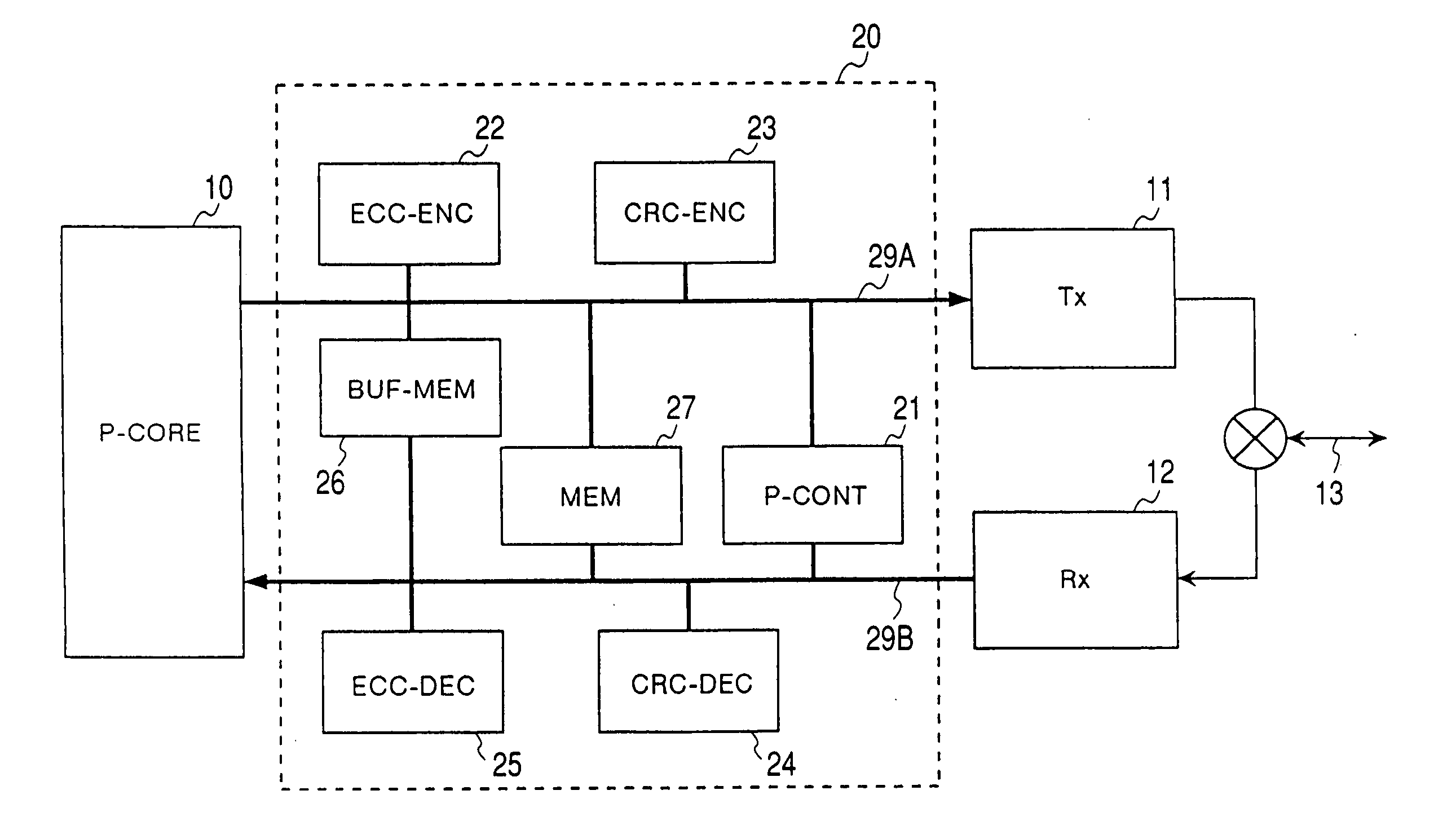
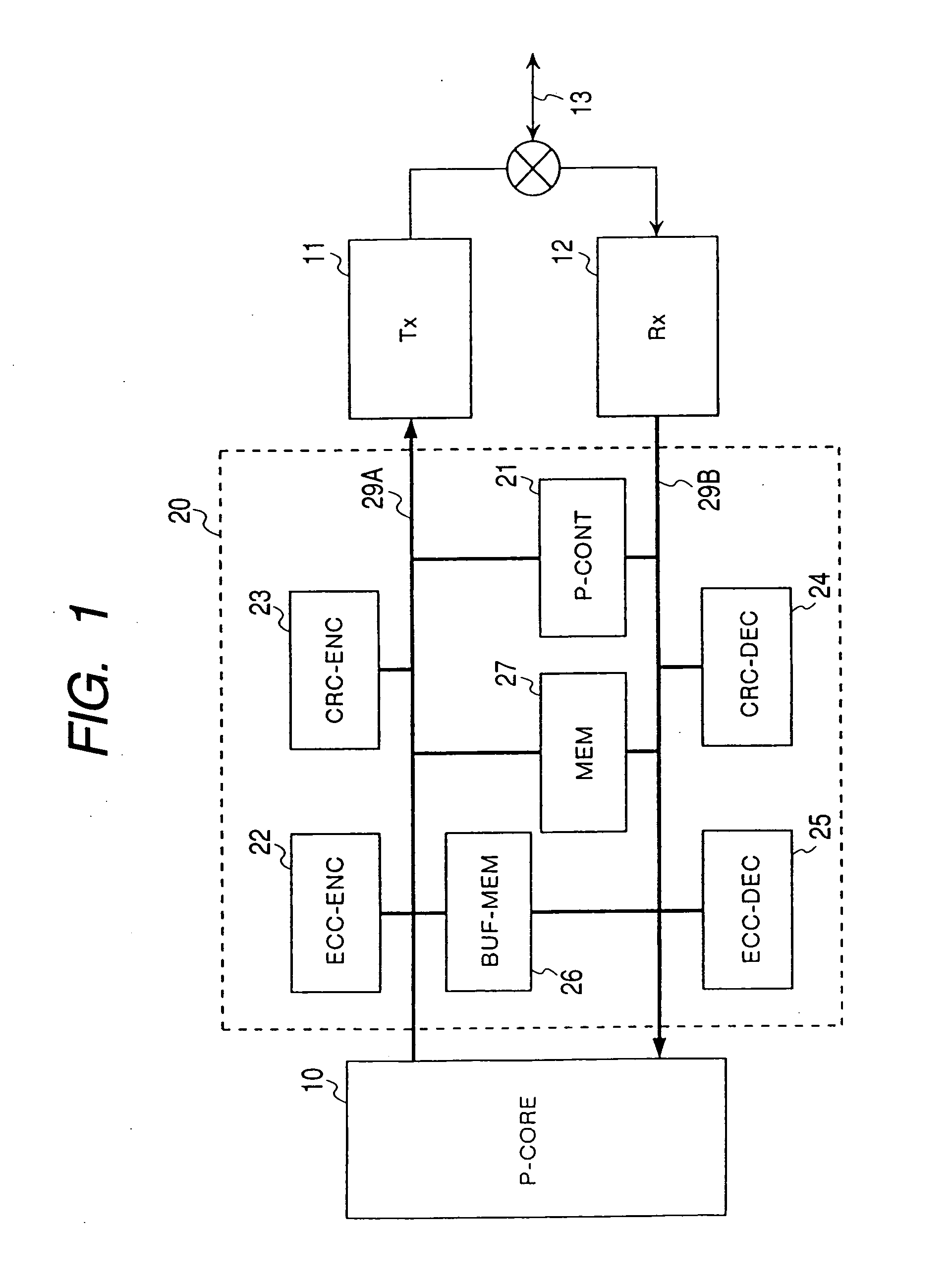
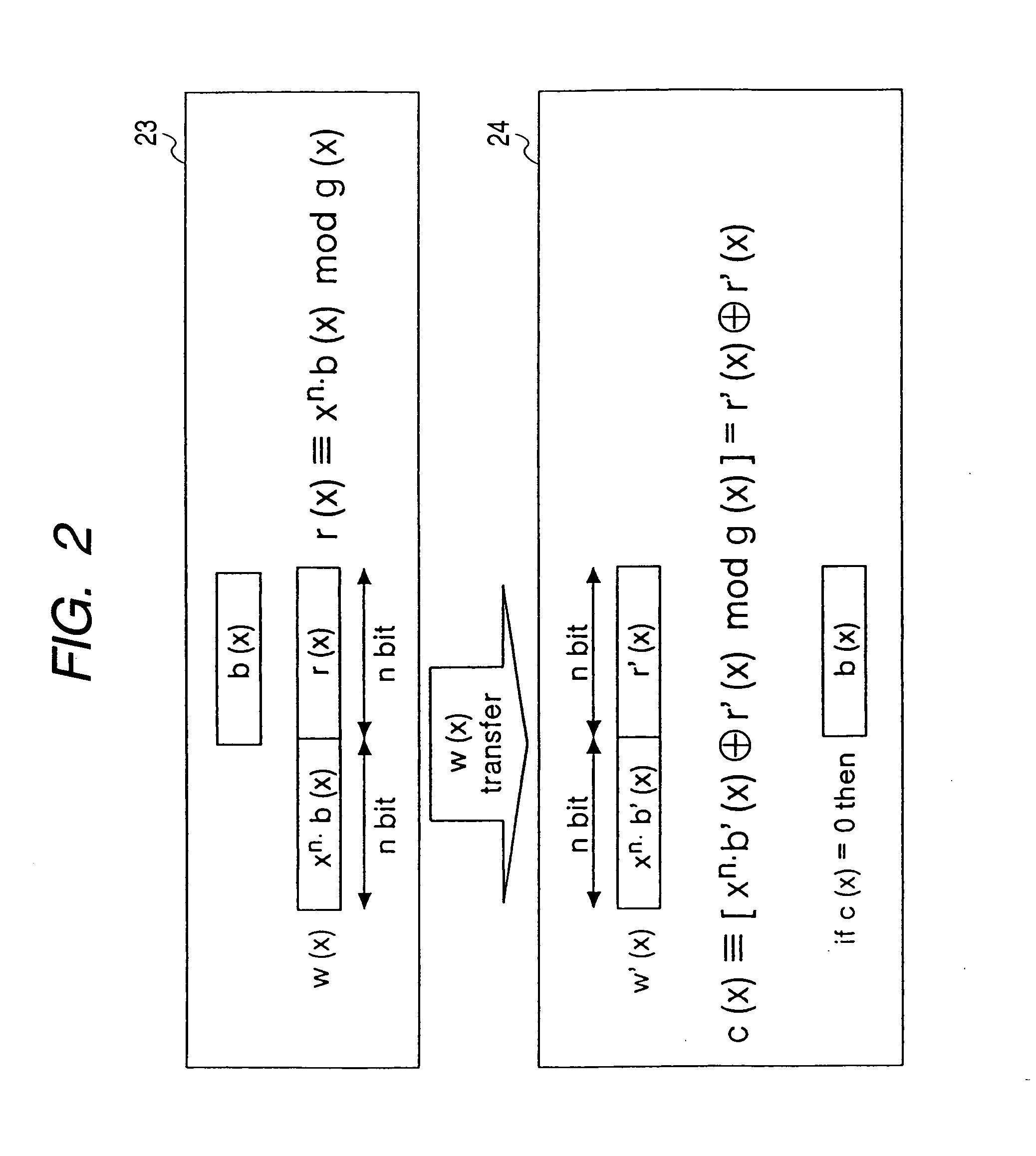
Patents
Literature
933results about "Computations using residue arithmetic" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
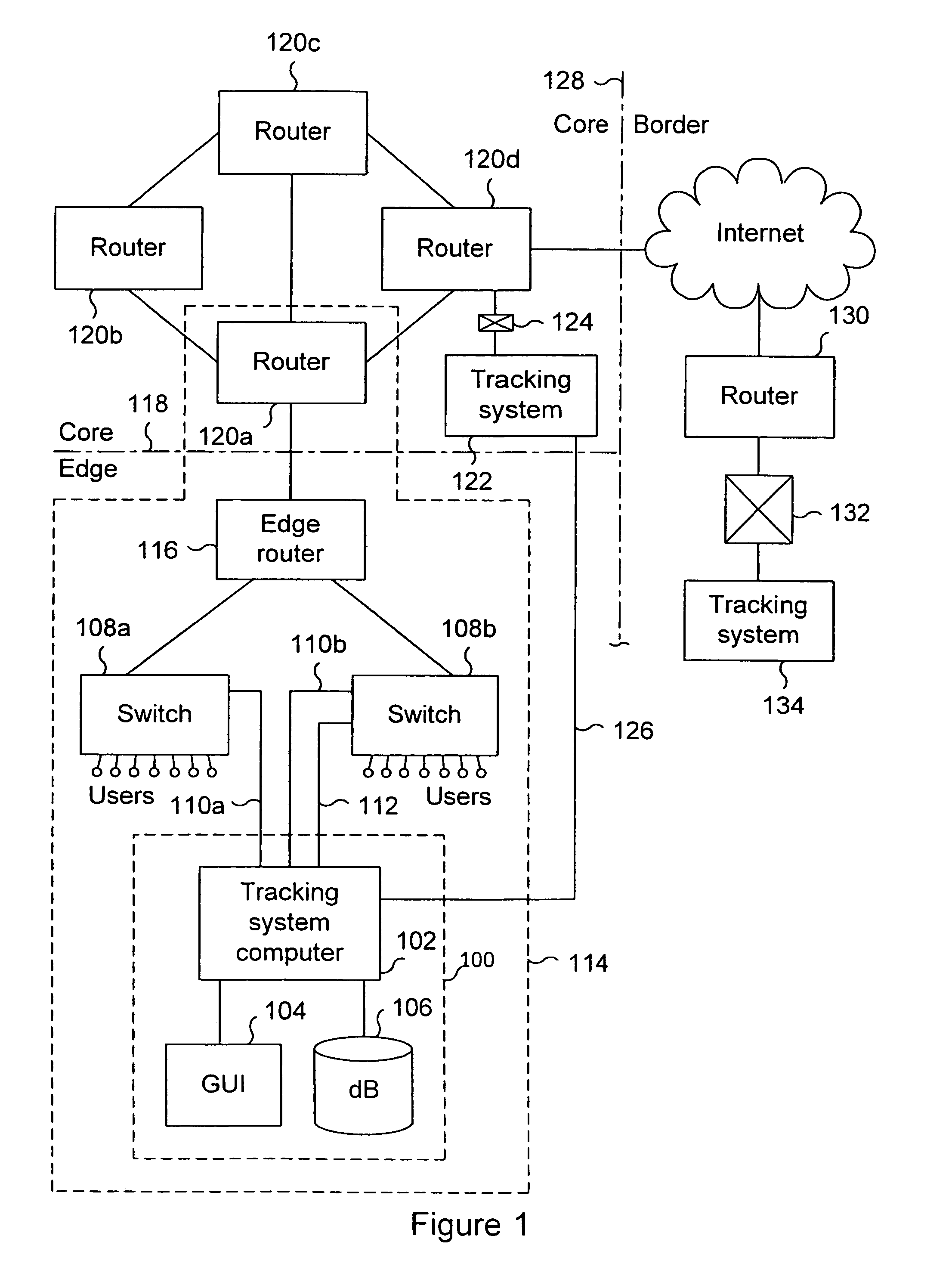
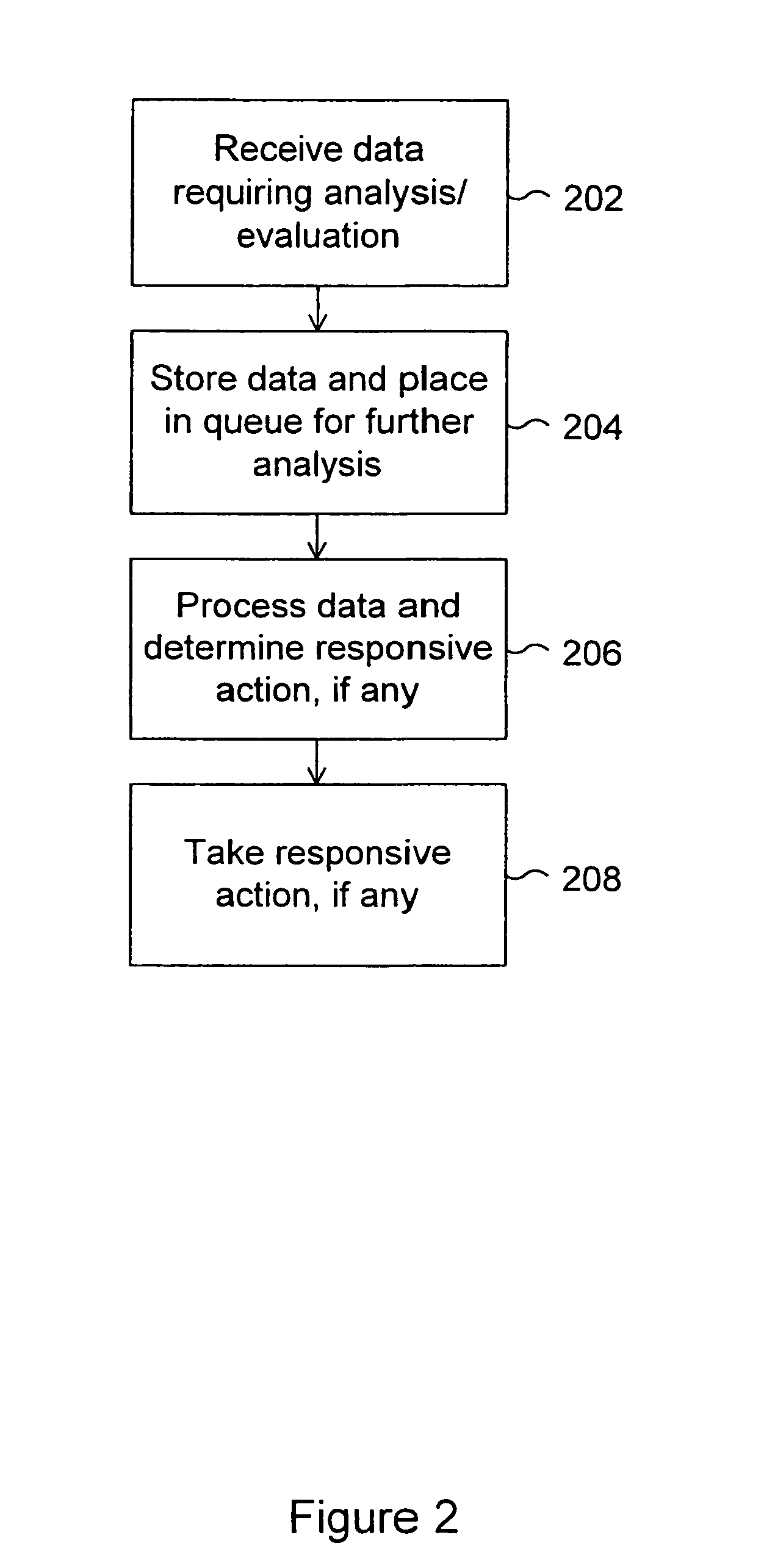
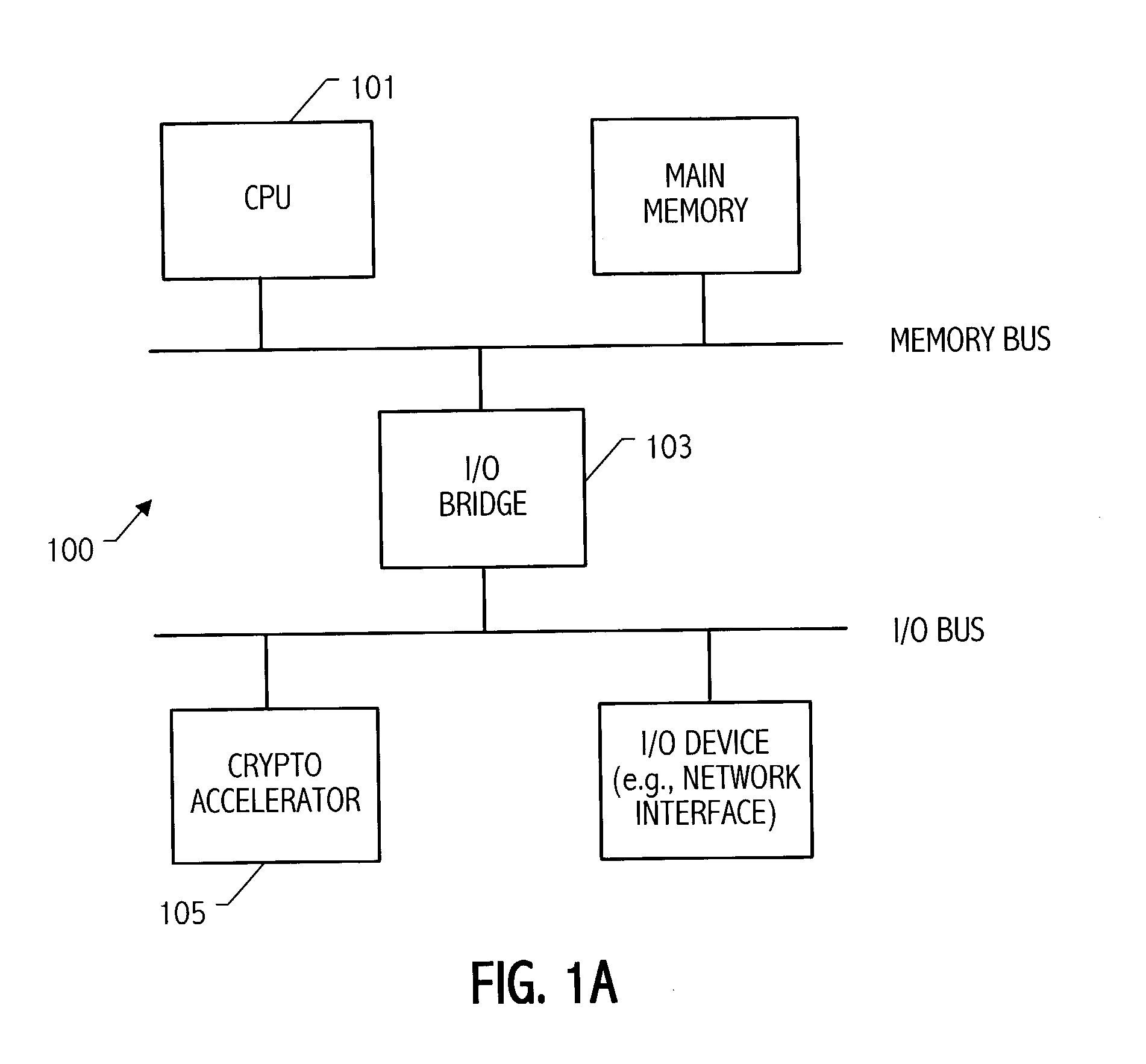
System and method for tracking the source of a computer attack
InactiveUS6971028B1Memory loss protectionDigital computer detailsAdministrative domainData placement
A system and method are disclosed for detecting and processing attacks on a computer network. Data indicating an attack may be taking place is received. The data is associated with an event. The data is placed in a selected one of a plurality of queues of data to be processed. The data in the queue is processed. Each queue is configured to store one or more sets of data, each set of data being associated with an event to be processed. An administrative domain may be notified that an attack may be taking place. The destination administrative domain may or may not be associated with other than the sending administrative domain. The source of an attack may be identified. Messages associated with an attack may be tracked back to identify a point of attack at which messages associated with the attack are entering a network.
Owner:CA TECH INC
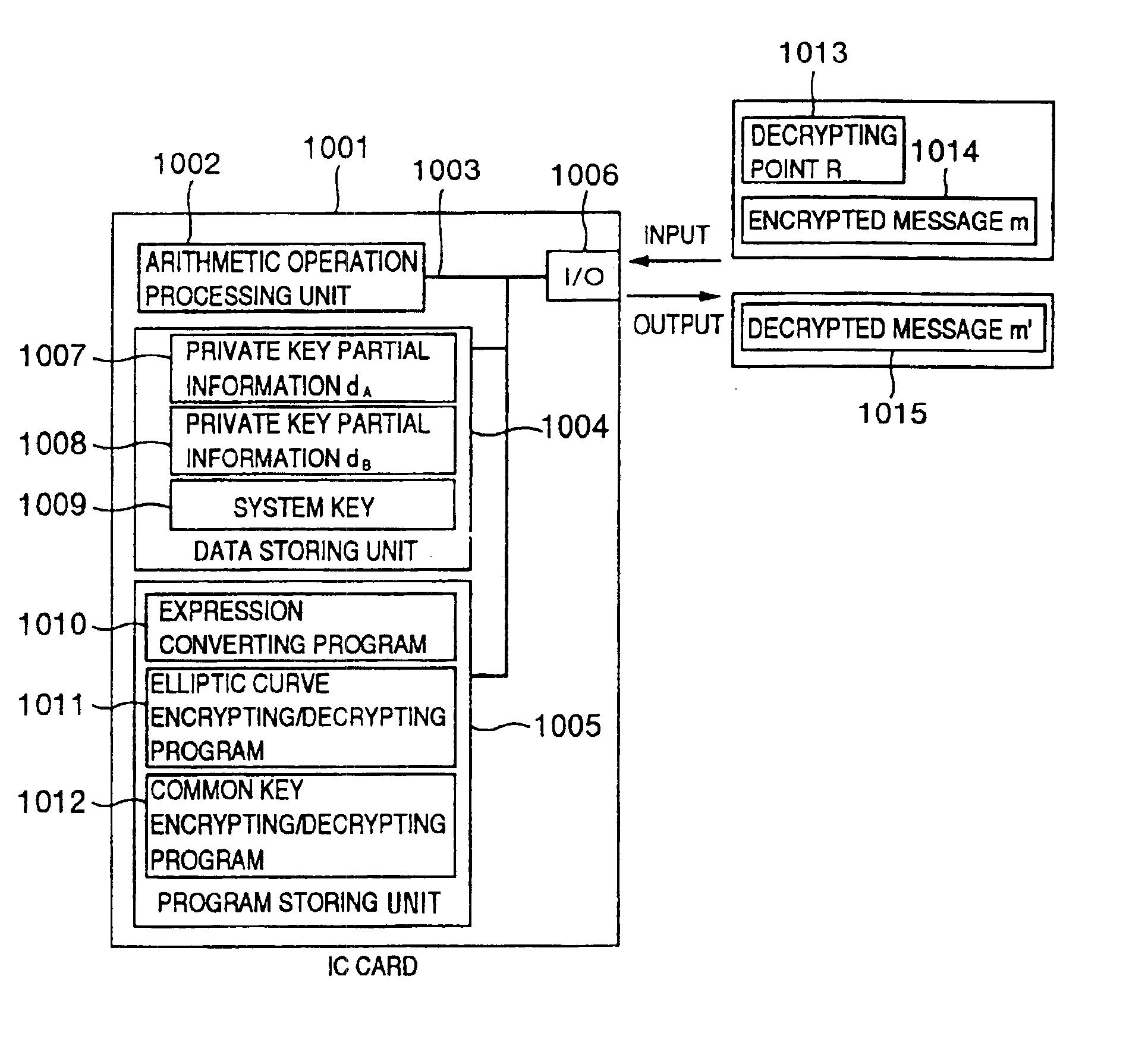
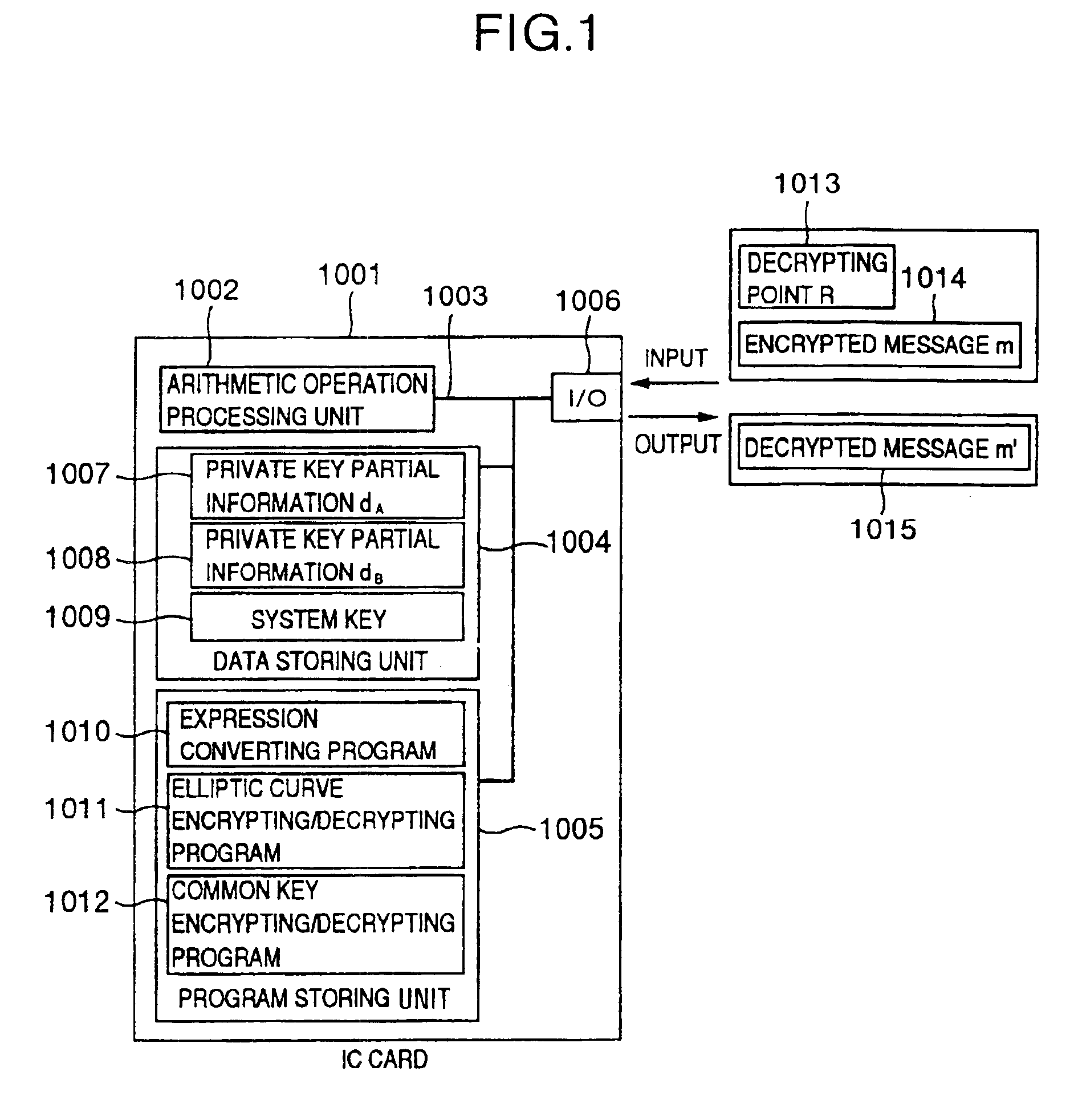
Processing apparatus, program, or system of secret information
InactiveUS6873706B1Reduce correlationTotal current dropKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationComputer hardwarePower analysis
To provide a secure cryptographic device such as an IC card which can endure TA (Timing Attack), DPA (Differential Power Analysis), SPA (Simple Power Analysis), or the like as an attaching method of presuming secret information held therein, when the secret information held in the card or another information which is used in the secret information or an arithmetic operation using such secret information when such an arithmetic operation is performed is shown by a plurality of expressing methods and the arithmetic operation is performed, thereby making an arithmetic operation processing method different each time the arithmetic operation is performed and making each of an arithmetic operation time, an intensity of a generated electromagnetic wave, and a current consumption different.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
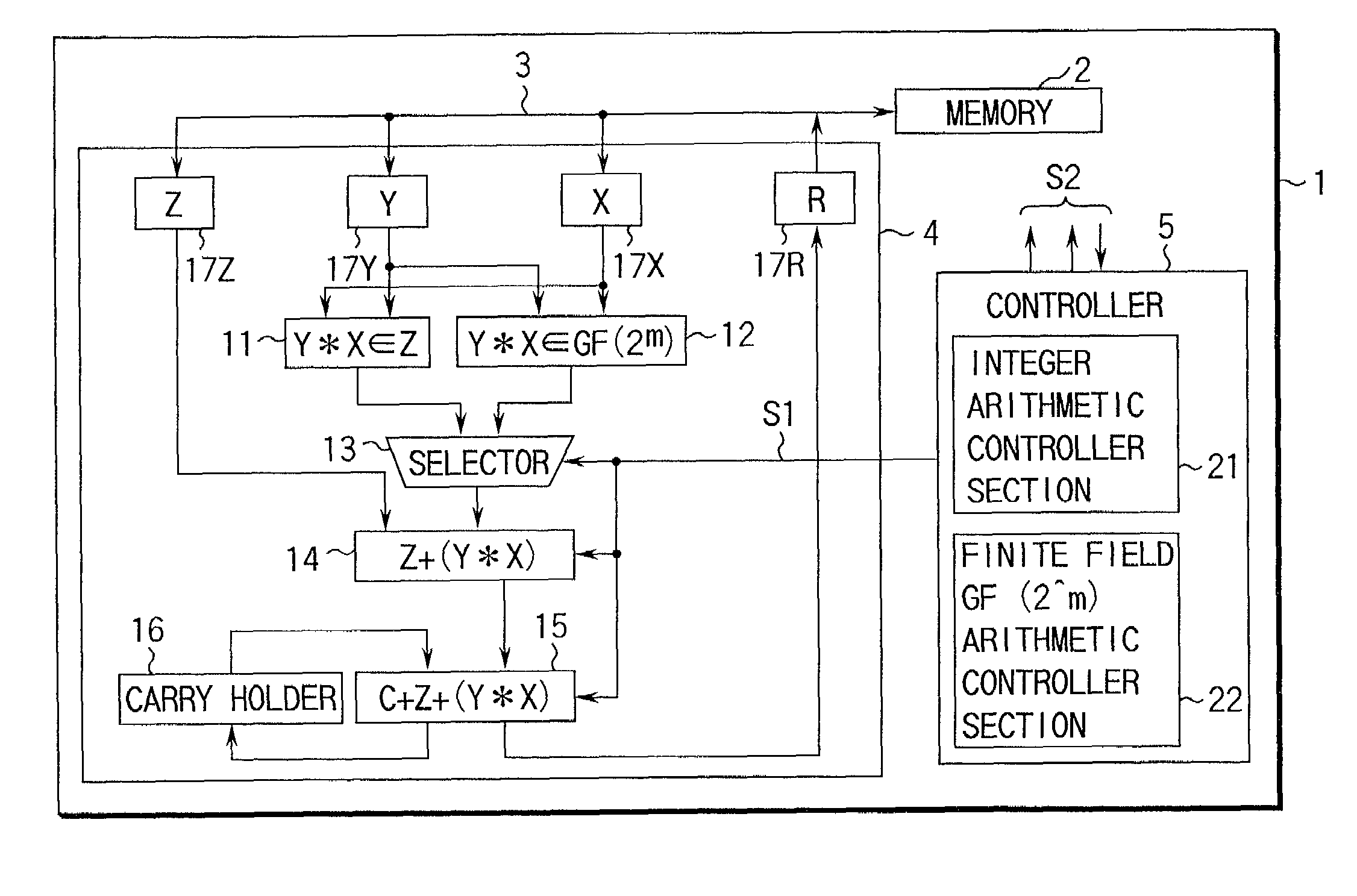
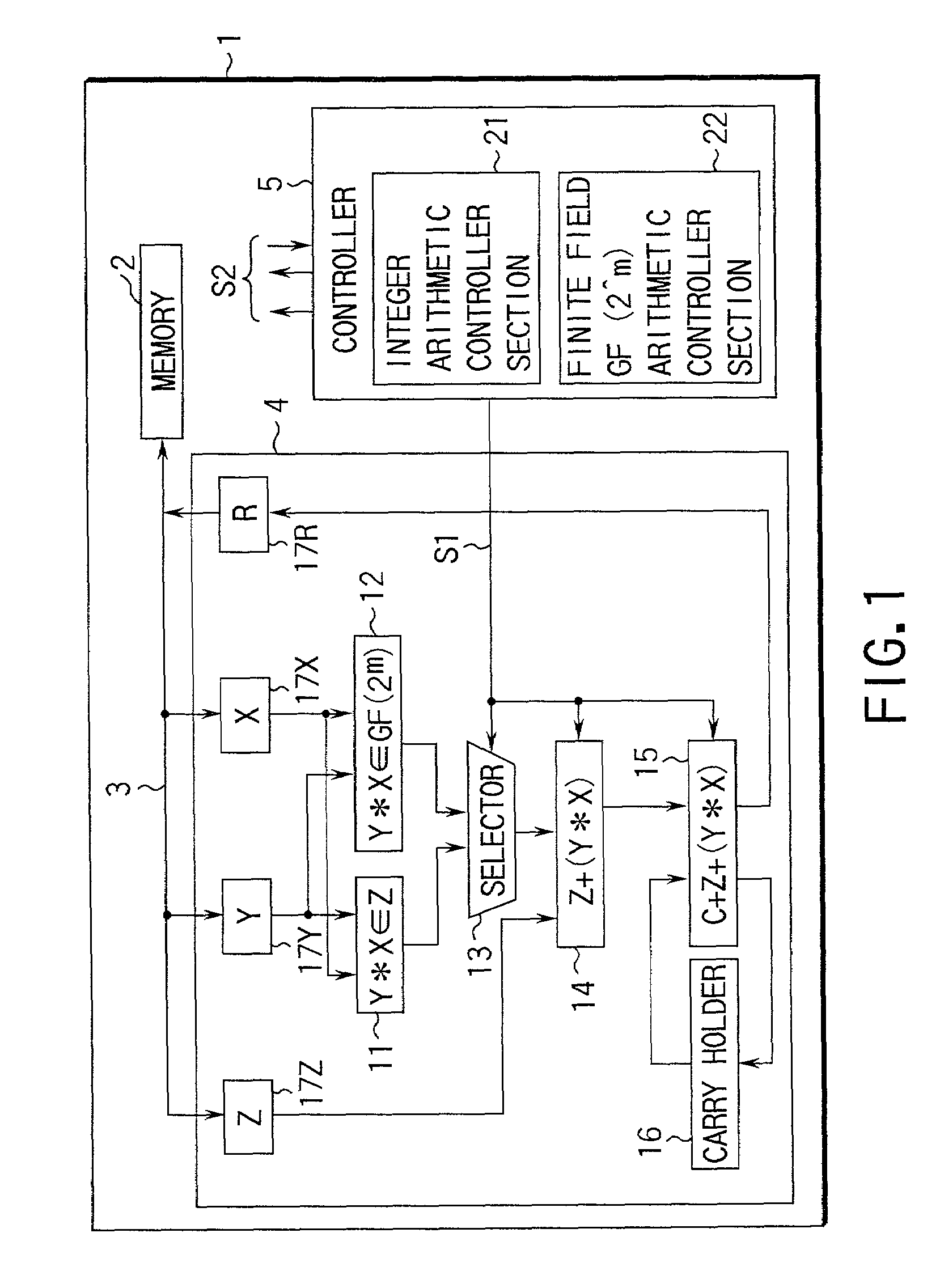
Arithmetic method and apparatus and crypto processing apparatus for performing multiple types of cryptography
InactiveUS7277540B1Computations using contact-making devicesDigital computer detailsComputer scienceArithmetic circuits
An arithmetic apparatus for performing a long product-sum operation includes an integer unit arithmetic circuit, a finite field GF(2^m) based unit arithmetic circuit logically adjacent to the integer unit arithmetic circuit, a selector for selecting the integer unit arithmetic circuit or the finite field GF(2^m) based unit arithmetic circuit, and an adder circuit which has a buffer for storing interim result data, adds the interim result data to the result data obtained by one of the integer unit arithmetic circuit and the finite field GF(2^m) based unit arithmetic circuit which is selected by the selector, propagates a carry in an integer unit arithmetic operation, and propagates no carry in a finite field GF(2^m) based unit arithmetic operation.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
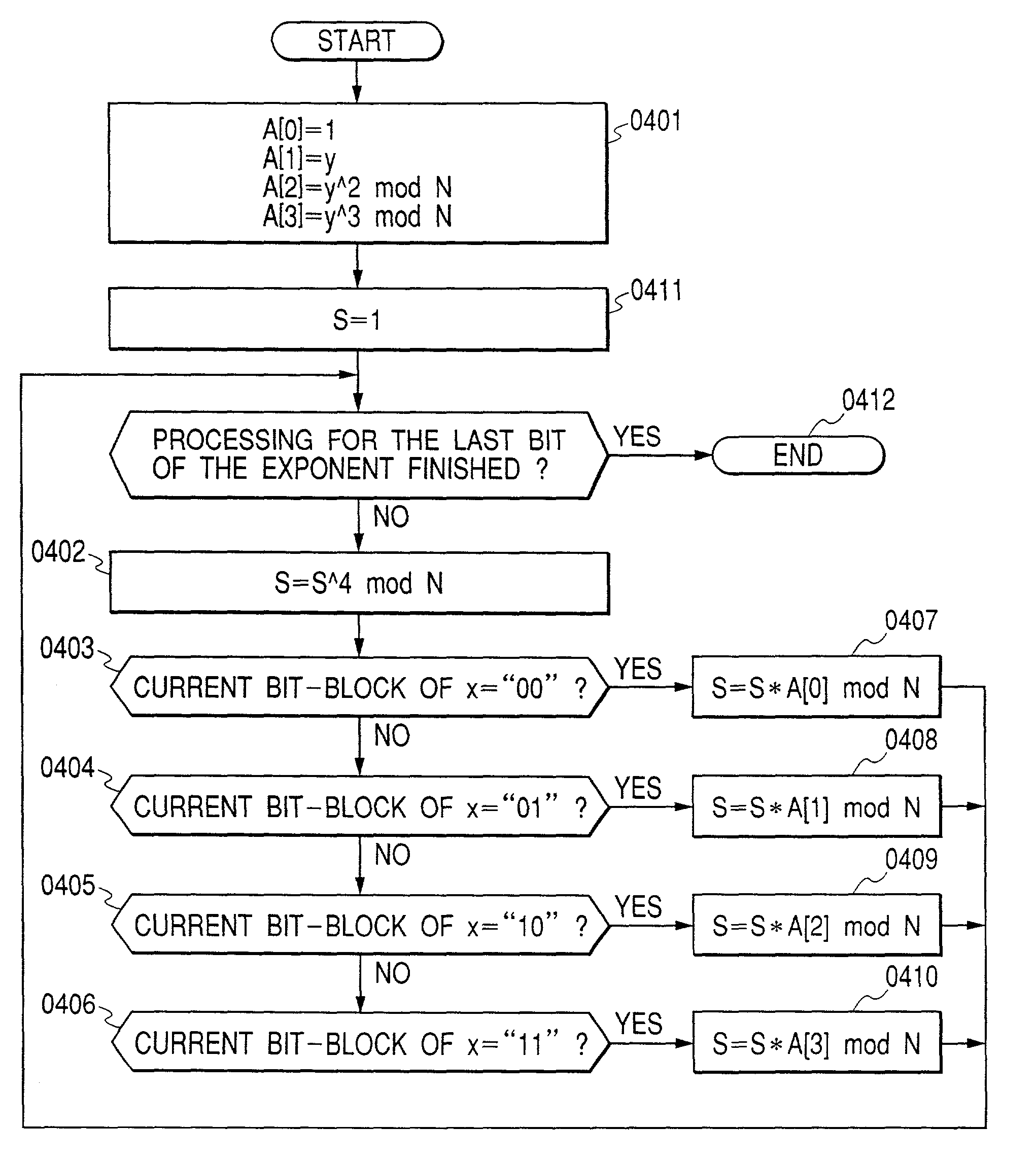
Method and apparatus for masking modulo exponentiation calculations in an integrated circuit
InactiveUS6064740APublic key for secure communicationComputation using non-contact making devicesComputer hardwareIntegrated circuit
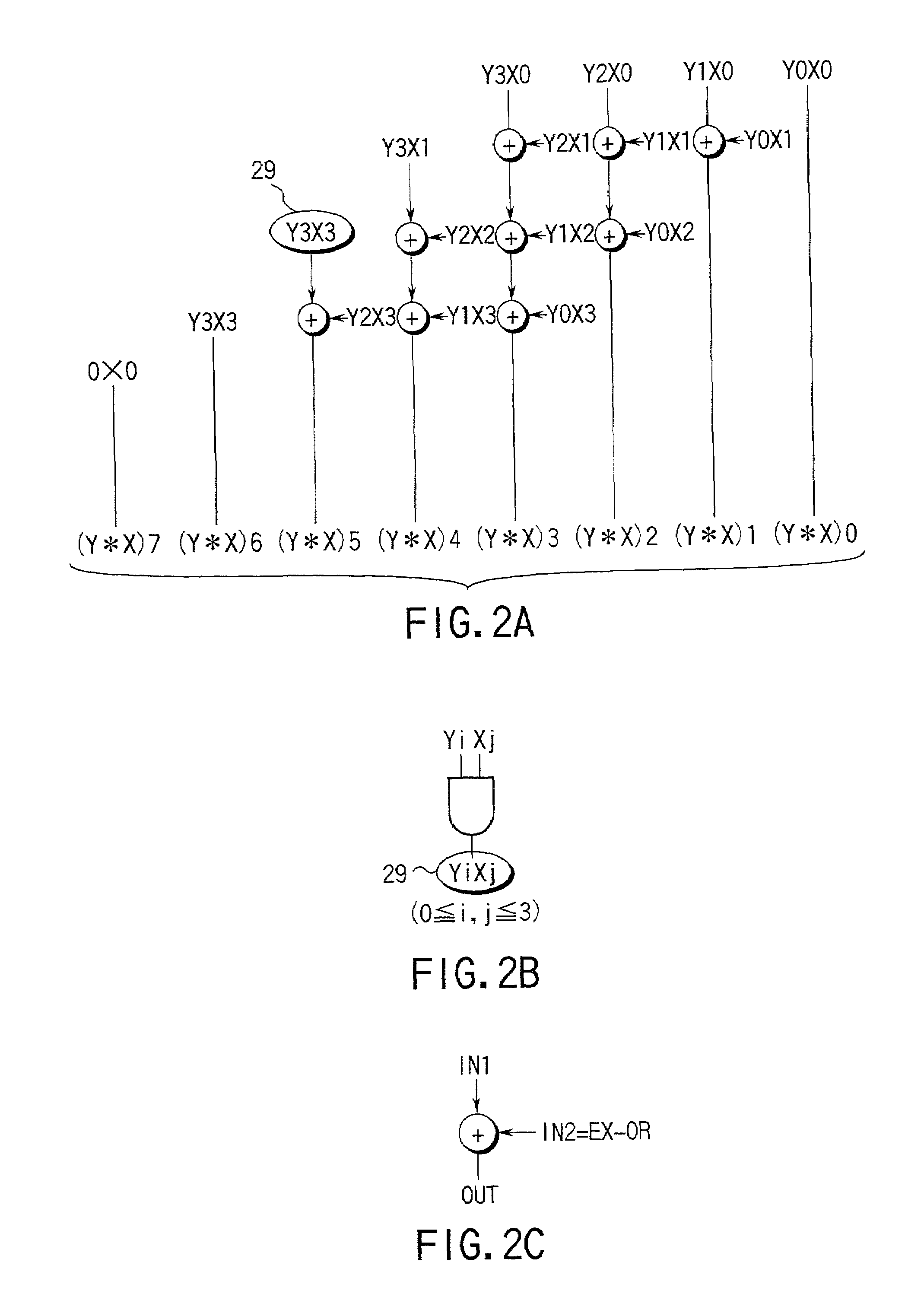
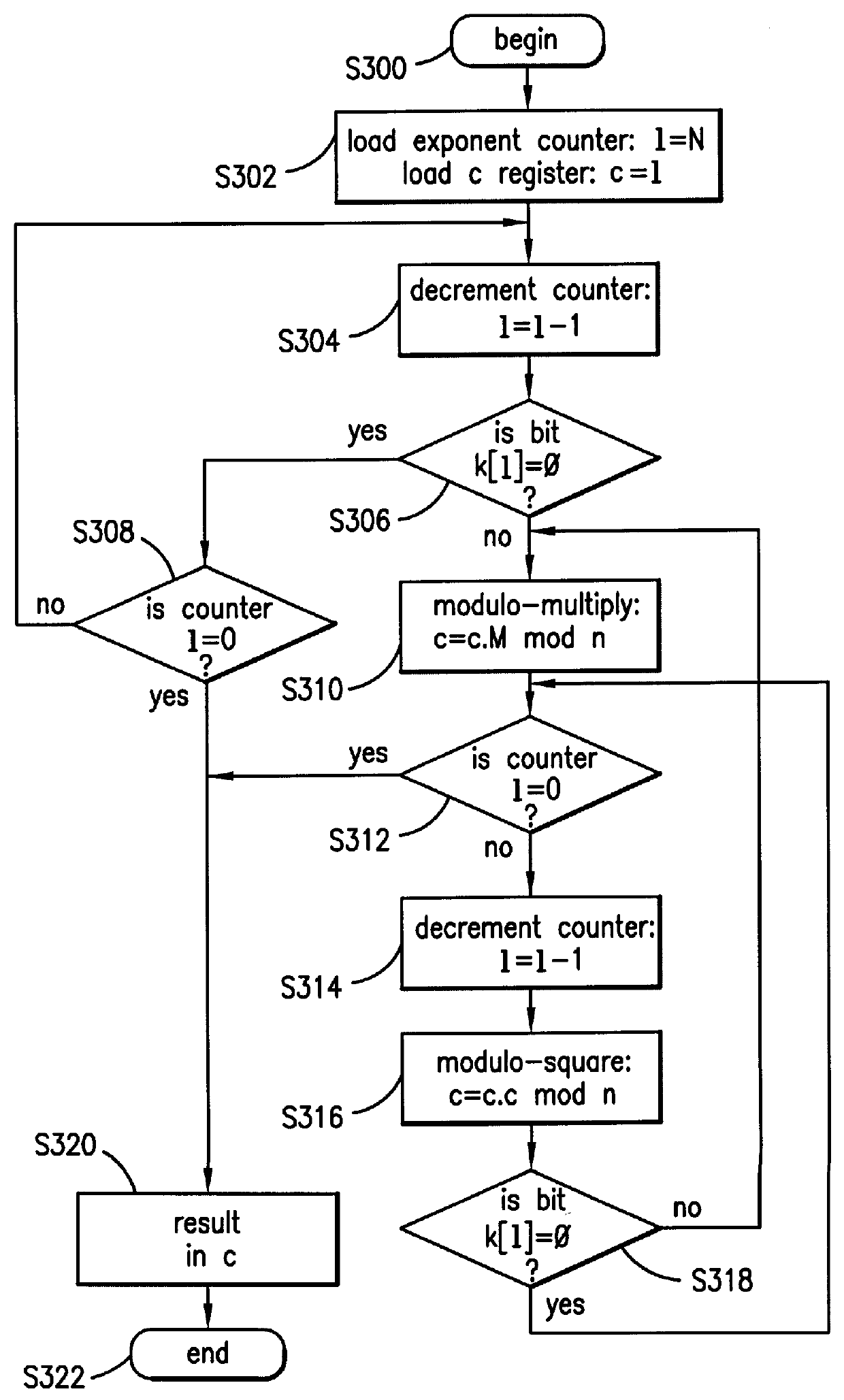
Circuitry which performs modular mathematics to solve the equation C=Mk mod n and n is performed in a manner to mask the exponent k's signature from timing or power monitoring attacks. The modular exponentation function is performed in a normalized manner such that binary ones and zeros in the exponent are calculated by being modulo-squared and modulo-multiplied.
Owner:MAXIM INTEGRATED PROD INC
Ring arithmetic method, system, and apparatus
ActiveUS20030044004A1Public key for secure communicationData switching by path configurationComputer scienceBit numbering
A data encryption method performed with ring arithmetic operations using a residue number multiplication process wherein a first conversion to a first basis is done using a mixed radix system and a second conversion to a second basis is done using a mixed radix system. In some embodiments, a modulus C is be chosen of the form 2w-L, wherein C is a w-bit number and L is a low Hamming weight odd integer less than 2(w-1) / 2. And in some of those embodiments, the residue mod C is calculated via several steps. P is split into 2 w-bit words H1 and L1. S1 is calculated as equal to L1+(H12x1)+(H12x2)+ . . . +(H12xk)+H1. S1 is split into two w-bit words H2 and L2. S2 is computed as being equal to L2+(H22x1)+(H22x2)+ . . . +(H22xk)+H2. S3 is computed as being equal to S2+(2x1+ . . . +2xk+1). And the residue is determined by comparing S3 to 2w. If S3<2w, then the residue equals S2. If S3>2w, then the residue equals S3-2w.
Owner:NCIPHER LIMITED ACTING BY & THROUGH ITS WHOLLY OWNED SUBSIDIARY NCIPHER +1
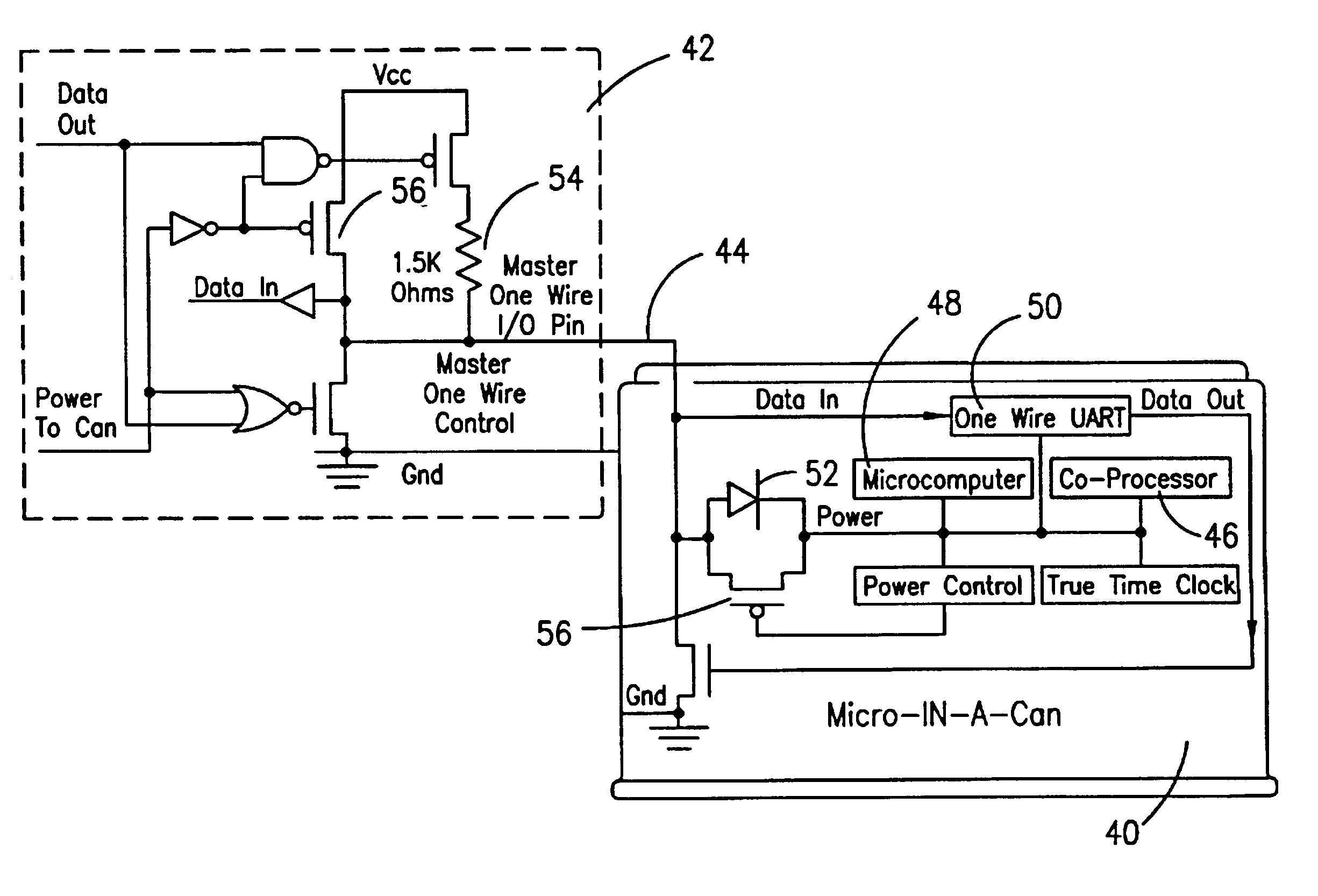
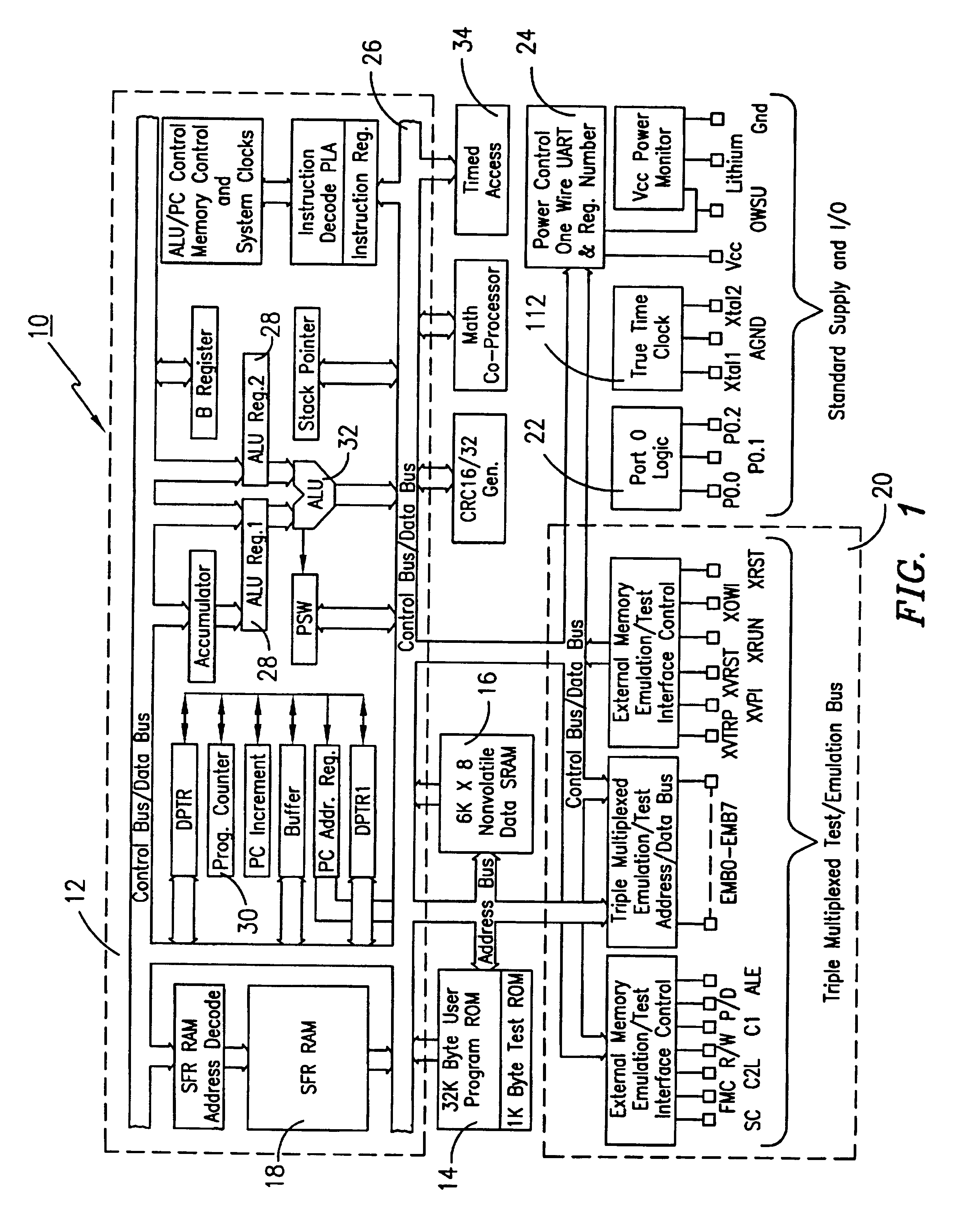
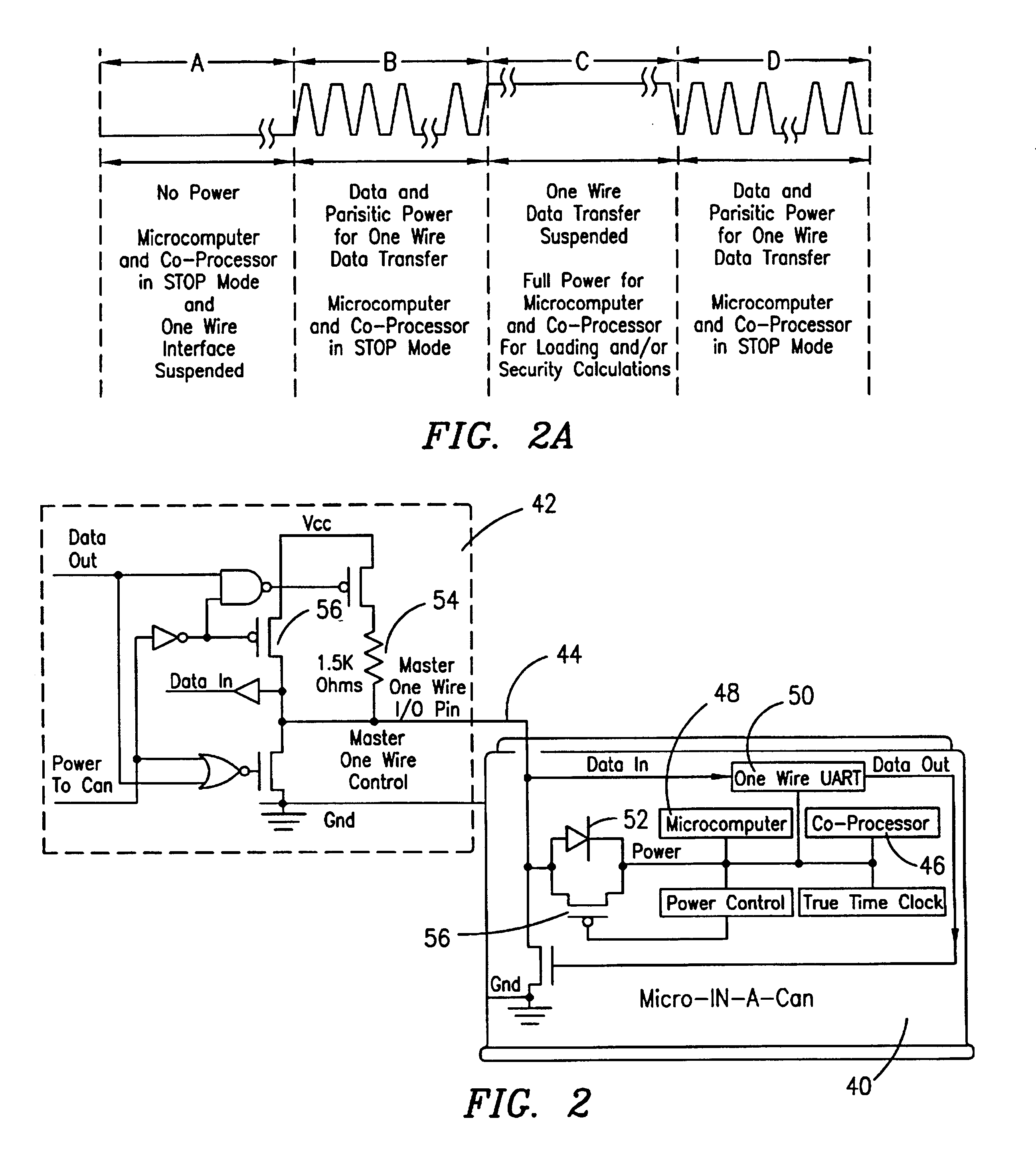
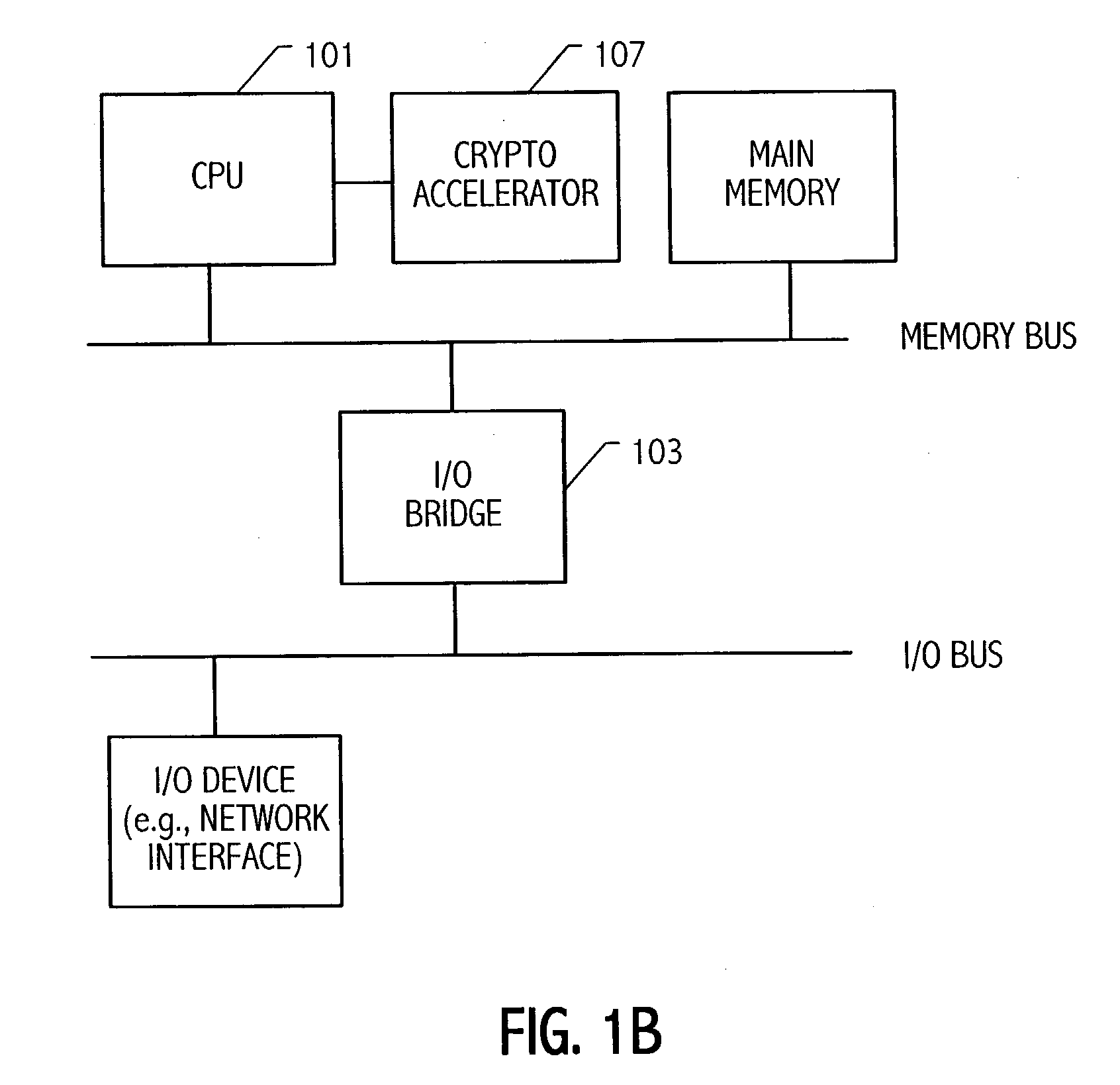
Microprocessor with coprocessing capabilities for secure transactions and quick clearing capabilities
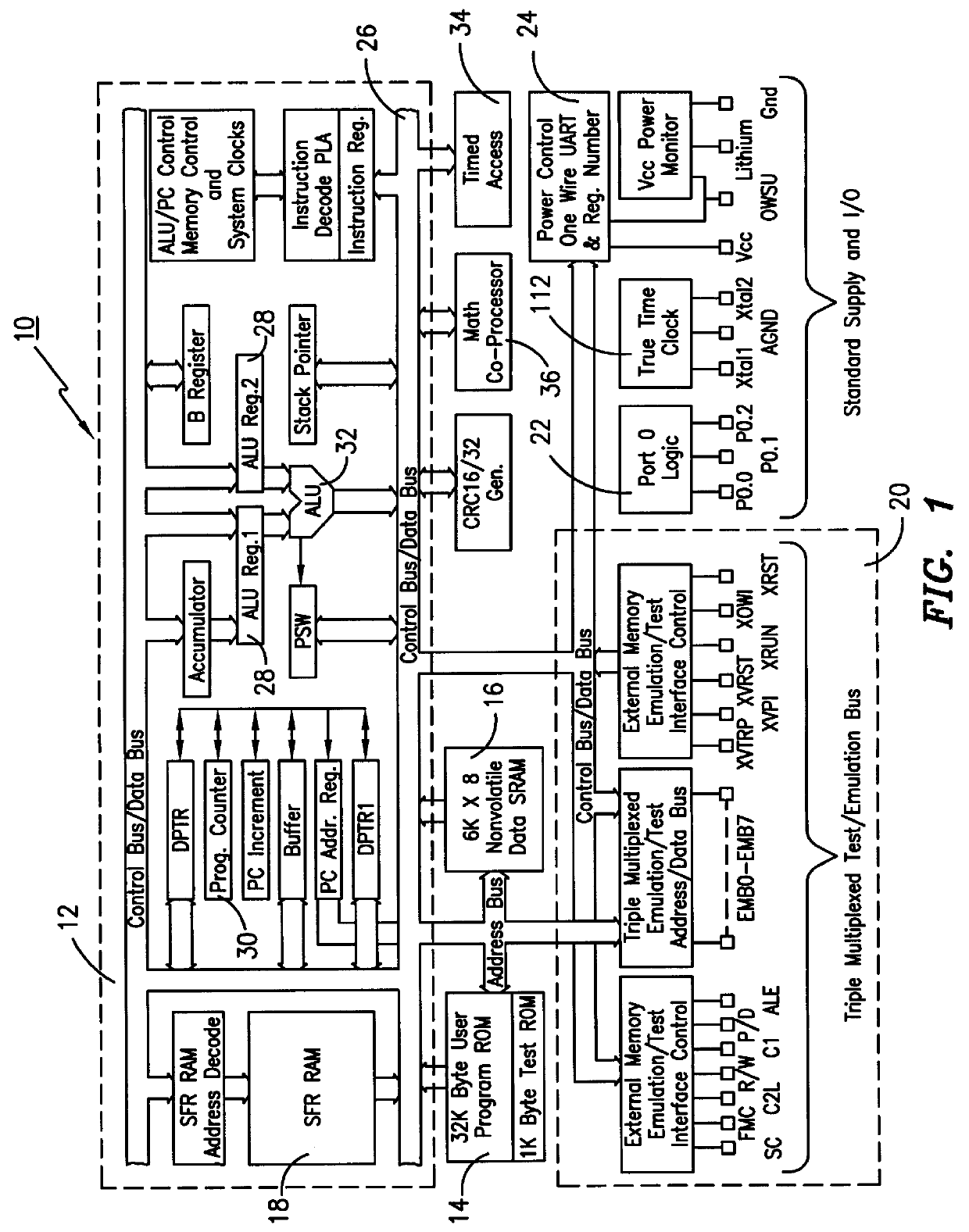
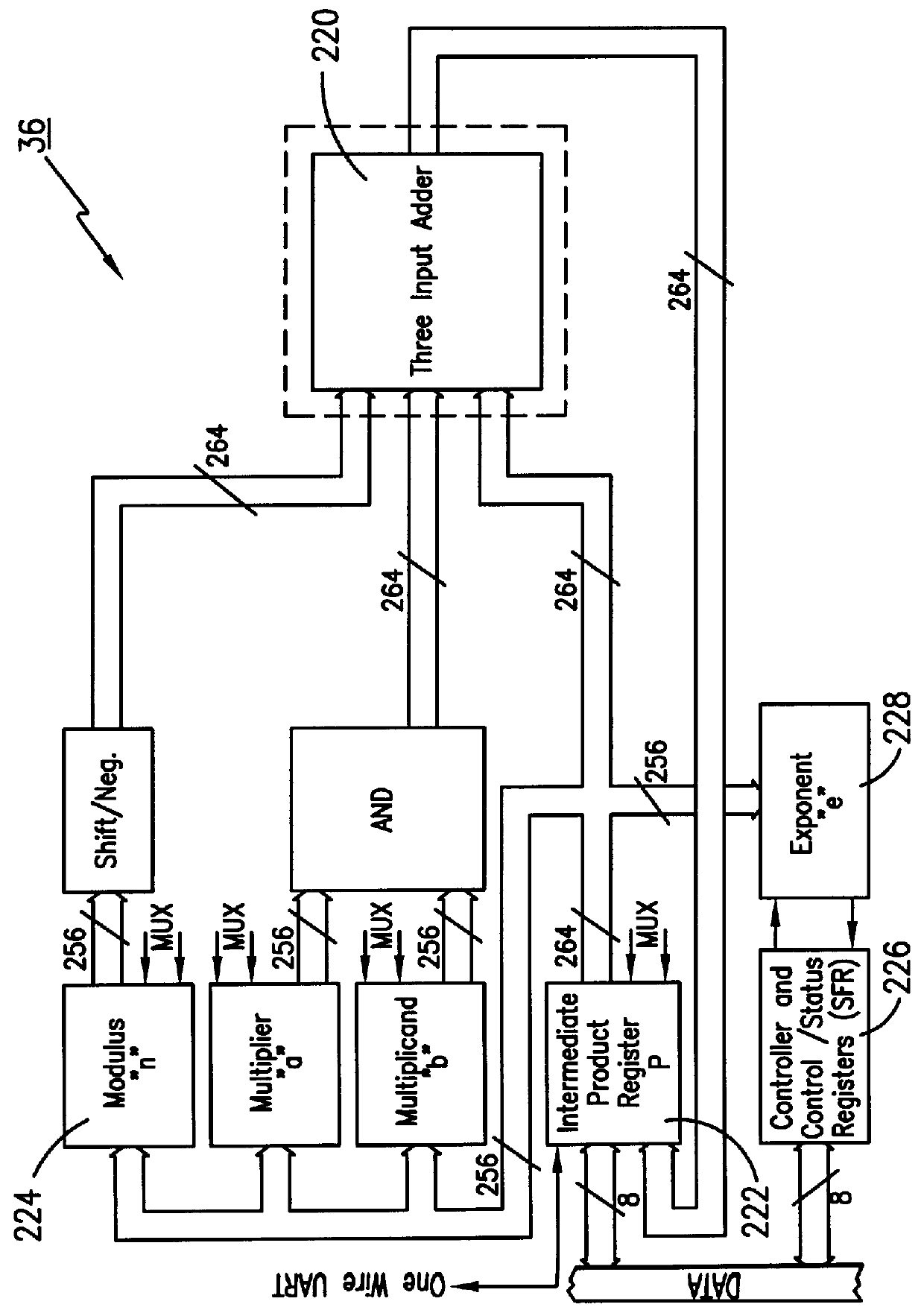
InactiveUS6219789B1Key distribution for secure communicationRandom number generatorsComputer moduleWire protocol
An electronic module having at least a microprocessor and co-processor on a single integrated circuit. The electronic module can be contained in a small housing. The electronic module provides secure bidirectional data communication via a data bus. The electronic module may include an integrated circuit comprising a microprocessor, and a co-processor adapted to handle 1,024-bit modulo mathematics primarily aimed at RSA calculations. The electronic module is preferably contained in a small token sized metallic container and will preferably communicate via a single wire data bus which uses a one-wire protocol.
Owner:MAXIM INTEGRATED PROD INC
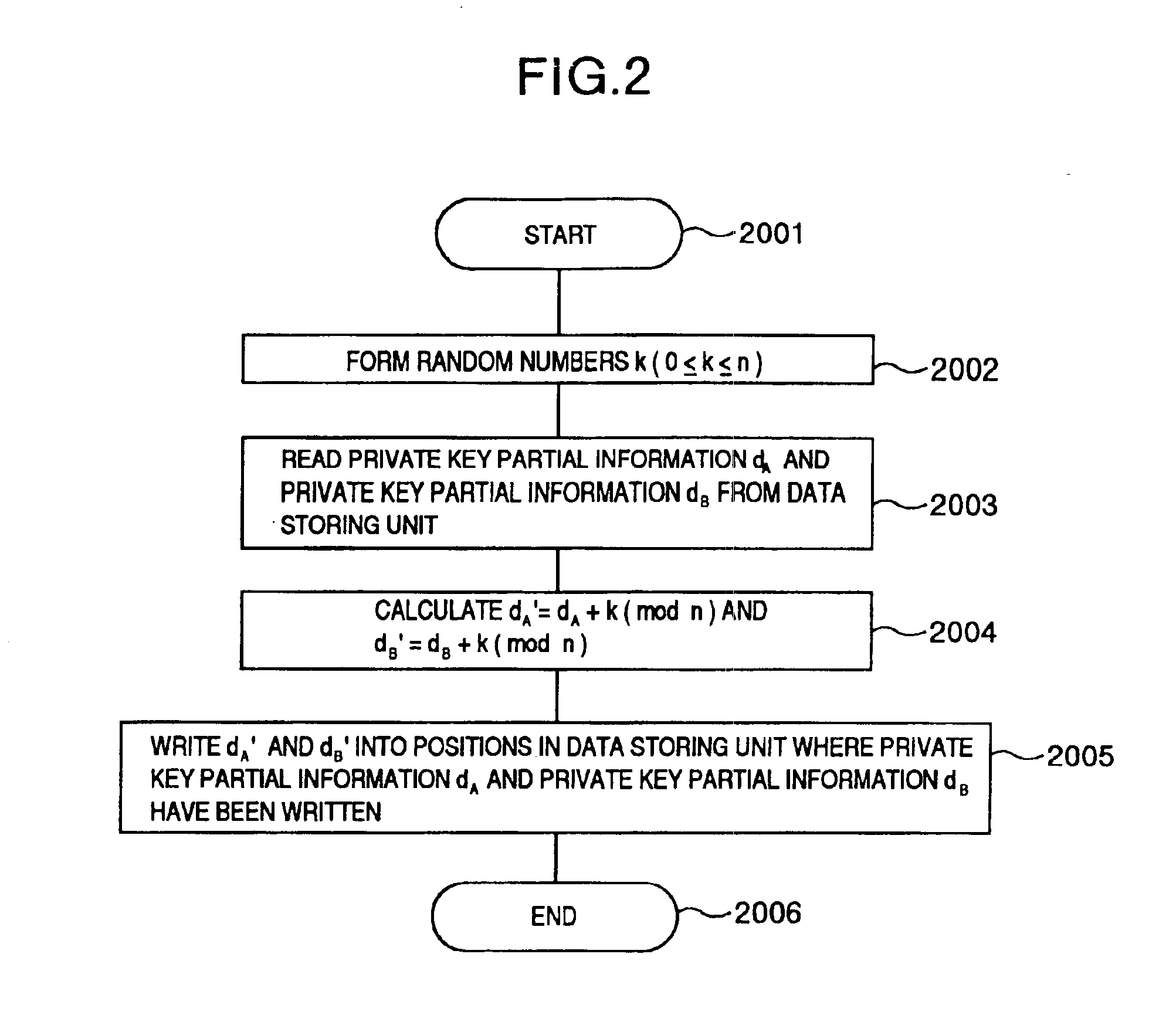
Attack-resistant implementation method
InactiveUS6986054B2Improve efficiencyEliminate characteristicKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationComputer hardwareInformation processing
The present invention makes it difficult for unauthorized parties to estimate processing and a secret key based upon the waveforms of power consumption of an IC card chip by changing a processing order in the IC card chip so that it is not estimated by the attackers. In an information processing apparatus comprising storing means having a program storing part for storing programs and a data storing part for storing data, an operation processing unit, means for inputting data to be operated on in the operation processing unit, and means for outputting operation processing results on the data by the operation processing unit, an arithmetic operation method is provided which comprises the steps of: for two integers K1 and K2, when finding a value F(K, A) of a function F satisfying F(K1+K2, A)=F(K1, A)◯F(K2, A) (◯ denotes an arithmetic operation in a communtative semigroup S. K designates an integer and A designates an element of S), decomposing the K to the sum of m integers K[0]+K[1]+ . . . K[m−1]; using T(0), T(1), . . . T(m−1) resulting from rearranging a string of the m integers 0, 1, . . . m−1 by permutation T (the result corresponds one for one to the integer string 0, 1, . . . m−1); and operating on terms F(K[T(0)], A) to F(K[T(m−1)], A) on the right side ofF(K, A)=F(K[T(0)], A)◯F(K[T(1)], A)◯ . . . F(K[T(m−1)], A) . . . (expression 1)in the order of F(K[T(0)], A), F(K[T(1)], A), . . . F(K[T(m−1)], A) to find F(K, A).
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Method and apparatus for elliptic curve cryptography and recording medium therefore
InactiveUS6876745B1Prevent leakageRandom number generatorsPublic key for secure communicationComputer hardwarePower analysis
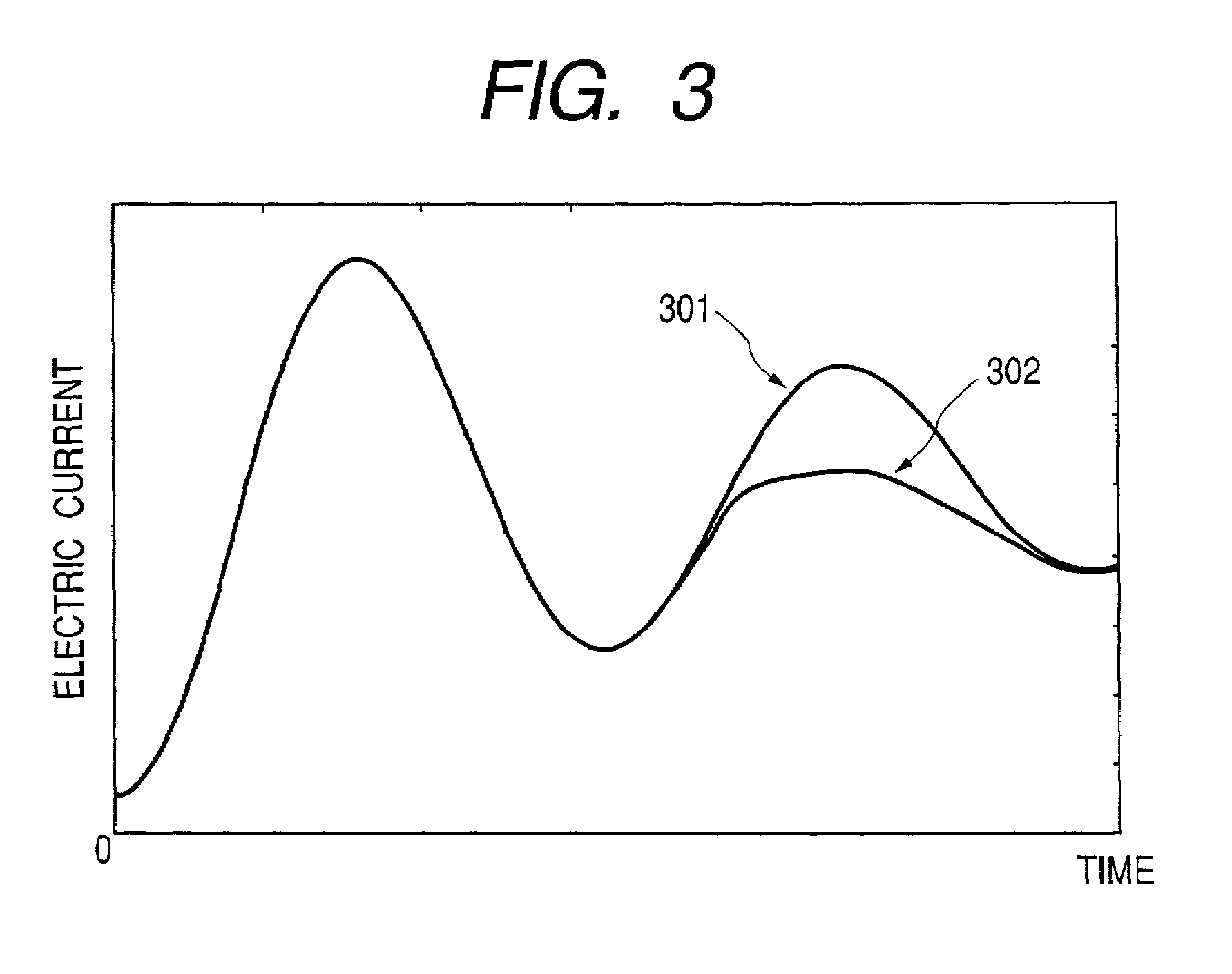
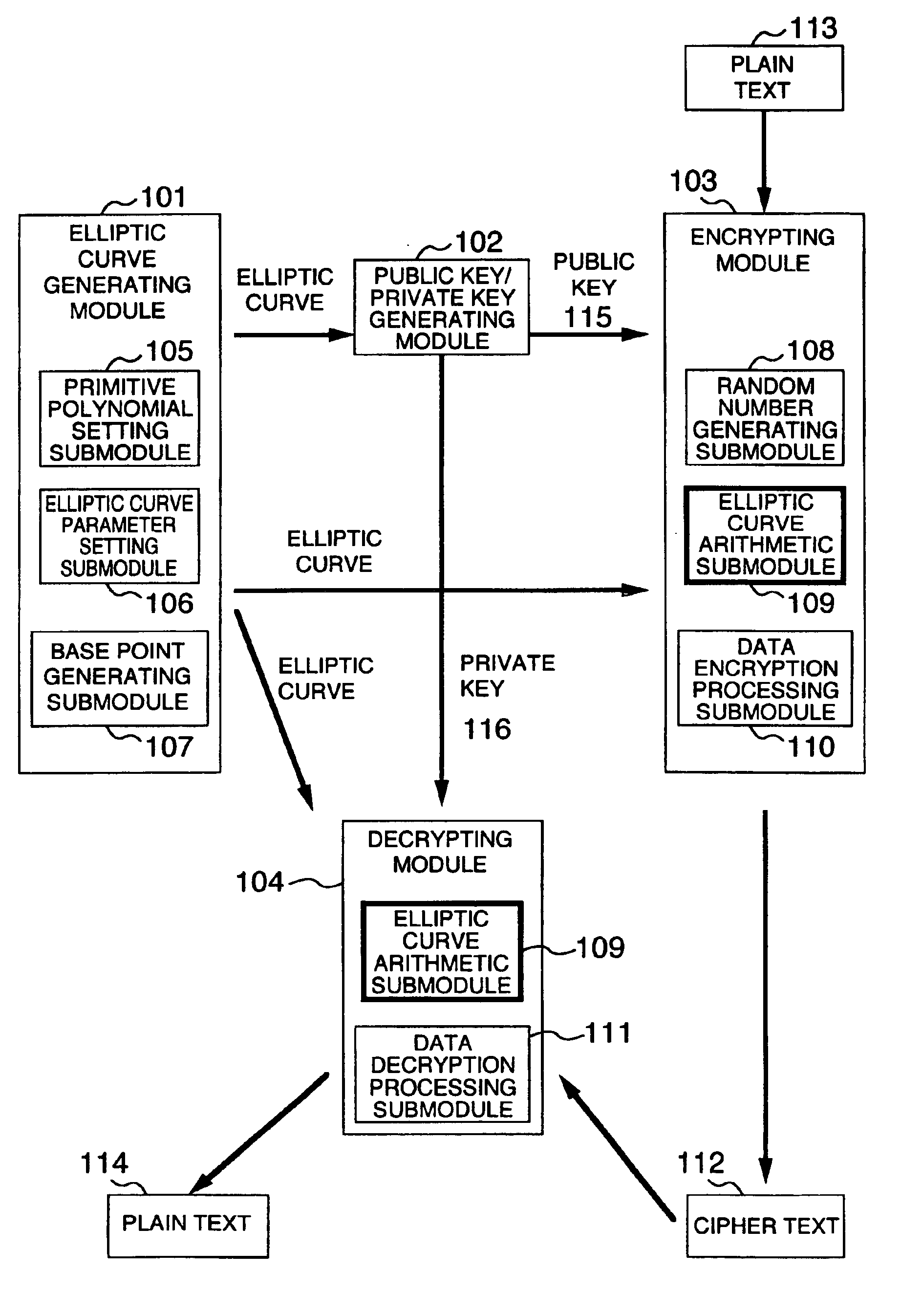
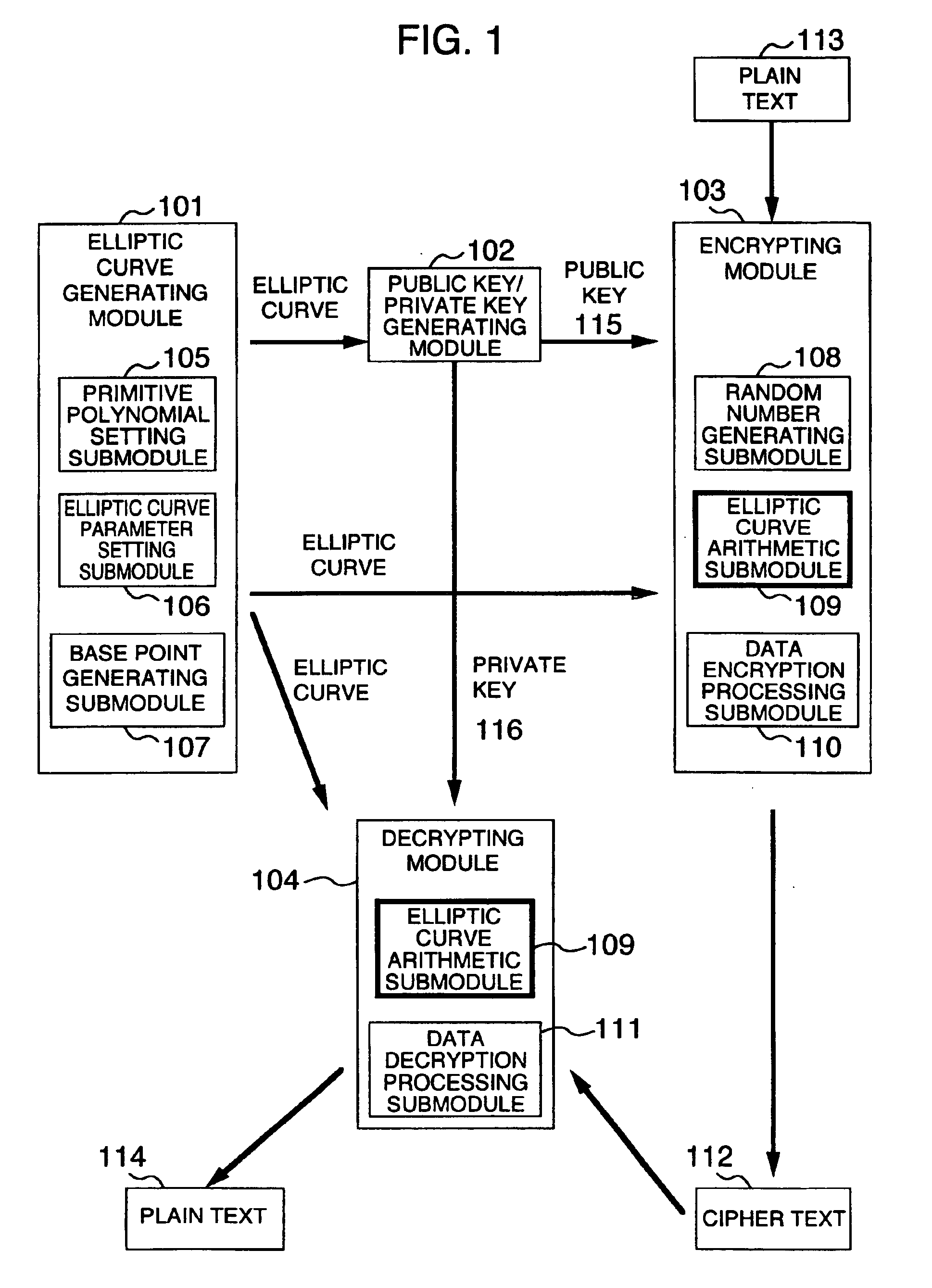
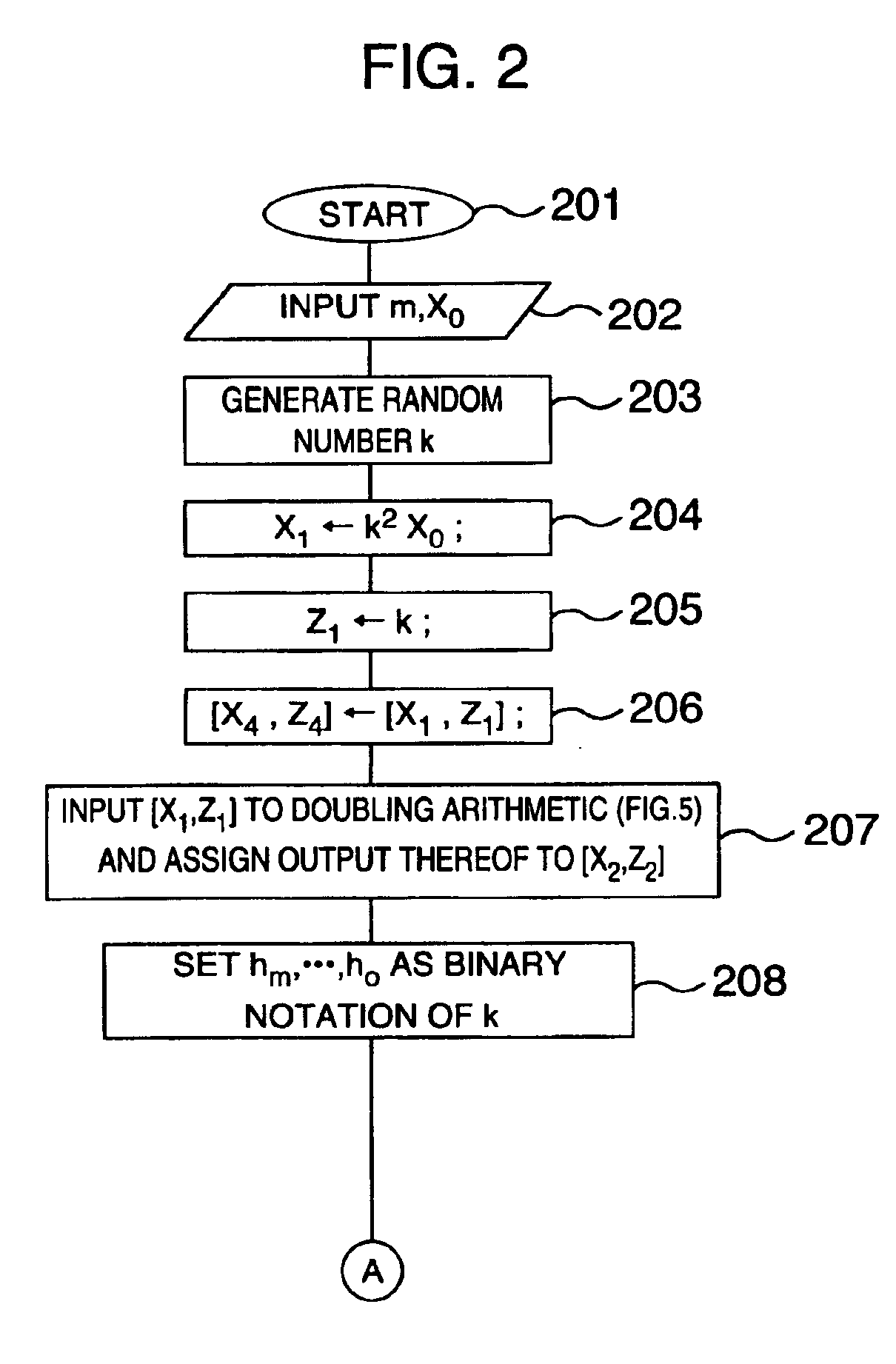
A method and an apparatus capable of realizing at a high speed an elliptic curve cryptography in a finite field of characteristic 2, in which the elliptic curve is given by y2+xy=x3+ax2+b (b≠0) and an elliptic curve cryptography method which can protect private key information against leaking from deviation information of processing time to thereby defend a cipher text against a timing attack and a differential power analysis attack are provided. To this end, an arithmetic process for executing scalar multiplication arithmetic d(x, y) a constant number of times per bit of the private key d is adopted. Further, for the scalar multiplication d(x, y), a random number k is generated upon transformation of the affine coordinates (x, y) to the projective coordinates for thereby effectuating the transformation (x, y)→[kx, ky, k] or alternatively (x, y)→[k2x, k3y, k]. Thus, object for the arithmetic is varied by the random number (k).
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Method and apparatus for fast elliptic encryption with direct embedding
InactiveUS6307935B1Public key for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationPlaintextEllipse
The present invention takes advantage of a quadratic-only ambiguity for x-coordinates in elliptic curve algebra as a means for encrypting plaintext directly onto elliptic curves. The encrypting of plaintext directly onto elliptic curves is referred to herein as "direct embedding". When performing direct embedding, actual plaintext is embedded as a "+" or "-" x-coordinate. The sender specifies using an extra bit whether + or - is used so that the receiver can decrypt appropriately. In operation their are two public initial x-coordinates such that two points P1+ and P1- lie respectively on two curves E+ and E-. A parcel of text xtext is selected that is no more than q bits in length. The curve (E+ or E-) that contains xtext is determined. A random number r is chosen and used to generate a coordinate xq using the public key of a receiving party. An elliptic add operation is used with the coordinate xq and the parcel of text to generated a message coordinate xm. A clue xc is generated using the random number and the point P from the appropriate curve E±. The sign that holds for xtext is determined and called g. The message coordinate xm, the clue xc, and the sign g are sent as a triple to the receiving party. The receiving party uses the clue xc and its private key to generate coordinate xq. Using the sign g and coordinate xq, the text can be recovered.
Owner:APPLE INC
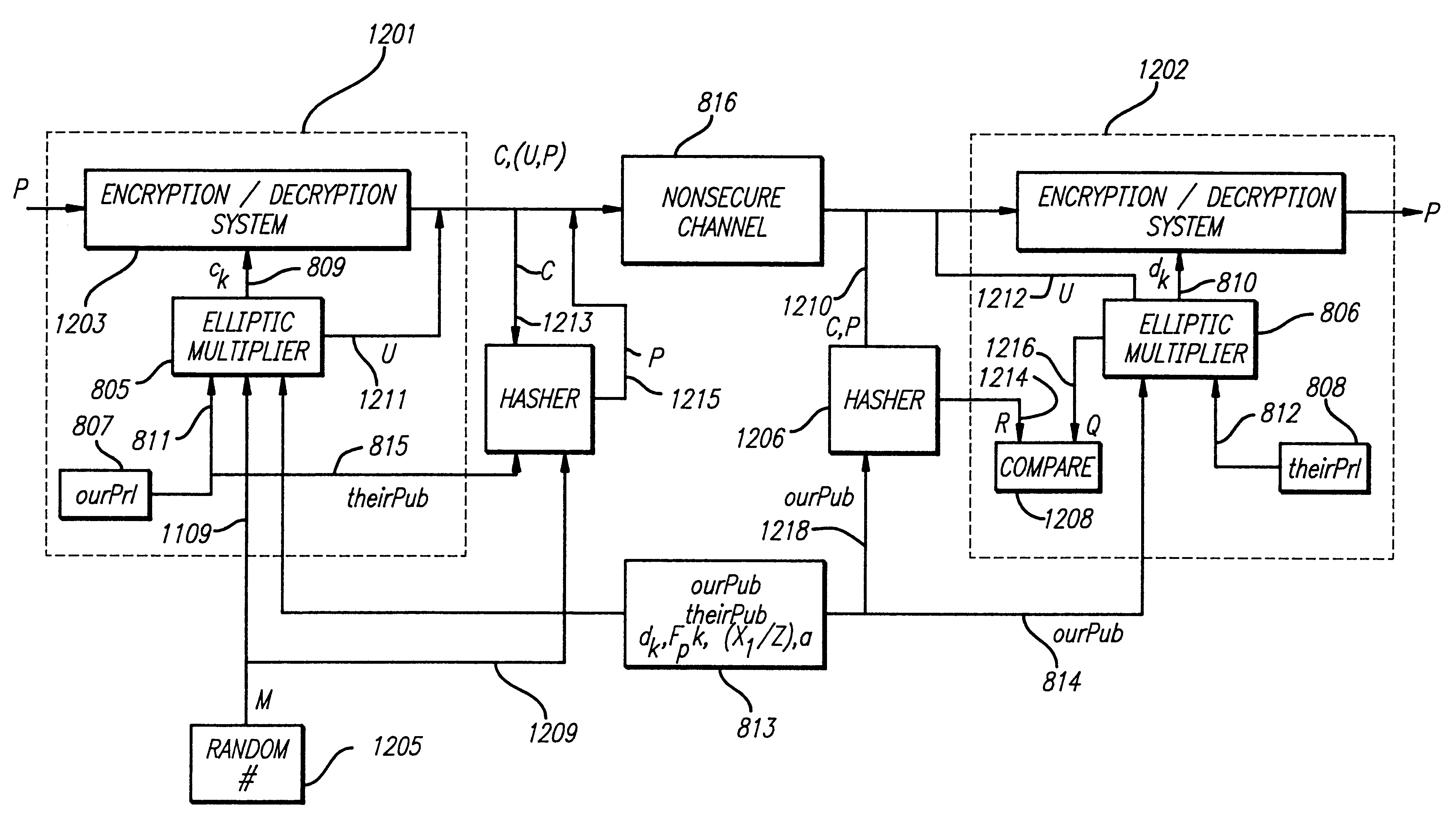
Cryptographic system incorporating a digitally generated chaotic numerical sequence
ActiveUS20090196420A1Data stream serial/continuous modificationSecret communicationNumbering systemData stream
A cryptographic system (CS) is provided. The CS (500) is comprised of a data stream receiving device (DSRD), a chaotic sequence generator (CSG) and an encryptor. The DSRD (602) is configured to receive an input data stream. The CSG (300) includes a computing means (3020, . . . , 302N-1) and a mapping means (304). The computing means is configured to use RNS arithmetic operations to respectively determine solutions for polynomial equations. The solutions are iteratively computed and expressed as RNS residue values. The mapping means is configured to determine a series of digits in the weighted number system based on the RNS residue values. The encryptor is coupled to the DSRD and CSG. The encryptor is configured to generate a modified data stream by incorporating or combining the series of digits with the input data stream.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
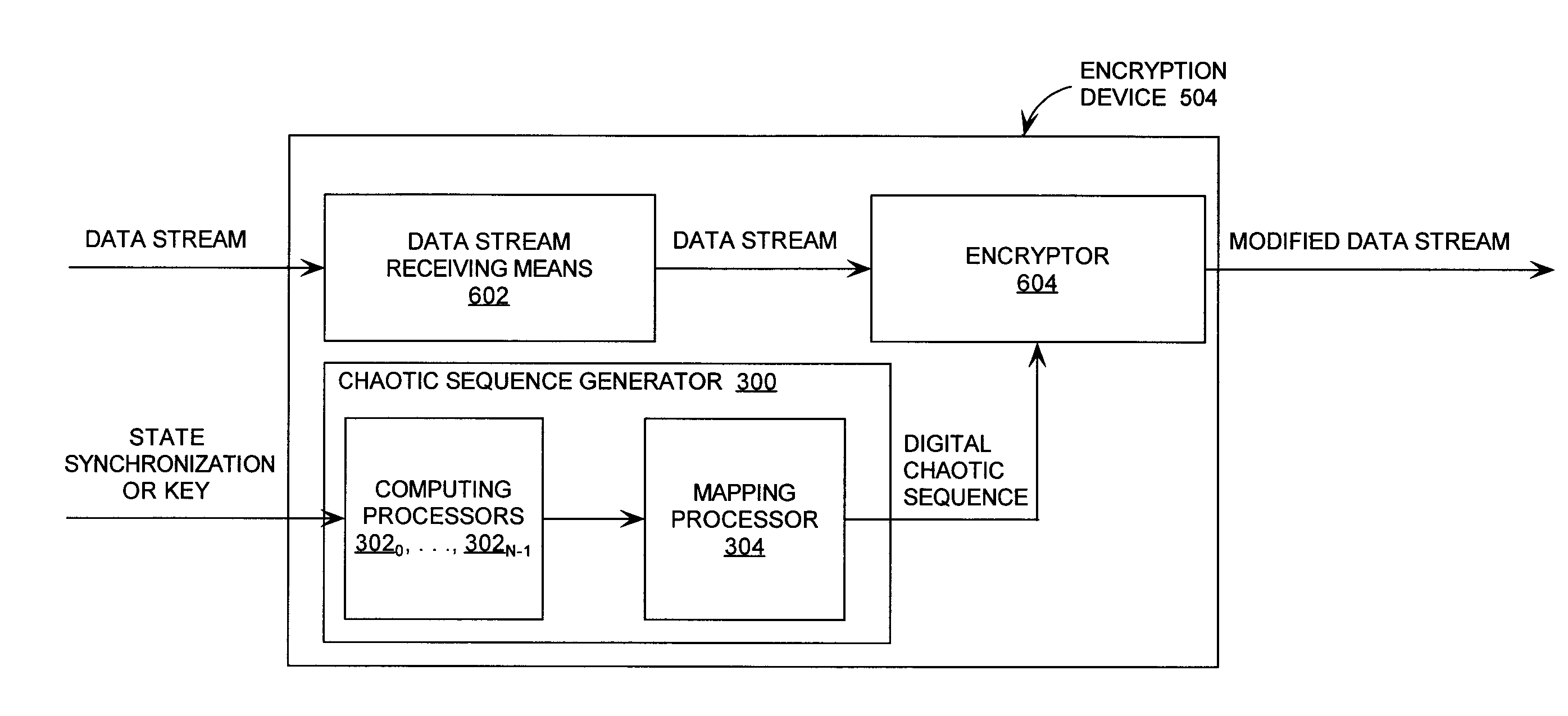
Digital Generation of a Chaotic Numerical Sequence
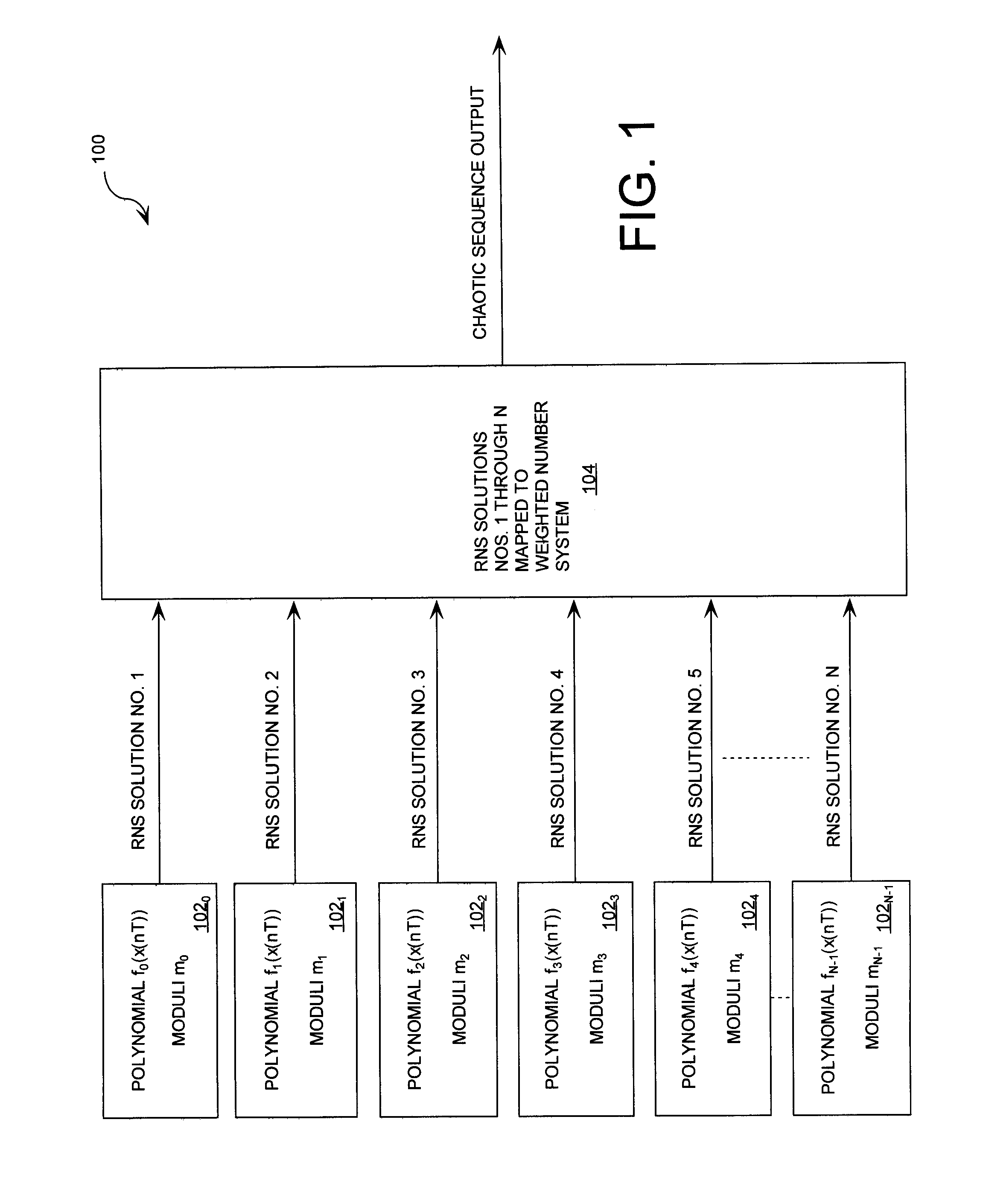
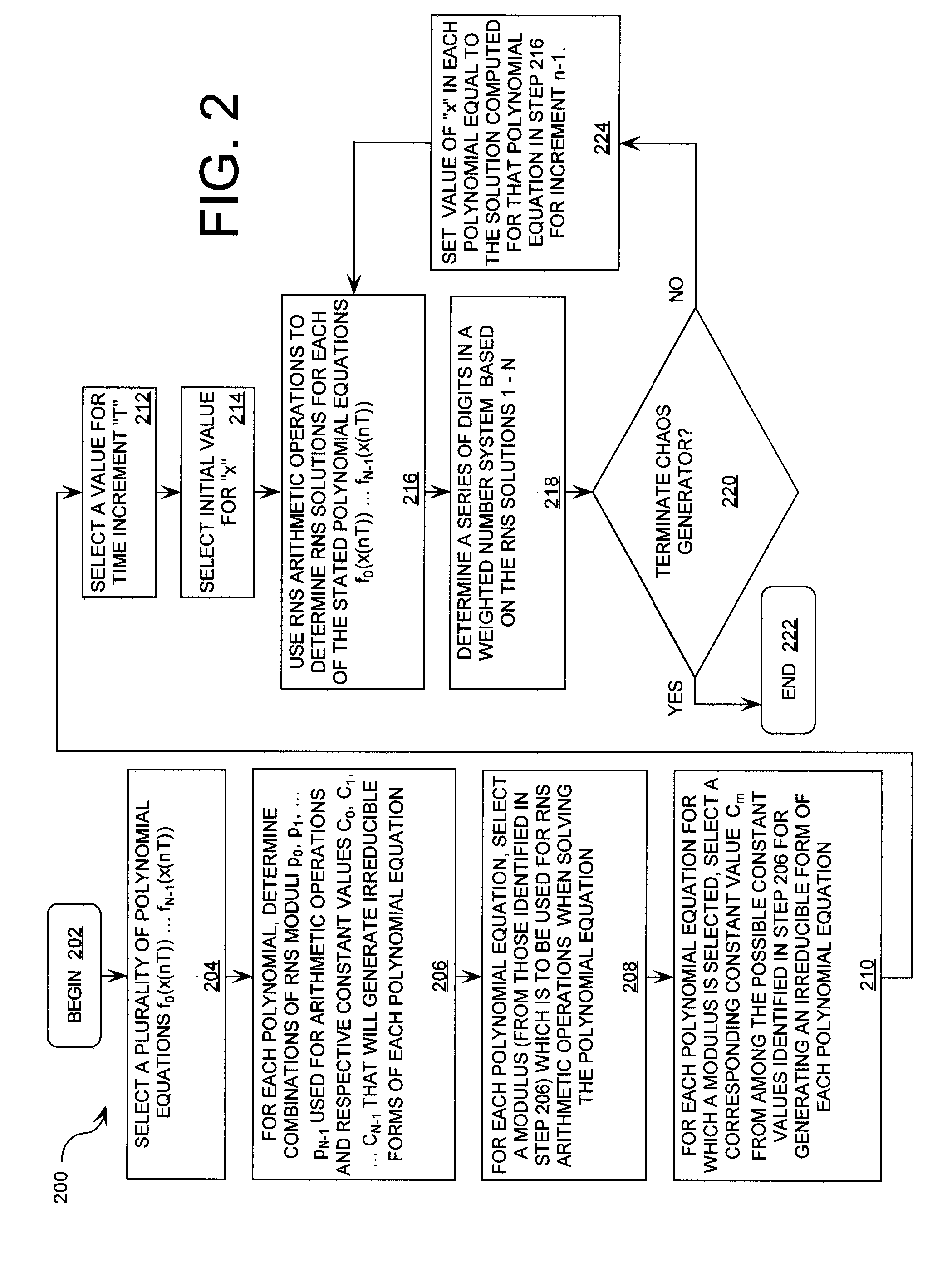
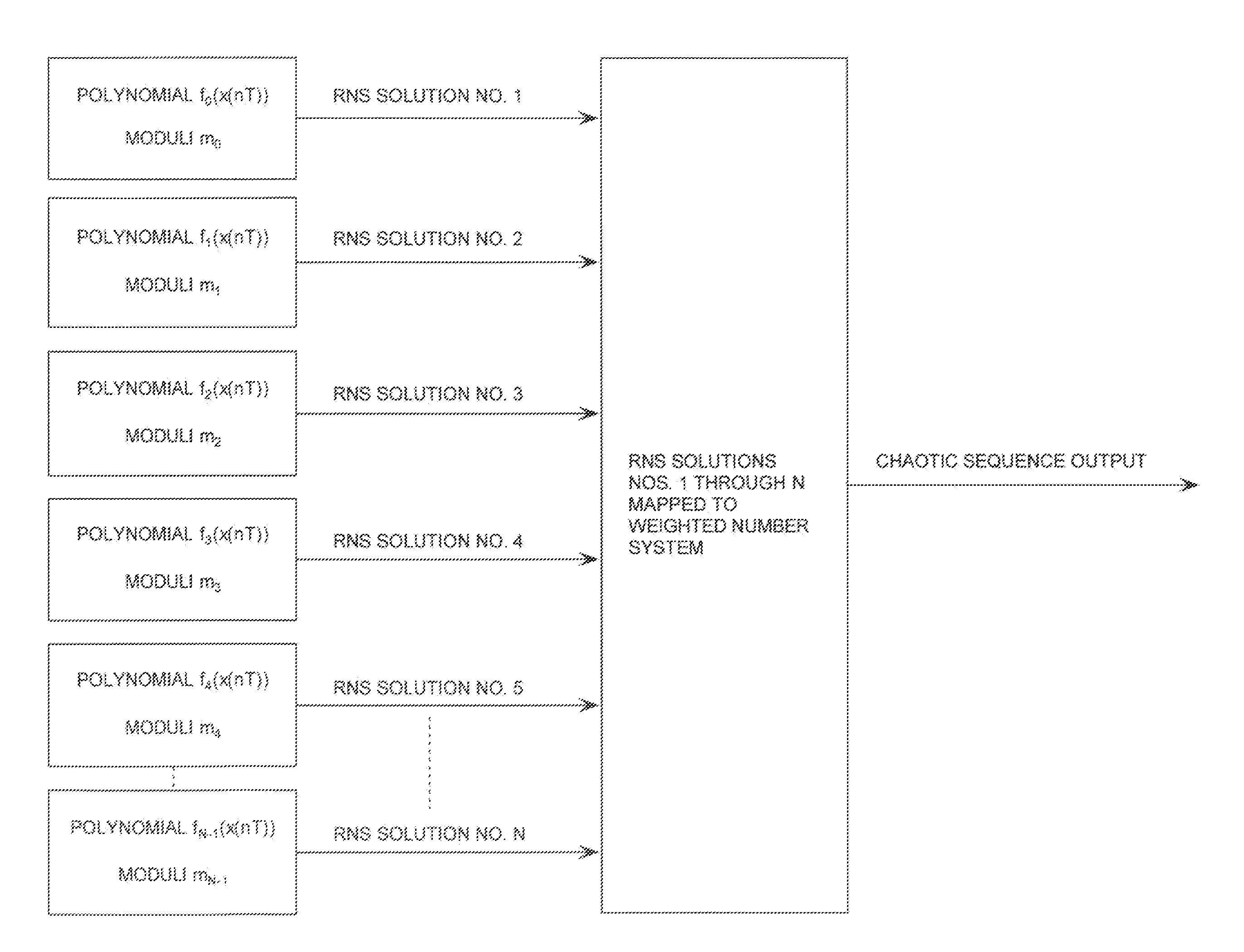
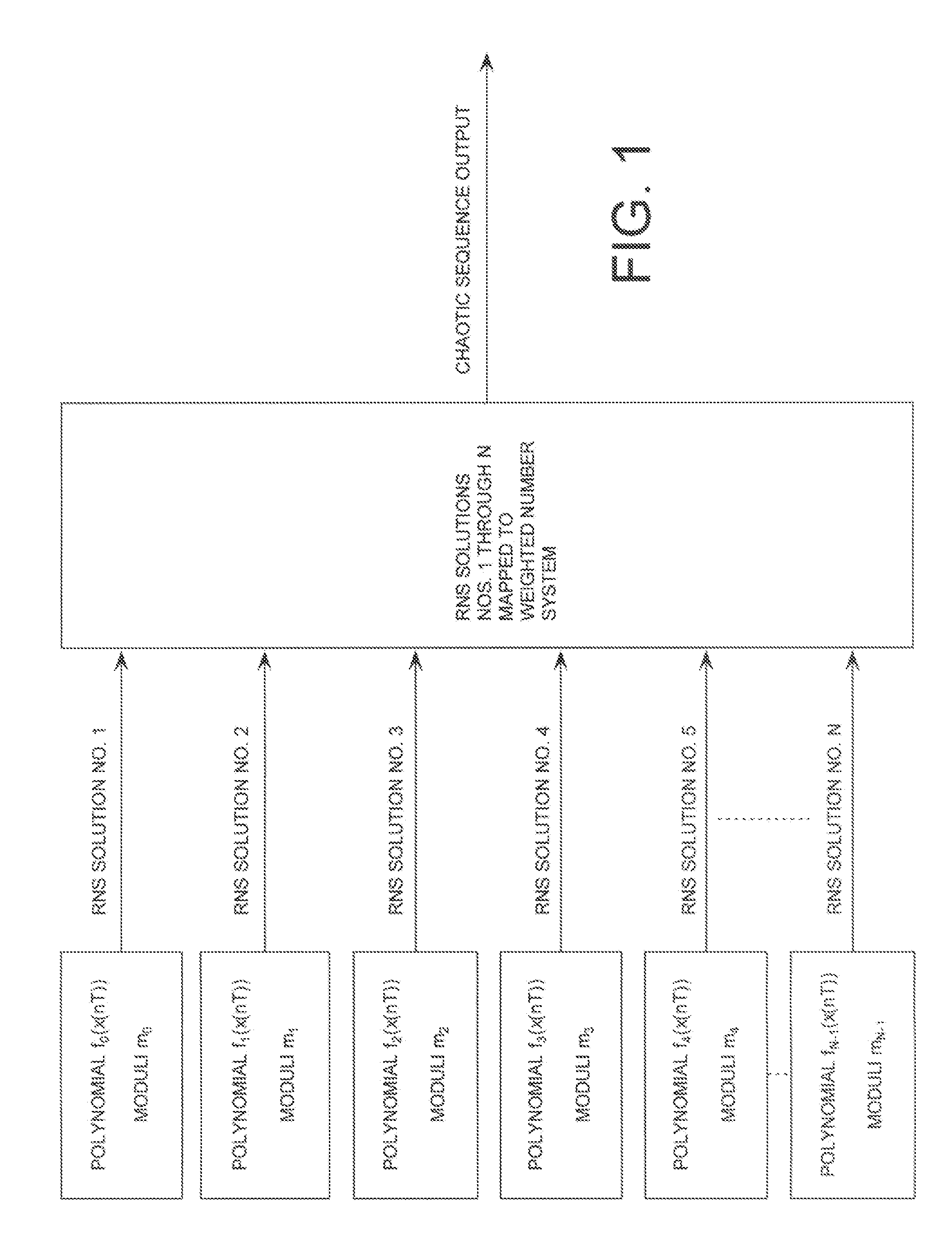
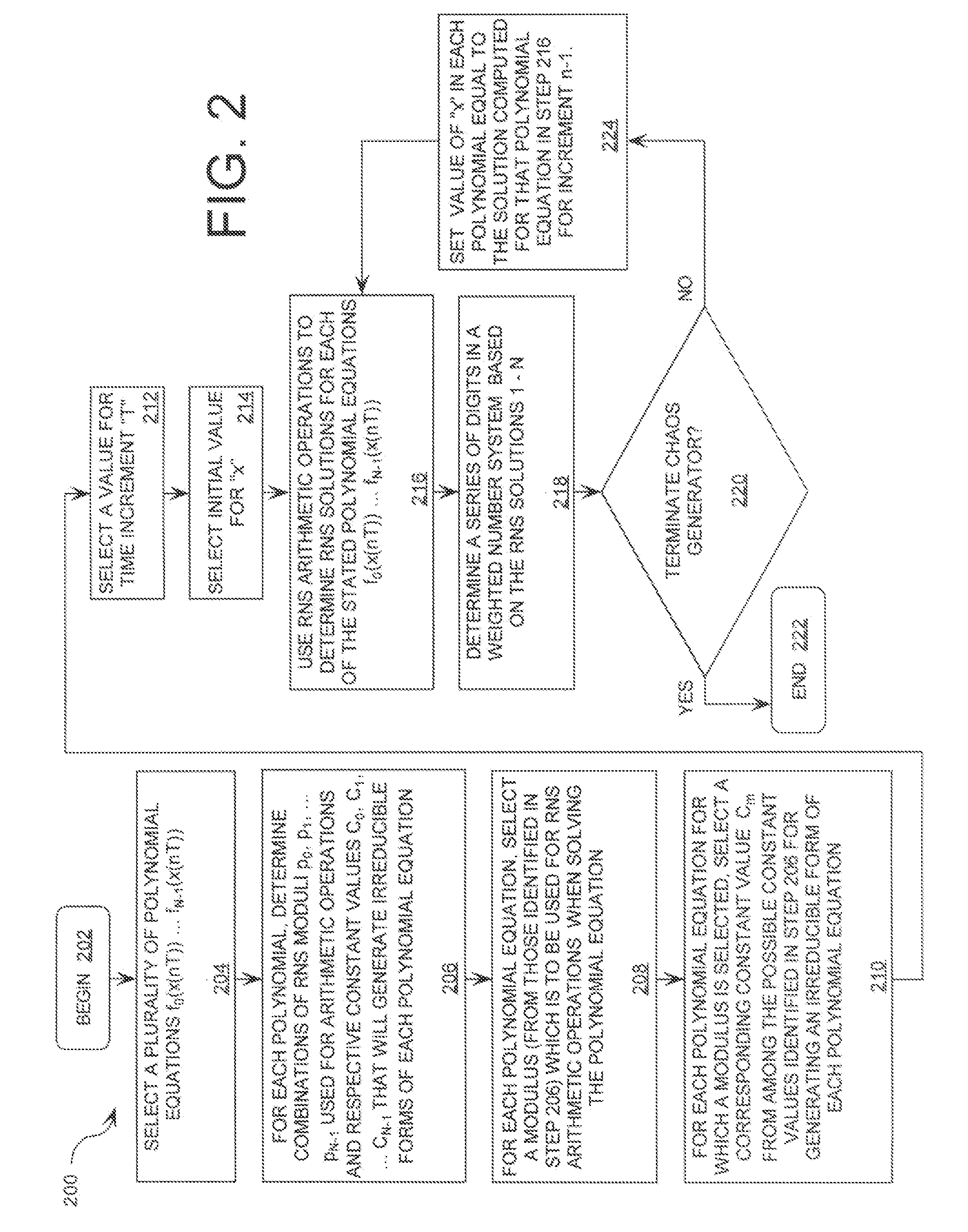
ActiveUS20080263119A1Random number generatorsComputations using residue arithmeticNumbering systemChinese remainder theorem
A method is provided for generating a chaotic sequence. The method includes selecting a plurality of polynomial equations. The method also includes using residue number system (RNS) arithmetic operations to respectively determine solutions for the polynomial equations. The solutions are iteratively computed and expressed as RNS residue values. The method further includes determining a series of digits in a weighted number system (e.g., a binary number system) based on the RNS residue values. According to an aspect of the invention, the method includes using a Chinese Remainder Theorem process to determine a series of digits in the weighted number system based on the RNS residue values. According to another aspect of the invention, the determining step comprises identifying a number in the weighted number system that is defined by the RNS residue values.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
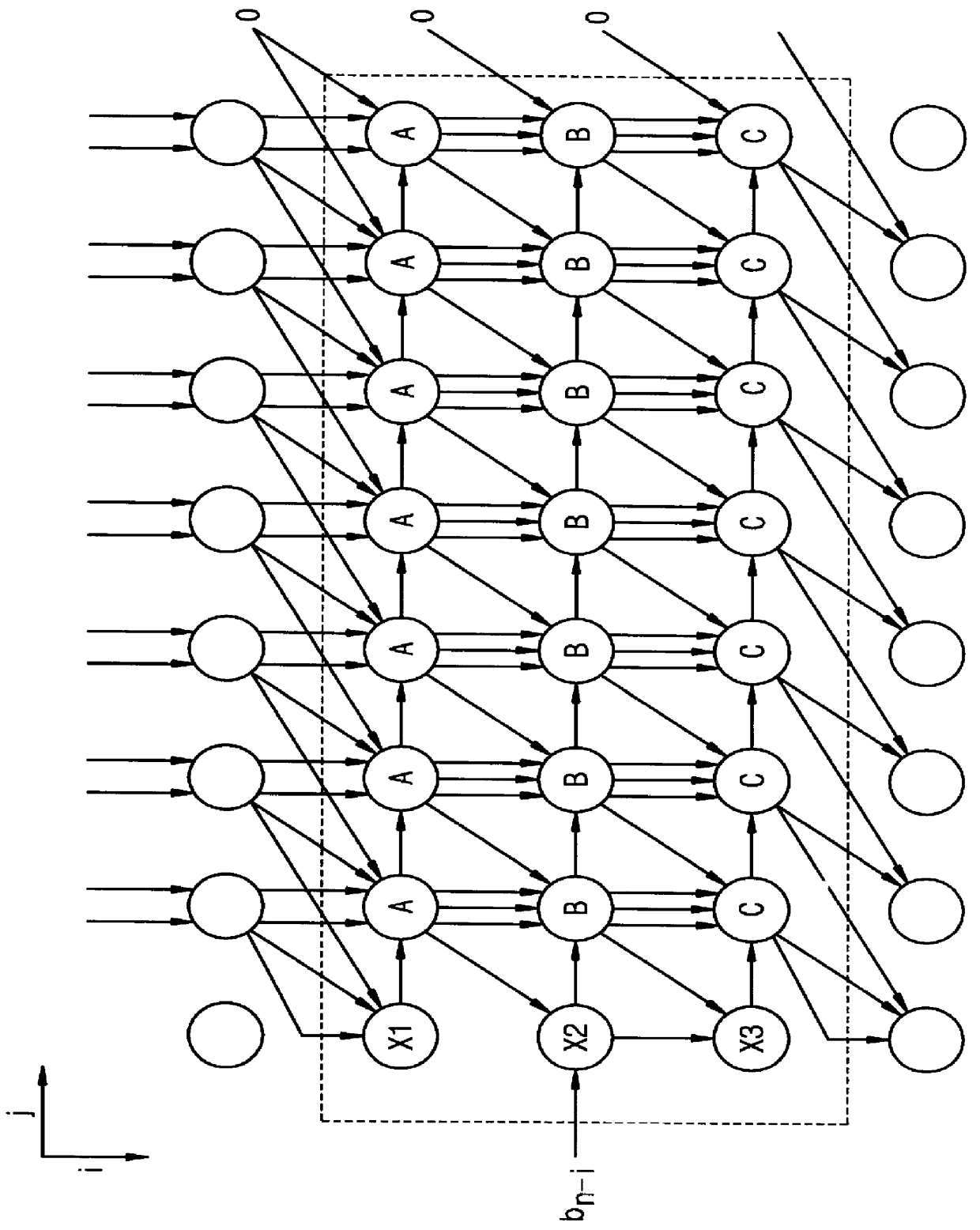
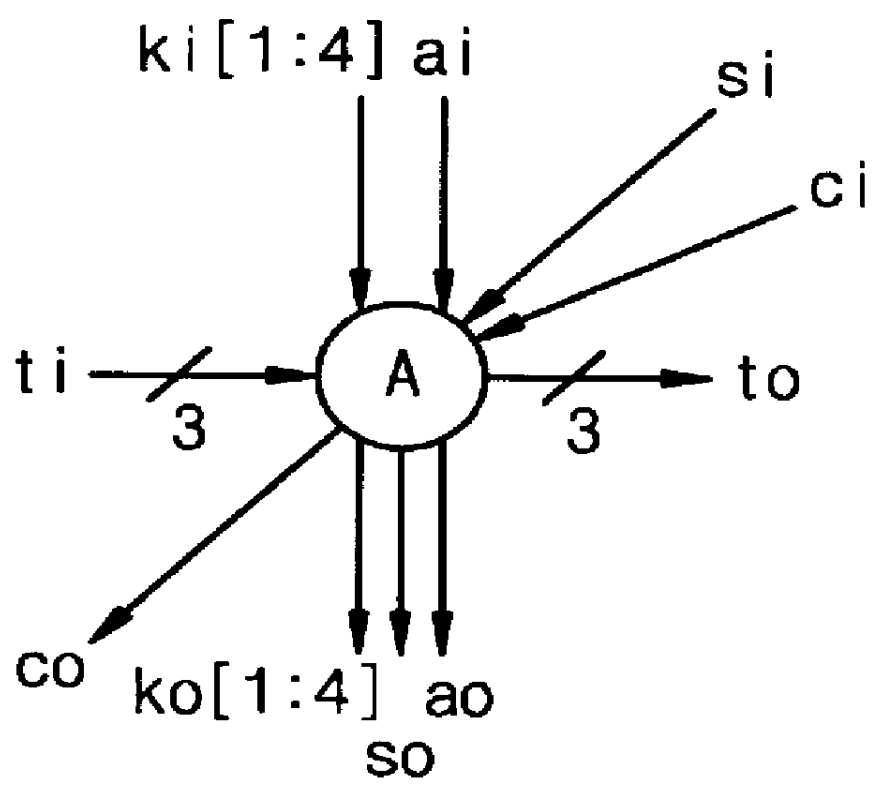
Device and method for modular multiplication
InactiveUS6151393AEasy mappingImprove performanceComputations using contact-making devicesComputation using non-contact making devicesEngineeringFine grain
A method and apparatus are disclosed for performing modular multiplication. Modular multiplication in accordance with the present invention includes precalculating a 2's complement of a given modulus and multiples of the 2's complement and calculating a total magnitude of end-around carries during the modular multiplication. The calculated multiples are selected depending on the total magnitude of the end-around carries, and the selected multiples are added. The disclosure includes array structures in accordance with the present invention. The invention includes an algorithm designed for Rivest-Shamir-Adelman (RSA) cryptography and based on the familiar iterative Homer's rule, but uses precalculated complements of the modulus. The problem of deciding which multiples of the modulus to subtract in intermediate iteration stages has been simplified using simple look-up of precalculated complement numbers, thus allowing a finer-grain pipeline. Regularity and local connections make the algorithm suitable for high-performance array implementation in FPGA's (field programmable gate arrays) or deep submicron VLSI's.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
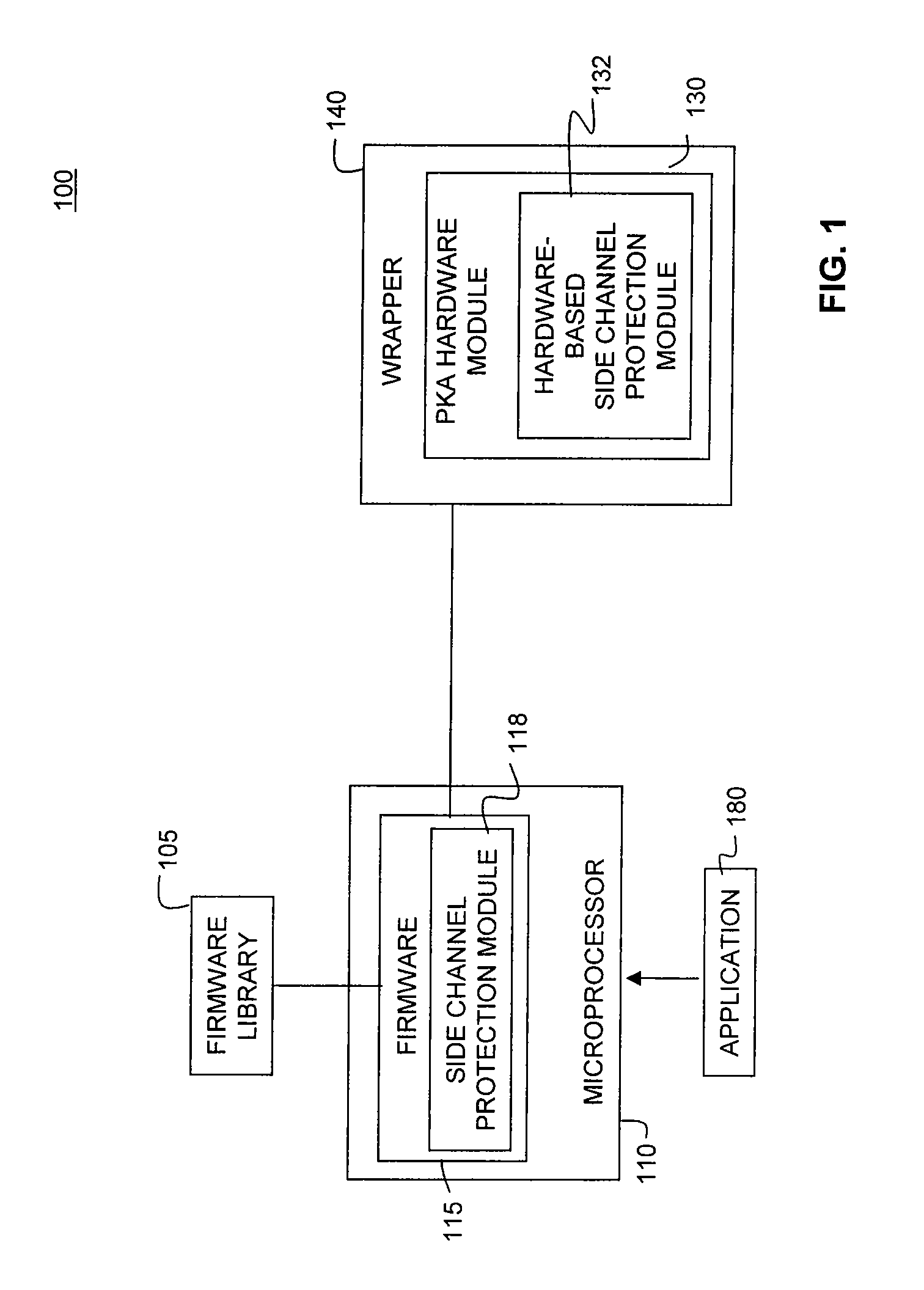
System and Methods for Side-Channel Attack Prevention
InactiveUS20090010424A1Internal/peripheral component protectionSecret communicationProcessor registerCryptosystem
A side channel attack utilizes information gained from the physical implementation of a cryptosystem. Software and hardware-based systems and methods for preventing side channel attacks are presented. Cryptographic hardware may introduce dummy operations to compensate for conditional math operations in certain functions such as modular exponentiation. Cryptographic hardware may also introduce random stalls of the data path to introduce alterations in the power profile for the operation. A cryptographic function may be mapped to a micro code sequence having a plurality of instructions. Firmware in the cryptosystem may alter the micro code sequence by altering the order of instructions, add dummy operations in the micro code sequence, break the micro code sequence into multiple sub micro code sequences and / or change the register location for source and destination operands used in the sequence. These alterations are designed to randomly change the timing and power profile of the requested function.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
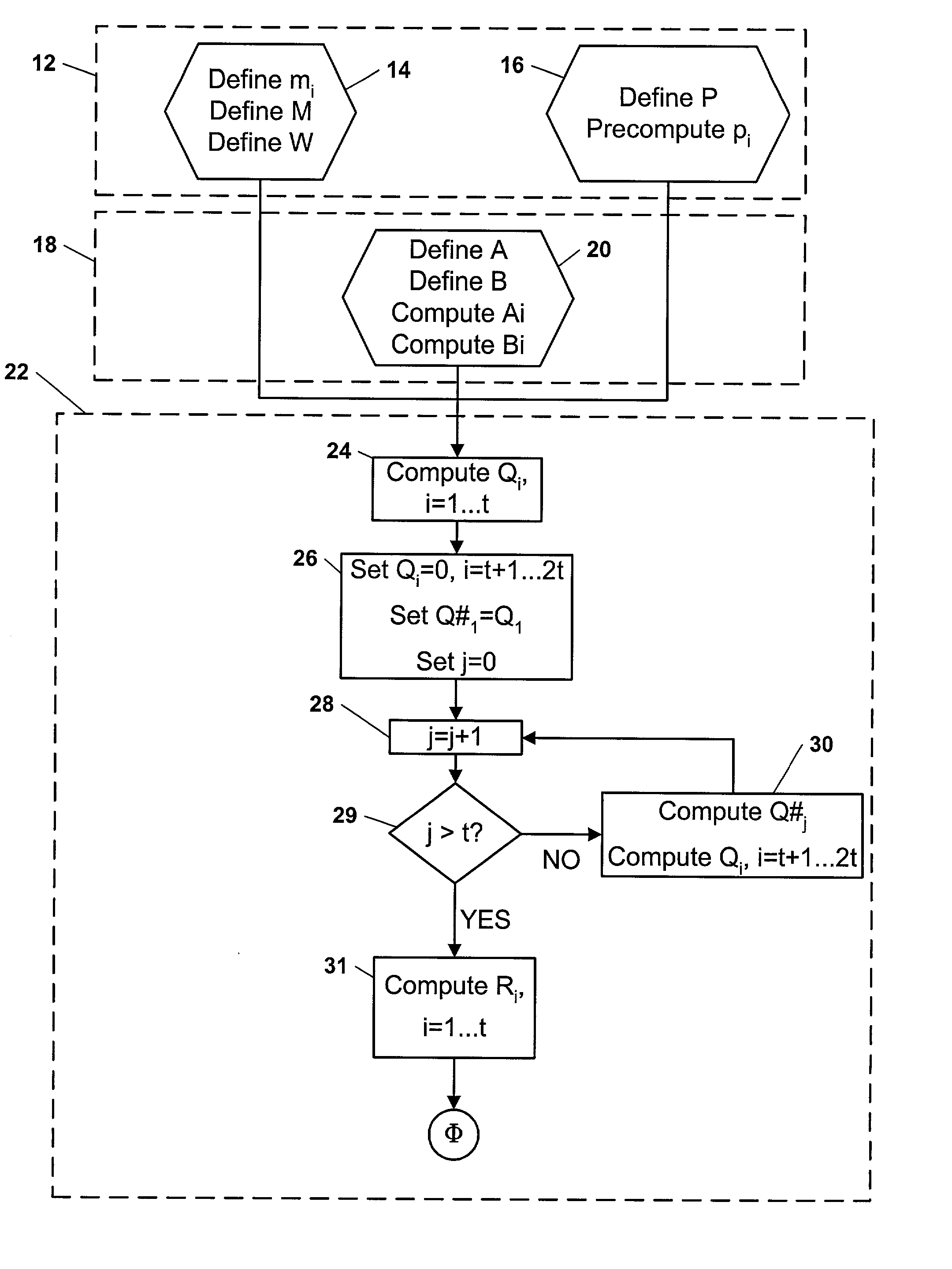
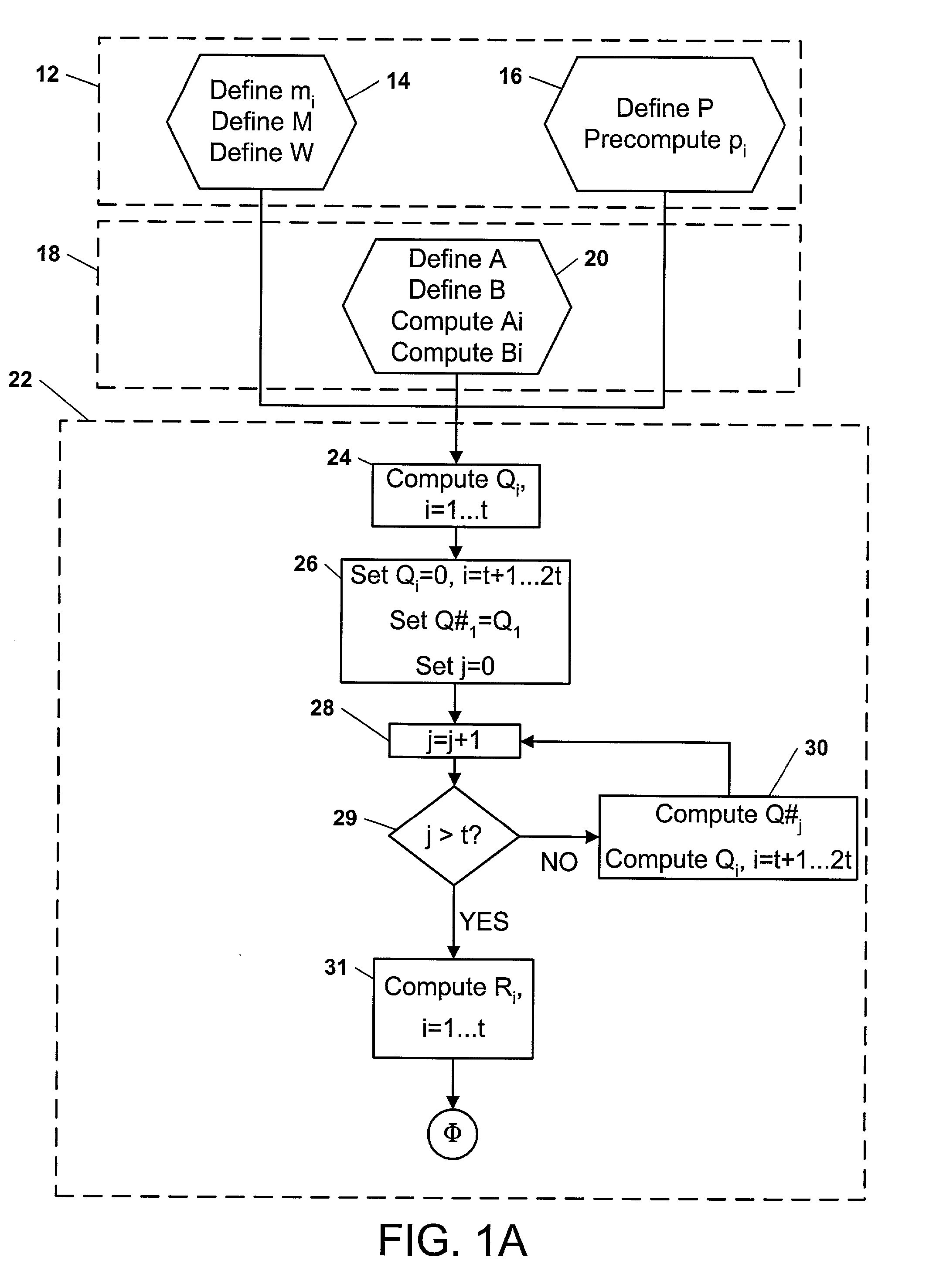
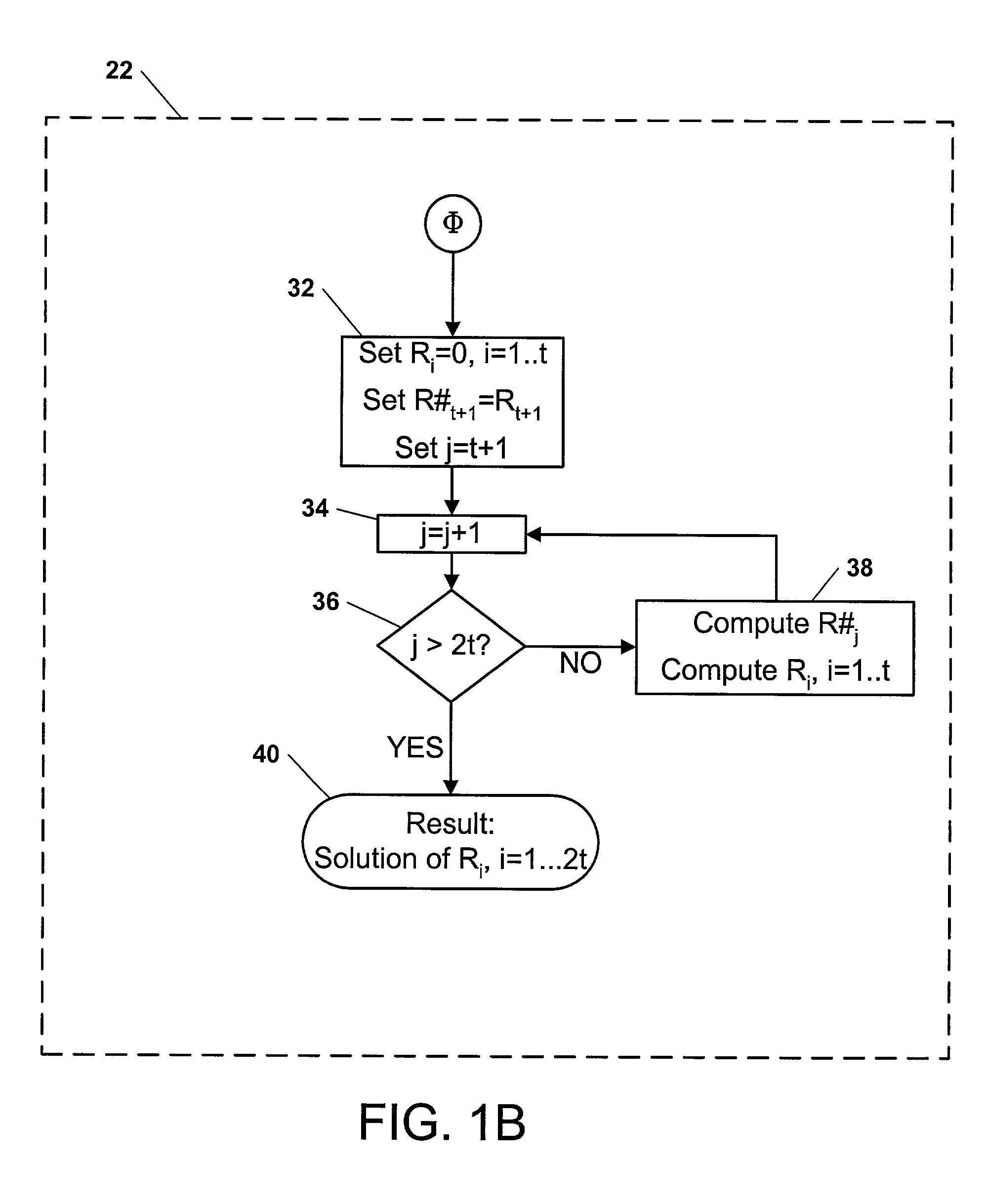
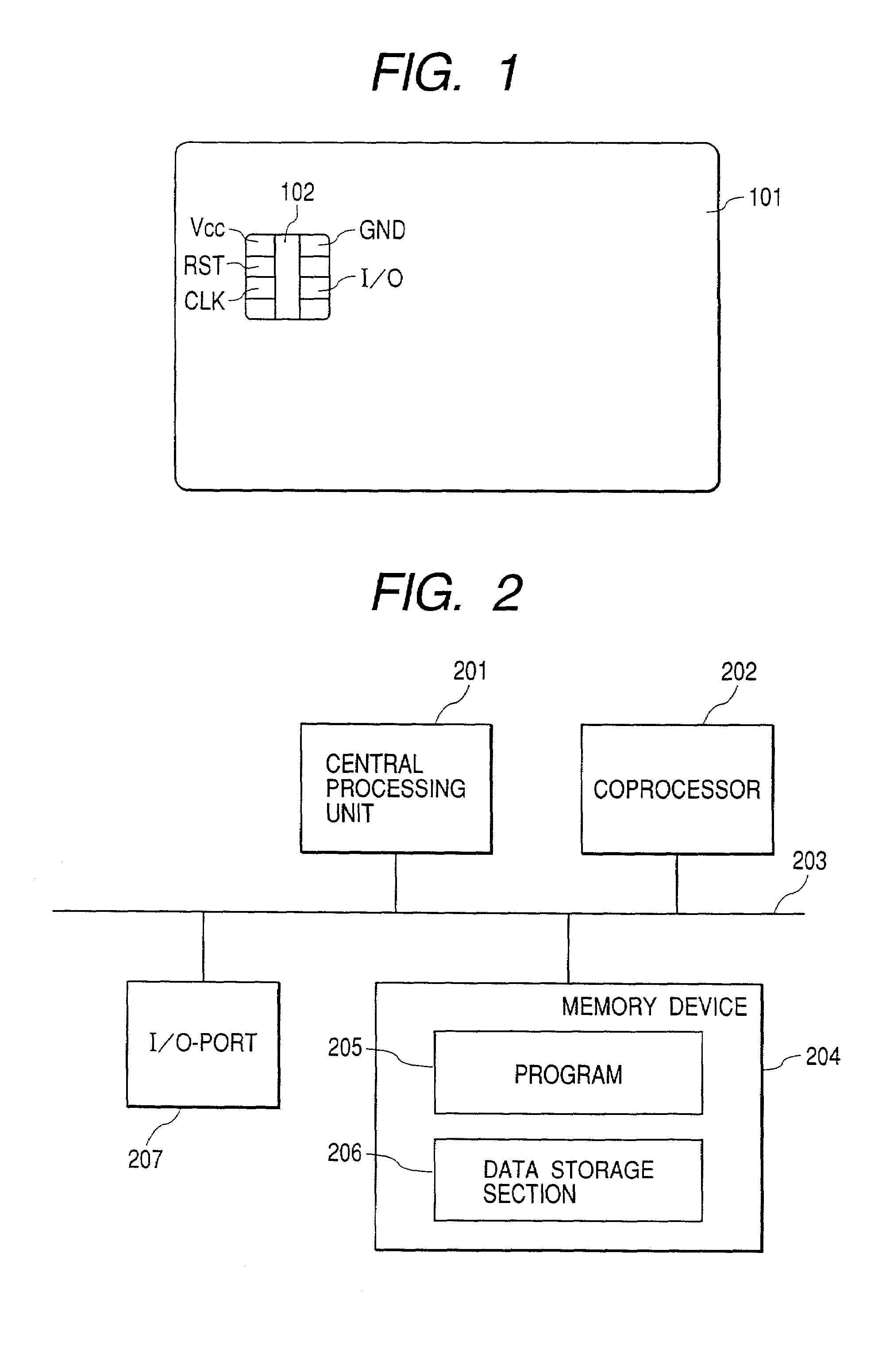
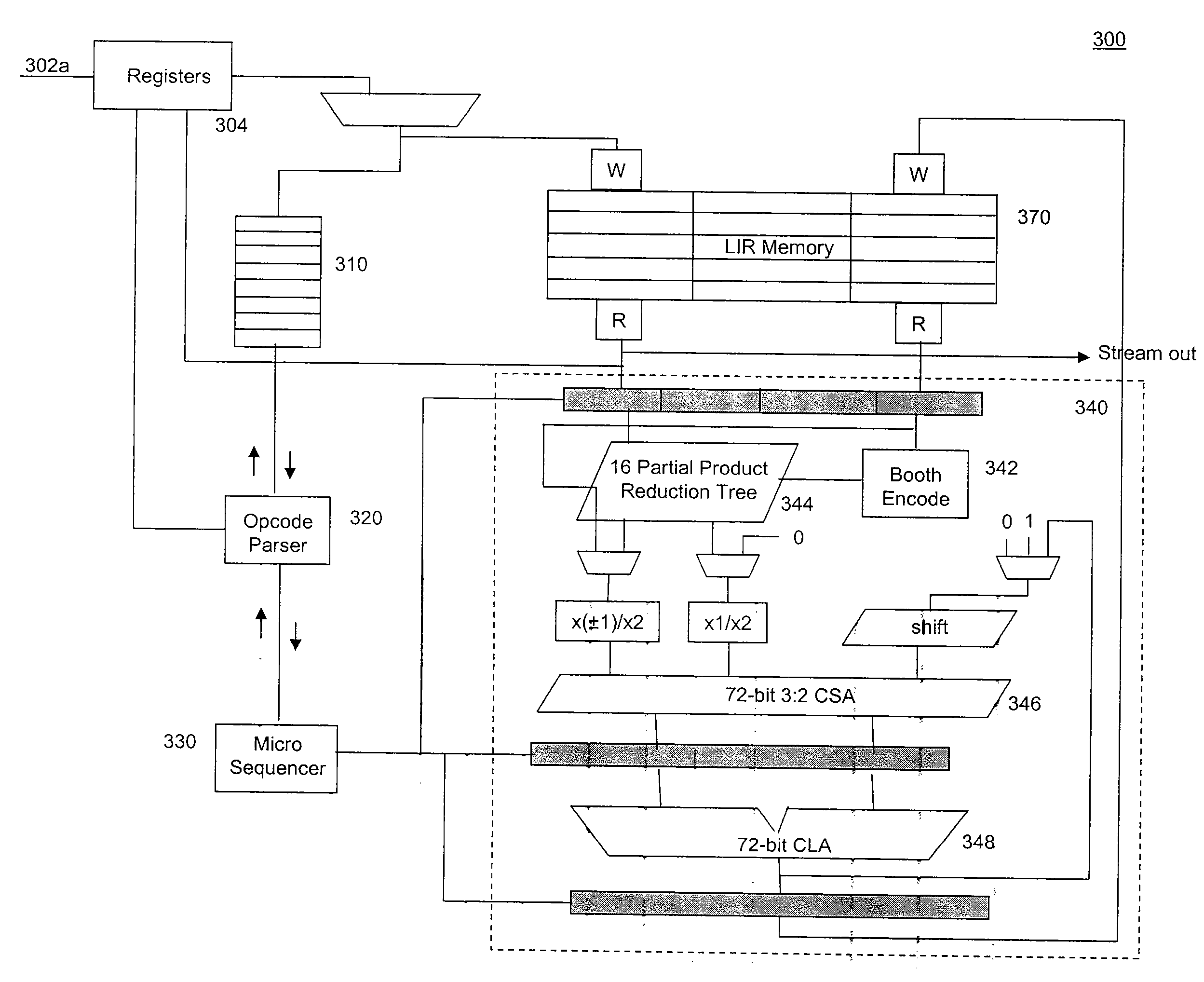
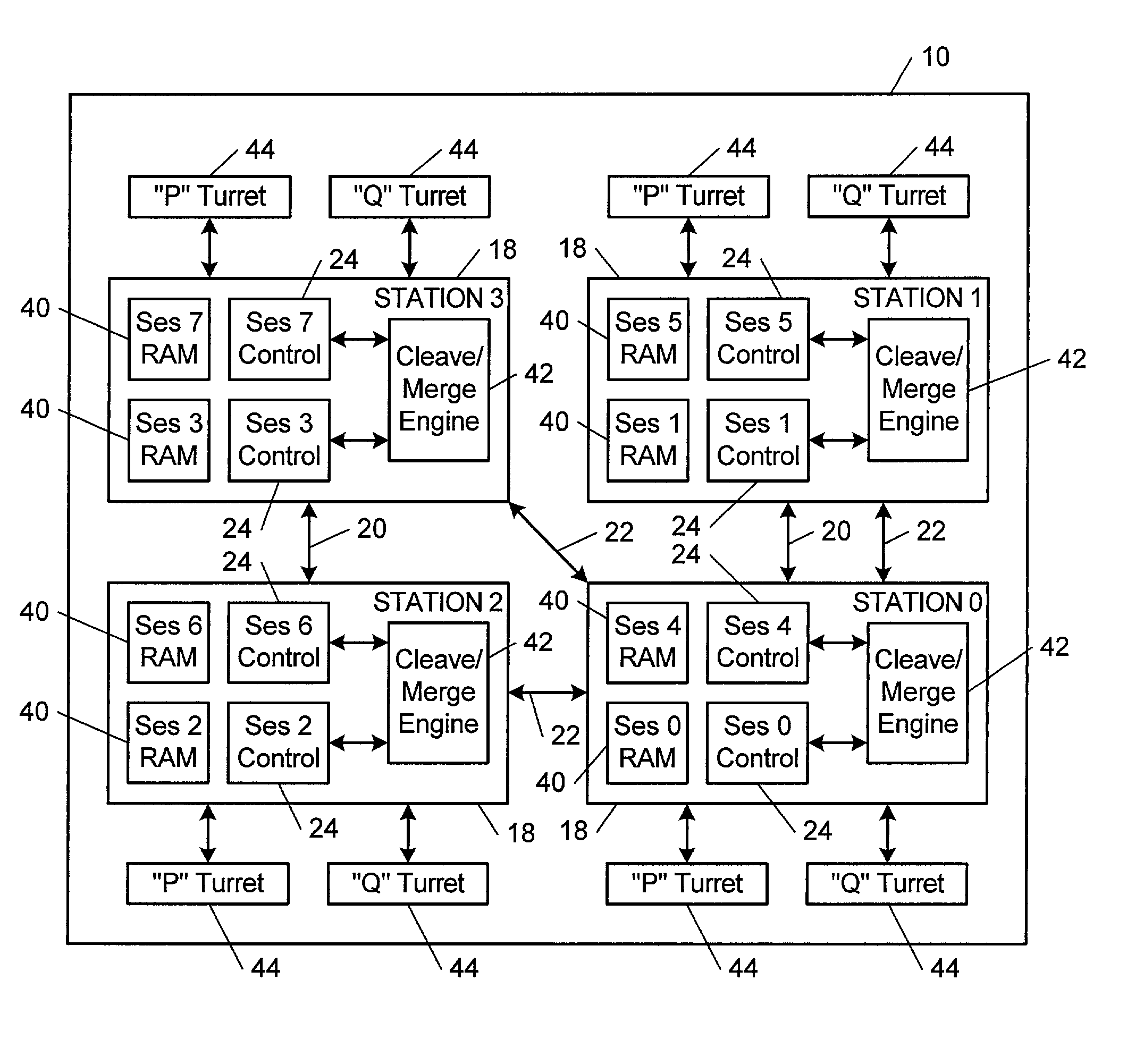
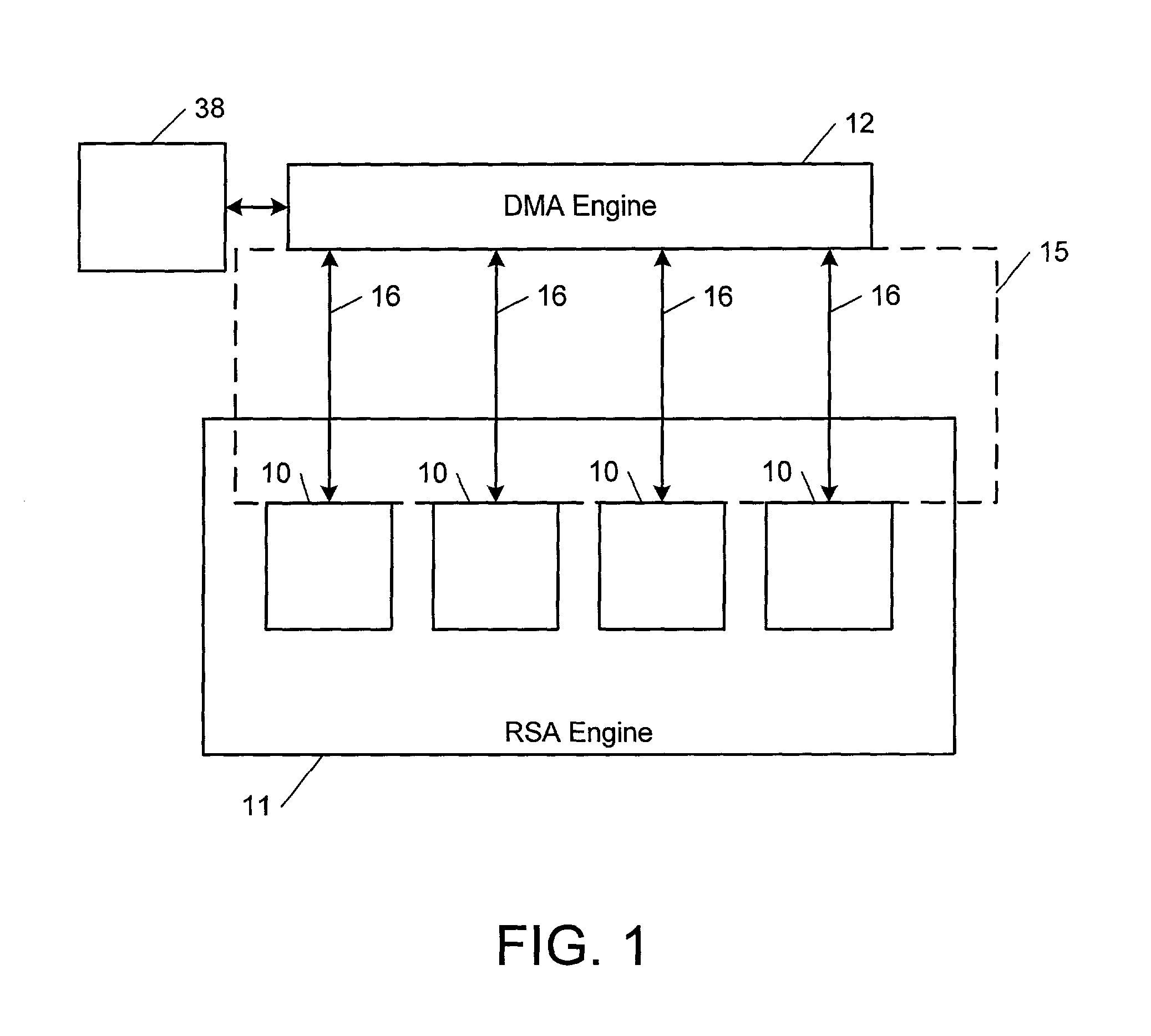
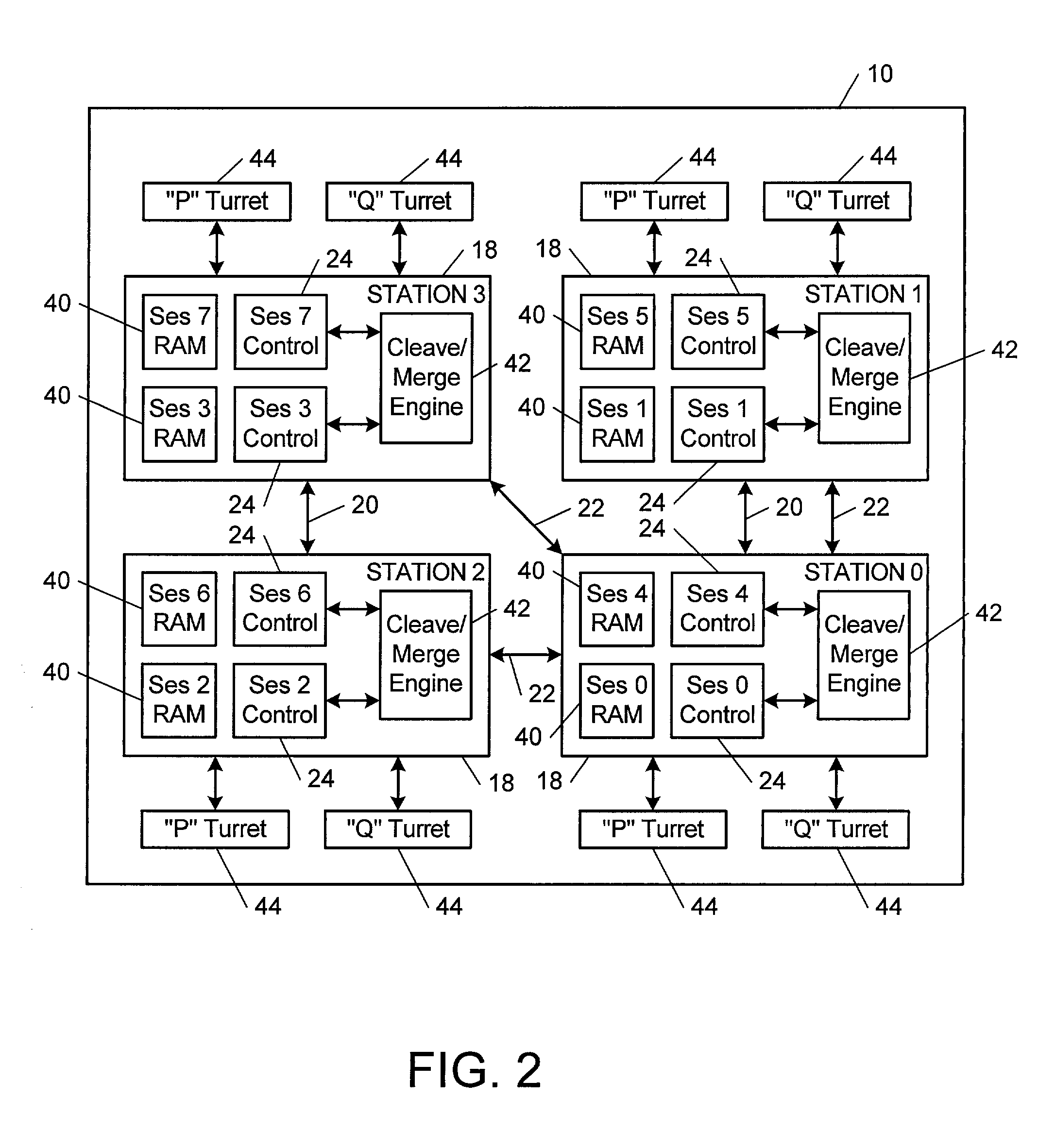
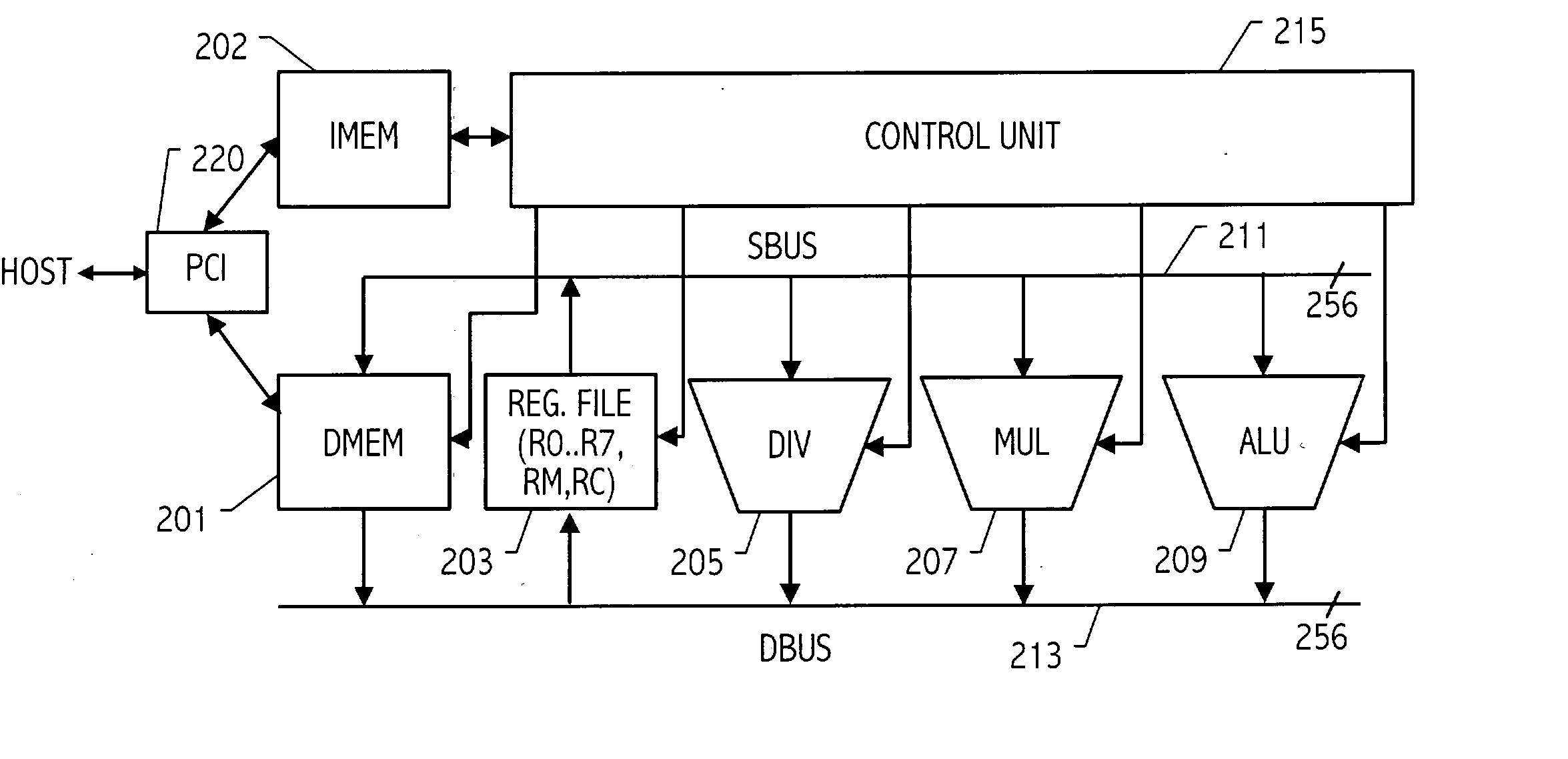
Computational method, system, and apparatus
A method, system, and apparatus for performing computations.In a method, arguments X and K are loaded into session memory, and X mod P and X mod Q are computed to give, respectively, XP and XQ. XP and XQ are exponentiated to compute, respectively, CP and CQ. CP and CQ are merged to compute C, which is then retrieved from the session memory.A system includes a computing device and at least one computational apparatus, wherein the computing device is configured to use the computational apparatus to perform accelerated computations.An apparatus includes a chaining controller and a plurality of computational devices. A first chaining subset of the plurality of computational devices includes at least two of the plurality of computational devices, and the chaining controller is configured to instruct the first chaining subset to operate as a first computational chain.
Owner:NCIPHER LIMITED ACTING BY & THROUGH ITS WHOLLY OWNED SUBSIDIARY NCIPHER +1
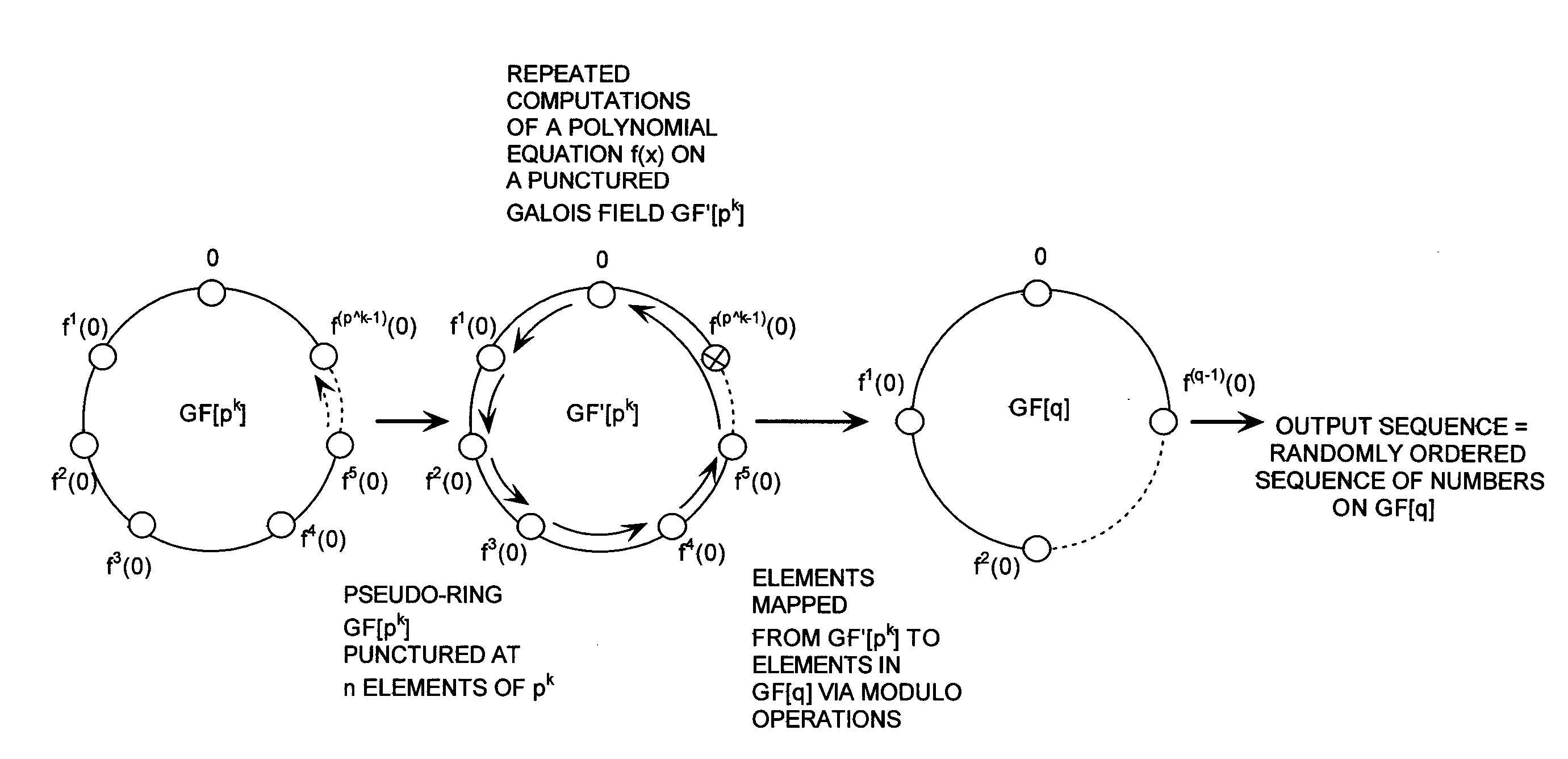
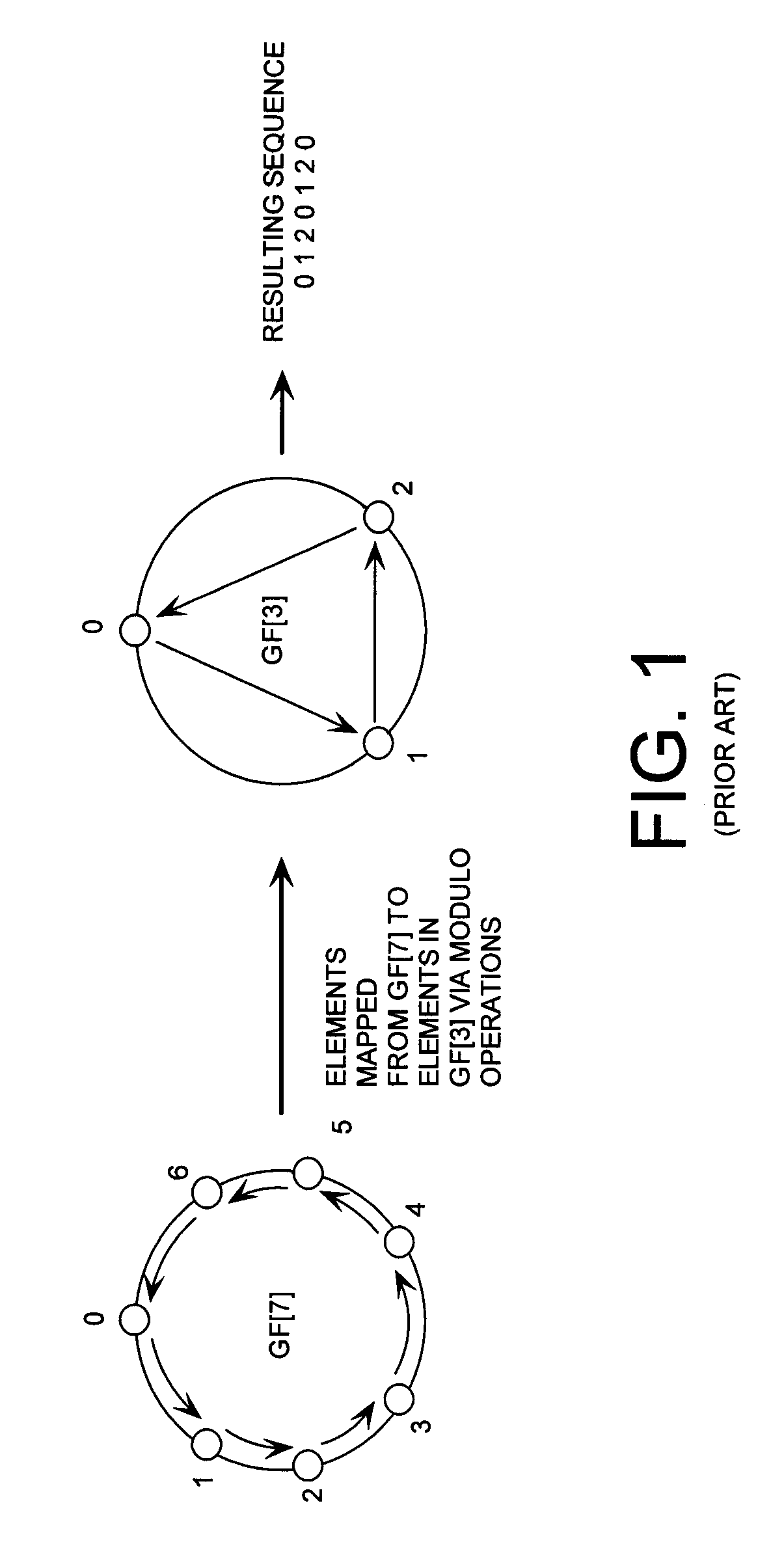
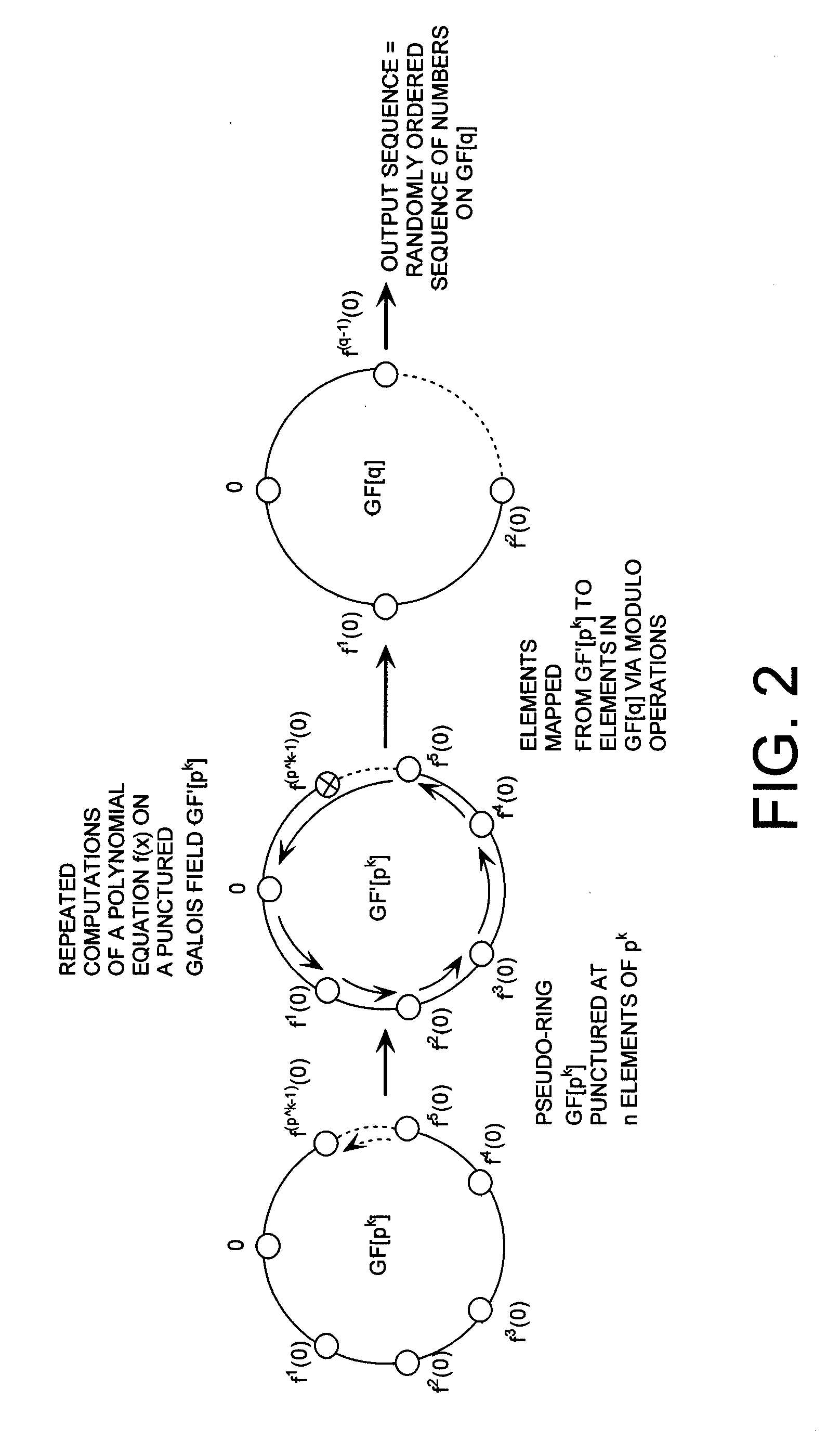
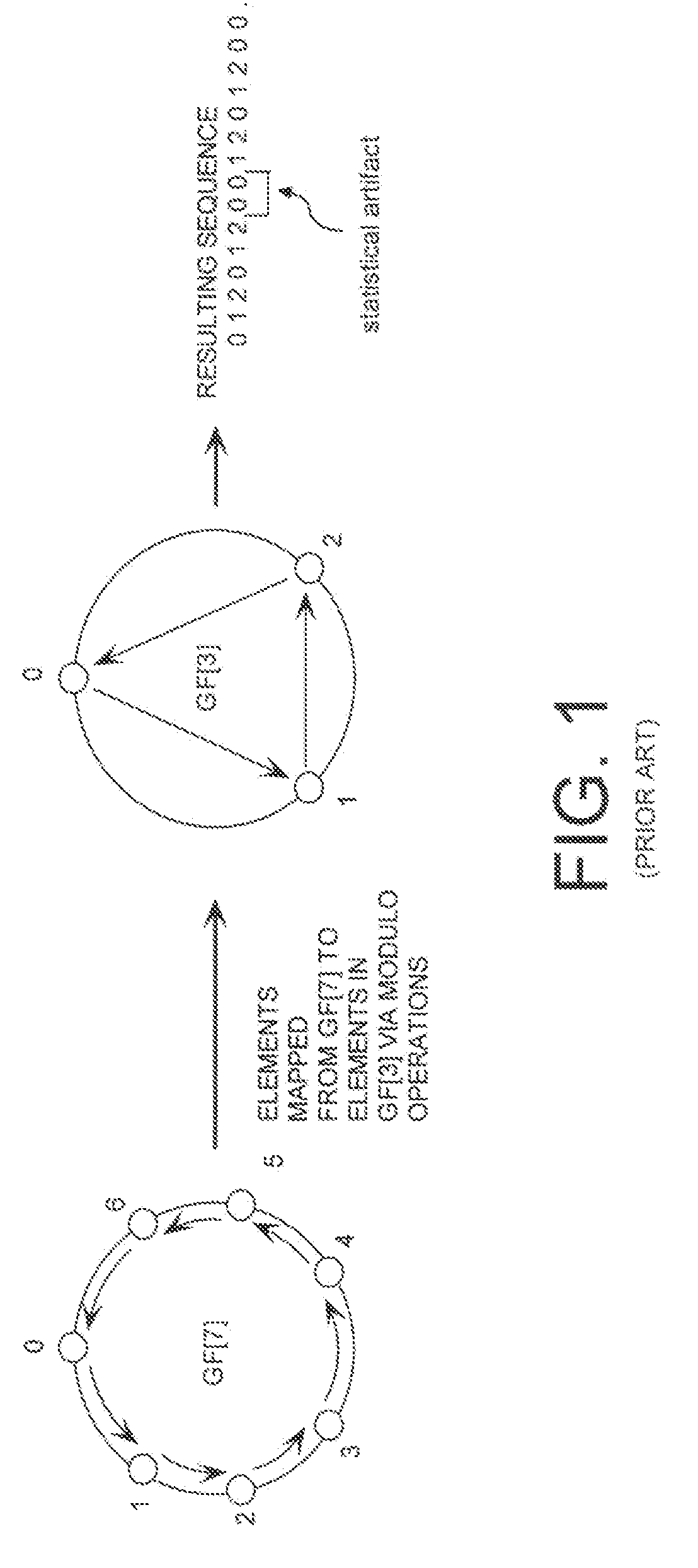
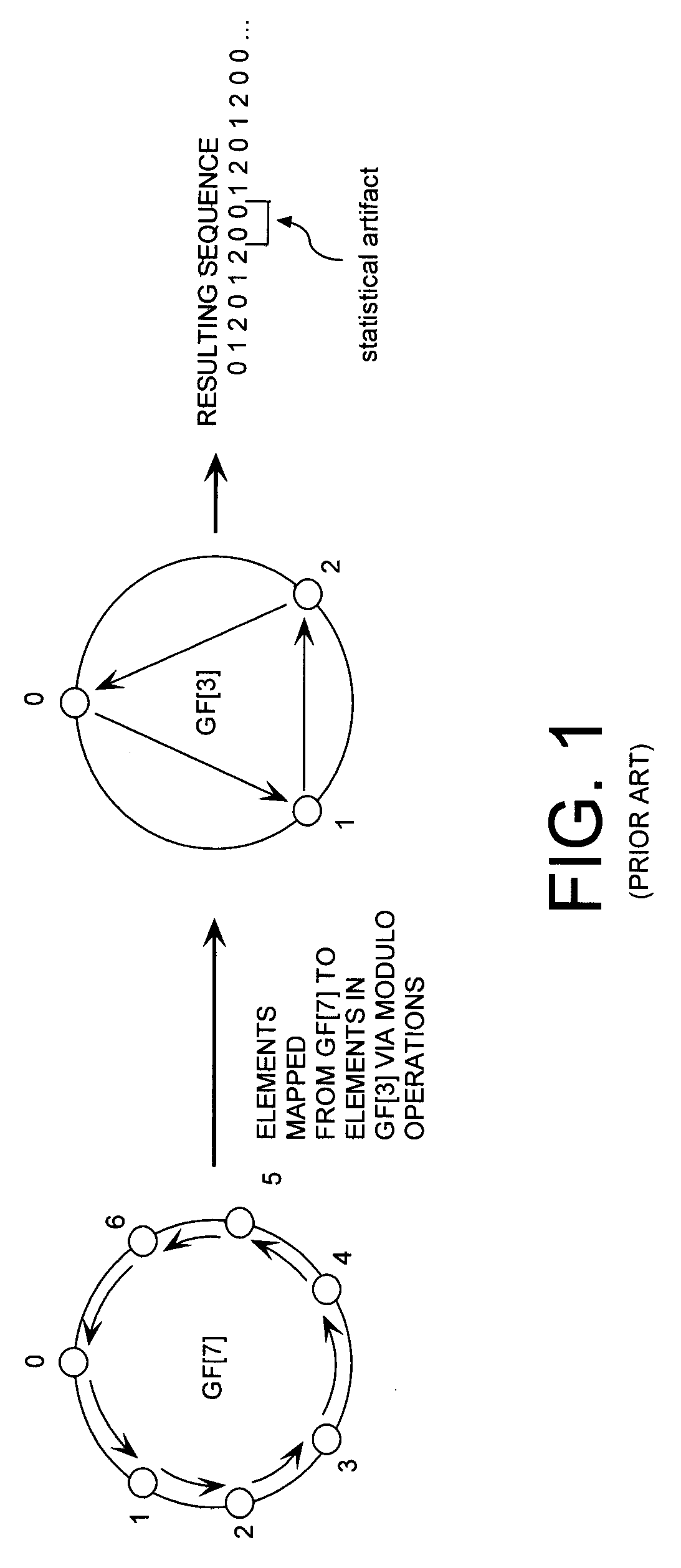
Cryptographic system configured to perform a mixed radix conversion with a priori defined statistical artifacts
ActiveUS20090202067A1Eliminate artifactsRandom number generatorsDigital computer detailsData streamComputer science
A cryptographic system (CS) is provided. The CS (800) comprises a data stream receiving means (DSRM), a generator (702), a mixed radix converter (MRC) and an encryptor (908). The DSRM (902) is configured to receive a data stream (DS). The generator is configured to selectively generate a random number sequence (RNS) utilizing a punctured ring structure. The MRC (704) is coupled to the generator and configured to perform a mixed radix conversion to convert the RNS from a first number base to a second number base. The encryptor is coupled to the DSRM and MRC. The encryptor is configured to generate an altered data stream by combining the RNS in the second number base with the DS. The punctured ring structure and the MRC are configured in combination to produce an RNS in the second number base which contains a priori defined statistical artifacts after the mixed radix conversion.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
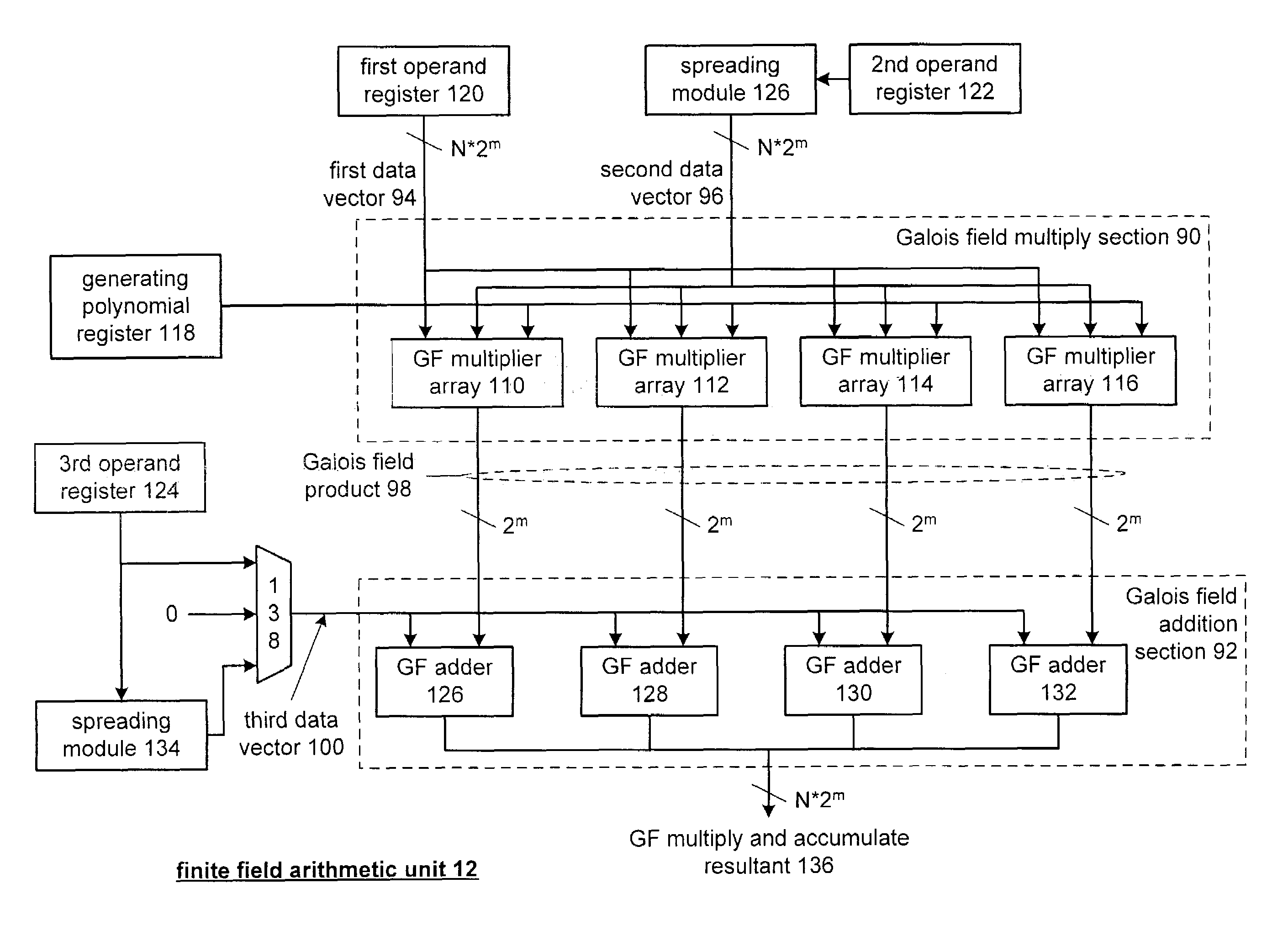
Galois field arithmetic unit for use within a processor
A Galois field arithmetic unit includes a Galois field multiplier section and a Galois field adder section. The Galois field multiplier section includes a plurality of Galois field multiplier arrays that perform a Galois field multiplication by multiplying, in accordance with a generating polynomial, a 1st operand and a 2nd operand. The bit size of the 1st and 2nd operands correspond to the bit size of a processor data path, where each of the Galois field multiplier arrays performs a portion of the Galois field multiplication by multiplying, in accordance with a corresponding portion of the generating polynomial, corresponding portions of the 1st and 2nd operands. The bit size of the corresponding portions of the 1st and 2nd operands corresponds to a symbol size of symbols of a coding scheme being implemented by the corresponding processor.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Code calculating device
A code computing apparatus with an error detection code (CRC) generating function and an elliptic curve cryptography (ECC) function, comprising a matrix element computation part 30 for generating matrix elements from parameter values set in first and second registers 201 and 202, a matrix element register 51 for holding the matrix elements generated by the matrix element computation part, and an inner product calculation part 40 for executing inner product calculation between the matrix elements held by the matrix element register and data set in a third register. The matrix element computation part selectively generates matrix elements for error detection and matrix elements for encryption by changing the parameters to be set in the first and second registers, and the inner product calculation part is shared to error control code generation and data encryption by altering the matrix elements to be held in the matrix element register.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Mixed Radix Number Generator with Chosen Statistical Artifacts
Owner:HARRIS CORP
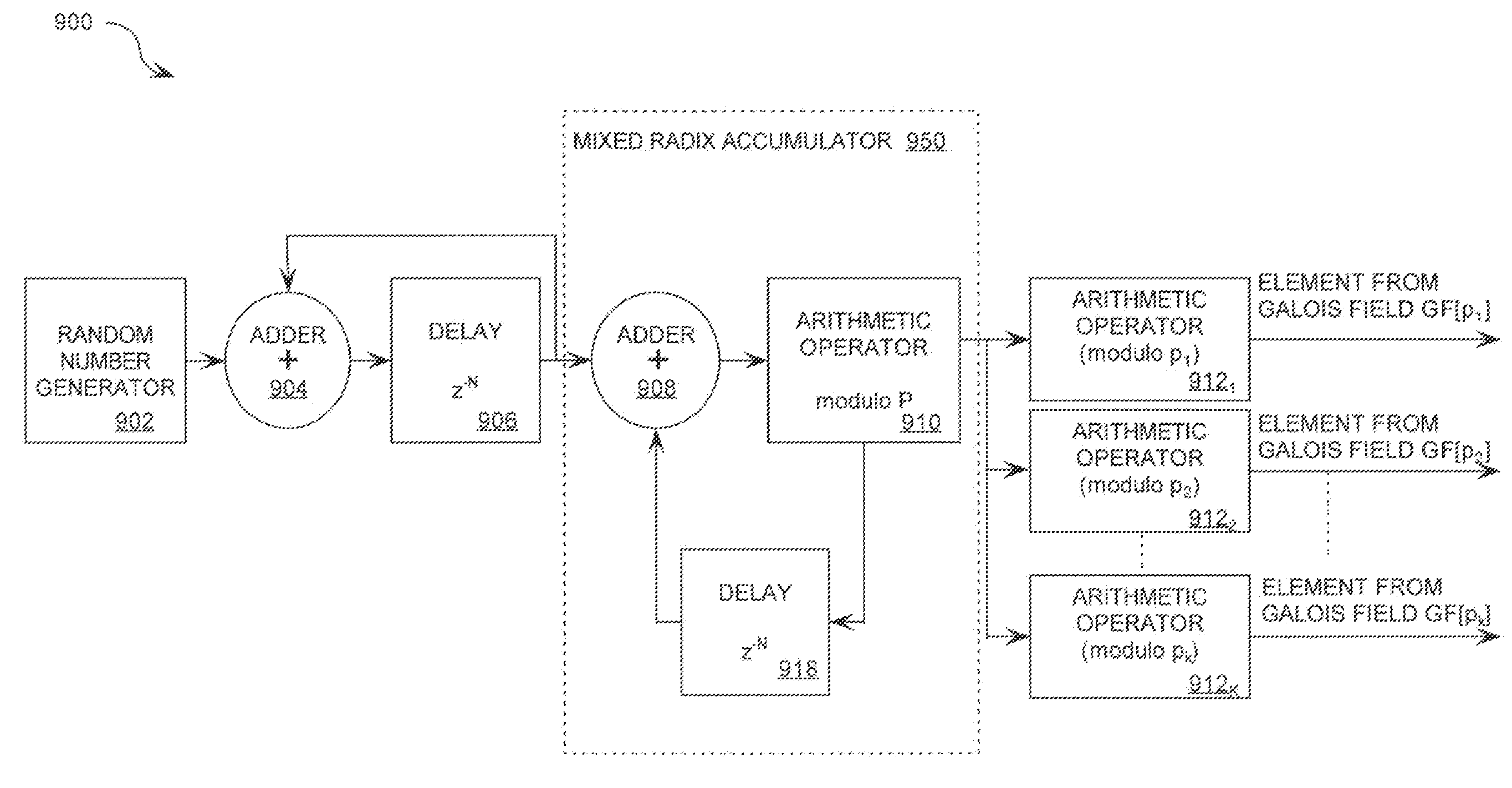
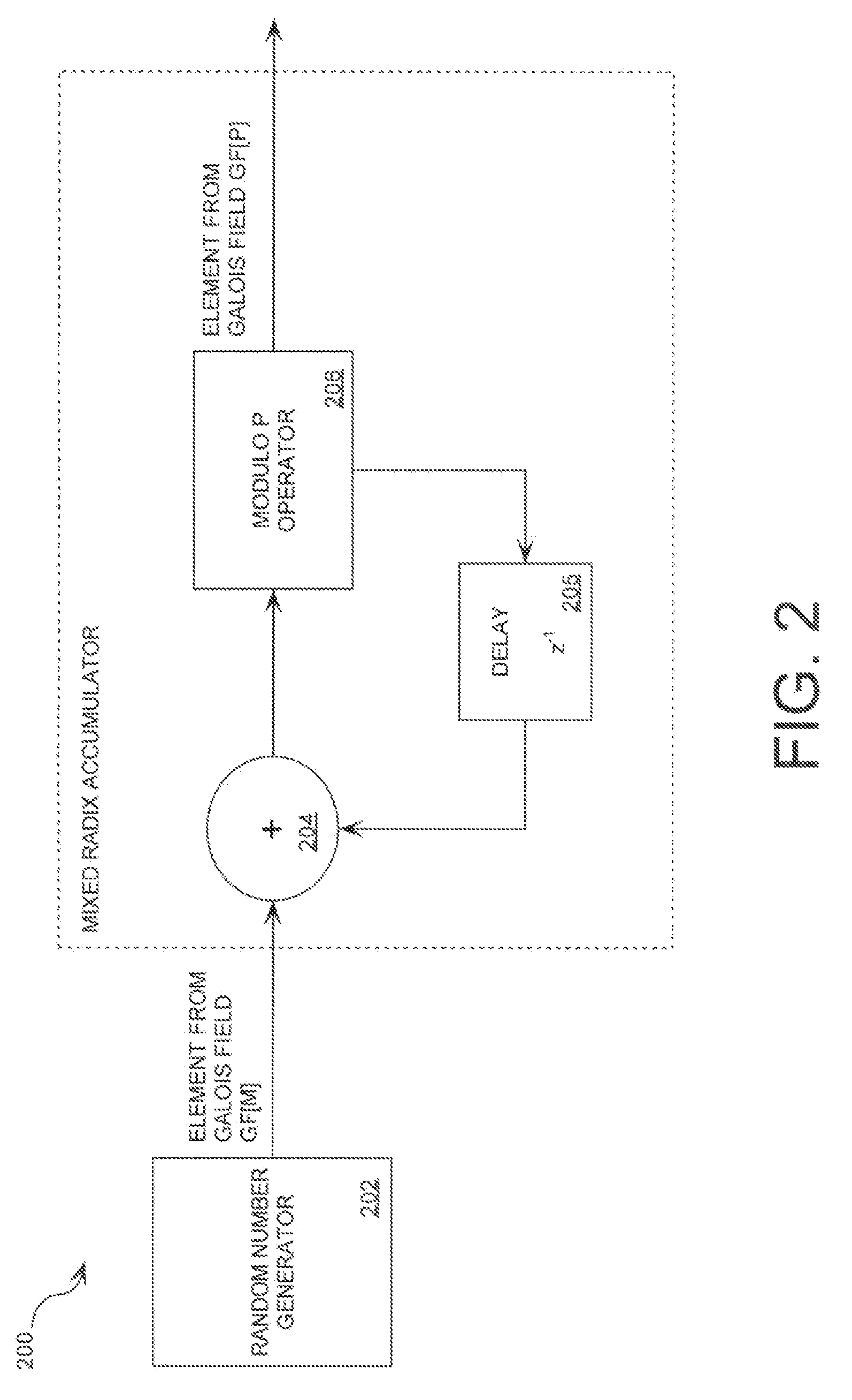
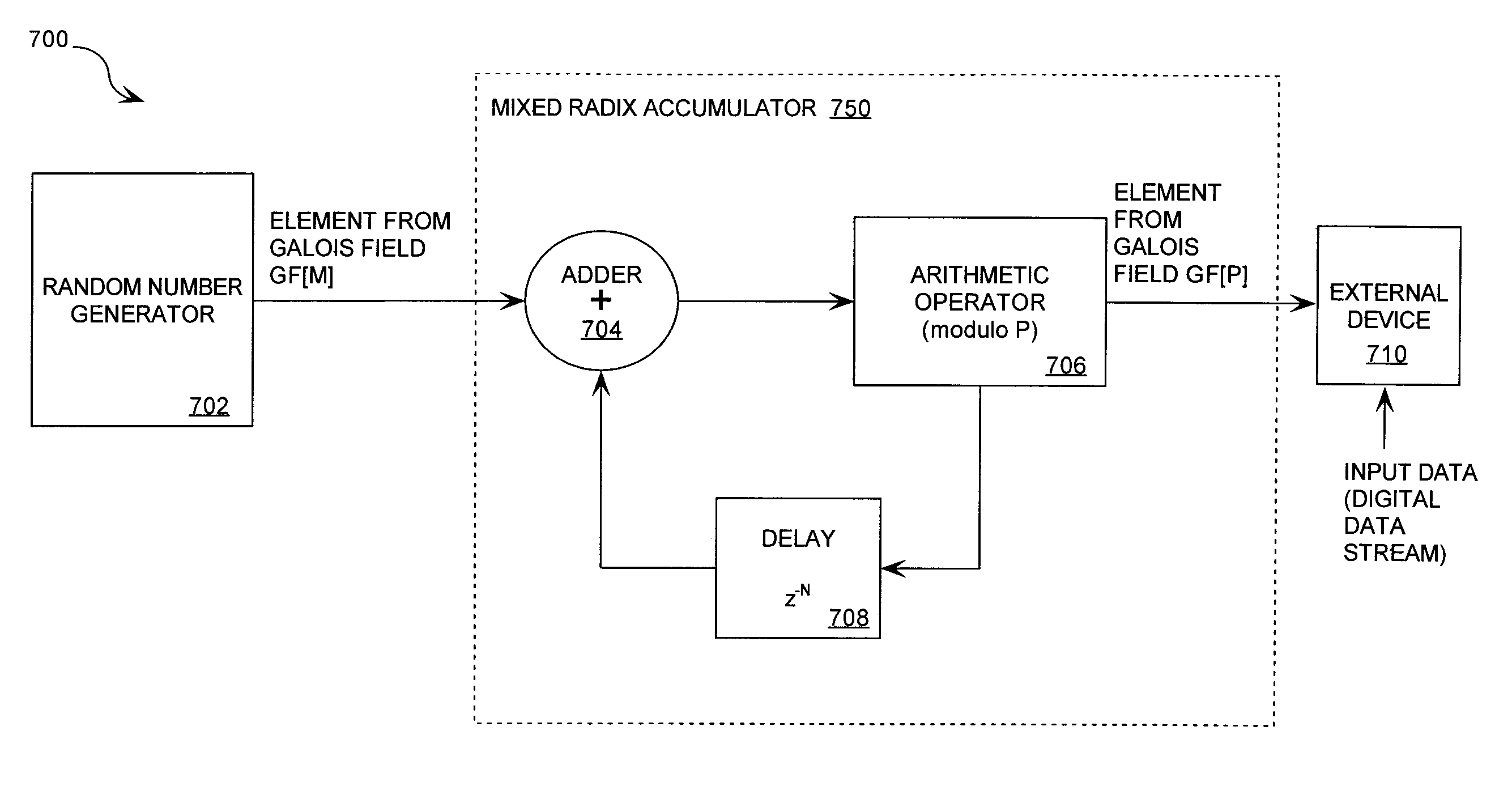
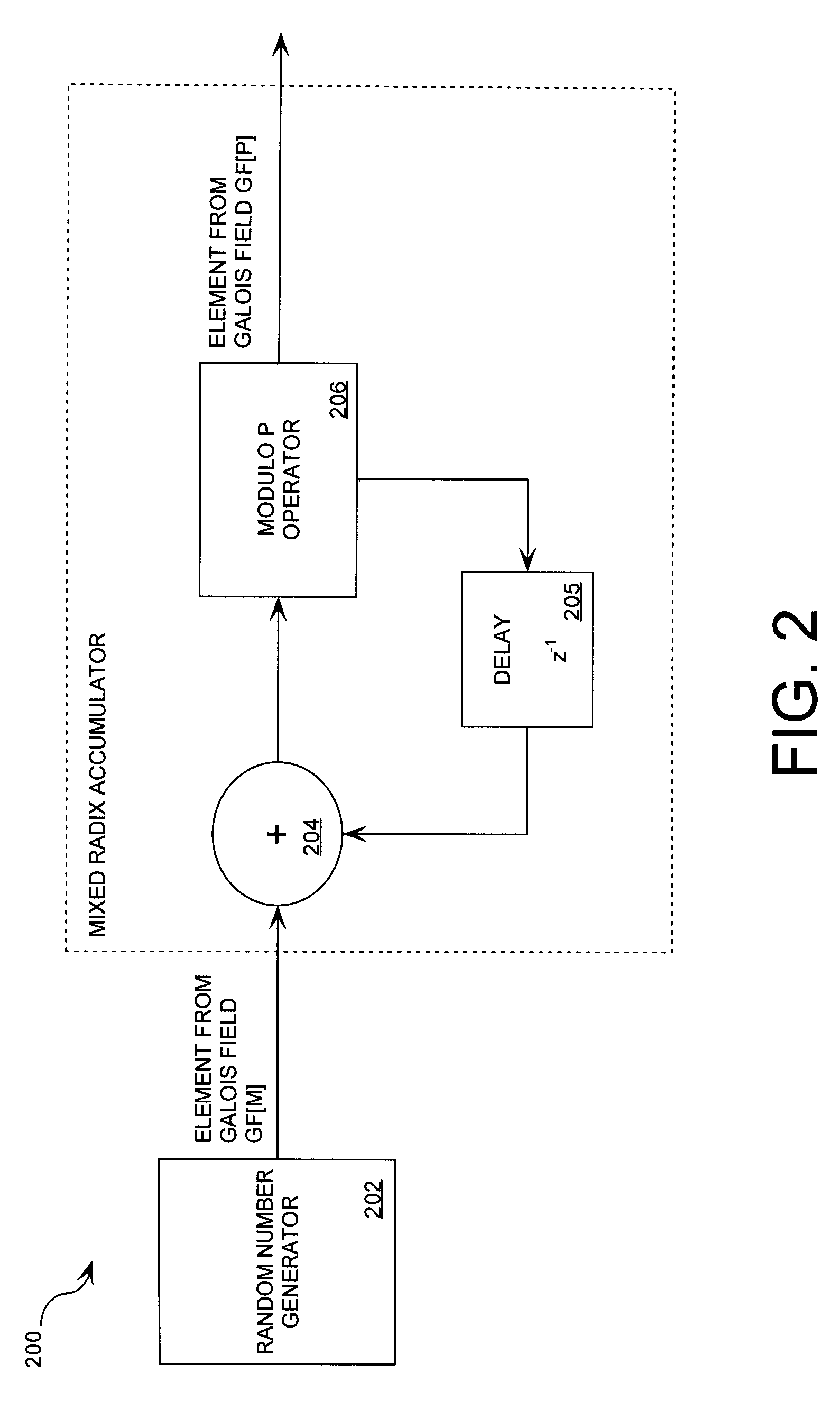
Cryptographic system including a mixed radix number generator with chosen statistical artifacts
A cryptographic system (1000) is provided. The cryptographic system includes a data stream receiving means (DSRM), a number generator (NG), a mixed radix accumulator (MRA) and an encryptor. The DSRM (1002) receives a data stream (DS). The NG (702) generates a first number sequence (FNS) contained within a Galois Field GF[M]. The MRA (750) is configured to perform a first modification to a first number (FN) in FNS. The first modification involves summing the FN with a result of a modulo P operation performed on a second number in FNS that proceeds FN. The MRA is also configured to perform a second modification to FN utilizing a modulo P operation. The MRA is further configured to repeat the first and second modification for numbers in FNS to generate a second number sequence (SNS). The encryptor (1004) is configured to generate a modified data stream by combining SNS and DS.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
Apparatus and method for efficient arithmetic in finite fields through alternative representation
InactiveUS6199087B1Digital computer detailsComputations using residue arithmeticTheoretical computer scienceOperand
A method and apparatus are shown for performing efficient arithmetic on binary vectors in a finite field. Typically, there is an efficient algorithm within an execution context, such as hardware or software, for performing a selected arithmetic operation on an operand. When the operand is in a first representative format and the efficient algorithm operates in an alternative representation format, then the operand is permutated from the first representative format to the alternative representation format. The efficient algorithm is then performed on the operand in the alternative representation format in order to obtain a result in the alternative representation format. The result is then permutated from the alternative representation format to the first representation format. Thus, efficient arithmetic is obtained by using the most efficient algorithm available in either the first representation format or the alternative representation format and permuting operands and results to the representation format corresponding to the most efficient algorithm available.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD CO
Modular multiplier
ActiveUS20030212729A1Computation using non-contact making devicesDigital computer detailsModular multiplierKaratsuba algorithm
Modular multiplication of two elements X(t) and Y(t), over GF(2), where m is a field degree, may utilize field degree to determine, at least in part, the number of iterations. An extra shift operation may be employed when the number of iterations is reduced. Modular multiplication of two elements X(t) and Y(t), over GF(2), may include a shared reduction circuit utilized during multiplication and reduction. In addition, a modular multiplication of binary polynomials X(t) and Y(t), over GF(2), may utilize the Karatsuba algorithm, e.g., by recursively splitting up a multiplication into smaller operands determined according to the Karatsuba algorithm.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
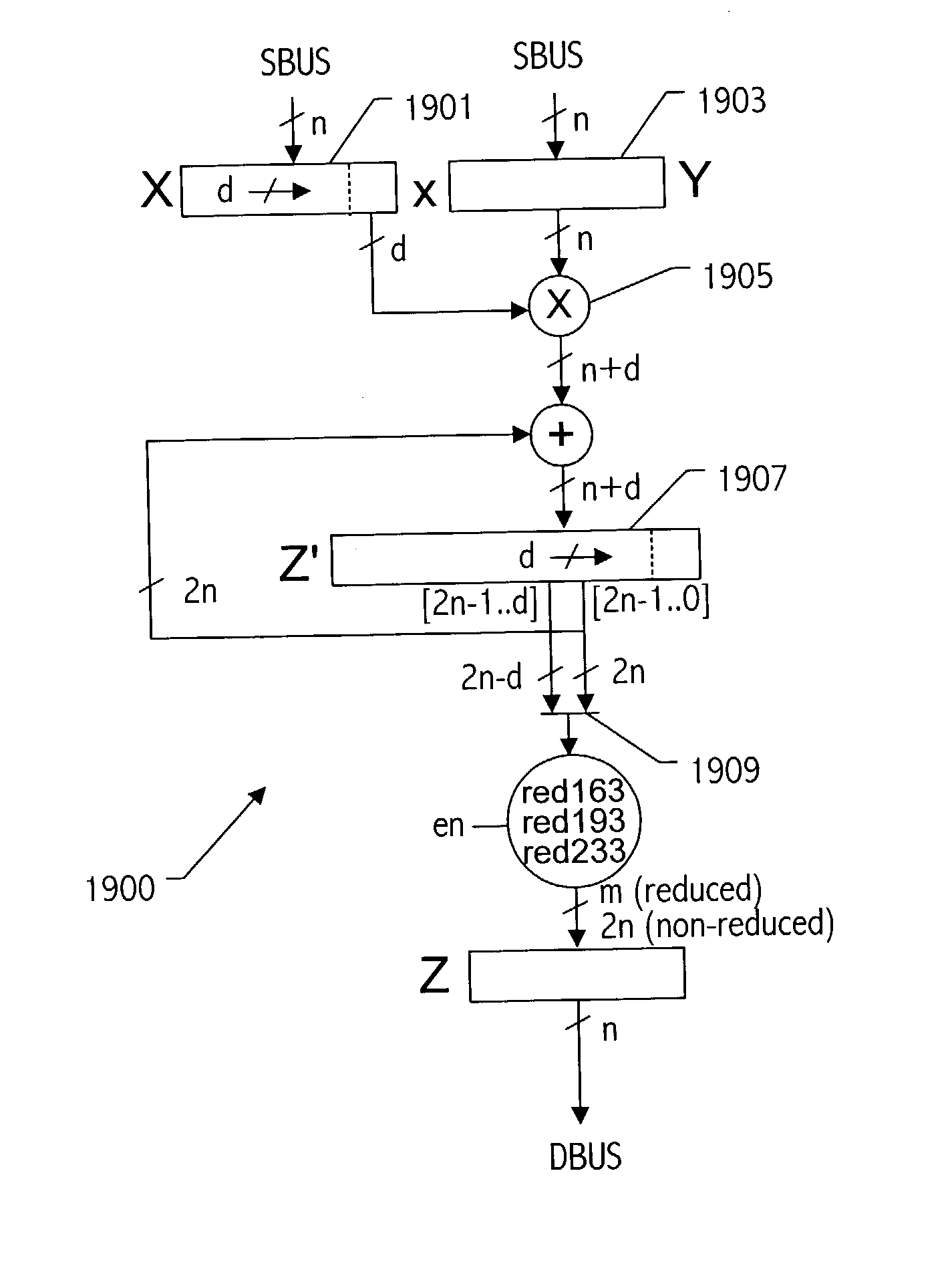
Generic implementations of ellipitic curve cryptography using partial reduction
ActiveUS20030208518A1Digital computer detailsComputations using residue arithmeticBinary multiplierOperand
A reduction operation is utilized in an arithmetic operation on two binary polynomials X(t) and Y(t) over GF(2), where an irreducible polynomial Mm(t)=t<m>+am-1t<m-1>+am-2t<m-2>+ . . . +a1t+a0, where the coefficients as are equal to either 1 or 0, and m is a field degree. The reduction operation includes partially reducing a result of the arithmetic operation on the two binary polynomials to produce a congruent polynomial of degree less than a chosen integer n, with m<=n. The partial reduction includes using a polynomial M'=(Mm(t)-t<m>)*t<n-m>, or a polynomial M''=Mm(t)*t<n-m >as part of reducing the result to the degree less than n and greater than or equal to m. The integer n can be the data path width of an arithmetic unit performing the arithmetic operation, a multiple of a digit size of a multiplier performing the arithmetic operation, a word size of a storage location, such as a register, or a maximum operand size of a functional unit in which the arithmetic operation is performed.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
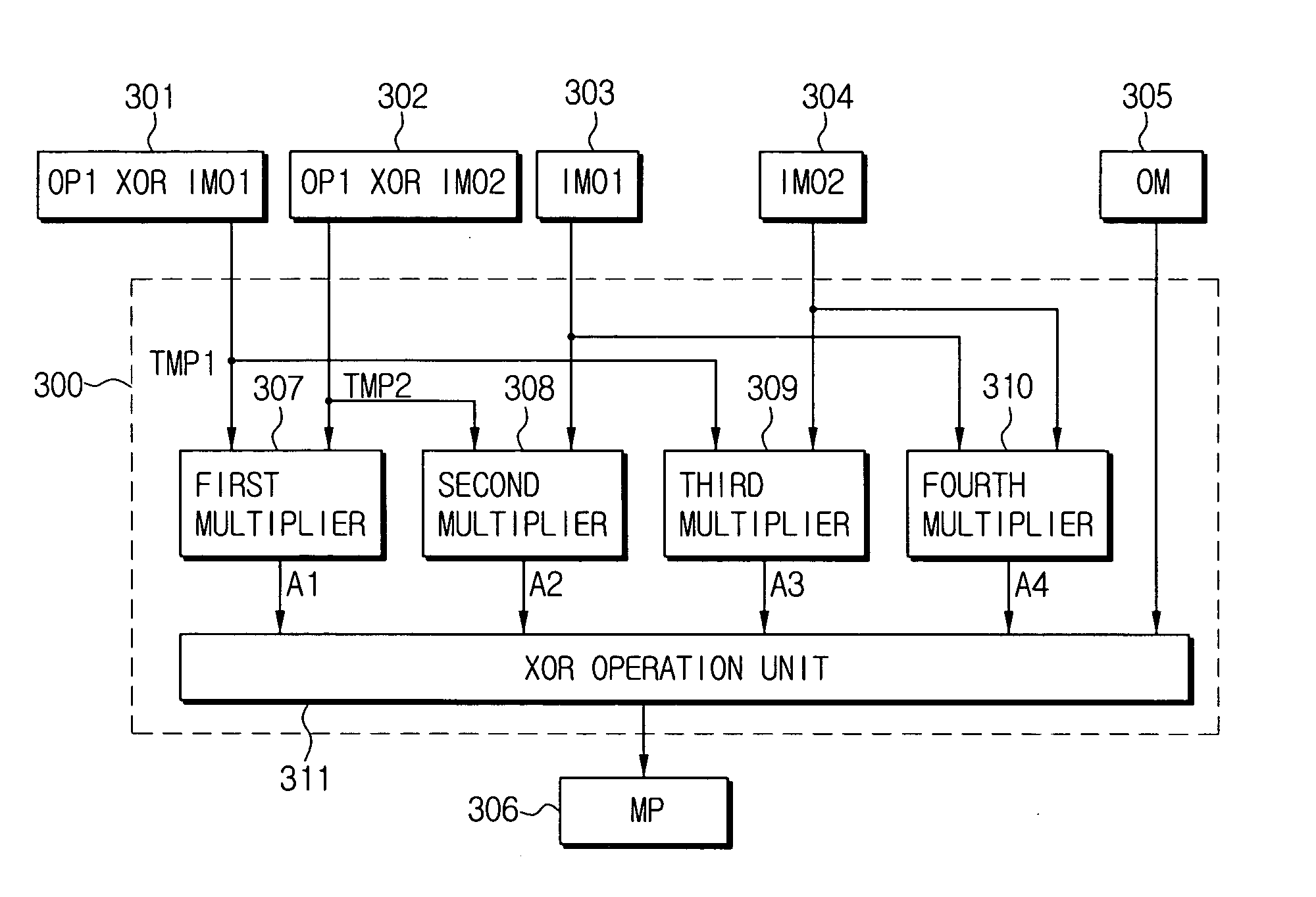
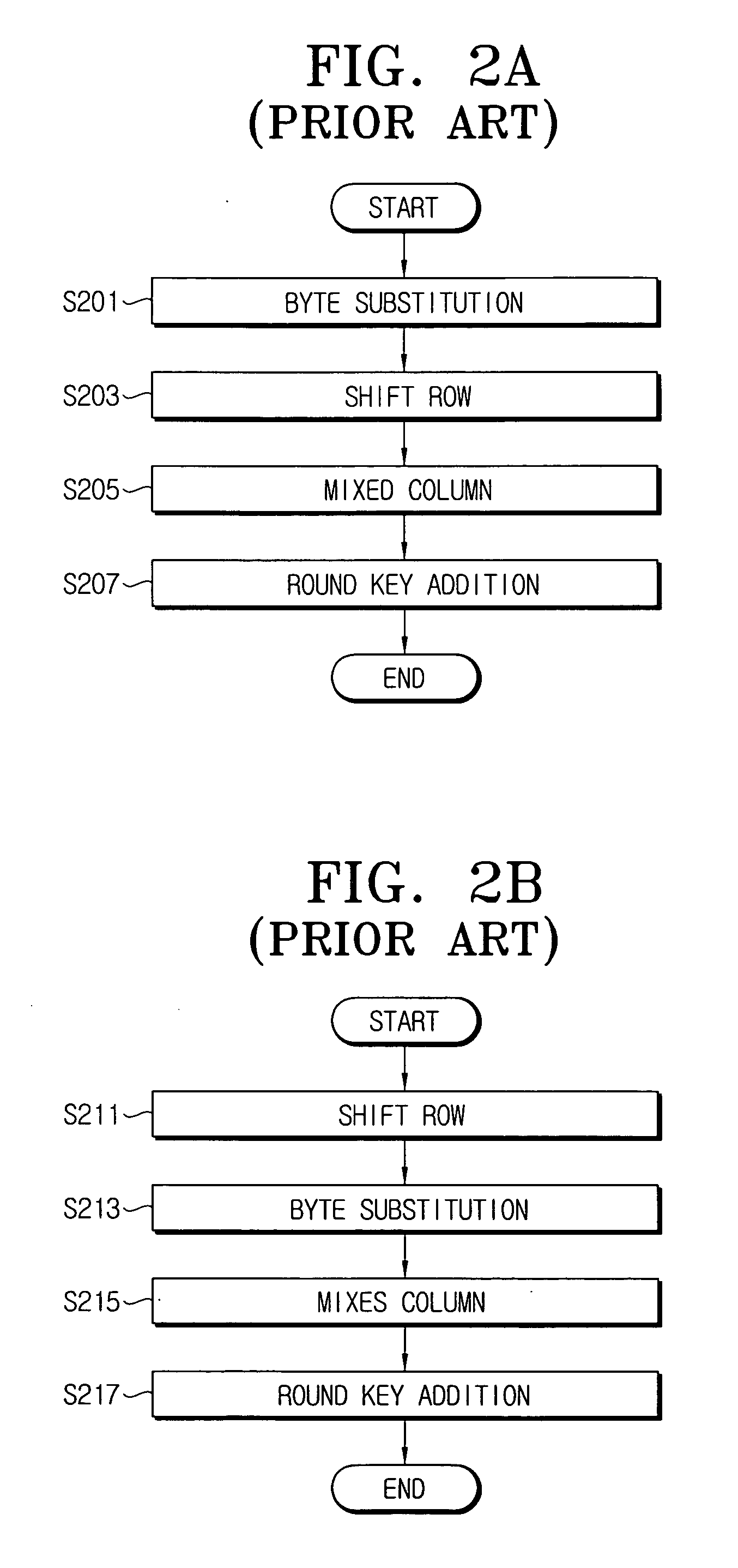
Method and apparatus for multiplication in Galois field, apparatus for inversion in Galois field and apparatus for AES byte substitution operation
InactiveUS20050283714A1Avoid attackEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesError detection/correctionByteComputer science
A method and apparatus for multiplication in a Galois field. The method of multiplication in a Galois field (GF) for preventing an information leakage attack by performing a transformation of masked data and masks in GF(2n) includes: receiving a plurality of first and second masked input data, a plurality of first and second input masks and an output mask; calculating a plurality of intermediate values by performing a multiplication of the plurality of masked input data and the plurality of input masks in GF(2n); and calculating a final masked output value by performing an XOR operation of the intermediate values and the output masks.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
System and method for sharing storage resources between multiple files
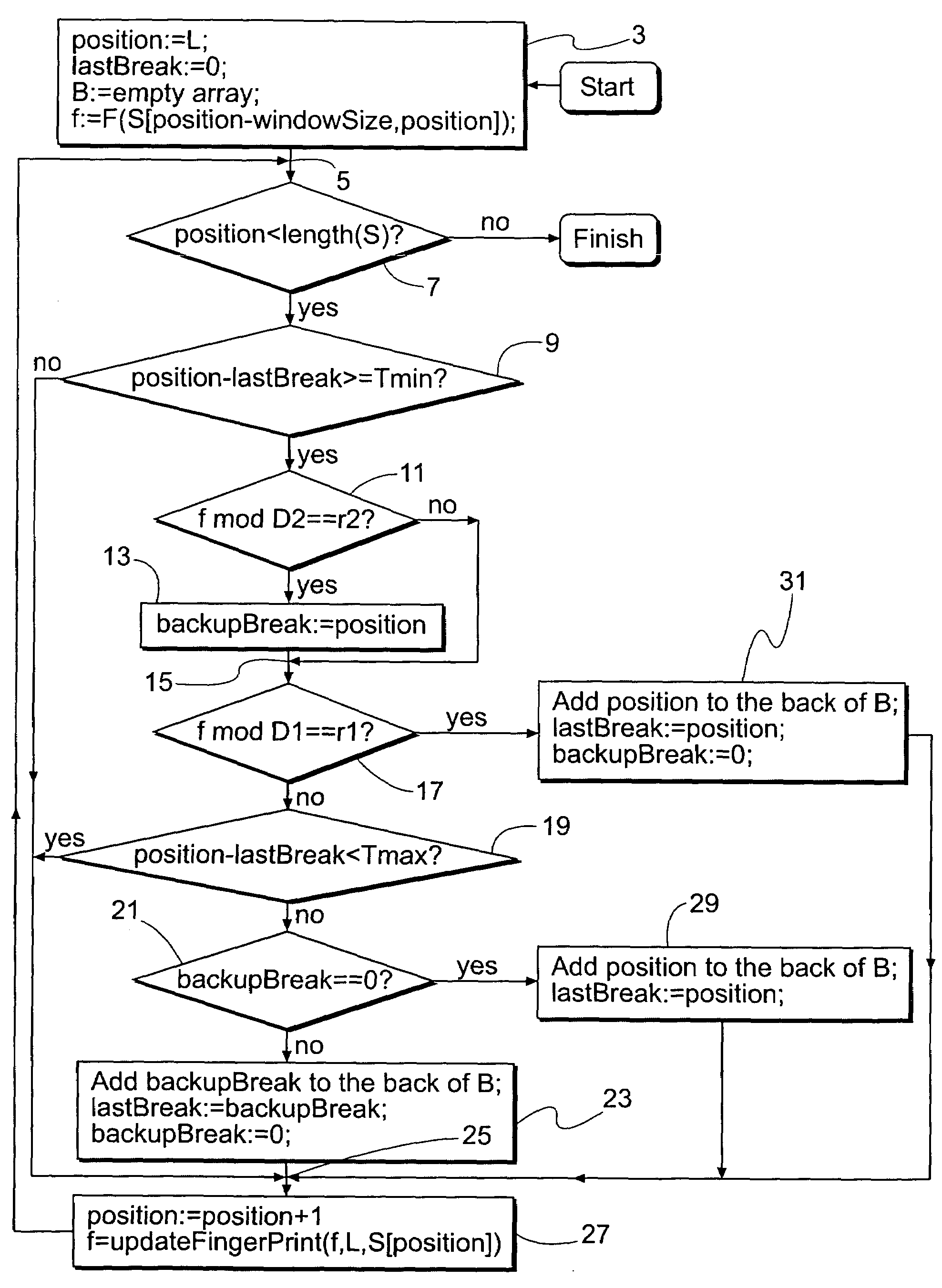
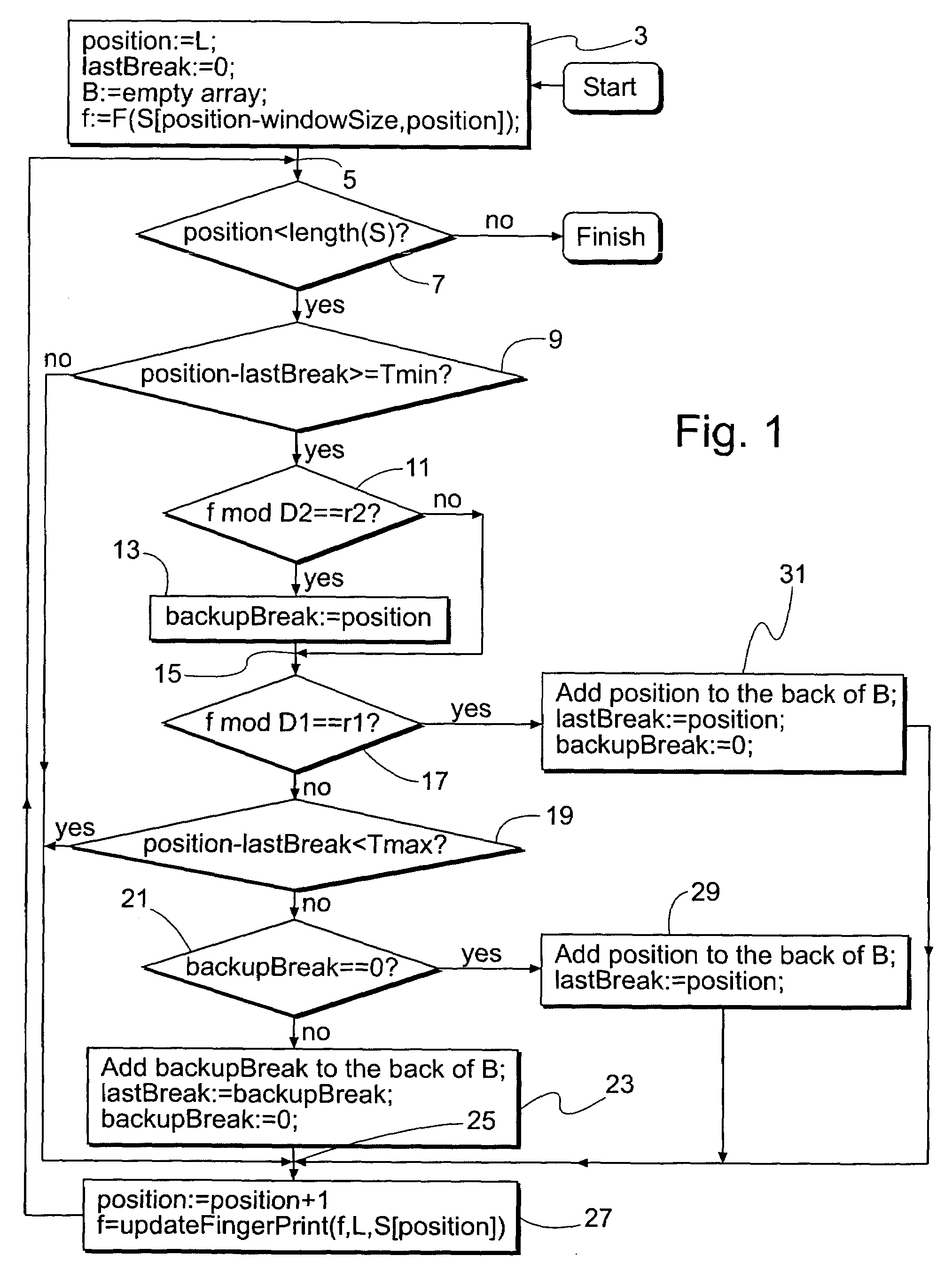
ActiveUS7269689B2Digital data information retrievalCharacter and pattern recognitionData setSlide window
An improved sliding window chunking apparatus and method comprising comparing a fingerprint value of each position in a data set to a second set of criteria, at least in instances when it doesn't satisfy a first set of criteria, and, if the value satisfies the second set of criteria, identifying the position as a potential breakpoint. Subsequently, if a fingerprint value that satisfies the first set of criteria is not found before a maximum chunk size is reached, the potential breakpoint can be designated as a breakpoint. Further improvement is possible by imposing minimum and maximum sizes on chunks. In some instances, more than two sets of criteria may be used to identify additional potential chunks to be used should subsets having fingerprint values satisfying either of the first two sets of criteria not be found.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
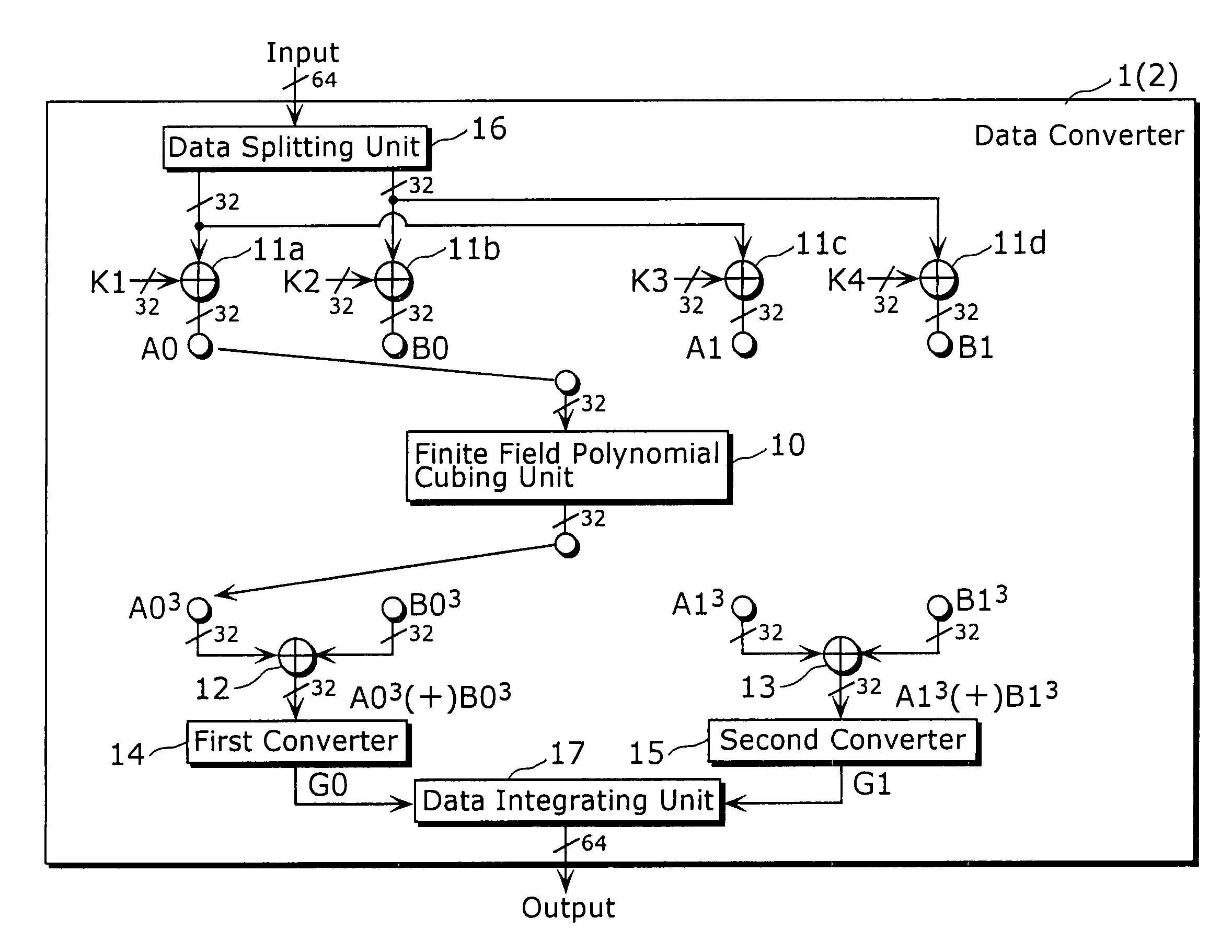
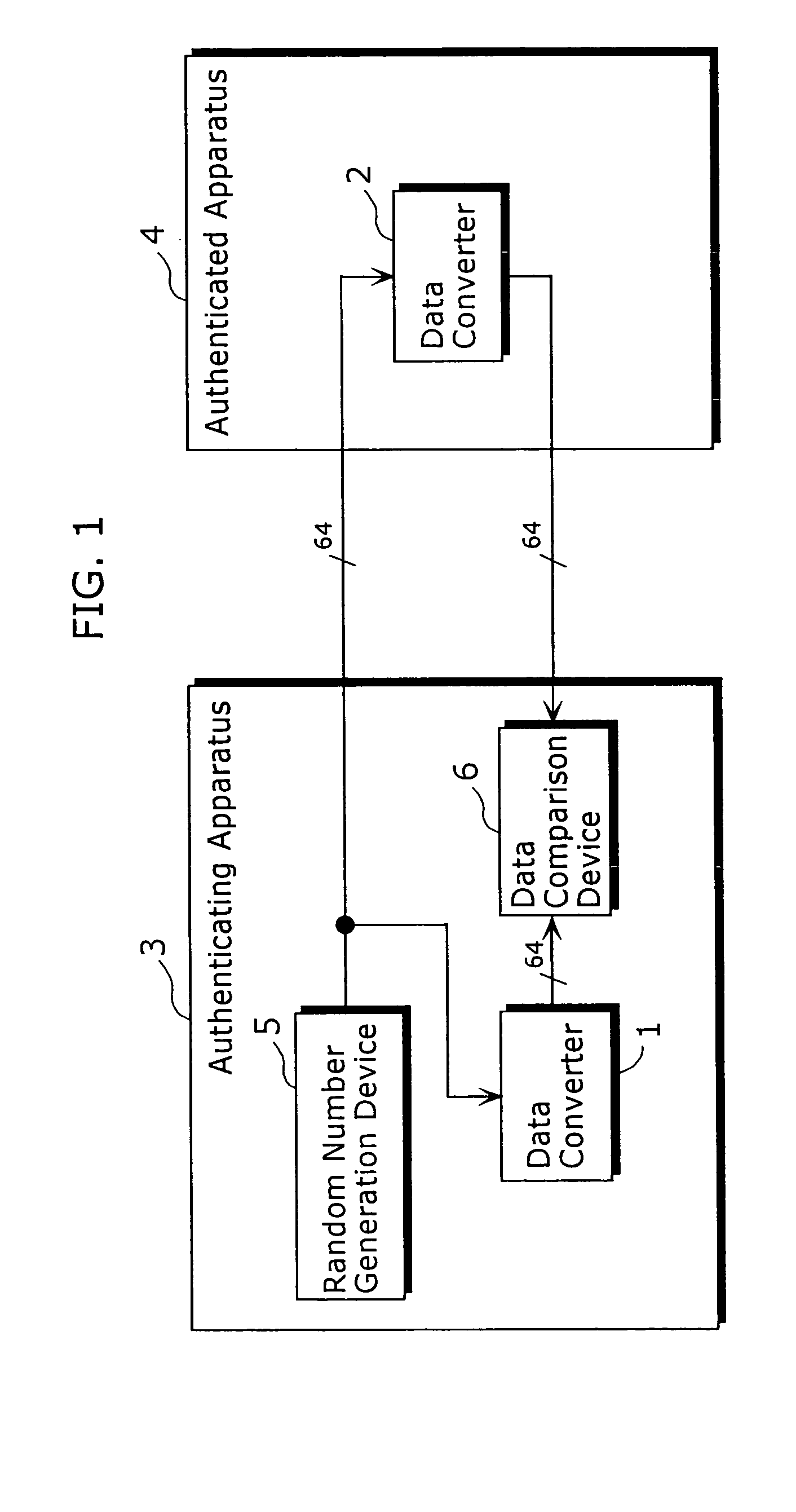
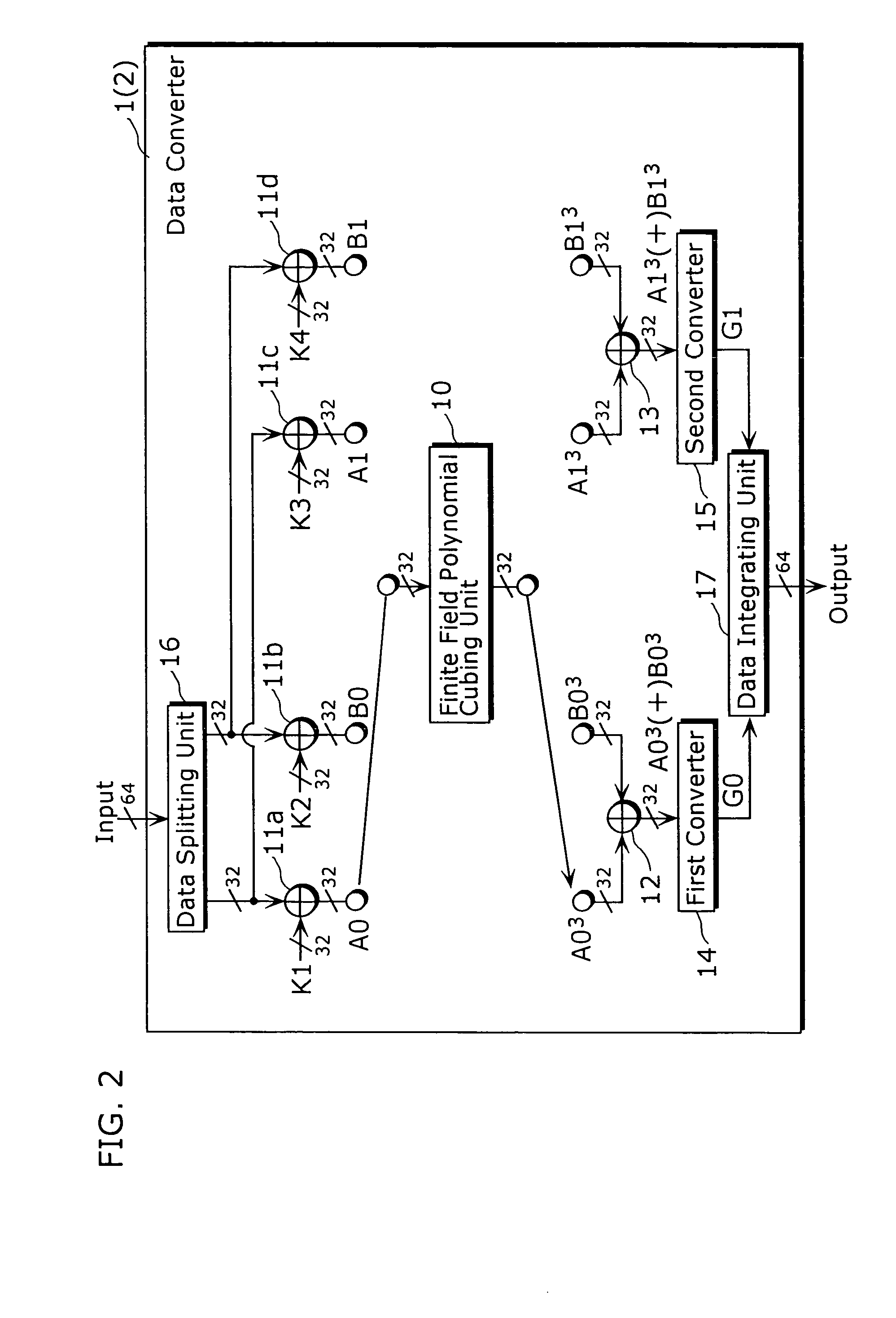
Data converter and method thereof
ActiveUS6995692B2Good data confusion performanceData augmentationError prevention/detection by using return channelUser identity/authority verificationData translationData splitting
A data converter (1) capable of reducing a size of the total implementation in a device is a processing apparatus that performs secret converting processing predetermined to input data with 64 bits, the data converter including a finite field polynomial cubing unit (10), data integrating units (11a) to (11d), (12) and (13), a first converter (14), a second converter (15), a data splitting unit (16), and a data integrating unit (17). The finite field polynomial cubing unit (10) performs cubing, on the 32 bits data, in the polynomial residue class ring with a value in the finite field GF (28) as a coefficient and respectively outputs data with 32 bits.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Method and apparatus for digital signature authentication
InactiveUS6049610APublic key for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationDigital signature
The present invention improves speed and reduces complexity in a digital signature scheme that uses elliptic algebra. The signature scheme generates two points that are compared. If the points do not match, the signature is not authentic. The present invention reduces computations by comparing only the x coordinates of the two generated points. The invention provides a scheme for deducing the possible values of the x-coordinate of a sum of two points using only the x coordinates of the original two points in question. The present invention provides a scheme that limits the possible solutions that satisfy the equation to two (the authentic signature and one other). Because of the large number of possible inauthentic solutions, the chance of a false authentic signature is statistically insignificant.
Owner:NEXT
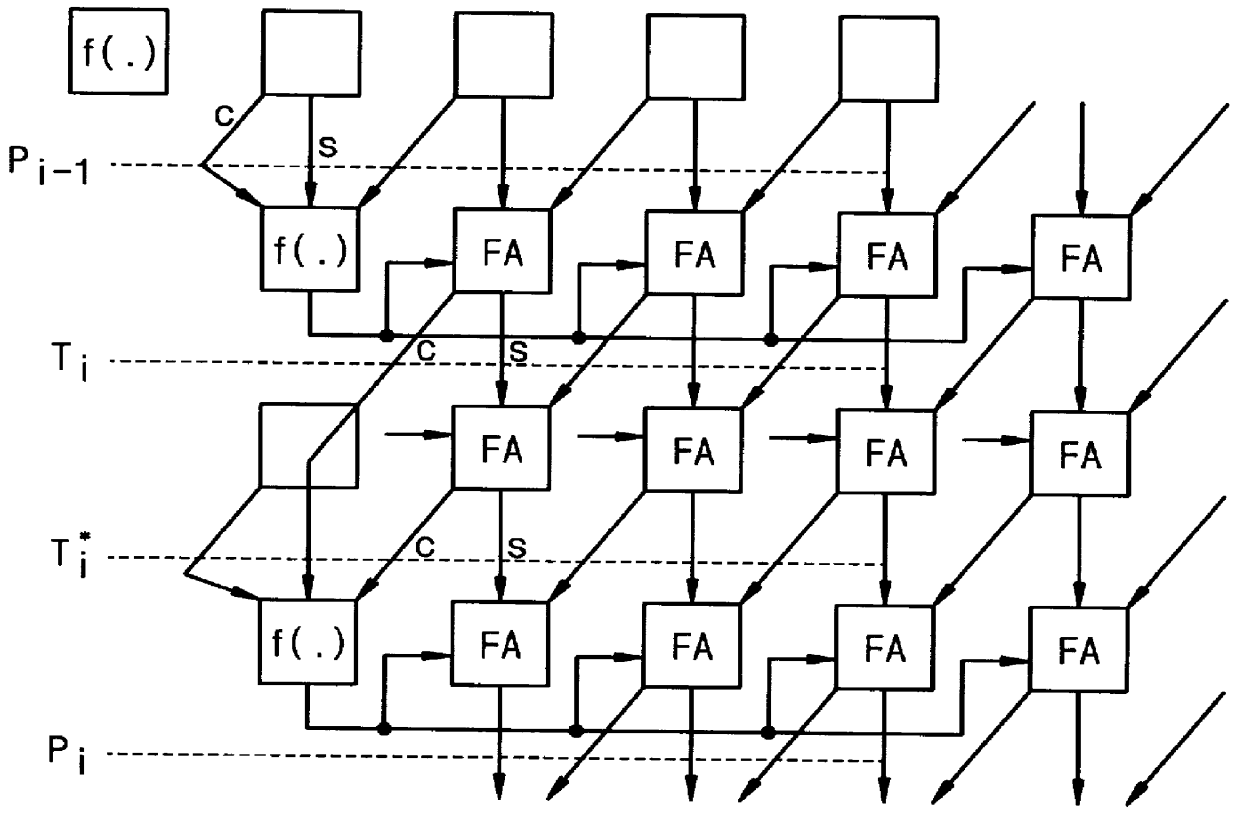
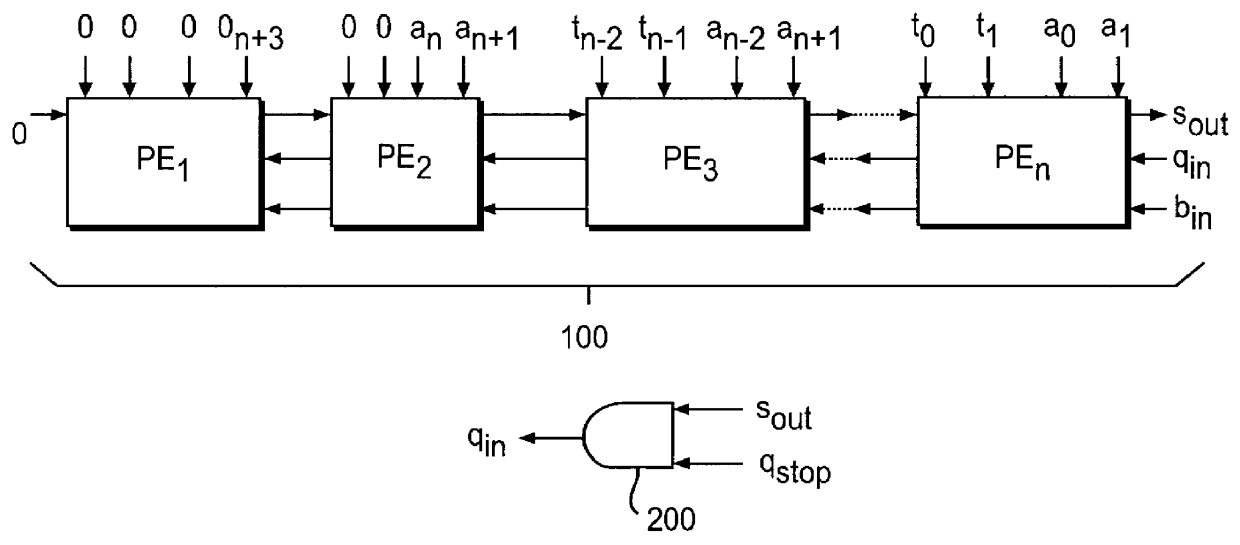
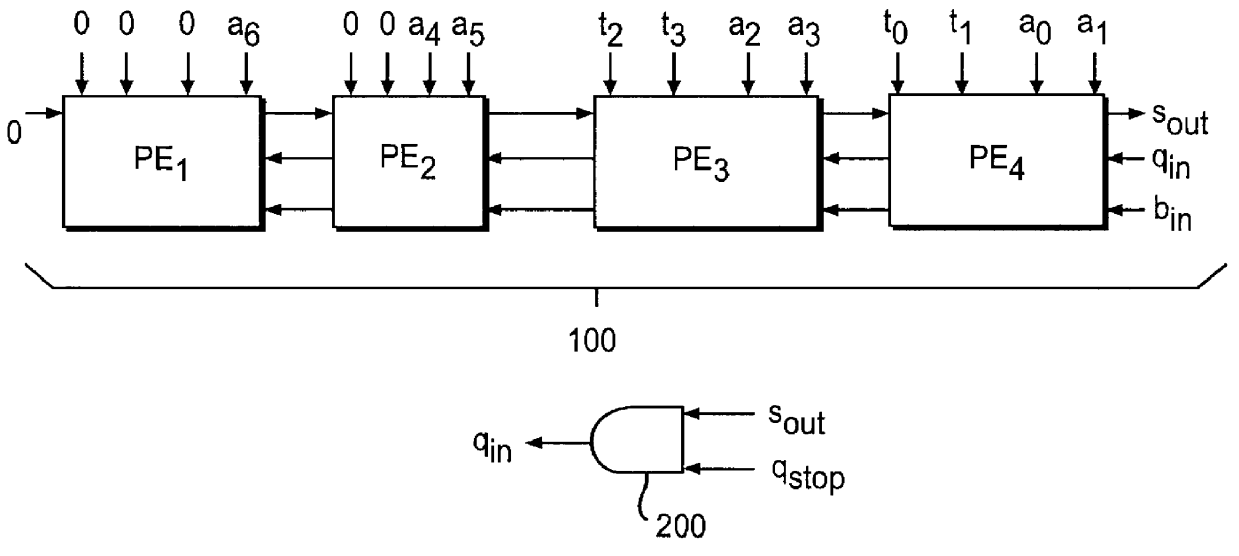
Systolic linear-array modular multiplier with pipeline processing elements
InactiveUS6061706ADegree of complexity can be reducedReduce manufacturing costComputations using residue arithmeticComputation using denominational number representationModularityCMOS
A systolic linear-array modular multiplier is provided, which can perform the modular multiplication algorithm of P. L. Montgomery more efficiently. The total execution time for n-bit modular multiplication is 2n+11 cycles. The modular multiplier includes a linear array of processing elements which is constructed based on a pipeline architecture that can reduce the computation procedure by one clock period. Each of the processing elements is simple in structure, which is composed of four full adders and fourteen flip-flops. For n-bit modular multiplication, a total number of 46n+184 gates is required, which is substantially less as compared to the prior art, so that manufacturing cost of the modular multiplier can be significantly reduced. These features make the modular multiplier suitable for use in VLSI implementation of modular exponentiation which is the kernel computation in many public-key cryptosystems, such as the RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman) system. With the 0.8 mu m CMOS technology, a clock signal up to 180 MHz can be used. In average, for n-bit modular multiplication, the encryption speed can reach 116 Kbit / s (kilobits per second), which is substantially twice that achieved by the prior art.
Owner:UNITED MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Elliptic curve cryptosystem apparatus, elliptic curve cryptosystem method, elliptic curve cryptosystem program and computer readable recording medium storing the elliptic curve cryptosystem program
InactiveUS20060093137A1Increase speedProvide securityPublic key for secure communicationUnauthorized memory use protectionSoftware engineeringMechanical engineering
An elliptic curve cryptosystem apparatus performing an elliptic curve cryptosystem process has a coordinate transforming unit for transforming coordinates (X:Y:Z) on a point P on an elliptic curve over a finite field GF(pˆm) to coordinates (r1×(X−s1):r2×(Y−s2):r3×(Z−s3)) (where, p is a prime number, m is an integer not less than 1, r1, r2 and r3 are integers not less than 1 and not larger than (p−1), s1, s2 and s3 are integer not less than 0 and not larger than (p−1), and a code “ˆ” represents power), and a scalar multiplication operating unit for performing scalar multiplication on the point on the elliptic curve transformed by the coordinate transforming unit, wherein at least one of the parameters s1, s2 and s3 has a value other than 0. The apparatus can perform the scalar multiplication in the elliptic curve cryptosystem, with resistance to side channel attacks.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Elliptic scalar multiplication system
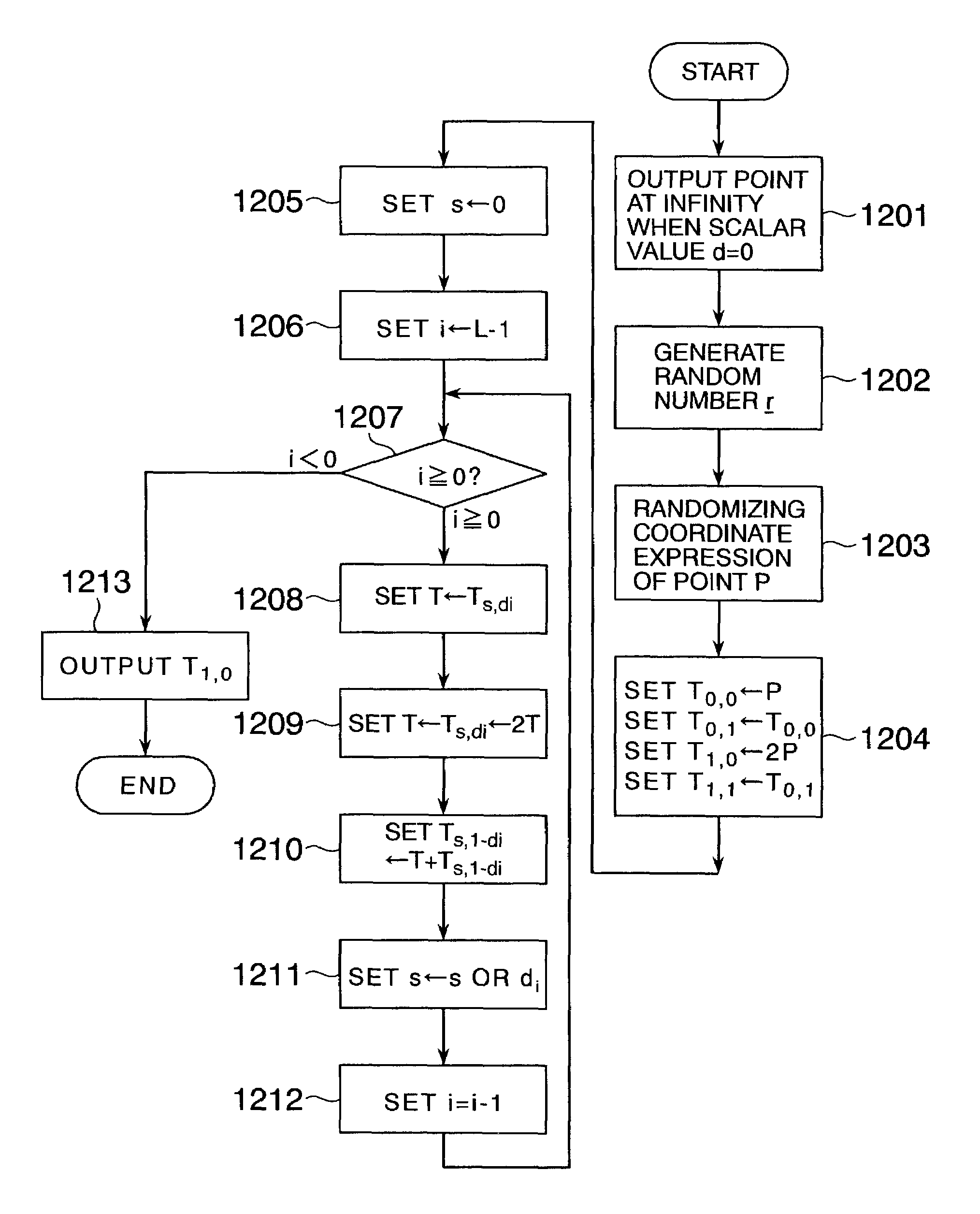
InactiveUS7308096B2Increase speedPublic key for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationAlgorithmScalar Value
In scalar multiplication method in which a point on an elliptic curve is randomized, but yet scalar multiplication can be calculated by the computational cost as much as that without randomization, an operation is carried out upon a point randomized and a point not randomized in a scalar multiplication method to calculate a scalar-multiplied point from a scalar value and a point on an elliptic curve. The result of the operation is randomized while the computational cost becomes as much as that without randomization.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Cryptography using finite fields of odd characteristic on binary hardware
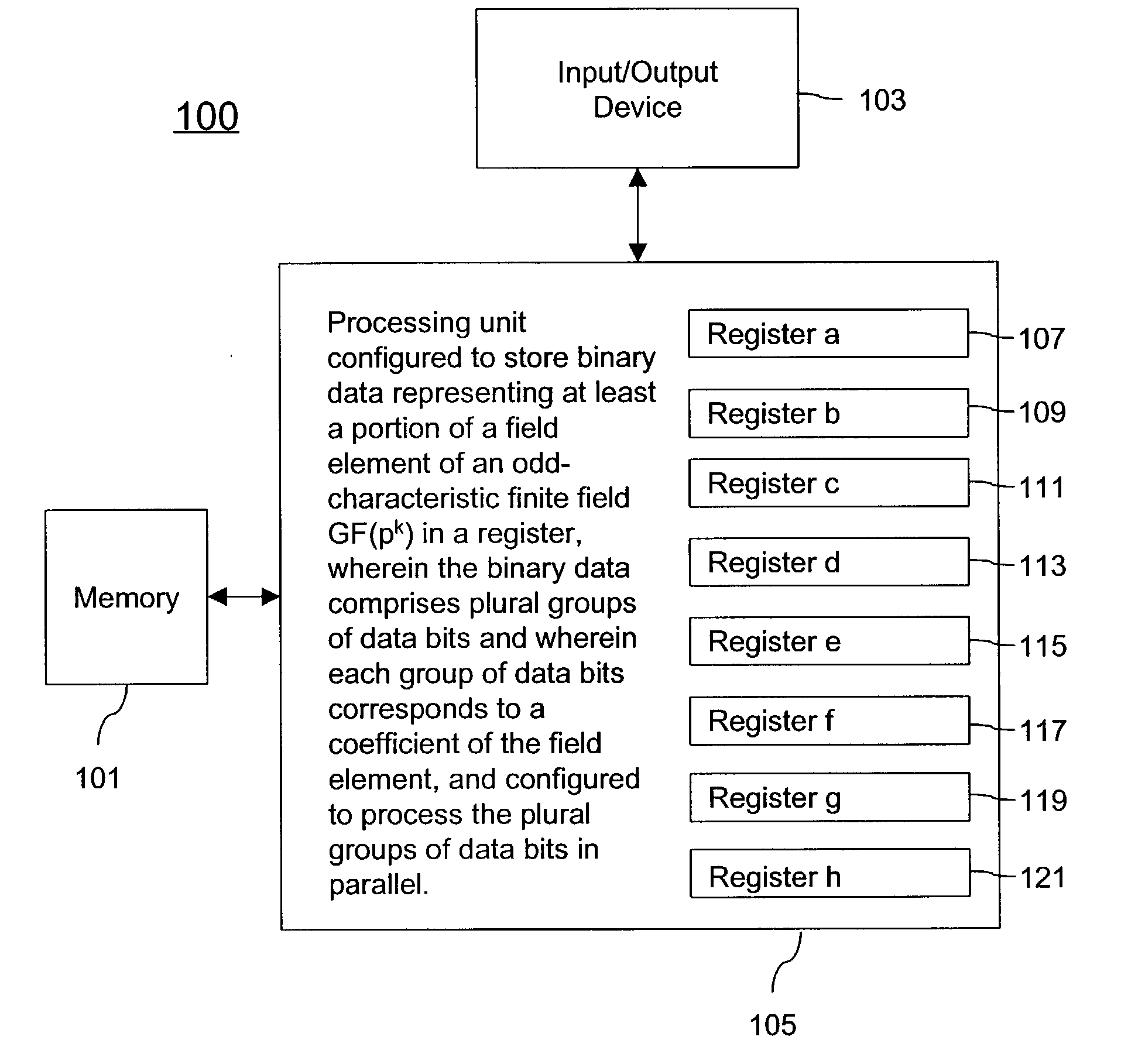
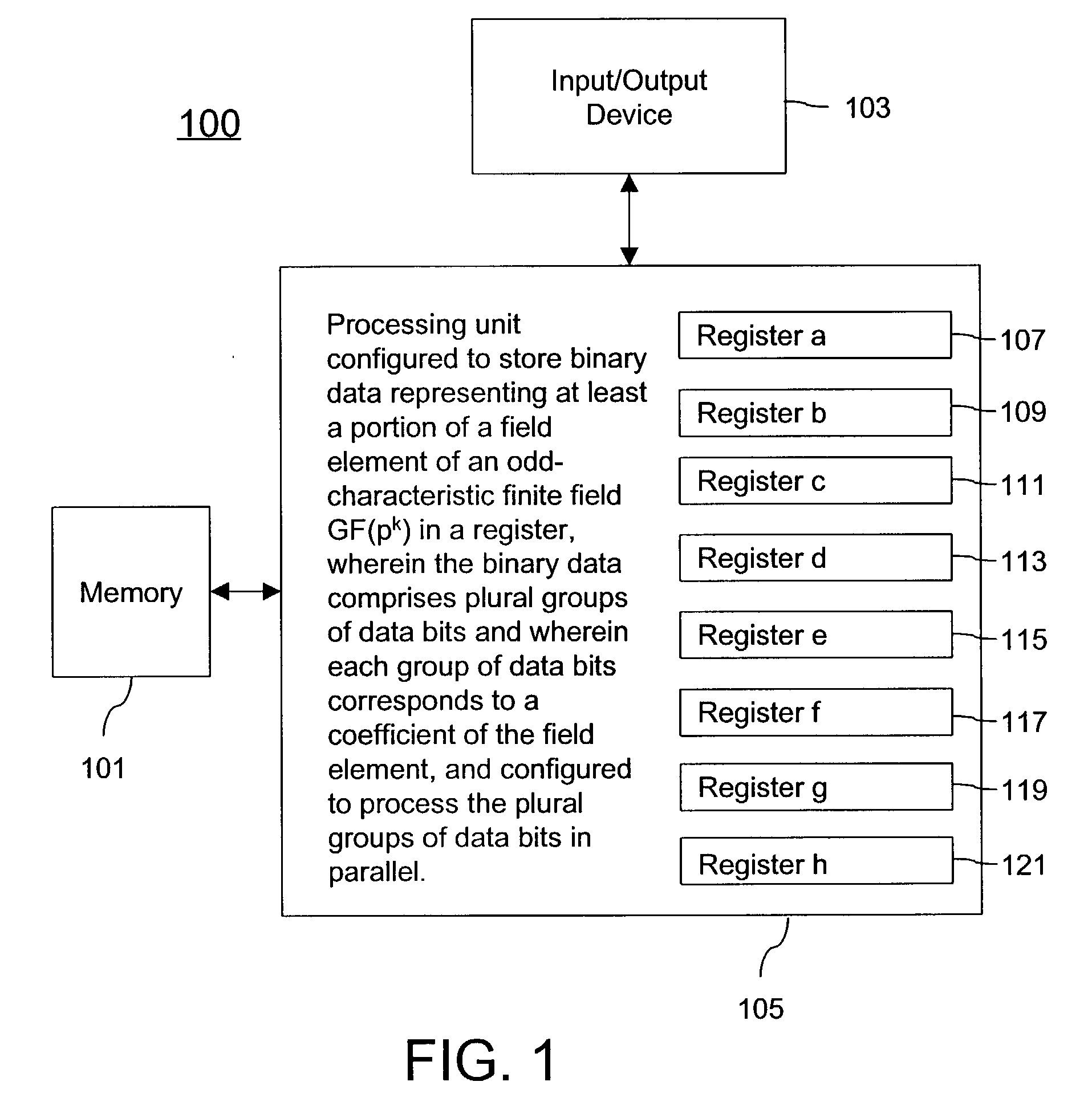
InactiveUS20060072743A1Speed up the calculation processReduce needPublic key for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationProcessing elementField element
A cryptographic method is described. The method comprises storing binary data representing at least a portion of a field element of an odd-characteristic finite field GF(pk) in a register, p being an odd prime number, the field element comprising k coefficients in accordance with a polynomial-basis representation, the binary data comprising plural groups of data bits, wherein each group of data bits represents an associated one of the k coefficients and processing the binary data in accordance with a cryptographic algorithm such that the plural groups of data bits are processed in parallel. An apparatus comprising a memory and a processing unit coupled to the memory to carry out the method is also described.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com