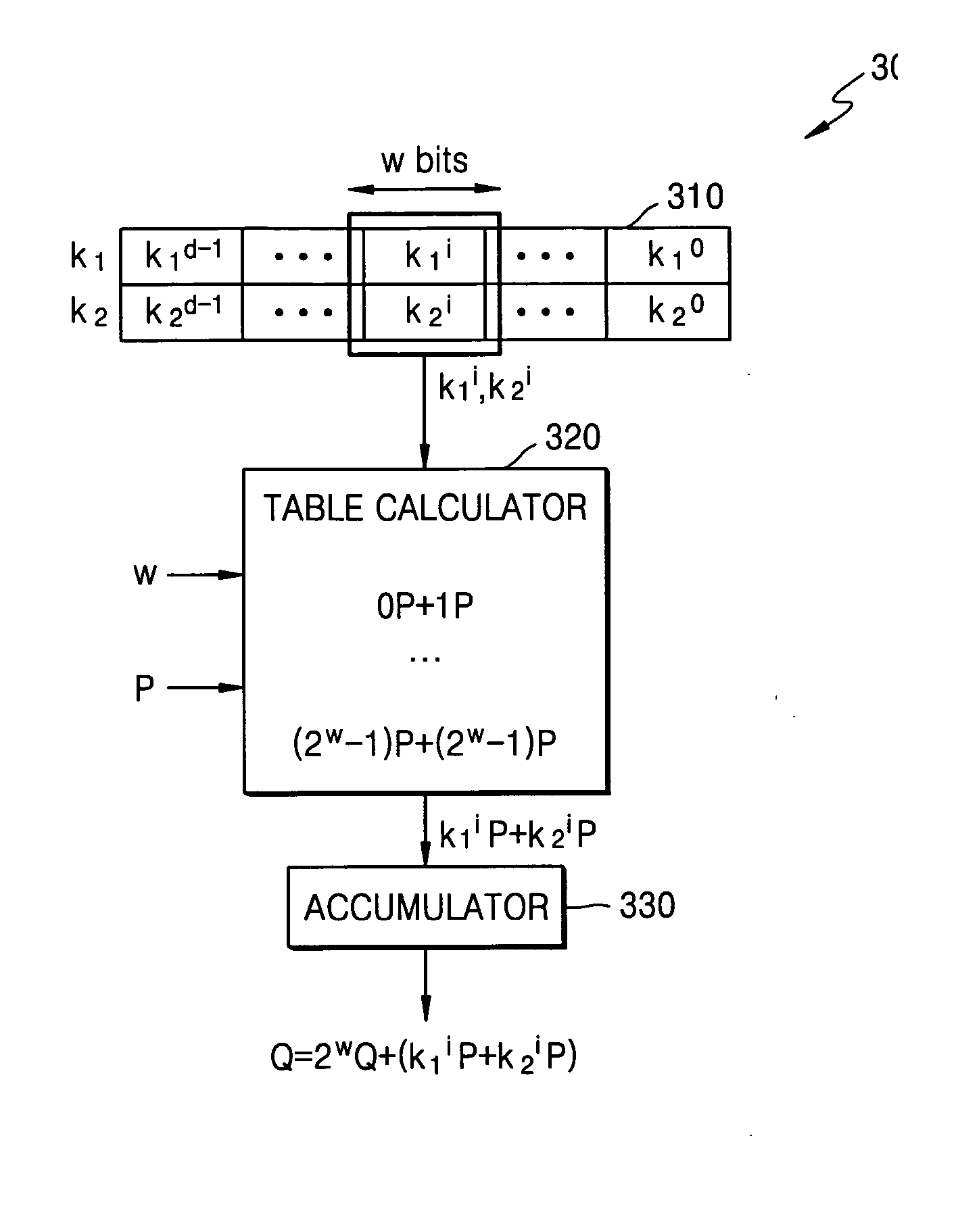
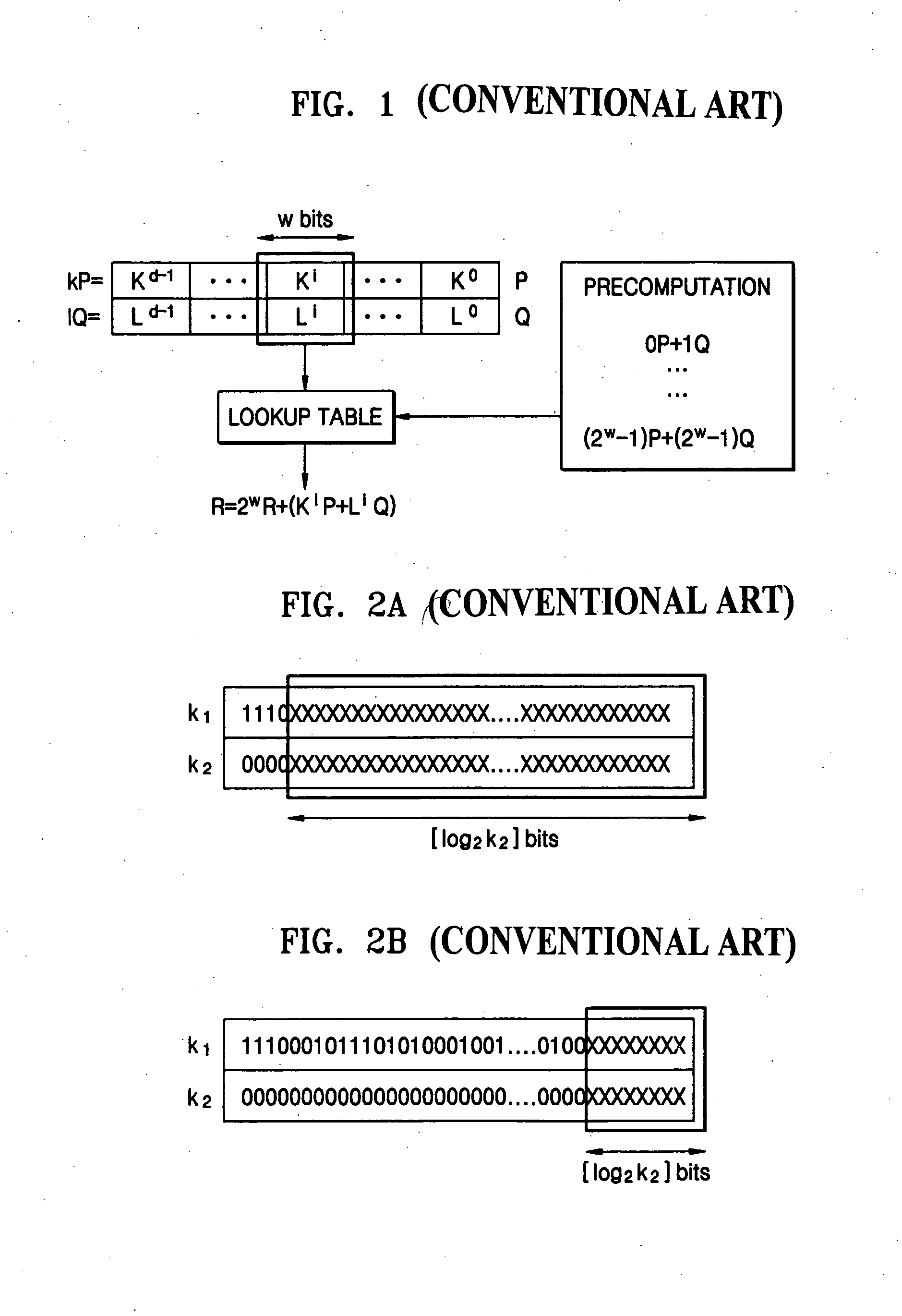
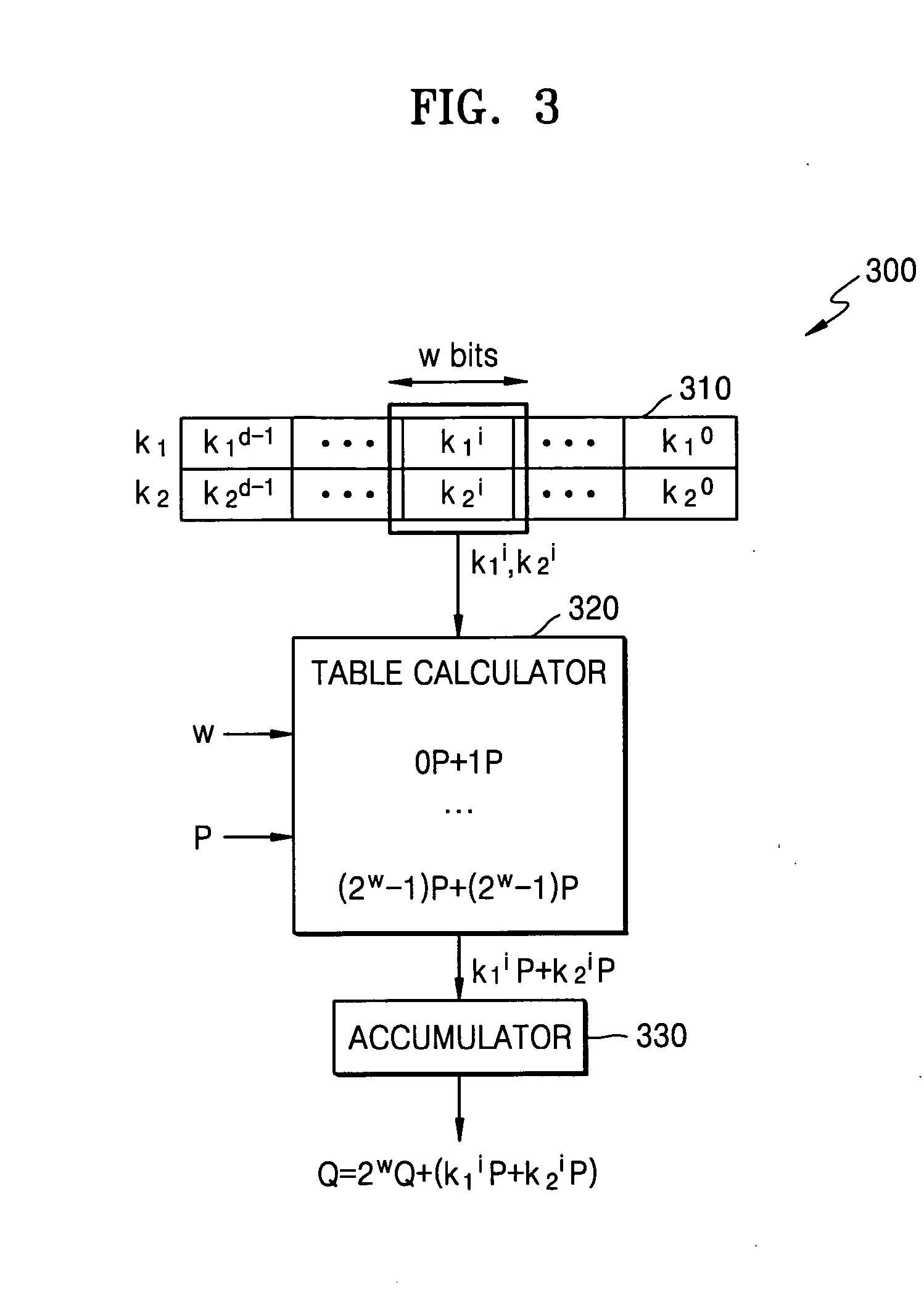
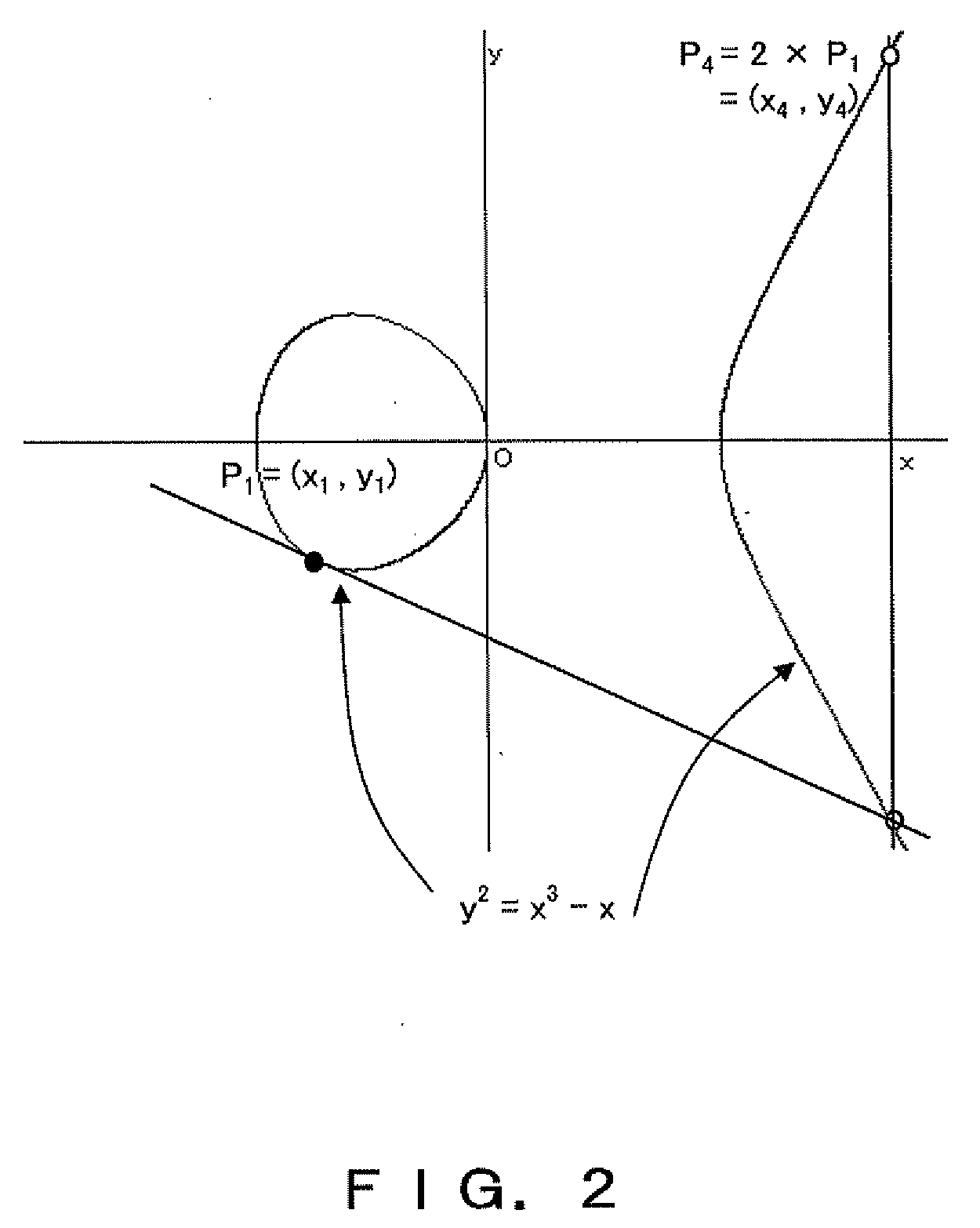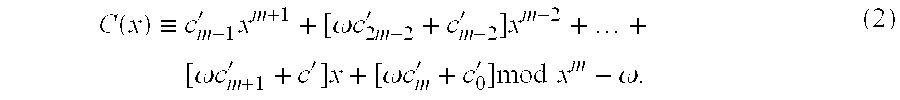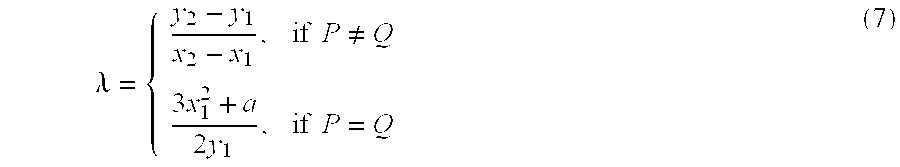Patents
Literature
199 results about "Scalar multiplication" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
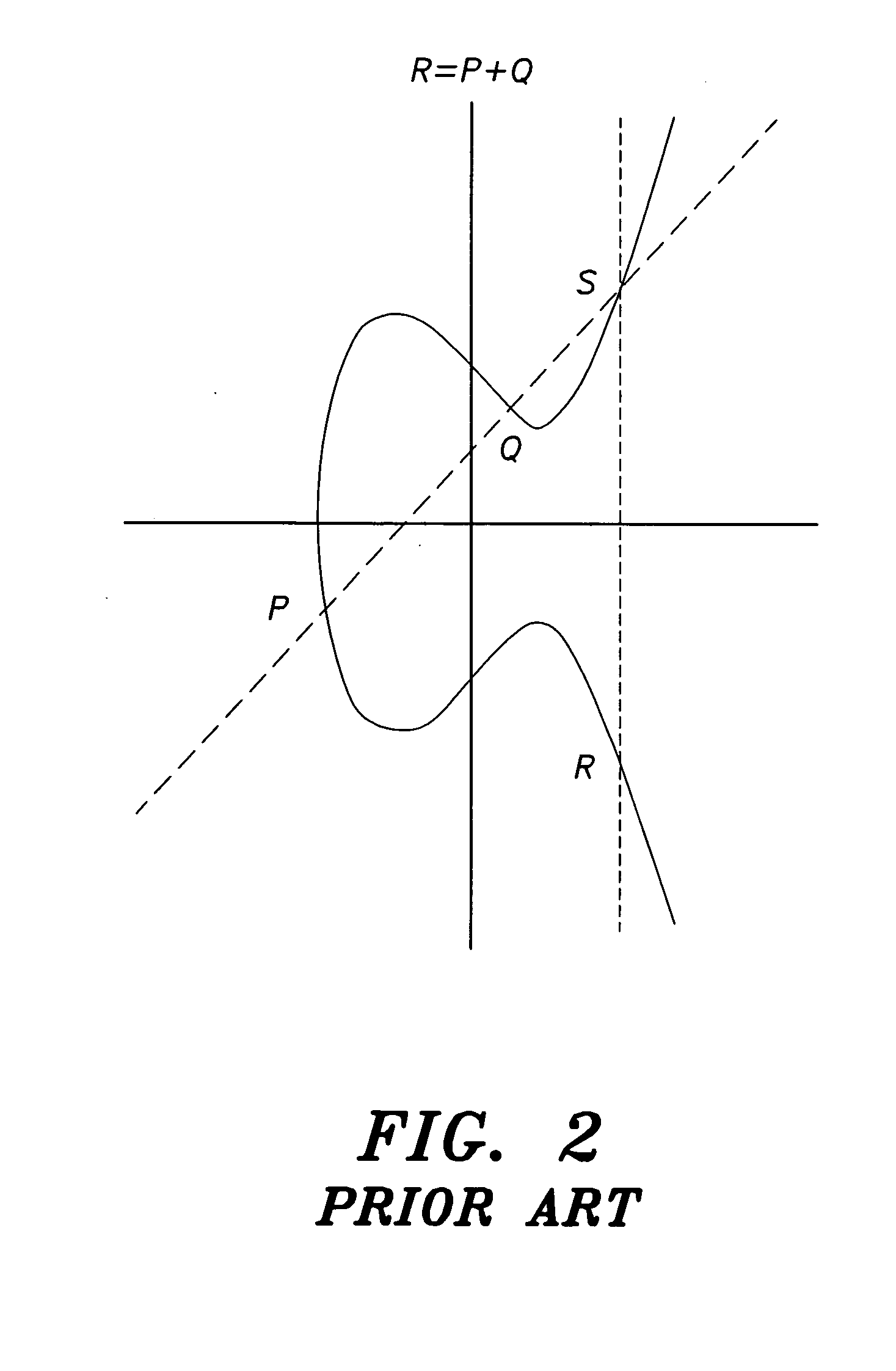
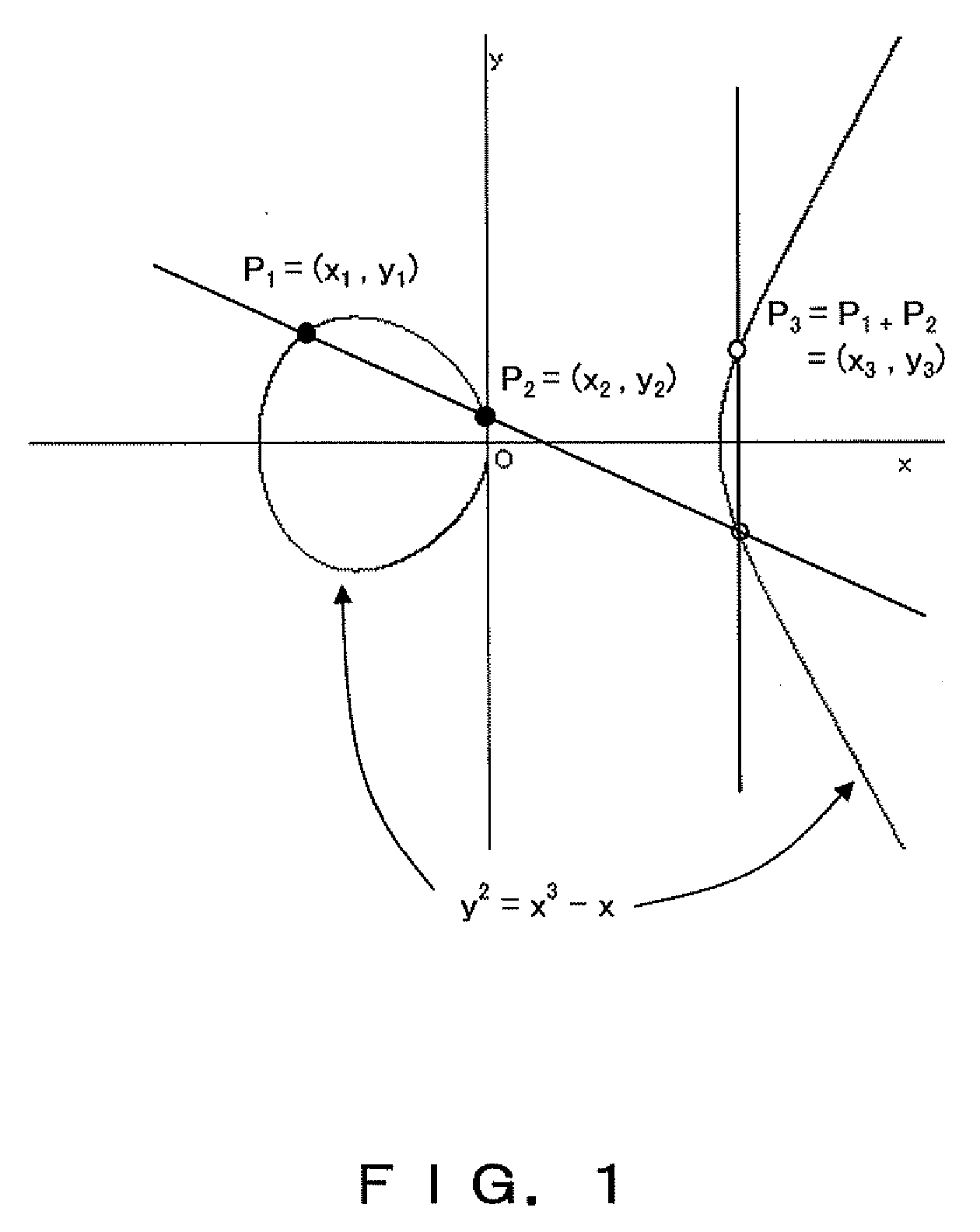
In mathematics, scalar multiplication is one of the basic operations defining a vector space in linear algebra (or more generally, a module in abstract algebra). In common geometrical contexts, scalar multiplication of a real Euclidean vector by a positive real number multiplies the magnitude of the vector without changing its direction. The term "scalar" itself derives from this usage: a scalar is that which scales vectors. Scalar multiplication is the multiplication of a vector by a scalar (where the product is a vector), and must be distinguished from inner product of two vectors (where the product is a scalar).
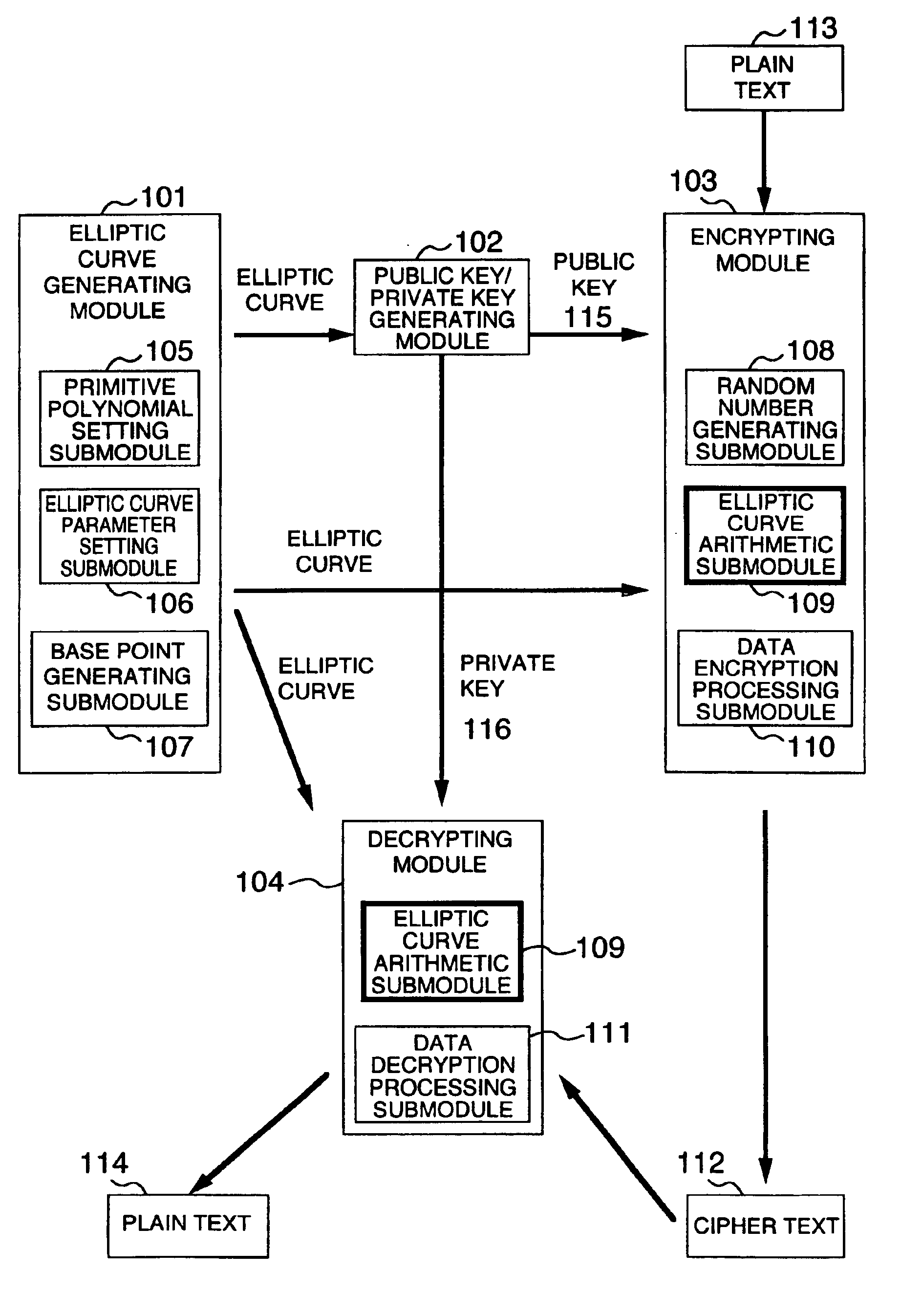
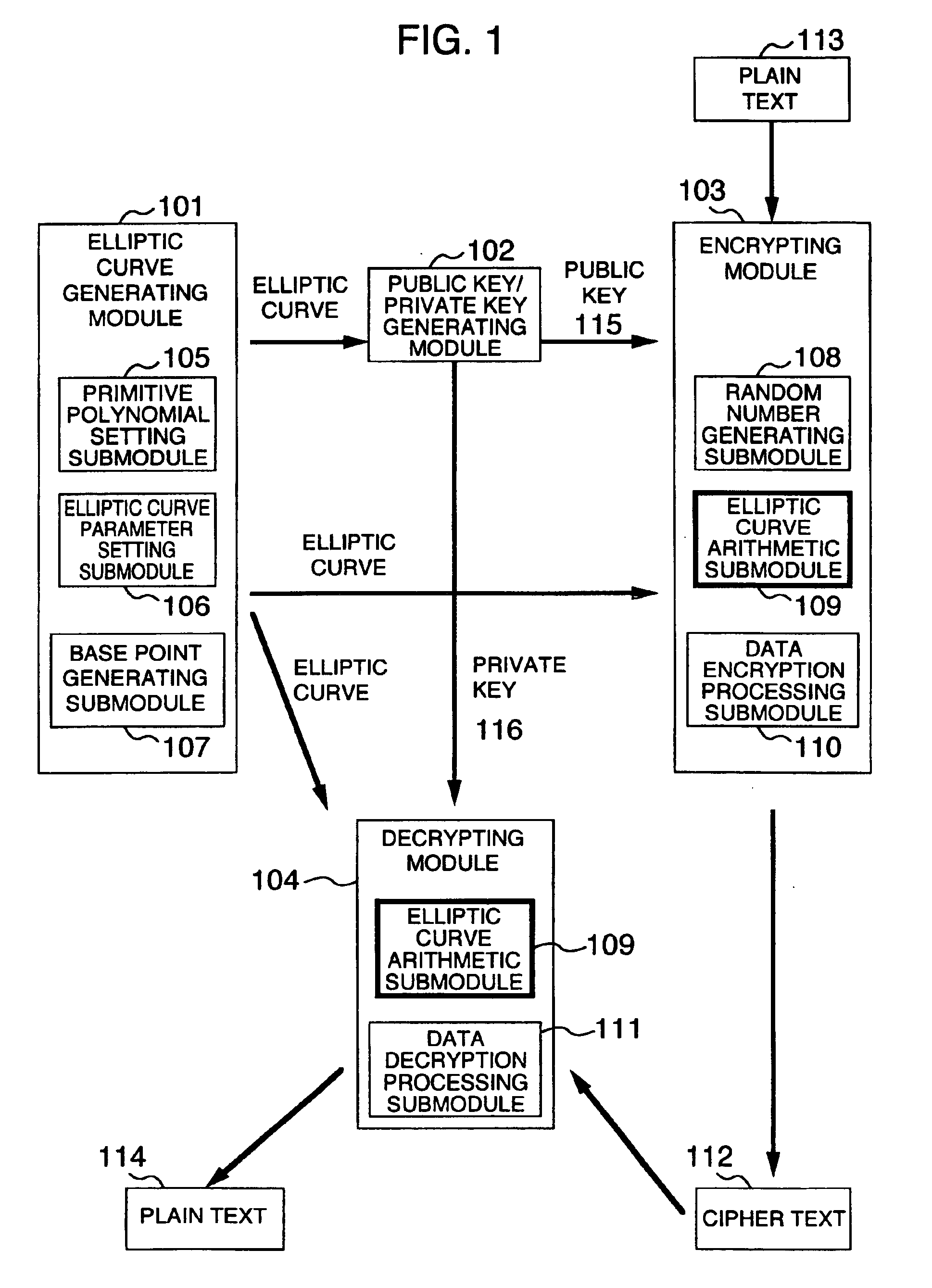
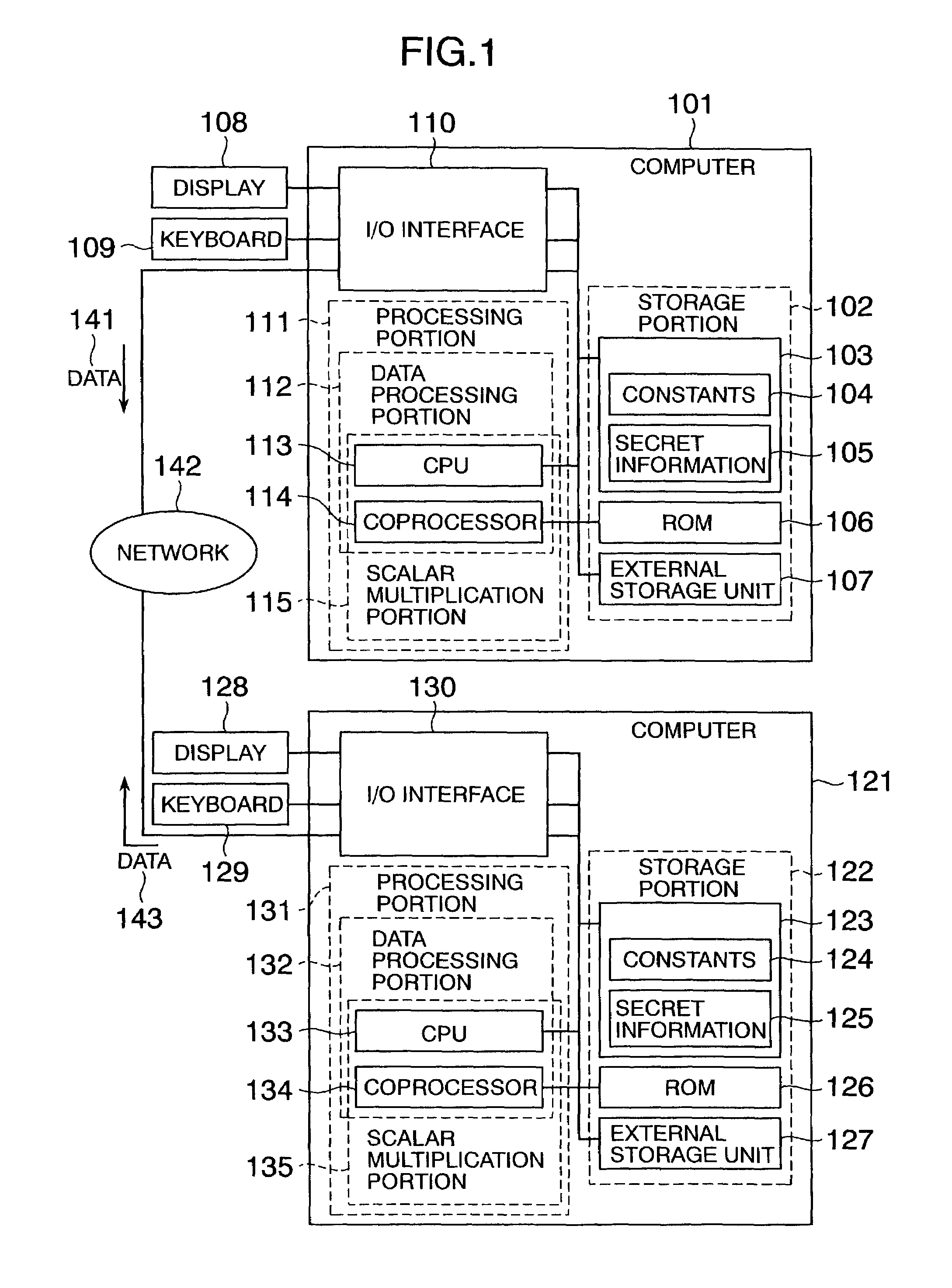
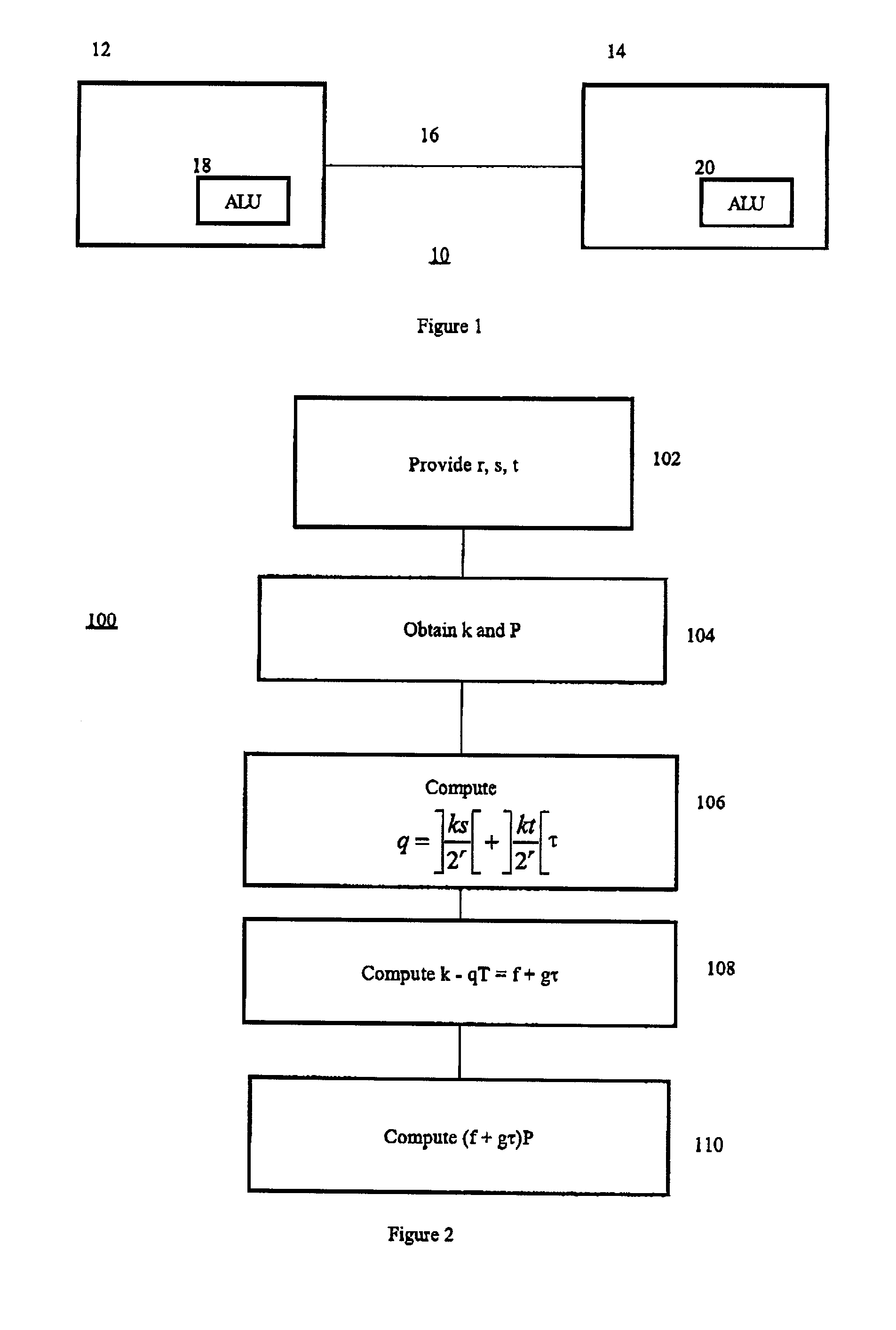
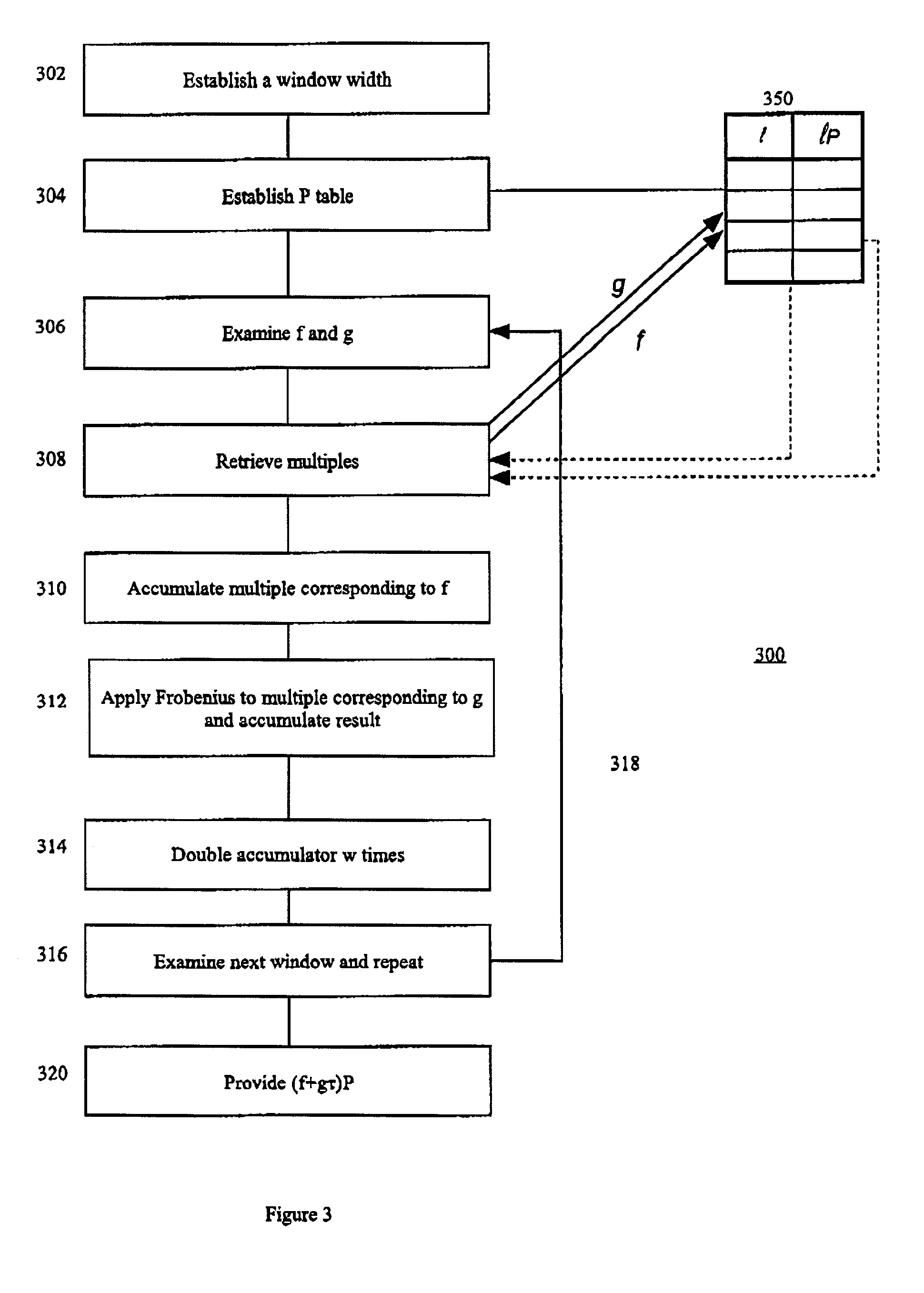
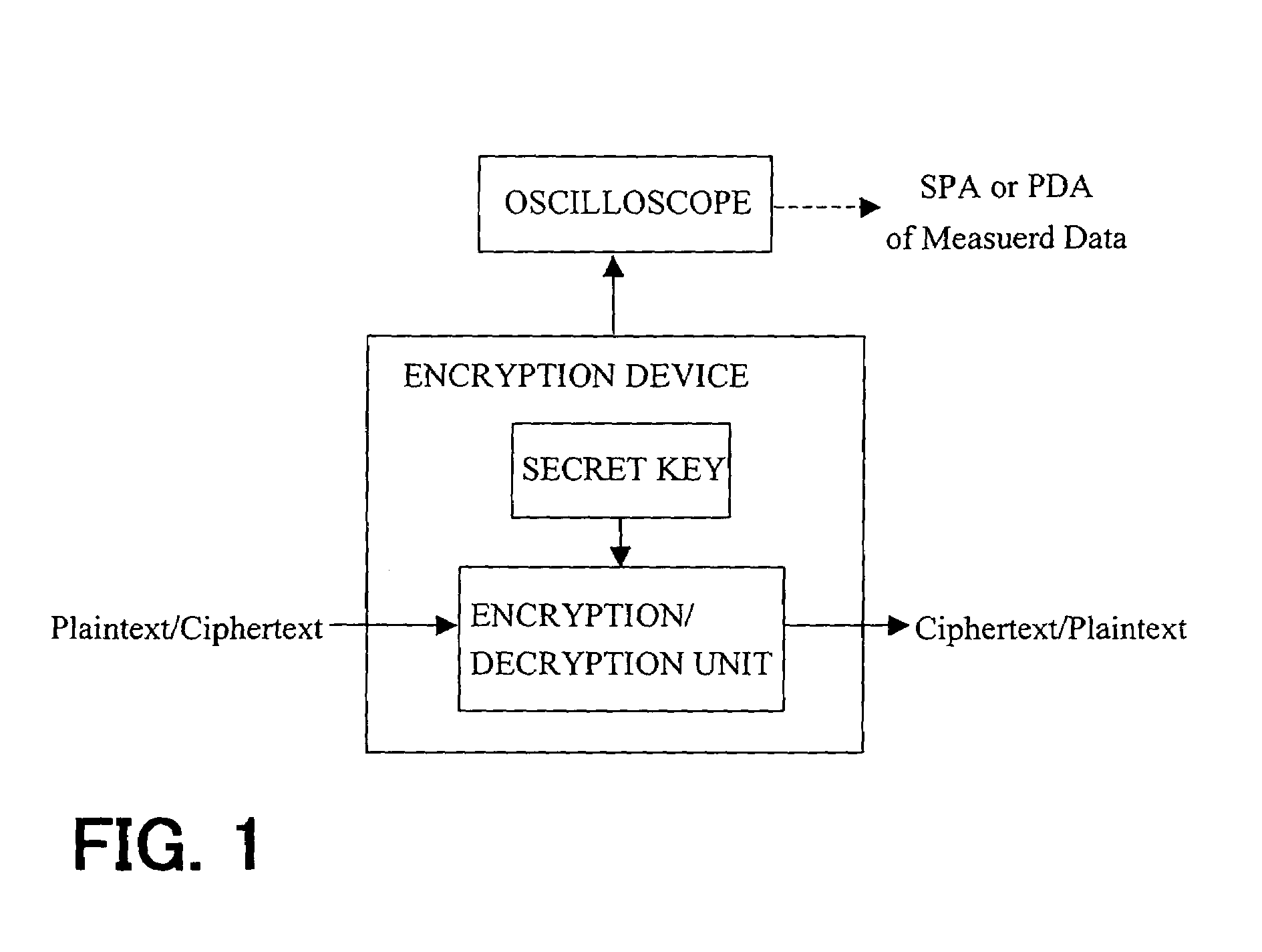
Method and apparatus for elliptic curve cryptography and recording medium therefore
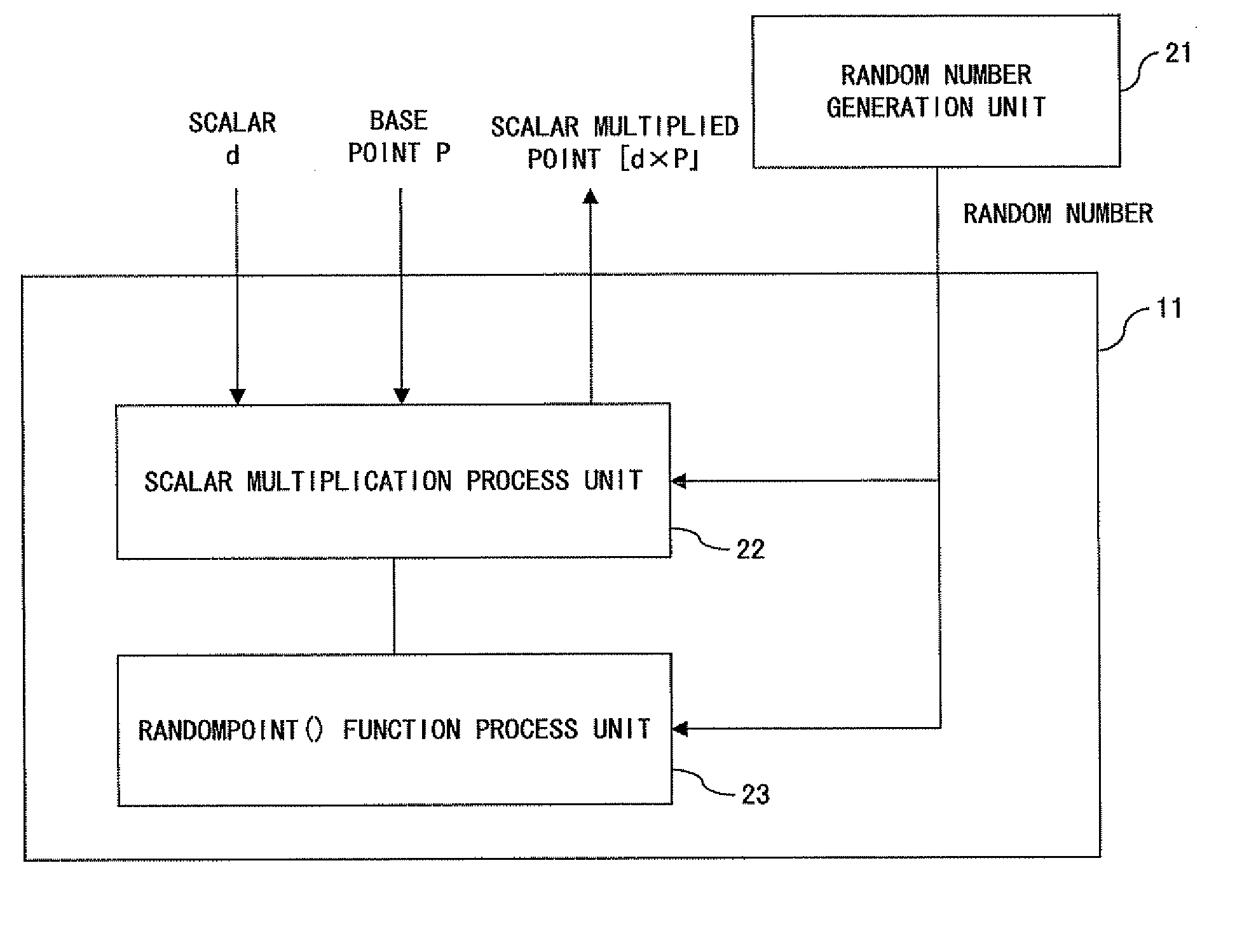
InactiveUS6876745B1Prevent leakageRandom number generatorsPublic key for secure communicationComputer hardwarePower analysis
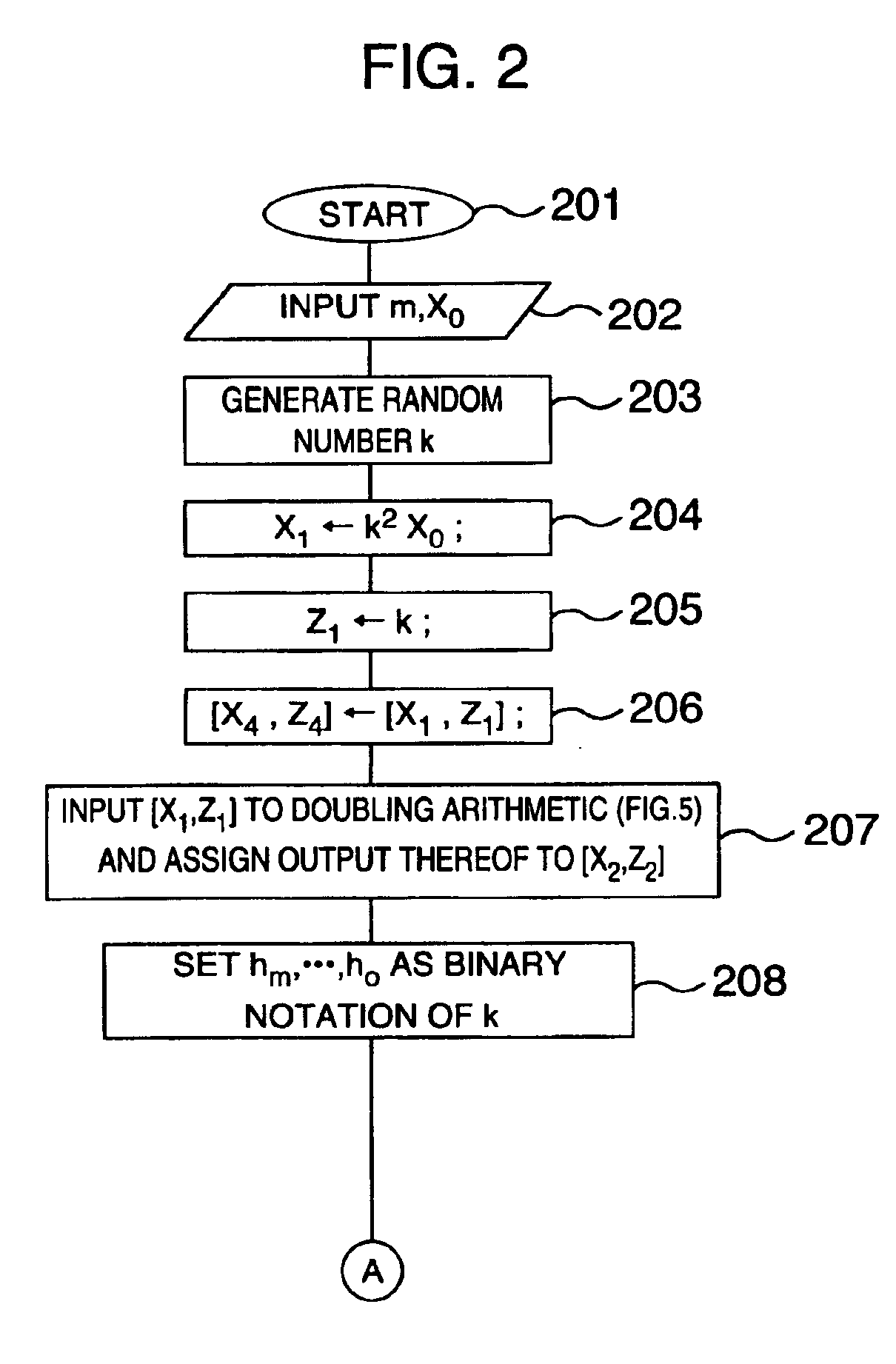
A method and an apparatus capable of realizing at a high speed an elliptic curve cryptography in a finite field of characteristic 2, in which the elliptic curve is given by y2+xy=x3+ax2+b (b≠0) and an elliptic curve cryptography method which can protect private key information against leaking from deviation information of processing time to thereby defend a cipher text against a timing attack and a differential power analysis attack are provided. To this end, an arithmetic process for executing scalar multiplication arithmetic d(x, y) a constant number of times per bit of the private key d is adopted. Further, for the scalar multiplication d(x, y), a random number k is generated upon transformation of the affine coordinates (x, y) to the projective coordinates for thereby effectuating the transformation (x, y)→[kx, ky, k] or alternatively (x, y)→[k2x, k3y, k]. Thus, object for the arithmetic is varied by the random number (k).
Owner:HITACHI LTD
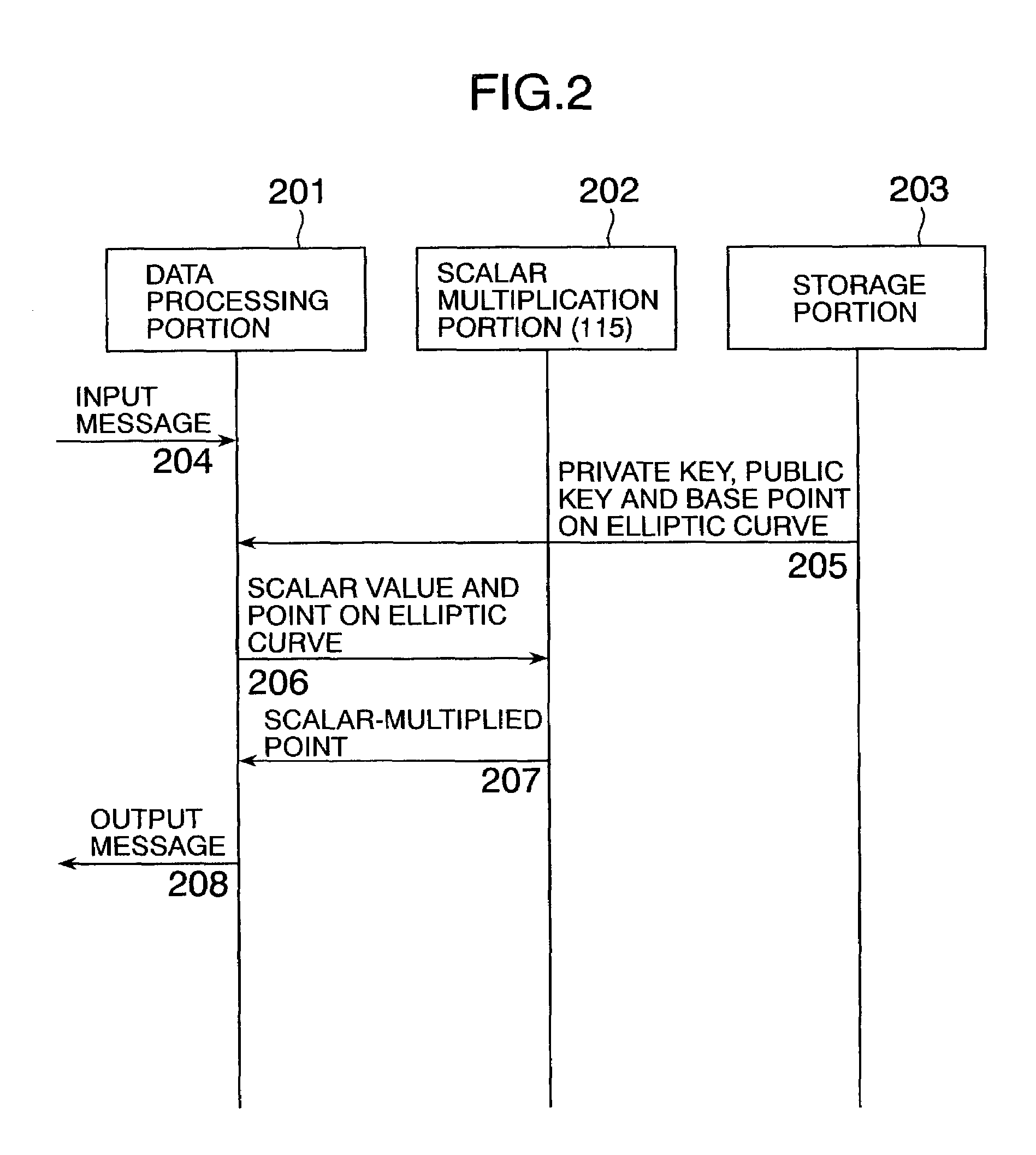
Elliptic scalar multiplication system
InactiveUS7308096B2Increase speedPublic key for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationAlgorithmScalar Value
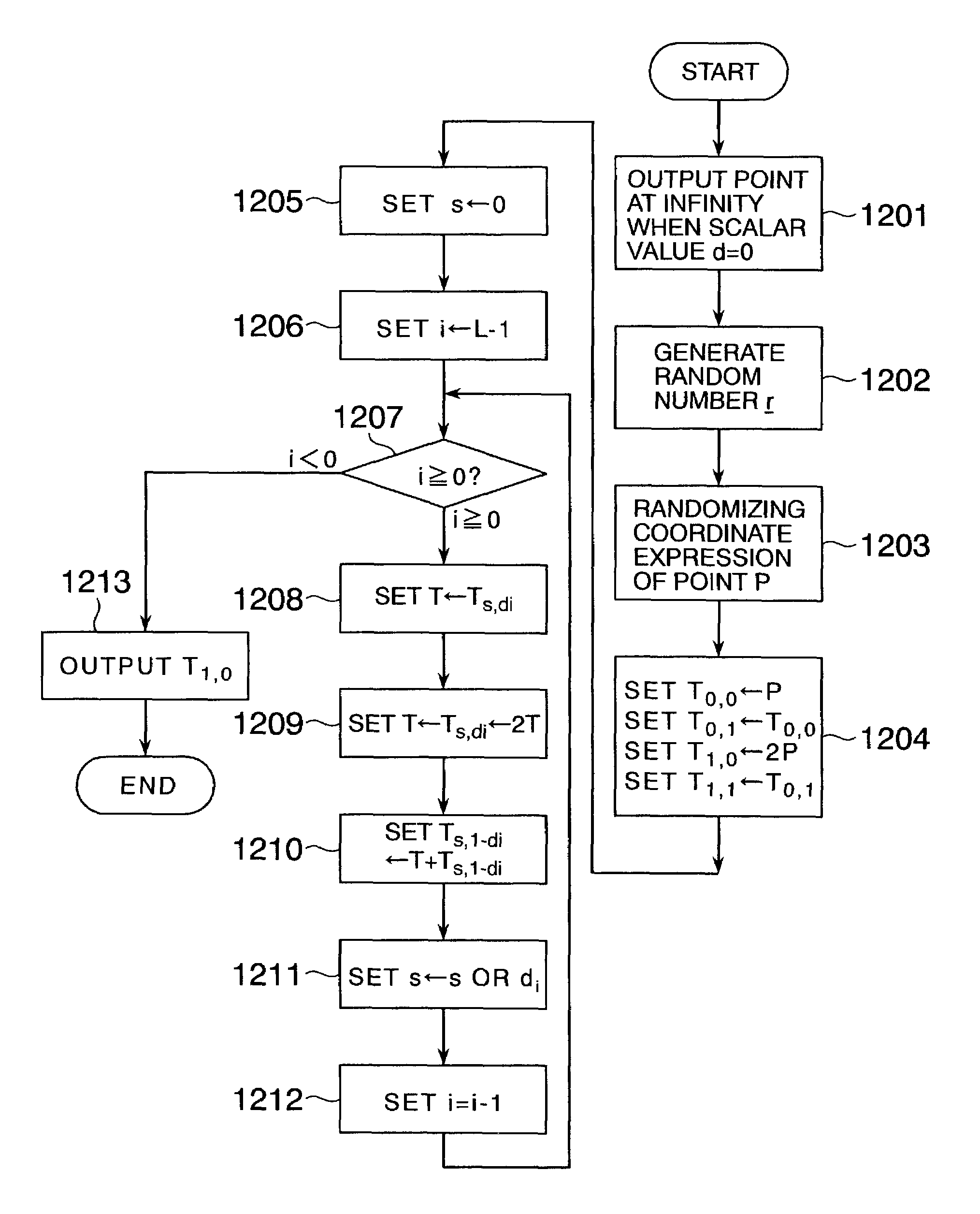
In scalar multiplication method in which a point on an elliptic curve is randomized, but yet scalar multiplication can be calculated by the computational cost as much as that without randomization, an operation is carried out upon a point randomized and a point not randomized in a scalar multiplication method to calculate a scalar-multiplied point from a scalar value and a point on an elliptic curve. The result of the operation is randomized while the computational cost becomes as much as that without randomization.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
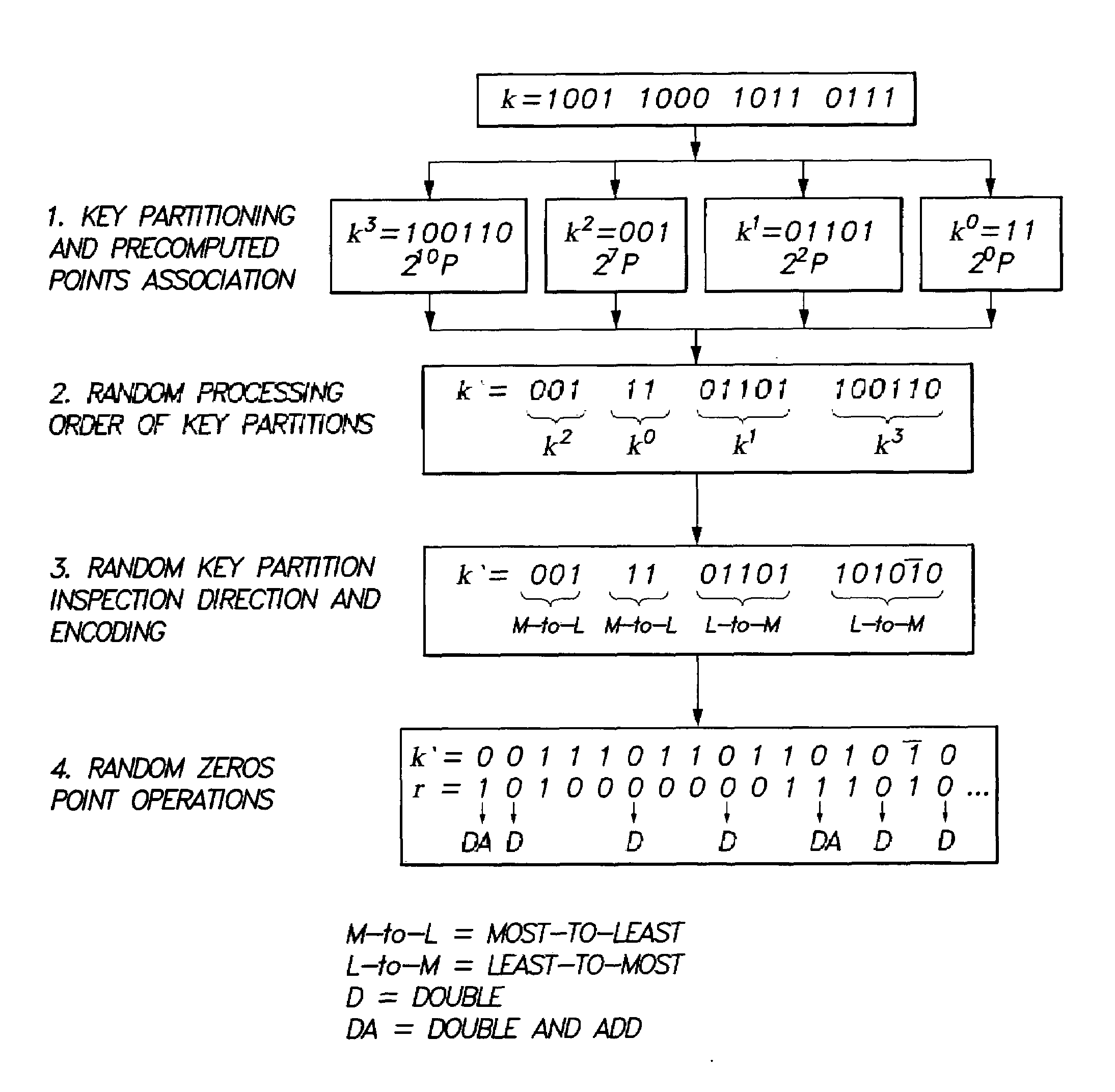
Method for elliptic curve scalar multiplication
InactiveUS20090214023A1Improve the immunityImprove securityDigital data processing detailsSecret communicationPower analysisCountermeasure
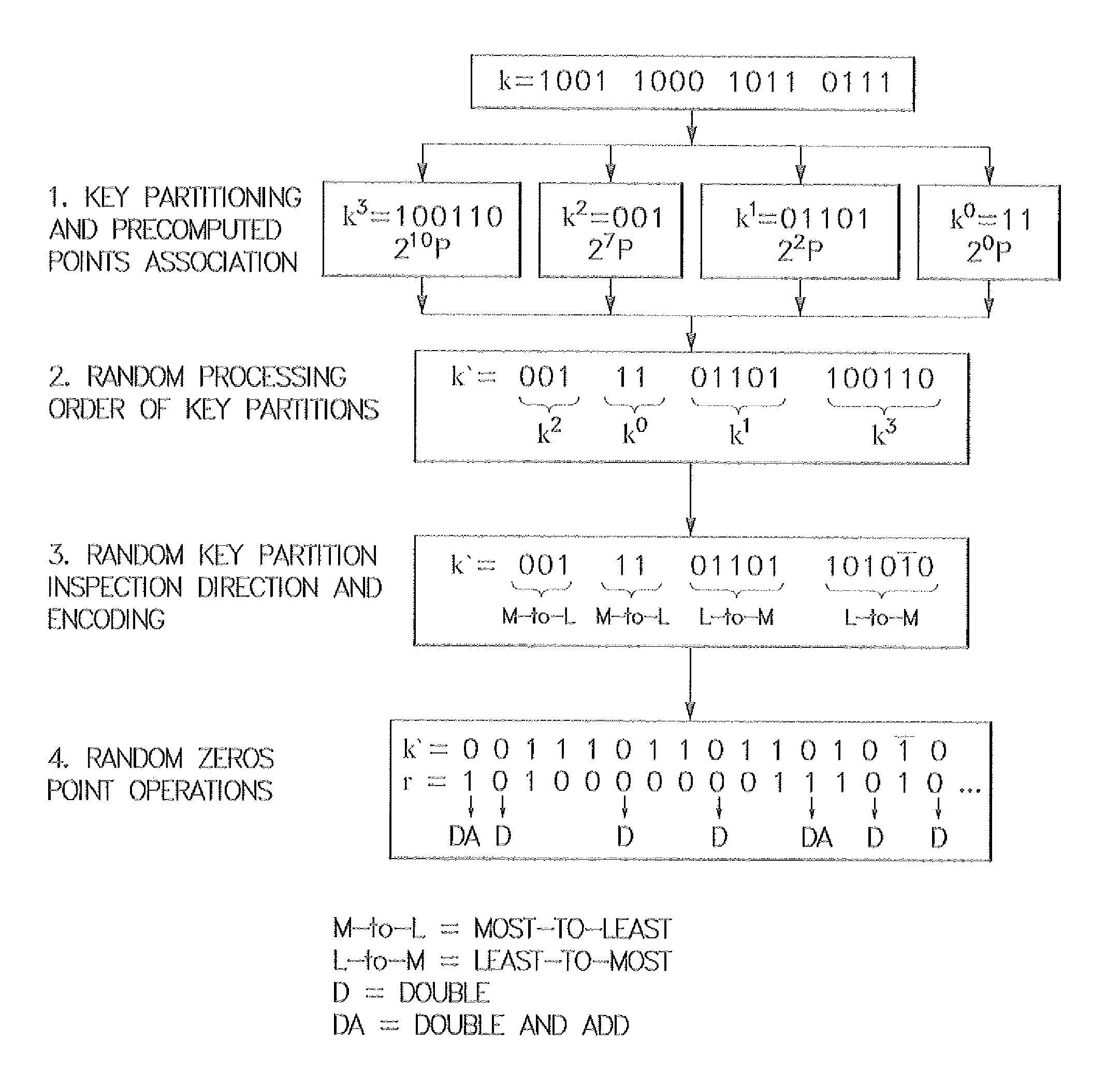
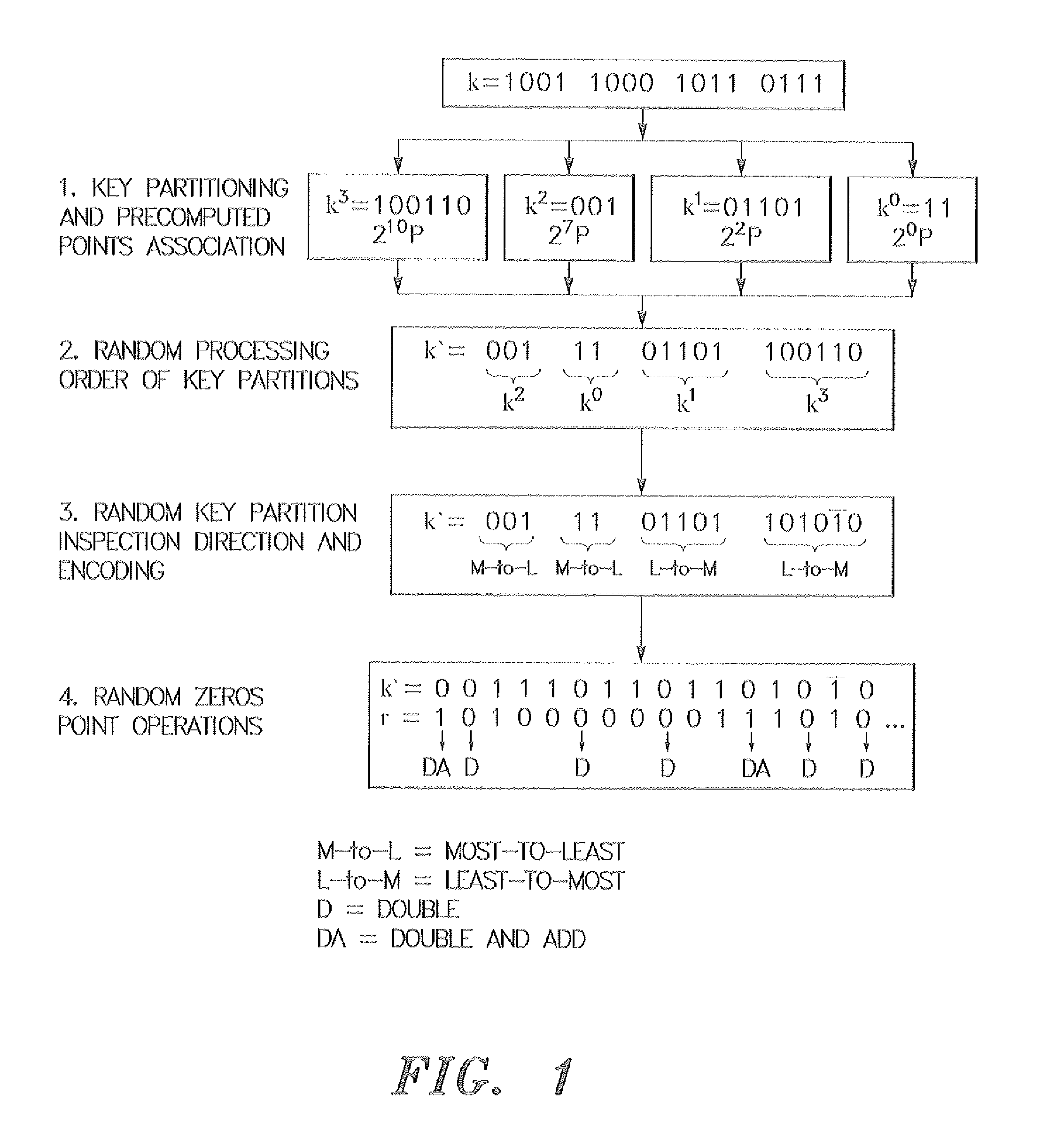
The method for elliptic curve scalar multiplication may provide several countermeasures to protect scalar multiplication of a private key k by a point P to produce the product kP from power analysis attacks. First, the private key, k, is partitioned into a plurality of key partitions, which are processed in a random order, the resulting points being accumulated to produce the scalar product kP. Second, in each partition, the encoding is randomly selected to occur in binary form or in Non-Adjacent Form (NAF), with the direction of bit inspection being randomly assigned between most-to-least and least-to-most. Third, in each partition, each zero in the key may randomly perform a dummy point addition operation in addition to the doubling operation. The method may be implemented in software, smart cards, circuits, processors, or application specific integrated circuits (ASICs) designed to carry out the method.
Owner:KING FAHD UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND MINERALS
Tamper-proof elliptic encryption with private key
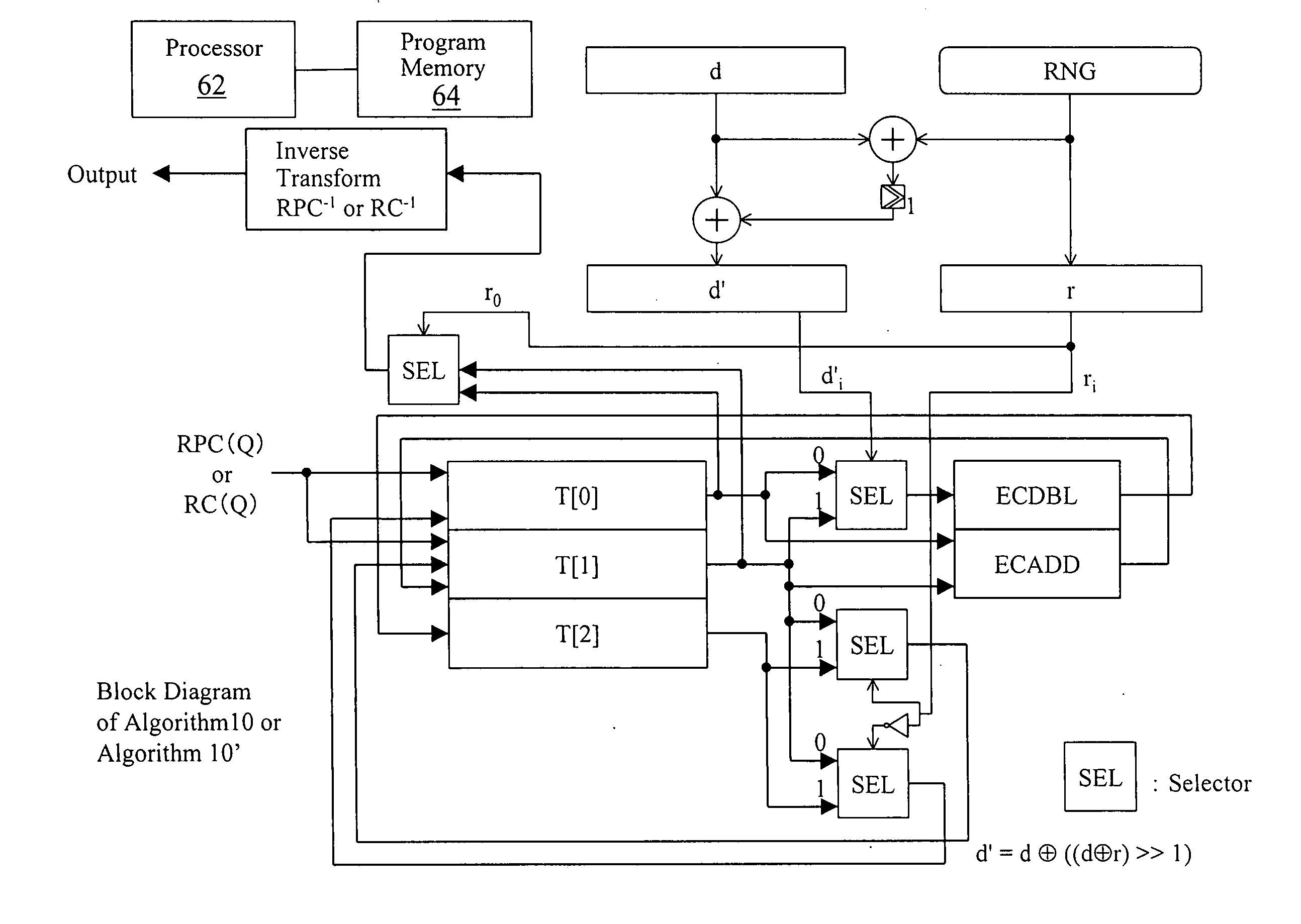
ActiveUS20050152541A1Public key for secure communicationSecret communicationData storingScalar multiplication
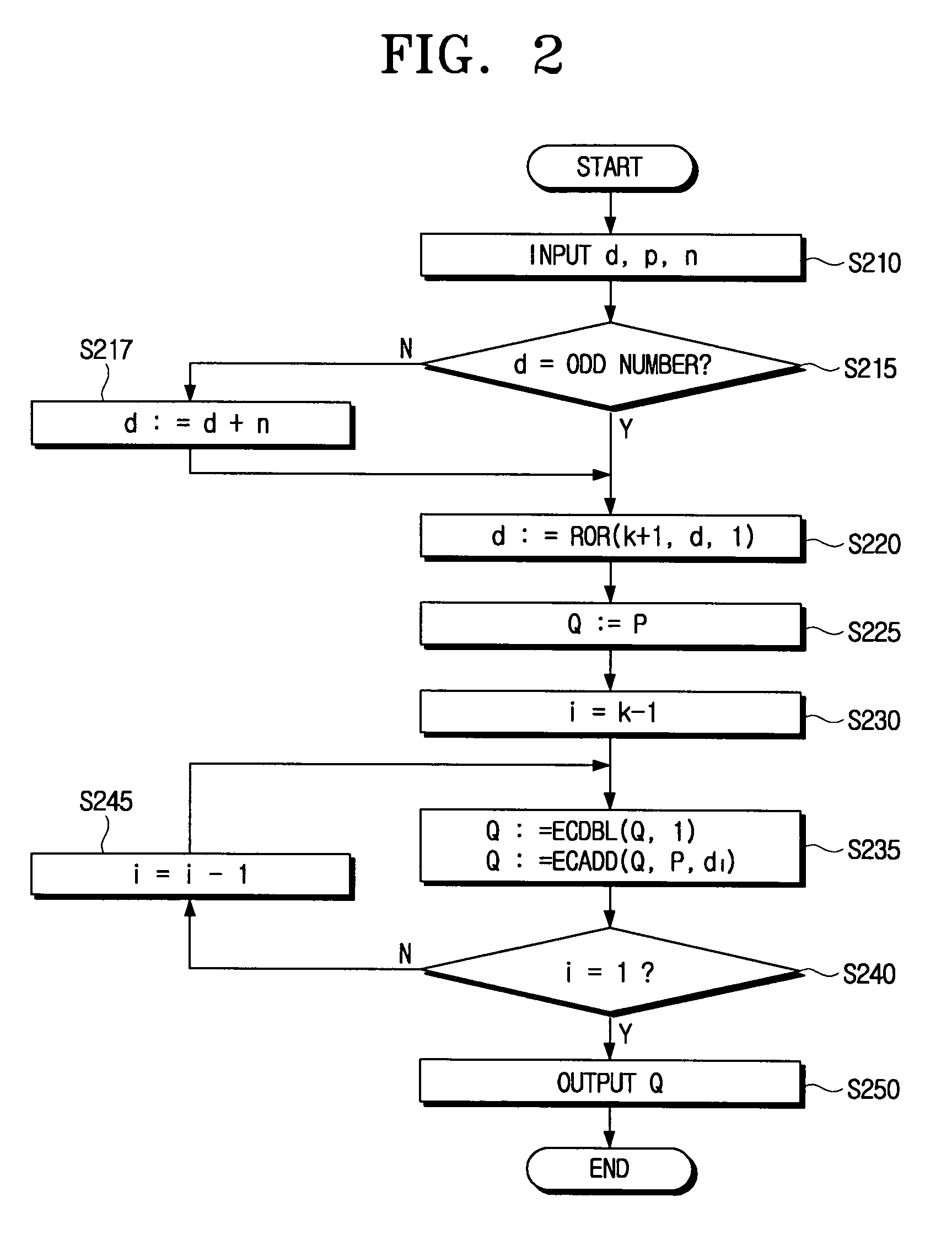
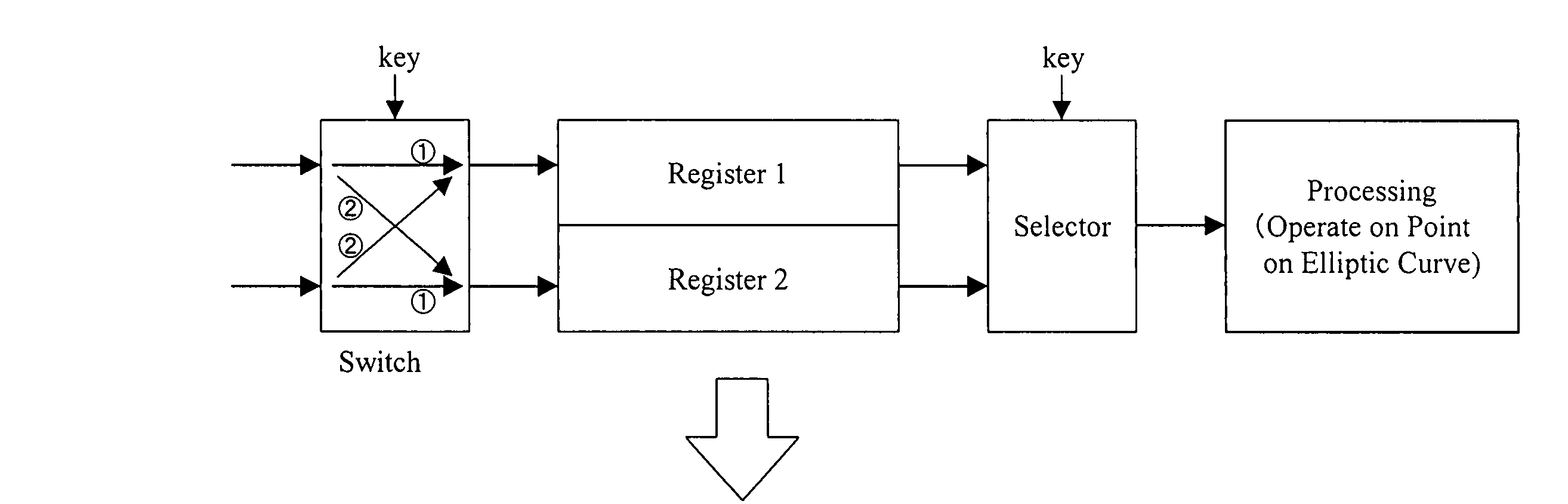
An encryption device (FIG. 15) performs elliptic curve encryption using a secret key. The encryption device includes: operation means (ECDBL, ECADD) for performing scalar multiplication of a point on an elliptic curve; storage (T[0]-T[2]) having a plurality of data storing areas; and means (SEL) for determining, in accordance with a bit sequence of a given value (d) and with a random value (RNG), an address of one of the plurality of data storage areas that is to be coupled to the operation means for each scalar multiplication.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Cryptographic method capable of protecting elliptic curve code from side channel attacks
ActiveUS20050169462A1Requires minimizationSafe and efficientKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationScalar multiplicationElliptic curve cryptography
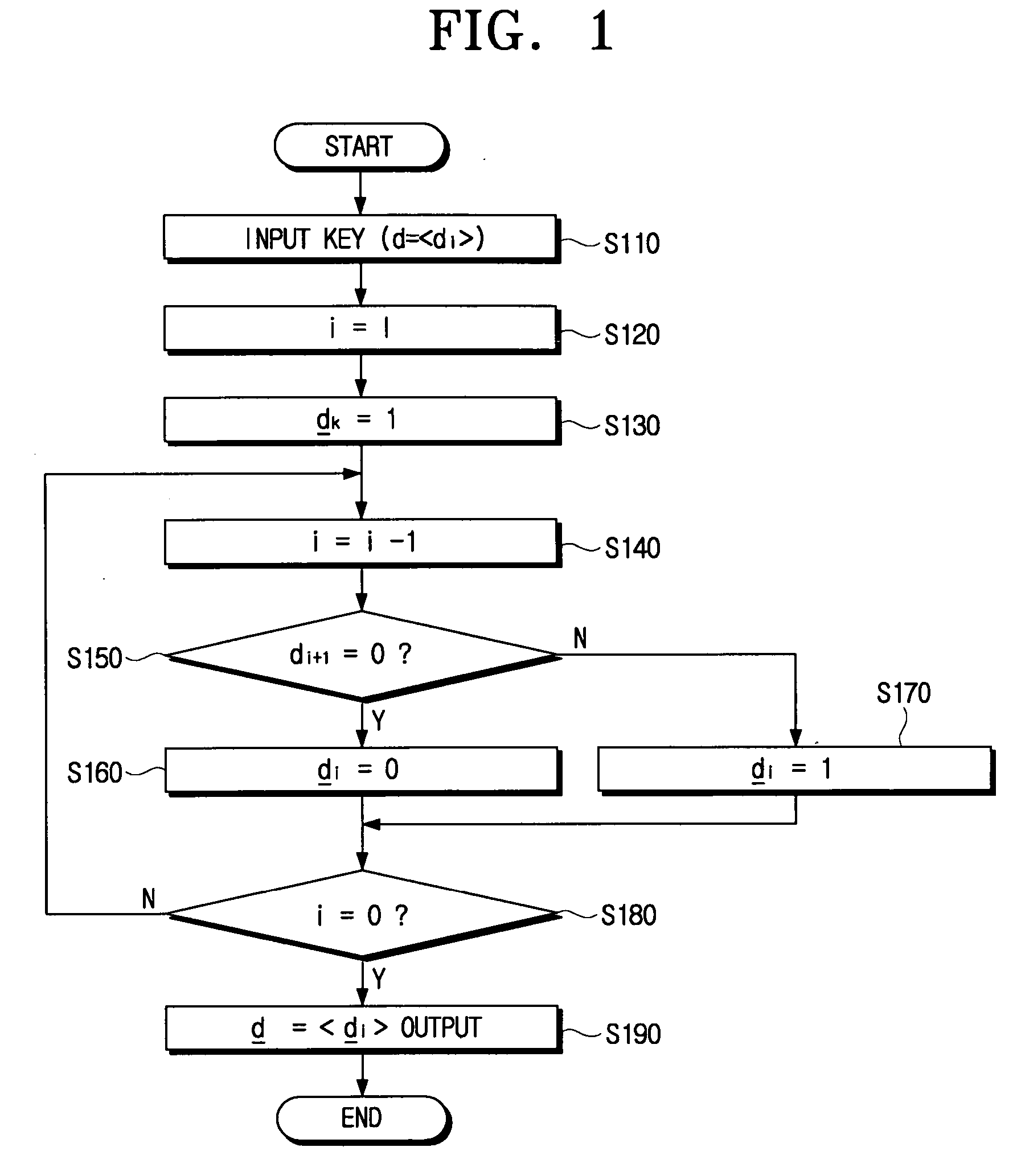
An elliptic curve cryptography method which generates a public key for use in a communication encryption using an elliptic curve, including: changing a number of a secret key (d) of (k) bits to an odd number; encoding the secret key to yield an encoded secret key (d) in which a most significant bit (MSB) is (1) and a rest positional number is (1) or (−1); and computing the public key (Q=Dp) by multiplying the encoded secret key (d) by a predetermined point (P) on the elliptic curve by a scalar multiplication.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Cryptographic device having tamper resistance to power analysis attack
InactiveUS20080025500A1Improve securityIncrease the difficultyRandom number generatorsPublic key for secure communicationPower analysisTamper resistance
A randomly selected point on an elliptic curve is set as the initial value of a variable and calculation including a random point value is performed in an algorithm for calculating arbitrary scalar multiple operation on an elliptic curve when scalar multiplication and addition on an elliptic curve are defined, then a calculation value obtained as a result of including a random point is subtracted from the calculation result, whereby an intended scalar multiple operation value on an elliptic curve is determined.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Cryptographic system and method for encrypting input data
ActiveUS20080044010A1Multiple keys/algorithms usageDigital data processing detailsModular exponentiationScalar multiplication
A cryptographic system and method for encrypting input data, in which an example system includes a table calculator configured to calculate table values composed of one of scalar multiplication values by Elliptic Curve (EC) operation, or exponentiation values by modular exponentiation operation, based on input data and the number of a portion of bits of each of secret keys. The table calculator may output one of scalar multiplication values or exponentiation values corresponding to a window that includes given bits of each of the secret keys from among the calculated table values. A logic circuit may be configured to output encrypted data by accumulating the output scalar multiplication values or by performing involution on the output exponentiation values.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
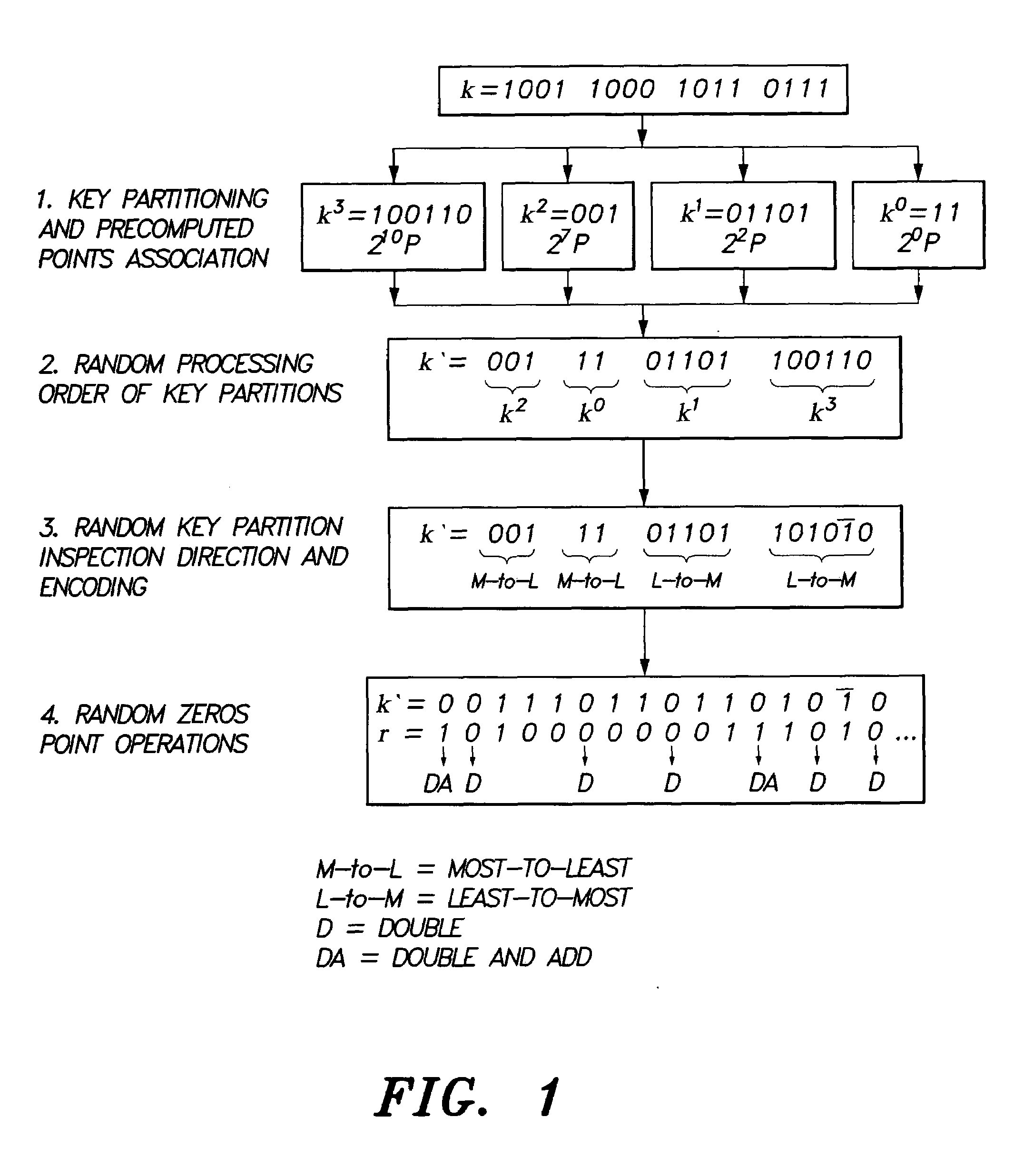
Method for elliptic curve scalar multiplication
InactiveUS20120008780A1Improve the immunityImprove securityDigital data processing detailsSecret communicationSmart cardScalar multiplication
The method for elliptic curve scalar multiplication may provide several countermeasures to protect scalar multiplication of a private key k by a point P to produce the product kP from power analysis attacks. First, the private key, k, is partitioned into a plurality of key partitions, which are processed in a random order, the resulting points being accumulated to produce the scalar product kP. Second, in each partition, the encoding is randomly selected to occur in binary form or in Non-Adjacent Form (NAF), with the direction of bit inspection being randomly assigned between most-to-least and least-to-most. Third, in each partition, each zero in the key may randomly perform a dummy point addition operation in addition to the doubling operation. The method may be implemented in software, smart cards, circuits, processors, or application specific integrated circuits (ASICs) designed to carry out the method.
Owner:KING FAHD UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND MINERALS
Method and apparatus for elliptic curve scalar multiplication
ActiveUS7215780B2Reducing a scalar modulo a truncatorKey distribution for secure communicationSecret communicationAlgorithmModularity
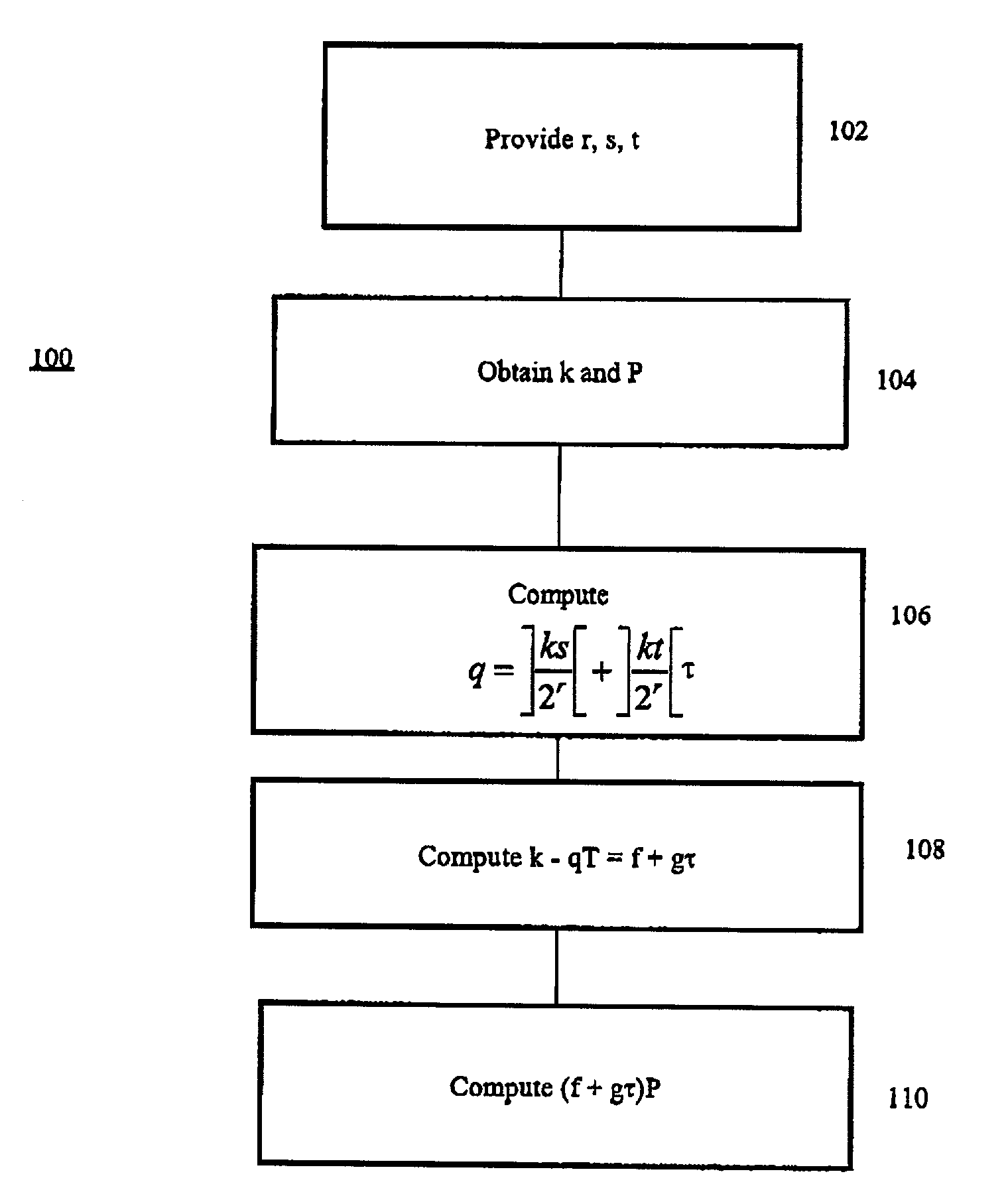
The applicants have recognized an alternate method of performing modular reduction that admits precomputation. The precomputation is enabled by approximating the inverse of the truncator T, which does not depend on the scalar.The applicants have also recognized that the representation of a scalar in a τ-adic representation may be optimized for each scalar that is needed.The applicants have further recognized that a standard rounding algorithm may be used to perform reduction modulo the truncator.In general terms, there is provided a method of reducing a scalar modulo a truncator, by pre-computing an inverse of the truncator. Each scalar multiplication then utilizes the pre-computed inverse to enable computation of the scalar multiplication without requiring a division by the truncator for each scalar multiplication.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
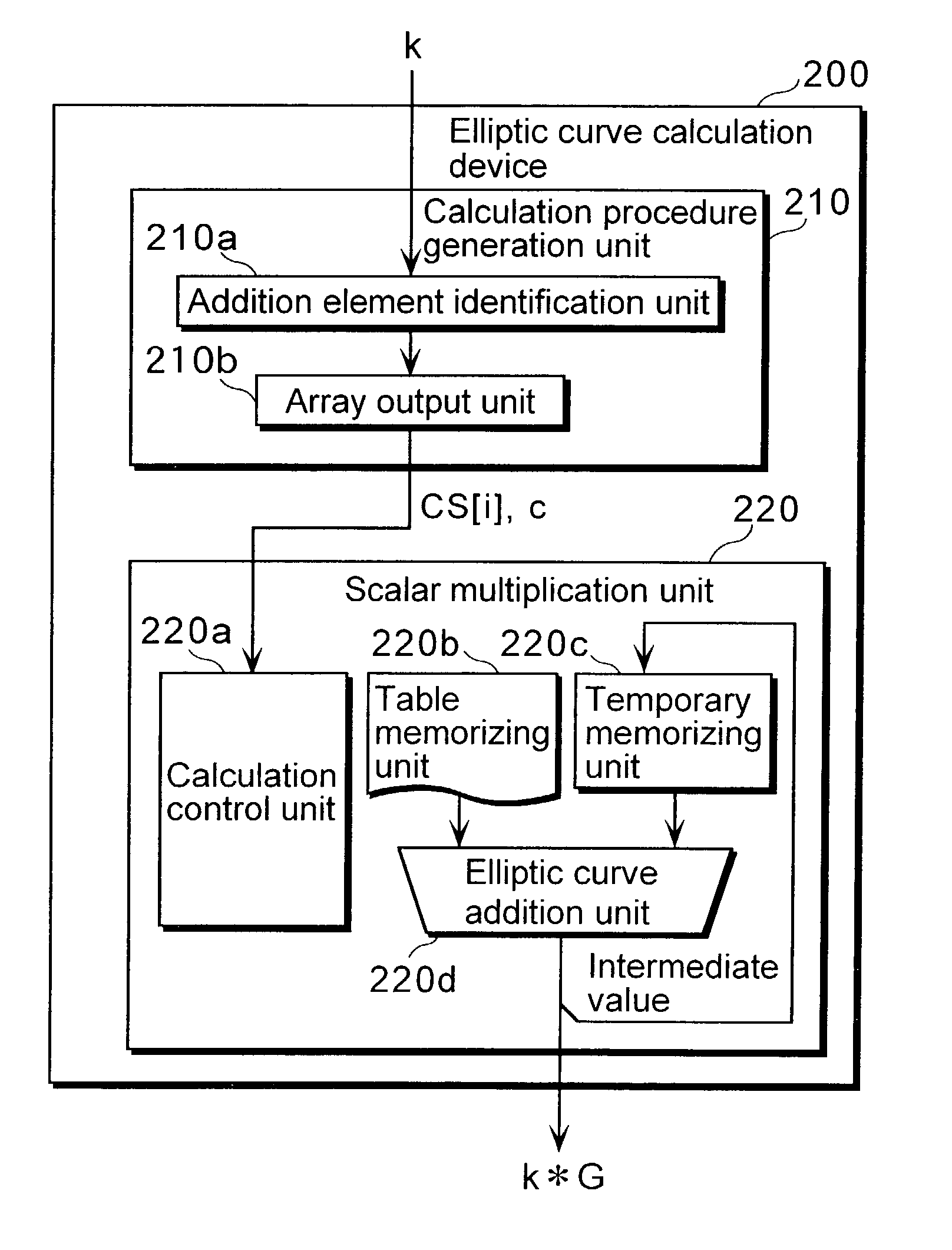
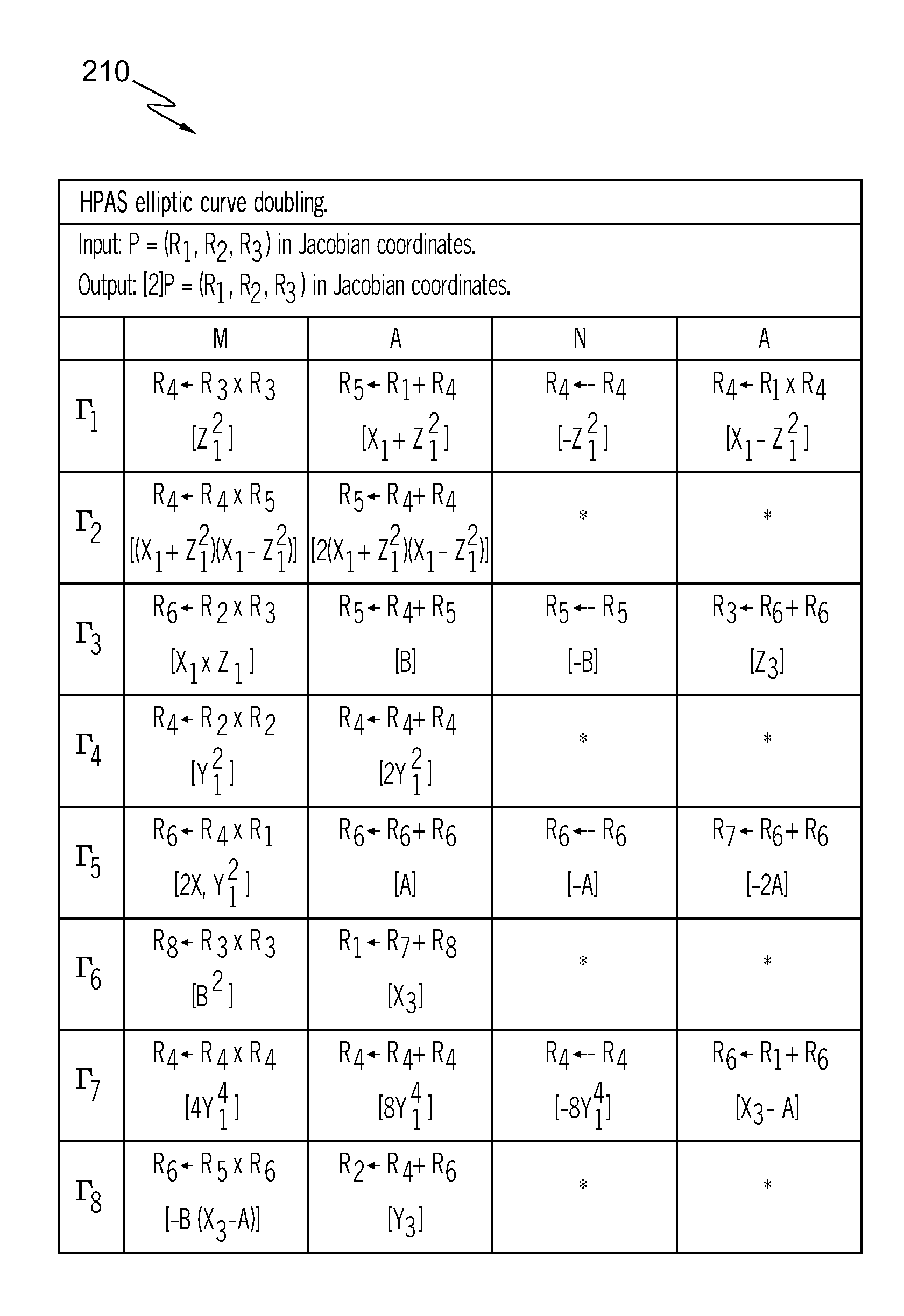
Device and method for calculation on elliptic curve
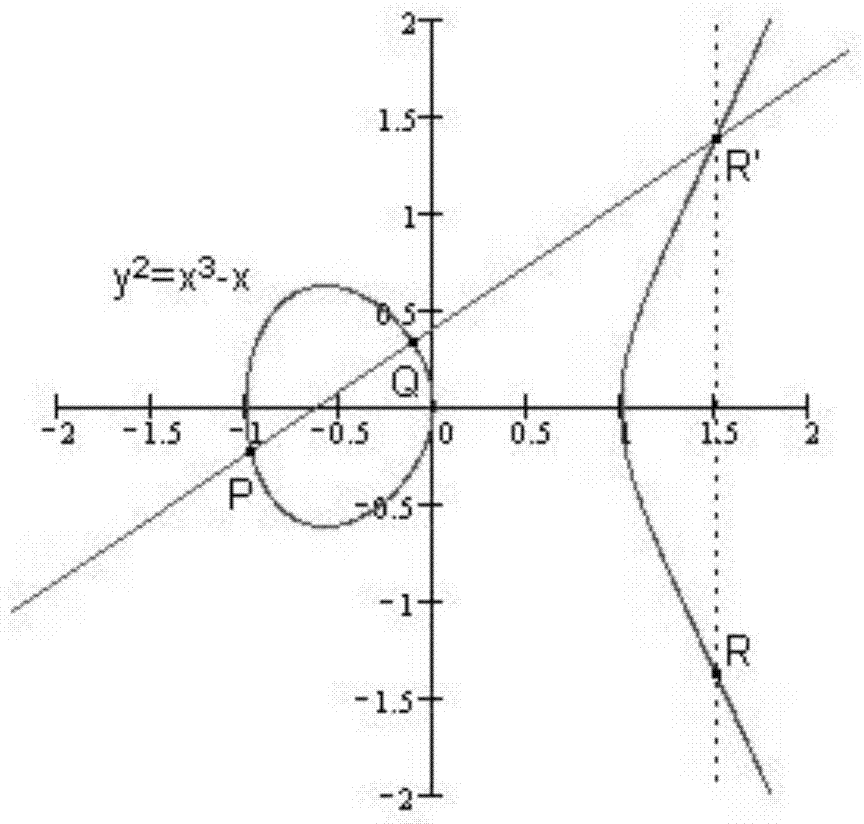
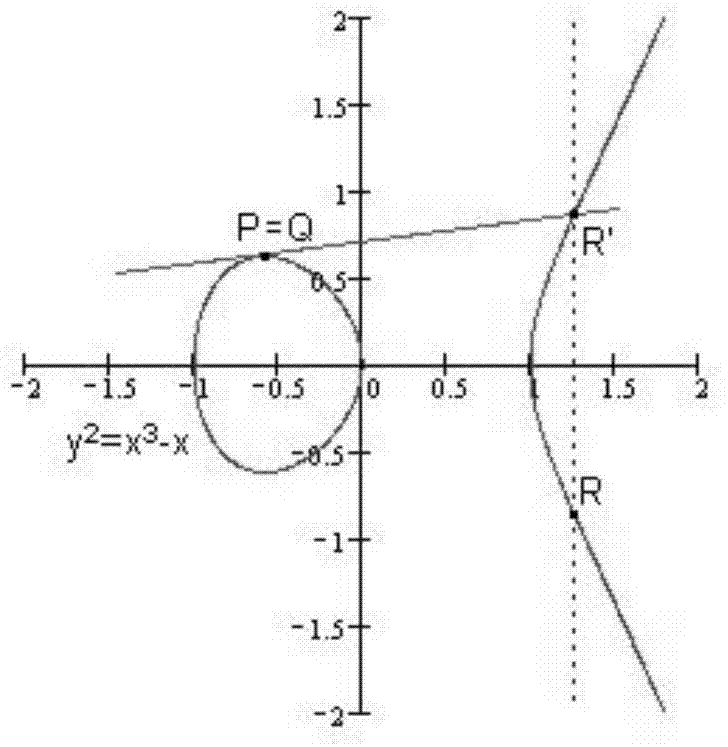
InactiveUS20030142820A1Public key for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationEllipseAlgorithm
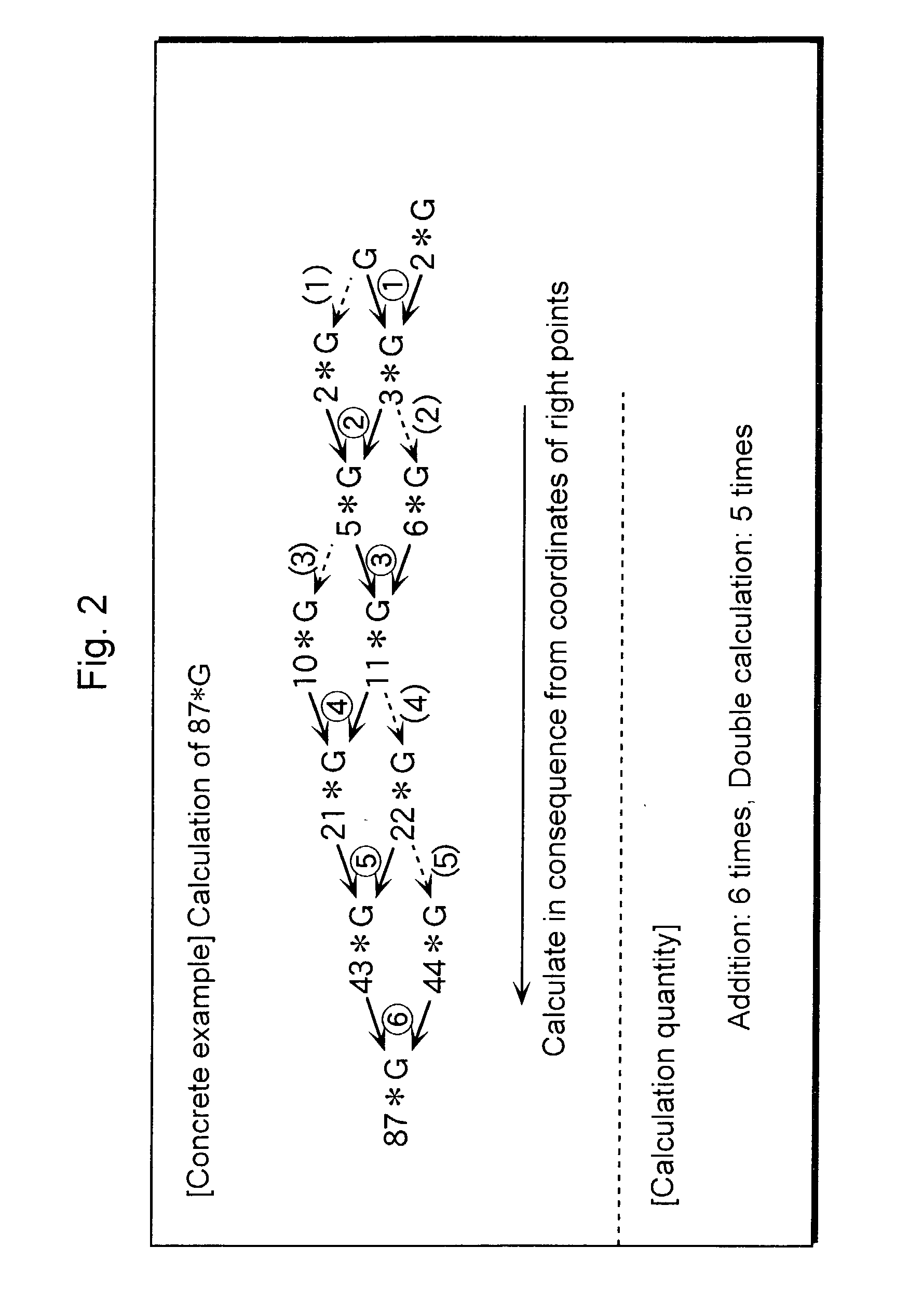
In scalar multiplication method using a Montgomery-type elliptic curve, a high-speed elliptic curve calculation device that can use effectively a table that stores coordinates of a certain scalar multiple points like points multiplied by exponentiation of two to a certain point G and so forth. An elliptic curve calculation device 200 that receives an arbitrary integer k of n bits and outputs scalar-multiplied points against a point G on a Montgomery-type elliptic curve E on an infinite field F that is given in advance comprises: a calculation procedure generation unit 210 that generates a calculation procedure that addition on the elliptic curve E with either of G, 2*G, 22*G, . . . , 2n-1*G as the first addition element is repeated and a scalar multiplication unit 220 that calculates the scalar-multiplied points k*G by repeating addition on the elliptic curve E, referring to a table memorizing unit 220b that stores values (coordinates) of exponentiation of two against the point G and complying with the generated calculation procedure.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
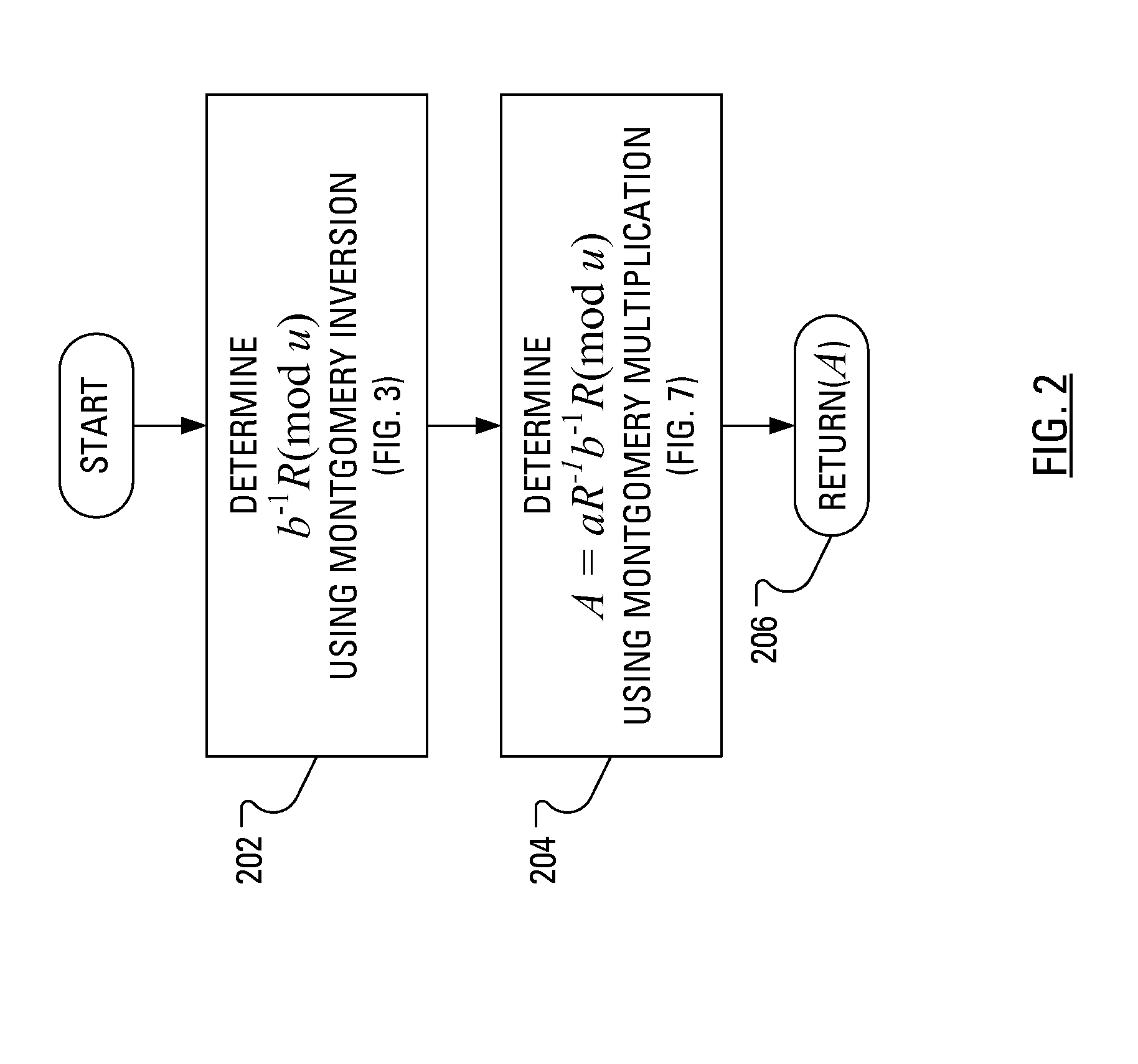
Method and Apparatus for Performing Elliptic Curve Scalar Multiplication in a Manner that Counters Power Analysis Attacks
ActiveUS20080219437A1Public key for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsComputer hardwarePower analysis
When multiplicative splitting is used to hide a scalar in an Elliptic Curve scalar Multiplication ECSM operation, the associated modular division operation employs the known Almost Montgomery Inversion algorithm. By including dummy operations in some of the branches of the main iteration loop of the Almost Montgomery Inversion algorithm, all branches of the algorithm may be viewed, from the perspective of a Power Analysis-based attack, as equivalent and, accordingly, devoid of information useful in determining the value of the scalar, which may be a cryptographic private key.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
Cryptography method on elliptic curves
InactiveUS7218735B2Public key for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationKey exchangeEllipse
A cryptography method for generating probabilistic digital signatures and / or for a key-exchange a protocol and / or for an encryption algorithm is based on the use of a public key algorithm on abnormal binary elliptic curve, such as a Koblitz curve. A point P (x, y) is selected, and pairs (ki, Pi) are stored with Pi being the point corresponding to the scalar multiplication of the point P by ki. A random variable (k) is generated and a point C is calculated that corresponds to the scalar multiplication of P by k. The generation of the random variable (k) and the calculation of the point C are performed simultaneously.
Owner:GEMPLU
Method for efficient computation of odd characteristic extension fields
InactiveUS7069287B2Acceptable computational performanceLow costDigital computer detailsSecret communicationMicrocontrollerTheoretical computer science
A method for implementing an elliptic curve or discrete logarithm cryptosystem on inexpensive microprocessors is disclosed which provides for advantageous finite field computational performance on microprocessors having limited computational capabilities. The method can be employed with a variety of commercial and industrial imbedded microprocessor applications such as consumer smart cards, smart cards, wireless devices, personal digital assistants, and microprocessor controlled equipment. In one embodiment, a Galois Field (GF) implementation based on the finite field GF((28−17)17) is disclosed for an Intel 8051 microcontroller, a popular commercial smart card microprocessor. The method is particularly suited for low end 8-bit and 16-bit processors either with or without a coprocessor. The method provides for fast and efficient finite field multiplication on any microprocessor or coprocessor device having intrinsic computational characteristics such that a modular reduction has a greater computational cost than double precision, long number additions or accumulations. The disclosed method offers unique computational efficiencies in requiring only infrequent subfield modular reduction and in employing an adaptation of Itoh and Tsujii's inversion algorithm for the group operation. In one embodiment, a core operation for a signature generation, an elliptic curve scalar multiplication with a fixed point, is performed in a group of order approximately 2134 in less than 2 seconds. In contrast to conventional methods, the method does not utilize or require curves defined over a subfield such as Koblitz curves.
Owner:WORCESTER POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE
Cryptographic Computation Method, Cryptographic System, and Computer Program
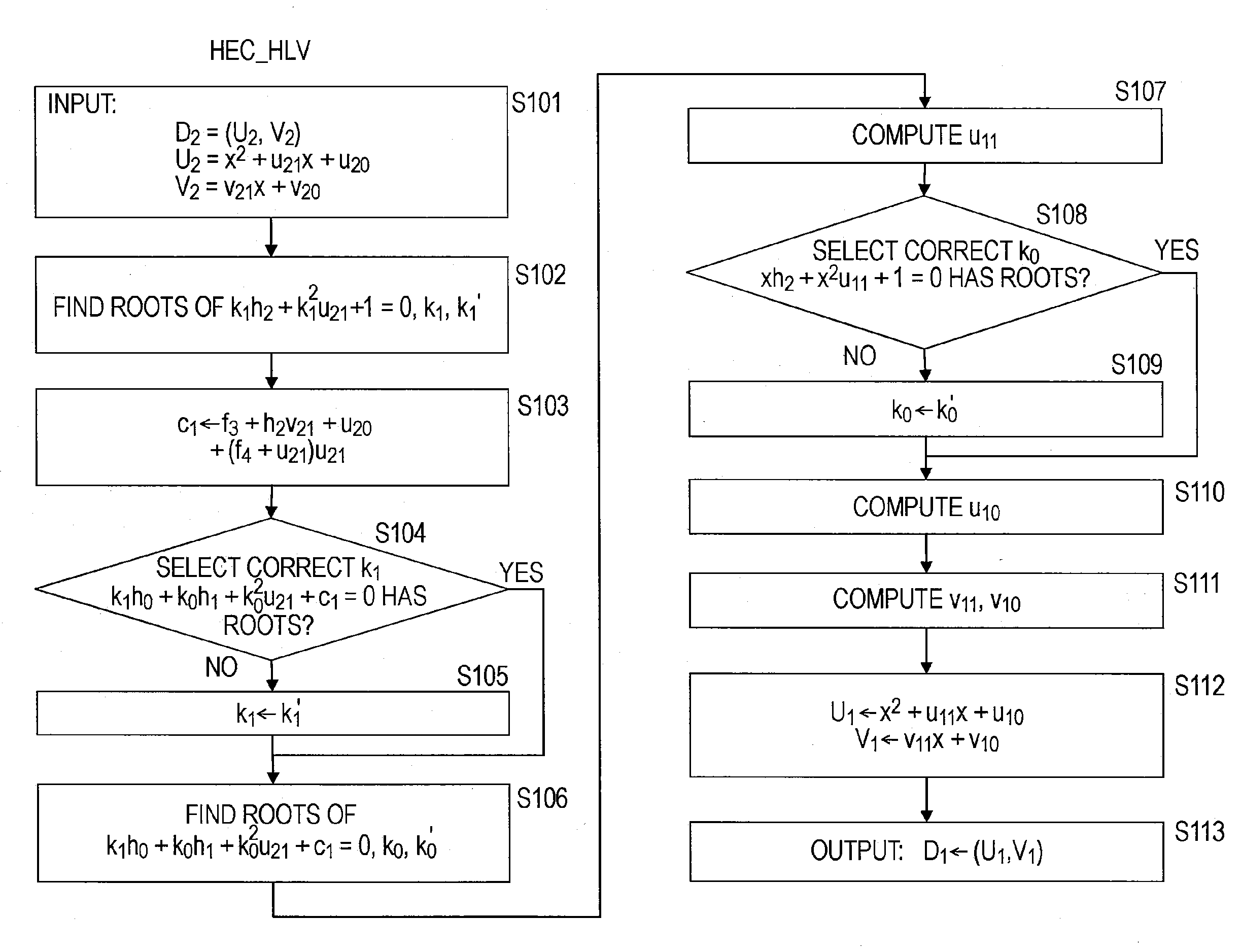
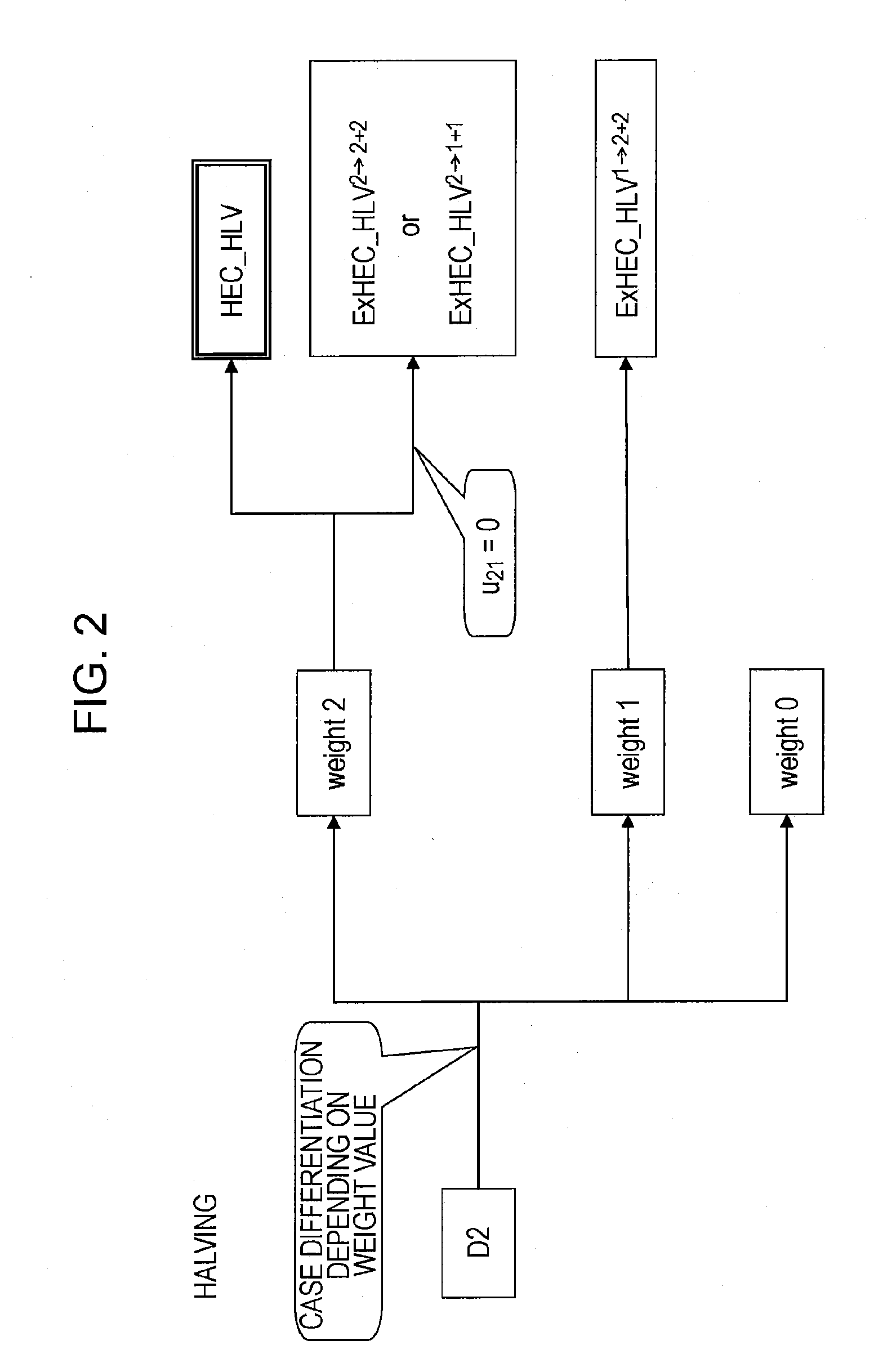
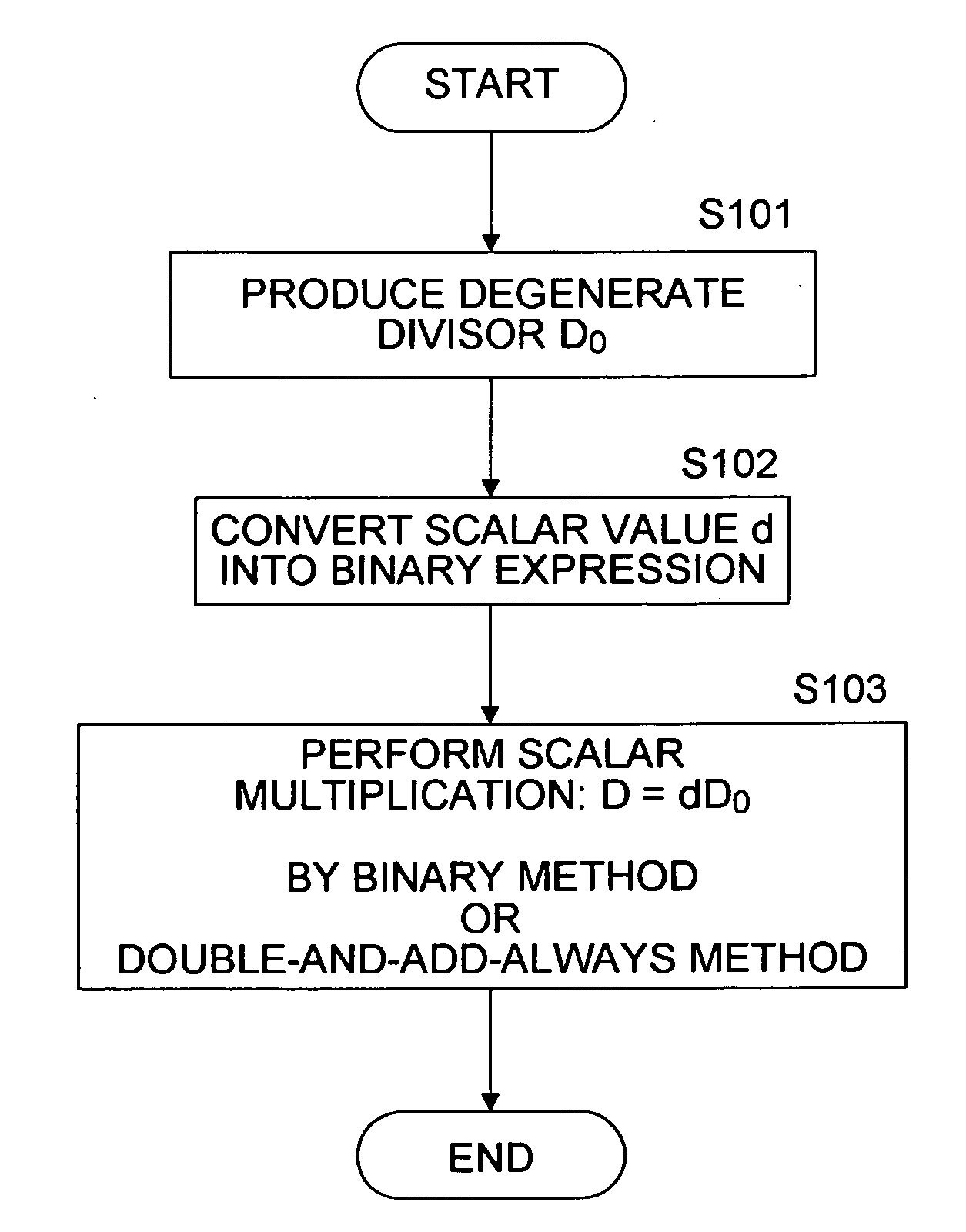
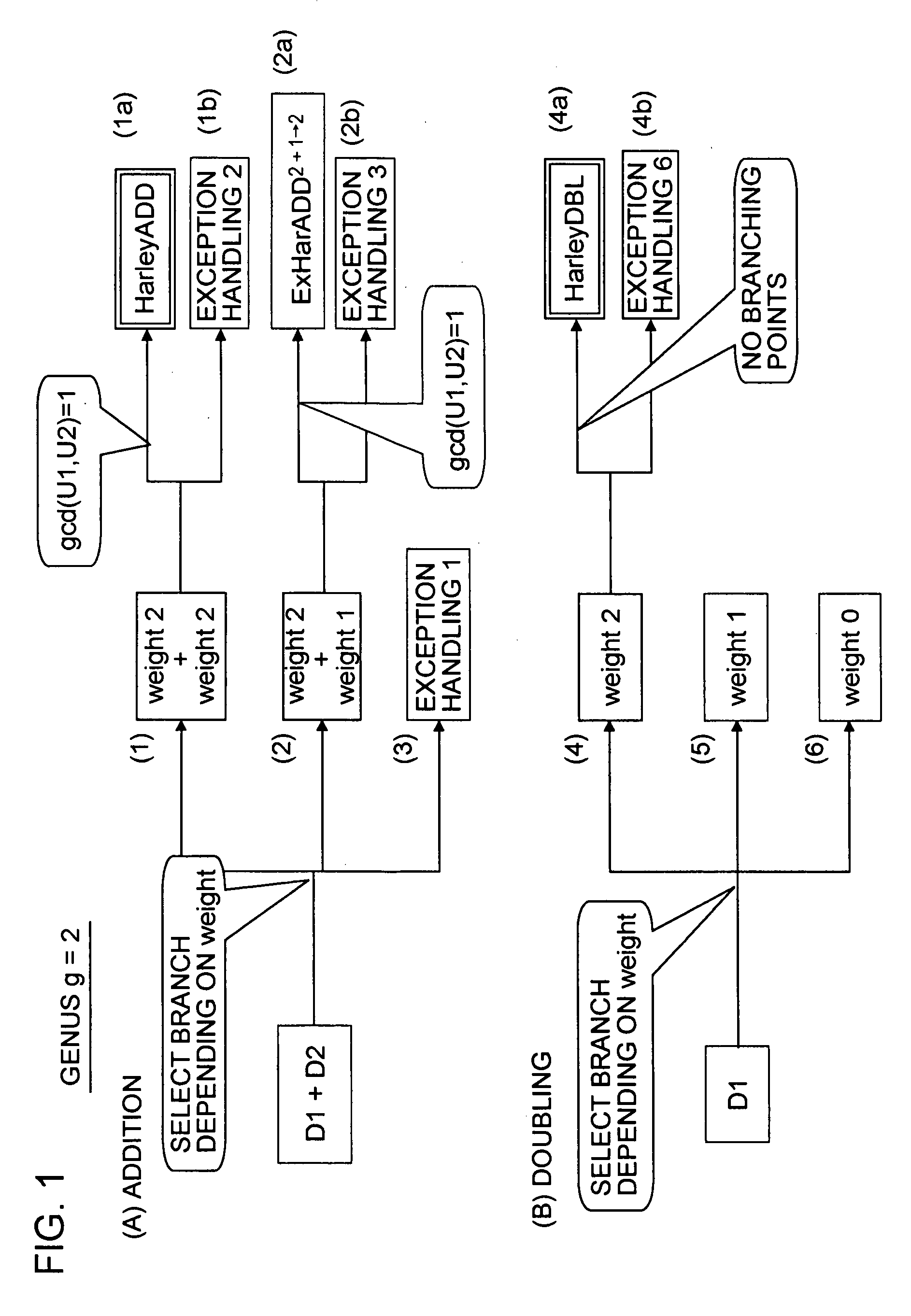
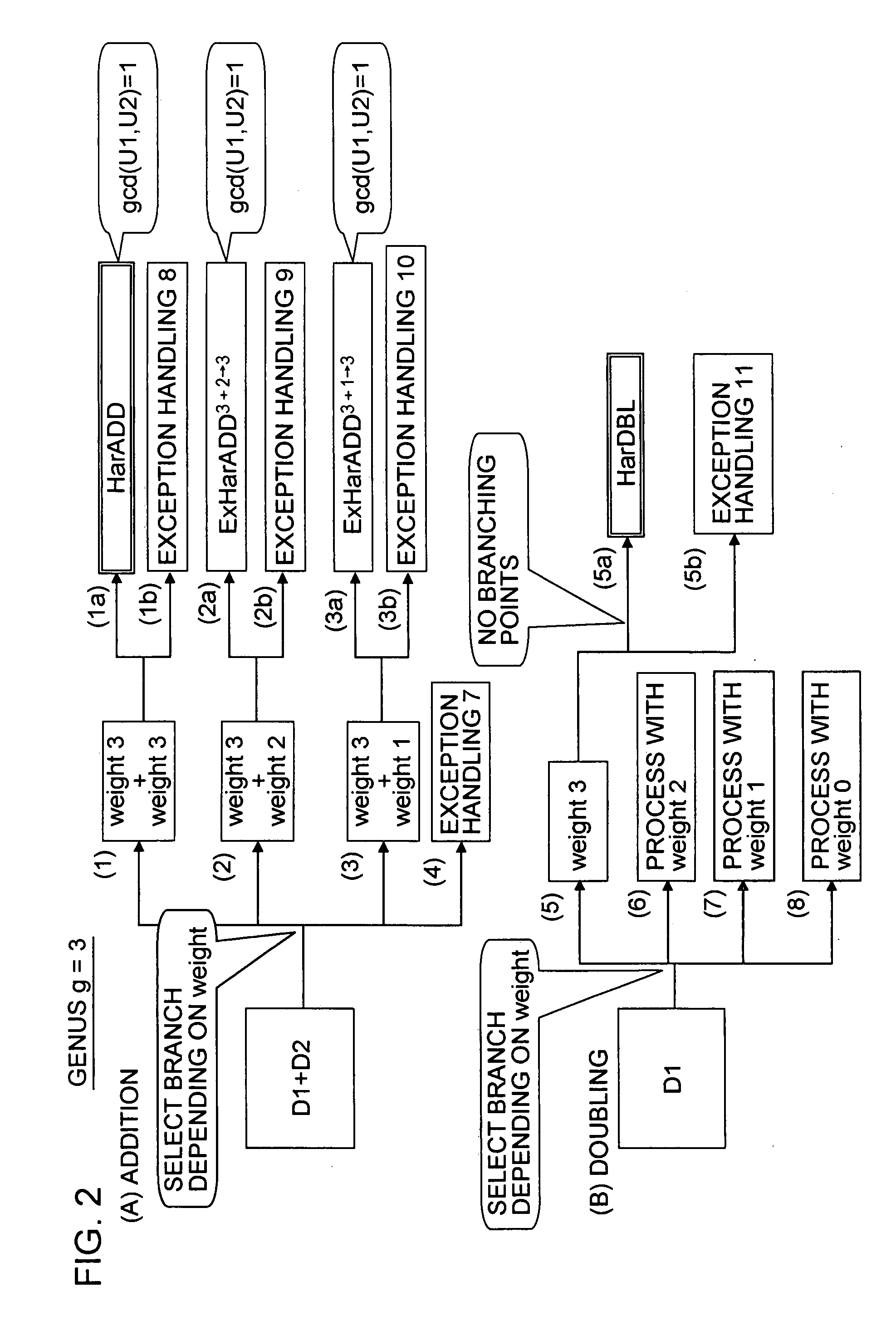
InactiveUS20080095357A1Reduce computing timeFast HECCEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesDigital data processing detailsComputational scienceHyperelliptic curve cryptography
A system and method for achieving secure and fast computation in hyperelliptic cryptography is realized. Fast scalar multiplication is achieve by executing computing operations including halving as computing processing in scalar multiplication with respect to a divisor D in hyperelliptic curve cryptography. For example, computing operations including halving are executed in scalar multiplication with respect to a divisor D on a hyperelliptic curve of genus 2 in characteristic 2 having h(x)=x2+x+h0, f4=0 as parameters, a hyperelliptic curve of genus 2 in characteristic 2 having h(x)=x2+h1x+h0, f4=0 as parameters, or a hyperelliptic curve of genus 2 in characteristic 2 having h(x)=x as a parameter. Further, reduced complexity and faster computation are realized through the application of a table that records which of k1, k1′, (k0, k0′) is correct on the basis of a computed value of [½iD] with respect to a fixed divisor D, and through a reduction in the number of inversion operations.
Owner:SONY CORP
Method and system for atomicity for elliptic curve cryptosystems
InactiveUS20090046851A1Digital data processing detailsPublic key for secure communicationEllipseChannel analysis
A method and system are provided for atomicity for elliptic curve cryptosystems (ECC-systems). The method includes a side channel atomic scalar multiplication algorithm using mixed coordinates. The algorithm including repeating a sequence of field operations for each elliptic curve addition or doubling operation to provide an atomic block, wherein an atomic block appears equivalent by side-channel analysis. The mixed coordinates are chosen based on a ratio of I / M where I and M are the time required to execute an inversion and a multiplication in the ground field respectively. If the I / M ratio is less than 60, a mixture of affine and Jacobian coordinates are used during scalar multiplication. If the I / M ratio is 60 or more, a mixture of Chudnovsky-Jacobian and Jacobian coordinates are used during scalar multiplication. The method is optimized for elliptic curves over Fp defined by an equation of the form y2=x3+ax+b, where a, b ε Fp, having a=−3.
Owner:DOORDASH INC
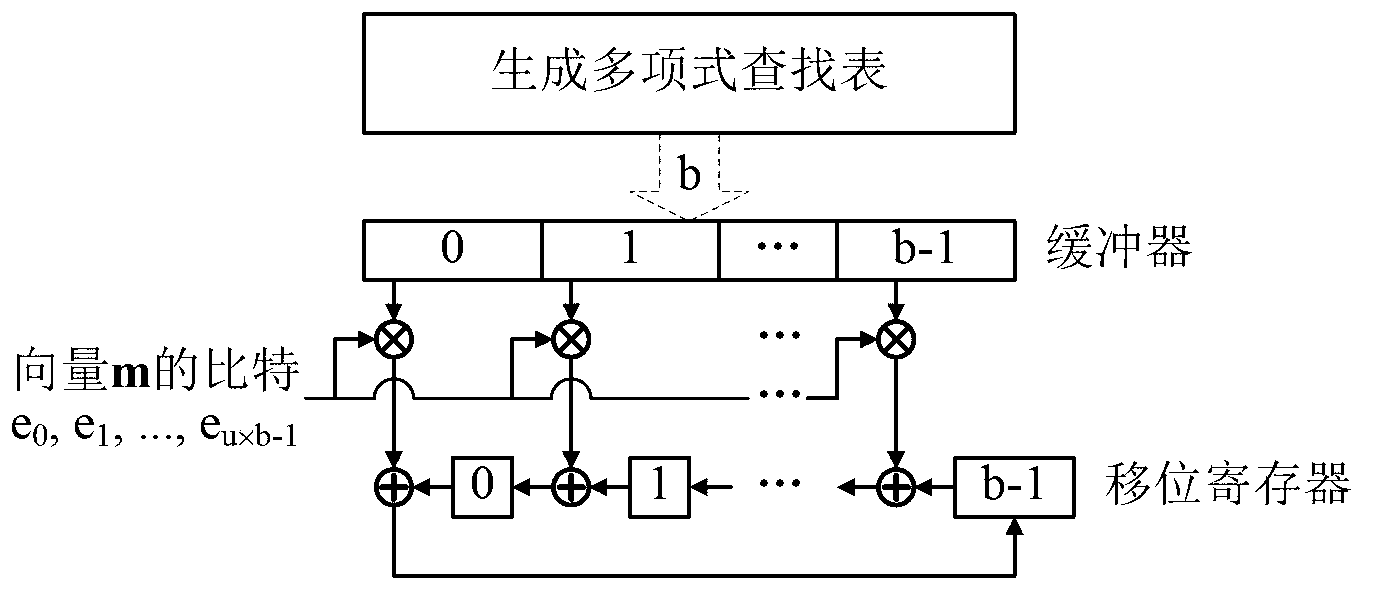
Quasi-cyclic LDPC serial encoder based on ring shift left
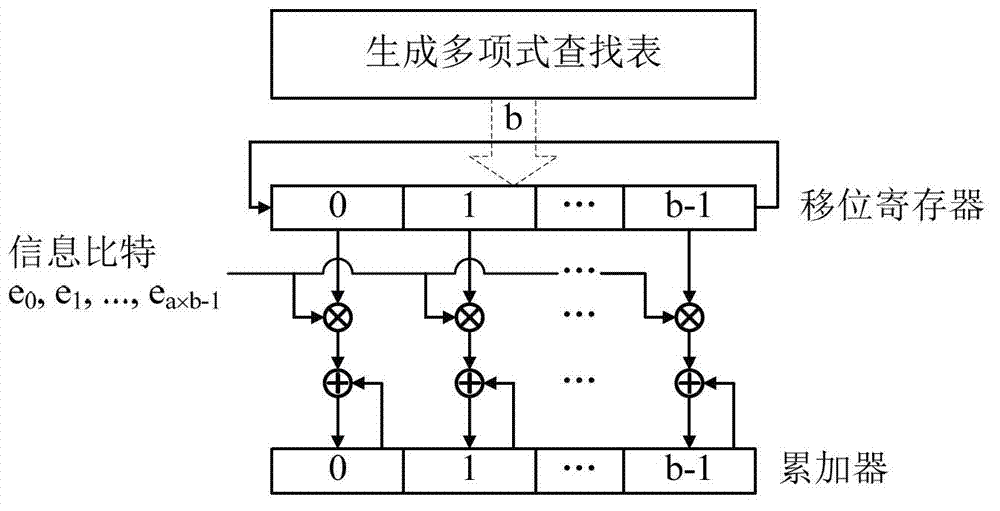
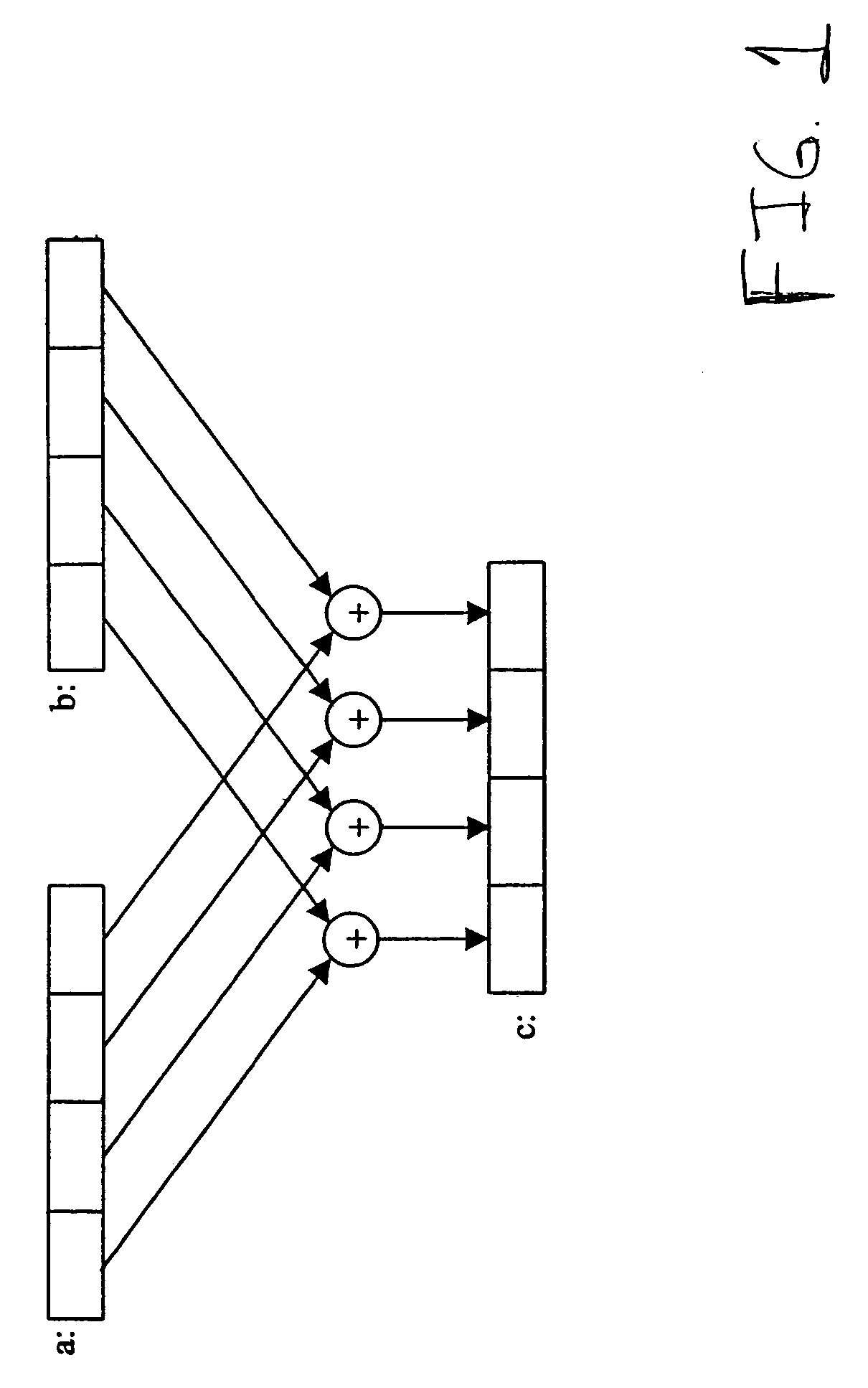
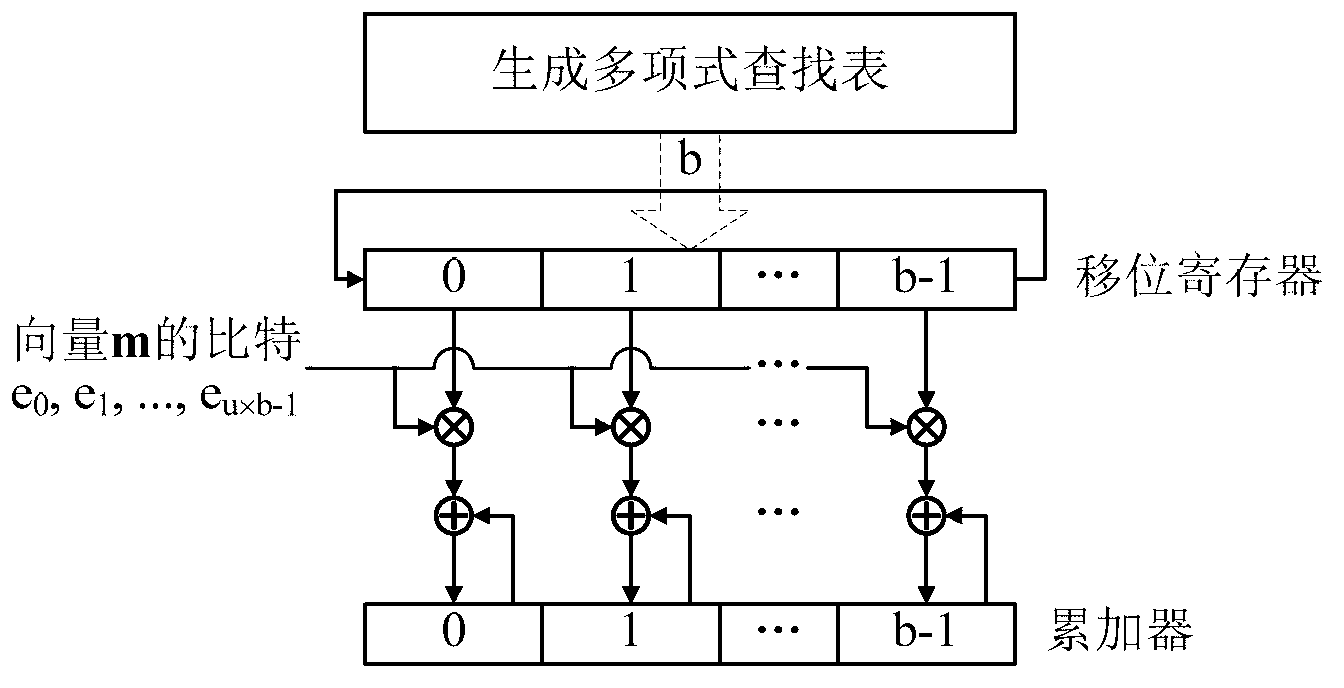
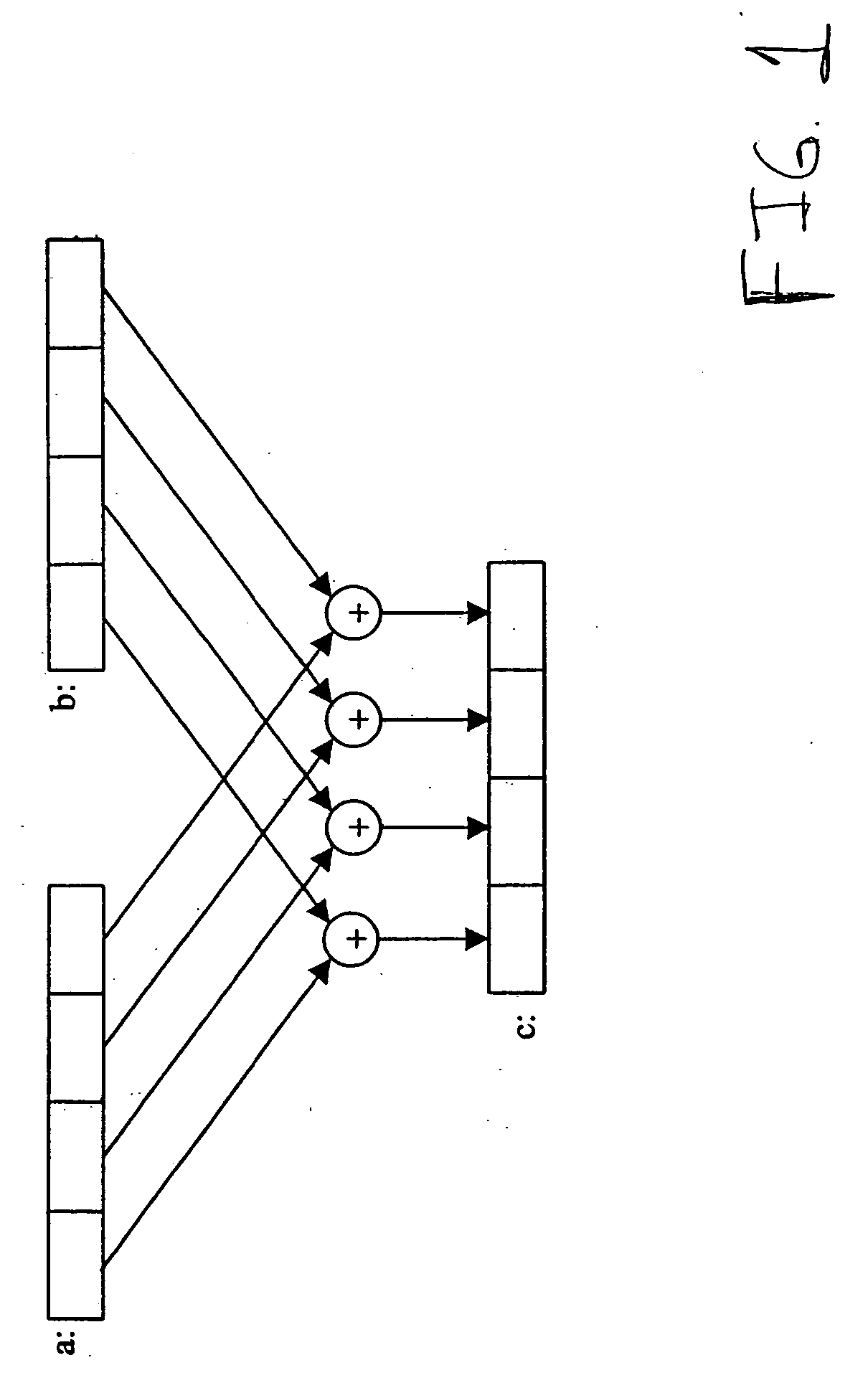
InactiveCN103248372ASimple structureReduce power consumptionError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsCode conversionShift registerBinary multiplier
The invention provides a quasi-cyclic LDPC serial encoder based on ring shift left, which includes c generator polynomial lookup tables of all cyclic matrix generator polynomials in a prestored generated matrix, c b-bit binary multipliers for performing scalar multiplication to information bit and generator polynomials, c b-bit binary adders for performing modulo-2 adding to product and content of shifting registers, and c b-bit shifting registers for storing the sum of ring shift left for 1 bit, and finally, the checking data is stored in the c shifting registers. The serial encoder provided by the invention has the advantages of few registers, simple structure, low power consumption, low cost and the like.
Owner:RONGCHENG DINGTONG ELECTRONICS INFORMATION SCI & TECH CO LTD
Cryptographic Processing Apparatus
InactiveUS20070291937A1Minimize the numberIncrease resistancePublic key for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsComputer hardwareHyperelliptic curve cryptography
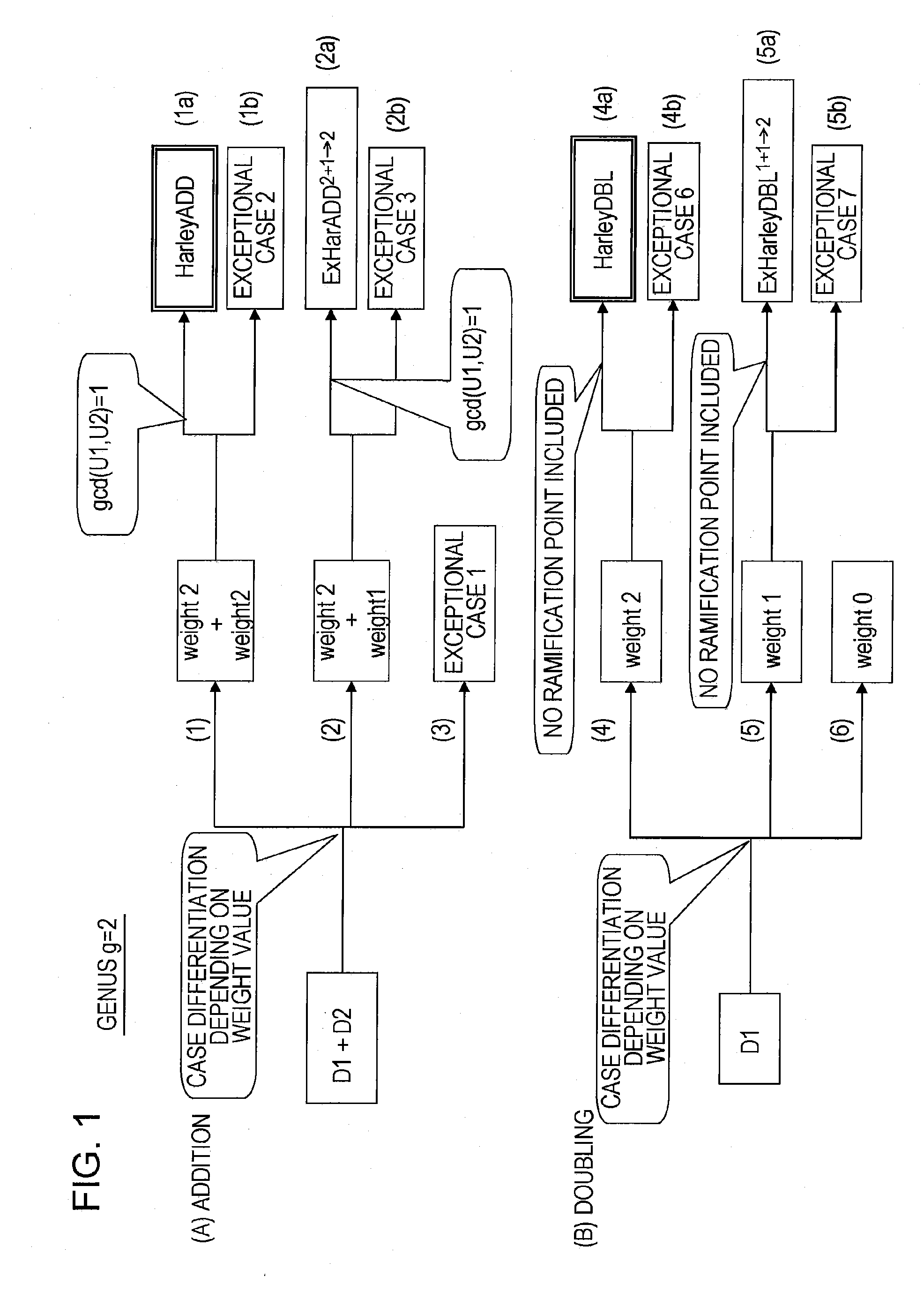
An apparatus and a method for performing a hyperelliptic curve cryptography process at a high speed in a highly secure manner are provided. A base point D is produced such that the base point D and one or more of precalculated data in addition to the base point used in a scalar multiplication operation based on a window algorithm are degenerate divisors with a weight smaller than genus g of a hyperelliptic curve. An addition operation included in the scalar multiplication operation based on the window algorithm is accomplished by performing an addition operation of adding a degenerate divisor and a non-degenerate divisor, whereby a high-speed operation is achieved without causing degradation in security against key analysis attacks such as SPA.
Owner:SONY CORP
SM2 signature algorithm protection method for resisting error attack based on lattice
ActiveCN104852805AFull resistanceAvoid being leakedUser identity/authority verificationDigital data protectionScalar multiplicationComputer security
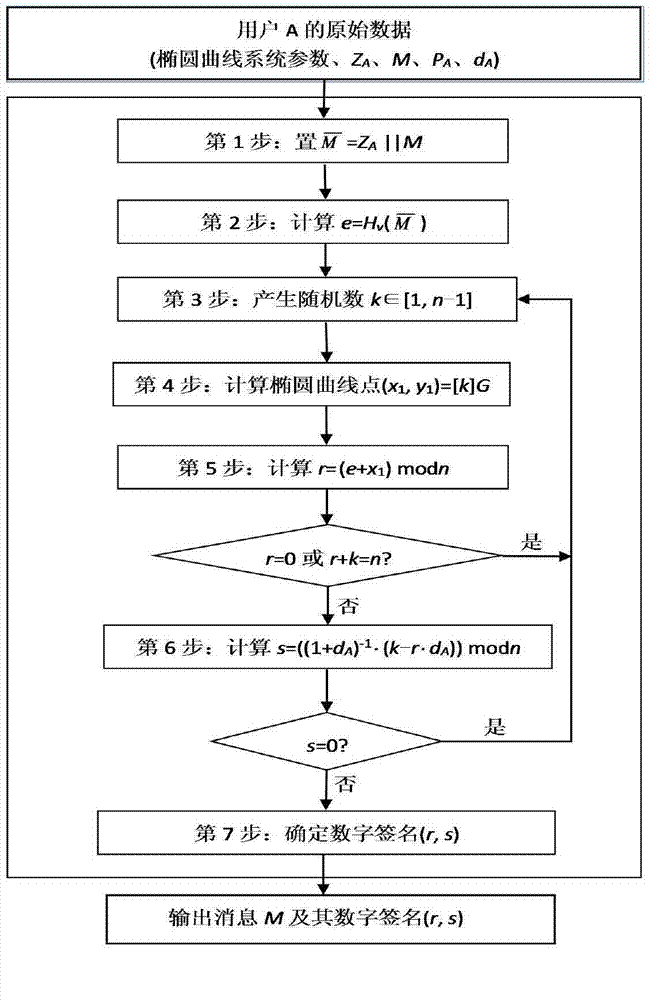
The present invention discloses an SM2 signature algorithm protection method for resisting error attack based on lattice. The method comprises the following steps: (1) a signer A carries out Hash operation on an inputted message M to be signed and combines an operation result ZA and the message M to obtain M<->, (2) M<-> is subjected to hashing compression to obtain a pre-processing result e, (3) two random numbers k and w are generated, the scalar multiplication kG of the random number k and a base point G and the scalar multiplication wPA of the random number w and a public key PA are calculated respectively, then the above two scalar multiplications are summed to an elliptic curve point Q, (4) the coordinate x1 mode n add of e and point Q is calculated to obtain an r value, (5) private keys dA, k, w, r are subjected to substitution to obtain a signature result s. By using the method provided by the invention, the lattice attack of an SM2 signature algorithm can be effectively and comprehensively resisted.
Owner:INST OF SOFTWARE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +2
Identity authentication system based on elliptic curve
InactiveCN101296075APublic key for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationIdentity recognitionDigital content
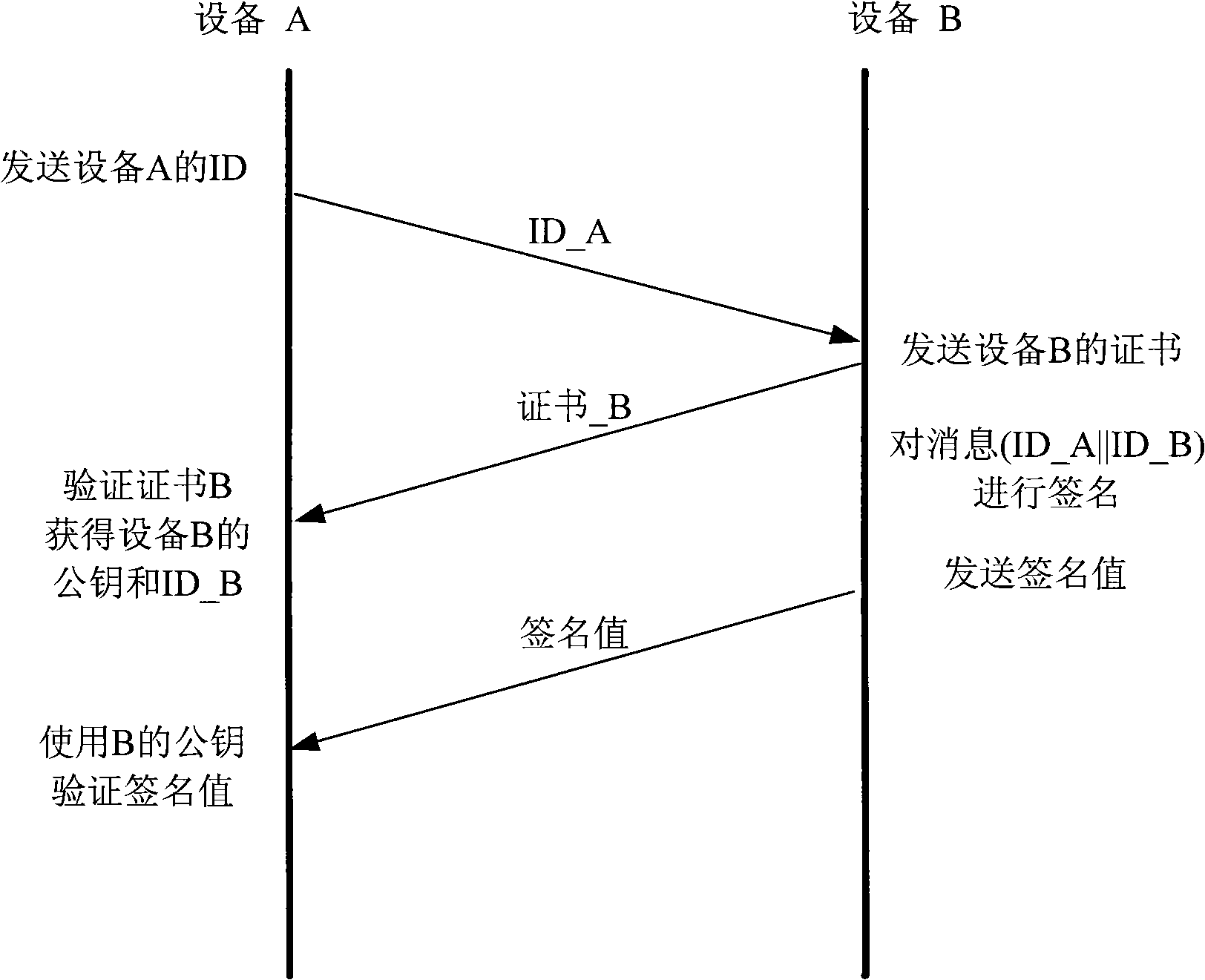
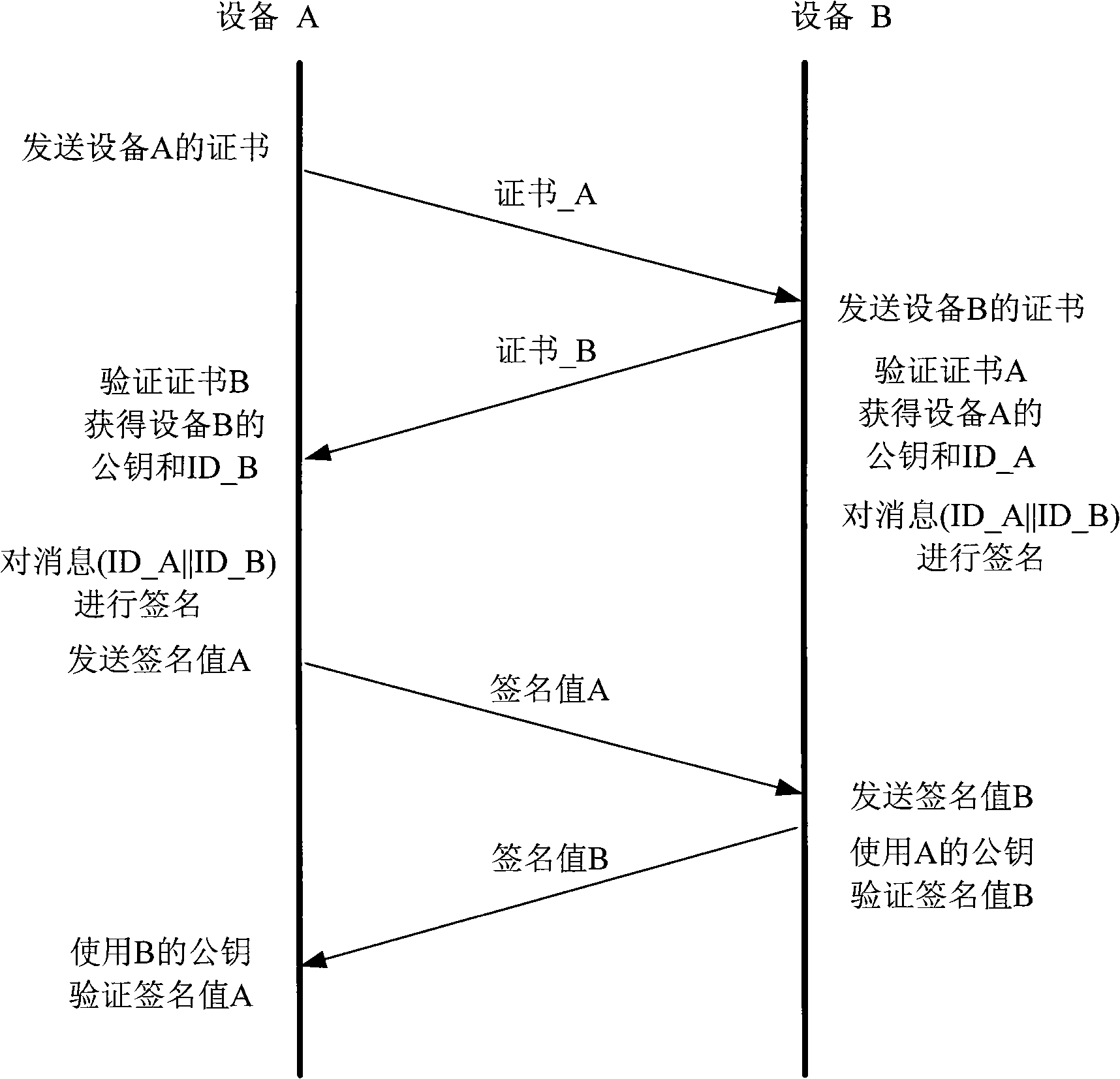
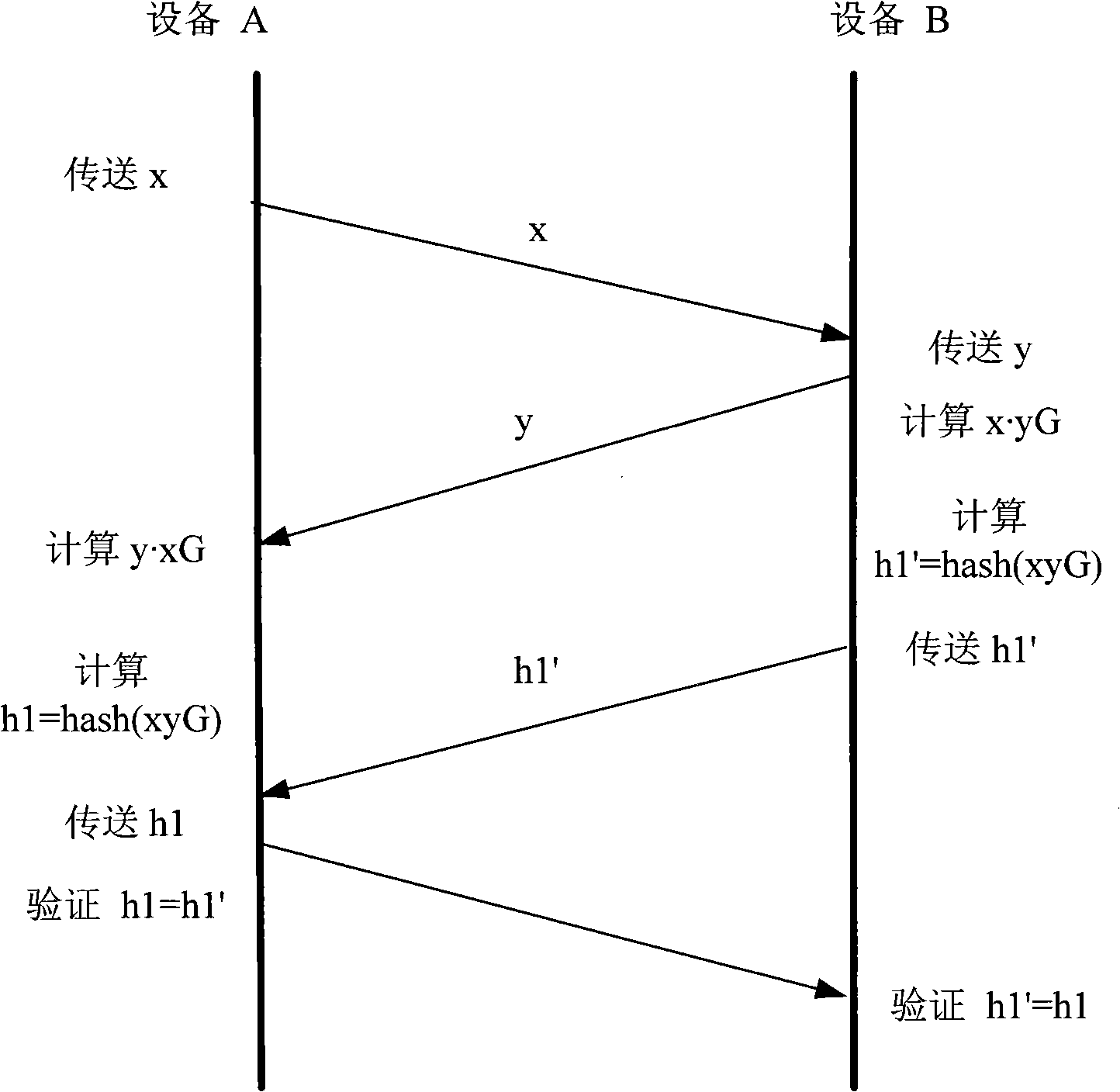
The invention discloses an identity authentication system based on an elliptic curve. A public key and private key pair, a DH cipher code exchange protocol and hashing functions preset in equipment are used for realizing fast identity authentication, thus preventing the identity authentication by using complicated arithmetic in a public key certificate system, such as a certificate chain and digital signature. The public and private key pair of equipment A are x and xG, and the public and private key pair of equipment B are y and yG; when carrying out the identity authentication, the equipment A and the equipment B exchange x and y (or xG and yG), then both calculate scalar multiplication xyG. The equipment A and the equipment B utilize hashing function H to operate each scalar multiplication result xyF so as to obtain hash value h1 and h1'; if h1=h1', both equipment are legal. The system can be used in software and hardware environments, such as digital content protection interface, e-business, banking system, smart card, and identity authentication, etc.
Owner:SICHUAN PANOVASIC TECH
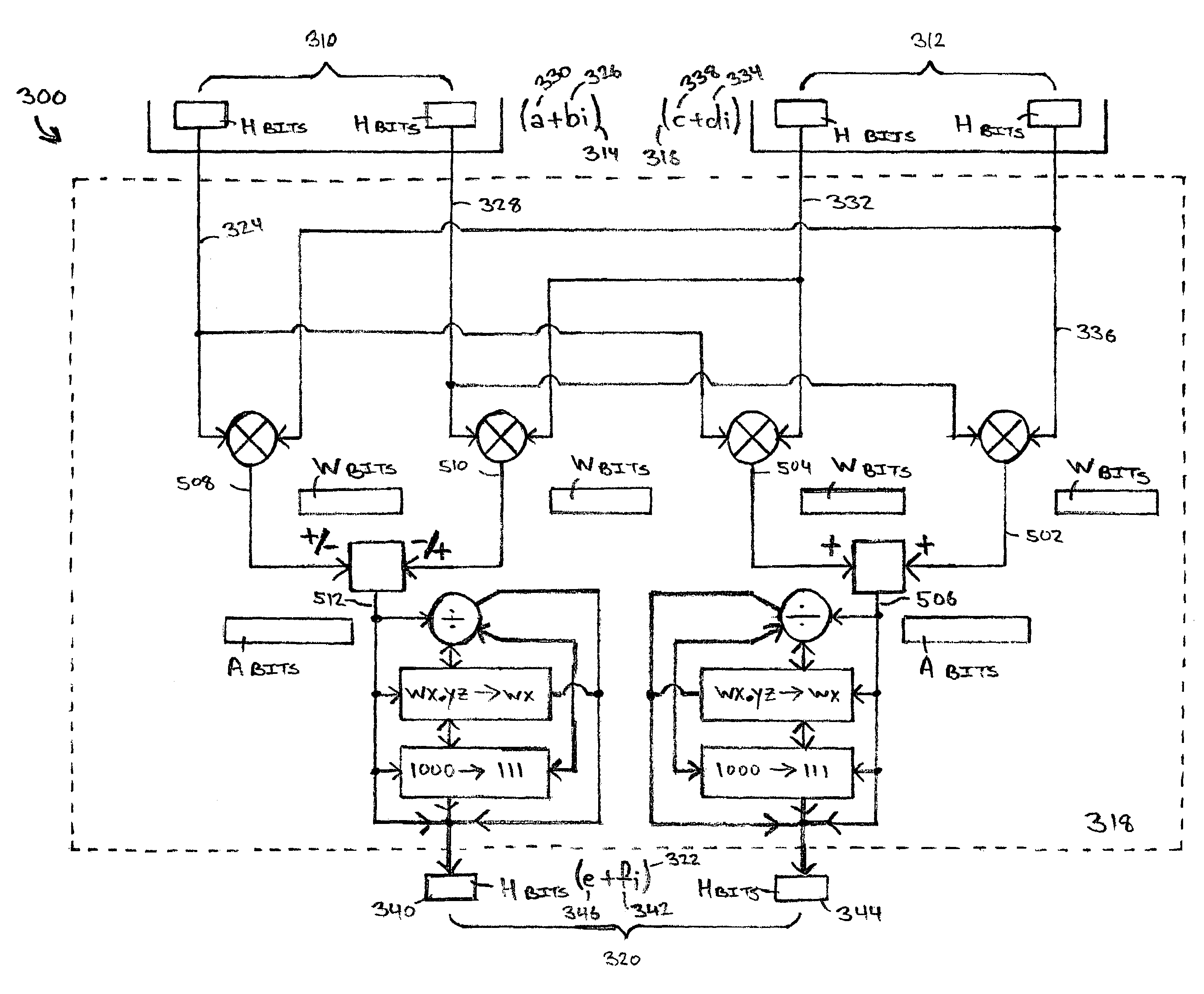
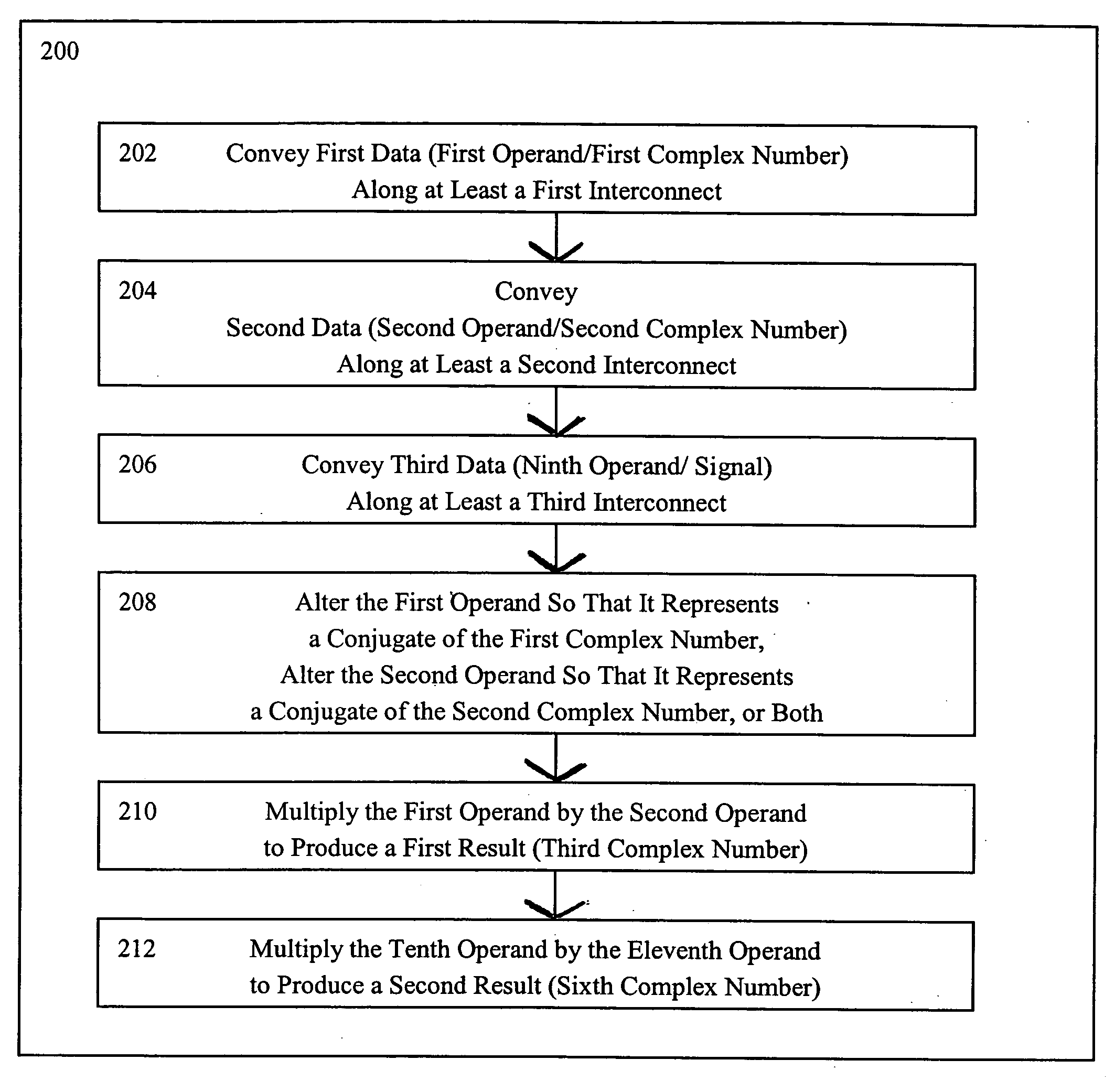
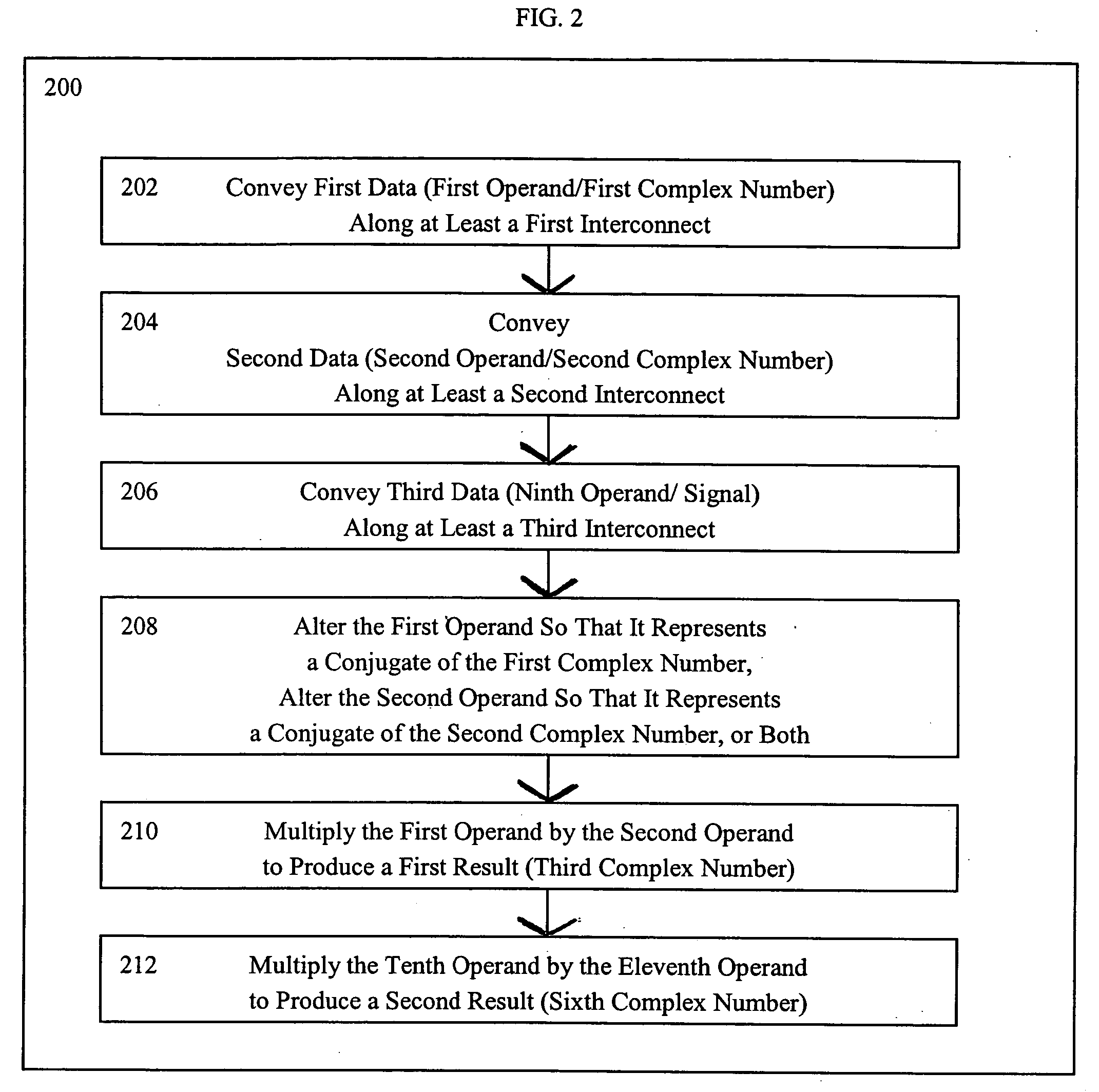
Systems for performing multiplication operations on operands representing complex numbers
InactiveUS7546329B2Computation using non-contact making devicesDigital computer detailsExecution unitOperand
A method for multiplying, at an execution unit of a processor, two complex numbers in which all four scalar multiplications, concomitant to multiplying two complex numbers, can be performed in parallel. A real part of a first complex number is multiplied at the execution unit by a real part of a second complex number to produce a first part of a real part of a third complex number. An imaginary part of the first complex number is multiplied at the execution unit by an imaginary part of the second complex number to produce a second part of the real part of the third complex number. A first arithmetic function is performed at the execution unit between the first part of the real part of the third complex number and the second part of the real part of the third complex number. The imaginary part of the first complex number is multiplied at the execution unit by the real part of the second complex number to produce a first part of an imaginary part of the third complex number. The real part of the first complex number is multiplied at the execution unit by the imaginary part of the second complex number to produce a second part of the imaginary part of the third complex number. A second arithmetic function is performed at the execution unit between the first part of the imaginary part of the third complex number and the second part of the imaginary part of the third complex number.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
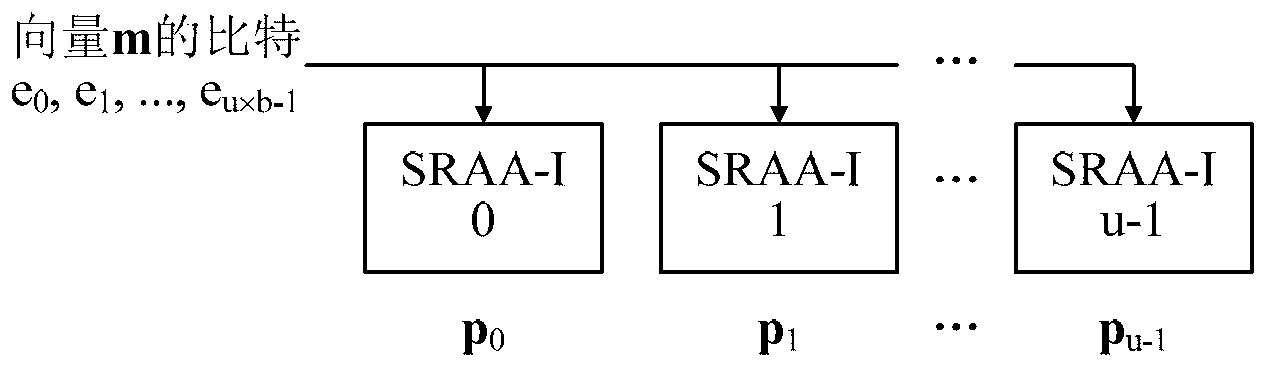
Quasi-cyclic matrix serial multiplier based on rotate left
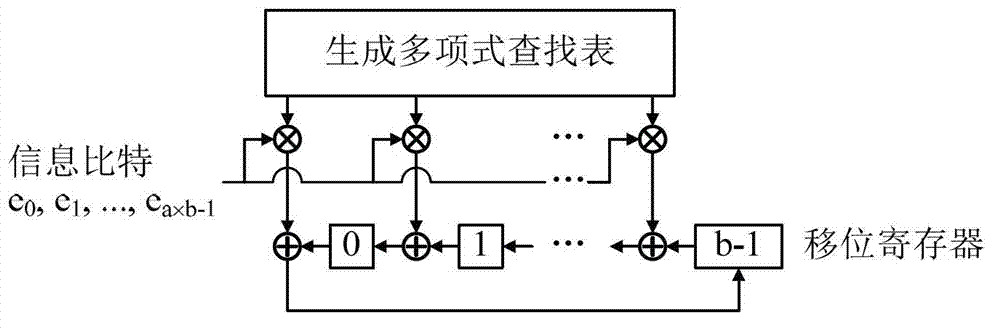
InactiveCN103268217ASimple structureReduce power consumptionDigital data processing detailsShift registerBinary multiplier
The invention provides a quasi-cyclic matrix serial multiplier based on rotate left. The quasi-cyclic matrix serial multiplier is used for implementing multiplication of a vector m and a quasi-cyclic matrix F in QC-LDPC (quasi-cyclic low-density parity-check) approximate lower triangular encodings. The multiplier comprises u generated polynomial lookup tables, u b-bit binary multipliers, u b-bit binary summators and u b-bit shift registers. The generated polynomial lookup tables are used for pre-storing quasi-cyclic matrix generated polynomial in the matrix F. The b-bit binary multipliers are used for performing scalar multiplication of the vector m data bit and the generated polynomial. The b-bit binary summators are used for performing modulo-2 adding of products and shift register contents. The b-bit shift registers are used for storing sums of 1-bit movements subjected to rotate left. The quasi-cyclic matrix serial multiplier has the advantages of small number of registers, simple structure, low power consumption and cost and the like.
Owner:RONGCHENG DINGTONG ELECTRONICS INFORMATION SCI & TECH CO LTD
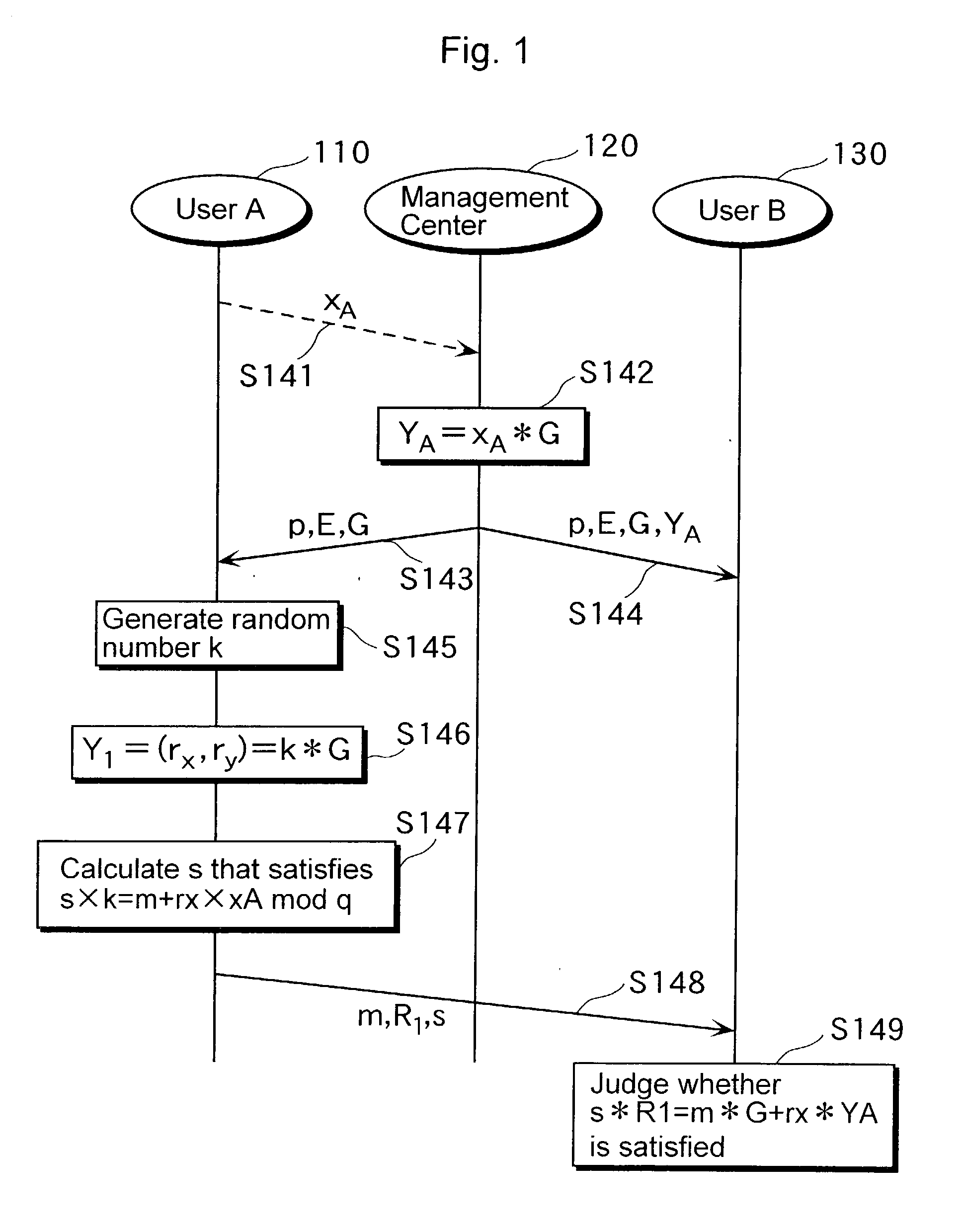
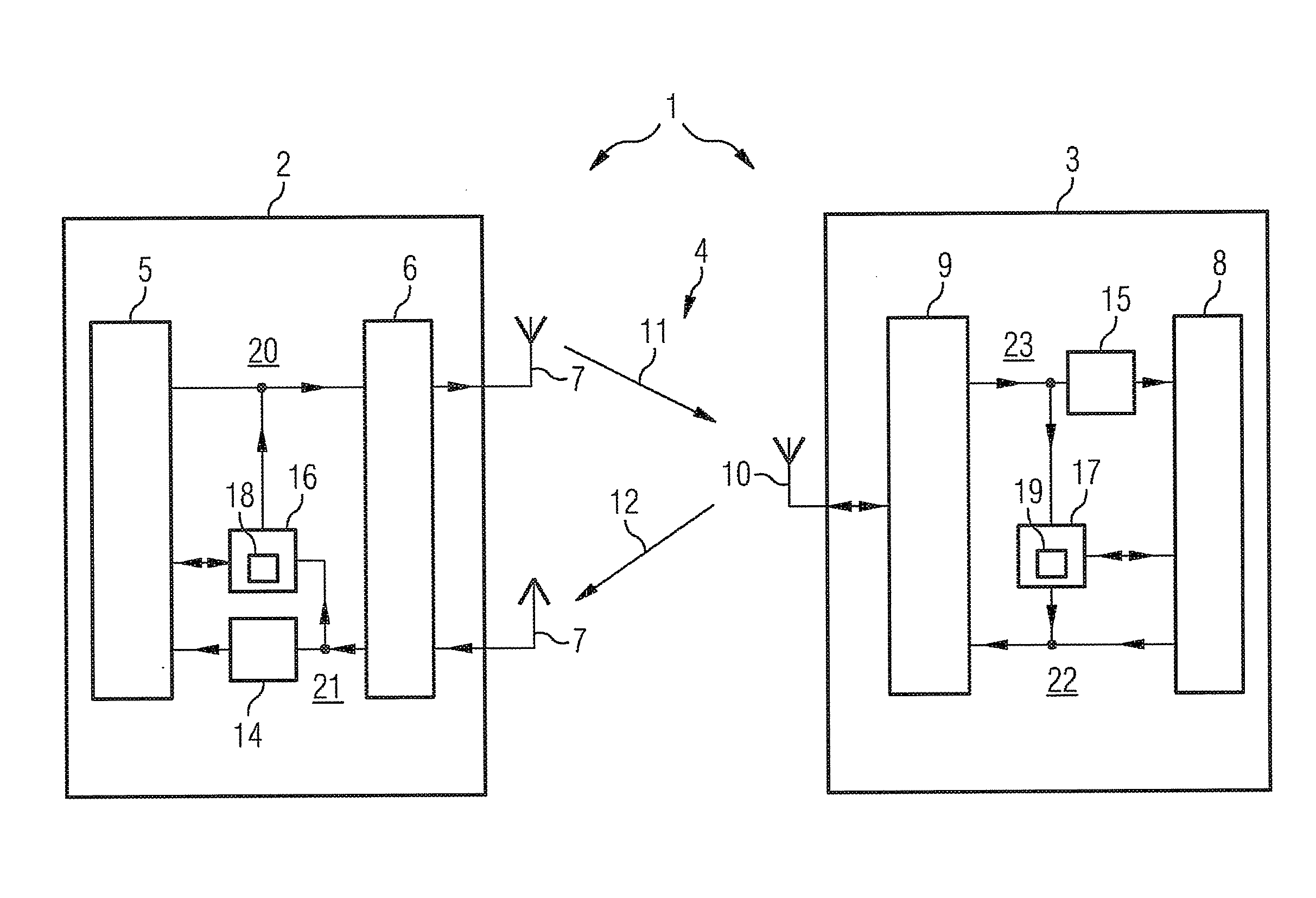
Method for the encrypted data exchange and communication system
ActiveUS20090292921A1Less timeRaise security concernsDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationComputer hardwareCommunications system
The embodiments relate to a method for the encrypted data exchange between subscribers of a communication system using cryptography based on elliptical curves, wherein upon a query by a first subscriber a scalar multiplication is calculated by the second subscriber, wherein merely part of the result of the scalar multiplication is returned to the first subscriber as a response. The invention relates to a communication system.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Methods for performing multiplication operations on operands representing complex numbers
InactiveUS20050071414A1Computation using non-contact making devicesDigital computer detailsOperandExecution unit
A method for multiplying, at an execution unit of a processor, two complex numbers in which all four scalar multiplications, concomitant to multiplying two complex numbers, can be performed in parallel. A real part of a first complex number is multiplied at the execution unit by a real part of a second complex number to produce a first part of a real part of a third complex number. An imaginary part of the first complex number is multiplied at the execution unit by an imaginary part of the second complex number to produce a second part of the real part of the third complex number. A first arithmetic function is performed at the execution unit between the first part of the real part of the third complex number and the second part of the real part of the third complex number. The imaginary part of the first complex number is multiplied at the execution unit by the real part of the second complex number to produce a first part of an imaginary part of the third complex number. The real part of the first complex number is multiplied at the execution unit by the imaginary part of the second complex number to produce a second part of the imaginary part of the third complex number. A second arithmetic function is performed at the execution unit between the first part of the imaginary part of the third complex number and the second part of the imaginary part of the third complex number.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
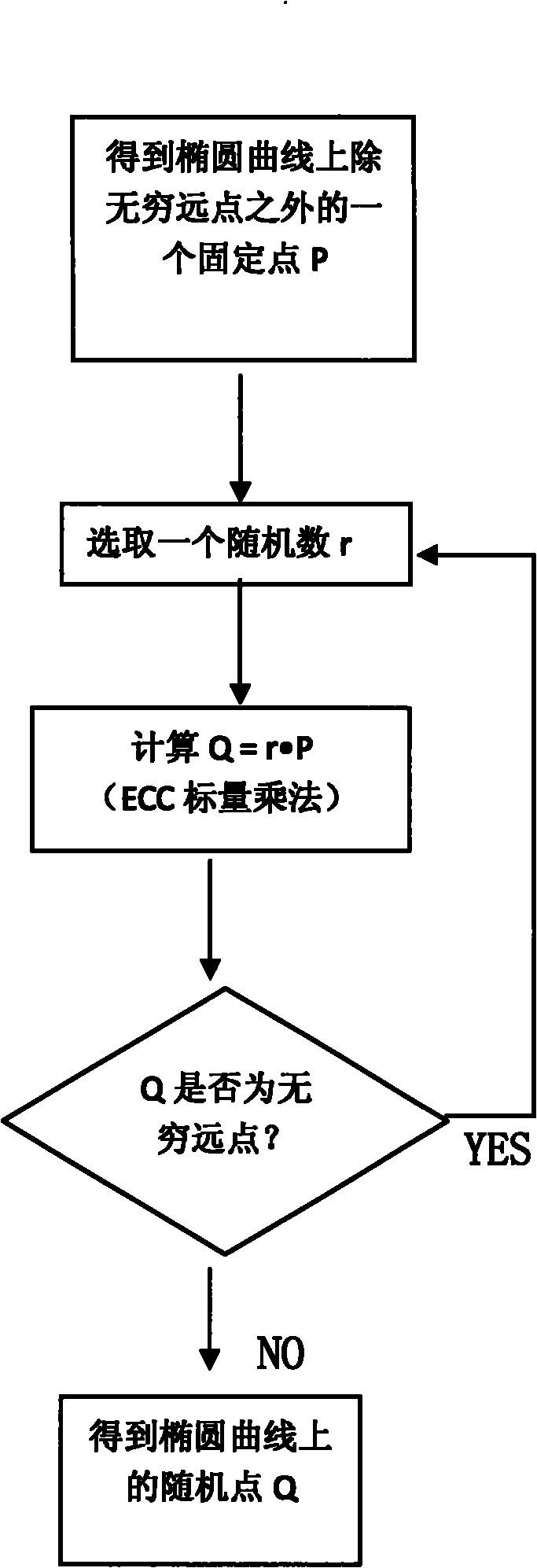
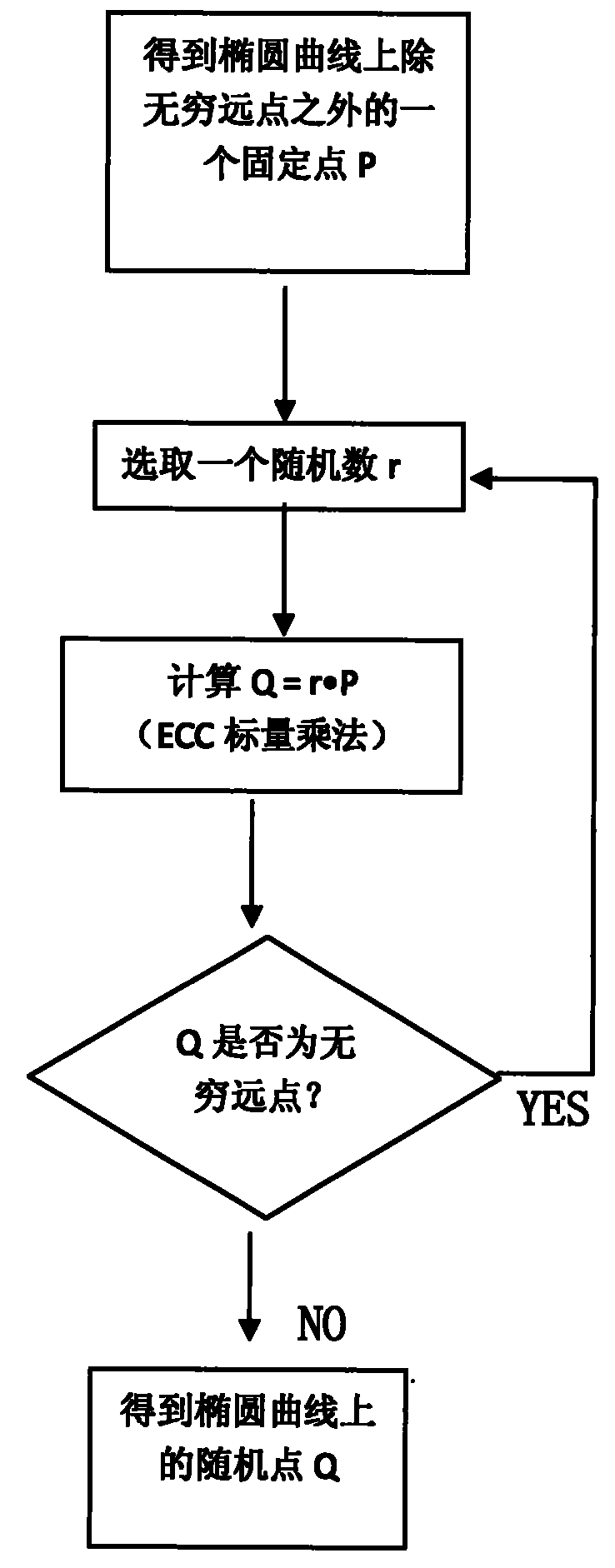
Random point generation method suitable for elliptic curve cryptography (ECC) safety protection
The invention discloses a random point generation method suitable for elliptic curve cryptography (ECC) safety protection. The method comprises the following steps: (1) finding a fixed point P on a certain elliptic curve except an infinite point; (2) selecting a random number r; (3) calculating scalar multiplication of r and P to obtain a calculation result Q; (4) determining whether Q is the infinite point, if yes, returning to the step (2), and otherwise, executing the step (5); and (5) obtaining the random point Q on the certain elliptic curve. The method can obviate the large amount of modular multiplication by obviating the evolution of large numbers or the operation for solving a quadratic equation with one unknown. Therefore, the method provided by the invention can greatly improve the operation speed and reduce the time for generating the random point on the elliptic curve.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAHONG INTEGRATED CIRCUIT
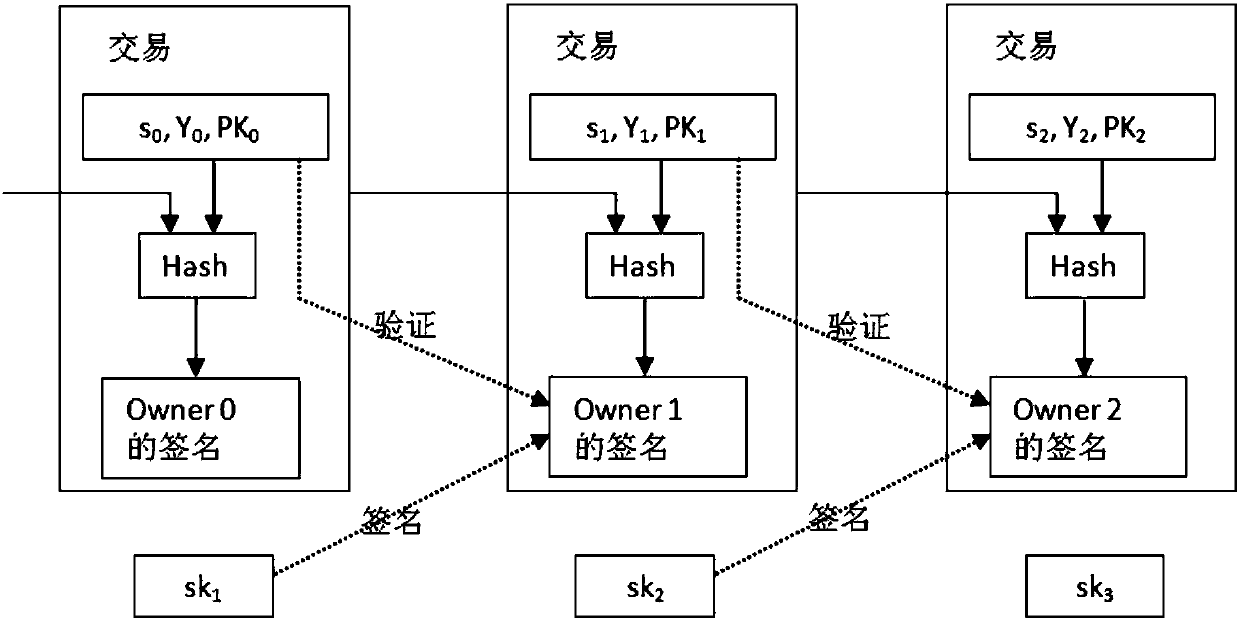
Acentric digital currency transaction method based on public and private key pair derivation
ActiveCN107784580AEnhanced anonymityStrong anonymityFinancePayment protocolsDigital currencyGeneration process
The invention relates to an acentric digital currency transaction method based on public and private key pair derivation; a receiver can scan on a public account book to calculate collection public and private key pairs according to the transfer time, thus reducing data storage; each transaction forms a new collection address, thus enhancing the digital currency anonymous property; only one time elliptical curve scalar multiplication calculation is added on the computational complexity in an implicit certificate generation process, thus easily reducing stronger anonymous property; a transaction initiator actively forms a new collection address in the process instead of using the new collection address issued by the receiver; each person only processes a long term public key, and new publicand private key pairs can be calculated according to the public messages on the public account book and the long term public and private key pairs, thus reducing the public and private key pair storage space; transaction graph analysis is hard to receive.
Owner:DATA COMM SCI & TECH RES INST +1
Tamper-proof elliptic encryption with private key
ActiveUS7536011B2Public key for secure communicationSecret communicationTamper resistanceScalar multiplication
An encryption device performs elliptic curve encryption using a secret key. The encryption device includes an operation unit for performing scalar multiplication of a point on an elliptic curve a storage unit having a plurality of data storing areas and a determiner unit for determining, in accordance with a bit sequence of a given value (d) and with a random value (RNG), an address of one of the plurality of data storage areas that is to be coupled to the operation means for each scalar multiplication.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Method for scalarly multiplying points on an elliptic curve
InactiveUS20090136025A1Optimal reduction attributesReduce weightPublic key for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsEllipsePolynomial representations of cyclic redundancy checks
A method performs scalar multiplication of points on an elliptic curve by a finite expandable field K of a first field Fp of a p>3 characteristic, wherein said characteristic p has low Hamming weight and the expandable field has a polynomF(X)+Xd−2 of order d in the polynomial representation thereof.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Method for calculating elliptic curve scalar multiplication
InactiveUS20170091148A1Heavy loadAffect performance of processComputations using residue arithmeticCoding/ciphering apparatusEngineeringScalar multiplication
An elliptic curve scalar multiplication apparatus stores a prime number p and information of a first point, the prime number p defining a field of definition Fp, which defines a first curve, which is a Weierstrass form elliptic curve, and expressed as p=p0+p1c+ . . . +p1cn−1, (where c equals 2f and f is an integer equal to or larger than 1 that is units of breaking data into pieces in multiple-precision integer arithmetic executed by the elliptic curve scalar multiplication apparatus), calculates a Montgomery constant k0, work, and h1, executes doubling of a second point, which is calculated from the first point, by Montgomery multiplication that uses k0, work, and h1, adds a third point and fourth point, which are calculated from the first point, by Montgomery multiplication that uses k0, work, and h1; and calculates a scalar multiple of the first point, based on a result of the doubling and the addition.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Method for improving elliptic curve scalar multiplication efficiency
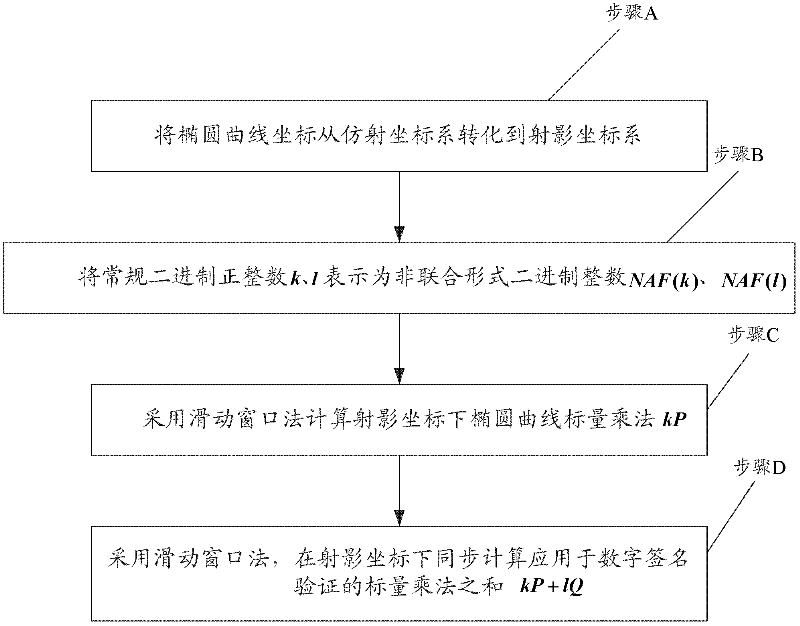
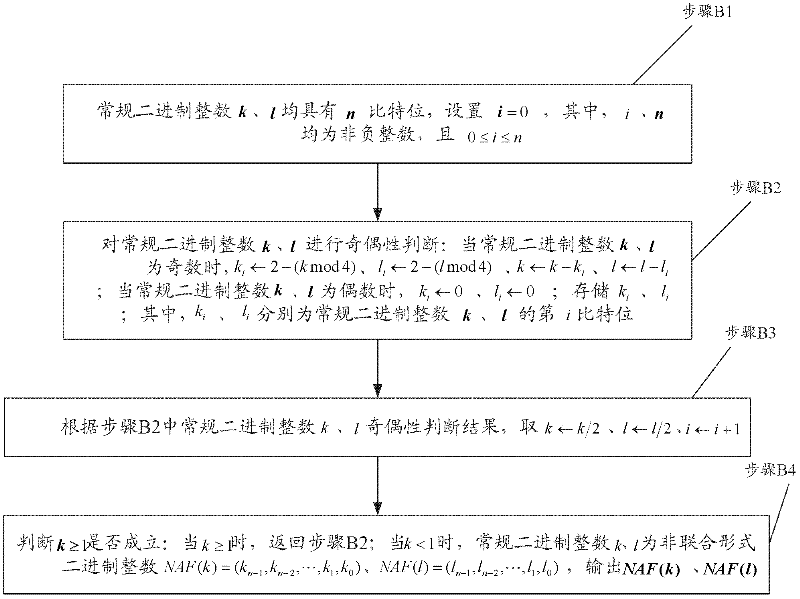
InactiveCN102387015APublic key for secure communicationSecurity arrangementComputer hardwareSlide window
The invention provides a method for improving an elliptic curve scalar multiplication efficiency. The method comprises the following steps: converting an elliptic curve coordinate from affine coordinates to projective coordinates; expressing conventional binary integers k and 1 as non-adjacent forms (NAF) NAF (k) and NAF(1); using a sliding window method to calculate the elliptic curve scalar multiplication kP under the projective coordinates; using the sliding window method to synchronously calculate a sum of the scalar multiplication kP+1Q which is applied in digital signature verification under the projective coordinates. Operation time is short and a needed storage capacity is small. The method can be widely used in a wireless sensor network (WSN).
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
Elliptic curve encryption processing method, elliptic curve encryption processing apparatus, and program
InactiveUS7177422B2Increase speedSpeed up the processPublic key for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationComputer hardwareComputation process
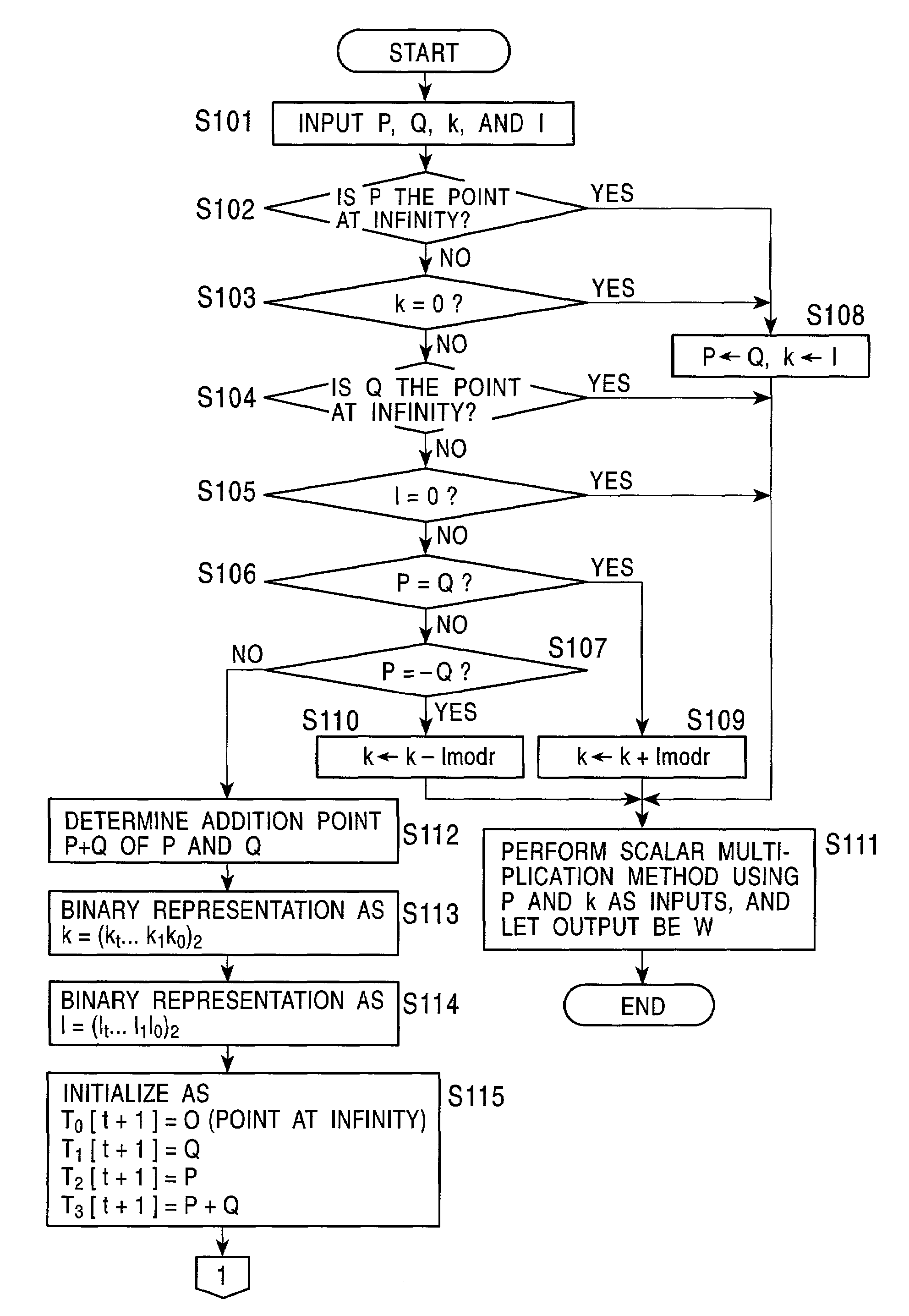
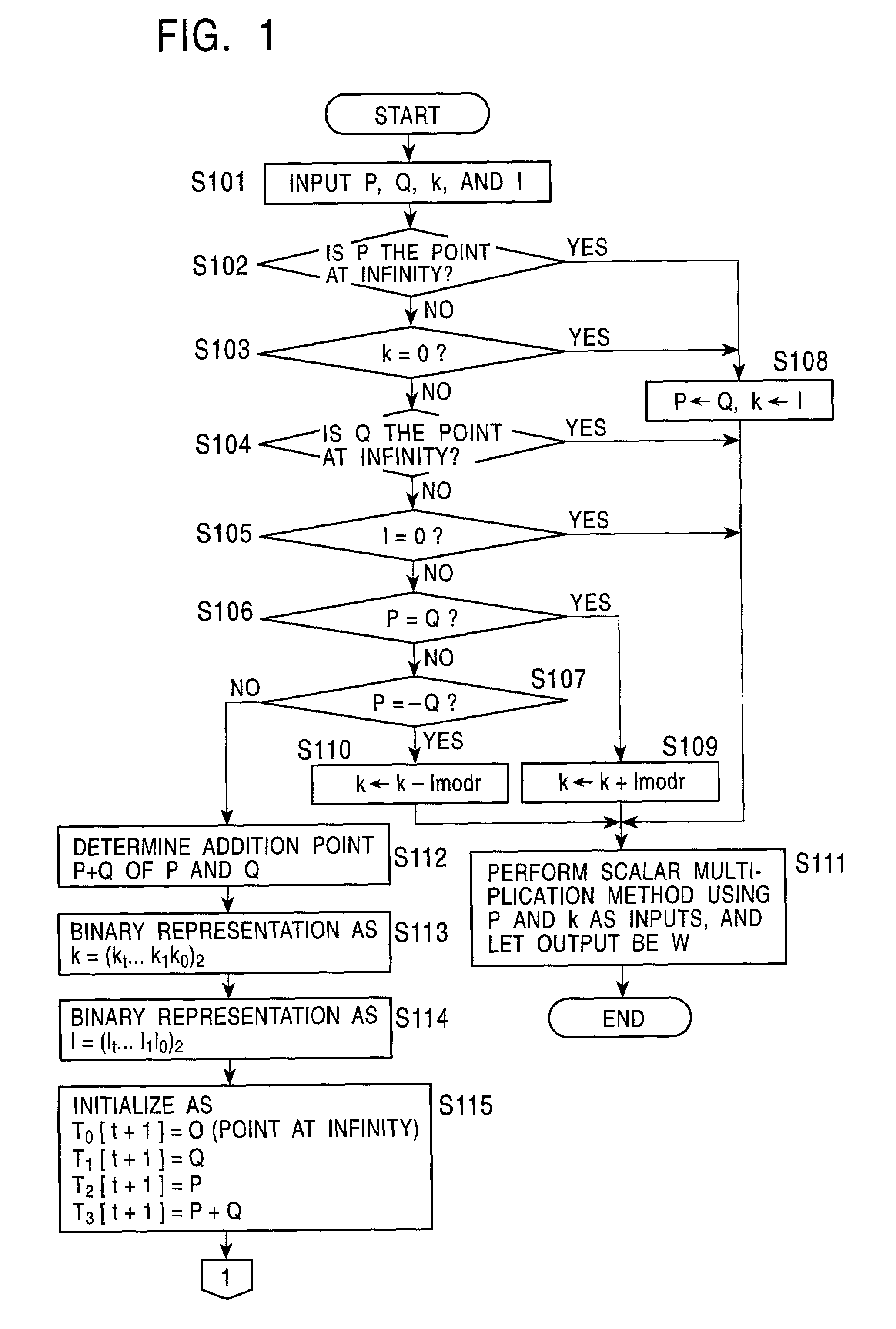
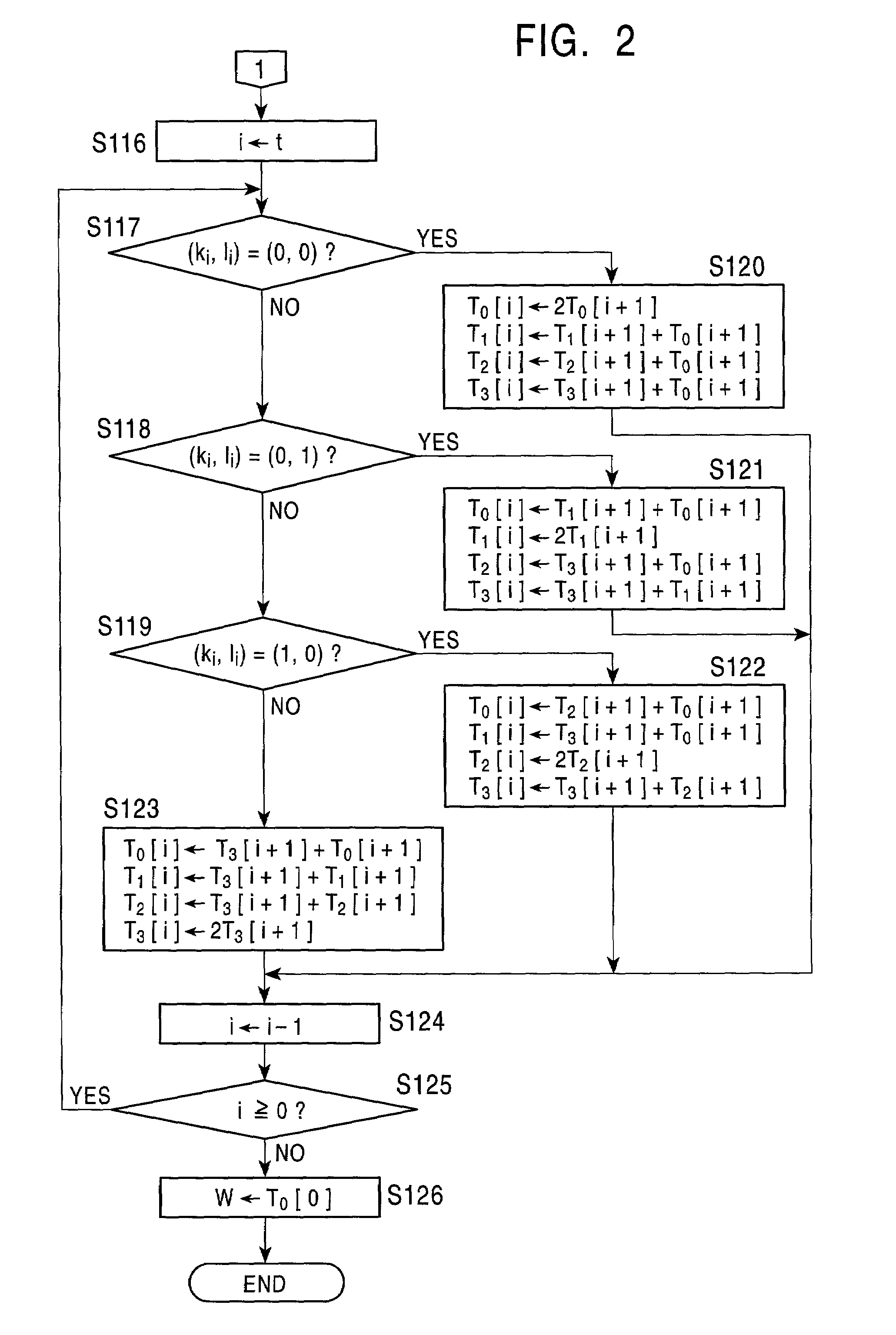
An elliptic curve encryption processing method and an elliptic curve encryption processing apparatus enable high-speed elliptic curve encryption processing computations to be realized. In elliptic curve encryption processing computations, two scalar multiplications, kP and lQ, are not performed separately, but the computation process of kP+lQ is performed simultaneously. In the computation of scalar multiplications, kP and lQ are set on a Montgomery elliptic curve By2=x3+Ax2+x. On the basis of a combination of each bit value of k and l from the high-order bits of the binary representation data of the scalar quantities k and l, a computation relation of the next four points based on the computed four points is selected, and based on the selected relation, a process of computing the next four points is repeatedly performed to eventually compute kP+lQ.
Owner:SONY CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com