bit floating point data representations
InactiveUS7330864B2Better trade-offSolve the lack of precisionCode conversionDigital computer details16-bitFloating point
A method for providing a 16-bit floating point data representation where the 16-bit floating point data representation may be operated upon by a microprocessors native floating point instruction set. The method contemplates the use a variety of techniques for converting the 16-bit floating point number into a representative native floating point value. Thereafter, the native microprocessor floating point instruction set may perform operations upon the converted data. Upon completion, the native floating point data representation may be converted back into the 16-bit floating point value.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
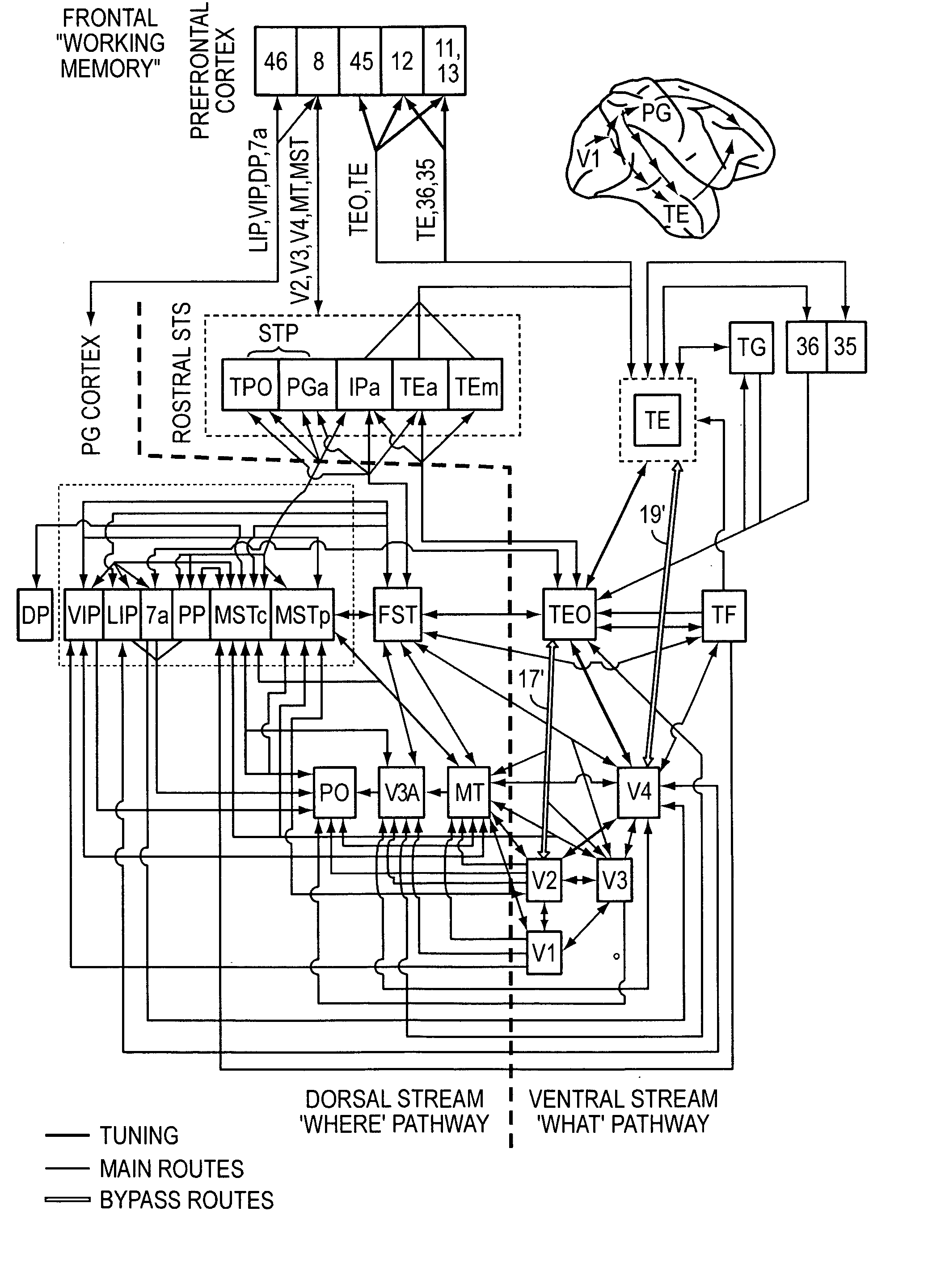
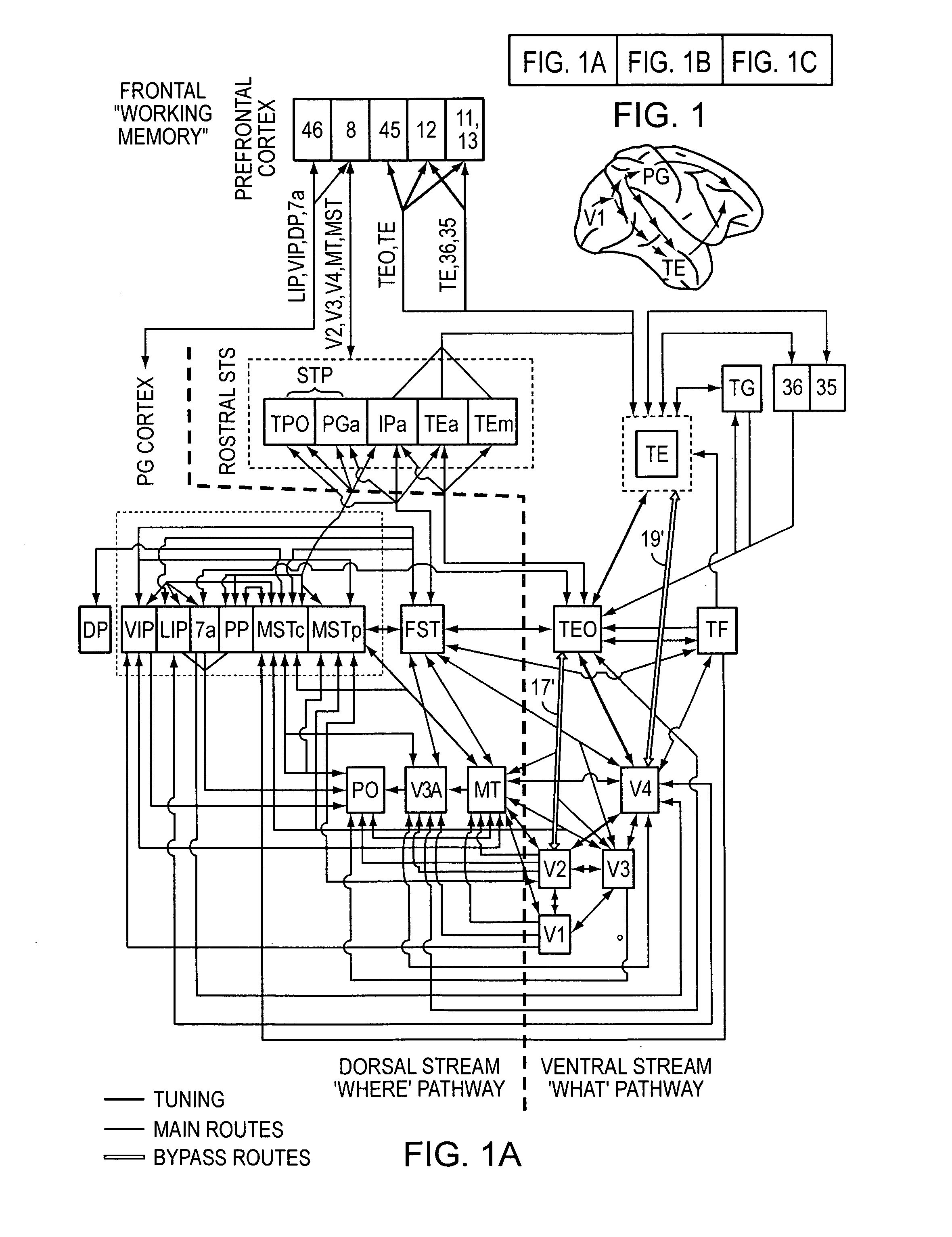
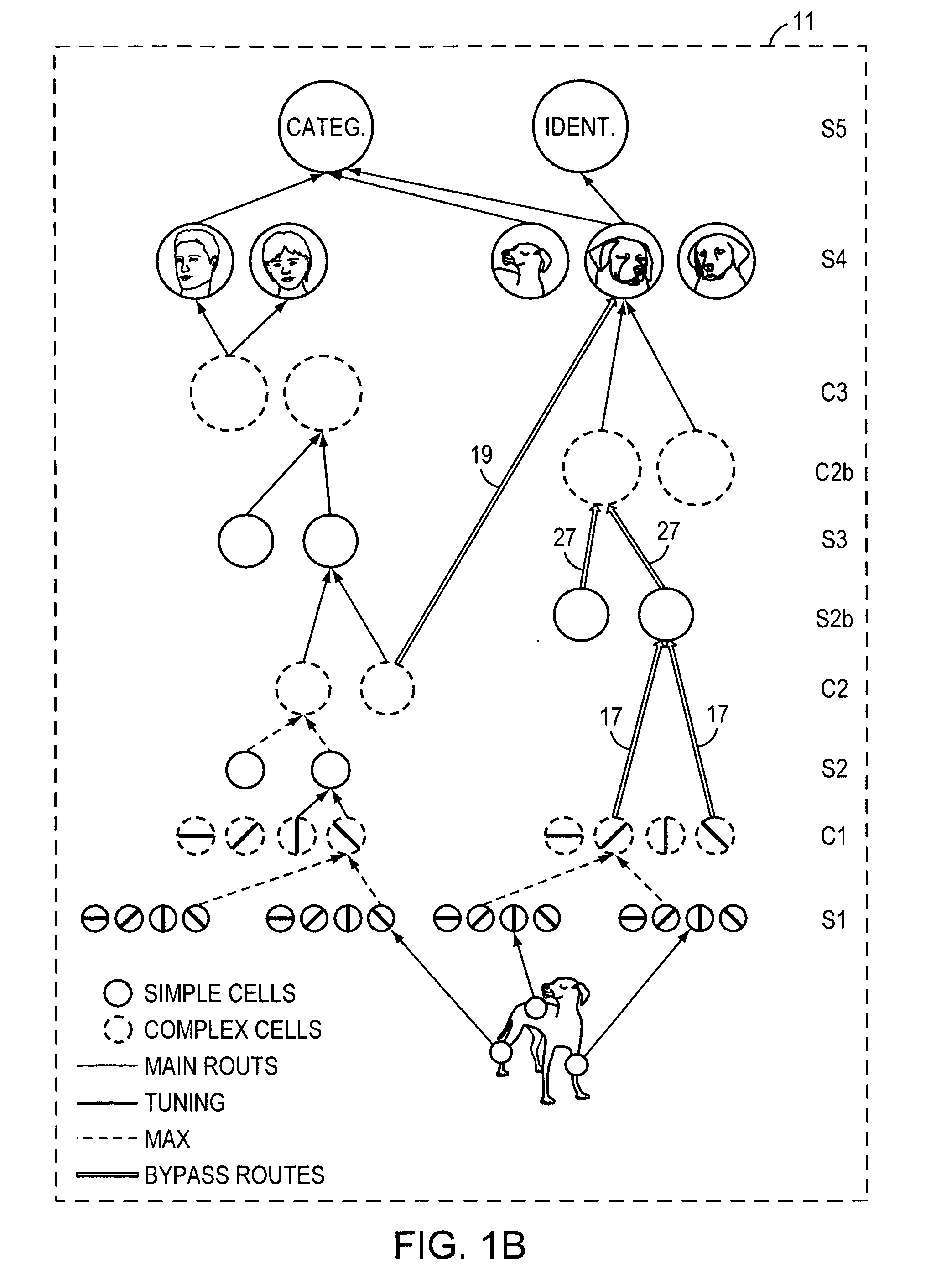
High-performance vision system exploiting key features of visual cortex
InactiveUS20080071710A1Better trade-offLittle inputDigital computer detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionVisual cortexVisual recognition
An artificial visual recognition system and method employ a digital processor and a model executed by the digital processor. The model has a loose hierarchy of layers. Each layer, from a lowest hierarchy level to a top level, provides relatively increasing selectivity and invariance of the input image. The hierarchy allows bypass routes between layers. On output, the model produces feature recognition and classification of an object in the input image. In some embodiments, windowing means provide windows of the input image to the model, and the model responds to shape-based objects in the input image. In another feature, segmenting means segment the input image and enables the model to determine texture-based objects in the input image.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
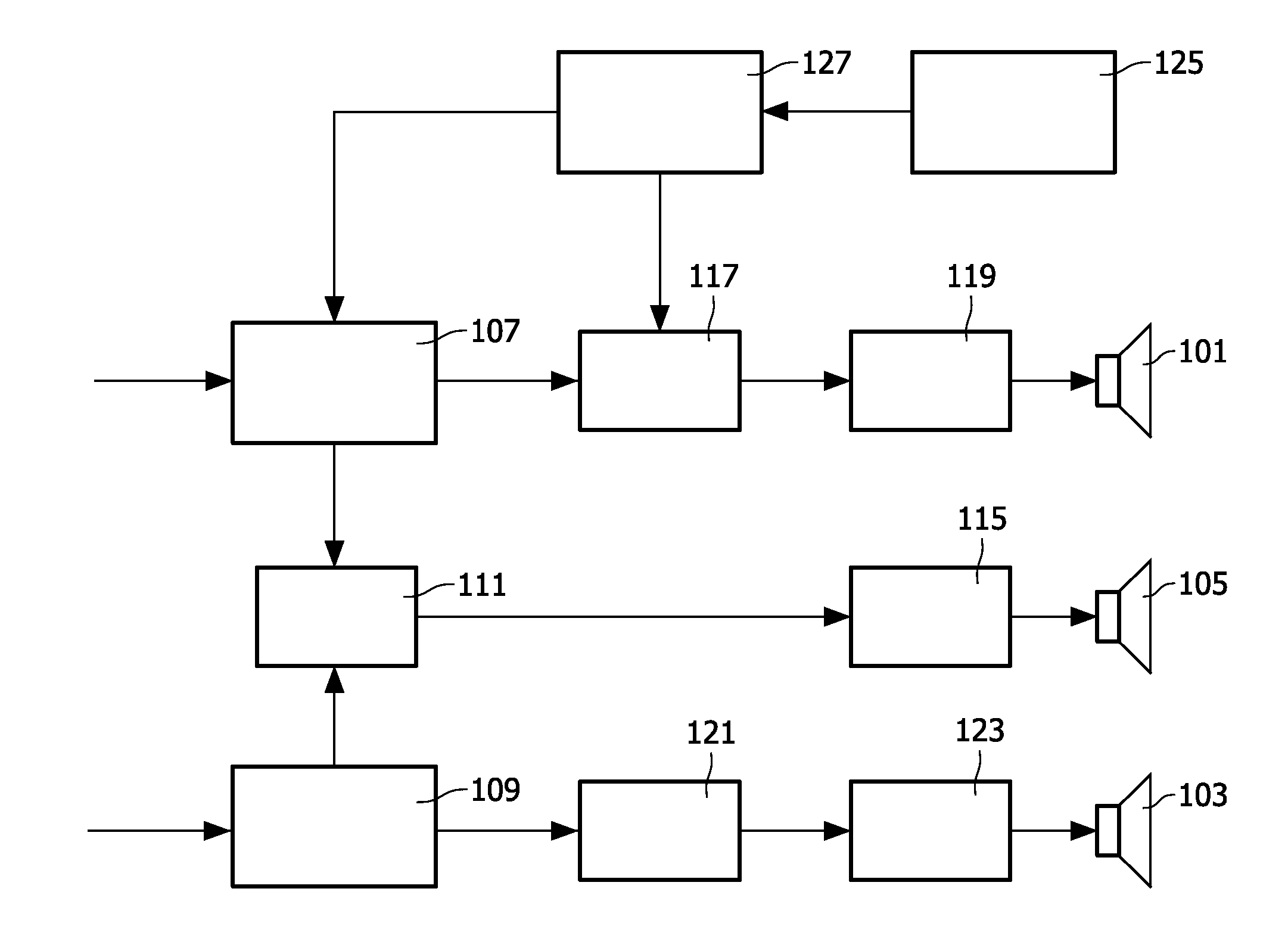
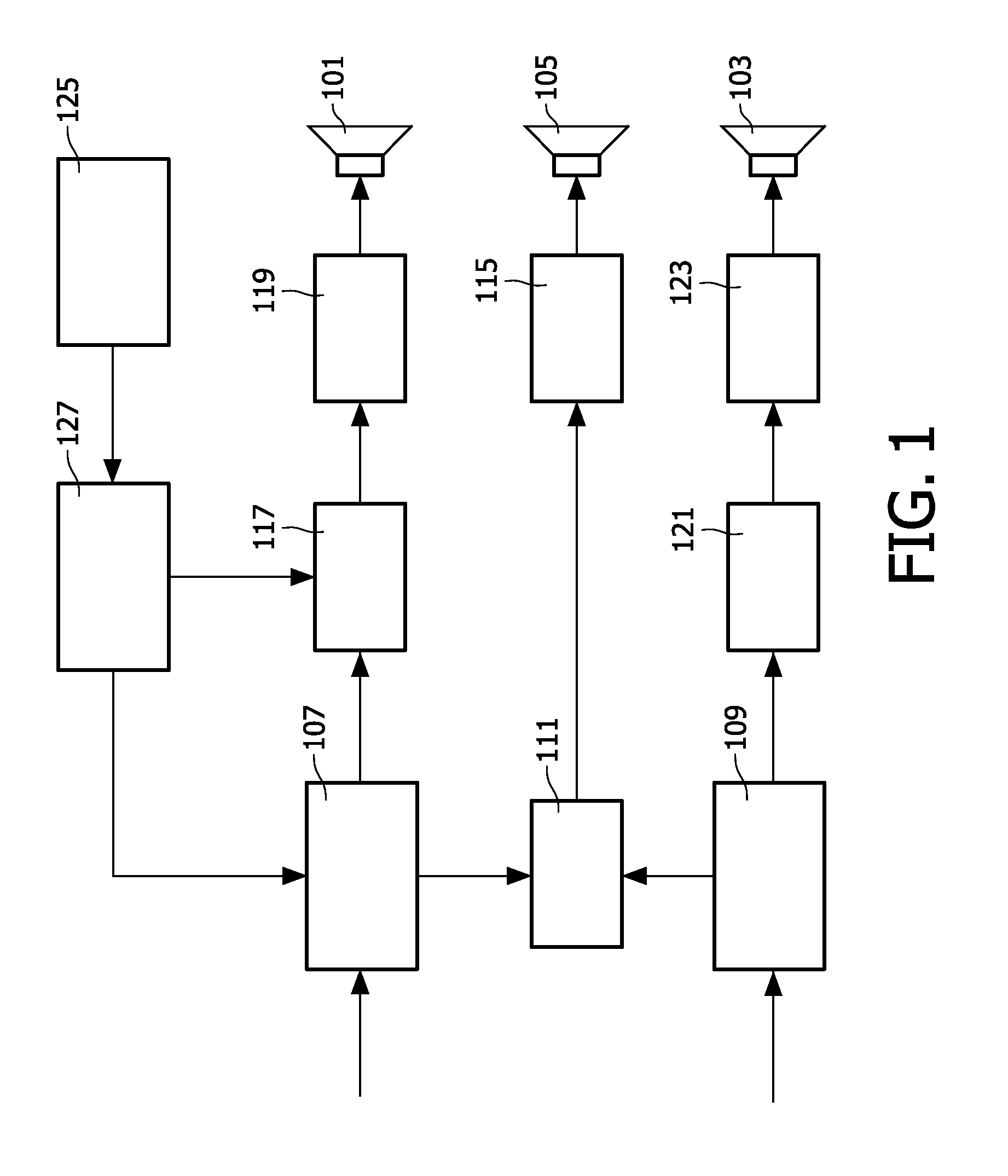
Driving of multi-channel speakers
InactiveUS20120033818A1Improve performanceReduced driver excursionTransducer protection circuitsFrequency response correctionEngineeringSubwoofer
A drive system comprises a splitter (107) which generates a low frequency signal and high frequency signal from an input signal. A first drive circuit (111, 115) is coupled to the splitter (117) and generates a drive signal for an audio driver (105) from the low frequency signal. A second drive circuit (117, 119) is coupled to the splitter (117) and generates a drive signal for a second audio driver (101) from the high frequency signal. The second drive circuit (117, 119) provides a bass frequency extension for the second audio driver (101) by applying low frequency boost to the low frequency signal. A processor (125) determines a driver excursion indication for the second audio driver (101) and a controller (127) performs a combined adjustment of a cross-over frequency for the high and low frequency signals and a characteristic of the low frequency boost based on the driver excursion indication. The invention may provide improved interworking between e.g. a subwoofer and satellite speakers.
Owner:MMD HONG KONG HLDG LTD
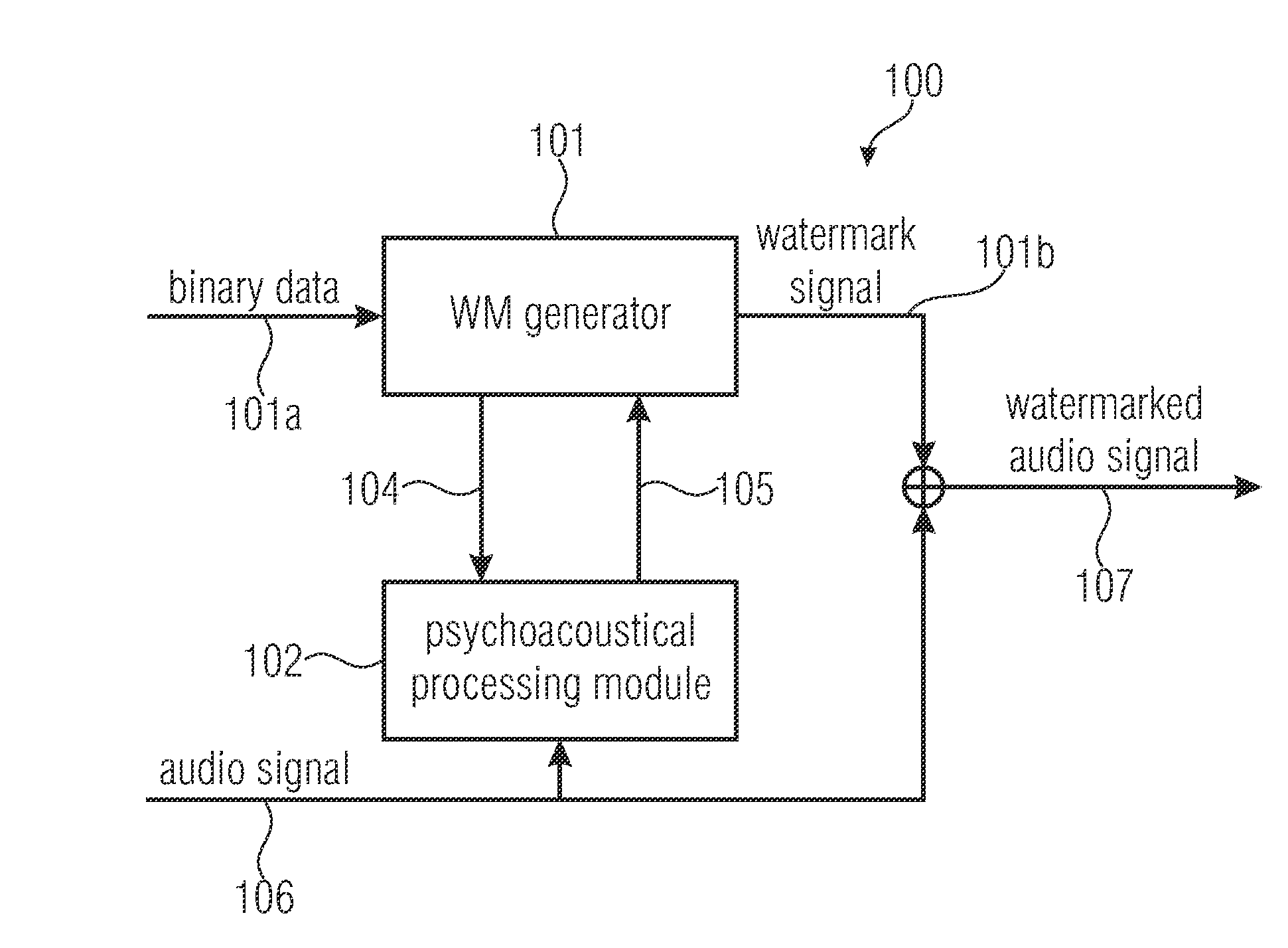
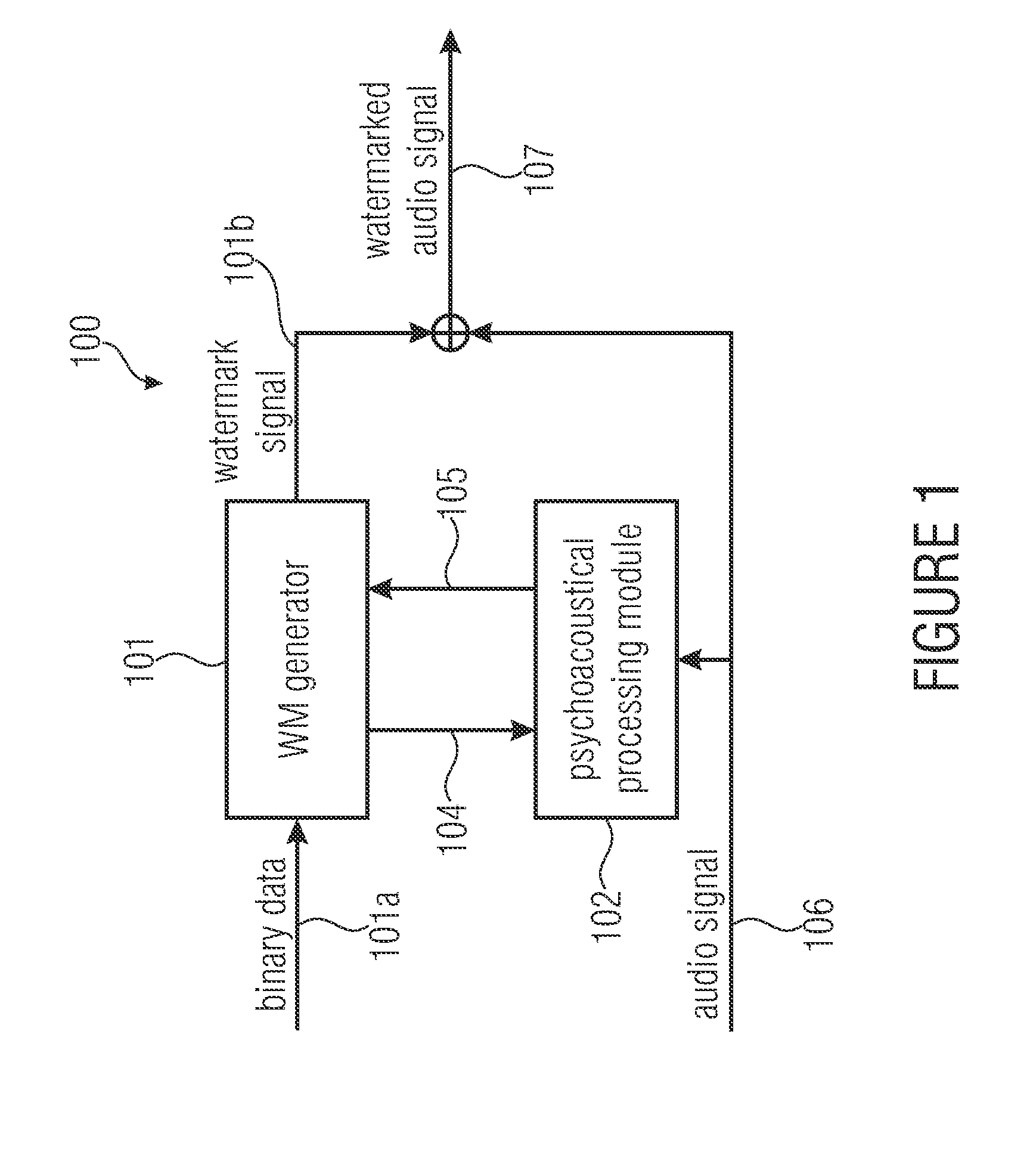
Watermark signal provision and watermark embedding
ActiveUS20130218314A1Good trade-offBetter trade-offSpeech analysisBroadcast information monitoringAudio signalWatermark embedding
A watermark signal provider provides a watermark signal suitable for being hidden in an audio signal when the watermark signal is added to the audio signal, such that the watermark signal represents watermark data. The watermark signal provider includes a psychoacoustical processor for determining a masking threshold of the audio signal; and a modulator for generating the watermark signal from a superposition of sample-shaping functions spaced apart from each other at a sample time interval of a time-discrete representation of the watermark data, each sample-shaping function being amplitude-weighted with a respective sample of the time-discrete representation, multiplied by a respective amplitude weight depending on the masking threshold, the modulator being configured such that the sample time interval is shorter than a time extension of the sample-shaping functions; and the respective amplitude weight also depends on samples of the time-discrete representation neighboring the respective sample in time.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com